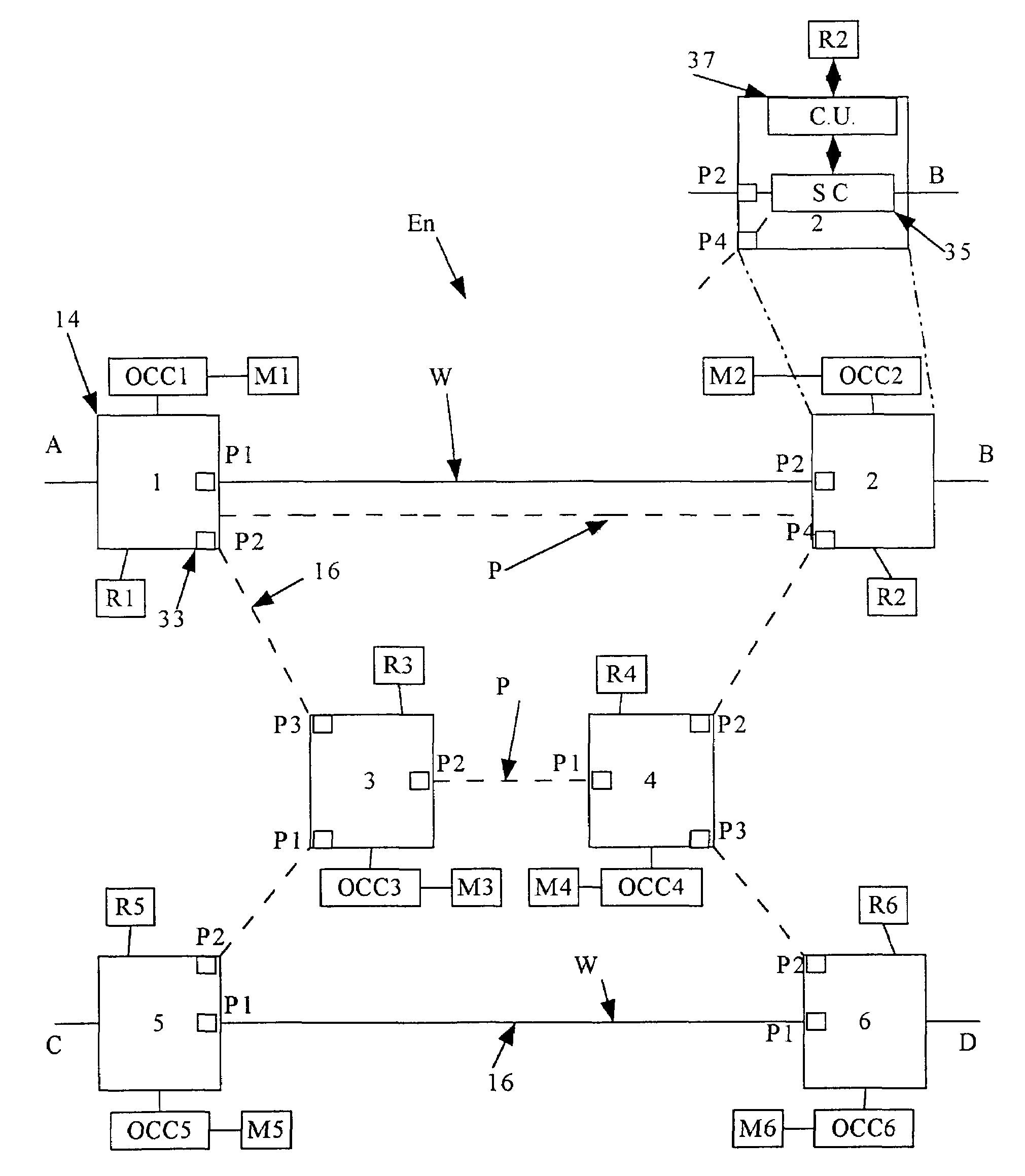Patents
Literature
46 results about "Shared mesh" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
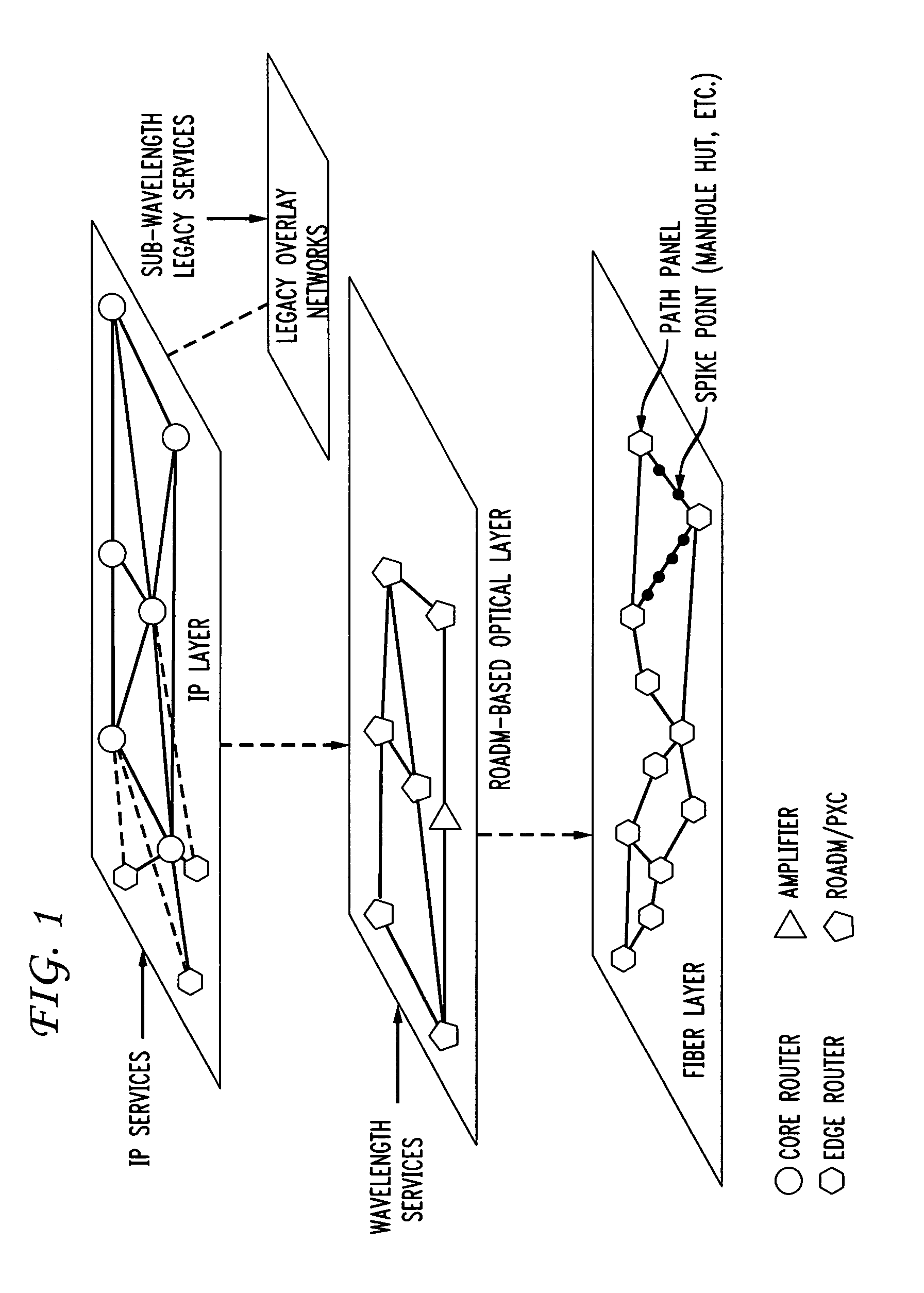
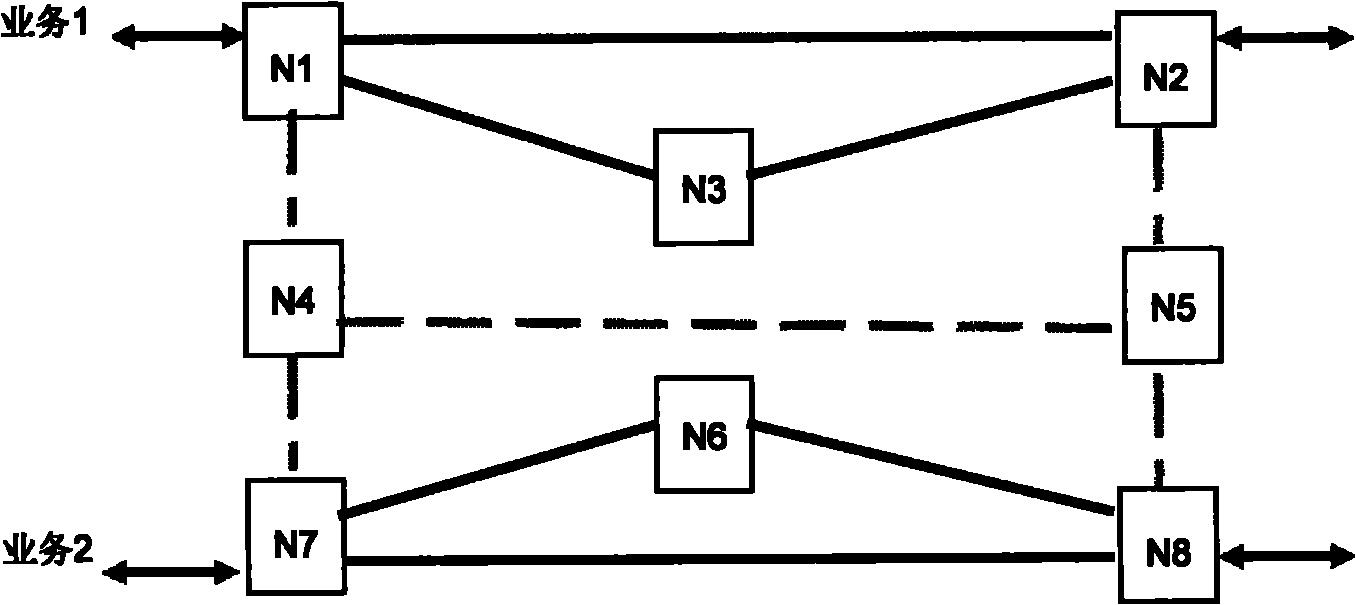
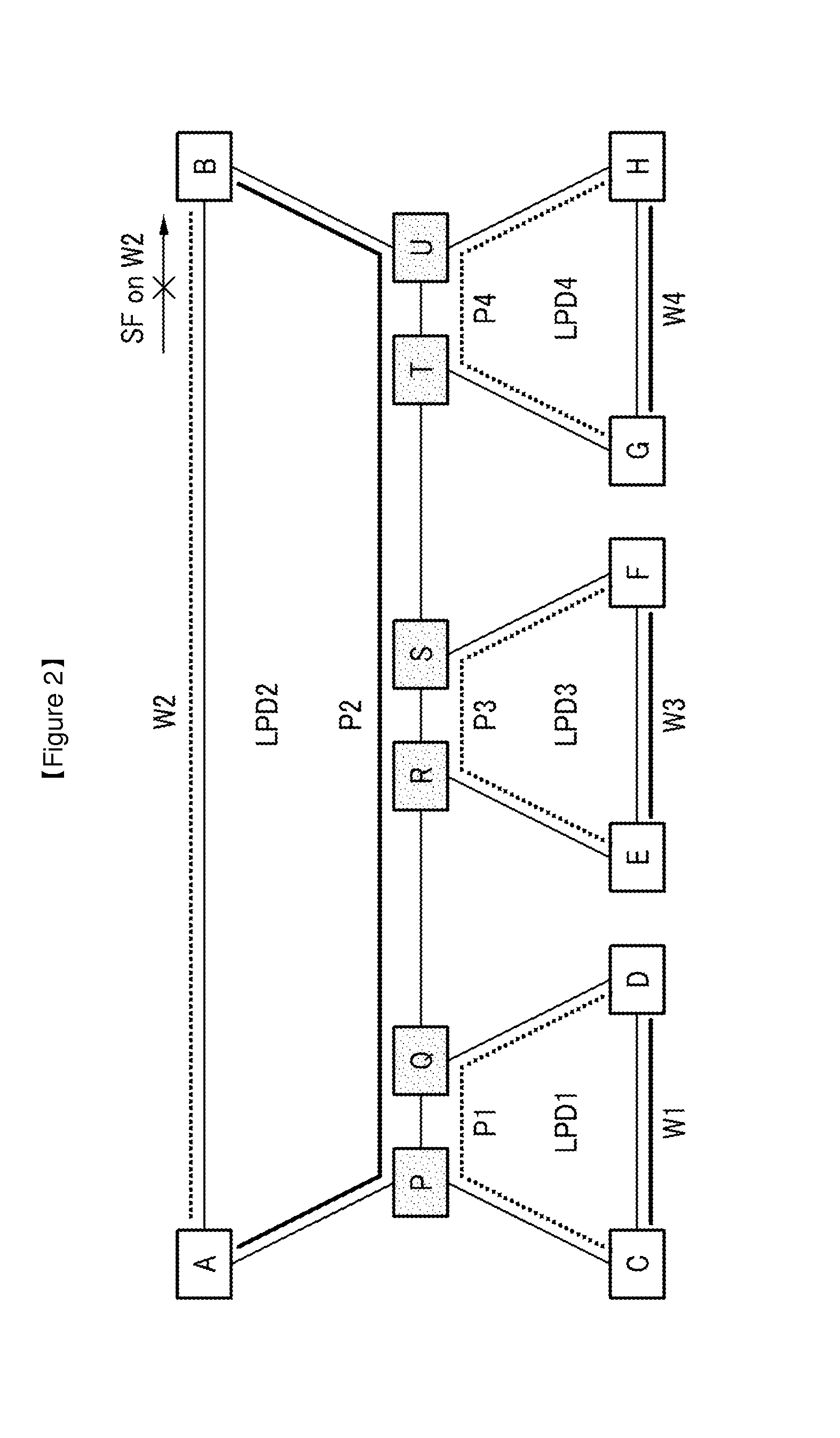
A shared mesh (also known as 'traditional' or 'best effort' mesh) is a wireless mesh network that uses a single radio to communicate via mesh backhaul links to all the neighboring nodes in the mesh. This is a first generation mesh where the total available bandwidth of the radio channel is ‘shared’ between all the neighboring nodes in the mesh. The capacity of the channel is further consumed by traffic being forwarded from one node to the next in the mesh – reducing the end to end traffic that can be passed. Because bandwidth is shared amongst all nodes in the mesh, and because every link in the mesh uses additional capacity, this type of network offers much lower end to end transmission rates than a switched mesh and degrades in capacity as nodes are added to the mesh.
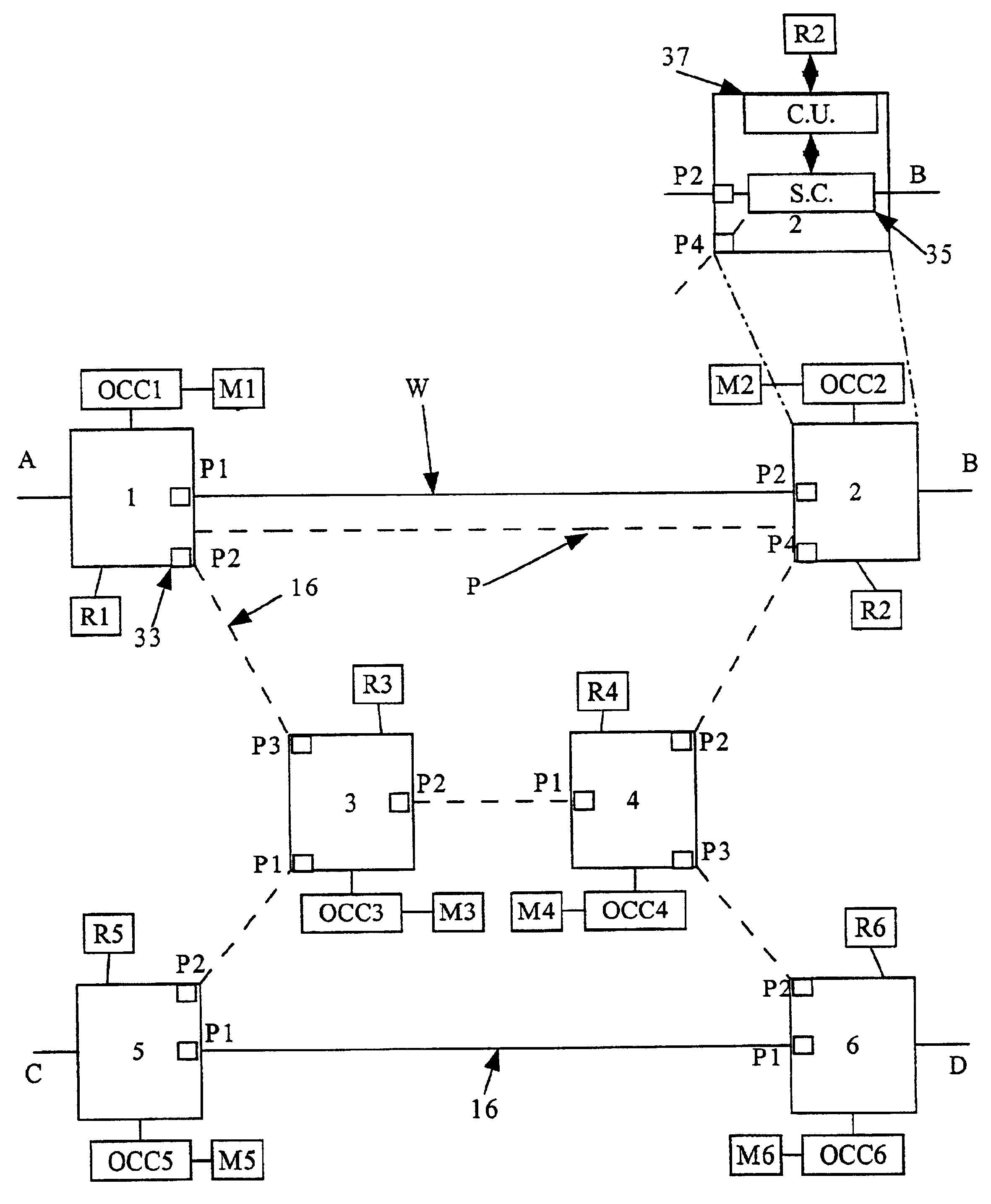
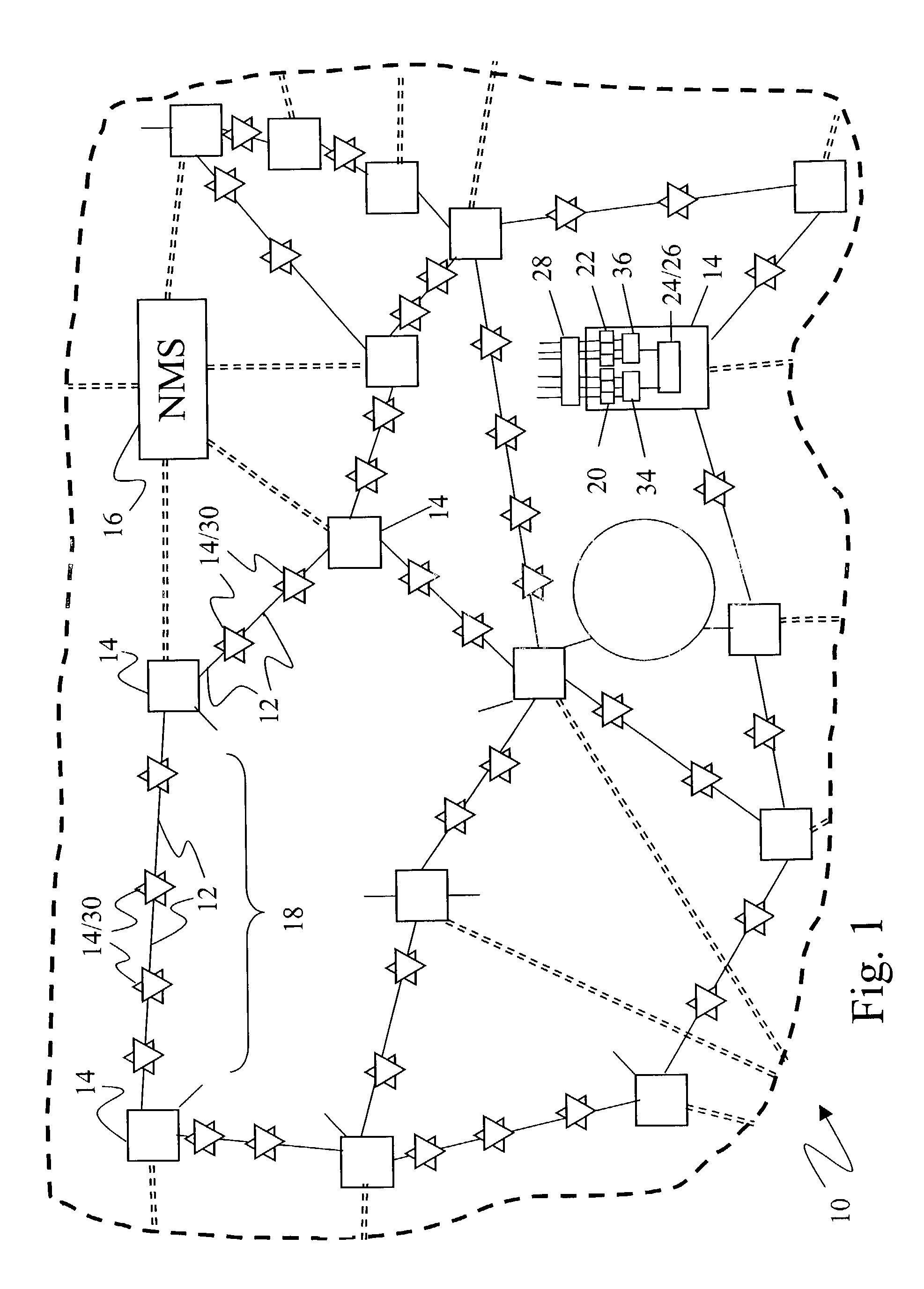
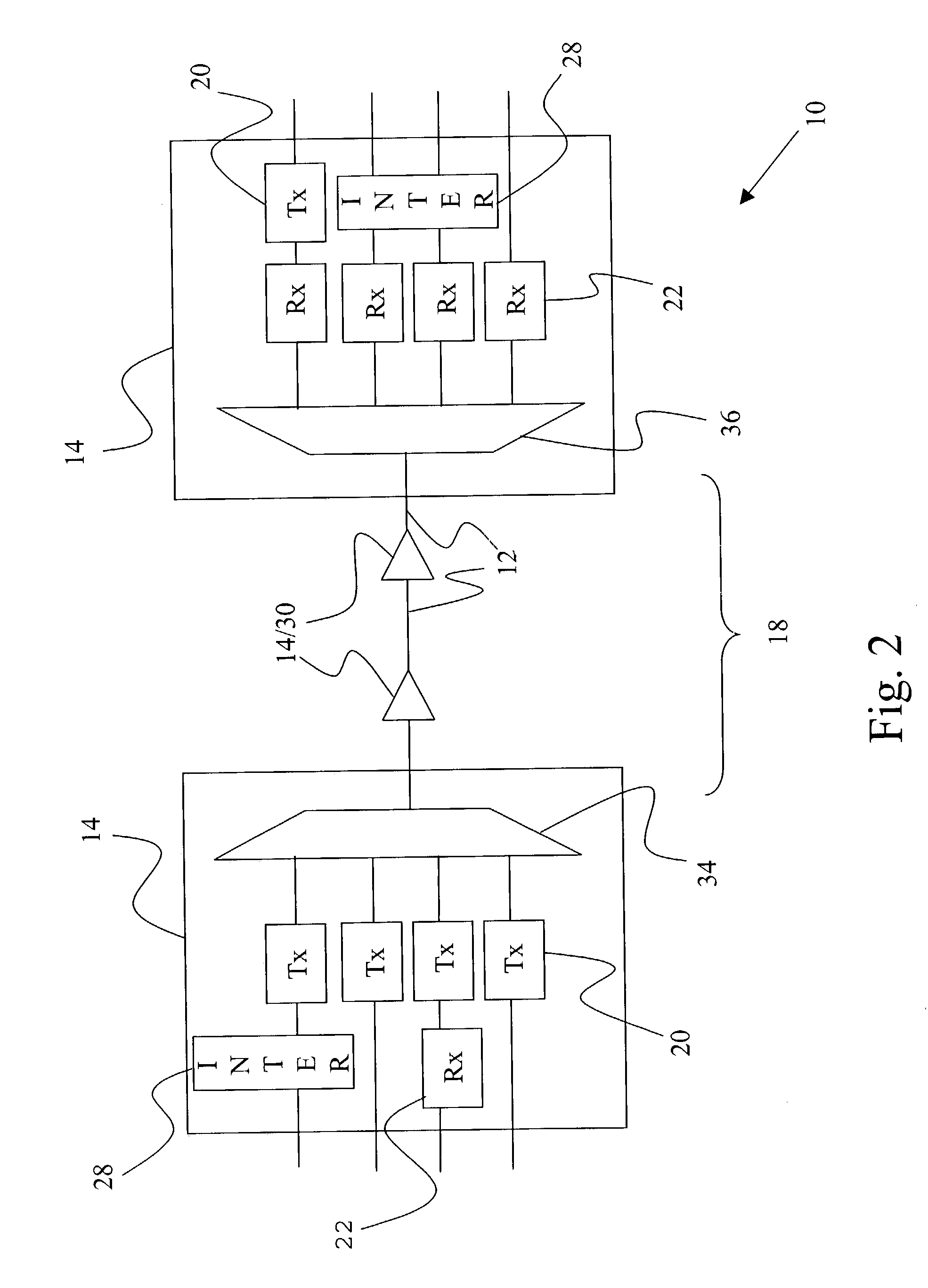
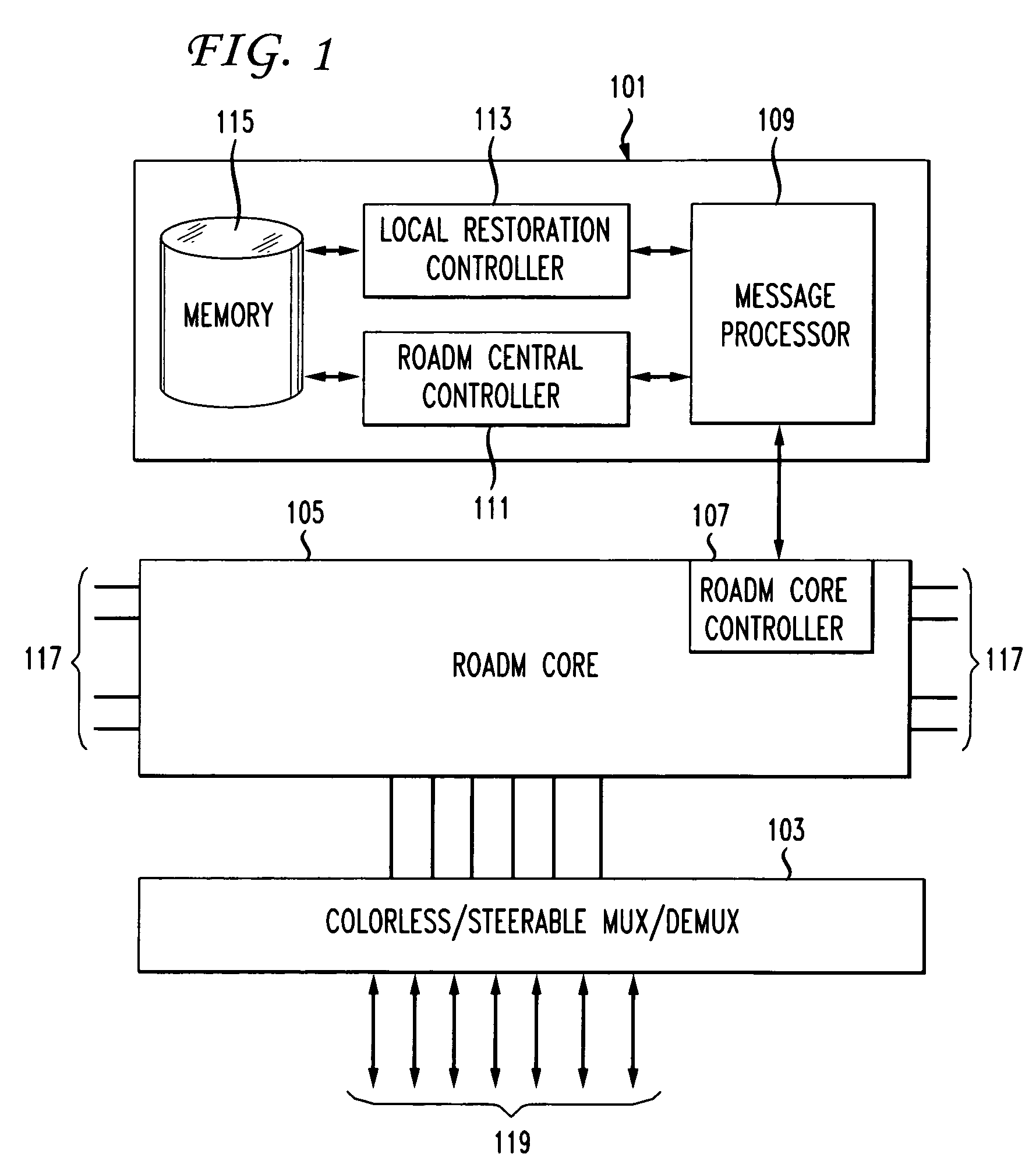
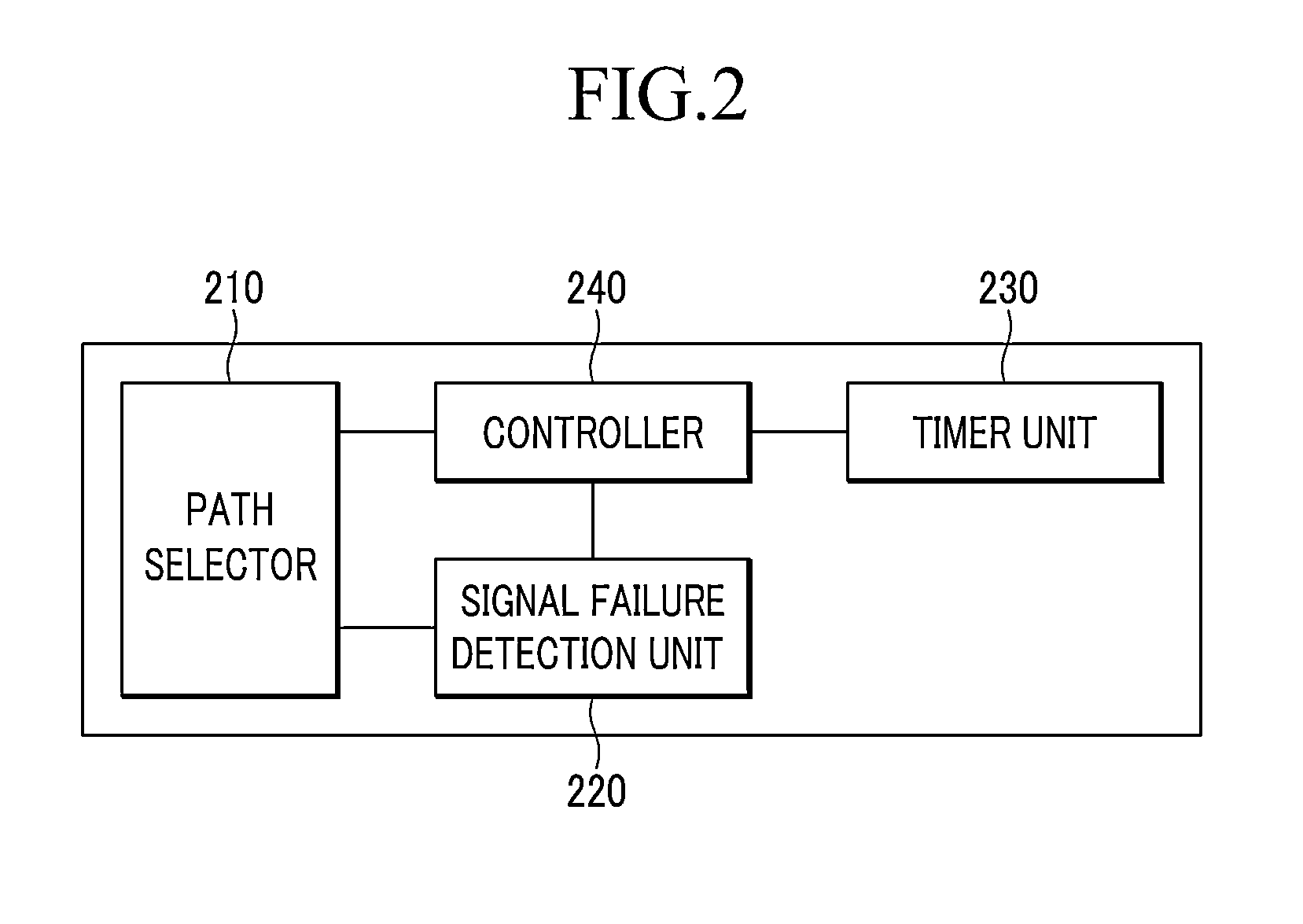
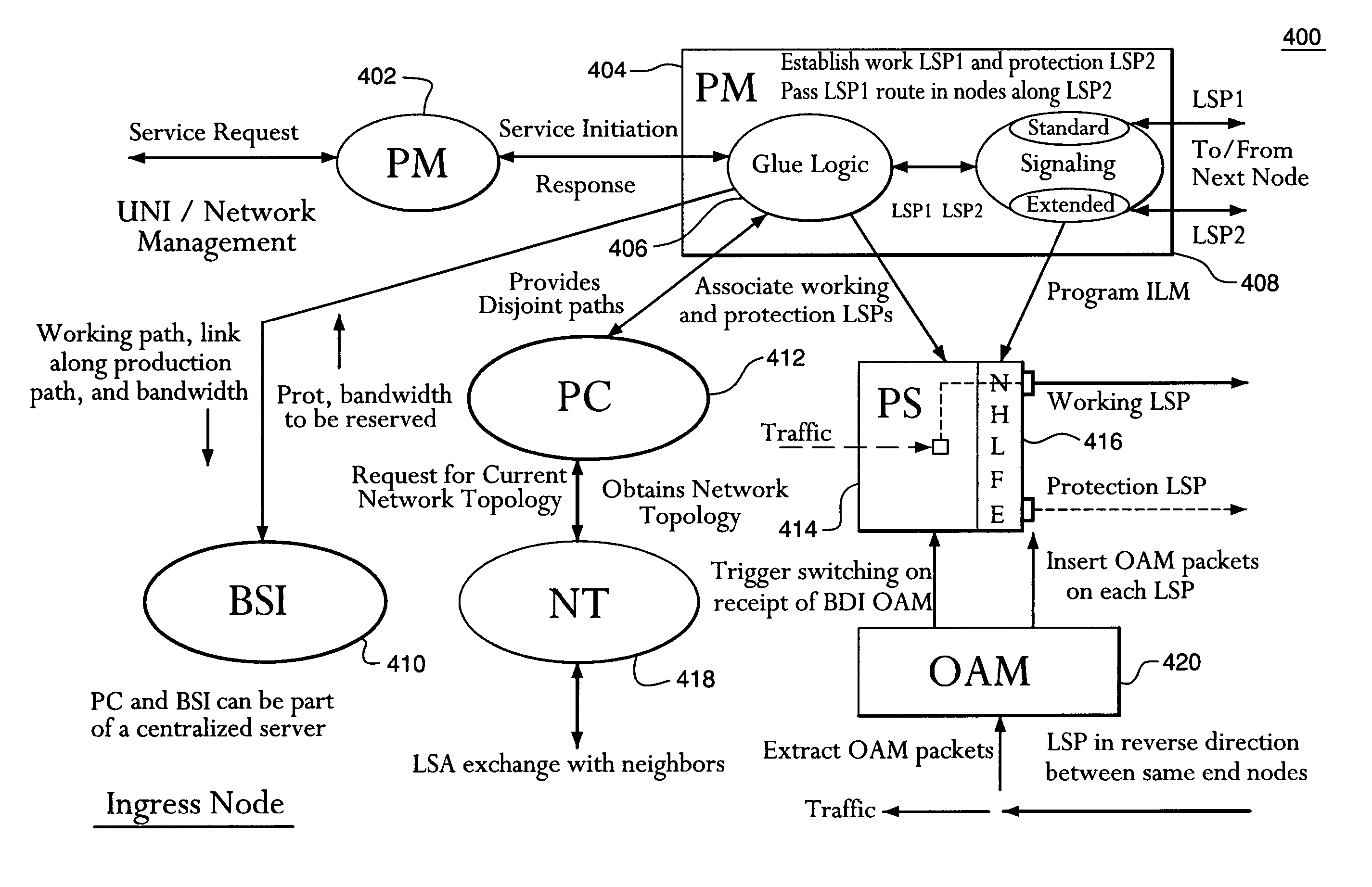
Shared mesh signaling algorithm and apparatus
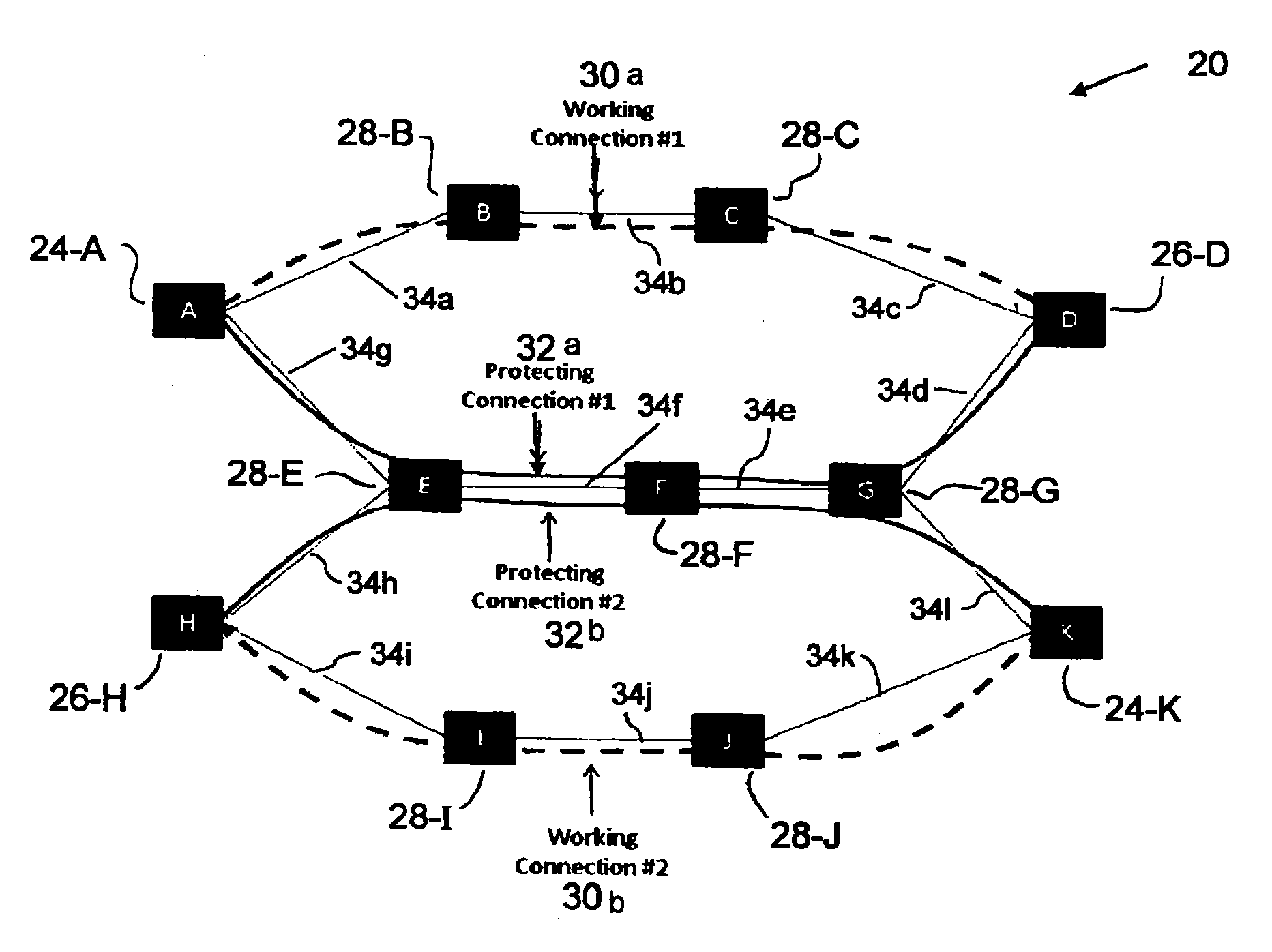
