Patents
Literature
182results about "Digital adaptive filters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
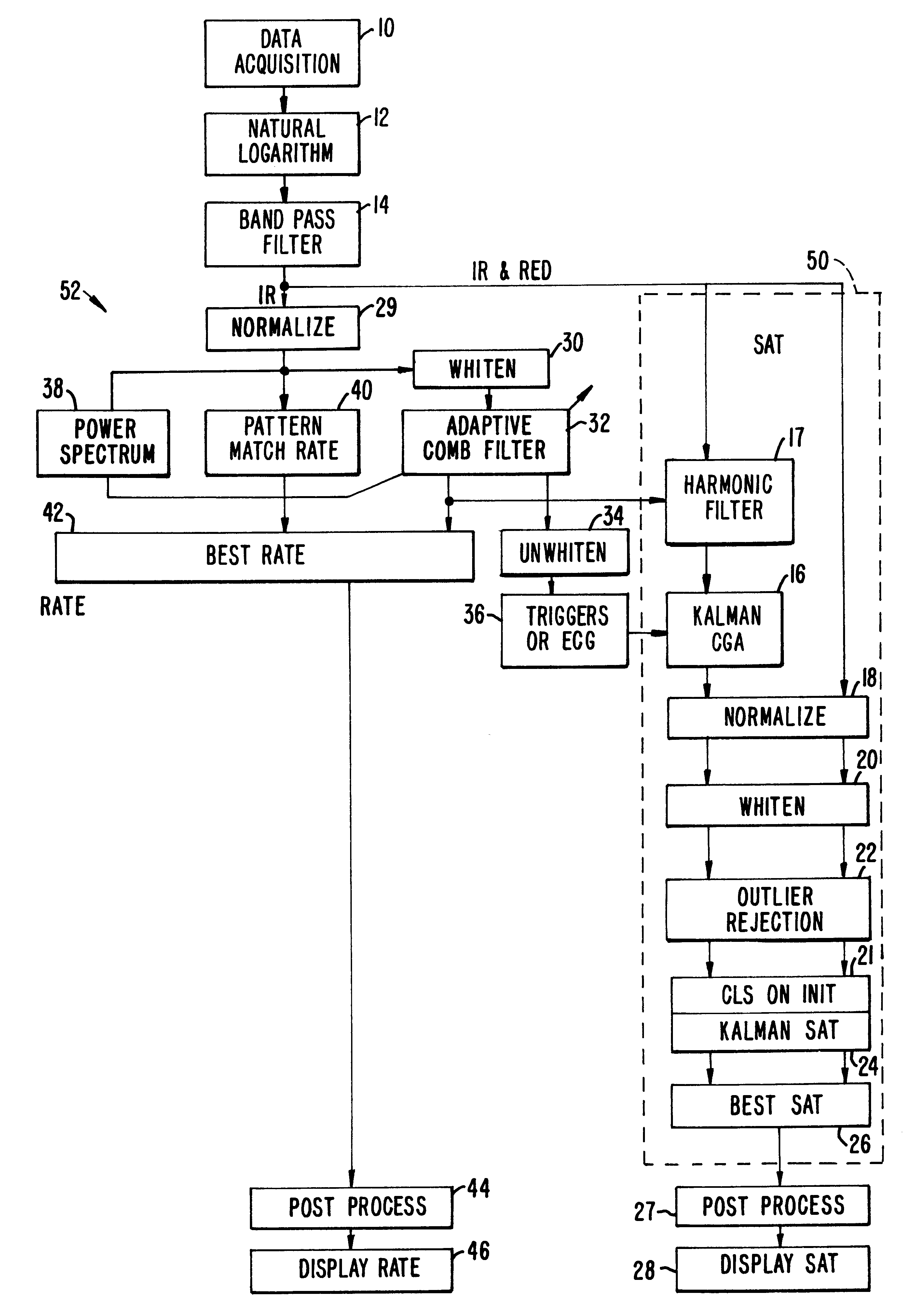
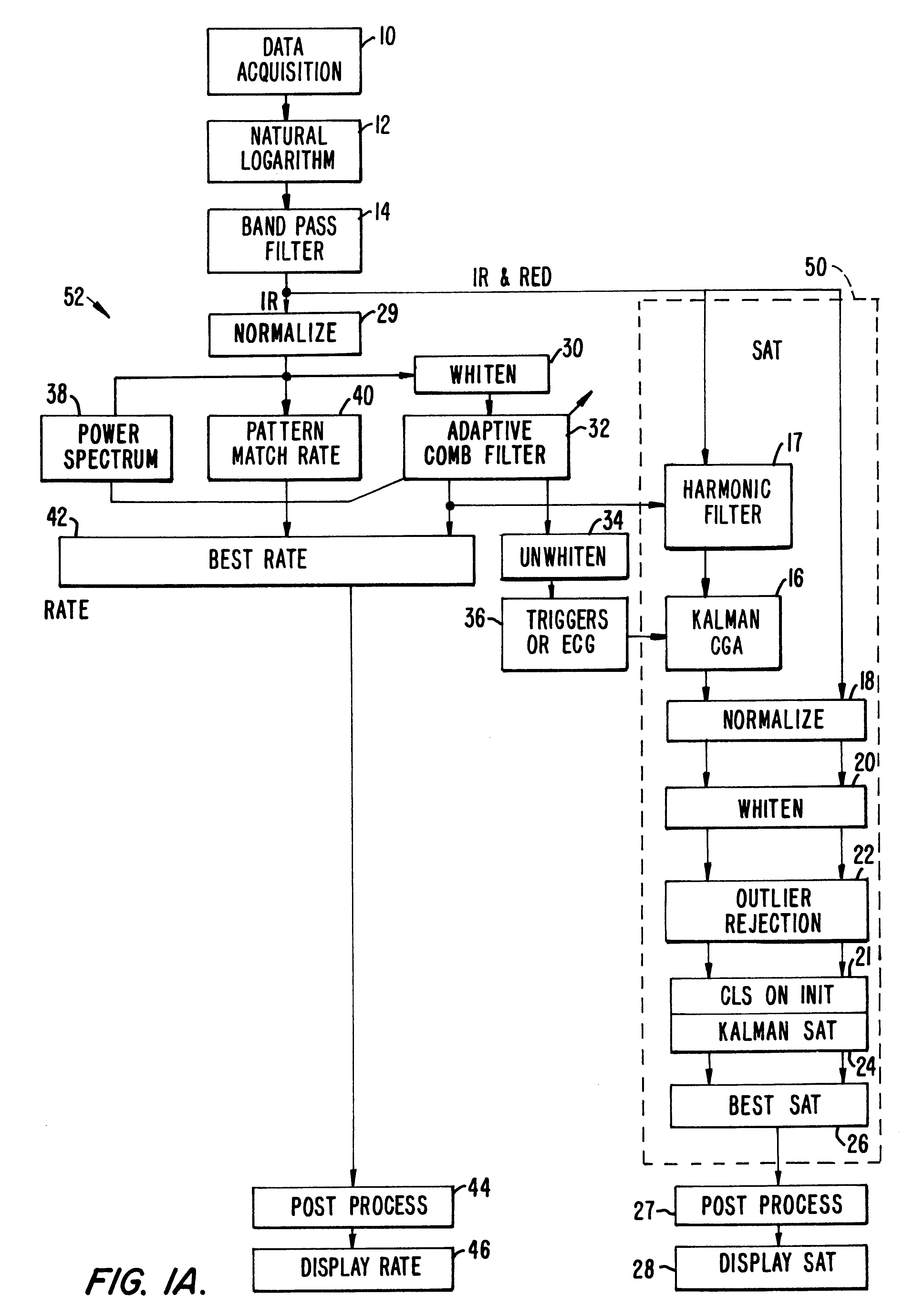
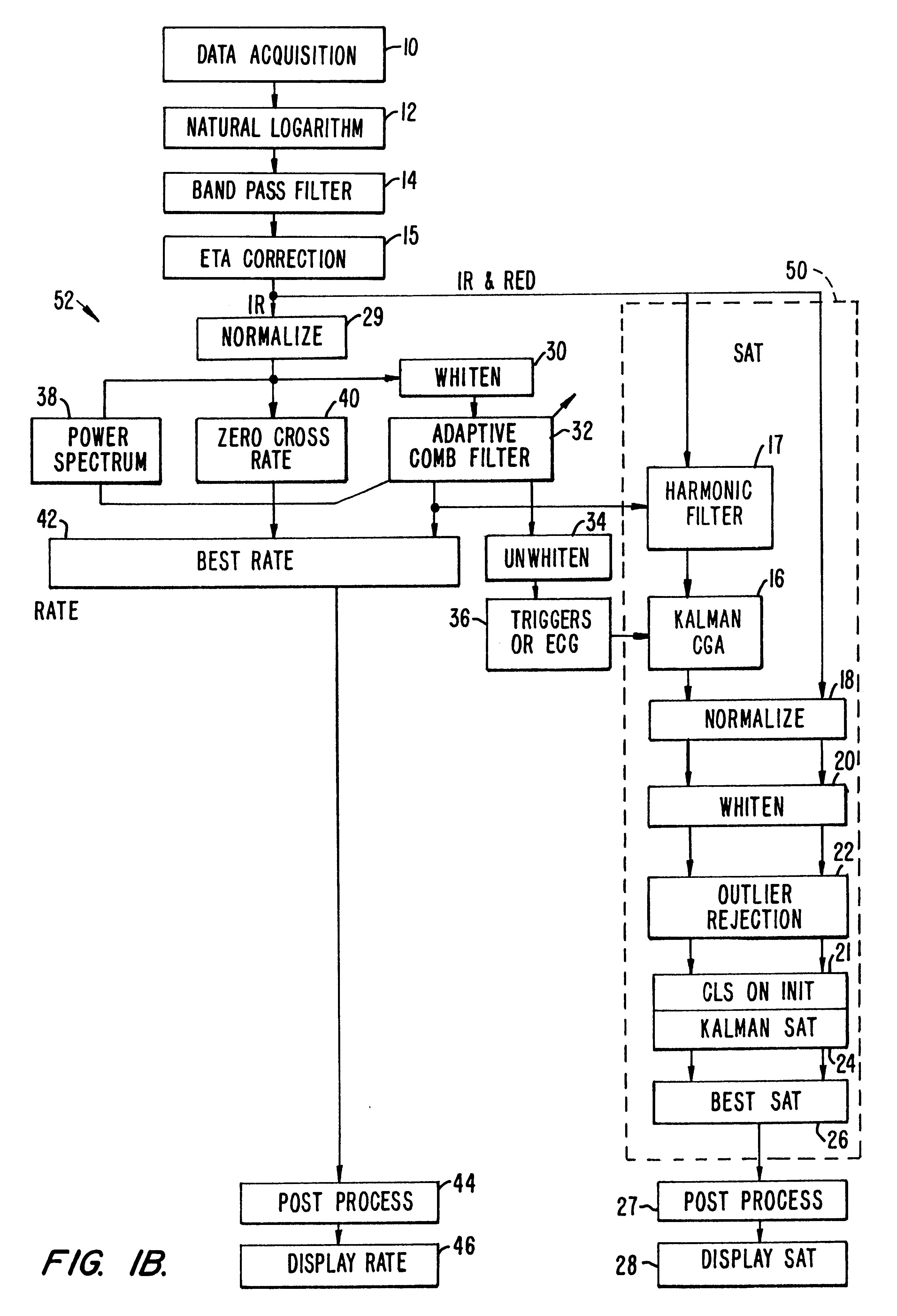
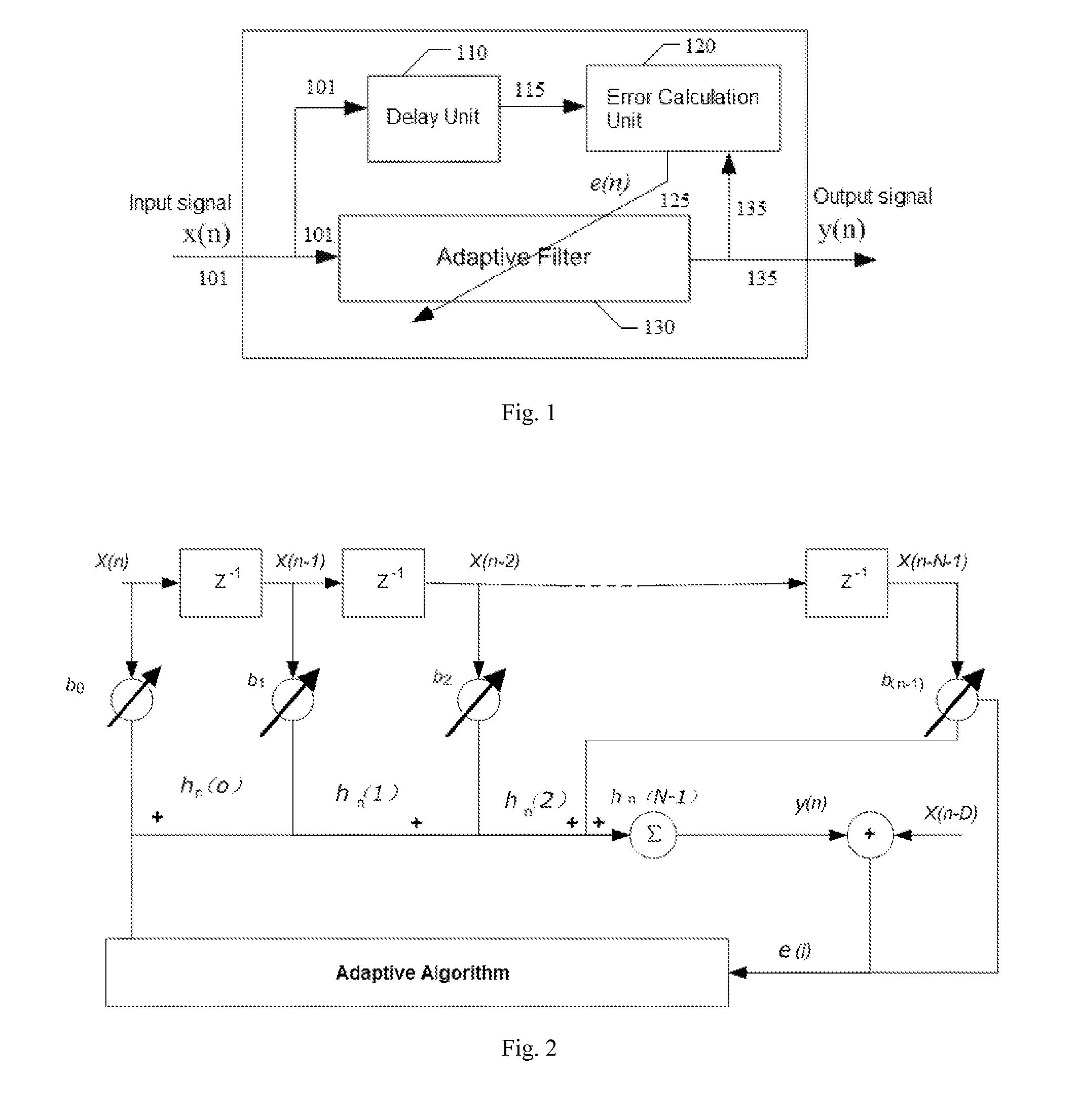
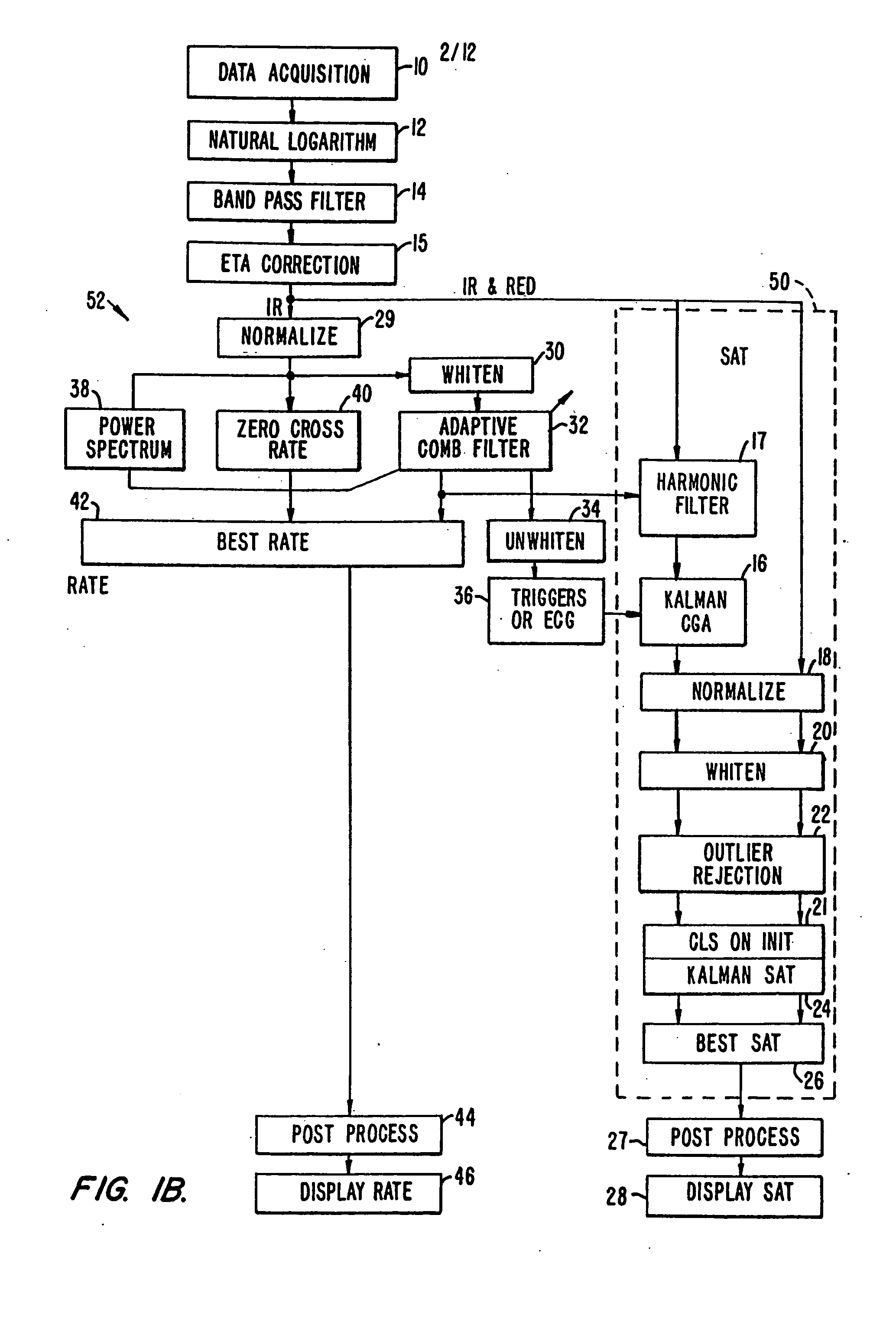
Method and apparatus for estimating physiological parameters using model-based adaptive filtering
InactiveUS6836679B2Reduce the impact of noiseDigital adaptive filtersDiagnostics using spectroscopySelf adaptiveEngineering
A method and apparatus for reducing the effects of noise on a system for measuring physiological parameters, such as, for example, a pulse oximeter. The method and apparatus of the invention take into account the physical limitations on various physiological parameters being monitored when weighting and averaging a series of measurements. Varying weights are assigned different measurements, measurements are rejected, and the averaging period is adjusted according to the reliability of the measurements. Similarly, calculated values derived from analyzing the measurements are also assigned varying weights and averaged over adjustable periods. More specifically, a general class of filters such as, for example, Kalman filters, is employed in processing the measurements and calculated values. The filters use mathematical models which describe how the physiological parameters change in time, and how these parameters relate to measurement in a noisy environment. The filters adaptively modify a set of averaging weights to optimally estimate the physiological parameters.
Owner:NELL COR PURITAN BENNETT INC (US)
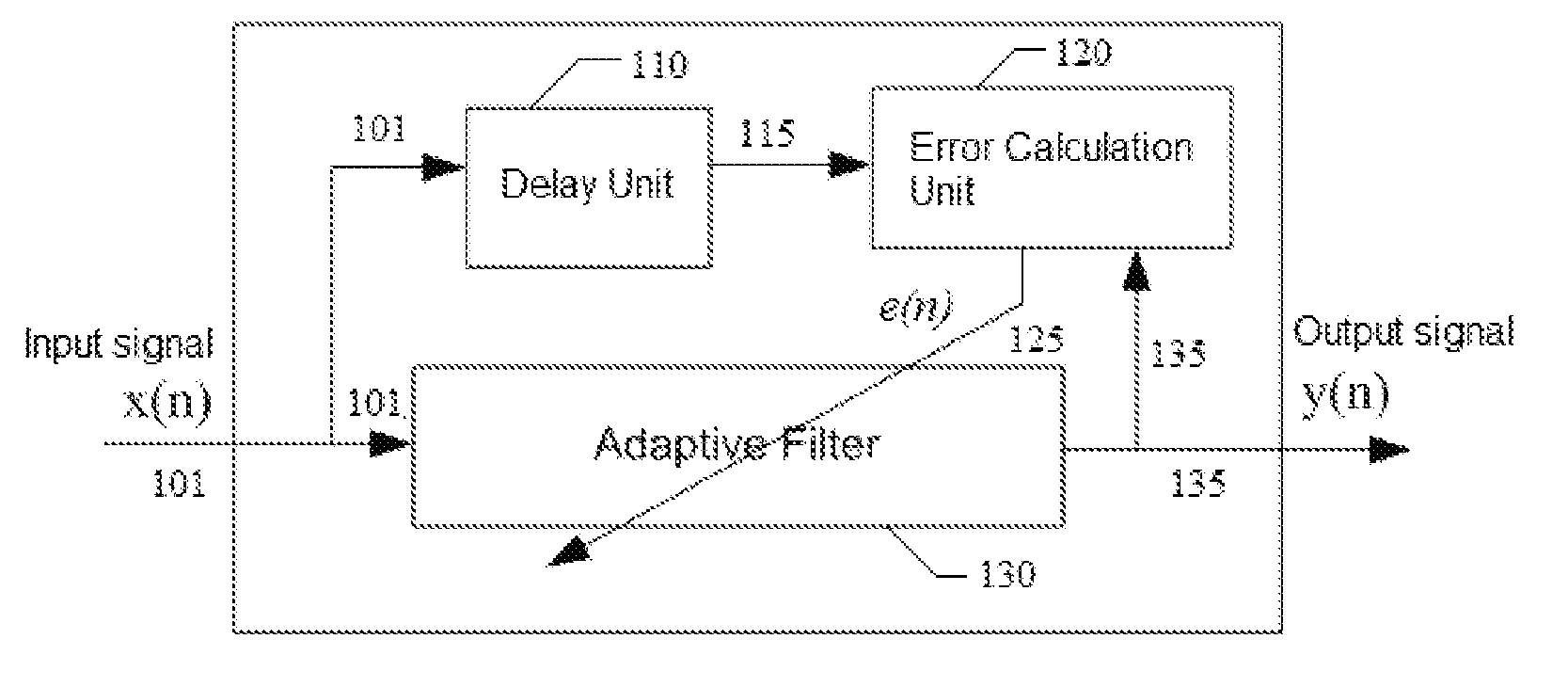
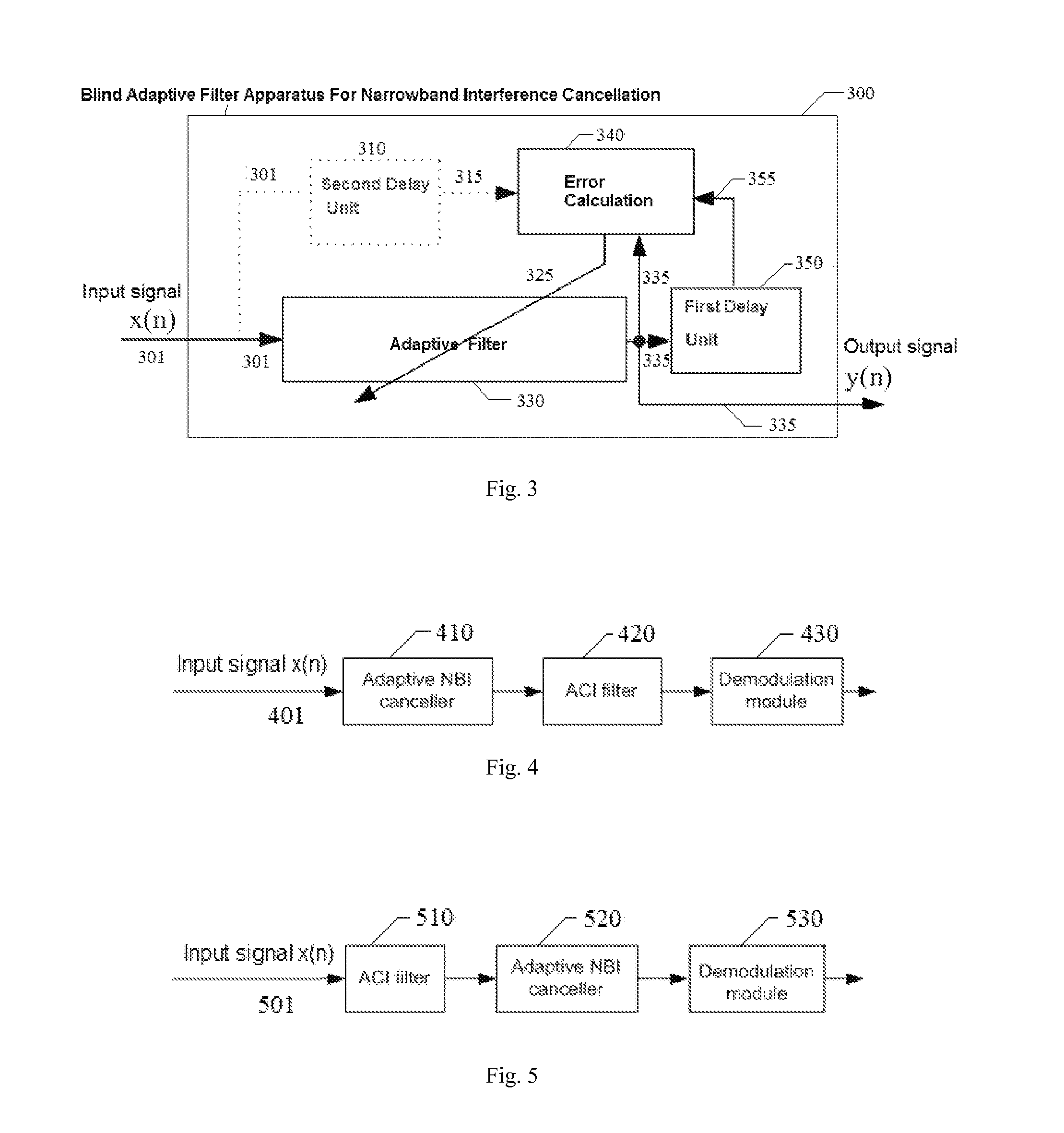
Blind adaptive filter for narrowband interference cancellation
ActiveUS20110305306A1Wide applicationError preventionDigital adaptive filtersSelf adaptiveSweep rate
The present invention relates to a blind adaptive filter for narrowband interference cancellation, which includes an adaptive filter, a delay unit coupled to the adaptive filter for generating a delayed signal with a predetermined delay length from the output signal of the adaptive filter, and an error calculation unit coupled to the adaptive filter and the delay unit. The error calculation unit compares the output signal from the adaptive filter and the delayed signal from the delay unit to extract error information, and feedback the first error information to the adaptive filter. The first error information is formed of a transfer function including a number of coefficients, and used to adjust the adaptive filter and remove interference in the next input signal. The disclosed technique is also applicable in wideband receivers, as well as resisting multiple strong narrowband interferences having a frequency sweep rate of tens of milliseconds.
