Patents
Literature
275 results about "Source element" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Source Element (Binding) (ASSL) Identifies the source of data to which the parent element is bound.
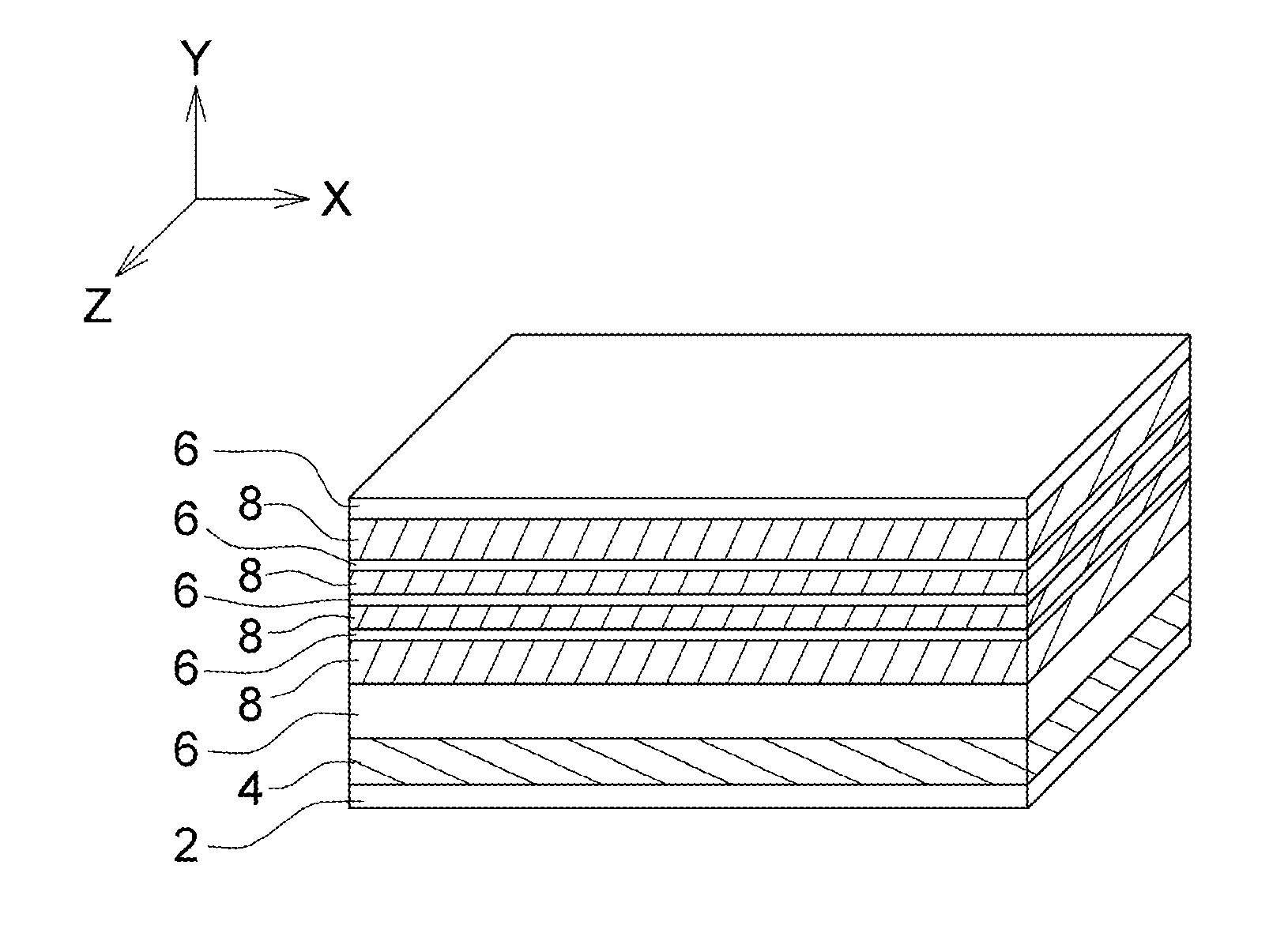
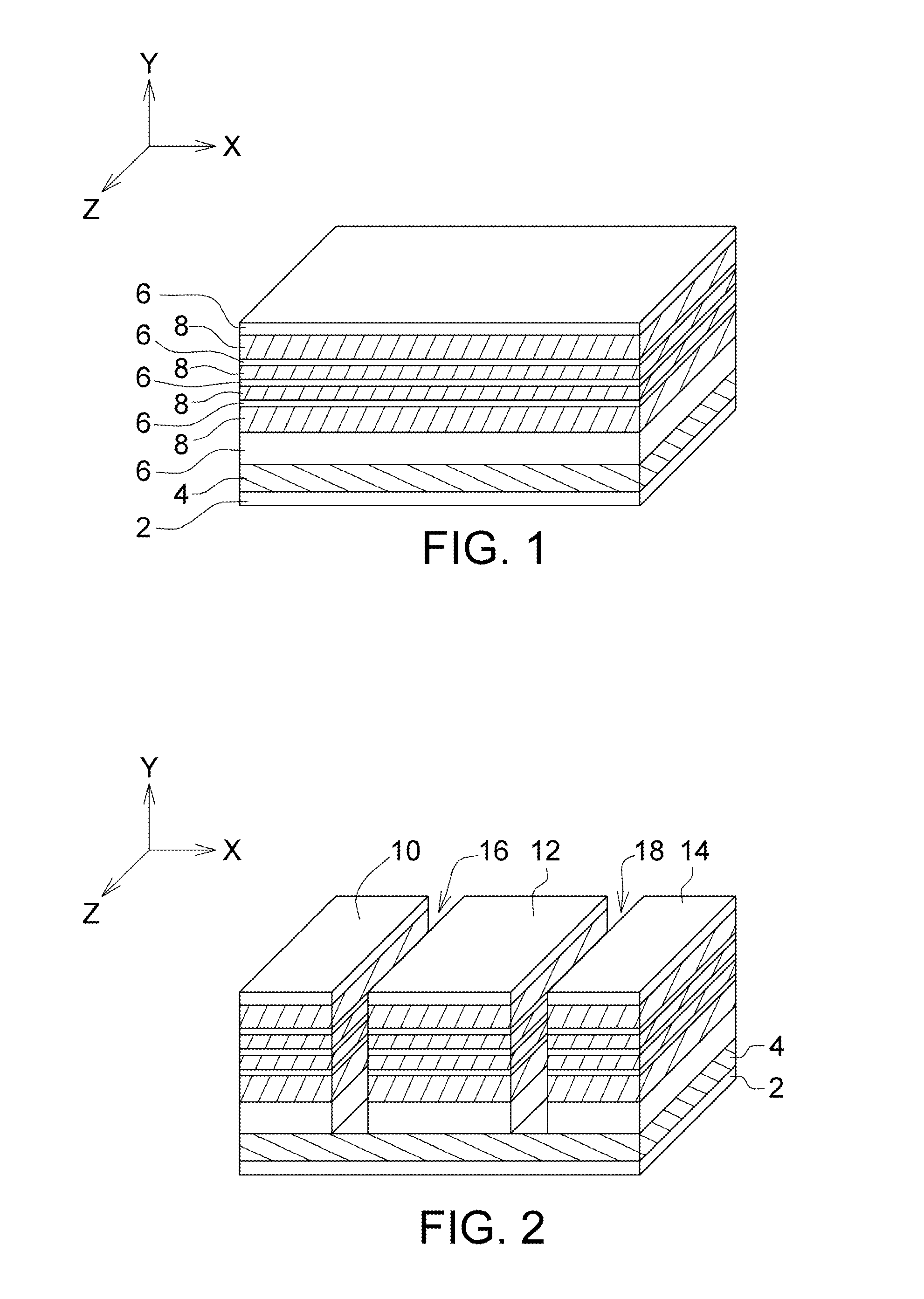
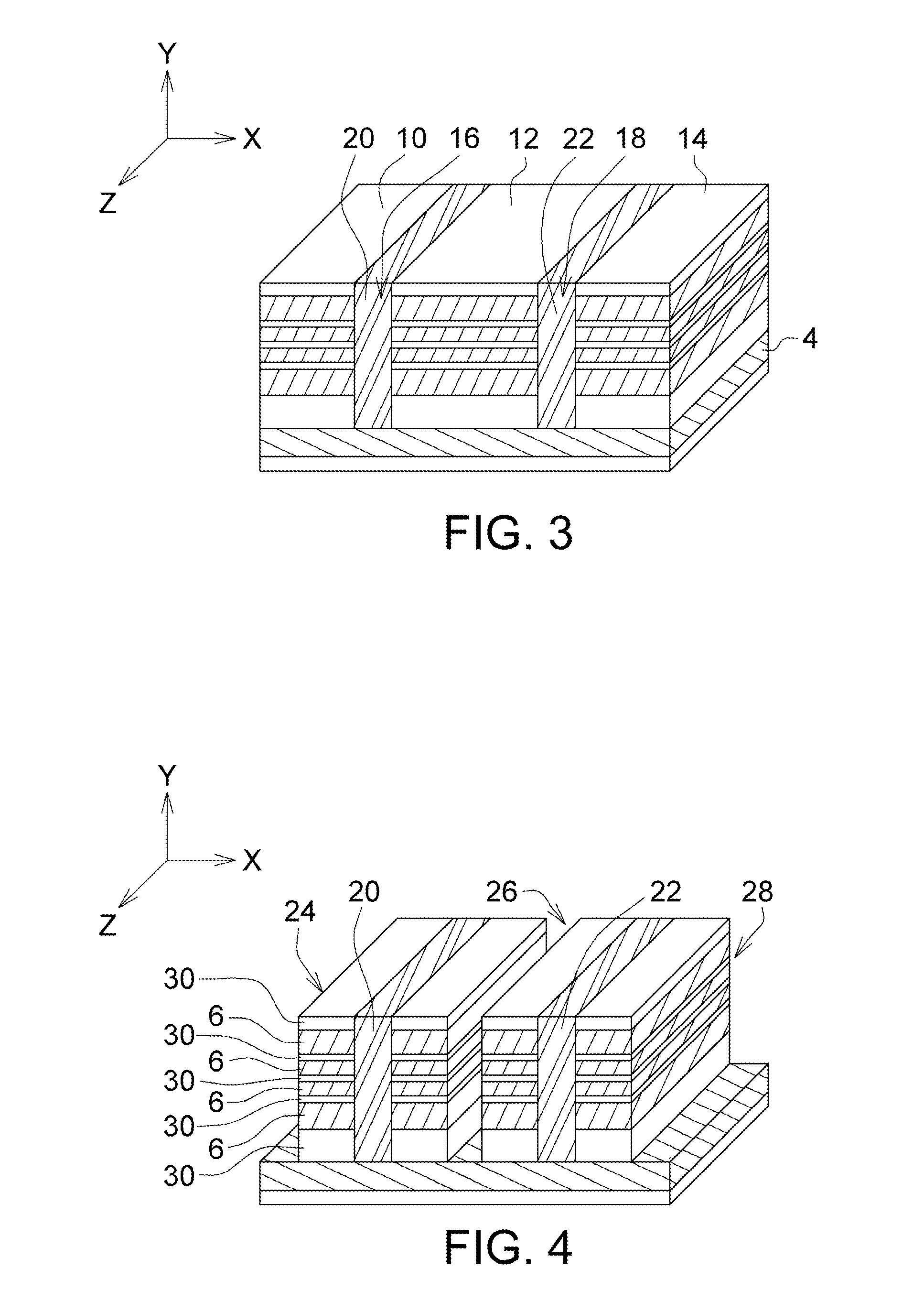
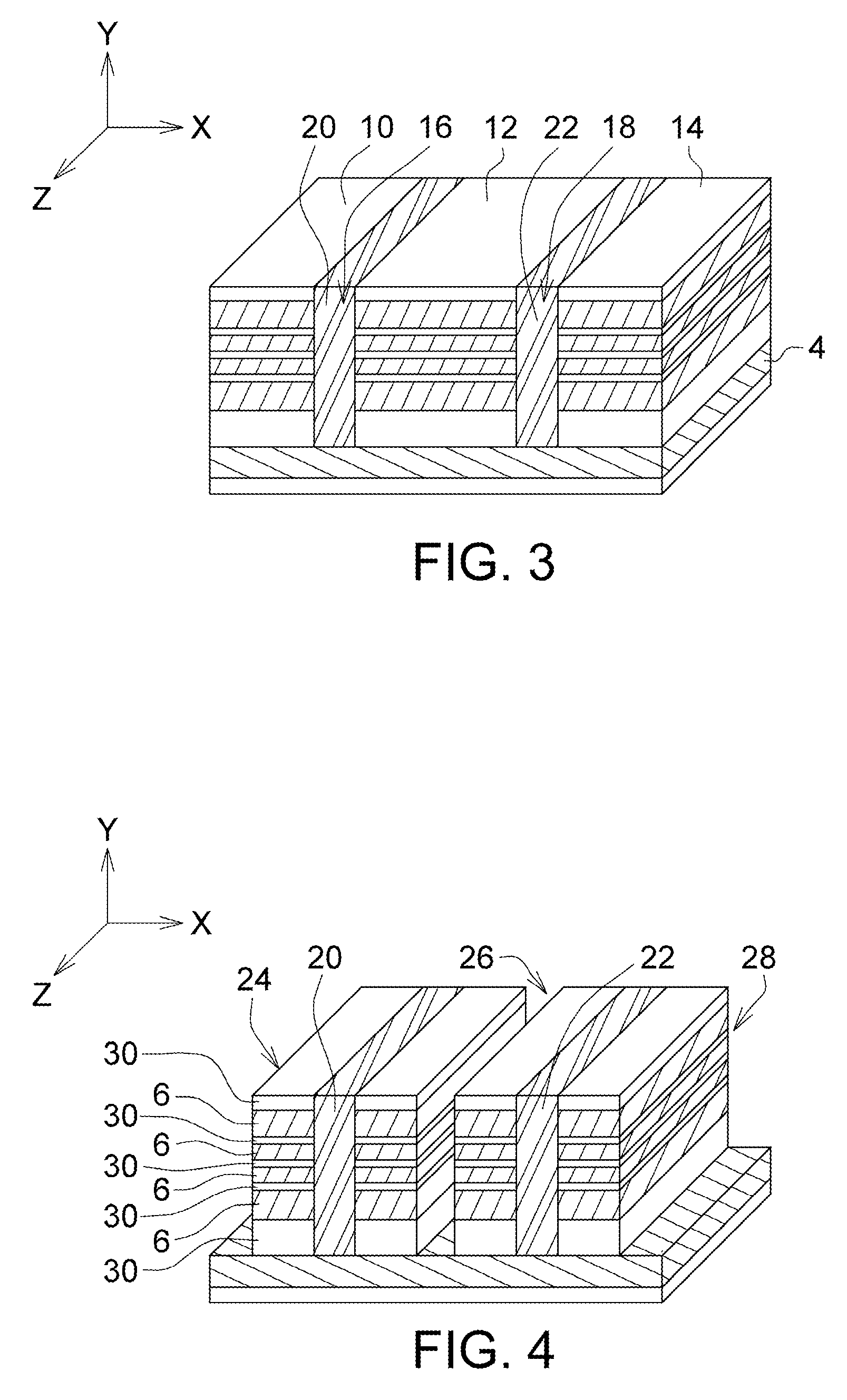
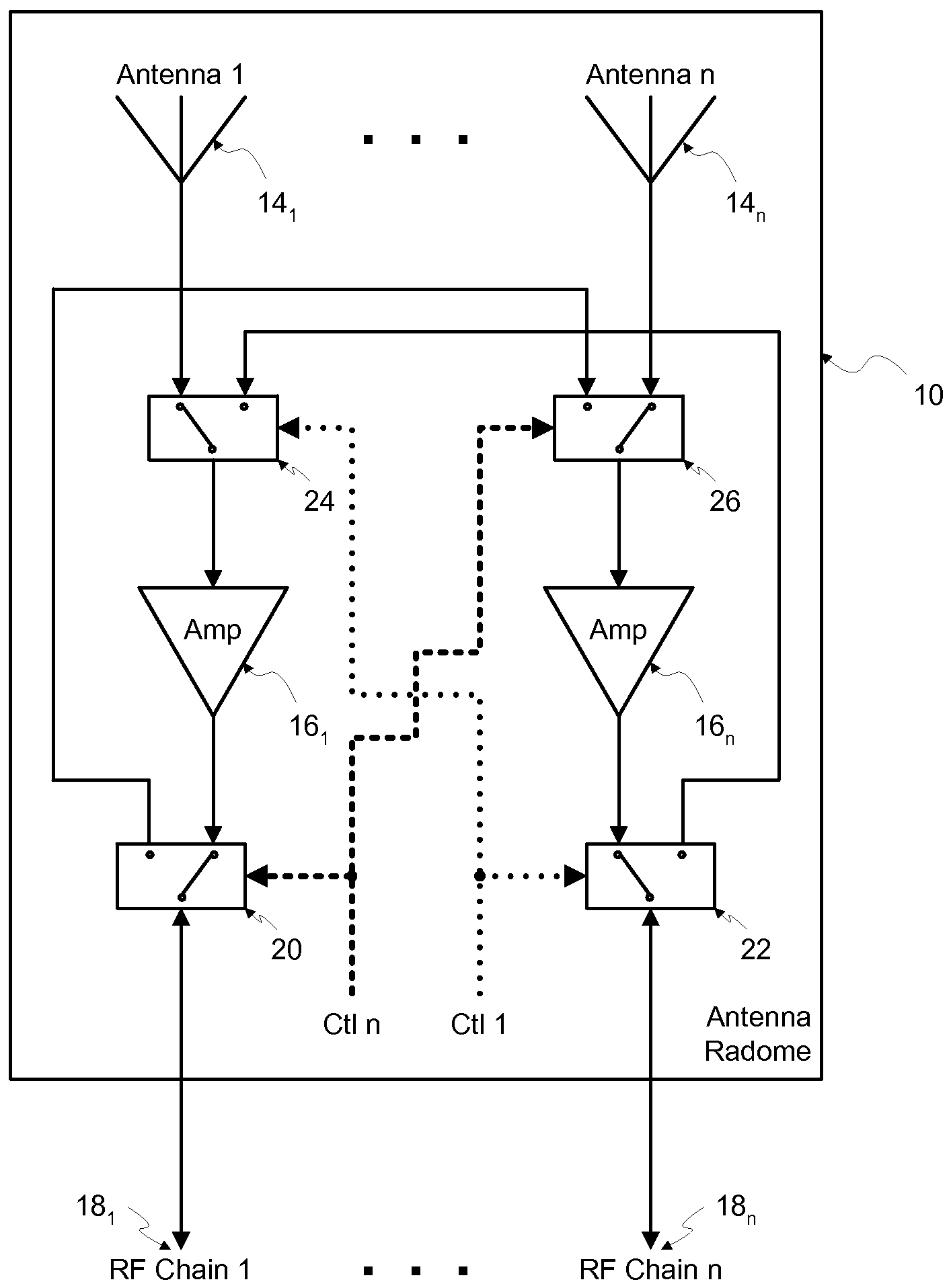
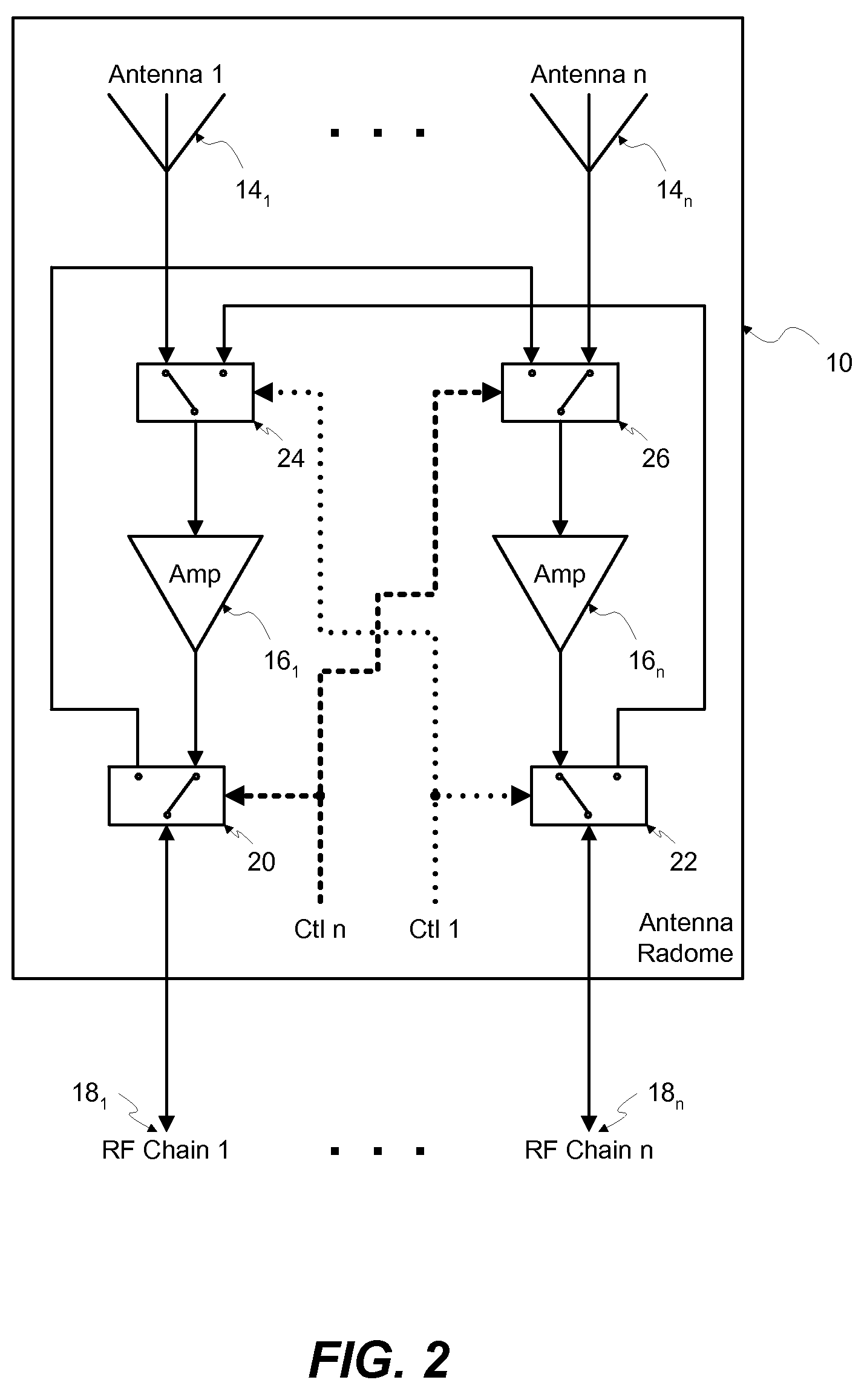
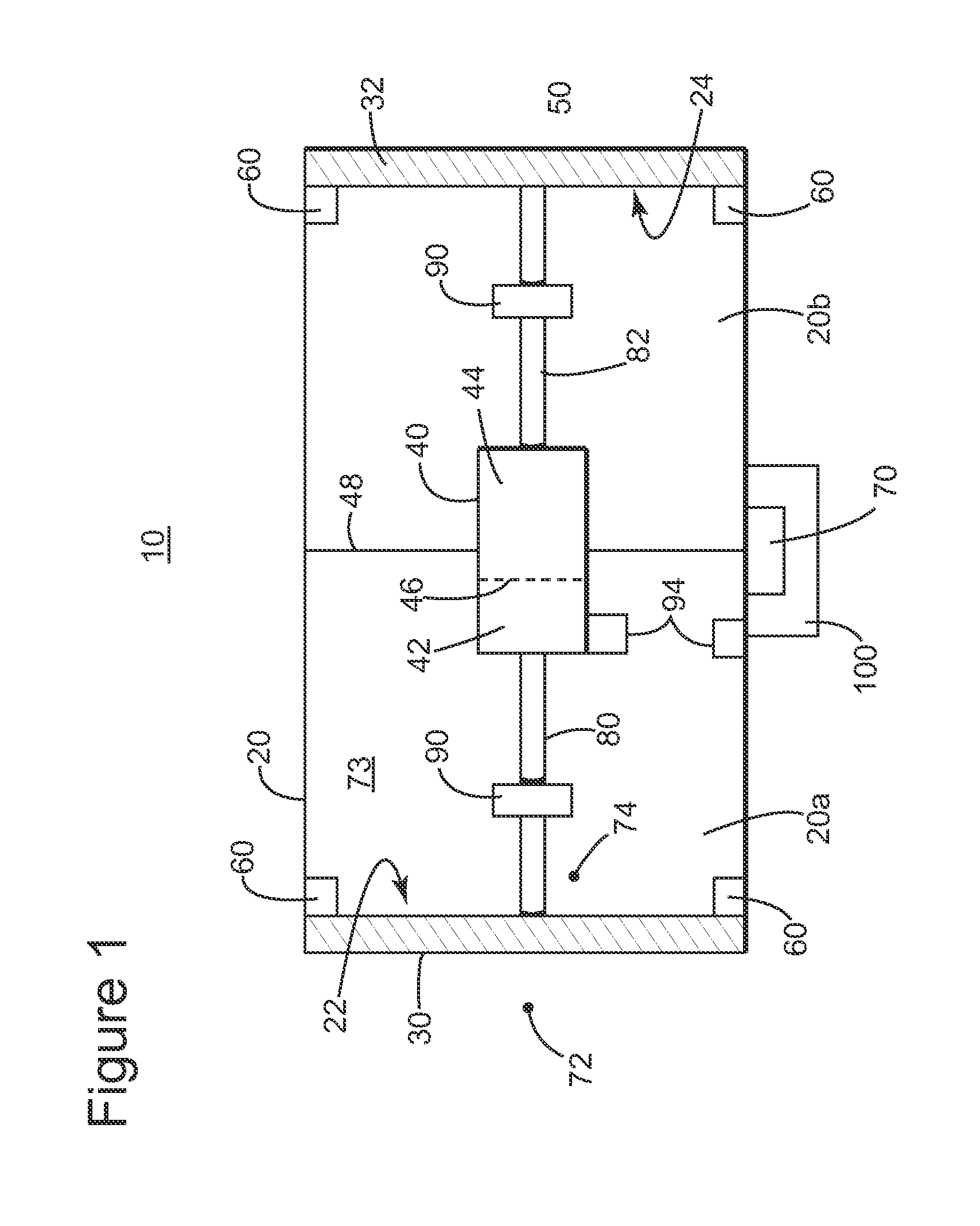
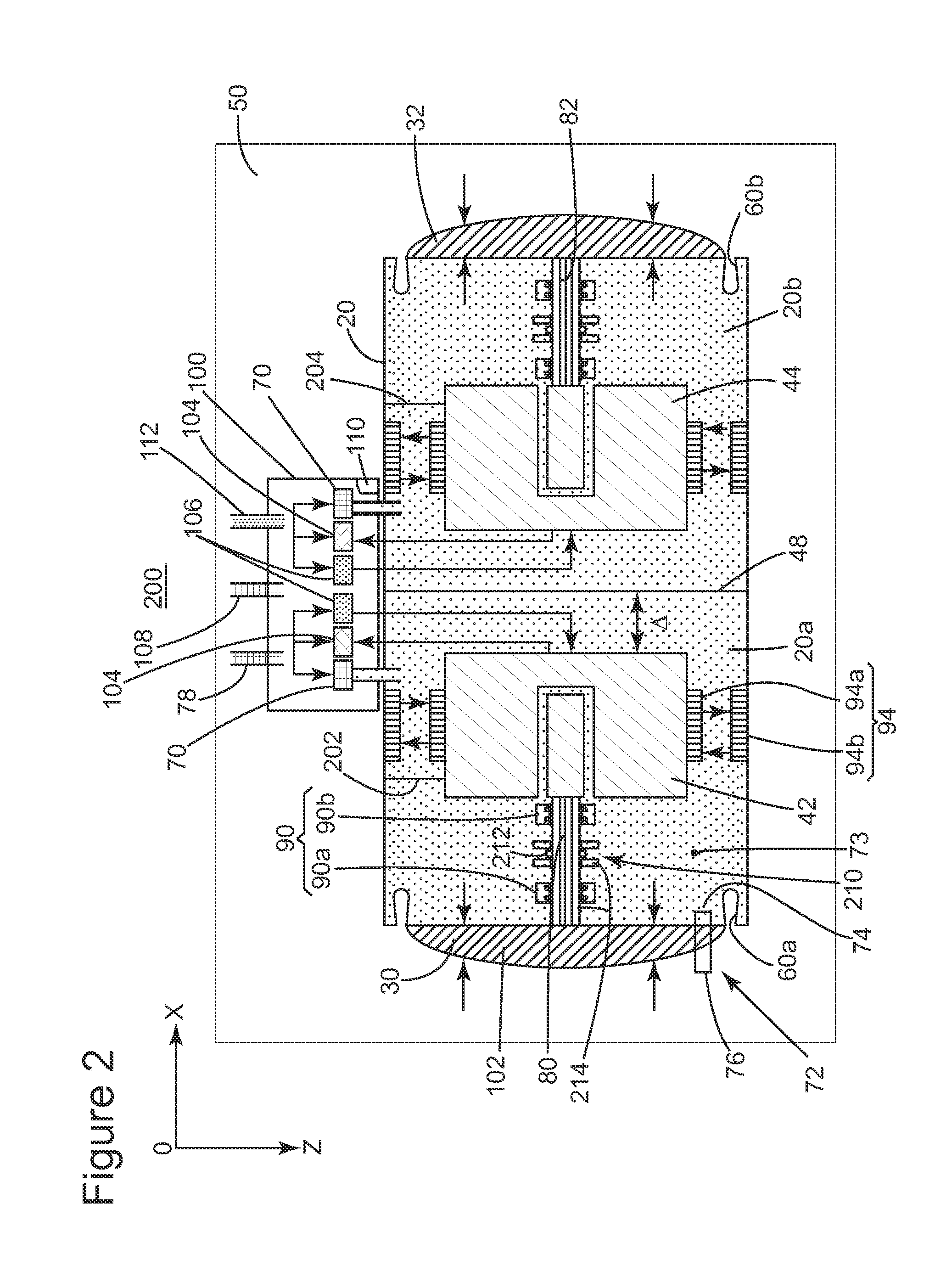
Memory Device, Manufacturing Method and Operating Method of the Same
ActiveUS20120182808A1Small scaling featureImprove performanceSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesDielectricSource element
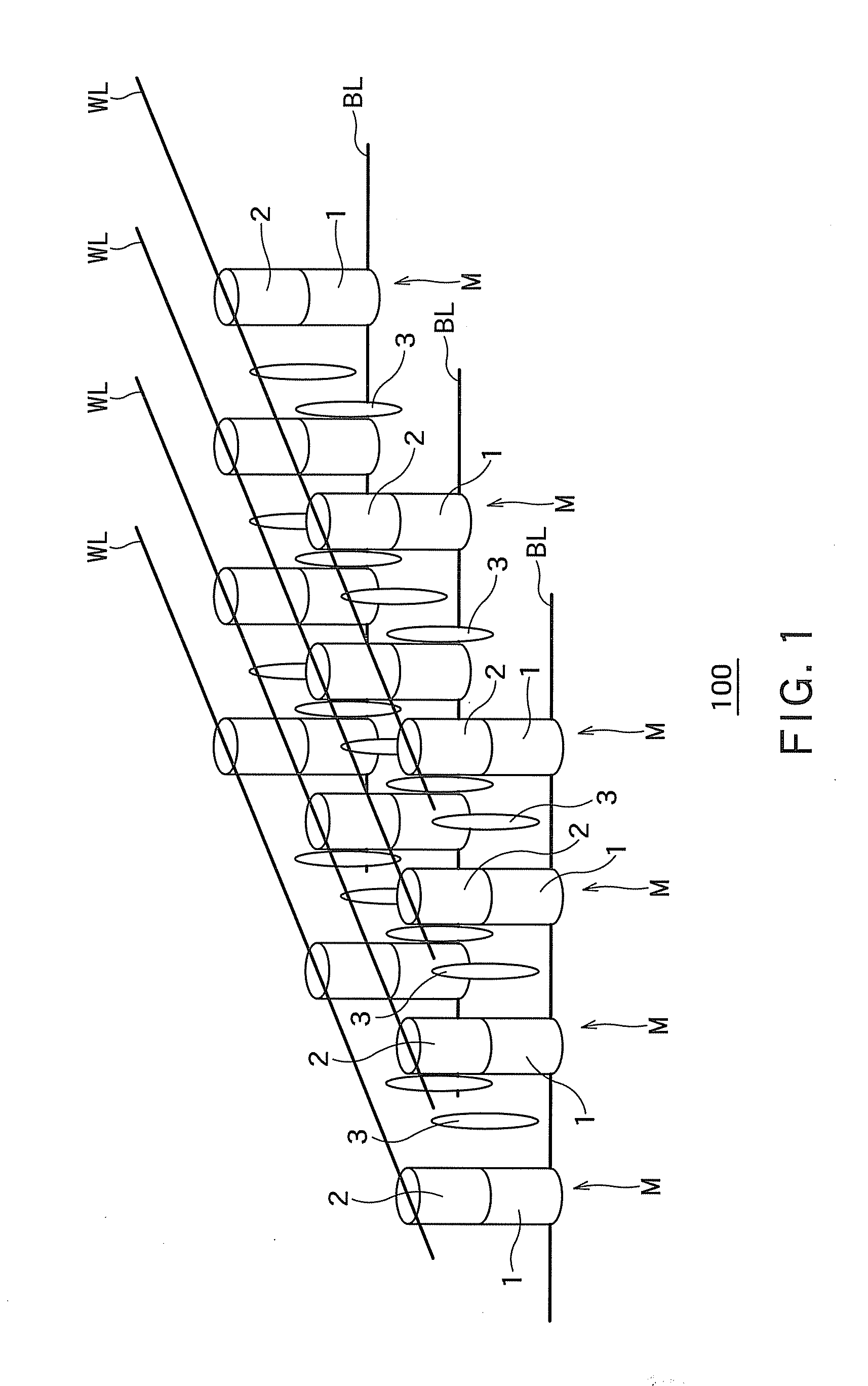
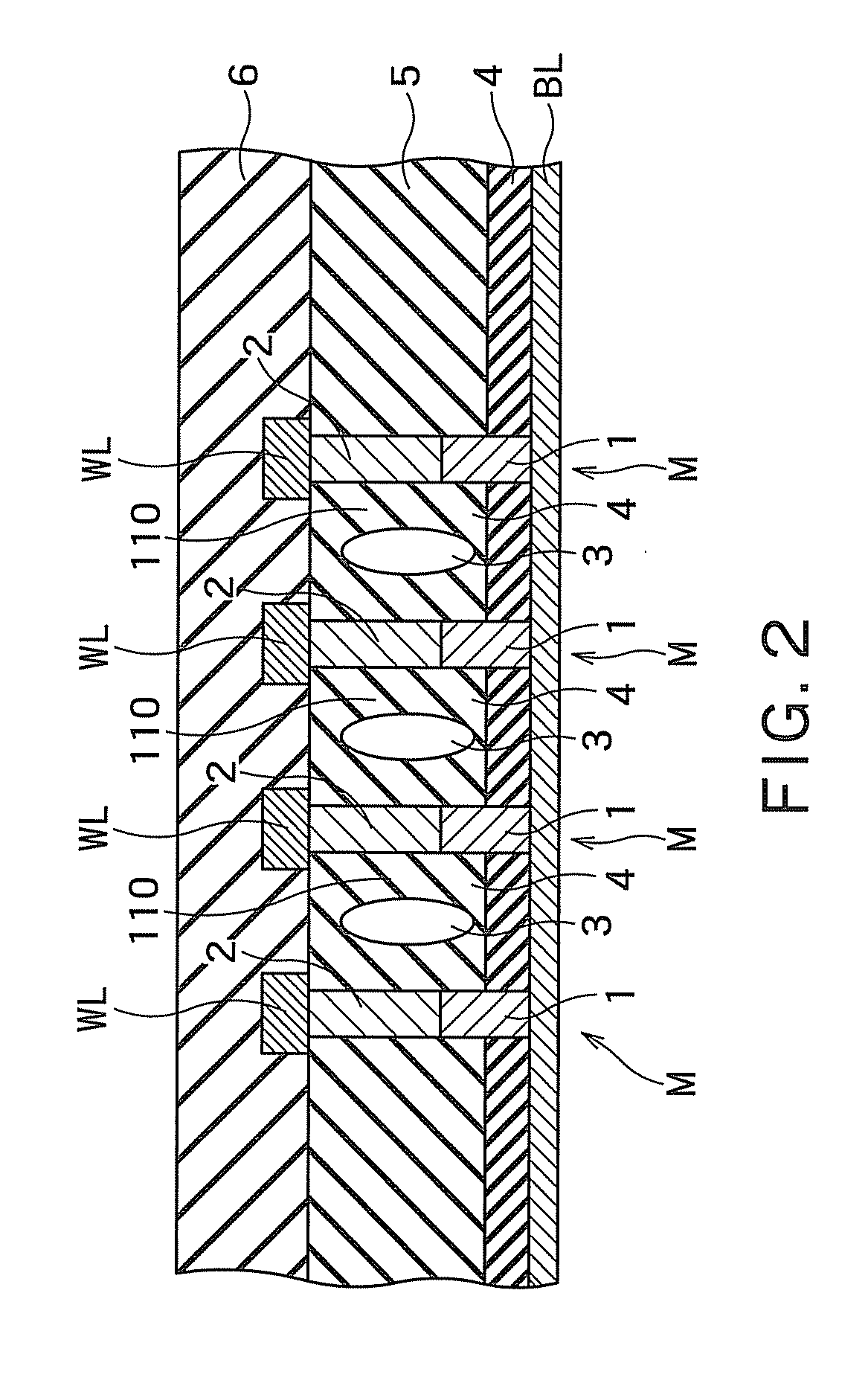
A memory device, a manufacturing method and an operating method of the same are provided. The memory device includes a substrate, stacked structures, a channel element, a dielectric element, a source element, and a bit line. The stacked structures are disposed on the substrate. Each of the stacked structures includes a string selection line, a word line, a ground selection line and an insulating line. The string selection line, the word line and the ground selection line are separated from each other by the insulating line. The channel element is disposed between the stacked structures. The dielectric element is disposed between the channel element and the stacked structure. The source element is disposed between the upper surface of the substrate and the lower surface of the channel element. The bit line is disposed on the upper surface of the channel element.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Apparatus and method for thin film deposition
InactiveUS20020086106A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSource elementEngineering