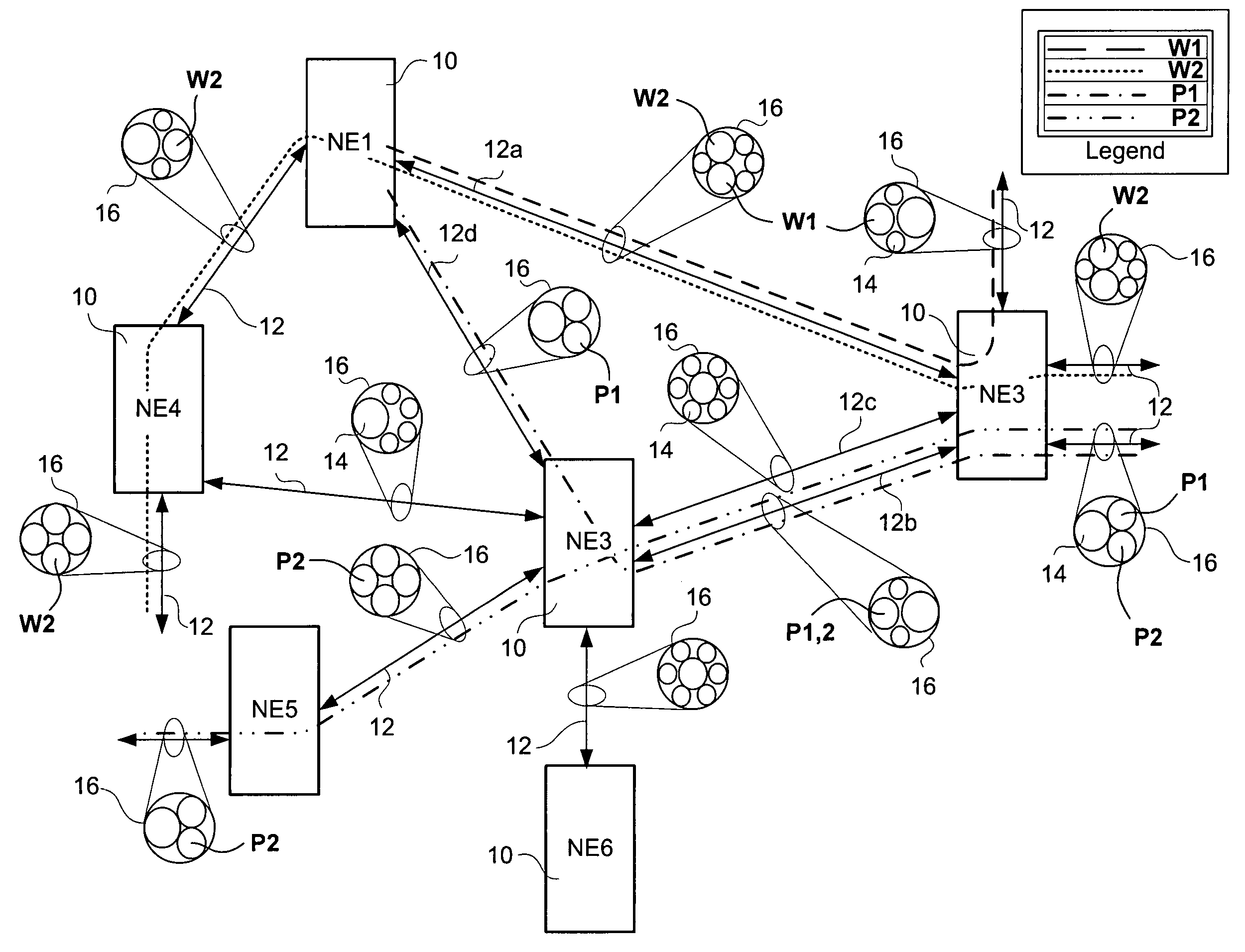
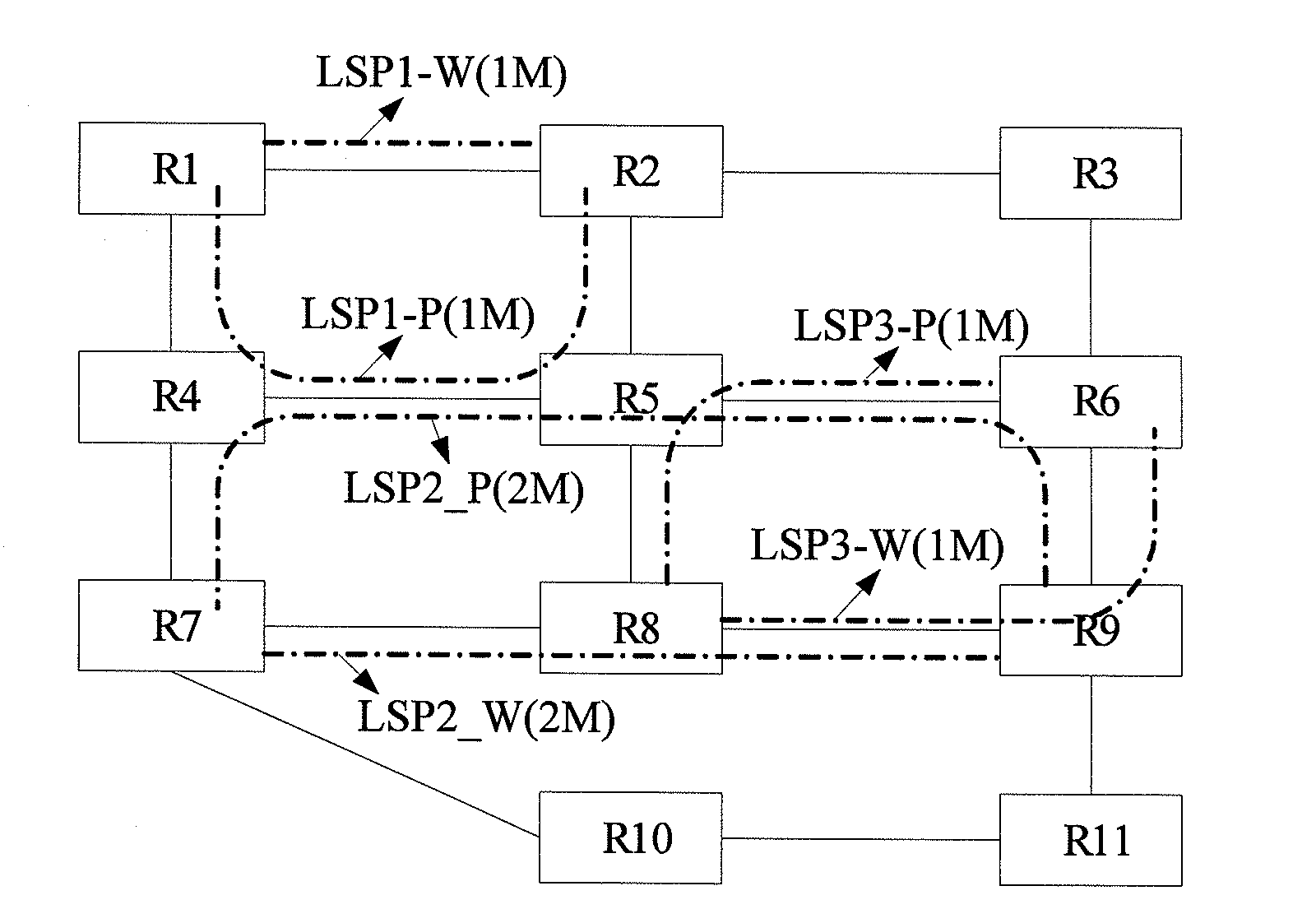
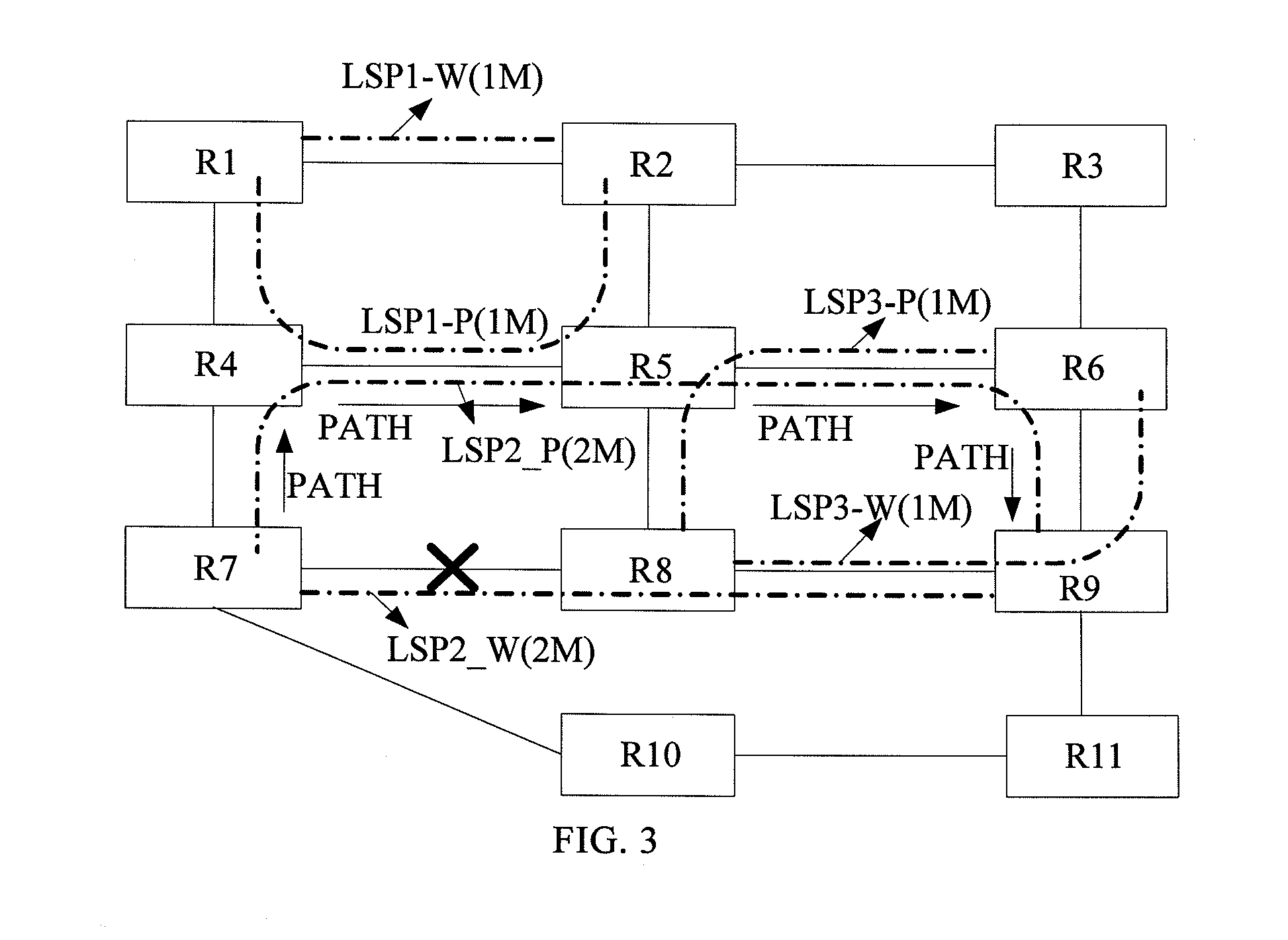
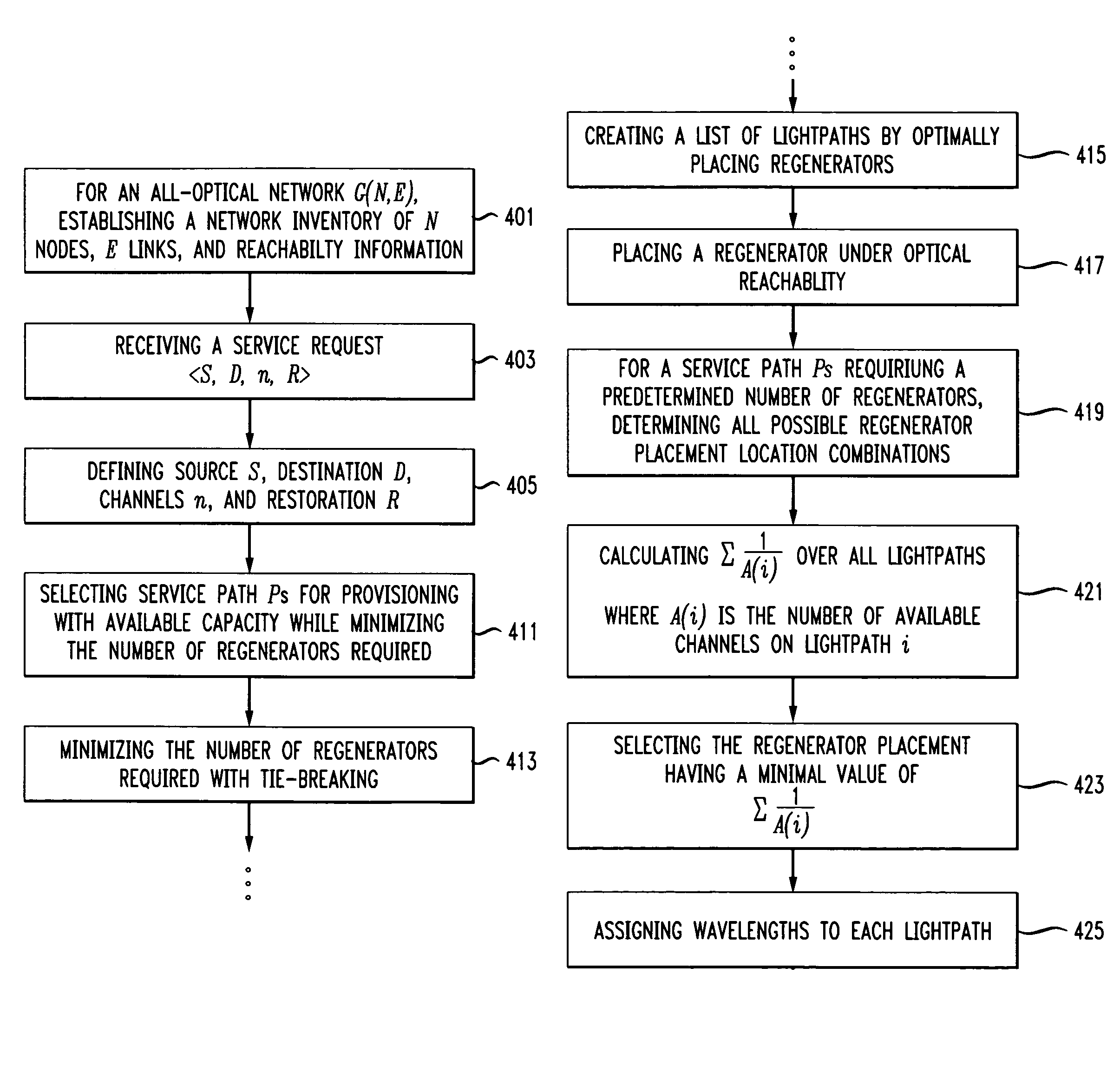
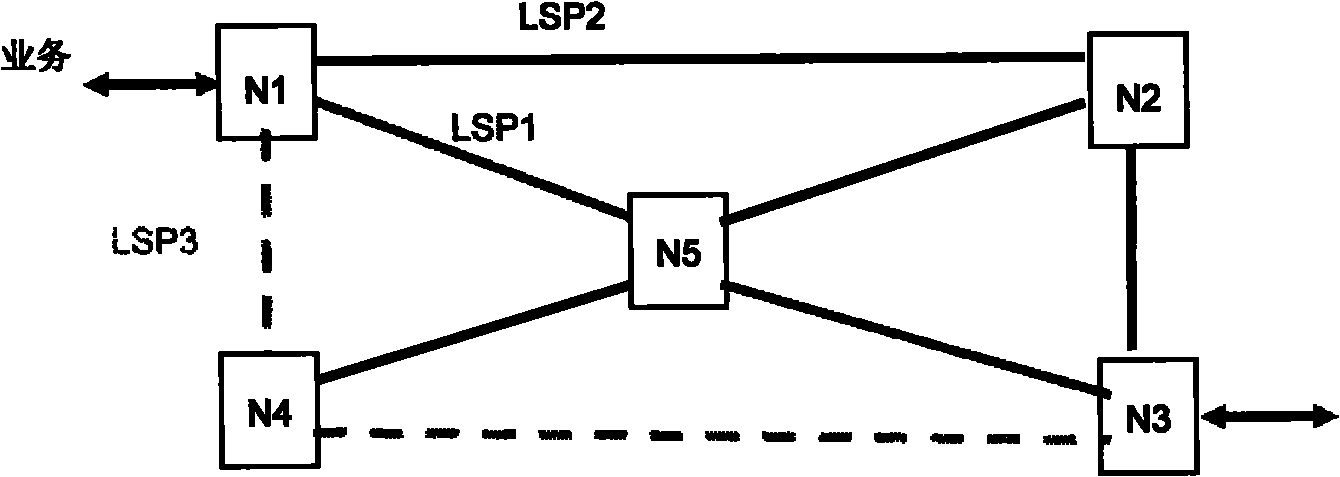
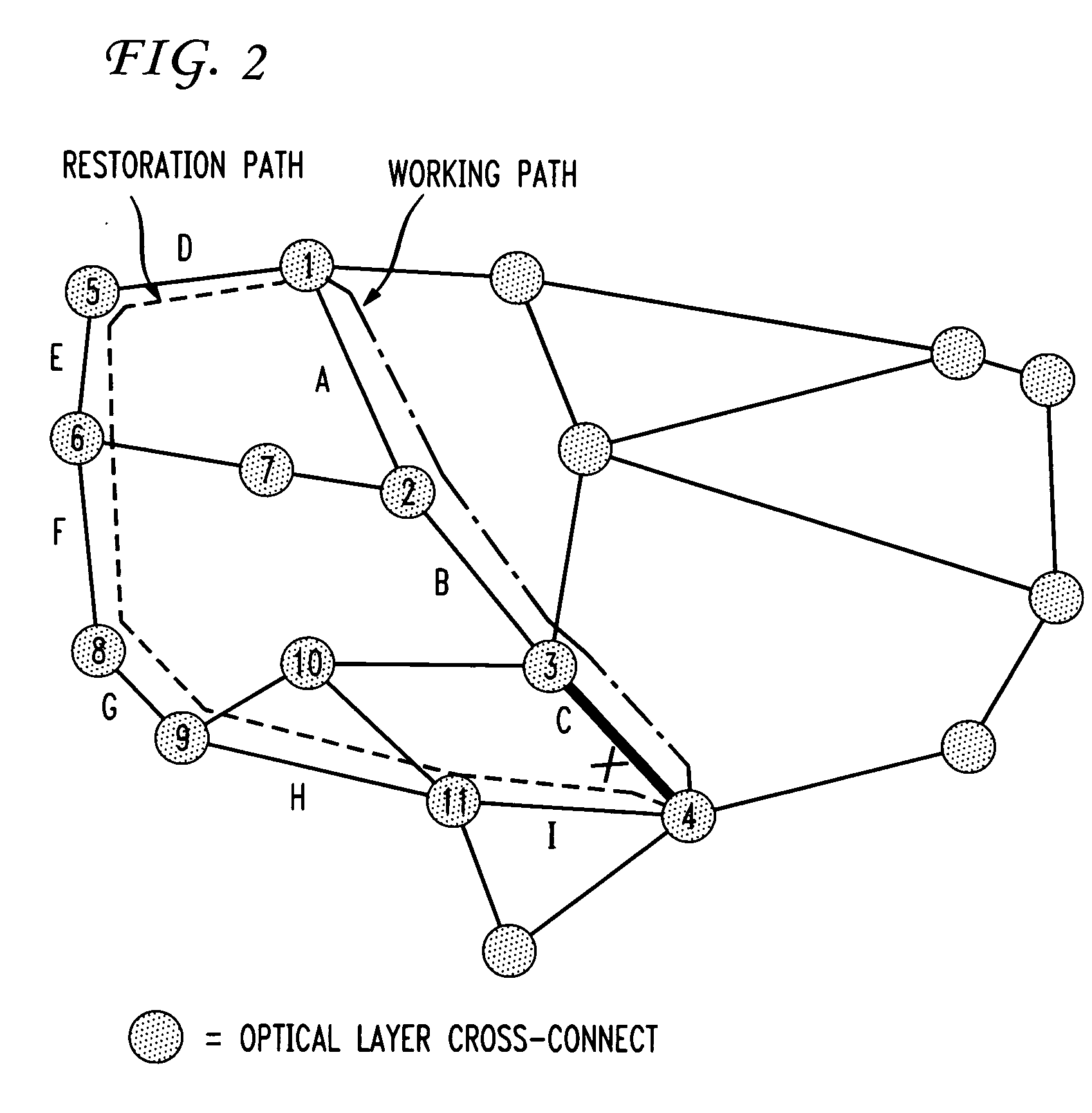
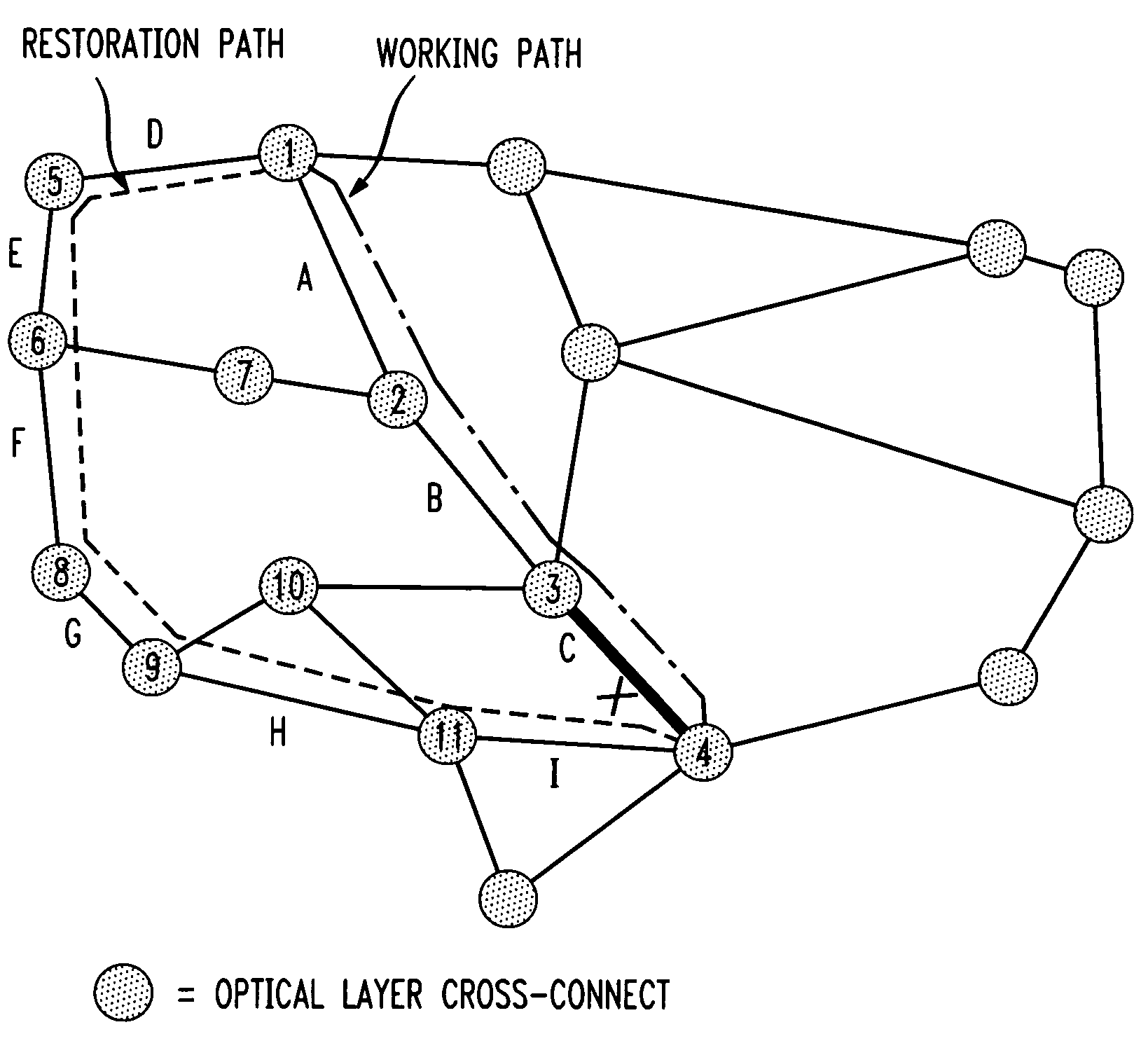
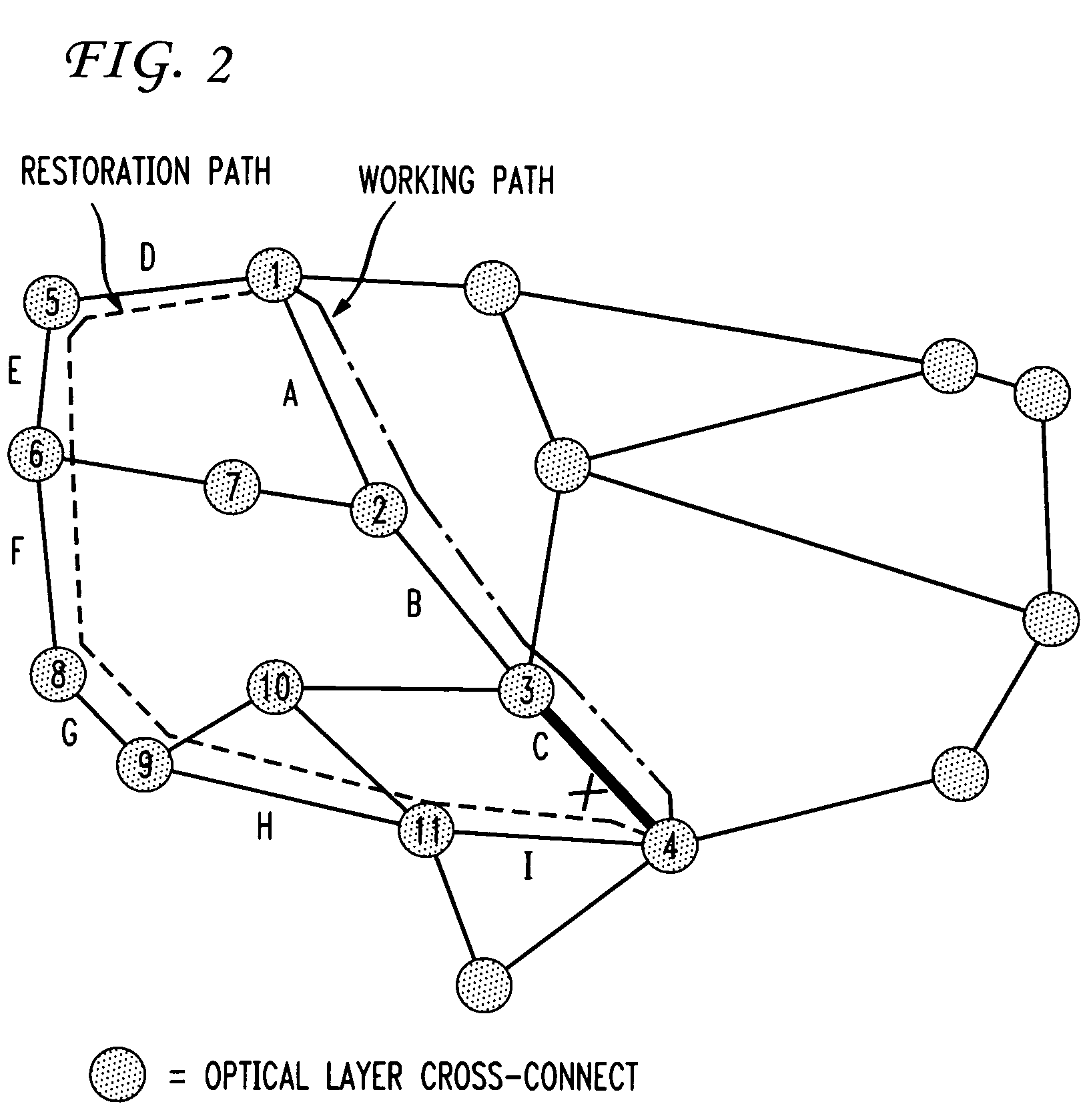
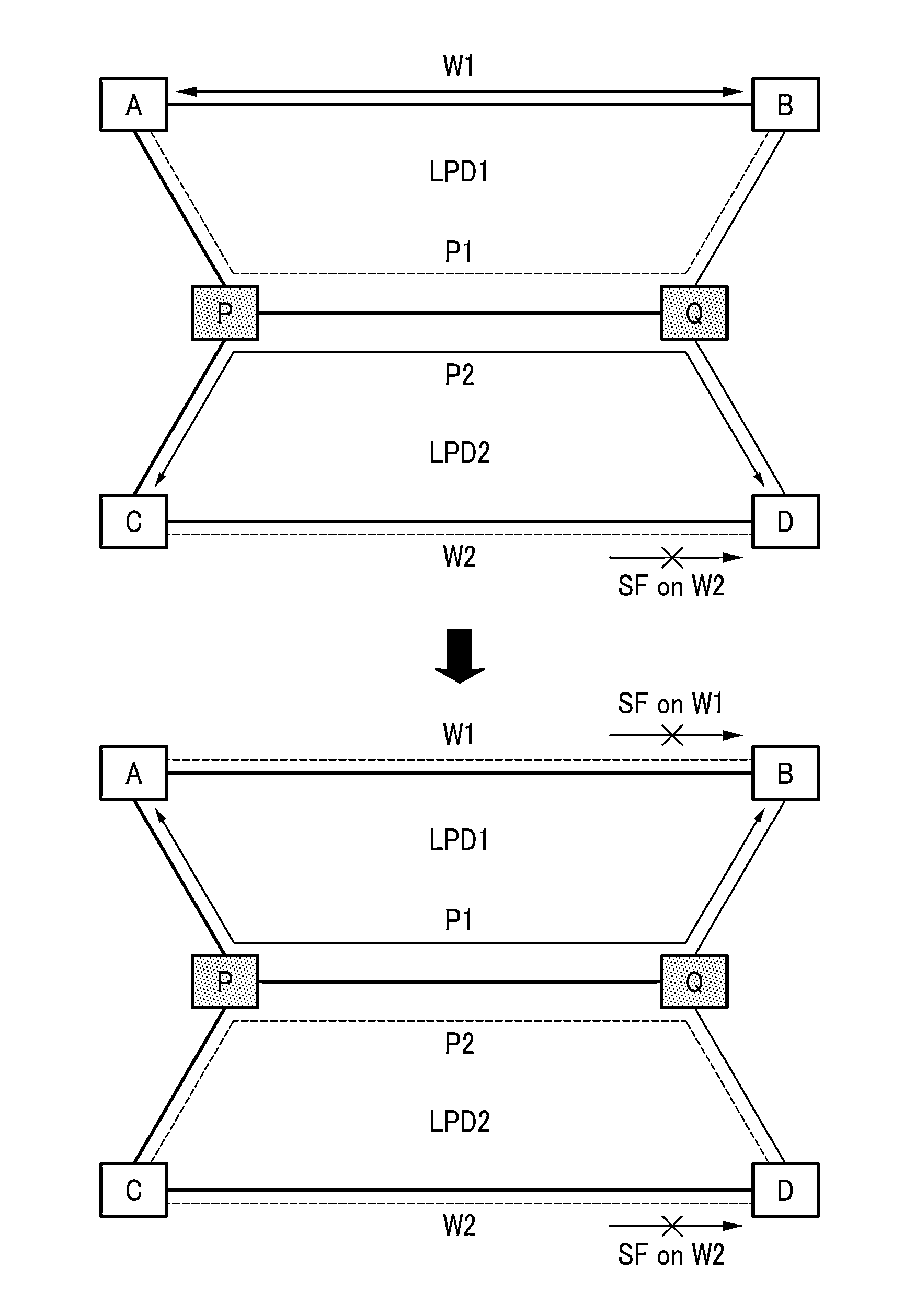
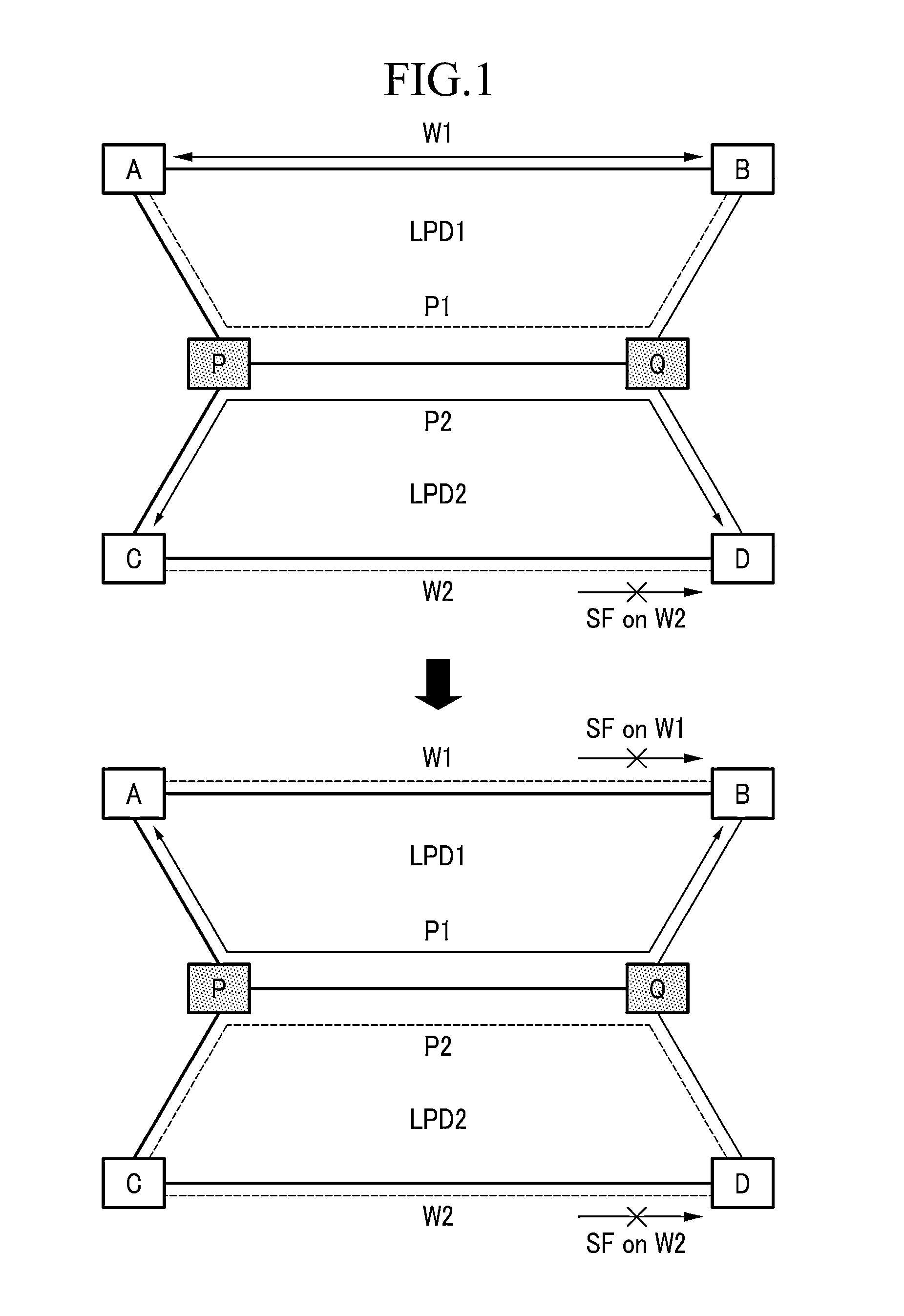
A shared mesh protection scheme defines an associated protection path when a working connection is established. During the protection path definition, the corresponding protection path information is sent down to a switch card of network elements making up the protection path. Upon detection of the failure, the network elements using an overhead byte message will inform the routing source network element of the connection of the failure in the working path. The overhead bytes used are interrupt driven bytes located in the line and path overhead of network traffic. The routing source node of the connection will then send the corresponding overhead byte messages down the protection path to provide for protection path establishment according to the preloaded data located at the switch card. It should be noted that each connection can have a source and termination element which relates to the source from where the corresponding