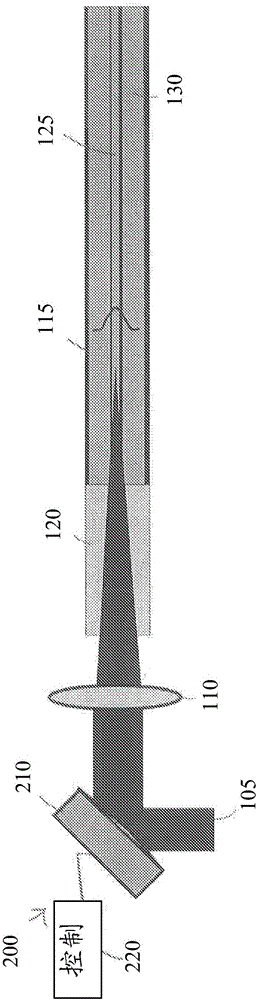
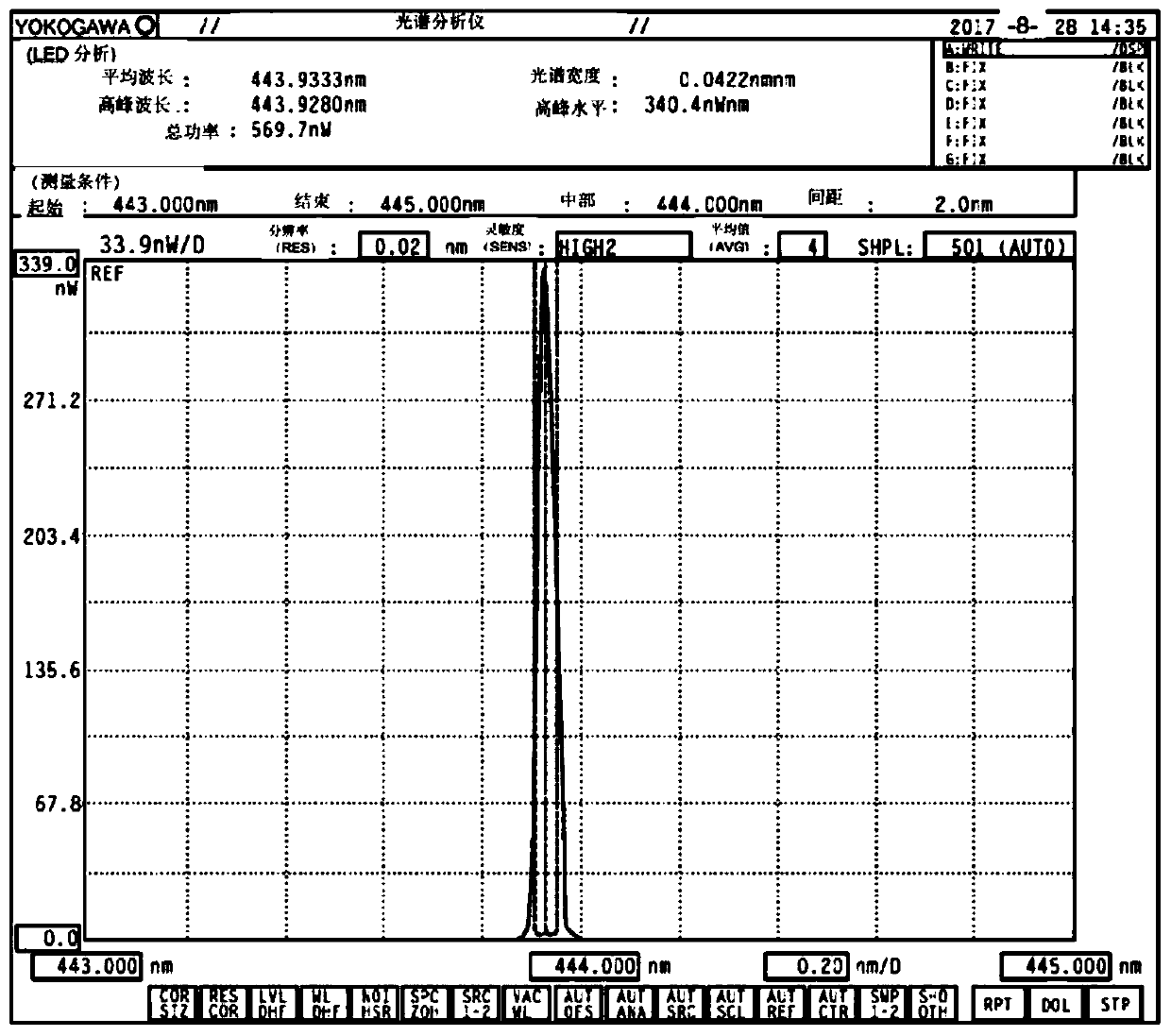
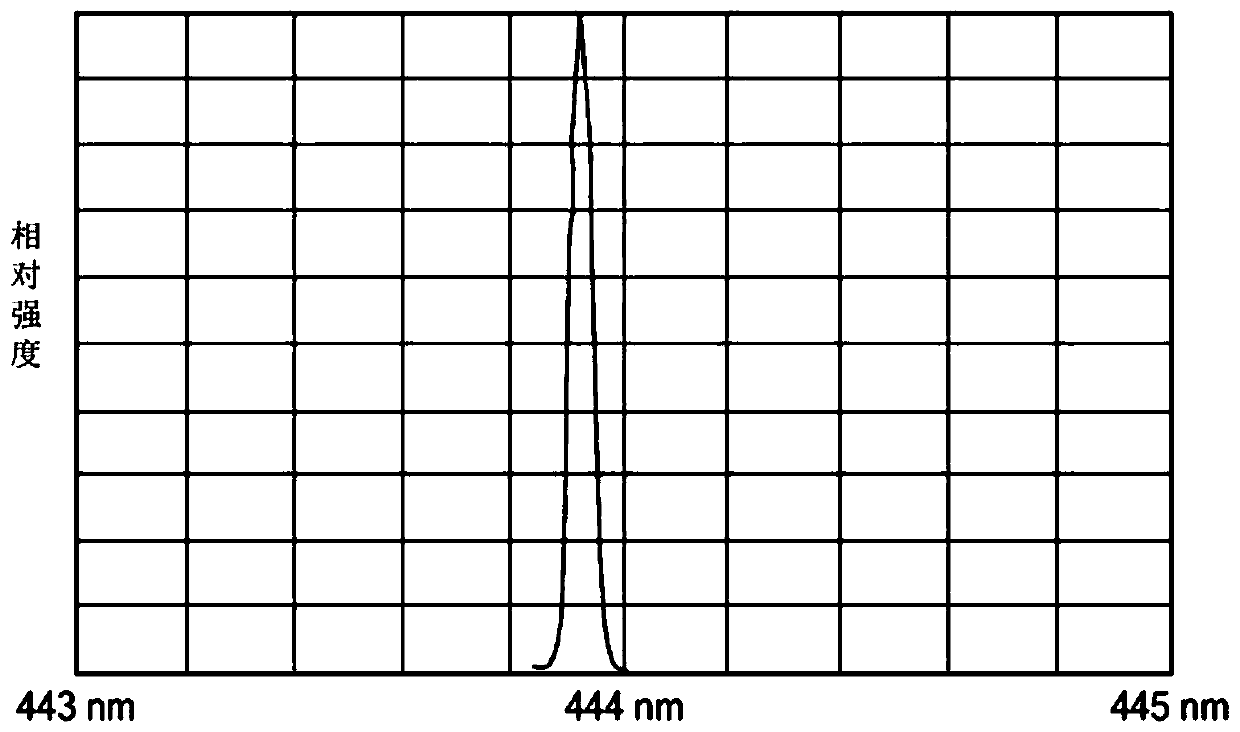
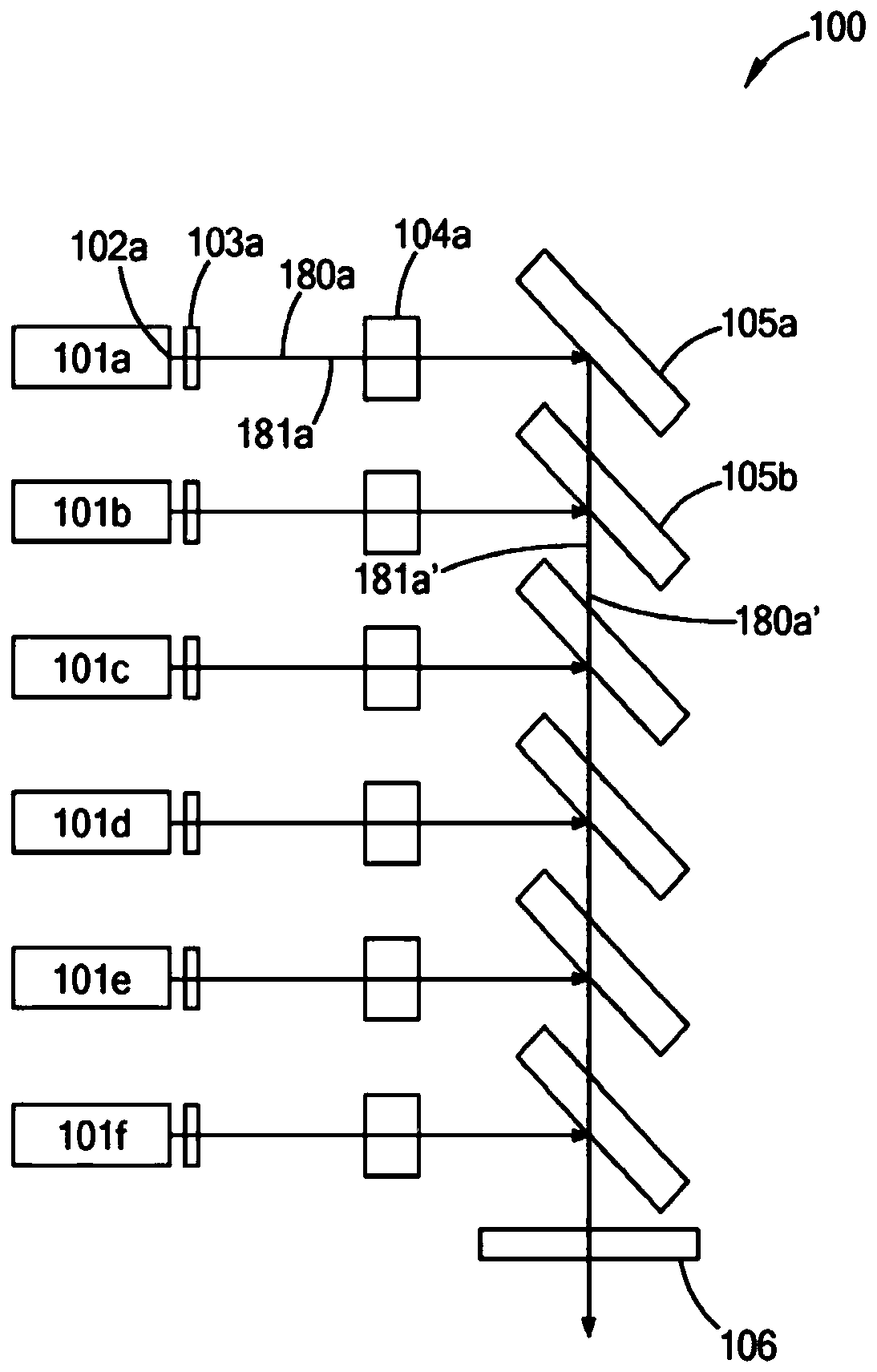
Patents
Literature
46 results about "Beam parameter product" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
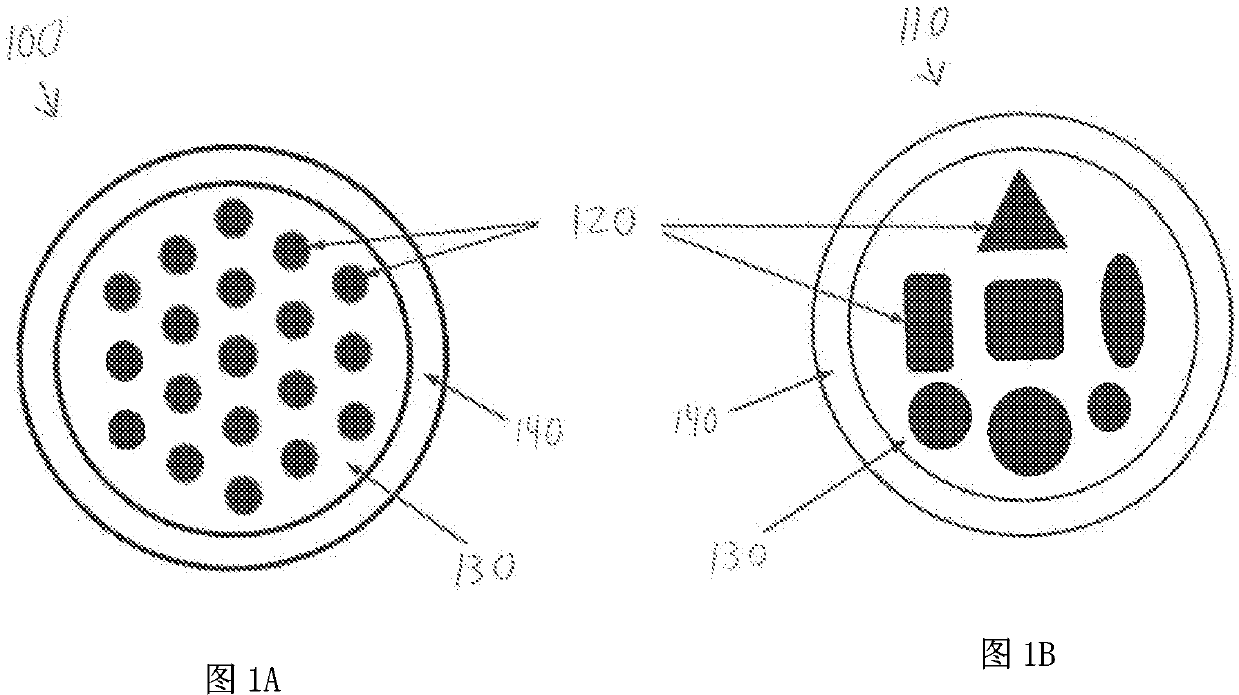
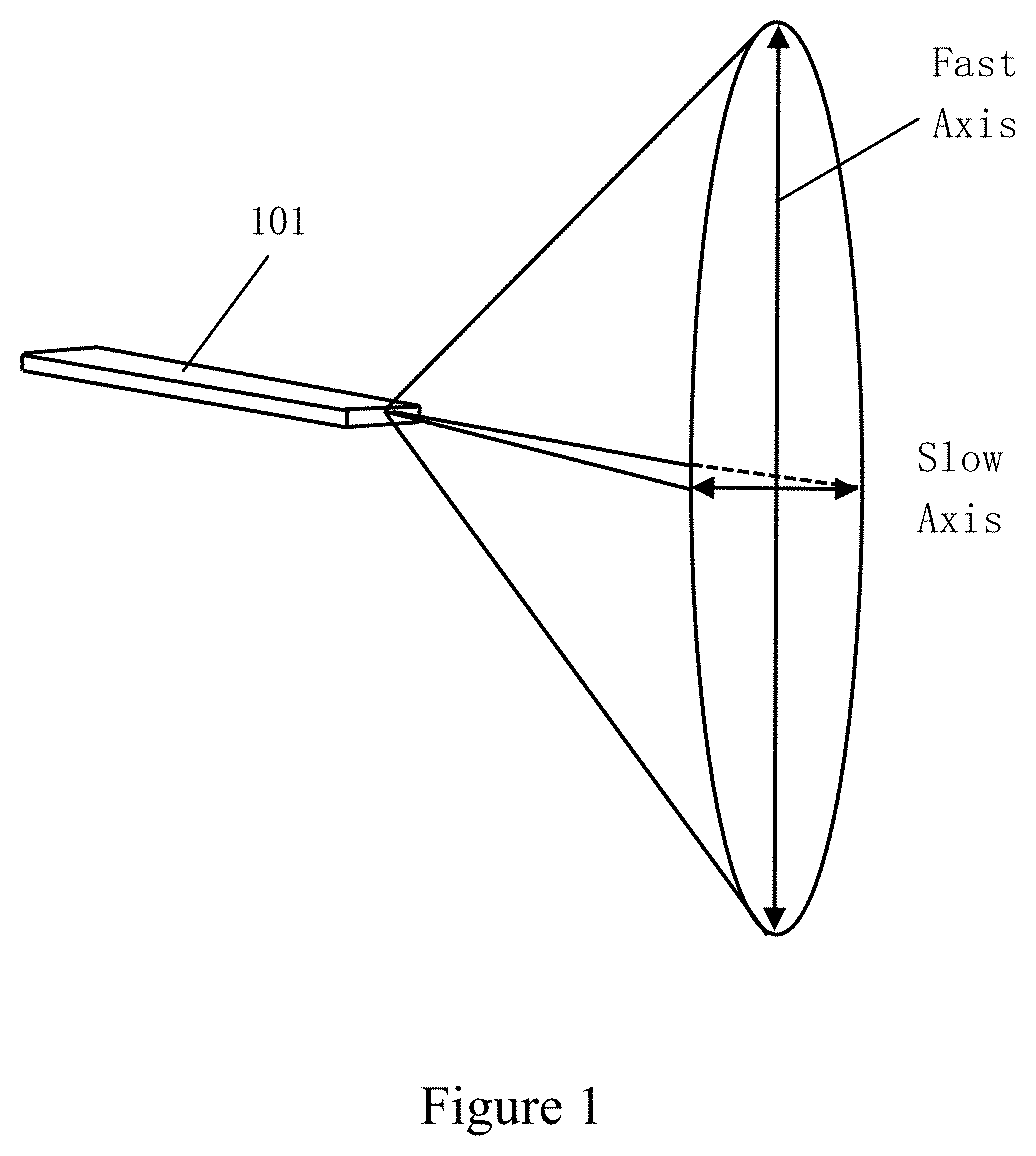
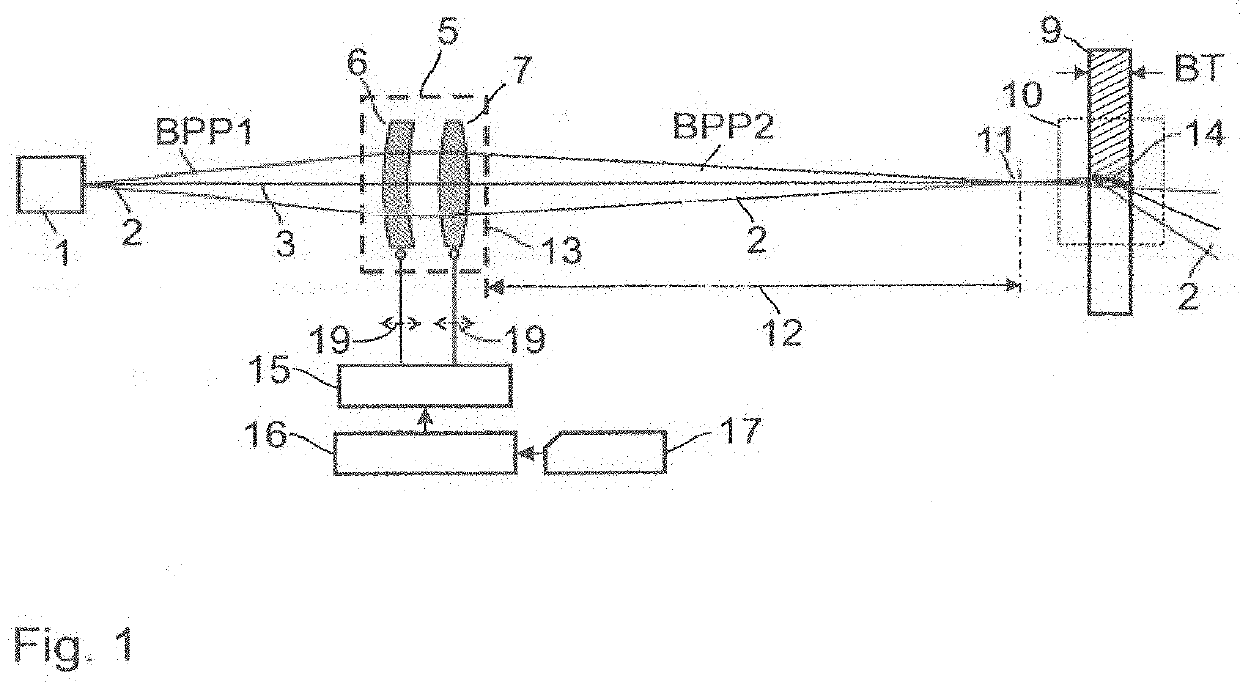
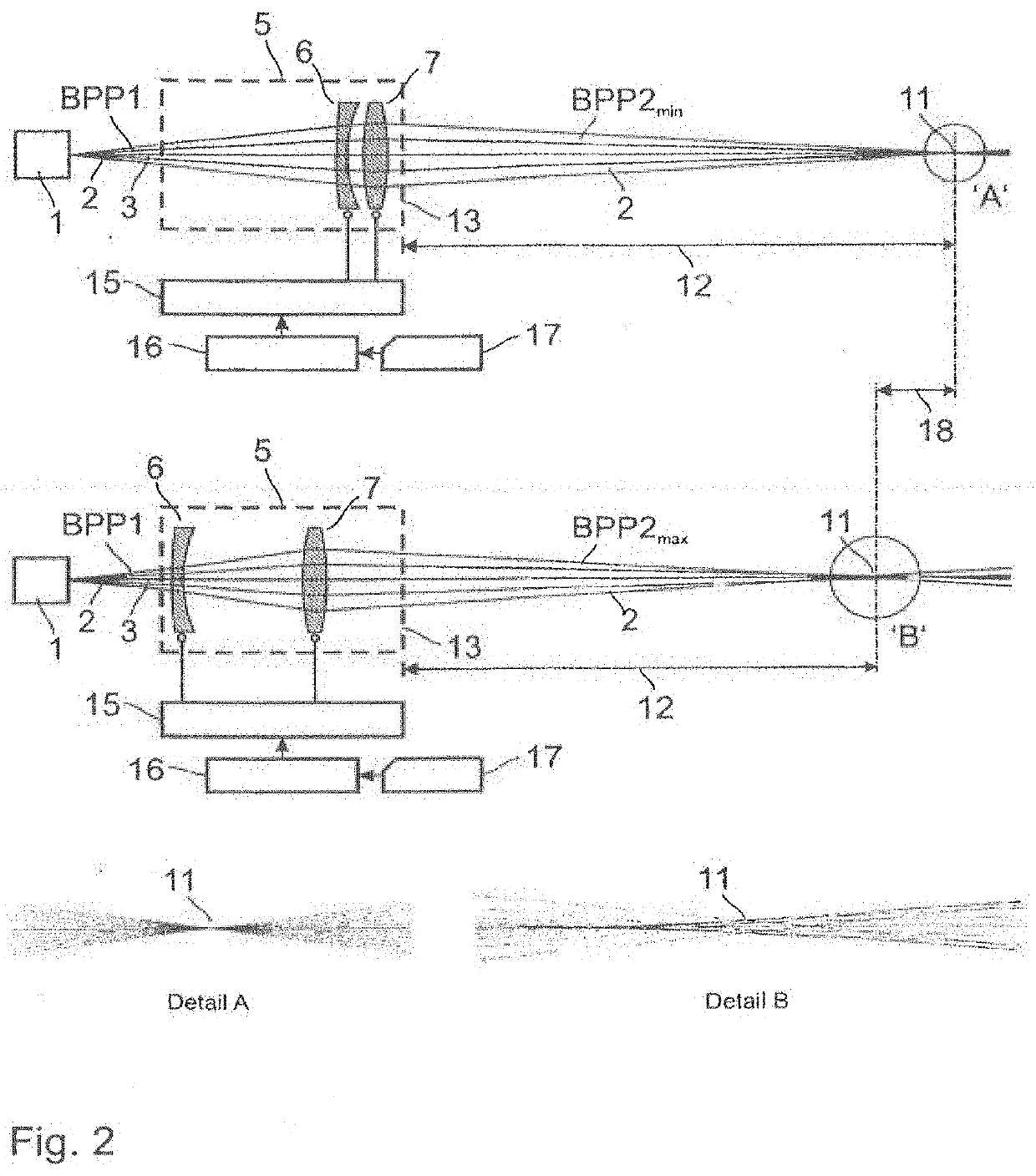
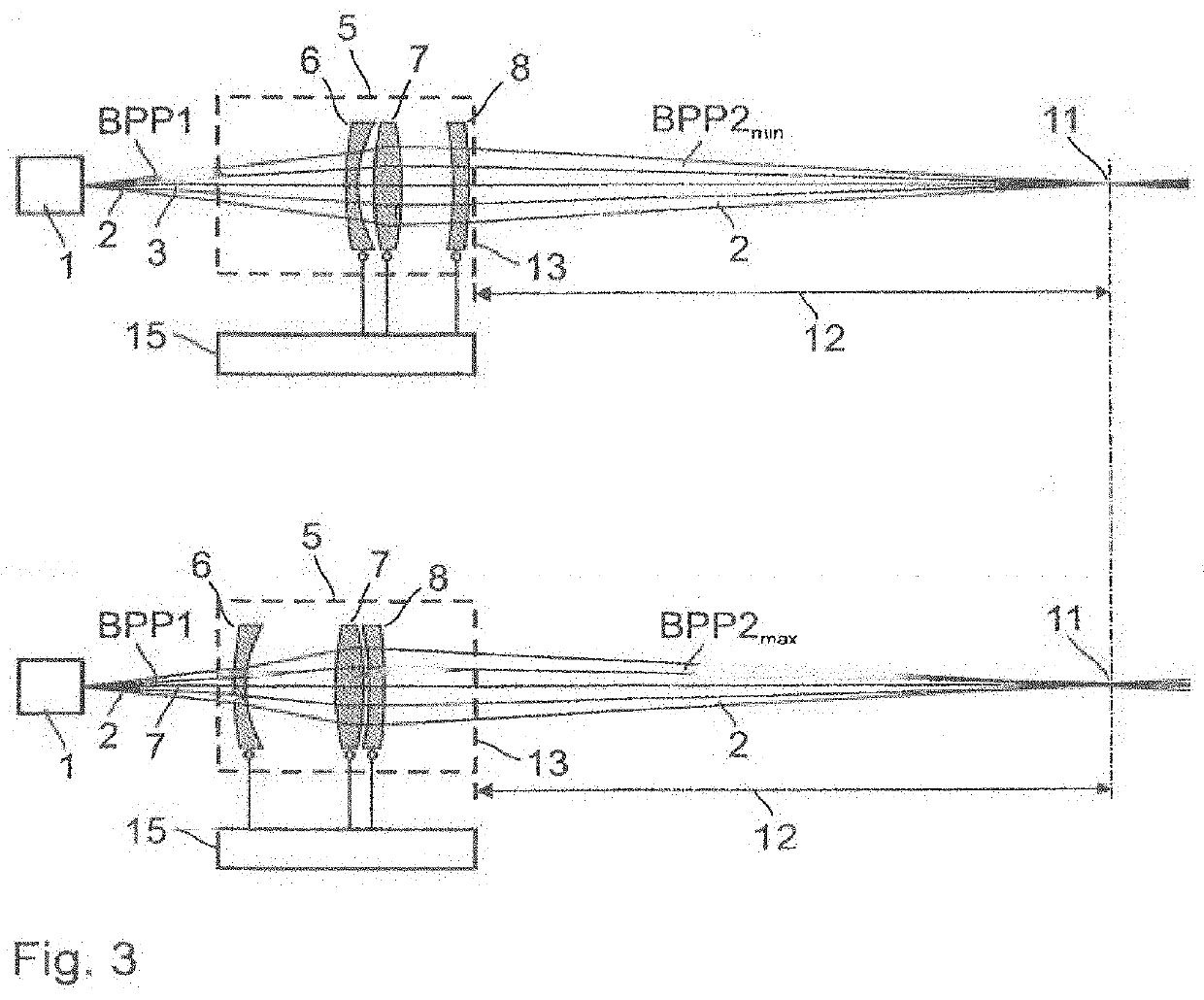
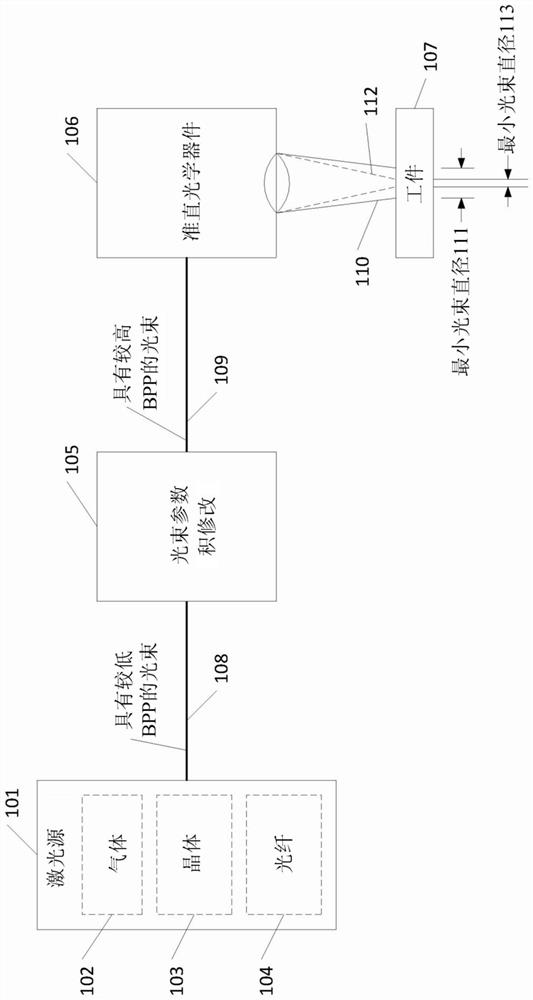
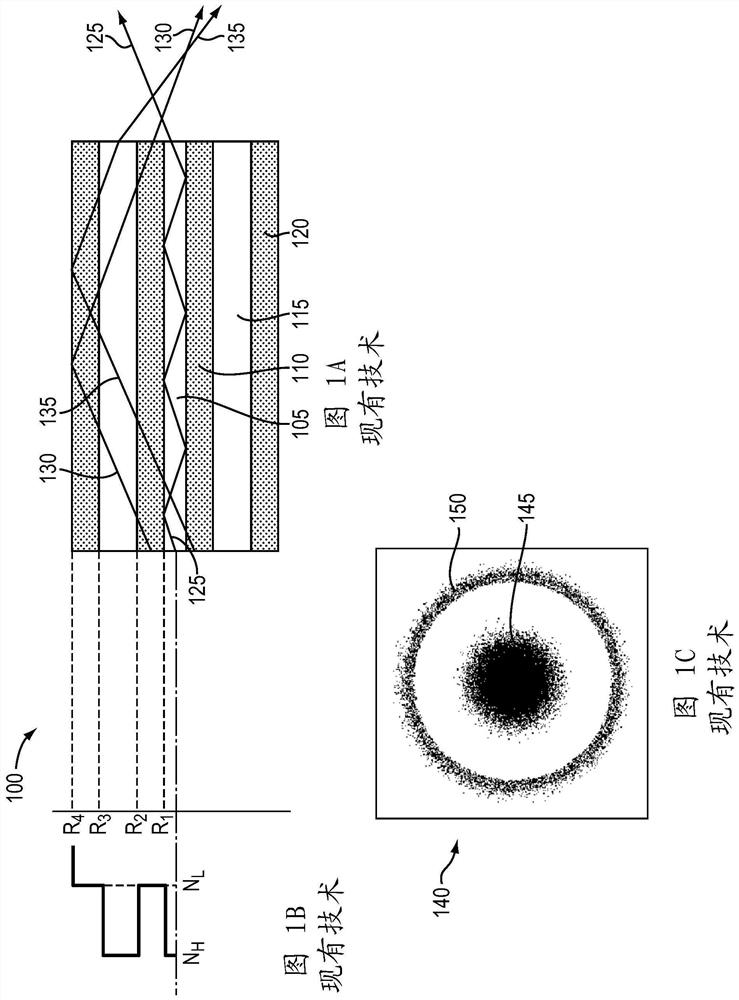
In laser science, the beam parameter product (BPP) is the product of a laser beam's divergence angle (half-angle) and the radius of the beam at its narrowest point (the beam waist). The BPP quantifies the quality of a laser beam, and how well it can be focused to a small spot. A Gaussian beam has the lowest possible BPP, λ/π, where λ is the wavelength of the light. The ratio of the BPP of an actual beam to that of an ideal Gaussian beam at the same wavelength is denoted M² ("M squared").
