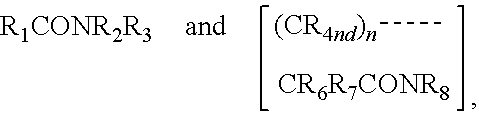Patents
Literature
269results about "Cleaning and washing methods" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of hydrophilizing materials
InactiveUS6863933B2Easy to controlGood removal effectInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsRadiation applicationsPolymer scienceNanoparticle
Coating compositions, methods and articles of manufacture comprising a nanoparticle system employing same to impart surface modifying benefits for all types of soft surfaces, and in some cases, hard surfaces, are disclosed. In some embodiments, dispersement of nanoparticles in a suitable carrier medium allows for the creation of coating compositions, methods and articles of manufacture that create multi-use benefits to the modified surfaces. These surface modifications can produce long lasting or semi-permanent multi-use benefits that, in some embodiments, may include at least one of the following improved surface properties: cleaning, wettability, liquid strike-through, comfort, stain resistance, soil removal, malodor control, modification of surface friction, reduced damage to abrasion and color enhancement, relative to the surfaces unmodified with such nanoparticle systems.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Process and composition for cleaning soft tissue grafts optionally attached to bone and soft tissue and bone grafts produced thereby
InactiveUS6024735AEfficient removalEfficient formationSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsPresent methodAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to compositions effective for the cleansing of mammalian soft tissue optionally attached to bones, and particularly the removal of blood deposits and bone marrow therefrom. The compsotions are composed of an aqueous solution containing as its essential ingredients a detergent having a functionality of the nature of a polyoxyethylene-23-lauryl either, a detergent having a functionality of the nature of exyethylated alkylphenol, and water, where the compositions are free from any membrane stabilizers. The present invention is also directed to a method and composition for cleaning cadaveric soft tissue optionally attached to bone to produce soft tissue grafts optionally attached to bone suitable for transplantation into a human. The present method involves removing bone marrow elements, blood deposits and any bacteria, virus or fungi contamination, from the donor bone and / or associated soft tissues.
Owner:LIFENET HEALTH
Automatic dishwashing compositions containing a halogen dioxide salt and methods for use with electrochemical cells and/or electrolytic devices
InactiveUS6921743B2Inorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsElectrolysed waterPhosphate
The present invention relates to automatic dishwashing detergent compositions and methods of using compositions comprising halogenated salts, phosphate and / or silicate in conjunction with electrolyzed water in automatic dishwashing appliances comprising an electrochemical cell and / or electrolytic device for treating tableware to improve cleaning, sanitizing and stain removal by controlling hardness, corrosion and dispersancy.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Cleaning submicron structures on a semiconductor wafer surface
InactiveUS20060042651A1Electrostatic cleaningSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAcoustic energyPhysical chemistry
Cleaning solutions and cleaning methods targeted to particular substrates and structures in semiconductor fabrication are described. A method of cleaning fragile structures having a dimension less than 0.15 um with a cleaning solution formed of a solvent having a surface tension less than water while applying acoustic energy to the substrate on which the structures are formed is described. Also, a method of cleaning copper with several different cleaning solutions, and in particular an aqueous sulfuric acid and HF cleaning solution, is described. Also, methods of cleaning both sides of a substrate at the same time with different cleaning solutions applied to the top and the bottom are described.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Enhancement of color on surfaces
InactiveUS6872444B2Easy to controlGood removal effectInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsPigmenting treatmentNanoparticleMaterials science
Coating compositions, methods and articles of manufacture comprising a nanoparticle system employing same to impart surface modifying benefits for all types of soft surfaces, and in some cases, hard surfaces, are disclosed. In some embodiments, dispersement of nanoparticles in a suitable carrier medium allows for the creation of coating compositions, methods and articles of manufacture that create multi-use benefits to the modified surfaces. These surface modifications can produce long lasting or semi-permanent multi-use benefits that, in some embodiments, may include at least one of the following improved surface properties: cleaning, wettability, liquid strike-through, comfort, stain resistance, soil removal, malodor control, modification of surface friction, reduced damage to abrasion and color enhancement, relative to the surfaces unmodified with such nanoparticle systems.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Extraction cleaning with heating
A portable surface cleaning apparatus comprises a fluid dispensing system including at least one fluid supply tank, a dispensing nozzle for applying a cleaning fluid to a surface to be cleaned, and a block heater for heating the fluid to be applied to the surface to be cleaned to a temperature less than boiling; a fluid recovery tank for holding recovered fluid; a suction nozzle; a working air conduit extending between the recovery tank and the suction nozzle; and a vacuum source in fluid communication with the recovery tank for generating a flow of working air from the suction nozzle through the working air conduit and into the recovery tank to thereby recover fluid from the surface to be cleaned.
Owner:BISSELL INC
Monitoring cleaning of surfaces
ActiveUS20060223731A1Enhancing cleaning programEasy to cleanBacteriaDiagnosticsSurface cleaningEngineering
A method for monitoring cleaning of a surface includes applying an amount of transparent indicator material to an area of a surface and measuring the amount of transparent indicator material remaining on the surface. The transparent indicator material may be fixed on the surface by drying and, when a fluorescent material, may be measured through exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Owner:KLEANCHECK SYST
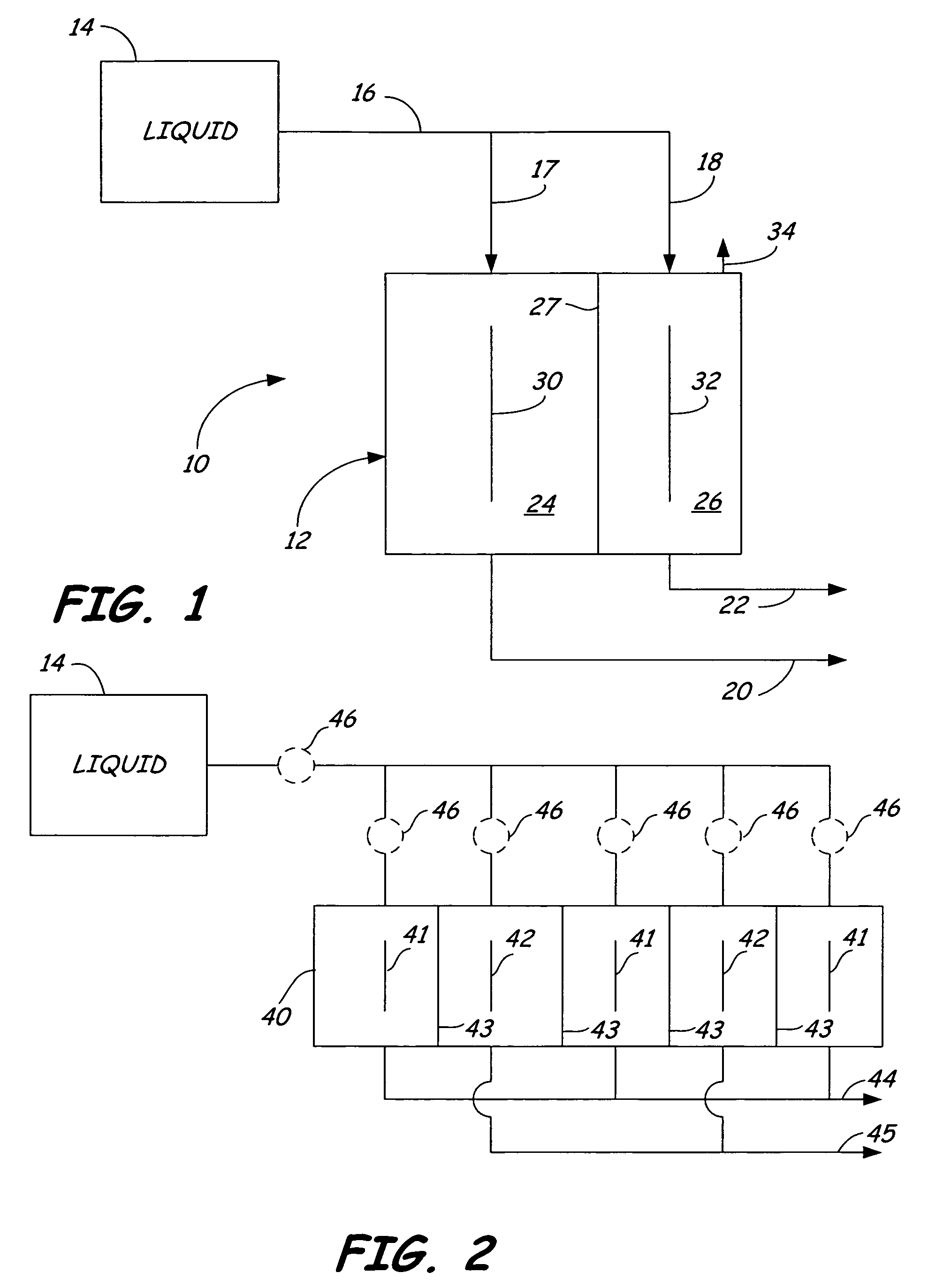
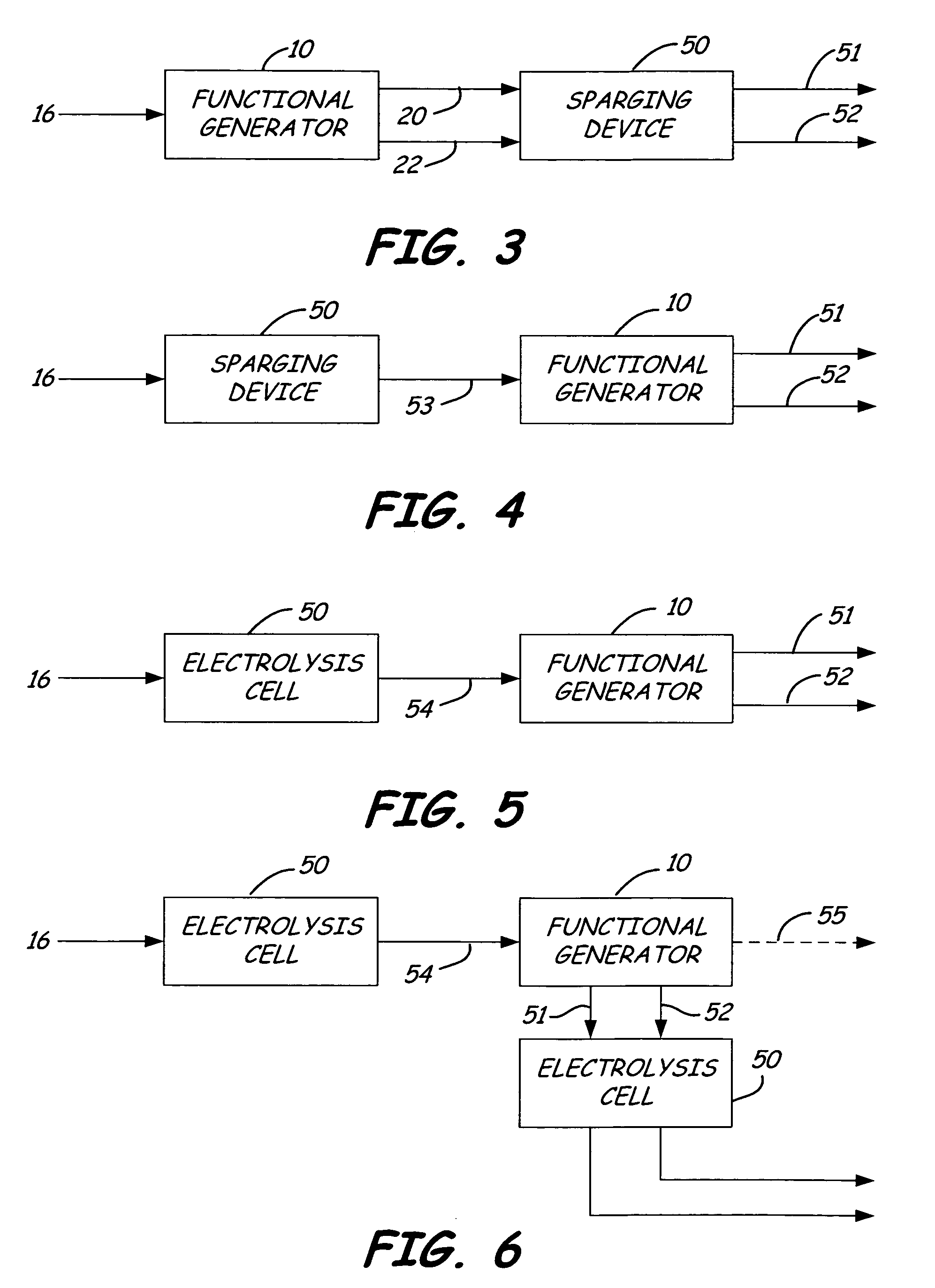
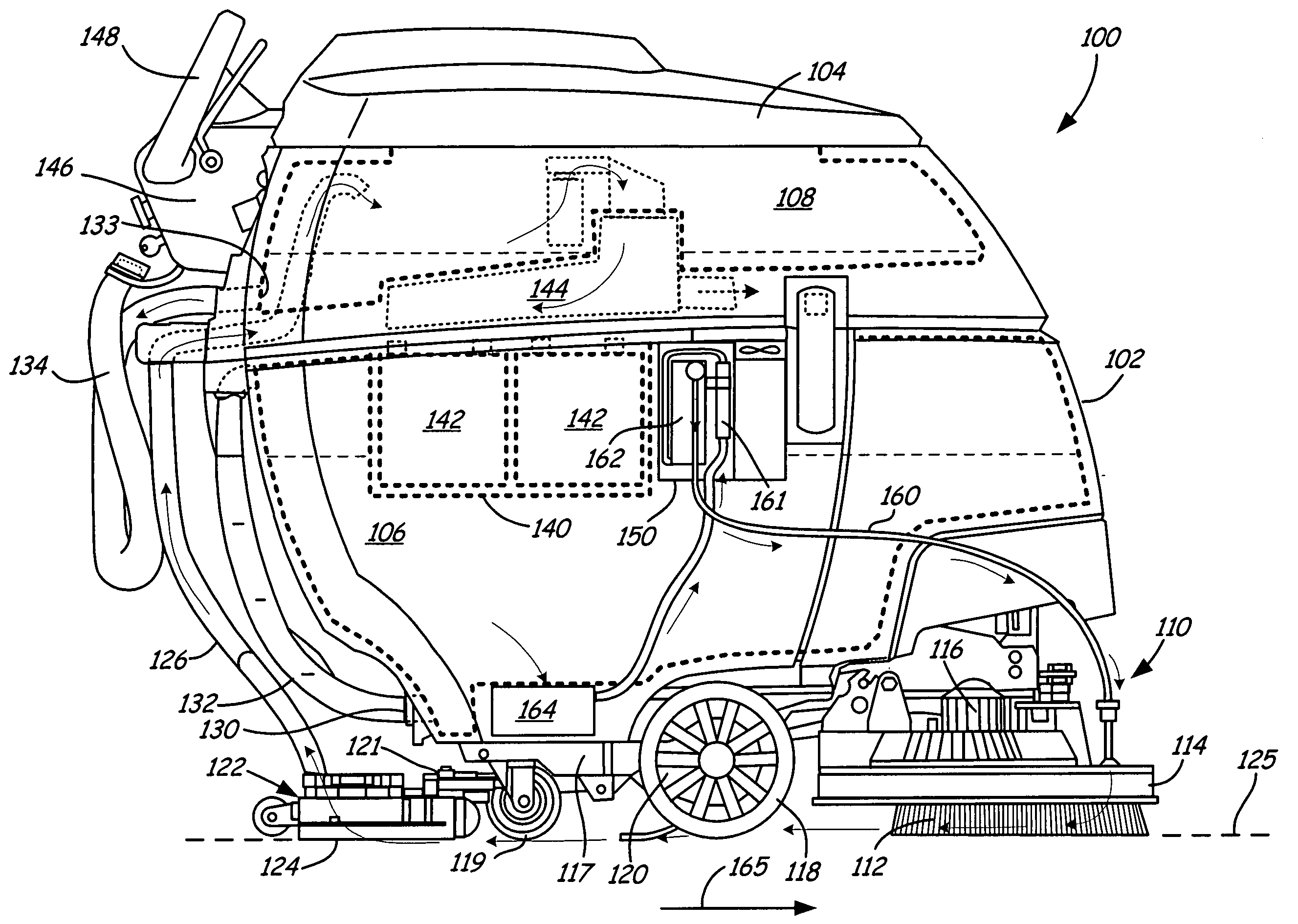
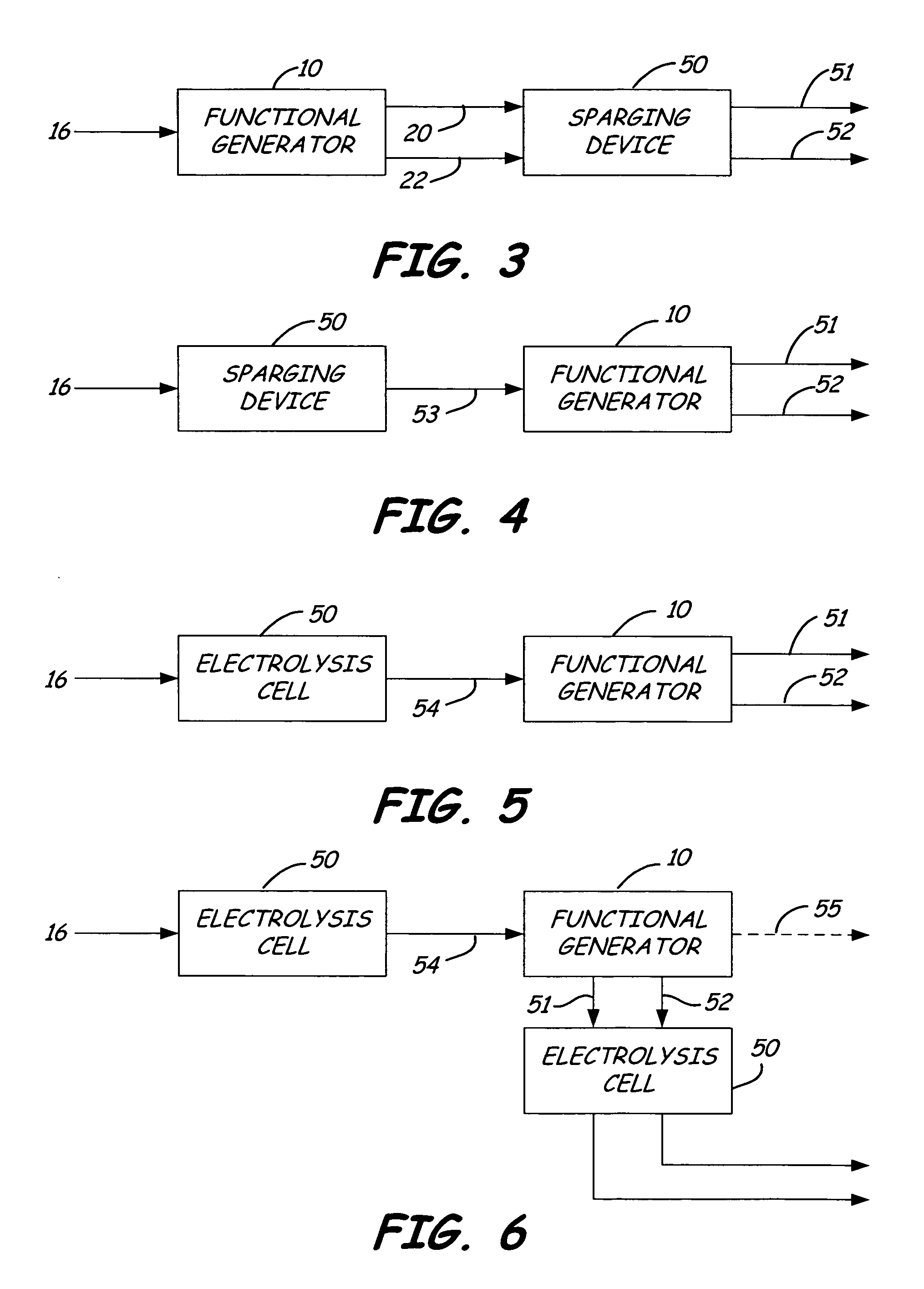
Method of producing a sparged cleaning liquid onboard a mobile surface cleaner
A method is provided, which includes moving a mobile floor cleaning machine along a floor. Onboard the mobile floor cleaning machine, a liquid is sparged by electrolysis. The sparged liquid is dispensed from the mobile floor cleaning machine.
