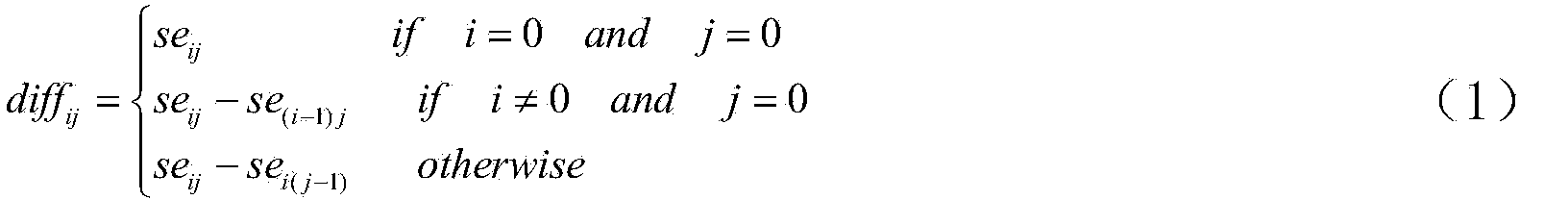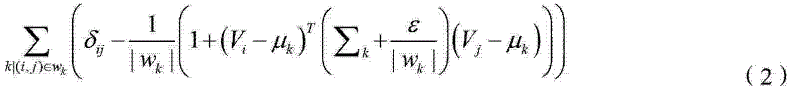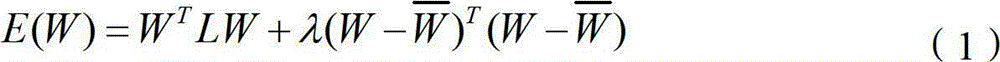Patents
Literature
383 results about "Information recovery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
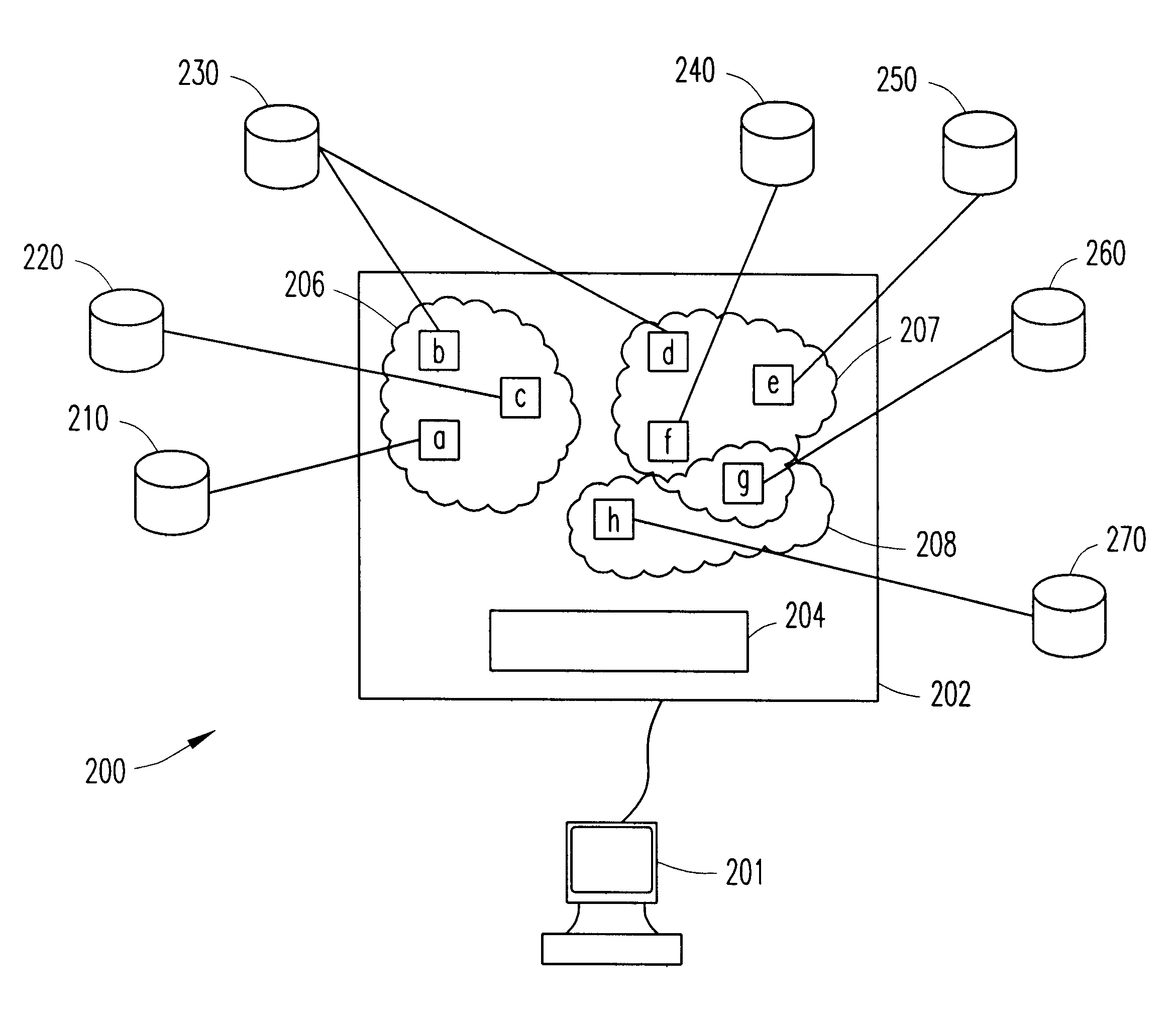
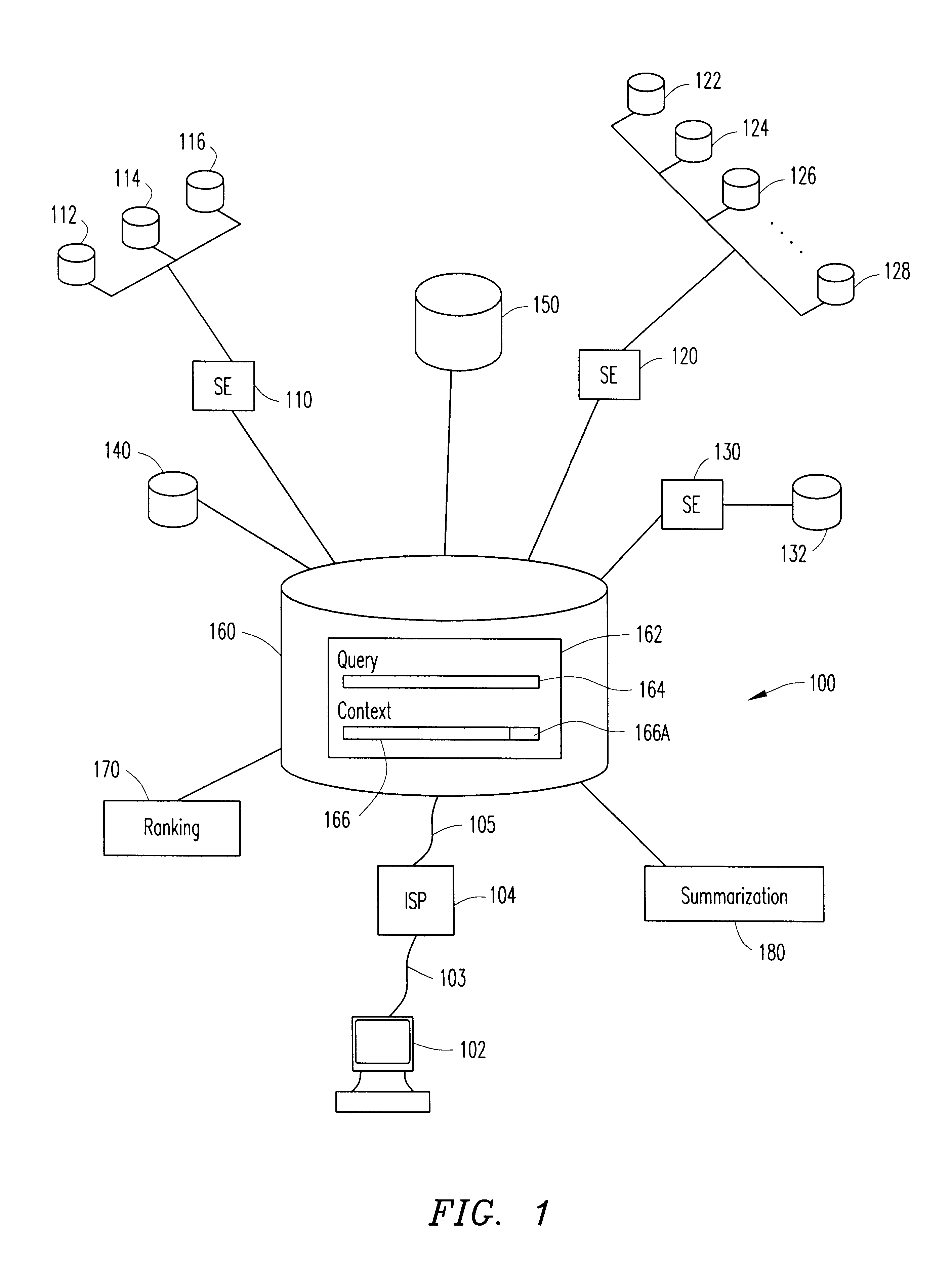
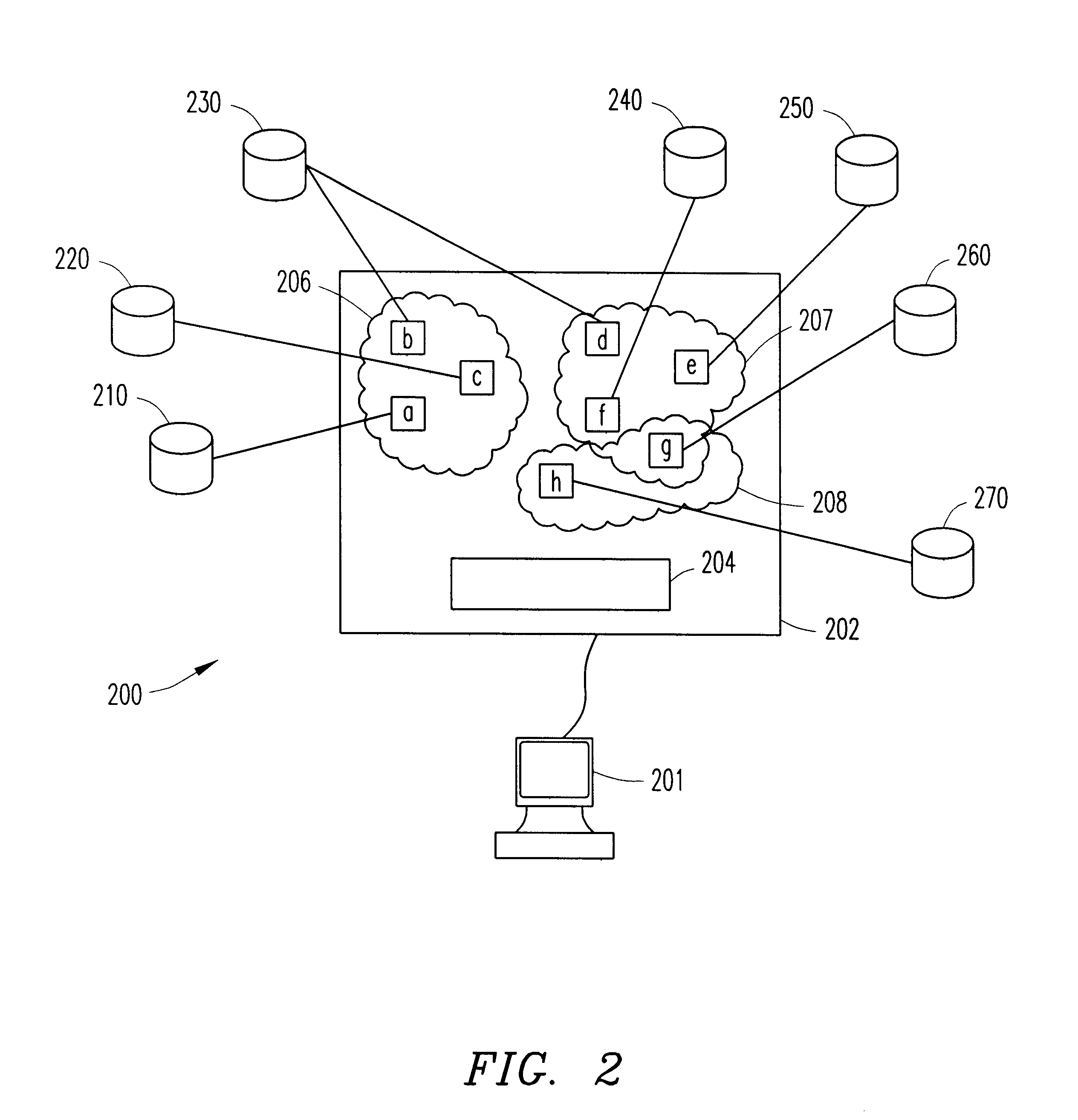
Search engine system and method utilizing context of heterogeneous information resources
InactiveUS6490579B1Data processing applicationsWeb data indexingInformation recoveryInformation resource
A system and method for facilitating the retrieval of information from a system of distributed computers or information resources is disclosed. In particular, the system and method of the present invention improves upon metasearch techniques by including information resource profiles that provide directives to the metasearch engine for facilitating information recovery. These information resource profiles additionally allow for metasearches to recover information from non-indexed information resources such as when browsing the web. Contextual searching is further provided via a grouping of the information resource profiles. The present invention is further directed to tools for the creation and management of the information resource profiles.
Owner:PEROT SYSTEMS
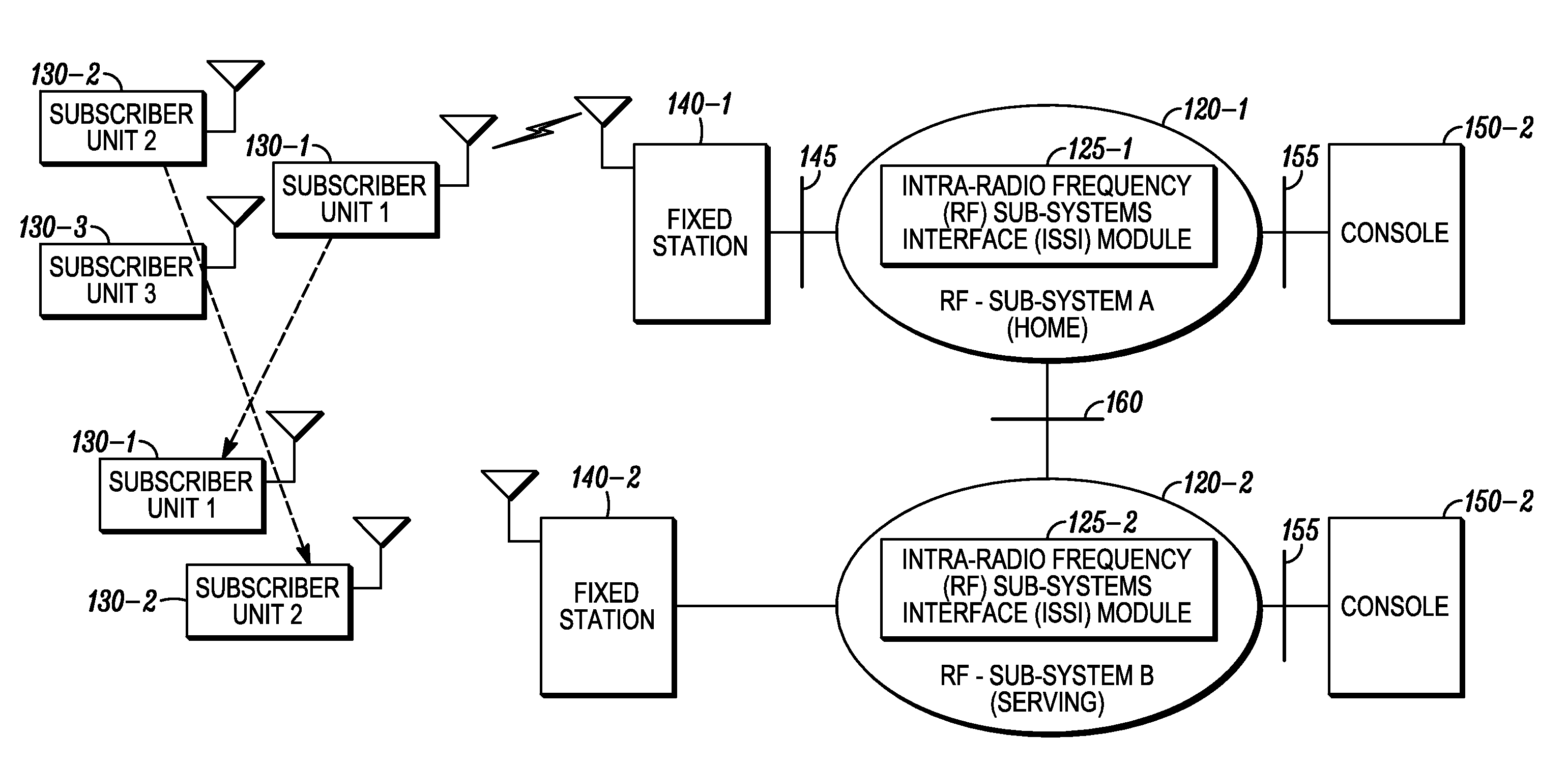
Methods, systems and apparatus for recovering registration information
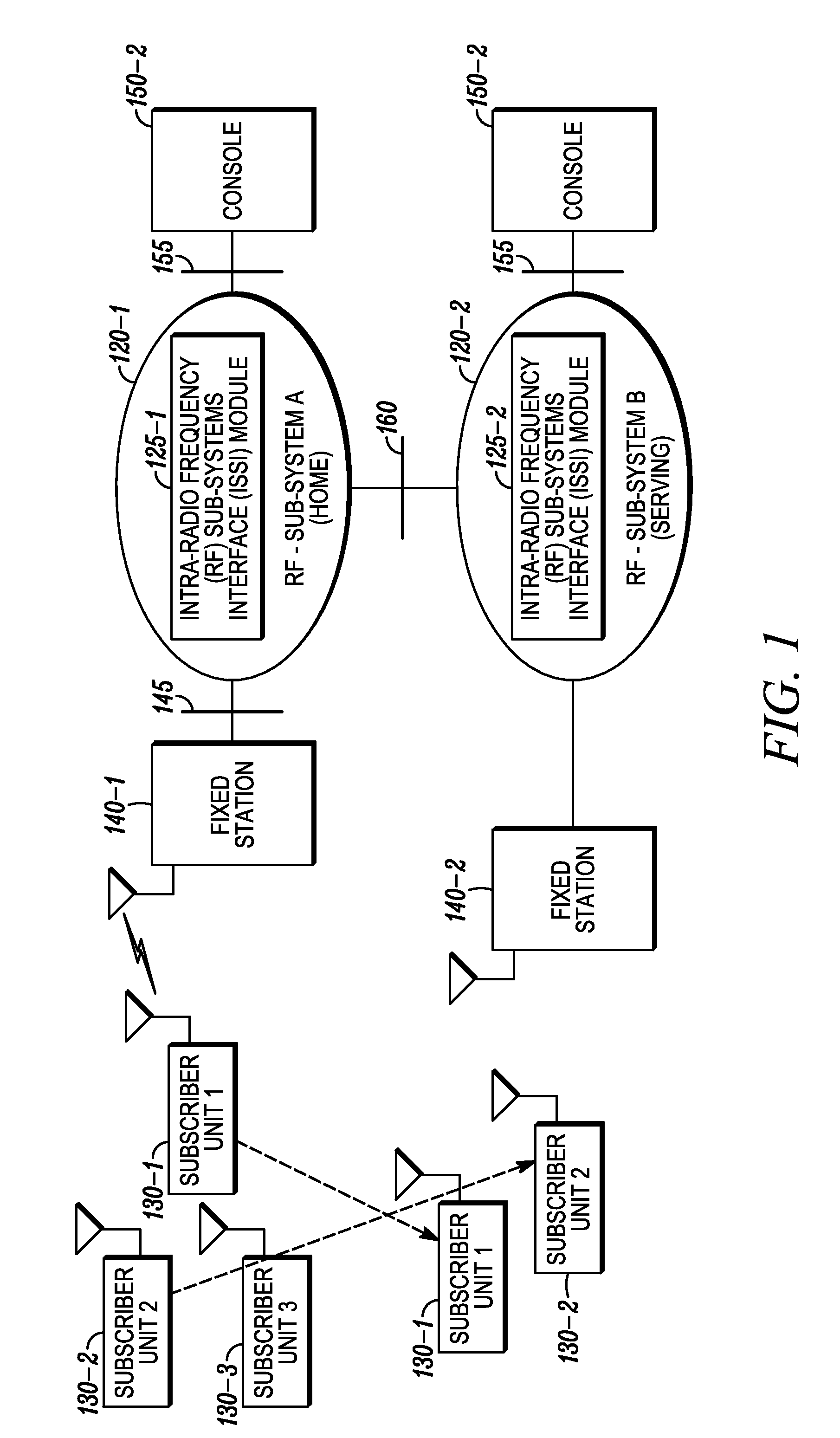
Methods, systems and apparatus are provided for recovering registration information at a home network when the home network determines that it has experienced a loss of the registration information. The home network communicates a triggering message to at least one visited network to initiate registration information recovery, and the visited network responds to the triggering message by communicating registration information for objects that are located at the visited network and that are associated with the home network. These objects may include, for example, subscriber units and / or talk groups that are associated with the home network and have roamed to the visited network.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
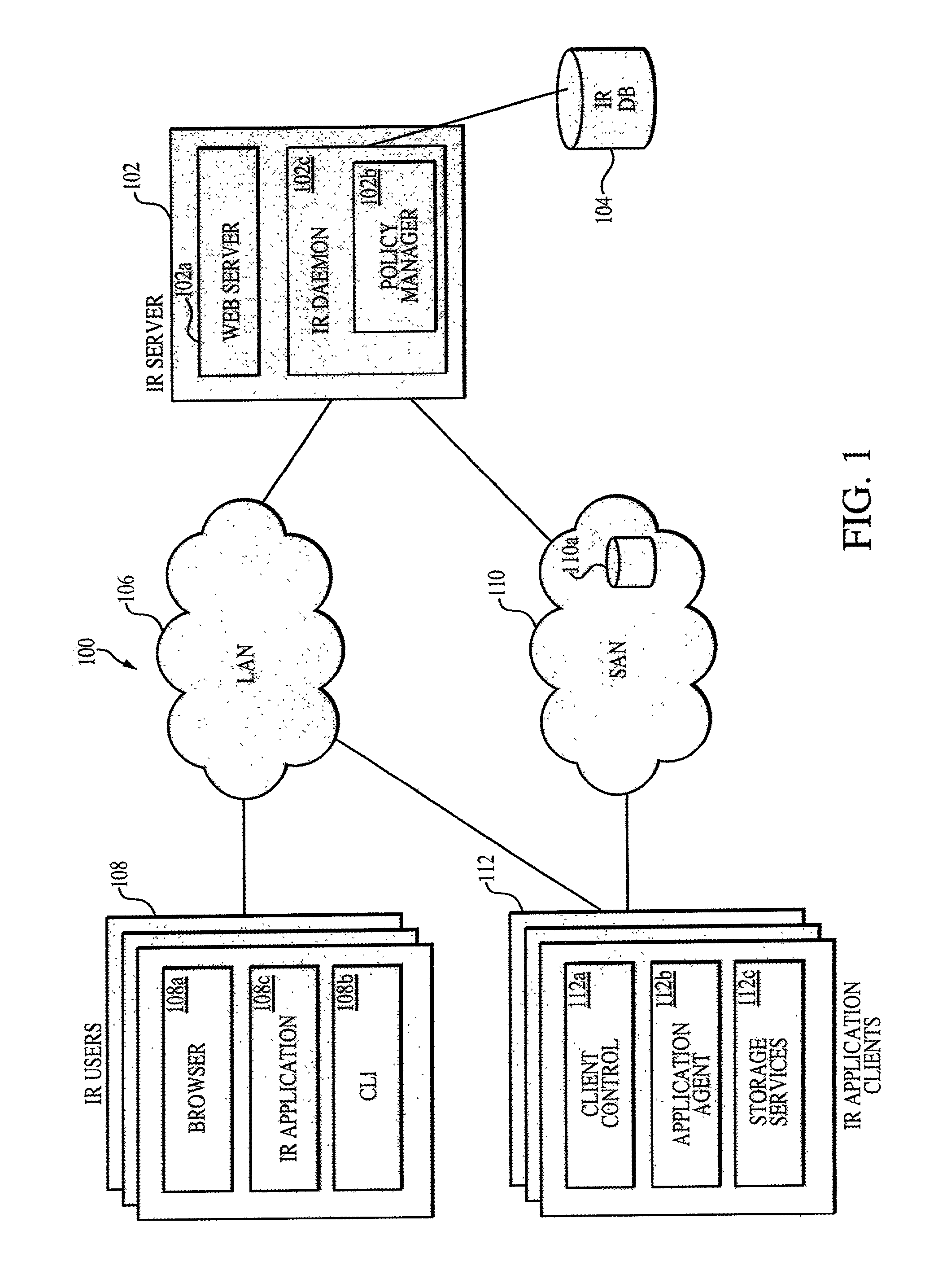
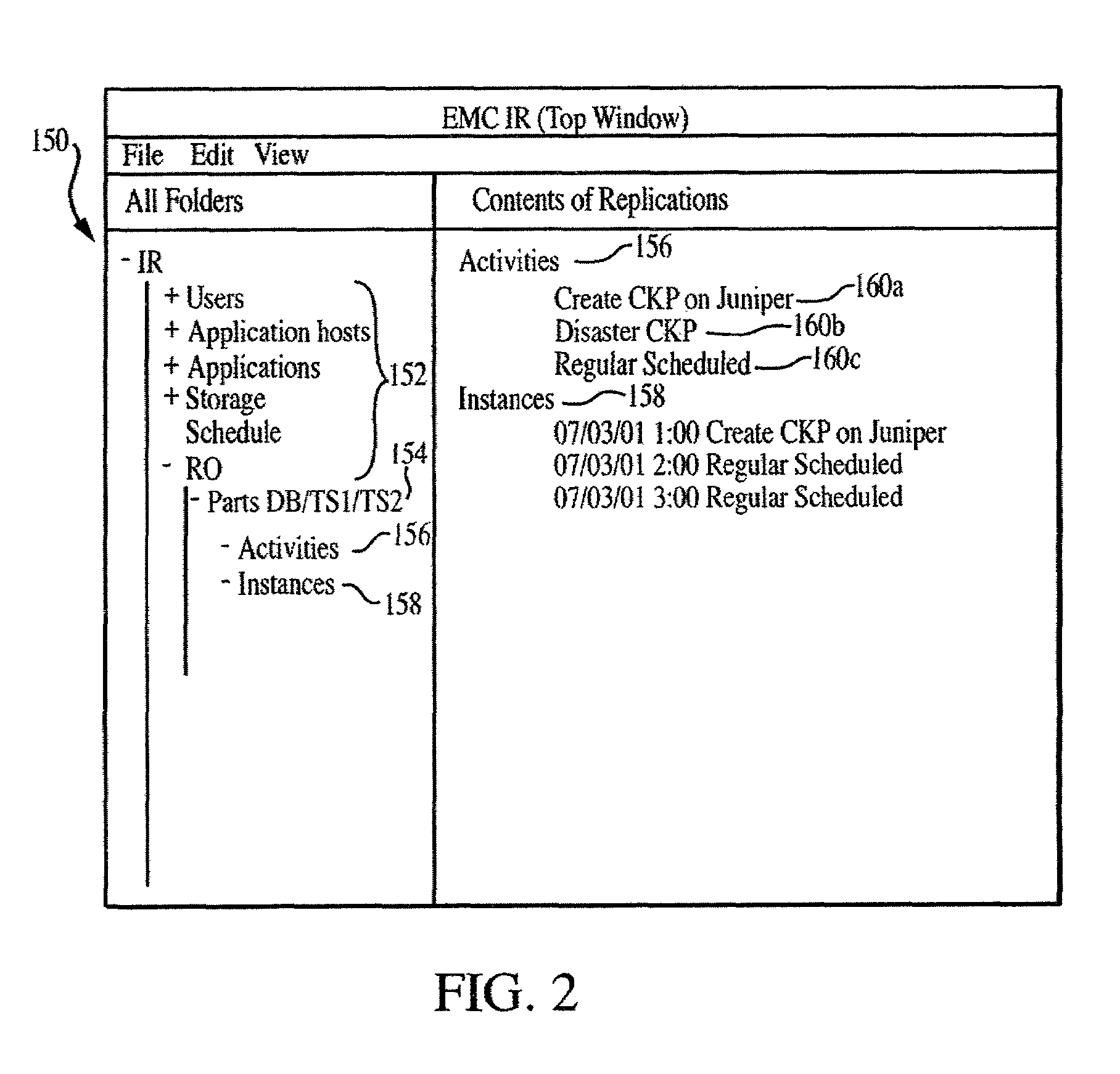
Information replication system having automated replication storage
InactiveUS6978282B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsInformation recoveryDistributed computing
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
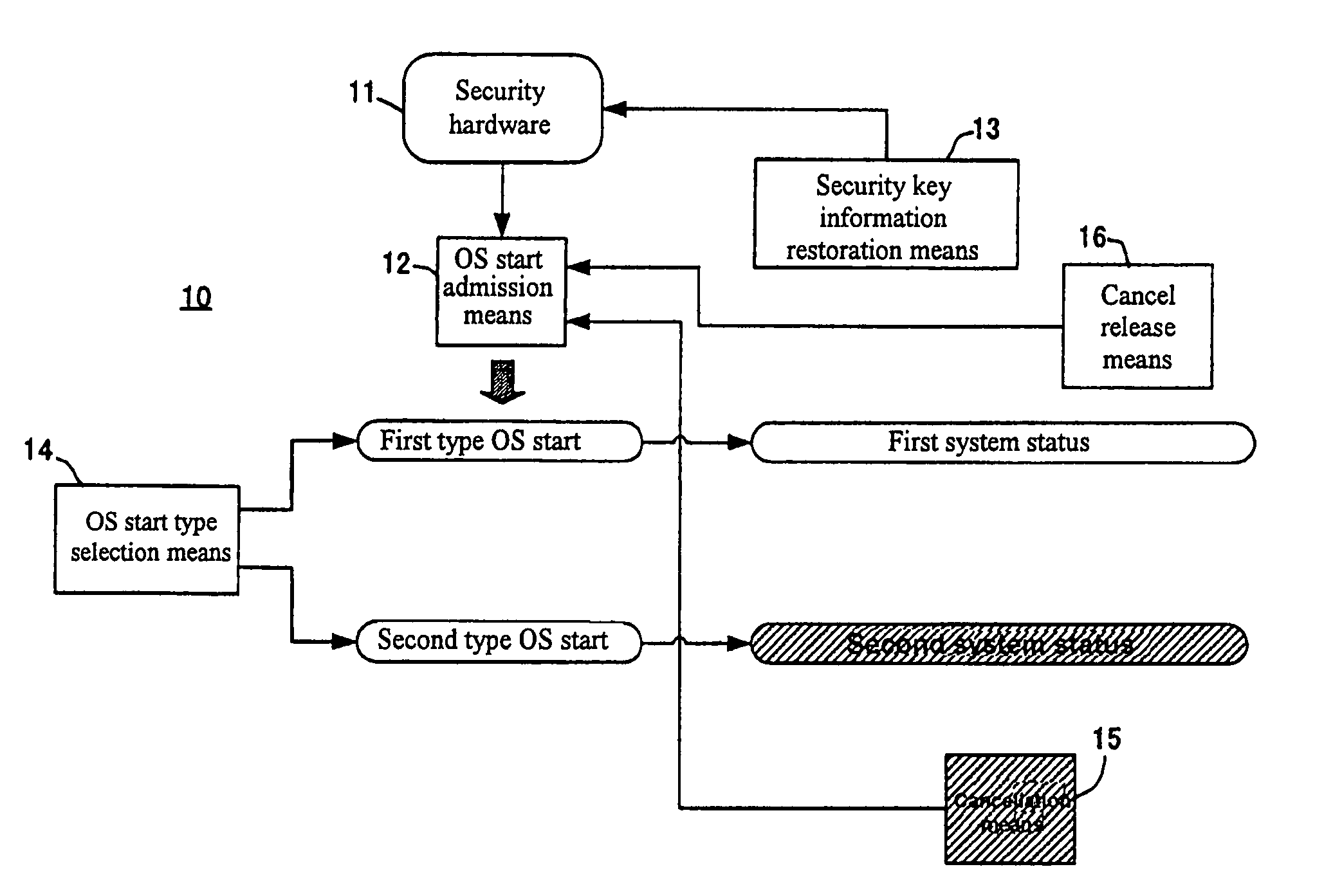
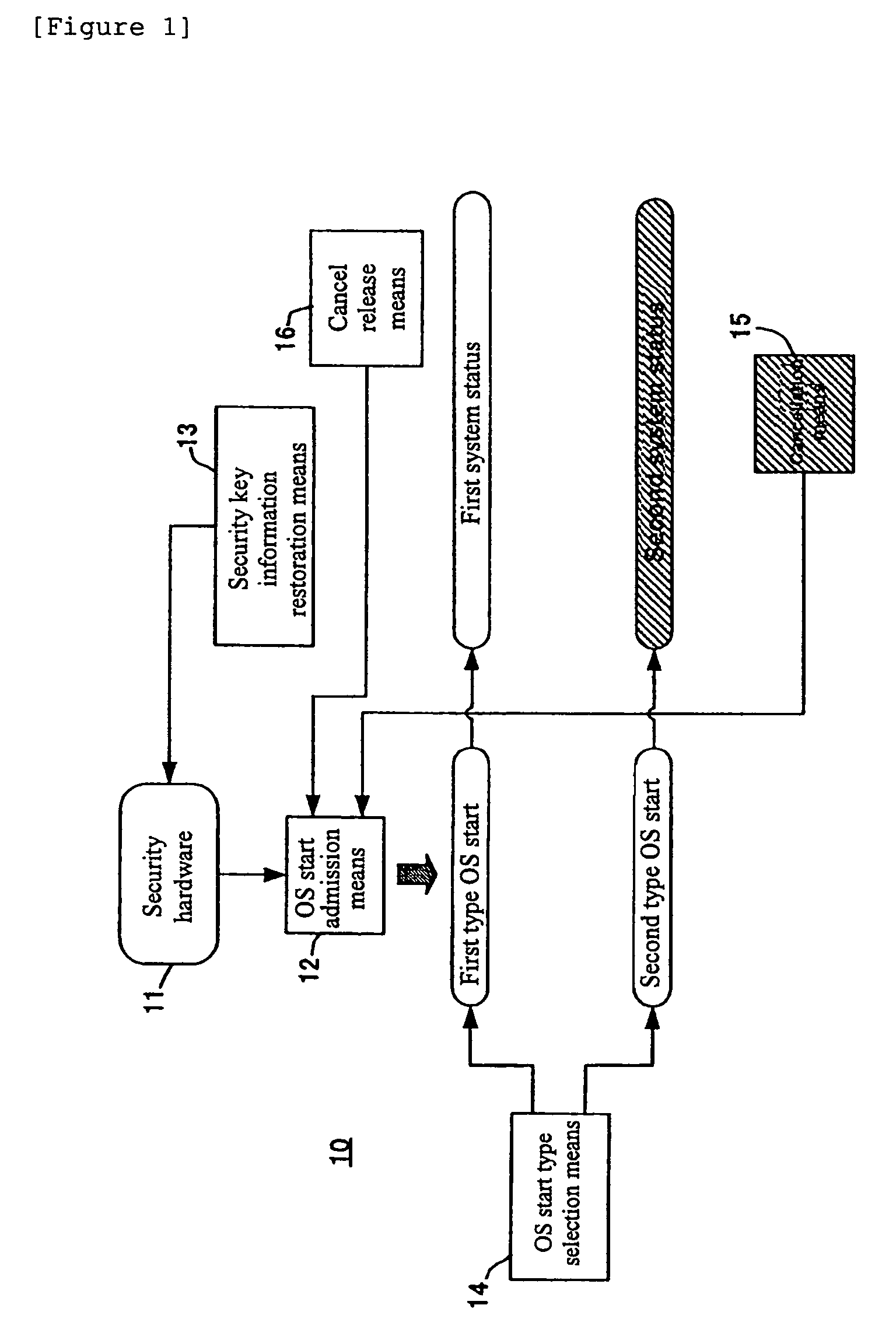
Information processing apparatus for secure information recovery
ActiveUS7290276B2Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsInformation processingInformation recovery
In an information processing apparatus for performing user certification when an OS starts based on security key information of security hardware, a need has arisen to restore the security key information before replacement of the security hardware replaced for troubleshooting. A cancellation means is generated in a second system status generated by a functionally restricted second type OS start such as a safe mode. Although the user certification based on the security key information of the security hardware is usually performed in a first type OS start, the cancellation means cancels it. Thus, it is possible to put the information processing apparatus in a first system status without undergoing the user certification so as to restore the security key information. A cancel release means releases cancellation of the user certification so that the user certification on the first type OS start is restored after the restoration of the security key information.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
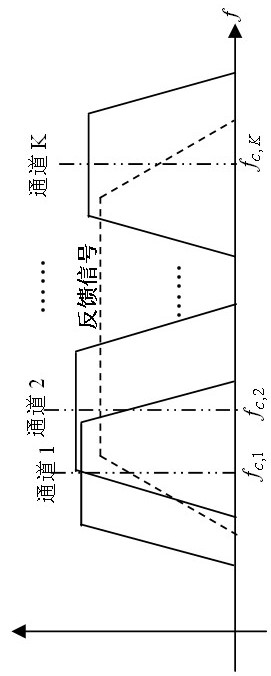
Optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexed communications with nonlinearity compensation
InactiveUS20090190929A1Improve throughputImprove performancePolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsInformation recoveryEngineering
