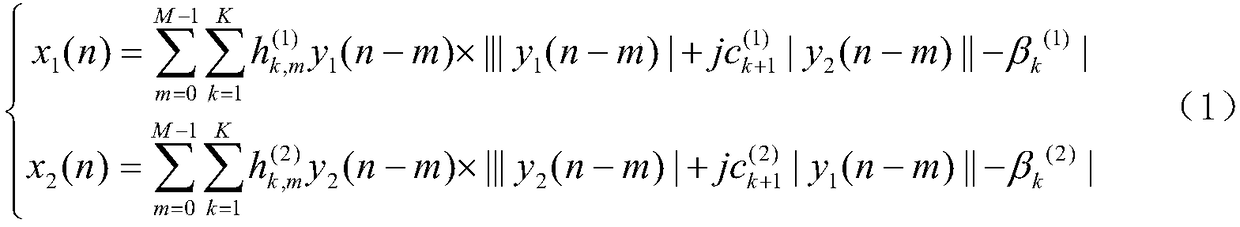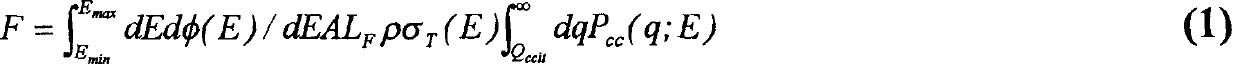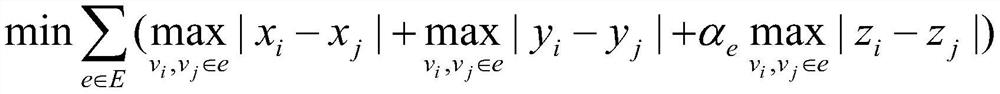Patents
Literature
93results about How to "Fast calculation time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
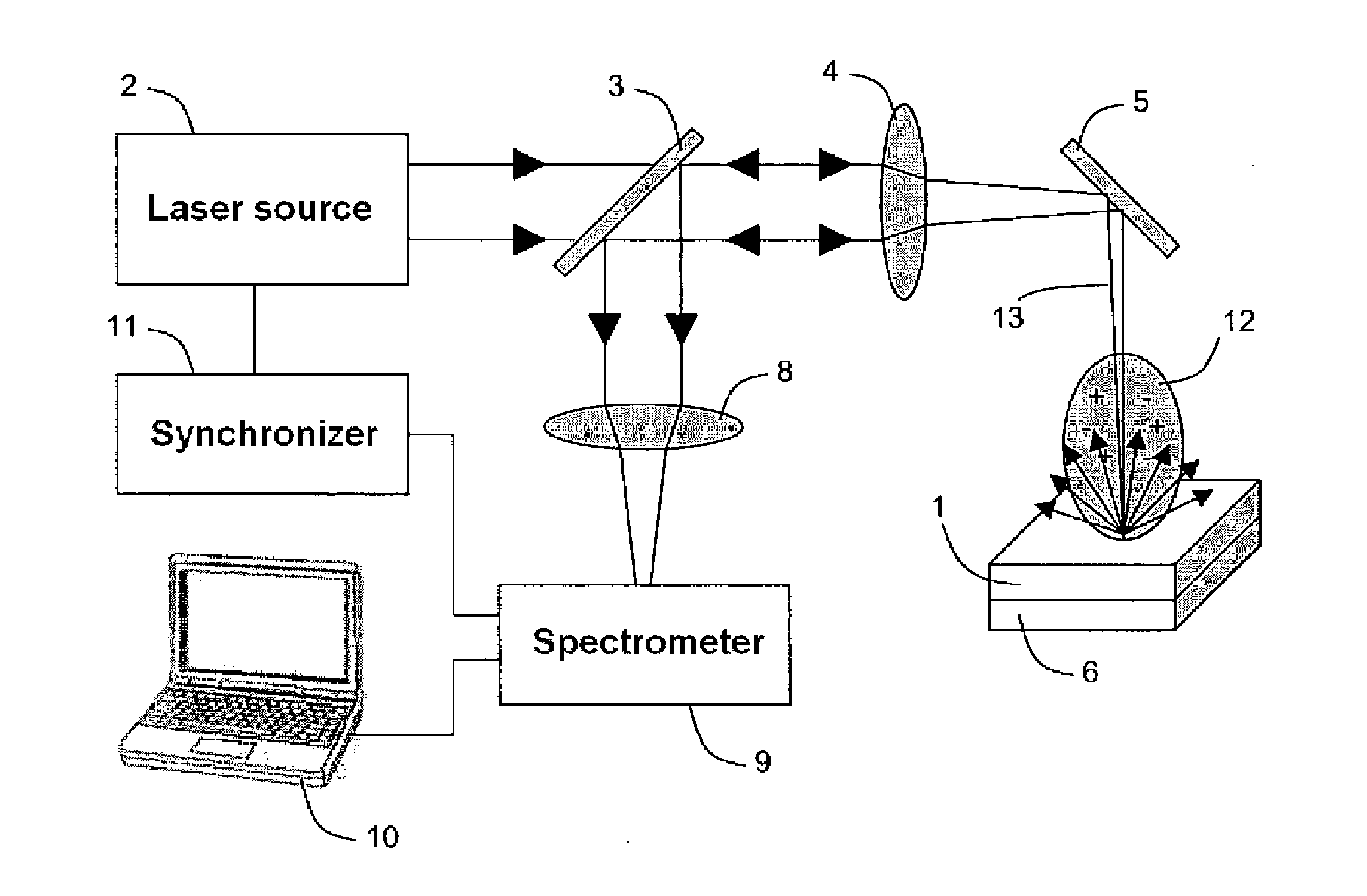
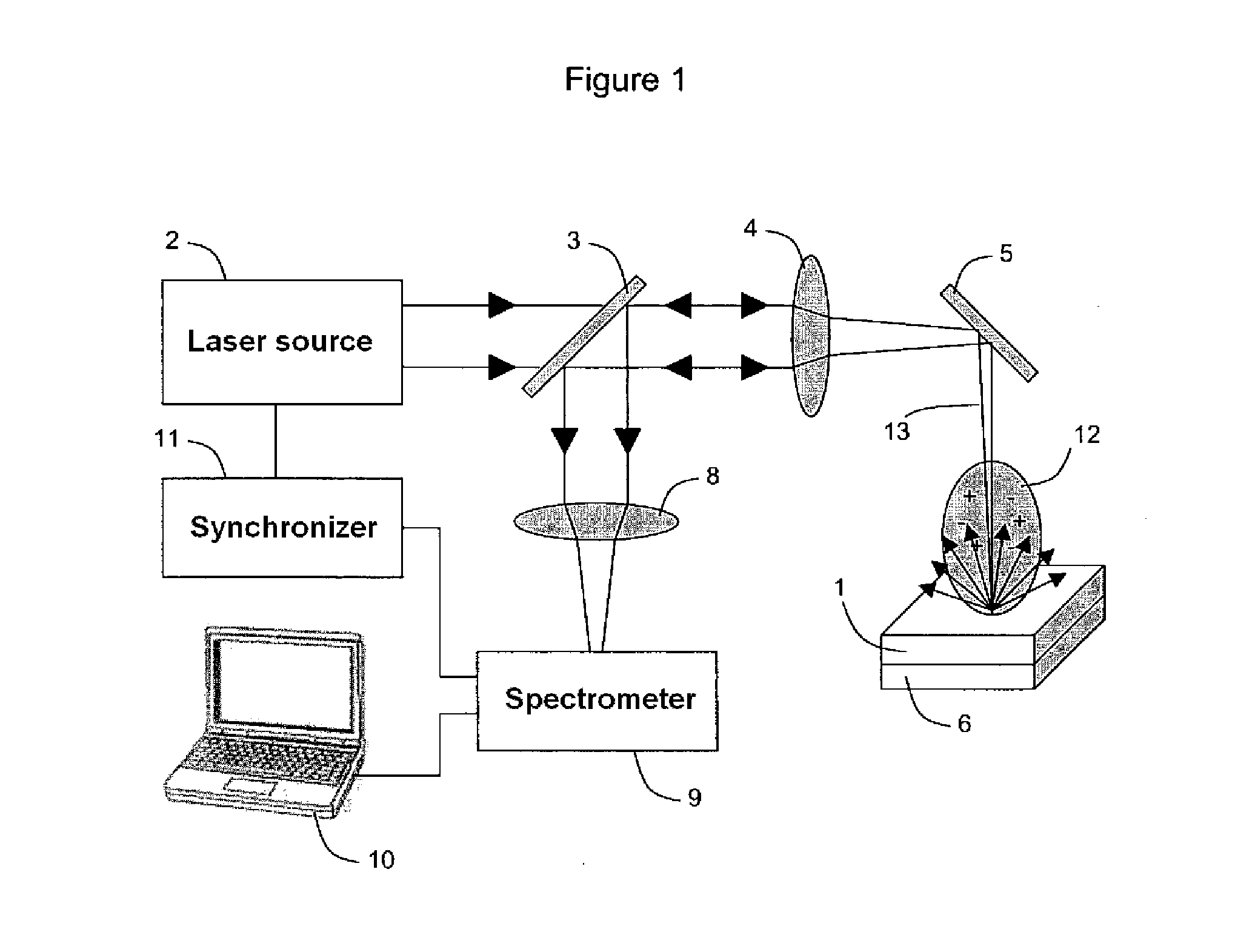
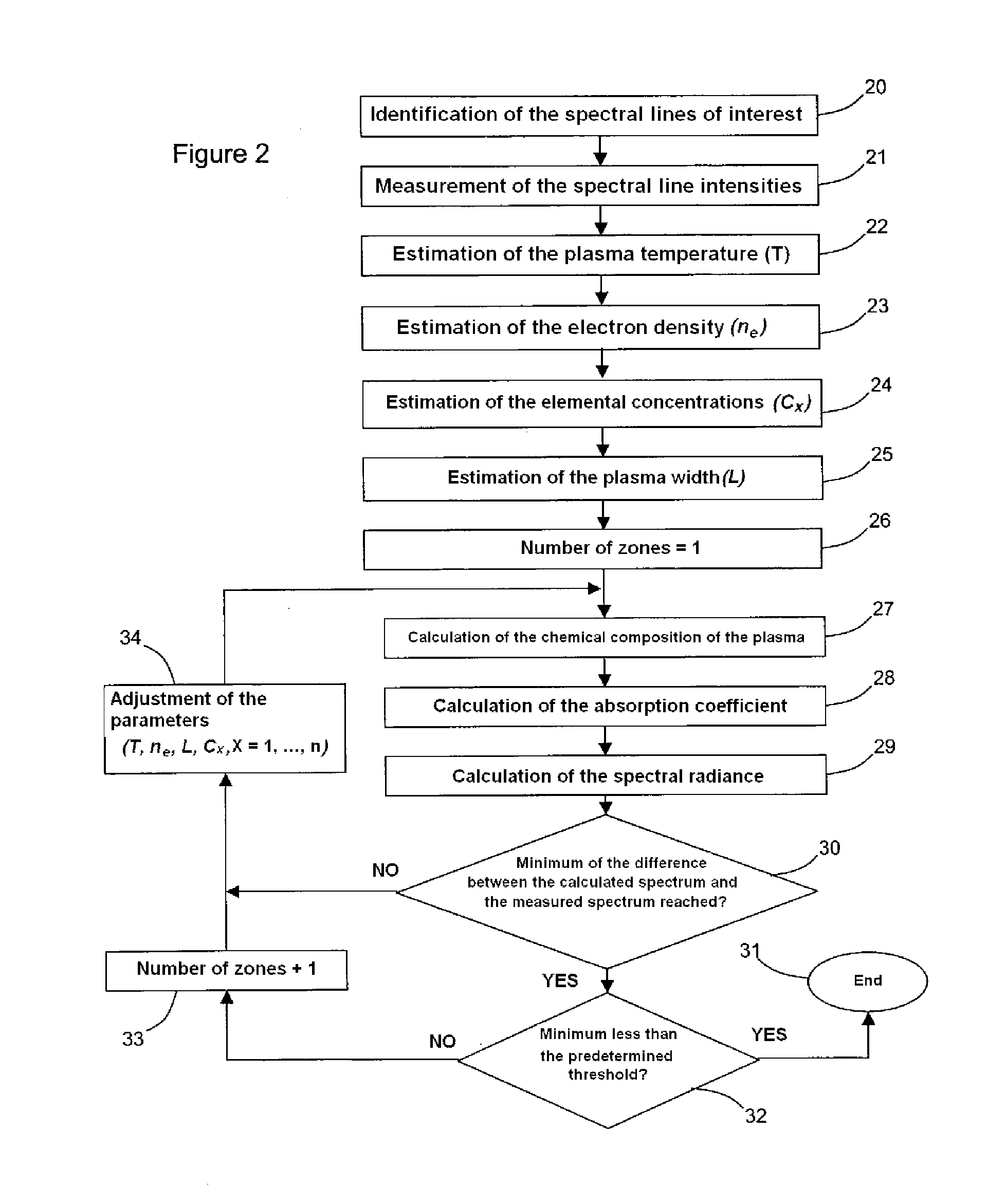
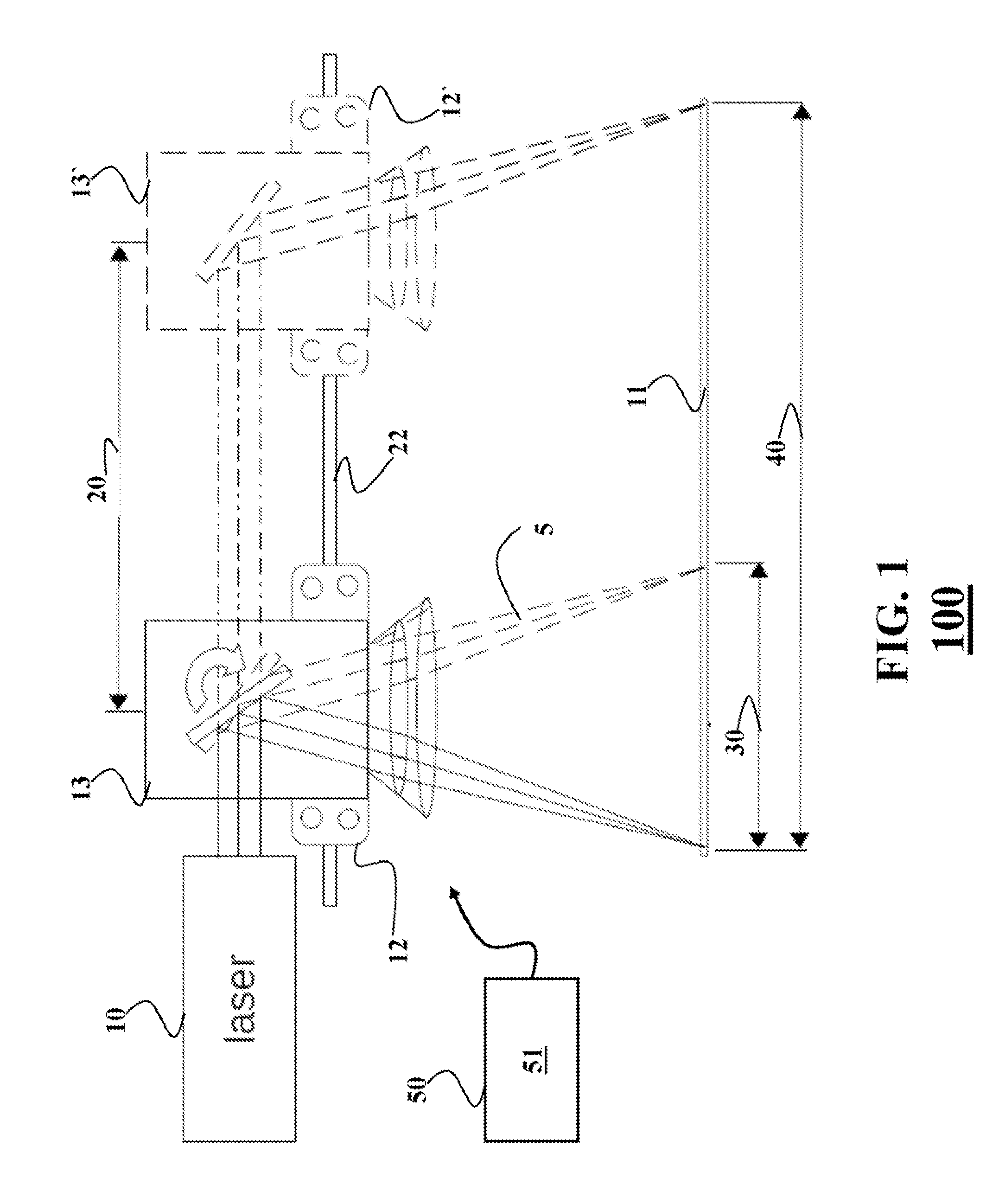
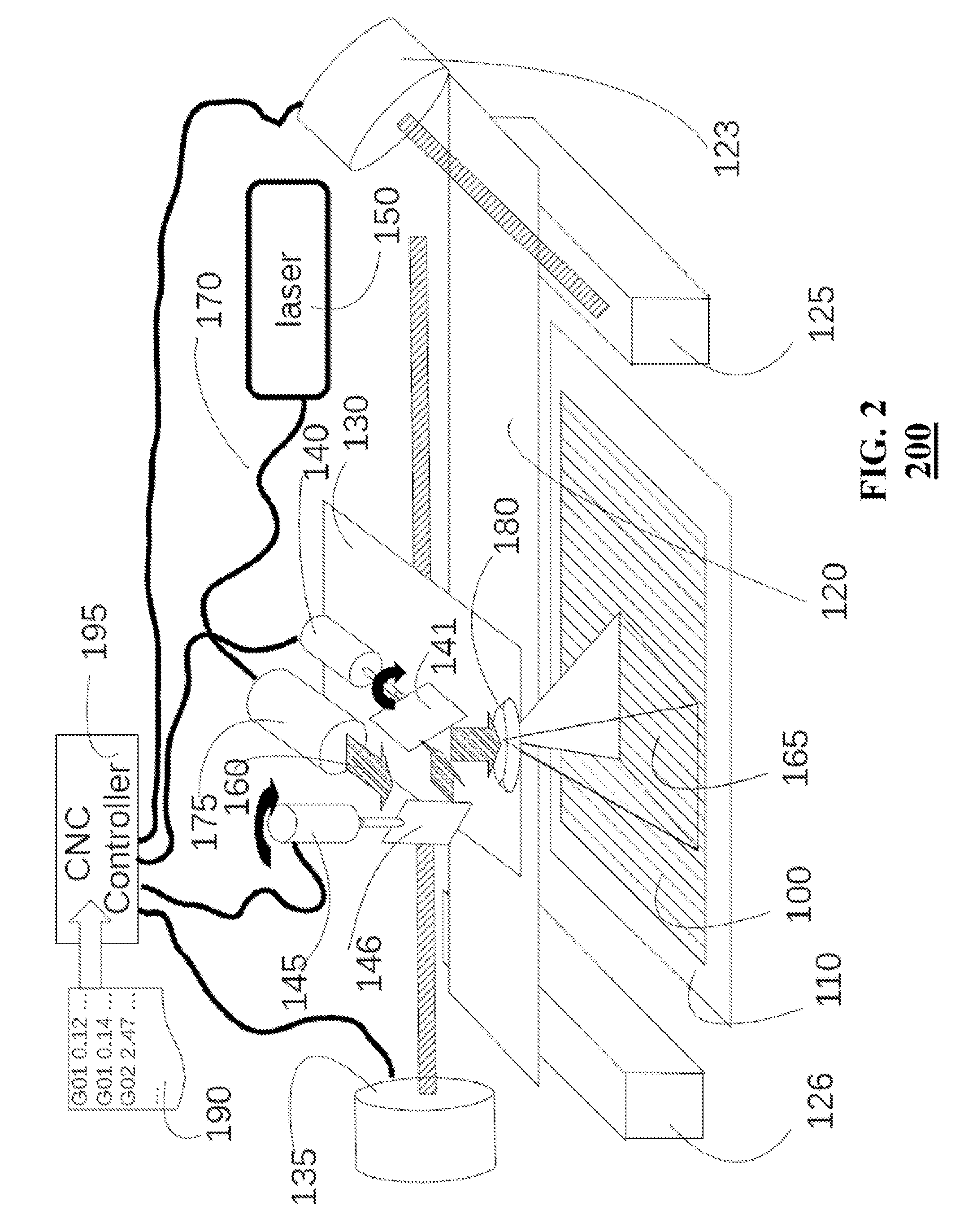
System and method for quantitative analysis of the elemental composition of a material by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS)
ActiveUS20120029836A1Quick calculationShort calculation timeEmission spectroscopyAnalysis by thermal excitationElemental compositionChemical composition
A system and method for measuring elemental concentrations of a material from a sample containing several elements by LIBS analysis. The material is heated to generate plasma and its chemical composition is determined from spectral analysis of its radiation. The spectral lines of interest are identified among those emitted by the constituents of each element composing sample. The intensities of the spectral lined identified are measured. From an estimate of temperature, electron density and relative concentration values, the chemical composition of the plasma is calculated. The absorption coefficient according to wavelength is calculated for the spectral zones of the lines of interest. From an estimate of the plasma width, the spectral radiance of the plasma is calculated for the same spectral zones and then a comparison of the intensity and shape of the spectrum thus calculated with those of the spectrum measured is performed. These calculations and this comparison are repeated iteratively in order to adjust the temperature, electron density, relative values of the elemental concentrations and width of the plasma.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Determining Trajectories of Redundant Actuators Jointly Tracking Reference Trajectory
InactiveUS20140114463A1Fast computation timeNumber of usedSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical controlError toleranceActuator
A method determines trajectories of redundant actuators of a machine including a first actuator and a second actuator. The method determines a first trajectory of the first actuator tracking a reference trajectory with an error tolerance, wherein the error tolerance is a function of a constraint of the second actuator, and determines a second trajectory of the second actuator based on a difference between the reference trajectory and the first trajectory.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Short-term load predicting method based on quick fuzzy rough set
ActiveCN104239968ASmall amount of calculationReduce lossesForecastingInformation technology support systemLoad forecastingFuzzy rough sets
The invention discloses a short-term load predicting method based on a quick fuzzy rough set. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, electrical load data recorded by an electricity meter installed in a power grid are collected, and an initial attribute decision table is constructed; secondly, a fuzzy subordinate function of the condition attribute and the decision attribute is determined; thirdly, the attribute reduction is carried out according to the quick fuzzy rough set method, and the reduction condition attribute is obtained; fourthly, the reduction condition attribute serves as input data of a neural network to train normalized historical load data; fifthly, the neural network obtained through training is utilized for carrying out the short-term load prediction on an electric power system; sixthly, reverse normalization processing is carried out on the obtained normalization value of the maximum load of the prediction day, and a short-term electric power load prediction result is obtained and is the maximum load of the prediction day. The computing amount of the fuzzy rough set attribute reduction is small, the computing time is short, and the computing efficiency is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
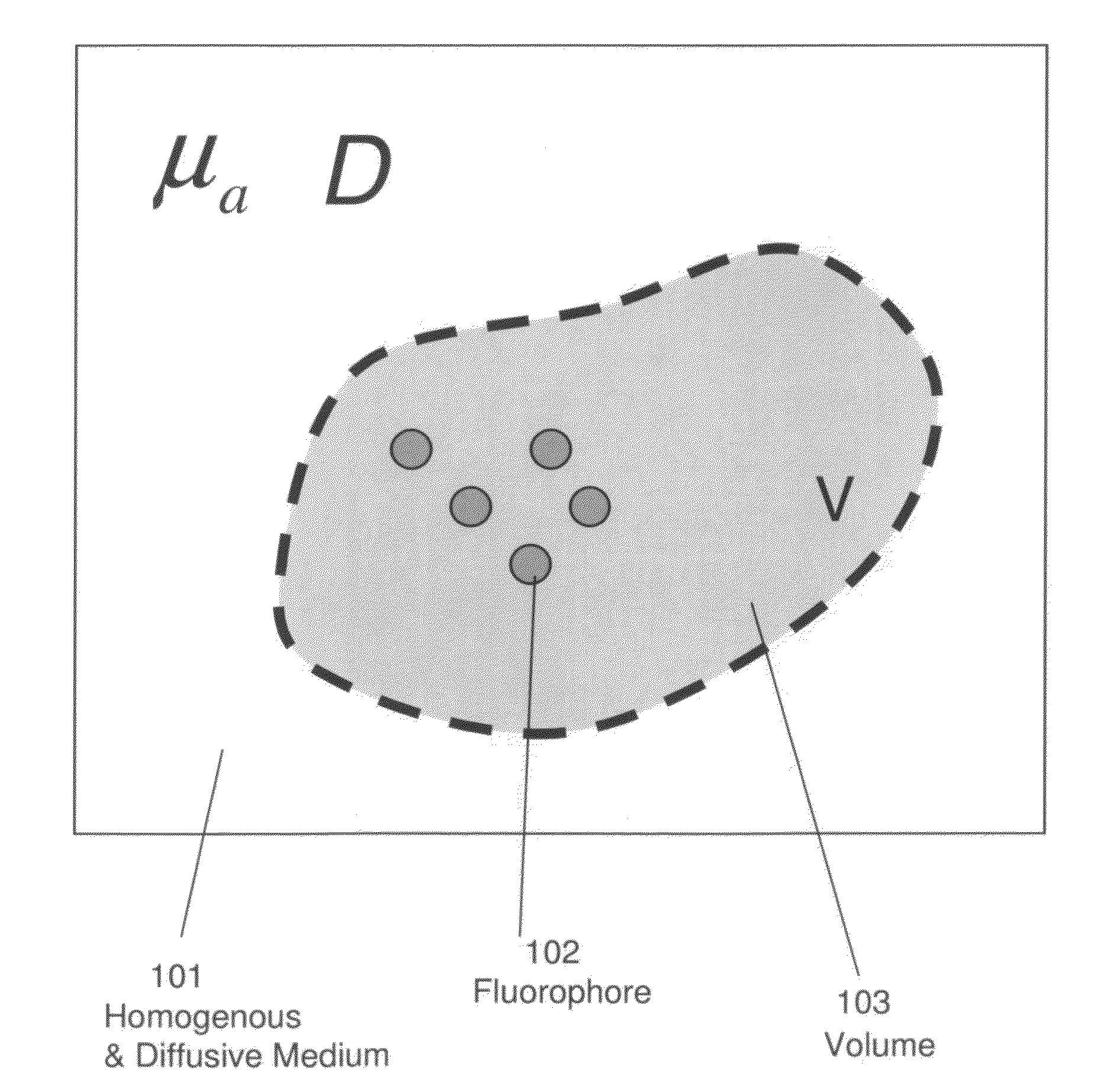
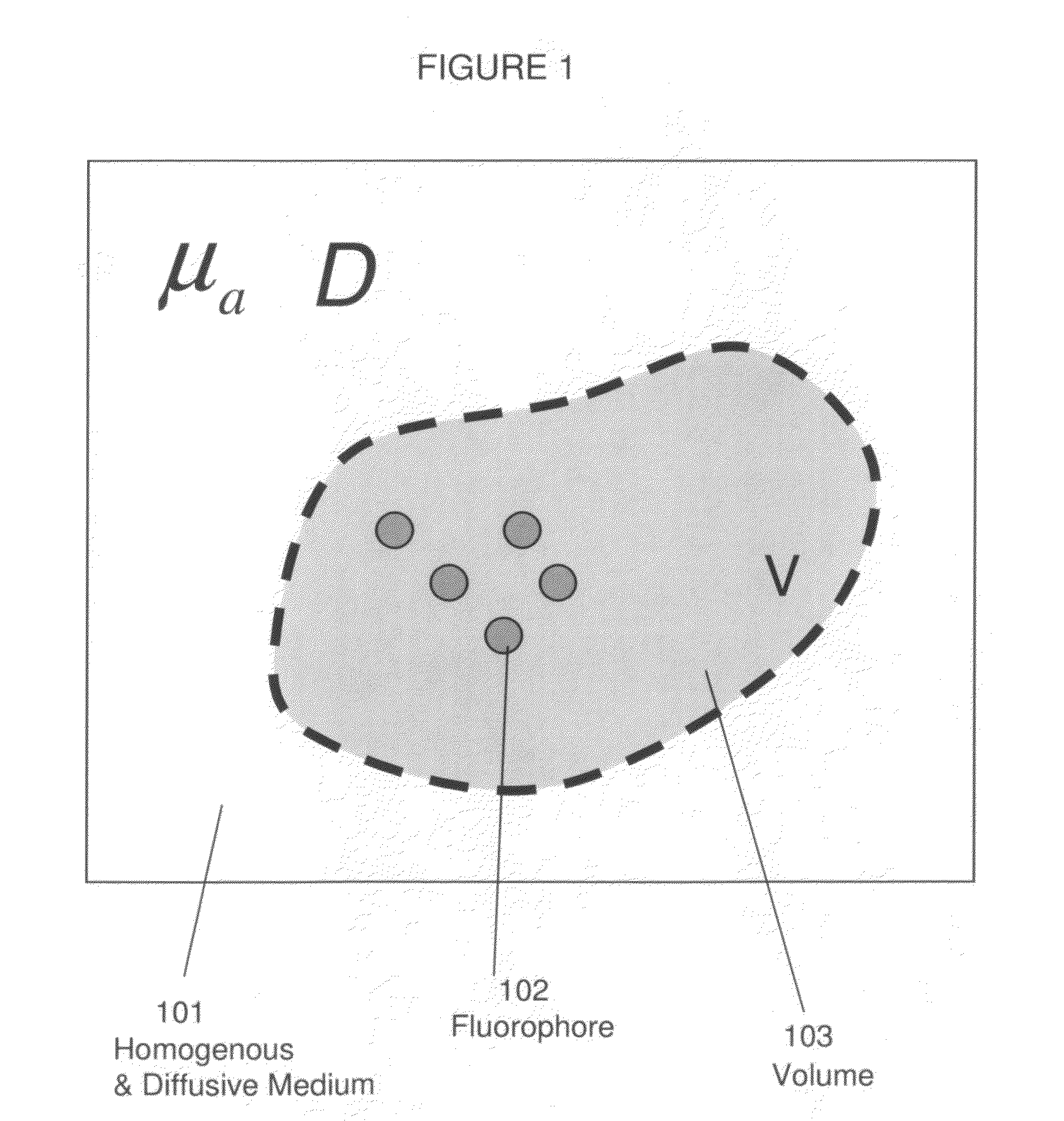
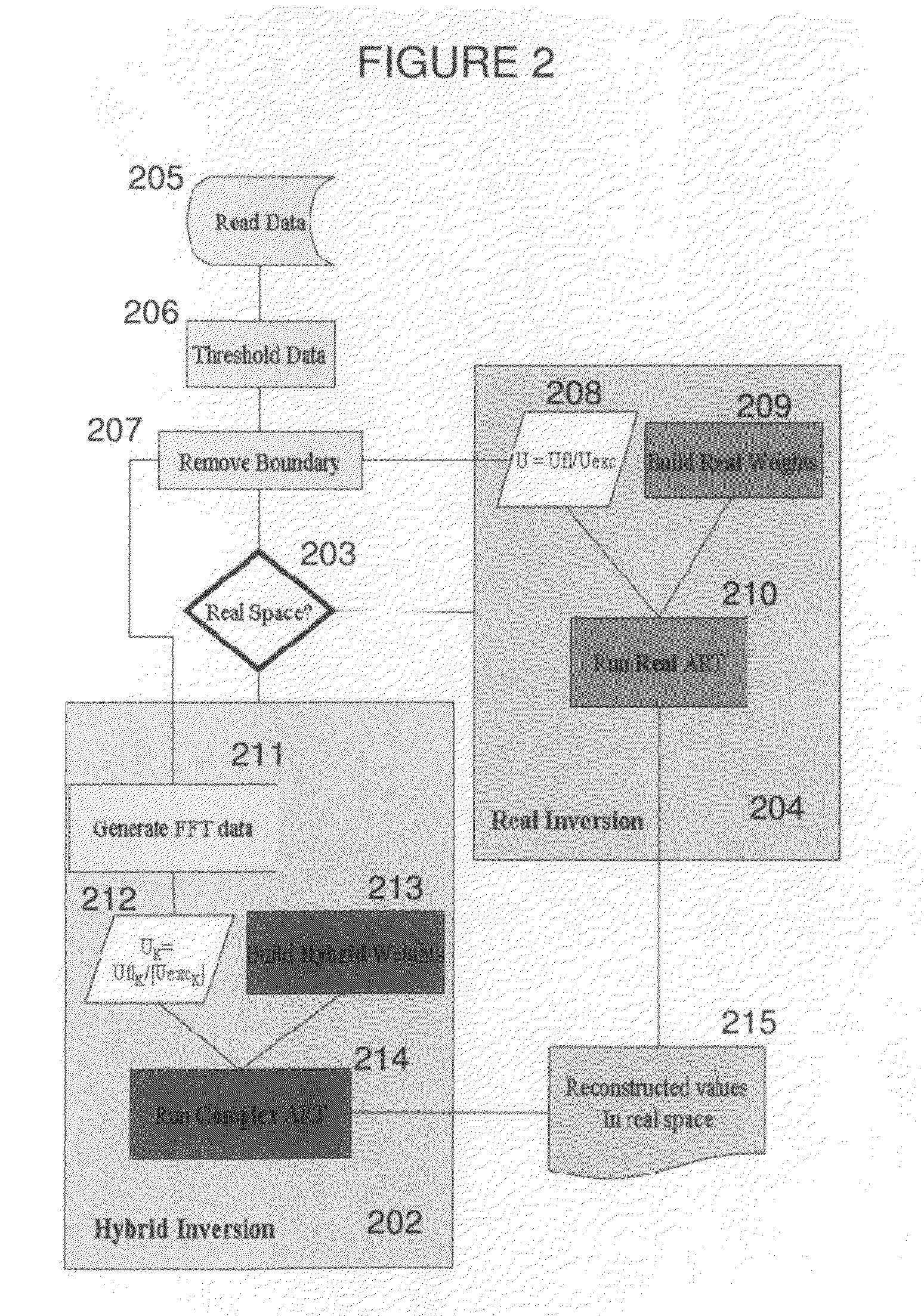
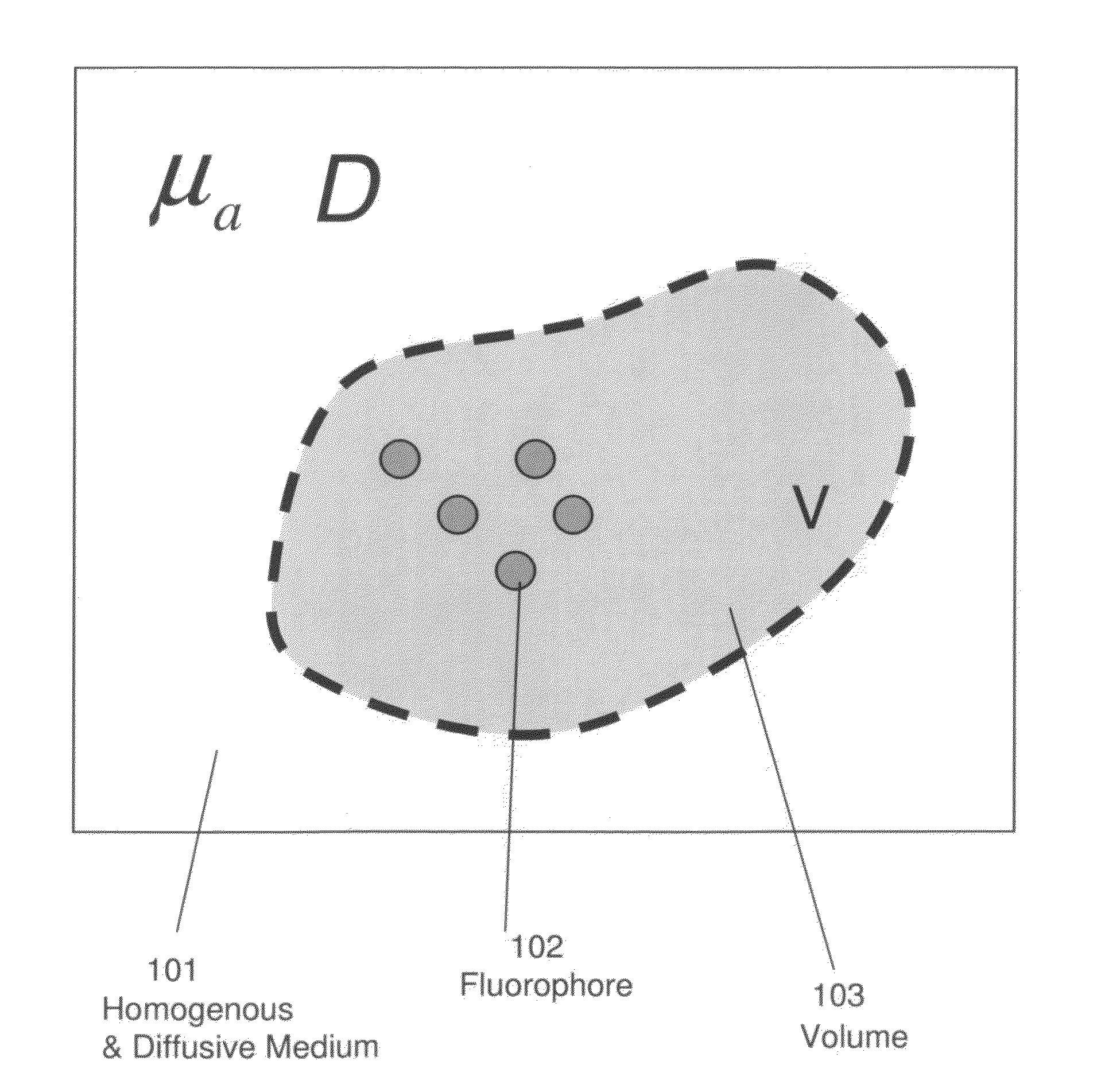
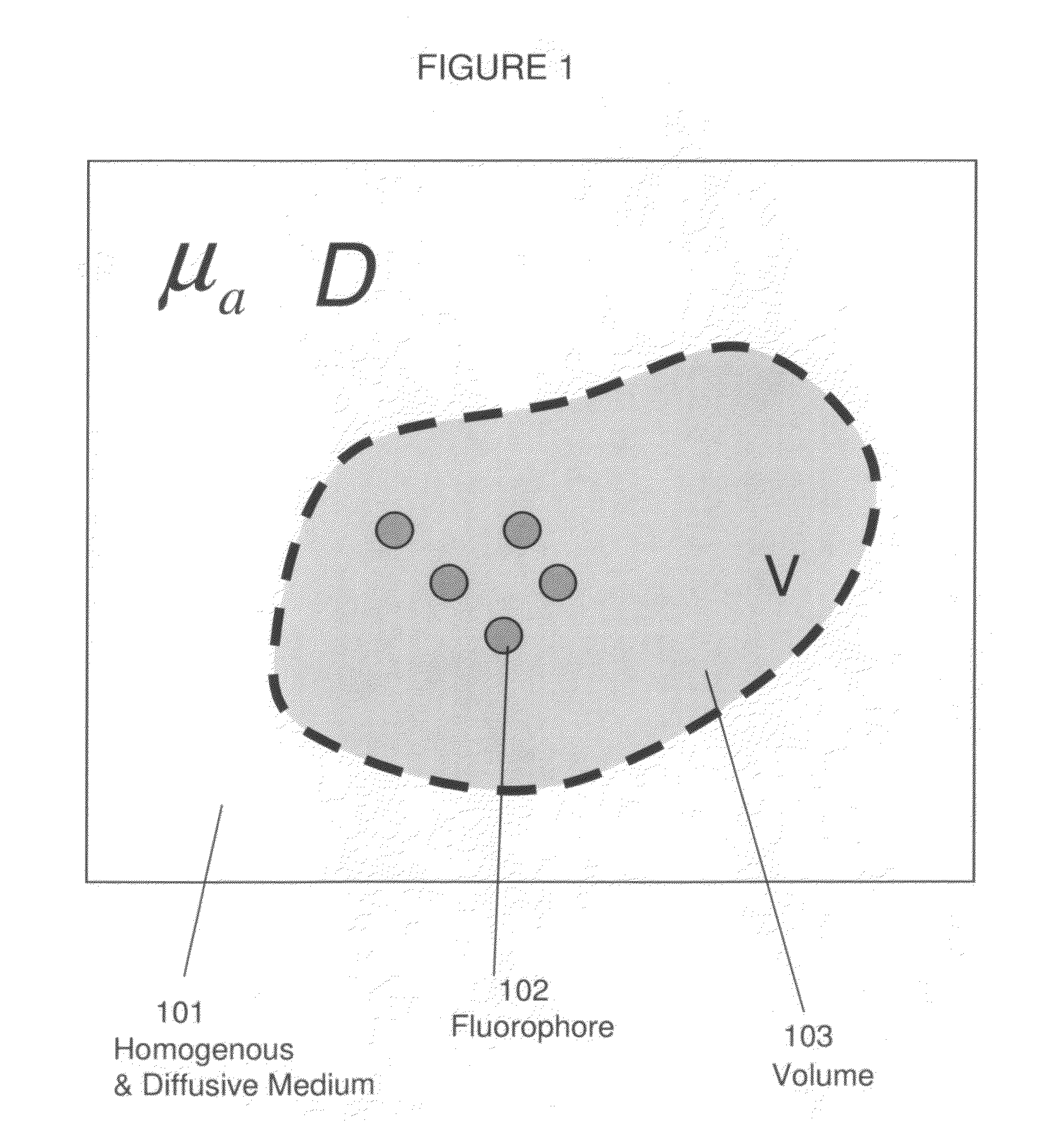
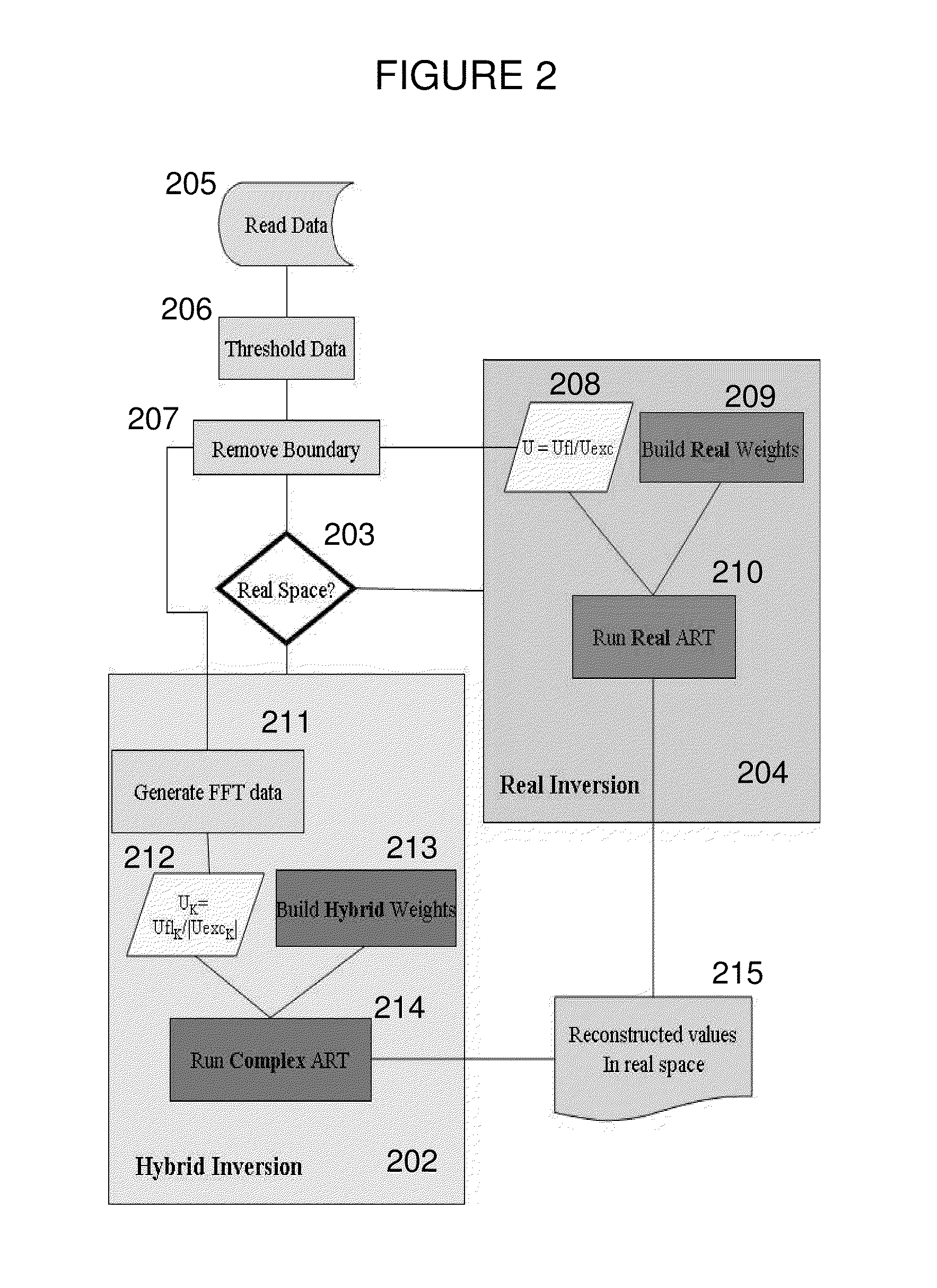
Systems and methods for tomographic imaging in diffuse media using a hybrid inversion technique
ActiveUS20110060211A1Fast rebuildGood tomographic reconstruction performanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsReconstruction from projectionTomographic reconstructionFluorophore