The apparatus for forming a thin film includes a reaction chamber having a top portion, a sidewall portion and a bottom portion; a gas injector penetrating the top portion and letting a source element pass therethrough; a distributor connected to the gas injector, wherein a plurality of injection holes are formed in the distributor and the source element is injected through the plurality of injection holes; and u substrate heating member positioned in a reaction space defined by the top, bottom and sidewall portions of the reaction chamber, and arranged below the distributor.
Owner:JUSUNG ENG
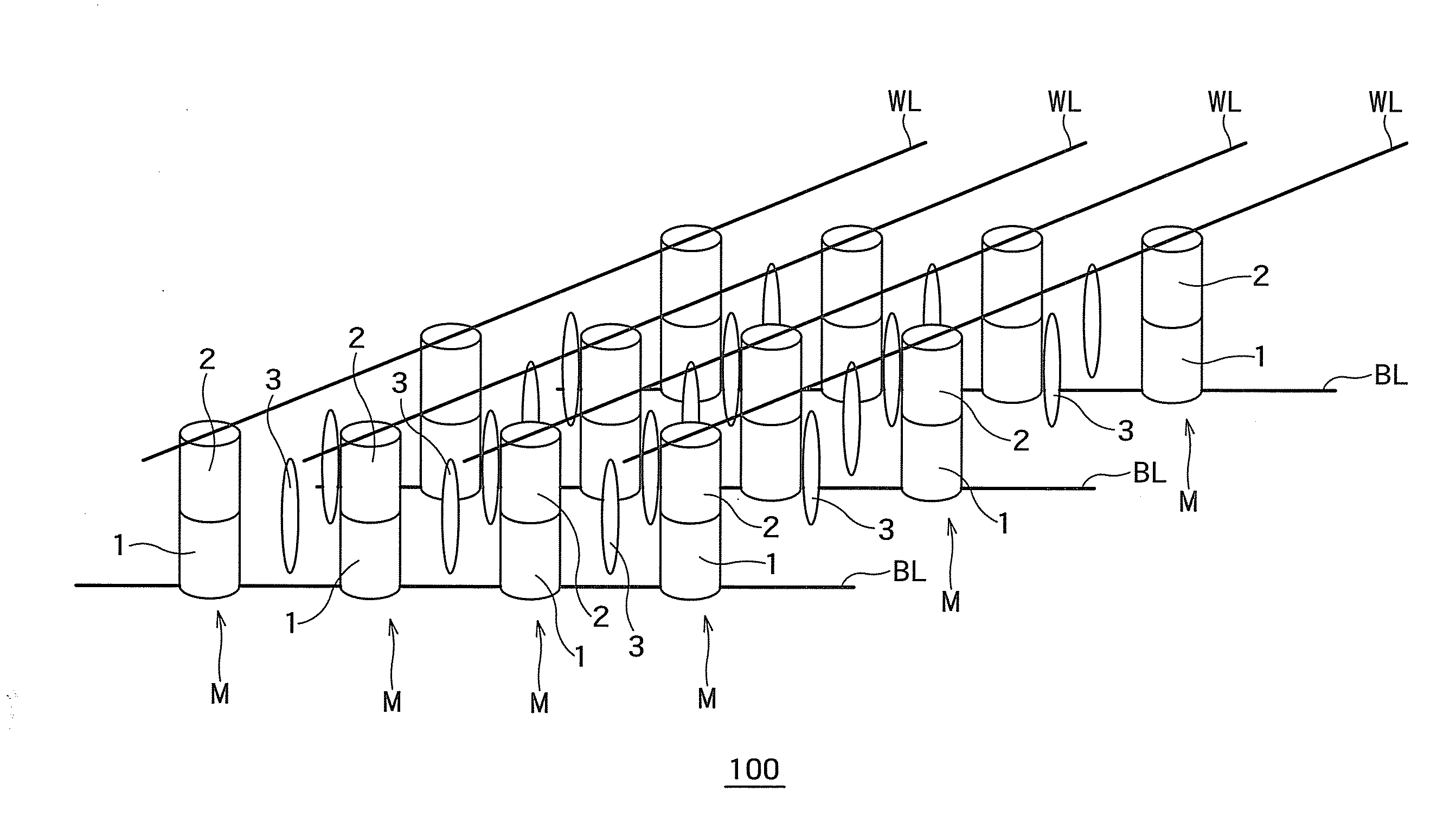
Memory device, manufacturing method and operating method of the same
ActiveUS8363476B2Small scaling featureImprove performanceSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesDielectricBit line
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
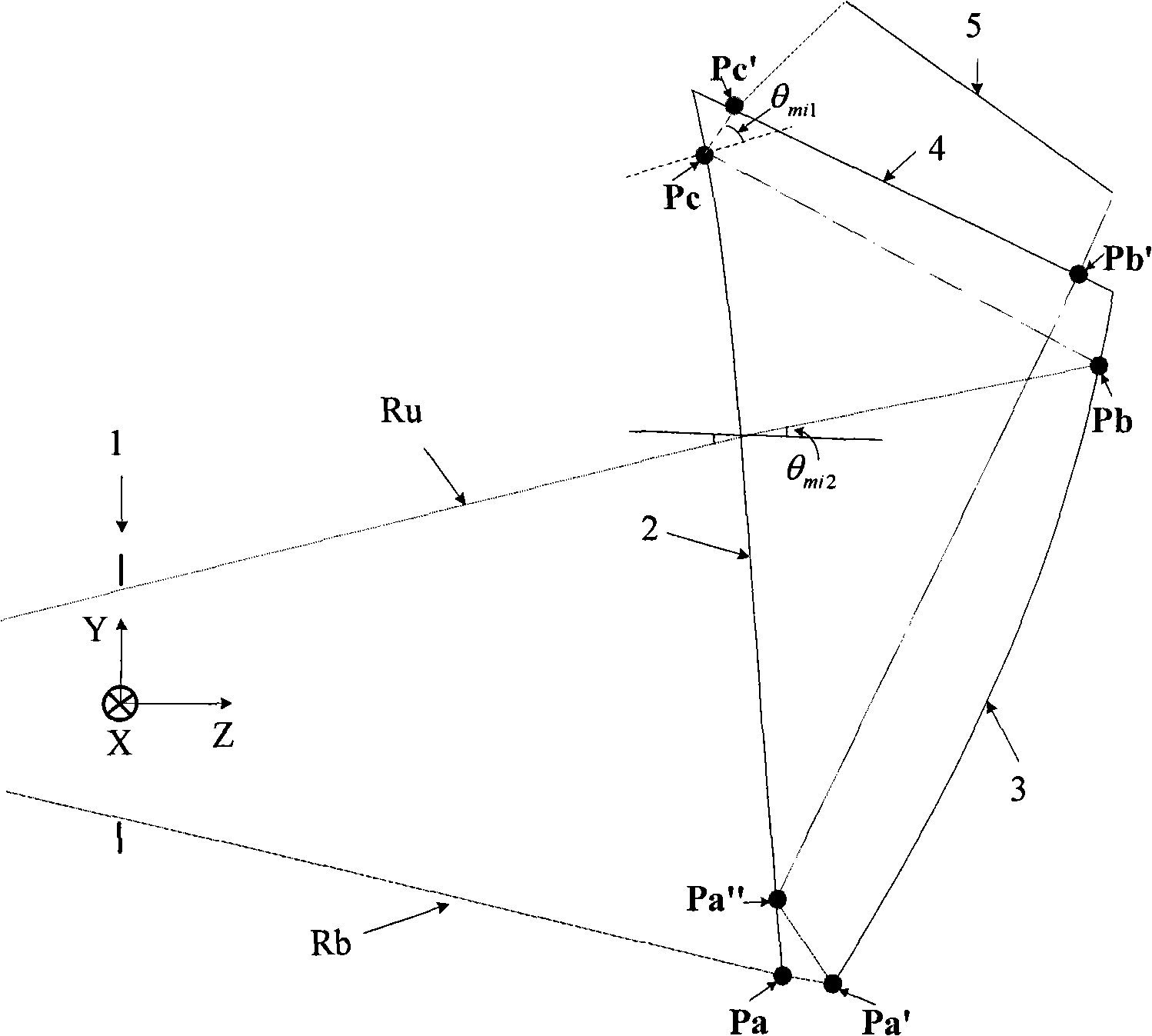
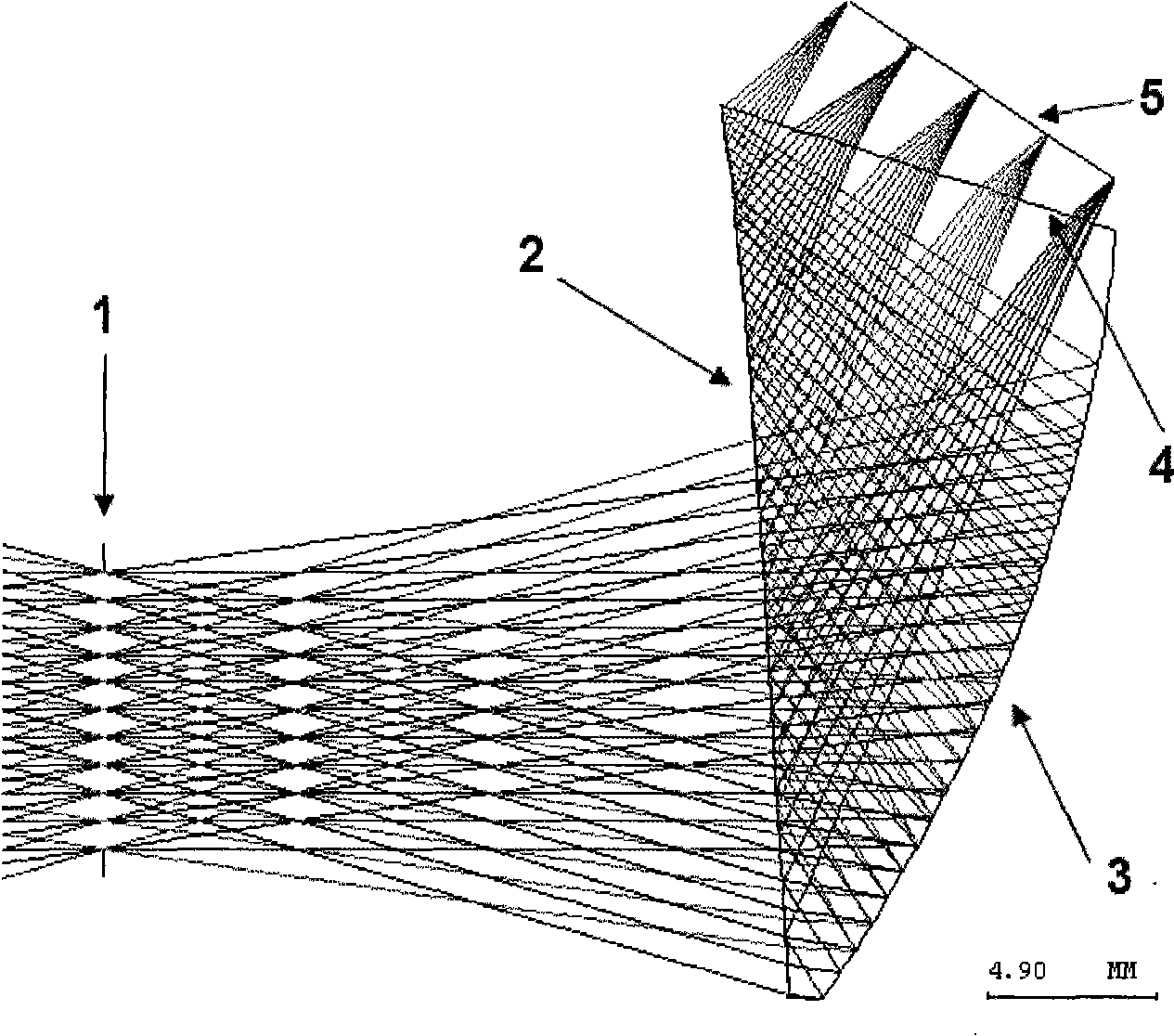
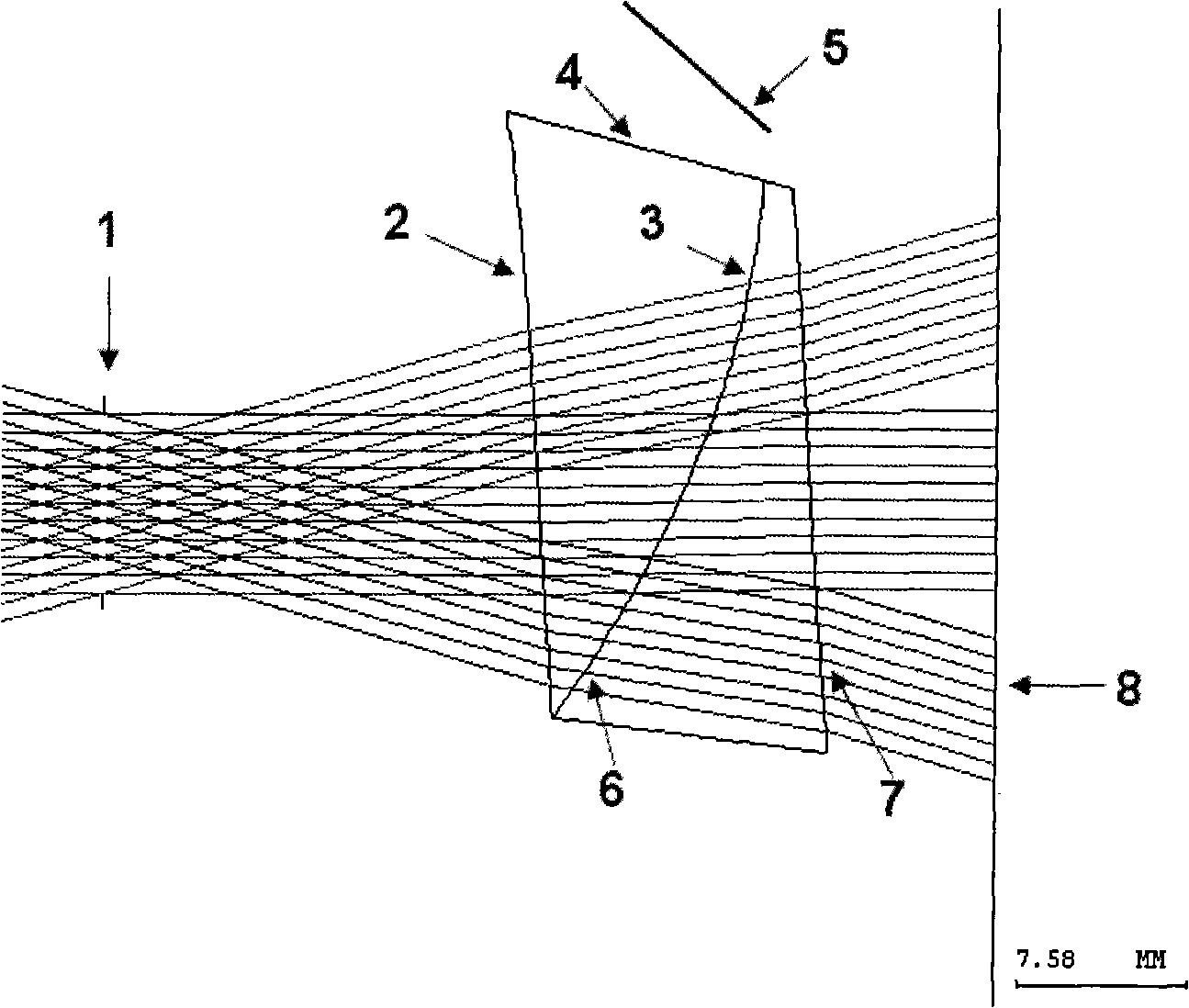
Optical system of light and small-sized big angular field free curved surface prism helmet display
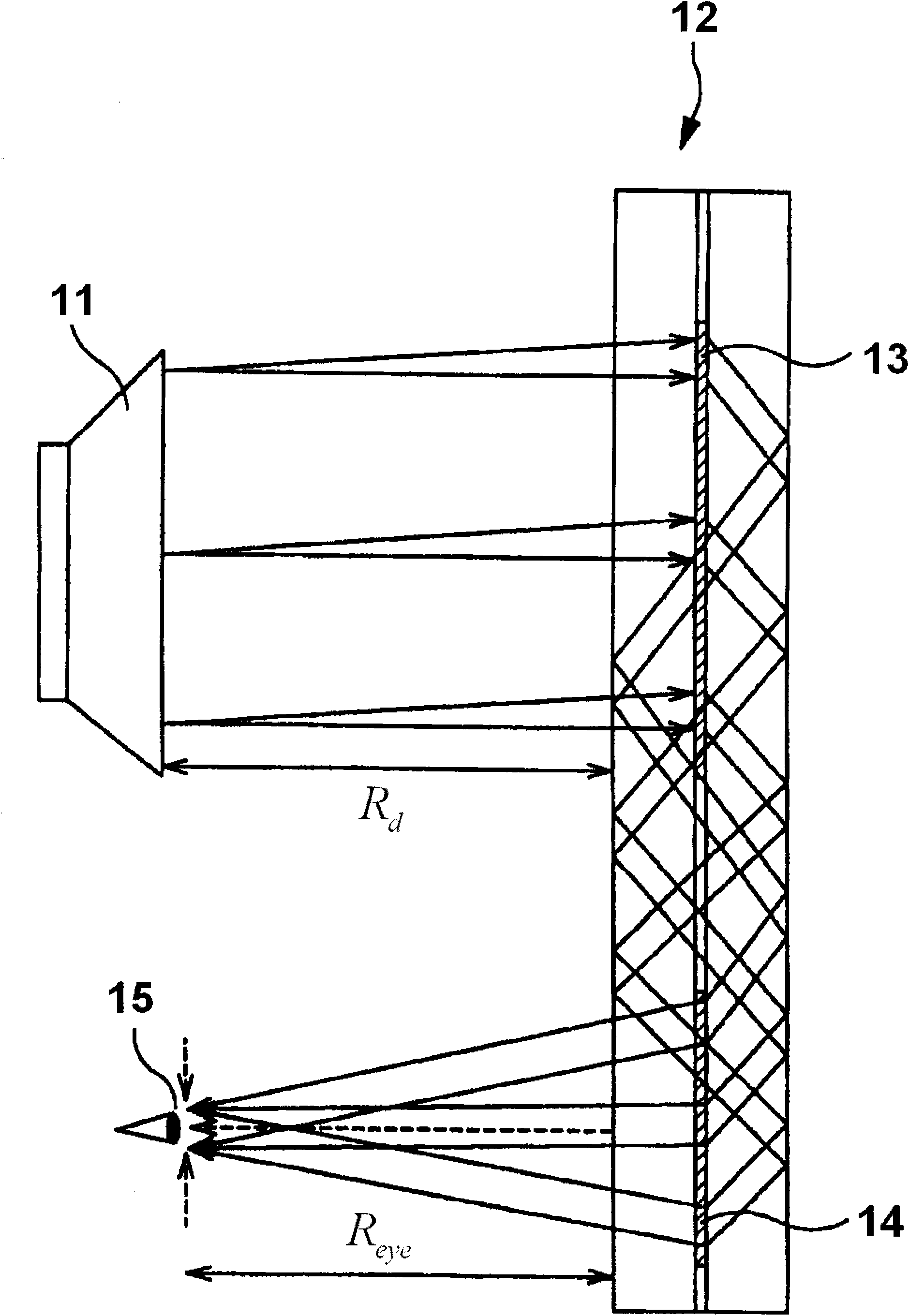
The invention relates to a small and light wide-field free-form surface prism HMD optical system, which belongs to the field of optical system and device design and is applied to the virtual reality and augmented reality field. The invention comprises a free-form surface prism with three optical surfaces, and a micro-image display; the free-form surface prism is made of plastic glass materials with the refractive index greater than 1; the three free-form optical surfaces are concave surfaces, which meet one of the three surface-type equations, and the location relationship of each surface meets three condition equations; the incident angle formed between the widest-field upper edge rays emitted by an LCD and the second free-form surface meets the total reflection conditions; and an image source element is an LCD of 0.61 or 0.59 inches. The small and light wide-field free-form surface prism HMD optical system is light and compact and has the advantages of good aberration correction and high light energy utilization rate; the optical system enables the observer to see clear images in a wide field of view, and the displayed images do not have apparent brightness attenuation and can not easily cause visual fatigue to the observer.
