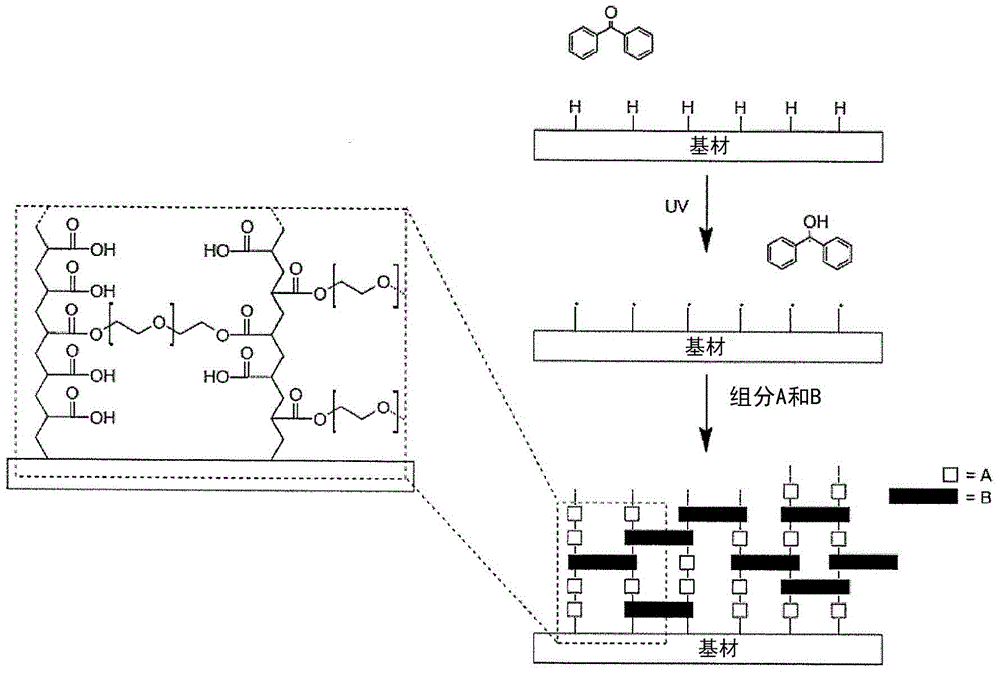
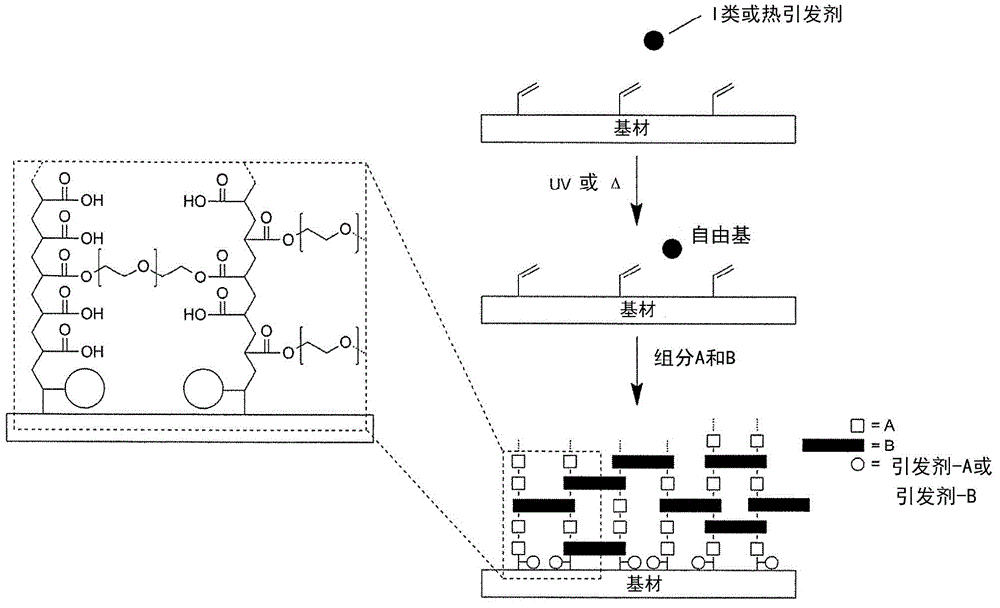
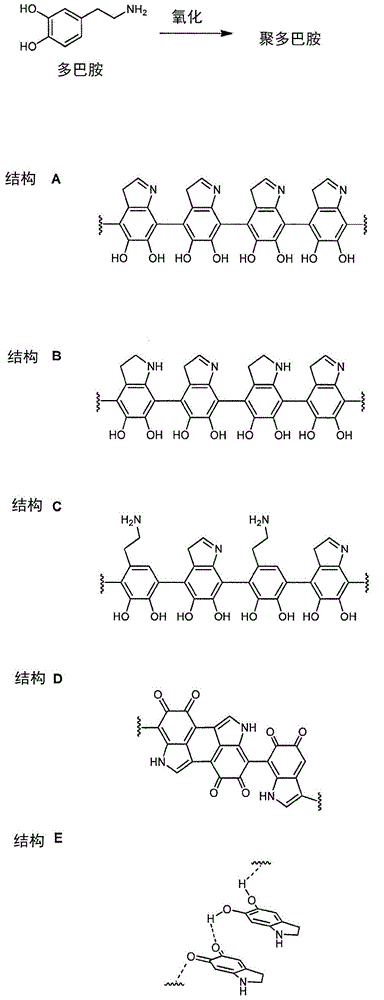
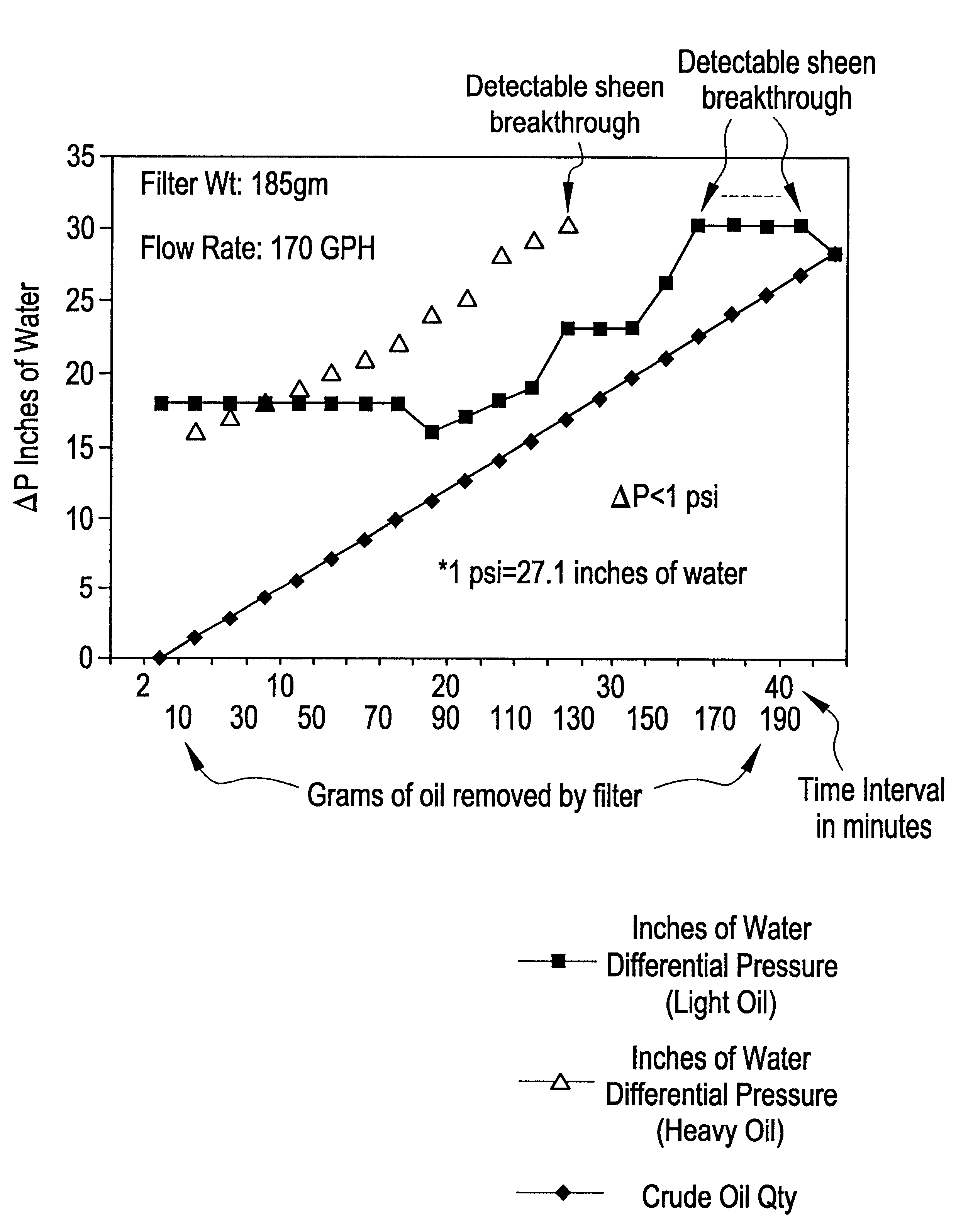
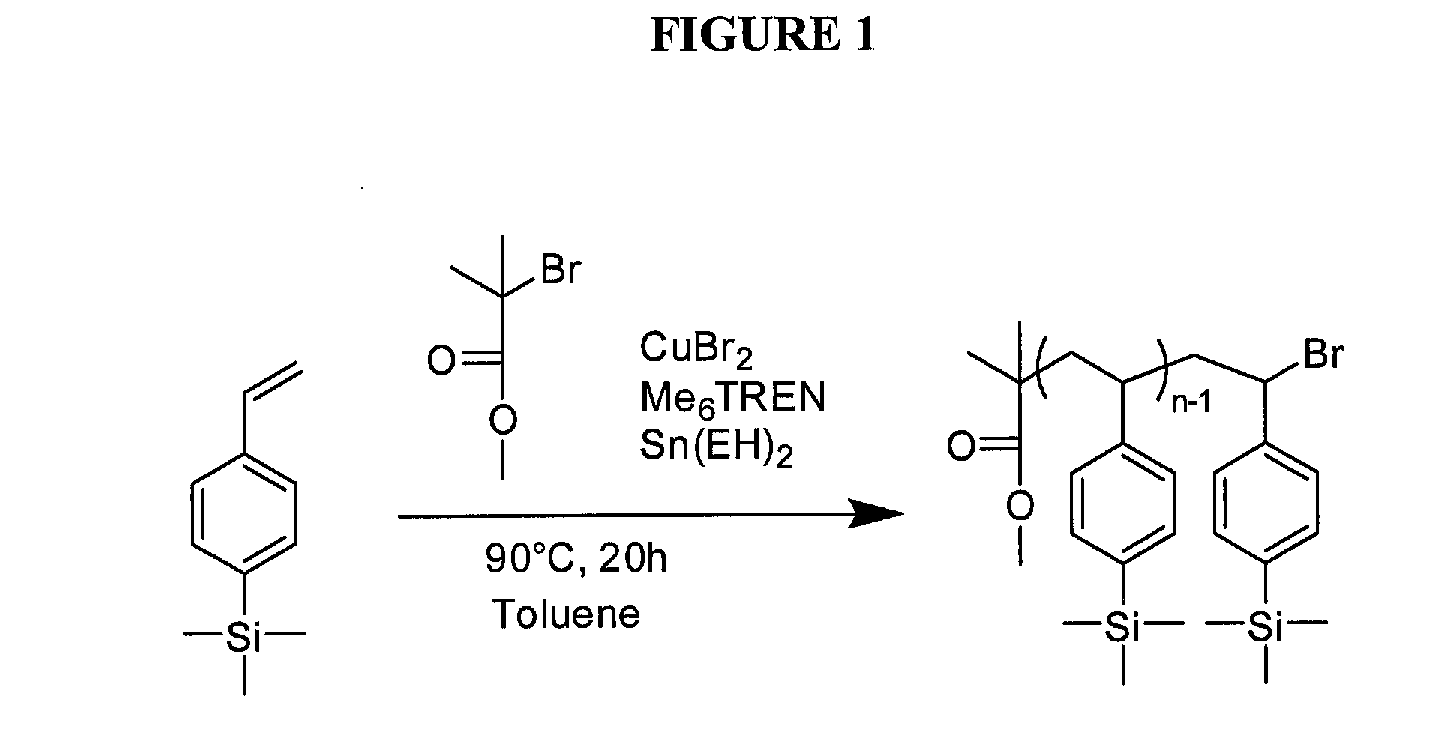
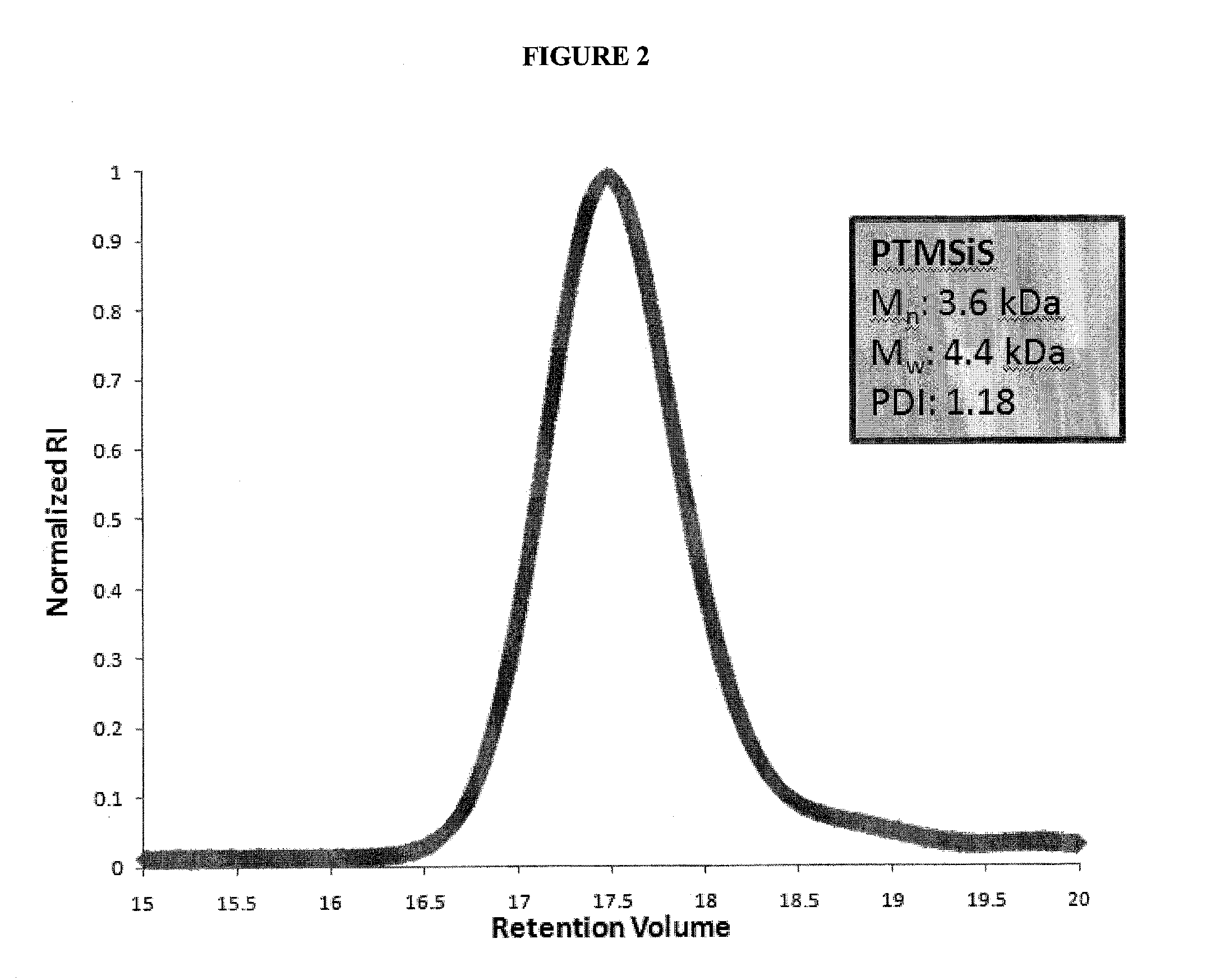
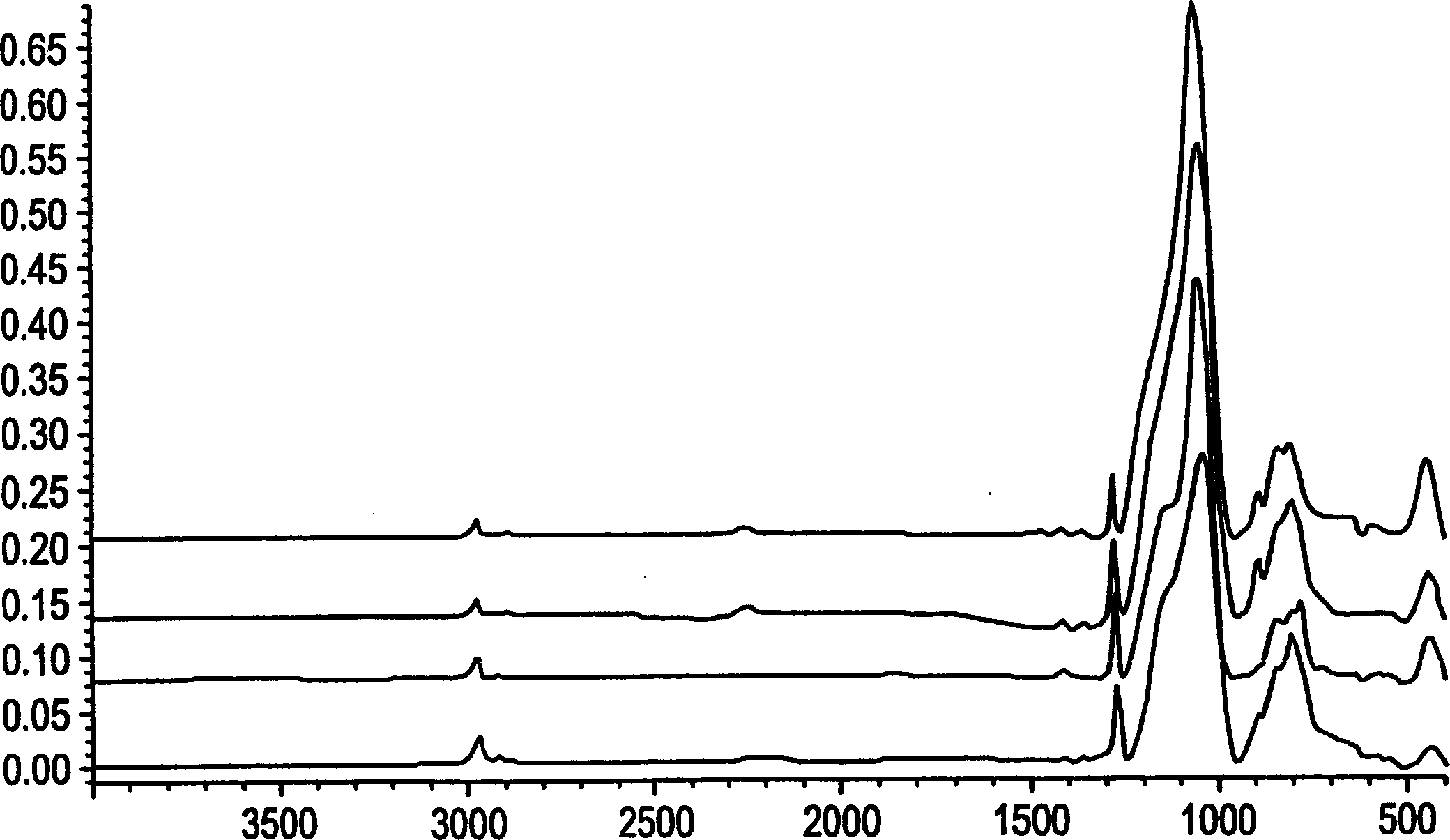
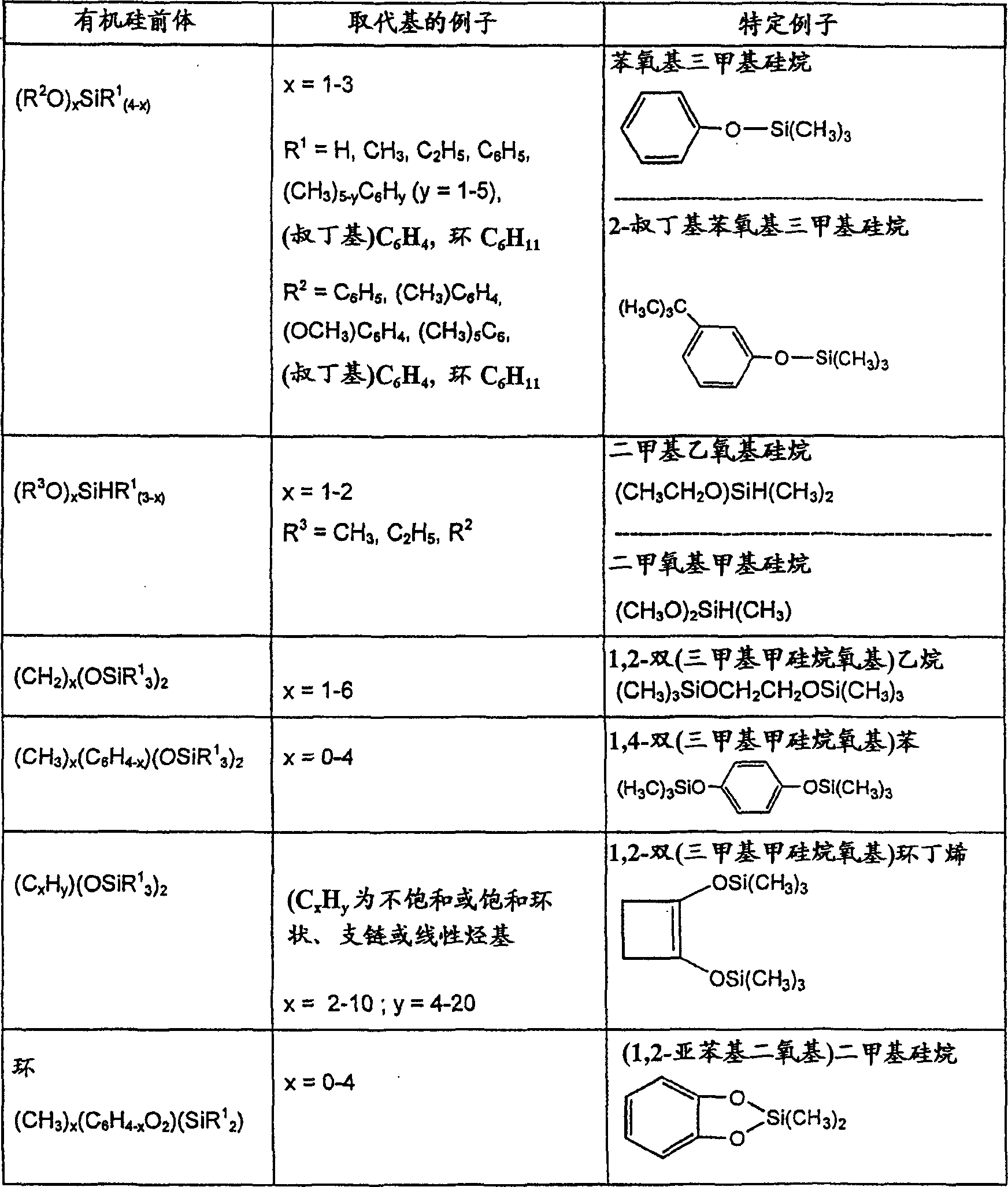
Patents
Literature
129 results about "Alkyne formation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula CnH2n−2.