The invention relates to systems and methods for tomographic imaging in diffuse media employing a fast reconstruction technique. A hybrid Fourier approach is presented that enables the fast tomographic reconstruction of large datasets. In certain embodiments, the invention features methods of in vivo fluorescence molecular tomographic (FMT) reconstruction of signals, reporters and / or agents (i.e., contrast agents or probes) in a diffusive medium (e.g., a mammalian subject). The method preserves the three-dimensional fluorophore distribution and quantitative nature of the FMT approach while substantially accelerating its computation speed, allowing FMT imaging of larger anatomies.
Owner:VISEN MEDICAL INC
Underwater multi-target tracking method
InactiveCN103645487AOvercoming the Constraints of ManeuveringIncrease flexibilitySatellite radio beaconingComputation complexityMulti target tracking
Disclosed in the invention is an underwater multi-target tracking method. A wireless sensor network positioning system comprises a plurality of sensor nodes, a cluster head node and a control system. For the system positioning, an improved resampling non-augmented tasteless particle filtering algorithm is used to realize target positioning based on sensor network configuration. Because the algorithm fully utilizes information measured at current time at the current orientation to estimate a particle posterior probability density function, a defect that particle selection has blindness according to a PF algorithm is overcome, so that the approximate and better positioning precision can be realized under the circumstances that a few particles exist. Moreover, there is no need to expand the state dimension in a vector, so that the calculation complexity can be substantially reduced, the calculation time is improved, and the system can be realized in real time.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
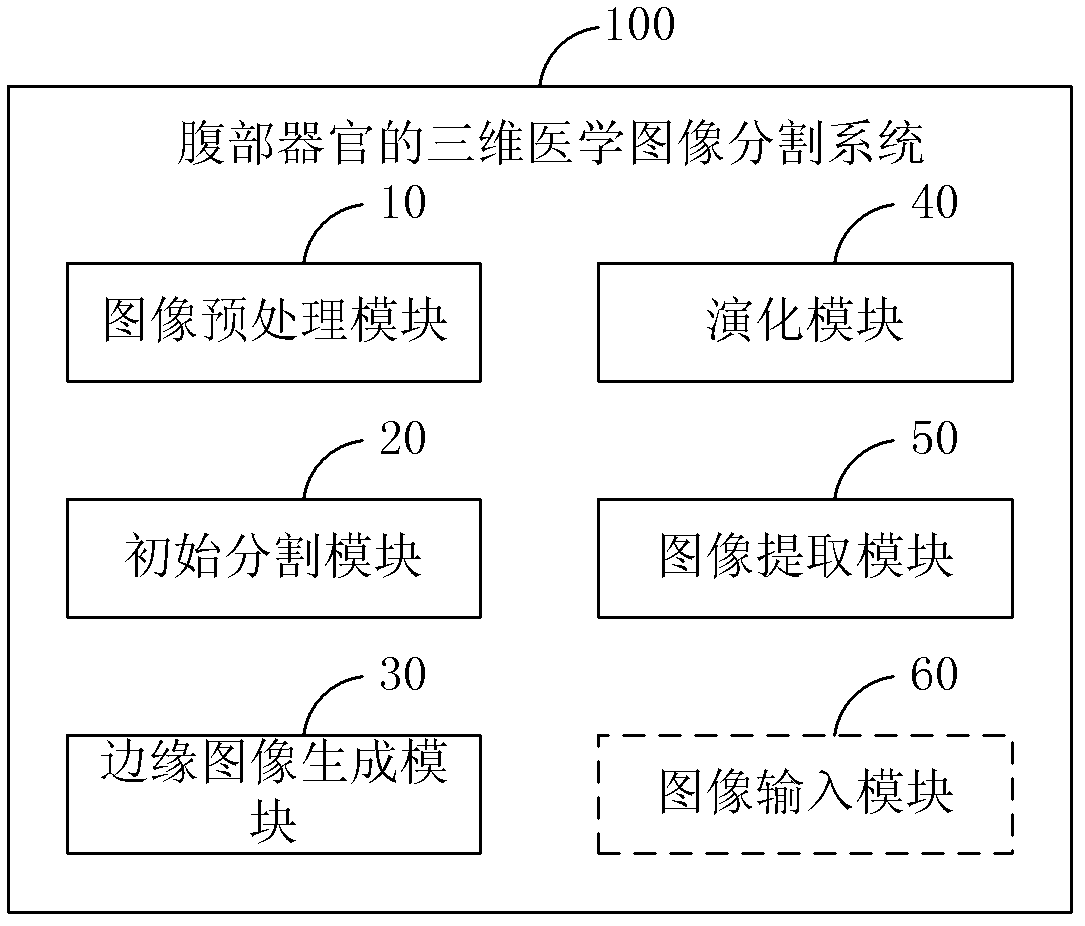
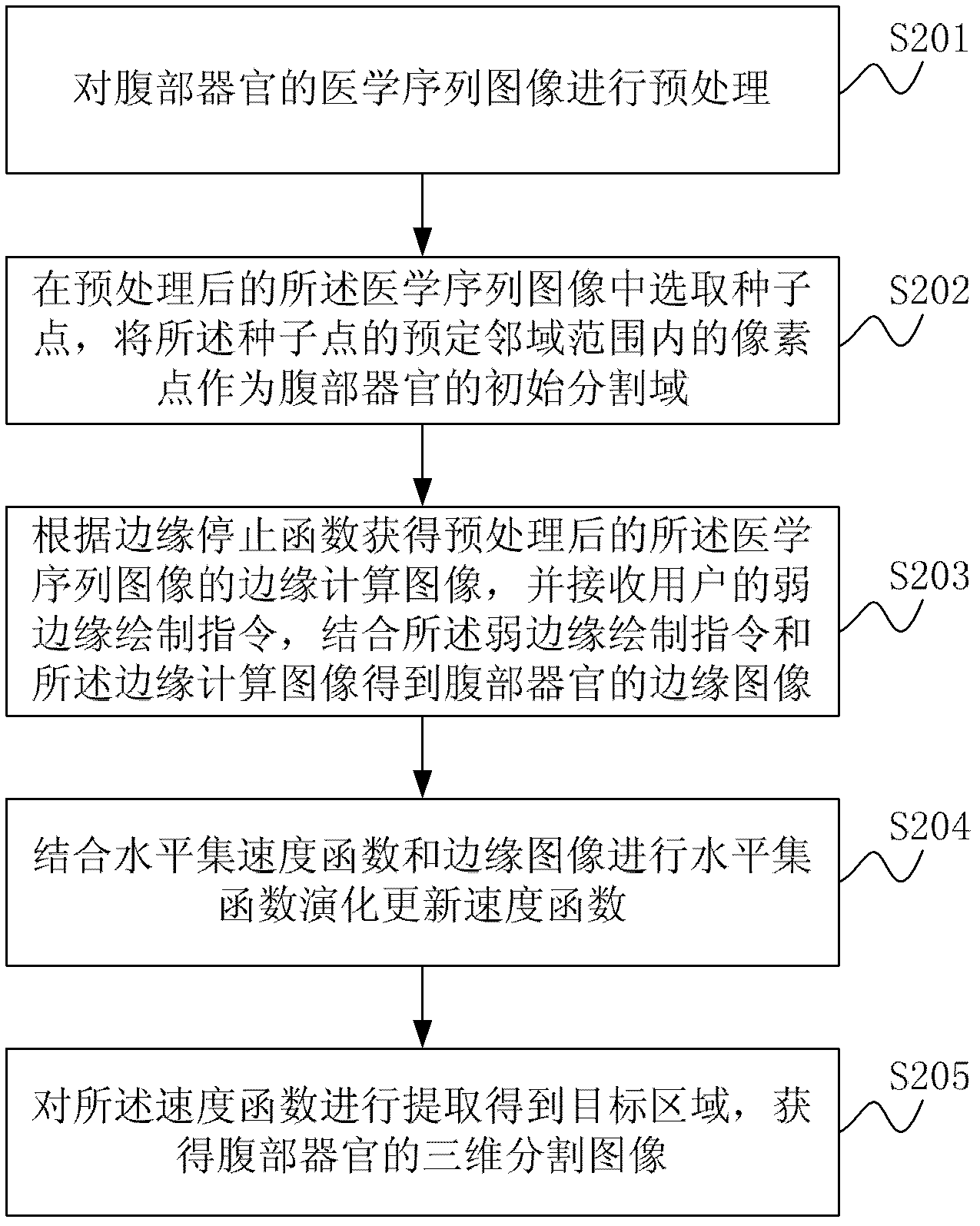
Method and system for dividing up three-dimensional medical image of abdominal organ
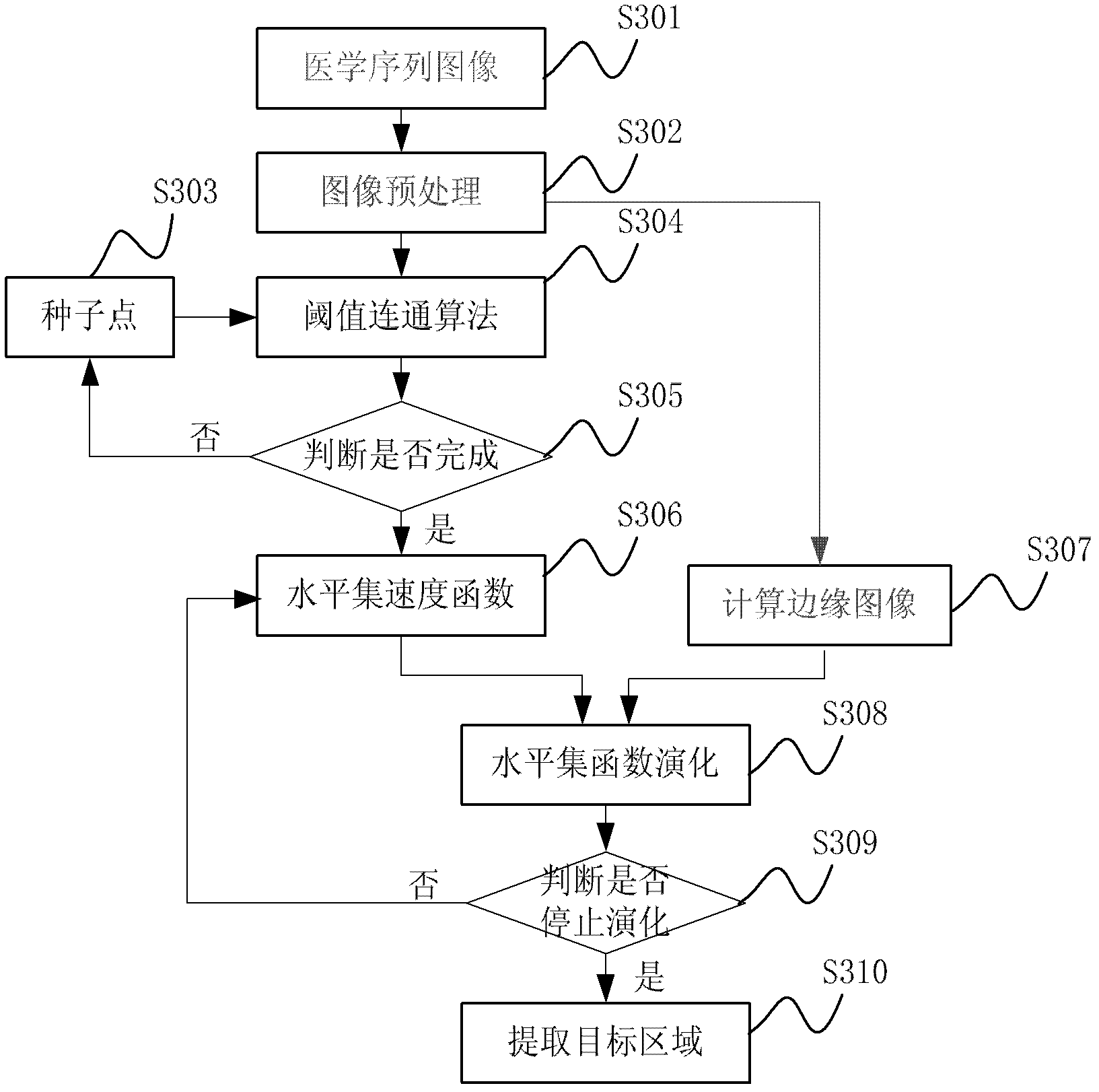
InactiveCN102306373AQuality improvementEasy to analyzeImage enhancementImage segmentationVelocity function
The invention discloses a method and a system for dividing up a three-dimensional medical image of an abdominal organ. The method comprises the following steps of: preprocessing a medical sequence image of the abdominal organ; selecting a seed point from the preprocessed medical sequence image, and using a pixel point in a preset neighborhood range of the seed point as an initial division region of the abdominal organ; acquiring an edge calculation image of the preprocessed medical sequence image according to an edge stop function, and receiving a feebleness edge drawing instruction of a user to obtain an edge image of the abdominal organ by combining the feebleness edge drawing instruction with the edge calculation image; performing level set function evolution to update a velocity function by combining a level set velocity function with the edge image; and extracting the velocity function to obtain a target region. Therefore, according to the invention, the problem of fuzzy boundary in medical image division is solved by using a user interaction type input boundary fuzzy boundary, and the quality of the three-dimensional division image of the abdominal organ is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN YORATAL DMIT
Quick measurement method for blade curved surface
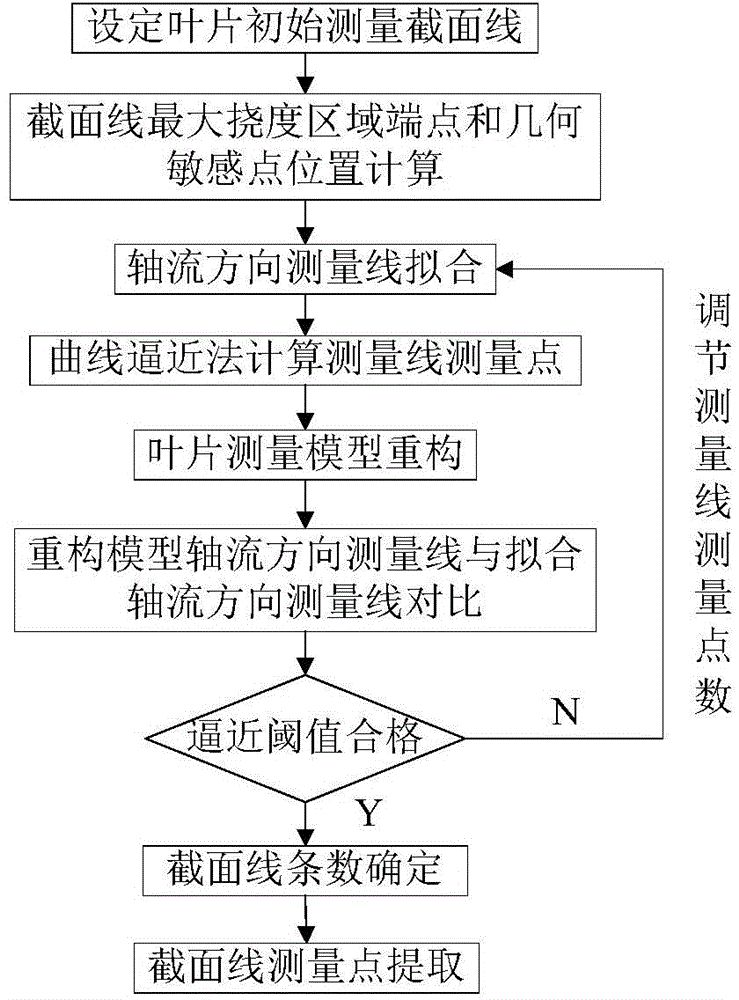
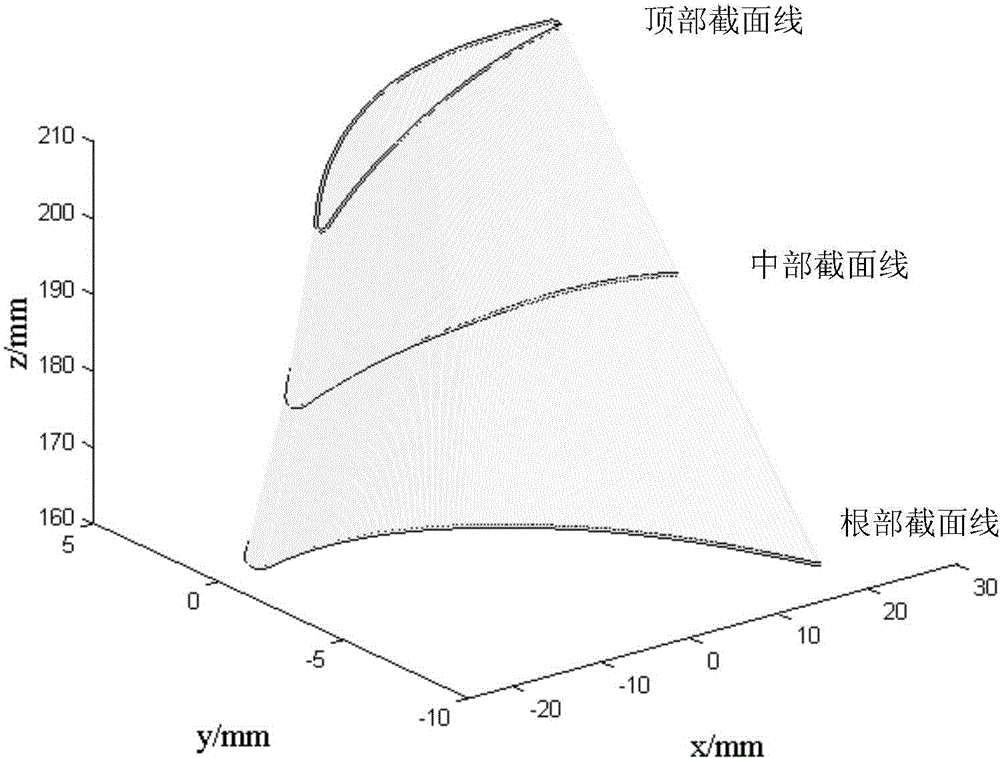
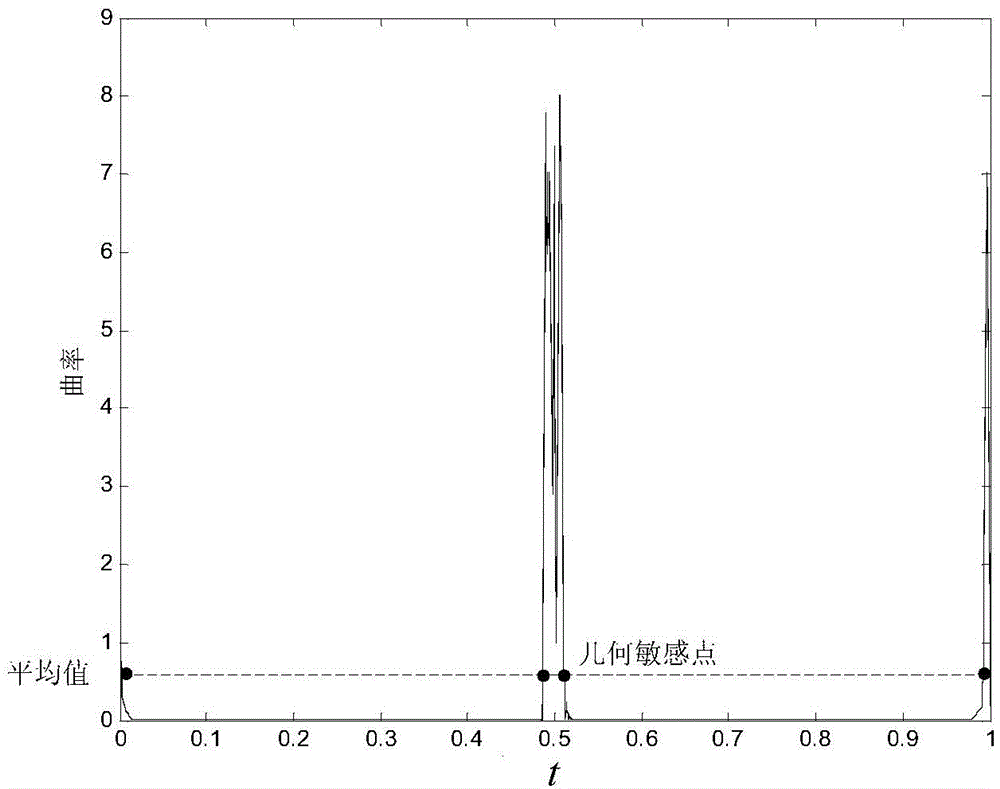
InactiveCN104864829AGuaranteed dynamic performanceGuaranteed measurement accuracyMeasurement devicesMeasurement pointEngineering
The invention relates to a quick measurement method for a blade curved surface, belonging to the field of blade measurement. The method comprises the following steps: firstly determining endpoints of the maximum deflection region of section lines and geometric sensitive positions of front and back edges; planning a measurement curve of an axial direction of a blade; calculating measurement points of the axial curve by virtue of a curve approximation method so as to further determine the measurement section of the blade; partitioning the region according to the drastic characteristic of the curvature of the section line; quickly extracting the measurement points of the section line by virtue of double rules of the curvature and Hausdorff distance; and planning a measurement point set of each section line. The method has the advantages that the measurement of the blade curved surface is carried out by applying the method, so that the quantity of the measurement points is greatly reduced, and the measurement efficiency of the blade is remarkably improved on the premise of ensuring the precision of the profile of the blade.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Parallel computing hardware structure based on separation and combination thought
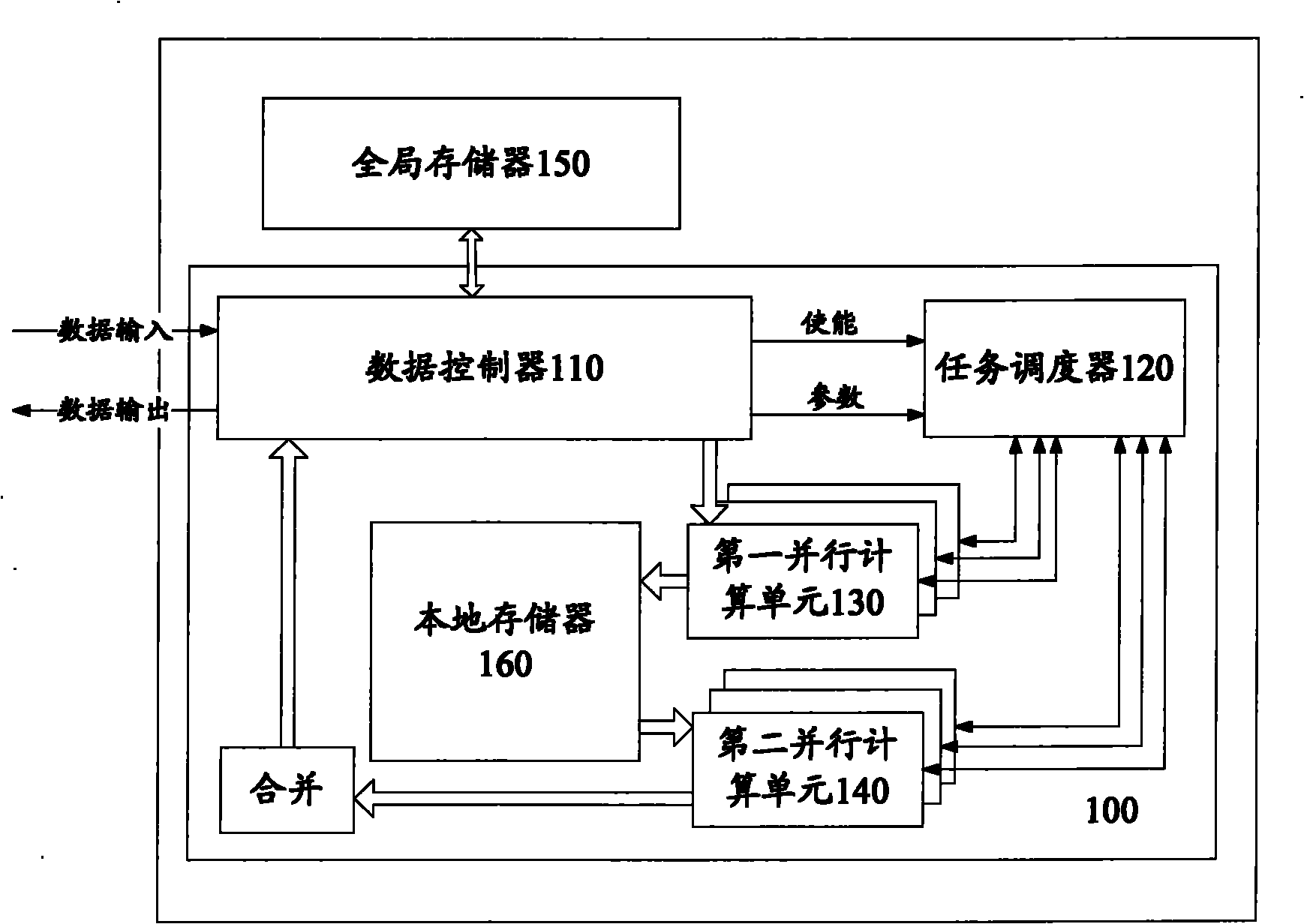
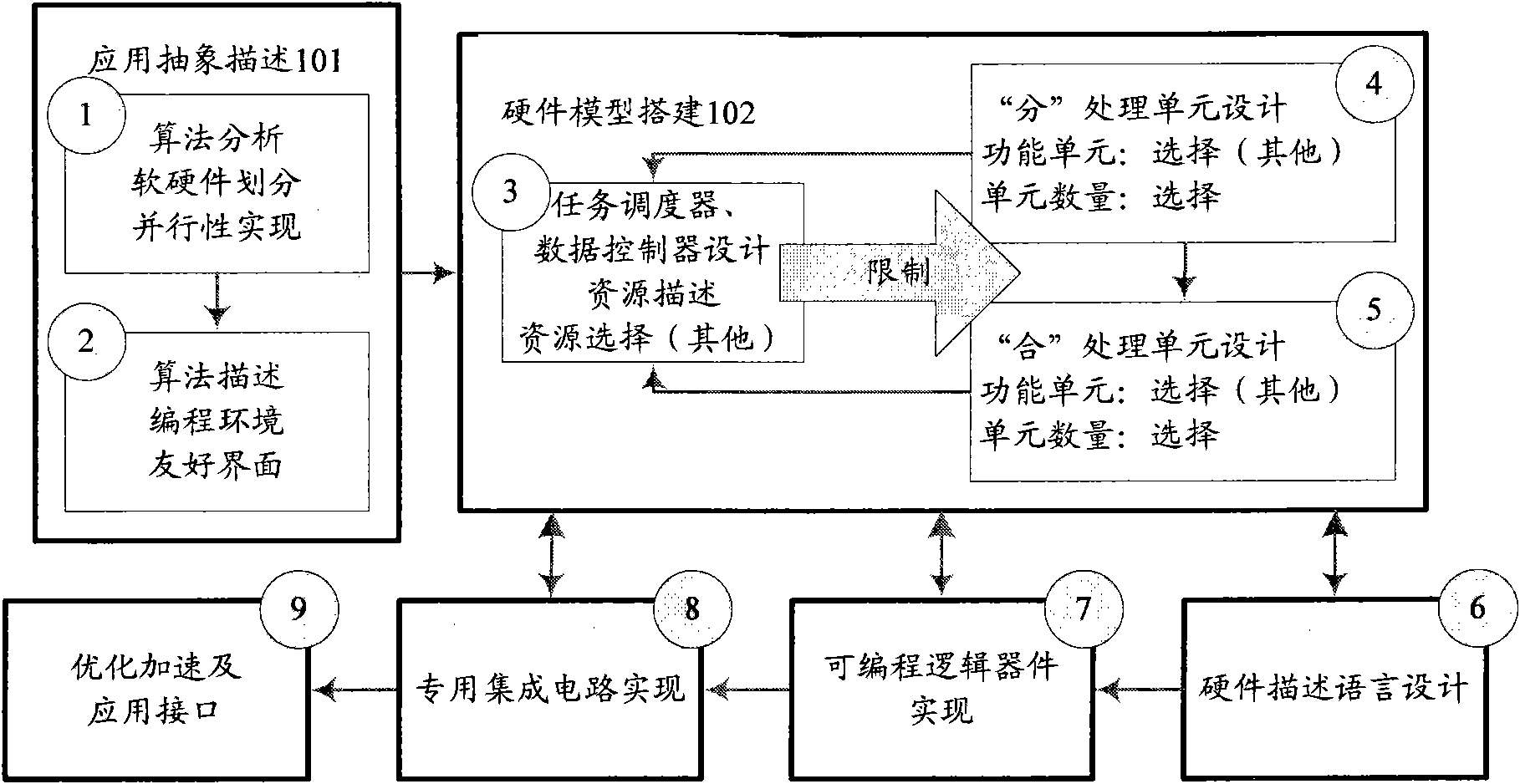
