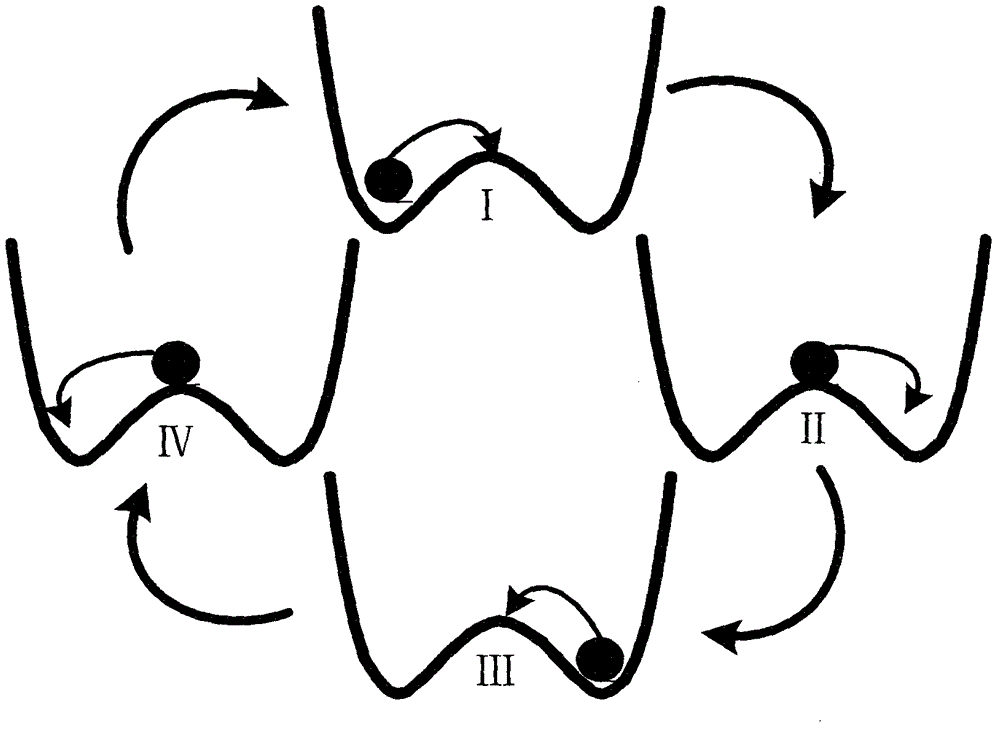
Power distribution network fault line selection method based on variable-scale bi-stable system
A distribution network fault and steady-state system technology, applied in the direction of fault location, etc., can solve the problem of less research on power systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0140] 1 simulation model
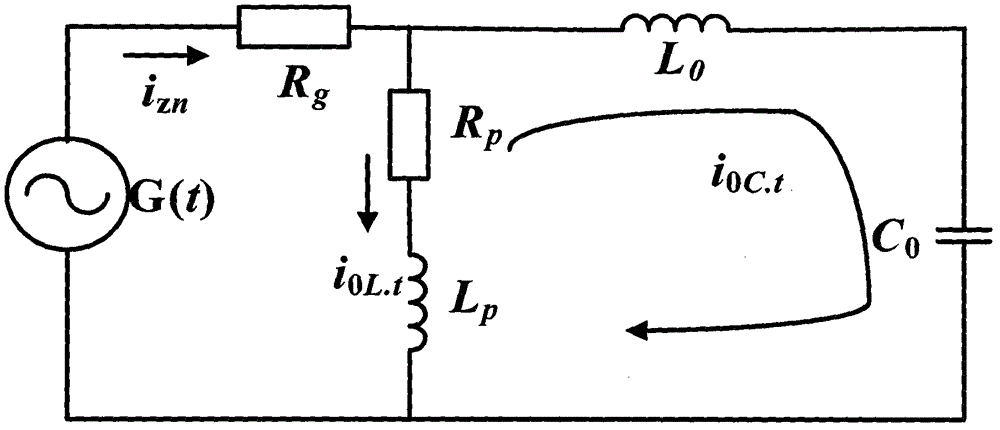
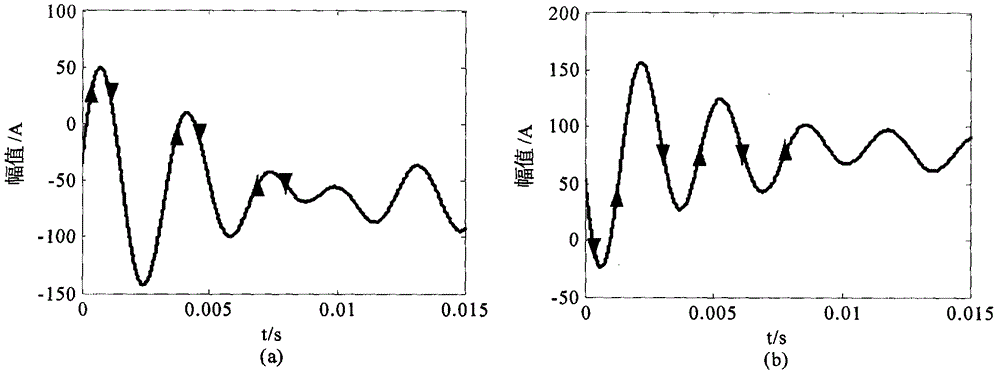
[0141] The present invention uses ATP-EMTP to do single-phase grounding simulation experiments, and the simulation model is as follows Figure 5 As shown, the specific electrical parameters of the model are as follows:
[0142] Line: Overhead line positive sequence parameter R 1 = 0.17Ω / km, L 1 = 1.2mH / km, C 1 =9.697nF / km; zero sequence parameter R 0 = 0.23Ω / km, L 0 =5.48mH / km, C 0 = 6nF / km. Cable line positive sequence parameter R 11 = 0.193Ω / km, L 11 =0.442mH / km, C 11 =143nF / km; zero sequence parameter R 00 =1.93Ω / km, L 00 =5.48mH / km, C 00 = 143nF / km.
[0143] Transformer: 110 / 10.5kV; high-voltage side single-phase neutral point coil resistance 0.40Ω, inductance 12.2Ω; low-voltage side single-phase coil resistance 0.006Ω, inductance 0.183Ω; excitation current 0.672A, excitation flux 202.2Wb, magnetic circuit resistance 400kΩ. Load: always use delta connection, Z L =400+j20Ω. Arc suppression coil: When simulating the arc suppressio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com