Patents
Literature
137 results about "Protection domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
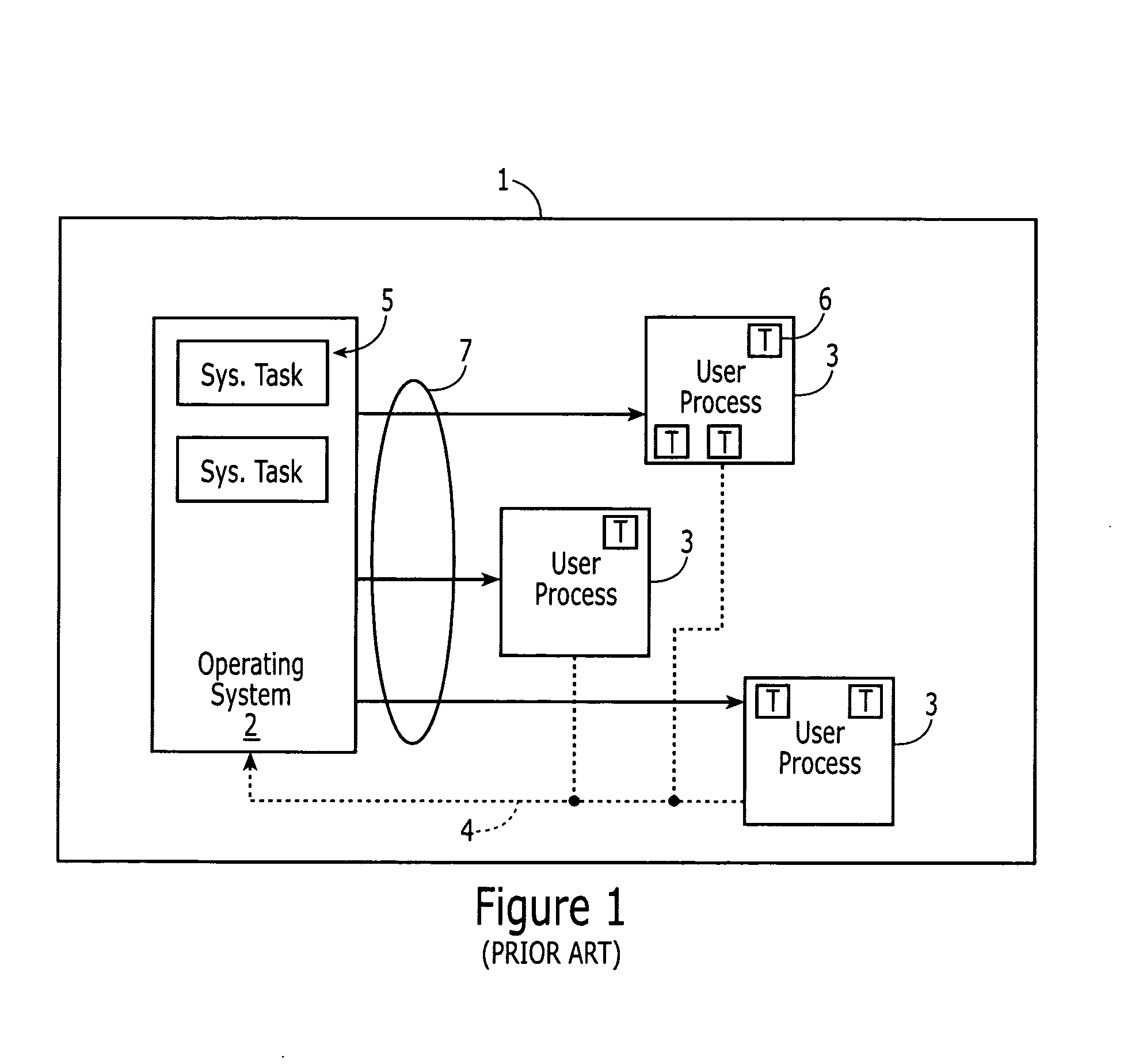
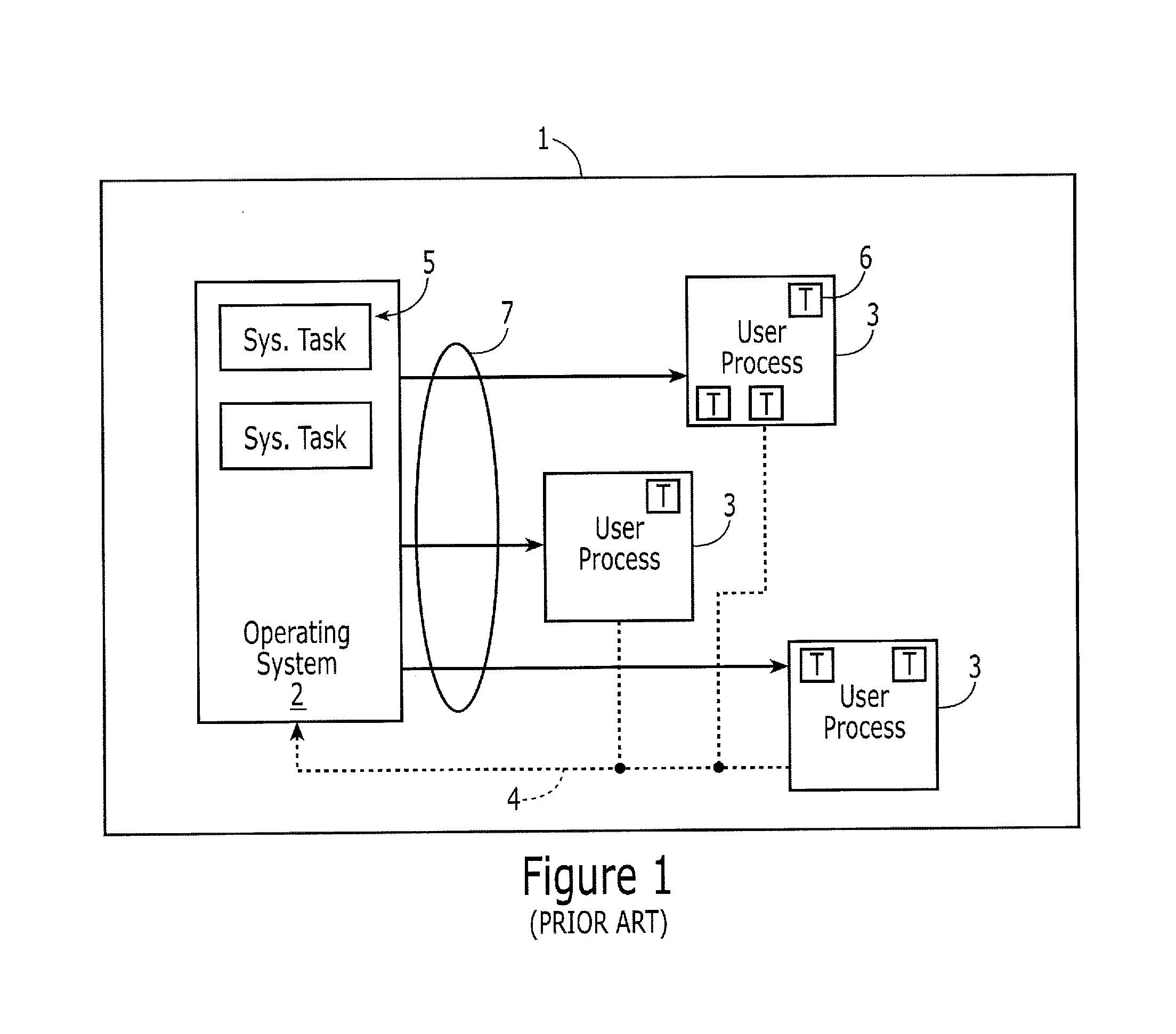
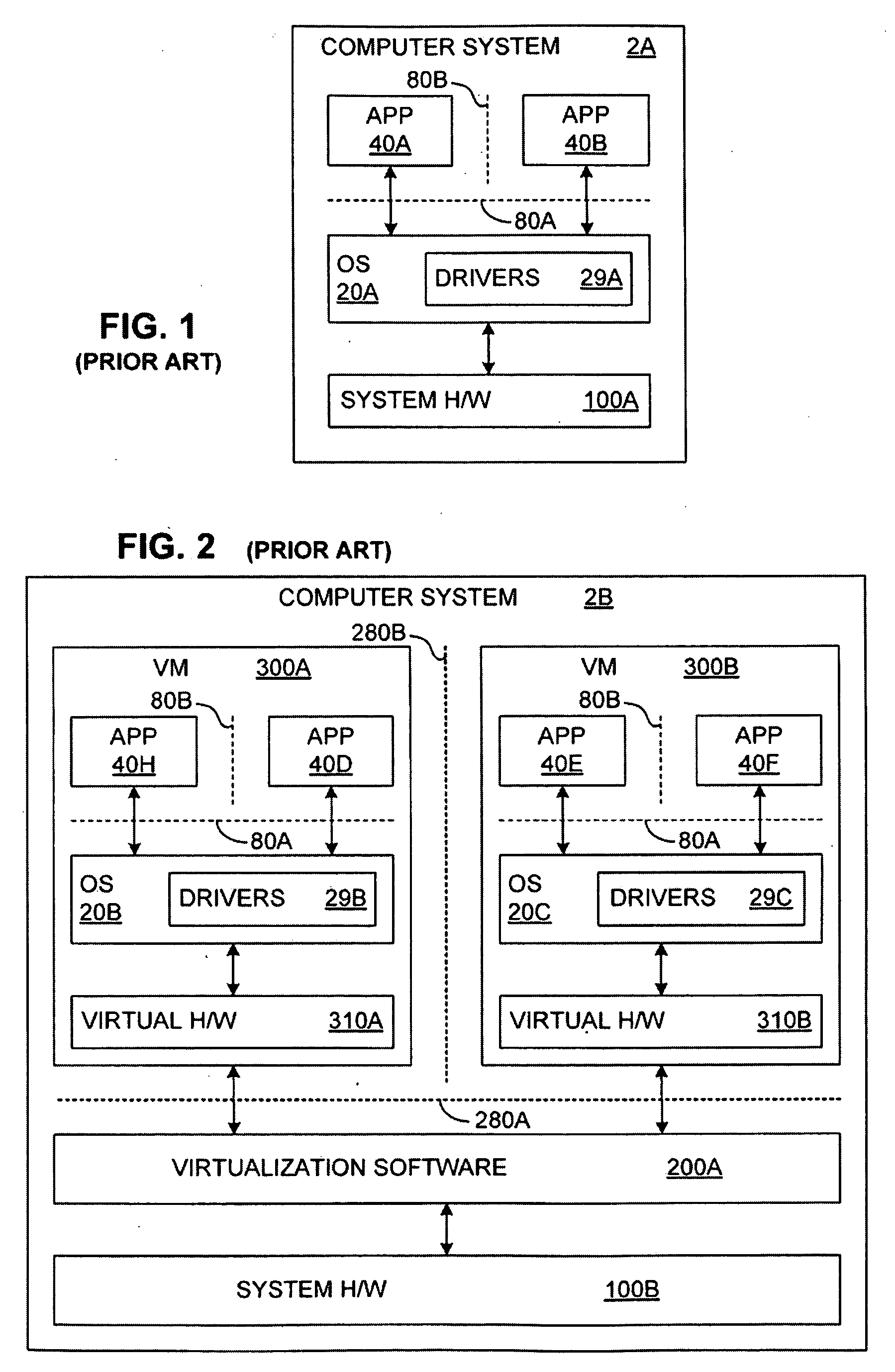
Integrating operating systems and run-time systems
InactiveUS6546546B1Specific access rightsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationOperational systemApplication software
The Virtual Machine is viewed by many as inherently insecure despite all the efforts to improve its security. This invention provides methods, apparatus, and computer products to implement a system that provides operating system style protection for code. Although applicable to many language systems, the invention is described for a system employing the Java language. Hardware protection domains are used to separate Java classes, provide access control on cross domain method invocations, efficient data sharing between protection domains, and memory and CPU resource control. Apart from the performance impact, these security measures are all transparent to the Java programs, even when a subclass is in one domain and its superclass is in another, when they do not violate the policy. To reduce the performance impact, classes are grouped and shared between protection domains and map data lazily as it is being shared. The system has been implemented on top of the Paramecium operating system used as an example of an extensible operating system application.
Owner:IBM CORP
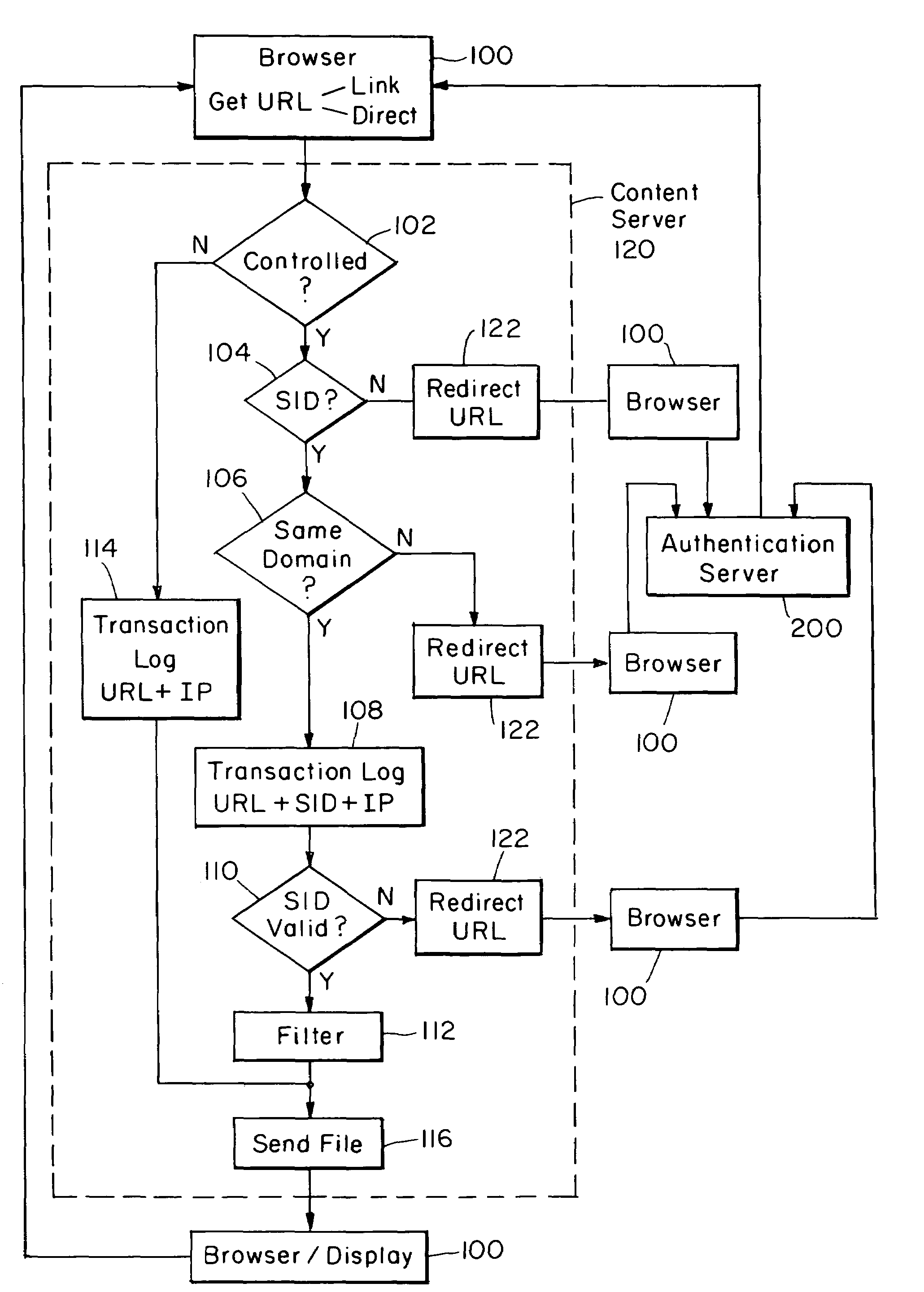
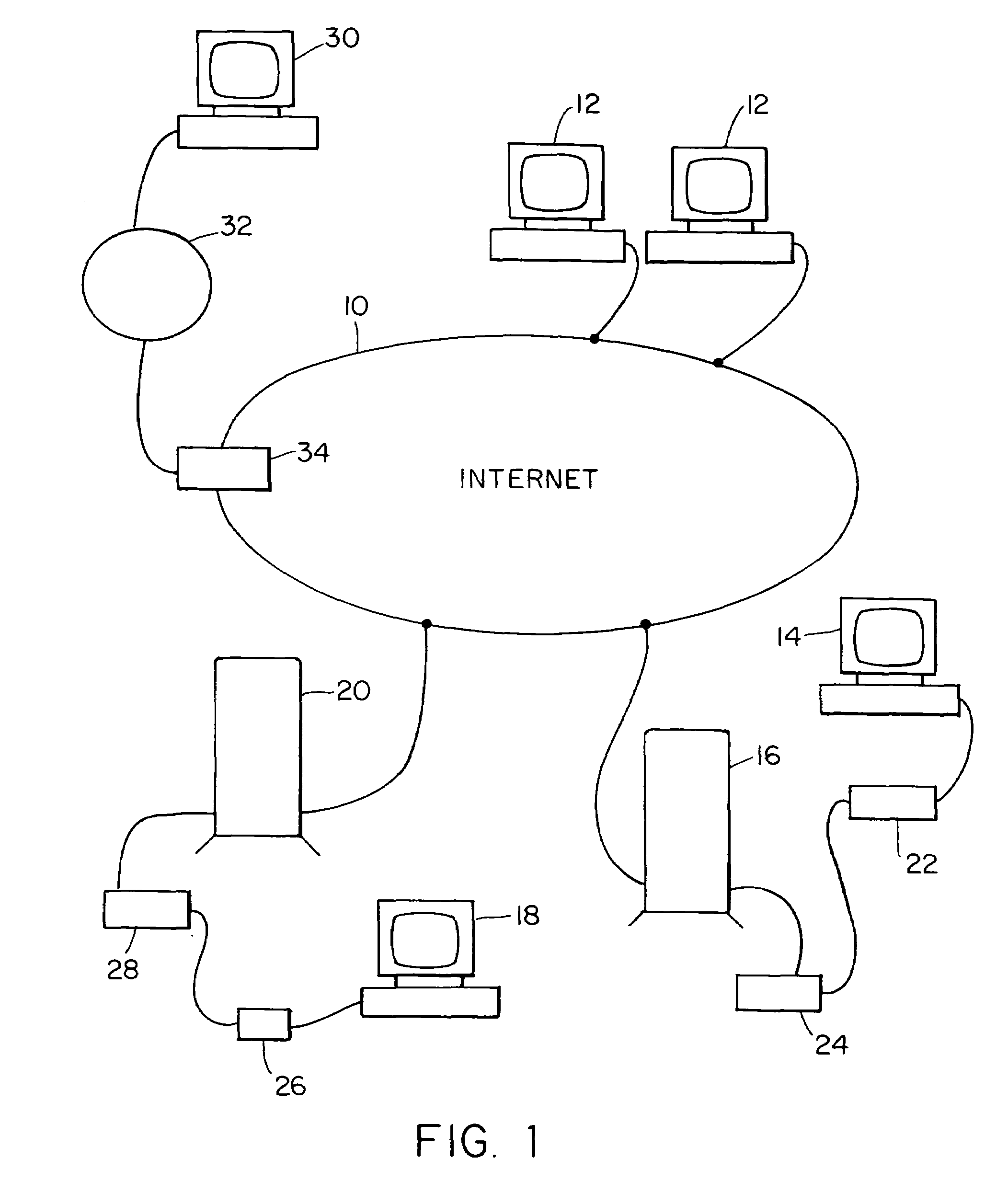
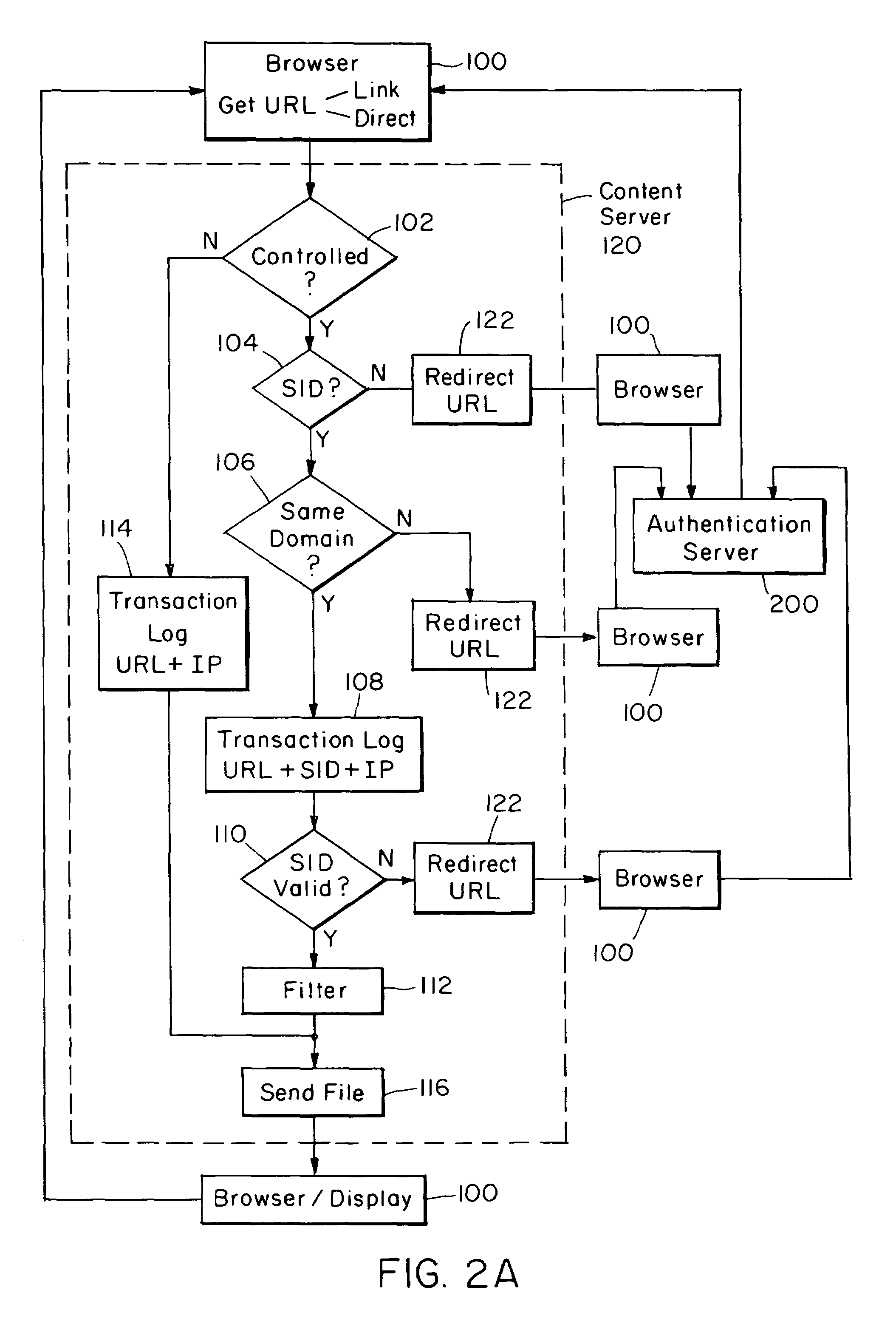
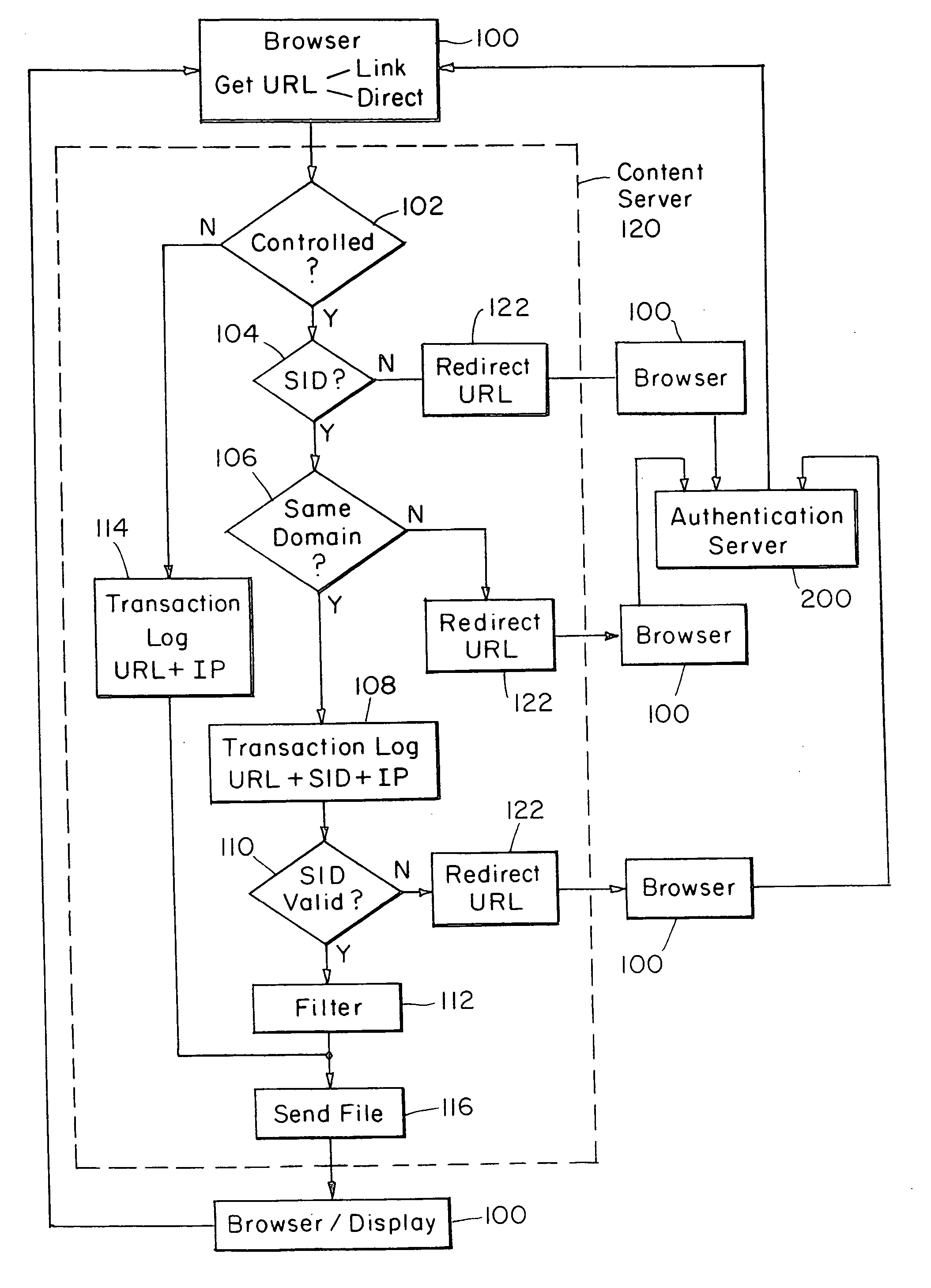
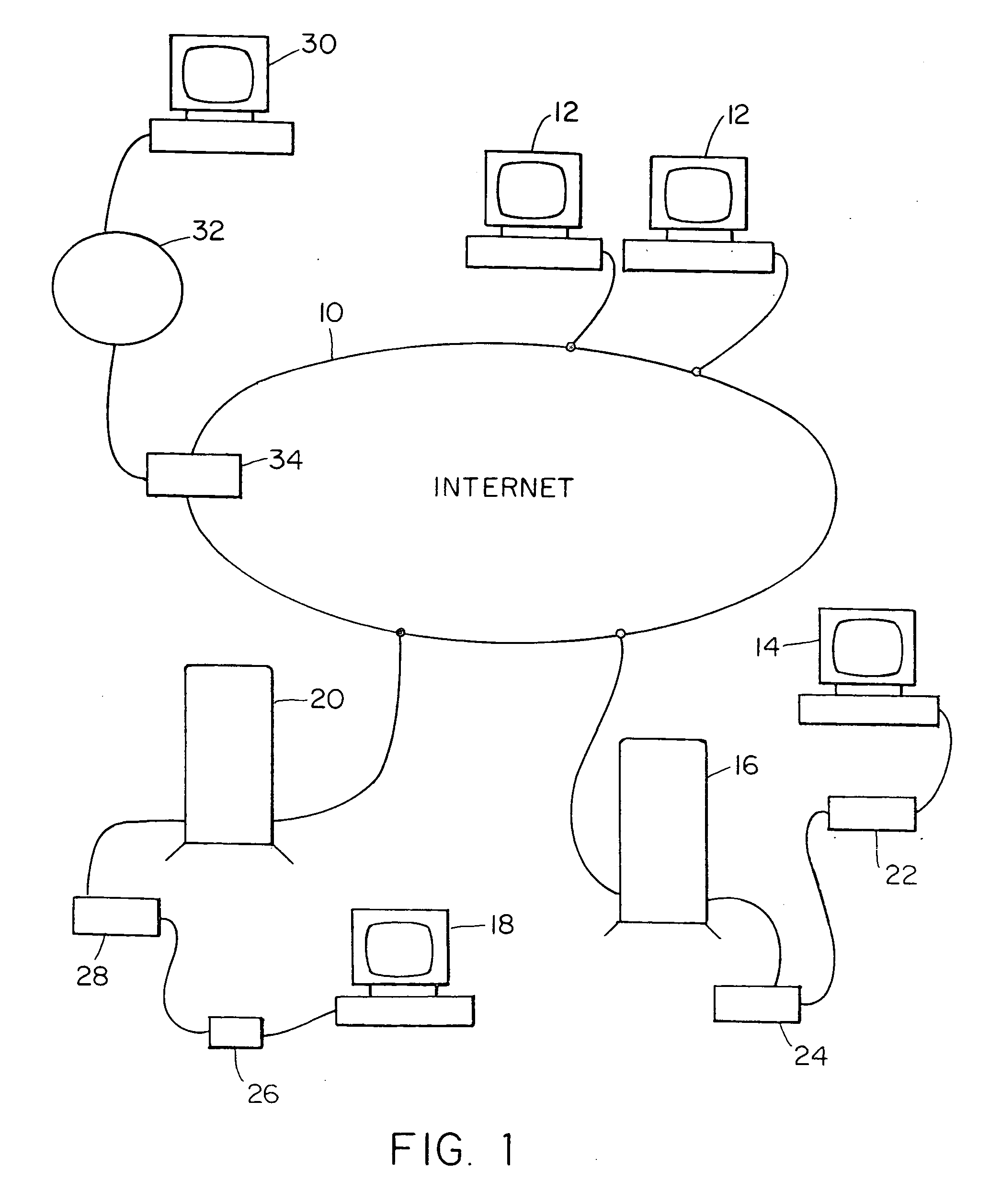
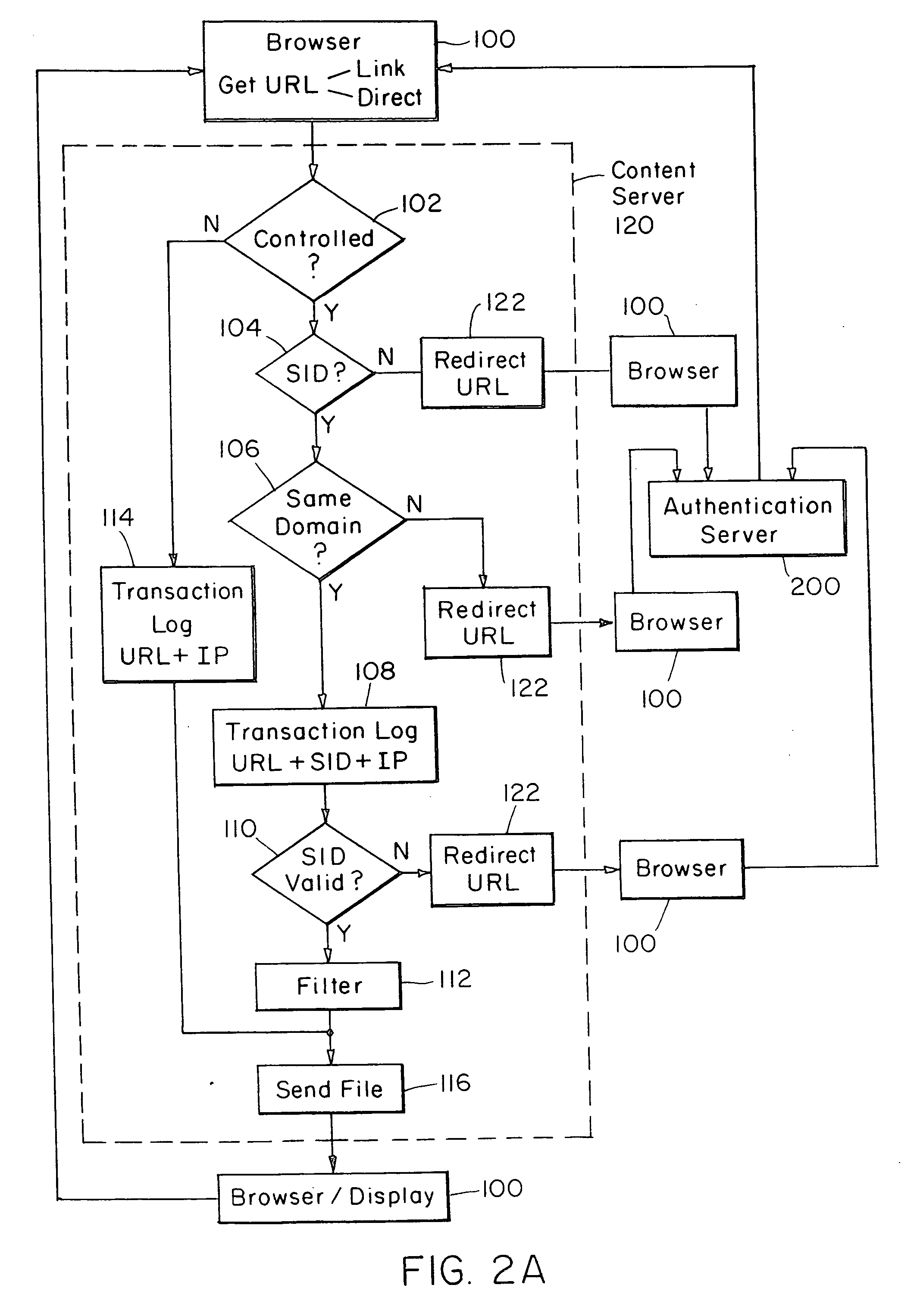
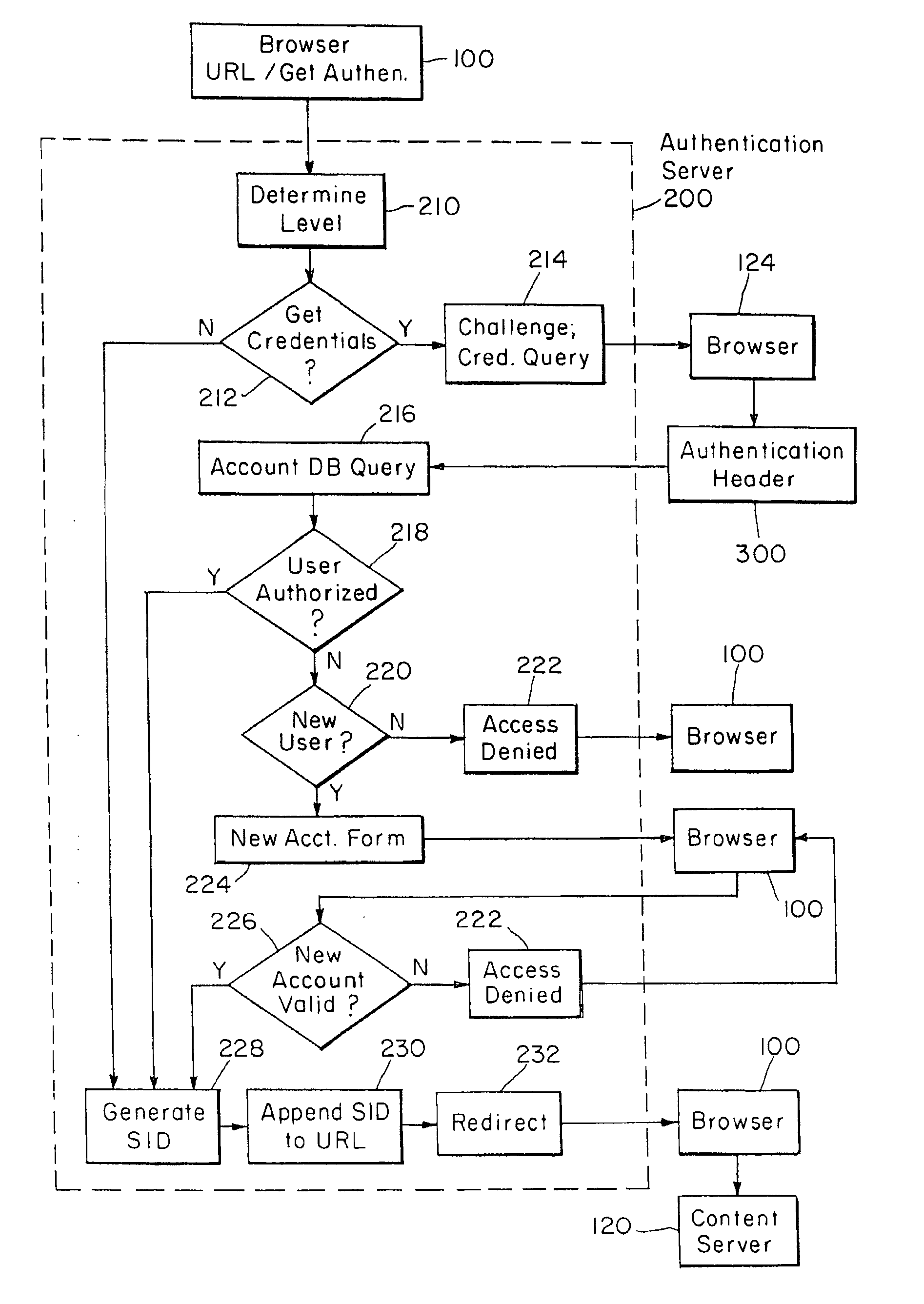
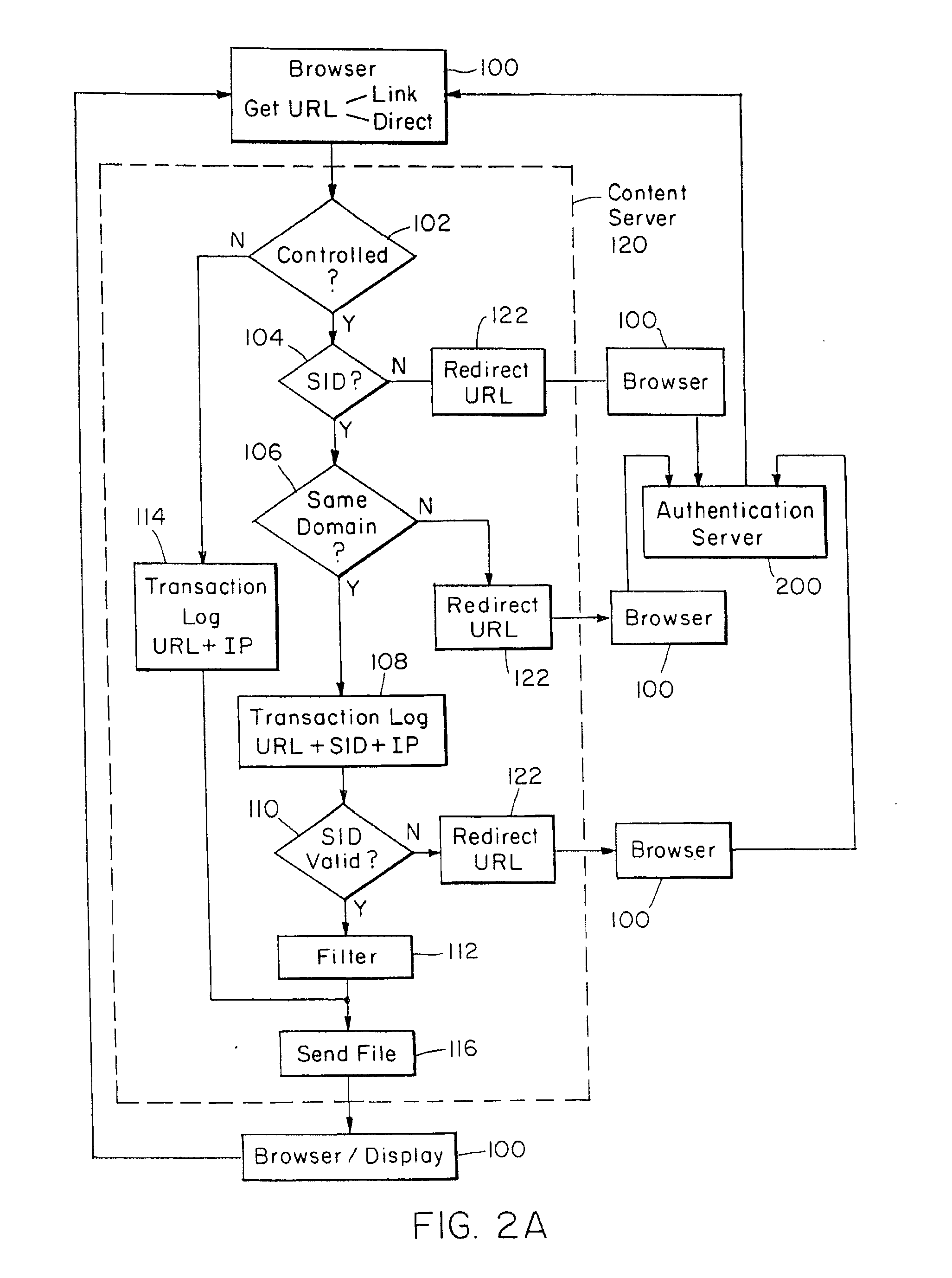
Internet server access control and monitoring systems
InactiveUS7272639B1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionProtection domainMonitoring system
This invention relates to methods for controlling and monitoring access to network servers. In particular, the process described in the invention includes client-server sessions over the Internet. In this environment, when the user attempts to access an access-controlled file, the server subjects the request to a secondary server which determines whether the client has an authorization or valid account. Upon such verification, the user is provided with a session identification which allows the user to access to the requested file as well as any other files within the present protection domain.
Owner:SOVERAIN IP LLC
