Patents
Literature
80results about How to "Remove distortion effects" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spot-size effect reduction
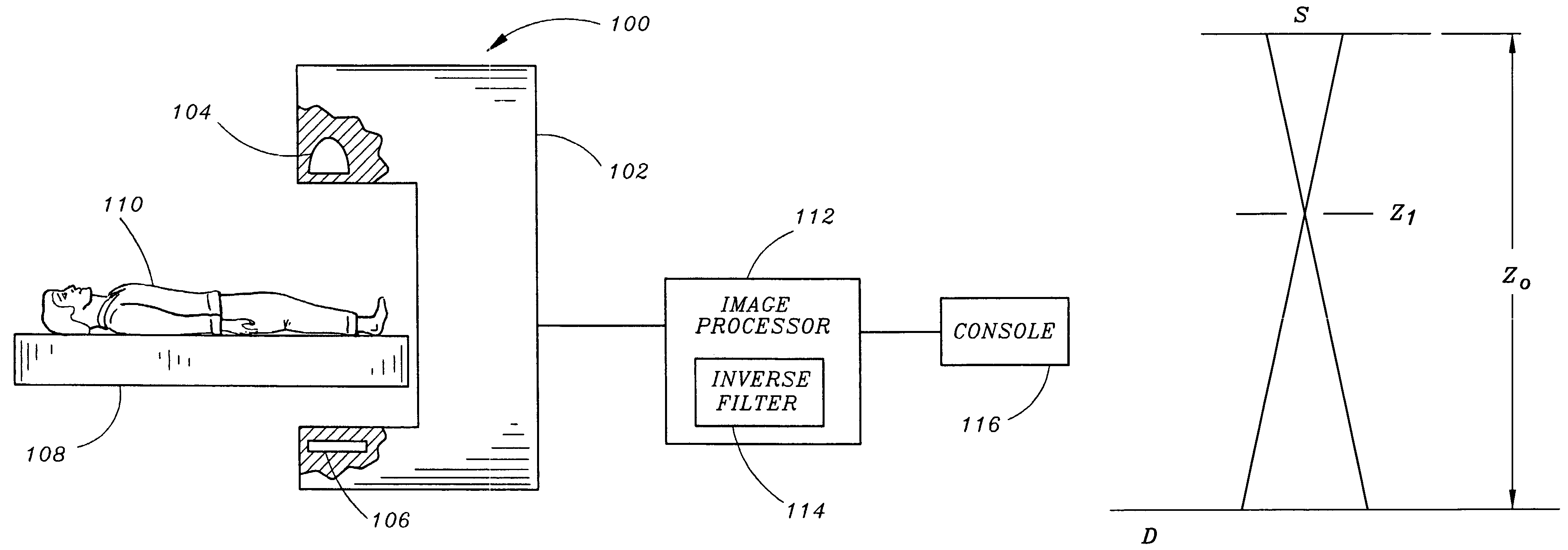
InactiveUS7418078B2Reduce adverse effectsImprove image qualityRadiation/particle handlingTomographyX-rayRadiography
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
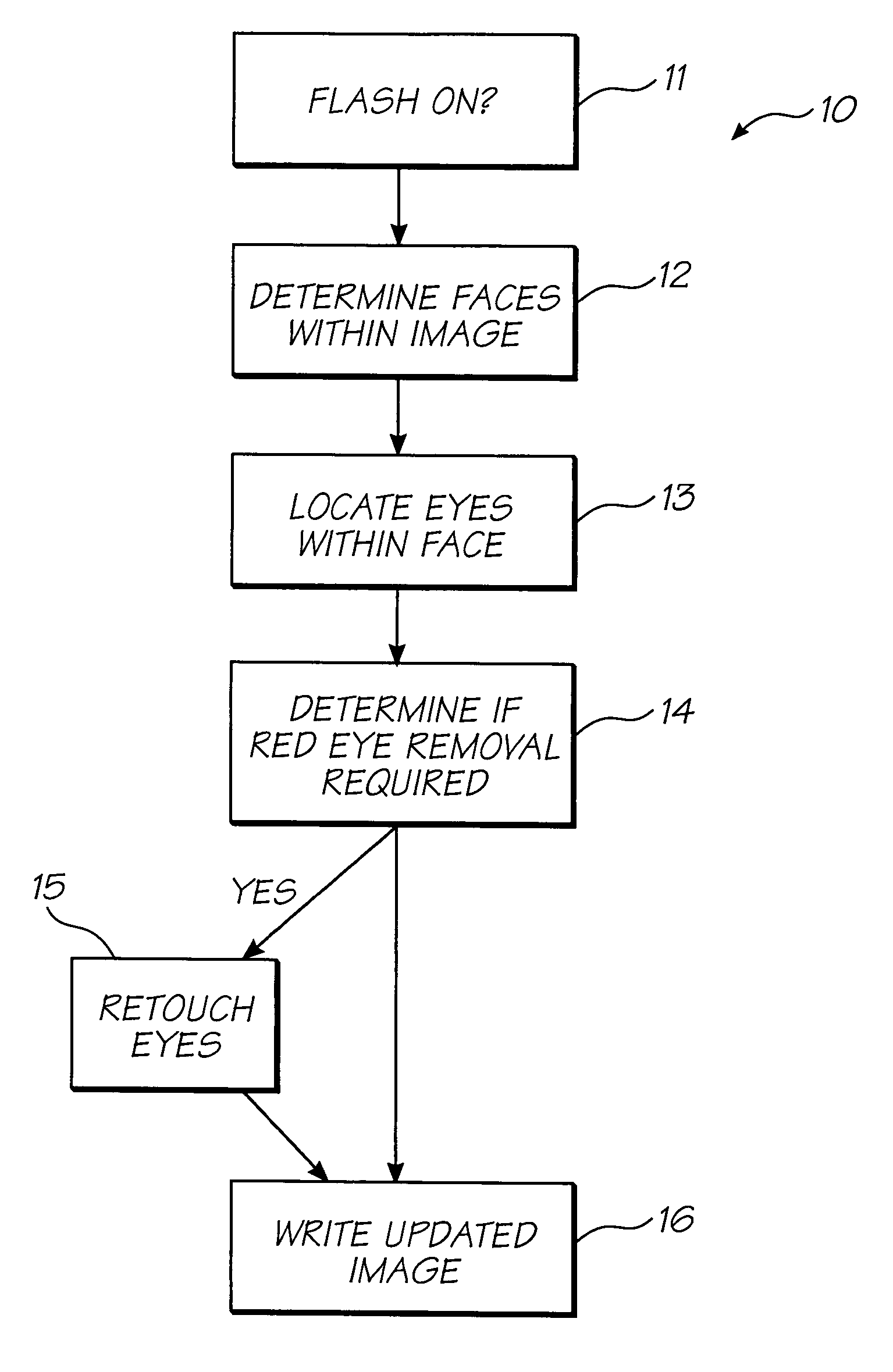
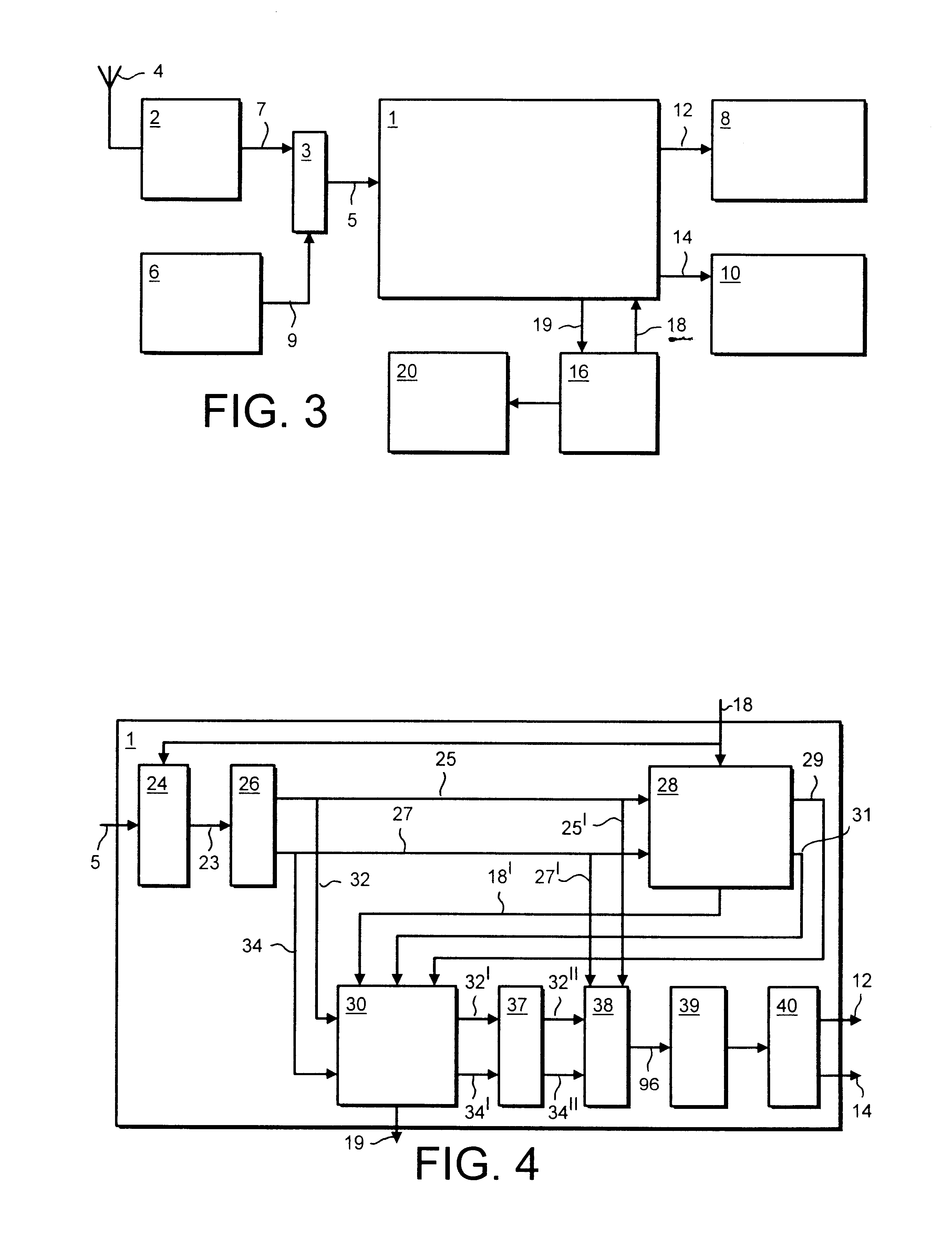
Method of processing digital image to correct for flash effects
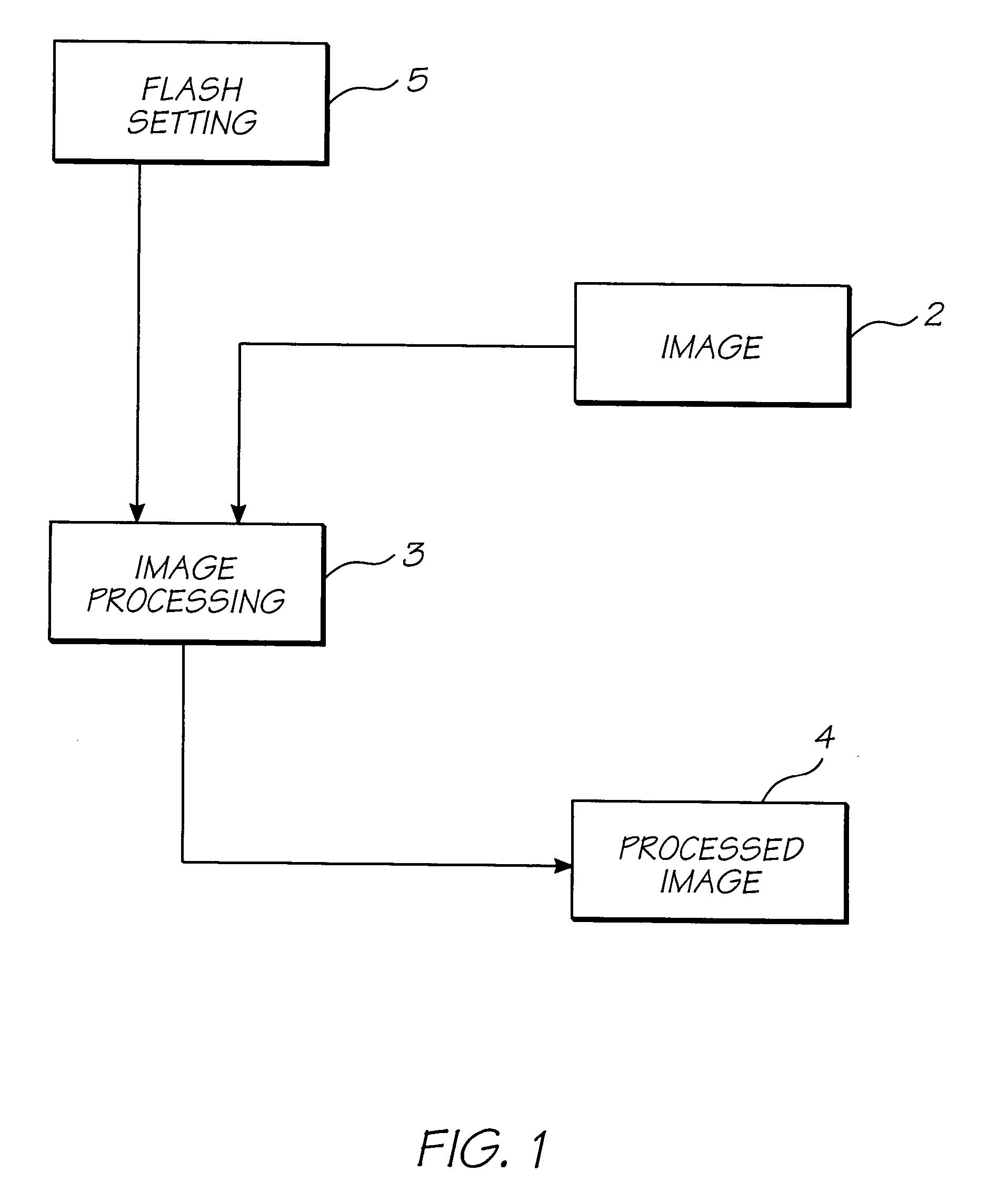
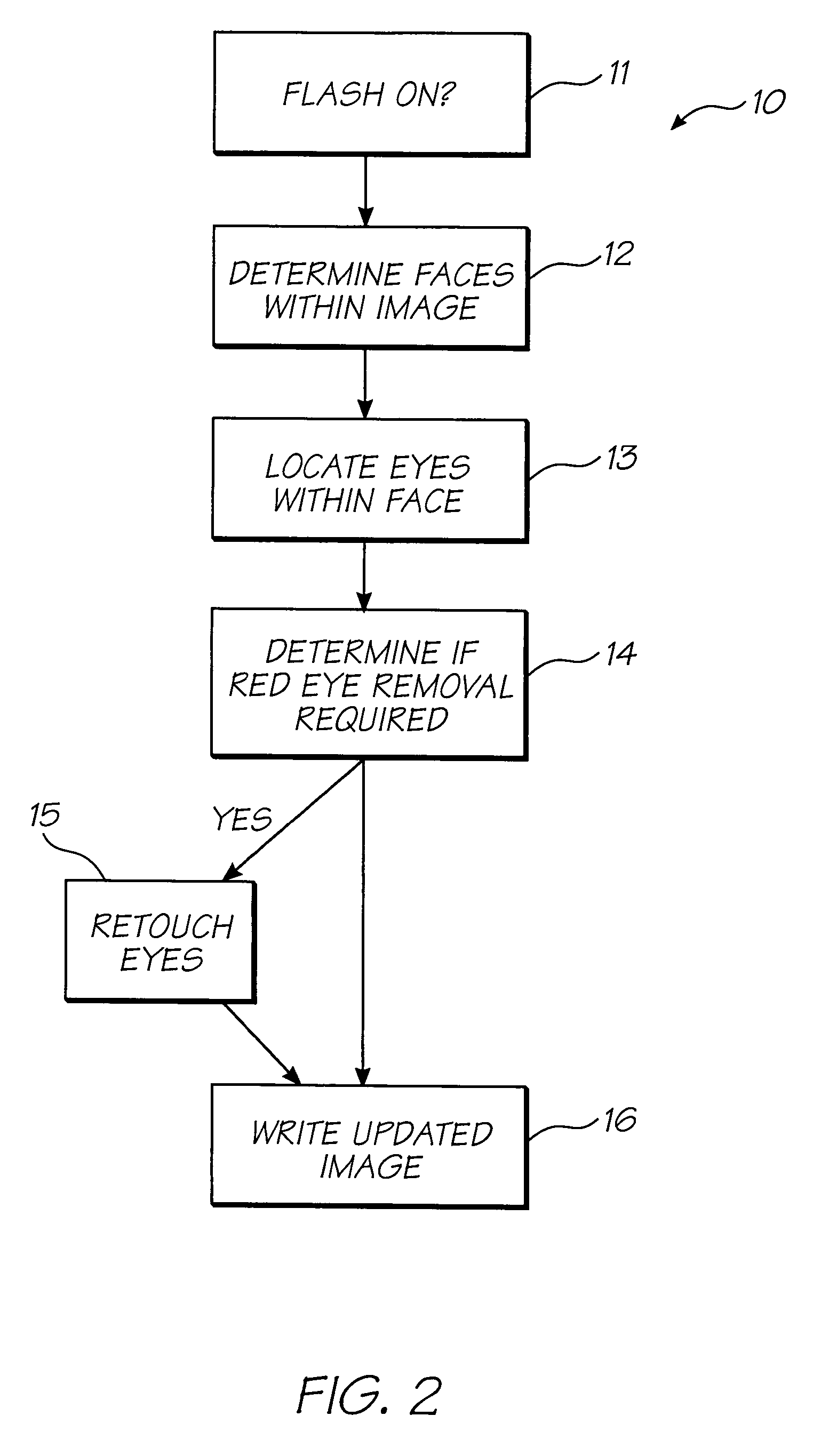
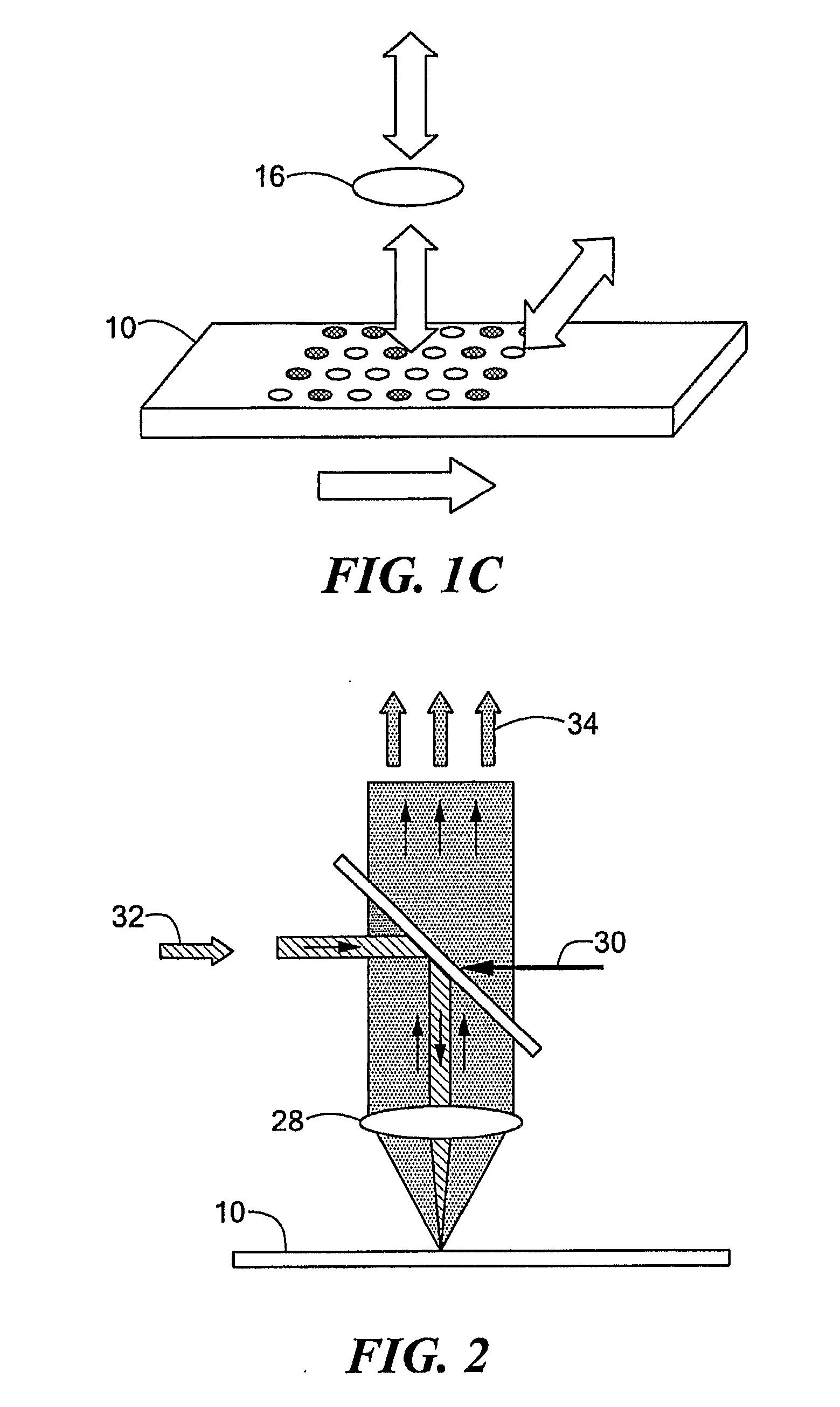
InactiveUS7724282B2Reduce impactRemove distortion effectsTelevision system detailsTypewritersDigital imageDistortion
An image captured by a digital camera with a flash is processed by locating distortions of said captured image due to said flash such as “red-eye” effects and removing them. The process includes the steps of determining if the flash is on (step 11), if so, determining any faces within the captured image (step 12), locating eyes within said faces (step 13), determining if “red-eye” removal is required (step 14), and if so, correcting for such effects (step 15) and storing corrected image (step 16) in a memory device of the digital camera.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
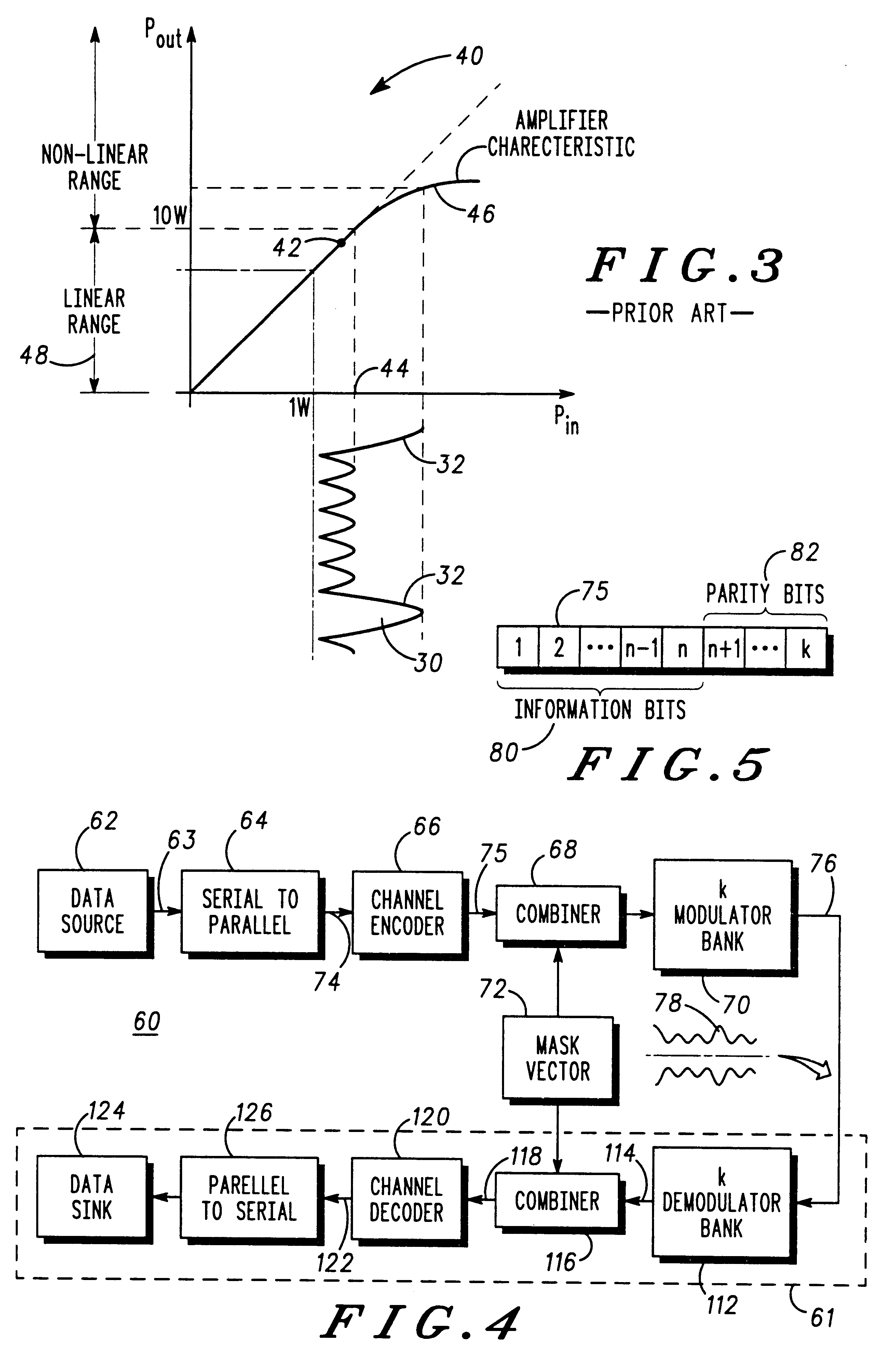
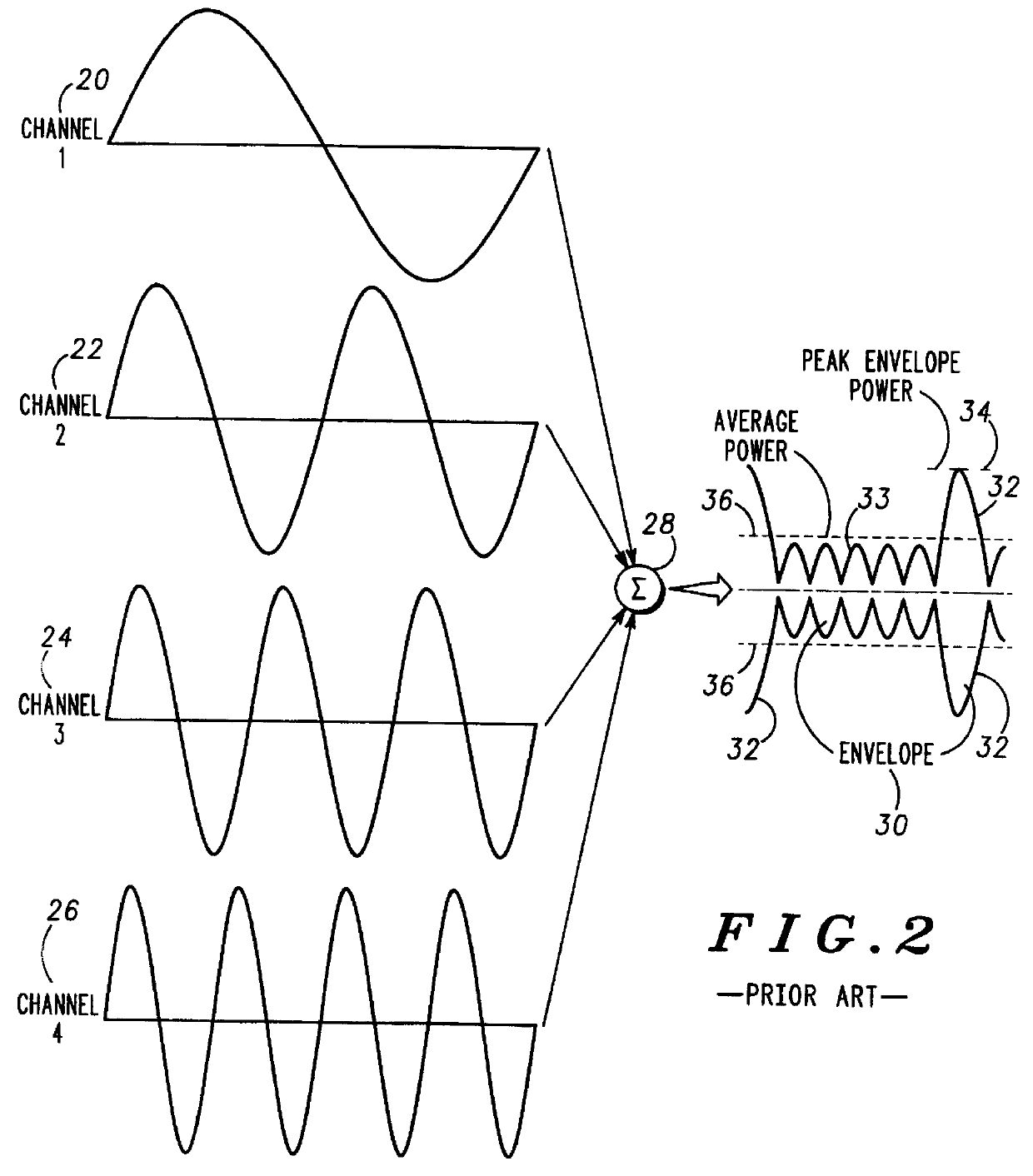
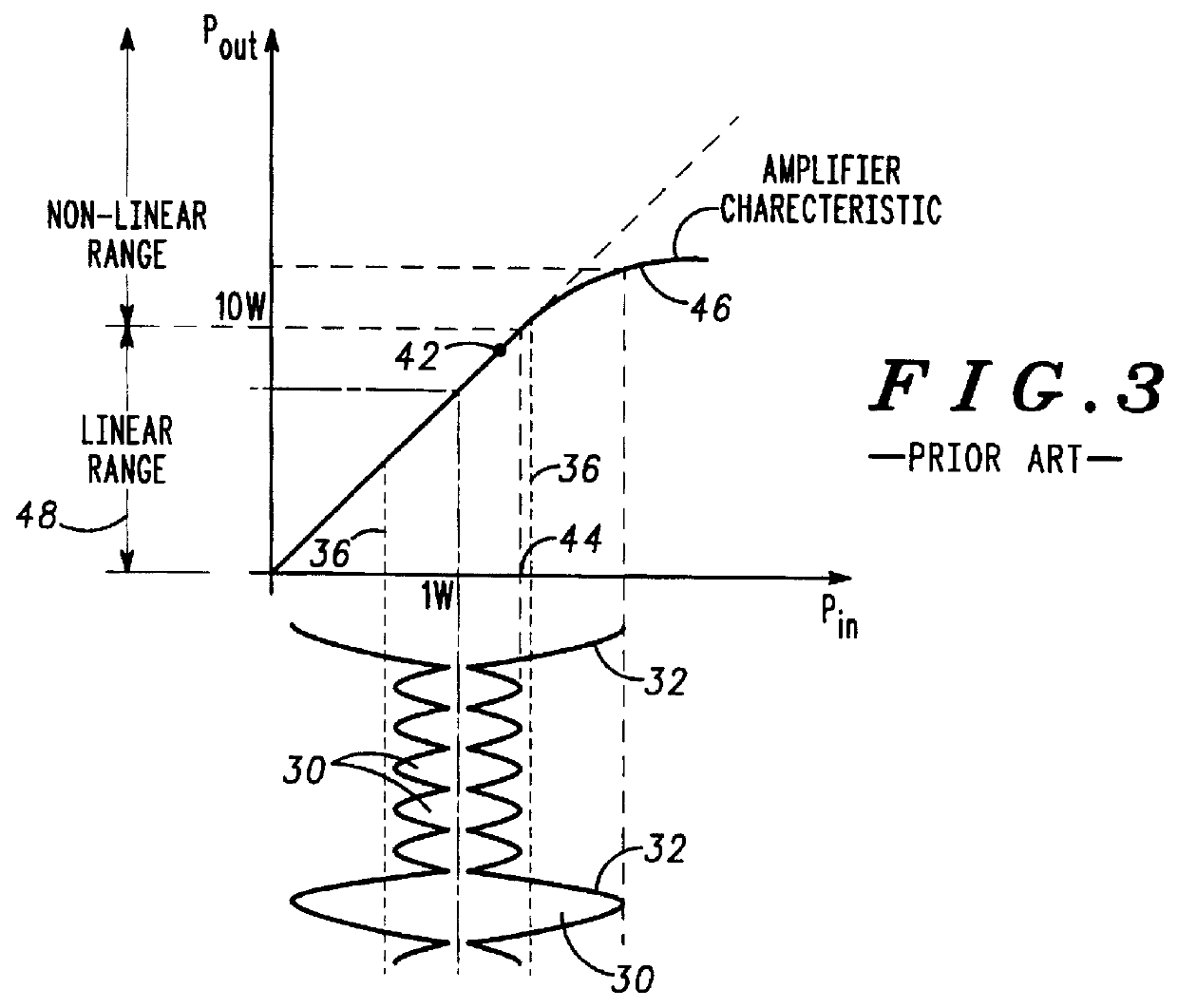
Multicarrier communication system and method for peak power control
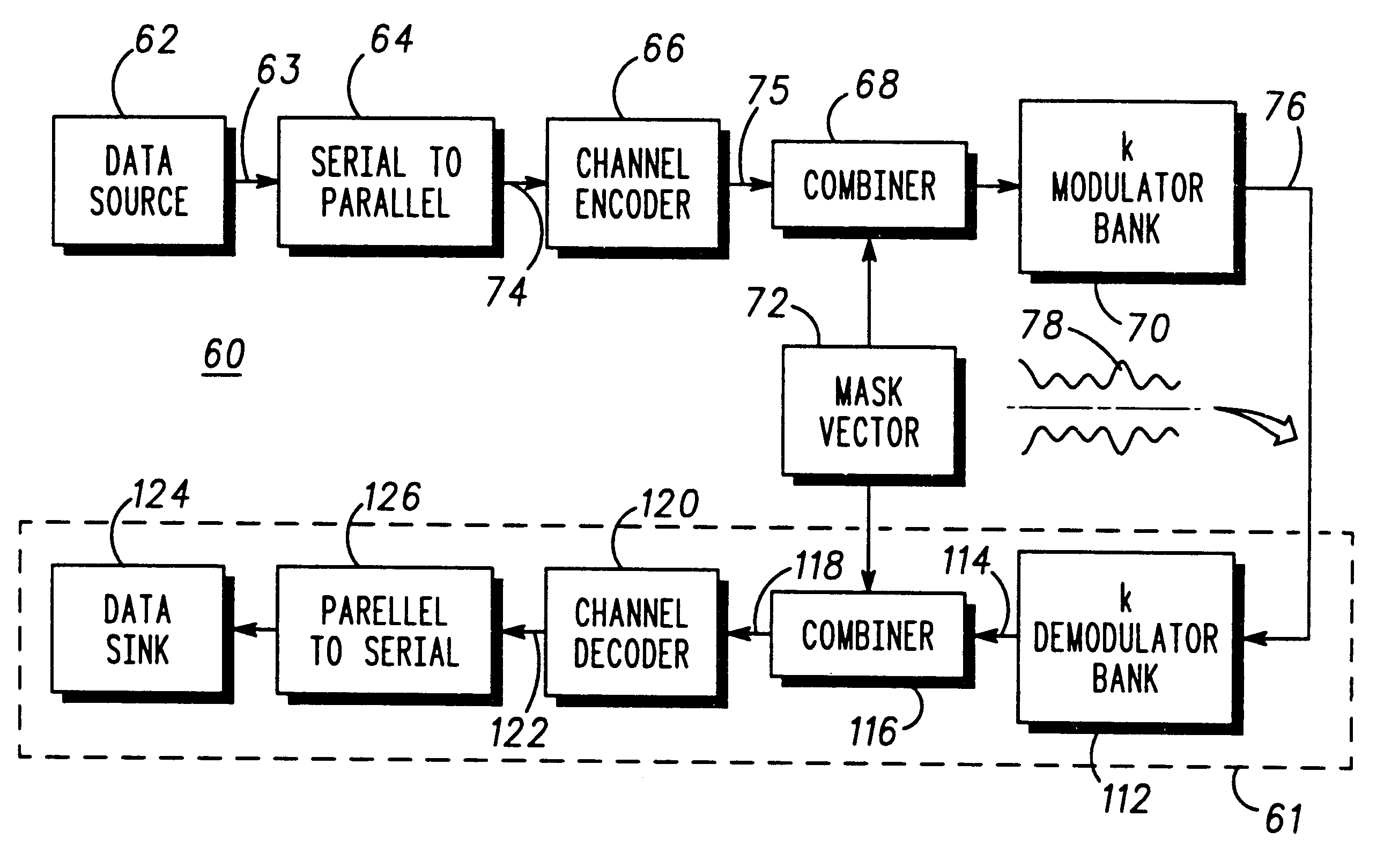
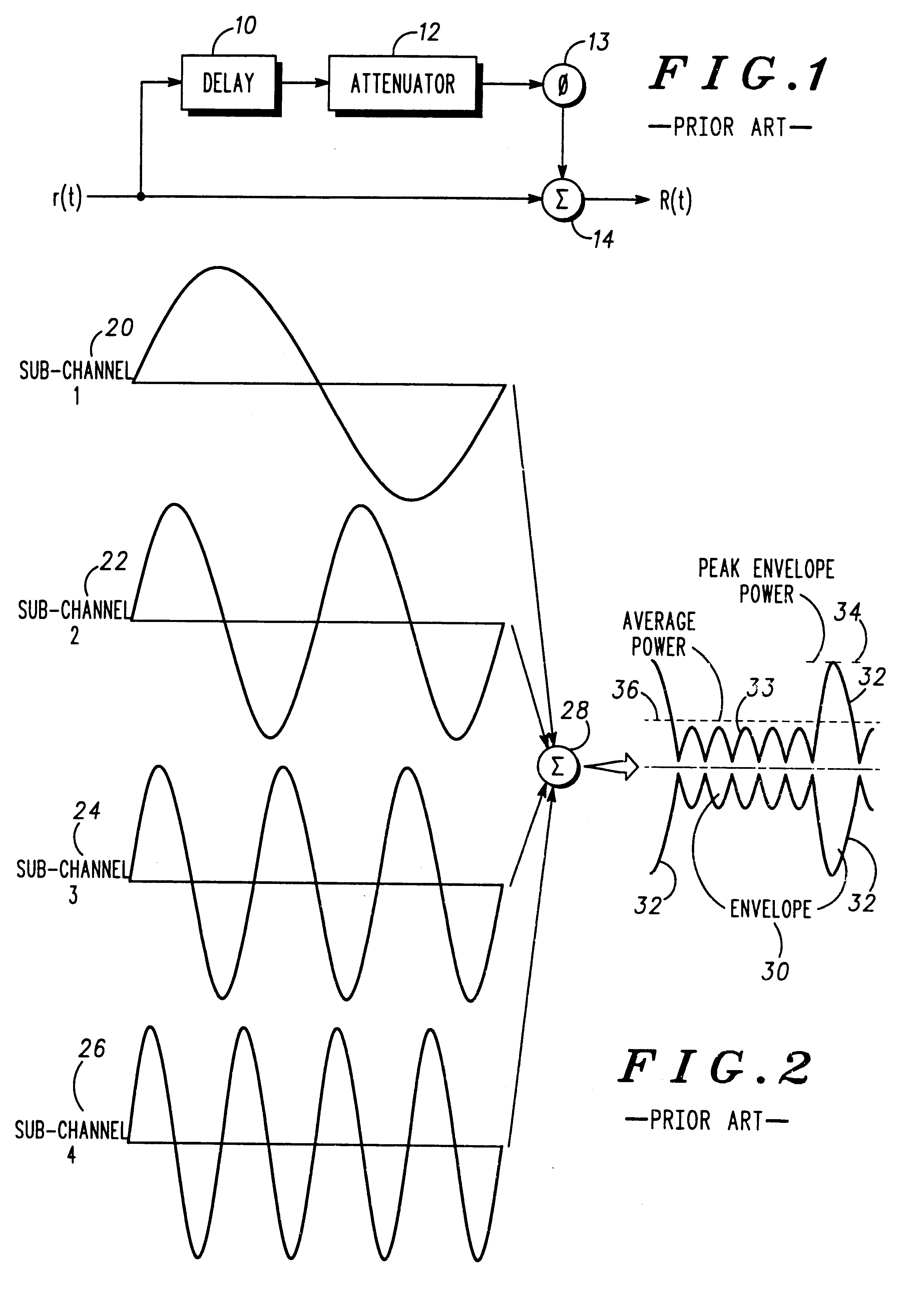
InactiveUS6307892B1Remove distortion effectsImprovement in PMEPRSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemPeak value
A communication device for simultaneously transmitting information on multiple sub-channels encodes information for each of the multiple sub-channels with a coding scheme to produce channel encoded information. A mask vector derived from a redundancy in the coding scheme, encodes the channel encoded information to transform the channel encoded information into codewords having pairwise Euclidean distance properties identical to those of the channel encoded information, Modulation of the sub-channels in accordance with the codewords in a modulator then produces a composite signal envelope having a peak-to-mean error power ratio (PMEPR) reduced relative to a PMEPR for correspondingly modulated channel encoded information.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Filter for multicarrier communication system and method for peak power control therein