Owner:BEIJING NEDPLUSAR DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
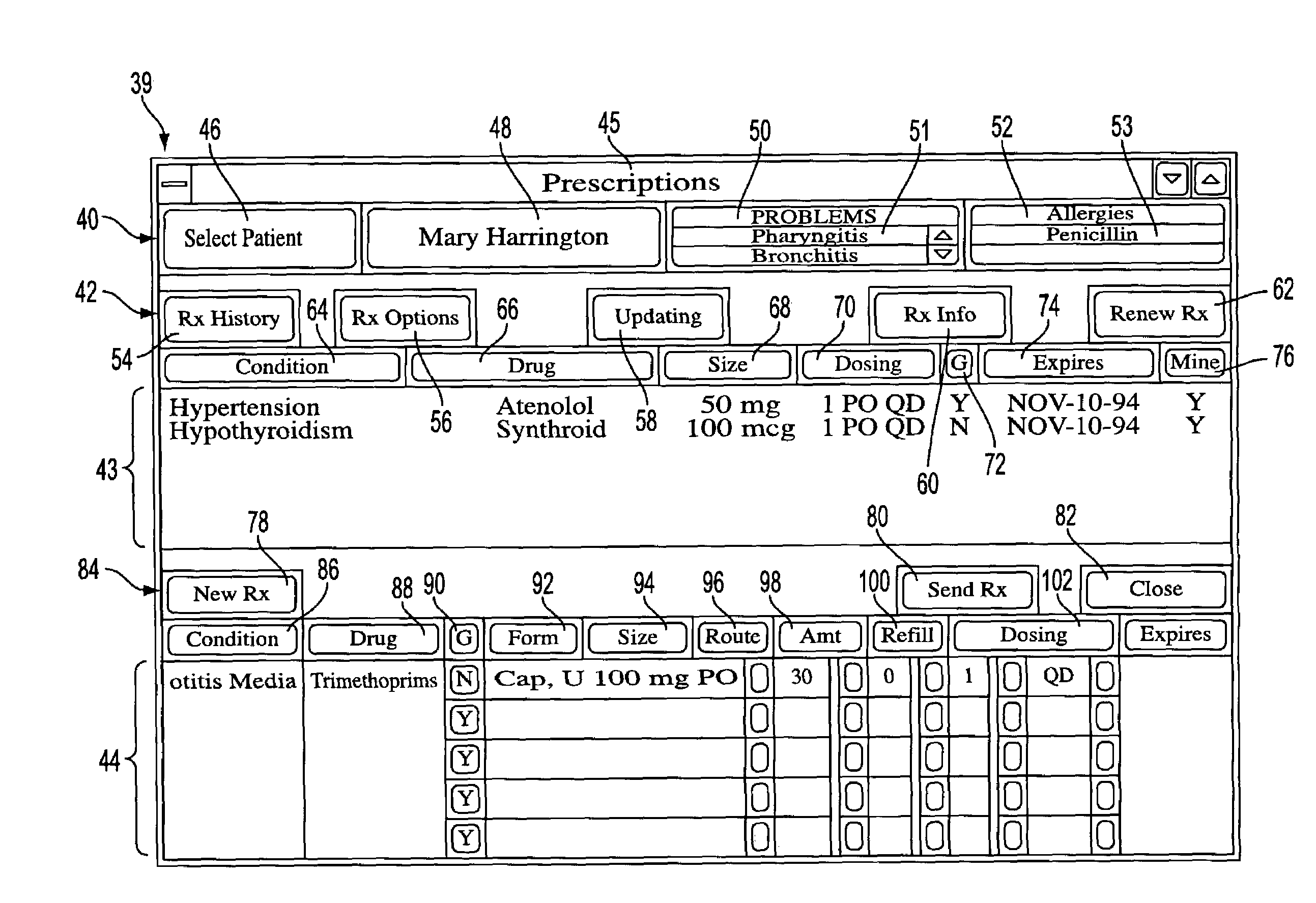
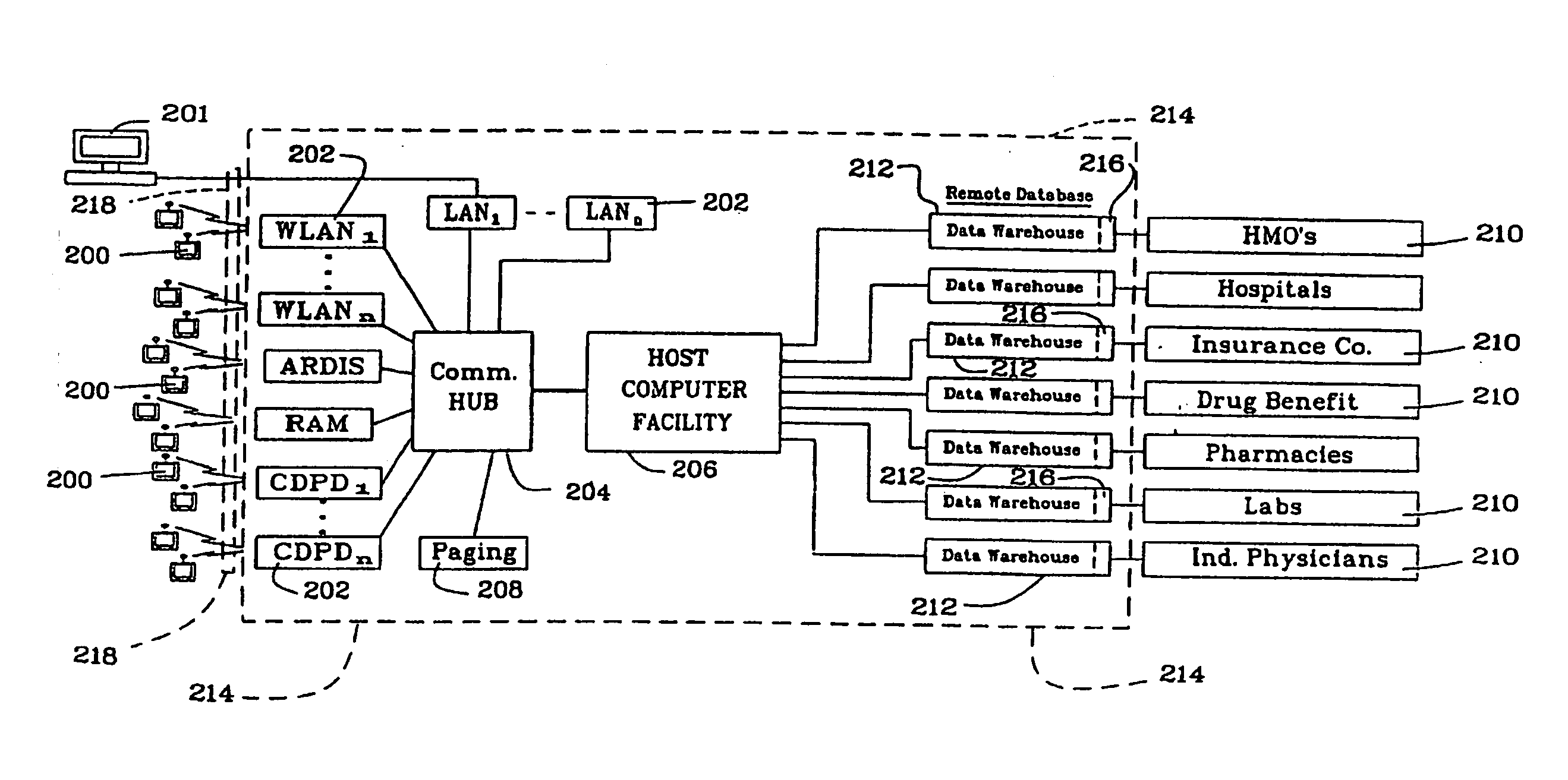
Computerized prescription system for gathering and presenting information relating to pharmaceuticals
InactiveUS7483839B2Quality improvementLow costFinanceDrug and medicationsIntelligent NetworkData retrieval
A wirelessly deployable, electronic prescription creation system for physician use captures into a prescription a patient condition-objective of the prescribed treatment and provides for patient record assembly from source elements, with privacy controls for patient and doctor, adverse indication review and online access to comprehensive drug information including scientific literature. Extensions to novel multi-drug packages and dispensing devices, and an “intelligent network” remote data retrieval architecture as well as onscreen physician-to-pharmacy and physician-to-physician e-mail are also provided.
Owner:CYBEAR
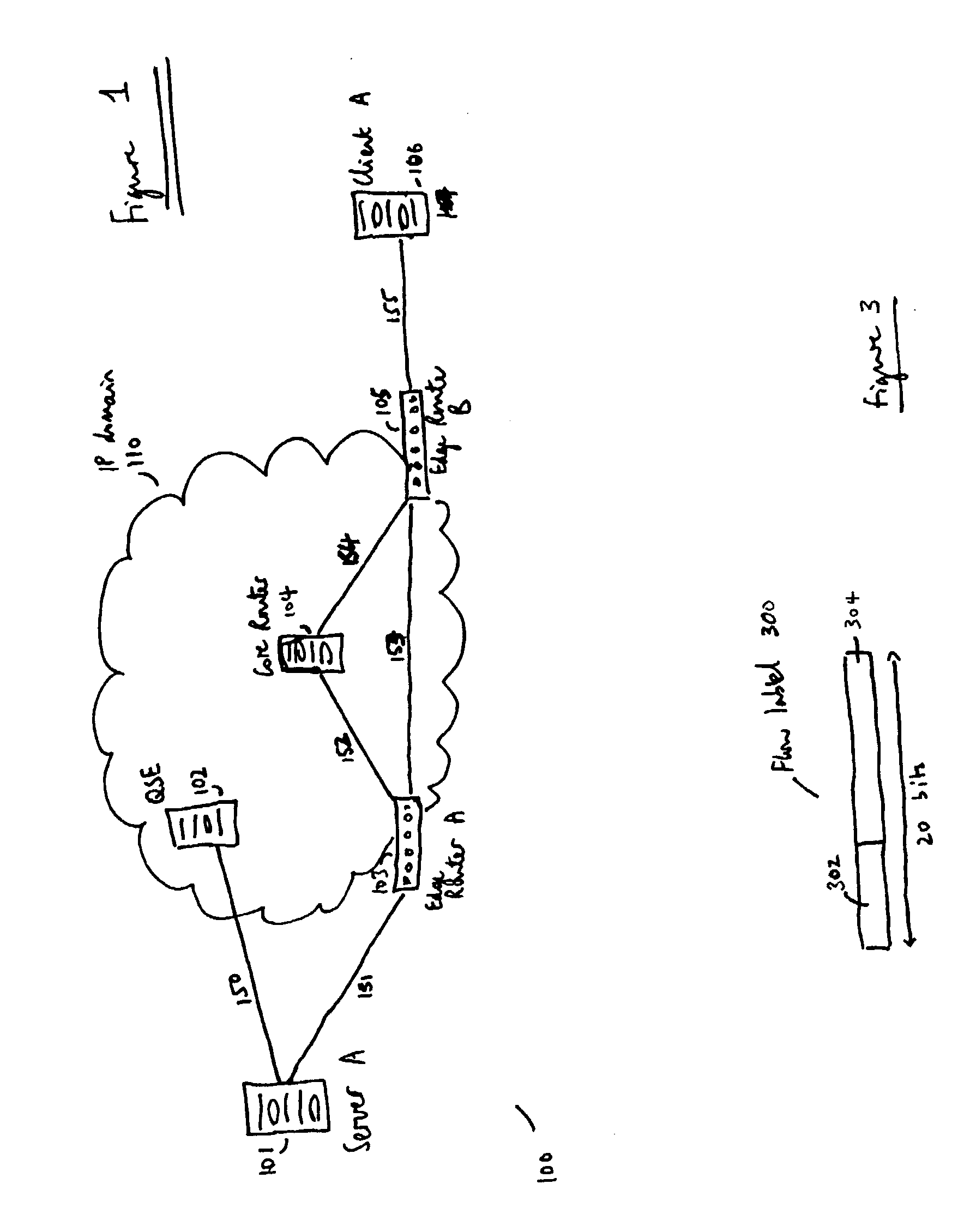
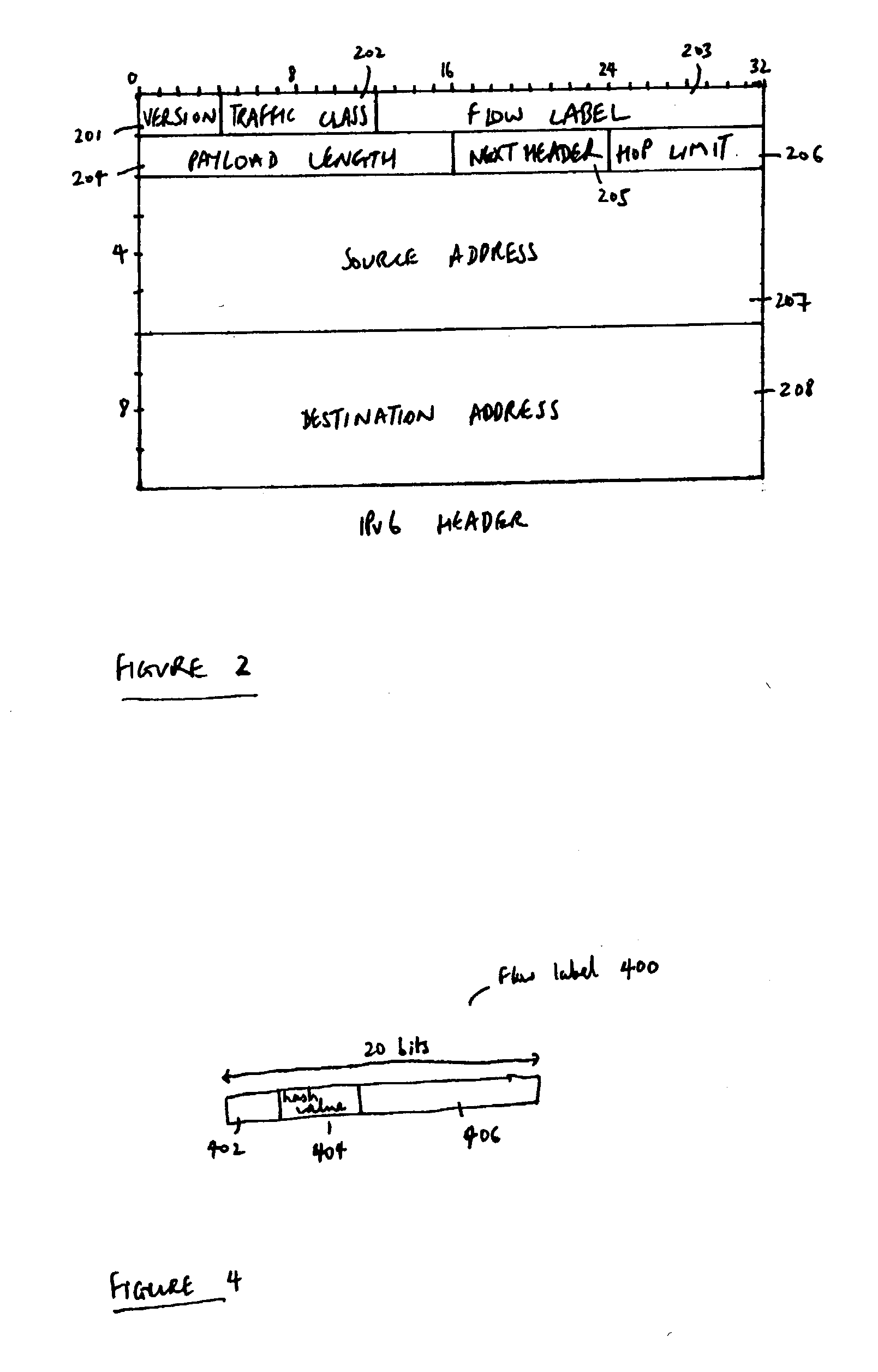
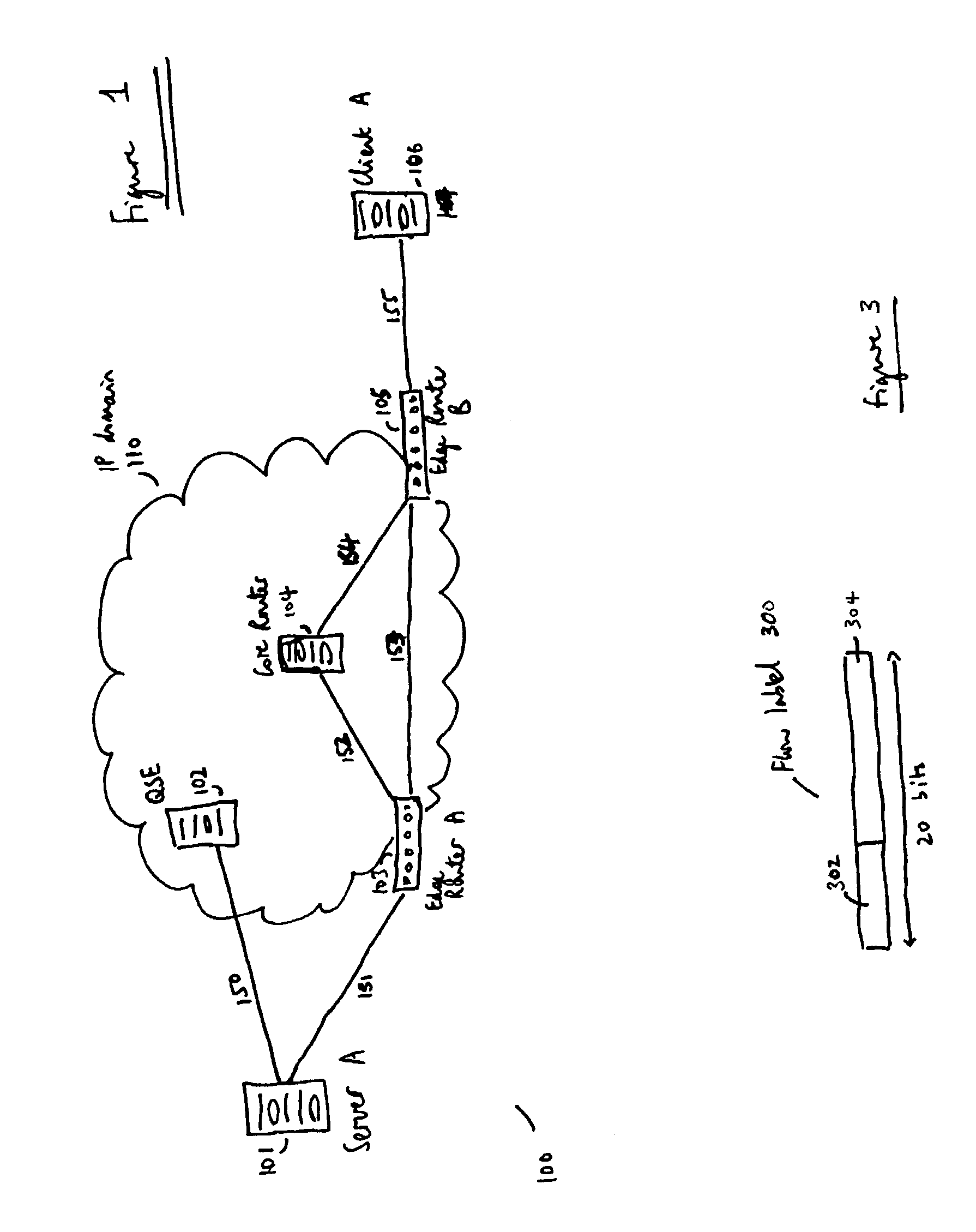
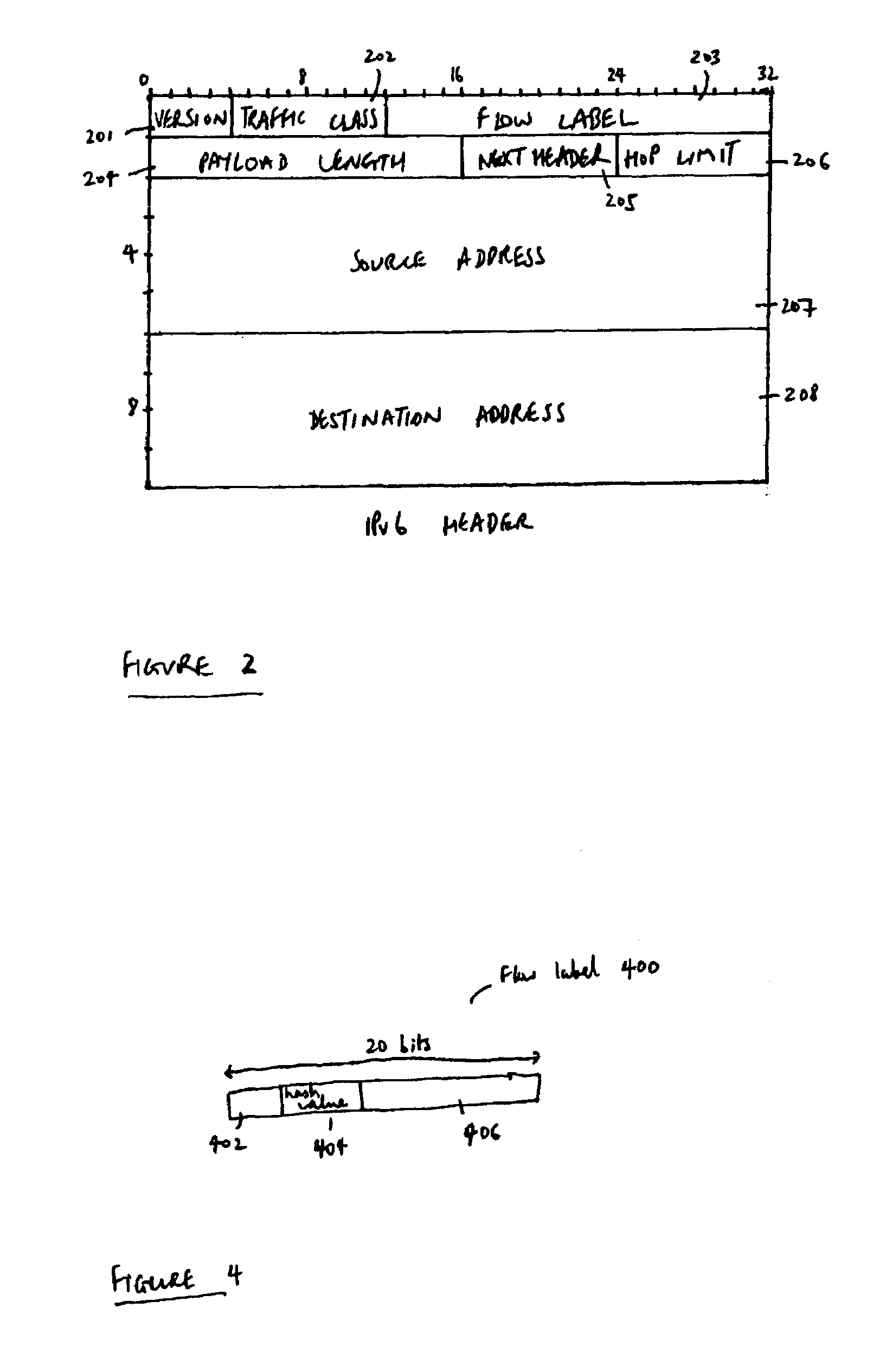
Flow labels
ActiveUS20040125797A1Easy to useValid verificationData switching by path configurationNetwork data managementQuality of serviceData stream
There is disclosed a system for monitoring a packet data flow, comprising: a data flow source element including: determining means adapted to determine a quality of service identifier for the data flow; first generating means adapted to generate an encoded value in dependence on the quality of service identifier; allocating means adapted to allocate the quality of service identifier and the encoded value to the flow label for each data packet of the data flow; and transmitting means for forwarding data packets including flow labels to a routing domain; and a routing domain interface element including: receiving means for receiving data packets from the data flow source; second generating means adapted to generate a further encoded value in dependence on the quality of service identifier in a flow label of a data packet; comparing means adapted to compare the further encoded value to the encoded value in the flow label; and routing means adapted to selectively route the data packets in dependence on the comparing step.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
Method and apparatus for using barrier phases to limit packet disorder in a packet switching system
InactiveUS6967926B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionCommunications systemSource element
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for using barrier phases to limit the disorder of packets which may be used in a computer or communications system. In one packet switching system, source nodes include an indication of their current barrier state in sent packets. For each barrier state, a predetermined range of sequence numbers may be used or a predetermined number of packets may be sent by a source node. The source, destination, and switching nodes are systematically switched between barrier phases, which is typically performed continuously in response to the flow of barrier request and barrier acknowledgement packets or signals. Each source node broadcasts to all forward connected nodes a barrier request to change to a next barrier state. After a switching node has received a barrier request on all incoming links, the switching node propagates the barrier request. Upon receiving barrier requests over all links, each destination stage relays an acknowledgement message to all connected source elements, which then send a barrier acknowledgement in much the same way, and each source element changes its barrier state causing the sequence number or counting space to be reset, and newly sent packets to indicate the new barrier state. Upon receiving all its barrier acknowledgement messages, each destination stage changes its barrier state, and then the destination can manipulate (e.g., resequence, reassemble, send, place in an output queue, etc.) packets marked with the previous barrier state as it knows that every packet from the previous barrier state has been received. This transition of barrier phases and limiting the number of packets sent per barrier phases may be used to limit the range of the sequence number space and the size of outgoing, resequencing, and reassembling buffers, as well providing a packet time-out mechanism which may be especially useful when non-continuous sequence numbers or time-stamps are included in packets for resequencing and / or reassembly purposes.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Prescription management system
InactiveUS20100161353A1Quality improvementReducing prescription costData processing applicationsDrug and medicationsIntelligent NetworkData retrieval
A wirelessly deployable, electronic prescription creation system for physician use captures into a prescription a patient condition-objective of the prescribed treatment and provides for patient record assembly from source elements, with privacy controls for patient and doctor, adverse indication review and online access to comprehensive drug information including scientific literature. Extensions to novel multi-drug packages and dispensing devices, and an “intelligent network” remote data retrieval architecture as well as onscreen physician-to-pharmacy and physician-to-physician e-mail are also provided.
Owner:CYBEAR
Method of forming a building panel or surface element and such a building panel and surface element
ActiveUS20160369507A1Increase and decrease and heat conductivityImprove propertiesConstruction materialLamination ancillary operationsEngineeringSource element
A method of forming a building panel or a surface element, including providing a substrate, applying a sub-layer on the substrate, applying a mesh structure on the sub-layer, and applying heat and pressure to the mesh structure such that the sub-layer at least partially fills meshes of the mesh structure. Also, to such a building panel and a surface element.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
Shared mesh signaling algorithm and apparatus
A shared mesh protection scheme defines an associated protection path when a working connection is established. During the protection path definition, the corresponding protection path information is sent down to a switch card of network elements making up the protection path. Upon detection of the failure, the network elements using an overhead byte message will inform the routing source network element of the connection of the failure in the working path. The overhead bytes used are interrupt driven bytes located in the line and path overhead of network traffic. The routing source node of the connection will then send the corresponding overhead byte messages down the protection path to provide for protection path establishment according to the preloaded data located at the switch card. It should be noted that each connection can have a source and termination element which relates to the source from where the corresponding connection was set-up rather than the direction of the payload transmission. Therefore, once the failure has occurred the source elements will send messages using overhead bytes to the corresponding network elements along the protection path. Accordingly, routing tables located at the switch card of the network elements, set-up when the working path connections were initially established, determine this dynamically allocated protection path environment.
