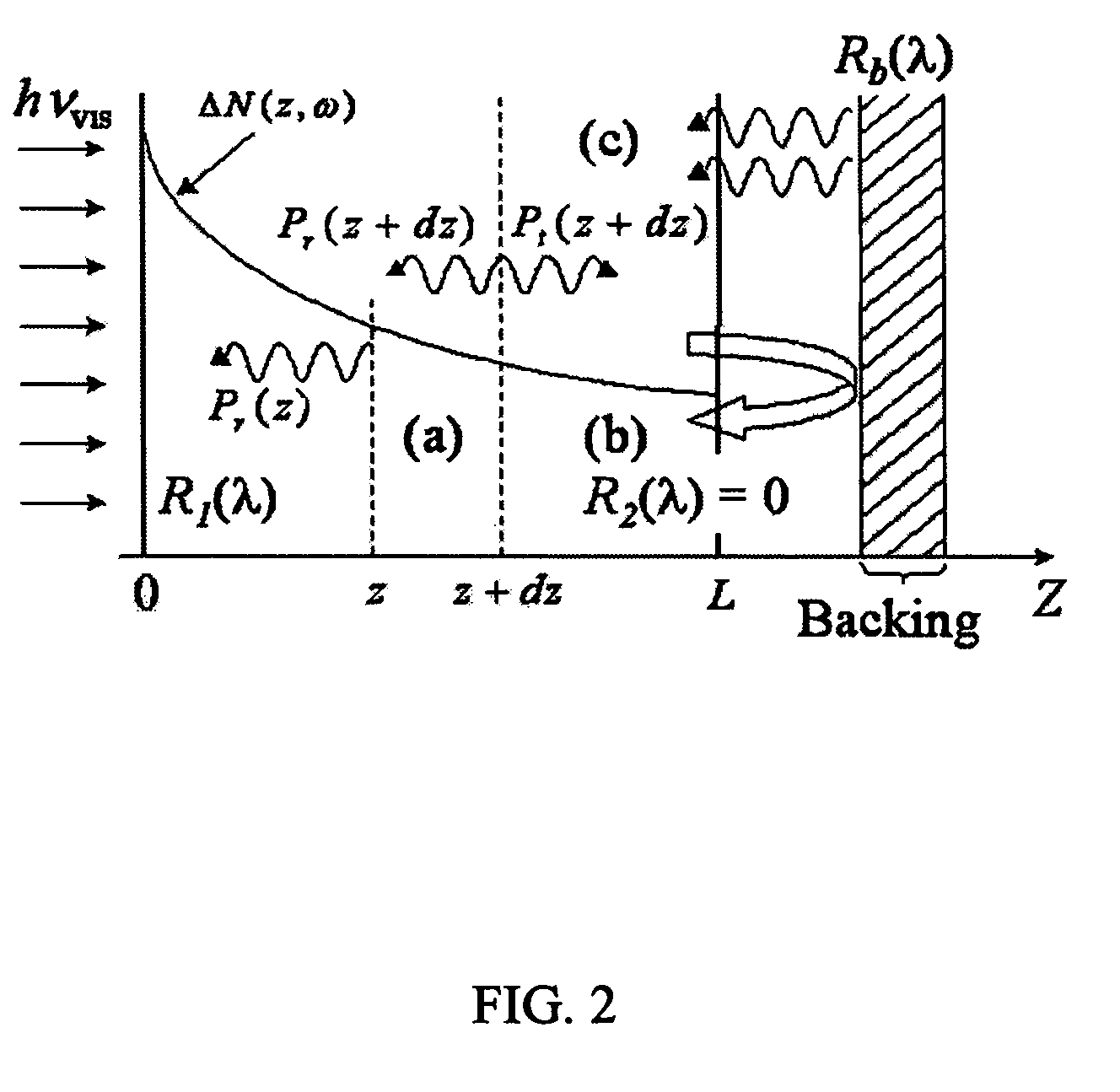
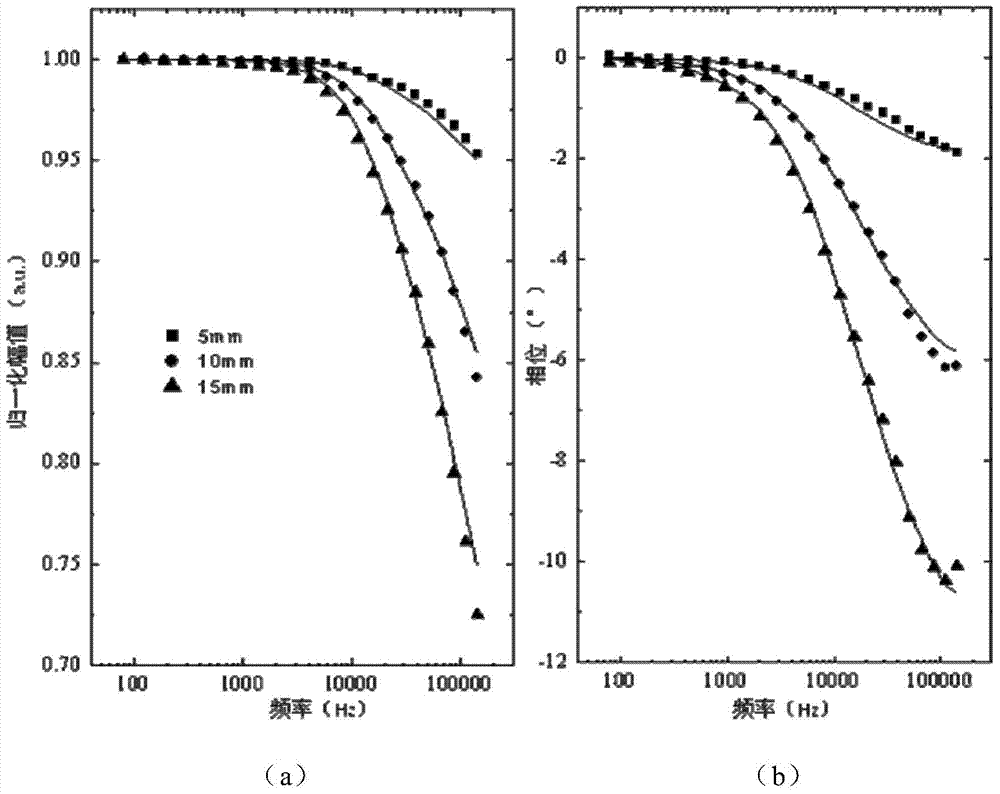
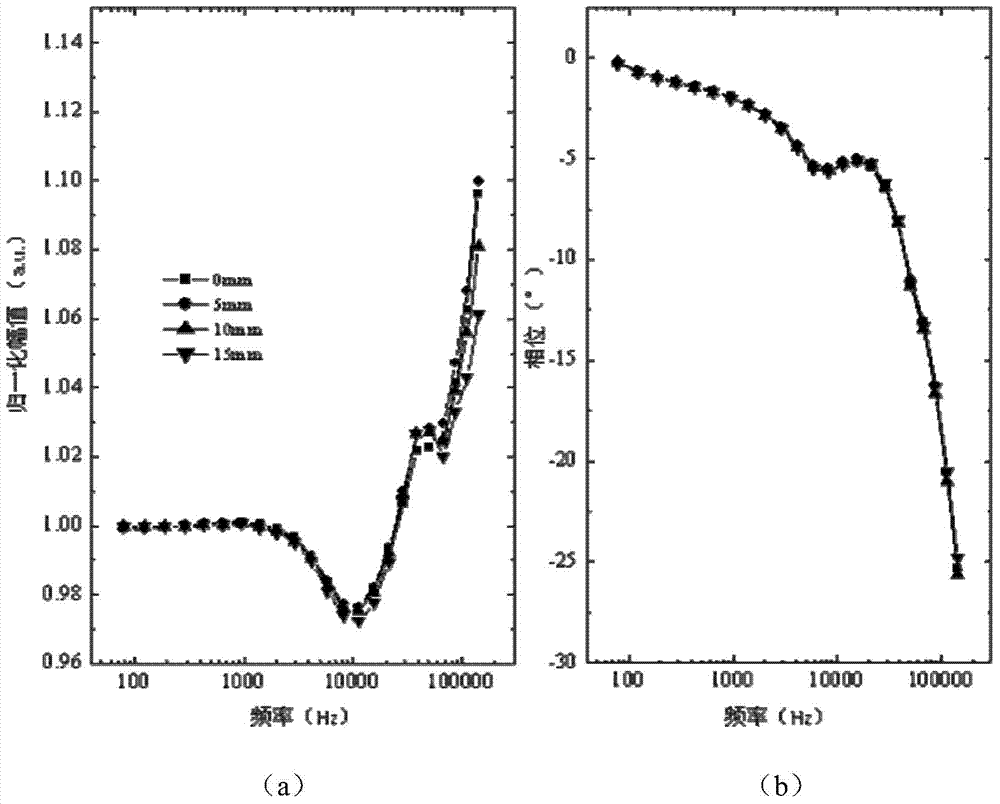
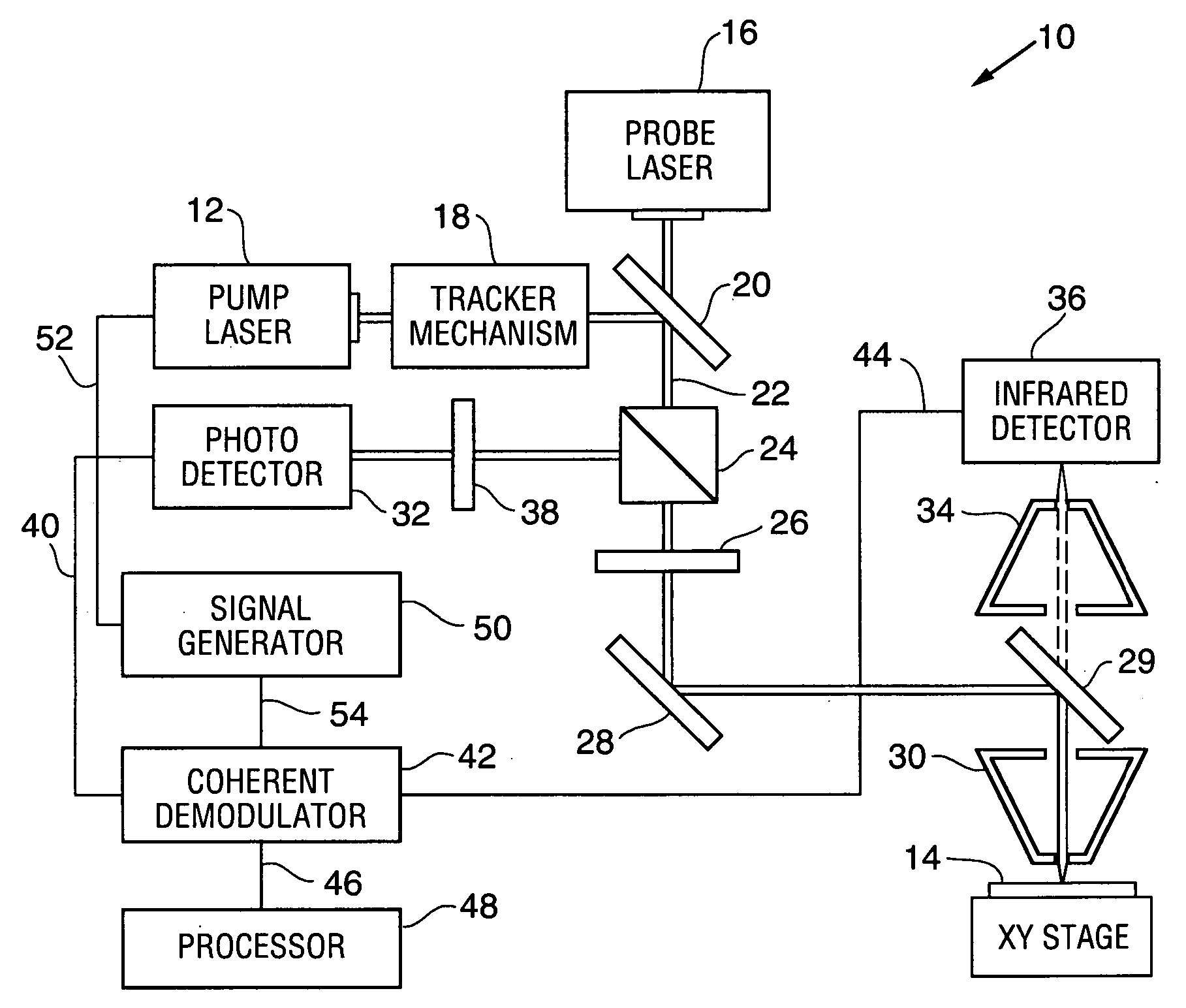
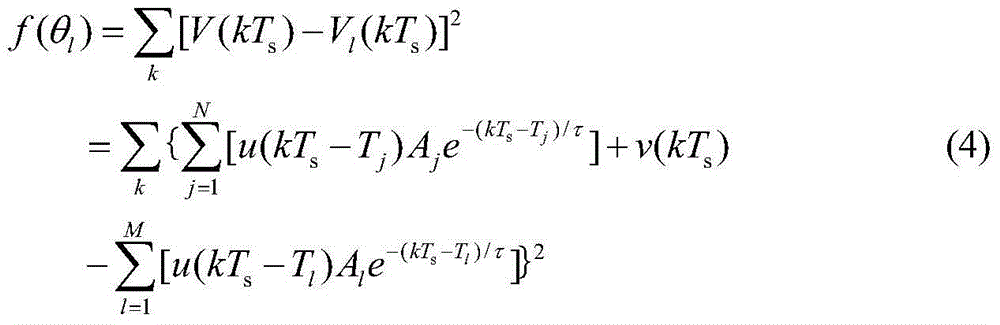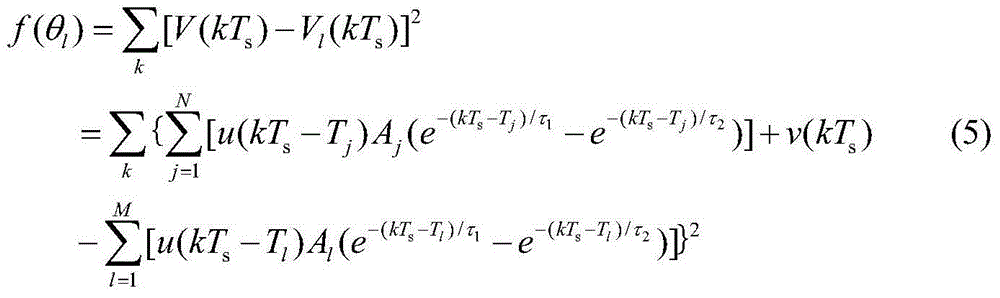Patents
Literature
67 results about "Radiometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Radiometry is a set of techniques for measuring electromagnetic radiation, including visible light. Radiometric techniques in optics characterize the distribution of the radiation's power in space, as opposed to photometric techniques, which characterize the light's interaction with the human eye. Radiometry is distinct from quantum techniques such as photon counting.
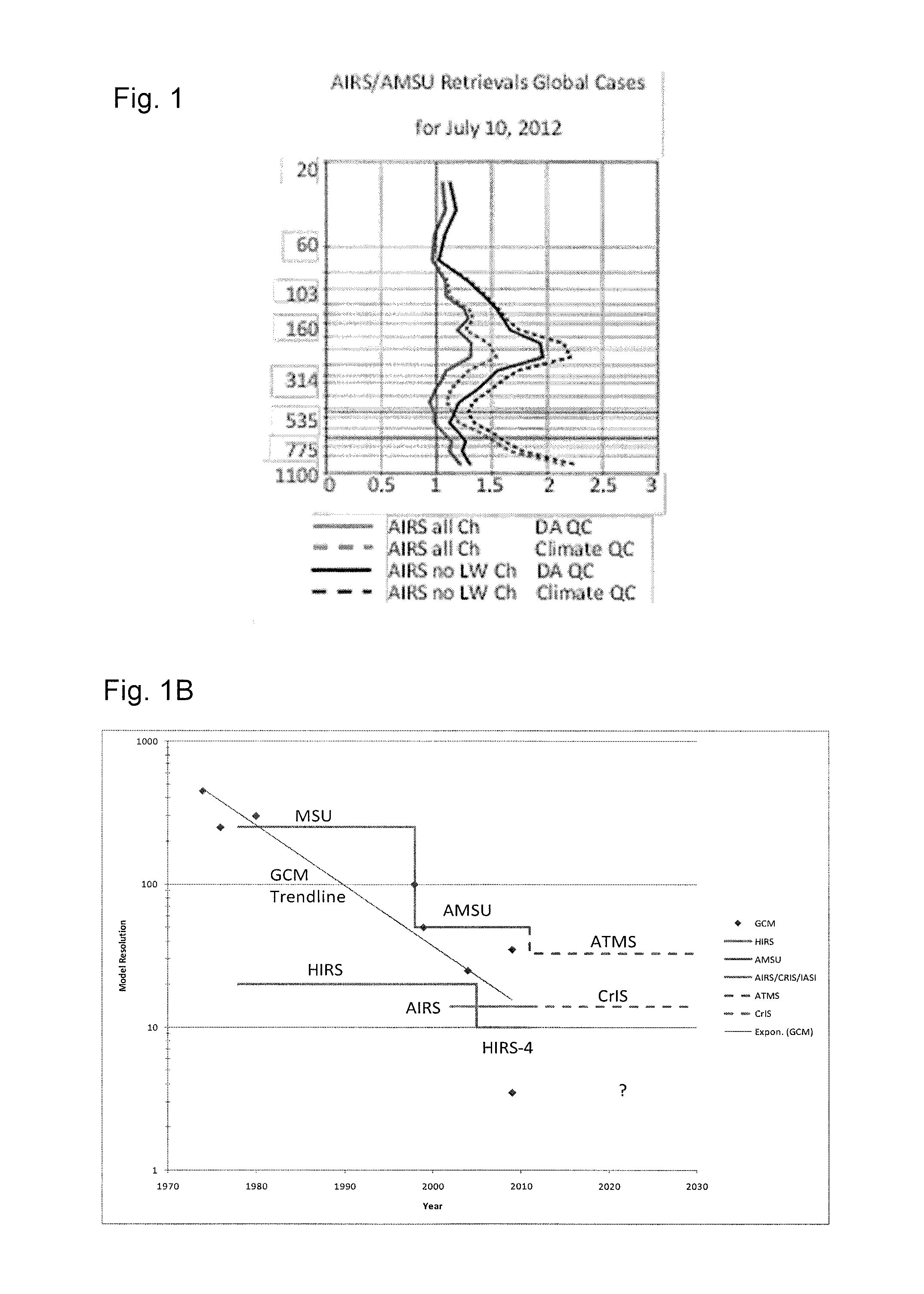
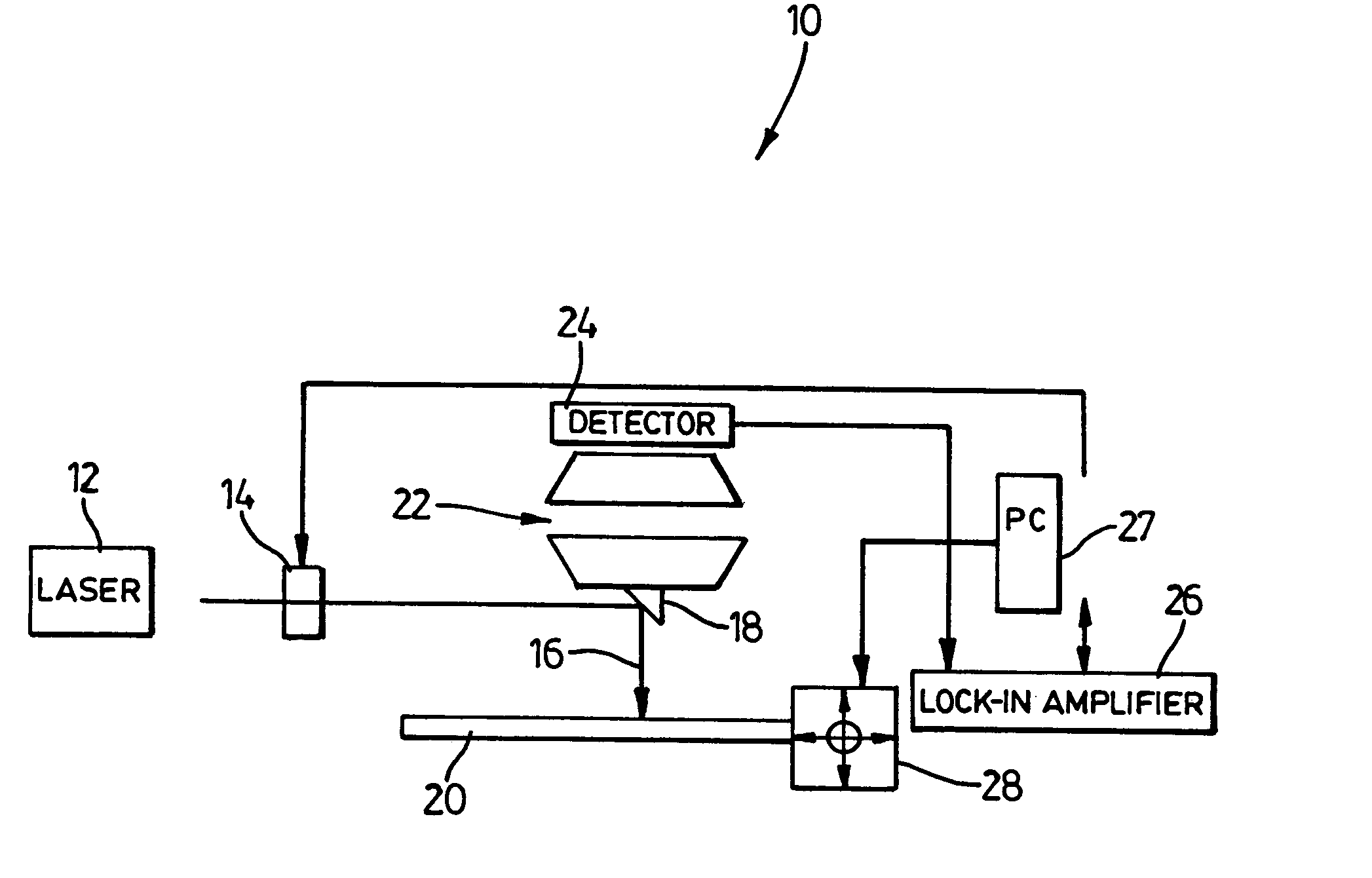
Portable radiometry and imaging apparatus
InactiveUS6849849B1Protection elementEasy to installRadiation pyrometrySolid-state devicesParticulatesEngineering
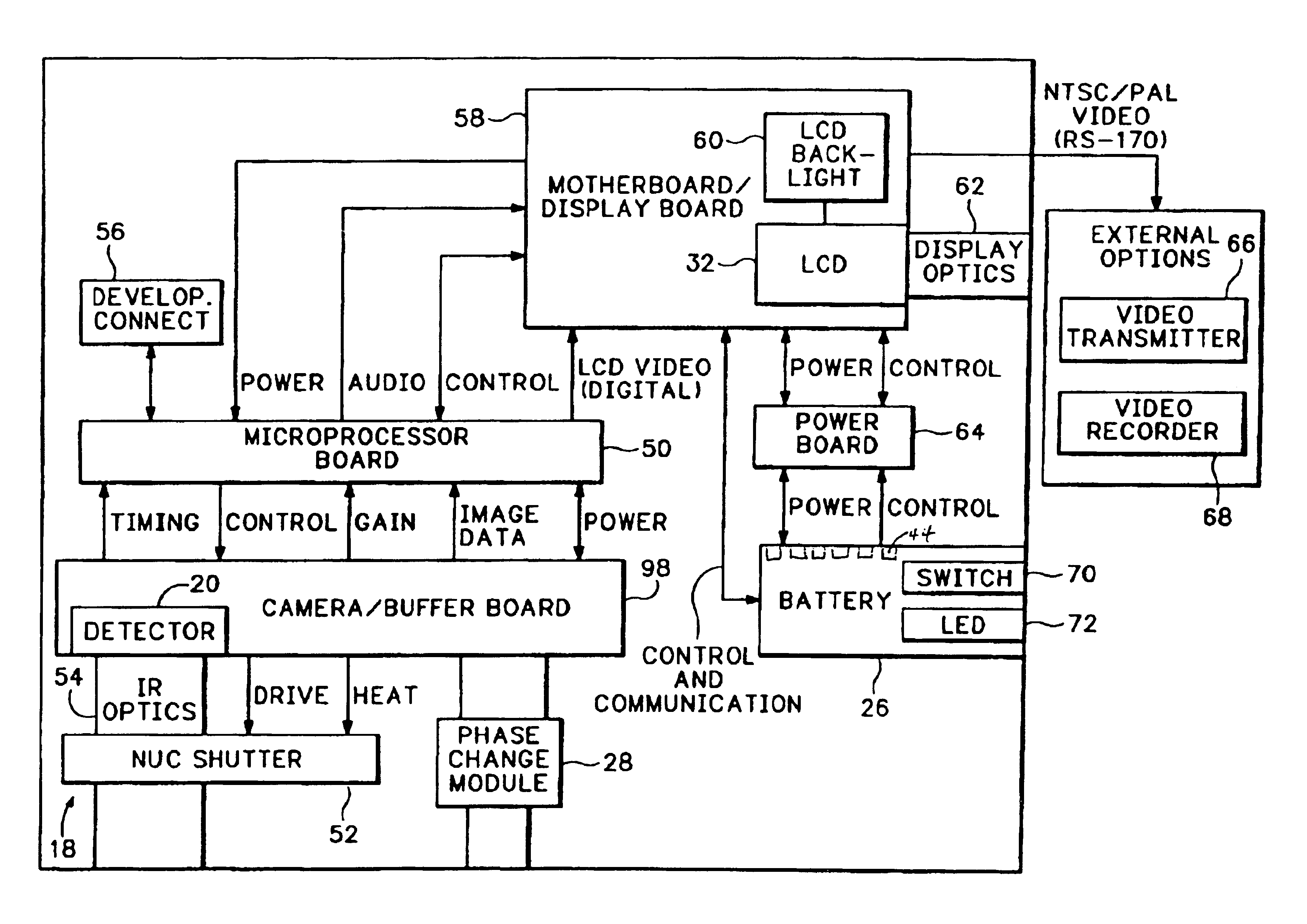
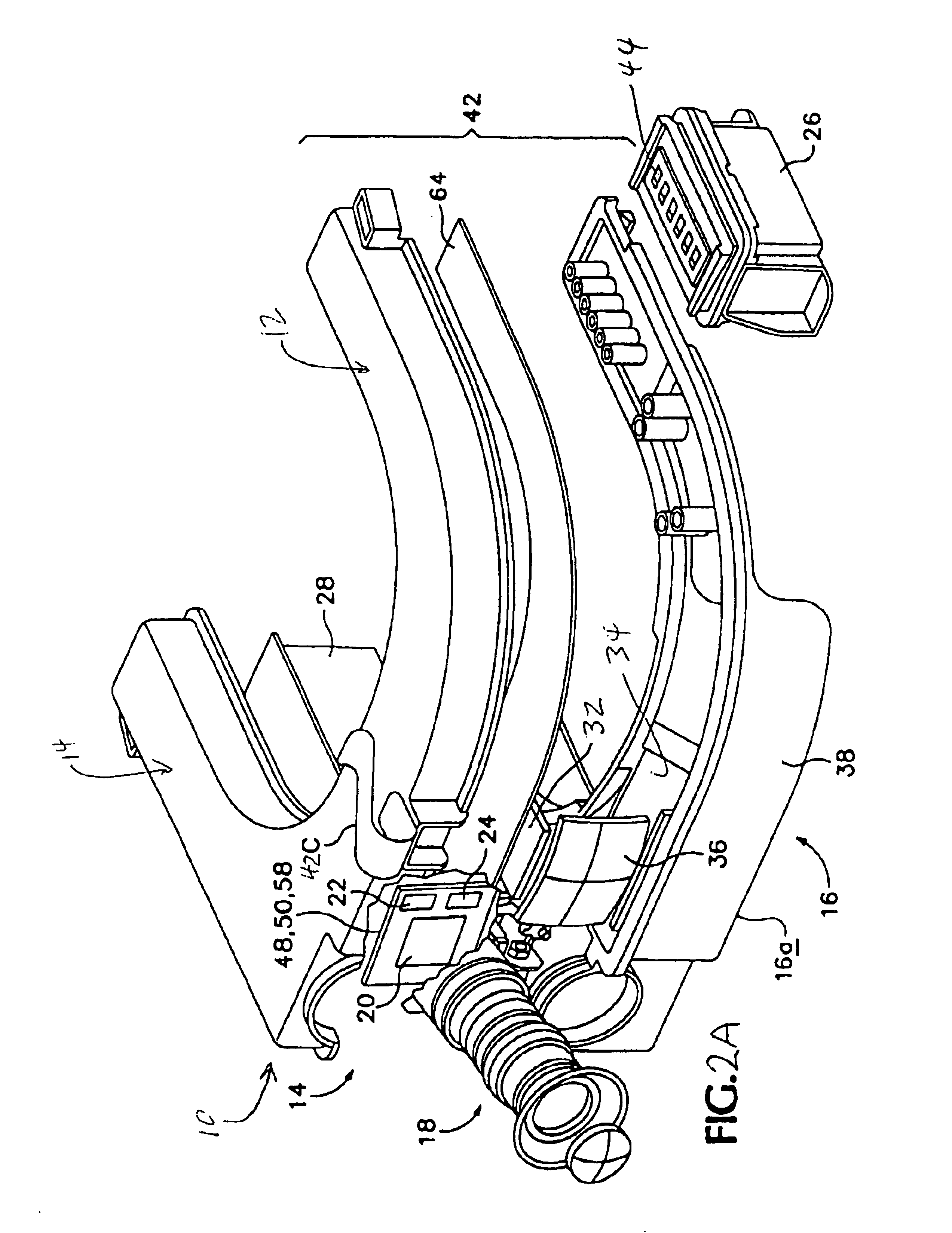
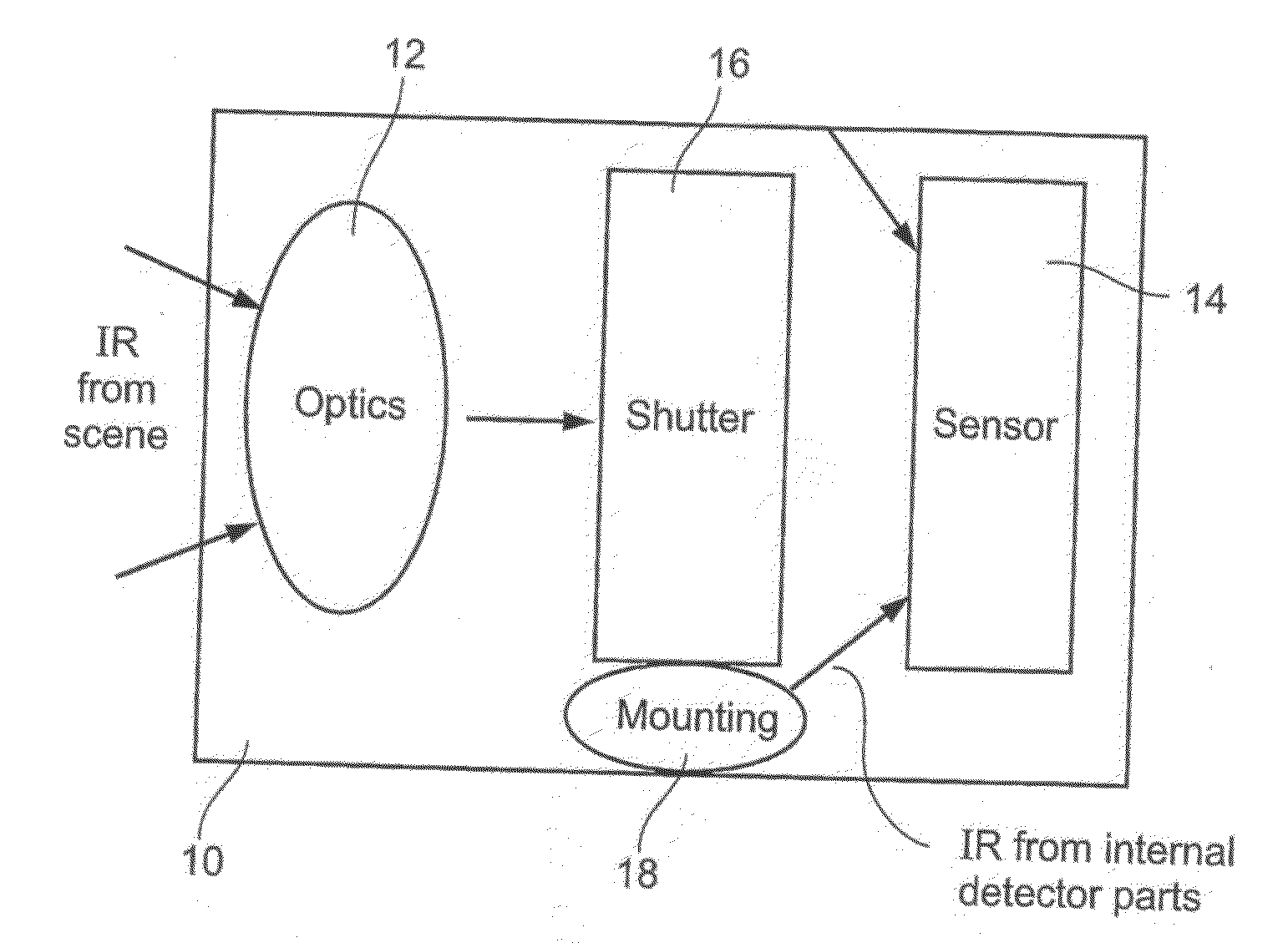
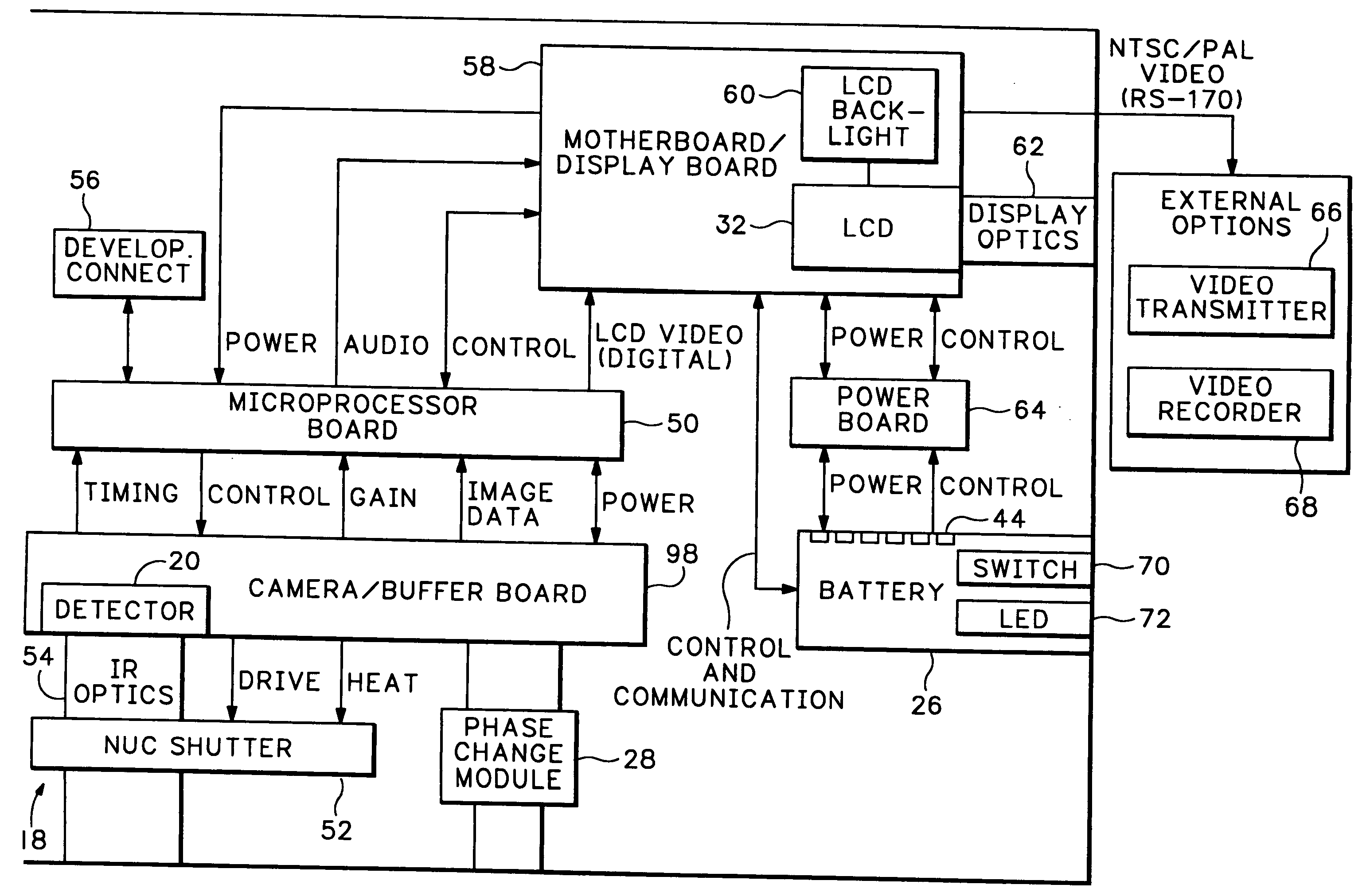
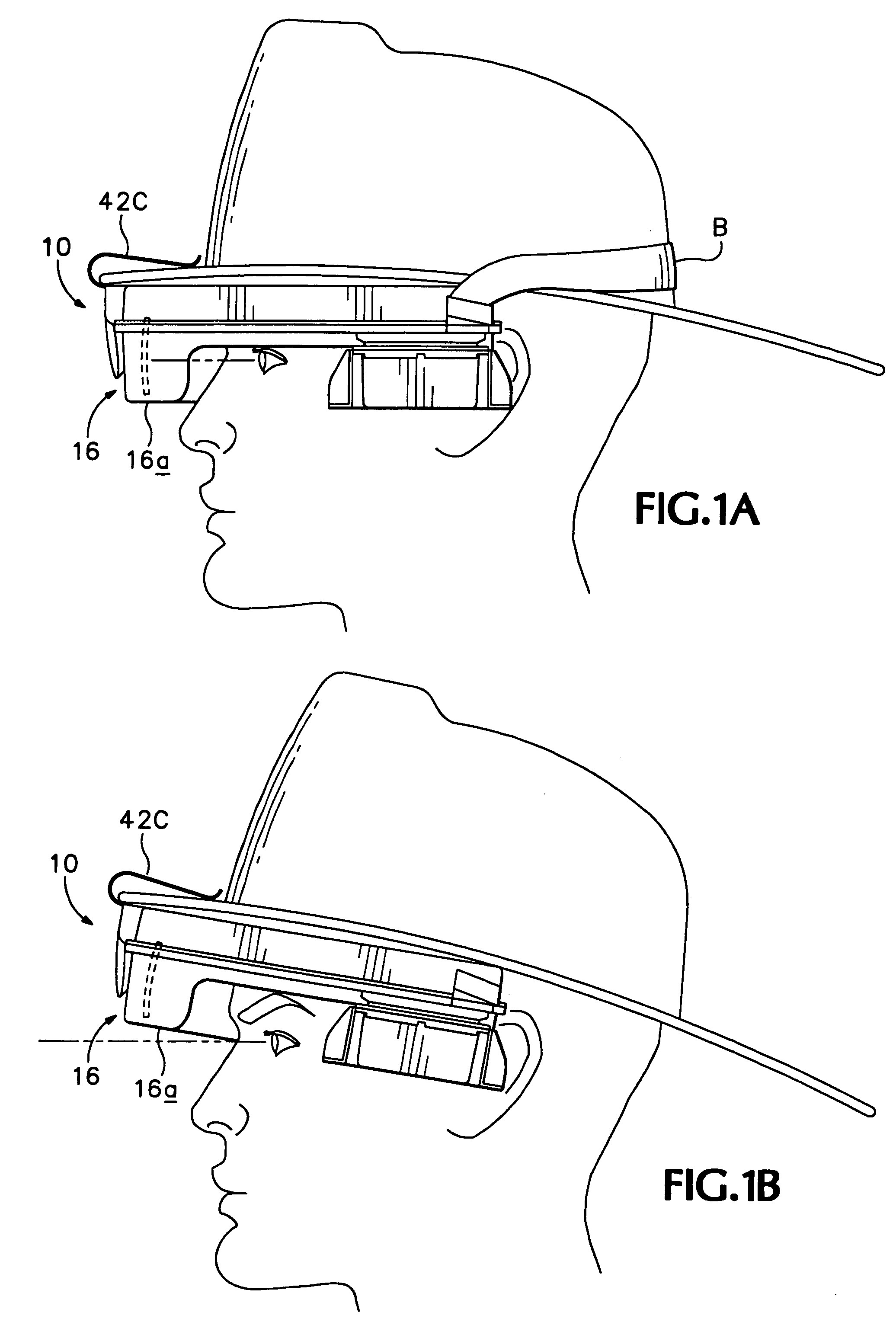
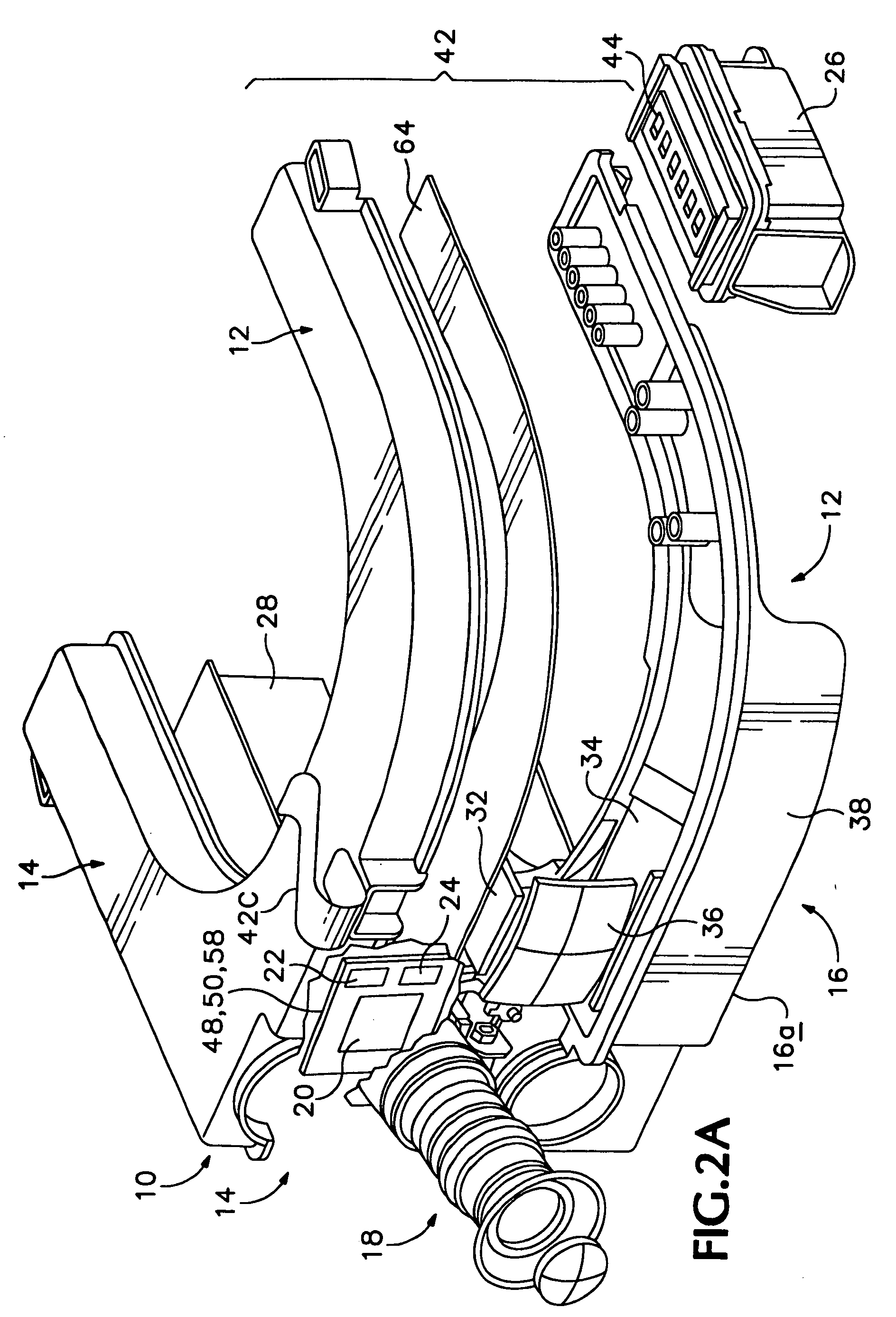
An infrared (IR) camera and associated electronics including power are integrated into portable, self-contained, vision-enhancement apparatus useful in environments of dense air-borne particulate and thermal extremes such as encountered in fire fighting situations, in accordance with the invention. The IR camera is integral with a self-contained power supply so that the system is portable and requires no umbilical cord or other external connections. The camera includes an imager that is preferably an un-cooled focal plane array, and associated imaging, storing, processing and displaying electronics that are cooled in the extreme thermal environment using an integral plural phase heatsink.
Owner:TELEDYNE FLIR LLC
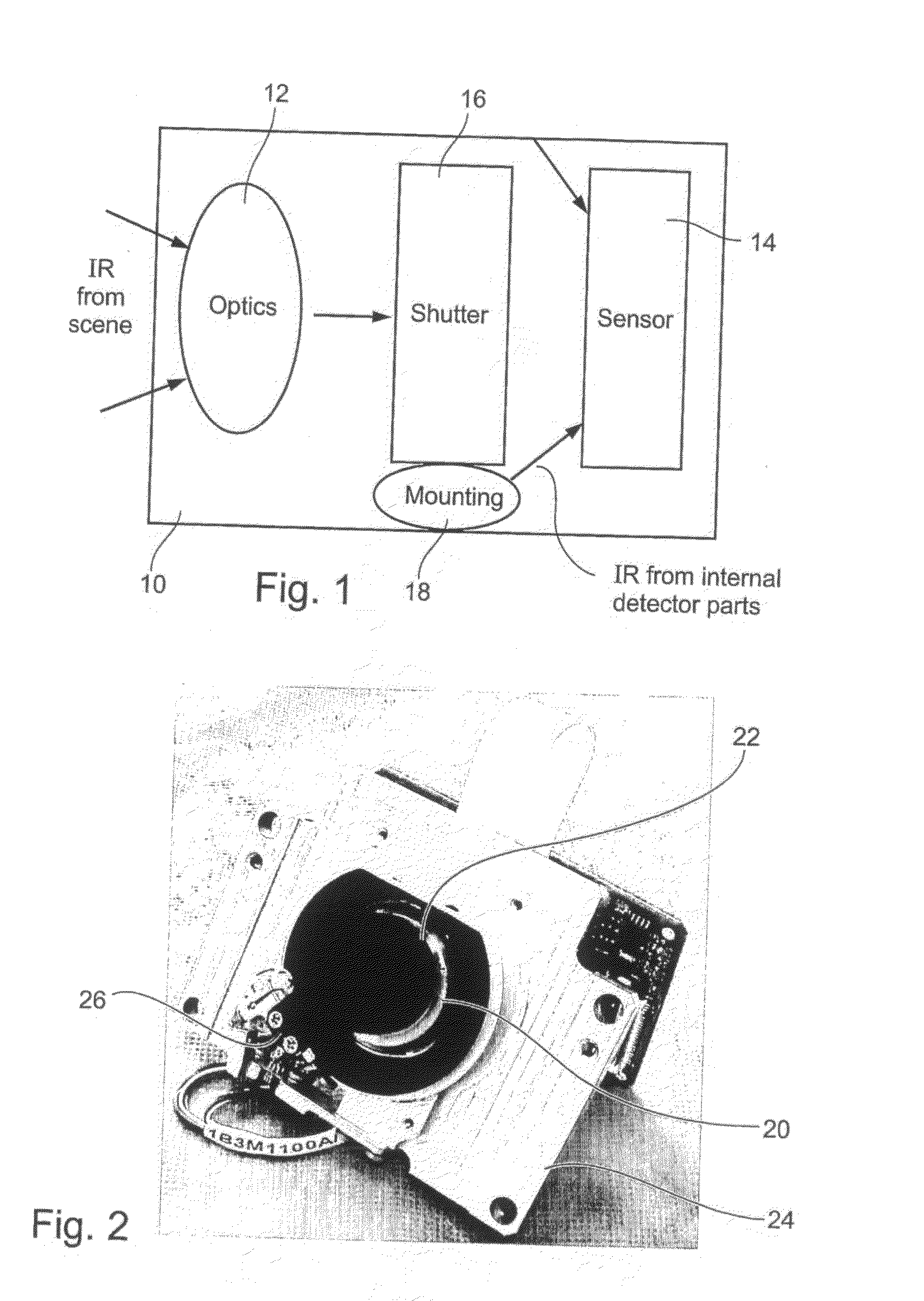
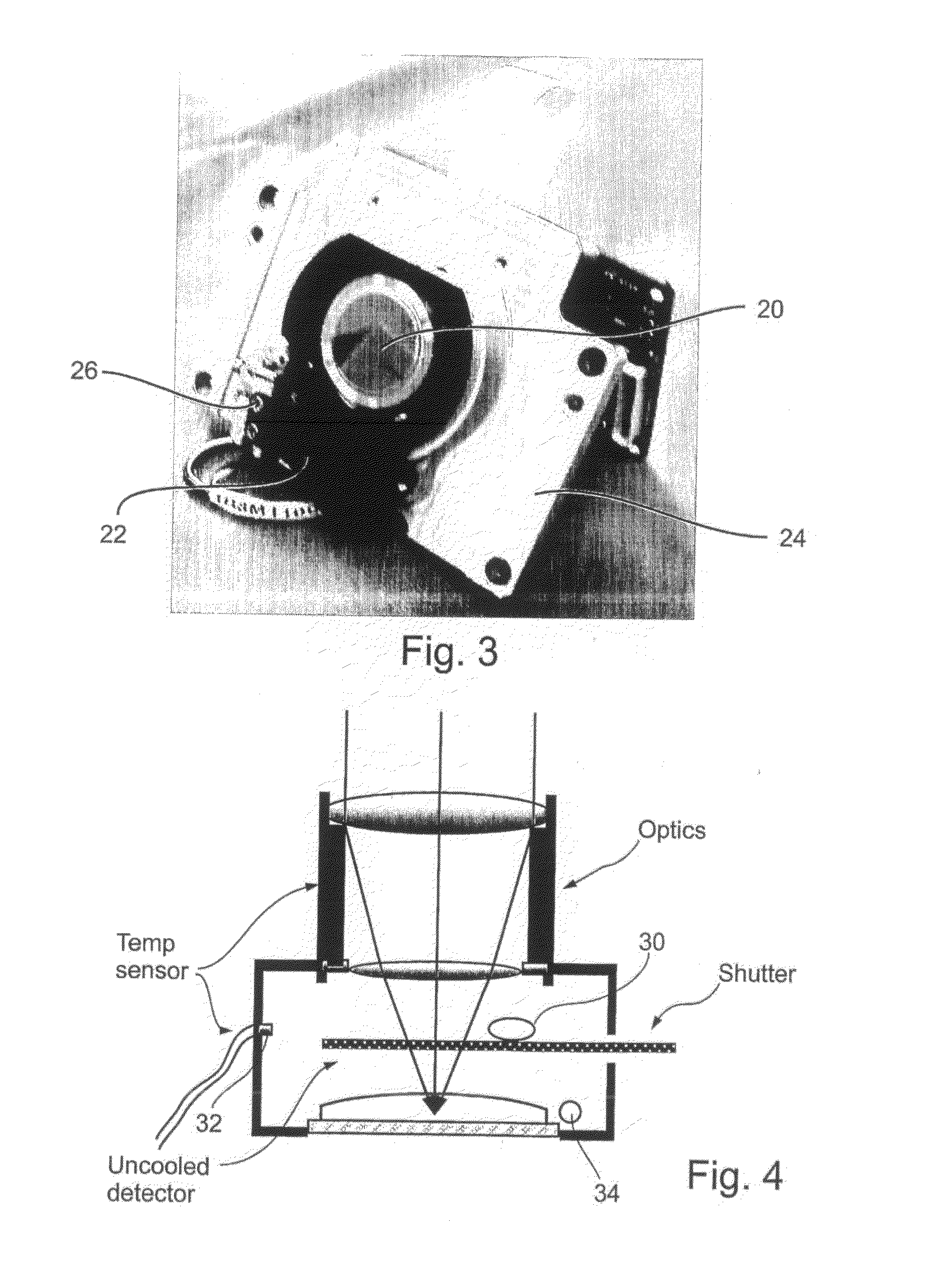
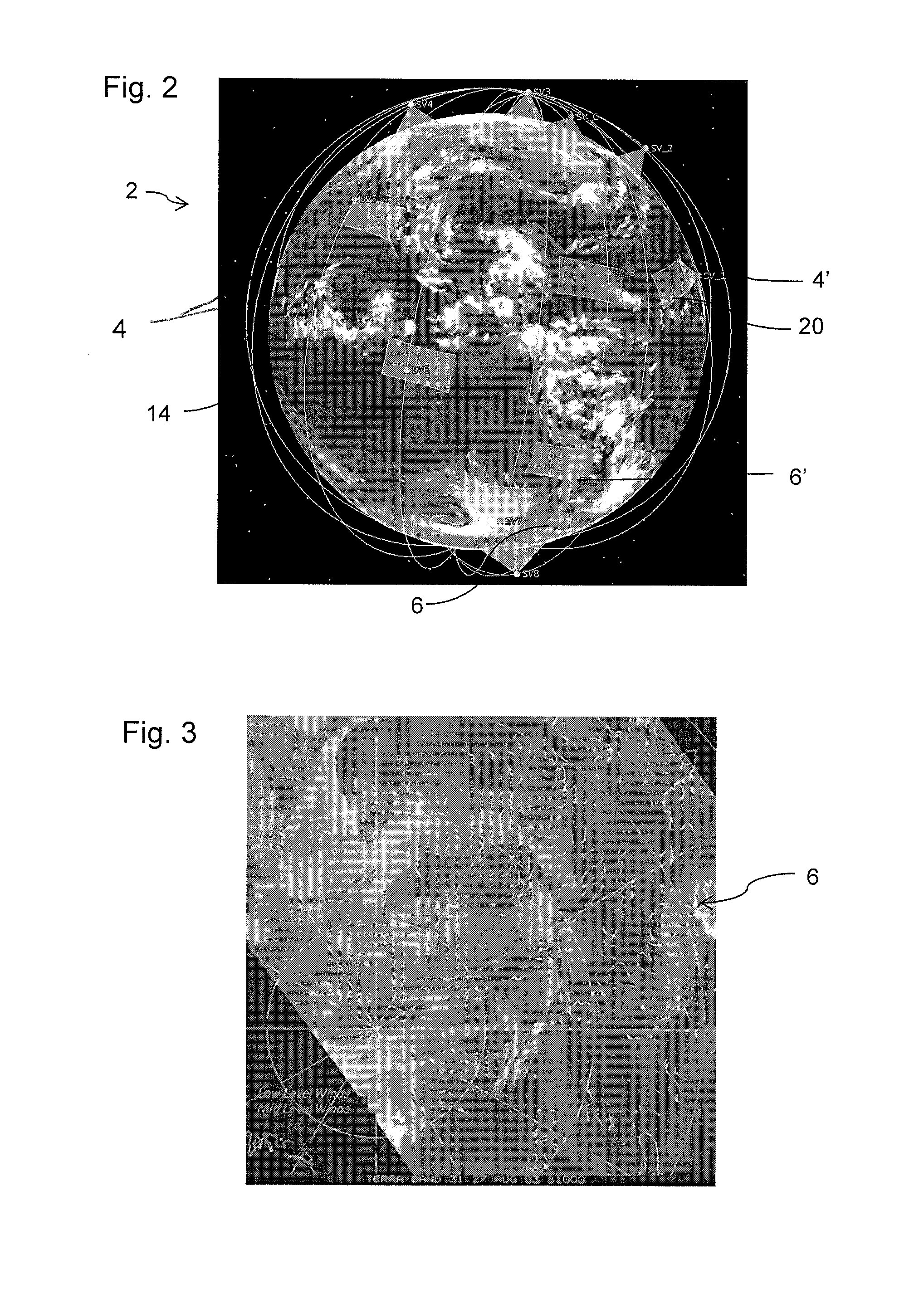
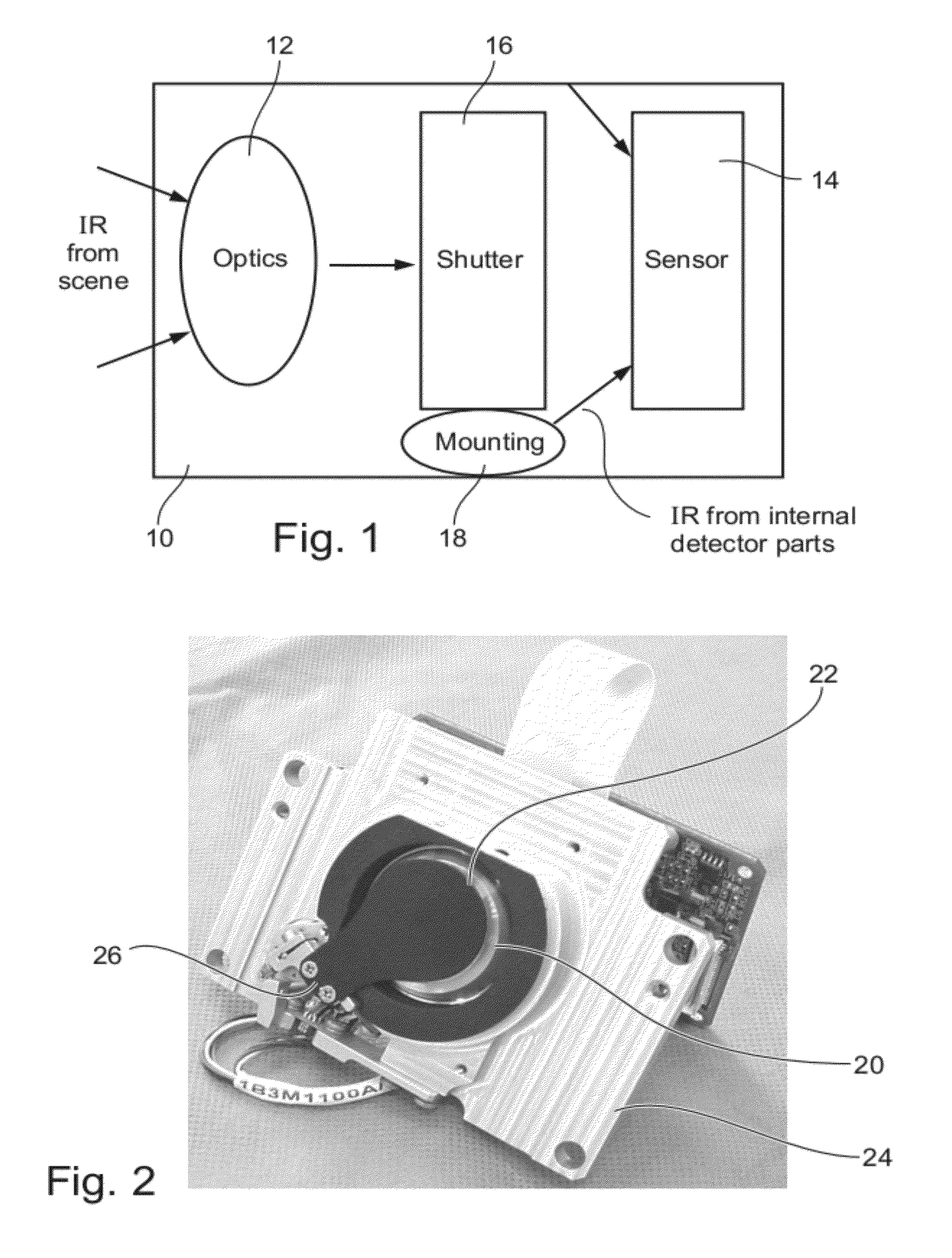
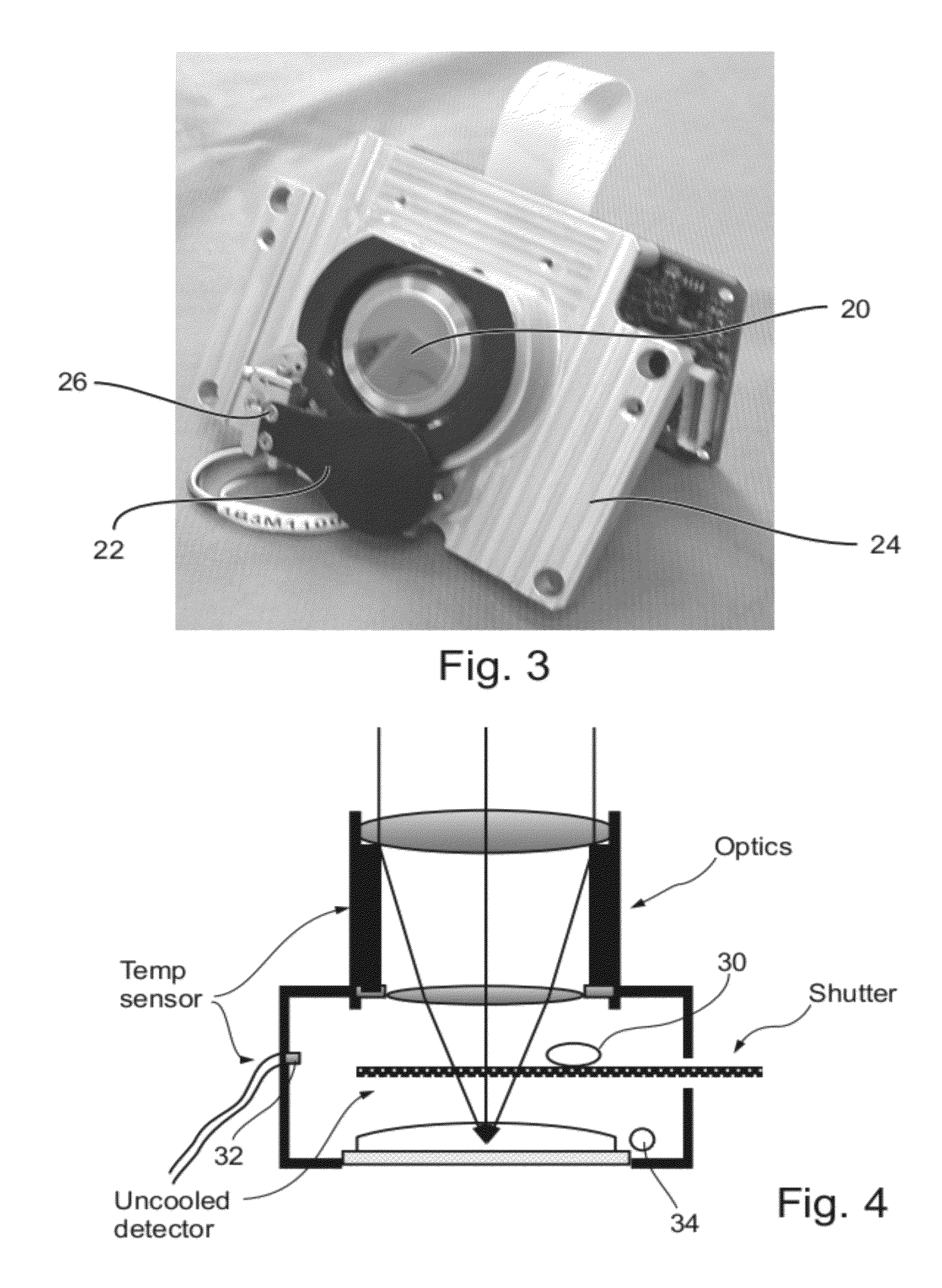
Radiometry Using an Uncooled Microbolometer Detector
InactiveUS20080210872A1Television system detailsRadiation pyrometryTemperature responseMicrobolometer
An infra-red imaging camera comprises focusing optics for gathering infra-red energy from an external scene, and an uncooled and unshielded detector arranged to detect infra red energy. Internal temperature sensing together with approximation of the temperature response of the camera provides a time varying calibration that allows the infra-red energy received at the detector to be used as a temperature measurement for objects in the camera's field of view.
Owner:OPGAL
Thermoluminescence measurements and dosimetry with temperature control of the thermoluminescent element
ActiveUS20060043314A1Rapid responseEasy to optimizeElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesTemperature controlDosimetry radiation
A thermoluminescence (TL) dosimetry (TLD) system comprises at least one TLD element that is controllably heated and which temperature is monitored in real time using an infrared (IR) radiometry subsystem that provides respective IR radiation inputs to a control subsystem. The control subsystem uses the inputs to effect the heating control. The TLD system further comprises a TL measuring subsystem for measuring TL emission data from each heated TLD element, the TL data used in obtaining a does curve indicative of the total radiation to which the TLD element has been exposed.
Owner:KATZIR ABRAHAM
Scanning apparatus
InactiveUS6587246B1Limited power requirementMinimum inertiaTelevision system detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsRadarDetector array