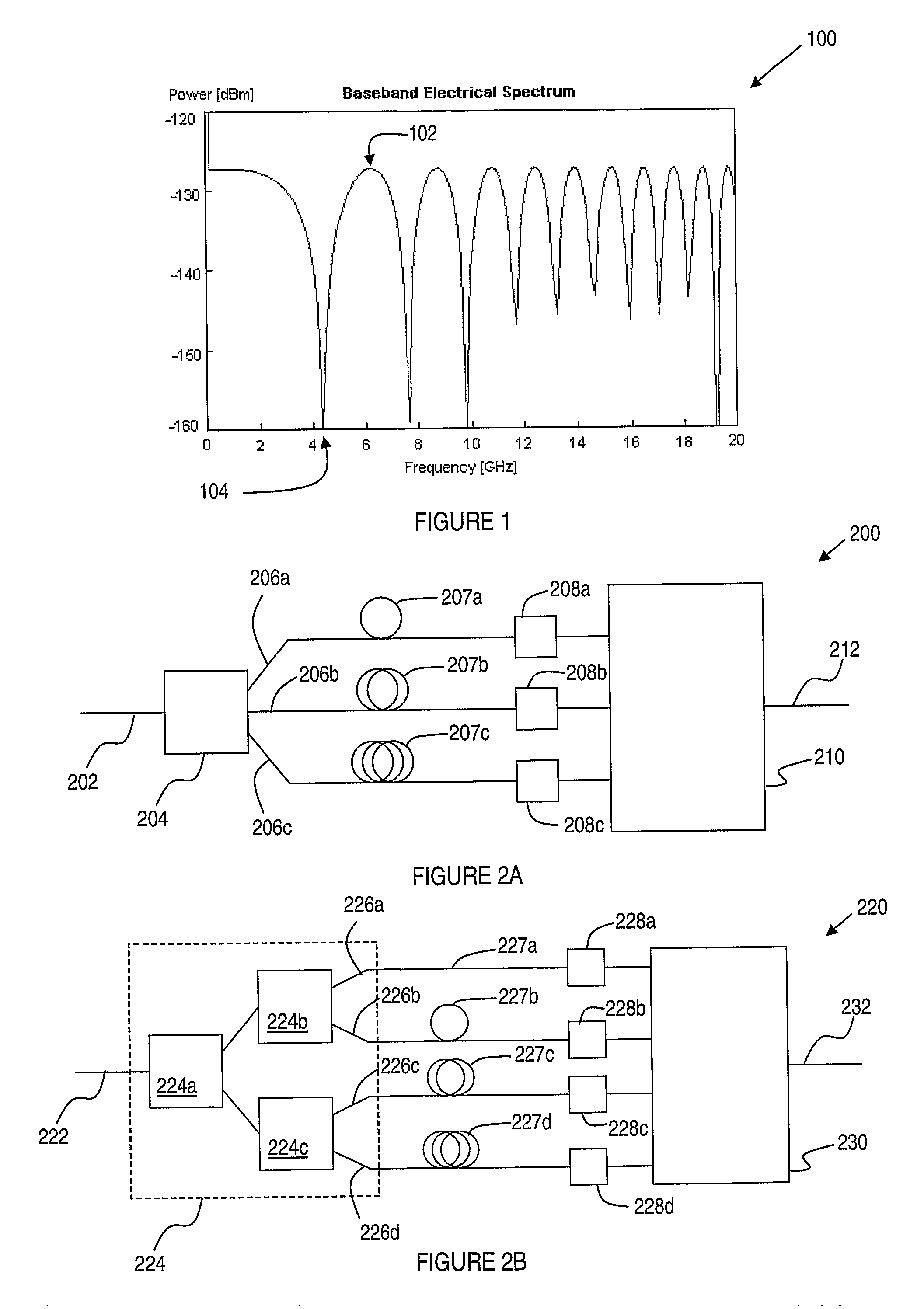
The present invention discloses a transmitter and receiver for optical communications system, which provide compensation of the optical link nonlinearity. M-PSK modulating is used for data embedding in an optical signal in each WDM channel using orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) technique. At the receiver side electrical output signals from a coherent optical receiver are processed digitally with the link nonlinearity compensation. It is followed by the signal conversion into frequency domain and information recovery from each subcarrier of the OFDM signal. At the transmitter side an OFDM encoder provides a correction of I and Q components of a M-PSK modulator driving signal to compensate the link nonlinearity prior to sending the optical signal to the receiver.
Owner:CELIGHT
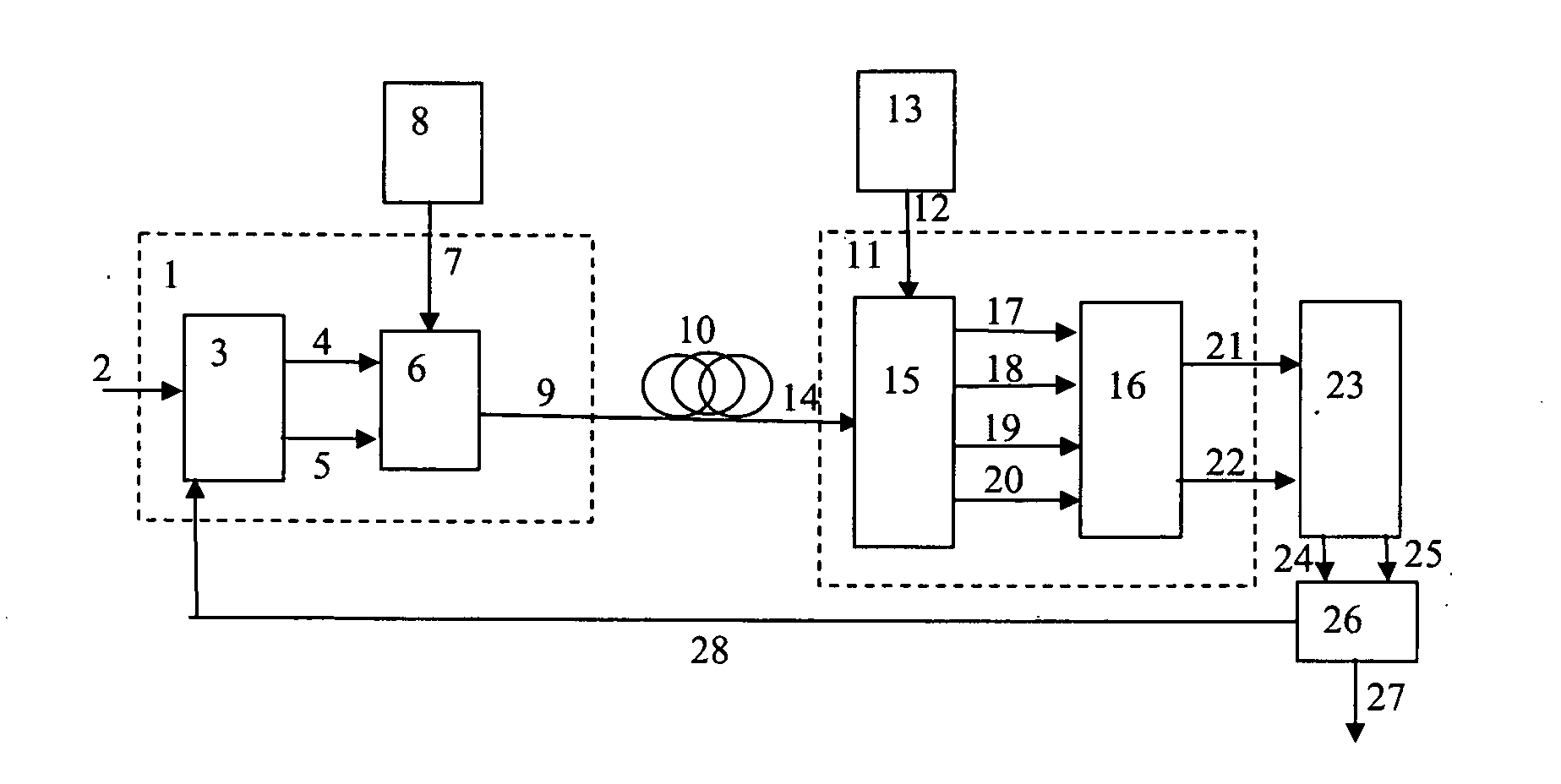
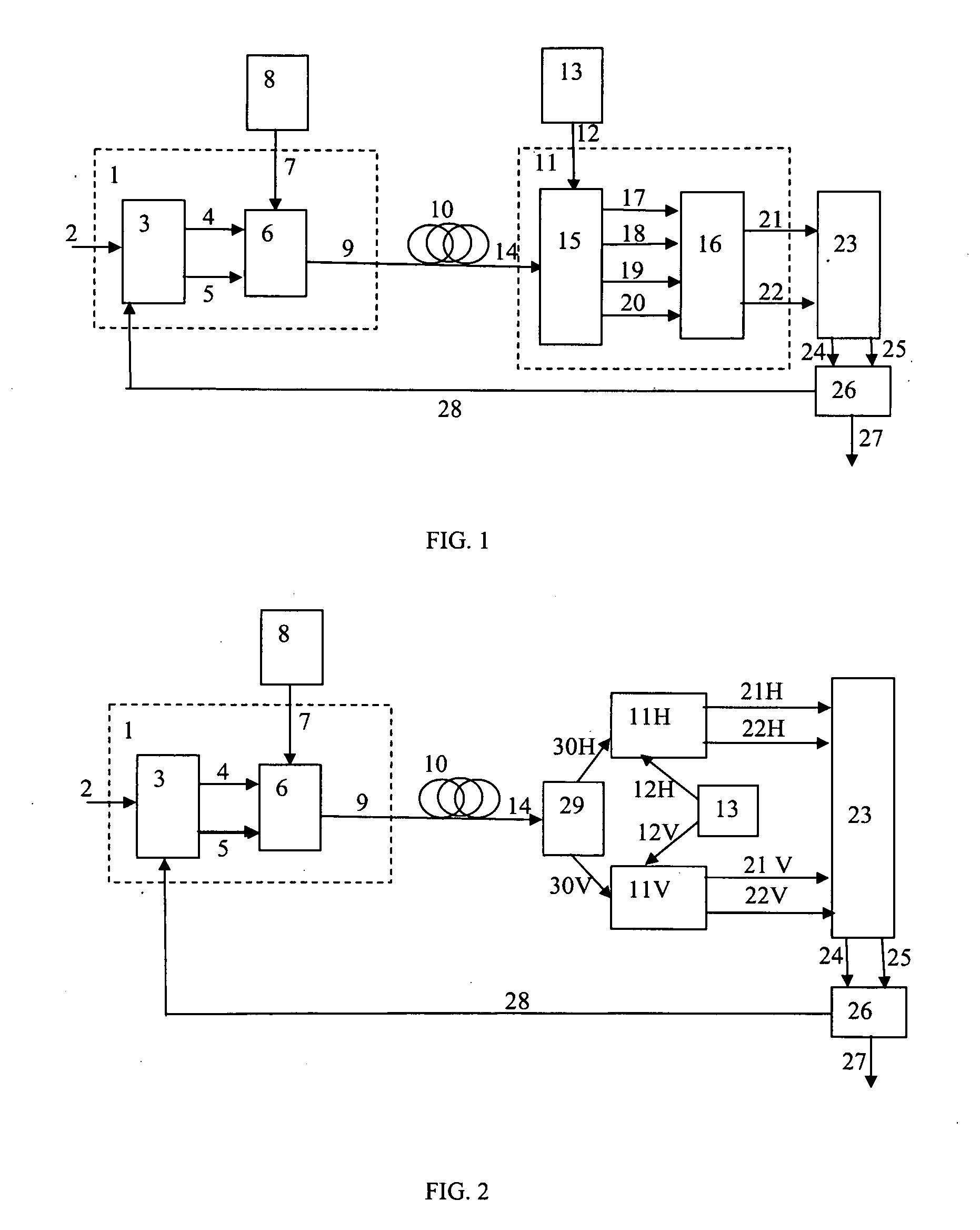
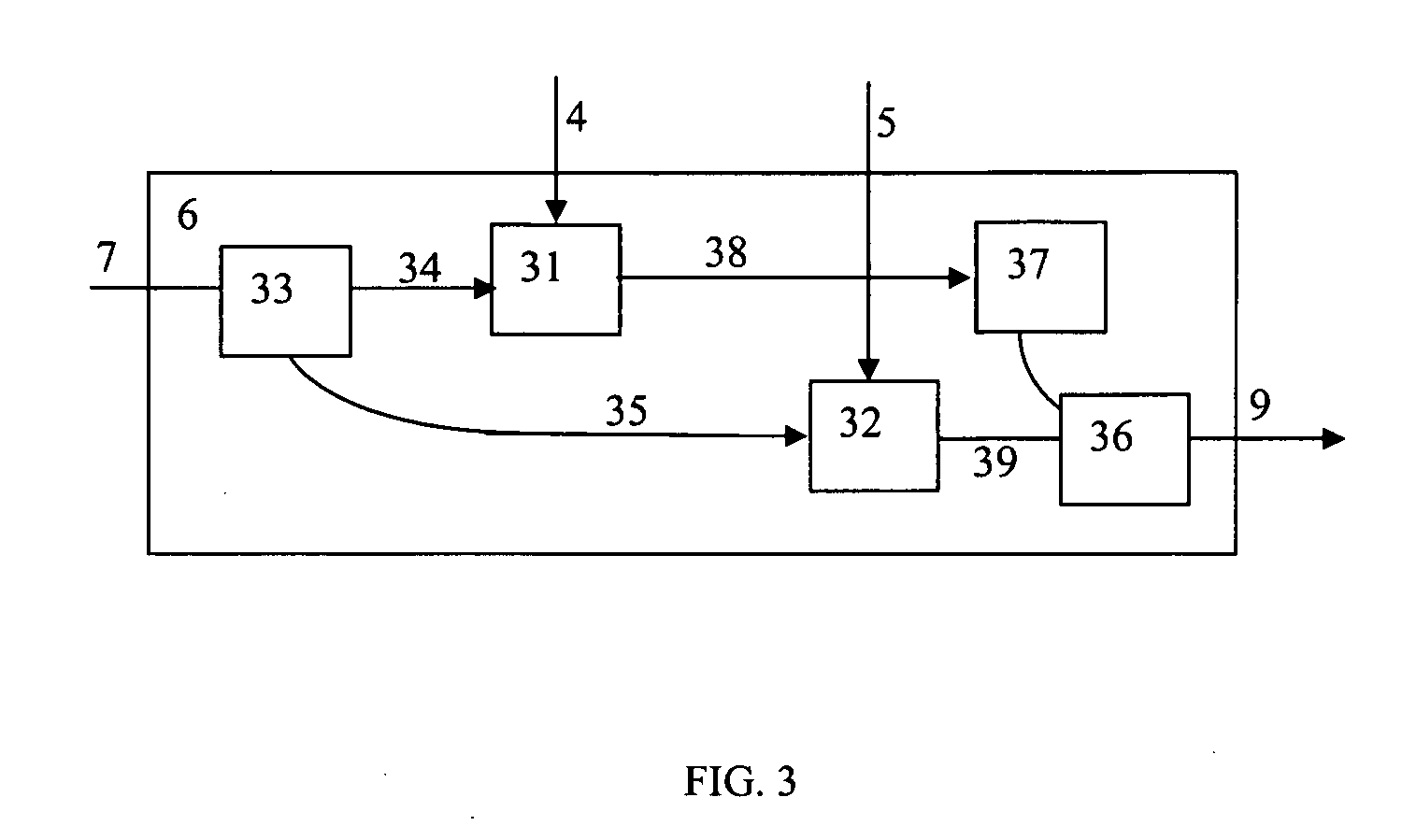
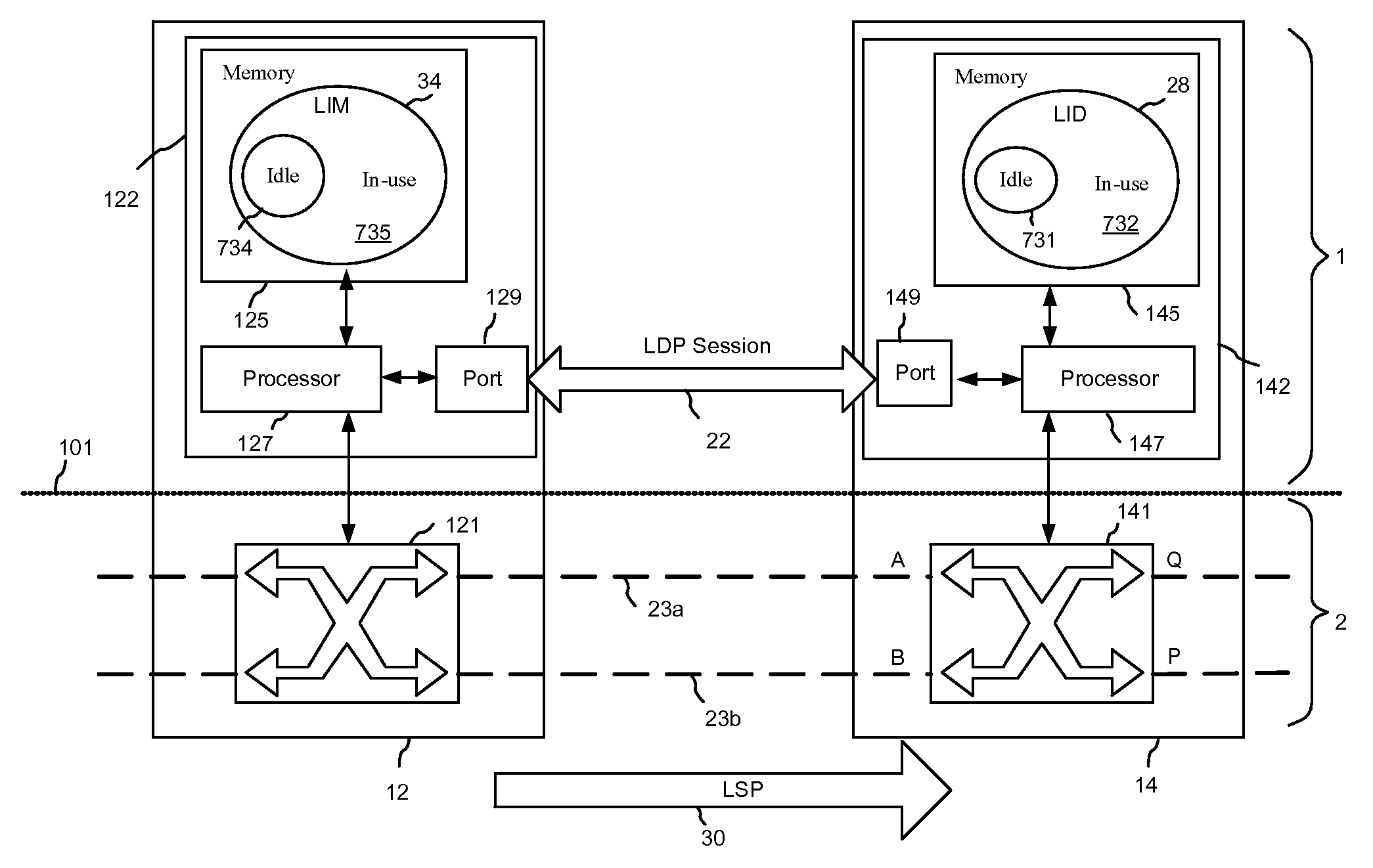
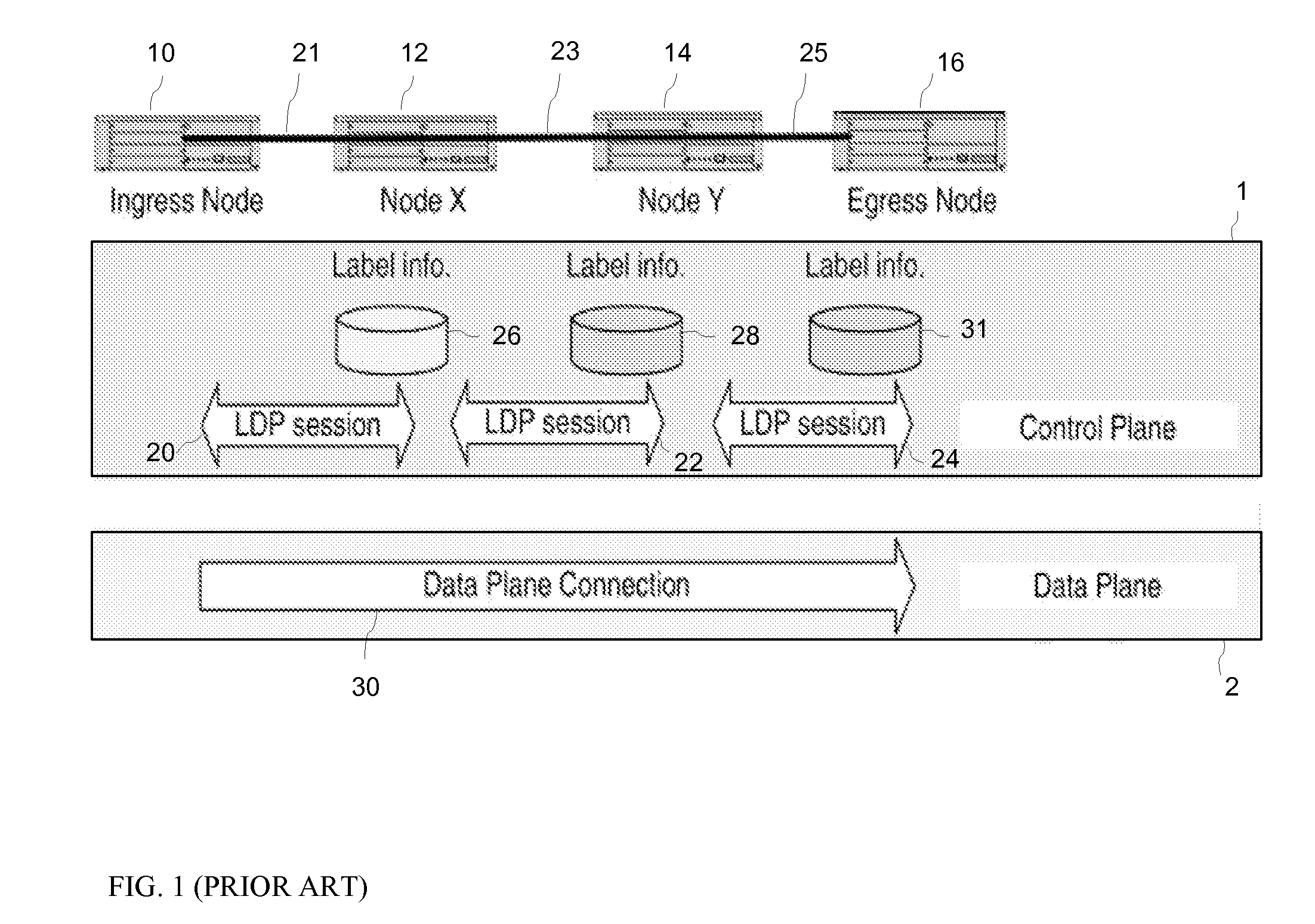
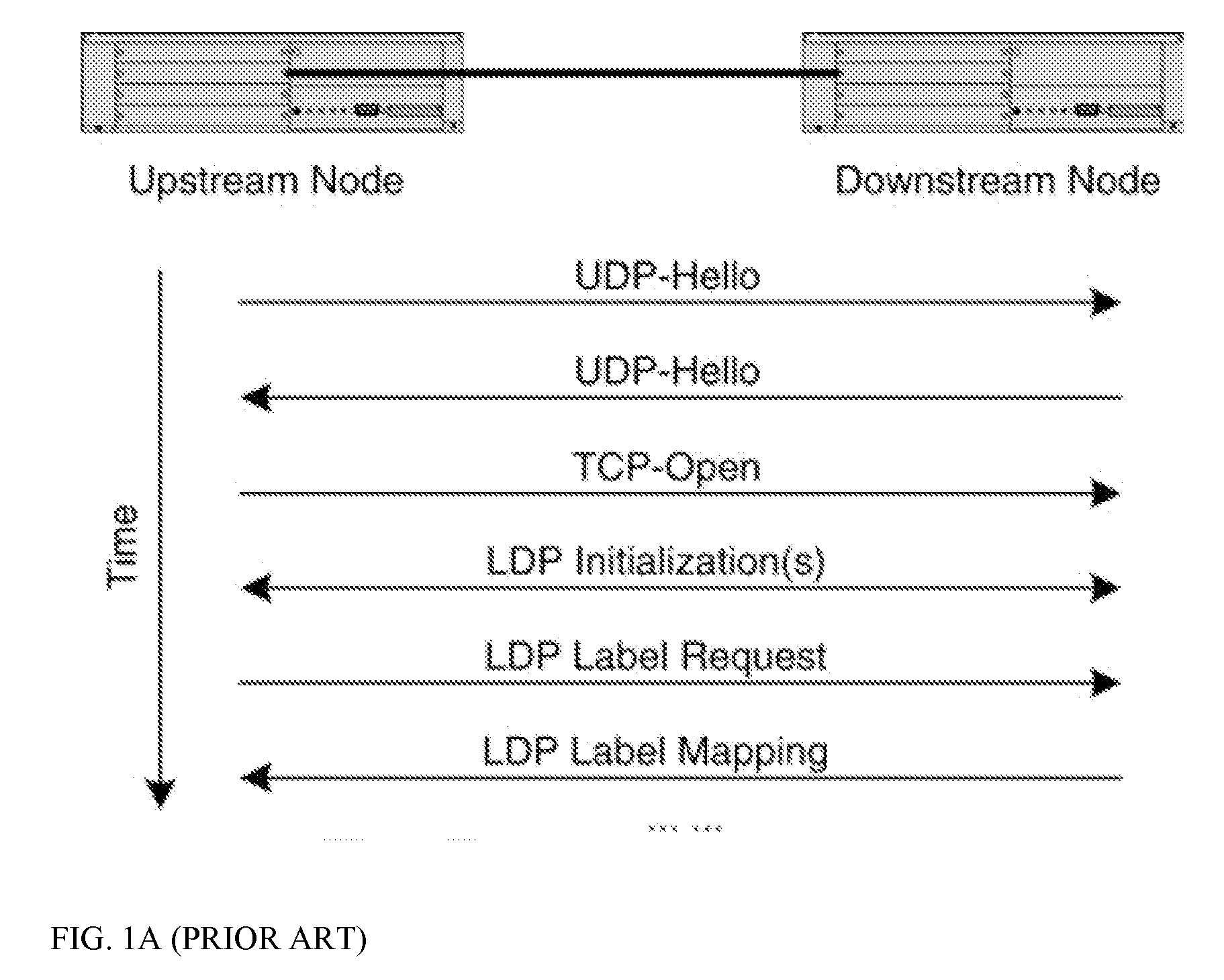
Recovery from Control Plane Failures in the LDP Signally Protocol
InactiveUS20070053359A1Promote recoveryTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationInformation recoveryTwo step
The invention provides a distributed back-up mechanism and a two-step method for facilitating fast control plane recovery in a switched network network. In a preferred embodiment, a Label Information Database (LID) maintained at a control node of a GMPLS network is mirrored to an upstream node using the Label Distribution Protocol (LDP). After a control plane interruption resulting in the LDP restart, the control node, using the mirrored information at the upstream node, conducts first a fast coarse LID recovery wherein only the idle labels are identified, to enable the restarted LDP session to process new connection setup. A detailed LDP state information recovery performs in the background in parallel to the normal LDP operations, e.g. using on-demand LDP queries.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
Image hiding and authentication method based on secret sharing
ActiveCN103761702AImprove securityDifferences in Statistical PropertiesImage data processing detailsPattern recognitionHash function
The invention discloses an image hiding and authentication method based on secret sharing, and belongs to the technical field of secret image sharing. The image hiding and authentication method is characterized by comprising the steps that firstly, difference Huffman encoding is conducted on a secret image, every three generated bit sequences are set to be one group to be converted into decimal numbers which are used as coefficients of a sharing polynomial in the Shamir (k, n) threshold scheme, the k and the n are positive integers, the k is smaller than or equal to the n, and n shadow images are generated; secondly, n significant carrier images are selected, the generated shadow images are embedded into the carrier images in a matrix encoding mode, authentication bits generated by the hash function are also embedded into the carrier images, and n disguise images are formed and are in the charge of n different participants respectively. The disguise images generated through the image hiding and authentication method has higher visual quality, existence of secret information cannot be perceived by attackers easily, and the safety of the secret information is ensured. Meanwhile, before the secret information is recovered, the disguise images provided by each participant need to be authenticated, only the disguise images passing through authentication can participate in recovery of the secret information, and the safety of the secret information is further strengthened.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Information replication system mounting partial database replications
ActiveUS7076685B2Easy to understandInput/output to record carriersError preventionInformation recoveryTablespace
