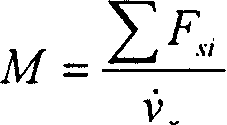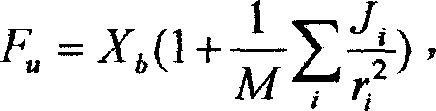Patents
Literature
31 results about "Sticking coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sticking coefficient is the term used in surface physics to describe the ratio of the number of adsorbate atoms (or molecules) that adsorb, or "stick", to a surface to the total number of atoms that impinge upon that surface during the same period of time. Sometimes the symbol Sc is used to denote this coefficient, and its value is between 1 (all impinging atoms stick) and 0 (no atoms stick). The coefficient is a function of surface temperature, surface coverage (θ) and structural details as well as the kinetic energy of the impinging particles.
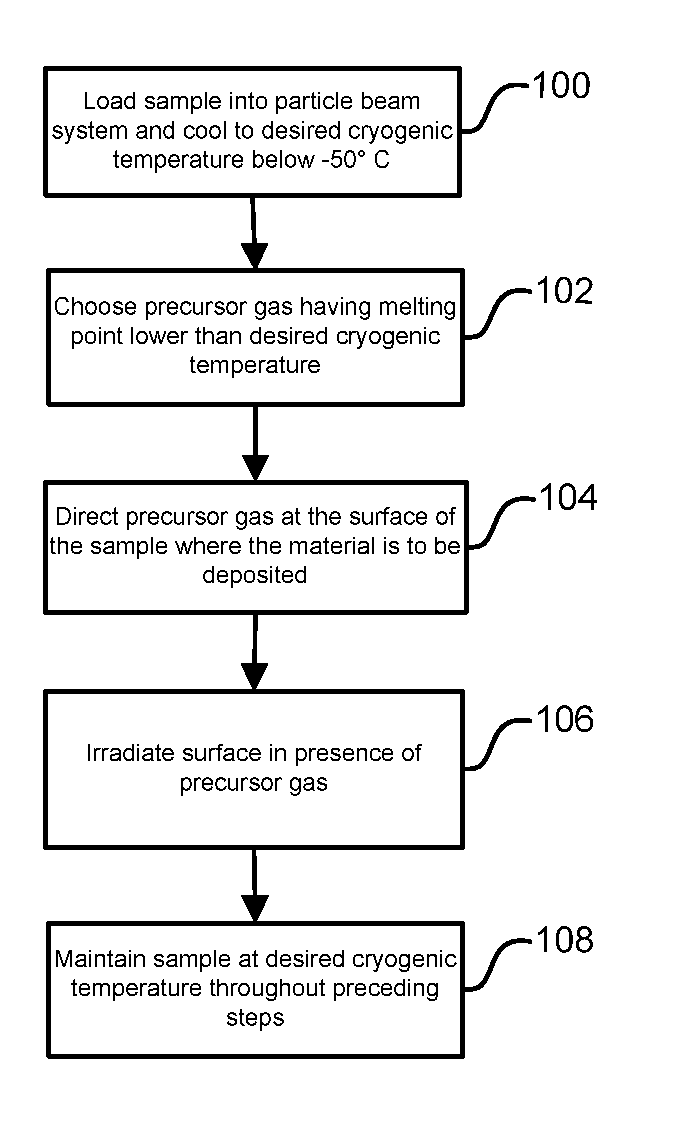
Beam-Induced Deposition at Cryogenic Temperatures
ActiveUS20120003394A1Easy to usePretreated surfacesChemical vapor deposition coatingAlkaneAlkyne formation
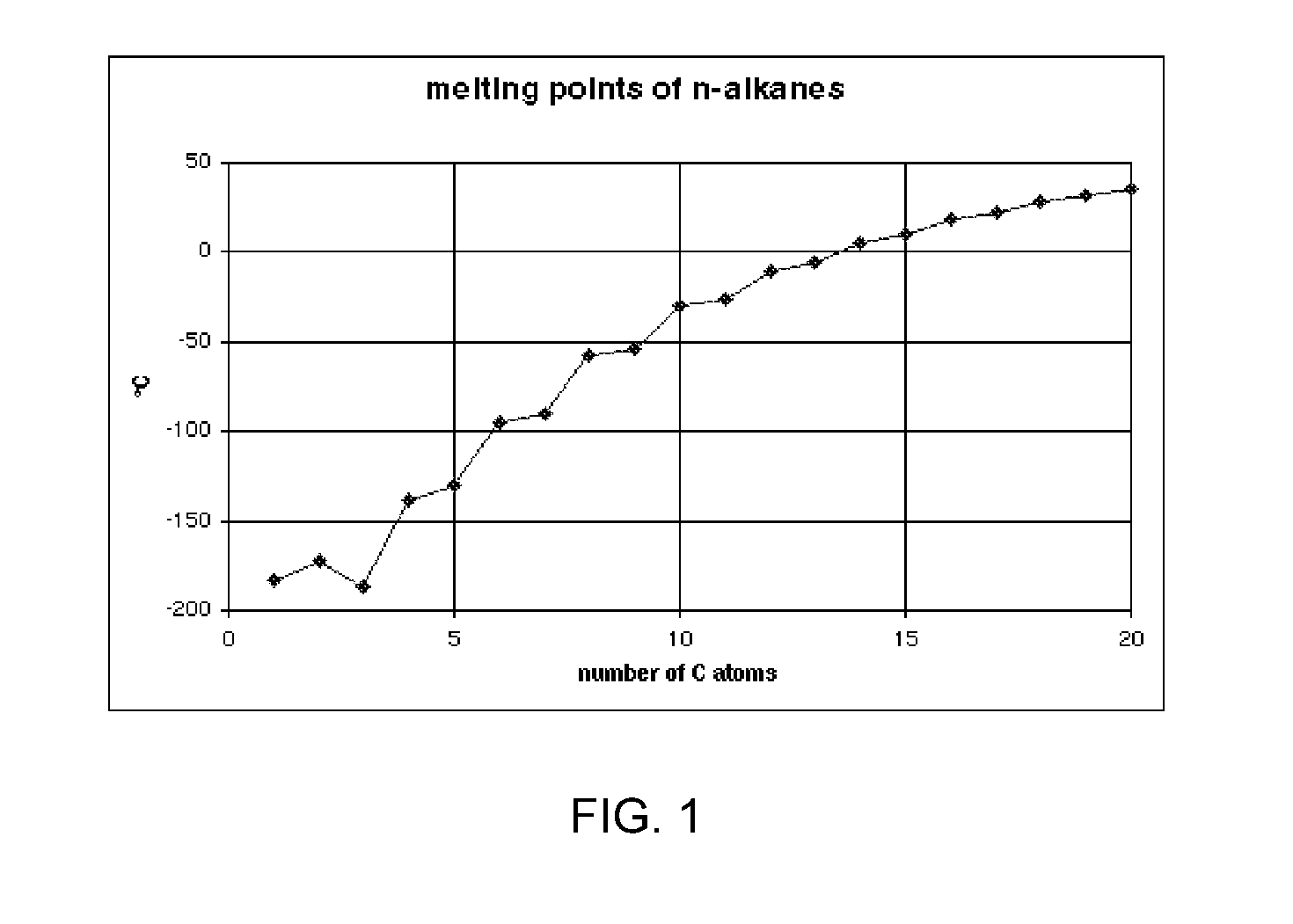
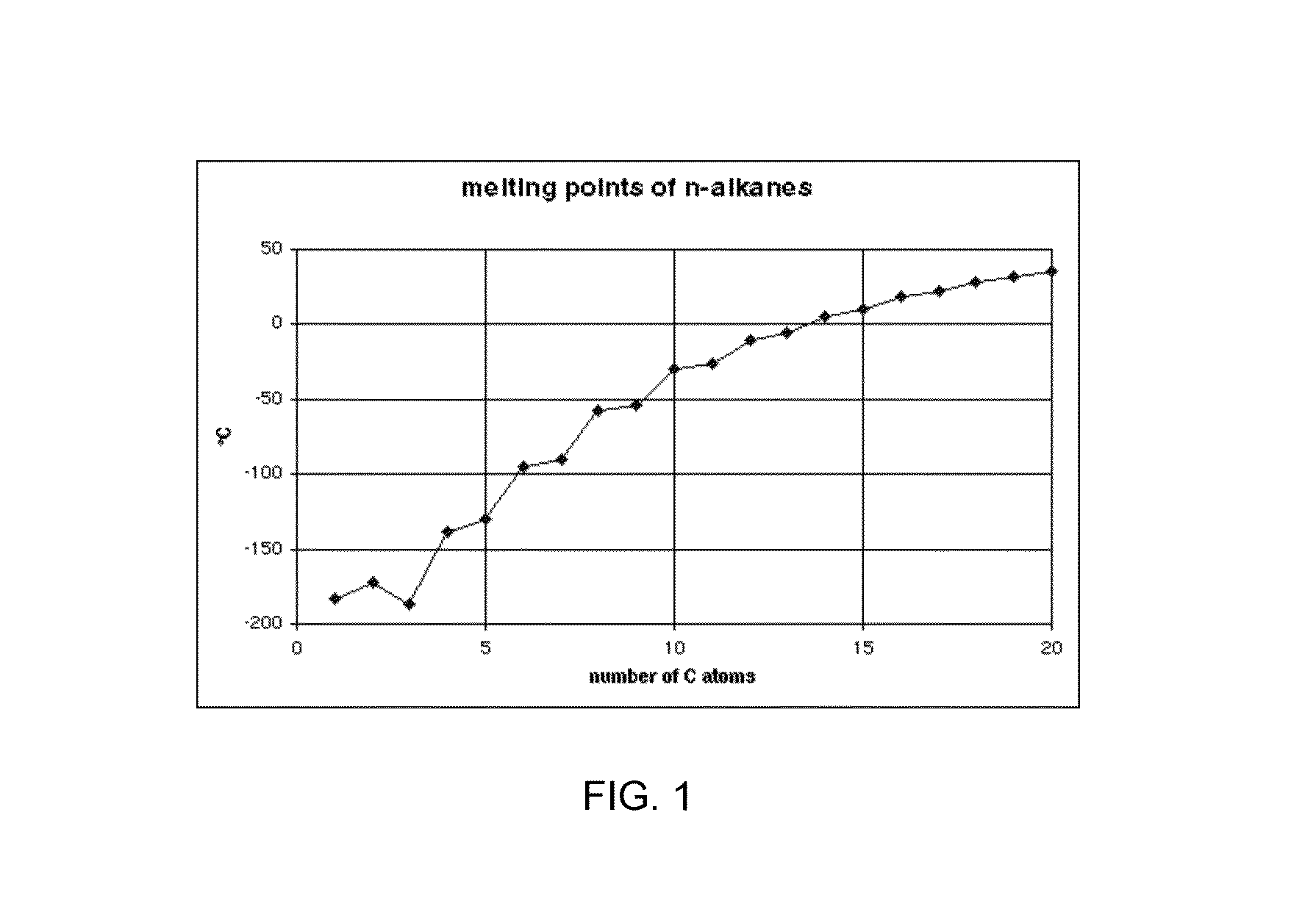
A method of depositing material onto a substrate at cryogenic temperatures using beam-induced deposition. A precursor gas is chosen from a group of compounds having a melting point that is lower than the cryogenic temperature of the substrate. Preferably the precursor gas is chosen from a group of compounds having a sticking coefficient that is between 0.5 and 0.8 at the desired cryogenic temperature. This will result in the precursor gas reaching equilibrium between precursor molecules adsorbed onto the substrate surface and precursor gas molecules desorbing from the substrate surface at the desired cryogenic temperature. Suitable precursor gases can comprise alkanes, alkenes, or alkynes. At a cryogenic temperature of between −50° C. and −85° C., hexane can be used as a precursor gas to deposit material; at a cryogenic temperature of between −50° C. and −180° C., propane can be used as a precursor gas.