Internet server access control and monitoring systems
InactiveUS20060095526A1Discounts/incentivesMultiple digital computer combinationsProtection domainMonitoring system
This invention relates to methods for controlling and monitoring access to network servers. In particular, the process described in the invention includes client-server sessions over the Internet. In this environment, when the user attempts to access an access-controlled file, the server subjects the request to a secondary server which determines whether the client has an authorization or valid account. Upon such verification, the user is provided with a session identification which allows the user to access to the requested file as well as any other files within the present protection domain.
Owner:SOVERAIN IP LLC
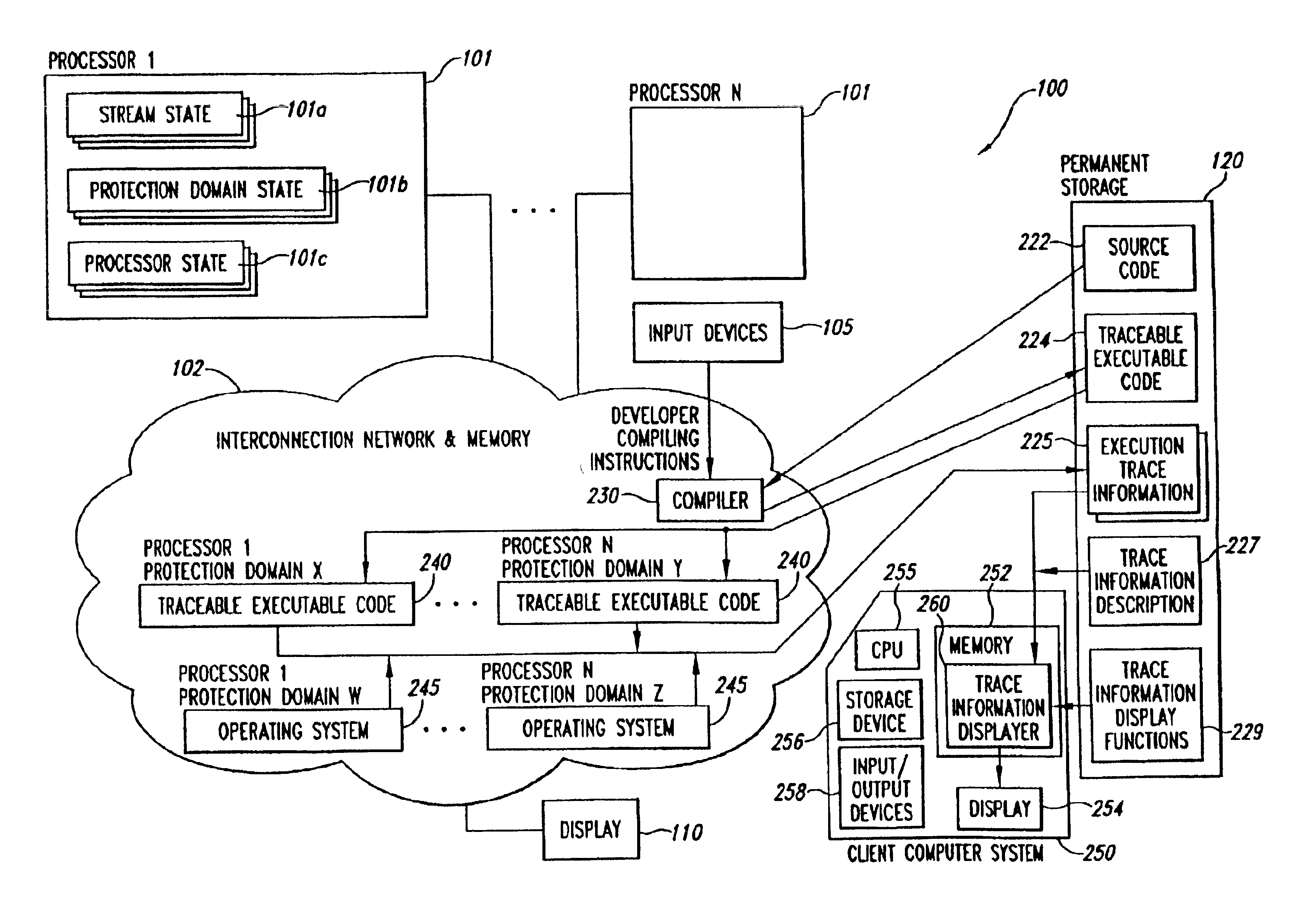
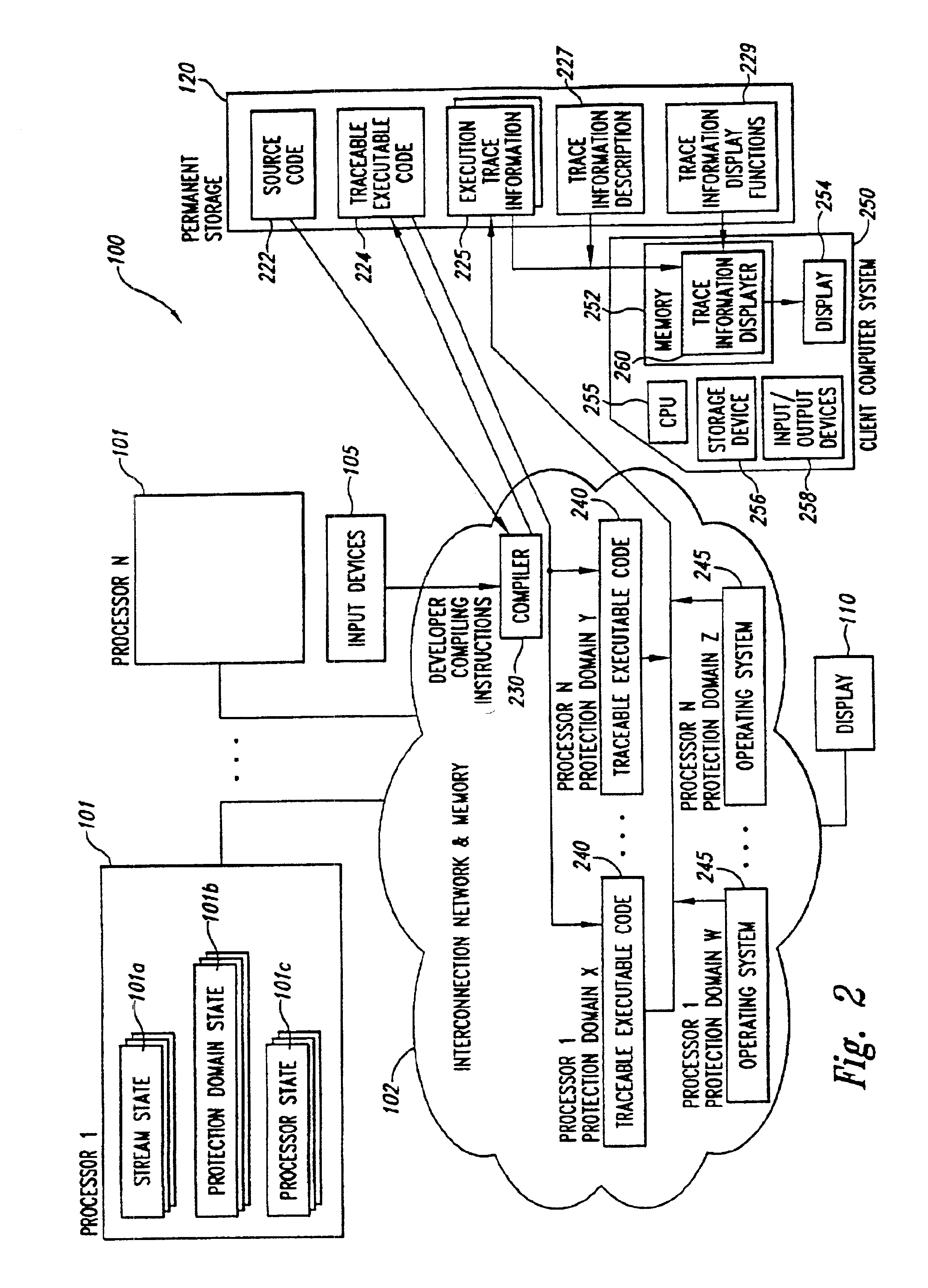
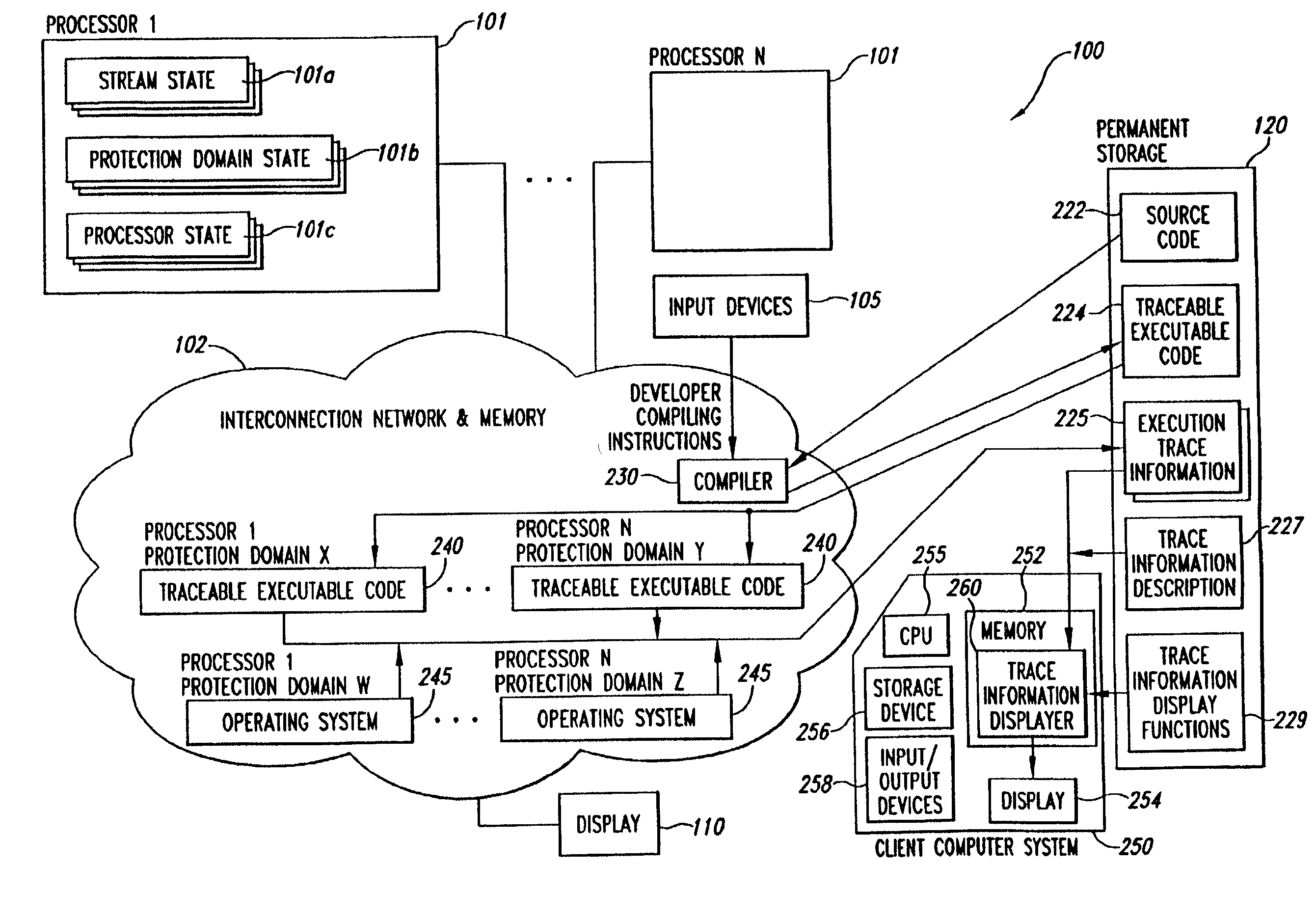
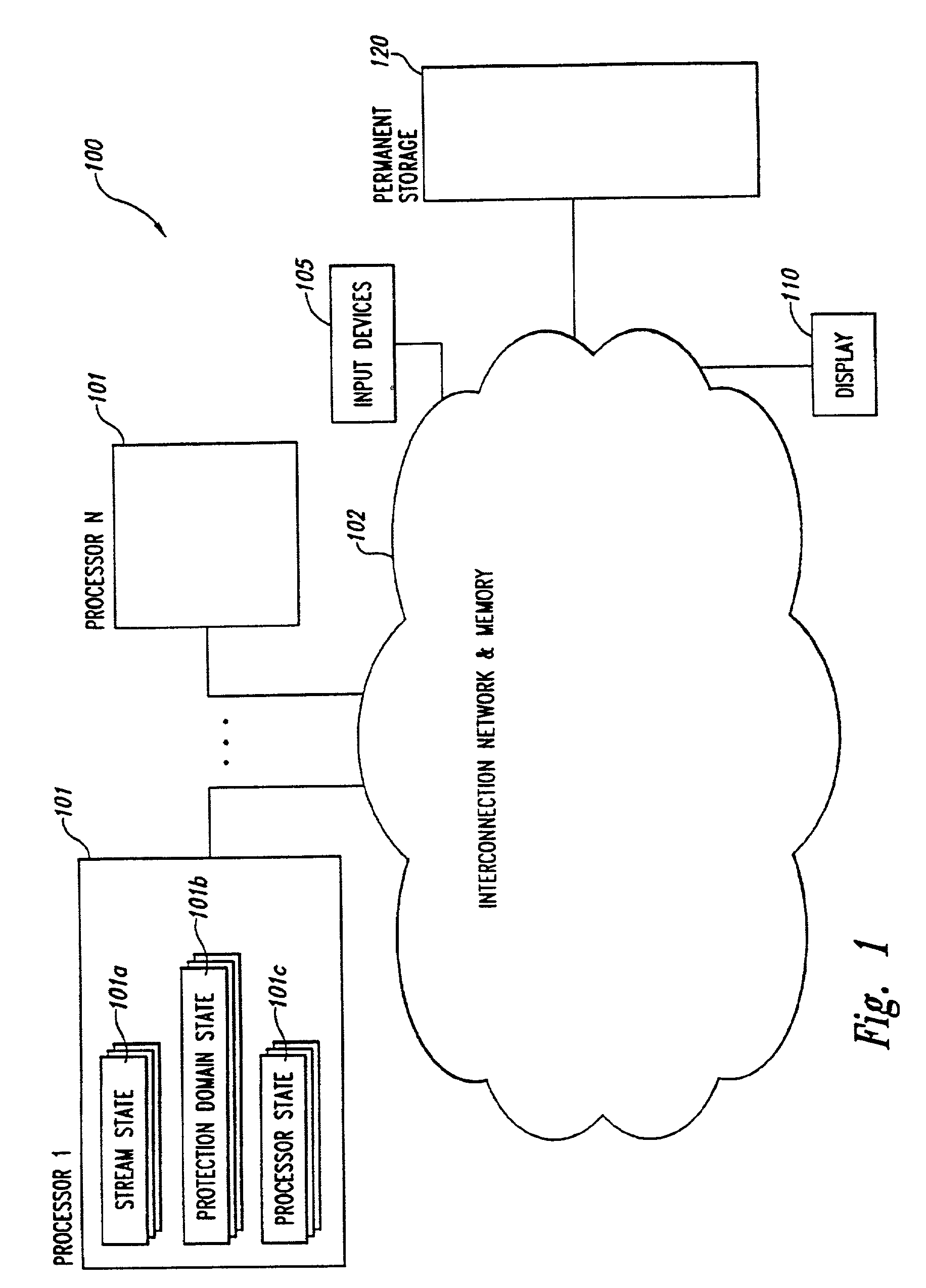
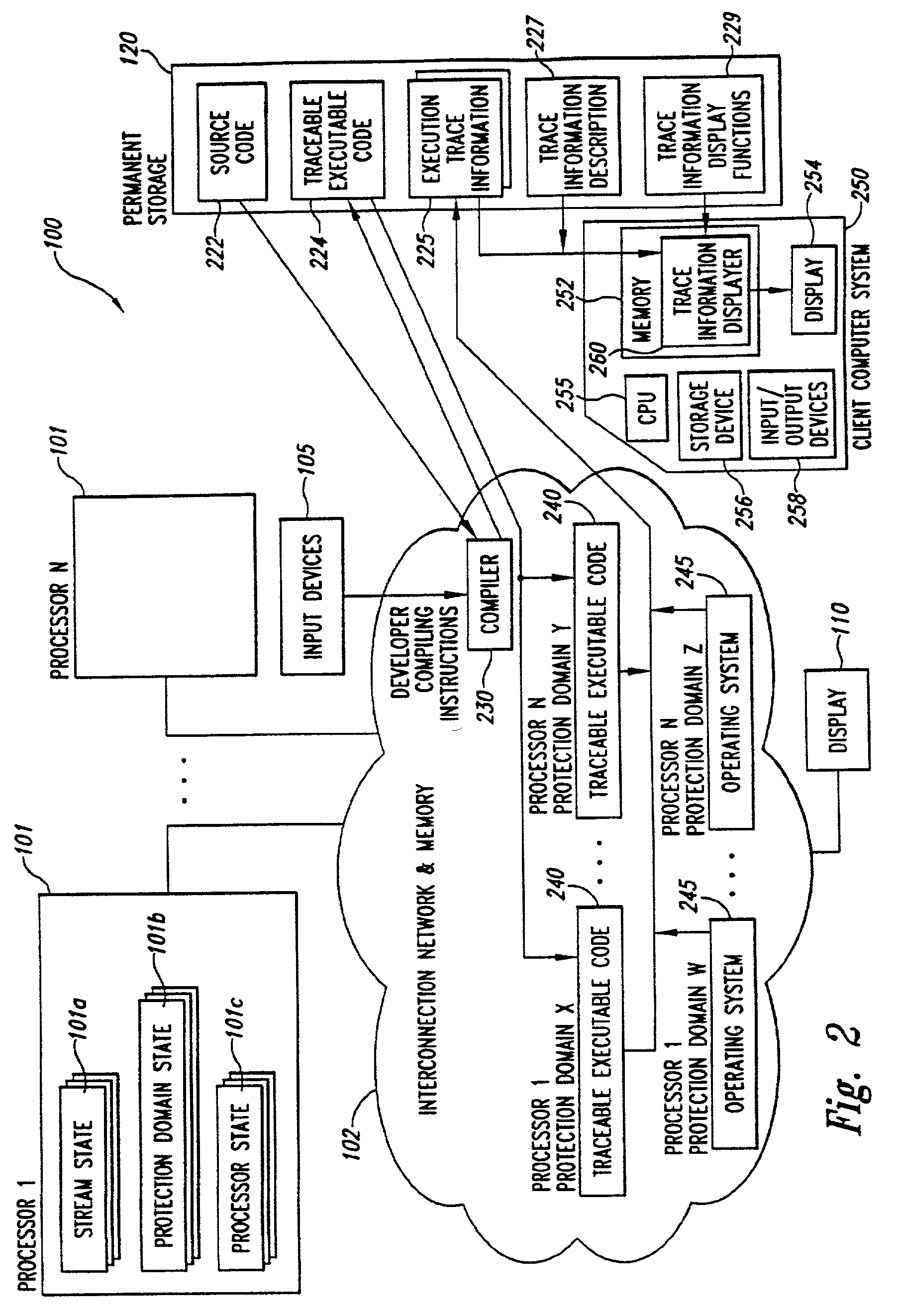
Parallelism performance analysis based on execution trace information
A system for conducting performance analysis for executing tasks. The analysis involves generating a variety of trace information related to performance measures, including parallelism-related information, during execution of the task. In order to generate the trace information, target source code of interest is compiled in such a manner that executing the resulting executable code will generate execution trace information composed of a series of events. Each event stores trace information related to a variety of performance measures for the one or more processors and protection domains used. After the execution trace information has been generated, the system can use that trace information and a trace information description file to produce useful performance measure information. The trace information description file contains information that describes the types of execution events as well as the structure of the stored information. The system uses the trace information description file to organize the information in the trace information file, extracts a variety of types of performance measure information from the organized trace information, and formats the extracted information for display. The system can use default or user-defined functions to extract and format trace information for display. After the system displays one or more types of performance measure information, a user of the system can then interact with the system in a variety of ways to obtain other useful performance analysis information.