connection was set-up rather than the direction of the payload transmission. Therefore, once the failure has occurred the source elements will send messages using overhead bytes to the corresponding network elements along the protection path. Accordingly, routing tables located at the switch card of the network elements, set-up when the working path connections were initially established, determine this dynamically allocated protection path environment.
Owner:CIENA
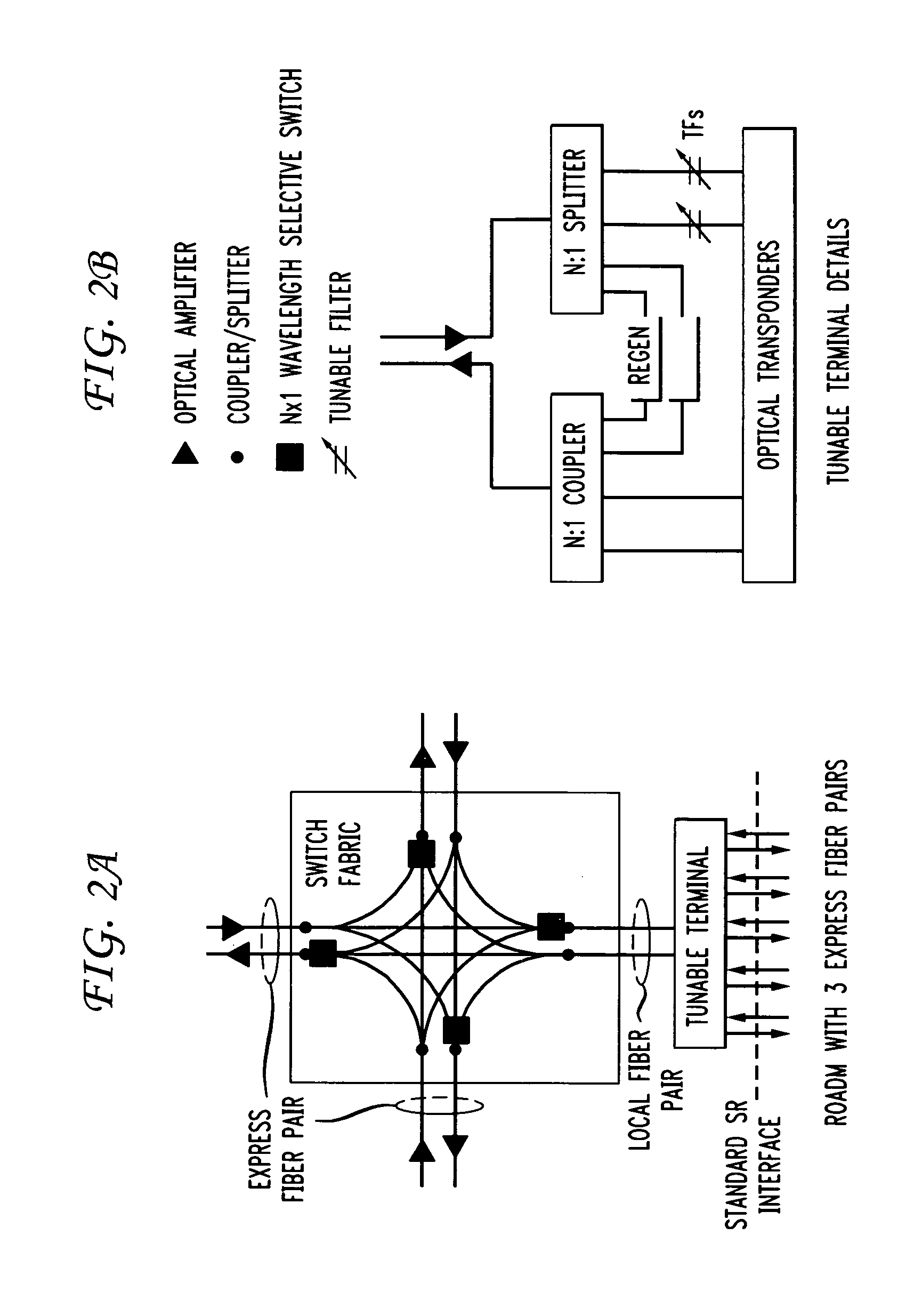
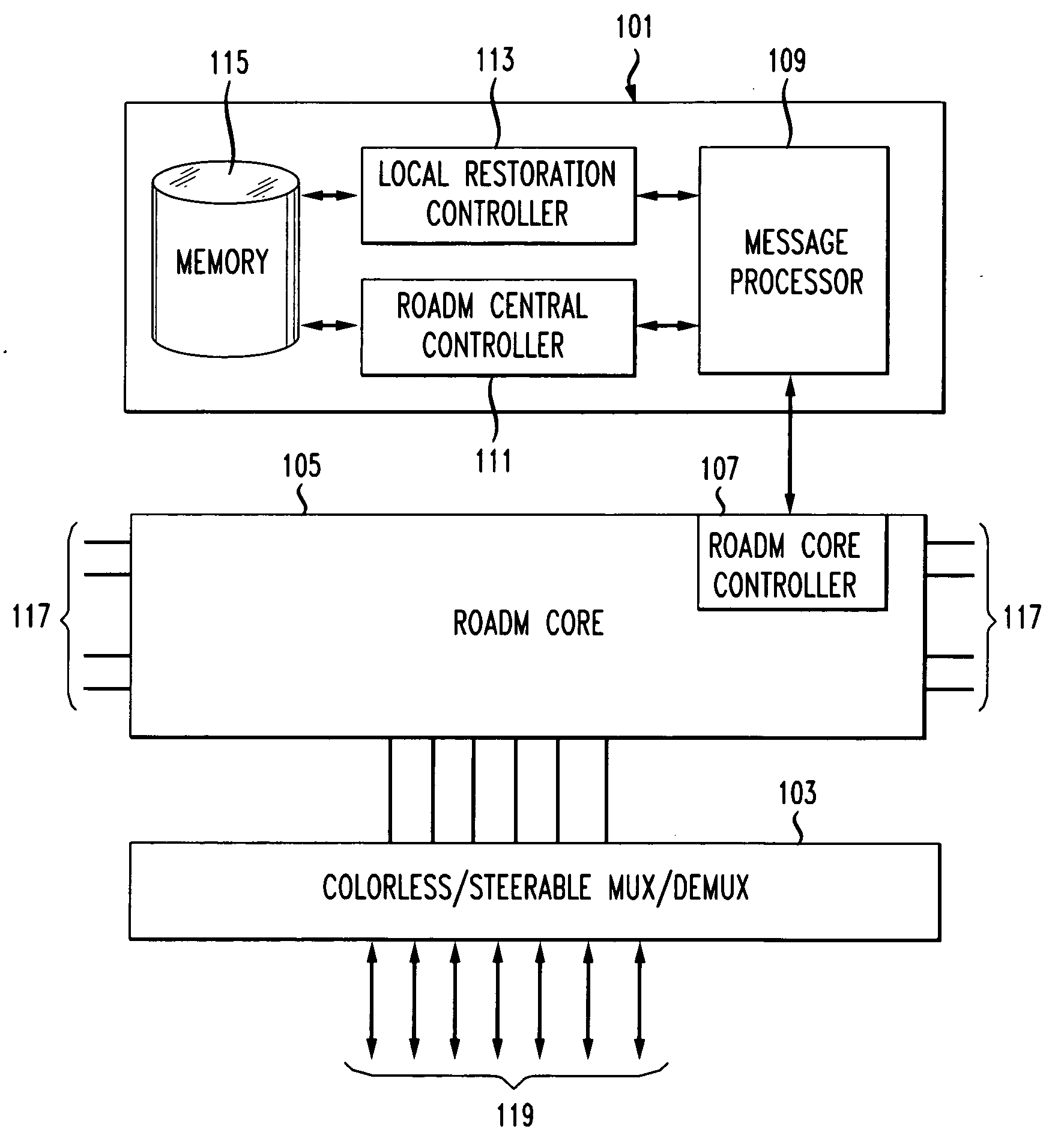
Optical transmission systems, devices, and methods
ActiveUS7606494B1Improve operational flexibilityEfficient and low optical communicationMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCommunications systemTransmission system
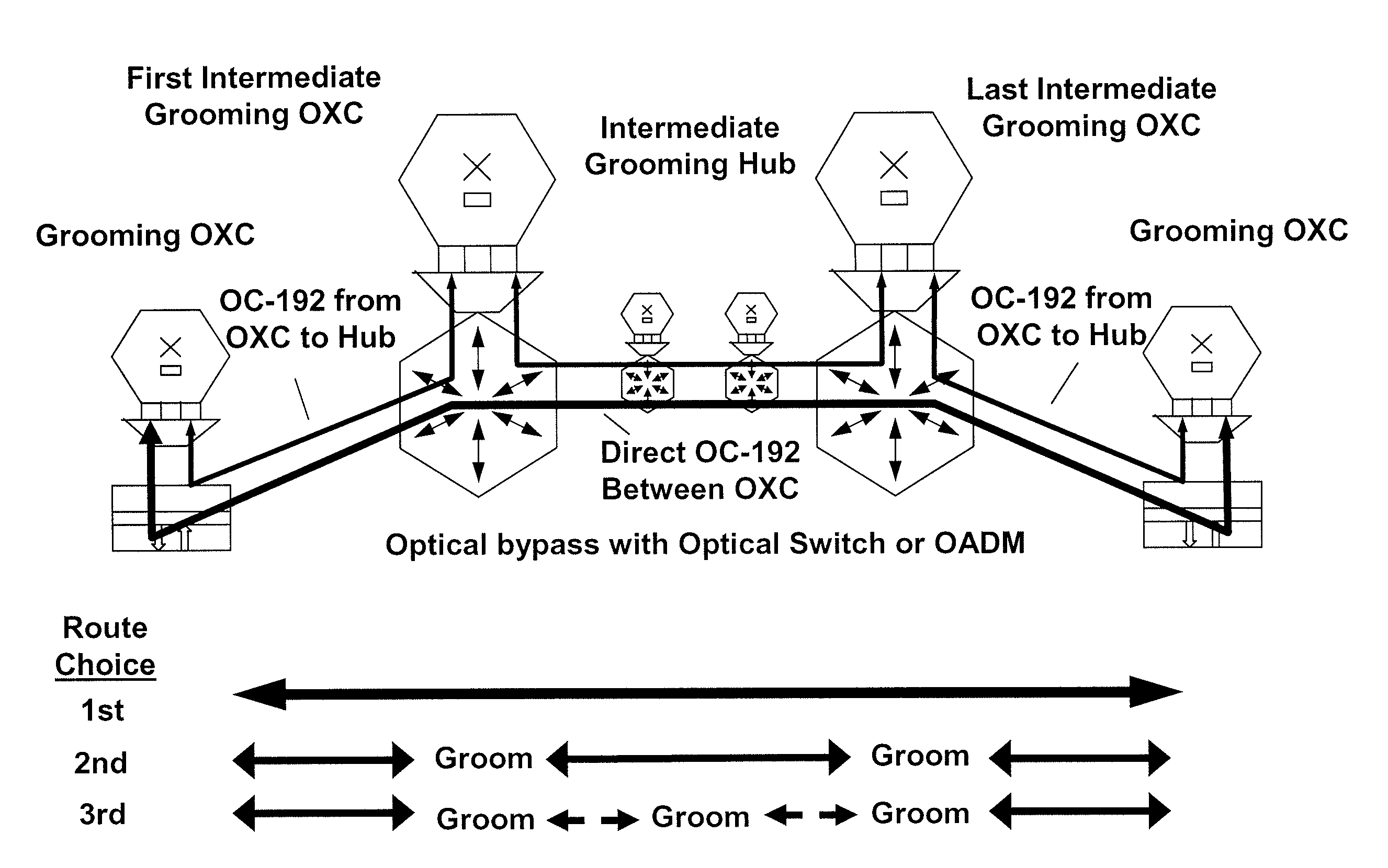
Optical communications systems including grooming, protection, restoration, and migration on a unified network platform, and using a unified control plane. The systems may include combinations of optical bypass and mesh restoration, may include combinations of shared mesh and dedicate protection, and may be combinations of long haul, extended long haul, and ultra long haul systems. The systems may also include a configurable DWDM tier to accommodate dynamic traffic patterns, thereby allowing for increased operational flexibility.