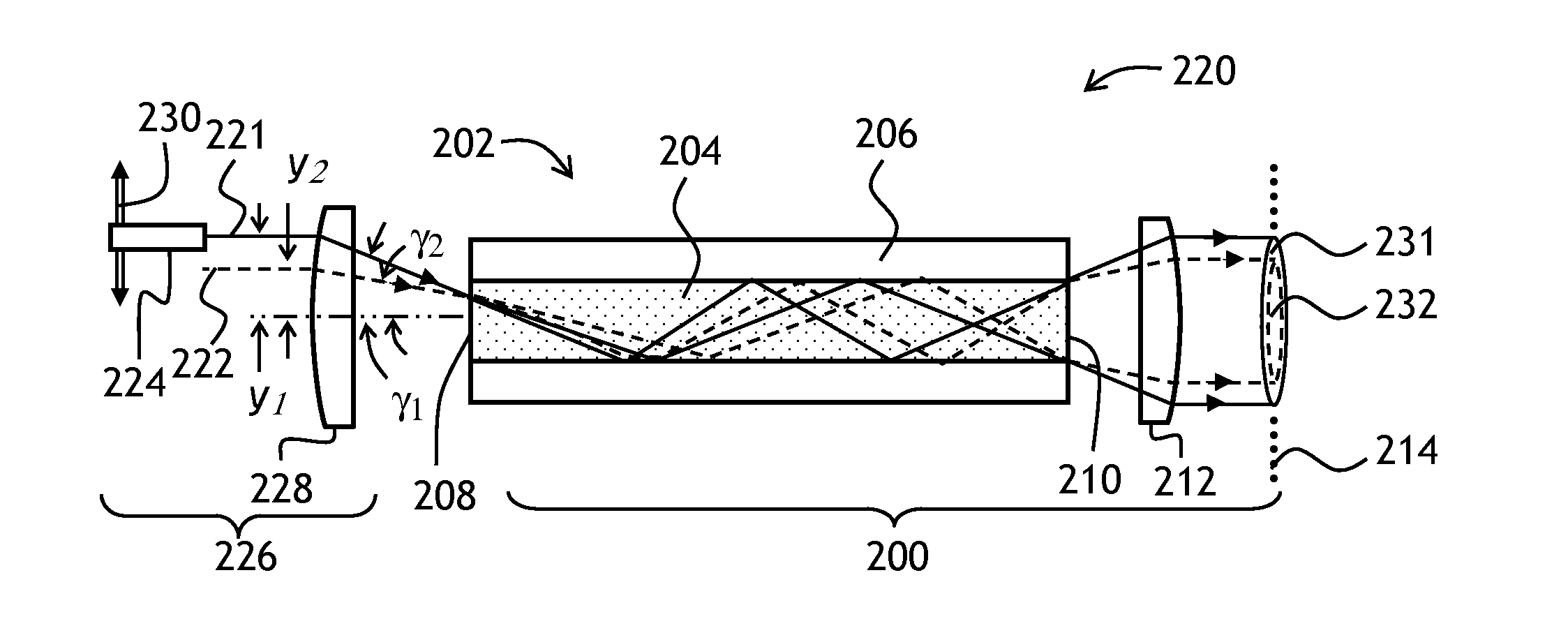
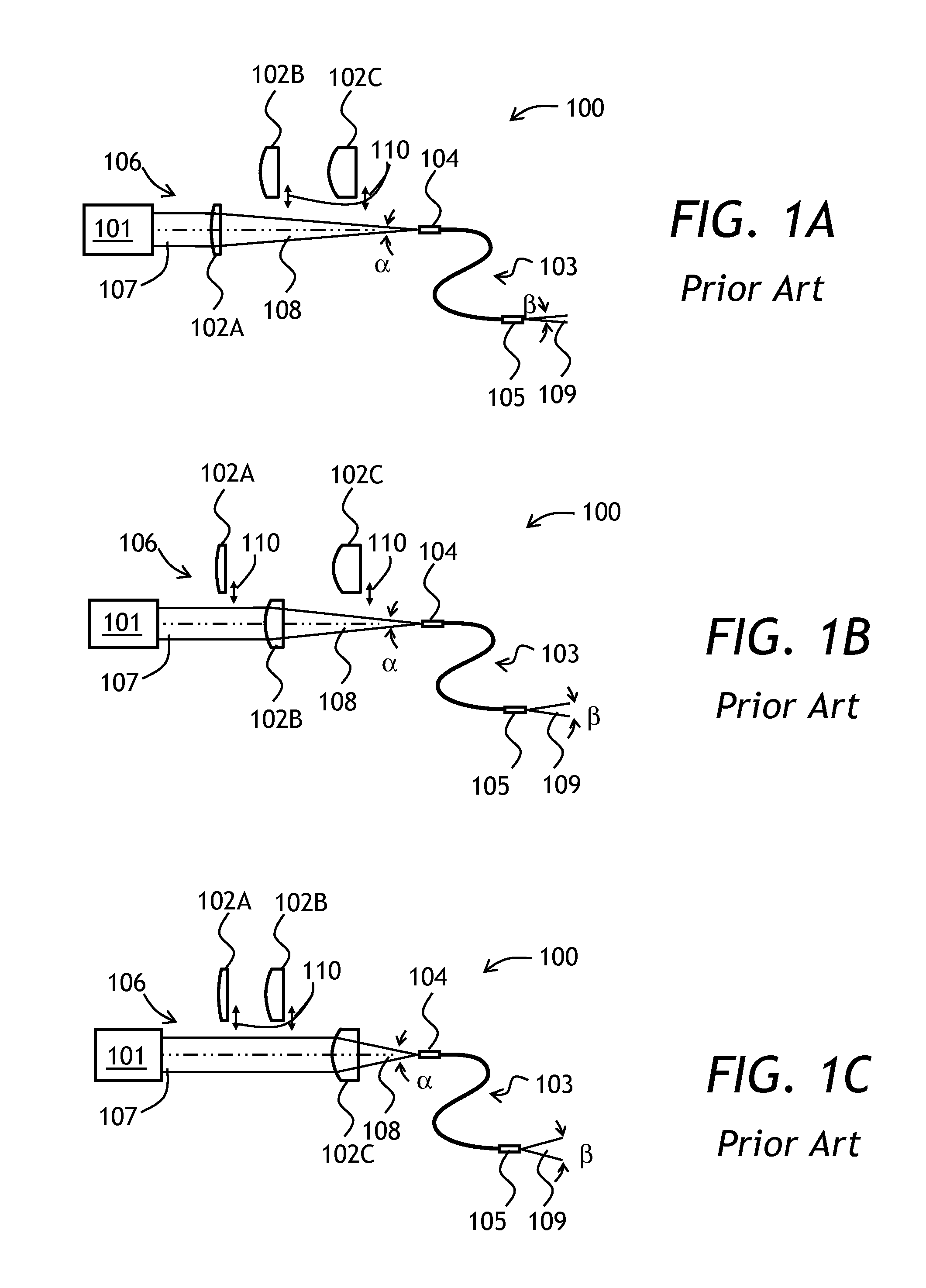
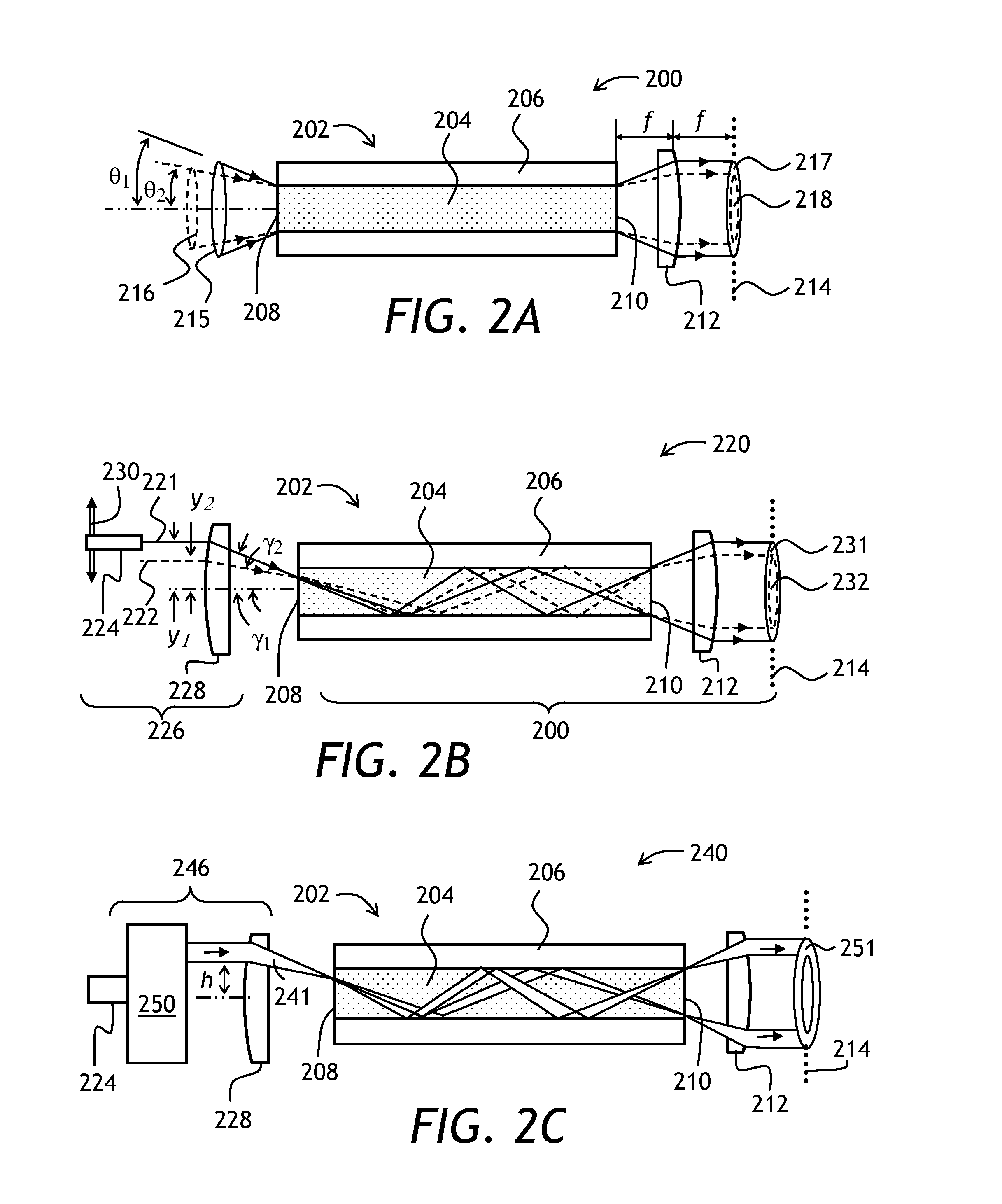
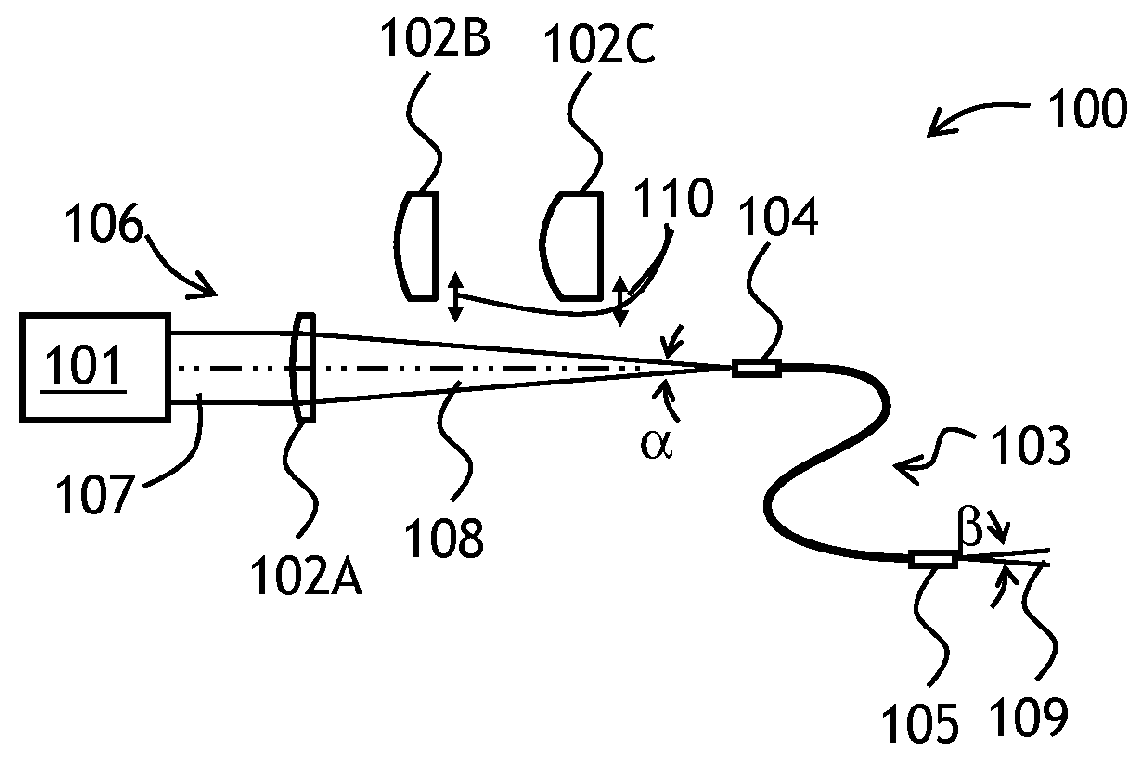
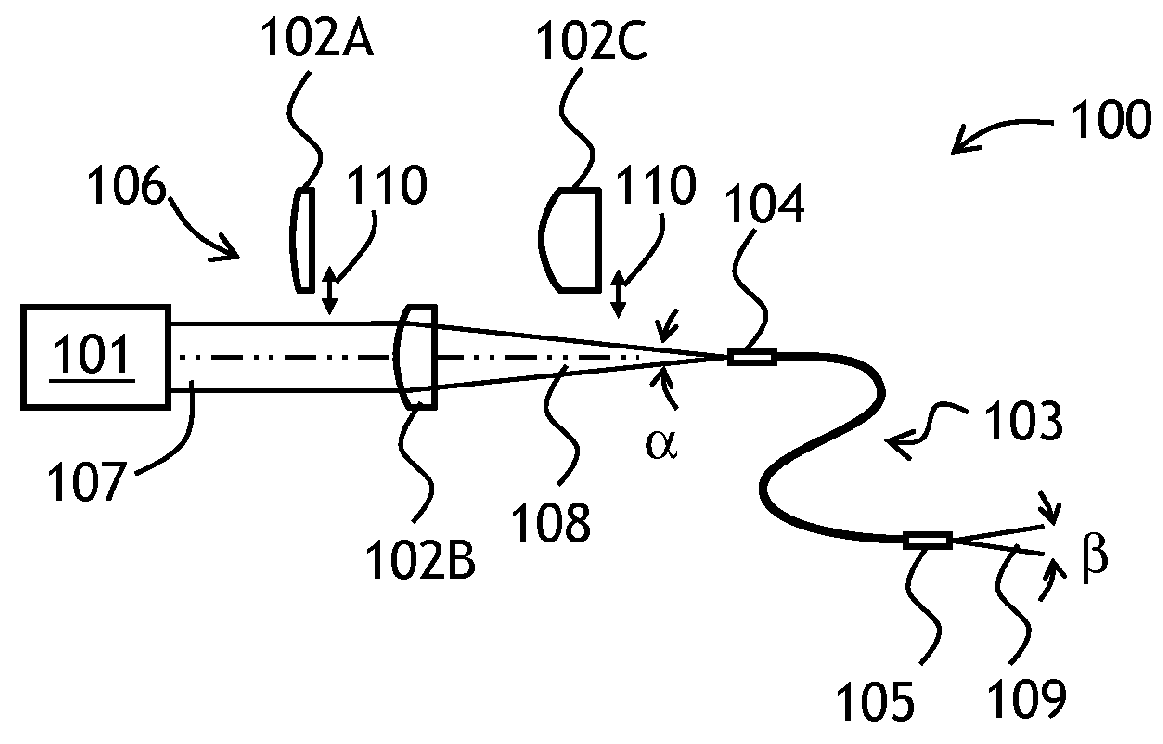
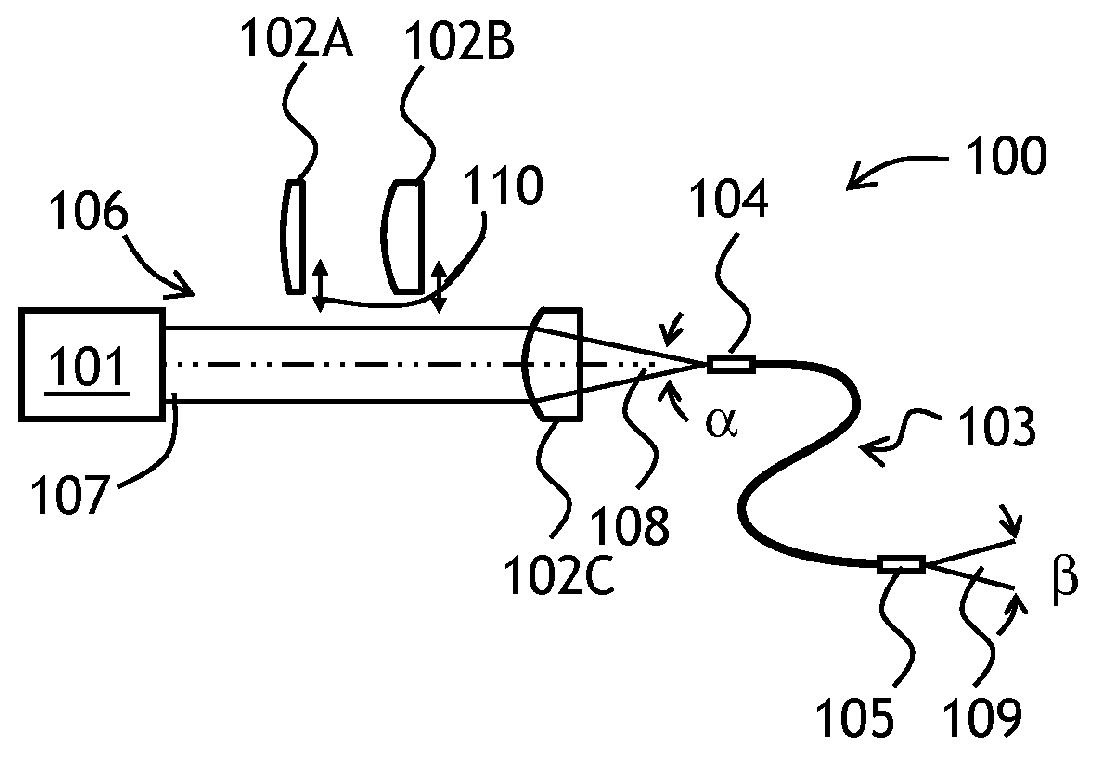
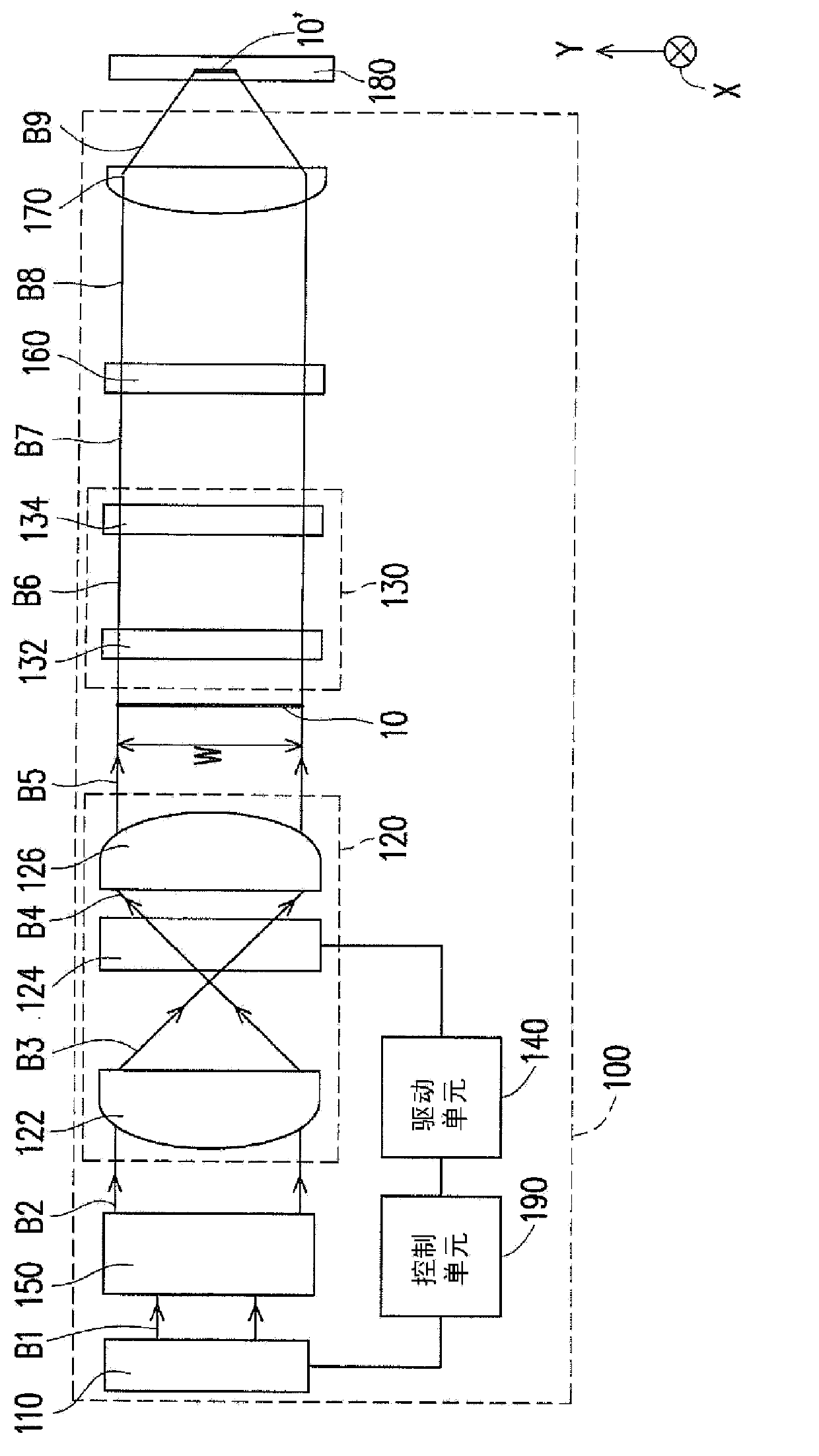
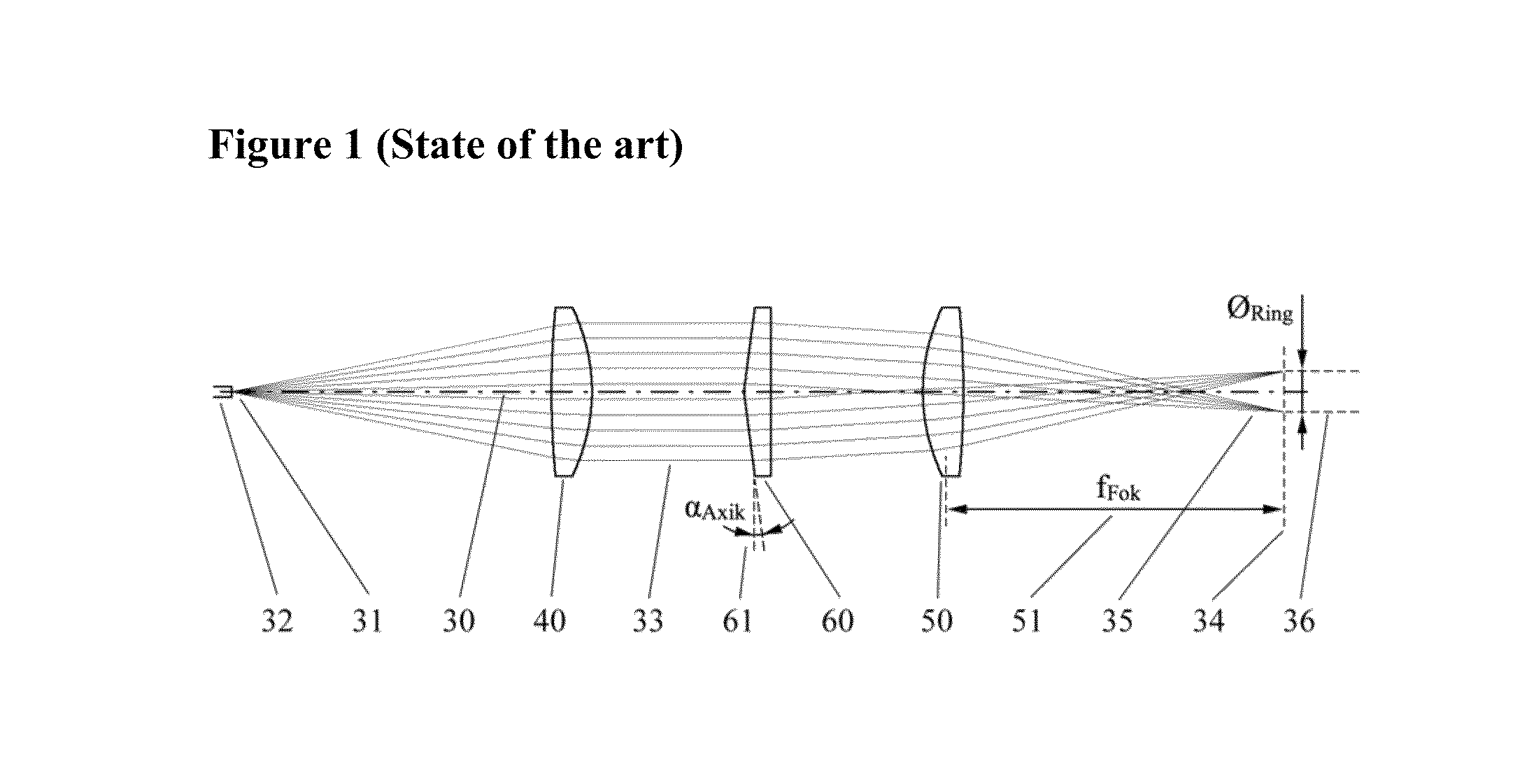
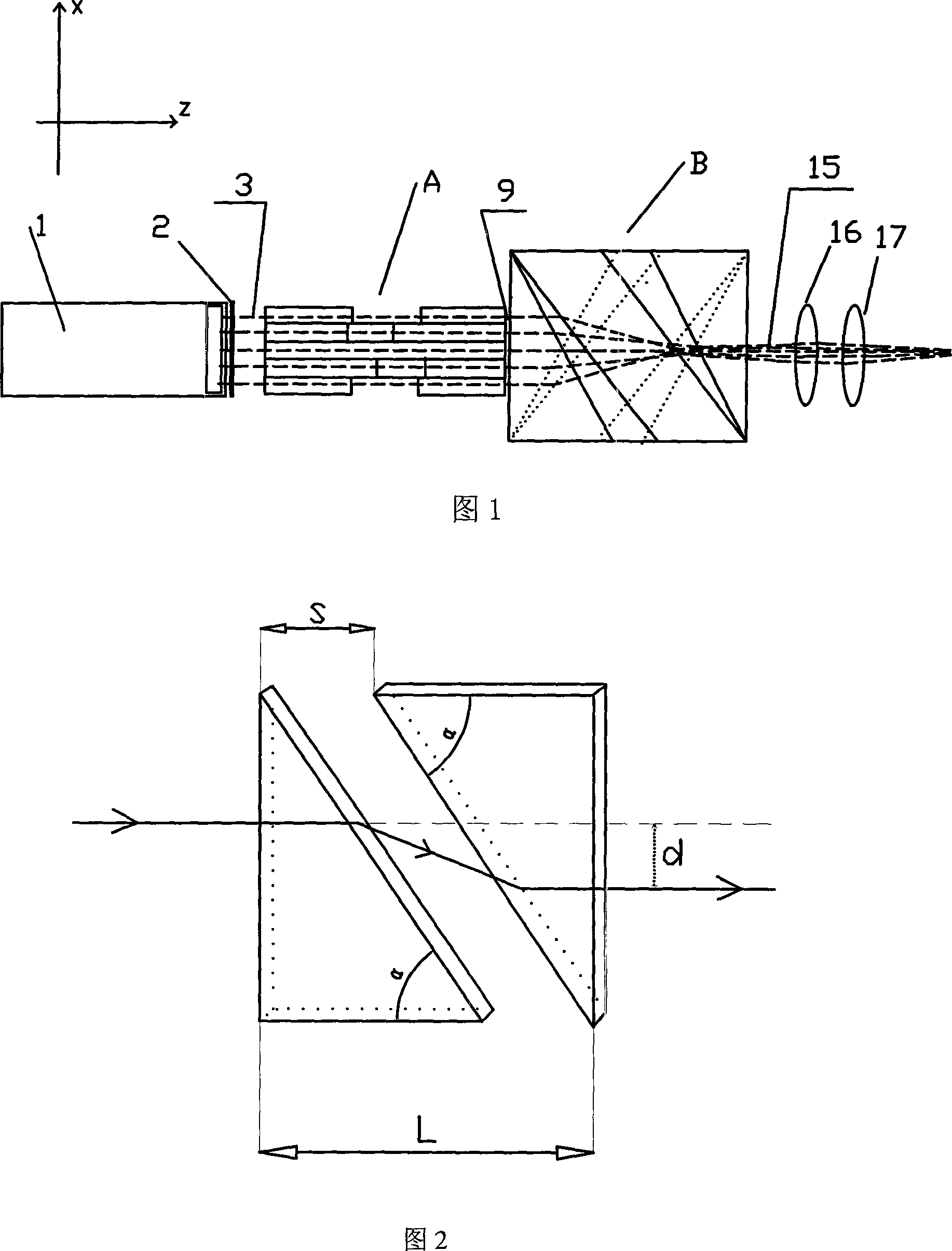
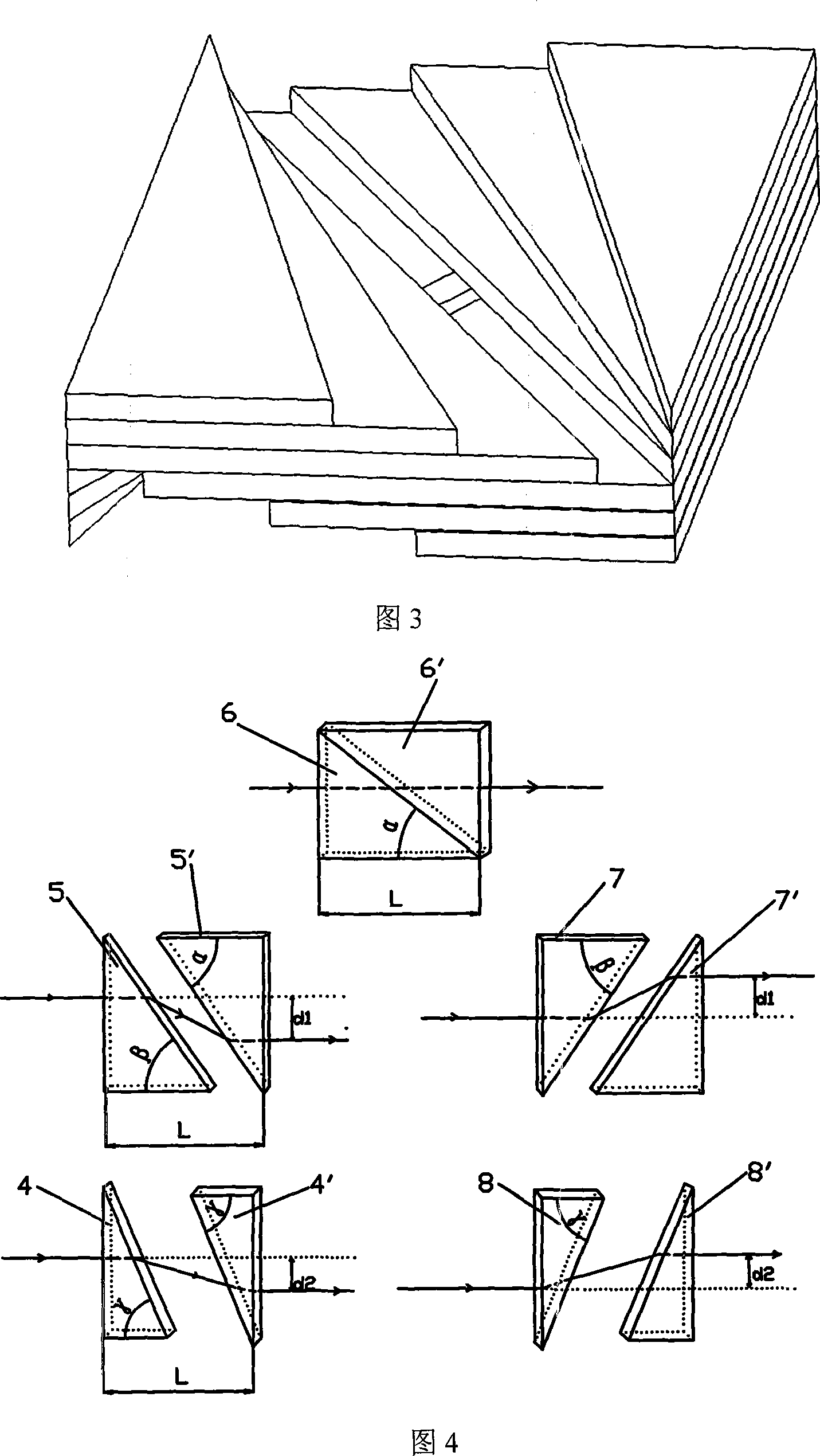
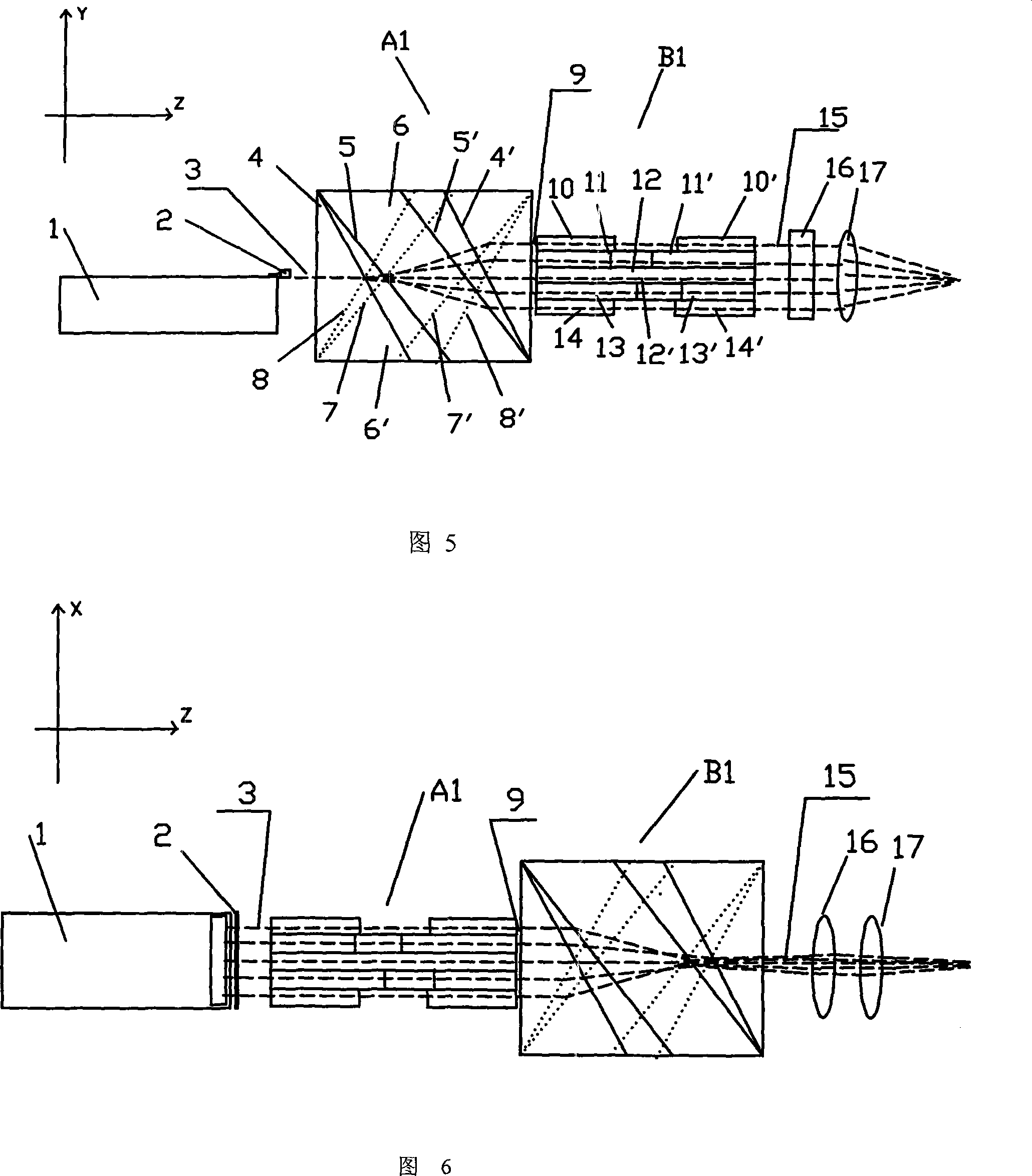
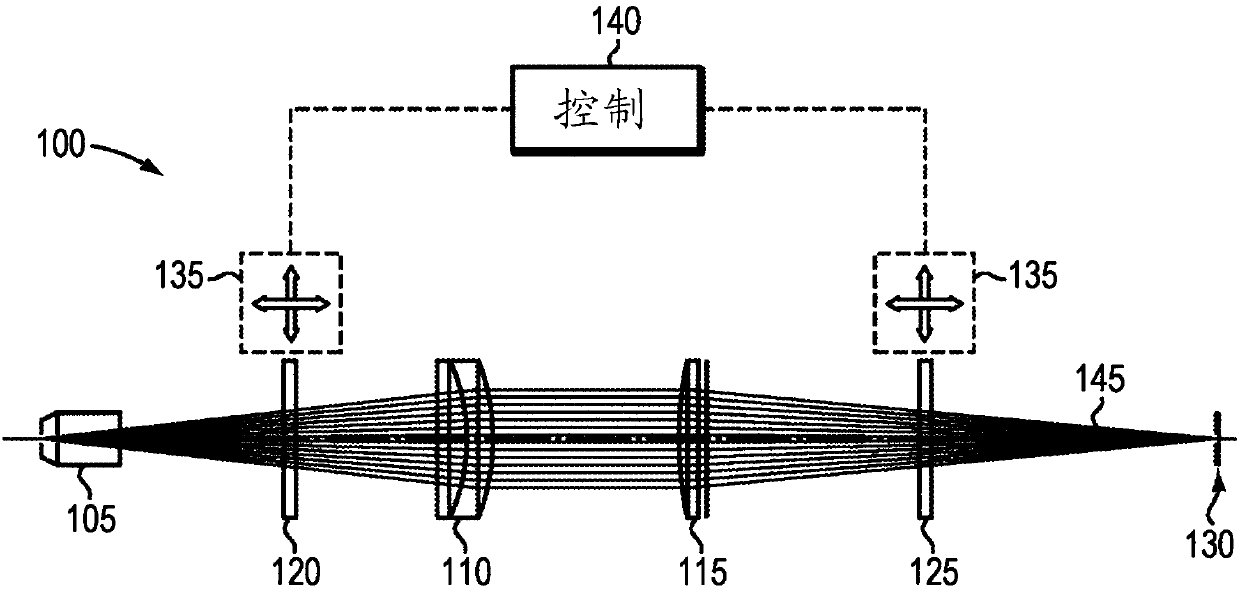
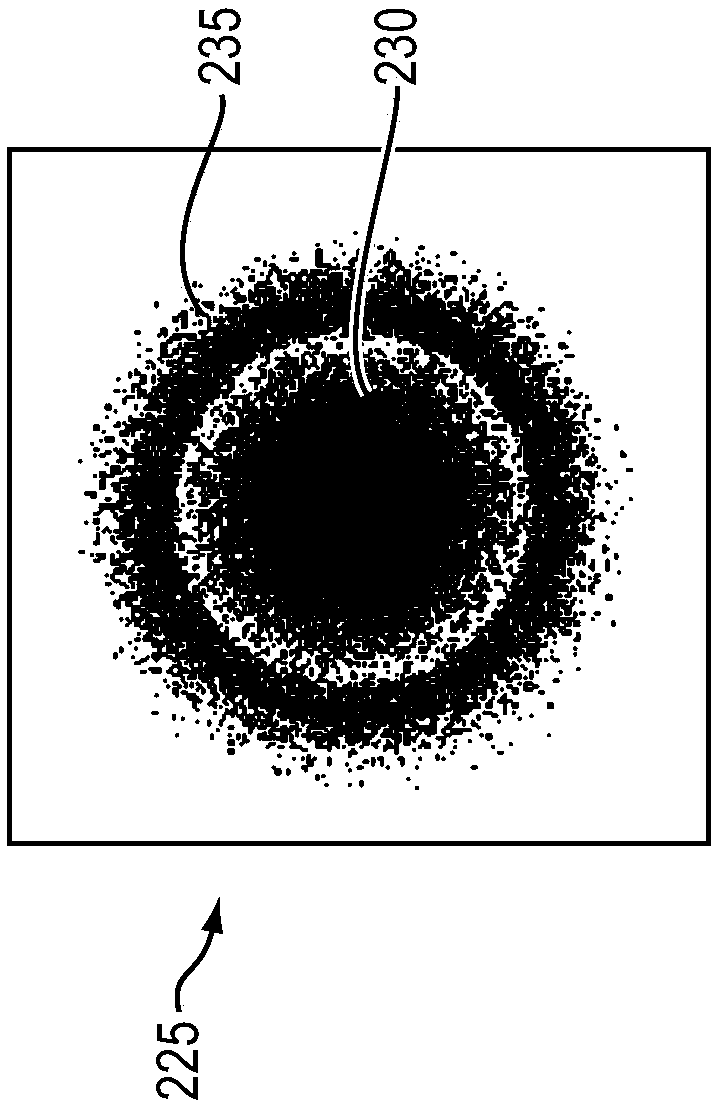
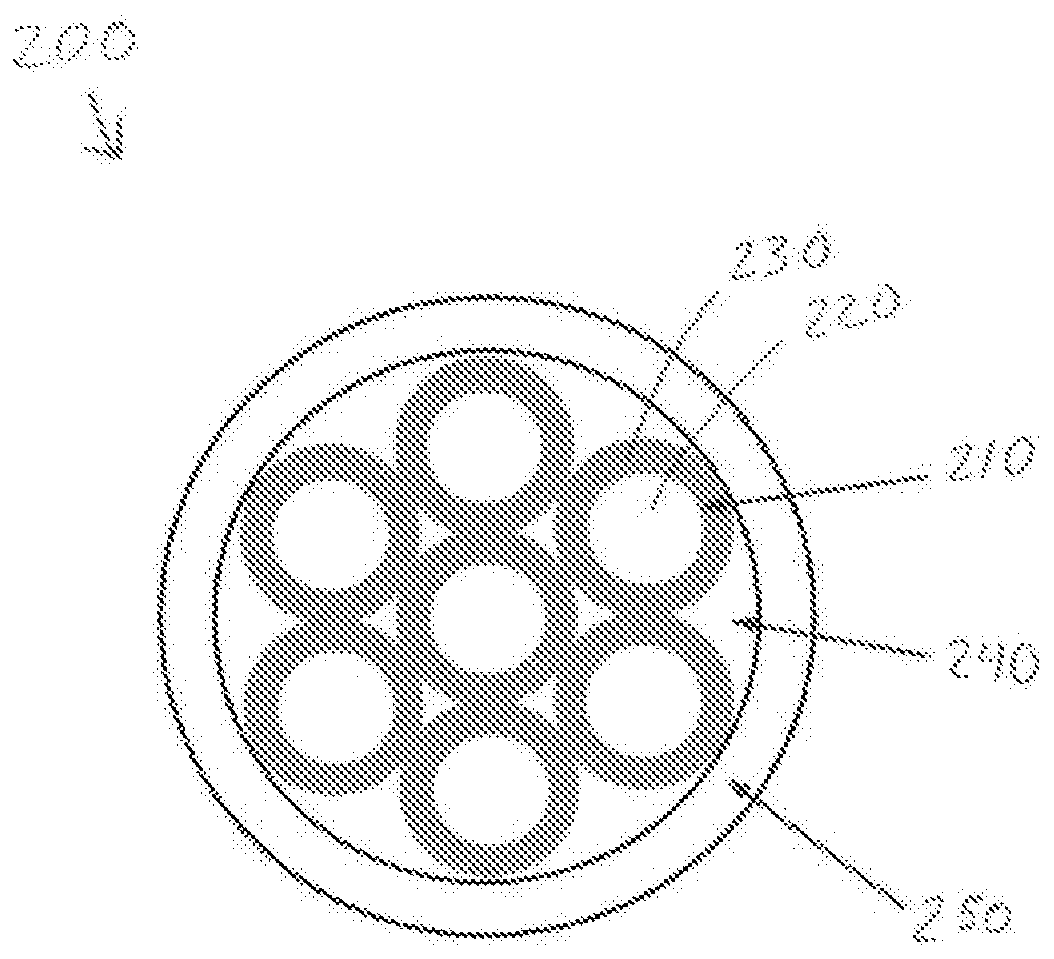
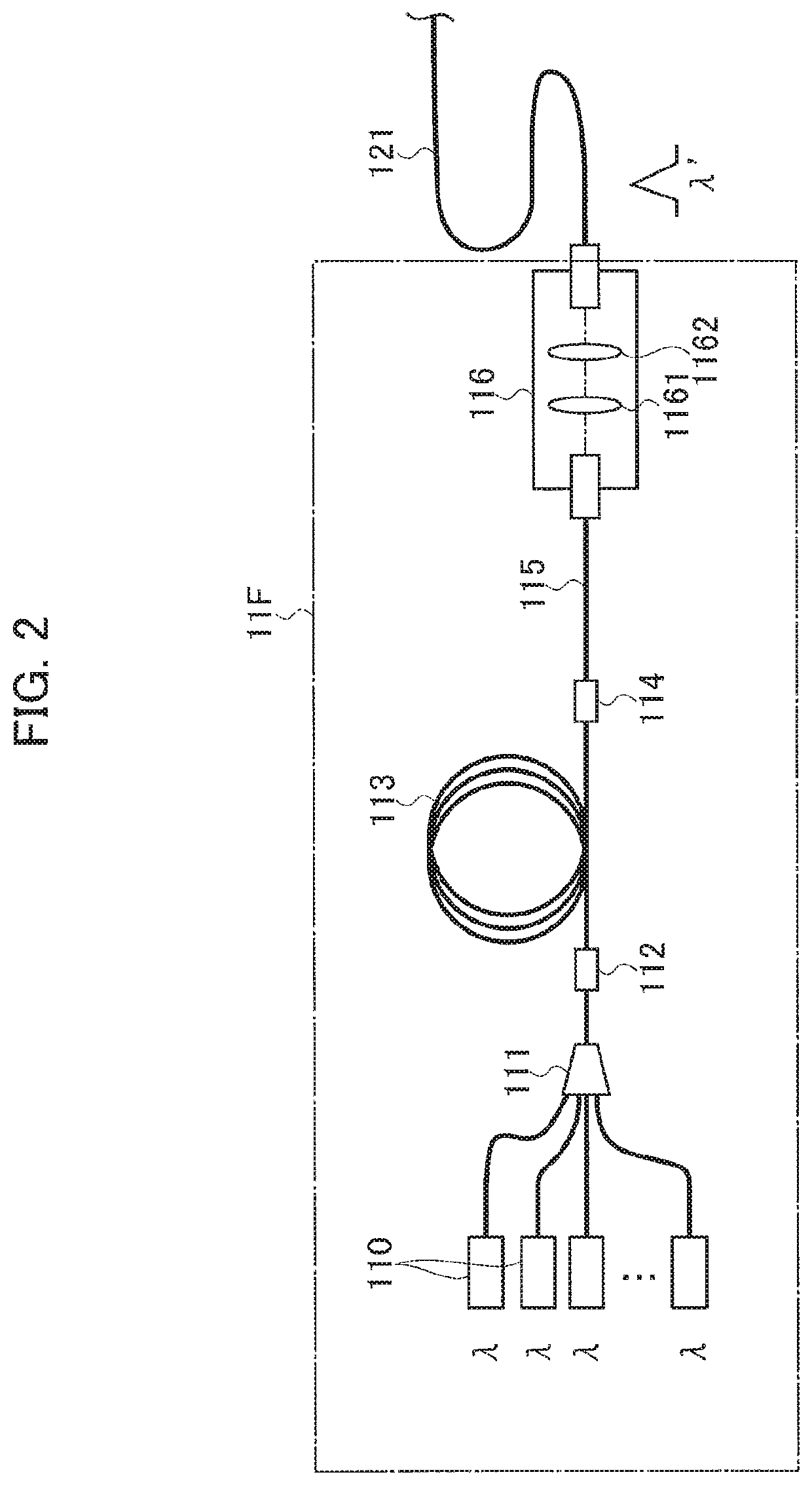
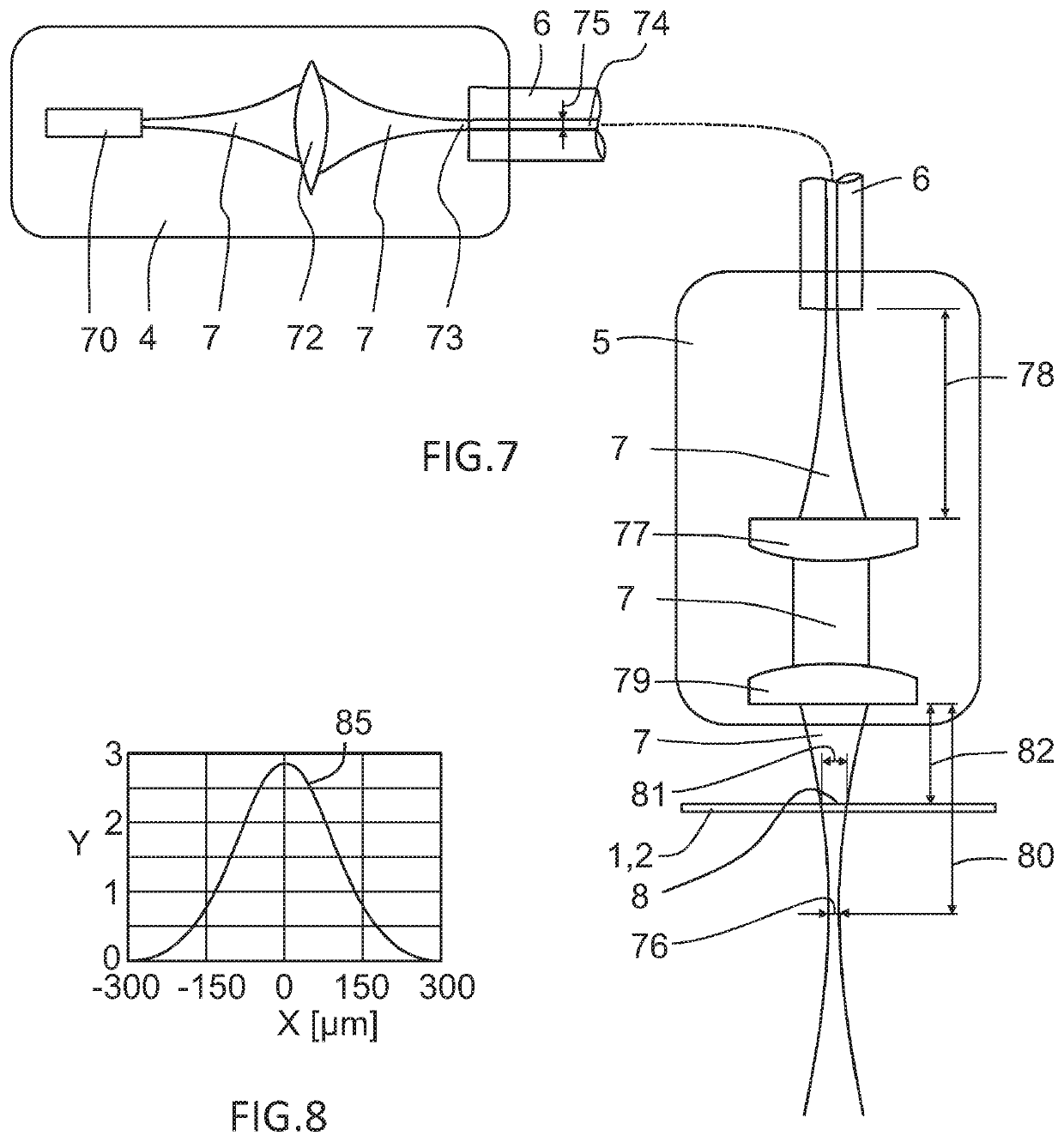
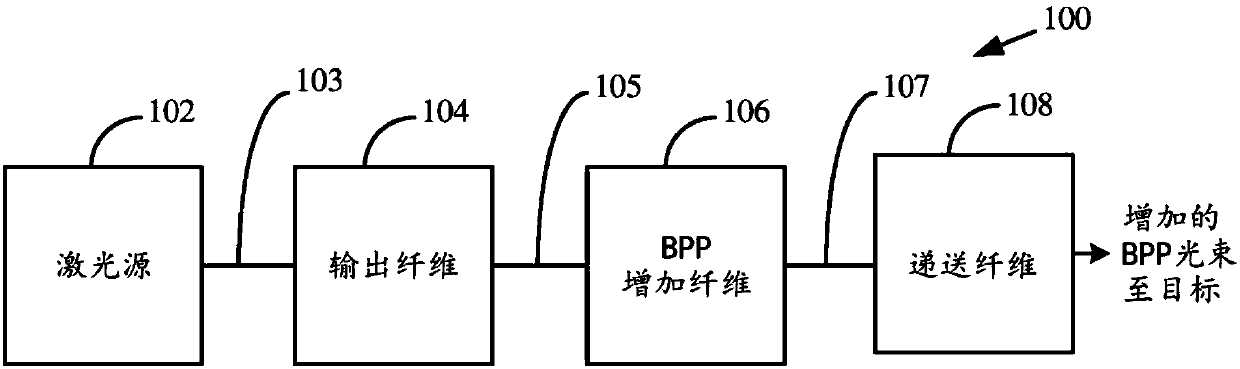
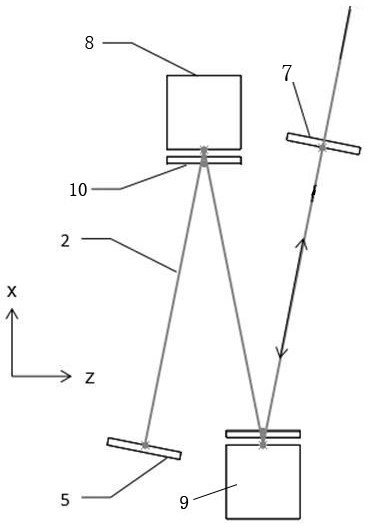
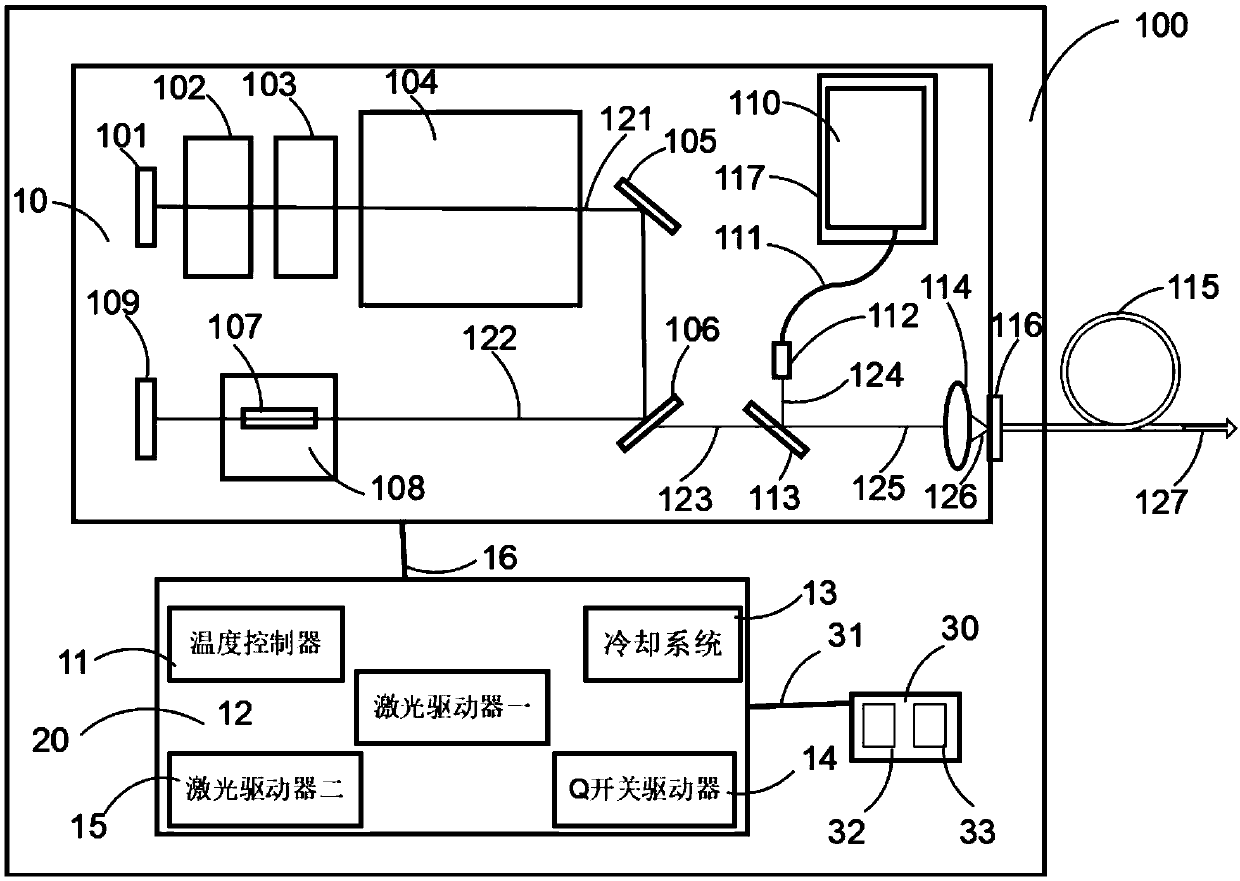
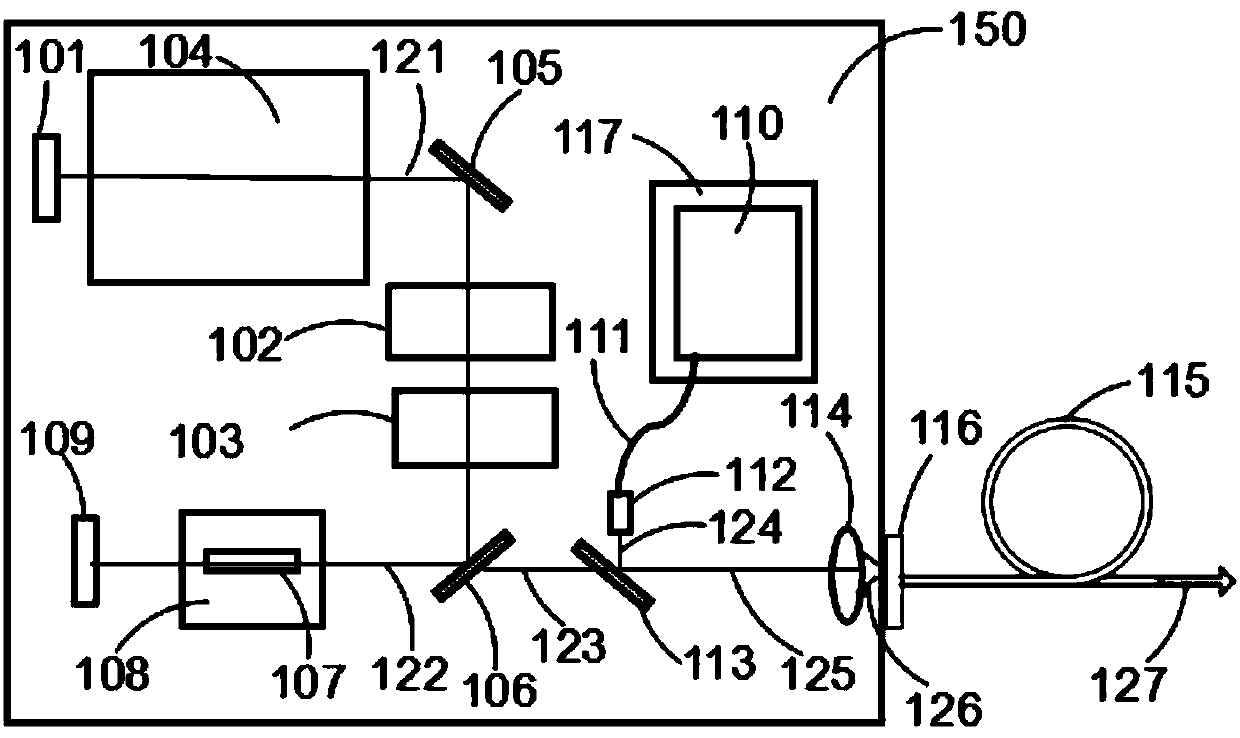
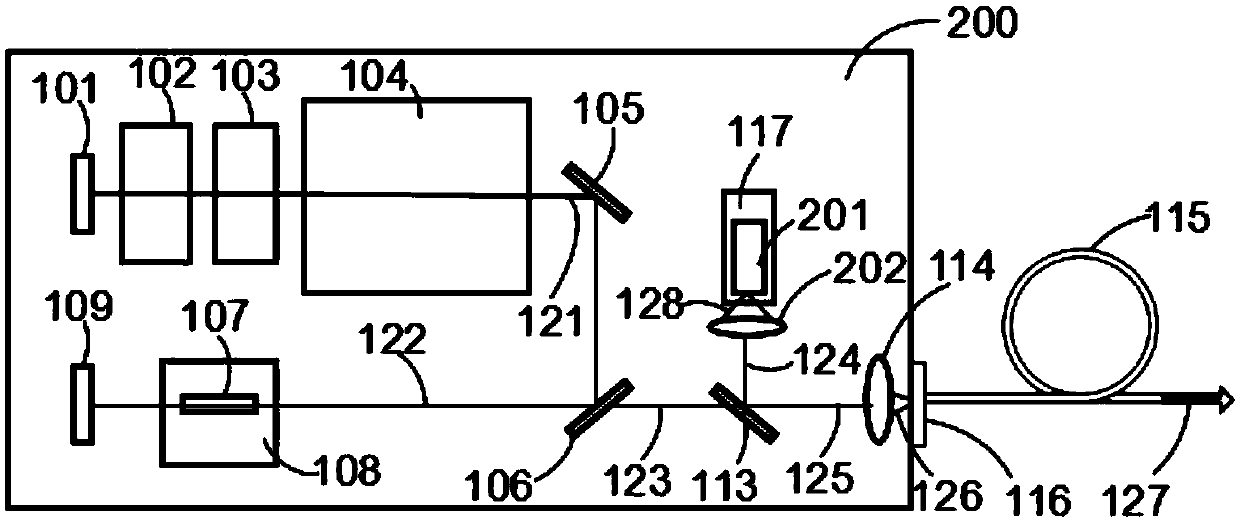
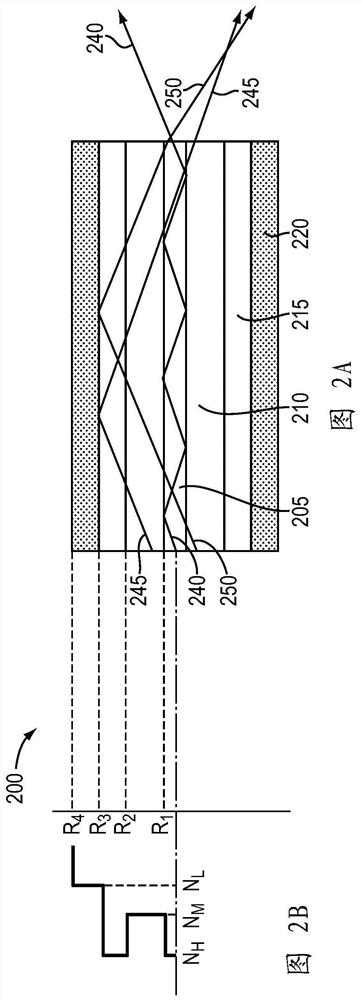
Varying beam parameter product of a laser beam
ActiveUS20130148925A1Short focal lengthClear processLaser detailsCoupling light guidesLaser processingLight beam
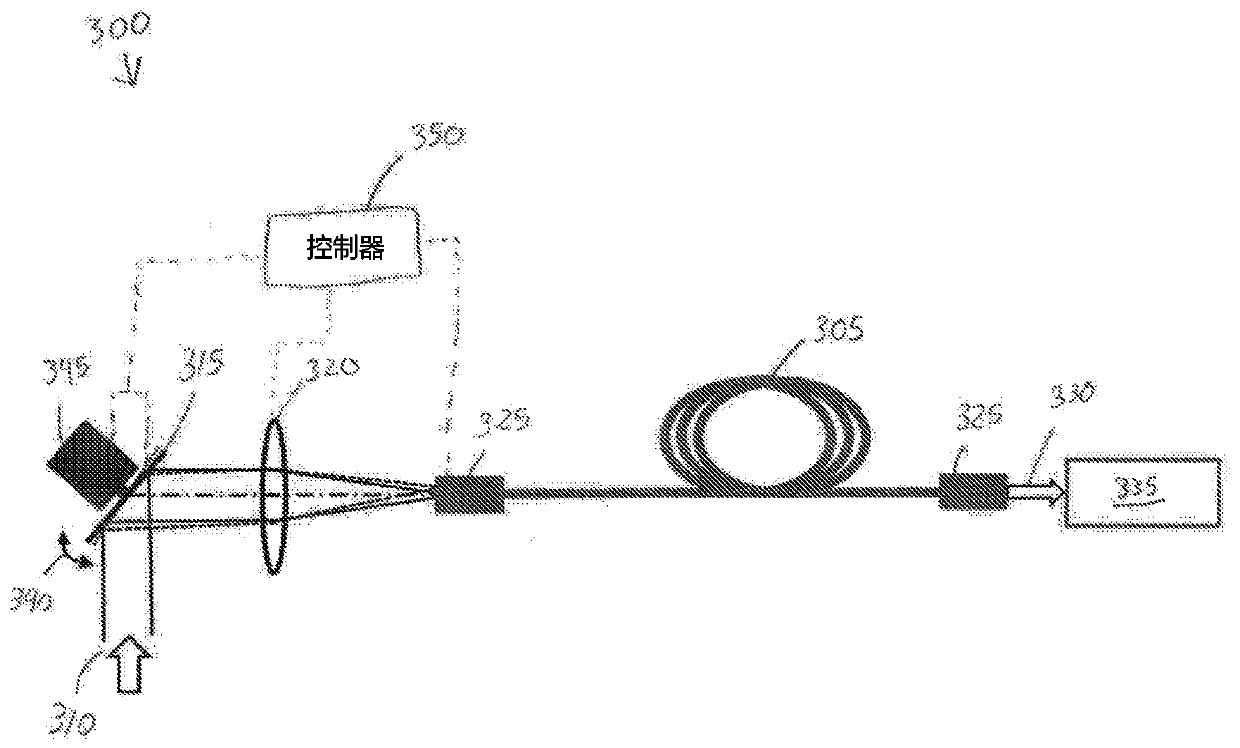
An optical delivery waveguide for a material laser processing system includes a small lens at an output end of the delivery waveguide, transforming laser beam divergence inside the waveguide into a spot size after the lens. By varying the input convergence angle and / or launch angle of the laser beam launched into the waveguide, the output spot size can be continuously varied, thus enabling a continuous and real-time laser spot size adjustment on the workpiece, without having to replace the delivery waveguide or a process head. A divergence of the laser beam can also be adjusted dynamically and in concert with the spot size.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Varying beam parameter product of a laser beam
