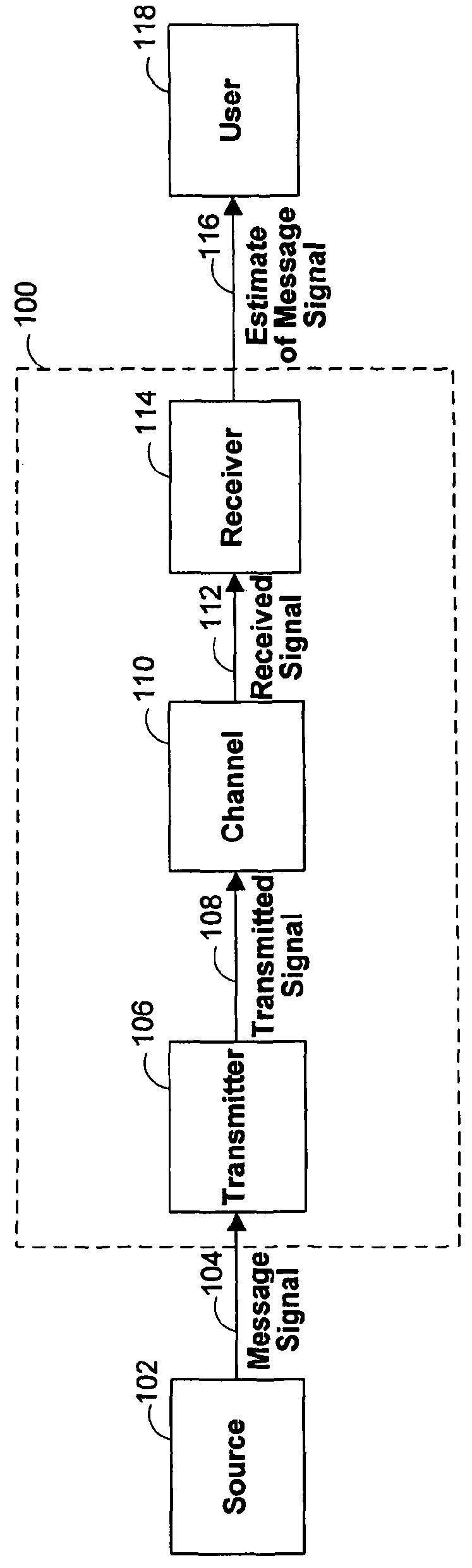
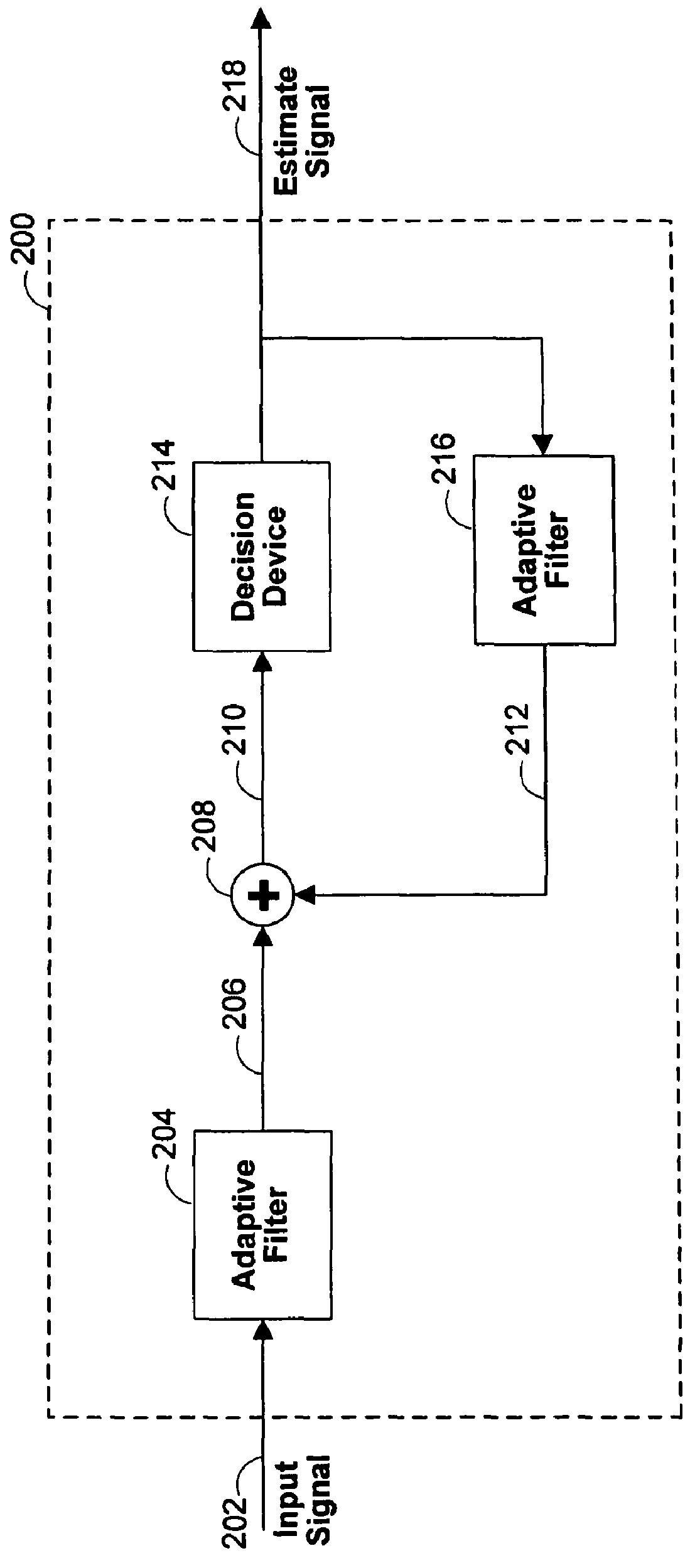
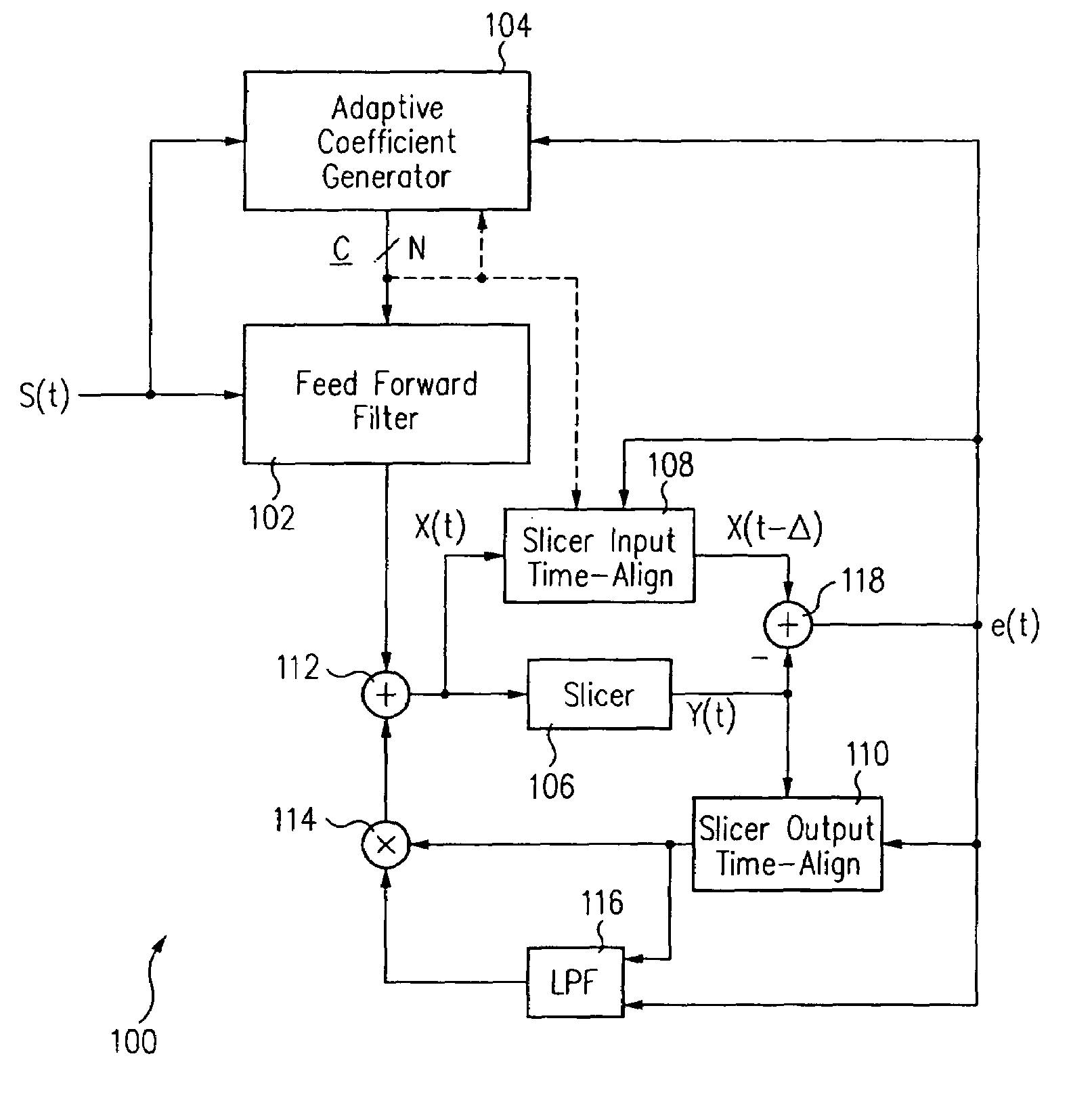
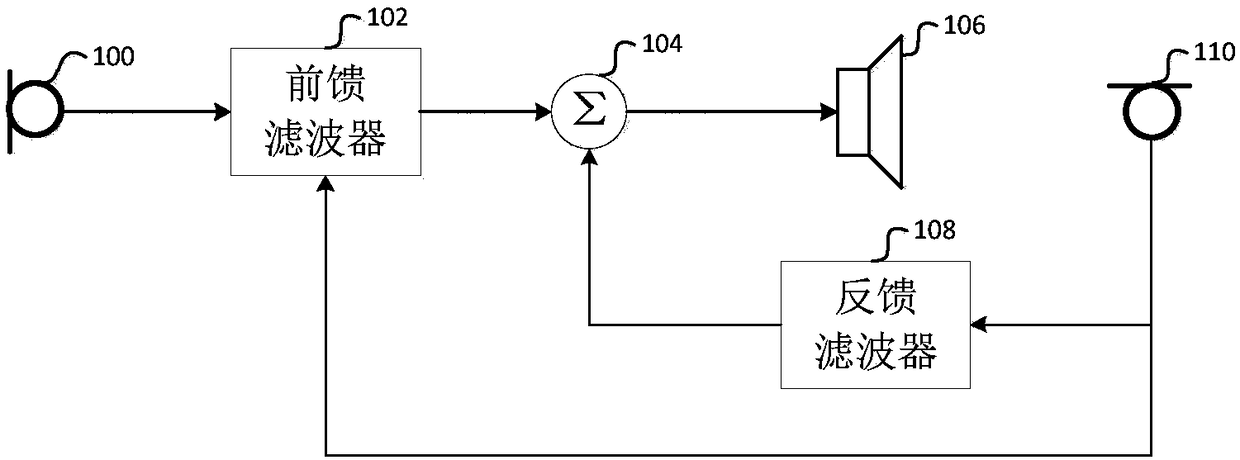
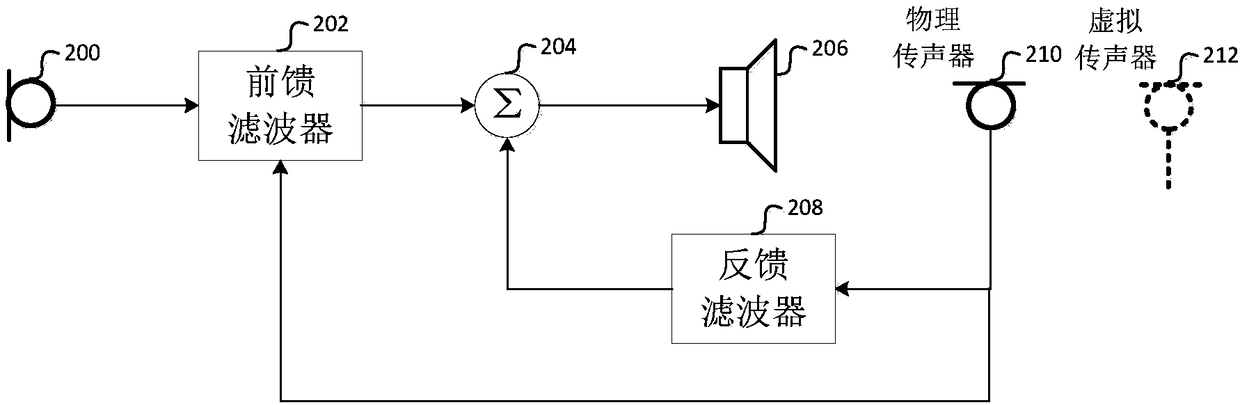
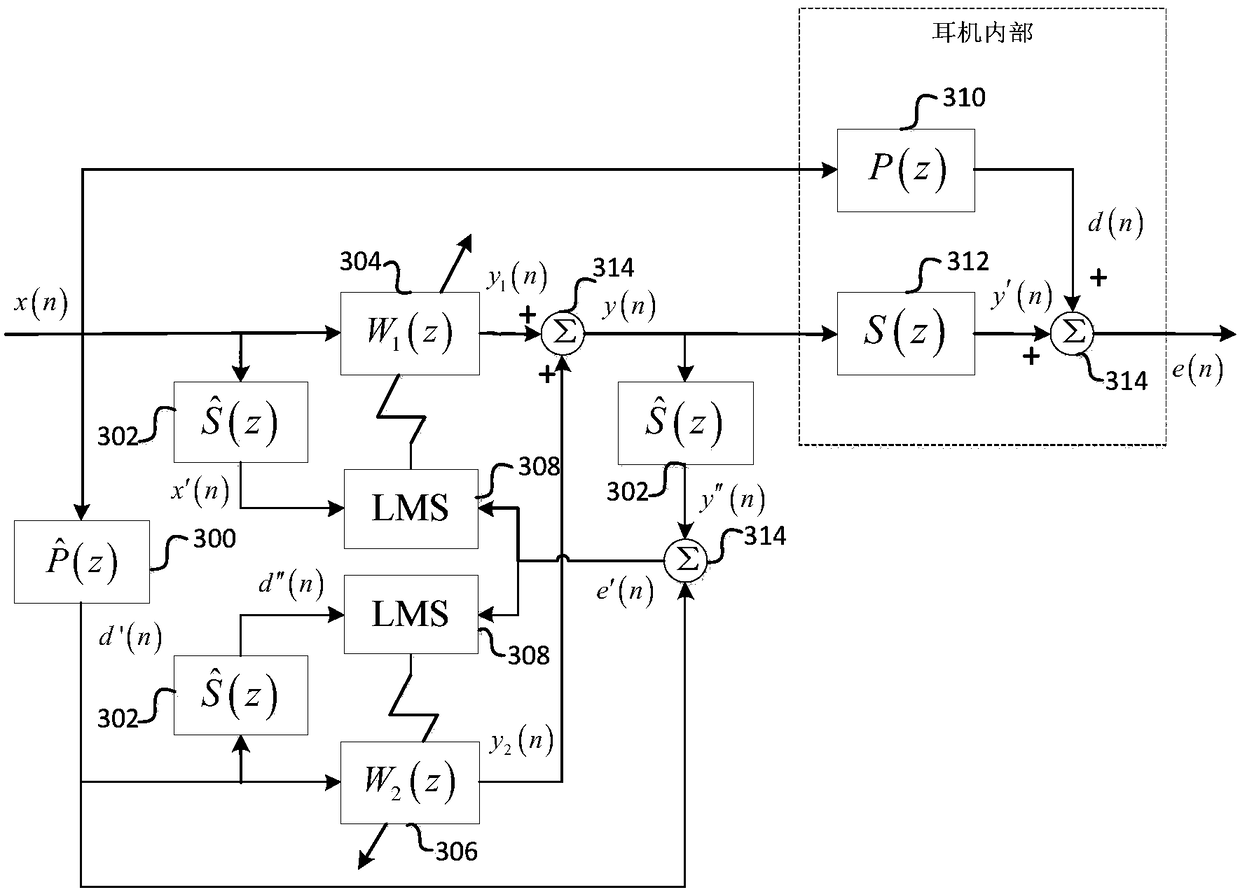
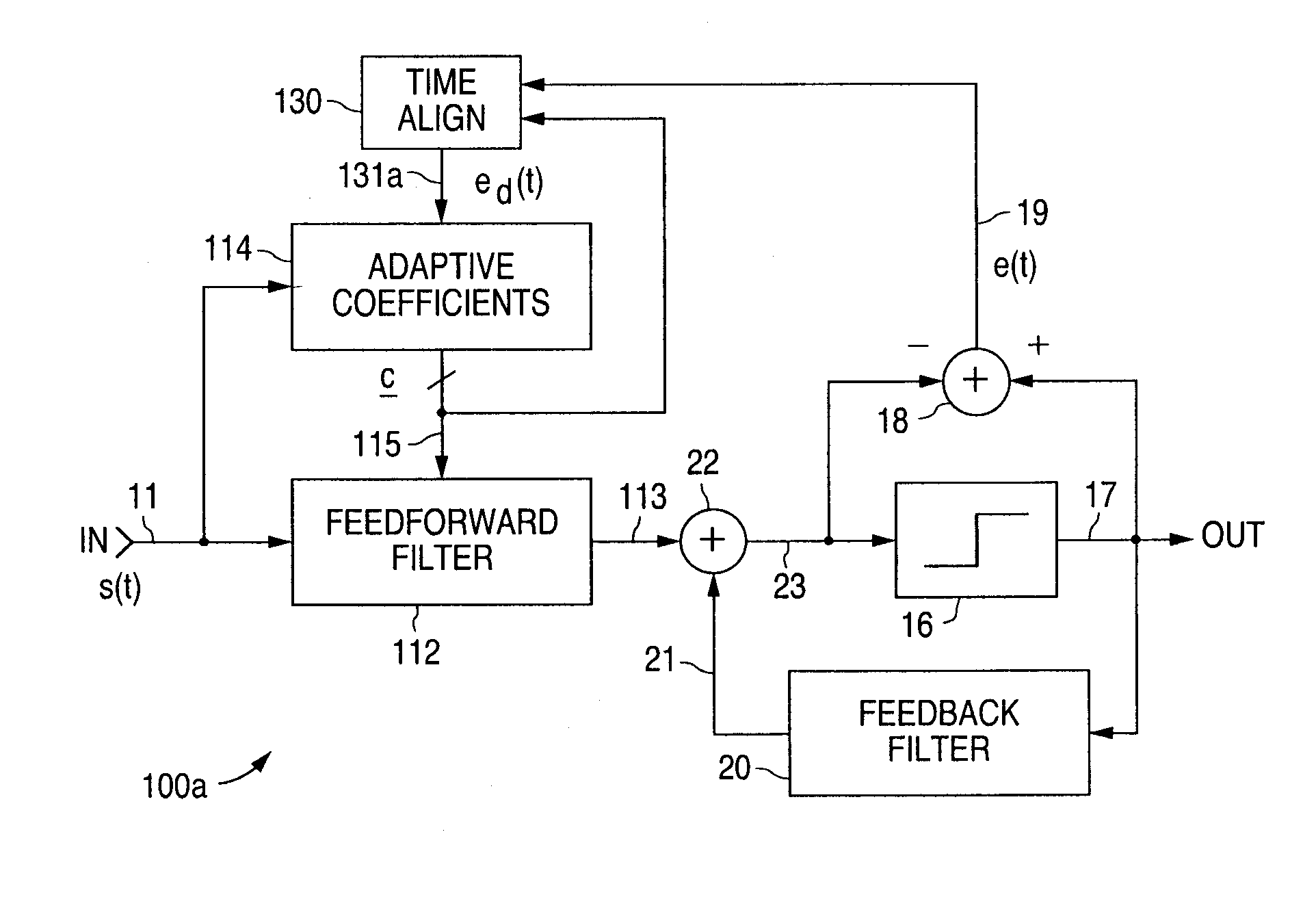
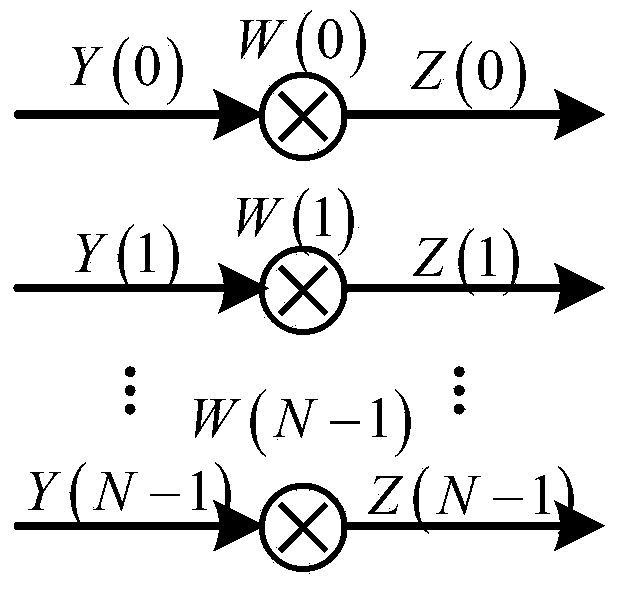Patents
Literature
171 results about "Feedforward filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
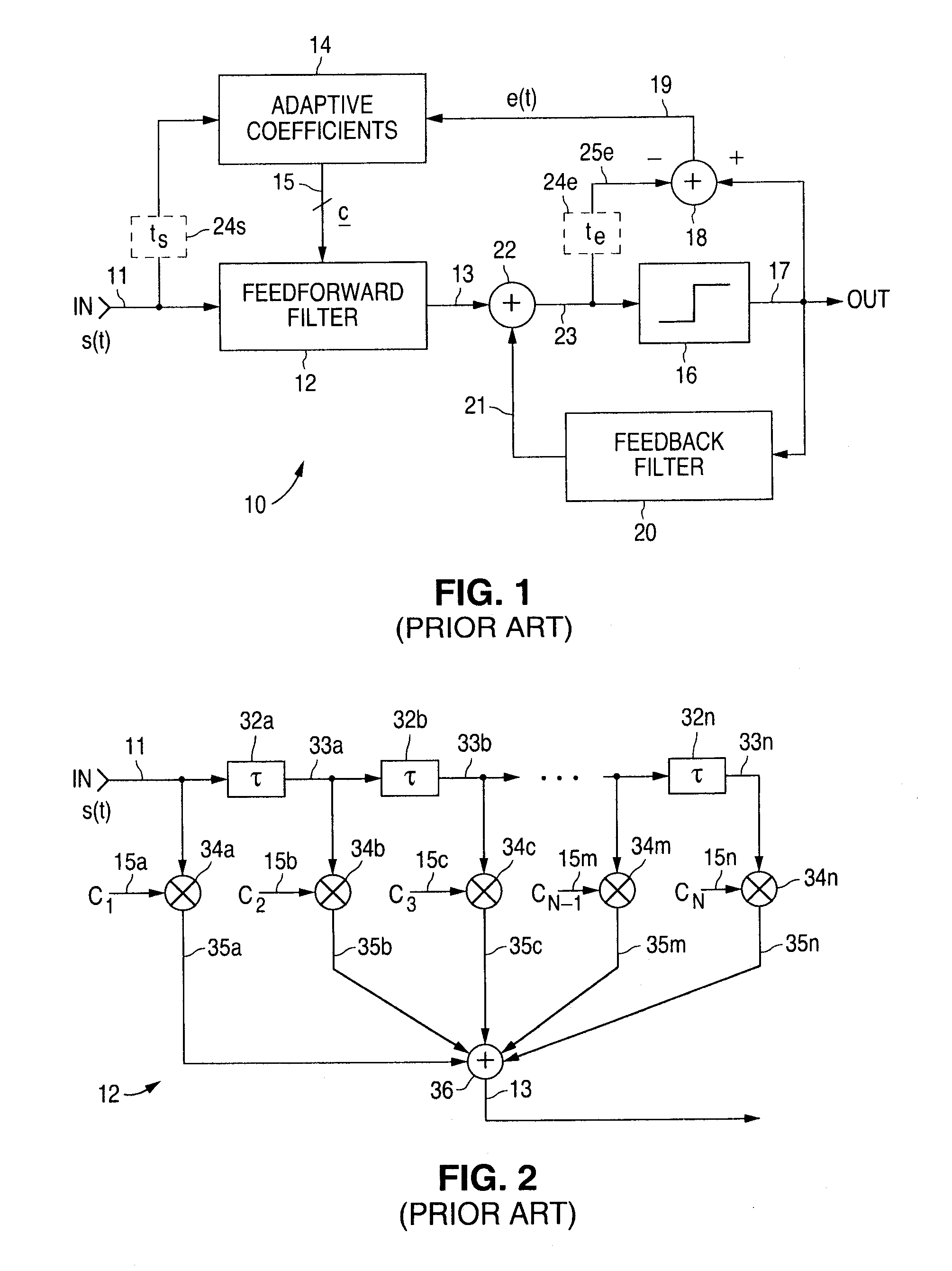
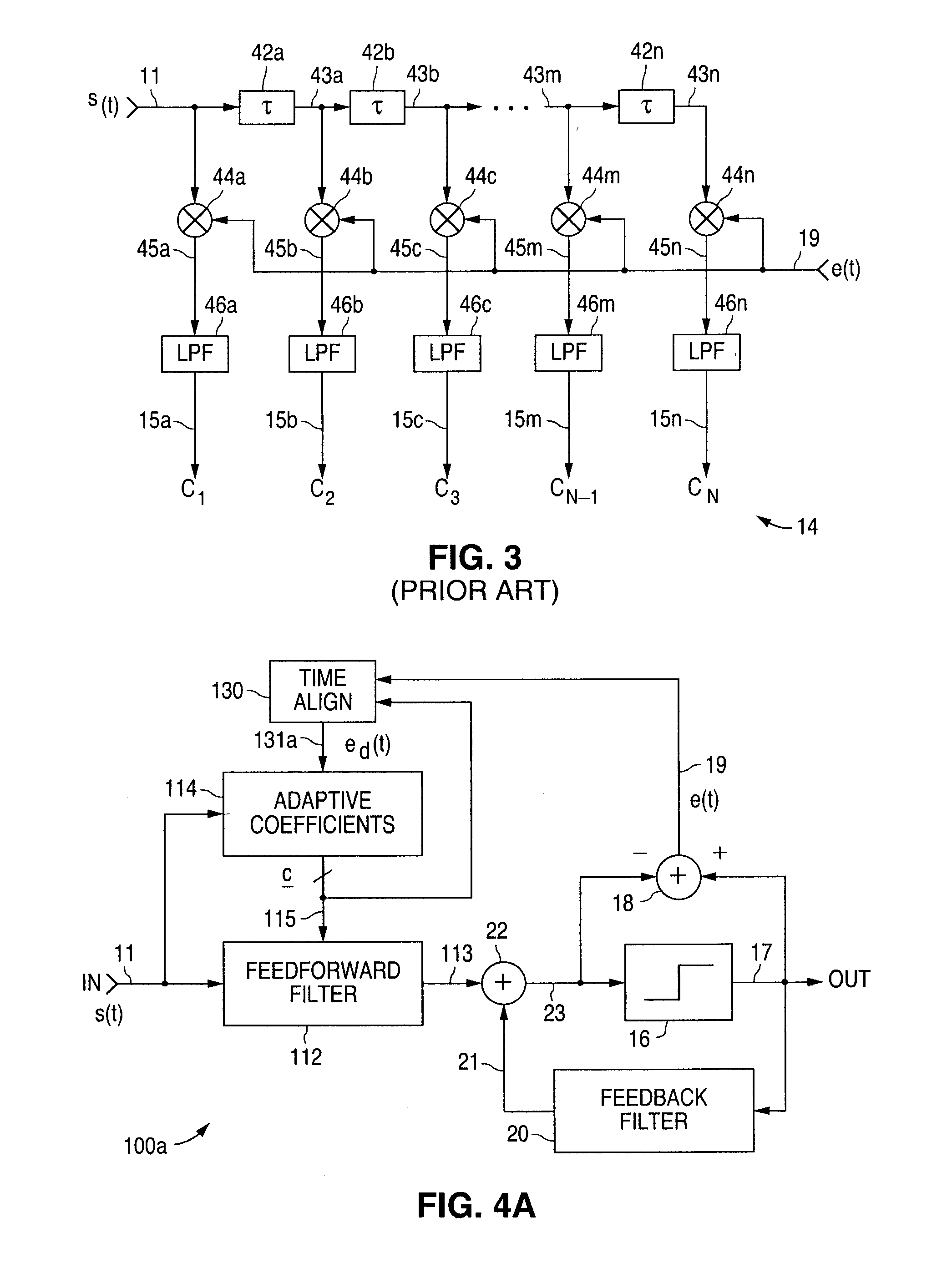
Method and apparatus for adaptively compensating channel or system variations in precoded communications system
InactiveUS6400761B1Reduce distractionsImprove performanceMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsPrecodingCommunications system
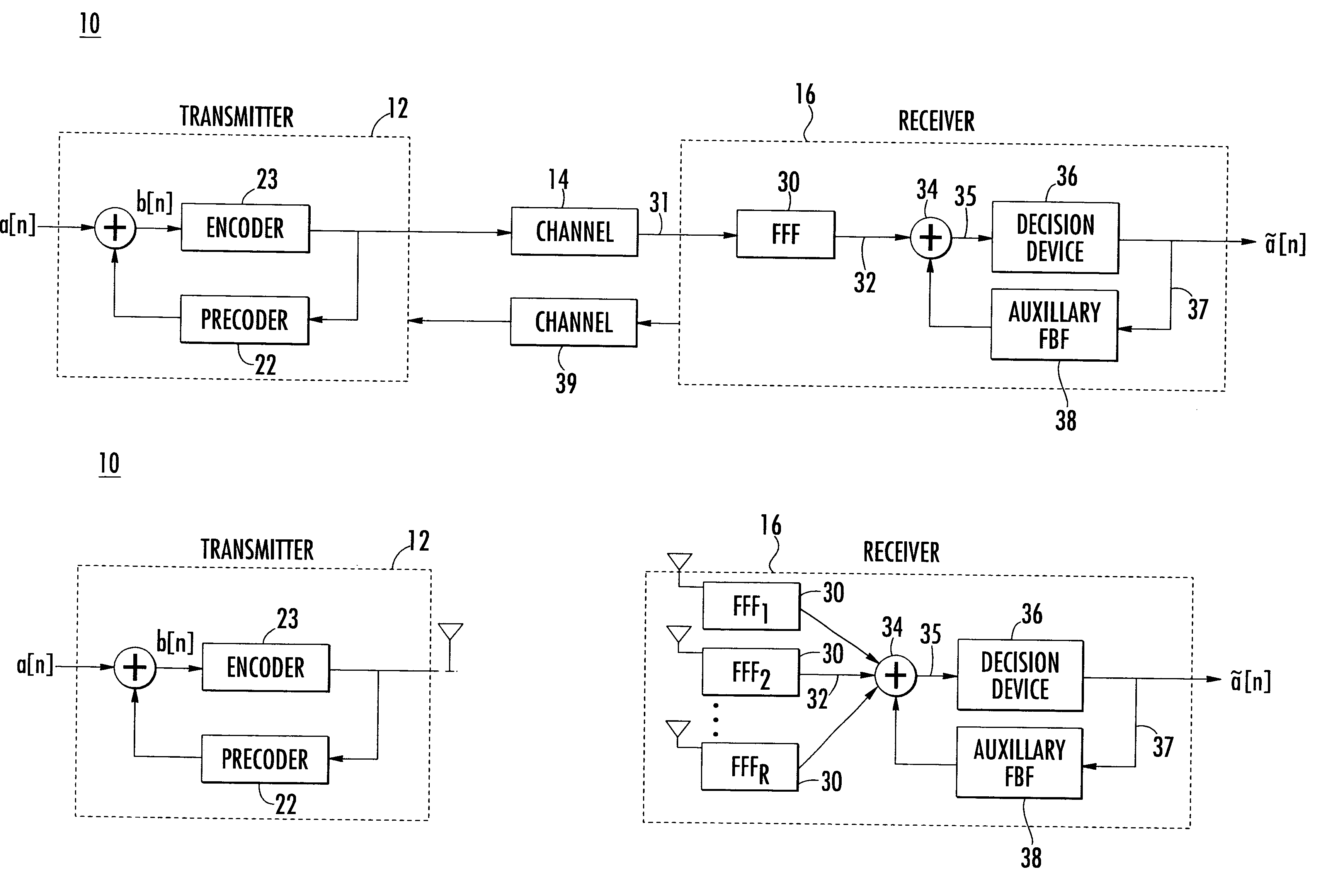
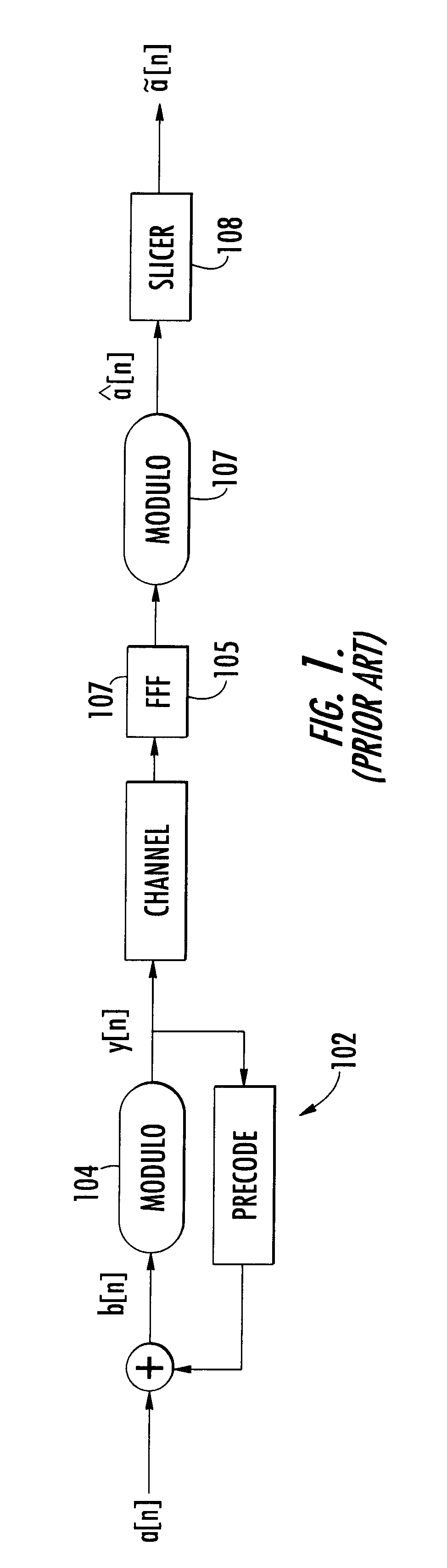
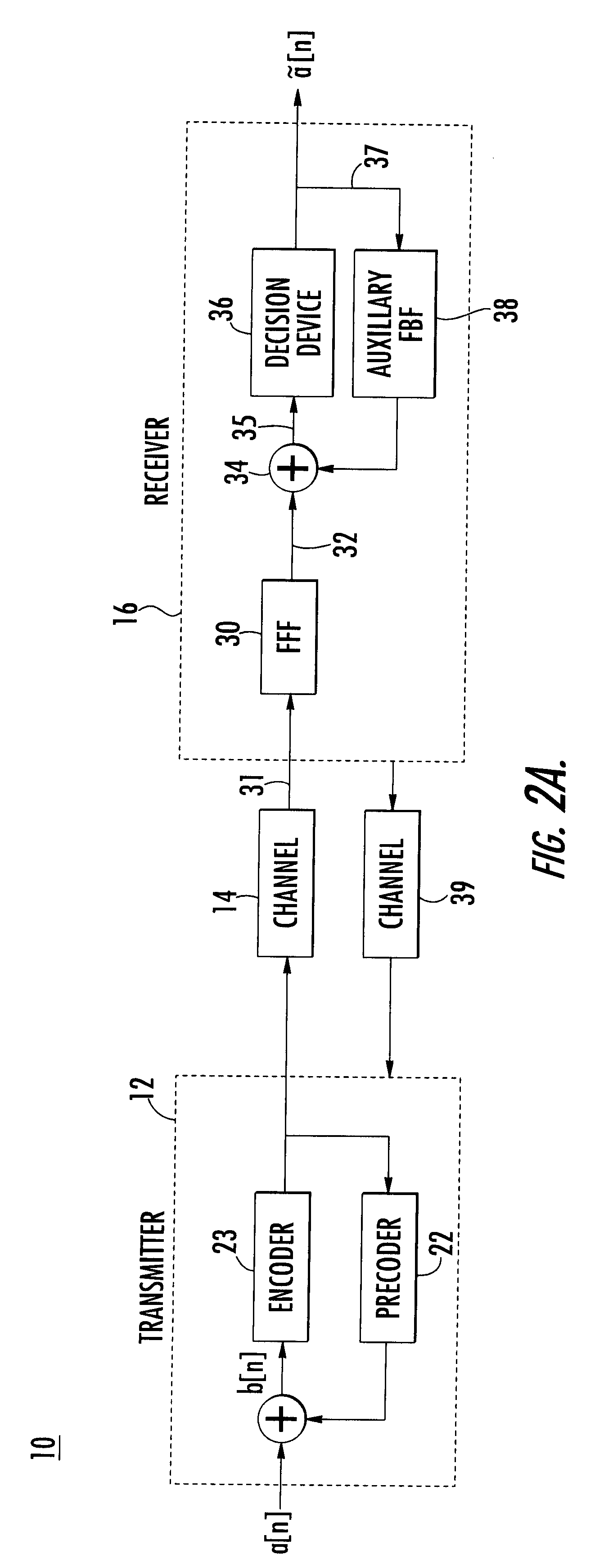
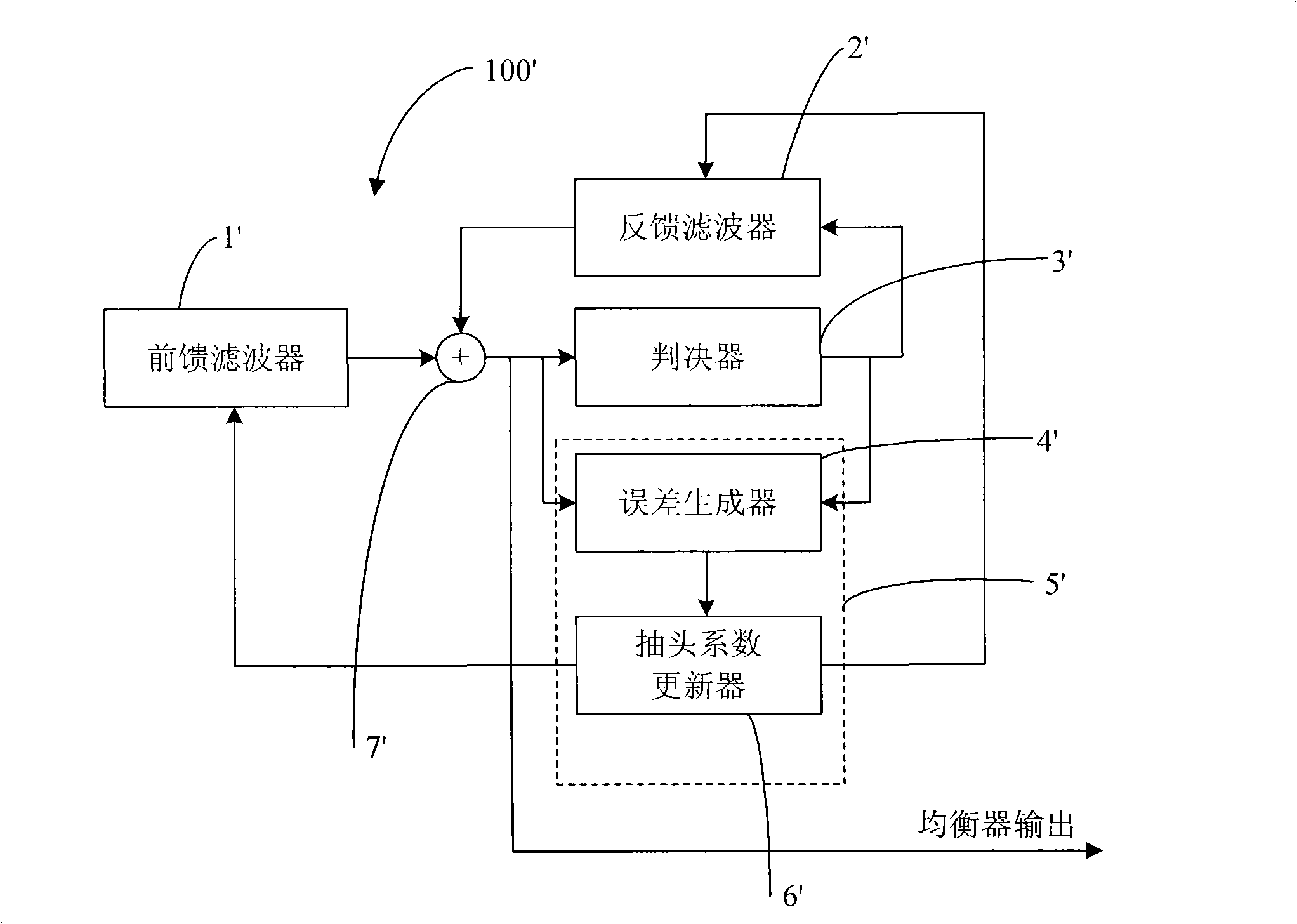
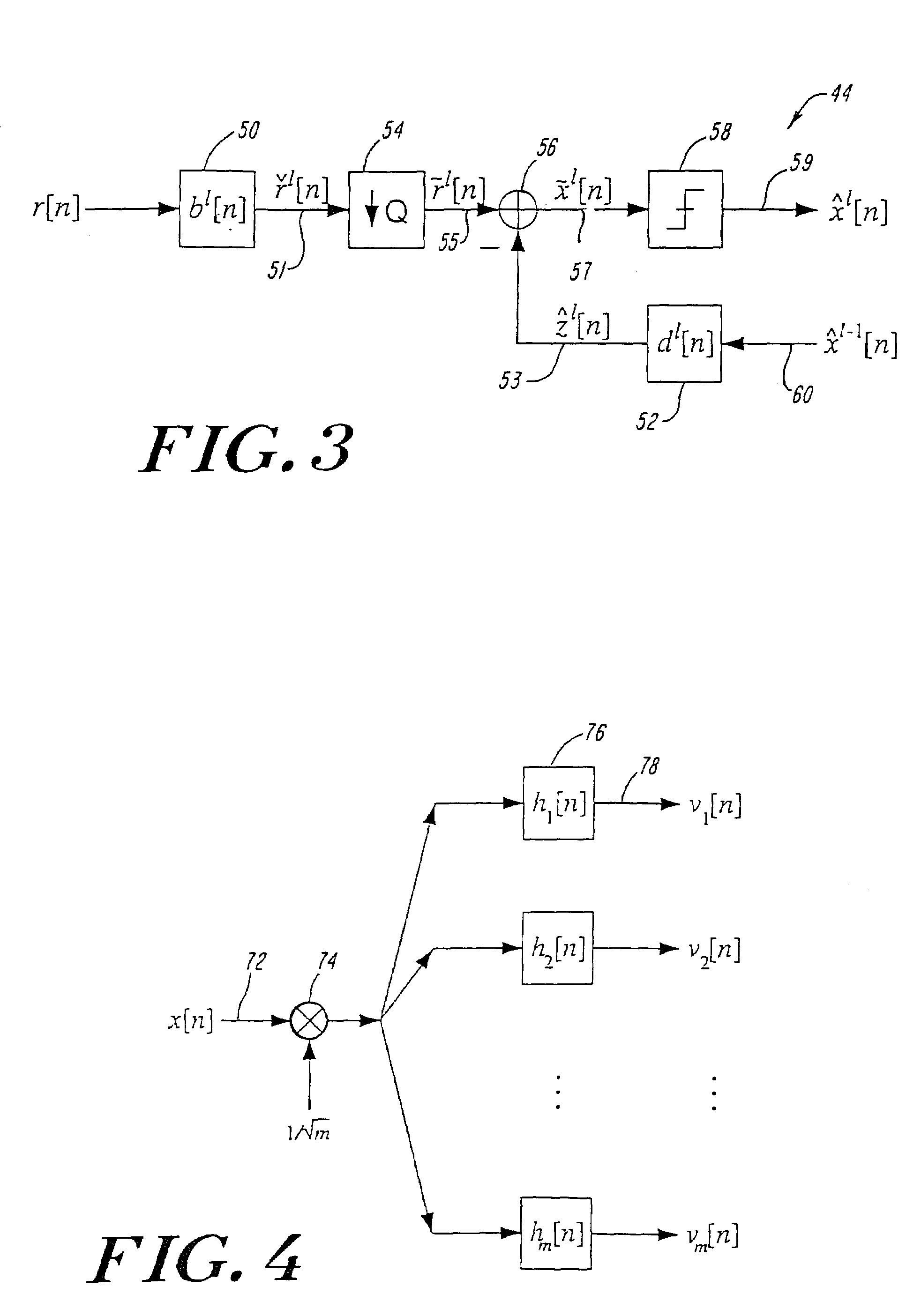
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for adaptively compensating for channel or system variations in which adaptive compensation is used in the receiver of a digital communication system. The transmitter of the digital communication system includes precoding. The adaptive receiver compensation mitigates the interferences not removed by the transmitter precoder. In an embodiment of the invention, the adaptive compensation can be performed using an adaptive feedforward filter (FFF) and a feedback filter (FBF) in the receiver. The FBF output is generated based on previous values of estimates of the transmitted precoded sequence. The determined value of the FBF coefficients can be periodically relayed to the transmitter to update the precoder coefficients of the transmitter. Alternatively, the value of the FBF coefficients can be relayed to the transmitter after the value of the coefficients exceeds a predetermined threshold. Accordingly, the receiver adaptively and automatically compensates for misadjustments of the fixed transmitter precoder with respect to the actual channel at a given point in time.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Apparatus For And Method Of Controlling A Feedforward Filter Of An Equalizer
InactiveUS20070201544A1Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsPhase correctionComplex representation
A method of controlling a feedforward filter of an equalizer includes the steps of generating a complex representation of an output of the feedforward filter and generating a representation of a decision from an output of the equalizer. The complex representation and the decision representation are correlated to obtain a phase error estimate. A phase correction value is generated based on the phase error estimate and used to adjust the phase of the output of the feedforward filter.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
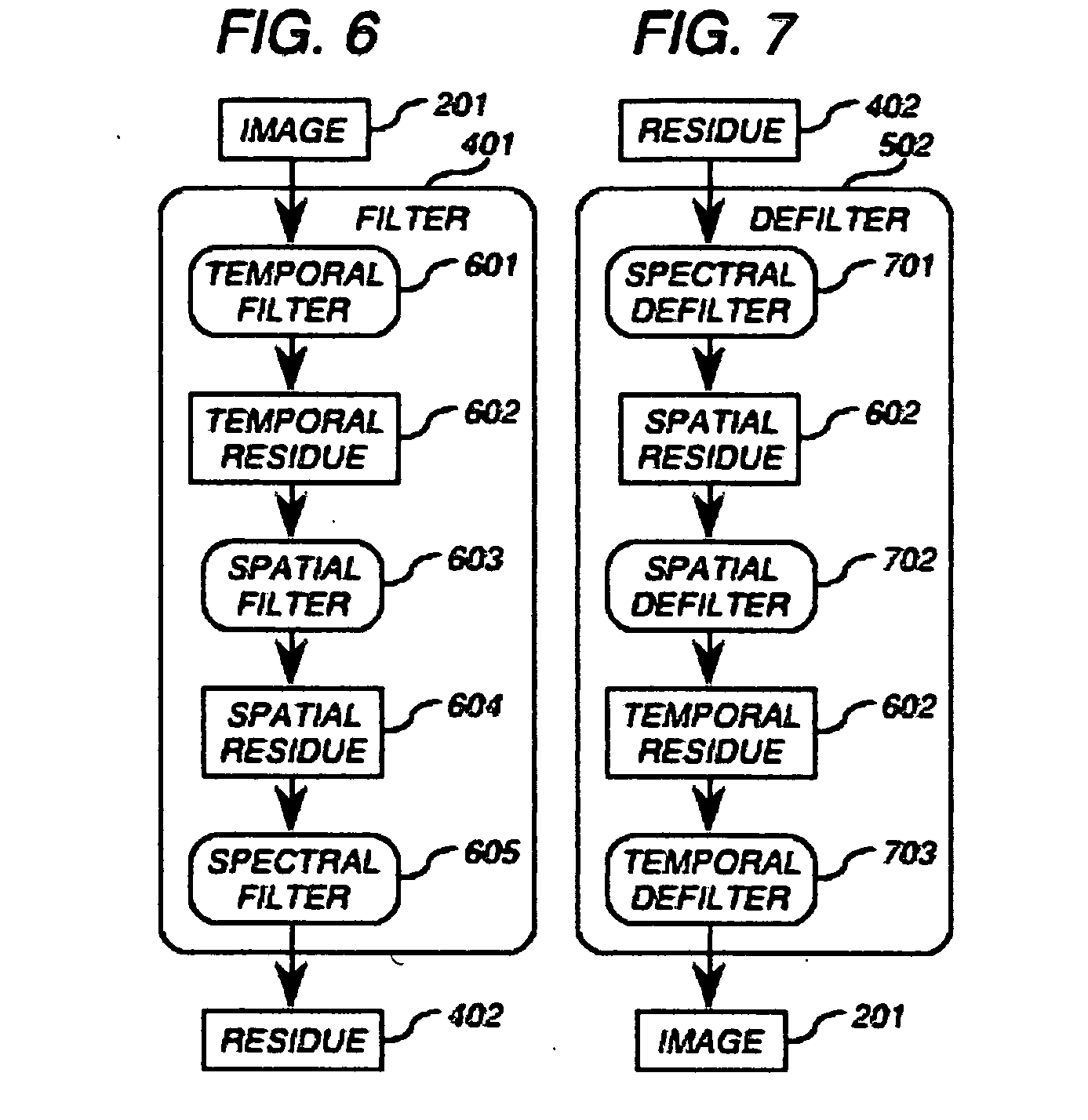
Method and apparatus for faster-than-real-time lossless compression and decompression of images
InactiveUS20080219575A1Maximize compression ratioMinimized on demandCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationFrequency spectrumContext independent