InactiveUS6128351ARemove distortion effectsReduce the ratioSecret communicationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemWaveform shaping
PCT No. PCT / EP97 / 02486 Sec. 371 Date Jun. 4, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jun. 4, 1998 PCT Filed May 15, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 45987 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 4, 1997A communication device (60) for simultaneously transmitting independent information (82) on multiple channels comprises a modulator (66) and at least two matched filters (68-70). Each matched filter has a unique predetermined characteristic that is a time-reversed, complex conjugate of a complex waveform shape (72) produced by the modulator (66) in response to a channel encoder previously supplying known codeword vectors (75) to the modulator (66). Therefore, a composite signal envelope (82) produced for transmission by the communication device (60) of FIG. 4 has a reduced peak-to-mean envelope power ratio (PMEPR), since relatively large excursions in complex waveform shapes subsequently generated by the modulator (66) are unmatched by the unique filter characteristics while relatively small excursion are matched and therefore enhanced.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Complex neural network channel prediction method
ActiveCN105142177AEfficient extractionRemove distortion effectsBiological neural network modelsWireless communicationAlgorithmNetwork communication
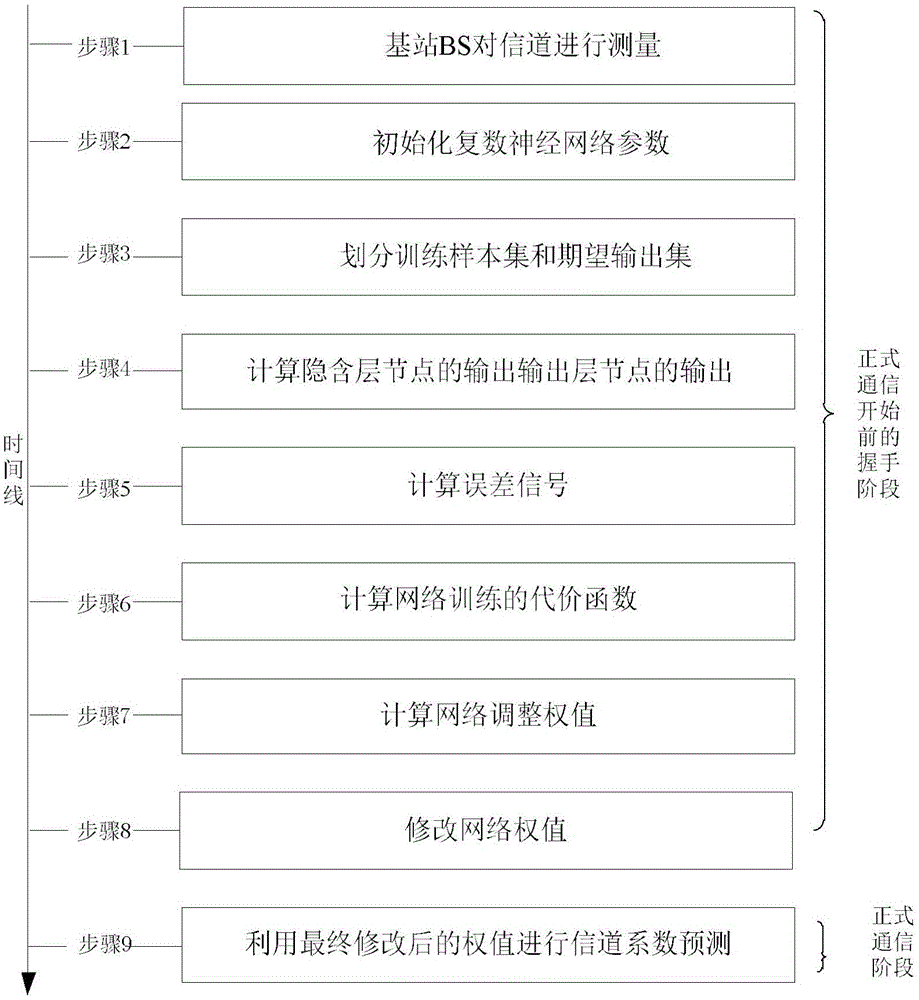
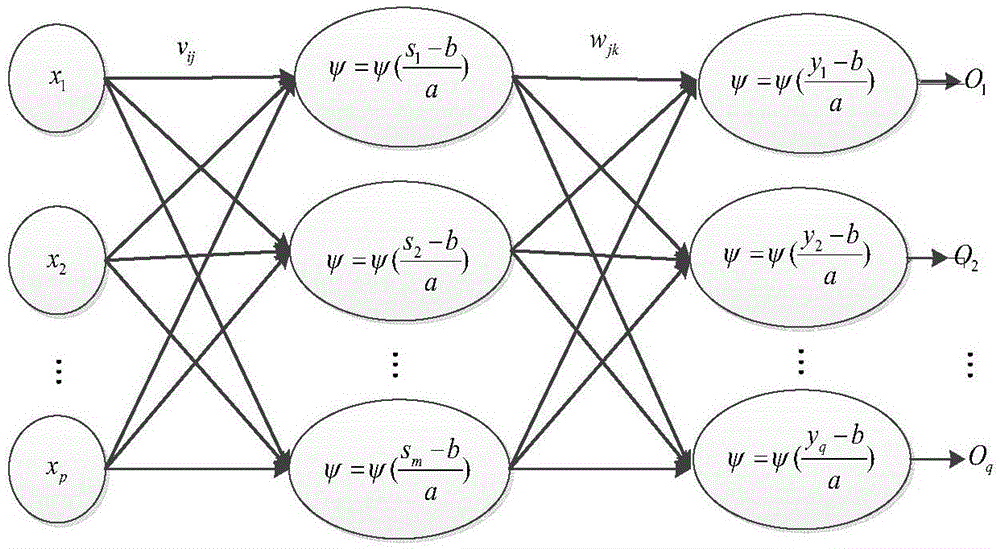
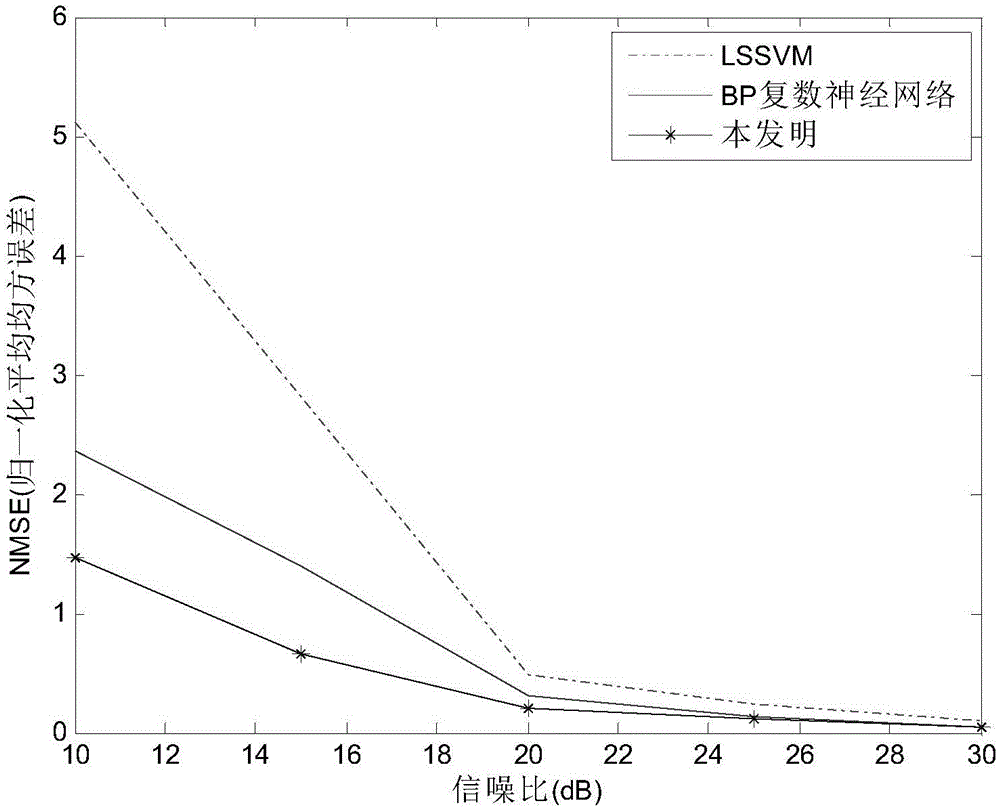
The invention discloses a complex neural network channel prediction method, and mainly aims to solve the problem of channel fading caused by channel time variation in an MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) system. According to the technical scheme, the complex neural network communication prediction method comprises the following steps: 1, measuring a channel by a base station to obtain a channel coefficient training sequence containing an estimation error; 2, acquiring a corresponding training sample and desired output according to the obtained channel coefficient sequence; 3, inputting a training sample to perform complex wavelet neural network training in order to obtain a final network weight; and 4, performing channel coefficient prediction through a trained complex wavelet neural network by the base station. The method is simple, convenient and feasible, has a good effect, and is suitable for lowering the influence of the channel time variation on an MIMO system channel.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