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC
Method for restoration and normalization in a mesh network
InactiveUS7652983B1Minimal service traffic interruptionAchieve performanceLaser detailsError preventionBandwidth reservationDistributed computing
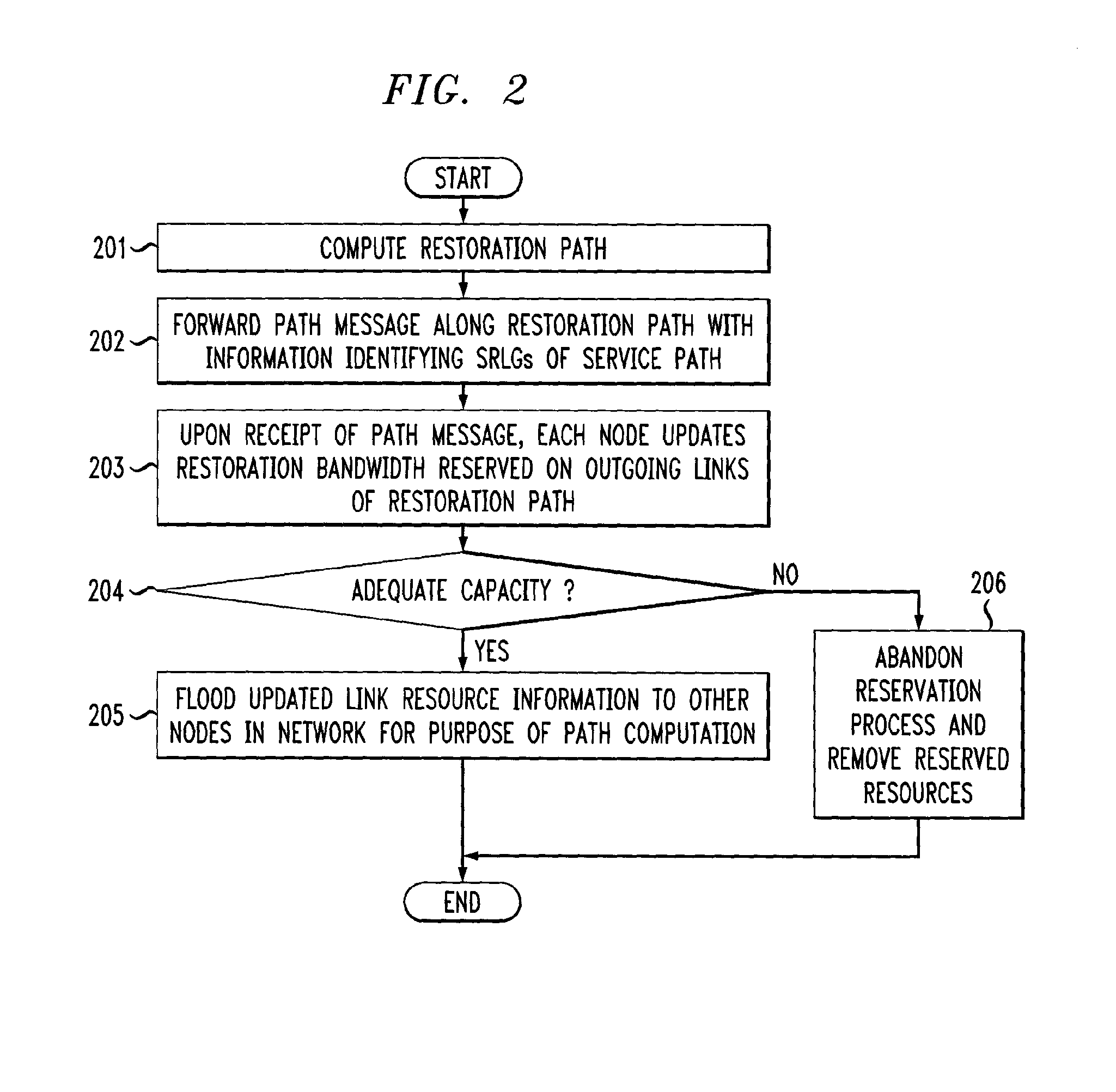
The present invention is directed to methods for signaling that enable bandwidth reservation, path restoration, path normalization, and path removal in a mesh network that supports shared mesh restoration.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Optical transmission systems, devices, and methods
InactiveUS20100129078A1Improve operational flexibilityEfficient, low cost optical communications systemsMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCommunications systemTransmission system
Optical communications systems including grooming, protection, restoration, and migration on a unified network platform, and using a unified control plane. The systems may include combinations of optical bypass and mesh restoration, may include combinations of shared mesh and dedicate protection, and may be combinations of long haul, extended long haul, and ultra long haul systems. The systems may also include a configurable DWDM tier to accommodate dynamic traffic patterns, thereby allowing for increased operational flexibility.
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC
Supporting oam on protecting connections in shared mesh protection environment
A method for detecting the liveliness and synchronizing the control-plane and data-plane on protecting connections in a shared mesh network environment through methods for probing the protecting connection conditions by sending in-band messages; and synchronization of control plane and data plane by using LSP-ping messages on the protecting connections.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Method and apparatus for protection switch messaging on a shared mesh network
InactiveUS20050088963A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionMessage processingData transmission
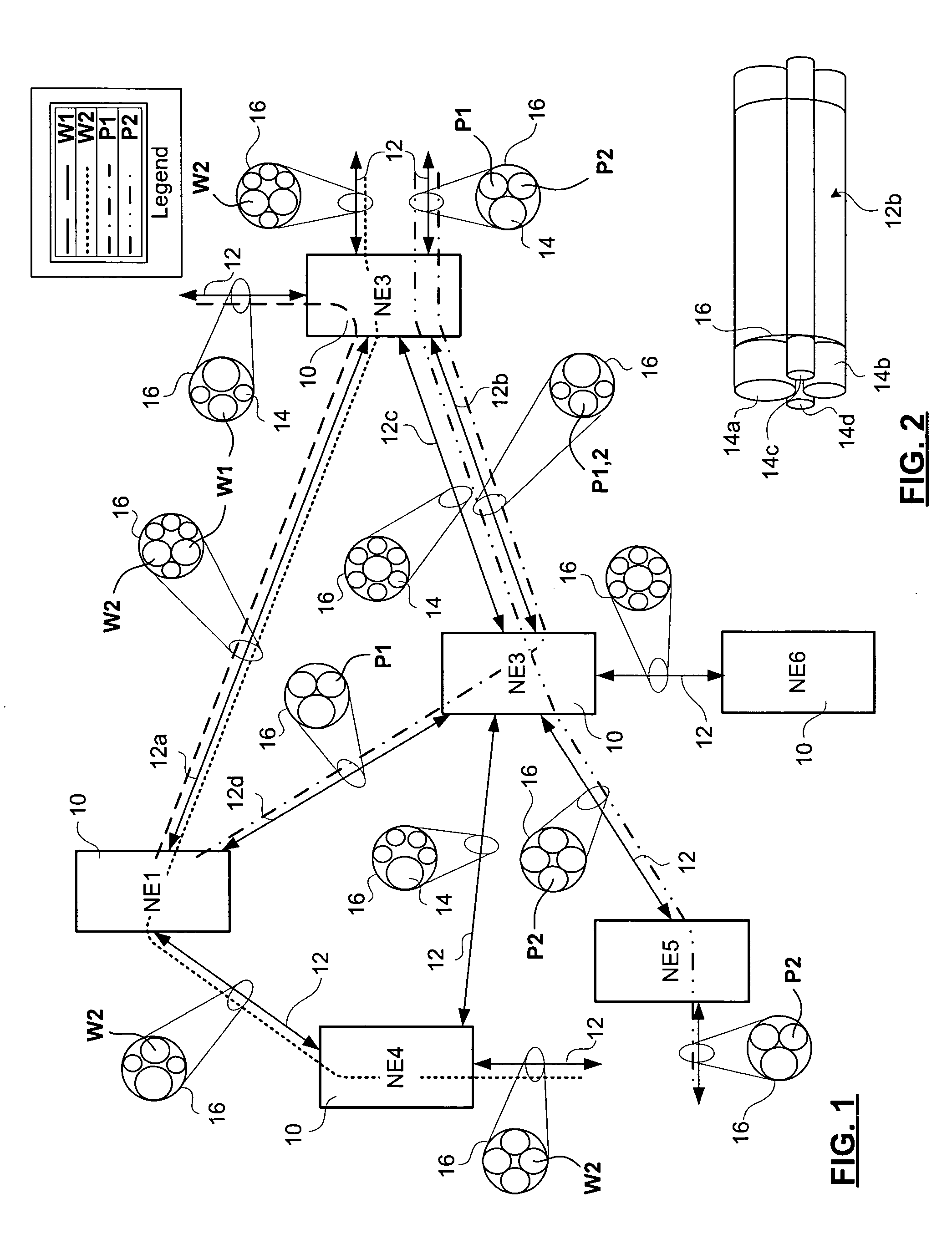
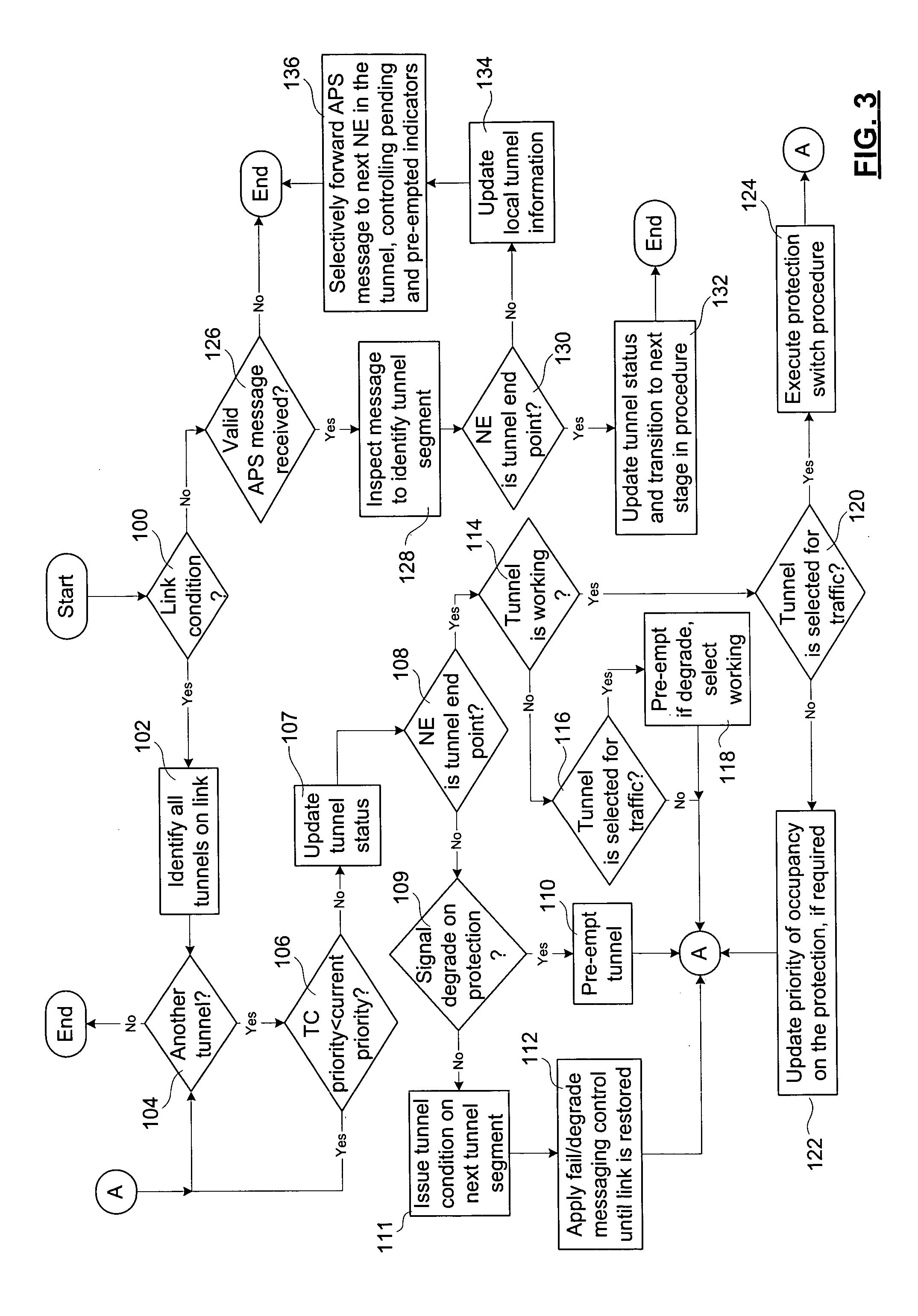
A method for processing automatic protection switch (APS) messages at a network element in a tunnel provisioned across a data transport network in order to provide for distributed processing of protection switch request messages involves receiving new APS message at the NE; determining whether the NE is an end point of the tunnel, or a tandem of the tunnel and processing the message accordingly. If the NE is a tandem, message processing involves using local information about tunnel segments of the tunnel only maintained by the NE, to update the local information, and to selectively forward the updated information to adjacent NEs of the tunnel. If the NE is an end point, it updates a status of the tunnel. In a preferred embodiment all NEs are responsible for controlling pending and preemption indicators, and for initiating tunnel condition messages, and the end point NEs are responsible for initiating all other messages.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
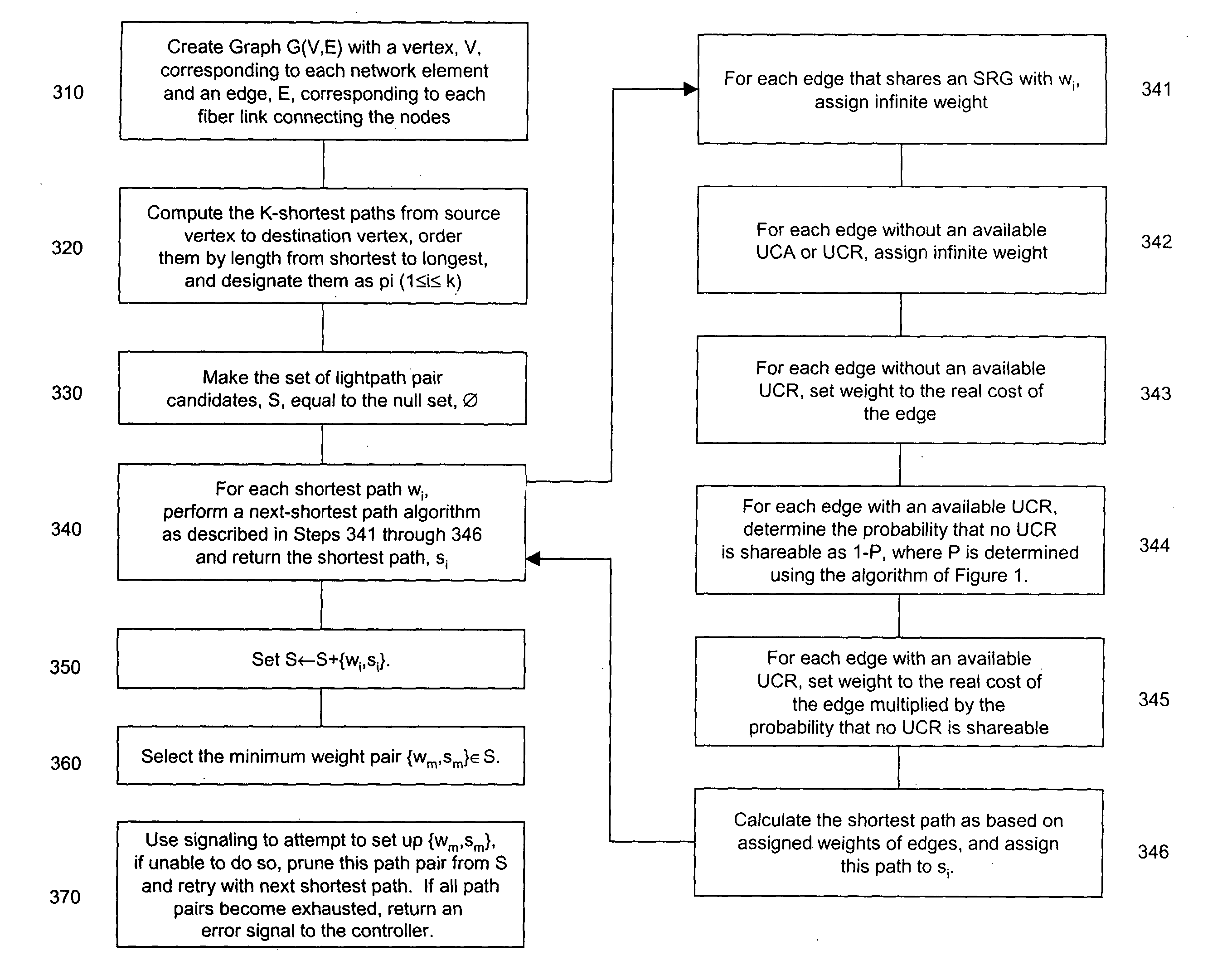
Method for stochastic selection of improved cost metric backup paths in shared-mesh protection networks
InactiveUS20050025058A1Efficient sharingReduce the amount requiredError preventionTransmission systemsCost metricBackup path
A method of path selection in shared-mesh restoration networks that results in efficient use of network resources, using only the network state information available locally at each network element. The method uses probability theory to develop an estimate of protection channel sharing opportunities and encourages sharing of protection channels if possible
Owner:SUMMIT TECH SYST LP
Method and device for recovering a shared mesh network
InactiveUS20080117806A1Easy to implementBetter compatibleMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionNetwork connectionNetwork management
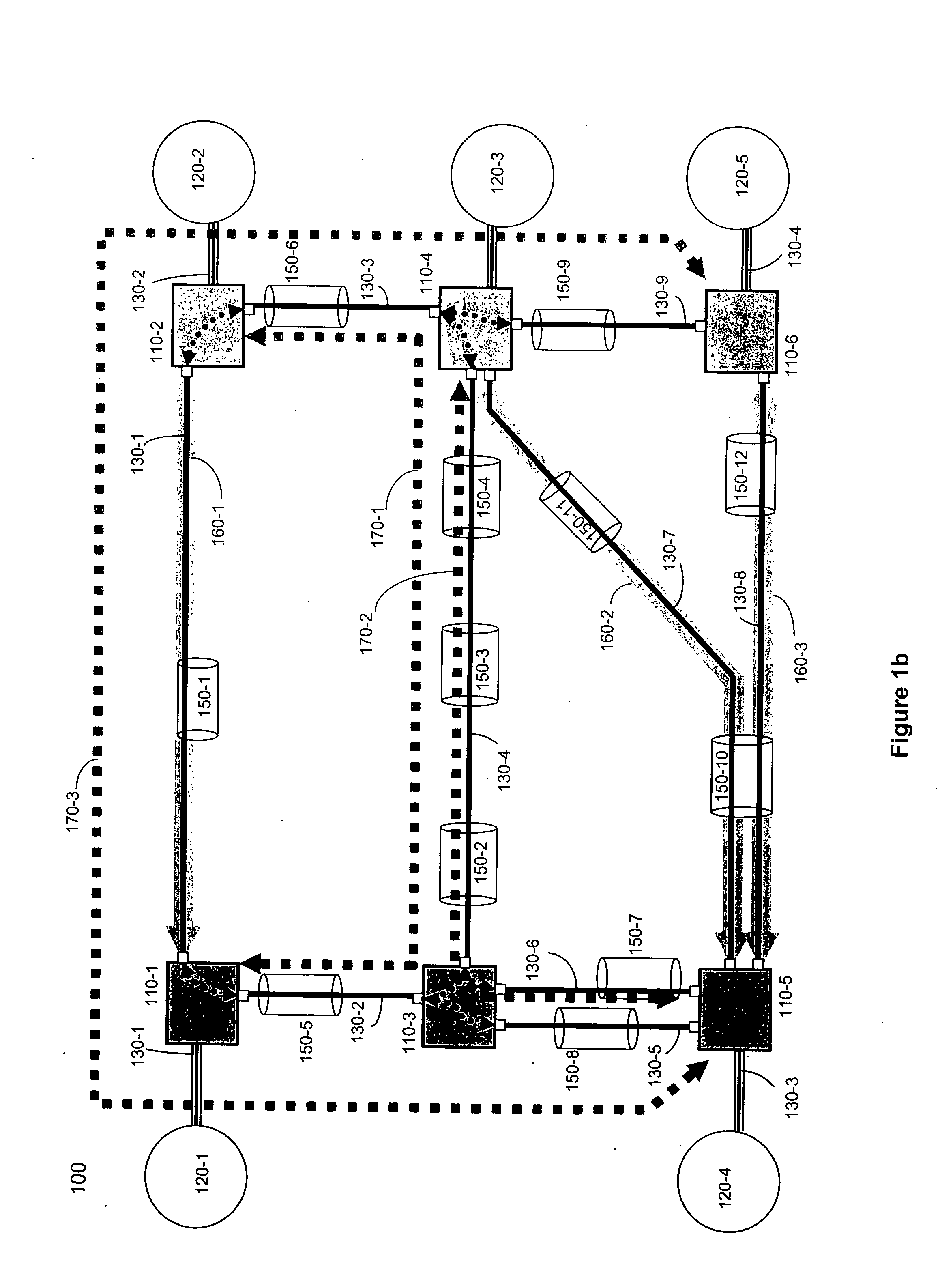
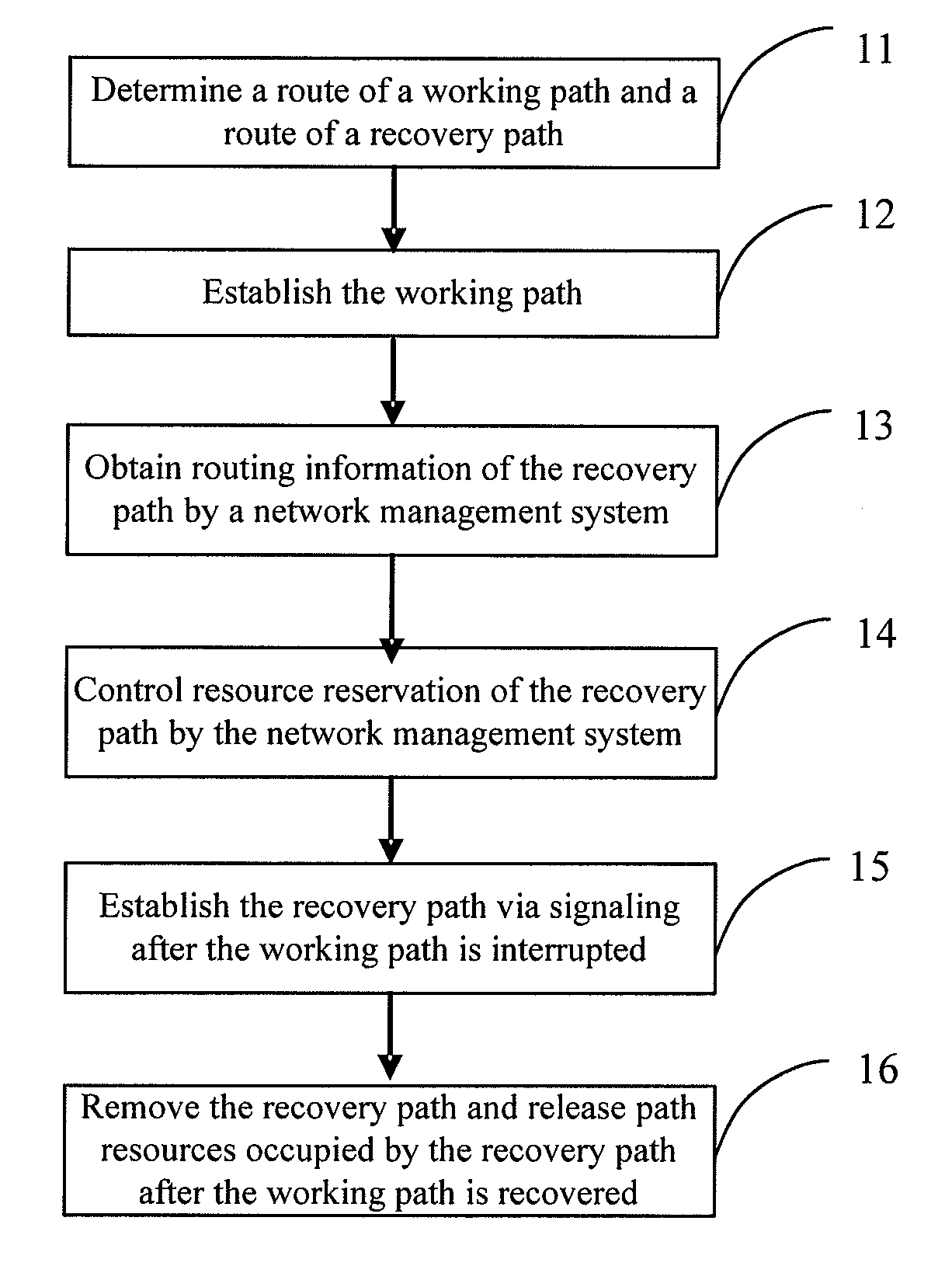
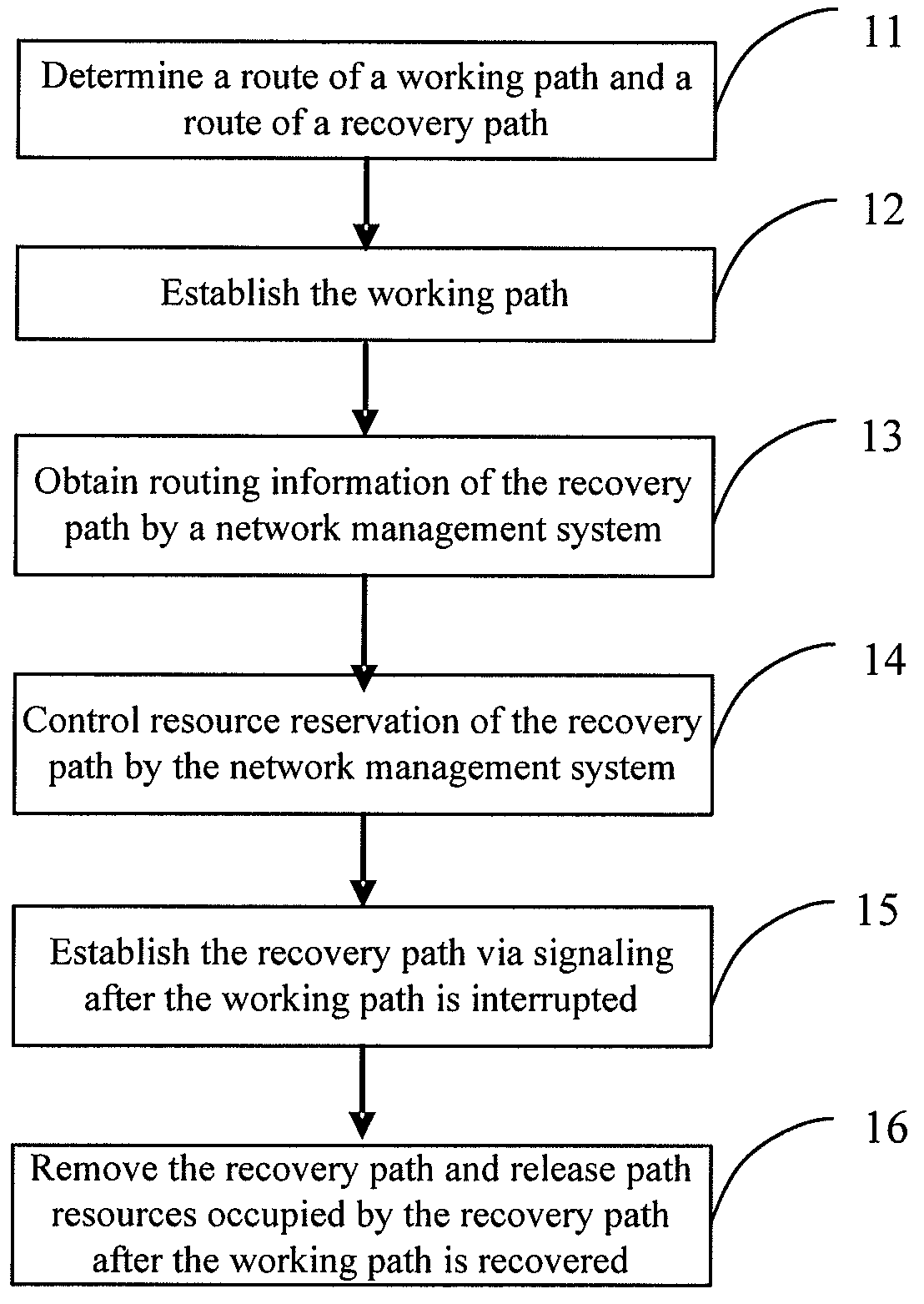
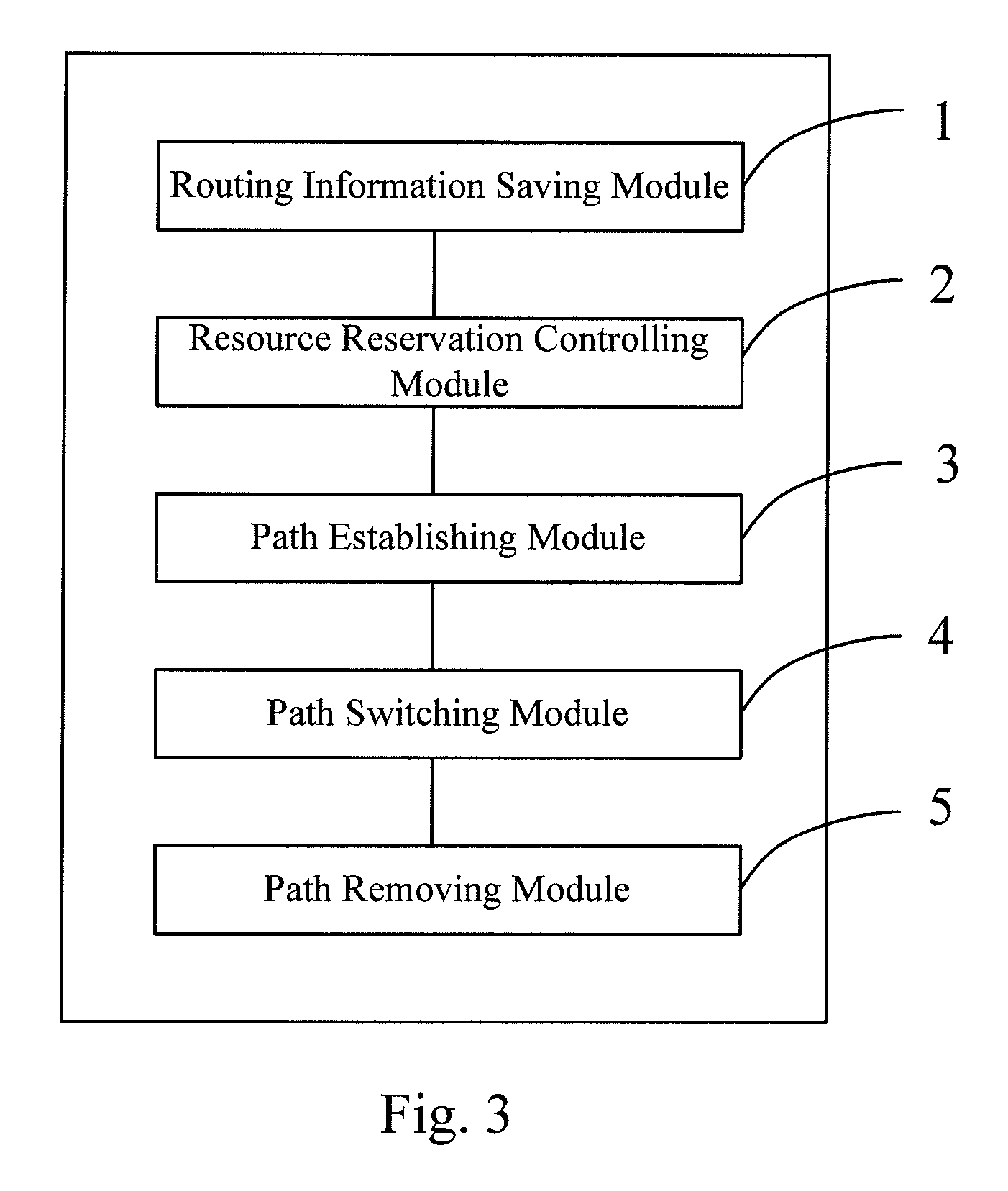
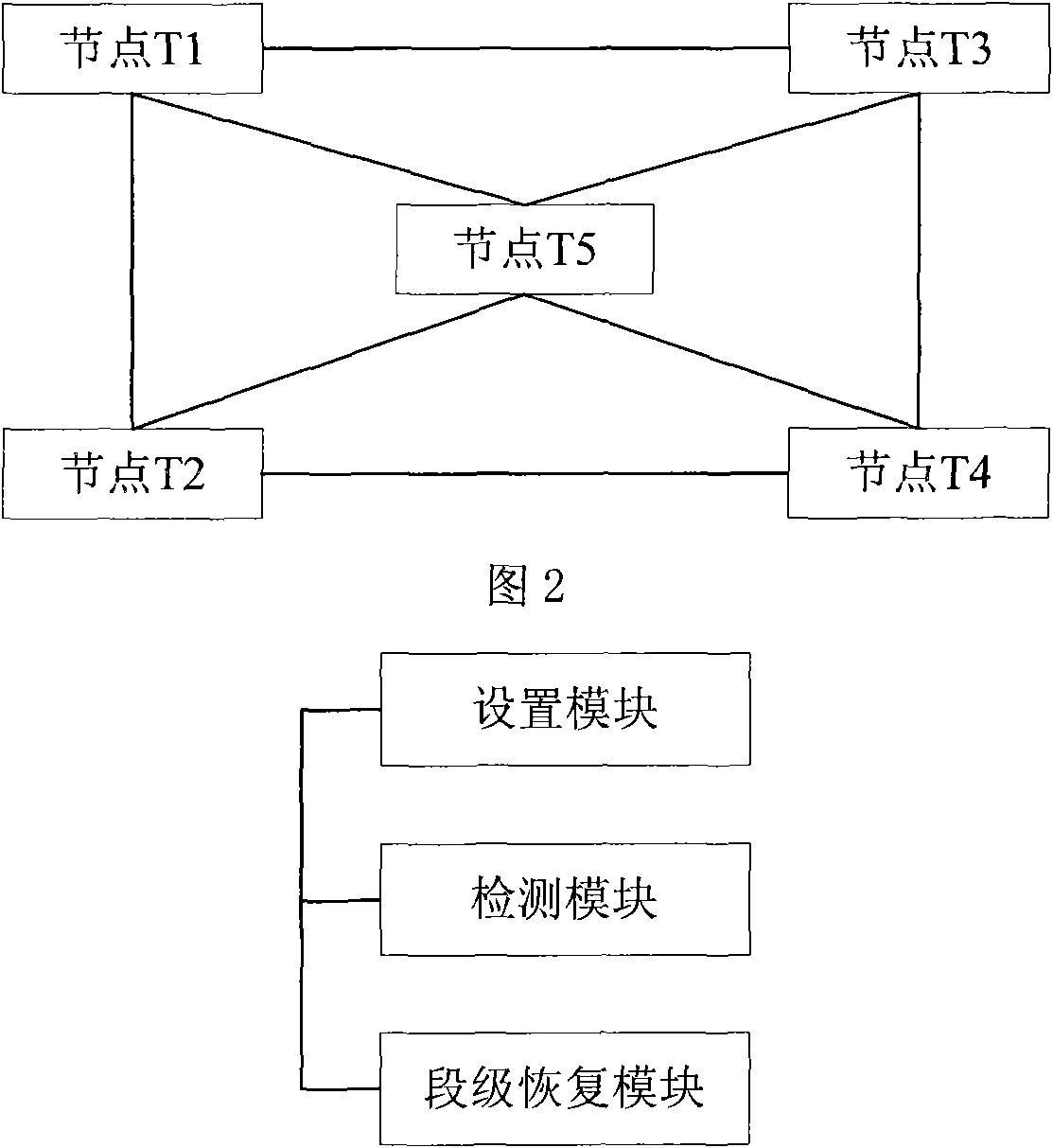
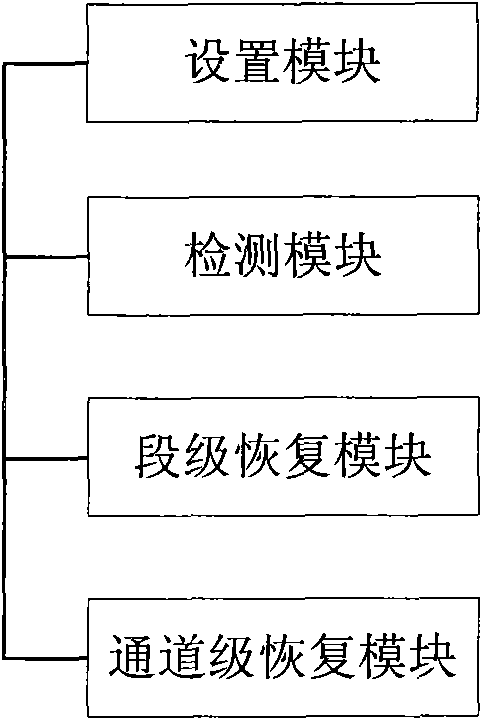
One embodiment of the present invention discloses a method and device for recovering a shared mesh network. The core idea of the method lies in that: a network ingress node of network connection service determines and saves routing information of a recovery path; after a working path is established successfully, a network management system controls resource reservation of the recovery path; and after the working path is interrupted, the network ingress node of the network connection service initiates an establishing procedure of the recovery path by using the reserved resources according to the saved routing information of the recovery path, and switches services on the working path to the recovery path for transmission. The technical solutions of the invention are easy to implement, and can be realized by using existing protocols; moreover, it can be well compatible with existing devices.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and network device for realizing shared mesh protection