Owner:FEI CO
Sanitary Tissue Products and Methods for Making Same
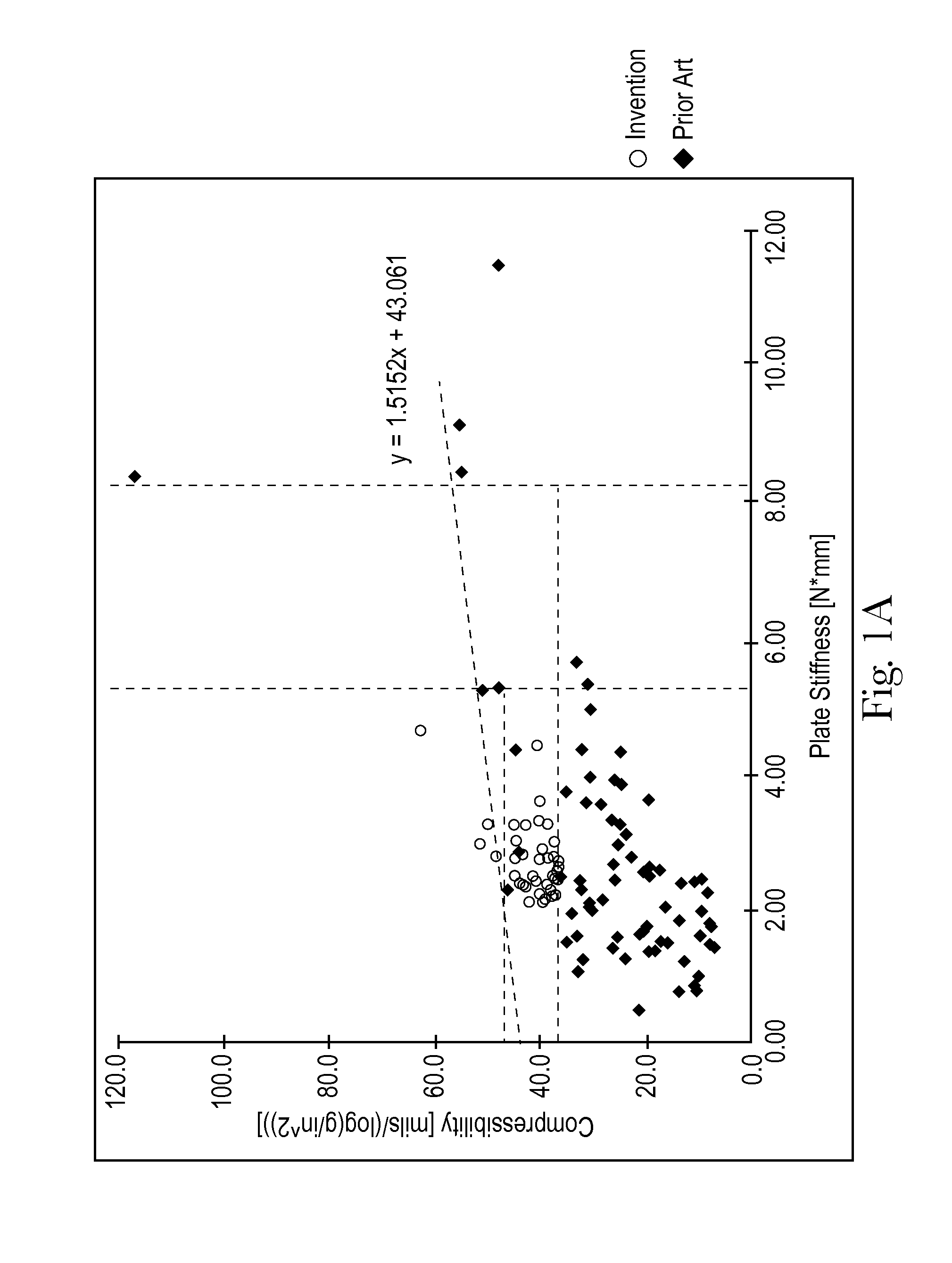
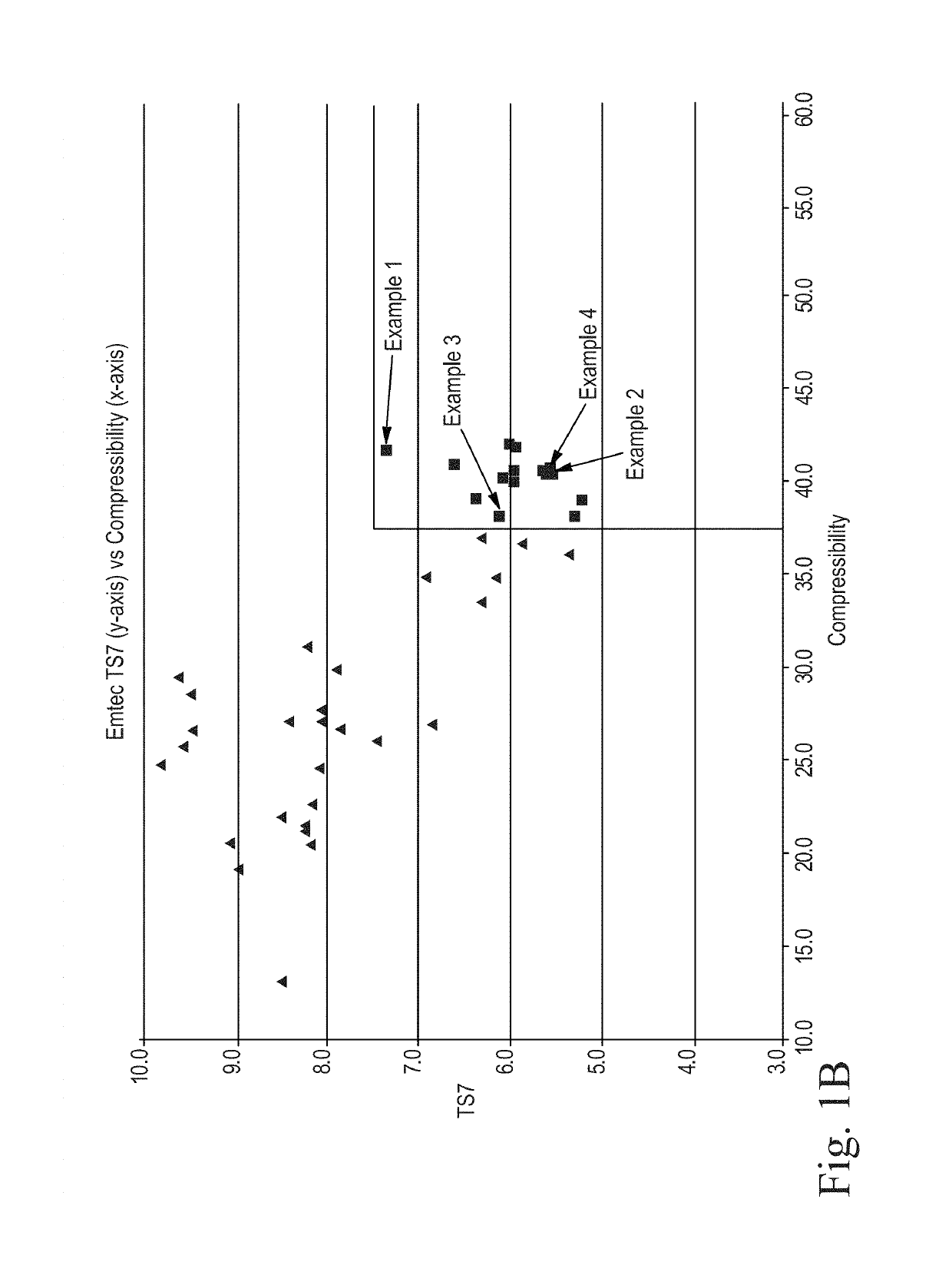
ActiveUS20150176218A1Improve compression performanceIncrease stiffnessNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperFiber3d patterning
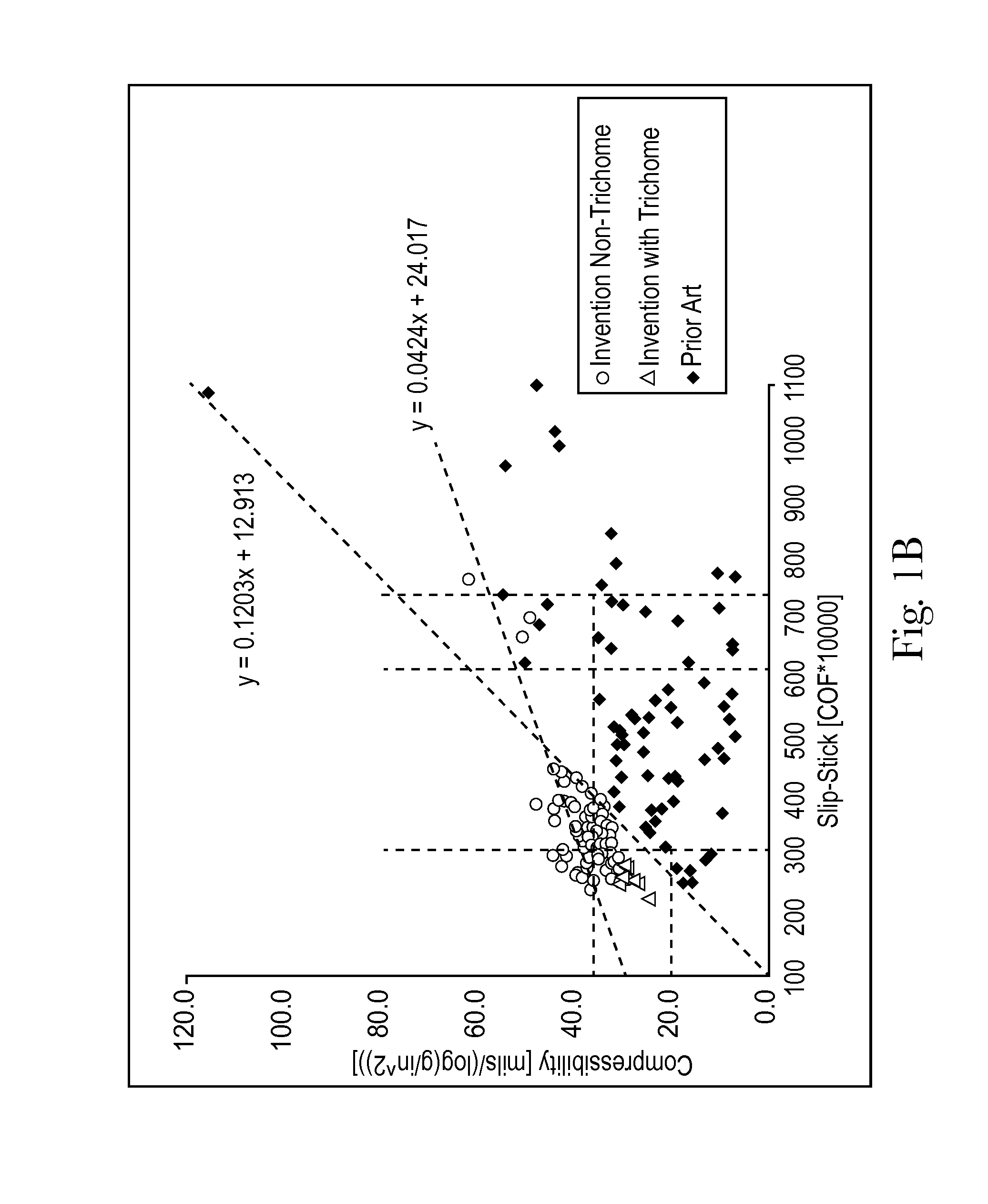
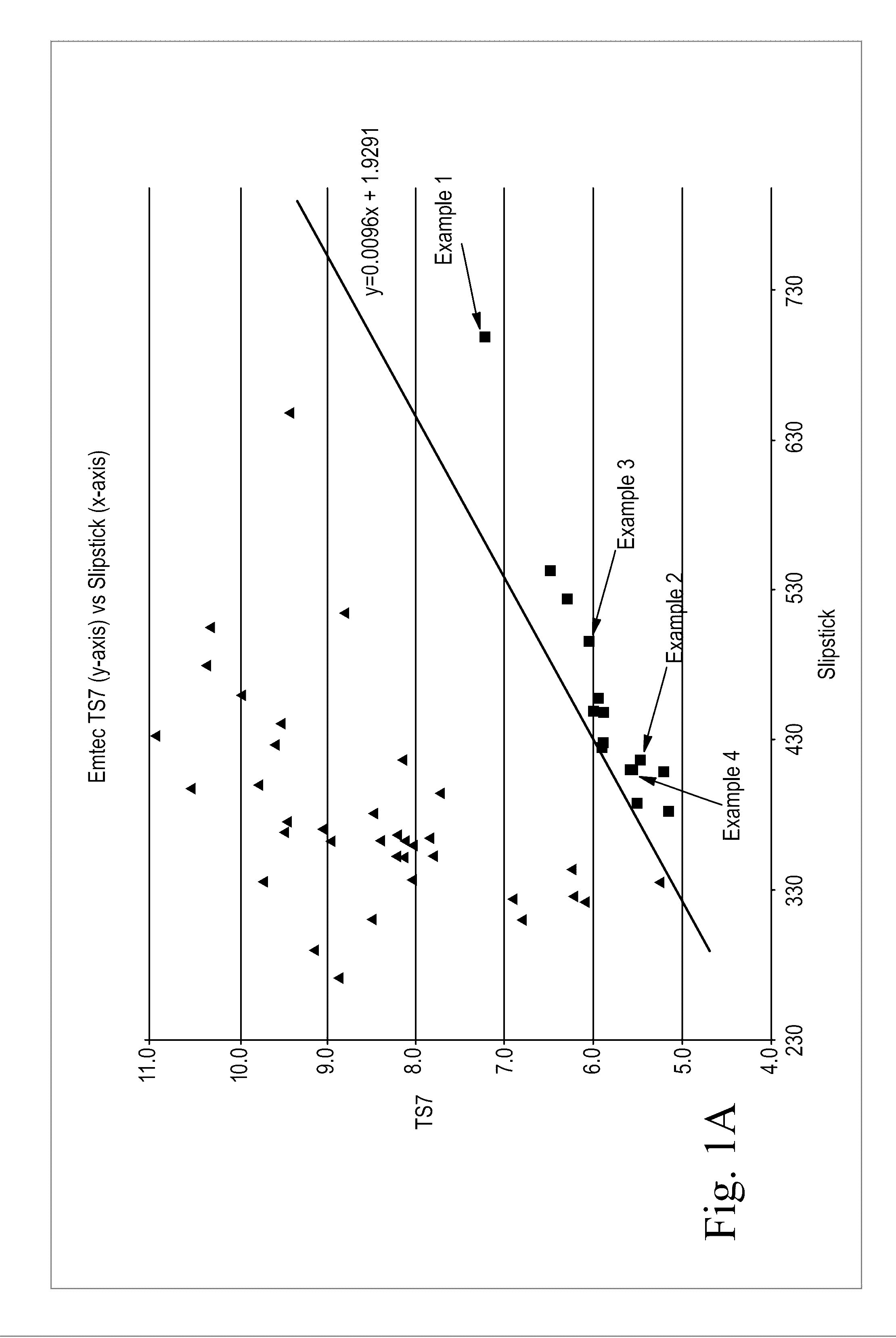
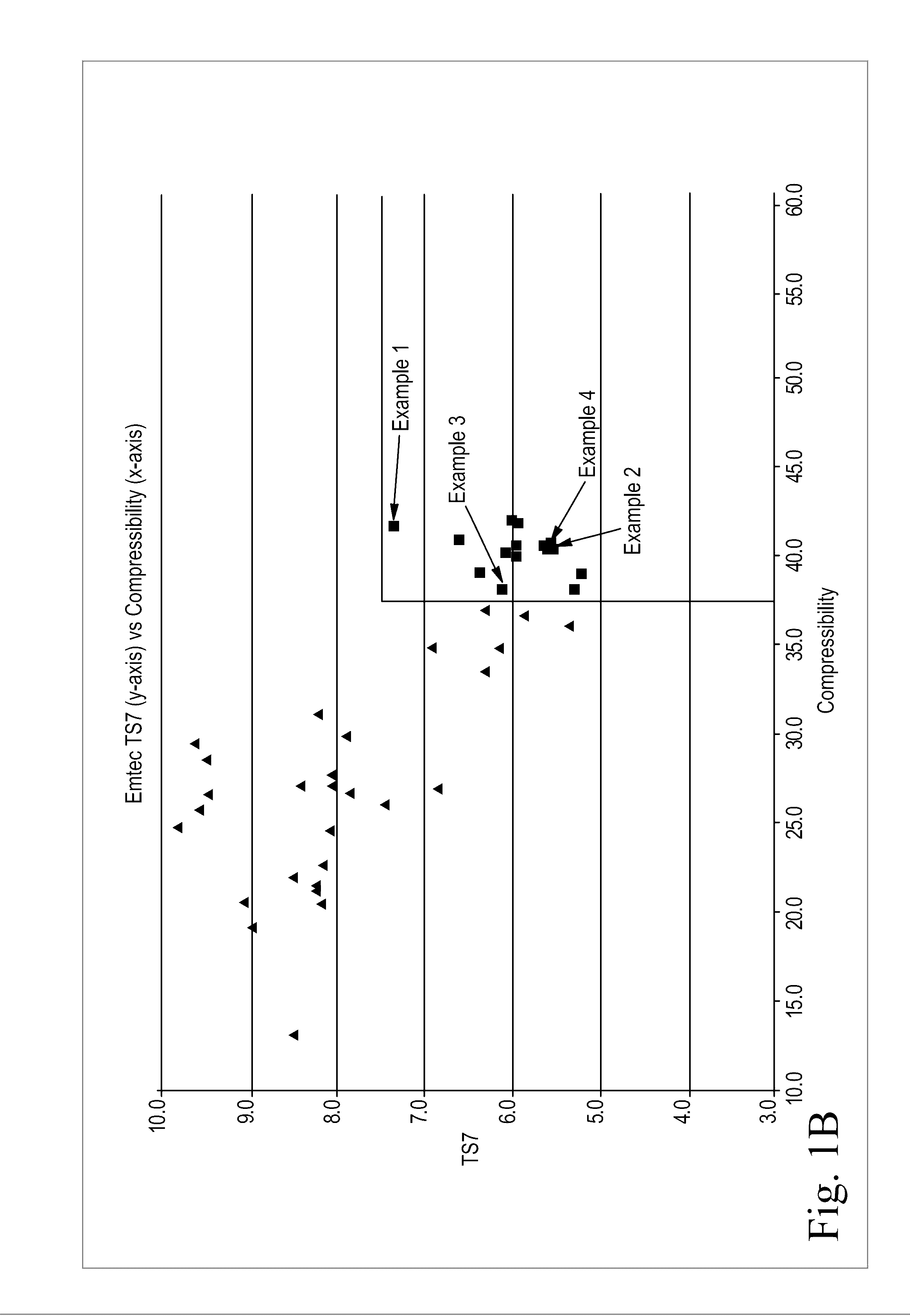
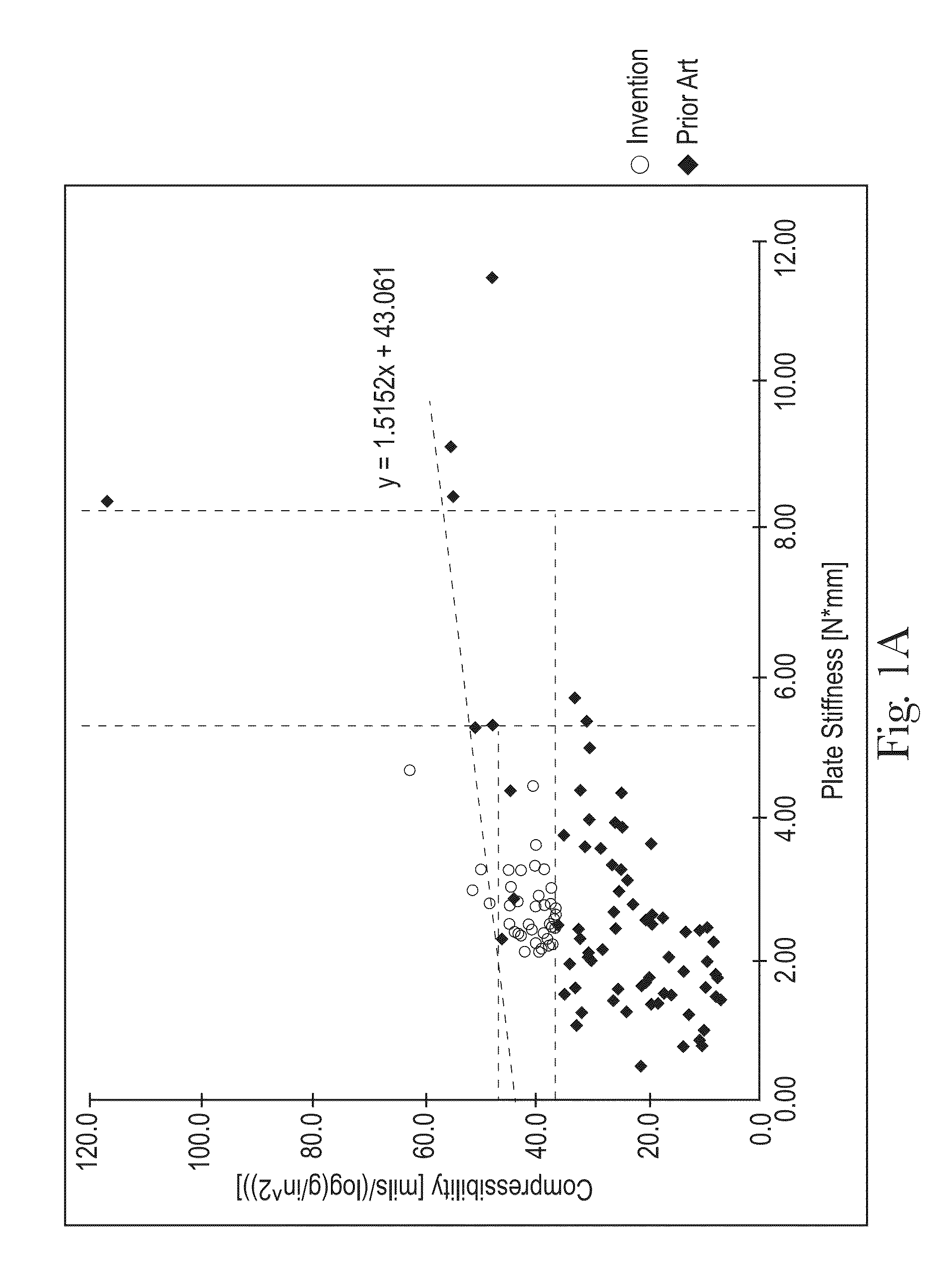
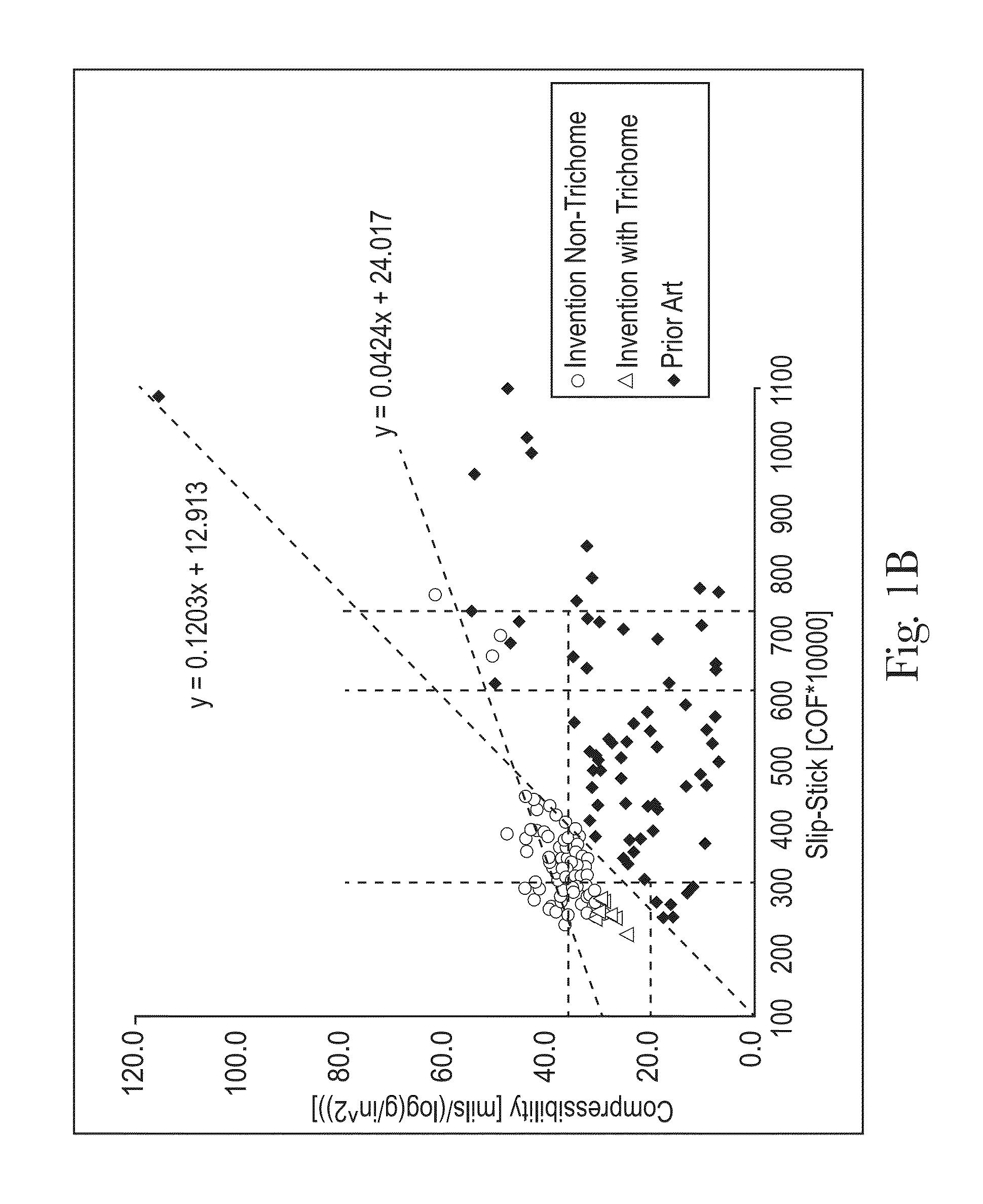
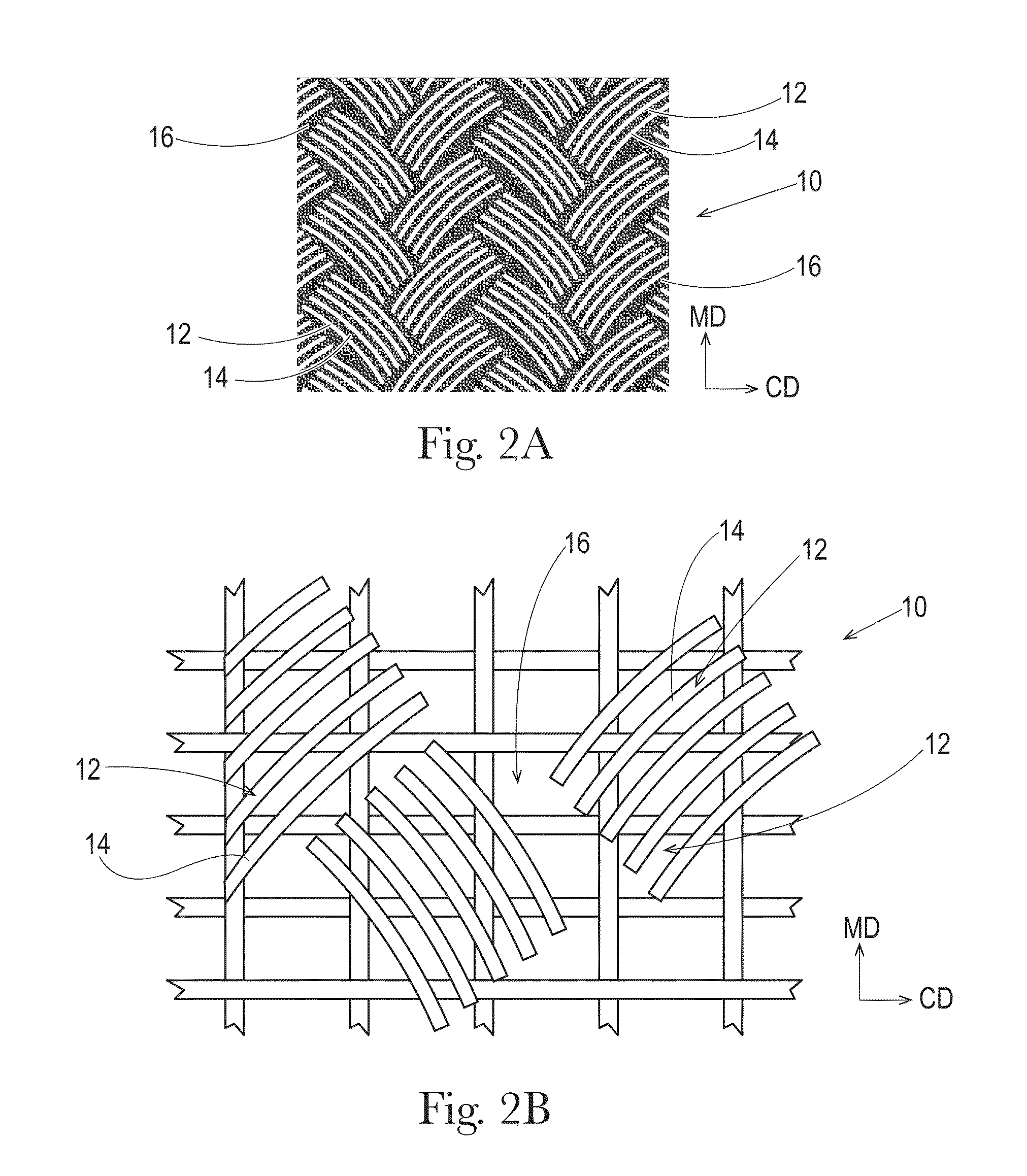
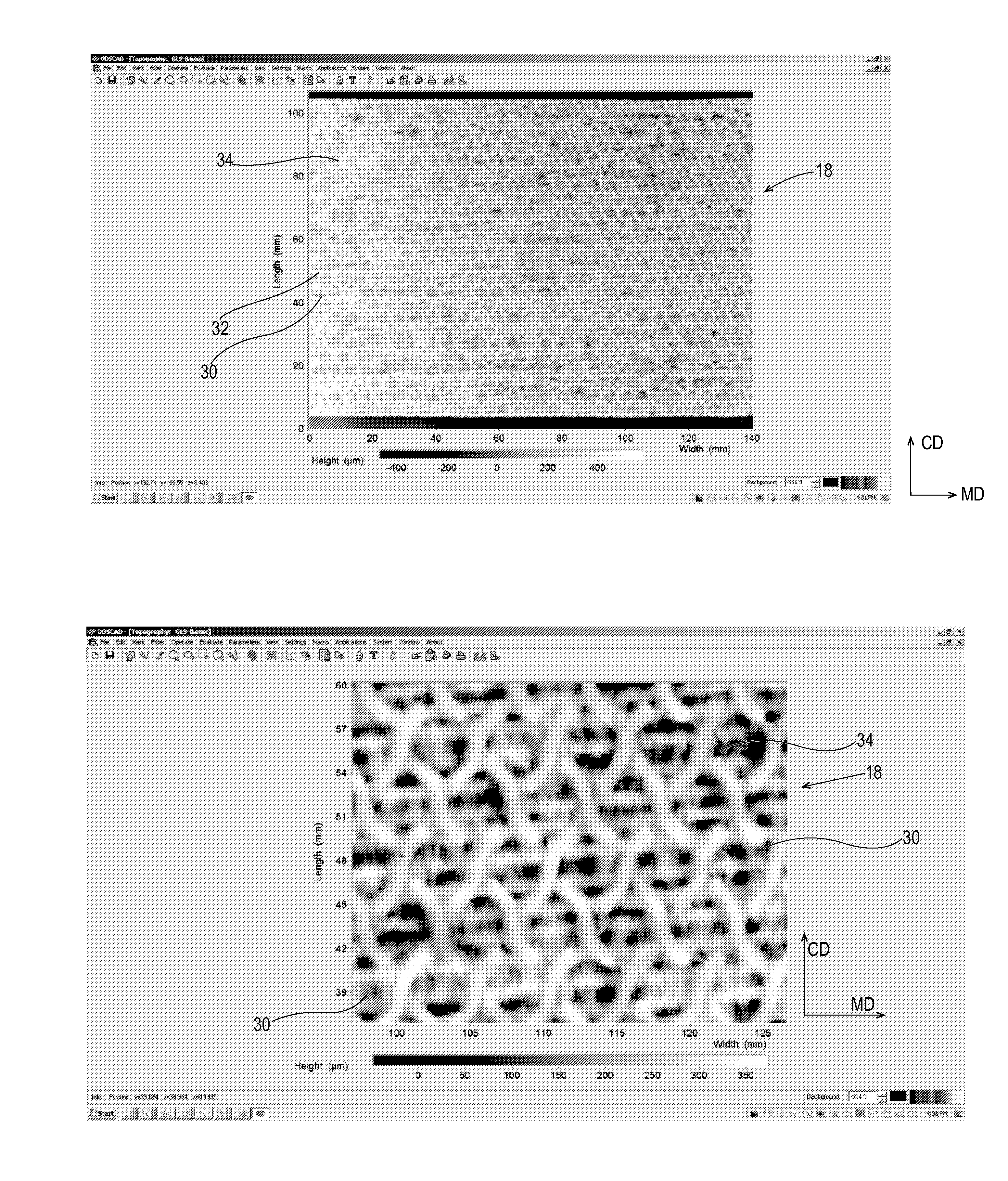
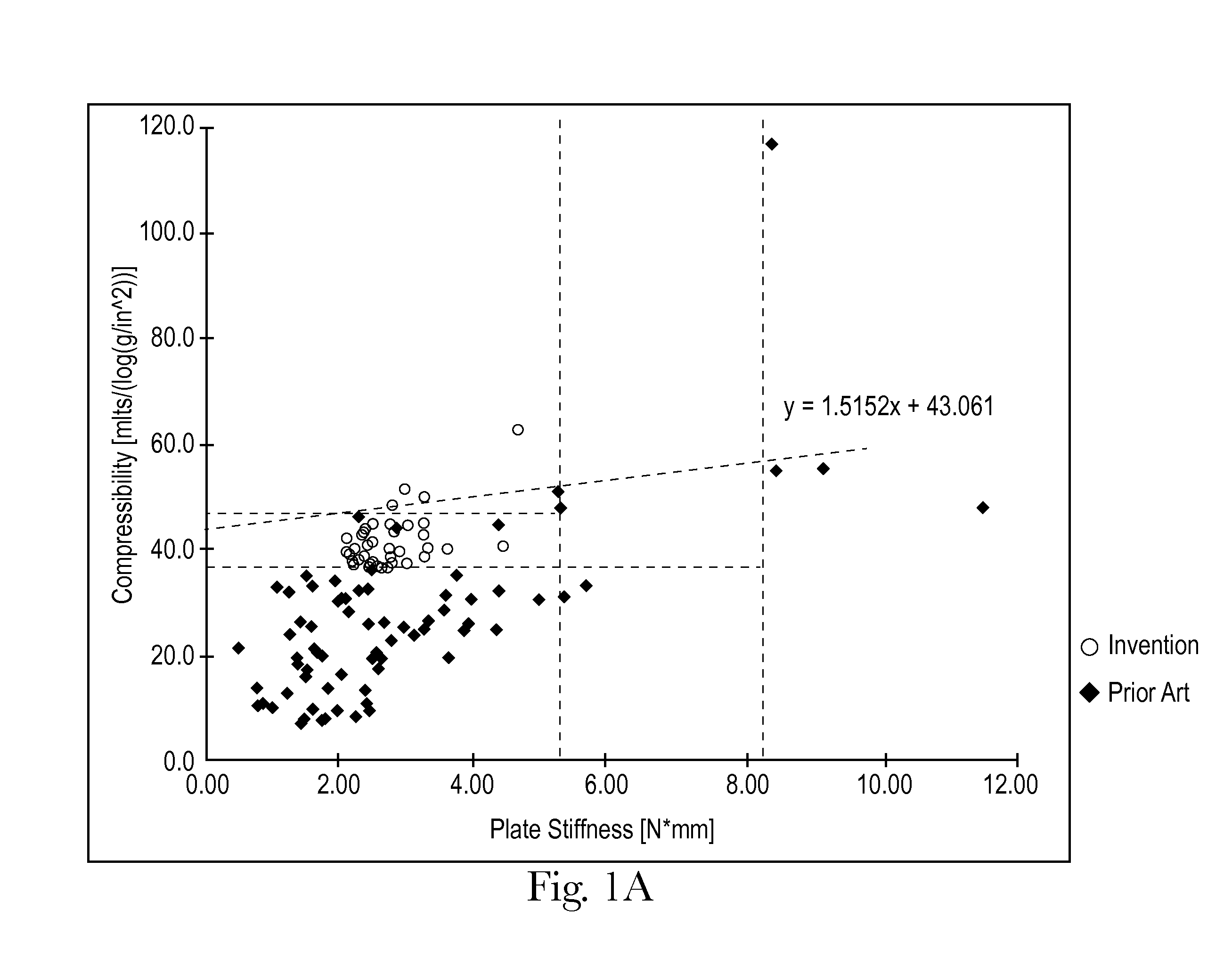
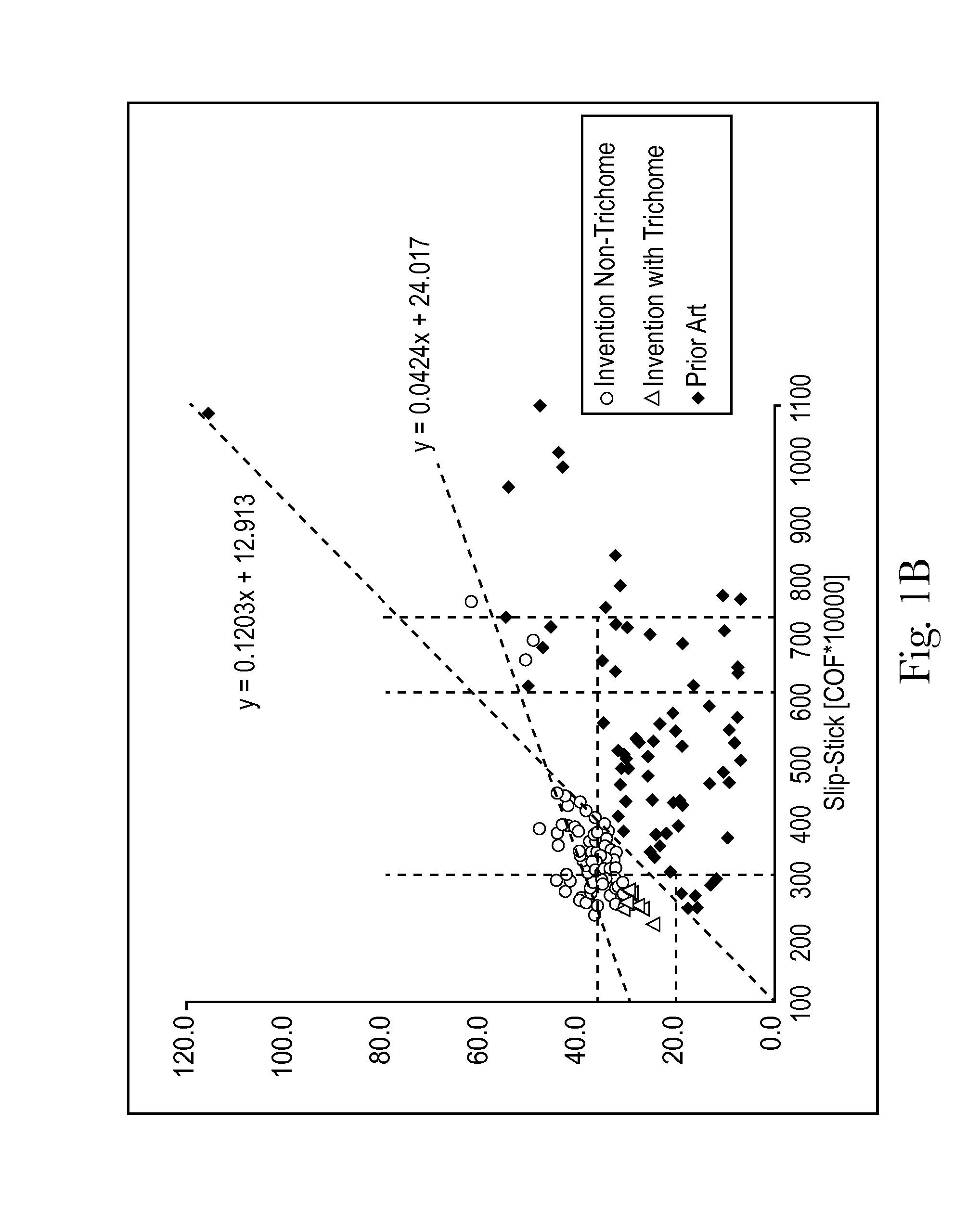
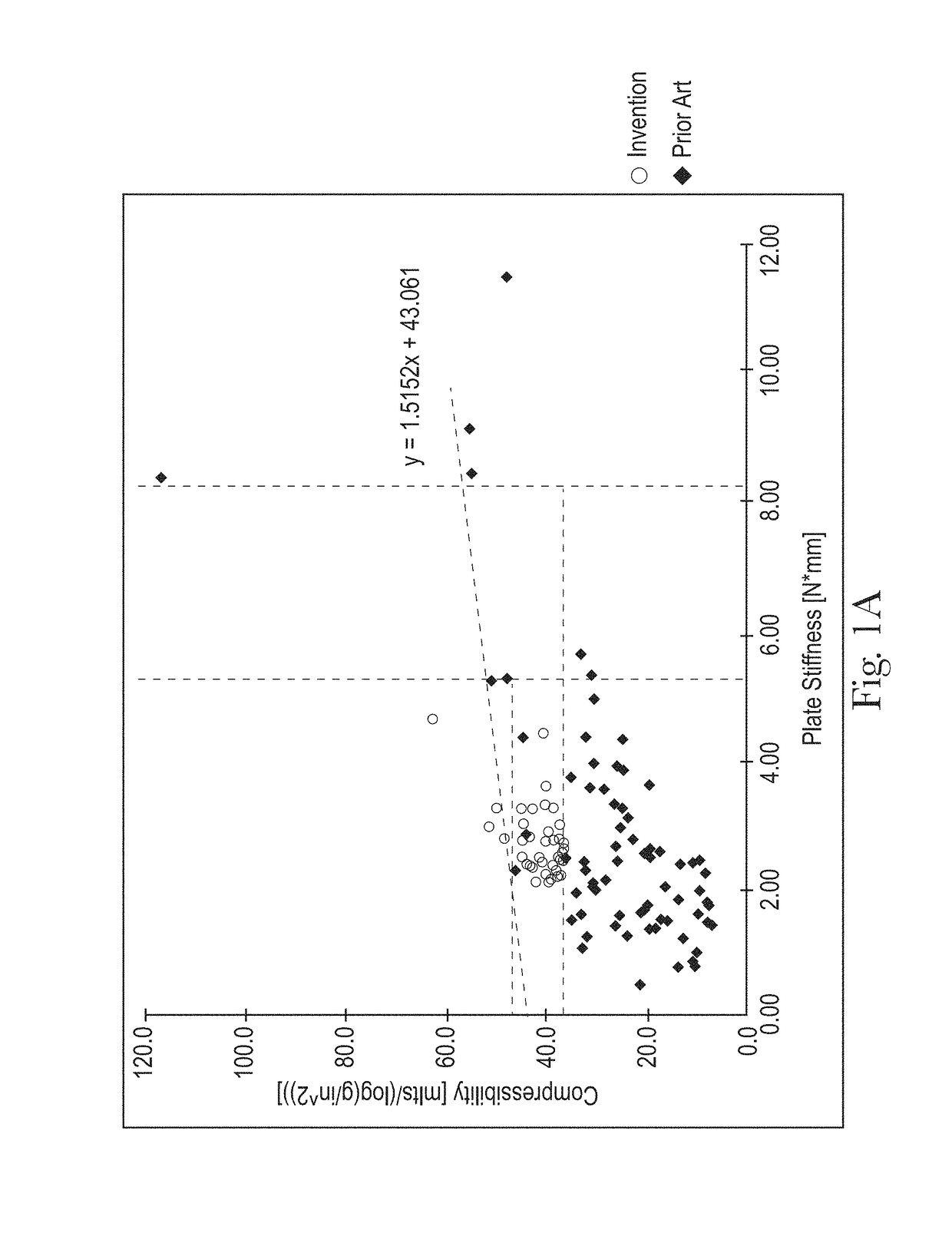
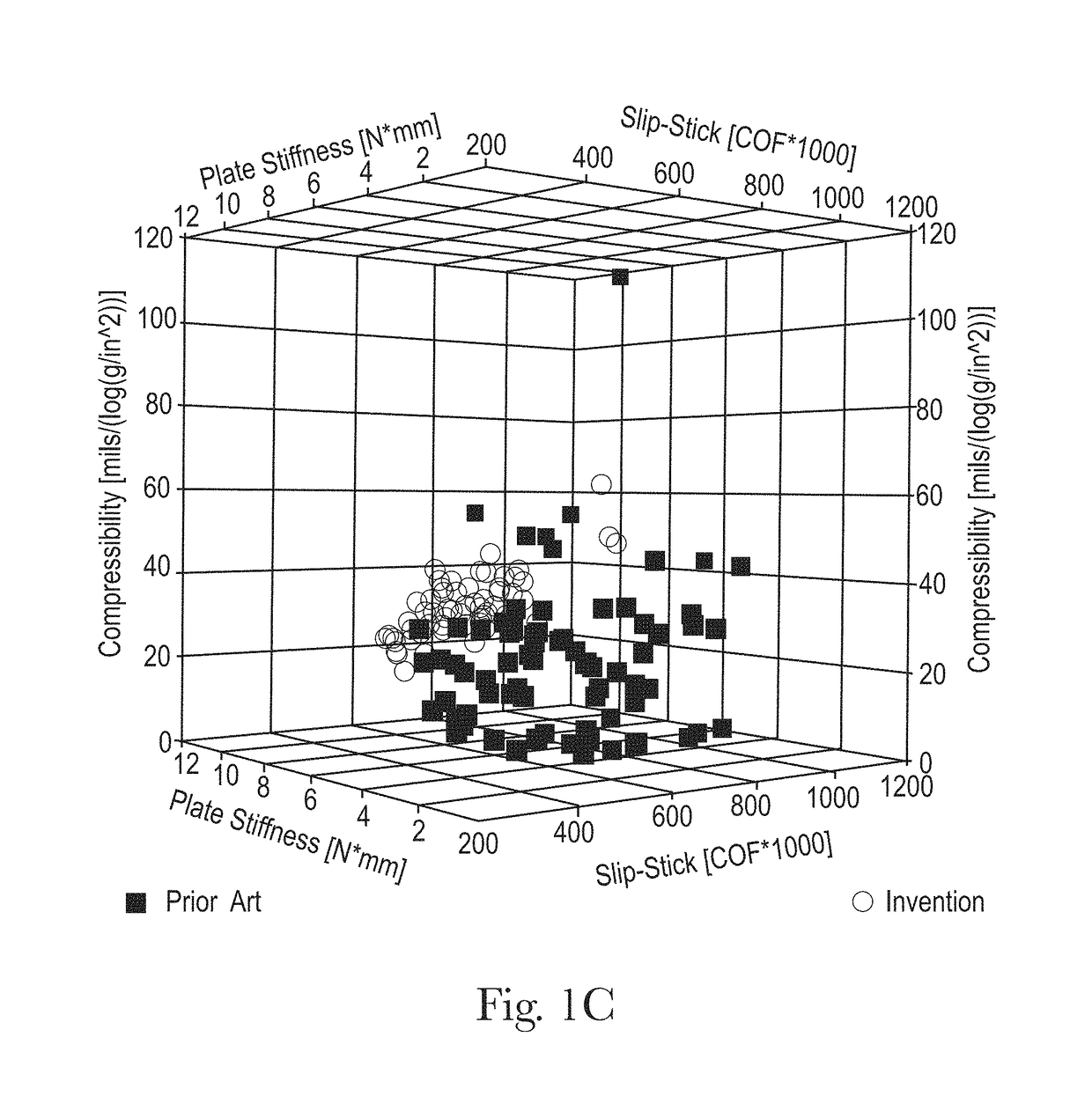
Sanitary tissue products employing 3D patterned fibrous structure plies having a surface comprising a novel three-dimensional (3D) pattern such that the 3D patterned fibrous structures and / or sanitary tissue products employing the fibrous structures exhibit novel cushiness as evidenced by compressibility of the fibrous structures and / or sanitary tissue products, novel flexibility as evidenced by plate stiffness of the fibrous structures and / or sanitary tissue products, and / or surface smoothness as evidenced by slip stick coefficient of friction of the fibrous structures and / or sanitary tissue products, and methods for making same, are provided.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Sanitary Tissue Products
ActiveUS20150176216A1Increase coefficient of frictionImprove compression performanceNon-fibrous pulp additionMechanical working/deformationFiberCompressibility