Owner:CIENA
Method and system for stylesheet execution interactive feedback
InactiveUS7337391B2Easy to FeedbackImprove understandingDigital computer detailsNatural language data processingProgramming languageSource element
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
Sampling in volumetric computed tomography
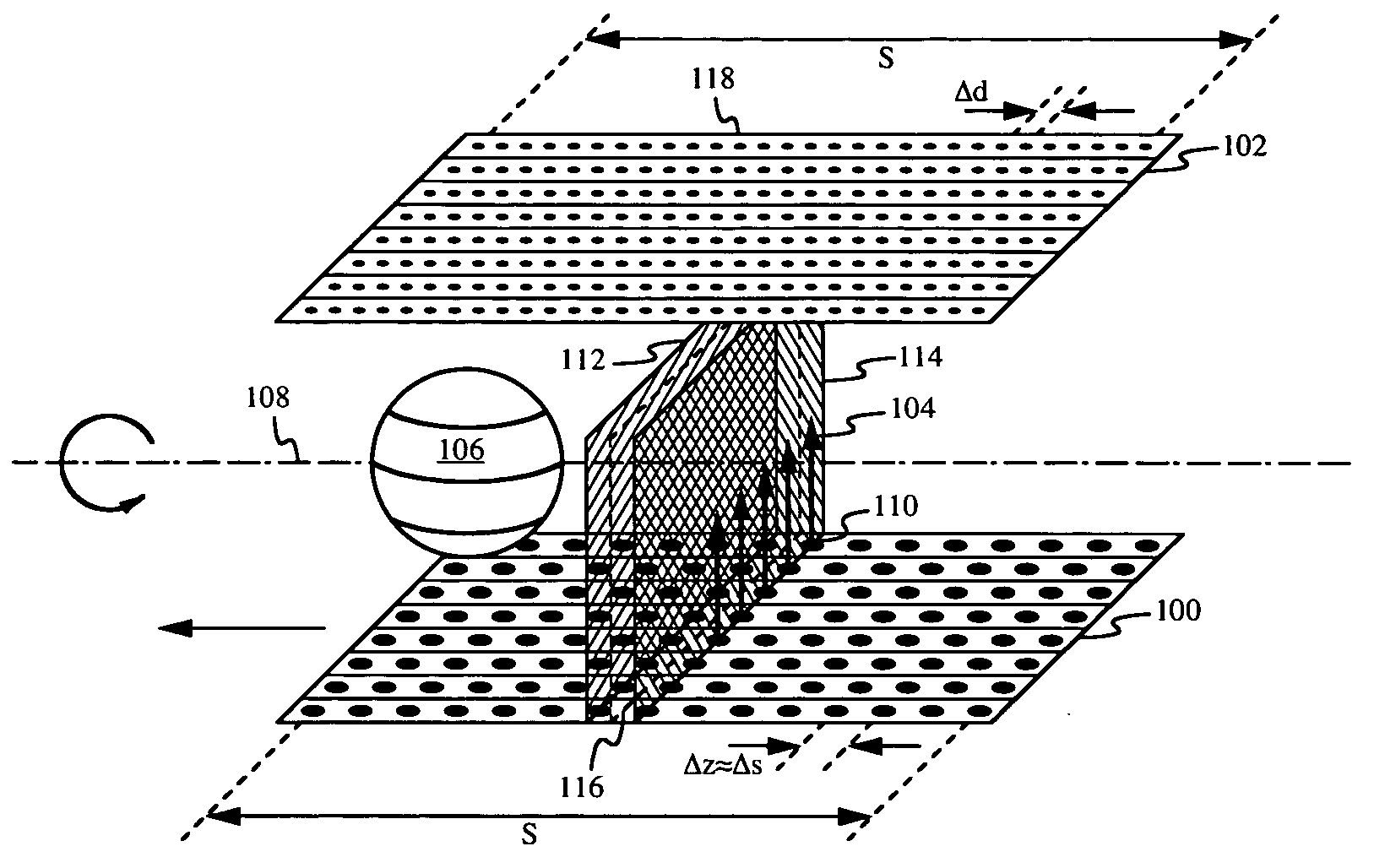
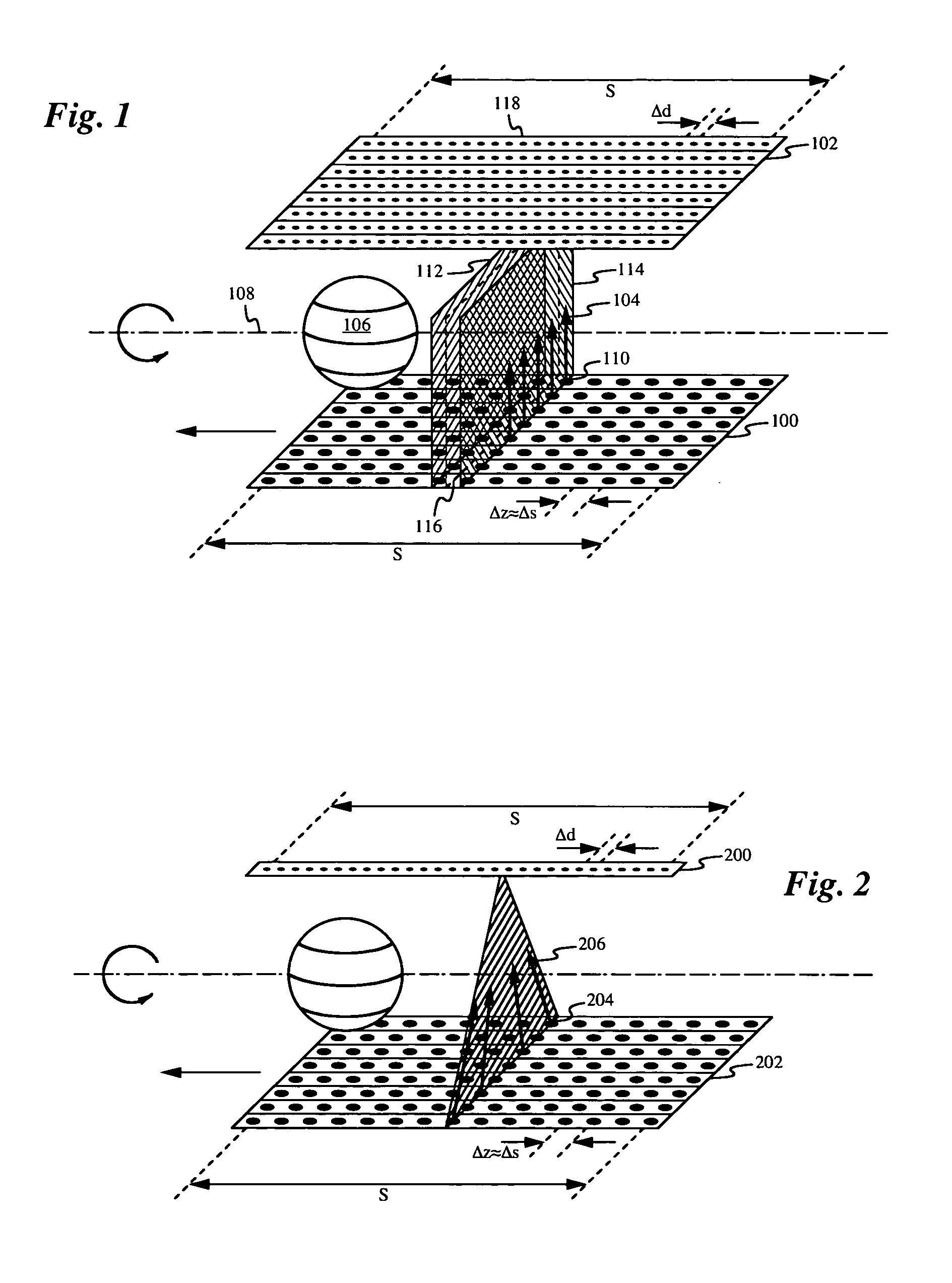
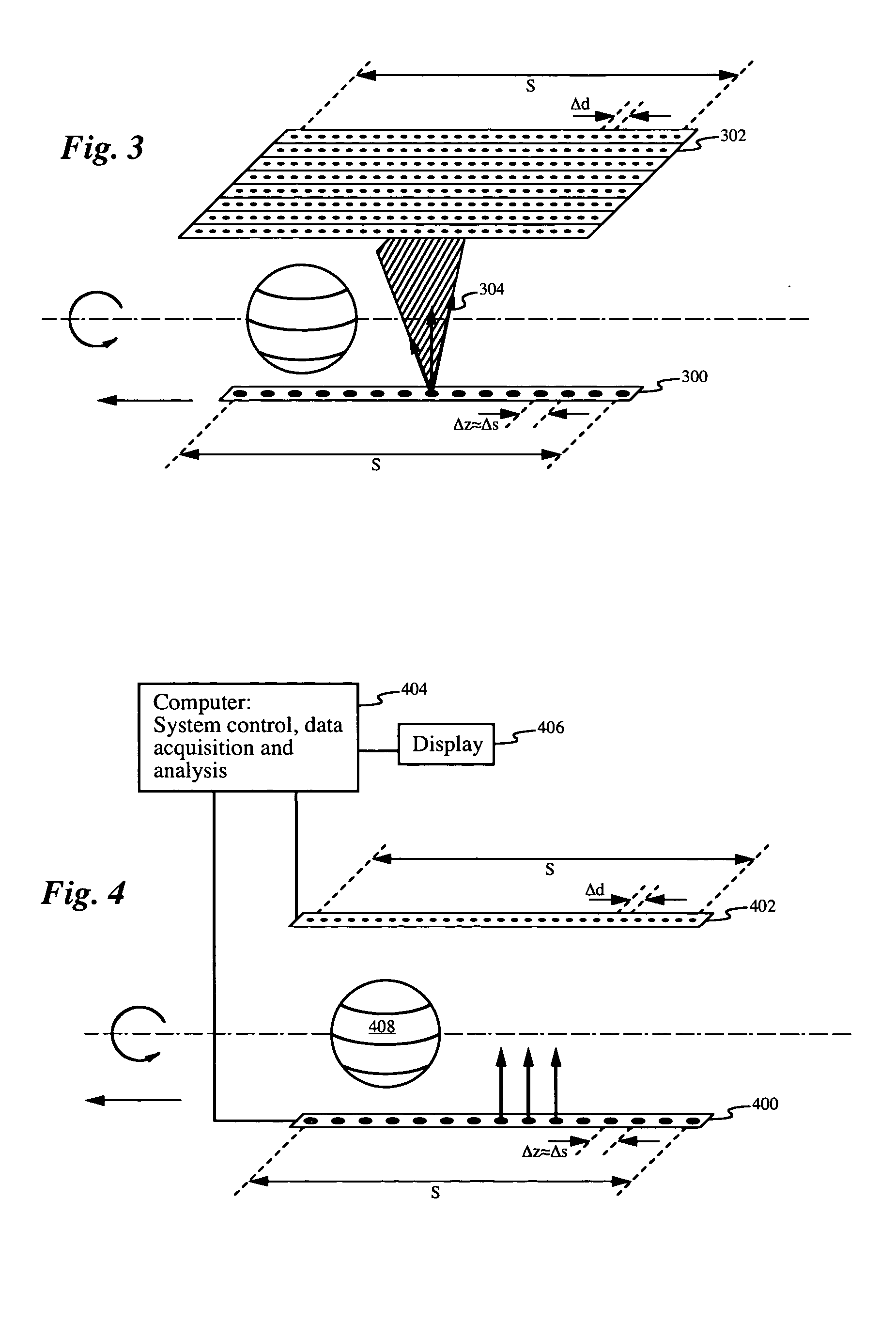
ActiveUS20060045234A1Reducing z-dependenceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayComputational physics
A volumetric computed tomography method includes translating a discrete element x-ray source and detector relative to the patient or object in a z-direction parallel to the axis of rotation. As the source rotates through the angles of a single rotation, it is simultaneously translated by a distance comparable to the discrete spacing distance between individual source elements in the z-direction. The small translation is designed so that the axial planes passing through discrete source element rows are not distinguished from axial planes passing between the discrete source element rows, thereby eliminating the z-dependence of the system and associated sampling problems.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Surface light source device of side light type, liquid crystal display and light guide plate
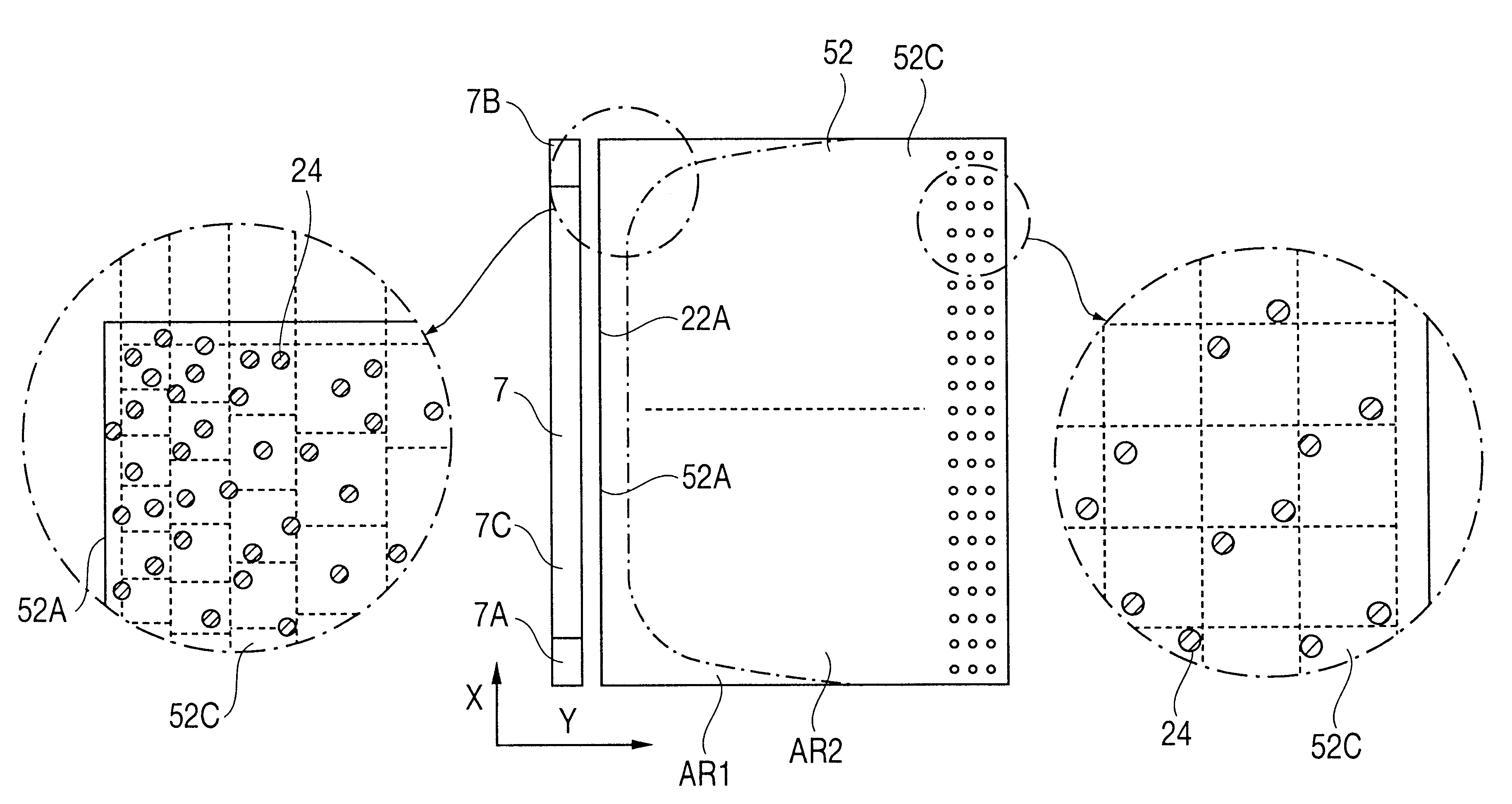
InactiveUS6412968B1Solve the lack of brightnessShow cabinetsMechanical apparatusLiquid-crystal displayLight guide
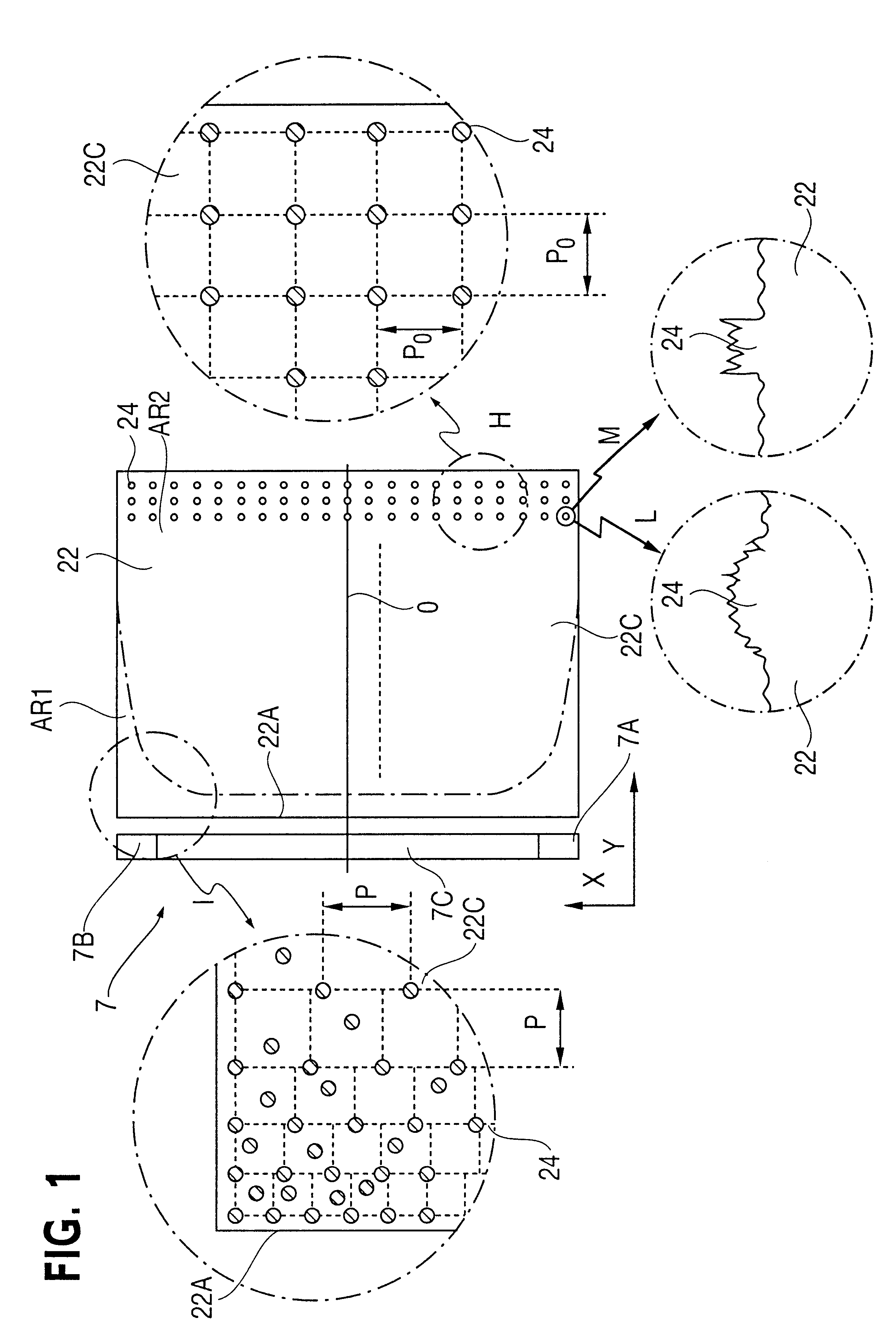
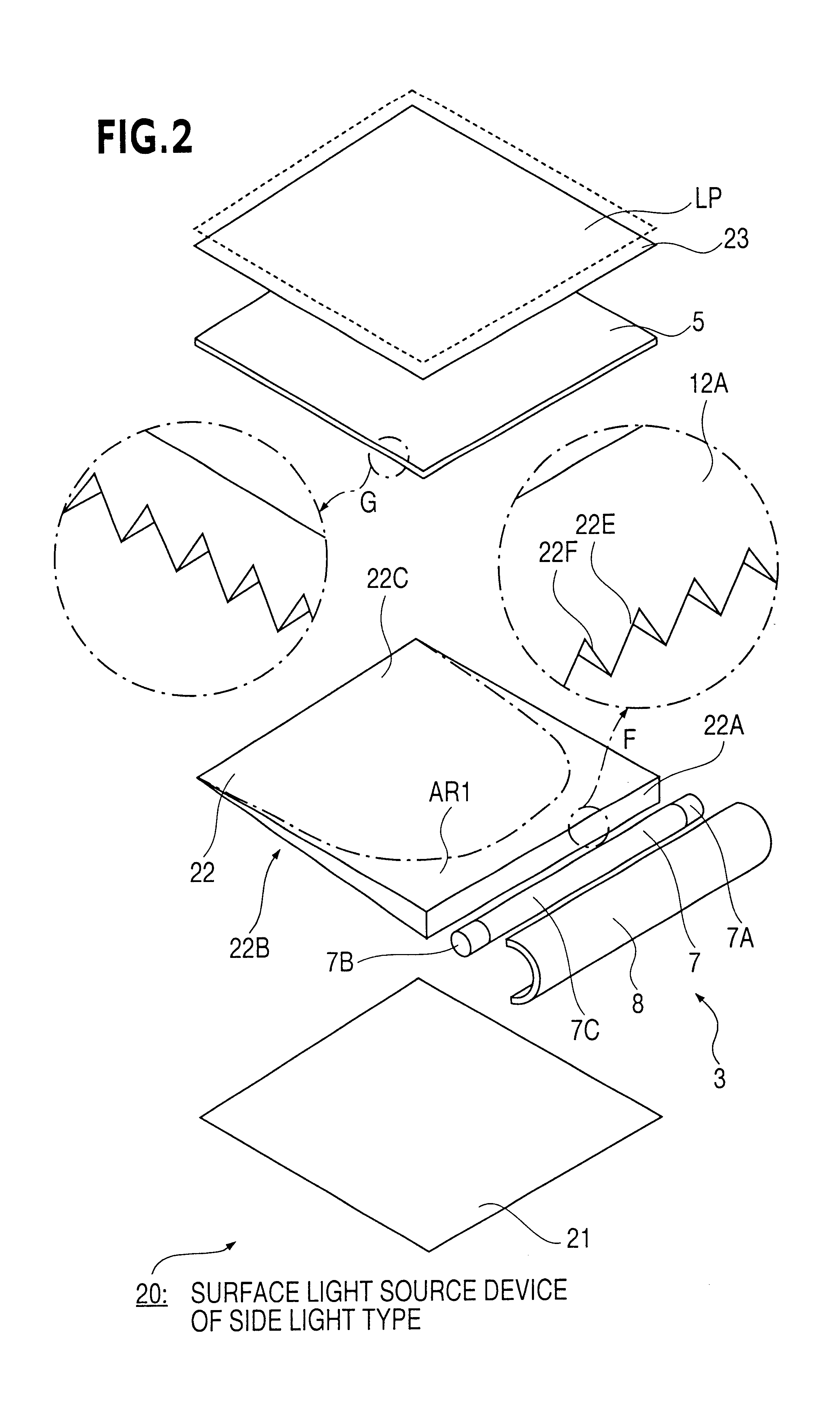
A surface light source device of side light type 40 comprises a guide plate 42, a primary light source 3 comprising a wedge-shaped light source element 7 and a reflector 8, a reflection sheet 21, a prism sheet 41 and a light-scattering sheet 23. The guide plate 42 is wedge-shaped in cross-section and has a back surface 42B and an emission surface 42C. The emission surface 42C is a prism surface. A scattering pattern 24 is provided on the back surface 42B. The scattering pattern 24 comprises a great number of micro-dots, which are sufficiently small that they are hardly visible. Covering rate of the micro-dots is high near an incidence surface 42A, especially at the corners, thereby preventing brightness reduction in a region AR1. Irregularity of the dot arrangement avoids moaré streaks caused in relation to a color filter arrangement of a liquid crystal panel.
