Method for determining a mutation in genomic dna, use of the method and kit for carrying out said method
A genome and gene technology, applied in the field of implementing the method or kit for the purpose, can solve the problems of unnecessary treatment and wrong treatment of patients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 9
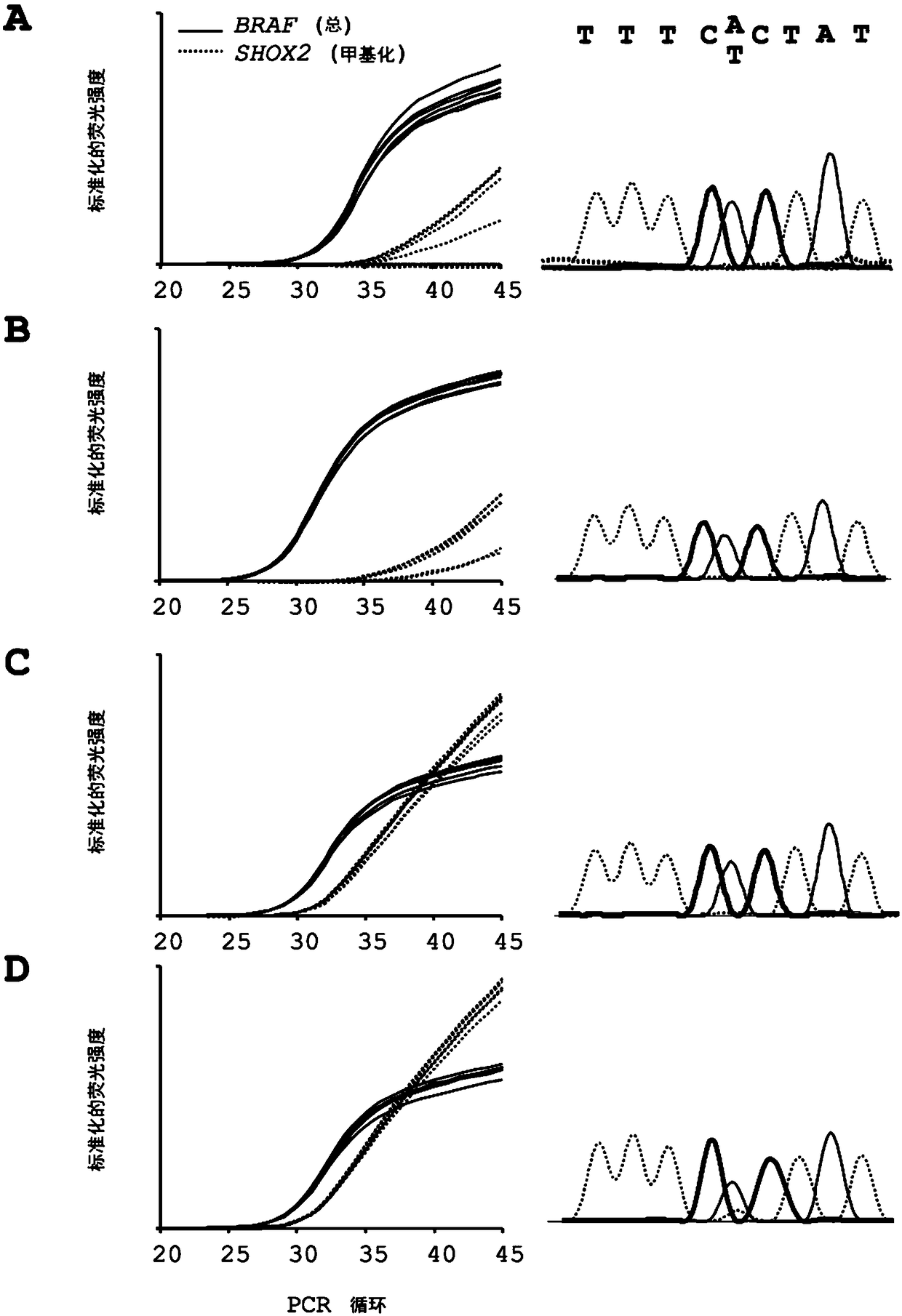
[0197] In a preferred use of the method for prediction, a prediction of a patient's response to treatment with at least one active ingredient selected from the group consisting of alkylating chemotherapeutics, cytostatics, therapeutic monoclonal antibodies and inhibitory agents, especially tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Particular preference is given to making predictions regarding active ingredients selected from the group consisting of Temozolomide, Cetuximab, Bevacizumab, AG-221, AGI-5198, AG-120, AG-881 or combinations thereof.
[0198] In a preferred variant of the method for the follow-up of a patient's malignant disease it is contemplated that steps B) and C) are in a manner that allows quantitative determination of the methylation status of at least one mutation and / or at least one CpG-dinucleotide under conditions. Preferably, the use of the method for follow-up of a malignant disease then comprises the steps of: i) providing a first sample with genomic DNA from a patie...