Owner:TENNANT COMPANY
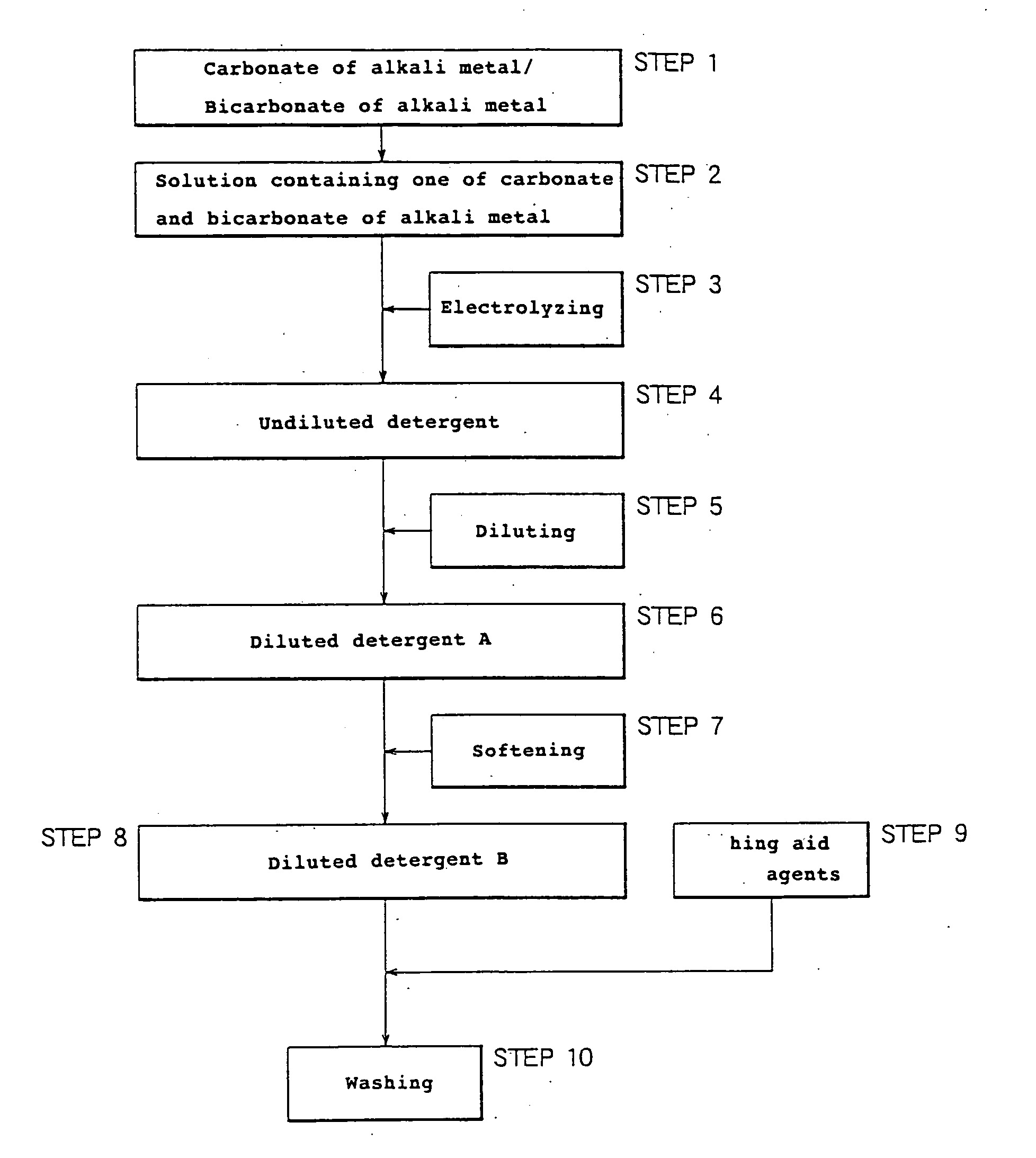
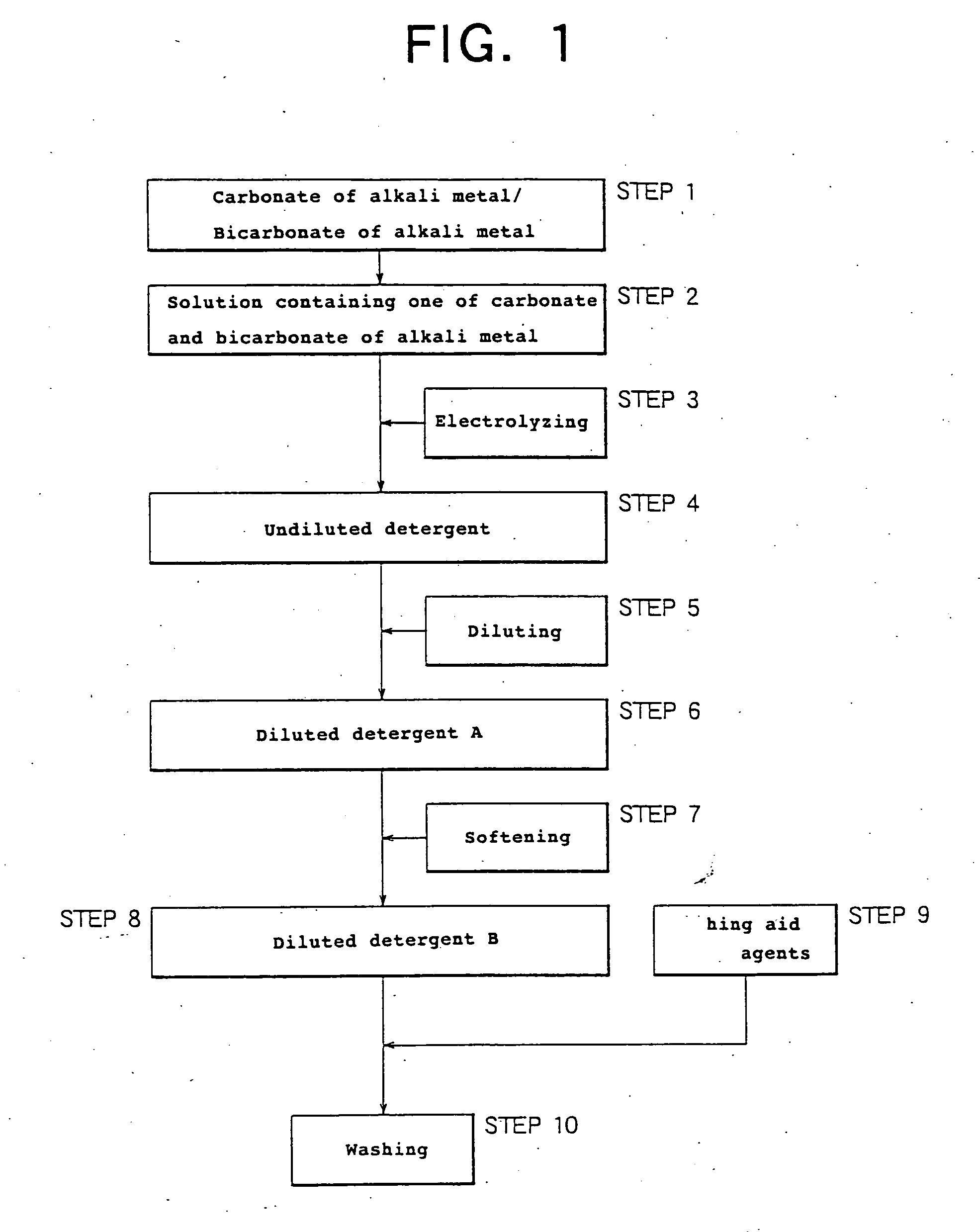
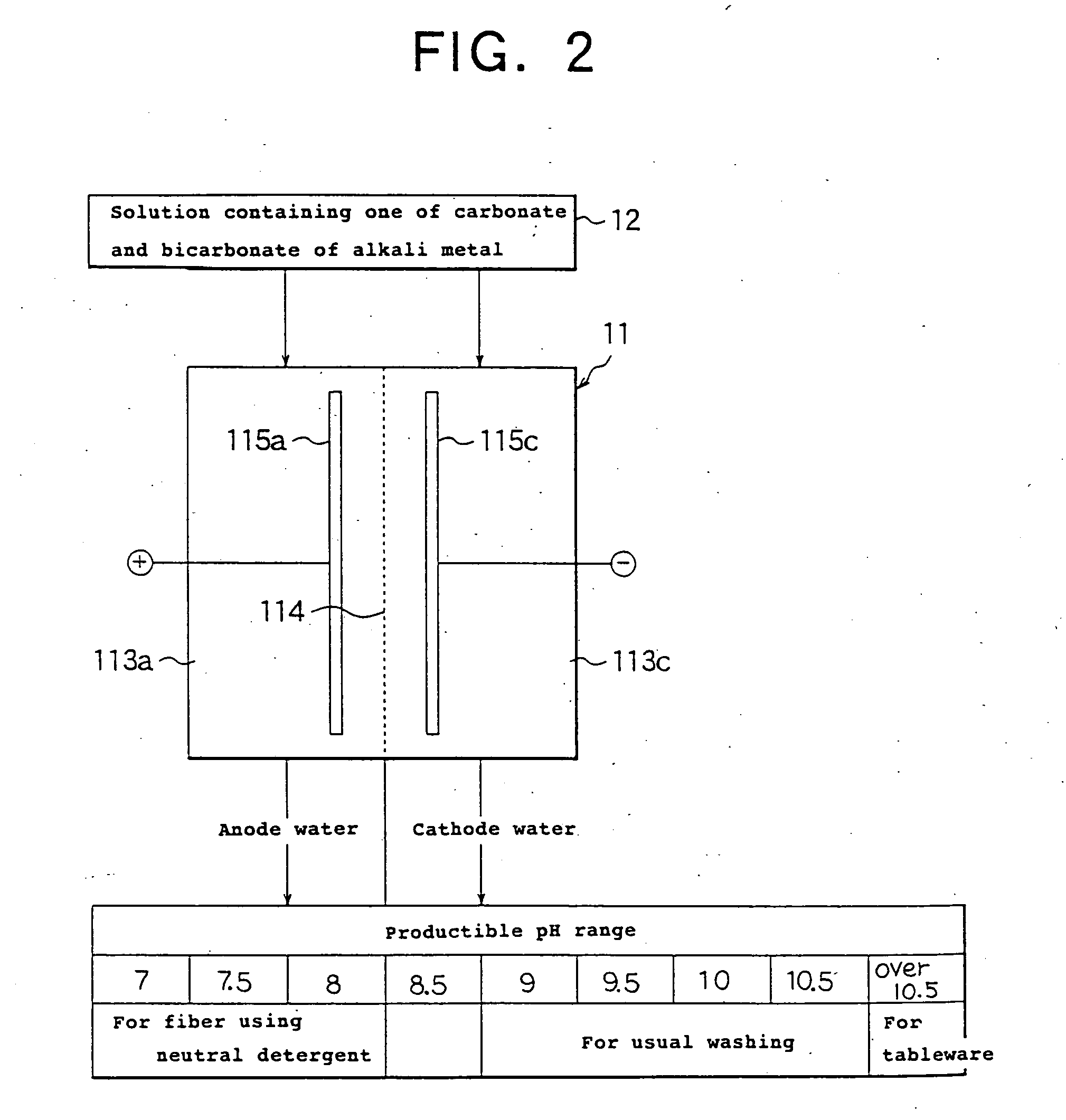
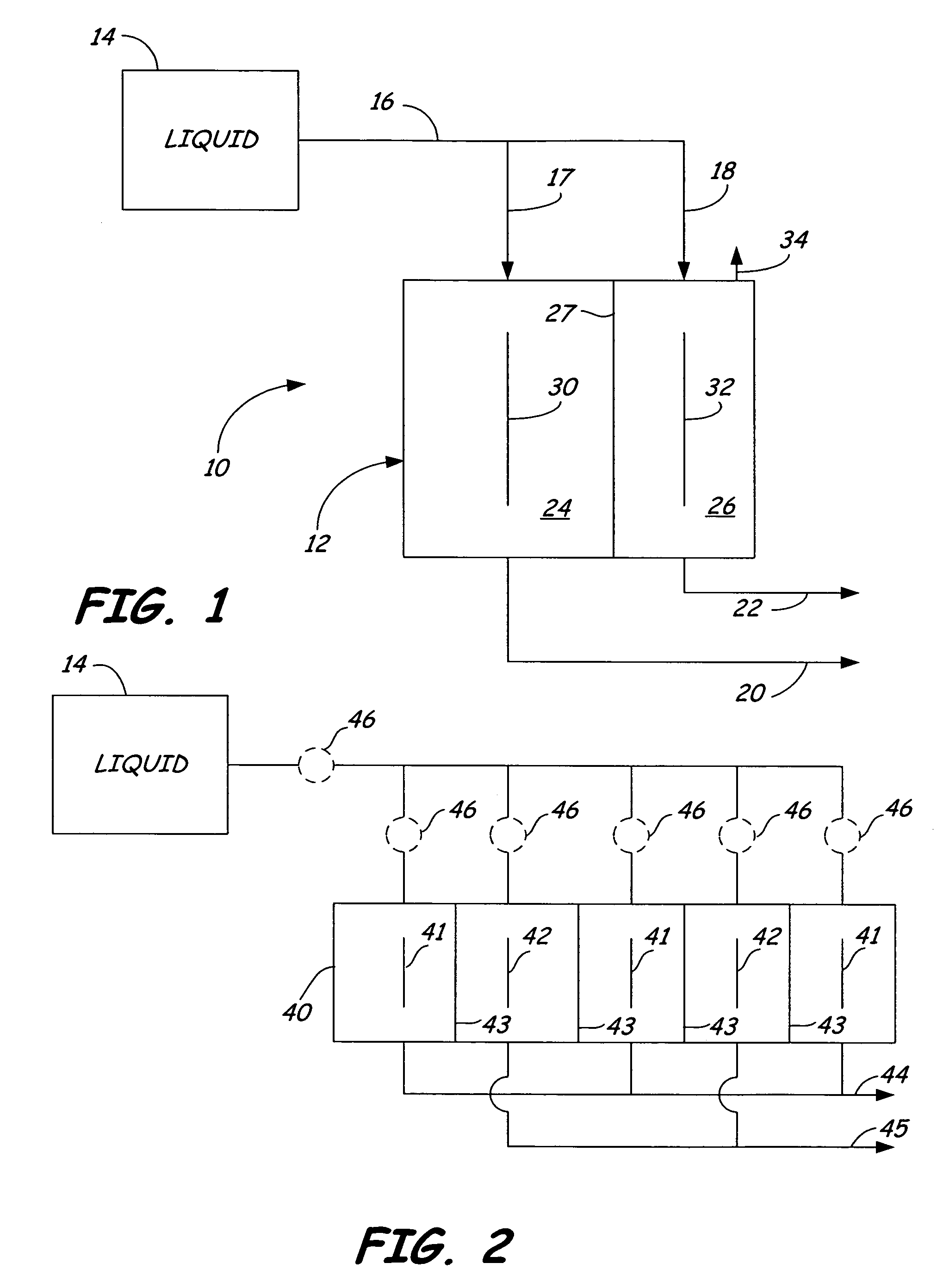
Production method of detergent and producing apparatus
InactiveUS20040250323A1Easy to handleEasy to adjustInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsCellsElectrolysisCarbonate
Owner:MIZ CO LTD
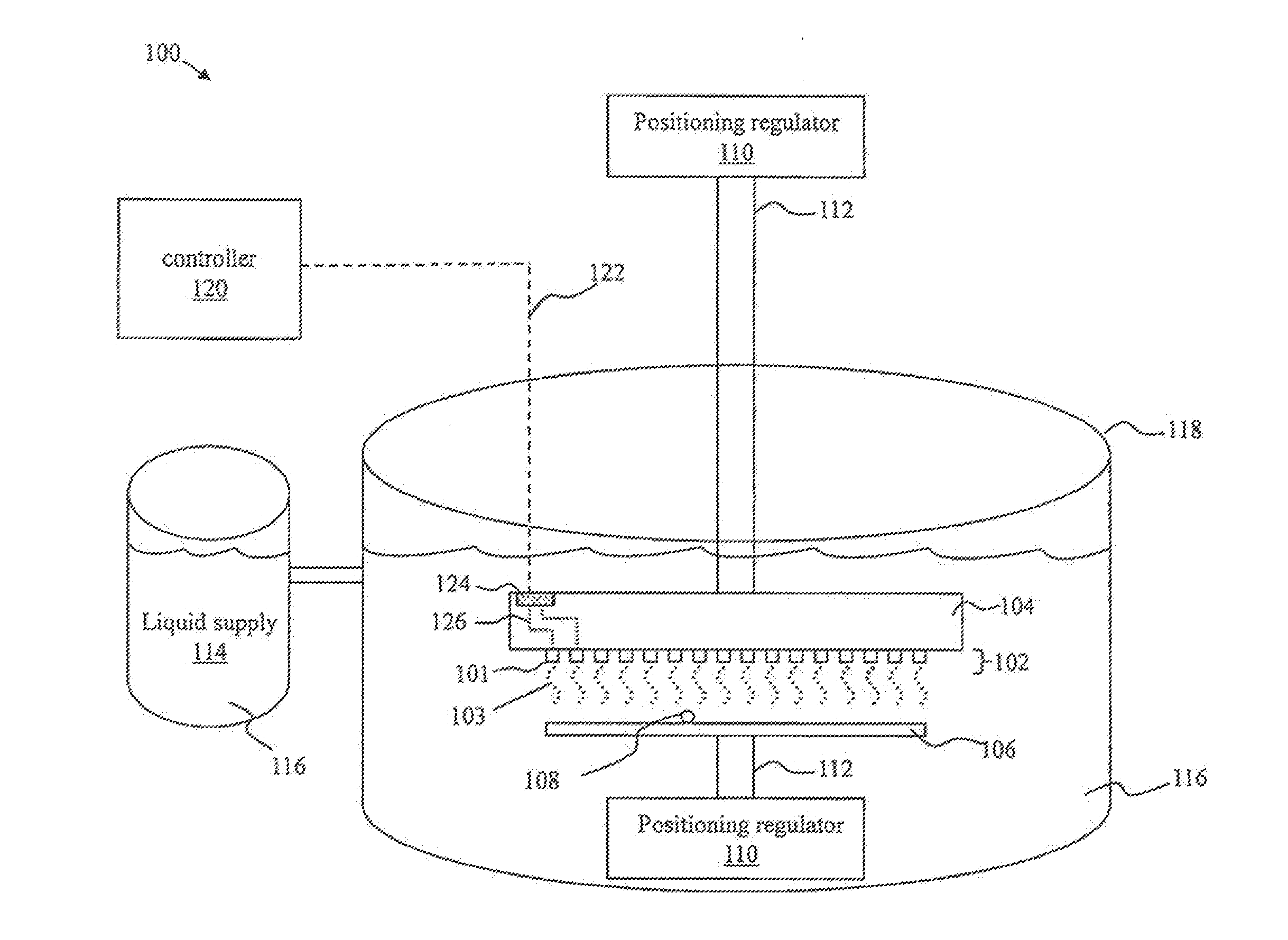
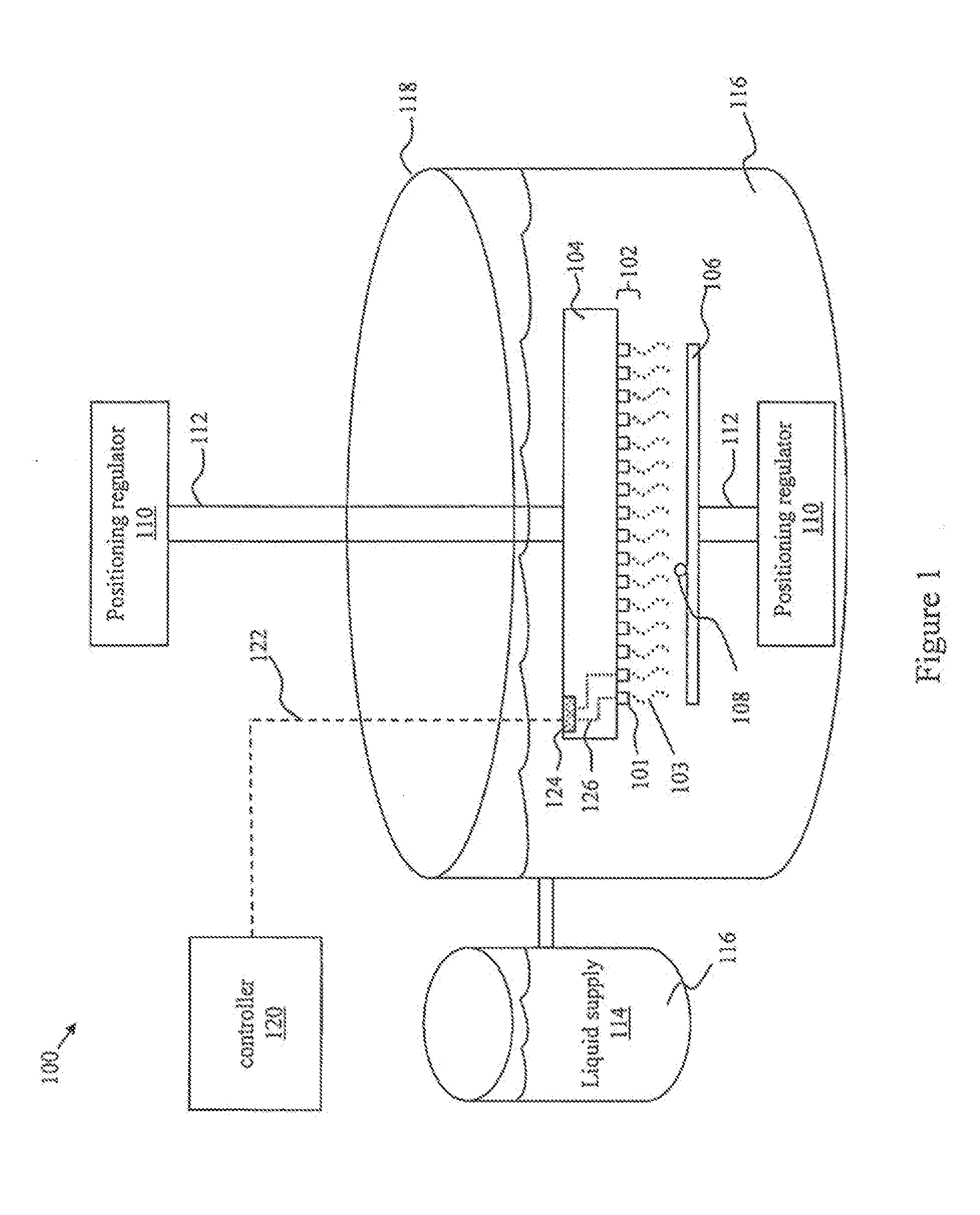
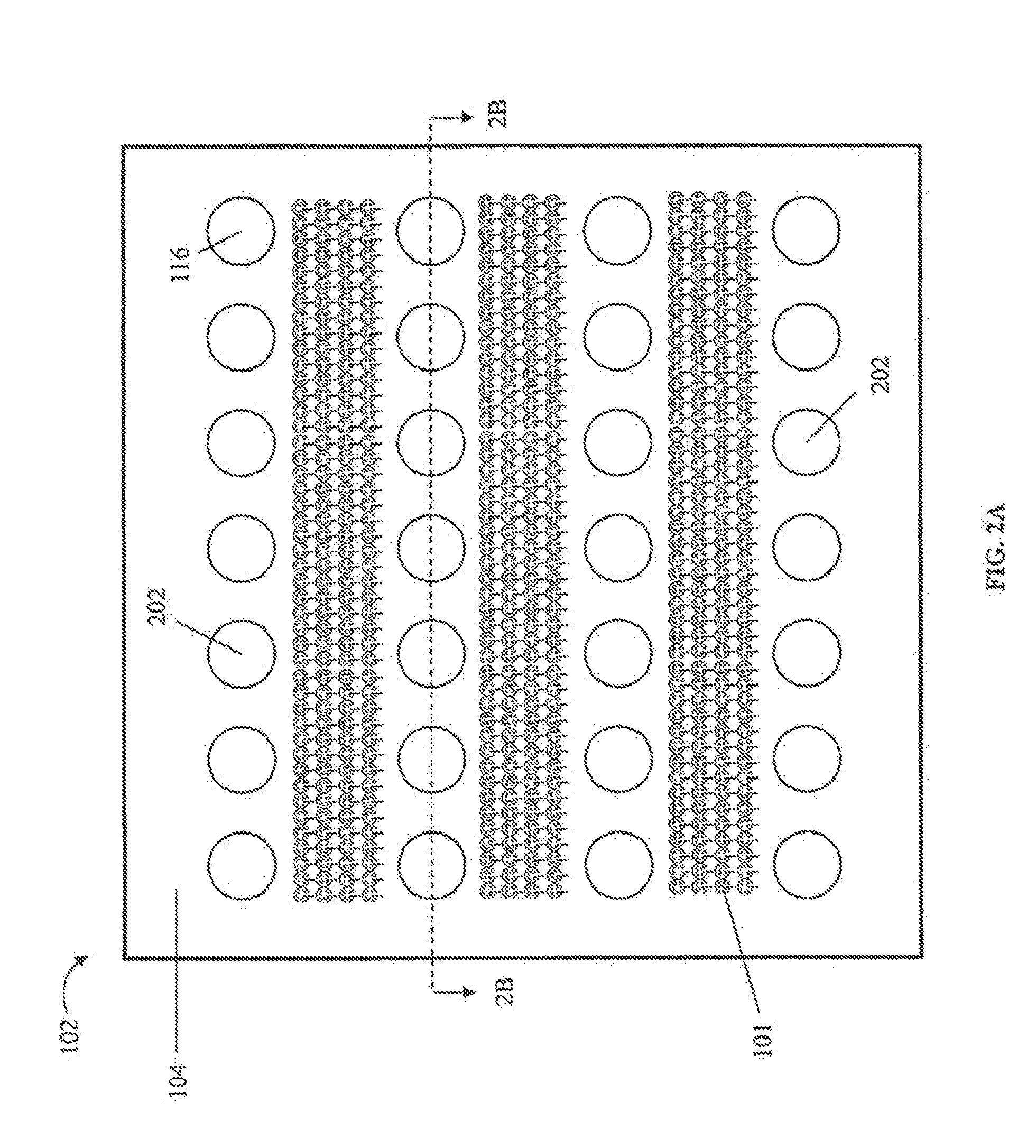
Surface Cleaning Method and Apparatus Using Surface Acoustic Wave Devices
InactiveUS20150206738A1Safe removalSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic cleaningTarget surfaceSurface cleaning
An apparatus, system, and method for cleaning surfaces is presented. One embodiment of the system includes an array of surface acoustic wave (SAW) transducers coupled to a substrate. The system may include a positioning mechanism coupled to at least one of a target surface or the array of SAW transducers, and configured to position the array of SAW transducers within an effective cleaning distance of a target surface. The system may also include a cleaning liquid supply arranged to provide cleaning liquid for coupling the array of SAW transducers to the target surface. The system may further include a controller coupled to the array of SAW transducers and configured to activate the array of SAW transducers. At least one of the SAW transducers may be formed to focus cleaning liquid on a focal point and jet cleaning liquid in a direction substantially out of the place of the SAW transducer.
Owner:SEMATECH
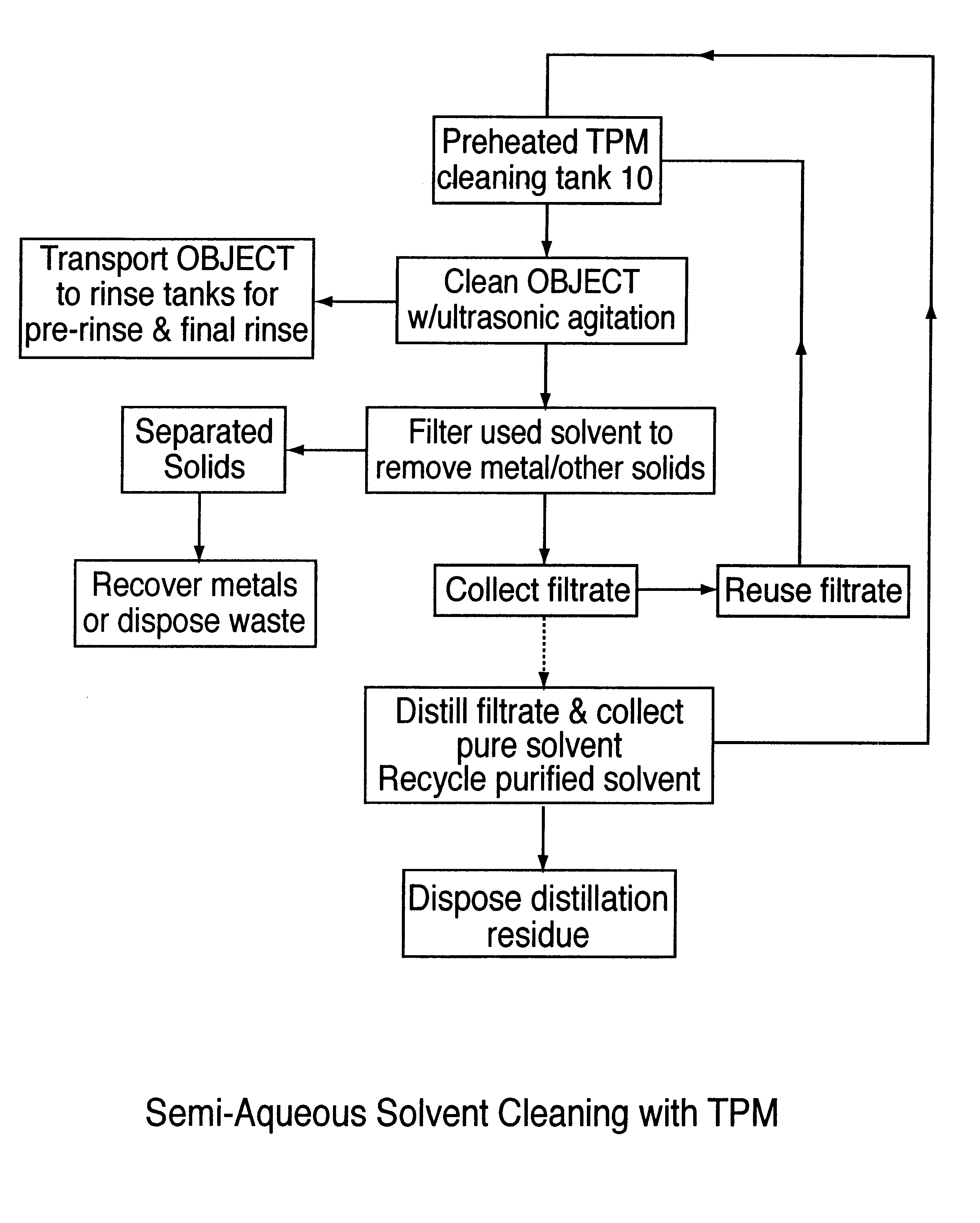
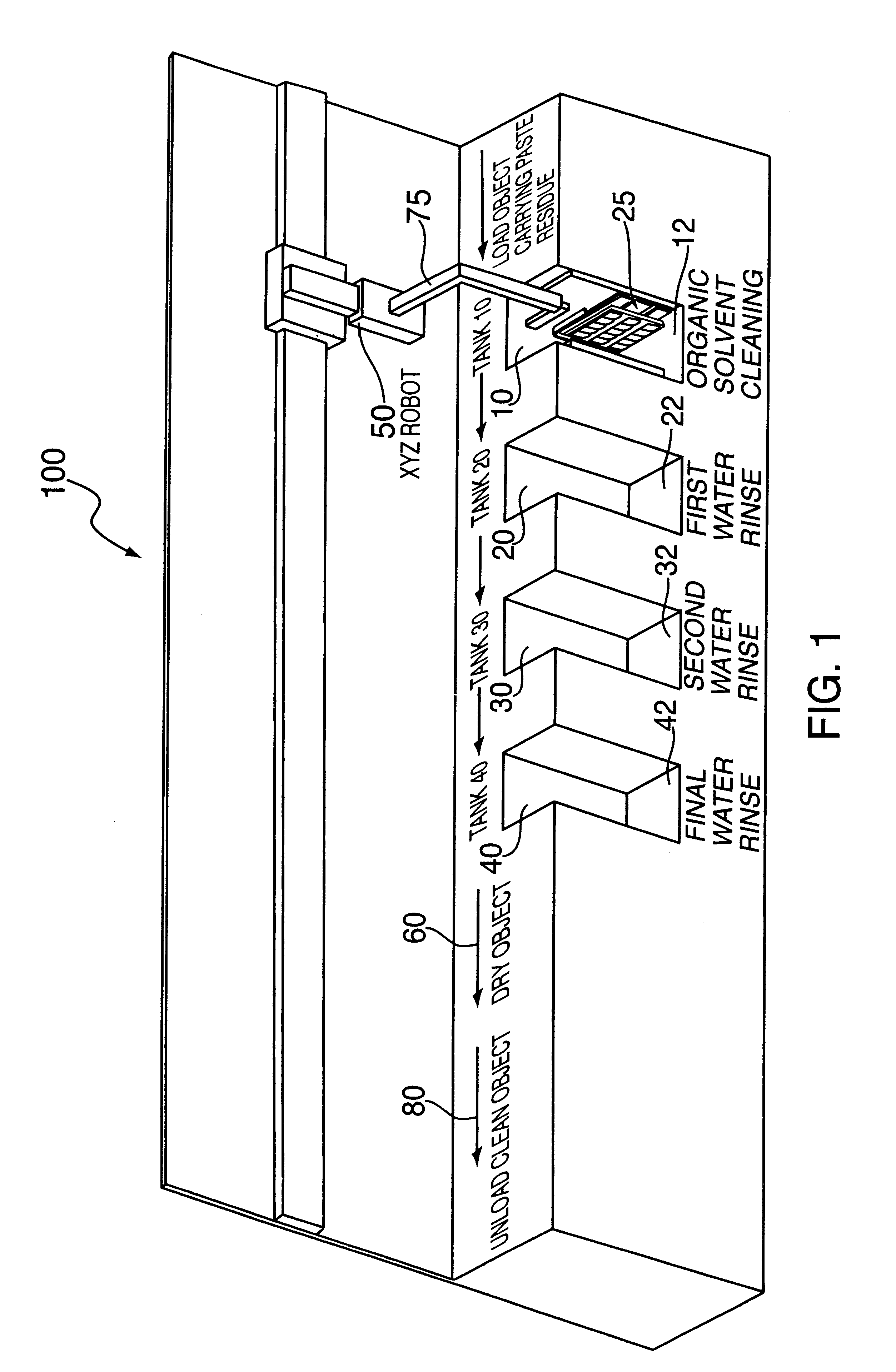
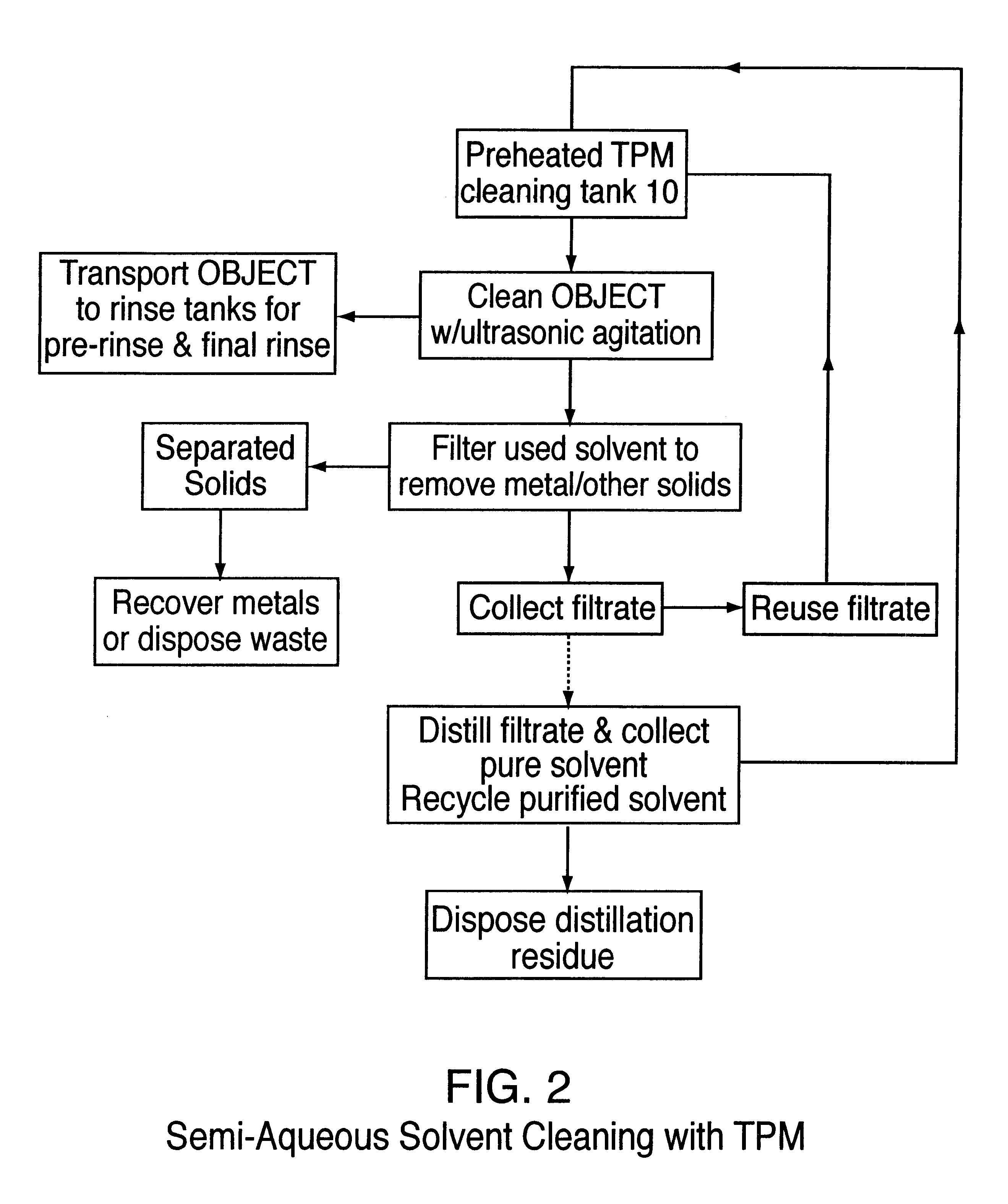
Semi-aqueous solvent cleaning of paste processing residue from substrates
A process of cleaning of objects that relate to semiconductor fabrication processes, such as, for example, conductive paste screening in the production of multilayer ceramic substrates and composite solder paste by stencil printing in electronic circuit assembly. Specifically, the process removes a metal / polymer composite paste from screening masks and associated paste making and processing equipment used in printing conductive metal pattern onto ceramic green sheet in the fabrication of semiconductor packaging substrates. The process also cleans solder paste residue