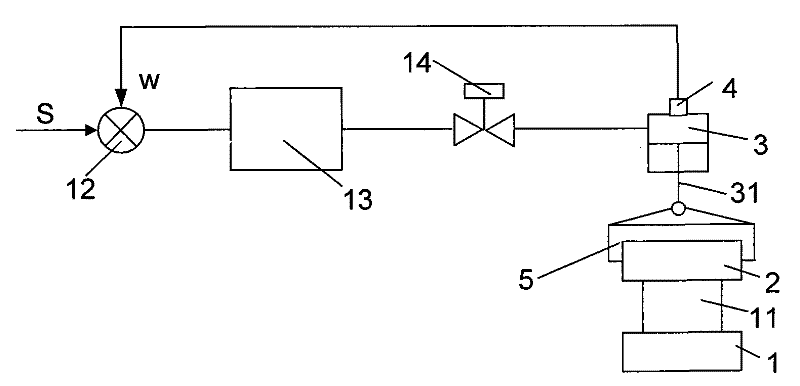
Roll gap control method for soft reduction technology for continuous casting
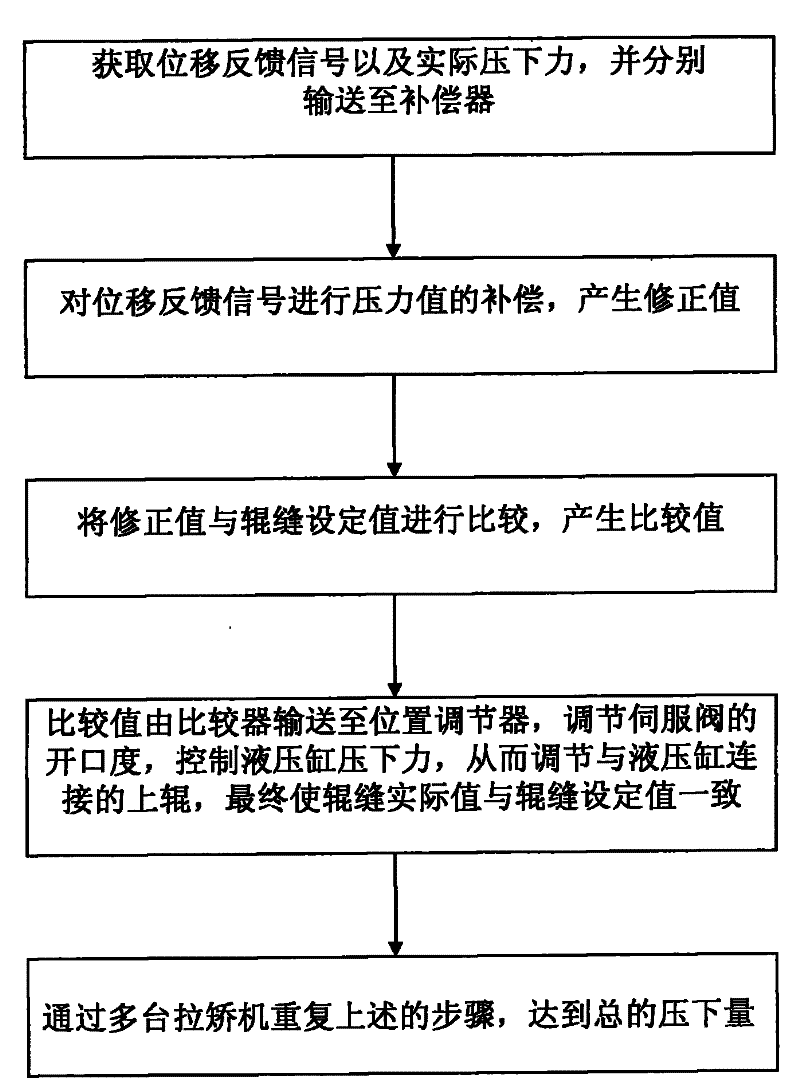
The invention discloses a roll gap control method for a soft reduction technology for continuous casting. The method comprises the following steps: respectively obtaining a displacement feedback signal and an actual reduction force of an upper roll of a withdrawal and straightening unit by a displacement sensor and a pressure sensor, and conveying the displacement feedback signal and the actual reduction force to a compensator; performing pressure value compensation on the displacement feedback signal so as to generate a corrected value, and transmitting the corrected value to a comparator; comparing the corrected value with a set value for the roll gap so as to generate a comparison value; transmitting the comparison value to a position regulator by the comparator, adjusting opening of aservo valve and controlling a reduction force of a hydraulic cylinder so as to adjust the upper roll connected with the hydraulic cylinder so that the actual value and the set value for the roll gap are consistent with each other; and performing stepwise reduction by utilizing the upper rolls of a plurality of withdrawal and straightening units so as to reach total rolling reduction. In the method, by adopting the measure of pressure value compensation for the displacement feedback signal, the influence of distortion of the displacement feedback signal on the displacement sensor resulting from greater reduction force applied to a casting blank can be eliminated, thus creating a good condition for achieving ideal metallurgical process effect by utilizing the soft reduction technology.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Screw threaded fastener and fastening system
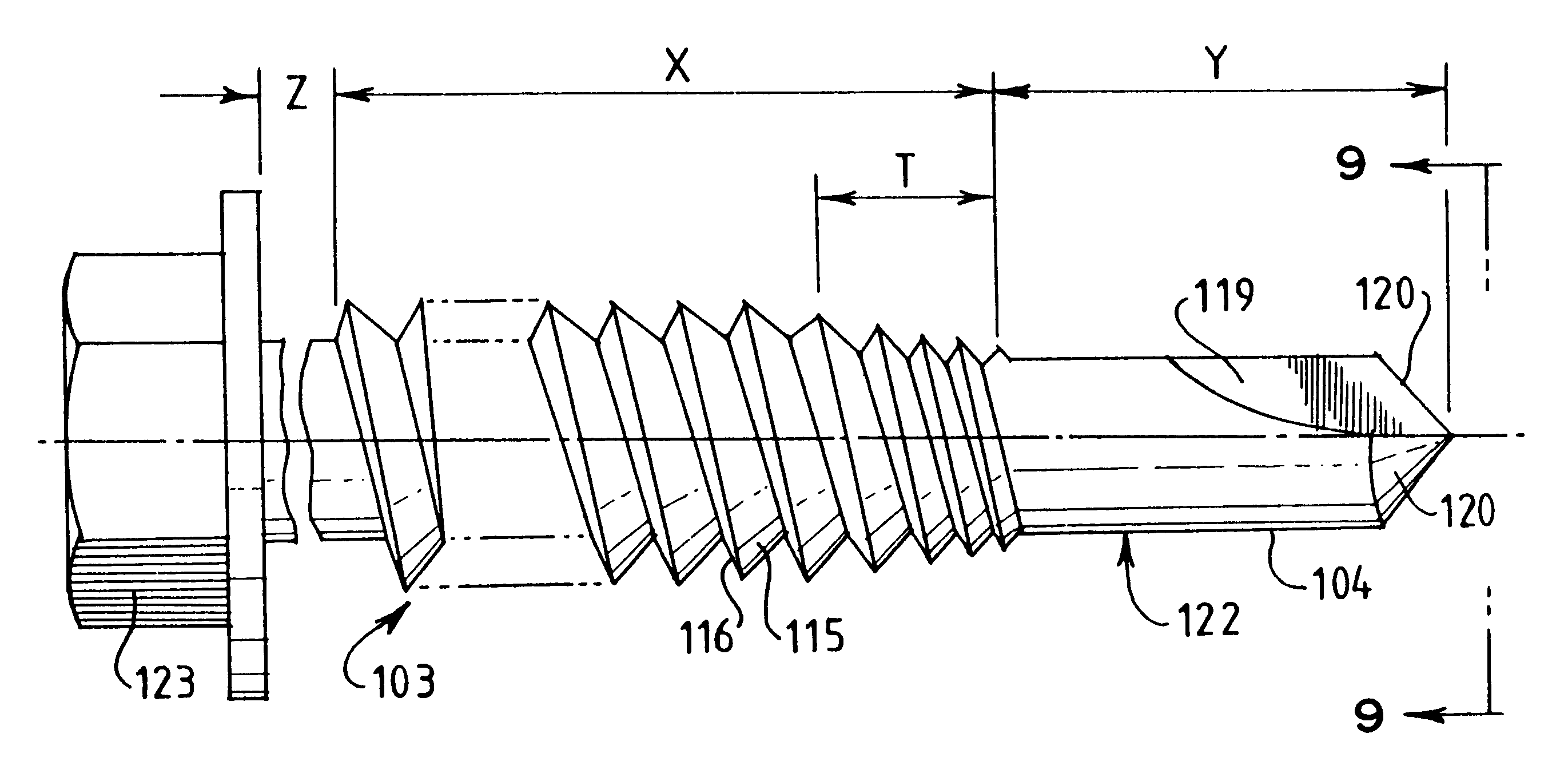
InactiveUS6185896B1Fast fasteningHighly resistant to failureRoof covering using slabs/sheetsRoof covering using tiles/slatesThin metalTrailing edge
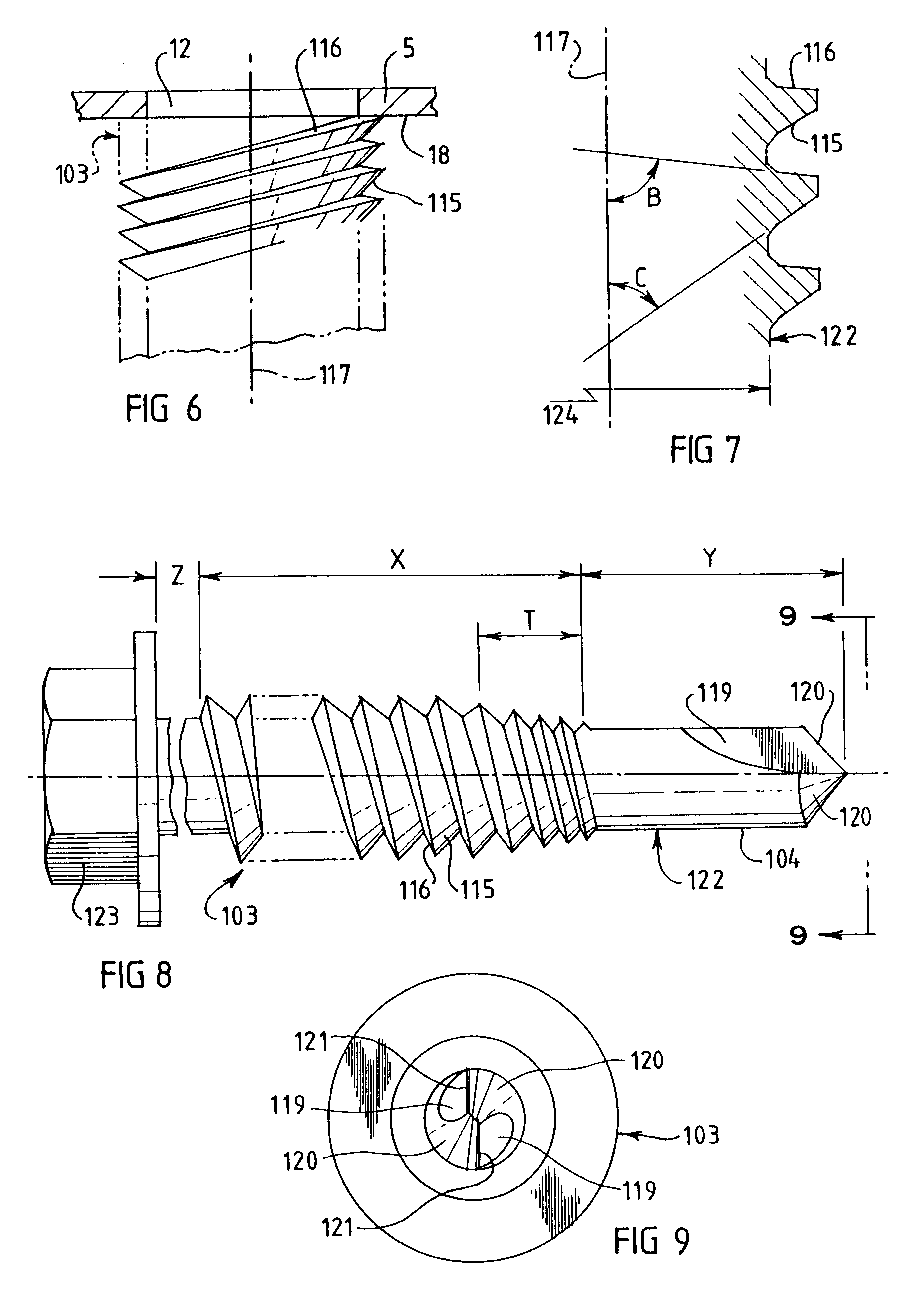