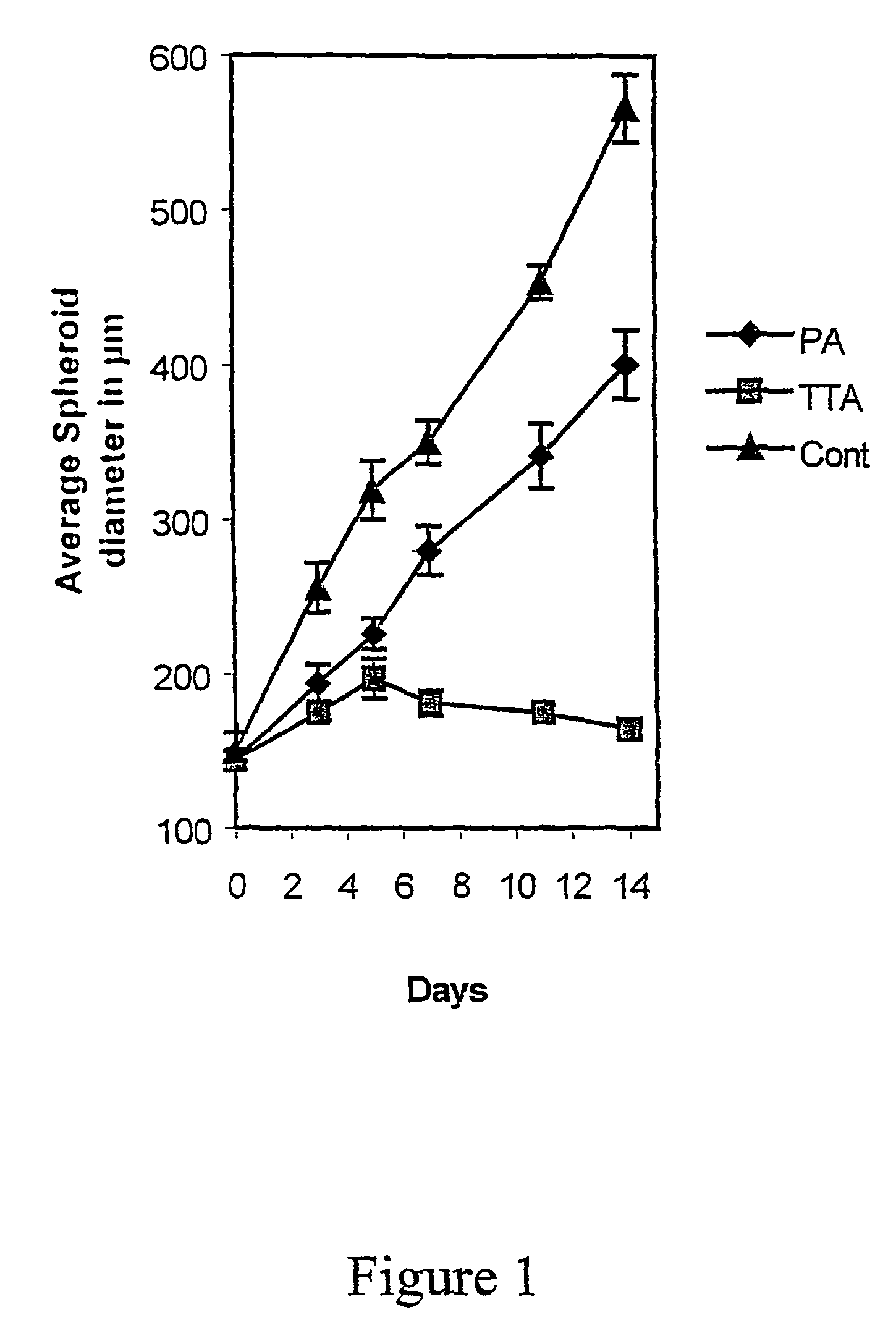
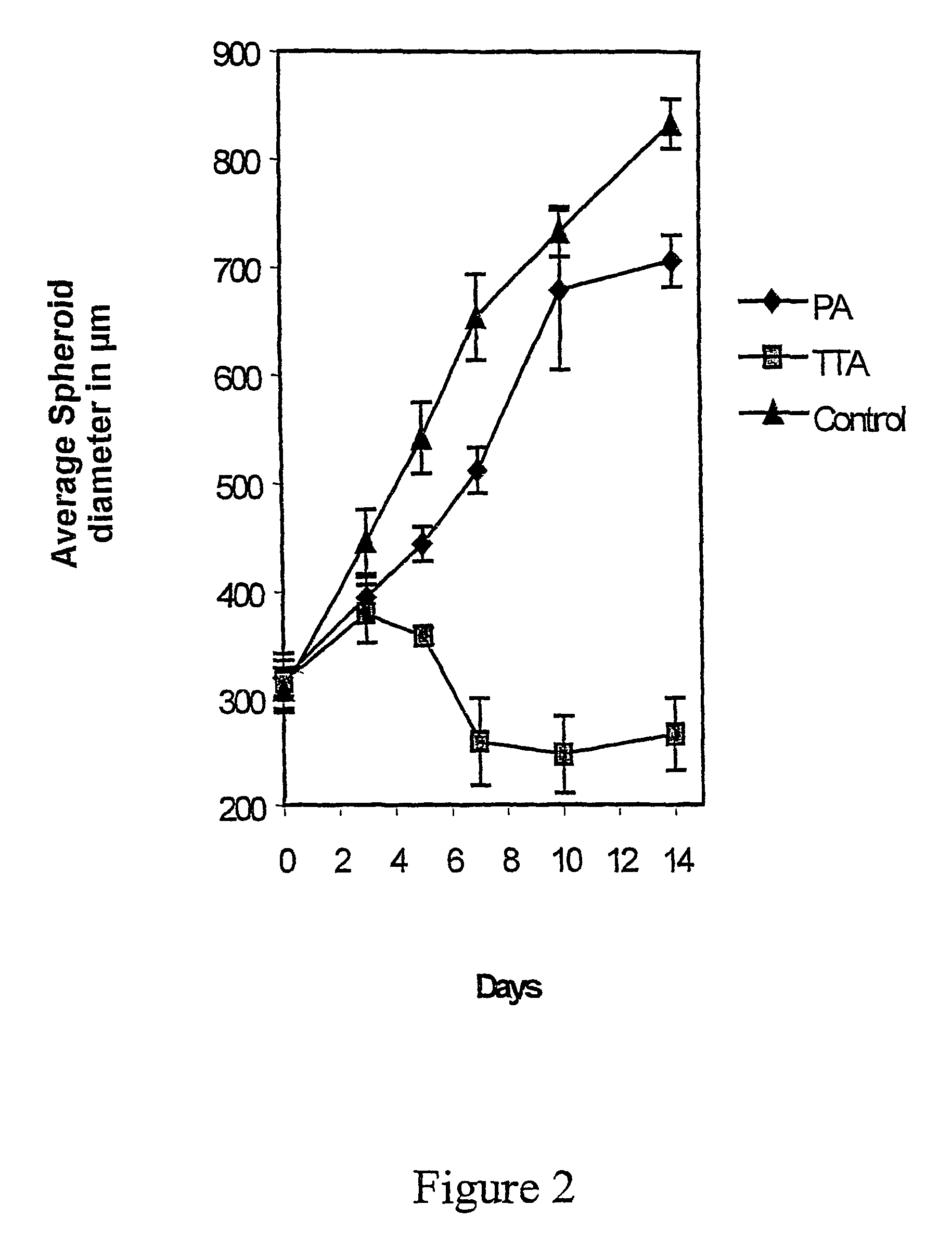
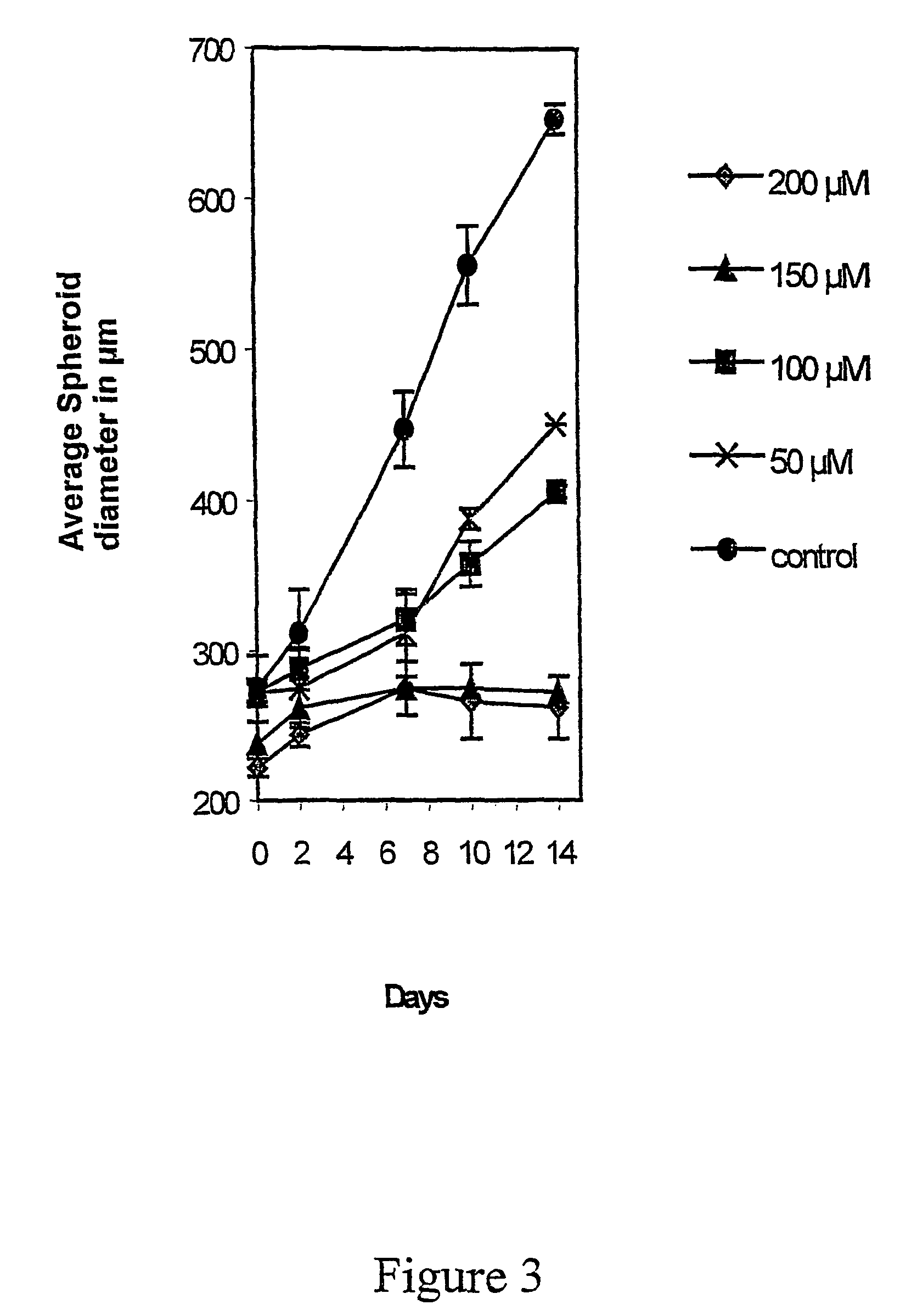
Formulation for paclitaxel
A pharmaceutical formulation is provided for delivering paclitaxel in vivo comprising: water and micelles comprising paclitaxel and a pharmaceutically-acceptable, water-miscible solubilizer forming the micelles, the solubilizer selected from the group consisting of solubilizers having the general structuresR1COOR2, R1CONR2, and R1COR2,wherein R1 is a hydrophobic C3-C50 alkane, alkene or alkyne and R2 is a hydrophilic moiety. The solubilizer is selected such that it does not have a pKa less than about 6.
Owner:SUPERGEN
Oral formulation for paclitaxel
A pharmaceutical formulation is provided for delivering paclitaxel in vivo comprising: water and micelles comprising paclitaxel and a pharrnaceutically-acceptable, water-miscible solubilizer forming the micelles, the solubilizer selected from the group consisting of solubilizers having the general structureswherein R1 is a hydrophobic C3-C50 alkane, alkene or alkyne and R2 is a hydrophilic moiety. The solubilizer is selected such that it does not have a pKa less than about 6.
Owner:SUPERGEN
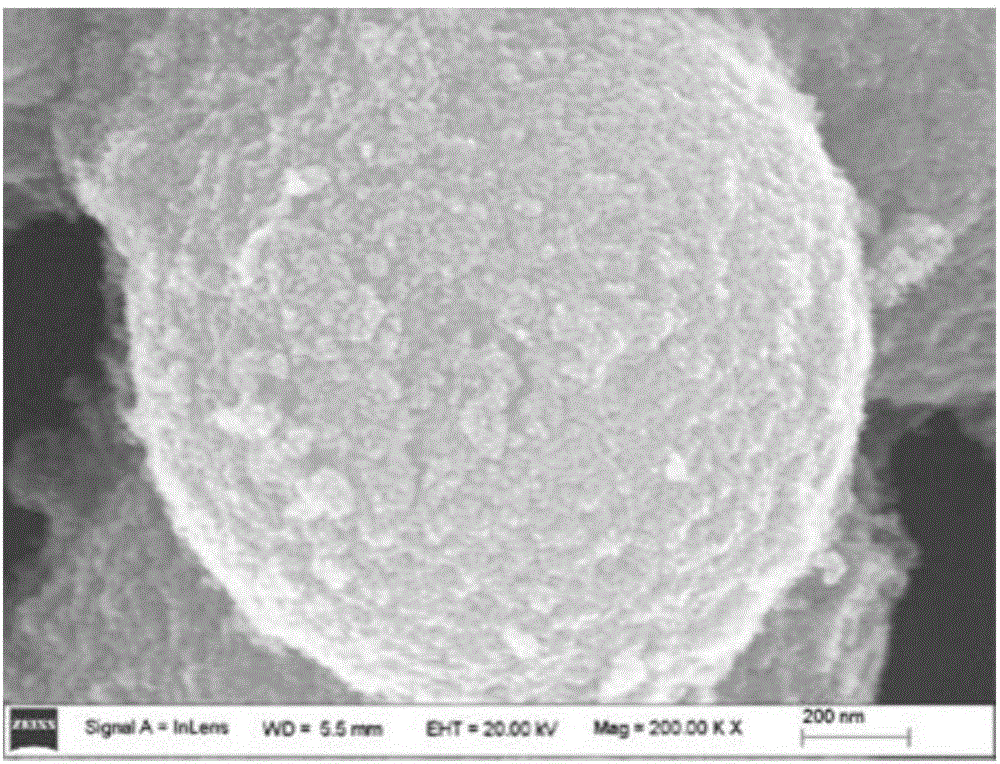
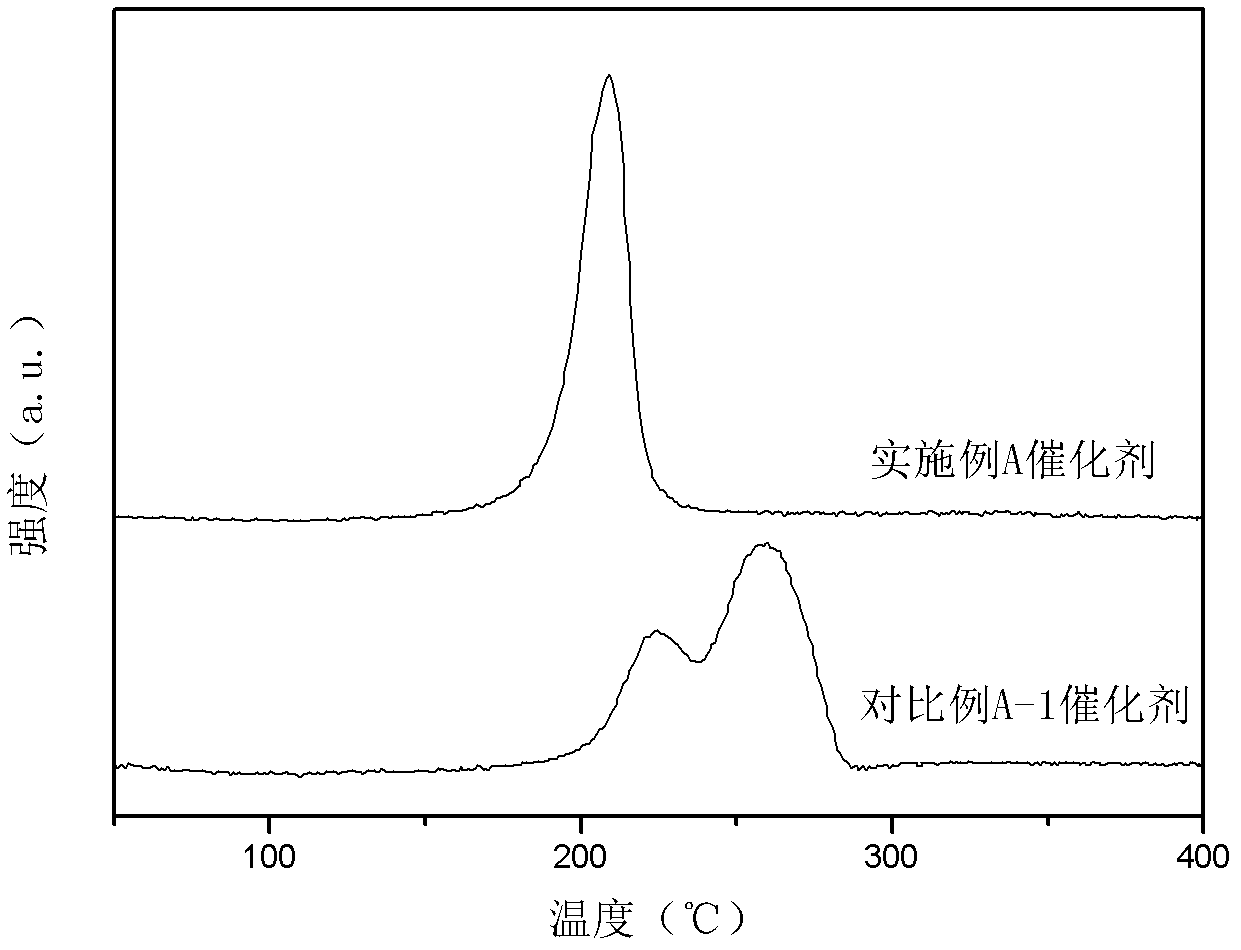
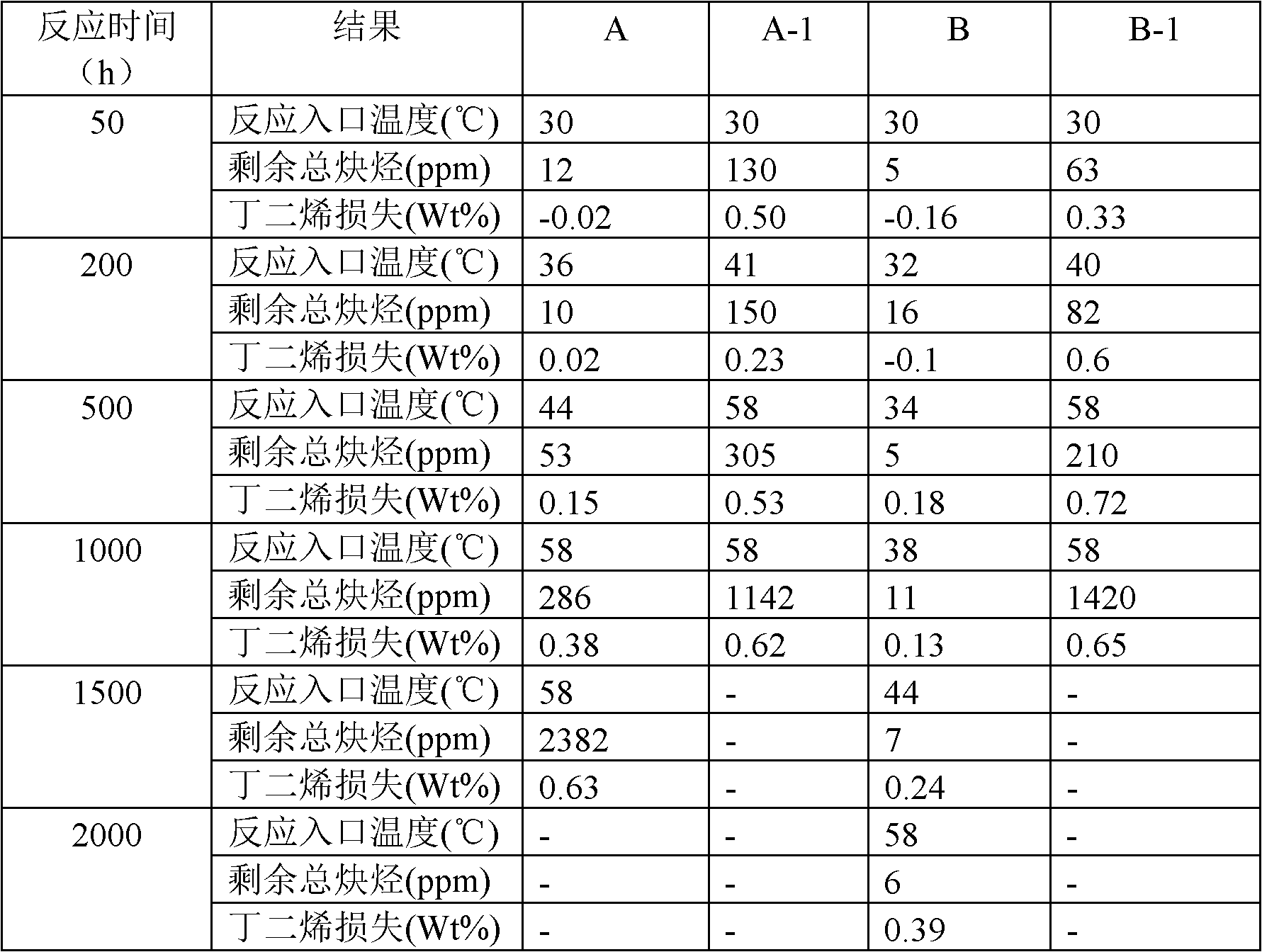
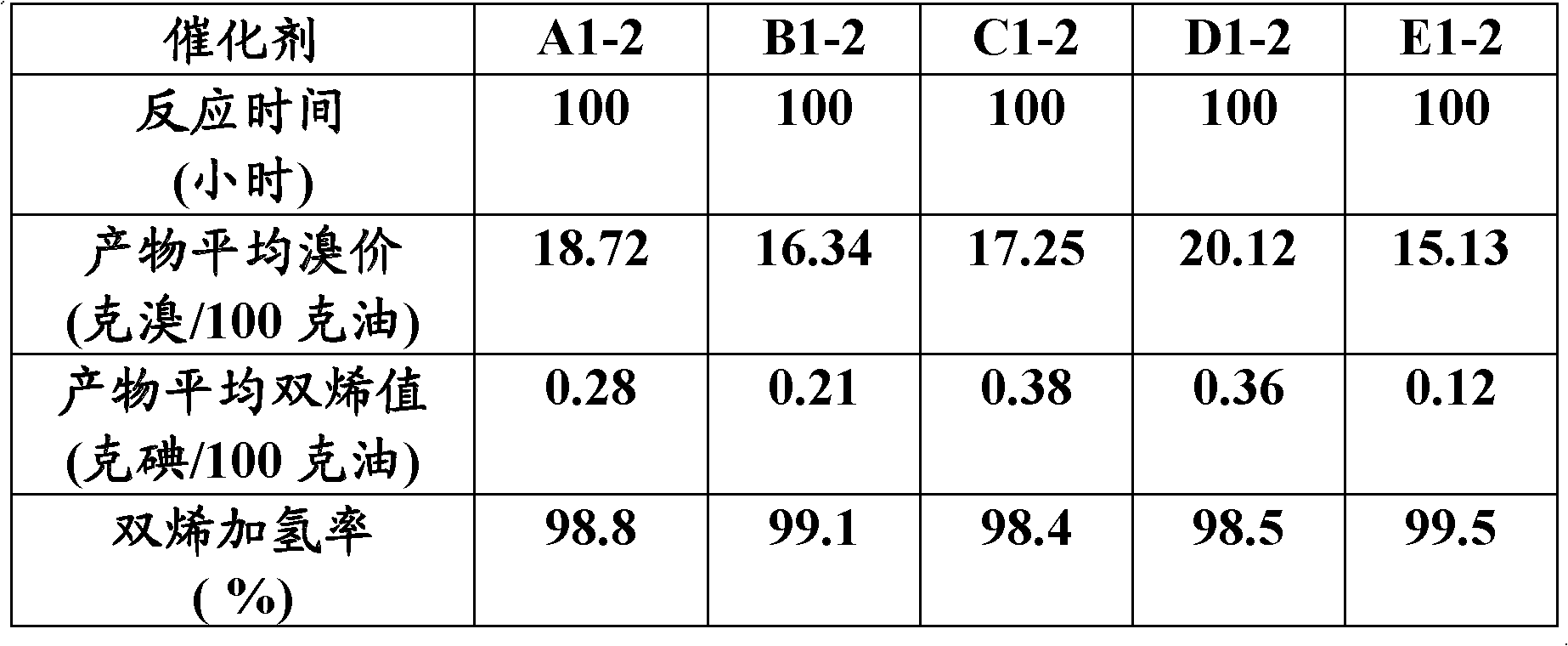
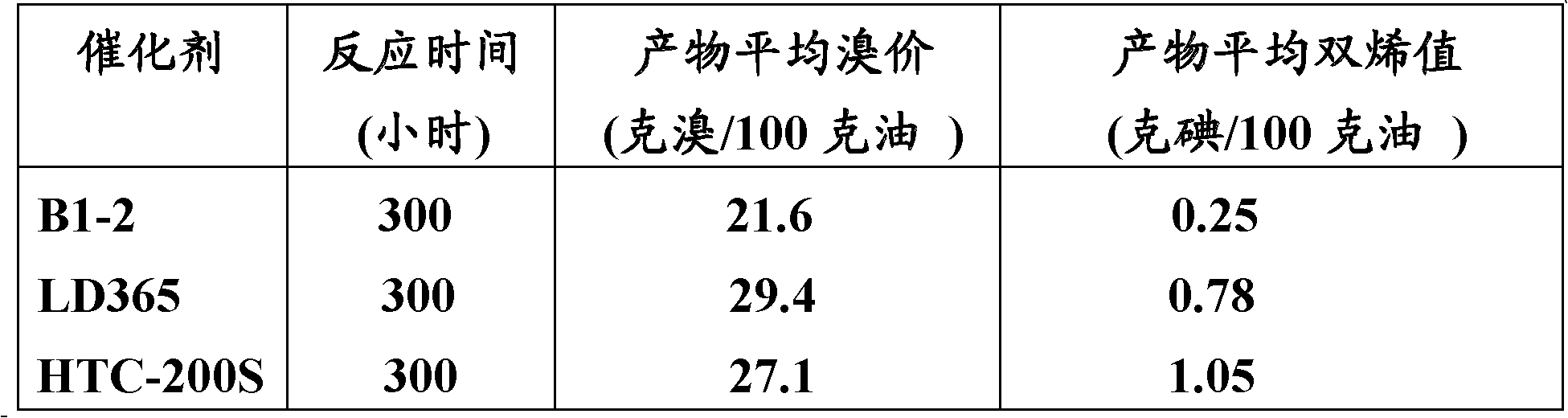
Copper catalyst for selective hydrogenation of mixed C4 and preparation method of copper catalyst