An information recovery system mounts partial database replications, such as selected tablespaces, on a target host.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Storage apparatus using nonvolatile memory as cache and mapping information recovering method for the storage apparatus
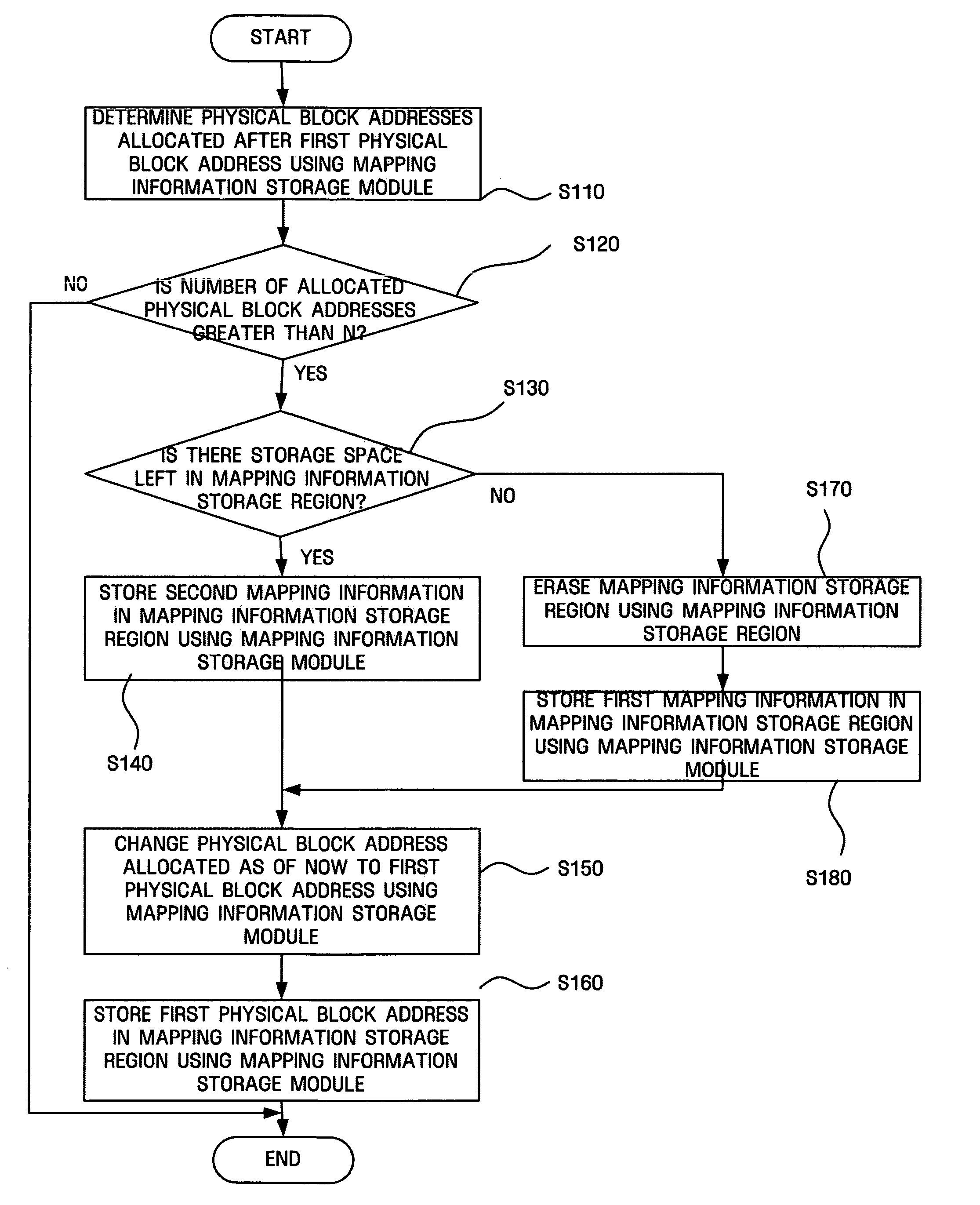
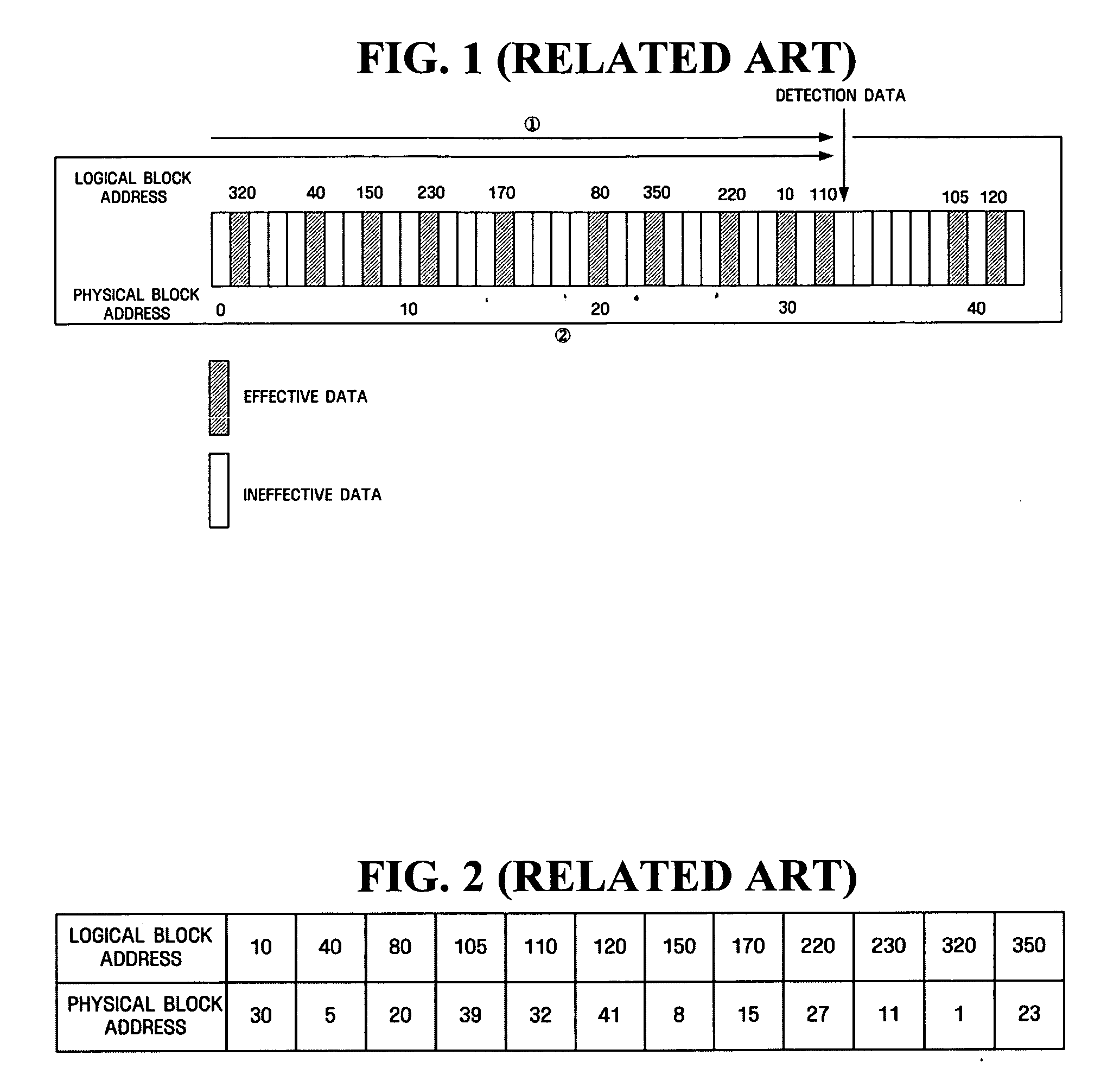
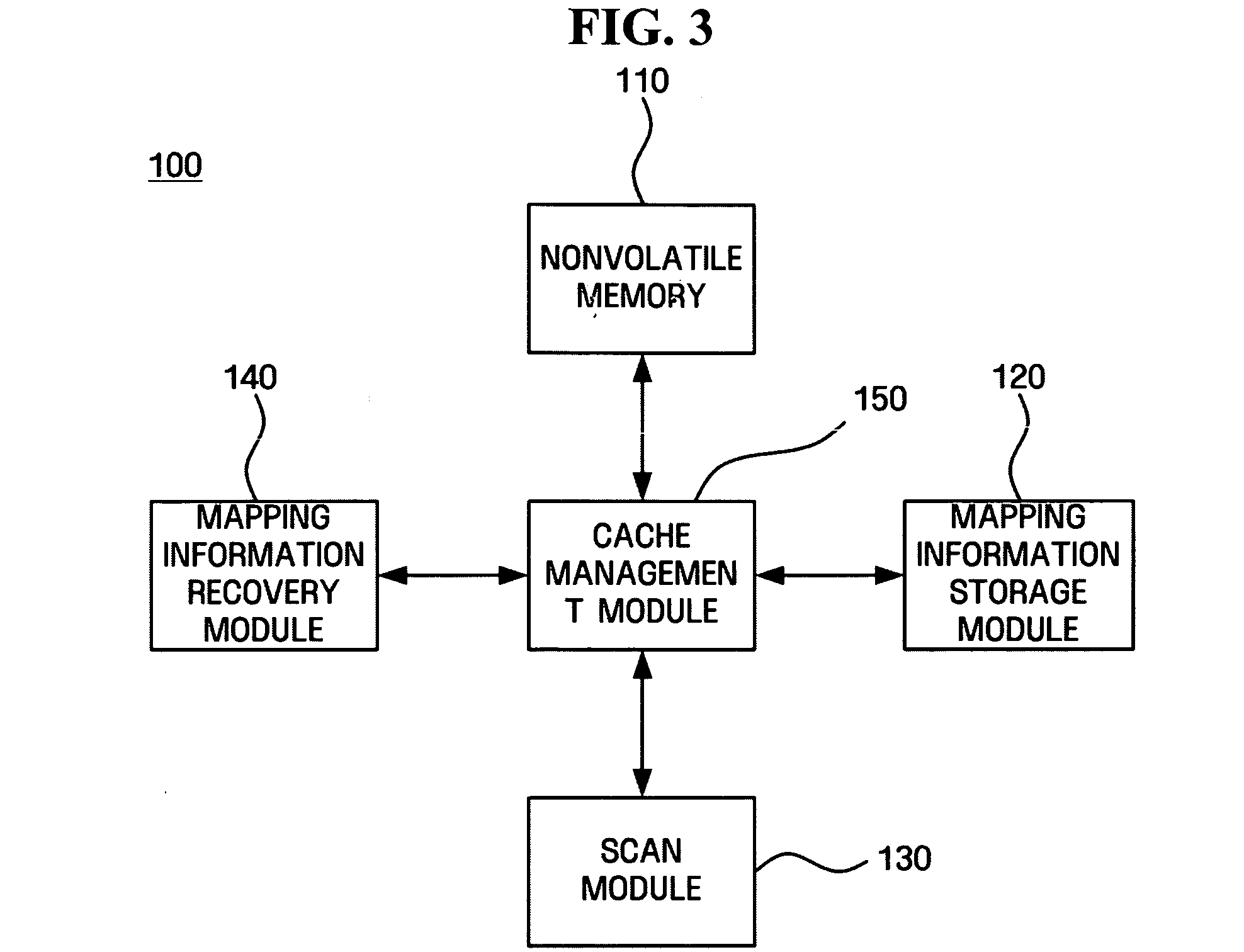
ActiveUS20070204100A1Promote recoveryMemory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionInformation recoveryOperating system
A storage apparatus using a nonvolatile memory as a cache and a mapping information recovering method for the storage apparatus are provided. The storage apparatus includes a mapping information storage module which stores in the nonvolatile memory mapping information of the nonvolatile memory and a first physical block address allocated when the mapping information is stored; a scan module which scans the first physical block address through a second physical block address allocated currently; and a mapping information recovery module which recovers the mapping information between the first physical block address and the second physical block address based on a result of the scan by the scan module.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
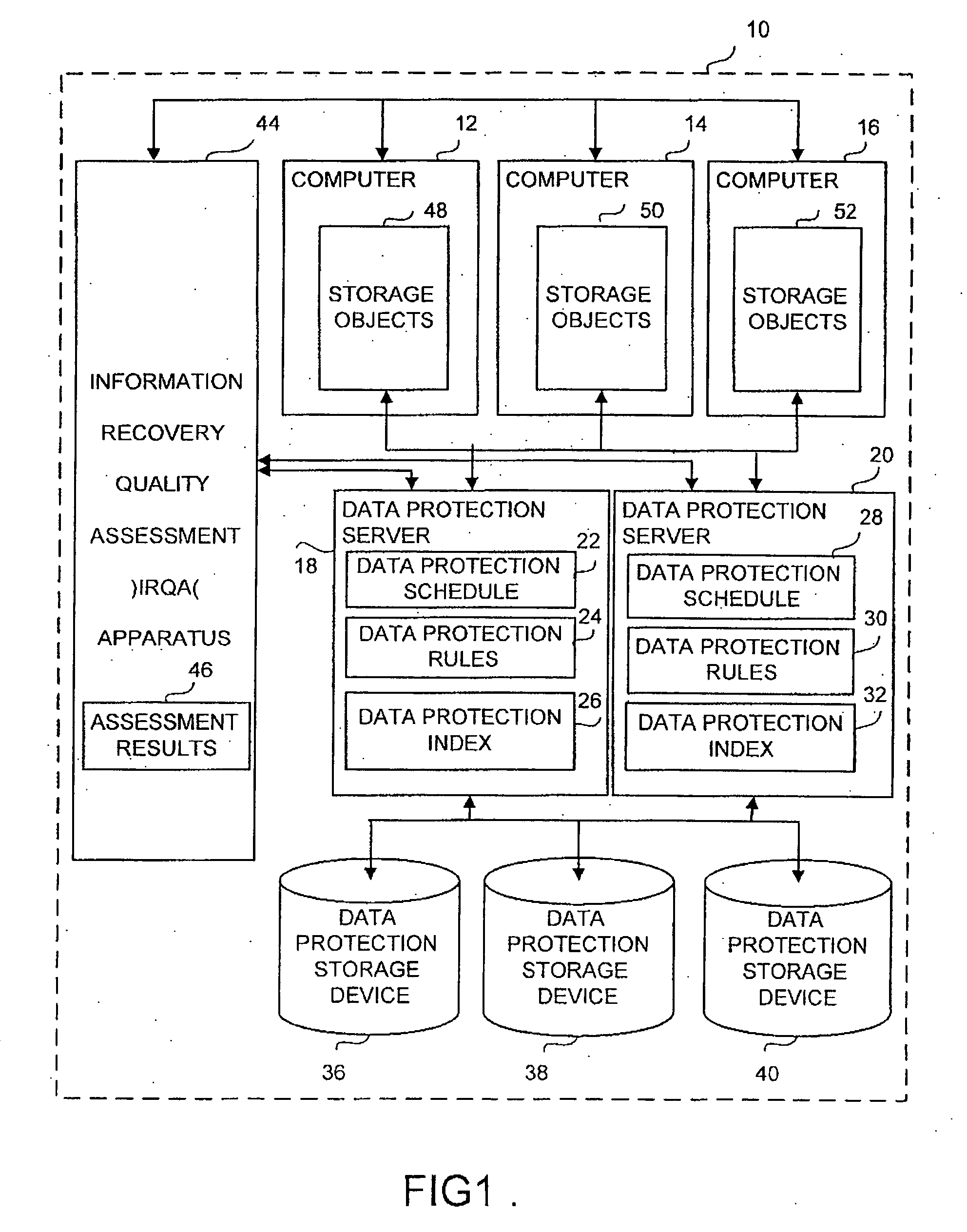
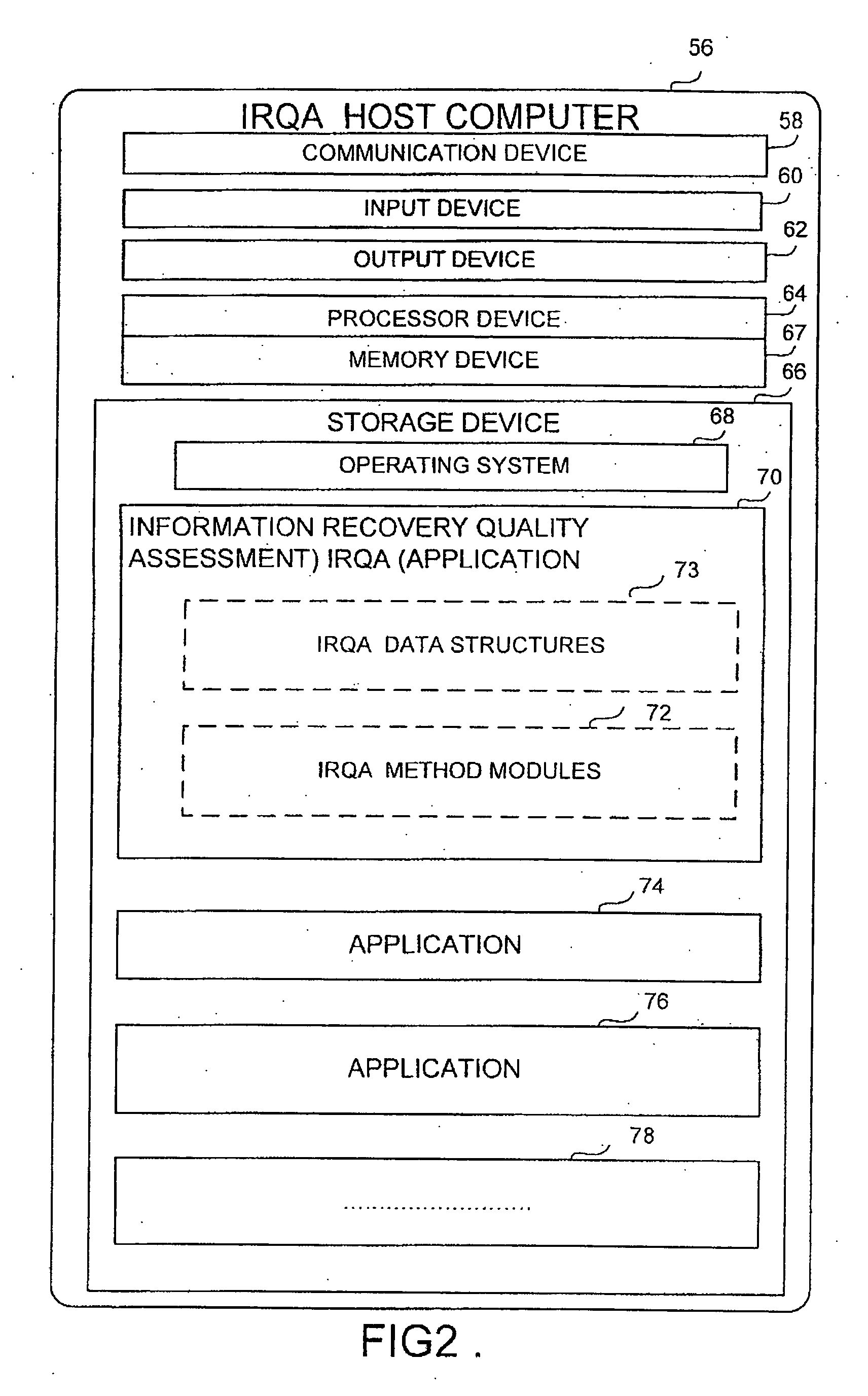
Apparatus and method for information recovery quality assessment in a computer system
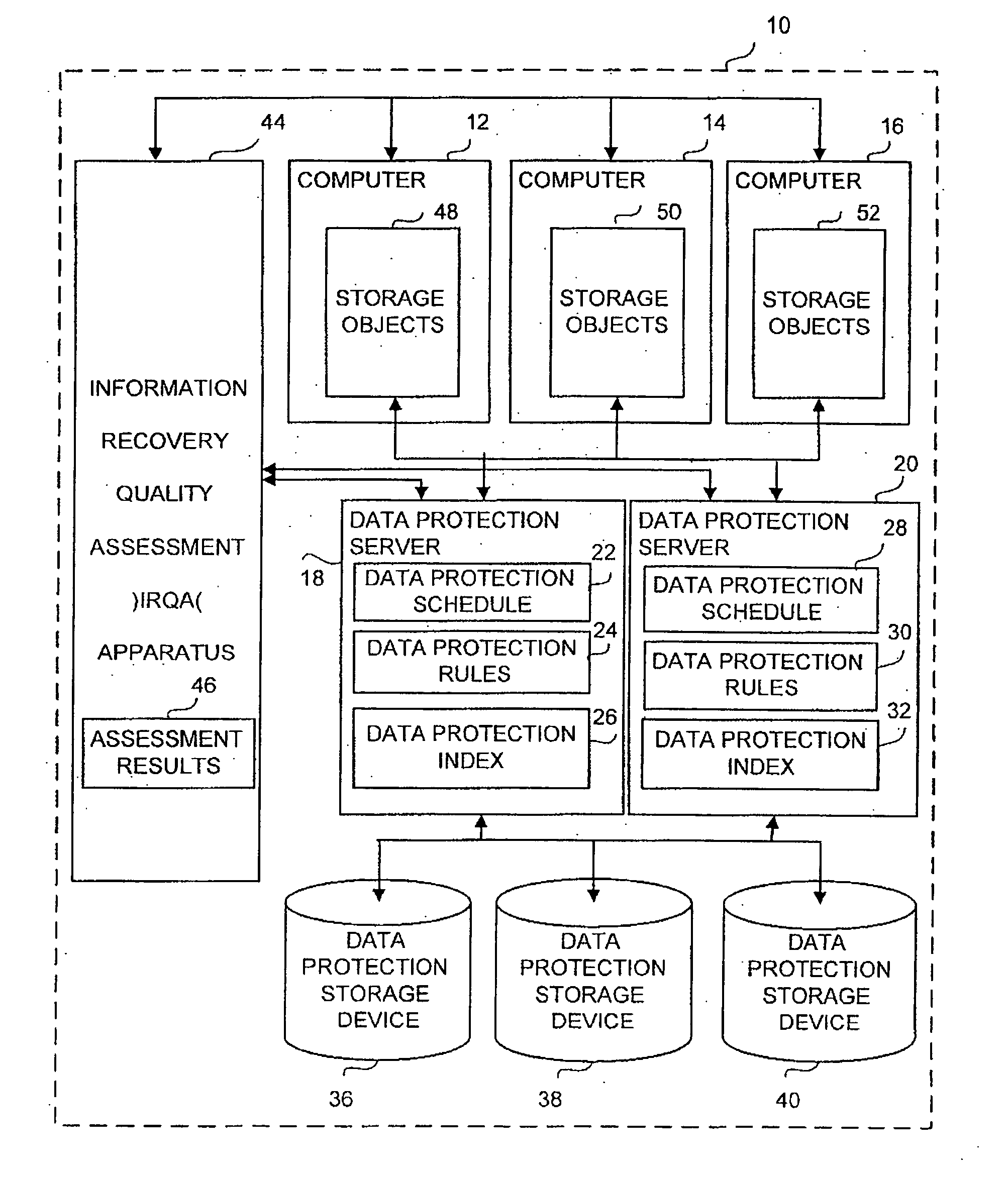
ActiveUS20060288183A1Error detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsInformation recoveryProtection domain
An apparatus and method for information recovery quality assessment in a computing environment is disclosed. This includes a group of inter-related software modules and associated data structures that analyze and assess the recoverability of the network data through the data protection configuration setup and a previously performed data protection process. It examines in a comprehensive manner the recoverability perspective across a pre-defined data protection domain, such as a computer network with an organization. The results of the examination provide for the display of inconsistencies of data protection configuration and previously performed data protection processes that consequently result in problems of recovering the network objects in an appropriate manner.
Owner:EMC BENELUX R L
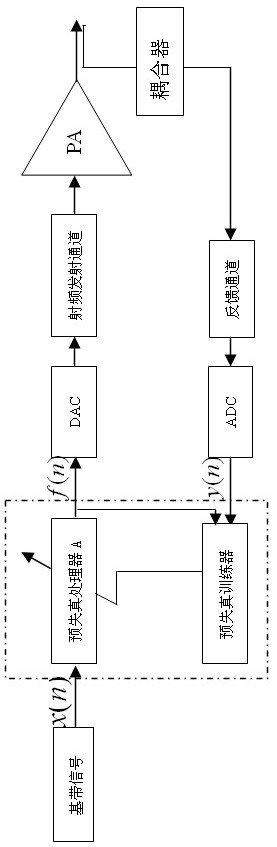
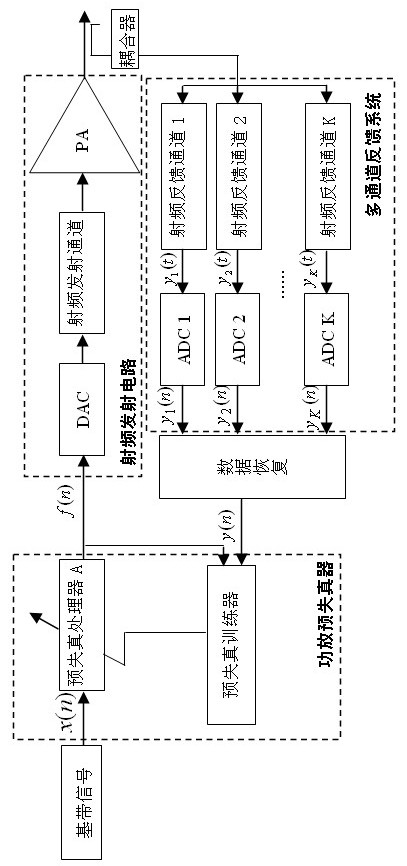
Power amplifier linearization correcting circuit and method based on multi-channel feedback
ActiveCN102055411ASolve problems that are difficult to achieve high linearityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersNonlinear distortionFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a power amplifier linearization correcting circuit and method based on multi-channel feedback, relates to a linearization technology in the technical field of communication, and aims to provide a power amplifier linearization correcting circuit and method capable of self-adaptively regulating a predistortion parameter of a system by tracking the linearization characteristic of a radio frequency power amplifier. The power amplifier linearization correcting method is technically characterized in that a signal output by a power amplifier is subjected to frequency spectrumdivision and is coupled to a feedback system by utilizing a plurality of paths of channels; a data recovery circuit recovers a plurality of paths of feedback information to form a path of signal; a predistortion trainer calculates the predistortion parameter by utilizing a baseband signal and a recovered feedback signal; a predistortion trainer A adds a predistortion signal complementing a nonlinear distorted signal of the power amplifier according to the predistortion parameter; and the predistortion signal in the baseband signal is counteracted in the power amplifier, thereby realizing the linearization correction of the power amplifier. The invention is mainly used for nonlinear predistortion correction of a radio frequency signal emission system.