Owner:MONTAGE TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
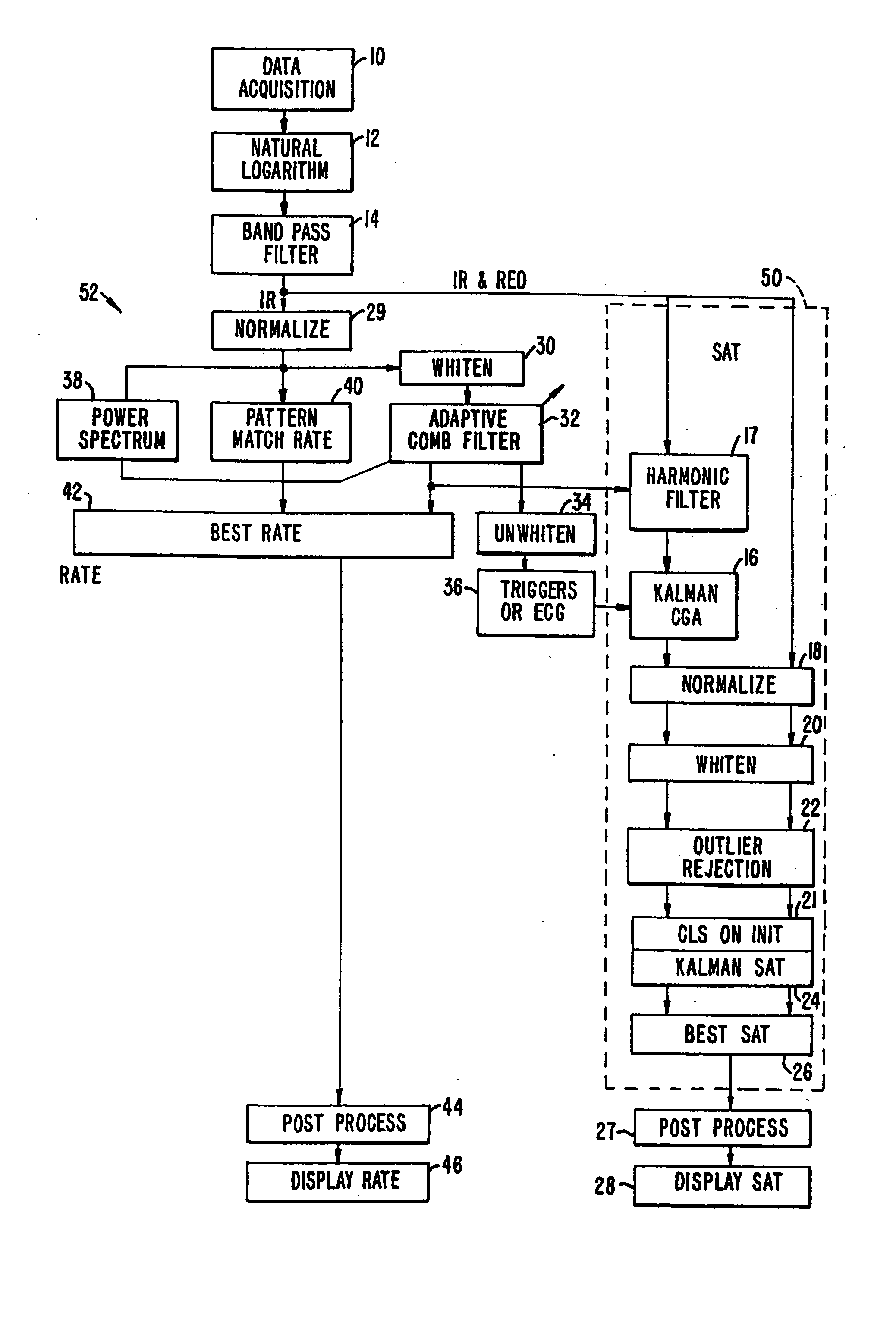
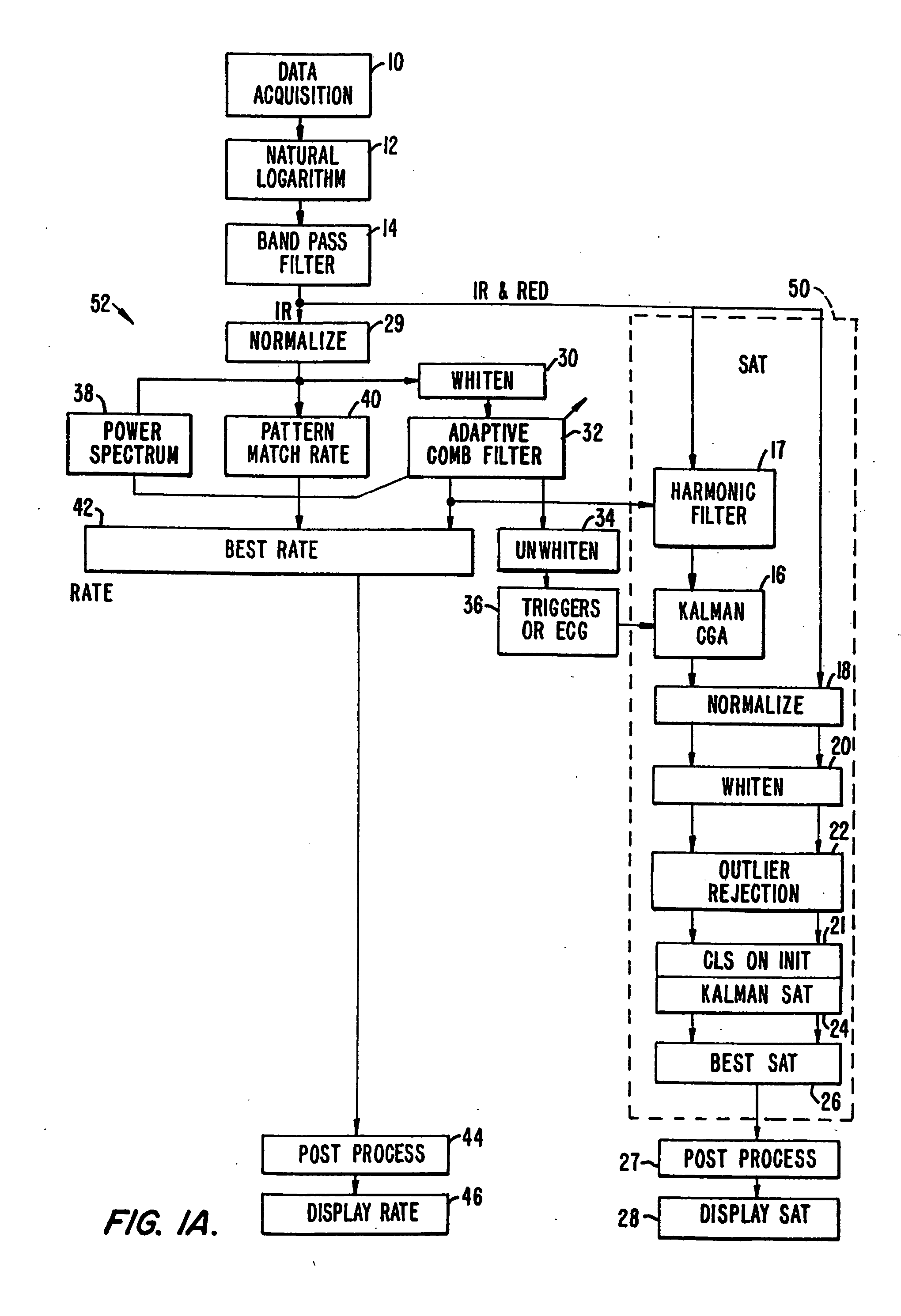
Method and apparatus for estimating a physiological parameter
InactiveUS20050085735A1Reduce impactGood estimateDigital adaptive filtersDiagnostics using spectroscopyFrequency spectrumPulse rate
In a physiological monitor, a method and an apparatus for determining a patient's pulse rate using data corresponding to a plurality of wavelengths of electromagnetic energy transmitted through the tissue of the patient. The method includes tracking the pulse rate in the data using an adaptive comb filter, the data having signal portions corresponding to the pulse rate and signal portions corresponding to noise, periodically calculating a frequency power spectrum of one of the wavelengths, and using the frequency power spectrum in a pulse rate calculator to determine the pulse rate or to verify the pulse rate calculated by the pulse rate calculator.
Owner:NELLCOR PURITAN BENNETT LLC
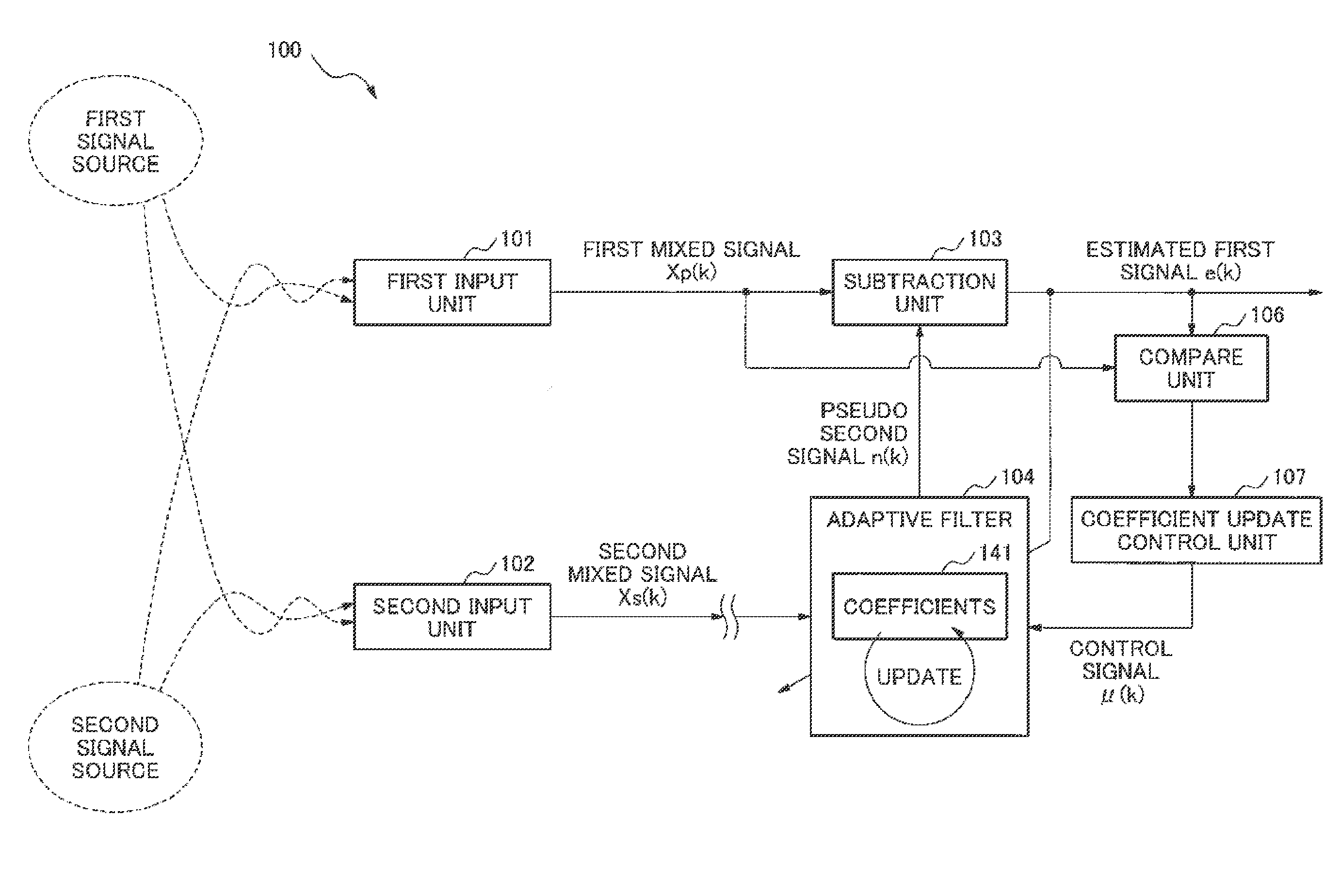
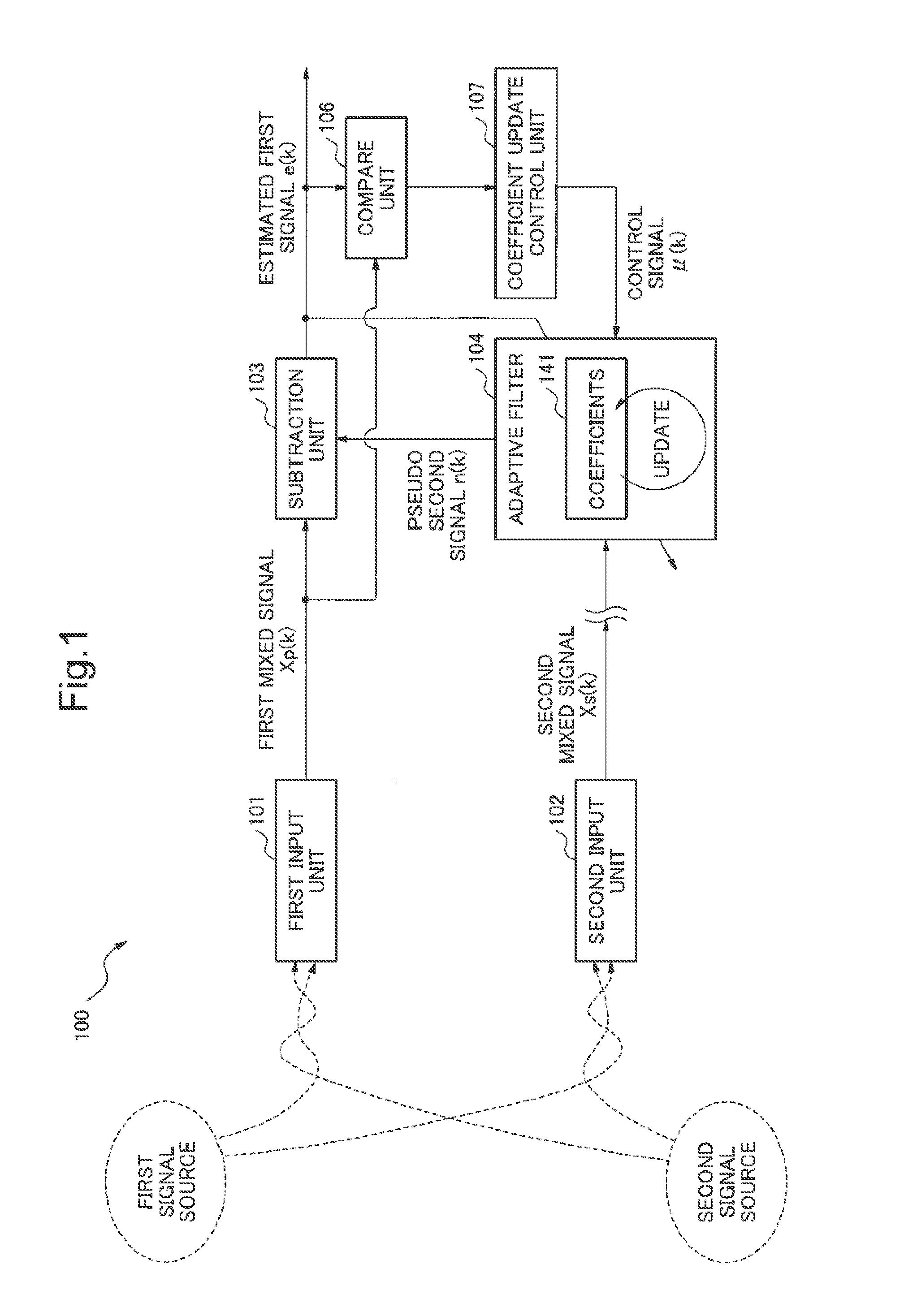
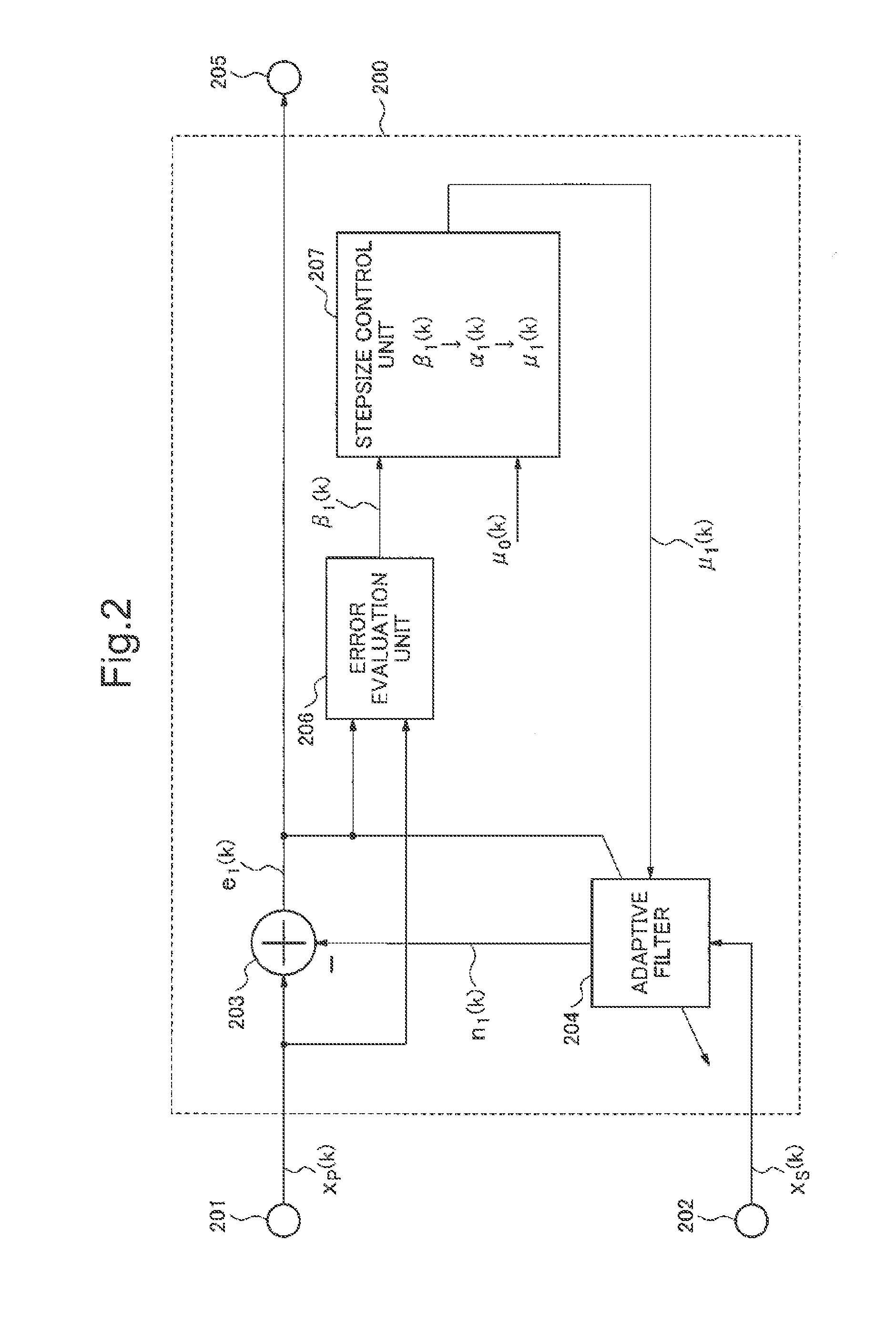
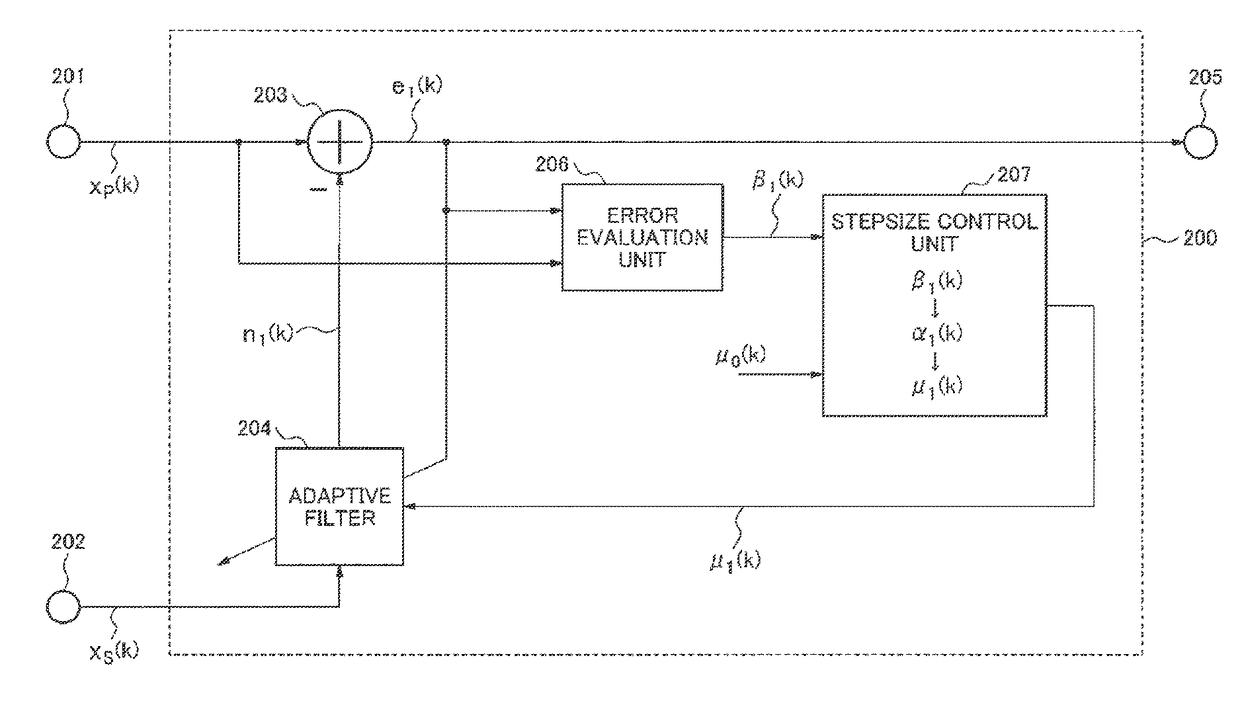
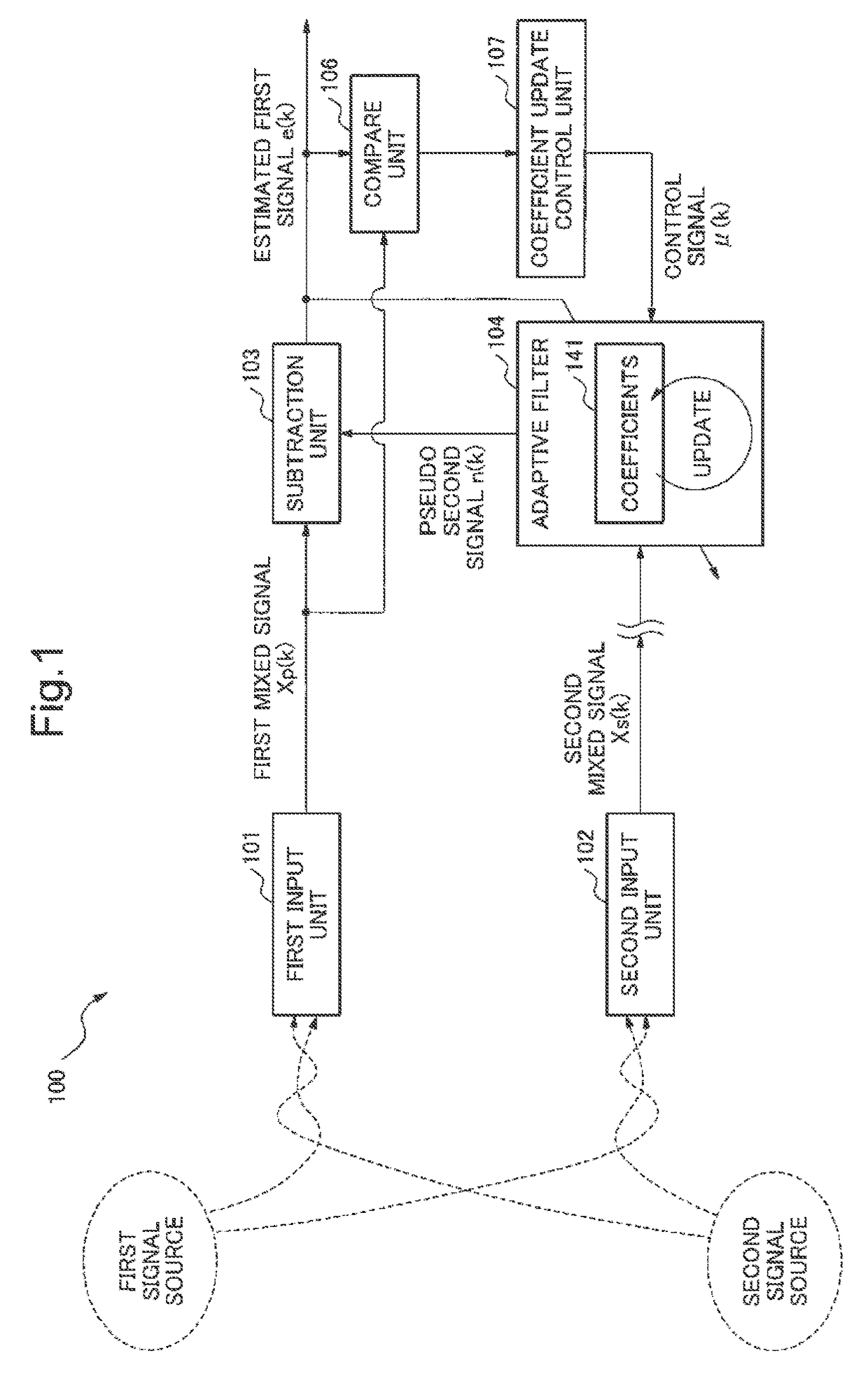
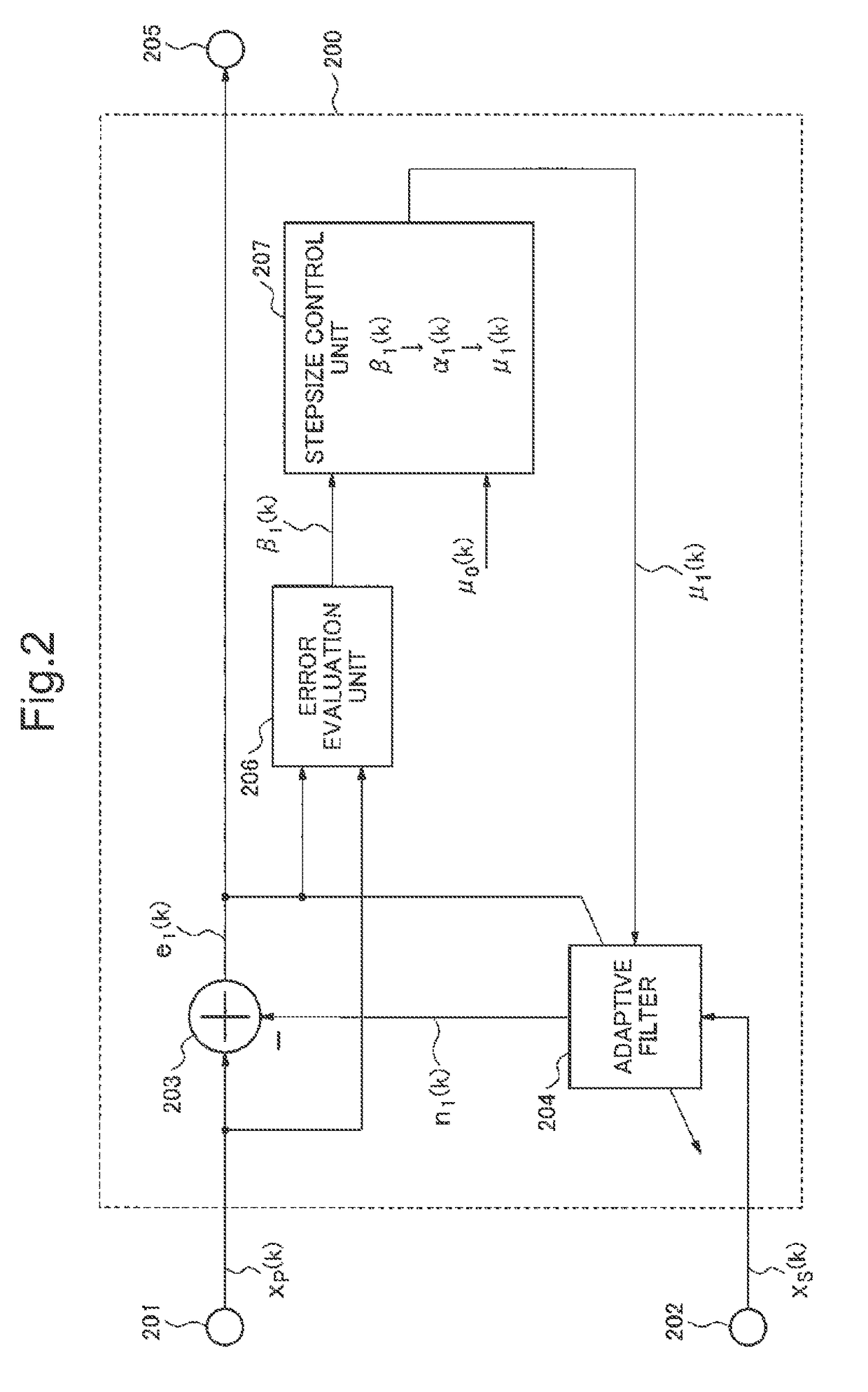
Signal processing device, signal processing method and signal processing program
ActiveUS20130191119A1Reduce processing costsWithout delayInterconnection arrangementsDigital adaptive filtersAdaptive filterLow distortion
From a mixed signal in which a first signal and a second signal are mixed, the second signal is removed at low processing cost and without delay. As a result, an estimated first signal which has low residue of the second signal and low distortion is obtained.An estimated first signal is generated by subtracting a pseudo second signal which is estimated to be mixed in a first mixed signal in which a first signal and a second signal are mixed from the first mixed signal. The pseudo second signal is obtained by a first adaptive filter using a second mixed signal in which the first signal and the second signal are mixed in a different proportion from the first mixed signal. A coefficient update amount of the first adaptive filter is made smaller as compared with a case when the estimated first signal is smaller than the first mixed signal, in case the estimated first signal is larger than the first mixed signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
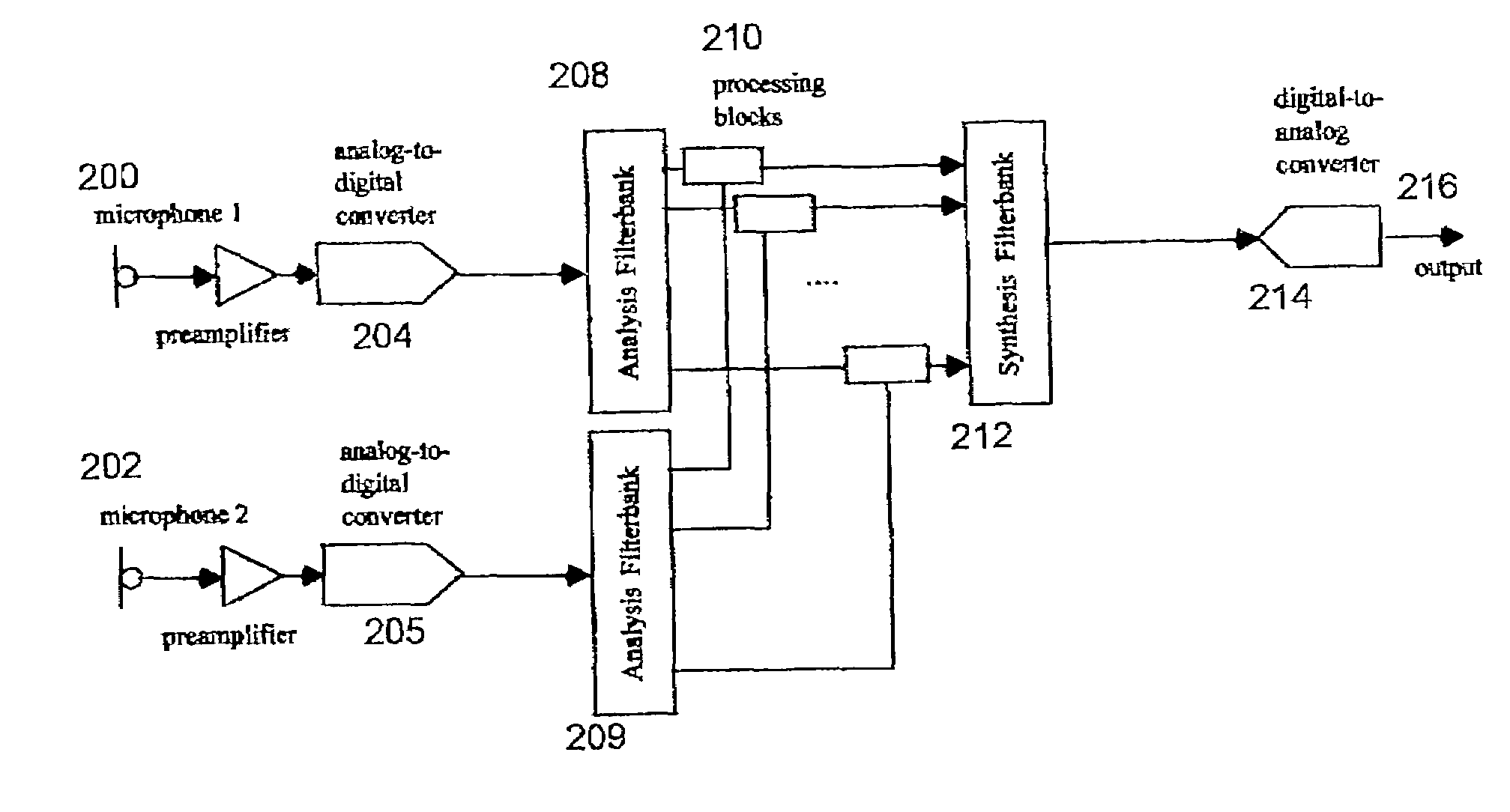
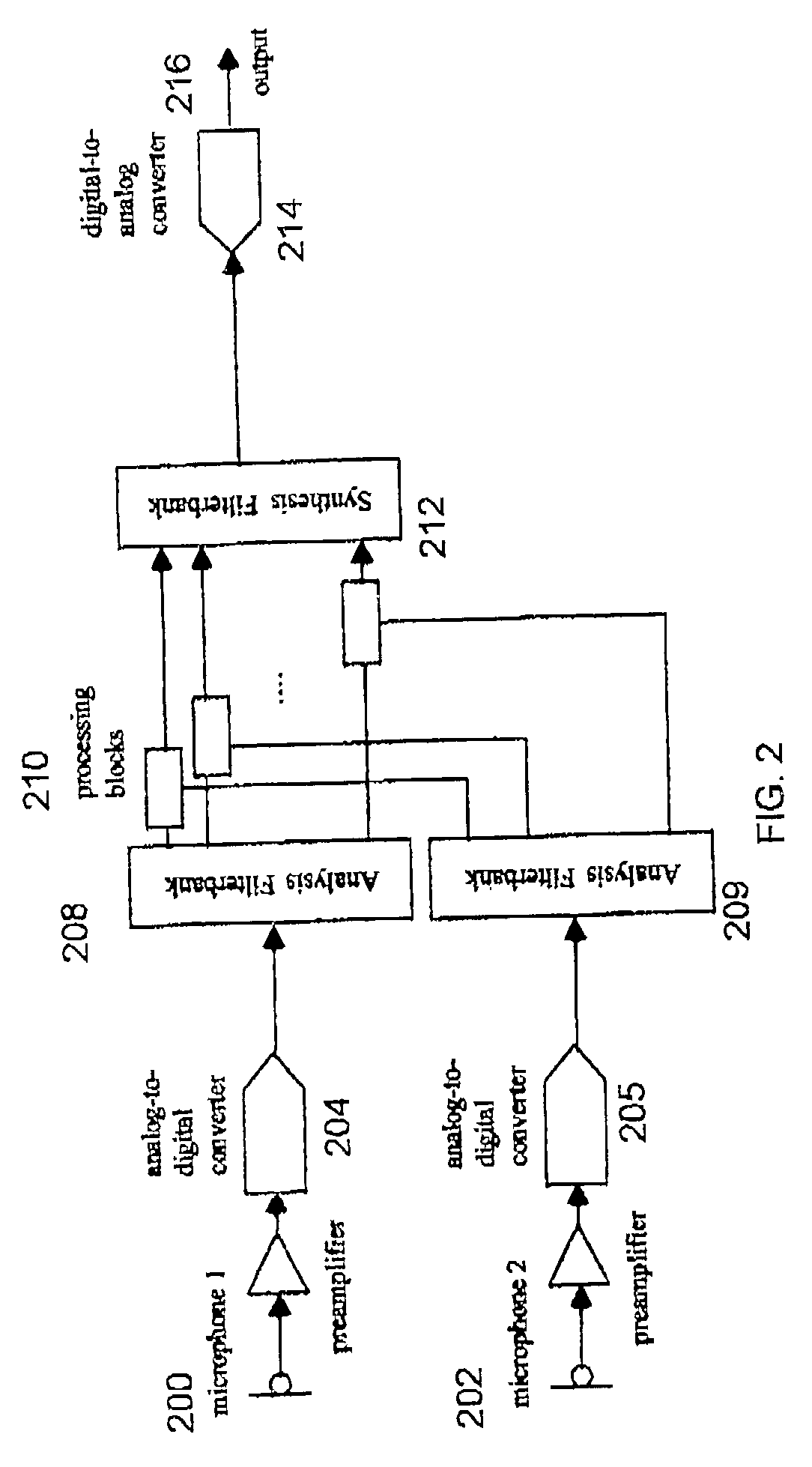
Sub-band adaptive signal processing in an oversampled filterbank
