Method and apparatus for optimizing performance and battery life of electronic devices based on system and application parameters
a technology of electronic devices and system parameters, applied in the field of processing systems or devices, can solve the problems of reducing the amount of time between battery recharge or replacement, reducing the processing capability of portable electronic devices, and not as rapid improvement in battery capacity and energy density, so as to reduce the power consumption of electronic devices and extend the operating life of devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
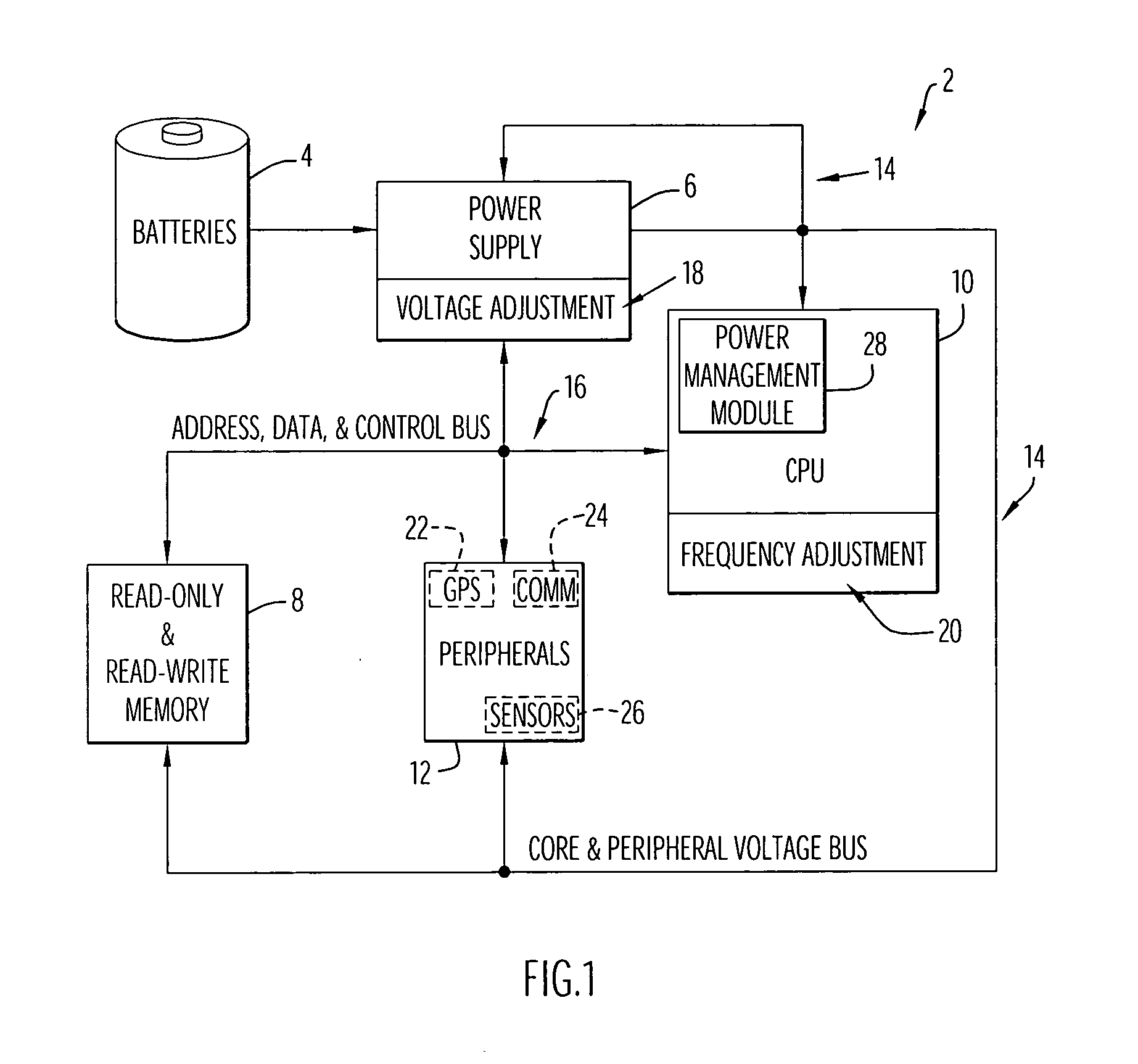
[0026] An exemplary computer system employing the dynamic power management of the present invention is illustrated in FIG. 1. By way of example, the present invention is described with respect to a computer system; however, the present invention may be employed by any electronic device including a processing system or processor to reduce power consumption by that device. Specifically, computer system 2 includes a power source or batteries 4, a power supply 6, memories 8, a processor or CPU 10 and peripherals 12. The power supply receives power from batteries 4 and provides appropriate power signals to the various computer system components (e.g., memories 8, processor 10, peripherals 12, etc.) via a power bus 14. The power supply is typically implemented by a conventional power supply and includes a voltage adjustment module 18 (e.g., in the form of hardware (such as circuitry) and / or software) to control the voltage provided by that supply. Processor 10 is typically implemented by ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com