The present invention is a method and apparatus for compressing and decompressing data. In particular, the present invention provides for (de-)compressing naturalistic color-image and moving-image data, including high-precision and high-definition formats, with zero information loss, one-sample latency and in faster than real time on common computing platforms, resulting in doubled transmission, storage, and playback speed and doubled transmission bandwidth and storage capacity, and hence in doubled throughput for non-CPU-bound image-editing tasks in comparison with uncompressed formats. The present invention uses a nearly symmetrical compression-decompression scheme that provides temporal, spatial, and spectral compression, using a reversible condensing / decondensing filter, context reducer, and encoder / decoder. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, the compression filter is implemented as a cascade of quasilinear feedforward filters, with temporal, multidimensional spatial, and spectral stages, where appropriate, in that order, whose support consists of adjacent causal samples of the respective image. The decompressor cascades quasilinear feedback inverse filters in the reverse order. The filters can be implemented with mere integer addition, subtraction, and either one-dimensional table lookup or constant multiplication and binary shifting, depending on the computing environment Tables permit the data precision to be constrained throughout to that of the image samples. The encoder uses a table of prefix codes roughly inversely proportional in length to their probability, while the decoder uses chunked decode tables for accelerated lookup. In the fastest and simplest mode, the code tables are context-independent. For greater power, at the cost of a reduction in speed, the code tables are based on the temporal, multidimensional spatial, and spectral adjacent causal residue samples, where contexts with similar probability distributions are incoherently collapsed by a context reducer using one-dimensional lookup tables followed by implicitly multidimensional lookup tables, to minimize the overall table size. The invention's minimal resource requirements makes it ideal for implementation in either hardware or software.
Owner:WITTENSTEIN ANDREAS
Adaptive equalizer, decoding device, and error detecting device
InactiveUS20050135472A1Adequate equalization processingExtra processingMultiple-port networksModification of read/write signalsEqualizationOptical recording
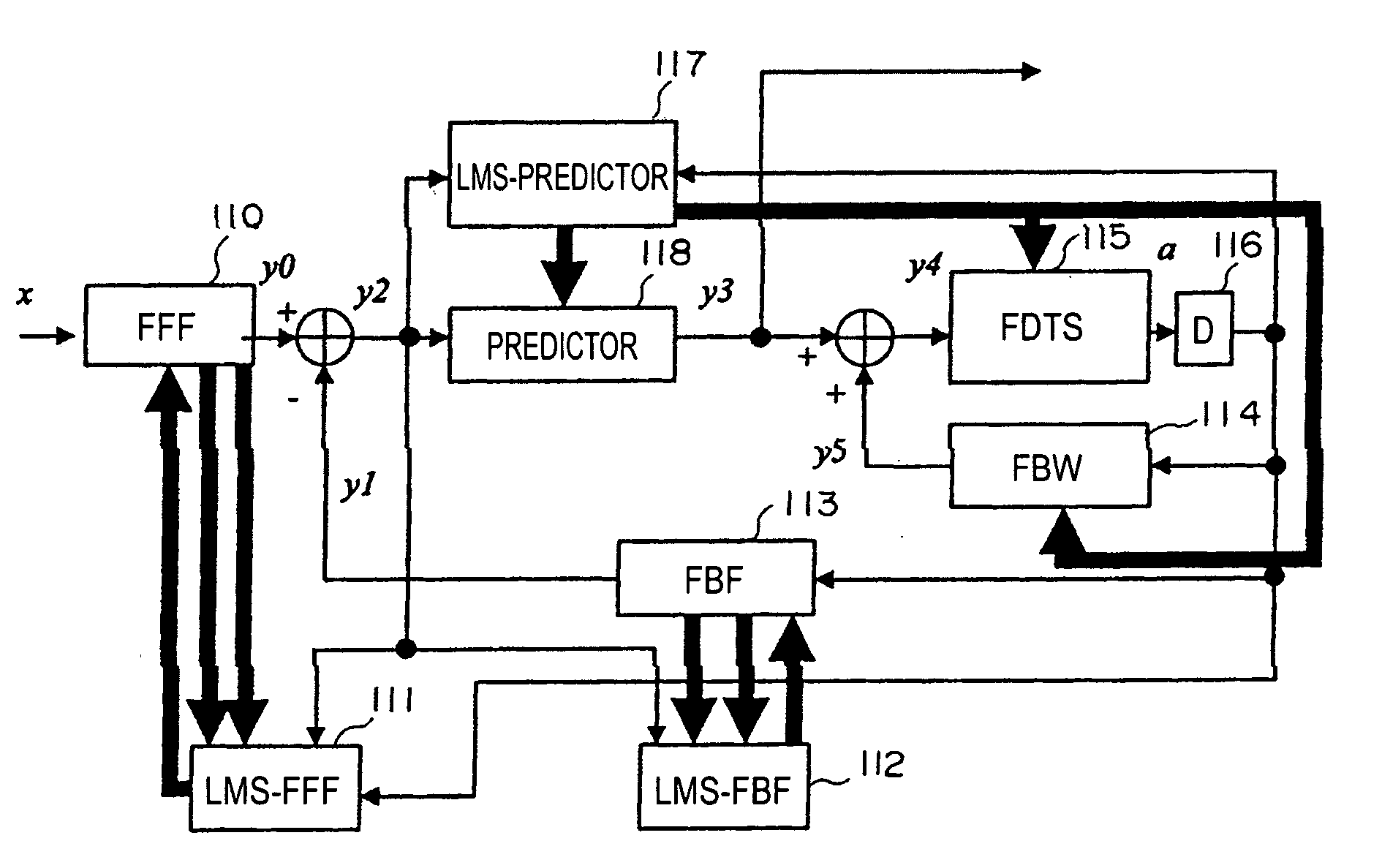
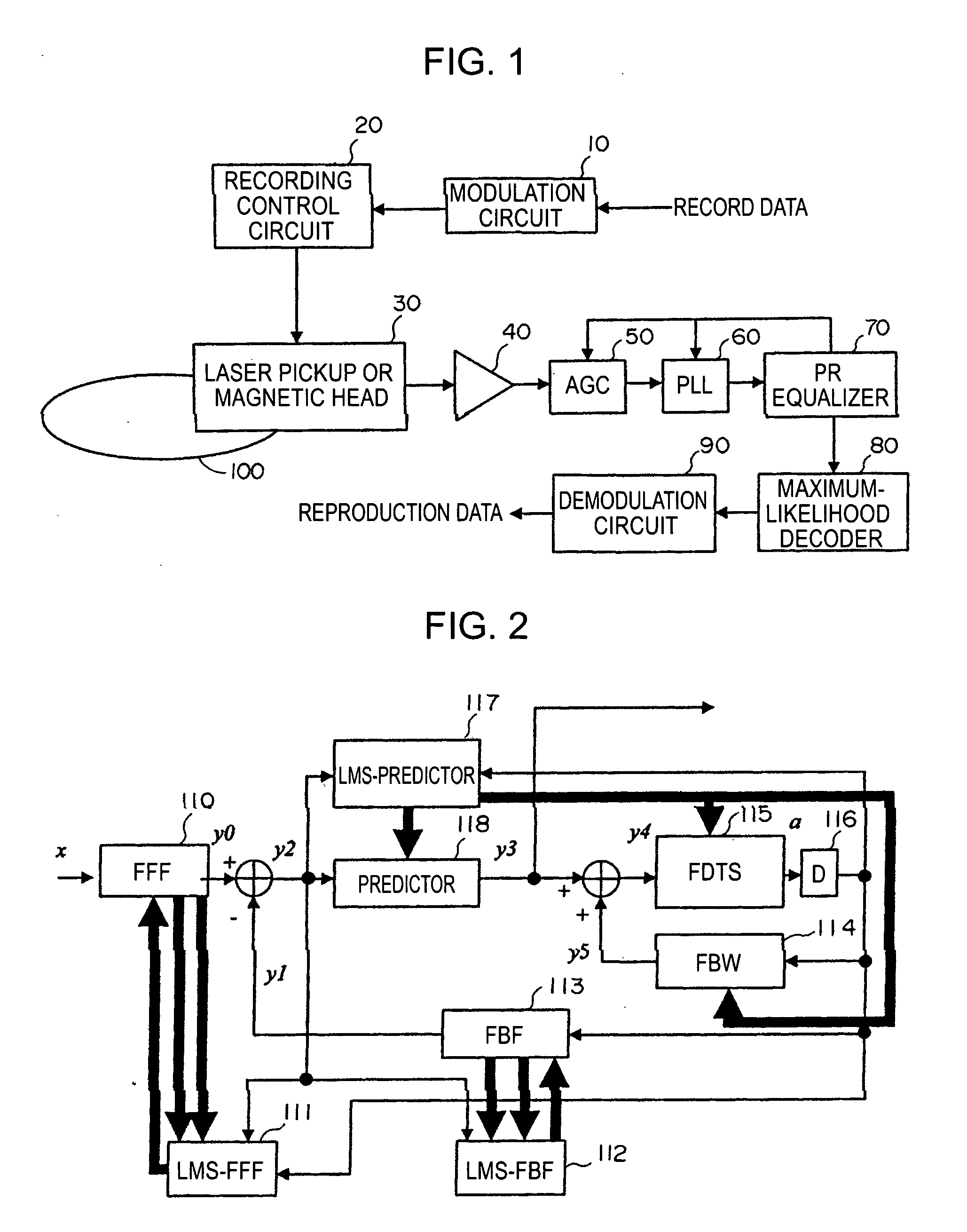
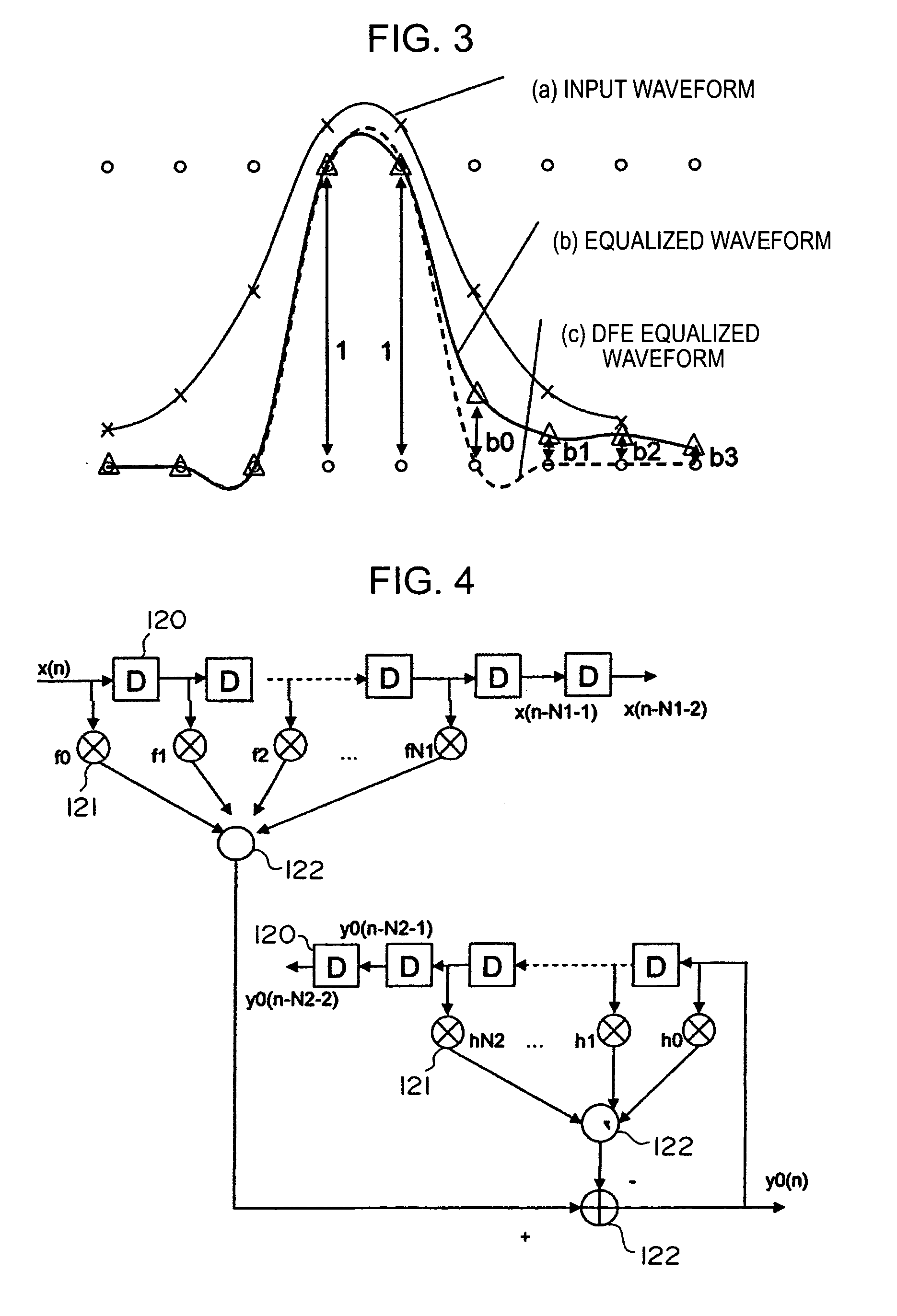
In a waveform equalizer for a communication apparatus, a magnetic recording apparatus, or an optical recording / reproducing apparatus, a feed-forward filter (FFF) is provided and, at a subsequent stage, a decision feedback equalizer (DFE) or a fixed delay tree search / decision feedback equalizer (FDTS / DFE) employing FDTS for a determination unit is provided. Partial response (PR) is performed on only a first portion of inter-symbol interference (ISI) of a waveform equalized by the FFF and equalization that does not consider subsequent response (i.e., trailing-edge ISI) is performed. A feed-back filter (FBF) generates a response for the trailing-edge ISI and the DFE structure subtracts the generated response from a response provided by the FFF so that a result becomes a partial response.