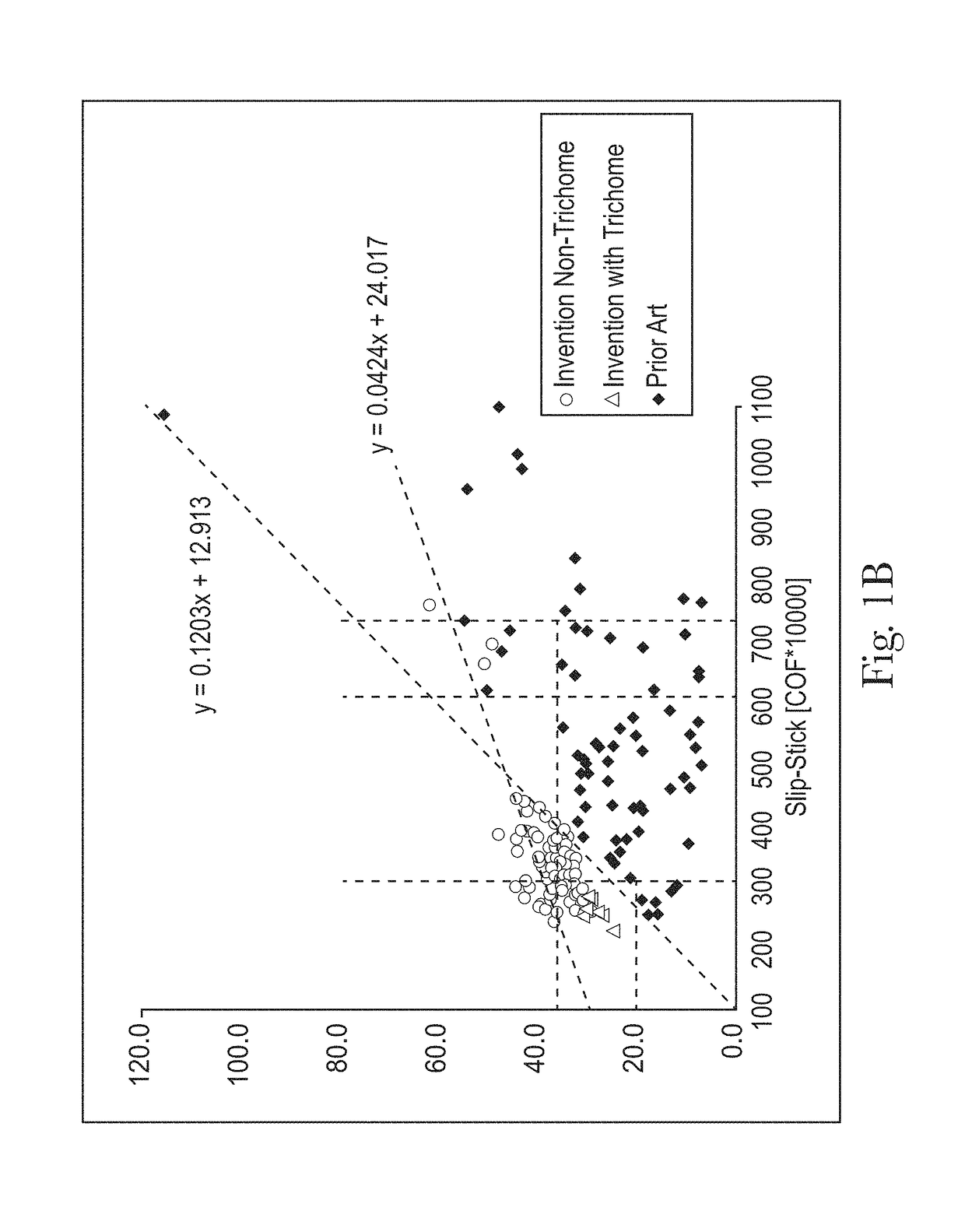
Sanitary tissue products employing fibrous structures that exhibit novel combination of slip stick coefficient of friction and compressibility properties and methods for making same.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Sanitary tissue products and methods for making same
ActiveUS9315945B2Cushier, more flexibleImprove compression performanceMechanical working/deformationPaper/cardboardFiber3d patterning
Sanitary tissue products employing 3D patterned fibrous structure plies having a surface comprising a novel three-dimensional (3D) pattern such that the 3D patterned fibrous structures and / or sanitary tissue products employing the fibrous structures exhibit novel cushiness as evidenced by compressibility of the fibrous structures and / or sanitary tissue products, novel flexibility as evidenced by plate stiffness of the fibrous structures and / or sanitary tissue products, and / or surface smoothness as evidenced by slip stick coefficient of friction of the fibrous structures and / or sanitary tissue products, and methods for making same, are provided.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Sanitary Tissue Products
ActiveUS20170022670A1Increase valueImprove surface mobilityApplied substance rearrangementPaper/cardboardFiberCompressibility
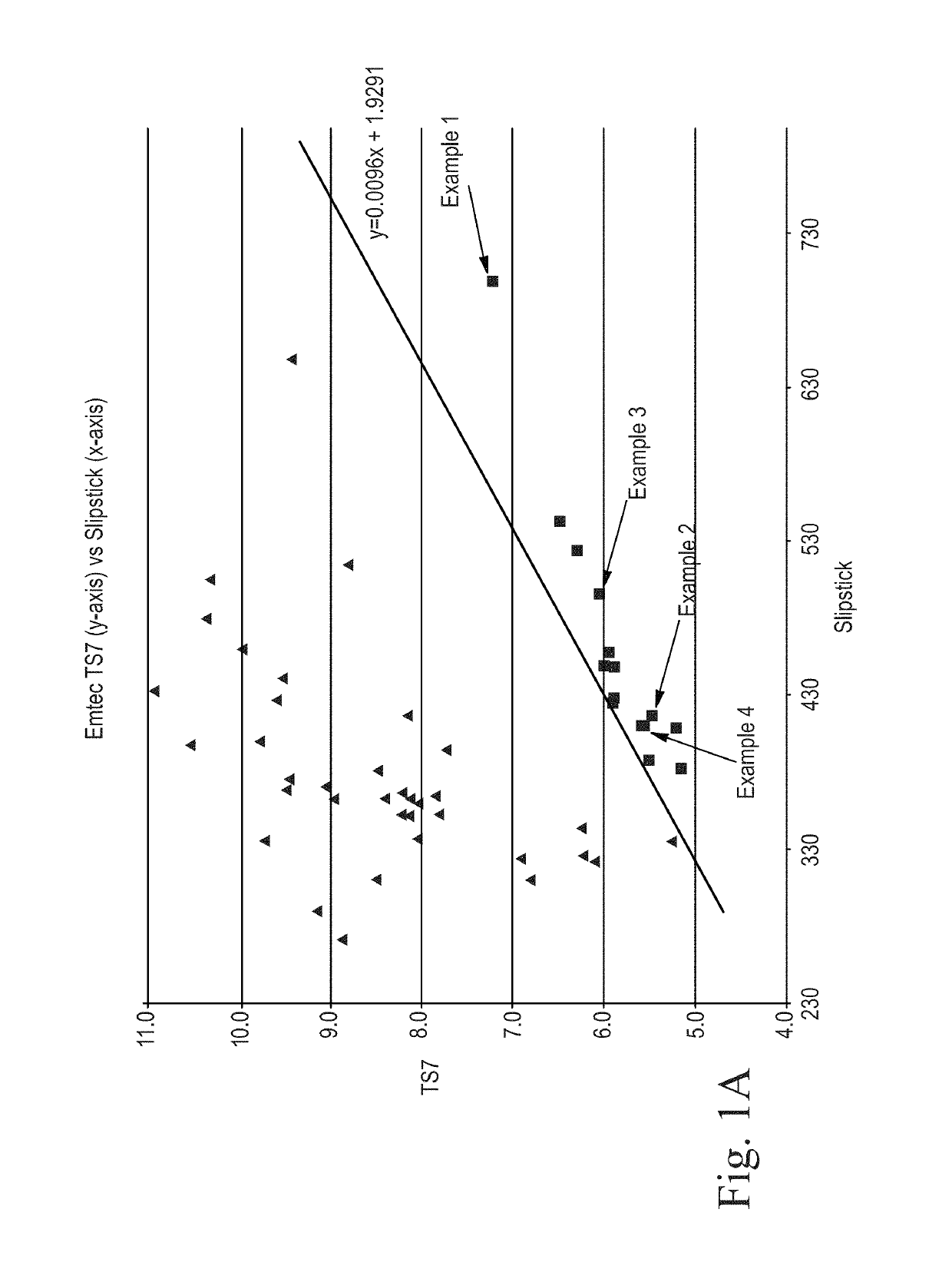
Sanitary tissue products employing fibrous structures that exhibit novel combination of average TS7 values and slip stick coefficient of friction and / or compressibility properties and methods for making same.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Sanitary tissue products
ActiveUS9404222B2Smoother and cushierIncrease coefficient of frictionPaper/cardboardChemical/chemomechanical pulpFiberCompressibility
