Coating for substrate
A technology of substrate and substrate surface, applied in coatings, catheters, prostheses, etc., can solve problems such as difficulties in designing and manufacturing coatings
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
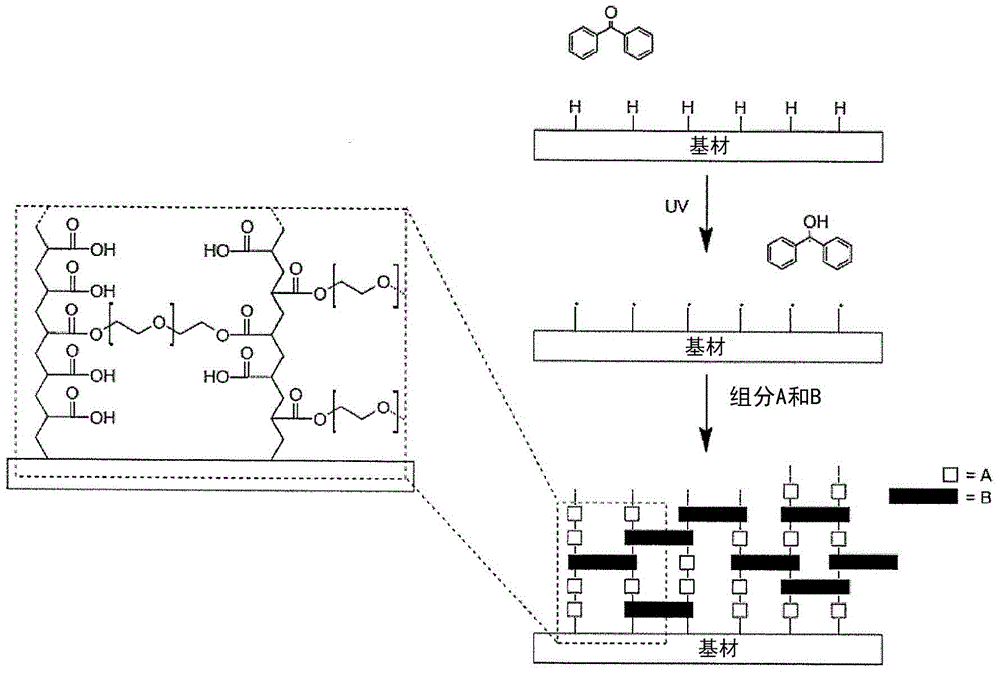
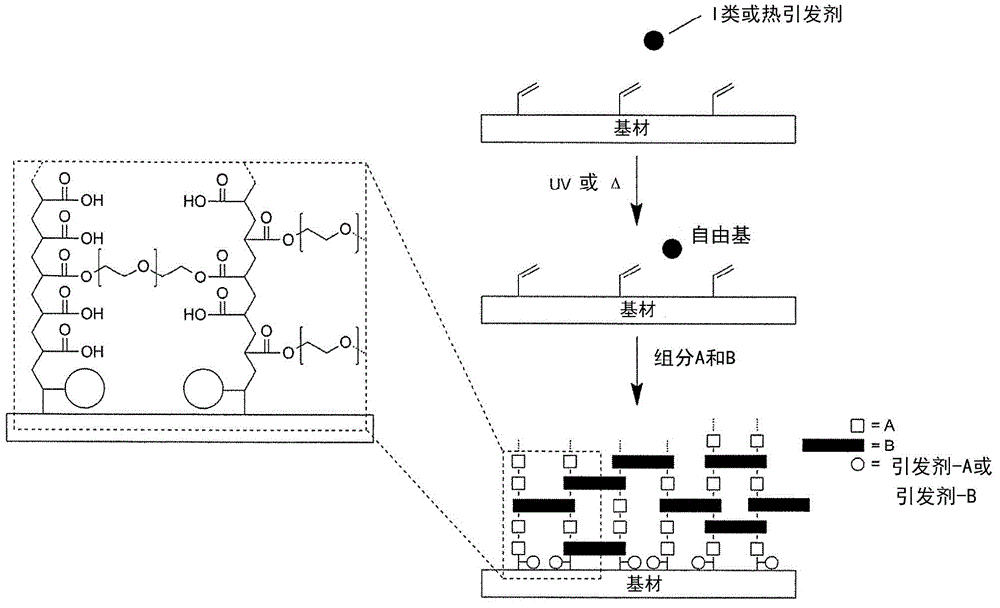
[0209] In a first embodiment, the covalent linkage between the substrate surface and the hydrophilic coating is formed by the reaction of surface-bound radicals on the substrate surface with components of the hydrophilic coating, wherein the surface-bound The free radicals are formed by abstracting hydrogen atoms from the substrate surface.
[0210] like figure 1 As shown, in this embodiment, polymerization is initiated when the free radical initiator in the liquid phase contacts the surface to abstract hydrogen atoms from the substrate surface to form surface bound free radicals. Surface bound free radicals react with components A, B and C and D (when present and capable of such reactions – figure 1Only at least one reaction of components A and B) to covalently attach the copolymer to the surface is shown. Copolymers can pass through all of Components A, B and C and D (when present) (or at least through a copolymer that was previously present as Component A or Component B...
Embodiment 1
[0458] Example 1: Formation of a polymeric surface primer coating comprising extractable hydrogen atoms on a substrate
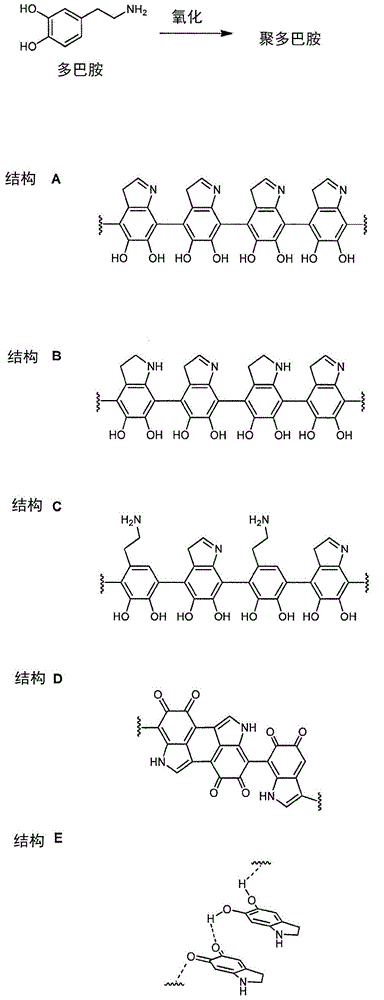
[0459] In the following examples, polydopamine surface primer coatings were formed on various substrates. When exposed to the polymerization solution, the QCM crystals and the PVC pipe substrate were horizontally aligned. All other substrates are aligned vertically. The polydopamine coating was subsequently analyzed for uniformity, adhesion and other properties and the results are given in Example 1a.
Embodiment 11
[0460] Example 1.1 Preparation of a polydopamine surface primer coating on a PEBAX shaft at pH 8 and using Pretreatment method A
[0461] PEBAX axes were preconditioned according to Method A. Submerge the pretreated shaft in a deionized aqueous solution of tris buffer (1.21 g / L) and APS (0.6 g / L) and adjust the pH to 8.0 using HCl (1 M). Dopamine (1 g / L) was added to the solution and polymerization was allowed to proceed for 15, 30, 60 or 120 minutes. The polydopamine-primed shafts were rinsed with EtOH and dried at room temperature prior to analysis.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com