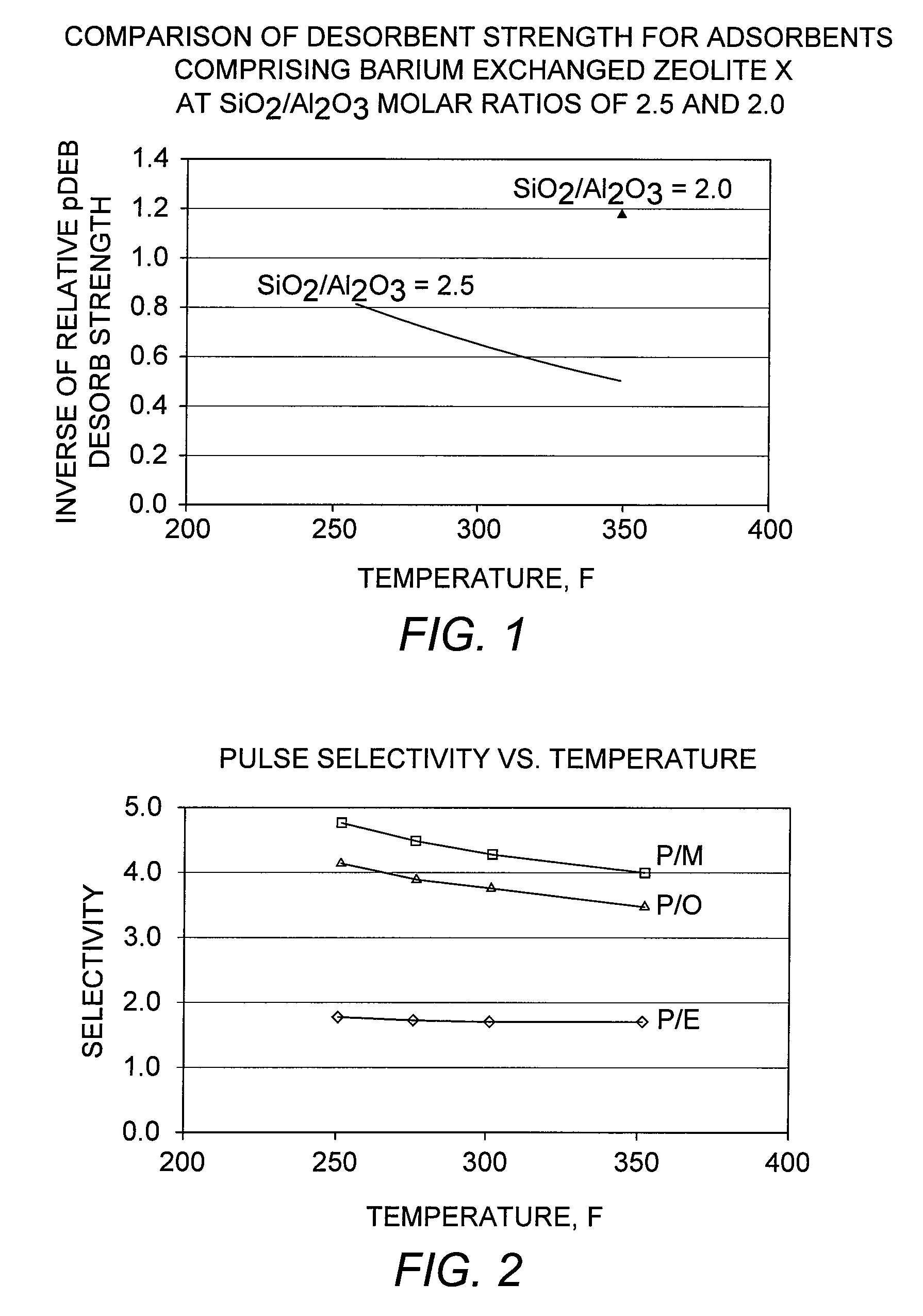
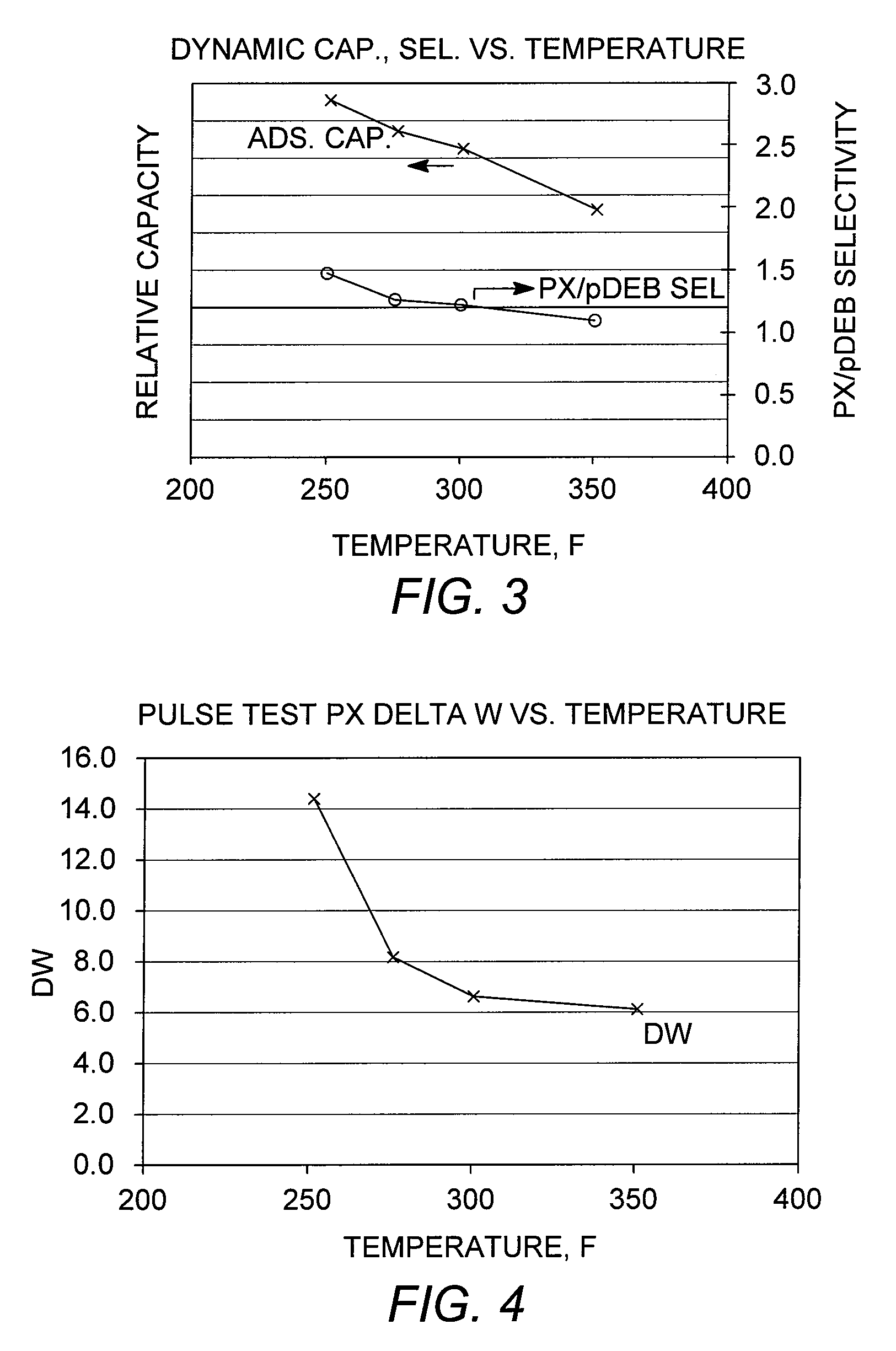
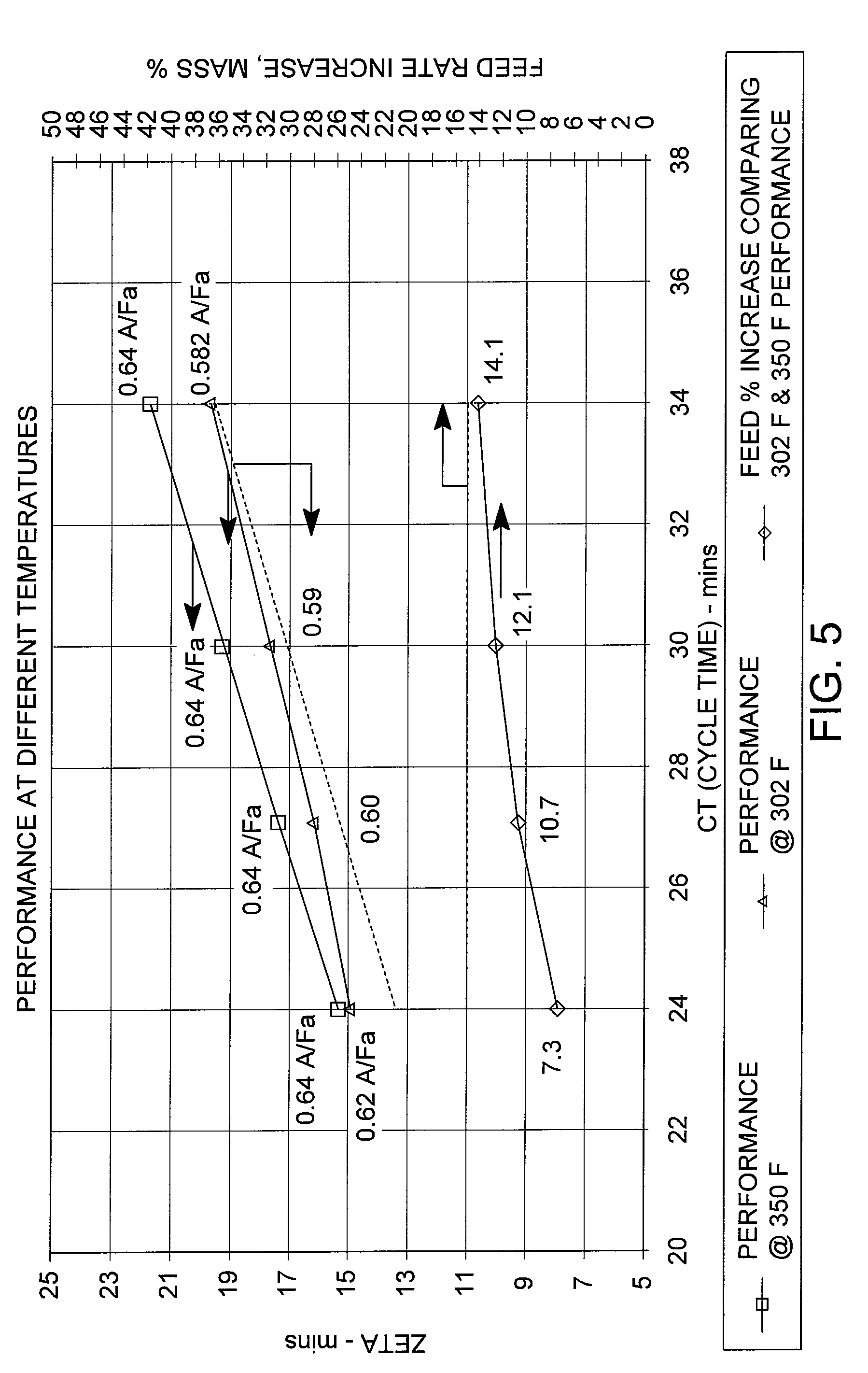
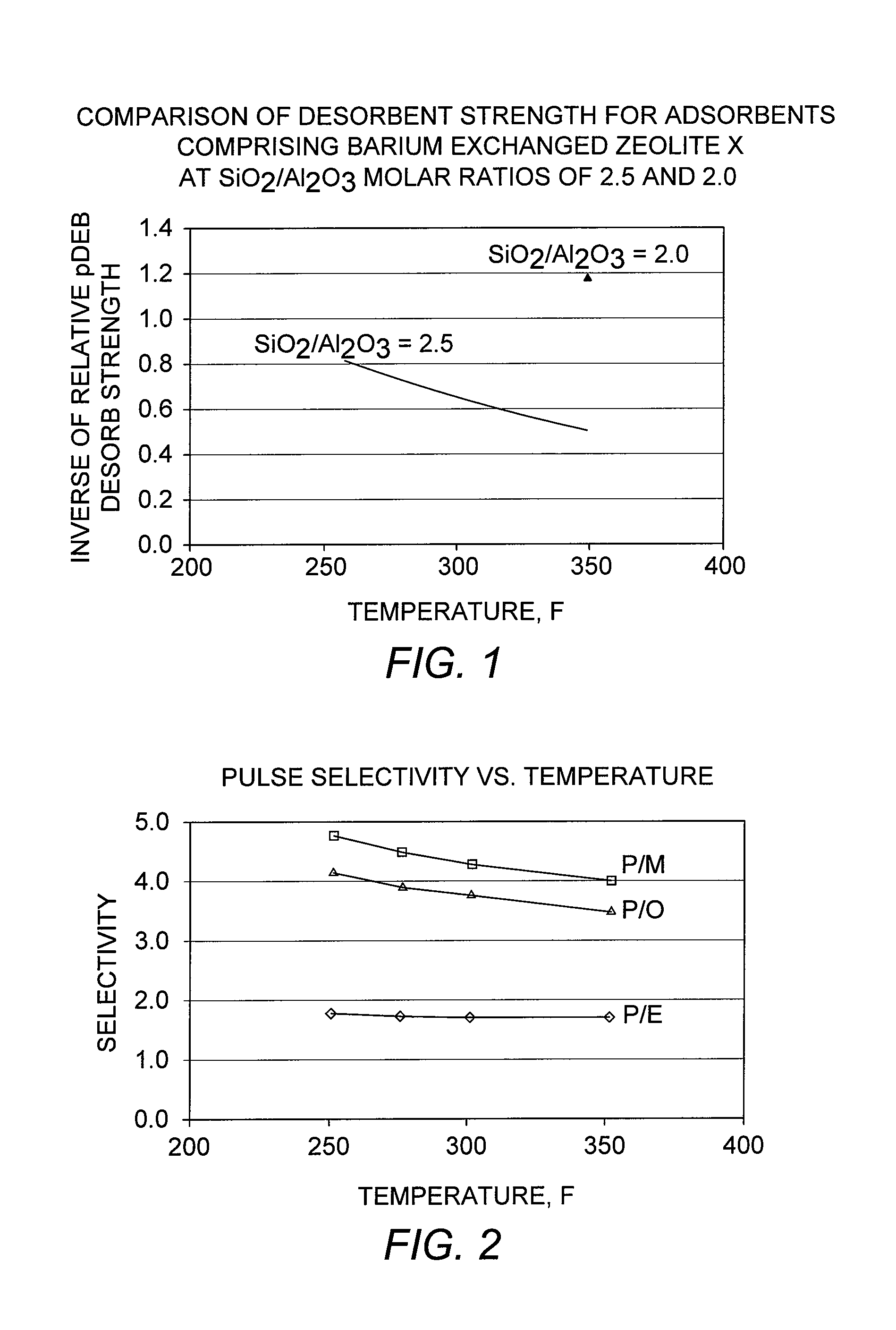
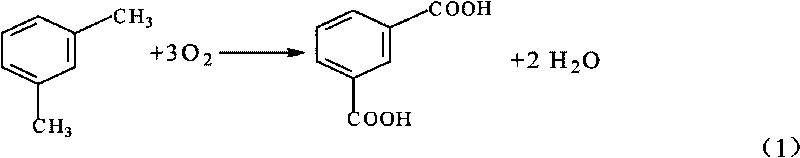
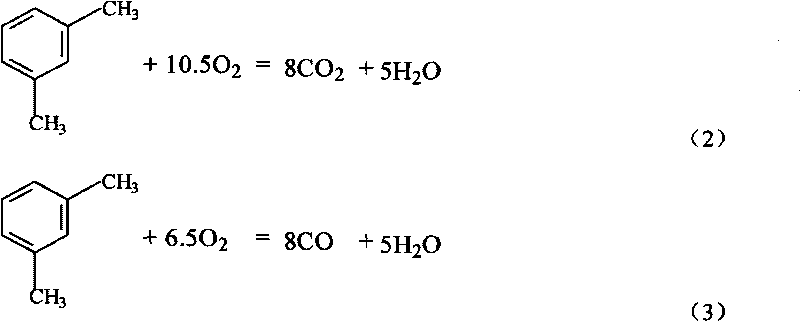Patents
Literature
138 results about "Meta-xylene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
M-Xylene (meta-xylene) is an aromatic hydrocarbon. It is one of the three isomers of dimethylbenzene known collectively as xylenes. The m-stands for meta-, indicating that the two methyl groups in m-xylene occupy positions 1 and 3 on a benzene ring.
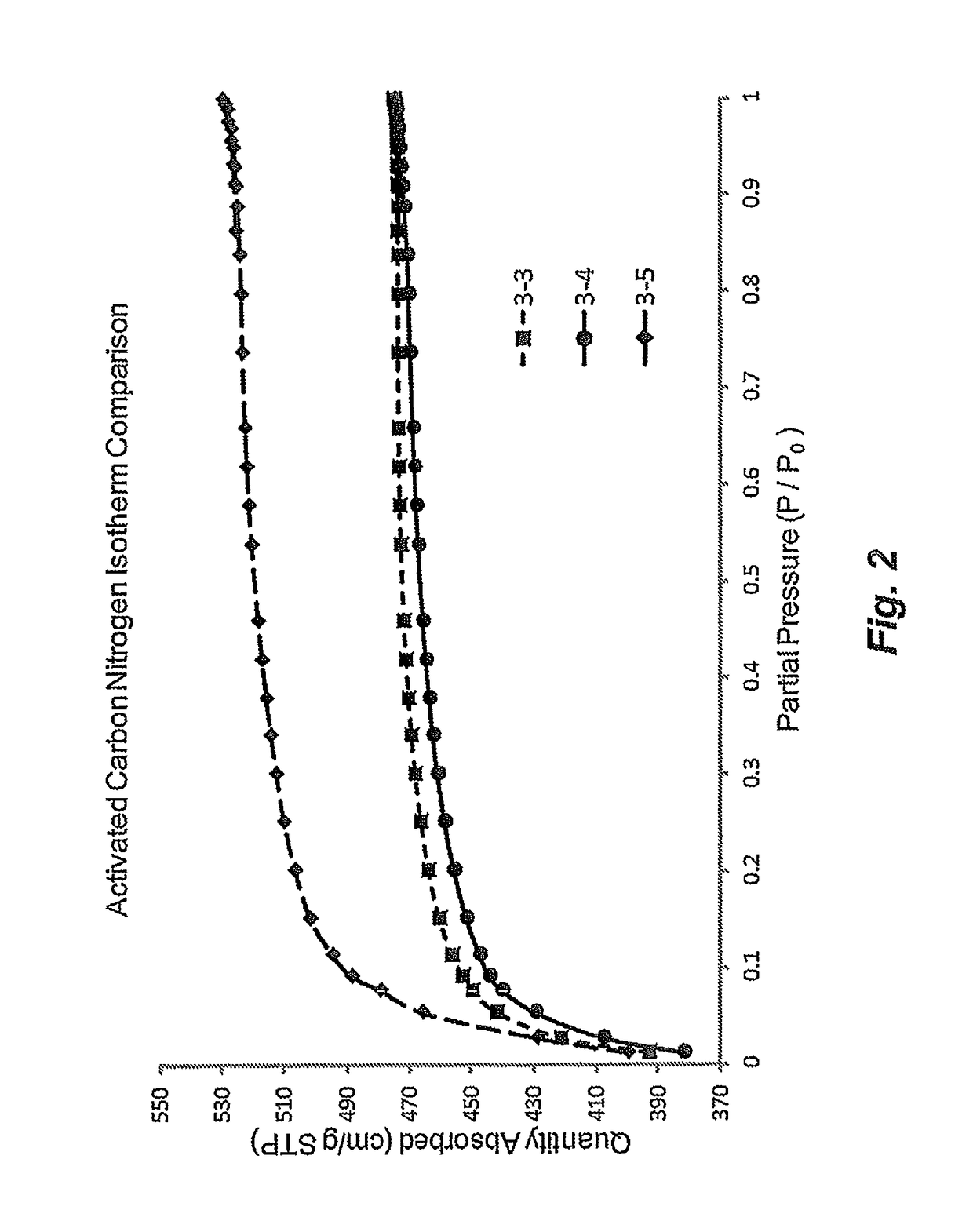
Binderless adsorbents with improved mass transfer properties and their use in the adsorptive separation of para-xylene
ActiveUS7812208B2Improve performanceImprove mass transfer effectOther chemical processesMolecular-sieve and base-exchange compoundsProduction rateSorbent
Owner:UOP LLC
Binderless adsorbents and their use in the adsorptive separation of para-xylene
ActiveUS7820869B2Improve performanceIncrease mass transfer rateMaterial nanotechnologyMolecular sieve catalystsProduction rateSorbent
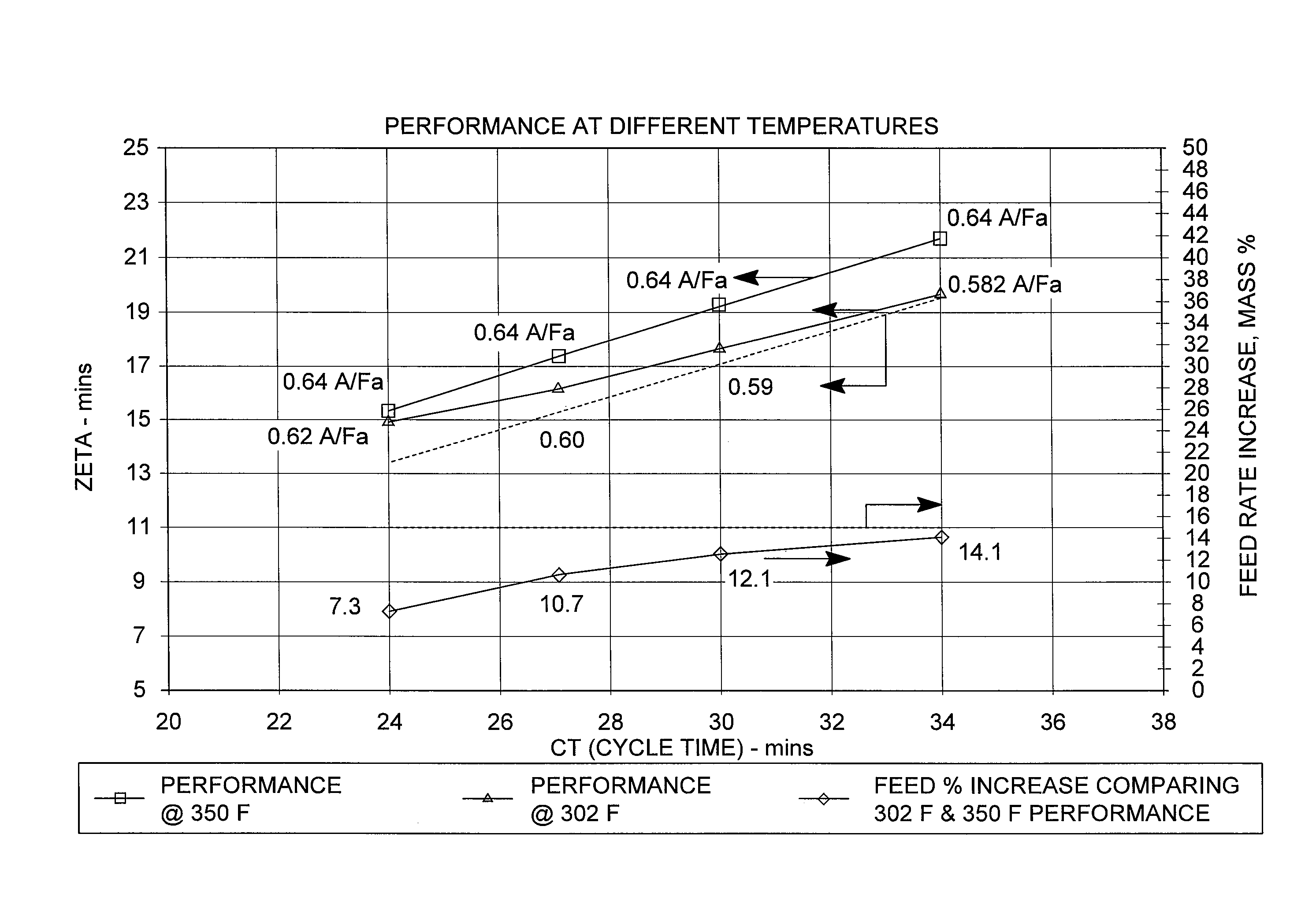
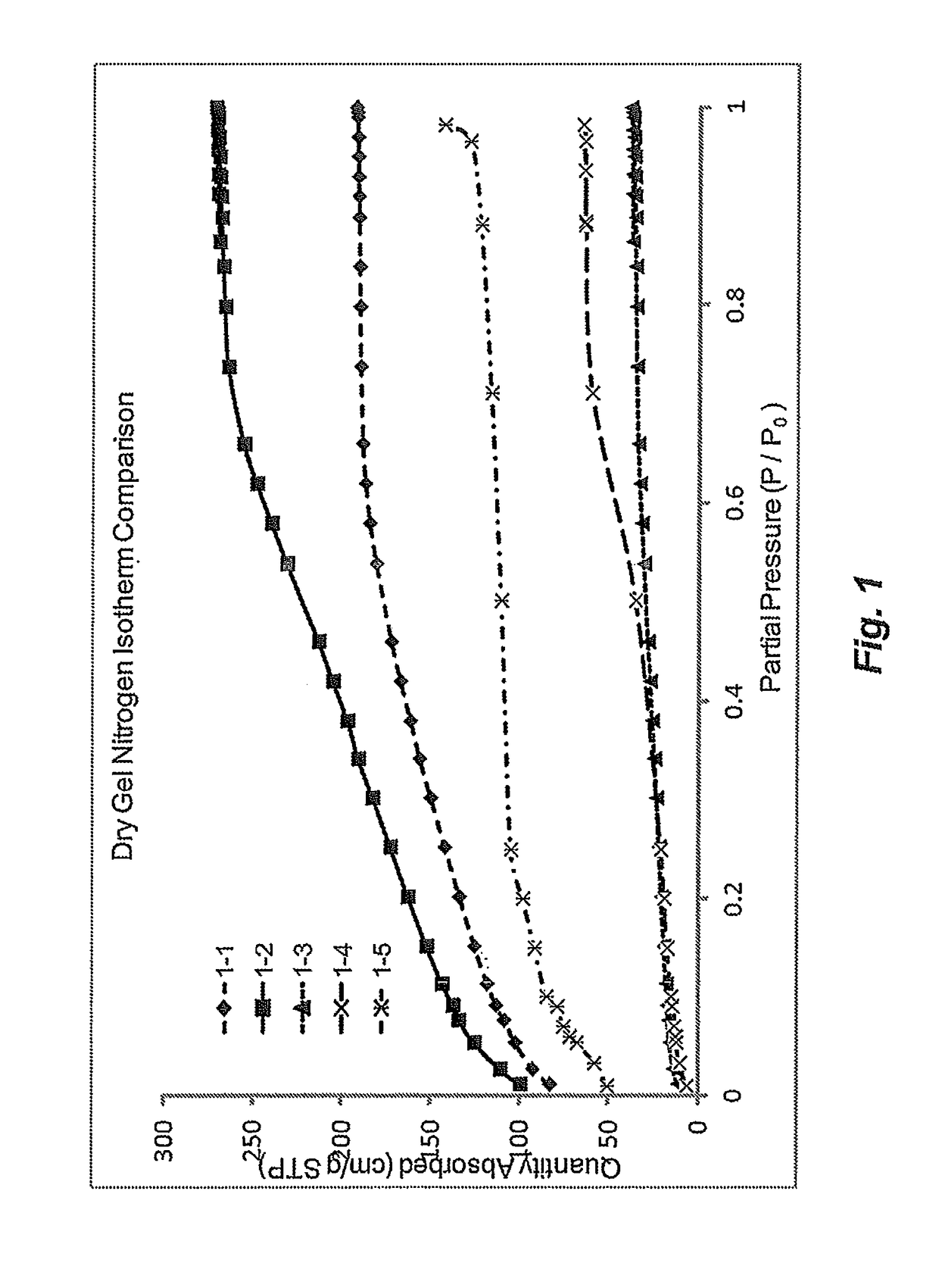
Adsorbents and methods for the adsorptive separation of para-xylene from a mixture containing at least one other C8 aromatic hydrocarbon (e.g., a mixture of ortho-xylene, meta-xylene, para-xylene, and ethylbenzene) are described. Suitable binderless adsorbents (e.g., formulated with the substantial absence of an amorphous material that normally reduces selective pore volume), particularly those with a water content from about 3% to about 5.5% by weight, improve capacity and / or mass transfer. These properties are especially advantageous for improving productivity in low temperature, low cycle time adsorptive separation operations in a simulated moving bed mode.