Owner:ENPLAS CORP +1
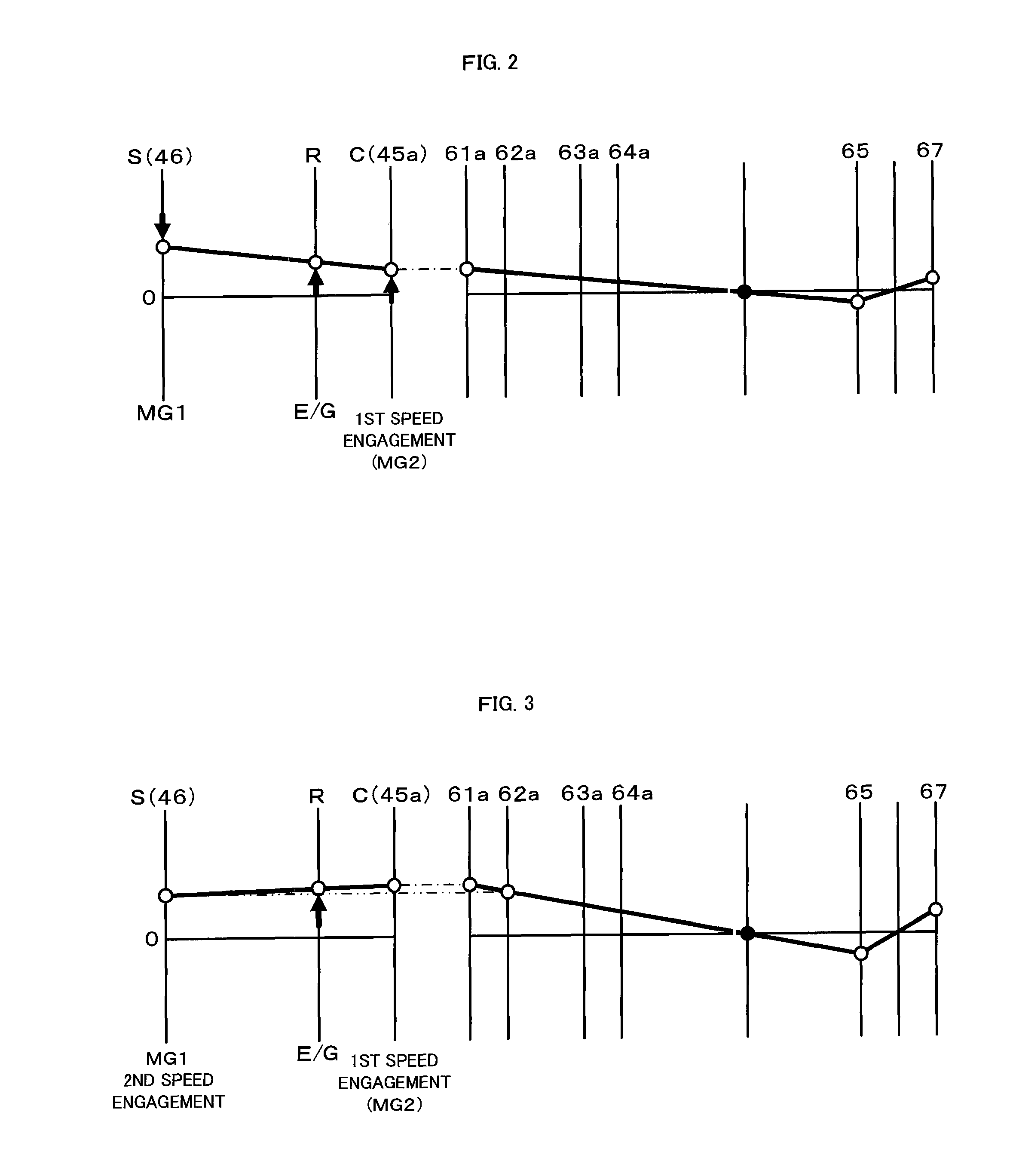
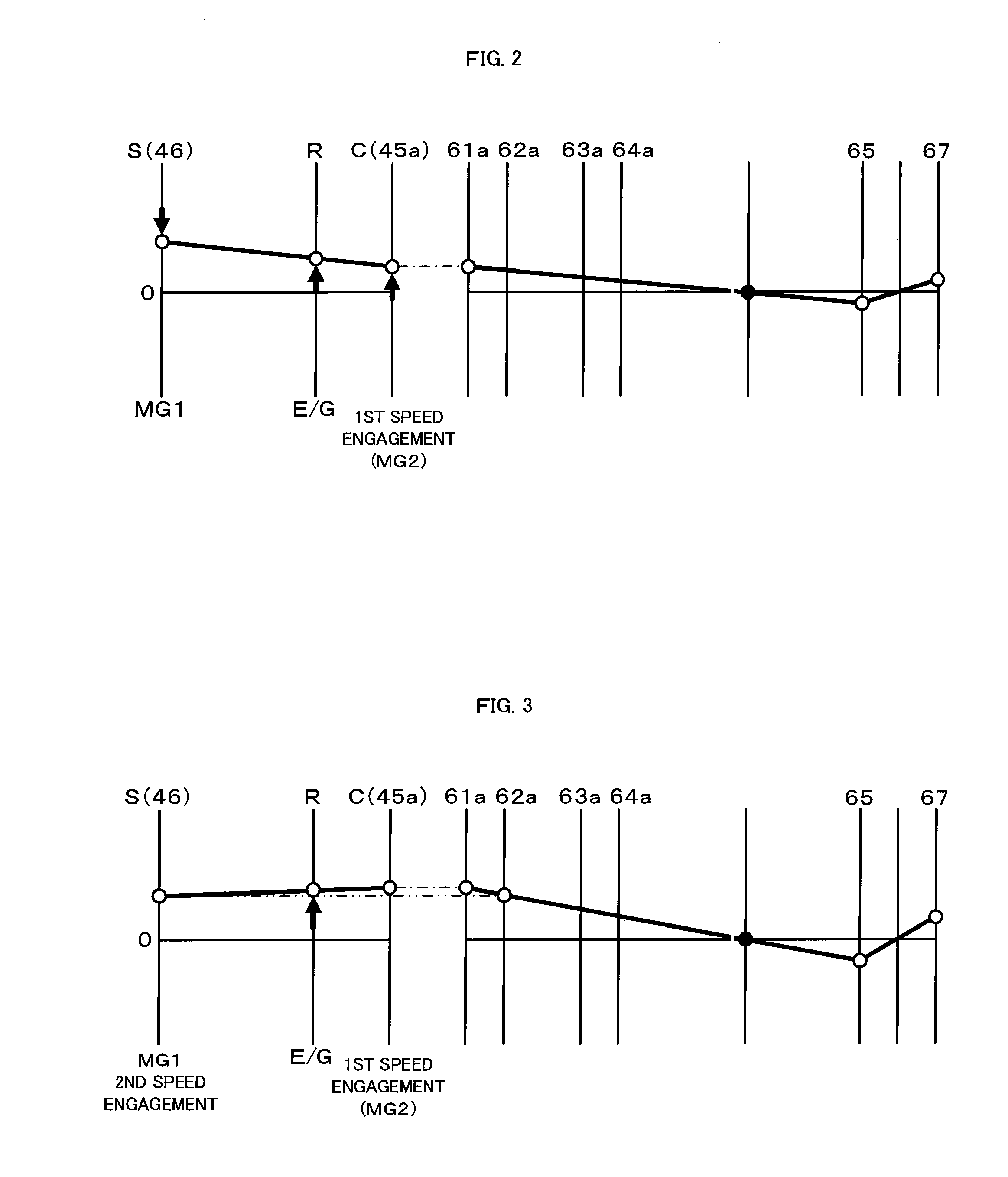
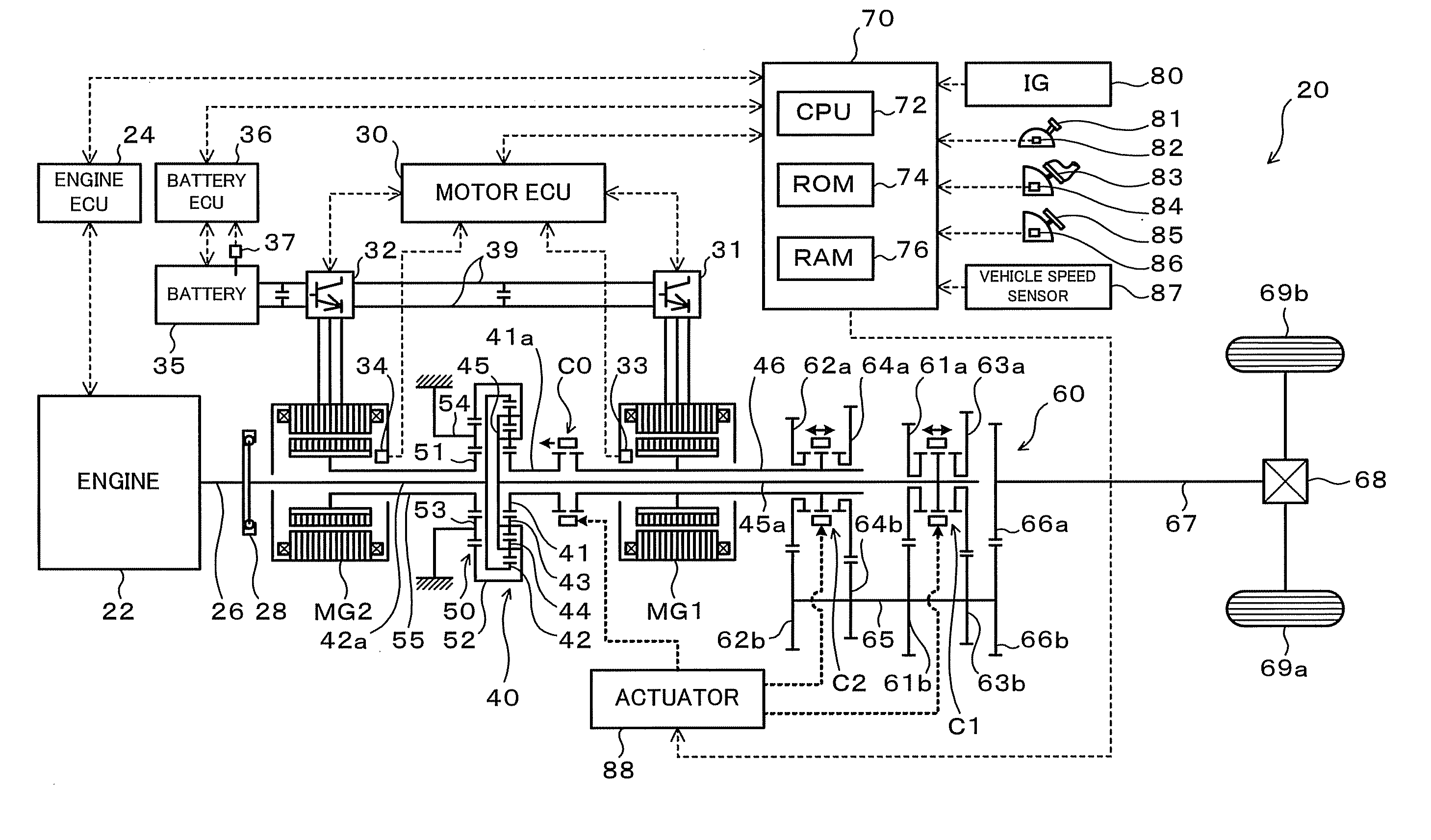
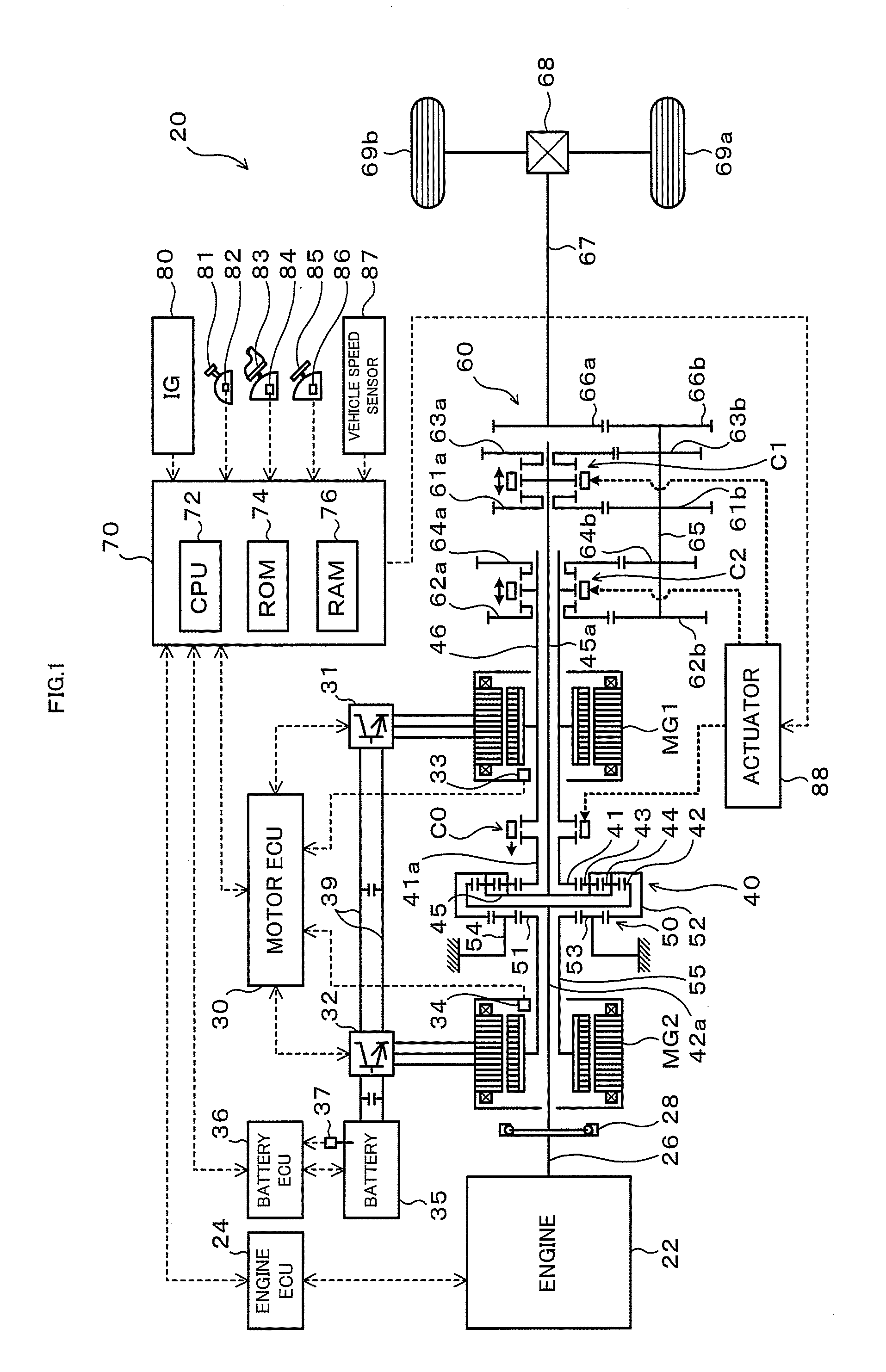
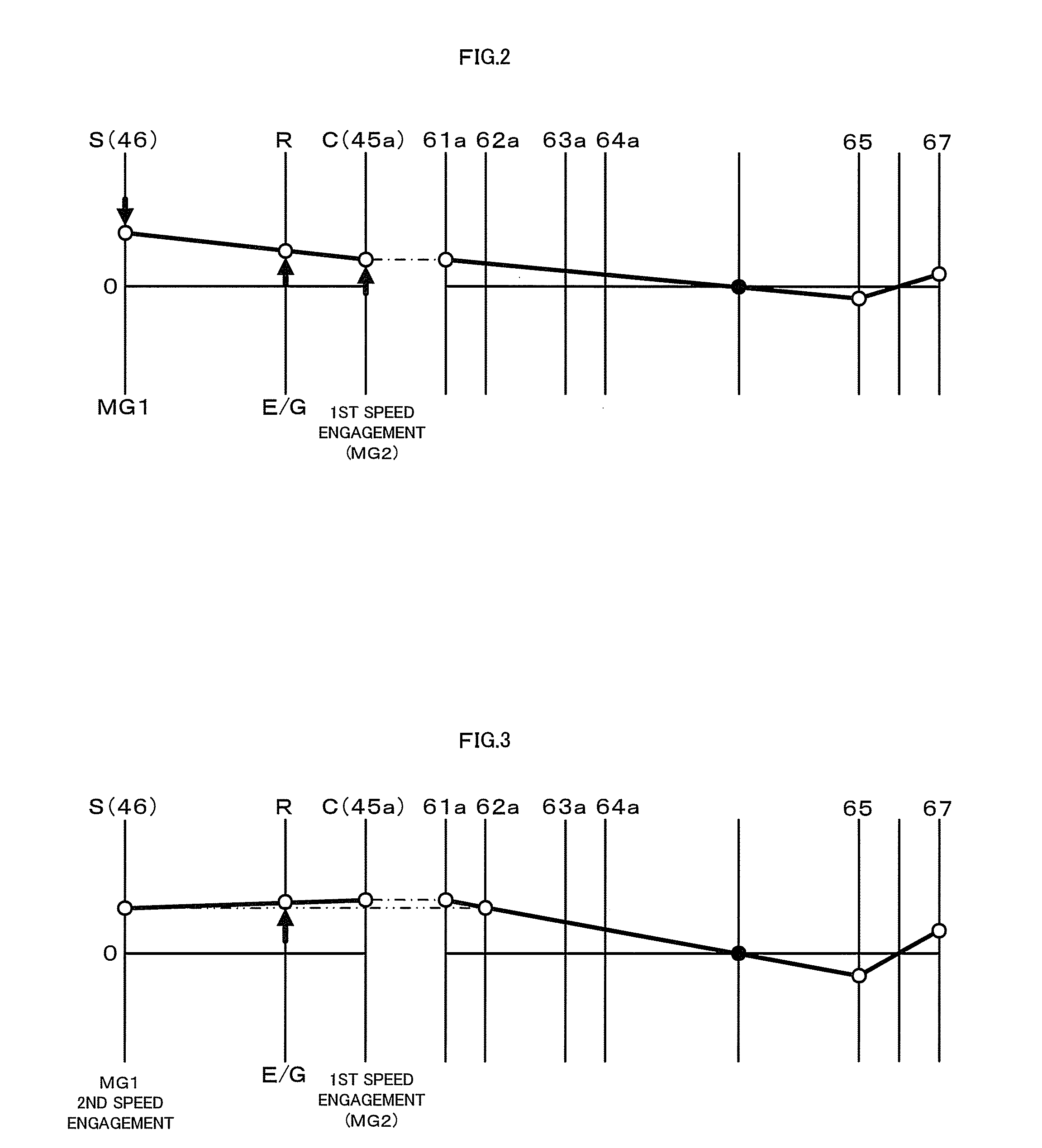
Power output apparatus, hybrid vehicle having the same, and method of controlling the power output apparatus
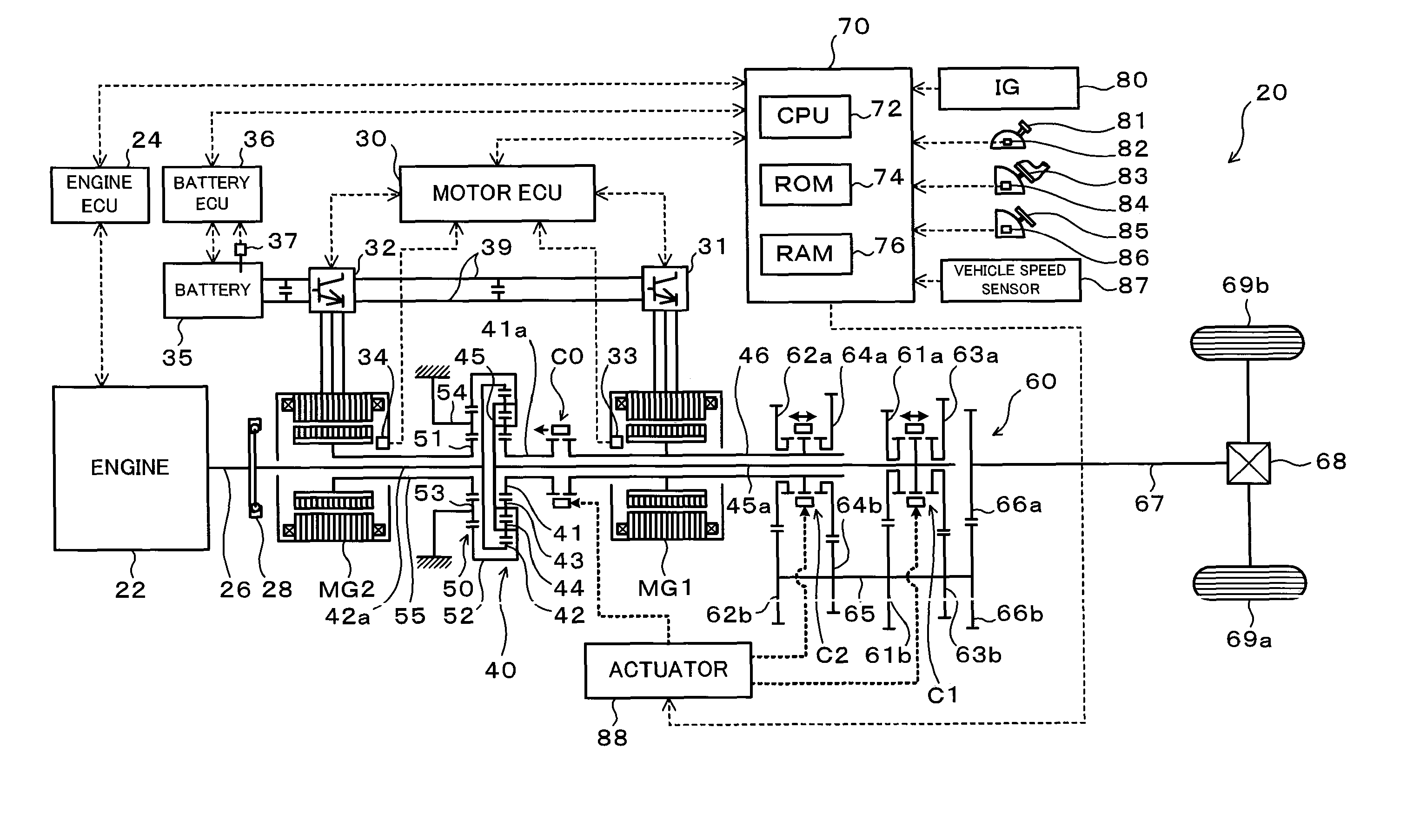
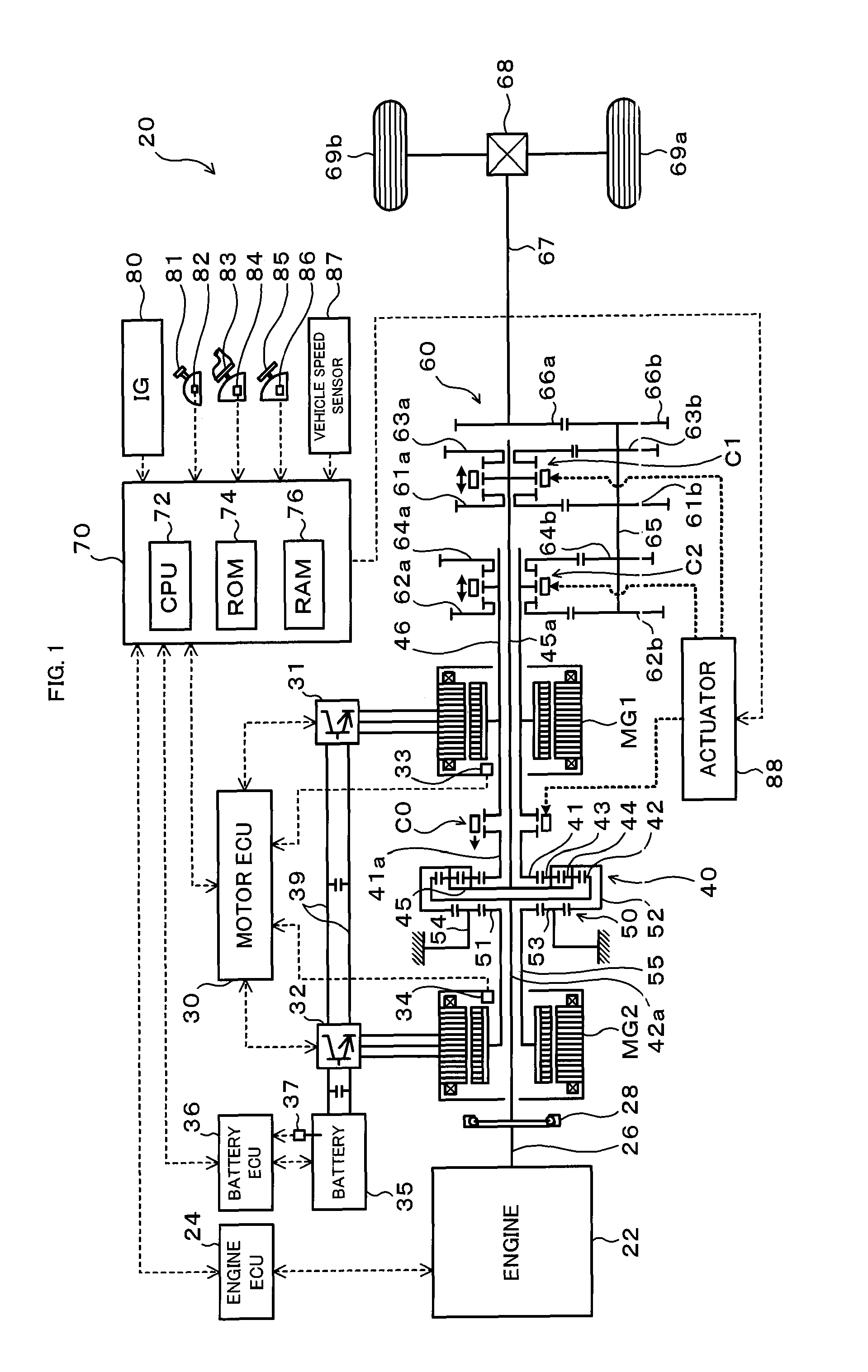
InactiveUS8100207B2Accurate outputChange speedHybrid vehiclesElectric motor startersCouplingDrive shaft
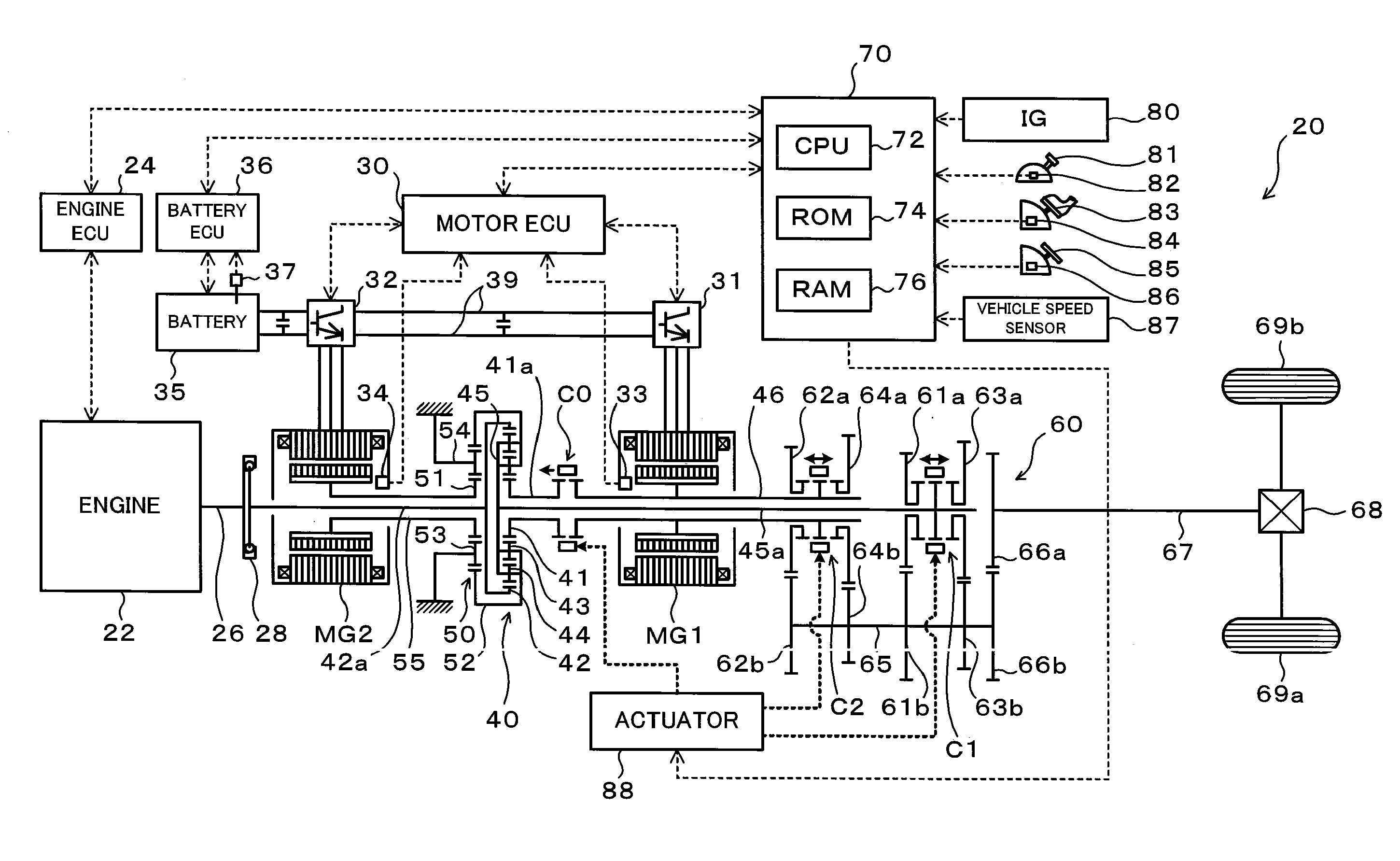
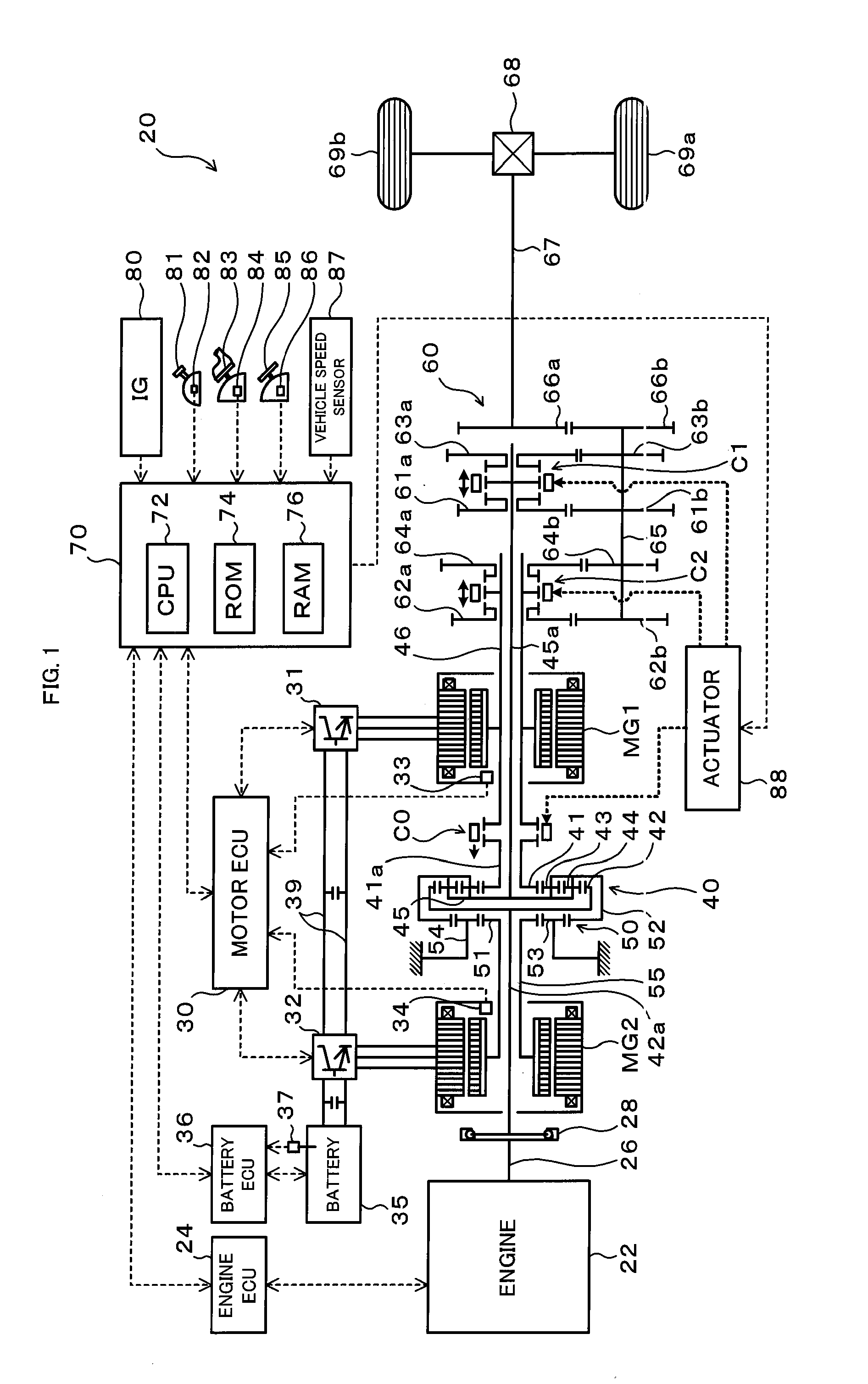
The hybrid vehicle transfers power between the two motors, releases a coupling between one of the motors and the drive shaft, adjusts the rotation speed of one of the motors which is released from the coupling to the drive shaft by the transmission so as to enable drive source element connection, and connects the clutch as well as cranks the engine by either one or the other motor when the engine is started while the clutch is released, the engine is stopped, both the motors are coupled to the drive shaft as well as at least one of the motors is caused to output power.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
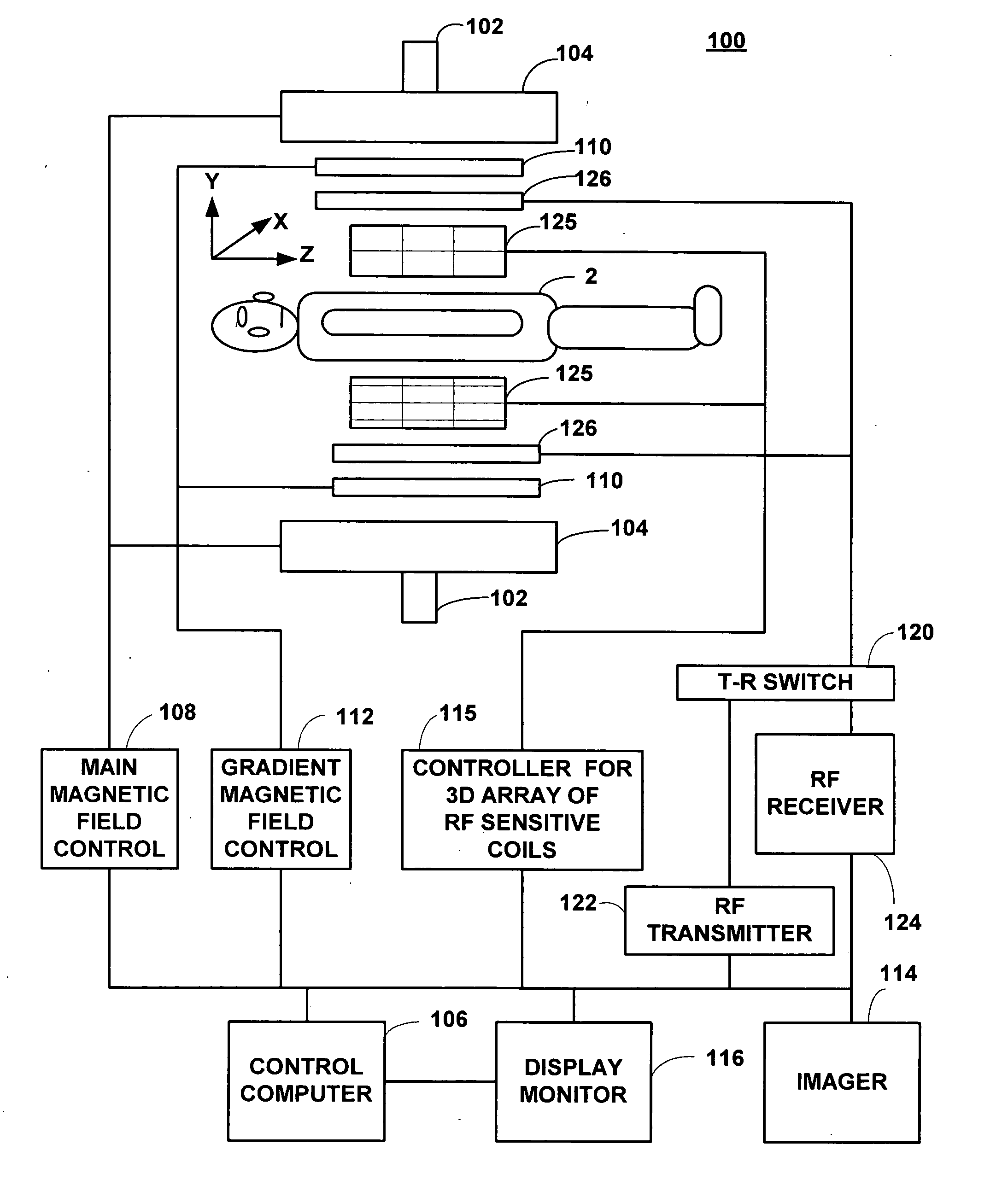
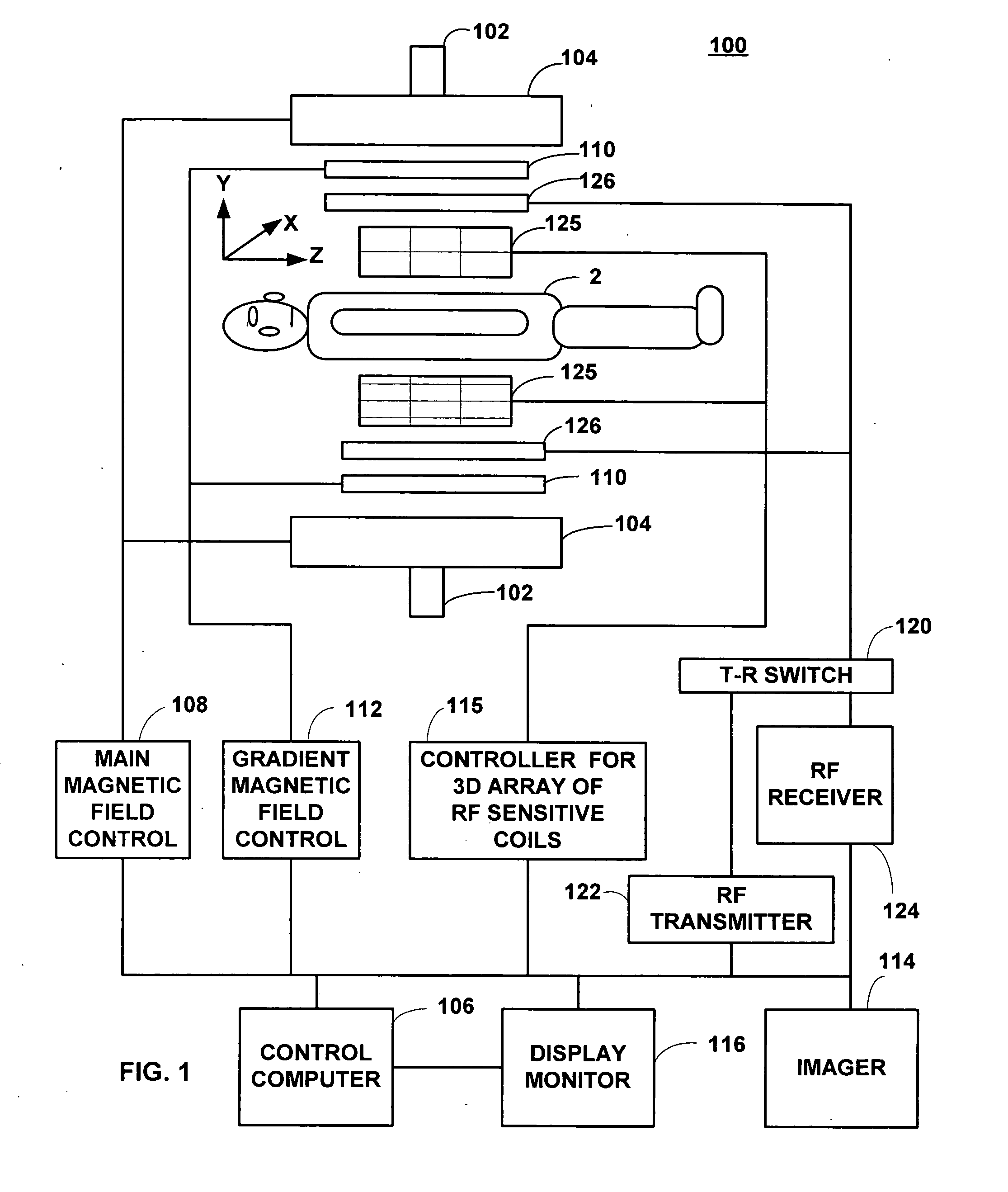
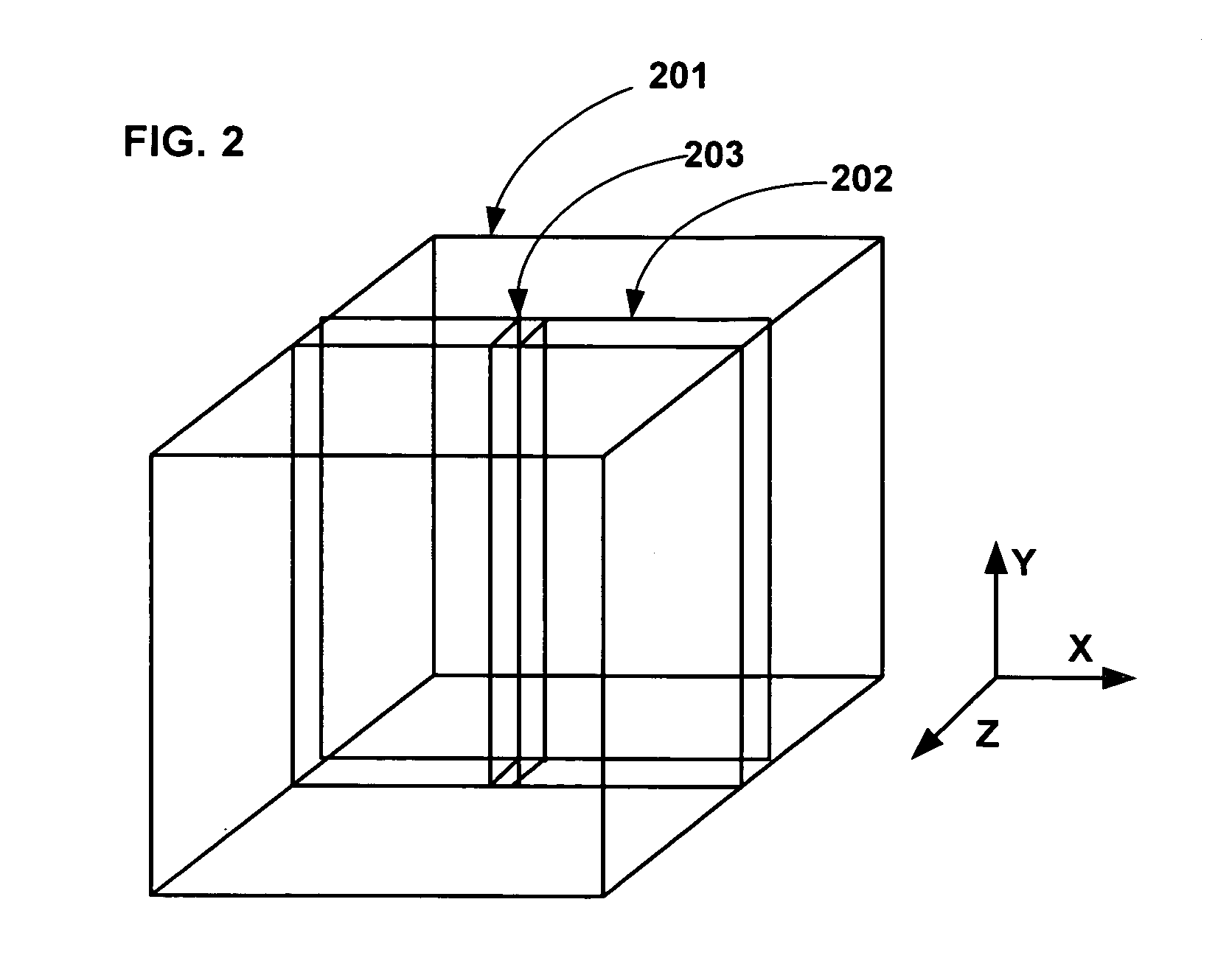
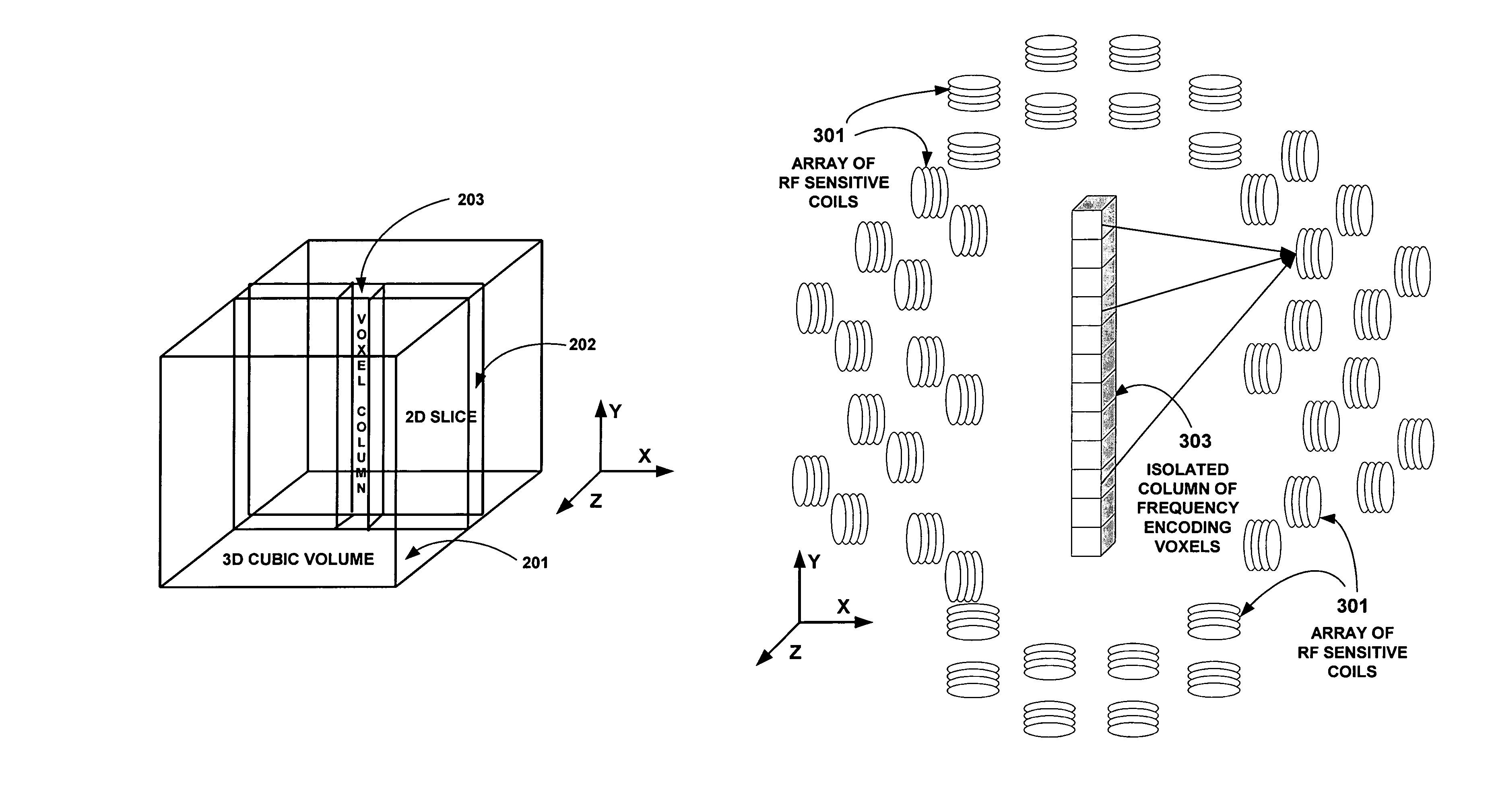
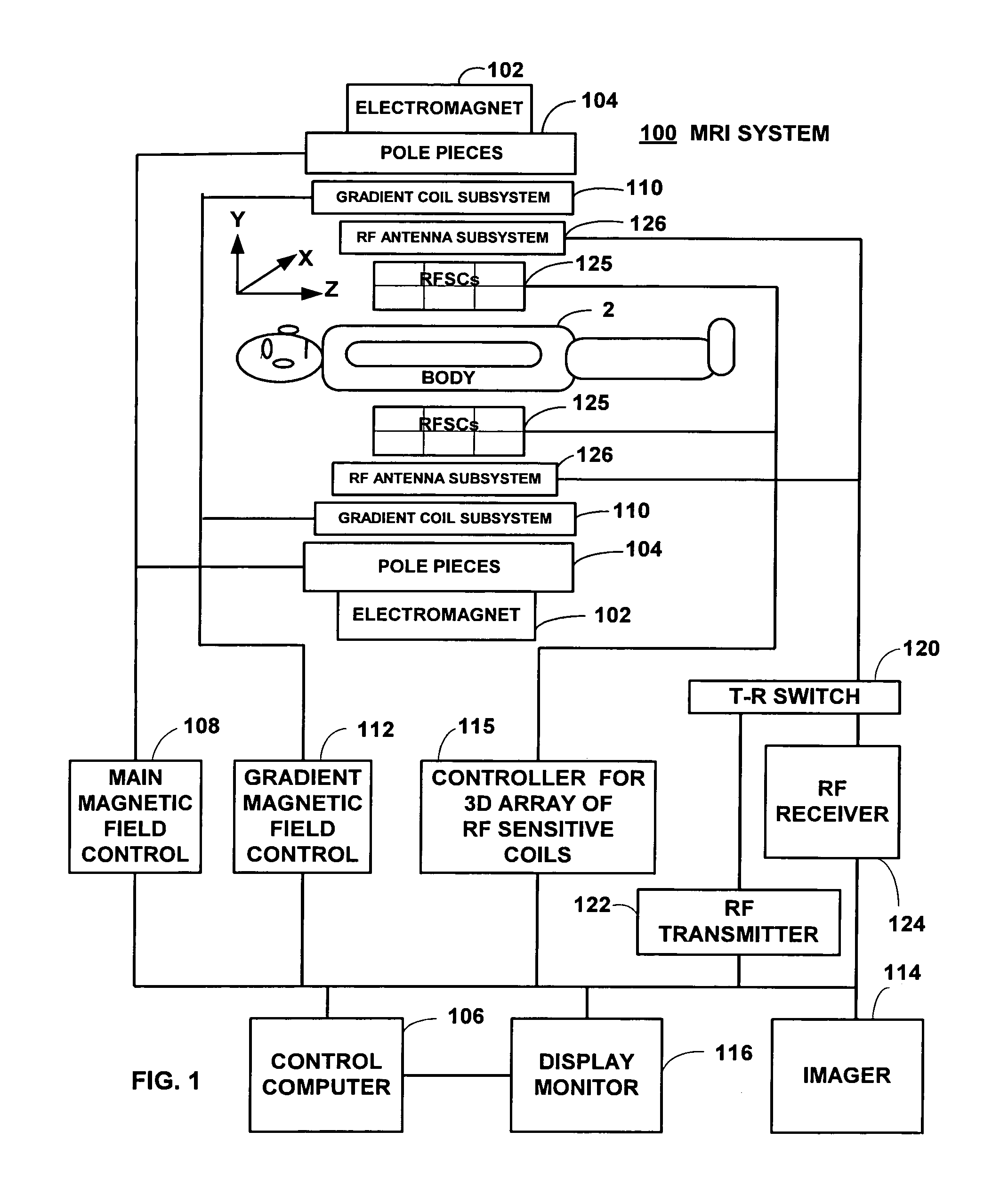
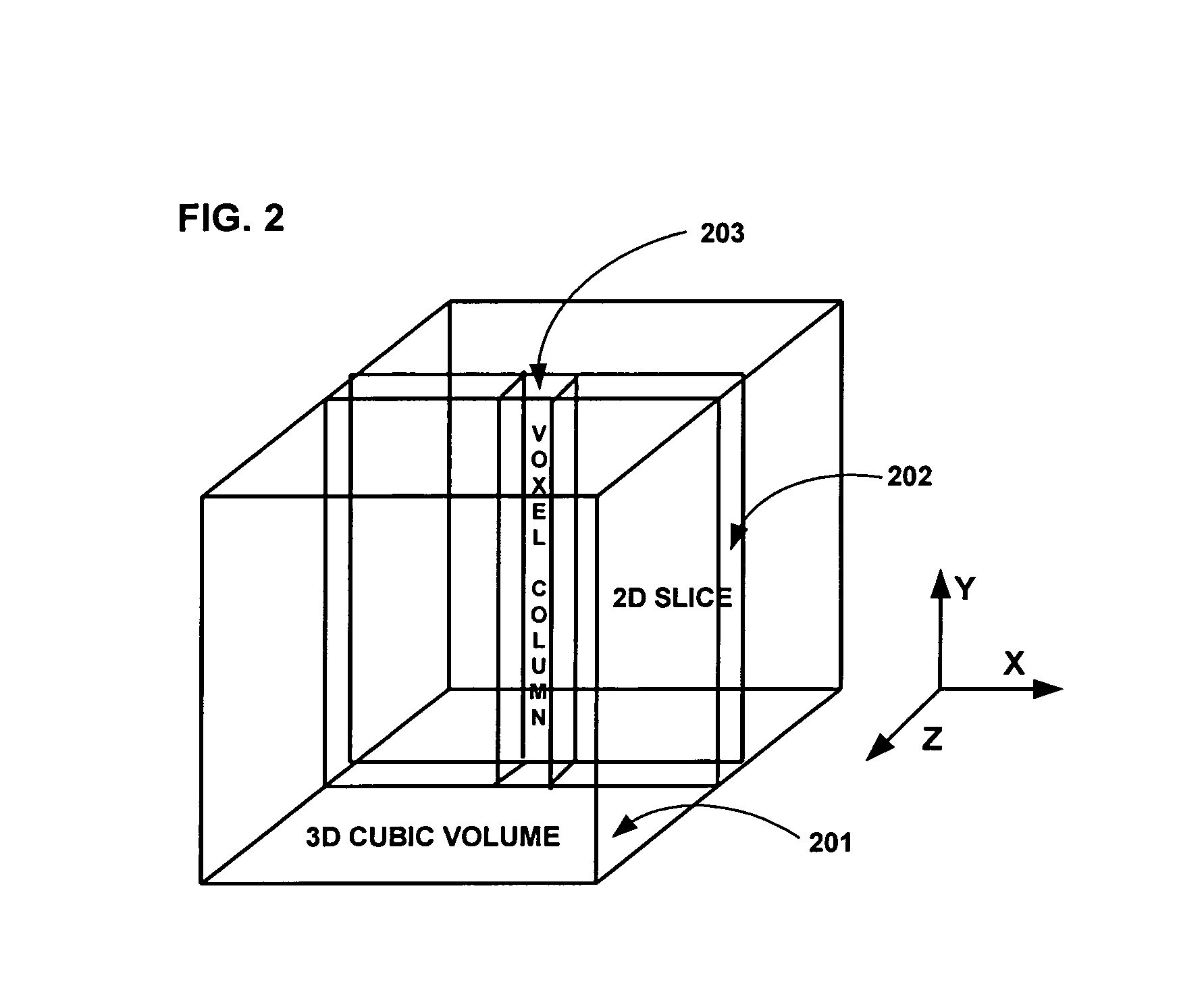
Field image tomography for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20110115485A1Shorten the length of timeReduce usageMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionObject basedSystem matrix
Field Image Tomography (FIT) is a fundamental new theory for determining the three-dimensional (3D) spatial density distribution of field emitting sources. The field can be the intensity of any type of field including (i) Radio Frequency (RF) waves in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), (ii) Gamma radiation in SPECT / PET, and (iii) gravitational field of earth, moon, etc. FIT exploits the property that field intensity decreases with increasing radial distance from the field source and the field intensity distribution measured in an extended 3D volume space can be used to determine the 3D spatial density distribution of the emitting source elements. A method and apparatus are disclosed for MRI of target objects based on FIT. Spinning atomic nuclei of a target object in a magnetic field are excited by beaming a suitable Radio Frequency (RF) pulse. These excited nuclei emit RF radiation while returning to their normal state. The intensity or amplitude distribution of the RF emission field g is measured in a 3D volume space that may extend substantially along the radial direction around the emission source. g is related to the 3D tomography f through a system matrix H that depends on the MRI apparatus, and noise n through the vector equation g=Hf+n. This equation is solved to obtain the tomographic image f of the target object by a method that reduces the effect of noise.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
Distributed built-in test and performance monitoring system for electronic surveillance
InactiveUS7683842B1Precise maintenanceAccurate performanceReceivers monitoringSpatial transmit diversityCritical positionDistributed testing
A distributed test system for implementing enhanced BIT (Built-In-Test) within an ESM (Electronic Surveillance Monitoring) or RF receiver system. The distributed test system includes a system processor, a programmable RF source element or other comparable test signal generating arrangement, and switched path coupled elements and various measurement elements, each embedded at strategic locations within the ESM system so as to effect maximum path coverage and test benefit.
Owner:ADVANCED TESTING TECH