The invention discloses a copper catalyst for selective hydrogenation of mixed C4 and a preparation method of the copper catalyst. The copper catalyst comprises an alumina carrier, 5-50% of active component (Cu), and 0.1-20% of an assistant (one or more of Ag, Co, Fe, Mn, Ni, Zn, Cr and Pd). In the preparation process of the catalyst, organic amine is added to be subjected to complexing with a metal component to effectively improve the uniformity and the dispersibility of alloy formed on the surface of the catalyst. The copper catalyst is used for the process of removing alkyne through selective hydrogenation by the mixed C4, and has good selectivity and long operation cycle.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
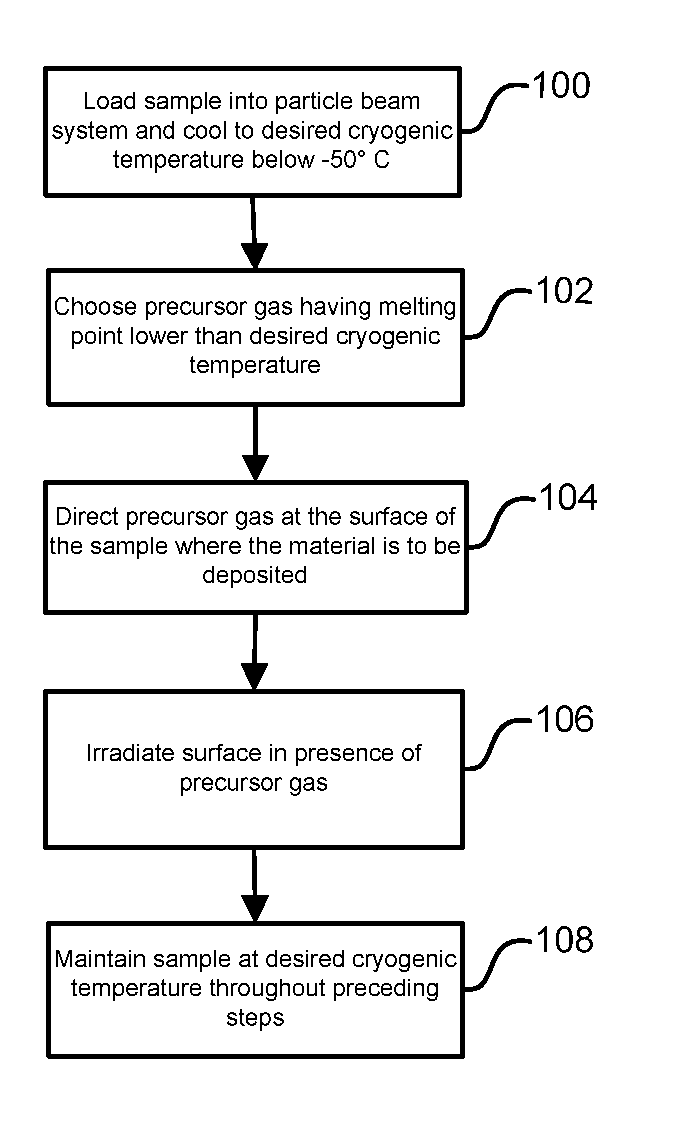
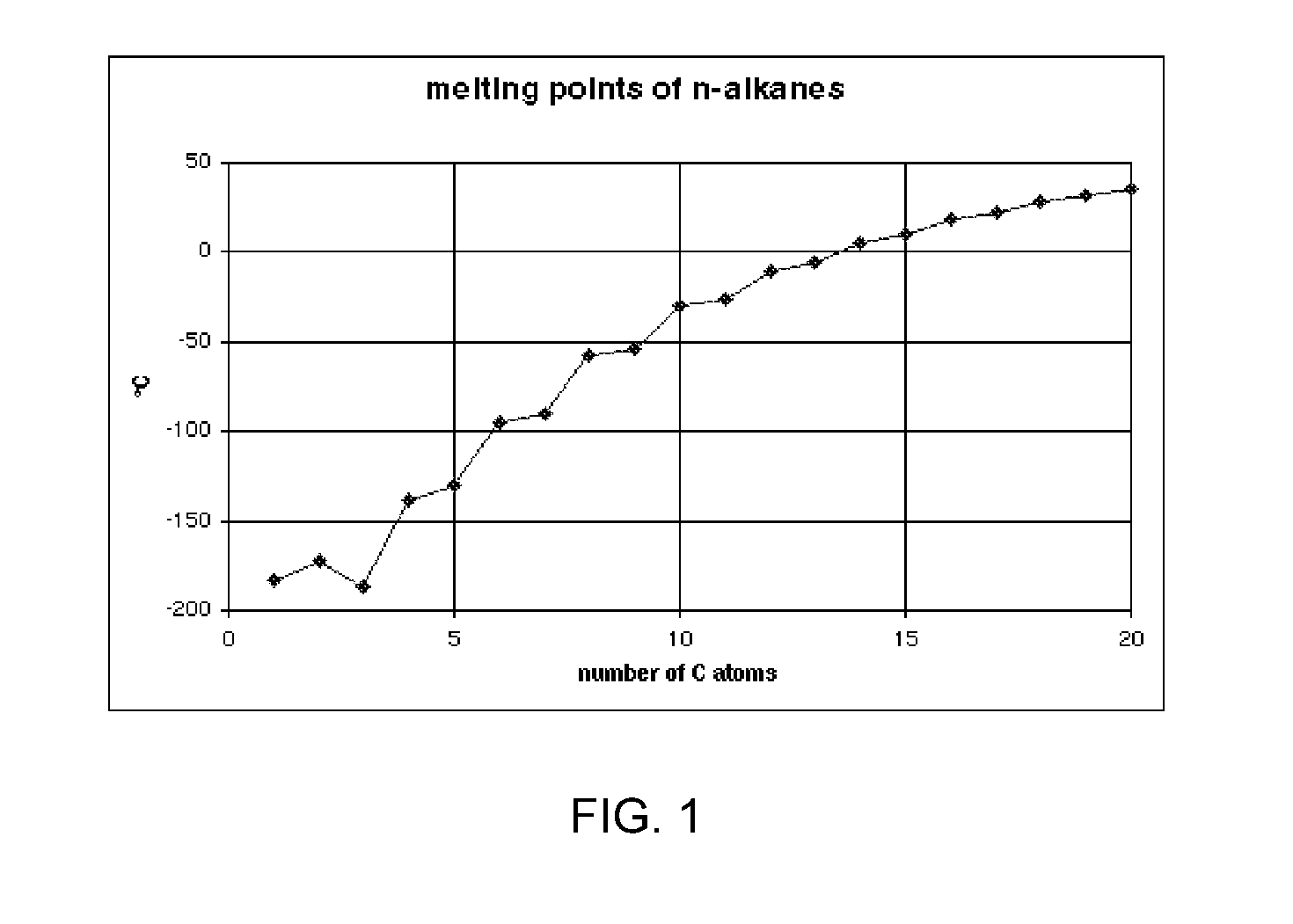
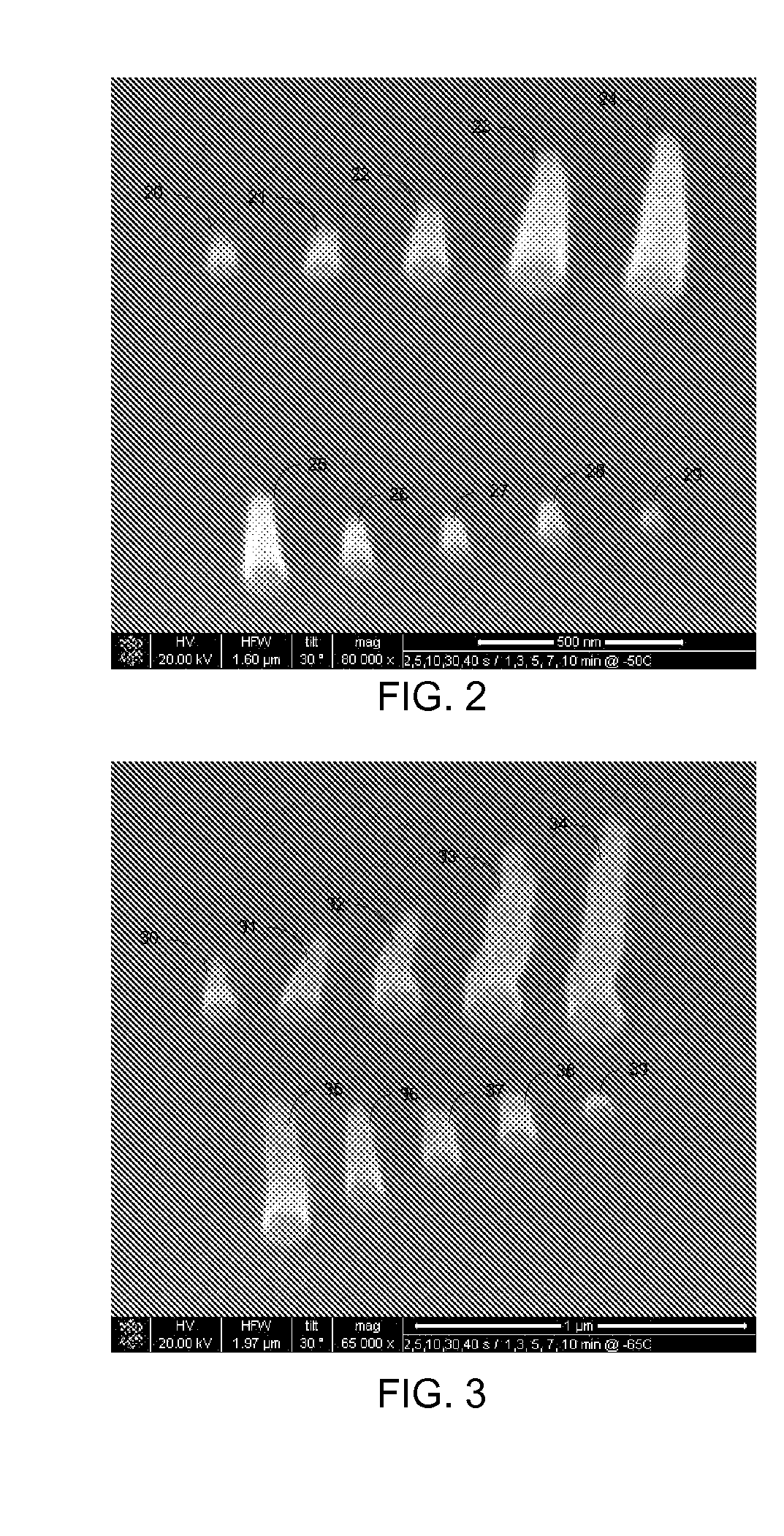
Beam-Induced Deposition at Cryogenic Temperatures
ActiveUS20120003394A1Easy to usePretreated surfacesChemical vapor deposition coatingAlkaneAlkyne formation
A method of depositing material onto a substrate at cryogenic temperatures using beam-induced deposition. A precursor gas is chosen from a group of compounds having a melting point that is lower than the cryogenic temperature of the substrate. Preferably the precursor gas is chosen from a group of compounds having a sticking coefficient that is between 0.5 and 0.8 at the desired cryogenic temperature. This will result in the precursor gas reaching equilibrium between precursor molecules adsorbed onto the substrate surface and precursor gas molecules desorbing from the substrate surface at the desired cryogenic temperature. Suitable precursor gases can comprise alkanes, alkenes, or alkynes. At a cryogenic temperature of between −50° C. and −85° C., hexane can be used as a precursor gas to deposit material; at a cryogenic temperature of between −50° C. and −180° C., propane can be used as a precursor gas.