An optical delivery waveguide for a material laser processing system includes a small lens at an output end of the delivery waveguide, transforming laser beam divergence inside the waveguide into a spot size after the lens. By varying the input convergence angle and / or launch angle of the laser beam launched into the waveguide, the output spot size can be continuously varied, thus enabling a continuous and real-time laser spot size adjustment on the workpiece, without having to replace the delivery waveguide or a process head. A divergence of the laser beam can also be adjusted dynamically and in concert with the spot size.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
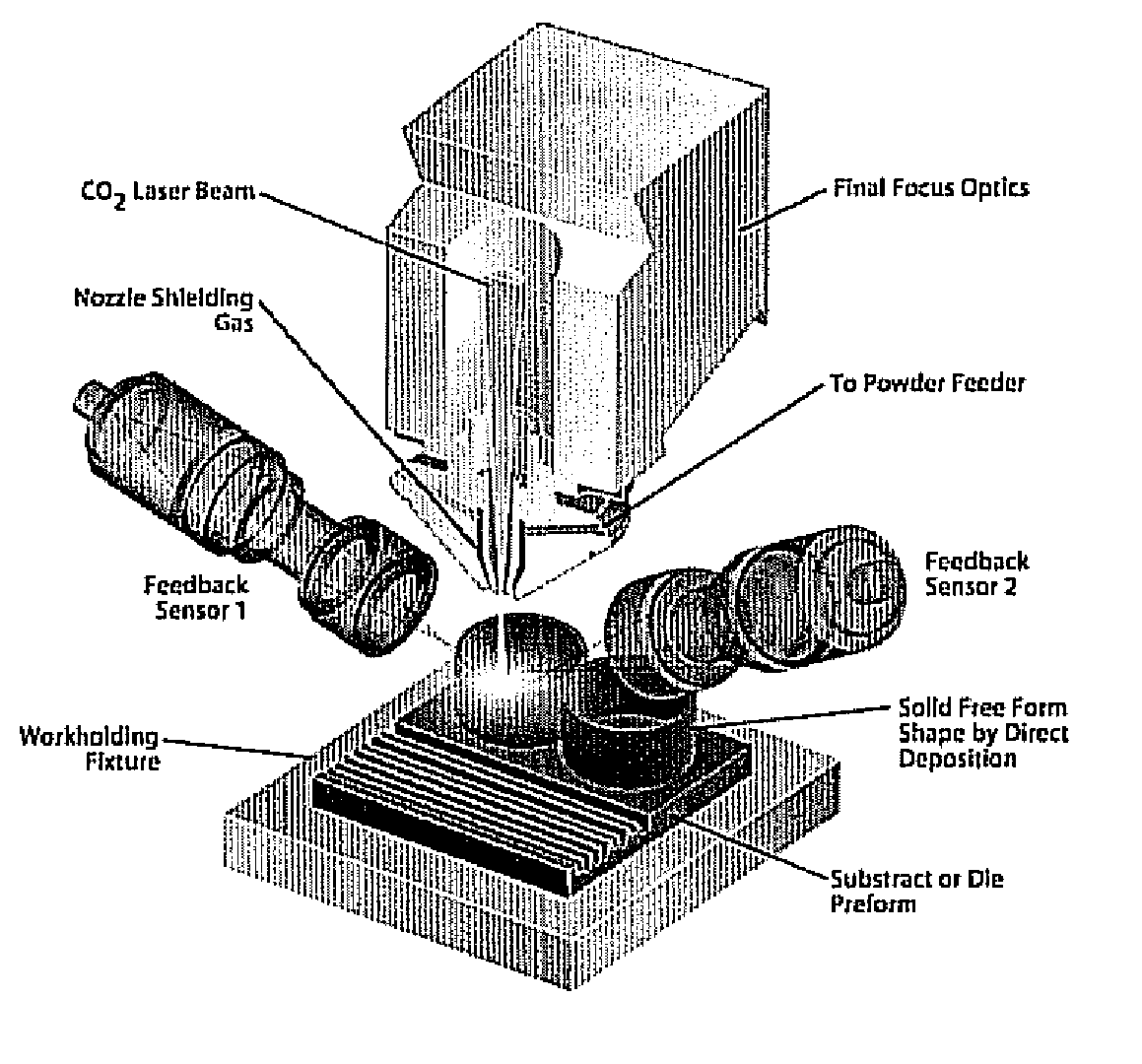
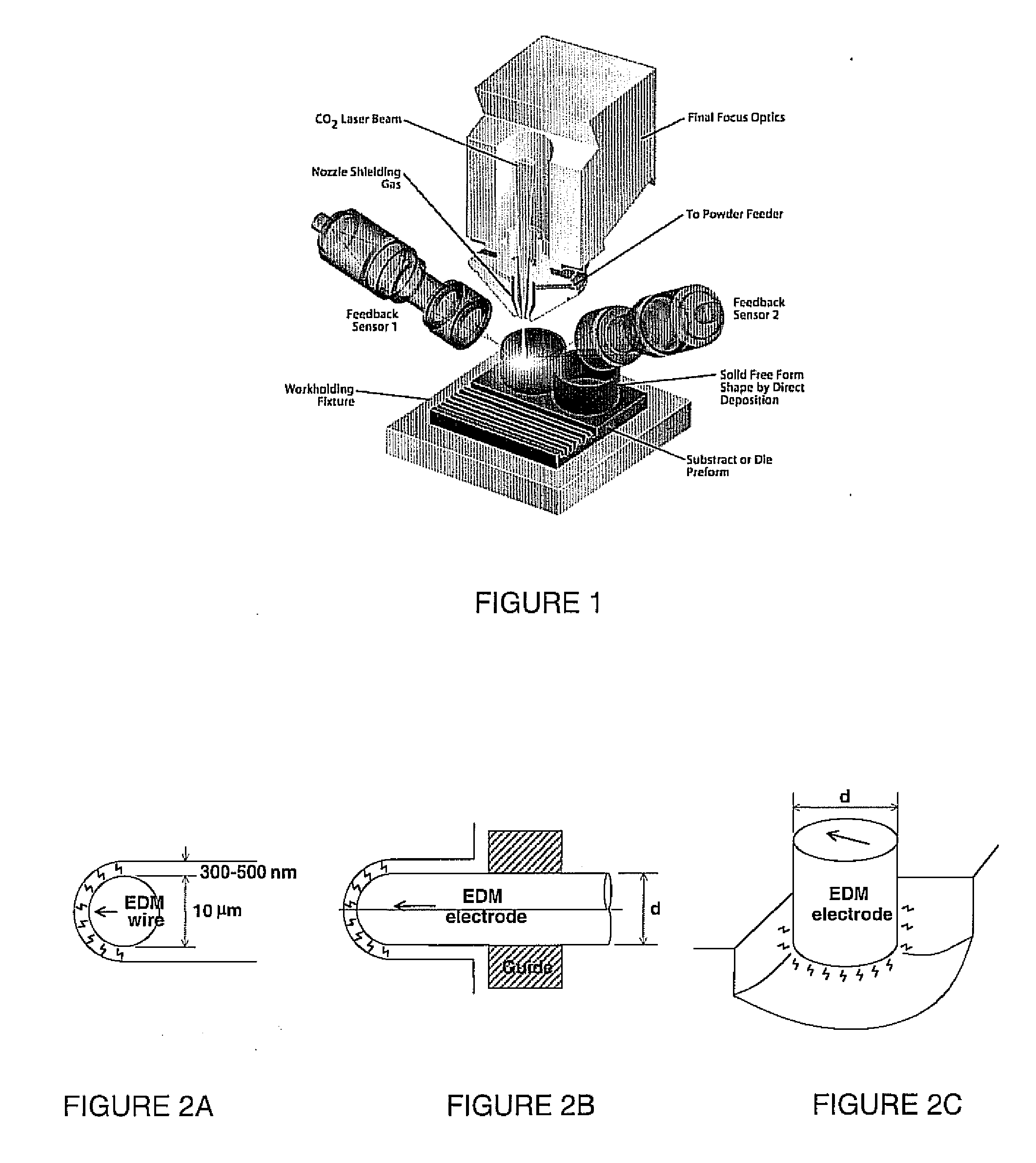
High-speed, ultra precision manufacturing station that combines direct metal deposition and edm
ActiveUS20070205184A1Fast transferImprove efficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusElectric discharge heatingEngineeringWorkstation
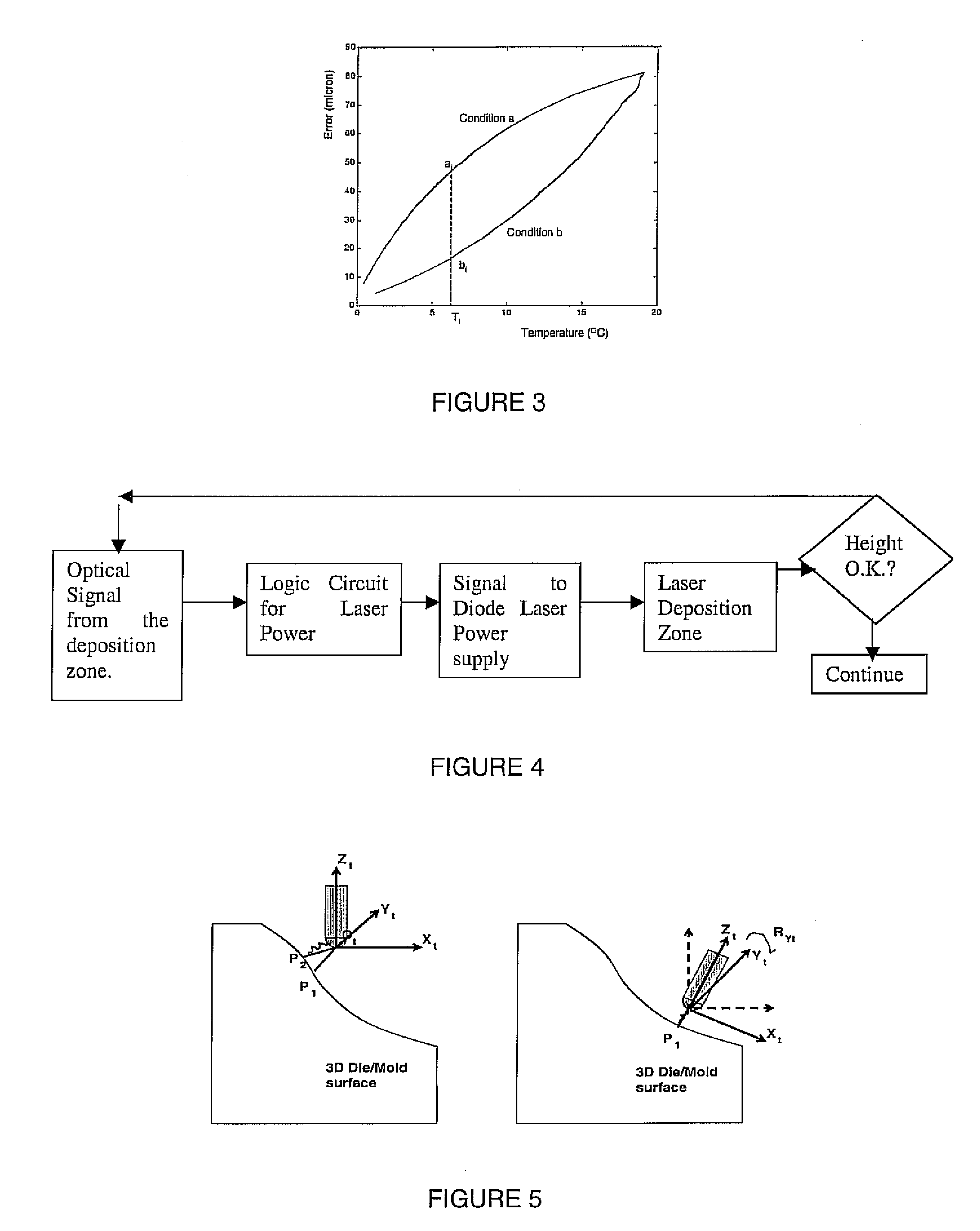
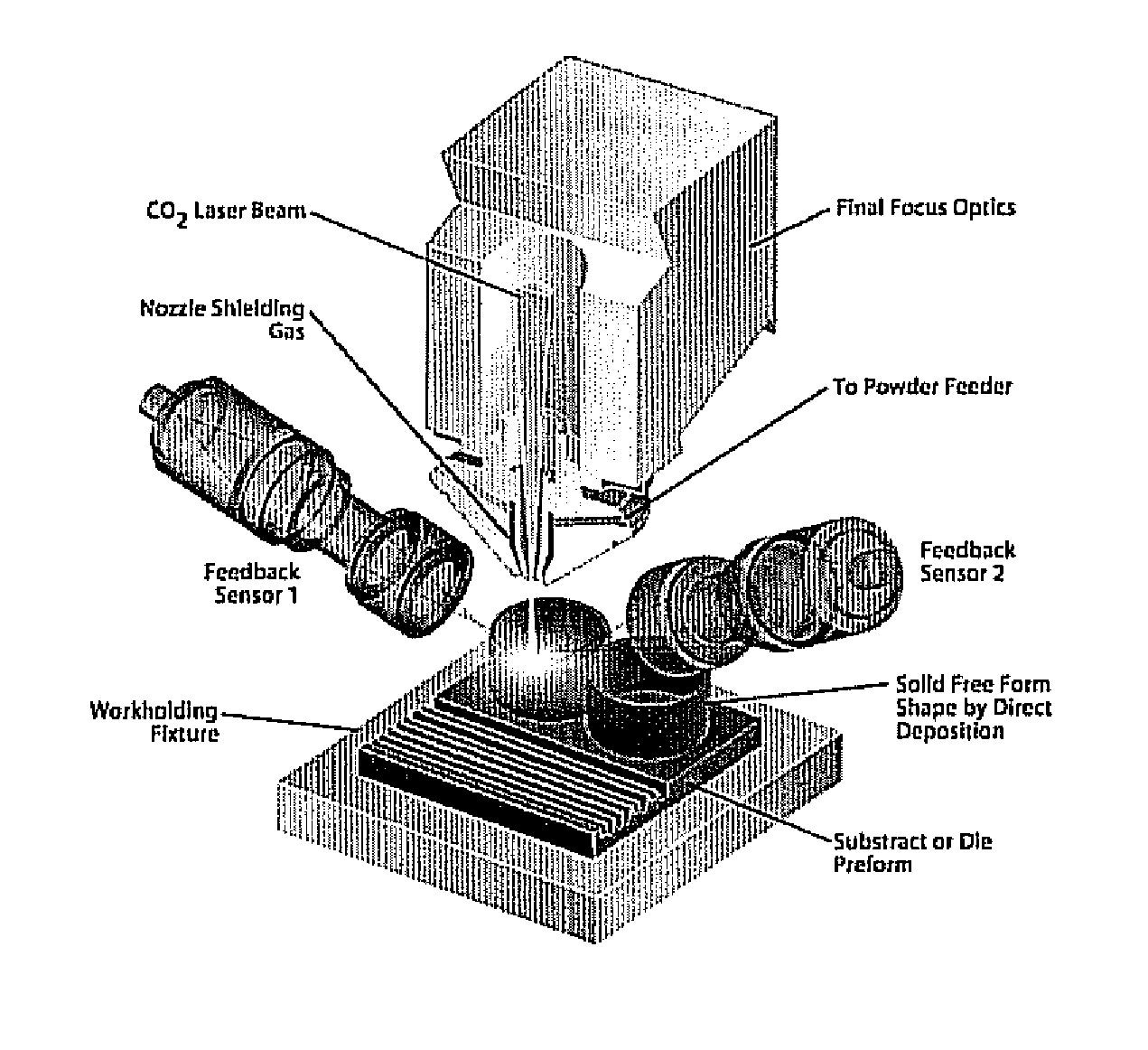
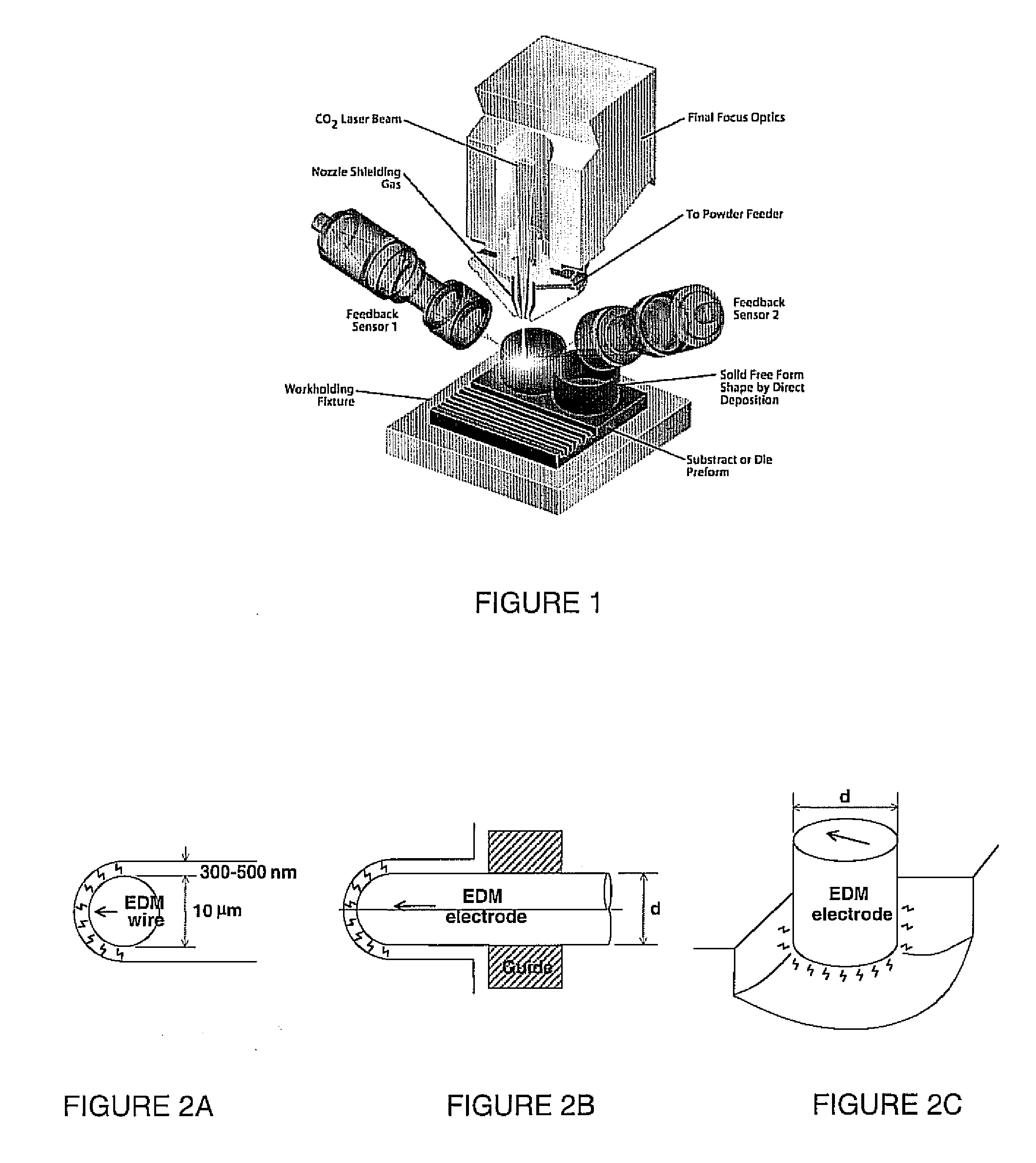
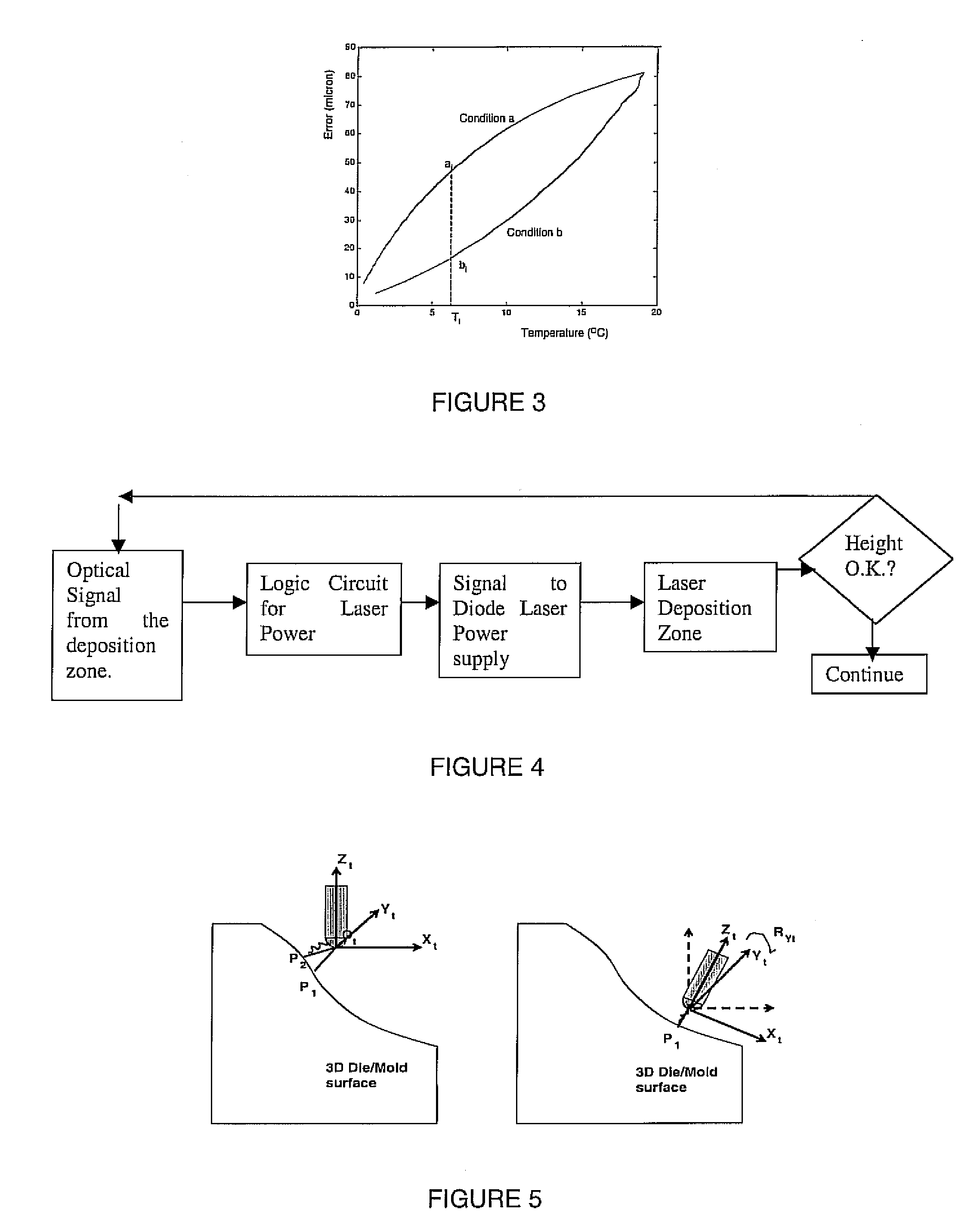