from stencil printing equipment used in electronic module assembly surface mount technology for SMT discretes, solder column attachment, and BGA (Ball Grid Array) attachment on ceramic chip carrier or for screening solder paste onto printed circuit board. More particularly, paste residue is cleaned from metal, ceramic, and plastic substrates by a non-alkaline semi-aqueous cleaning method employing high boiling propylene glycol alkyl ether or mixtures of propylene glycol alkyl ether and propylene glycol solvents.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Automatic dishwashing compositions and methods for use with electrochemical cells and/or electrolytic devices
InactiveUS20050075257A1Improved tableware cleaningImproved sanitizingInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsElectrolysisPhosphate
The present invention relates to automatic dishwashing detergent compositions and methods of using compositions comprising halogenated salts, phosphate and / or silicate in conjunction with electrolyzed water in automatic dishwashing appliances comprising an electrochemical cell and / or electrolytic device for treating tableware to improve cleaning, sanitizing and stain removal by controlling hardness, corrosion and dispersancy.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
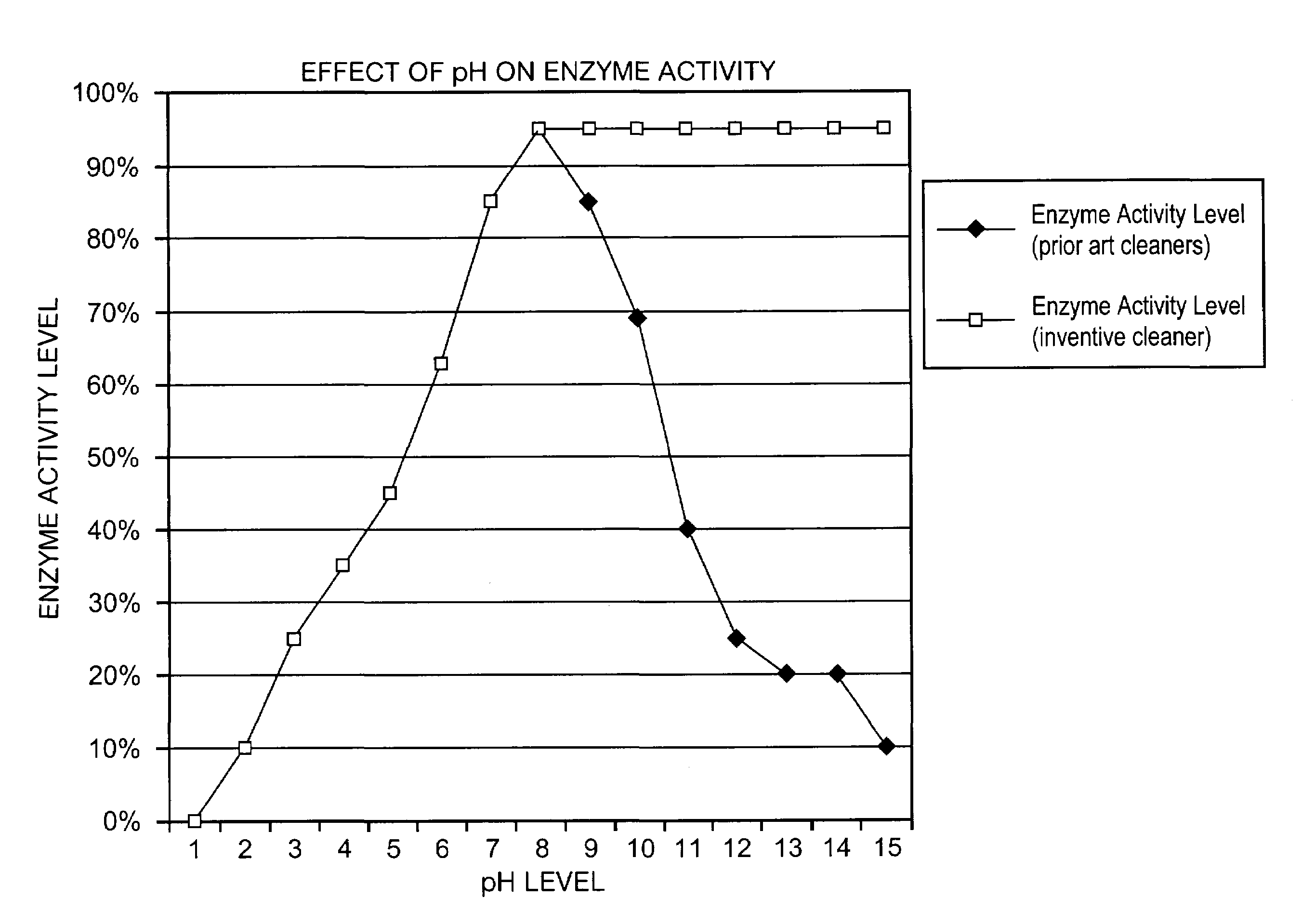
Enzymatic cleaner having high pH stability
InactiveUS20030089381A1High activityImprove efficiencyOrganic detergent compounding agentsSoap detergents with inorganic compounding agentsMicroorganismOrganic matter
The present invention is directed to a cleaning composition comprising: (a) an enzyme in an amount effective to promote cleaning; (b) viable microorganisms in an amount effective to degrade and promote the degradation of organic materials; (c) a surfactant; and (d) an aqueous carrier; said cleaning composition maintaining at least 95% enzymatic activity at a pH range of from about 5.5 to about 13.5.
Owner:TREYCO SUPPLY
Enzymatic cleaner having high pH stability
InactiveUS7183248B2Organic detergent compounding agentsSoap detergents with inorganic compounding agentsMicroorganismOrganic matter
The present invention is directed to a cleaning composition comprising: (a) an enzyme in an amount effective to promote cleaning; (b) viable microorganisms in an amount effective to degrade and promote the degradation of organic materials; (c) a surfactant; and (d) an aqueous carrier; said cleaning composition maintaining at least 95% enzymatic activity at a pH range of from about 5.5 to about 13.5.