A screw threaded fastener (103) has an elongate shank (122) with a drilling tip (104) at one end and a head (123) at the other end. A screw thread extends along at least a part of the length of the shank (122). The trailing flank (116) of the thread subtends an angle (B) relative to the axis (117) of the fastener which approaches 90° and is greater than the angle (C) subtended by the leading flank (115). The screw is for use in fixing sheets of material a1 to thin metal battens (5) and the angle between the trailing flank (116) and the adjacent thin metal section (18) of the batten (9), being reduced in comparison to a conventional thread form, lessens the distorting effect of the thread on the batten (9) under relatively high pull-out loads.
Owner:W A DEUTER
Manifold for a horn loudspeaker and method
InactiveUS20030132056A1Direct controlRemove distortion effectsSound producing devicesFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsEngineeringLine array
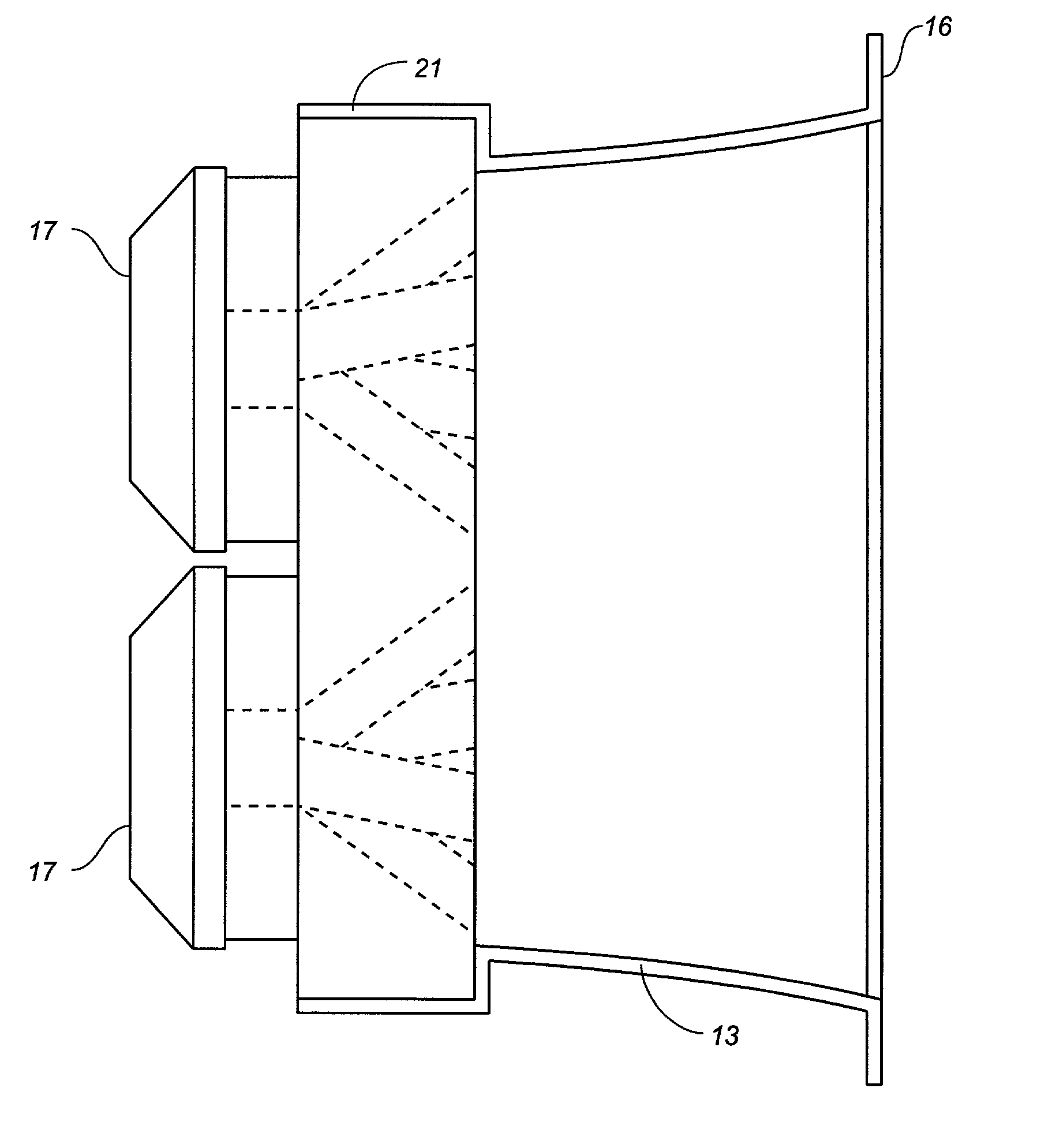
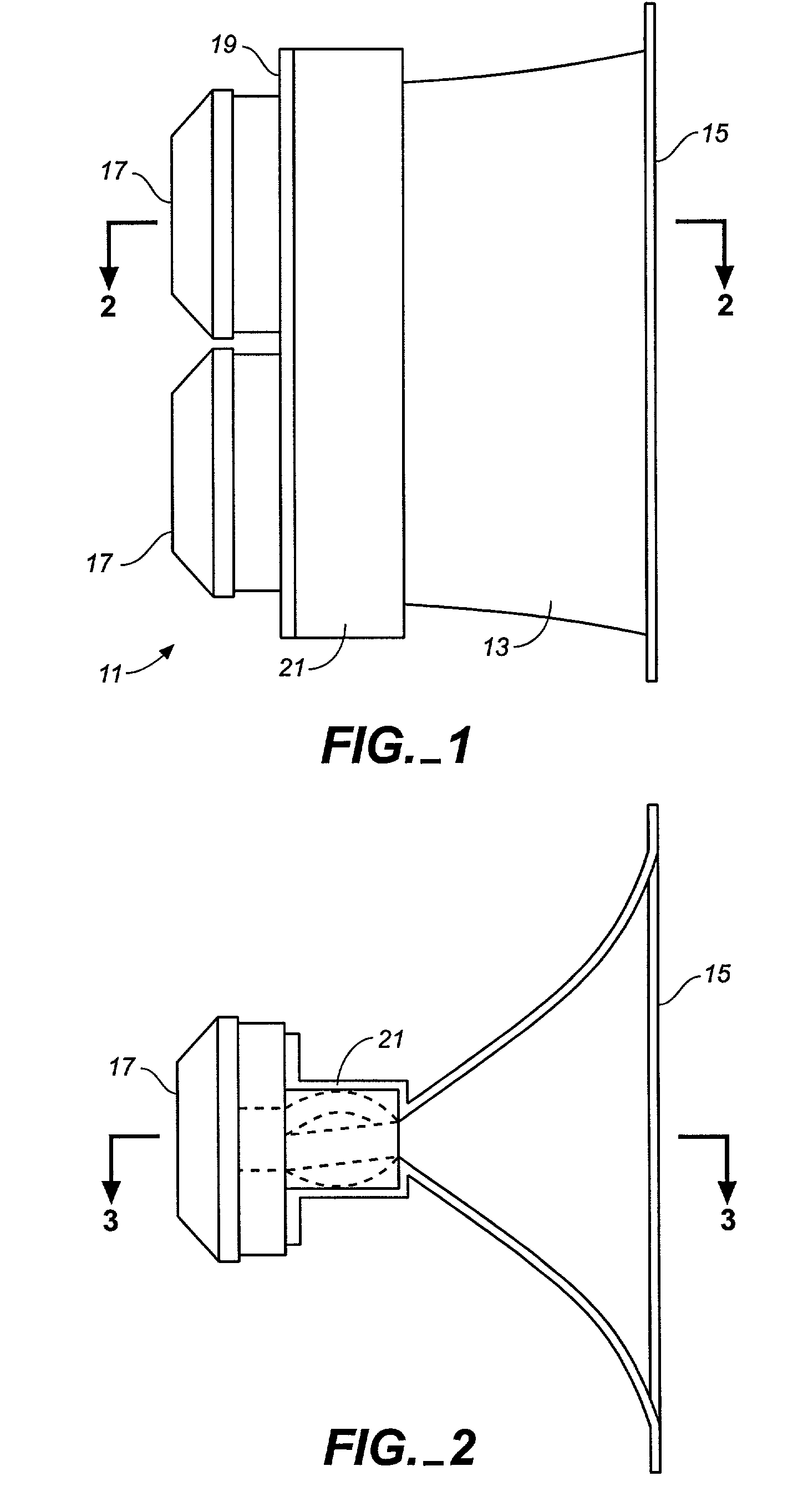
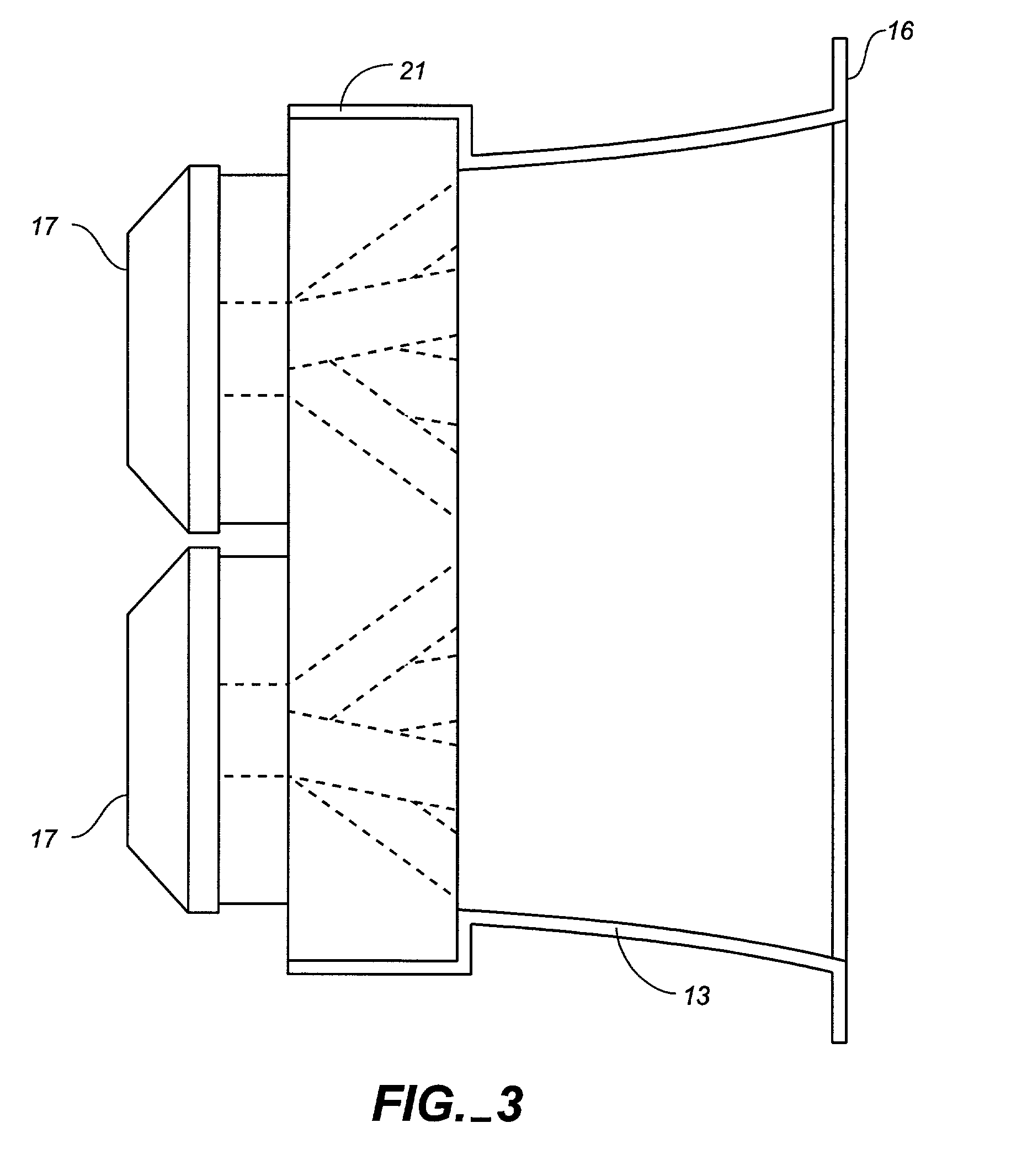
A manifold for a horn loudspeaker has an input end having at least one input port for receiving acoustic power from at least one acoustic driver, and an output end for delivering acoustic power to the throat end of the horn. The output end of the manifold has at least two and suitably multiple output ports. An acoustic power waveguide is provided for each output port and connects each of the output ports to the input port of the manifold. Acoustic power received by the input port is divided between the acoustic waveguides such that it is delivered to the aligned output ports to simulate a line array of acoustic power sources.
Owner:MEYER SOUND LABORATORIES
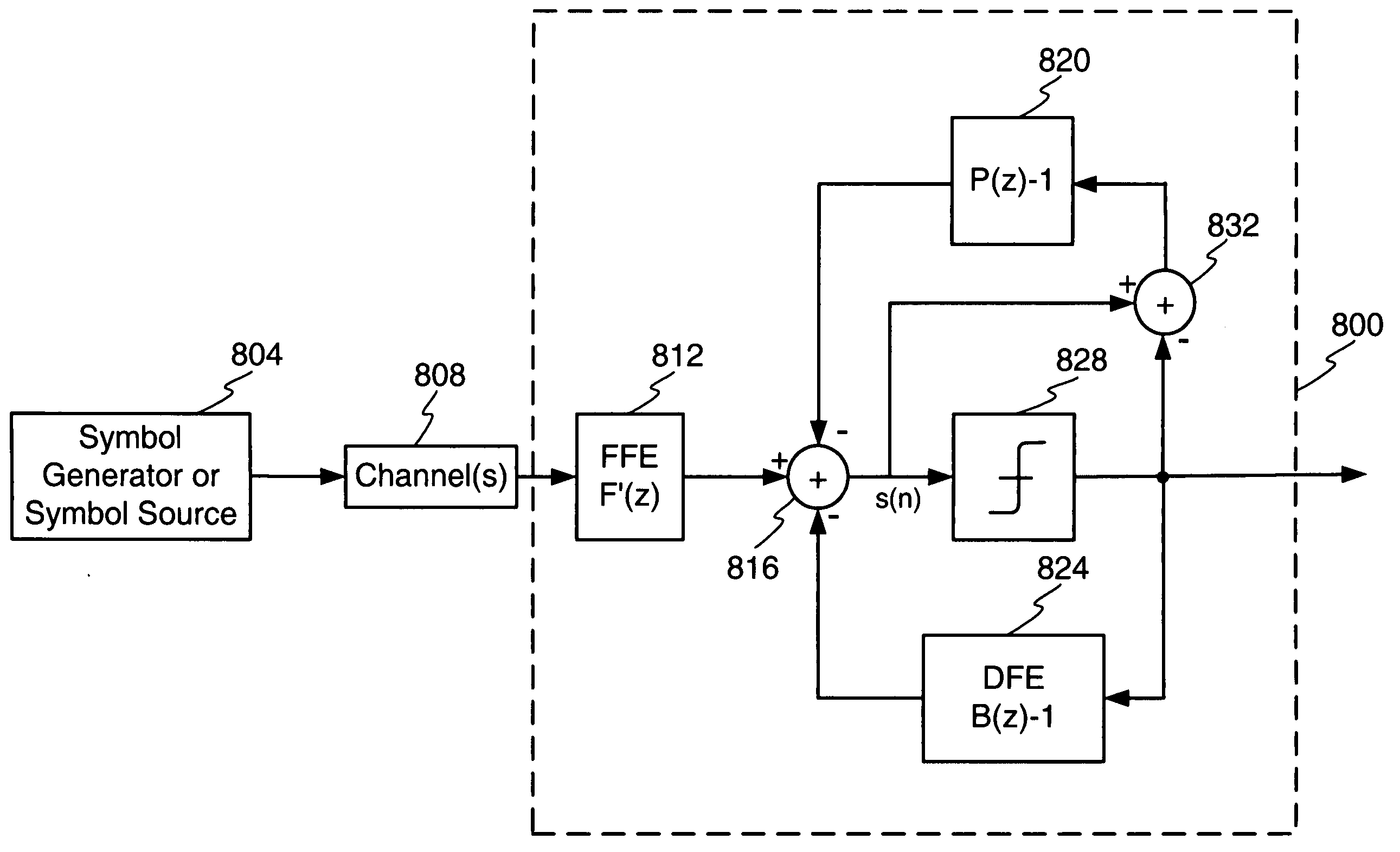
Method and apparatus for channel equalization
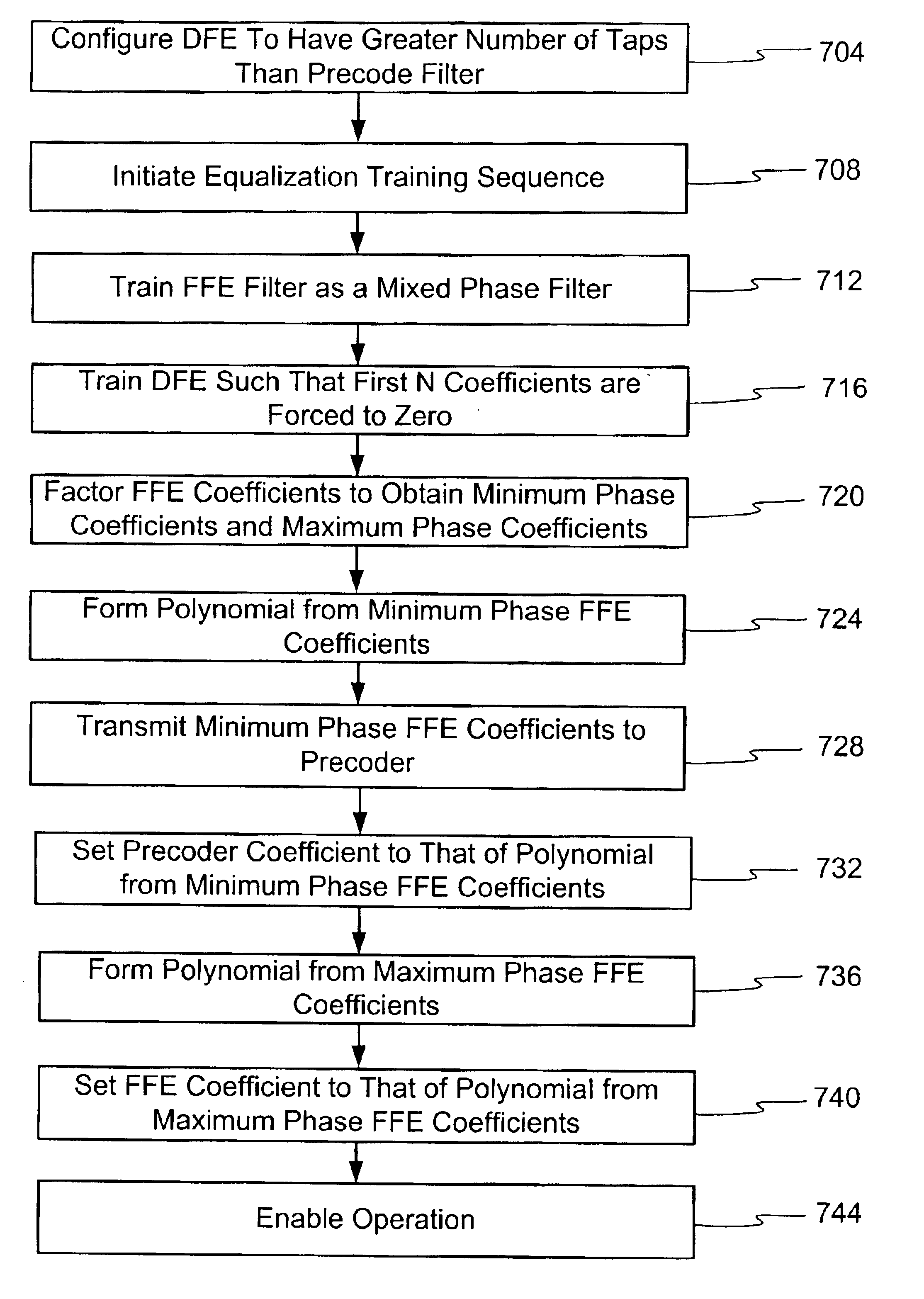
InactiveUS6961373B2Remove distortion effectsMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationEngineeringMaximum phase
A method and apparatus is disclosed to overcome the effects of intersymbol interference during data transmission. Overcoming the effects of intersymbol interference makes possible higher data transmission rates for a given error rate. In one embodiment a receiver-transmitter pair is configured with a precode filter at the transmit side and a feed forward filter and a feedback filter at the receive side. Filter coefficients are calculated to reduce the undesirable effects of the channel, such as intersymbol interference. In one embodiment a training process occurs with the feedforward filter and a feedback filter, such that the first N coefficients of the feedback filter are set to zero. Thereafter, the coefficients of the feedforward filter are subject to spectral factorization and separated into minimum phase roots and maximum phase roots. The minimum phase roots comprise the precode filter coefficients and the maximum phase roots are established as feedforward filter coefficients.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