Owner:SONY CORP
Efficient tapped delay line equalizer methods and apparatus
ActiveUS8199804B1Efficient and reliable equalizationEnsure correct executionMultiple-port networksSpatial transmit diversityEngineeringEqualization
Methods and apparatus are provided for performing equalization of communication channels. In an embodiment of the invention, at least one tap can be selected from a set of feedforward taps of feedforward filter circuitry, where each tap of the selected at least one tap has a magnitude that is greater than or substantially equal to a magnitude of any tap of the set of feedforward taps that is not in the selected at least one tap. In addition, at least one tap can be added to a set of taps of feedback filter circuitry in communication with the feedforward filter circuitry. The invention advantageously allows for more efficient and reliable equalization of communication channels.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
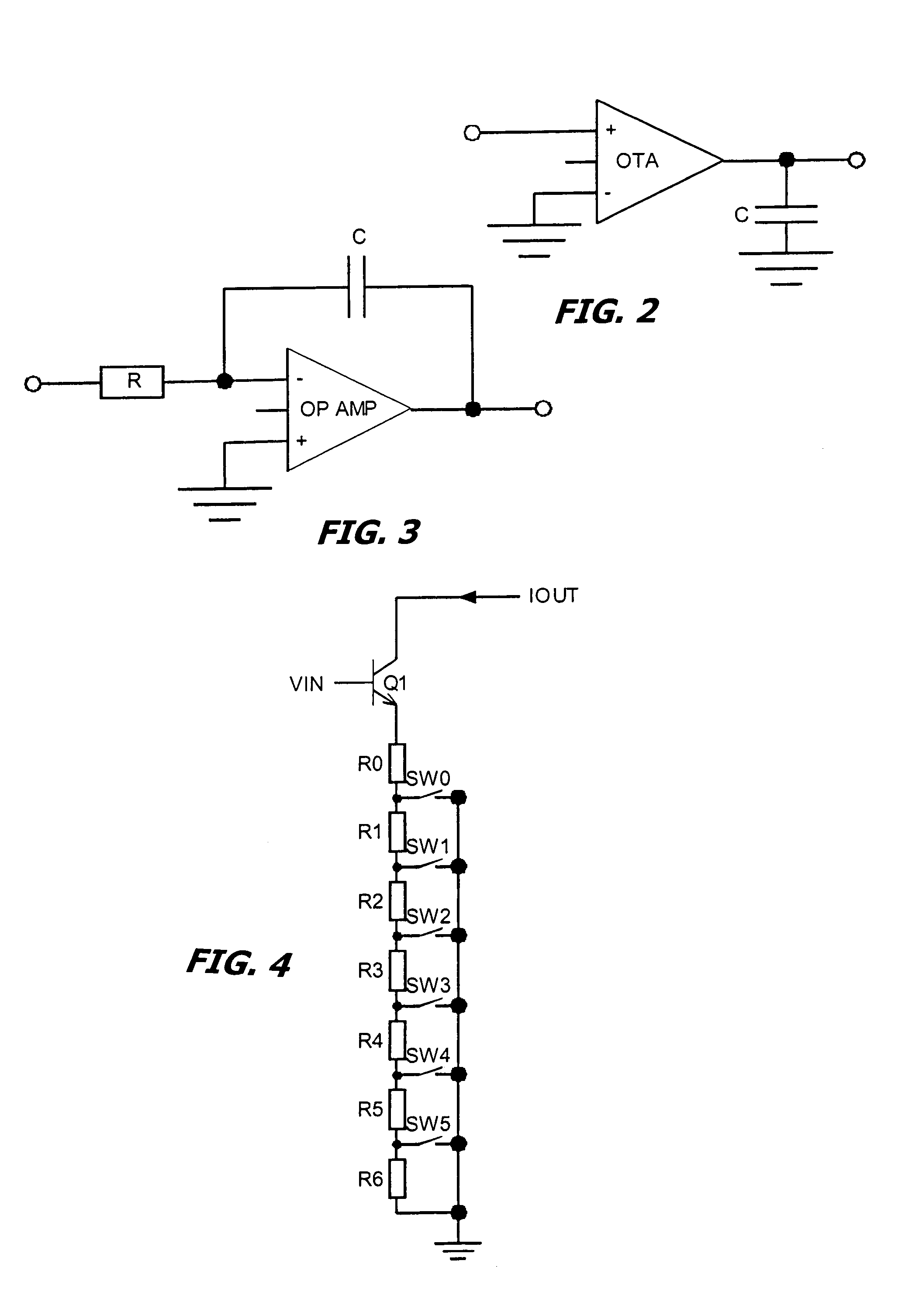
Adaptation structure and methods for analog continuous time equalizers
InactiveUS7016406B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce bit error rateMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsForward error correctionFeedforward filter
Tap coefficients for fractionally-spaced equalizers are updated iteratively using error statistics from an input bit stream and an output bit stream, such as from a forward error correction circuit. The process continues until the errors converge to a sufficiently small number. Knowledge of the error patterns are used apriori to adaptively change the tap coefficients in a feedforward filter.
Owner:SCINTERA NETWORKS
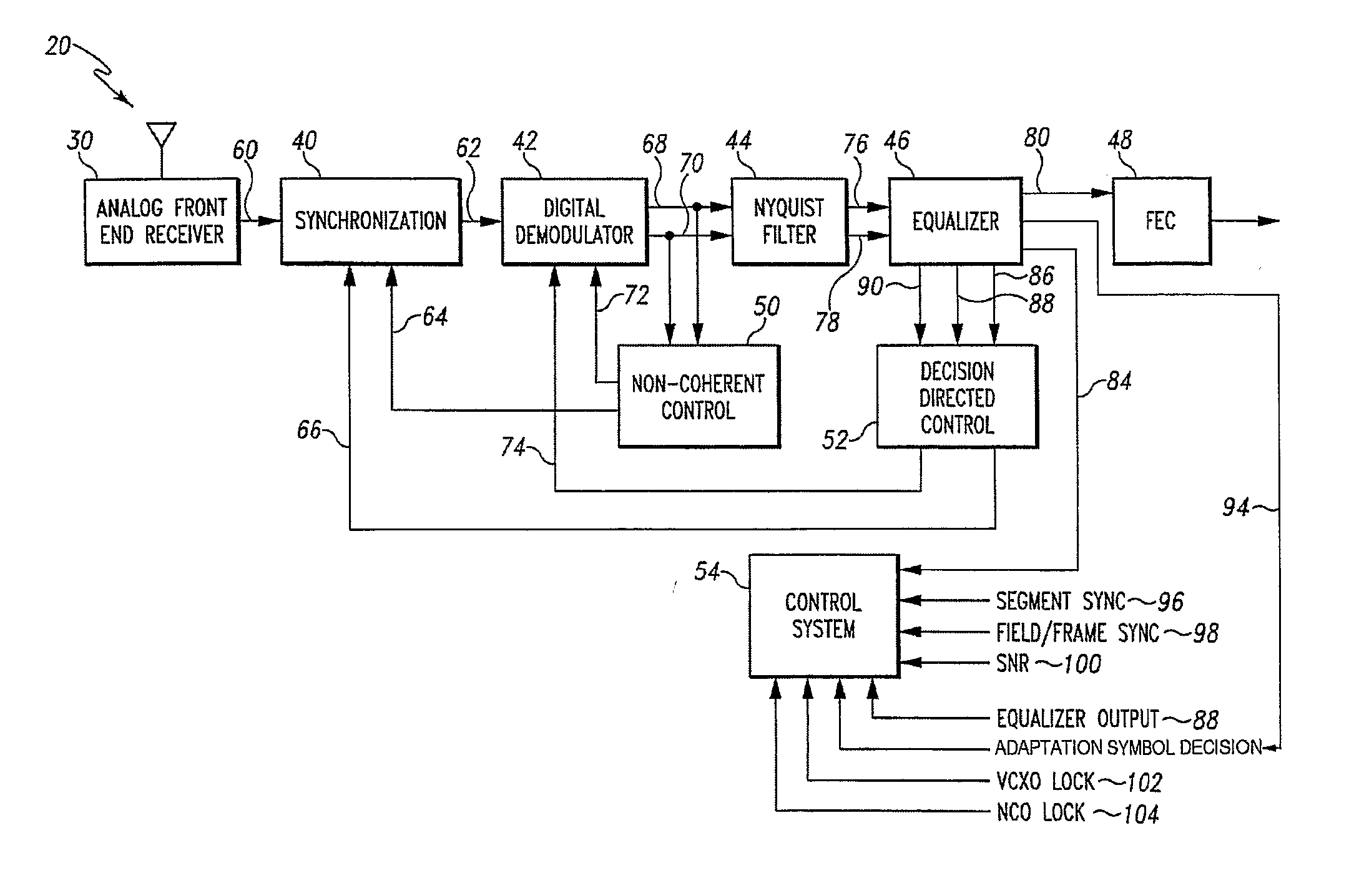
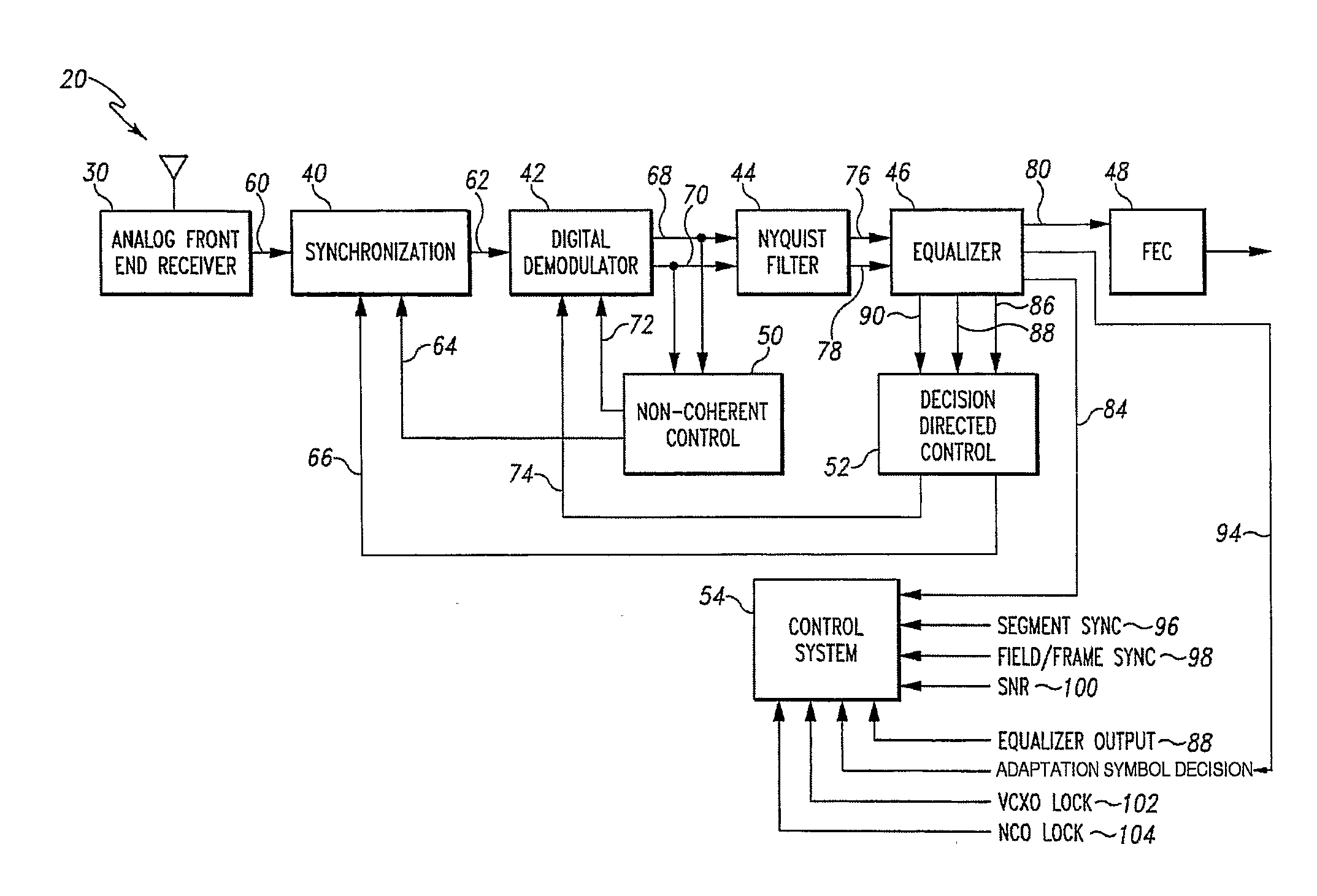
Advanced Digital Receiver
A digital receiver for processing a signal received from a channel includes a digital demodulator and an equalizer coupled to the digital demodulator. The equalizer includes a feedforward filter and a decision feedback equalizer (DFE), wherein the feedforward filter includes a plurality of feedforward filter taps. Coefficients are associated with the plurality of feedforward filter taps and the values of all of the coefficients associated with the plurality of feedforward filter taps are dynamically determined.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
Method and apparatus for channel equalization
InactiveUS6961373B2Remove distortion effectsMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationEngineeringMaximum phase
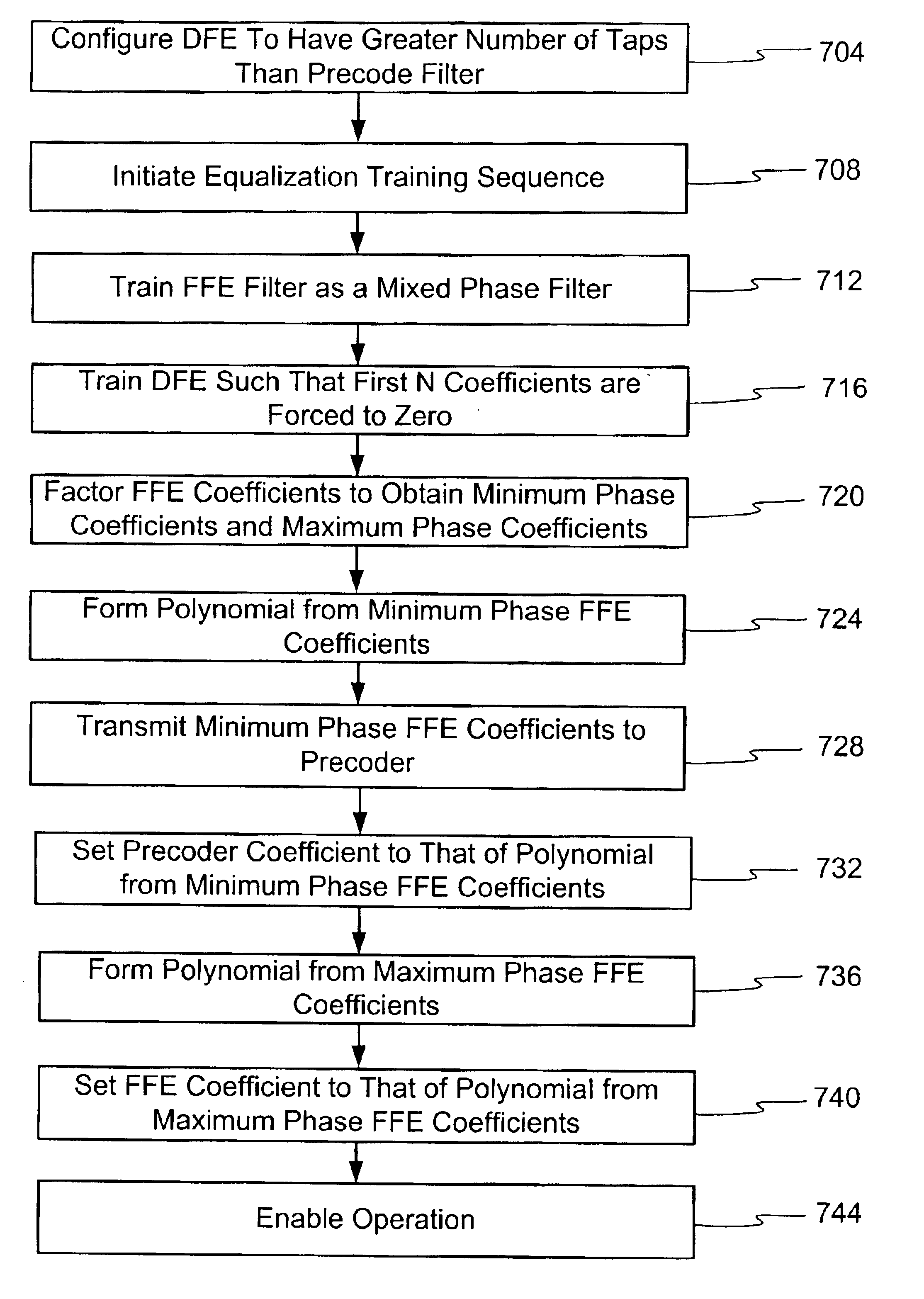
A method and apparatus is disclosed to overcome the effects of intersymbol interference during data transmission. Overcoming the effects of intersymbol interference makes possible higher data transmission rates for a given error rate. In one embodiment a receiver-transmitter pair is configured with a precode filter at the transmit side and a feed forward filter and a feedback filter at the receive side. Filter coefficients are calculated to reduce the undesirable effects of the channel, such as intersymbol interference. In one embodiment a training process occurs with the feedforward filter and a feedback filter, such that the first N coefficients of the feedback filter are set to zero. Thereafter, the coefficients of the feedforward filter are subject to spectral factorization and separated into minimum phase roots and maximum phase roots. The minimum phase roots comprise the precode filter coefficients and the maximum phase roots are established as feedforward filter coefficients.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Self-adaptive active noise reduction method for error-free microphone
ActiveCN108428445AAvoid stabilityAvoid complexitySound producing devicesActive noise controlAlgorithmWeight coefficient
The invention discloses a self-adaptive active noise reduction method for an error-free microphone. According to the method, only one reference microphone is used for achieving active noise reduction;the method comprises the steps that firstly, transfer functions of a main channel and a secondary channel are estimated in advance, an error signal of a target noise-reduction point is estimated in real time by utilizing a received reference signal, and then weight coefficient vectors of a feedforward filter and a feedback filter are updated by using the error signal; the output of the feedforward filter and the output of the feedback filter are superimposed to obtain the output of an infrasound source. By means of the method, an error microphone required in a traditional self-adaptive activenoise reduction method is not needed, the problems of insufficient algorithm stability, complicated earphone structure and the like generally existing in traditional self-adaptive active noise reduction can be solved, and therefore the applicability and stability of the self-adaptive active noise reduction algorithm are greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Adaptive signal equalizer with adaptive error timing and precursor/postcursor configuration control
InactiveUS20070230557A1Substantial avoidance of “driftingEnhanced signalTelevision system detailsMultiple-port networksAdaptive filterData signal
An adaptive signal equalizer with a feedforward filter in which the feedback error signal and corresponding incoming data signal are dynamically aligned in time using signal interpolation, and further, to control the precursor / postcursor filter taps configuration, thereby producing more adaptive filter tap coefficient signals for significantly improved and robust signal equalization.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
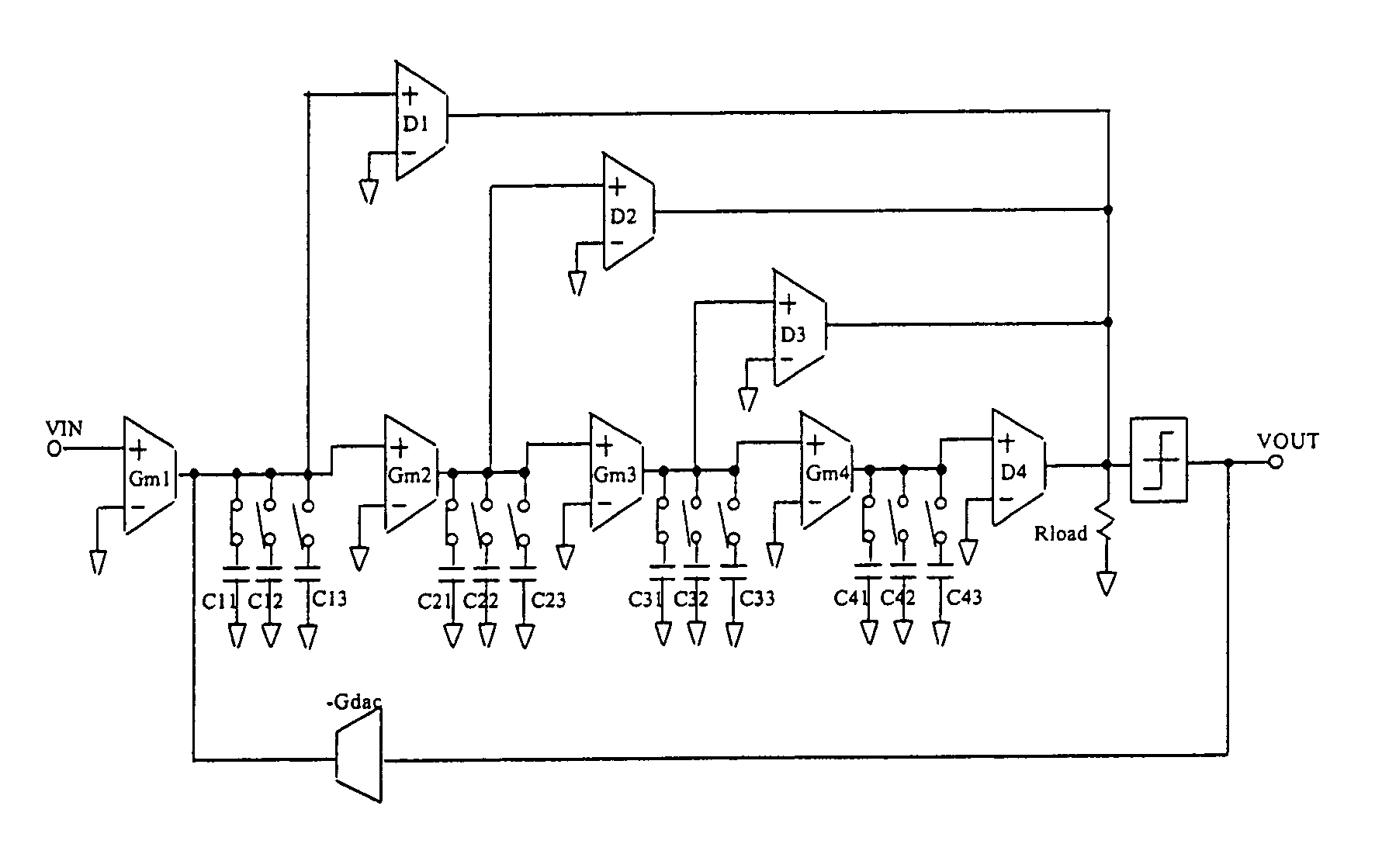
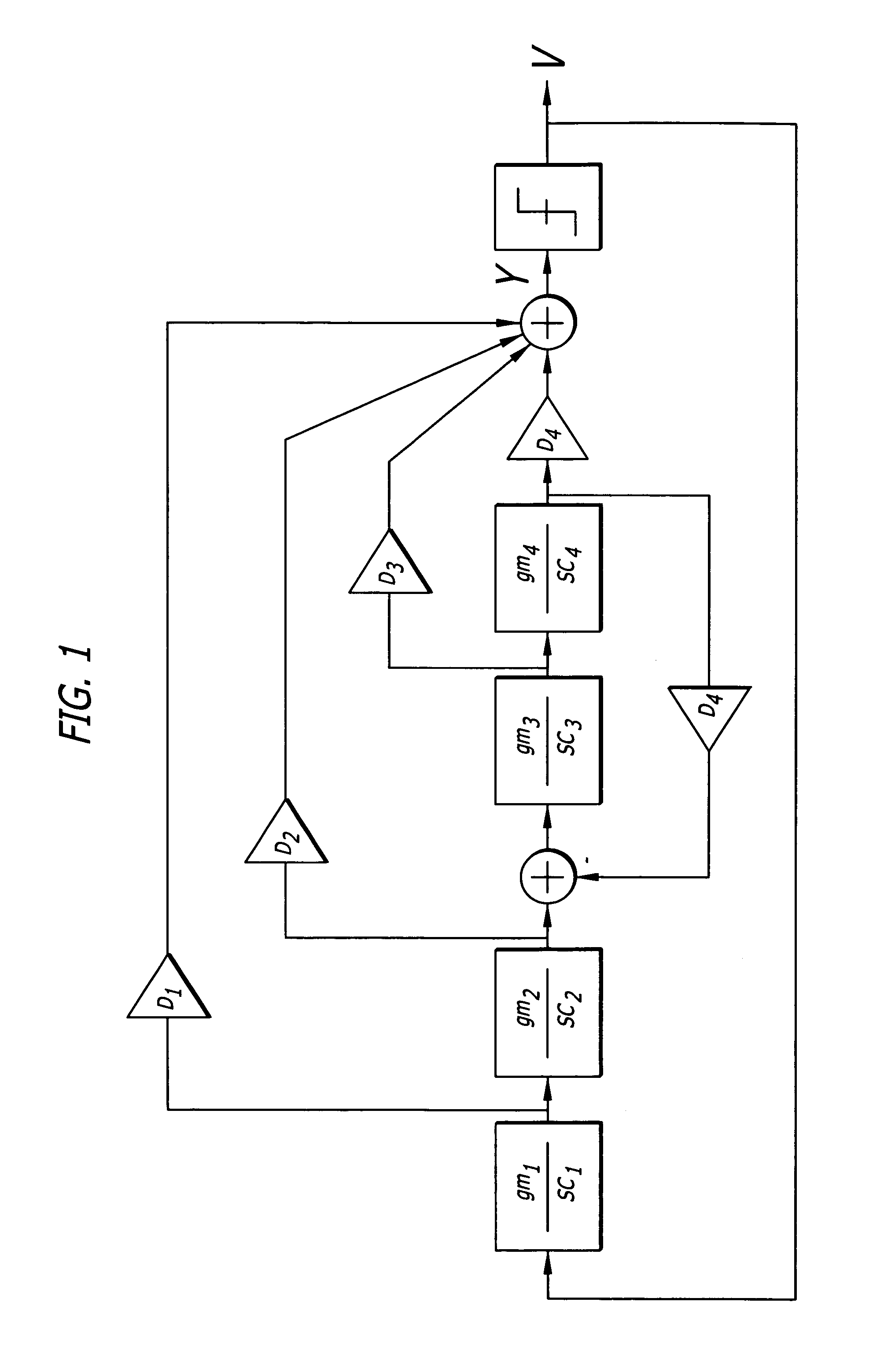
Process variation trim/tuning for continuous time filters and Delta-Sigma analog to digital converters
Continuous time filters and Δ-Σ analog to digital converters and methods for process variation trim / tuning. In feed forward filters, the resistance of feed forward transconductance elements are adjusted to compensate for process variation in the GM / SC values in the filters. Since all. GM / SC values are subject to the same RC process variation, and the resistance in all feed forward transconductance elements is also subject to the same R process variation, the resistance in the feed forward transconductance elements may be adjusted in accordance with analytically predetermined factors based on a single measurement of the RC process variation for each filter to compensate for the overall RC process variation. Various embodiments are disclosed, both as feed forward filters and as Δ-Σ analog to digital converter systems using such filters.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
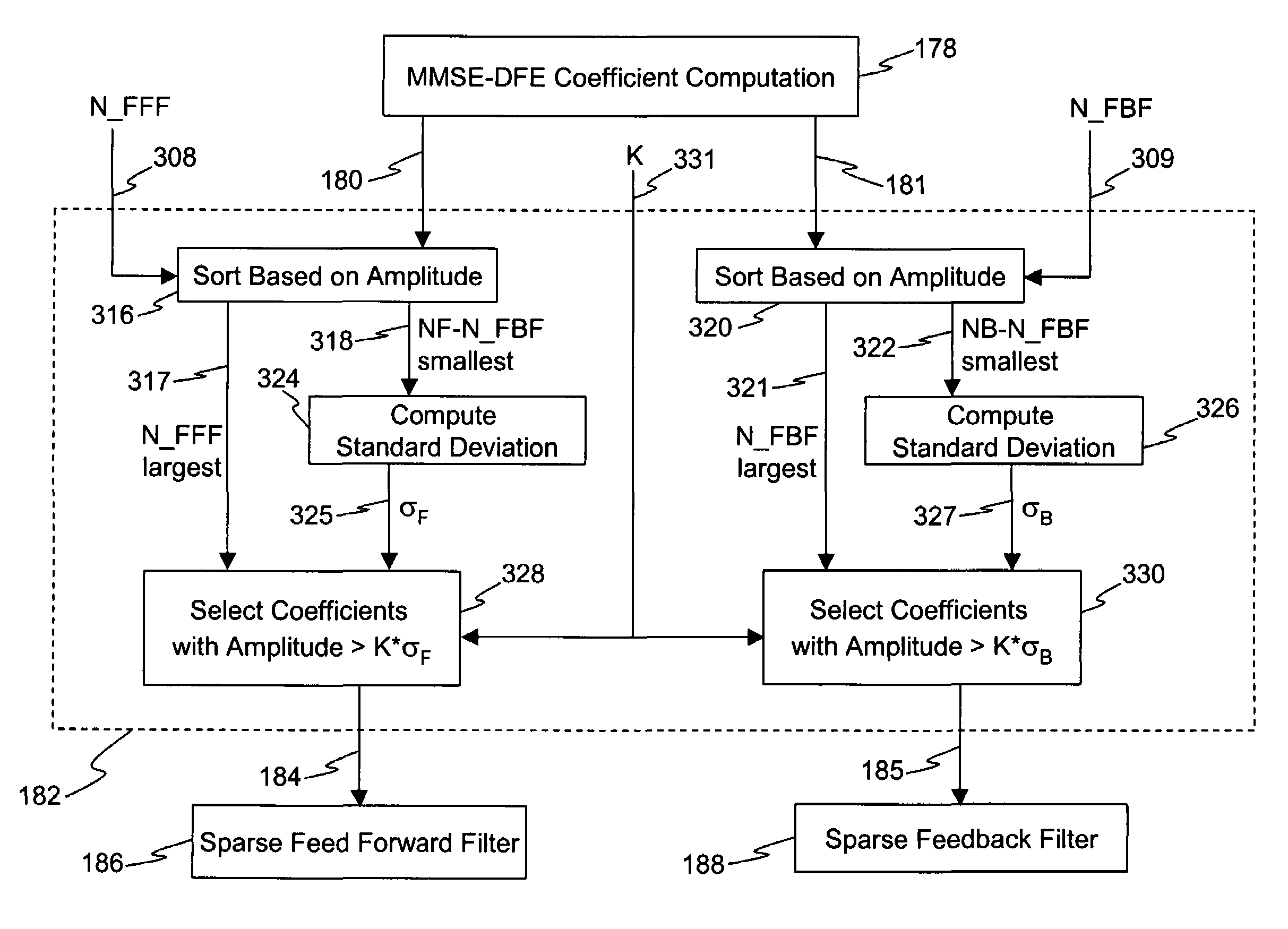
Method and apparatus for single burst equalization of single carrier signals in broadband wireless access systems
InactiveUS7388910B2Avoid disadvantagesNear optimal receptionMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTime domainChannel impulse response
A receiver implementing a single carrier single burst equalization (SC-SBE) method is capable of achieving near optimal reception of individual single carrier RF bursts by making an accurate estimate of the burst's propagation channel impulse response (CIR). The SC-SBE method uses a CIR based coefficient computation process to obtain filter coefficients for a minimum mean square error decision feedback equalizer (MMSE-DFE). The MMSE-DFE filter computation process computes a sufficiently large number of coefficients for the DFE filters, i.e., the feed forward filter (FFF) and feedback filter (FBF), so that each filter spans the maximum anticipated length of the CIR. In order to implement the filters efficiently, a coefficient selection process eliminates less significant computed FFF and FBF coefficients. The resulting FFF and FBF are sparse filters in that most of the taps in the filter delay lines do not have a filter coefficient. Such filters may be efficiently implemented in the time domain.