Owner:TREYCO SUPPLY
Surfactant
InactiveUS20070167343A1Efficient and advanced cleaningInhibitionNon-ionic surface-active compoundsAnionic surface-active compoundsNitrogenProton
To provide a surfactant which is obtainable by using substantially no alkali metal, has excellent readhesion prevention ability of finely-pulverized particles at the time of cleaning, and is capable of quite efficient and advanced cleaning. In the present invention, a surfactant which comprises a neutralized salt (AB1) and / or neutralized salt (AB2) is used. Neutralized salt (AB1): a neutralized salt (AB1) which comprises an acidic compound (A1) containing at least each one of an acid group (X1) of an acid having the difference of heat of formation in an acid dissociation reaction (Q1) of 3 to 200 kcal / mol and a hydrophobic group (Y) containing 1 to 36 carbon atoms, and a nitrogen-containing basic compound (B) having the difference of heat of formation in a proton addition reaction of 10 to 152 kcal / mol, wherein (X1) is at least one species selected from a sulfonic acid group, and the like. Neutralized salt (AB2): a neutralized salt (AB2) which comprises a polymer (A2) having at least one acid group (X2) within the molecule, and the nitrogen-containing basic compound (B) having the difference of heat of formation in a proton addition reaction of 10 to 152 kcal / mol.
Owner:SANYO CHEM IND LTD
Method, process, chemistry and apparatus for treating a substrate
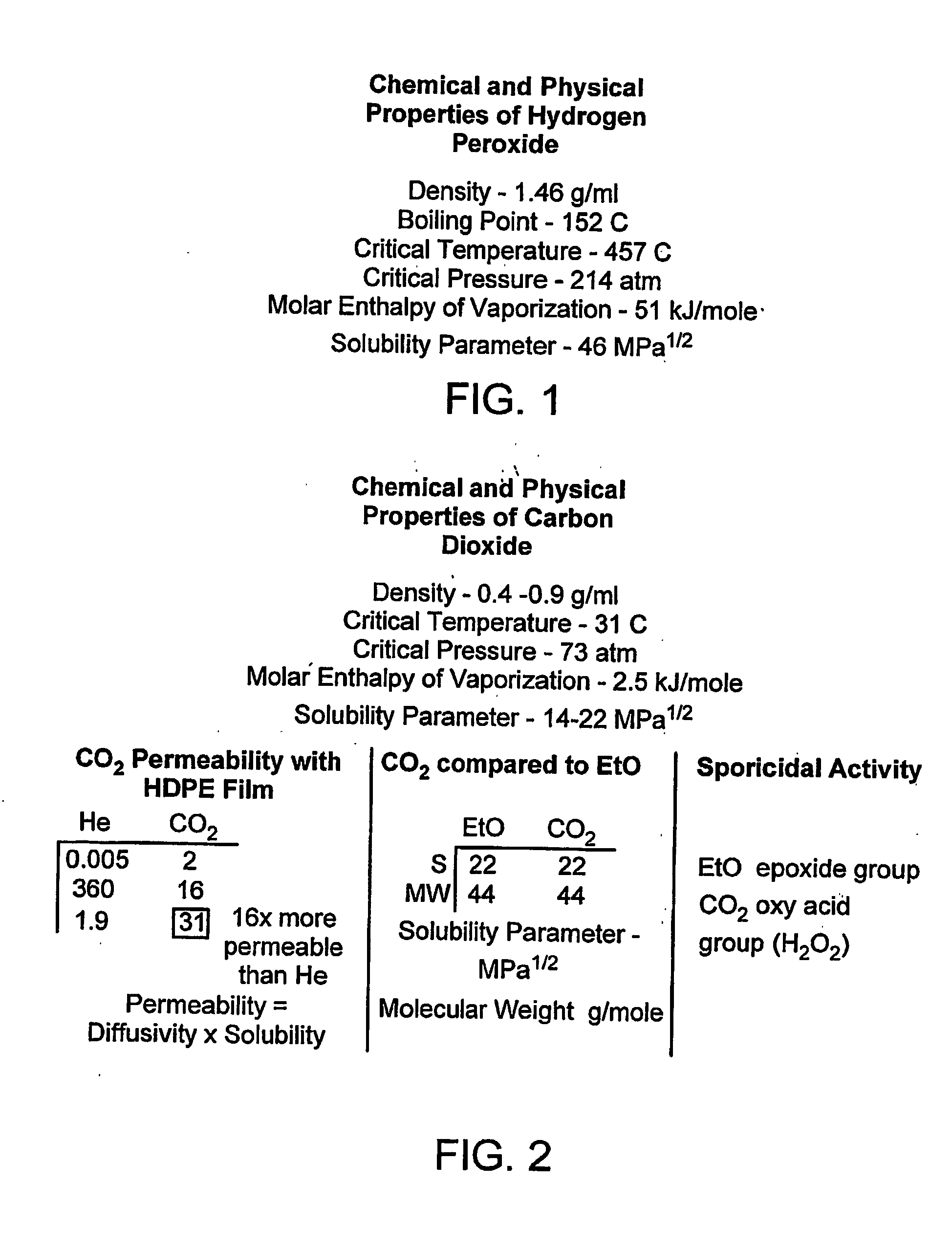
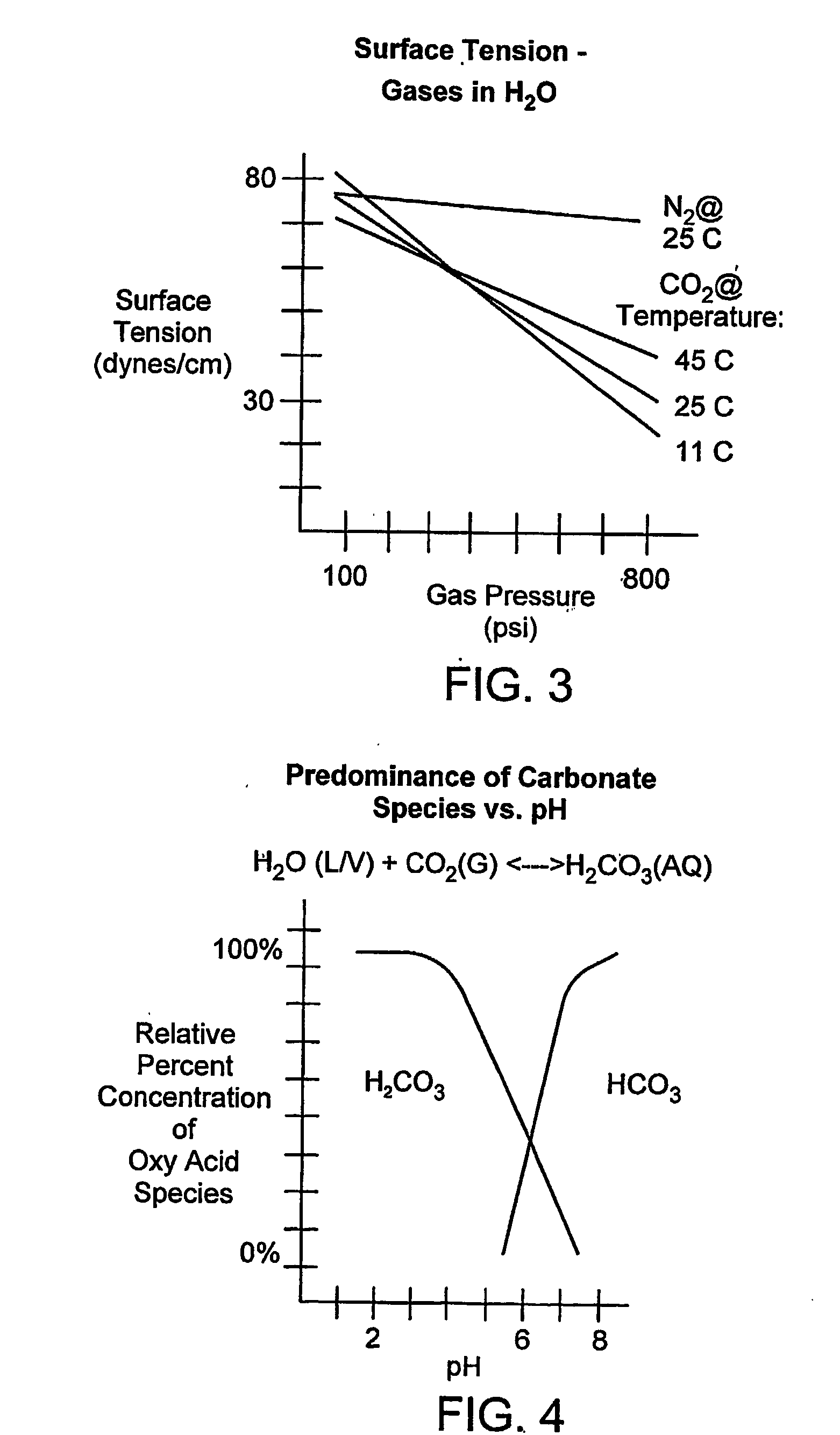
InactiveUS20050260107A1Much of lightEfficiently usPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesSynthetic resin layered productsCarbon dioxideChemistry
The invention provides new methods for synthesis of percarbonic acid and methods of using percarbonic acid compositions for the treatment of substrates. The invention is particularly useful for cleaning, disinfecting and / or sterilizing a substrate using percarbonic acid or a percarbonic acid-carbon dioxide mixture. The invention further provides an apparatus suitable for use in the substrate treatment methods provided herein. The invention also provides methods and apparatus for the real time monitoring of the treatment processes provided herein.