A direct-metal deposition (DMD) processing stage and a 5DOF (degree of freedom) dry micro-EDM (mEDM) stage are integrated to provide the submicron scale resolution necessary for the ultra-precision processing of work pieces. The DMD processing stage includes optical feedback for dimensional control utilizing a high-power, fiber-coupled diode laser with fast response time and small beam parameter product. The electrical discharge machining (EDM) stage is a dry EDM stage using an inert gas with appropriate dielectric properties to perform the surface finishing operations. The system further includes one or more surface treatment operations to obtain a desired level of surface hardness or wear resistance and / or to minimize the distortion induced in treating the surface.
Owner:DM3D TECH
High-speed, ultra precision manufacturing station that combines direct metal deposition and EDM
ActiveUS8629368B2Fast transferImprove efficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusElectric discharge heatingEngineeringBeam parameter product
A direct-metal deposition (DMD) processing stage and a 5DOF (degree of freedom) dry micro-EDM (mEDM) stage are integrated to provide the submicron scale resolution necessary for the ultra-precision processing of work pieces. The DMD processing stage includes optical feedback for dimensional control utilizing a high-power, fiber-coupled diode laser with fast response time and small beam parameter product. The electrical discharge machining (EDM) stage is a dry EDM stage using an inert gas with appropriate dielectric properties to perform the surface finishing operations. The system further includes one or more surface treatment operations to obtain a desired level of surface hardness or wear resistance and / or to minimize the distortion induced in treating the surface.