Phase-change memory device and method of manufacturing the phase-change memory device
InactiveUS20100270527A1Resistance value variesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductancePhase-change memory
A phase-change memory device has a plurality of first wiring lines; a plurality of memory cells that are provided on the plurality of first wiring lines; a plurality of second wiring lines that are provided on the plurality of memory cells, respectively; and an interlayer insulating film that is formed between the plurality of first wiring lines and the plurality of second wiring lines and insulates the plurality of first wiring lines from the plurality of second wiring lines; wherein each of the memory cells includes a heat source element that is supplied with a current and generates heat and a phase-change element that is changed to an amorphous state or a crystalline state according to a cooling speed after being heated by the heat source element, a resistance value of the phase-change element varying with the change in the state, and wherein a void is formed between the two adjacent memory cells in the interlayer insulating film.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Power output apparatus, hybrid vehicle having the same, and method of controlling the power output apparatus
InactiveUS20100113213A1Improve driving performanceImprove fuel consumption performanceHybrid vehiclesEngine controllersCouplingDrive shaft
The hybrid vehicle transfers power between the two motors, releases a coupling between one of the motors and the drive shaft, adjusts the rotation speed of one of the motors which is released from the coupling to the drive shaft by the transmission so as to enable drive source element connection, and connects the clutch as well as cranks the engine by either one or the other motor when the engine is started while the clutch is released, the engine is stopped, both the motors are coupled to the drive shaft as well as at least one of the motors is caused to output power.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Power output apparatus, hybrid vehicle with the same, and method for controlling power output apparatus
InactiveUS20100012405A1Guaranteed normal transmissionIncrease powerHybrid vehiclesPower operated startersControl powerDrive shaft
There is provided a hybrid vehicle 20 which stops an engine 22 in a state in which a drive source element connection by a clutch C0 is released; a transmission 60 is used to couple only one of the motors MG1 and MG2 to a drive shaft 67; and one of the motors MG1 and MG2 is caused to output power; at this time, in order to start the engine 22, a rotation speed of the other one of the motors MG1 and MG2 which does not correspond to a current speed ratio γ and is not connected to the drive shaft 67 is adjusted so as to enable the drive source element connection; and the clutch C0 is connected as well as the engine 22 is cranked by the motor MG1 or MG2.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
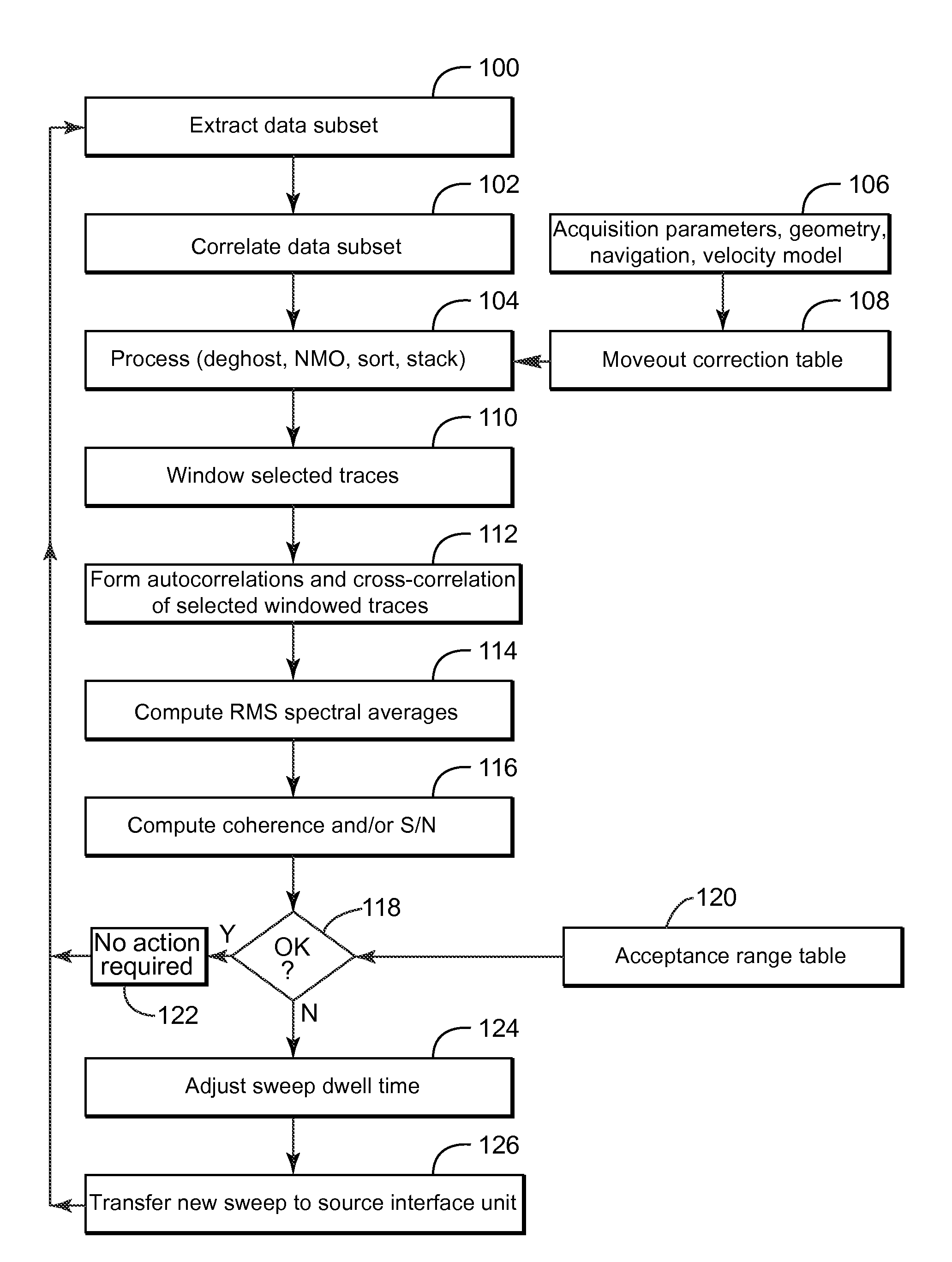
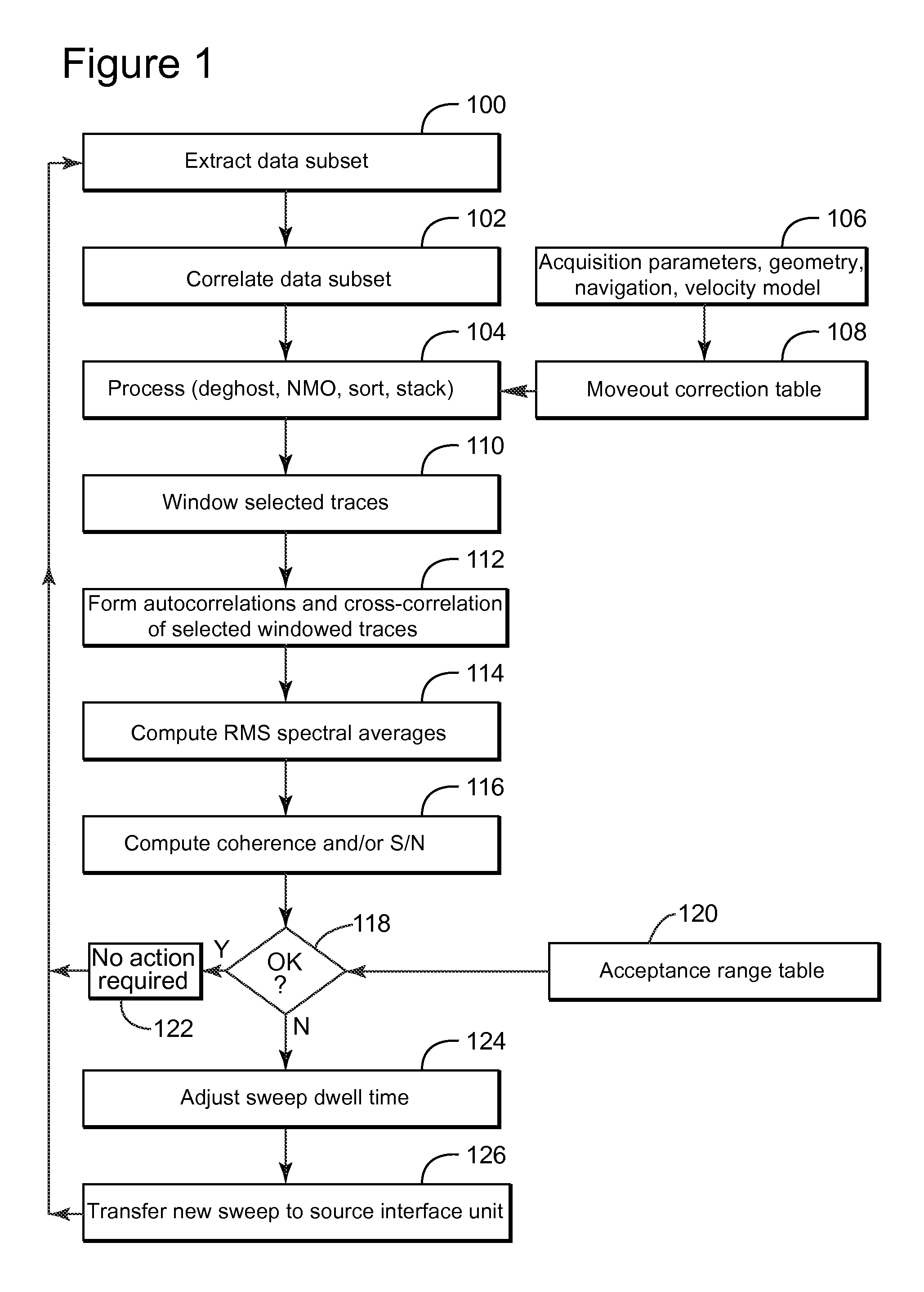
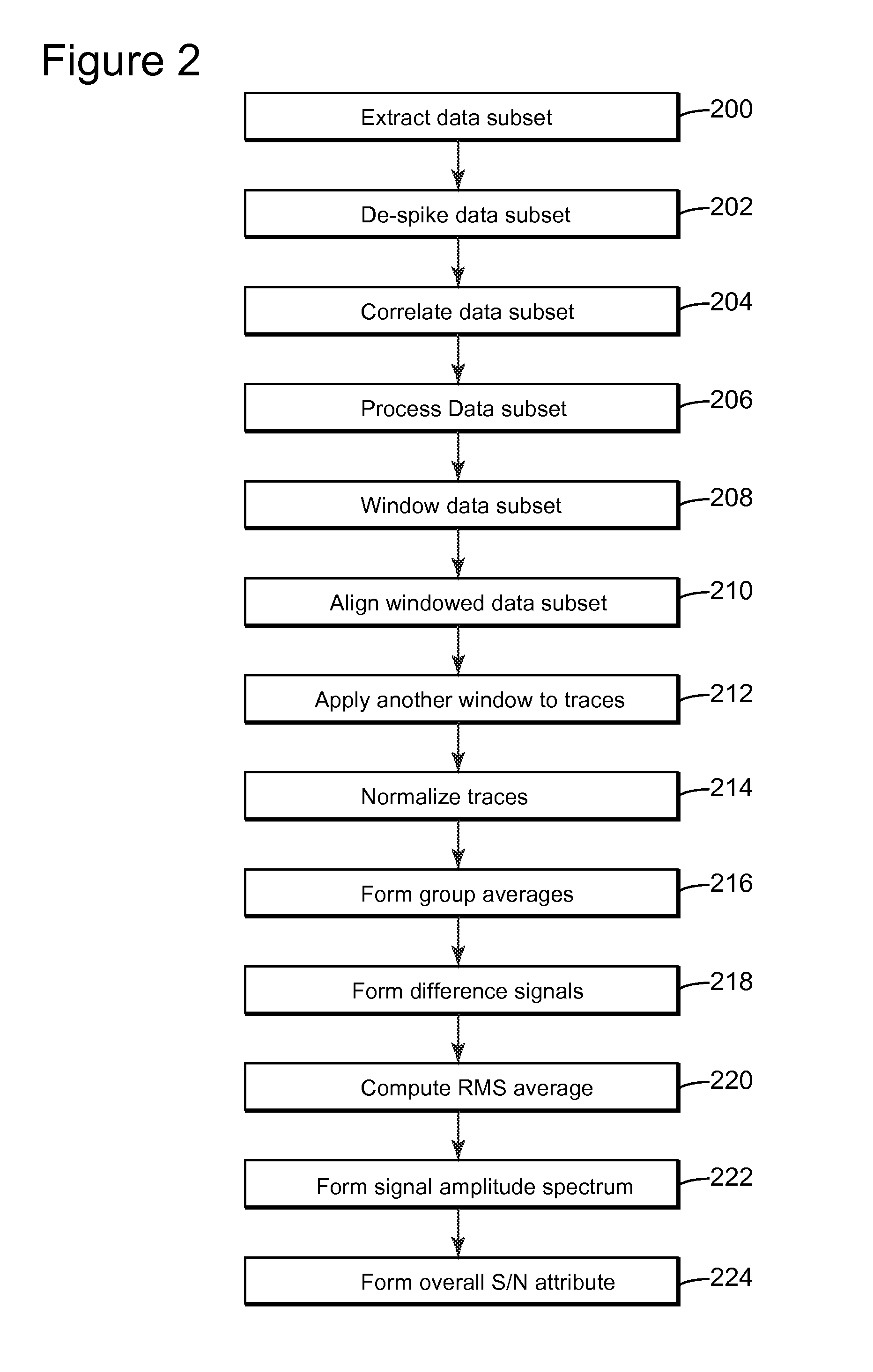
Adaptive sweep method and device for seismic exploration
InactiveUS20140043937A1Seismic data acquisitionSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveySound sources
Controller and method for adapting a frequency sweep for a vibro-acoustic source element that is configured to generate acoustic waves during a seismic survey. The method includes driving a seismic source element to generate a current frequency sweep; recording seismic data with plural seismic sensors in response to the current frequency sweep; selecting, during the seismic survey, a data subset of the seismic data, wherein the data subset has a size less than 10% of the seismic data; calculating with a processing device an attribute based on the data subset; and calculating a new frequency sweep based on the attribute.