Sanitary tissue products employing fibrous structures that exhibit novel combination of slip stick coefficient of friction and compressibility properties and methods for making same.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Sanitary Tissue Products
ActiveUS20150176217A1Improve compression performanceIncrease stiffnessNon-fibrous pulp additionMechanical working/deformationCompressibilityBiomedical engineering
Sanitary tissue products employing fibrous structures that exhibit a novel combination of compressibility properties, plate stiffness properties, and slip stick coefficient of friction properties, and methods for making same.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
FIB milling of copper over organic dielectrics
ActiveUS7060196B2Electric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsCharged particle beamNitropropane
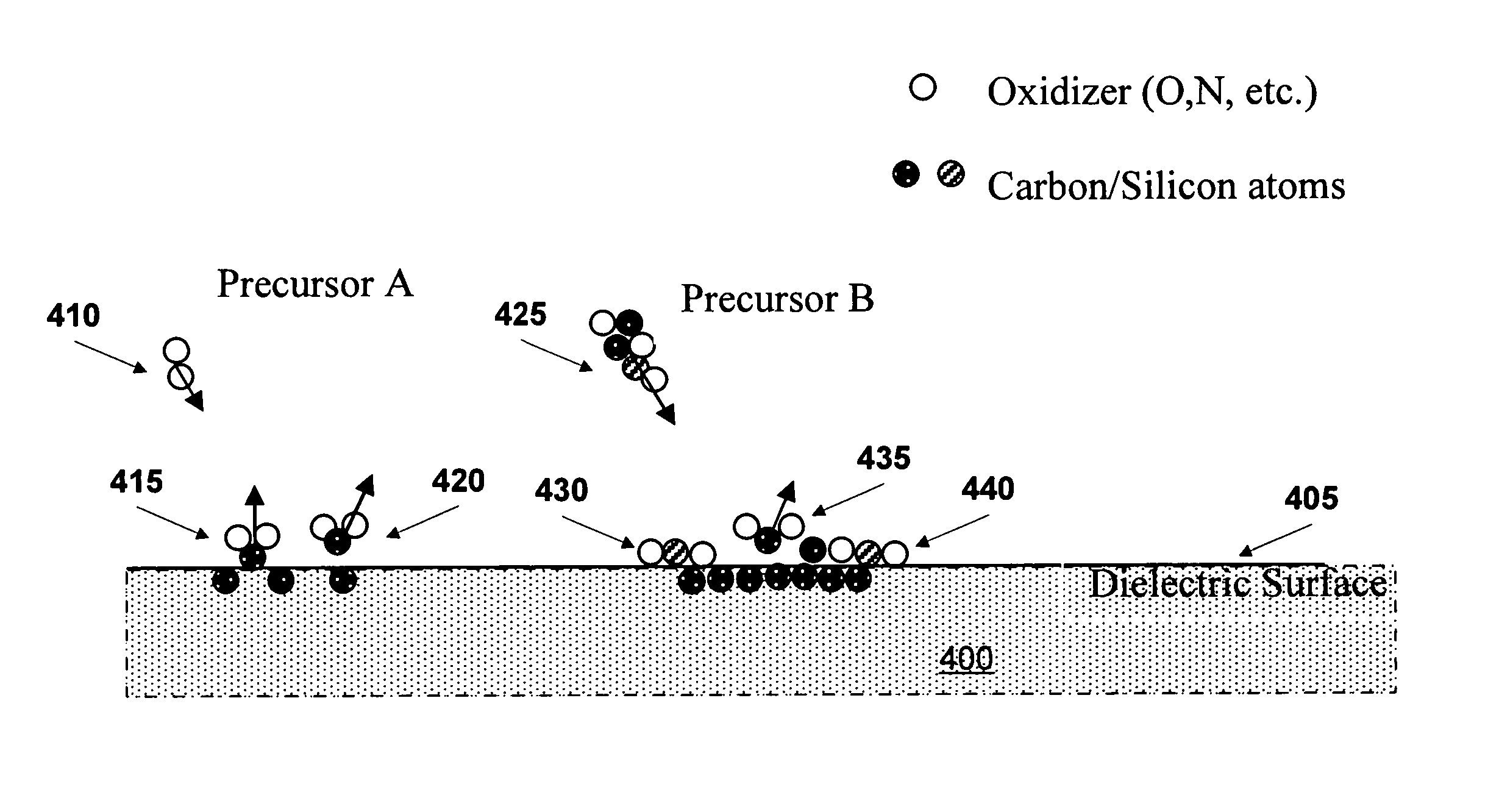
Apparatus and processes are disclosed for milling copper adjacent to organic low-k dielectric on a substrate by directing a charged-particle beam at a portion of the copper and exposing the copper to a precursor sufficient to enhance removal of the copper relative to removal of the dielectric, wherein the precursor contains an oxidizing agent, has a high sticking coefficient and a long residence time on the copper, contains atoms of at least one of carbon and silicon in amount sufficient to stop oxidation of the dielectric, and contains no atoms of chlorine, bromine or iodine. In one embodiment, the precursor comprises at least one of the group consisting of NitroEthanol, NitroEthane, NitroPropane, NitroMethane, compounds based on silazane such as HexaMethylCycloTriSilazane, and compounds based on siloxane such as Octa-Methyl-Cyclo-Tetra-Siloxane. Products of the processes are also disclosed.