Owner:WILLIAM A YOUNG GASKET CORP
Signal-based electrochemical methods for automatic dishwashing
InactiveUS20060096618A1Improve cleanlinessImproved sanitizingInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsTableware washing/rinsing machine detailsSpecific timeElectrochemical cell
Methods of improving tableware cleaning, sanitizing and stain removal using an automatic dishwashing appliance containing an electrochemical cell and / or electrolytic device. The methods comprise steps for generating electrolyzed water by intermittently activating and / or intermittently deactivating the cell so as to sequentially provide a bleaching species at specific times during the wash and / or rinse cycle. Said methods include a signal-sensing system capable of detecting a composition comprising a signal-providing agent, methods of using said compositions, and articles of manufacture.
Owner:PRICE KENNETH NATHAN +3
Substrate cleaning method, cleaning solution, cleaning apparatus and semiconductor device
InactiveUS20030150477A1Prevent oxygen from dissolvingLiquid degasificationElectrostatic cleaningAtmospheric airSemiconductor
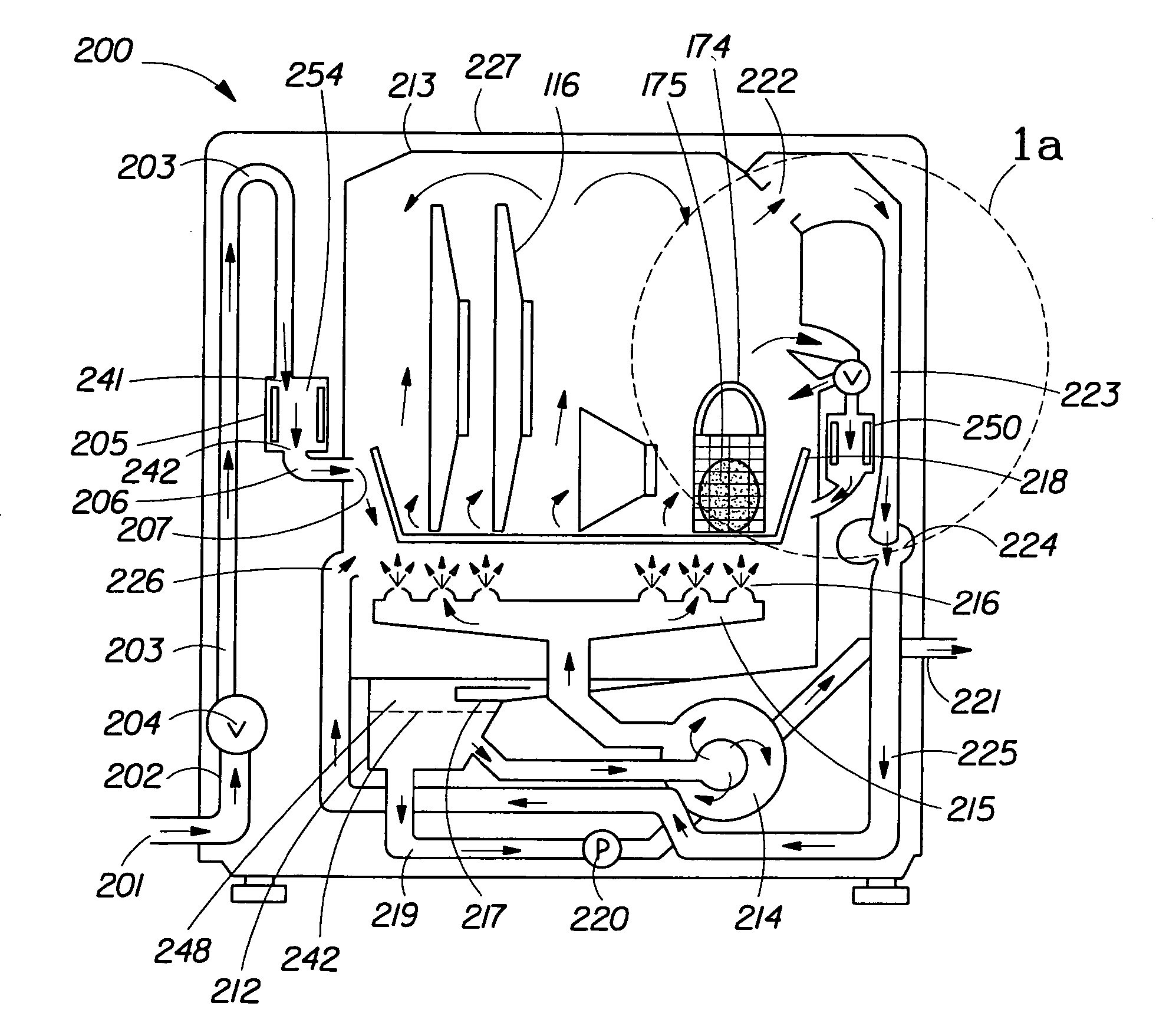
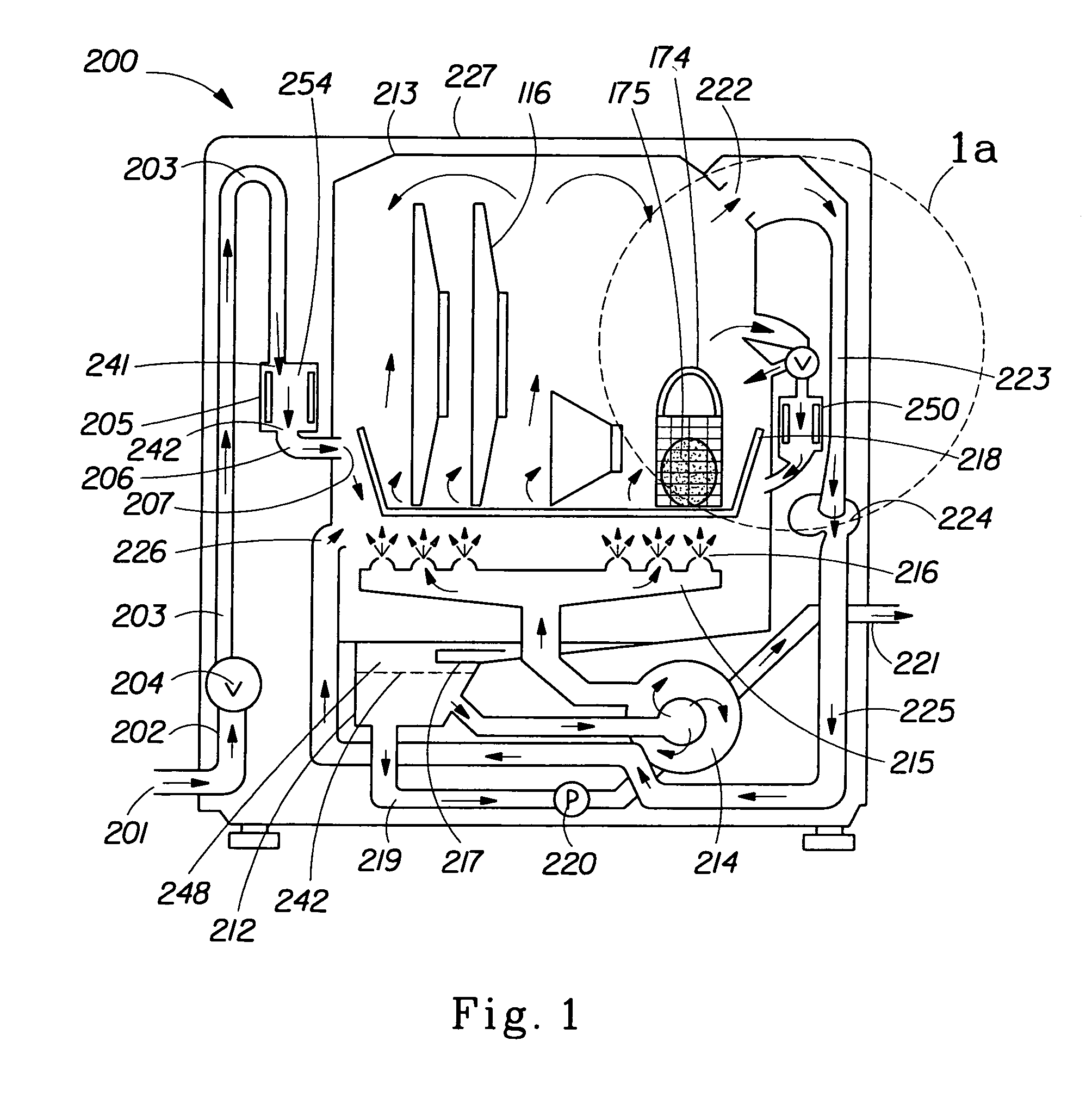
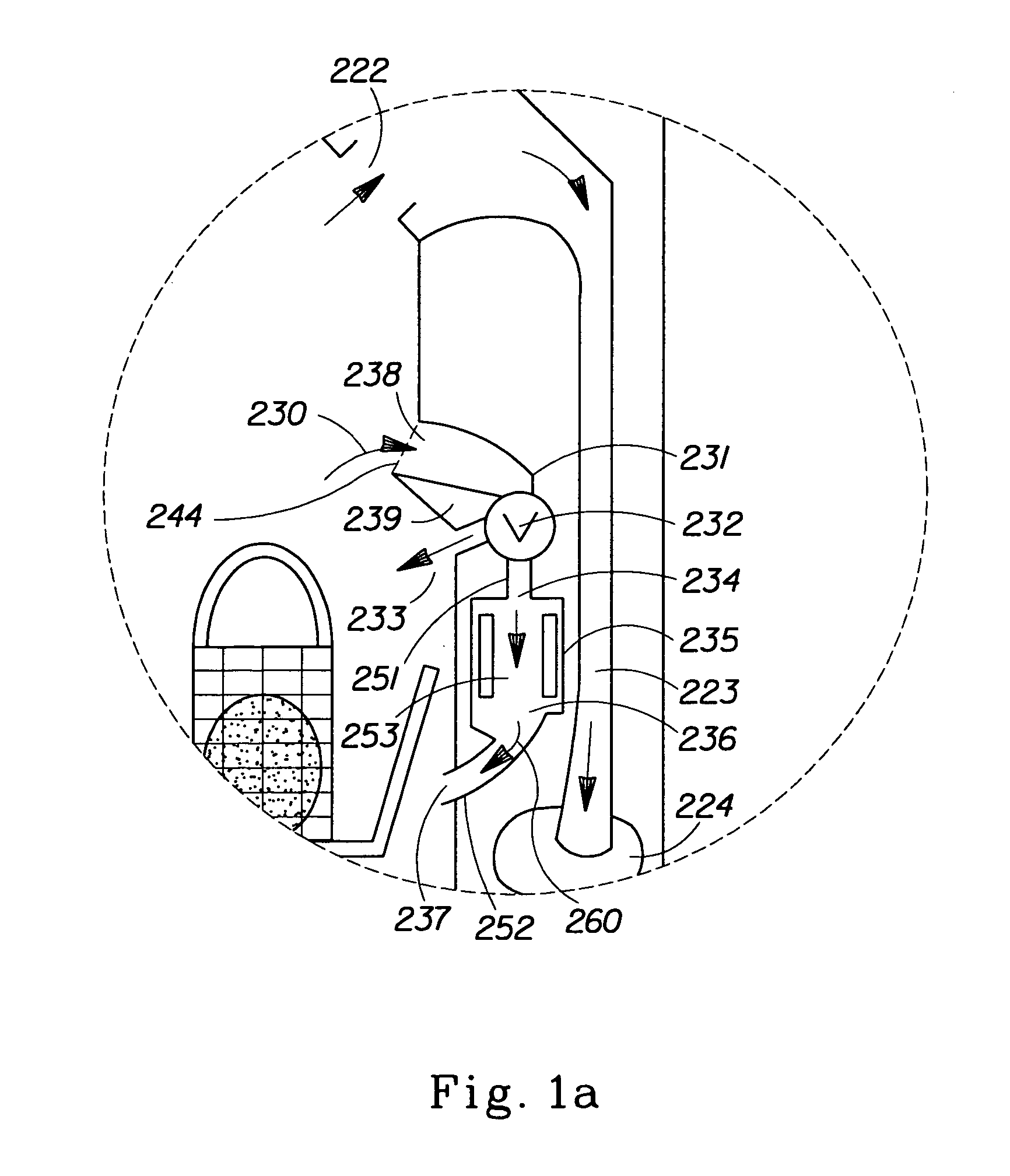
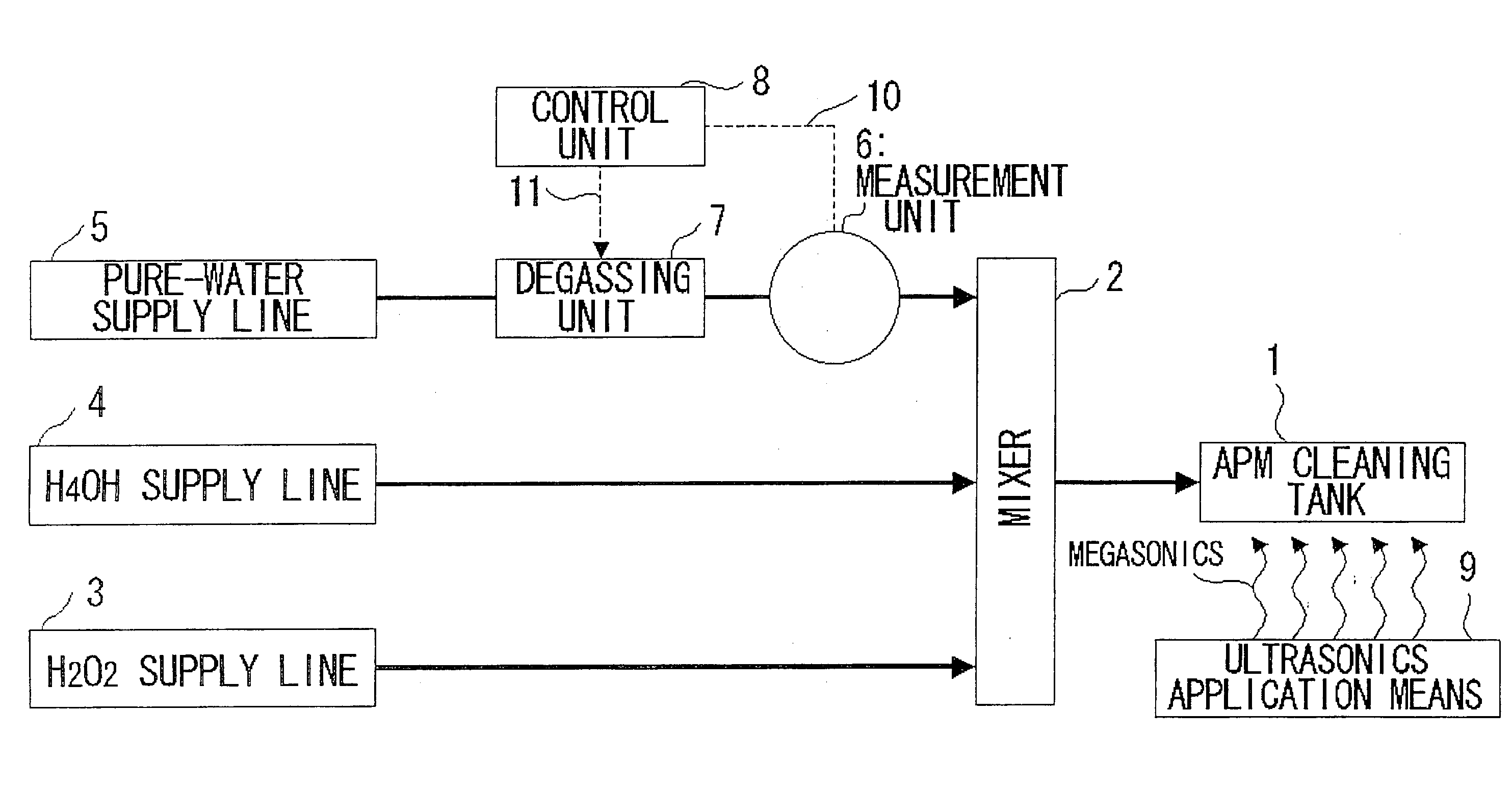
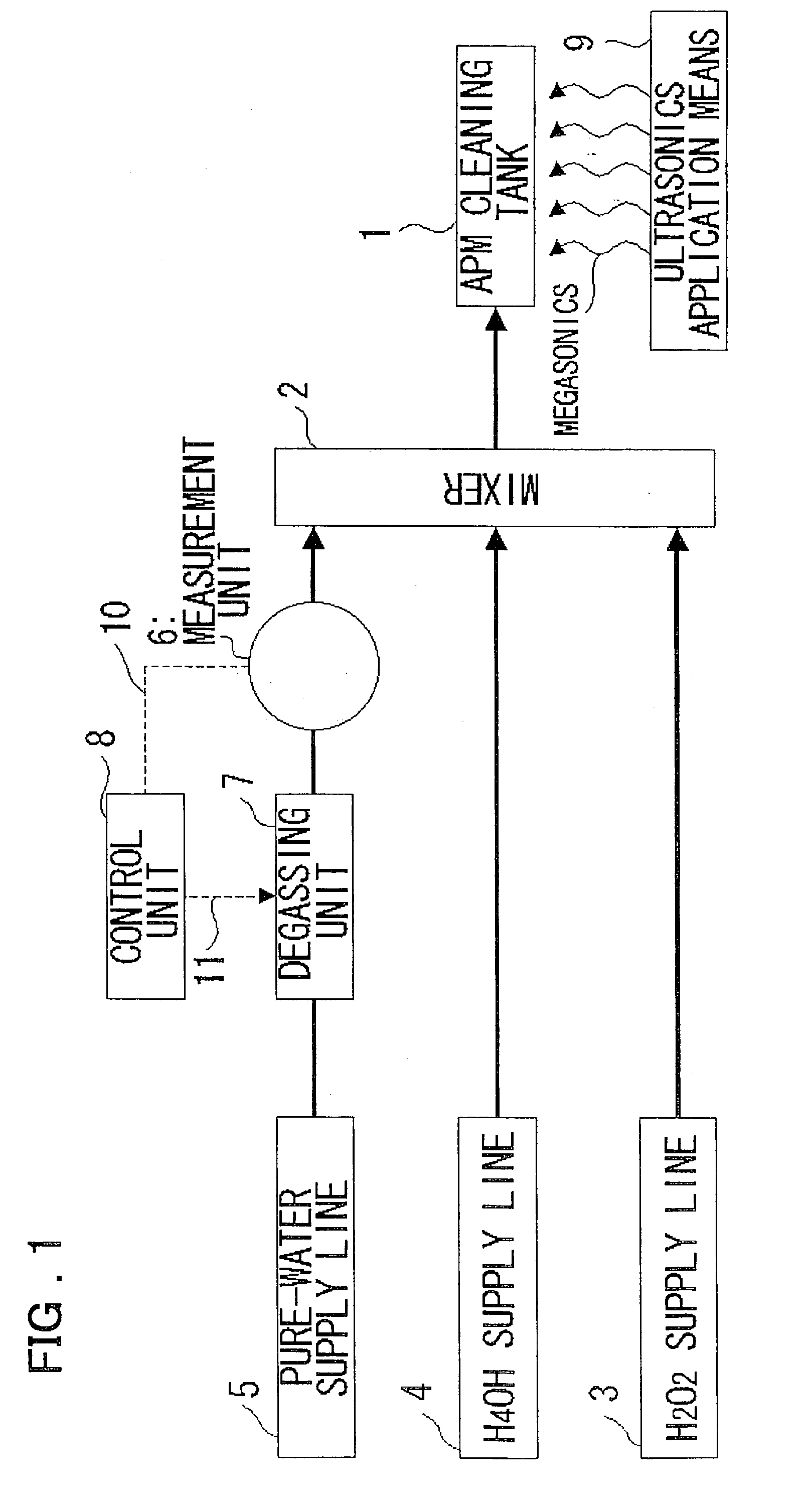
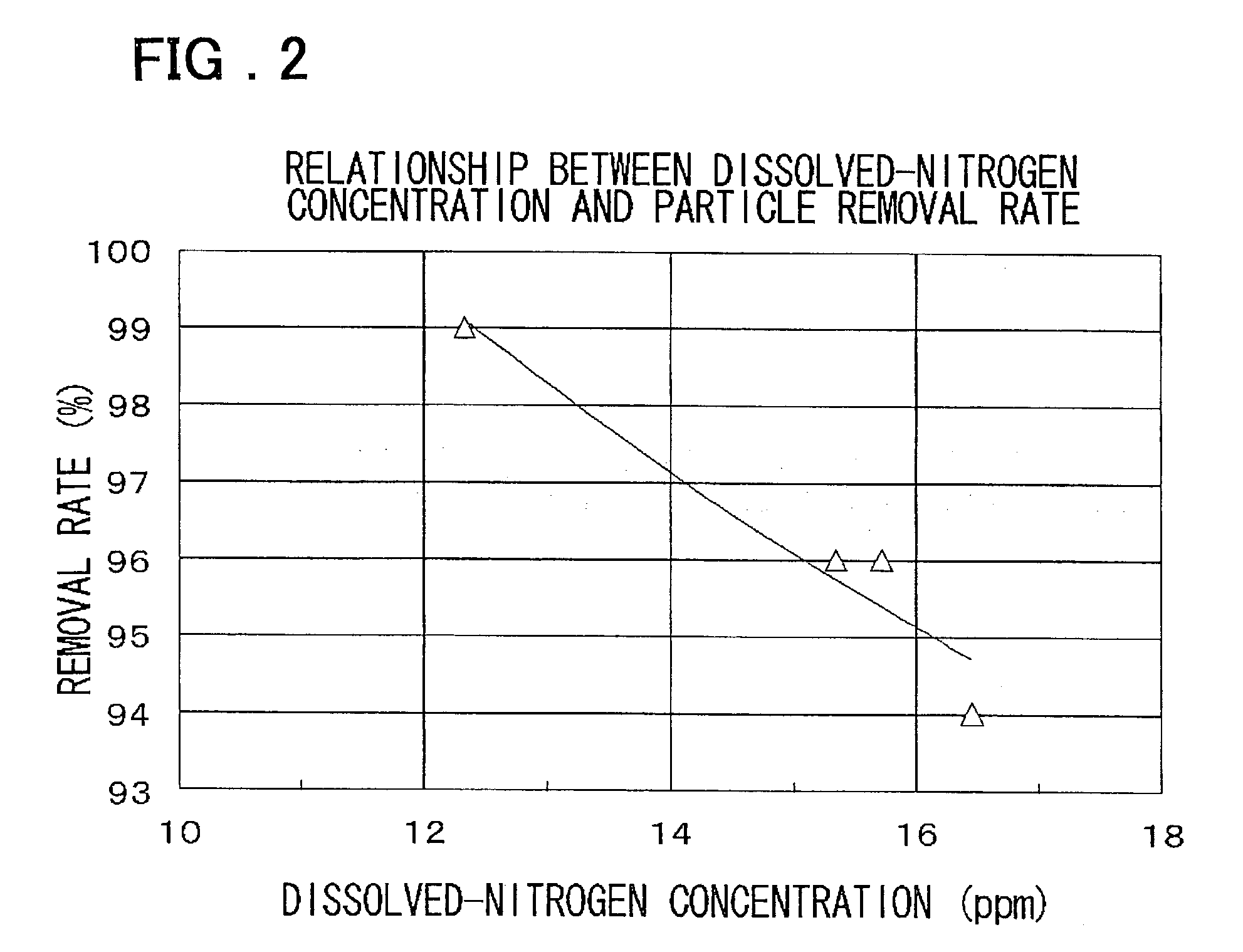
Disclosed is a substrate cleaning method for removing particles from a substrate includes a first step of adjusting the concentration of dissolved nitrogen in pure water, so as to be less than or equal to the concentration of dissolved nitrogen in equilibrium with the atmosphere (about 16 ppm), in a supply line that supplies the pure water, and a second step of cleaning a substrate by supplying a cleaning tank with a cleaning solution produced by mixing at least hydrogen peroxide with the pure water adjusted at the first step, and applying an ultrasonic wave to the cleaning solution in which the substrate is immersed.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Detergent composition
InactiveUS20060079437A1Inorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsOrganic solventWater soluble
The present invention relates to a detergent composition containing (a) 2 to 30% by weight of an inorganic alkali, (b) 0.5 to 20% by weight of at least one surfactant selected from an anionic surfactant and a nonionic surfactant, (c) 0.01 to 2% by weight (based on calcium ion) of a calcium salt, (d) 0.1 to 15% by weight of a calcium ion-sequestering agent, (e) 1 to 30% by weight of a water-soluble organic solvent and (f) 20 to 95% by weight of water.
Owner:KAO CORP
Azeotropic compositions comprising methyl perfluoropentene ethers for cleaning applications
The present disclosure provides azeotropic and azeotrope-like compositions comprised of methylperfluoropentene ethers and at least one of methanol, ethanol, 2-propanol, hexane, heptane, trans-1,2-dichloroethylene, ethyl formate, methyl formate, HFE-7100, HFE-7200 and 1-bromopropane or combinations thereof. The present disclosure also provides for methods of use for the azeotropic and azeotrope-like compositions.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Nanoelectronic and microelectronic cleaning compositions