Owner:UOP LLC
Production of a xylene isomer in three stages: separation, isomerization with a catalyst with an EUO zeolite base and transalkylation with recycling of C10-aromatic compounds
A process for the production of at least one xylene isomer, paraxylene, metaxylene or orthoxylene from an aromatic feedstock that has 7 to 10 carbon atoms per molecule. The process comprises a stage for transalkylation of C7- and C9-aromatic compounds, a stage for separation of xylenes and a stage for isomerization of xylenes. The isomerization catalyst used in the process comprises at least one EUO zeolite composition whose crystals are grouped in aggregates that have a grain size with a value of Dv,90 less than or equal to 500 microns and at least one element of group VIII.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Binderless adsprbents and their use in the adsorptive separation of para-xylene
ActiveUS20090326309A1High adsorbent capacity/mass transfer propertyIncreased para-xylene productivityMaterial nanotechnologyMolecular sieve catalystsSorbentSimulated moving bed
Adsorbents and methods for the adsorptive separation of para-xylene from a mixture containing at least one other C8 aromatic hydrocarbon (e.g., a mixture of ortho-xylene, meta-xylene, para-xylene, and ethylbenzene) are described. Suitable binderless adsorbents (e.g., formulated with the substantial absence of an amorphous material that normally reduces selective pore volume), particularly those with a water content from about 3% to about 5.5% by weight, improve capacity and / or mass transfer. These properties are especially advantageous for improving productivity in low temperature, low cycle time adsorptive separation operations in a simulated moving bed mode.
Owner:UOP LLC
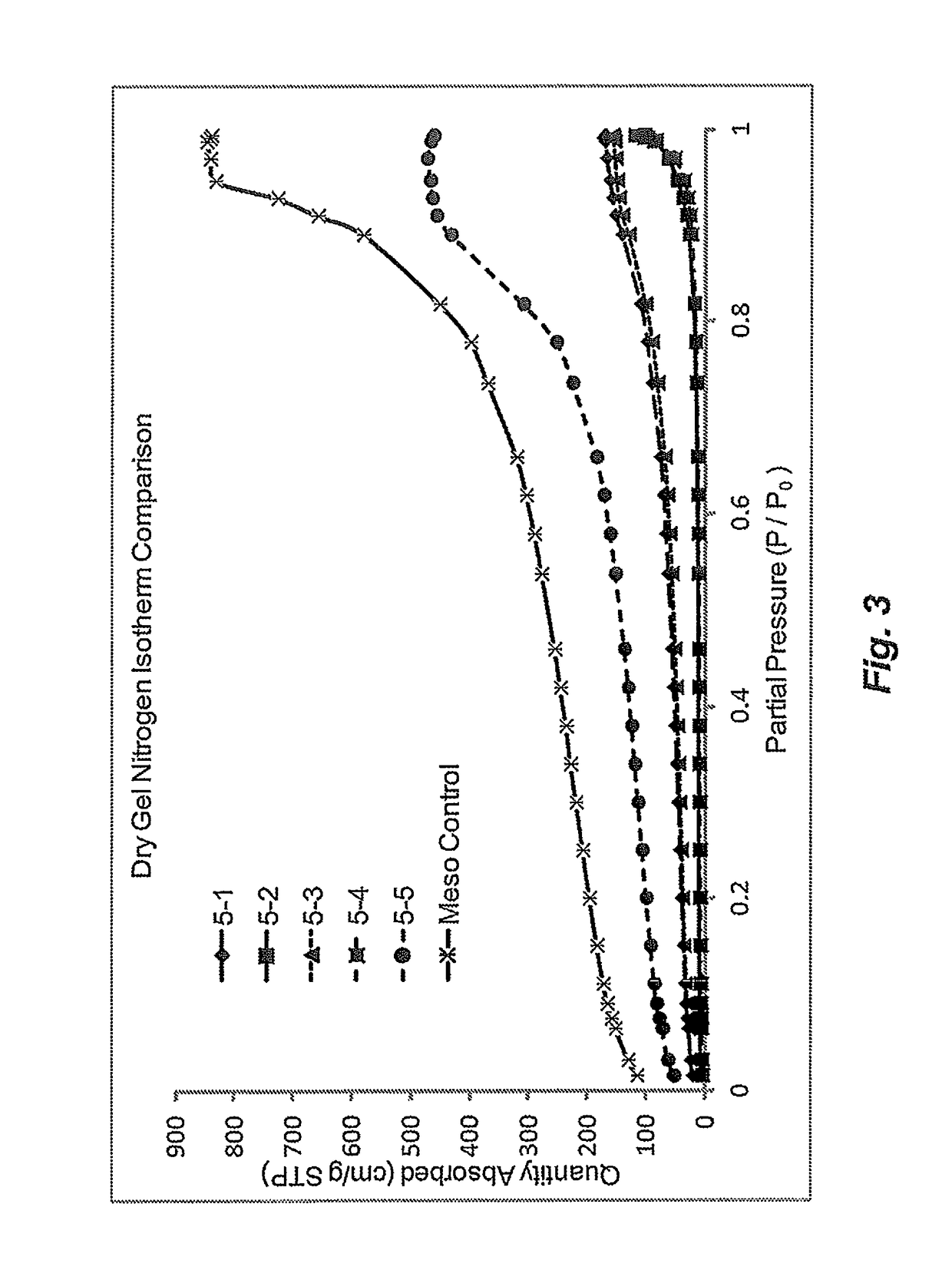
Preparation of polymeric resins and carbon materials
Methods for making carbon materials are provided. In at least one specific embodiment, the method can include combining one or more polymer precursors with one or more liquids to produce a mixture. The mixture can be an emulsion, dispersion, or a suspension. The liquid can include hexane, pentane, cyclopentane, benzene, toluene, o-xylene, m-xylene, p-xylene, diethyl ether, ethylmethylketone, dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, mineral oils, paraffin oils, vegetable derived oils, or any mixture thereof. The method can also include aging the mixture at a temperature and time sufficient for the polymer precursor to react and form polymer gel particles having a volume average particle size (Dv,50) of the polymer particles in gel form greater than or equal to 1 mm. The method can also include heating the polymer gel particles to produce a carbon material.
Owner:GEORGIA PACIFIC CHEM LLC
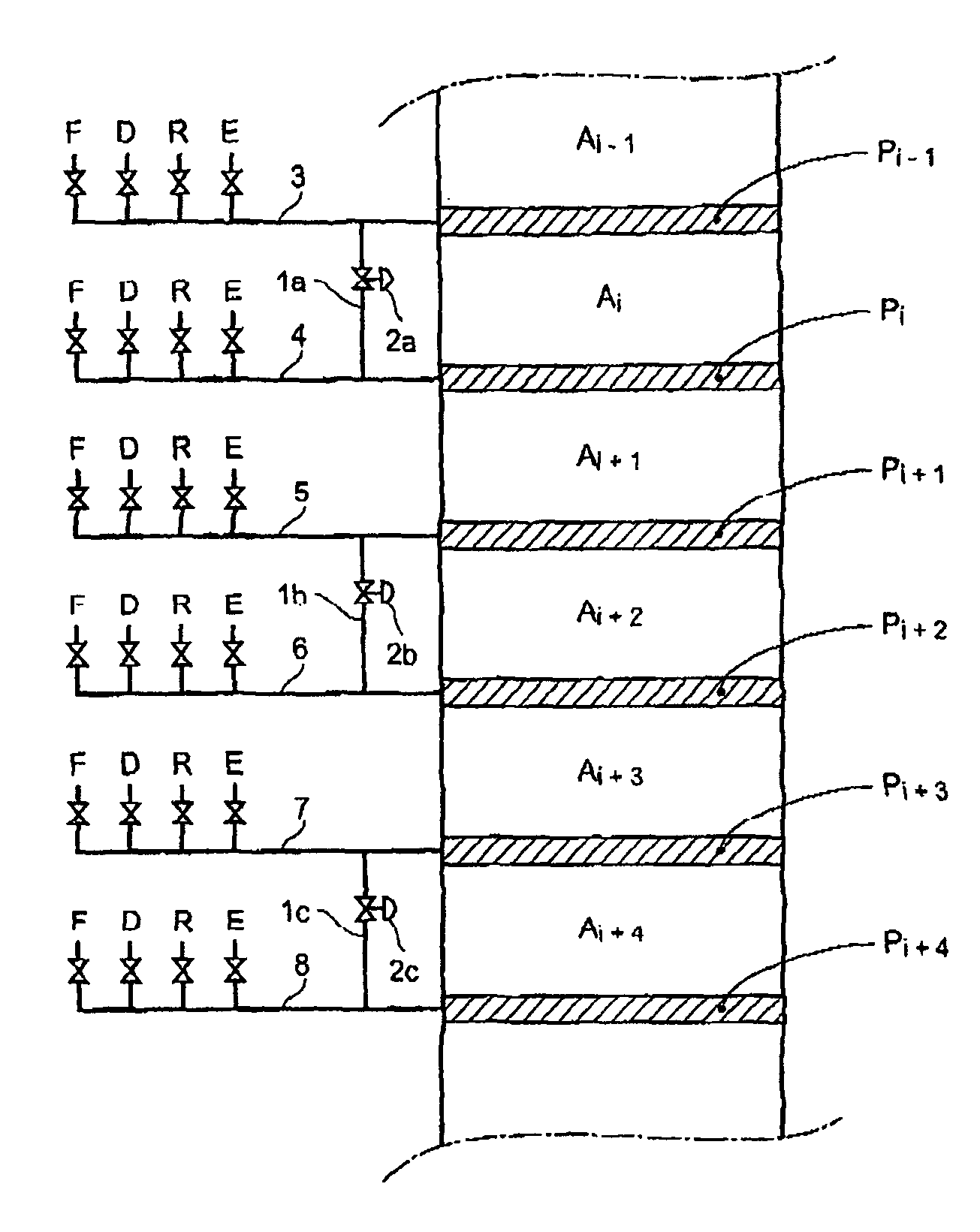
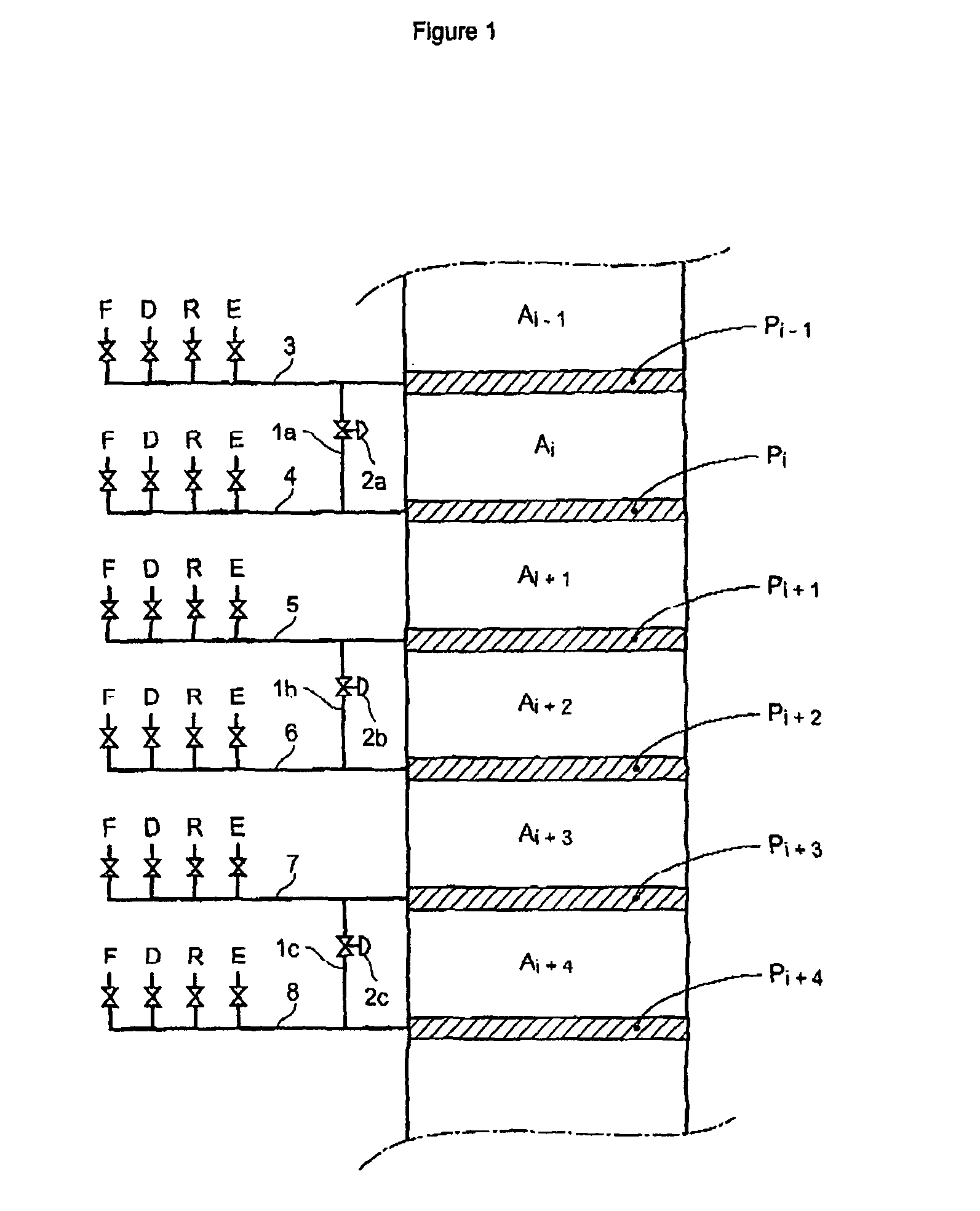