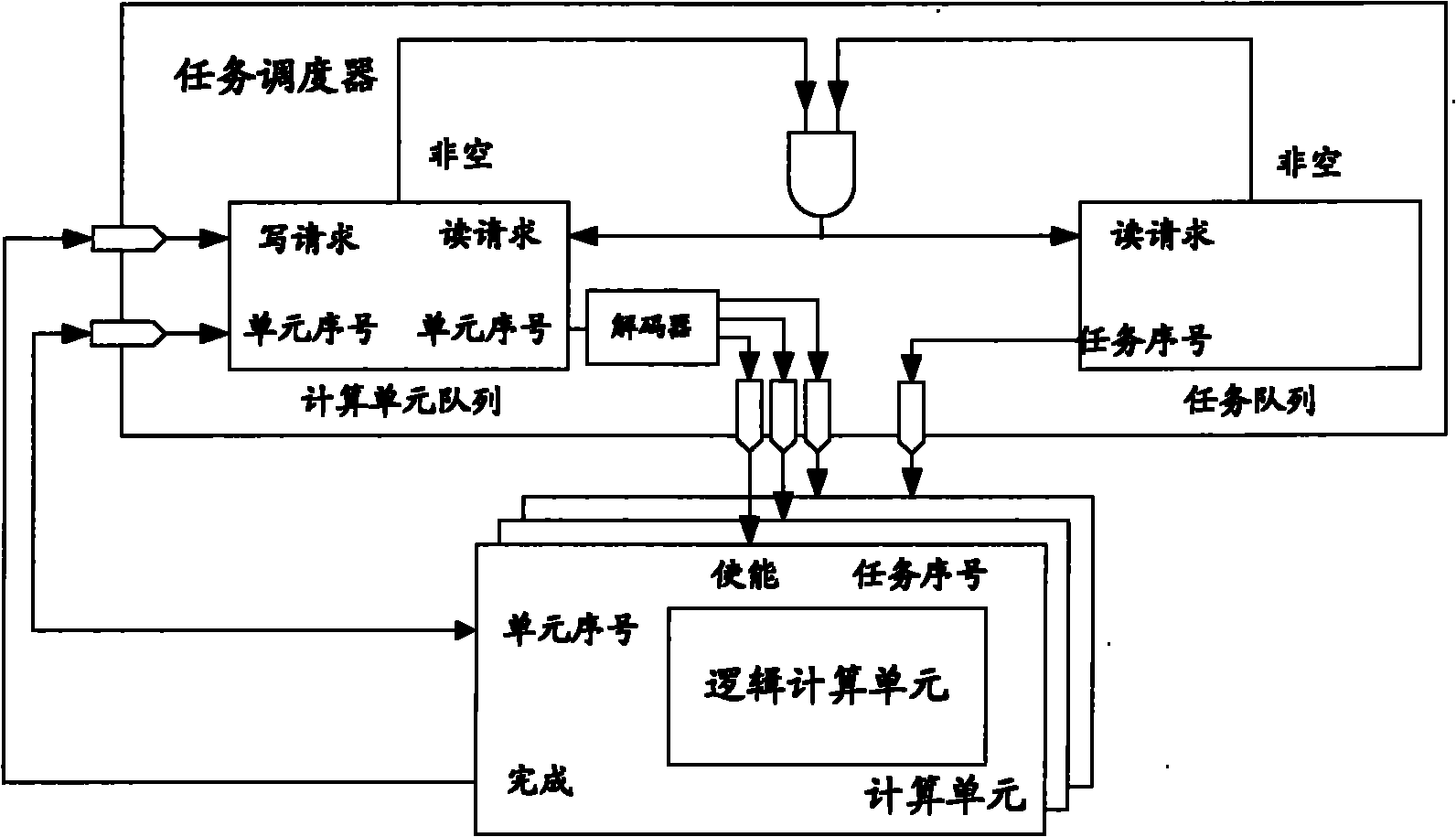
ActiveCN101833439AReduce Design ComplexityReduce designResource allocationConcurrent instruction executionHardware structureData control
The invention provides a parallel computing hardware structure based on a separation and combination thought, which comprises a plurality of first parallel computing units, a plurality of second computing units, a task dispatcher used for controlling a plurality of the first parallel computing units and a plurality of the second parallel computing units, a global memory used for storing global data, a local memory for storing intermediate results computed by a plurality of the first parallel computing units and providing the intermediate results to a plurality of the second computing units after starting computation, and a data controller used for providing data for a plurality of the first parallel computing units and the task dispatcher. By adopting the hardware structure applied in parallel computing and provided by the embodiment of the invention, design thoughts such as dispatching, synchronizing and communicating can be effectively covered, so a designer can directly focus on the description of a computation part of an algorithm, thus reducing design complexity of a parallel circuit and shortening circuit design and realization time to a large degree.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Fish-eye camera-based human detection system
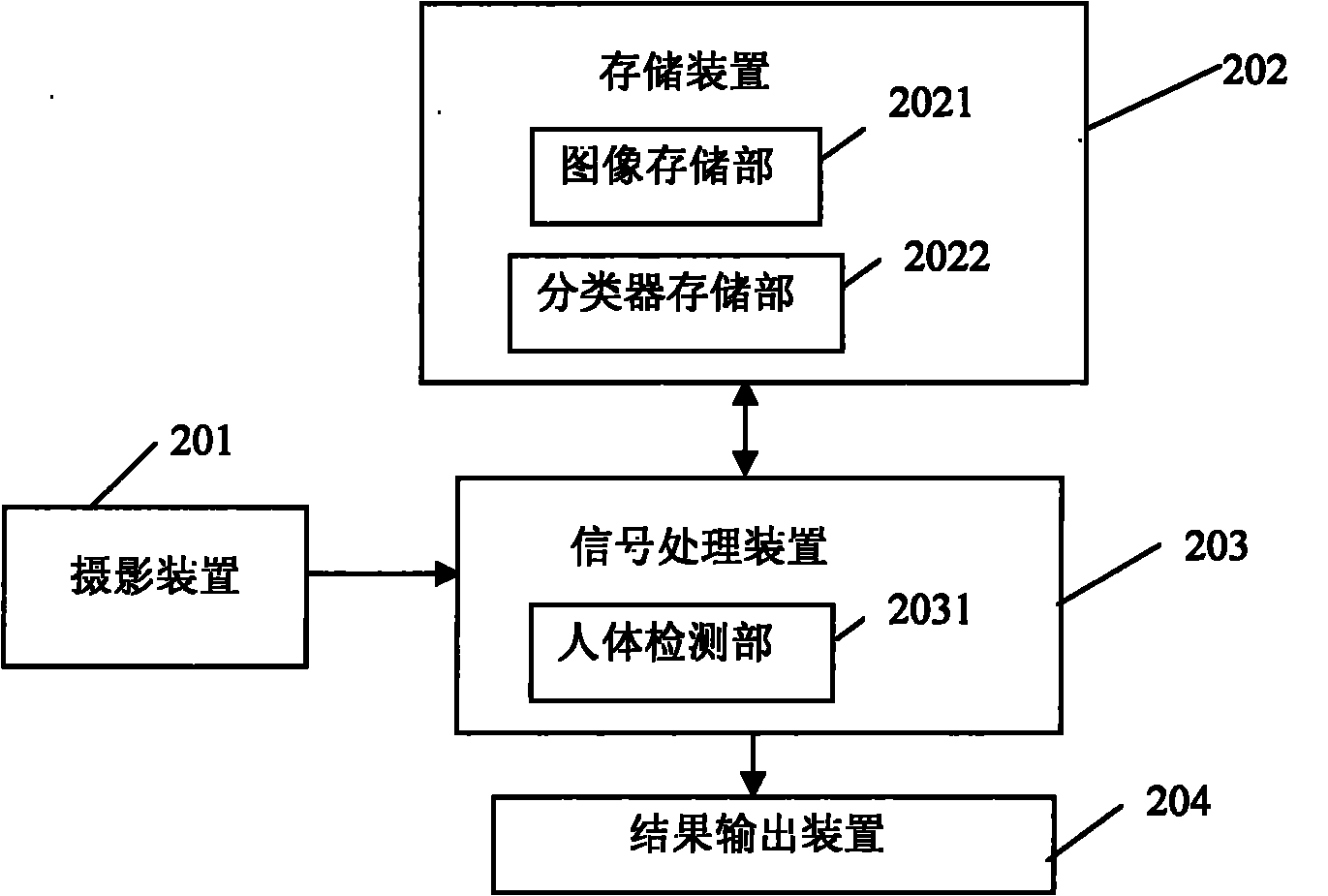
InactiveCN101859376AImprove transmission efficiencyImprove system efficiencyImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionDisplay deviceRadiology
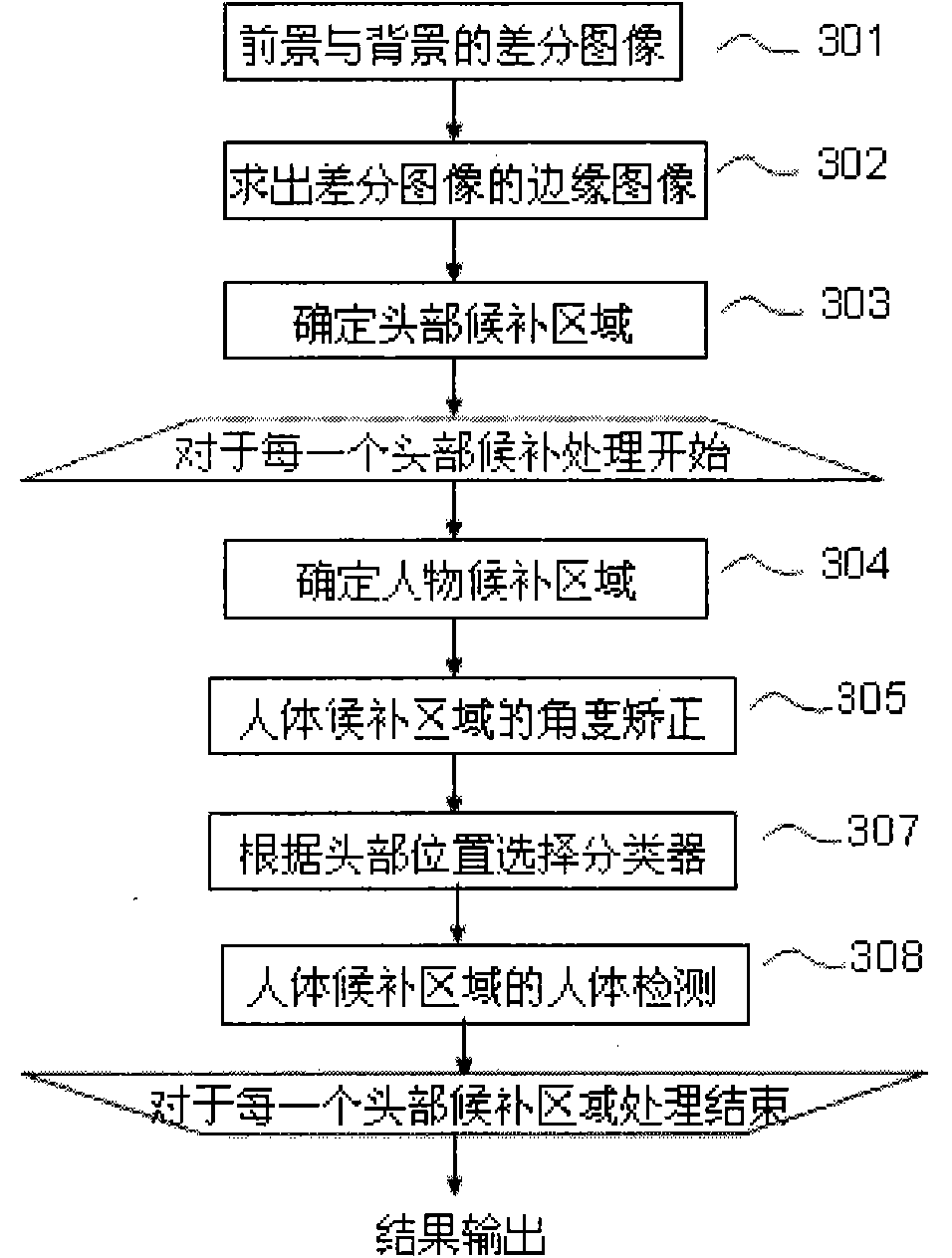
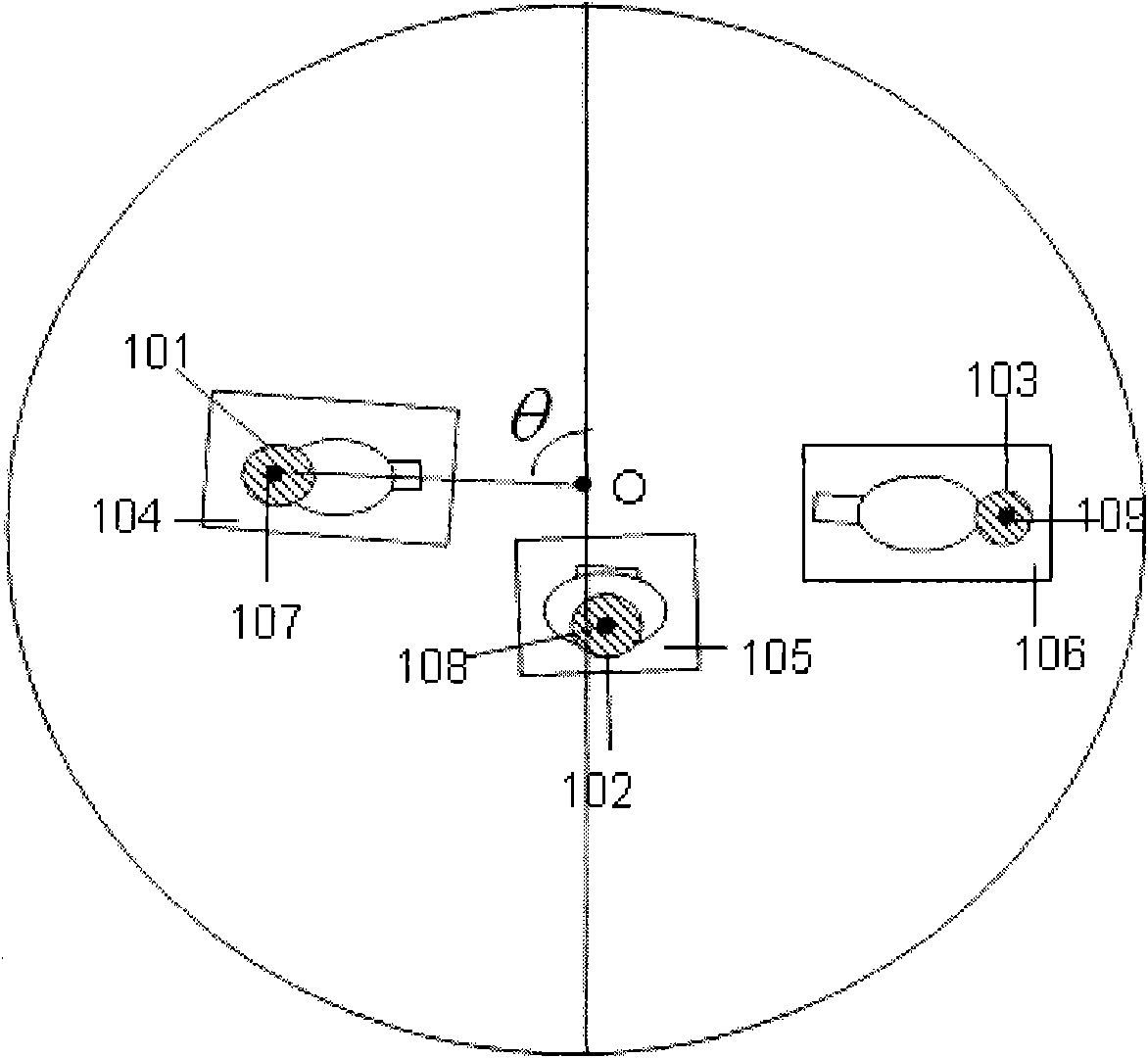
The invention discloses an automatic monitoring system which uses one camera to realize large extent monitoring and has no dead corner. In the system, a photographic device transmits the shot picture to a signal processing device; a storage device is connected with the signal processing device, the storage device stores background image and head candidate area in an image storage part according to the command of the signal processing device and also stores a classifier for judging whether a human body exists in the image, in a classifier storage part; a result output device is connected with the signal processing device; and when the system detects a person exists, a monitor is used to display the image, send an abnormal signal and transmit the image to the user side. The system adopts a fish-eye camera with the visible angle of 180 degrees to realize the human detection to the fish-eye image. By using the invention, the human body in the fish-eye image can be correctly detected, all the human areas in the video image can be determined, the human areas can be rectified to form two-dimensional images, and the two-dimensional images can be displayed in a display device and sent to the user side.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Legalized method used for mixed height standard cell circuit design
InactiveCN106971042ALegalization problem solvingLegalization issues meetCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsVery-large-scale integrationDecomposition
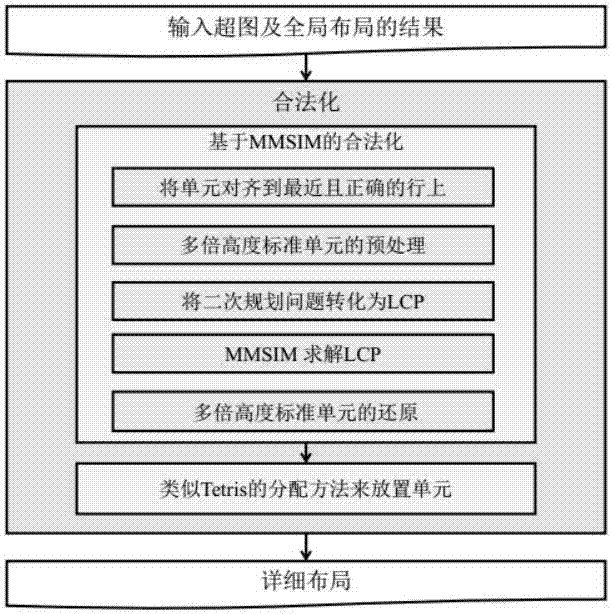
The invention relates to a legalized method used for mixed height standard cell circuit design. The technical scheme of the method comprises the following key points: (1) according to a cell position sequence obtained according to a global layout, carrying out relaxation on the right boundary constraint of a layout area, and converting a legalization problem of a mixed height standard cell into a corresponding LCP (Linear Complementary Problem), wherein the legalization problem can be effectively solved by an existing optimization method; (2) carrying out decomposition on a matrix in the converted LCP in a proper way, and using MMSIM (Matrix MultiSplitting Iterative Method) to solve the converted LCP, wherein the proper matrix decomposition meets MMSIM convergence requirements, and meanwhile, calculation time is greatly quickened; and (3) by use of the method, simultaneously optimizing all cells instead of optimizing cells one by one, and considering the legalization problem from a global perspective. An experiment result indicates that an efficient and practical legalization result (especially for a large-scale living example) can be provided, and the requirement of a mixed height standard cell legalization stage of existing VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) can be met.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method for upscaling an image and apparatus for upscaling an image
InactiveUS20170132759A1Improve super-resolutionSuitable solutionImage enhancementImage analysisHat matrixImage resolution
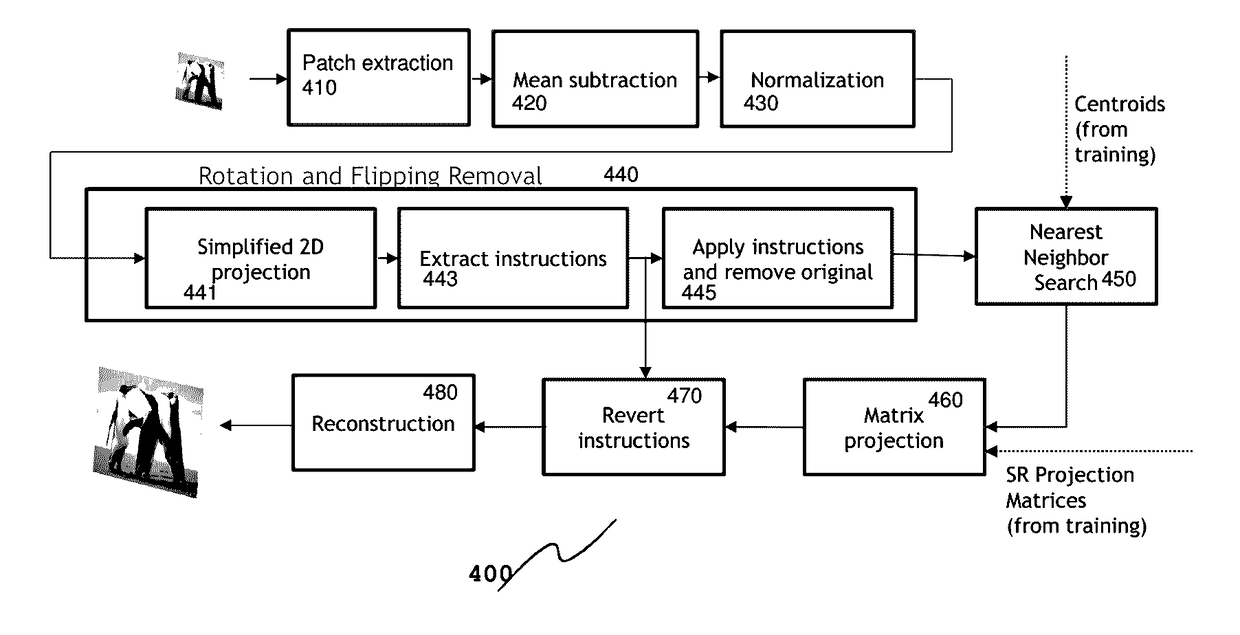