ActiveUS7110554B2Fast convergenceImprove efficiencyEar treatmentDigital technique networkTime domainSignal quality
An adaptive signal processing system for improving a quality of a signal. The system includes an analysis filterbank for transforming a primary information signal in time domain into oversampled sub-band primary signals in frequency domain and an analysis filterbank for transforming a reference signal in time domain into oversampled sub-band reference signals. Sub-band processing circuits process the signals output from the filterbanks to improve a quality of an output signal. A synthesis filterbank can combine the outputs of the sub-band processing circuits to generate the output signal.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Parallel decimator adaptive filter and method for all-rate gigabit-per-second modems
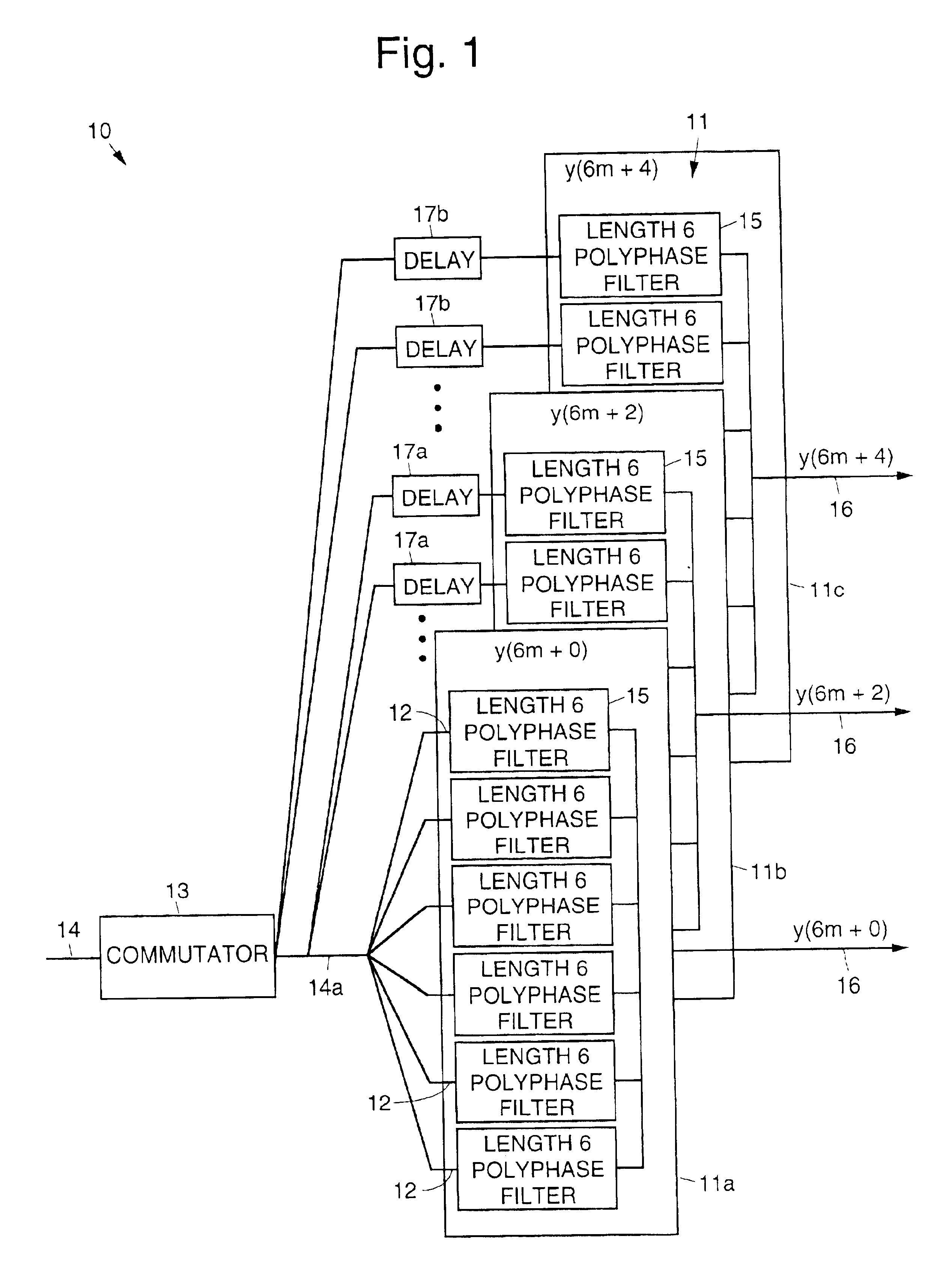
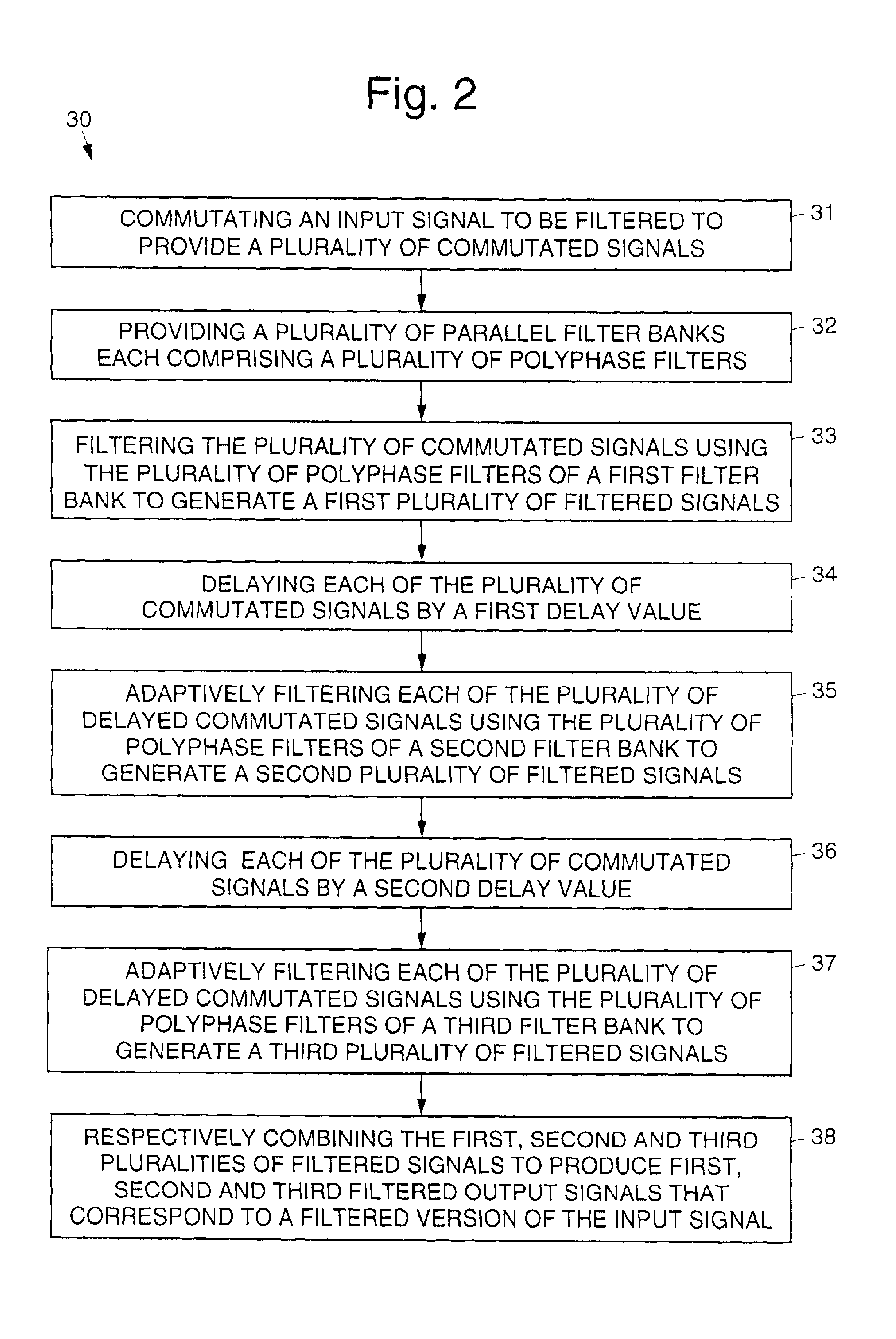
InactiveUS6889238B2Extend effective filter lengthEfficient productionDigital adaptive filtersComplex mathematical operationsHigh rateAdaptive filter
Parallel adaptive filters and filtering methods that enable processing of an input signal in a circuit that has an clock speed many times slower than the input rate of the input signal that is processed. A polyphase decimator structure processes a data stream requiring a low pass filtered bandlimited (low-rate) output that is used for high-rate output structures. The filters and methods break an input data stream into parallel paths that efficiently produce a bandlimited (decimated, low-rate) filtered output. Each of the parallel paths is processed at a decimated rate to provide a filtered output signals corresponding to a filtered version of the input signal.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
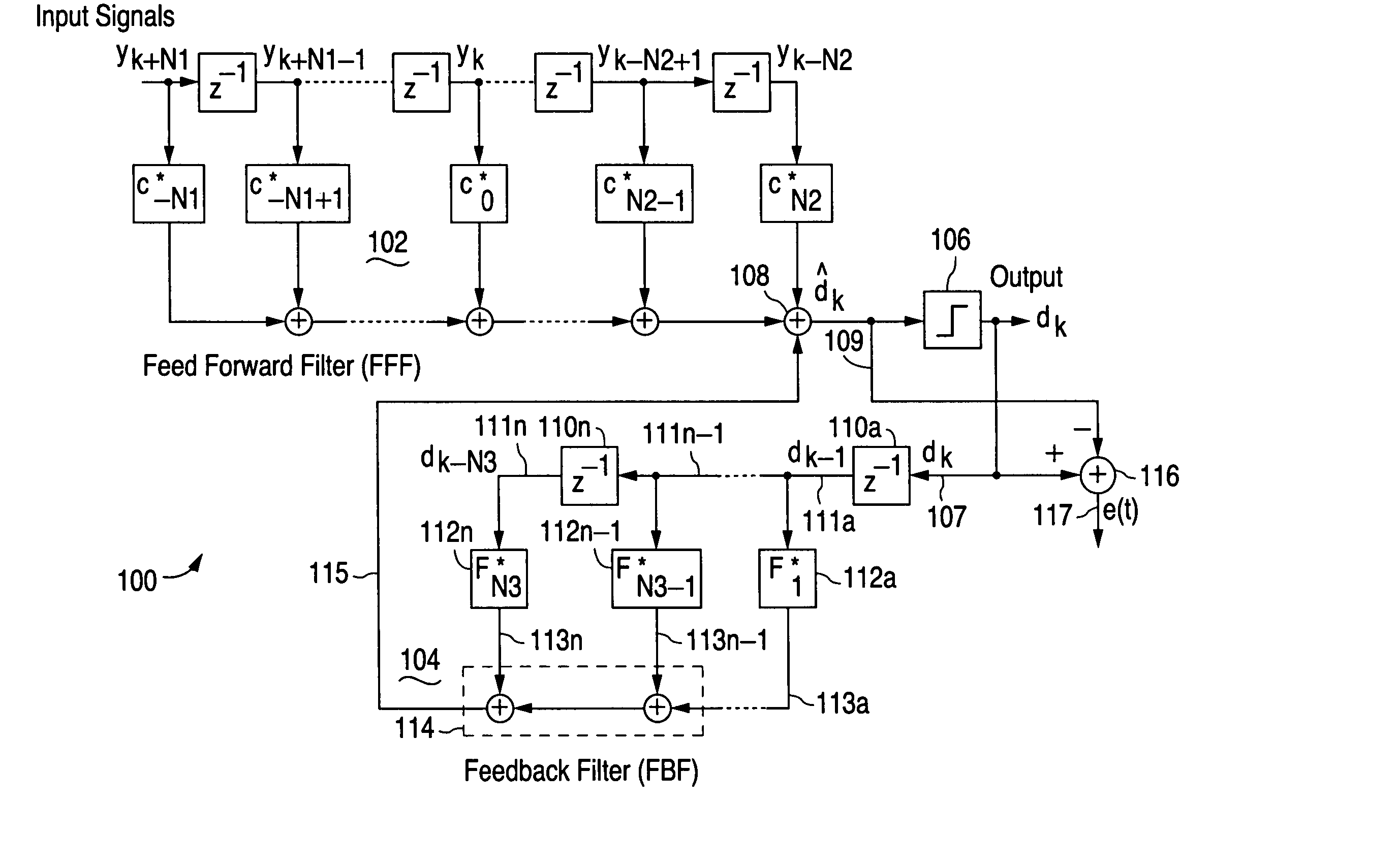
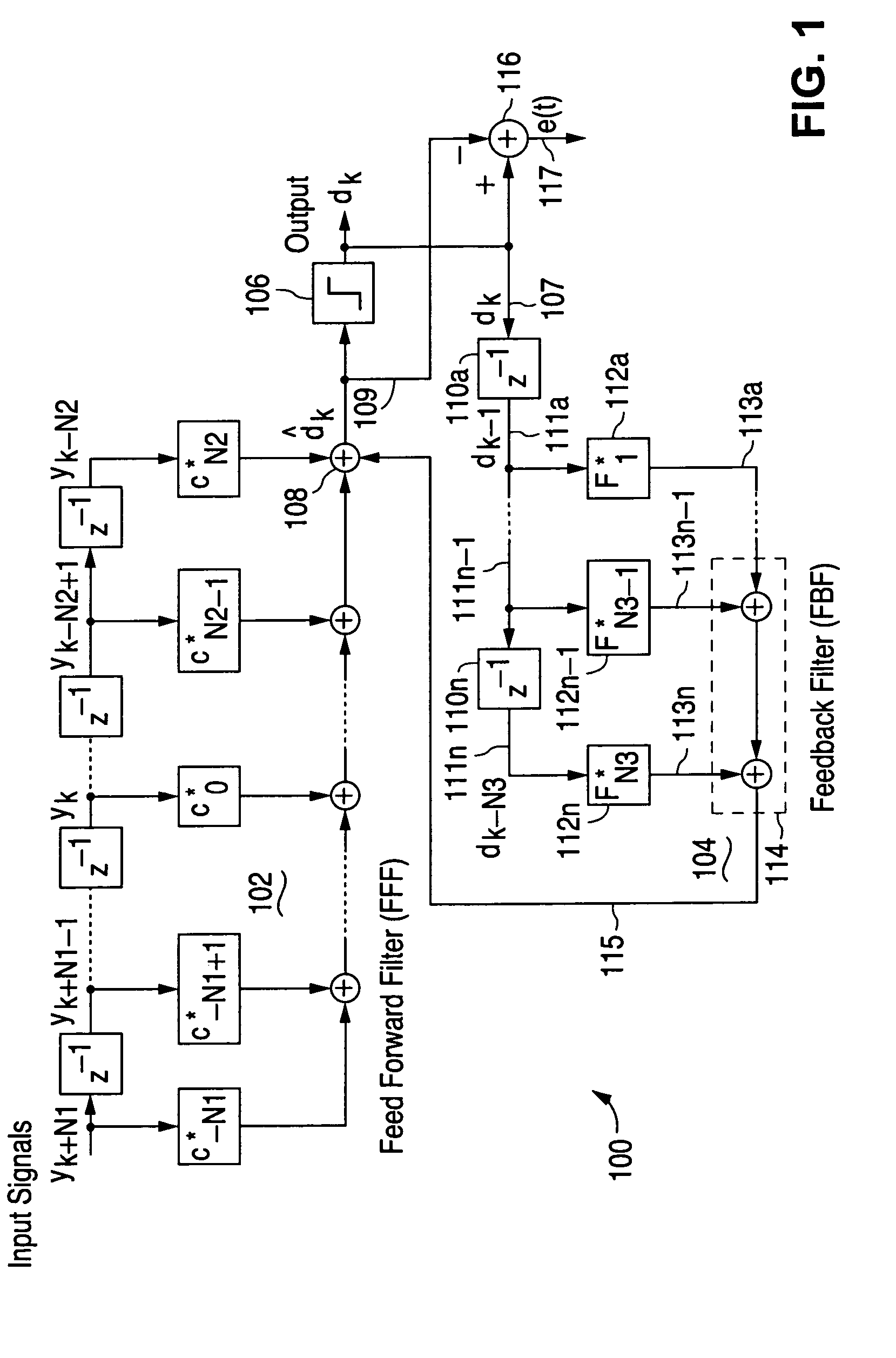
Decision feedback equalizer with dynamic feedback control
InactiveUS20050190832A1Promote recoveryMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsData signalFeedback control
A decision feedback equalizer with dynamic feedback control for use in an adaptive signal equalizer. Timing within the decision feedback loop is dynamically controlled to optimize recovery of the data signal by the output signal slicer.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
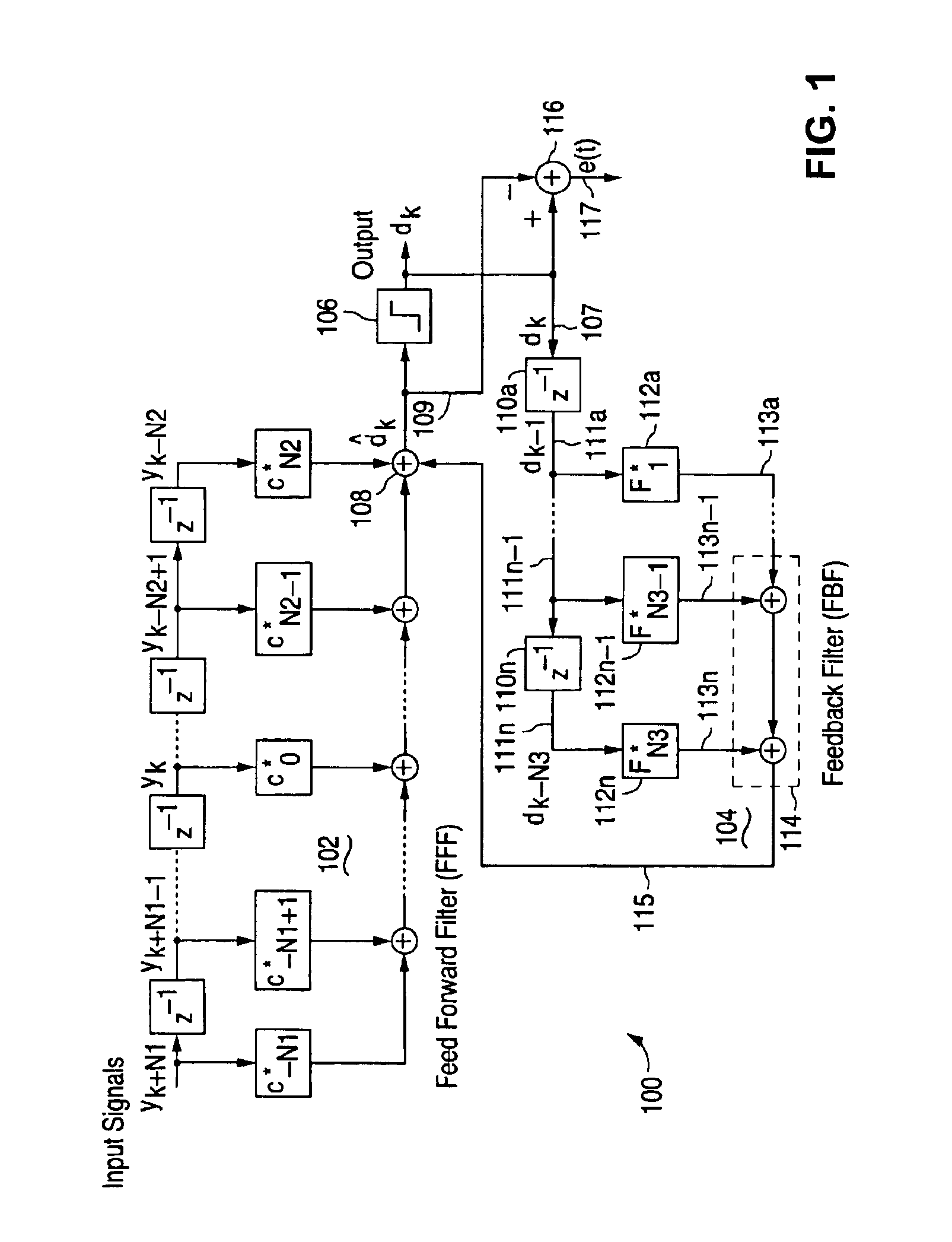
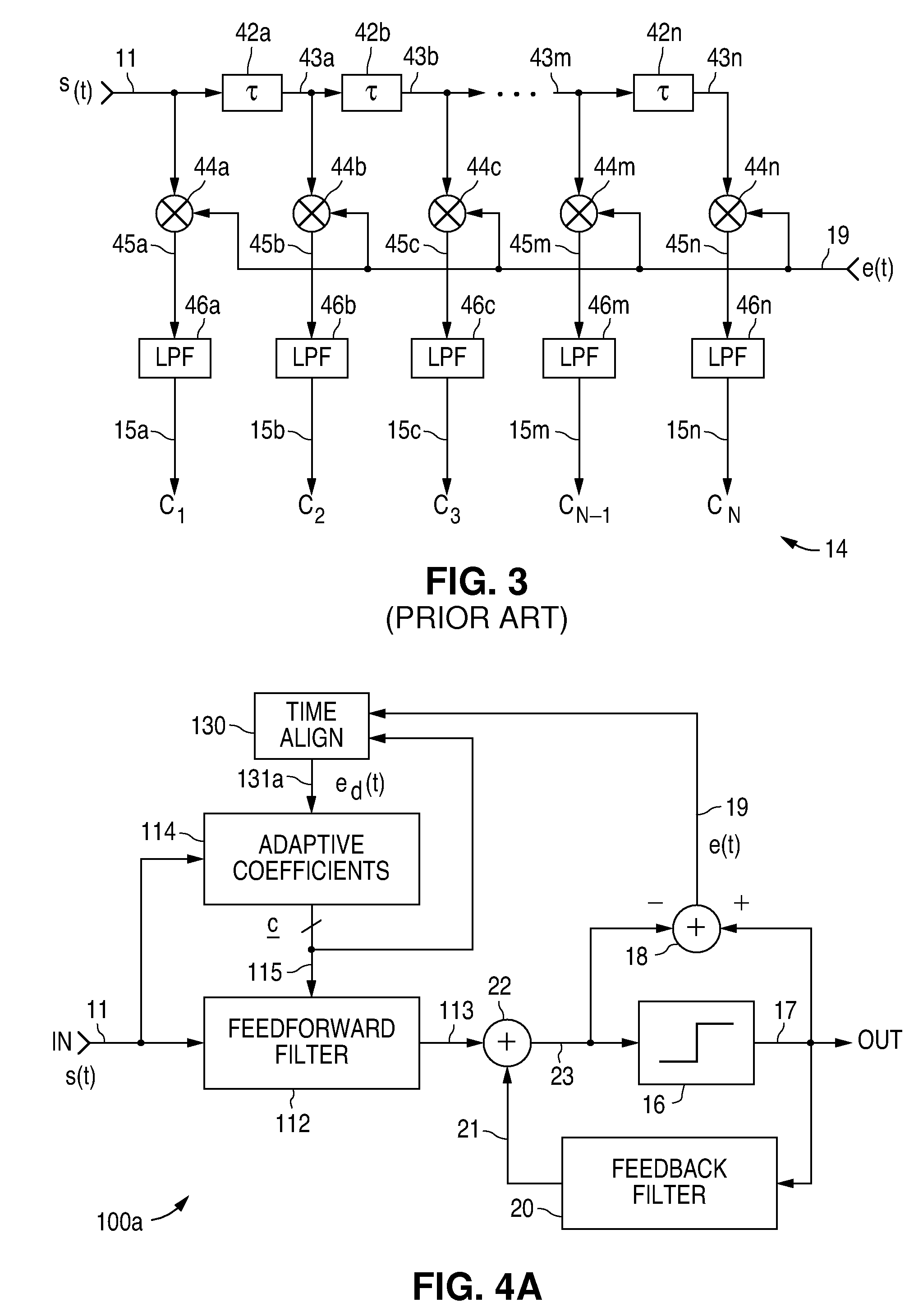
Digital filter adaptively learning filter coefficient
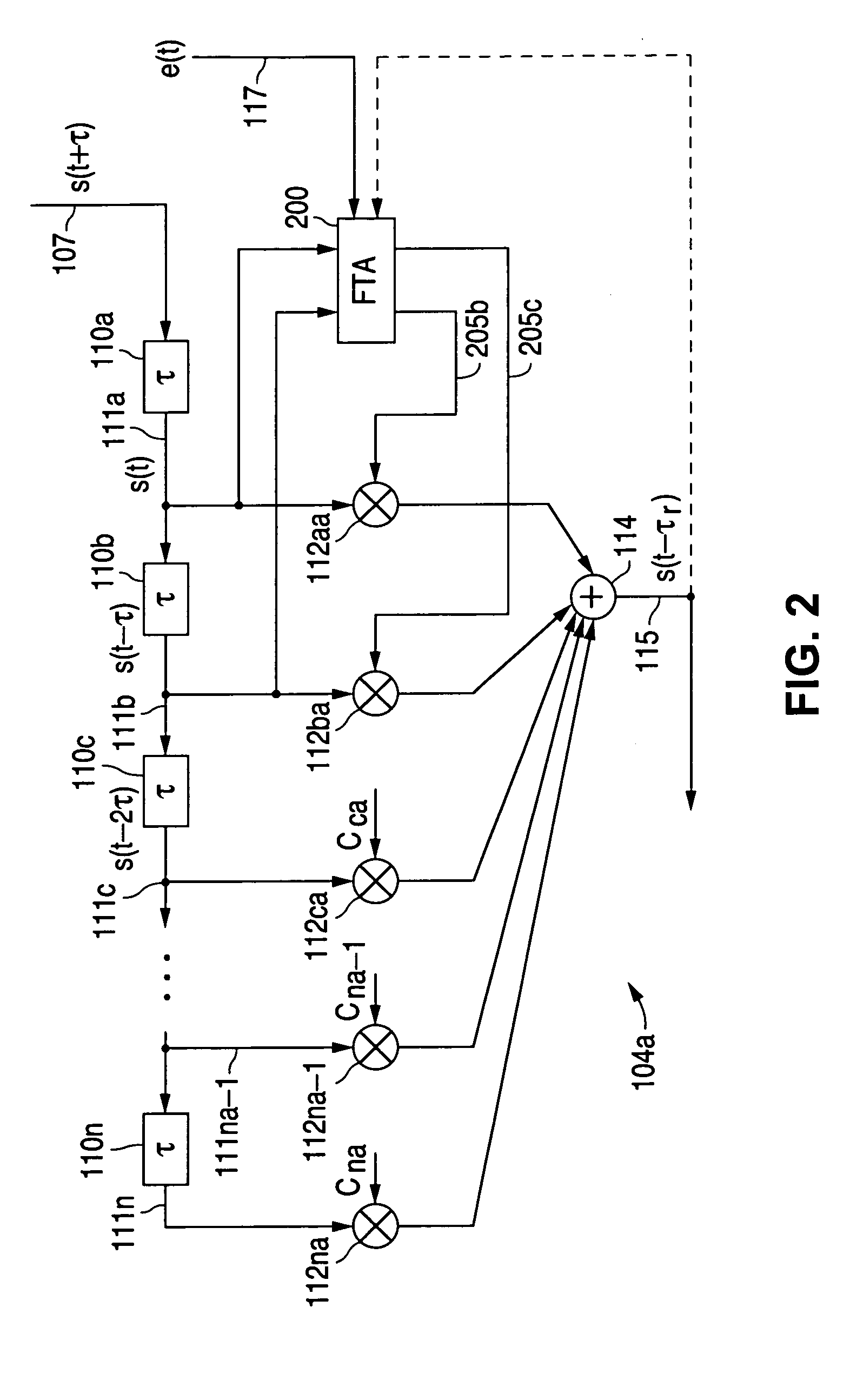
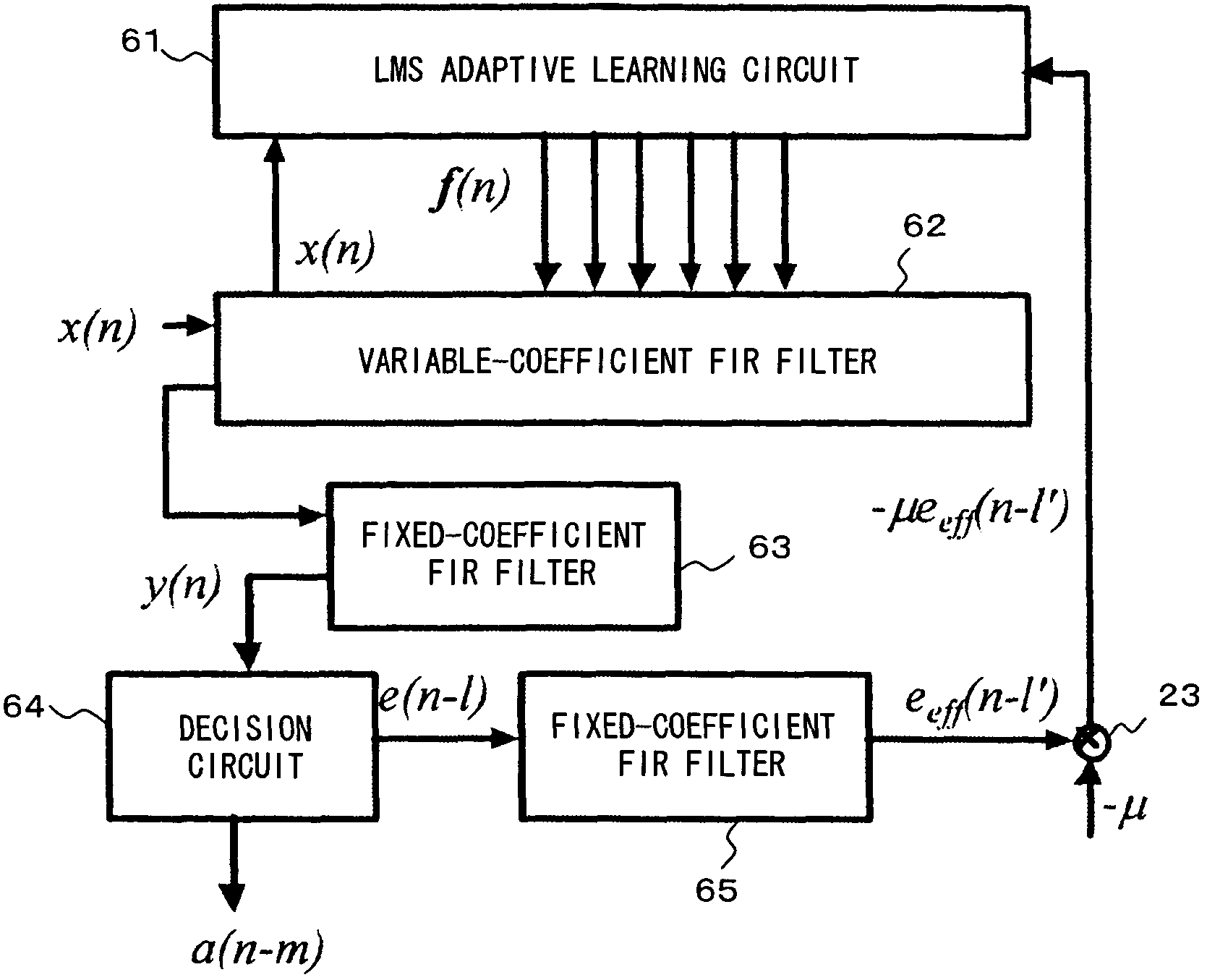
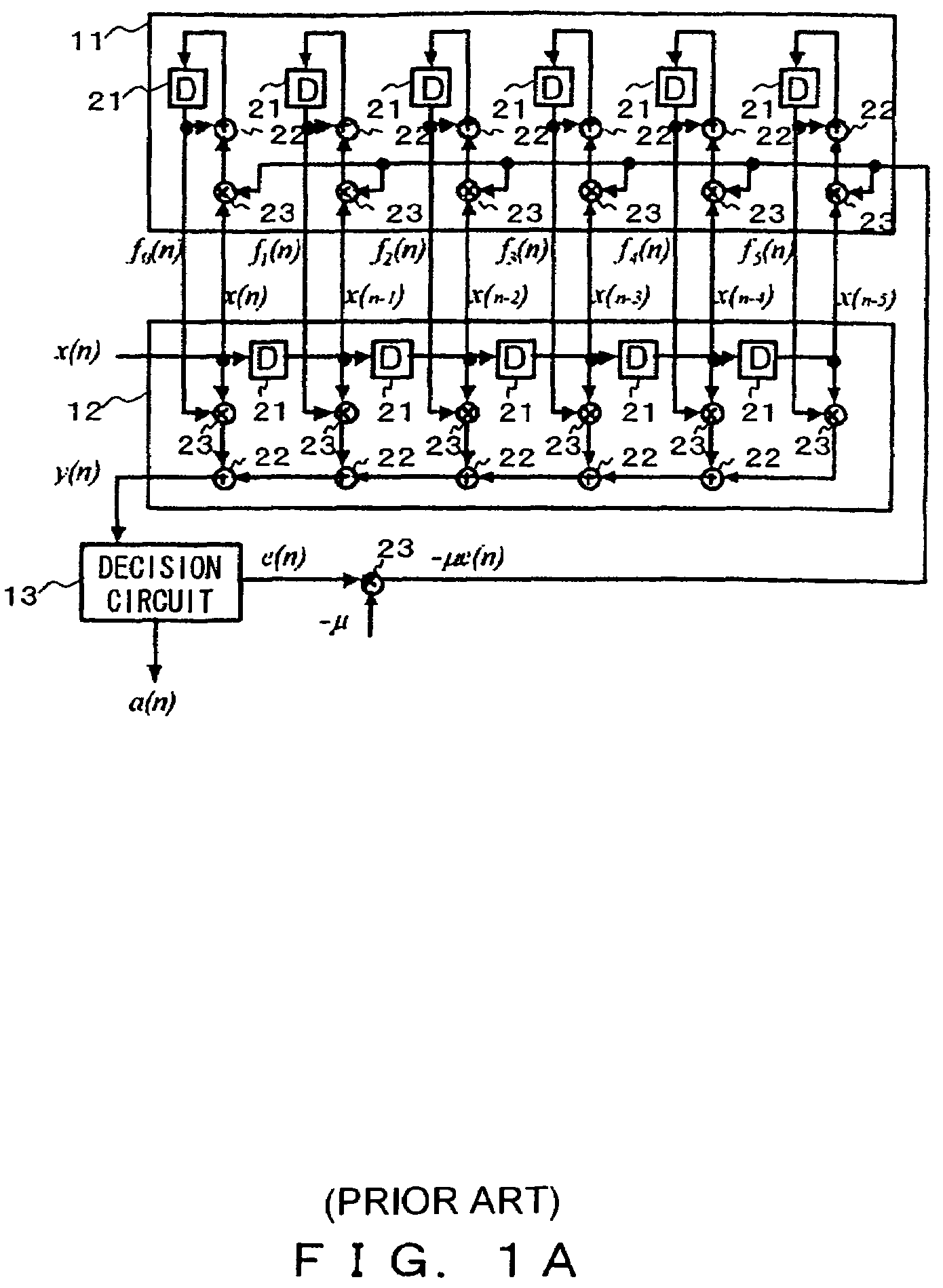
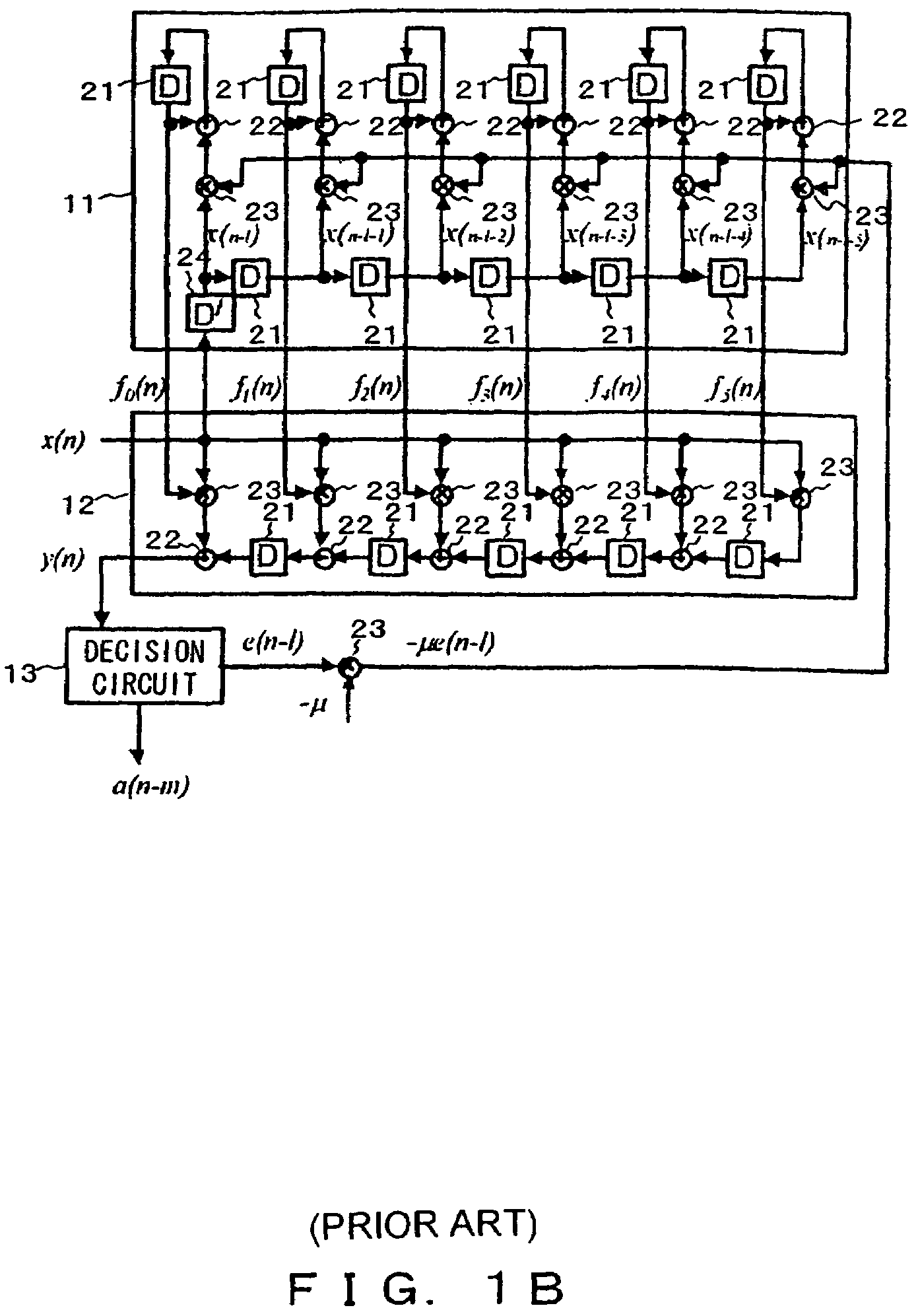