Owner:ADVANCED RECEIVER TECH
Time-domain automatic-adaptive equalizer and equalizing method thereof
ActiveCN101527697AImprove stabilityGood signal effectTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTime domainSelf adaptive
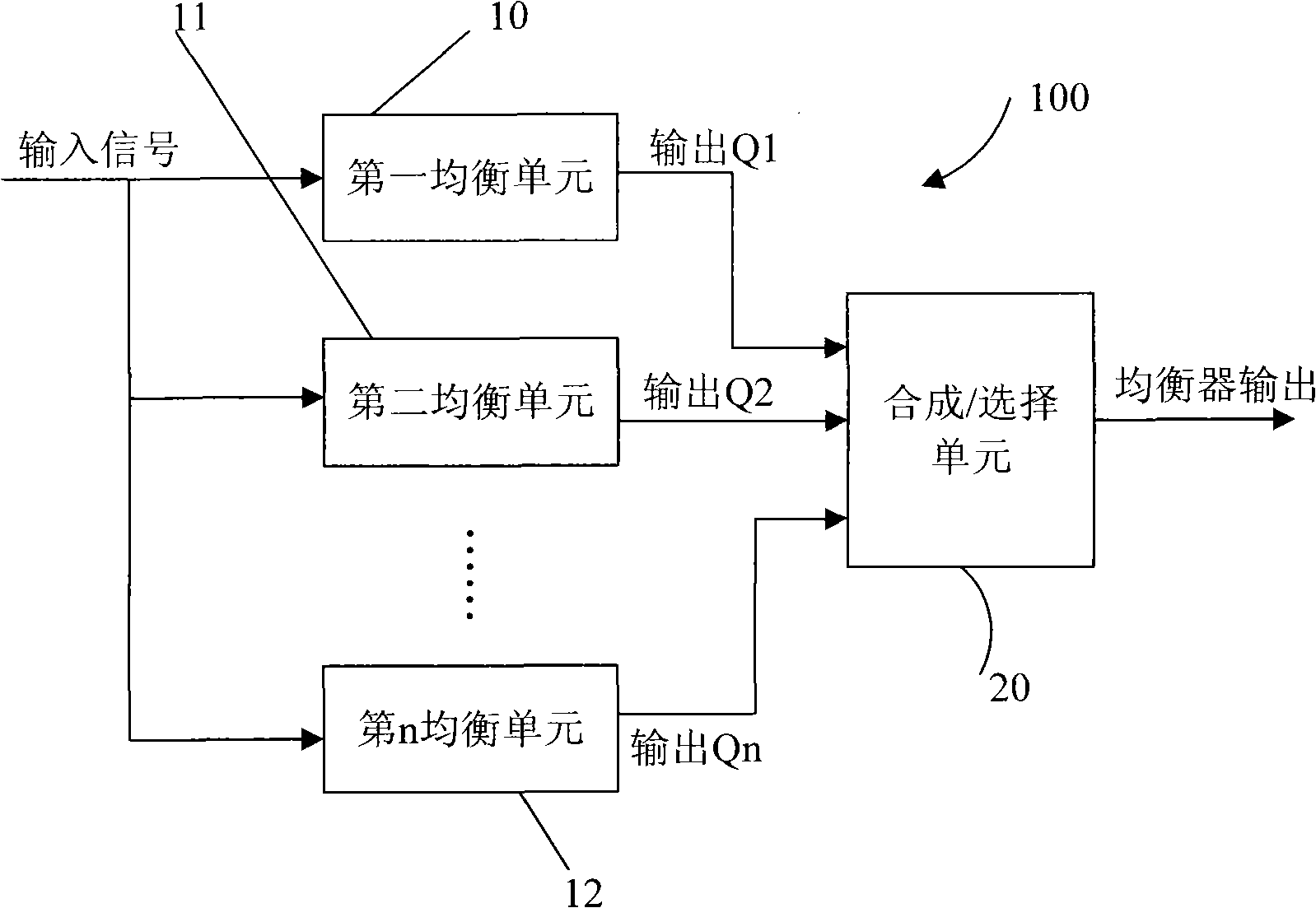
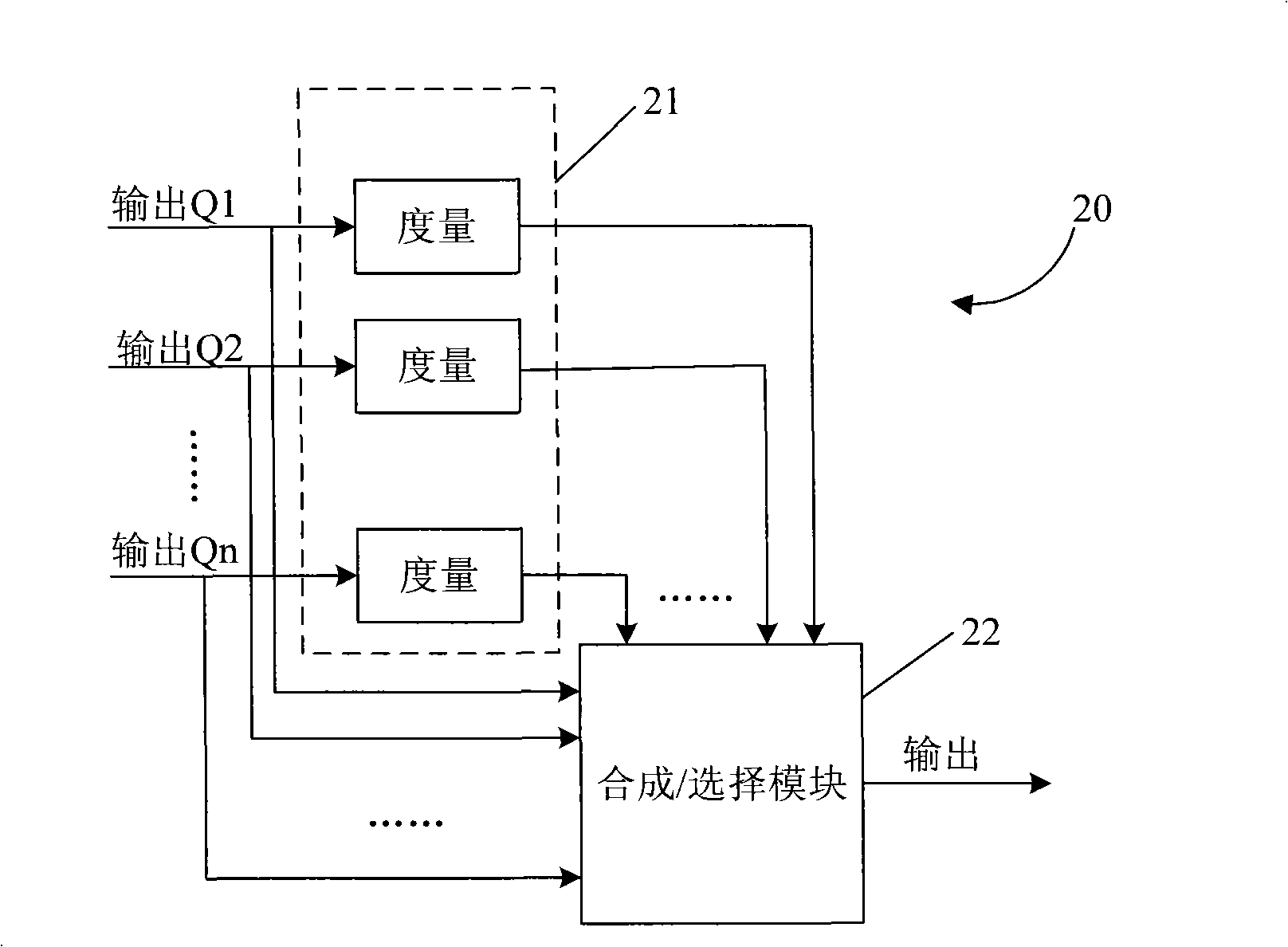
The invention discloses a time-domain automatic-adaptive equalizer and an equalizing method thereof, wherein the time-domain automatic-adaptive equalizer comprises a plurality of equalizing units and is used for equally compensating the same input signal and outputting a plurality of paths of different equalized output signals, wherein every equalizing unit comprises a feedforward filter used for eliminating the front path of an input signal, a feedback filter used for eliminating the back path of an input signal, a decision device, an error generator, a tap coefficient renovator and a combination / selection unit used for selecting or combining a plurality of paths of different equalized output signals, and the formed output signal is the output of the time-domain automatic-adaptive equalizer. The invention differently equalizes the same input signal to output a plurality of paths of different output signals. A plurality of signals are optimized by selecting different equalizing structures and equalizing methods according to the condition of the environment of the actual-used signal path to obtain the equalizing signal of good stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI HIGH DEFINITION DIGITAL TECH IND
Equalizer and feedback equalization method
InactiveCN105553898ASmall amount of calculationImprove convergence speedTransmitter/receiver shaping networksComputation complexityEngineering
The invention discloses an equalizer, which comprises a feed-forward filter, a first adder, a feedback filter, a second adder and a filter tap coefficient determination unit, wherein the feed-forward filter carried out feed-forward filtering on an underwater acoustic communication training sequence; the first adder adds the underwater acoustic communication training sequence subjected to feed-forward filtering and an output of the feedback filter together and outputs an adding result to the feedback filter; the second adder adds the output of the first adder and an expected output d(n) of the equalizer together; and the filter tap coefficient determination unit determines tap coefficients of the feed-forward filter and the feedback filter according to the output of the second adder. According to the equalizer and the feedback equalization method, a channel model is simplified, the calculated amount for design of the equalizer is reduced and the rate of convergence of an algorithm is improved, so that the algorithm can be converged at a smaller convergence residual, the computational complex is reduced and the equalization performance is improved.
Owner:THE THIRD RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
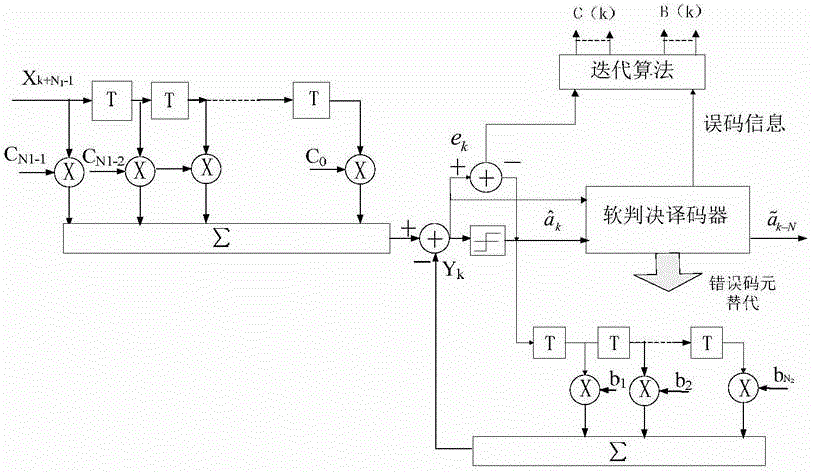
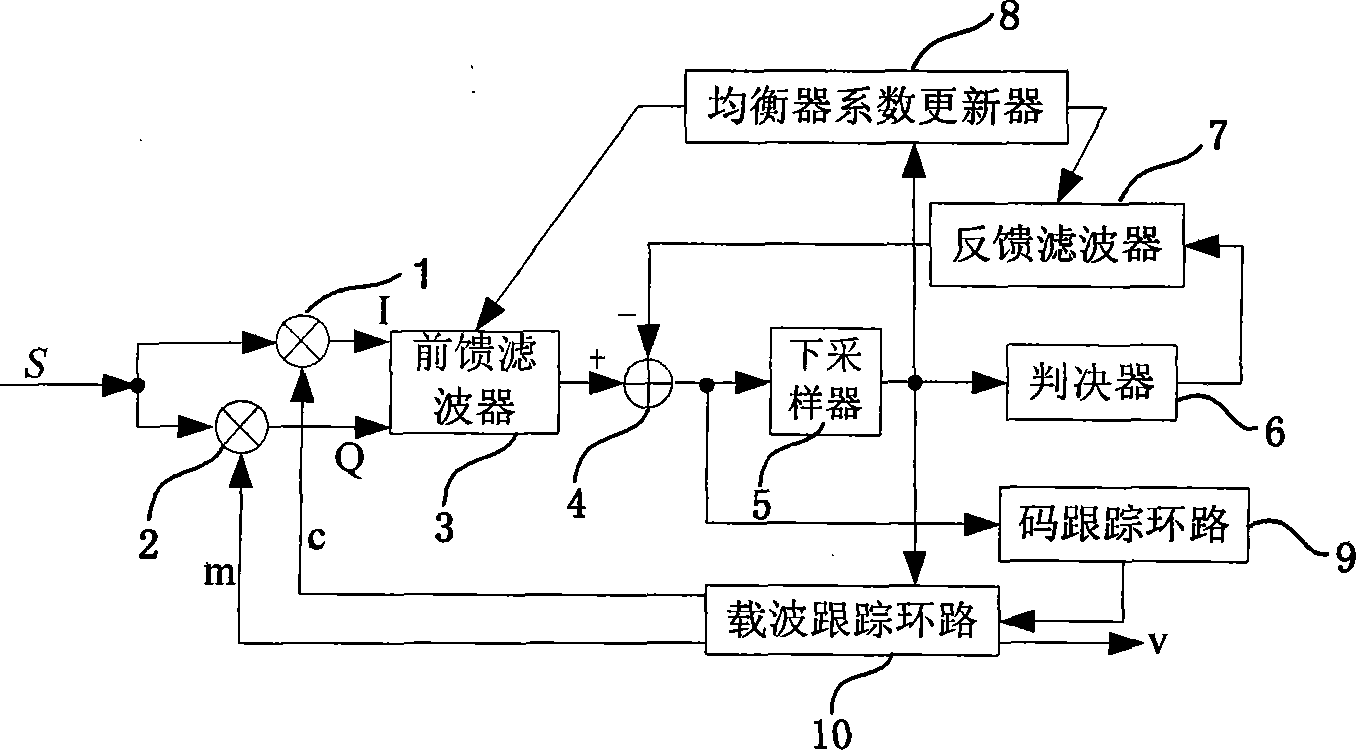
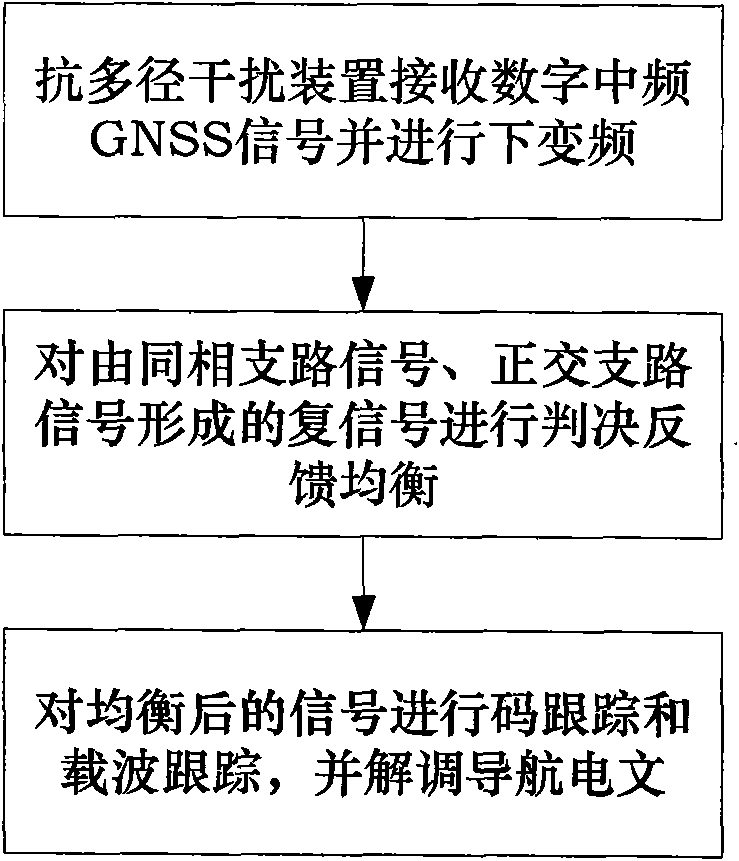
Anti-multipath interference device of GNSS receiving system and method thereof
ActiveCN101807940AHigh measurement accuracyImproved tracking loop structureRadio transmissionMultipath interferenceFrequency conversion
The invention discloses an anti-multipath interference device of a GNSS receiving system and a method thereof. The device comprises a first multiplier, a second multiplier, a feedforward filter, an adder, a down sampler, a decision device, a feedback filter, an equalizer coefficient updating device, a code tracking loop and a carrier tracking loop. The method comprises the steps of firstly using the anti-multipath interference device for receiving digital intermediate frequency GNSS signals and carrying out down frequency conversion, then carrying out decision feedback equalization on complexsignals formed by in-phase branch signals and orthogonal branch signals, finally carrying out code tracking and carrier tracking on the signals after equalization and demodulating a navigation message. The device and the method thereof can effectively resist the impacts of multipath interference, when the multipath interference exists in a channel, the pseudo code tracking precision after introducing the method into the tracking loop is higher than the tracking precision of the typical early-late DLL loop, thereby improving the measurement precision of pseudo range and being conductive to precise positioning.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Hard disk drive vibration cancellation using adaptive filter
InactiveUS7486470B1Record information storageMaintaining head carrier alignmentHard disc driveResonance
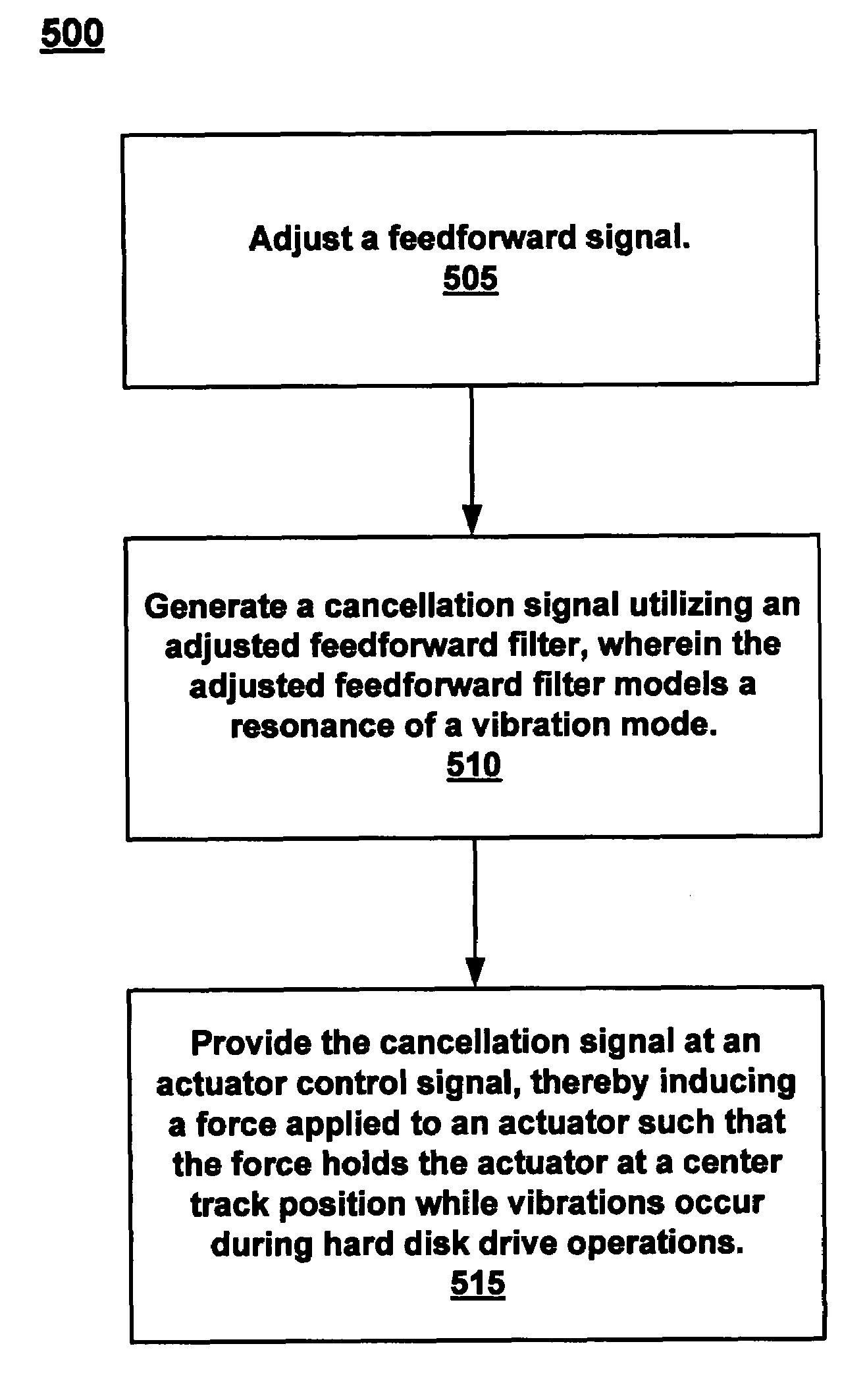
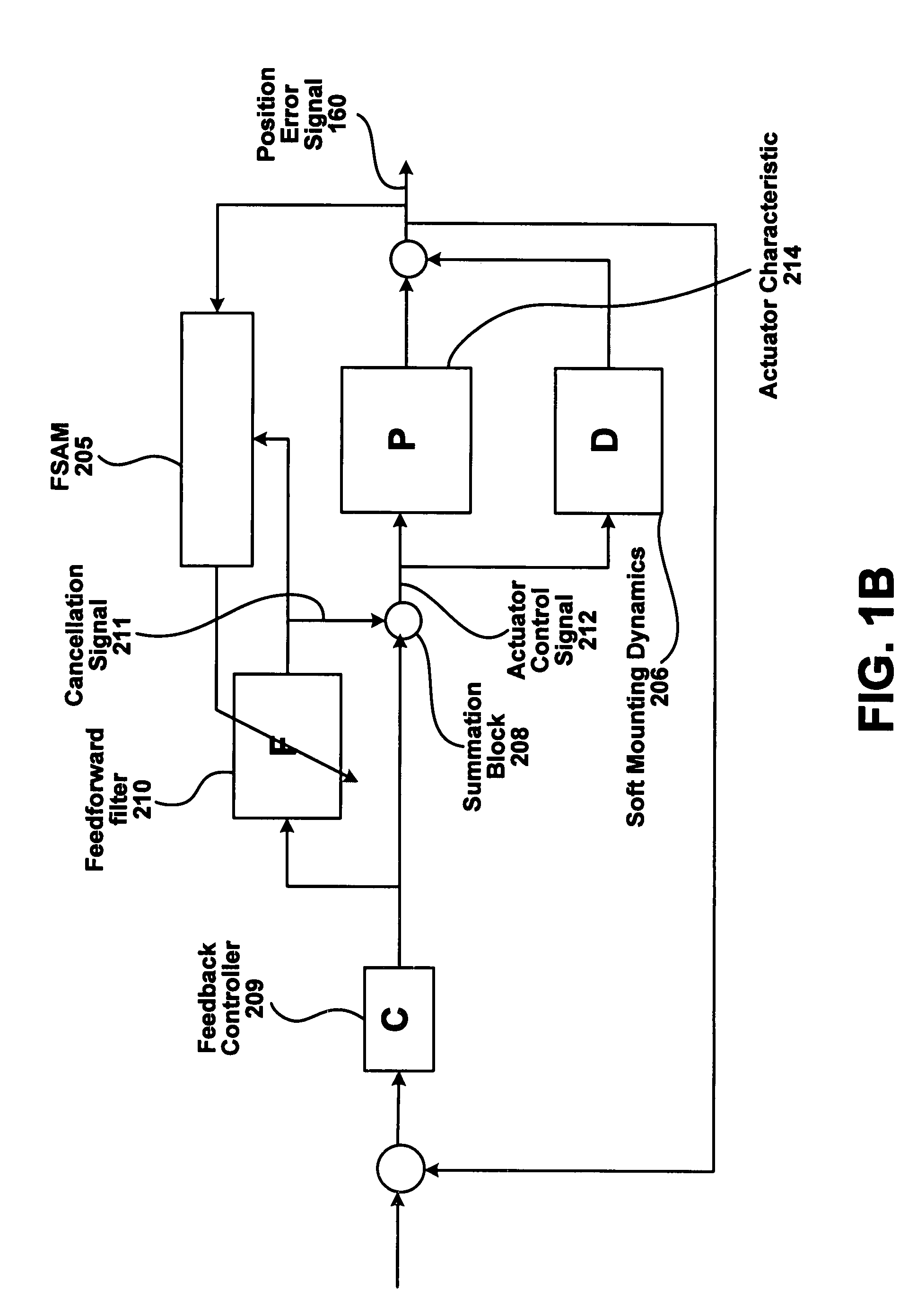
A method of reducing the effect of vibrations associated with seek operations is disclosed. A feedforward filter is adjusted. A cancellation signal is then generated utilizing an adjusted feedforward filter, wherein the cancellation signal models a resonance of a vibration mode. The cancellation signal is provided at an actuator control signal, thereby inducing a force applied to an actuator such that the force holds the actuator at a track center position while vibrations occur during hard disk drive operations.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Active noise reduction method and system and earphone
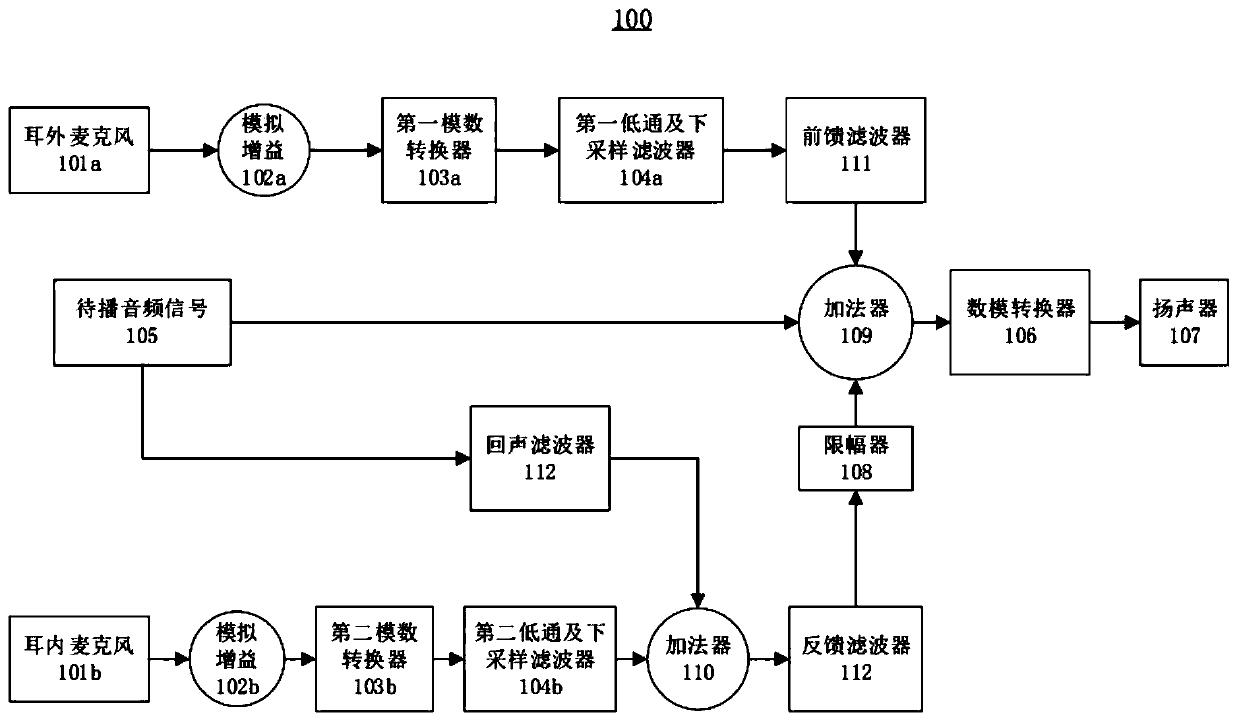
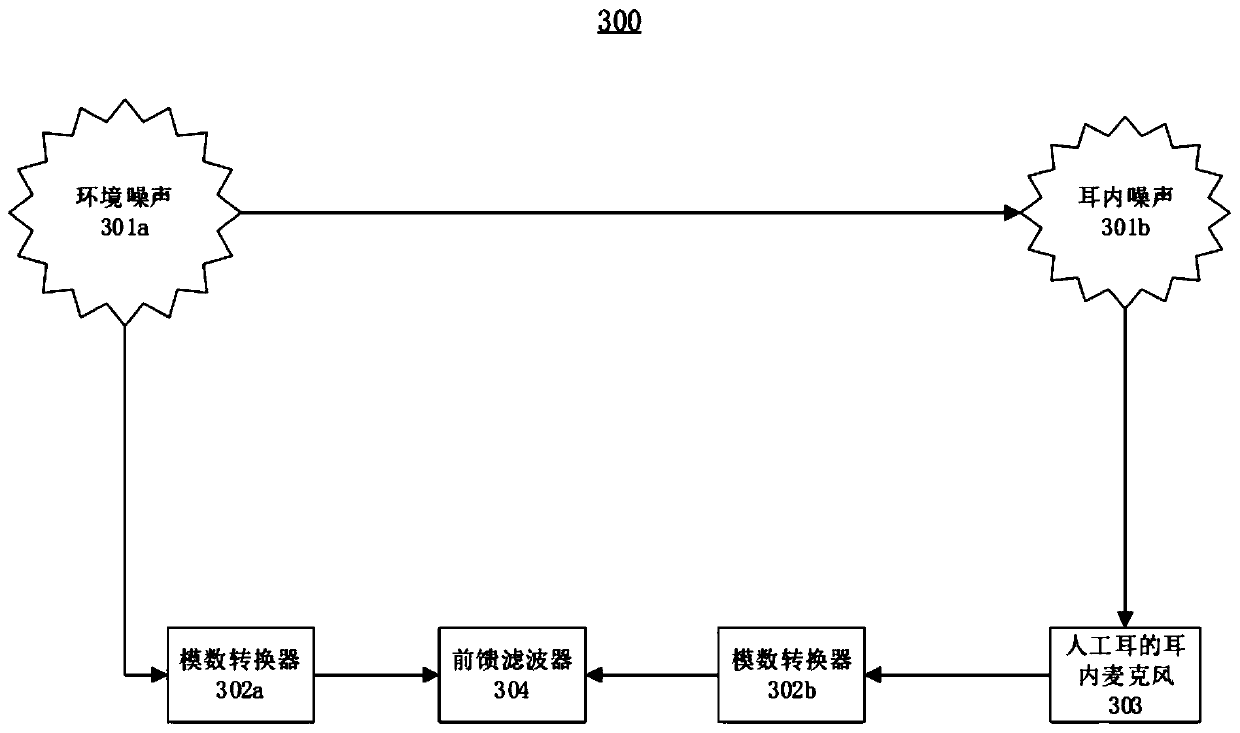
ActiveCN110996209AImprove noise reductionEnhance listening experienceEarpiece/earphone noise reductionHeadphonesNoise reduction
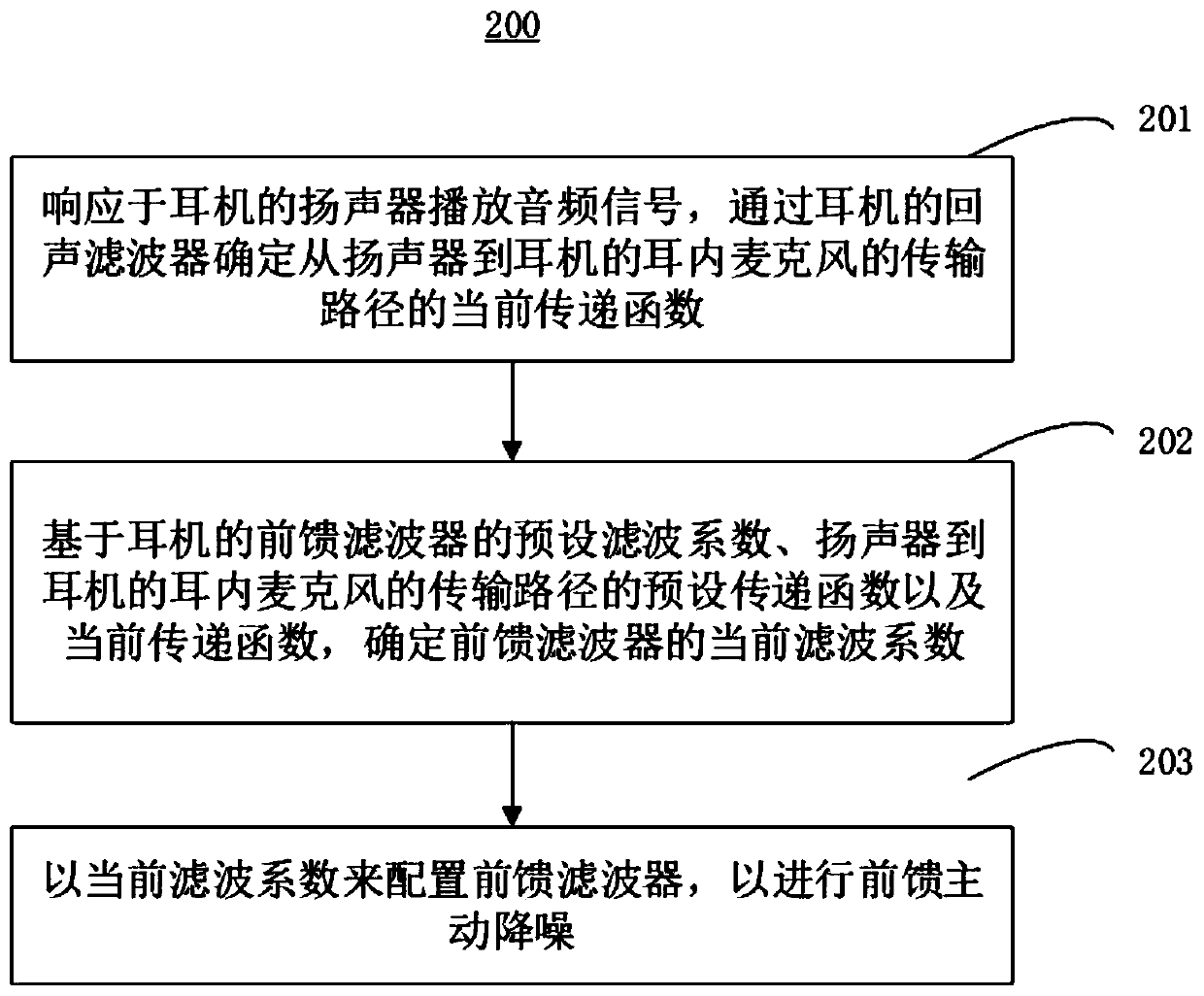
The invention relates to an active noise reduction method and system, and an earphone, and the method comprises the steps: responding to an audio signal played by a loudspeaker of the earphone, and determining a current transfer function of a transmission path from the loudspeaker to an in-ear microphone of the earphone through an echo filter of the earphone; determining a current filter coefficient of a feed-forward filter based on a preset filter coefficient of the feed-forward filter of the earphone, a preset transfer function of a transmission path from the loudspeaker to an in-ear microphone of the earphone and a current transfer function; and configuring a feed-forward filter according to the current filter coefficient so as to carry out feed-forward active noise reduction. Through active adaptive adjustment of the current filter coefficient of the feed-forward filter, the influence of different wearing modes and different ear canal structures on the noise reduction system can bereduced, the noise reduction effect of the earphone is improved, and meanwhile, the listening experience of a user is improved.