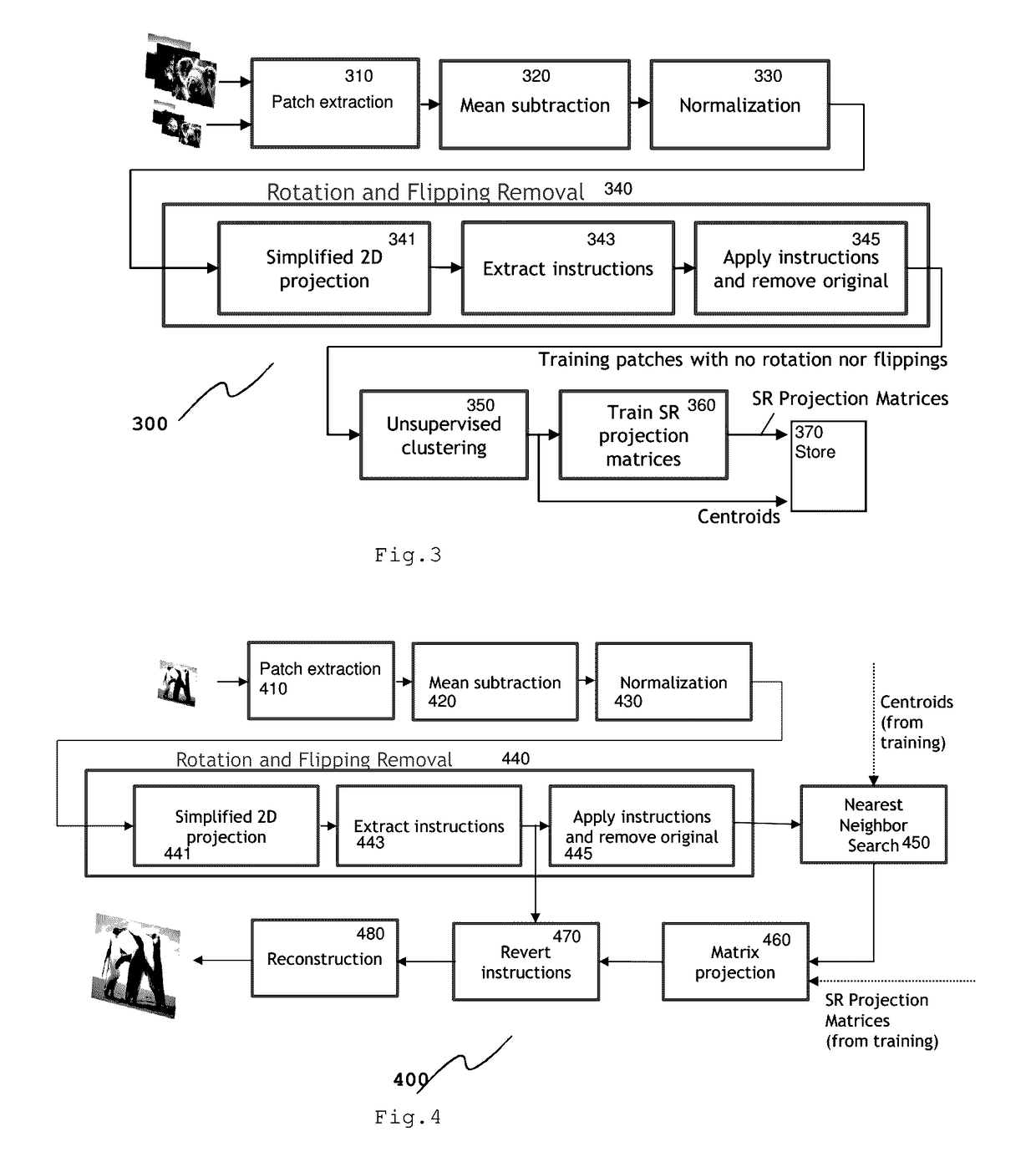
Image super-resolution (SR) generally enhance the resolution of images. One of SR's main challenge is discovering mappings between low-resolution (LR) and high-resolution (HR) image patches. The invention learns patch upscaling projection matrices from a training set of images. Input images are divided into overlapping patches, which are normalized and transformed to a defined orientation. Different transformations can be recognized and dealt with by using a simple 2D-projection. The transformed patches are clustered, and cluster specific upscaling projection matrices and corresponding cluster centroids determined during training are applied to obtain upscaled patches. The upscaled patches are assembled to an upscaled image.
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
Power distribution network fault line selection method based on variable-scale bi-stable system
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
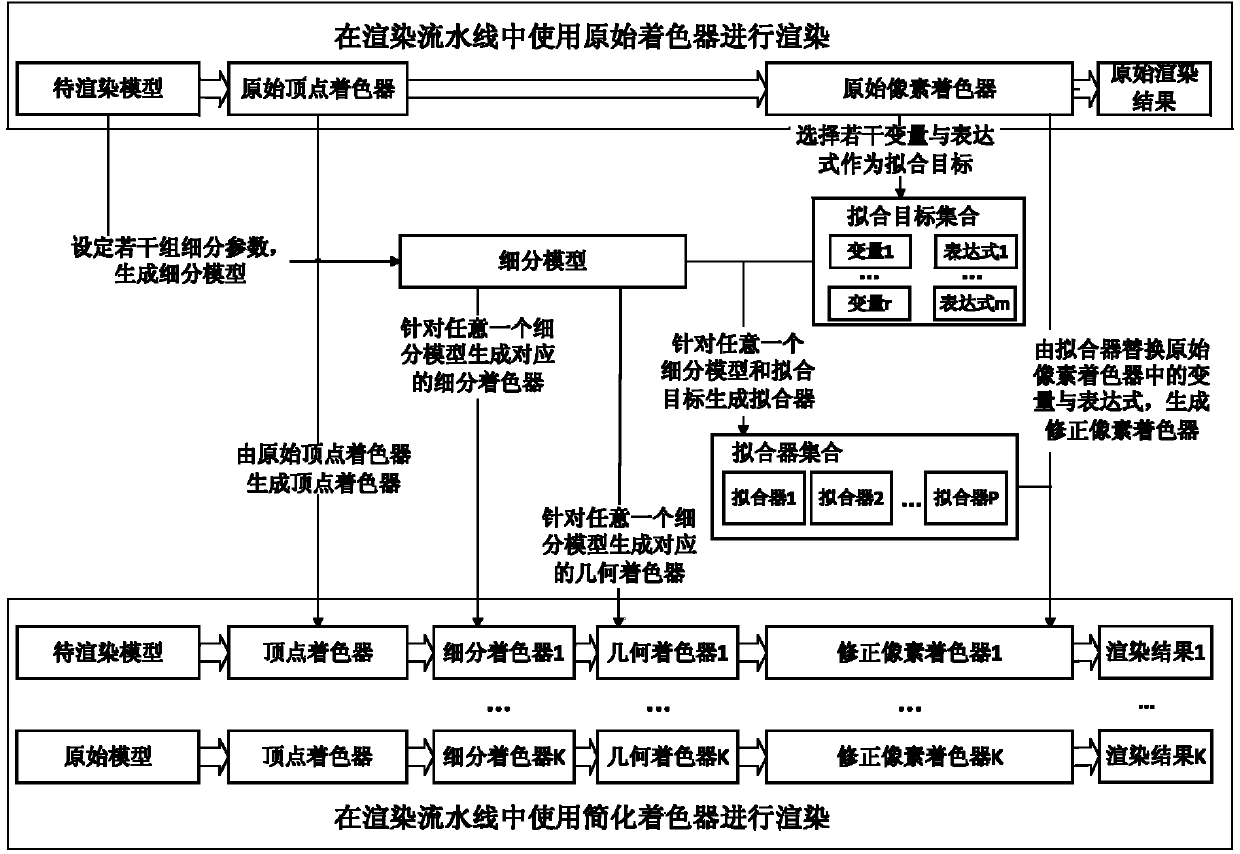
Shader classification method and device based on surface signal fitting and tessellation and graphics rendering method
ActiveCN104183008ASimple calculationFast calculation time3D-image renderingClassification methodsGeometry shader
The invention discloses a shader classification method and device based on surface signal fitting and tessellation and a graphics rendering method. A subdivision shader and a geometry shader are inserted into an original shader by utilizing a tessellation method to subdivide a rendering model, a fitting machine is used for calculating the values of a variable and an expression, in a corresponding subdivision pel of the subdivision model, in an original pixel shader, and the formed fitting machine is inserted into the original pixel shader to replace value calculation to the corresponding variable or expression so as to simplify the calculation of the original pixel shader and shorten calculation time. Furthermore, since the subdivision shader and the geometry shader are inserted, fitting calculation can be carried out on the subdivision pel so as to improve fitting precision and reduce rendering errors brought by simplifying the shader.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SENSETIME TECH DEV CO LTD
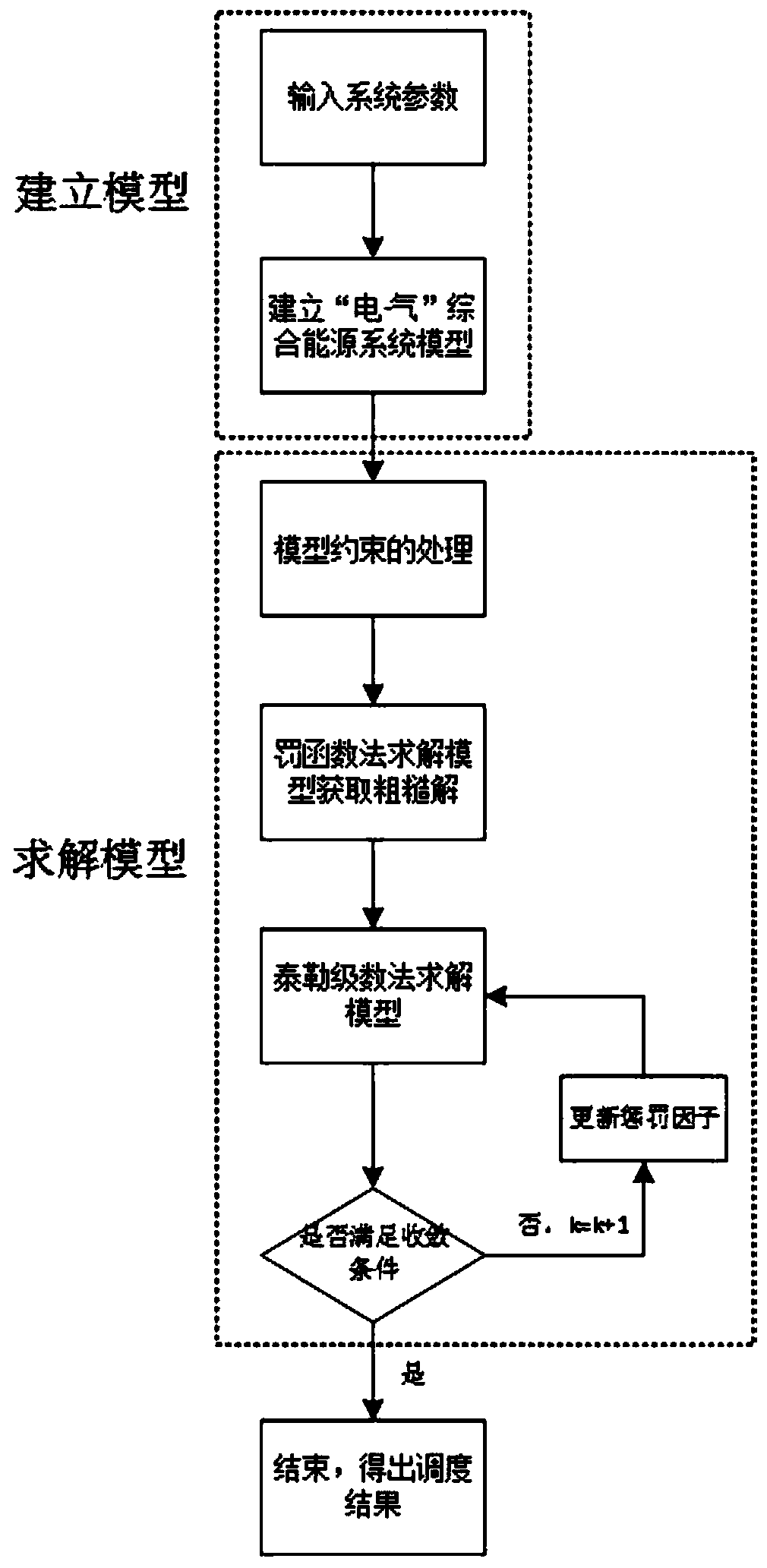
Day-ahead scheduling method of electricity-gas integrated energy system
ActiveCN110070213AImprove management efficiencyFast convergenceForecastingResourcesIntegrated energy systemElectric power system
The invention belongs to the technical field of electric power system operation and control of energy Internet, and more specifically relates to a day-ahead scheduling method of an electricity-gas integrated energy system. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing an electricity-gas integrated energy system day-ahead scheduling model, including establishing a power network model,establishing a natural gas network model, establishing a gas turbine set model, establishing a non-gas turbine set model and establishing a system operation cost minimum model; S2, performing constraint processing on the electric-gas integrated energy system day-ahead scheduling model established in the step S1; and S3, solving the model: firstly obtaining a rough solution by using a penalty function solving model, then solving the model by using a Taylor series method, and forming iterative optimization by using sequential second-order cone programming. The penalty function method and the Taylor series method are combined, and the sequential second-order cone programming method is utilized, a set of day-ahead scheduling algorithm of the electricity-gas integrated energy system is designed. The algorithm has good convergence and accuracy, and the calculation time is prolonged.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
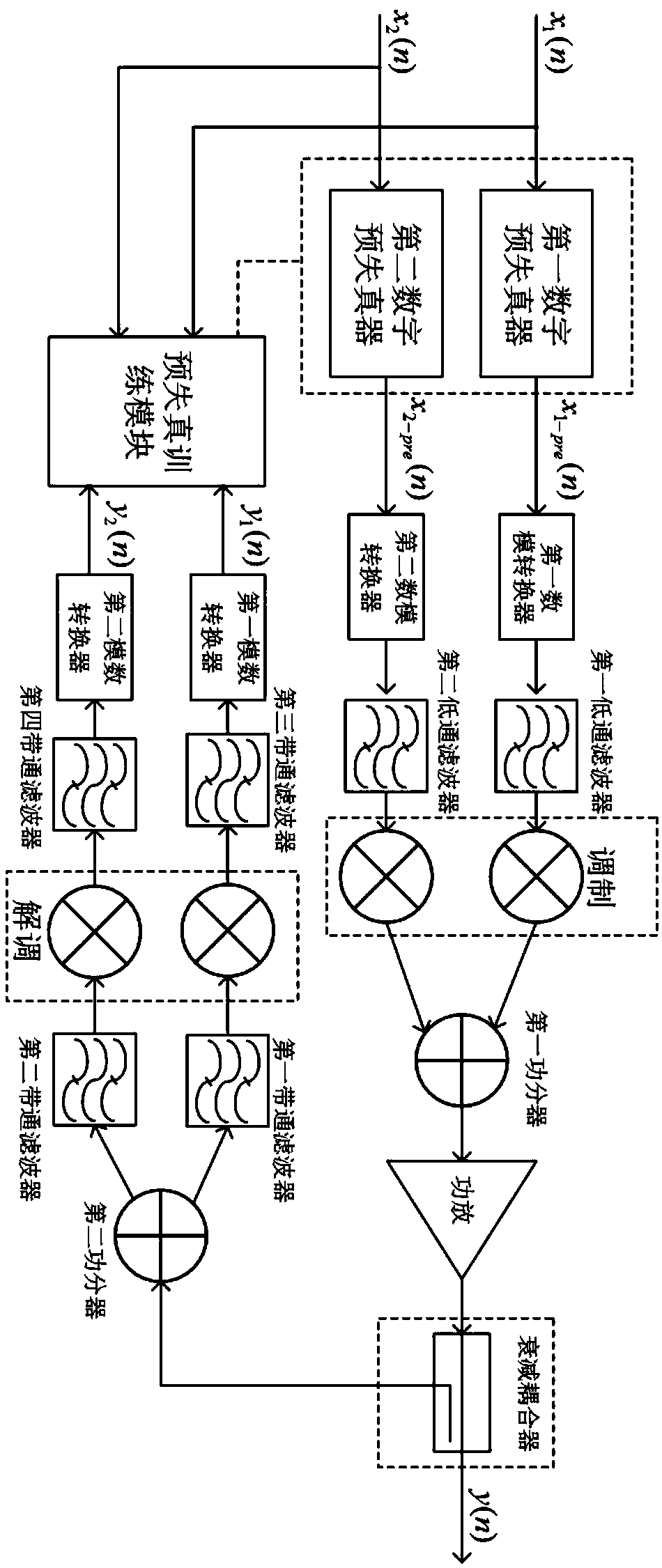
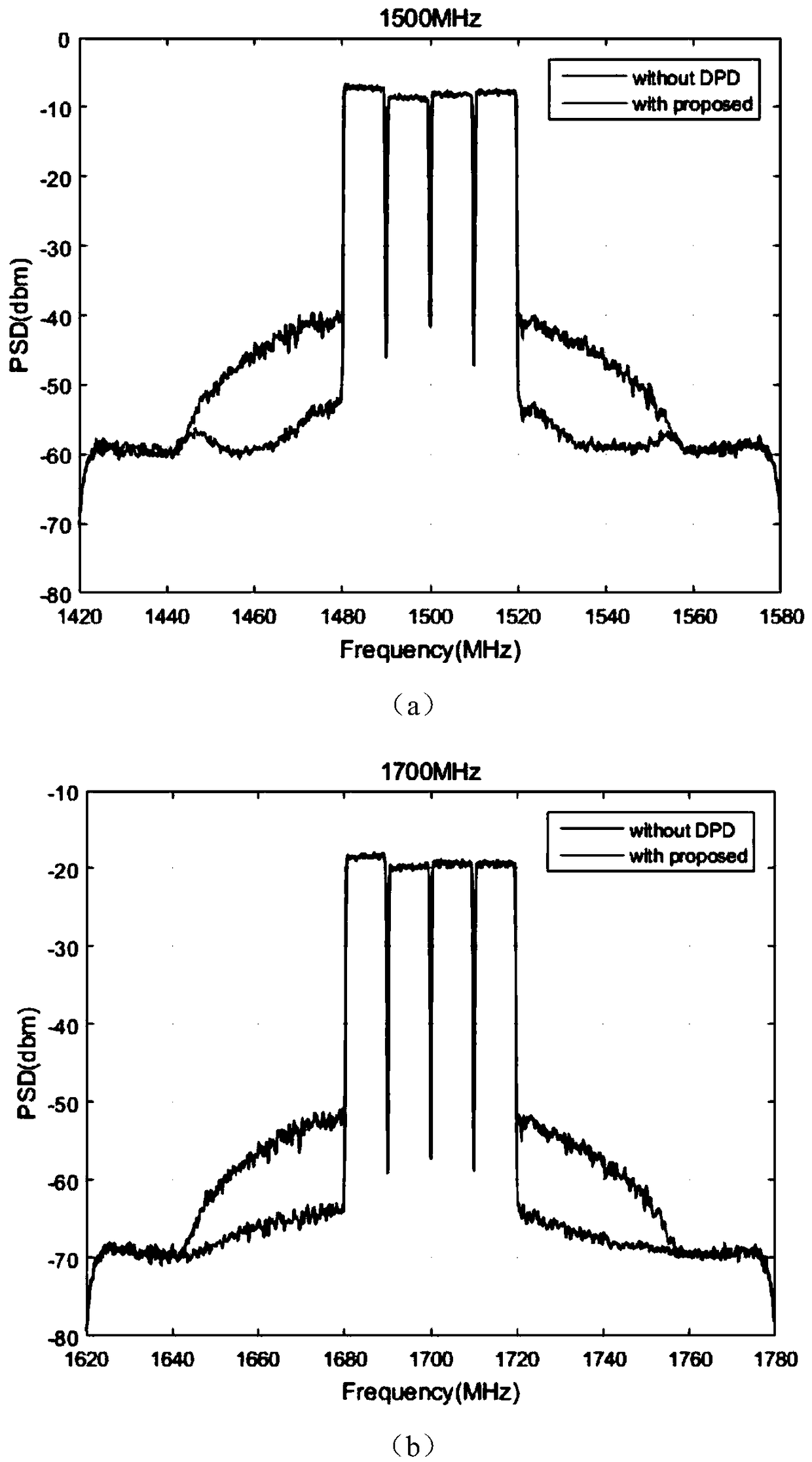
Double-frequency power amplifier digital predistortion device and method based on piecewise linear function
ActiveCN109347452AReduce the number of parametersSave computing resourcesPower amplifiersAmplifier detailsUltrasound attenuationDigital analog converter
The invention discloses a double-frequency power amplifier digital predistortion device and method based on a piecewise linear function, which comprises a first digital pre-distorter, a second digitalpre-distorter, a first digital-to-analog converter, a second digital-to-analog converter, a first low-pass filter, a second low-pass filter, a first modulator, a second modulator, a first power divider, a power amplifier, an attenuation coupler, a second power divider, a first band-pass filter, a second band-pass filter, a first demodulator, a second demodulator, a third band-pass filter, a fourth band-pass filter, a first analog-to-digital converter, a second analog-to-digital converter and a predistortion training module. The invention also discloses a double-frequency power amplifier digital predistortion method based on the piecewise linear function. The device and the method in the invention reduce the number of parameters in the existing 2D-DPD double-frequency power amplifier predistortion model, thereby reducing the implementation difficulty and consumed computing resource of a model in the FPGA and accelerating the computing time of the optimal model parameter.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