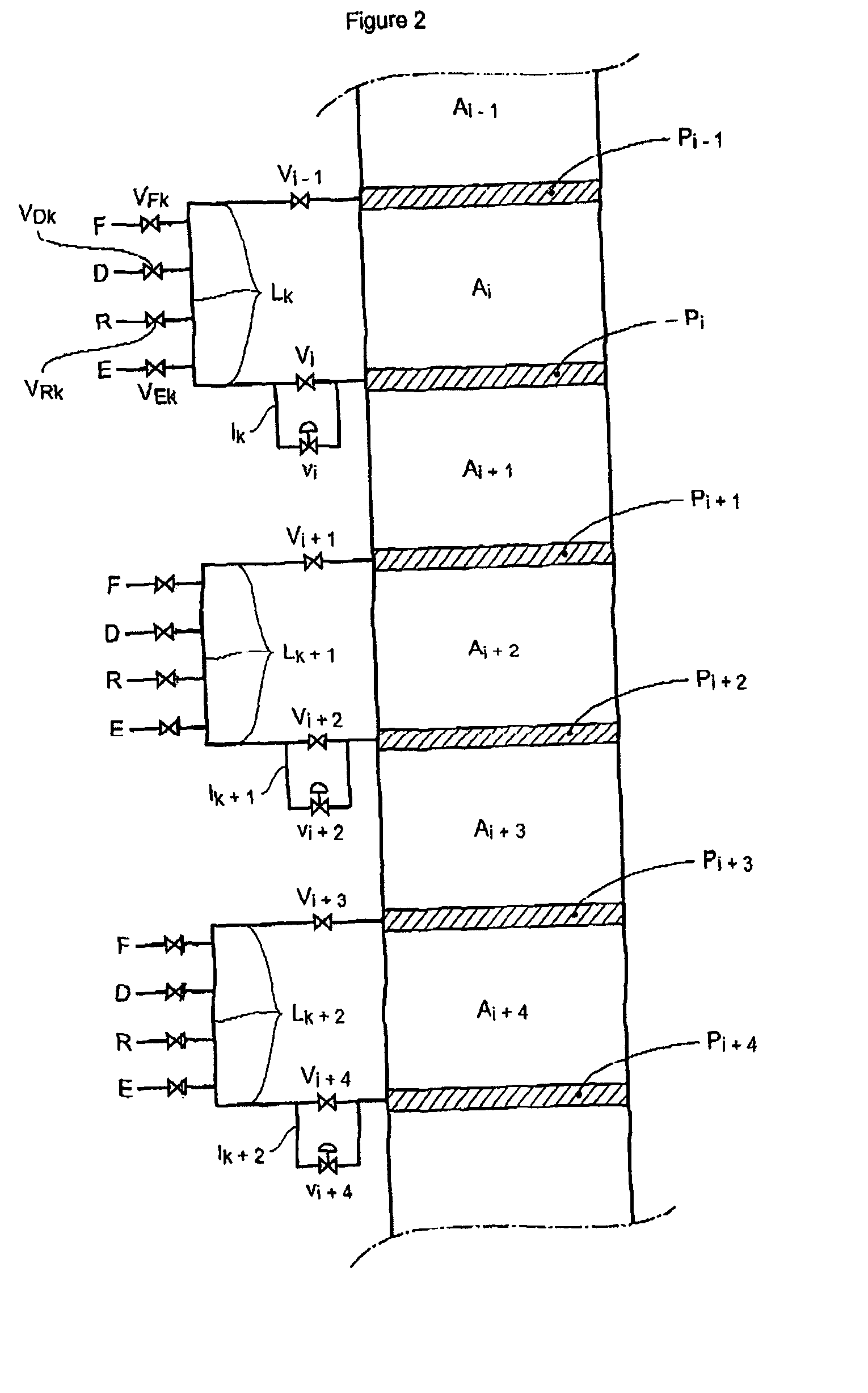
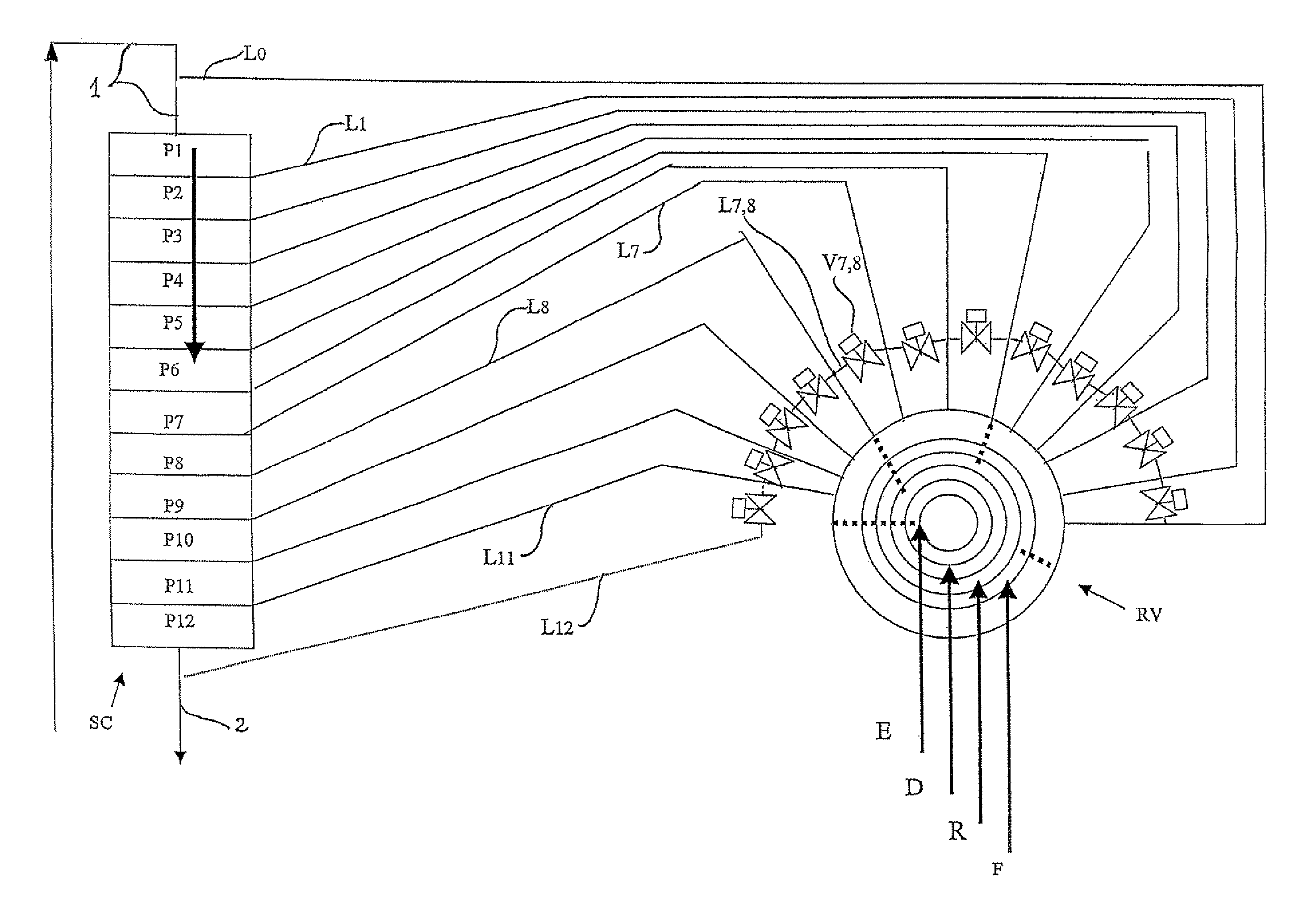
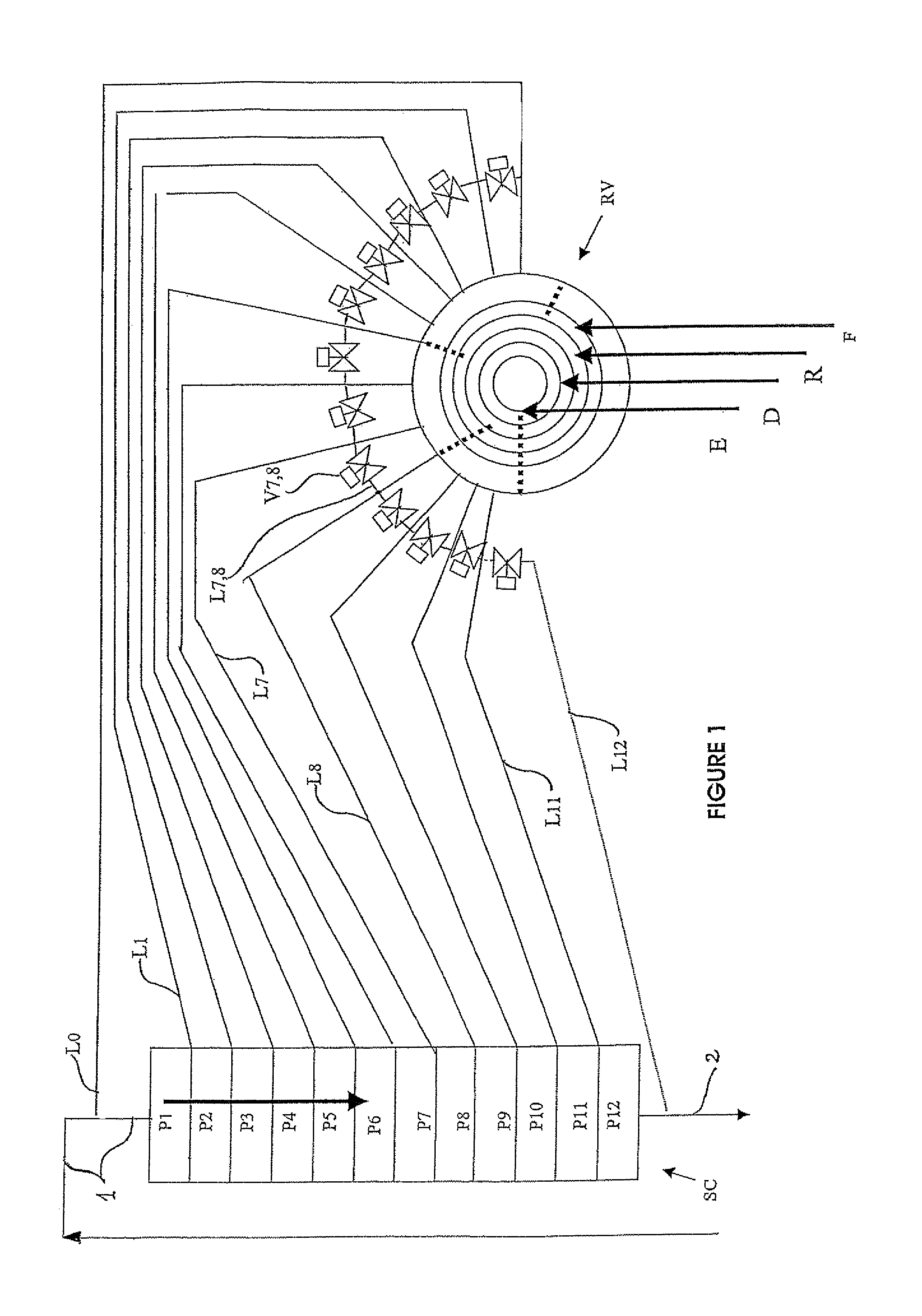
Process and device for simulated moving bed separation with a reduced number of valves and lines
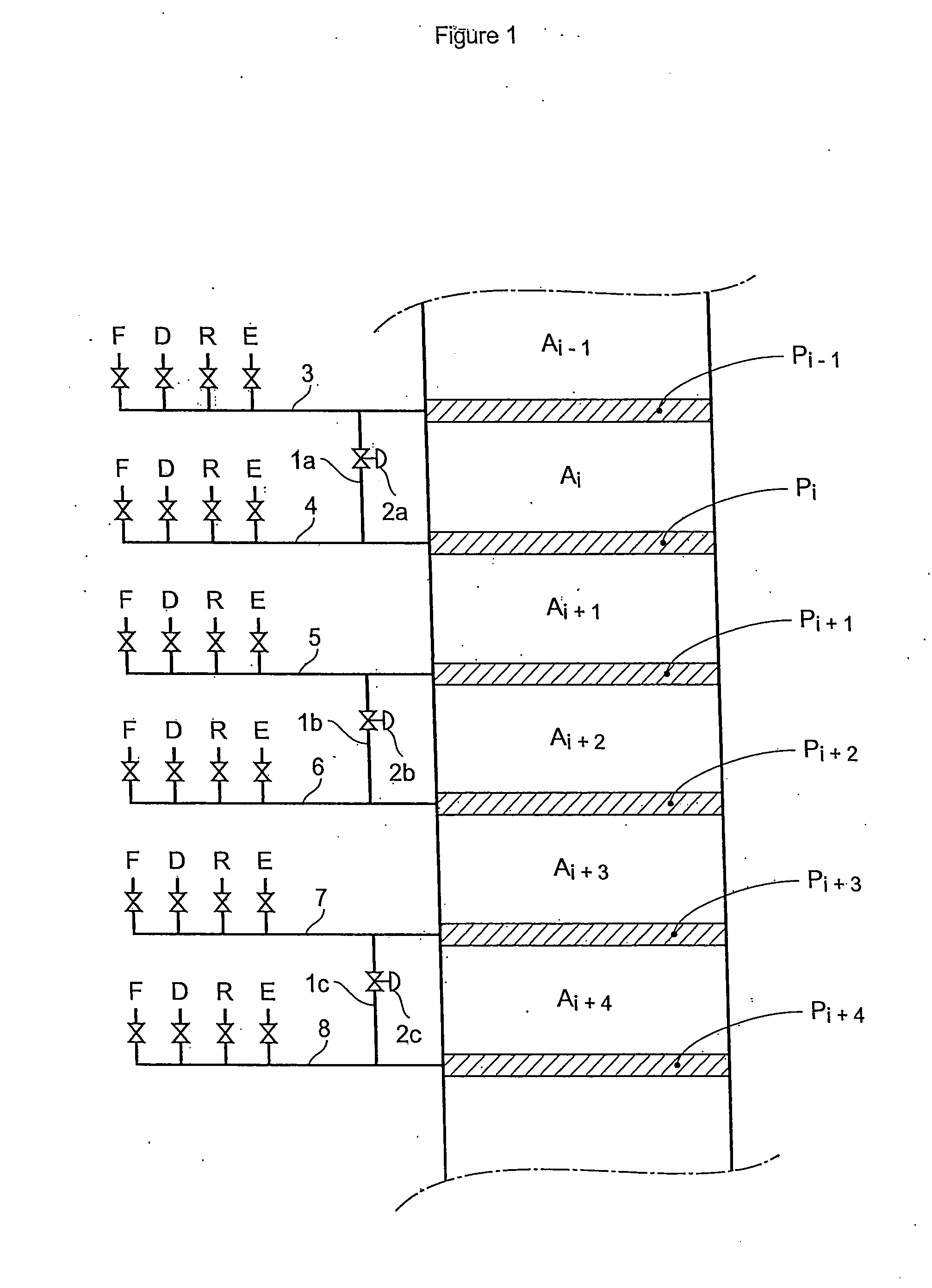
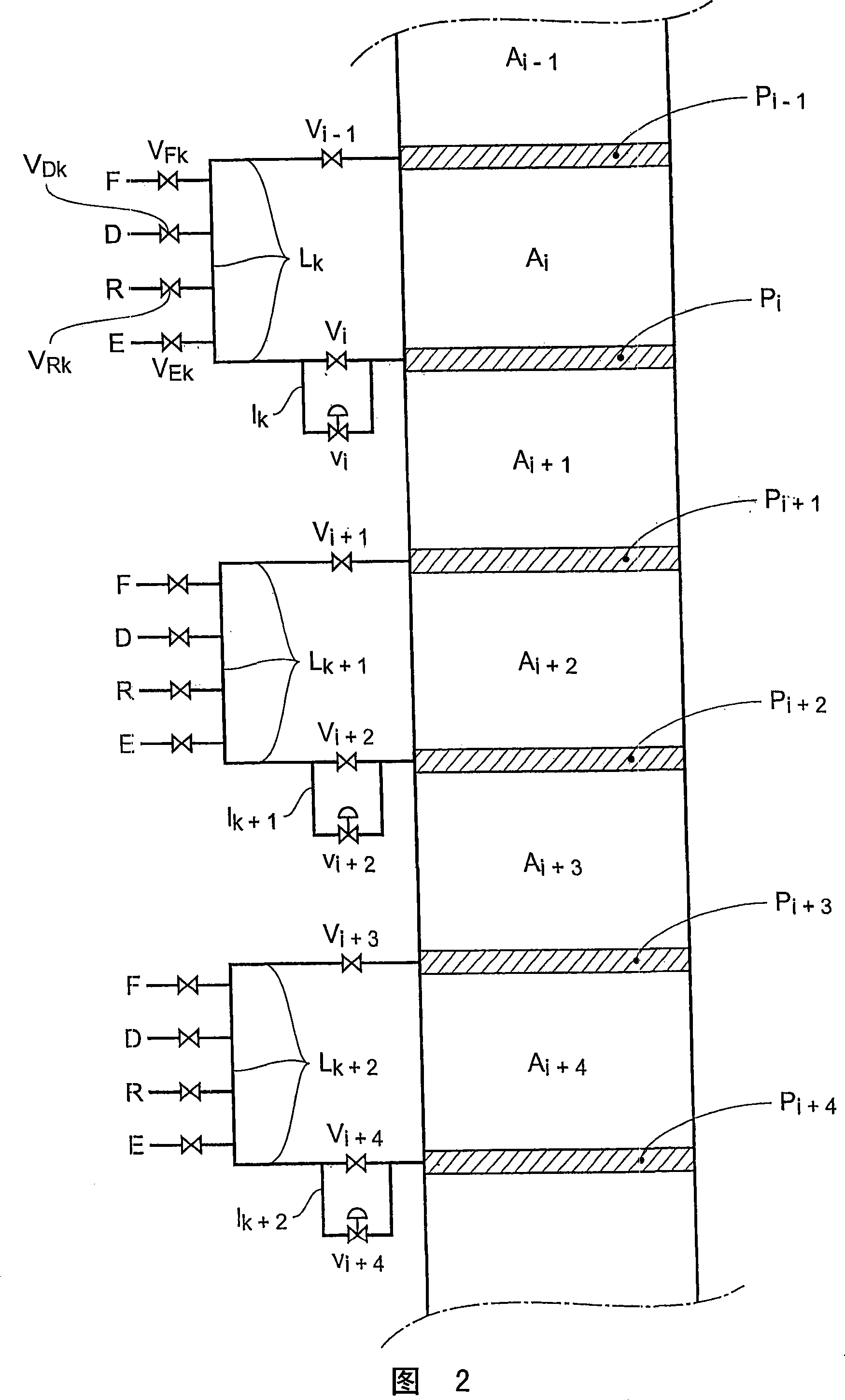
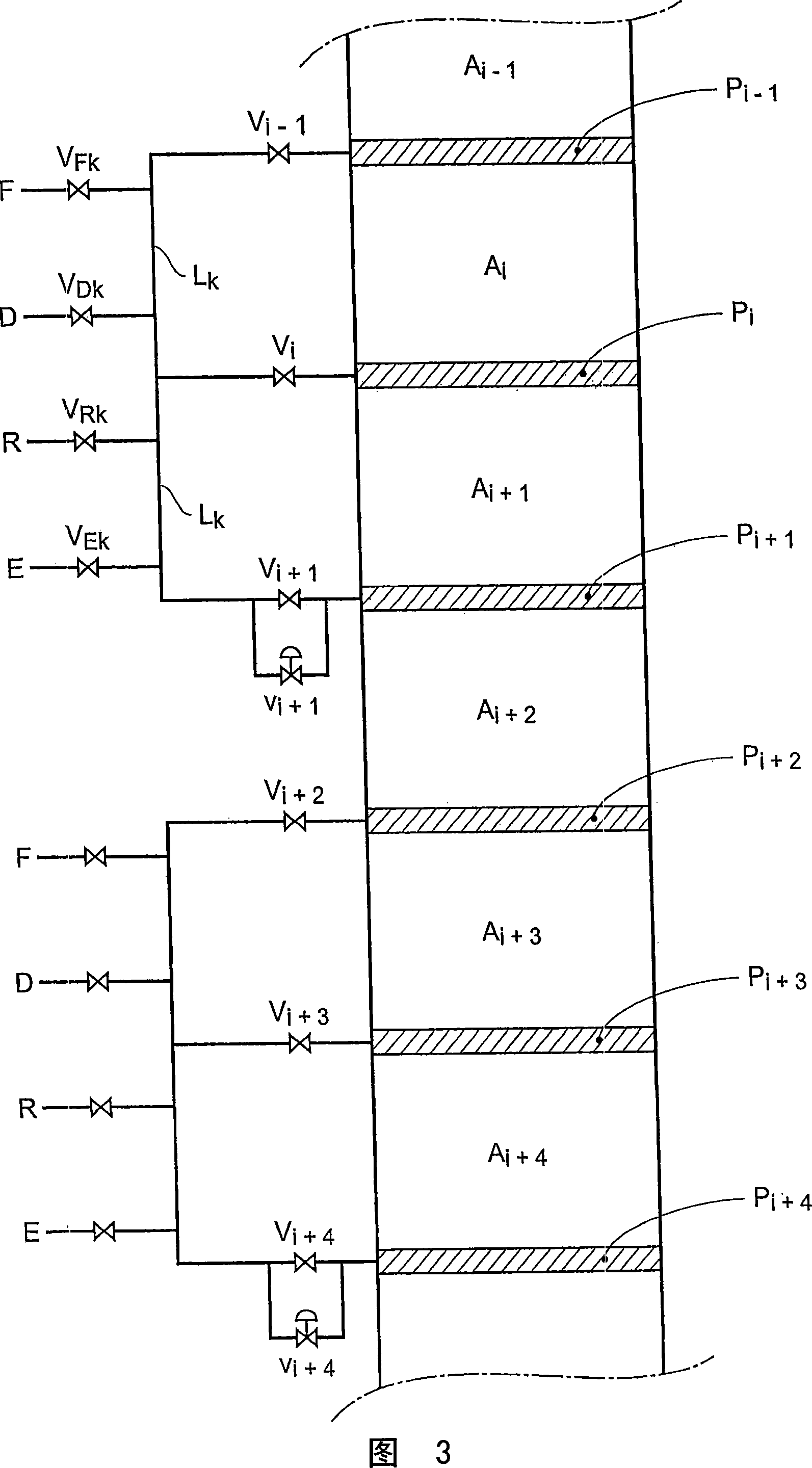
InactiveUS20080237132A1Reduce in quantityReduce disadvantagesComponent separationIon-exchanger regenerationSimulated moving bedMeta-xylene
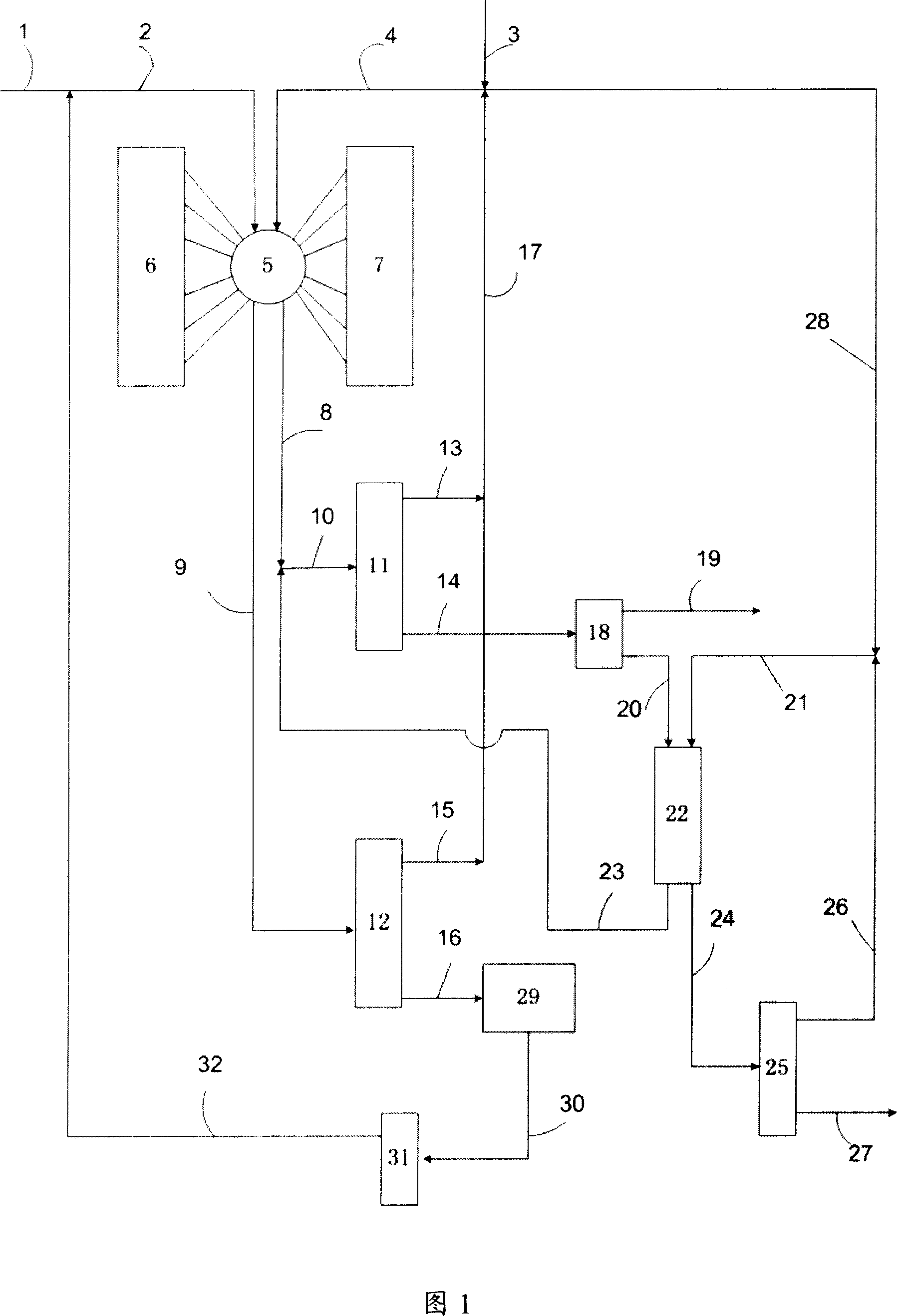
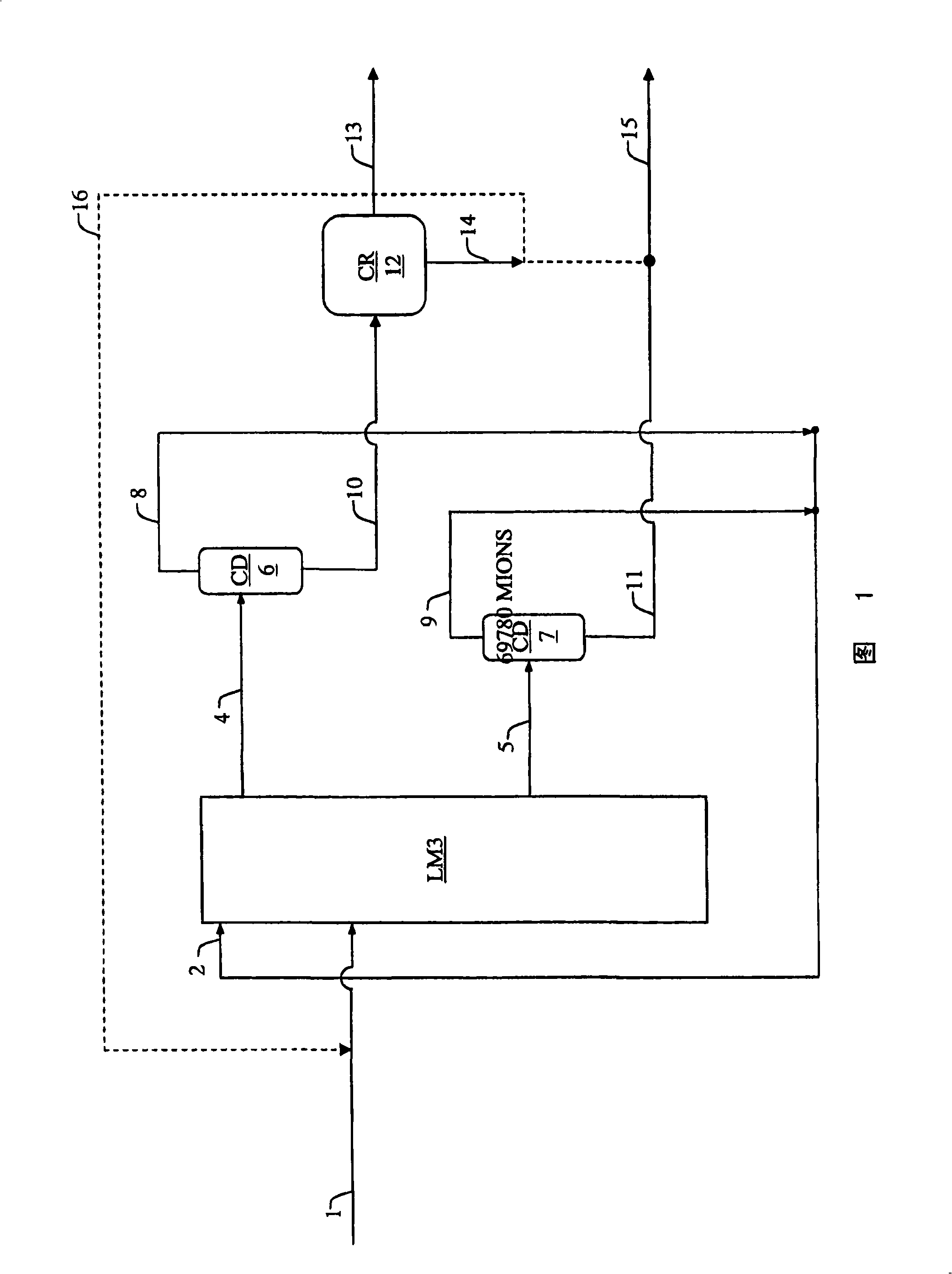
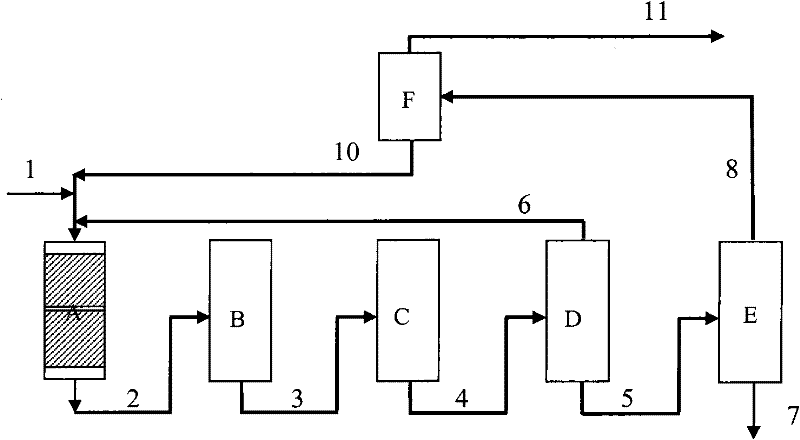
The invention concerns a simulated moving bed adsorption separation device comprising a limited number of valves. According to the invention, the device comprises a column with a plurality of sectors Sk with 2 superimposed plates Pi with a single distribution network, each sector Sk comprising an external principal bypass line Lk connected to each plate Pi of Sk via a plate valve Vi. Each line Lk comprises a flow limitation means and is connected to each of the fluid networks via a single valve.Further, the connectors of lines Lk onto the column are offset by at most 20° inside Sk to limit the volume of lines Lk, and are offset by a mean angle in the range 70° to 110° between two neighbouring sectors Sk and Sk+1 so as not to weaken the column mechanically. The plates preferably comprise panels DMEi,j with parallel segments the direction of which varies from plate to plate or per group of 2 plates.The invention also concerns a separation process using said device, in particular to separate para-xylene or meta-xylene from an aromatic C8 cut.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
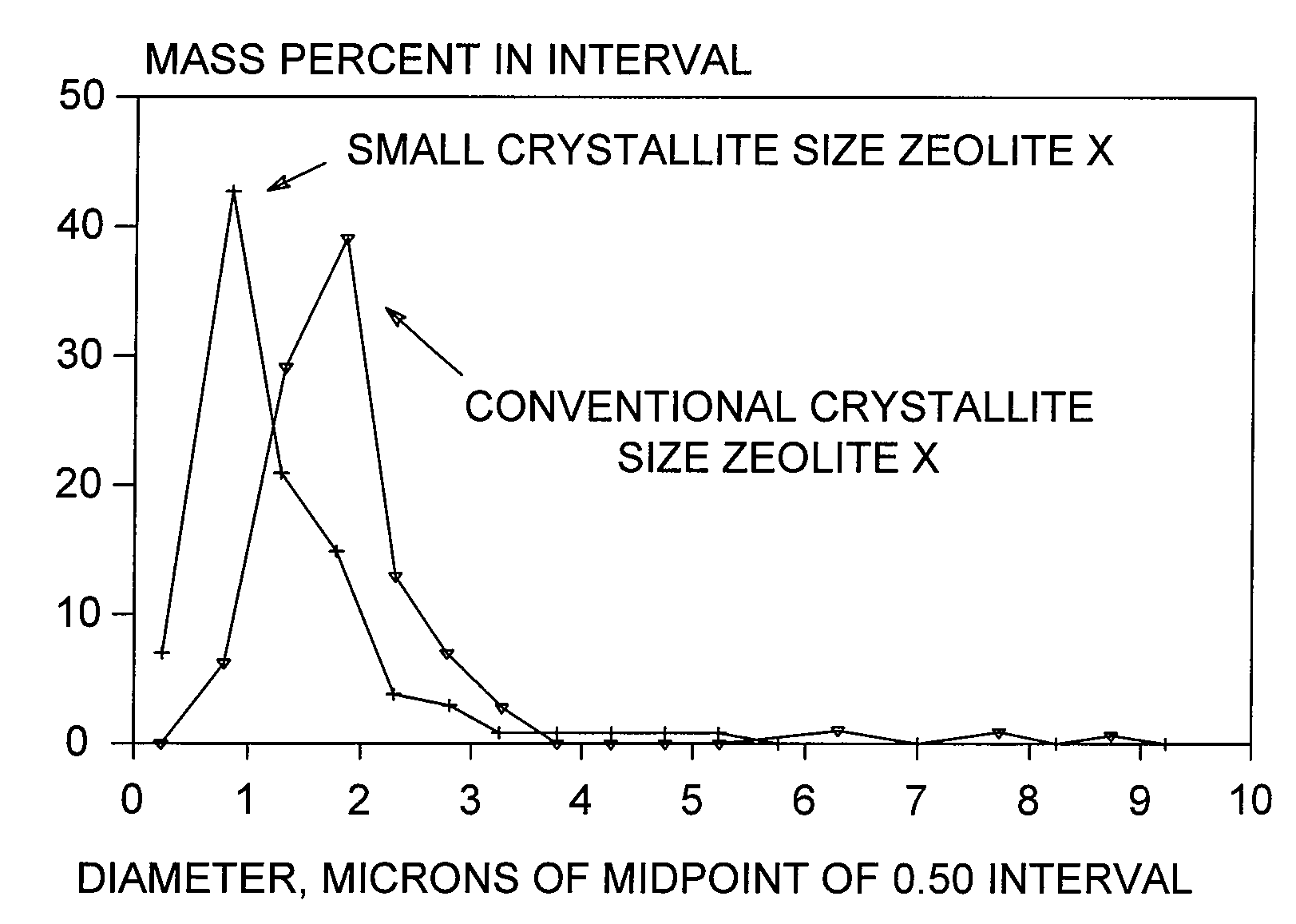
Binderless adsorbents with improved mass transfer properties and their use in the adsorptive separation of para-xylene
ActiveUS20100076243A1Improve performanceImprove mass transfer effectOther chemical processesMolecular-sieve and base-exchange compoundsProduction rateSorbent
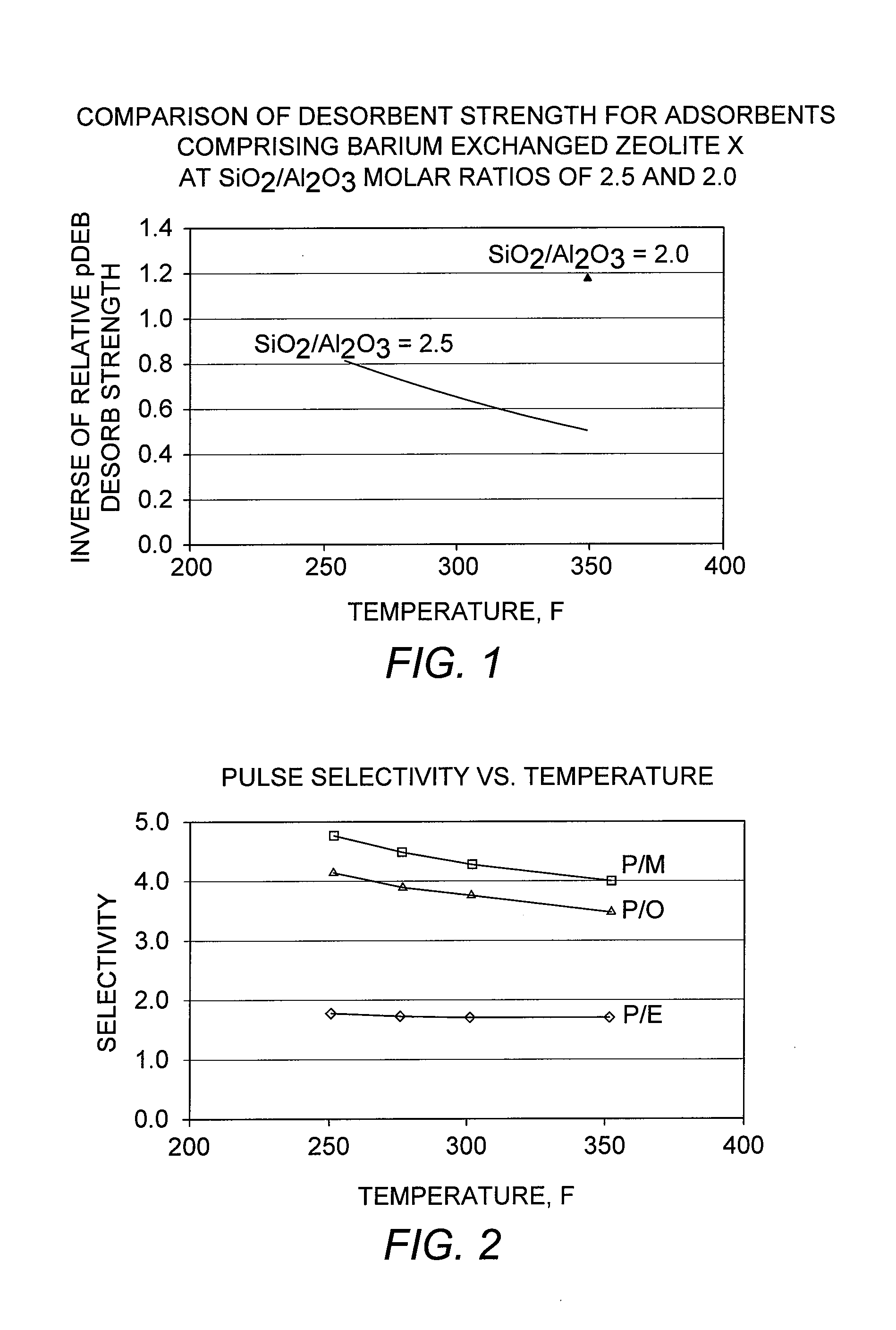
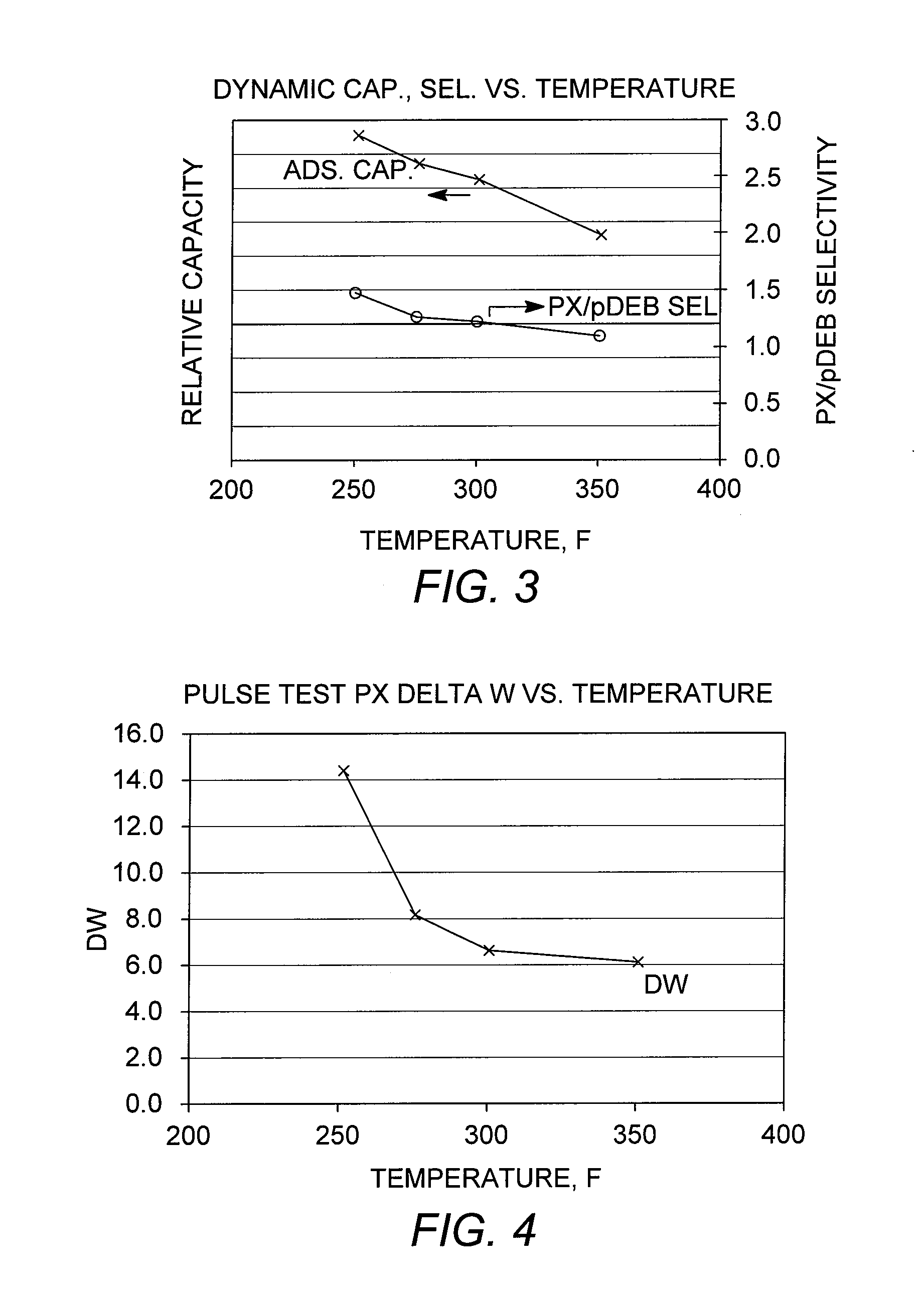
Adsorbents and methods for the adsorptive separation of para-xylene from a mixture containing at least one other C8 aromatic hydrocarbon (e.g., a mixture of ortho-xylene, meta-xylene, para-xylene, and ethylbenzene) are described. Suitable adsorbents comprise small-crystallite-size zeolite X having an average crystallite size of less than 1.8 microns. The adsorbents may be binderless (e.g., formulated with the substantial absence of an amorphous material that normally reduces selective pore volume) to further improve capacity and mass transfer. These properties are especially advantageous for improving productivity in low temperature, low cycle time adsorptive separation operations in a simulated moving bed mode.