Owner:CRAY
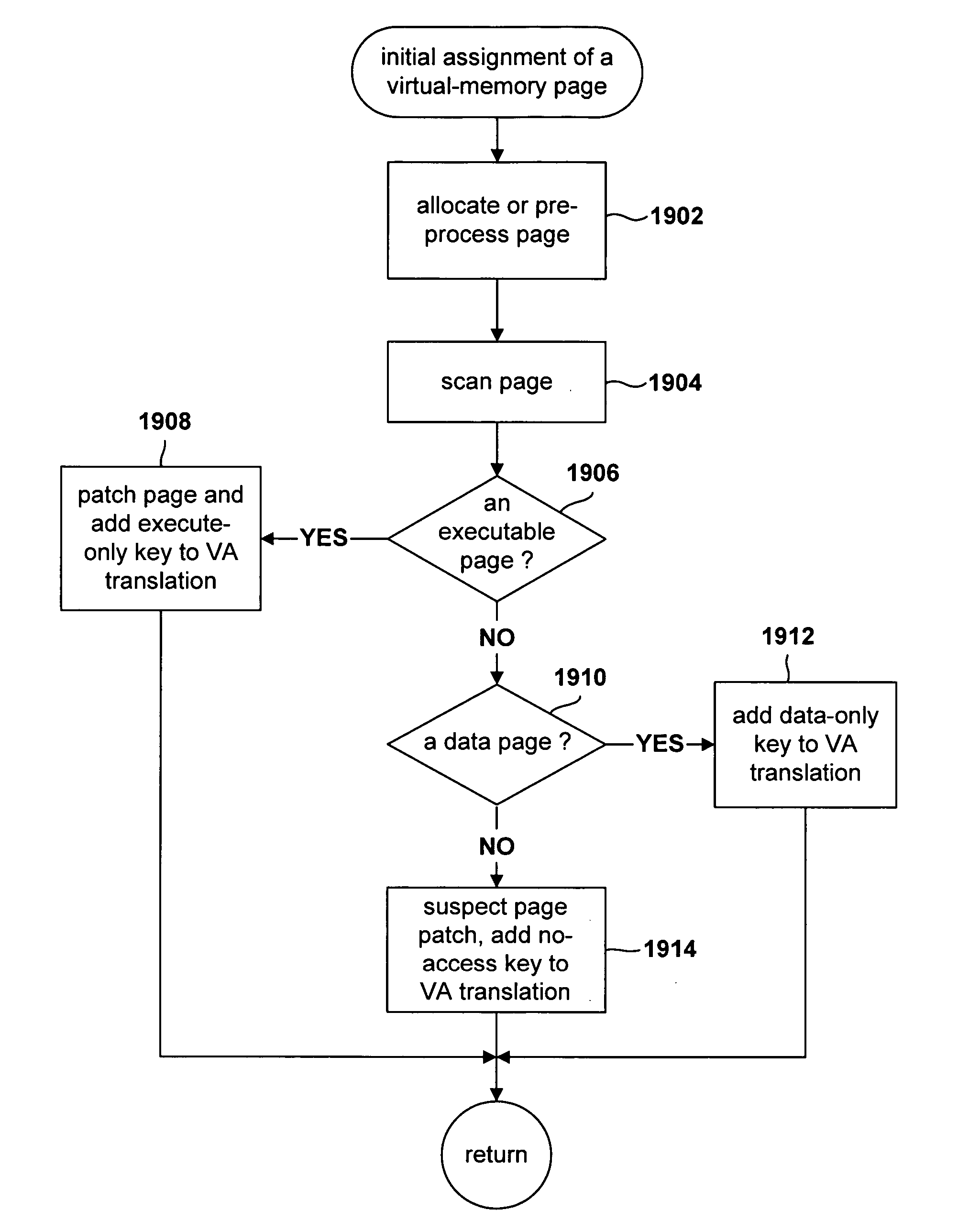
Method for monitoring access to virtual memory pages
InactiveUS20060036830A1Internal/peripheral component protectionMemory systemsVirtual memoryOperational system
Various embodiments of the present invention are directed to efficient methods for virtual-machine monitors to detect, at run time, initial attempts by guest operating systems and other higher-level software to access or execute particular instructions or values corresponding to the particular instructions, that, when accessed for execution, need to be emulated by a virtual-machine monitor, rather than directly accessed by guest operating systems. In certain embodiments of the present invention, the virtual-machine monitor assigns various guest-operating-system-code-containing memory pages to one of a small number of protection-key domains. By doing so, the virtual-machine monitor can arrange for any initial access to the memory pages assigned to the protection-key domains to generate a key-permission fault, after which the key-permission-fault handler of the virtual-machine monitor is invoked to arrange for subsequent, efficient access or emulation of access to the protected pages. In alternative embodiments, protection domains can be implemented by using page-level access rights or translation-lookaside-buffer entry fields.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
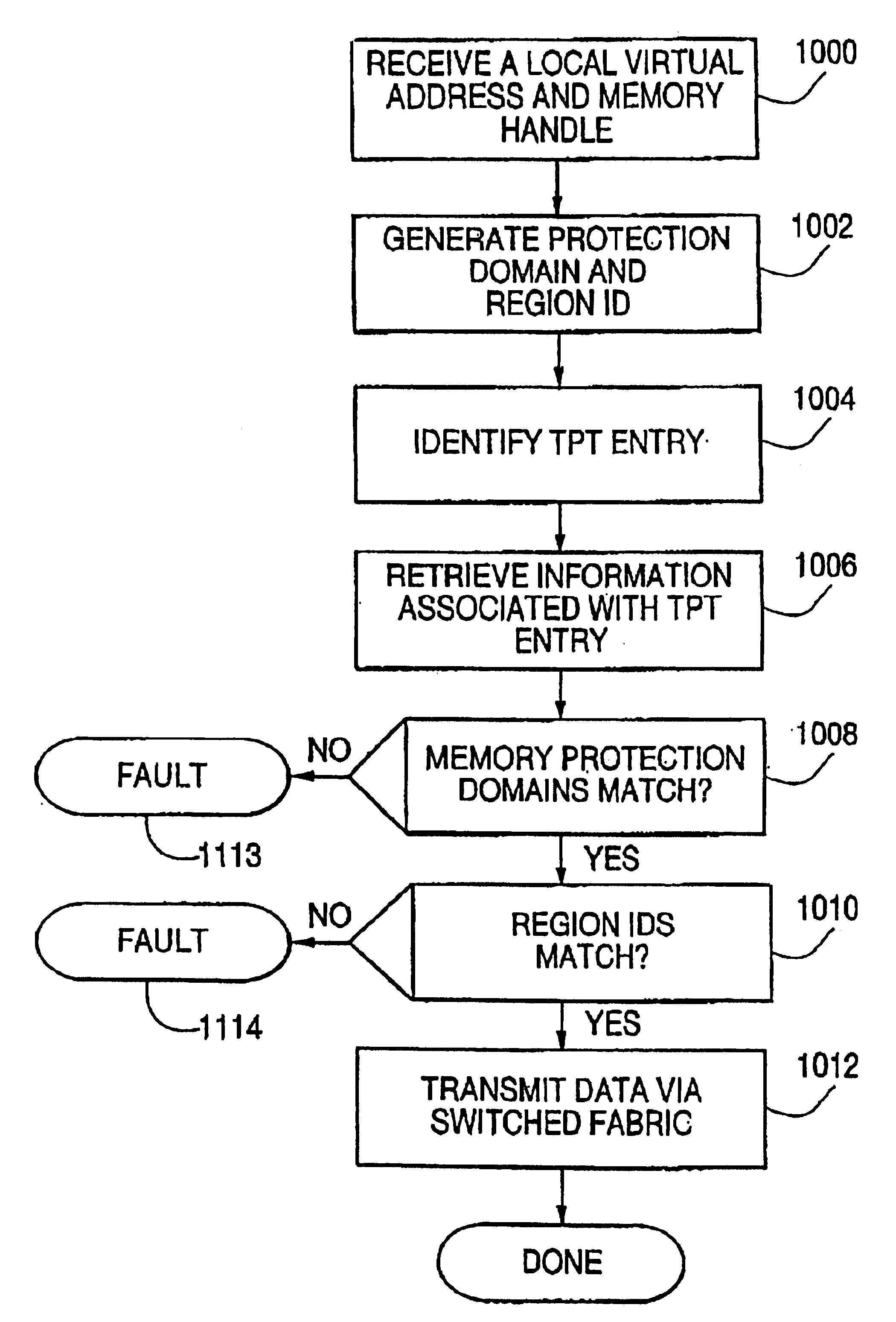
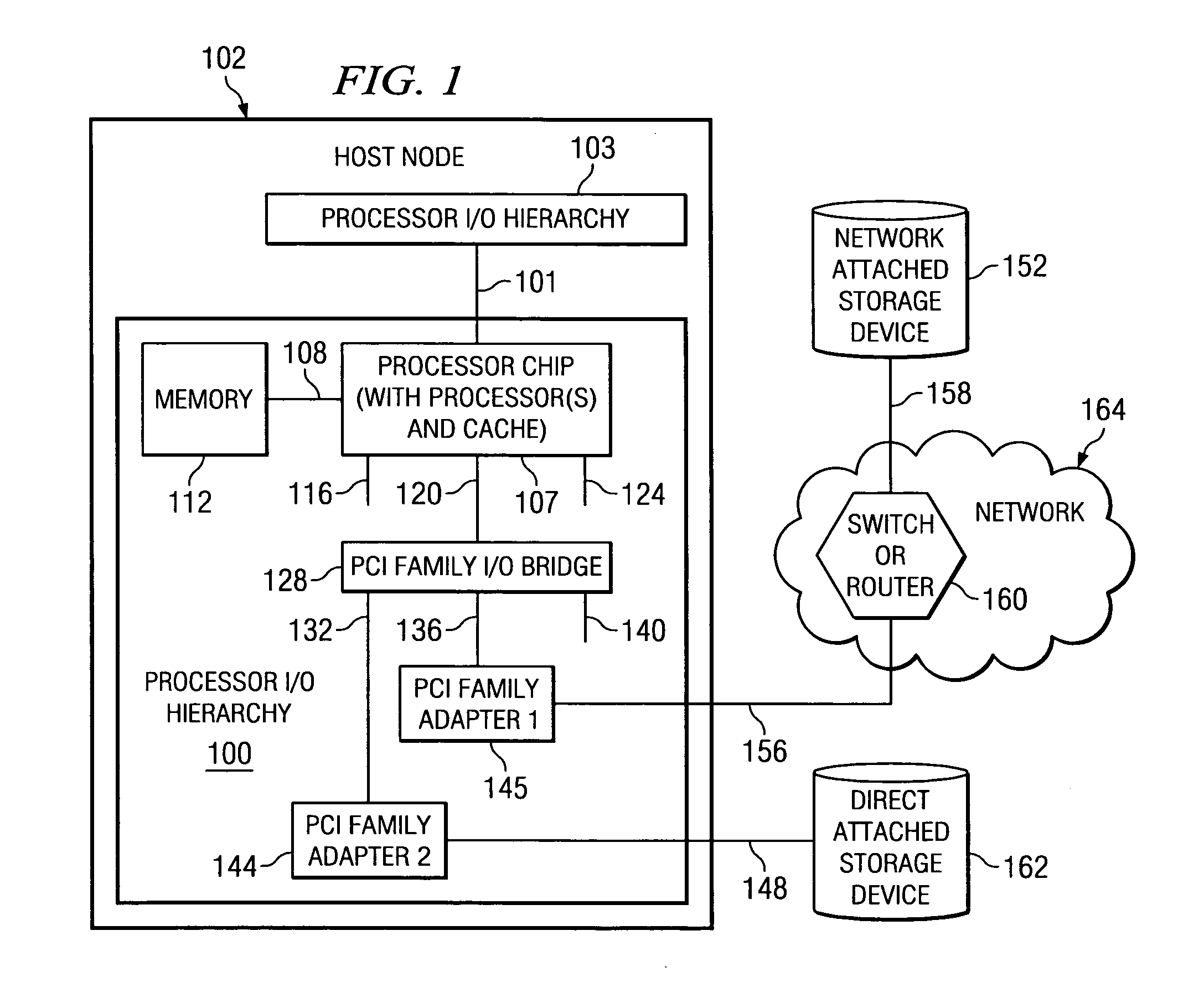
Translation and protection table and method of using the same to validate access requests
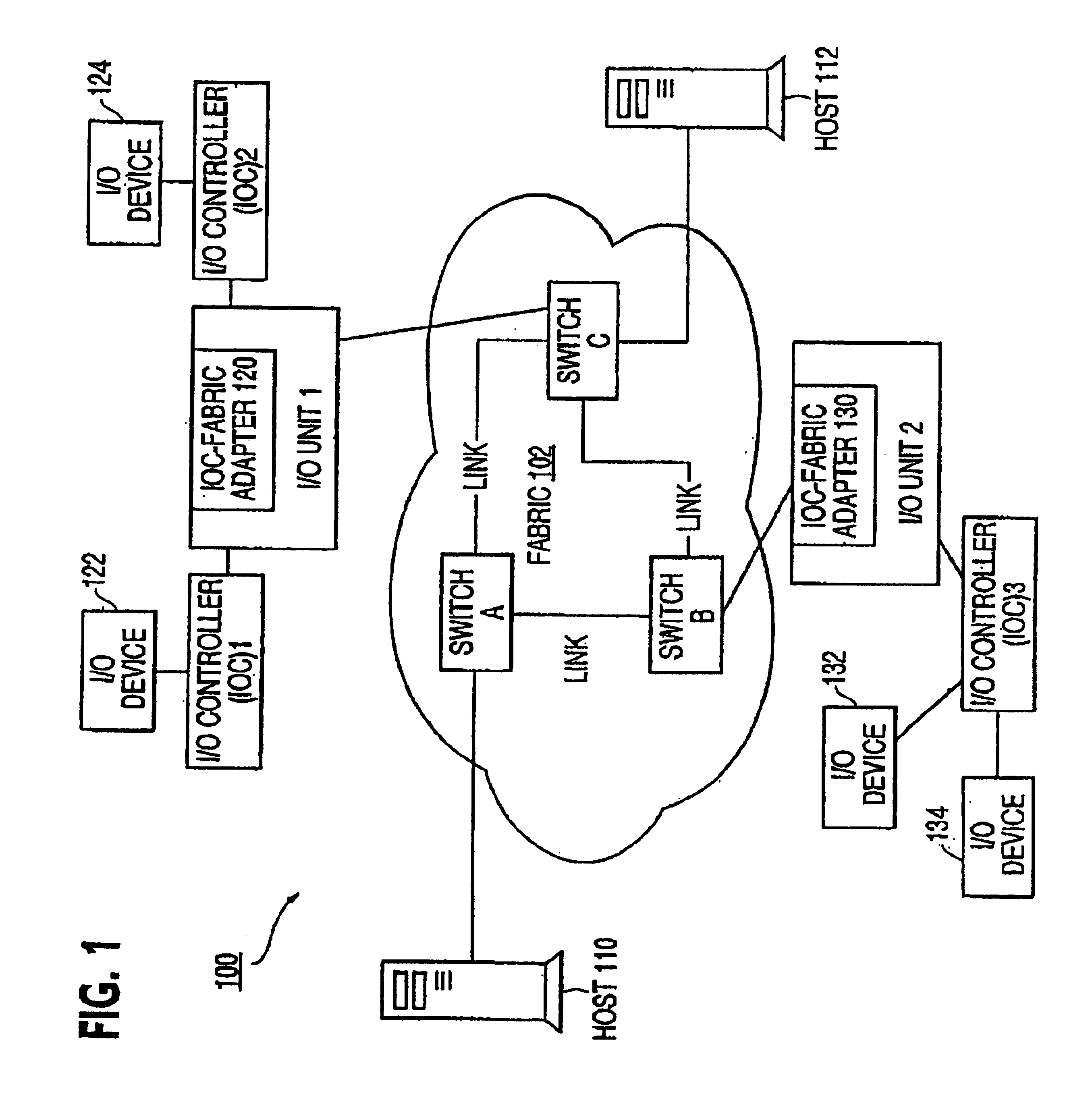
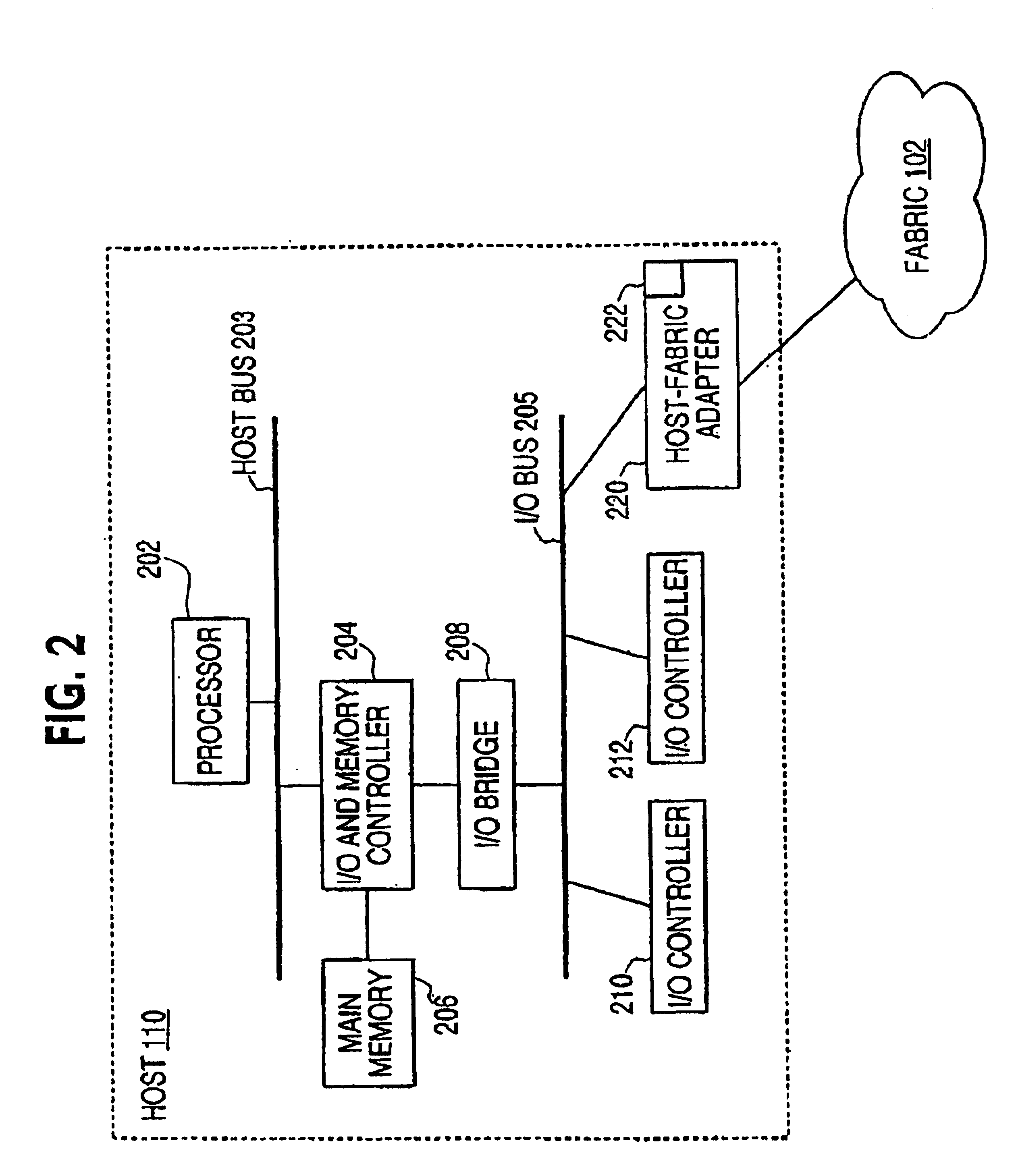
InactiveUS6859867B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationUnauthorized memory use protectionProtection domainHost memory
A host may be coupled to a switched fabric and include a processor, a host memory coupled to the processor and a host-fabric adapter coupled to the host memory and the processor and be provided to interface with the switched fabric. The host-fabric adapter accesses a translation and protection table from the host memory for a data transaction. The translation and protection table entries include a region identifier field and a protection domain field used to validate an access request.
Owner:INTEL CORP
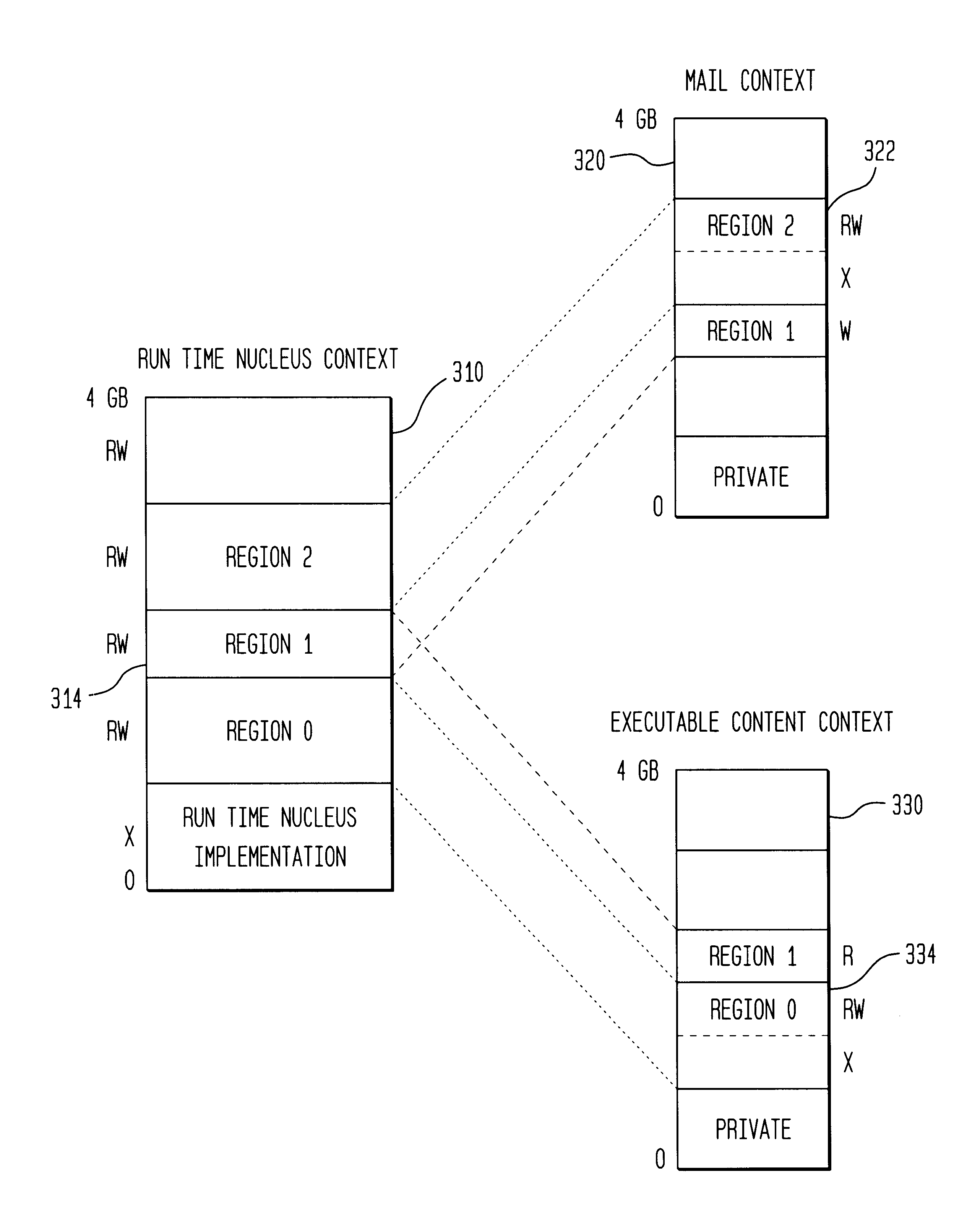
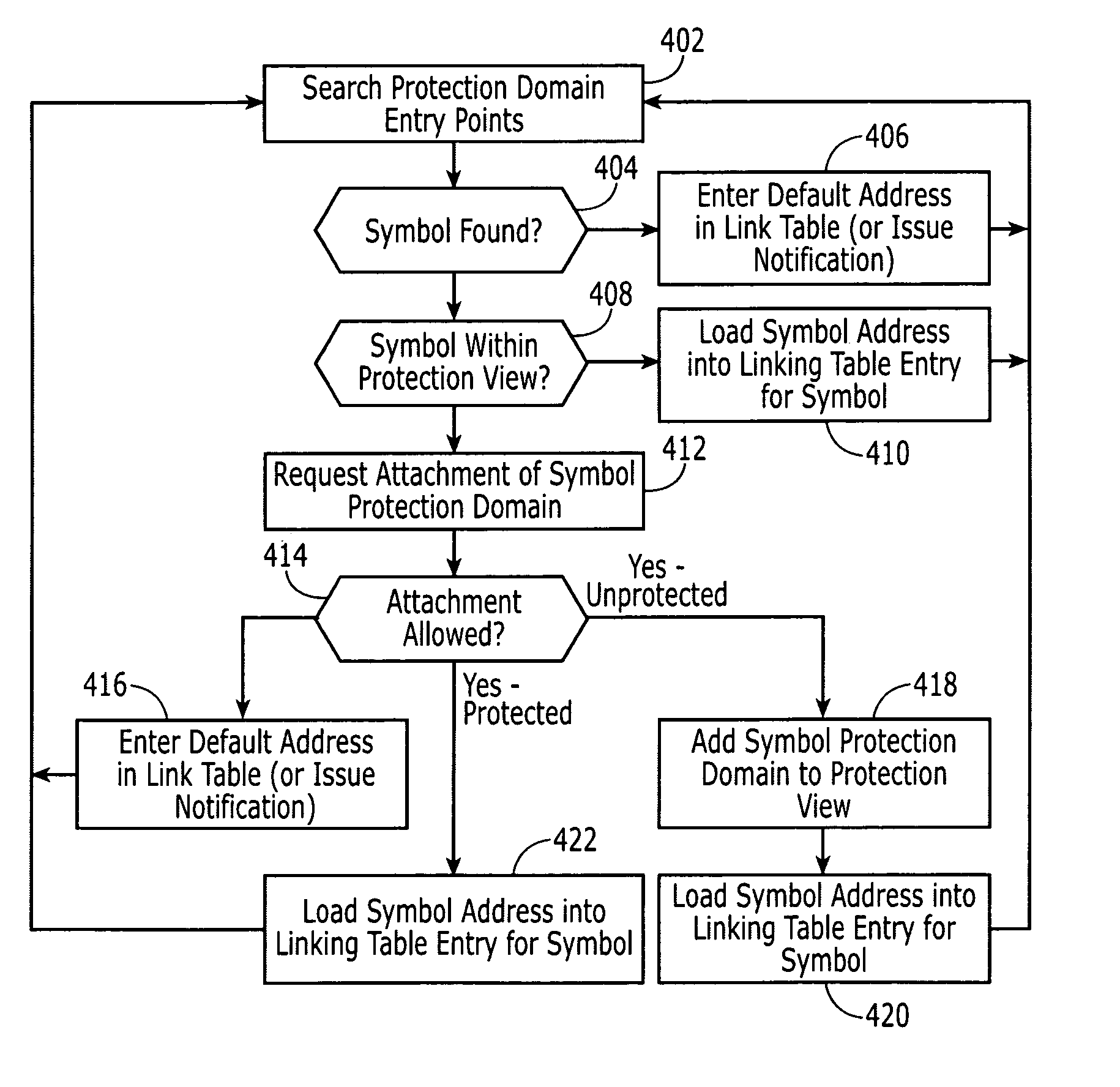
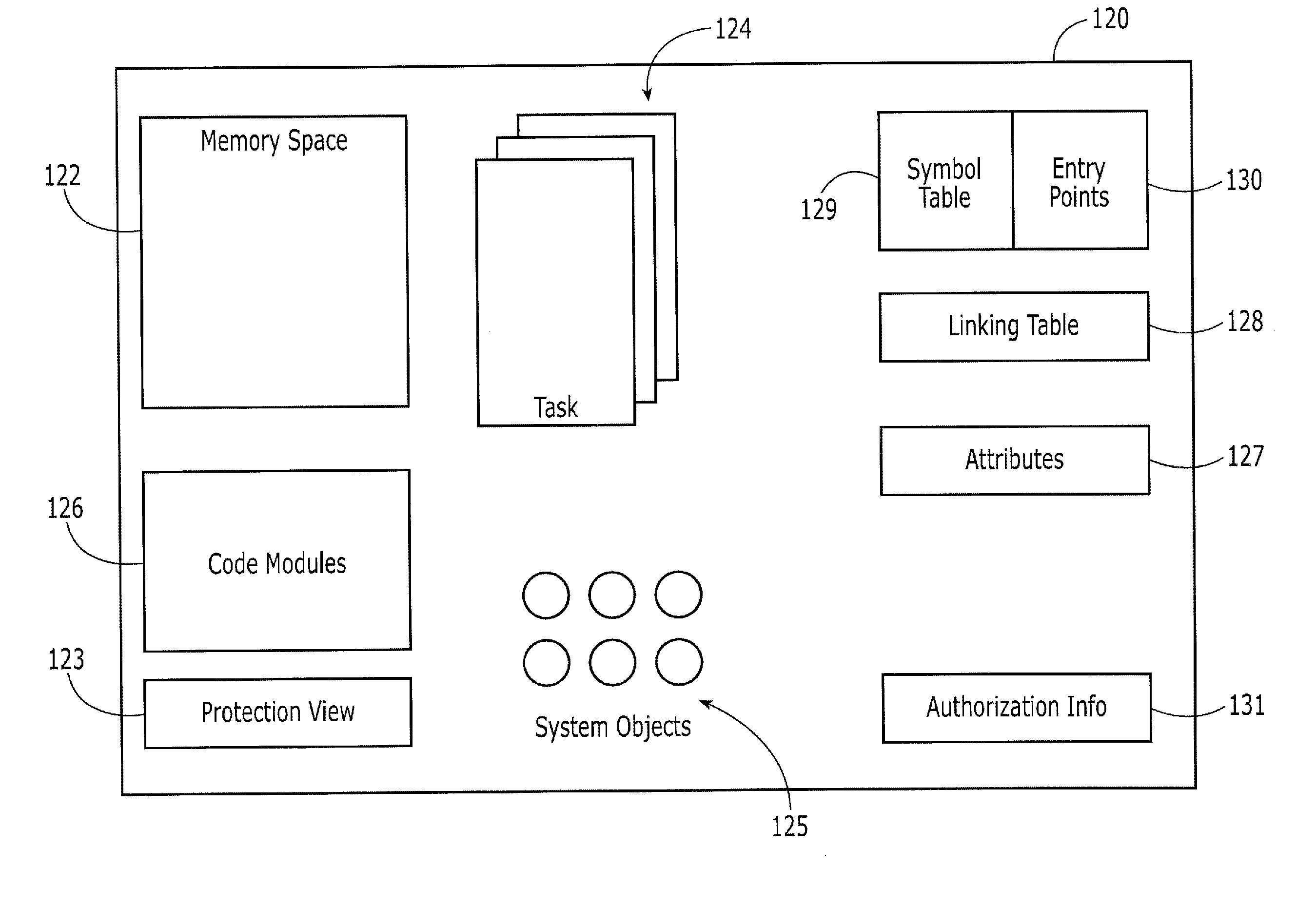
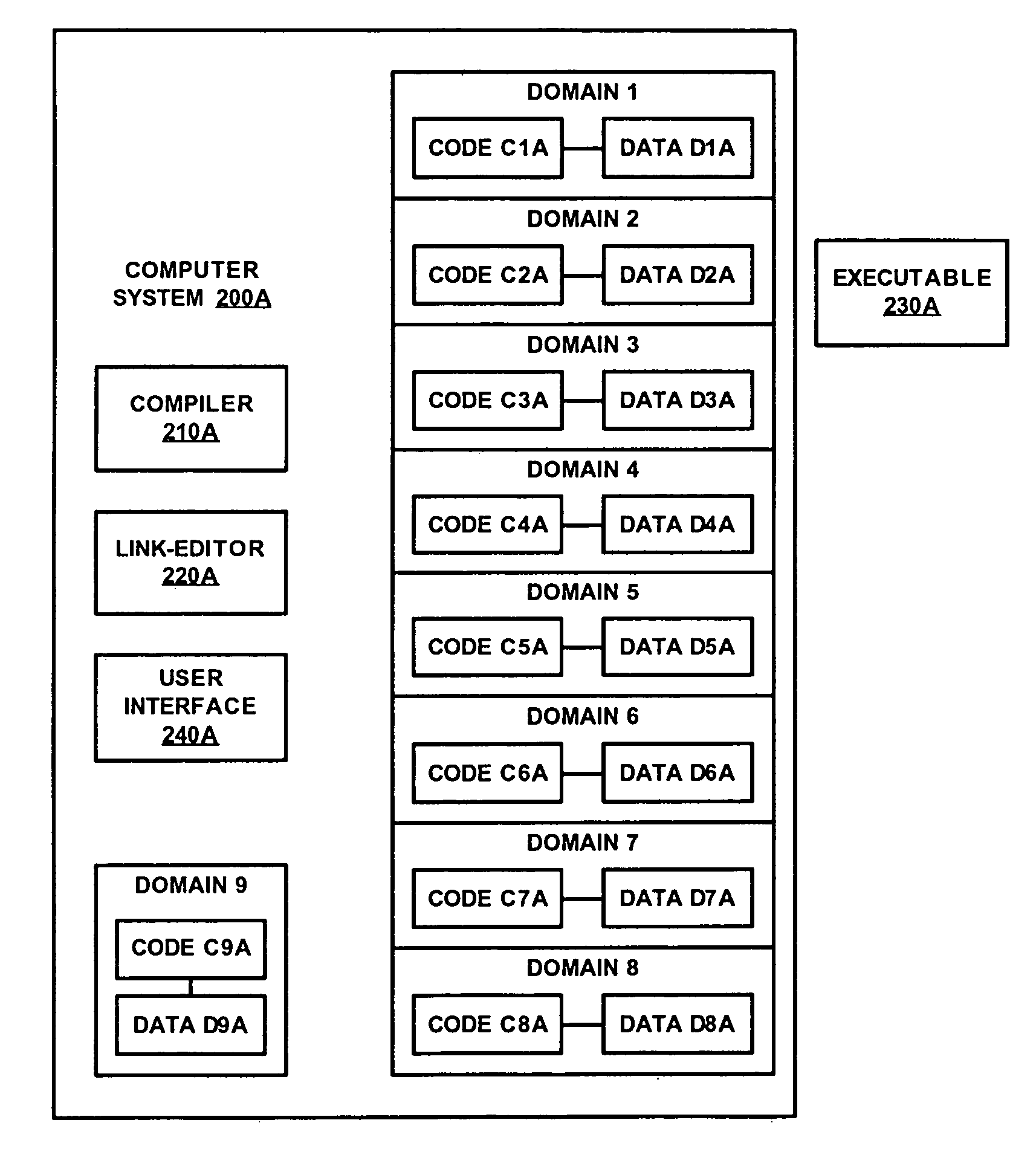
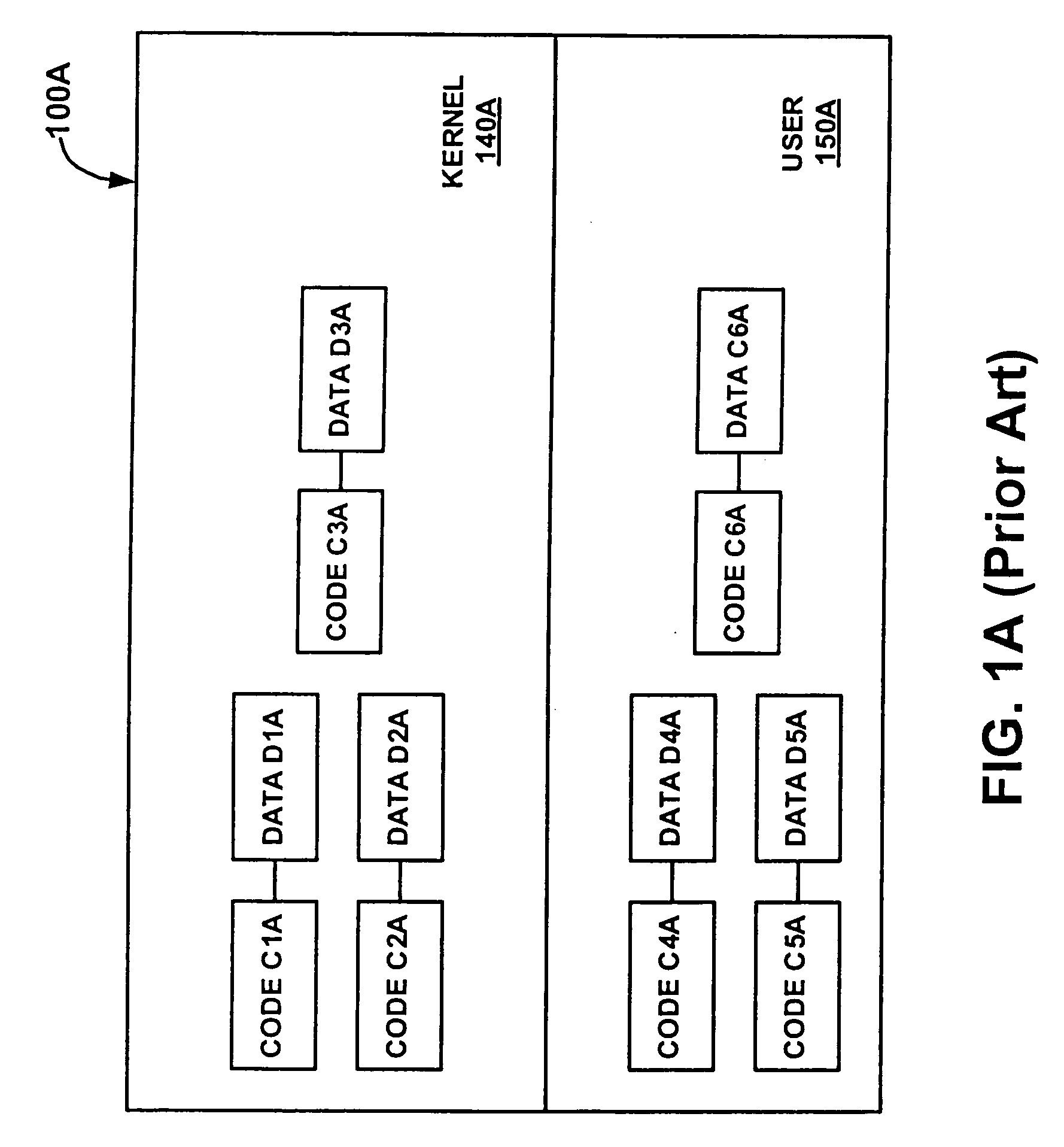
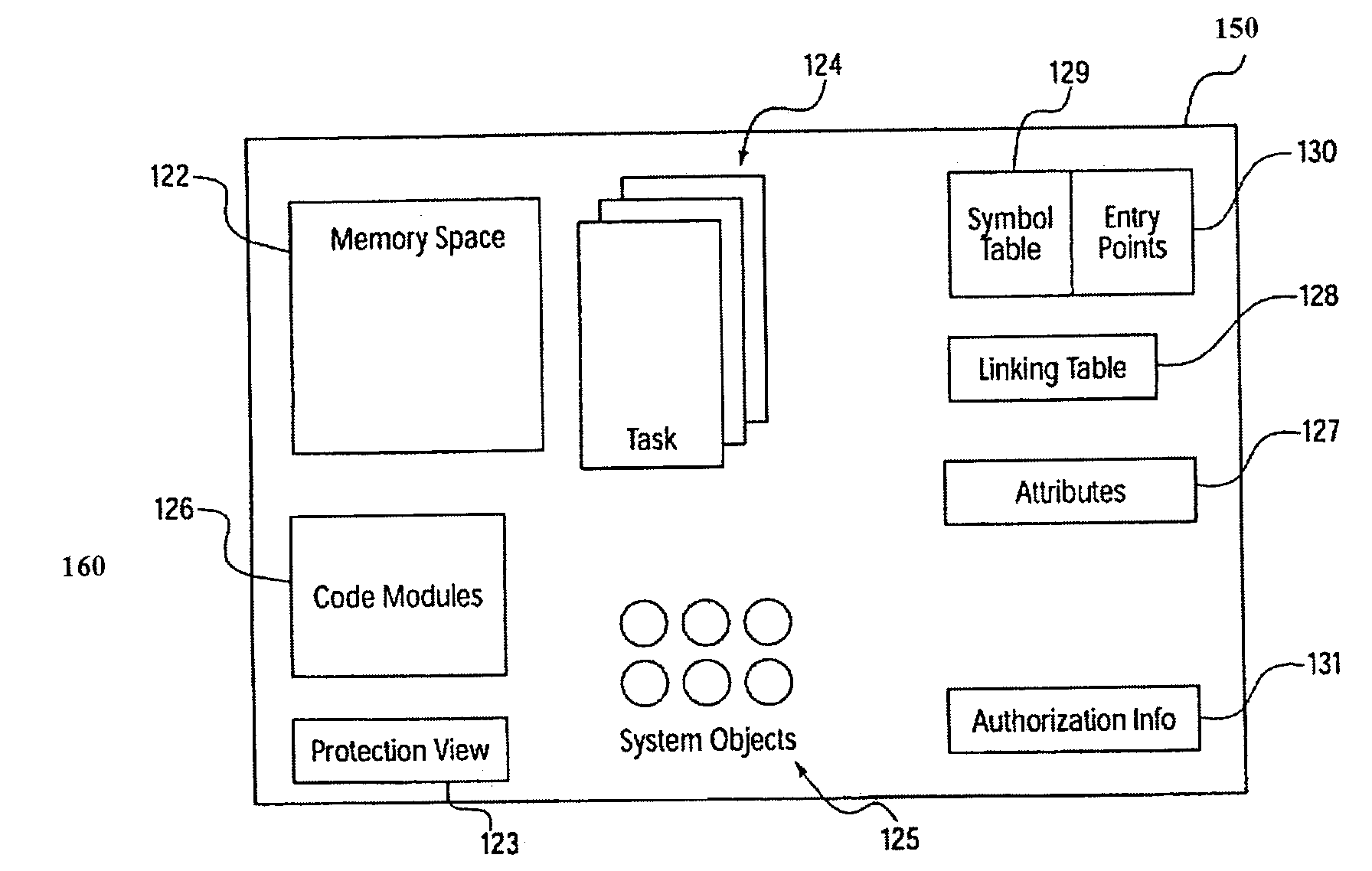
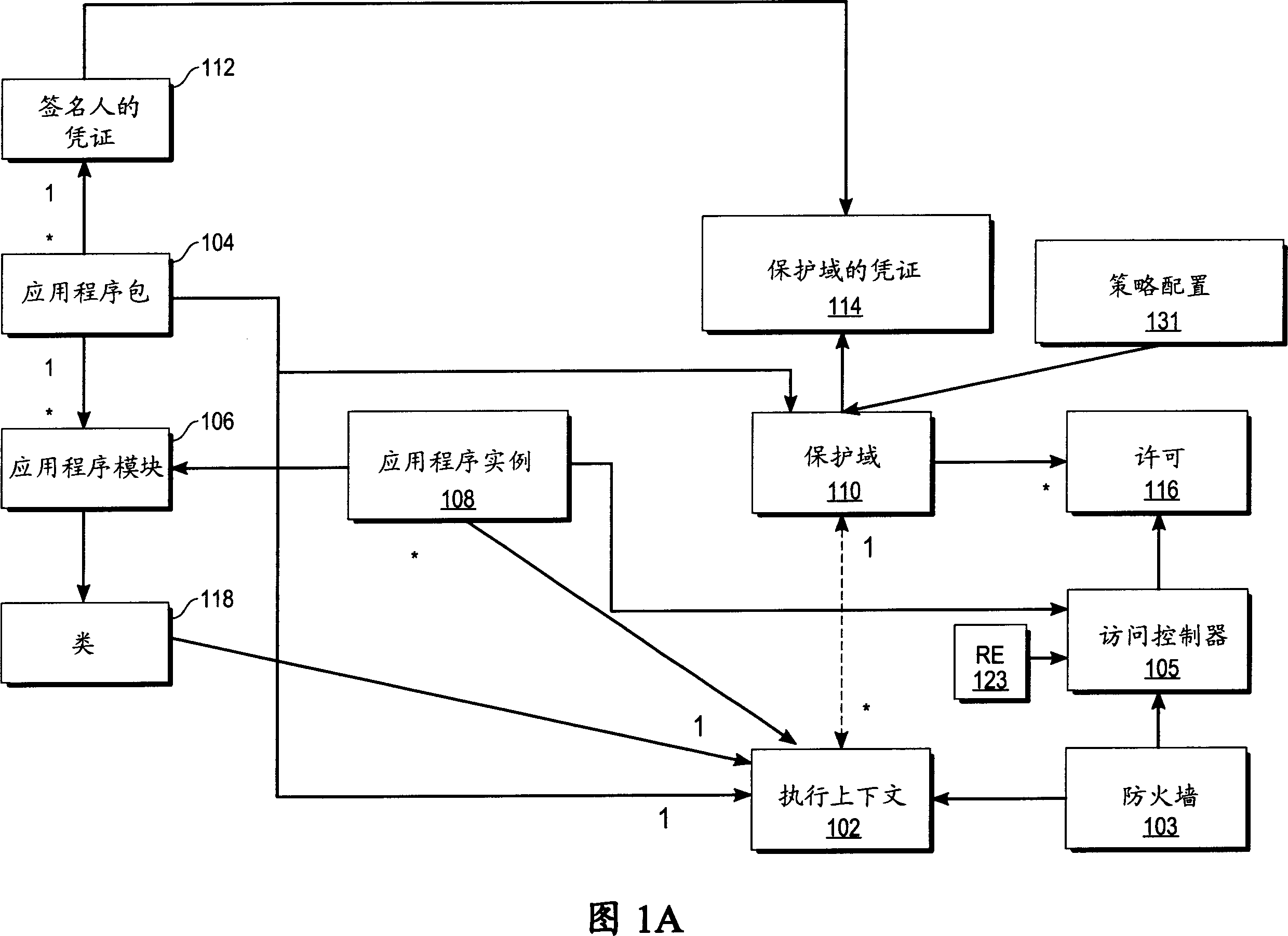
Protection domains for a computer operating system
A protection domain system is implemented to provide protection for applications executing in a computing environment. Protection domains are allocated system resources and may contain executing tasks. The protection domain system may allow tasks to access resources in other protection domains to which attachments have been made. Attachment is transparent to the software developer. The protection domain system provides flexibility in implementing operating system services and defining protection hierarchies.
Owner:WIND RIVER SYSTEMS
Internet server access control and monitoring systems
This invention relates to methods for controlling and monitoring access to network servers. In particular, the process described in the invention includes client-server sessions over the Internet. In this environment, when the user attempts to access an access-controlled file, the server subjects the request to a secondary server which determines whether the client has an authorization or valid account. Upon such verification, the user is provided with a session identification which allows the user to access to the requested file as well as any other files within the present protection domain.
Owner:SOVERAIN IP LLC