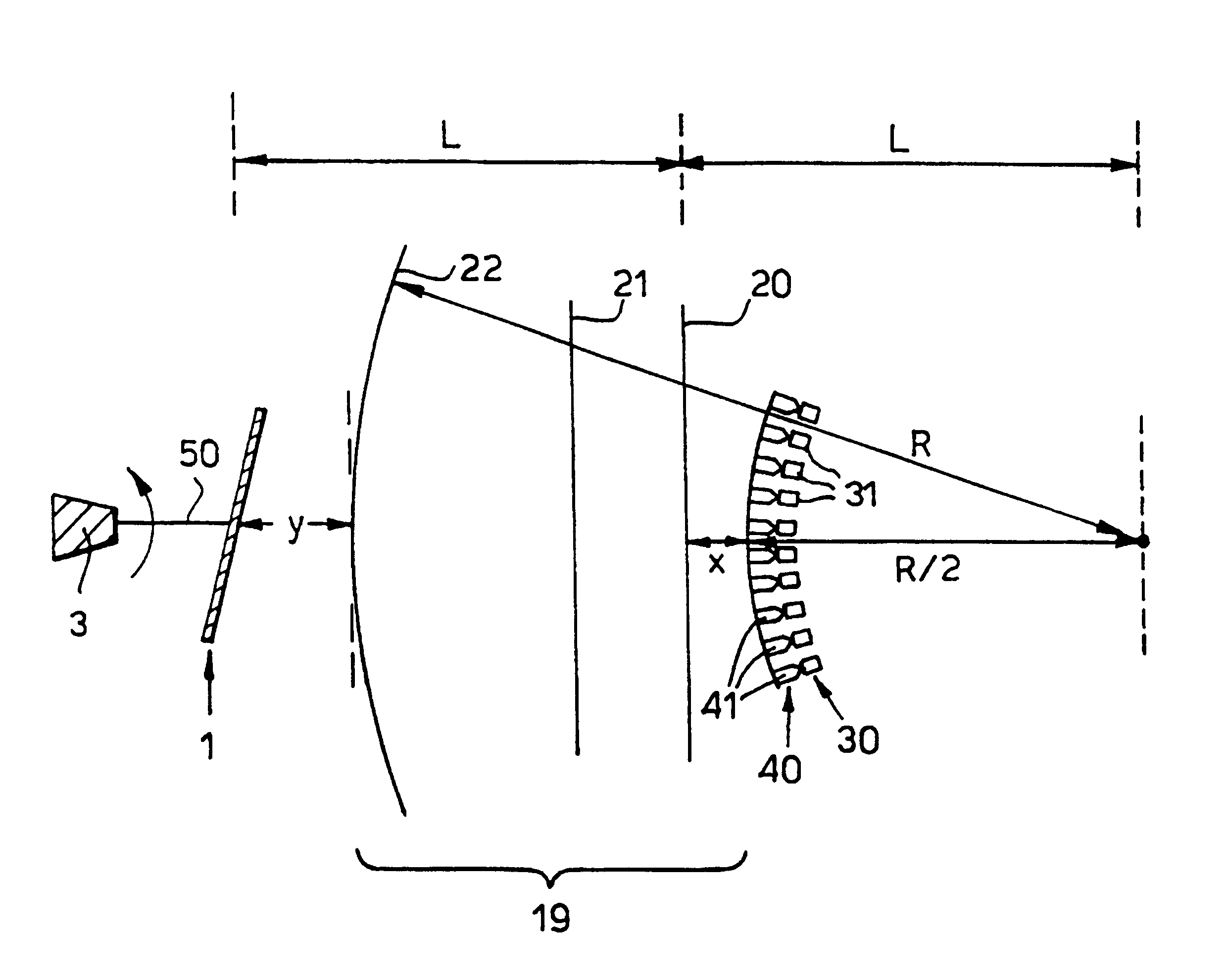
Scanning apparatus which may be used in a real-time passive millimeter wavelength imaging system or in other radiometry systems. The apparatus scans input radiation from a scene and output radiation is transmitted to a receiver system, for example a millimeter wave imaging camera or a radar receiver. The apparatus comprises a rotatable reflective plate having an axis of rotation passing through the centre of its surface and a lens arrangement for selectively transmitting and focusing radiation having a particular direction of polarisation. The apparatus may also comprise a feed horn array comprising a plurality of feed horns, the feed horns forming part of a spherical surface having a radius of curvature substantially equal to R / 2 and being concentric with the third substantially spherical polarising element. The apparatus may further comprise a detector array comprising a plurality of detector elements. The detector array may form part of a millimeter wave imaging camera.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
Integrated modeling method for infrared radiation characteristic of complicated target
ActiveCN105243289ASave human effortSave moneySimulator controlSpecial data processing applicationsBidirectional reflectance distribution functionRadiation model
The invention discloses an integrated modeling method for an infrared radiation characteristic of a complicated target. A bidirectional reflection distribution function model of infrared radiation on the surface of the complicated target and an infrared radiation model of non-uniform tail flame gas are considered based on a radiometry spectral ray tracking method; in a ray tracking process, the pixel on the focal plane of a detector is sampled, thus generating ray bundles, and an intersection between each ray and the complicated target in a scene is calculated; a radiation reflection value of each intersection is calculated, and the radiation brightness obtained by all the rays of the pixel is subjected to sampling and reconstruction, thus obtaining the radiation brightness with a spectral form at the pixel of the detector; finally, a required infrared spectrum band is integrated, thus obtaining a target infrared radiation characteristic value received by the detector. According to the integrated modeling method, the spectral ray tracking method runs through the whole solving process, and a solving model suitable for a ray tracking form is constructed, so that the integrated modeling method is suitable for infrared radiation characteristic simulation of a tail-flame-containing complicated target aircraft under a specific flying state.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
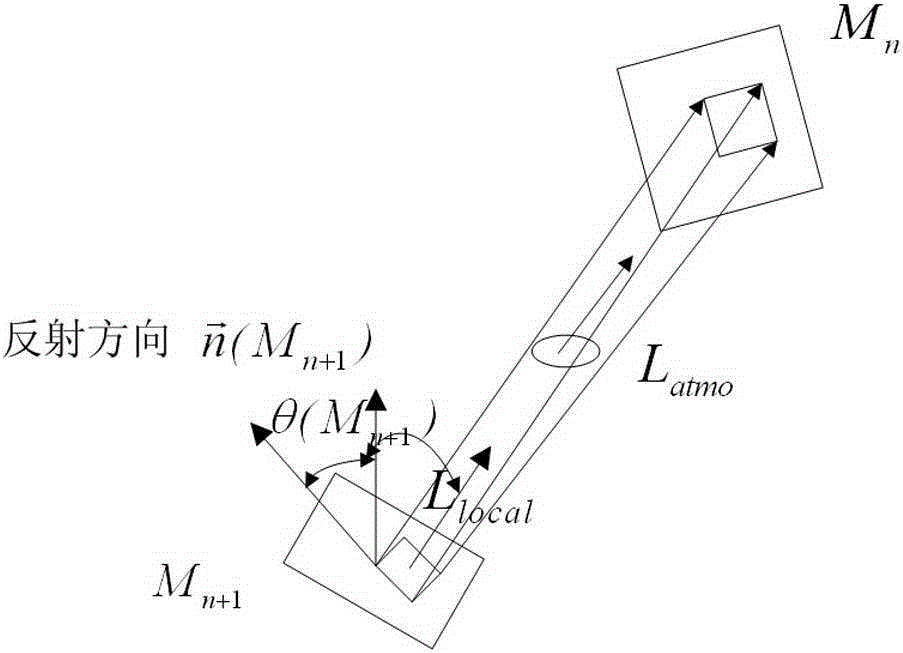
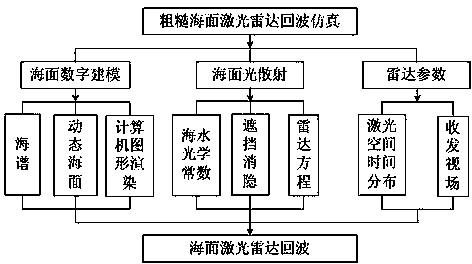
Method for dynamic sea surface laser pulse wave beam echo simulation
InactiveCN103472443ARealize Backscatter Echo SimulationSolve the needs of the optical characteristics of the sea environmentWave based measurement systemsSea wavesOpenGL
The invention relates to a method for dynamic sea surface laser pulse wave beam echo simulation. The method for dynamic sea surface laser pulse wave beam echo simulation comprises the following steps that according to a sea spectrum statistic model, a dynamic sea surface is generated by means of the reverse-FFT technology, and the parameters such as the wind speed, the wave height and the sea wave period are considered through the model; space energy distribution and the pulse shape of each emitted laser wave beam are measured, space-time distribution of any laser wave beam is obtained through fitting, and section spatial light intensity distribution at any distance is determined