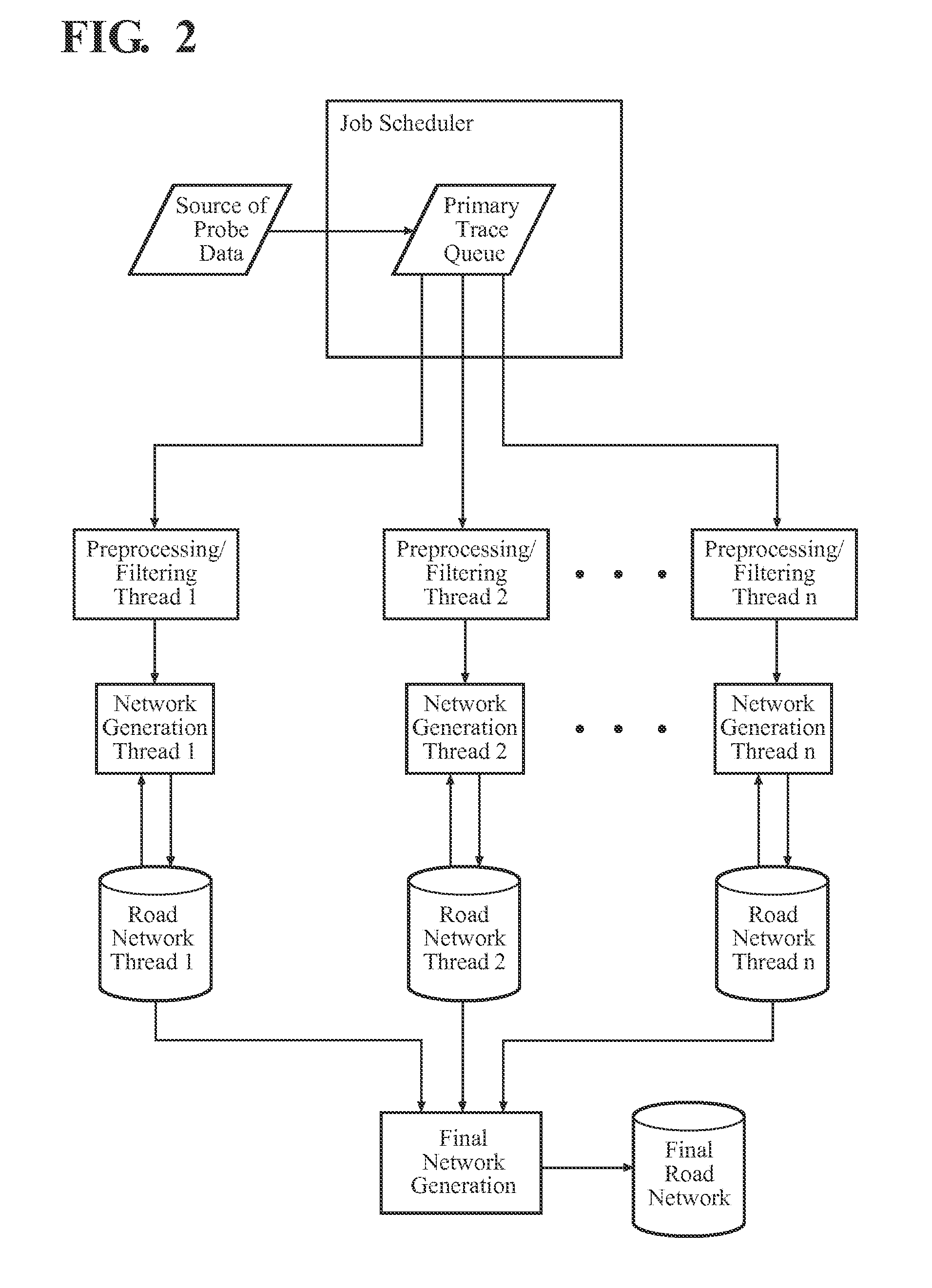
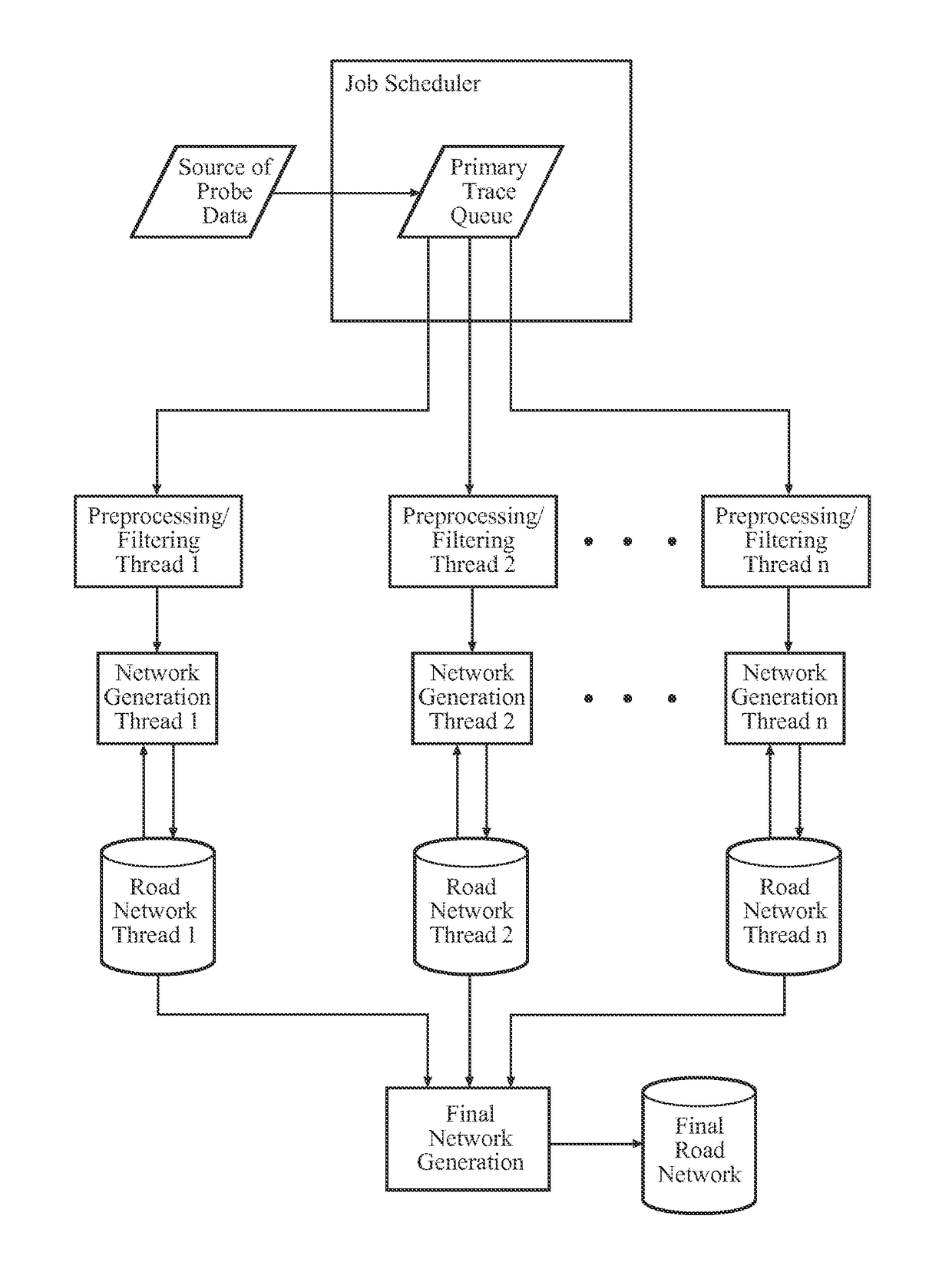
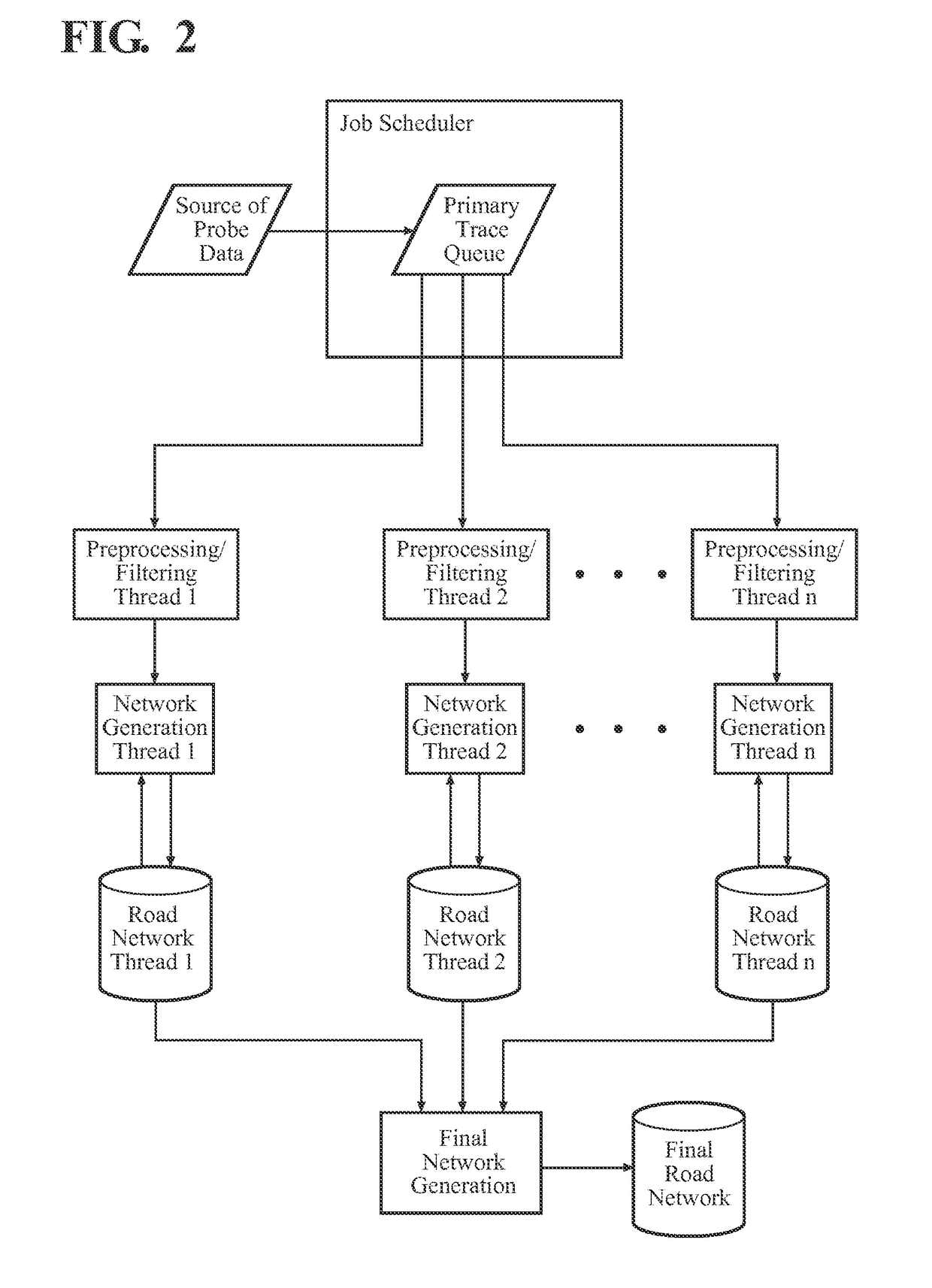
Seamless network generation
ActiveUS20140163875A1Faster processing timeAccelerate computationInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlNetwork generationTechnical standard
A system and method for generating a seamless road network of a large geographical area includes a plurality of GPS probe traces extending across a geographical area. The probe traces are divided into sub-sets base on criteria, such as accuracy. A plurality of threads simultaneously employ the sub-sets traces to generate an independent network of the entire geographical area. The networks generated using sub-sets having a high accuracy are preferred over networks generating using sub-sets having a lower accuracy. The independent networks are combined to form a seamless networks of road segments.
Owner:TOMTOM GERMANY
Energy internet harmonic power flow calculating method
InactiveCN107069733AImprove accuracyFast calculation timeAc networks with different sources same frequencyHarmonic reduction arrangementPower flowTotal harmonic distortion
The invention provides an energy internet harmonic power flow calculating method. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining electric quantity of nodes in an energy internet; carrying out modeling on each output power of each indeterminate node by utilizing a backward cloud generator to obtain characteristic values, wherein each indeterminate node is a node, the output power of which is uncertain and which is corresponding to DG; obtaining an uncertainty interval of the output power according to the characteristic values; carrying out one-time deterministic load flow calculation on each output power in the uncertainty interval to obtain a central value of flow output; obtaining flow output range according to the central value of the flow output; calculating harmonic current of each node according to the flow output in the range; calculating harmonic parameters of components, except the DG, in the energy internet; carrying out calculation according to the harmonic parameters and the harmonic current to obtain harmonic voltage of each node; and calculating voltage total harmonic distortion of the nodes according to the harmonic voltage of the nodes. The method has the advantages of being accurate in calculation and high in calculation efficiency.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
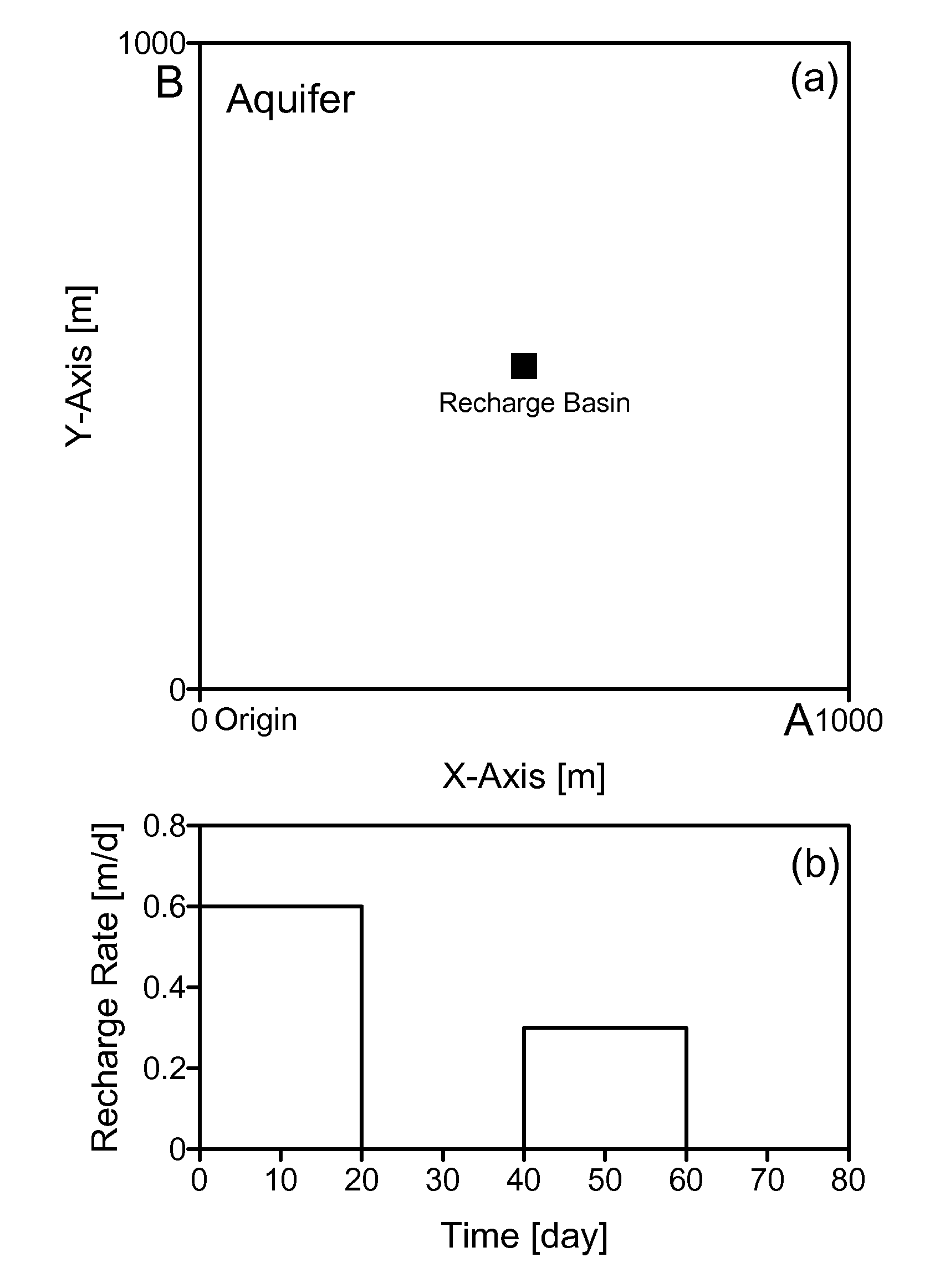
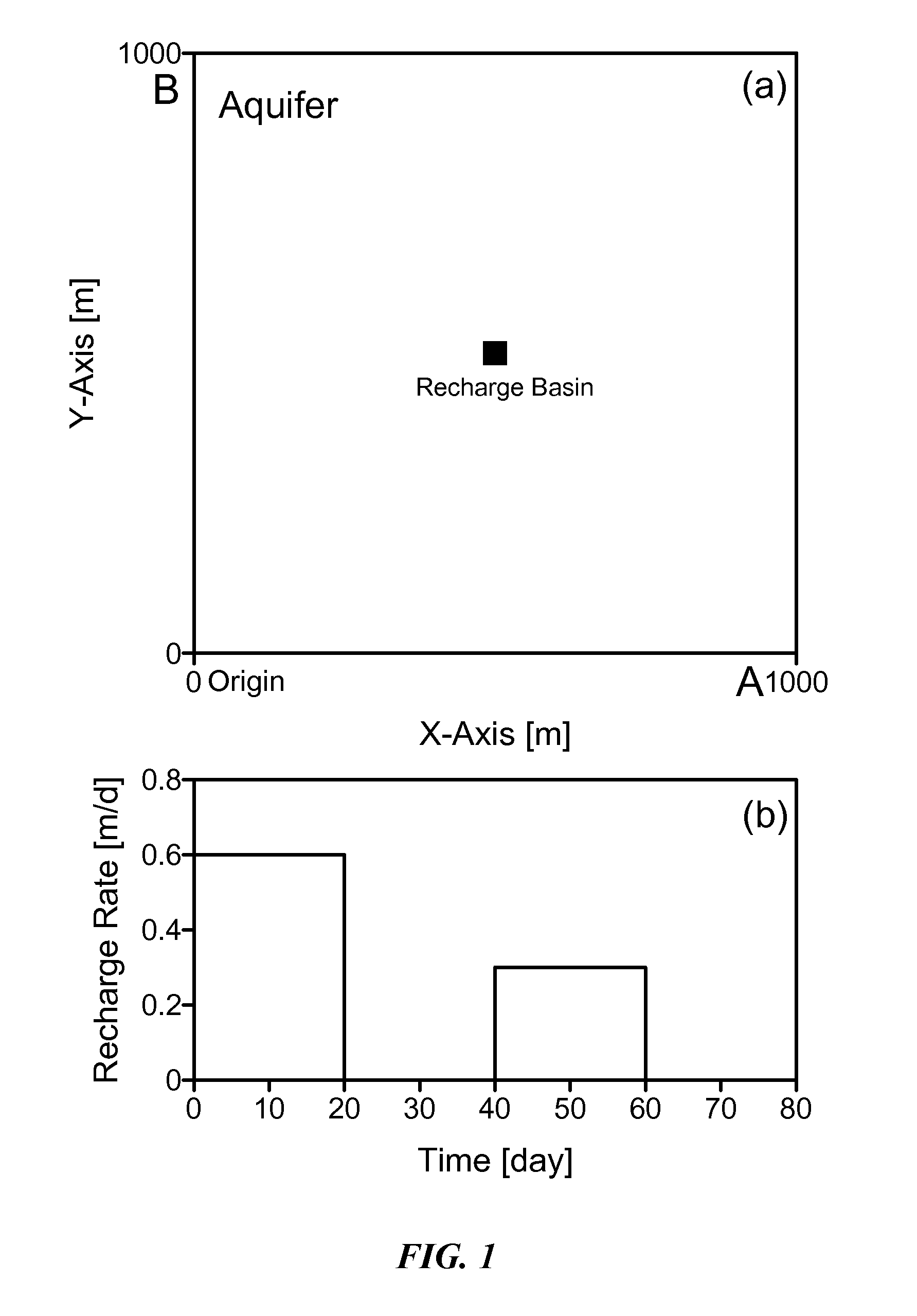
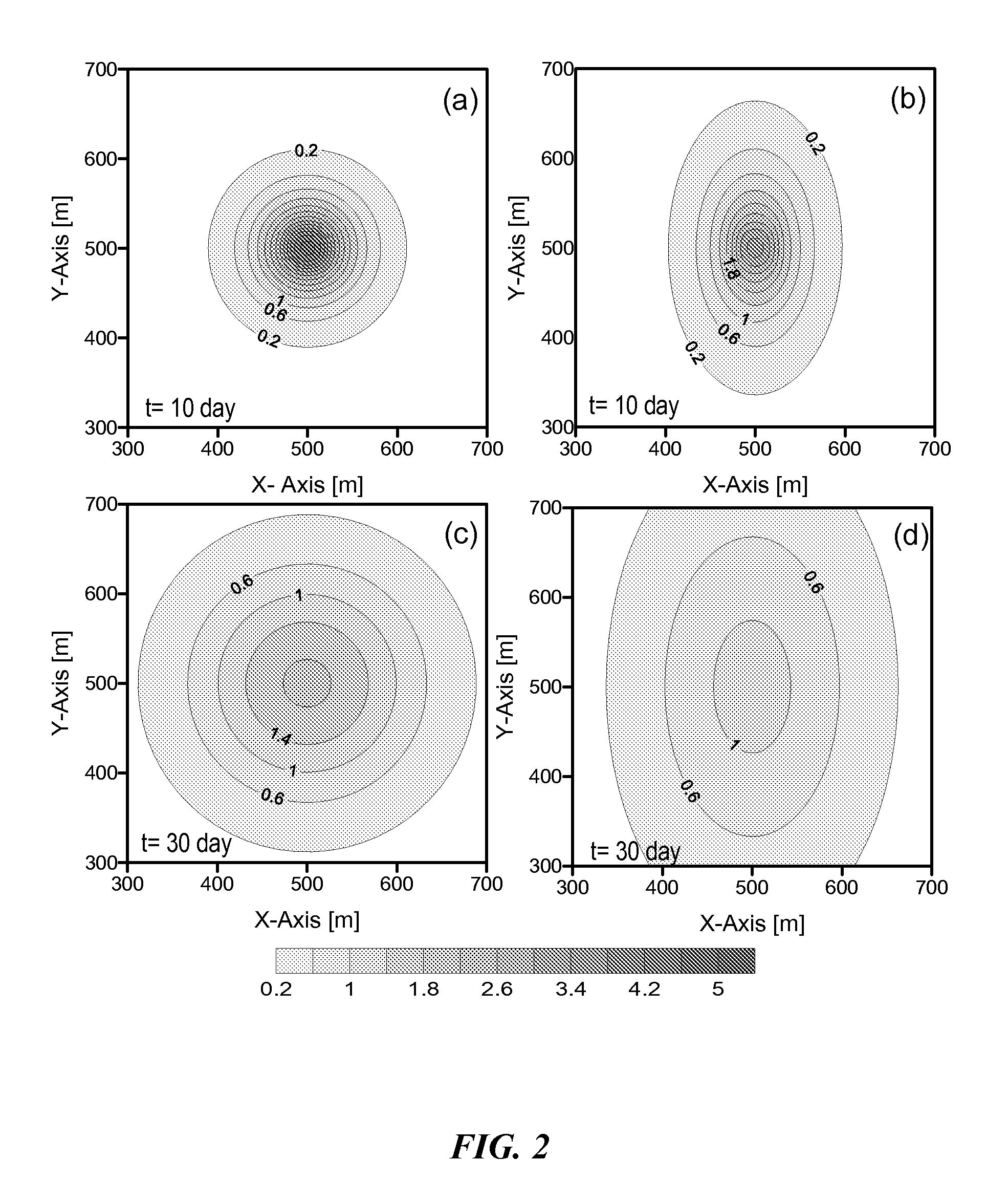
Method of predicting the dynamic behavior of water table in an anisotropic unconfined aquifer having a general time-varying recharge rate from multiple rectangular recharge basins
InactiveUS20090024369A1Fast computation timeFast calculation timeFluid removalComputation using non-denominational number representationWater levelAnisotropy
The present invention relates to development of a method of predicting the dynamic behavior of water table in an anisotropic unconfined aquifer having a general time-varying recharge rate from multiple rectangular recharge basins. Each basin can have a different dimension and nature of rate of recharge. Aquifer can have prescribed head, zero flux, or a combination of both types of boundary conditions.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method and system for lowering action of soft error caused by radiation
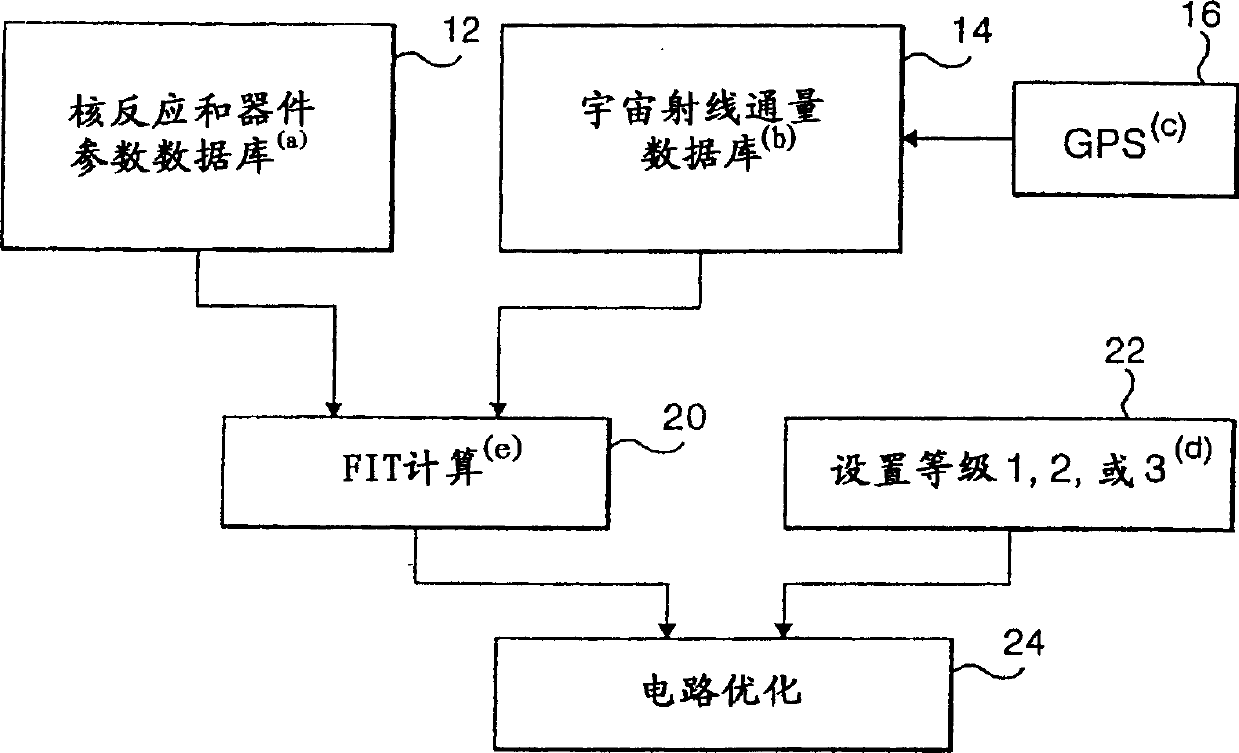
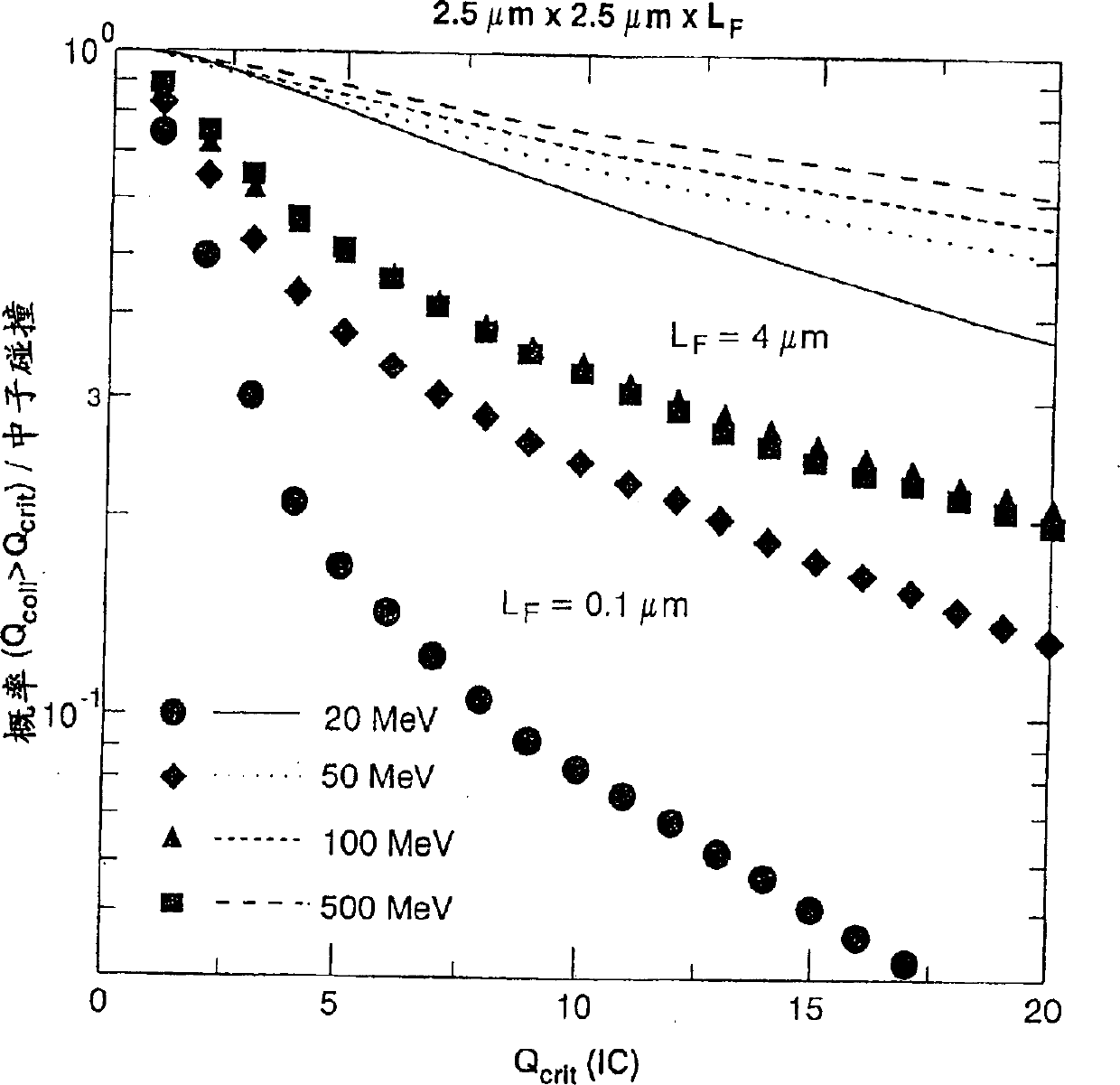
InactiveCN1480841AFast calculation timeOrder of magnitude improvement in computation timeError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsComputer scienceRadiation induced
A method and system for mitigating the impact of radiation induced in a data processor incorporating integrated circuits. The method comprises the steps of determining the location of the data processor, determining a set of radiation sources and intensities at that location, and estimating the soft error rate of the data processor as a function of the determined radiation intensities and geometric characteristics of said integrated circuits to provide an estimate value. The data processor is modified (either hardware or software) in response to the estimate value at times the estimate value exceeds a predetermined value.