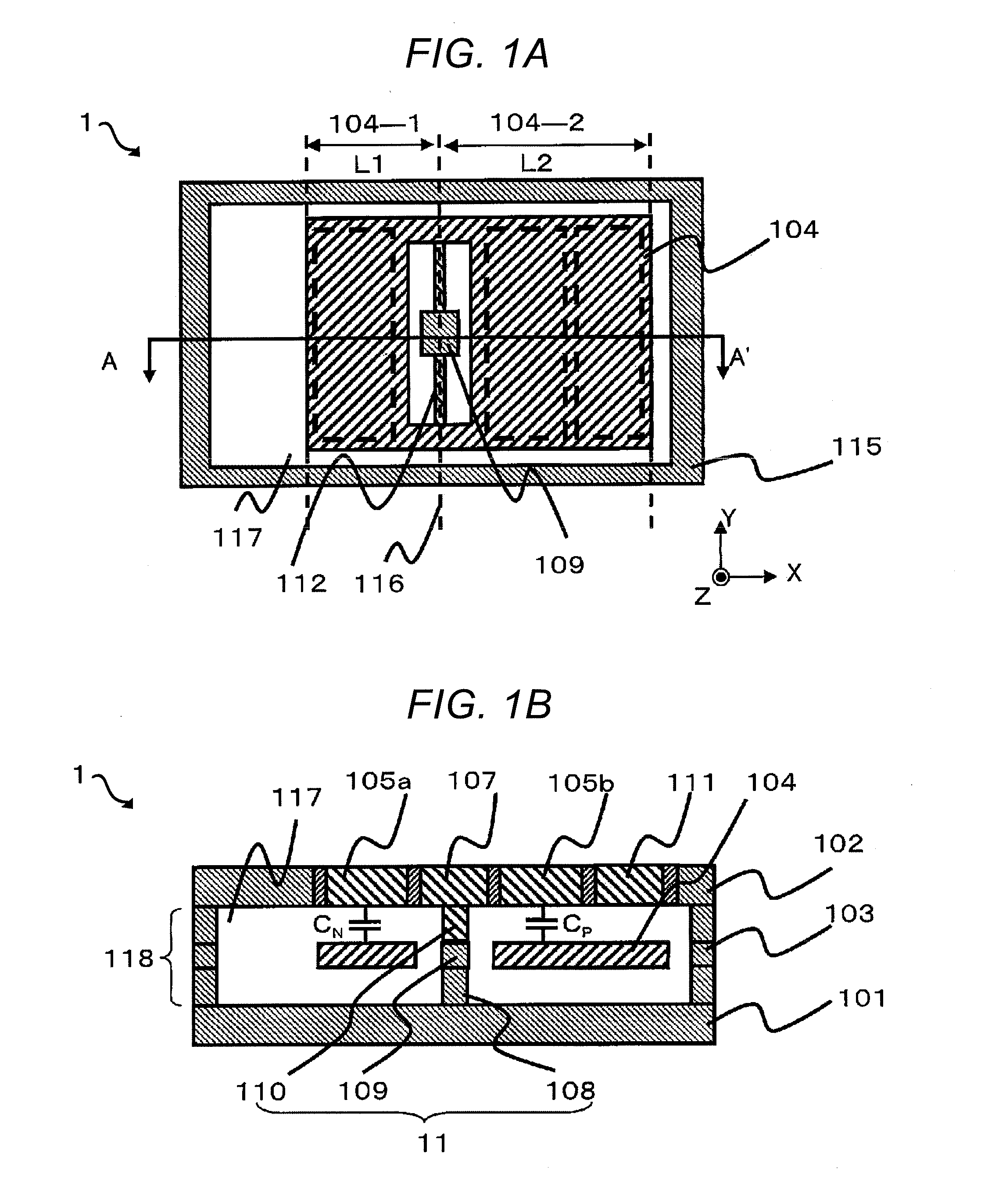
Inertial Sensor
A movable part rotates about a rotation axis, which passes through a support, when an inertial force in a detecting direction is applied to an inertial sensor. The movable part includes a first region and a second region displaced in a direction opposite to a direction of the first region when the inertial force is applied. A second substrate includes first and second detection electrodes opposed to the first and second regions, respectively. The first detection electrode and the second detection electrode are provided symmetrically with respect to the rotation axis. A cavity is provided symmetrically with respect to the rotation axis. In a direction perpendicular to the detecting direction and a direction in which the rotation axis extends, a length from the rotation axis to an end of the first region and a length from the rotation axis to an end of the second region are different.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Fiber Optic Interrogated Microslide, Microslide Kits and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20090161100A1Eliminate the problemEliminates adverse optical effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscope slideFiber
The present invention provides a substrate that overcomes the performance limitations of conventional microscope slides, microarrays, or microtiter plates when optically interrogated through the thickness of the substrate. With conventional microscope slides, image quality and resolution are degraded as a result of distortions introduced by imaging through the thickness of the glass. Fiber Optic Interrogated Microslides (FOI) consist of many fiber optics that have been fused together. When sliced and polished to form microscope slides, the fibers effectively transfer optical images from one surface of the microslide to the other. The finished microslide is the optical equivalent of a zero thickness window. The image of an object on the top surface is transferred to the bottom surface allowing it to be viewed without focusing through the thickness of the slide. In addition to providing improved image quality, FOI microslides allow objects to be directly imaged without complex and expensive focusing optics.