based on energy conservation; a laser radar wave beam back scattering echo radar equation is established based on the radiometry, rough surface processing is conducted on a water surface element, and the water surface element is expressed through a bidirectional reflection distribution function; drawing, coloring, rendering, real-time animation, hidden-line elimination and clipping of the scene are completed based on a computer graphic base OpenGL. The method for dynamic sea surface laser pulse wave beam echo simulation can be applied to different sea condition model machine dynamic intersection virtual experiments, facilitate development of sea surface pulse echo scattering mechanism study, and save a large amount of cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
Device and method for making weather observations using infrared spectral radiometry
ActiveUS20160187535A1Low costReduce the total massRadiation pyrometryWeather condition predictionNatural satelliteMotion vector
A method of weather observations by a constellation comprises at least a first duster of three micro-satellites each orbiting around earth, and each micro-satellites comprises a spectrometer. Orbiting the three micro-satellites of the first duster around the earth in three separate orbits offset with respect to one another. Staggering the three micro-satellites with respect to one another as they orbit. Selecting the offset and the staggering, of each of the three micro-satellites with respect to one another, so that each one of the three micro-satellites have a substantially identical viewing area as each one of the three micro-satellites orbits around the earth. Sequentially collecting observations, from each of the three micro-satellites, as the micro-satellites orbit around the earth and observe substantially identical viewing areas, to separately gather atmospheric measurements and provide critical data for weather forecasting by infrared temperature and humidity soundings and motion vector winds of the earth.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Highly accurate calibration of microwave radiometry devices
InactiveUS20140035779A1High precision calibrationEliminate reflectionsWave based measurement systemsThermometers using physical/chemical changesMicrowave radiometryWavelength
Systems and methods are disclosed for highly accurate calibration of microwave radiometry devices by defeating reflections from a cryogenic blackbody calibration target and, further, defeating a standing wave established between reflecting features at the device and at the blackbody calibration target. The preferred disclosed system includes adaptations for effective Brewster angle presentation of radiation emanating from the target to the radiometry device. Other embodiments are taught for substantially eliminating or randomizing the standing wave in both wavelength dependent and independent applications.
Owner:RADIOMETRICS CORP
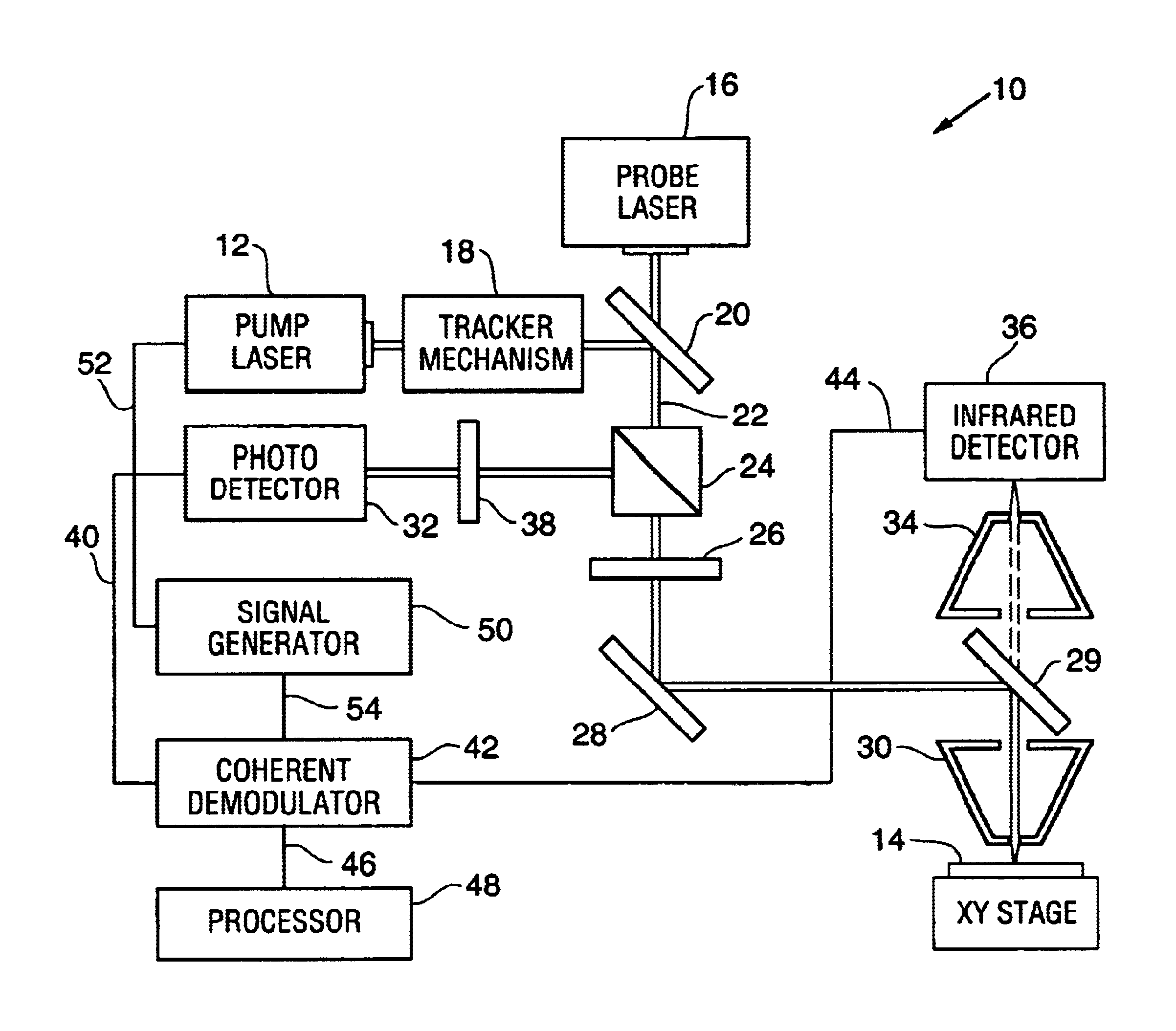
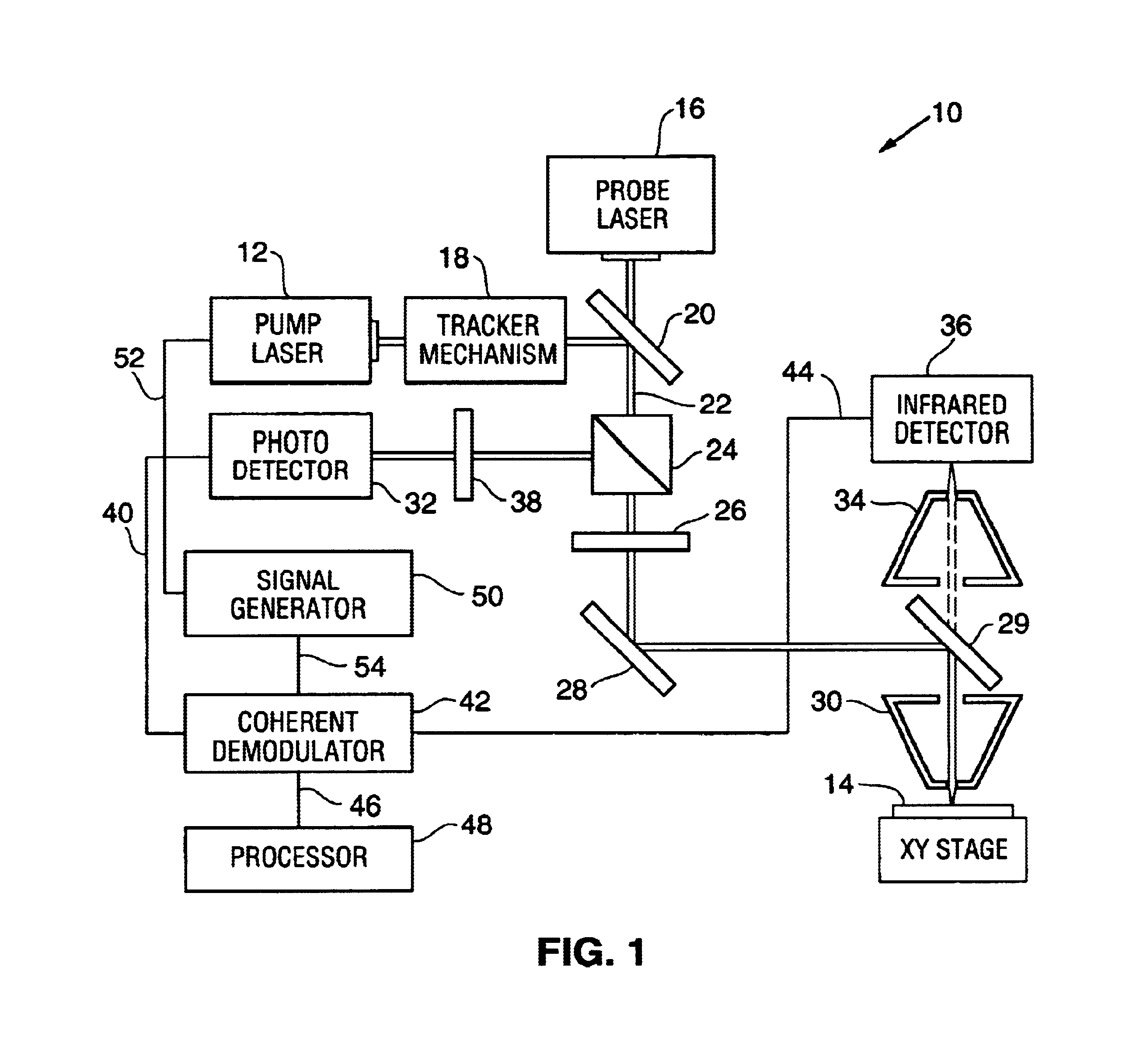
Method and system for combined photothermal modulated reflectance and photothermal IR radiometric system
A method and apparatus for evaluating a semiconductor wafer. A combination of a photothermal modulated reflectance method and system with a photothermal IR radiometry system and method is utilized to provide information which can be used to determine properties of semiconductor wafers being evaluated. The system and method can provide for utilizing a common probe source and a common intensity modulated energy source. The system and method further provide an infrared detector for monitoring changes in infrared radiation emitted from a sample, and photodetector for monitoring changes in beam reflected from the sample.