Owner:IBM CORP
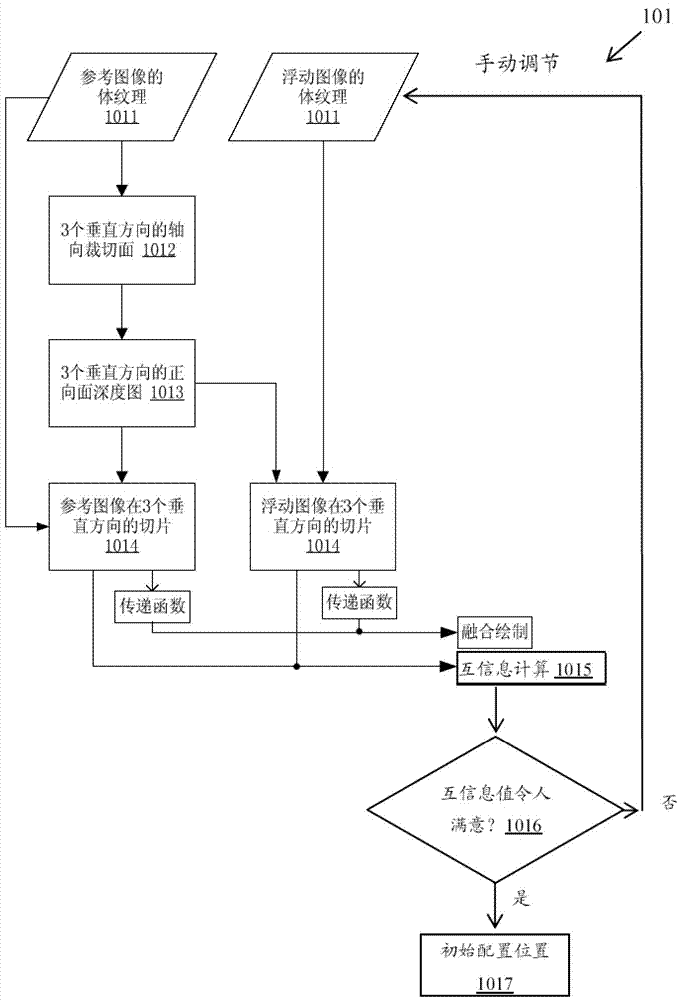
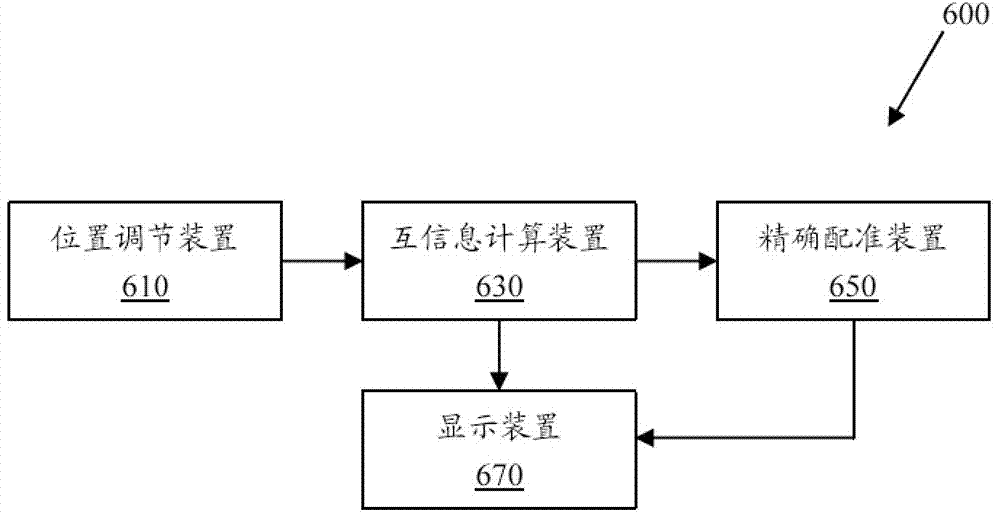
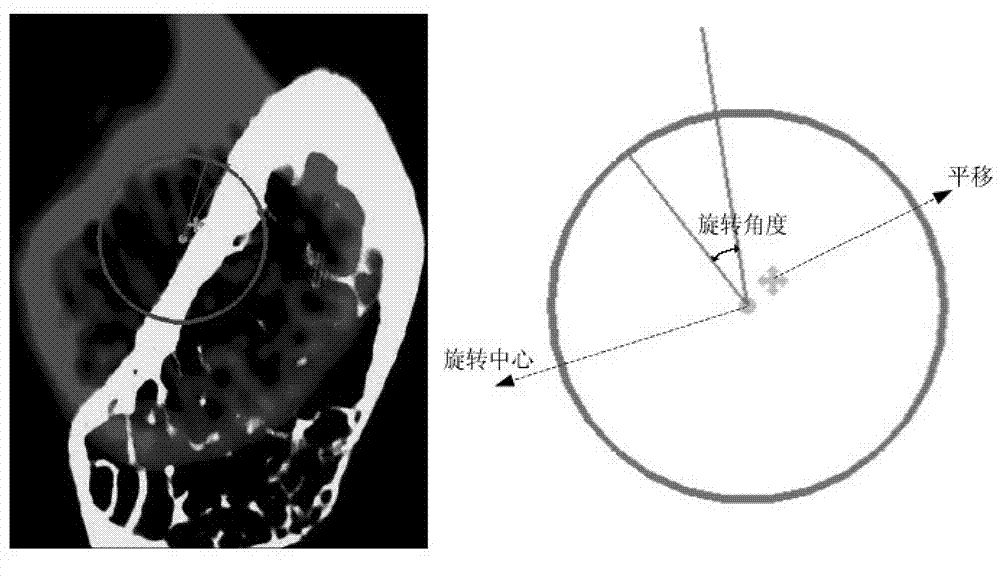
Method and equipment for interactively registering medical three-dimensional image
The invention discloses a method and equipment for interactively registering a medical three-dimensional image. The method for interactively registering the medical three-dimensional image includes that manually regulating the medical three-dimensional image based on the mutual information of the medical three-dimensional image and a reference image in several vertical space directions, and re-calculating the mutual information according to a preset time interval and / or regulating times in the regulating process; manually regulating the medical three-dimensional image based on the re-calculated mutual information to obtain an expected initial registration position; automatically and precisely registering the medical three-dimensional image and reference image based on the initial registration position, wherein the precise registration is performed through the mutual information value of the medical three-dimensional image and reference image in several vertical space directions.
Owner:NUCTECH CO LTD +1
Systems and methods for tomographic imaging in diffuse media using a hybrid inversion technique
ActiveUS8401618B2Fast rebuildFast calculation timeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsReconstruction from projectionTomographic reconstructionFluorophore
Owner:VISEN MEDICAL INC
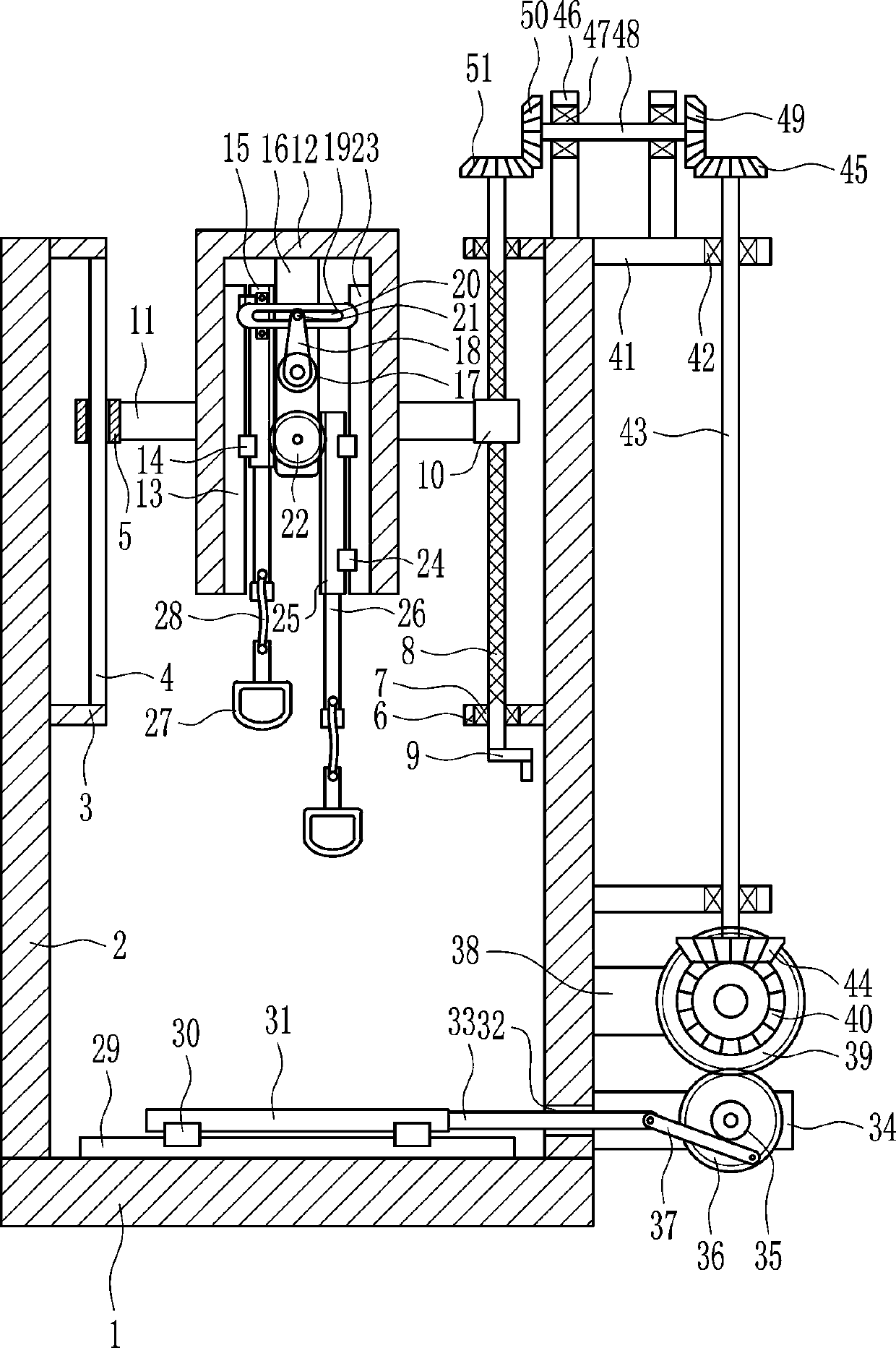
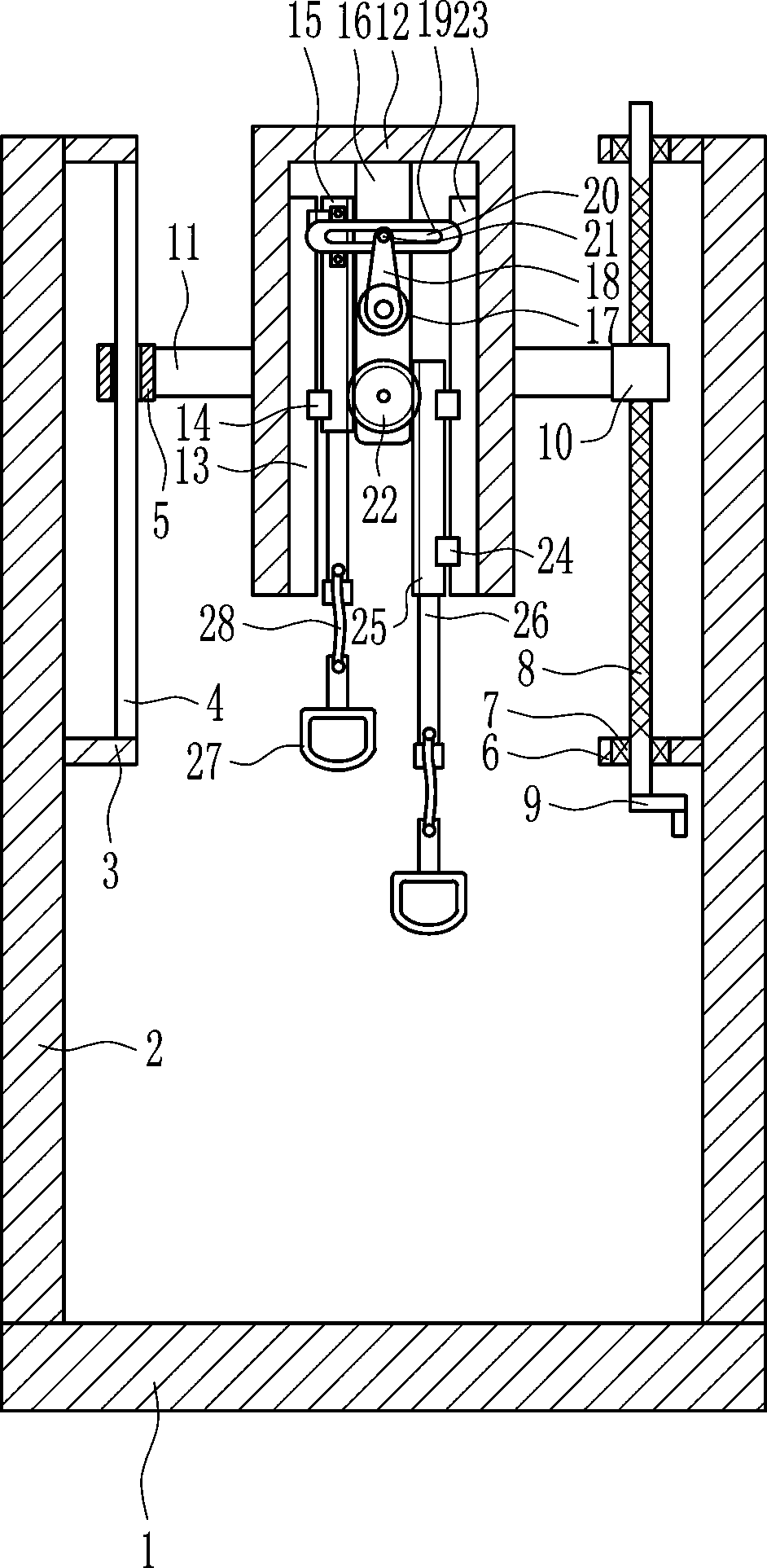
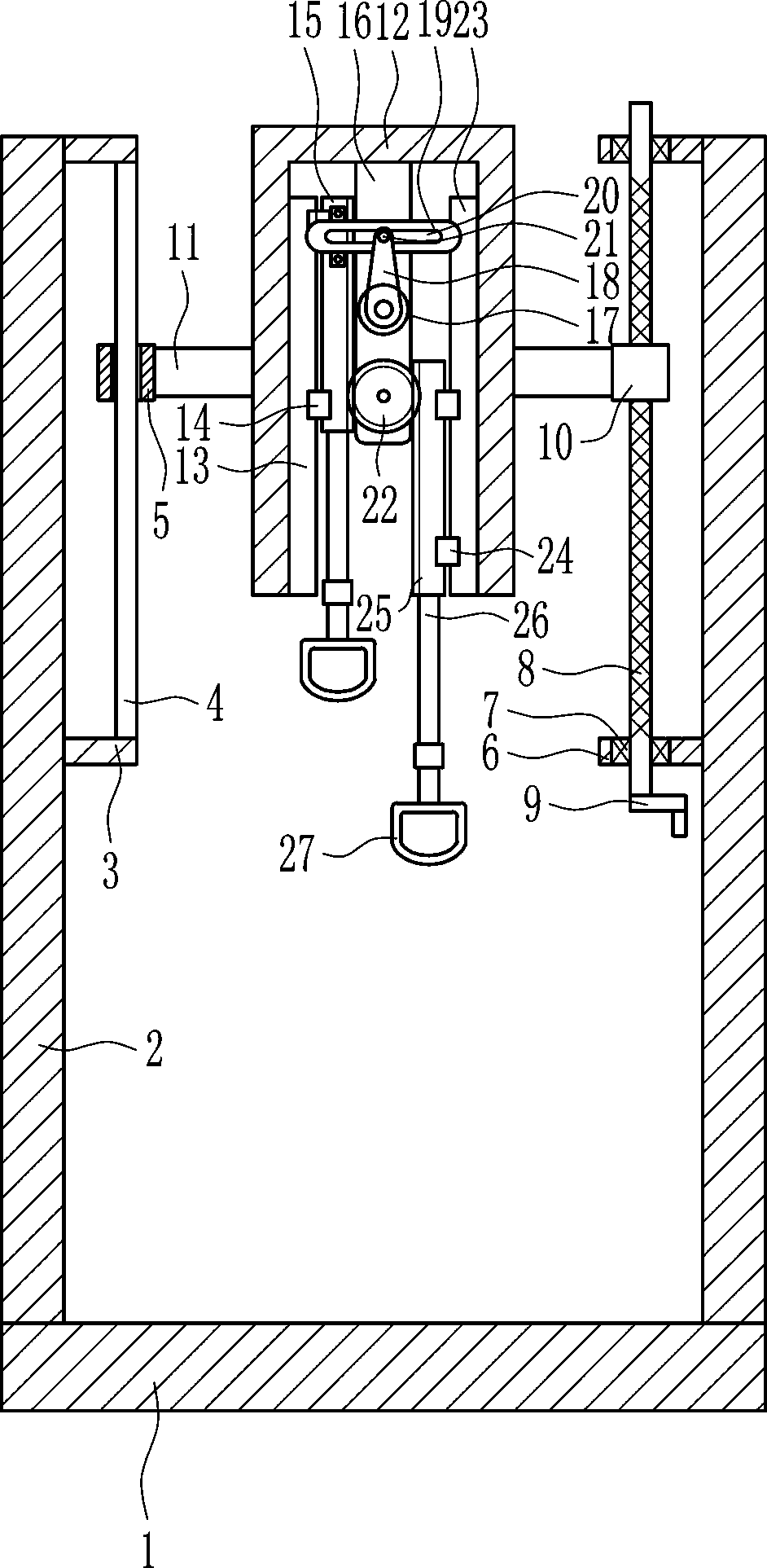
Orthopedic arm rehabilitation device
InactiveCN108031074AEffective recoveryAccurate calculationMuscle exercising devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationSteel ball
The invention relates to orthopedic rehabilitation devices, particularly to an orthopedic arm rehabilitation device. The orthopedic arm rehabilitation device is efficient in rehabilitation, high in safety coefficients and capable of accurately calculating amount of exercise. The orthopedic arm rehabilitation device comprises a base, supports, first connecting plates, a guide bar, a guide sleeve, athird connecting plate and the like. The left and the right of the top of the base are vertically connected with the supports; the upper portion of the right surface of the left support is connectedwith two first connecting plates, between which the guide bar is connected and provided with the guide sleeve. The orthopedic arm rehabilitation device can stretch the arms of a patient through vertical movement of pull rings to effectively rehabilitate the arms; through regular and quantitative steel ball conveying, the orthopedic arm rehabilitation device can accurately calculate time to achievethe effects of high rehabilitation efficiency, high safety coefficient and accurate exercise amount calculation.