Protection Domains for a Computer Operating System
A protection domain system is implemented to provide protection for applications executing in a computing environment. Protection domains are allocated system resources and may contain executing tasks. The protection domain system may allow tasks to access resources in other protection domains to which attachments have been made. Attachment is transparent to the software developer. The protection domain system provides flexibility in implementing operating system services and defining protection hierarchies.
Owner:WIND RIVER SYSTEMS
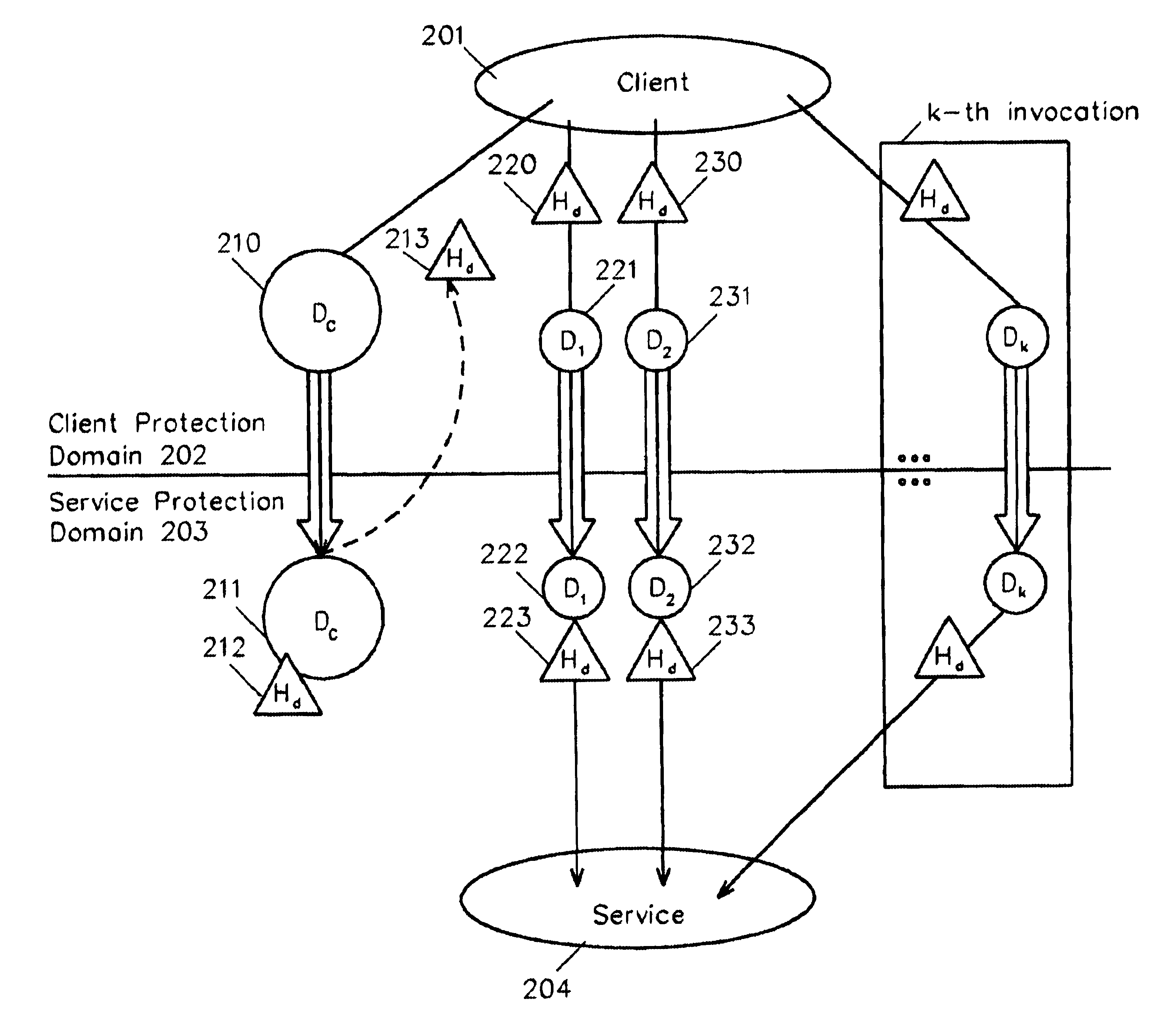
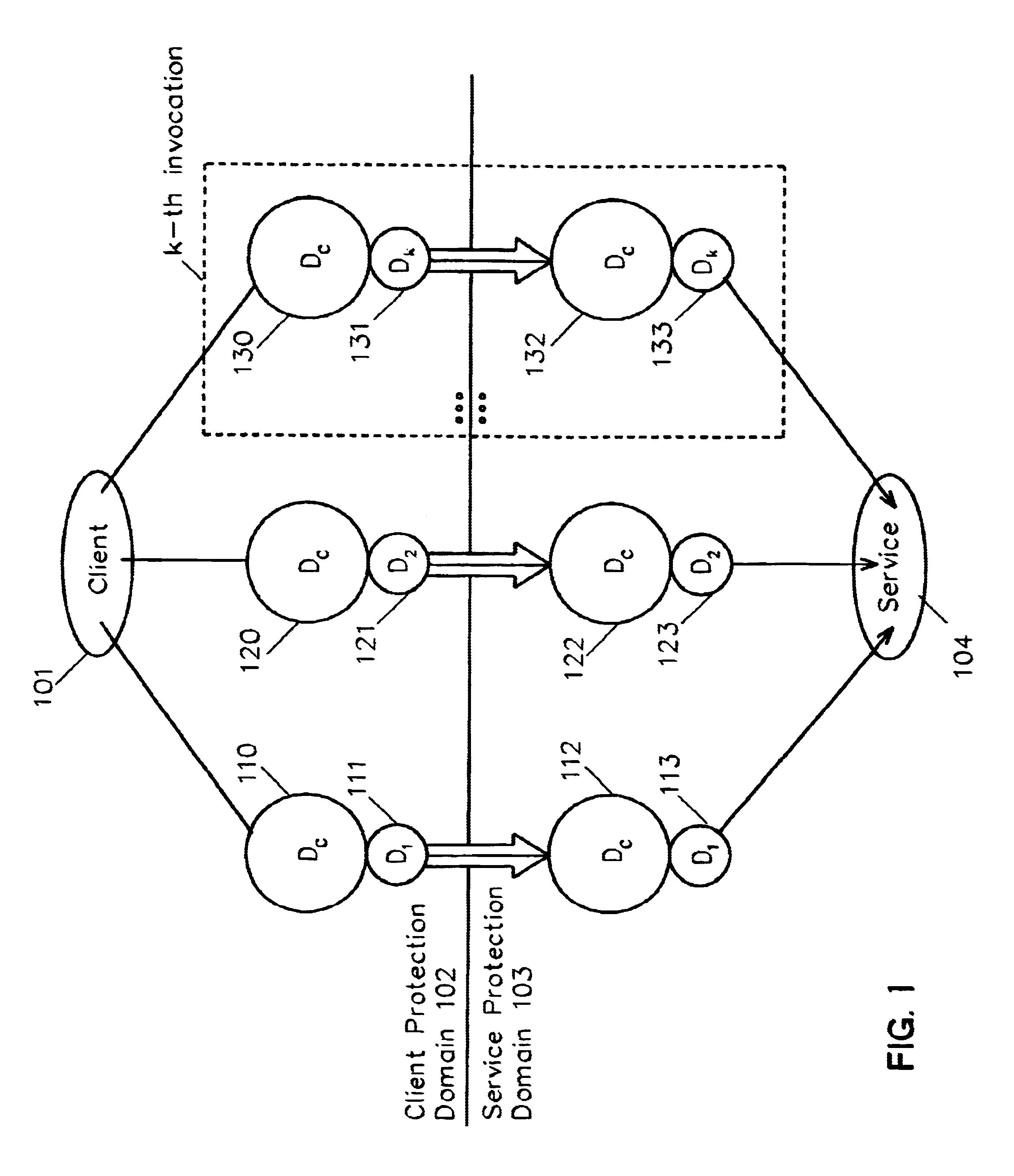
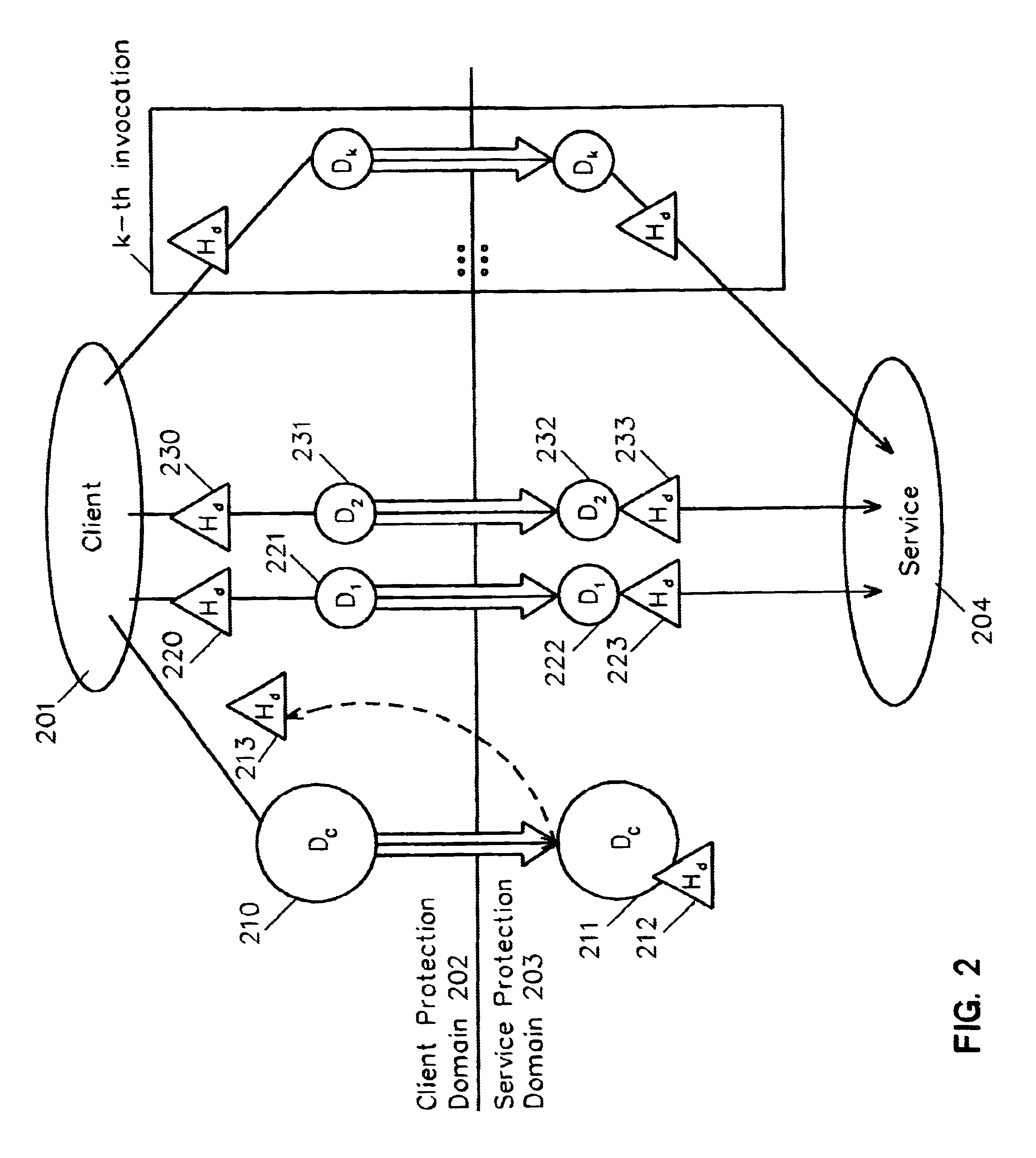
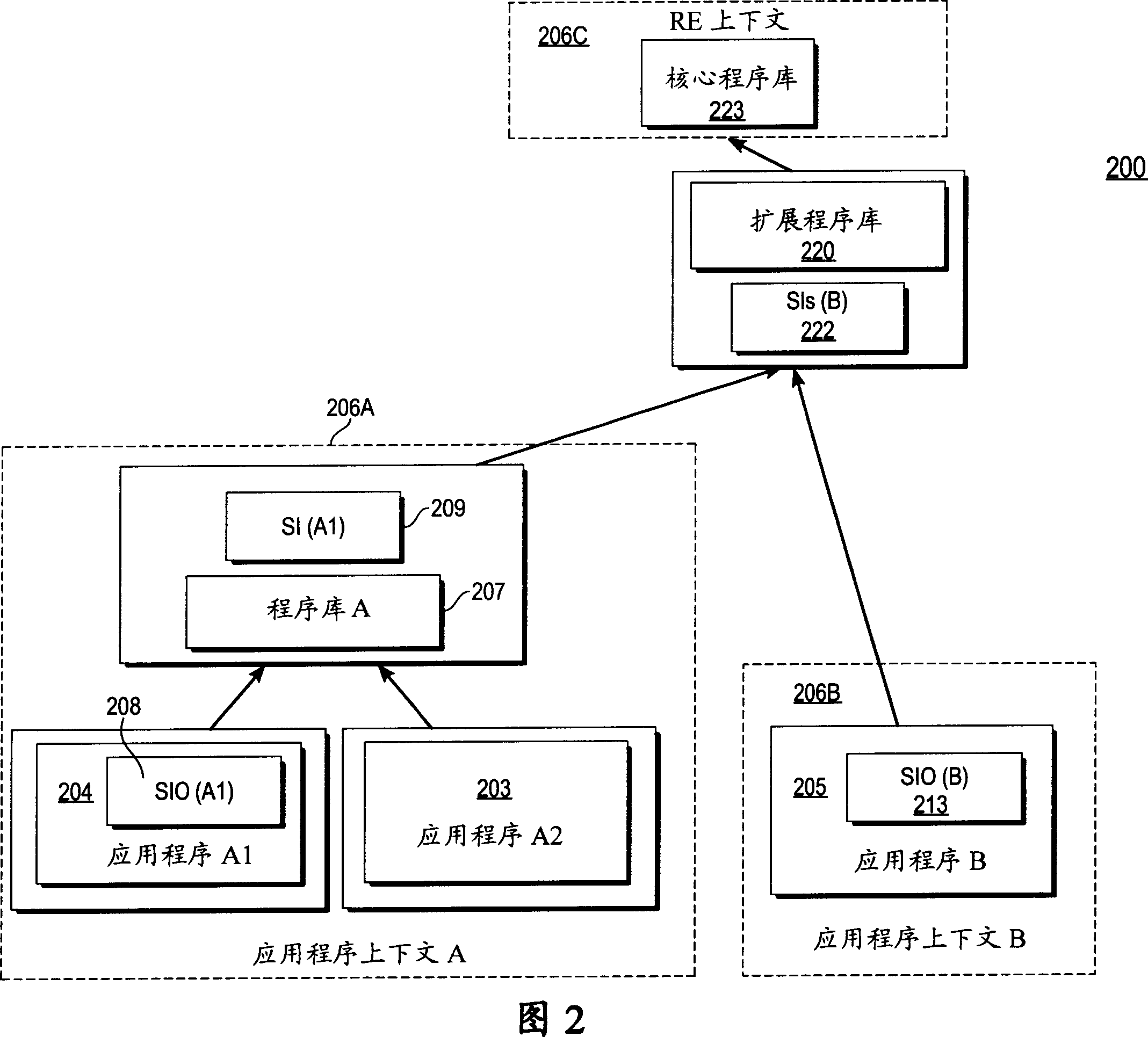
Method and system for cross-domain service invocation using a single data handle associated with the stored common data and invocation-specific data
InactiveUS6934757B1Eliminate needInterprogram communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsComposite servicesService domain
A system and method whereby a client can transfer data to a service on the same or another protection domain and obtain a handle to it, the handle being defined as any mutually agreed-upon token that refers to the data, and which is usually much shorter than the data. The handle may then be passed to a service in lieu of again transferring the data. For example, in the case of a client sending the same data to multiple destinations, the invention allows the data to be transferred from the client protection domain to the service protection domain once using the data transfer operation. The client can then call the communication service any number of times by passing a handle to the instance of the data in the service protection domain, thus obviating the need to repeatedly transfer the data between the client and the service. An alternative embodiment allows the client to aggregate service invocations which are to operate on common data and to transfer a composite service invocation to a service domain using the data handle. The invention can be applied among local entities within one protection domain, between two protection domains at one location, between remote protection domains, across networks, between clients and routers, etc.
Owner:IBM CORP
Parallelism performance analysis based on execution trace information
A system for conducting performance analysis for executing tasks. The analysis involves generating a variety of trace information related to performance measures, including parallelism-related information, during execution of the task. In order to generate the trace information, target source code of interest is compiled in such a manner that executing the resulting executable code will generate execution trace information composed of a series of events. Each event stores trace information related to a variety of performance measures for the one or more processors and protection domains used. After the execution trace information has been generated, the system can use that trace information and a trace information description file to produce useful performance measure information. The trace information description file contains information that describes the types of execution events as well as the structure of the stored information. The system uses the trace information description file to organize the information in the trace information file, extracts a variety of types of performance measure information from the organized trace information, and formats the extracted information for display. The system can use default or user-defined functions to extract and format trace information for display. After the system displays one or more types of performance measure information, a user of the system can then interact with the system in a variety of ways to obtain other useful performance analysis information.