Owner:THERMA WAVE INC
Method and apparatus for carrying out a mox fuel rod quality control
InactiveUS20060056566A1Nuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringQuality controlRadioactive contamination
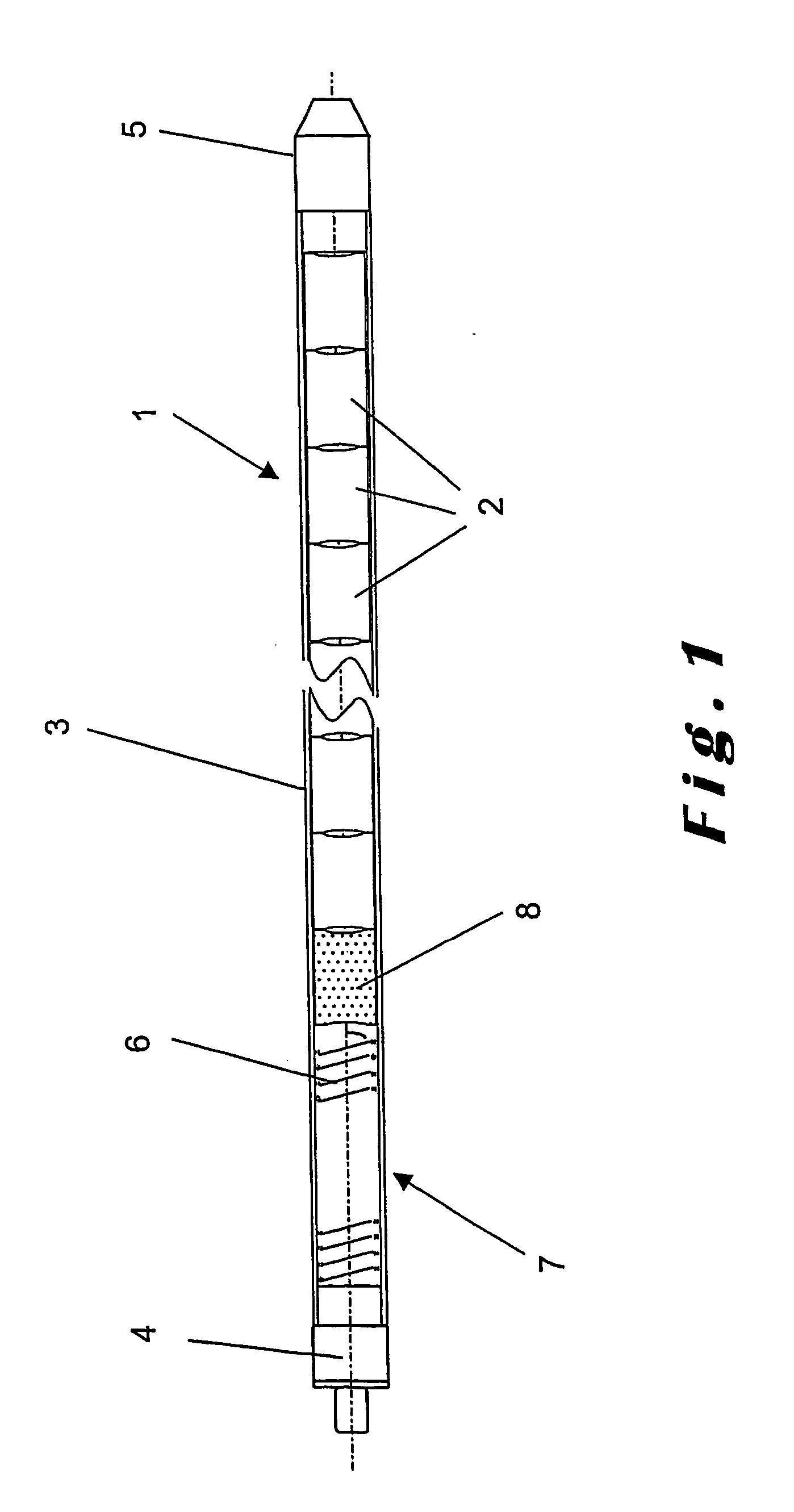
A method for carrying out a comprehensive quality control of MOX fuel rods, including measurement of plutonium content of pellets contained in the rod, check of internal structure and constituents in the rod, including the detection of rogue pellets, and measurement of dimensional characteristics and radioactive contamination along the rod surface, by moving the fuel rod axially, performing concurrently the measurements and checks along the fuel rod moved axially, using radiometry and radiography. An apparatus for carrying out the method.
Owner:BELGONUCLEAIRE SA
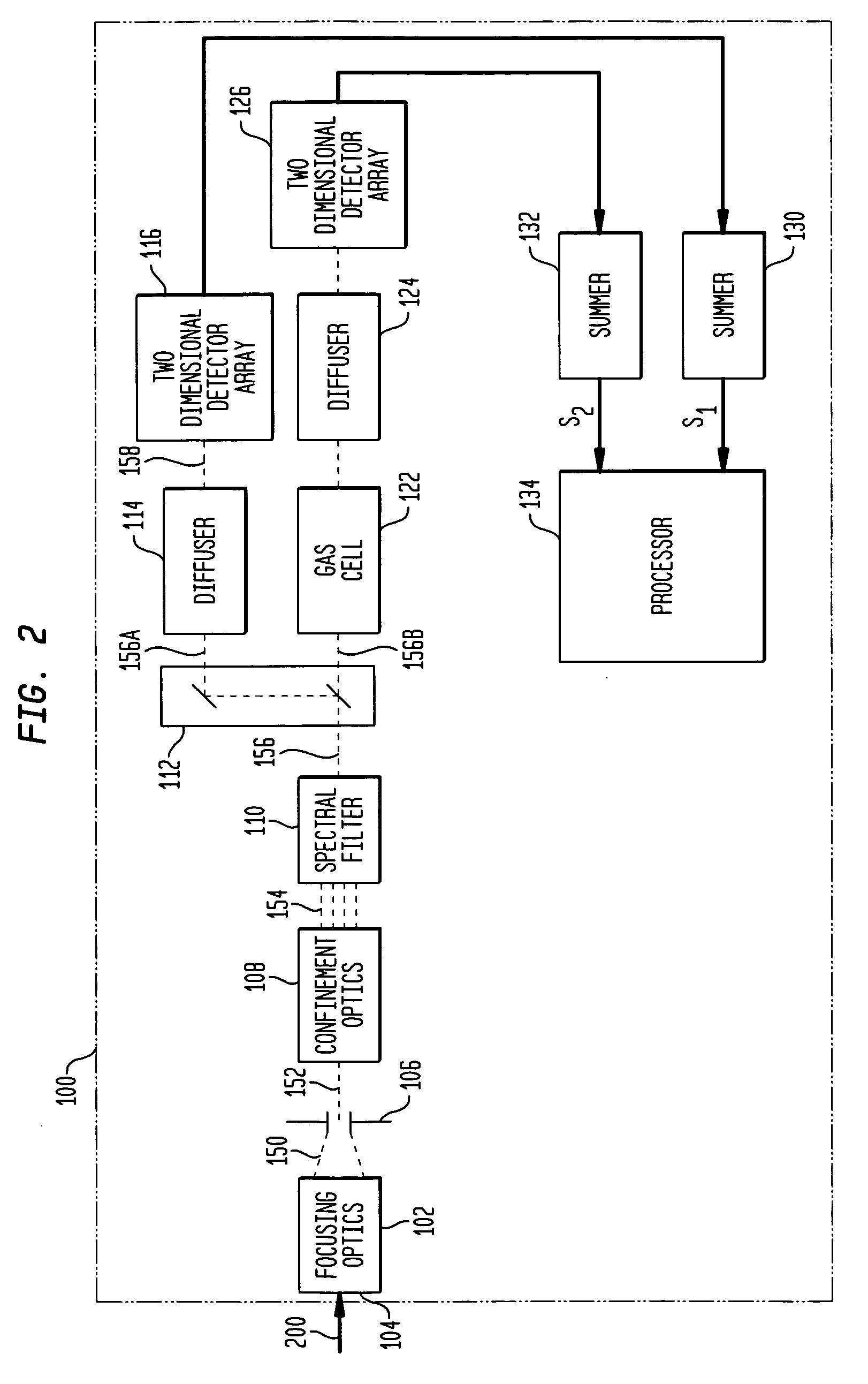
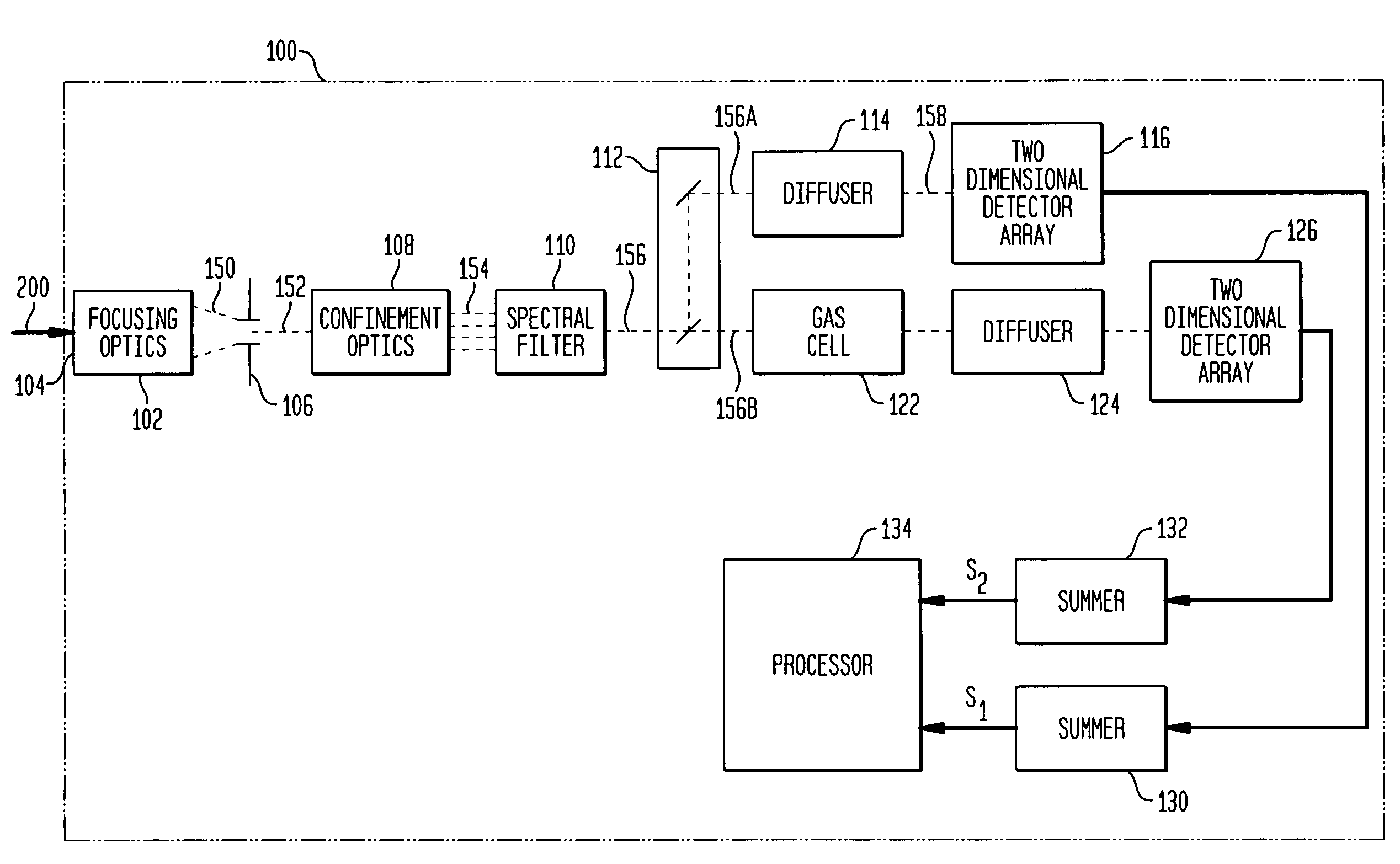
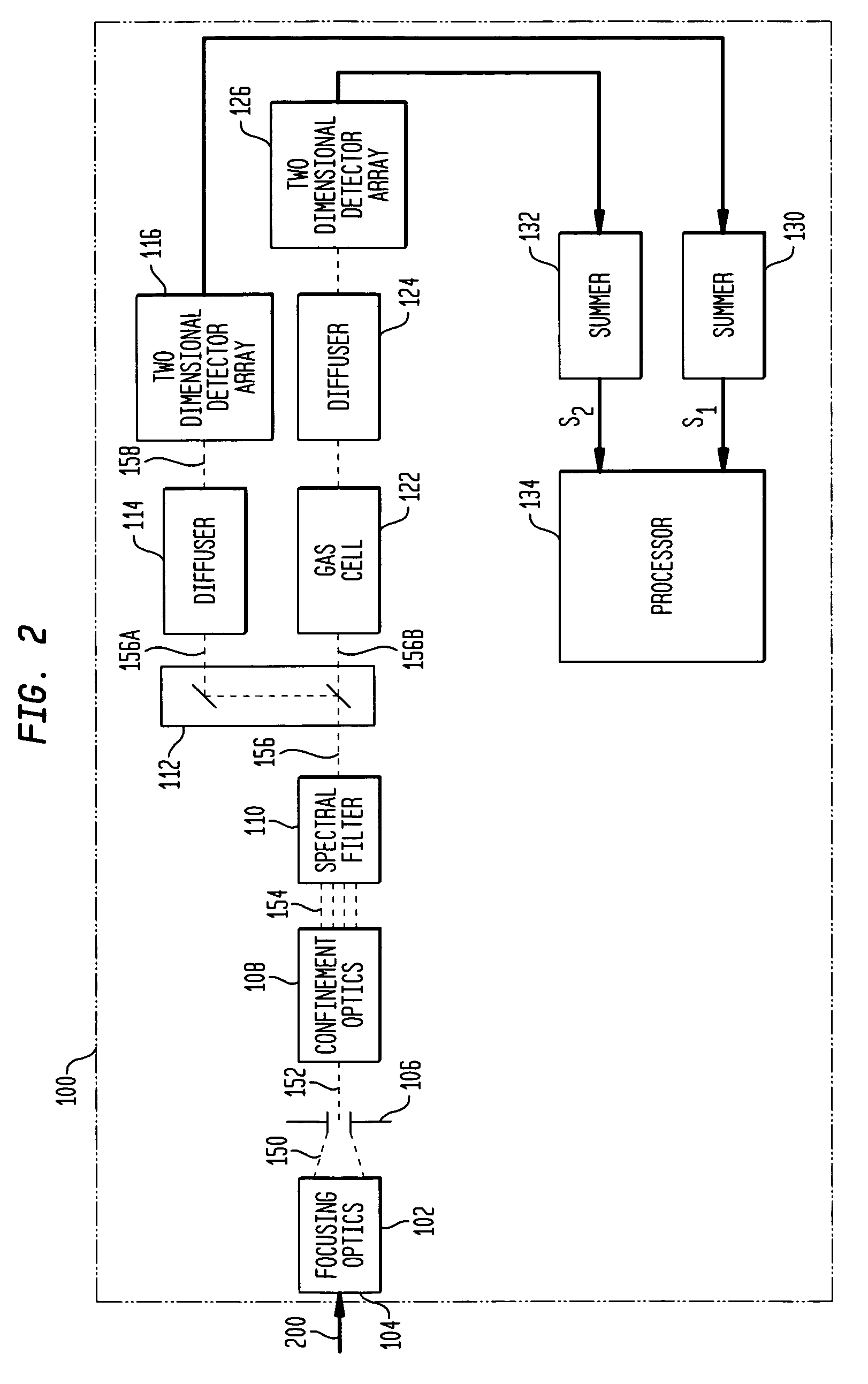
Internally-calibrated, two-detector gas filter correlation radiometry (GFCR) system
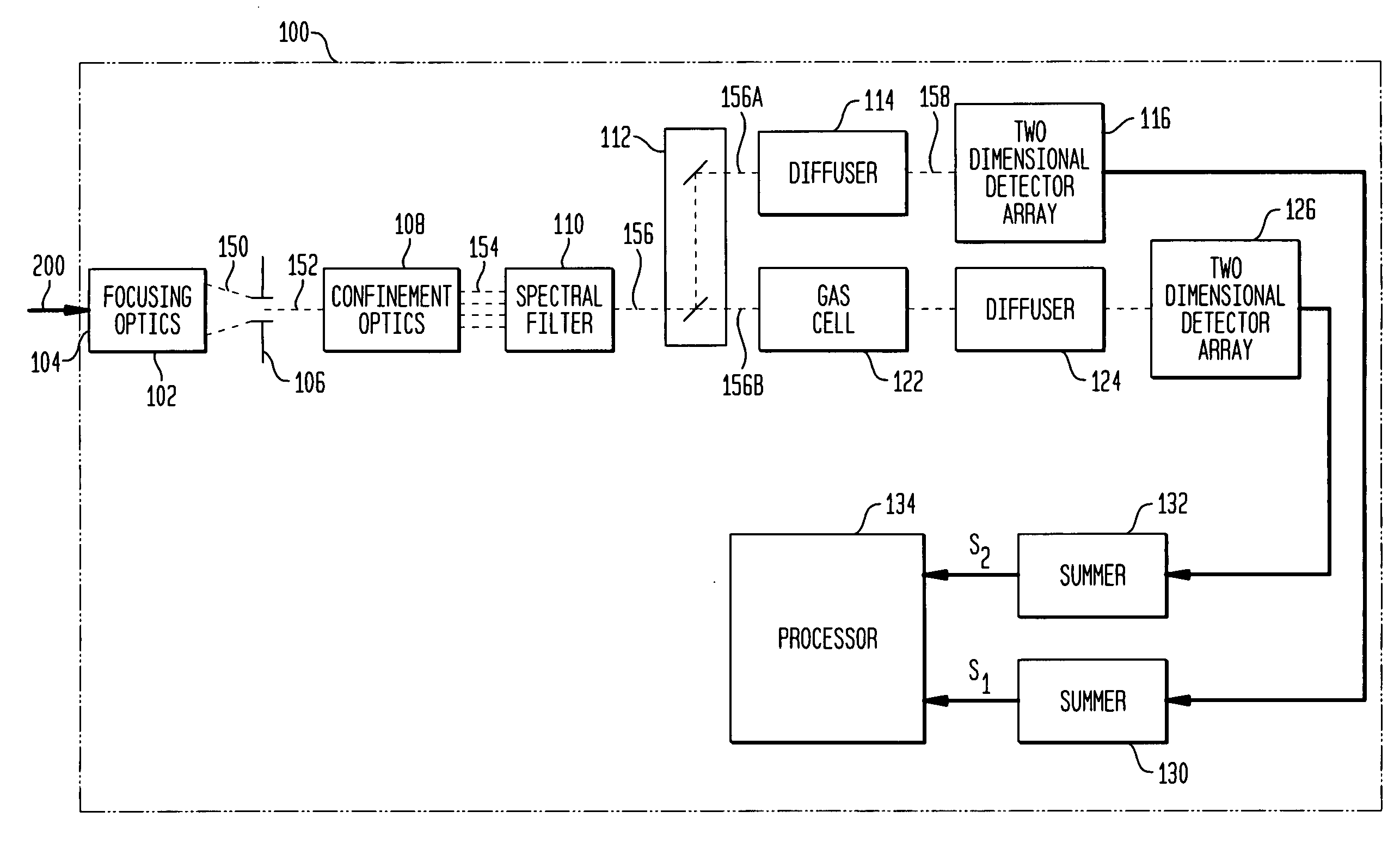
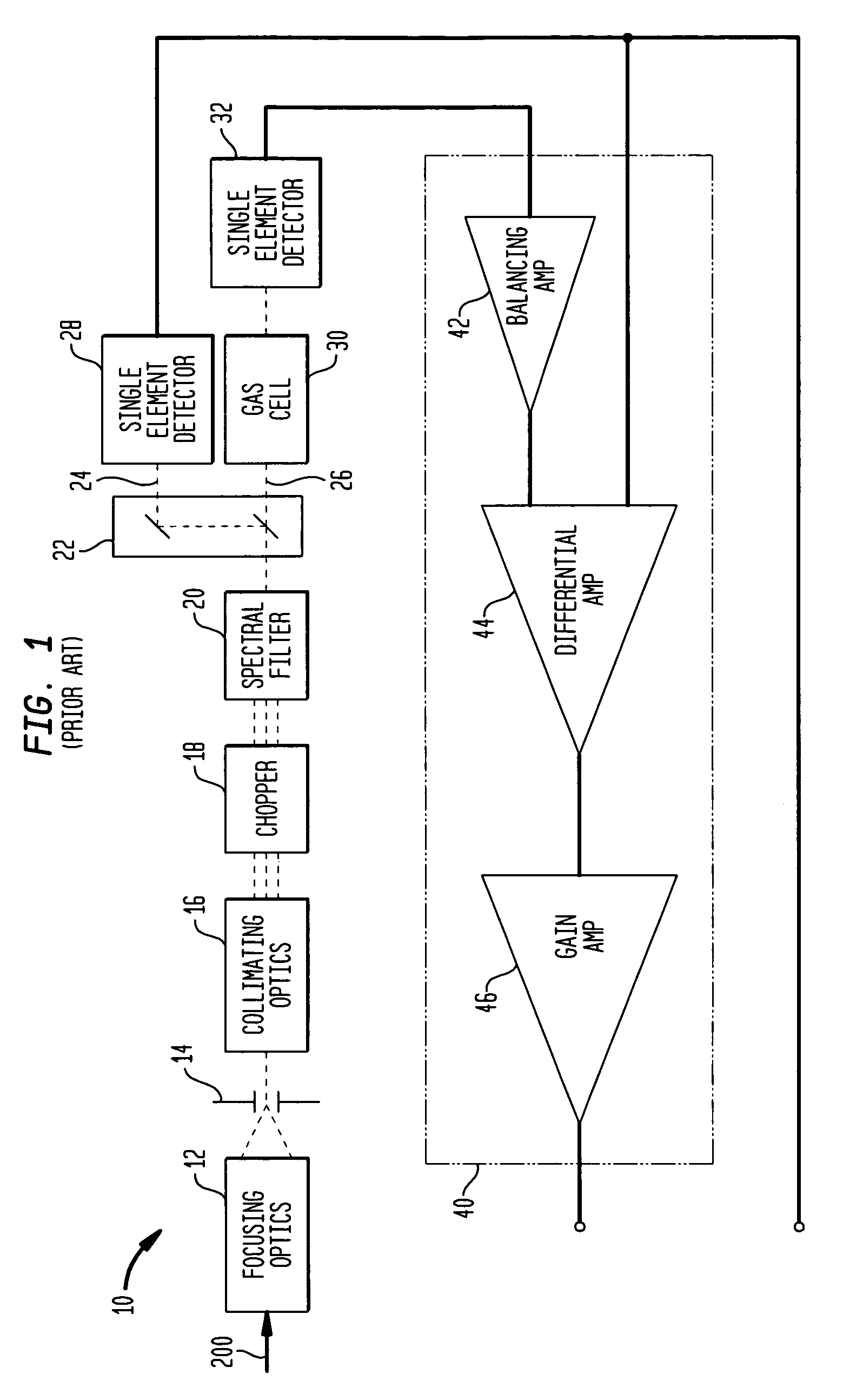
InactiveUS20080180677A1Accurate CalibrationEasy CalibrationRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansSpectral bandsField of view
An entrance aperture of a GFCR system receives light from a scene of interest. The light is focused to form an image at a focal plane. Light associated with a selected field-of-view of the image at the focal plane is then confined to a spectral band at which a gas of interest absorbs. The confined light is split into first and second paths. A calibrating light is selectively produced from within the optical train at the focal plane. A portion of the calibrating light traverses each of the first and second paths. A region that is substantially non-interfering with respect to the spectral band is disposed in the first path. A gas cell filled with the gas of interest is disposed in the second path. The light passed through the region and through the gas cell is independently detected and used to generate output signals indicative of the light so-detected. The output signals are processed with the output signals generated by the light from the selected field-of-view of the image being used to generate a measure of the gas of interest and the output signals generated by the portion of the calibrating light traversing the first and second paths being used to calibrate the GFCR system.