Owner:CHENGDU KAITENG SIFANG DIGITAL RADIO & TELEVISION EQUIP CO LTD
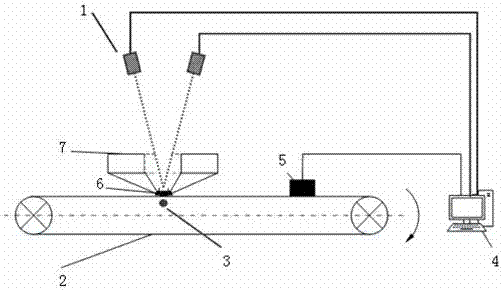
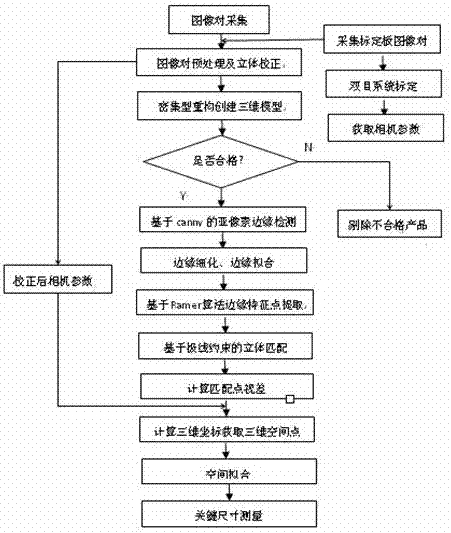
Binocular-stereoscopic-vision-based workpiece detection and three-dimensional measurement system and detection method
InactiveCN106969706ALess edge burrsHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisInformation recoveryImaging processing
The invention provides a real-time workpiece detection and three-dimensional measurement method based on binocular stereoscopic vision and an image processing system for realizing the method. A measuring system is composed of an image acquisition module, a camera calibration module, an image preprocessing module, a stereo correction module, a three-dimensional information recovery module and a detection and measurement module. Therefore, real-time and non-contact detection and measurement of workpieces in batches can be realized.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
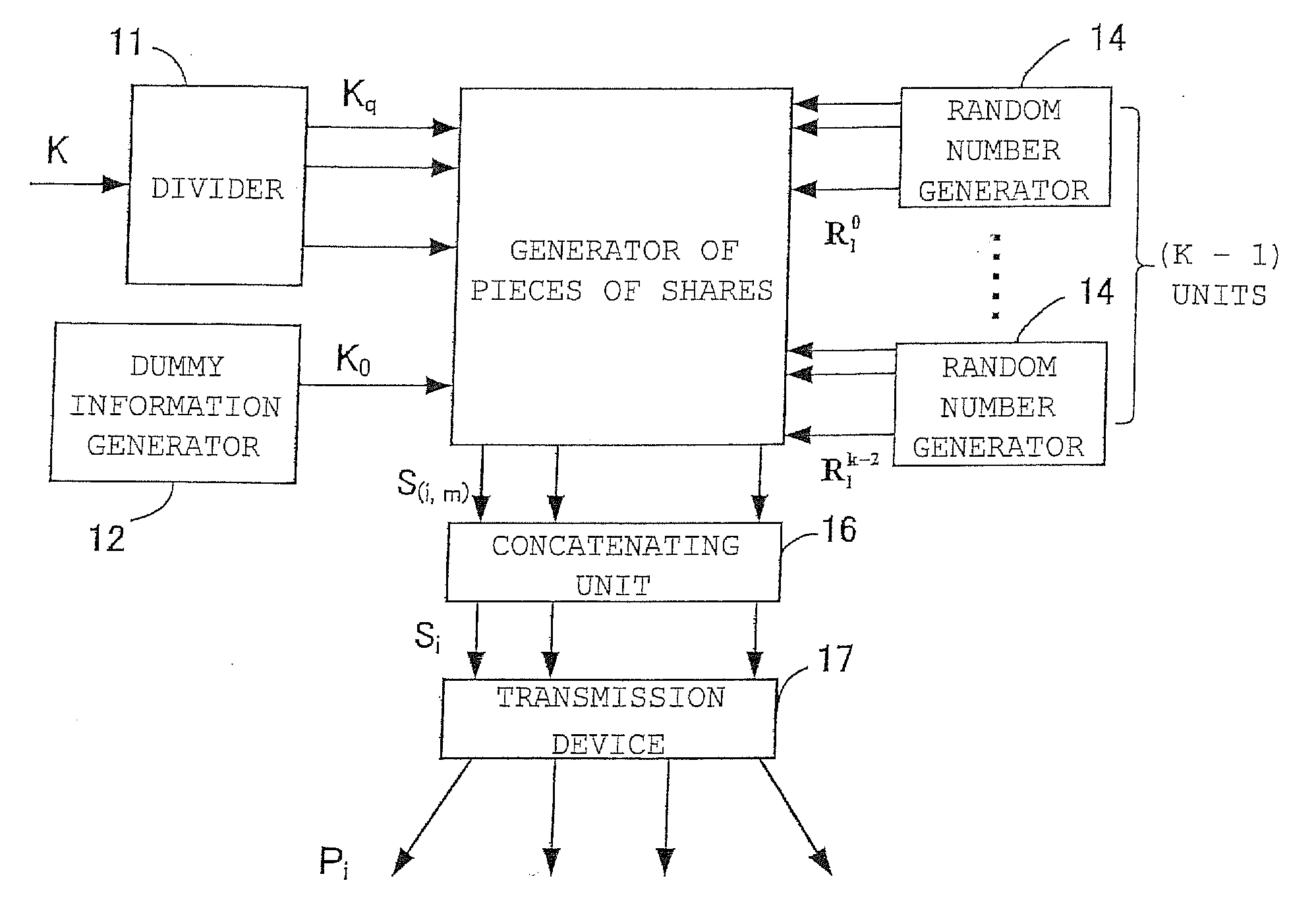
Threshold secret sharing apparatus, threshold secret sharing scheme, secret information decryption method, and program for the same
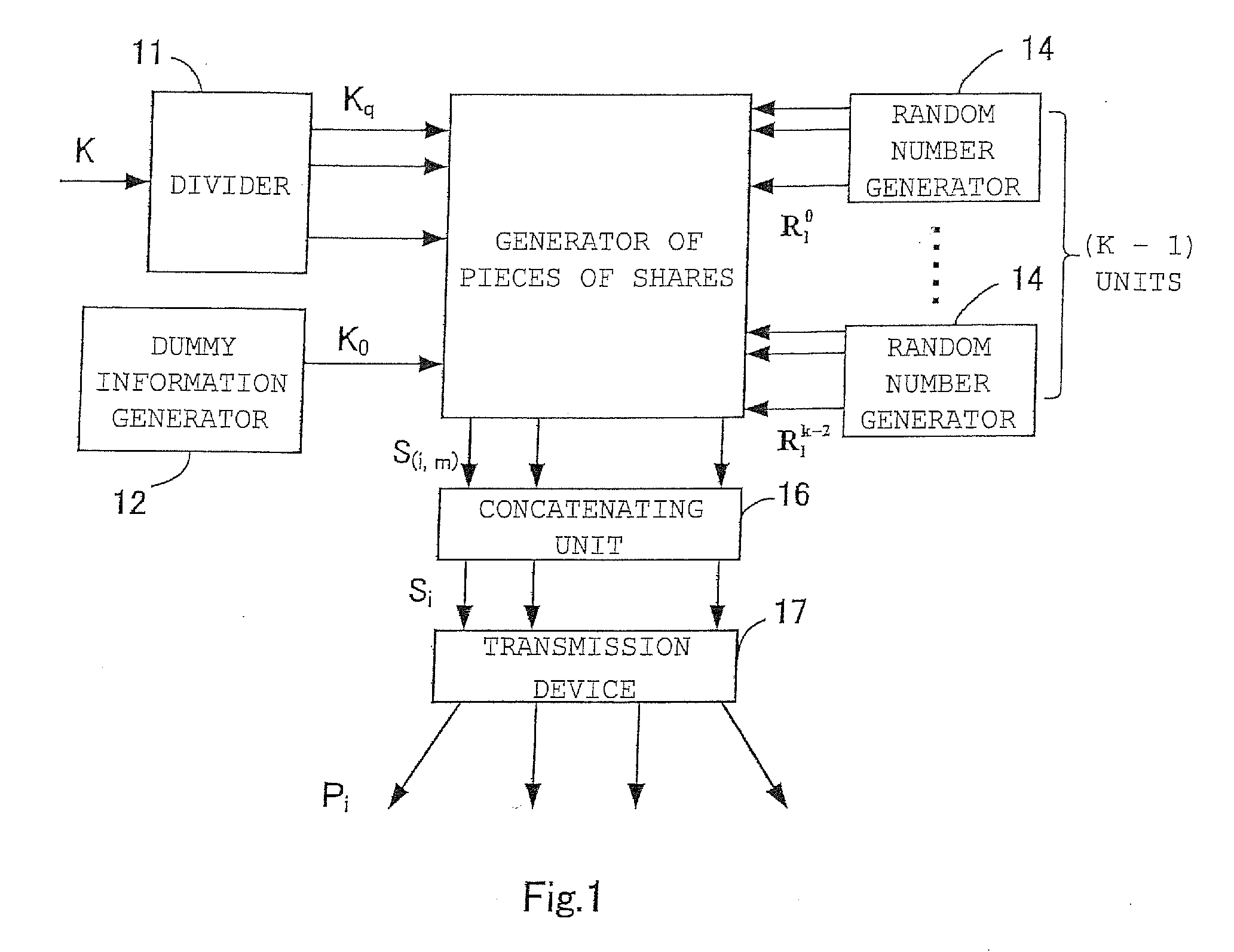
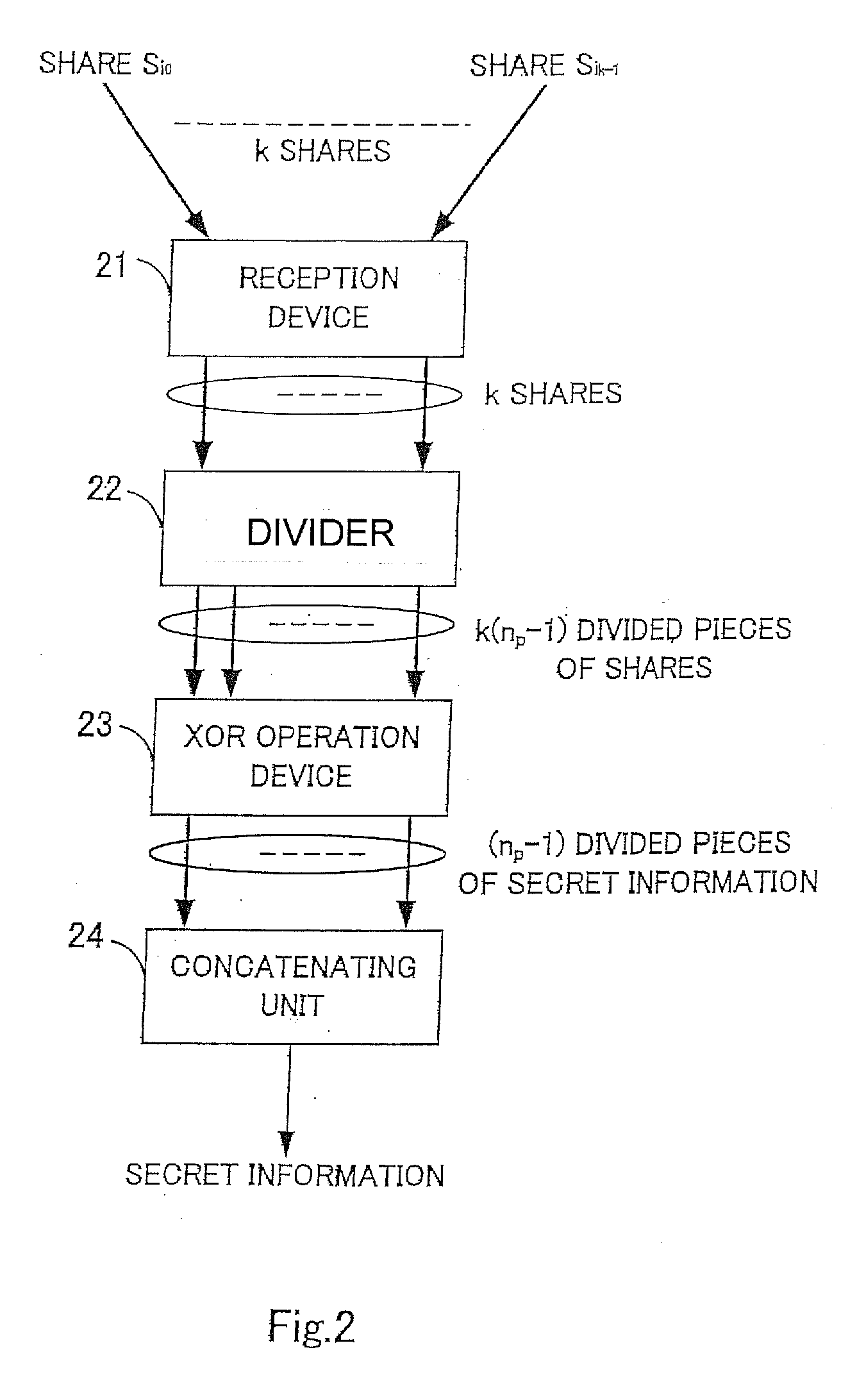
ActiveUS20080205637A1High speed machiningDigital data protectionSecret communicationInformation recoveryExclusive or
A threshold secret sharing apparatus, a threshold secret sharing scheme, a secret information recovery apparatus a secret information recovery method, and a program thereof are provided using XOR computation, thereby offering a general (k,n) threshold secret sharing scheme with high computation speed. Secret information K is divided into (np−1) divided pieces of secret information Kq (np is a prime number which is equal to or greater than a secret distribution number n). Furthermore, dummy secret information K0 is generated. Moreover, random numbers R, which are pairwise independent are generated. Then, pieces of shares are created using exclusive-OR (XOR) operations based upon the dummy secret information K0, the divided piece of secret information Kq, and the random numbers R. The pieces of shares thus generated are concatenated so as to generate n shares Si, thereby providing a (k,n) threshold secret sharing scheme.
Owner:KDDI CORP
Collaborative communication method and collaborative communication system based on non-orthogonal multiple access
InactiveCN108601088ASimultaneous accessImprove spectral efficiencySource coding adaptationSignalling characterisationInformation recoverySuperposition coding
The invention discloses a collaborative communication method based on non-orthogonal multiple access, and the method comprises the following steps: a relay node receives a source node signal and channel state information; the relay node decodes the source node signal through successive interference cancellation to obtain a decoded signal; superposition coding is executed for the coded signal according to a power distribution coefficient, the relay node sends the superposed signal to a plurality of destination nodes simultaneously through performing downlink non-orthogonal multiple access withthe plurality of destination nodes; the destination nodes perform decoding and information recovery for the superposed signal through successive interference cancellation; according to channel state information and user requirements, transmitting power and the power distribution coefficients of all the nodes are calculated, and a plurality of source nodes send the obtained information to the relaynode through performing uplink non-orthogonal multiple access with the relay node. In the method and the system provided by the invention, the non-orthogonal multiple access technology is used, userrate is satisfied, total consumption of the system is minimized, the number of access users is expanded effectively, spectrum efficiency of the system is promoted, and power consumption of the systemis reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
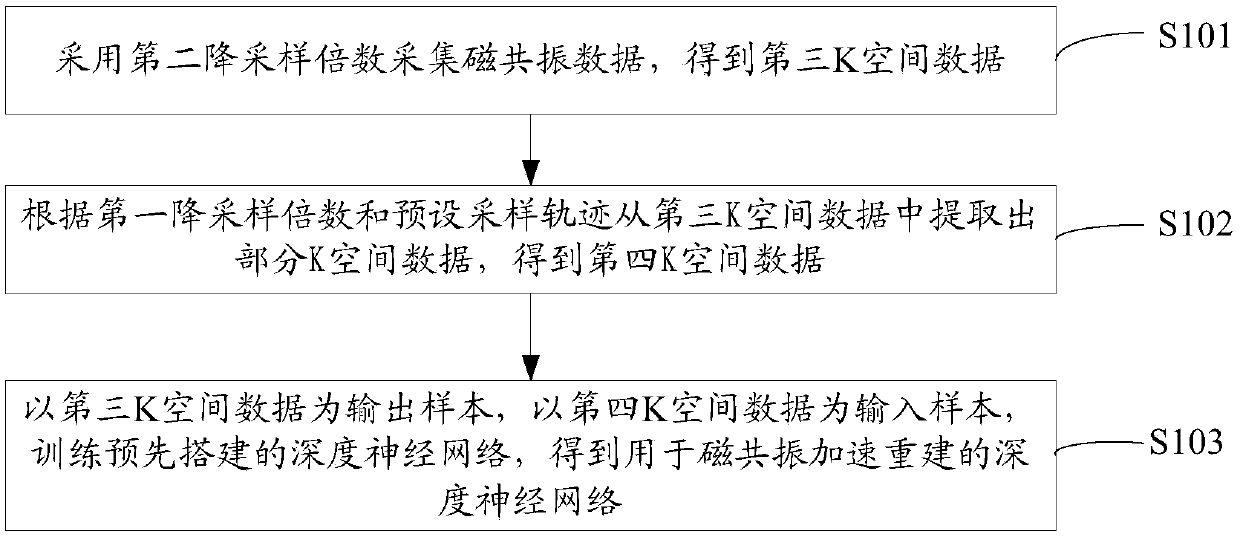
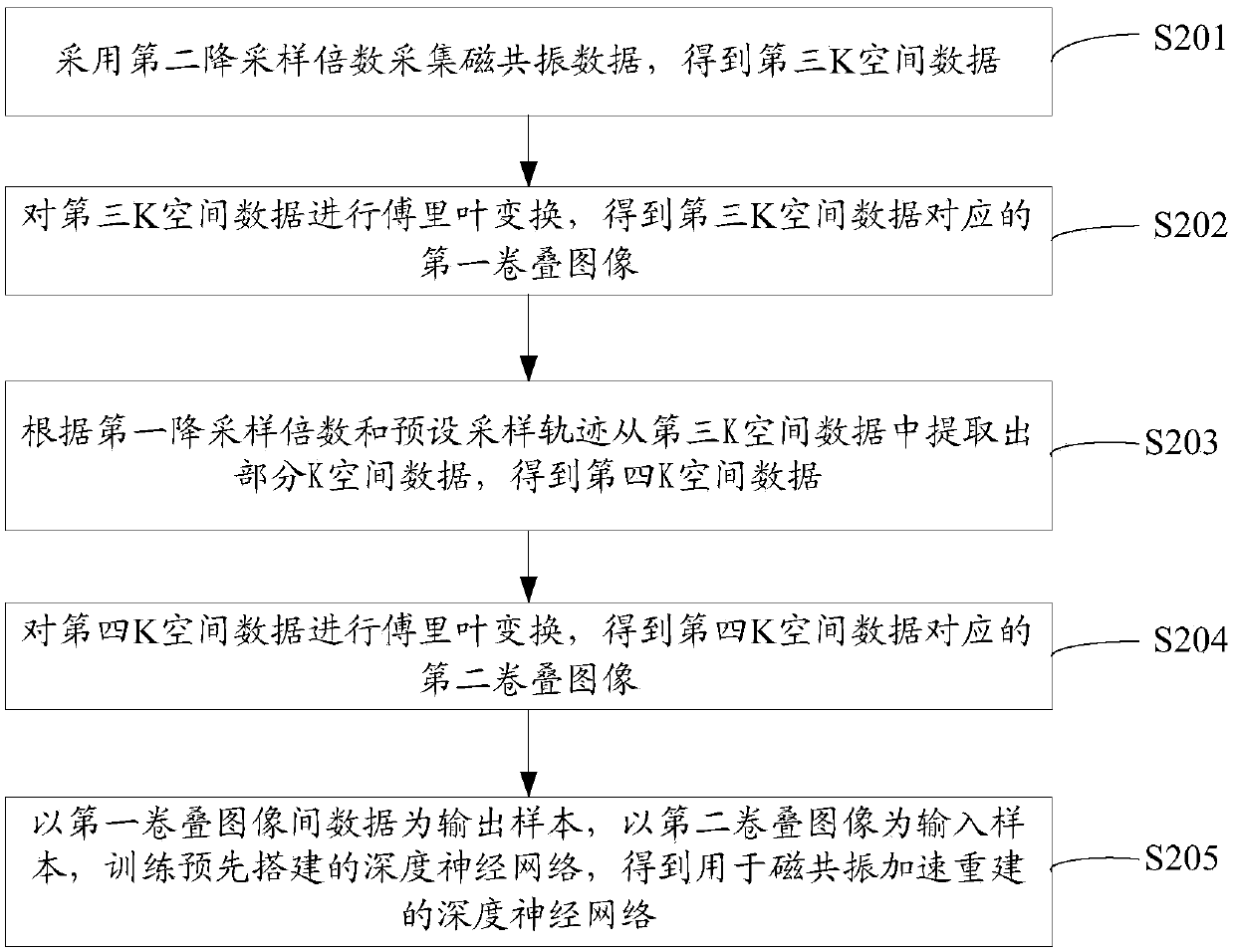
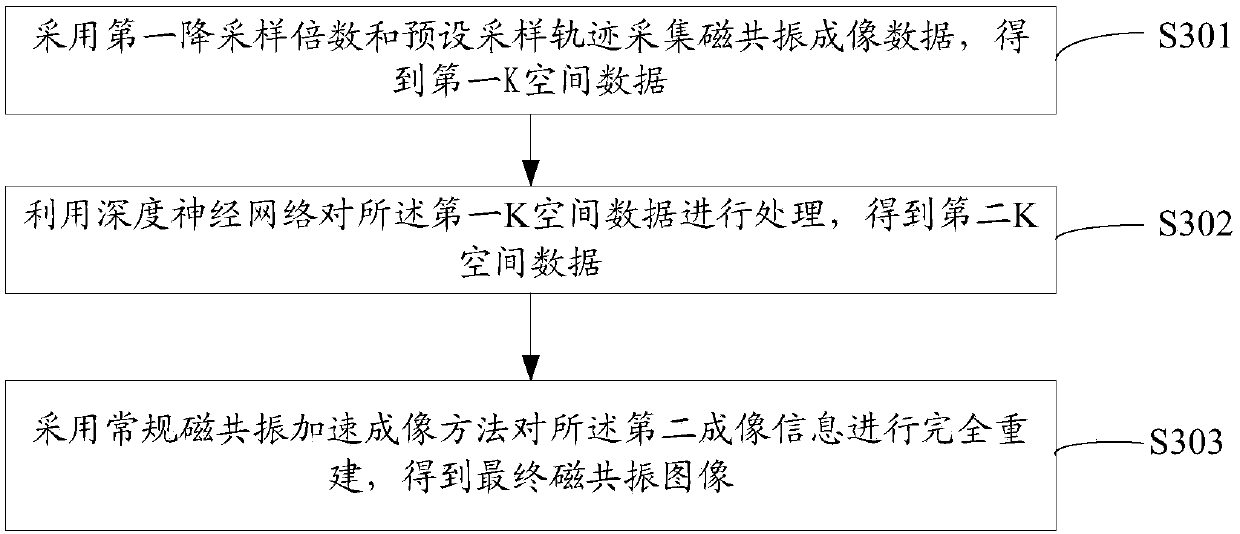
Magnetic resonance imaging method and device
ActiveCN109557489AShort acquisition timeMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringAcquisition timeResonance
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance imaging method and device. The method combines a deep network model with a conventional acceleration reconstruction method in sequence. Firstly, the deep network model is used for recovering first imaging information with a high downsampling multiple to second imaging information with a low downsampling multiple, then, the conventional acceleration reconstruction method is used for completely reconstructing the second imaging information with the low downsampling multiple, and therefore, a final magnetic resonance image is obtained. Therefore, in the magnetic resonance imaging method provided by the invention, the output training sample of the deep neural network used for magnetic resonance quick imaging is not full sampling or super-full sampling data but is downsampling data, so that the output training sample of the training deep neural network can be obtained through a conventional downsampling method, the output training sample can be obtained through short collection time, and therefore, the deep neural network can be applied to a magnetic resonance imaging application scene with limited collection time, such as abdomen scanning.