Owner:CRAY
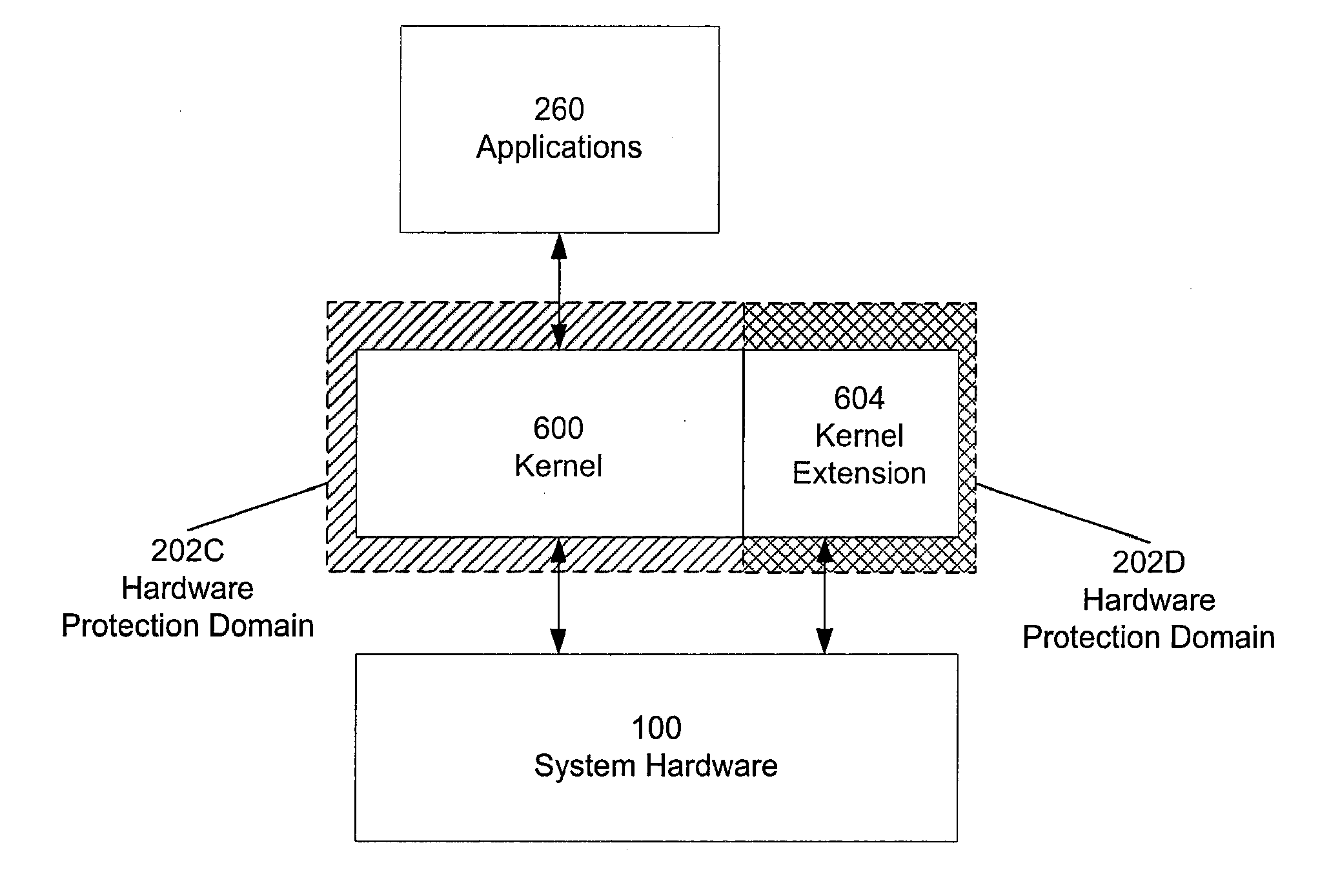
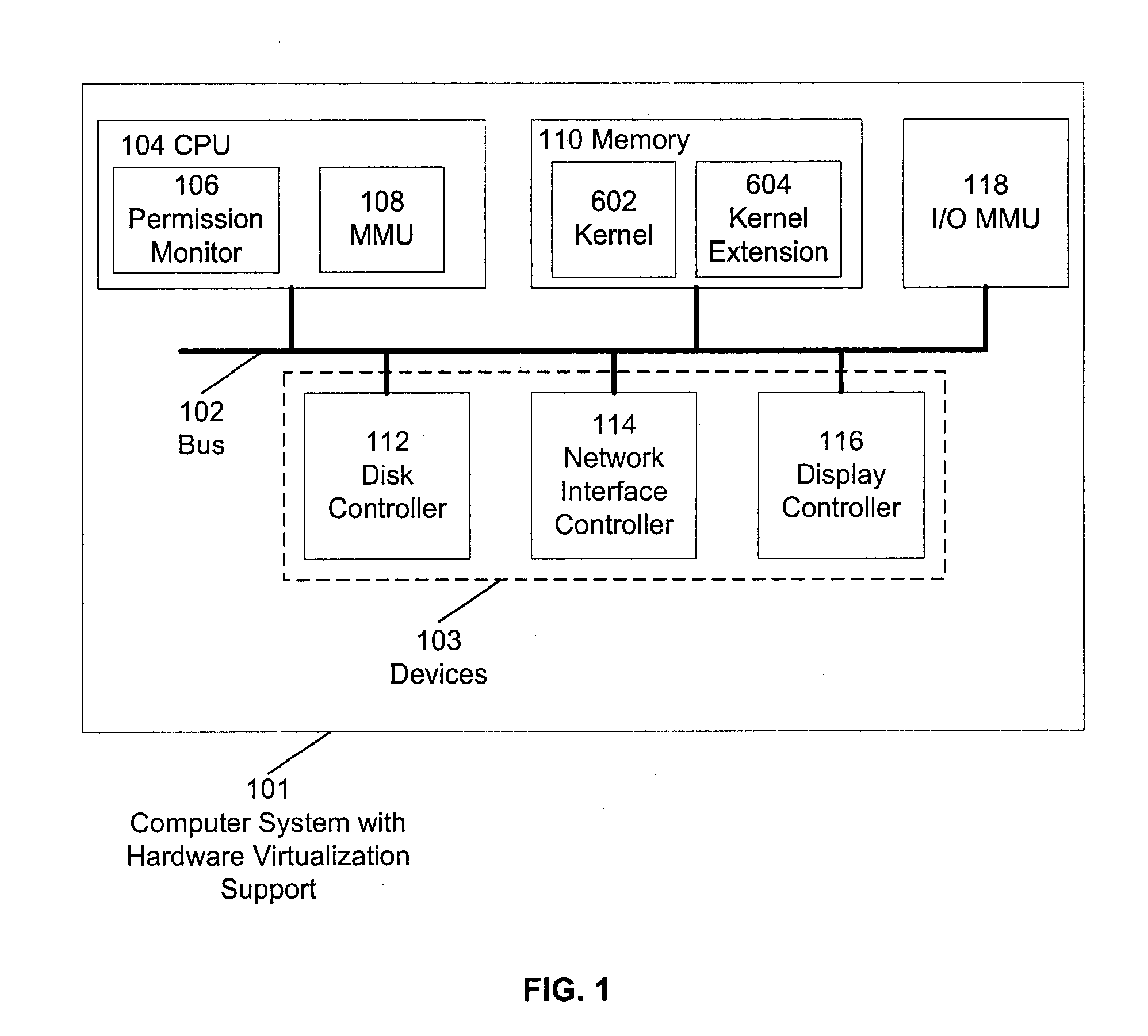
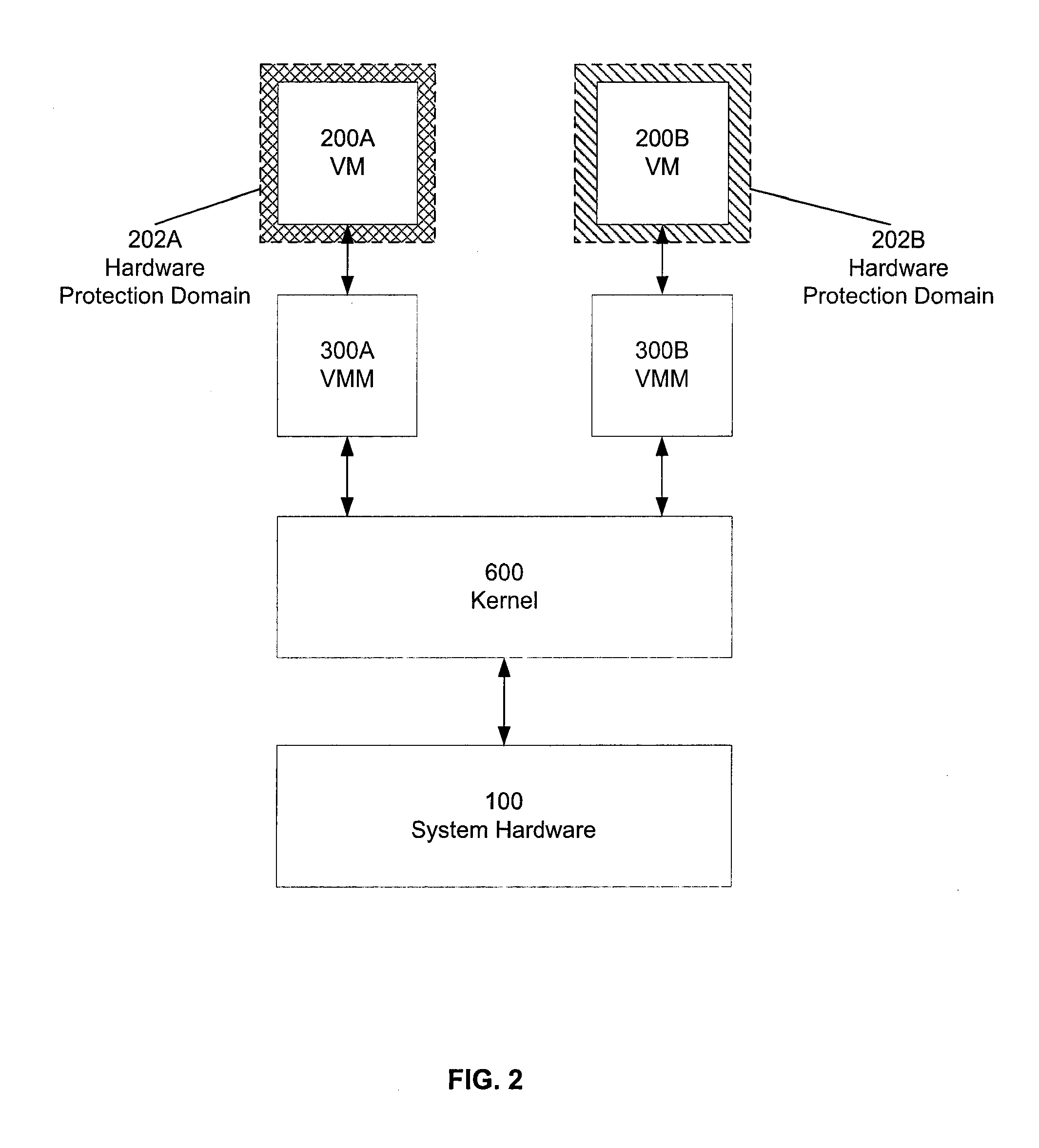
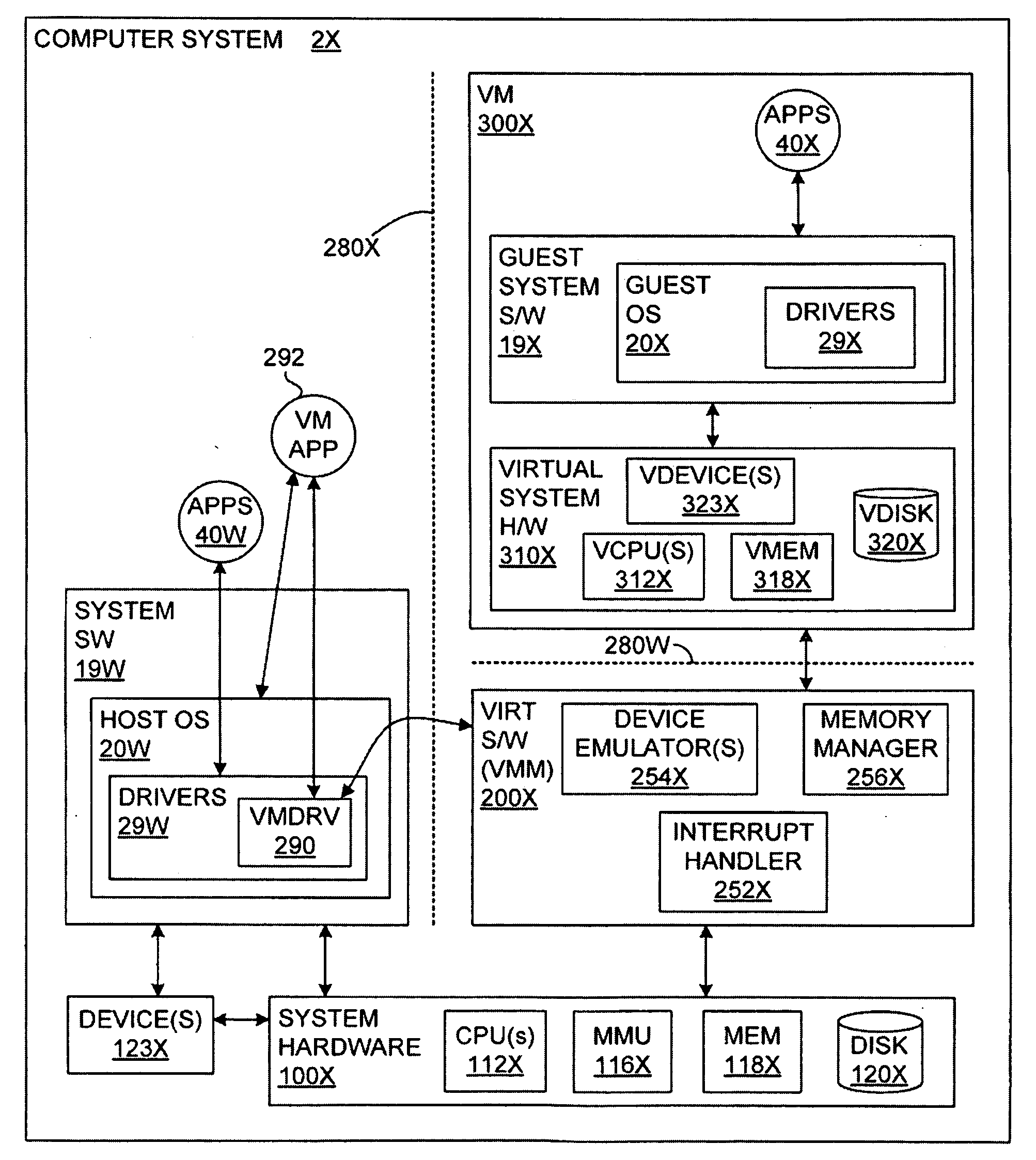
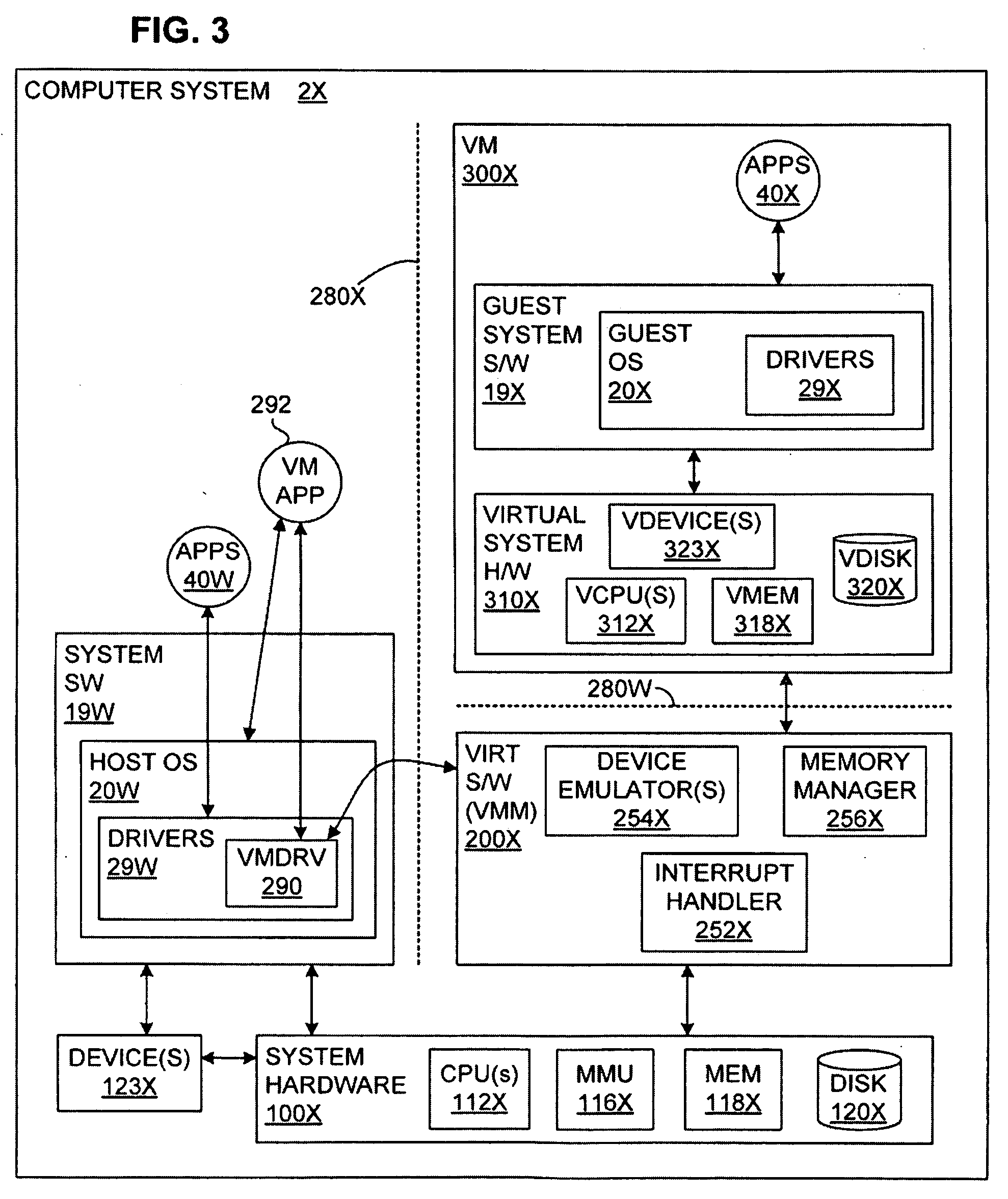
Virtualization Hardware For Device Driver Isolation
ActiveUS20080148048A1Solve insufficient computing resourcesSolve insufficient resourcesMultiprogramming arrangementsPlatform integrity maintainanceVirtualizationComputer resources
Hardware virtualization support is used to isolate kernel extensions. A kernel and various kernel extensions are executed in a plurality of hardware protection domains. Each hardware protection domain defines computer resource privileges allowed to code executing in that hardware protection domain. Kernel extensions execute with appropriate computer resource privileges to complete tasks without comprising the stability of the computer system.
Owner:VMWARE INC
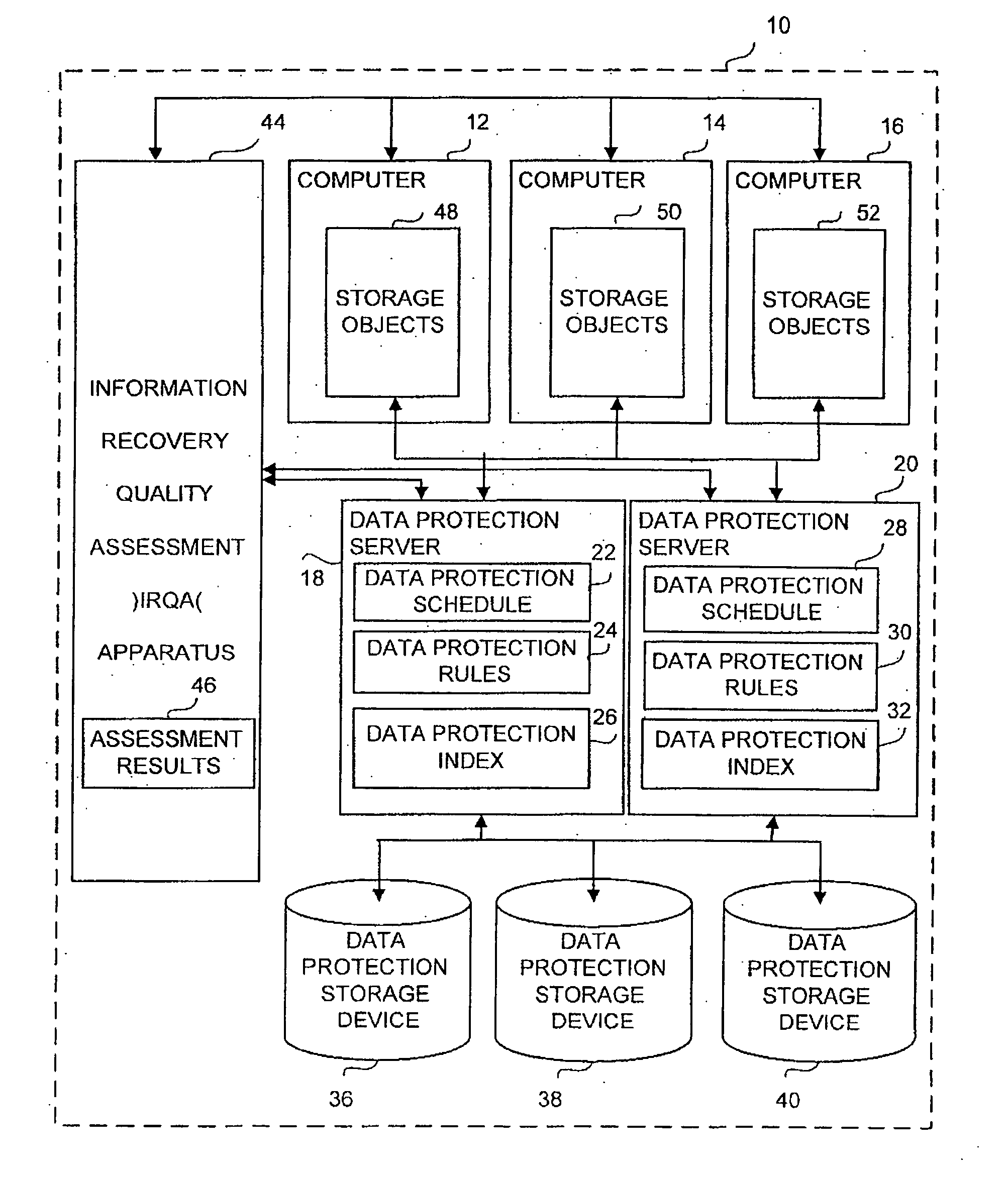
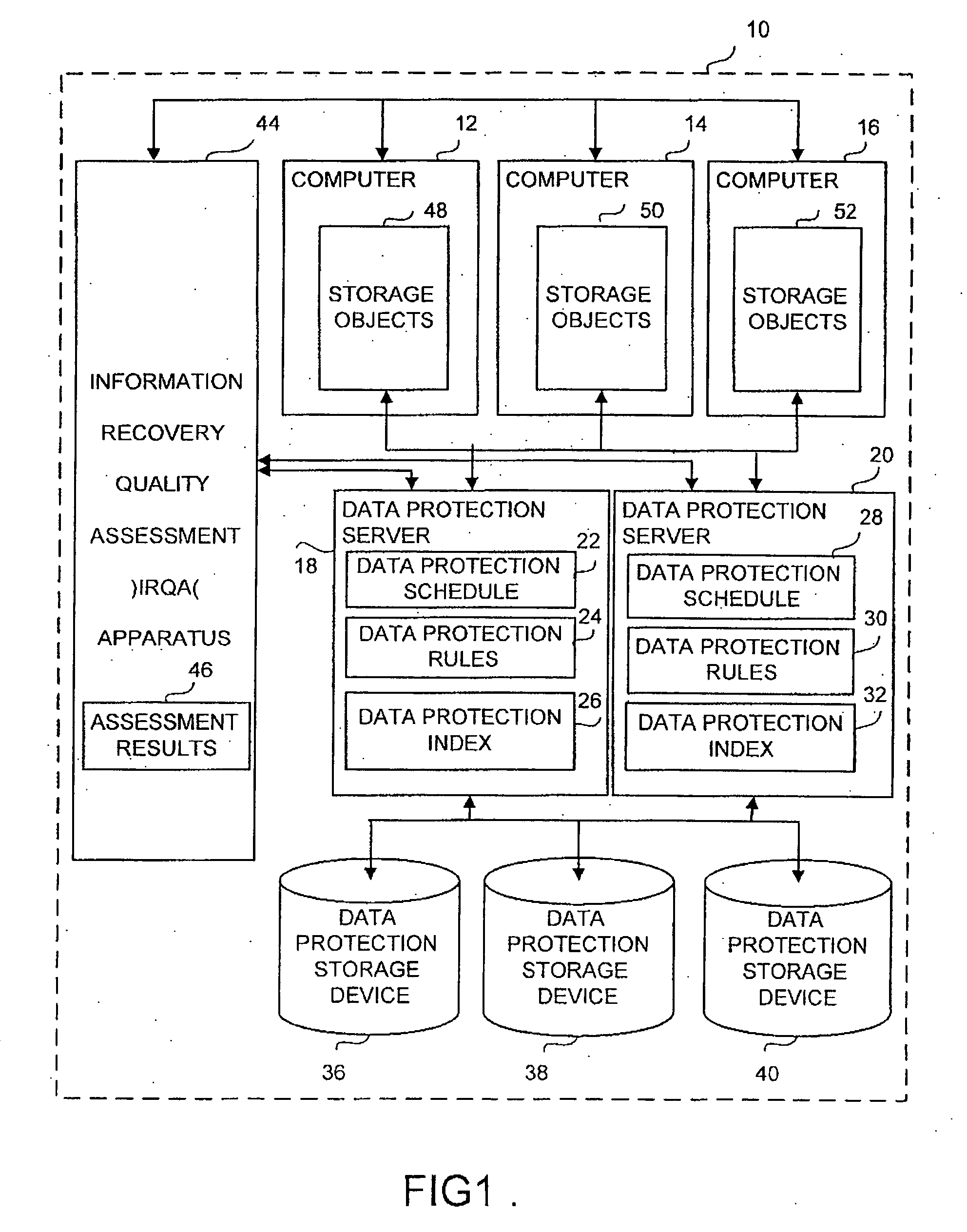
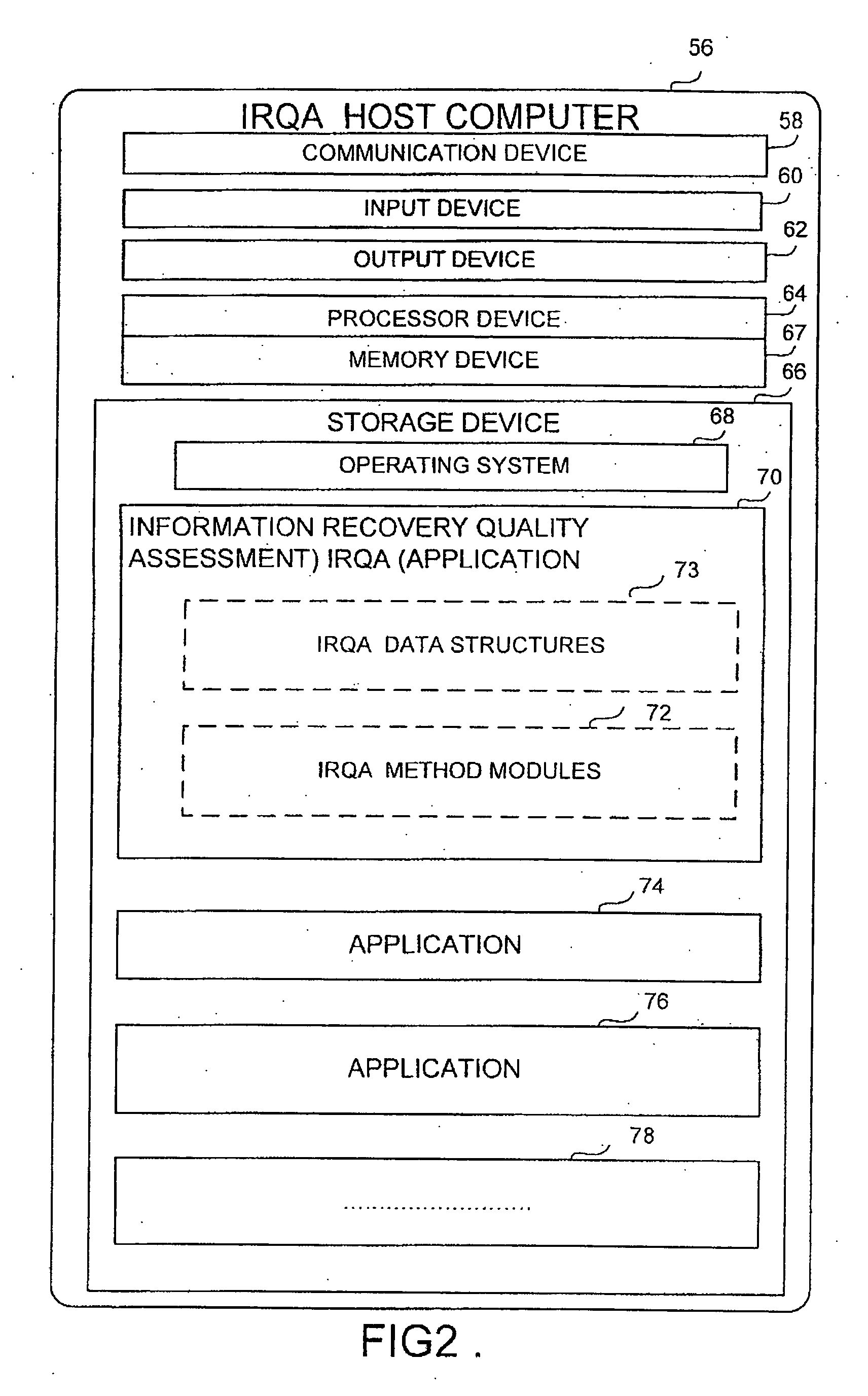
Apparatus and method for information recovery quality assessment in a computer system
ActiveUS20060288183A1Error detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsInformation recoveryProtection domain
An apparatus and method for information recovery quality assessment in a computing environment is disclosed. This includes a group of inter-related software modules and associated data structures that analyze and assess the recoverability of the network data through the data protection configuration setup and a previously performed data protection process. It examines in a comprehensive manner the recoverability perspective across a pre-defined data protection domain, such as a computer network with an organization. The results of the examination provide for the display of inconsistencies of data protection configuration and previously performed data protection processes that consequently result in problems of recovering the network objects in an appropriate manner.