Owner:INCOM INC
Method and apparatus for channel equalization
InactiveUS20050025229A1Reduce effectRemove distortion effectsMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationData transmissionIntersymbol interference
A method and apparatus is disclosed to overcome the effects of intersymbol interference during data transmission. Overcoming the effects of intersymbol interference makes possible higher data transmission rates for a given error rate. In one embodiment a receiver processing system a first, second and third filter, such that the second and third filter comprise feedback filters. Filter coefficients are calculated to reduce the undesirable effects of the channel, such as intersymbol interference. A training process occurs to establish the first filter as a mixed phase filter and the third filter as minimum phase filter. The second filter is configured based on the transfer function of the channel and one or more coefficients may be set to a predetermined value.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
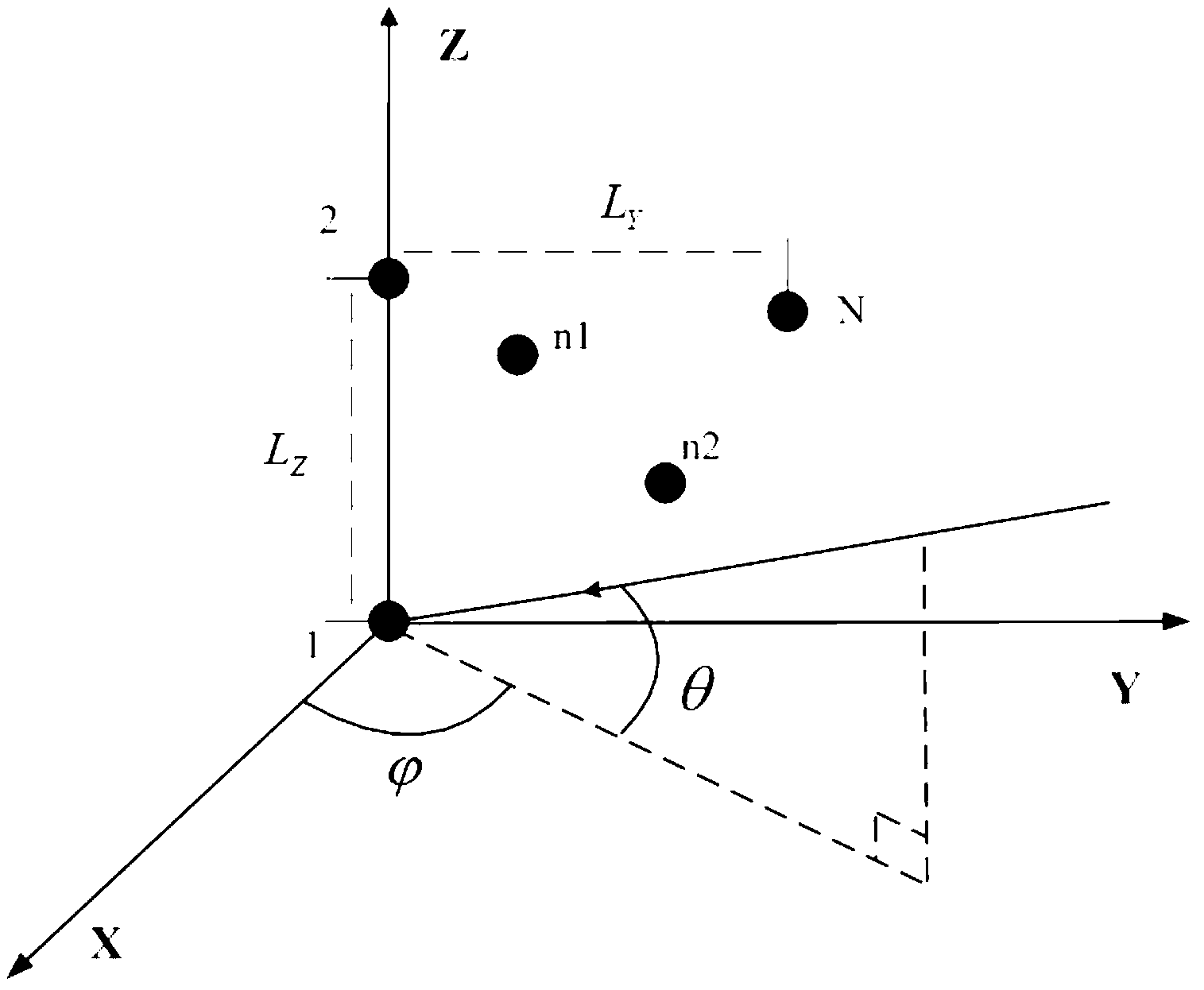
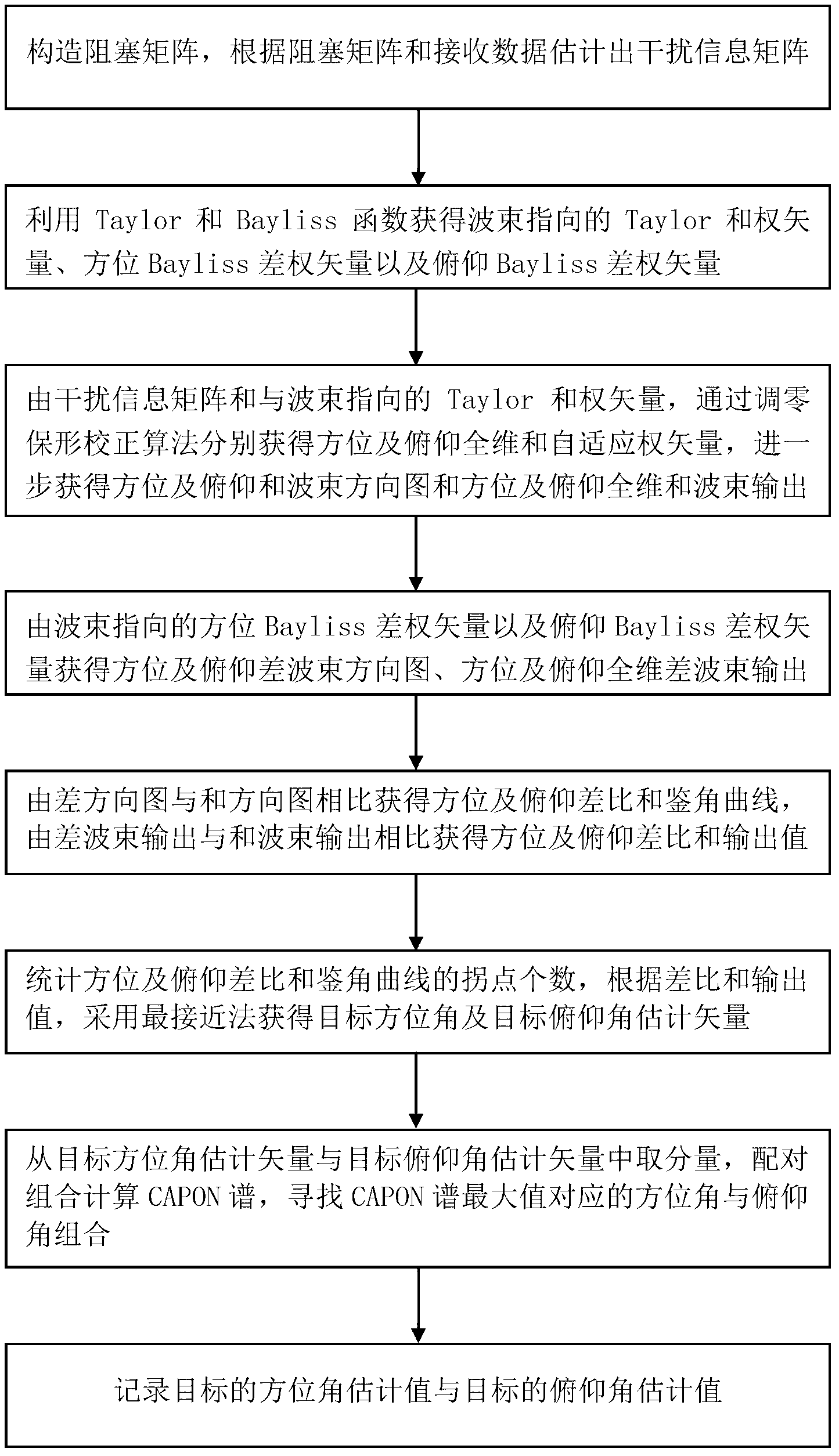
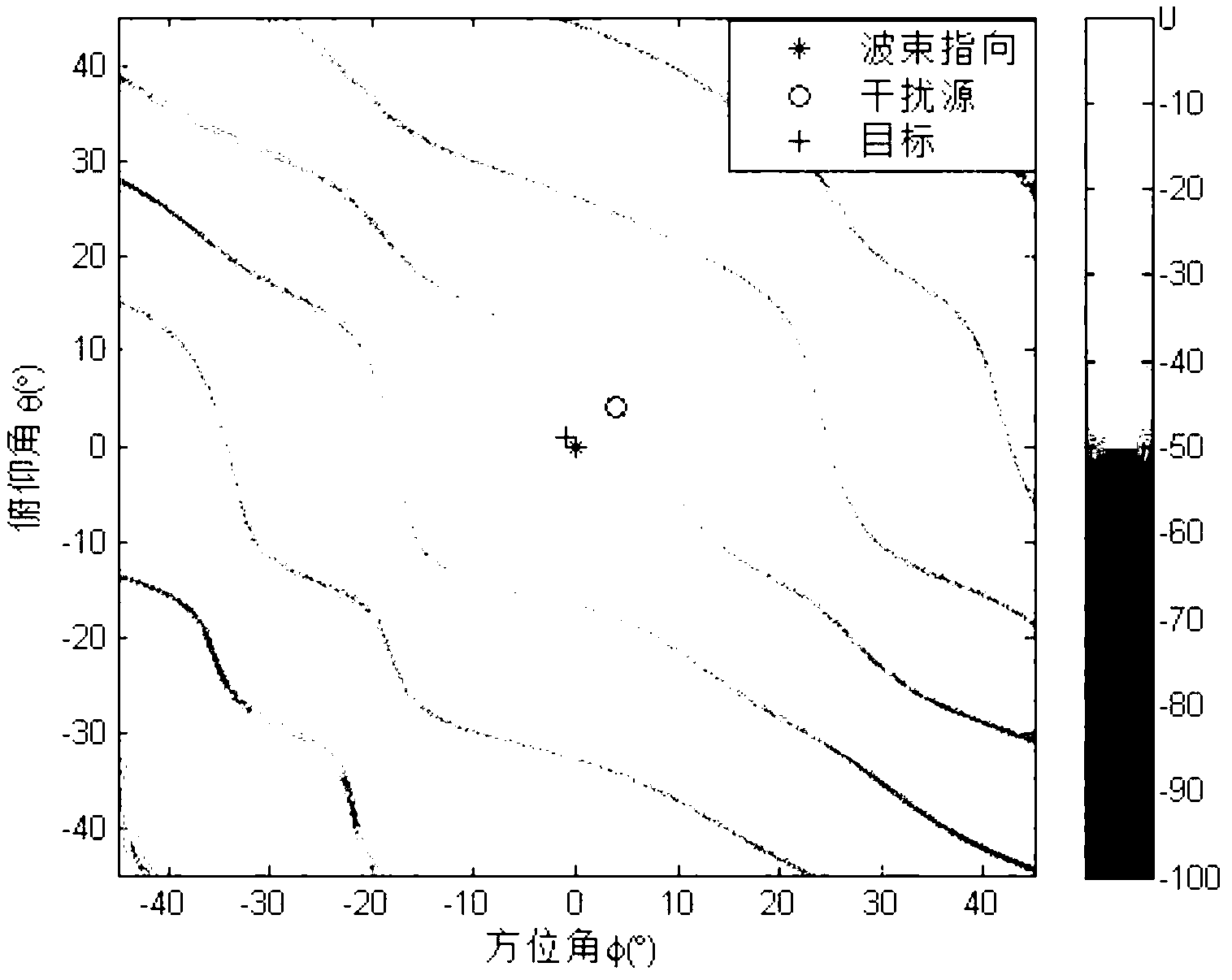
Full-dimension and difference angle measurement method for zero setting conformal calibration of a planar phased array
ActiveCN103235292AWithout sacrificing interference performanceRemove distortion effectsWave based measurement systemsCorrection algorithmSelf adaptive
The invention relates to a full-dimension and difference angle measurement method for zero setting conformal calibration of a planar phased array. The method comprises the following steps: evaluating to obtain an interference information matrix according to a block matrix and received data; obtaining a beam pointing Taylor sum weight vector and a direction / pitch Bayliss difference weight vector through Taylor and Bayliss functions; obtaining a direction / pitch full-dimension sum self-adaptive weight vector