Owner:DM3D TECH
Laser cutting method and equipment, with means for modifying the laser beam quality factor by a diffractive optical component
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
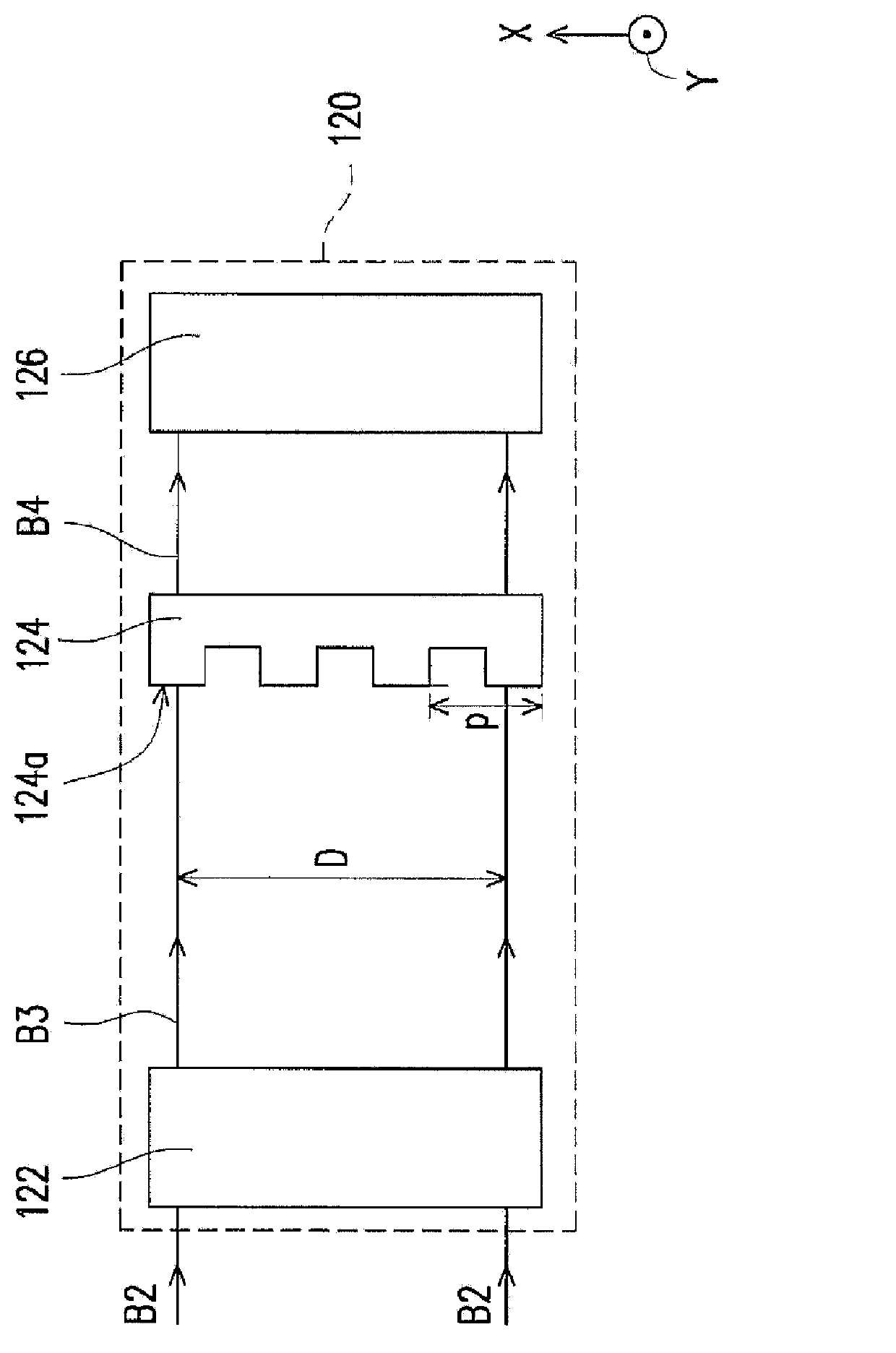
Beam generating apparatus
A beam generating apparatus includes a laser light source, a speckle suppressing module, a light homogenizing module and a driving unit. The laser light source outputs a laser beam. The speckle suppressing module includes two biconic lenses and a diffuser. The first biconic lens is disposed on a transmission path of the laser beam. The diffuser is located on the transmission path of the laser beam between the first and second biconic lenses. The light homogenizing module is disposed on the transmission path of the laser beam from the second biconic lens. The driving unit drives the diffuser to move with respect to the laser beam so that the ratio of the M2 of the laser beam exiting from the second biconic lens in a first direction to the M2 thereof in a second direction is greater than 2, wherein the two directions are substantially perpendicular to each other.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
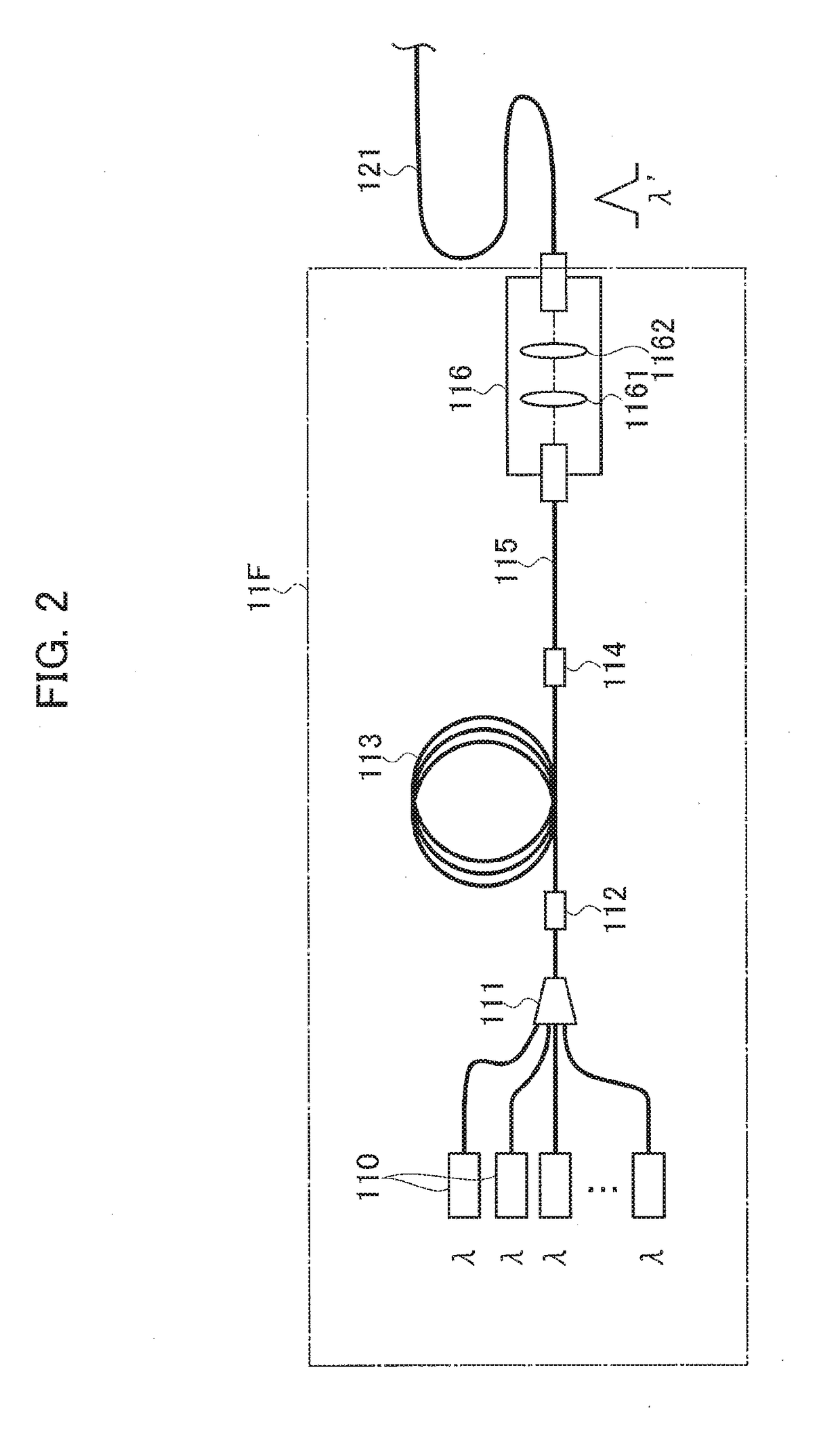
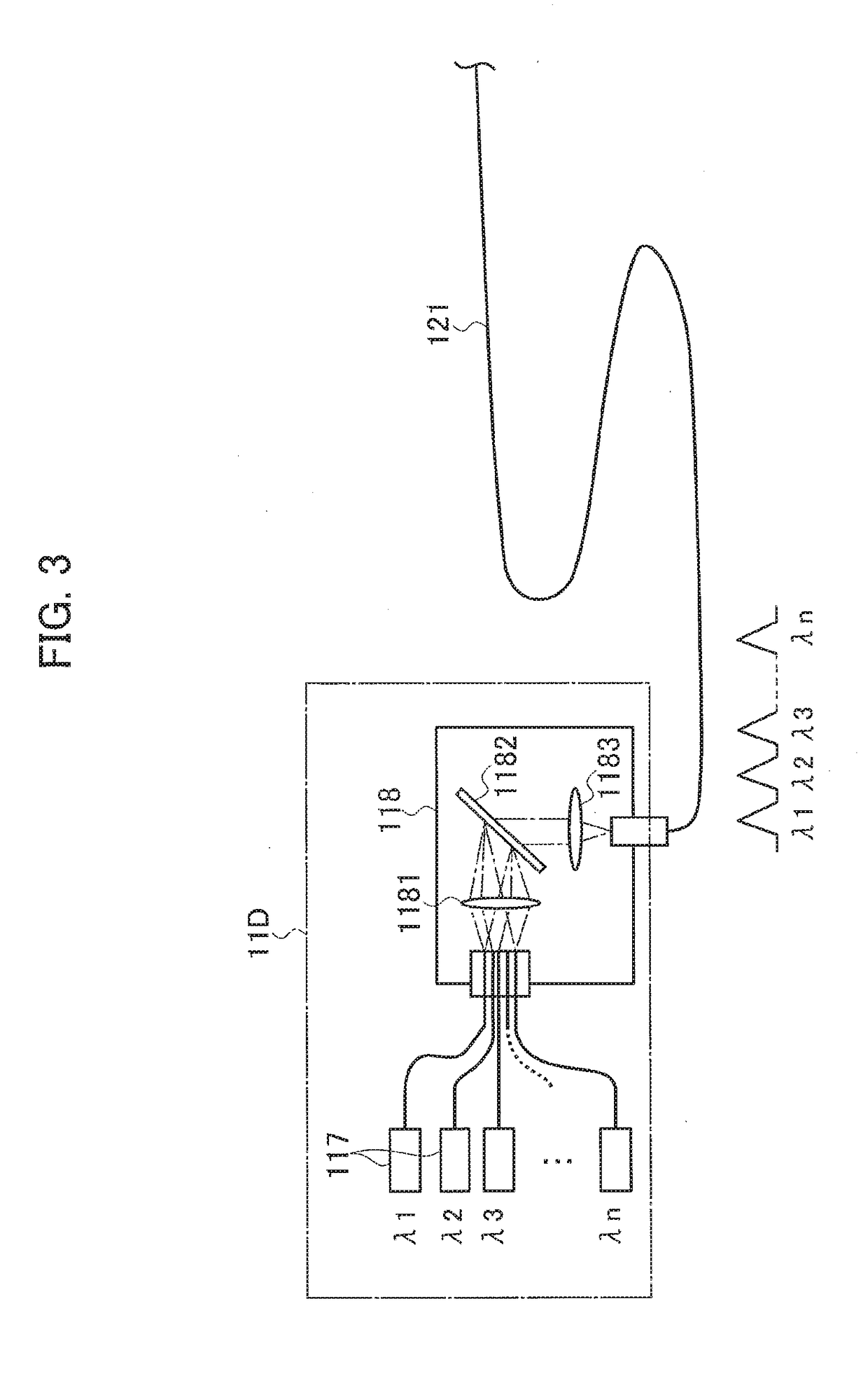
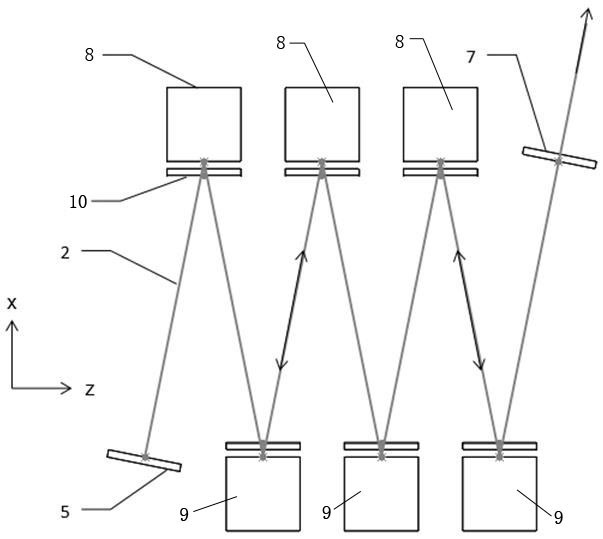
Systems and methods for multiple-beam laser arrangements with variable beam parameter product
In various embodiments, a beam-parameter adjustment system and focusing system alters a spatial power distribution of a plurality of radiation beams before the beams are coupled into an optical fiber.
Owner:陈斌 +6
Multi kw class blue laser system
PendingCN111512507AOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser output parameters controlGratingEngineering
The invention may be embodied in other forms than those specifically disclosed herein without departing from itMulti-kW-class blue (400-495 nm) fiber- delivered lasers and module configurations. In embodiments, the lasers propagate laser beams having beam parameter products of < 5 mm*mrad, which are used in materials processing, welding and pumping a Raman laser. In an embodiment the laser systemis an integration of fiber-coupled modules, which are in turn made up of submodules. An embodiment has sub-modules having a plurality of lensed blue semiconductor gain chips with low reflectivity front facets. These are locked in wavelength with a wavelength spread of < 1 nm by using volume Bragg gratings in an external cavity configuration. An embodiment has modules having of a plurality of submodules, which are combined through wavelength multiplexing with a bandwidth of < 10 nm, followed by polarization beam combining. The output of each module is fiber- coupled into a low NA fiber. In an embodiment a kW-level blue laser system is realized by fiber bundling and combining multiple modules into a single output fiber.
Owner:NUBURU INC
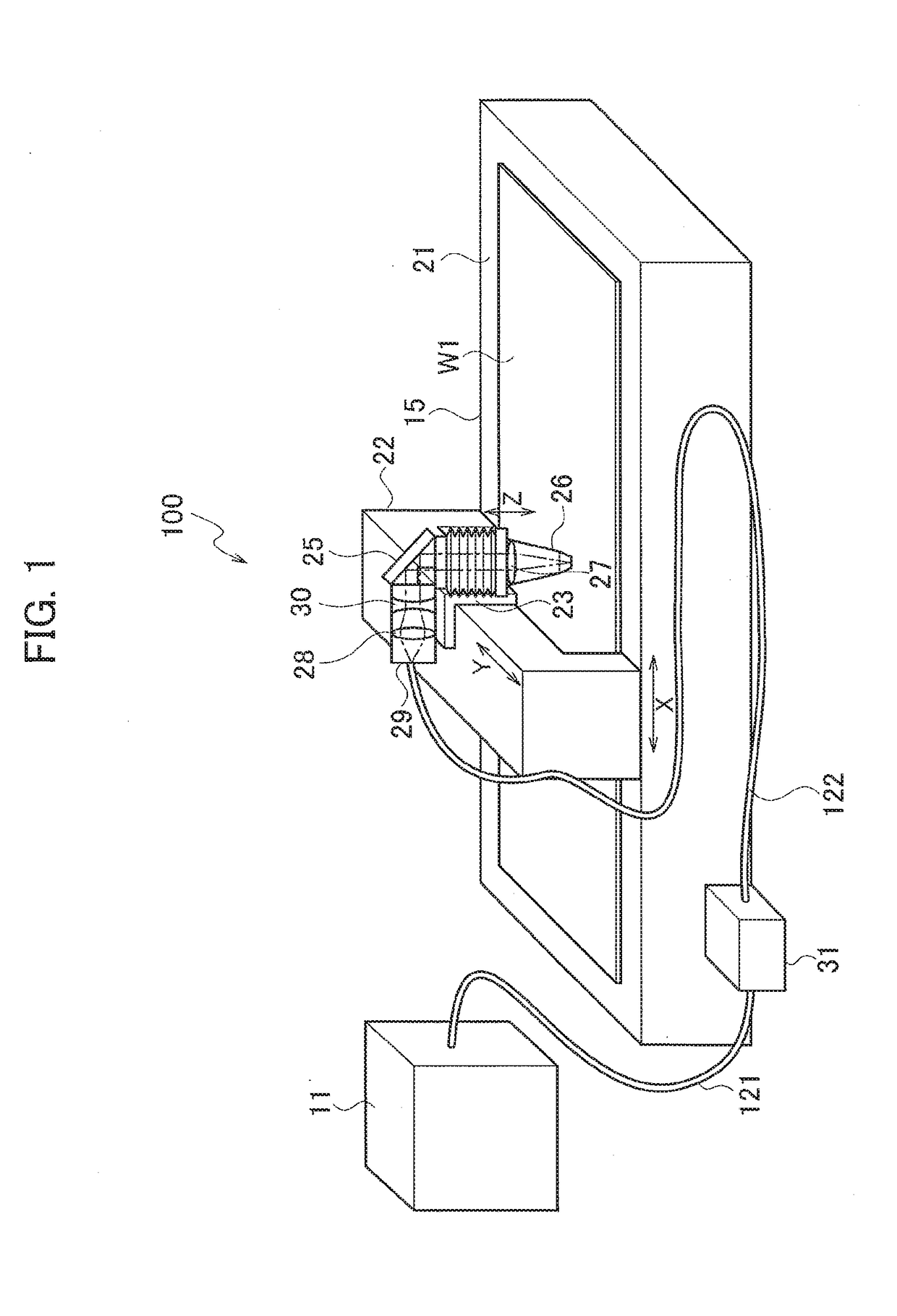
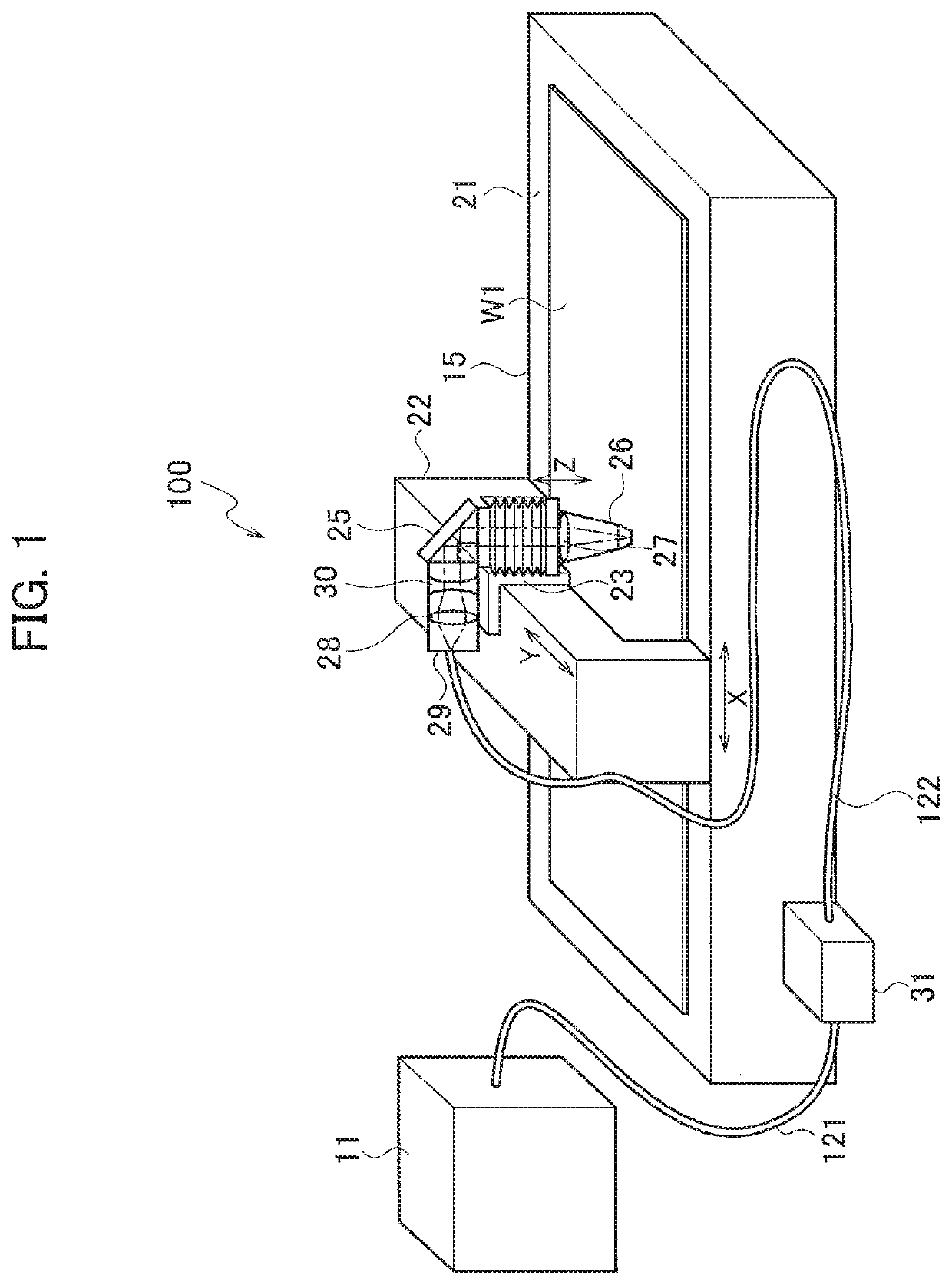
Laser processing machine
A laser processing machine includes a beam parameter product variable device, and a beam diameter variable device. The beam parameter product variable device sets beam parameter products of a laser beam to a predetermined value. The beam diameter variable device includes a first lens that is movable in an optical axis direction and having a positive focal length, and converts divergent light of a laser beam emitted from an emission end of the laser beam into convergent light, and a second lens that is movable in the optical axis direction and having a negative focal length on which the convergent light is incident. A third lens having a positive focal length, focuses the laser beam emitted from the beam diameter variable device, and irradiates a plate material with the focused laser beam.
Owner:AMADA HLDG CO LTD
Optical device for beam shaping
