Device and method for making weather observations using infrared spectral radiometry
a technology of infrared spectral radiometry and instruments, applied in the field of atmospheric measurements, can solve problems such as substantial errors in the assigned wind velocity vector, and achieve the effects of reducing the required size of the infrared spectrometer, reducing operating temperature, and reducing siz
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0051]The present invention may be understood by reference to the following detailed description, which should be read in conjunction with the appended drawings. It is to be appreciated that the following detailed description of various embodiments is by way of example only and is not meant to limit, in any way, the scope of the present invention.
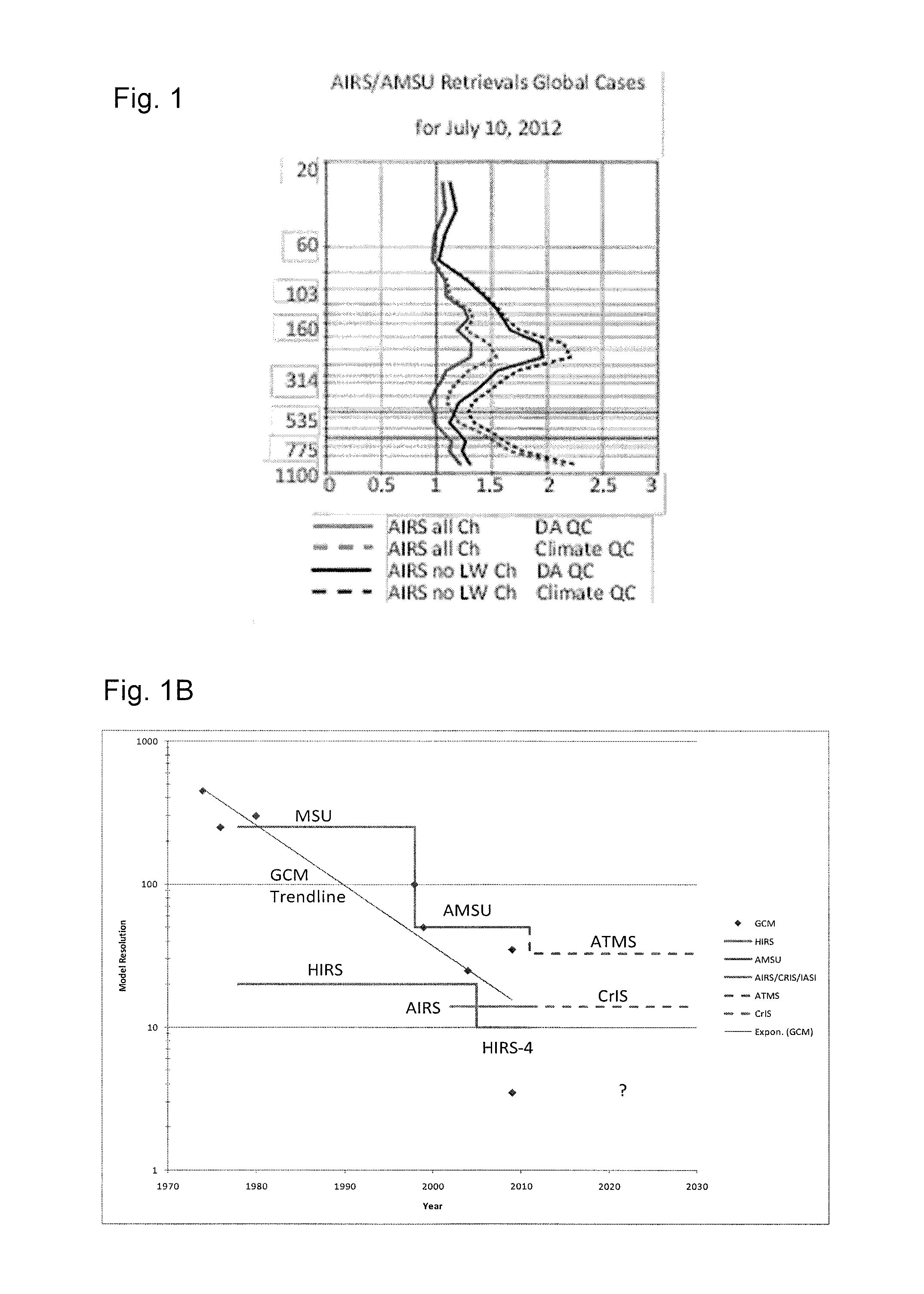
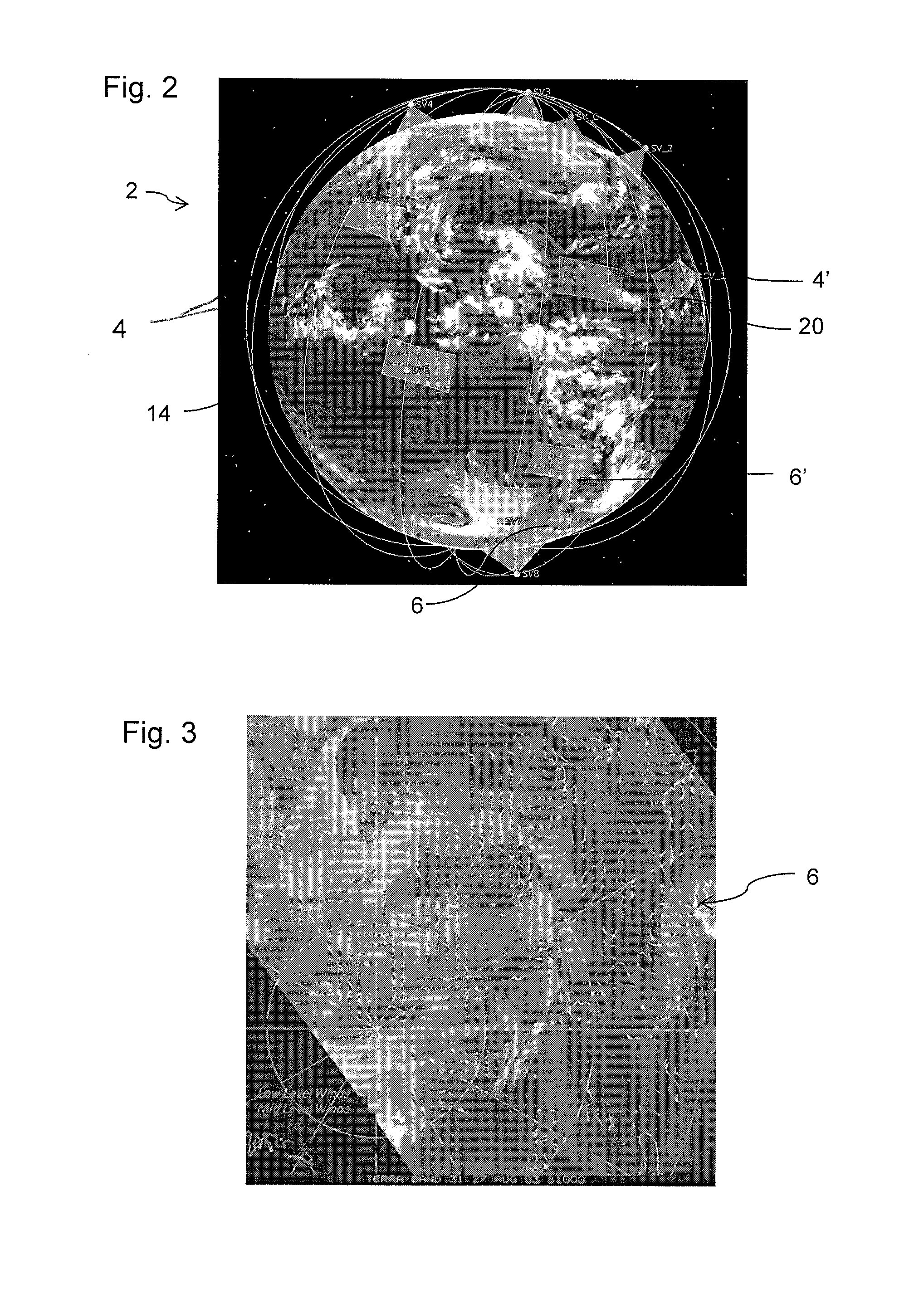
[0052]Turning now to FIG. 2, a brief description concerning the various satellite systems and constellations 4, of the system 2 of the present invention will now be briefly discussed. FIG. 1B is a schematic drawing showing temperature and humidity sounding constellations 4, according to one embodiment of the invention. A first constellation 4 comprises at least eight different separate micro-satellite 4′, which provide observations of the same area every 90 minutes. A second constellation 6, comprises at least three separate micro-satellite 6′ which provide three similar but separate observations of a region and each of the observations are...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com