InactiveUS20090163396A1Improved and superior cleaningImproved and superior and stripping photoresistElectrostatic cleaningOrganic/inorganic per-compounds compounding agentsHafniumSolvent
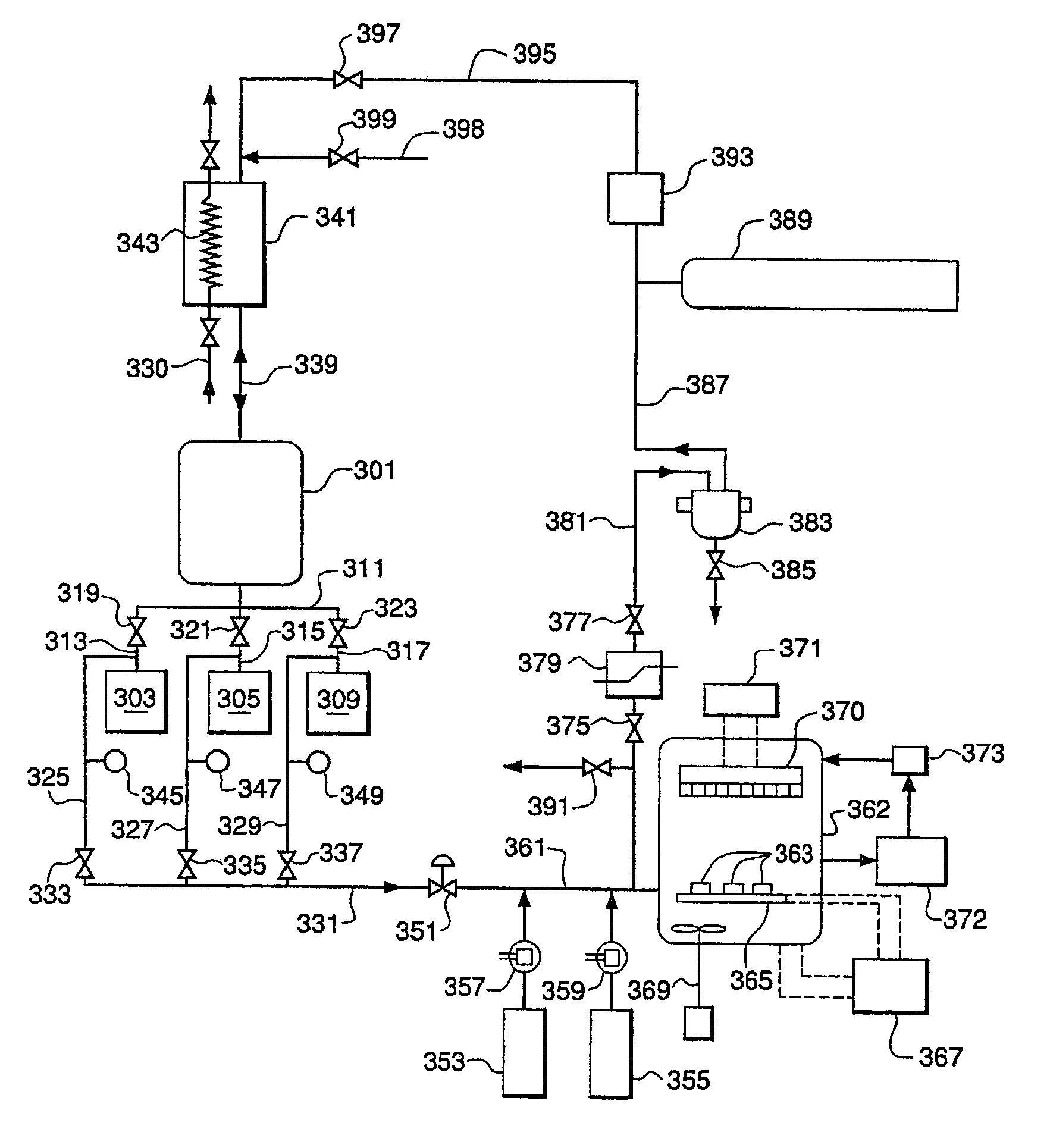
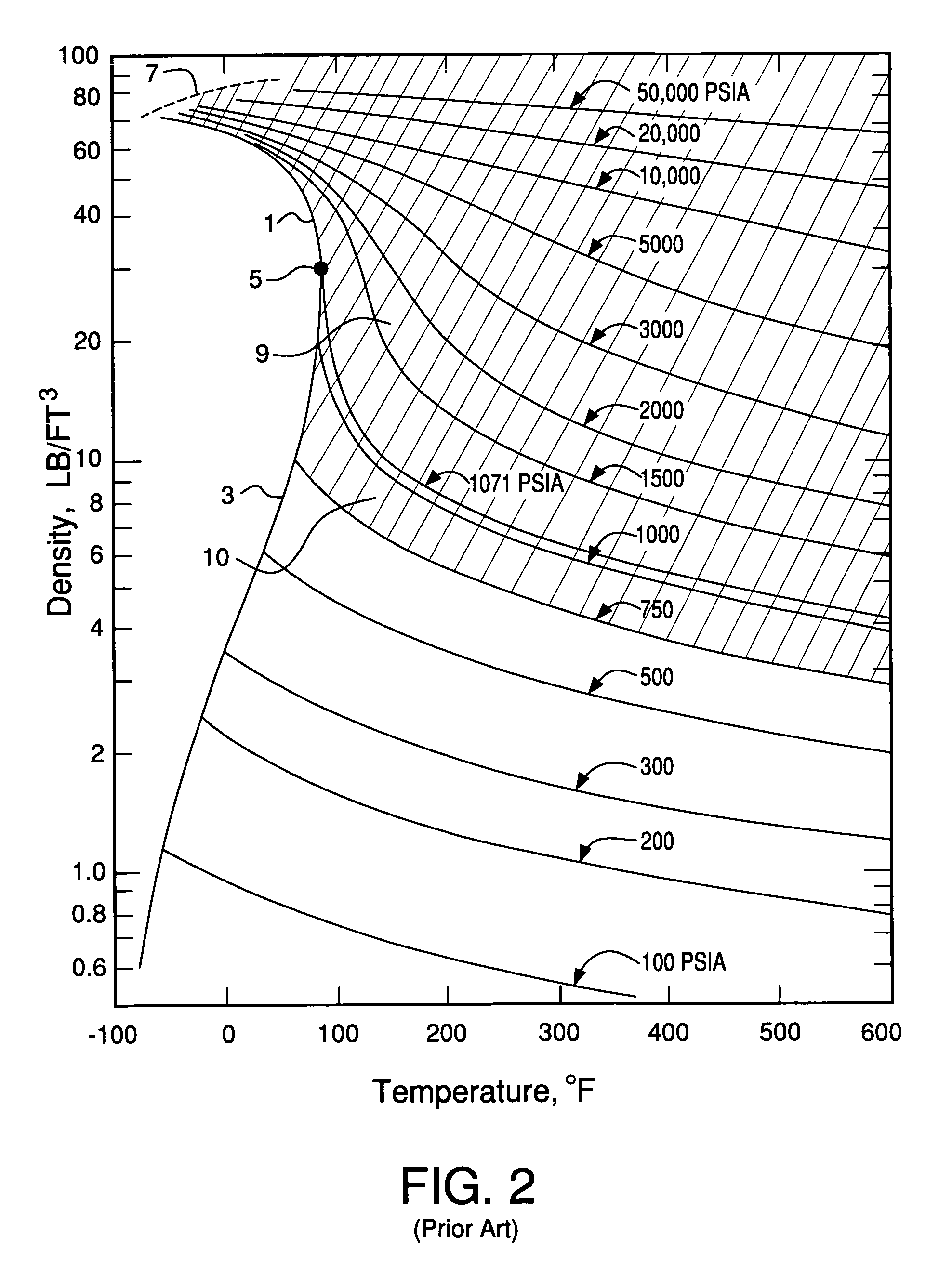
Nanoelectronic and microelectronic cleaning compositions for cleaning nanoelectronic and microelectronic substrates under supercritical fluid state conditions, and particularly cleaning compositions useful with and having improved compatibility with nanoelectronic and microelectronic substrates characterized by silicon dioxide, sensitive low-κ or high-κ dielectrics and copper, tungsten, tantalum, nickel, gold, cobalt, palladium, platinum, chromium, ruthenium, rhodium, iridium, hafnium, titanium, molybdenum, tin and other metallization, as well as substrates of Al or Al(Cu) metallizations and advanced interconnect technologies, are provided by nanoelectronic and microelectronic cleaning compositions comprising nanoelectronic and microelectronic cleaning compositions of this invention are provided by compositions comprising: (1) a supercritical main fluid reaching a supercritical fluid state at a temperature of 250° C. or less and a pressure of 600 bars or less (592.2 atm, 8702.3 psi), and (2) as a secondary fluid, a modifier formulation selected from the following formulations: a) a formulation comprising: an oxidizing agent; a polar organic solvent selected from the group consisting of amides, sulfones, sulfolenes, selenones and saturated alcohols; and optionally other components; b) a silicate free formulation comprising: a polar organic solvent selected from the group consisting of amides, sulfones, selenones and saturated alcohols; a strong alkaline base; and optionally other components; c) a formulation comprising: from about 0.05% to 30% by weight of one or more non-ammonium producing strong base containing non-nucleophilic, positively charged counter ions; from about 0.5 to about 99.95% by weight of one or more corrosion inhibiting solvent compounds, said corrosion inhibiting solvent compound having at least two sites capable of complexing with metals; and optionally other components; d) a formulation comprising: from about 0.05 to 20% by weight of one or more non-ammonium producing, non-HF producing fluoride salt; from about 5 to about 99.95% by weight of water, organic solvent or both water and organic solvent; and optionally other components; and e) a formulation comprising: from about 0.05% to 30% by weight of one or more non-ammonium producing strong base containing non-nucleophilic, positively charged counter ions; from about 5 to about 99.95% by weight of one or more steric hindered amide solvents; and optionally other components.