Owner:SHANGHAI NEUSOFT MEDICAL TECH LTD
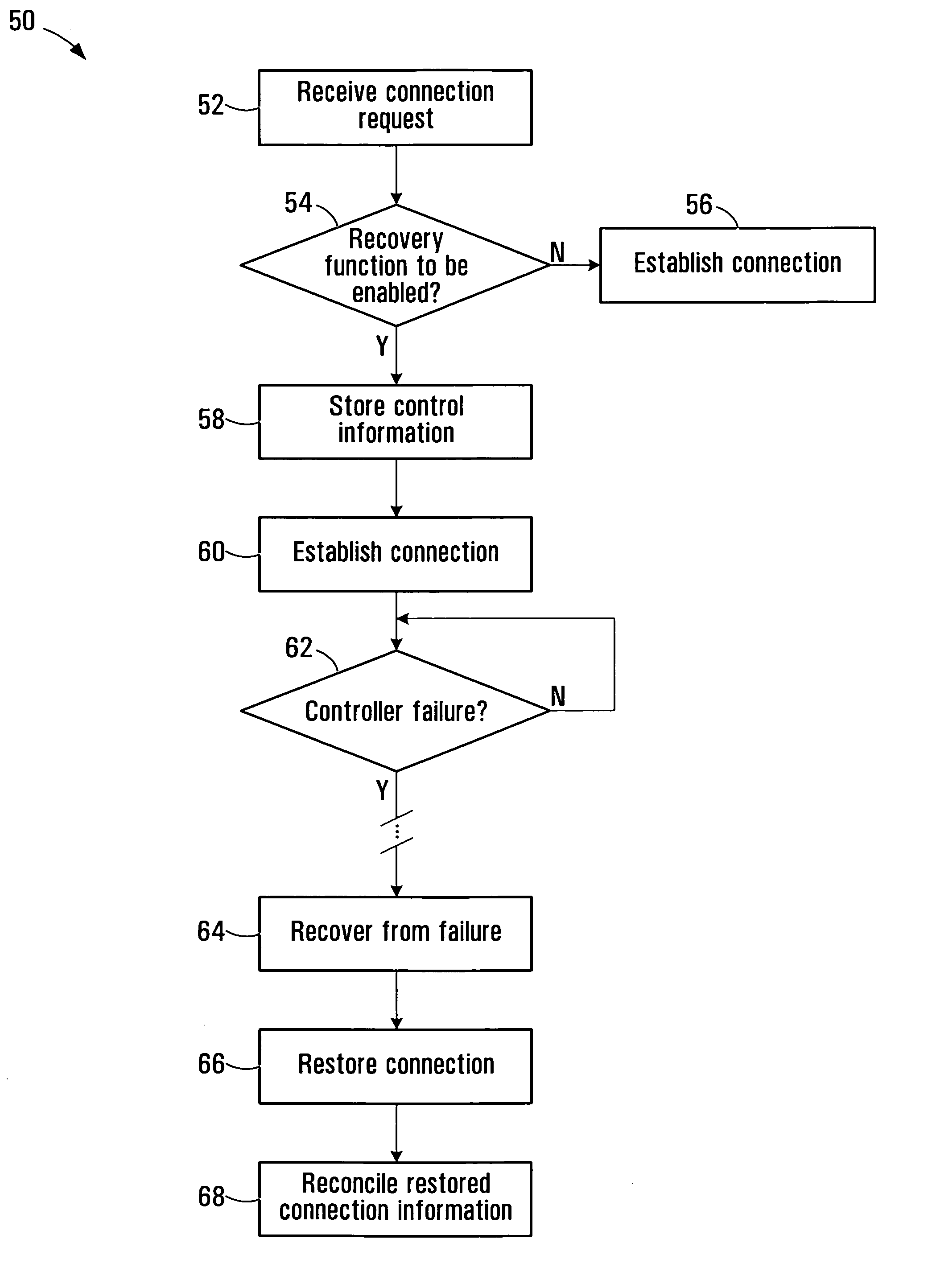
Communication connection control systems and methods
InactiveUS20070133394A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData connectionInformation recovery
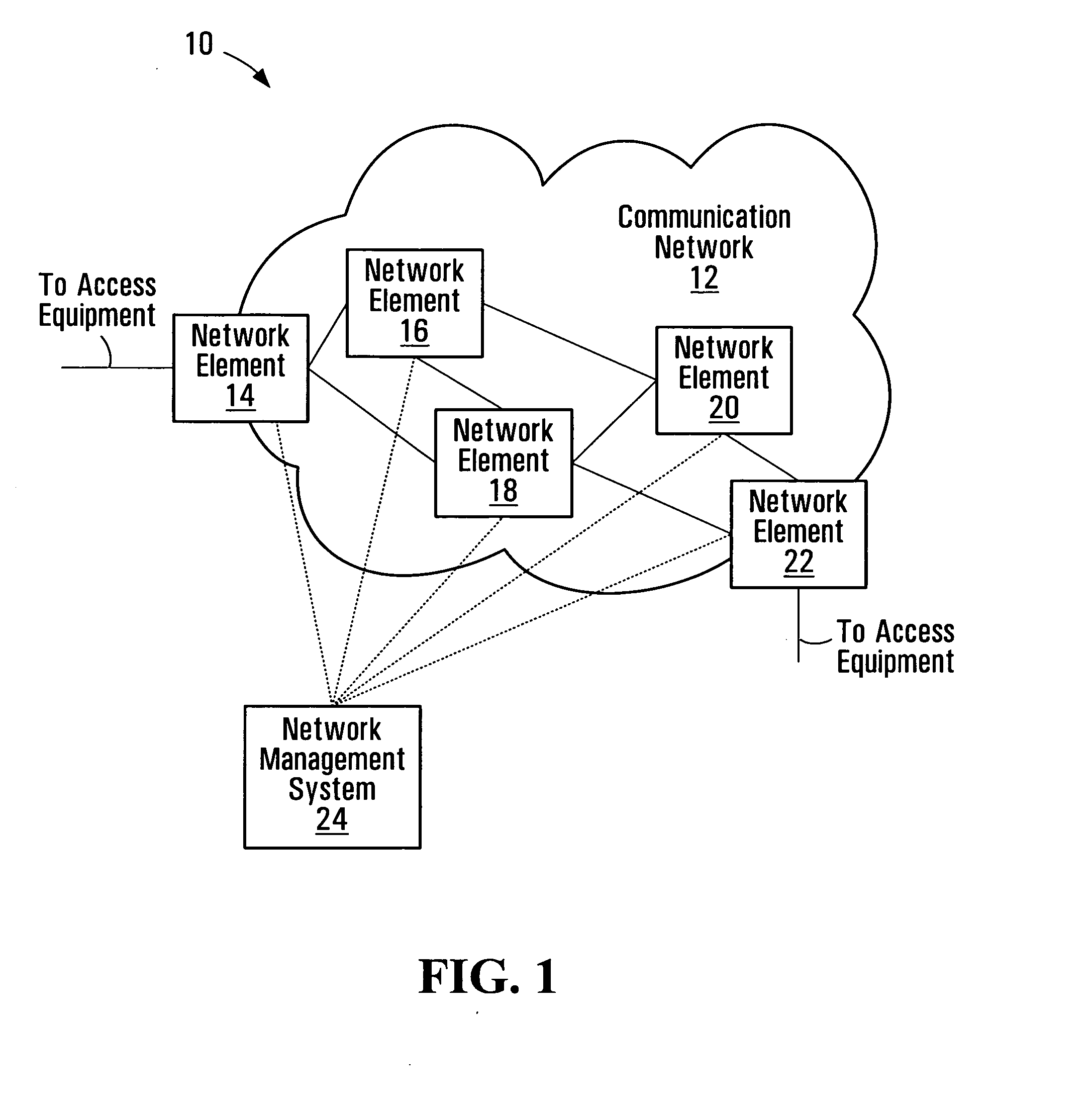
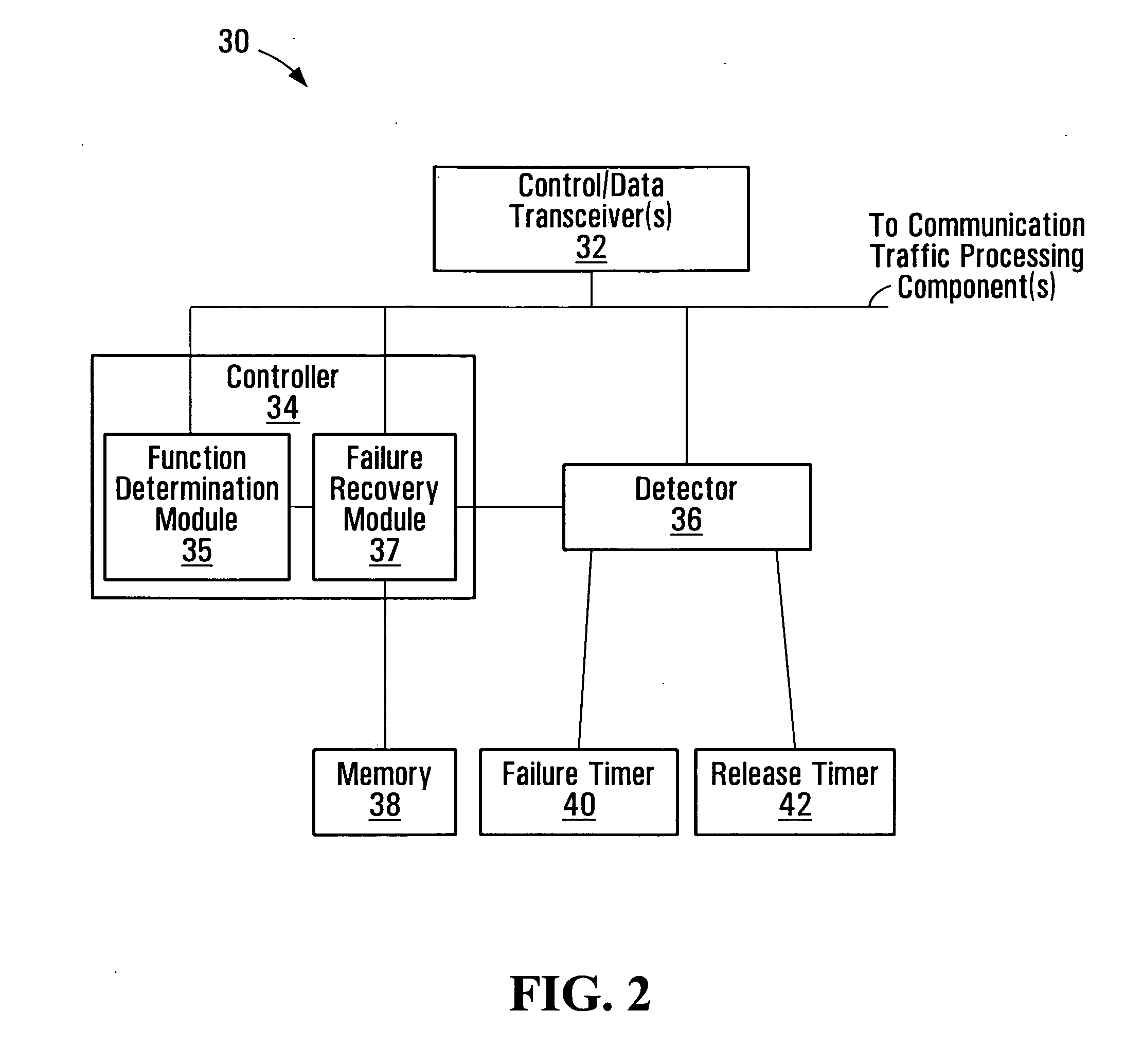
Communication connection control systems and methods are disclosed. If a control failure recovery function is to be enabled for a data communication connection established by a communication connection controller by communicating control information with a remote controller, an indication that the control failure recovery function is supported at the controller is included in the control information communicated with the remote controller. Each of the controller and the remote controller may support, for example, either or both of a local control information recovery function or a resynchronization function to reduce the amount of time that the data connection is interrupted during a temporary failure of one of the controllers.
Owner:RPX CORP
Enhanced fiber nodes with cmts capability
InactiveUS20070050835A1Increase functional densityReduce power consumptionModulated-carrier systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsFiberFrequency spectrum
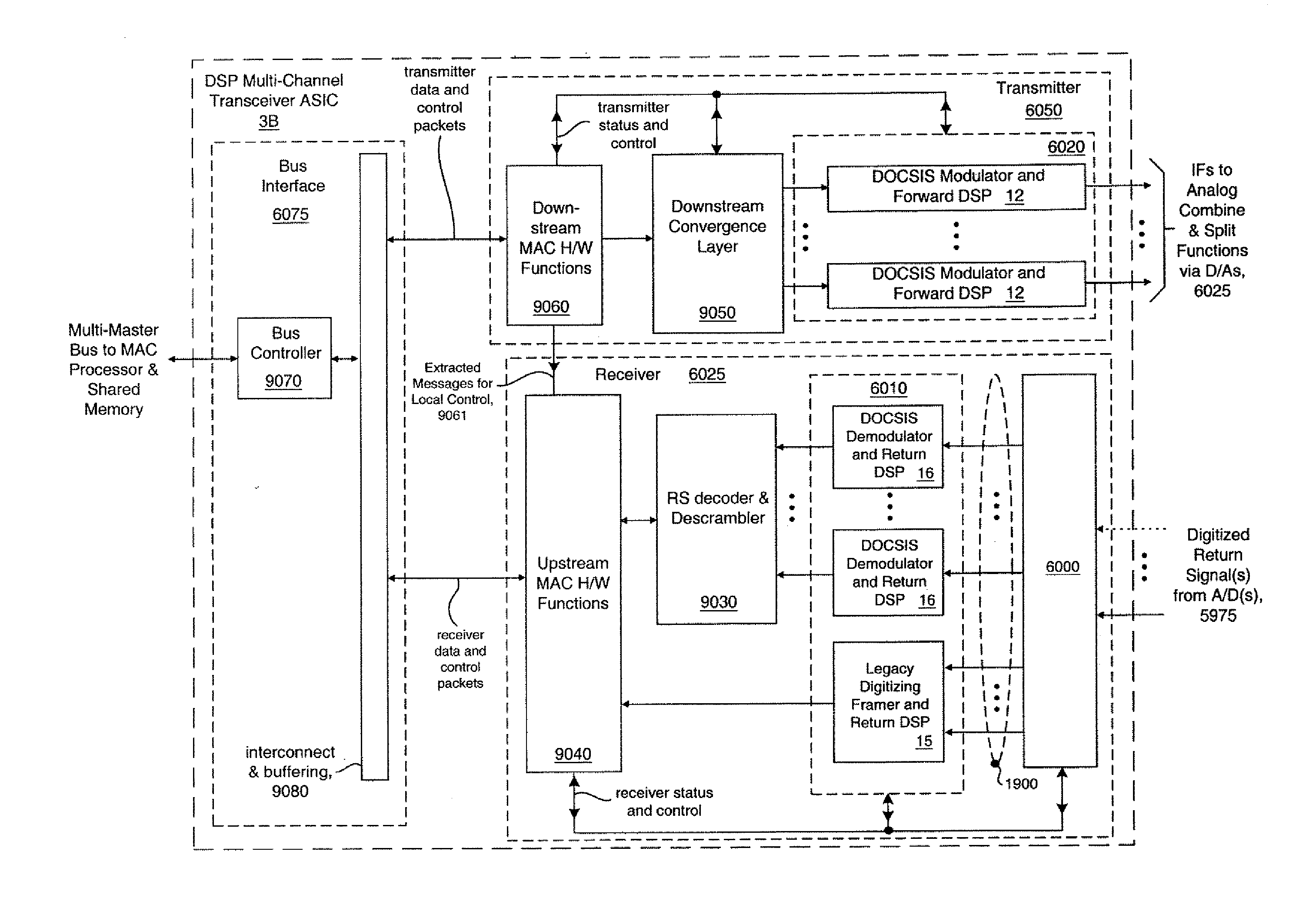
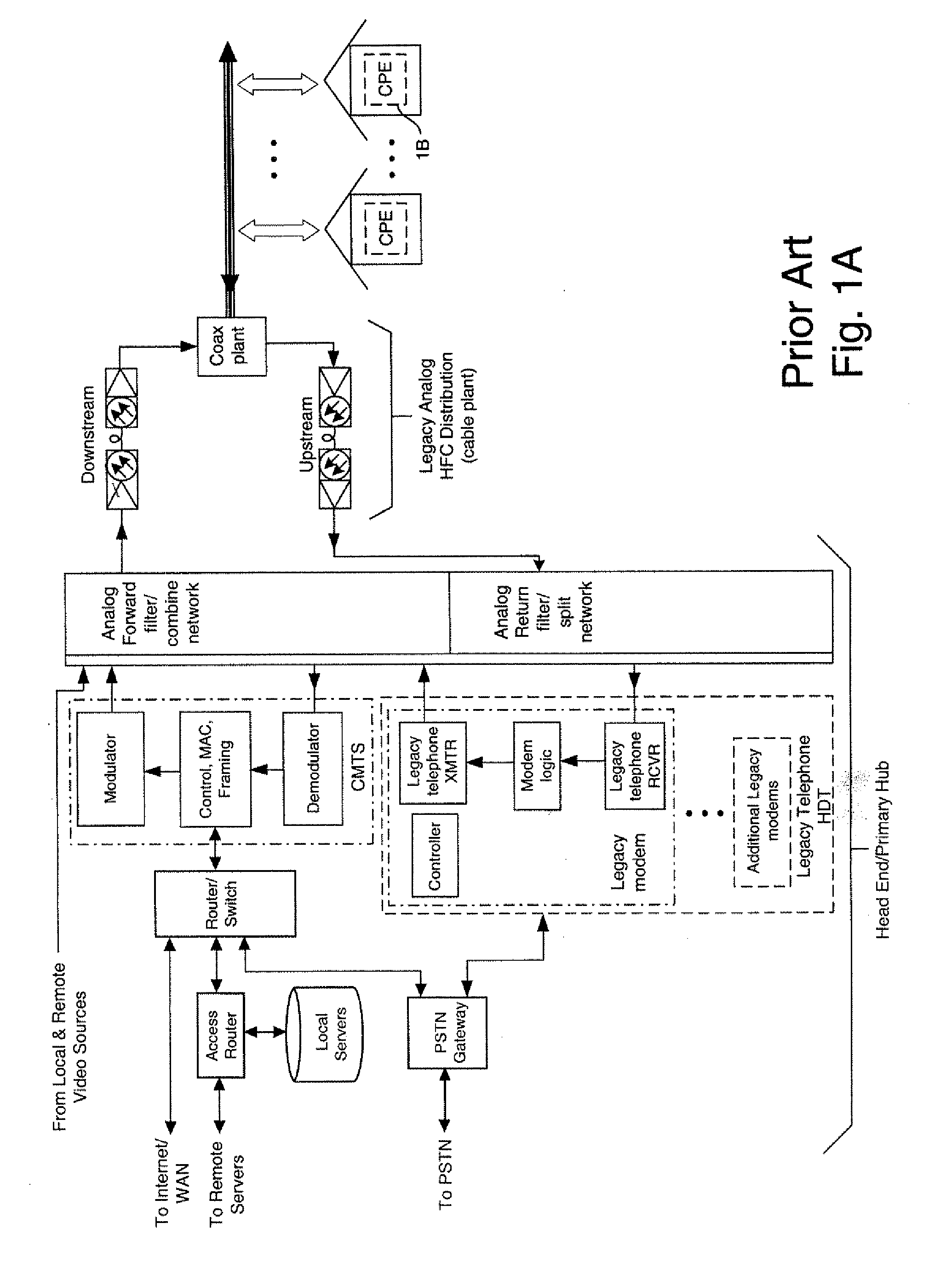
Enhanced Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) functionality, including programmable digital domain modulators and demodulators for dynamic channel assignment, is incorporated into Fiber Nodes (FNs) or mini Fiber Nodes (mFNs), yielding enhanced Fiber Nodes (eFNs). These eFns distribute CMTS functionality deep into Hybrid-Fiber-Coax Networks (HFCN) rather than centralizing the CMTS functions within a single location. Moving the cable modem terminations closer to the subscribers shortens the analog RF paths required to support cable modems. Communication of both subscriber data and CMTS control data is performed over Ethernet-compatible packet networks between the field-based CMTSs and an upstream facility (e.g., the Head End), which includes an Internet gateway. Packet data for multiple subscriber cable modems is easily compressed and merged over common network paths, reducing cabling plant complexity and increasing bandwidth utilization. This approach dramatically reduces the infrastructure cost per cable modem. Distributing CMTS functionality among multiple eFNs also reduces demands on already stretched resources at the Head End for space, power, and HVAC. For HFCN channels containing signals with modulation or encoding schemes that are unknown or best processed upstream, the invention also provides for tunneling their spectrum over the same packet network as used for the cable modem data. The channels to he tunneled are isolated using digital receivers, translated to baseband, their data framed, merged with cable modem subscriber data, and transmitted over the packet network. Upstream, the framed channel data is parsed and the original channel spectrum reconstructed to permit information recovery.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
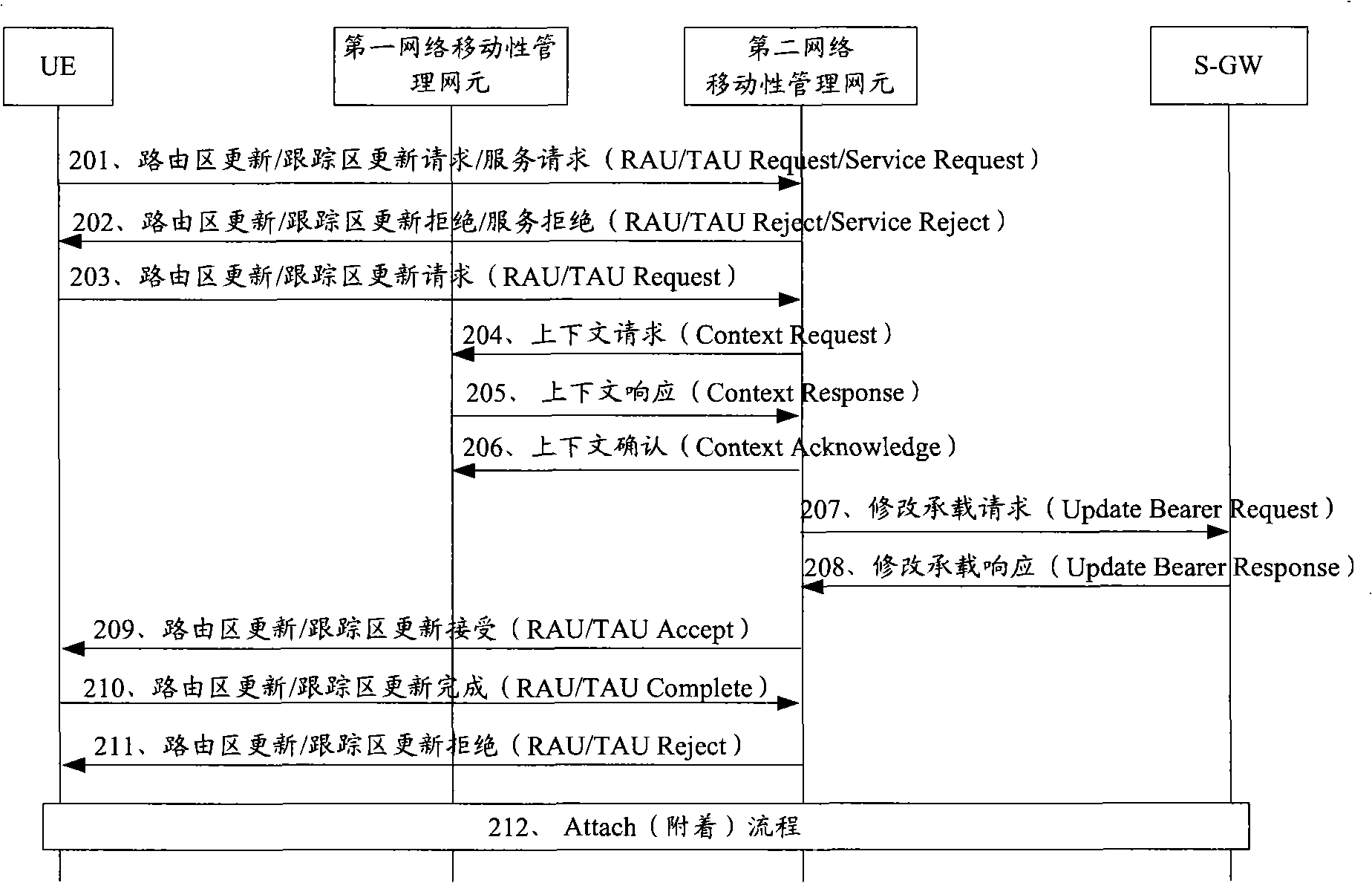
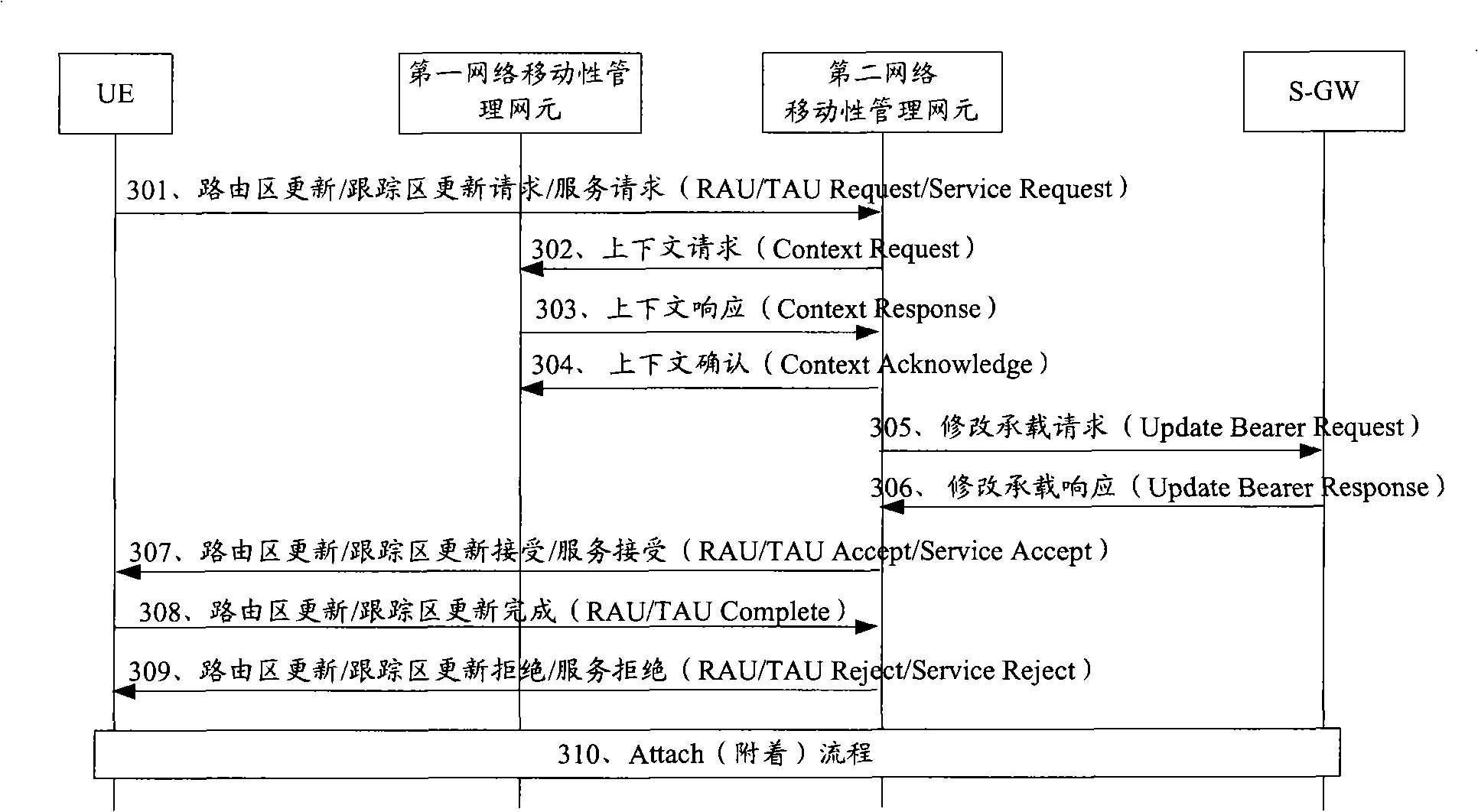
Method for recovery of context after user conceal separation, network element and system
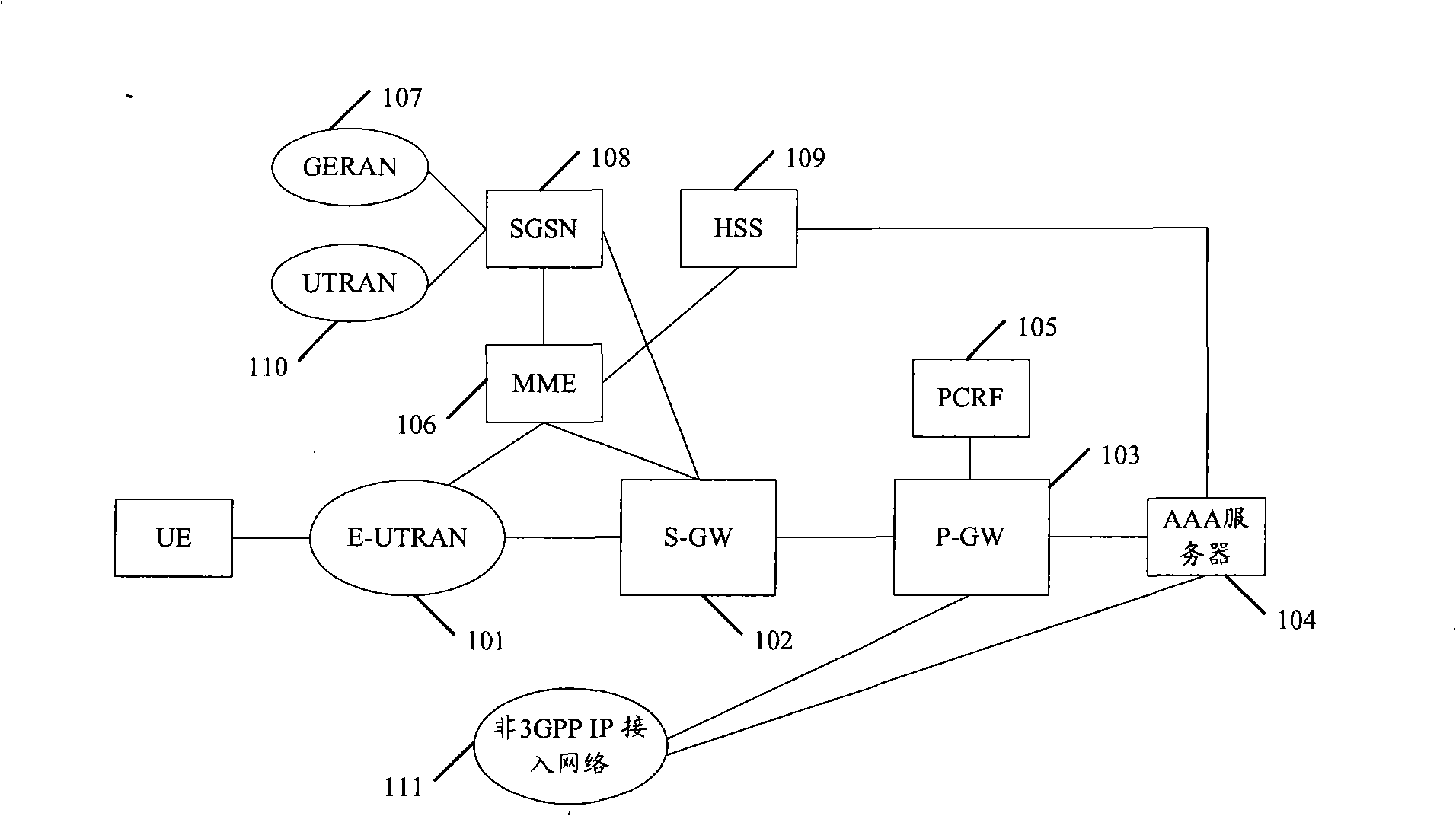
The invention discloses a user implicit separated context recovery method, net element and system. The method in the invention comprises: mobile management net element of second network receives an information from user equipment, when learning that the user equipment is implicit separated according to the informatioin, obtaining the mobile management net element address of first network in at least one network according to the obtained identification information of at least one network except the second network of the user equipment; obtaining the context information of the user equipment from the mobile management net elements in the first network according to the obtained mobile management net element address of the first network; and recovering the context of the user equipment according to the obtained context information. The invention need not re-establish the context of user equipment, so the IP address used by the user equipment does not change, and the service used by the user before can also be used, thereby the user experience is improved.