Owner:G & A TECHN SOFTWARE
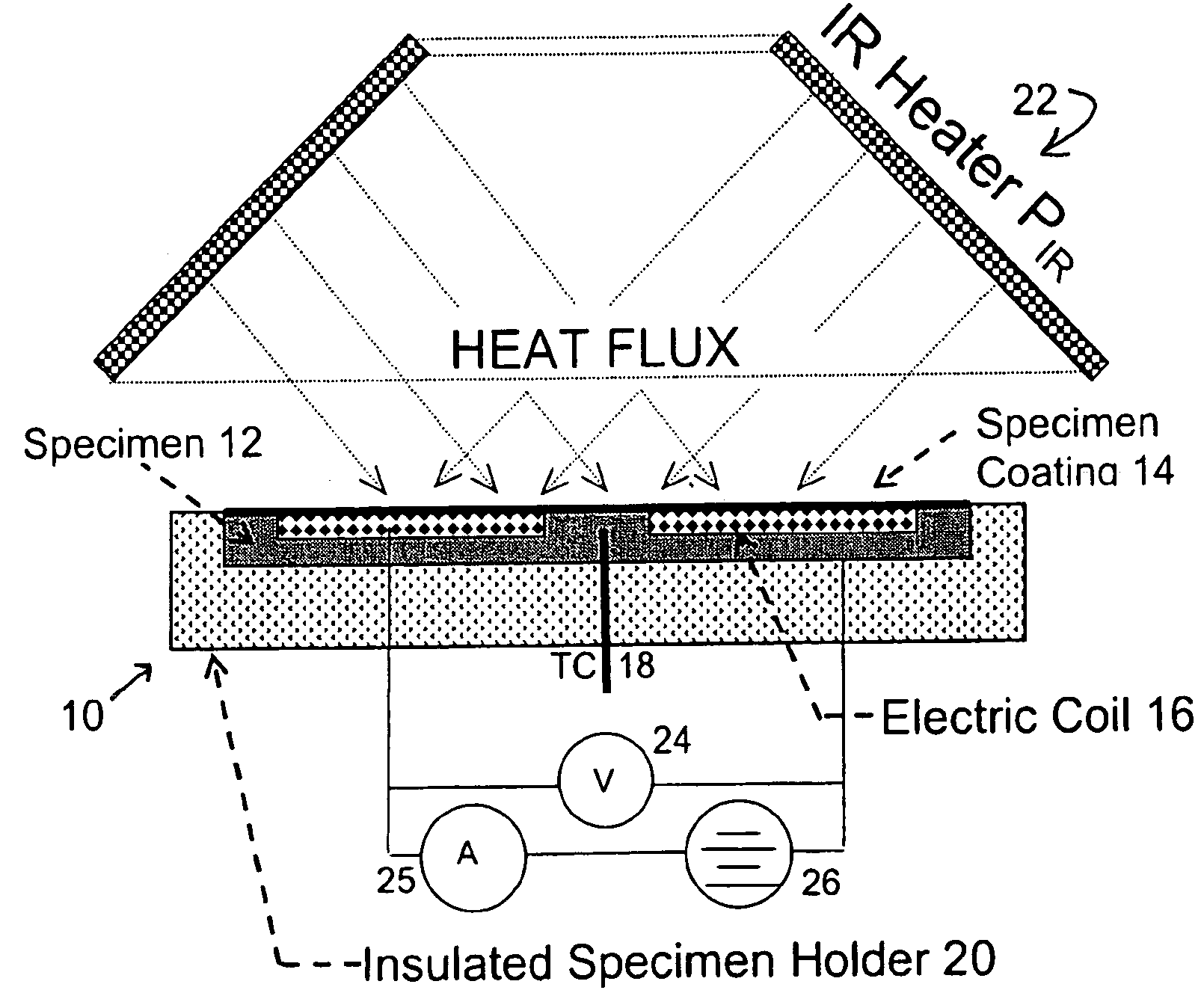
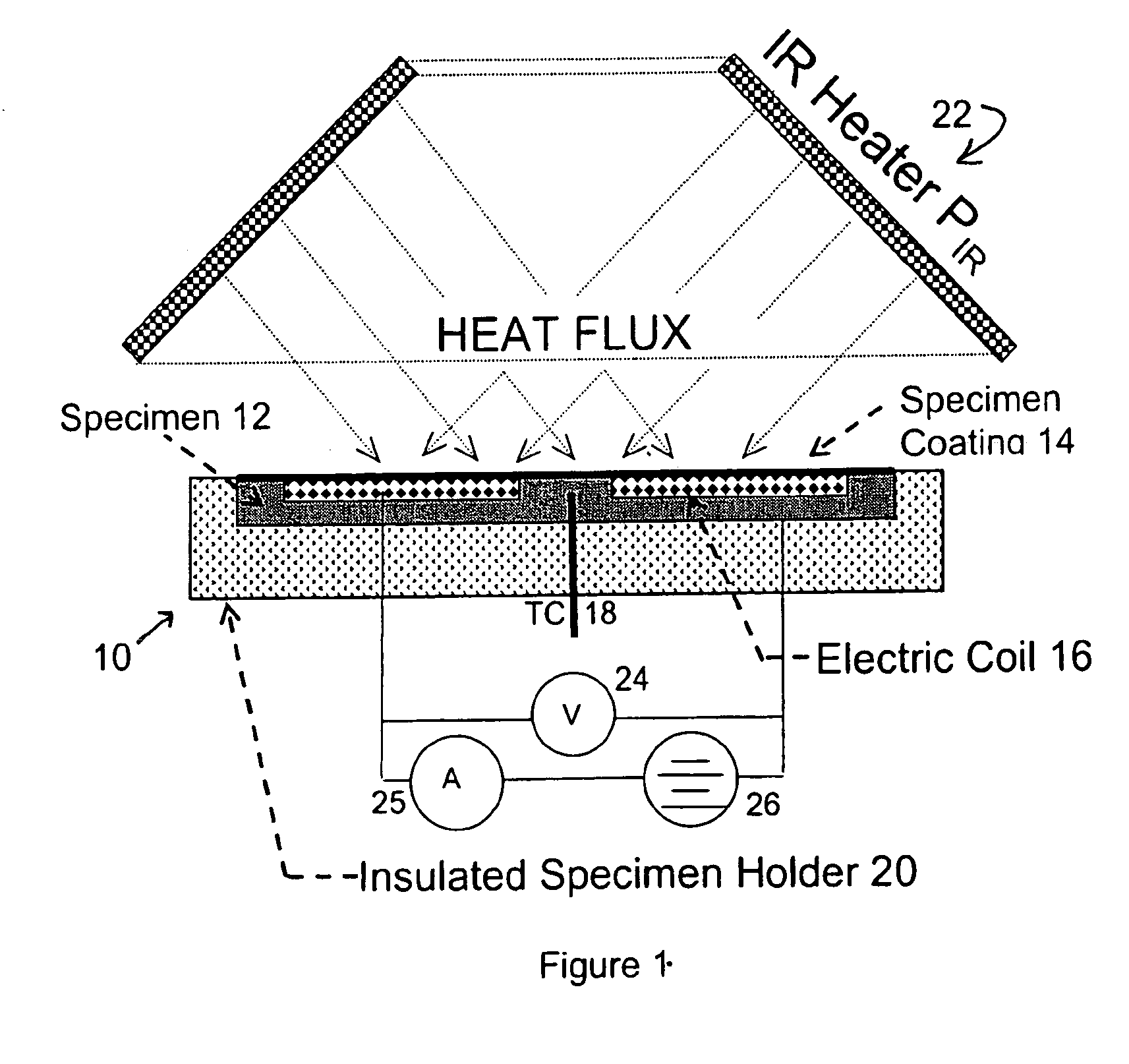
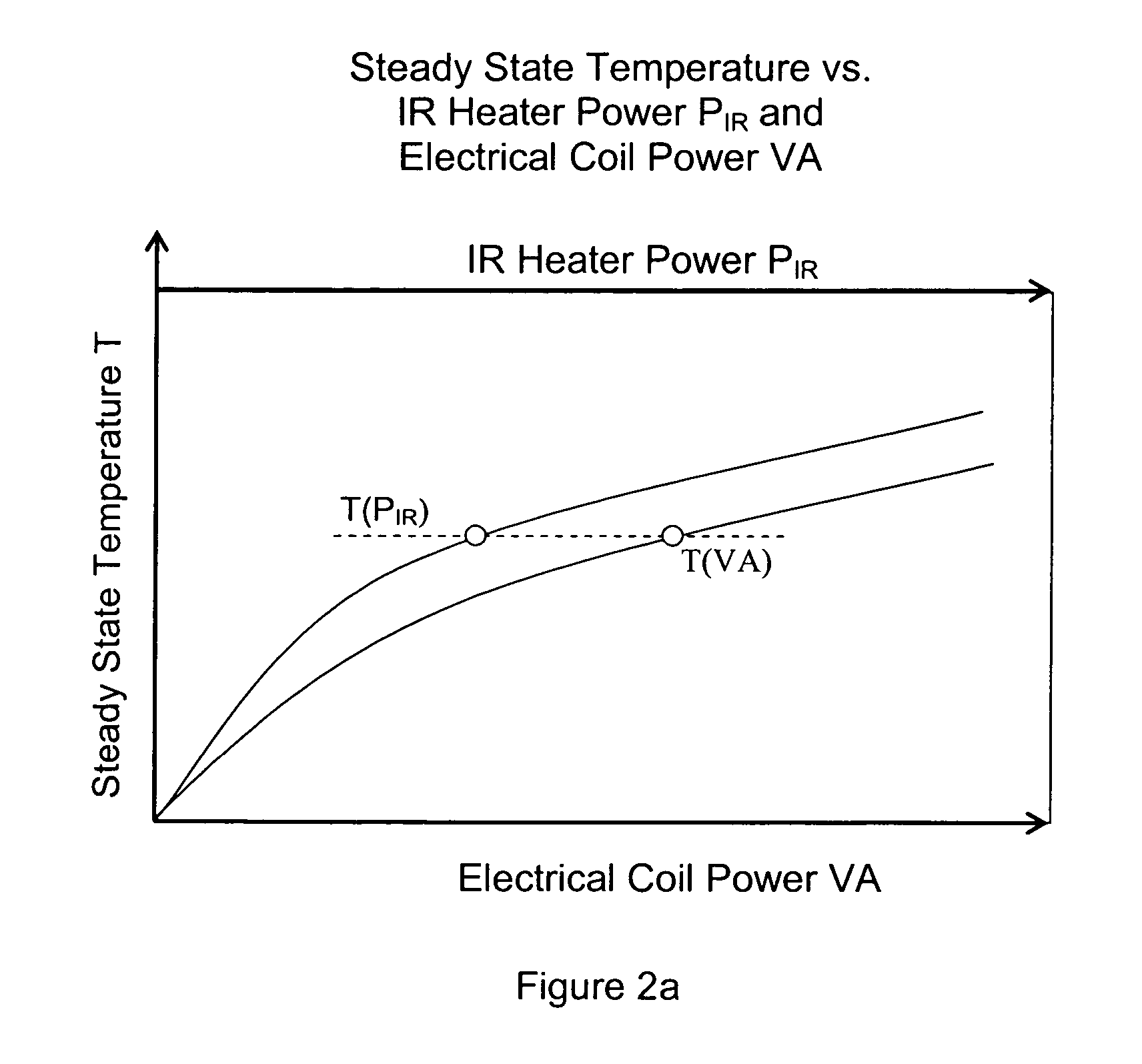
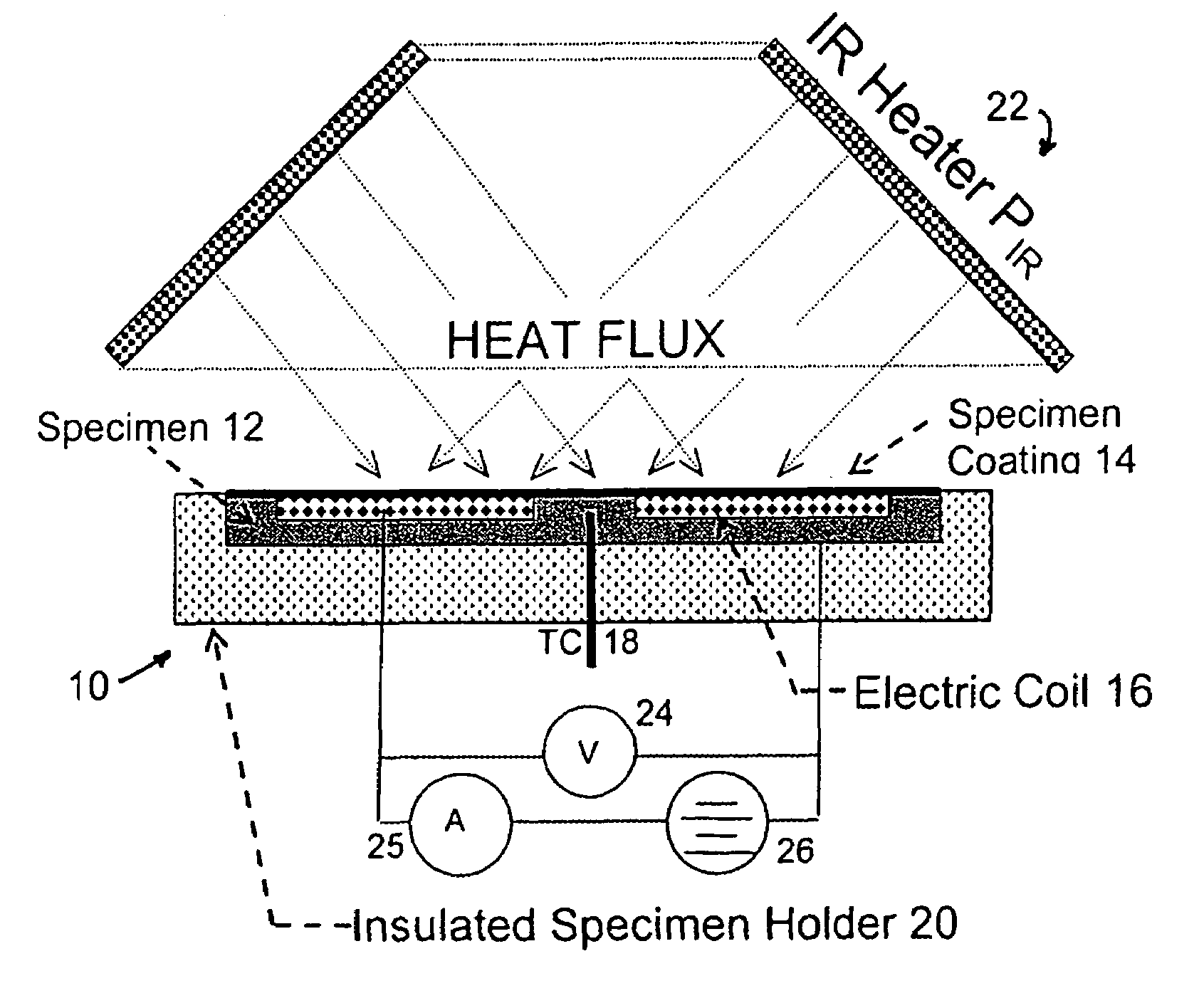
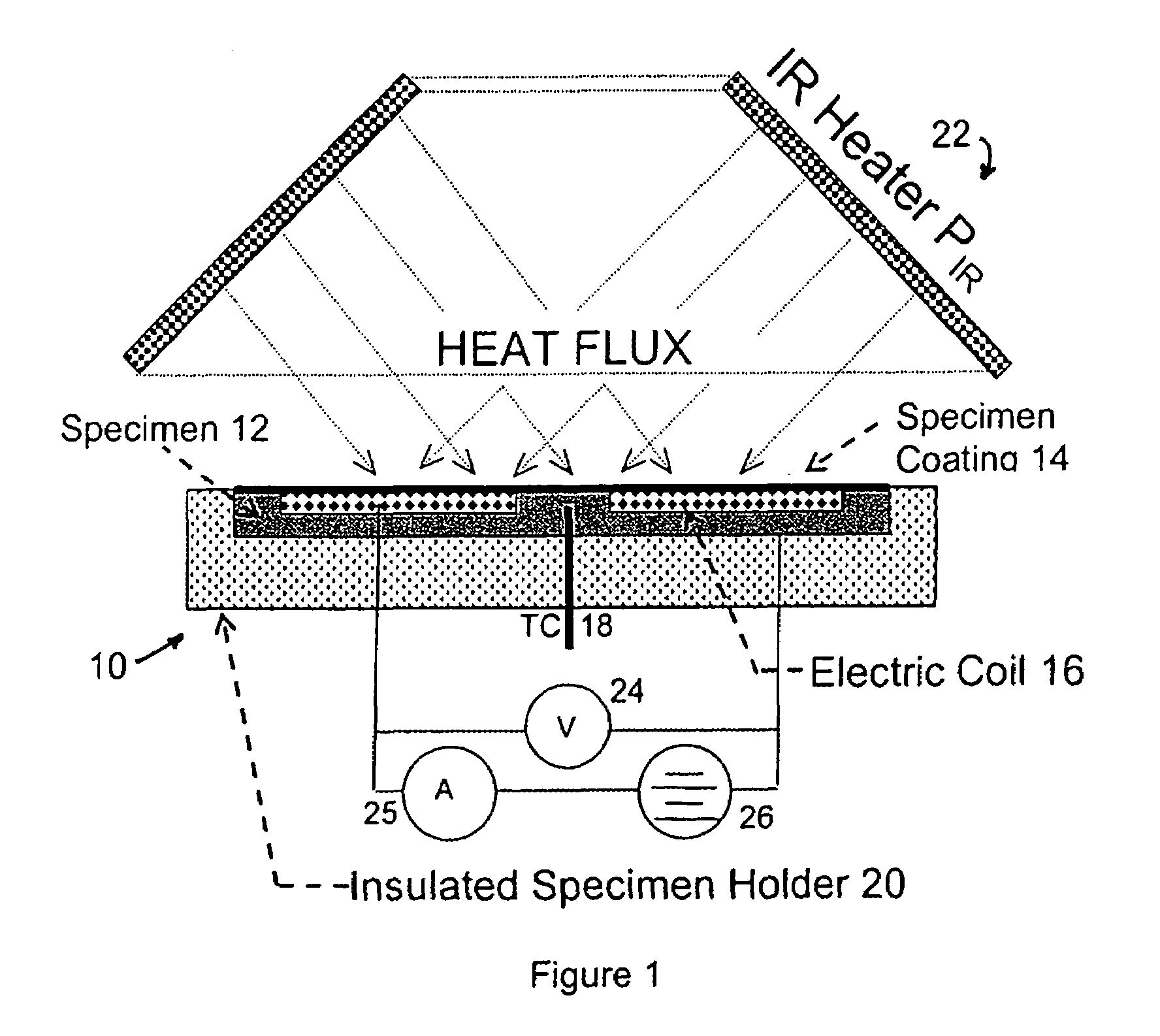
Device and method for measuring absorbed heat flux in a fire test apparatus
InactiveUS20050078732A1Overcomes possible measurement errorAccurate measurementMaterial thermal conductivityThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsHeat fluxEngineering
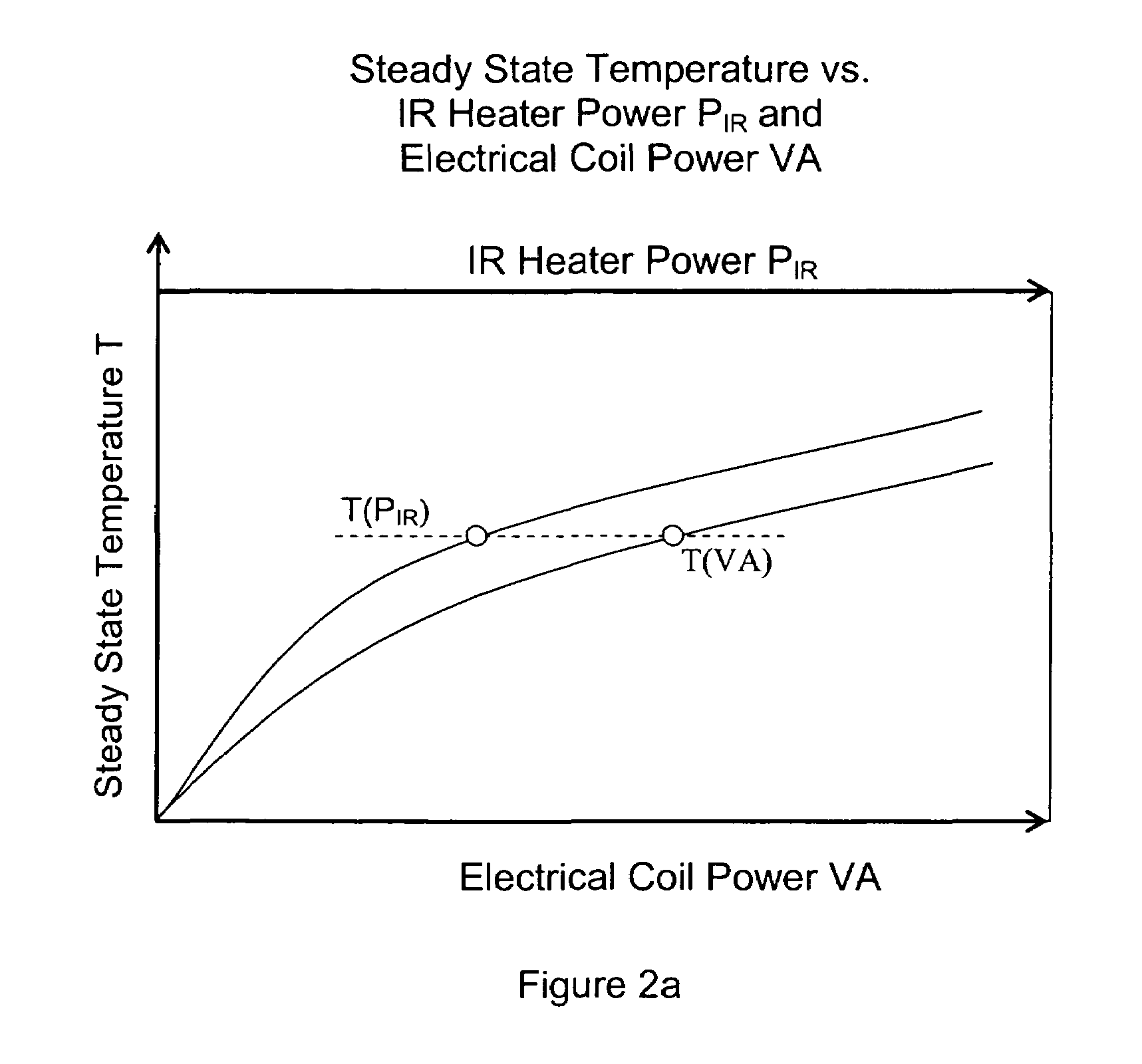
A device for measuring the flux received by a specimen in fire test apparatuses has a copper disk or plate of the same dimensions and the same type of surface coating as a typical material specimen, an embedded heating coil and thermocouple, and an insulated sample holder similar to that used for a specimen. The transient response of the embedded thermocouple is measured for several different levels of imposed incident radiation without electrical heating and for several different known levels of electrical heating without any imposed radiation. The principle of Electrical Substitution Radiometry (ESR) is applied, and the transient responses to incident radiation and electrical heating under identical thermal conditions are compared to determine the amount of incident radiation that is actually absorbed by the device while it is being irradiated. The situations are kept thermally identical, thereby insuring that all effects due to heat losses (e.g. convection, radiation and conduction) are exactly the same.