ActiveUS20100232287A1Easy to implementFlexible protectionError preventionTransmission systemsState variationLabel switching
A method and a network device for realizing shared mesh protection are provided. The method includes the following steps. If a status change of a working label switching path (LSP) is detected, routing information and bandwidth information about the working LSP are notified to every node on a protection LSP corresponding to the working LSP. Every node on the protection LSP calculates a maximal reserved bandwidth of a link based on the received routing information and bandwidth information and adjusts a shared protection bandwidth of the link according to the maximal reserved bandwidth.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Shared mesh restoration with pre-configured standby lightpaths
ActiveUS8150257B1Minimize the numberLaser detailsOptical multiplexCross connectionRestoration method
Systems and methods are described for restoring wavelength services in mesh networks using pre-configured, standby lightpaths. The standby lightpaths are pre-cross-connected lightpaths that provide connectivity between switching nodes having a fiber link of degree-2 or higher. The restoration method overcomes the problem of optical impairments for long haul connections, avoids wavelength power balancing delays, provides wavelength conversion for capacity efficiency, and allows sharing of links across nonsimultaneous failures.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Shared mesh signaling method and apparatus
In a mesh network, a network element for providing protection switching in a 1:N shared mesh protection scheme having a first protection path associated with a pair of working paths selected from the N working paths is disclosed. The network element comprising: (a) a link for connecting the network element to a first working path of the pair of working paths in a path layer of the network, the path layer including a plurality of interconnected network elements; (b) a routing table accessible by the network element, the routing table for having local protection channel information associated with a local protection segment separate from the first protection path, the local protection segment connecting the network element and one of the interconnected network elements adjacent to the network element; and (c) an identification module for using the local protection channel information to identify an available protection channel on the local protection segment in the event of failure of a local working segment of the first working path, the local working segment connecting the network element and said one of the adjacent interconnected network elements; wherein the available local protection channel on the local protection segment is used to switch local network bandwidth from the failed local working segment to the local protection segment after the failure has been detected. Selection functions are also disclosed.
Owner:CIENA
Method and apparatus for shared mesh protection switching
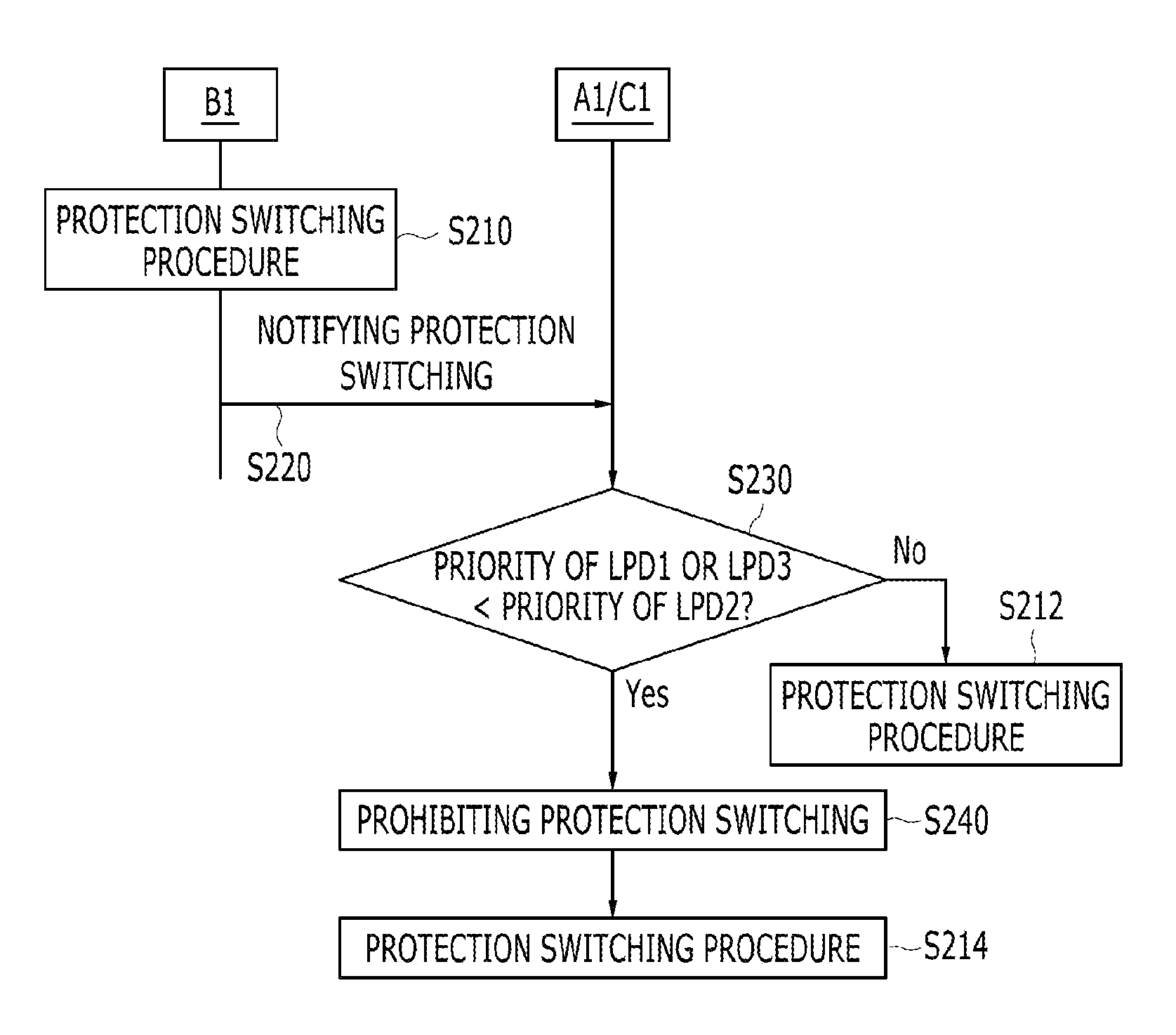
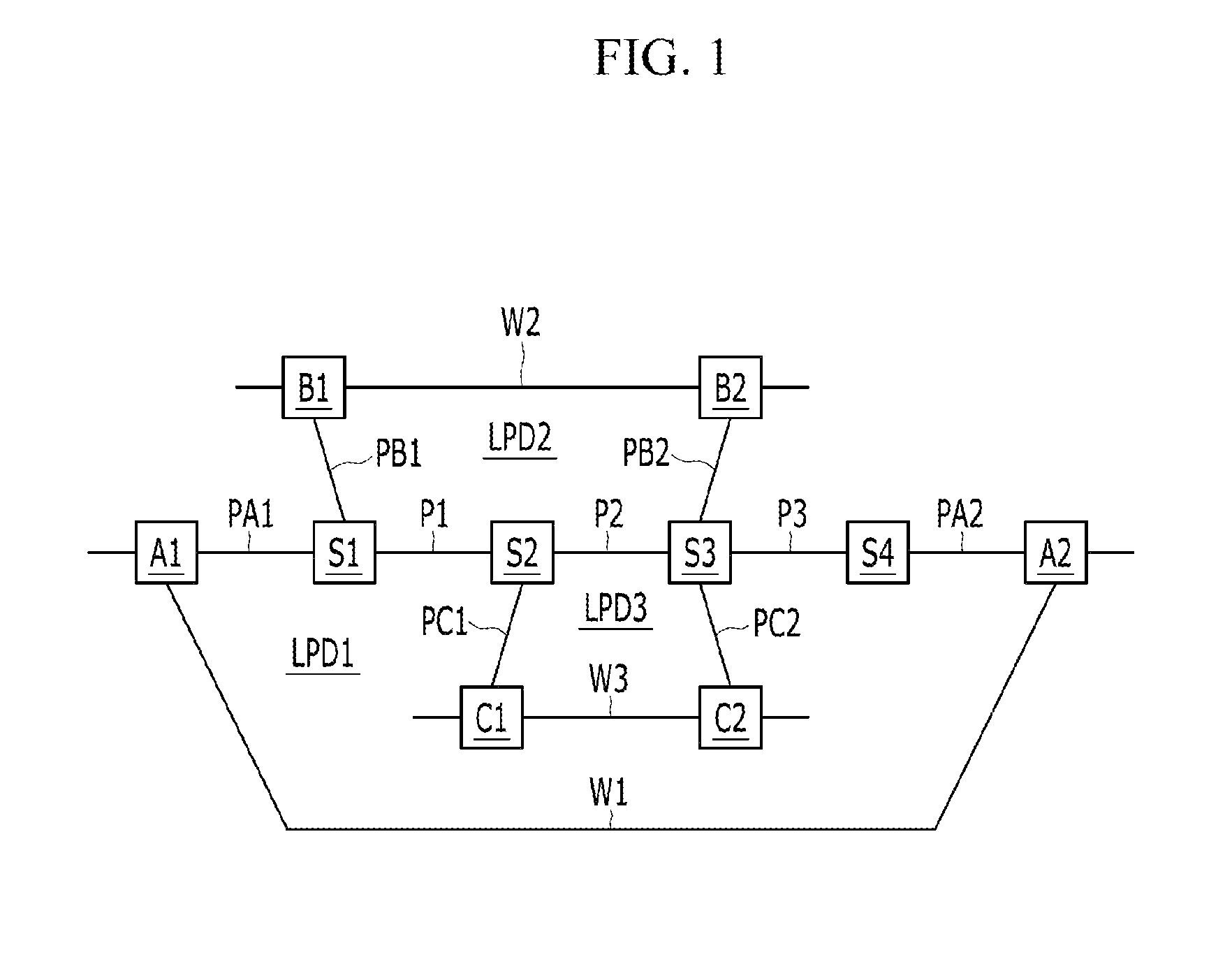
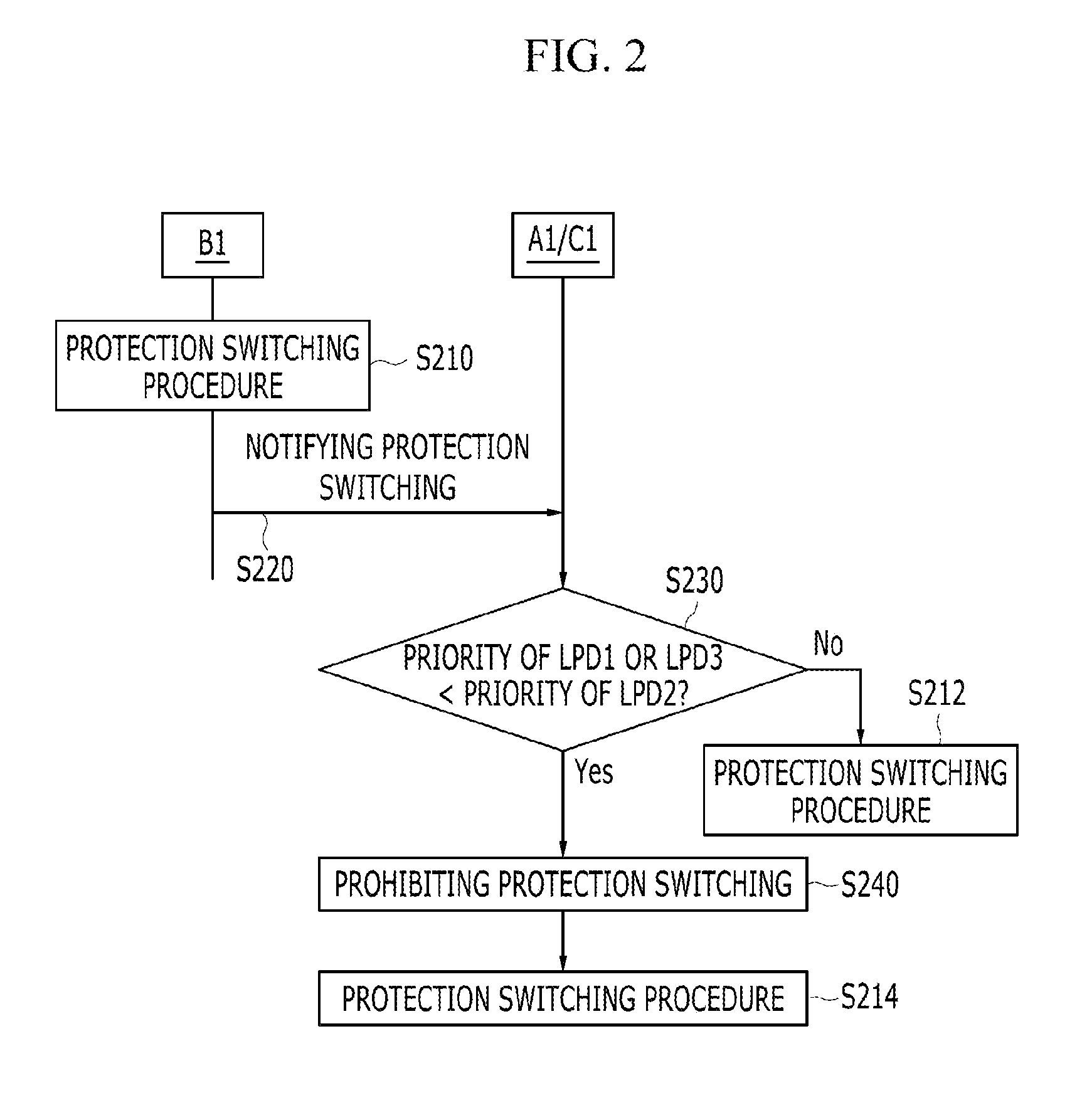
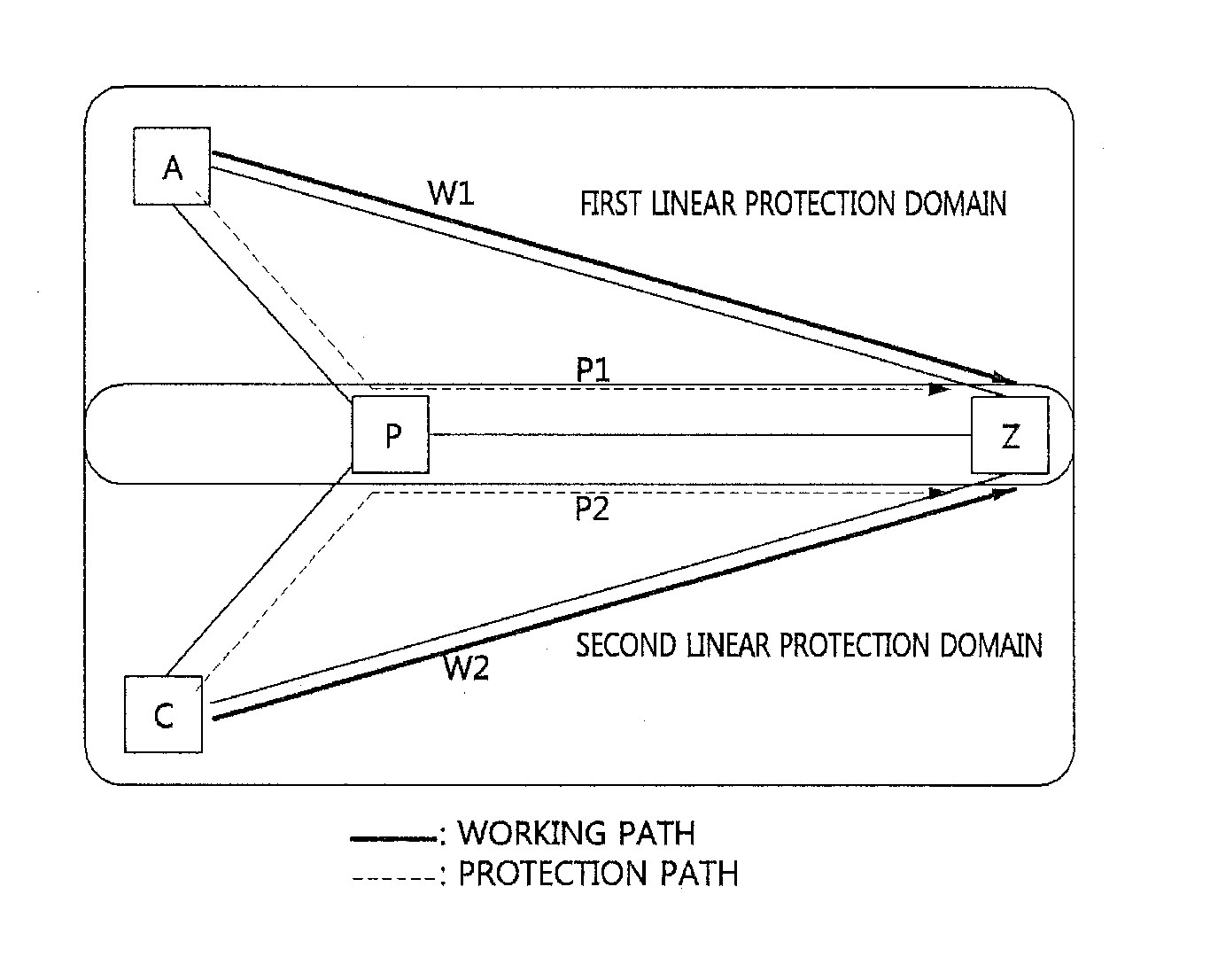
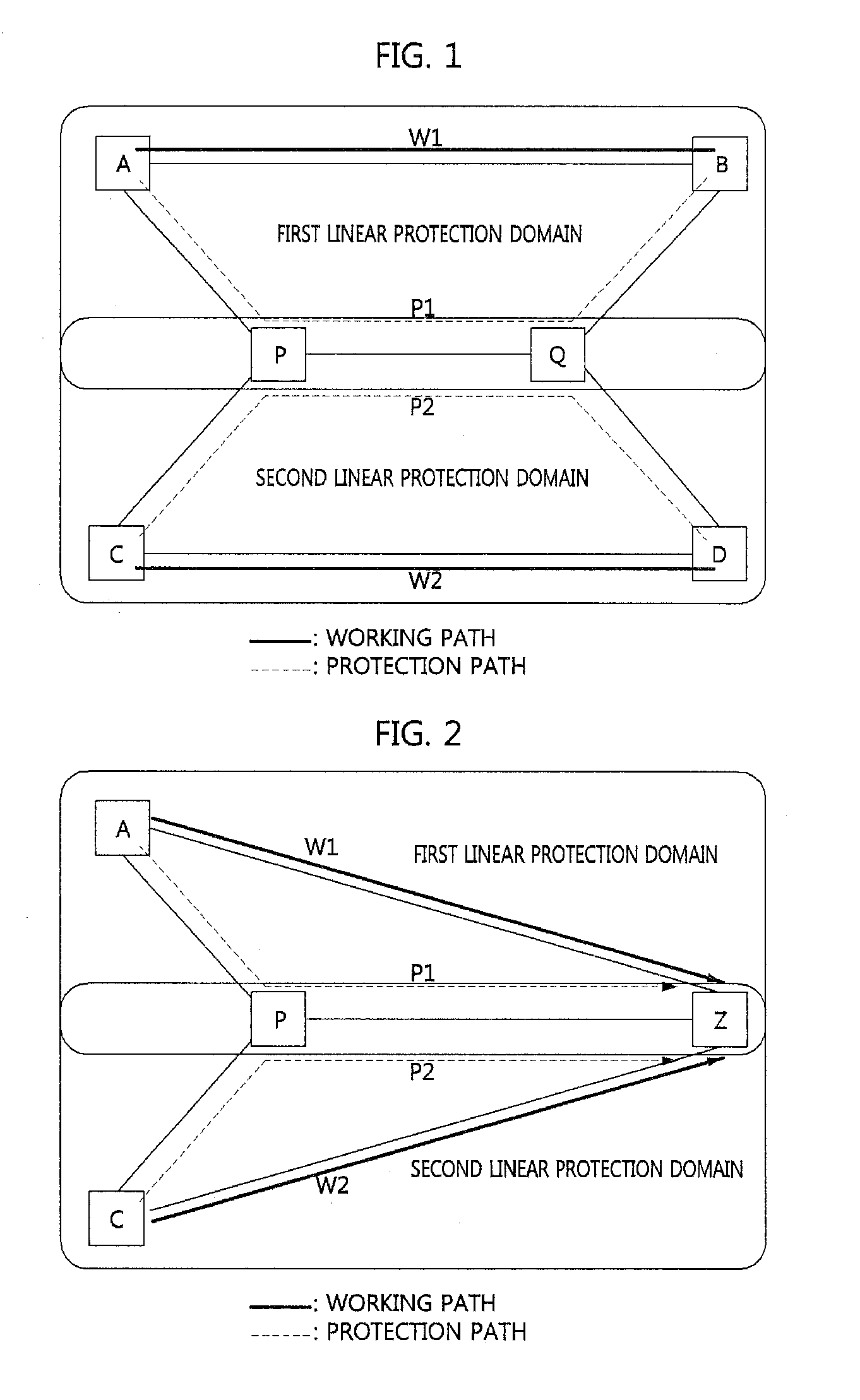
ActiveUS20120294140A1Raise priorityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsProtection domainComputer science
A method for protection switching in a shared node where protection resources of a plurality of end-to-end linear protection domain are shared is provided. The shared node receives a first protection switching event message notifying that a protection switching event occurs from a first node of a first end-to-end linear protection domain, and determines whether to prohibit protection switching on a second end-to-end linear protection domain by comparing a priority of the first end-to-end linear protection domain with a priority of the second end-to-end linear protection domain.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Sharing meshed protection realizing method and system