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
Method for protecting and restoring continuous data
ActiveCN101739313AWrite small amount of dataEasy and efficient adjustmentRedundant operation error correctionInformation recoveryRestoration method
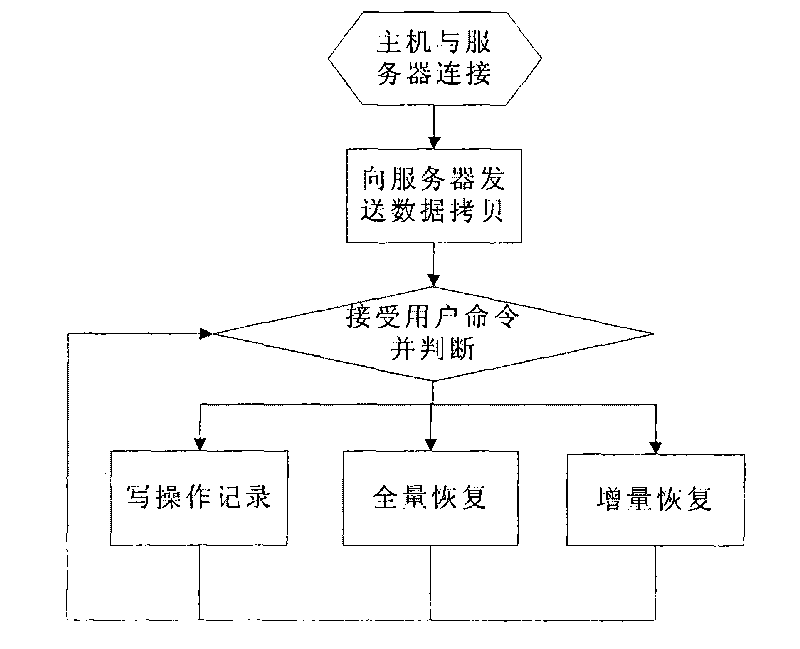
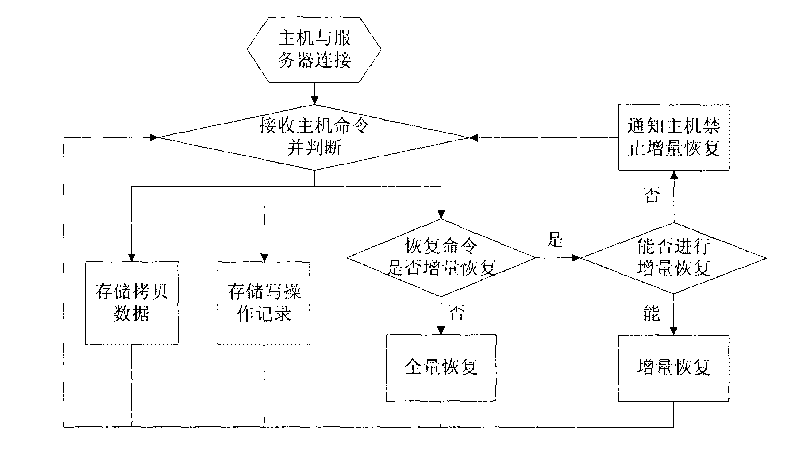
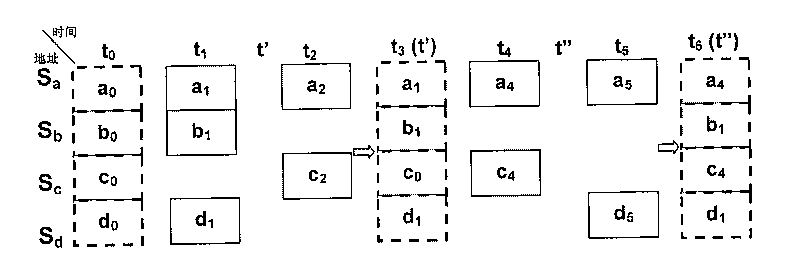
The invention relates to a method for protecting and restoring continuous data, belongs to the computer data storage and backup method and aims to solve the problem that appropriate restoring time is difficult to identify by the existing method for protecting and restoring continuous data. In the invention, a host computer process and a server process are provided, the two processes are carried out in parallel; the host computer process comprises the following steps: initiating connection, copying, host computer command judgment, recording write operation info, carrying out full restoration and incrementation storage; the server process comprises the following steps: accepting connection, storing copied data by the server, command judgment by the server, write operation info storage by the sever, restoring request judgment and restoring data. With the method of the invention adopted, user requests for storing data to any-point-in-time can be supported and write data needed for completing restoration can be minimized; in addition, restoration time can be more conveniently and more effectively adjusted to seek appropriate recovery points and data loss can be minimized. The host computer and the server are separated, so that when a local host computer hard disk is damaged, data restoration can still be carried out.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
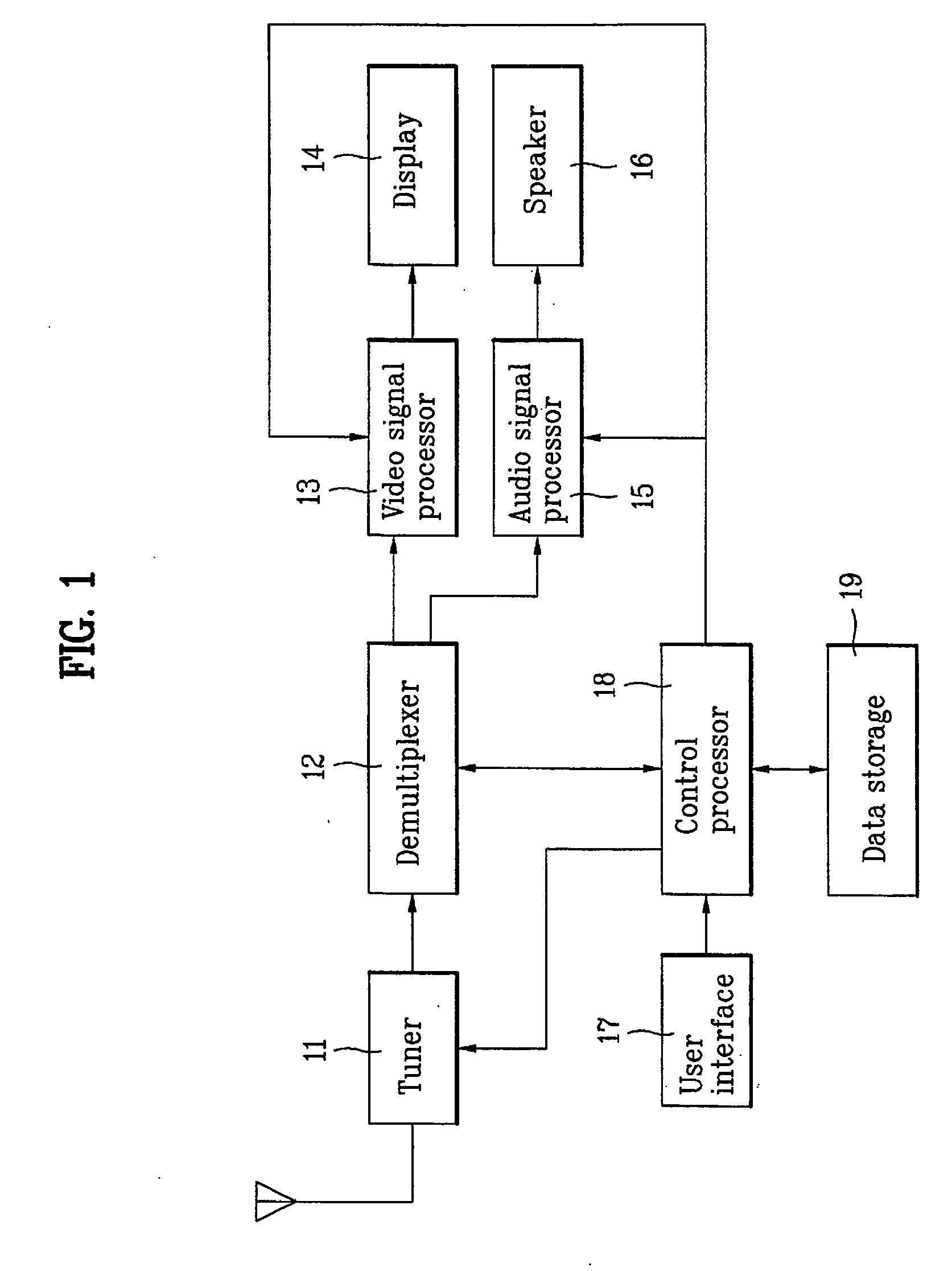
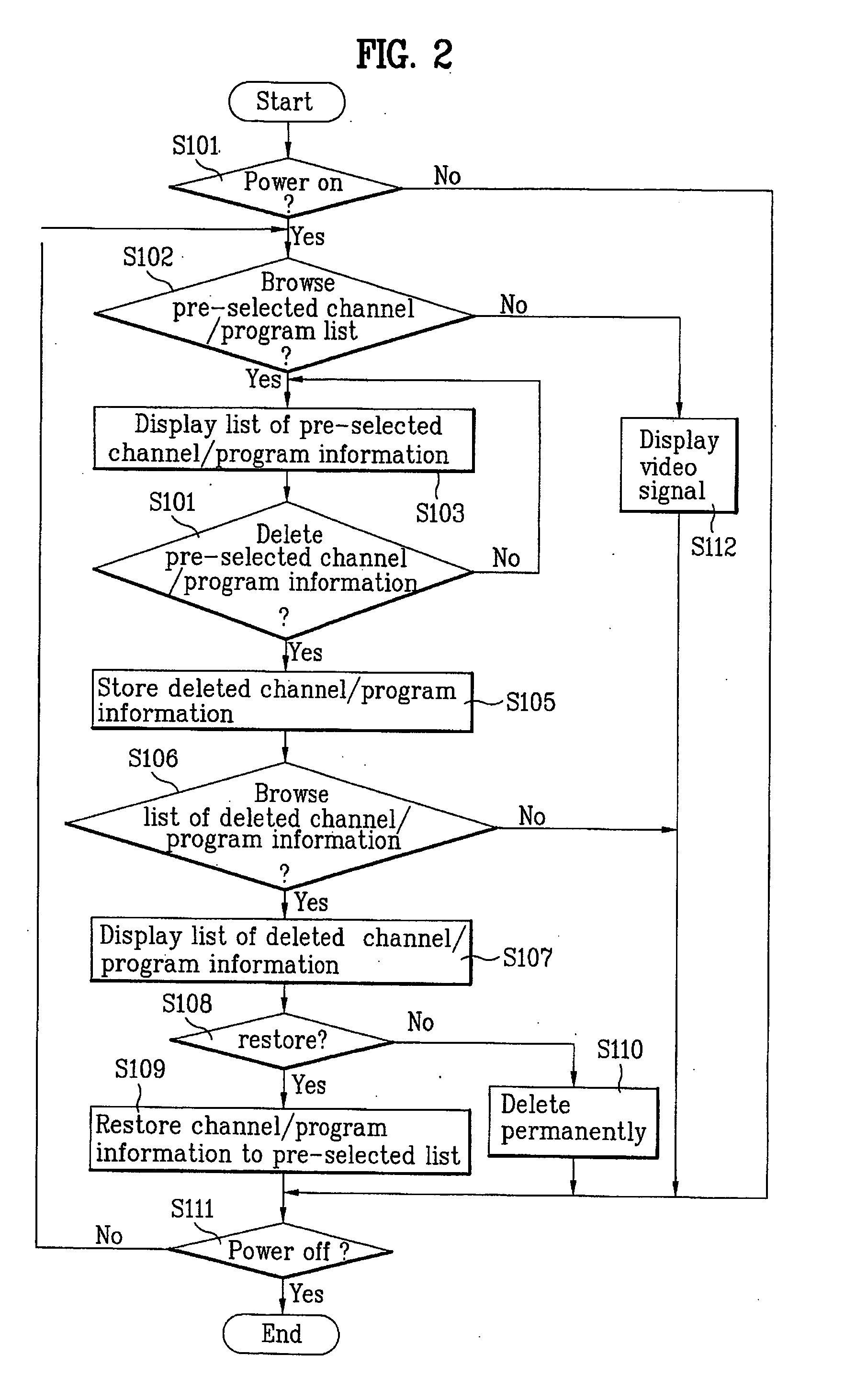
Display device and method of managing list of channel information in video display device
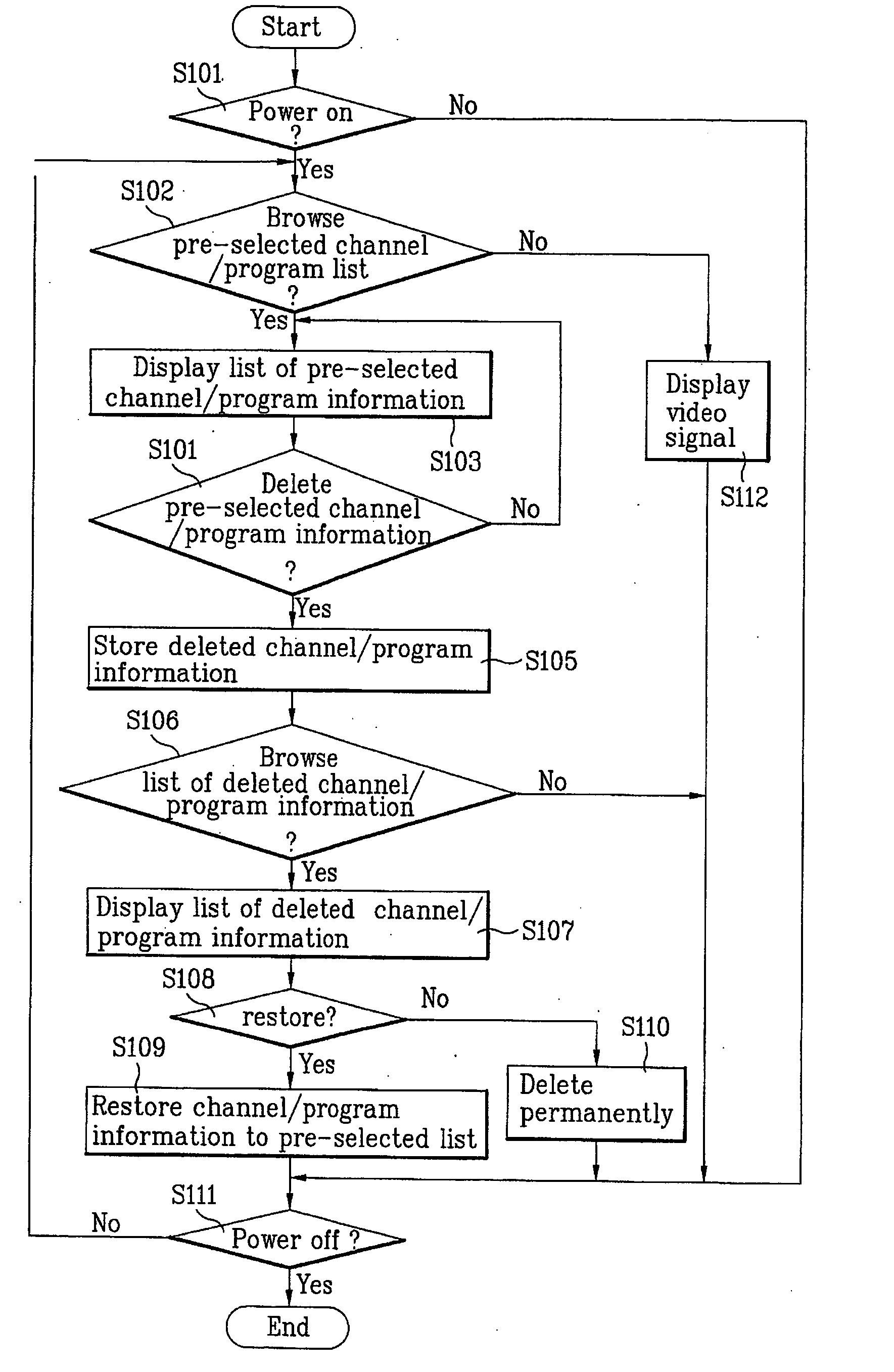
ActiveUS20050177848A1Television system detailsColor television detailsInformation recoveryDisplay device
A display device and method of managing a list of channel information in a video display device are provided. The display device includes the steps of displaying a first window including a first list of pre-selected channel and / or program information, storing at least one channel and / or program information deleted from the first window to a data storage, displaying a second window including a second list of deleted channel and / or program information stored in the data storage, and selectively restoring a channel and / or program information selected from the second list to the first list.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
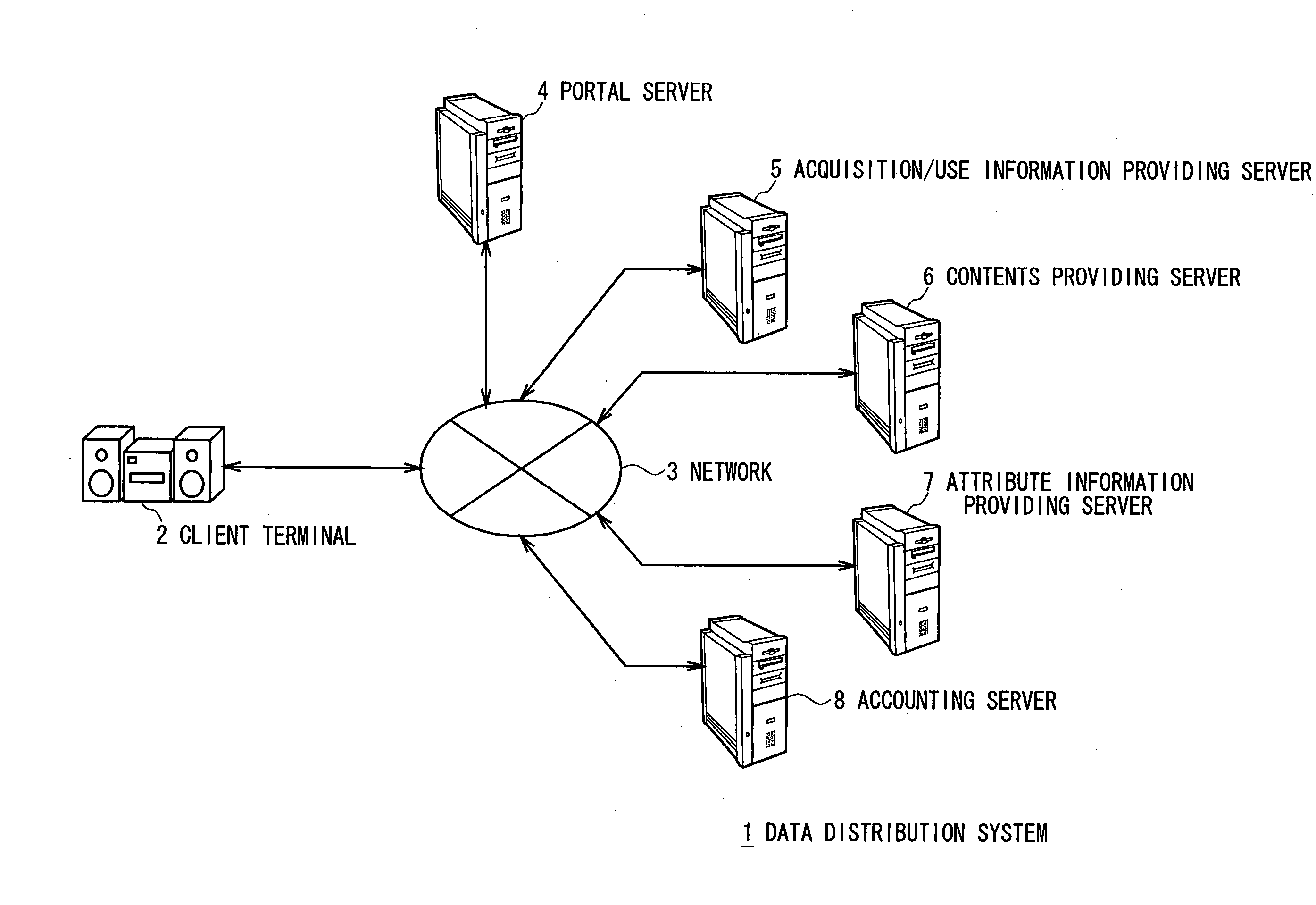
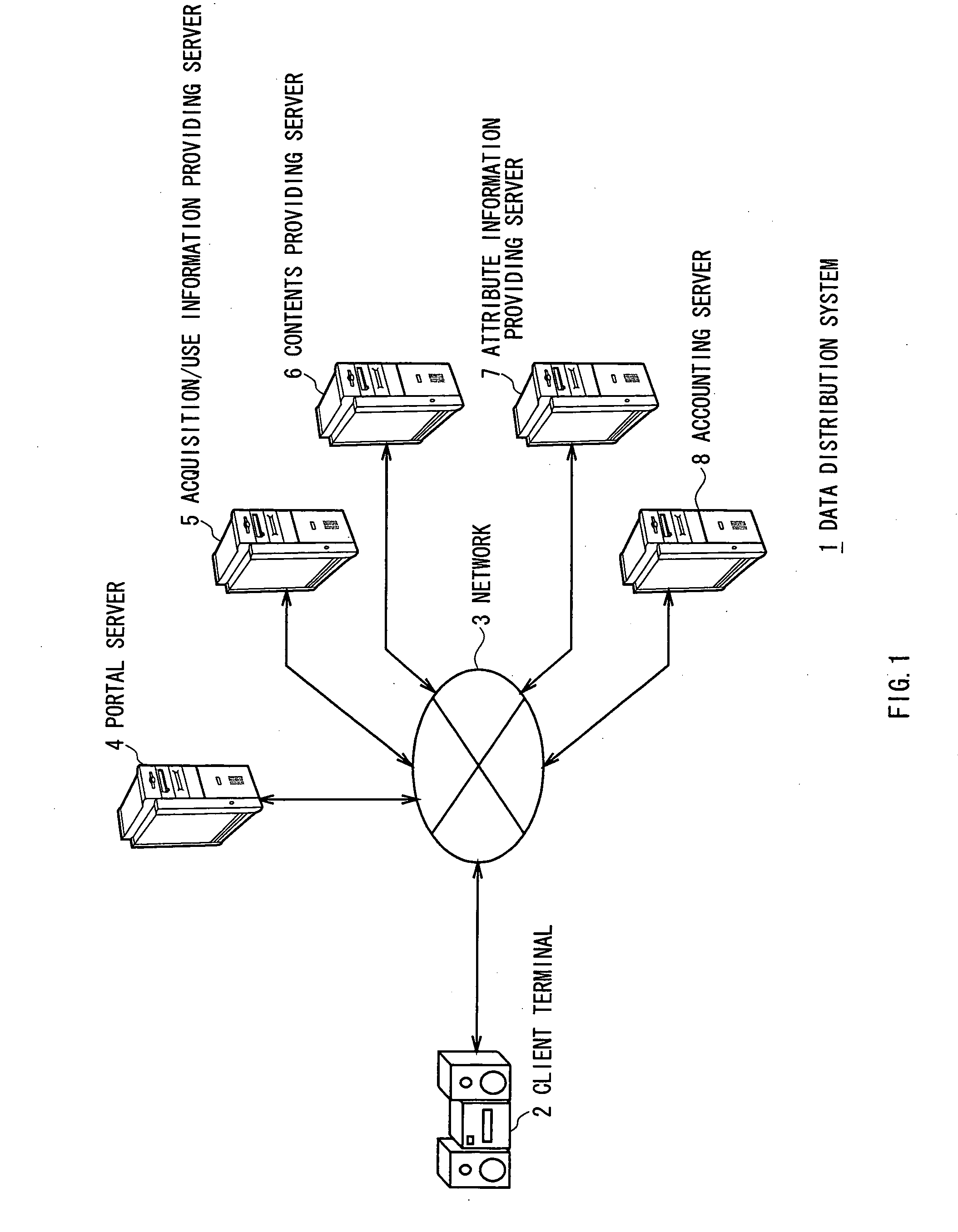
Attribute information acquiring method
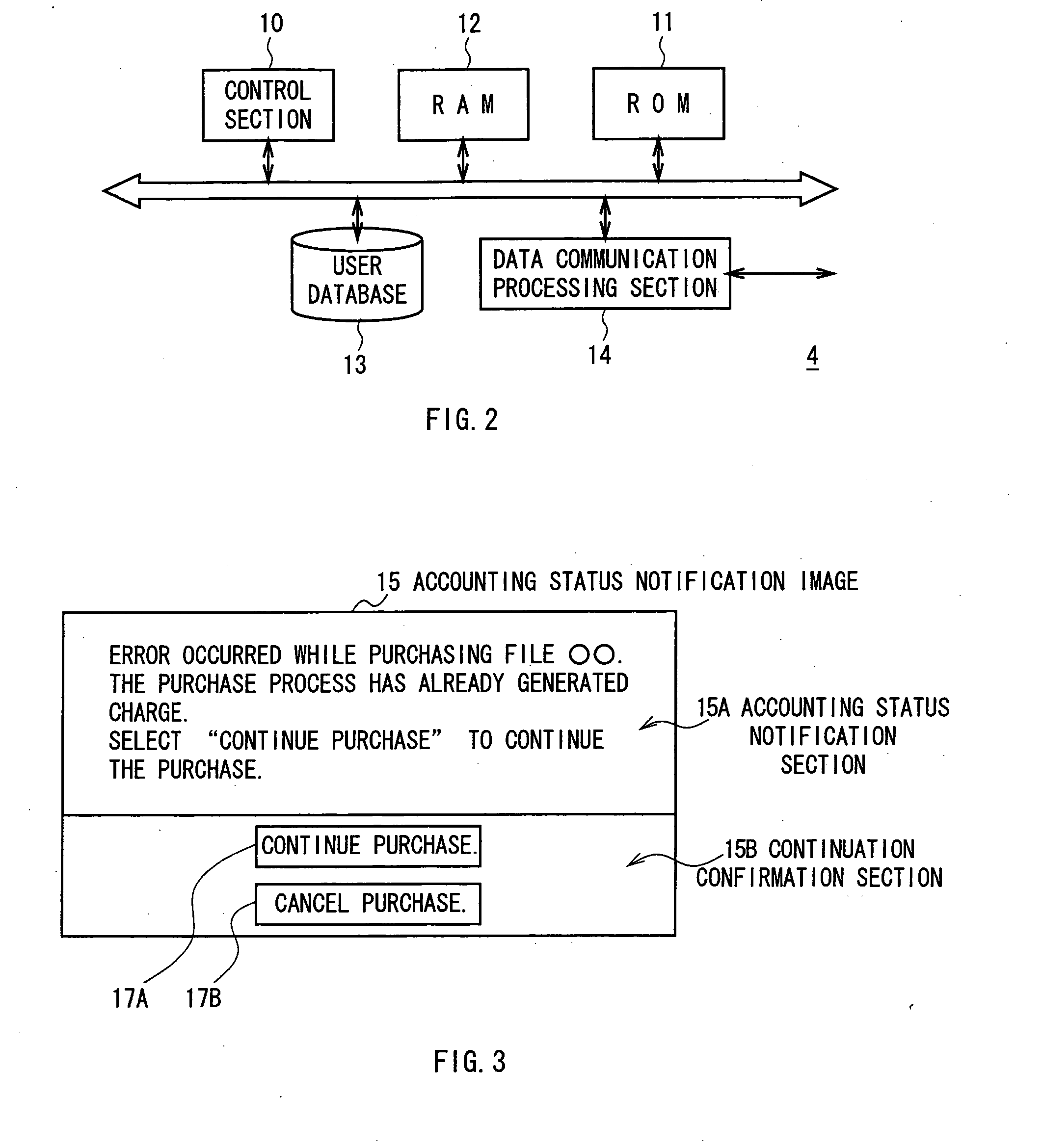
ActiveUS20070033192A1Accurate processingDigital computer detailsOffice automationInformation recoveryData storing
This invention can handle a communicable state restored from disconnection of a communication line. According to the invention, if the communication line is disconnected while a client terminal 2 requests to acquire a contents attribute file 47 that corresponds to a set of contents data stored in a hard disk and receives the file 47 and subsequently the communication line restores a communicable state, the client terminal 2 requests accounting status notification information to a portal server 4 and receives accounting status notification images 15 and 16 transmitted to it in response so that it can be notified if the accounting process had been completed by the time when the communication was disconnected while receiving the contents attribute file 47 and subsequently the communication n line restored a communicable state by accounting status notification information so that it can reliably handle the situation that arises when the communication line restores a communicable state from disconnection.