Owner:BESTECHNIC SHANGHAI CO LTD
Fast generalized decision feedback equalizer precoder implementation for multi-user multiple-input multiple-output wireless transmission systems
InactiveUS20100232494A1Reduce computing costImprove performanceMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsCapacity lossTransport system
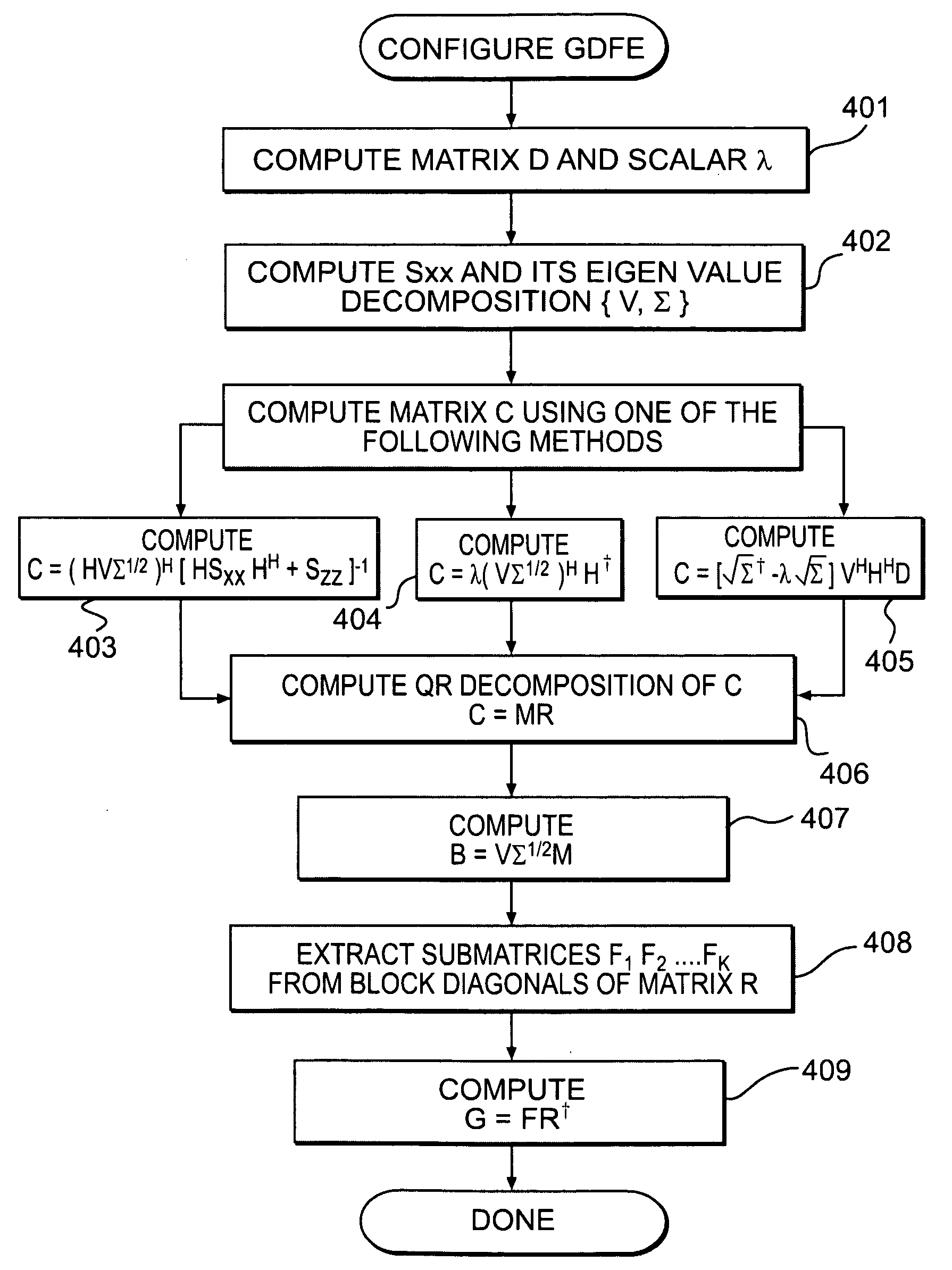
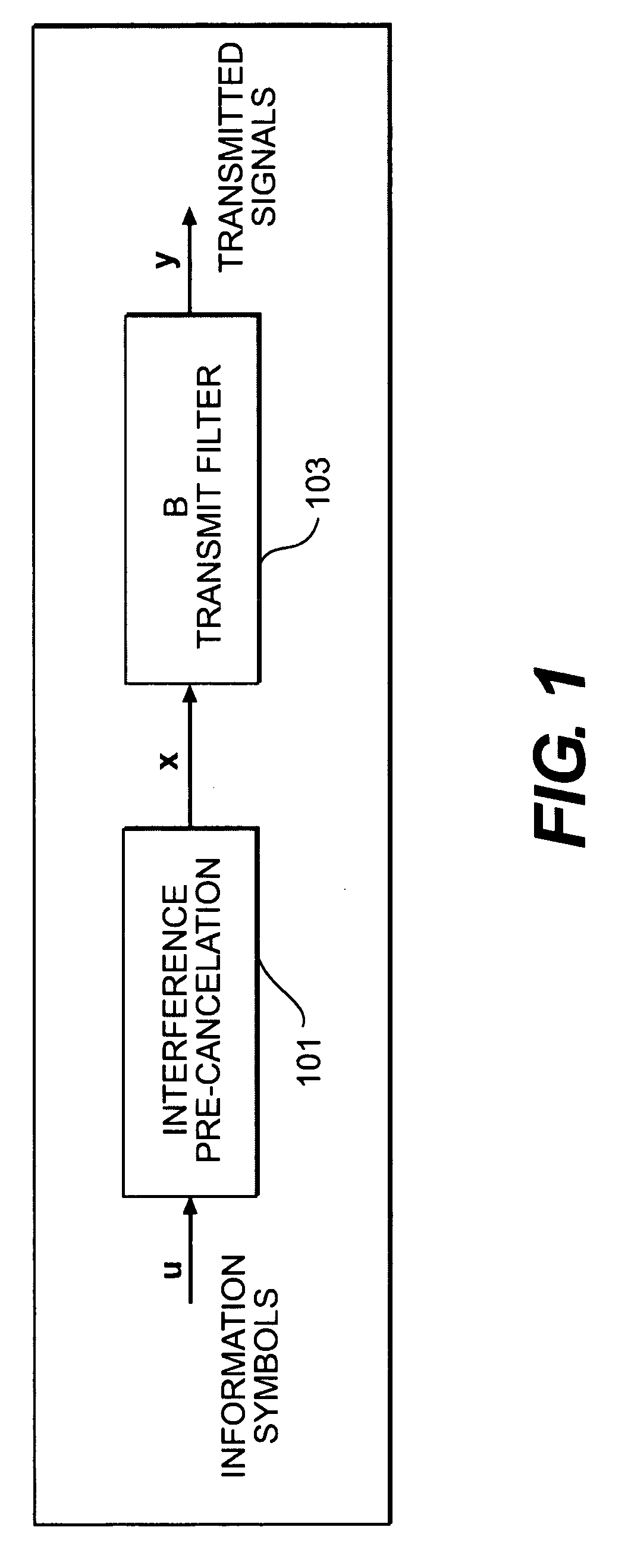
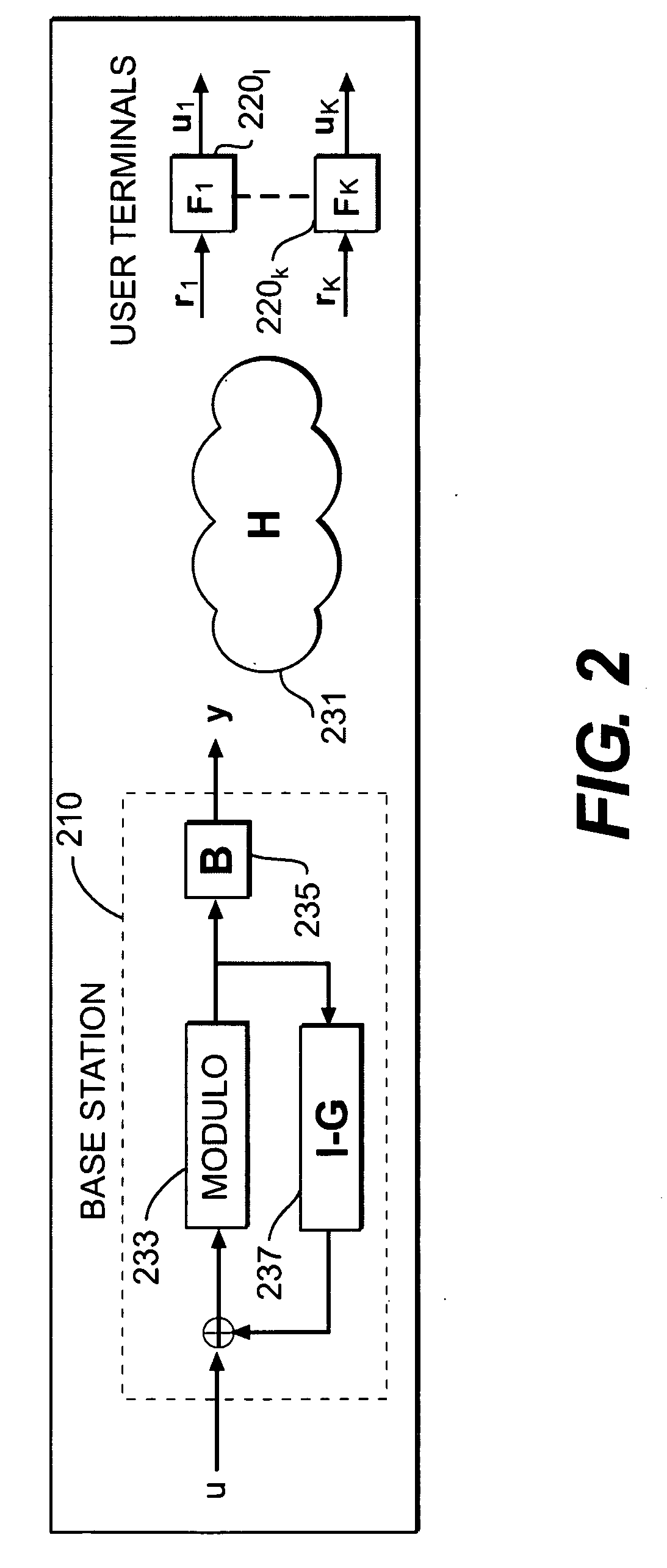
A technique is used to realize a generalized decision feedback equalizer (GDFE) Precoder for multi-user multiple-input multiple-output (MU-MIMO) systems, which significantly reduces the computational cost while resulting in no capacity loss. The technique is suitable for improving the performance of various MU-MIMO wireless systems including future 4G cellular networks. In one embodiment, a method for configuring a GDFE precoder in a base station of a MU-MIMO wireless system having k user terminals, each user terminal having associated therewith a feedforward filter. The method comprises computing a filter matrix C using one of a plurality of alternative formulas of the invention; and, based on the computation of the filter matrix C, computing a transmit filter matrix B for a transmit filter used to process a symbol vector obtained after a decision feedback equalizing stage of the GDFE precoder, a feedforward filter matrix F, and an interference pre-cancellation matrix G.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Block-iterative equalizers for digital communication system
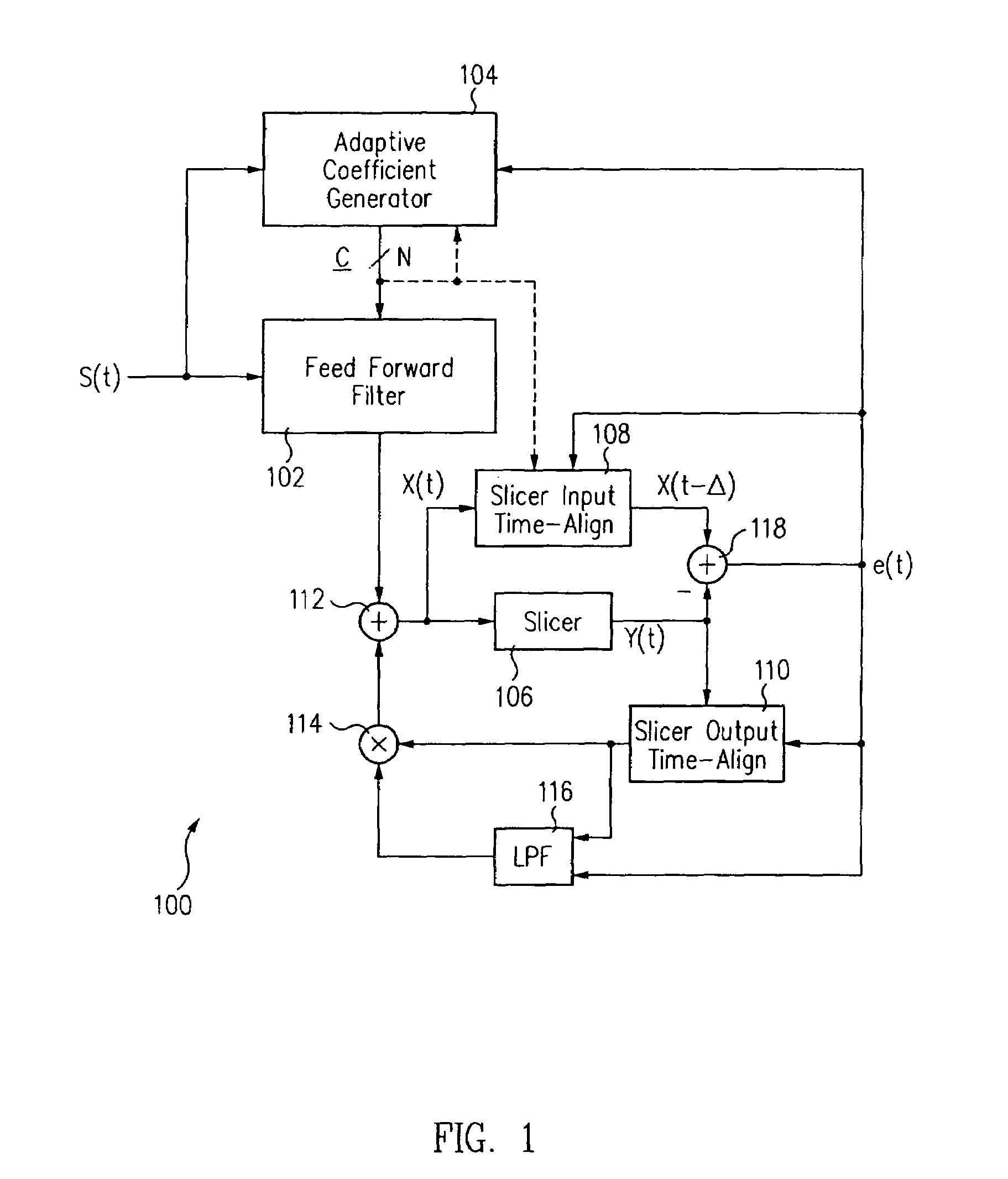
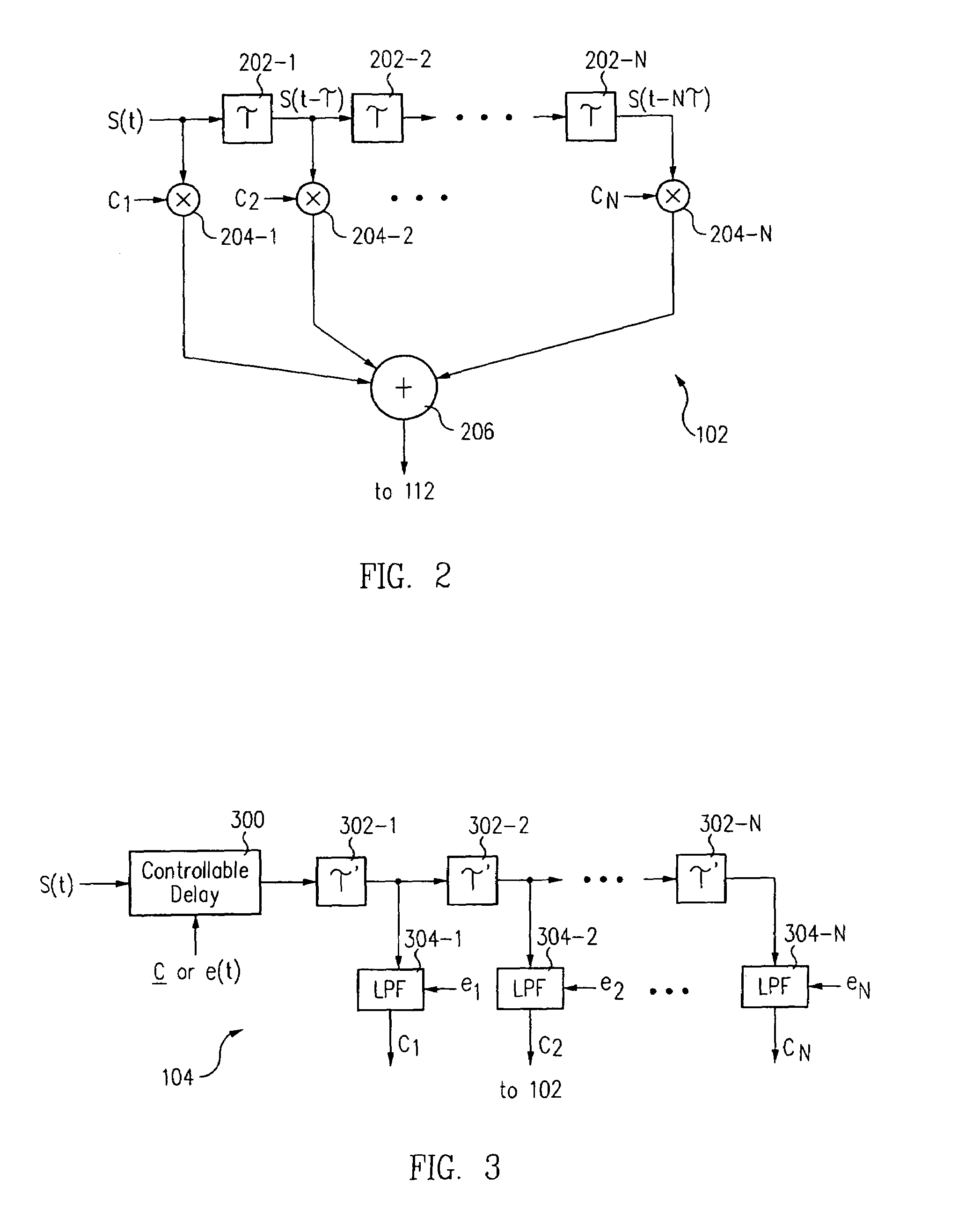
InactiveUS7292661B1Improve system performanceLess received signal powerMultiple-port networksError preventionCommunications systemComputer science
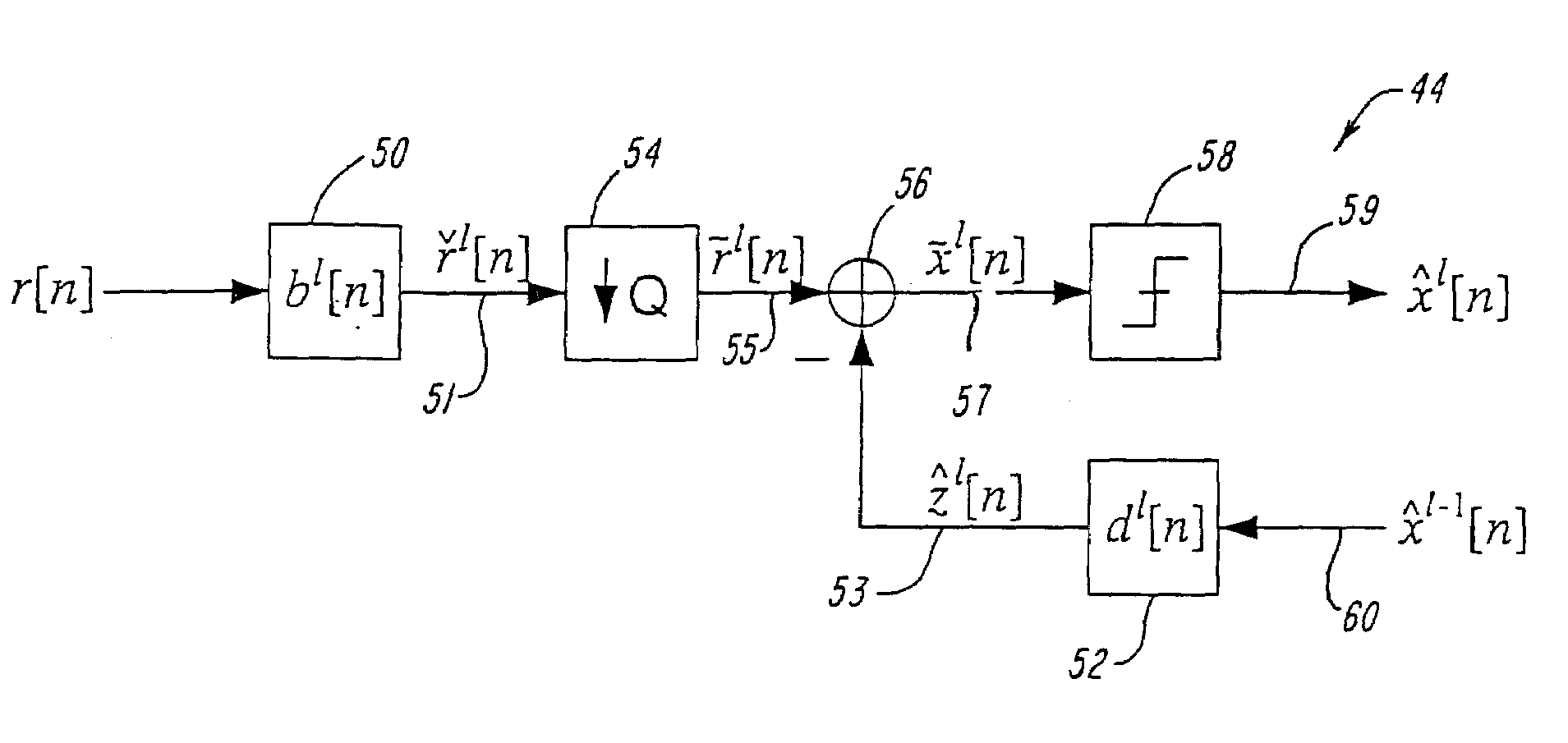
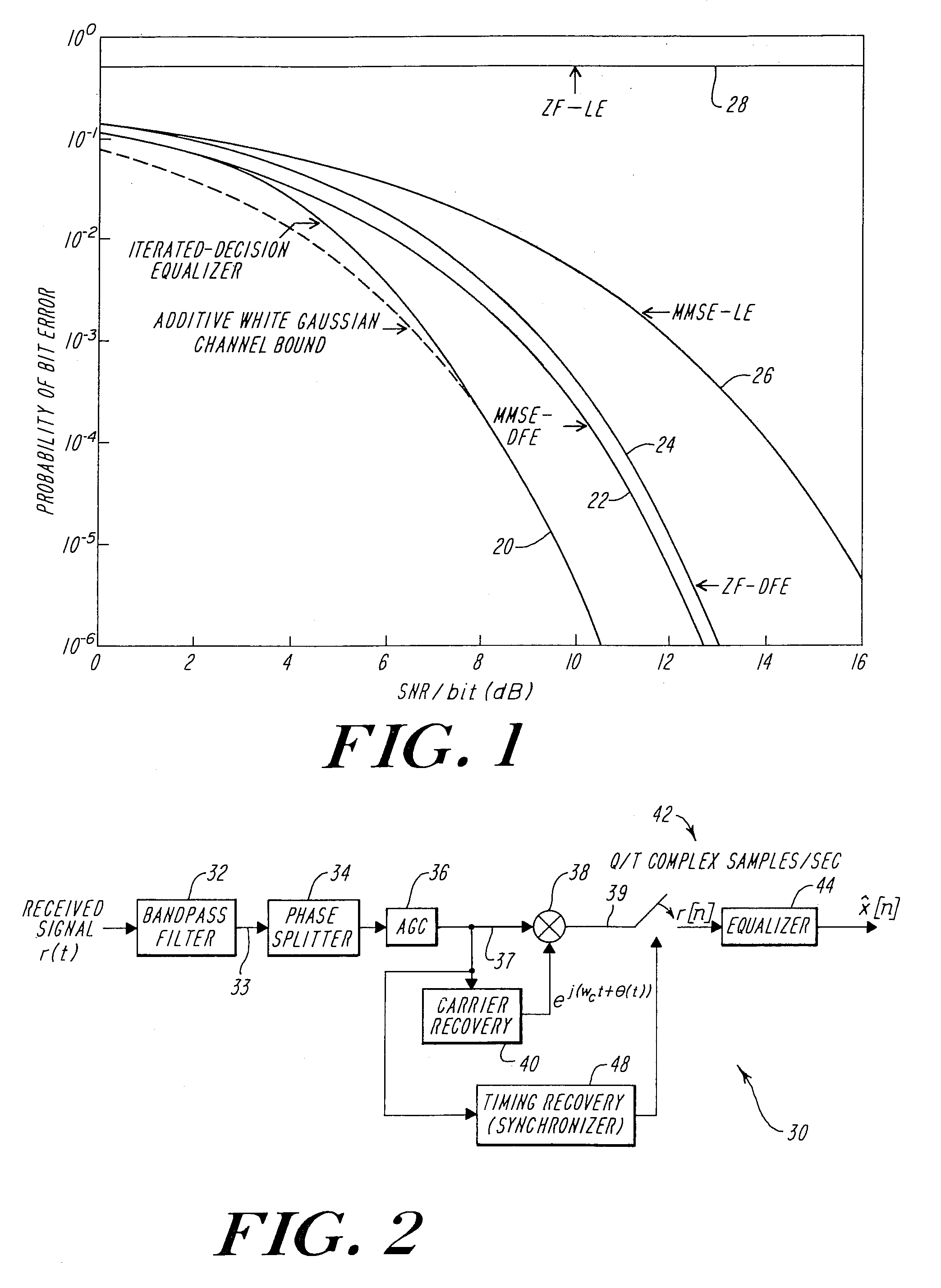
A block-iterative equalizer is adapted for use in contemporary digital communication system receivers. In a preferred embodiment, data received over a communication channel is processed by a linear feed-forward filter and the resulting filtered signal is provided to a slicer which makes a first set of tentative symbol decisions. During later iterations, the same received data is processed by the linear feed-forward filter, the feed-forward filter parameters being modified at each iteration based on the received data and the tentative decisions are themselves filtered by a second, “feed-back” filter and used to improve the tentative decisions.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
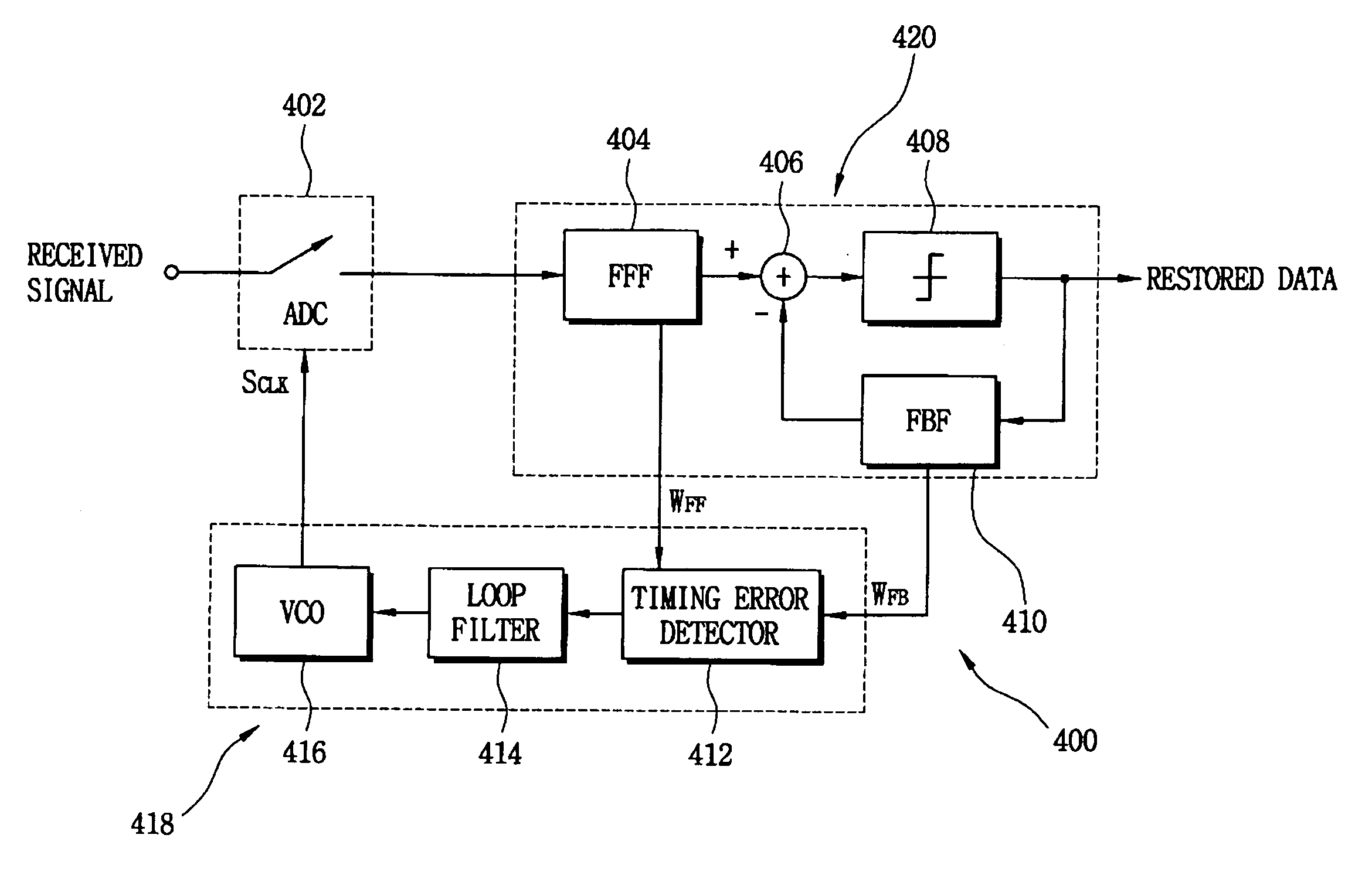
Timing recovery circuit and timing recovery method
A timing recovery circuit for a receiver may include a timing error detector that generates a timing error based on differences between coefficients of a feed-forward filter and a feed-back filter. The timing recovery circuit may include a loop filter which generates a control voltage signal based on the timing error, and a voltage controlled oscillator that generates a sampling clock for the receiver based on the generated control voltage signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