Owner:UOP LLC
Method for adsorbing-crystal separation of paraxylene and ethylbenzene from C8 aromatic
ActiveCN101045671ALarge amount of processingHigh purityAdsorption purification/separationCrystallisation purification/separationO-XyleneIsomerization
An adsorbing-crystallizing process for separating p-xylene and ethylbenzene from C8 arylhydrocarbon includes such steps as adsorptive separation to obtain the first material flow containing ethylbenzene and p-xylene and the second material flow containing meta-xylene and o-xylene, crystallizing for separating p-xylene from the first material flow, and adsorbing for separating ethylbenzene from the residual mother liquid.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Process for separating meta-xylene from a feed of aromatic hydrocarbons
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Process for separating meta-xylene from a feed of aromatic hydrocarbons by liquid phase adsorption
InactiveUS20070038012A1Improve diffusivityReduce moisture contentSolid sorbent liquid separationHydrocarbonsDesorptionMeta-xylene
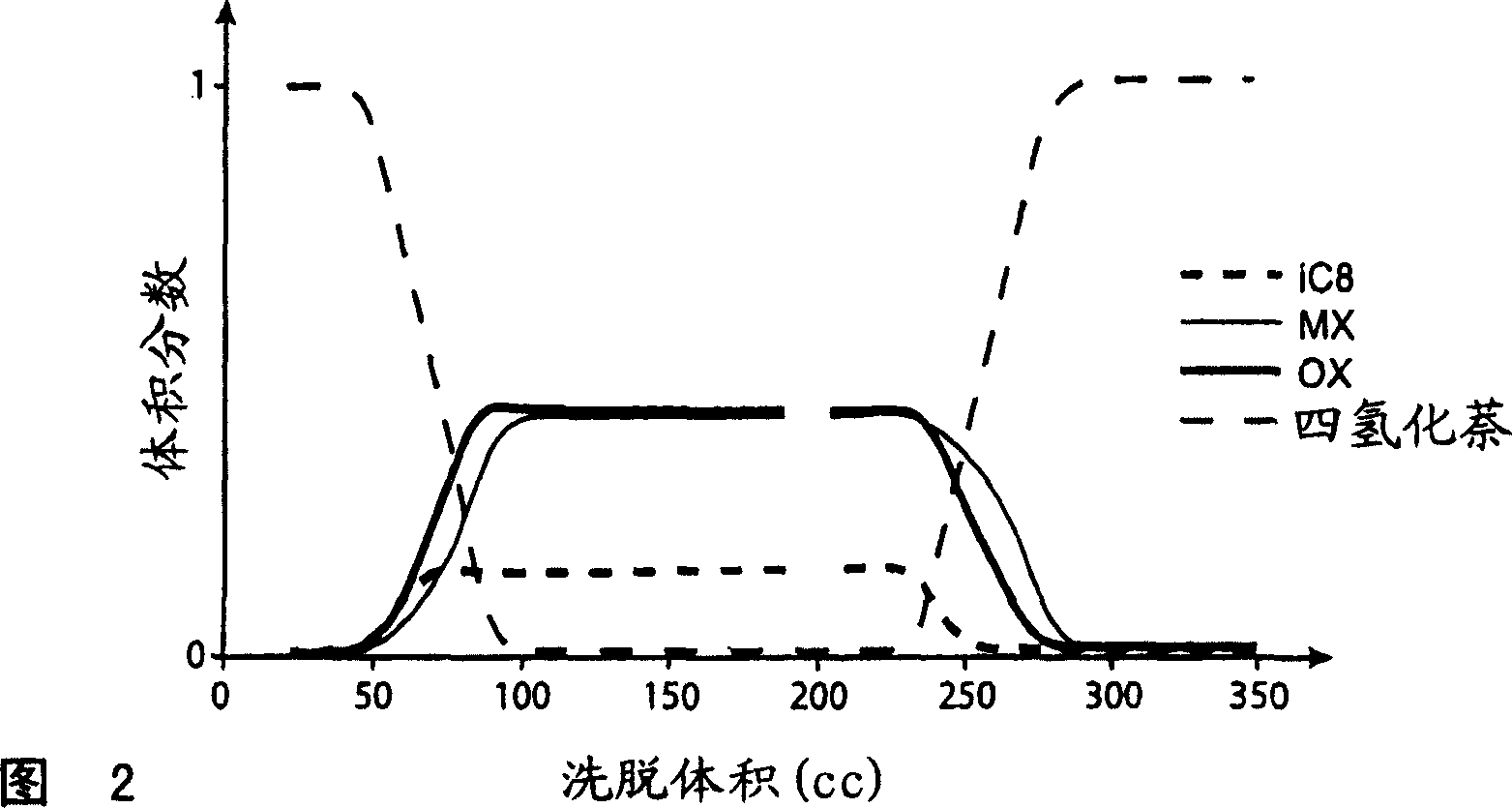
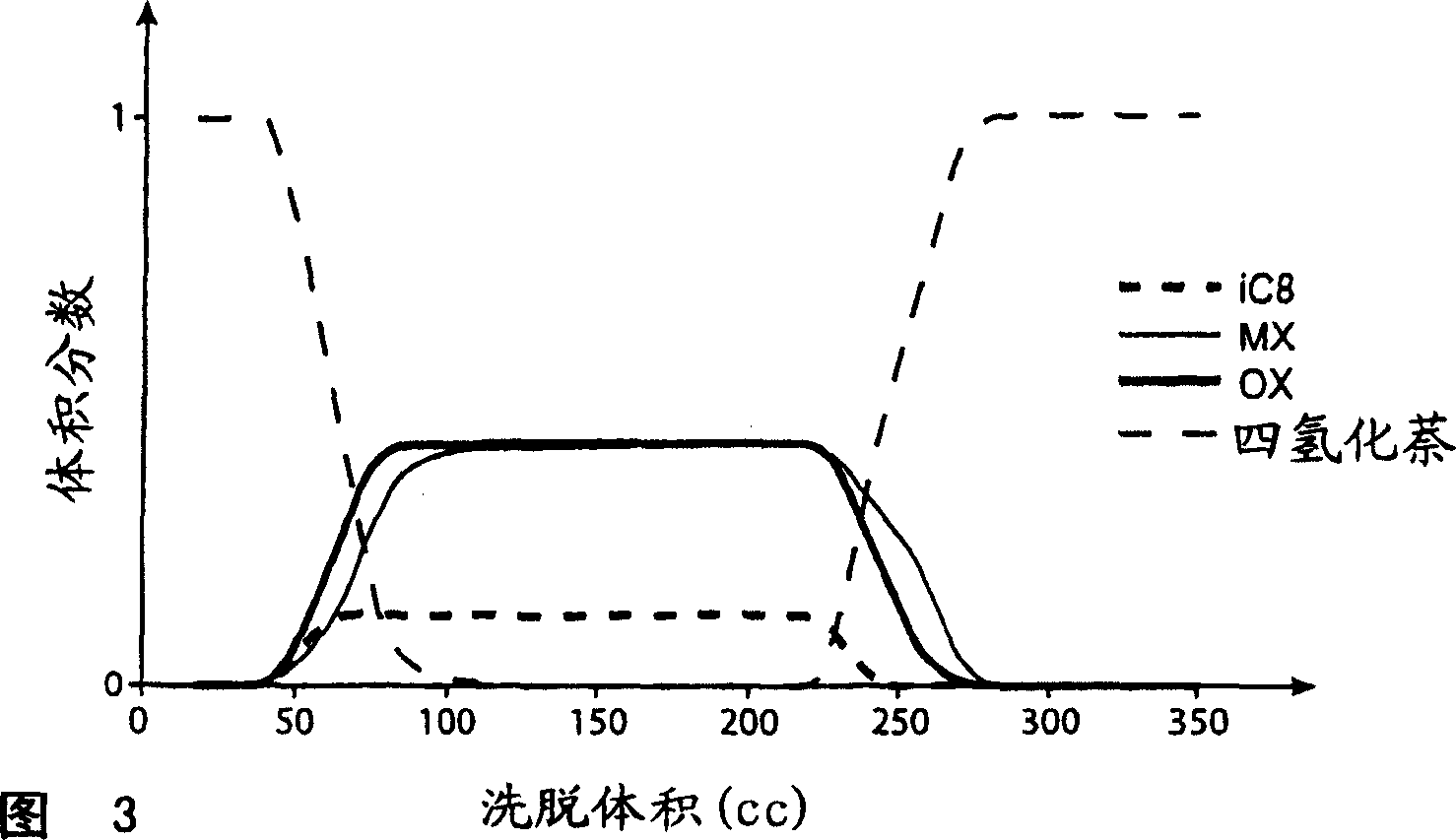
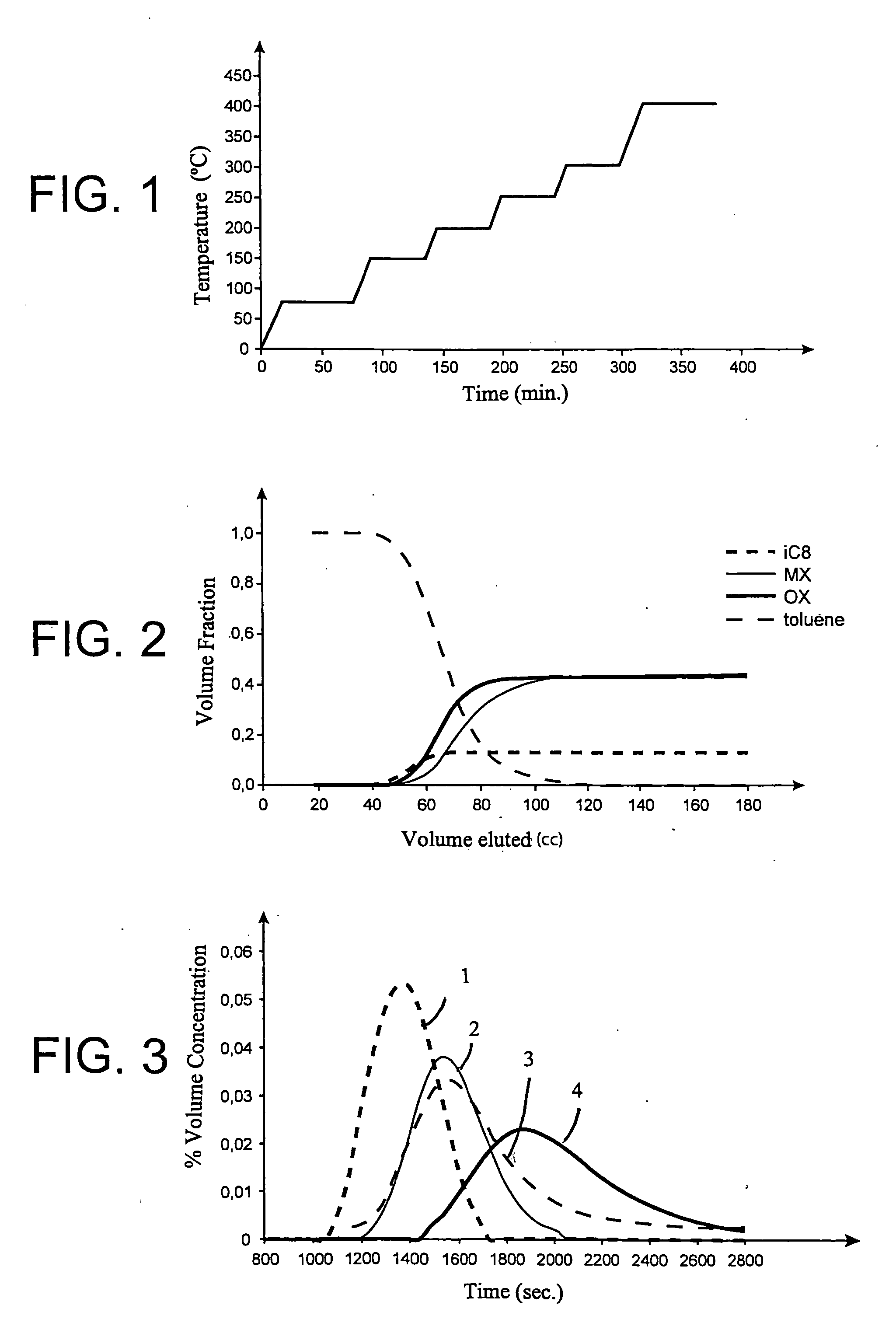
The invention concerns a process for separating meta-xylene from a hydrocarbon feed comprising isomers containing 8 carbon atoms, comprising: a step for bringing said feed into contact with a faujasite type zeolite adsorbant, the water content of the adsorbant being in the range 0 to 1% by weight and the adsorption temperature being from 160° C. to 180° C.; a desorption step employing a solvent selected from toluene, indane and mixtures thereof.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
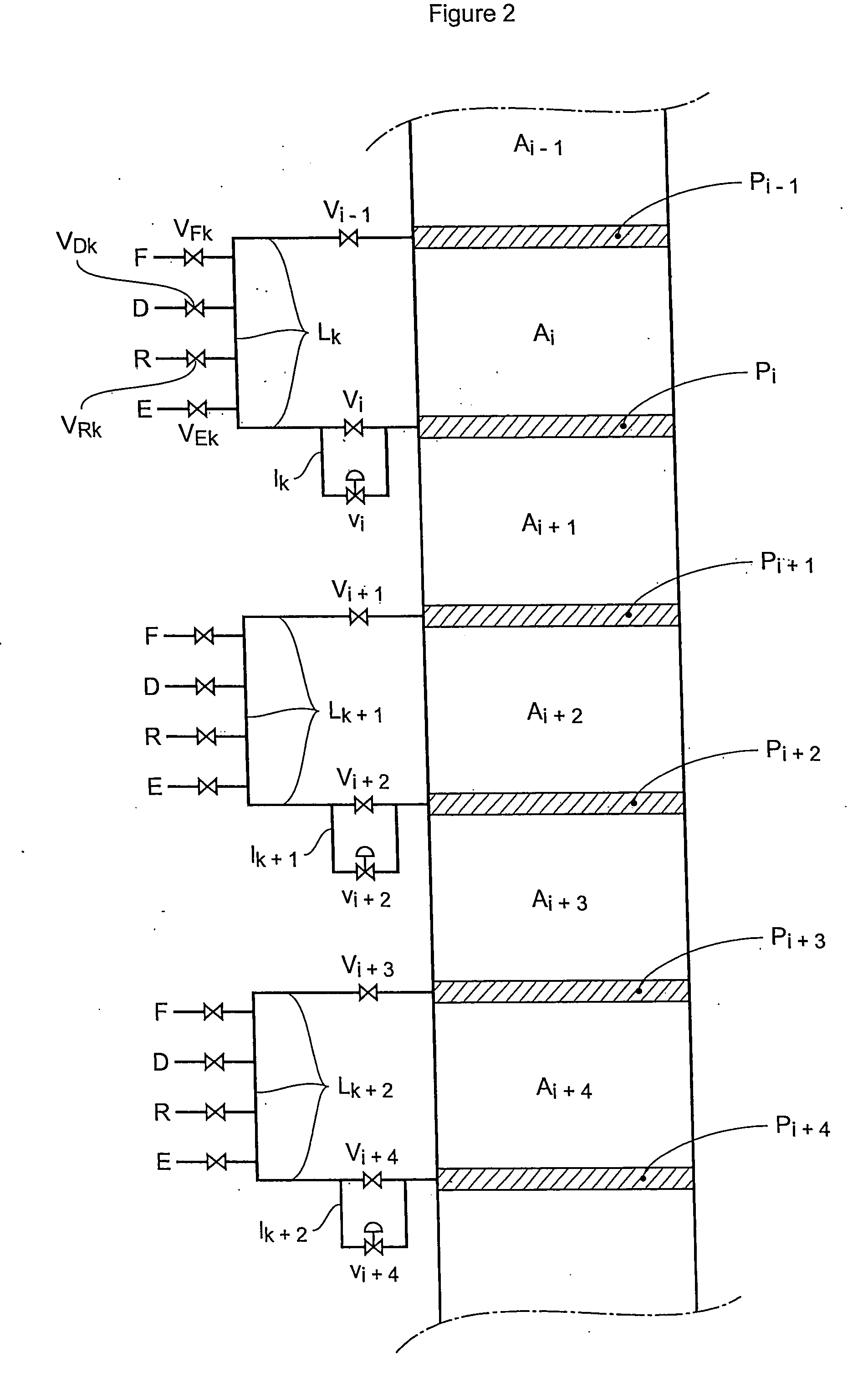
Process and device for simulated moving bed seperation with a reduced number of valves
InactiveUS20080041788A1Reduce in quantityReduce disadvantagesIon-exchange process apparatusGas treatmentIsolation valveLine tubing
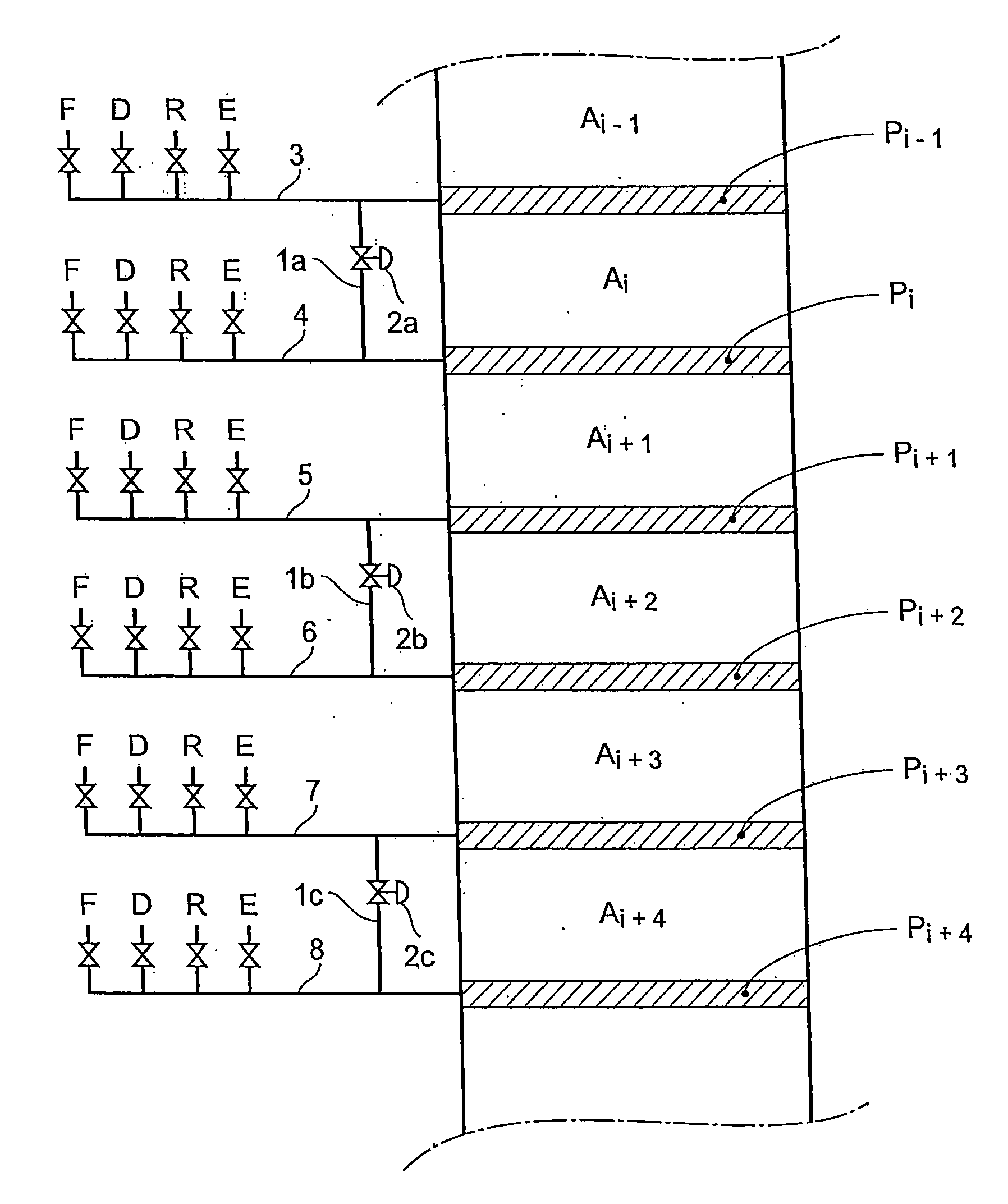
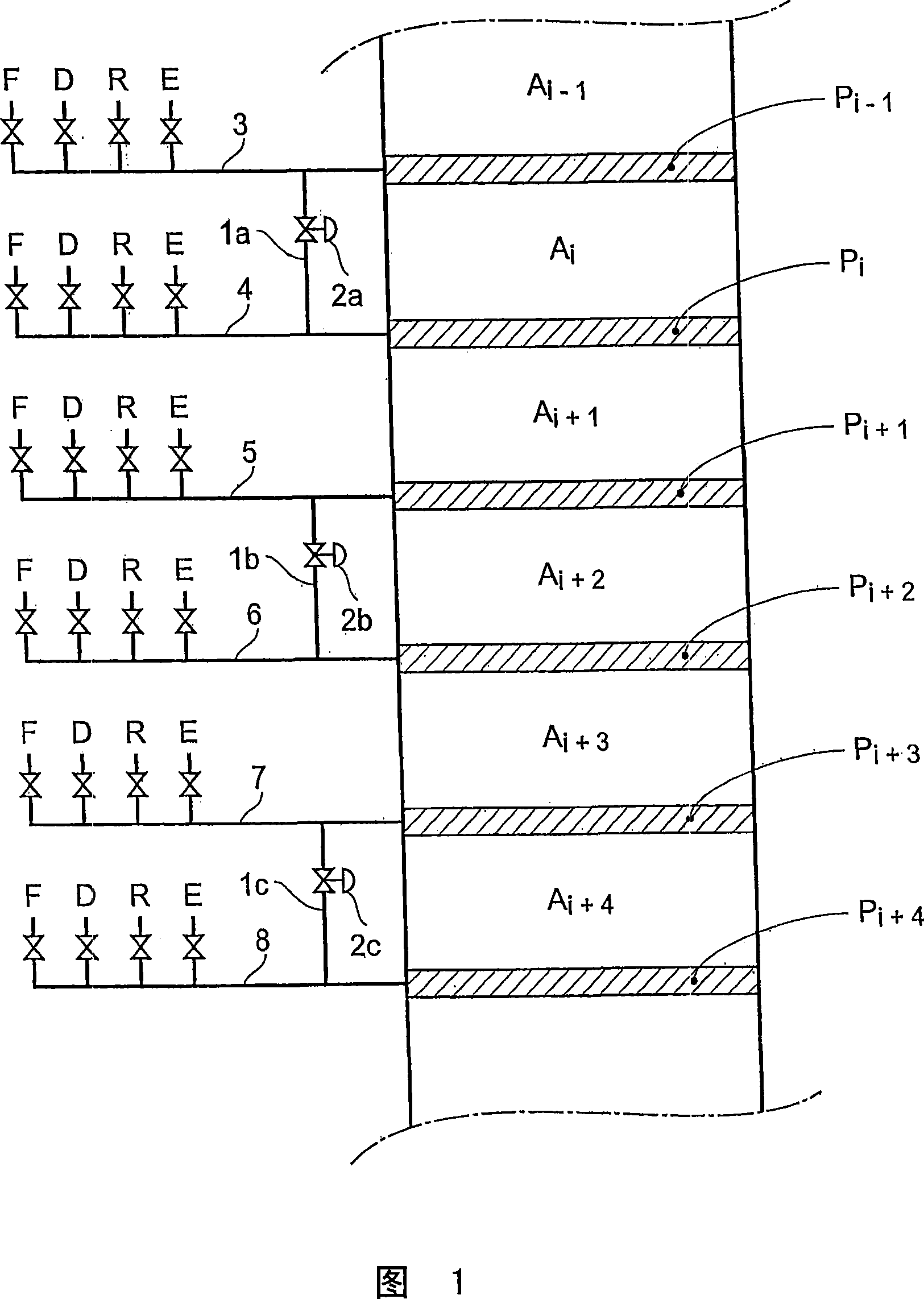
The invention concerns a simulated moving bed (SMB) separation device comprising a column, beds Ai of adsorbent separated by plates Pi with a single distribution and extraction network for fluids, in particular feed F, desorbant D, raffinate R and extract E, and a plurality of two-way valves for distribution of said fluids, said valves being limited in number compared with the prior art. According to the invention, the column is divided into a plurality of sectors Sk with 2 or 3 superimposed plates, each sector Sk comprising an external bypass line Lk connected to each plate Pi of Sk via a connector comprising a plate valve Vi. Each line Lk comprises a controlled means for limiting its internal flow, and is connected to each of the fluid networks F, D, R, E via a single line comprising a single controlled two-way isolation valve to supply for sequential supply or withdrawal of the corresponding fluid F, D, R or E towards or from the sector Sk under consideration. The invention also concerns a separation process using said device or the use of said device for the separation of para-xylene or meta-xylene from an aromatic C8 cut.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Adsorbent and process for the separation of meta-xylene from aromatic hydrocarbons
ActiveUS7728187B2Improve performanceGreat massMaterial nanotechnologyHydrocarbonsMeta-xyleneOrtho-xylene
Owner:UOP LLC
Method of joint produce pare xylene and metaxylene including two stage separation