Owner:DCG SYST
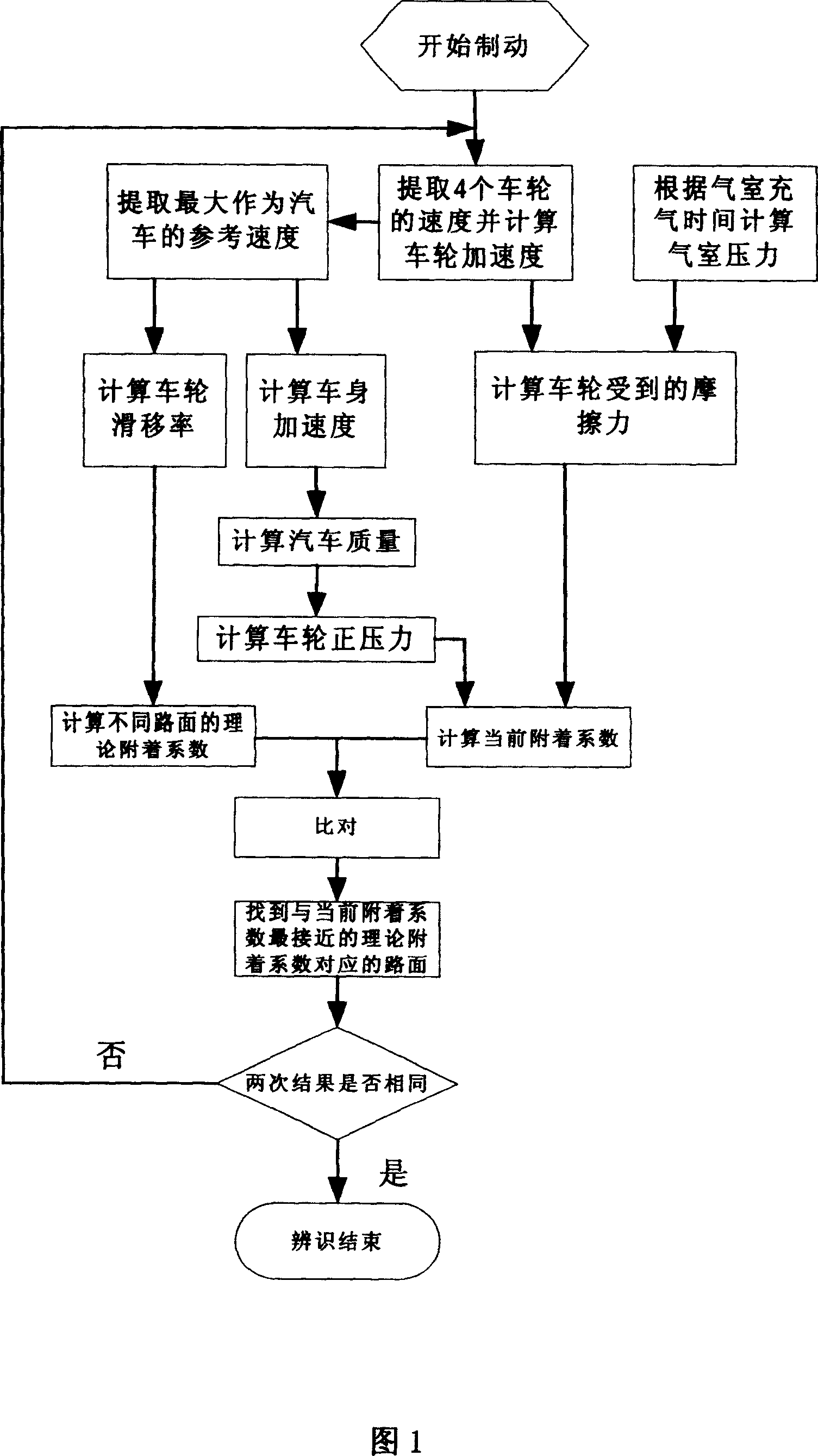
Cargo vehicle ABS road identification method
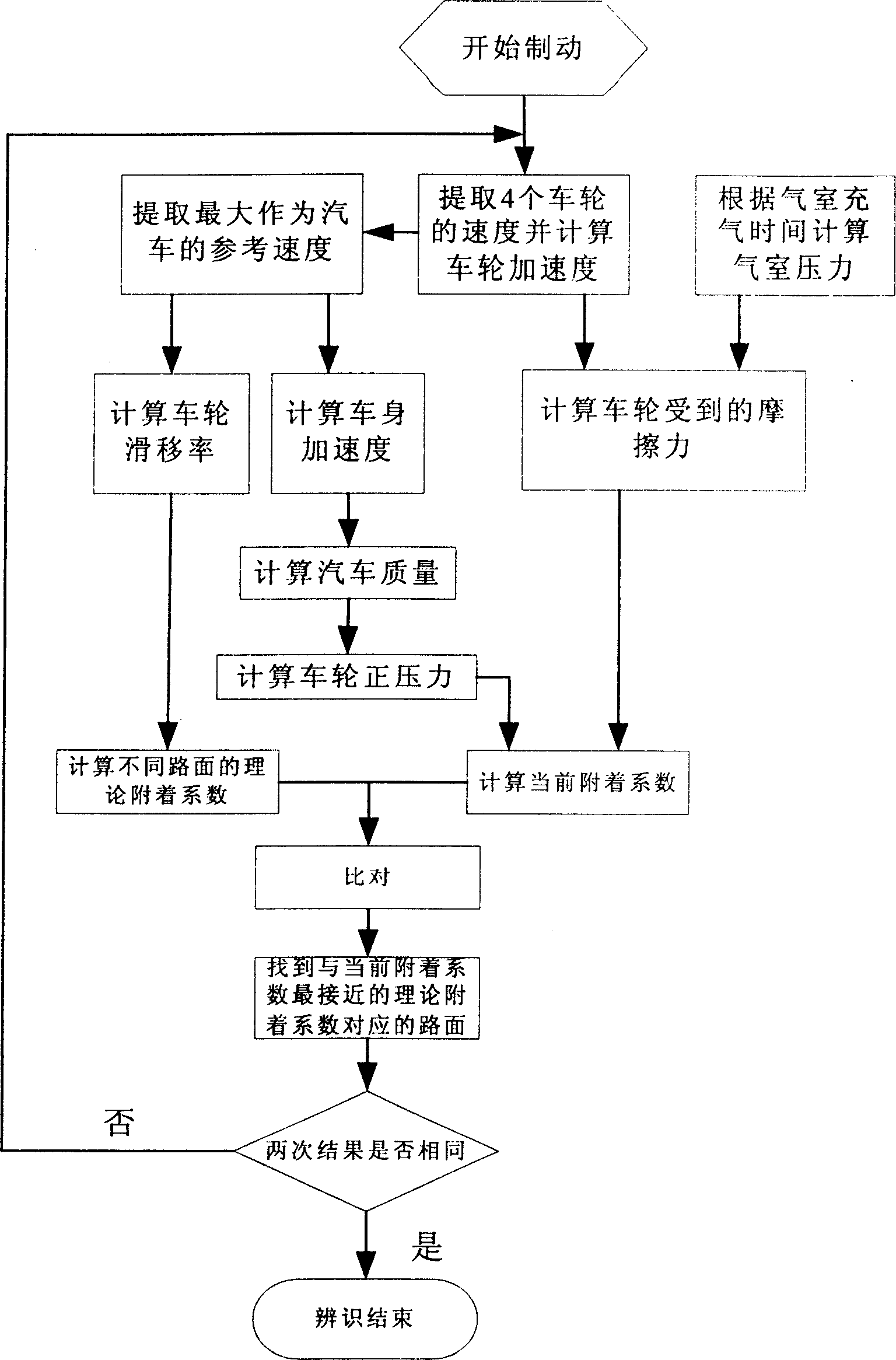
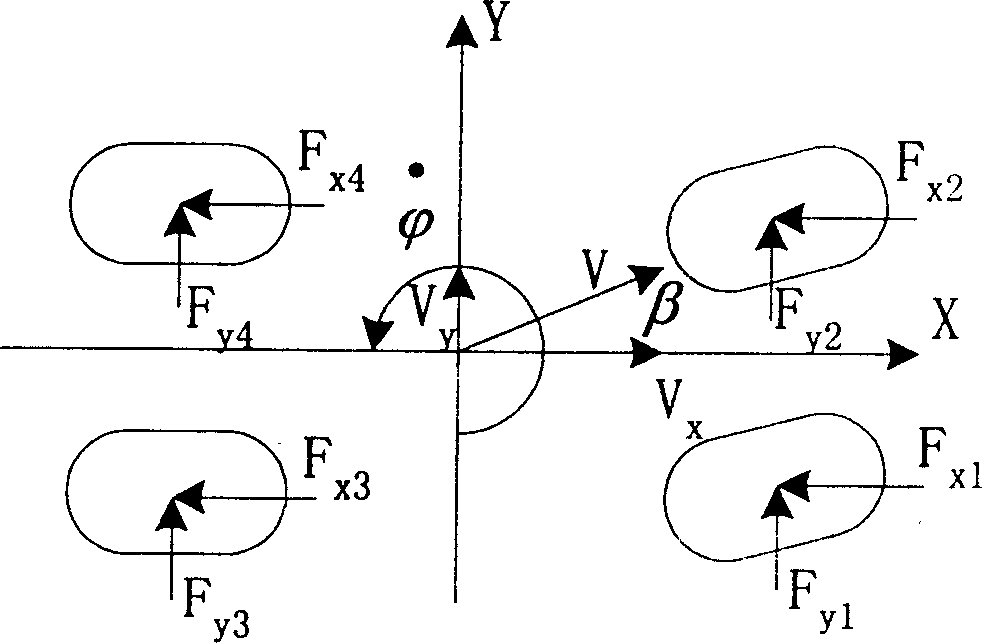
This invention relates to a road identifying method for the ABS of camion brakes, which takes the maximum speed of the wheel as the reference then computes the friction of each wheel endured by the earth based on the angular acceleration of the wheel then to compute the mass of the vehicle and its parameter in loading to get the positive pressure of the wheel so as to get the sticking coefficient of the earth, then to compute the slip ratio and the theoretical sticking coefficient of different roads under the current slip ratio according to a theoretical formula to compare the two coefficients to identify the situation of the road.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
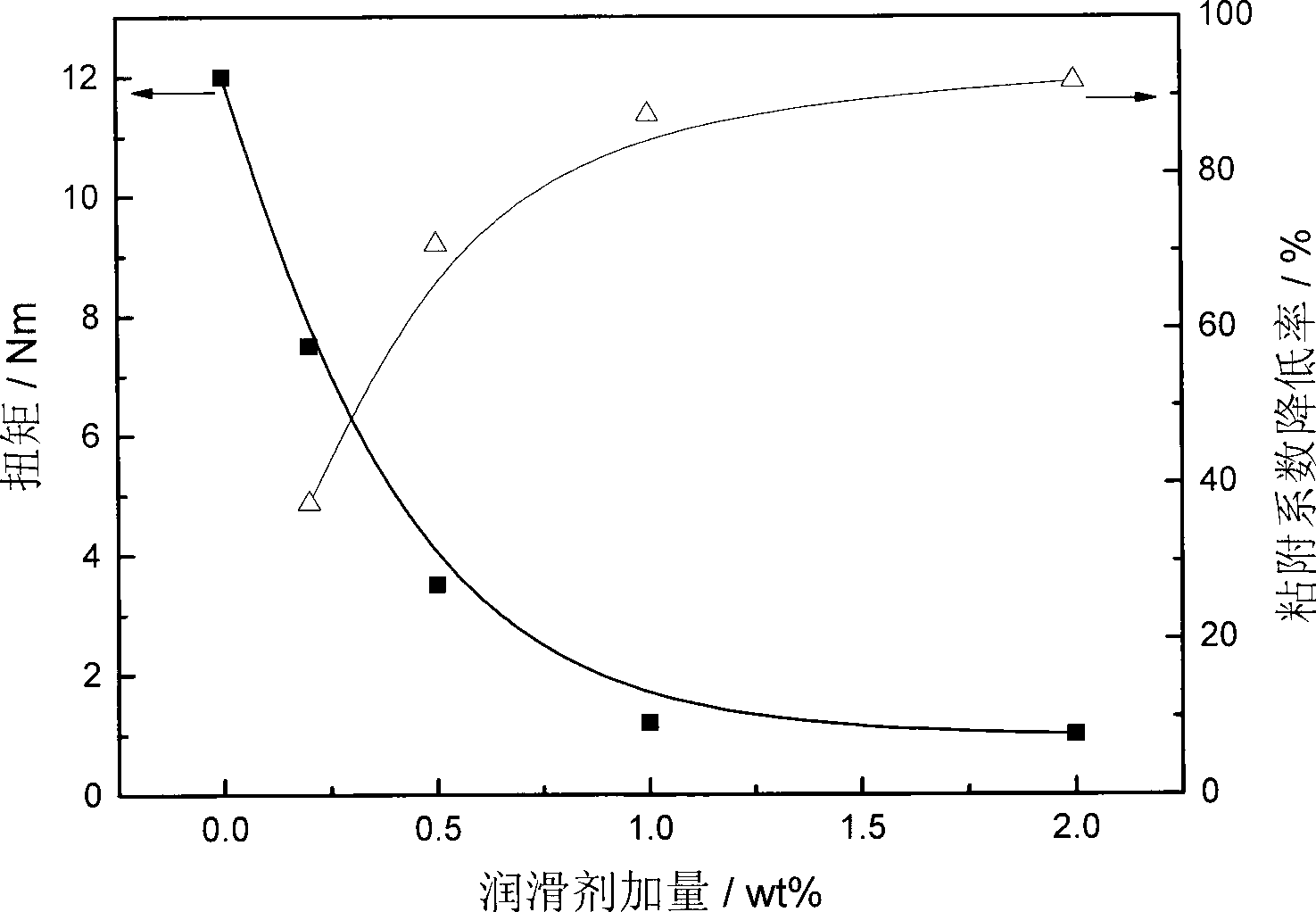
Lubricant for drilling fluids and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101423752AImprove dispersion stabilityEasy to operateDrilling compositionSlurryLubrication
The invention discloses a lubricant for drilling fluid and a preparation method thereof. Oil-phase nonionic surfactant is added to a reactor and stirred for reaction, so as to obtain the lubricant. The method has the characteristics that the method is simple to operate, low in requirements on equipment and environment, easy to realize and capable of effectively reducing and regulating sticking coefficient. The lubricant prepared by the method has the characteristics of good dispersibility in prepared slurry, small particle size and good lubrication effect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Sanitary tissue products
ActiveUS10060077B2Cushier, more flexible, and smootherImprove compression performanceMechanical working/deformationPaper/cardboardFiberFrictional coefficient
Sanitary tissue products employing fibrous structures that exhibit a novel combination of compressibility properties, plate stiffness properties, and slip stick coefficient of friction properties, and methods for making same.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Sanitary tissue products
ActiveUS10240296B2Improve surface mobilityGood “cushiness”Paper/cardboardApplied substance rearrangementFiberCompressibility
Sanitary tissue products employing fibrous structures that exhibit novel combination of average TS7 values and slip stick coefficient of friction and / or compressibility properties and methods for making same.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Etching method
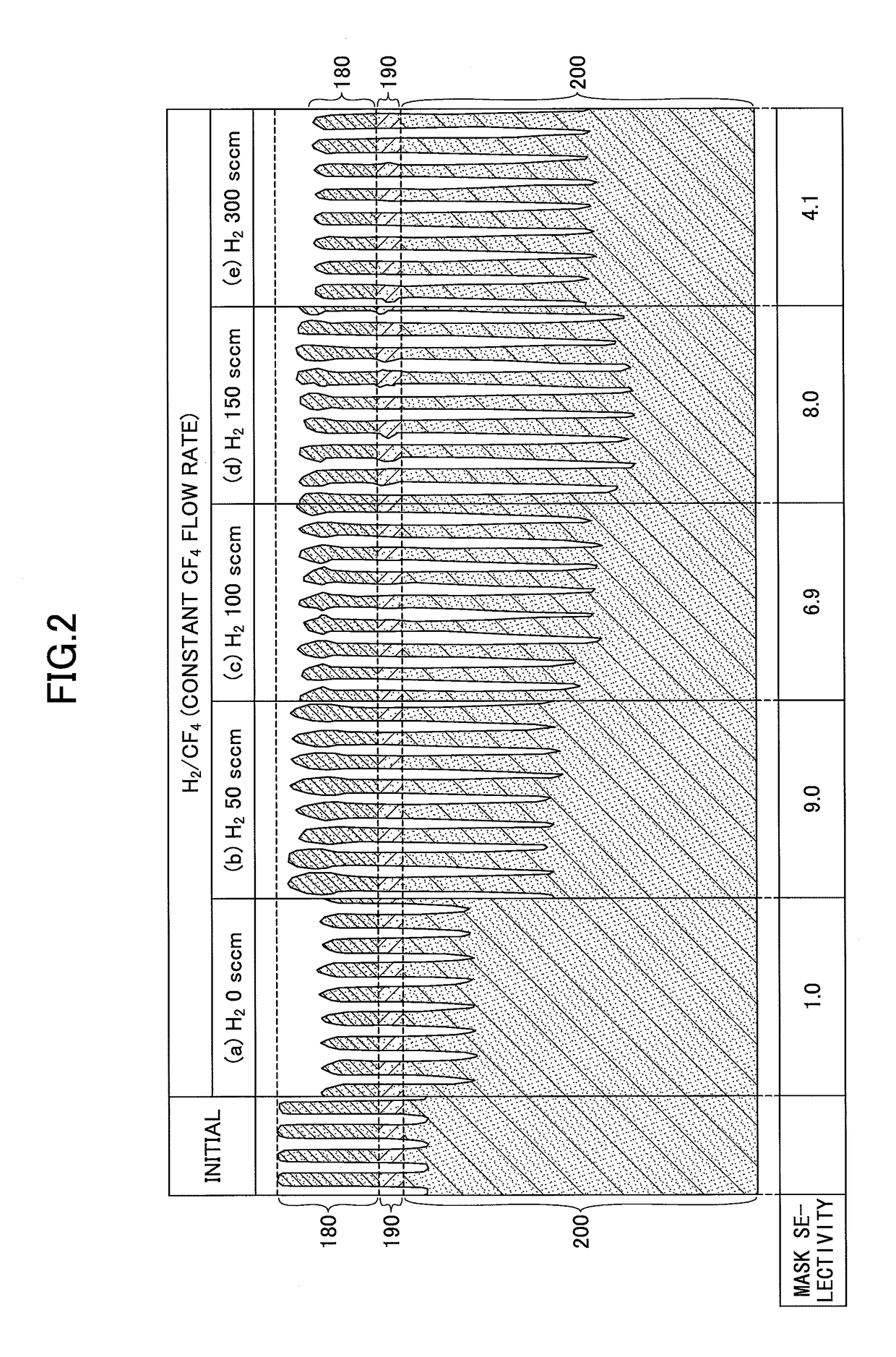
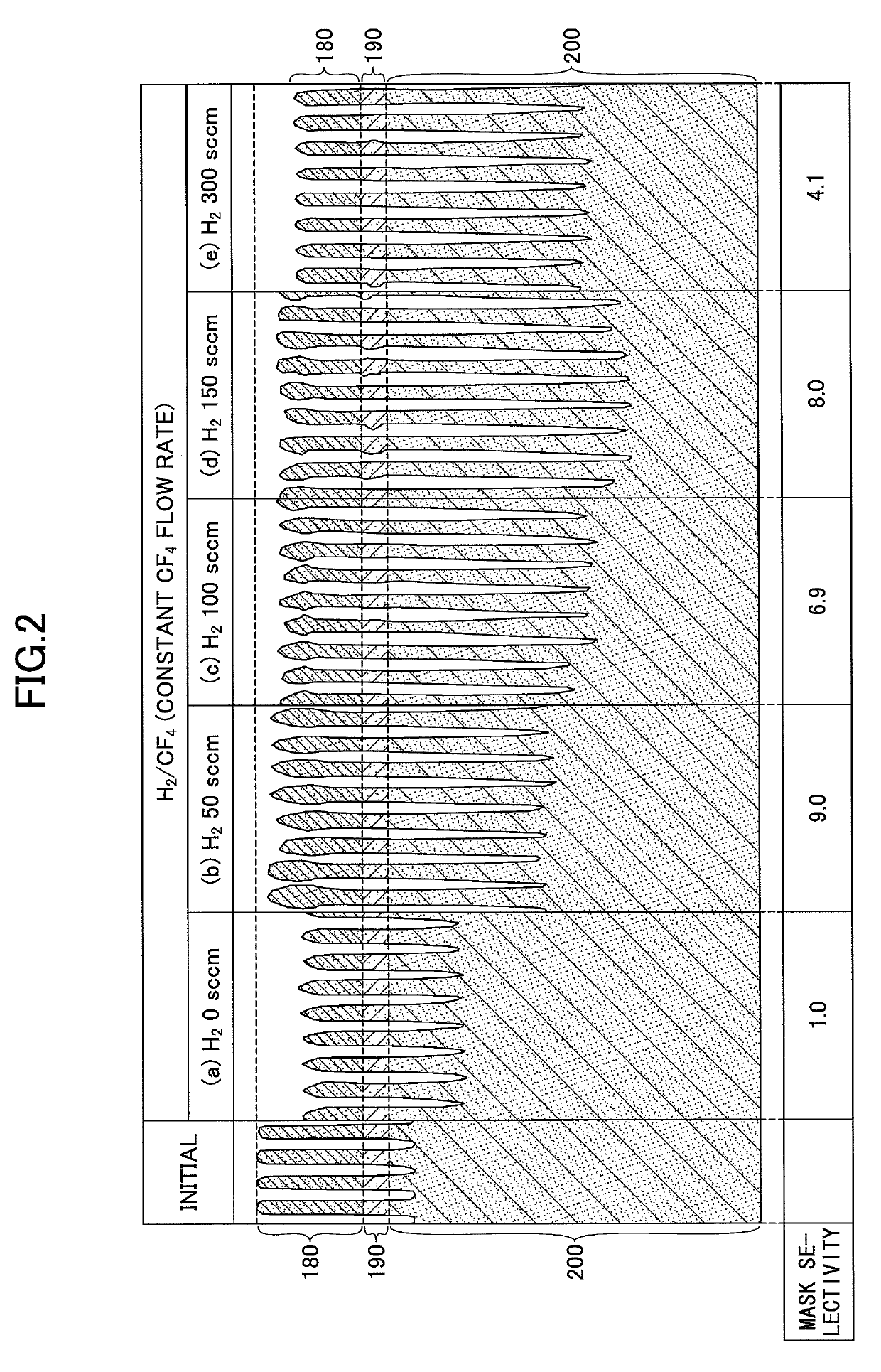
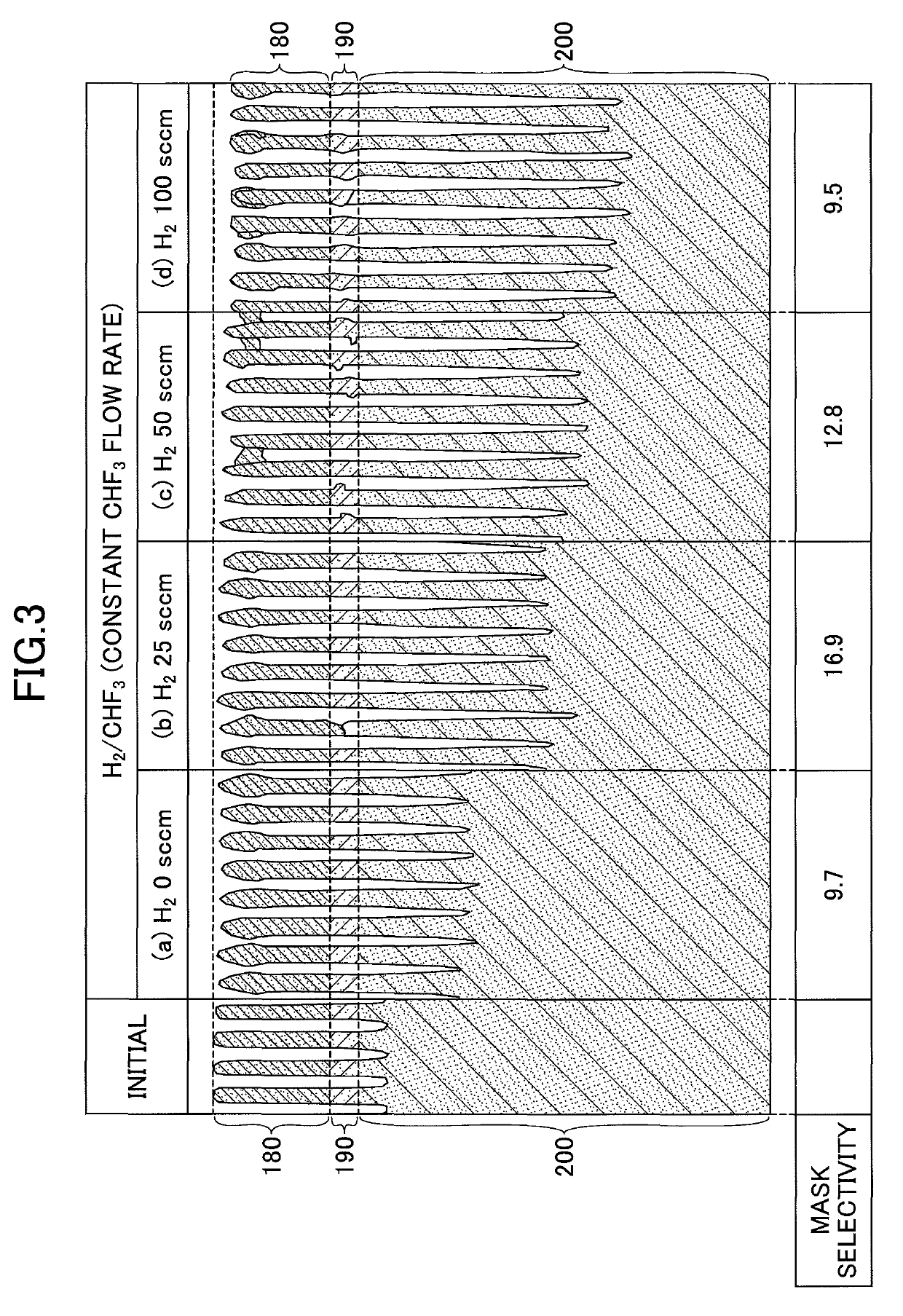