Owner:CGG SERVICES SA
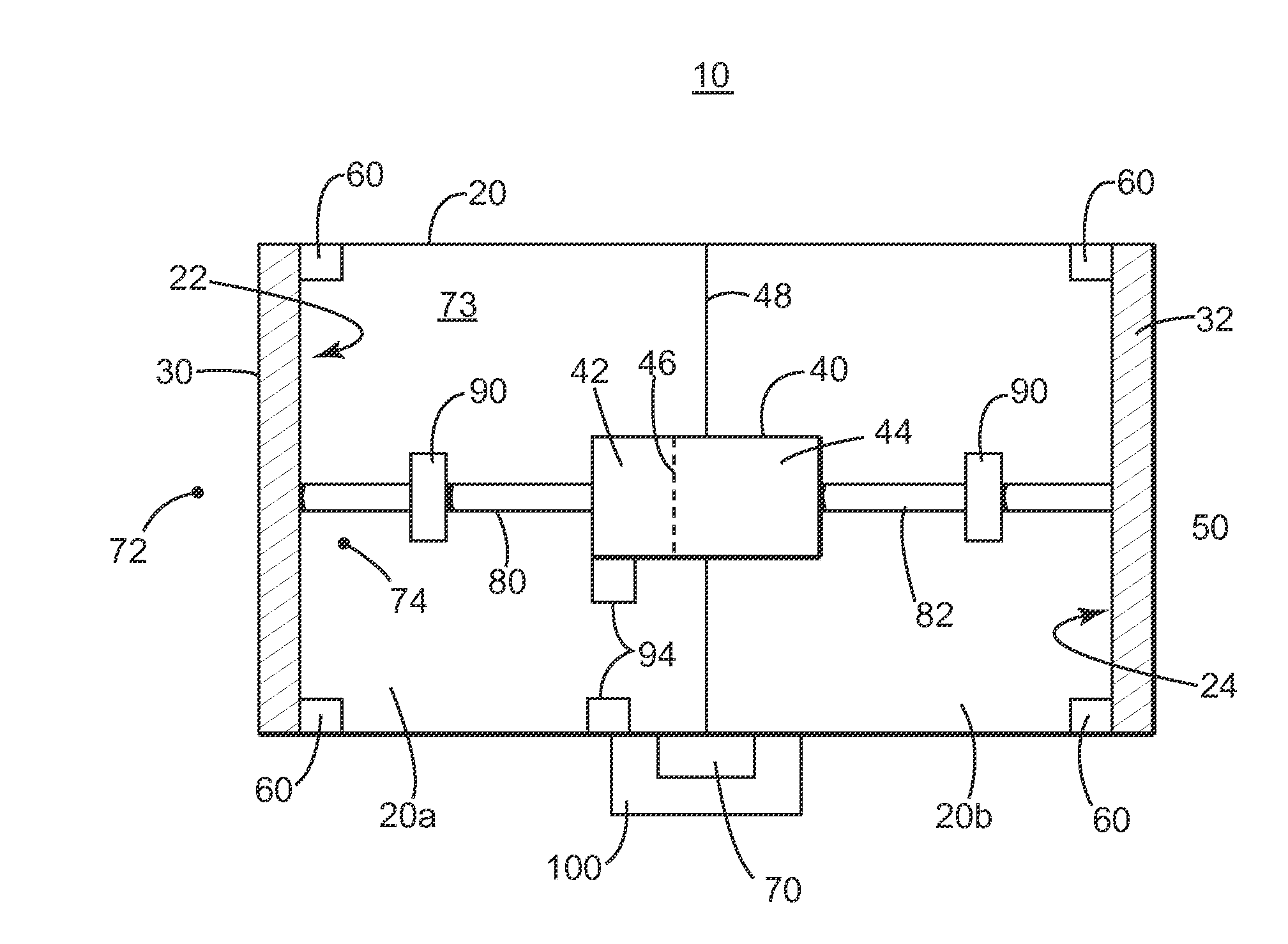
Source for marine seismic acquisition and method
Method, source and seismic vibro-acoustic source element configured to generate acoustic waves under water. The seismic vibro-acoustic source element includes an enclosure having first and second openings; first and second pistons configured to close the first and second openings; an actuator system provided inside the enclosure and configured to actuate the first and second pistons to generate a wave having first frequency; and a pressure mechanism attached to the enclosure and configured to control a pressure of a fluid inside the enclosure such that a pressure of the fluid is substantially equal to an ambient pressure of the enclosure.
Owner:CGG SERVICES SAS
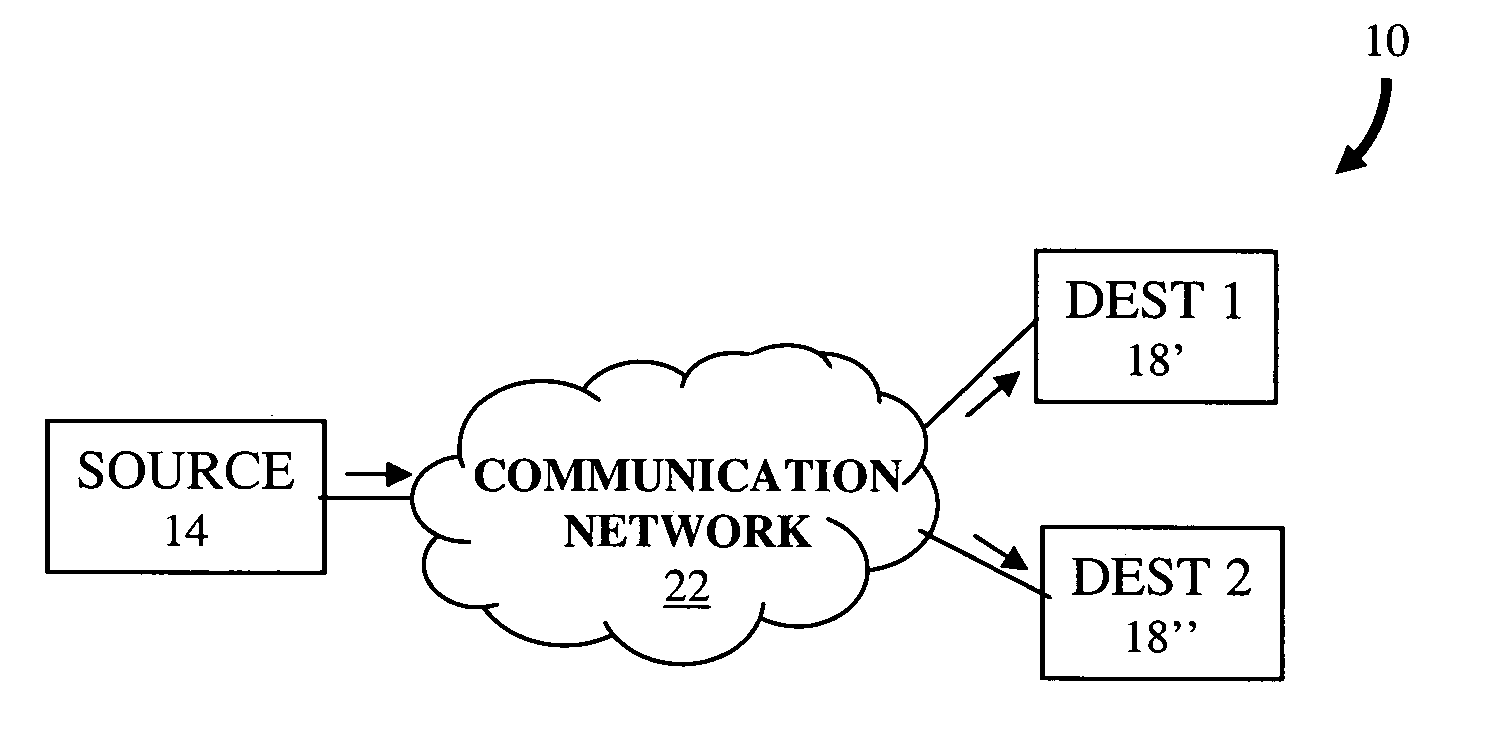
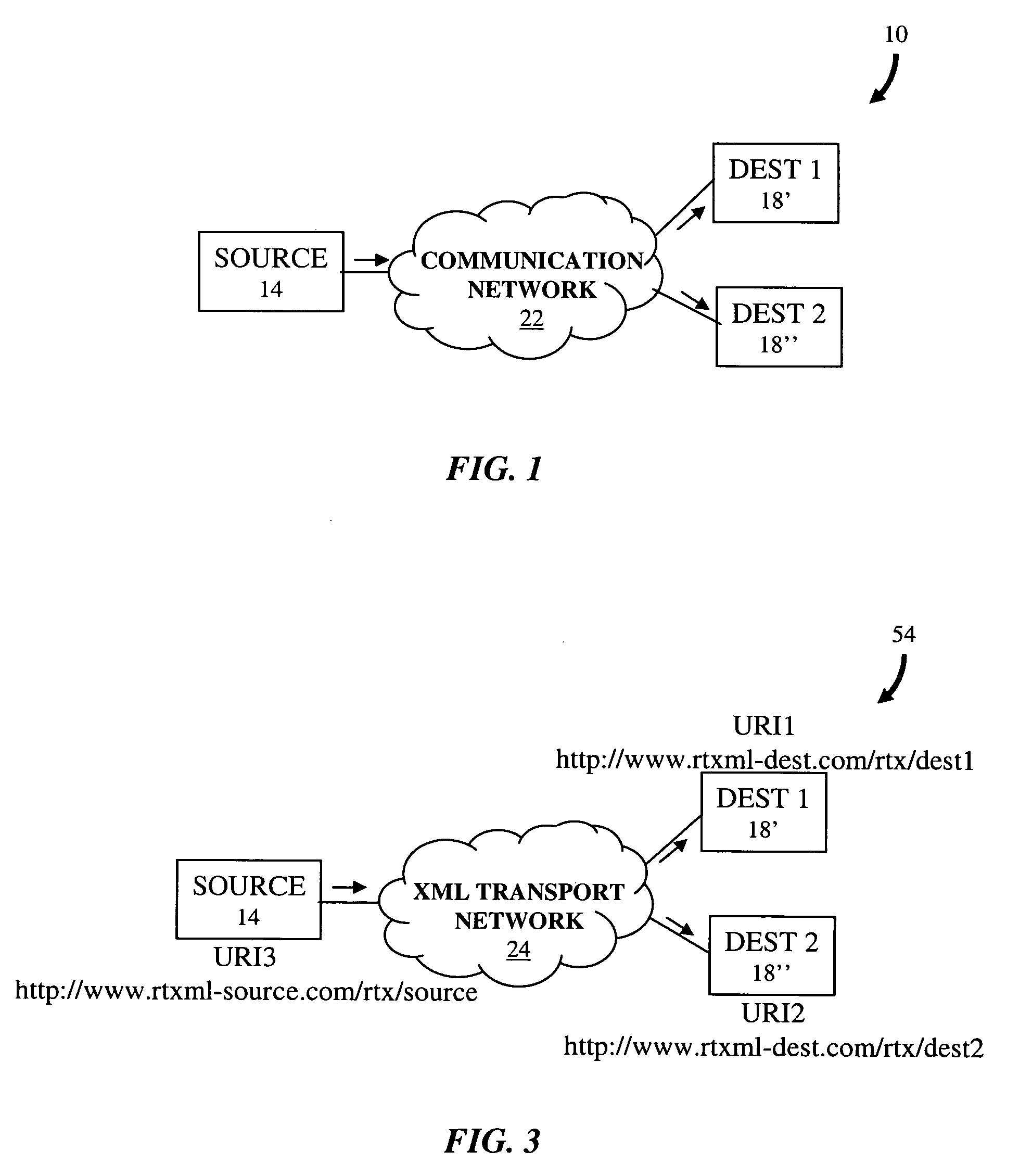
Real-time XML messaging protocol
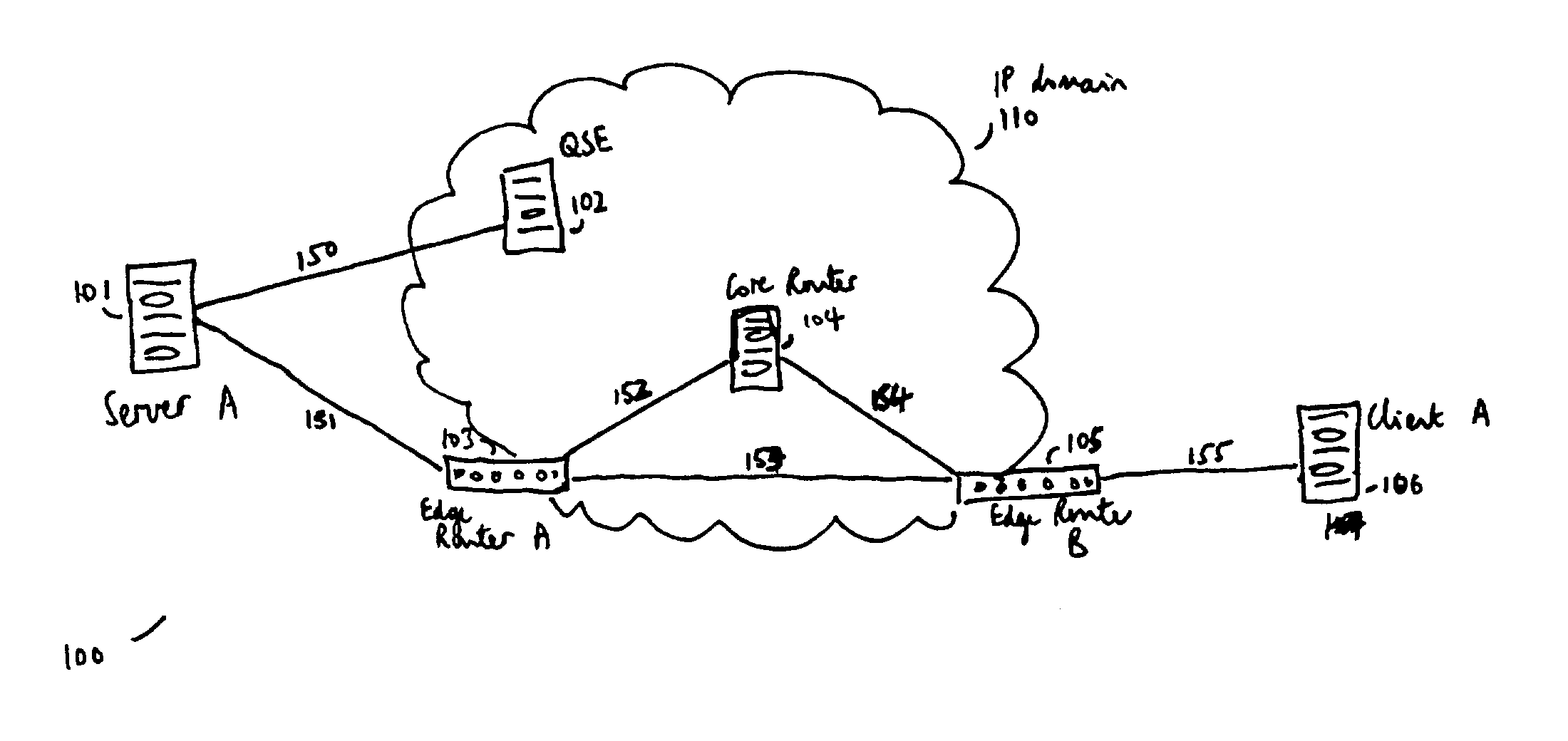
ActiveUS20070124725A1FinanceAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingUnique identifierSource element
Described are a method and a system for using XML in a real-time message for transmission of data from a source to a destination over a network. The real-time XML message includes a header element and a body element. The header element includes one or more destination elements and one source element, each having a unique identifier and a set of pre-defined and user-defined real-time properties. The body element of the message includes the data to be carried to the destination in plain or encoded XML content. XML addresses are proposed as the identifier of the source and destination, and an XML naming service can look up an XML address from the canonical name of the source and destination. Advantageously, the real-time message can be transported through the network using XML addresses included in the destination and source elements of the message.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Field image tomography for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS8378682B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionObject basedSystem matrix
Field Image Tomography (FIT) is a fundamental new theory for determining the three-dimensional (3D) spatial density distribution of field emitting sources. The field can be the intensity of any type of field including (i) Radio Frequency (RF) waves in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), (ii) Gamma radiation in SPECT / PET, and (iii) gravitational field of earth, moon, etc. FIT exploits the property that field intensity decreases with increasing radial distance from the field source and the field intensity distribution measured in an extended 3D volume space can be used to determine the 3D spatial density distribution of the emitting source elements. A method and apparatus are disclosed for MRI of target objects based on FIT. Spinning atomic nuclei of a target object in a magnetic field are excited by beaming a suitable Radio Frequency (RF) pulse. These excited nuclei emit RF radiation while returning to their normal state. The intensity or amplitude distribution of the RF emission field g is measured in a 3D volume space that may extend substantially along the radial direction around the emission source. g is related to the 3D tomography f through a system matrix H that depends on the MRI apparatus, and noise n through the vector equation g=Hf+n. This equation is solved to obtain the tomographic image f of the target object by a method that reduces the effect of noise.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
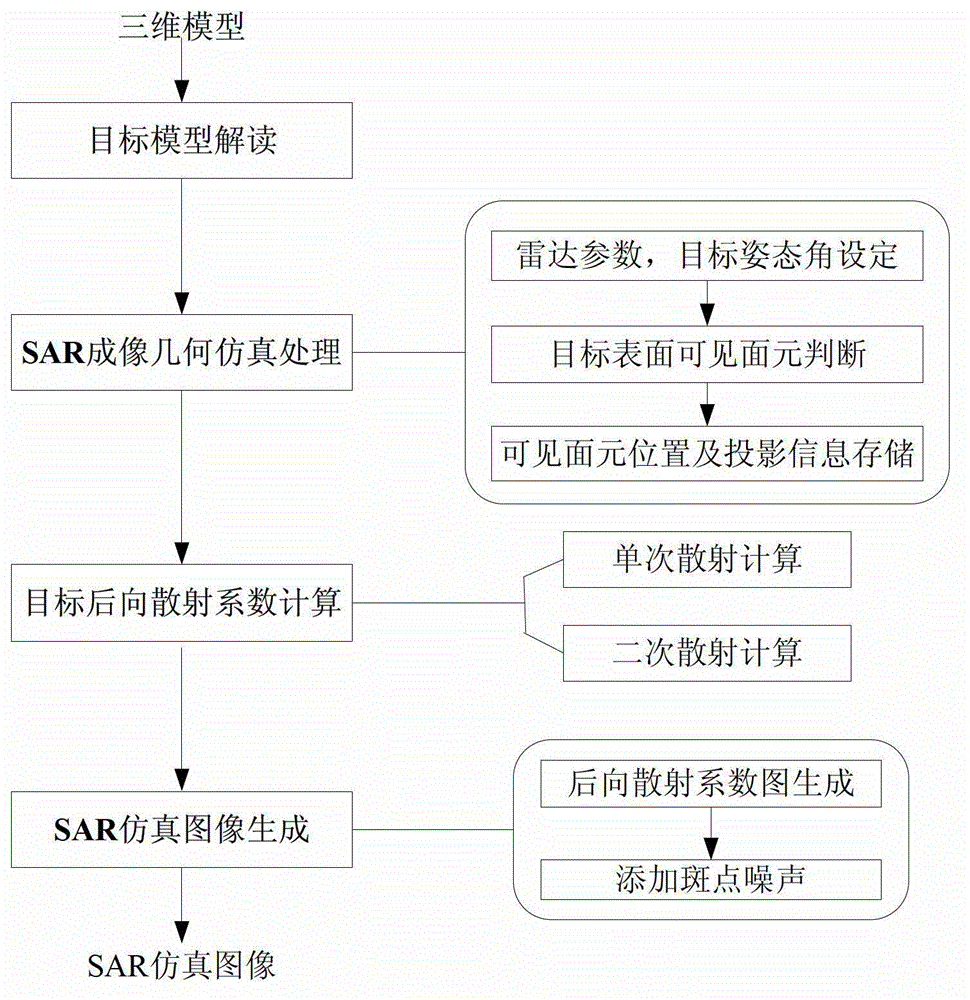
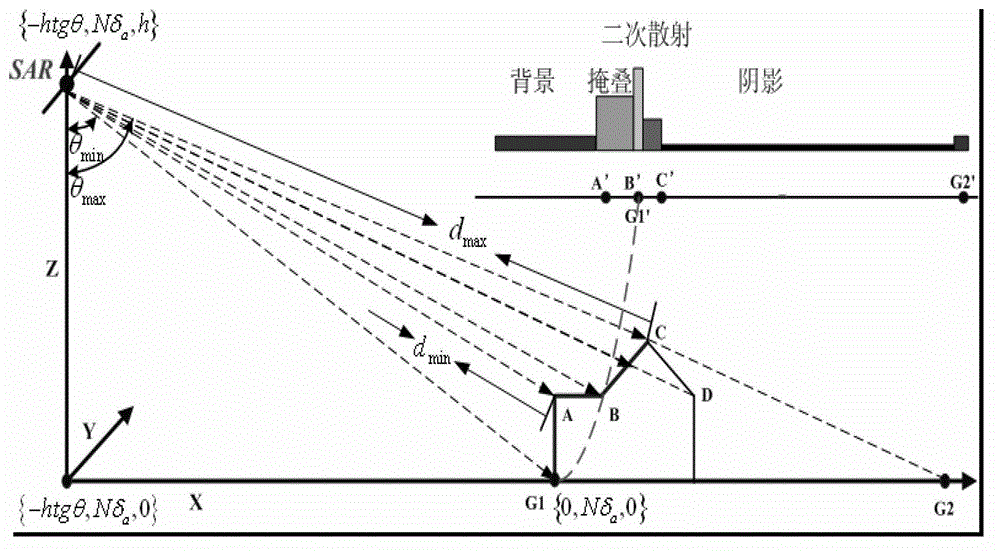
Geometric structure based complex target SAR image simulation method
InactiveCN103336272AOvercome the shortcomings of limited processing of scattering effectsQuick judgmentRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging interpretationImage resolution
The invention aims to provide a geometric structure based complex target SAR image simulation method, which can acquire simulation images with various viewing angles and various resolution ratios, and is used for assisting SAR image interpretation and automatic identification of complex targets. The method comprises the steps of: first, reading files of a target 3D model and acquiring spatial information, that is, calculating normal vectors of triangular surface elements through reading the vertex coordinates of triangular surface elements on the surface of the target and acquiring the spatial information of the target; second, carrying out SAR imaging geometrical simulation, that is, judging the surface element which receives radar signals on the surface of the target according to radar side looking imaging principles and recording the projection position of each of the visible surface element on the image; third, calculating the relative back scattering intensity of each position of the target model; and fourth, producing an SAR simulation image.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
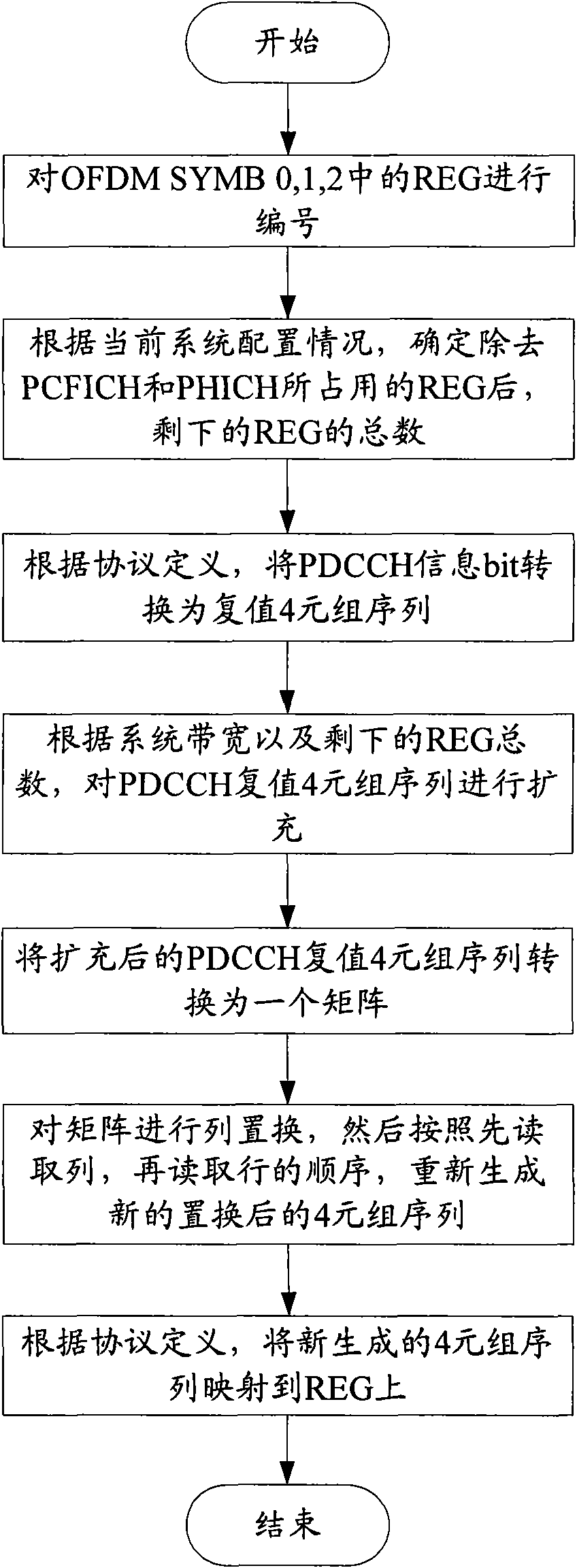
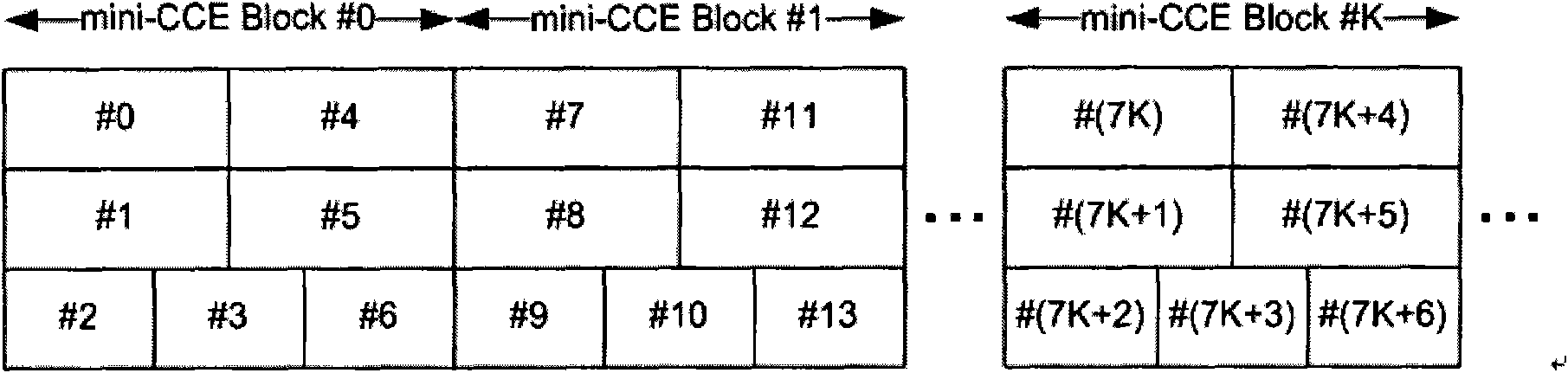
Method and device for mapping control channel sources
ActiveCN101605023AReduce distractionsIncrease diversity effectError prevention/detection by using return channelMulti-frequency code systemsAutomatic repeat requestResource element