Owner:FEI CO
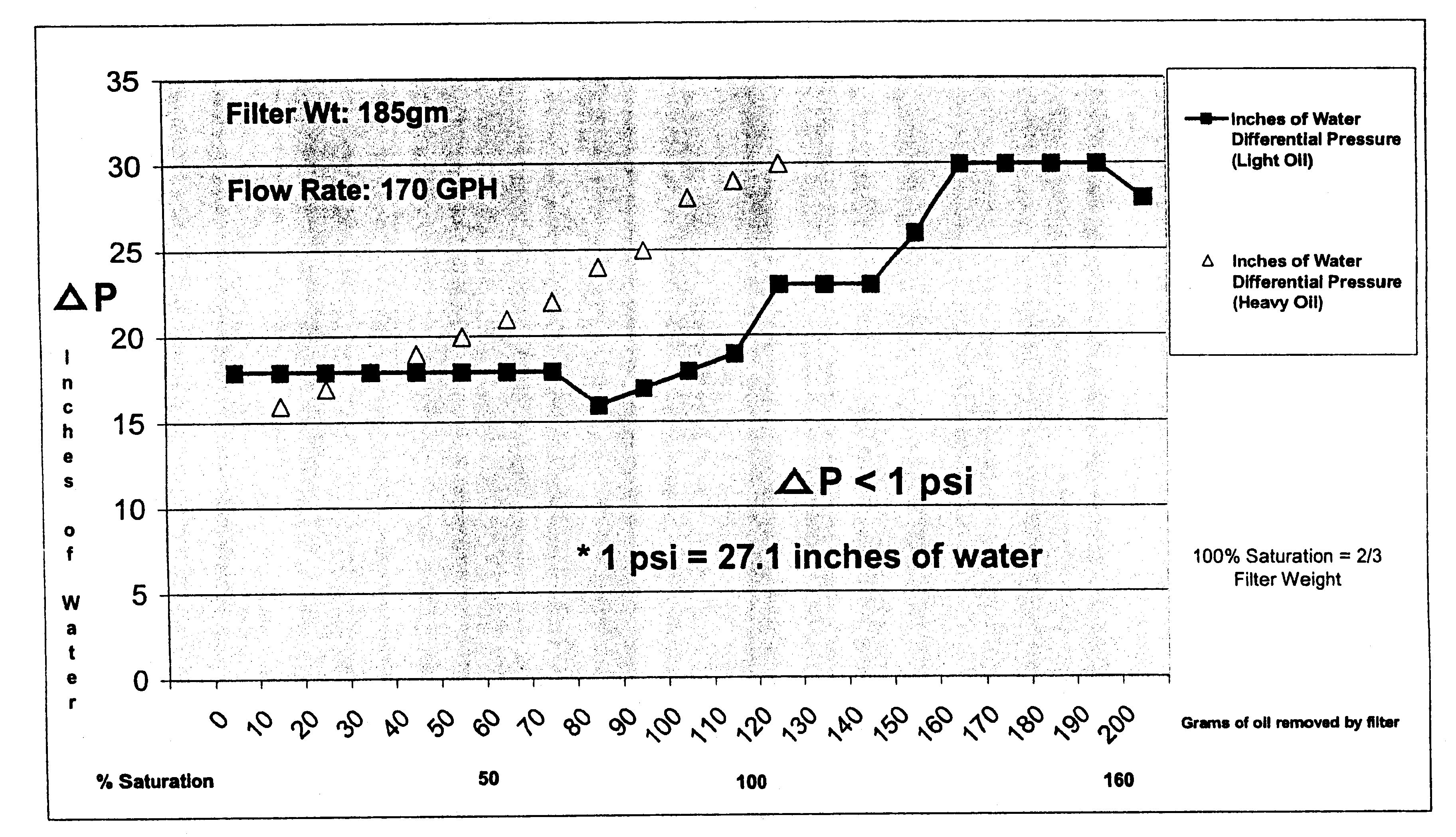
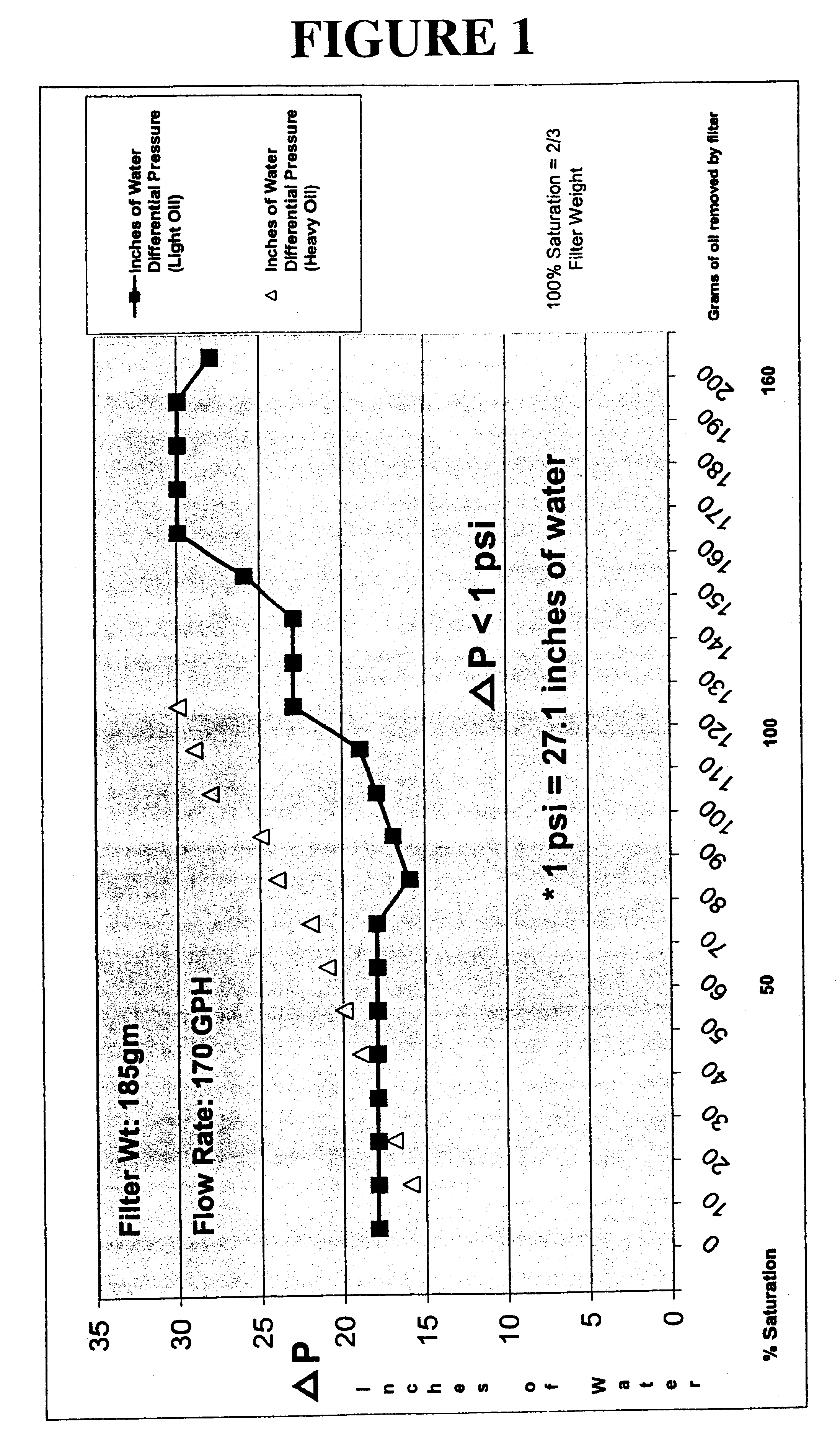
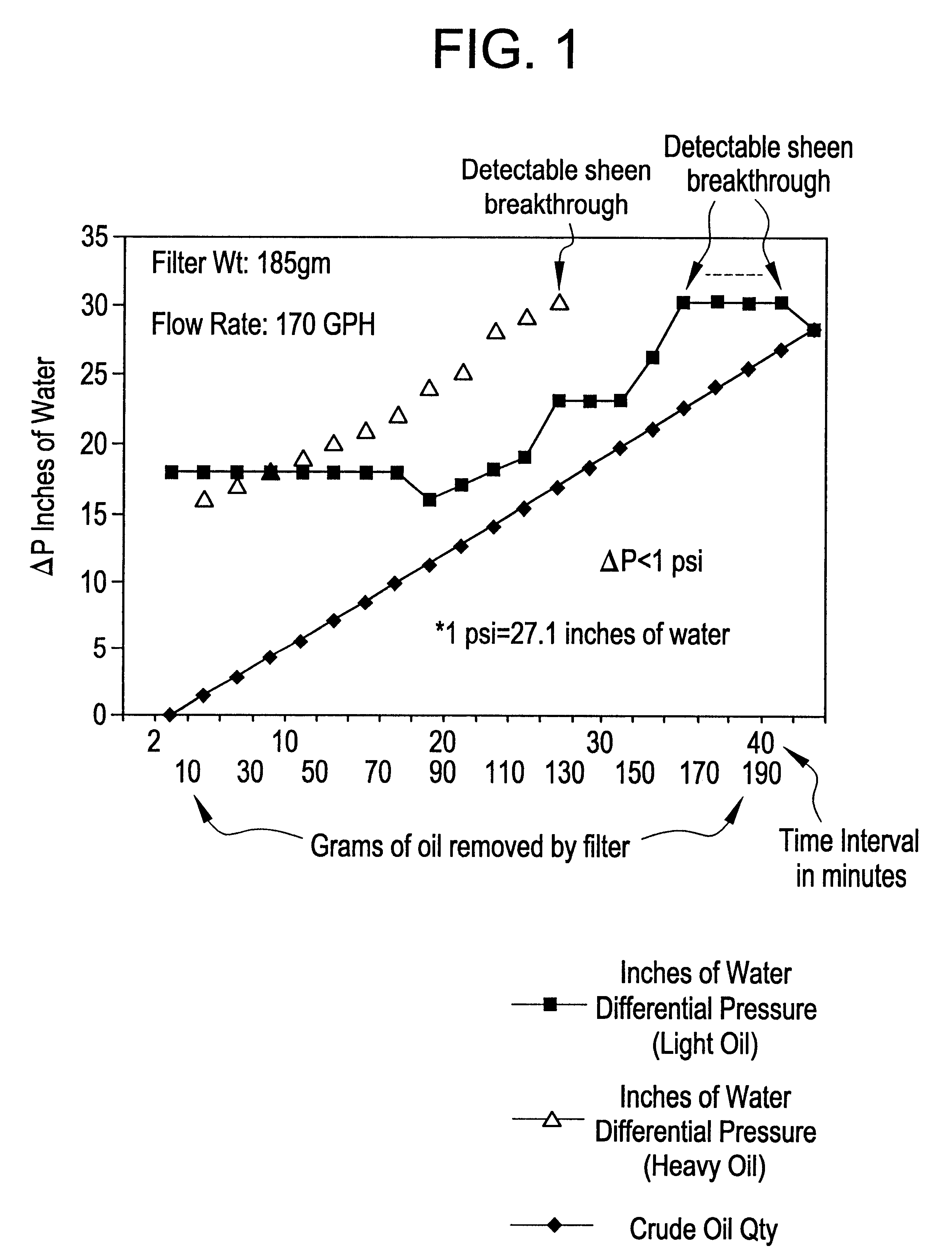
Protection of crossflow membranes from organic fouling
InactiveUS6491822B2Reduce and eliminate tendencyEasy to clogSolid sorbent liquid separationLoose filtering material filtersMethacrylateFiltration
A method for improving the efficiency and usable life in a cross flow membrane filter used to remove contaminants from bilgewater. The bilgewater is passed upstream of the cross filter membrane through a fluid-pervious filtration media which has been infused with an absorbtion composition comprising a homogeneous thermal reaction product of an oil component selected from the group consisting of glycerides, fatty acids, alkenes, and alkynes, and a methacrylate or acrylate polymer component. The contaminants are thereby immobilized at the media. The purified output from the infused filtration media is then provided as input for the cross flow membrane filter.
Owner:MYCELX TECH CORP
Coating for substrate
ActiveCN104936626ALow particle sensitivityIncreased durabilitySurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismHydrophilic monomerCross-link
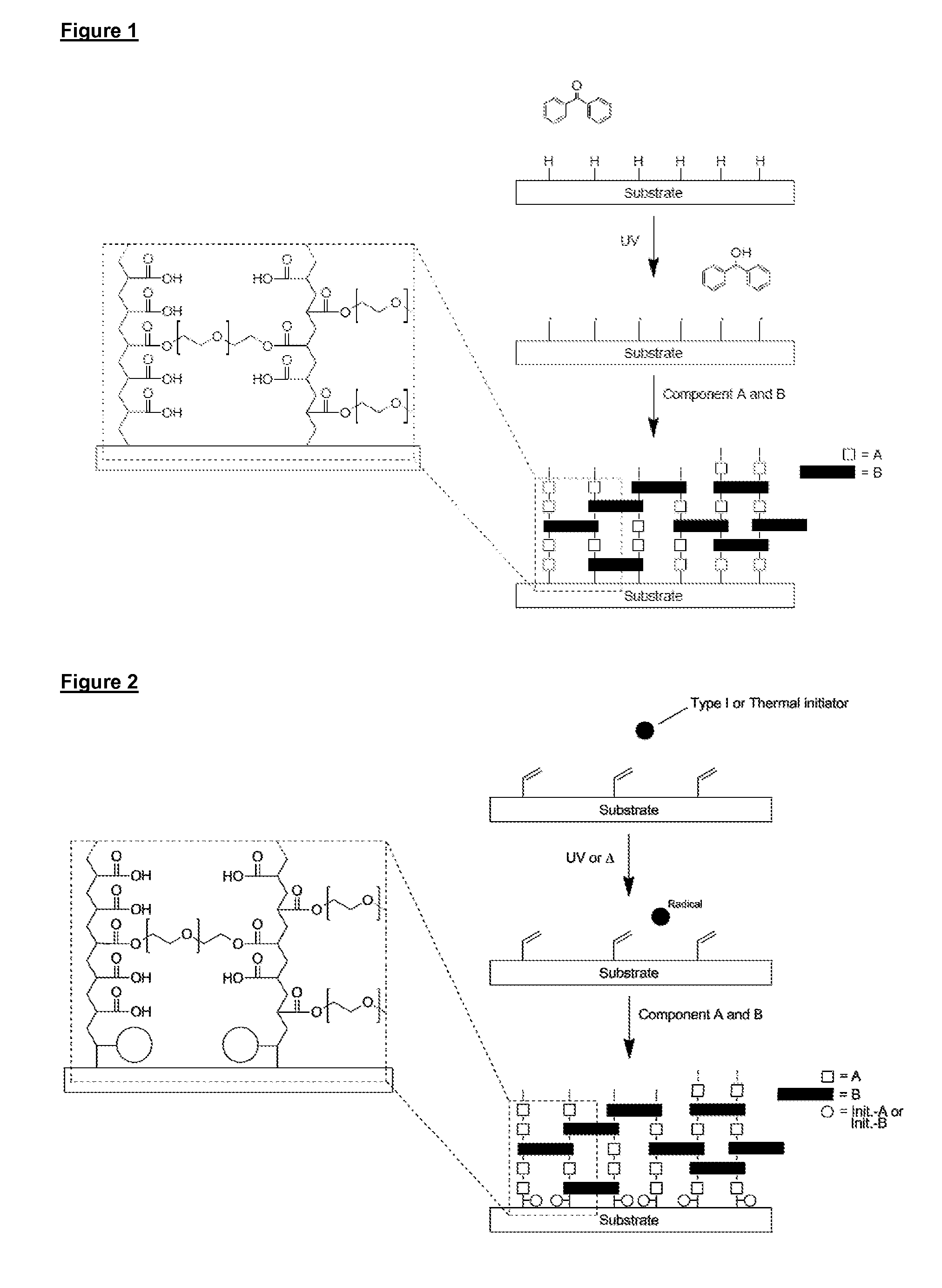
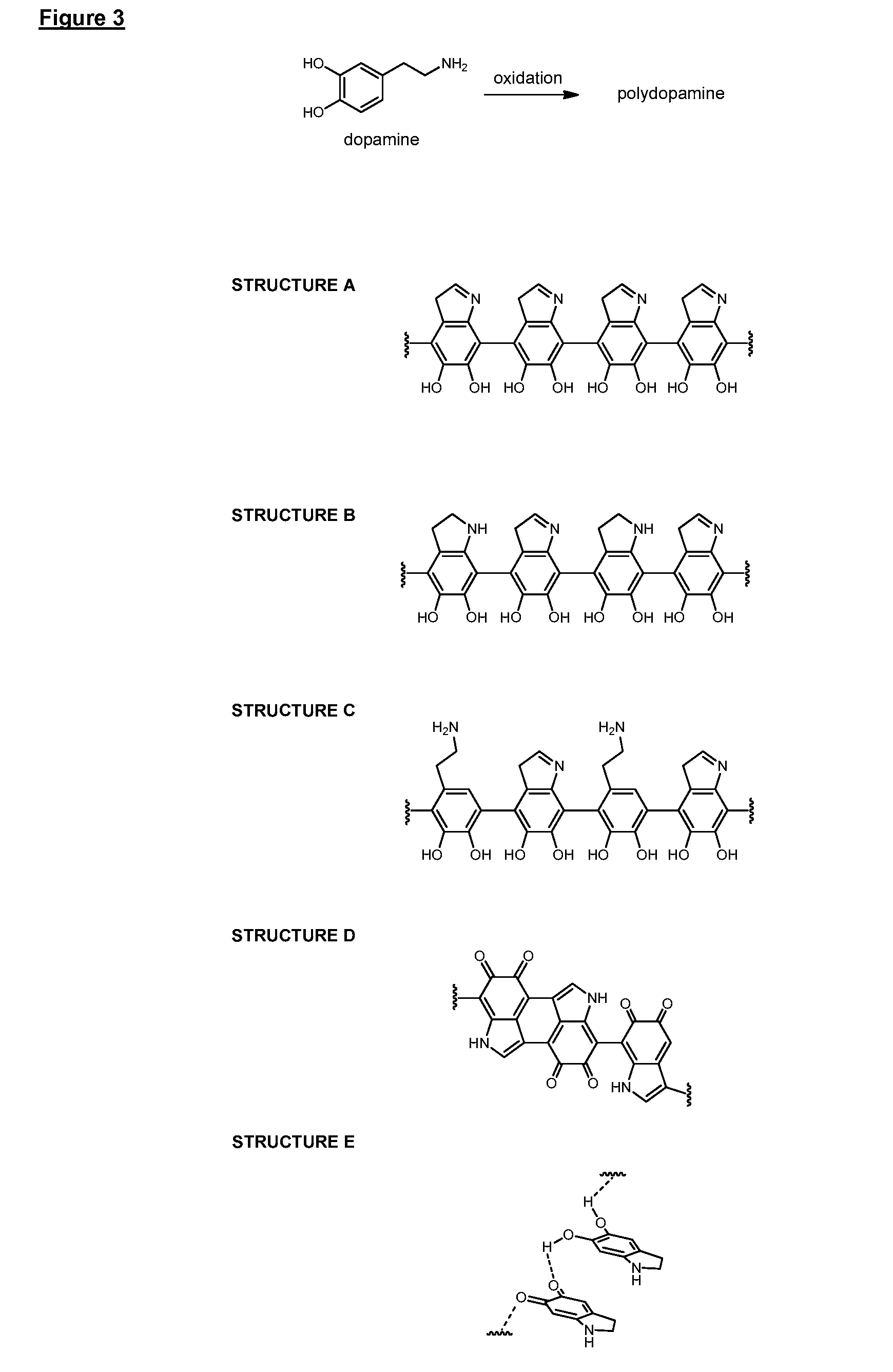
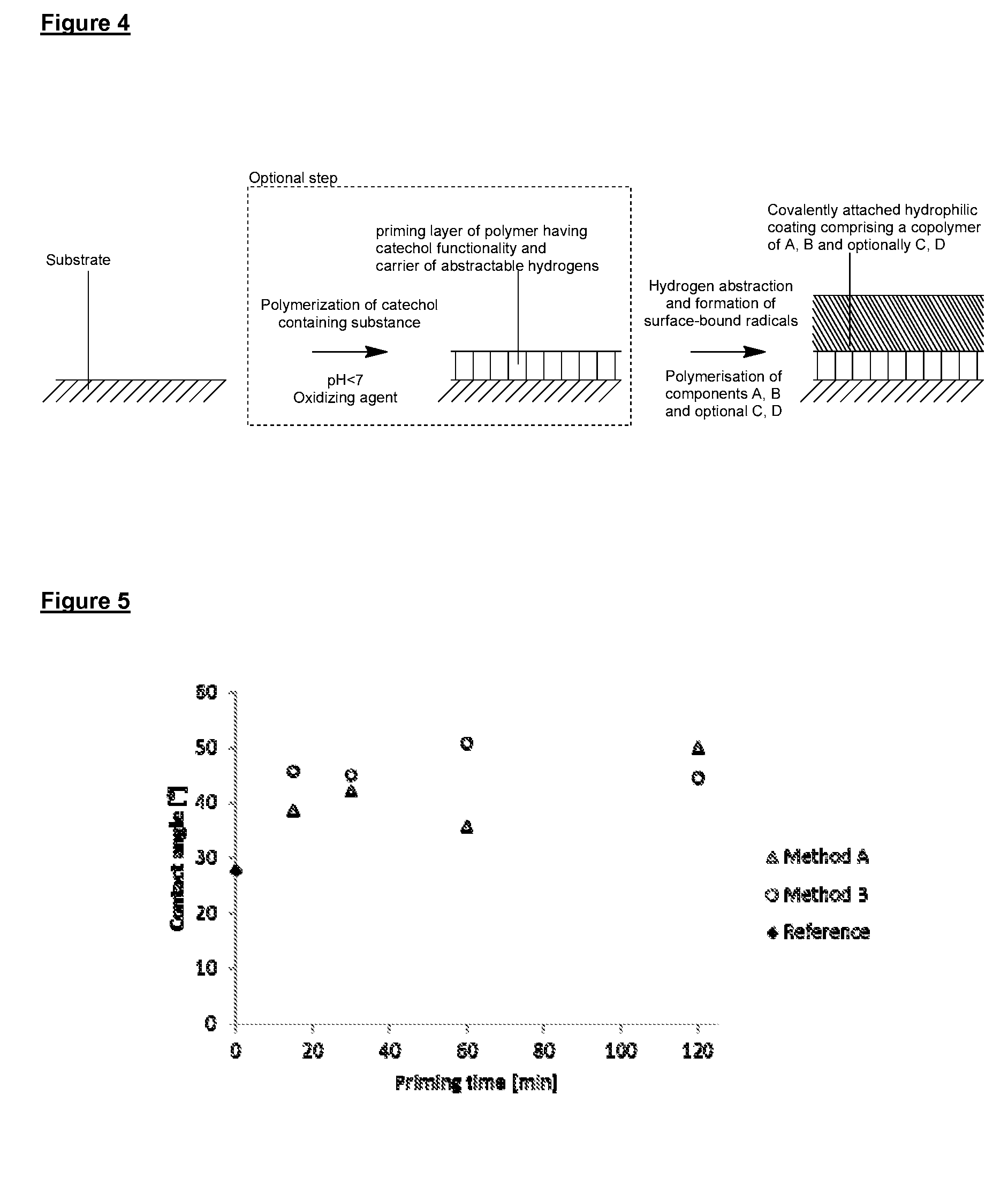
There is provided inter alia a substrate with a surface having a hydrophilic coating comprising a cross-linked copolymer of components A and B, and optional components C and D; wherein component A comprises one or more C2-C16 hydrophilic monomers each bearing one or more alkene and / or alkyne groups; component B comprises one or more hydrophilic polymers each bearing two or more alkene and / or alkyne groups; component C, if present, comprises one or more beneficial agents each bearing one or more alkene or alkyne groups; and component D, if present, comprises one or more low molecular weight cross-linking agents each bearing two or more functional groups independently selected from thiol, alkene and alkyne groups; wherein the cross-linked copolymer is formed by radical polymerisation involving the alkene and / or alkyne groups of components A, B and C (if present) and involving the functional groups of component D (if present); wherein the hydrophilic coating optionally comprises component E which comprises one or more beneficial agents, wherein component E does not form a copolymer with components A, B, C (if present) and D (if present); and wherein the hydrophilic coating is covalently attached to the surface of the substrate.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
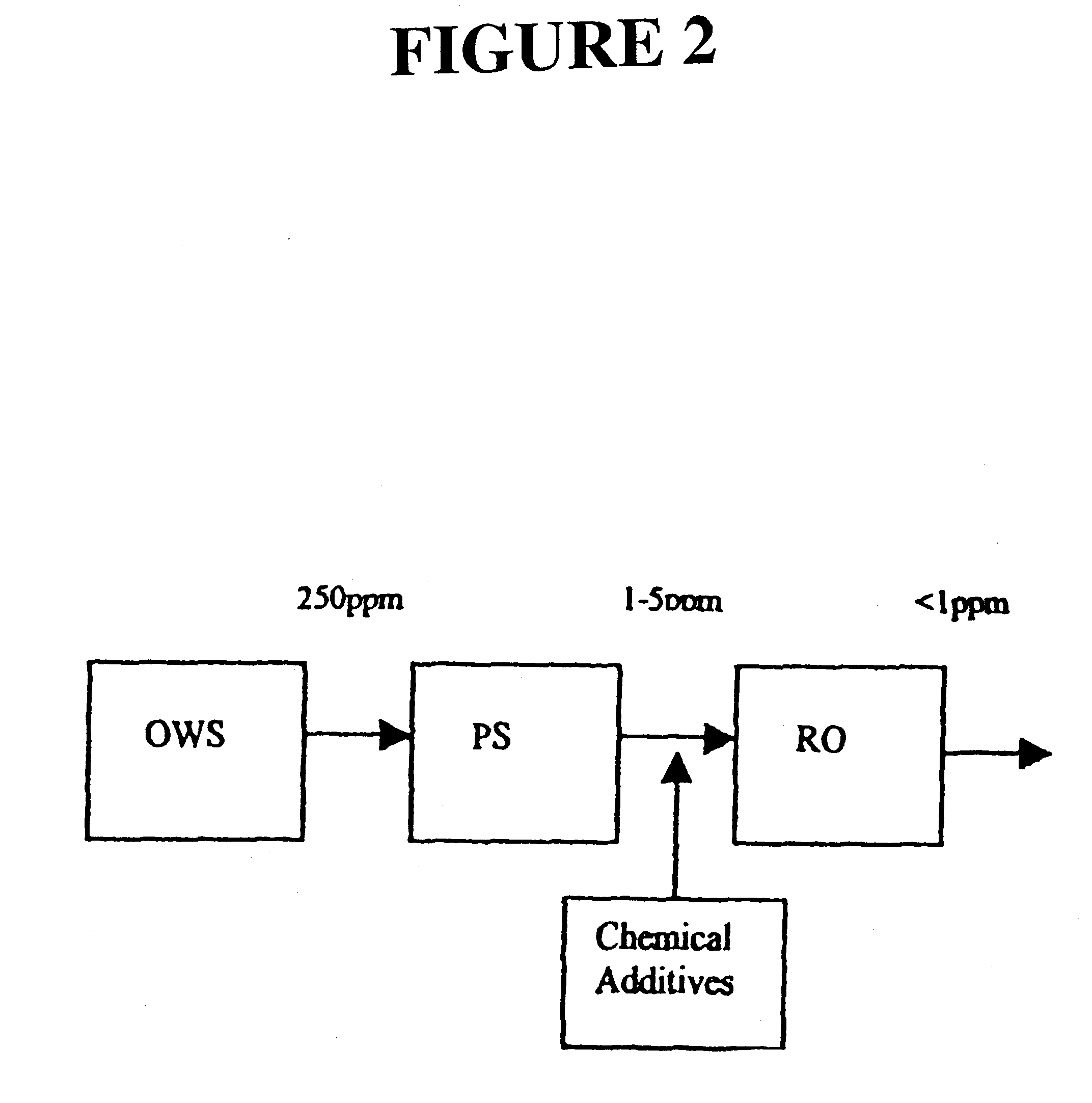
Method and apparatus for removing pernicious contaminants from bilgewater discharge
A method and apparatus for removing contaminants from an oily bilgewater. In the method the bilgewater is passed through a fluid-pervious filtration media which has been infused with an absorbtion composition comprising a homogeneous thermal reaction product of an oil component selected from the group consisting of glycerides, fatty acids, alkenes, and alkynes, and a methacrylate or acrylate polymer component. The contaminants are thereby immobilized at said media, and the purified bilgewater having passed through the filtration media is discharged, e.g. into a body of navigable water.
