Optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexed communications with nonlinearity compensation
a technology of orthogonal frequency division and multiplexing, applied in multiplex communication, polarisation multiplex system, phase-modulated carrier system, etc., can solve the problems of impracticality, long system latency, and inability to ensure the control of relative optical phase shifts. achieve the effect of improving performance and high throughpu
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024]This disclosure describes a number of embodiments of one or more optical transmission systems and elements. Within this disclosure, the term “optical” indicates electromagnetic range at or near optical frequencies; this includes visible light and so-called “near-visible” light such as near infrared, infrared, far infrared and the near and far ultra-violet spectra. The preferred operating range is around 1.5 micron.
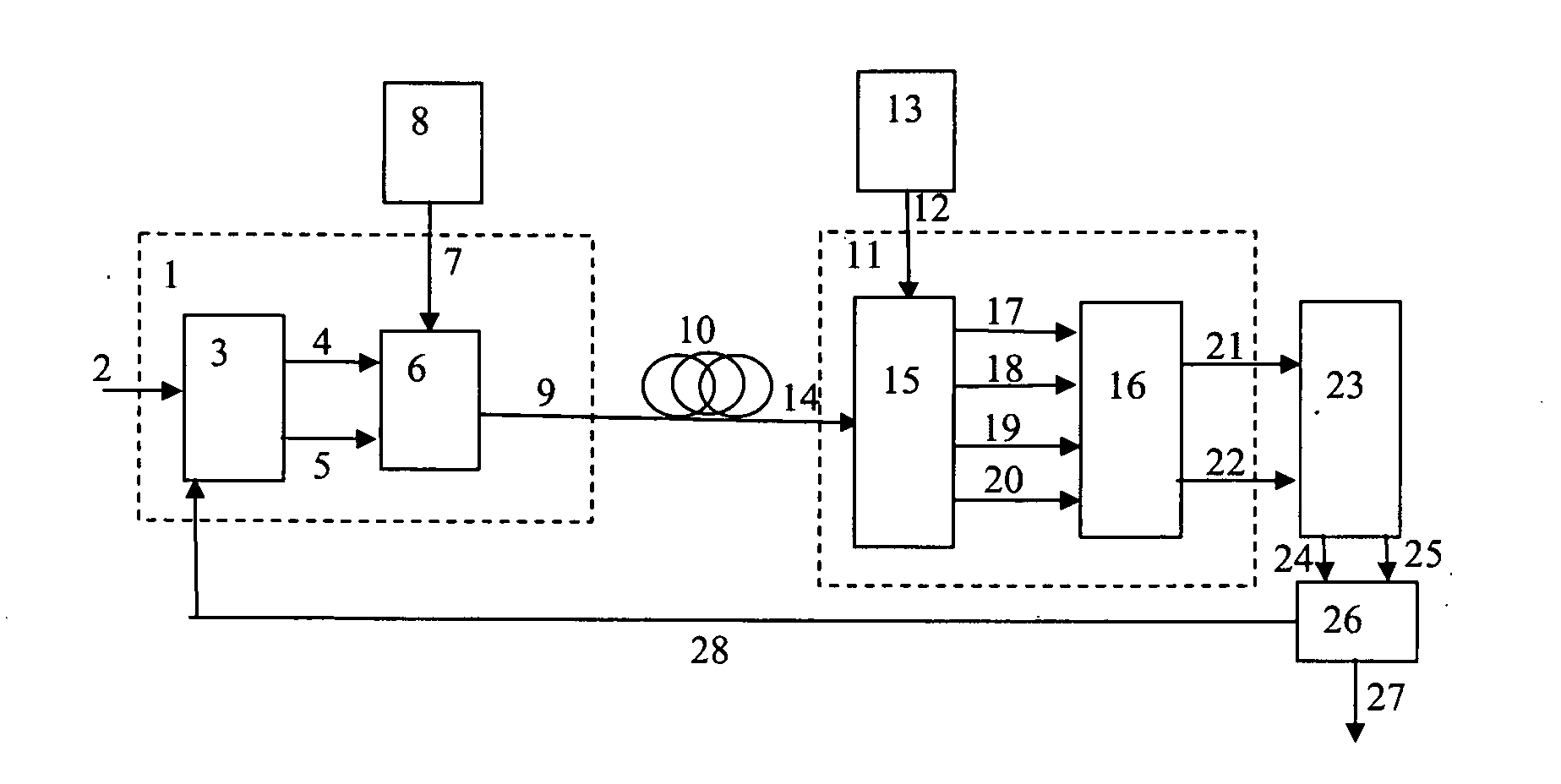
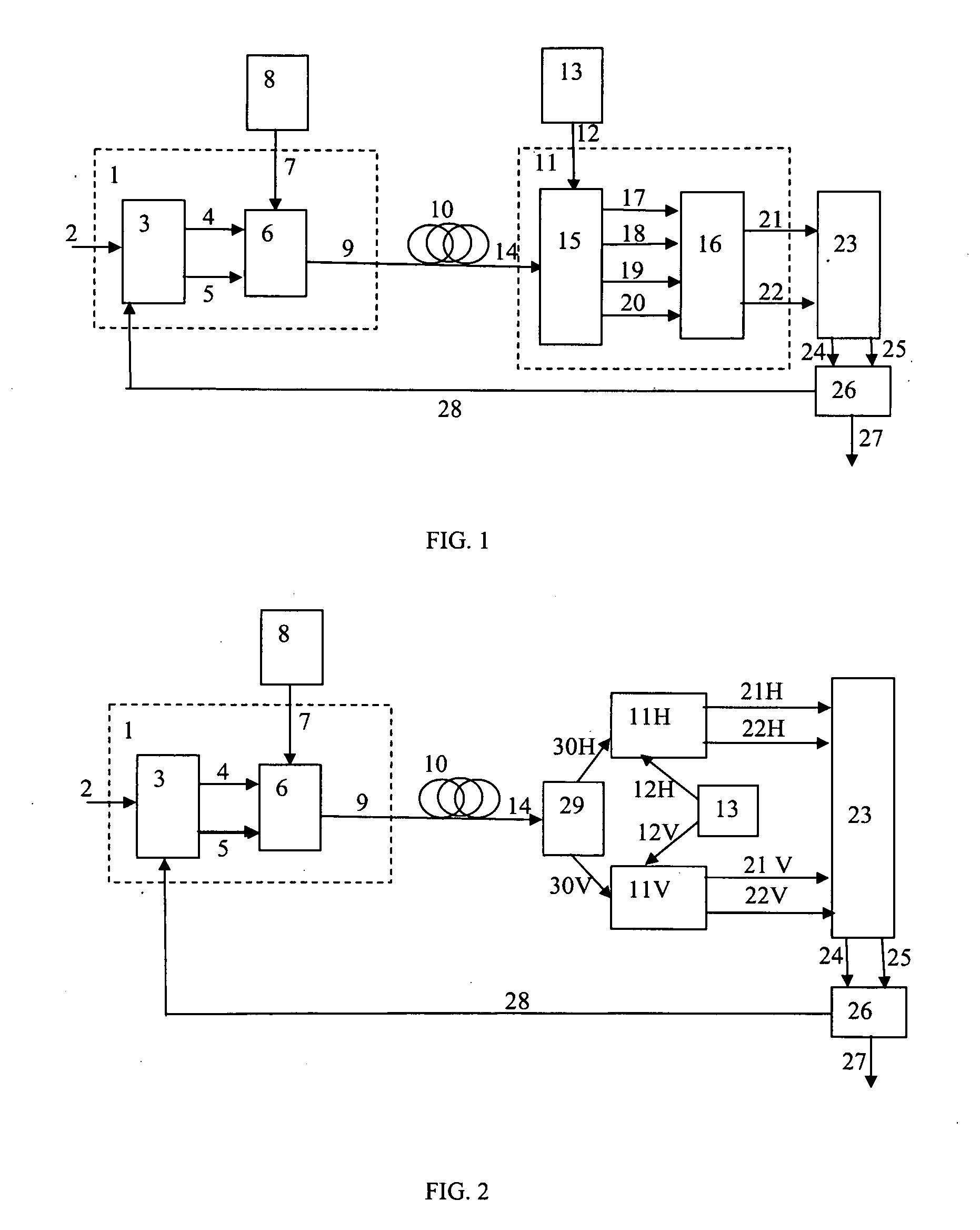
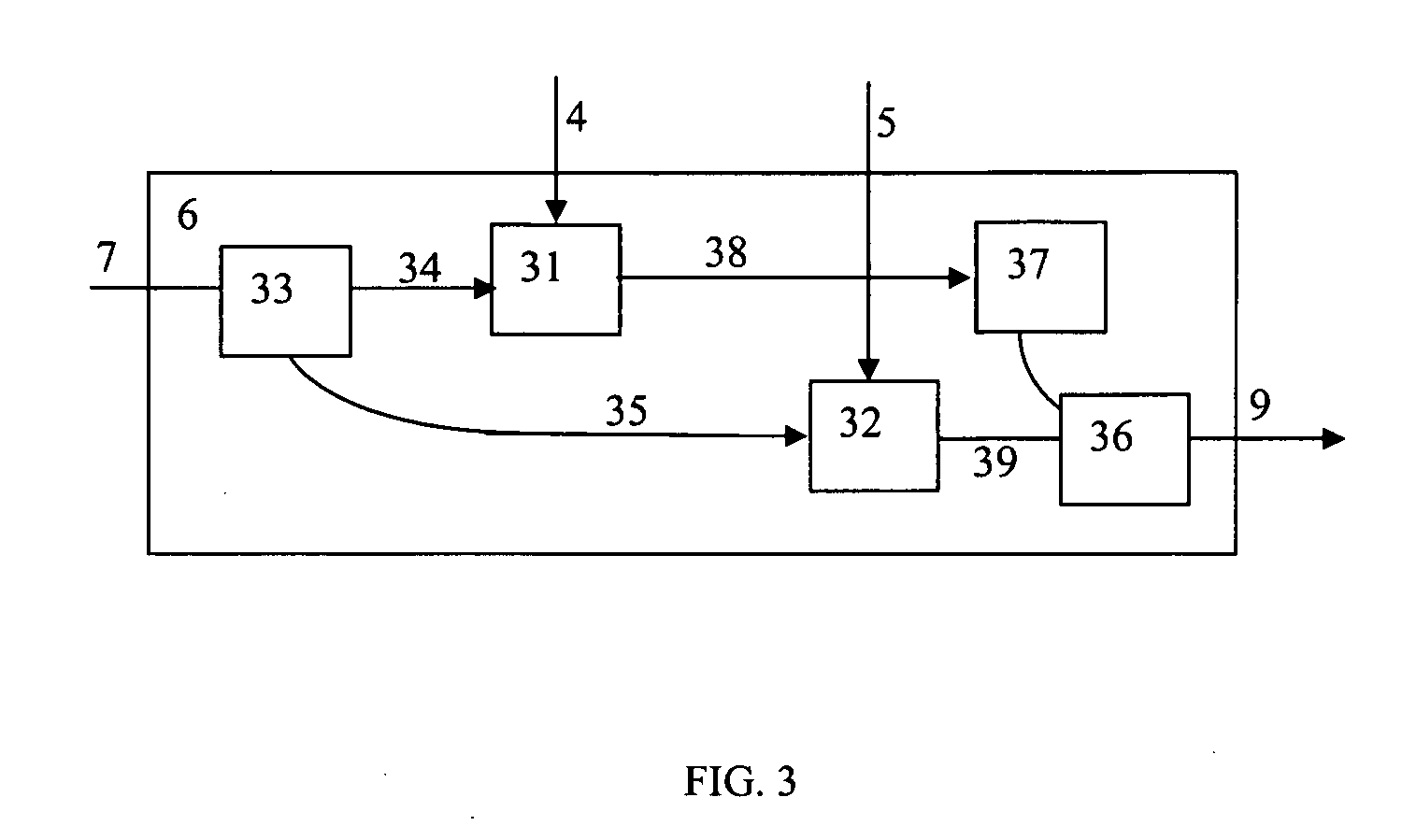
[0025]FIG. 1 illustrates a point-to-point OFDM data transmission system using coherent detection. In a transmitter I a digital data stream 2 enters an OFDM encoder 3, which outputs two analog signals 4 and 5 (I and Q) driving an optical modulator 6. The modulator 6 applies the modulation to a light beam 7 emitted by a light source 8. The signal 9 transmitted via an optical link 10 is received by coherent receivers 11. Local oscillator optical signal 12 coming from a light source 13 enters the coherent receiver 11 and interferes with the optical signal 14. The receive...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com