Owner:FACTORY MUTUAL RES
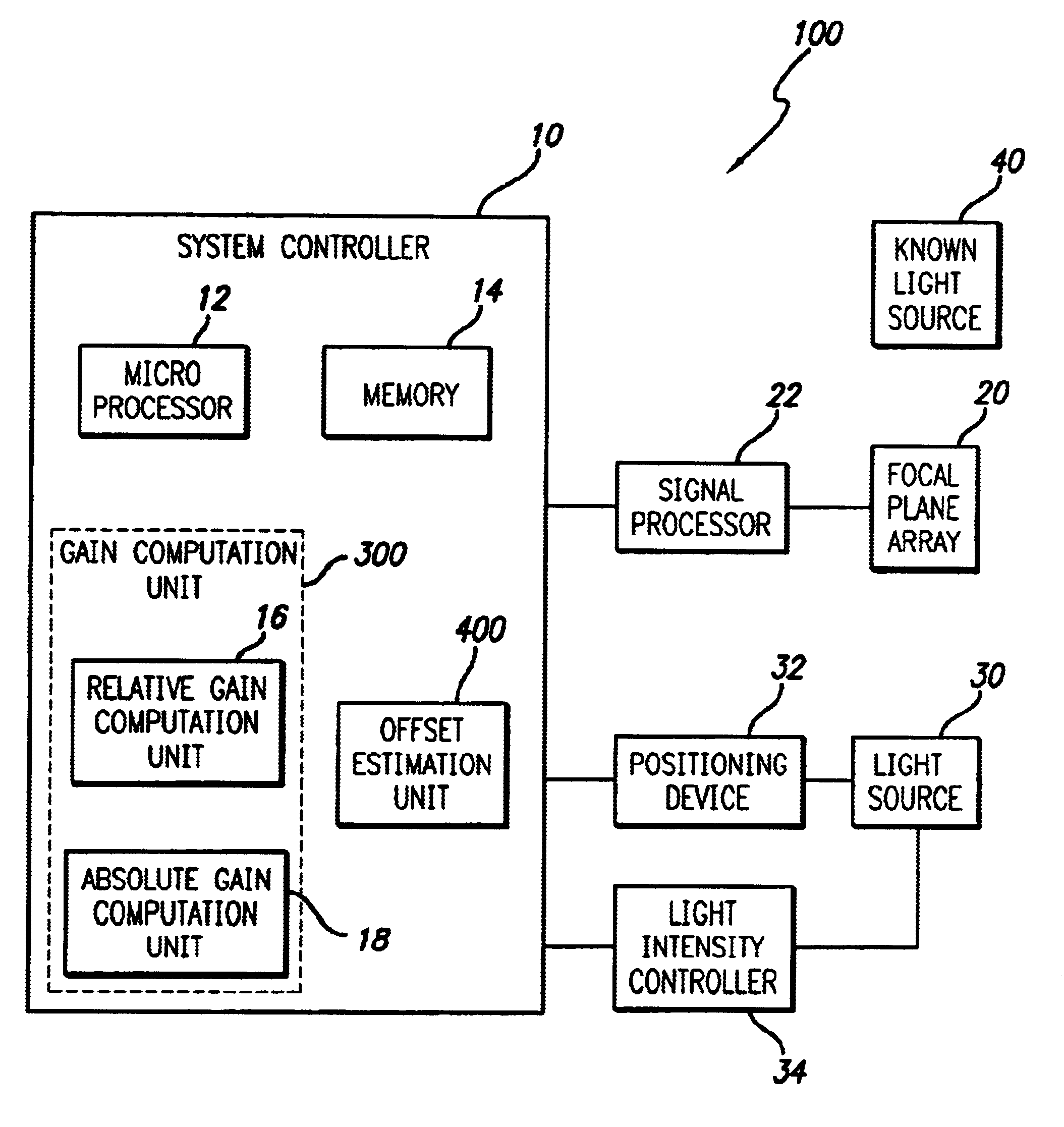
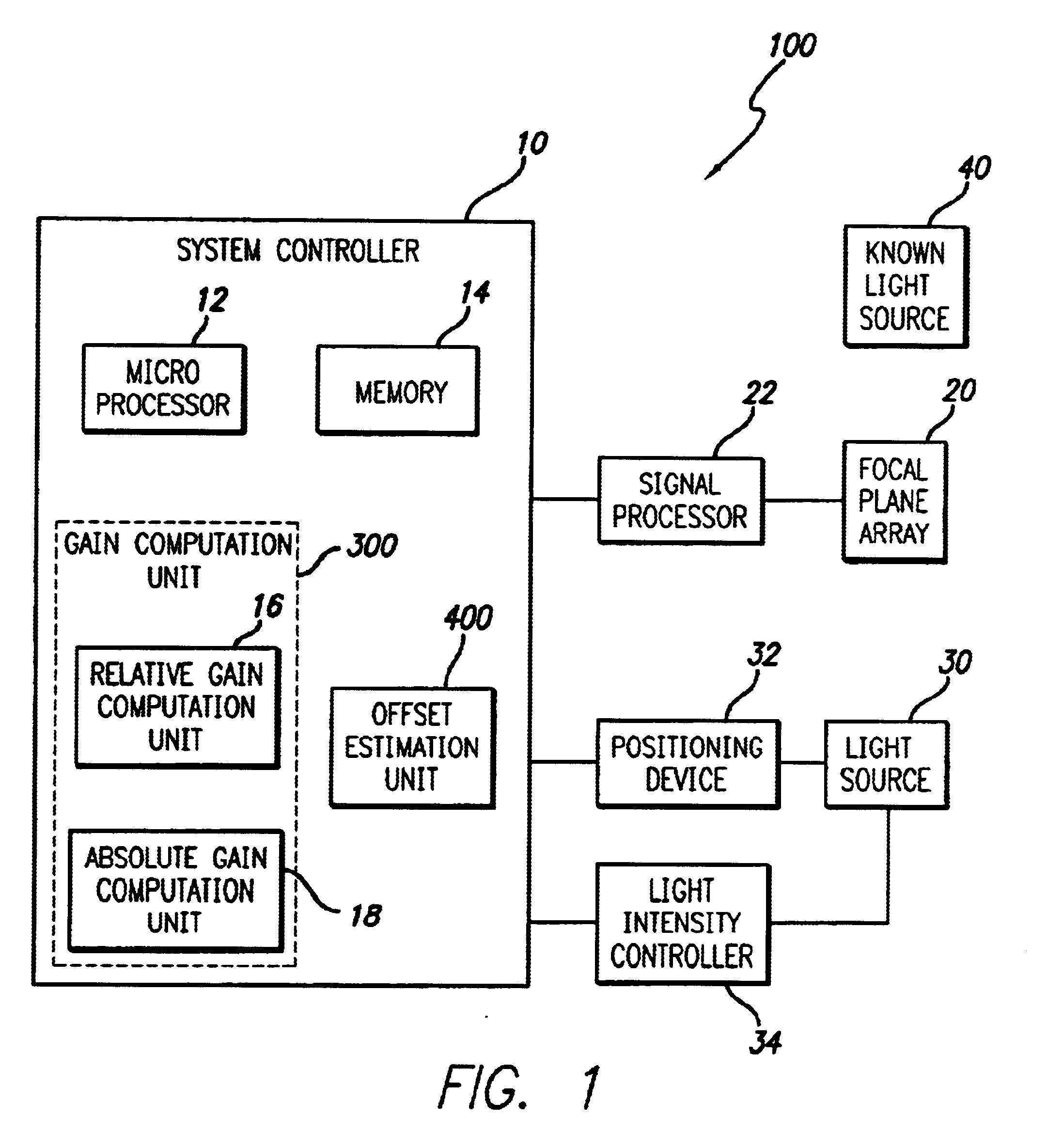
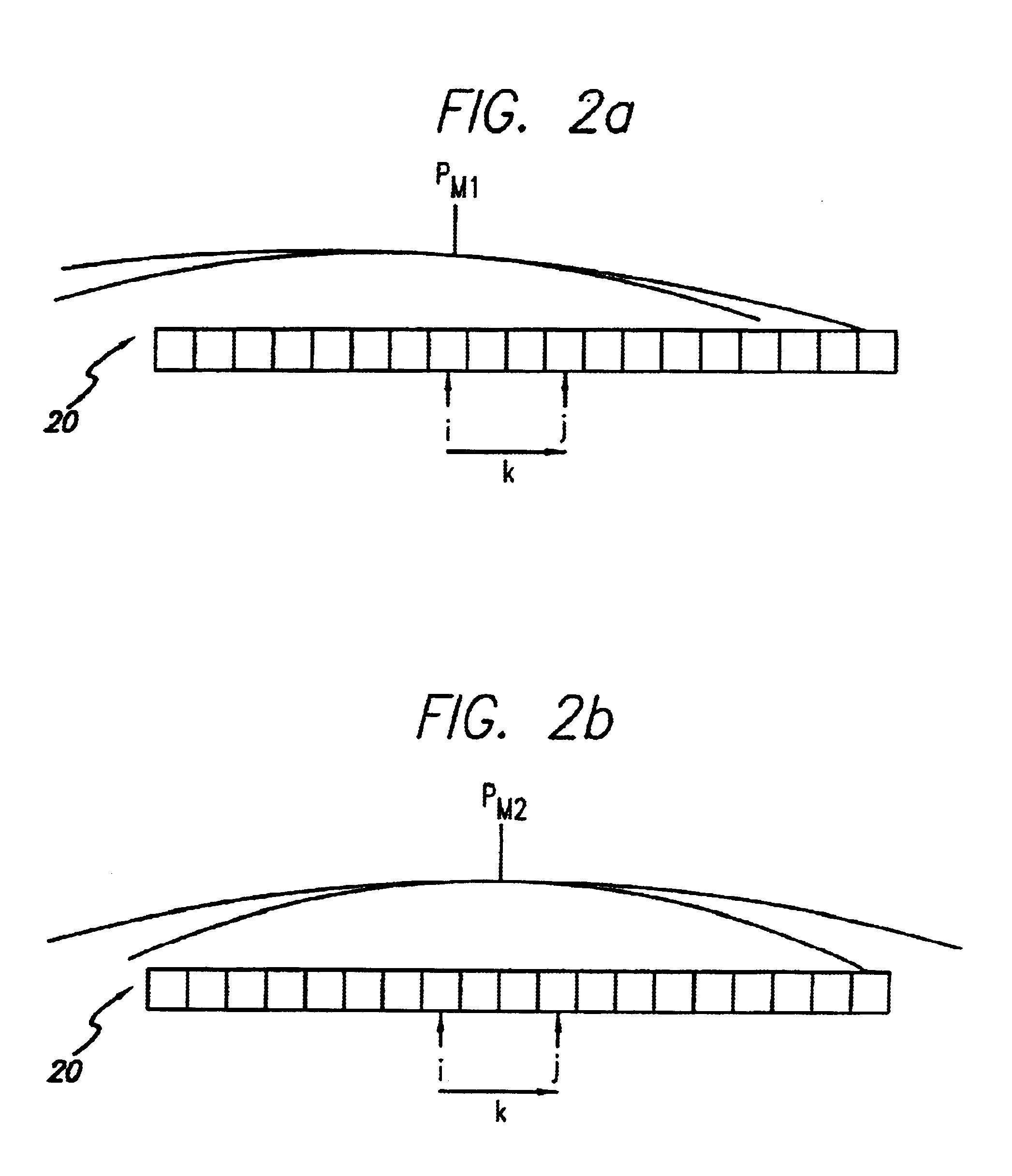
Radiometry calibration system and method for electro-optical sensors
InactiveUS20030025067A1Television system detailsRadiation pyrometryElectro-optical sensorShift vector
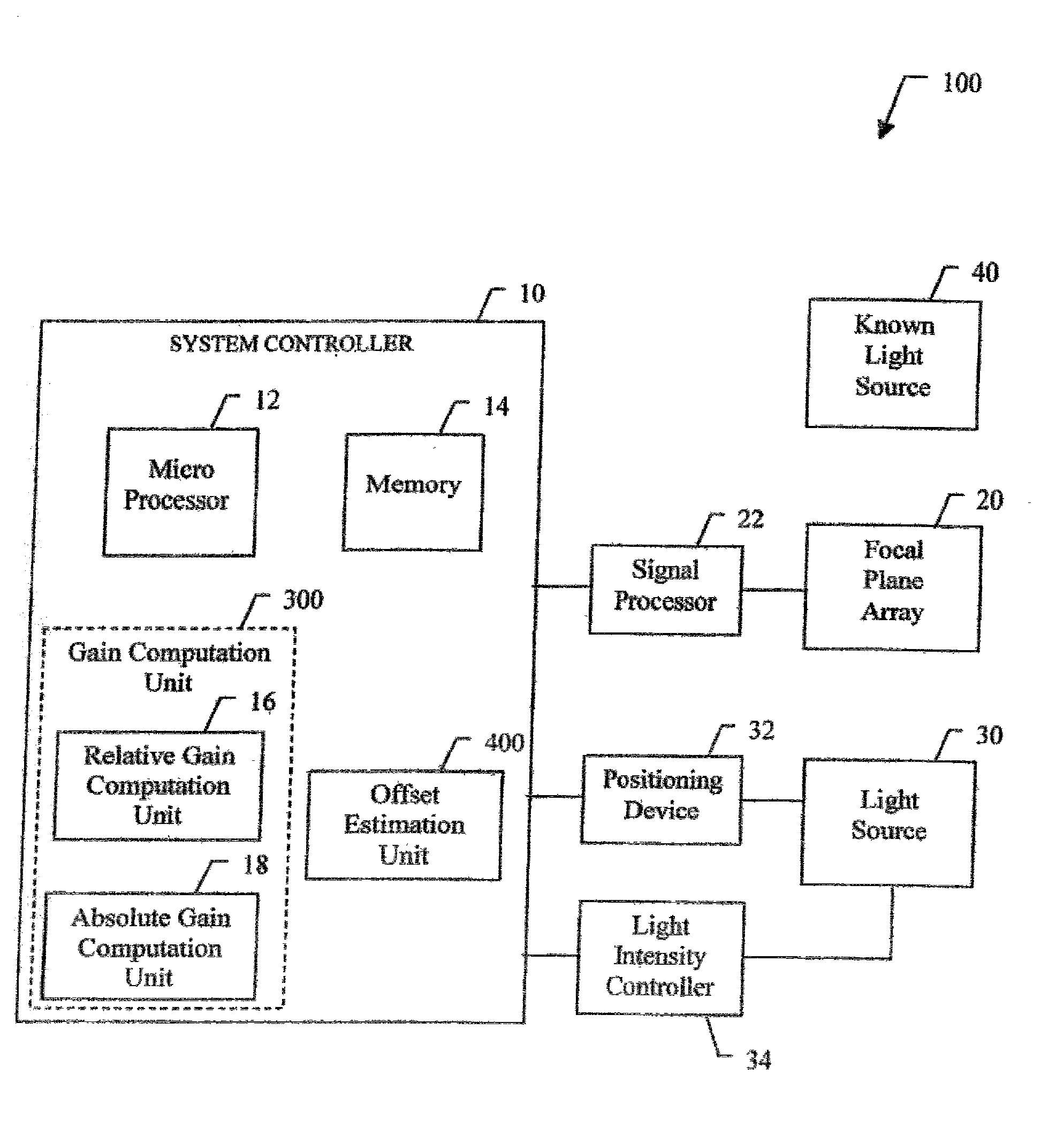
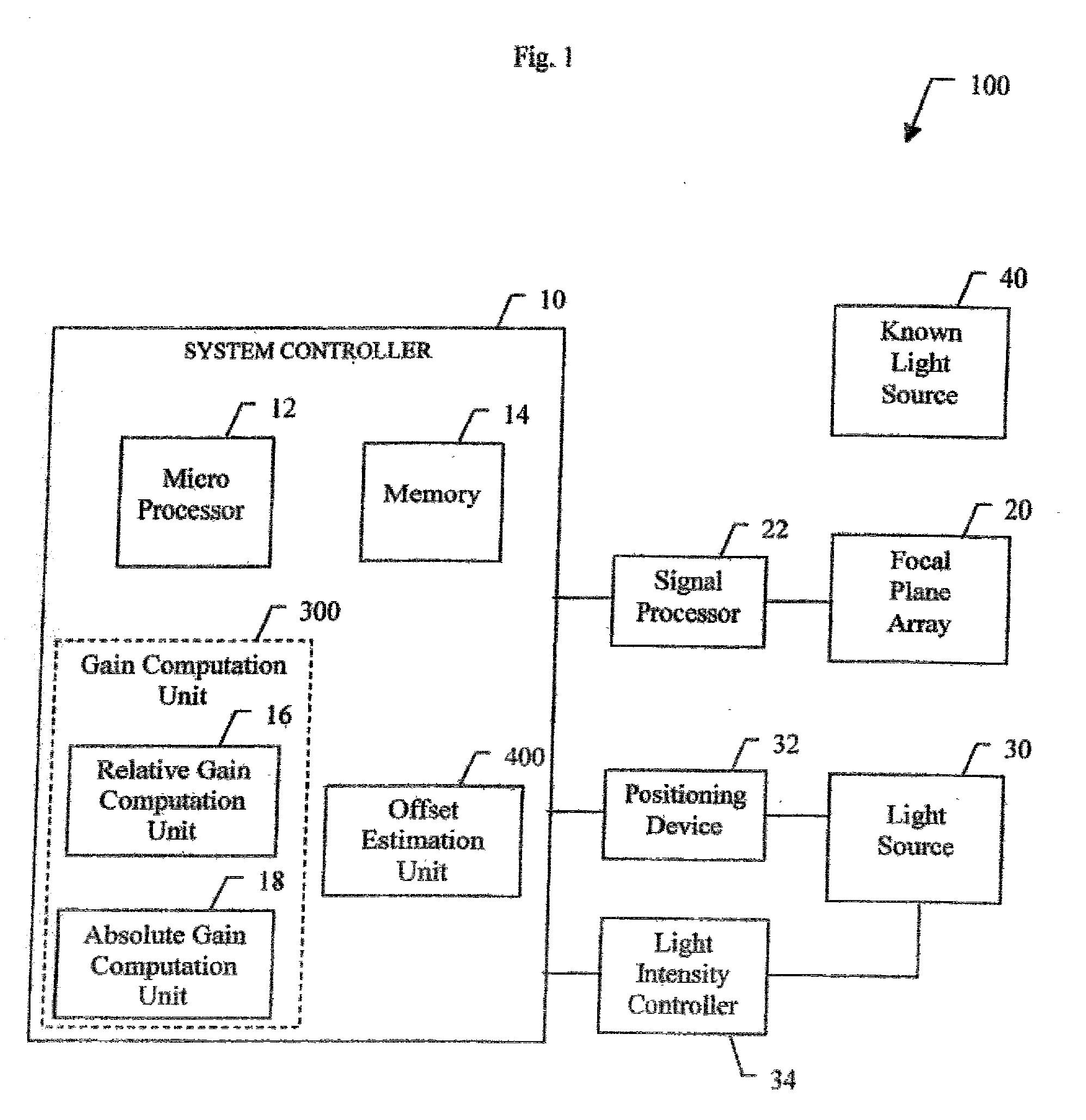
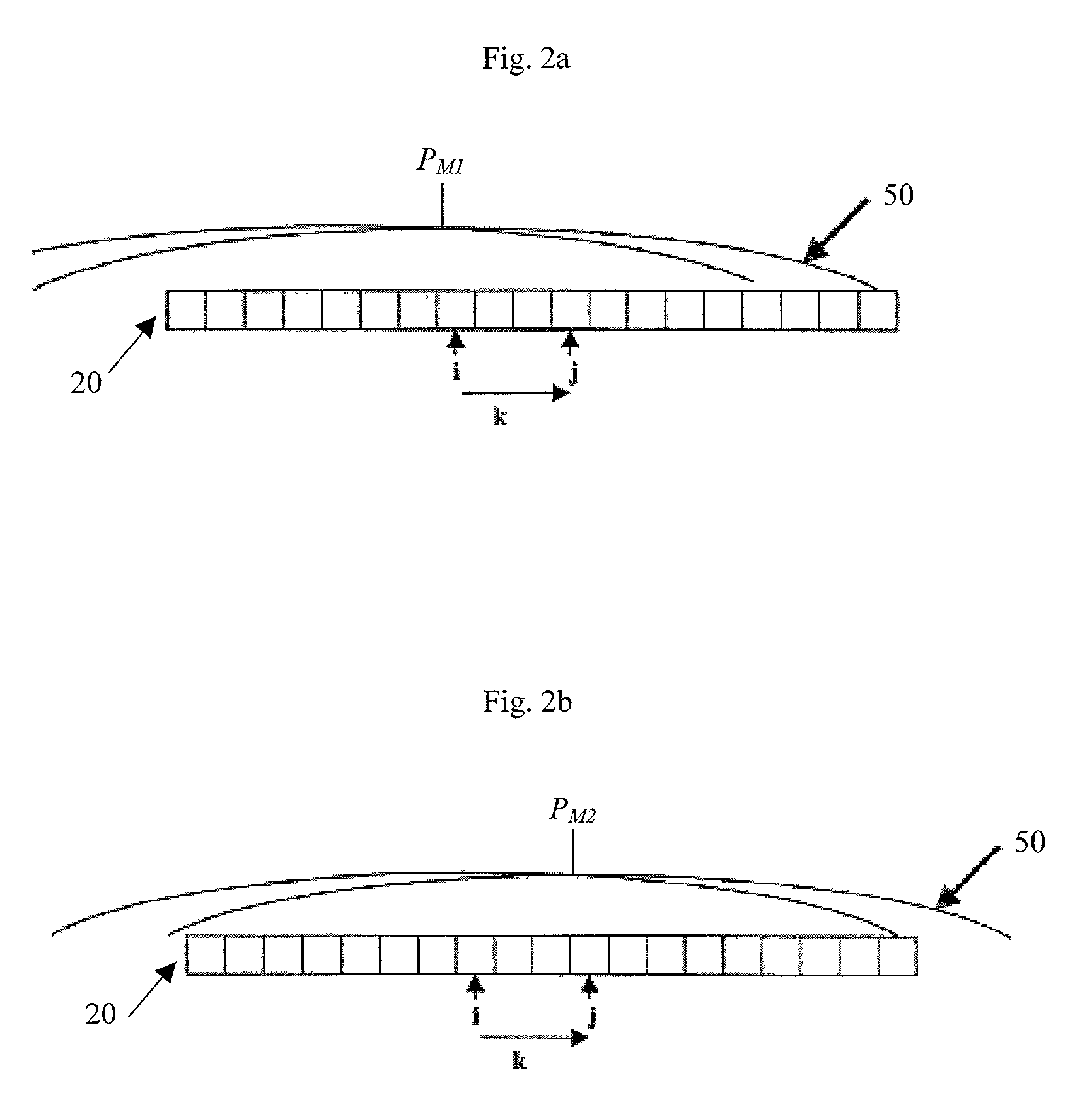
A system (100) and method for focal plane array calibration using an internal non-uniform calibration source (30). In the illustrative embodiment, the system (100) includes a first mechanism (16) for calculating a relative gain of each detector element in the focal plane array (20) relative to at least one reference element, a second mechanism (17) for obtaining the absolute gain of the reference element, and a third mechanism (18) for calculating the absolute gains for all other detector elements using the relative gains in conjunction with the absolute gain of the reference element. The relative response of each pixel is calculated from measurements of the response of each pixel using an internal calibration source (30) at two or more different source positions, and two illumination intensities at each position. Measurements using a pair of source positions separated by k pixels establishes the relative response of the ith pixel with respect to the (i+k)th pixel. Through this recursive relationship and other pairs of source position with a different shift vector k, the relative response of every pixel in the FPA can be established. Then, the absolute radiometric calibration of at least one reference pixel is accomplished using a known external source (40), such as a star. The absolute response calibration of each pixel can then be obtained using the recursive relationship in combination with the reference pixels.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Radiometry using an uncooled microbolometer detector
An infra-red imaging camera comprises focusing optics for gathering infra-red energy from an external scene, and an uncooled and unshielded detector arranged to detect infra red energy. Internal temperature sensing together with approximation of the temperature response of the camera provides a time varying calibration that allows the infra-red energy received at the detector to be used as a temperature measurement for objects in the camera's field of view.
Owner:OPGAL
Apparatus and method for determining analyte content in a fluid
ActiveUS20090173145A1Accurate and reliable processAccurately passedRadiation pyrometryDirection finders using radio wavesWater useOil and grease
An apparatus and method to determine analytes in a fluid. One aspect of the present invention is for the determination of the oil content of water using UV, near-IR, IR or Raman spectroscopy or radiometry. In certain embodiments, a solid membrane material absorbs analytes from fluid brought into contact with it. The membrane is subsequently placed in a FTIR spectrometer, which spectrometer is enabled to determine the concentration of analytes in fluid by calibration. Certain embodiments can determine the type of hydrocarbon present, and thus can differentiate Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons (TPH) from Total Oil and Grease (TOG), without any separate sample preparation.
Owner:ORONO SPECTRAL SOLUTIONS
Thermal instrument engine
An engine for use in a thermal instrument. The engine includes an infrared camera module and may also include a visible light camera module. The engine includes several temperature sensors mounted on a printed circuit board assembly that permit the engine to provide improved radiometry functionality and improved fine offset compensation capabilities.
Owner:JOHN FLUKE MFG CO INC
Portable radiometry and imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20060081778A1Protection elementEasy to install and removeMaterial analysis by optical meansTelescopesParticulatesEngineering
Owner:TELEDYNE FLIR LLC
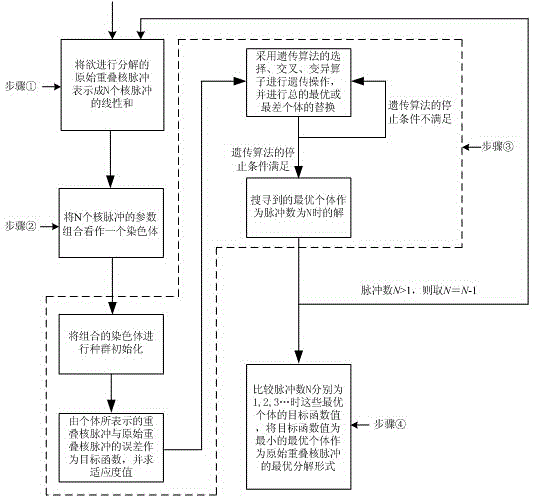
Overlap kernel pulse separation method
InactiveCN105989410AReduce abandonment rateImprove accuracyGenetic modelsMutation operatorGenetic algorithm
The invention discloses an overlap kernel pulse separation method, which comprises the following steps: firstly, expressing an original overlap kernel pulse to be separated, which is obtained in radiometry, as the linear sum of N nuclear pulses; then, taking the parameter composition of the N nuclear pulses as a chromosome; and finally, taking the error of the overlap kernel pulse represented by an individual and the original overlap kernel pulse as a target function, adopting the selection, cross and mutation operators of a genetic algorithm, and obtaining an optimal individual after a multi-generation operation so as to obtain the parameter value of each pulse, i.e. realizing the separation of the overlap kernel pulse. When N takes different values, the overlap kernel pulse is subjected to the same separation to obtain new optimal individuals, and the optimal individual with a minimum target function value is selected from the optimal individuals to serve as a final solution. A result indicates that the overlap kernel pulse separation method based on a population searching technology is an optimal combination for searching the kernel pulse from the global meaning to realize the separation of the overlap kernel pulse so as to obtain the parameter of each kernel pulse.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
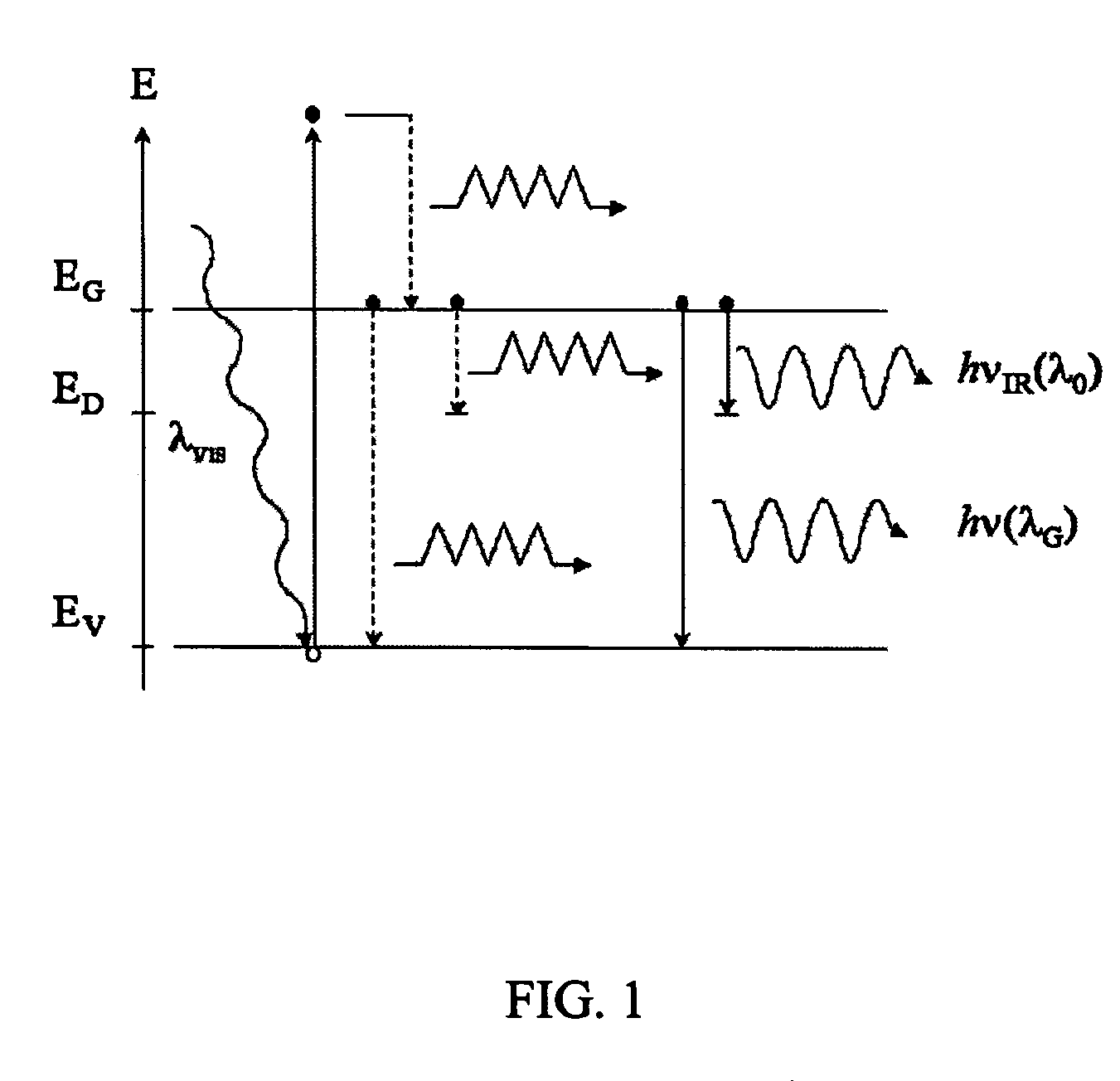
Method of photocarrier radiometry of semiconductors
ActiveUS7045786B2Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansSemiconductor materialsCarrier signal
The present invention relates to metrologic methodologies and instrumentation, in particular laser-frequency domain infrared photocarrier radiometry (PCR), for contamination and defect mapping and measuring electronic properties in industrial Si wafers, devices and other semiconducting materials. In particular the invention relates to the measurement of carrier recombination lifetime, τ, carrier diffusivity, D, surface recombination velocities, S, carrier diffusion lengths, L, and carrier mobility, μ, as well as heavy metal contamination mapping, ion implantation mapping over a wide range of dose and energy, and determination of the concentration of mobile impurities in SiO2 layers on semiconductor substrates. The present invention provides a method and complete photocarrier radiometric apparatus comprising novel signal generation and analysis techniques (carrier-wave interferometry) as well as novel instrumental hardware configurations based on the physical principle of photocarrier radiometry. The method comprises (a) optical excitation of the sample with a modulated optical excitation source and (b) detection of the recombination-induced infrared emission while filtering any Planck-mediated emissions. The present invention provides an instrumental method for detecting weak inhomogeneities among semiconducting materials that are not possible to detect with conventional single-ended photocarrier radiometry. The method comprises (a) irradiating both sides of the sample with modulated optical excitation sources that are 180 degrees out of phase with respect to one another and (b) monitoring the diffusion of the interfering, separately generated carrier waves through the corresponding recombination-induced IR emissions for PCR detection, or the use of an alternative detection scheme that monitors a sample property dependent on the carrier wave transport in the sample.