Owner:李吉利
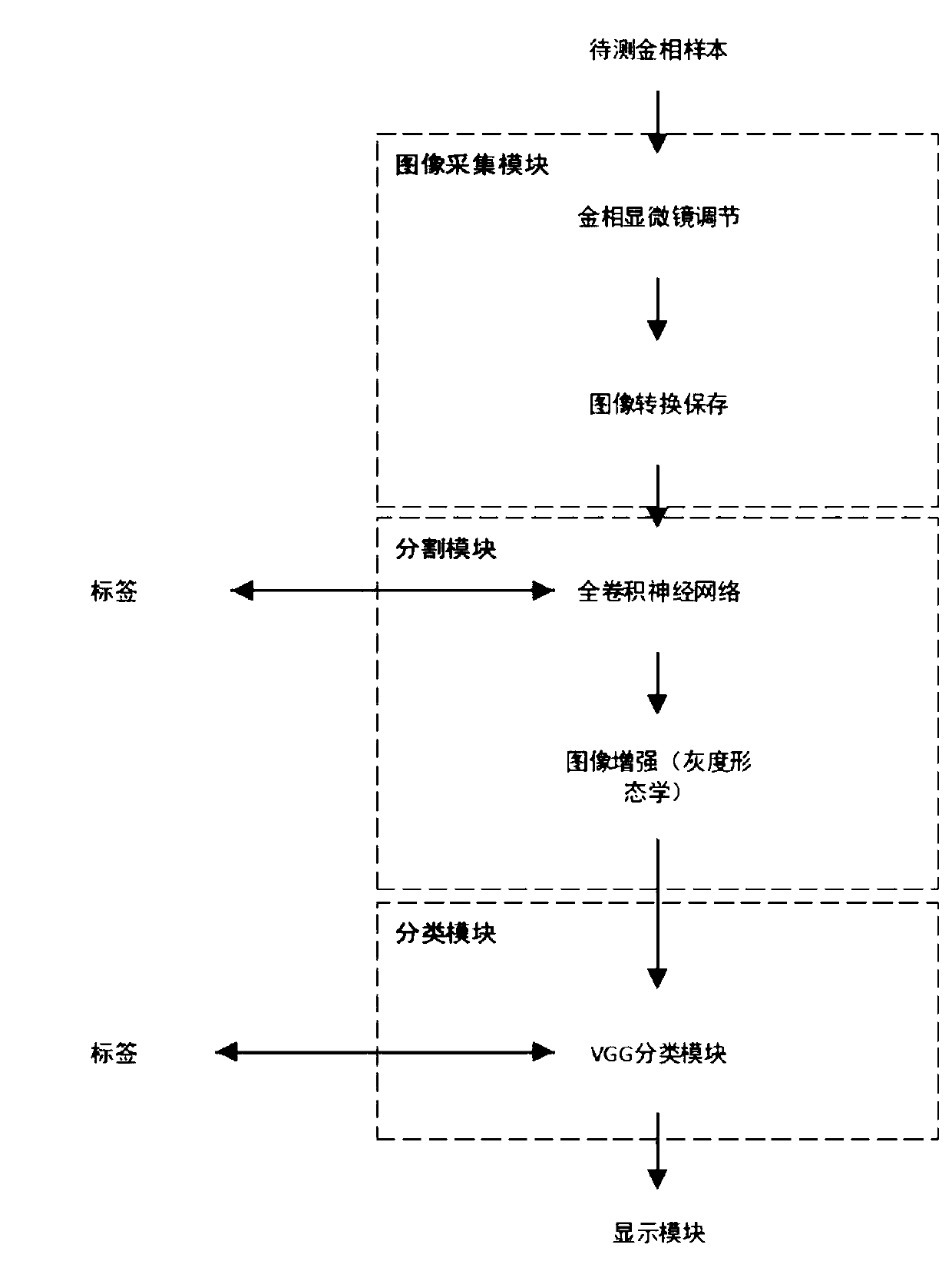
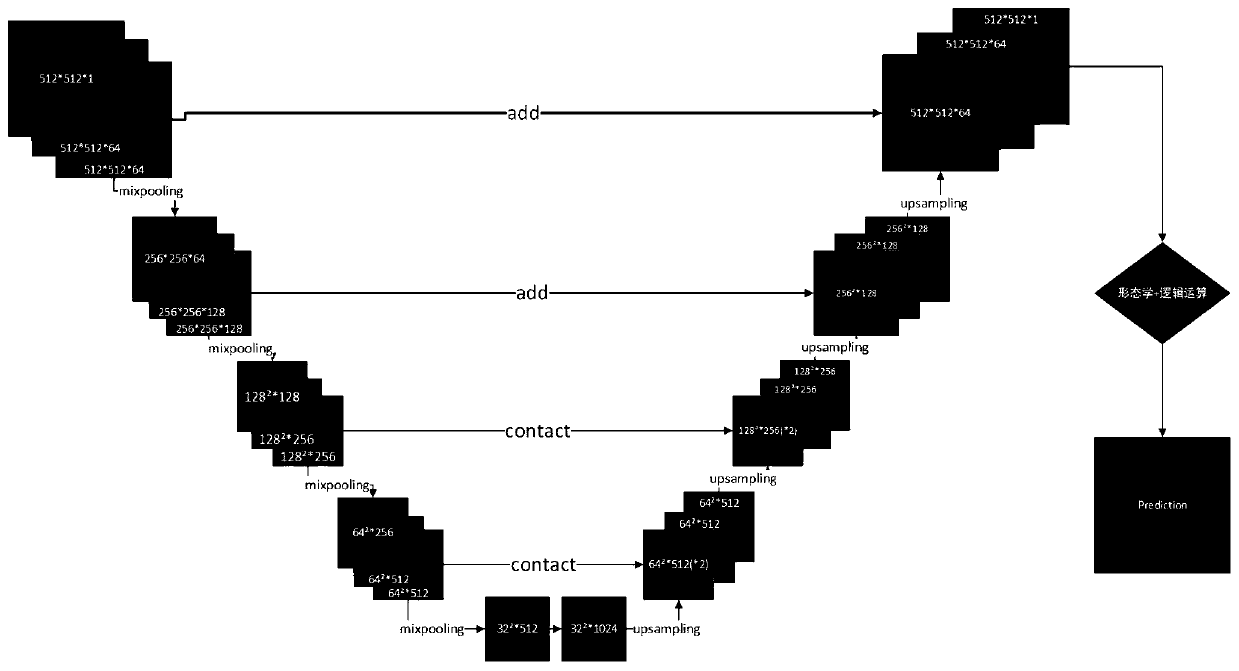
Intelligent metallographic detection rating method and system based on deep learning
ActiveCN110956092AAvoid cumbersomeAvoid stabilityImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionEngineering
The invention provides an intelligent metallographic detection rating method and system based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a metal sample image; making improvement on the basis of a U-net full convolutional neural network to obtain the construction of the improved full convolutional neural network; automatically segmenting the acquired metal sample image through an improved full convolutional neural network to obtain a metallographic segmentation image; performing automatic rating classification on the obtained metallographic segmentation map through adeep neural network. According to the method, the deep learning algorithm is adopted, the improvement is carried out on the basis of the U-net full convolutional neural network, the complexity and instability of traditional image manual feature extraction are avoided, and meanwhile, the applicability of feature extraction is improved based on parameter optimization of a gradient descent method; the method is based on the deep neural network, so the system calculation time is greatly improved, and tedious classification calculation is avoided; the method is high in segmentation and classification accuracy, segmentation and grading are fused through one key, multi-step operation of a traditional method is avoided, and the method is flexible and convenient.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
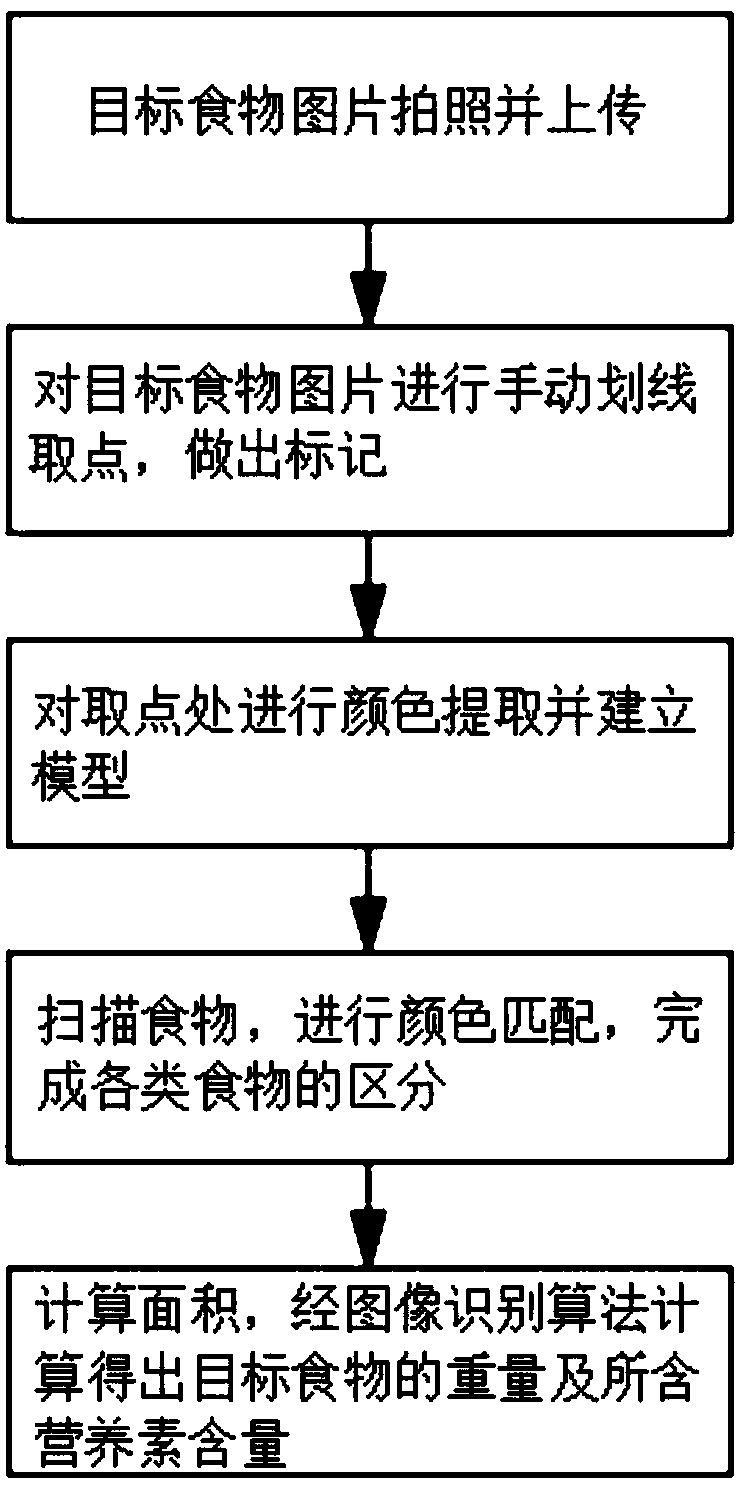
Food weight and nutrient content identification method based on image recognition
InactiveCN108364675AFast calculation timeImprove accuracyImage analysisNutrition controlRecognition algorithmColor matching
The invention relates to a food weight and nutrient content identification method based on image recognition. The method comprises the steps that a target food picture is acquired; point acquiring andmarking are carried out on the acquired food picture; a selected picture path and the data of point acquiring and marking are calculated, and each value of point acquiring and marking is labeled; thetarget food picture is acquired according to the picture path, and color extraction and color modeling are carried out on a point acquiring place according to the data and label of point acquiring and marking; a target food is scanned, and color matching is carried out to complete the classification of various foods; scanning and matching are carried out on a terminal; a recognition algorithm iscalled to calculate the area of the target food; and through the acquired area data and the acquired density and nutrients of the target food, the weight of the target food and the nutrients containedin the target food are calculated to acquire the weight of the target food and the nutrients contained in the target food. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple and quickoperation and high recognition accuracy.
Owner:明纳信息技术深圳有限公司
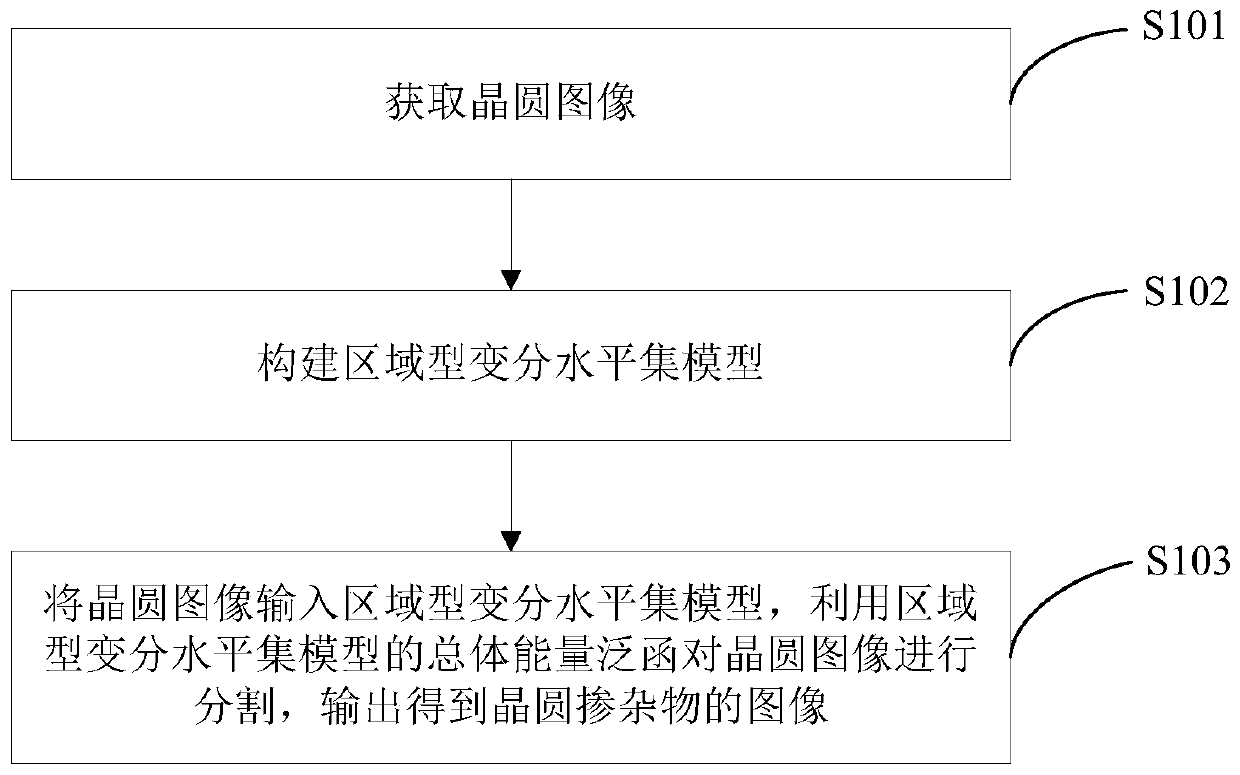
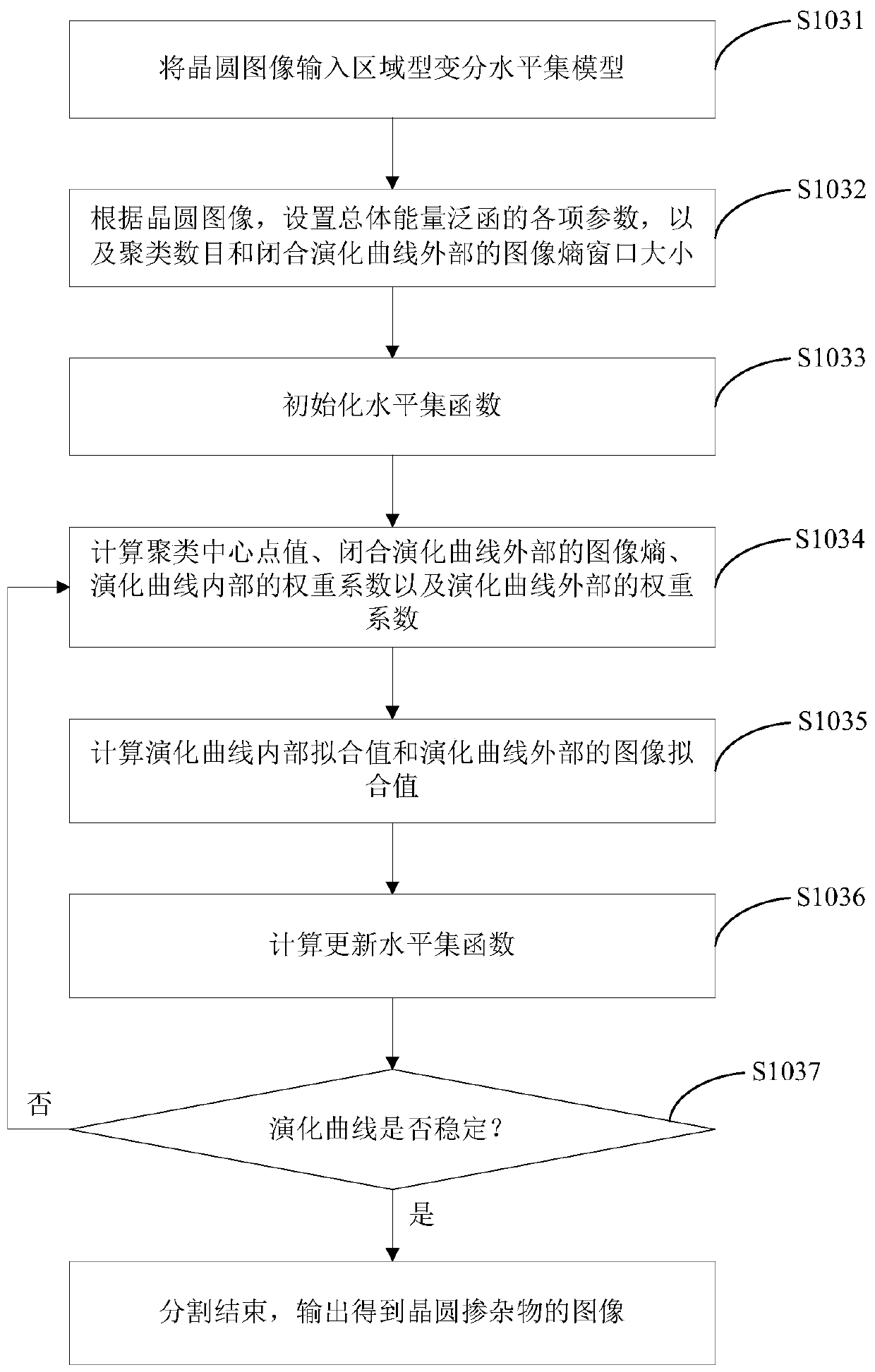
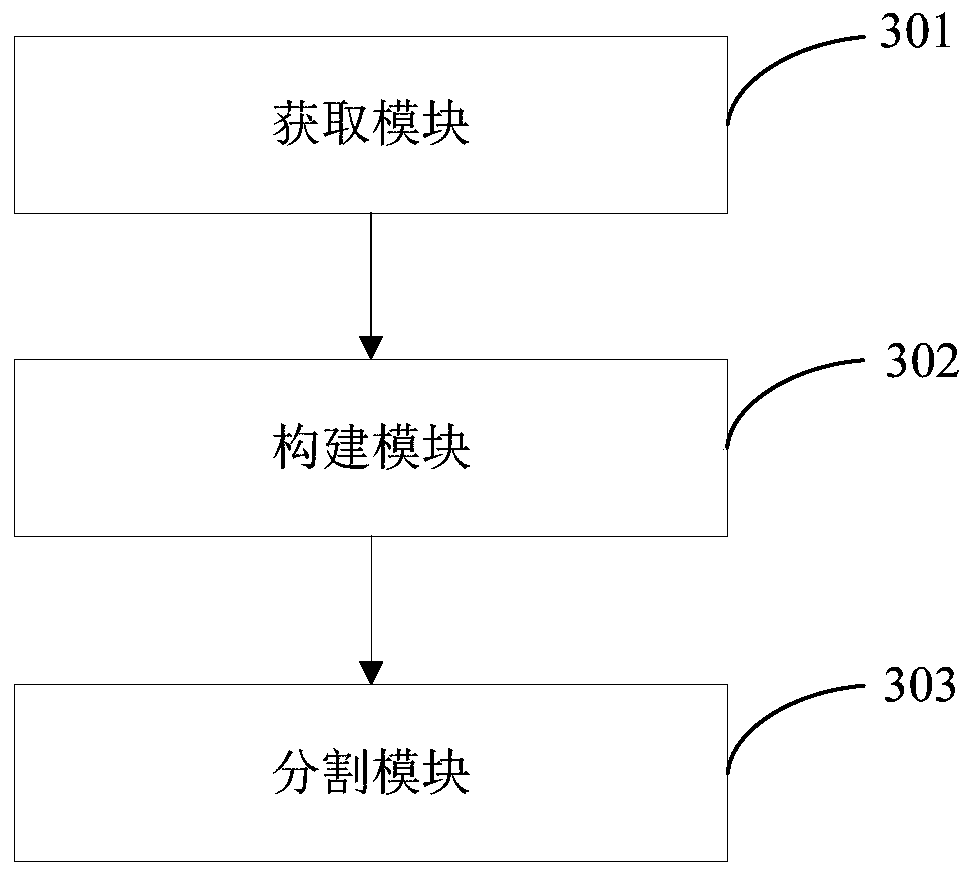
Image segmentation method and system for wafer dopant, computer device and storage medium
ActiveCN109978843AAccurate segmentationImproving Image Segmentation AccuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionDopant
The invention discloses an image segmentation method and system for a wafer dopant, a computer device and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a wafer image; constructing a regional variation level set model; inputting the wafer image into a regional variational level set model, segmenting the wafer image by using the total energy functional of the regional variational level set model, and outputting to obtain a wafer dopant image; the system comprises an acquisition module, a construction module and a segmentation module. According to the method, the wafer image influenced by the noise is input into the constructed regional variation level set model, and the wafer image is segmented by using the total energy functional of the regional variation level set model, sothat the wafer dopant can be accurately segmented from the wafer image, and the image segmentation precision with low contrast ratio can be improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Global layout method for 2.5D packaged FPGA
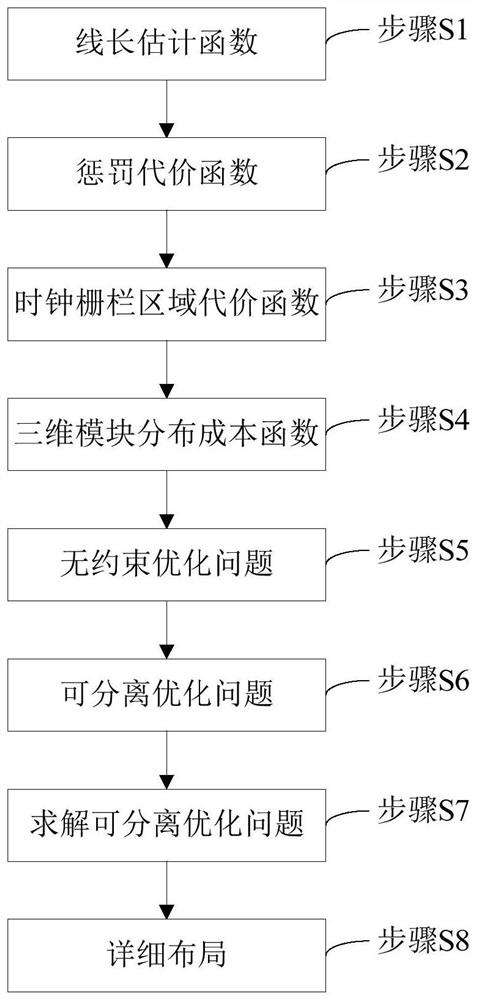
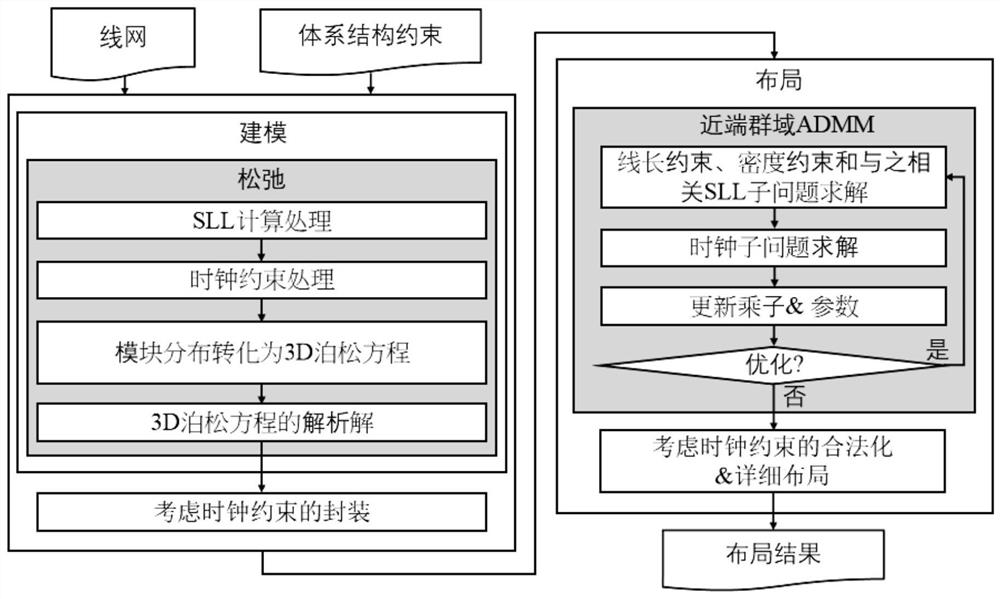
InactiveCN113139361ASolving SLL problemsExact analytical solutionCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsLayoutEngineering
The invention relates to a global layout method for a 2.5D packaged FPGA, and the method comprises the following steps: defining a line length constraint condition through a line length estimation function, constraining a super-long line SLL through a penalty cost function, processing clock constraint through a clock fence area cost function, constraining module distribution through a three-dimensional module distribution cost function based on a 3D Poisson equation, expressing the global layout method of the 2.5D packaged FPGA as an unconstrained optimization problem including a line length estimation function, a penalty cost function, a clock fence area cost function and a three-dimensional module distribution cost function, expressing the unconstrained optimization problem as a separable optimization problem with linear constraints, and solving the separable optimization problem by adopting a near-end group domain ADMM; and carrying out detailed layout by using clock constraint legalization so as to realize layout legalization. According to the global layout method, layout calculation time is shortened, super-long lines are remarkably reduced on a base layer meeting clock constraint and line length constraint, and a more effective legalized layout result is obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI FUDAN MICROELECTRONICS GROUP
Computer simulation of photolithographic processing
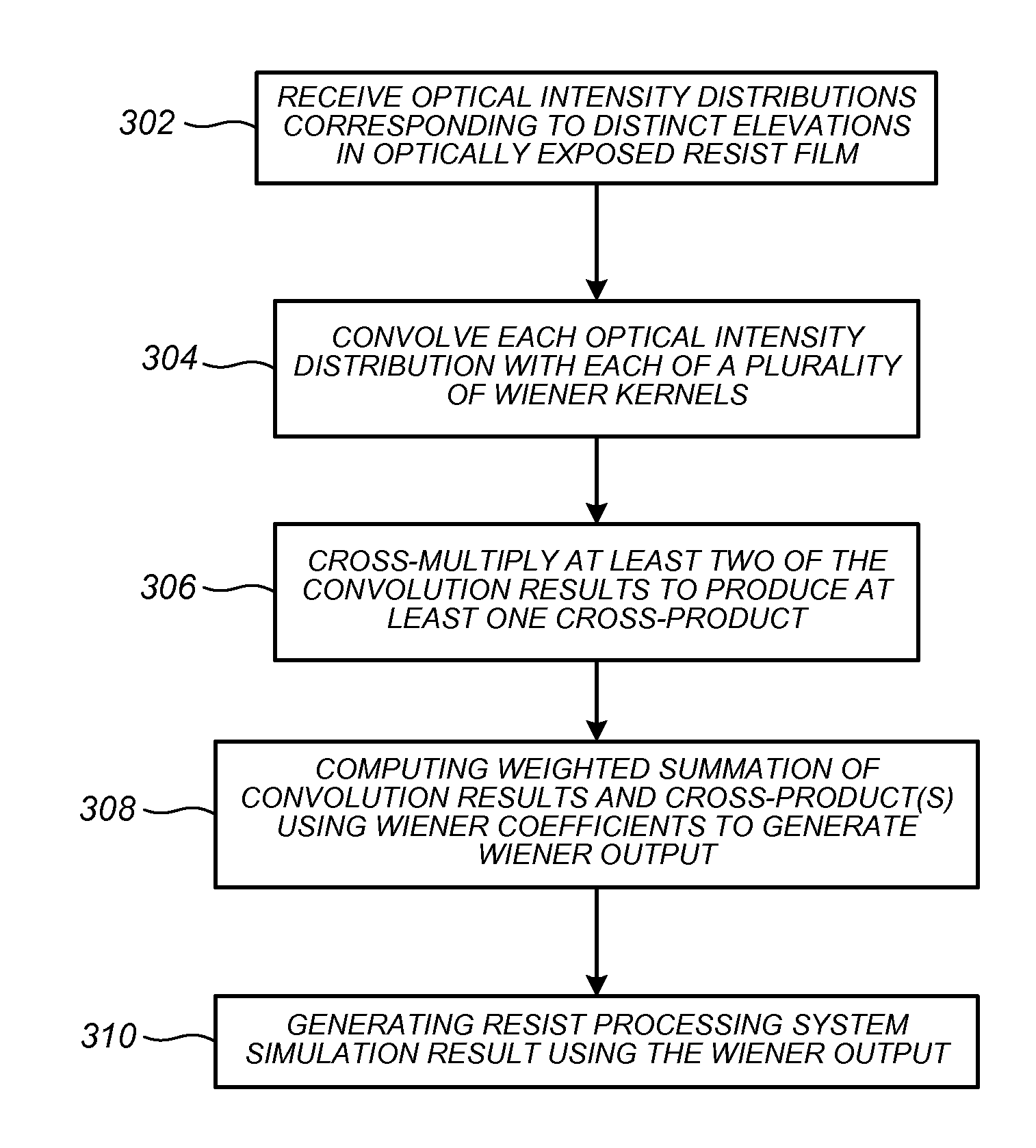
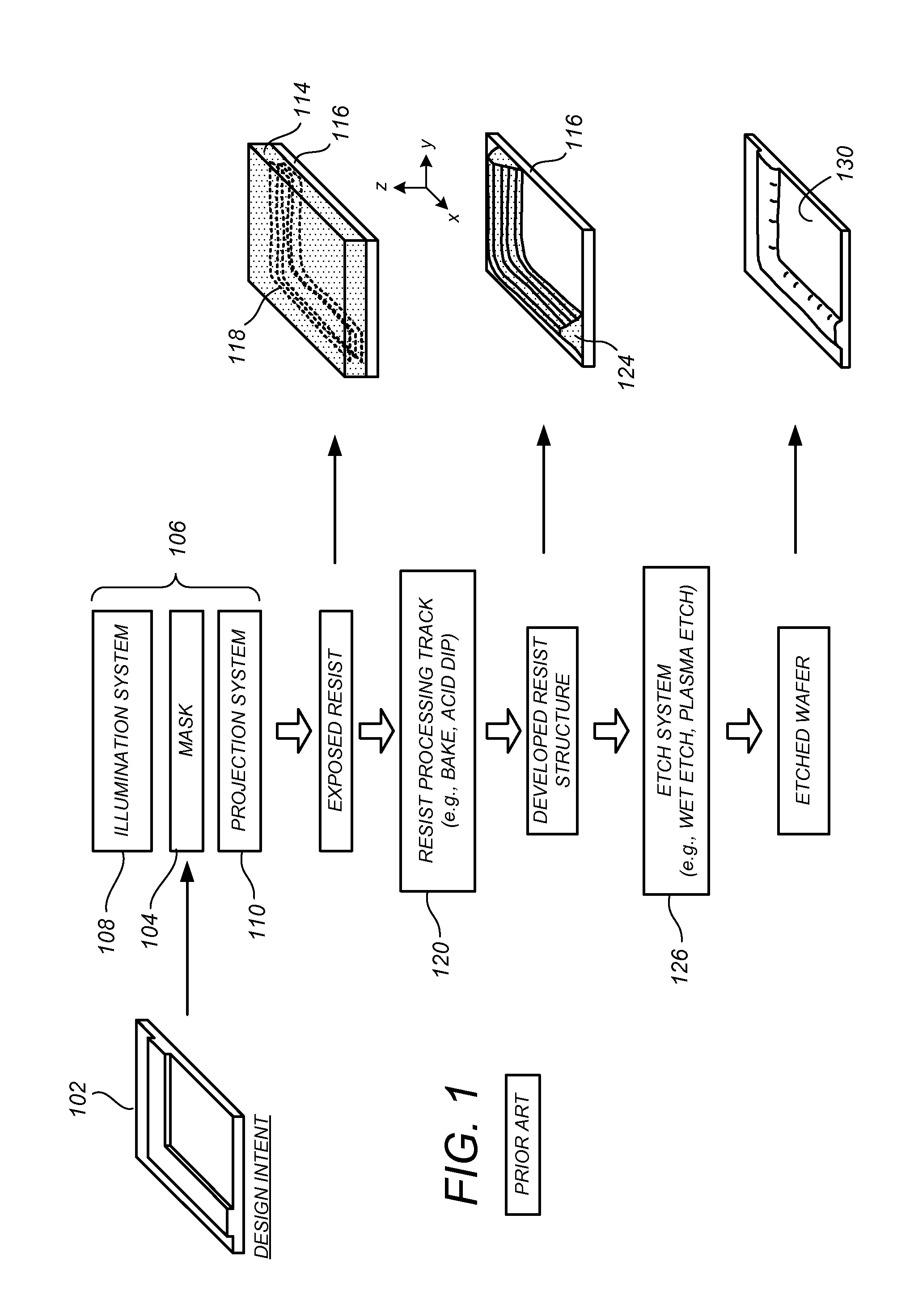
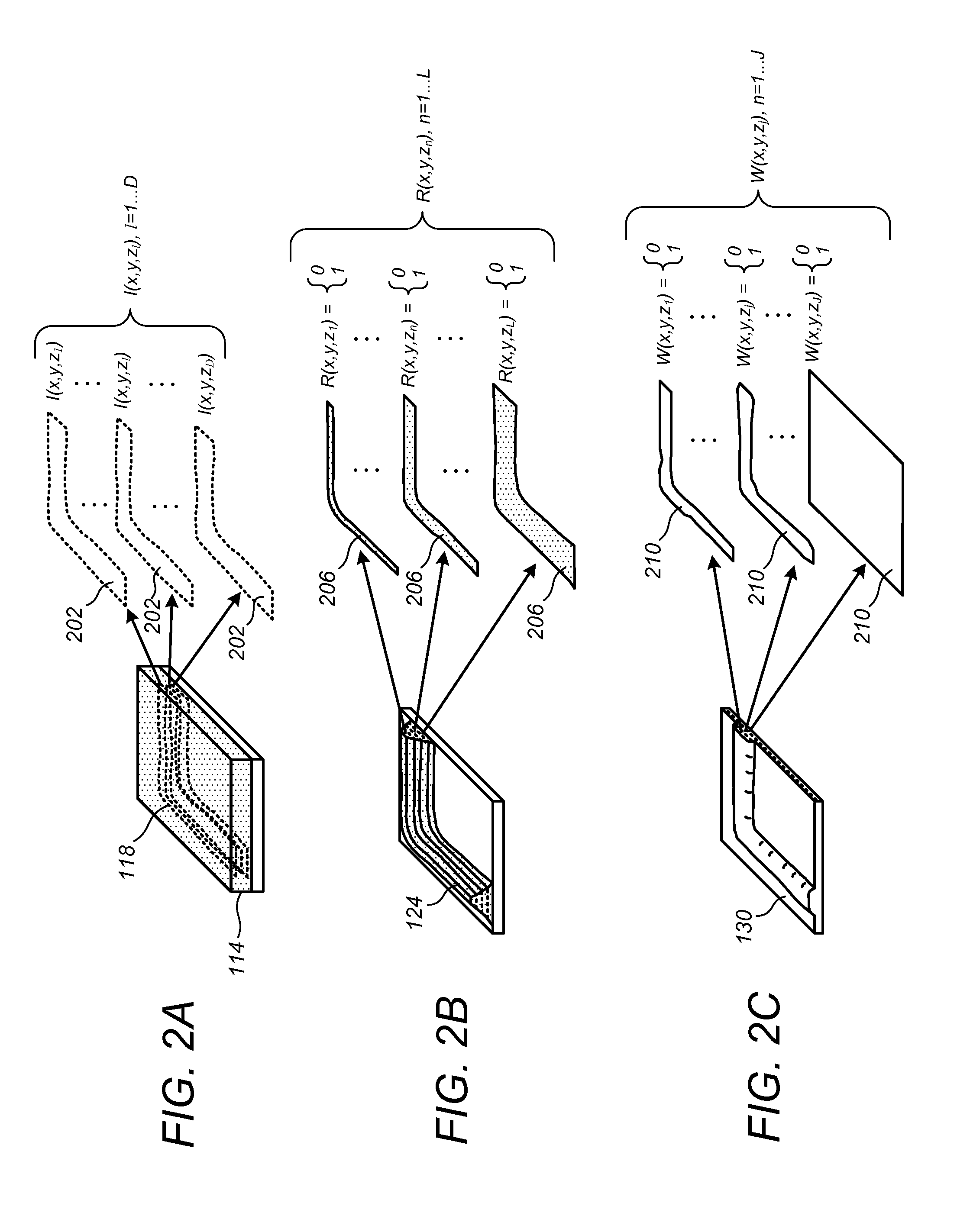
InactiveUS20120158384A1Improve usabilityFast calculation timePhotomechanical apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationResistNonlinear model
Methods, systems, and related computer program products for photolithographic process simulation are disclosed. In one preferred embodiment, a resist processing system is simulated according to a Wiener nonlinear model thereof in which a plurality of precomputed optical intensity distributions corresponding to a respective plurality of distinct elevations in an optically exposed resist film are received, each optical intensity distribution is convolved with each of a plurality of predetermined Wiener kernels to generate a plurality of convolution results, and at least two of the convolution results are multiplied to produce at least one cross-product. A weighted summation of the plurality of convolution results and the at least one cross-product is computed using a respective plurality of predetermined Wiener coefficients to generate a Wiener output, and a resist processing system simulation result is generated based at least in part on the Wiener output.
Owner:OLAMBDA
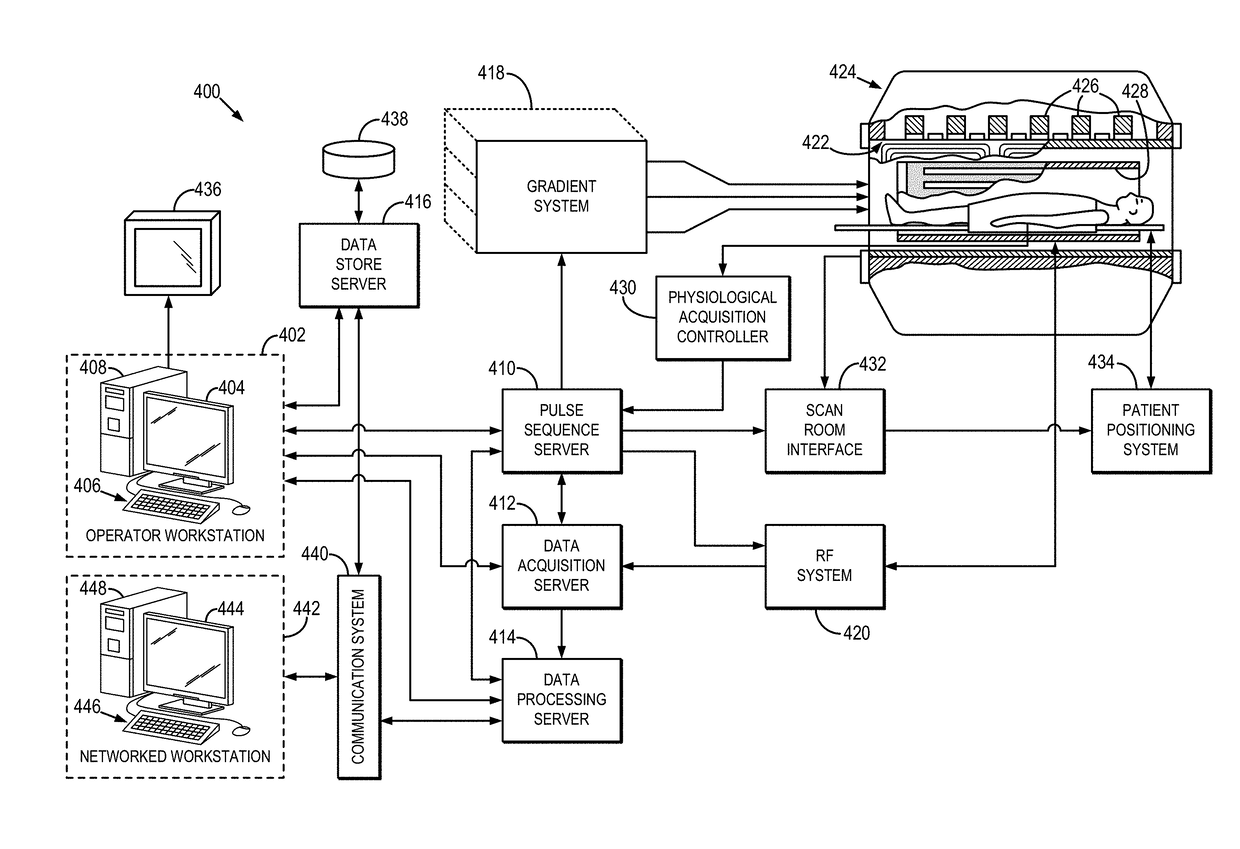
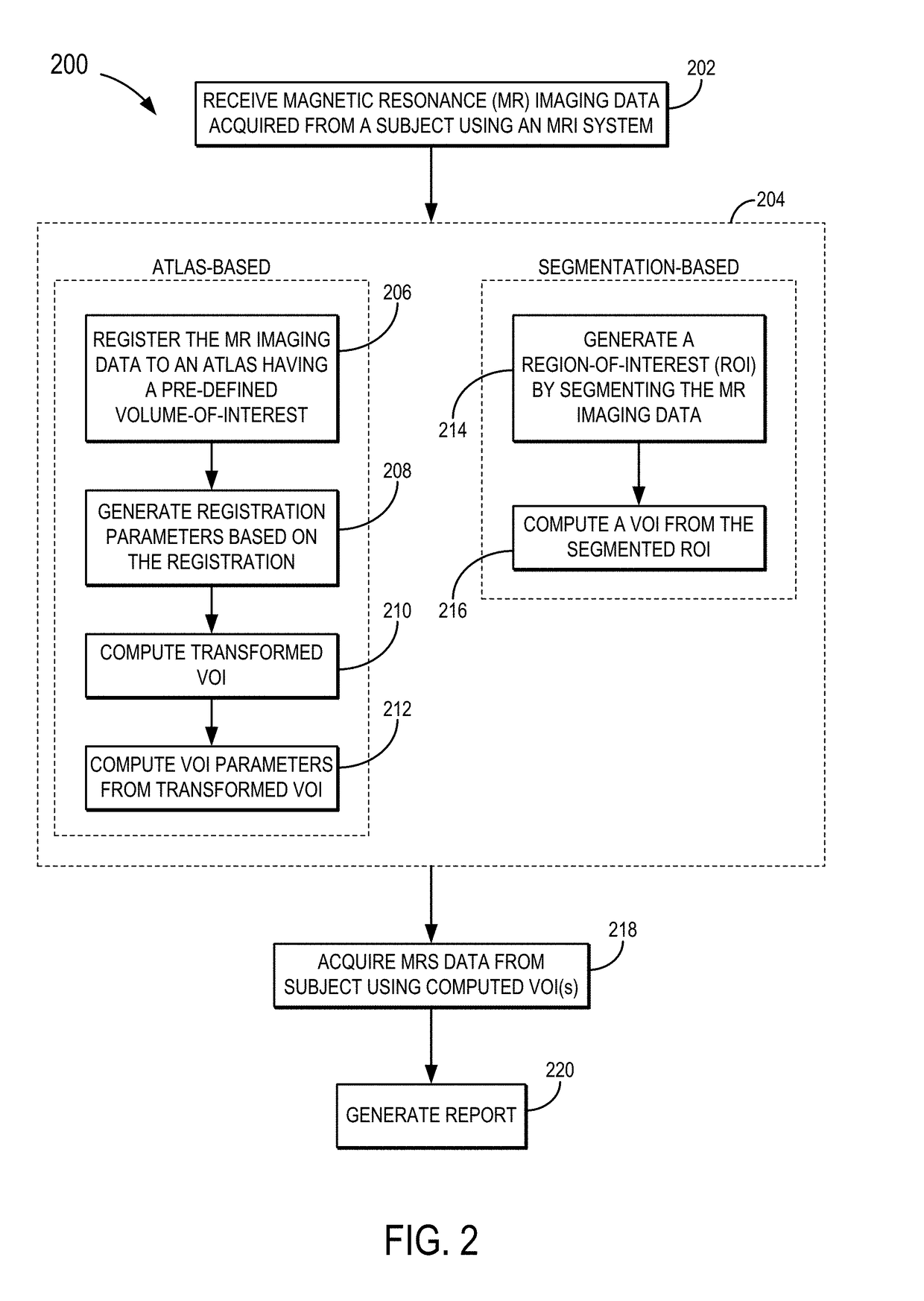
Systems and methods for automatic voxel positioning in magnetic resonance spectroscopy
ActiveUS20180156883A1Improve consistencyFast calculation timeImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelResonance
Systems and methods for automated voxel positioning in magnetic resonance spectroscopy (“MRS”) are provided. In some aspects, a method includes receiving magnetic resonance (“MR”) imaging data acquired from a subject using an MR imaging system and registering the MR imaging data to an atlas having a pre-defined volume of interest (“VOI”), or segmenting a region of interest (“ROI”) directly from the MR data. The method also includes generating registration parameters based on the registration, and computing a transformed VOI using the pre-defined VOI in the atlas and the registration parameters. Alternatively, the VOI may be obtained by directly estimating it from the ROI.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
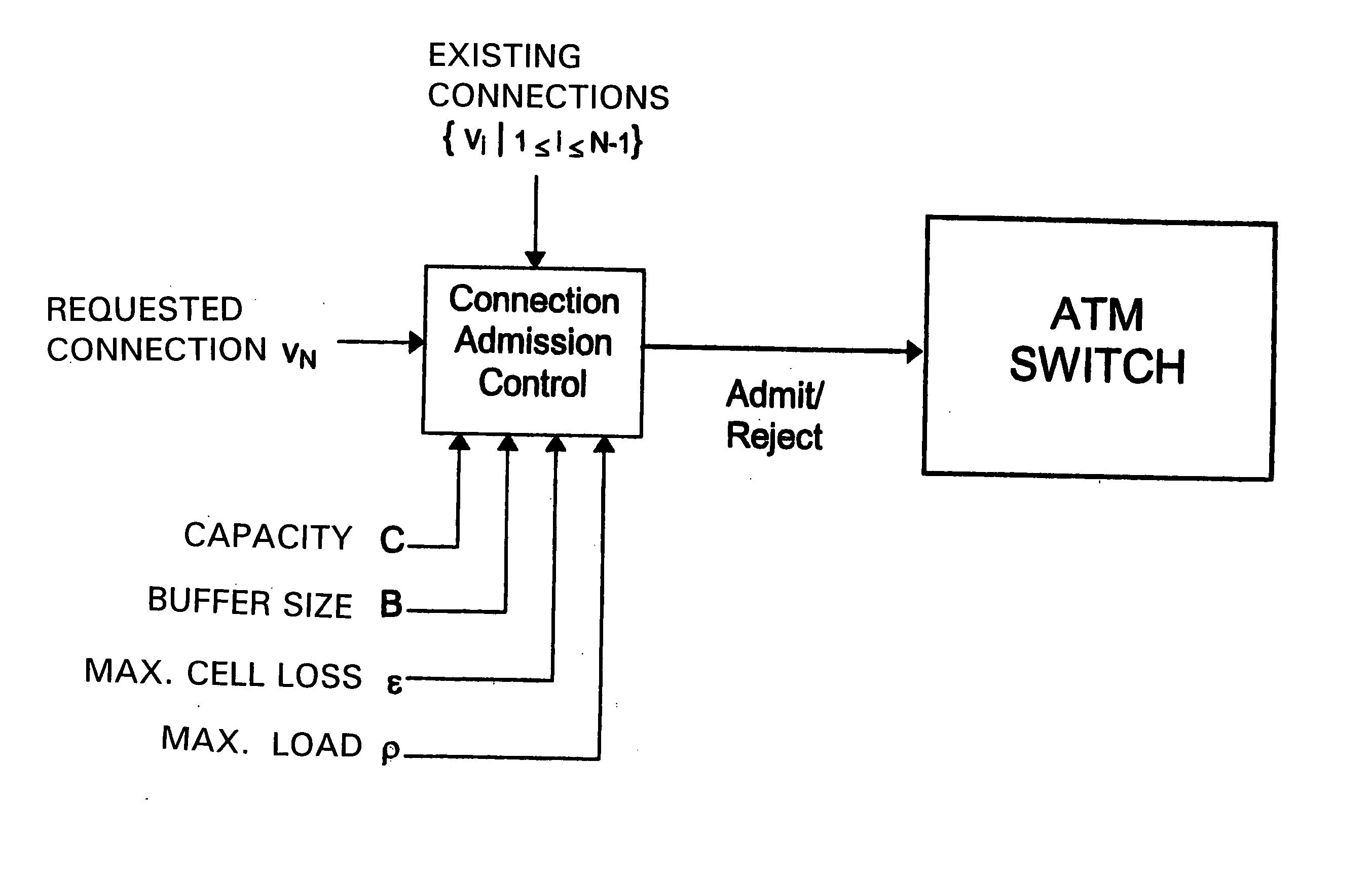
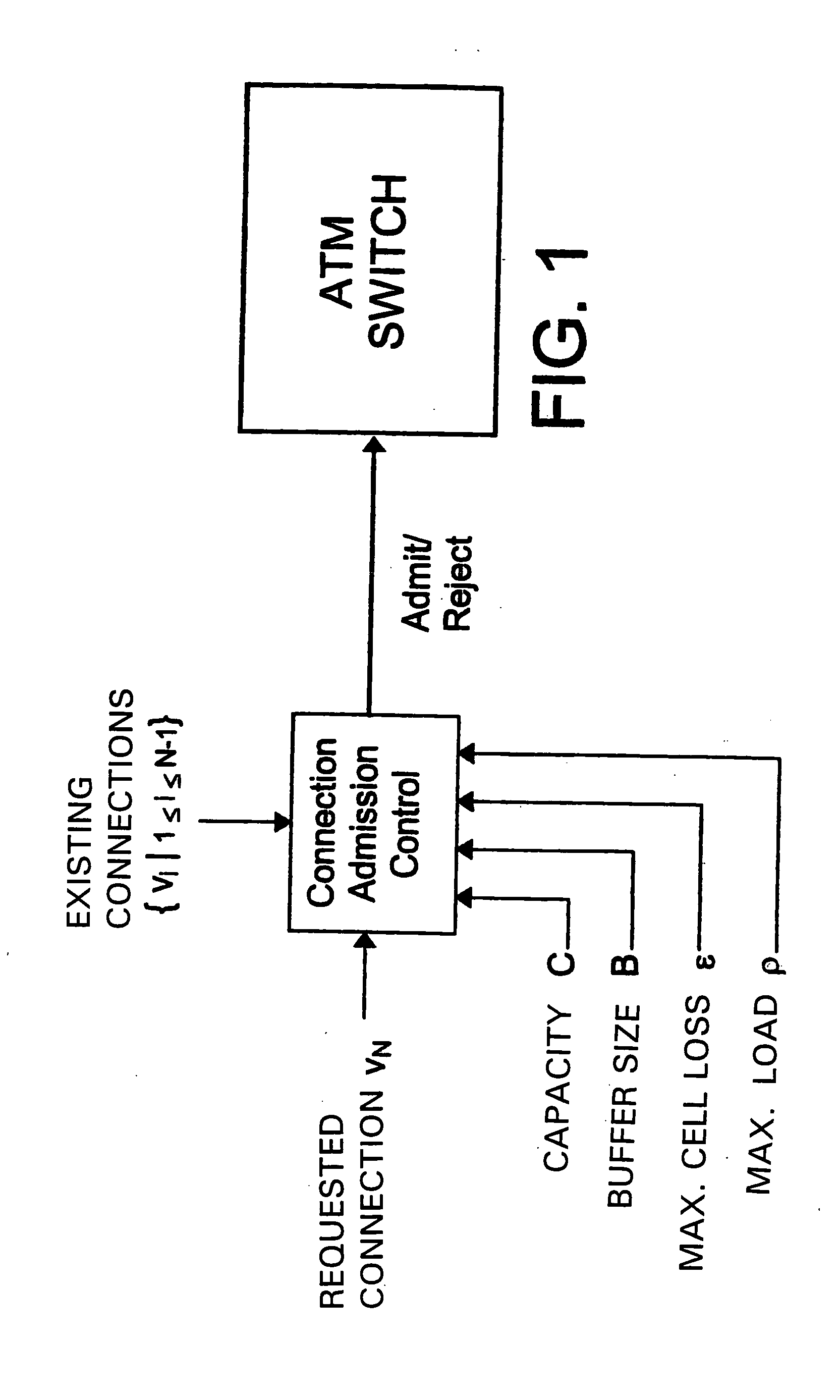
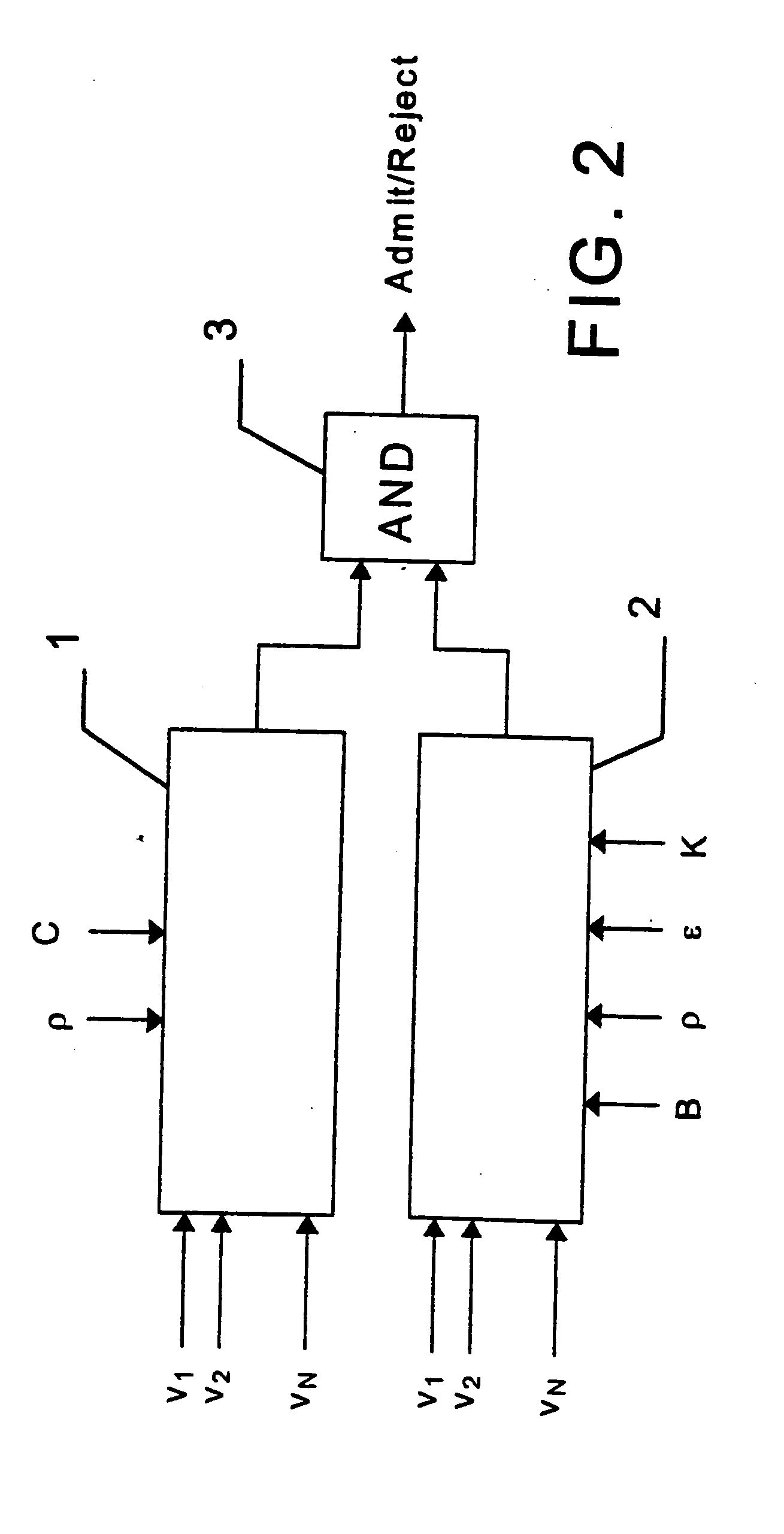
ATM connection admission control device for DBR connections
InactiveUS20050038903A1Improve practicalityNumerically stableMultiple digital computer combinationsStore-and-forward switching systemsTraffic volumeAdmission control
Owner:KONINK KPN NV
Seamless network generation
ActiveUS9599476B2Efficiently generate and updateError associated with step is avoidedInstruments for road network navigationMaps/plans/chartsNetwork generationRoad networks
A system and method for generating a seamless road network of a large geographical area includes a plurality of GPS probe traces extending across a geographical area. The probe traces are divided into sub-sets base on criteria, such as accuracy. A plurality of threads simultaneously employ the sub-sets traces to generate an independent network of the entire geographical area. The networks generated using sub-sets having a high accuracy are preferred over networks generating using sub-sets having a lower accuracy. The independent networks are combined to form a seamless networks of road segments.
Owner:TOMTOM GERMANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com