InactiveCN1379007ASmall sizeEthylbenzene content limitDistillation purification/separationHydrocarbonsDistillationSimulated moving bed
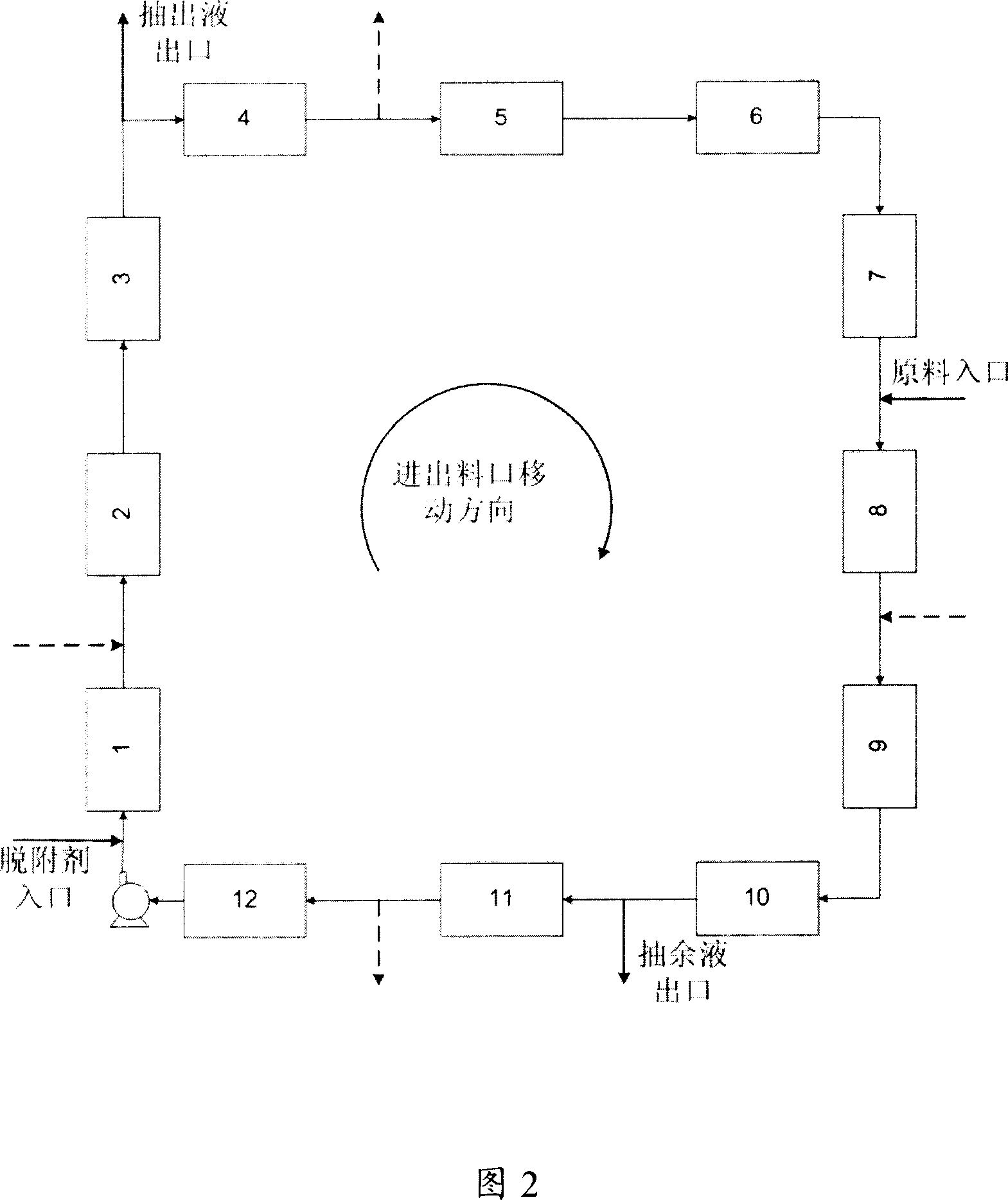
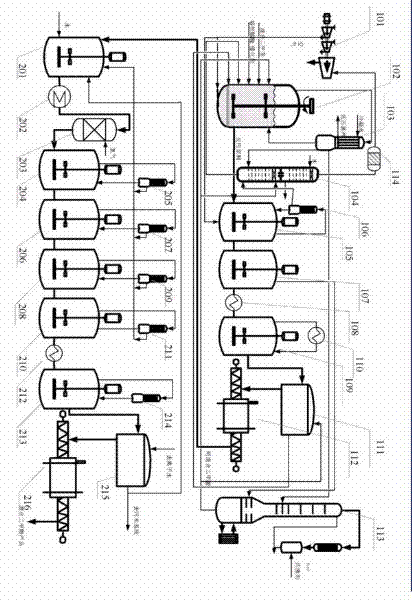
A process for the co-production of m-xylene and p-xylene from hydrocarbon feedstocks is described, which involves two separate steps. The first separation step of the method is a simulated moving bed system in a countercurrent manner in the chromatographic column. The chromatographic column contains at least five sections, including continuous or intermittent injection of material, injection of desorbent, extraction of extract, raffinate and intermediate raffinate. Distill the extract to obtain p-xylene with a purity of at least 99.7%. The raffinate rich in m-xylene is distilled to extract the desorbent, and then injected into the countercurrent simulated moving bed to continuously provide the extract and raffinate. One of these two streams is rich in m-xylene. Distillation of the most m-xylene-rich stream yields m-xylene with a purity greater than 99%.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
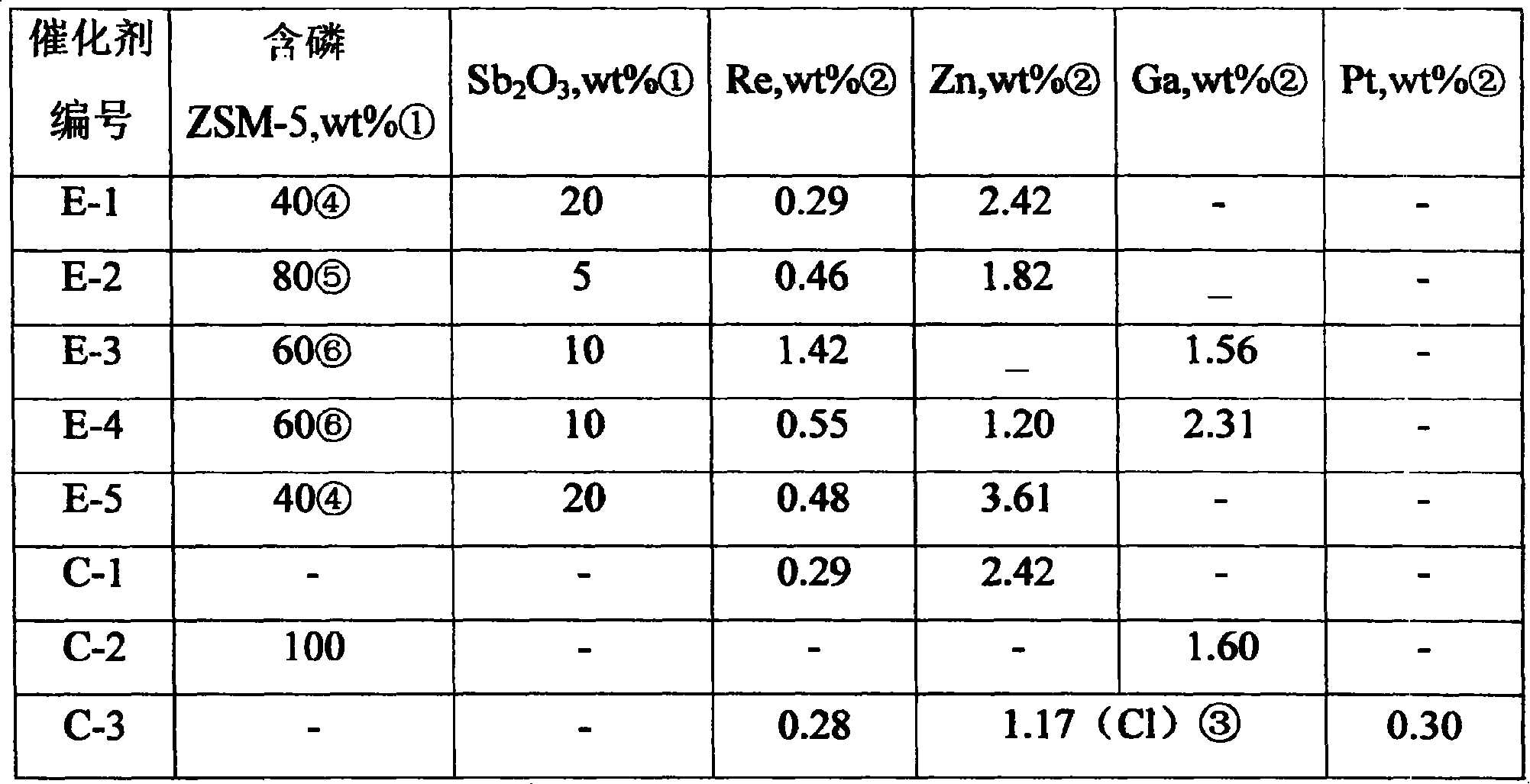
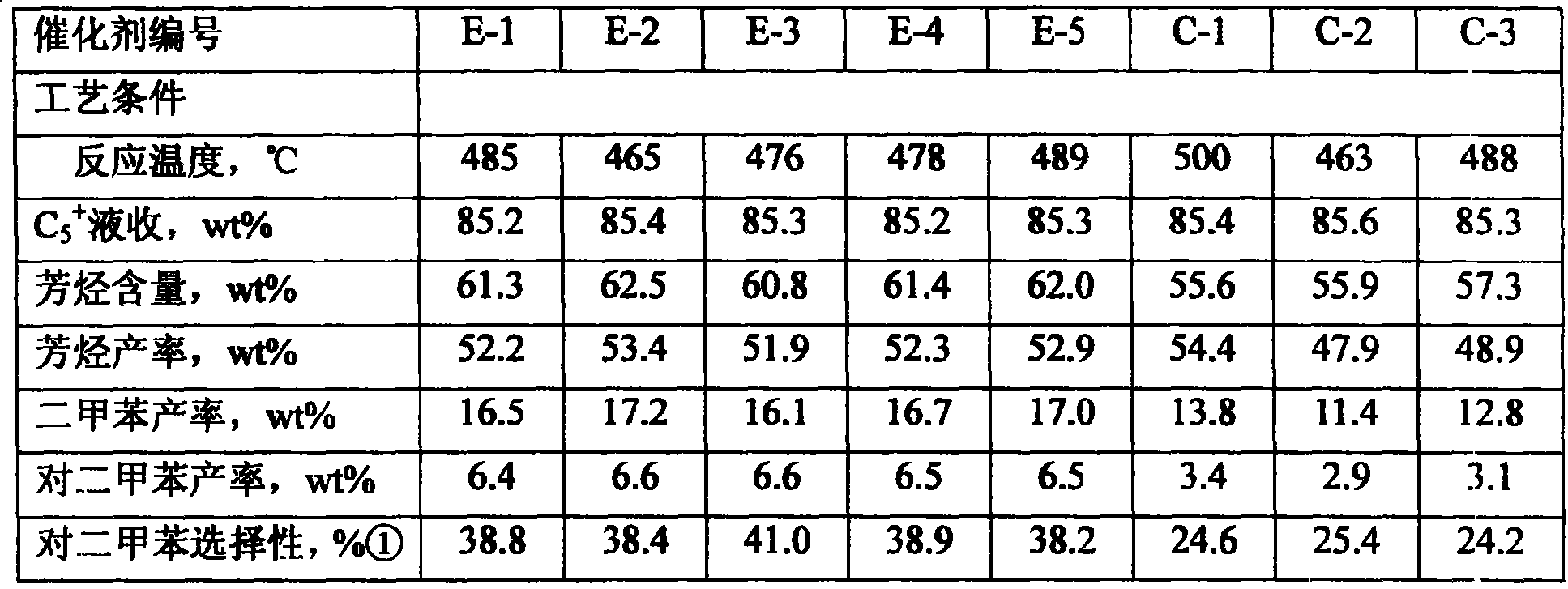
Reforming catalyst and application in high selectivity production of para-xylene of the same
ActiveCN101172252ALow costStrong resistance to sulfur and nitrogen poisoningMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbonsStrong acidsHigh selectivity
The invention discloses reforming catalyst and the application in the preparation of para xylene reforming high selectivity and taking saturated hydrocarbon, cycloparaffinic hydrocarbon and naphtha as the raw material. The carrier of the catalyst includes mesoporous molecular sieve, antimony oxide and inorganic melt-resistant oxide, wherein, the mesoporous molecular sieve includes 0.5 wt percent to 10.0 wt percent of phosphorus pentoxide. The surfaces of the antimony oxide and the molecular sieve included in the catalyst are contacted to facilitate the strong acid position on the surface of the molecular sieve to be intoxicated, so as to lower the reaction activity center with poor selectivity, and to maintain a passage reaction site with high selectivity; meanwhile the invention adopts phosphorus pentoxide modified molecular sieve to adjust the internal surface of the molecular sieve, particularly to adjust the size of the passage of the molecular sieve, so as to further contract the size of the passage to restrain the generation of the nonideal products of ortho xylene and meta xylene, and to improve the selectivity of the ideal product para xylene.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Process and device for simulated moving bed seperation with a reduced number of valves
InactiveCN101143274ALimit statistical failure riskImprove reliabilityGas treatmentComponent separationIsolation valveSorbent
The present invention relates to a simulated moving bed (SMB) separation plant comprising a column, adsorbent beds Ai separated by plates Pi, with a single distribution of fluids, in particular feed F, desorbent D, raffinate R and extract E With extraction nets, and multiple two-way valves for the fluid distribution, the number of these valves is limited compared to the prior art. According to the invention, the column is divided into a number of sections Sk with 2 or 3 superimposed plates, each section Sk comprising an external bypass line Lk connected to each plate of Sk through a connecting pipe comprising a plate valve Vi. Each line Lk includes control means to limit the flow therein, and is connected to each fluid network F, D, R, E by a single line including a single controllable two-way isolation valve for sequentially separating The respective fluid F, D, R or E is supplied to or withdrawn from the considered segment Sk. The invention also relates to a separation process using such a device, or the use of such a device for the separation of para-xylene or meta-xylene from aromatic C8 fractions.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