The invention concerns an optical device and its application to generate an adjustable wave front deformation of a laser beam and thus to generate an adjustable beam spot geometry in the focal plane of laser optics. For this purpose, a device is provided which allows adjusting and modifying a laser beam in such a way that a beam spot, the shape of which can be adjusted continuously based on the original focal shape, is generated after focusing the beam, i.e. at least one dimension parameter of the shape of the beam spot has to be variable and adjustable so that the beam parameter product of the beam can also be modified without having to modify the focal position.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Beam parameter product (BPP) control by varying fiber-to-fiber angle
An apparatus includes a laser system that includes a first fiber having an output end and situated to propagate a first laser beam with a first beam parameter product (bpp) and a second fiber having an input end spliced to the output end of the first fiber at a fiber splice so as to receive the first laser beam and to form a second laser beam having a second bpp that is greater than the first bpp,wherein the output end of the first fiber and the input end of the second fiber are spliced at a tilt angle so as to increase the first bpp to the second bpp.
Owner:NLIGHT INC
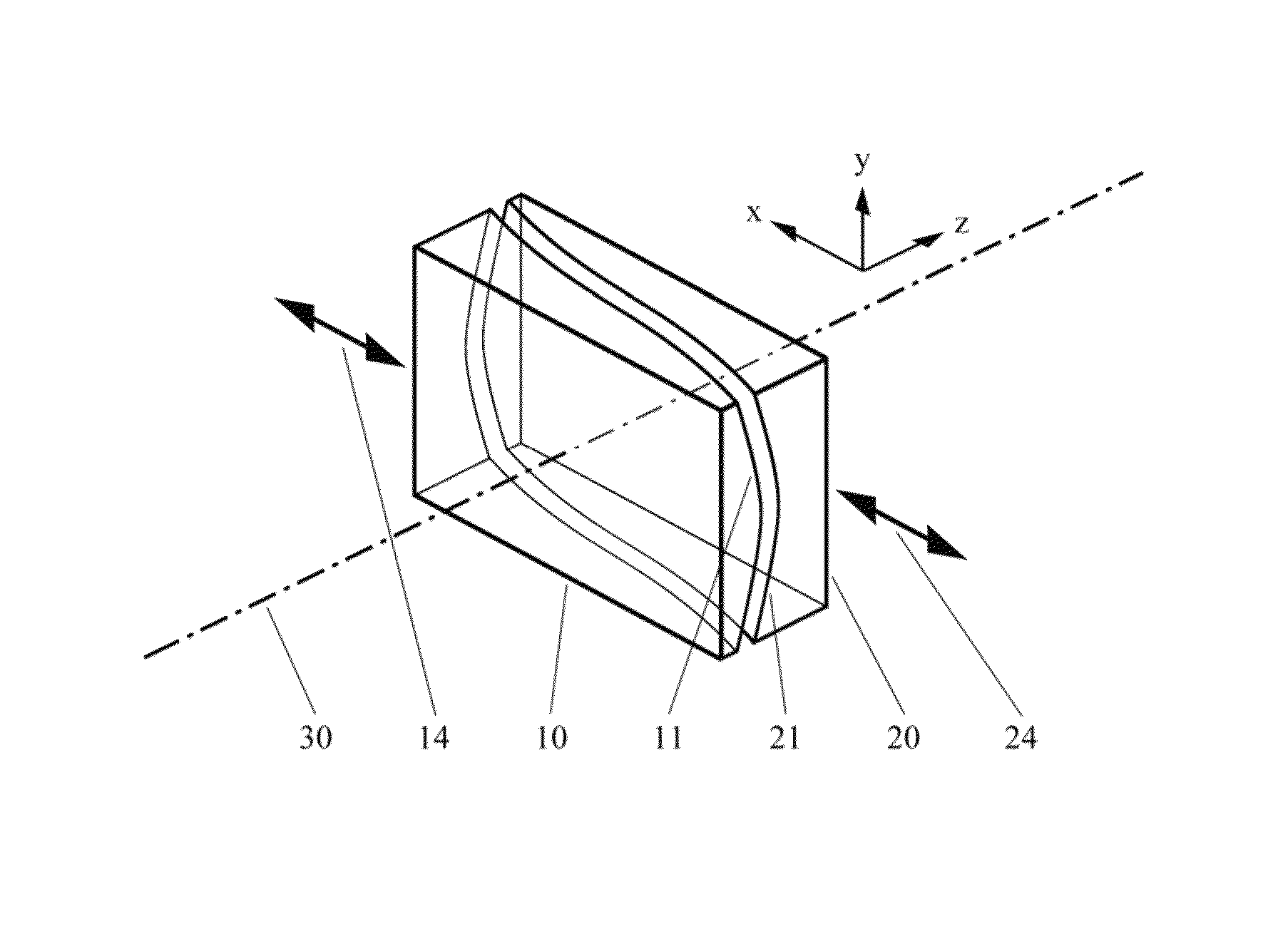
Apparatus and Method For Laser Processing A Material
PendingUS20190262949A1Reduce decreaseHigh beam qualityMulticore optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideLaser processingOptoelectronics
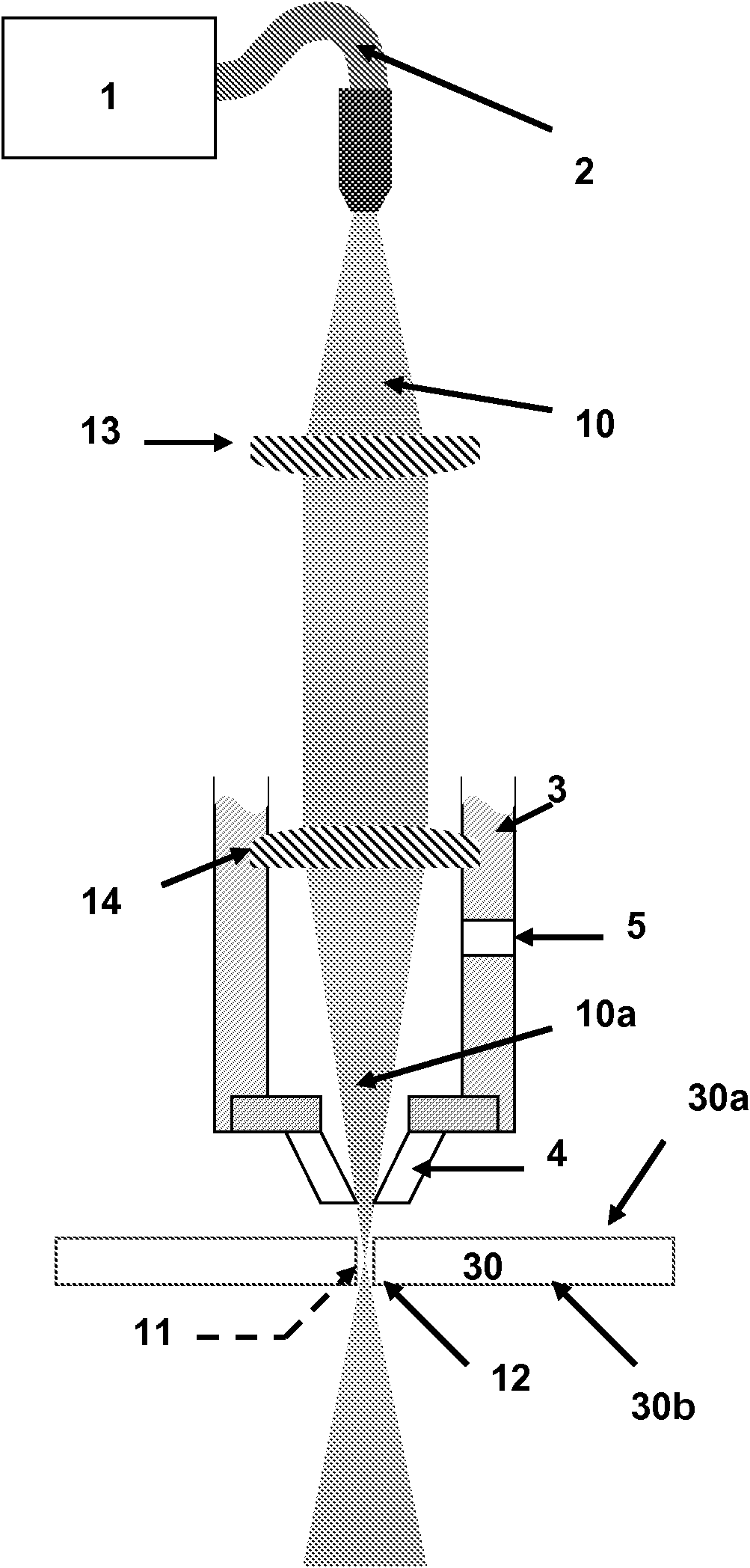
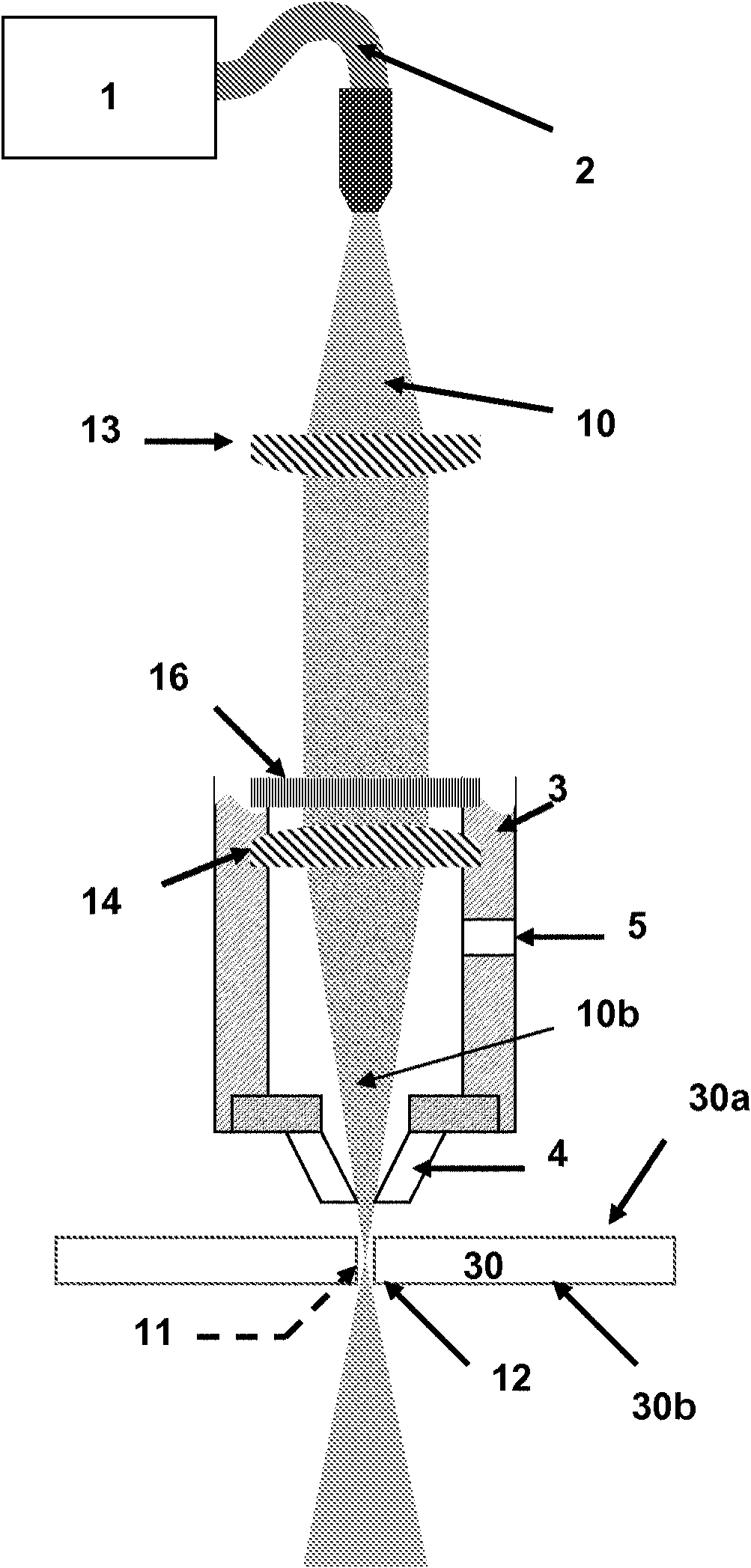
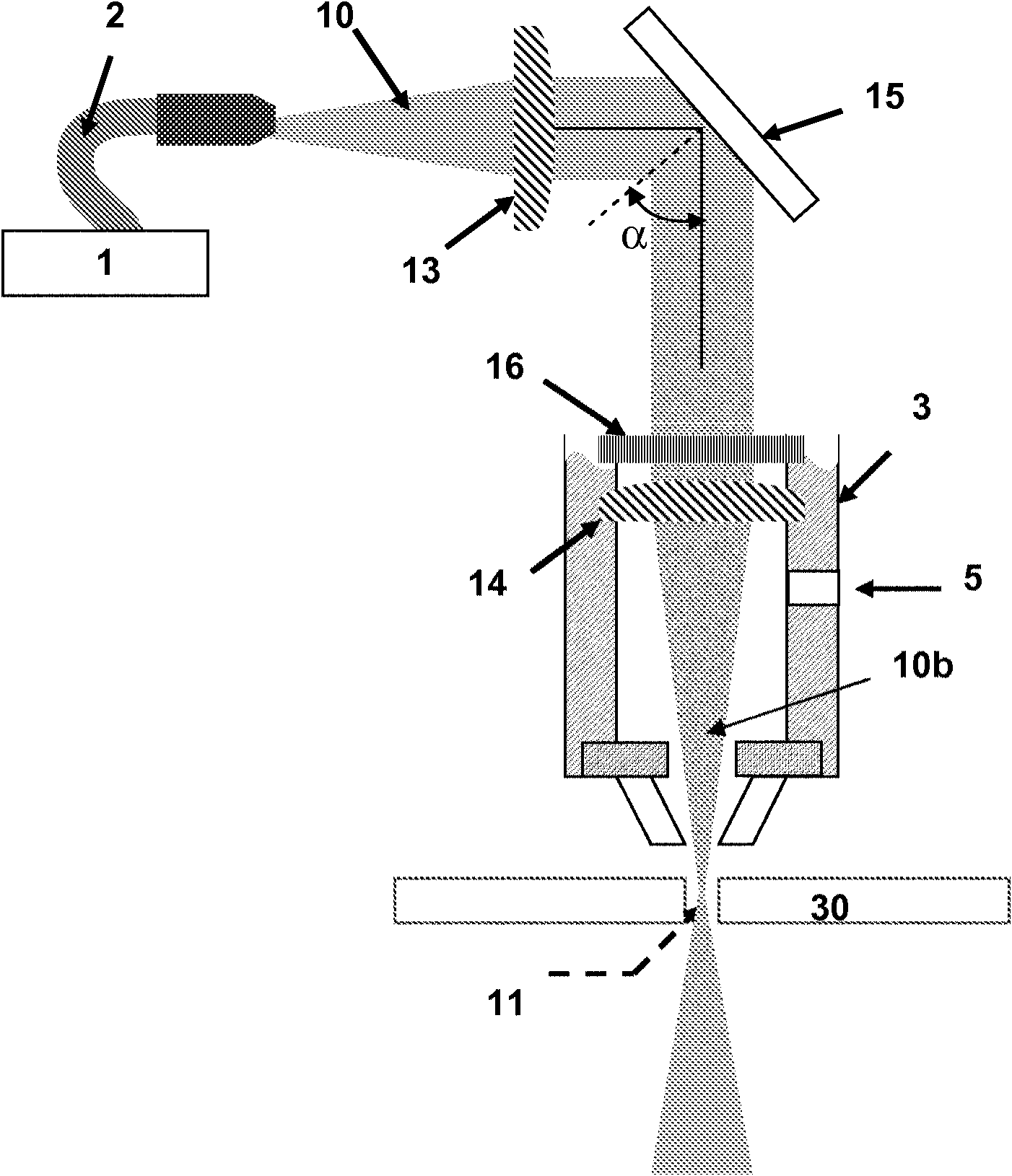
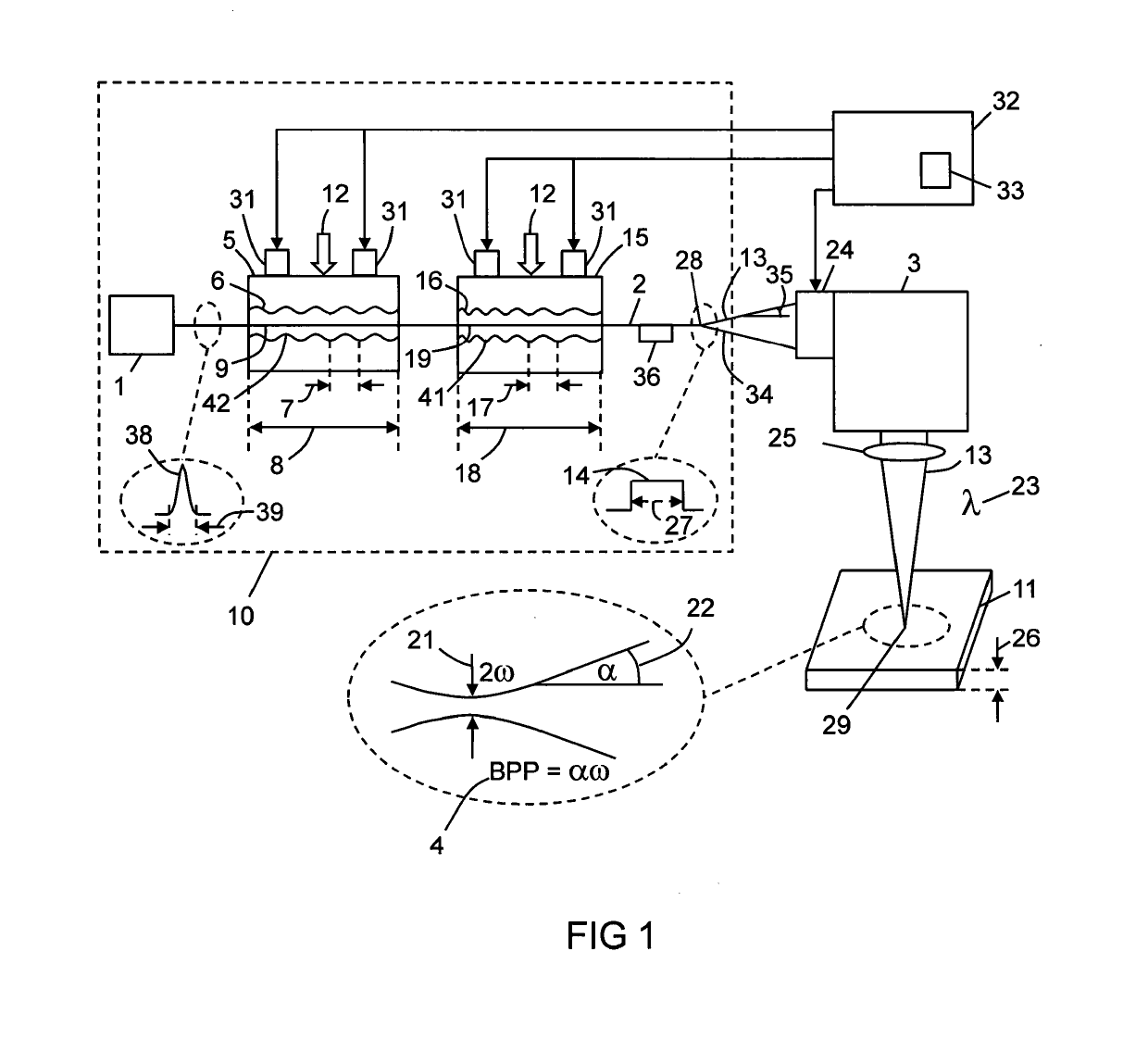
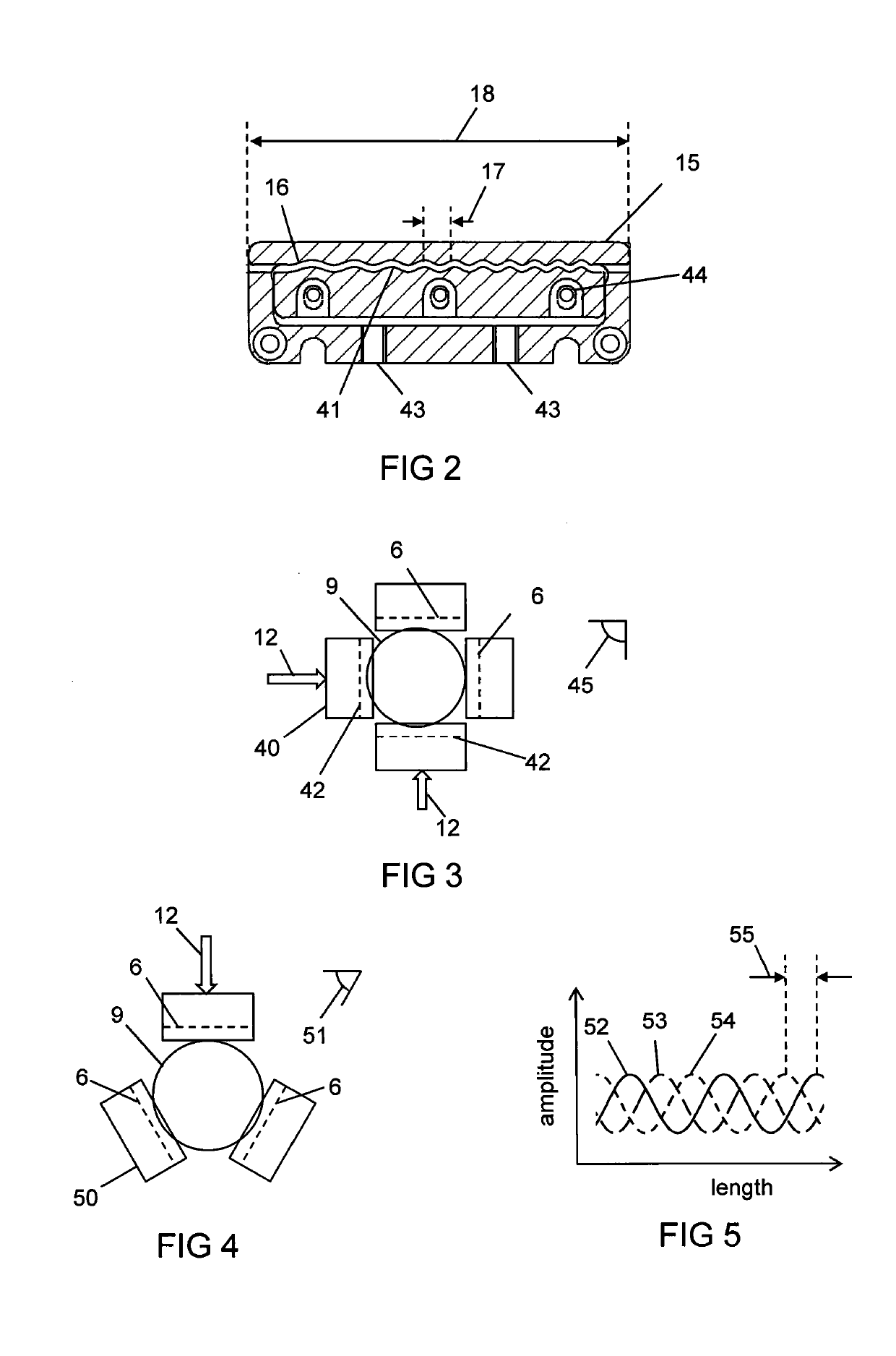
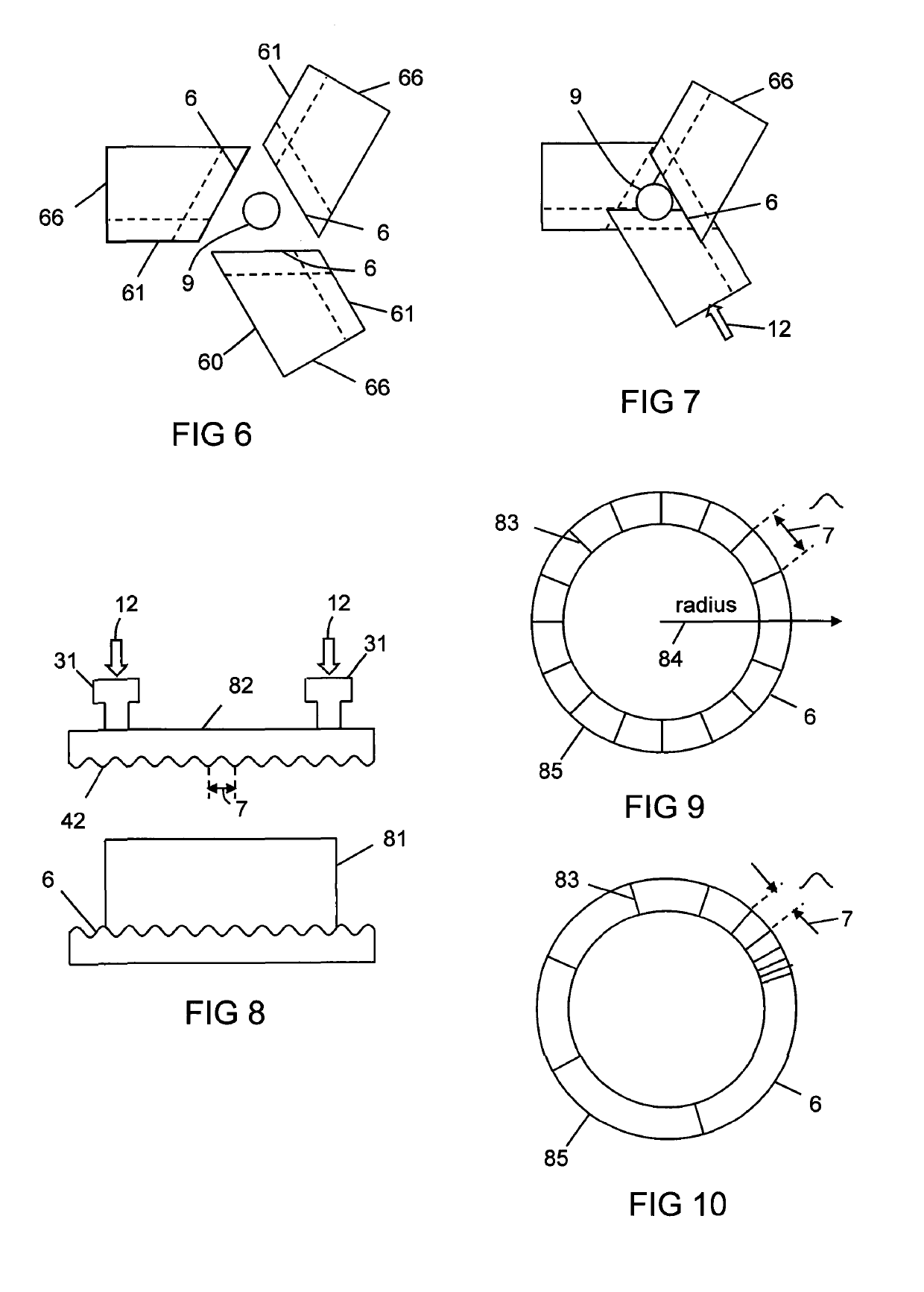
Apparatus (10) for laser processing a material (11), which apparatus comprises a laser (1) and a beam delivery cable (2), wherein: the laser (1) is connected to the beam delivery cable (2); the beam delivery cable (2) is configured to transmit laser radiation (13) emitted from the laser (1), and the laser radiation (13) is defined by a beam parameter product (4); and the apparatus (10) is characterized in that: the apparatus (10) includes at least one squeezing mechanism (5) comprising a periodic surface (6) defined by a pitch (7); a length (8) of optical fibre (9) that forms part of the laser (1) and / or the beam delivery cable (2) is located adjacent to the periodic surface (6); and the squeezing mechanism (5) is configured to squeeze the periodic surface (6) and the length (8) of the optical fibre (9) together with a squeezing force (12); whereby the beam parameter product (4) is able to be varied by adjusting the squeezing force (12).
Owner:SPI LASERS UK
Beam shaping device for semiconductor laser
InactiveCN103424872AHigh beam qualityEasy to manufactureOptical elementsSemiconductor packageDivergence angle
A beam shaping device for a semiconductor laser is characterized in that (i) a light-emitting area of a semiconductor laser tube core is linearly amplified by an optical amplifying element, (ii) the light-emitting area is sectioned, each section is optically transformed in a 90-degree rotating manner by a 90-degree optical rotating element, (iii) spatial translation is performed on each section by an optical translation element, so that the sections are closer, and gaps among the sections are narrowed, (iv) an image in the light-emitting area is properly linearly reduced by an optical reduction element, so that a linear size and a divergence angle adapting to output are formed. By the aid of the device, the BPP (beam parameter product) of an output beam of the semiconductor laser is decreased, beam quality is improved, and a powerful technological path is provided for manufacture of a high-power semiconductor pump laser and a high-power direct semiconductor laser system.
Owner:JIANGSU SKYERALASER TECH
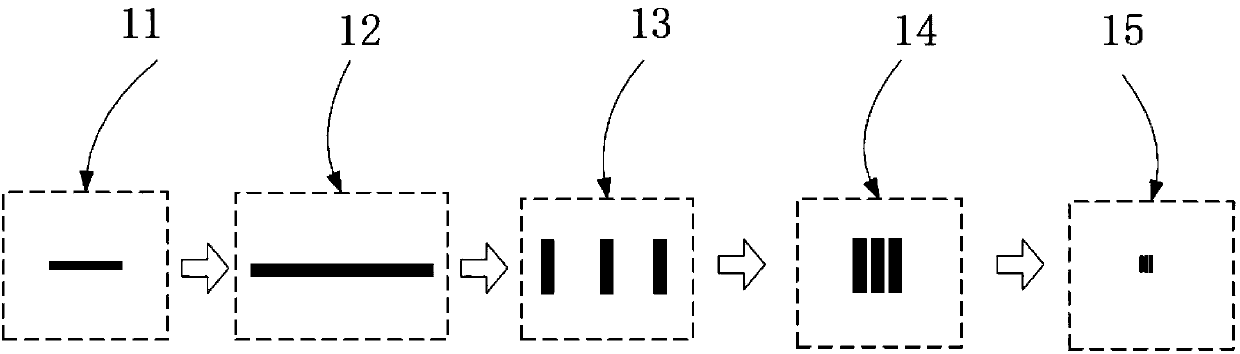
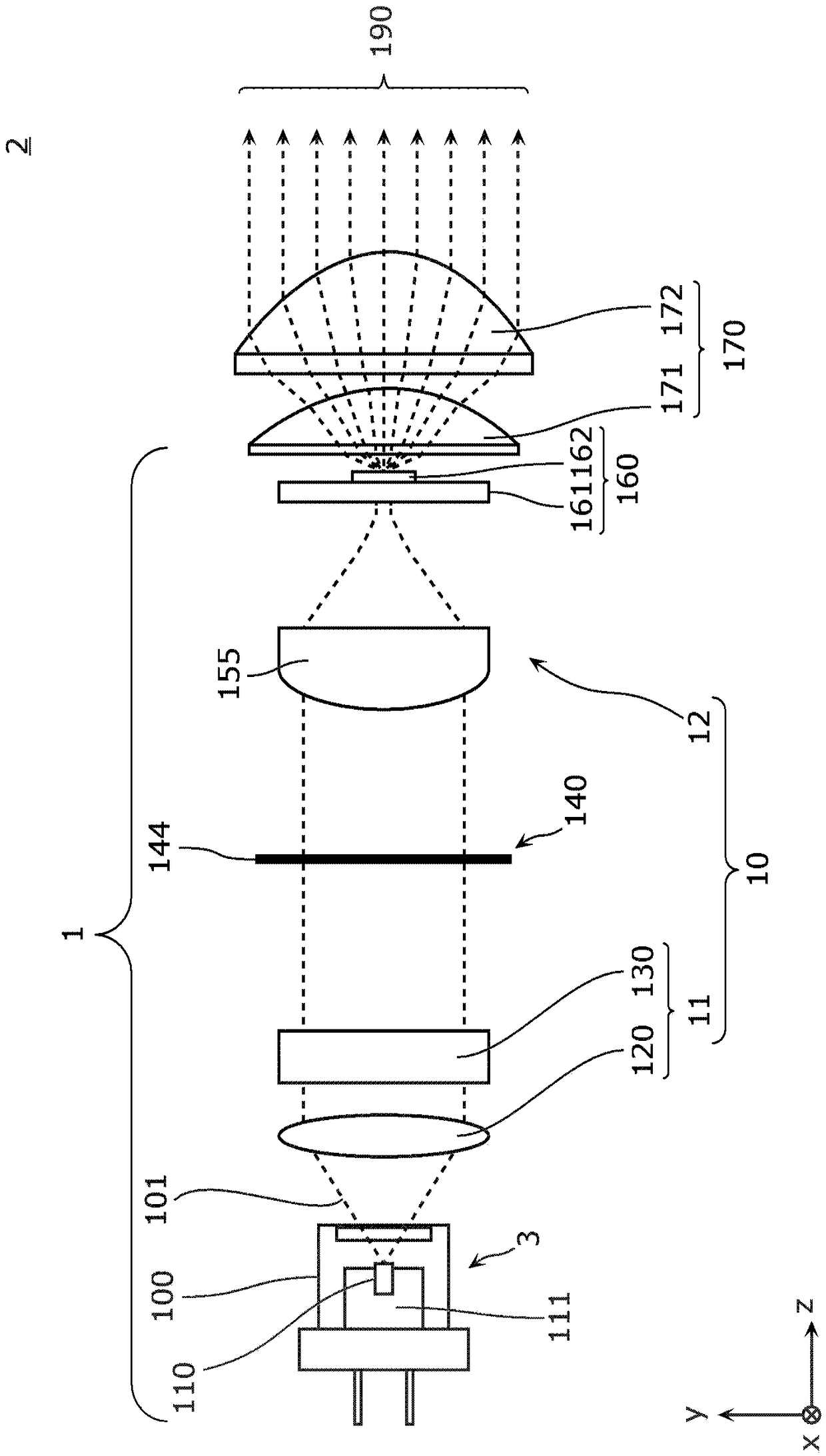
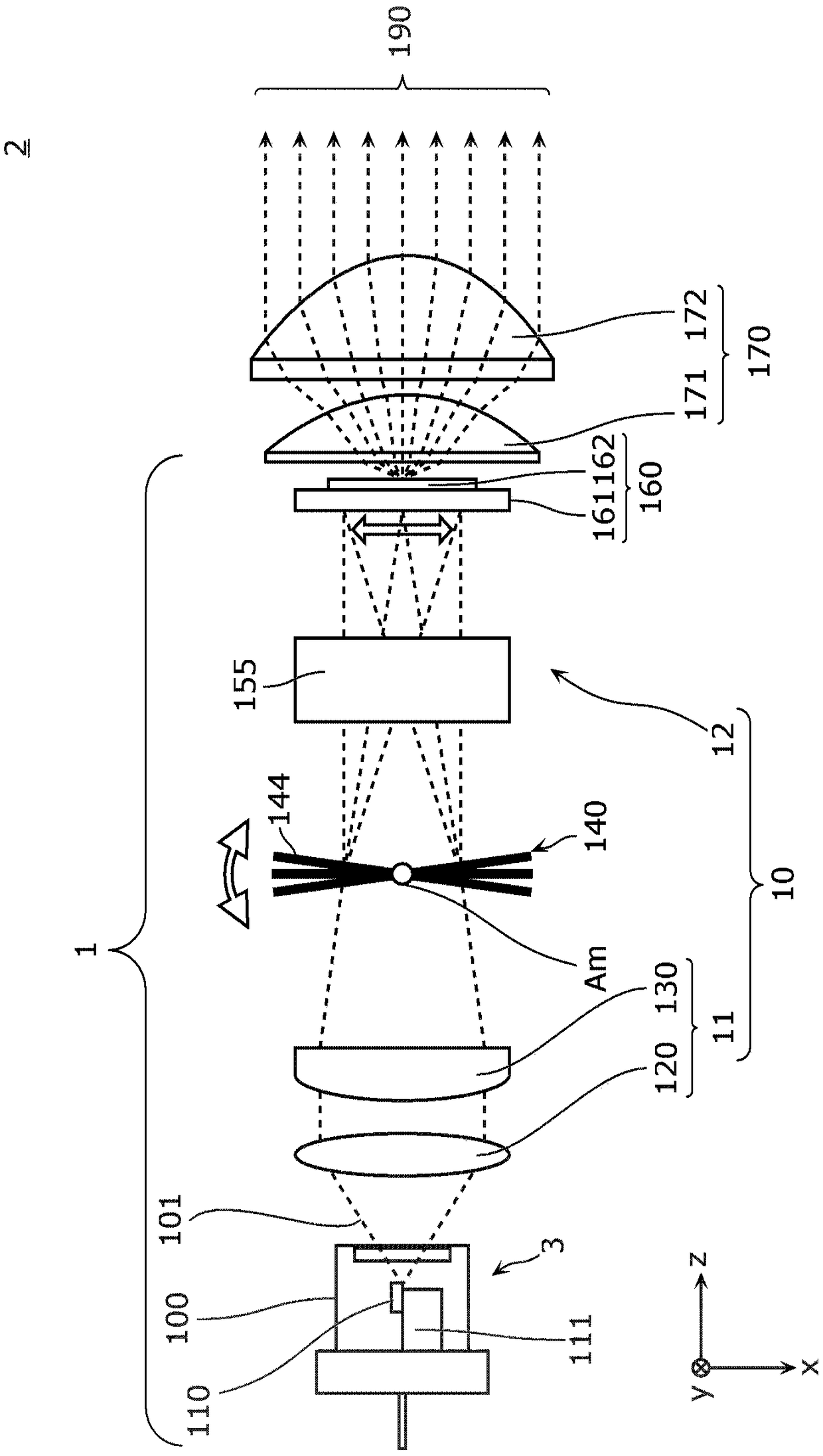
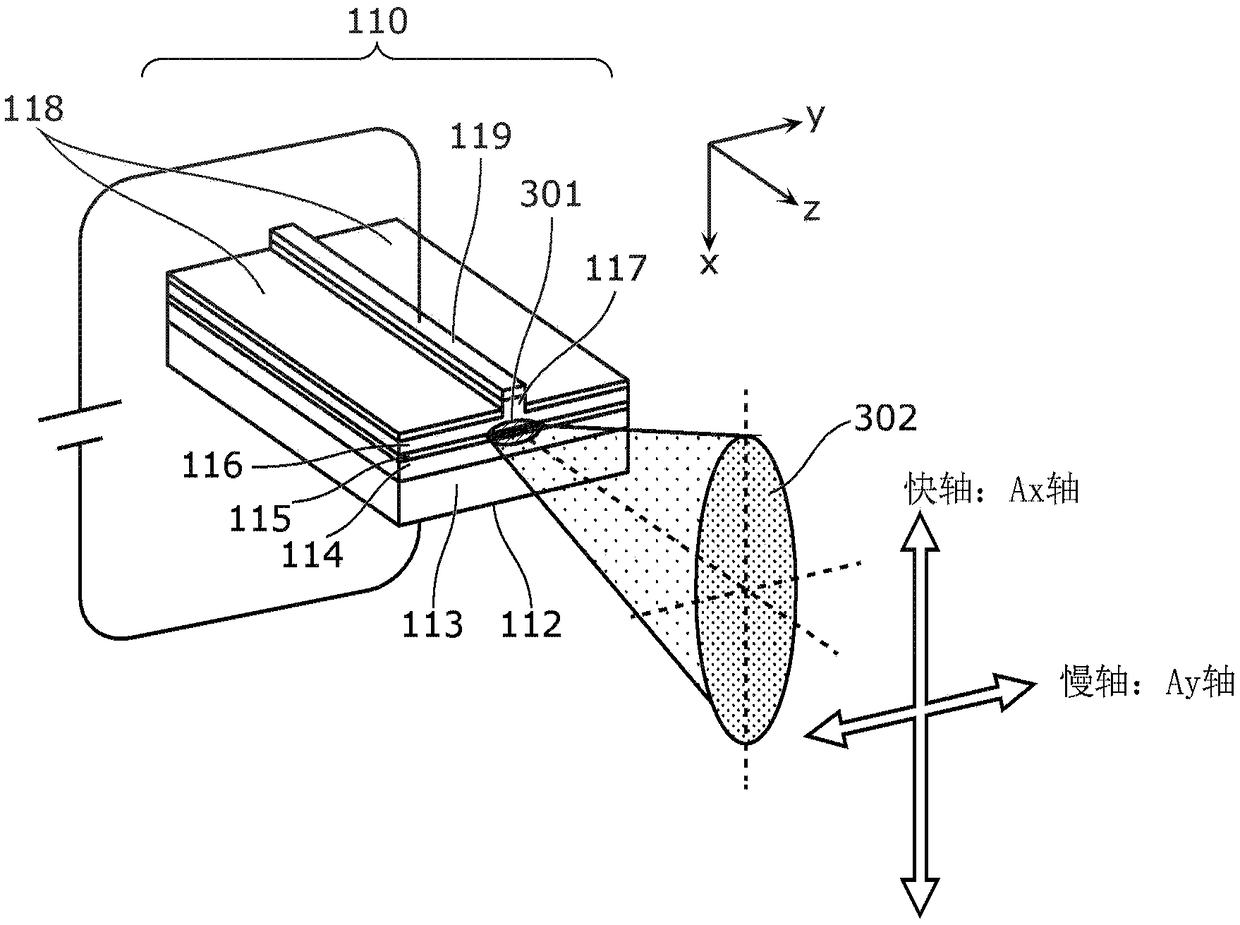
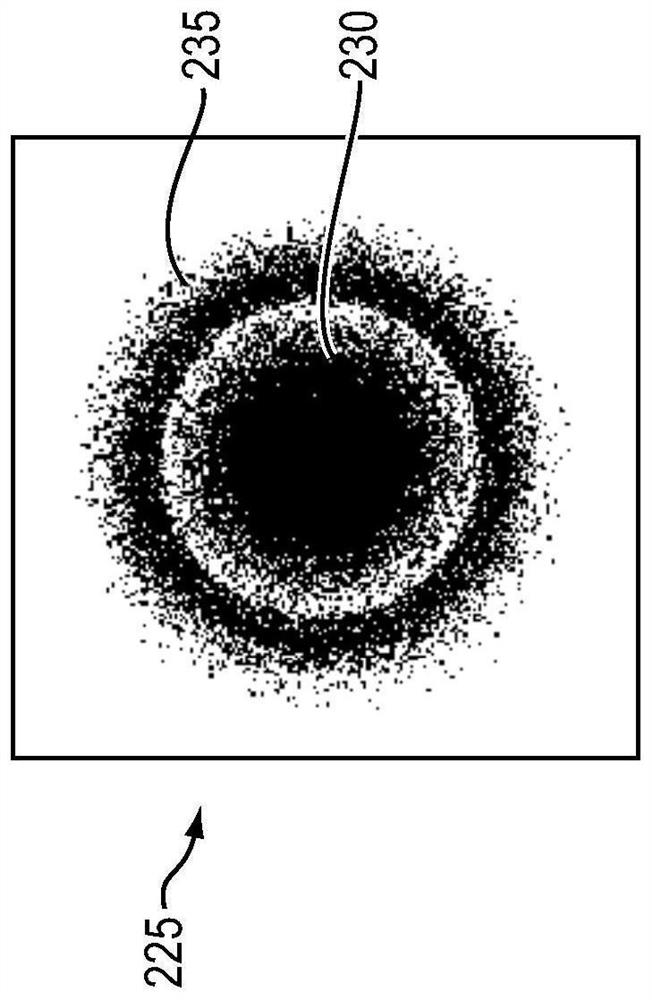
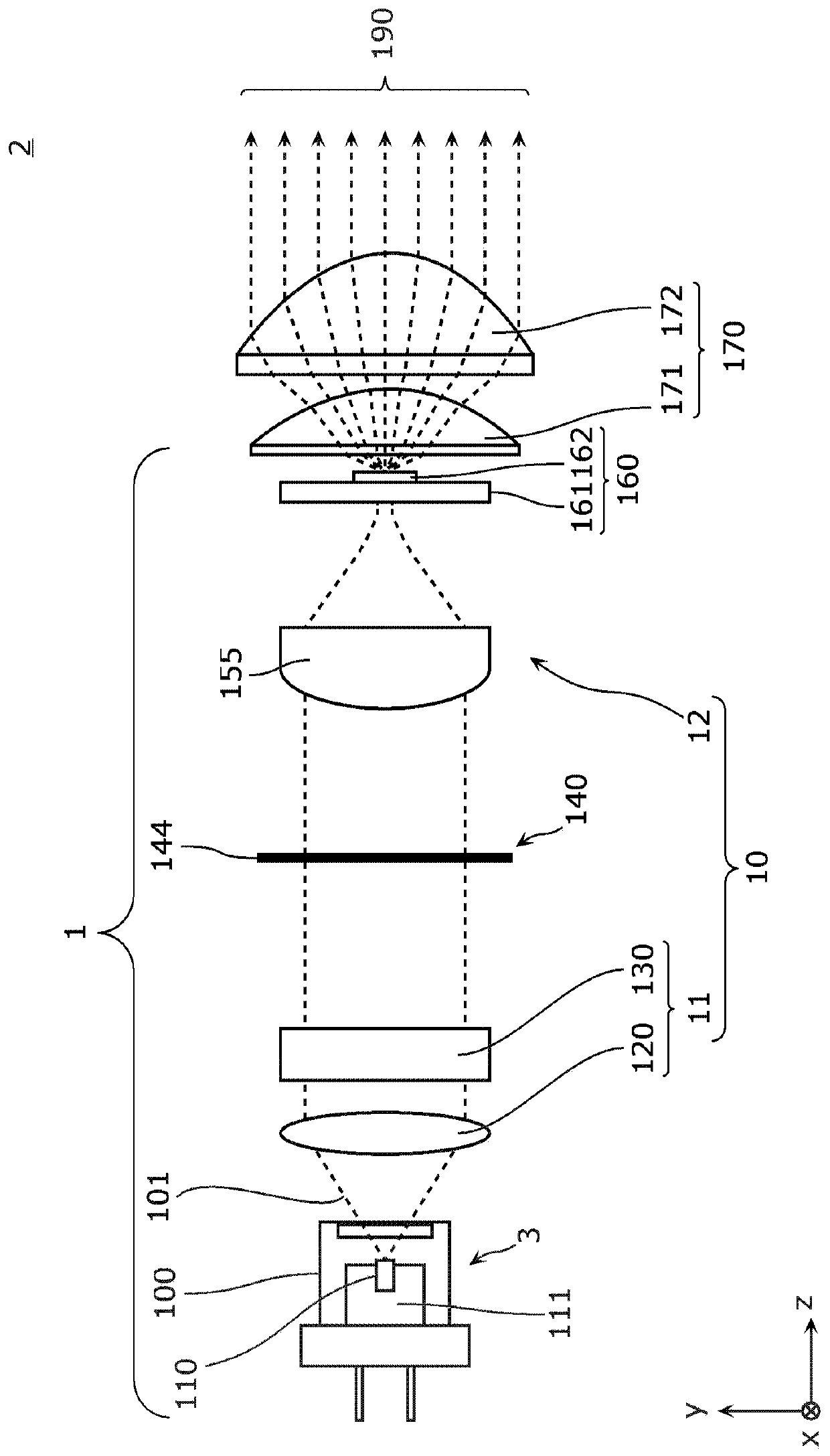
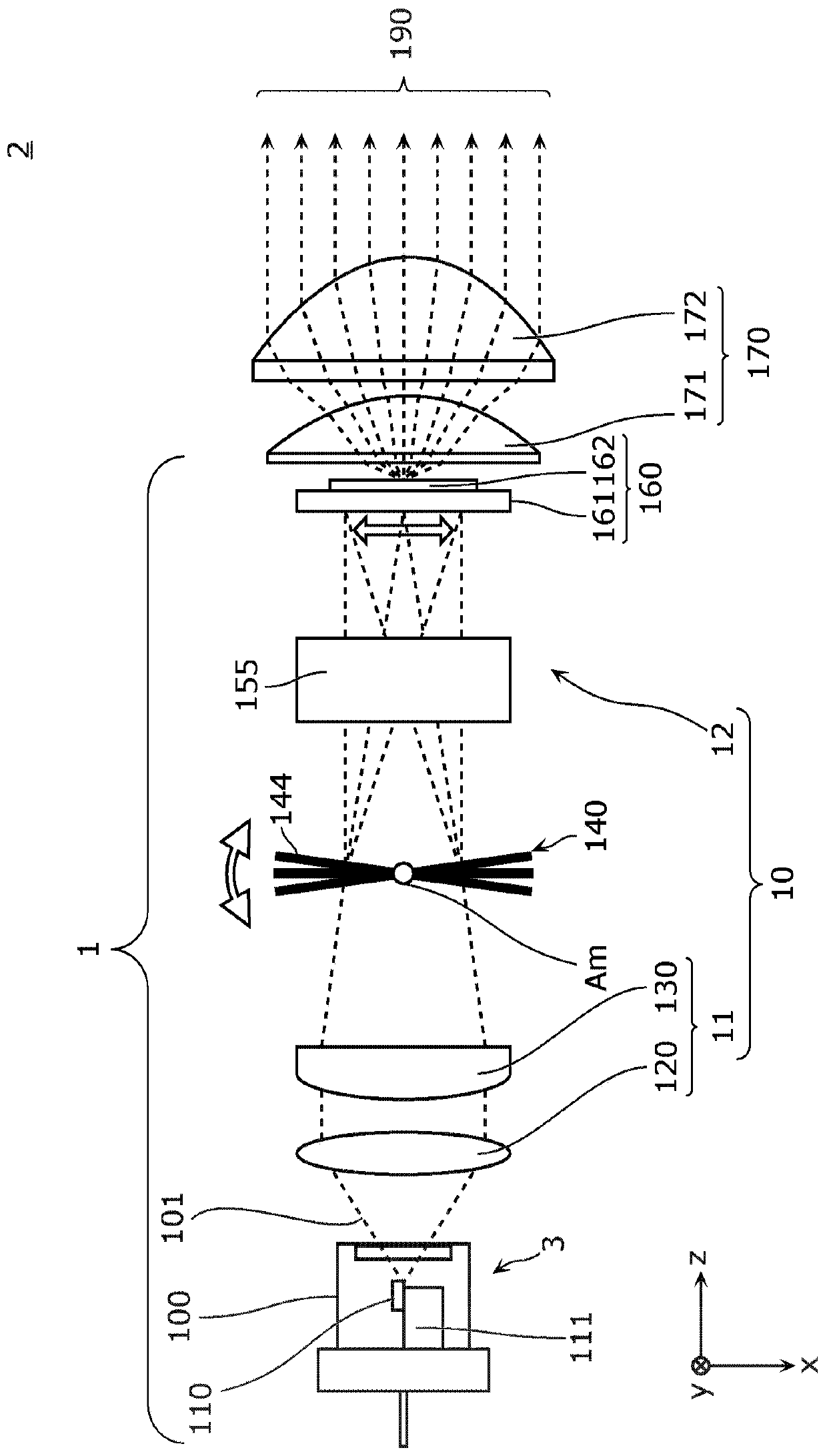
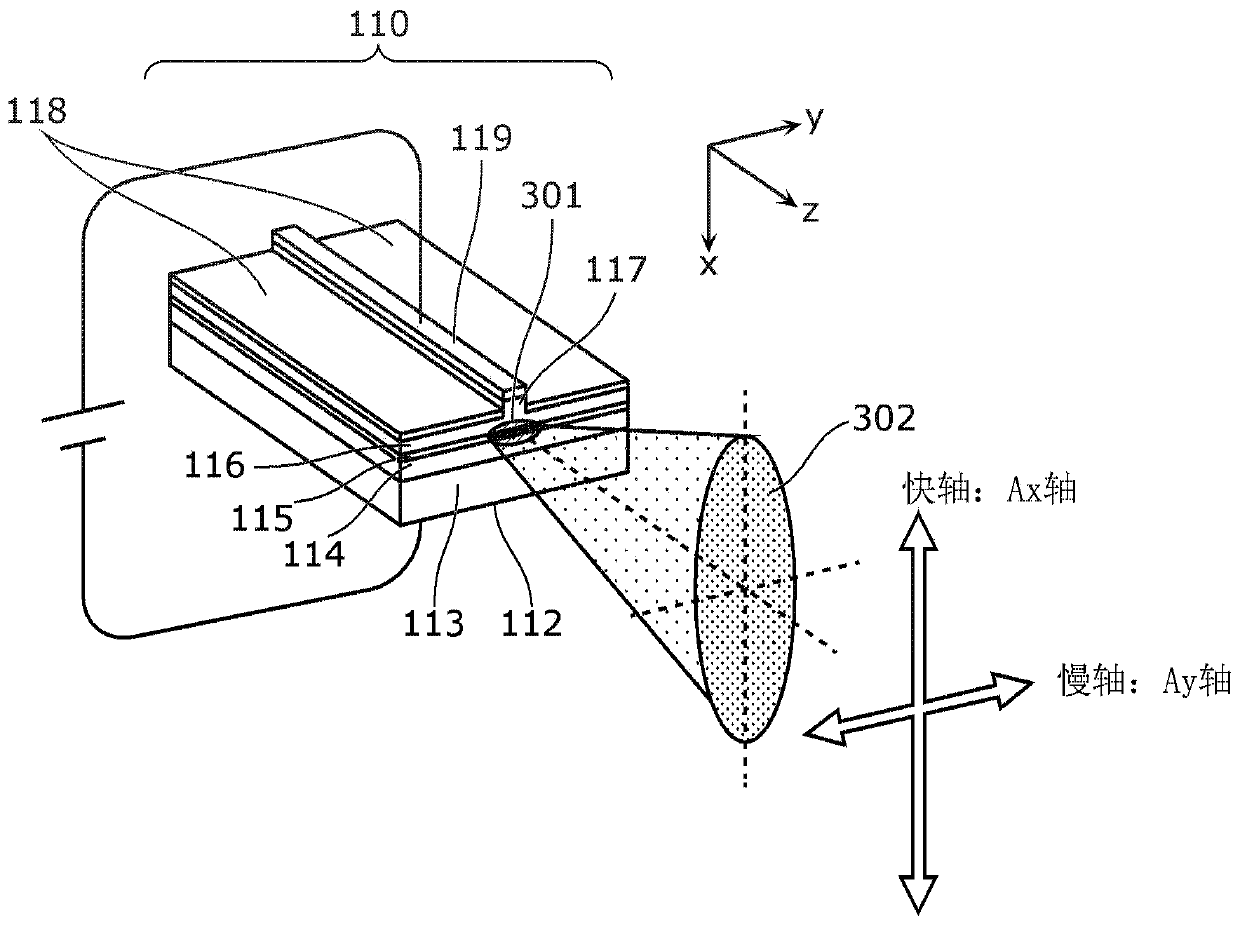
Light emission device and illumination device