Owner:AVANTOR PERFORMANCE MATERIALS LLC
Methods and Apparatus for Laser Cleaning
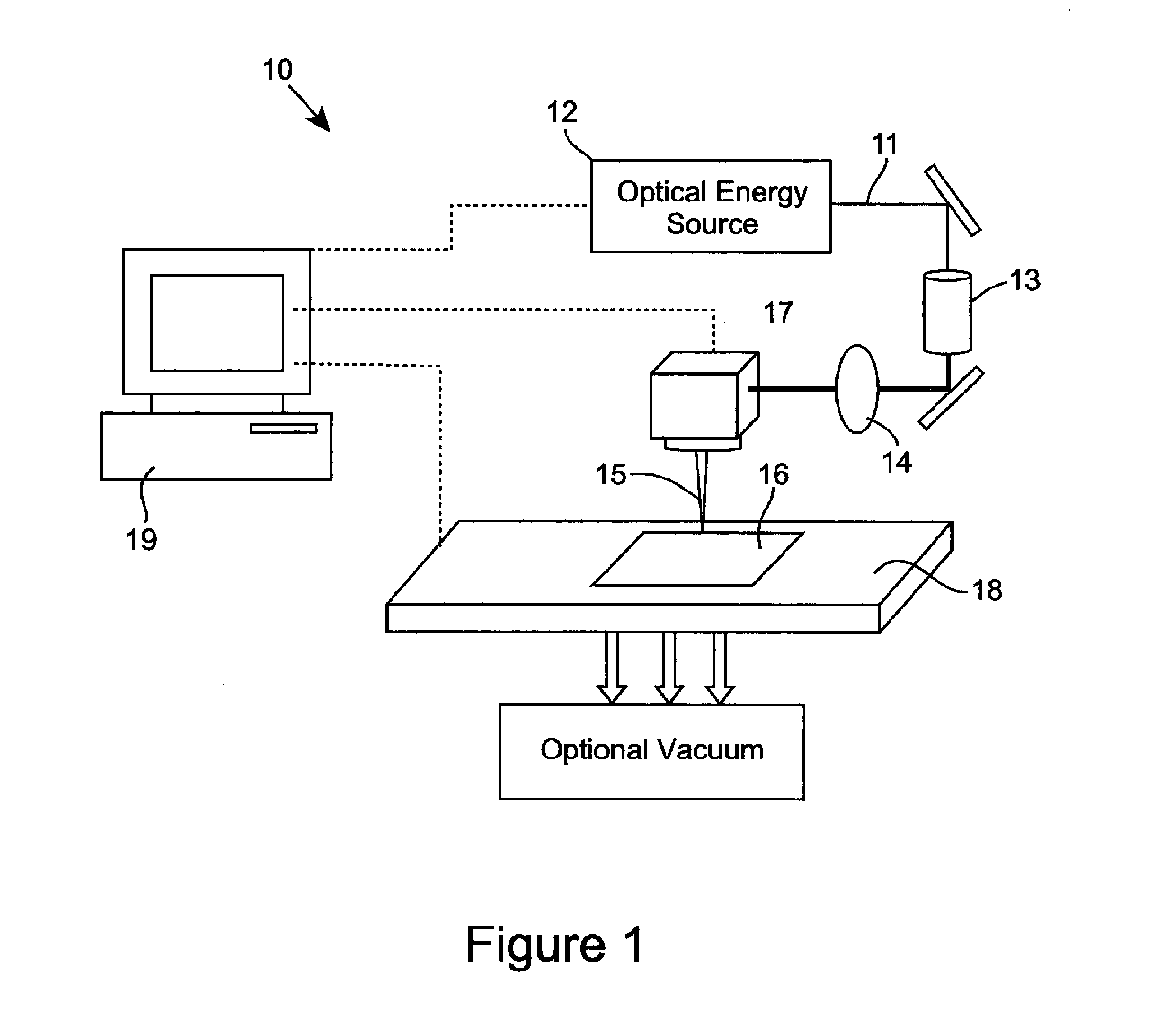
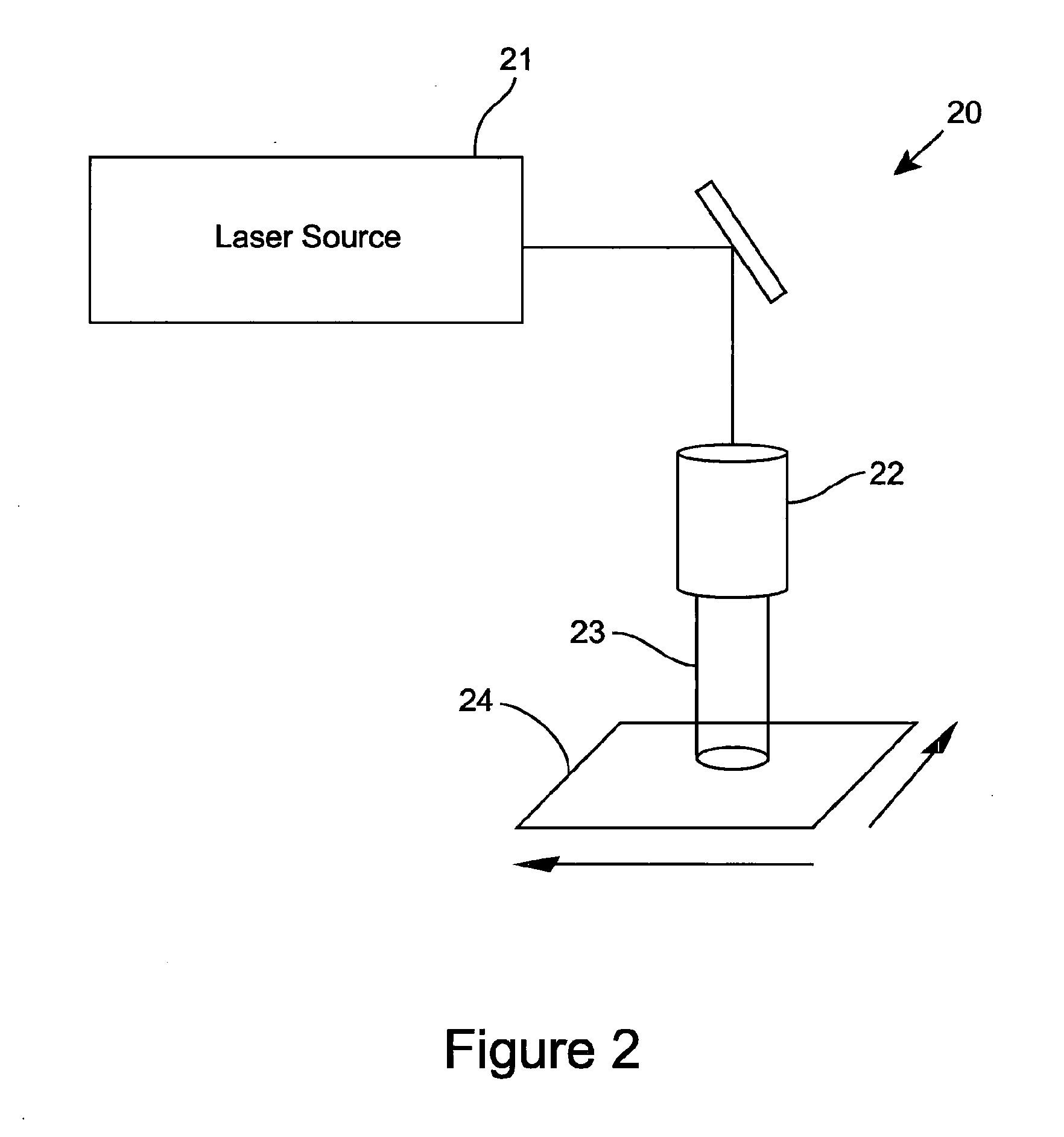
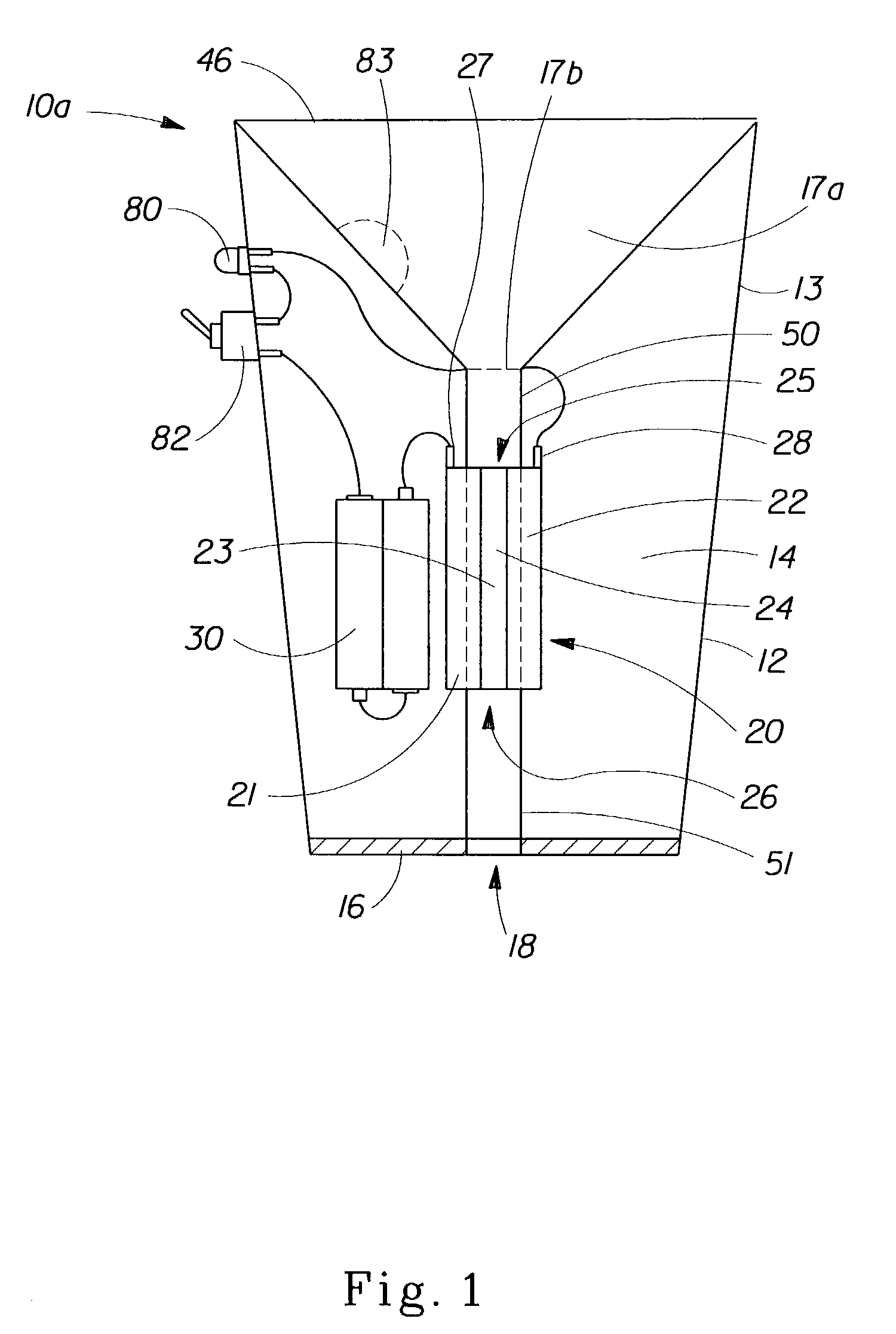
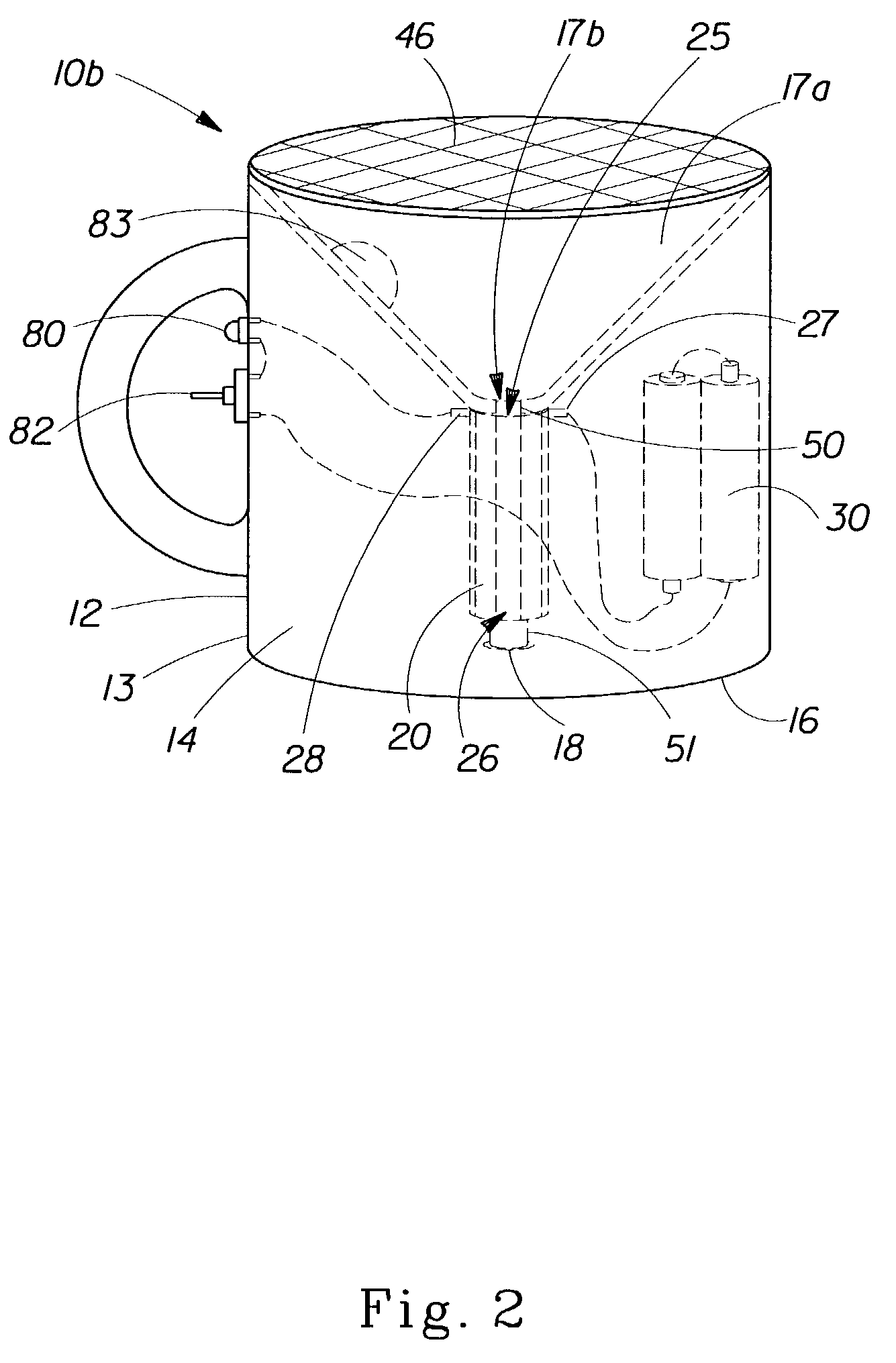
ActiveUS20150225891A1Reduce the amount of waterLaser beam fibre treatmentDry-cleaning apparatusEngineeringCleansing Agents
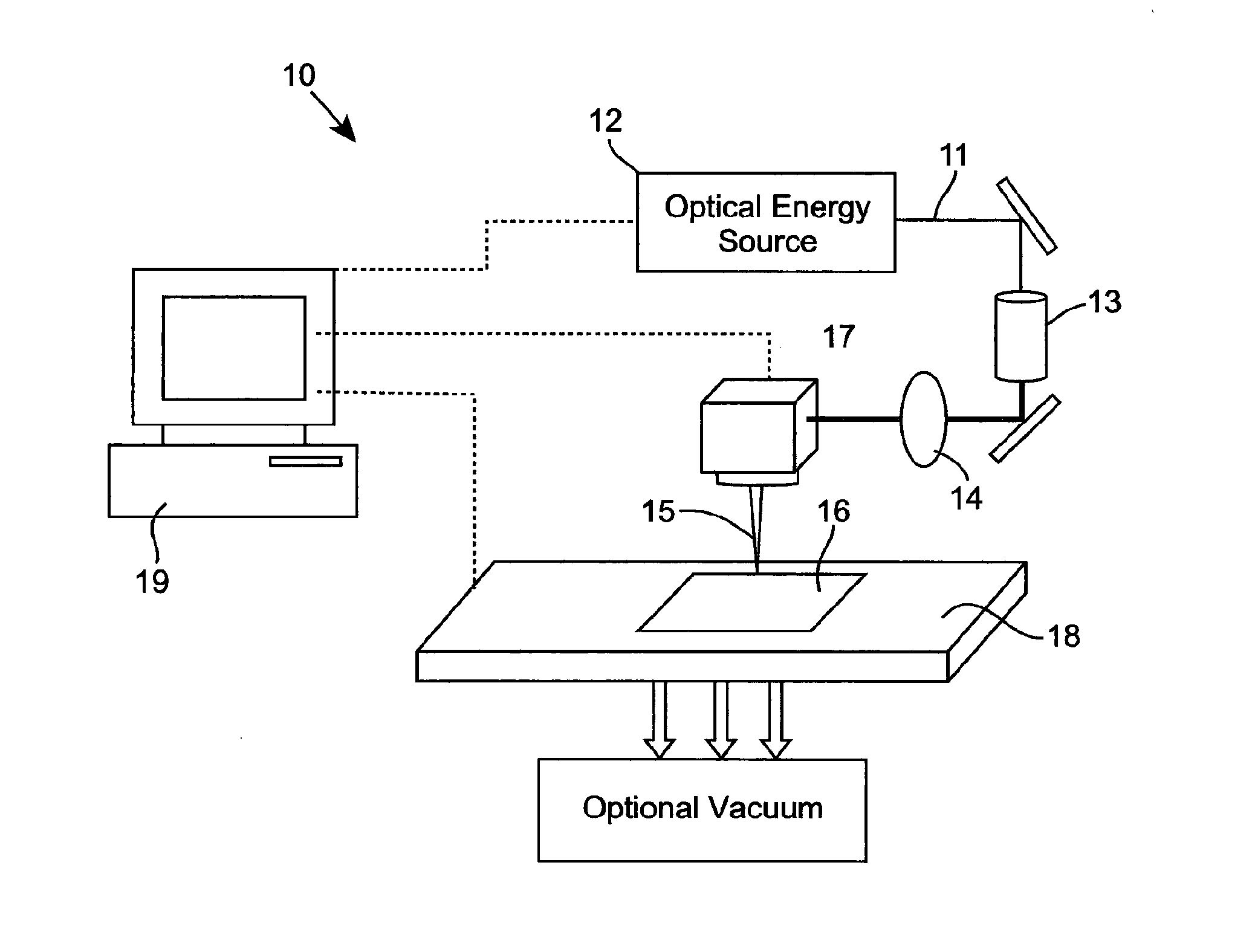
A method of cleaning a substrate (16, 24, 34, 64, 71, 82, 102, 165, 171, 181, 201, 300, 310) with optical energy can comprise applying optical energy from a source of optical energy (12, 21, 31, 91, 103, 114, 121, 131, 141, 151, 164, 191, 202) to the substrate. The method can comprise applying the optical energy to a substrate having a cleaning agent applied thereto, the optical energy having one or more optical parameters selected for cleaning the substrate. The method can comprise reading data from a data bearing element (173) associated with the substrate, communicating the data to a processor (154) associated with a cleaning appliance (10, 30, 40, 60, 70, 80, 90, 110, 120, 130, 140, 150, 161, 200) comprising the source of optical energy, wherein the processor, responsive to the communicated data, controls the cleaning of the substrate with the optical energy. The method can comprise slidingly contacting the substrate with a work surface, said work surface comprising an aperture (83, 117) and emanating optical energy from the aperture for cleaning the substrate. A cleaning appliance can comprise an appliance body (80, 90, 104, 125) comprising an aperture for emanating optical energy for cleaning the substrate and an optical transmission pathway arranged for propagating optical energy received from an optical energy source to said aperture. The appliance can be adapted and constructed for delivering a cleaning agent to the substrate. The appliance can include a processor, a data interface in communication with the processor, and can be configured such that the processor outputs signals that control the cleaning of the substrate, the processor being configured for controlling, responsive to data received by the data interface and via the output signals, the substrate cleaning. The cleaning appliance can include a suction pump (142) for removing material from the substrate.