An etching method for etching a silicon oxide film is provided that includes generating a plasma from a gas including a hydrogen-containing gas and a fluorine-containing gas using a high frequency power for plasma generation, and etching the silicon oxide film using the generated plasma. The fluorine-containing gas includes a hydrofluorocarbon gas, and the sticking coefficient of radicals generated from the hydrofluorocarbon gas is higher than the sticking coefficient of radicals generated from carbon tetrafluoride (CF4).
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Adhesion promotion for etch by-products
InactiveUS7176140B1Easy and efficient and effective and inexpensive and reliableSufficient sticking coefficient for adherenceElectrostatic cleaningSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
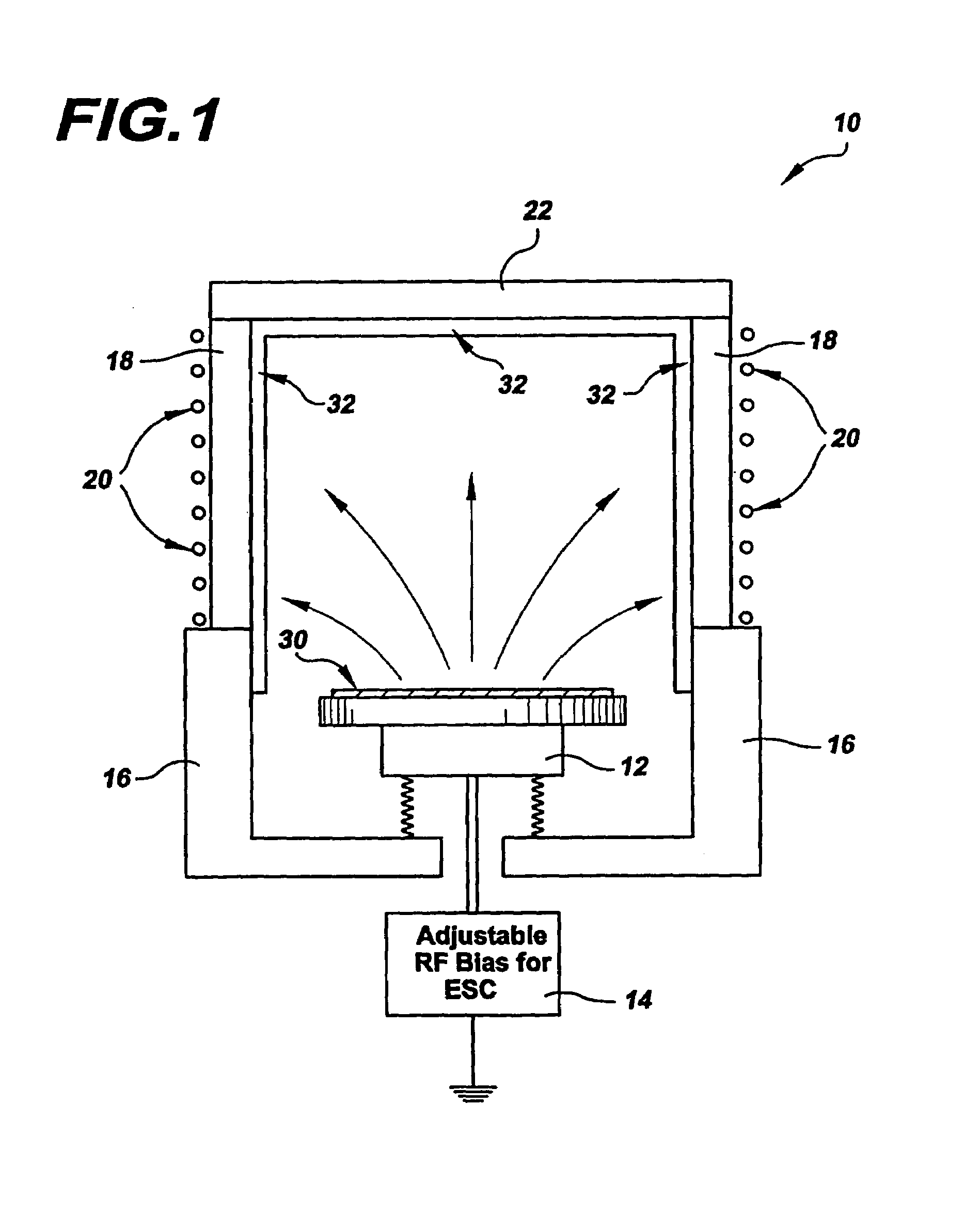
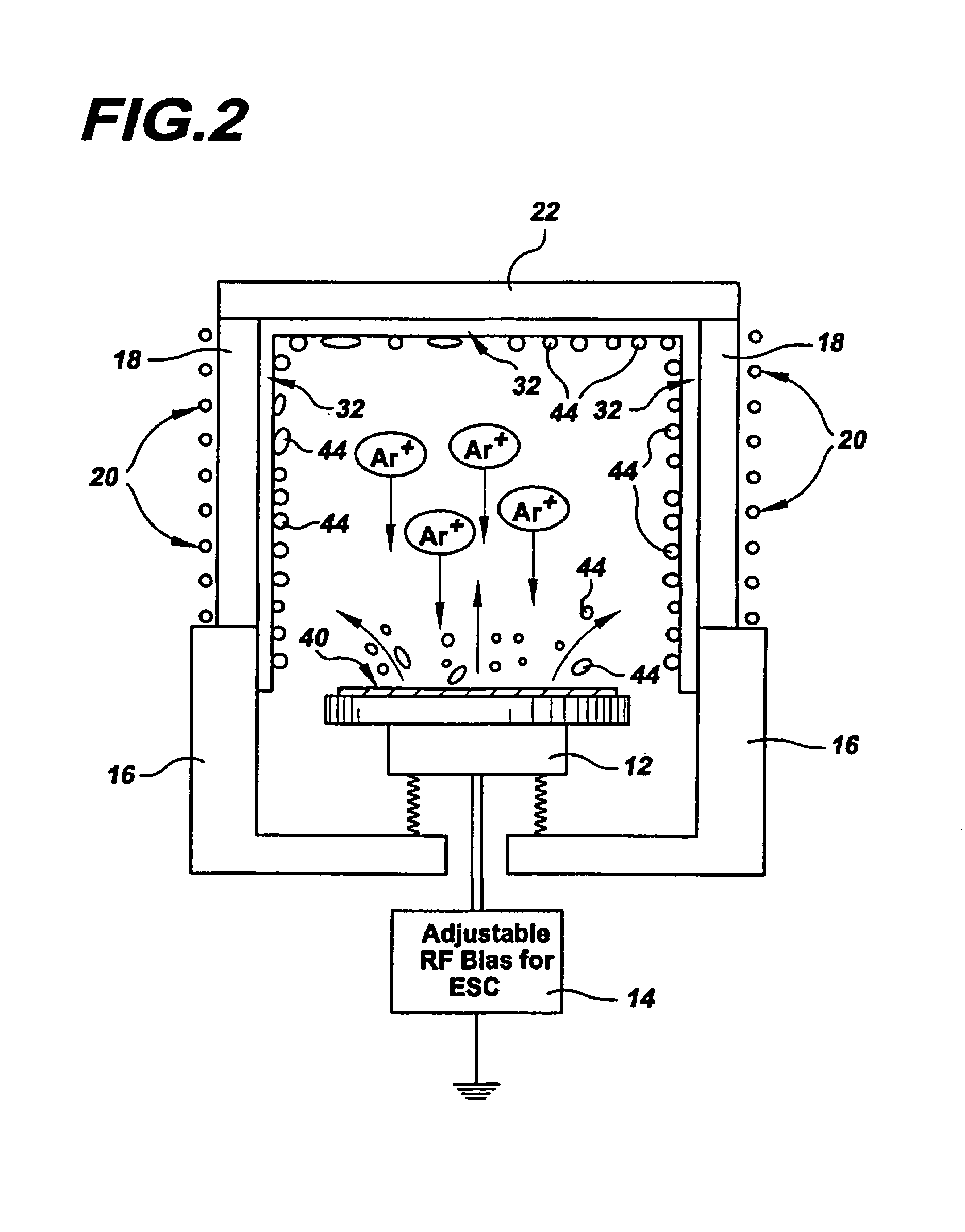
Methods and apparatus for cleaning a semiconductor substrate that significantly reduce the number of particles falling onto the substrate during cleaning by coating all interior surfaces within a processing chamber with an adhesion film that has an increased sticking coefficient for any subsequently arriving etched species to promote a continuous film growth and improve adhesion of such etched species. Due to its increased sticking coefficient, this adhesion film reduces surface mobility of any arriving by-products to enable the growth of the continuous film of etched species. The continuous film of etched species adheres firmly to the adhesion film such that the etched species are prevented from flaking off and falling onto the substrate being cleaned. The methods and apparatus may clean a plurality of semiconductor substrates, whereby a plurality of adhesion films are sequentially deposited over a plurality of continuous film growths of removed materials for cleaning the substrates.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Multi-Step Atomic Layer Deposition Process for Silicon Nitride Film Formation
InactiveUS20170107614A1Increase concentrationIncrease deposition rateChemical vapor deposition coatingNitrogenAtomic layer deposition
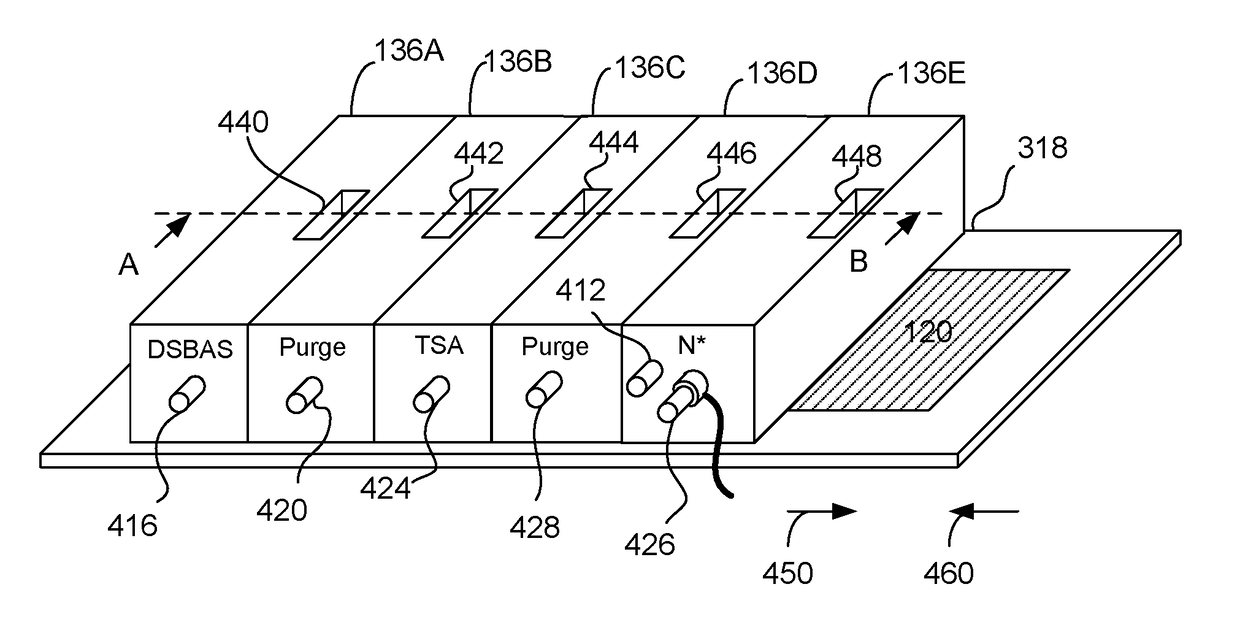
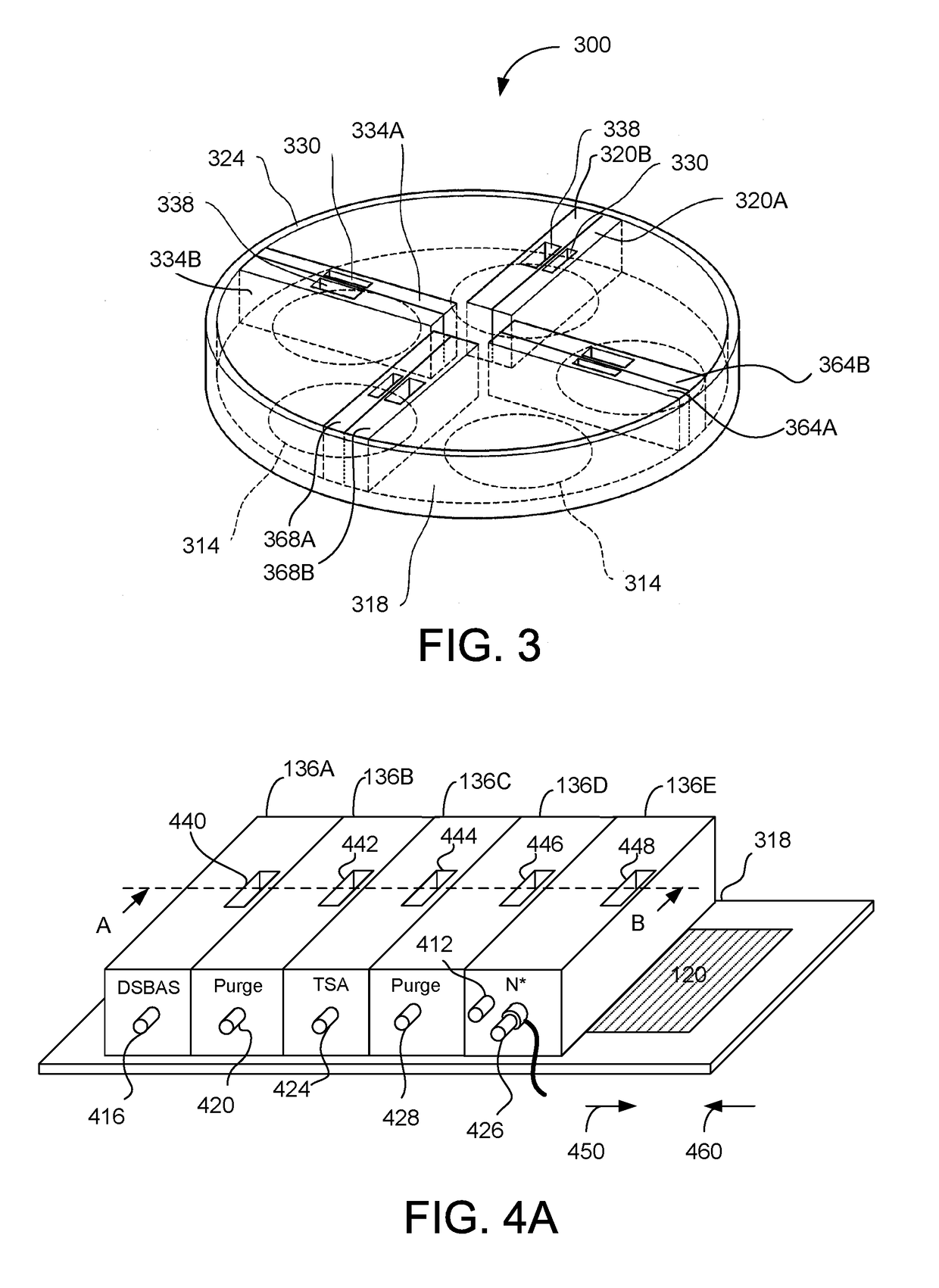
One or more silicon nitride layers are deposited onto a substrate by exposing the surface of the substrate to radicals to activate the surface of the substrate. A silicon-containing first precursor with a high sticking coefficient is injected onto the substrate. A second precursor including molecules each having at least two Si atoms is injected onto the substrate. The first precursor has a higher sticking coefficient than the second precursor. The substrate is treated with nitrogen radicals N* to form multiple layers of silicon nitride per radical exposure. This results in high-quality silicon nitride films with high deposition rate.