Owner:MYCELX TECH CORP
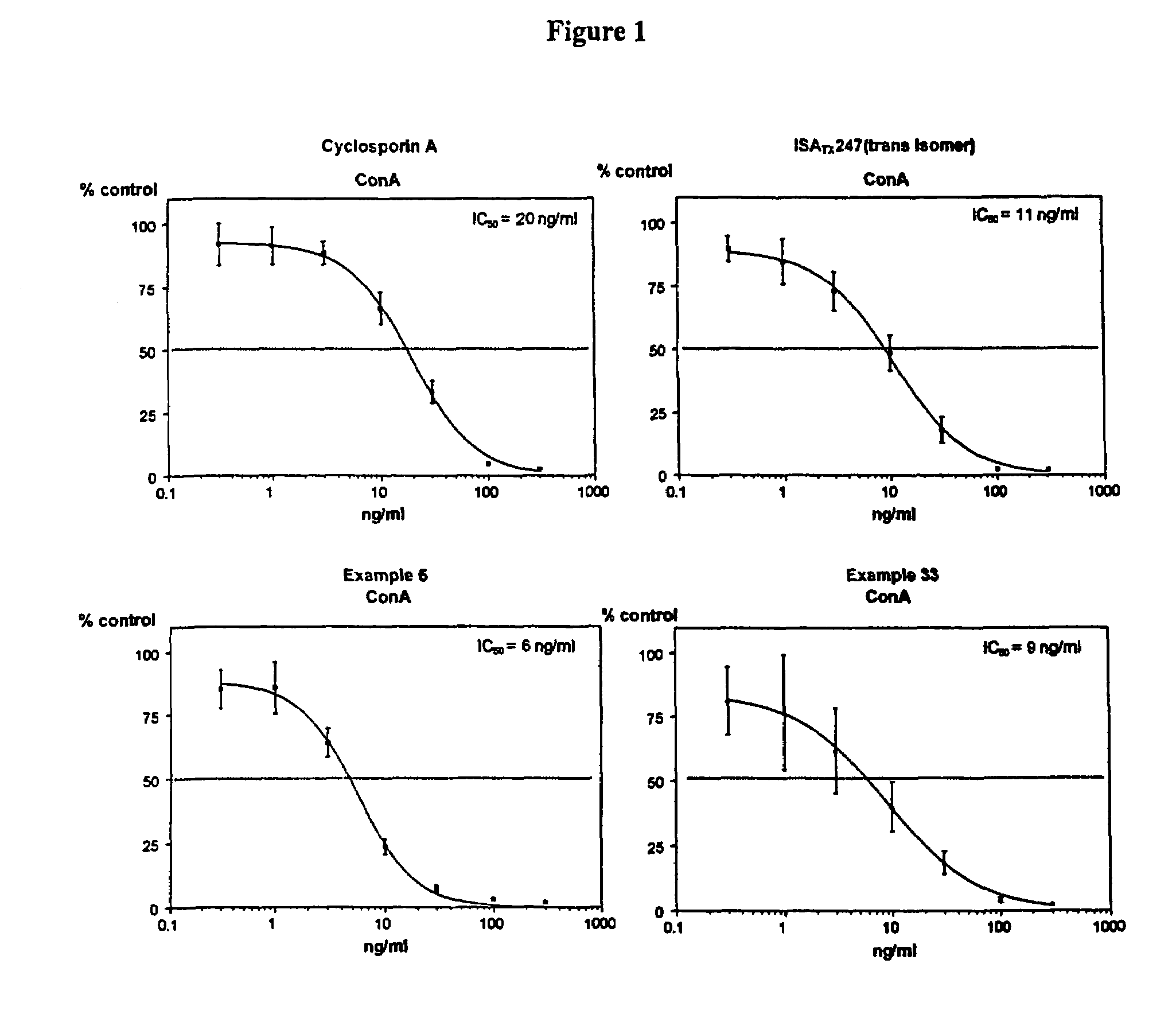
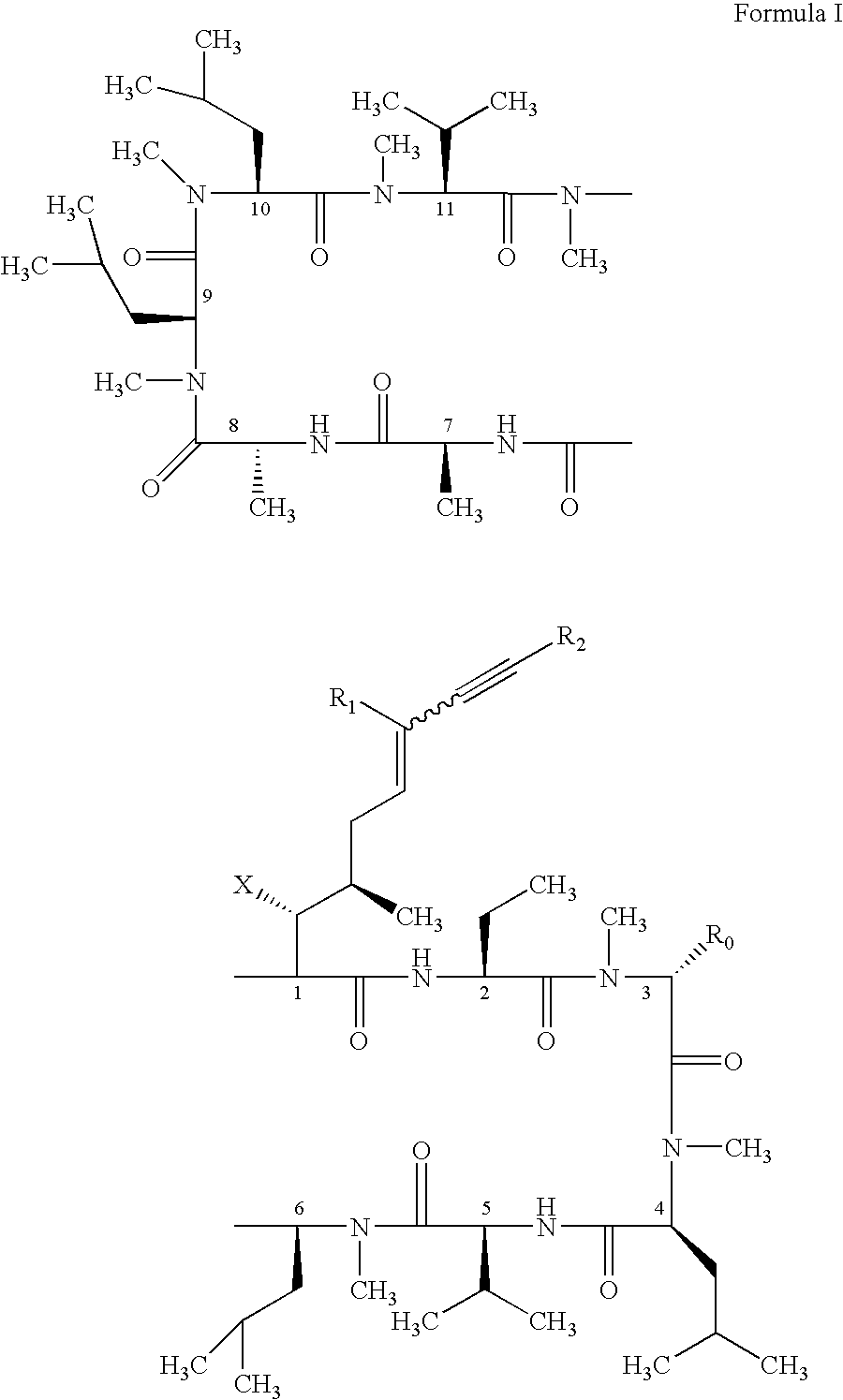
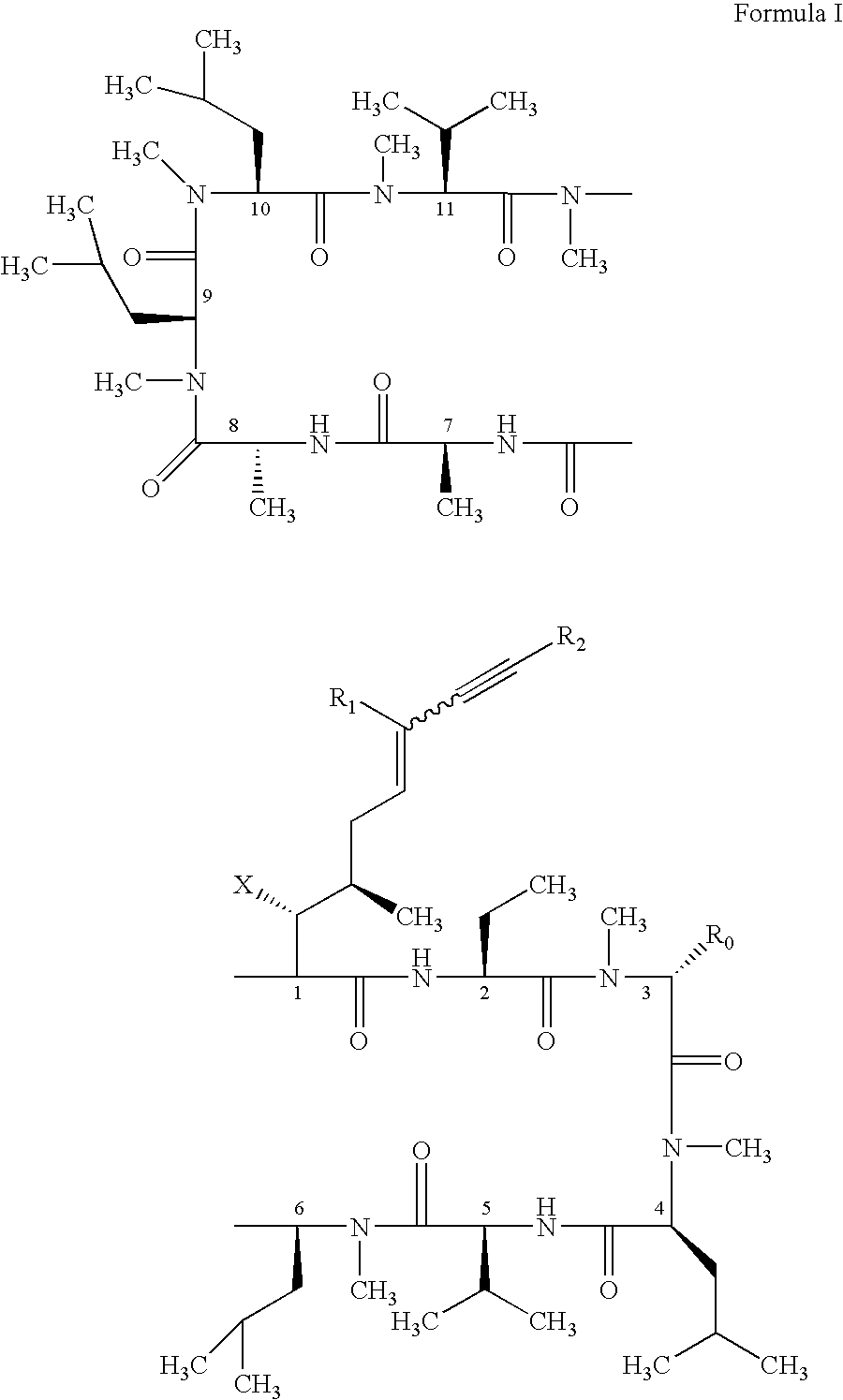
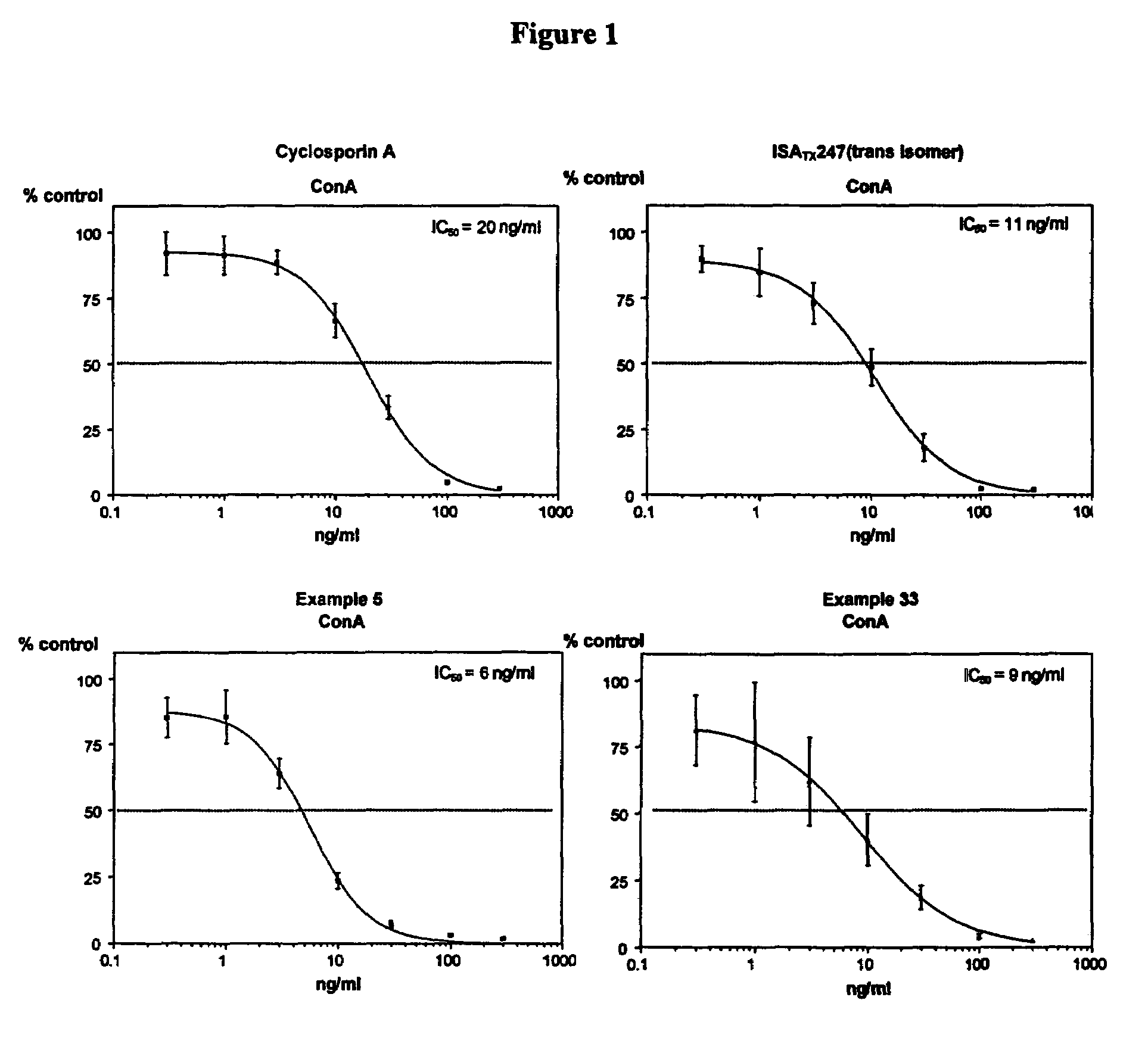
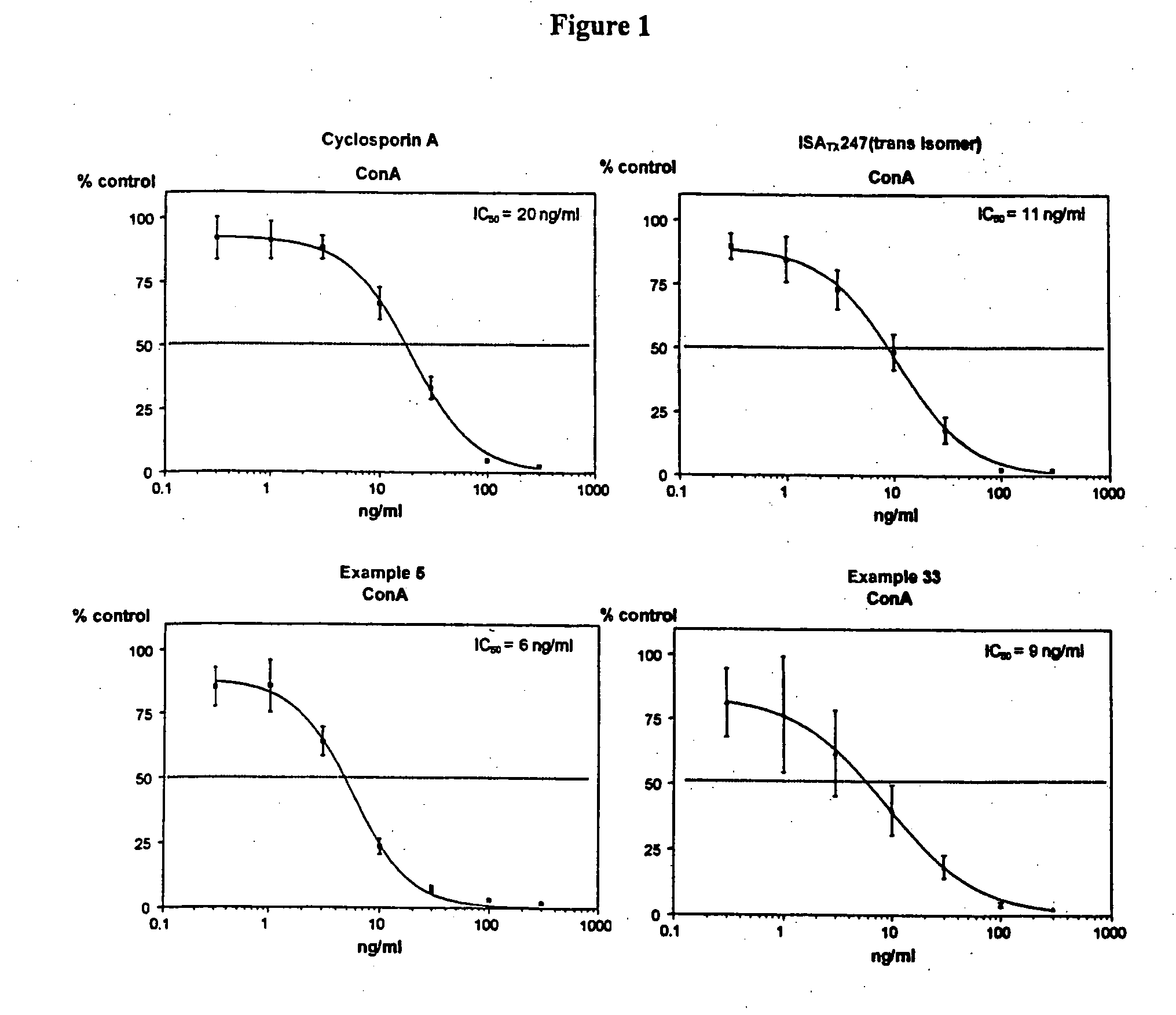
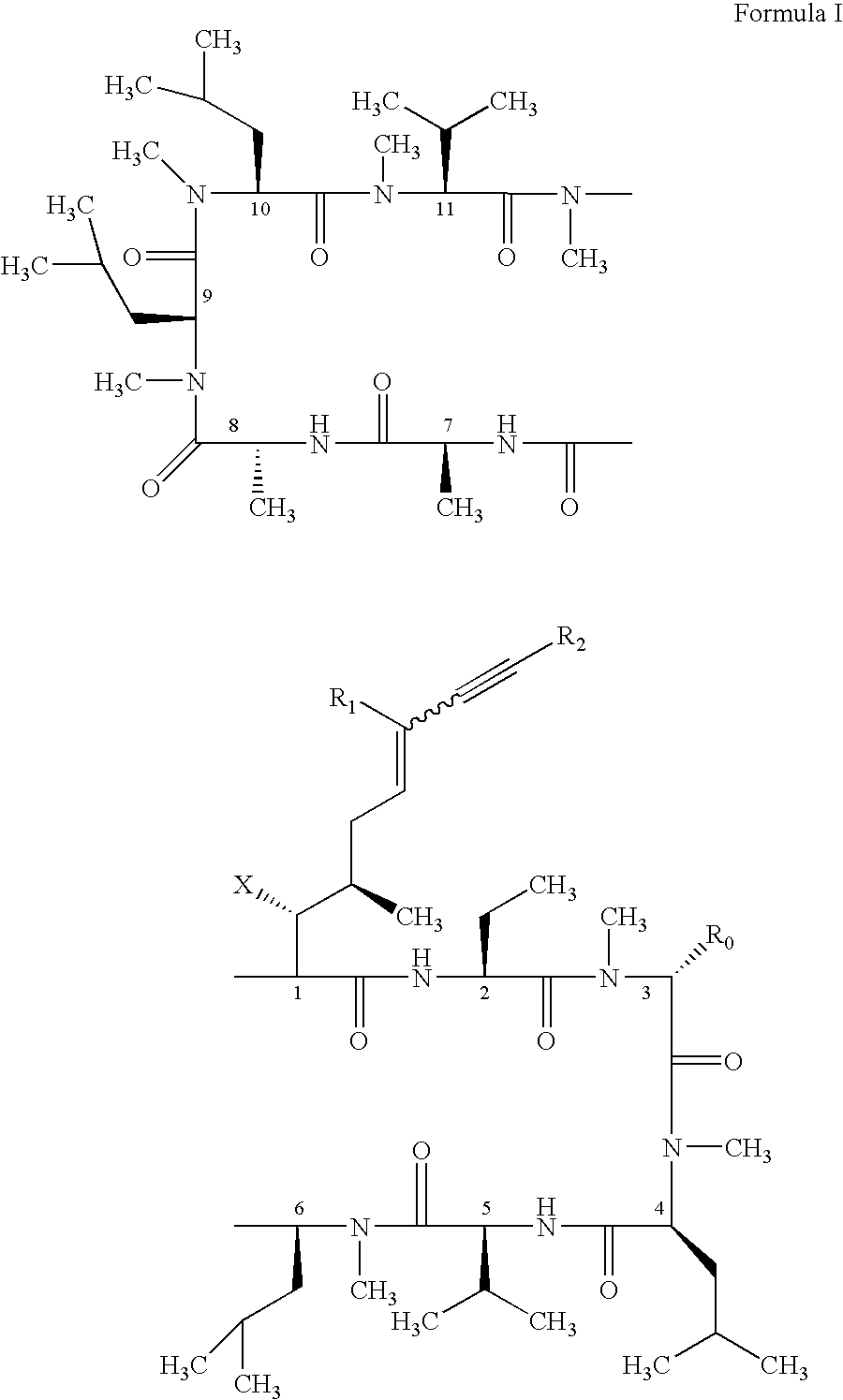
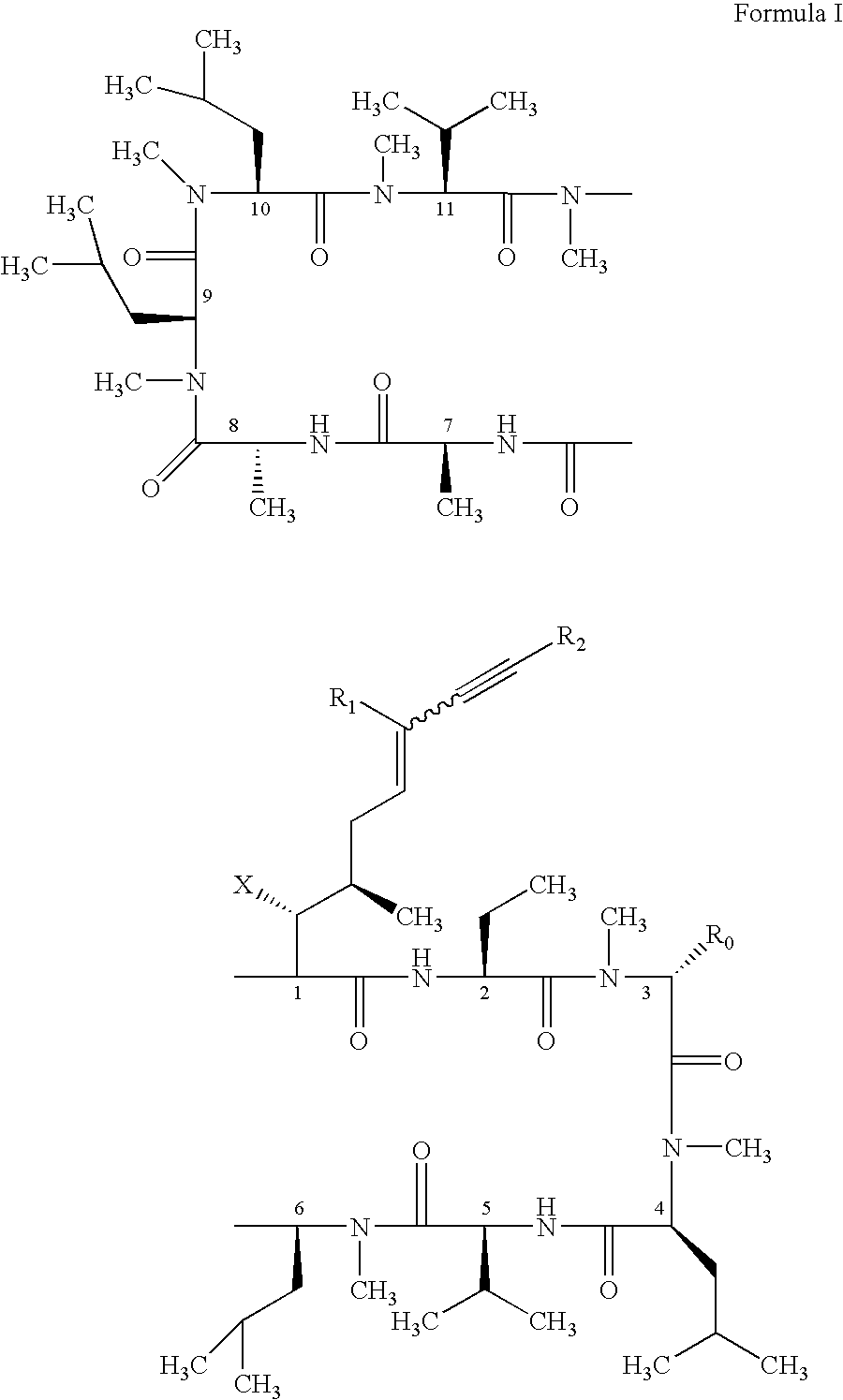
Use of cyclosporin alkyne/alkene analogues for preventing or treating viral-induced disorders
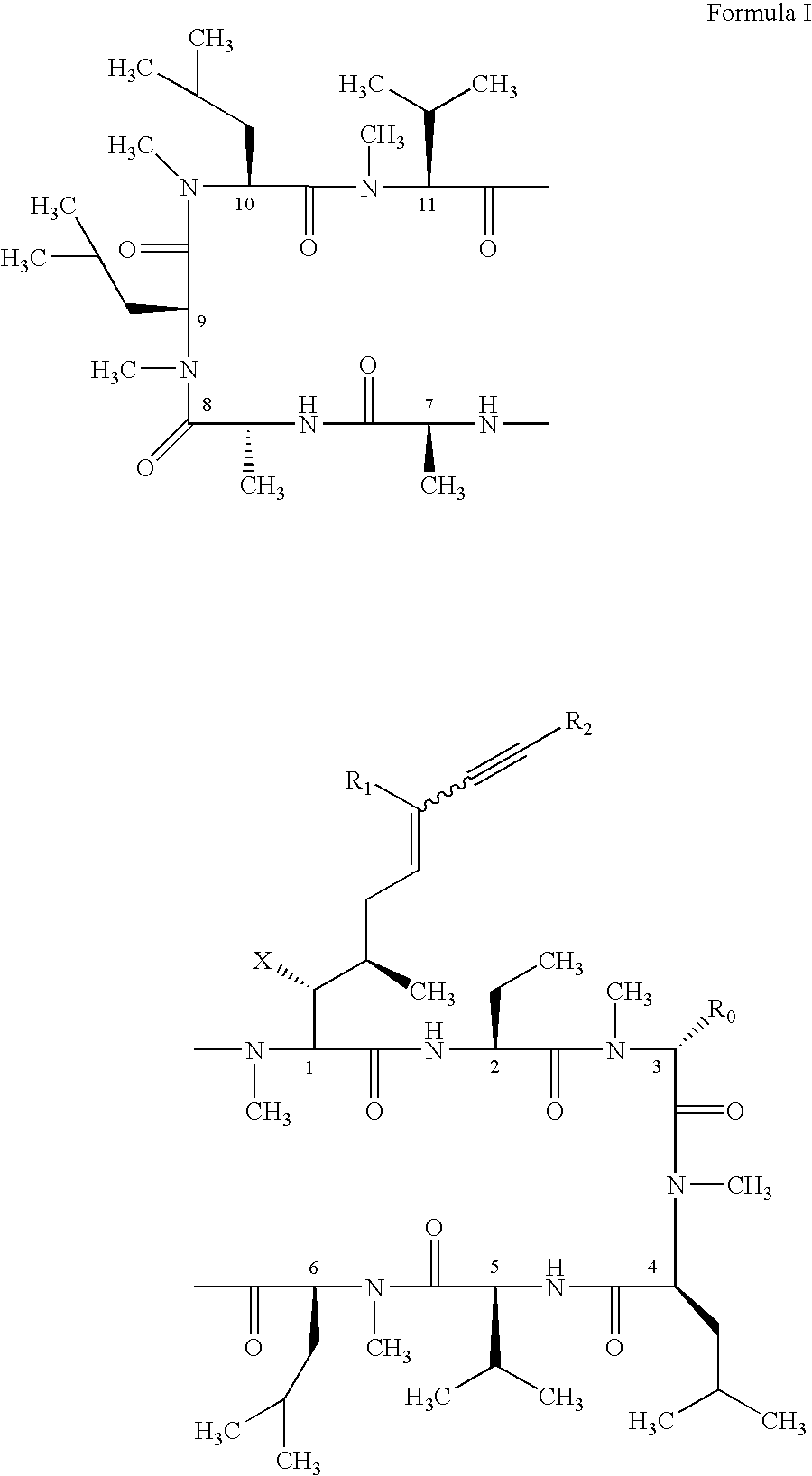
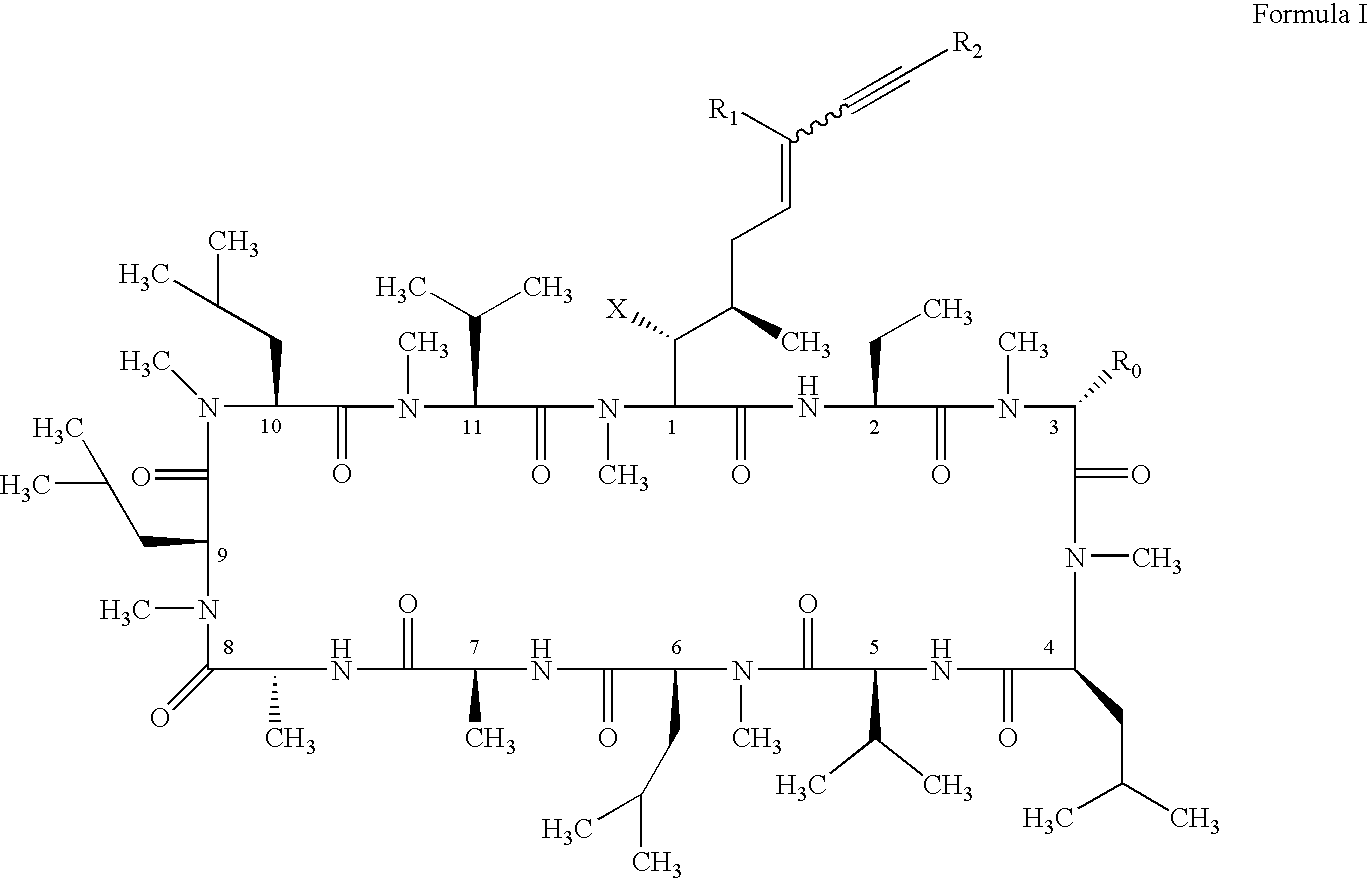
The present invention relates to methods of preventing or treating a mammal with a viral-induced disorder. The method involves administering to the mammal a therapeutically effective amount of a compound represented by Formula I, as shown below:or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, with X, R0, R1, and R2 defined herein, under conditions effective to prevent or treat the viral-induced disorder.
Owner:ALBANY MOLECULAR RESEARCH INC
Coating for substrate
ActiveUS20140221522A1Highly durableHighly lubriciousCosmetic preparationsImpression capsCross-linkHydrophilic monomer
There is provided inter alia a substrate with a surface having a hydrophilic coating comprising a cross-linked copolymer of components A and B, and optional components C and D; whereincomponent A comprises one or more C2-C16 hydrophilic monomers each bearing one or more alkene and / or alkyne groups;component B comprises one or more hydrophilic polymers each bearing two or more alkene and / or alkyne groups;component C, if present, comprises one or more beneficial agents each bearing one or more alkene or alkyne groups; andcomponent D, if present, comprises one or more low molecular weight cross-linking agents each bearing two or more functional groups independently selected from thiol, alkene and alkyne groups;wherein the cross-linked copolymer is formed by radical polymerisation involving the alkene and / or alkyne groups of components A, B and C (if present) and involving the functional groups of component D (if present);wherein the hydrophilic coating optionally comprises component E which comprises one or more beneficial agents, wherein component E does not form a copolymer with components A, B, C (if present) and D (if present);and wherein the hydrophilic coating is covalently attached to the surface of the substrate.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
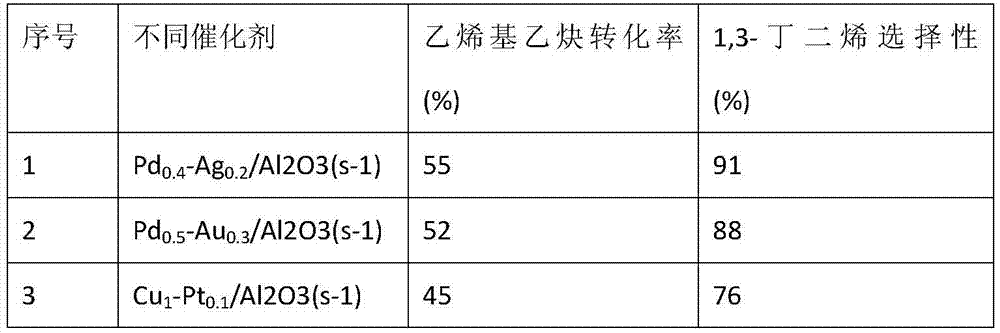