InactiveUS7421017B2Good coefficientMultiple-port networksDigital technique networkTarget signalLinear filter
A linear filter feeds back an error signal generated using the output of an adaptive filter to a learning circuit. The learning circuit learns the coefficients of the adaptive filter using the error signal. The coefficients of the linear filter are determined depending on the generation method of a target signal for error minimization. In a signal interpolation type timing recovery digital filter, the coefficients of an inverse interpolation filter are determined in such a way as to minimize an error of a signal after interpolation.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Digital adaptive equalizer for T1/E1 long haul transceiver
InactiveUS6980592B1Exact matchMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsFinite impulse responseIir filtering
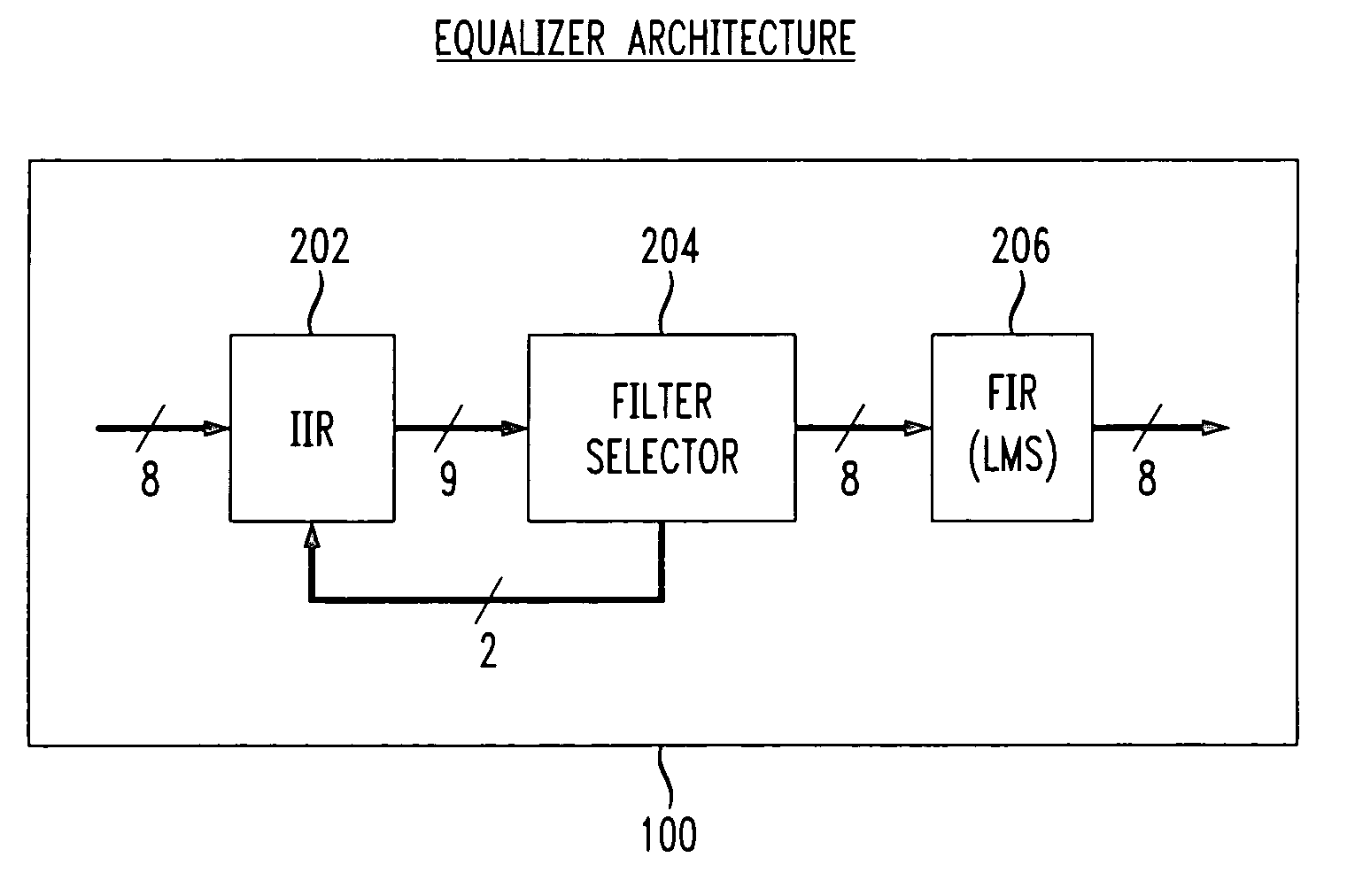
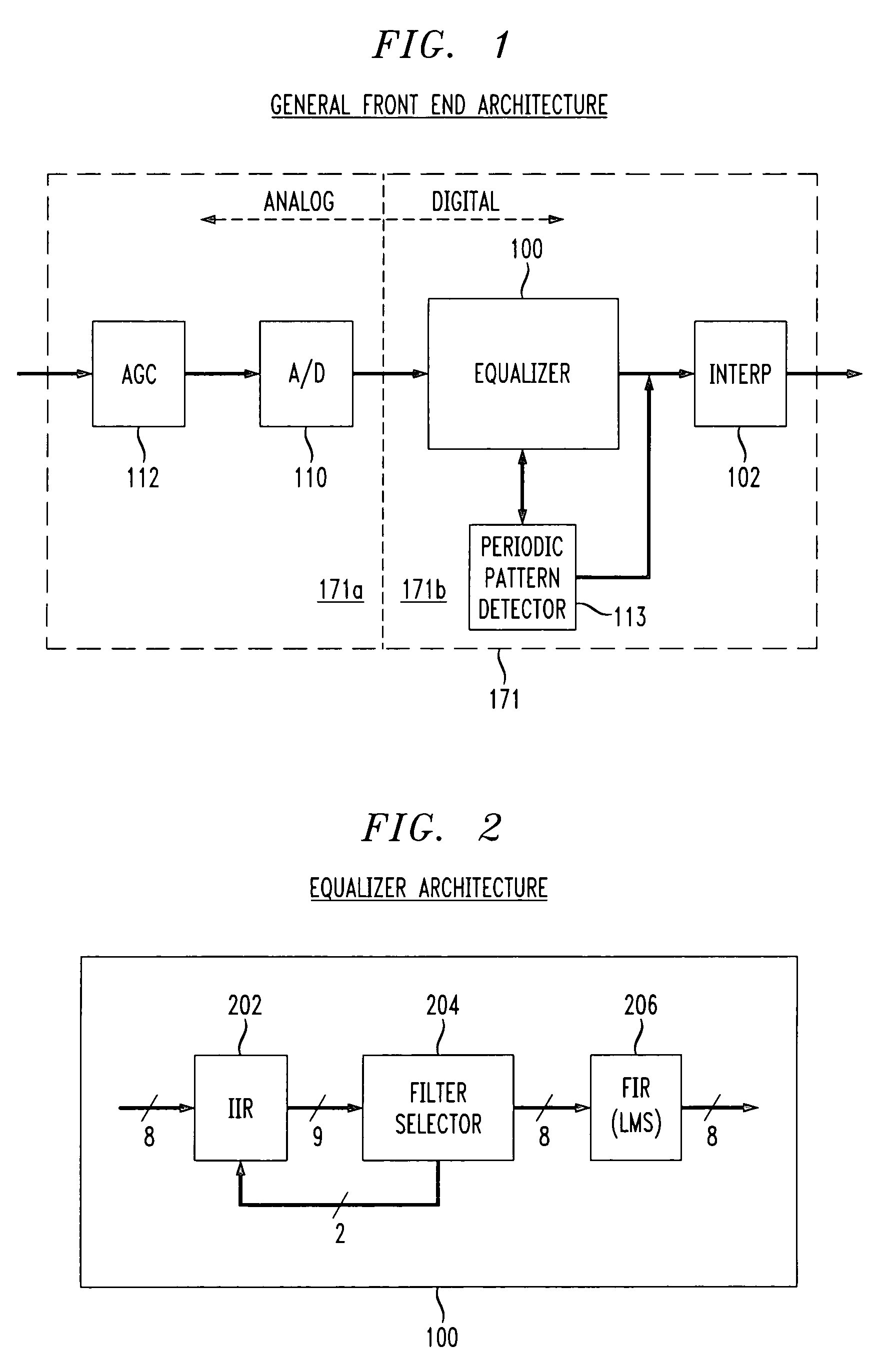
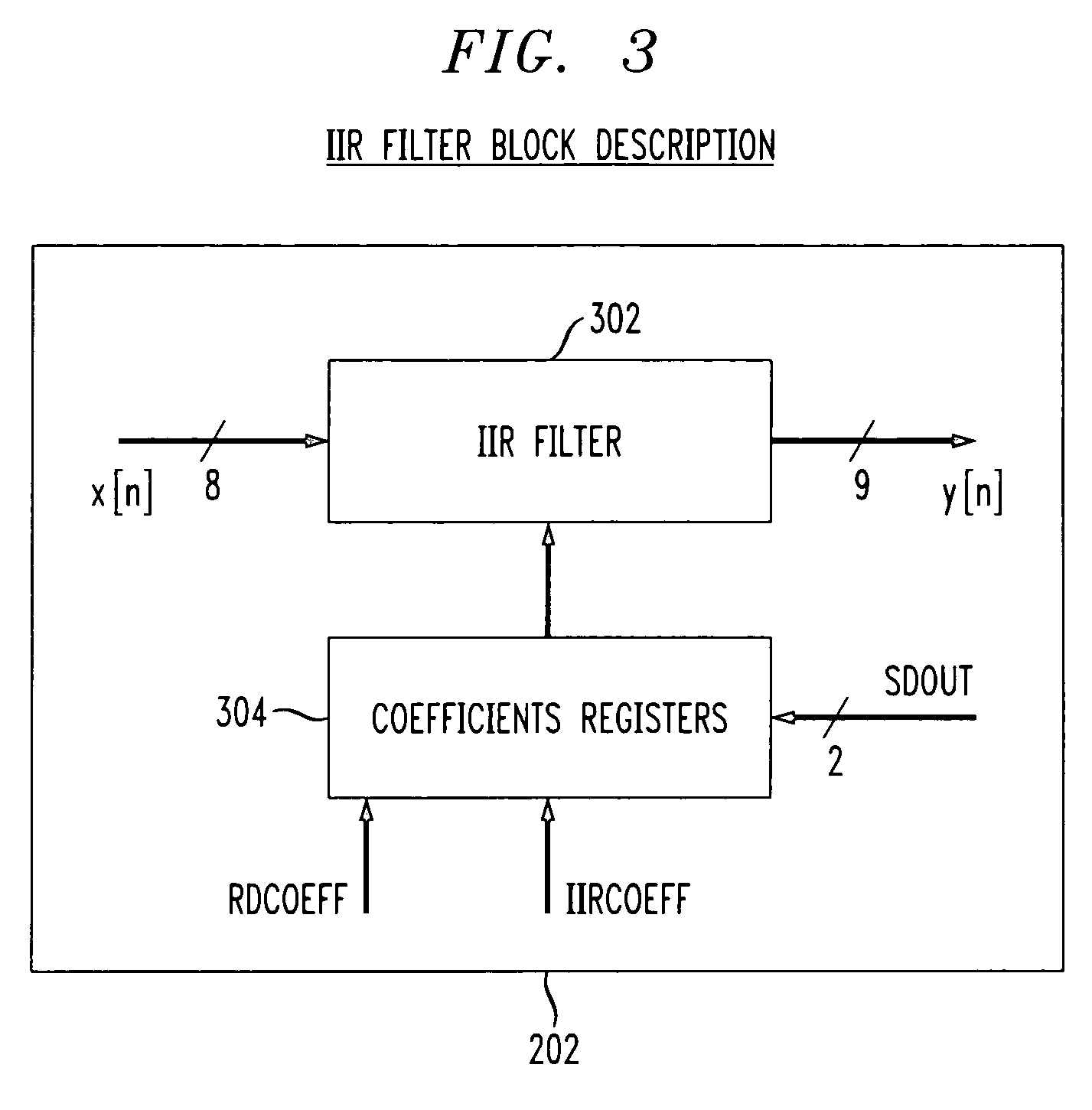
The present invention relates to the implementation of a digital adaptive equalizer for a T1 / E1 long haul transceiver which is capable of adapting to a wide range of cable types, cable lengths, and / or other data transmission impairments, particularly when the transmission path type and / or length are unknown. The digital adaptive equalizer contains two filter blocks, i.e., an IIR filter and a FIR filter, together with a filter selector block to select a best IIR filter based on an error estimation of the received data. Only a few sets of coefficients are found to be necessary to allow proper digital equalization of a large number of cable types and / or lengths. A filter selector block selects a desired set of coefficients corresponding to the optimum IIR filter. The coefficients may be programmed into volatile memory (e.g., RAM) or non-volatile memory (e.g., Flash). Alternatively, the coefficients may be hardwired into the IIR filter. The back end of the digital adaptive equalizer contains an adaptive finite impulse response (FIR) filter. In the disclosed embodiment, the FIR filter uses a least mean square (LMS) algorithm for adaptation to the unknown or changed T1 or E1 transmission channel or medium. The adaptive FIR filter adjusts the output from the IIR filter to accurately match the inverse response of the unknown channel used to transmit the received T1 / E1 signal. Equalization may be temporarily frozen if periodic patterns are detected in the received T1 / E1 signal. A restored T1 or E1 signal is output from the FIR filter, and thus from the digital adaptive equalizer.