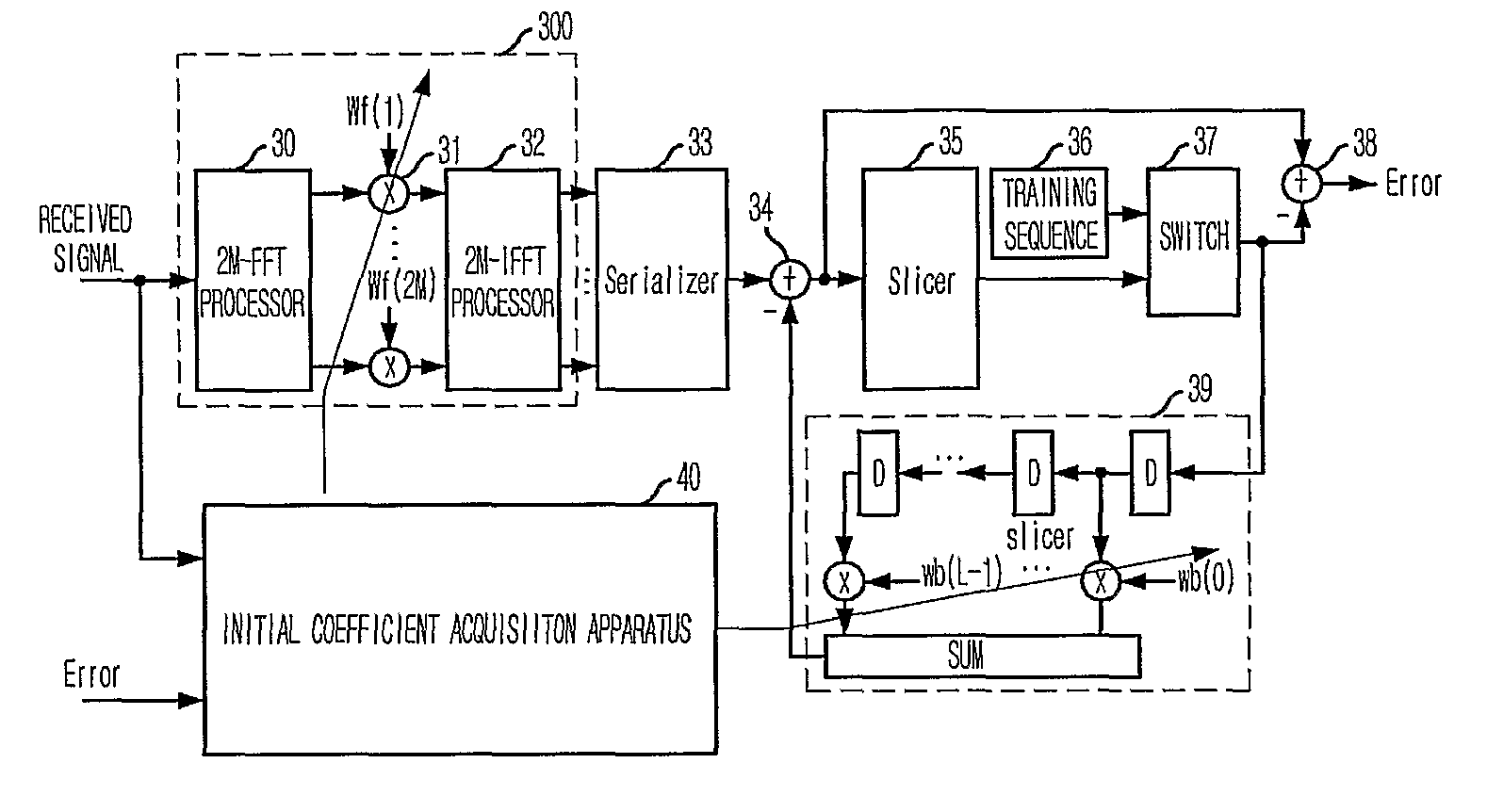
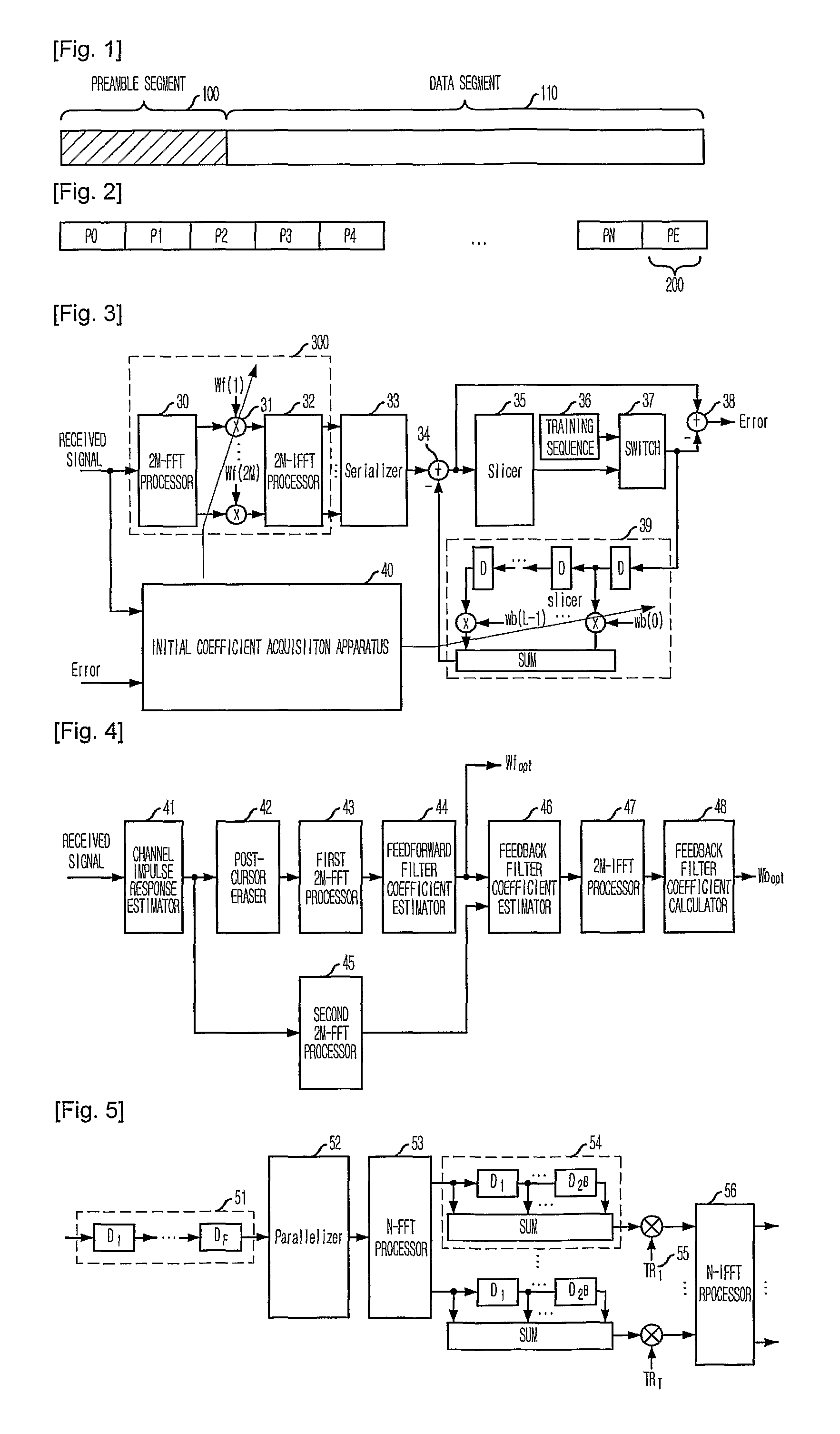
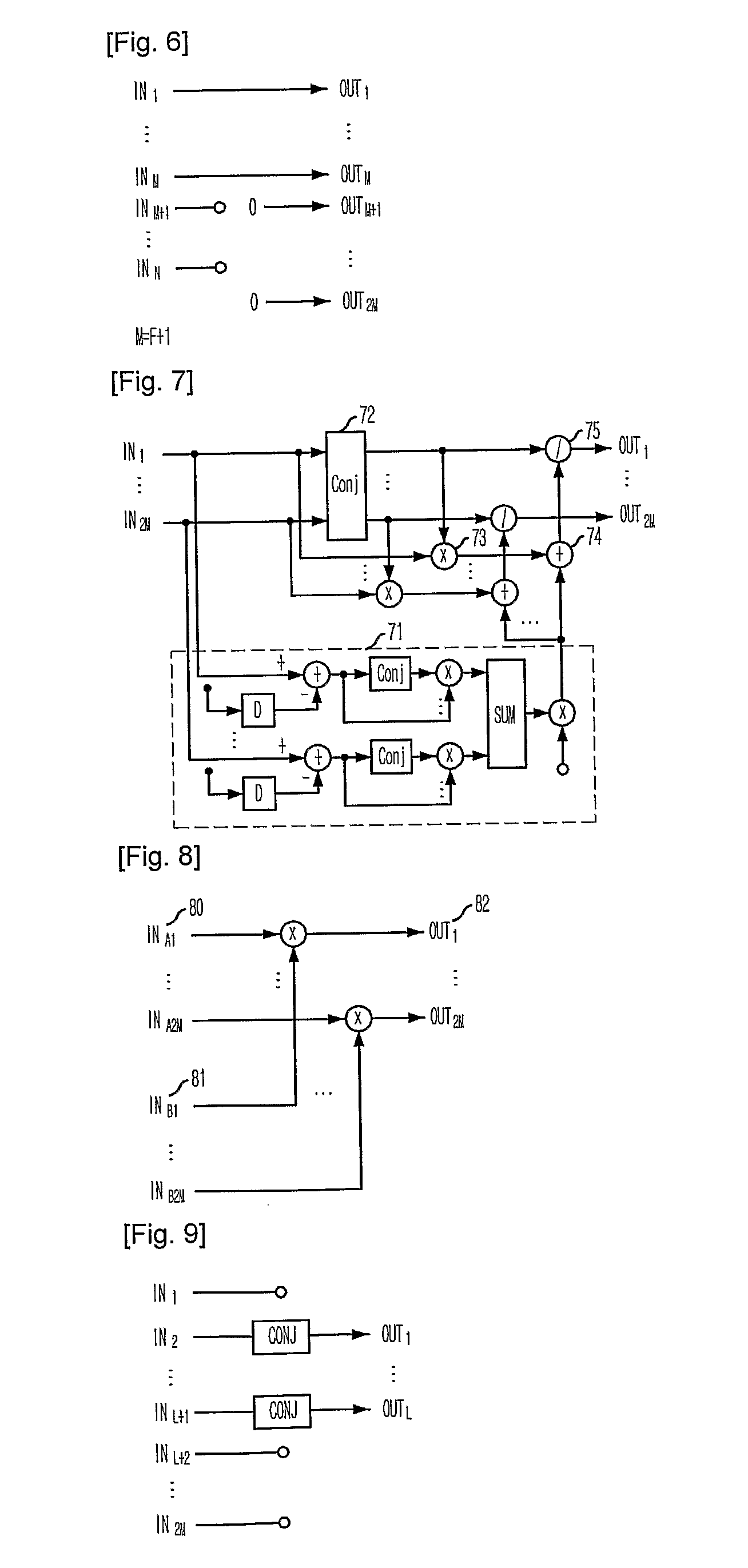
Apparatus and method for acquiring initial coefficient of decision feedback equalizer using fast fourier transform
InactiveUS20100046599A1Small amount of calculationEasy to implementMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTime domainFast Fourier transform
Provided is an apparatus and method for acquiring an initial coefficient of a DFE using an FFT. The apparatus includes a channel impulse response estimating unit for estimating a non-causal impulse response by delaying a received signal of a time domain and transforming it into frequency domain signals; a feedforward filter coefficient acquisition unit for extracting a predetermined number of signals from the non-causal channel impulse response signals estimated by the channel impulse response estimating unit, and transforming the same into frequency domain signals to acquire an initial coefficient of a feedforward filter; and a feedback filter coefficient acquisition unit for transforming the non-causal channel impulse response signals estimated by the channel impulse response estimating unit into frequency domain signals, multiplying the same by the initial coefficient of the feedforward filter, and transforming the results of multiplication into time domain signals to calculate an initial coefficient of a feedback filter.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
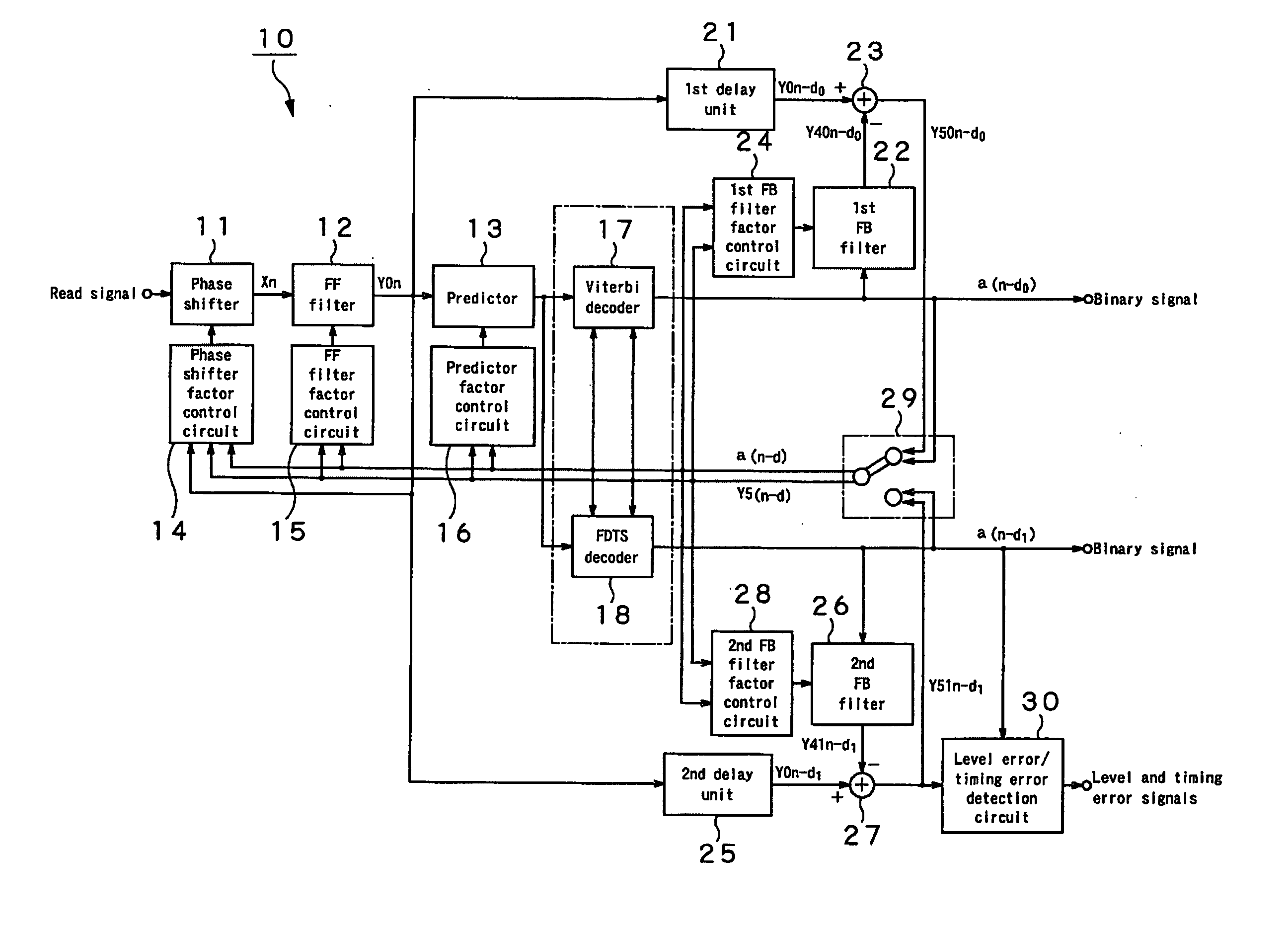
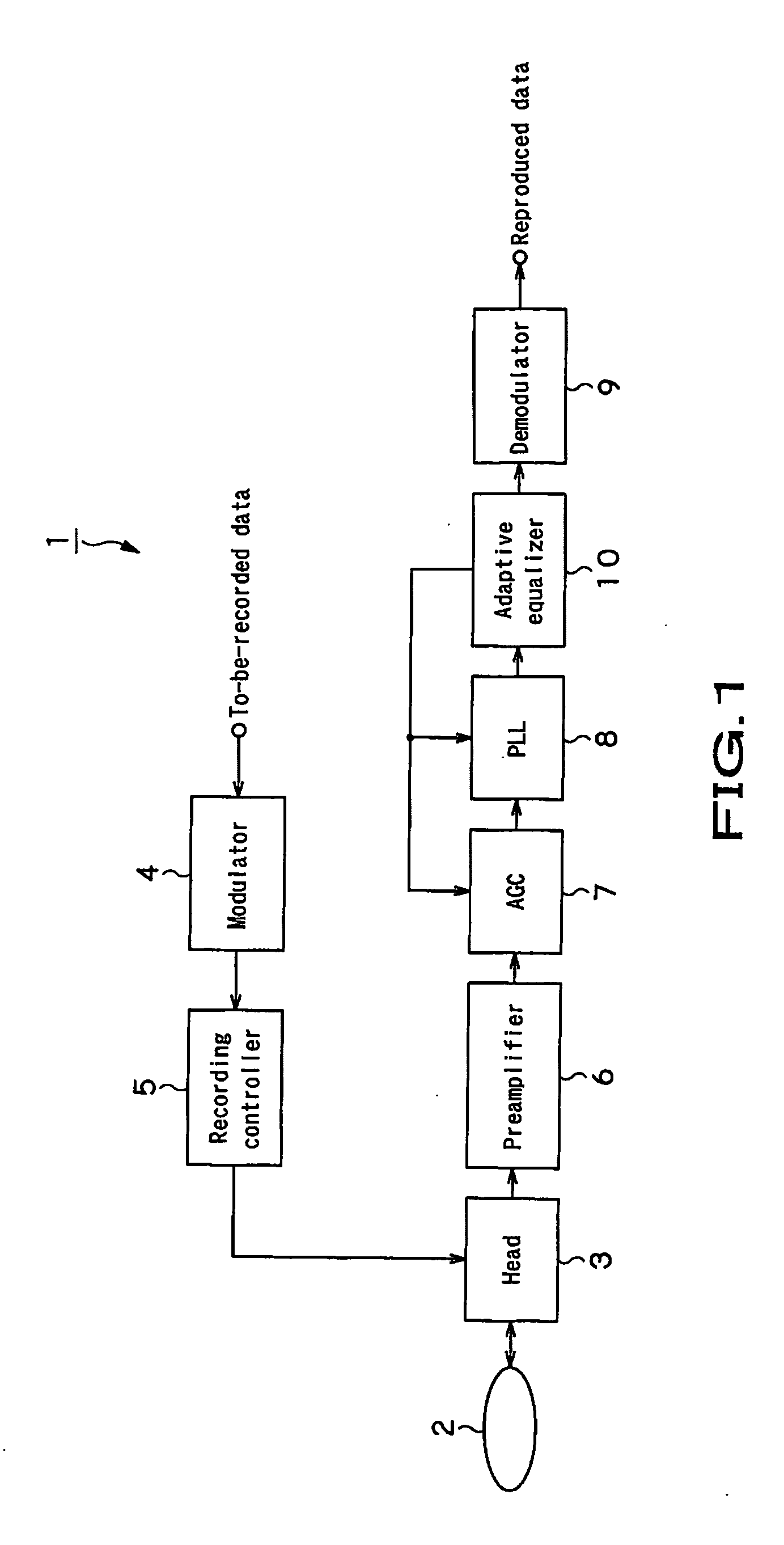
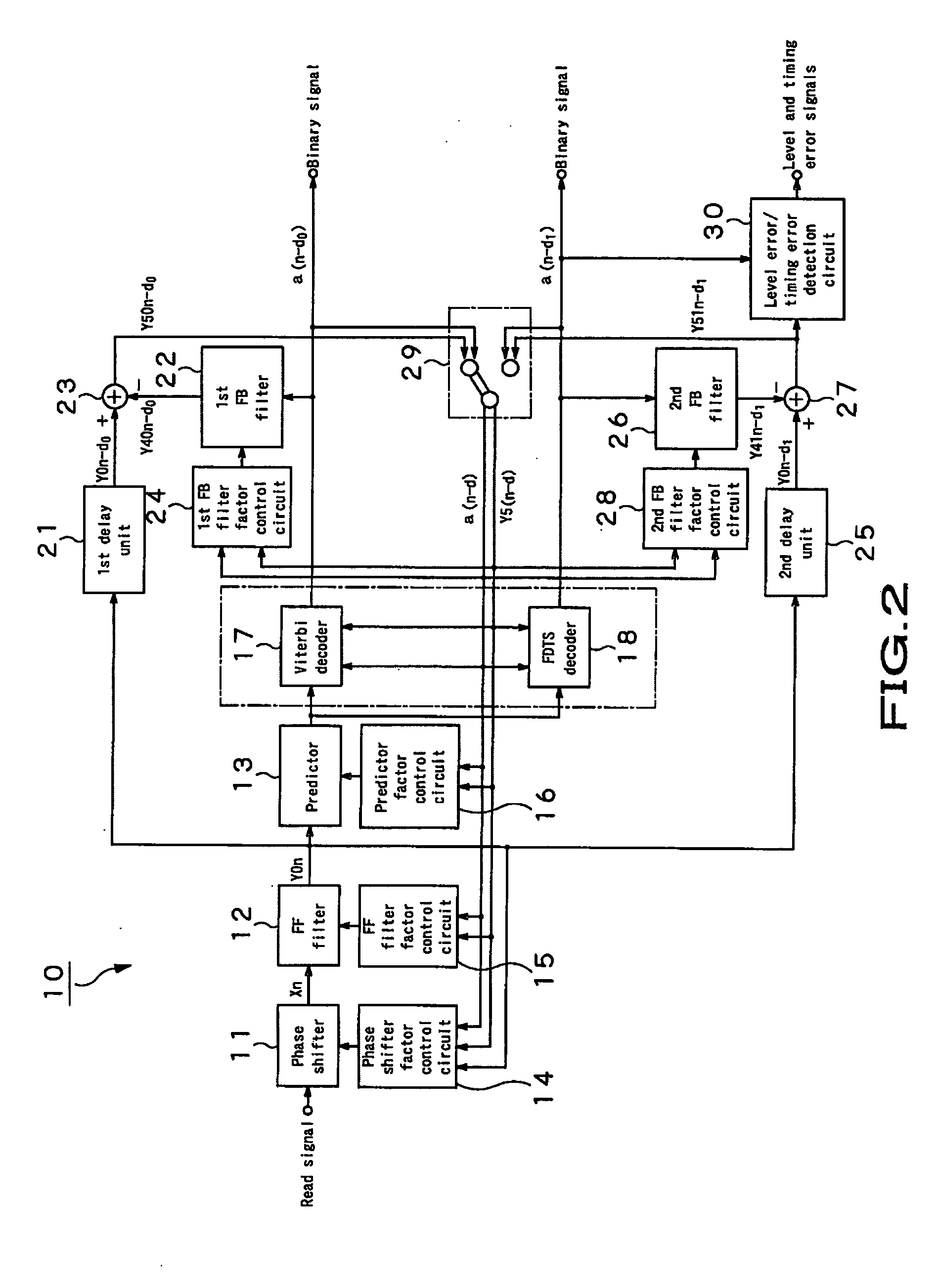
Adaptive equalizing apparatus and method
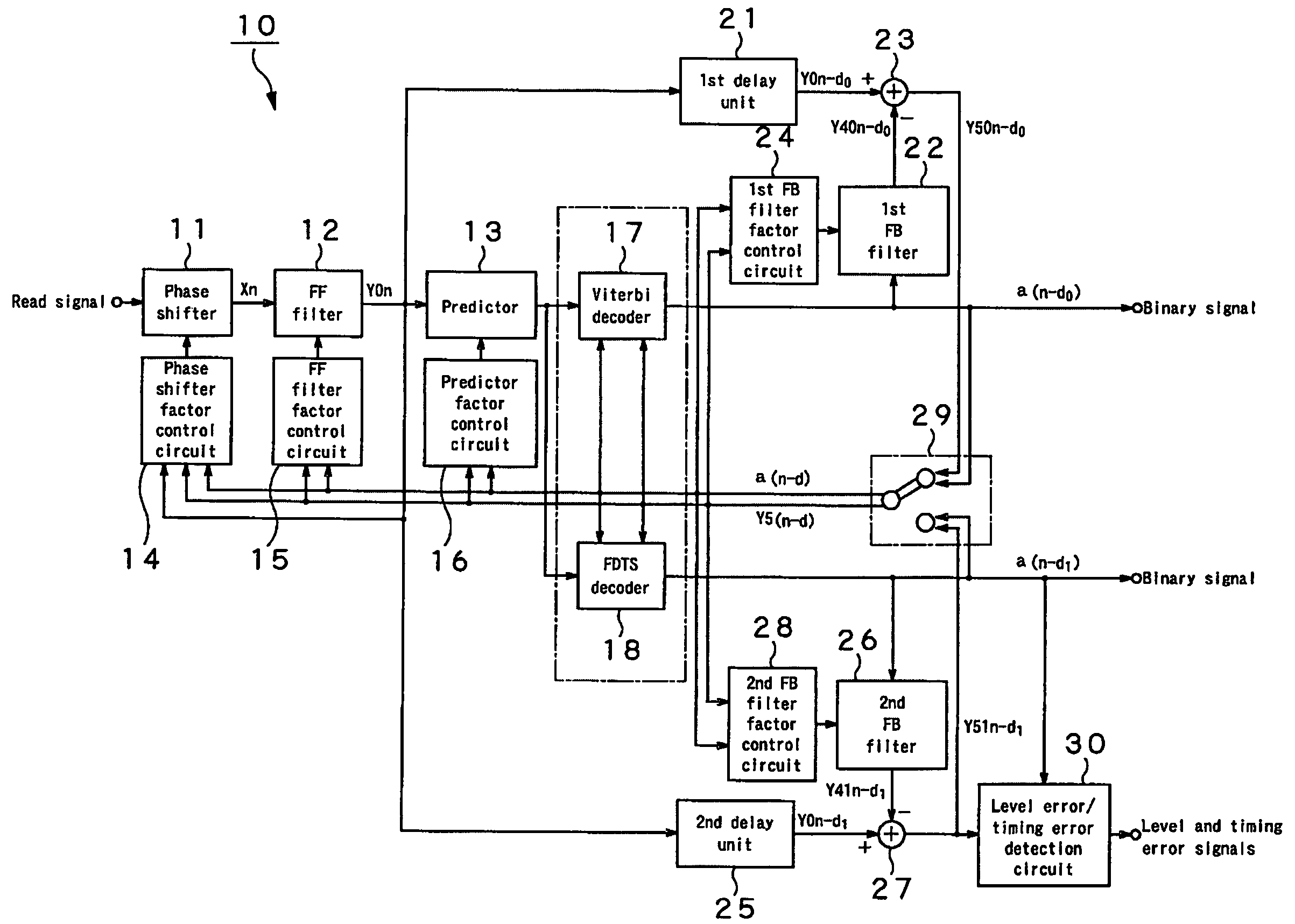
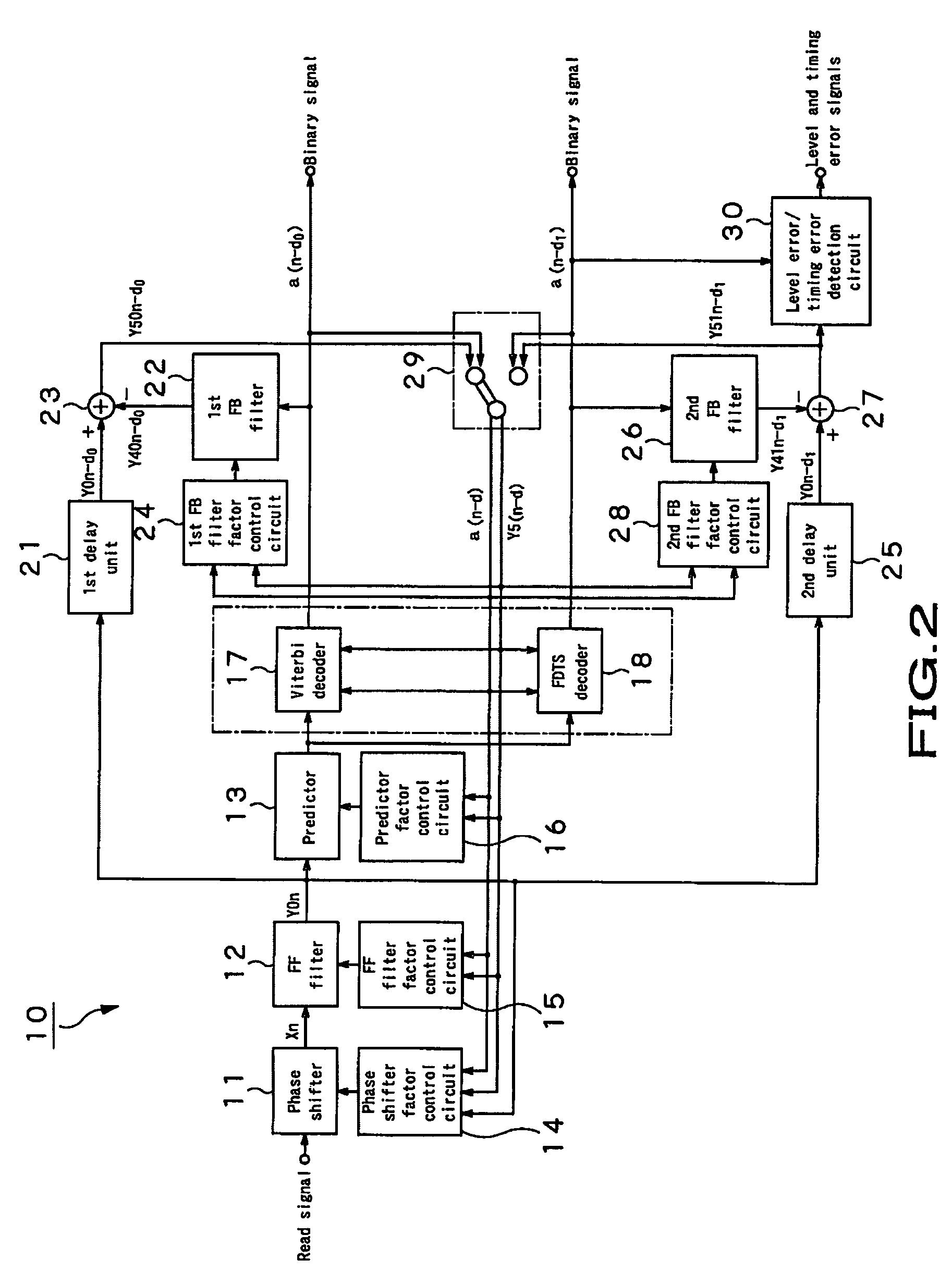
InactiveUS20050226316A1Error rateImprove performanceMultiple-port networksError preventionLeading edgeEqualization
The present invention provides an adaptive equalizing apparatus that can positively remove the leading ISI, and make a maximum-likelihood decoding and an optimum equalization on the basis of the result of the maximum-likelihood decoding with consideration being given to the asymmetry of an input waveform. The adaptive equalizing apparatus includes a feedforward filter to filter the read signal, a maximum-likelihood decoder making maximum-likelihood decoding of the signal filtered by the feedforward filter to generate the binary signal, a feedback filter to filter the binary signal supplied from the maximum-likelihood decoder, a delay unit delaying the signal filtered by the feedforward filter by a processing time of the maximum-likelihood decoder, and a subtracter subtracting the signal supplied from the feedback filter from the signal supplied from the delay unit. In the feedback filter, the tap factor is controlled on the basis of the binary signal generated by the maximum-likelihood decoding to generate a distortion of a partial response after the leading edge of the binary signal and an ISI response after the trailing edge. In the feedforward filter, the tap factor for the signal supplied from the subtracter is controlled to be a partial response.