Pd-Ag/Al2O3-TiO2 catalyst for selective hydrogenation of cracked gasoline or its fractions, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102728351ALow temperature hydrogenation activity is highImprove performanceRefining by selective hydrogenationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsActive componentAlkyne formation
The invention relates to a Pd-Ag / Al2O3-TiO2 catalyst for selective hydrogenation of cracked gasoline or its fractions. The catalyst comprises an Al2O3-TiO2 composite as a carrier, and active components of Pd and Ag loaded on the carrier, wherein the Pd content accounts for 0.15-0.5wt% of the total weight of the catalyst, and the Ag content accounts for 0.8-4.5wt% of the total weight of the catalyst. Compared with same catalysts, the catalyst for the hydrogenation of the cracked gasoline or its fractions of the invention has the advantages of high hydrogenation selectivity at a low temperature, strong As impurity resistance, large charging capacity and stable activity. In addition, the invention also relates to a preparation method of the catalyst. The catalyst of the invention can also be used for the selective hydrogenation of alkynes and / or diolefins of other petroleum hydrocarbons.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
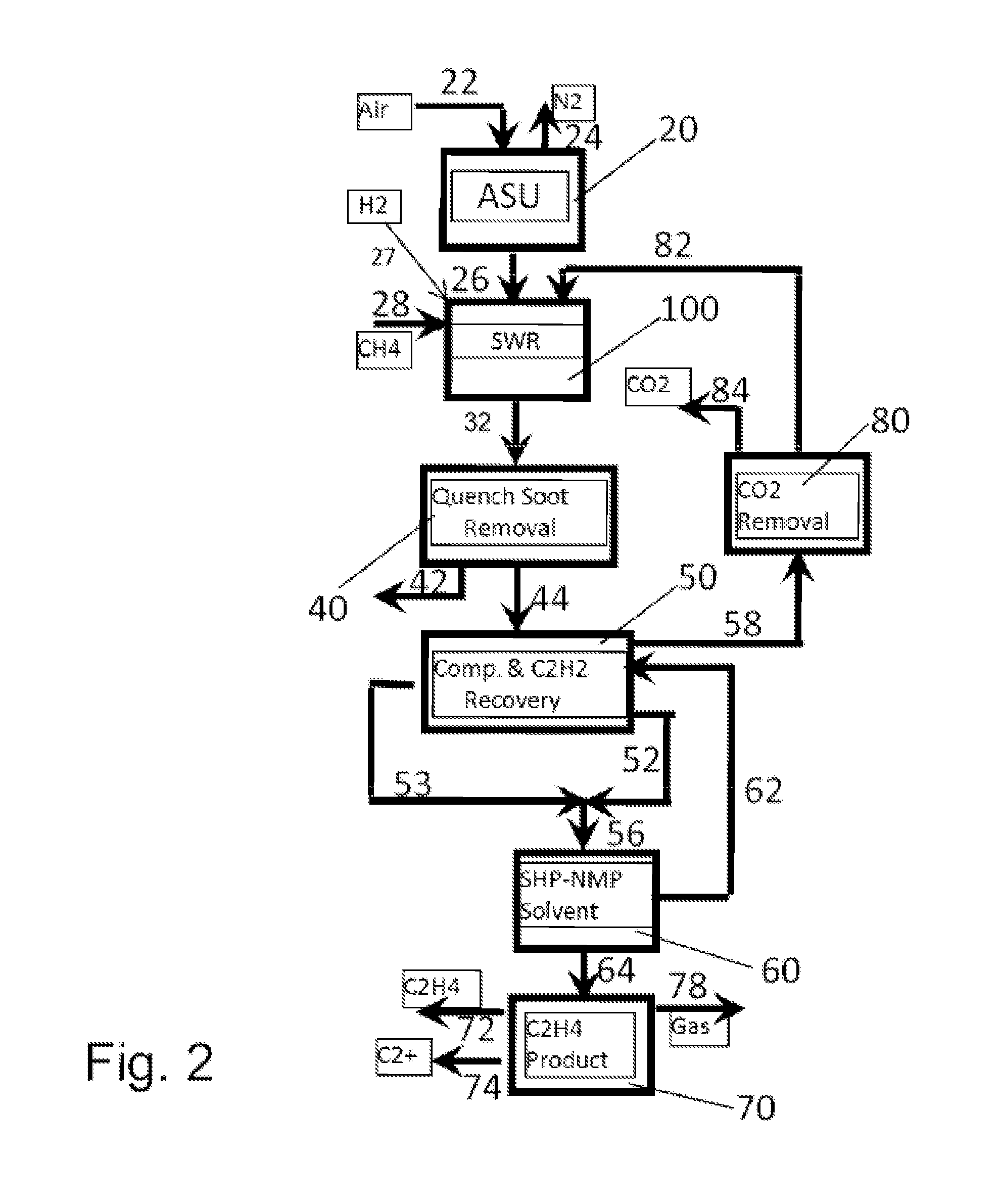
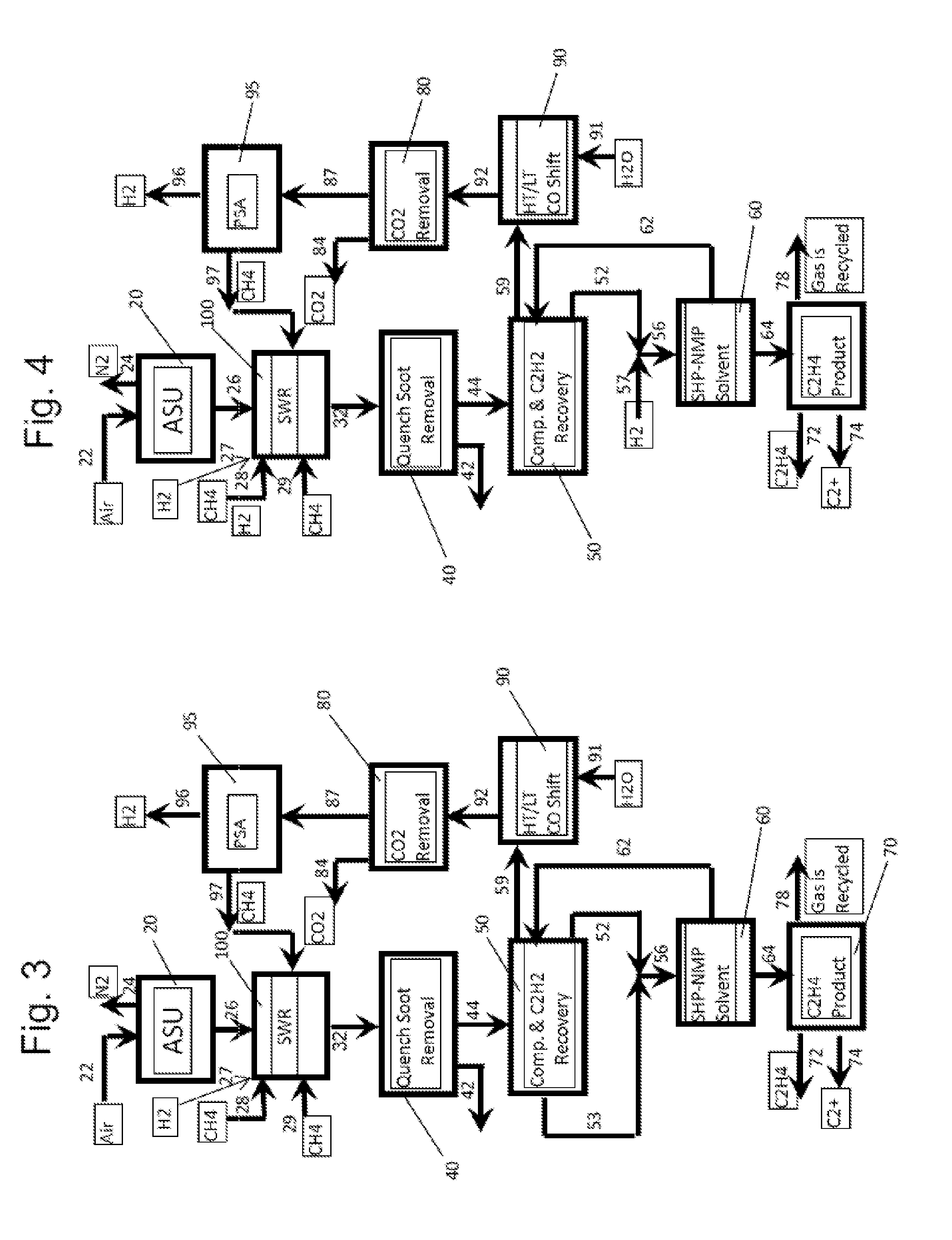
High efficiency processes for olefins, alkynes, and hydrogen co-production from light hydrocarbons such as methane
InactiveUS20140058149A1Process environmental protectionIncreases overall C selectivityThermal non-catalytic crackingHydrocarbon by hydrogenationMethanationOxygen
High efficiency processes for producing olefins, alkynes, and hydrogen co-production from light hydrocarbons are disclosed. In one version, the method includes the steps of combusting hydrogen and oxygen in a combustion zone of a pyrolytic reactor to create a combustion gas stream, transitioning a velocity of the combustion gas stream from subsonic to supersonic in an expansion zone of the pyrolytic reactor, injecting a light hydrocarbon into the supersonic combustion gas stream to create a mixed stream including the light hydrocarbon, transitioning the velocity of the mixed stream from supersonic to subsonic in a reaction zone of the pyrolytic reactor to produce acetylene, and catalytically hydrogenating the acetylene in a hydrogenation zone to produce ethylene. In certain embodiments, the carbon efficiency is improved using methanation techniques.