Owner:WOODROW SCI LTD
Process of treating a carpet with a composition comprising a zeolite
InactiveUS20050037937A1Inorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsSurface-active detergent compositionsChemistryZeolite
The present invention relates to a process of treating a fabric with a composition comprising an activated zeolite.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
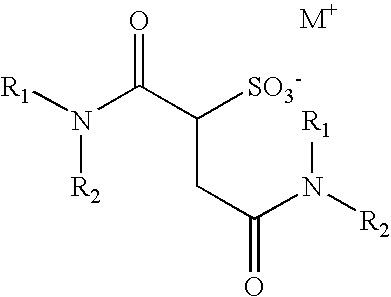
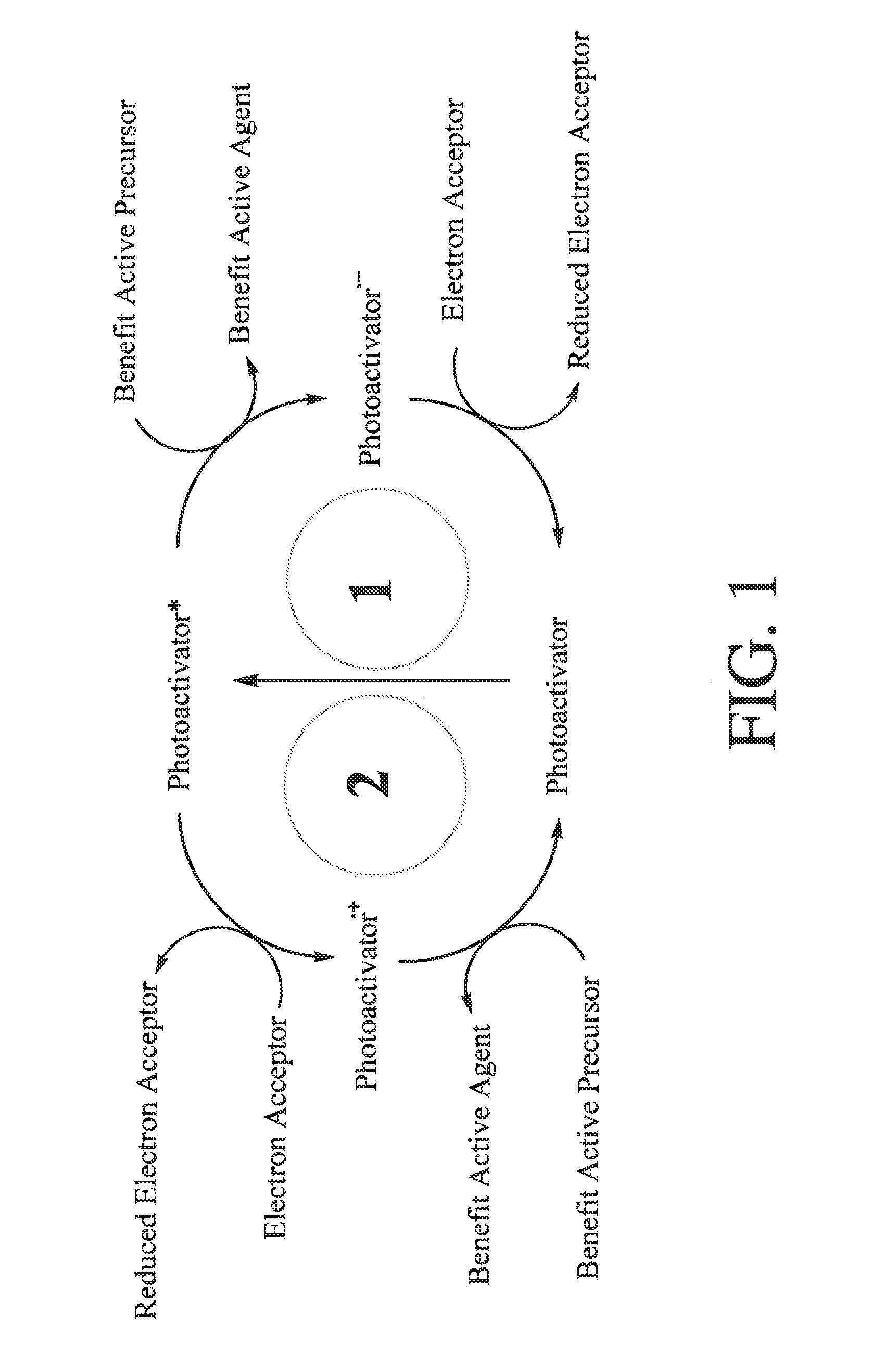
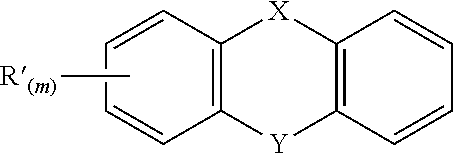
Consumer Product Compositions
InactiveUS20150210964A1Eliminating biofilmInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsBiocideExcited stateActive agent
Consumer product compositions comprise a water soluble organic photoactivator, an electron acceptor which accepts an electron from the photoactivator when the photoactivator is in a photo-excited state and / or reduced state, and a benefit active precursor which converts into a benefit active agent via electron transfer. The electron acceptor is preferably not covalently linked to the photoactivator. Also disclosed are methods of making a benefit active, comprising exposing the consumer product compositions to light, preferably having a wavelength greater than about 350 nm.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Processing of semiconductor components with dense processing fluids and ultrasonic energy
InactiveUS7267727B2Reduce frequencyPressurized chemical processElectrostatic cleaningSonificationConstant frequency
Method for processing an article with a dense processing fluid in a processing chamber while applying ultrasonic energy during processing. The dense fluid may be generated in a separate pressurization vessel and transferred to the processing chamber, or alternatively may be generated directly in the processing chamber. A processing agent may be added to the pressurization vessel, to the processing chamber, or to the dense fluid during transfer from the pressurization vessel to the processing chamber. The ultrasonic energy may be generated continuously at a constant frequency or at variable frequencies. Alternatively, the ultrasonic energy may be generated intermittently.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Methods for Shaping Fibrous Material and Treatment Compositions Therefor
The present invention relates to a method of shaping a fibrous material and treatment compositions therefor. The method comprises providing a treatment composition comprising an active agent and a photocatalyst, applying the treatment composition to the fibrous material to form a treated fibrous material, mechanically shaping the treated fibrous material, and exposing the treated fibrous material to electromagnetic radiation. The treatment composition comprises an active agent, wherein the active agent comprises a non-acid carbonyl or an equivalent of non-acid carbonyl; and a photocatalyst.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
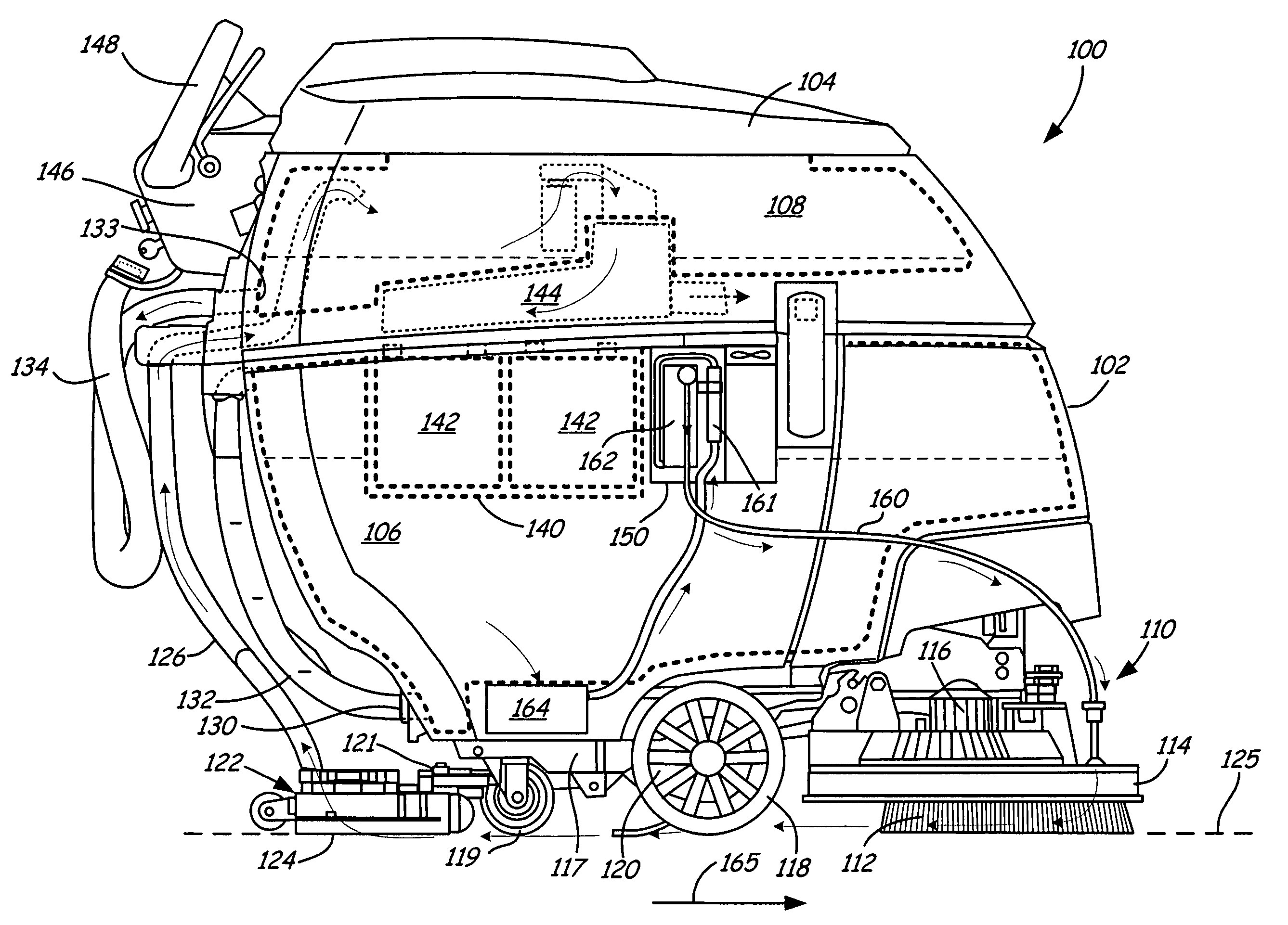
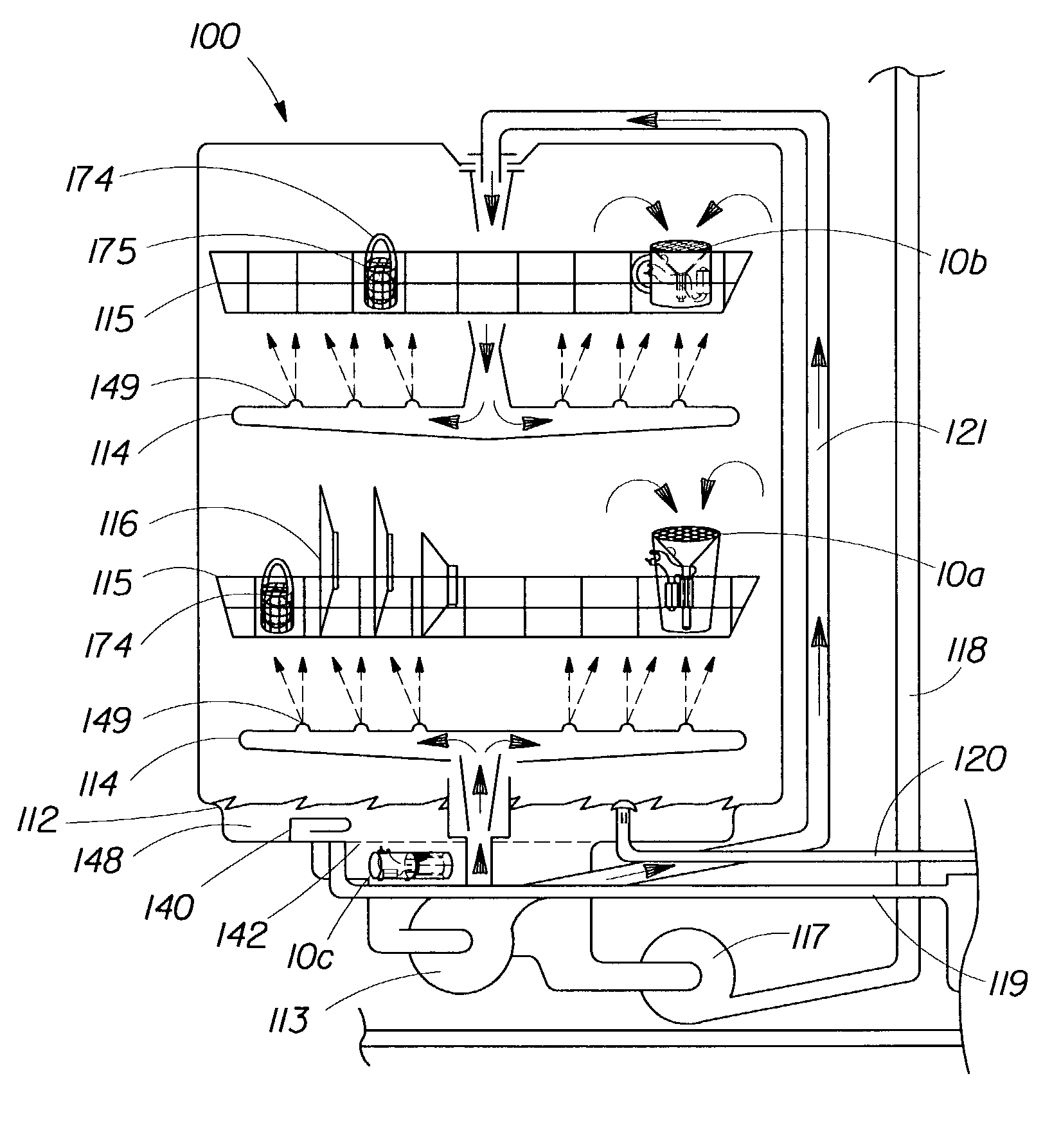
Method for generating electrochemically activated cleaning liquid
Owner:TENNANT COMPANY
Fluorometric method for monitoring a clean-in-place system
InactiveUS20060286676A1Less harshTesting beveragesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceClean-in-placeChemical substance
The invention pertains to a method for fluorometrically monitoring a Clean-In-Place (“CIP”) system and for fluorometrically monitoring the dosage of chemical added to the CIP system. Monitoring of the said CIP system can be based upon fluormetrically monitoring the fluorescent tracer, chemical or both, which are added to the CIP system.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Monitoring Cleaning of Surfaces
ActiveUS20090248499A1Enhancing cleaning programOptical radiation measurementDetergent dyesSurface cleaningUltraviolet radiation
Owner:KLEANCHECK SYST
Self-contained, self-powered electrolytic devices for improved performance in automatic dishwashing
ActiveUS7413637B2Improve cleanlinessImprovement in sanitizingInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsTableware washing/rinsing machine detailsElectrolysisElectrochemical cell
An automatic dishwashing appliance comprising an unattached electrolytic device which comprises an unattached electrochemical cell capable of generating electrolyzed water in the wash and / or rinse cycle, and more particularly to the unattached electrolytic device itself, methods of use, and articles of manufacture.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com