Owner:INTEL CORP
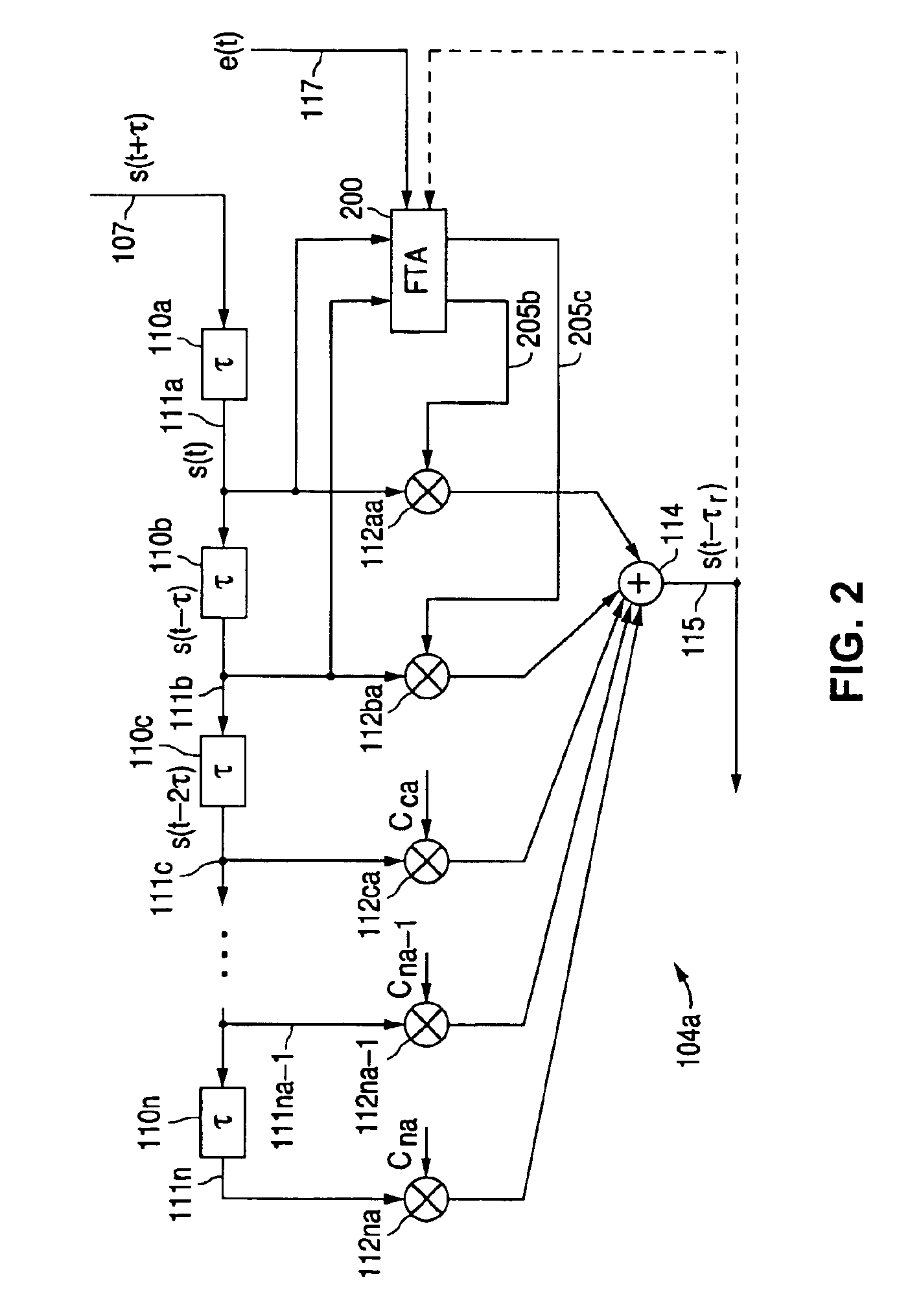
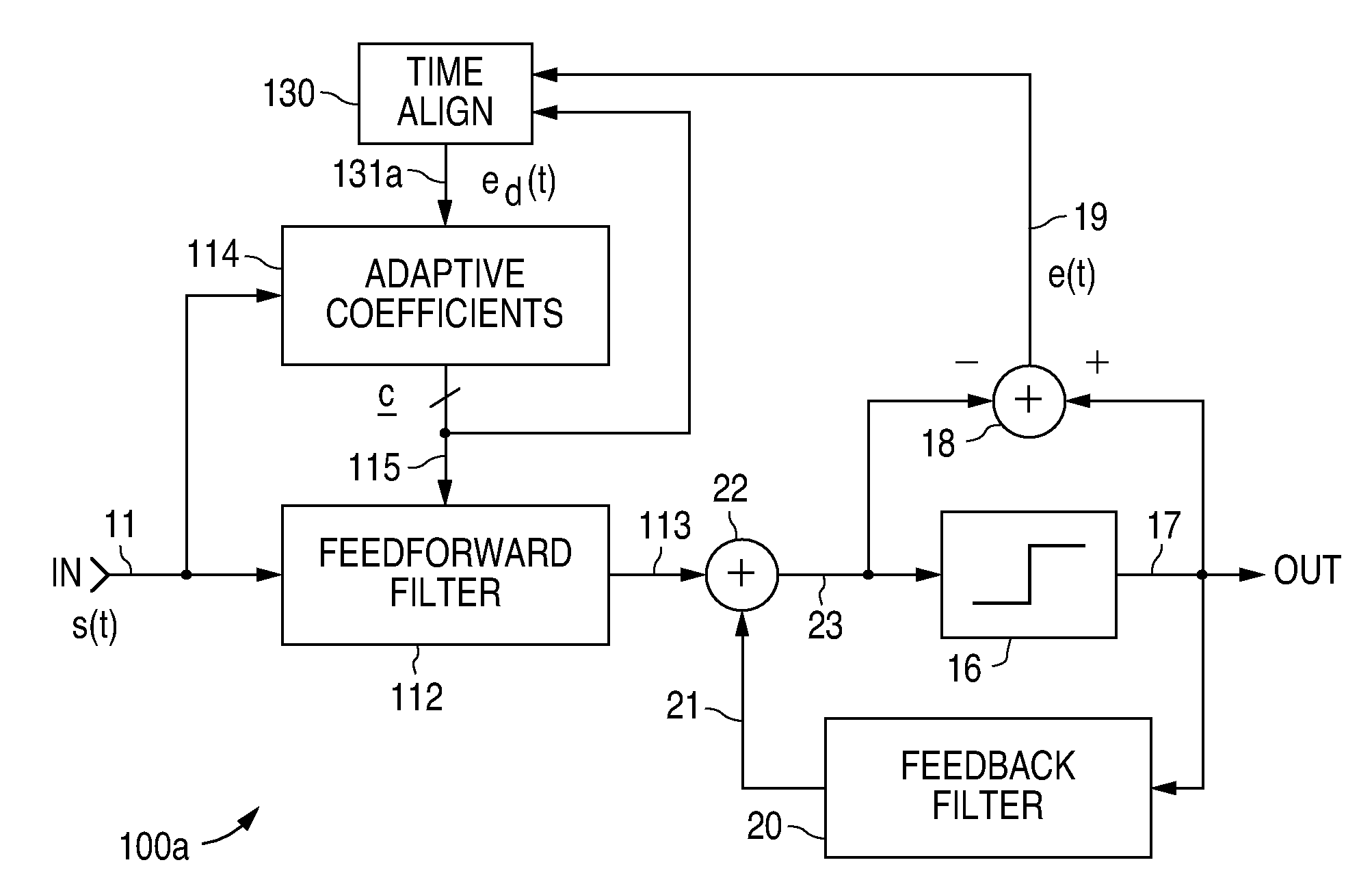
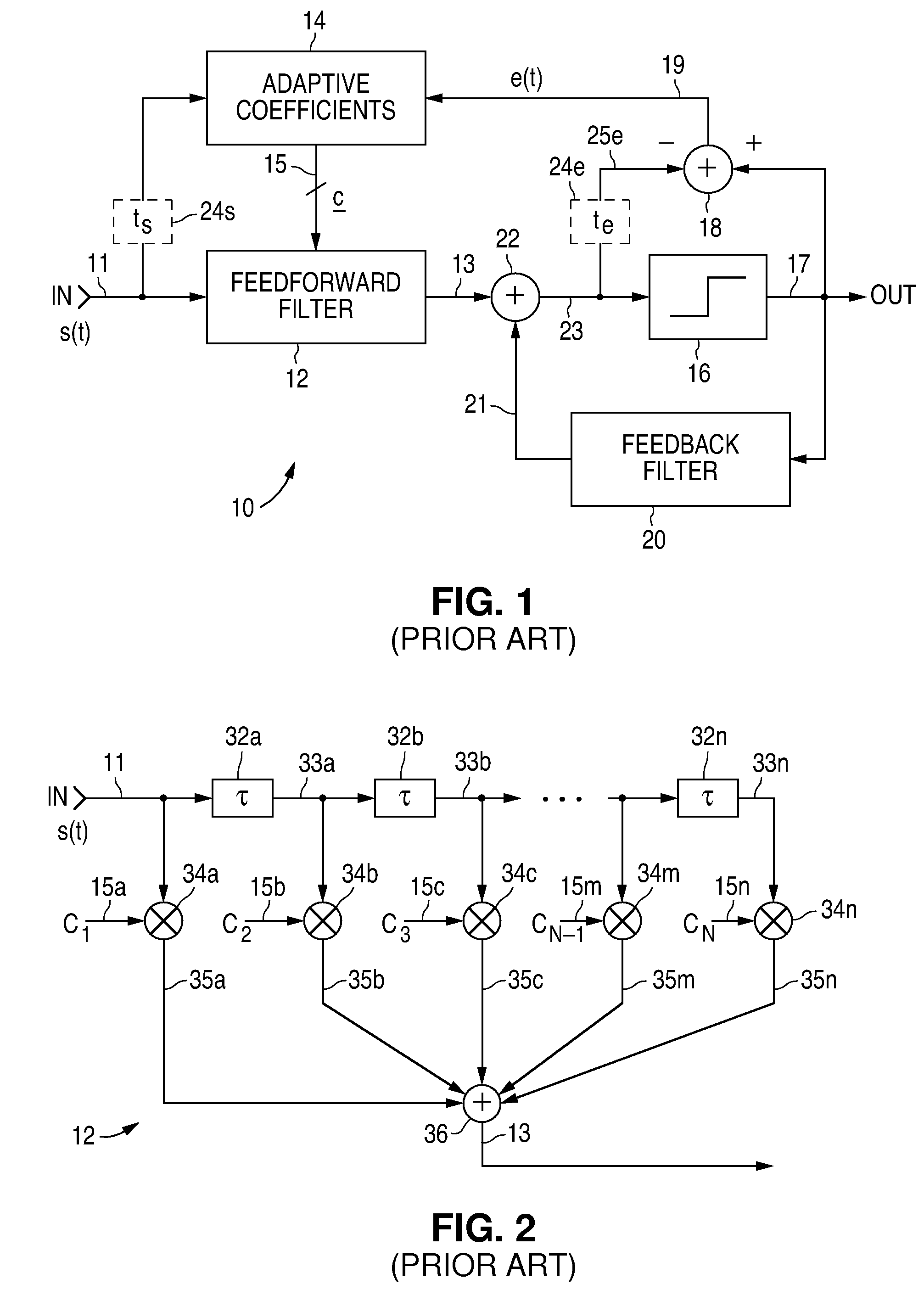
Adaptive signal equalizer with adaptive error timing and precursor/postcursor configuration control
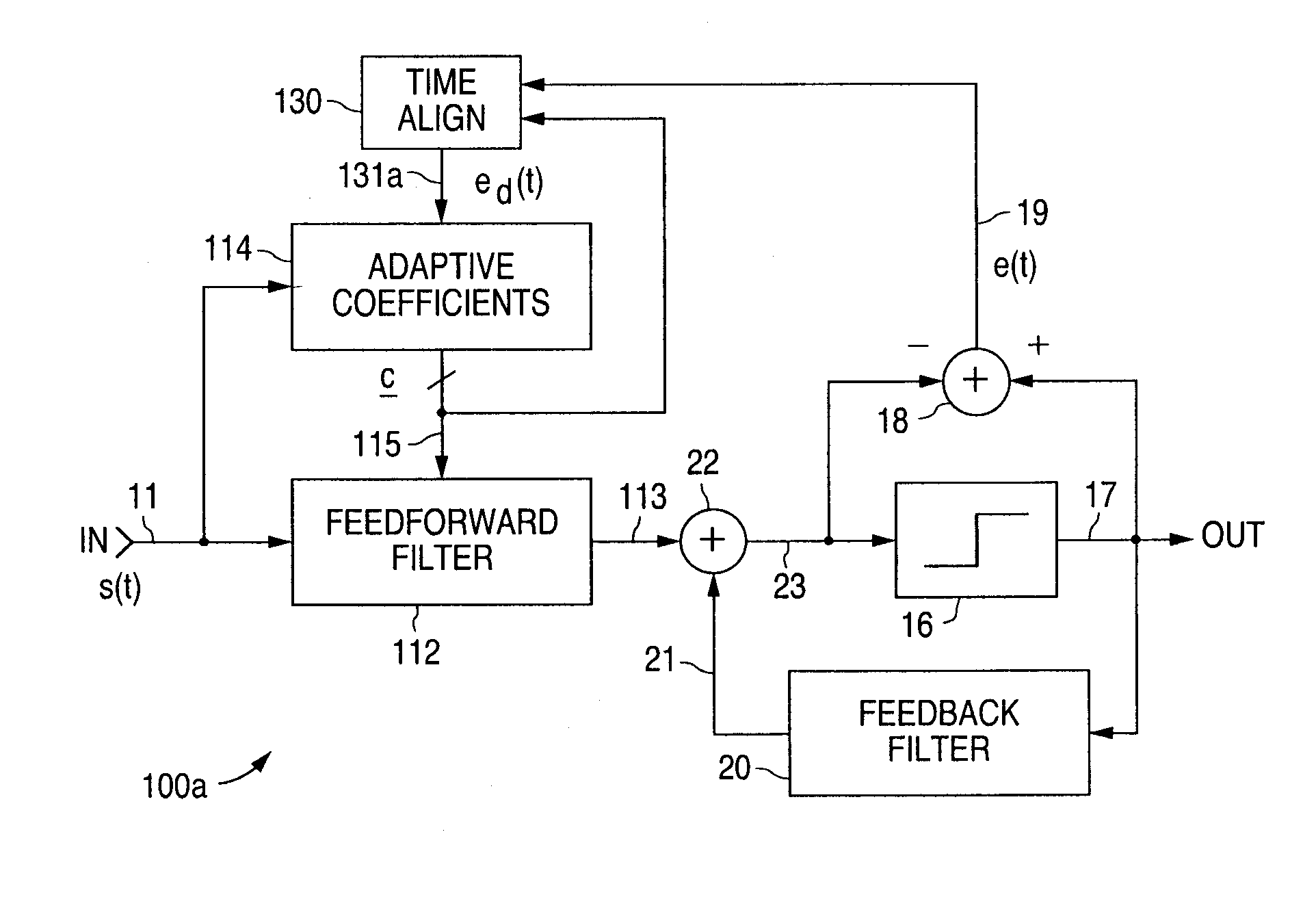
InactiveUS20070230557A1Substantial avoidance of “driftingEnhanced signalTelevision system detailsMultiple-port networksAdaptive filterData signal
An adaptive signal equalizer with a feedforward filter in which the feedback error signal and corresponding incoming data signal are dynamically aligned in time using signal interpolation, and further, to control the precursor / postcursor filter taps configuration, thereby producing more adaptive filter tap coefficient signals for significantly improved and robust signal equalization.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Audio enhancement system
An audio enhancement system is provided for compensating for distortions (e.g., linear distortions) of a sound signal reproduced by an audio system in a listening room. The audio enhancement system includes analysis filters that generate a plurality of analysis output signals from an audio signal to be enhanced. The system also includes synthesis filters that generate an enhanced audio signal from a number of synthesis input signals. The number of analysis output signals and the number of synthesis input signals preferably are equal. Signal processing elements between the analysis filters and the synthesis filters generate one of the synthesis input signals from a respective one of the analysis output signals to perform an inverse filtering for linearizing an unknown transfer function indicative of the audio system and the listening room in the respective frequency range.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Circuit and method for suppressing interference components in received signal
InactiveUS20080013657A1Improve adaptabilitySuppress interferenceMultiple-port networksError preventionAdaptive filterSelf adaptive
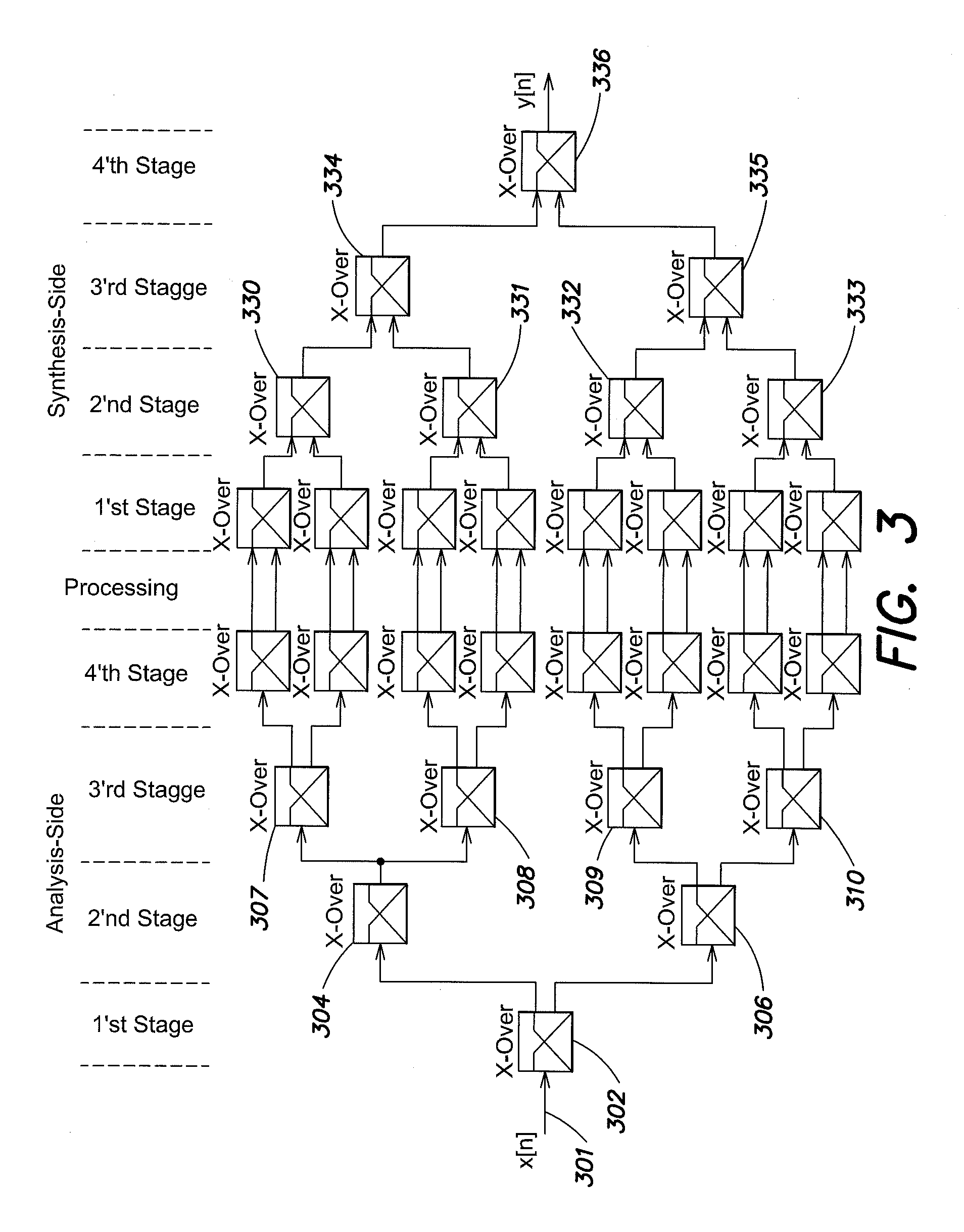
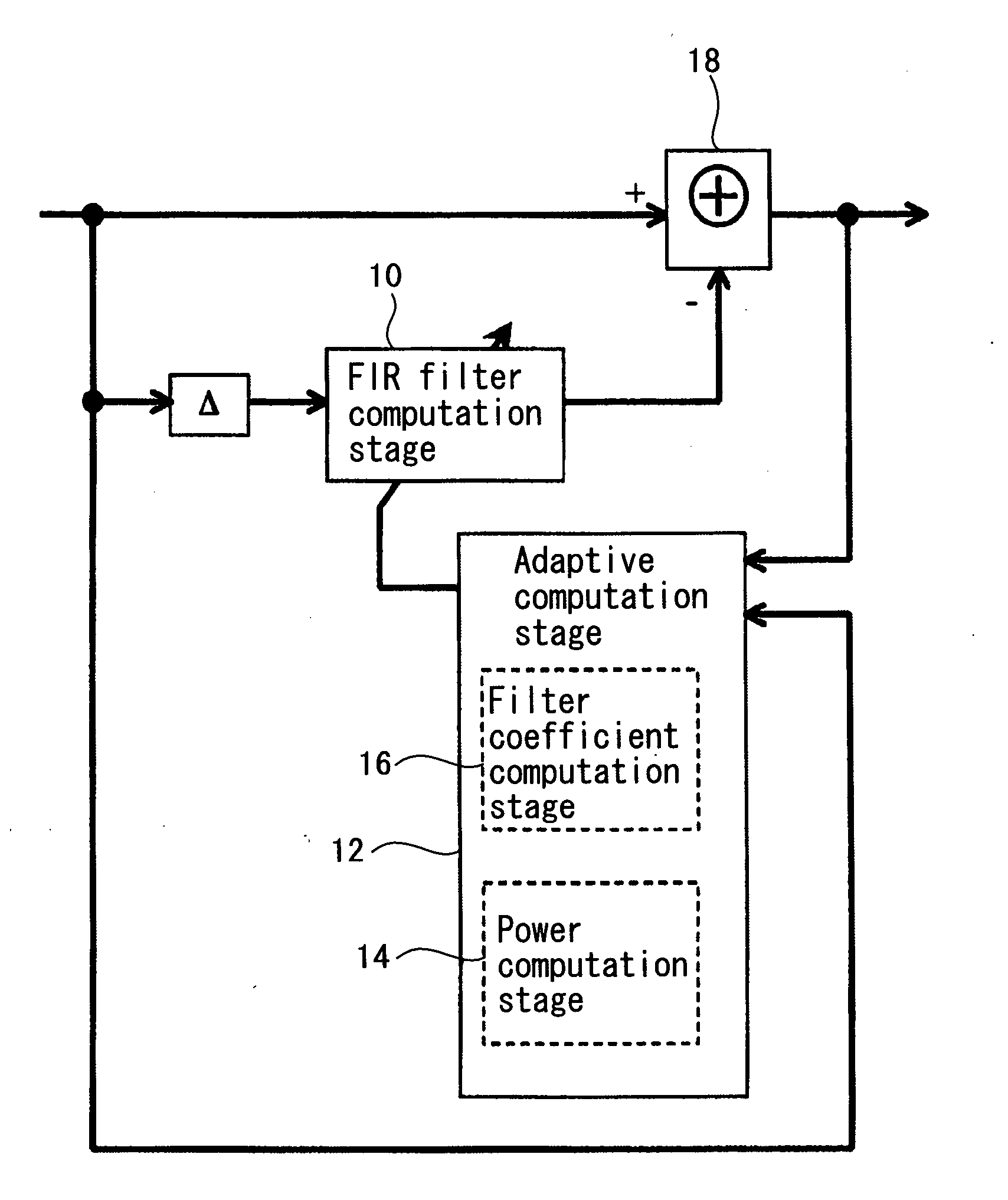
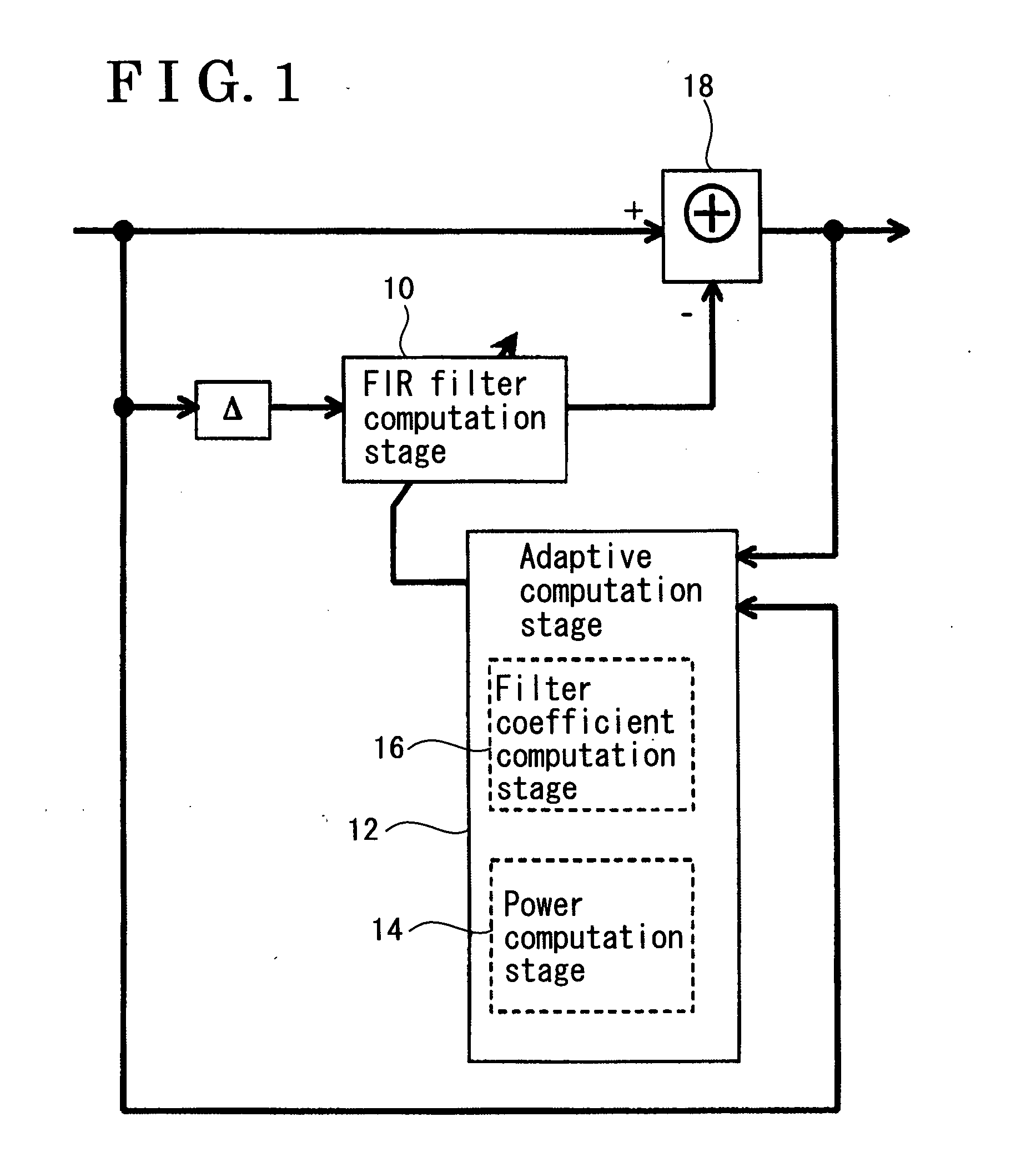
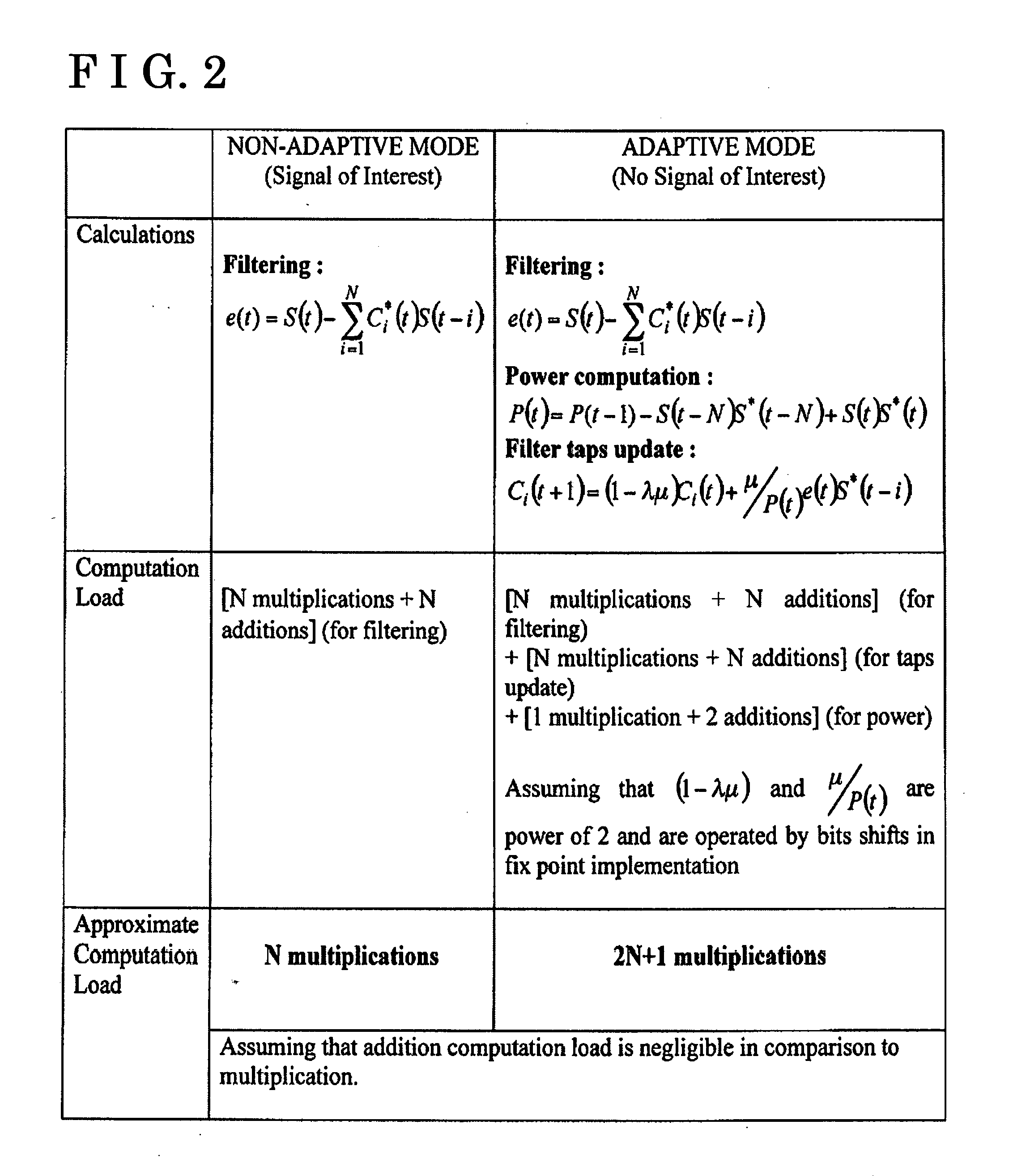
A circuit and method for suppressing interference components in a received signal are provided. The circuit includes an adaptive filter configured to process a first quantity of digital signal samples per unit time when the adaptive filter is operating in a first mode, and a second quantity of digital signal samples per unit time when operating in a second mode, wherein the first quantity is less than the second quantity. The method includes implementing an adaptive filter configured to operate in an adaptive mode and in a second mode having a reduced adaptability compared to the adaptive mode; operating the adaptive filter in the adaptive mode to process a first quantity of digital signal samples per unit time; and operating the adaptive filter in the second mode to process a second quantity of digital signal samples per unit time; wherein the first quantity is less than the second quantity.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
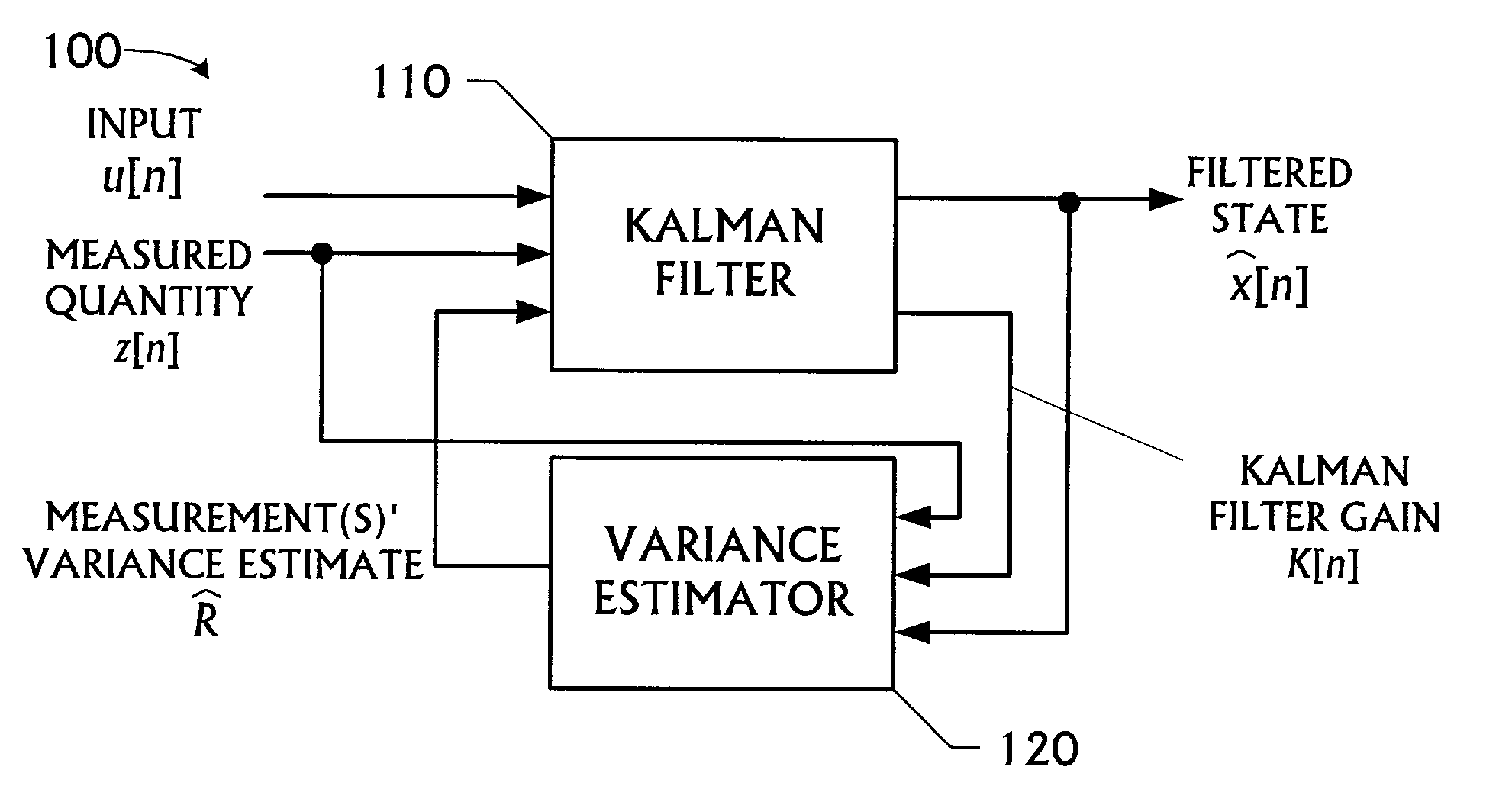
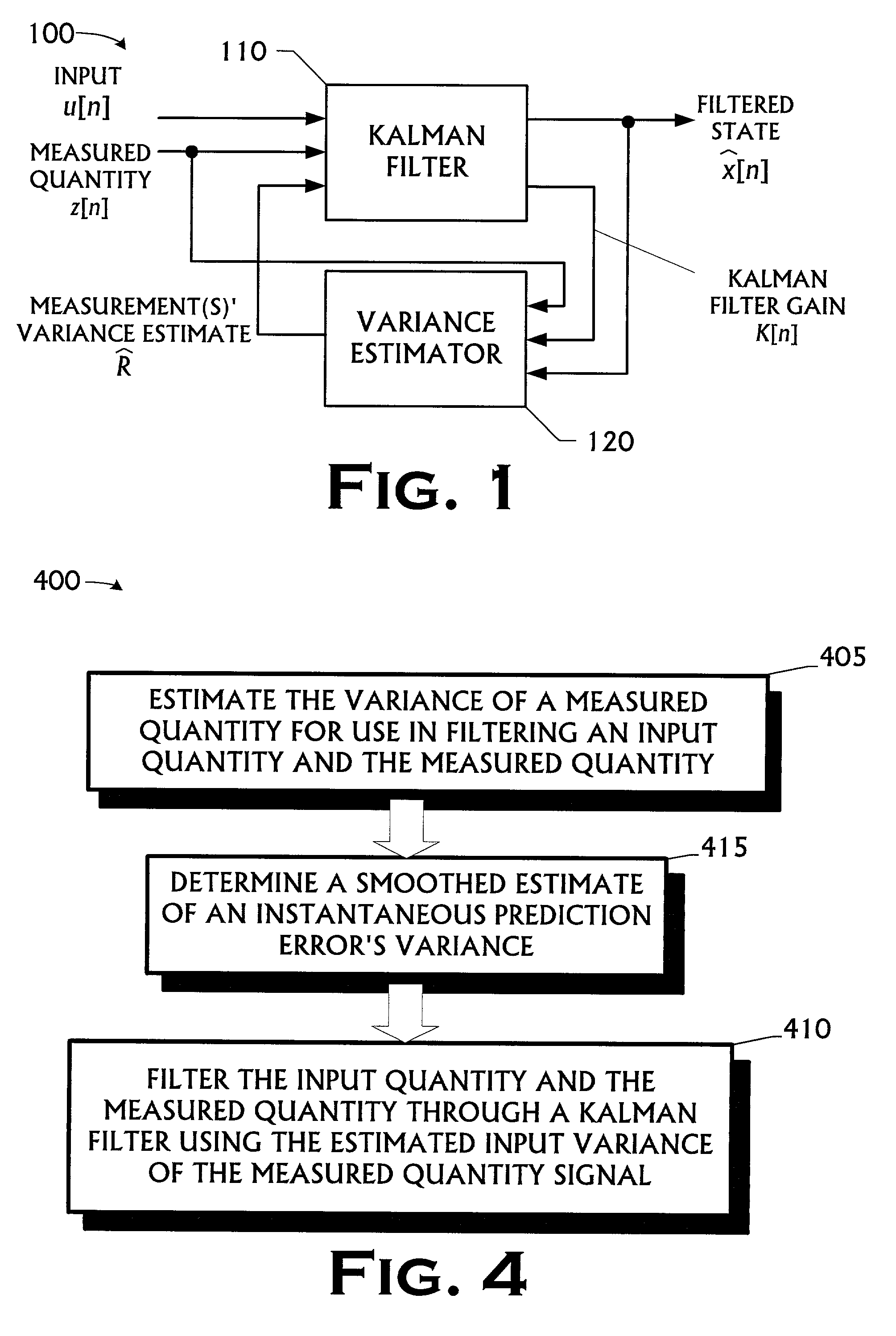
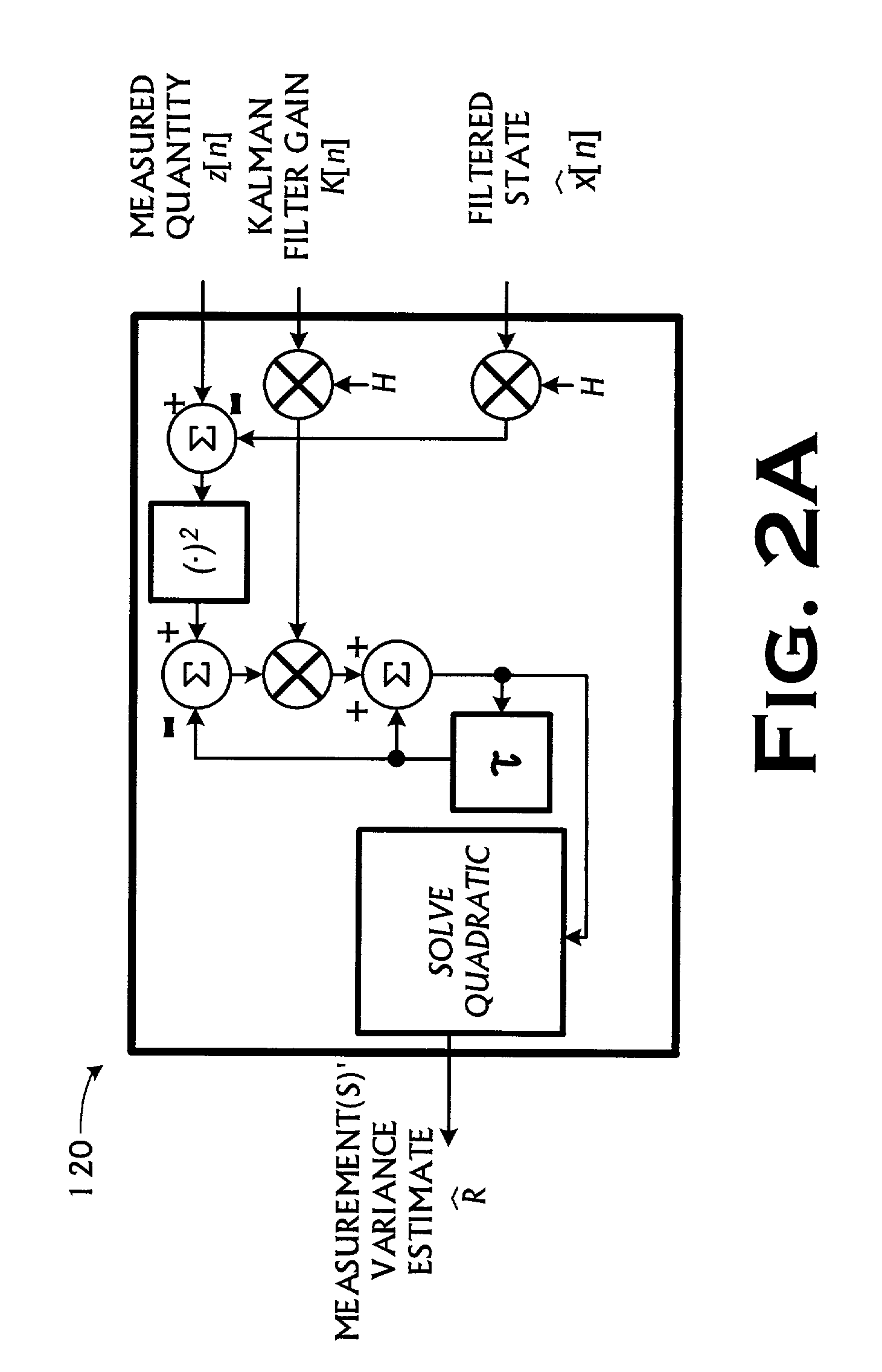
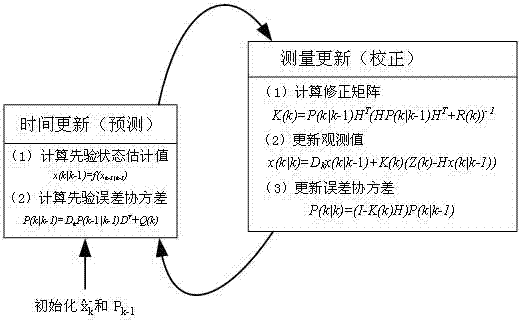
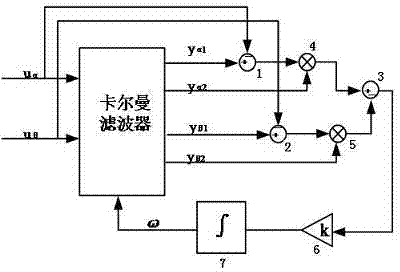
Kalman filter with adaptive measurement variance estimator
A Kalman filtering technique employing an adaptive measurement variance estimator is disclosed. The Kalman filtering technique includes a signal filtering mechanism, the signal filtering mechanism futher includes a Kalman filter and a variance estimator. The variance estimation used in the filtering includes estimating the variance of the measured quantity signal and generating the variance estimate signal for use in filtering the input signal and the measured quantity signal, wherein estimating the variance of the measured quantity signal includes determining a smoothed estimate of the measured quantity's variance from the measured quantity signal. The invention also manifests itself as a method for filtering and estimating, a program storage medium encoded with instructions that, when executed by a computer, performs such a method, an electronic computing device programmed to perform such a method, and a transmission medium over which the method is performed.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