Owner:UOP LLC
Process of obtaining an isoprene-enriched FCC C5 fraction and selective polymerization of isoprene from said fraction
ActiveUS20060020095A1Low costEasy to operateHydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrocarbon purification/separationO-Phosphoric AcidDehydrogenation
A process is described for obtaining, from an “FCC” initial C5 fraction, a final C5 fraction which is enriched with isoprene and purified and usable for the selective polymerization of isoprene. A process is also described for obtaining an isoprene homopolymer from a polymerization medium comprising isoprene and at least one methyl butene, such as said “FCC” C5 fraction which is enriched with isoprene and purified. The process of obtaining the final fraction from the initial C5 fraction includes: a catalytic hydrogenation reaction of said initial C5 fraction by a palladium-based catalyst, which produces an intermediate C5 fraction comprising n-pentenes in a mass ratio which is less than 0,1% and methyl butanes; a dehydrogenation reaction applied to the intermediate C5 fraction, which includes methyl butanes to produce the final fraction, and purification of the final fraction to obtain a purified fraction which is practically devoid of disubstituted alkynes, true alkynes and cyclopentadiene, and the mass fraction of the methyl butenes in the intermediate fraction is <30%. The process for obtaining an isoprene homopolymer includes the step of reacting, in the presence of isoprene and at least one methyl butene, a catalytic system based on a conjugated diene, a rare earth salt of an organic phosphoric acid in suspension, an alkylating agent, and a halogen donor.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
Hydrogenation catalyst preparation, hydrogenation catalyst and application
ActiveCN106861691ASimple manufacturing processSimple processHydrocarbon by hydrogenationCatalyst activation/preparationHydrogenation reactionAlloy
The invention provides a hydrogenation catalyst preparation method and application of hydrogenation catalyst in selective hydrogenation reaction. Aluminum oxide is utilized as a carrier; the hydrogenation catalyst is prepared from boehmite; cane sugar, glucose and soluble starch are added into carrier precursor in a preparation process to serves as structural aids and are roasted in inert atmosphere and air sequentially, and roasting temperature is 450 to 1000 DEG C. Active ingredients of the catalyst are loaded by an impregnation method, and the active ingredients are chosen from alloy which is prepared from one or several of metal Ru, Pd and Pt and one or several of Cu, Ag and Au. The catalyst can be applied to olefin preparation by alkyne selective hydrogenation reaction.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cyclosporin alkyne analogues and their pharmaceutical uses
InactiveUS7378391B2High activityPossess utility in the treatmentSenses disorderNervous disorderChemical structureCyclosporins
The compounds of the present invention are represented by the chemical structure found in Formula I:or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, with X, R0, R1, and R2 defined herein.
Owner:ALBANY MOLECULAR RESEARCH INC
Fatty acid analogues for the treatment of cancer
A fatty acid analogue of the general formula: R1-[xi-CH2]n—COOR2, wherein R1 is: a C2-C24 alkene with one or more double bonds and / or with one or more triple bonds, and / or a C2-C24 alkyne, and / or a C1-C24 alkyl, or a C1-C24 alkyl substituted in one or several positions with one or more compounds selected from the group comprising fluoride, chloride, hydroxy, C1-C4 alkoxy, C1-C4 alkylthio, C2-C5 acyloxy or C1-C4 alkyl, and wherein R2 represents hydrogen or C1-C4 alkyl, and wherein n is an integer from 1 to 12, and wherein i is an odd number and indicates the position relative to COOR2, and wherein Xi independent of each other are selected from the group comprising O, S, SO, SO2, Se and CH2, and with the proviso that at least one of the Xi is not CH2, and or a salt, prodrug or complex thereof is used in the treatment and / or prevention of primary and secondary metastatic neoplasms.
Owner:THIA MEDICA AS
Composite metal oxide loading active metal catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106732567ASimple processSmall sizeHydrocarbon by hydrogenationCatalystsPetrochemicalPetroleum
The invention provides a composite metal oxide loading active metal catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst is formed by loading an active metal component by a composite metal oxide serving as a carrier. The catalyst has the characteristics that the active metal component is highly and stably dispersed on the surface of the carrier, the crystal shape is complete, the size is uniform, the particle size is 1 to 5 nm, and the particle size distribution range is small. The preparation method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: dissolving two or three soluble metal salts in deionized water to prepare a mixed salt solution, mixing the mixed salt solution with an alkaline precipitator, and carrying out crystallizing, washing, drying and roasting to obtain a composite metal oxide carrier which is of a uniform microspherical structure and has an average diameter of 0.3 to 3.0 [mu]m; steeping the carrier in steeping liquid to enable the carrier to be coated with the metal salts, and carrying out drying, roasting and reduction to obtain the catalyst. The catalyst can be applied to various alkyne hydrogenation reaction processes in the fields of petrochemical engineering, fine chemical engineering and the like, and is outstanding in catalysis property and easy to recycle and reuse.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
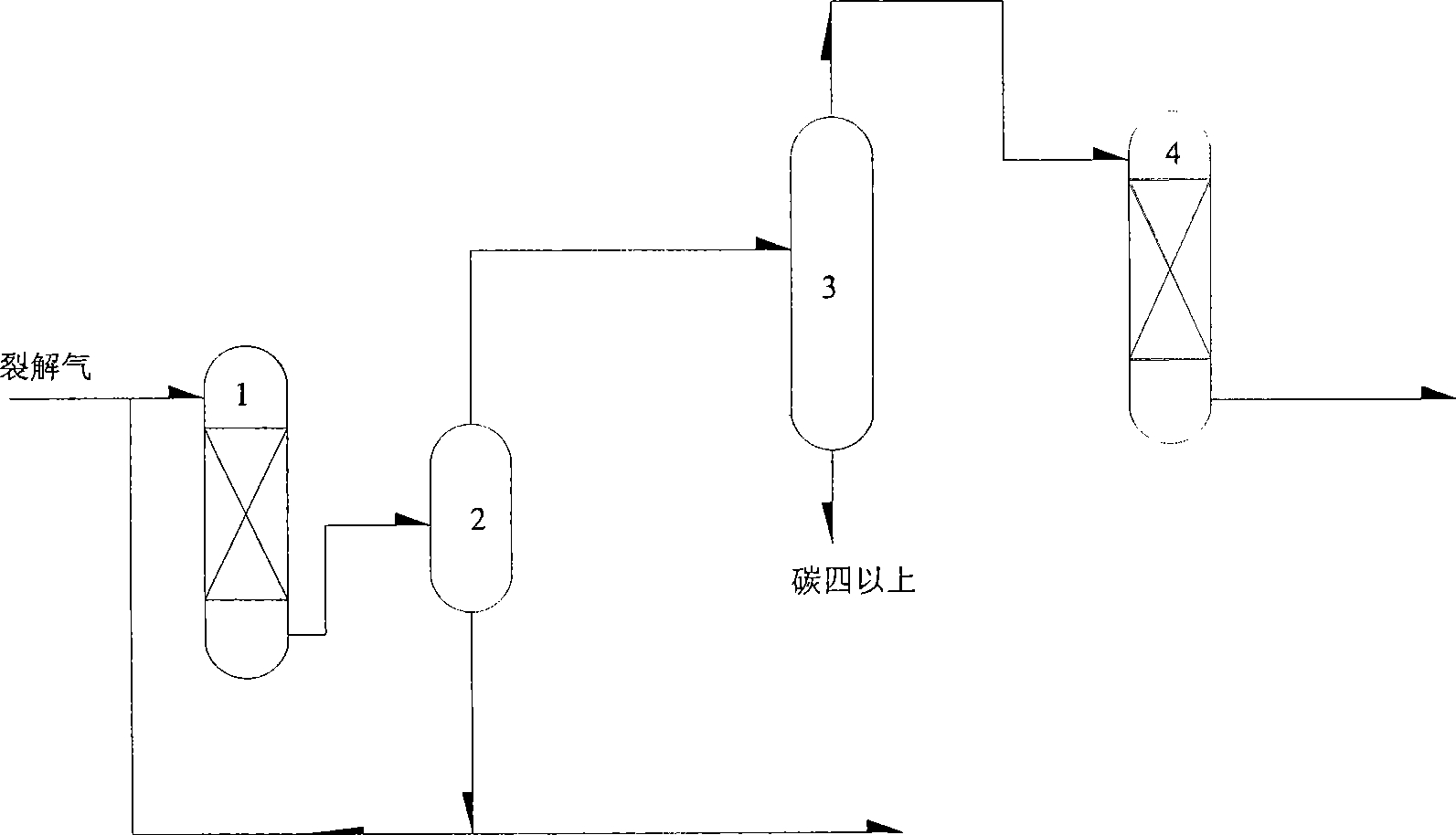
Selective hydrogenation method of acetylene hydrocarbon and dialkene in cracking gas
ActiveCN101451077AReduce the numberReduce hydrogen contentHydrocarbon by hydrogenationRefining by selective hydrogenationUnsaturated hydrocarbonHigh energy
The invention discloses a selective hydrogenation method for acetylene hydrocarbon and diene in pyrolysis gas and belongs to the technical field of selective hydrogenation of unsaturated hydrocarbon. In order to solve the problems in the prior art of high energy consumption, large equipment size, high operation cost, incapable of improvement of C3 selectivity, and the like, due to the facts that liquid phase flow of a mixed phase hydrogenation reactor contains a large amount of C3, C4 and C5 components, can not realize full rinse in the reactor, and repeatedly enters into a front depropanizing tower. The invention provides the method which comprises: carrying out preferential selective hydrogenation of C2-C10 highly unsaturated hydrocarbon (acetylene hydrocarbon and diene) on the upstream of the front depropanizing tower; condensing heavy components above C6 through dephlegmation; and using the heavy components as the fluid phase flow of the mixed phase hydrogenation reactor. The method makes full use of the liquid phase flow of the mixed phase hydrogenation reactor, reduces feeding quantity of the front depropanizing tower, energy consumption and equipment investment, and is propitious to improve selectivity.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Use of cyclosporin alkyne/alkene analogues for preventing or treating viral-induced disorders
InactiveUS20070232531A1Potent immunosuppressive activityDevoid of immunosuppressive activityBiocideDigestive systemCyclosporinsAlkyne formation
The present invention relates to methods of preventing or treating a mammal with a viral-induced disorder. The method involves administering to the mammal a therapeutically effective amount of a compound represented by Formula I, as shown below: or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, with X, R0, R1, and R2 defined herein, under conditions effective to prevent or treat the viral-induced disorder.
Owner:ALBANY MOLECULAR RESEARCH INC
Oligosaccharide/silicon-containing block copolymers for lithography applications
InactiveUS20130022785A1Improve etch selectivitySmall structureMaterial nanotechnologySugar derivativesChemistryAzide
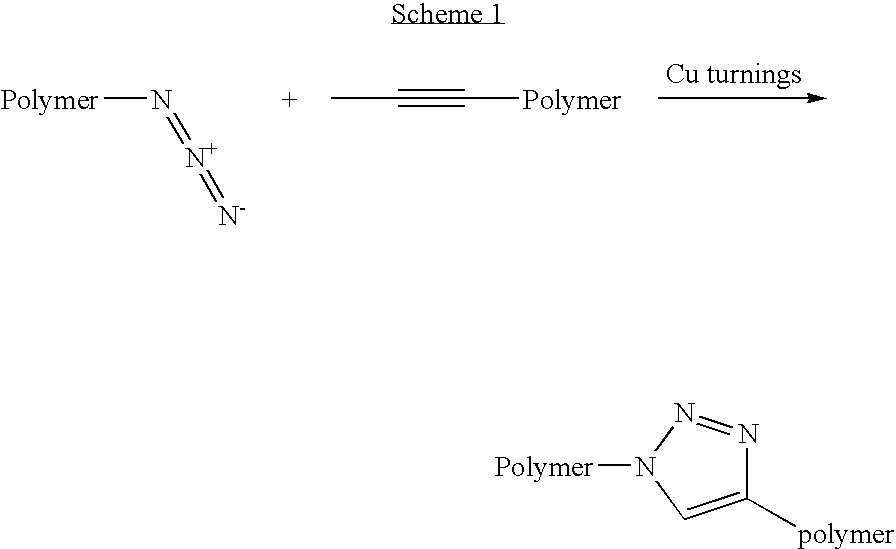
The present invention discloses diblock copolymer systems that self-assemble to produce very small structures. These co-polymers consist of one block that contains silicon and another block comprised of an oligosaccharide that are coupled by azide-alkyne cycloaddition.
Owner:CERMAV CNRS +1
Paclitaxel formulation
A pharmaceutical formulation is provided for delivering paclitaxel in vivo comprising: paclitaxel, a water-miscible amide and a pharmaceutically-acceptable, water-miscible solubilizer selected from the group consisting of solubilizers having the general structures <paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>R1COOR2, R1CONR2, and R1COR2, < / in-line-formula>wherein R1 is a hydrophobic C3-C50 alkane, alkene or alkyne and R2 is a hydrophilic moiety.
Owner:SUPERGEN
Method of forming low dielectric constant interlayer dielectric film
InactiveCN1644753ALiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEpoxyThin membrane
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Addition-Reaction-Curable Silicone Rubber Composition and a Molded Article Therefrom
An addition-reaction-curable silicone rubber composition comprising: 0.001 to 5 mass % of a metal deactivator and 0.001 to 5 mass % of a curing-retarder selected from an alcohol derivative having carbon-carbon triple bonds, an enzyne compound, an alkenyl-containing low-molecular-weight organosiloxane compound, or an alkyne-containing silane; and a molded body produced by curing the aforementioned addition-reaction-curable silicone rubber composition. The addition-reaction-curable silicone rubber composition is capable of producing a molded silicone rubber body, which is obtained with low compression set without resorting to secondary thermal treatment.
Owner:DOW TORAY CO LTD
Process for the manufacture of functional PFPE derivative
A process for the manufacture of a functional (per)fluoropolyether derivative comprising at least one triazole group, such process comprising: (1) reacting a (per)fluoropolyether hydroxyl derivative having at least one hydroxyl group [derivative (PFPE-OH)] with an activating agent, to yield an activated (per)fluoropolyether hydroxyl derivative comprising at least one activated hydroxyl group [derivative (a-PFPE-OH)]; (2) reacting said activated (per)fluoropolyether hydroxyl derivative [derivative (a-PFPE-OH)] with at least one azide salt to yield a functional (per)fluoropolyether derivative comprising at least one azido group [derivative (PFPE-N3)]; and (3) reacting said functional (per)fluoropolyether derivative comprising at least one azido group [derivative (PFPE-N3)] with a hydrocarbon compound having a terminal alkyne group to yield a functional (per)fluoropolyether derivative comprising at least one triazole group [derivative (PFPE-azole)].
