Recovery method for front-section defluorination of waste lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery and battery technology, applied in battery recycling, waste collector recycling, secondary batteries, etc., can solve problems such as accelerated equipment corrosion, poor fluorine removal effect, and impact on product quality, so as to save energy consumption and raw materials The effect of low cost and equipment requirements and high recycling rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
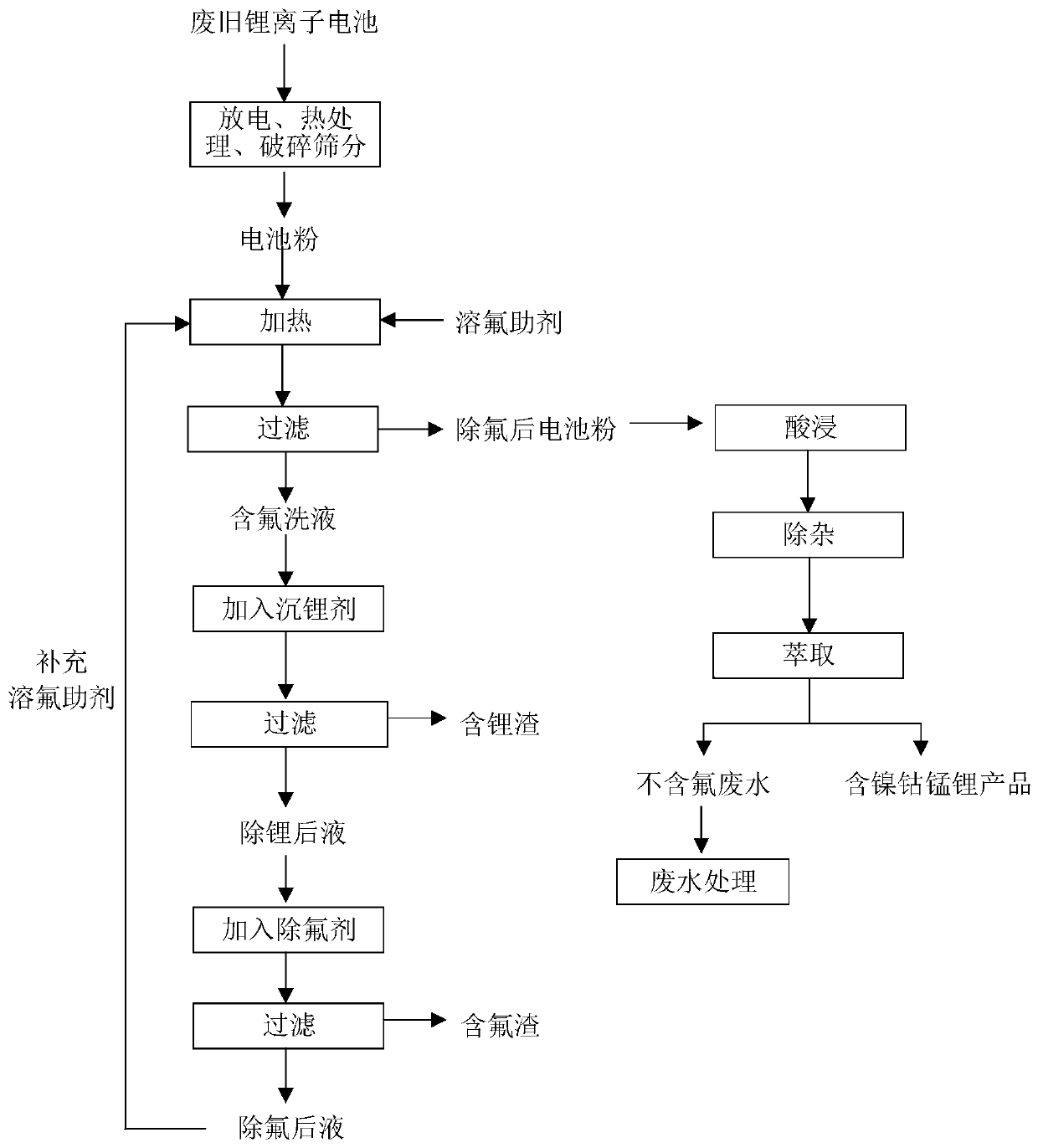
[0058] A recovery method for removing fluorine from the front end of a waste lithium-ion battery, comprising the following steps:
[0059] (1) Carry out heat treatment after discharging the waste lithium-ion battery, after crushing and sieving, obtain fluorine-containing lithium cobaltate battery powder;
[0060] (2) Mix 50 g of battery powder with a fluorine content of about 1.24% and a sodium sulfate solution of 3.8 times the theoretical molar amount of fluorine at a mass-to-volume ratio of 1:25 to obtain a mixed slurry;
[0061] (3) Stir the mixed slurry obtained in step (2) at a constant temperature of 80°C for 1 hour, and filter to obtain the defluorinated battery powder 1-1 and fluorine-containing lotion;
[0062] (4) Add 1.3 times the theoretical molar amount of sodium phosphate to the fluorine-containing lotion, stir at a constant temperature of 85°C for 1 hour, and filter to obtain lithium phosphate slag and lithium-removed liquid;
Embodiment 2
[0067] A recovery method for removing fluorine from the front end of a waste lithium-ion battery, comprising the following steps:
[0068] (1) Carry out heat treatment after discharging the waste lithium-ion battery, after crushing and sieving, obtain fluorine-containing lithium cobaltate battery powder;
[0069] (2) Mix 50 g of battery powder with a fluorine content of about 1.24% and 7.6 times the theoretical molar amount of sodium carbonate solution at a mass-to-volume ratio of 1:20 to obtain a mixed slurry;
[0070] (3) Stir the mixed slurry obtained in step (2) at a constant temperature of 80°C for 2 hours, and filter to obtain the defluorinated battery powder 2-1 and fluorine-containing lotion;
[0071] (4) Add sodium carbonate with 1.2 times the theoretical molar amount of lithium to the fluorine-containing lotion, stir for 2 hours at a constant temperature of 90°C, and filter to obtain lithium carbonate slag and lithium-removed liquid;
[0072] (5) Add magnesium hydro...
Embodiment 3
[0076] A recovery method for removing fluorine from the front end of a waste lithium-ion battery, comprising the following steps:
[0077] (1) Carry out heat treatment after discharging the waste lithium-ion battery, after crushing and sieving, obtain fluorine-containing ternary battery powder;
[0078] (2) Mix 50 g of battery powder with a fluorine content of about 0.897% and 3.8 times the theoretical molar amount of ammonium carbonate solution at a mass-to-volume ratio of 1:25 to obtain a mixed slurry;
[0079] (3) Stir the mixed slurry obtained in step (2) at a constant temperature of 90°C for 2 hours, and filter to obtain the defluorinated battery powder 3-1 and fluorine-containing lotion;
[0080] (4) Add sodium phosphate of 1.4 times the theoretical molar amount of lithium to the fluorine-containing lotion, stir for 2 hours at a constant temperature of 80°C, and filter to obtain lithium phosphate slag and lithium-removed liquid;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com