Owner:SONY CORP
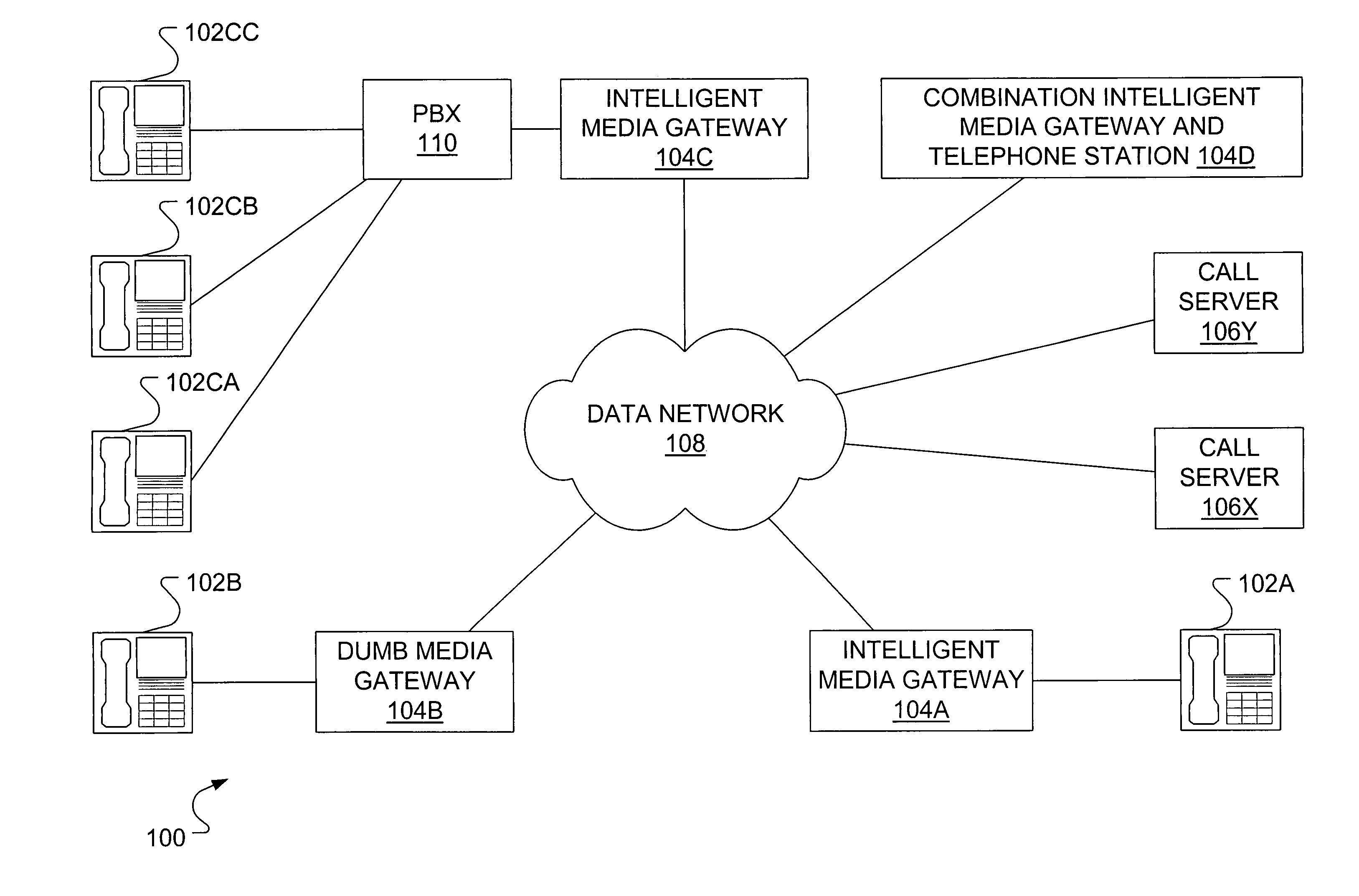
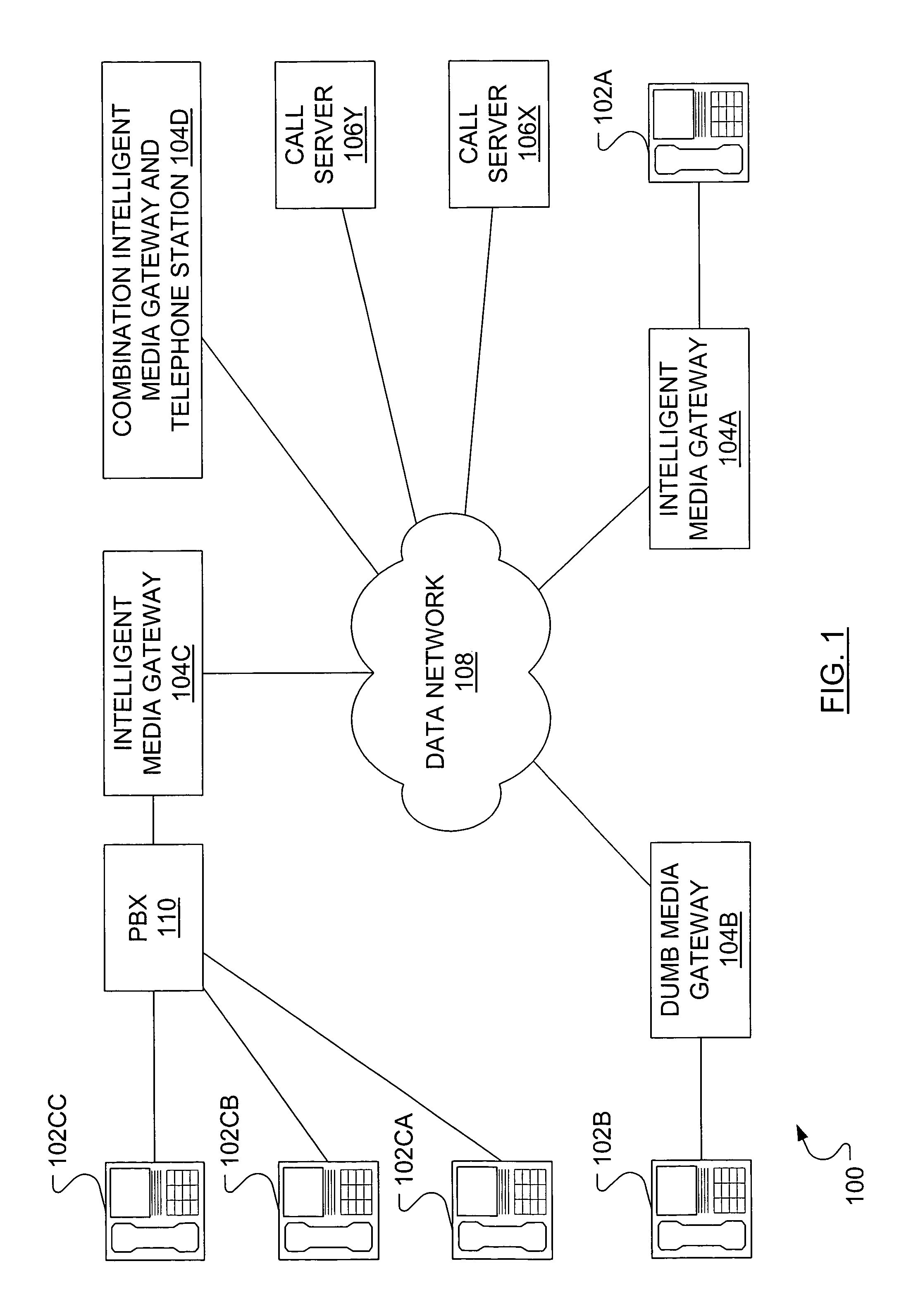
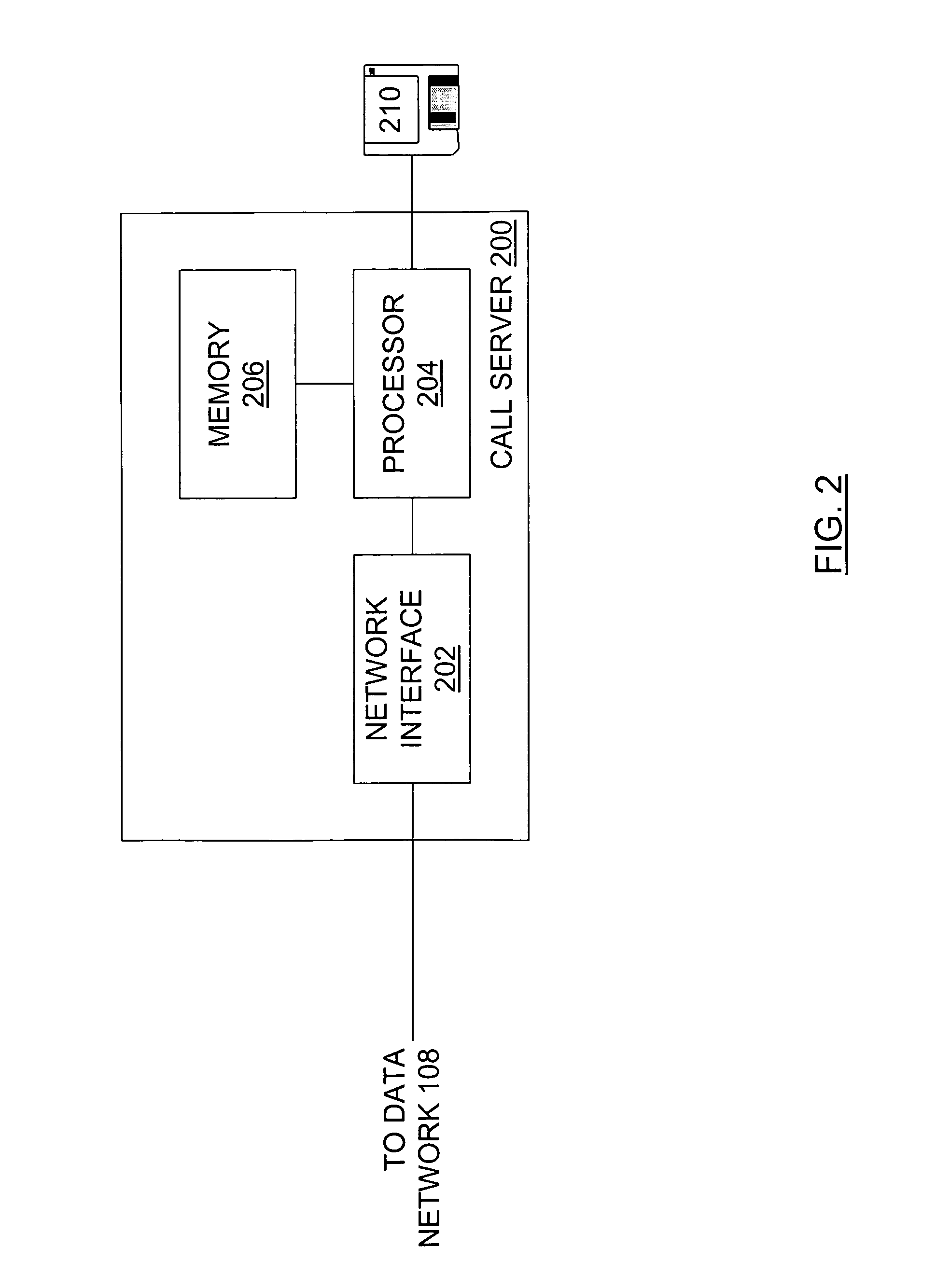
Media gateway connection information recovery
InactiveUS7533174B1Necessary performanceLower performance requirementsInterconnection arrangementsSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsInformation recoveryTelephone network
In a packet-based telephony network, a media gateway provides information on active media path connections to an active call server. For instance, this data may be provided to a backup call server to keep the backup call server in a warm standby mode. The backup call server polls a media gateway to retrieve a table of information on active media path connections. The polling may be done periodically or only during switchover from the active call server to the backup call server. After switchover, the backup call server has all necessary details about active media path connections to provide accurate billing information. Alternatively, after a temporary failure at the active call server, the active call server may send a request to the media gateway to retrieve a table of information on active media path connections.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Identity authentication method and system
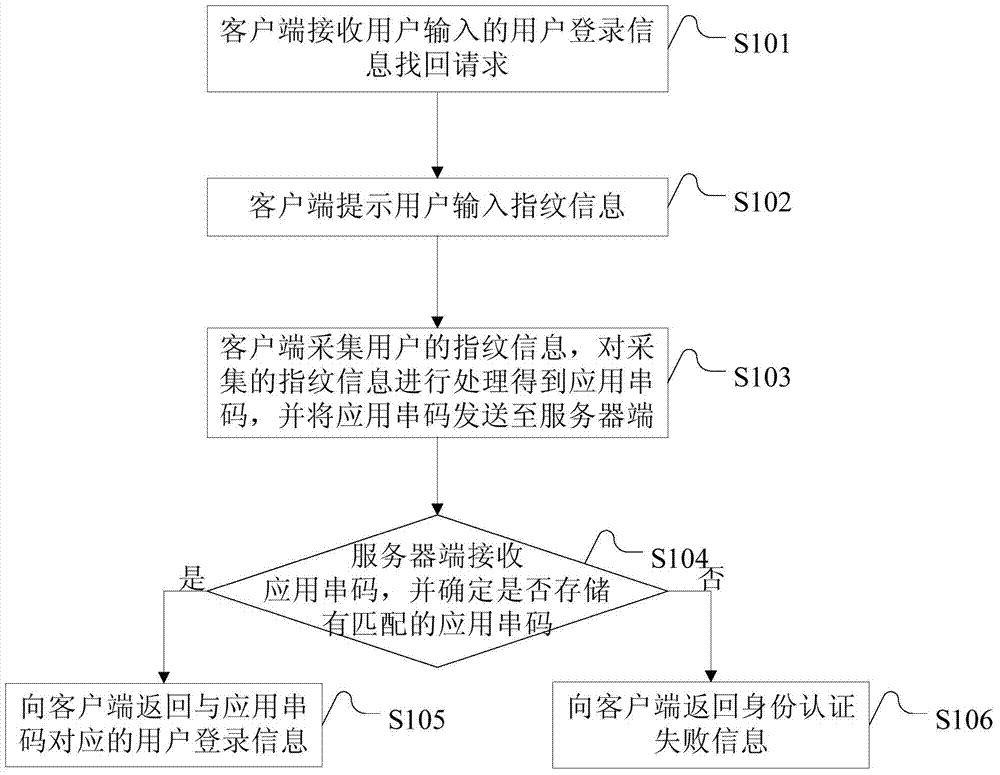
InactiveCN103618604ATimely authenticationGet it back in timeUser identity/authority verificationDigital data authenticationInformation recoveryUser input
The invention discloses an identity authentication method and system. The identity authentication method comprises the following steps: a client side receives a user login information recovery request input by a user; the client side prompts the user to input fingerprint information; the client side collects the fingerprint information of the user, processes the collected fingerprint information to obtain an application code string and sends the application code string to a server side; the server side receives the application code string and determines whether an application code string matched with the received application code string exists; if the application code string matched with the received application code string exists, user login information corresponding to the application code string is returned to the client side; if the application code string matched with the received application code string does not exist, identity authentication failure information is returned to the client side. According to the identity authentication method and system, by means of the identity authentication mode that the fingerprint information of the user is collected when the user forgets login information, the collected fingerprint information is processed to obtain the application code string, and the application code string is sent to the server side for matching, effective information can be provided for the user in time for identity authentication, and the user can conduct login in time or recover a user name or a password in time.
Owner:CHINA UNITED NETWORK COMM GRP CO LTD
Threshold secret information distribution and recovery method and device
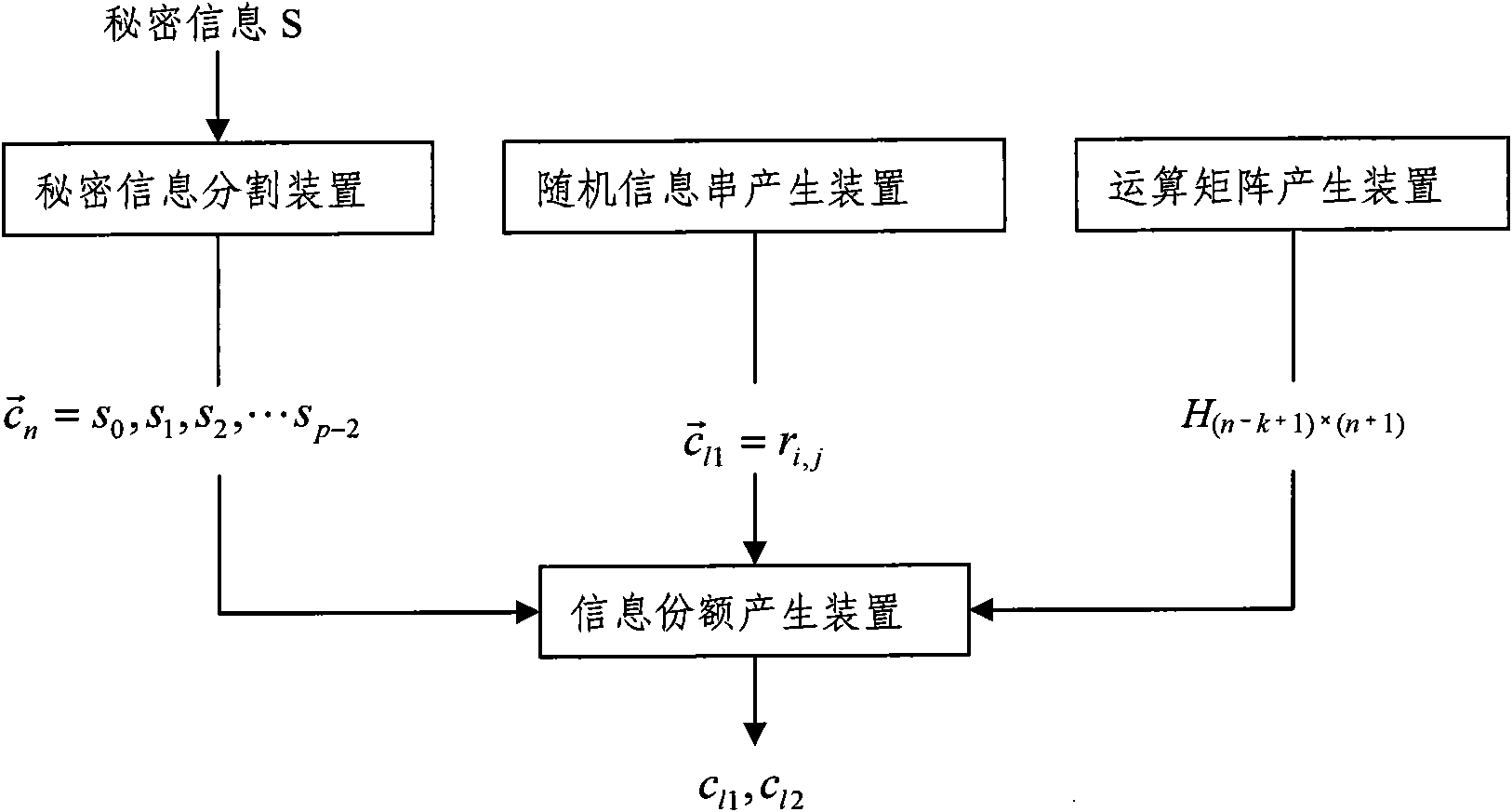
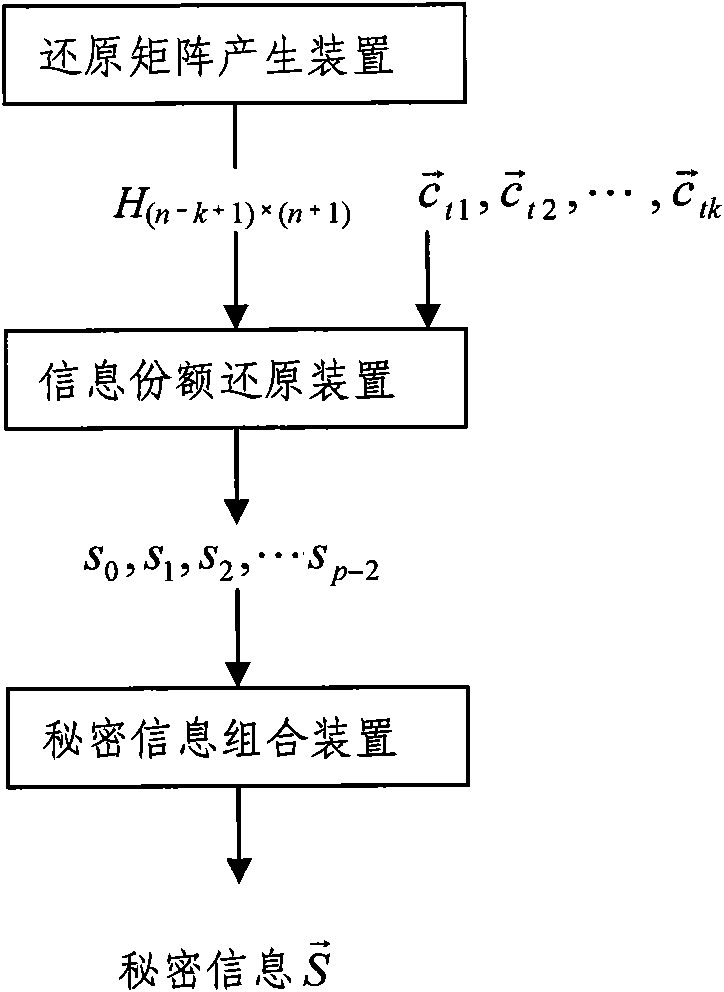
InactiveCN101882992AReduce computing loadImprove efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationInformation recoveryAlgorithm
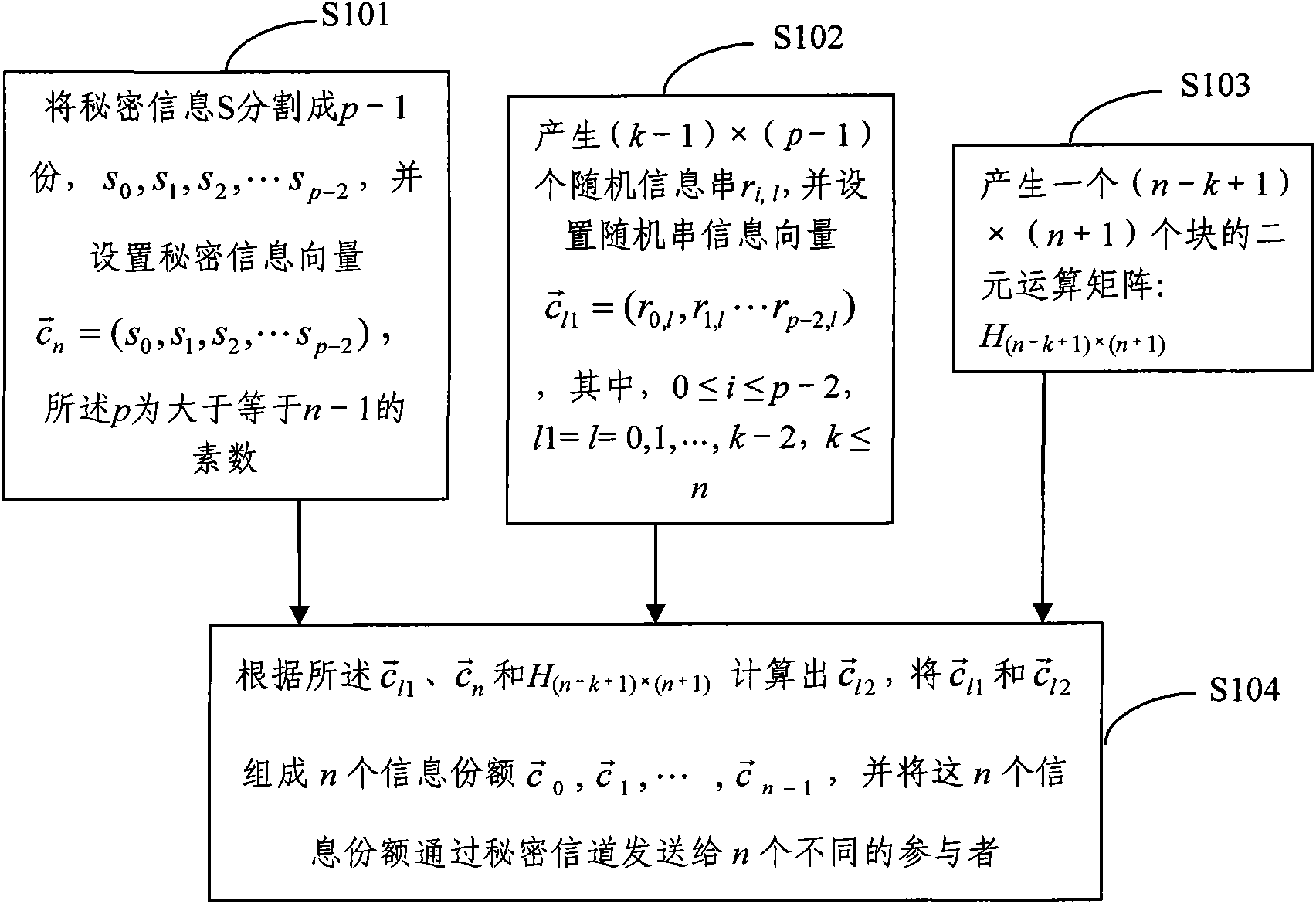
The invention discloses a threshold secret information distribution method which divides secret information into n-numbered information portions. The method comprises the following steps: dividing secret information into p-1 parts, wherein p is a prime and is not less than n-1; generating (k-1)*(p-1) random information strings; generating a binary operation matrix with (n-k+1)*(n+1) blocks; and generating n-numbered information portions according to the p-1 parts of secret information, the random information strings and the binary operation matrix, and distributing to n-numbered sharers. The invention also discloses a threshold secret information recovery method, wherein when at least random k-numbered information portions are known, secret information is recovered. The invention also discloses a threshold secret information distribution device and recovery device. The closer k is to n, the lower computational loads and higher efficiencies the threshold secret distribution and recovery devices have; and the distribution and recovery of threshold secret information can be completed by the same device.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
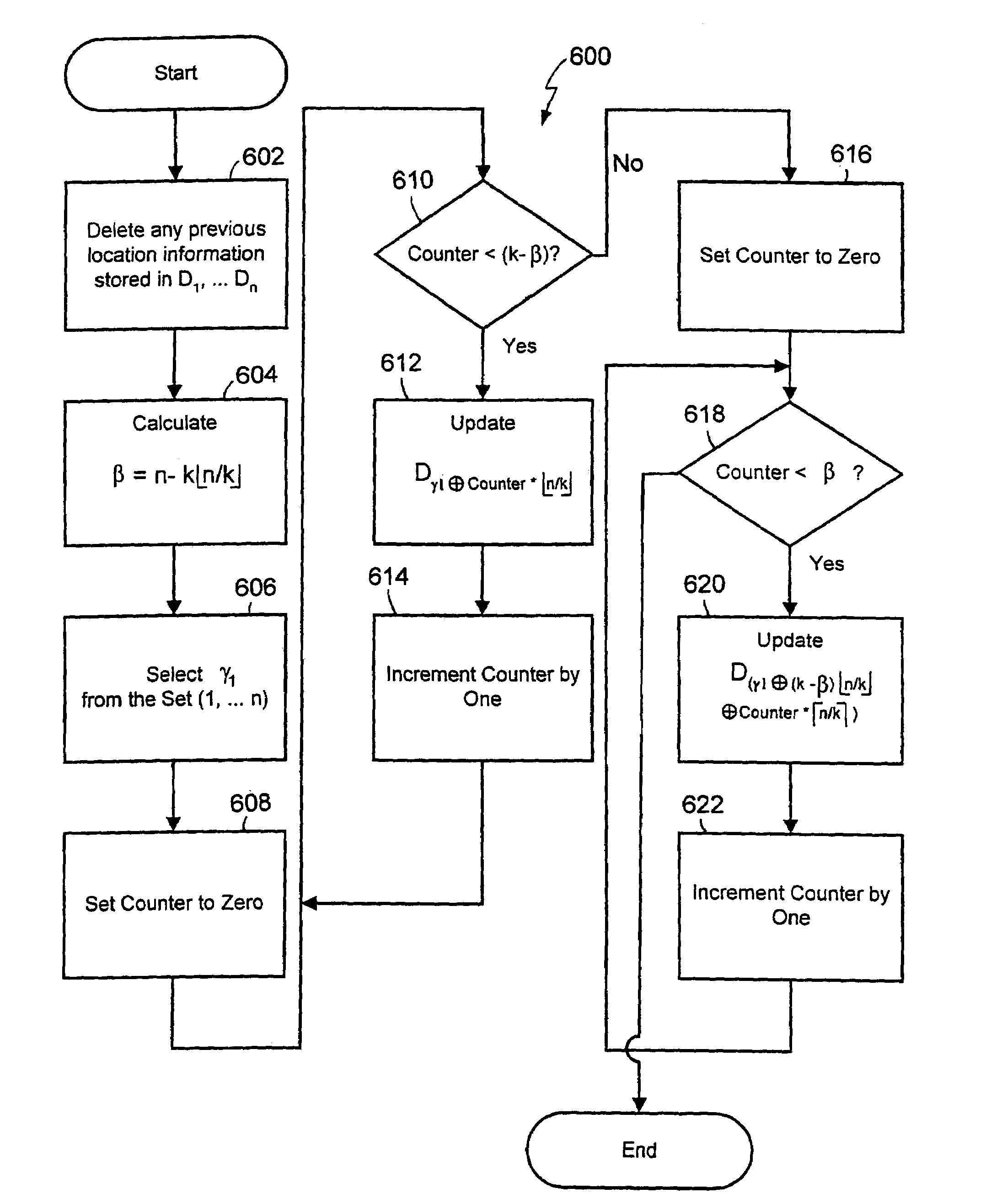
Location information recovery and management for mobile networks
InactiveUS7113795B2Easy to implementGuaranteed recovery periodData processing applicationsSpecial service for subscribersInformation recoveryRecovery period
Systems and methods for recovering and managing location information in mobile communication networks using a fast recovery protocol and load balanced query and update processes. According to the fast recovery protocol, if a location update processor does not receive a message from a global database server acknowledging receipt by the global database server of a location update message after a predetermined retry interval has elapsed since the location update message was sent by the location update processor, the location update processor sends a location update retry message after each predetermined retry interval elapses until the location update processor receives an acknowledgement message from the global database server. The global database server can use the location update retry messages and the predetermined retry interval to recover from a database or link failure. The recovery period using the fast recovery protocol is bounded by the predetermined retry interval. The fast recovery protocol can also be used in a system having a distributed location information database architecture. The load balanced query and update processes can be used to query and update, respectively, the databases of the distributed location information database architecture.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
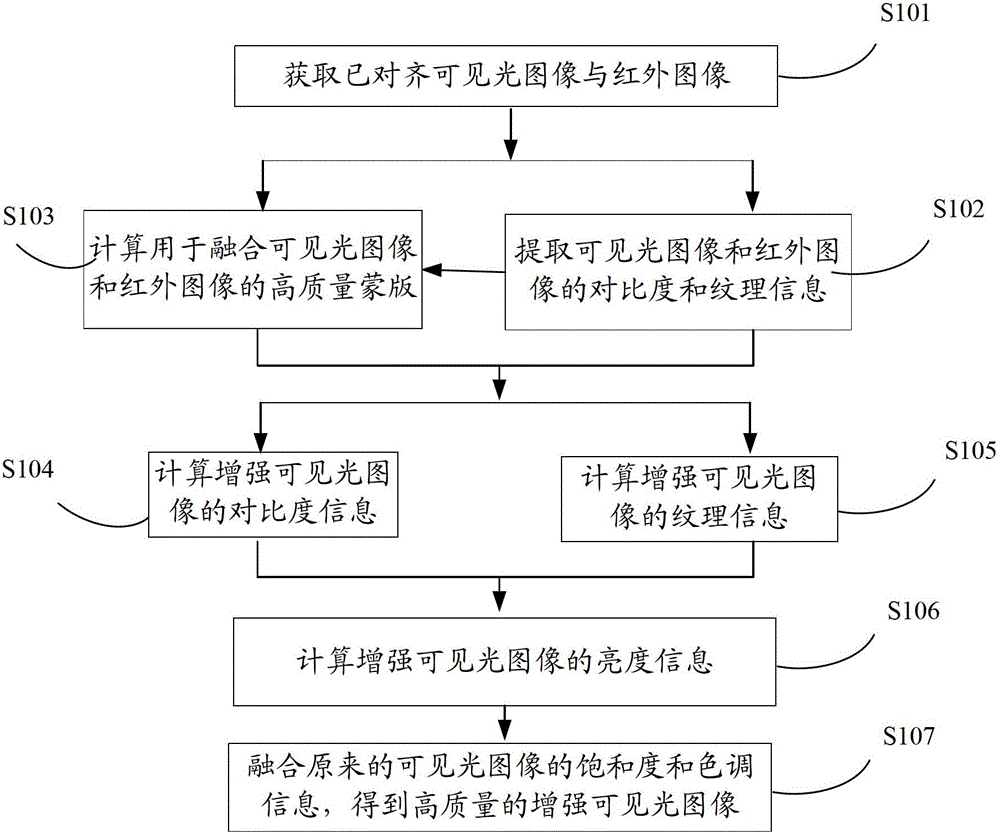
Image enhancement method
The invention provides an image enhancement method, comprising steps that: a visible-light image and an infrared image are collected; reversible transformation is carried out on the brightness and the dimension of the visible-light image and the infrared image to obtain contrast information and texture information of the visible-light image and the infrared image; a mask is calculated on the basis of the saturation and the brightness of the visible-light image; the mask is used to migrate the visible-light image and the infrared image, and the contrast information for enhancing the visible-light image is calculated; the mask is used to migrate the visible-light image and the infrared image, and the texture information for enhancing the visible-light image is calculated; reversible transformation is carried out to obtain the brightness of the enhanced visible-light image; and the enhanced visible-light image is obtained on the basis of the brightness of the enhanced visible-light image, the saturation of the visible-light image and tone mixing. The image enhancement method of the embodiment of the invention can automatically realize high dynamic scene information recovery and achieve high qualified visible light image enhancement from two aspects of the contrast and the texture.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Circuit and method for extracting amplitude and phase information in a resonant system