through a zero setting conformal calibration algorithm; obtaining a direction / pitch sum and difference beam directional diagram, and direction / pitch full-dimension sum beam output and difference output through the self-adaptive weight vector and the difference weight vector; obtaining a direction / pitch difference ratio sum resolvable angle curve and a direction / pitch difference ratio sum output value; counting the number of inflection points of the direction / pitch difference ratio sum resolvable angle curve, and adopting a nearest method to obtain a target direction / pitch angle estimation vector; and calculating to obtain a CAPON spectrum of a direction / pitch angle estimation value, searching a direction / pitch angle combination corresponding to a maximum value of the CAPON spectrum, and obtaining a target direction / pitch angle estimation value.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
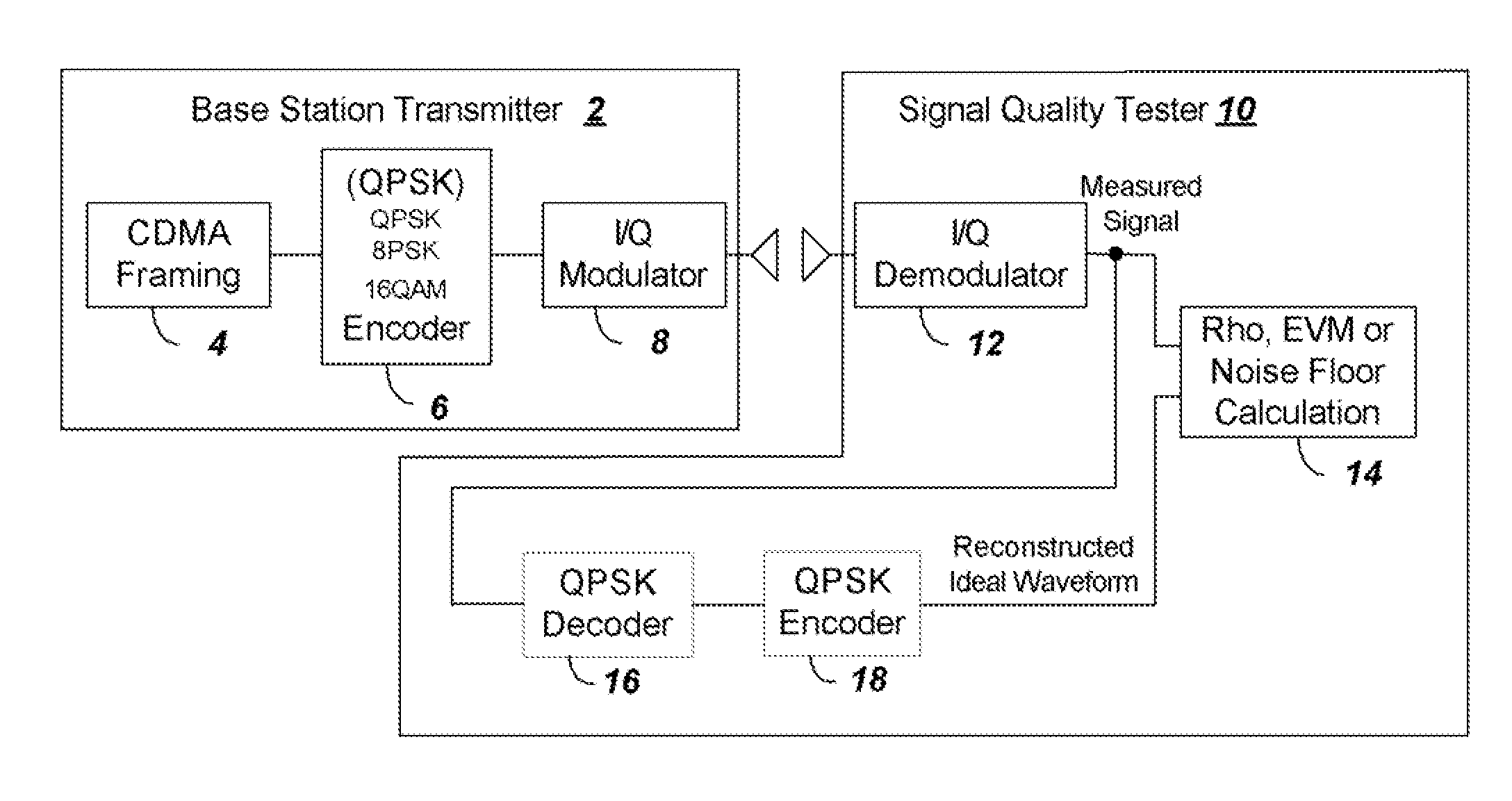
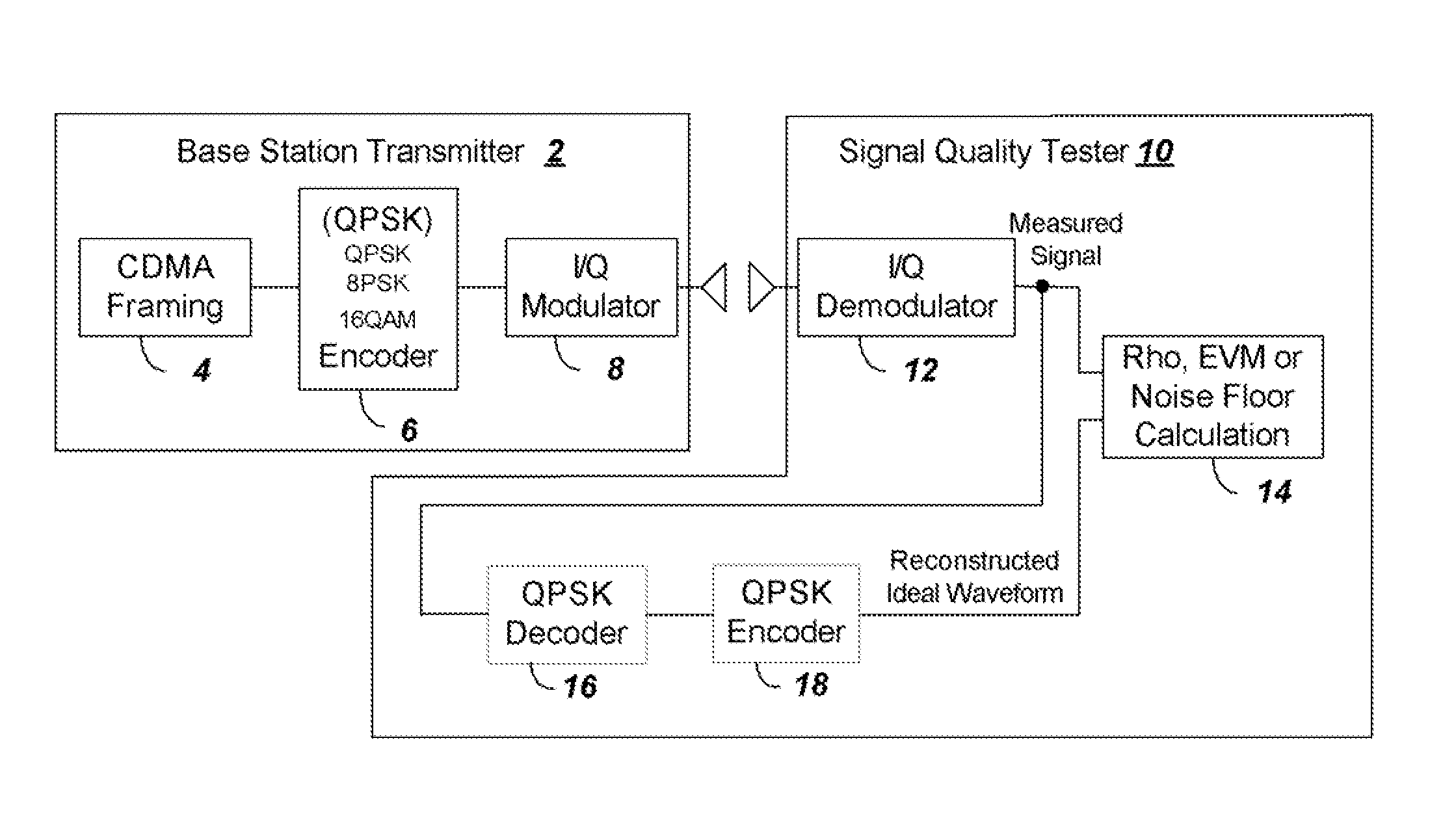
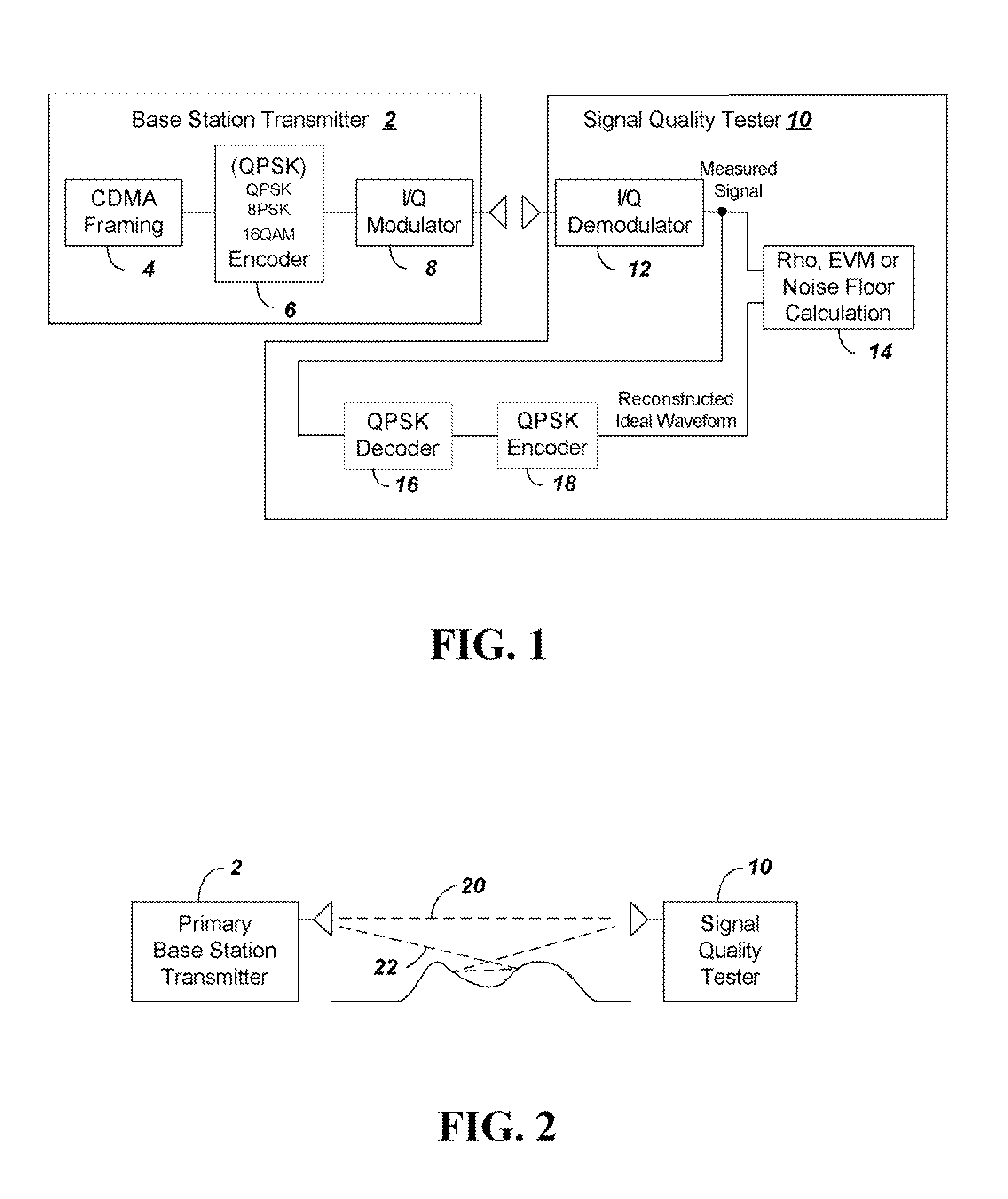
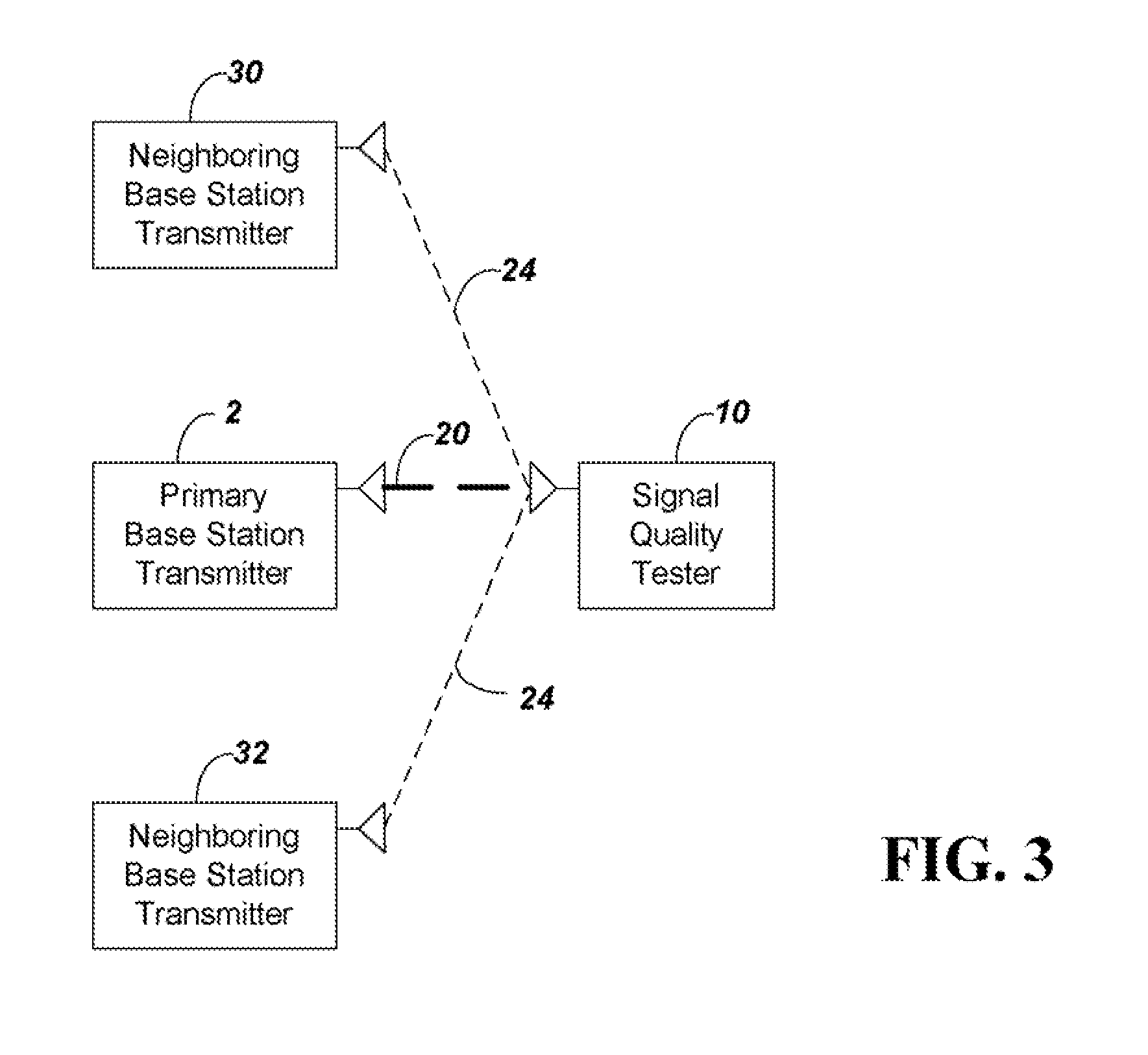
Method and apparatus to estimate wireless base station signal quality over the air
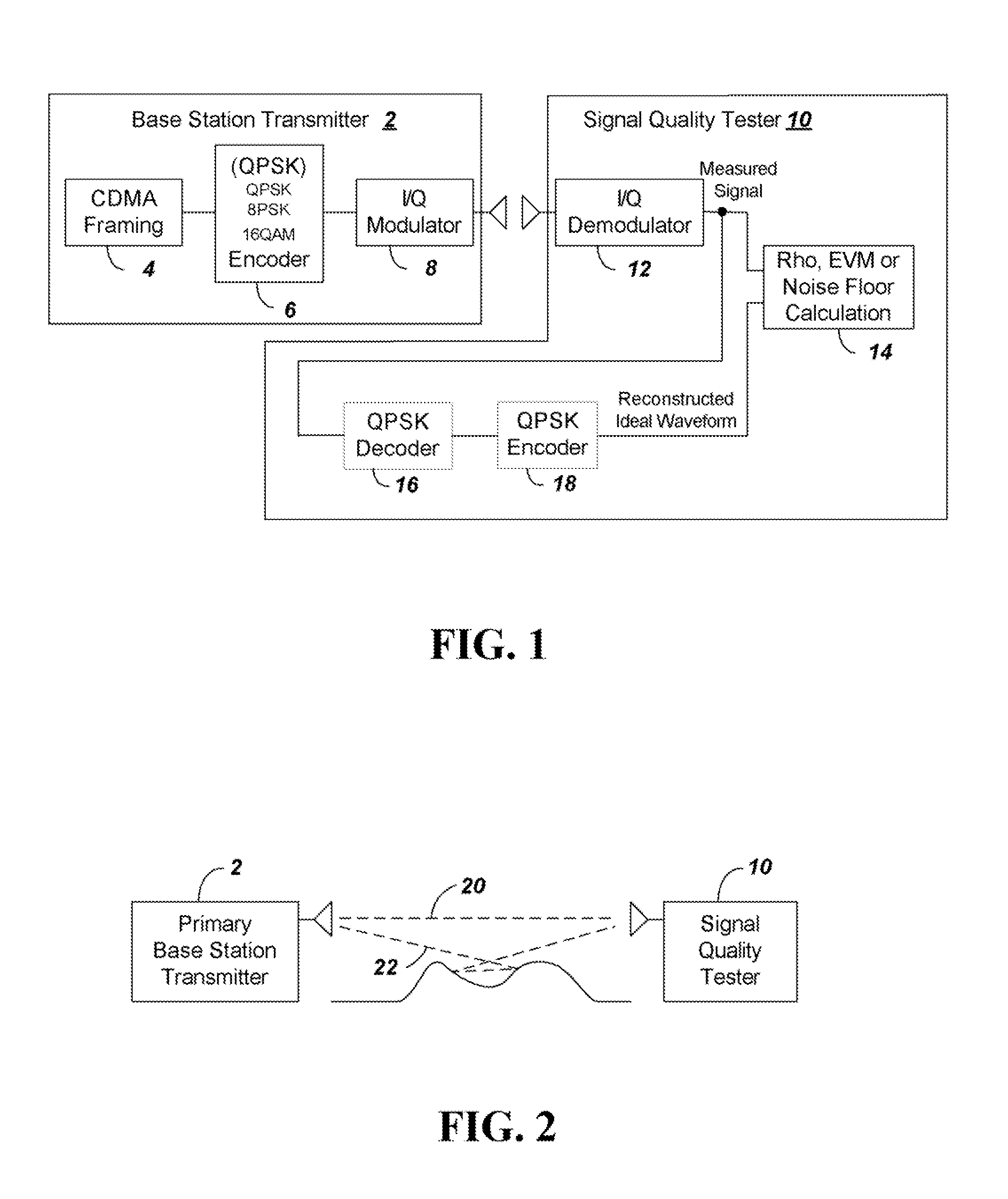
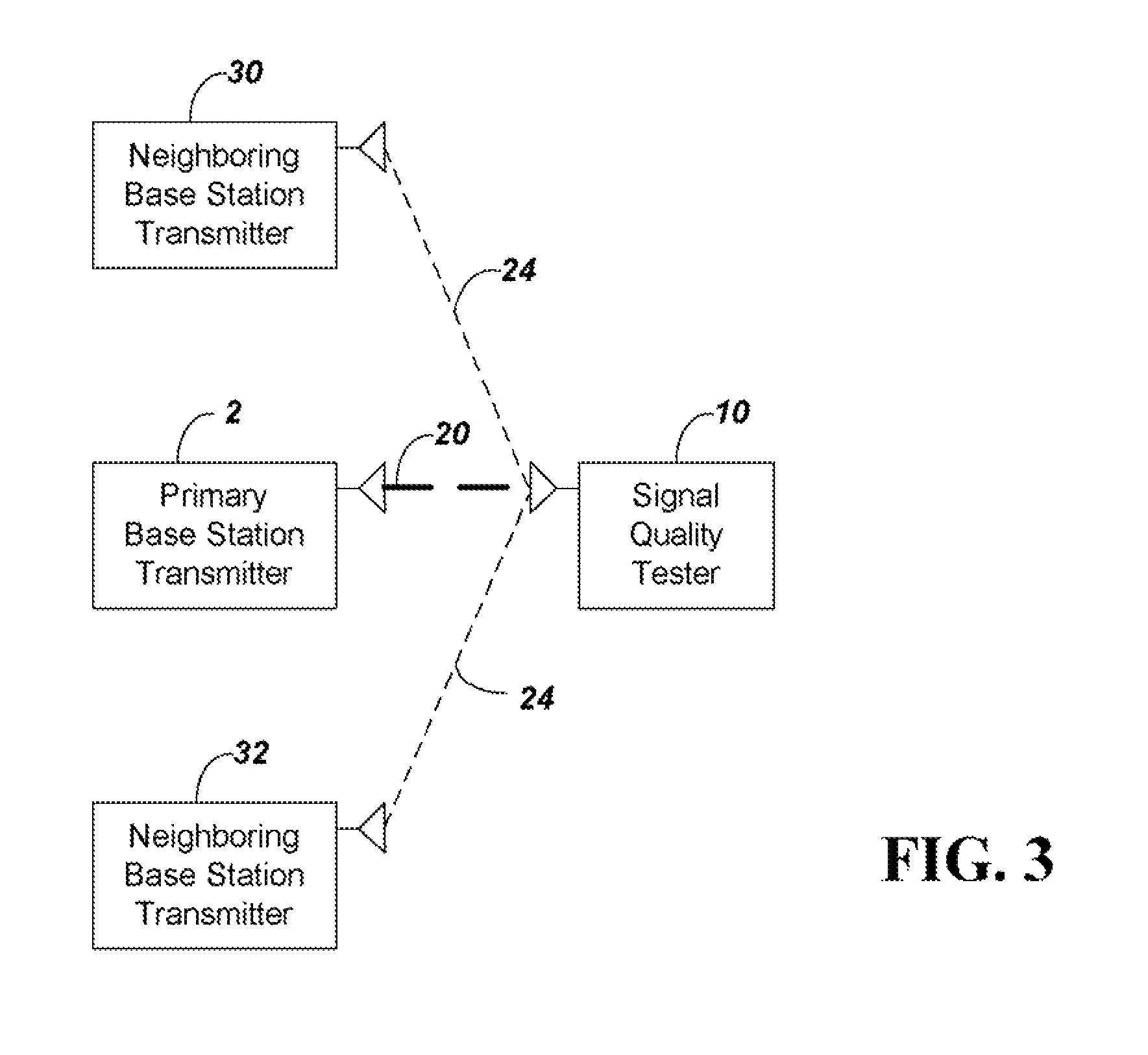
ActiveUS8169993B2Remove distortion effectsRemove distortionFrequency-division multiplexTransmission monitoringSignal qualitySignal on
Owner:ANRITSU CO
Electric power generators and systems comprising same
InactiveUS20120097211A1Increase the volume ratioIncrease power generationPhotovoltaic supportsPV power plantsLighter than airElectric power
An electric power generator comprising: at least one lighter than air balloon (LAB) with at least one photovoltaic array (PVA) embedded in a surface thereof; and a cable connecting the LAB to the ground and adapted to convey a buoyant gas to an inner volume of the LAB and also to convey an electric current generated by said PVA to a ground installation.