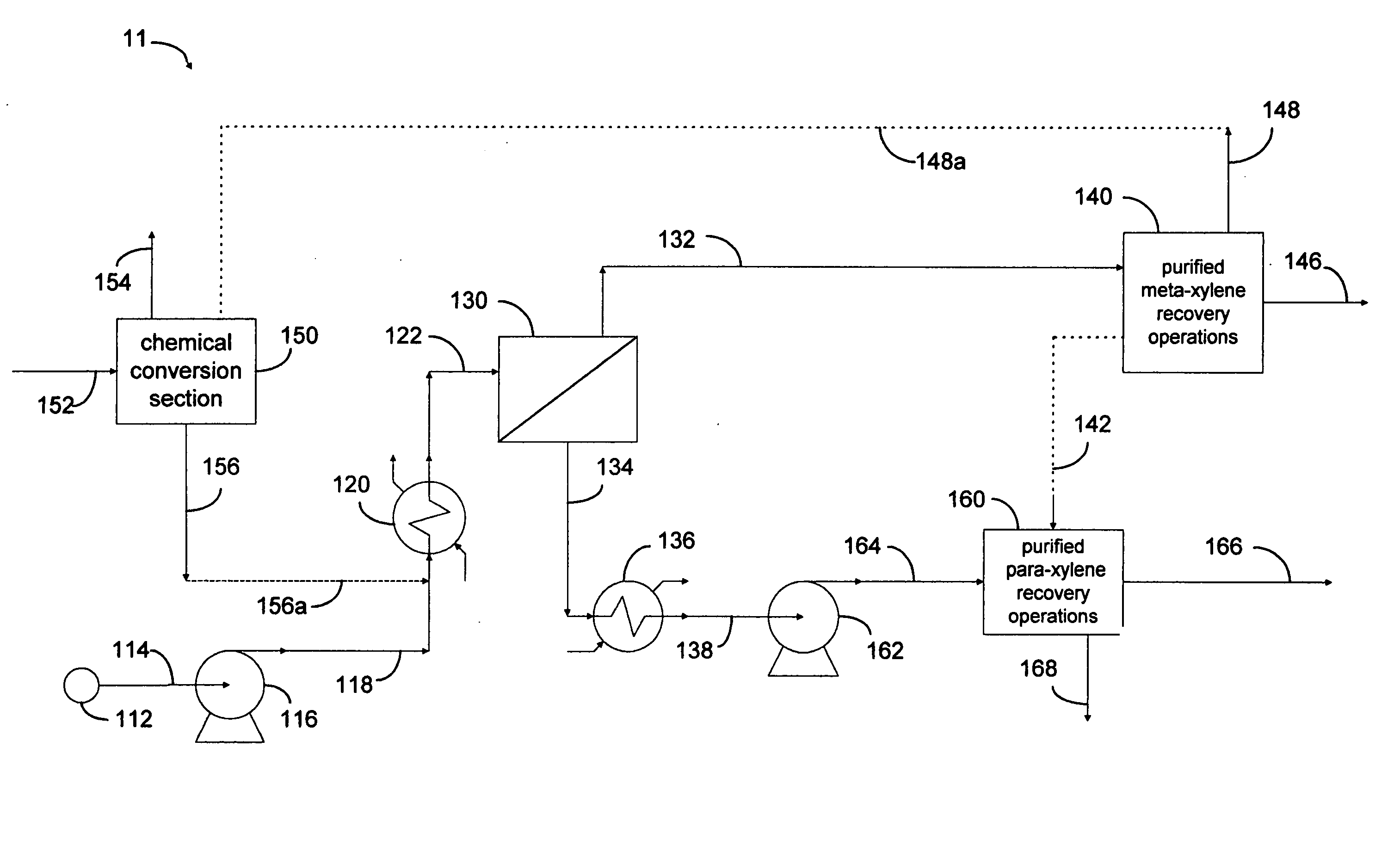
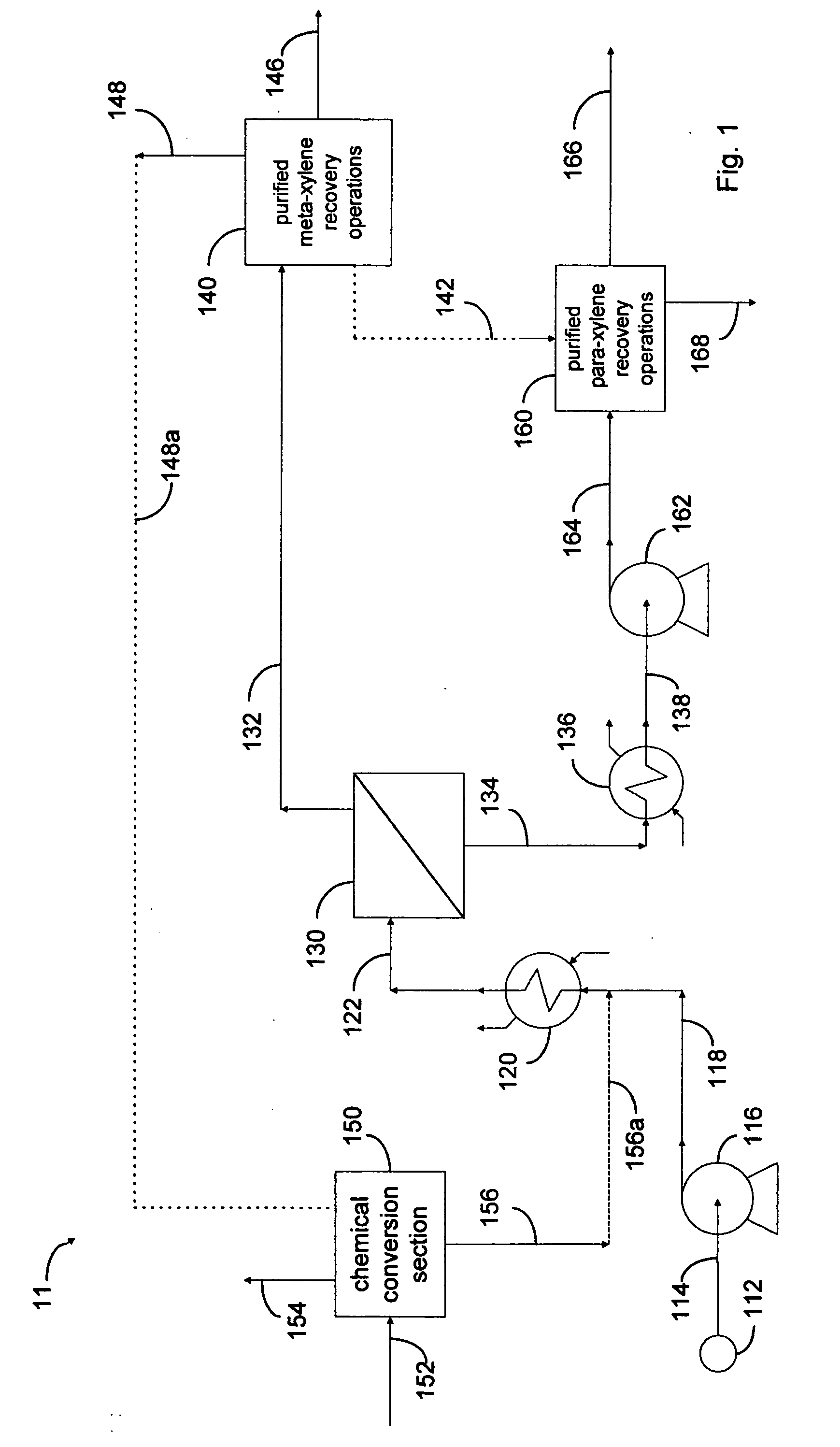
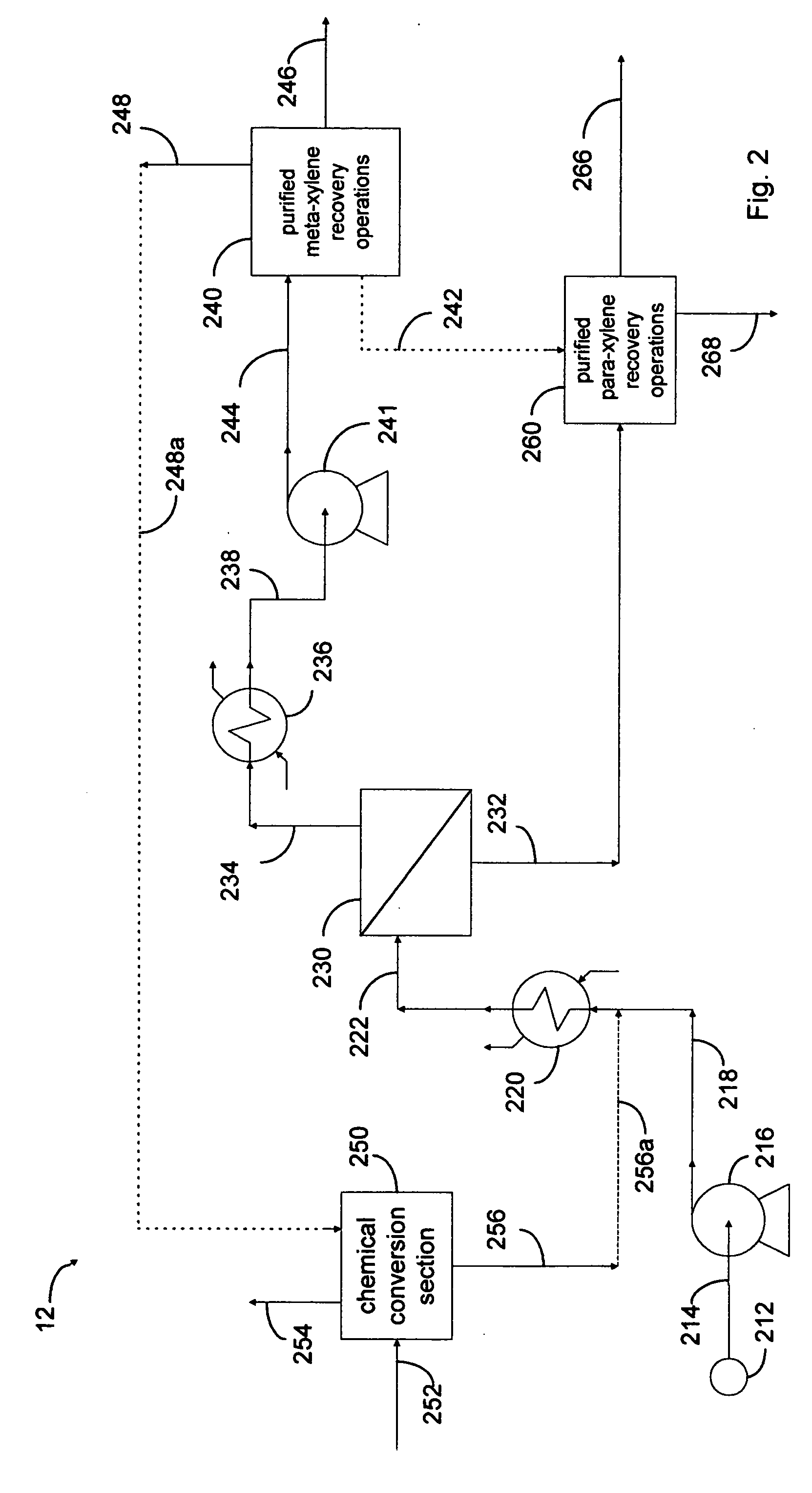
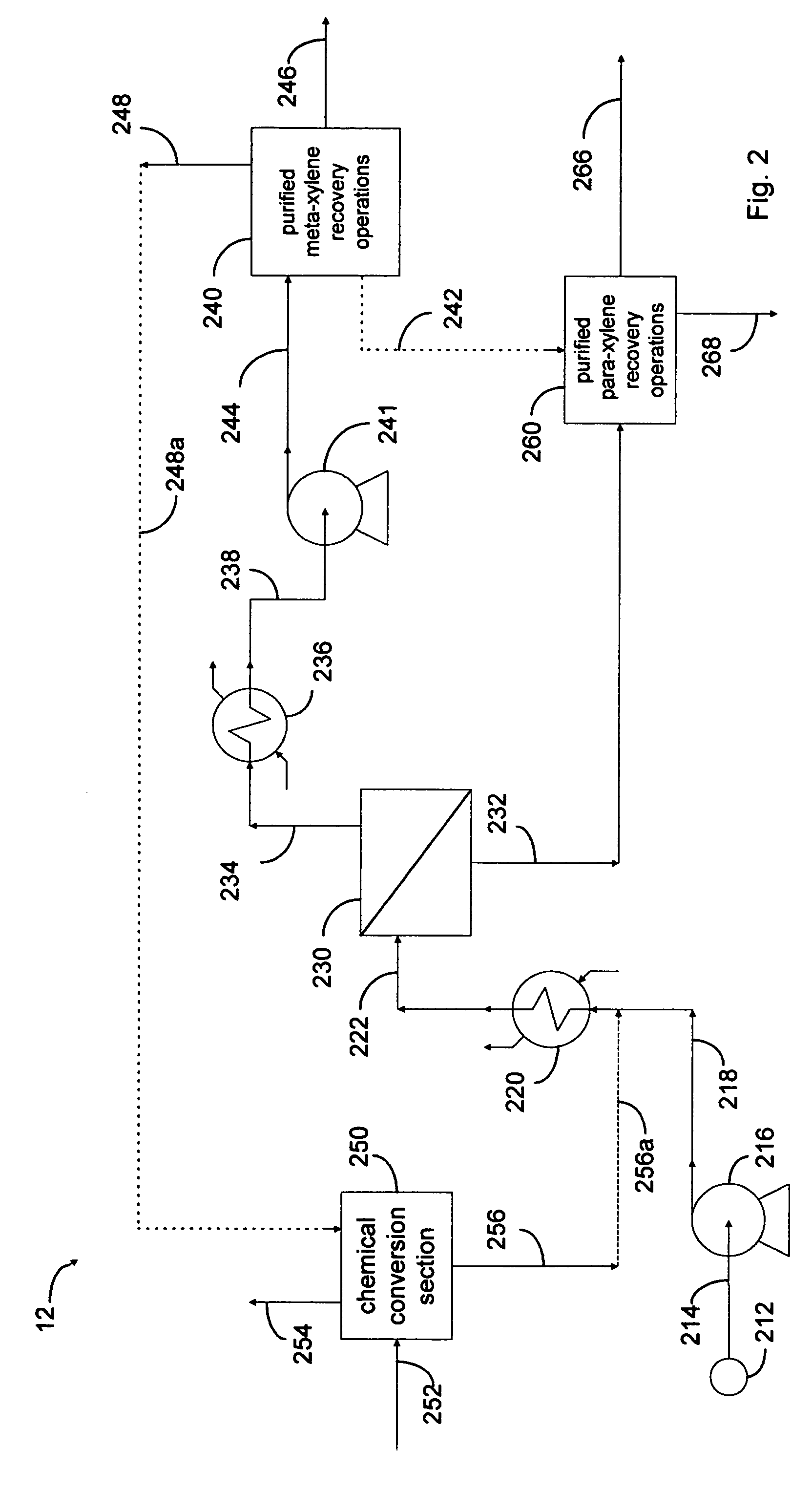
Xylene process using perm-selective separations
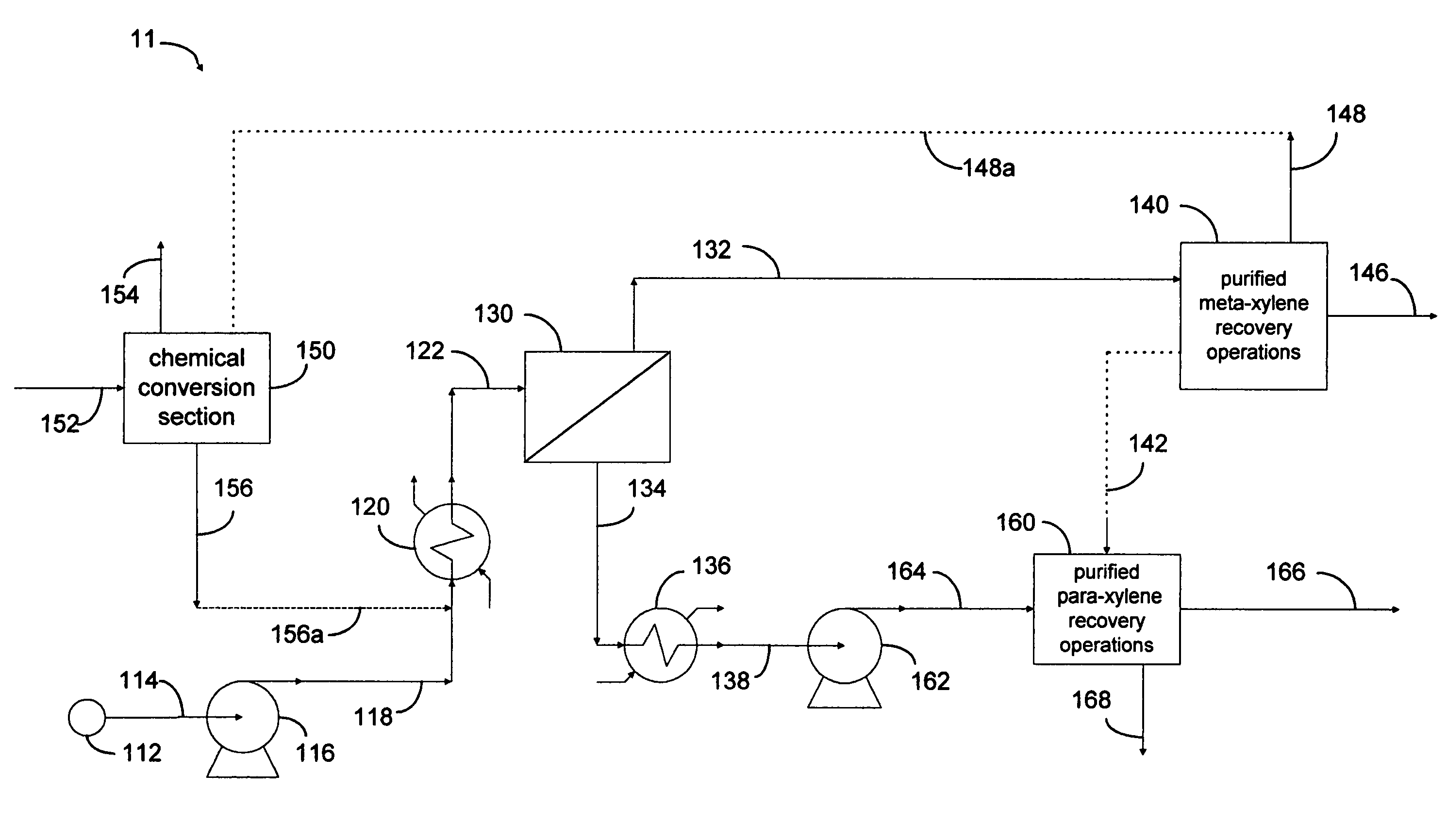
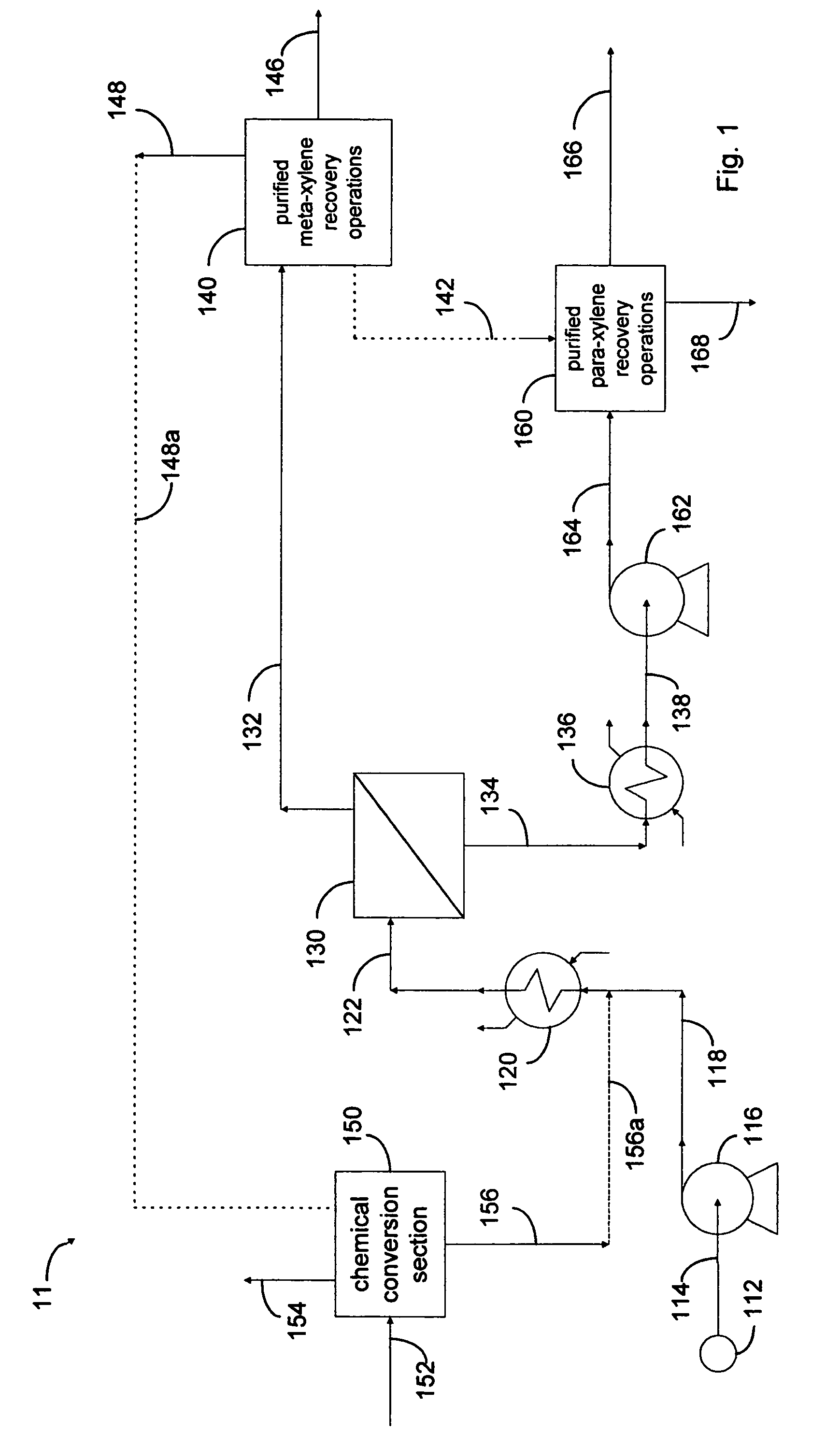
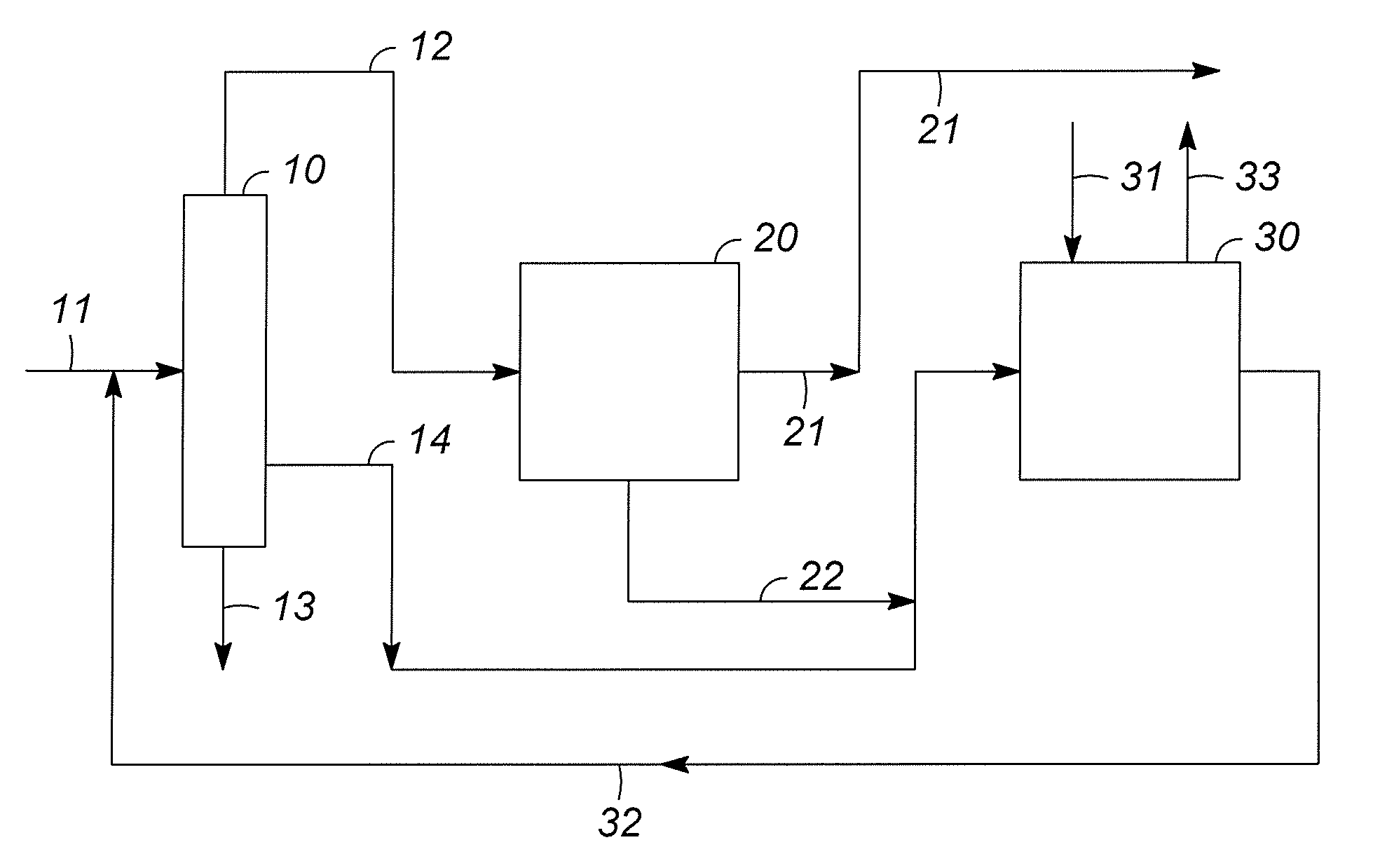
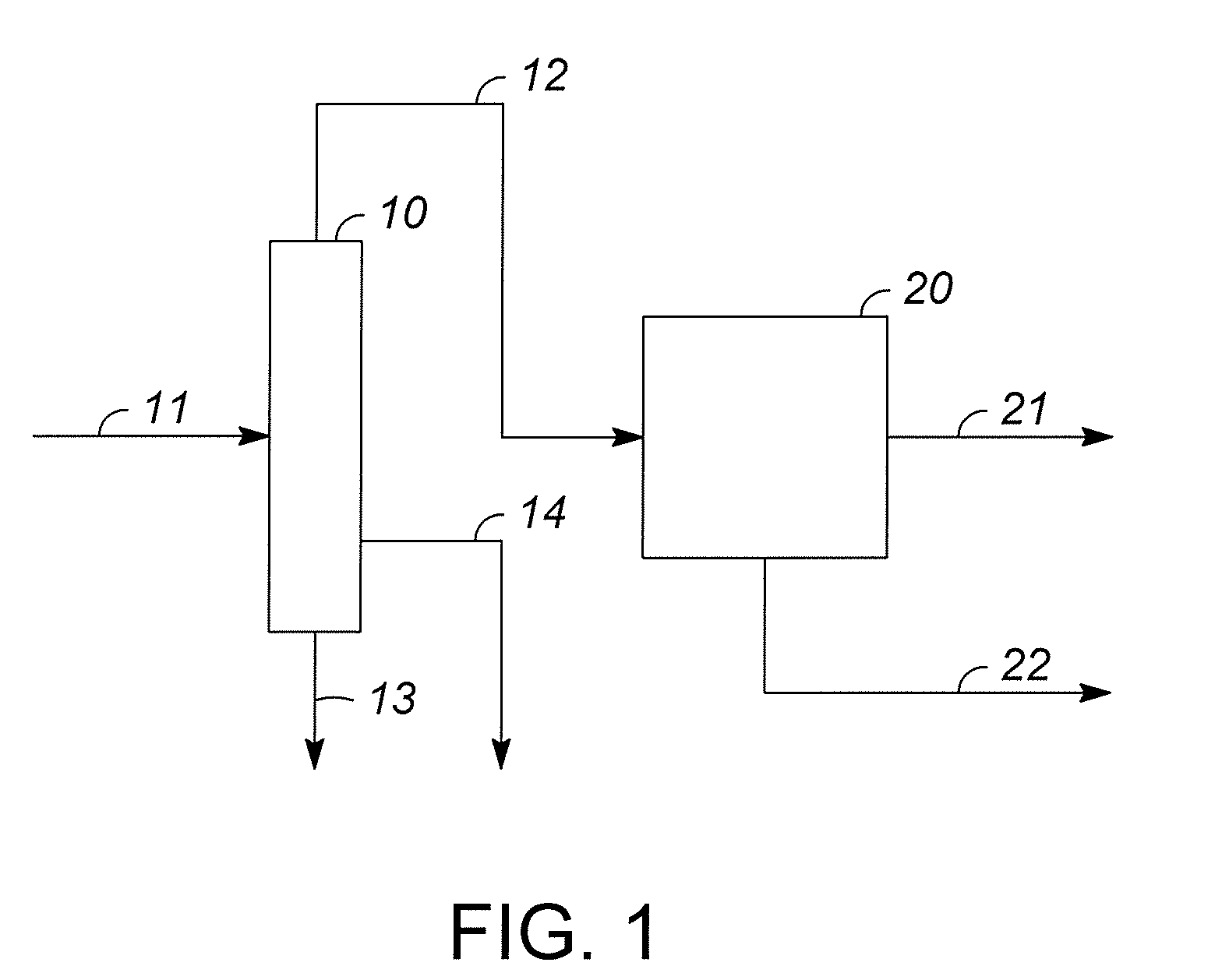
Processes are disclosed for production of purified products from a fluid mixtures of C8 aromatics by means of integration of perm-selective separations with purified product recovery operations. The perm-selective separations of the invention comprise of one or more devices using polymeric perm-selective membrane devices to separate a meta-xylene enriched stream from fluid mixtures of C8 aromatics thereby producing a fluid comprising the remaining aromatic compounds which advantageously includes para-xylene. Processes of the invention are particularly useful for recovery of very pure meta-xylene and para-xylene co-products from liquid mixtures even containing ethylbenzene as well as the three xylene isomers.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
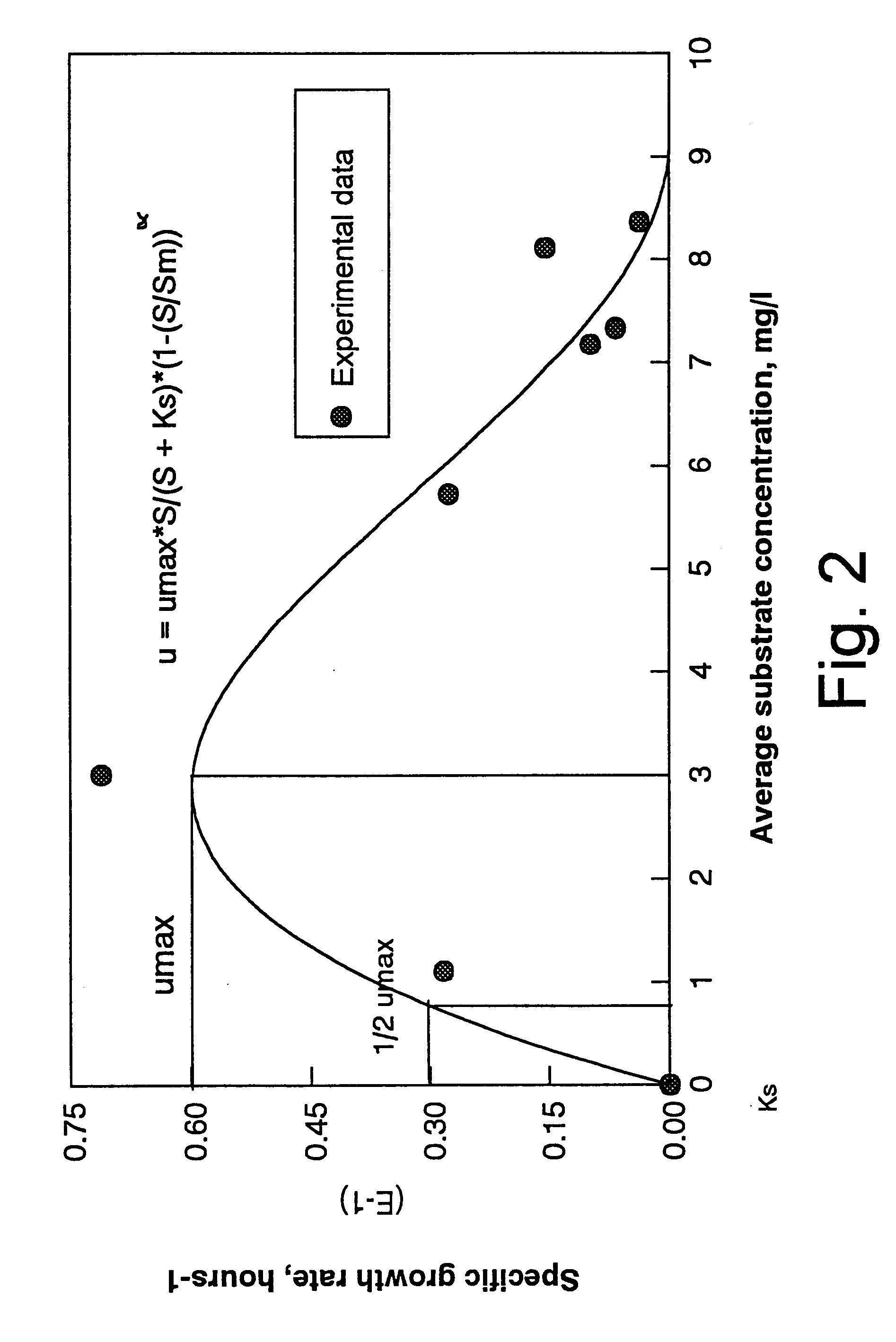
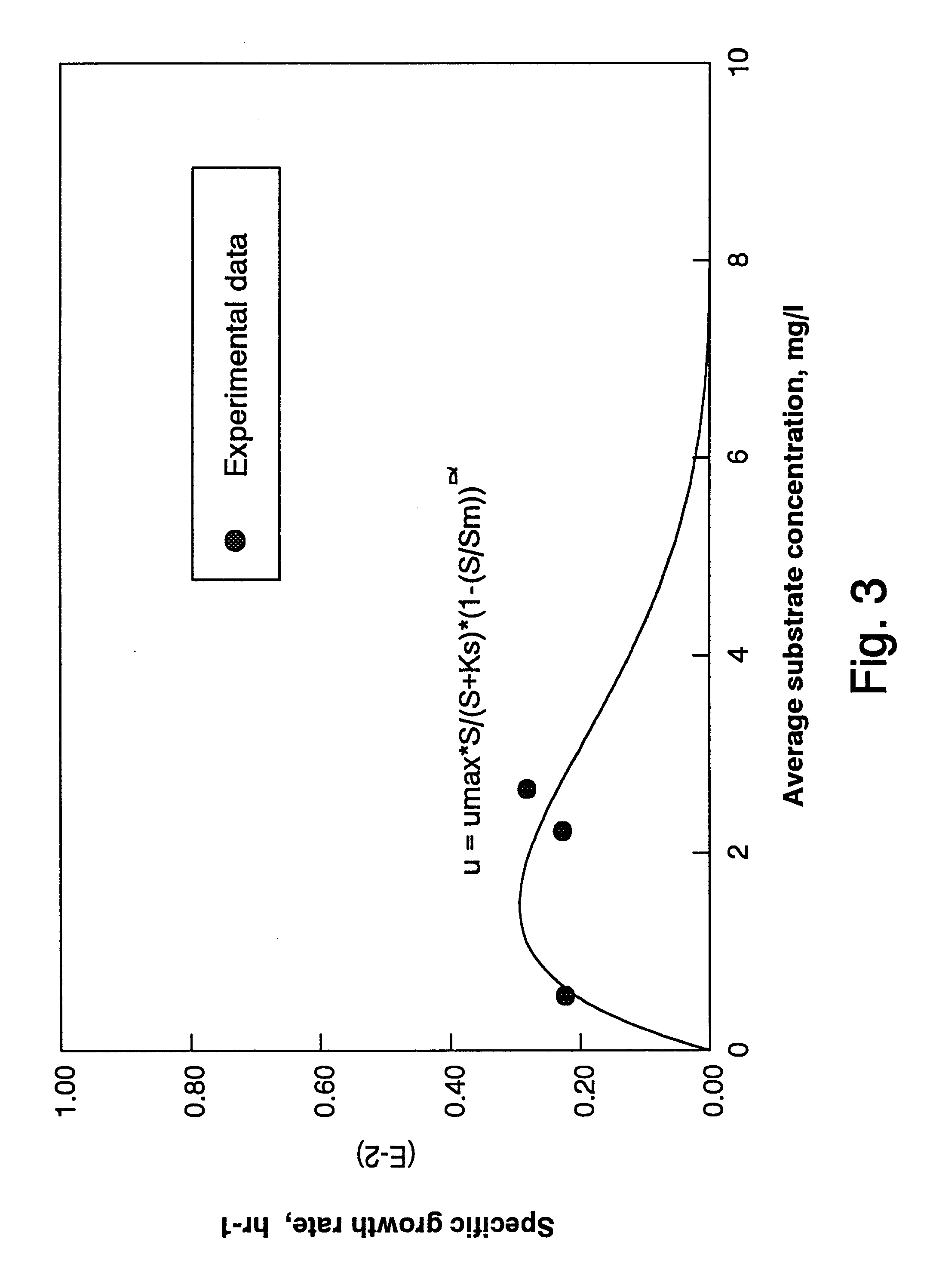
Anaerobic biodegradation of unsaturated, saturated, aromatic and halogenated hydrocarbons
An apparatus and method for anaerobic biodegradation, bioremediation or bioprocessing of hydrocarbons dissolved in an aqueous matrix, such as wastewater, groundwater, or slurry. Dissolved alkanes (saturated hydrocarbons), alkenes (unsaturated hydrocarbons), aromatic hydrocarbons and / or halogenated hydrocarbons are metabolized or cometabolized. In one form, the invention involves introducing an aqueous stream comprising at least one dissolved aromatic hydrocarbon (such as benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, o-xylene, m-xylene, p-xylene, phenol, o-cresol, m-cresol, or p-cresol) and a dissolved oxide of nitrogen [such as nitrate (NO3-), nitrite (NO2-), nitric oxide (NO) and nitrous oxide (N2O)] to a reactor, and operating said reactor under conditions that support denitrification of the aromatic hydrocarbon. Alternatively, the aqueous stream may comprise at least one alkane (such as ethane) and / or at least one alkene (such as ethene or ethylene) and biodegradation of these compounds is accomplished. In a preferred form, the aqueous stream also comprises at least one dissolved halogenated hydrocarbon (such as tetrachloroethylene, trichloroethylene, or 1,1,1-trichloroethane) and dehalogenation of the halogenated hydrocarbon is accomplished. The reactor may be a continuous stirred tank reactor, a batch (or sequencing batch) reactor, a plug-flow reactor, a fixed-film reactor, or a pore space in an underground aquifer in situ. The reactor is operated in such a way that molecular oxygen is excluded from the space or zone in which the biodegradation is occurring and the other requirements of denitrifying bacteria are met. In some implementations, kinetic control (control of mean cell residence time) is used to enrich a denitrifying culture in the reactor.