Owner:SONY CORP
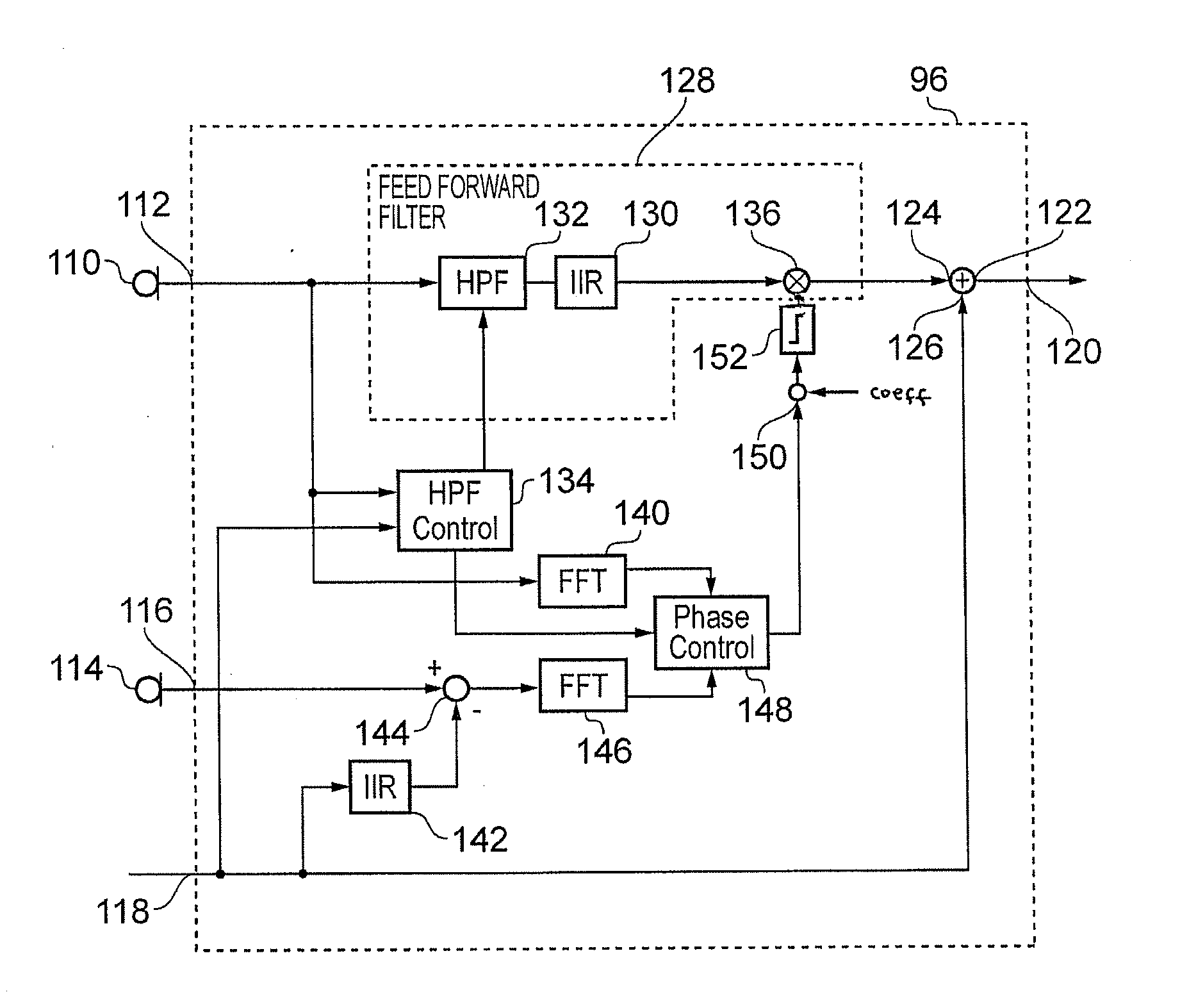
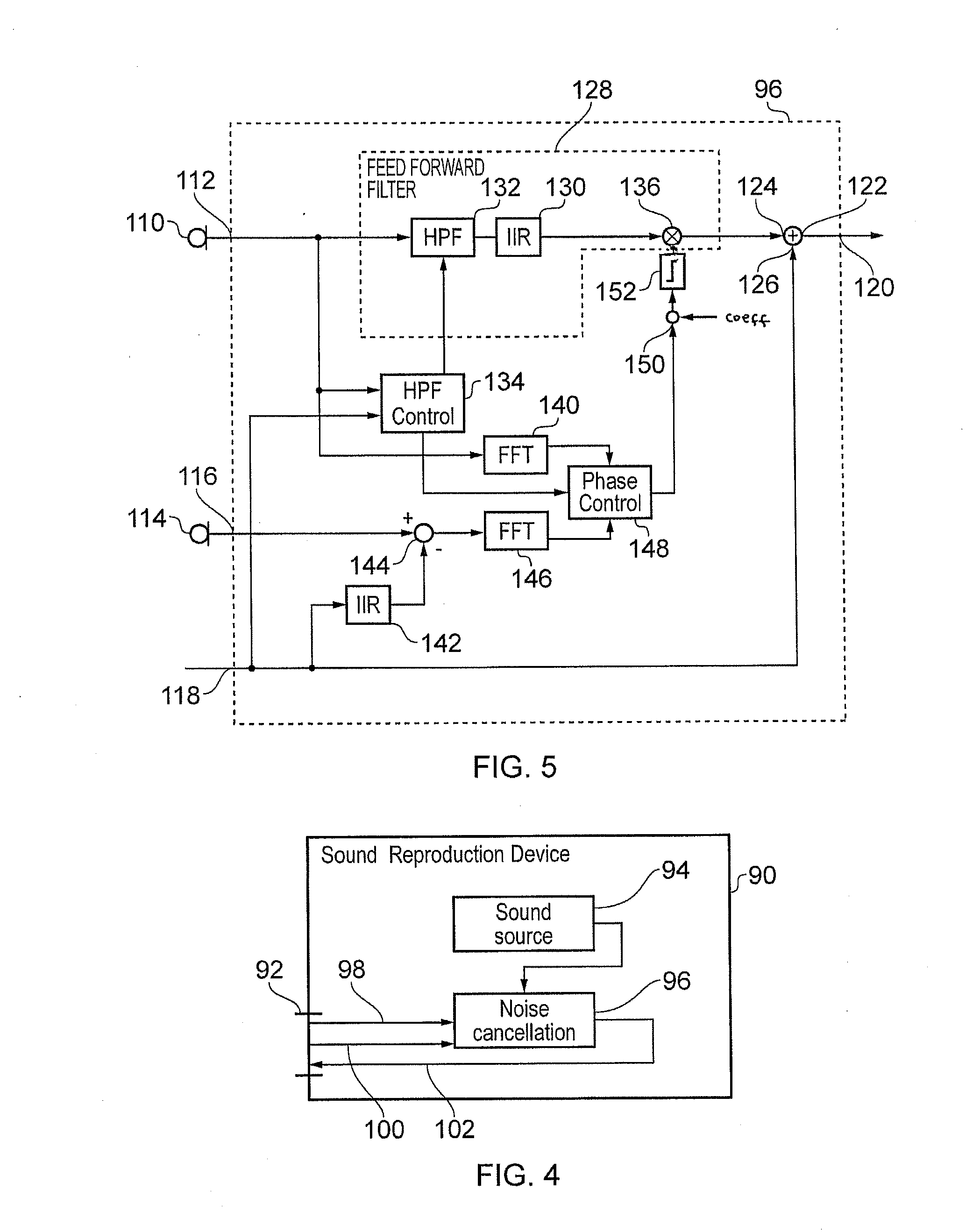
Noise cancellation
A noise cancellation signal is generated by generating an ambient noise signal, representing ambient noise, and generating a noise cancellation signal, by applying the ambient noise signal to an feedforward filter, where the feedforward filter comprises a high-pass filter having an adjustable cut-off frequency, and by applying a controllable gain. The noise cancellation signal is then applied to a loudspeaker, to generate a sound to at least partially cancel the ambient noise. An error signal is generated, representing unwanted sound in the region of the loudspeaker. The phase of the ambient noise signal is compared to a phase of the error signal, and the gain is controlled on the basis of a result of the comparison, taking account of a phase shift introduced by the high-pass filter when performing the comparison.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
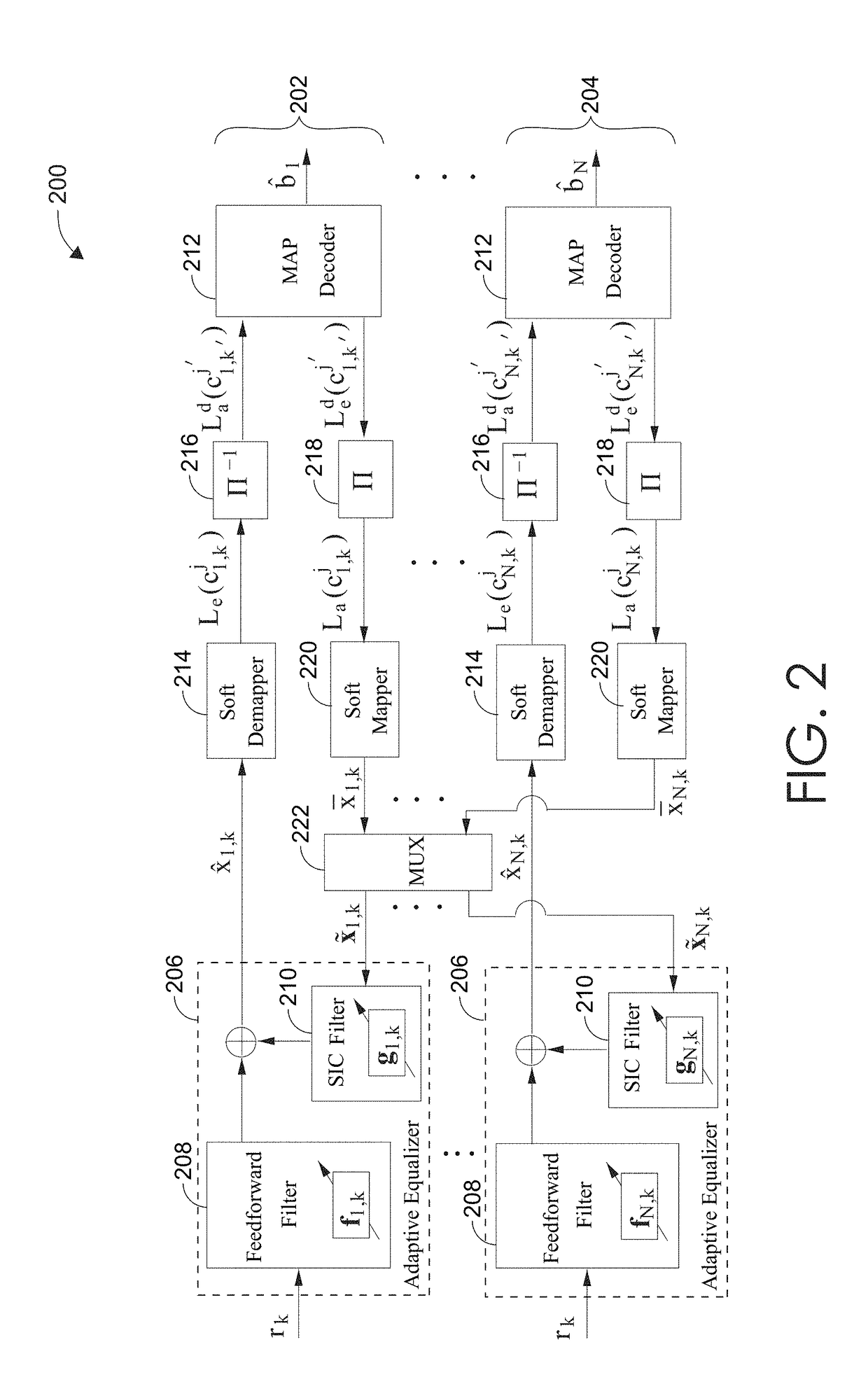
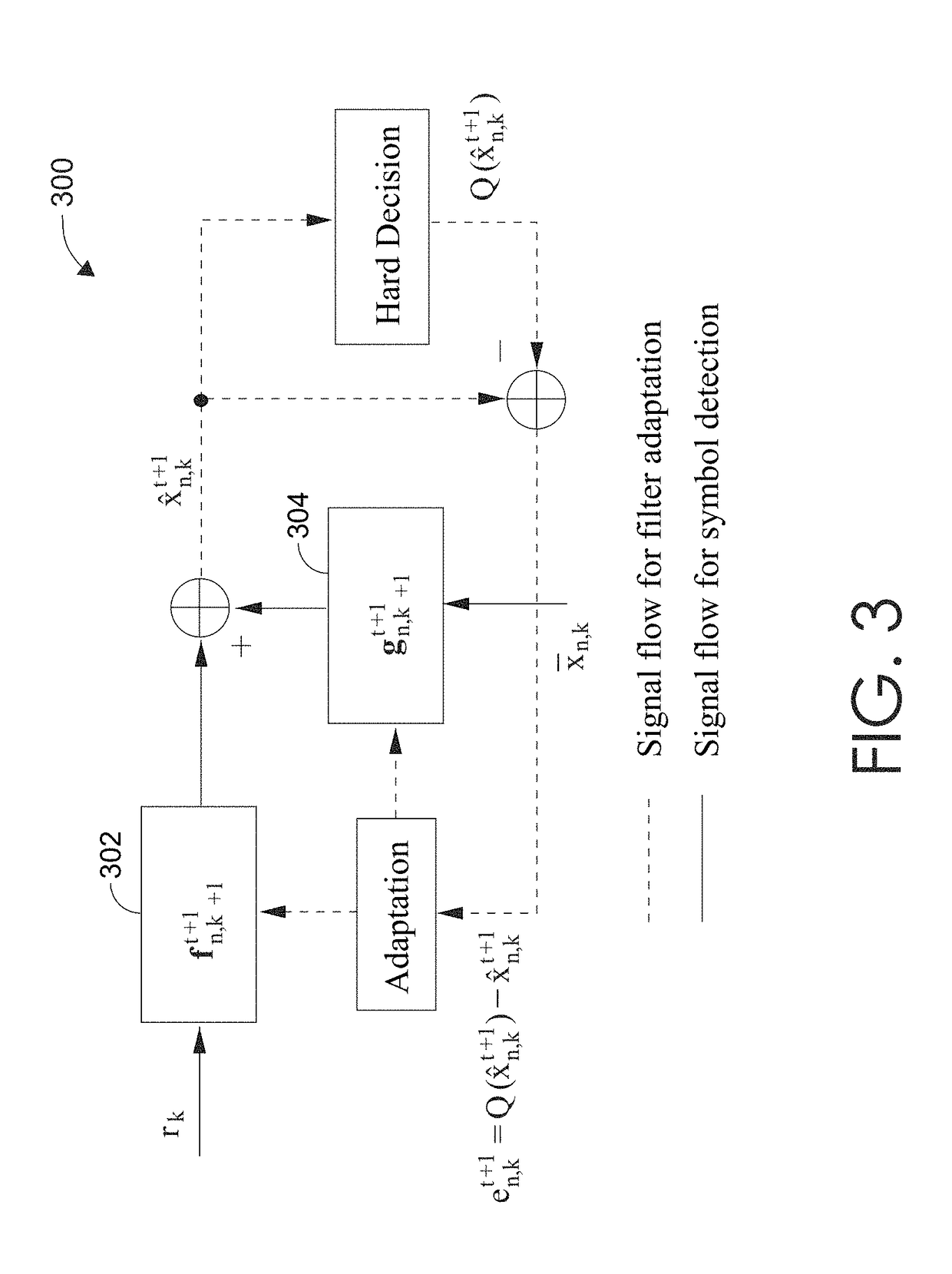
Turbo receivers for multiple-input multiple-output underwater acoustic communications
ActiveUS20190068294A1Easy to detectImprove fidelityMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionMultiple inputFeedforward filter
Systems and methods for underwater communication using a MIMO acoustic channel. An acoustic receiver may receive a signal comprising information encoded in at least one transmitted symbol. Using a two-layer iterative process, the at least one transmitted symbol is estimated. The first layer of the two-layer process uses iterative exchanges of soft-decisions between an adaptive turbo equalizer and a MAP decoder. The second layer of the two-layer process uses a data-reuse procedure that adapts an equalizer vector of both a feedforward filter and a serial interference cancellation filter of the adaptive turbo equalizer using a posteriori soft decisions of the at least one transmitted symbol. After a plurality of iterations, a hard decision of the bits encoded on the at least one transmitted symbol is output from the MAP decoder.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Channel equalizer, channel equalization method, and tap coefficient updating method
InactiveUS20070047637A1Multiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationTransmission channelEngineering
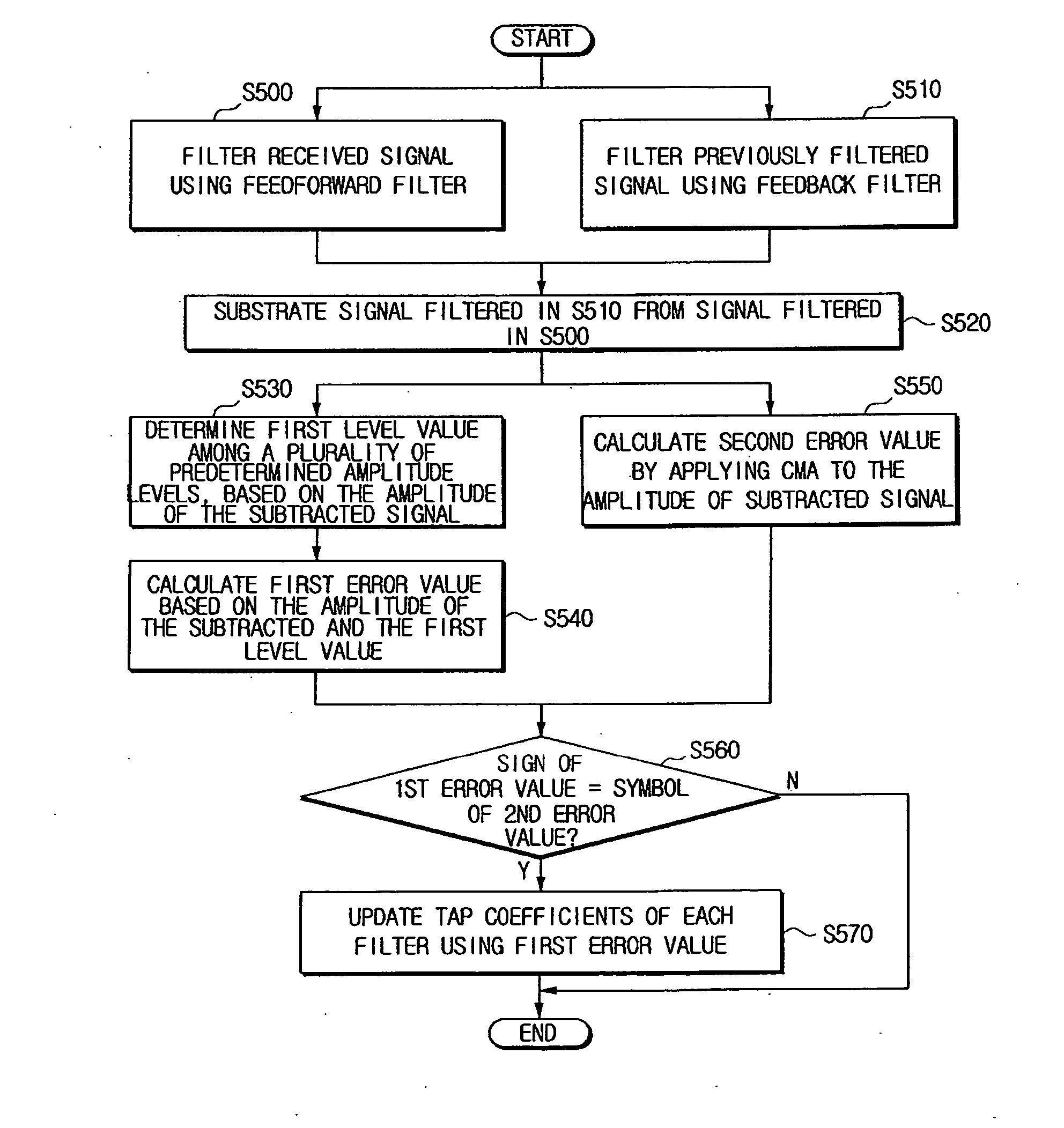
A channel equalizer to equalize a signal received over a transmission channel, includes a feedforward filter to filter the received signal, a level determination unit to determine a first level value among a plurality of predetermined amplitude levels based on an amplitude of an output signal of the feedforward filter, and an error calculation unit to calculate a first error value based on the amplitude of the output signal of the feedforward filter and the first level value and to output the first error value to the feedforward filter so that the feedforward filter updates a tap coefficient thereof using the first error value. As such, the channel equalizer is capable of operating independently of a phase error by using the amplitude of the received signal in channel equalization, whereby a variety of designs can be available for the channel equalizer regardless of a sequence of a carrier recovery operation and a channel equalization operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Decision-feedback channel equalizer usable with a digital receiver and method thereof
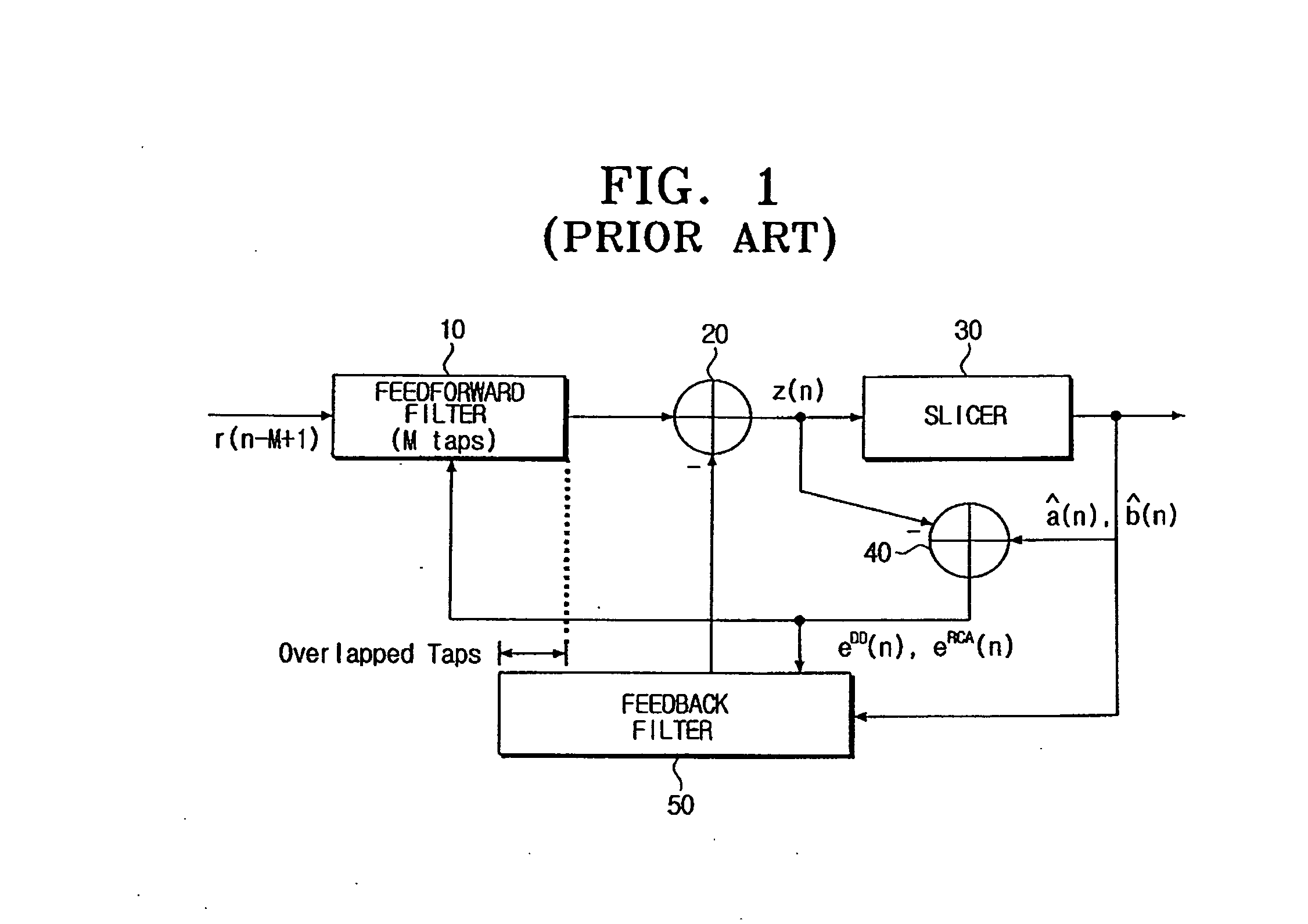
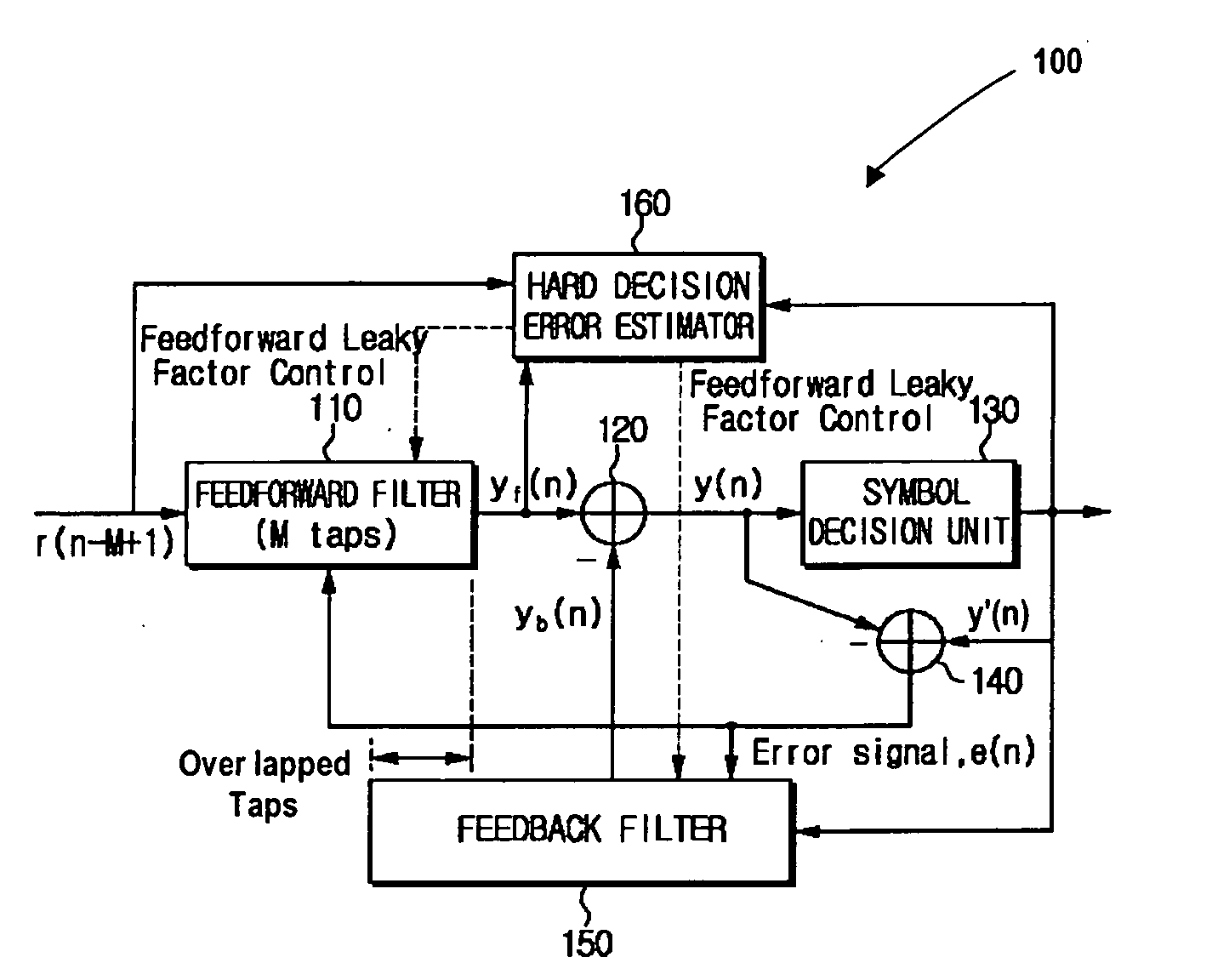
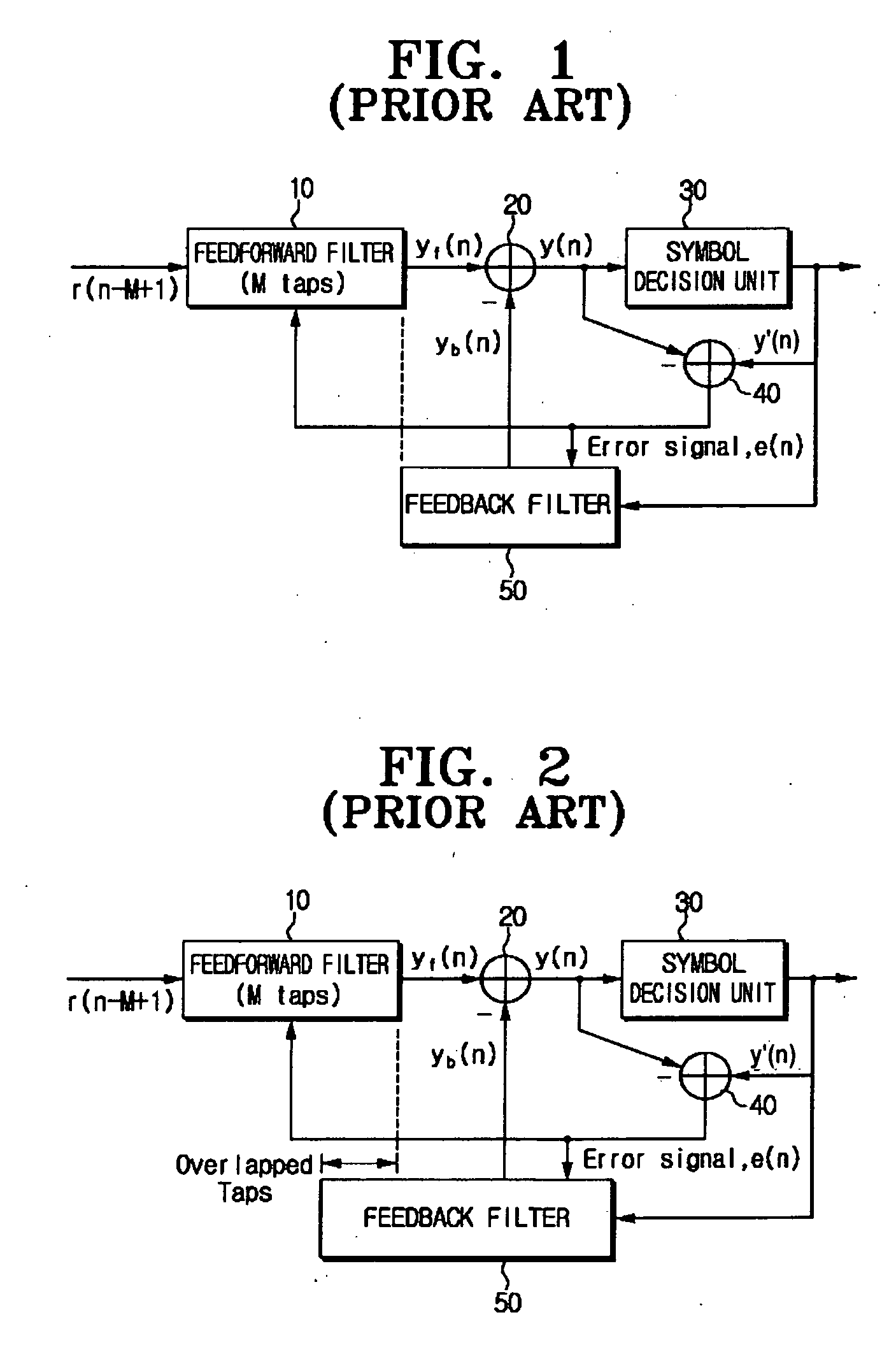
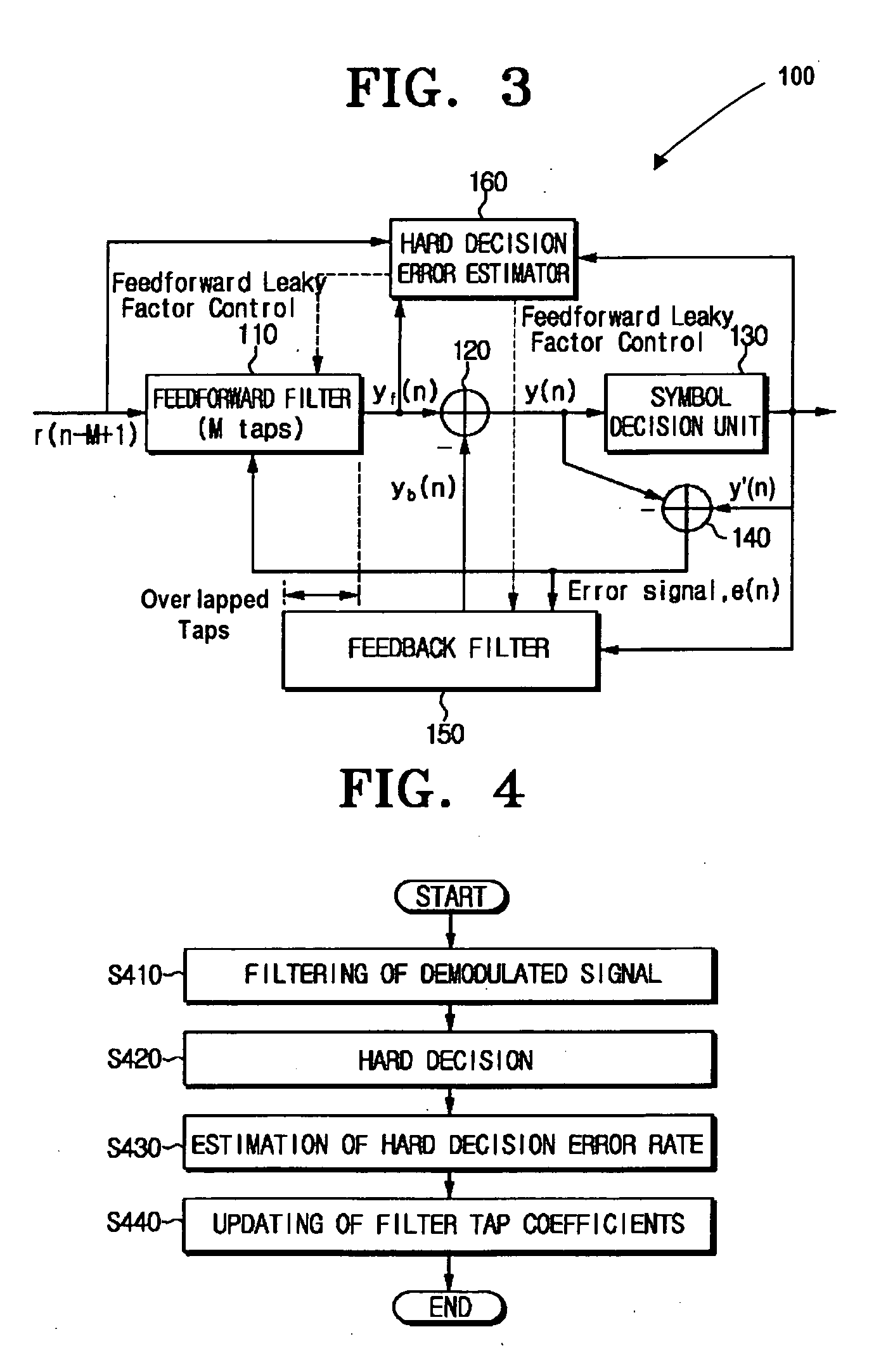
InactiveUS20060176948A1Reduce symbol error rateLower capability requirementsMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsControl theorySelf adaptive
A decision feedback channel equalizer of a digital receiver includes a feedforward filter to receive and filter a demodulated signal to remove one or more ghost signals, a hard decision unit to decide a decision value based on a first signal outputted from the feedforward filter, a feedback filter to receive and filter the decision value, and to output a second signal, and a hard decision error estimator to estimate a hard decision error rate based on the demodulated signal, the first signal and the decision value, and to control the equalizer to update tap coefficients of the feedforward filter and the feedback filter according to the hard decision error rate. Accordingly, the tap coefficients of the feedforward filter and the feedback filter may be adjusted adaptively based on the hard decision error rate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Adaptive equalizing apparatus and method
InactiveUS7551668B2Error rateImprove performanceMultiple-port networksError preventionLeading edgeEqualization
An adaptive equalizing apparatus that can positively remove the leading Inter Symbol Interference (ISI), make a maximum-likelihood decoding and an optimum equalization on the basis of the result of the maximum-likelihood decoding with consideration being given to the asymmetry of an input waveform. The adaptive equalizing apparatus includes a feedforward filter, a maximum-likelihood decoder, a feedback filter, a delay unit, and a subtracter. In the feedback filter, the tap factor is controlled on the basis of the binary signal generated by the maximum-likelihood decoding to generate a distortion of a partial response after the leading edge of the binary signal and an ISI response after the trailing edge. In the feedforward filter, the tap factor for the signal supplied from the subtracter is controlled to be a partial response.