The present invention is provided with: a light source unit (3) that emits excitation light (101); a light deflection unit (140) that deflects the excitation light (101); a wavelength conversion unit(160) that is irradiated with the excitation light (101) deflected by the light deflection unit (140), converts the excitation light (101) into wavelength-converted light of a different wavelength, and emits said wavelength-converted light; and a light-condensing unit (10) that condenses the excitation light (101) on the wavelength conversion unit (160). The light-condensing unit (10) comprises: afirst optical system (11) that is disposed between the light source unit (3) and the light deflection unit (140); and a second optical system (12) that is disposed between the light deflection unit (140) and the wavelength conversion unit (160). If an axis in a direction in which a beam parameter product of the excitation light (101) is at a minimum is referred to as the Ax axis, and an axis in adirection orthogonal to the Ax axis is referred to as the Ay axis, in a cross section orthogonal to the travel direction of the excitation light (101), the focal distance in the Ay axis direction inthe second optical system (12) is shorter than the focal distance in the Ax axis direction.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
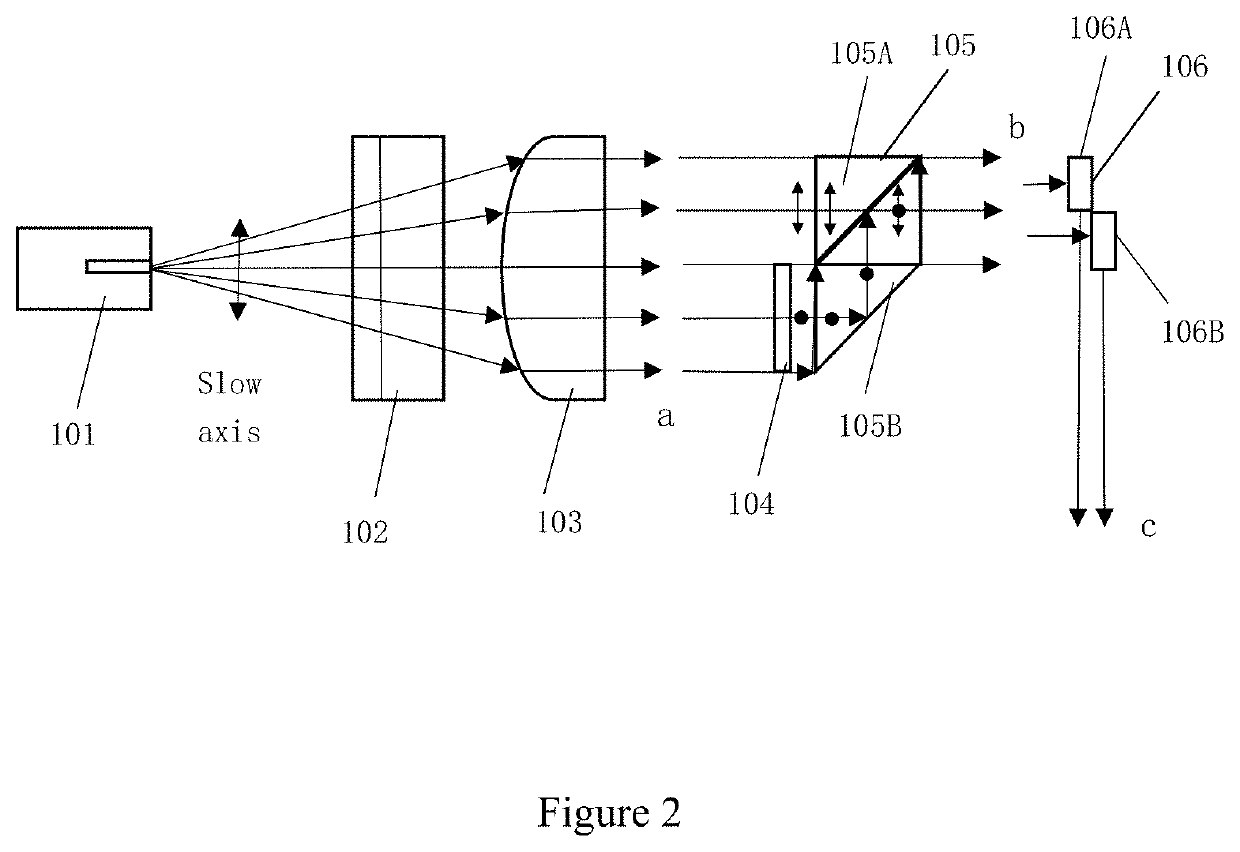
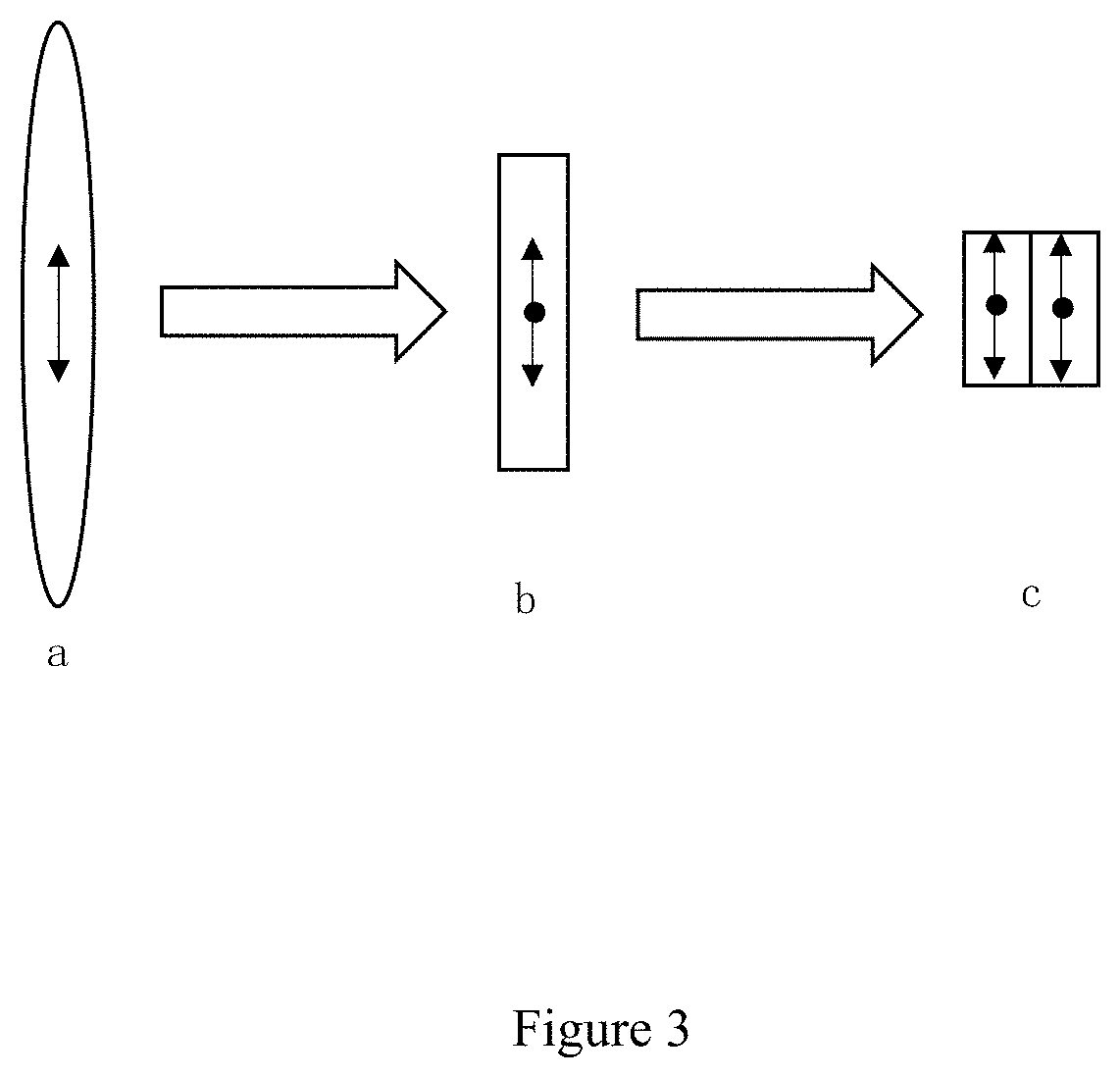
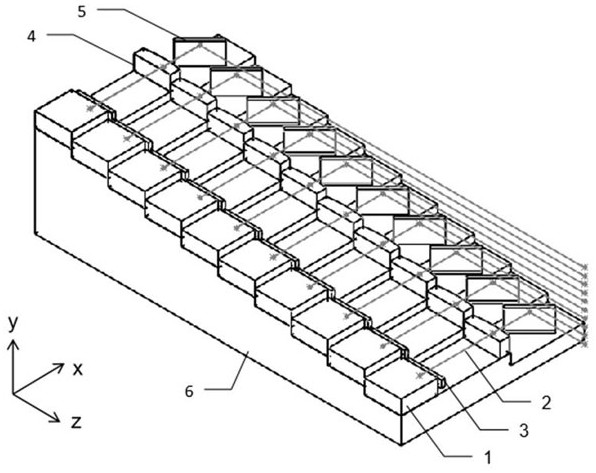
Optical beam parameter product symmetrization device of semiconductor laser array fast and slow axis
InactiveCN101221288BAchieve homogenizationEasy to installSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser arrangementsLaser technologyFlat glass
The invention relates to a homogenization device of a product of the beam parameters of a semiconductor laser array fast-slow shaft, belonging to the application field of laser technology and including a group of semiconductor laser array fast-slow shaft aligning micro-lens unit, a flat glass pile A, B and a focusing lens set. The light passing through the fast-slow shaft aligning micro-lens vertically injects on the flat glass pile A, a beam is divided into a plurality of portions and generates refraction excursion in the flat glass corresponding to each beam to obtain linear beams distributed in a ladder shape along the direction of the fast shaft of the laser array. The ladder shape linear beams pass through the flat glass pile B and the beams are led to generate reflection excursion along the direction of the slow shaft of the array and are further redistributed as linear beams according to a same beam recombining principle; therefore, the beams given out by the semiconductor laser array have a more approximate beam parameter product on the fast-slow shaft, namely, a balanced beam quality in the fast-slow shaft direction. Finally, a uniform focusing spot with high power density and brightness in the fast-slow shaft direction can be obtained by the focusing of the focusing lens set.
Owner:JIAXING DAHE LASER EQUIP
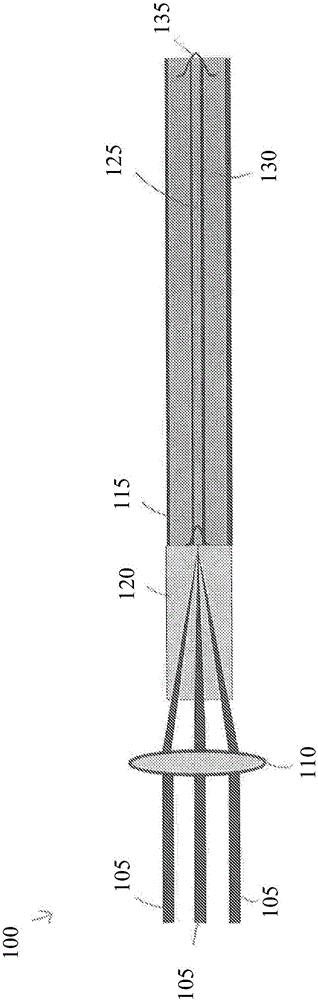
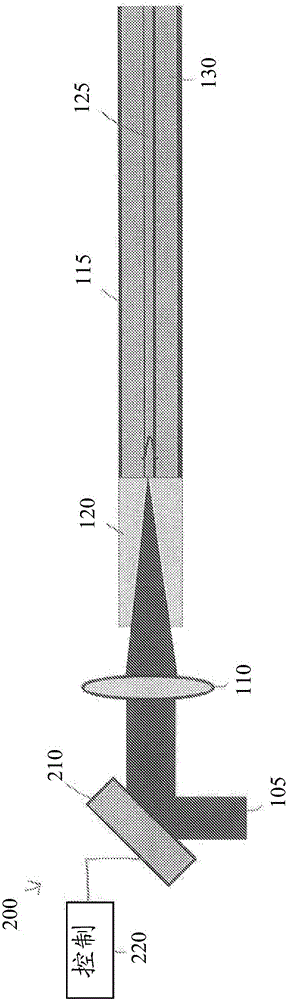
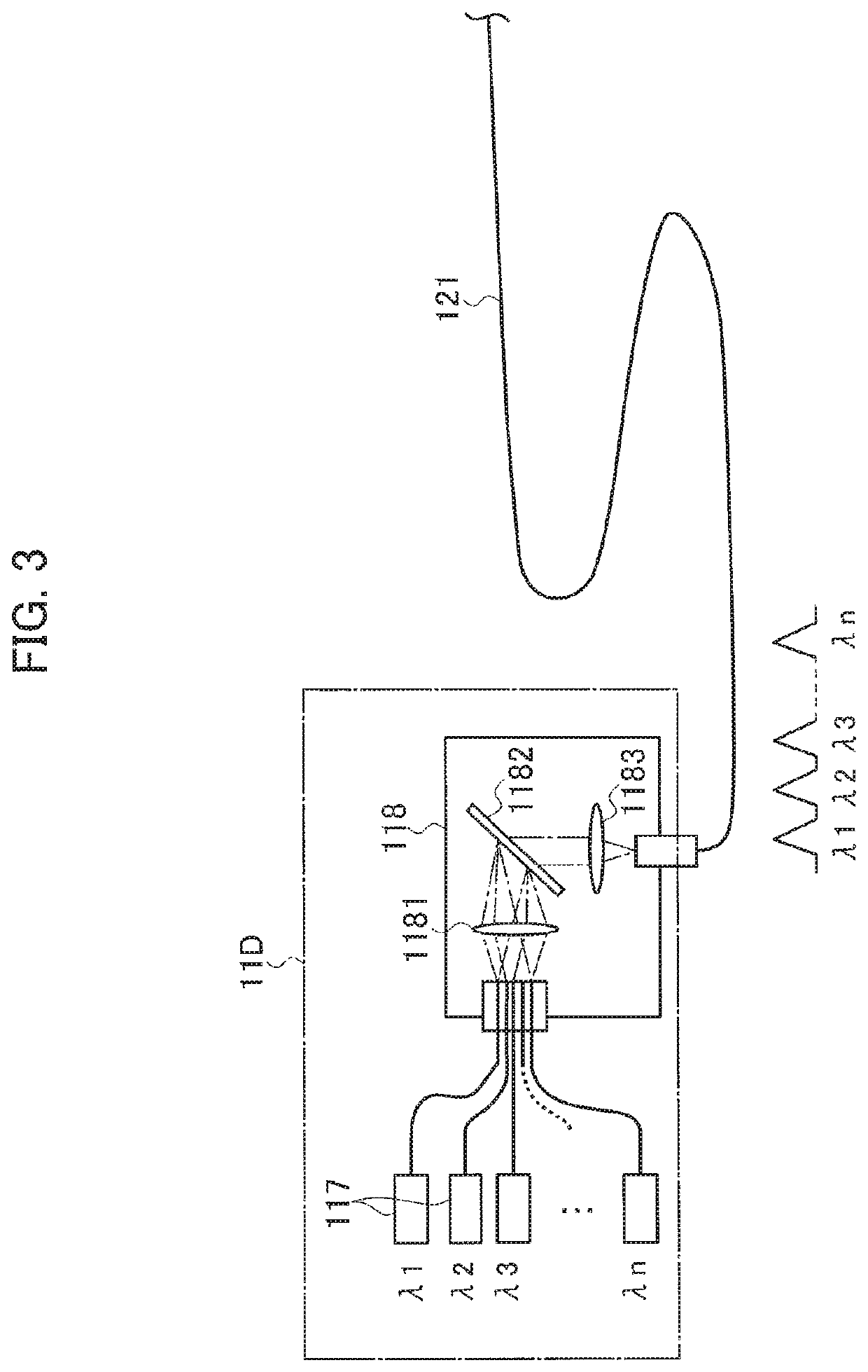
Optical element arrangements for varying beam parameter product in laser delivery systems
In various embodiments, laser delivery systems feature one or more optical elements for receiving a radiation beam and altering the spatial power distribution thereof, a lens manipulation system for changing a position of at least one optical element within the path of the radiation beam, and a controller for controlling the lens manipulation system to achieve a target altered spatial power distribution on a workpiece.
Owner:PANASONIC OF NORTH AMERICA +1
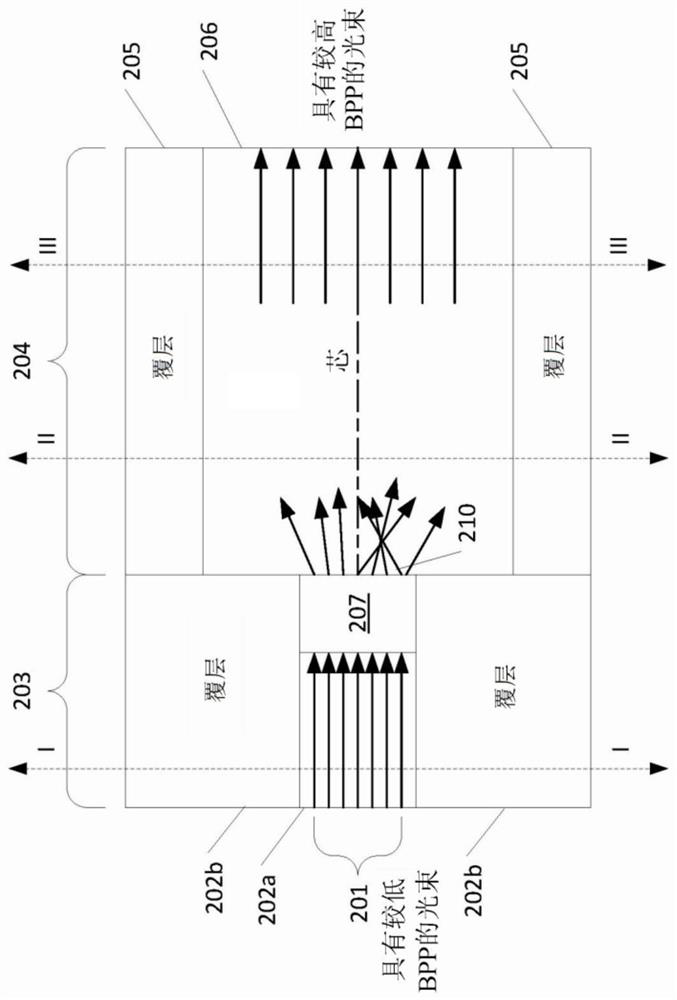
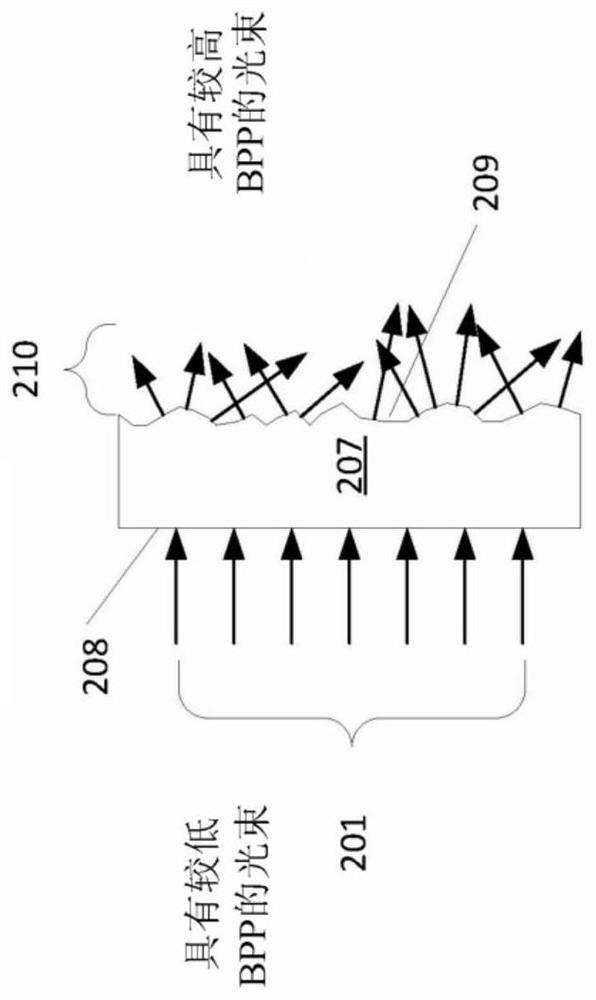
Optical fiber structures and methods for varying laser beam profile
ActiveCN108780189ALaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingLight beamComputational physics
In various embodiments, the beam parameter product and / or numerical aperture of a laser beam is adjusted utilizing a step-clad optical fiber having a central core, a first cladding, an annular core, and a second cladding.