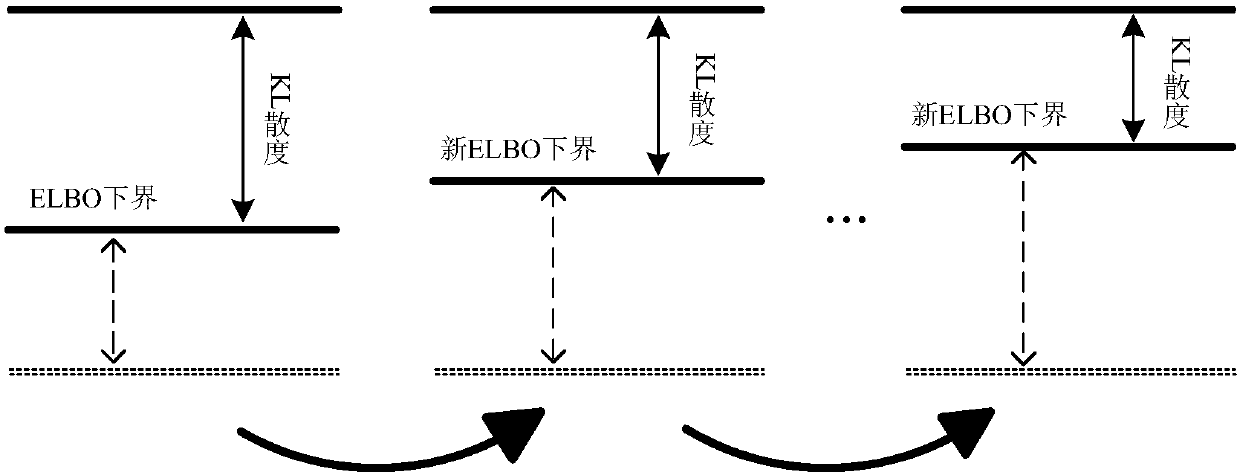
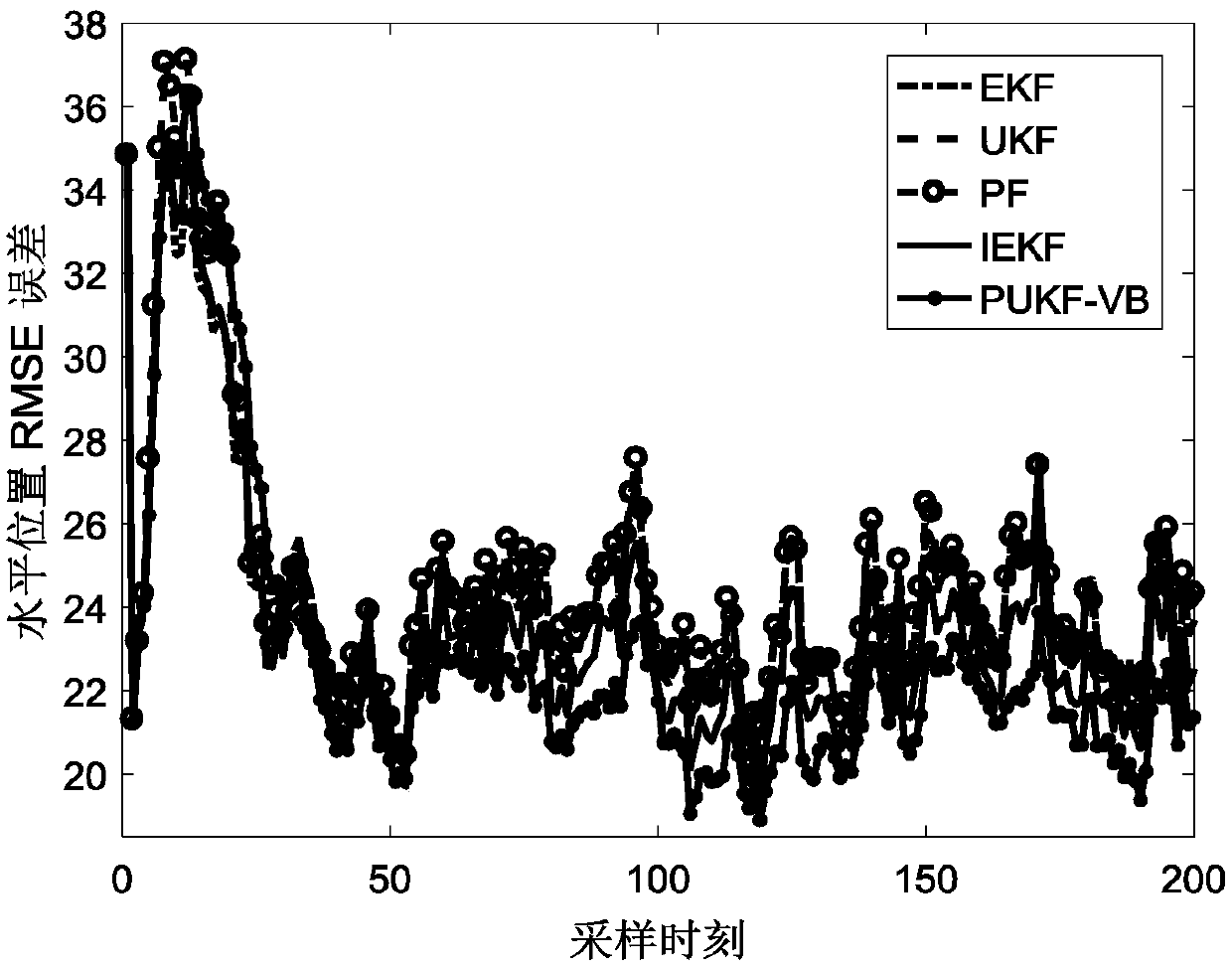
Design method for PNKF-VB
ActiveCN108599737AImprove State Estimation AccuracyIncrease flexibilityDigital technique networkDigital adaptive filtersKaiman filterAdaptive weighting
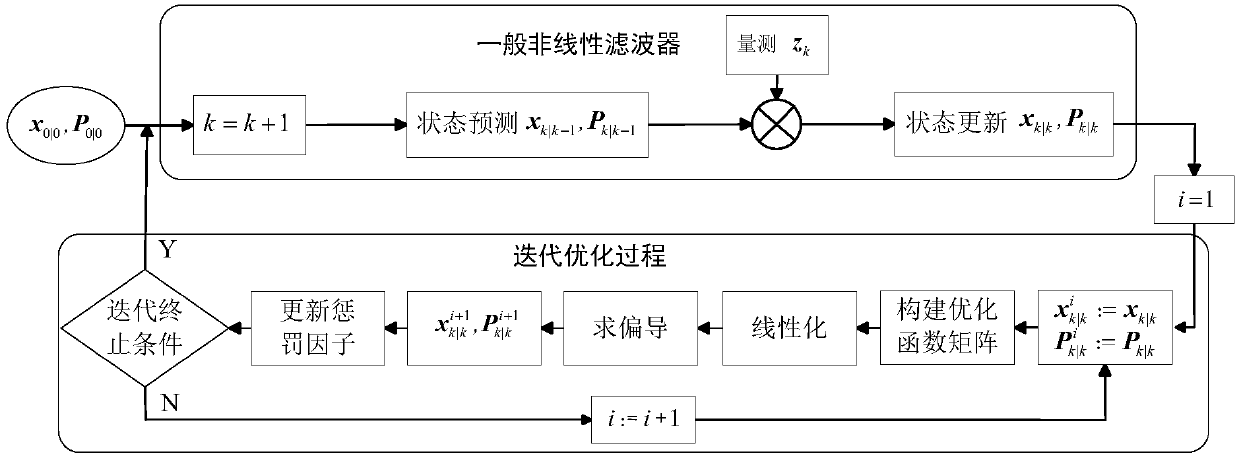
The invention provides a design method for PNKF-VB and relates to the field of a filter. According to the method, variational distribution approximate to a posterior probability density function is constructed under a Gaussian assumption condition; iteration approximation of state estimation is realized by taking KL (Kullback-Leibler) divergence as a penalty function; and the PNKF-VB is derived bytaking confidence lower bound maximization as a target function according to a variational Bayesian frame. According to the method, a relatively tight approximation form of the nonlinear state posterior probability density function can be obtained, so the state estimation precision is improved. The difficult solution problem of the integral of the posterior probability density function in a system state estimation process can be transformed into the problem of optimizing ELBO lower bound. The adaptive weighted KL divergence is taken as the penalty function, so the optimization flexibility isimproved and the state estimation precision is improved. The method has very high significance to nonlinear state estimation theory and practical engineering application.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
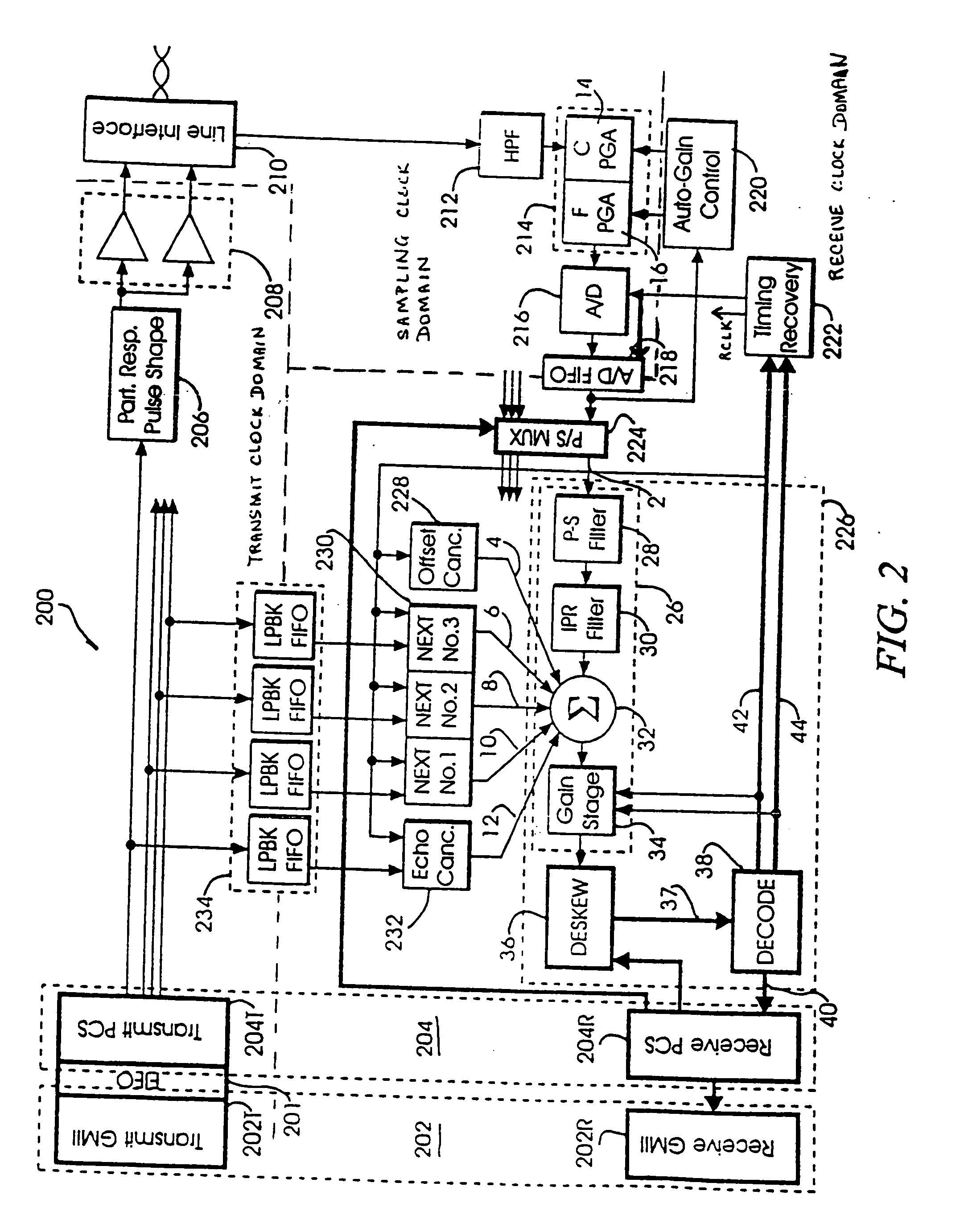
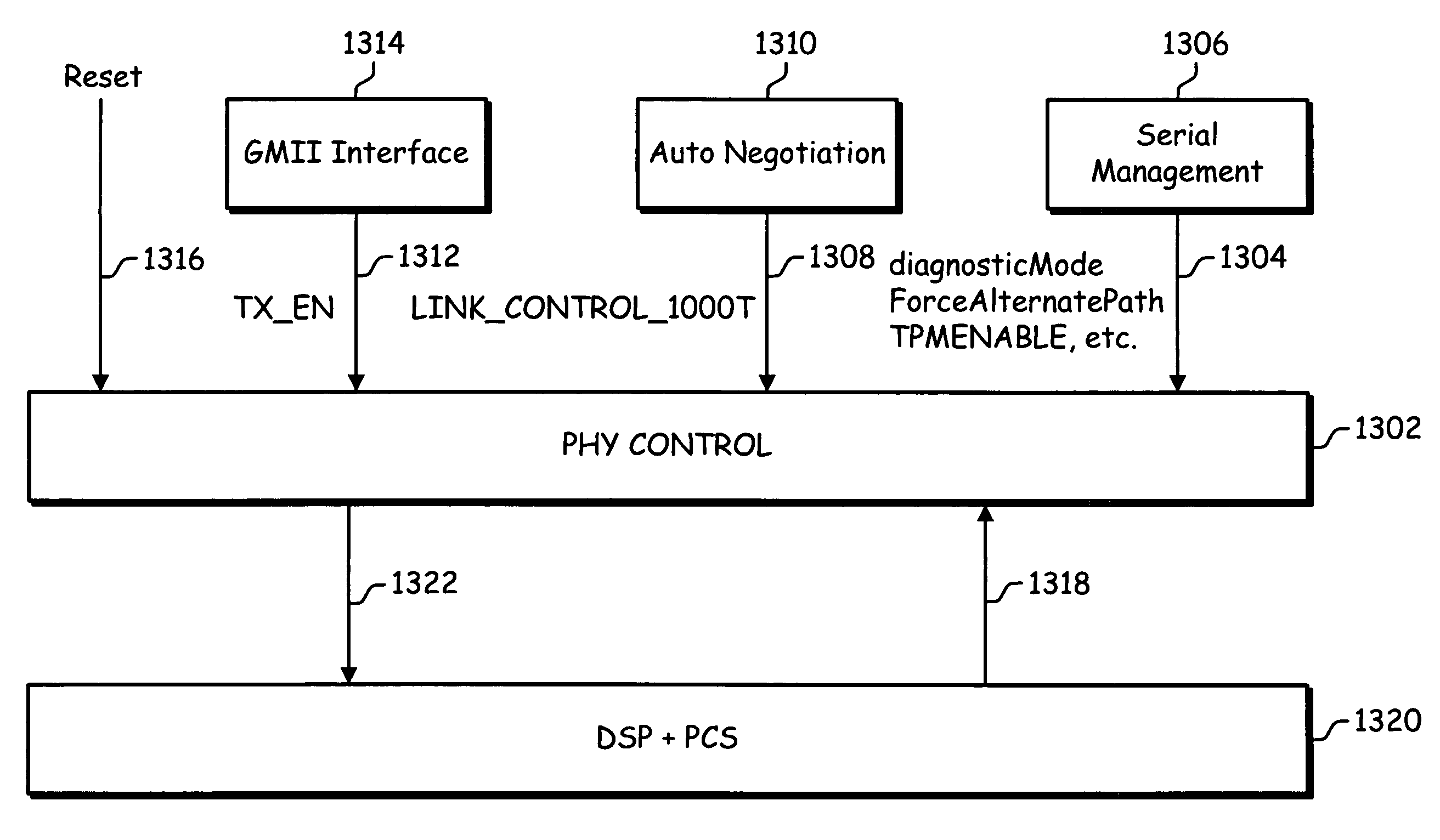
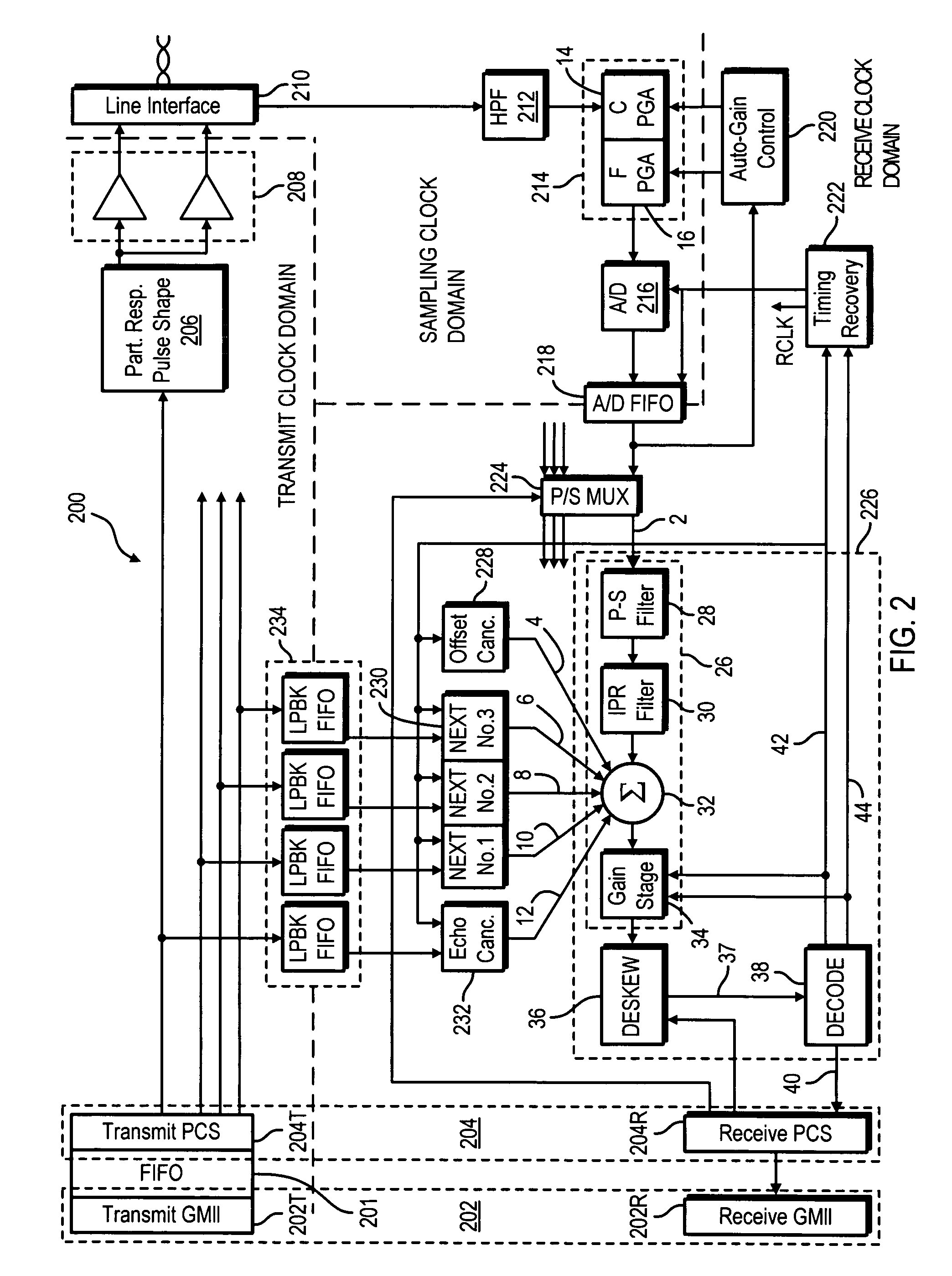
PHY control module for a multi-pair gigabit transceiver
InactiveUS20050041727A1Multiple-port networksChannel dividing arrangementsDigital signal processingSignal response
A method for controlling operation of a multi-pair gigabit transceiver. The multi-pair gigabit transceiver comprises a Physical Layer Control module (PHY Control), a Physical Coding Sublayer module (PCS) and a Digital Signal Processing module (DSP). The PHY Control receives user-defined inputs from the Serial Management module and status signals and diagnostics signals from the DSP and the PCS and generates control signals, responsive to the user-defined inputs, the status signals and diagnostics signals, to the DSP and the PCS.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
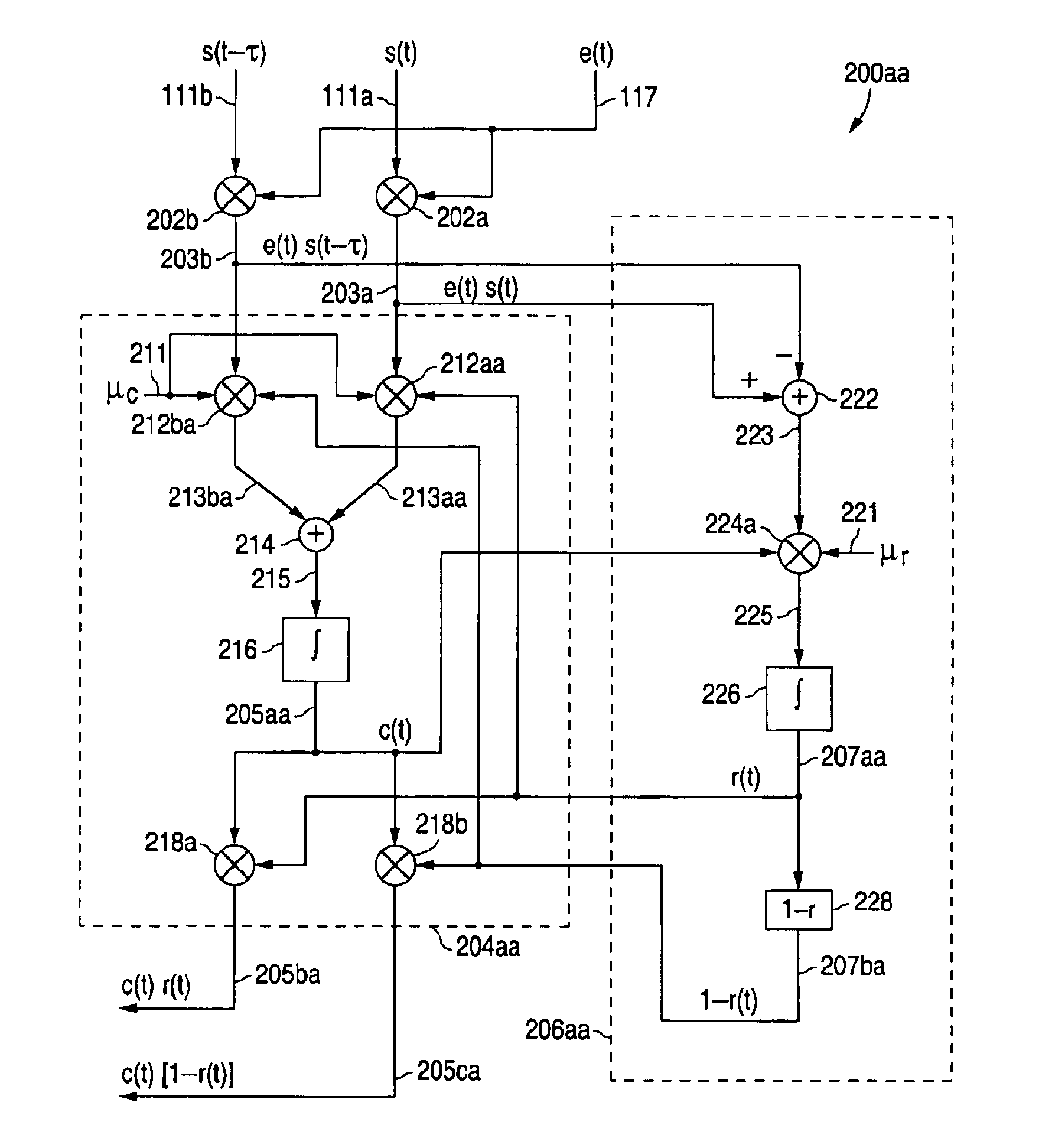
Adaptive coefficient signal generator for adaptive signal equalizers with fractionally-spaced feedback
ActiveUS6940898B2Avoid the needMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsFeedback circuitsEngineering
An adaptive coefficient signal generator for use in an adaptive signal equalizer with fractionally-spaced feedback. The signals representing the feedback tap coefficients are generated in conjunction with a timing interpolation parameter such that the fractionally-spaced feedback circuitry dynamically emulates symbol-spaced feedback circuitry.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD +1
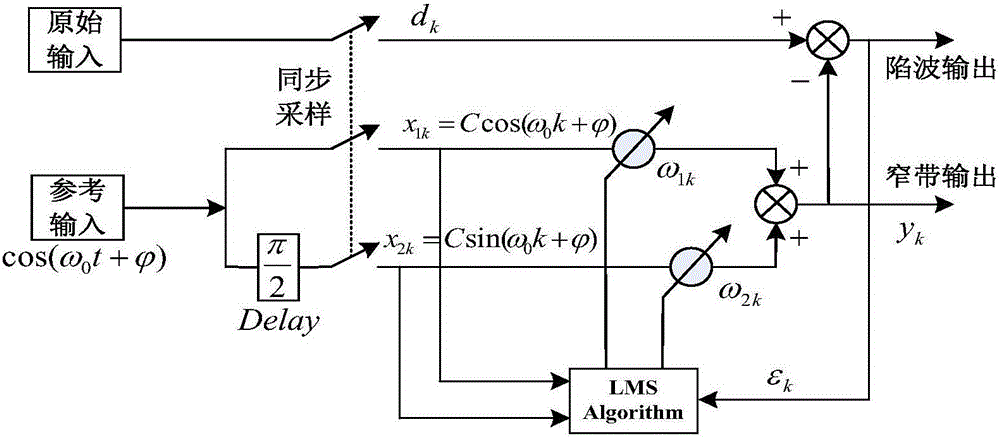
Multifunctional self-adaptive filter based on wavelet neural network and filtering method
The invention discloses a multifunctional self-adaptive filter based on a wavelet neural network and a filtering method. The filter comprises an input layer, wherein the input layer comprises an original input unit which is used for inputting an original signal and a reference input unit which is used for inputting a reference signal; a hidden layer, wherein in the hidden layer, a synchronous sampling unit samples the input original signal and then the signal is transmitted to a subtracter, and the synchronous sampling unit samples the input reference signal and then the signal is transmitted to an algorithm processing unit; and an output layer, wherein in the output layer, the output of the subtracter is taken as notch output, and the output of an adder is taken as narrowband output. According to the multifunctional self-adaptive filter based on the wavelet neural network (WNN), the filter can be taken as a notch filter for removing one or certain signals with determined frequency, and the filter also can be taken as a narrowband filter for passthrough of the signal with specific frequency.