Owner:SONY CORP
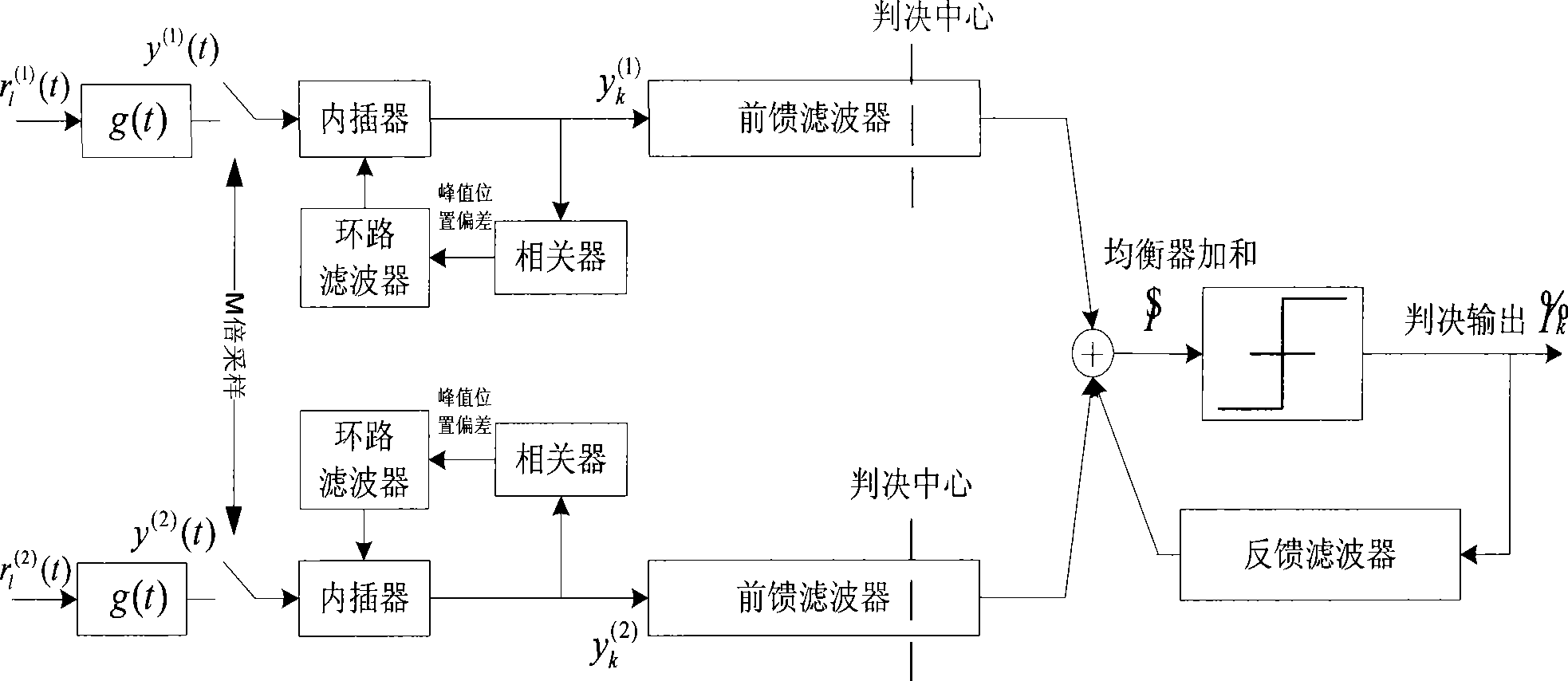
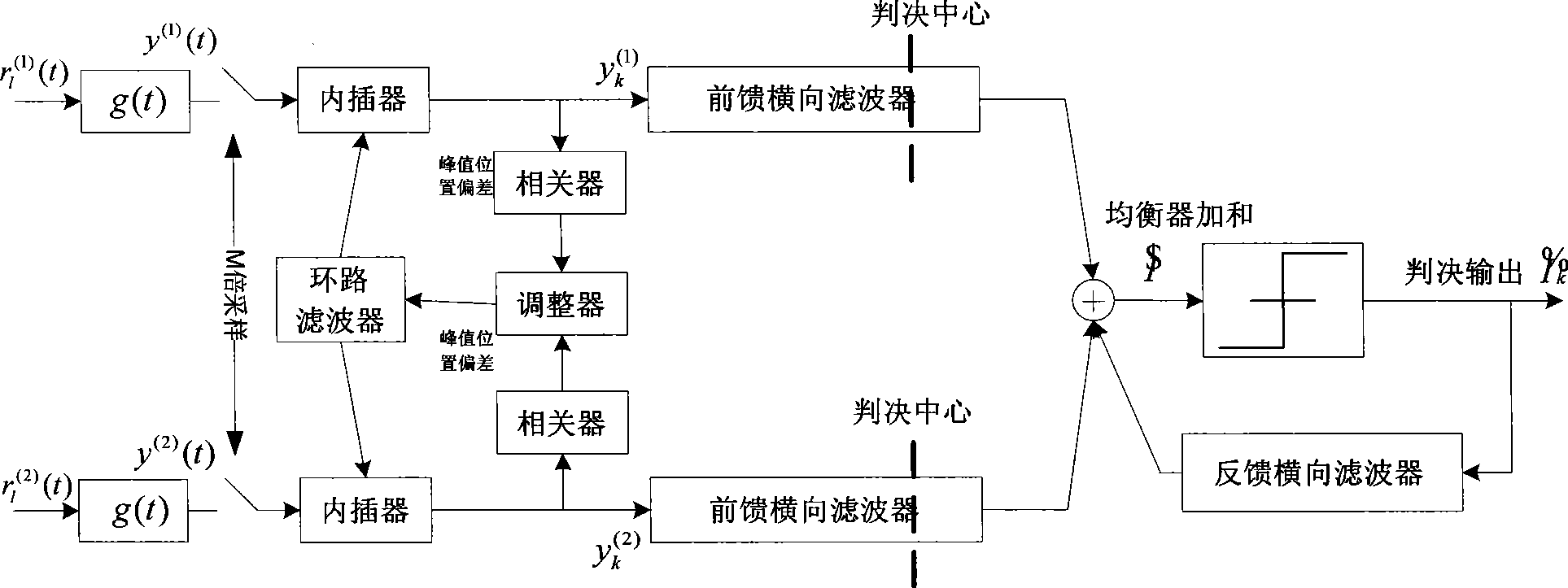
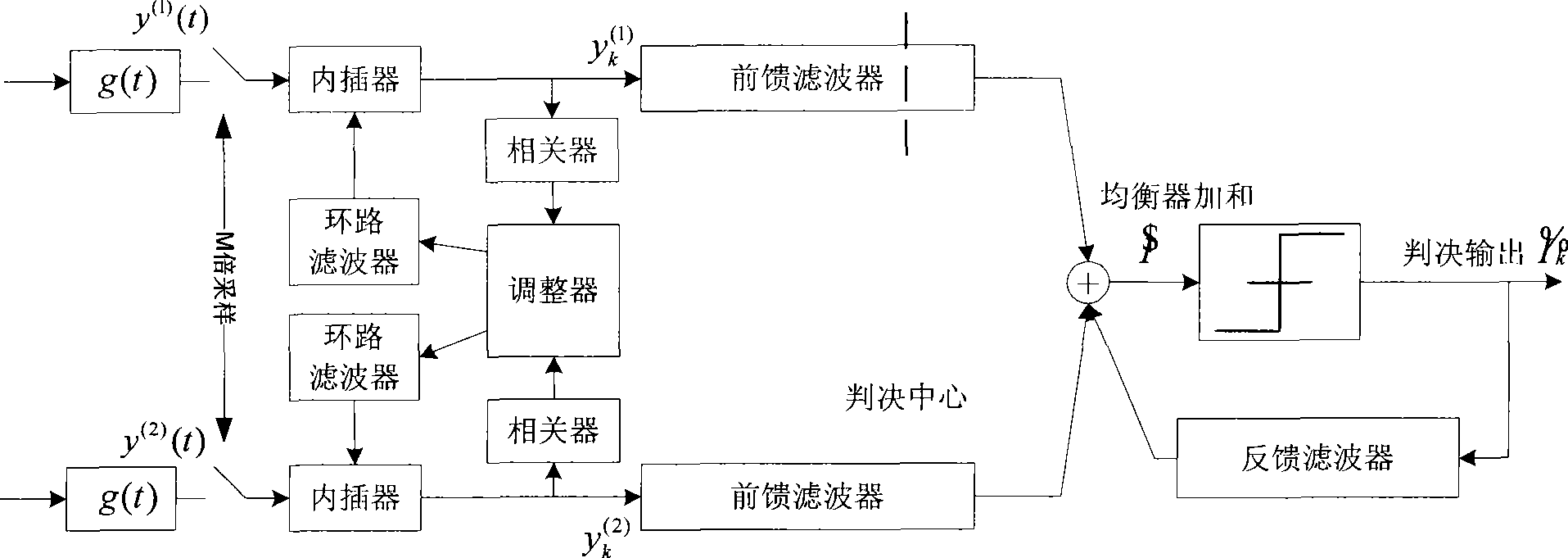
Method and apparatus for diversity reception by ground digital television broadcast transmission system
ActiveCN101500105AImprove robustnessHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsTransport systemCarrier signal
The invention discloses a diversity reception device and a method of a terrestrial digital television broadcast transmission system, wherein the device comprises a diversity signal channel tracker used for tracking the signal channel change of diversity signals and a diversity signal channel equalizer connected with the diversity signal channel tracker and used for withstanding multipath of the signal channel; the diversity signal channel tracker comprises N diversity signal channel tracking units corresponding to N-path diversity signals (N is not less than 2); and the diversity signal channel equalizer comprises N feedforward filters, feedback filters, and combination devices which combines the outputs of the N feedforward filters with the signals of the feedback filters. The invention can greatly improve the robustness of a terrestrial digital television broadcast single carrier receiving system, compared with the prior art, the invention can achieve the goals of greatly improving the sensitivity of receivers and reducing the error rate under the condition of poor dynamic signal channels.
Owner:SHANGHAI HIGH DEFINITION DIGITAL TECH IND
Channel equalization method based on bidirectional noise prediction decision feedback
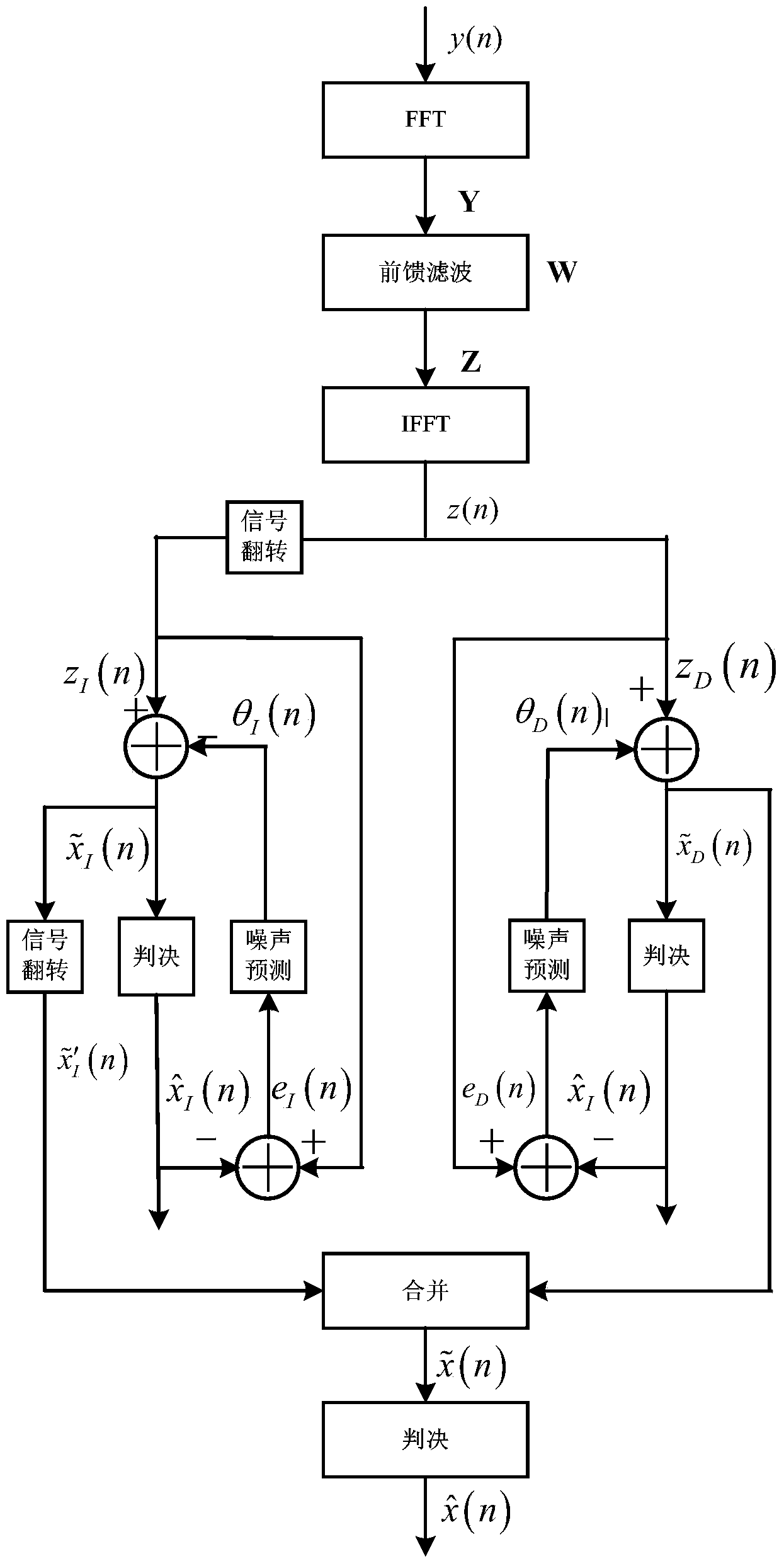
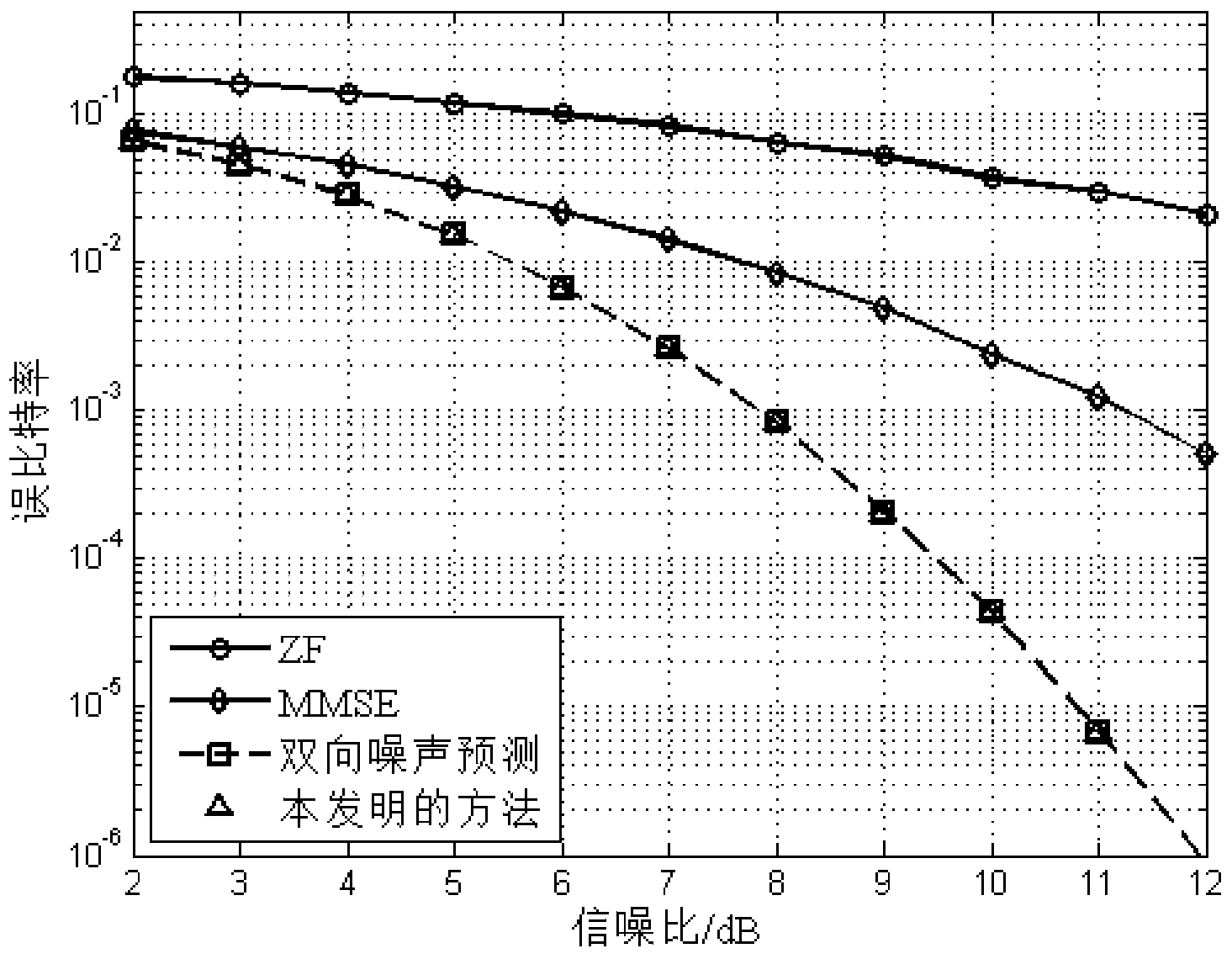
InactiveCN104022984ACounteract the effects of noiseImprove performanceTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTime domainAlgorithm
The invention discloses a channel equalization method based on bidirectional noise prediction decision feedback and mainly aims to solve a problem of high complexity of a traditional bidirectional noise prediction decision feedback algorithm. The method comprises steps that: 1, FFT conversion for a time domain signal is carried out to acquire a frequency domain signal; 2, feedforward filtering for the frequency domain signal is carried out; 3, IFFT conversion for the data after a feedforward filter is carried out to acquire a time domain signal; 4, signal overturning for the time domain signal is carried out; 5, positive noise prediction filtering for the signal before overturning is carried out; 6, reverse noise prediction filtering for the data after overturning is carried out; 7, the data acquired after positive noise prediction filtering and the data after reverse noise prediction filtering are combined to acquire a signal to be determined; and 8, the signal to be determined is determined to acquire a channel equalization result. According to the channel equalization method, only one feedforward filter is used, channel equalization complexity is reduced, the channel equalization method has stronger practicality and is suitable for a time varying channel having obvious multipath effects.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Spatial and temporal equalizer and equalization method
InactiveUS6862316B2High computational complexityFast convergenceMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationEngineeringEqualization
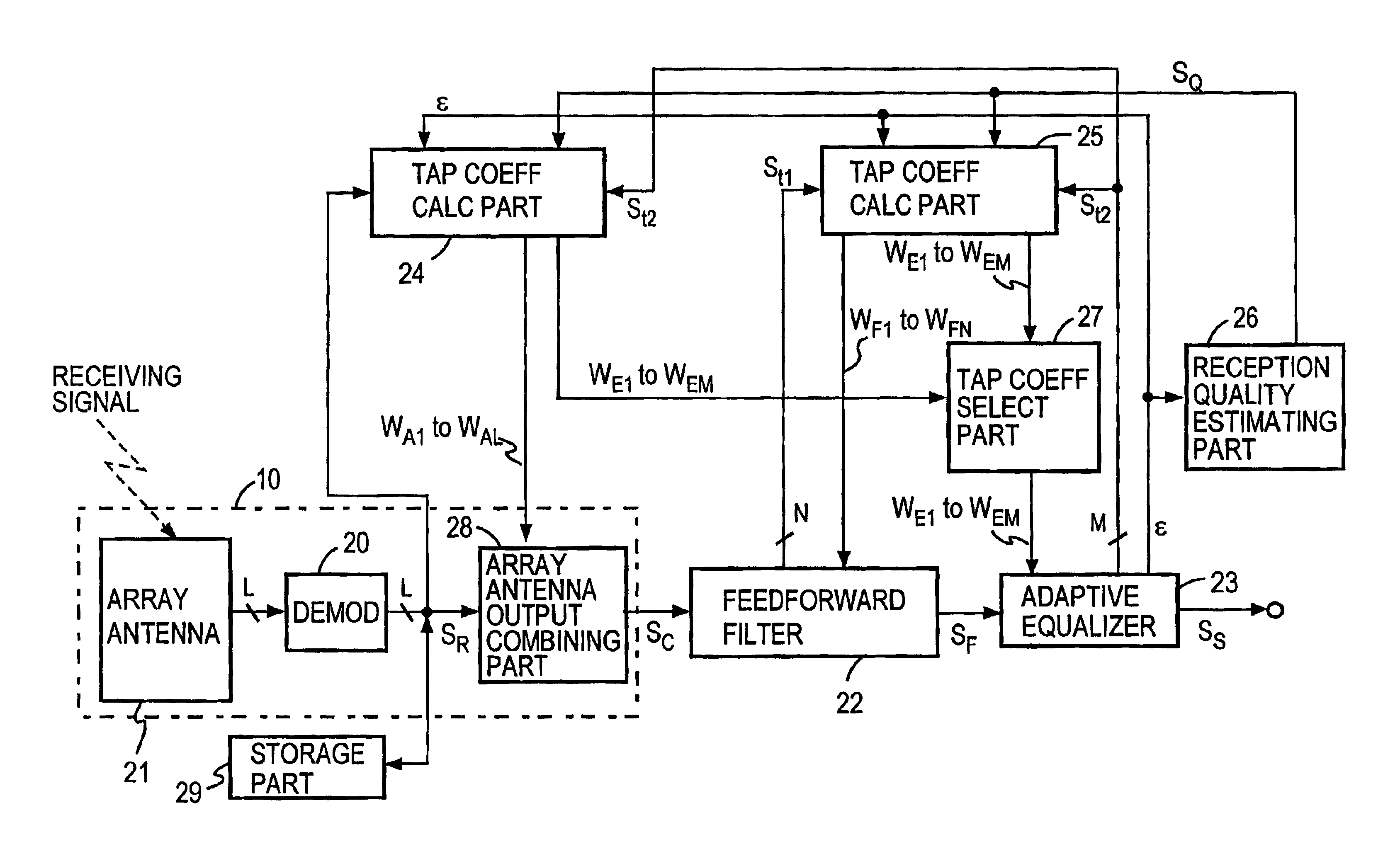
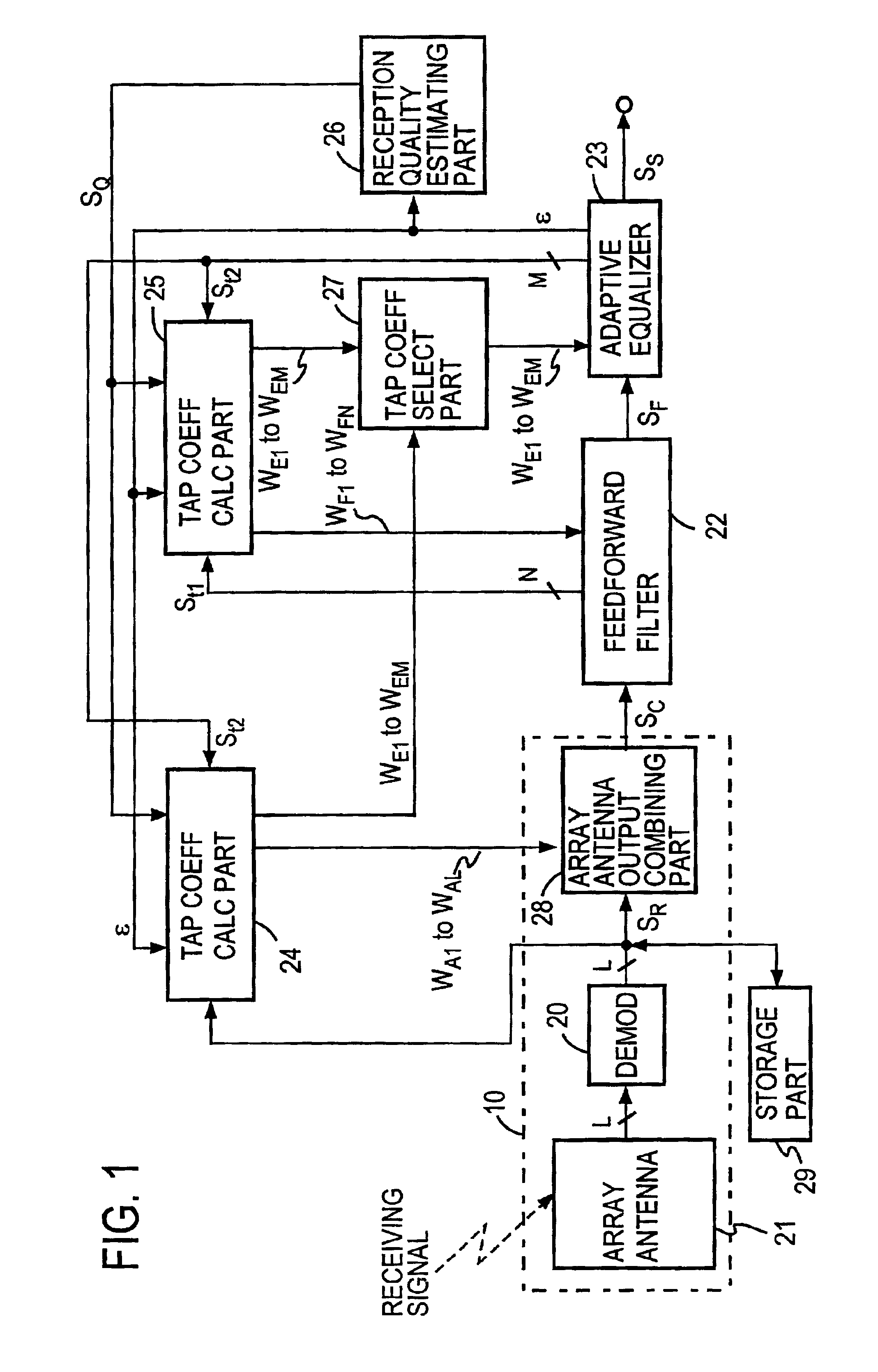
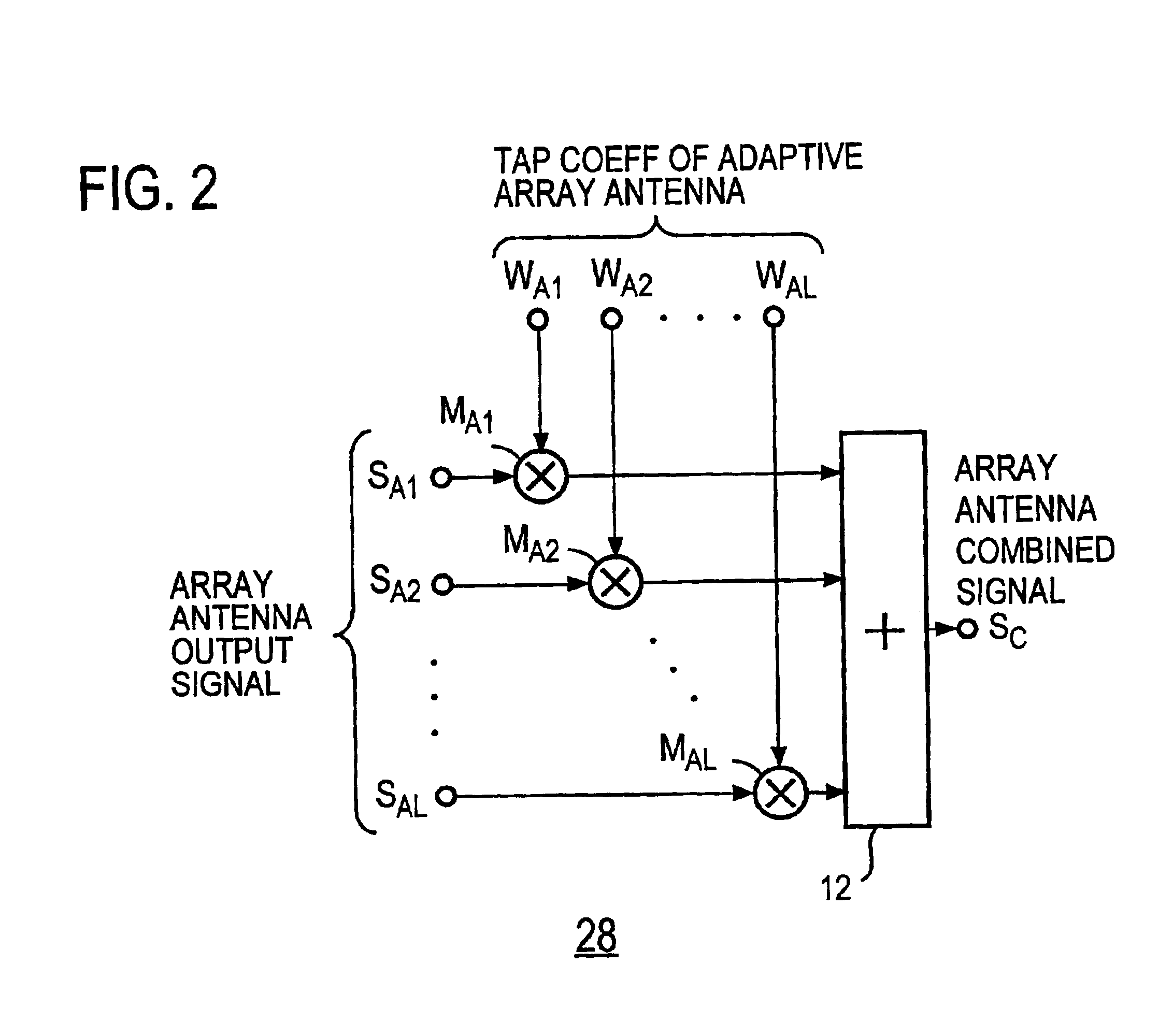
Outputs from respective elements of an array antenna 21 are demodulated, and the demodulated outputs are stored in storage means 29. The demodulated outputs are multiplied by tap coefficients of adaptive array antenna, then the multiplied outputs are combined by combining means 28, and the combined output is provided via a feed forward filter 22 to an adaptive equalizer 23, wherein it is equalized to obtain a decision symbol. During reception of a training signal the tap coefficients of adaptive array antenna and tap coefficients of the adaptive equalizer 23 are subjected to convergence processing by tap coefficient calculating means 24 so that an error signal becomes small, and then tap coefficients of the feed forward filter 22 and the adaptive equalizer 23 are subjected to convergence processing by tap coefficient calculating means 25 so that an error signal becomes small. Thereafter, the convergence processing by the means 24 and 25 is repeated, during which a training signal stored in storage means 29 is used, results of the immediately preceding convergence processing are used as initial values, and it is decided by receiving quality estimating means 26 whether the error signal has become sufficiently small relative to the received signal power.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com