The invention discloses a sharing meshed protection realizing method, comprising the following steps of: in sharing meshed protection, triggering a switching request by a fault detection node, and executing corresponding protection switching according to the response of a downstream node; and determining to transmit according to an appointed path by the downstream node according to the signaling content of the switching request, or responding to the request of an upstream node. The invention further discloses a sharing meshed protection realizing system, wherein a protection switching unit in the system is used for triggering the switching request by the fault detection node and executing the corresponding protection switching according to the response of the downstream node; and the downstream node is used for determining to transmit according to the appointed path according to the signaling content of the switching request or responding to the request of the upstream node. With the adoption of the method and system disclosed by the invention, the protection switching can be realized by the signaling content and transmission based on the sharing meshed protection.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Fault protection method and equipment
ActiveCN102143065AConsumption moderationEven consumptionError preventionStore-and-forward switching systemsResource consumptionComputer science
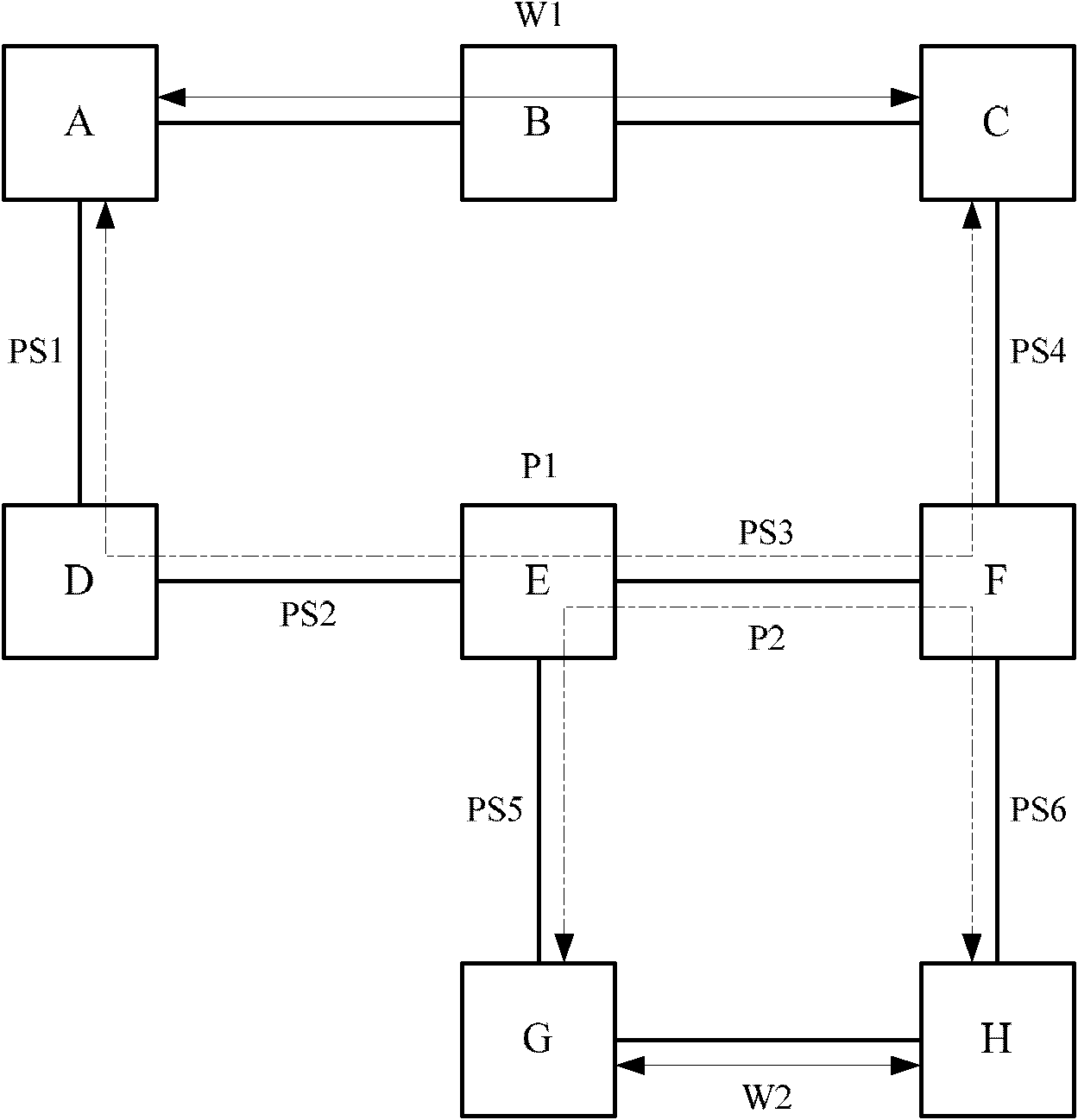
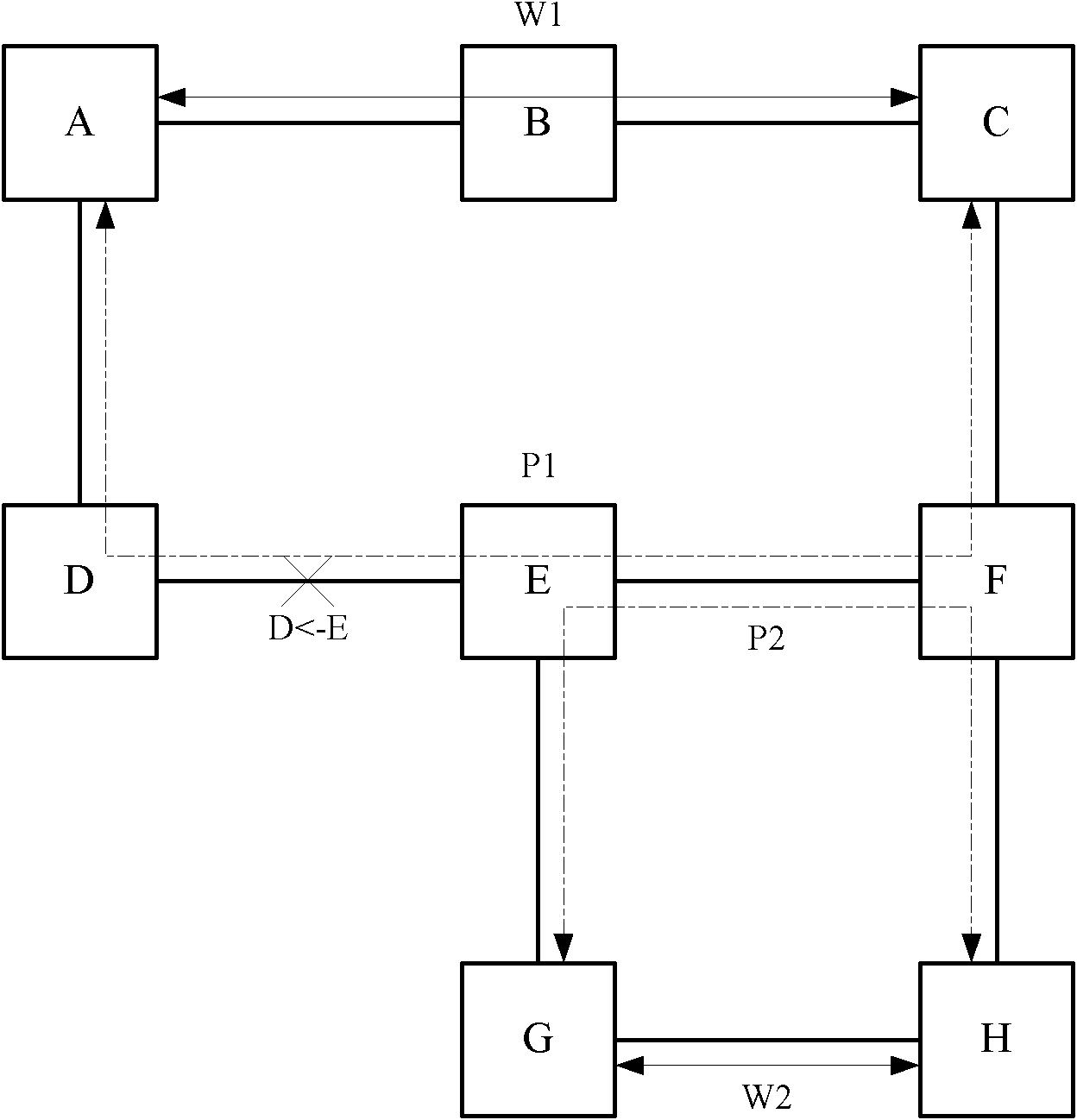
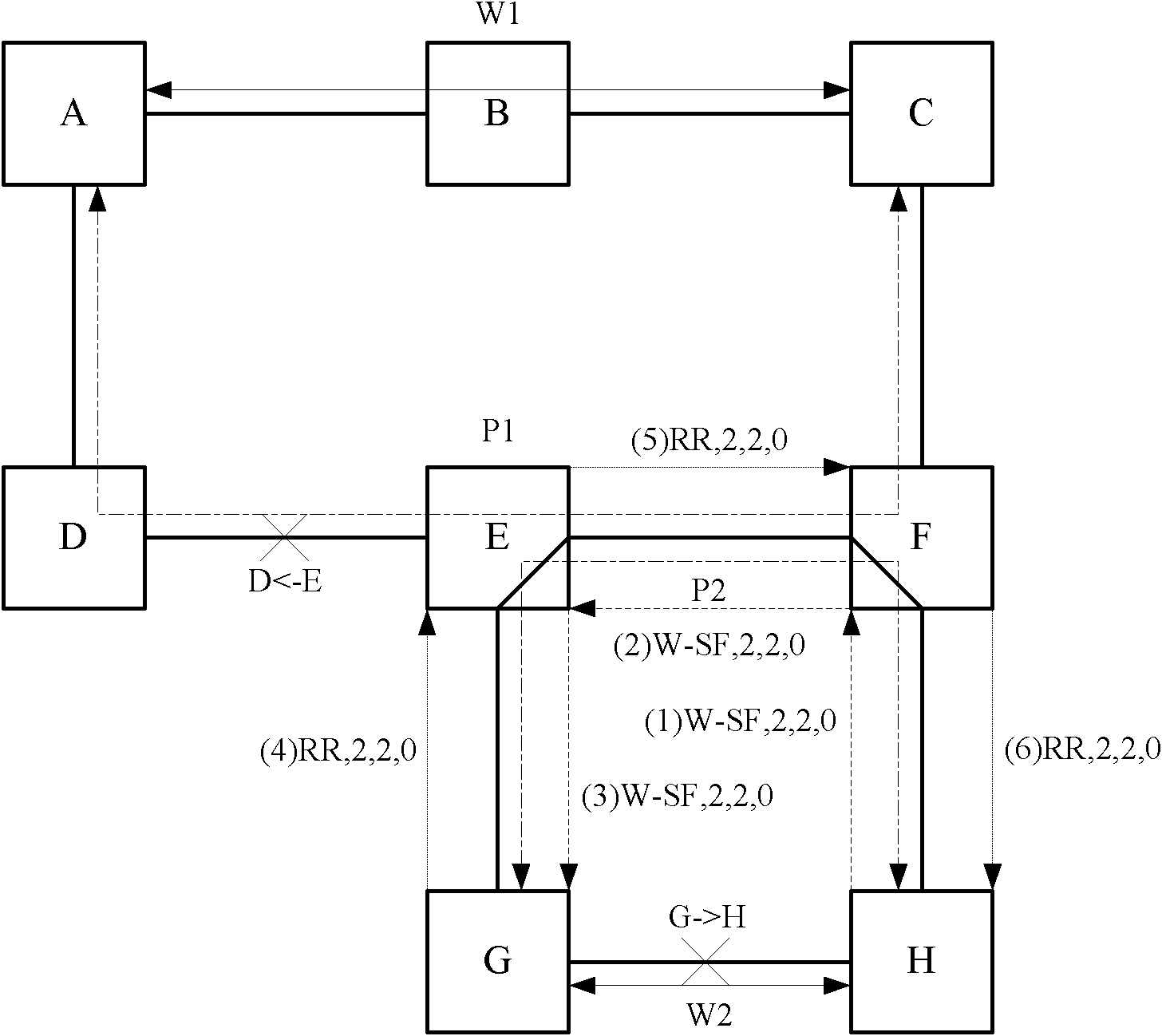
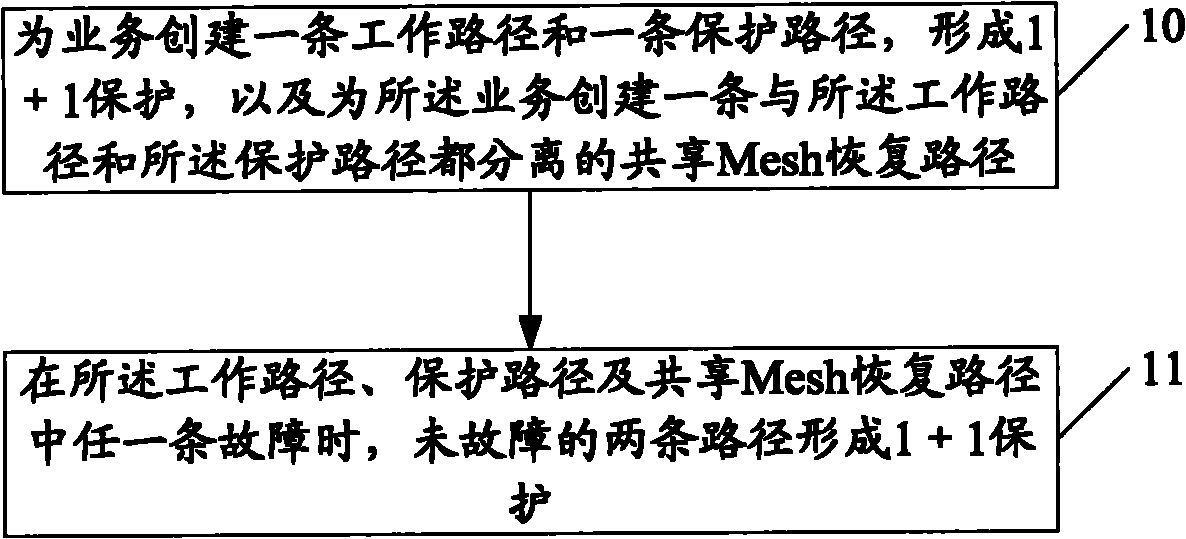
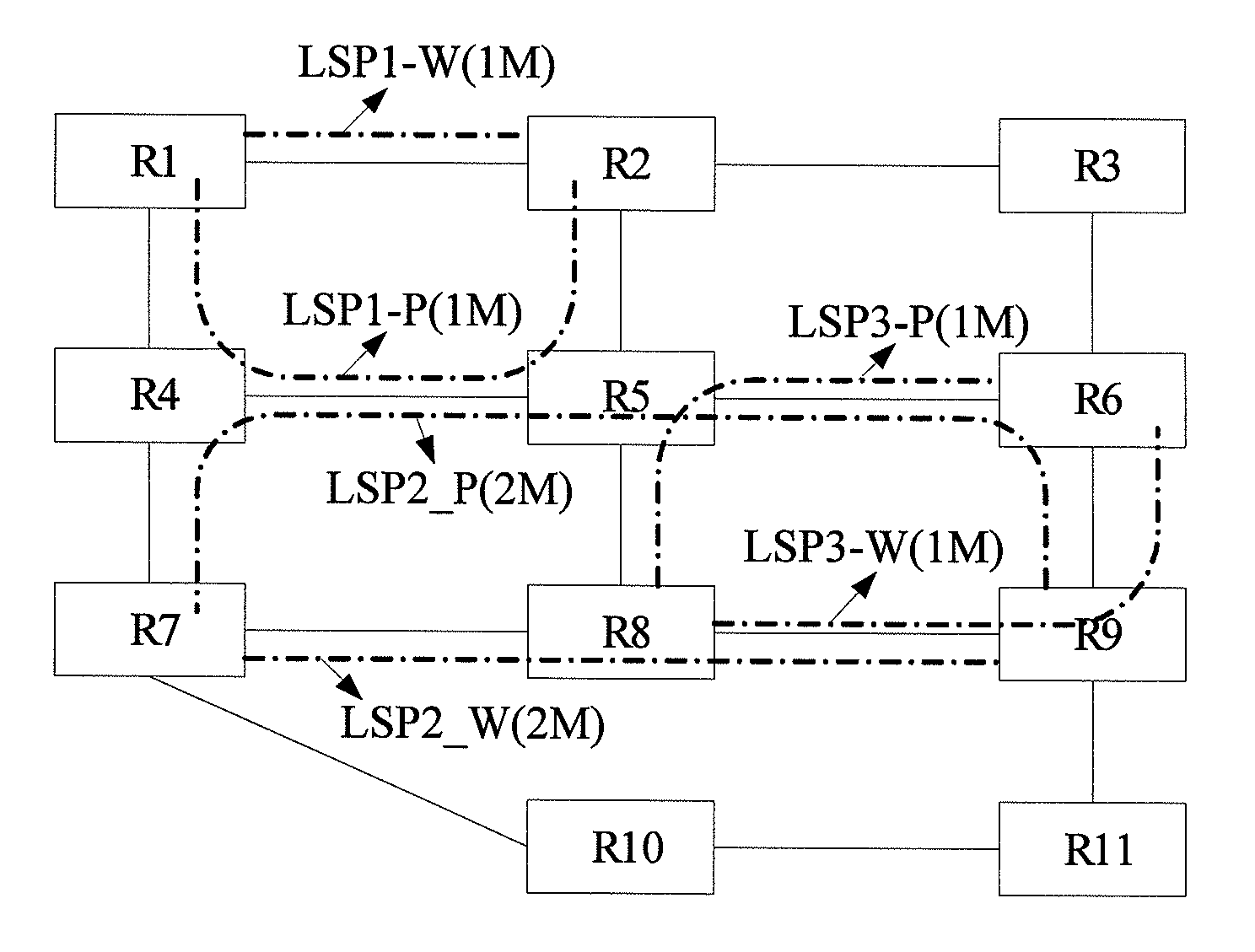
The invention discloses a fault protection method belonging to the technical field of communication. The method comprises the following steps: building a work path and a protective path for business to form 1+1 protection; building a shared Mesh recovery path separated from the work path and the protection path for the business; and when any one of the work path, the protection path and the shared Mesh path fails, the other two paths which do not fail form 1+1 protection. The embodiment of the invention also provides fault protection equipment. According to the embodiment of the invention, guaranteed fault protection is carried out two times, the purpose of resisting multiple faults and quickly protecting business can be achieved, bandwidth resource consumption is controlled to certain degree, and the protection capability and bandwidth consumption are balanced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Standby restoration signaling for optical networks
Systems and methods are described that provide a distributed restoration signaling protocol for shared mesh restoration with standbys for transparent optical networks.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Method for Restoration and Normalization in a Mesh Network
InactiveUS20100091647A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsBandwidth reservationDistributed computing
The present invention is directed to methods for signaling that enable bandwidth reservation, path restoration, path normalization, and path removal in a mesh network that supports shared mesh restoration.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
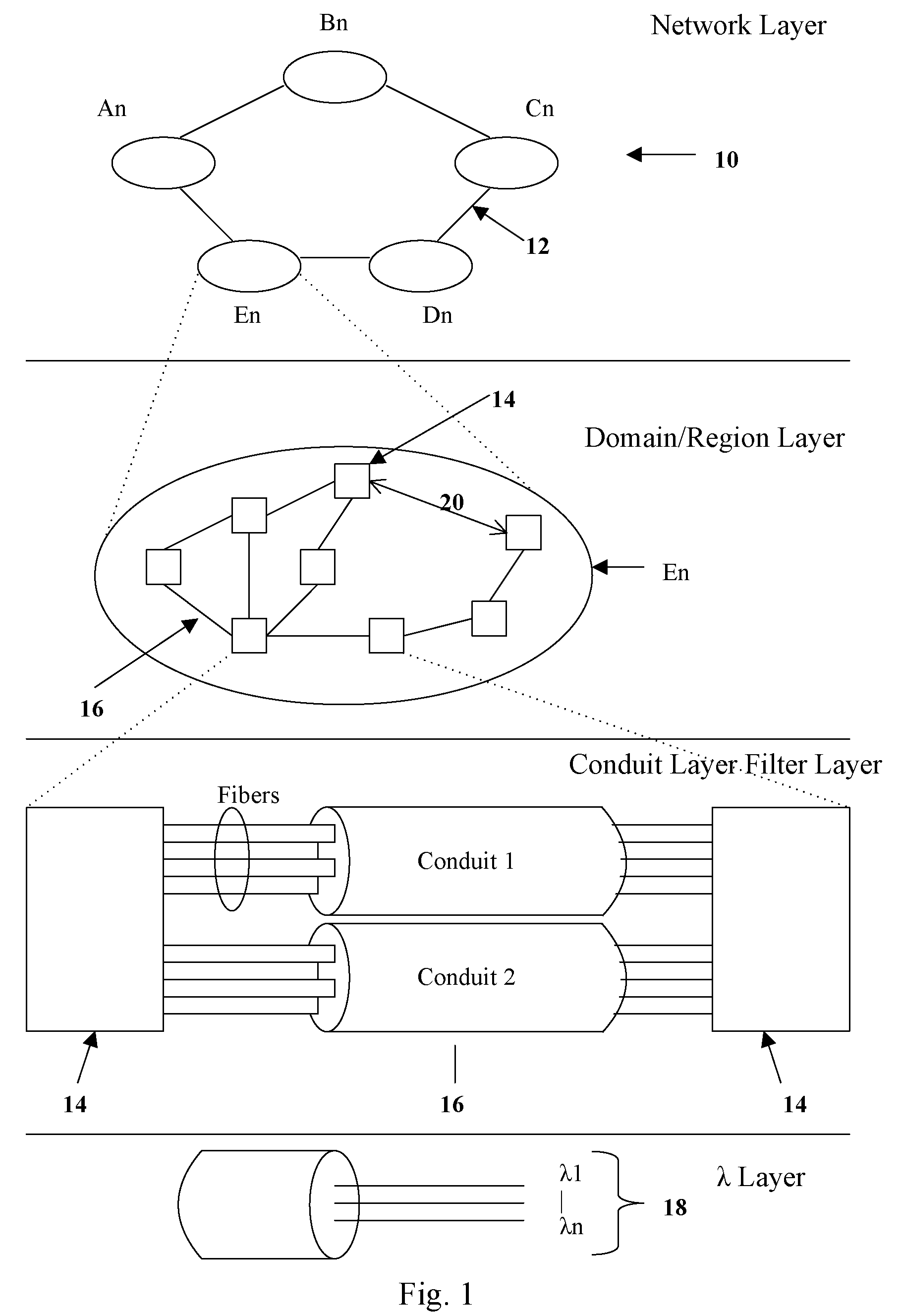
Process of optical WDM bus networking with DWDM expansion for the method of protected point to point, point to multipoint and broadcast connections
InactiveUS20050047713A1Low start-up costLow costMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberRing protection
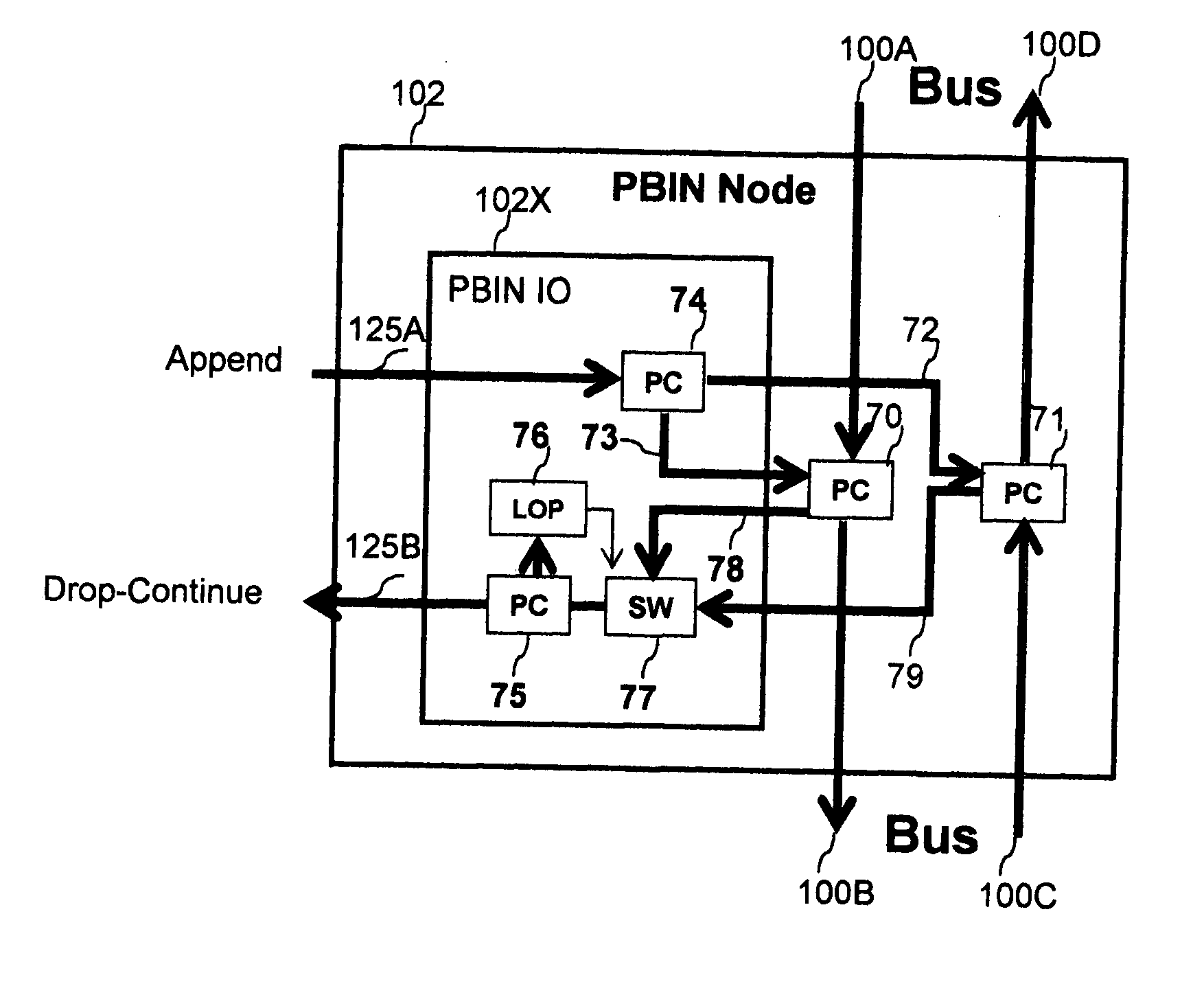
A process for all-optical multi-bus networking of two-fiber bidirectional buses with two-fiber bidirectional Bus-To-Bus Links for a method of shared mesh protected Point-To-Point, Point-To-Multipoint and Broadcast Networking with the steps of: providing protected Bus-To-Bus service networking and Bus-To-Bus protection networking and in-service expansion with more buses, in place of networking with isolated rings connected through un-protected ring-to-ring connections, providing capacity expansion by replacement of single Wavelength Division Multiplexed (WDM) optical signals in few, wide bandwidth WDM channels with a plurality of optical signals Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexed (DWDM) to each WDM channel, and switching few WDM optical channels with small size modular Switching Fabrics, in place of high startup-cost, high capacity DWDM systems switching many DWDM optical signals with expensive and unreliable large size Switching Fabrics, providing the Add / Drop capability integrated with the Append / Drop-Continue capability, to Append more DWDM optical signals to a WDM channel already partially occupied by DWDM optical signals at non overlapping carrier frequencies, in place of requiring to Drop those signals before new ones could be Added, providing optical switching capability integrated with selective broadcast capability of Added or arriving at the Bus or the Bus-To-Bus input terminals WDM channels in place of using external optical Power Couplers with reduced transmission reach, providing one local, shared mesh protection with bus protection loops integrated with dedicated 1+1 Dual Bus Interworking protection to protect Bus Link failures, Bus-to-Bus Link failures, and Switching Fabrics and other equipment failures with reserved as low as 25% of protection bandwidths, in place of ring protection with 50% of reserved protection bandwidth and un-protected ring-to-ring connections.