Owner:TERADIODE
Laser systems utilizing cellular-core optical fibers for beam shaping
ActiveCN110226269ACoupling light guidesActive medium shape and constructionLight beamBeam parameter product
In various embodiments, the beam parameter product and / or beam shape of a laser beam is adjusted by directing the laser beam across a path along the input end of a cellular-core optical fiber. The beam emitted at the output end of the cellular-core optical fiber may be utilized to process a workpiece.
Owner:PANASONIC OF NORTH AMERICA
Semiconductor laser shaping device
A semiconductor laser shaping device includes, along the light path of a semiconductor laser, a fast axis collimating lens, slow axis collimating lens, the half wave plate, a polarization beam combining prism, and a crawling prism group. The laser emitted by the semiconductor laser is collimated by a fast-axis collimating lens and then by a slow-axis collimating lens, and subsequently injected into a half wave plate and polarization beam combining prism, which compresses its spot size along the slow axis while keeping the spot size unchanged along the fast axis. The laser beam then passes through the crawling prism group, which shifts a portion of the light in the slow-axis direction to the fast-axis direction, which again compresses the light beam in the slow-axis direction. The device can reduce the beam size of a semiconductor laser in the slow-axis direction, reducing its beam parameter product and improving beam quality.
Owner:FUJIAN HITRONICS PHOTOELECTRIC CO LTD
Laser processing machine
Owner:AMADA HLDG CO LTD
Laser brazing process
PendingUS20200353550A1High-quality joint qualityVehicle componentsWelding/cutting media/materialsWire rodLight beam
A process for joining first and second metal workpieces by laser brazing for forming a vehicle structure includes providing the workpieces in contacting relationship so as to form an elongated contact region, wherein at least one of the workpieces is made of hot-dip galvanized steel material, supplying a laser beam having a beam parameter product lower than 10 mm·mrad from a laser source, guiding the laser beam through a laser focus head having a total optical magnification in the range of 1:0.5-1:1.5, directing the laser beam along the elongated contact region, wherein a beam spot formed where the laser beam hits the contact region has a size in the range of 2-6 mm, and supplying a consumable wire of filler material to the beam spot to melt the consumable wire and braze the workpieces together, wherein the consumable wire comprises at least 95% copper.
Owner:NINGBO GEELY AUTOMOBILE RES & DEV CO LTD
Flared laser oscillator waveguide
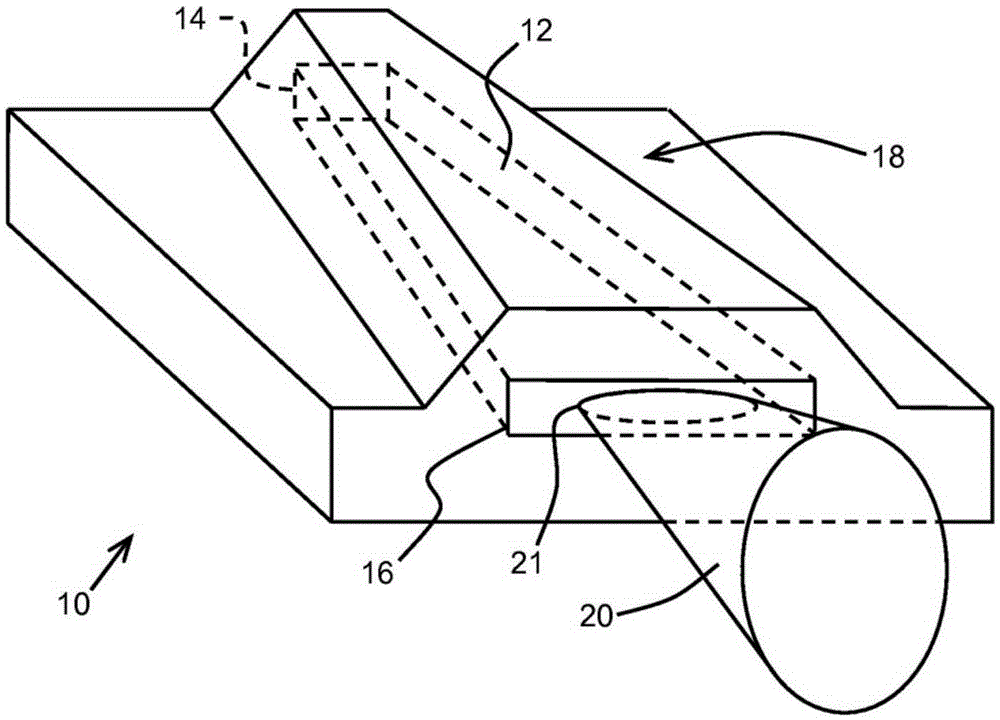
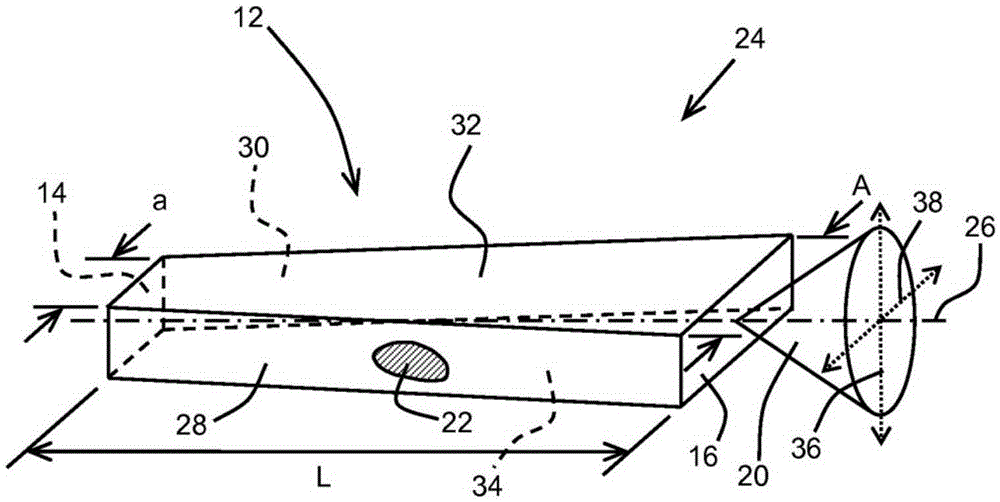
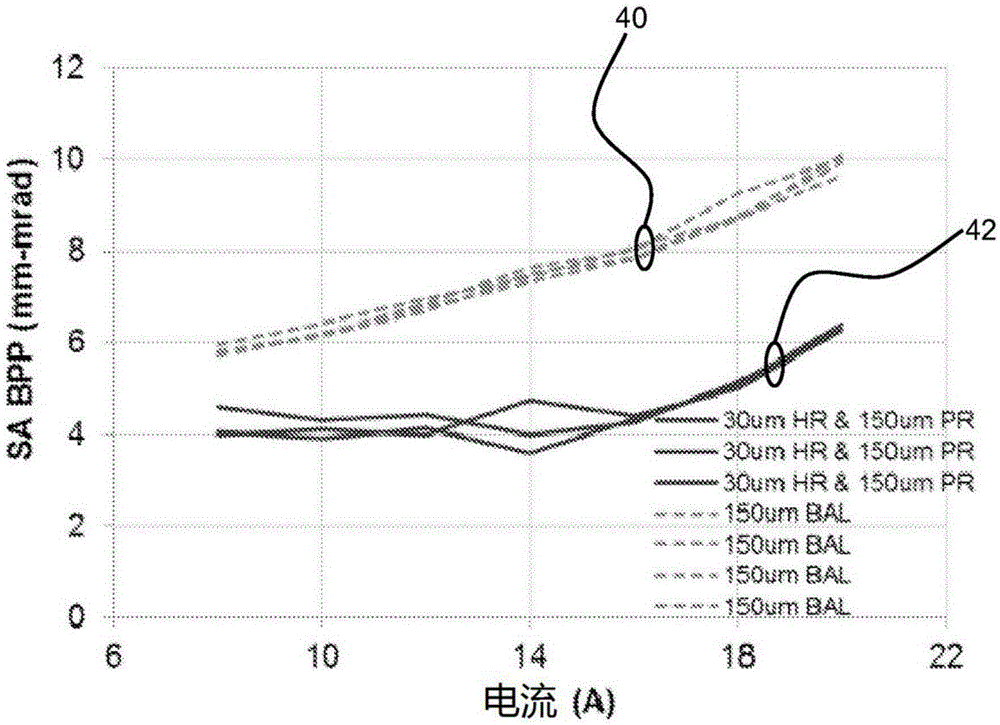
A broad area semiconductor diode laser device includes a multimode high reflector facet, a partial reflector facet spaced from said multimode high reflector facet, and a flared current injection region extending and widening between the multimode high reflector facet and the partial reflector facet, wherein the ratio of a partial reflector facet width to a high reflector facet width is n:l, where n>l. The broad area semiconductor laser device is a flared laser oscillator waveguide delivering improved beam brightness and beam parameter product over conventional straight waveguide configurations.
Owner:NLIGHT INC
Fiber with depressed central index for increased beam parameter product
ActiveCN107924023AOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingActive medium shape and constructionLight beamRefractive index
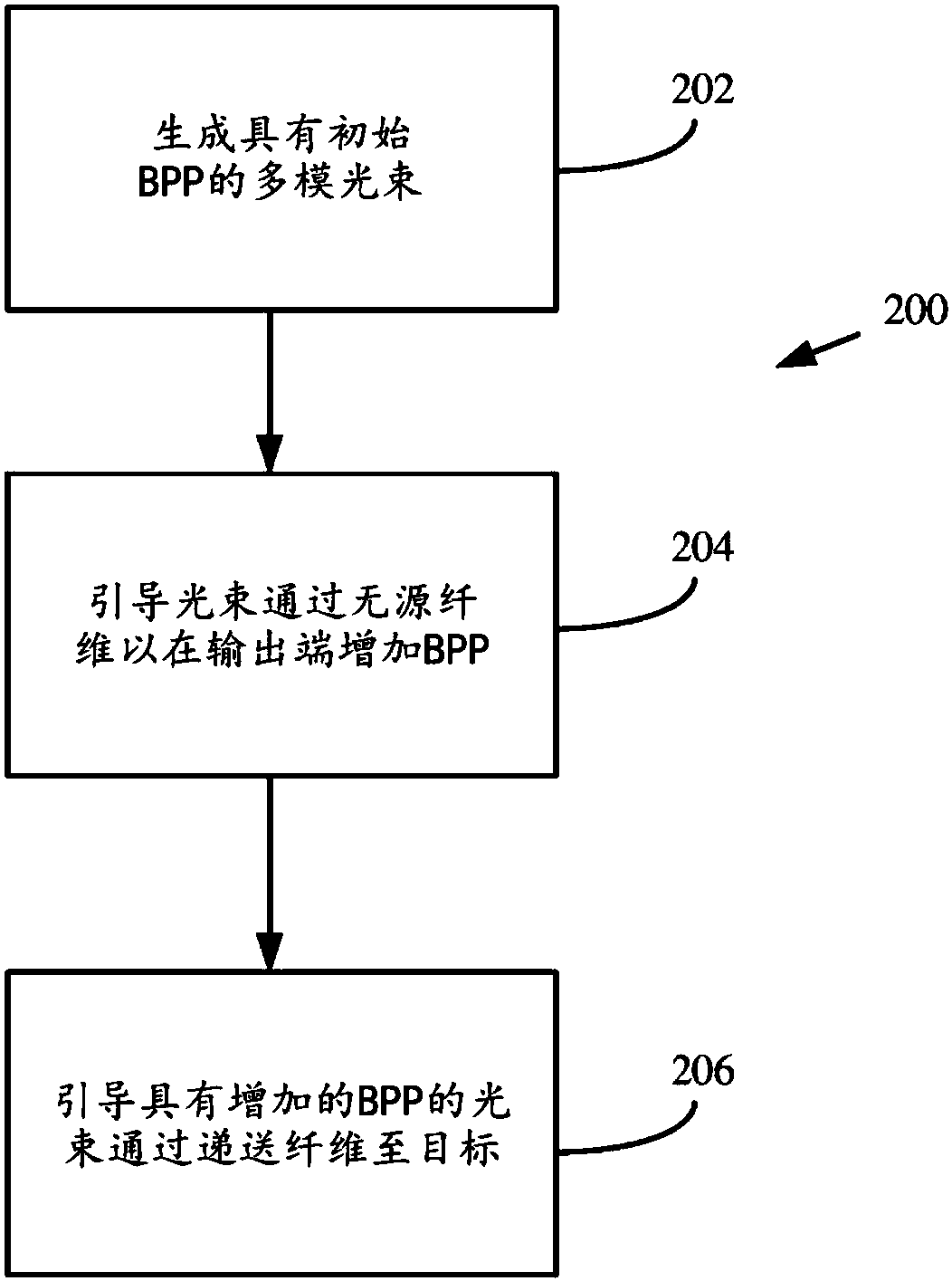
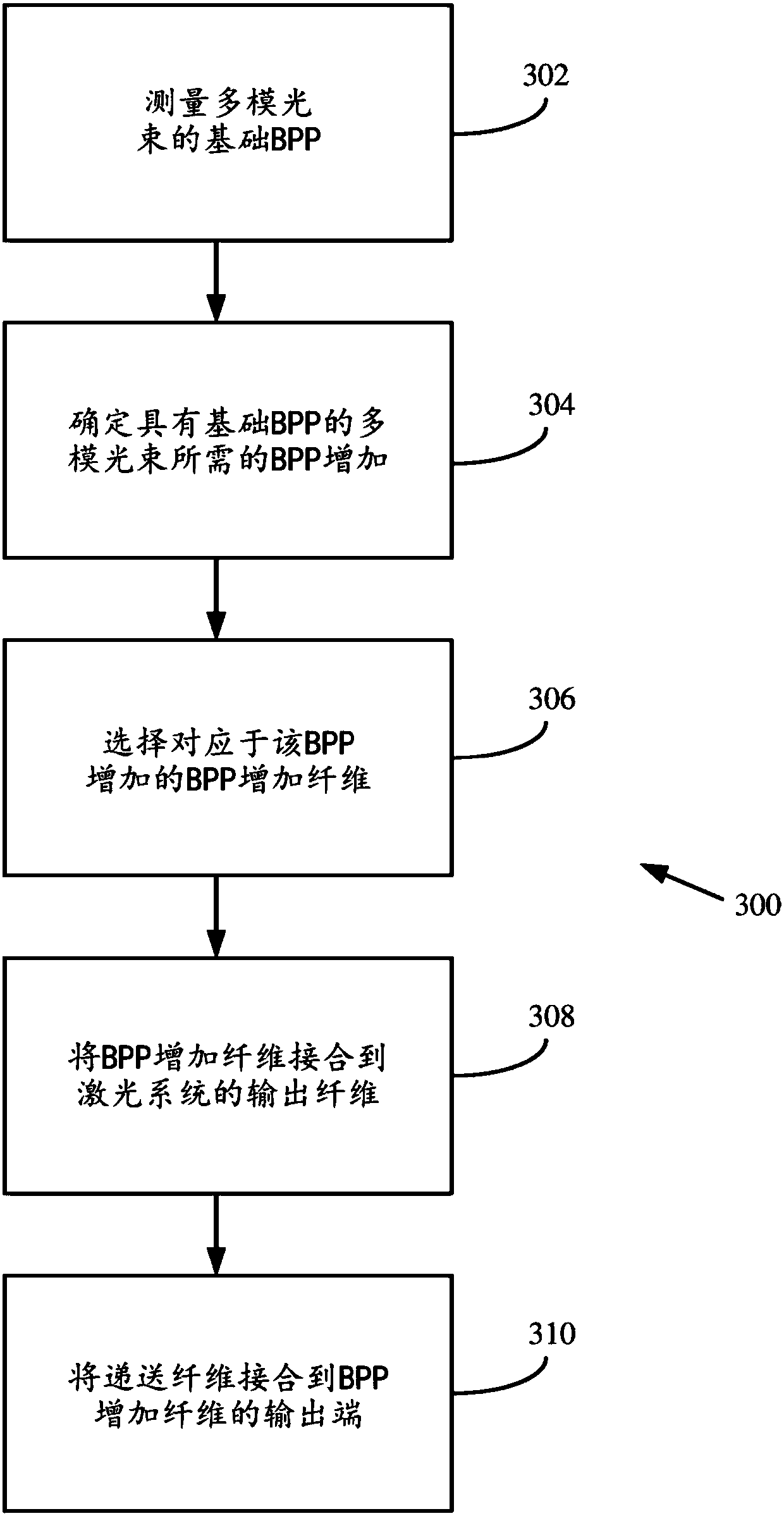
A method includes generating a multimode laser beam having an initial beam parameter product (bpp) and directing the multimode laser beam to an input end of a fiber so as to produce an output beam atan output of the fiber with a final bpp that is greater than the initial bpp. Another method includes measuring a base bpp associated with a multimode laser beam generated from a laser source and emitted from an output fiber output end, determining a bpp increase for the multimode laser beam, and selecting a bpp increasing optical fiber having an input end and an output end so that the multimode laser beam with the base bpp coupled to the input end has an output bpp at the output end of the bpp increasing optical fiber corresponding to the determined bpp increase.
Owner:NLIGHT INC
High-brightness external cavity semiconductor laser
PendingCN114784623AIncrease brightnessLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsLight beamErbium lasers
The invention provides a high-brightness external cavity semiconductor laser which comprises an external cavity, and the external cavity comprises a first laser single tube, a second laser single tube and an external cavity mirror. The first end of the first laser single tube and the first end of the second laser single tube are oppositely arranged, and the axis of the first laser single tube and the axis of the second laser single tube are not collinear; through adjustment of the outer cavity mirror, light beams emitted by the first laser single tube and the second laser single tube are subjected to turn-back oscillation in the outer cavity, coherent beam combination is carried out, and laser is output through the outer cavity mirror. The cost is low, the high-power laser beam can be obtained, the overall beam is kept close to the beam parameter product of one laser single tube, the laser beam quality is kept, and the brightness of the laser beam can be improved.
Owner:BWT BEIJING
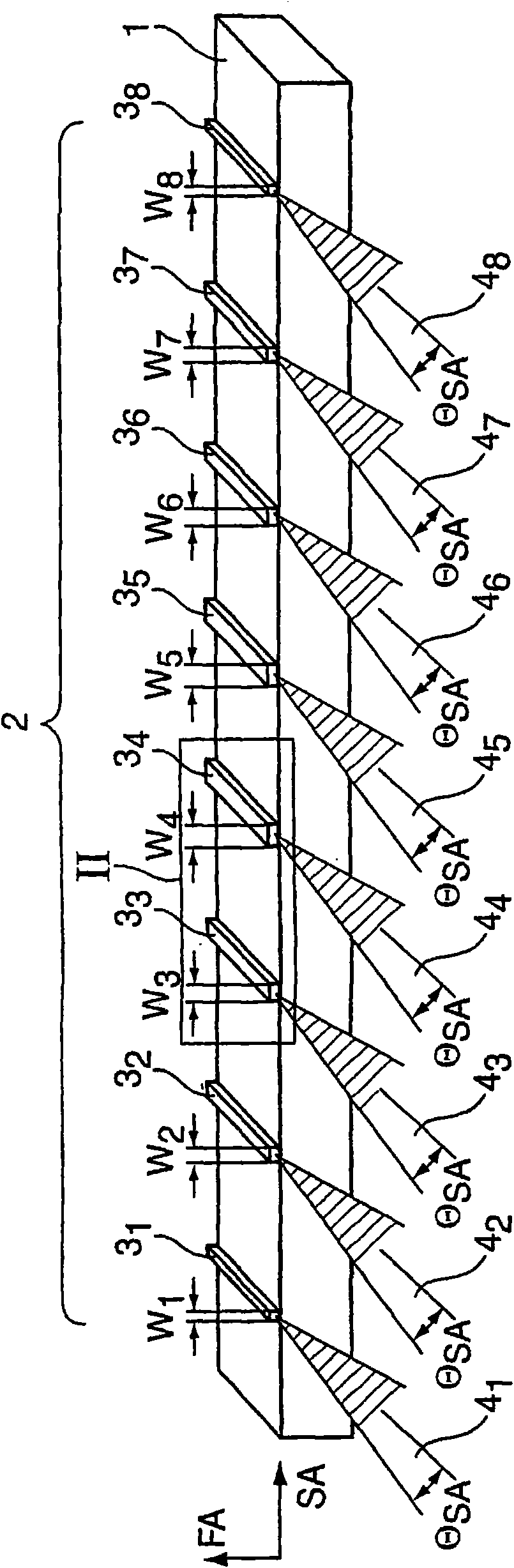
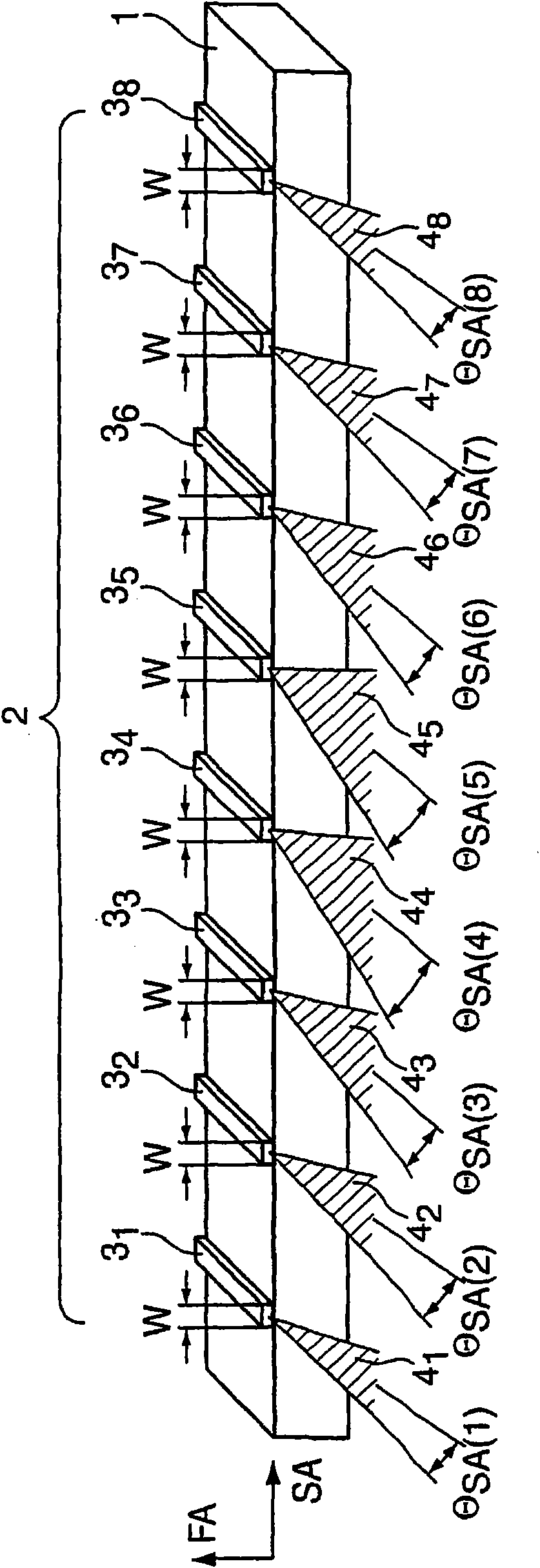
Diode laser structure to generate diode laser radiation with optimized fiber coupling radiation parameter product
ActiveCN101953039AEfficient inputIncrease input powerSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser arrangementsBeam parameter productDiode
In a diode laser structure (2) with a plurality of strip emitters (31 to 38) arranged side by side whose SA-axes are arranged in the same direction and at an offset to each other in this direction, wherein the beam parameter products (BPPSA) of at least a few of the strip emitters (31 to 38) are each shifted relative to the SA-axis, according to the invention the beam parameter product (BPPSA) of the strip emitters (31 to 38) decreases, starting from the middle of the diode laser structure (2), to the two edges of the diode laser structure (2), in particular in a mirror-symmetrical manner and / or from the middle of the diode laser structure (2).
Owner:TRUMPF LASER GMBH CO KG
Apparatus and method for material processing
InactiveUS20200331097A1Increase variabilityCost-effectiveCondensersLaser beam welding apparatusOptical propertyBeam source
Apparatuses and methods for material processing are disclosed. In an embodiment, an apparatus may include a source of electromagnetic radiation that emits the radiation in a beam with a defined power density distribution and beam-shaping optics variably shaping and focusing the radiation of the beam source. An optical axis of the radiation may be directed onto a processing zone. The apparatus may also include means for holding the radiation in a region wherein the radiation interacts with a material forming and moving in the processing zone; as well as an adjusting device that varies the second beam parameter product by changing at least one of a position and an optical property of at least one optical element. In an embodiment, a first optical element of the beam-shaping optics generates or increases the amount of an aberration; and a second optical element of the beam-shaping optics changes an amount of an aberration generated or increased by changing, using the adjusting device, a position or optical properties the first and / or the second optical element, such that the second beam parameter product is adjusted.
Owner:PETRING DIRK +3
Dual-wavelength high-power surgical instrument for prostate laser resection
PendingCN109602491AReduce Leakage PowerReduce widthSurgical instrument detailsFiberHigh power lasers
The present invention relates to the field of human body soft tissue combined treatment of continuous pumping of acousto-optic Q-switched solid visible laser and semiconductor near-infrared laser, andparticularly discloses a dual-wavelength high-power surgical instrument for prostate laser resection in the field of high-power laser prostatectomy. The dual-wavelength high-power surgical instrumentis characterized in that a laser head comprises a solid-state laser capable of outputting a green visible beam and a semiconductor laser capable of outputting a near-infrared laser beam, the green visible laser beam and near-infrared beam are coupled via an aspheric lens to surgical fibers having a core diameter of 400-800 [mu]m, the solid-state laser includes at least 2 sound field direction vertical cross-acousto-optic Q-switches and at least one laser nonlinear double-frequency crystal, and an output fiber of the semiconductor laser has a beam parameter product that is smaller than a beamparameter product of a surgical fiber. The dual-wavelength high-power surgical instrument has advantages of good safety, easy operation, low technical skill requirements for physicians, etc.
Owner:WEIHAI WEIGAO LASER MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Laser Beam Product Parameter Adjustments
PendingCN111864526AActive medium shape and constructionFibre with gratingsGratingFiber Bragg grating
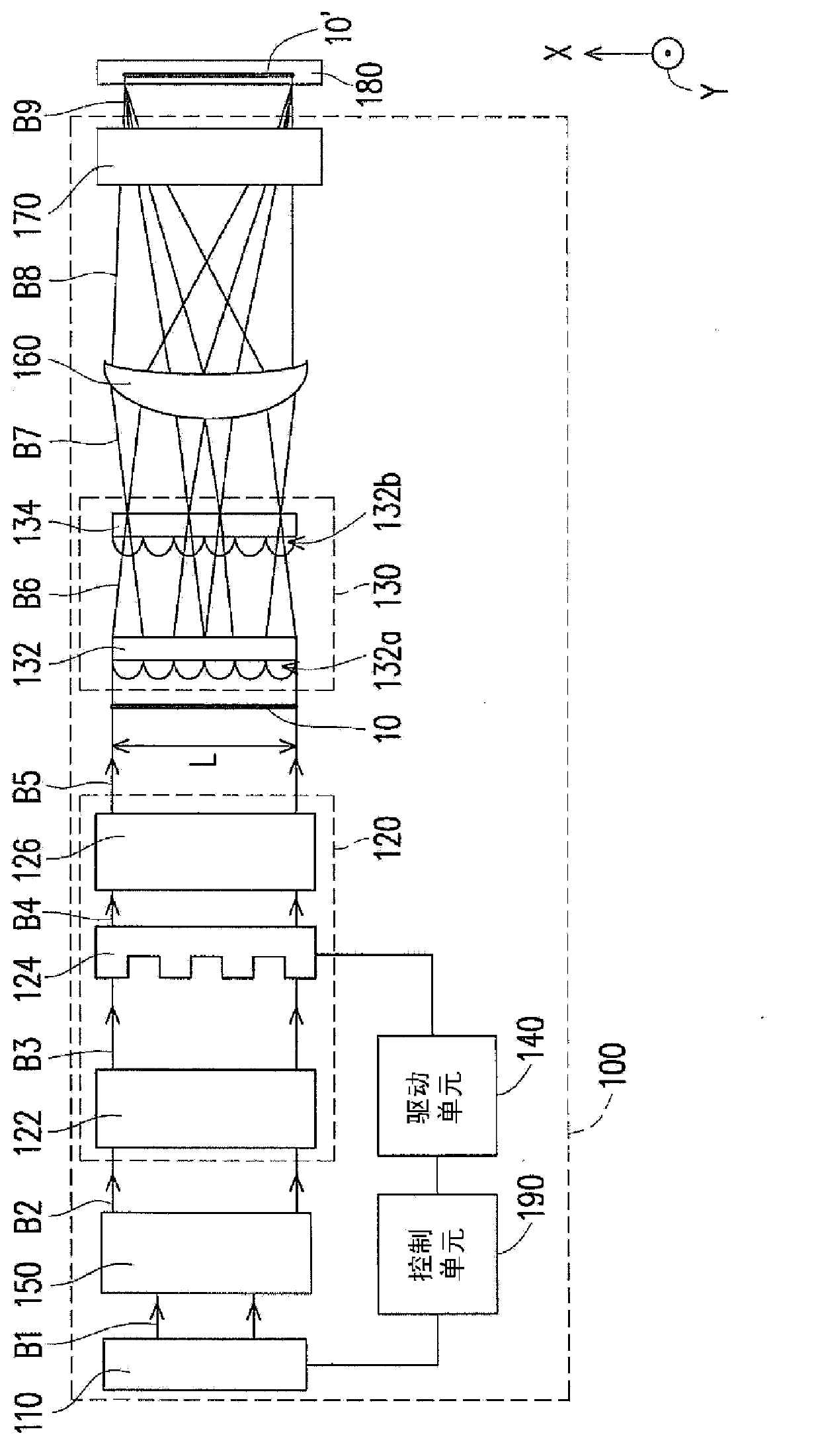
Systems, apparatuses, and methods are described for modifying a beam parameter product of a laser beam. The modified beam parameter product may increase the number of tasks that may be performed usinga given laser with its original beam parameter product. By increasing the beam parameter product of a laser, an initial low beam parameter product beam may be used to perform tasks requiring a higherbeam parameter product. The beam may be modified to redirect portions of the beam at different angles via one or more non-imaging refracting optical components or by one or more Fiber Bragg gratings.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Fiber structure and method for changing laser beam profile
In various embodiments, a stepped-cladding fiber having a central core, a first cladding, a ring core, and a second cladding is utilized to tune the beam parameter product and / or numerical aperture of the laser beam.
Owner:PANASONIC OF NORTH AMERICA
Lighting device and lighting device
Equipped with: a light source unit (3), which emits excitation light (101); a light deflection unit (140), which deflects the excitation light (101); a wavelength conversion unit (160), which is irradiated with the excitation light deflected by the light deflection unit (140) (101), convert the excitation light (101) into wavelength converted light with different wavelengths to emit; ), the first optical system (11) arranged between the light source part (3) and the light deflection part (140), and the first optical system (11) arranged between the light deflection part (140) and the wavelength conversion part (160) Two optical systems (12) constitute, in the section perpendicular to the direction of travel of the excitation light (101), the axis of the direction in which the beam parameter product of the excitation light (101) becomes the minimum is set as the Ax axis, and the axis perpendicular to the Ax axis is When the axis of the direction is the Ay axis, in the second optical system (12), the focus distance in the Ay axis direction is smaller than the focus distance in the Ax axis direction.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com