Owner:SOLVAY SOLEXIS
Alkyne-activated fluorogenic azide compounds and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20150276752A1Isotope introduction to sugar derivativesSilicon organic compoundsFluorescenceAlkyne formation
The present disclosure provides fluorogenic azide compounds. Also provided are methods of using the subject compounds for labelling a target biomolecule that includes an alkyne. In some embodiments, the method includes contacting the biomolecule with a fluorogenic azide compound, wherein the contacting results in covalent linkage of the compound with the alkyne moiety of the target biomolecule.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
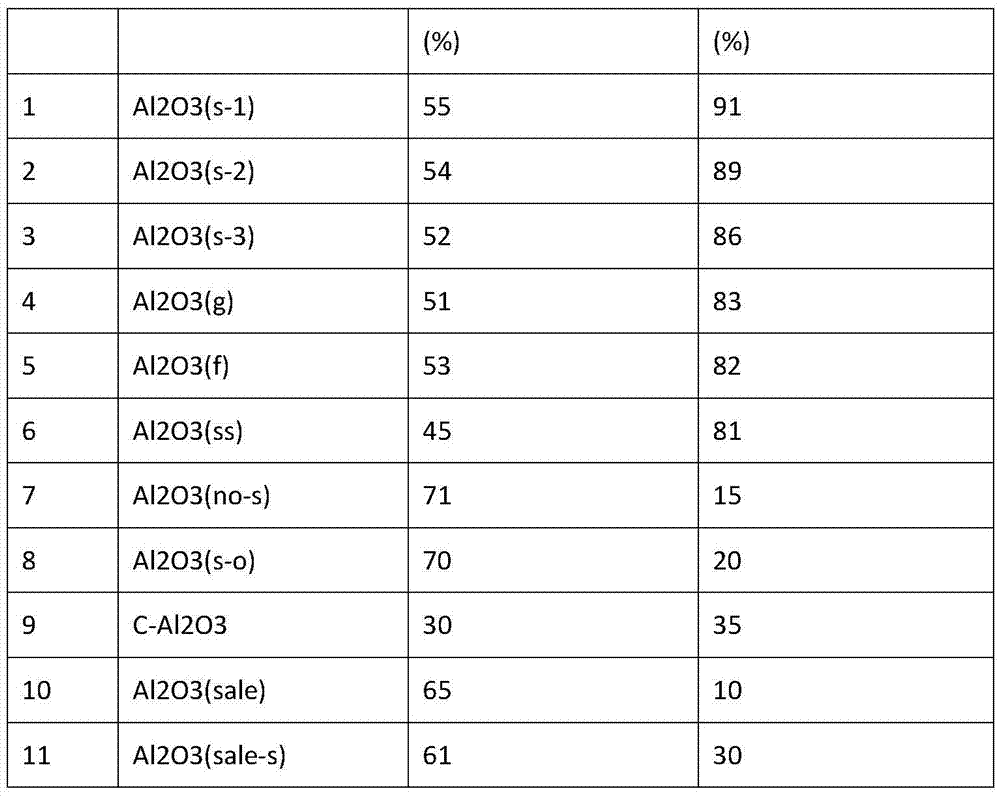
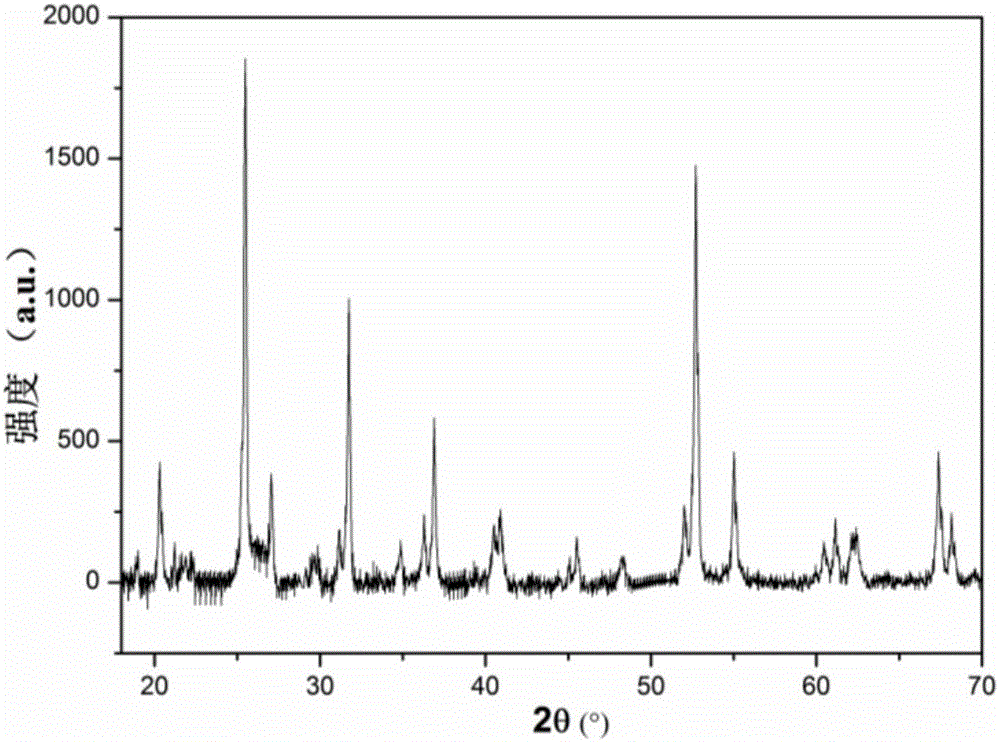
Selective hydrogenation catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105727951ASolve churnShort lifeHydrocarbon purification/separationHydrocarbonsActive componentAlkyne formation
The invention discloses a selective hydrogenation catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst is composed of a composite alumina / niobium oxide and active components. The catalyst includes 0.1-1.0 wt% of palladium, 2-10 wt% of lead, and 0.5-3.0 wt% of niobium oxide. The catalyst has high hydrogenation activity and selectivity, has good stability, and is suitable for selective hydrogenation alkyne removal for C4 material being high in alkyne content from extraction of butadiene.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
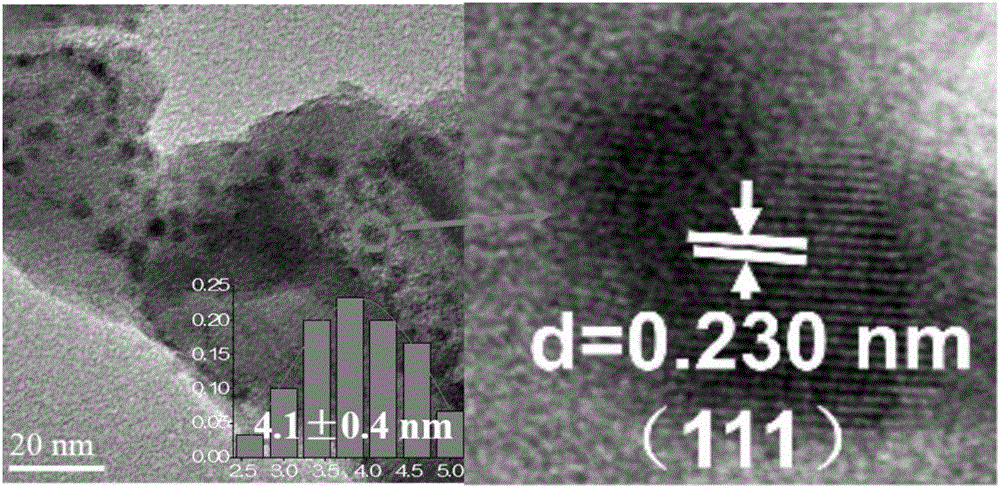
Loaded alloy catalyst for selective hydrogenation of alkyne and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108927156AHigh catalytic activityGood choiceHydrocarbon by hydrogenationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAlloyComposite oxide
The invention provides a loaded alloy catalyst for selective hydrogenation of alkyne and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the catalyst includes: dispersing metal salts containing Pd, M and Y in deionized water, using alkali as the precipitant, conducting coprecipitation reduction to obtain a bimetallic catalyst precursor, performing drying and roasting to form a PdMOx / YO2 composite oxide, and then conducting hydrogen reduction to obtain a PdM / YO2 catalyst. The active component of the catalyst is a palladium-containing alloy with a loading amount of 0.6-6wt% and a particle size of 1.5-5.5nm. The catalyst has the characteristics that: the active component is Pd-containing uniform alloy particles, and the alloy particles are stably inlaid on the carrier surface to produce metal-carrier strong interaction. The catalyst has excellent catalytic activity, selectivity and good recyclability in the reaction of olefin preparation by catalytic hydrogenation of alkyne.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Novel proton exchange membranes using cycloaddition reaction between azide and alkyne containing components
ActiveUS20060154129A1Improve stabilityReduce fuel cross-over rateIon-exchanger regenerationFinal product manufactureCross-linkTriazole antifungals
A process for making an ion-conducting polymer comprises cross-linking polymers having functional groups such as alkyne groups and azide groups. An example ion-conducting polymer has cross-links including nitrogen-containing heterocycles formed by the reaction between the functional groups, such as 1,2,3-triazole groups formed by a cycloaddition reaction between alkyne and azide groups. The ion-conducting polymer may be used in an ion-electrolyte membrane. Examples include a proton-electrolyte membrane useful for fuel cells.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD
Cetane number increasing process and additive for diesel fuel
InactiveUS20100094062A1Increase cetane numberOrganic chemistryLiquid carbonaceous fuelsGlycerolBy-product
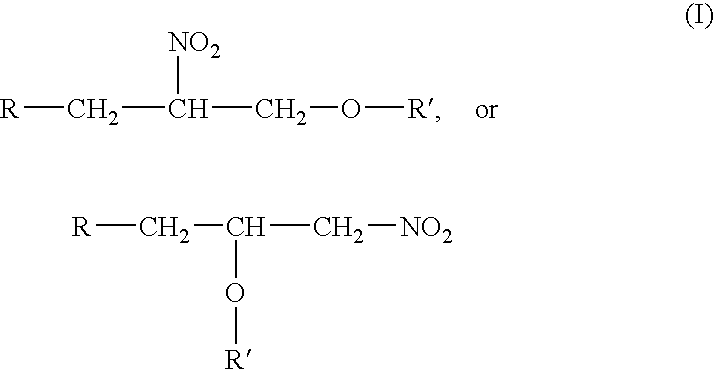
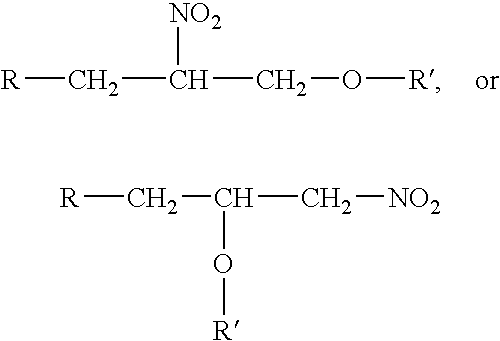
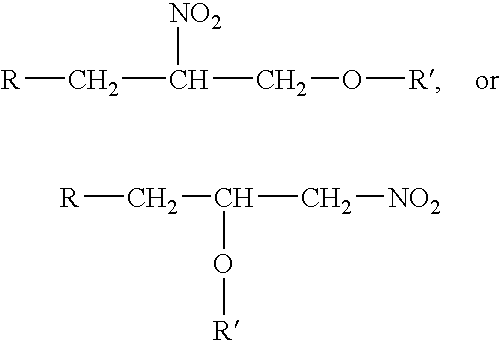
A cetane number increasing process and additive for diesel fuel, this additive being obtained by means of a less complex and more economic process which seeks to use by products in excess of supply on the market and to optimize the installed capacity of existing plants, the process producing a mixture of nitrated glycerol diethers is represented by the following general formula (I) where R can be: a hydrogen atom; or an R′—O group; and where R′ can be an alkene or alkyne or an unsaturated hydrocarbon formed by a number of carbon atoms ranging from 4 to 10 carbons.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
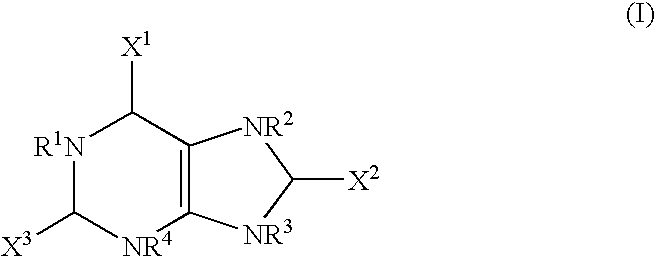
Methods of Treating Microbial Infections
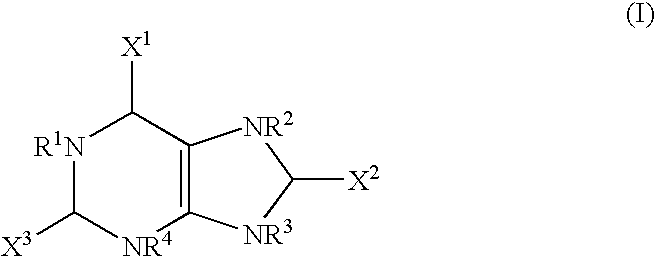
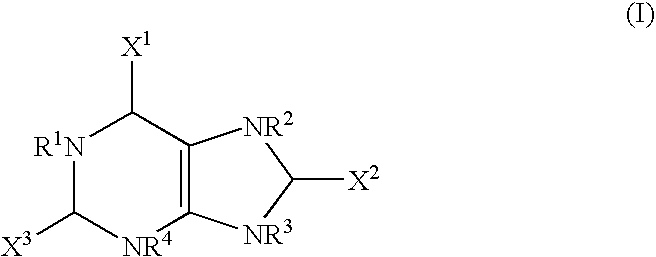
The present invention provides methods of treating microbacterial infections comprising administering to a subject in need thereof, a composition comprising a compound of formula I: wherein: X1, X2 and X3 are selected from the group consisting of oxygen, sulfur, aminoalkyl, alkoxy, aryl, and heteroaryl, unsubstituted or substituted; and R1, R2, R3 and R4 are selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, actinium, silicon, germanium, cyano, alkyl, alkoxy, allyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, alkylaryl, arylalkyl, aminoalkyl, alkylamino, alkene, alkyne, aryl, halide, alkylhalide, alkyloxyalkyl, thioalkyl, alkylthioalkyl, alkylamino, cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, unsubstituted or substituted; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The present invention further provides methods of treating bacterial infections comprising administering to a subject in need thereof, an effective amount of a pharmaceutical composition comprising uric acid, urate, derivatives thereof, salts and hydrates thereof and prodrugs thereof and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:PIPER MEDICAL
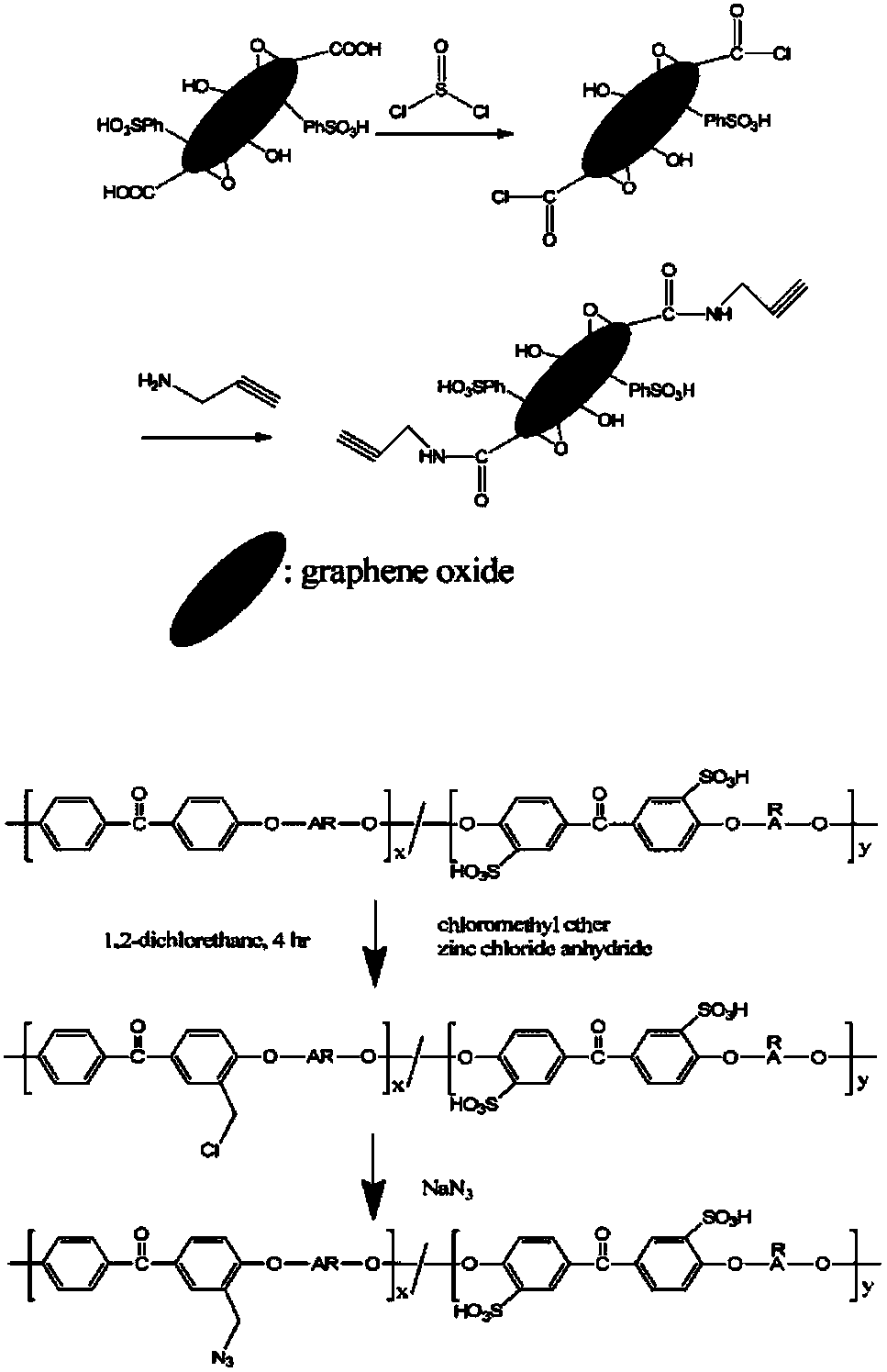
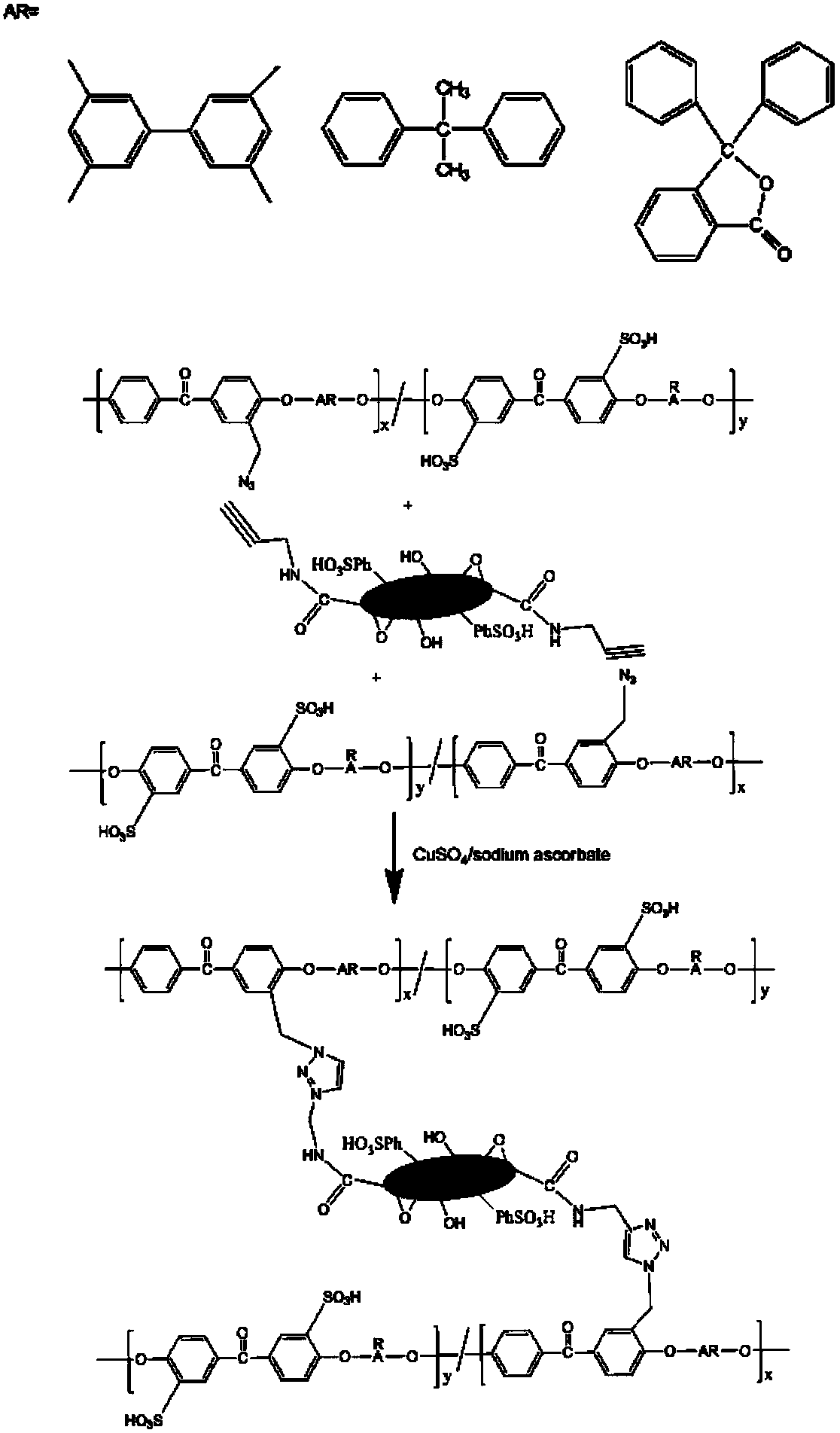
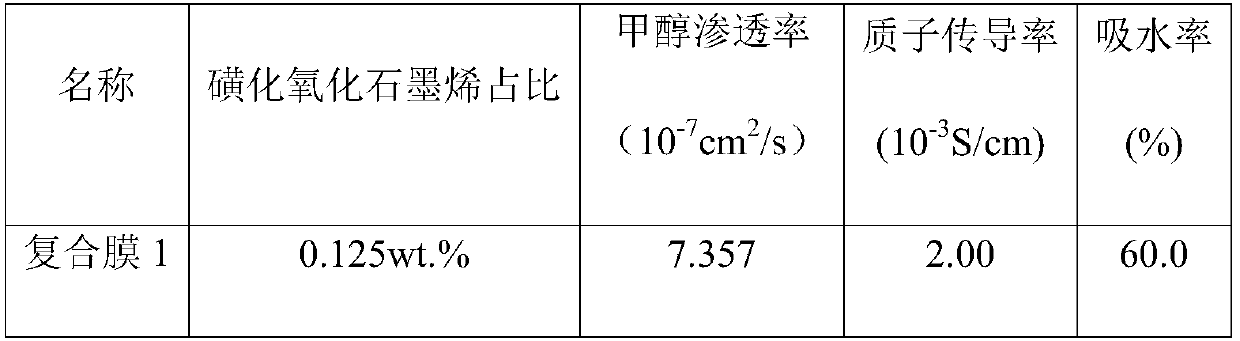
Preparation method of novel sulfonated polyetheretherketone/sulfonated graphene oxide composite proton exchange membrane
InactiveCN109535457AImprove thermal stabilityImprove mechanical propertiesCollectors/separatorsChemical industryChemical reaction
The invention discloses a preparation method of a novel sulfonated polyetheretherketone / sulfonated graphene oxide composite proton exchange membrane, and relates to the field of composite materials. SGO-C-triple bond-C is prepared; polyetheretherketone is dissilved in concentrated sulfuric acid to prepare sulfonated polyetheretherketone; SPEEK-CH2N3 is prepared through a chloromethylation reactionand an azidation reaction; SPEEK-SGO is prepared by a click chemical reaction of alkyne and azide under the catalysis of CuBr; and the SPEEK-SGO composite membrane is prepared by a solution casting blending phase transformation process in order to achieve the preparation and modification of the sulfonated polyetheretherketone membrane. The composite proton exchange membrane improves the proton conductivity, the coulombic efficiency and the power density of polymer membranes in fuel cells, and can be applied to the field of chemical industry.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com