Owner:VEECO ALD
Germanium doped n-type aluminum nitride epitaxial layers
InactiveUS7682709B1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenMolecular beam
A method of preparing an n-type epitaxial layer of aluminum nitride conductively doped with germanium comprises directing a molecular beam of aluminum atoms onto the growth surface of a substrate that provides an acceptable lattice match for aluminum nitride; directing a molecular beam of activated nitrogen to the growth surface of the substrate; and directing a molecular beam of germanium to the growth surface of the substrate; while maintaining the growth surface of the substrate at a temperature high enough to provide the surface mobility and sticking coefficient required for epitaxial growth, but lower than the temperature at which the surface would decompose or the epitaxial layer disassociate back into atomic or molecular species.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Etching method
ActiveUS20170178922A1Improvement factorParticle separator tubesSolid-state devicesHydrogenHigh frequency power
An etching method for etching a silicon oxide film is provided that includes generating a plasma from a gas including a hydrogen-containing gas and a fluorine-containing gas using a high frequency power for plasma generation, and etching the silicon oxide film using the generated plasma. The fluorine-containing gas includes a hydrofluorocarbon gas, and the sticking coefficient of radicals generated from the hydrofluorocarbon gas is higher than the sticking coefficient of radicals generated from carbon tetrafluoride (CF4).
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Control method and device of braking system
InactiveCN1478685AImplement dynamic allocationEasy to brakeBraking systemsEngineeringLoad distribution
A control method for the brake system of car or motorcycle, especially the PWM-type brake system, is based on the acceleration detection. It can realize the total mass (weight) detection, ground sticking coefficient detection, dynamic load distribution, optimal slide rate control and anti-seizing function. Its controller is also disclosed. Its advantages are simple structure and low cost.
Owner:朱筱杰
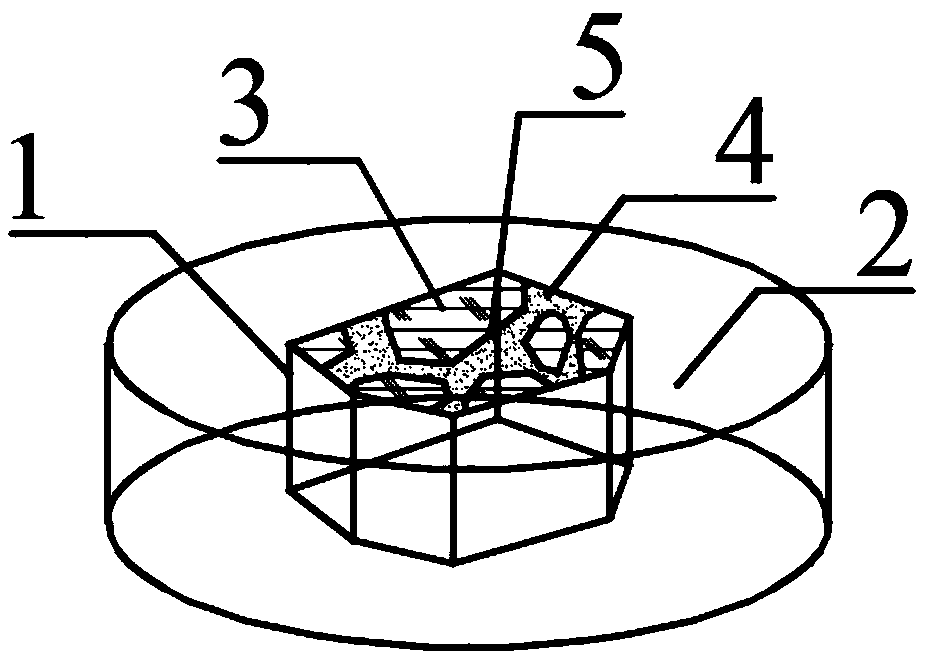
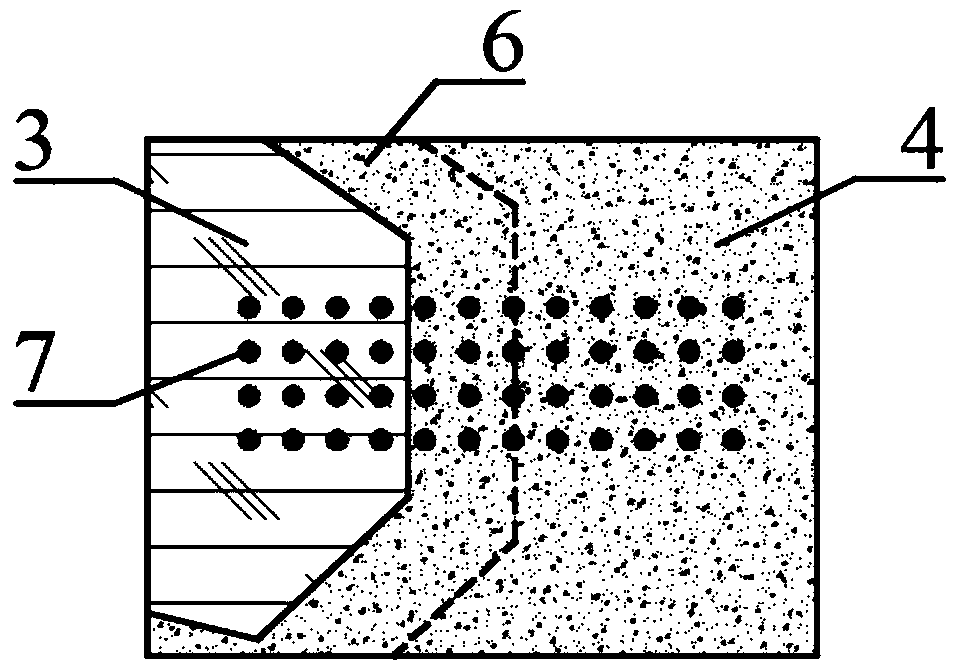
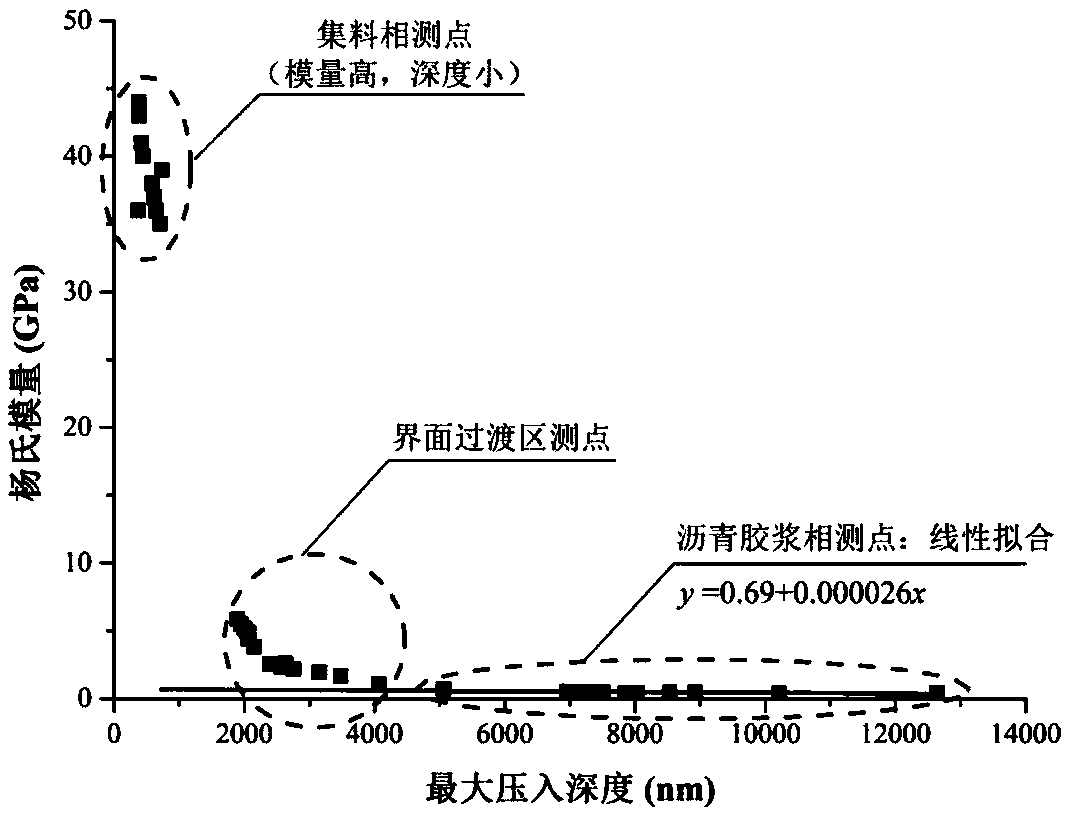
A test method for measuring the characteristic parameters of an interface transition zone of asphalt mixture
The invention discloses a test method for measuring the characteristic parameters of an interface transition zone of asphalt mixture. According to the phenomenon of mechanical property changes existing in an interface transition zone between aggregate and asphalt mortar, the method utilizes a nanoindentor to perform a micromechanical property test at the interface between the aggregate and the mortar in an asphalt mixture sample, equidistantly sets measuring points from the aggregate phase to the asphalt mortar phase to obtain the load-indentation depth curve of each point, calculates a modulus value, determines the number of the measuring points according to the modulus and indentation depth changing trend of each measuring point, and estimates the thickness of the interface transition zone by combining the distribution and interval of the measuring points, and therefore, the sticking coefficient of the interface transition zone can be calculated, and the quantitative characterizationof the thickness, mechanical properties, interaction strength and other characteristic parameters of the aggregate-asphalt mortar interface transition zone can be realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
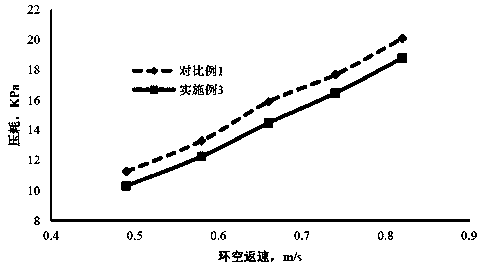
High-density low-frictional-resistance drilling fluid
ActiveCN104312557AReduce contentLow viscosity coefficientDrilling compositionPolymer scienceFiltration
The invention relates to a high-density low-frictional-resistance drilling fluid, and belongs to the technical field of oil-field drilling fluids. The high-density low-frictional-resistance drilling fluid employs water as a base liquid, and is obtained by mixing 1%-3% by mass of sodium bentonite, sodium carbonate accounting for 5% by mass of sodium bentonite, 0.5%-1.0% by mass of sodium hydroxide, 0.05%-0.1% by mass of tackifier A, 0.2%-0.5% by mass of filtrate reducer B, 0.5%-1.0% by mass of carboxymethyl cellulose sodium salt, 3.0%-5.0% by mass of sulfonated phenolic resin, 3.0%-5.0% by mass of sulfonated lignite, 2.0%-3.0% by mass of polymeric alcohol, 100% by mass of an organic salt C and 29.1%-122.2% by mass of barite, and performing high-temperature ageing. The drilling fluid has the temperature resistance up to 135 DEG C and the controllable density scope of 1.50-1.80 g / cm<3>, has good rheological property and filtration property at a high temperature, and has relatively low barite content, mud cake sticking coefficient and cyclic pressure dissipation, and relatively high inhibition performance.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
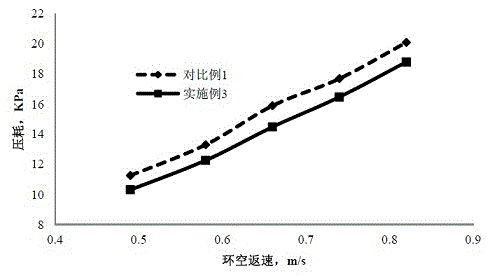
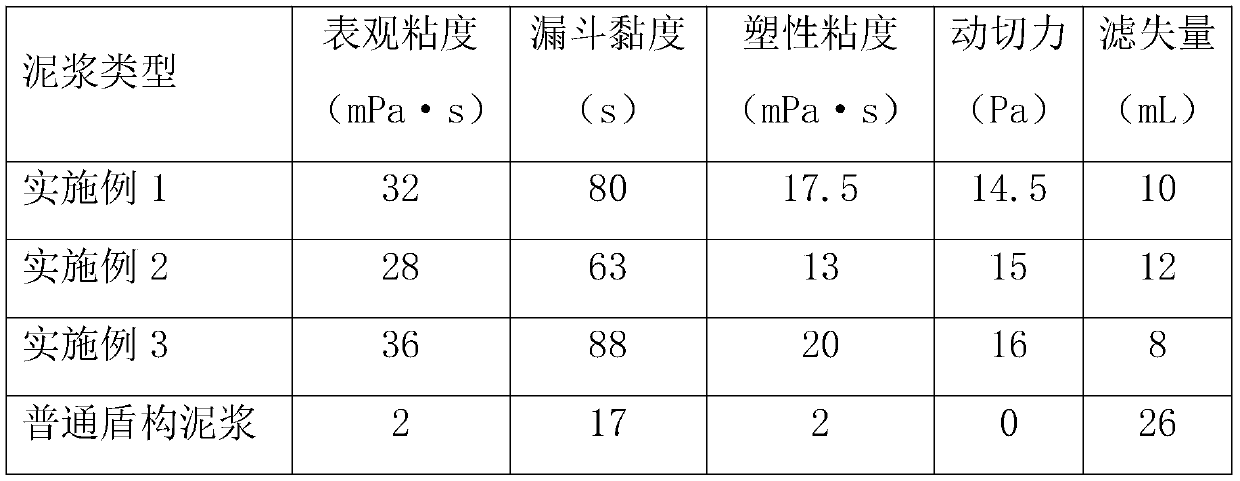
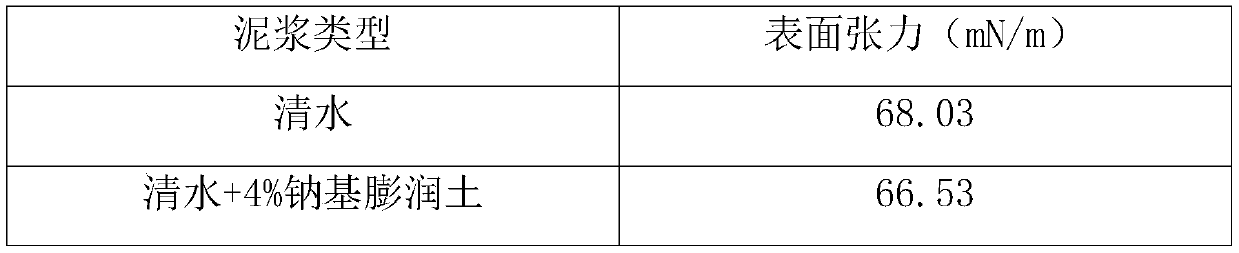
Shield mud system applicable to extra-large-diameter tunnel and preparation method
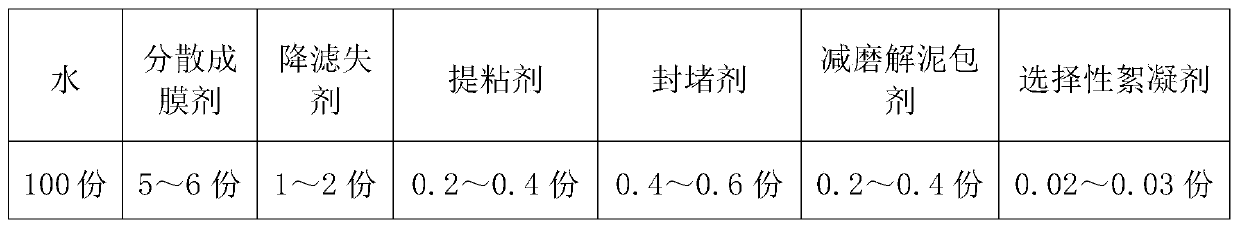
InactiveCN109762534AImprove recycling ratesQuality improvementDrilling compositionMud systemsFiltration
The invention provides a shield mud system applicable to an extra-large-diameter tunnel. The shield mud system is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by mass: 100 parts of water, 5 to 6parts of a dispersion film-forming agent, 1 to 2 parts of a filtration-reducing agent, 0.2 to 0.4 part of a viscosity improving agent, 0.4 to 0.6 part of a plugging agent, 0.2 to 0.4 part of an anti-wear and mud ball splitting agent and 0.02 to 0.03 part of a selective flocculating agent. The shield mud system provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that the shield mud system has unique 'lubrication and anti-wear performance' and has the effects of protecting a shield bit tool and improving the footage drilling efficiency; a dense mud film can be formed, the filtration loss amount is reduced and the soil pressure is balanced, so that the stability of a well wall is enhanced, the sticking coefficient can be reduced and a mud ball of the shield bit tool is prevented; and the shield mud system has good rheological performance, filtration-reducing performance and lubricating performance and can meet the requirements of shield mud drilling, and has the advantages of environment protection and low cost.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Beam-induced deposition at cryogenic temperatures
ActiveUS8796646B2Easy to useMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesAlkaneAlkyne
A method of depositing material onto a substrate at cryogenic temperatures using beam-induced deposition. A precursor gas is chosen from a group of compounds having a melting point that is lower than the cryogenic temperature of the substrate. Preferably the precursor gas is chosen from a group of compounds having a sticking coefficient that is between 0.5 and 0.8 at the desired cryogenic temperature. This will result in the precursor gas reaching equilibrium between precursor molecules adsorbed onto the substrate surface and precursor gas molecules desorbing from the substrate surface at the desired cryogenic temperature. Suitable precursor gases can comprise alkanes, alkenes, or alkynes. At a cryogenic temperature of between −50° C. and −85° C., hexane can be used as a precursor gas to deposit material; at a cryogenic temperature of between −50° C. and −180° C., propane can be used as a precursor gas.