The invention discloses a method for mapping control channel sources. The method comprises the following steps: confirming the number of source element groups occupied by a physical control format indicator channel (PCFICH) and a physical hybrid automatic repeat request indicator channel (PHICH) and the total number of the source element groups supported by a system; confirming a number NREG of the source element groups occupied by a physical downlink control channel (PDCCH) according to the confirmed total number and the number of the source element groups occupied by the PCFICH and the PHICH; expanding a complex value 4-tuple sequence of the PDCCH according to the NREG to obtain an expanded 4-tuple sequence; mapping the expanded 4-tuple sequence into a matrix according to a first preset mode; permuting the columns of the matrix to obtain a permutation matrix; reading the permutation matrix in a second preset mode to obtain a new 4-tuple sequence; and mapping the new 4-tuple sequence to the source element groups by a time priority principle. The invention also discloses a device for mapping the control channel sources. The invention can reduce the mutual interference among the control channels and improve the diversity effect of an OFDM technology.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Oxyopter type display device using holographic elements
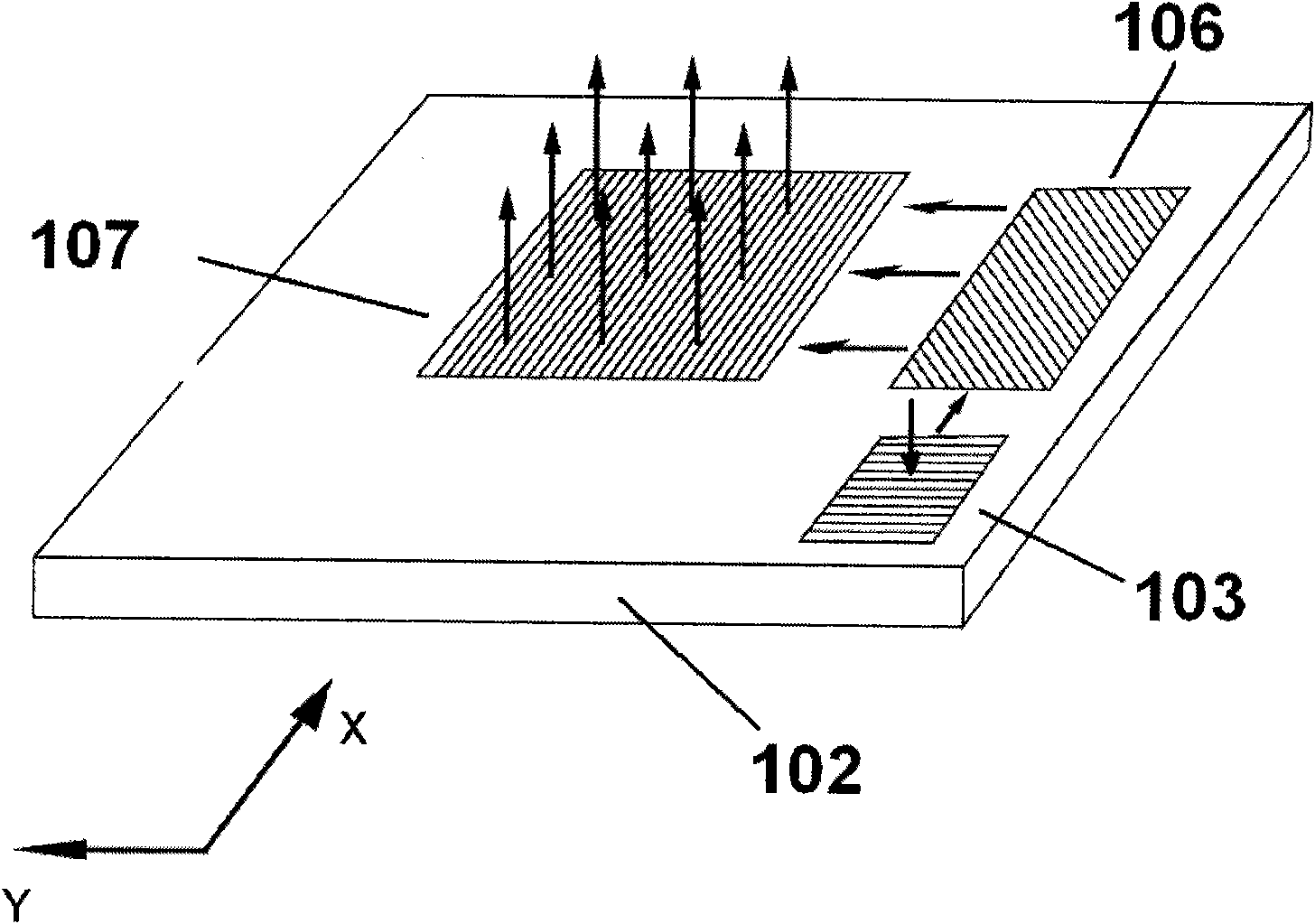
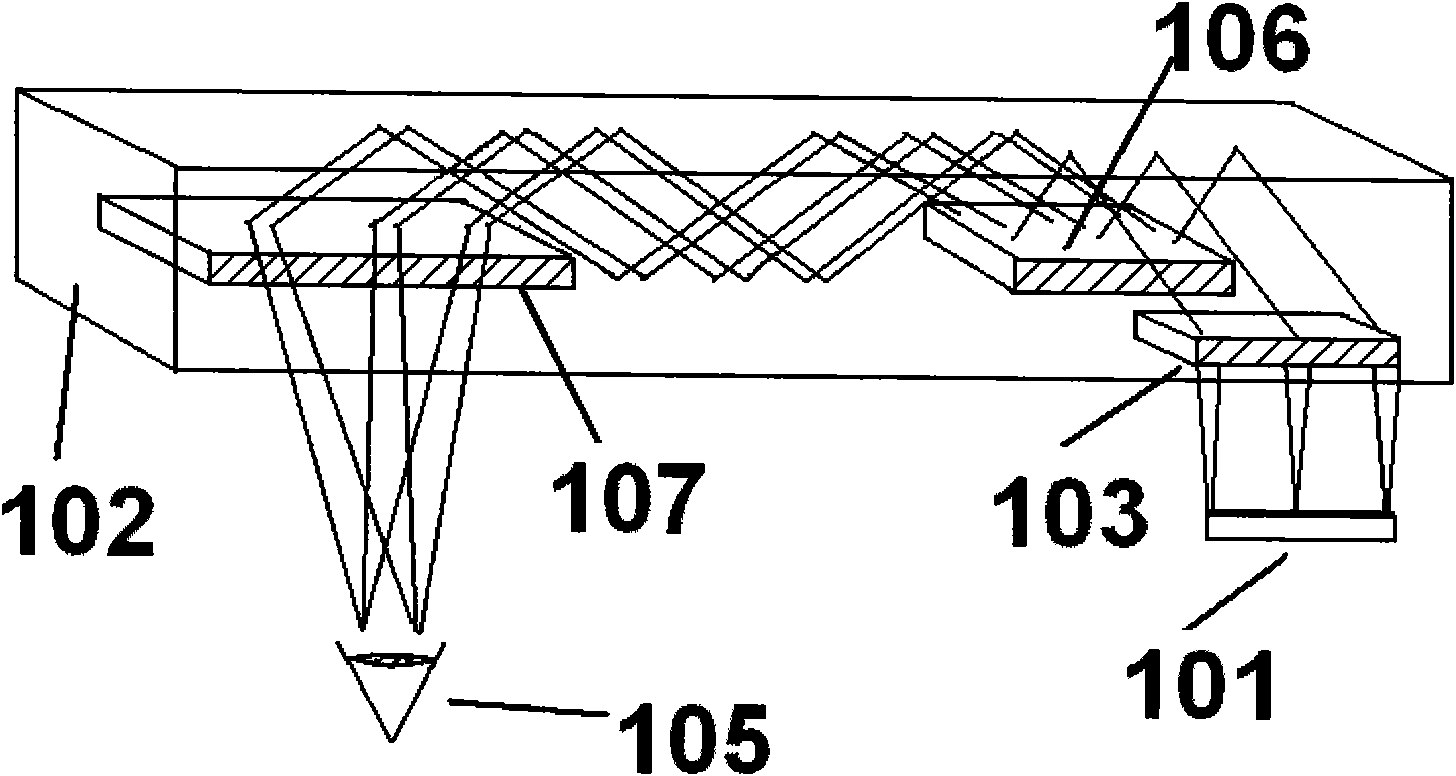
The invention relates to an optical system comprising three holographic elements, which can be used for a helmet-mounted display or a spectacle-mounted display. By using the optical display system, an image projected from an image source element can be subject to beam expansion by the three holographic elements and can be converted into divergent or convergent spherical waves for emission, thereby facilitating the wear of a user having a certain oxyopter. Because the display is realized by the holographic elements instead of lenses, the optical system provided by the invention is especially applicable to an ultra-thin display device, has the advantage of low manufacturing cost and can be customized according to user requirements.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Flow labels
ActiveUS7266121B2Easy to useValid verificationError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceData stream
There is disclosed a system for monitoring a packet data flow, comprising: a data flow source element including: determining means adapted to determine a quality of service identifier for the data flow; first generating means adapted to generate an encoded value in dependence on the quality of service identifier; allocating means adapted to allocate the quality of service identifier and the encoded value to the flow label for each data packet of the data flow; and transmitting means for forwarding data packets including flow labels to a routing domain; and a routing domain interface element including: receiving means for receiving data packets from the data flow source; second generating means adapted to generate a further encoded value in dependence on the quality of service identifier in a flow label of a data packet; comparing means adapted to compare the further encoded value to the encoded value in the flow label; and routing means adapted to selectively route the data packets in dependence on the comparing step.
Owner:CRYSTAL MOUNTAIN COMM LLC
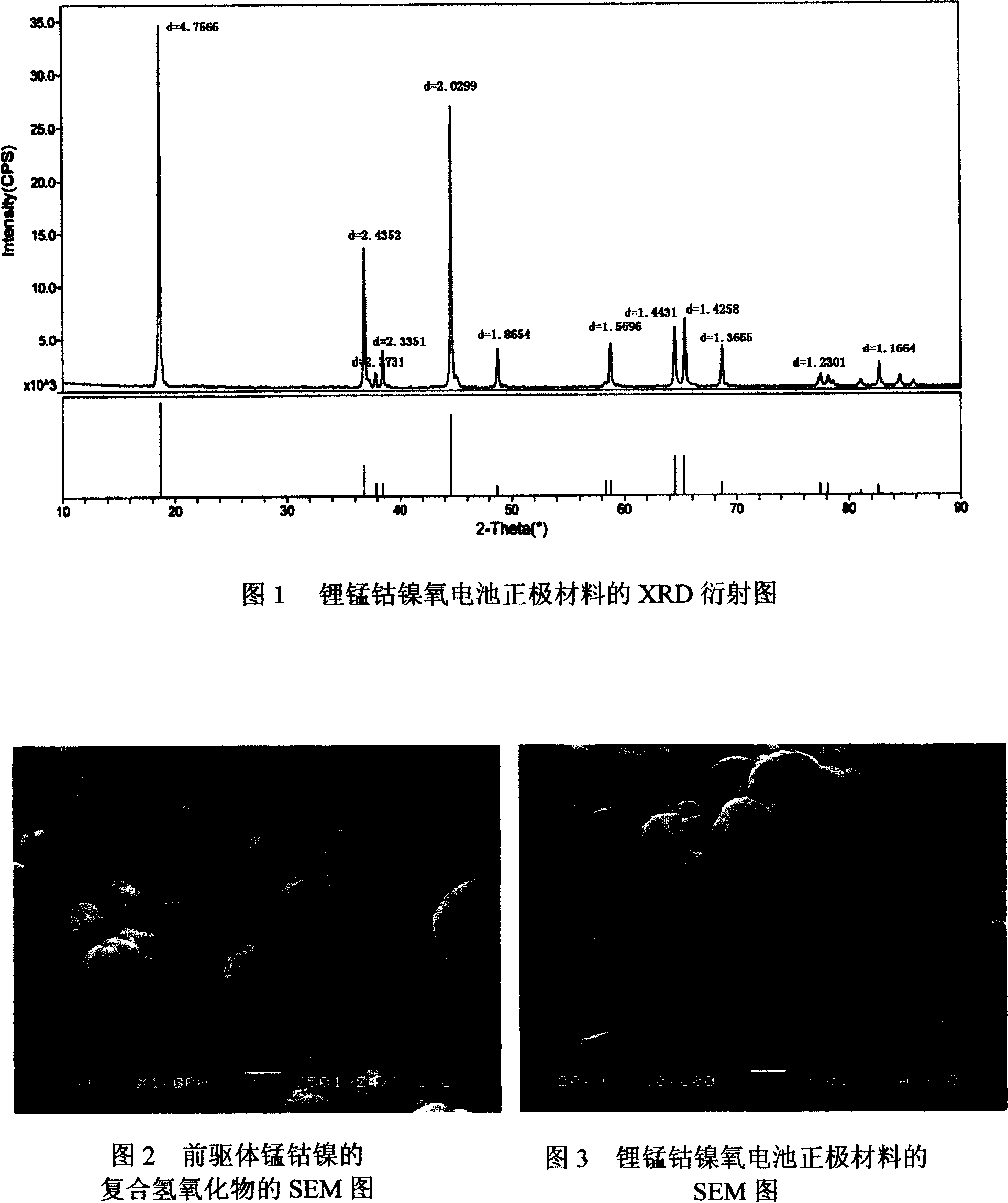
Lithium manganese cobalt nickle oxygen of manganese cobalt nickle triple lithium ionic cell positive material and its synthesizing method
InactiveCN101083321APrevent oxidationCrystal denseElectrode manufacturing processesLithium compoundsNickel saltManganese
The invention belongs to a manganese cobalt nickel three Yuan lithium ionization cell anode material, specifically relates to the lithium manganese cobalt nickel oxygen and its synthetic method. The high-capacity, the high safety performance of other battery positive electrode material is unable to compare with lithium manganese cobalt nickel oxygen, moreover low in price, the good compatibility with the electrolyte, the outstanding circulation performance, will certainly to thrust the market in the recent several years. The chemical formula of lithium manganese cobalt nickel oxygen is: The LiMn1 / 2Co1 / 4Ni1 / 4O2 crystal structure is a hexagonal system. The synthetic method of lithium manganese cobalt nickel oxygen is: (1) preparing the mix solution which is composed by the manganese salt, the cobalt blue, the nickel salt, under the agitation situation, joining the alloy salt brine, the complexing agent simultaneously in the reacting system according to the certain proportion distinction, simultaneously adjusts the join speed of alkali to maintain pH to be constant; After continuous feed certain times, filtrate and wash the precipitate to obtain the forerunner body. (2) Grinding and mixing lithium source element and forerunner body ball, after mixed evenly, compacting, roasting, and decomposing to obtain the lithium manganese cobalt nickel oxygen. Then cooling, grading, mixing to obtain the product.
Owner:湖南美特新材料科技有限公司
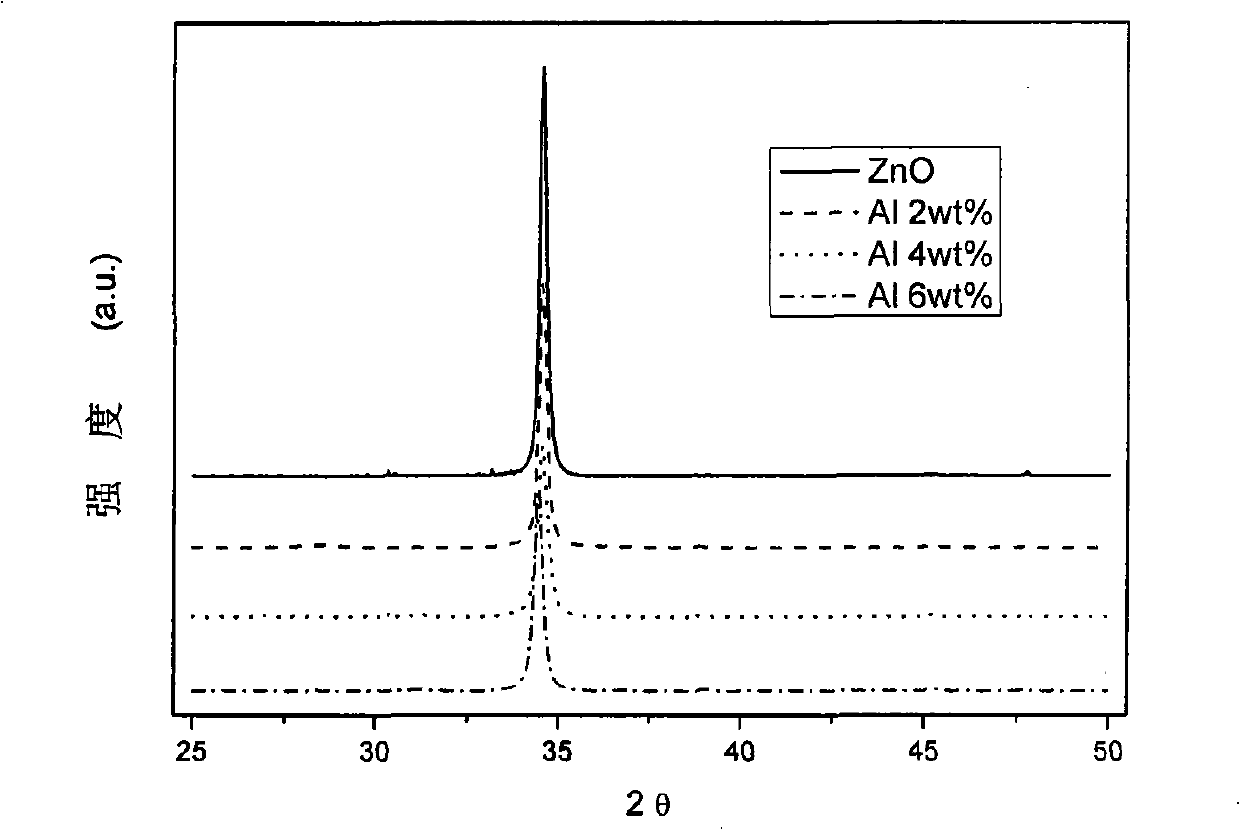
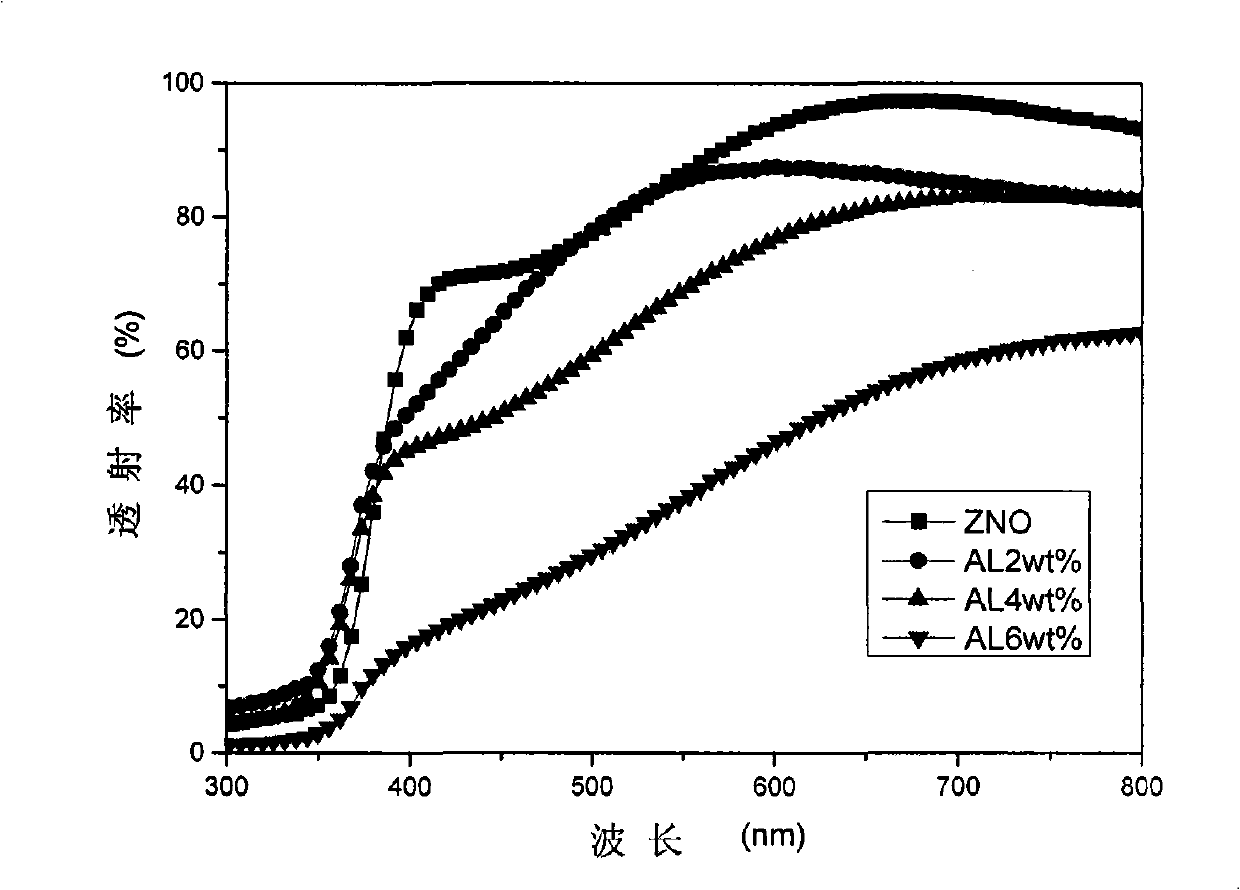
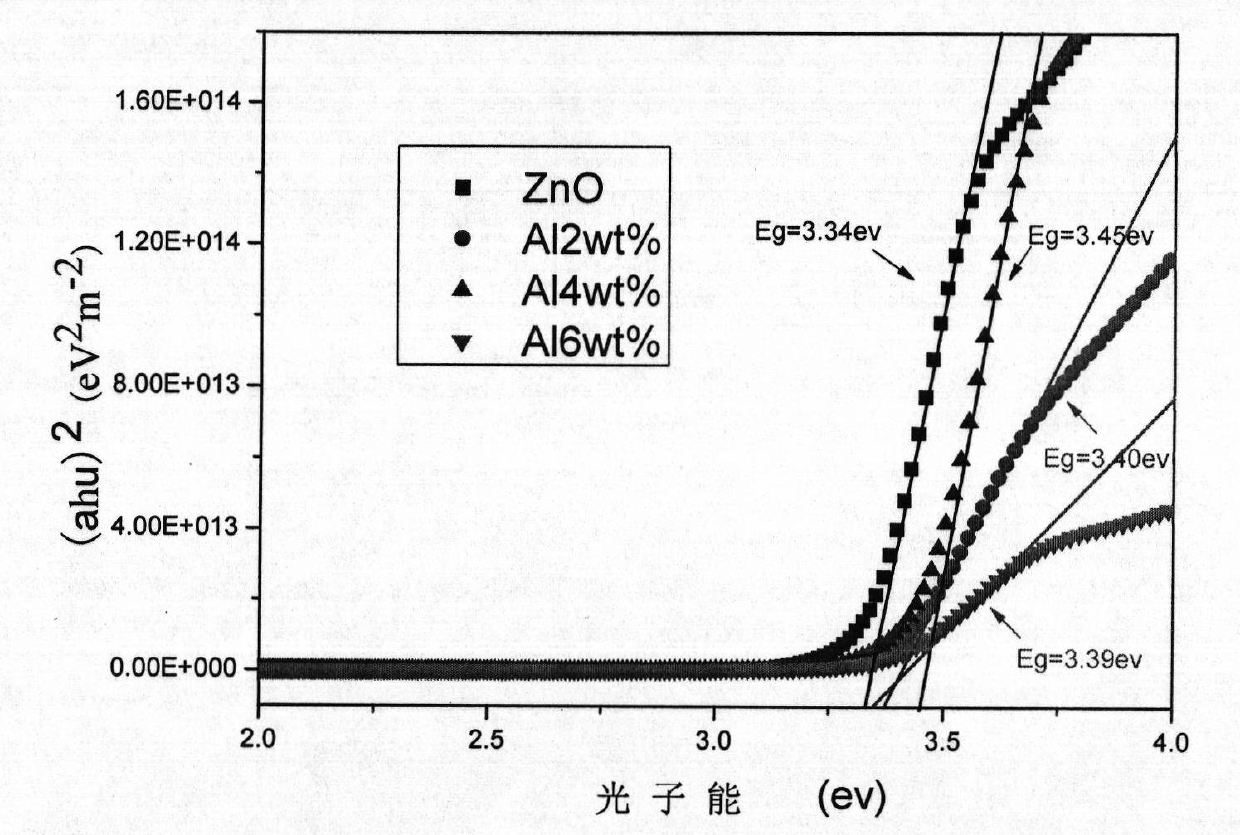
Method for preparing doped ZnO-based film through magnetron sputtering
InactiveCN101768728ALow costSimple and fast operationVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringRoom temperature
The invention provides a method for doping and growing ZnO-based film through magnetron sputtering. The method comprises the following steps: placing a substrate in the reaction chamber of a magnetron sputtering device, vacuumizing the reaction chamber to lower than 1*10<-4>Pa; separately placing ZnO target and doped source element target on the radio frequency target position and DC or electromagnetic target position of the turntable of the reaction chamber, introducing oxygen and argon, which are used as sputtering atmosphere, in a buffer chamber, fully mixing in the buffer chamber, introducing the mixed gas in a vacuum reaction chamber, performing sputtering growth when the pressure is 1-3Pa and the temperature of the substrate is below the room temperature; selecting a sample position and adjusting the sputtering times of the radio frequency target position and DC or electromagnetic target position through a preset program to alternately grow ZnO films and doped element layers; and after the growth placing the doped ZnO-based film in vacuum, air or nitrogen atmosphere to anneal for 30-60 minutes at 400-800 DEG C.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com