Owner:EMC BENELUX R L
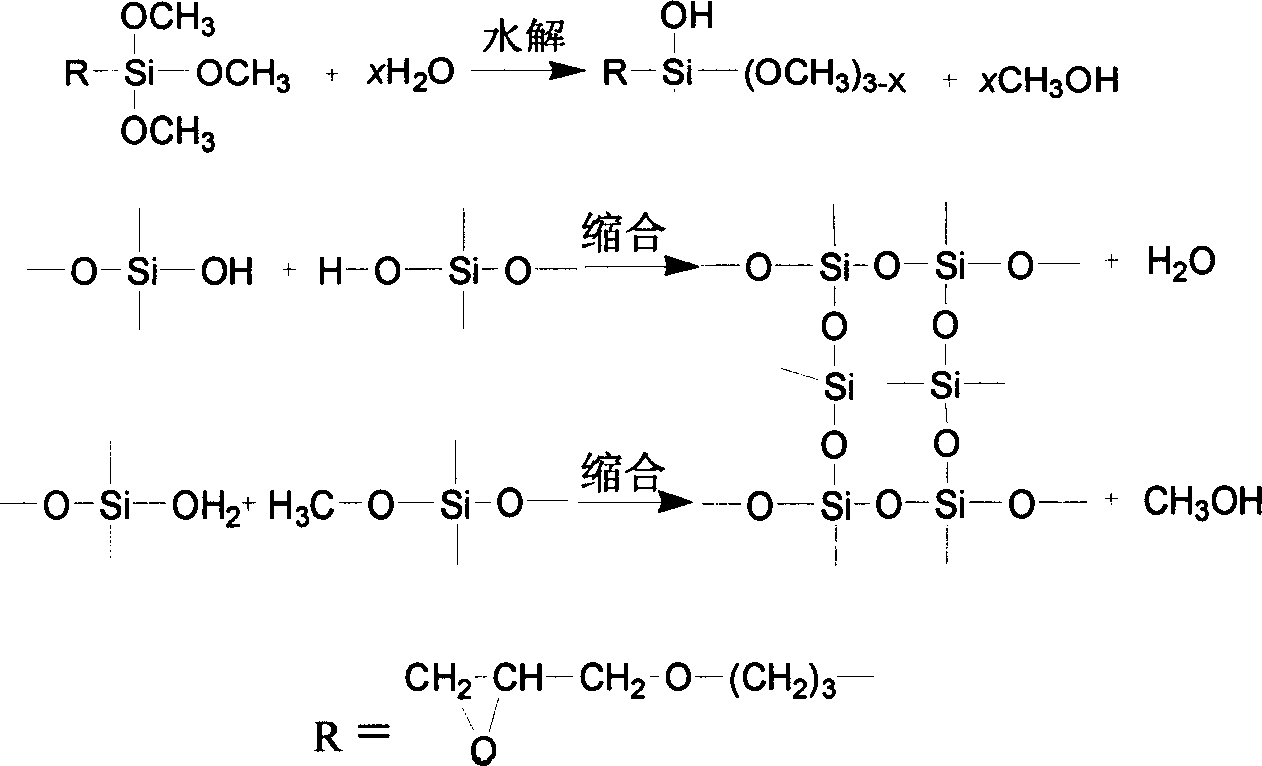
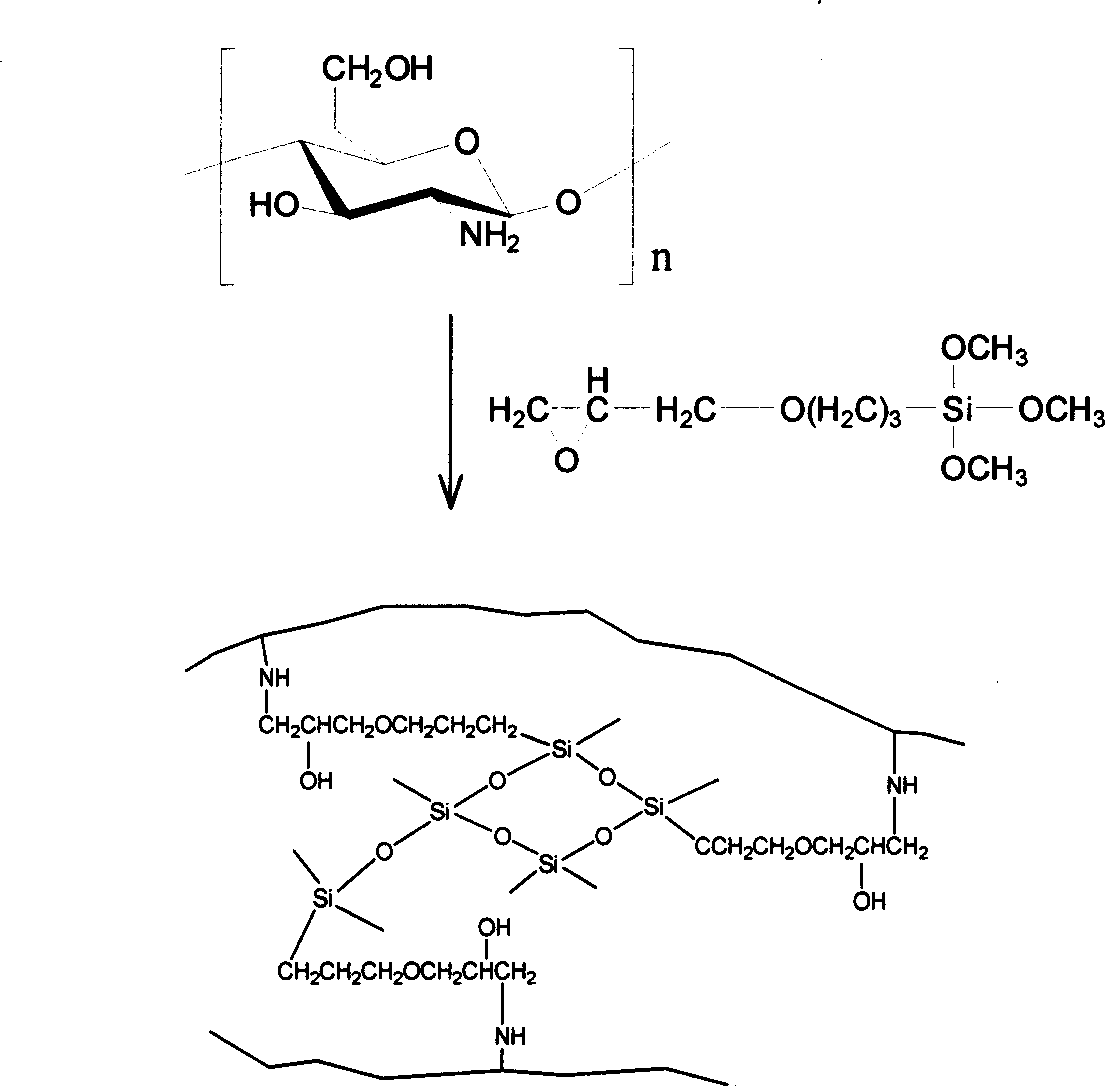
Novel silica gel loaded cross-linked chitosan adsorbent for heavy metal
InactiveCN1803275AEasy to removeEasy to operateOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionEpoxySorbent
The invention discloses a new-typed heavy metal ion adsorbent of silica loading crosslinking chitosan in the environment-protection domain, which is characterized by the following: the metal ion adsorbent adapts gamma-epoxy propyl-trimethyl silane with epoxy group and soluble inorganic silane agent as chitosan crosslinking agent; the chitosan crosslinking action is accomplished by the reaction of chitosan and epoxy group and the silane agent hydrolysis and condensation course. The invention displays simple course without organic solvent and environmental pollution, which can dispose the waste water with heavy metal ion.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cryptographic multi-shadowing with integrity verification
ActiveUS20090113216A1Privacy protectionImprove integrityMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationOperational systemProtection domain
A virtual-machine-based system that may protect the privacy and integrity of application data, even in the event of a total operating system compromise. An application is presented with a normal view of its resources, but the operating system is presented with an encrypted view. This allows the operating system to carry out the complex task of managing an application's resources, without allowing it to read or modify them. Different views of “physical” memory are presented, depending on a context performing the access. An additional dimension of protection beyond the hierarchical protection domains implemented by traditional operating systems and processors is provided.
Owner:VMWARE INC
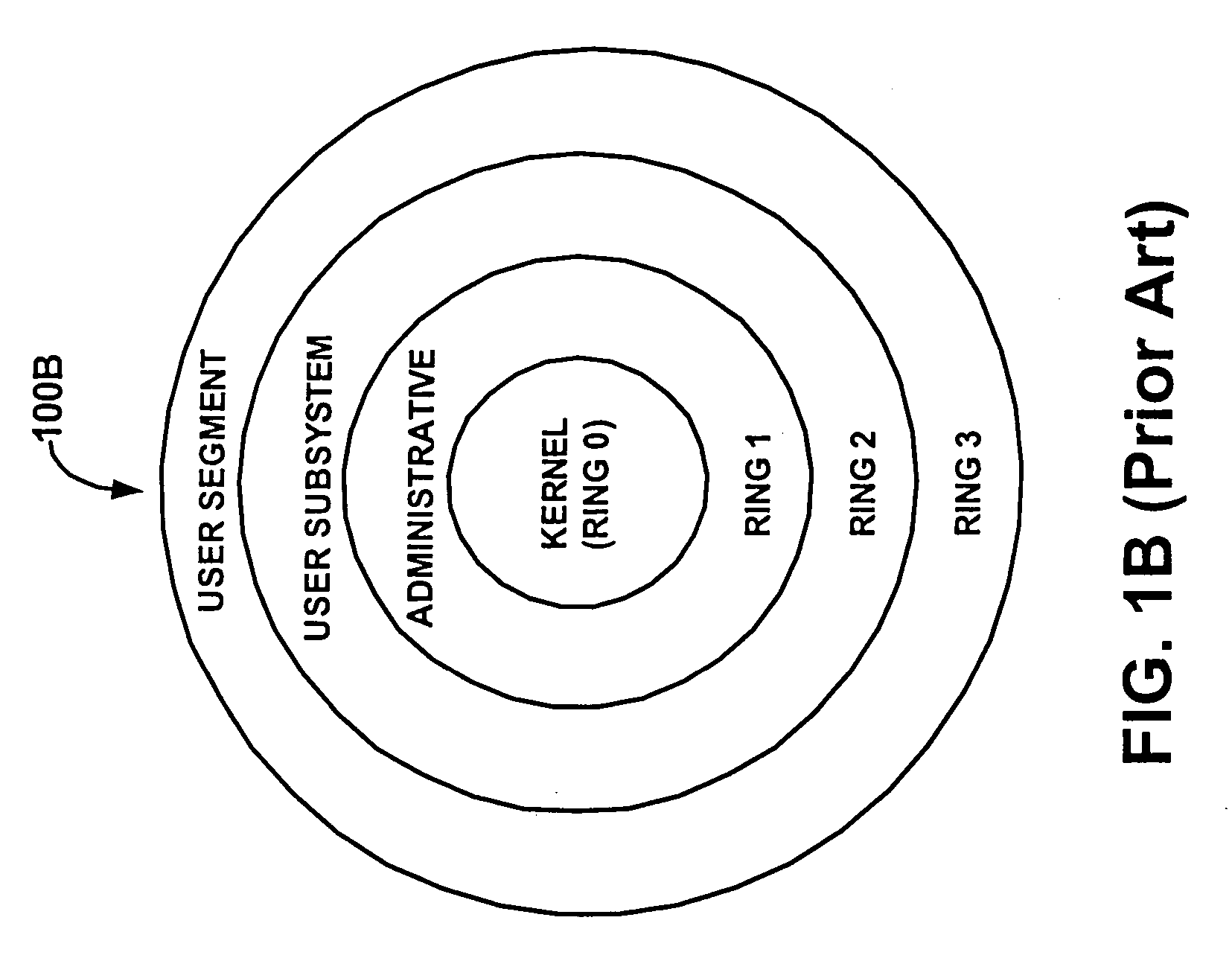
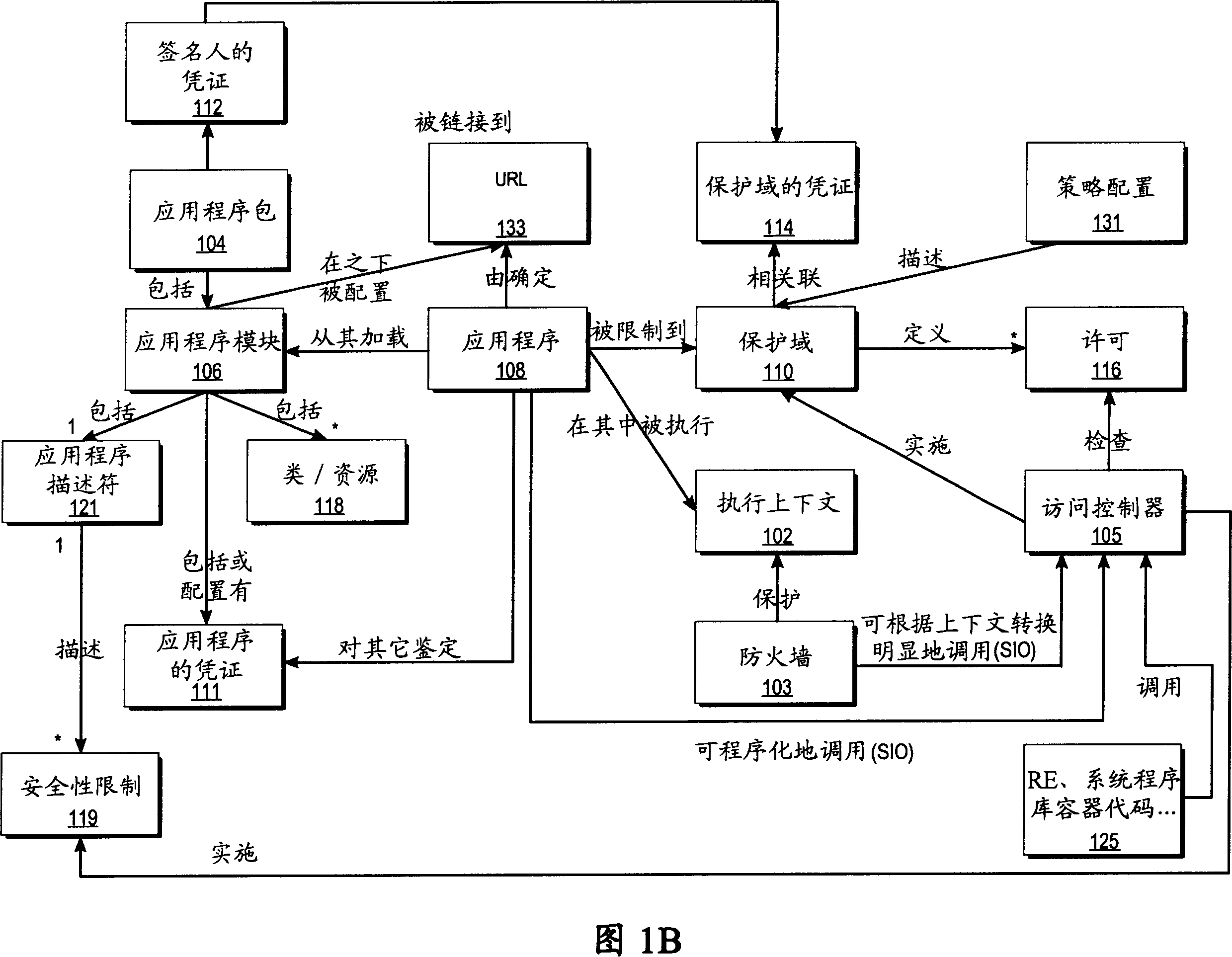
Providing a flexible protection model in a computer system by decoupling protection from computer privilege level
ActiveUS20050172138A1Flexible fine granularityReduce overheadSpecific access rightsDigital data processing detailsOperational systemProtection domain
Methods and systems for providing a flexible protection model in a computer system by decoupling protection from privilege are described. Information describing a relationship between the two or more domains that define types of protection and portions of code is received. The portions of code with the multiple domains that provide fine granularities of protection can be executed in the same privilege level. The relationship is not required to be linear. In addition, the overhead associated with crossing protection domains is relatively low with respect to traditional operating system context switching overhead.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
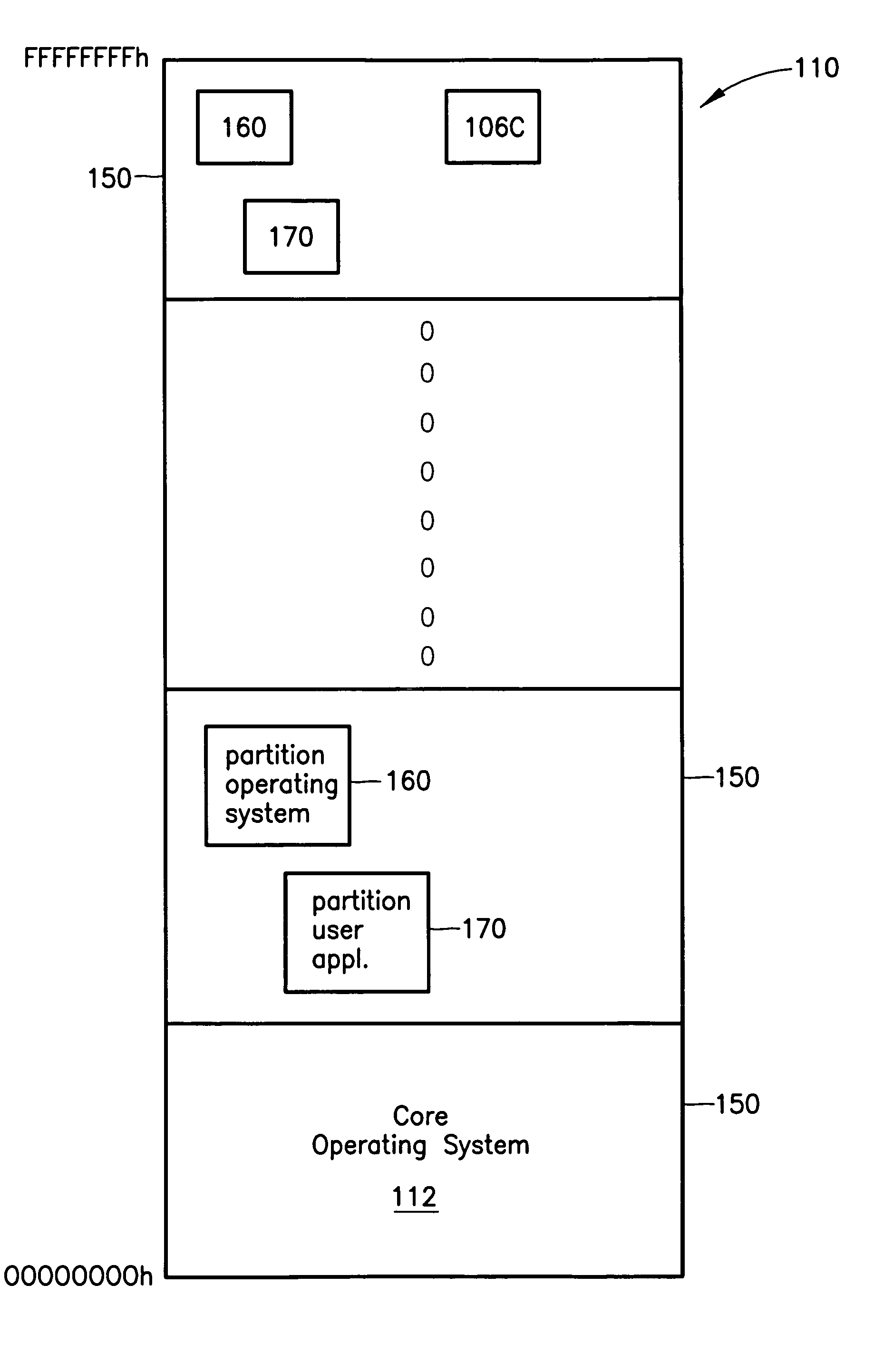
Health monitoring system for a partitioned architecture
ActiveUS6988226B2Error detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsOperational systemProtection domain
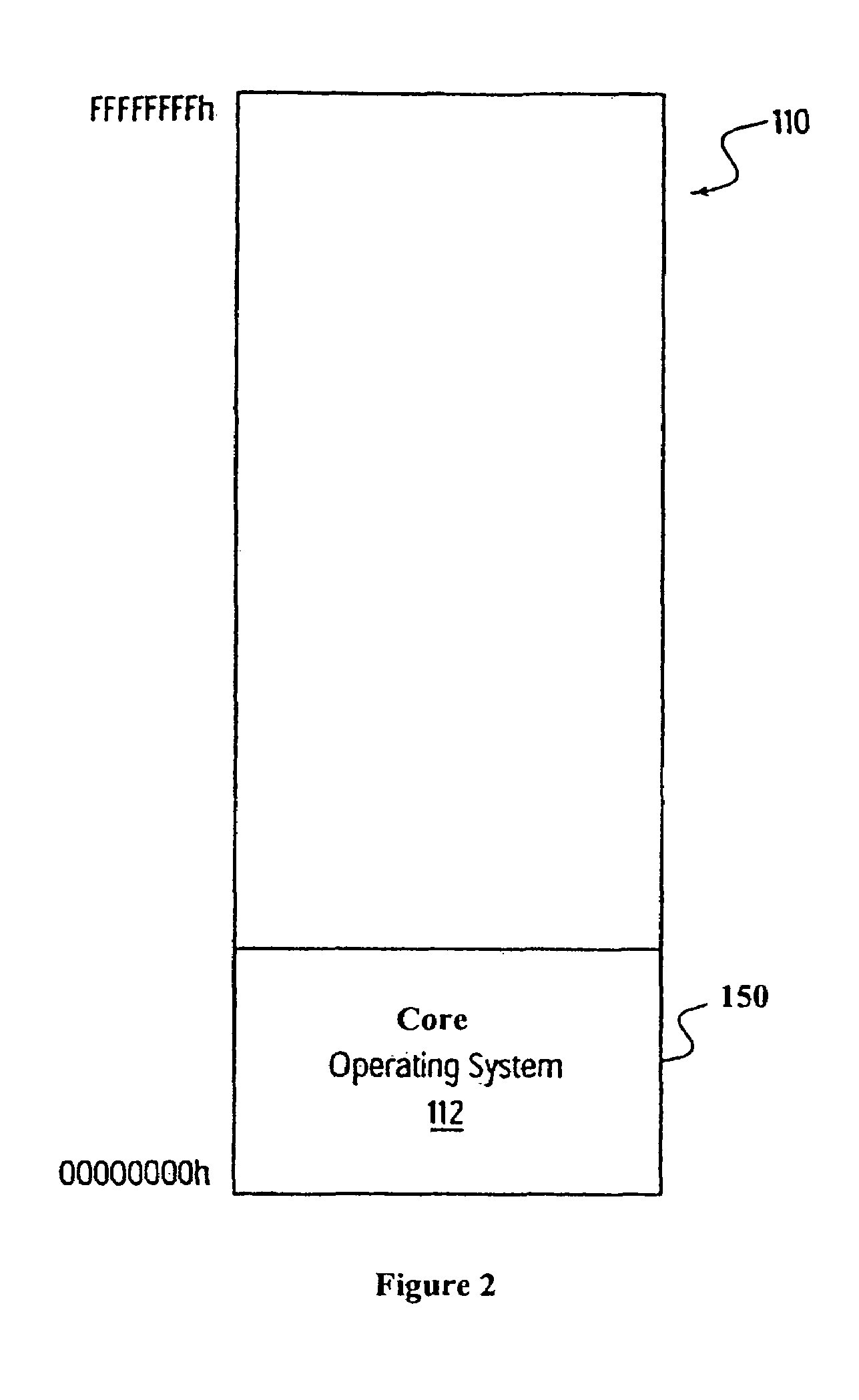
A computer system and method for operating a computer system is provided which comprises a core operating system and a system space having a number of memory locations. The core operating system is arranged to create a number of protection domains to partition the system space into a core operating system space and a plurality of partitions. A partition operating system, a partition user application, and a partition alarm handler is provided in each partition. Each partition operating system provides resource allocation services to the respective partition user application within the partition. An alarm dispatcher and a system alarm handler is provided in the core operating system space. The alarm dispatcher is configured to receive alarms and to dispatch the alarms to one of the alarm handlers.
Owner:WIND RIVER SYSTEMS
Two-level operating system architecture
InactiveUS7103745B2Resource allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationOperational systemProtection domain
A computer system is provided comprising a core operating system and a system space having a number of memory locations. The core operating system creates a number of protection domains to partition the system space. Each of the partitions includes a partition operating system and a partition user application. Each partition operating system provides resource allocation services to the respective partition user application within the partition.
Owner:WIND RIVER SYSTEMS
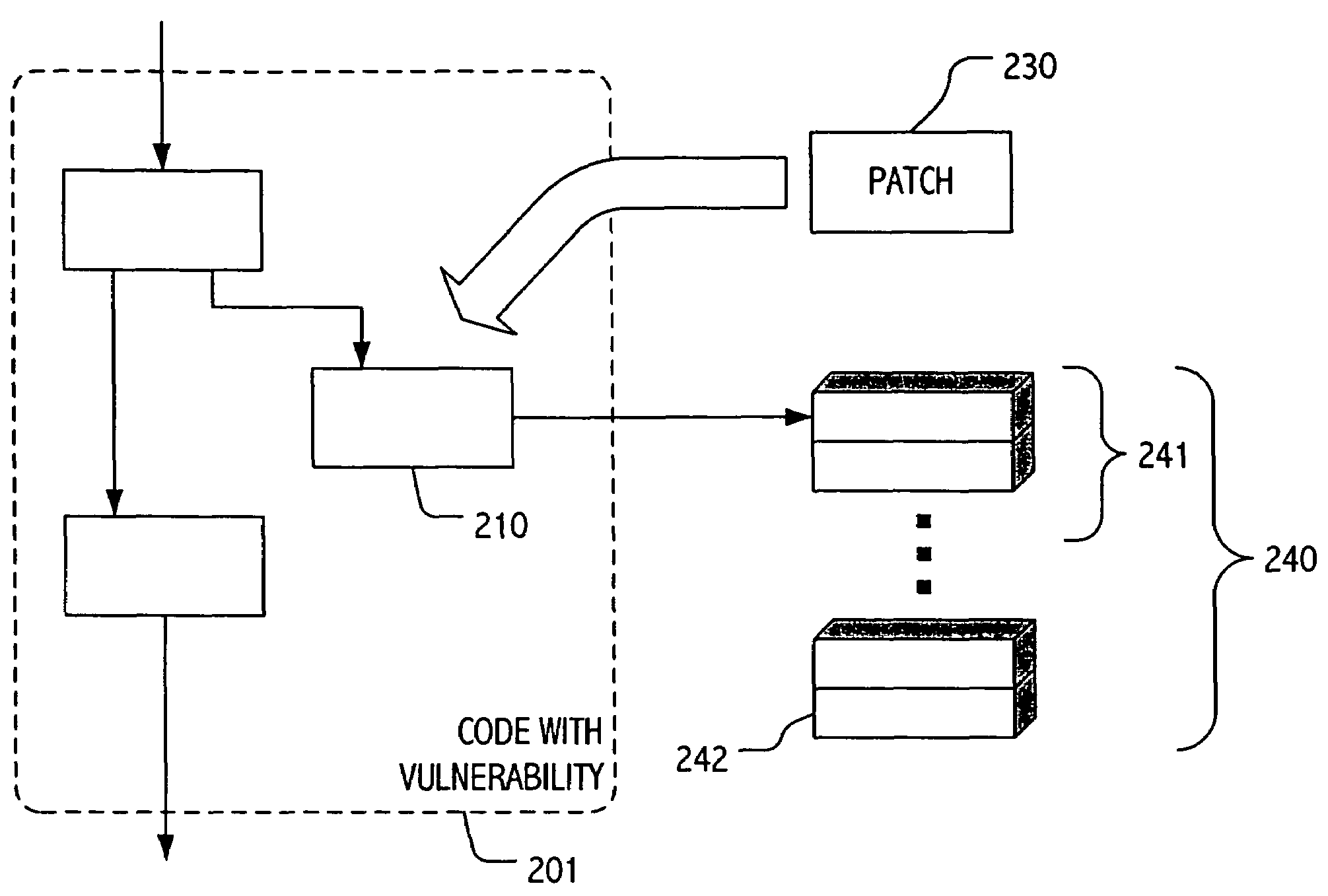
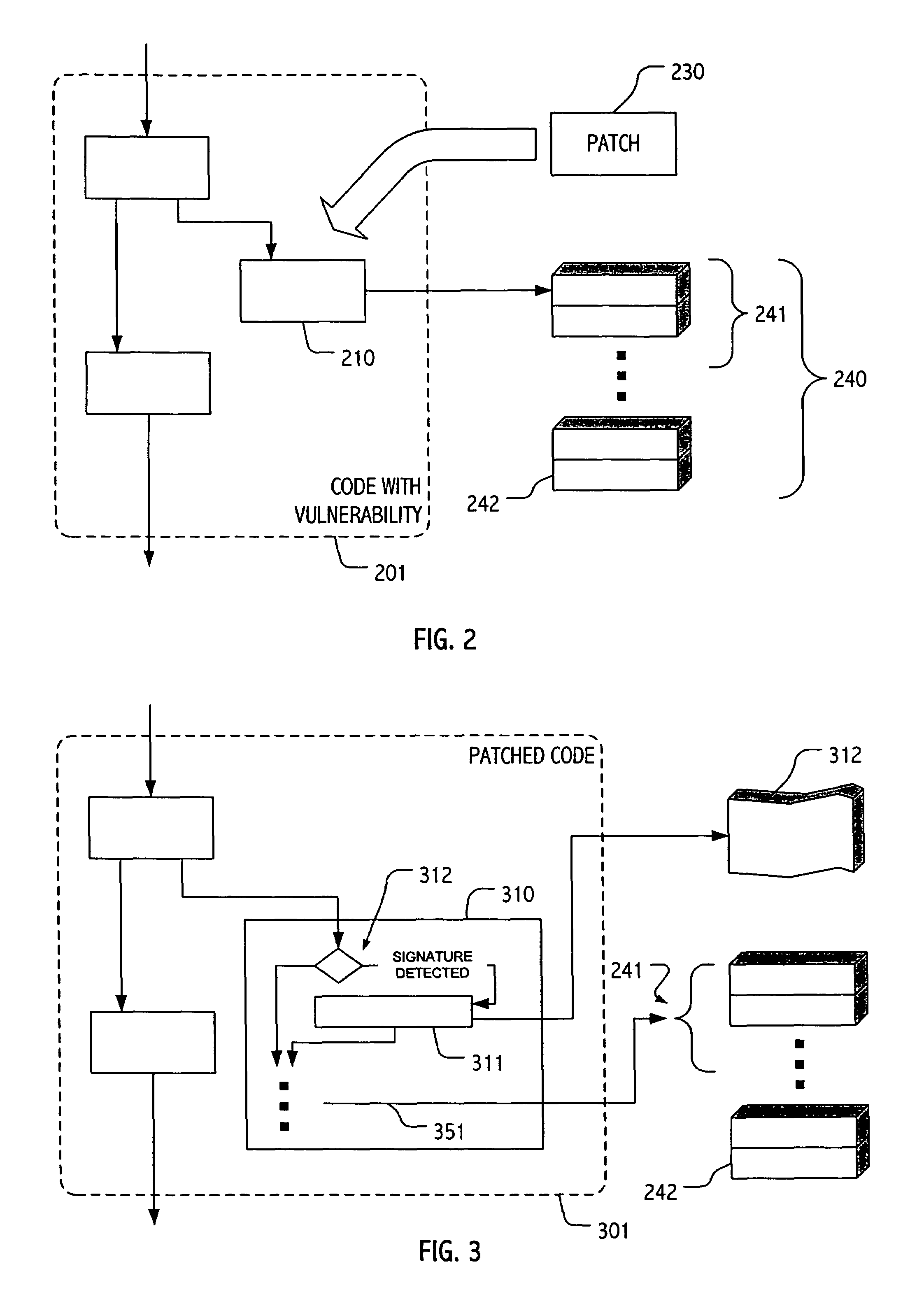
Computer security technique employing patch with detection and/or characterization mechanism for exploit of patched vulnerability
ActiveUS7647637B2Memory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionCharacterization testProtection domain
A patch or set of patches may be deployed, often to a subset of potentially vulnerable systems, to address a particular vulnerability while providing a facility to monitor and, in some cases, characterize post-patch exploit attempts. Often, such a patch will check for an exploit signature and, if an exploit attempt is detected or suspected, take an appropriate action. For example, the patch may include code to log indicative data or trigger such logging. In some exploitations, the patch may generate or contribute to a warning or advisory regarding an additional target (or targets) of the exploit and, if appropriate, initiate a patch or protective measure for the additional target(s). In some exploitations, the patch may simulate responses or behaviors suggestive (to an attacker) of unpatched code. In some exploitations, the patch may direct an exploit attempt to a service (or simulated service) hosted or executing in an isolated protection domain.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Far-end divect memory access invocating memory management unloading of network adapter
InactiveCN1487418AReduce usageMemory adressing/allocation/relocationUnauthorized memory use protectionRemote direct memory accessData treatment
A method, computer program product, and distributed data processing system for memory management. Memory regions are registered and have access rights and protection domains associated with them in response to receiving a request for a memory operation including a virtual address, which is used to address into a data structure. A second data structure is then used to translate the virtual address into physical addresses for the operation. A third data structure is used to allow an incoming request responsive to a remote operation being initiated.