Owner:ANTOSIK ROMAN
Apparatus and method for protection switching for mesh topology
InactiveUS20120082026A1Network resource can be efficientlyEfficient use ofError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsProtection domainFault occurrence
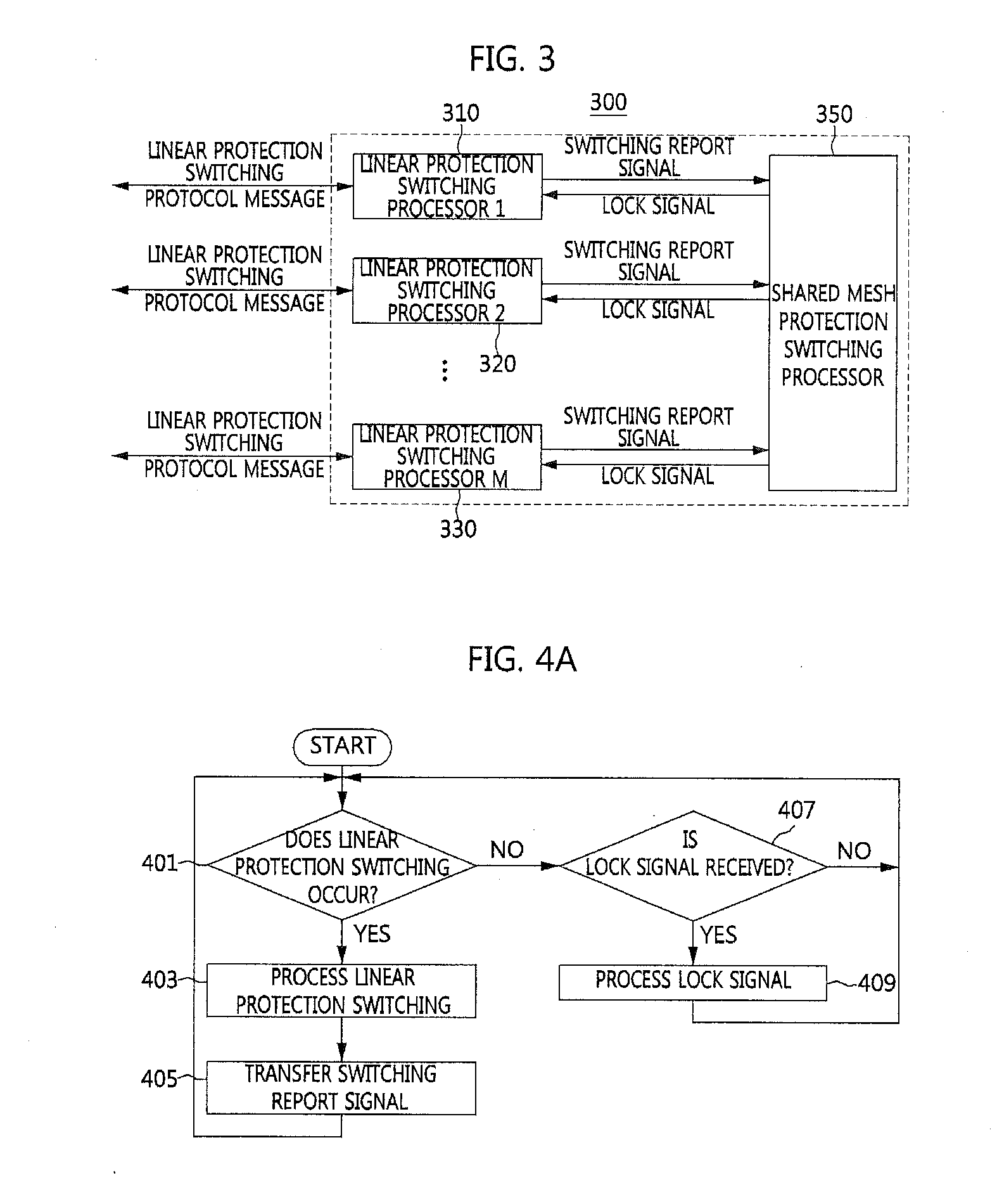
Provided are a shared mesh protection switching apparatus and method. The shared mesh protection switching apparatus includes a plurality of linear protection switching processors allocated to the linear protection domains respectively and configured to provide a switching report signal in response to fault occurrence in the corresponding linear protection domains or a linear protection switching operation, and perform a function of limiting use of the shared section in response to a provided lock signal, and a mesh protection switching processor configured to select at least one linear protection domain to be limited in use of the network resources of the shared section according to a predetermined reference when the switching report signal is provided and provide the lock signal to a linear protection switching processor corresponding to the at least one selected linear protection domain.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method and equipment for realizing share Mesh protection, and optical network system
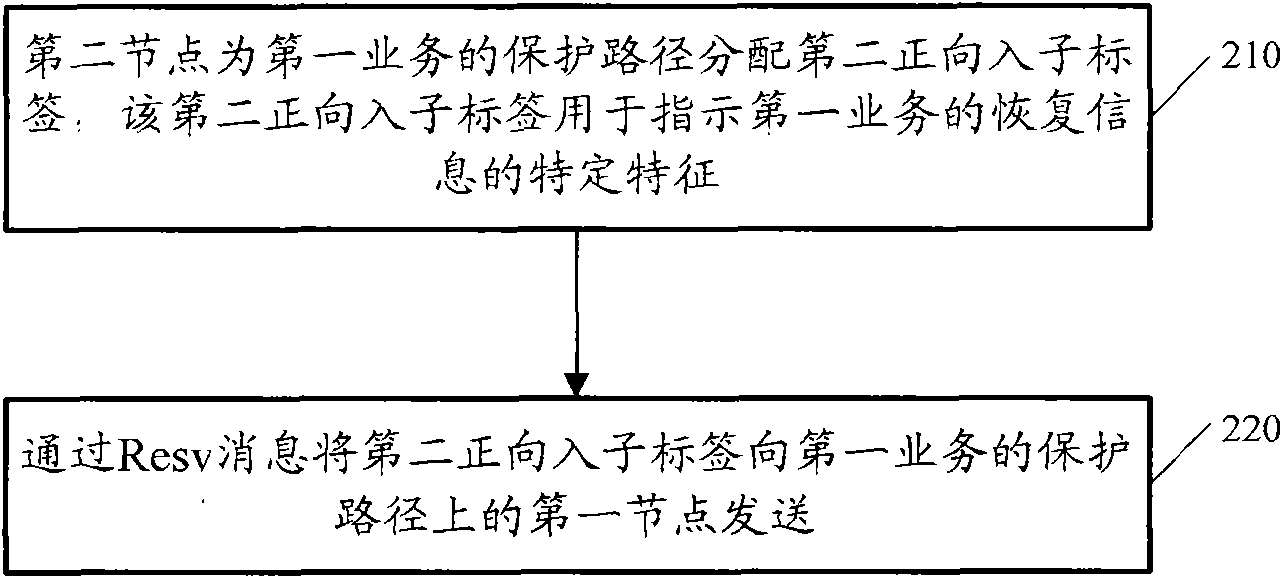
ActiveCN102104495AEasy to passSimplify configuration operationsMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic transmissionTelecommunicationsAutomatic protection switching
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and equipment for realizing share Mesh protection, and an optical network system. The method for realizing share Mesh protection comprises the following steps of: receiving a second type of message sent by a second node by a first node, wherein the second node carried by the second type of message is a second forward-in sub label distributed on a protection route of a first service, and the second forward-in sub label is used for indicating to carry a specific characteristic of restoring information of the first service; distributing a first forward-out sub label on the protection route of the first service according to the second forward-in sub label, wherein the first forward-out sub label and the second forward-in sub label have a corresponding relation; and transmitting the restoring information of the first service to the second node according to the instruction of the first forward-out sub label if the fault of the working route of the first service is known. By the scheme of the embodiment, each node on the protection route can easily and accurately determine a service to be restored so as to provide reliable support for subsequent service automatic protection switching.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and device for recovering a shared mesh network
InactiveUS7787362B2Easy to implementBetter compatibleMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionNetwork connectionNetwork management
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Standby restoration signaling for optical networks
Systems and methods are described that provide a distributed restoration signaling protocol for shared mesh restoration with standbys for transparent optical networks.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I LP
Method, system and equipment for service recovery
ActiveCN101646105AShorten recovery timeImprove resource utilizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksResource utilizationLabel switching
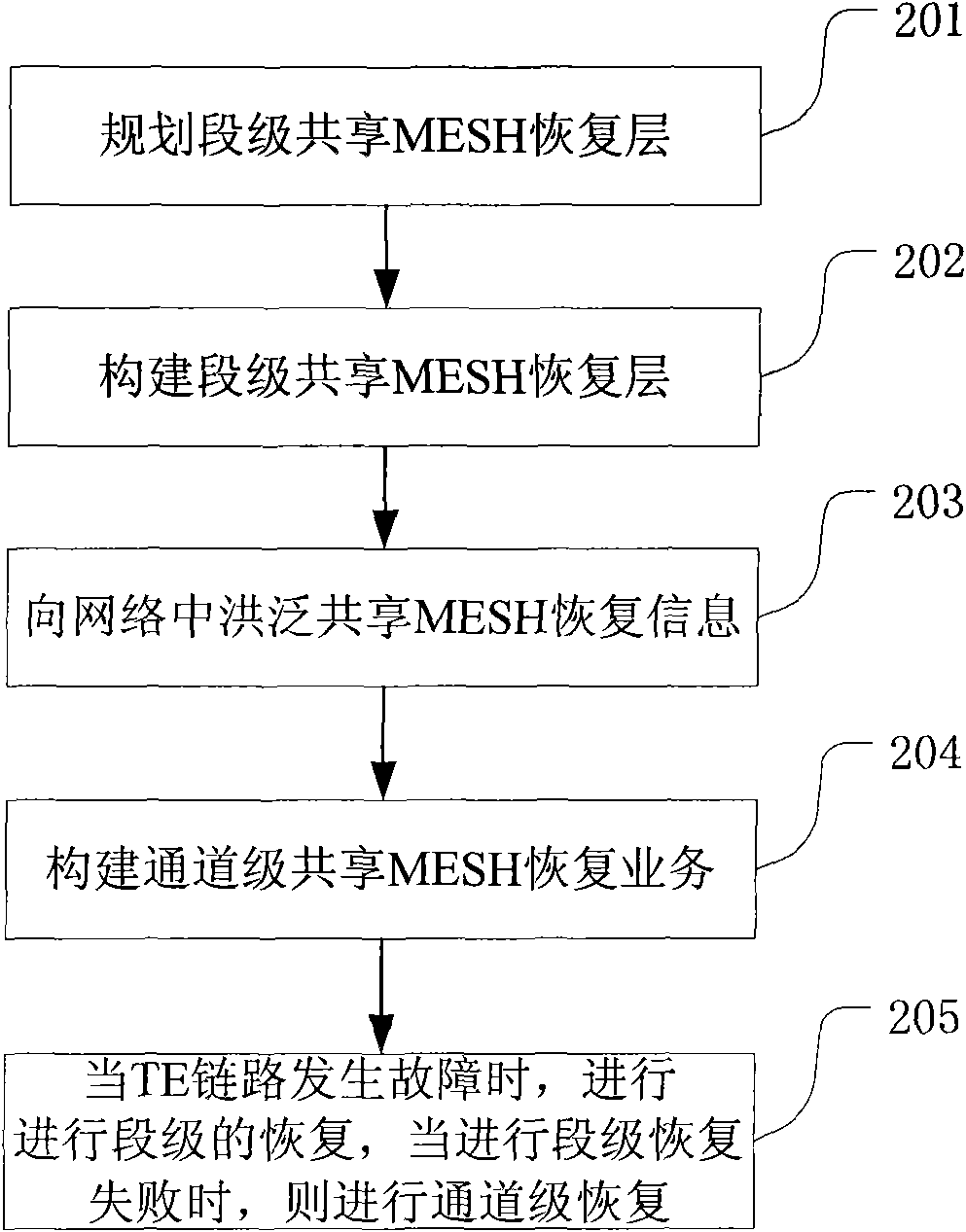
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method, a system and equipment for service recovery, which belong to the field of communication. The method comprises the following steps: setting the work resource of a traffic engineering link in a network in a sharing MESH recovery state; flooding the sharing MESH recovery state information into the network, wherein the sharing MESH recovery state information is used for notifying that the fault recovering mode of the work resource of the traffic engineering link is the segment level sharing MESH recovery; detecting whether the traffic engineering link has a fault or not; and recovering the service on the work resource of the traffic engineering link by switching N segment level forwarding adjacent label switching paths on the traffic engineering link to N corresponding segment level share MESH recovering paths when a fault is detected on the traffic engineering link. The technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention can reduce the service recovery time and meet the service requirement of a client when the bandwidth resource utilization is high.
Owner:乐陵市建兴装饰工程有限公司
Standby Restoration Signaling For Optical Networks
ActiveUS20120308224A1Reduce in quantityMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsSignaling protocolShared mesh
Systems and methods are described that provide a distributed restoration signaling protocol for shared mesh restoration with standbys for transparent optical networks.