Owner:MANDELIS ANDREAS +1
Portable radiometry and imaging apparatus
An infrared (IR) camera and associated electronics including power are systems, including devices and methods, for infrared imaging that can be switched or reprogrammed to produce or display at least two images associated with at least two temperature ranges.
Owner:TELEDYNE FLIR LLC
Superconducting radiometry apparatus
InactiveUS20100019152A1High resolution measurementHigh power measurementThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductancePeak value
There is provided a superconducting radiometry apparatus capable of performing, while sample-measuring, an energy correction in regard to a fluctuation of a peak value of an output signal, which is due to a radiation heat and a magnetic field from an outside. The superconducting radiometry apparatus is constituted by comprising a micro-calorie meter detecting an energy of a radiant ray as a temperature change, a signal detection mechanism for detecting a displacement of an electric current flowing to the micro-calorie meter, a shunt resistance which is connected in parallel to the micro-calorie meter and whose resistance value is smaller than the micro-calorie meter, a bias electric source connected to the micro-calorie meter and the shunt resistance and applying a constant voltage, a heat addition device adding a constant and already-known heat quantity to the micro-calorie meter, a peak value monitor measuring a peak value corresponding to an added heat quantity within an output signal from the signal detection mechanism while synchronizing with a heat quantity addition from the heat addition device, and an energy correction device correcting, on the basis of an output from the peak value monitor, so as to become a peak value corresponding to the heat quantity from the heat addition device.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH TECH SCI CORP
Method used for eliminating system frequency response influences on photo-carrier radiometry technology semi conducting material characteristic measuring equipment
InactiveCN103543130AImproved characteristic parametersEliminate the effects of characteristic measurementsAnalysis by material excitationExcitation beamSemiconductor materials
The invention discloses a method used for eliminating system frequency response influences on photo-carrier radiometry technology semi conducting material characteristic measuring equipment. The method is based on infrared radiation which is generated by a semi conducting material after absorption of focused excitation beams processed by strength periodic modulation; characteristic parameters of the semi conducting material are measured by collecting and measuring photo-carrier radiation signals; a relationship curve of the photo-carrier radiation signals and modulation frequency is obtained by changing the modulation frequency of the strength of the excitation beams; a relationship curve of the photo-carrier radiation signals and the modulation frequency under different excitation beam spot sizes is obtained by changing the space between a focusing lens and a sample; and frequency response function of the measuring equipment is obtained, and the influences of the frequency response function on semi conducting material characteristic measurement is eliminated by analyzing the relationship curve of the photo-carrier radiation signals and the modulation frequency under different excitation beam spot sizes. The method is capable of solving a problem that in traditional method measurement accuracy is influenced by relatively high measuring error, and increasing measuring accuracy of measurement on semi conducting material characteristic parameters.
Owner:TENGZHOU TENGHAI ANALYTICAL INSTR
Method and system for combined photothermal modulated reflectance and photothermal IR radiometric system
InactiveUS20050225765A1Optically investigating flaws/contaminationMaterial flaws investigationPhotodetectorLight beam
A method and apparatus for evaluating a semiconductor wafer. A combination of a photothermal modulated reflectance method and system with a photothermal IR radiometry system and method is utilized to provide information which can be used to determine properties of semiconductor wafers being evaluated. The system and method can provide for utilizing a common probe source and a common intensity modulated energy source. The system and method further provide an infrared detector for monitoring changes in infrared radiation emitted from a sample, and photodetector for monitoring changes in beam reflected from the sample.
Owner:THERMA WAVE INC
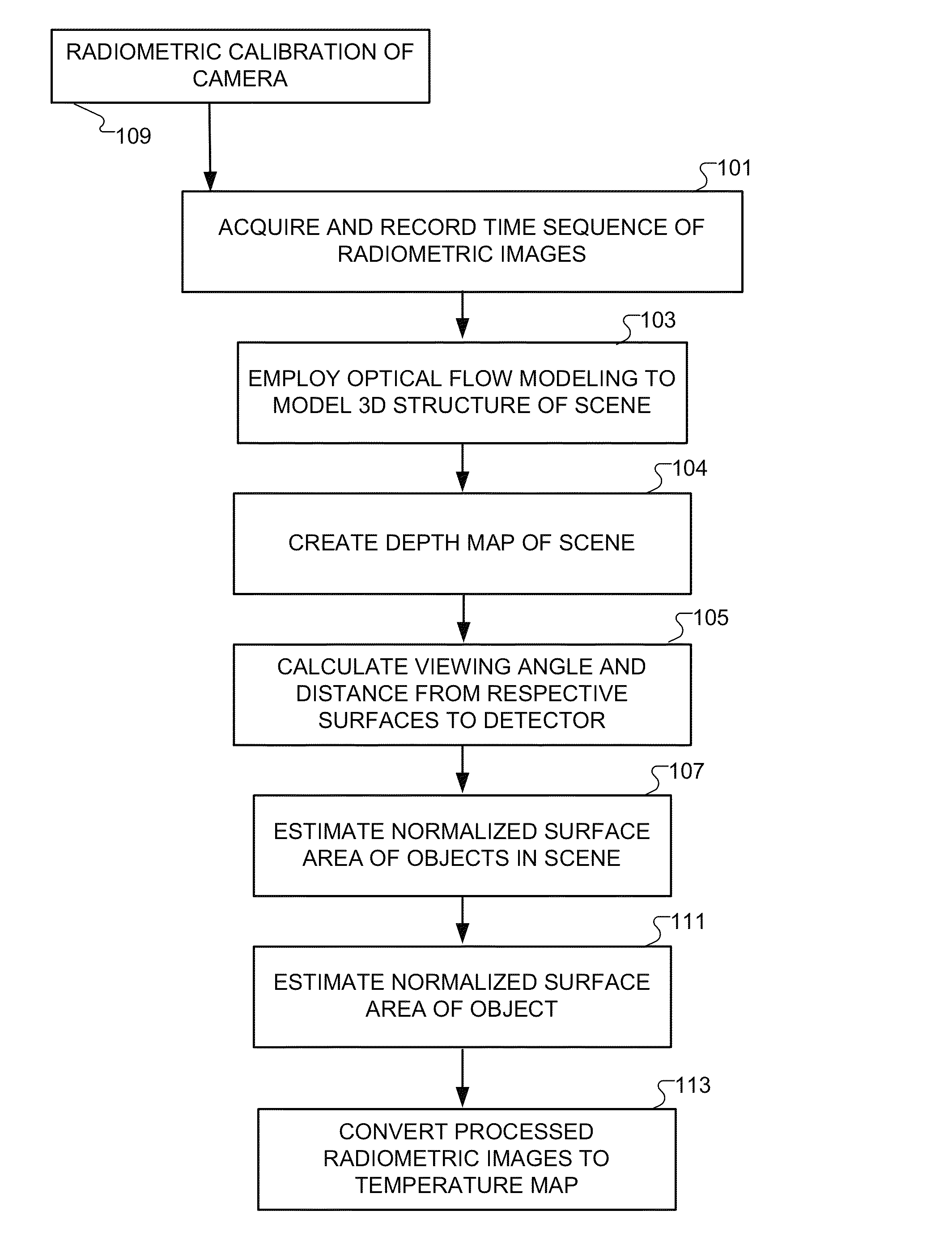
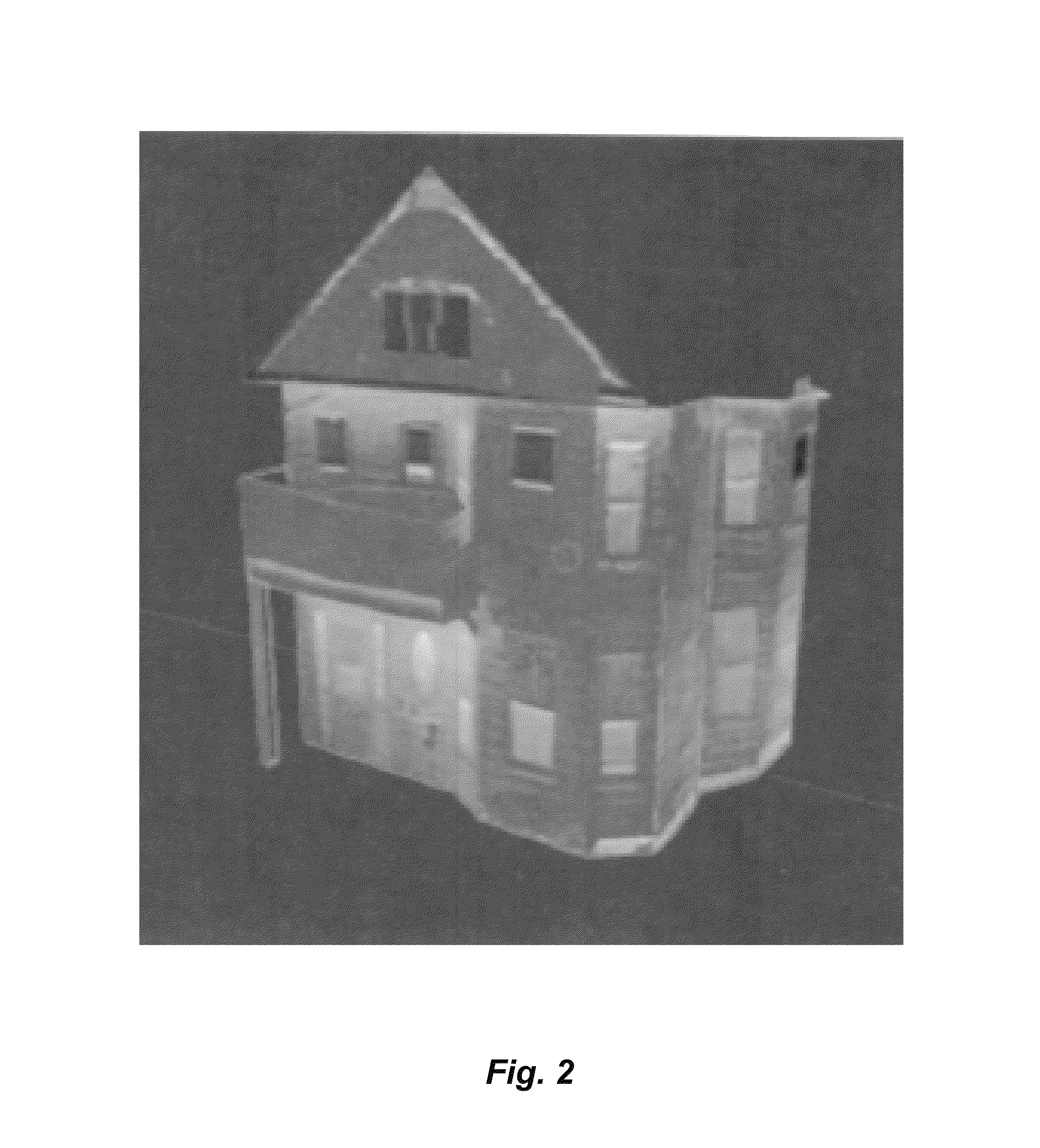
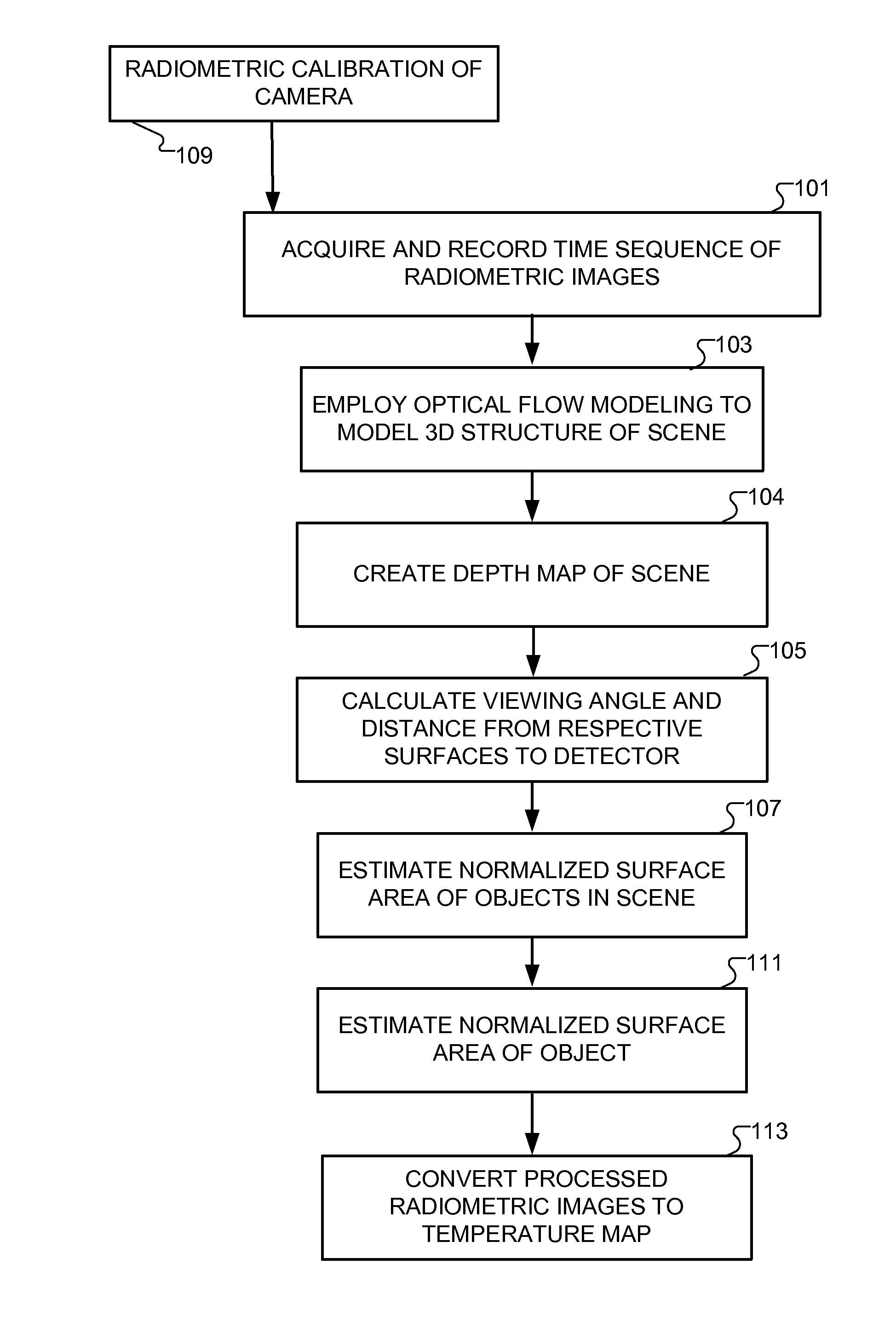
3D radiometry
InactiveUS8818079B2Material analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionEmissivityRadiometry
Methods and a computer program product for deriving temperature information with respect to surfaces within a scene that is imaged radiometrically. A time sequence of radiometric data is acquired in frames viewed from distinct angles. A three-dimensional structure of the scene is derived, allowing viewing angles and distances to the imaged surfaces to be inferred. Normalized surface areas of the imaged surfaces are calculated based on the inferred viewing angles and emissivities of the imaged surfaces are corrected accordingly. Corrections also account for background radiation impinging on the imaged surfaces. The radiometric data are converted to a perceptible temperature map of the imaged surfaces.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
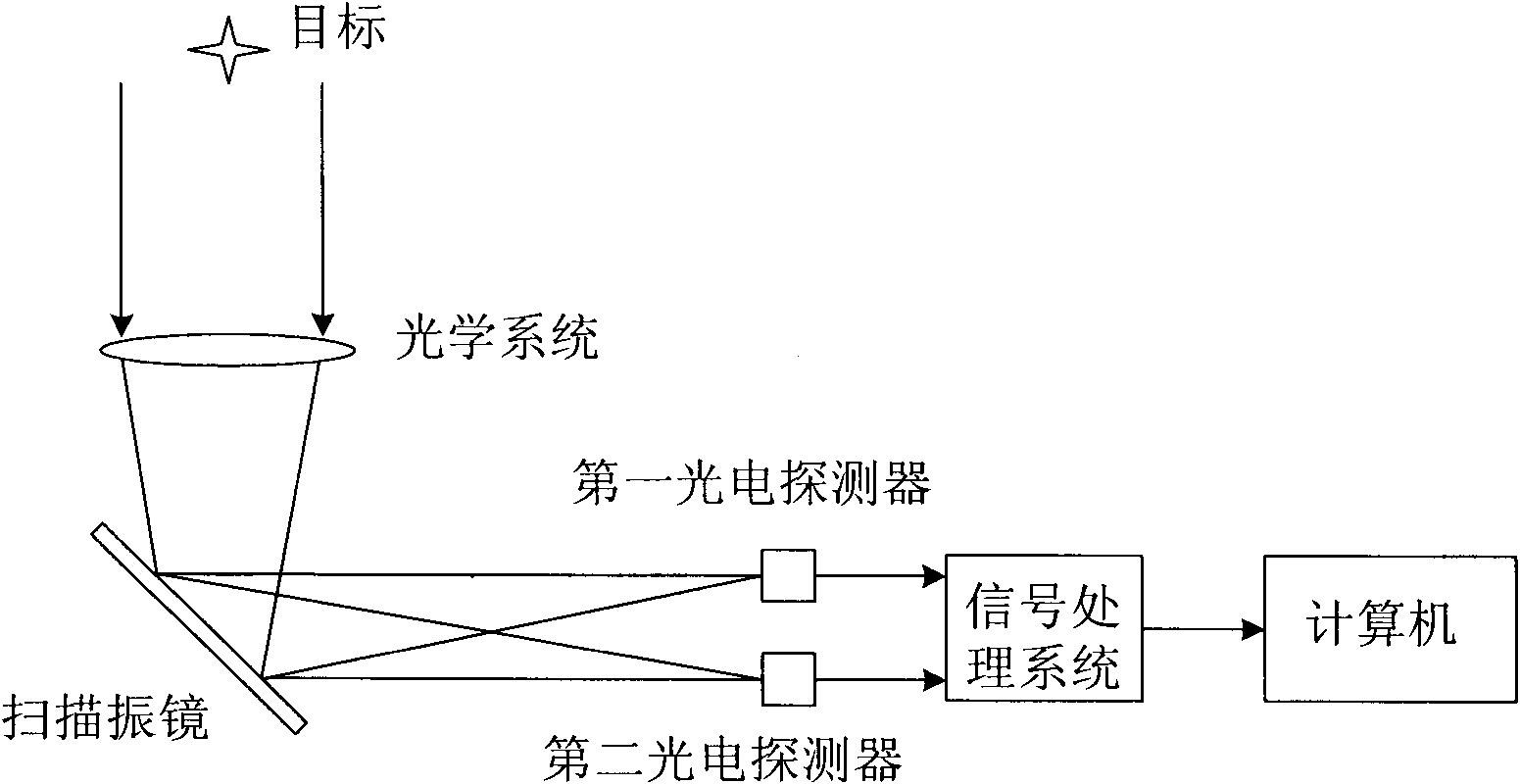
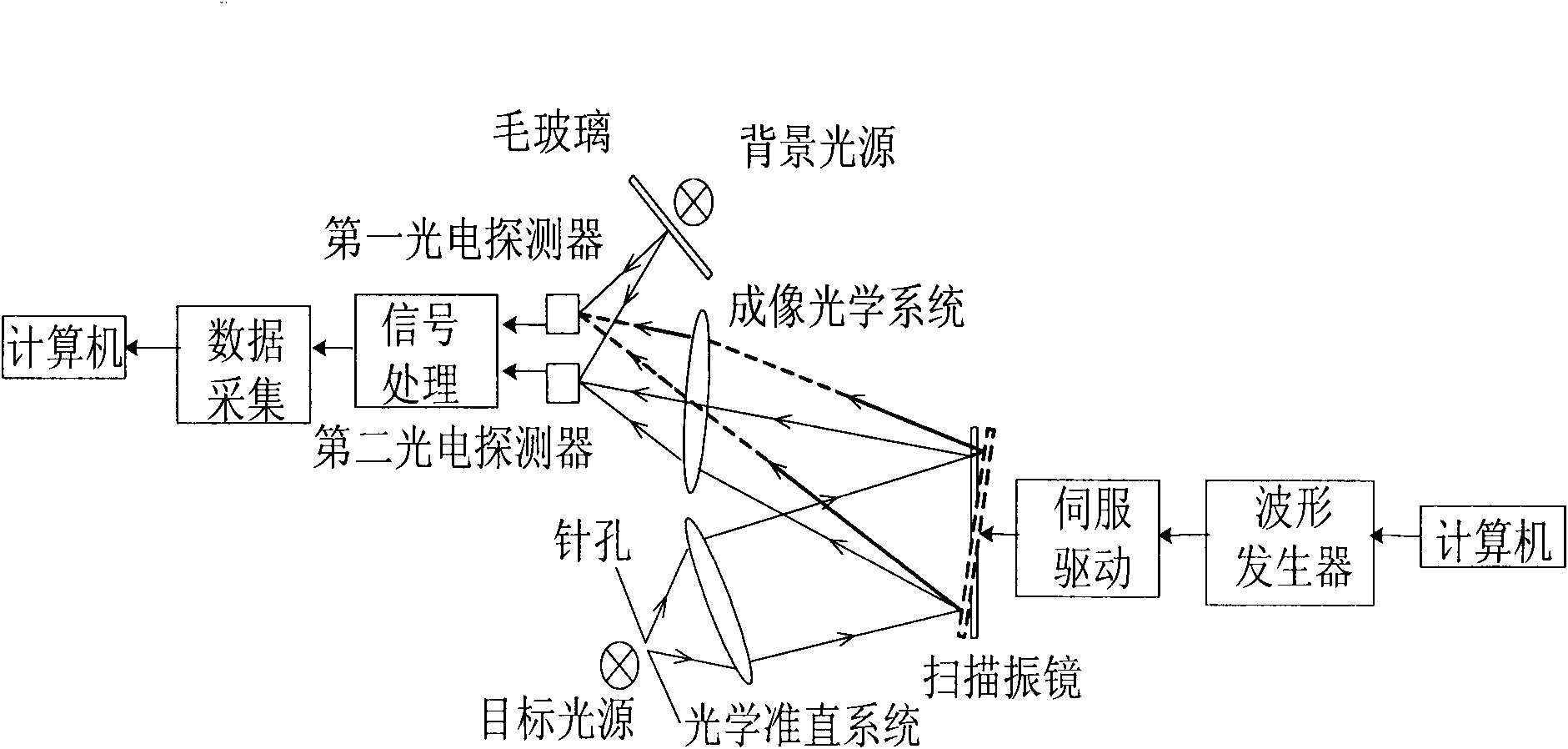
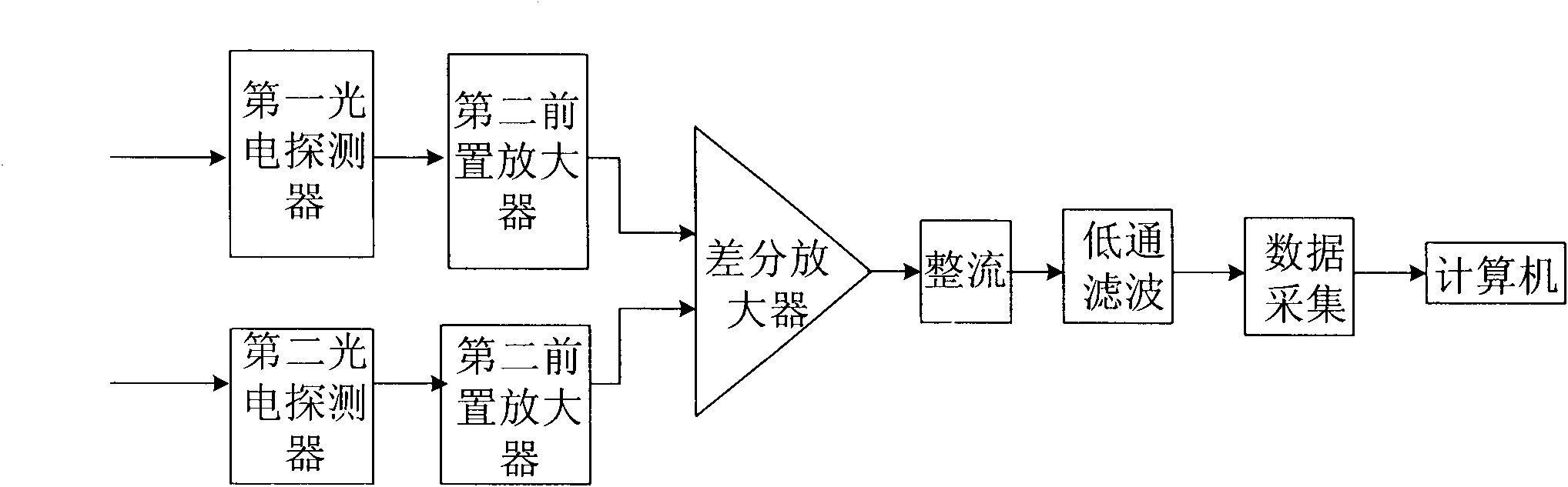
Real-time background deduction method for target radiometry
InactiveCN102338664AImprove real-time performancePyrometry using electric radation detectorsPhotovoltaic detectorsRadiometry
The invention discloses a real-time background deduction method for target radiometry. A target, a background, an optical system, a scanning vibration lens, a first photoelectric detector, a second photoelectric detector, a signal processing system and a computer are used for achieving the real-time deduction method, wherein the optical system is used for imaging the target; when the scanning vibration lens vibrates, the target is imaged on the first photoelectric detector and the second photoelectric detector in turn; when the target is imaged on the first photoelectric detector, the background is imaged on the second photoelectric detector; when the target is imaged on the second photoelectric detector, the background is imaged on the first photoelectric detector; and the signal processing system is used for subtracting the signals of the first photoelectric detector and the second photoelectric detector in real time, thereby efficiently eliminating the influence of the background on the target radiometry in real time and acquiring an accurate target radiometry value. Compared with an afterward background deduction method, the real-time background deduction method for the target radiometry provided by the invention has the advantages that the instantaneity is better and the change of target radiation intensity can be reflected in real time.