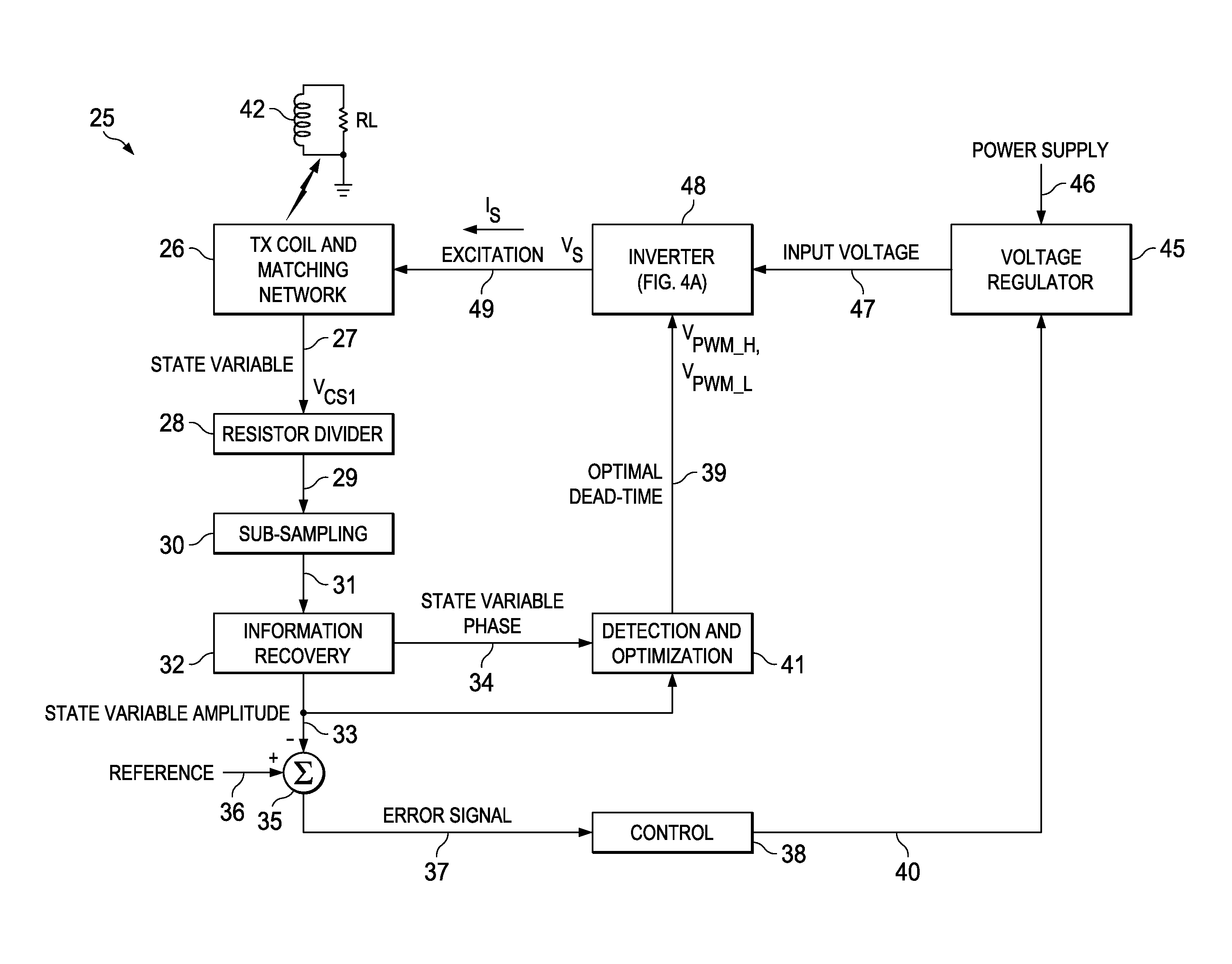
ActiveUS20140319921A1Way of increaseSimpler and flexible and cost-effectiveTransformersEfficient power electronics conversionInformation recoveryControl signal
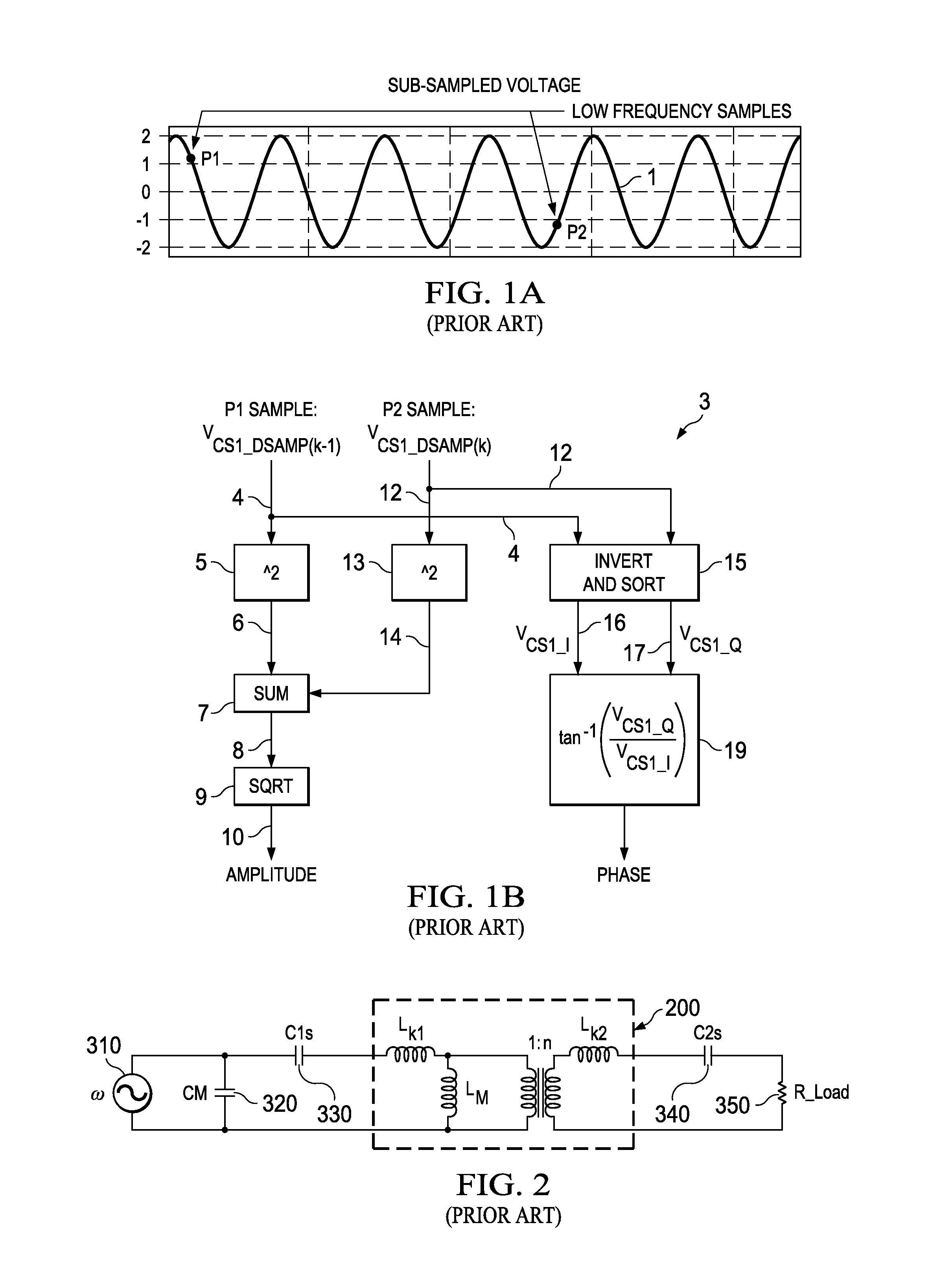
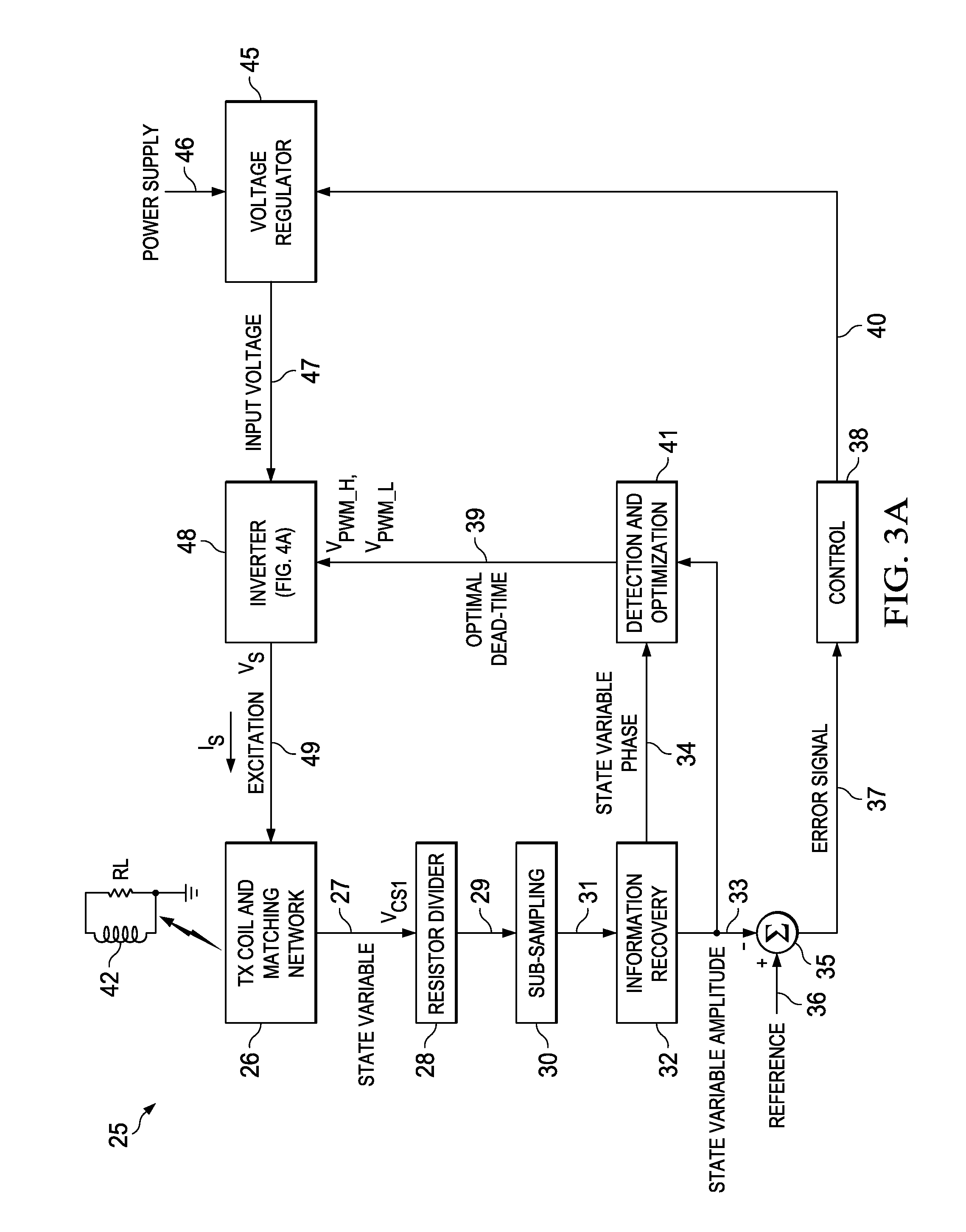
A resonant power transfer system includes resonant circuitry (26) including an inductor coil (59) and a resonant capacitor (51) coupled to a first terminal (27) of the inductor coil, wherein the inductor coil and the resonant capacitor resonate to produce an excitation signal (IS) and a state variable signal (VCS1). Sub-sampling circuitry (30) samples first and second points of the state variable signal at a rate which is substantially less than the RF frequency of the state variable signal. Information recovery circuitry (32) produces a state variable parameter signal representing a parameter (A) of the state variable signal from information in the first and second sampled points. Control circuitry (38) produces a first control signal in response to the state variable parameter signal. Detection and optimization circuitry (41) produces a second control signal in response to the state variable parameter signal. Voltage regulation circuitry (45) produces a regulated supply voltage in response to the first control signal. Switching inverter circuitry produces the excitation signal in response to the regulated supply voltage and the second control signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Multi-wavelength lamination imaging technology facing to three-dimensional information recovery
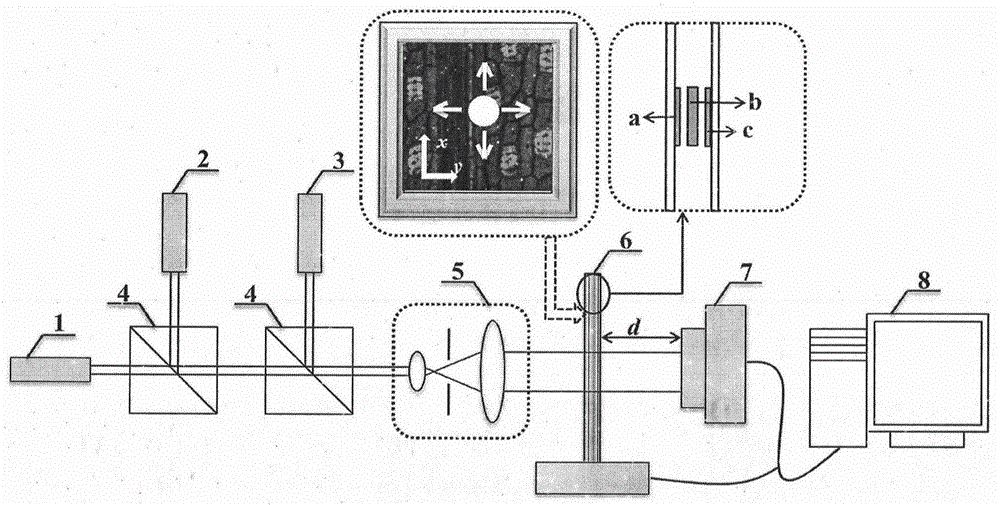
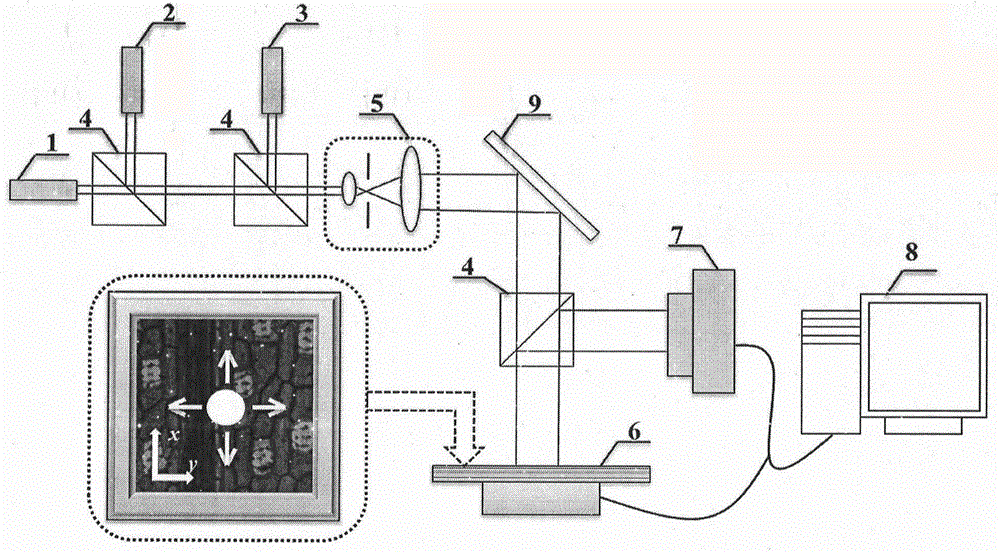
The invention discloses a multi-wavelength lamination imaging technology facing to three-dimensional information recovery. Samples to be tested are irradiated by various wavelengths and are translated successively in a lamination scanning way in a measurement plane, and corresponding series intensity images are recorded by an image sensor, the recorded series intensity images are processed, and a three-dimensional image of each sample to be tested can be obtained in a computer by an iterative reconstruction algorithm based on multi-wavelength lamination scanning. According to the selection of diffraction distance in a multi-wavelength lamination algorithm, the information of the surface layer, the bottom layer and each inner layer of each sample to be tested can be respectively recovered, i.e. the three-dimensional complex amplitude information of the sample to be tested can be recovered, and the problem that layers in the traditional lamination imaging are mutually overlapped and are difficult to distinguish can be effectively solved. According to the multi-wavelength lamination imaging technology, various wavelengths are adopted, so that the quality of the recovered image can be greatly improved, and meanwhile, the anti-noise capability of the system is better. The multi-wavelength lamination imaging technology has the advantages of high imaging efficiency and good transportability and is suitable for the three-dimensional imaging of the surface layer of a reflection-type object, the imaging of the surface layer and the bottom layer of a transmission-type thin object and the three-dimensional imaging of each layer of a transmission-type thick object.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
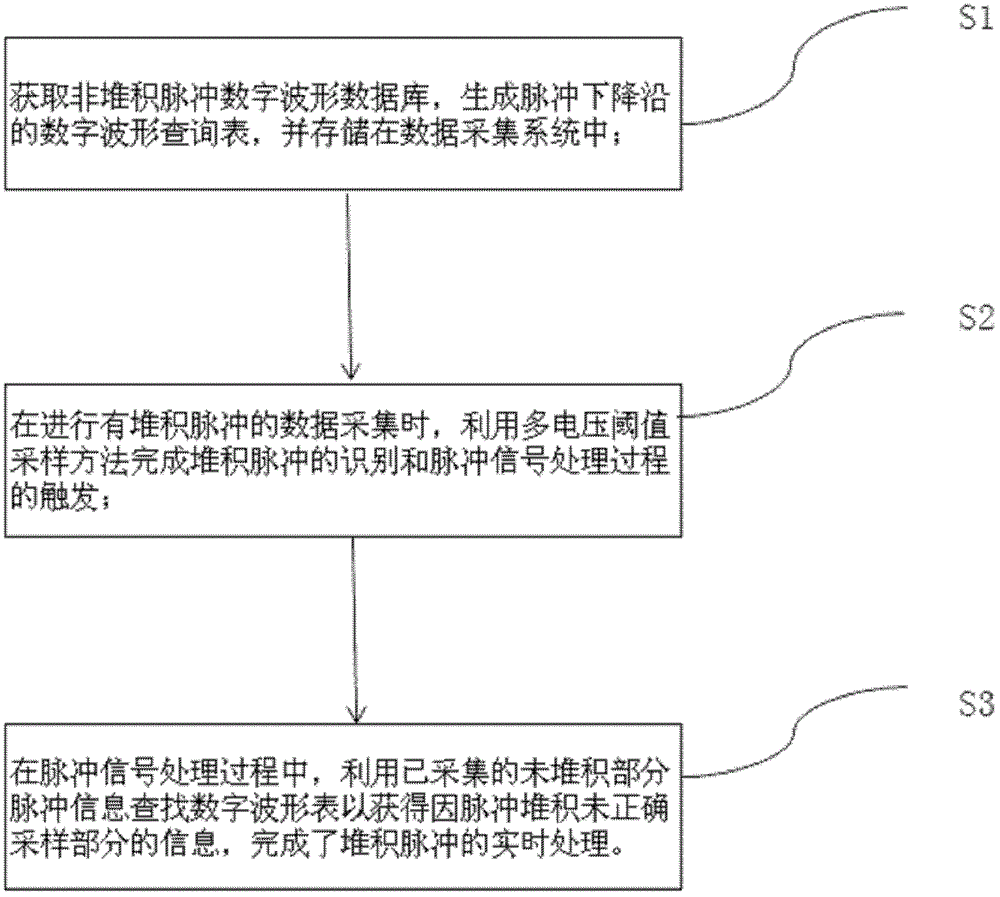
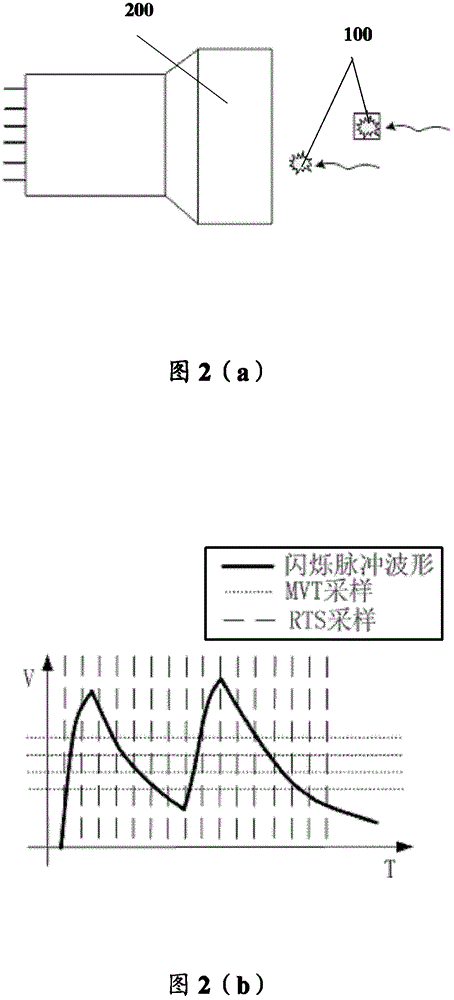
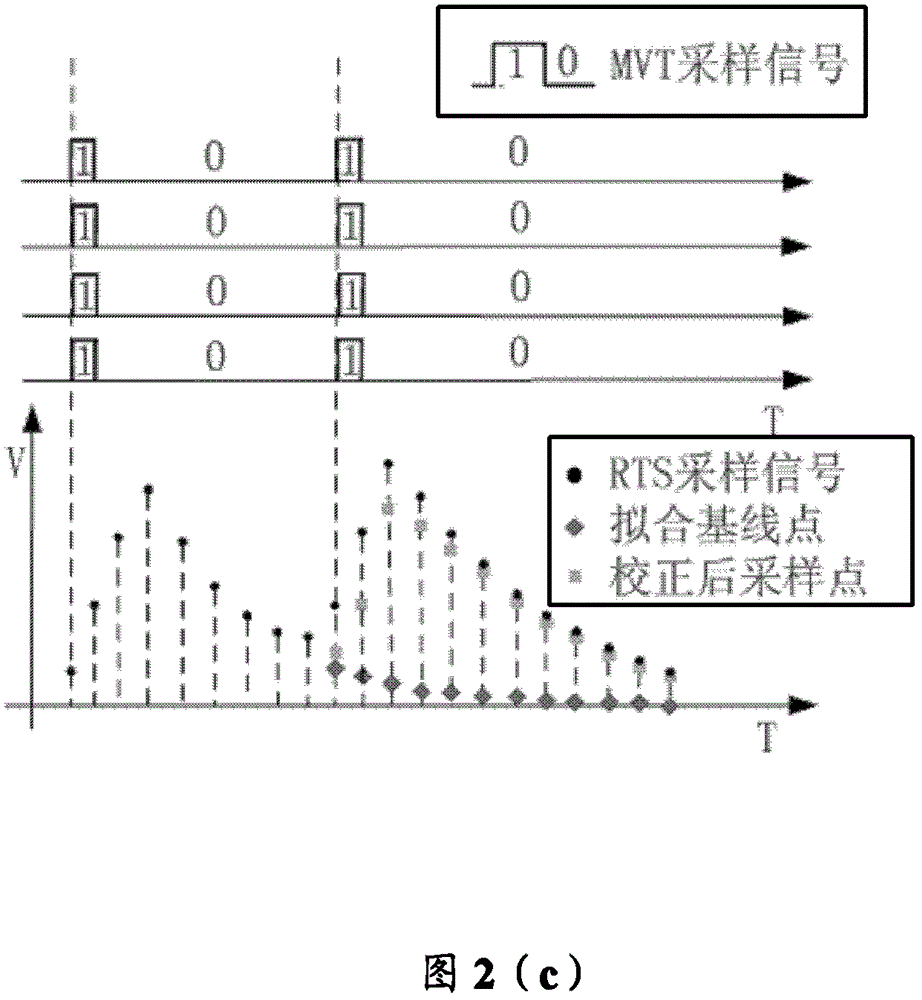
Pulse accumulation event real-time processing method and system
ActiveCN105212954APromote recoverySimple methodTomographyX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentCounting rateInformation recovery
A pulse accumulation event real-time processing method includes the steps of generating a fitting baseline value look-up table and a fitting energy value look-up table of a pulse falling edge, completing the recognizing of accumulated pulses and the triggering of the pulse signal processing process through a multi-voltage threshold value sampling method, obtaining information of a part not correctly sampled due to pulse accumulation through pulse prior information and collected pulse information in the form of the look-up tables, and completing real-time recovery of accumulated pulse information. The recognizing of high-counting-rate lower accumulated pulses and the triggering of the pulse signal processing process are completed through the multi-voltage threshold value sampling method, the information of the part not correctly sampled due to pulse accumulation is obtained through pulse prior information and collected pulse information in the form of the look-up tables, and the real-time recovery of the accumulated pulse information is completed. The method is simple and efficient and can be easily implemented on a detector-level real-time data collecting system, and an excellent accumulated pulse information recovery effect can still be achieved under the condition of a low sampling rate.
Owner:RAYCAN TECH CO LTD SU ZHOU
Reception of signals transmitted over a dispersive optical channel
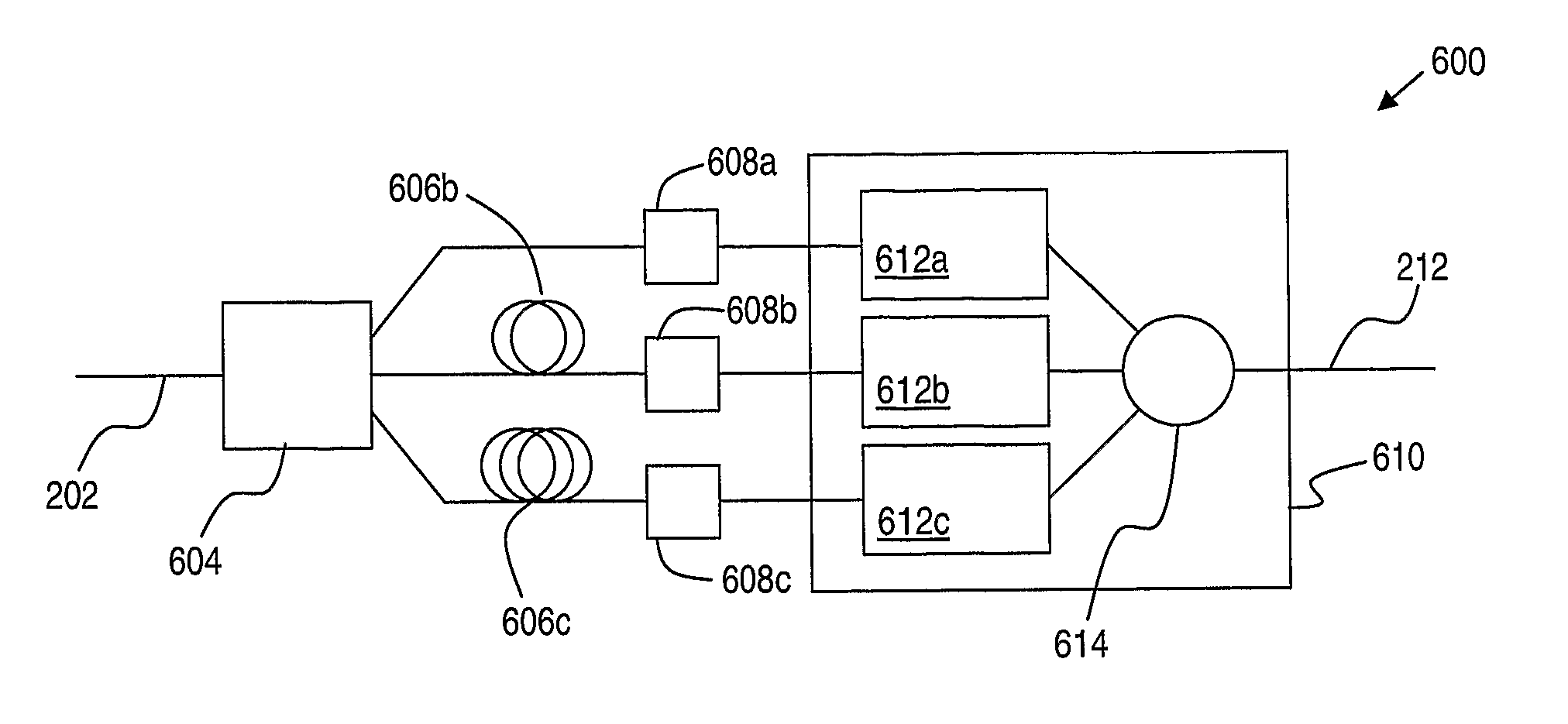
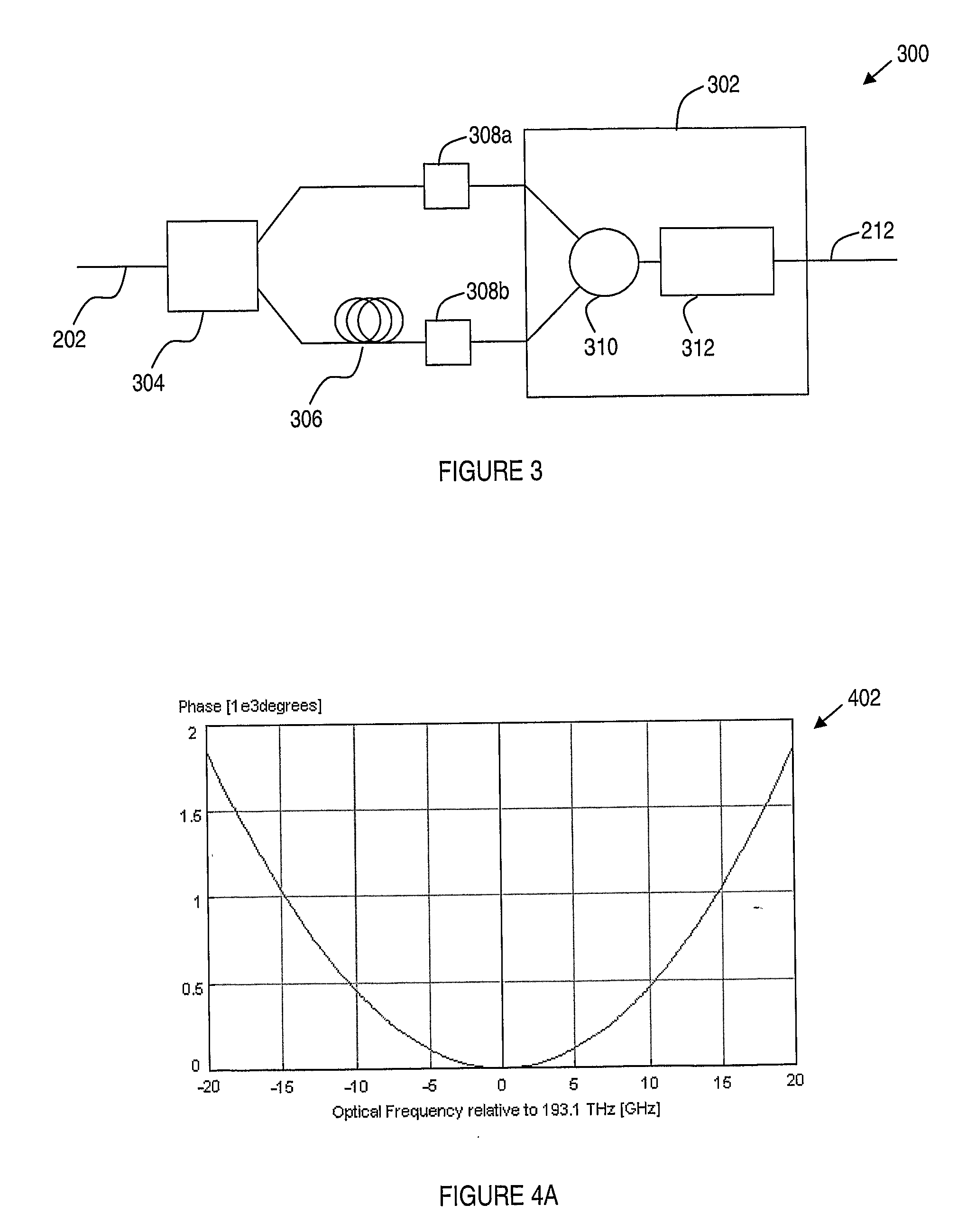
ActiveUS20100142951A1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityPolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsPhase shiftedInformation recovery
A receiver for recovering transmitted information carried by a received optical signal that has been affected by dispersion includes an optical splitter having an input port arranged to receive the received optical signal, and a plurality of output ports. A proportion of optical power at the input port is transmitted to each of the output ports. A plurality of optical detectors is operably connected to respective output ports of the optical splitter, for generating a corresponding plurality of electrical signals. Optical phase shifters are disposed between the output ports of the optical splitter and respective optical detectors. As a result, each optical phase shifter applies a frequency dependent phase shift to an optical signal passing therethrough. An electronic processor includes analog and / or digital electronic components configured to combine two or more of the plurality of electrical signals, or information recovered separately therefrom, in order to provide improved accuracy or reliability of information recovery as compared with detecting and processing only the received optical signal. The receiver is advantageously able to mitigate the effects of frequency-dependent fading which may occur in intensity modulation / direct detection optical transmission systems due to dispersion in optical transmission paths.
Owner:OFIDIUM PTY LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com