Owner:JINING POWER SUPPLY CO OF STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Adaptive signal equalizer with adaptive error timing and precursor/postcursor configuration control
ActiveUS7266145B2Improved signal equalizationMinimize timeMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsAdaptive filterData signal
An adaptive signal equalizer with a feedforward filter in which the feedback error signal and corresponding incoming data signal are dynamically aligned in time using signal interpolation, and further, to control the precursor / postcursor filter taps configuration, thereby producing more adaptive filter tap coefficient signals for significantly improved and robust signal equalization.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
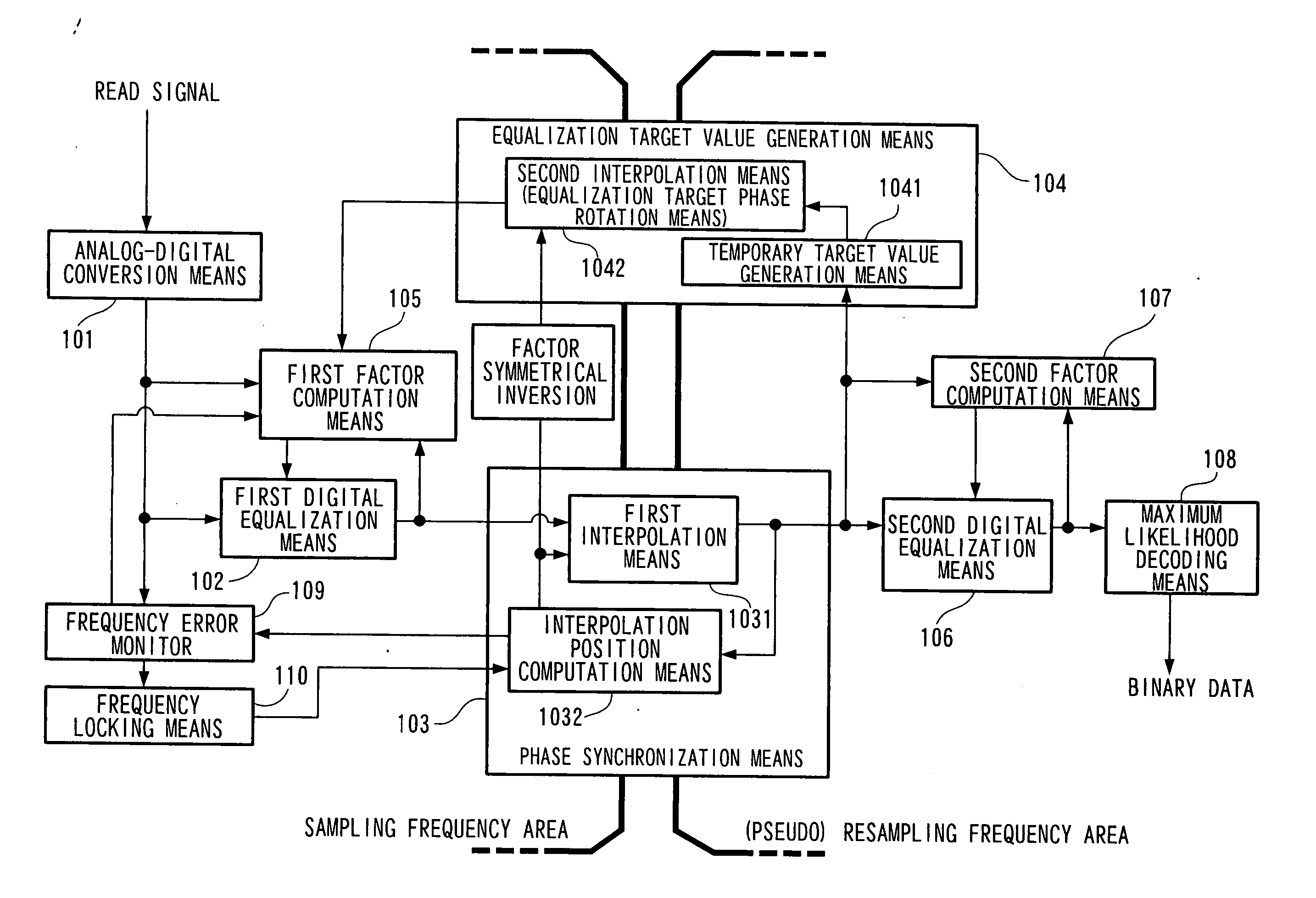
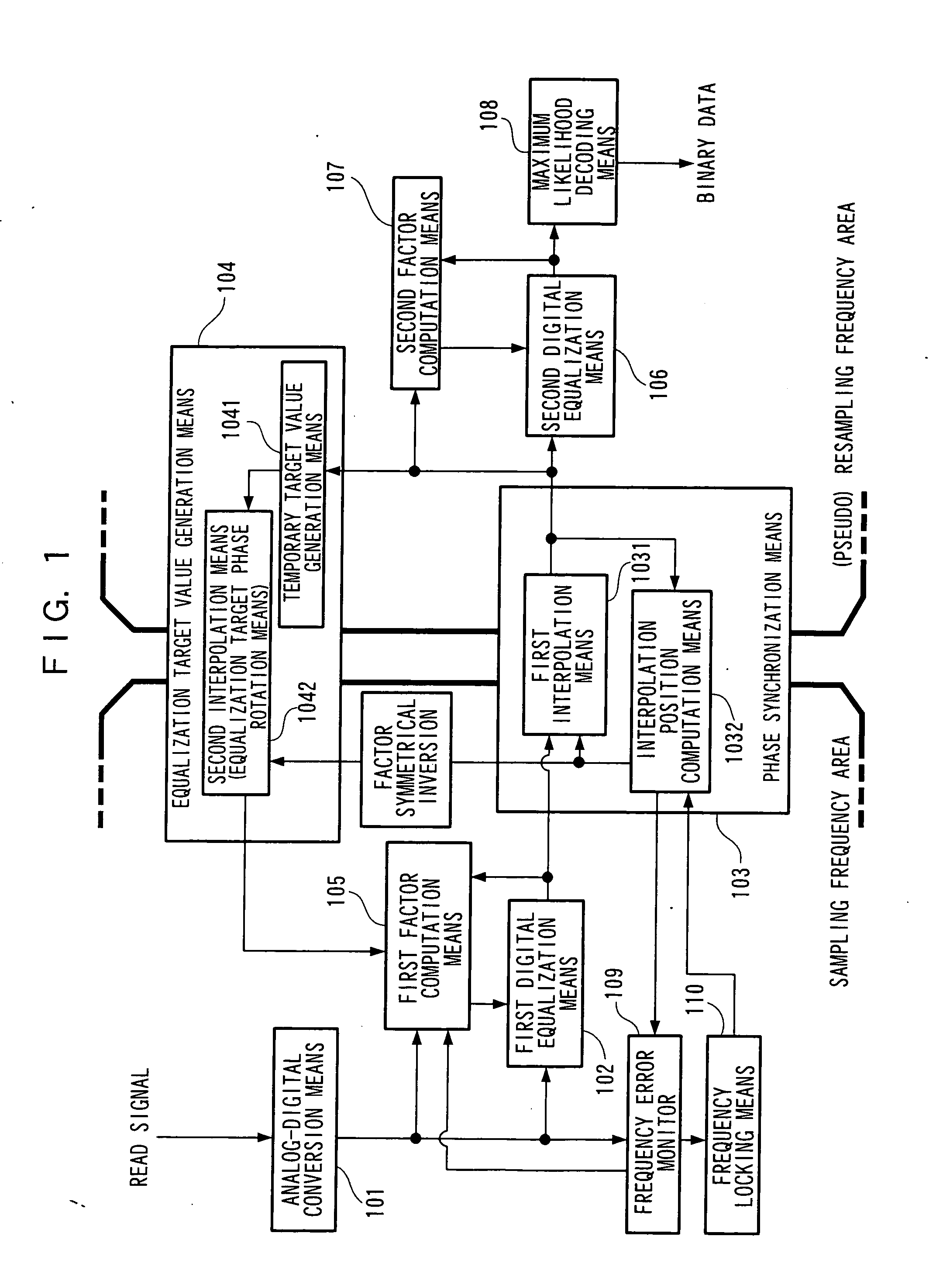
Adaptive equalization circuit and adaptive equalization method
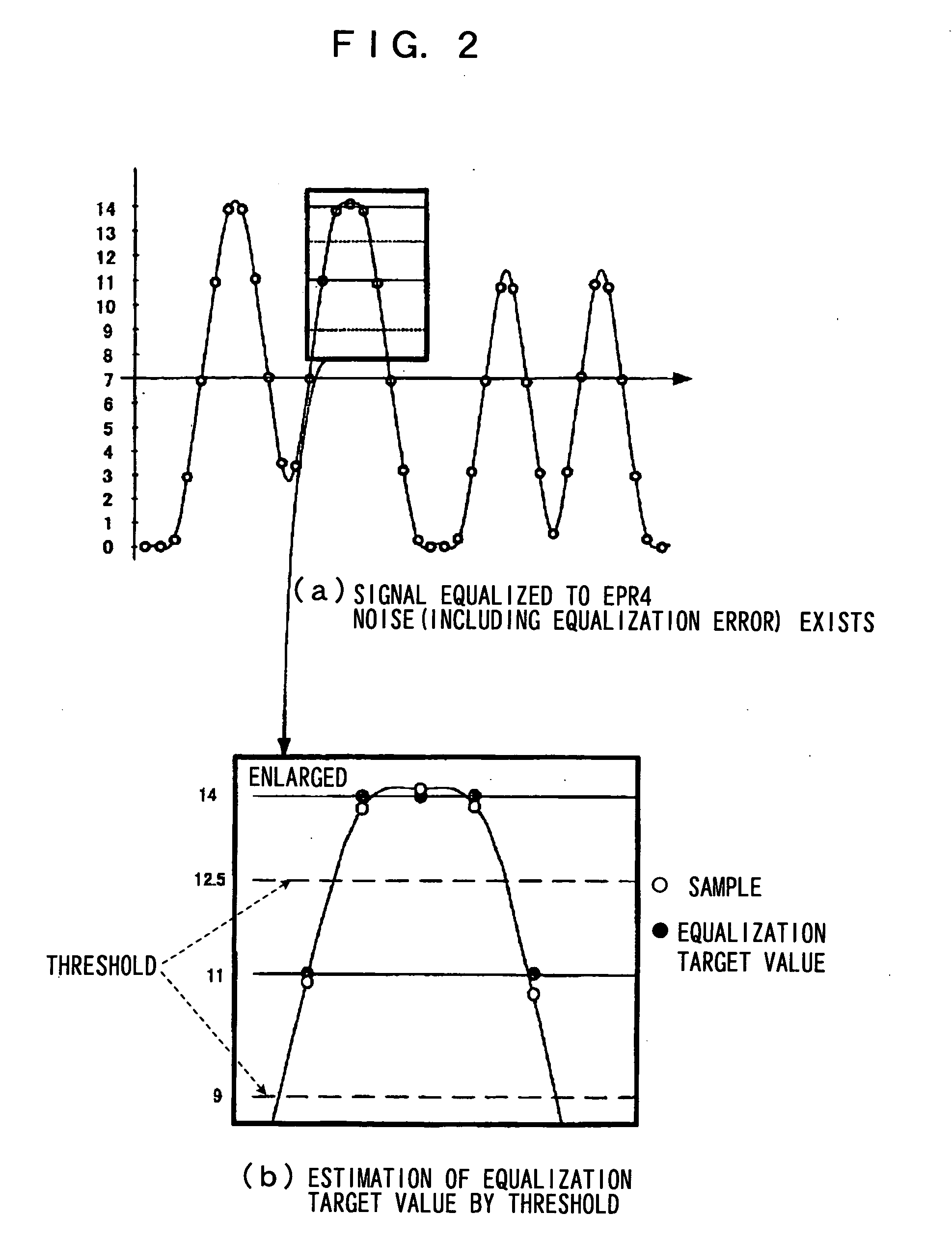
InactiveUS20060072379A1High playabilityMultiple-port networksModification of read/write signalsSignal qualityEngineering
The present invention provides an adaptive equalization circuit and adaptive equalization method that can perform signal processing on a small scale with good computation accuracy, and can improve the reproducing signal quality and improve the playability of abnormal signals. According to the present invention, an equalization target value (true target value) in the sampling frequency area is determined by the equalization target value generation means (104) from the signals in the resampling frequency area after phase synchronization is performed, and the tap factors of the pre-digital equalization means (102) can be adaptively computed from this equalization target value and the input / output signals of the pre-digital equalization means (102).
Owner:PANASONIC HEALTHCARE HLDG CO LTD
Audio enhancement system
An audio enhancement system is provided for compensating for distortions (e.g., linear distortions) of a sound signal reproduced by an audio system in a listening room. The audio enhancement system includes analysis filters that generate a plurality of analysis output signals from an audio signal to be enhanced. The system also includes synthesis filters that generate an enhanced audio signal from a number of synthesis input signals. The number of analysis output signals and the number of synthesis input signals preferably are equal. Signal processing elements between the analysis filters and the synthesis filters generate one of the synthesis input signals from a respective one of the analysis output signals to perform an inverse filtering for linearizing an unknown transfer function indicative of the audio system and the listening room in the respective frequency range.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Adaptive coefficient signal generator for adaptive signal equalizers with fractionally-spaced feedback
InactiveUS20060104342A1Avoid the needLong networkMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsEngineeringFeedback circuits
An adaptive coefficient signal generator for use in an adaptive signal equalizer with fractionally-spaced feedback. The signals representing the feedback tap coefficients are generated in conjunction with a timing interpolation parameter such that the fractionally-spaced feedback circuitry dynamically emulates symbol-spaced feedback circuitry.
Owner:SCINTERA NETWORKS
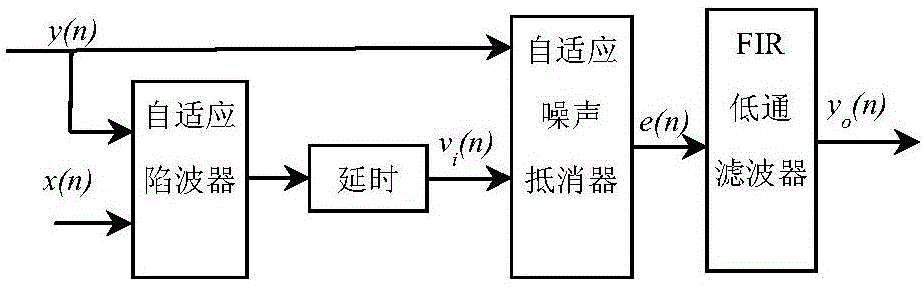
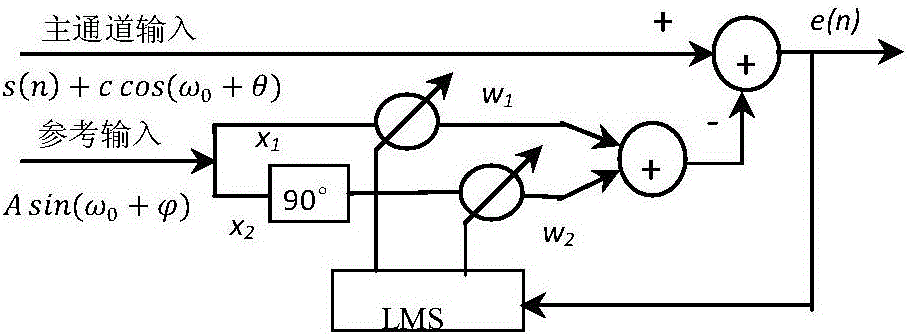
Method for eliminating pump stroke noise in mud impulse signals by aid of adaptive filtering algorithms
InactiveCN106301289AImprove signal-to-noise ratioEffective filteringDigital adaptive filtersAdaptive filtering algorithmFinite impulse response
The invention discloses a method for eliminating pump stroke noise in mud impulse signals by the aid of adaptive filtering algorithms. The method mainly includes three filtering steps implemented by the aid of an adaptive wave trap, an adaptive noise canceller and a FIR (finite impulse response) low-pass filter and particularly includes 1), filtering useful signals in original signals by the aid of the adaptive wave trap; 2), inputting the original singles into main channels of the adaptive noise canceller; 3), filtering the high-frequency noise in output signals of the adaptive noise canceller by the aid of the FIR low-pass filter so as to complete filtering. Reference signals at the step 2) are delay signals of the original signals without the useful signals, and error signals outputted by the adaptive noise canceller are the original signals without the pump stroke noise according to LMS (least mean square) criteria. The method has the advantages that the method can be used for carrying out noise removal processing on the mud impulse signals in measurement-while-drilling systems, effective filtering can be implemented on the premise that the useful signals are protected from being cancelled, the method is easy to implement, is universal in the aspect of mud impulse signal processing and has high practical value in the aspect of increasing signal-to-noise ratios of the mud impulse signals and reducing the communication bit error rates, and reliable filtering effects can be realized.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
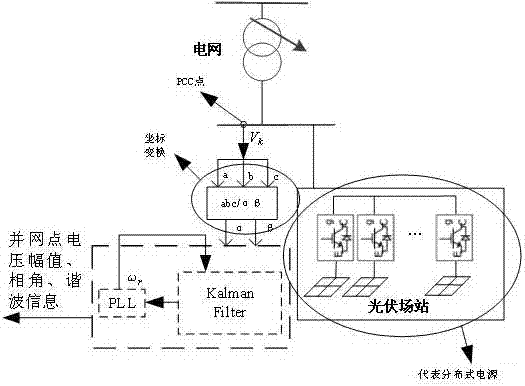
Method and system of observing power grid information based on Kalman filtering algorithm
ActiveCN107276220ALinear transitivityDigital adaptive filtersElectrical testingHarmonicState variable
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGXI ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD RES INST +1
Phy control module for a multi-pair gigabit transceiver
A method for controlling operation of a multi-pair gigabit transceiver. The multi-pair gigabit transceiver comprises a Physical Layer Control module (PHY Control), a Physical Coding Sublayer module (PCS) and a Digital Signal Processing module (DSP). The PHY Control receives user-defined inputs from the Serial Management module and status signals and diagnostics signals from the DSP and the PCS and generates control signals, responsive to the user-defined inputs, the status signals and diagnostics signals, to the DSP and the PCS.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Single-phase voltage sag rapid detection method
InactiveCN109507542ALower latencyHow to avoid harmonicsDigital adaptive filtersFault location by conductor typesAdaptive filterLow-pass filter
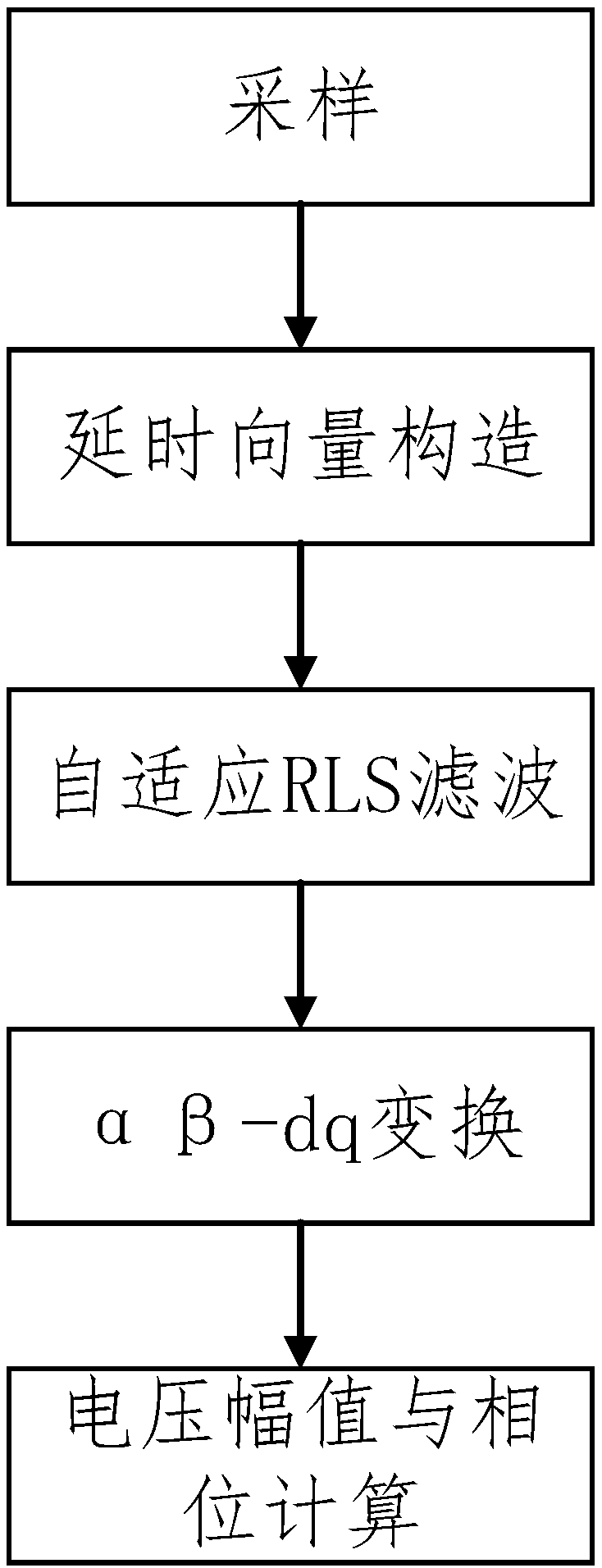
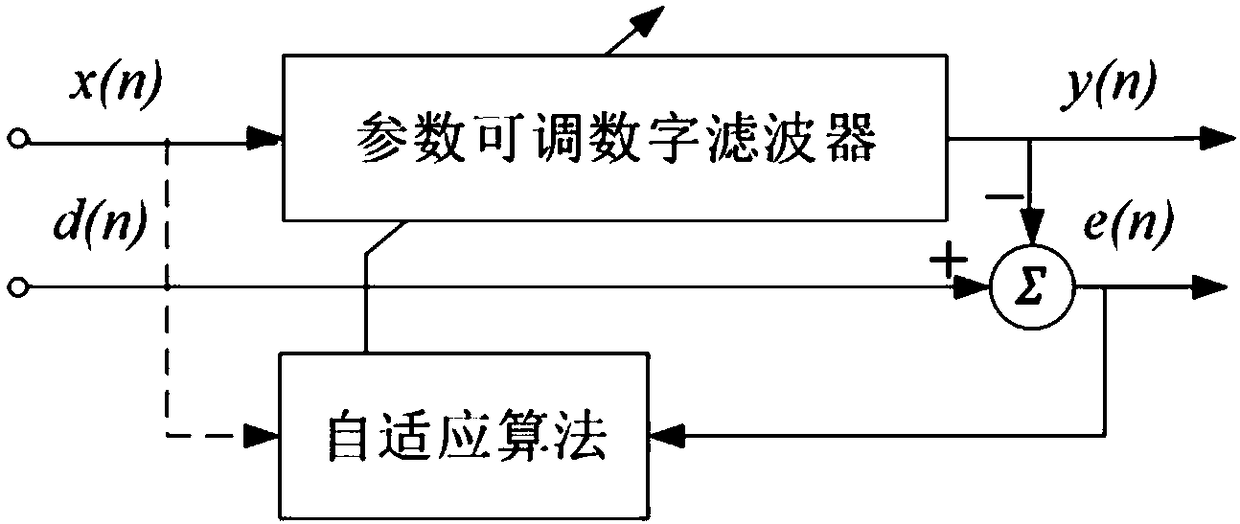
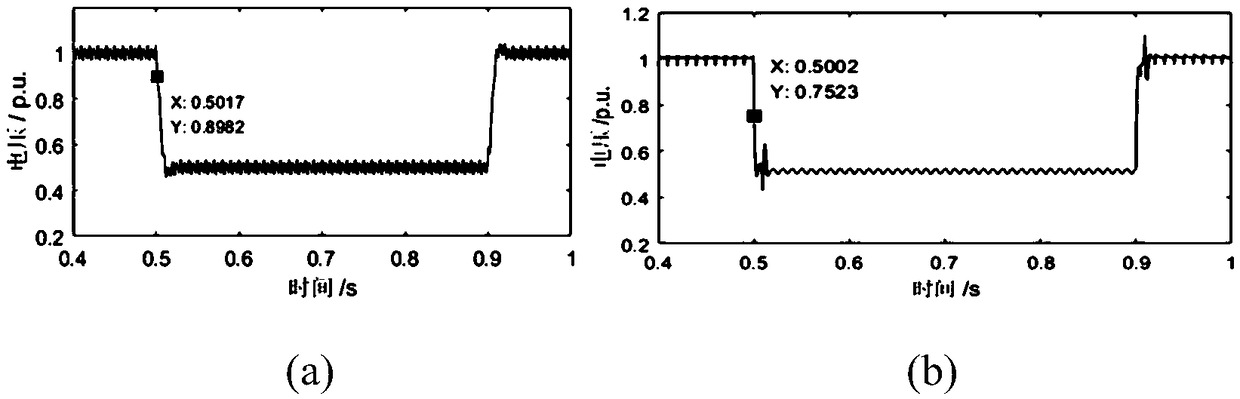
The invention discloses a single-phase voltage sag rapid detection method. Firstly, original data such as voltage and phase of a node is monitored; secondly, according to sampling data, u-alpha and u-beta components in an alpha-beta stationary coordinate system are obtained by means of a delay vector construction method; thirdly, a self-adaptive RLS filter is adopted for filtering to obtain a fundamental component; fourthly, alpha-beta-d q transformation is performed to obtain a d-axis direct current component and a q-axis direct current component of the fundamental component in a dq rotatingcoordinate system; finally, the voltage magnitude and phase are calculated according to the d-axis direct current component and the q-axis direct current component. By means of the method, on one hand, noise generated by signal errors and delay structures can be filtered out simultaneously; on the other hand, the influence of alpha-beta-d q transformation on a harmonic wave method is avoided. Finally, the self-adaptive filter is adopted for replacing a traditional low-pass filter, and the better effect of eliminating the condition of large harmonic wave content is achieved. The self-adaptive filter adopts a recursive least square (RLS) algorithm, and the higher initial convergence speed and higher detection accuracy are achieved.