Owner:SHANGHAI WINGTECH ELECTRONICS TECH
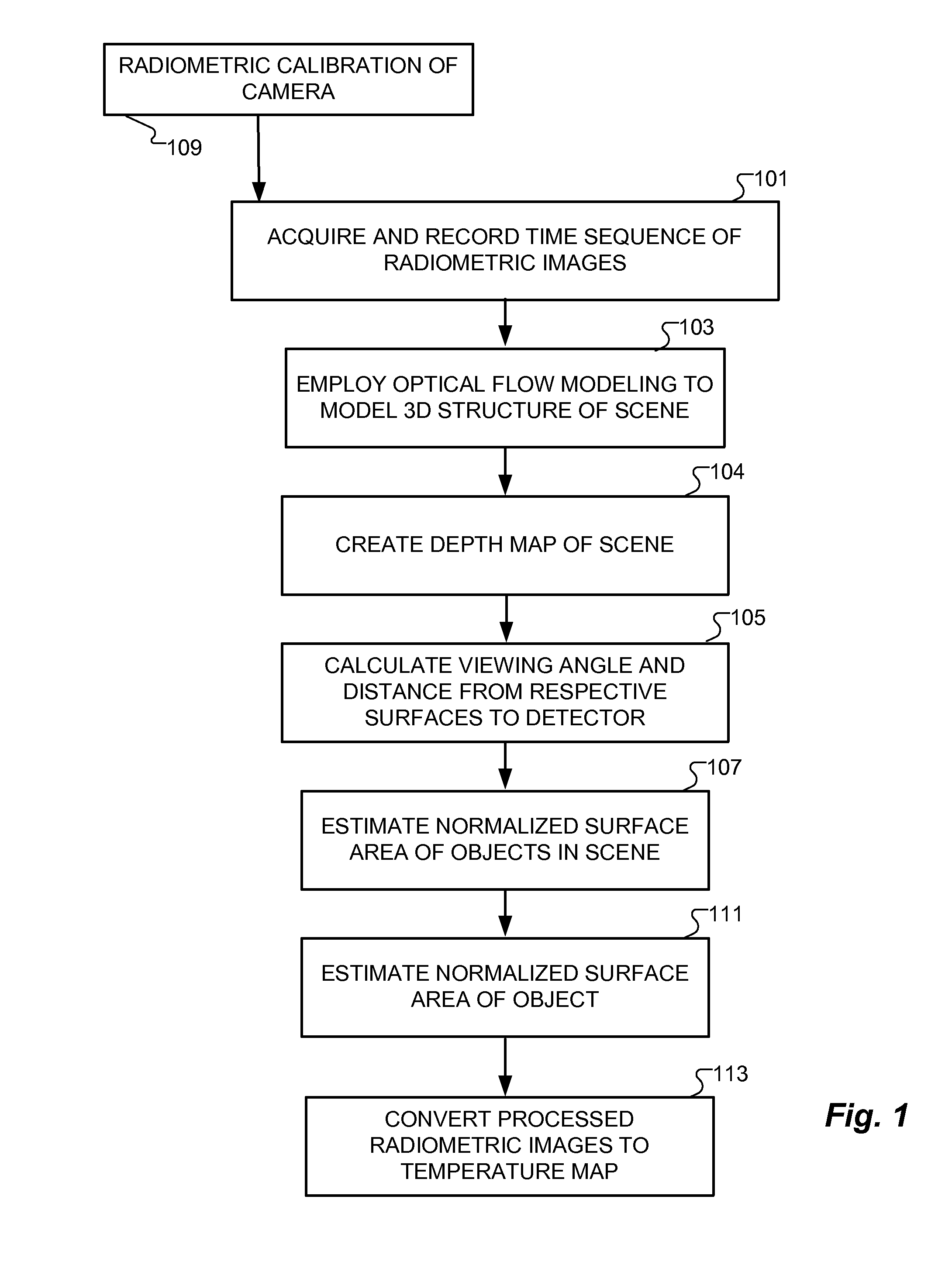
3D Radiometry
InactiveUS20140044340A1Character and pattern recognitionSensing radiation from moving bodiesEmissivityRadiometry
Methods and a computer program product for deriving temperature information with respect to surfaces within a scene that is imaged radiometrically. A time sequence of radiometric data is acquired in frames viewed from distinct angles. A three-dimensional structure of the scene is derived, allowing viewing angles and distances to the imaged surfaces to be inferred. Normalized surface areas of the imaged surfaces are calculated based on the inferred viewing angles and emissivities of the imaged surfaces are corrected accordingly. Corrections also account for background radiation impinging on the imaged surfaces. The radiometric data are converted to a perceptible temperature map of the imaged surfaces.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Device and method for measuring absorbed heat flux in a fire test apparatus
InactiveUS6971792B2Easy to measureAccurate measurementMaterial thermal conductivityThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsHeat fluxEngineering
Owner:FACTORY MUTUAL INSURANCE COMPANY
Internally-calibrated, two-detector gas filter correlation radiometry (GFCR) system
InactiveUS7423756B2Accurate CalibrationEasy CalibrationRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansSpectral bandsField of view
An entrance aperture of a GFCR system receives light from a scene of interest. The light is focused to form an image at a focal plane. Light associated with a selected field-of-view of the image at the focal plane is then confined to a spectral band at which a gas of interest absorbs. The confined light is split into first and second paths. A calibrating light is selectively produced from within the optical train at the focal plane. A portion of the calibrating light traverses each of the first and second paths. A region that is substantially non-interfering with respect to the spectral band is disposed in the first path. A gas cell filled with the gas of interest is disposed in the second path. The light passed through the region and through the gas cell is independently detected and used to generate output signals indicative of the light so-detected. The output signals are processed with the output signals generated by the light from the selected field-of-view of the image being used to generate a measure of the gas of interest and the output signals generated by the portion of the calibrating light traversing the first and second paths being used to calibrate the GFCR system.
Owner:G & A TECHN SOFTWARE
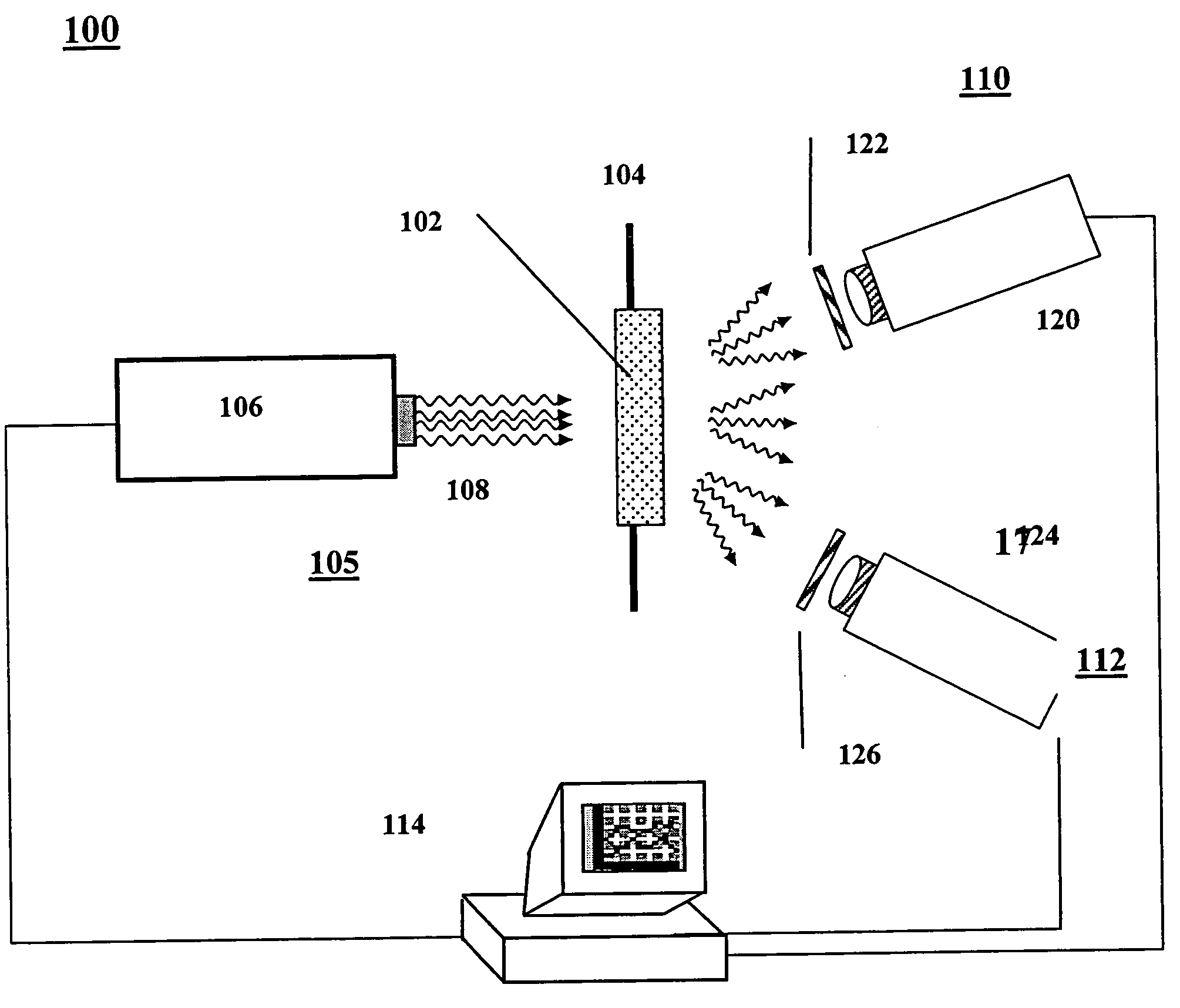
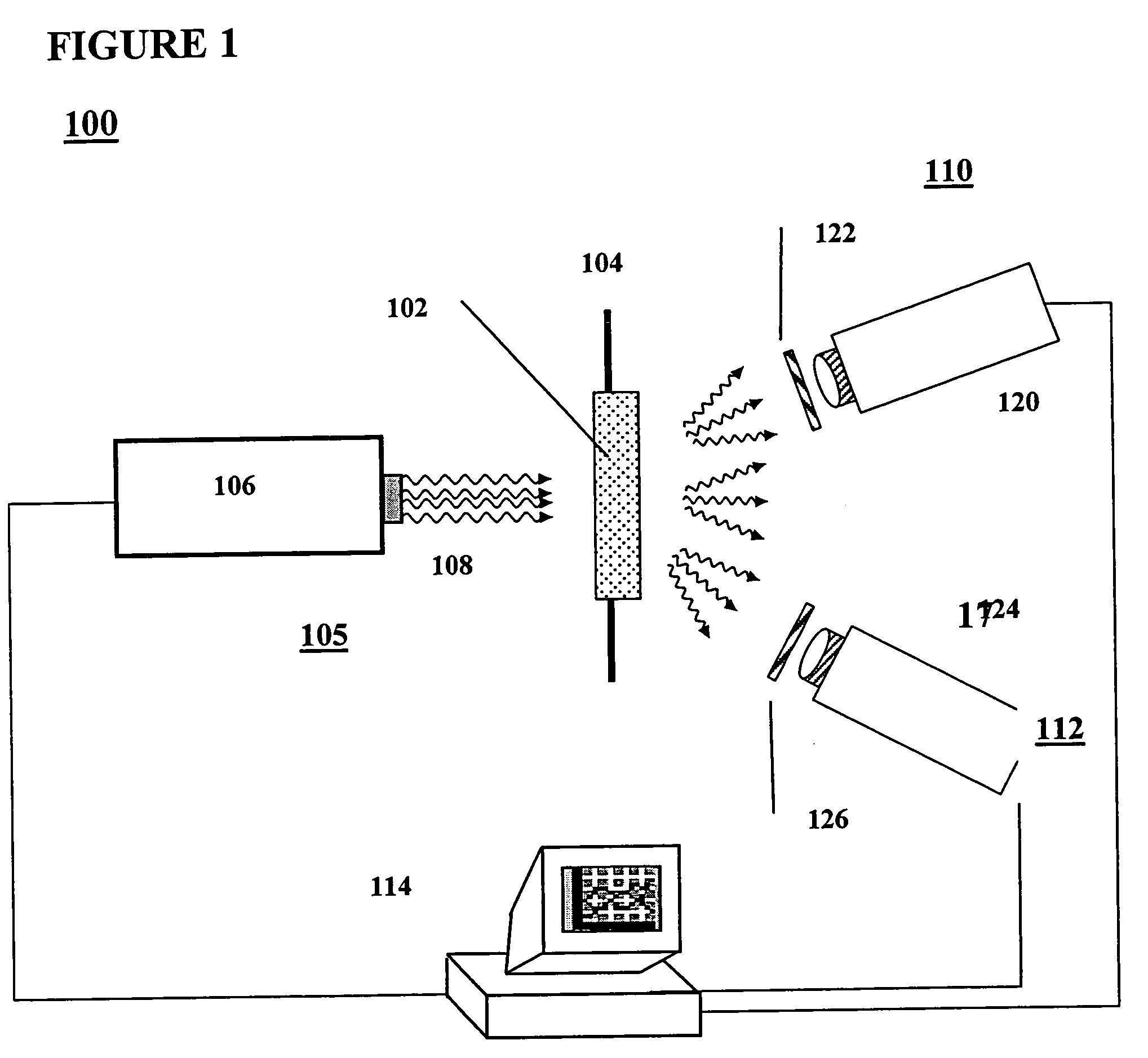
Radiometry calibration system and method for electro-optical sensors
A system (100) and method for focal plane array calibration using an internal non-uniform calibration source (30). In the illustrative embodiment, the system (100) includes a first mechanism (16) for calculating a relative gain of each detector element in the focal plane array (20) relative to at least one reference element, a second mechanism (17) for obtaining the absolute gain of the reference element, and a third mechanism (18) for calculating the absolute gains for all other detector elements using the relative gains in conjunction with the absolute gain of the reference element. The relative response of each pixel is calculated from measurements of the response of each pixel using an internal calibration source (30) at two or more different source positions, and two illumination intensities at each position. Measurements using a pair of source positions separated by k pixels establishes the relative response of the ipixel with respect to the (i+k)pixel. Through this recursive relationship and other pairs of source position with a different shift vector k, the relative response of every pixel in the FPA can be established. Then, the absolute radiometric calibration of at least one reference pixel is accomplished using a known external source (40), such as a star. The absolute response calibration of each pixel can then be obtained using the recursive relationship in combination with the reference pixels.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
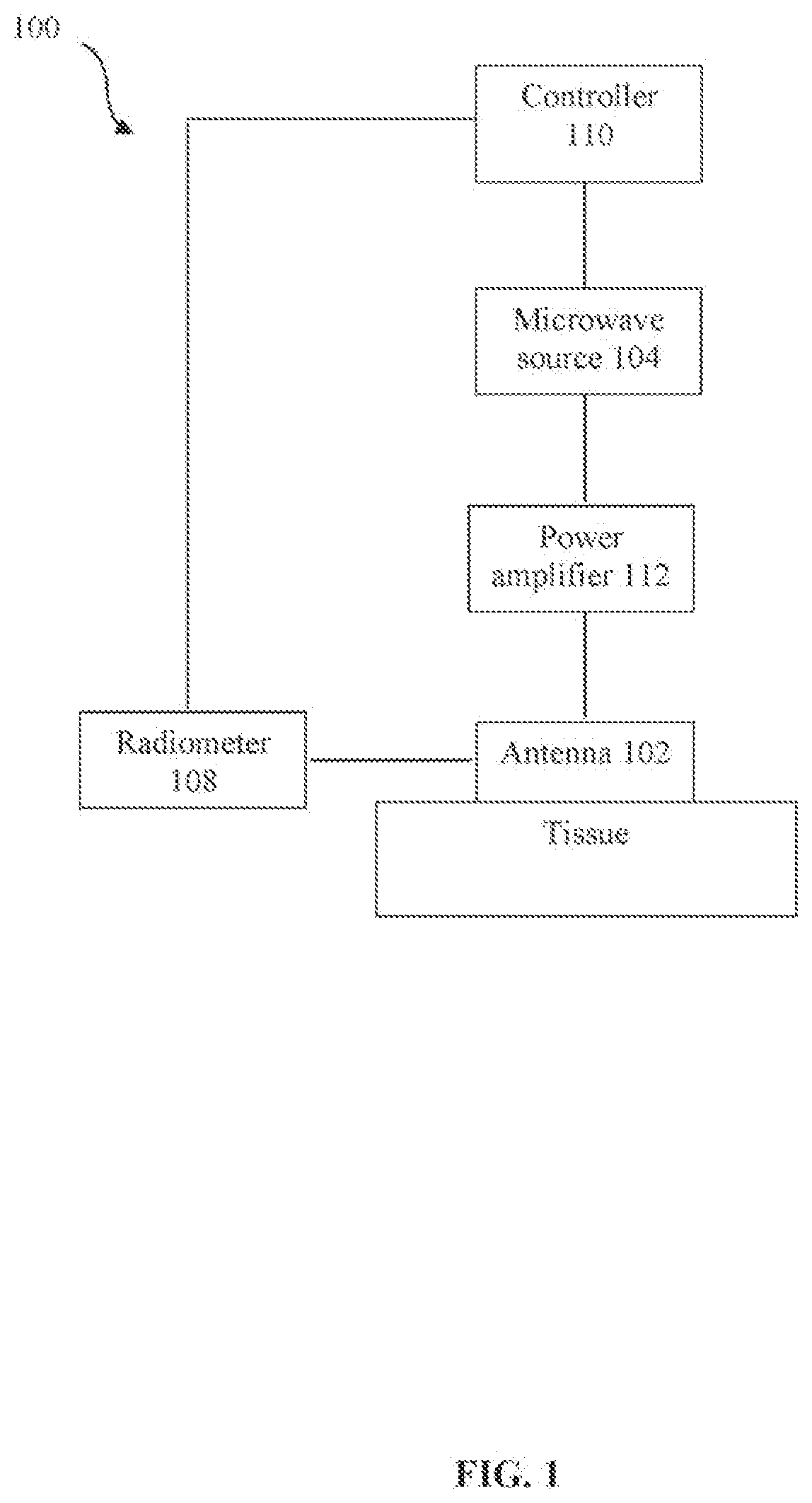
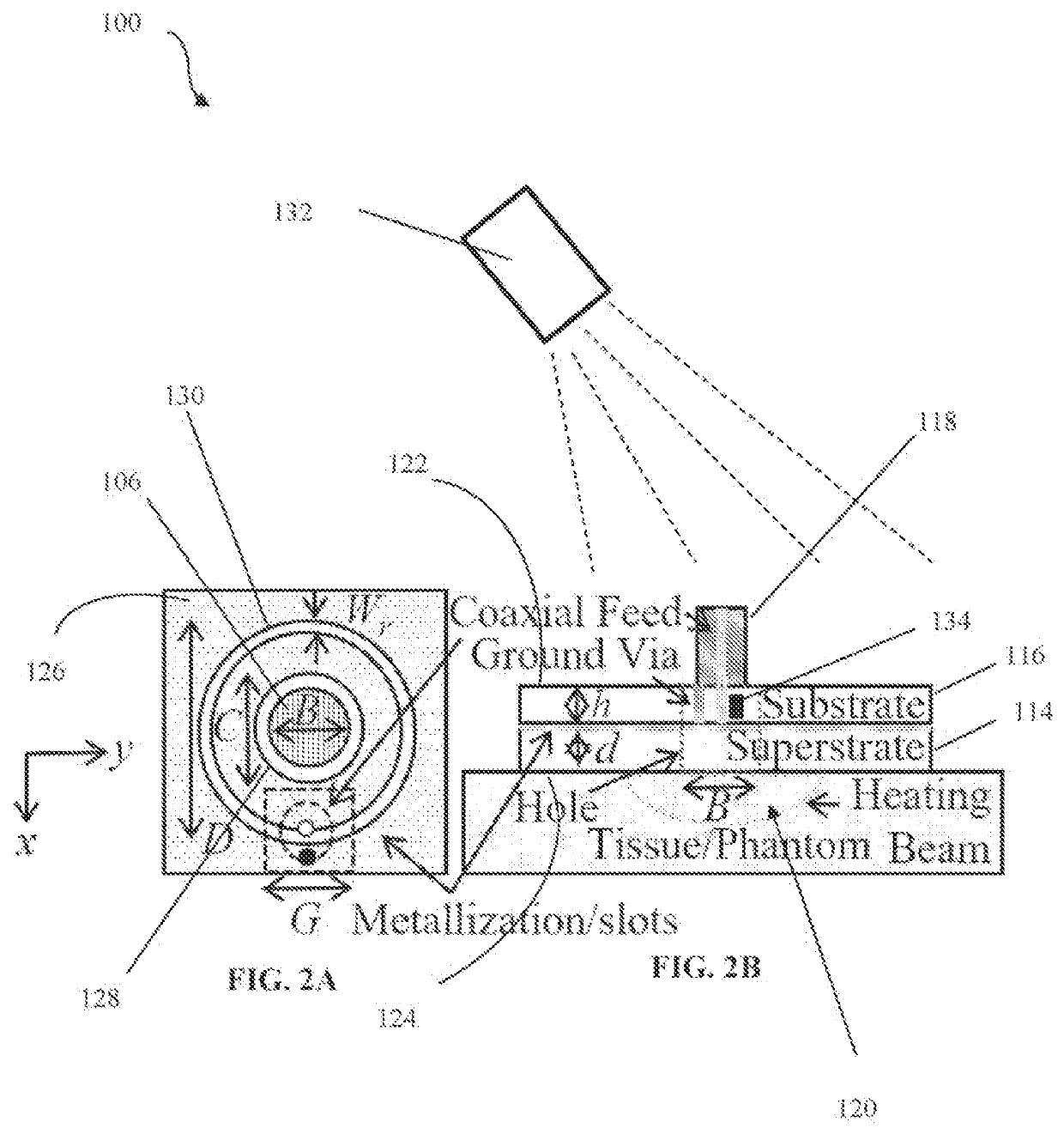
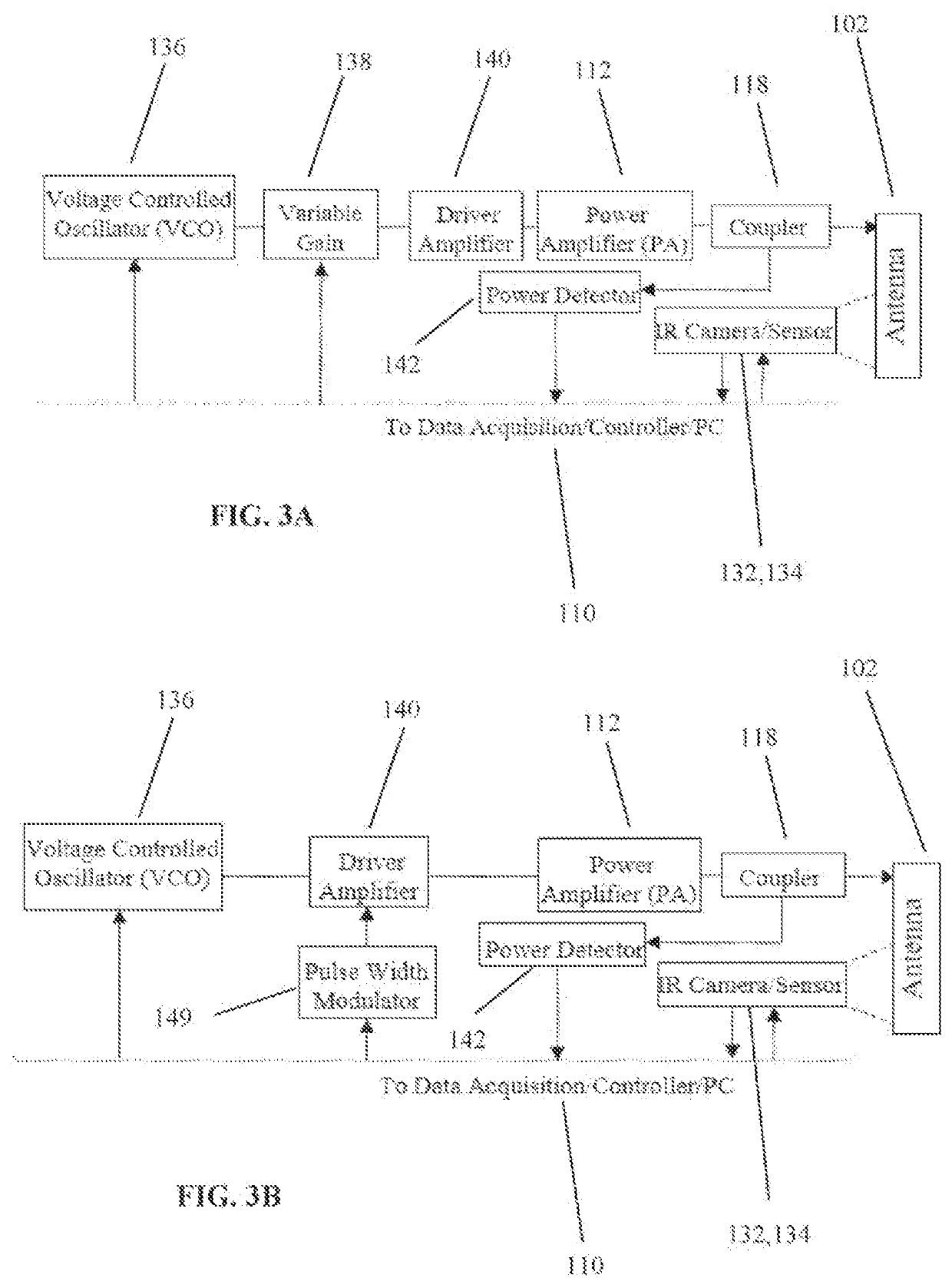
Assessment of skin perfusion using microwave heating and using infrared radiometry
Embodiments relate to use of microwave heating and infrared thermography for assessing perfusion. The system includes a microwave source, an antenna, and a radiometer. The microwave source generates microwave radiation at a frequency that is tuned to or near a resonance frequency by the antenna to output a microwave beam. The microwave beam is caused to be incident upon tissue and is converted to heat. The heated tissue emits infrared radiation that is monitored by the radiometer. The system allows for a low-cost, efficient, and non-invasive means to assess blood perfusion without radiofrequency interference. Use of infrared thermography is accomplished by the formation of the hole in the antenna structure. Use of an array of such antennas allows the measurement of perfusion for multiple points across a region of the body. The efficiency of the system is aided by adjusting the average microwave power by means of pulse width modulation.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com