Owner:IBM CORP
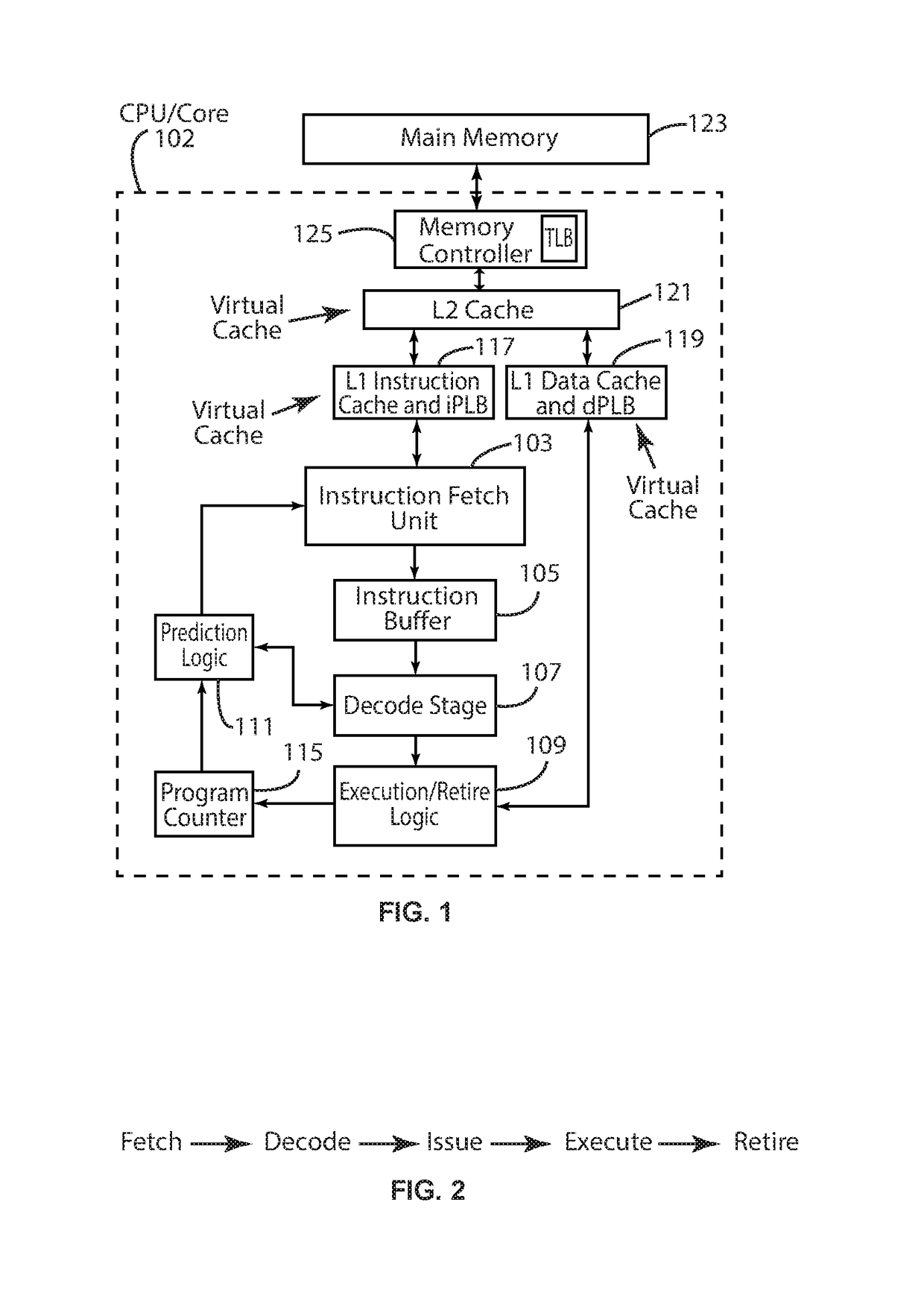
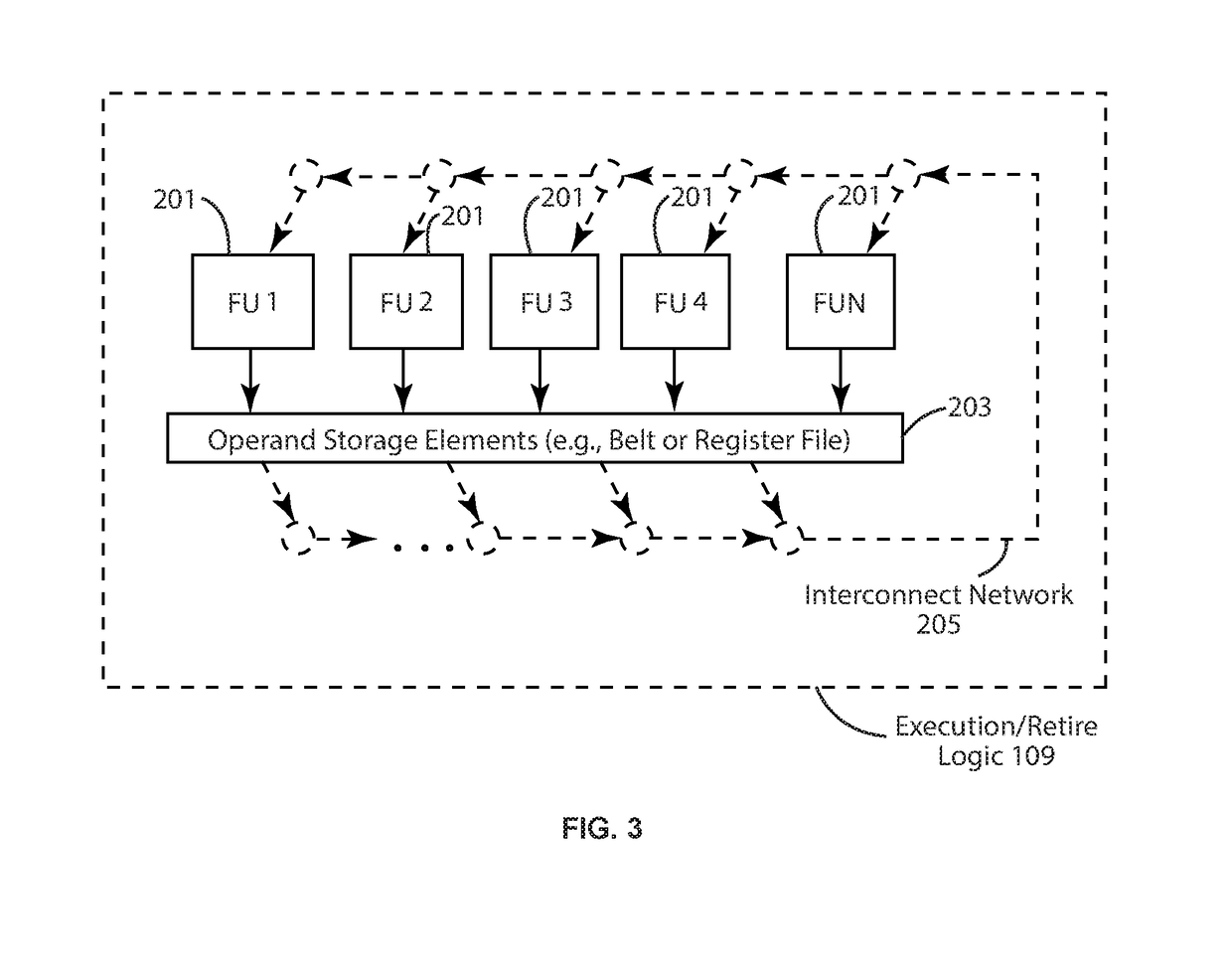
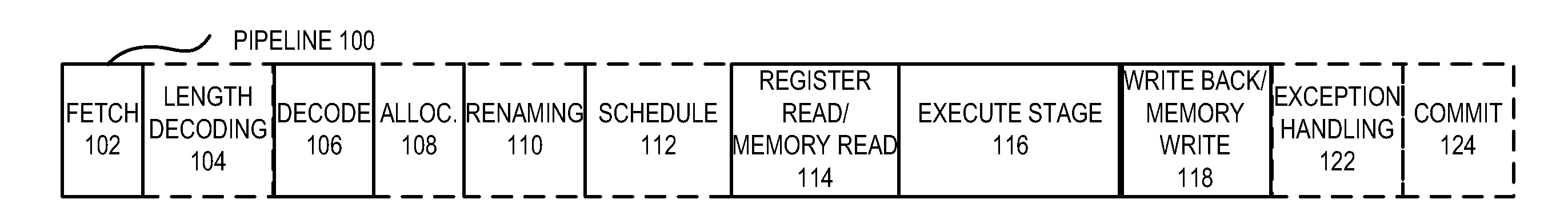
CPU Security Mechanisms Employing Thread-Specific Protection Domains
A computer processor includes an instruction processing pipeline that interfaces to a hierarchical memory system employing an address space. The instruction processing pipeline includes execution logic that executes at least one thread in different protection domains over time, wherein the different protection domains are defined by descriptors each including first data specifying a memory region of the address space employed by the hierarchical memory system and second data specifying permissions for accessing the associated memory region. The address space can be a virtual address space or a physical address space. The protection domains can be associated with different turfs each representing a collection of descriptors. A given thread can execute in a particular protection domain(turf), one protection domain (turf) at a time with the particular protection domain (turf) selectively configured to change over time.
Owner:MILL COMPUTING
Apparatus and method for fast failure handling of instructions
InactiveUS9053025B2Concurrent instruction executionNon-redundant fault processingProcessor registerProtection domain
A processor is described comprising: instruction failure logic to perform a plurality of operations in response to a detected instruction execution failure, the instruction failure logic to be used for instructions which have complex failure modes and which are expected to have a failure frequency above a threshold, wherein the operations include: detecting an instruction execution failure and determining a reason for the failure; storing failure data in a destination register to indicate the failure and to specify details associated with the failure; and allowing application program code to read the failure data and responsively take one or more actions responsive to the failure, wherein the instruction failure logic performs its operations without invocation of an exception handler or switching to a low level domain on a system which employs hierarchical protection domains.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and system for controlling access to network resources using resource groups
InactiveUS7225255B2Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlProtection domainComputerized system
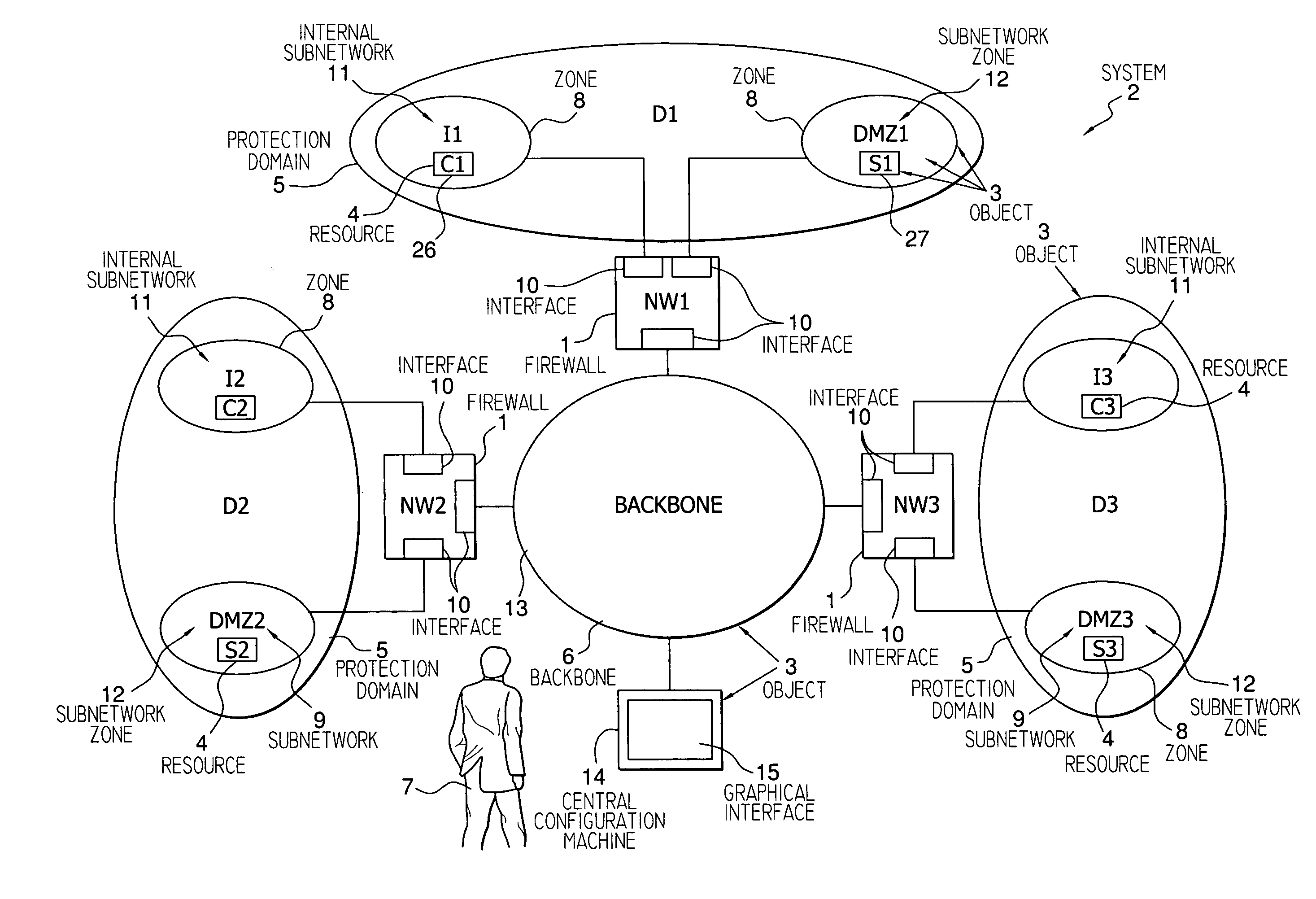
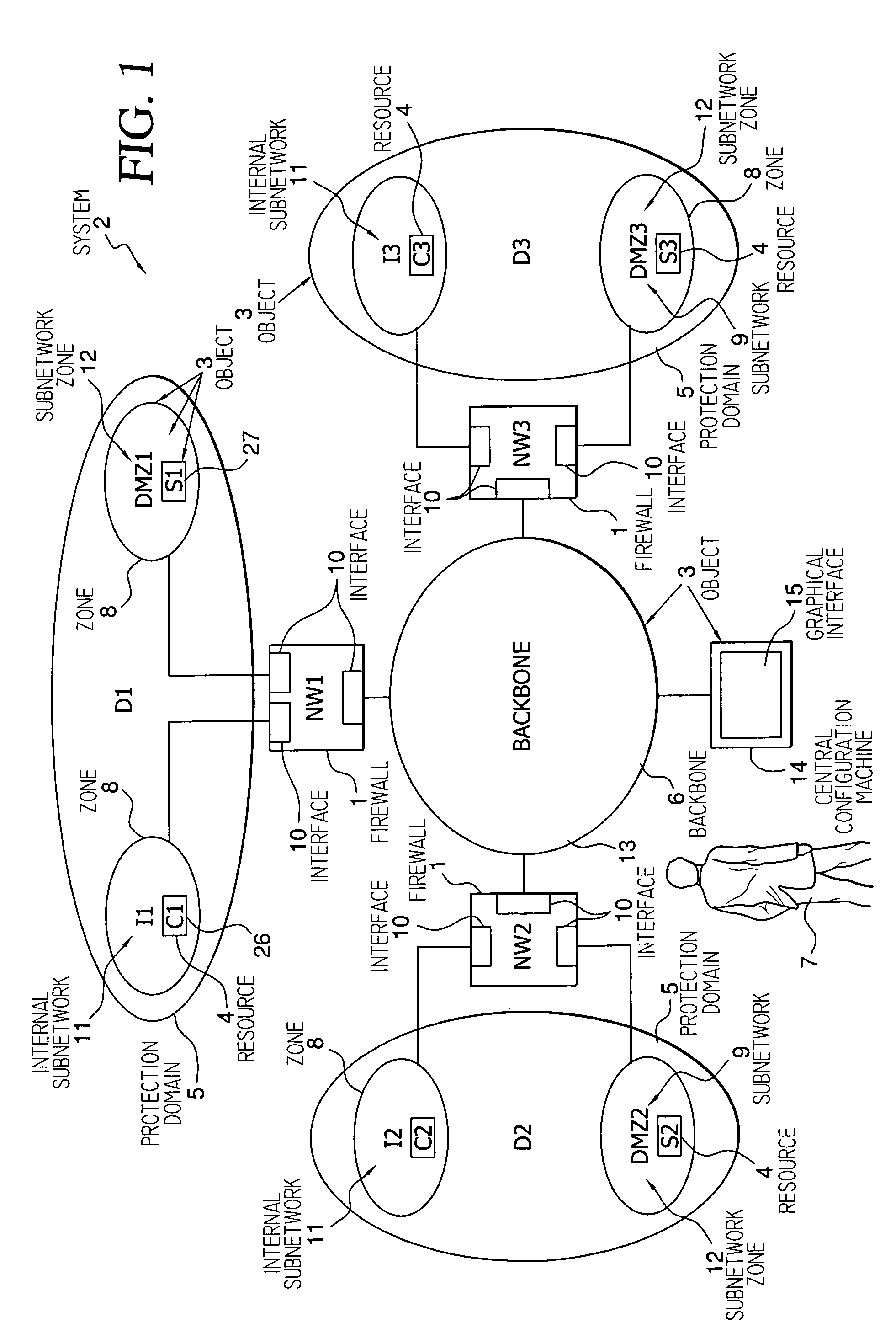
A method and device for configuring a firewall in a computer system employing a rule for controlling access between a source resource and a destination resource only if said source and destination resources belong to the same protection domain. At a central configuration machine, an access control rule is specified, including a scope, for each resource group, the scope, and thus the access control rule is capable of being interpreted by each of the plurality of firewalls differently depending on the value of the scope and network resource characteristics associated with each of the plurality of firewalls.
Owner:EVIDIAN
Method and apparatus for protection domain based security
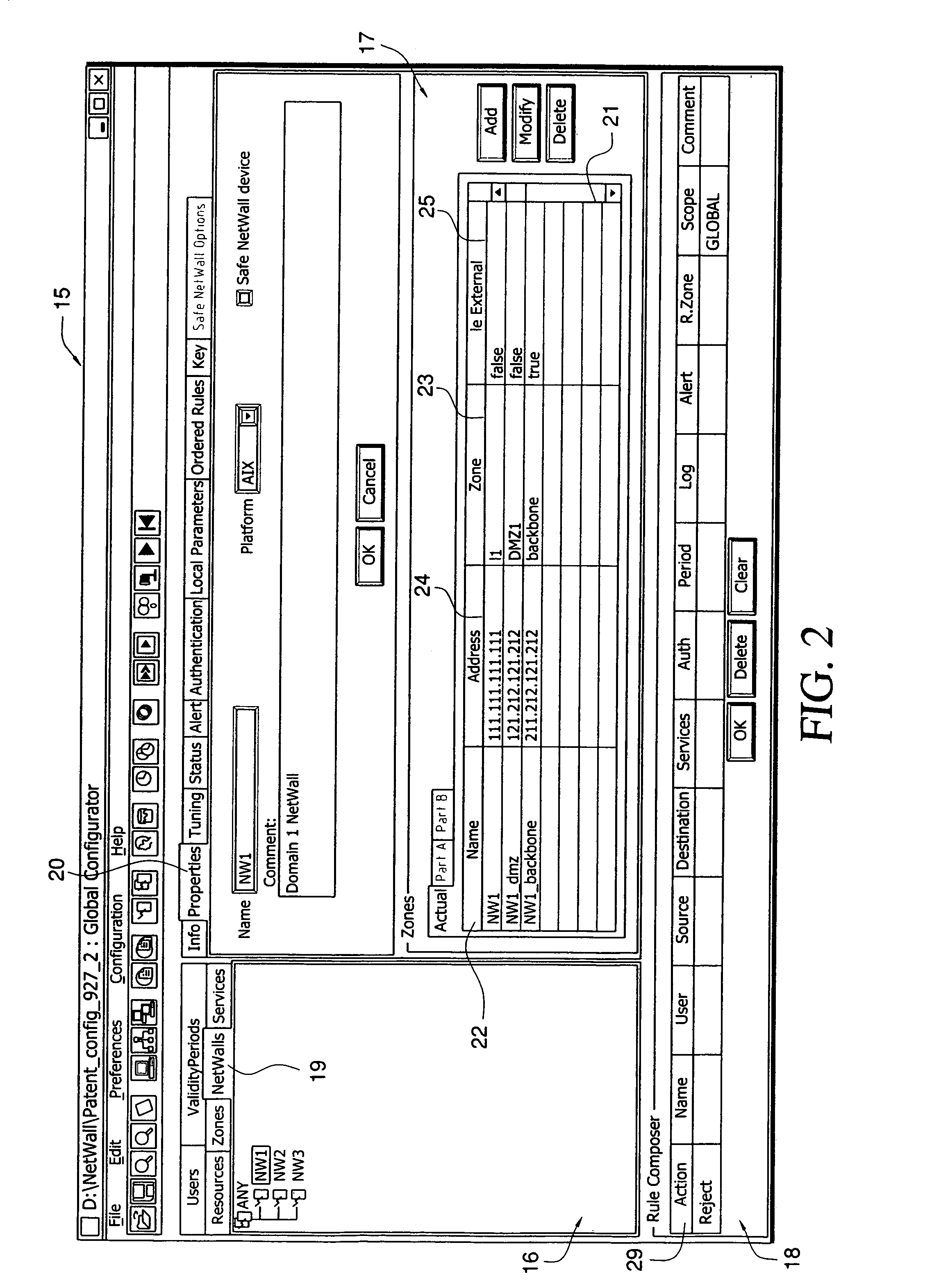
ActiveCN101004776AMultiprogramming arrangementsInternal/peripheral component protectionProtection domainApplication software
A first application instance is associated with a protection domain based on credentials (e.g.: a signed certificate) associated with a set of application code that, when executed, gives rise to the application instance. The first application instance executes in a first execution context. An indication is received that the first application instance seeks access to protected functionality associated with a second execution context. In response to receiving the indication, a determination is made as to whether the first application instance has permission to access the protected functionality. The determination is made by determining the protection domain with which the first application instance is associated, and determining if the protection domain with which the first application instance is associated is in the set of one or more protection domains.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
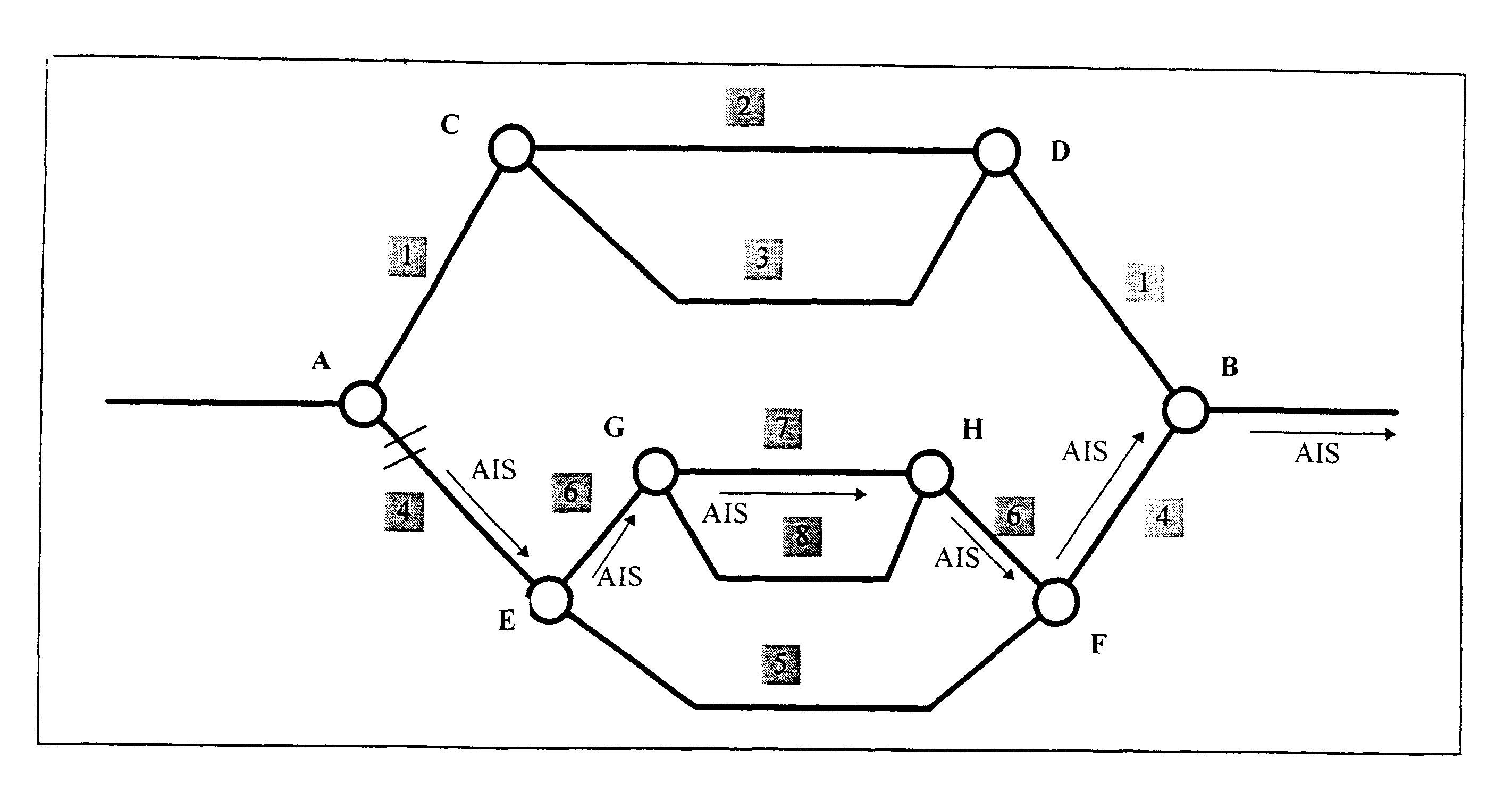
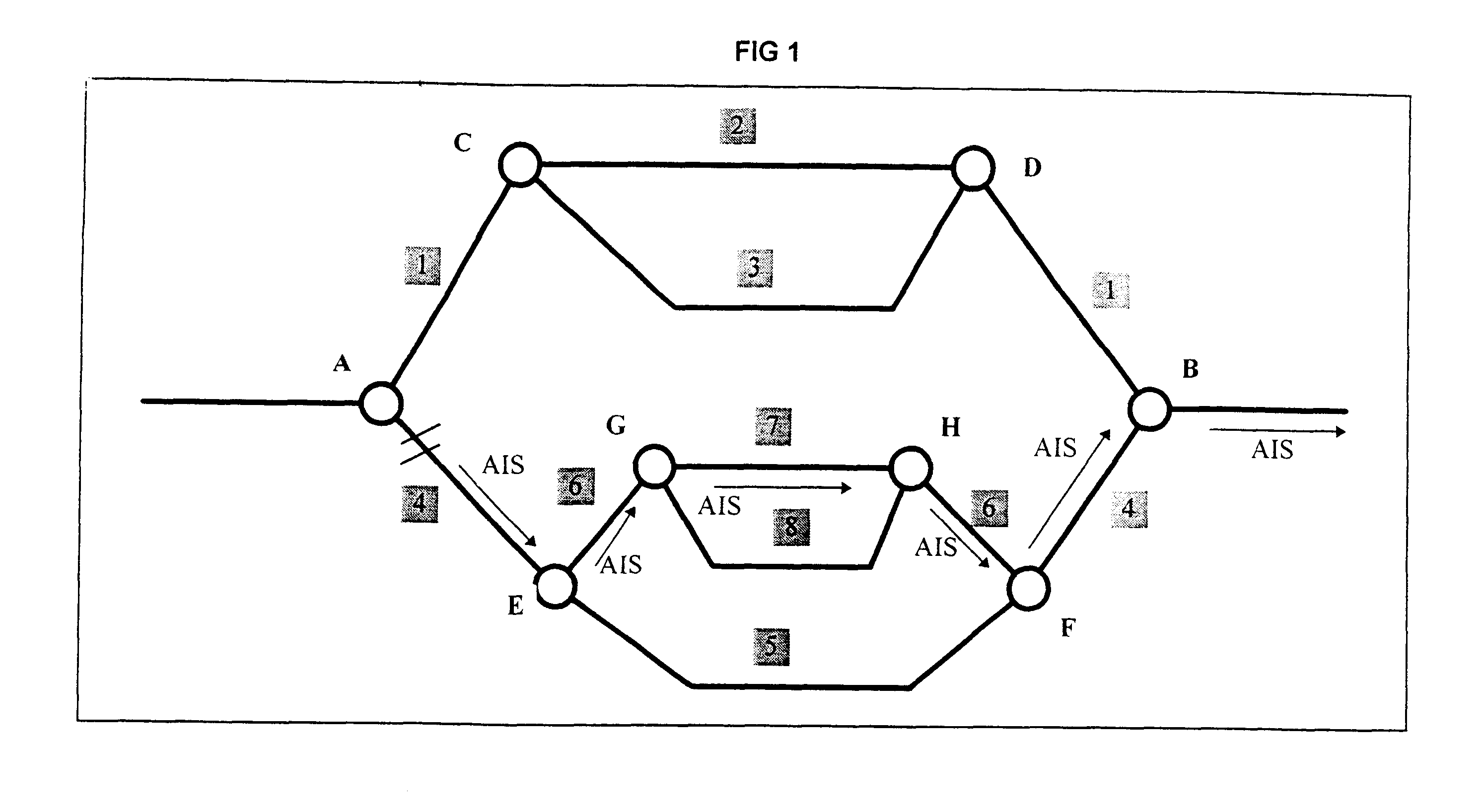
Method and apparatus for computing primary and alternate paths in mixed protection domain networks
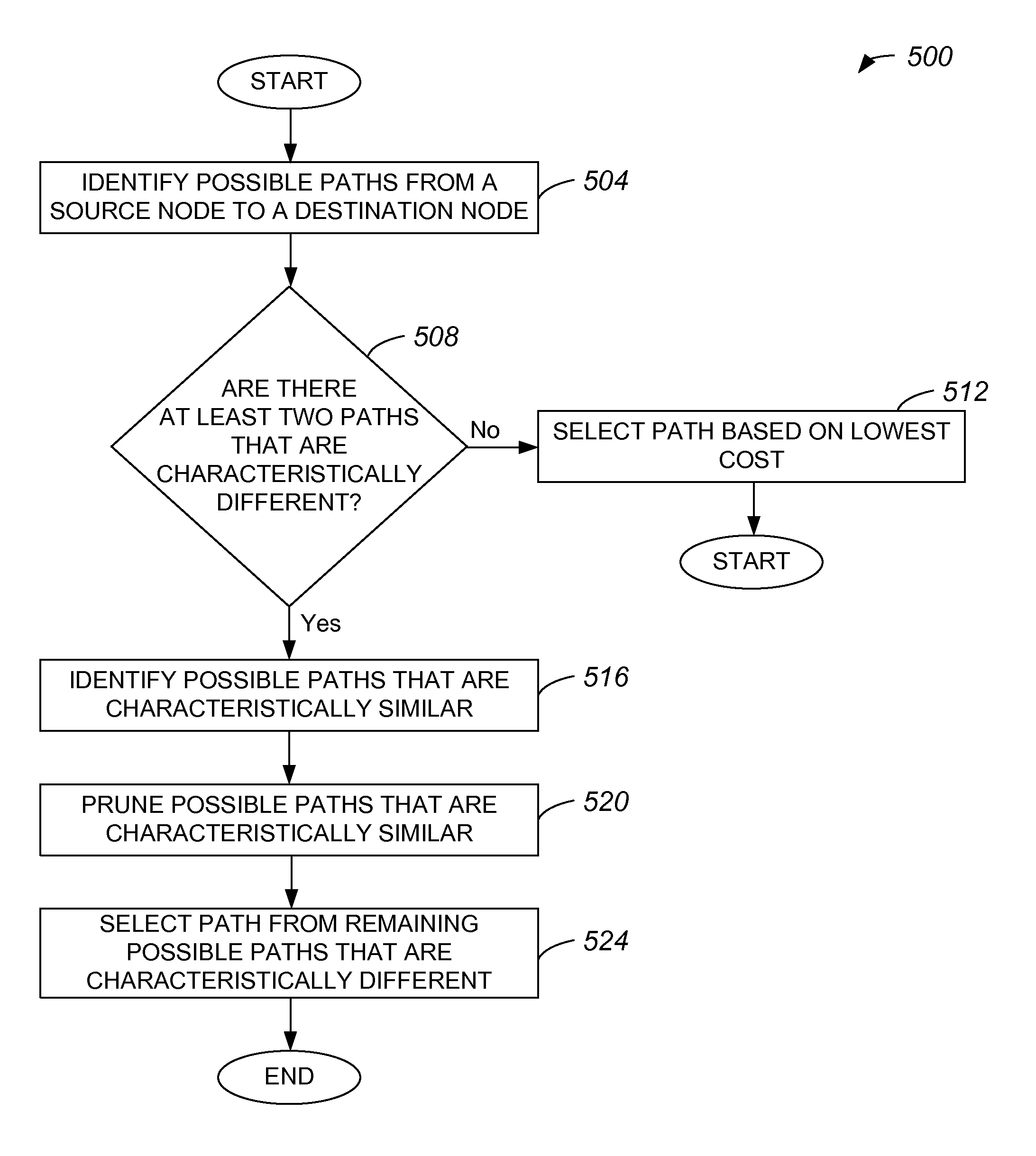
InactiveUS7082124B1Low costMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexProtection domainAutomatic routing
Methods and apparatus for automatically routing paths in a network with a mixed protection domain. According to one aspect, a method for computing a primary path within a network includes identifying a plurality of potential paths which are characteristically similar and are arranged between the source node and the destination node and selecting a first potential path from the plurality of potential paths which are characteristically similar. The first potential path is considered for use as an actual path between the source node and the destination node, while the other potential paths included in the plurality of potential paths which are characteristically similar are not considered for use as the actual path between the source node and the destination node.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