Owner:YESTECH
Process for producing high purity meta-xylene, comprising simulated moving bed adsorption and crystallization
InactiveCN101293807AHigh separation methodEconomic production conditionsDistillation purification/separationAdsorption purification/separationSimulated moving bedMeta-xylene
The invention concerns a process for producing high purity meta-xylene, comprising a step for separation by simulated moving bed adsorption starting from an aromatic C8 feed delivering a fraction which is rich in meta-xylene and a fraction which is depleted in meta-xylene, and a step for crystallization of the meta-xylene rich fraction. The purity of the meta-xylene produced is at least 99.5%.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Production method of mixed fragrant dioctyl phthalate
InactiveCN102584572AGood flexibilityFacilitate cross-linkingOrganic compound preparationChemical industryCatalytic oxidationCarboxylic acid
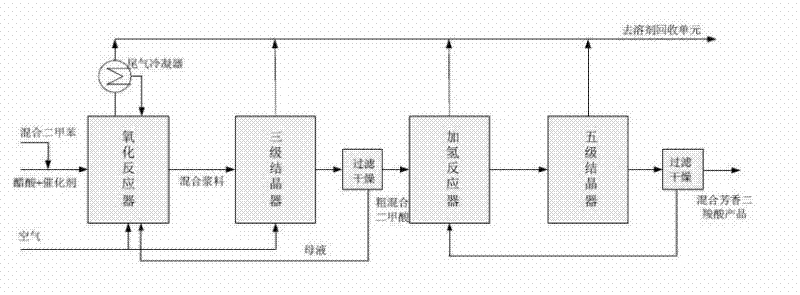
The invention discloses a production method and a device for preparing mixed fragrant dioctyl phthalate by taking mixed xylene as a raw material and through liquid-phase catalytic oxidation. The raw material is derived from products produced after the extract of C8 aromatic hydrocarbon is separated, or is prepared through paraxylene with higher purity (99 percent) and meta-xylene according to fixed proportion. The mixed xylene is positioned in a gas-liquid agitation reactor with higher temperature and higher pressure, and is directly oxidized by air under the condition of solvent and catalyst, so as to produce mixed fragrant carboxylic acid. The oxidation product is separated by hydrofining and multi-stage low temperature crystallization, so that a high purity mixed product only containing TA (terephthalic acid) and IA (m-phthalic acid) is obtained. The product can be used for polyester production directly, and separation is no longer required. In the mixed carboxylic acid produced by using the technology, TA and IA are in a molecular level high dispersion state, and the mixed carboxylic acid is used for producing polyester, so that the problems of quality instability of the polyester product and the like caused by uneven raw material mixing can be effectively reduced.
Owner:YISHENG DAHUA PETROCHEM
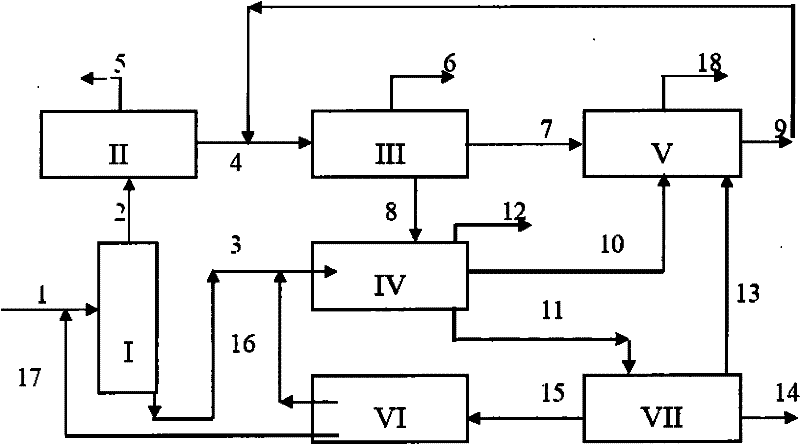
Co-production method for dimethyl benzene, meta dimethyl benzene and/or ortho dimethyl benzene
InactiveCN1408690ALow operating costDistillation purification/separationHydrocarbonsSimulated moving bedOrtho-xylene
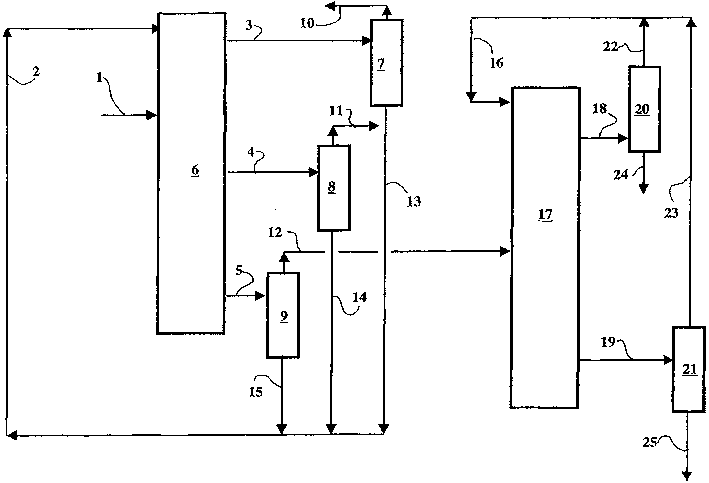
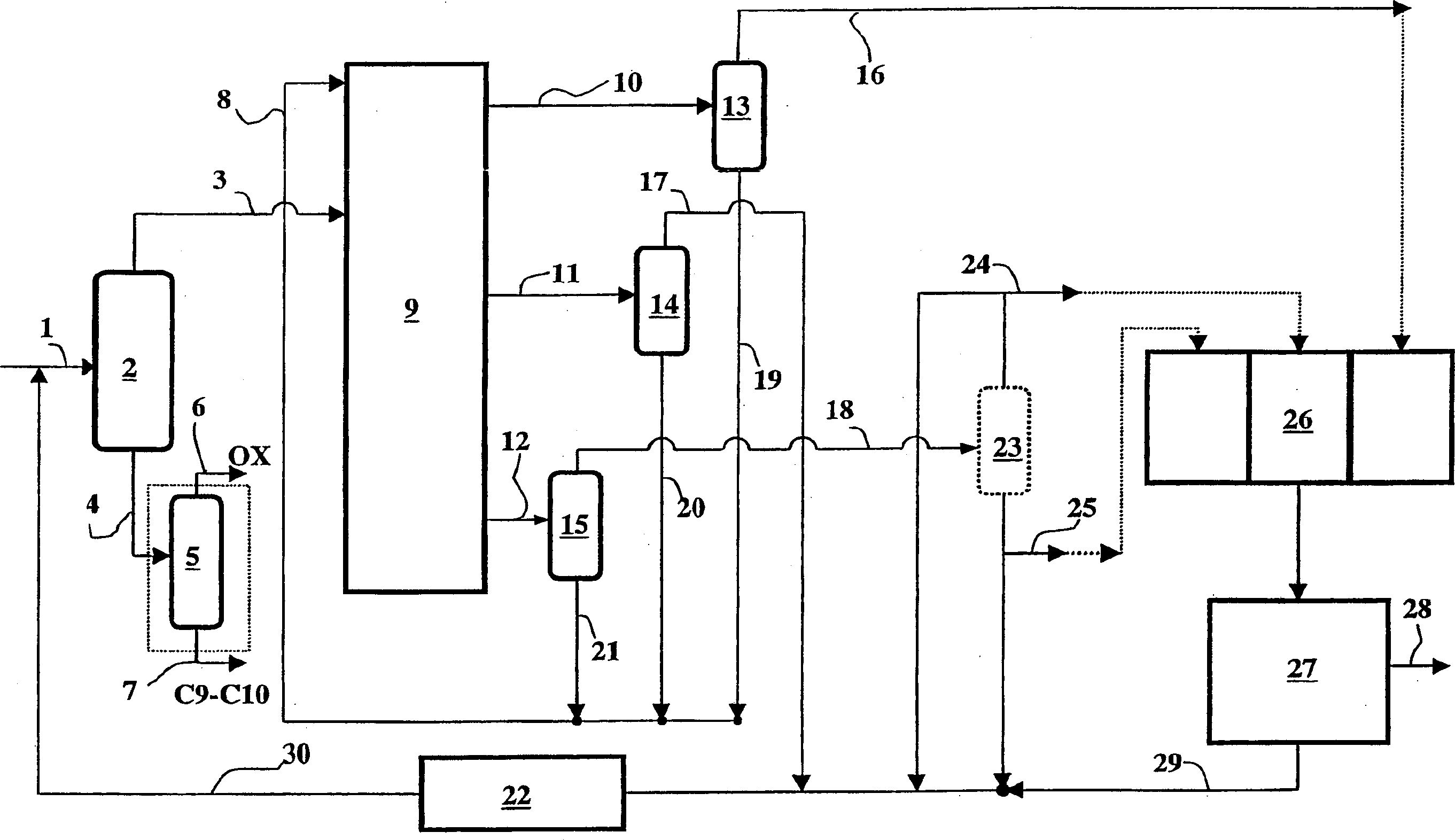
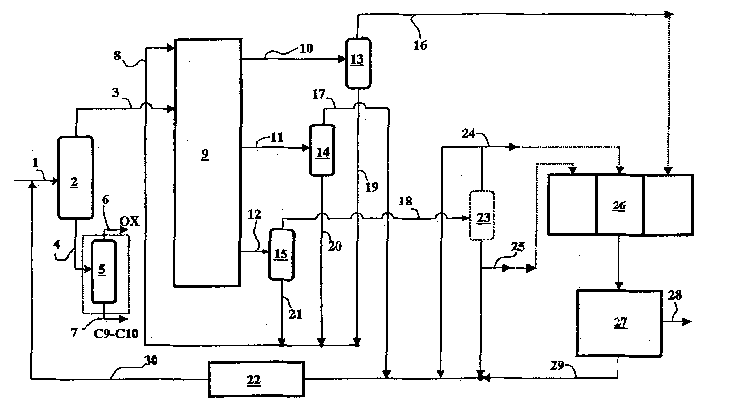
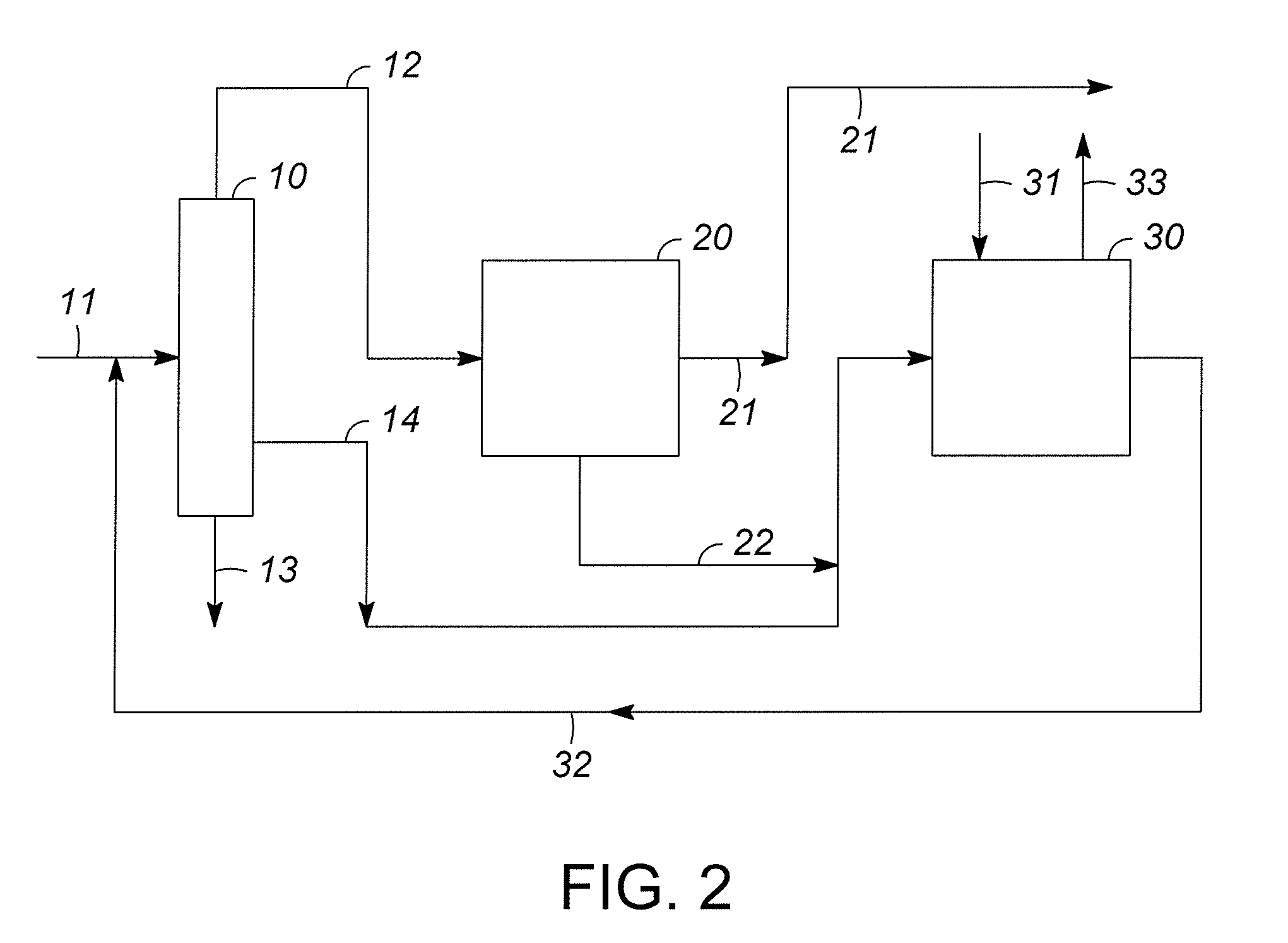
A process for co-production of paraxylene, metaxylene and / or orthoxylene from a hydrocarbon feedstock (1) that comprises [1] a separation stage of the feedstock in a simulated moving bed in a chromatographic column (9) that contains a number of beds of an adsorbent, interconnected in a loop, is described, whereby said column comprises an injection (3) of the feedstock, a draw-off (10) of an extract that consists of paraxylene and desorbent, an intermediate fraction (11) (extract or raffinate) that contains ethylbenzene, and a raffinate (12) that contains a mixture of metaxylene and orthoxylene that is virtually free of ethylbenzene and paraxylene and [2] a crystallization stage (27) of the metaxylene and / or orthoxylene fraction. Upstream from the adsorption zone and / or upstream from the crystallization zone, it is possible to distill the entering mixture to produce an orthoxylene-enriched fraction at the bottom and a metaxylene-enriched fraction at the top.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Xylene process using perm-selective separations
Processes are disclosed for production of purified products from a fluid mixtures of C8 aromatics by means of integration of perm-selective separations with purified product recovery operations. The perm-selective separations of the invention comprise of one or more devices using polymeric perm-selective membrane devices to separate a meta-xylene enriched stream from fluid mixtures of C8 aromatics thereby producing a fluid comprising the remaining aromatic compounds which advantageously includes para-xylene. Processes of the invention are particularly useful for recovery of very pure meta-xylene and para-xylene co-products from liquid mixtures even containing ethylbenzene as well as the three xylene isomers.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Adsorbents with improved mass transfer properties and their use in the adsorptive separation of para-xylene
ActiveUS20090326311A1Improve mass transfer effectIncreased para-xylene productivityHydrocarbonsAdsorption purification/separationProduction rateSimulated moving bed
Adsorbents and methods for the adsorptive separation of para-xylene from a mixture containing at least one other C8 aromatic hydrocarbon (e.g., a mixture of ortho-xylene, meta-xylene, para-xylene, and ethylbenzene) are described. Suitable adsorbents comprise zeolite X having an average crystallite size of less than 1.8 microns. The adsorbents provide improved mass transfer, which is especially advantageous for improving productivity in low temperature, low cycle time adsorptive separation operations in a simulated moving bed mode.
Owner:UOP LLC
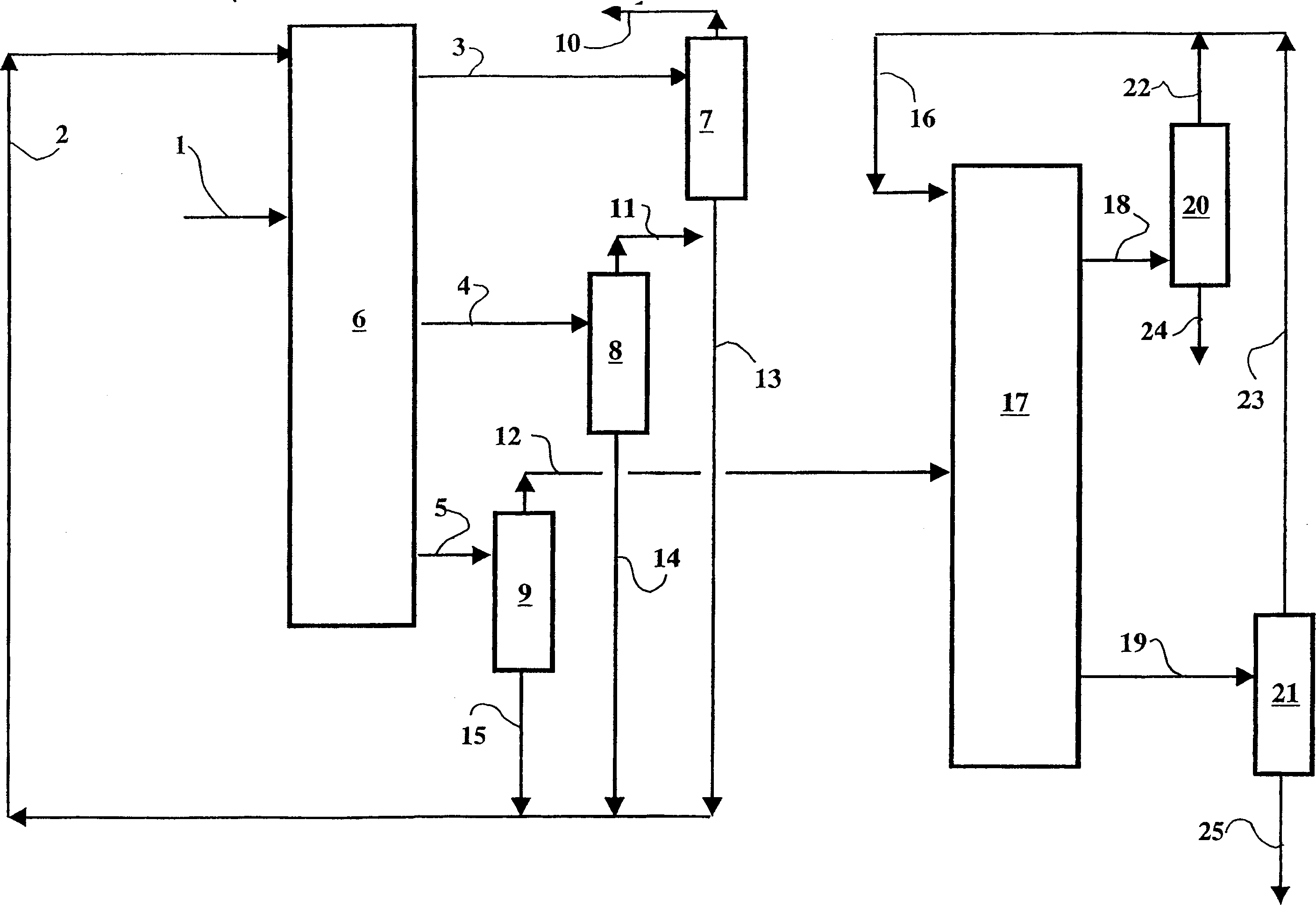
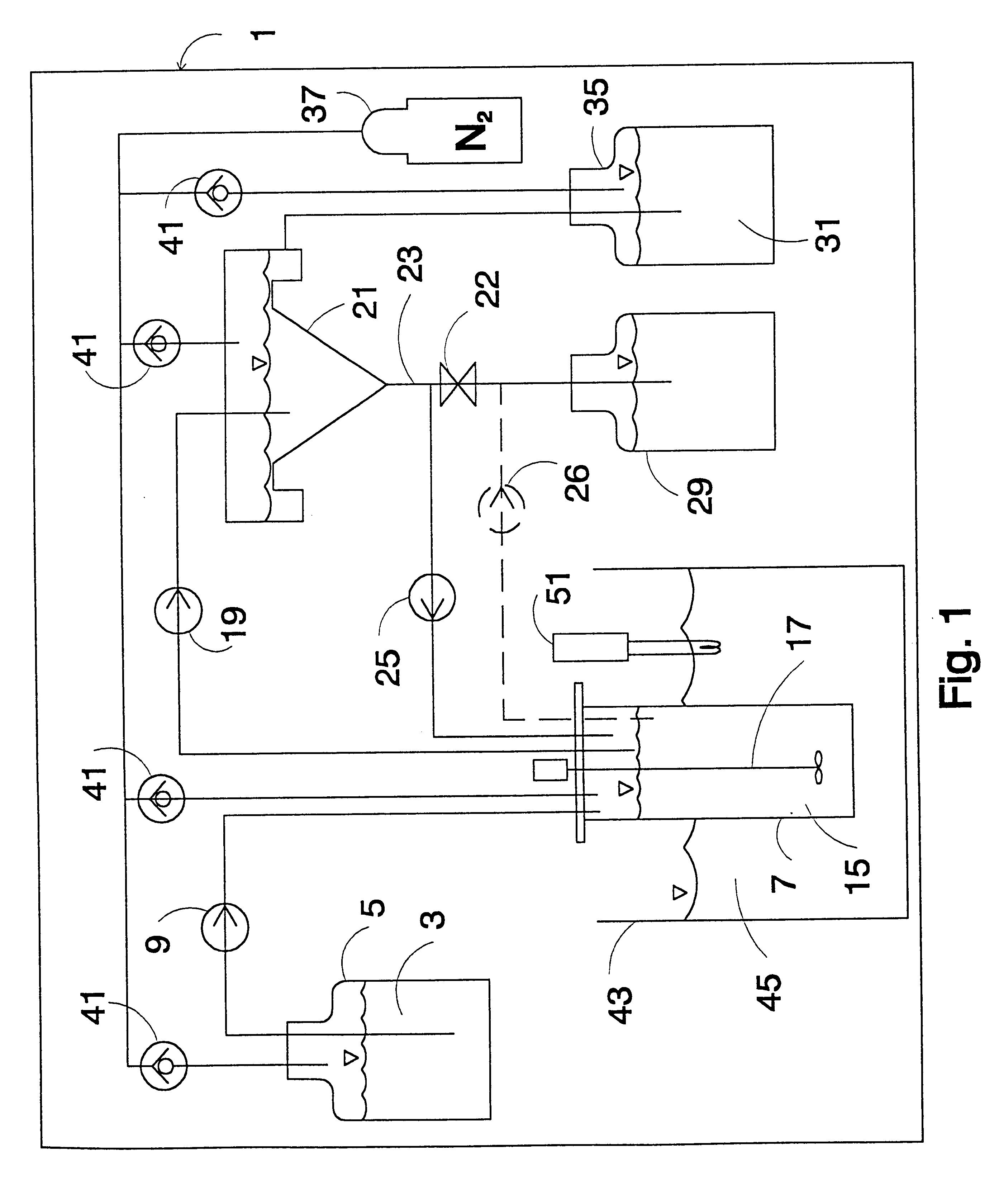
Simulated moving bed separation process and device
InactiveUS7473368B2Effective flushingHigh purityIon-exchange process apparatusGas treatmentSorbentSimulated moving bed
A simulated moving bed (SMB) separation device comprises at least one column, beds of adsorbent arranged in this column, trays Pi with a chamber Ci for distribution and extraction of fluids, a multi-way rotary valve for the distribution of the fluids feeding or leaving said trays, and junction lines Li between this valve and said trays. The SMB device also comprises a plurality of bypass lines Li,i+1 between adjacent lines, these bypasses being outside the multi-way rotary valve and situated in proximity to this valve, for the circulation of rinsing liquids with a small or zero concentration gradient. The invention makes it possible to use all types of distribution and extraction trays and all types of adsorbent loading, while preserving a high level of product purity. Application of the separation devices is in particular to the separation of paraxylene or metaxylene from a C8 aromatic charge.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Aromatic hydrocarbon alkyl transfer method for producing benzene and p-xylene
ActiveCN102190553AHigh PX contentIncrease concentrationHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbonsAlkyl transferIsomerization
The invention relates to an aromatic hydrocarbon alkyl transfer method for producing benzene and p-xylene, and the method is mainly used for solving the problems that in the prior art, an isomerization unit and a disproportionation unit of p-xylene just respectively process C8 aromatic hydrocarbon and toluene, and the equipment investment is large. The method comprises the following steps: a) feeding mixed xylene containing o-xylene and m-xylene and a toluene material into an aromatic hydrocarbon alkyl transfer process unit so as to generate an aromatic hydrocarbon alkyl transfer reaction under the hydrogen condition so as to generate an aromatic hydrocarbon material flow containing benzene and p-xylene after reaction; (b) successively passing the aromatic hydrocarbon material flow containing the benzene and the p-xylene through a benzene tower, a toluene tower and a xylene tower so as to separate out the benzene and the mixed xylene; and (c) feeding the mixed xylene in a absorption separation or freezing crystalline separation unit so as to generate the p-xylene, and feeding the unreacted toluene and xylene in the aromatic hydrocarbon alkyl transfer unit, wherein a composite catalyst bed layer is adopted in the aromatic hydrocarbon alkyl transfer process unit, aromatic hydrocarbon alkyl transfer reaction occurs to the upper catalyst bed layer, and toluene selectivity disproportional reaction is carried out on the lower catalyst bed layer with a shape-selective function. By using the technical scheme, the problem can be well solved; and the method can be applied to production of benzene and p-xylene.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