Owner:FEI CO
Methods for controlling plasma constituent flux and deposition during semiconductor fabrication and apparatus for implementing the same
ActiveCN103098184AElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTemperature controlSemiconductor
A time-dependent substrate temperature to be applied during a plasma process is determined. The time-dependent substrate temperature at any given time is determined based on control of a sticking coefficient of a plasma constituent at the given time. A time-dependent temperature differential between an upper plasma boundary and a substrate to be applied during the plasma process is also determined. The time-dependent temperature differential at any given time is determined based on control of a flux of the plasma constituent directed toward the substrate at the given time. The time-dependent substrate temperature and time-dependent temperature differential are stored in a digital format suitable for use by a temperature control device defined and connected to direct temperature control of the upper plasma boundary and the substrate. A system is also provided for implementing upper plasma boundary and substrate temperature control during the plasma process.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
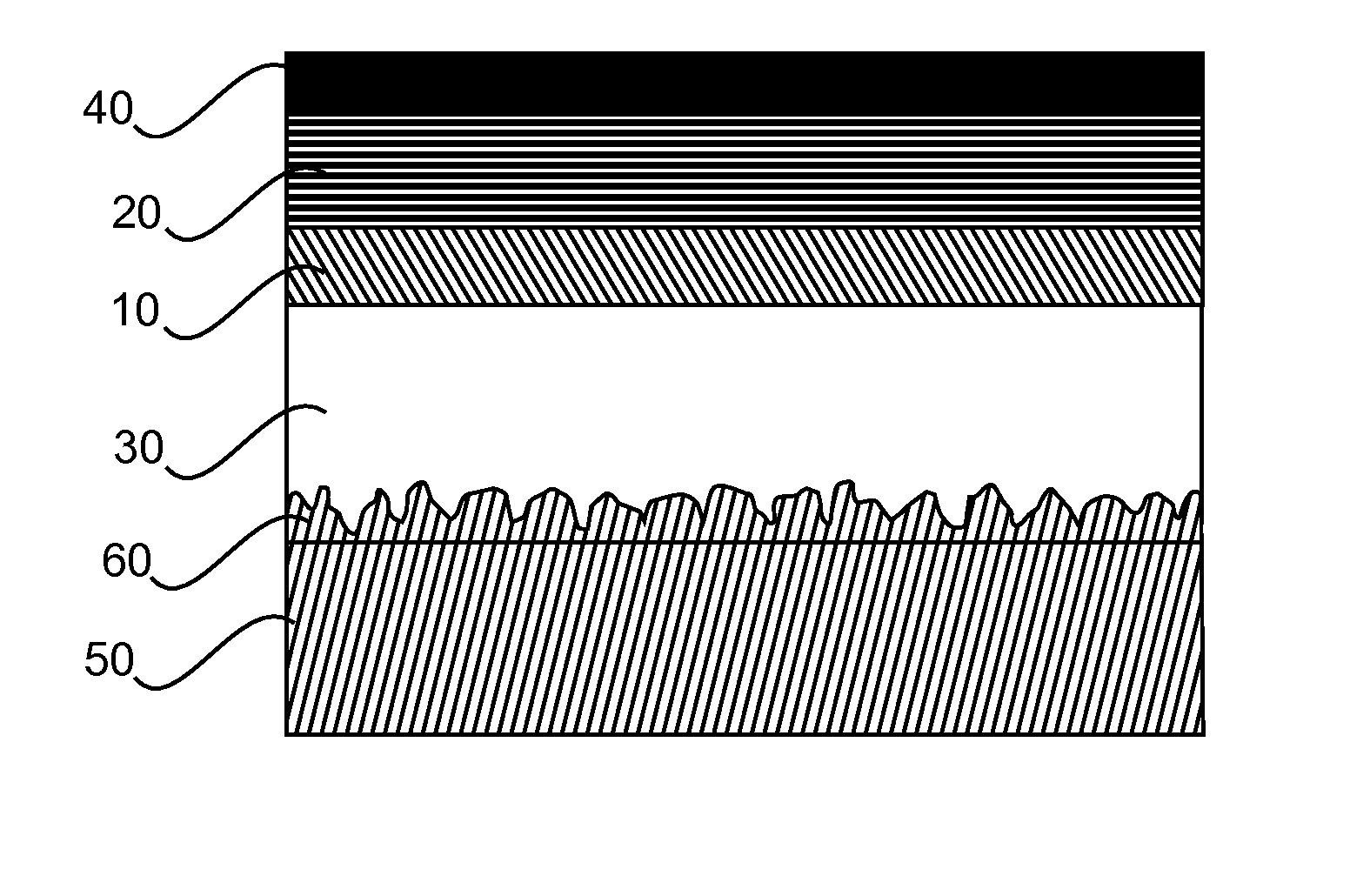
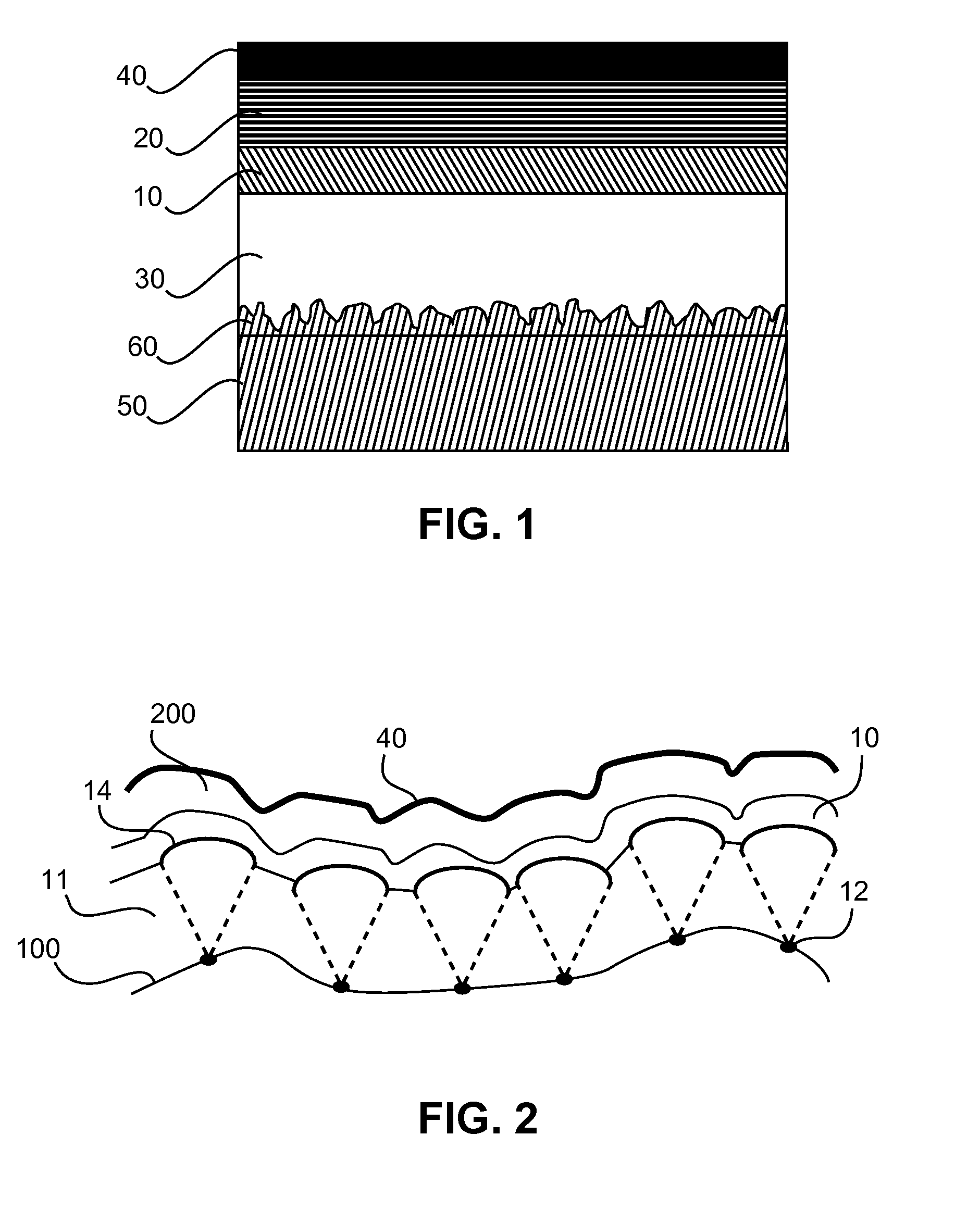
Light emitting device with improved internal out-coupling and method of providing the same
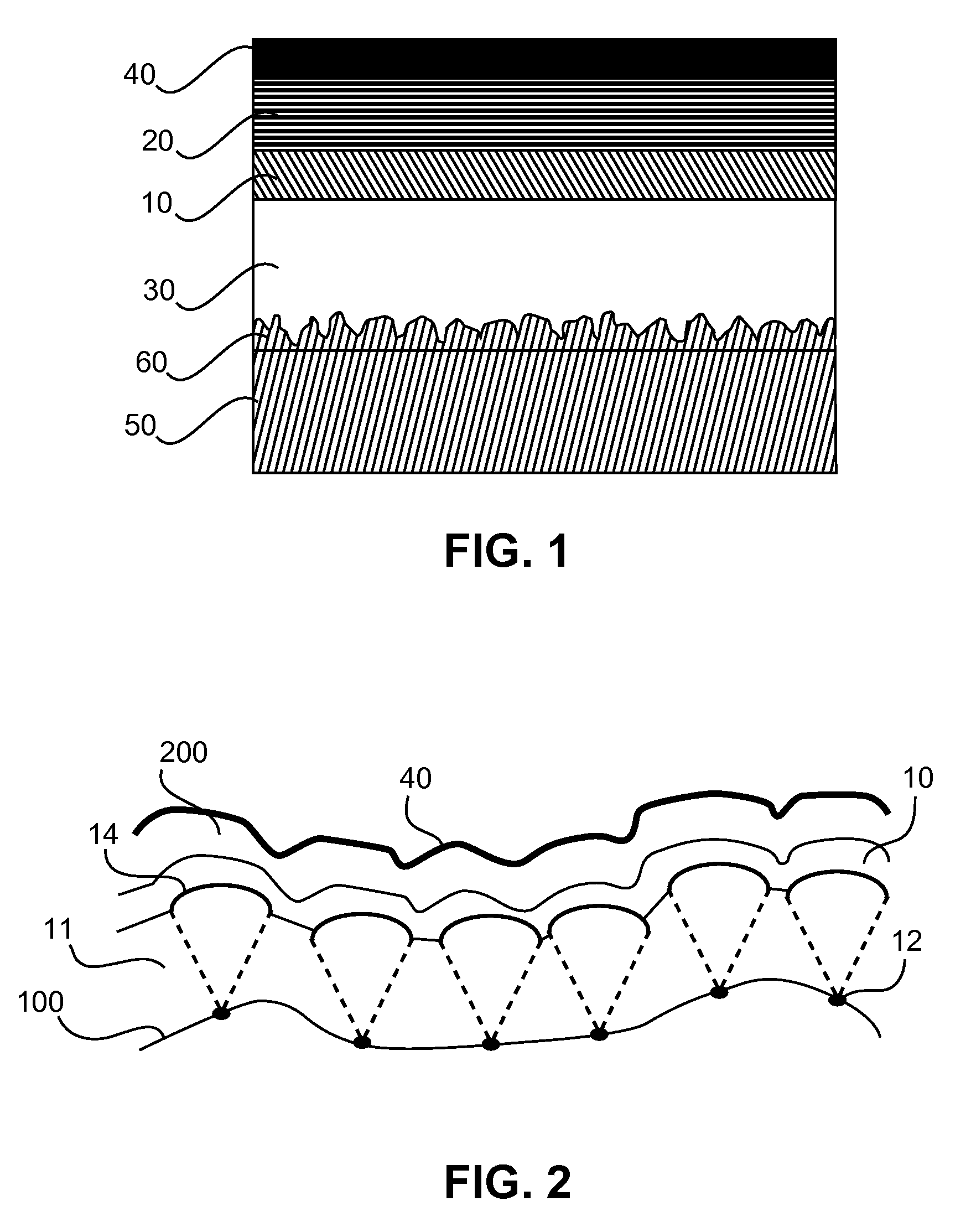
InactiveUS20150311476A1Sufficient scatteringStrong growthFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesFlat glassGas phase
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing a light emitting device with improved internal out-coupling by providing an intermediate layer (11) with a modulated surface. This is achieved by exposure of a flat glass surface (100) to a saturated etching fluid or by providing local changes in the chemical surface composition of the glass substrate or by depositing locally separated sub-μm particles. By removal of the etching fluid, either ultrafine particles (12) are deposited or defects are generated consisting of glass component areas of sub̂m-size extension with a high sticking coefficient with respect to the species deposited later on from the gas phase. These ultrafine particles or defects induce locally different growth by different sticking coefficients, with preferential columnar cone shaped growth, leading to small bumps (14) on the top surface of the intermediate layer (11), which are then over-coated with the layers (200) of the light emitting element and induce sufficient scattering by subsequent reflections.
Owner:OLEDWORKS GMBH
Automatic layer deposition process
InactiveUS20070161180A1Improve adhesion coefficientLow vapor pressureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsDeposition processAtomic layer deposition
The atomic layer deposition process according to the invention provides the following steps for the production of homogeneous layers on a substrate. The substrate is introduced into a reaction chamber. A first precursor is introduced into the reaction chamber, which first precursor reacts on the surface of the substrate to form an intermediate product. A second precursor is introduced into the reaction chamber, which second precursor has a low sticking coefficient and reacts with part of the intermediate product to form a first product. A third precursor is introduced into the reaction chamber, which third precursor has a high sticking coefficient and reacts with the remaining part of the intermediate product to form a second product. The second precursor and its first product reduce the effective sticking coefficient of the third precursor by partially covering the surface.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
A high-density low-friction drilling fluid
ActiveCN104312557BReduce contentLow viscosity coefficientDrilling compositionSodium BentonitePolymer science
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Cargo vehicle ABS road identification method
This invention relates to a road identifying method for the ABS of camion brakes, which takes the maximum speed of the wheel as the reference then computes the friction of each wheel endured by the earth based on the angular acceleration of the wheel then to compute the mass of the vehicle and its parameter in loading to get the positive pressure of the wheel so as to get the sticking coefficient of the earth, then to compute the slip ratio and the theoretical sticking coefficient of different roads under the current slip ratio according to a theoretical formula to compare the two coefficients to identify the situation of the road.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
A device for measuring mechanical friction and adhesion coefficient
InactiveCN104749096BImprove reliabilityLow costUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisAdhesion coefficientVertical plane
The invention relates to a mechanical friction and adhesion coefficient measuring device, which is used to measure the friction coefficient or adhesion coefficient of a piece to be tested, including a frame, a drive shaft, a friction disc, a force transmission shaft, a force measuring mechanism, Pressing mechanism and thrust mechanism, one end of the drive shaft is connected to the external drive device, and the other end is connected to the friction plate, the thrust mechanism and the test piece are sequentially installed on the force transmission shaft, and the test piece is in contact with the friction plate , one end of the force transmission shaft is connected to the force measuring mechanism, and the pressing mechanism is arranged at the other end of the force transmission shaft; the external driving device rotates the drive shaft, drives the friction disc to rotate, and simultaneously the force transmission shaft rotates in the vertical plane, By adjusting the pressing mechanism and the thrust mechanism, the force applied to the test piece is changed, and the friction coefficient or adhesion coefficient of the test piece is obtained according to the torque measured by the force-measuring mechanism. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages of high reliability, simple operation, low cost and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Light emitting device with improved internal out-coupling and method of providing the same
InactiveUS9349994B2Sufficient scatteringStrong growthFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesFlat glassGas phase
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing a light emitting device with improved internal out-coupling by providing an intermediate layer (11) with a modulated surface. This is achieved by exposure of a flat glass surface (100) to a saturated etching fluid or by providing local changes in the chemical surface composition of the glass substrate or by depositing locally separated sub-μm particles. By removal of the etching fluid, either ultrafine particles (12) are deposited or defects are generated consisting of glass component areas of sub^m-size extension with a high sticking coefficient with respect to the species deposited later on from the gas phase. These ultrafine particles or defects induce locally different growth by different sticking coefficients, with preferential columnar cone shaped growth, leading to small bumps (14) on the top surface of the intermediate layer (11), which are then over-coated with the layers (200) of the light emitting element and induce sufficient scattering by subsequent reflections.
Owner:OLEDWORKS GMBH
Phosphors for a plasma display panel, and a plasma display panel using the same
InactiveCN1329938CSmall difference in brightnessReduce the ratio of sticking to the fluorescent layerAlternating current plasma display panelsSolid cathode detailsPhosphorFluorescence
A plasma display panel, and phosphors for a plasma display panel are disclosed. The plasma display panel comprises first and second substrates each facing each other. Discharge sustain electrodes are positioned on the first substrate. A dielectric layer covers the discharge sustain electrodes. A MgO protective layer covers the dielectric layer. Address electrodes are positioned on the second substrate. Barrier ribs are arranged between the first and second substrates, creating a plurality of discharge cells. A phosphor layer is positioned on the second substrate between the barrier ribs in each discharge cell. The phosphor layer comprises a first non-fluorescent material and a second fluorescent material. The first fluorescent material has a MgO sticking coefficient greater than that of the second fluorescent material.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com