Owner:AT&T INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY I L P
Apparatus and method of shared mesh protection switching
InactiveUS20130083652A1Smoothly protection switchingReduce injectionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityAutomatic protection switching
A method of performing protection switching in which congestion does not occur at a shared segment and that can rapidly perform linear protection switching while using an 1-phase automatic protection switching protocol is provided. An end node that requests protection switching awaits by a time that is previously set to a timer and stops use of a shared protection segment for a standby time of the end node and thus traffic that is injected to a shared node reduces, whereby a congestion situation of a shared protection segment does not occur and thus a protection switching protocol is prevented from abnormally operating.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Demand Advertisement Method for Shared Mesh Protection Path Computation
A method includes the steps of: (1) generating, by circuitry of a first node, an advertising message including (a) a working path bandwidth demand; (b) an identification of at least two communication links in a shared risk link group of the working path; and (c) at least one protecting path and a bitmap indicative of failure of at least one first communication link in the shared risk link group that causes the at least one protecting path to be used; and (2) transmitting the advertising message from the first node to second nodes within a mesh network.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
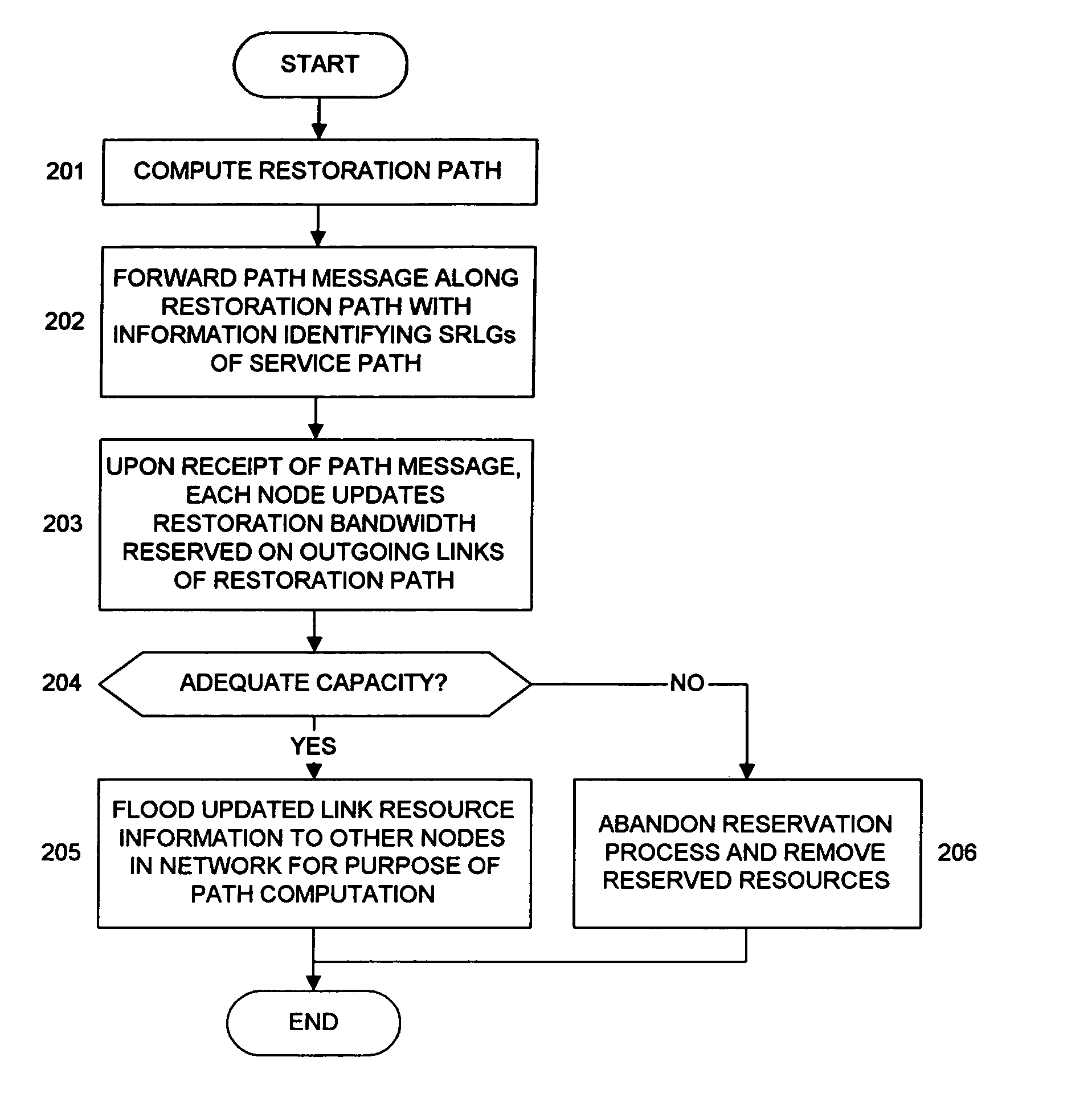
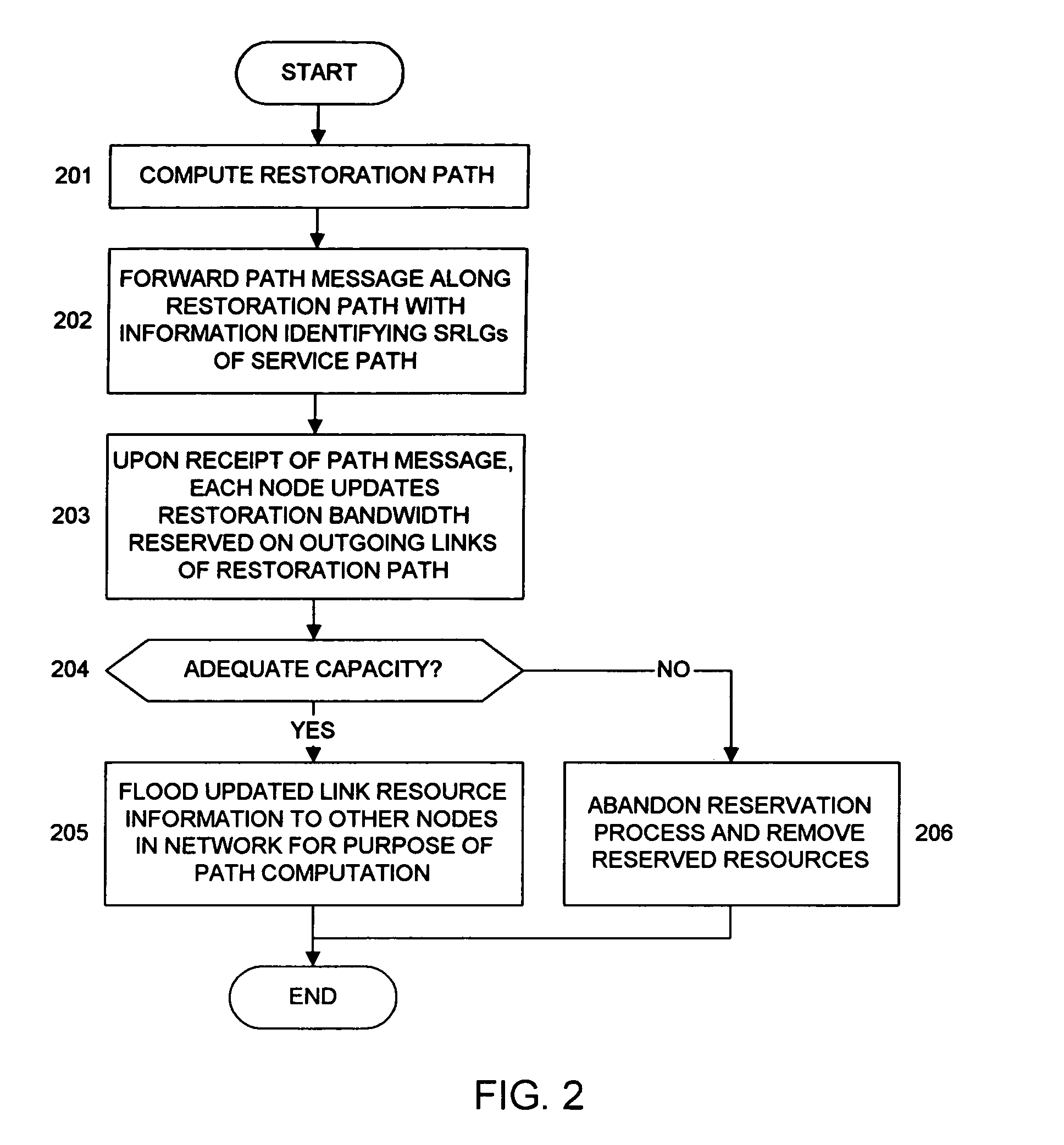
Sharing restoration path bandwidth in mesh networks
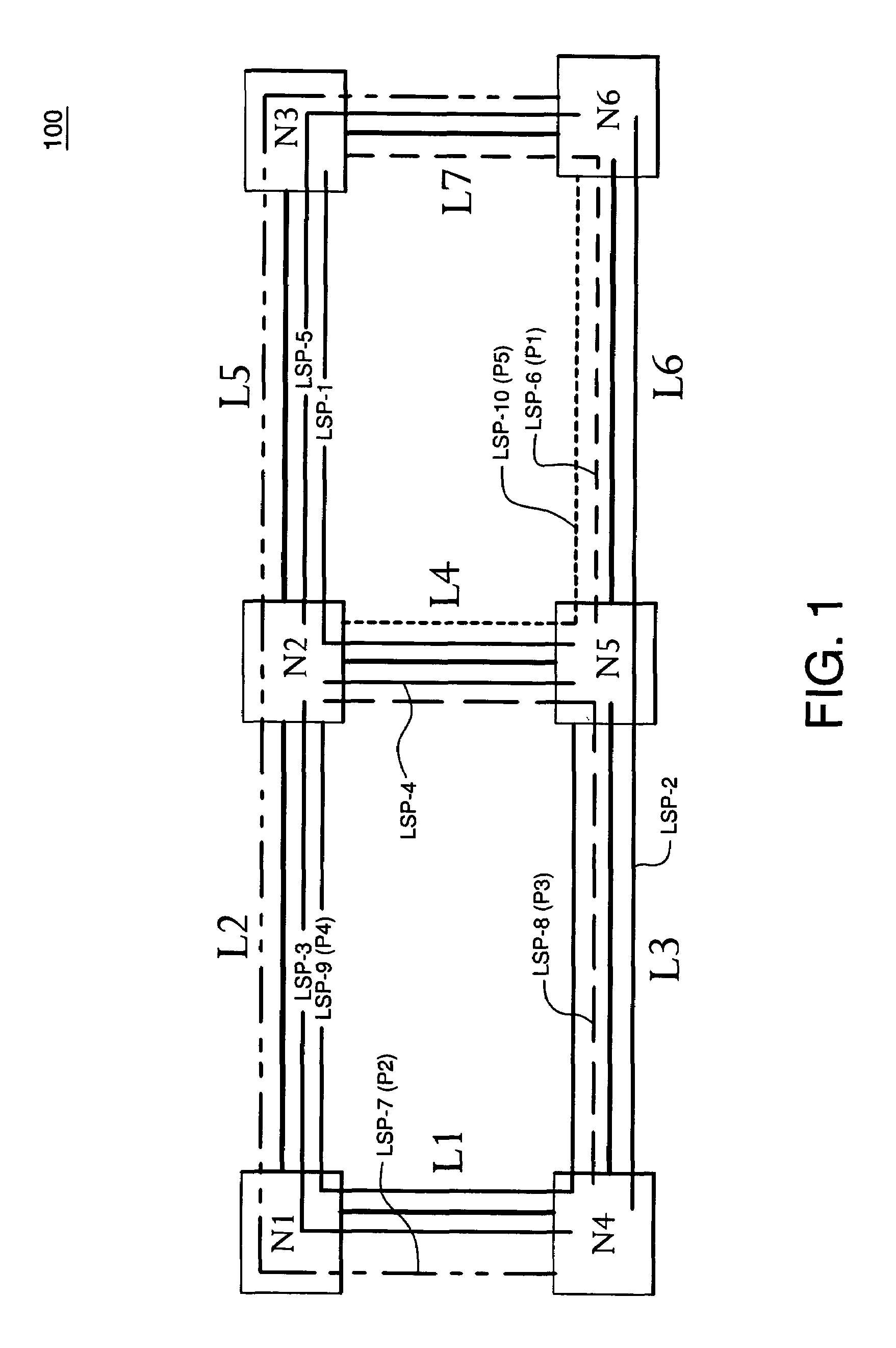
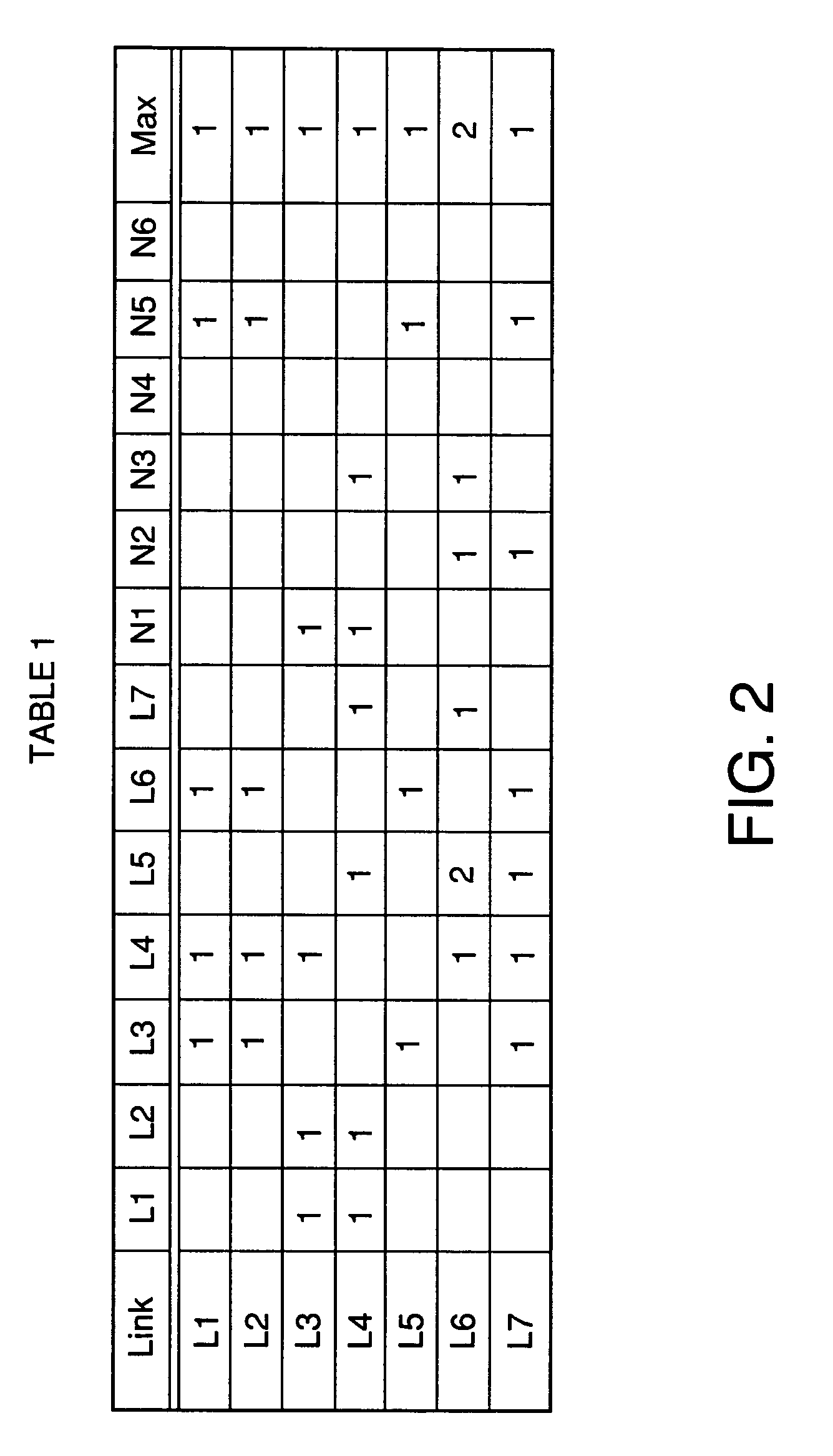
A shared mesh data network (SMDN) for path-based recovery at the packet level. In one implementation, a first link in the network is part of two or more different protection paths, where each protection path corresponds to a different primary path. A network manager determines how much protection bandwidth to reserve on the first link for the two or more protection paths in such a way that the protection bandwidth reserved on the first link is shared between the protection paths of the two or more primary paths. As such, the amount of protection bandwidth reserved on the first link can be less than the sum of the bandwidths of the two or more primary paths. The SMDN provides efficient sharing of protection capacity. Implementations of the SMDN are appropriate to multiprotocol label-switched (MPLS) optical networks.
Owner:PROVENANCE ASSET GRP LLC +1
Method and network device for realizing shared mesh protection
ActiveUS8406124B2Easy to implementGood serviceError preventionTransmission systemsLabel switchingDistributed computing
A method and a network device for realizing shared mesh protection are provided. The method includes the following steps. If a status change of a working label switching path (LSP) is detected, routing information and bandwidth information about the working LSP are notified to every node on a protection LSP corresponding to the working LSP. Every node on the protection LSP calculates a maximal reserved bandwidth of a link based on the received routing information and bandwidth information and adjusts a shared protection bandwidth of the link according to the maximal reserved bandwidth.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method of performing shared mesh protection switching
InactiveUS20140247712A1Abnormal operation of a shared mesh protection switching protocol can be fundamentally preventedError preventionTransmission systemsProtection domainAutomatic protection switching
A method of performing shared mesh protection switching in which congestion does not occur in a sharing segment and that quickly performs linear protection switching while using a 1-phase automatic protection switching protocol is provided. For protection switching of a working path that is included in a end-to-end linear protection domain having a high priority, because of congestion that may occur in a pre-emption process of stopping use of a shared protection segment of a working path that is included in a end-to-end linear protection domain having a low priority, a signal failure occurs at a protection path, and thus operation of a shared mesh protection switching protocol abnormally can be prevented.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
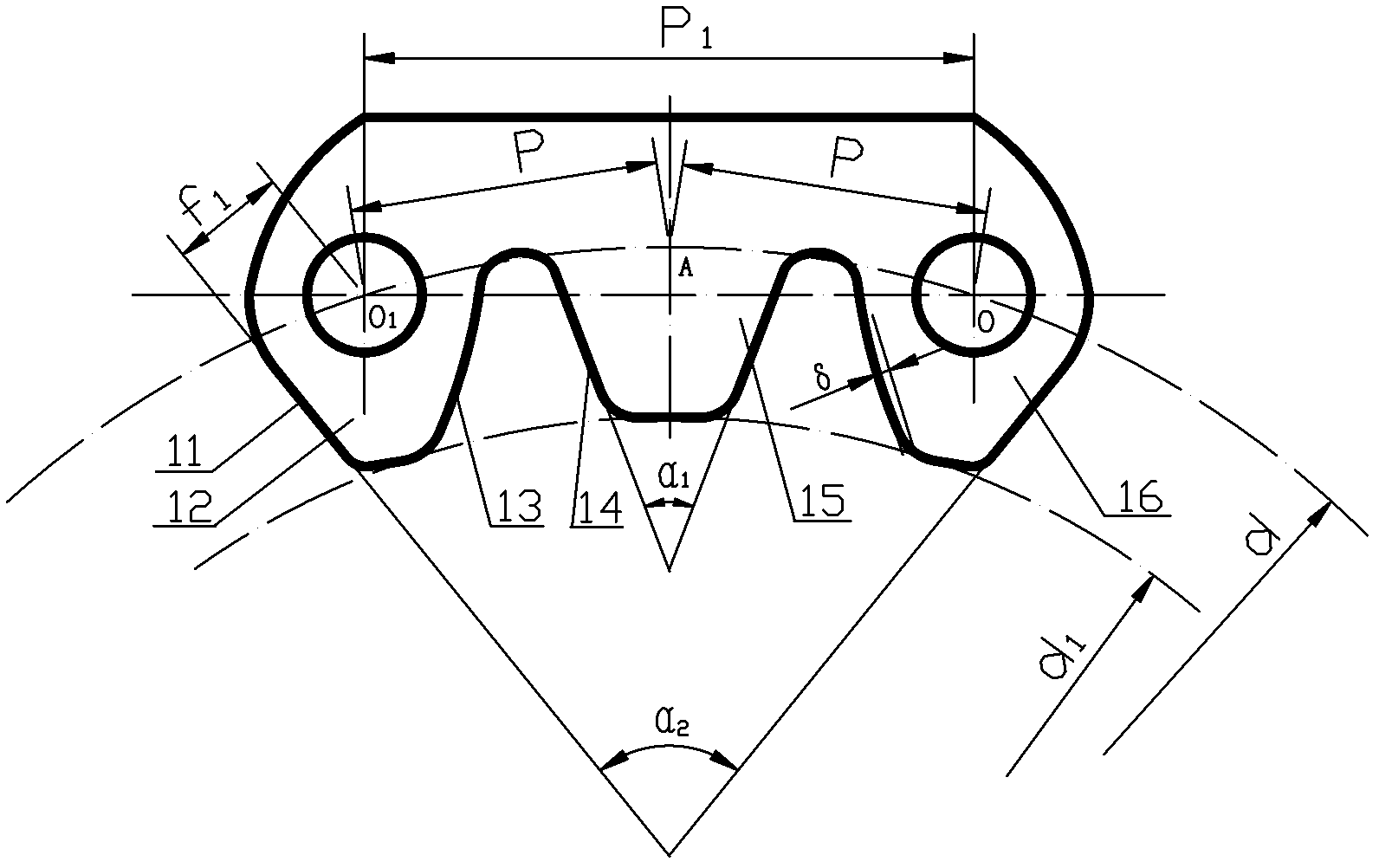
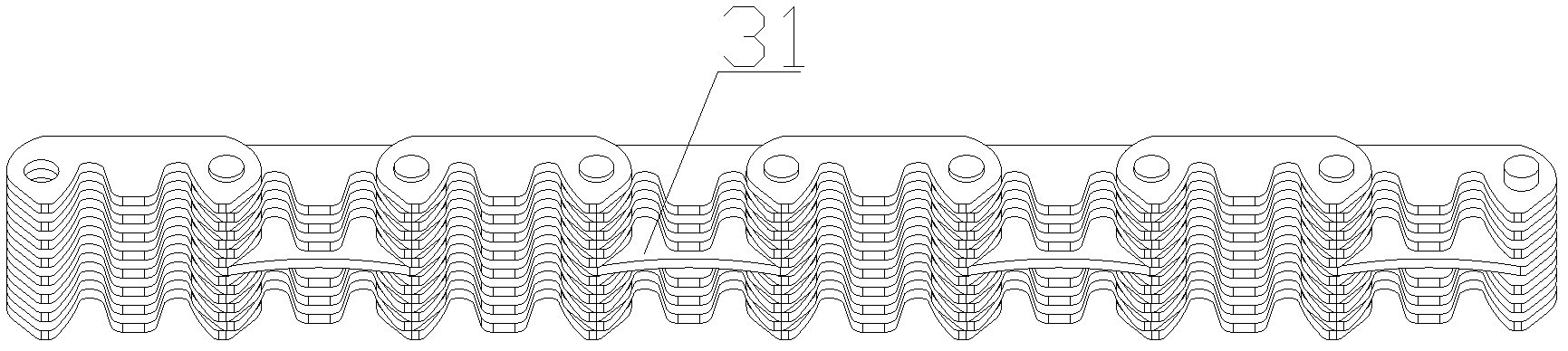
Double-pitch time-sharing meshing toothed chain chain plate
InactiveCN102287483ALight in massExtended service lifeConveyorsChain linksProduction lineMaterial consumption
The invention relates to a double-pitch time-sharing meshed tooth-shape chain board, belonging to the field of mechanical design and manufacture and chain driving. The chain board has double pitch on a meshing line, three teeth are distributed on each piece of the chain board, the outer tooth profile lines of the first and the third tooth profiles are straight lines, the apothem f1 of the chain board is 0.96-0.98 times than the apothem f of the standard tooth-shape chain board, the inner tooth profile line is a convex curve with a protrusion delta equal to 0.01f-0.03f, and the tooth profile line of the second tooth is a straight line tooth profile. The invention has the following advantages: when transporting and driving the same load, the chain board has stable tooth mesh-in and mesh-out, small shock and vibration and noise, less material consumption, high motion precision and good reliability, thus the chain board is particularly suitable for the transportation of the parts in an automobile assembly.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
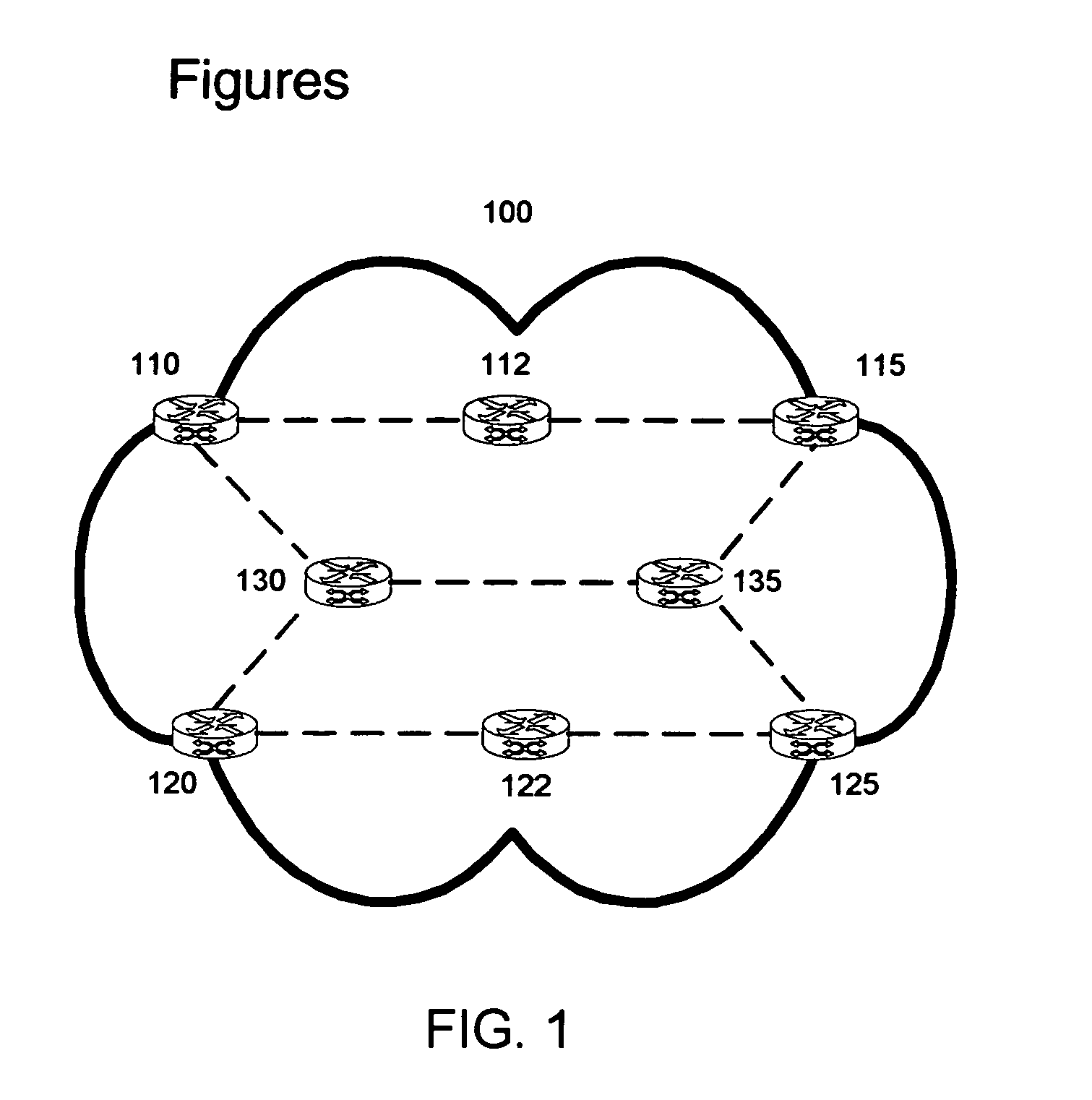
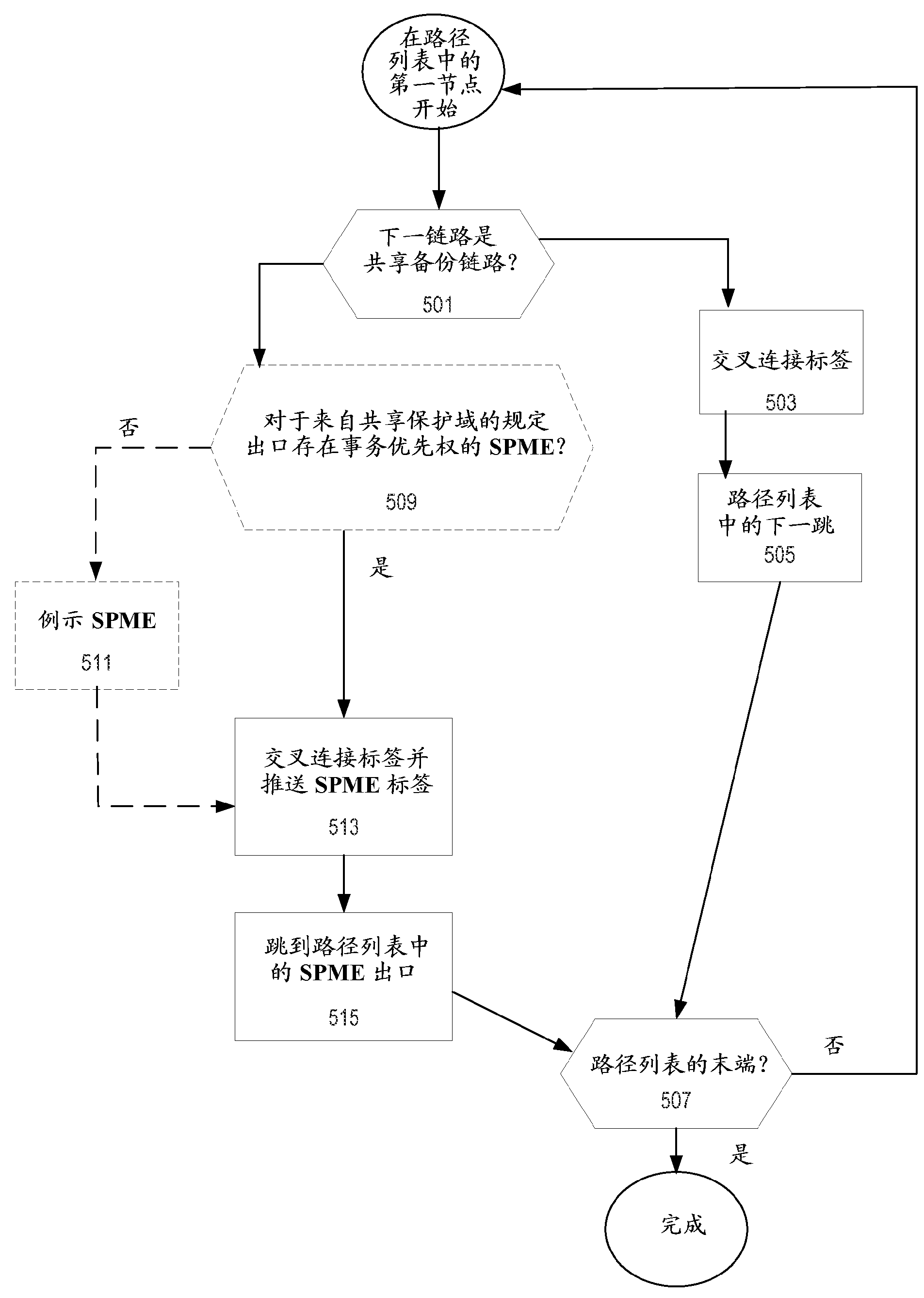
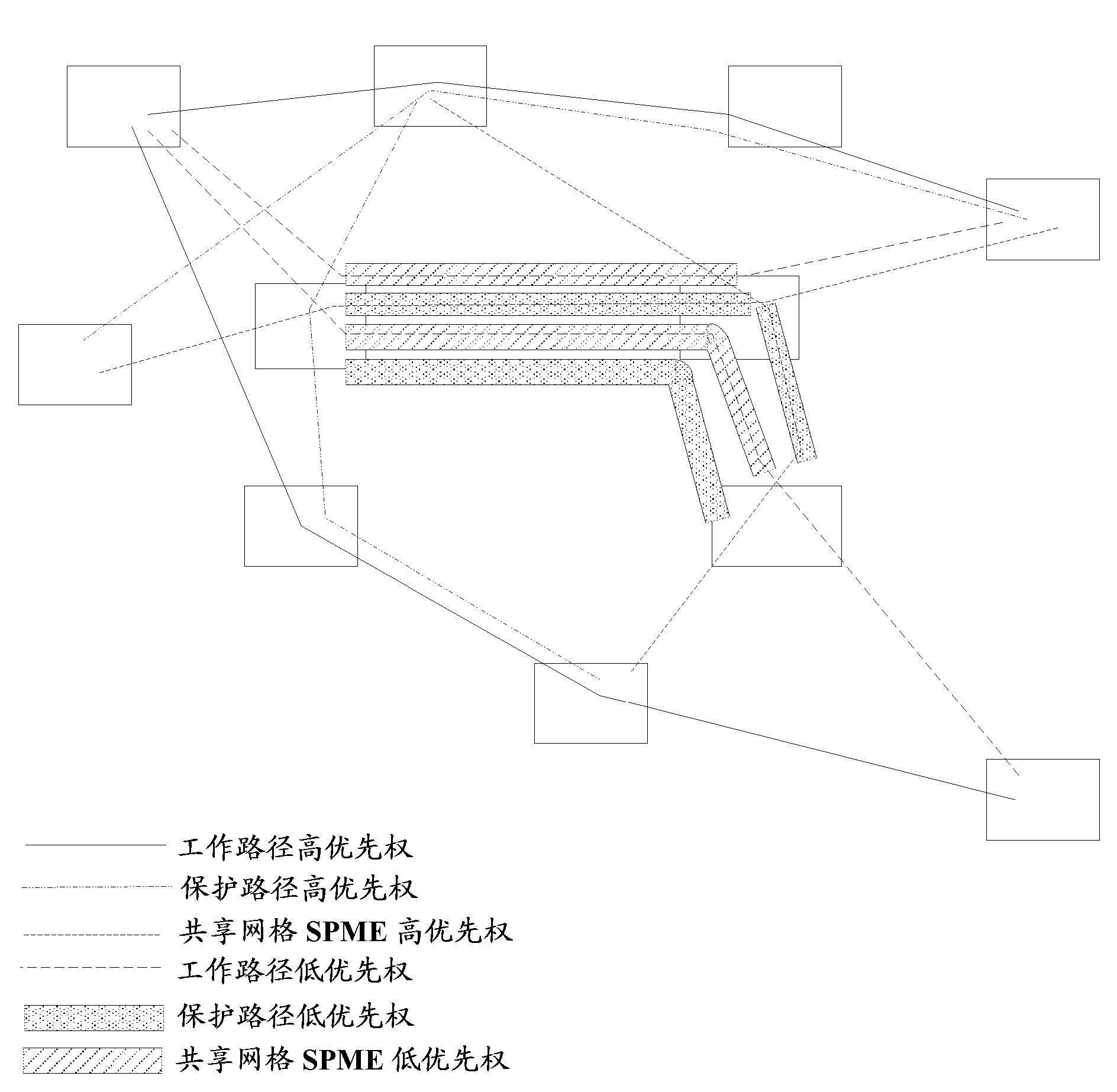
Use of sub path maintenance elements (SPMES) for multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) shared mesh protection
Embodiments of the invention include a computer-implemented method of shared backup path computation in an multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) network, the shared backup path to be used upon a failure of at least one working path of the MPLS network.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com