Embodiment 1
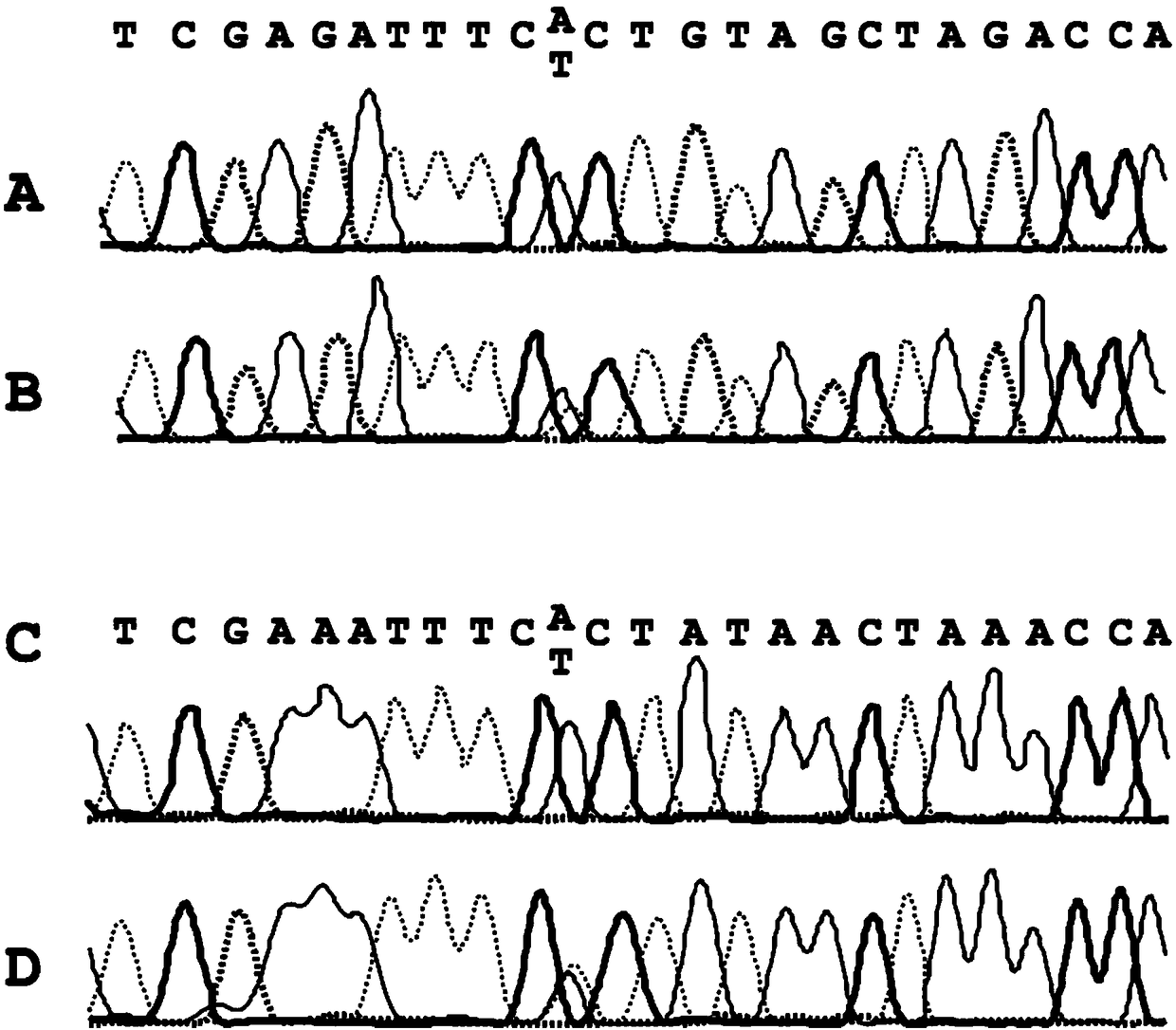
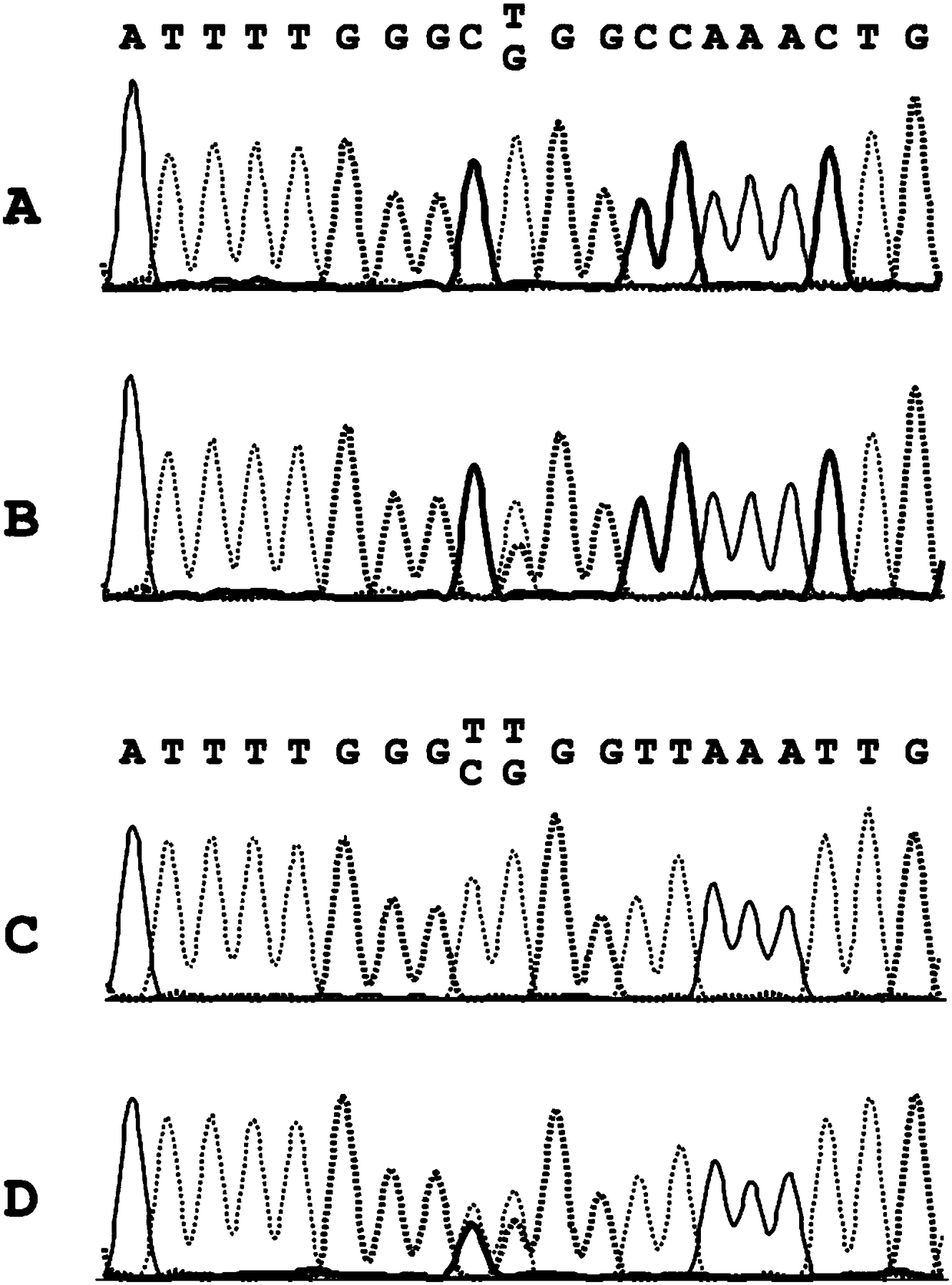
[0216] Example 1: Determination of point mutations in untransformed genomic DNA (reference)
[0217] Point mutations are those in which only a single nucleobase is affected by the change. The reliable determination of point mutations therefore places high demands on the specificity and sensitivity of molecular diagnostic assays.
[0218] As an example for a point mutation of high clinical relevance, the point mutation V600E within the BRAF gene was studied.
[0219] Genomic DNA to be analyzed can come from a variety of sources. For example, fixed tissue is used here. Three thin sections of 10 μm each of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded malignant melanoma and one tissue block of normal tissue (skin) adjacent to the melanoma were transferred to separate 2 ml reaction vessels. Subsequently, genomic DNA was extracted from the tissue sections. For this purpose the use of the QIAamp DNA FFPE tissue kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer's instructions ...
Embodiment 2
[0223] Example 2: Determining Point Mutations in Genomic DNA
[0224] In the extracted DNA from Example 1, in each case part of the genomic DNA was transformed according to the invention. Conversion can be accomplished, for example, by contacting the genomic DNA with bisulfite. Conversion is currently performed eg with the innuCONVERT bisulfite all-in-one kit (Analytik Jena, Jena, Germany). For this purpose, 2 μg of extracted DNA from each sample was transformed according to the manufacturer's instructions. The amount of converted DNA was then quantified using a NanoDrop ND-1000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
[0225] In the normal state, DNA is organized in the form of a double helix, which consists of two single strands that are reverse complementary to each other. One strand is called the positive or forward strand and the other is called the negative or reverse strand. After DNA conversion, eg with bisulfite, the plus and minus strand...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com