Owner:STATE GRID BEIJING ELECTRIC POWER +2
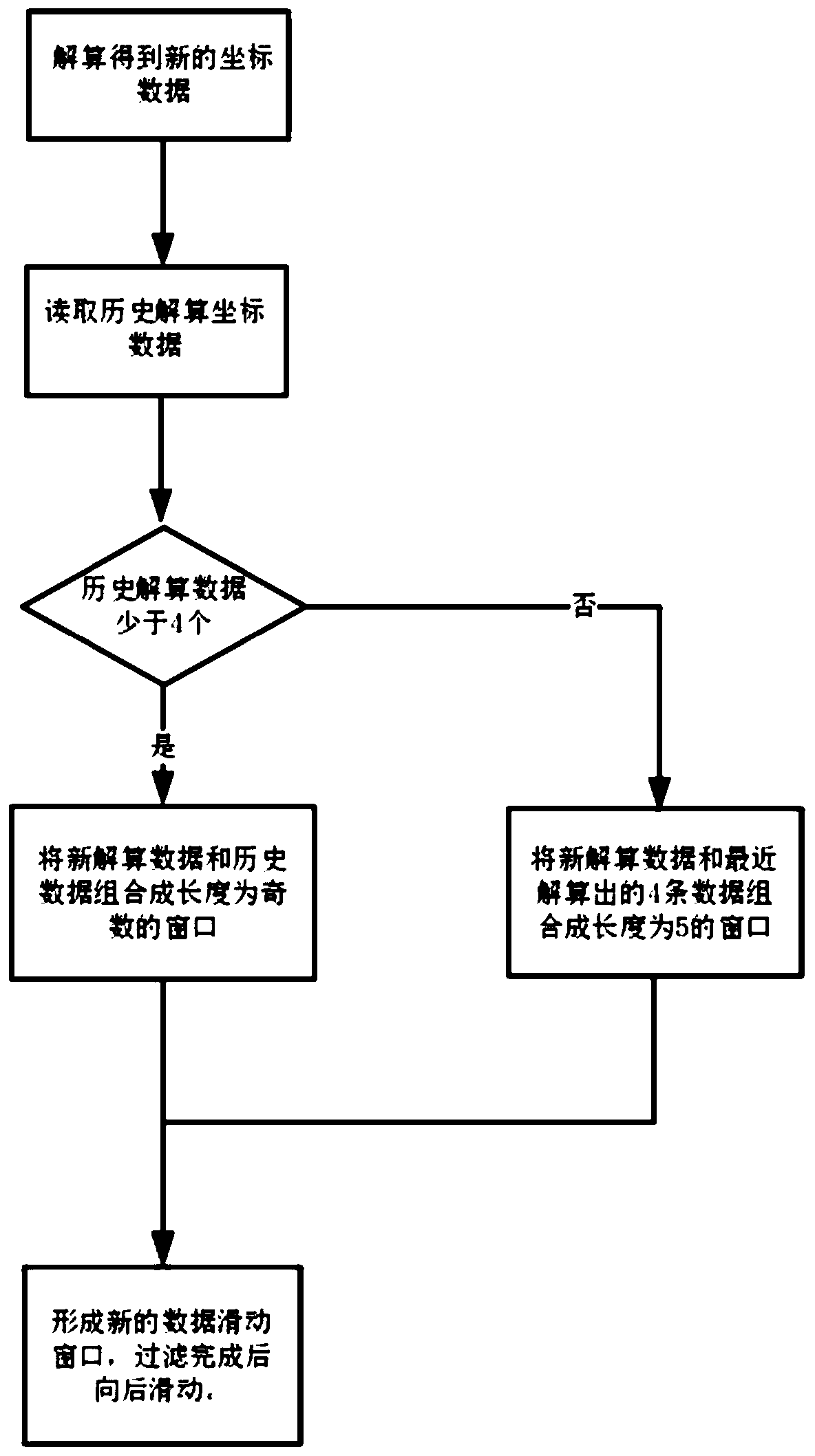
Method for carrying out dynamic filtering optimization based on real-time positioning trajectory data
ActiveCN110850363AImprove performanceGood effectNavigational calculation instrumentsDigital adaptive filtersData setAlgorithm
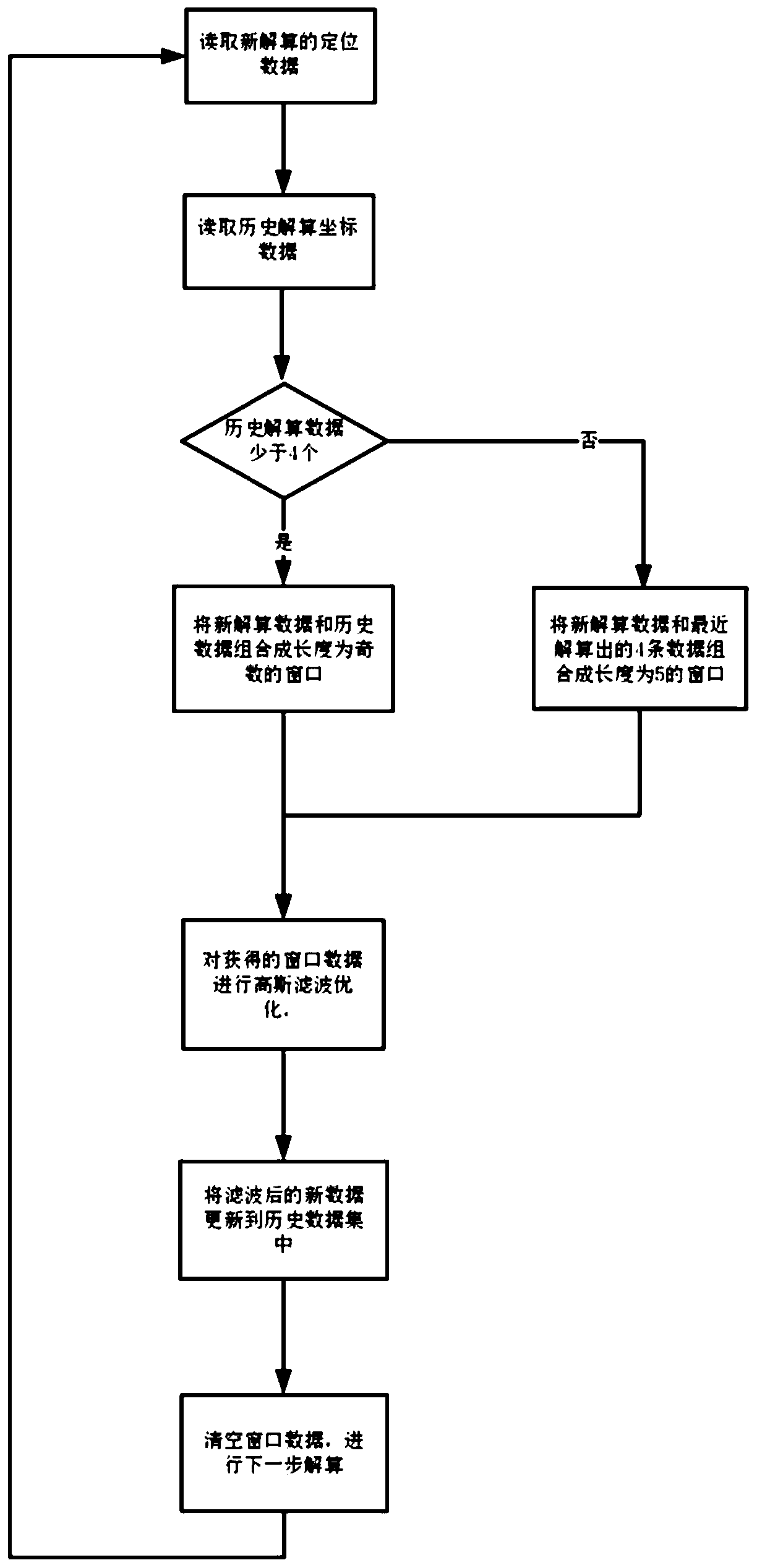
The invention provides a method for carrying out dynamic filtering optimization based on real-time positioning trajectory data. The method comprises the following steps: 1, reading positioning coordinate data calculated in real time; 2, reading positioning coordinate data obtained by historical calculation; 3, if the number of the historical calculation data is less than 4, turning to the step 4,otherwise, turning to the step 5; 4, fusing newly solved data and solved at most even number of historical data to form sliding window data with the length of odd number; 5, fusing the newly solved data and the recently solved four pieces of data to form sliding window data; 6, carrying out smoothing processing on the obtained window data; 7, adding newly resolved data into a historical data set after filtering, and updating the historical data subjected to smoothing processing in the window to the historical data set; 8, emptying the window data, carrying out positioning data calculation of the next step, turning to the step 1 after the calculation is completed, and reading the next piece of data.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
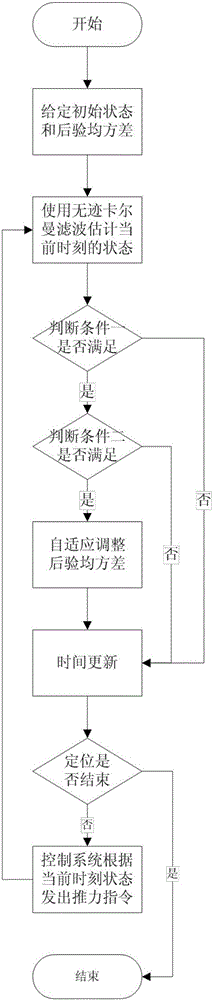
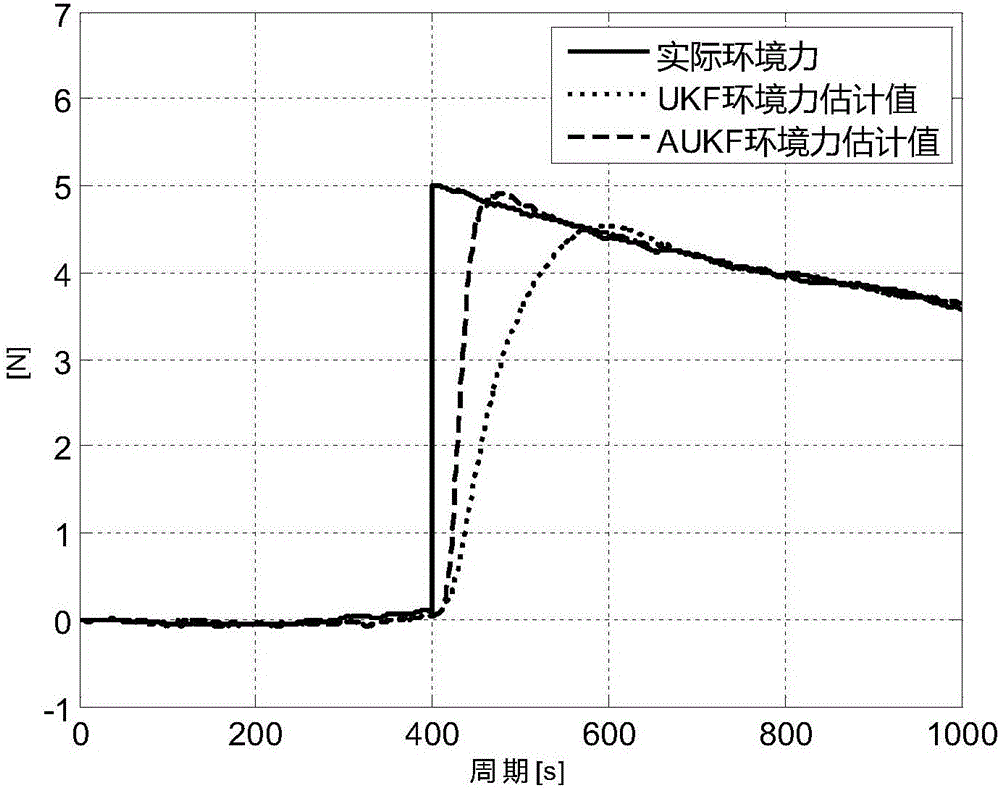
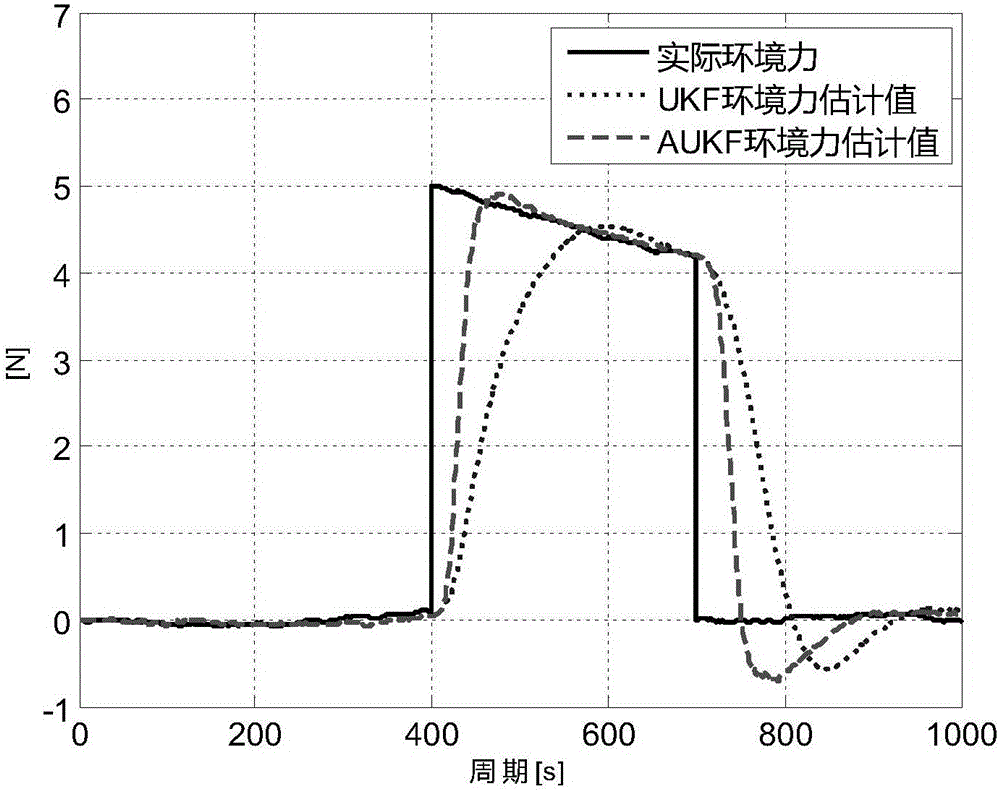
Self-adaption filtering method tracking environmental force sudden change in dynamic positioning
InactiveCN105807767AReduce the real positionReduce positioningDigital adaptive filtersSteering componentsControl systemState space
The invention relates to a self-adaption filtering method tracking environmental forces sudden change in dynamic positioning. The method includes steps of establishing a state space model of a ship system; using traceless Kalman filtering for estimating a state in the current moment; judging whether the environmental force in the current moment meets sudden change or not according to a judgment condition; performing self-adaption adjustment on posterior mean square error of the current moment if the judgment condition is met, which means environmental force sudden change occurs; judging positioning is completed or not; if the positioning is not finished, sending a thrust command of the next moment by a control system according to a position and the environmental force estimated by the self-adaption filtering so as to enable a ship to reach a positioning point and to hold at the positioning point; if the positioning is finished, finishing the whole cycle. According to the invention, environmental force sudden change can be judged and estimated value convergence to a real value can be realized quickly by modifying a posterior mean square error matrix, so that the controller can generate a thrust for compensating the environmental force and deviation between a real position and a set position can be reduced.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Signal processing device, signal processing method and signal processing program for noise cancellation
ActiveUS9805734B2Reduce processing costsWithout delayTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsDigital adaptive filtersAdaptive filterLow distortion
From a mixed signal in which a first signal and a second signal are mixed, the second signal is removed at low processing cost and without delay. As a result, an estimated first signal which has low residue of the second signal and low distortion is obtained.An estimated first signal is generated by subtracting a pseudo second signal which is estimated to be mixed in a first mixed signal in which a first signal and a second signal are mixed from the first mixed signal. The pseudo second signal is obtained by a first adaptive filter using a second mixed signal in which the first signal and the second signal are mixed in a different proportion from the first mixed signal. A coefficient update amount of the first adaptive filter is made smaller as compared with a case when the estimated first signal is smaller than the first mixed signal, in case the estimated first signal is larger than the first mixed signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
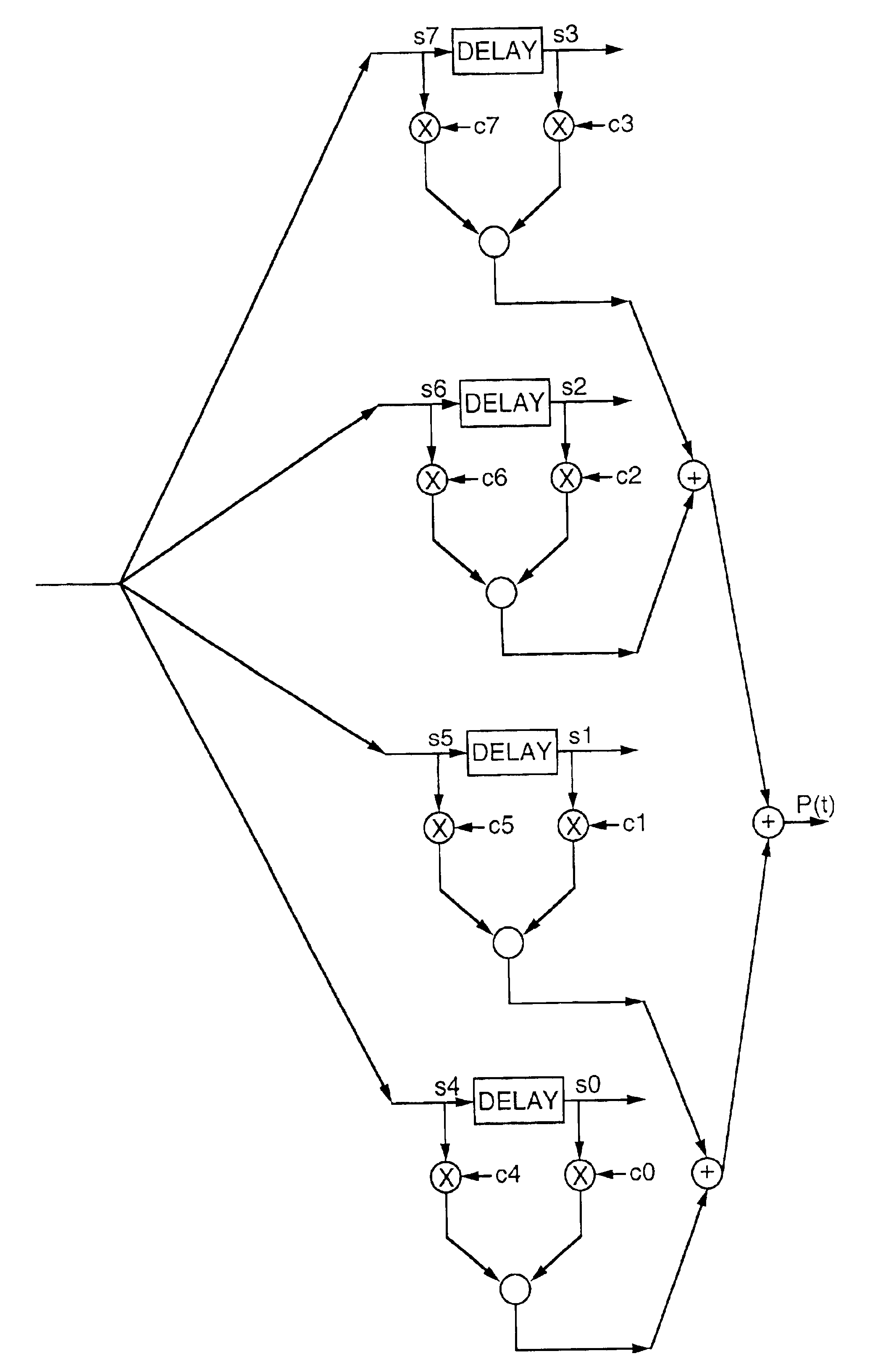
QR-RLS adaptive digital filter with 18-bit pipeline architecture
ActiveUS20120051475A1Fast calculation timeReliable detectionDigital adaptive filtersTransmissionFloating pointSymbol of a differential operator
A QR-RLS adaptive digital filter provides fast computation without excessive computational resources. 18-bit multipliers enhance speed, and a floating point inverse square root block adjusts dynamic range in 12-dB steps. A memory stores two P-matrix copies, one being delivered with rows shifted according to the clock speed so as to enhance pipeline processing. Embodiments reliably detect modulation schemes, demodulate strong signals by passing feedback bits between multiple stages, remove impulses due to lightening, etc, erase symbol estimates which exceed an error threshold, and add high frequency noise to avoid mathematical divergence caused by excessive S / N. A genetic method is provided for identifying asynchronous spreading codes with minimum correlations, whereby randomly selected candidates compete based on Frobenius norms of their correlations, the weakest being discarded and the process being iterated. A method is provided for selecting optimal filter sampling windows for simultaneously detected symbol streams having relative timing delays.
Owner:COLLISION COMM
Filtering method based on norm regularization discrete linear system, and discrete linear system
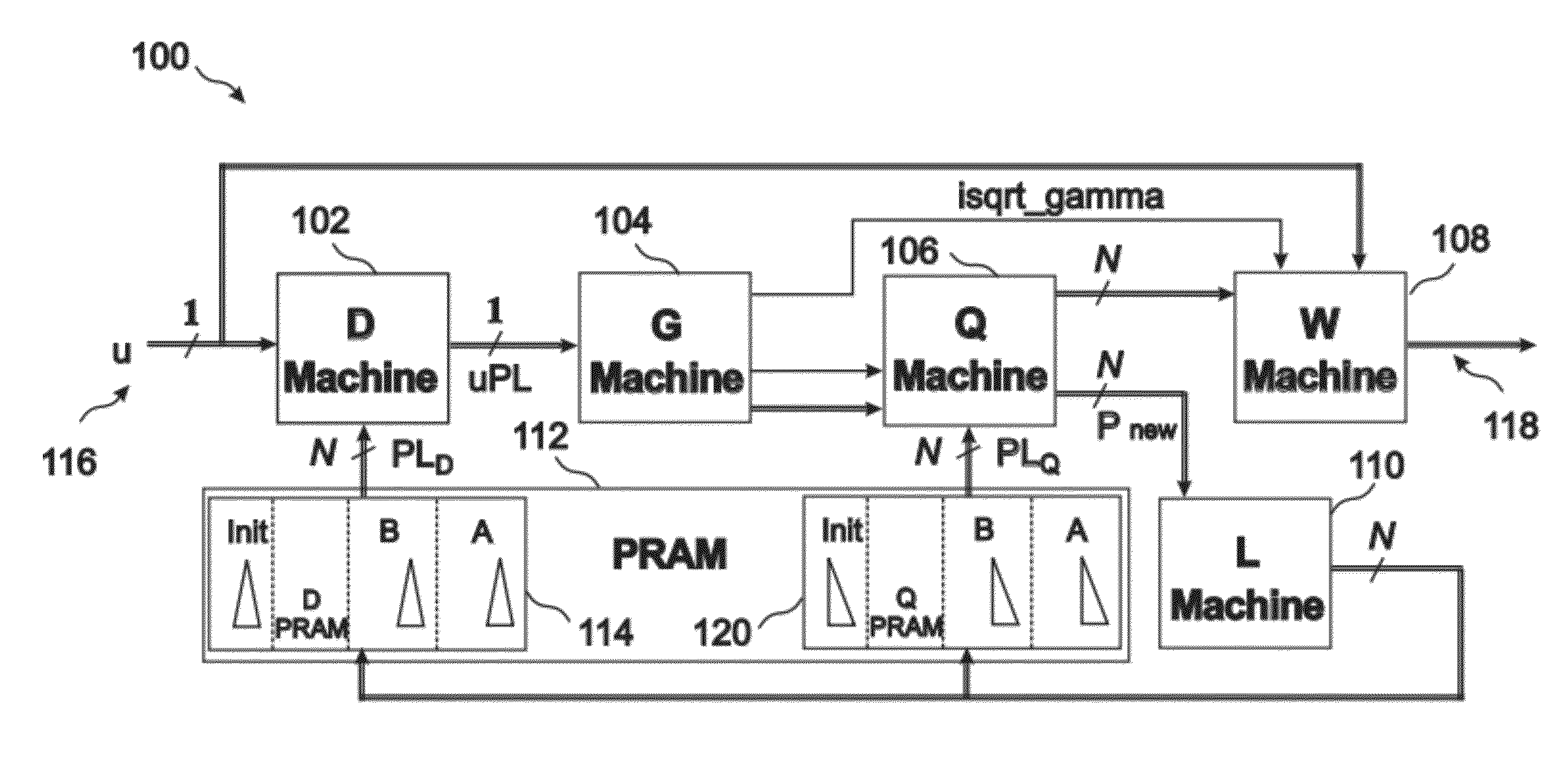
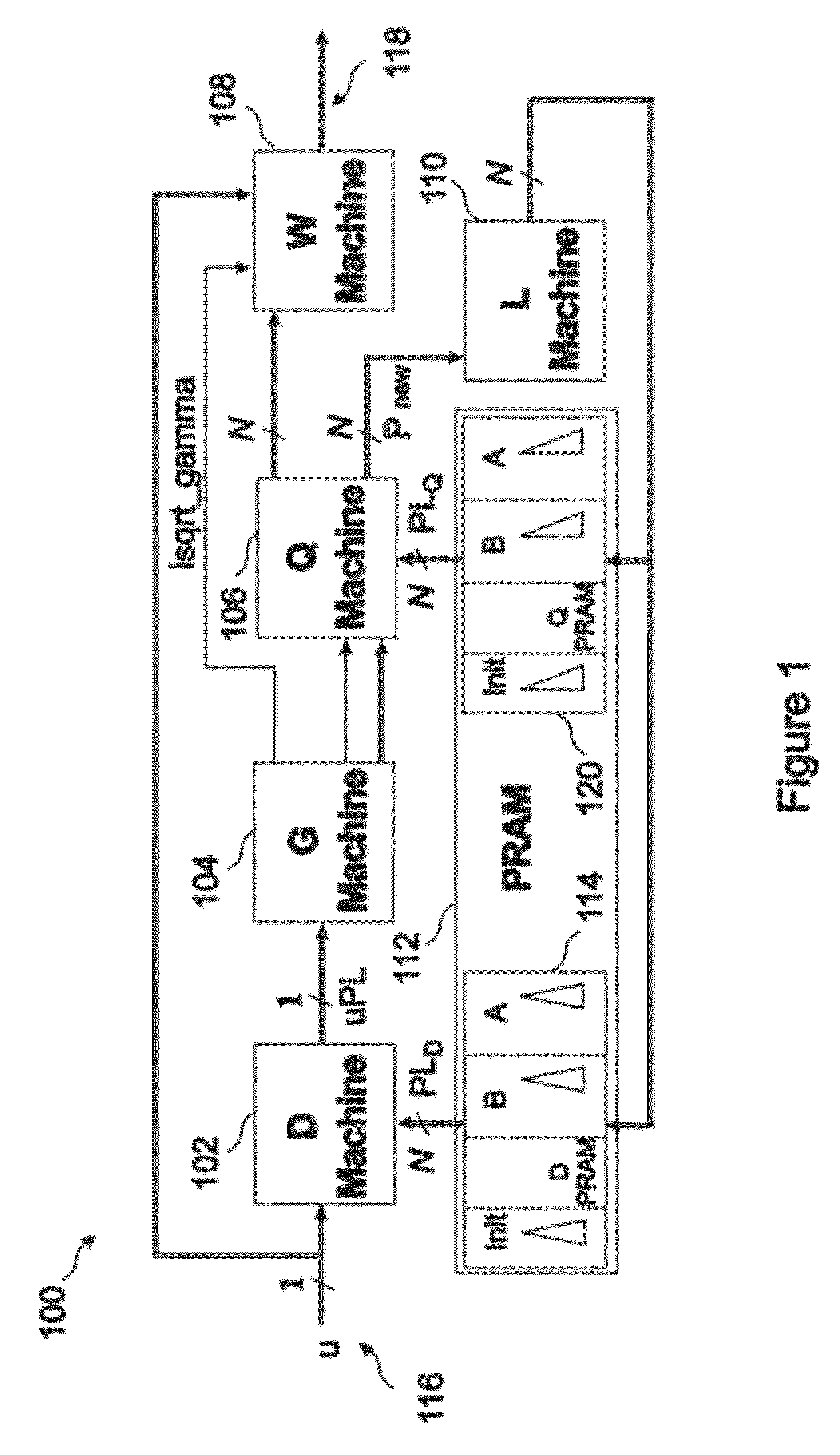
PendingCN111010145AProof of validityPromote sparse solutionsDigital technique networkDigital adaptive filtersPattern recognitionDiscrete linear system
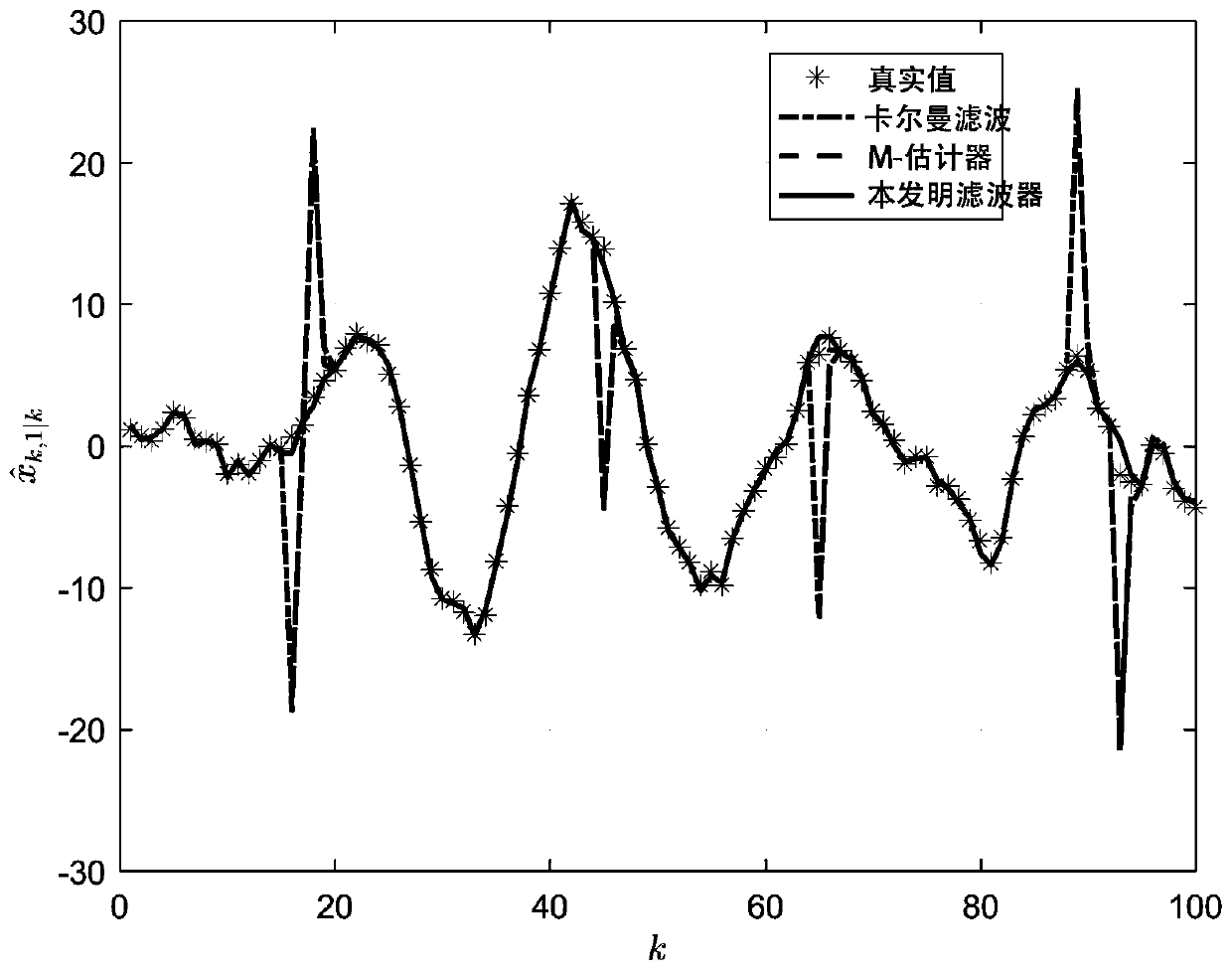
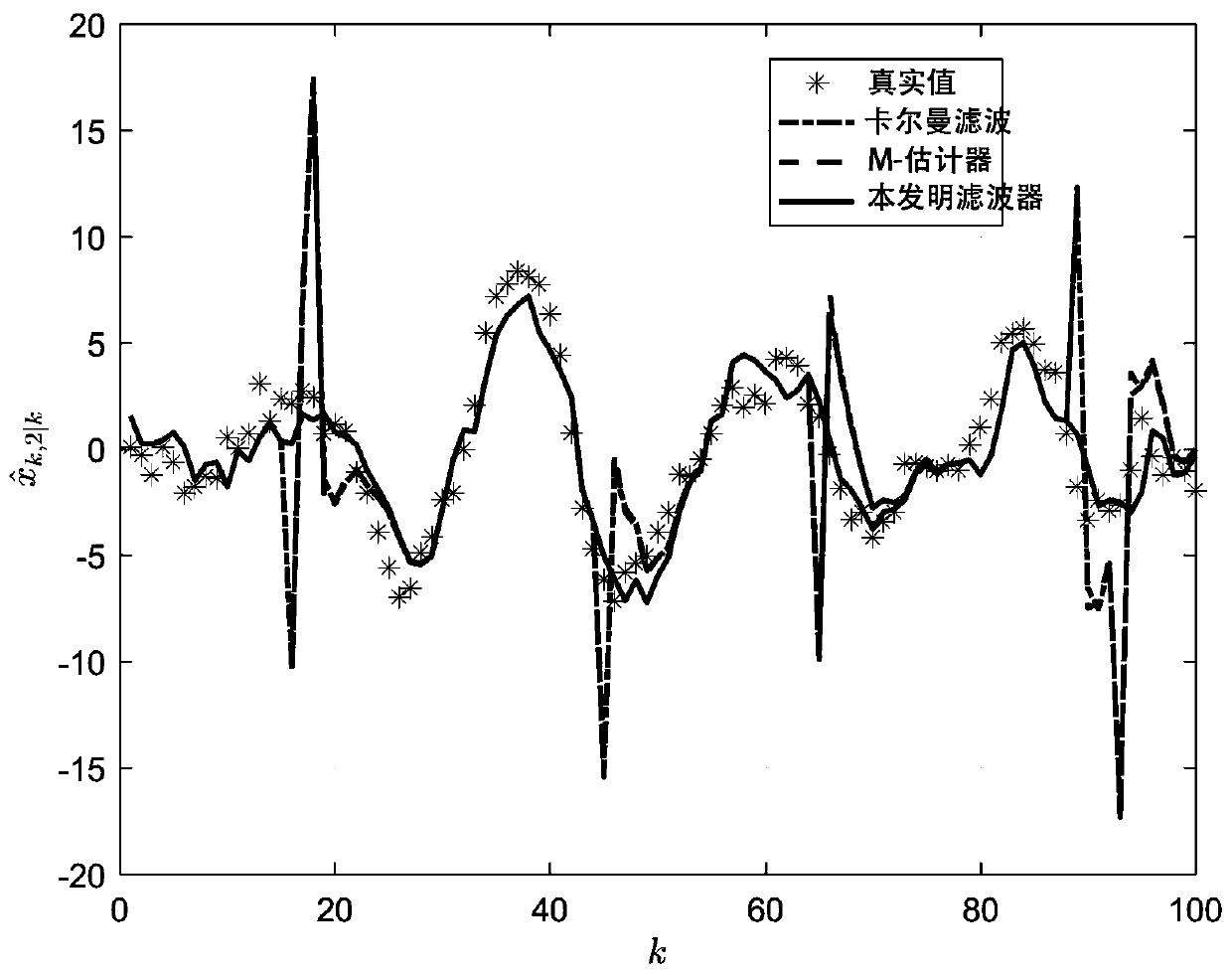
The invention belongs to the technical field of discrete linear system filtering, discloses a filtering method based on a norm regularization discrete linear system, and the discrete linear system, and uses l1-norm regularization to explicitly model and estimate an outlier and obtain a sparse solution. Due to the fact that explicit modeling is carried out on the outlier, the negative effect of theoutlier propagating through noise correlation can be estimated and reduced, and a more accurate estimation result can be obtained. According to the invention, the method provided by the invention provides the flexibility of allocating different penalty weights to the state outlier and the measurement outlier respectively, which is difficult to realize in a common M estimation method. By selectingproper regularization parameters, the proposed filter can be simplified into a linear optimal Kalman filter, so a good balance can be provided between robustness and optimality, and the effectivenessand superiority of the proposed robust filtering method are proved by using examples of simulation and experimental data.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com