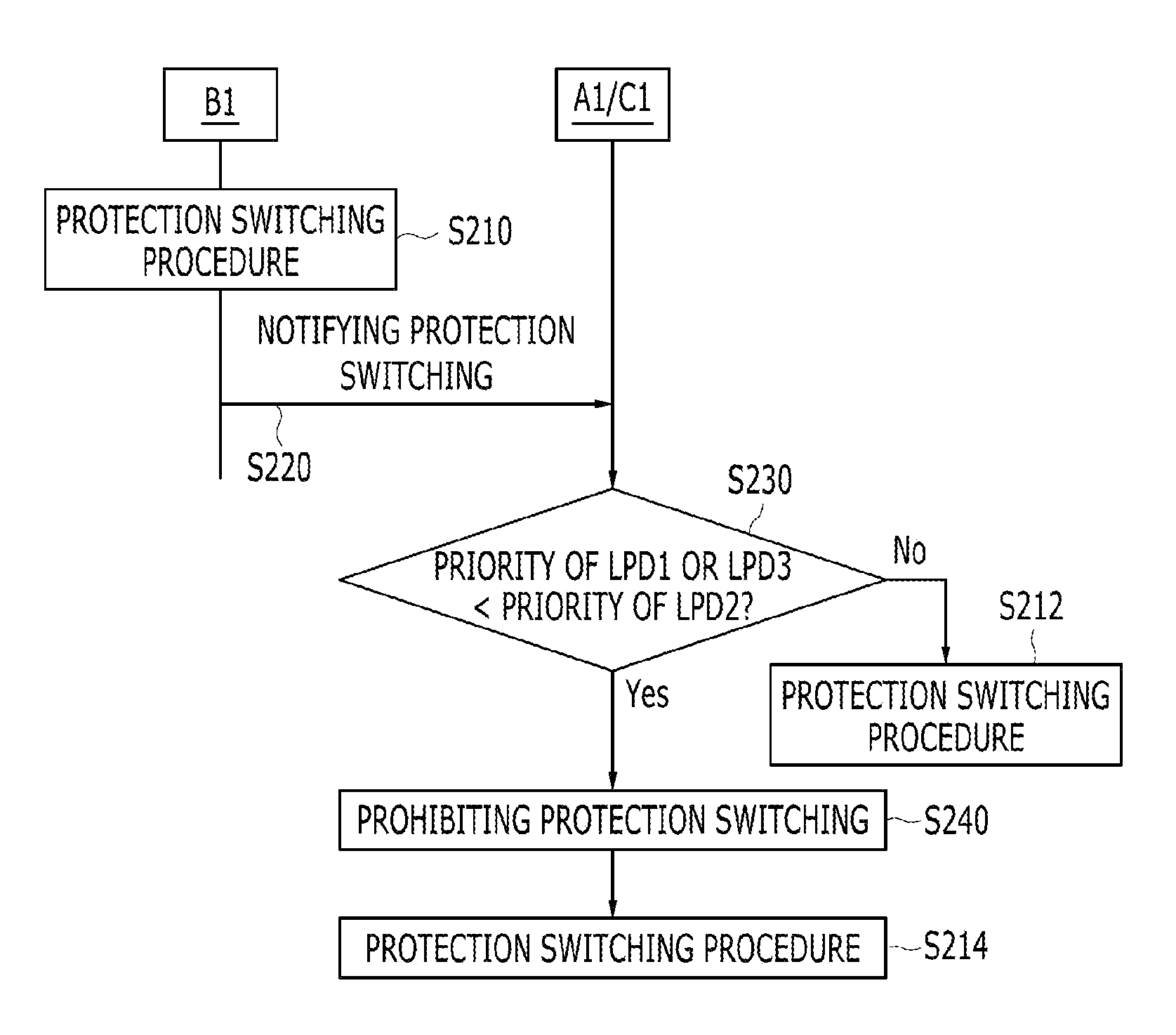
Method and apparatus for shared mesh protection switching
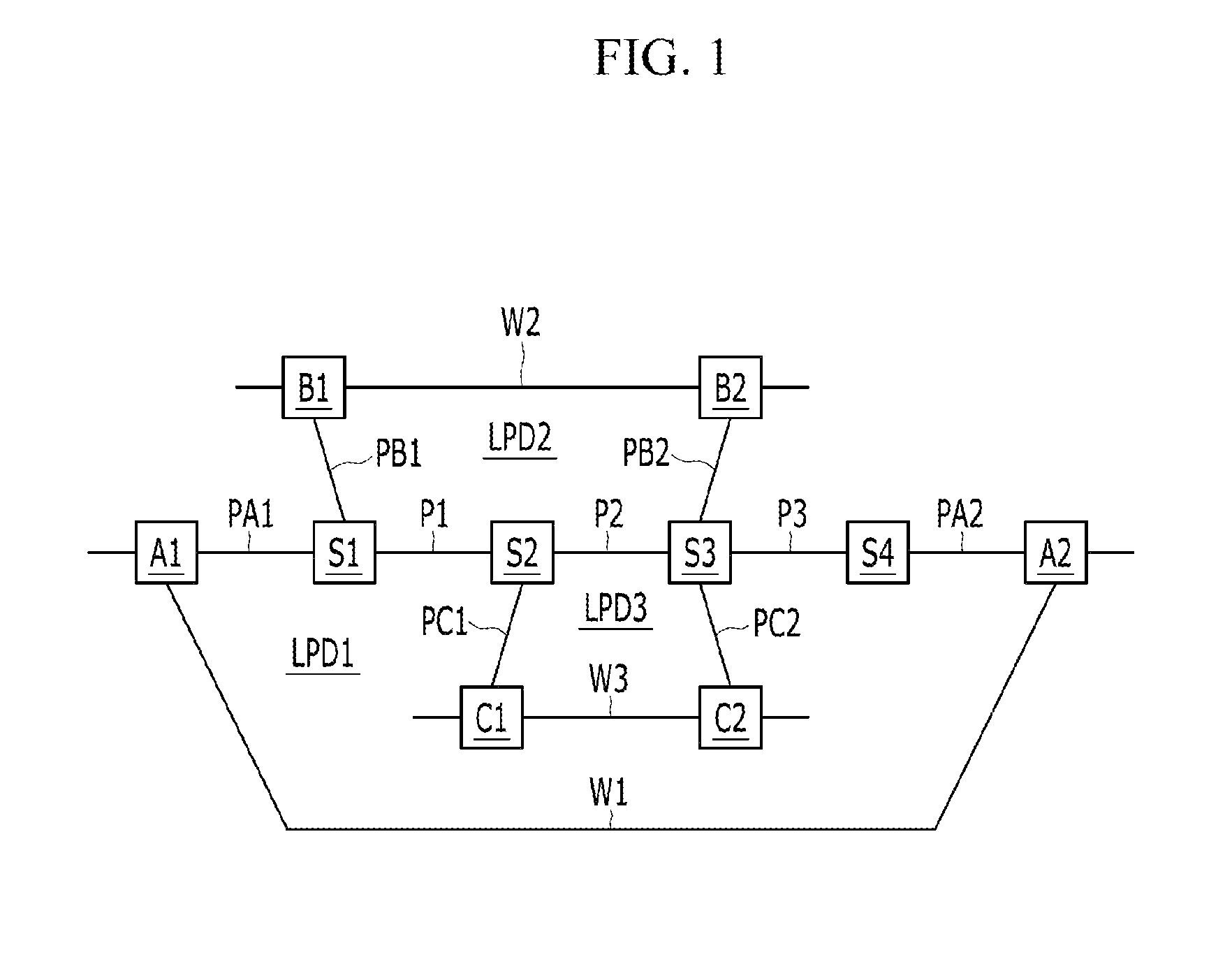
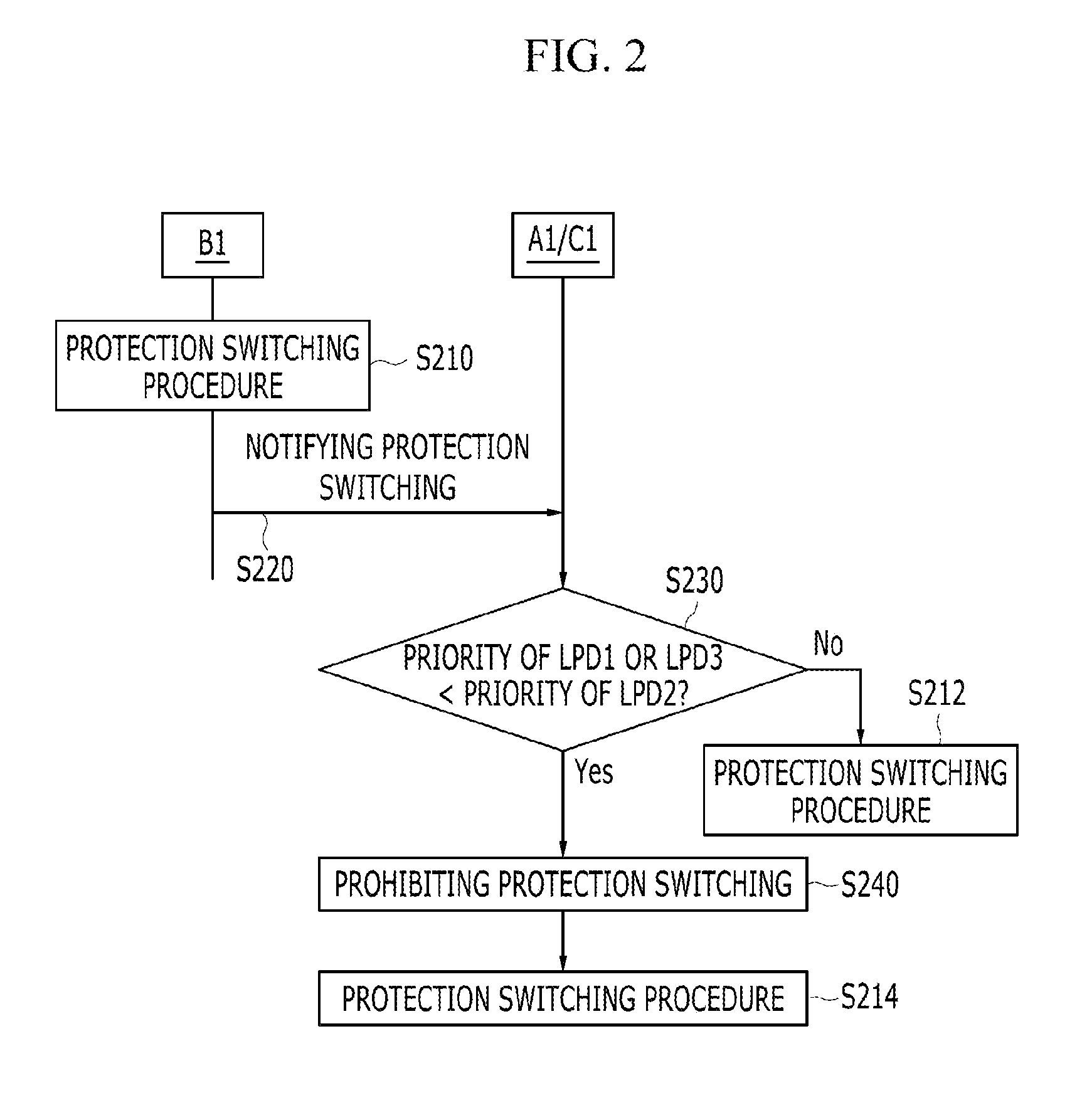
ActiveUS20120294140A1Raise priorityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsProtection domainComputer science
A method for protection switching in a shared node where protection resources of a plurality of end-to-end linear protection domain are shared is provided. The shared node receives a first protection switching event message notifying that a protection switching event occurs from a first node of a first end-to-end linear protection domain, and determines whether to prohibit protection switching on a second end-to-end linear protection domain by comparing a priority of the first end-to-end linear protection domain with a priority of the second end-to-end linear protection domain.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
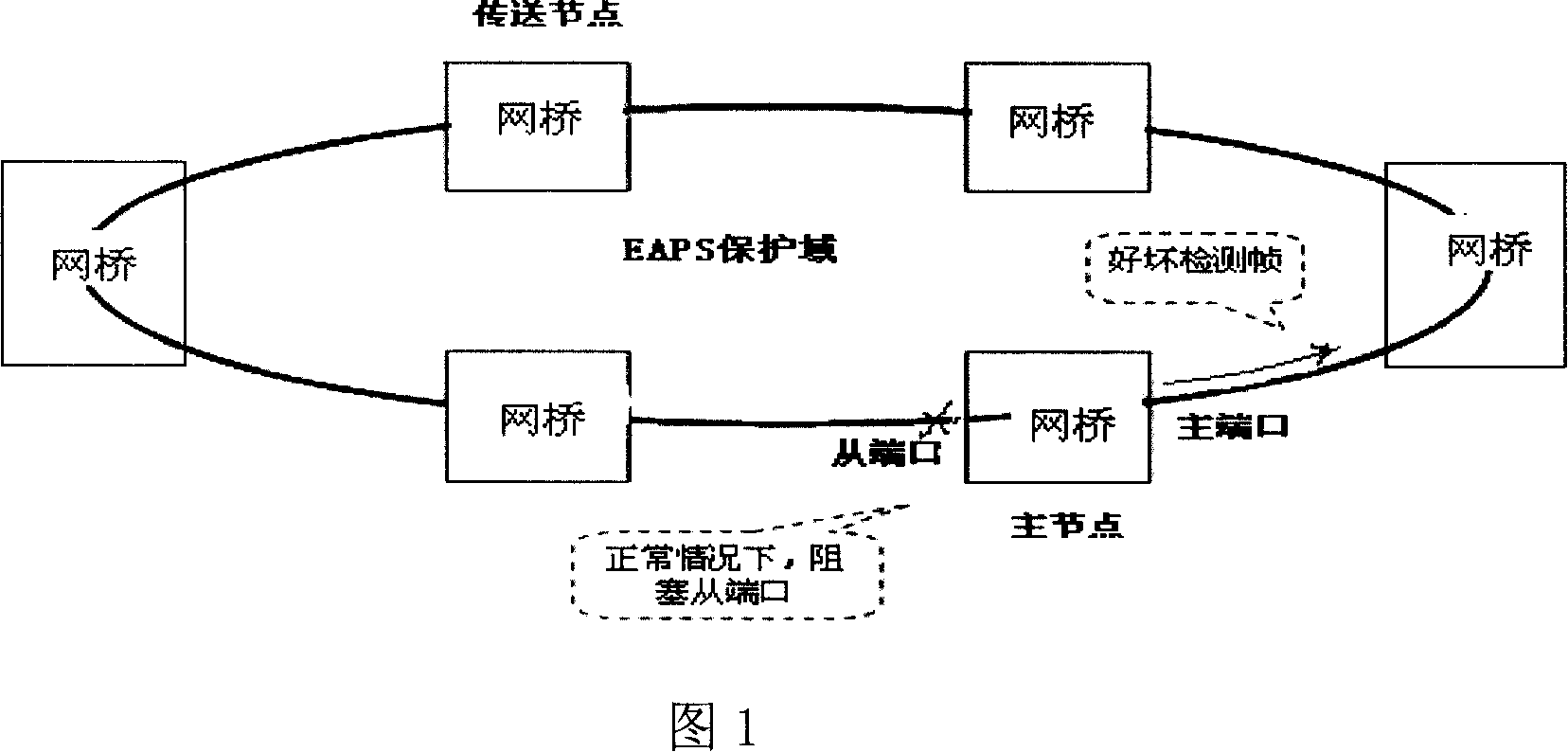
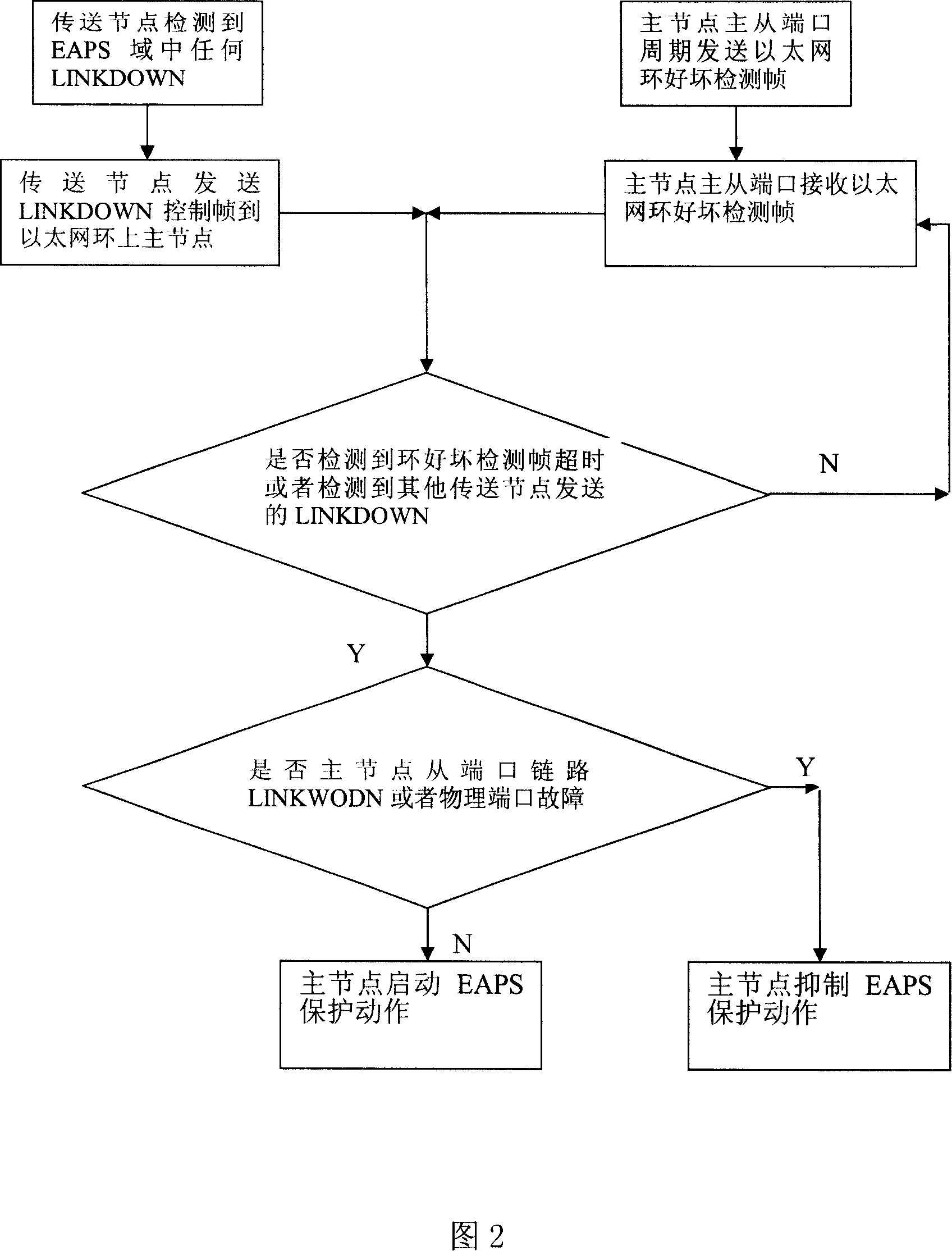
Ethernet automatic protection switching method
InactiveCN101127673AImprove stabilityAvoid oscillationError preventionData switching by path configurationAutomatic protection switchingProtection domain
The utility model relates to an Ethernet automatic protection switching method, comprising at least an alarm process or a polling process. The method comprises the following steps: A. judging whether the loop good and bad detection frame in the polling process is detected overtime, or the LINKDOWN signal sent by other transmission nodes in the alarm process is detected, and judging whether the secondary port link of the main node is dropped or the physical port is failed; B. when the secondary port link of the main node is dropped or the physical port is failed, the main node restrains EAPS protection action; when the physical port and the secondary port link of the main node is in normal operation, and the loop good and bad detection frame in the polling process is detected overtime, or the LINKDOWN signal sent by other transmission nodes in the alarm process is detected, then the main node starts EAPS protection action. Since the unsuitable protection action is restrained, the method prevents network topology oscillation and improves the stability of EAPS protection when the secondary port of the main node fails or the link interconnected with the secondary port of the main node fails in EAPS protection domain.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
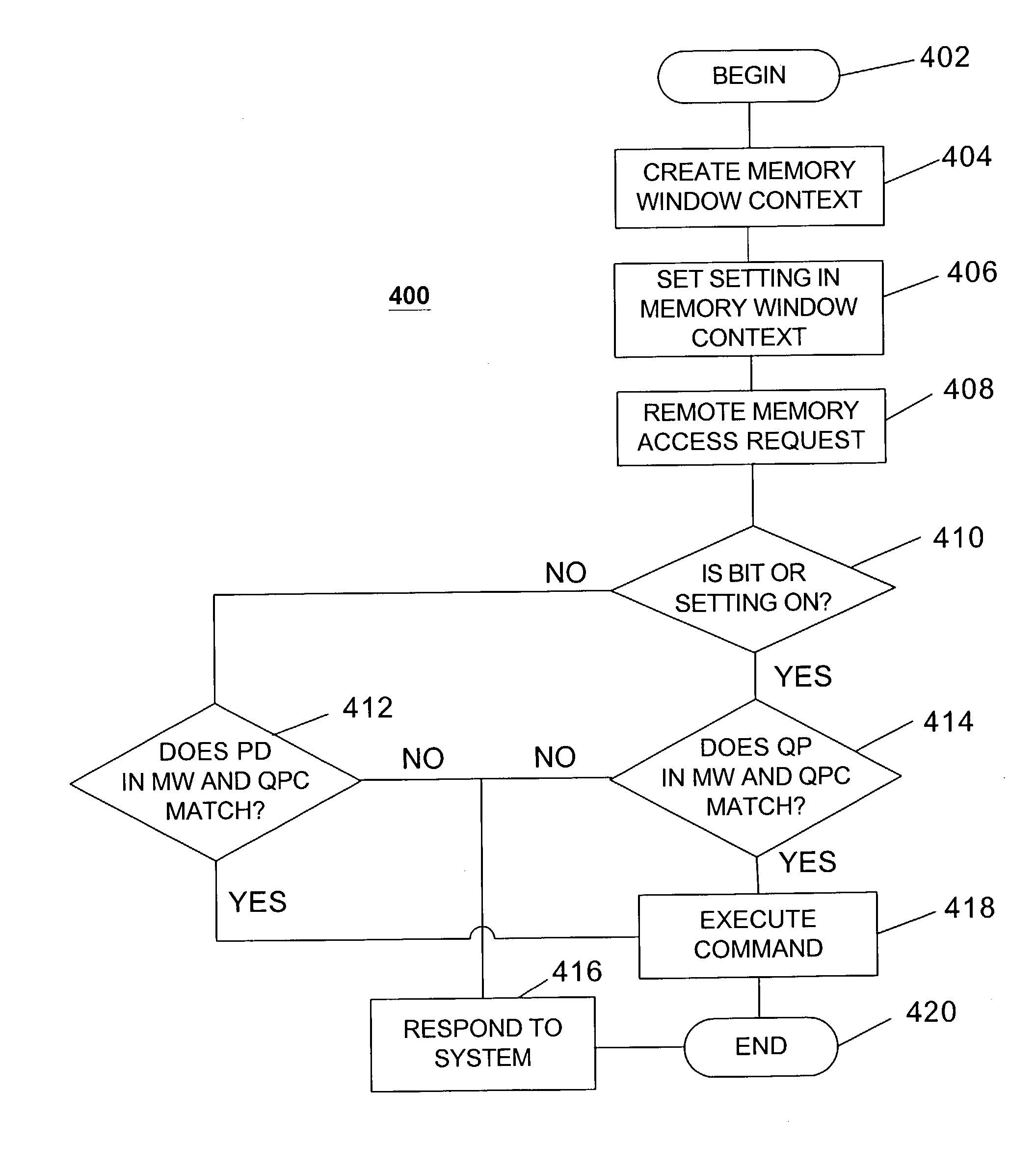
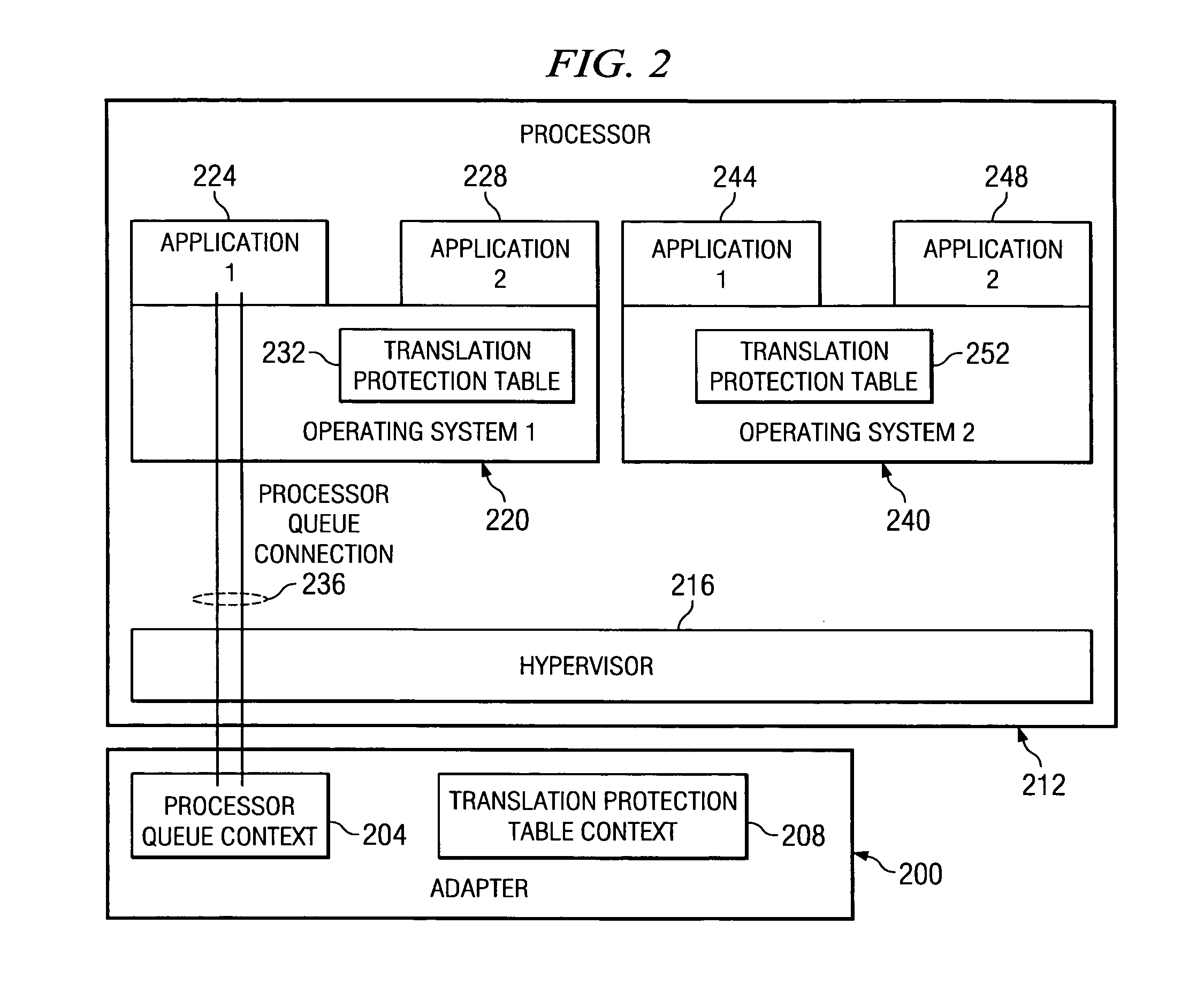
Queue pair/window association
ActiveUS20040193908A1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsProtection domainOperating system
The disclosed embodiments may relate to memory window access, which may include a memory window and protection domain associated with a process. The memory window access setting or bit may also allow a plurality of memory windows to be associated with a protection domain for a process. The memory window access setting or bit may allow access to the memory window to be for the queue pairs in a certain protection domain or a designated queue pair.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
System and method for processor queue to linear block address translation using protection table control based on a protection domain
InactiveUS20060265525A1Computer security arrangementsInput/output processes for data processingOperational systemProtection domain
Owner:IBM CORP
Method of protecting ATM connections in a telecommunications network
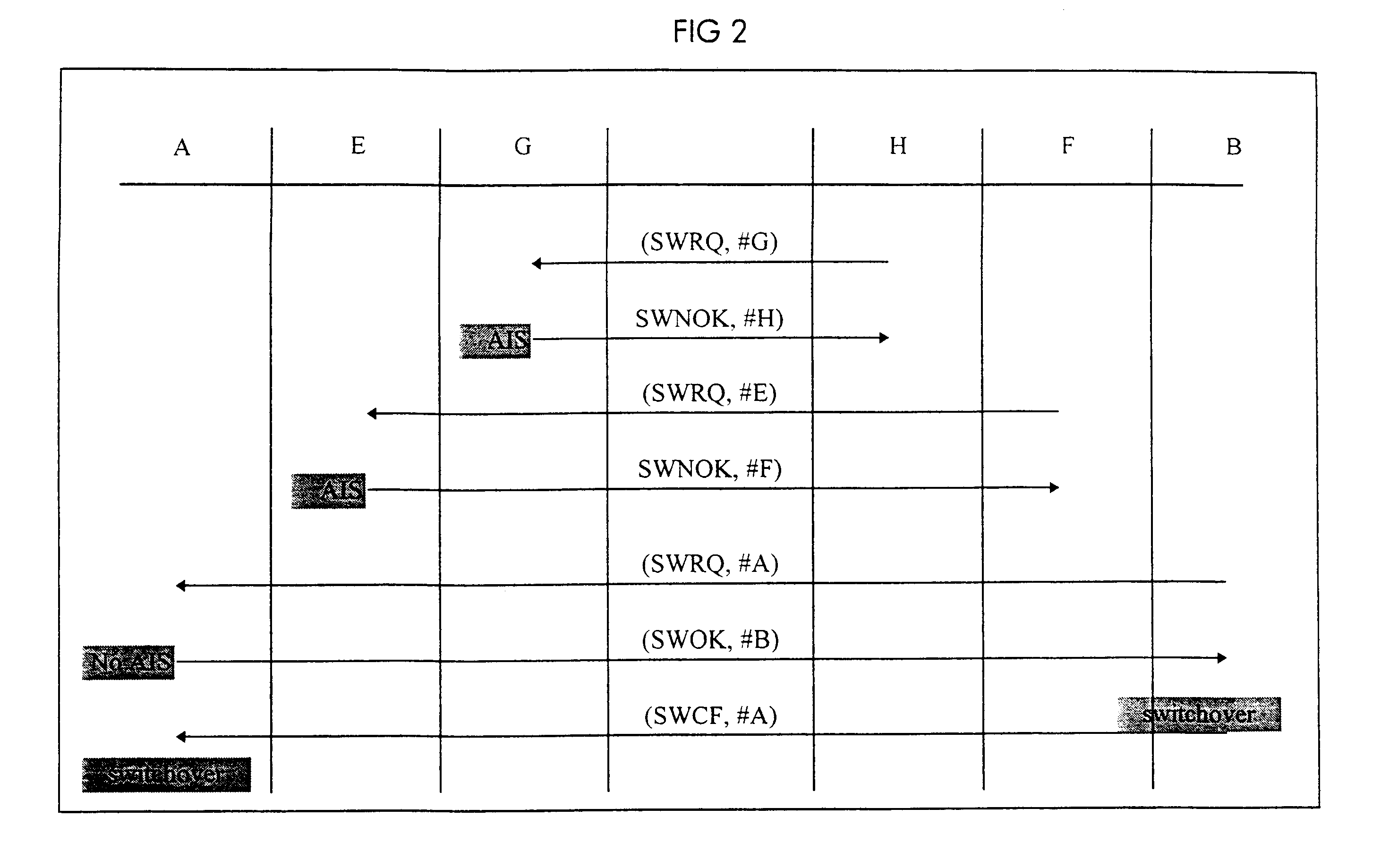
InactiveUS6542461B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsAlarm messageTelecommunications link
A method of protecting ATM connections in a telecommunications network including at least one protection domain which covers only a portion of a connection, each protection domain comprising a source node and a peer sink node. Each source node and its peer sink node can be interconnected by at least two alternative connection segments and can switch over from one connection segment to the other. Any node of the network can send an alarm message downstream over a current path and each node can store a connection fault status when it receives such an alarm message. Each sink node which receives the alarm message sends a switchover request message to its peer source node to request a switchover which is executed only if the peer source node has not itself stored an alarm message. The sink node switches over only if the peer source node has responded positively.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com