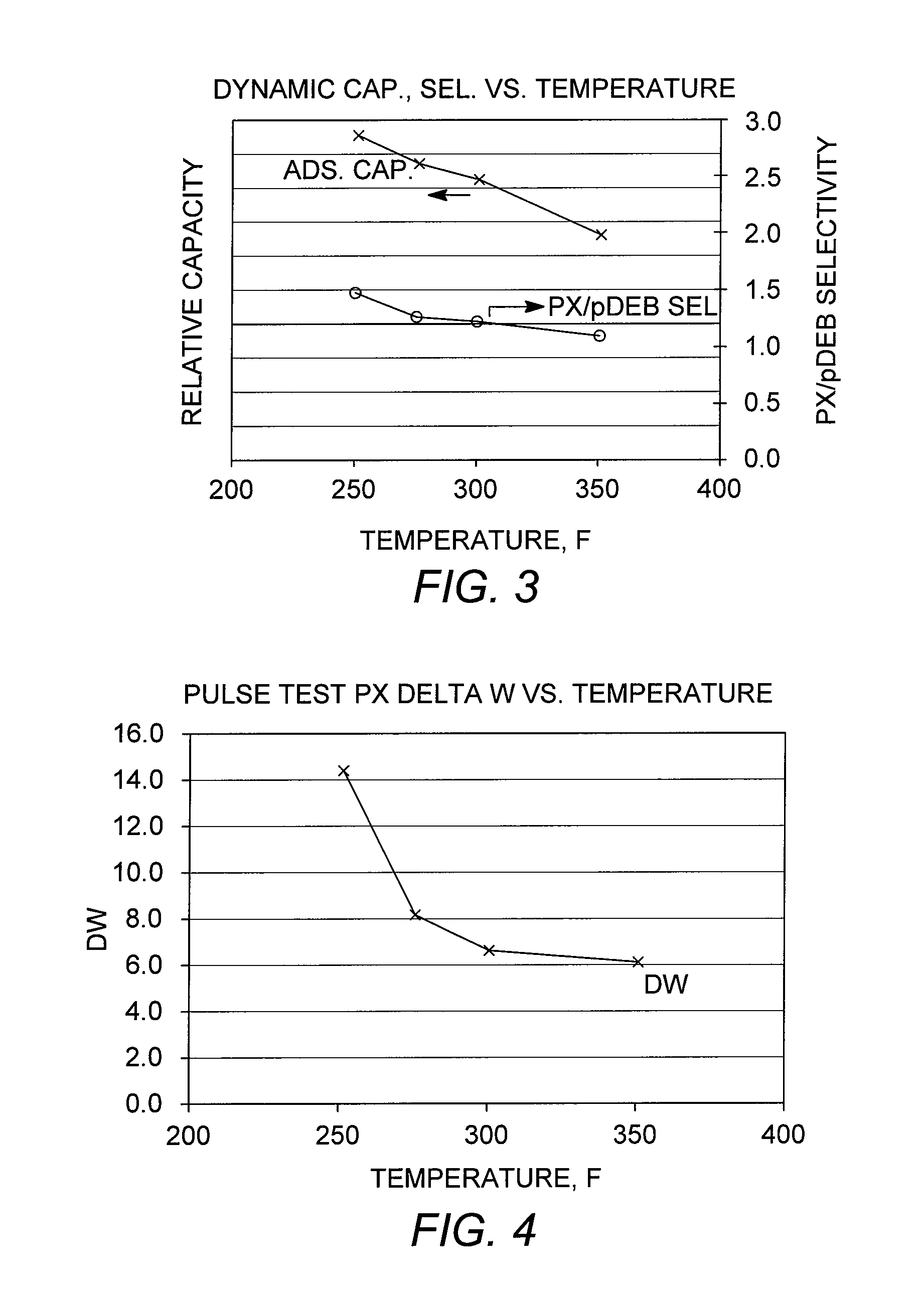
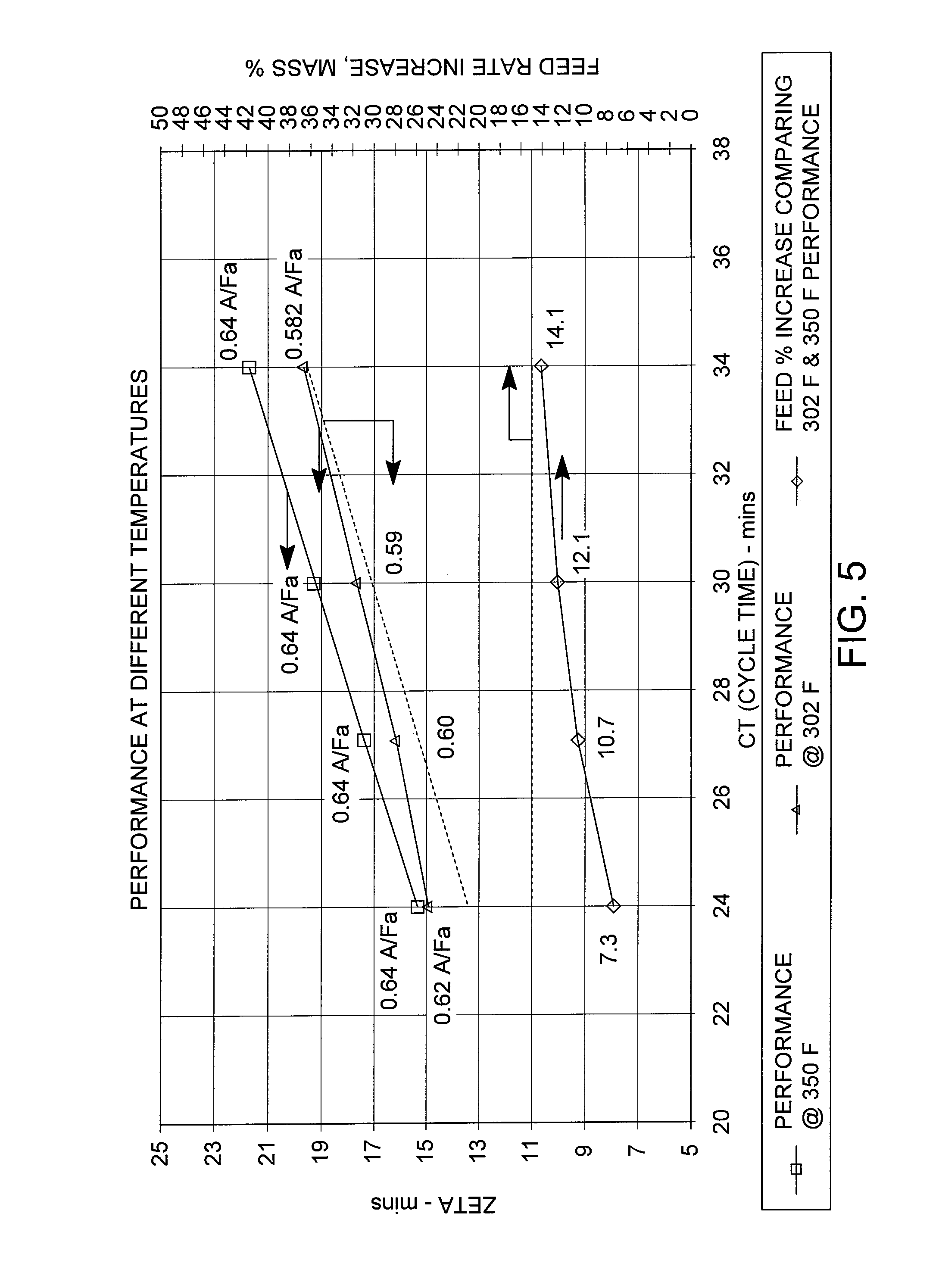
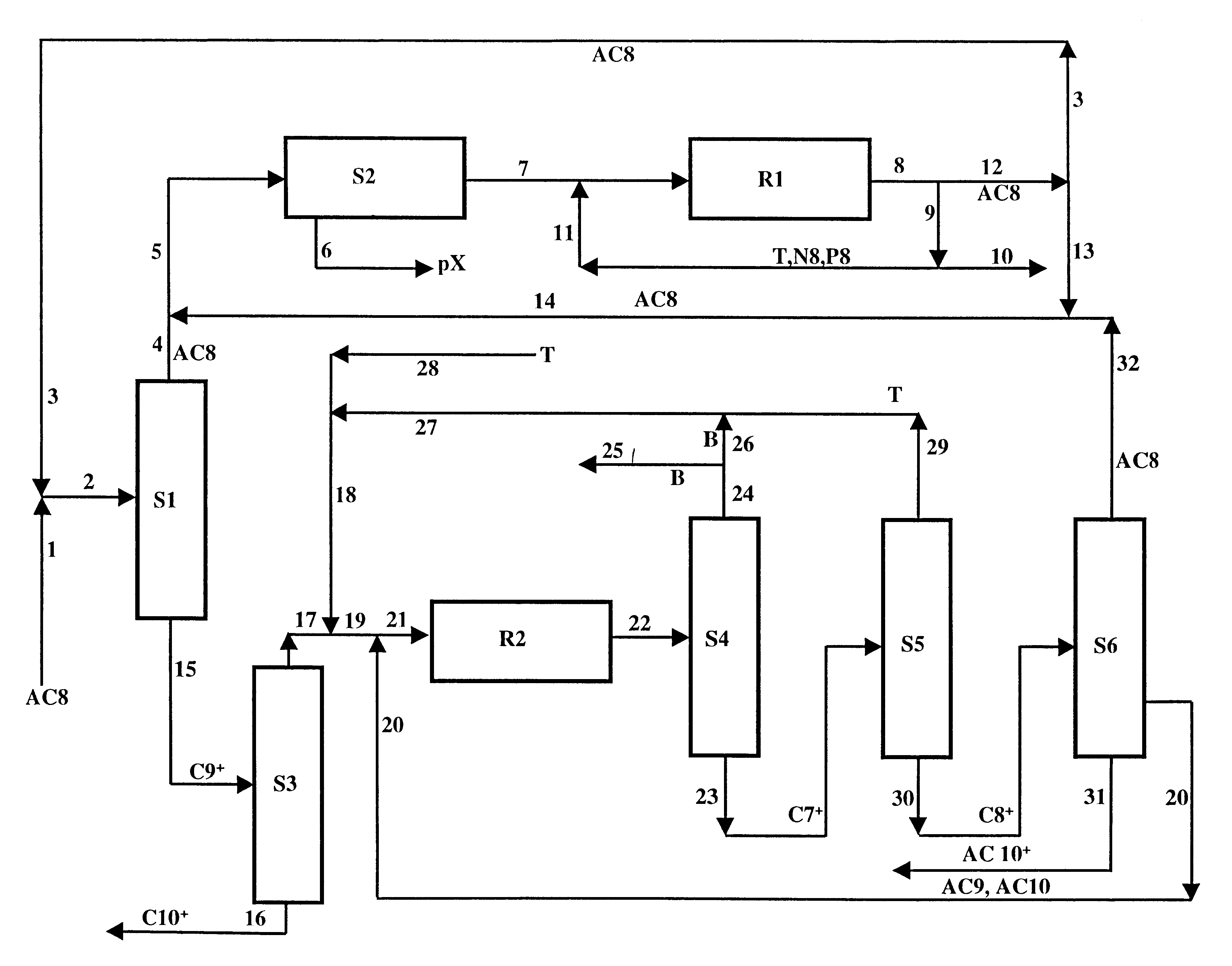
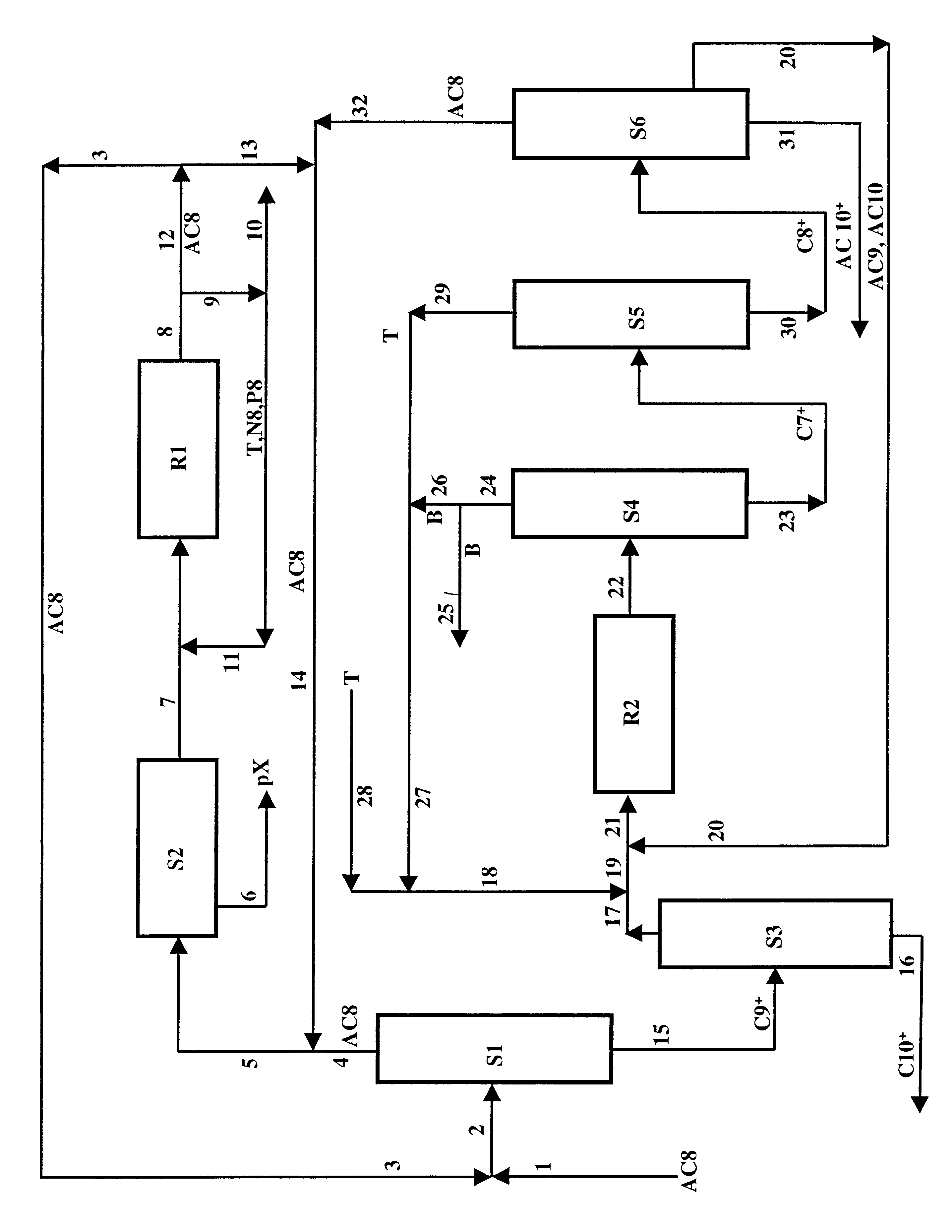
Process for Improved Meta-Xylene Yield from C8 Aromatics
ActiveUS20100305380A1Low costHydrocarbon by isomerisationDistillation purification/separationMeta-xyleneOrtho-xylene
Meta-xylene is recovered from admixture with other C8 aromatic hydrocarbons including ortho-xylene by liquid phase adsorptive separation. Performance is improved by reducing the concentration of ortho-xylene through adding a sidecut to a prefractionator preparing the feedstock to adsorptive separation.
Owner:UOP LLC
Monodisperse C* nano unit crystal material and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101550591APrecise shape controlEasy to operatePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsSingle crystalSolvent
The present invention provides a monodisperse C70 nano unit crystal material and a method for preparing same which belong to the technic field for preparing unit crystal material. The C70 nano unit crystal material has granular, bar or pipe shape with face-centred cubic structure. A saturated C70 meta-xylene solution is used as mother liquor, straight-chain saturated monohydric alcohol with various type is used as shape regulating agent. The preparing method includes steps as follows: mixing the mother liquor and the shape regulating agent, ultrasound shocking, standing, taking defecation scum on a basal lamina, volatilizing dissolvant and shape regulating agent naturally in room temperature and obtaining C70 nano crystal; then heating for removing dissolvant under pressure intensity 10(-5) and obtaining the product. The method can prepare C70 nano unit crystal material with granular shape, bar shape and pipe shape with regular size and shape; the product shape can be controlled accurately; the method is simple; the product provides an effective purpose for the nano device application which has better application prospect.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
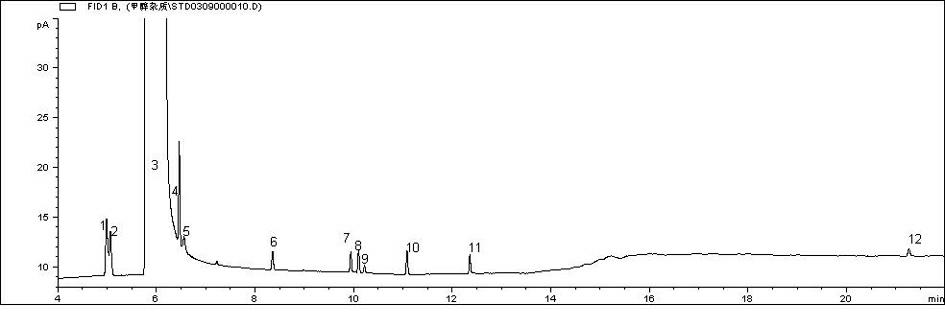
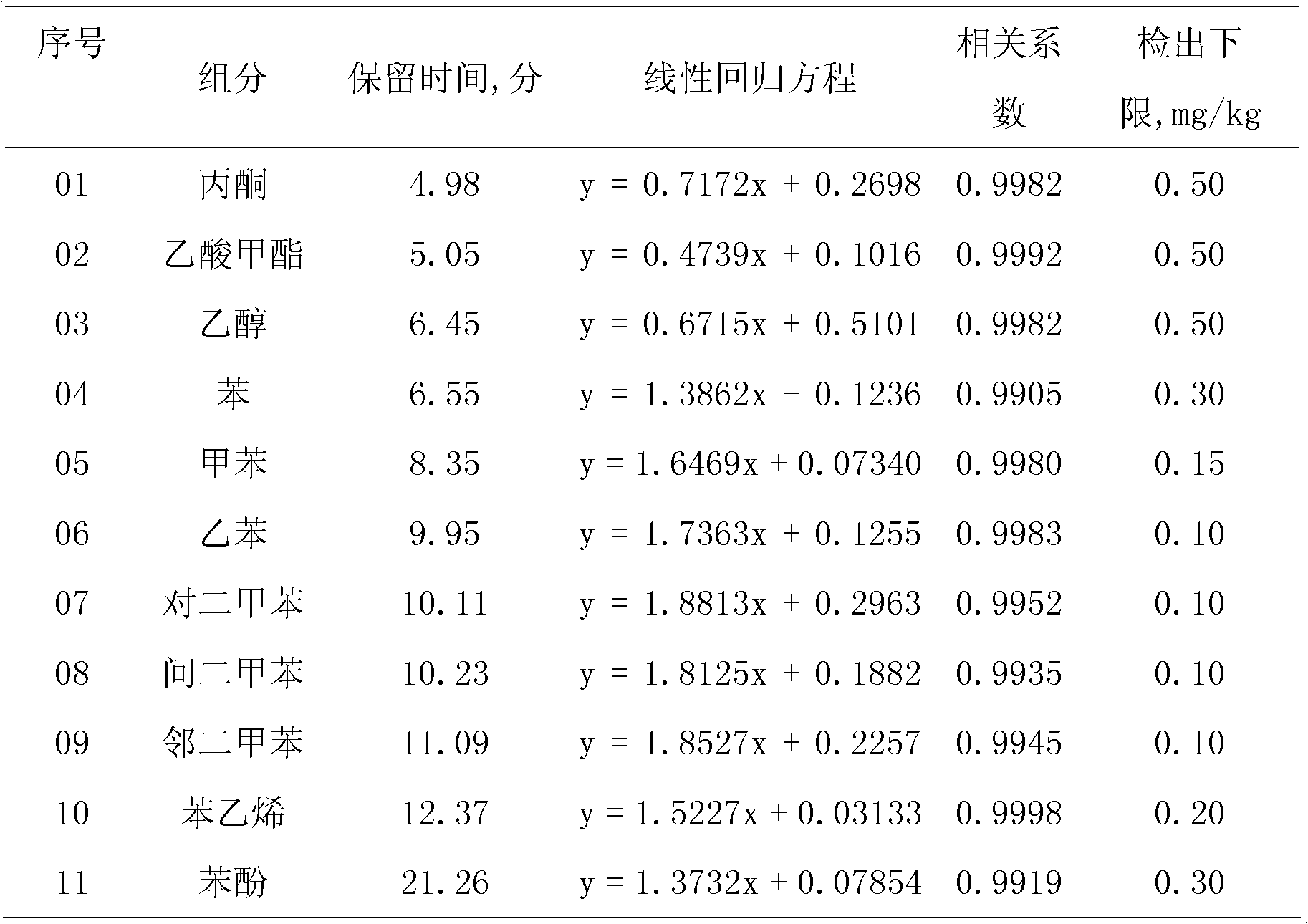
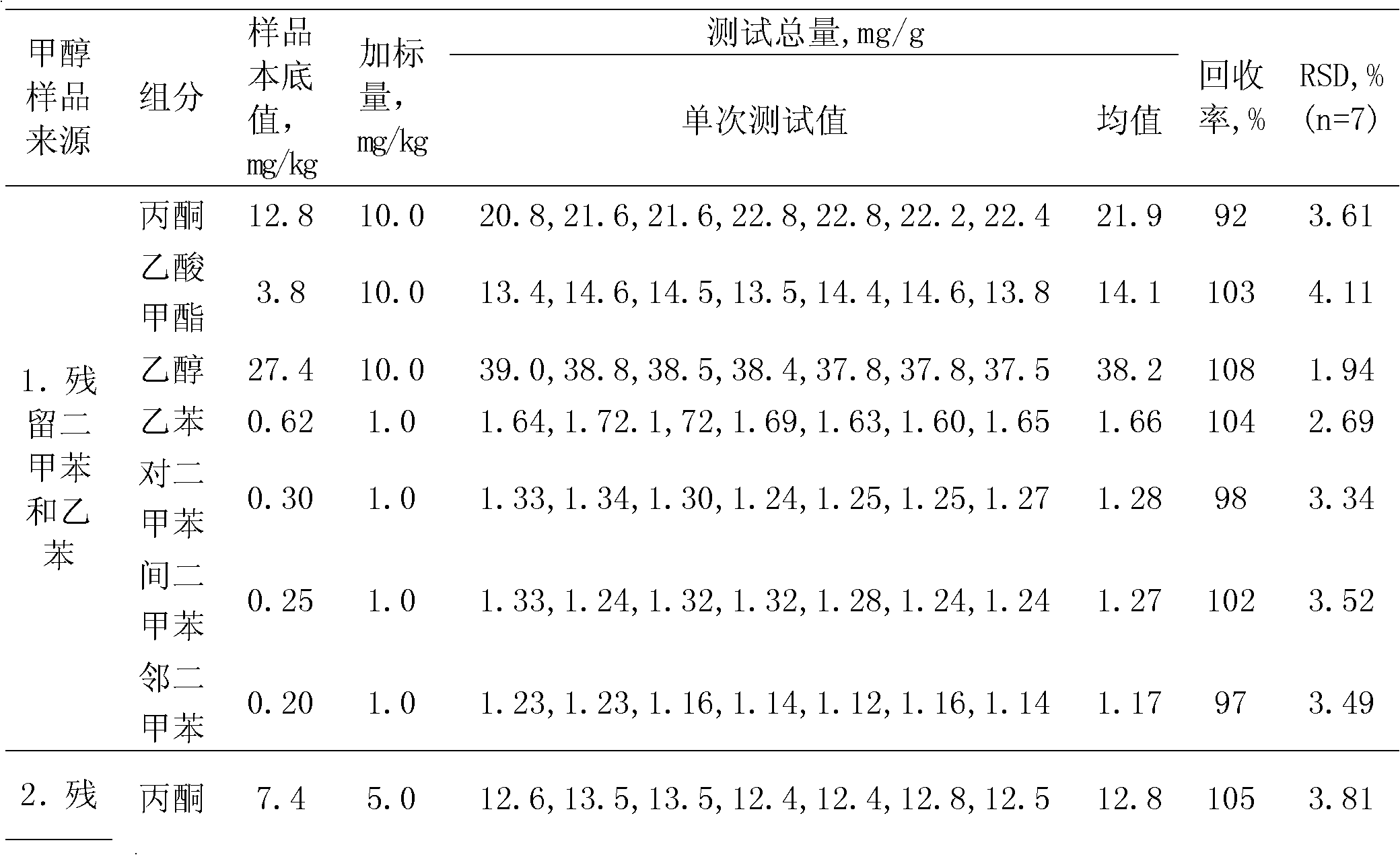
Method for determining coexisting impurities and trace arenes in methanol simultaneously
InactiveCN102253142AAccurate judgmentSave human effortComponent separationMaterial resourcesImpurity
The invention discloses a method for determining coexisting impurities and trace arenes in methanol simultaneously. In the method, gas chromatography is performed on methanol, and an external standard method is used for quantitatively determining the contents of the coexisting impurities and the trace arenes in the methanol, wherein the coexisting impurities refer to methyl acetate, acetone and ethanol, the trace arenes comprise the following components: benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, p-xylene, m-xylene, o-xylene, styrene and phenol. The coexisting components and the common arenes types in the methanol are considered in the method simultaneously, thus the simultaneous determination method for the eleven components in the methanol is established in an optimization manner. The simultaneous determination of multiple components is beneficial to saving of manpower and material resources to a great extent, acceleration of the detection speed, and accurate judgment of the polluted arenas types in methanol during storage and transportation. The method has the advantages of convenience for operation, low detection cost, accuracy, sensitivity and high efficiency.
Owner:太仓意发石化矿材检测有限公司
Method for preparing 2,4-dimethylbenzoic acid by using carbon dioxide carboxylation process
InactiveCN103319330ALow costMild reaction conditionsOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationWhite powderMeta-xylene
The invention discloses a method for preparing 2,4-dimethylbenzoic acid by using a carbon dioxide carboxylation process. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) orderly adding m-xylene and an aluminium trichloride catalyst according to a certain ratio in a reaction kettle with a stirring function, and sealing the reaction kettle; (2) leading carbon dioxide gas to the reaction kettle, replacing air and starting the stirring function, pressurizing to 0.2-0.7Mpa, and keeping the temperature at 25-40 DEG C to react for 5-10 hours; (3) adding a reactant to the m-xylene and diluted hydrochloric acid after reaction is finished, keeping below 30 DEG C to agitate for 20 minutes, stewing and layering; (4) adjusting pH value of an organic phase to about 11 by alkali, standing, and separating the water phase, adding the diluted hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH value to 2-3, separating out a lot of white powder, filtering and drying to obtain the product 2,4-dimethylbenzoic acid, wherein the mass ratio of the m-xylene to the aluminium trichloride catalyst is 1 to (0.10-0.35).
Owner:TAISHAN MEDICAL UNIV
Process for producing isophthalic acid
InactiveCN101704741ASlow down the combustion reaction rateReduce usageOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsReaction rateSolvent
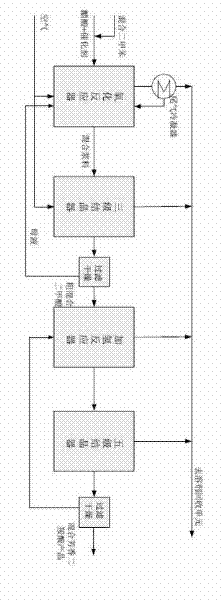
The invention relates to a method for producing isophthalic acid by using m-xylene. In a reactor, under the atmosphere of 6 to 20 and at the temperature of between 150 and 300 DEG C, a gas-liquid-solid three-phase reaction system is formed by the m-xylene serving as a raw material, air serving as an oxidant, acetic acid serving as solvent and active carbon loaded with 5 to 60 weight percent of heteropolyacid serving as a solid catalyst to oxide the m-xylene into the isophthalic acid. The method can reduce the combustion reaction rate of the acetic acid and the m-xylene, reduce the losses of the acetic acid and the m-xylene, avoid using bromine, reduce equipment corrosion, reduce pollution to environment, and realize green production of the isophthalic acid.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Synthesis method of 4-nitro m-xylene by selective nitration of bismuth nitrate
InactiveCN105175269AAvoid strong corrosiveRapid responseNitro compound preparationAcetic anhydrideSynthesis methods
A synthesis method of 4-nitro m-xylene by selective nitration of bismuth nitrate comprises the following steps: adding 3-7ml of petroleum ether to a round bottom flask under magnetic stirring, successively adding 2.0-4.0mmol of m-xylene, 2.0-10.0mmol of acetic anhydride, 2.0-4.0mmol of Bi(NO3)3.5H2O and 0.4-1.2g of a zeolite molecular sieve catalyst Hbeta (500); heating with refluxing for 2-6 h and terminating the reaction; filtering for removing the catalyst; and conducting liquid washing, dewatering and drying. The method can greatly improve the yield of 4-nitro m-xylene in a nitration product, and the nitration selectivity of m-xylene is significantly enhanced; and under the optimum conditions, the yield and selectivity of 4-nitro m-xylene reach 89.9% and 8.26. The method has the advantages of easy control of reaction conditions, short time consumption, simple process, low production cost, less pollution, and convenience for industrial production.
Owner:HEFEI NORMAL UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com