Owner:GURFIL PINCHAS +1
Processing signal samples of color video image to produce legalized color version of the image
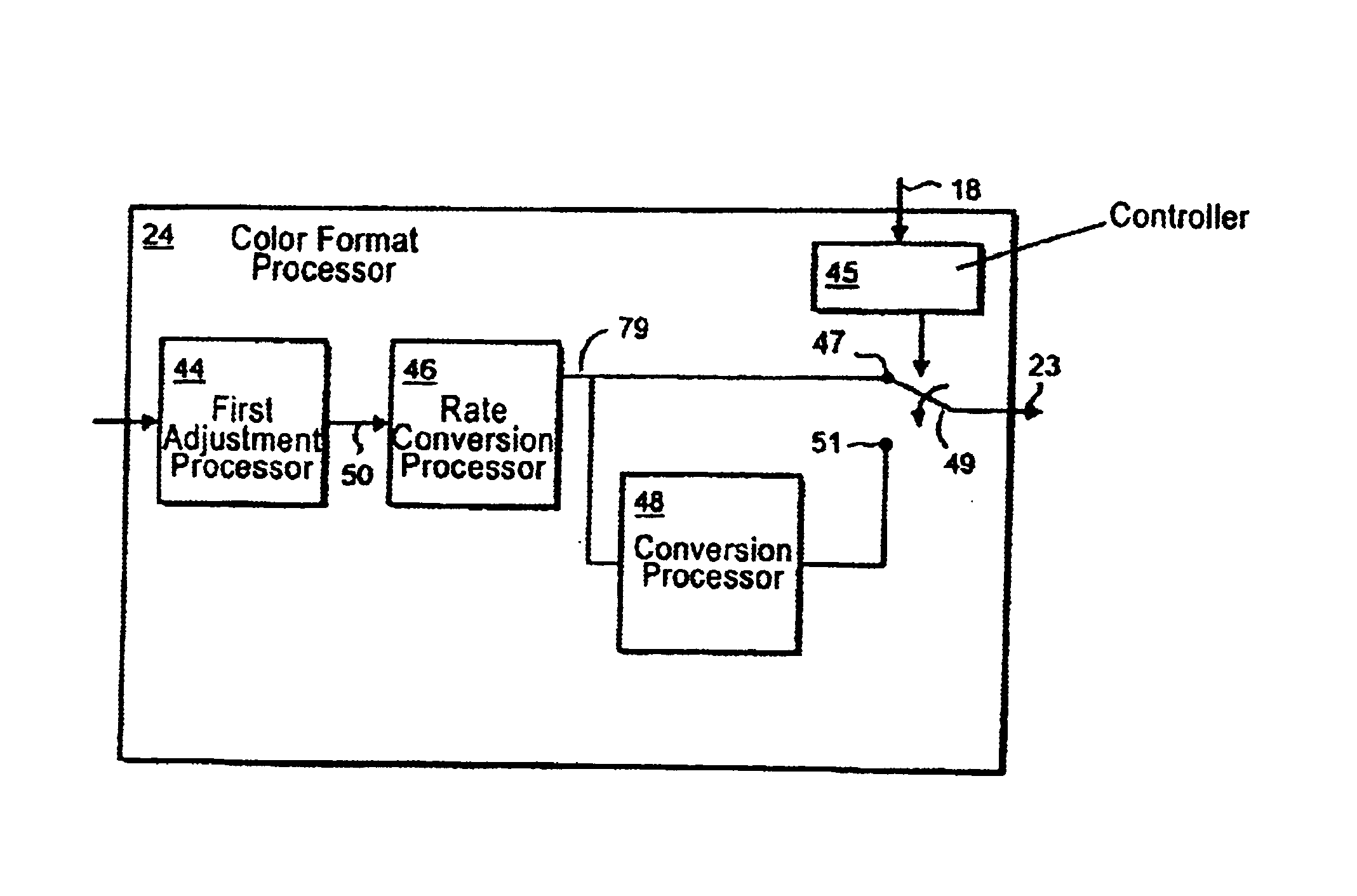
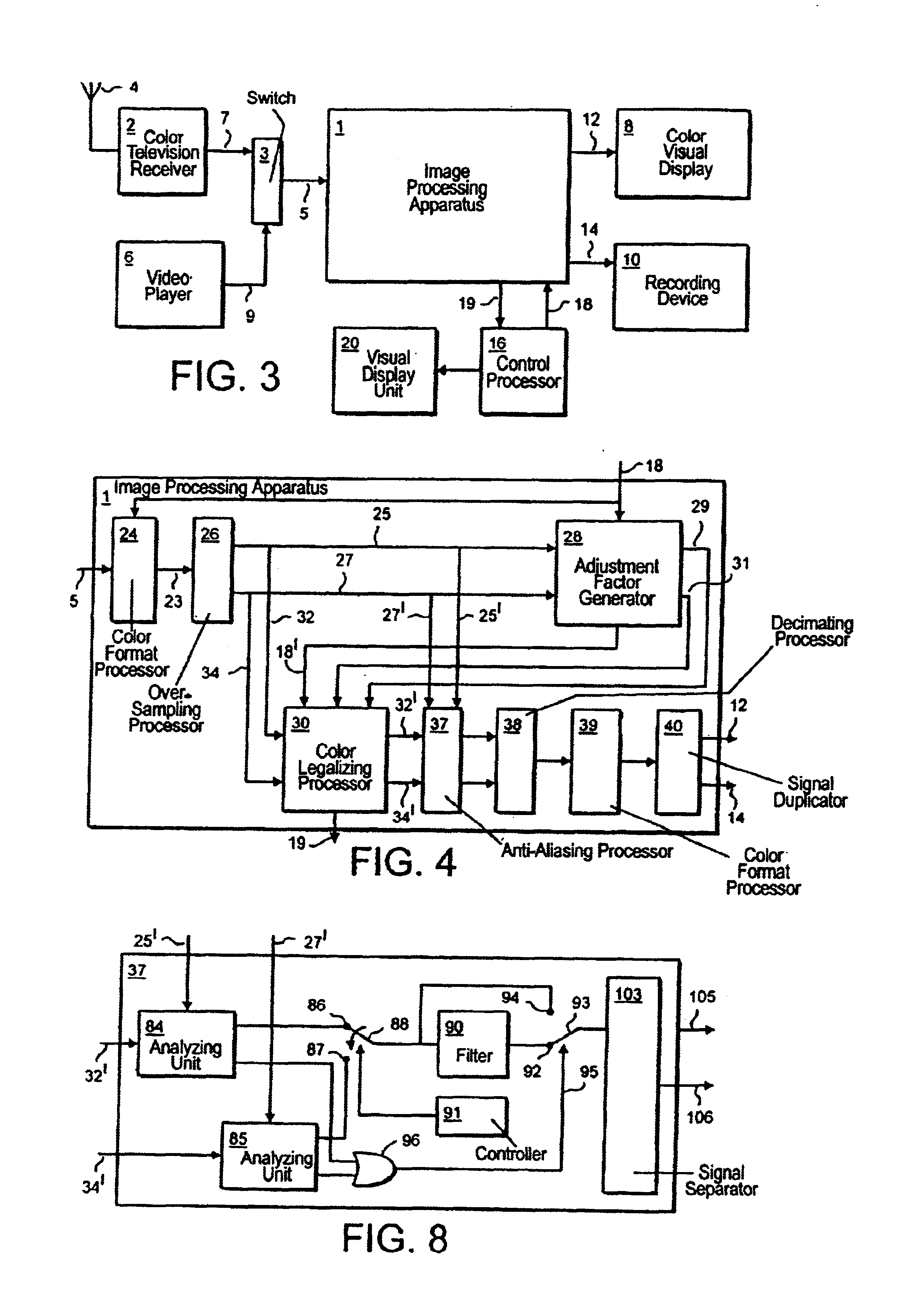
InactiveUS6734921B1Remove distortion effectsImprove representationTelevision system detailsTelevision with combined individual color signalPattern recognitionColor image
An image processing apparatus operates to process signal samples representative of at least part of a color video image to produce legal color signal samples representative of a legal color version of the image. The apparatus comprises an over sampling processor which operates to generate an over sampled version of the input signal samples by generating at least one extra signal sample for each base input signal sample, an adjustment factor generator, which operates to generate a plurality of adjustment factors which when combined with the input signal samples have an effect of converting illegal color pixels of the color image into legal color pixels, a color legalizer coupled to the adjustment factor generator, which operates to combine the adjustment factors with the input signal samples to produce the legalized color signal samples in an over sampled form, an anti-aliasing processor coupled to the color legalizer, which operates to filter selectively the over sampled version of the legalized color signal samples with an anti-aliasing filter in dependence upon whether the legalized color signal samples have changed with respect to the input signal samples and if the legalized color signal samples have not changed, bypassing the filter, and a decimating processor coupled to the color legalizer which operates to decimate the filtered legalised color signal samples to produce legalized signal samples having a sampling rate corresponding to that of the base input signal samples. The anti-aliasing processor filters the legalised color signal samples by selecting the base legalized color signal samples corresponding to the base input signal sample, where neither the base or the associated extra color signal samples have changed with respect to the input signal samples.
Owner:SONY UK LTD
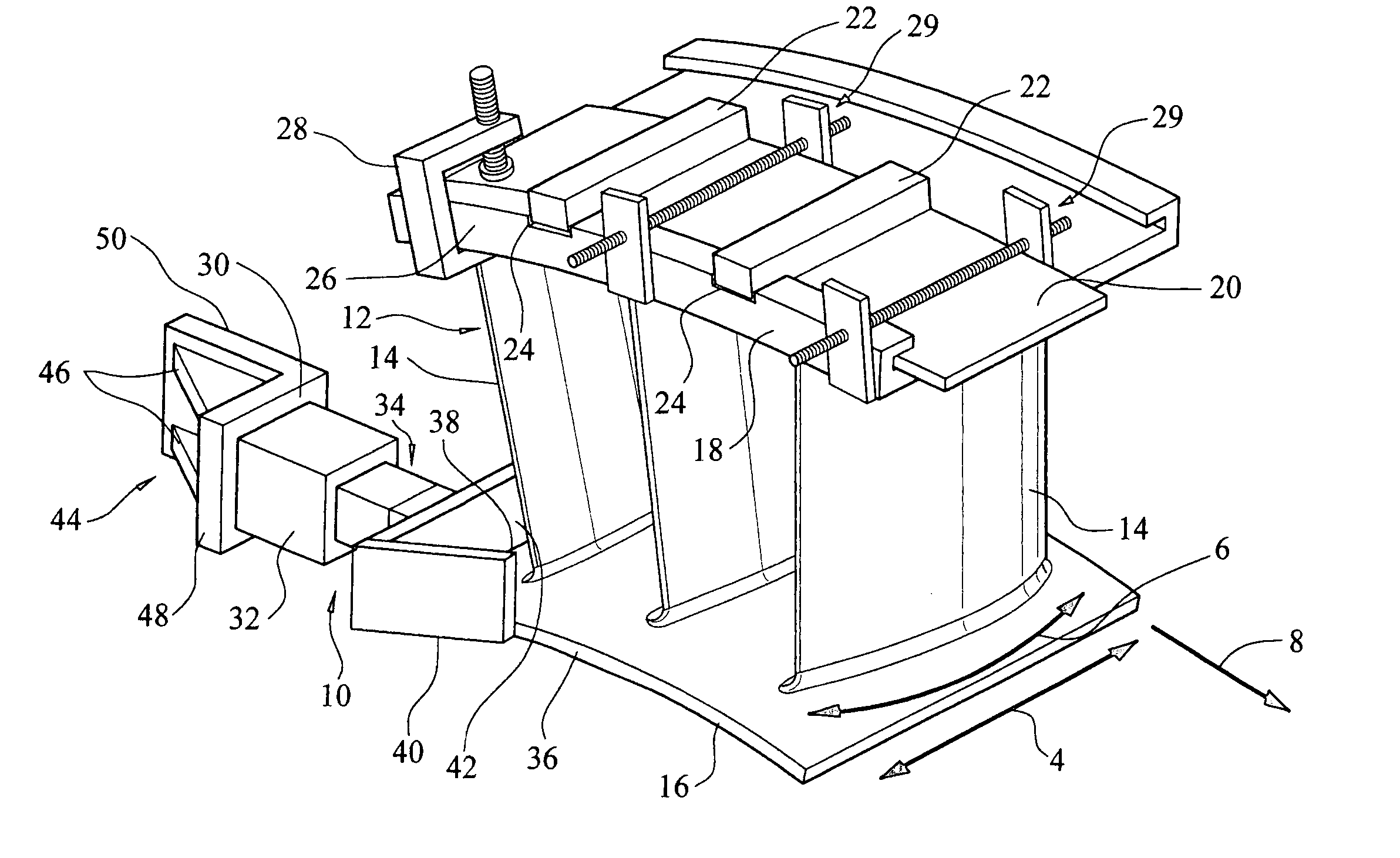
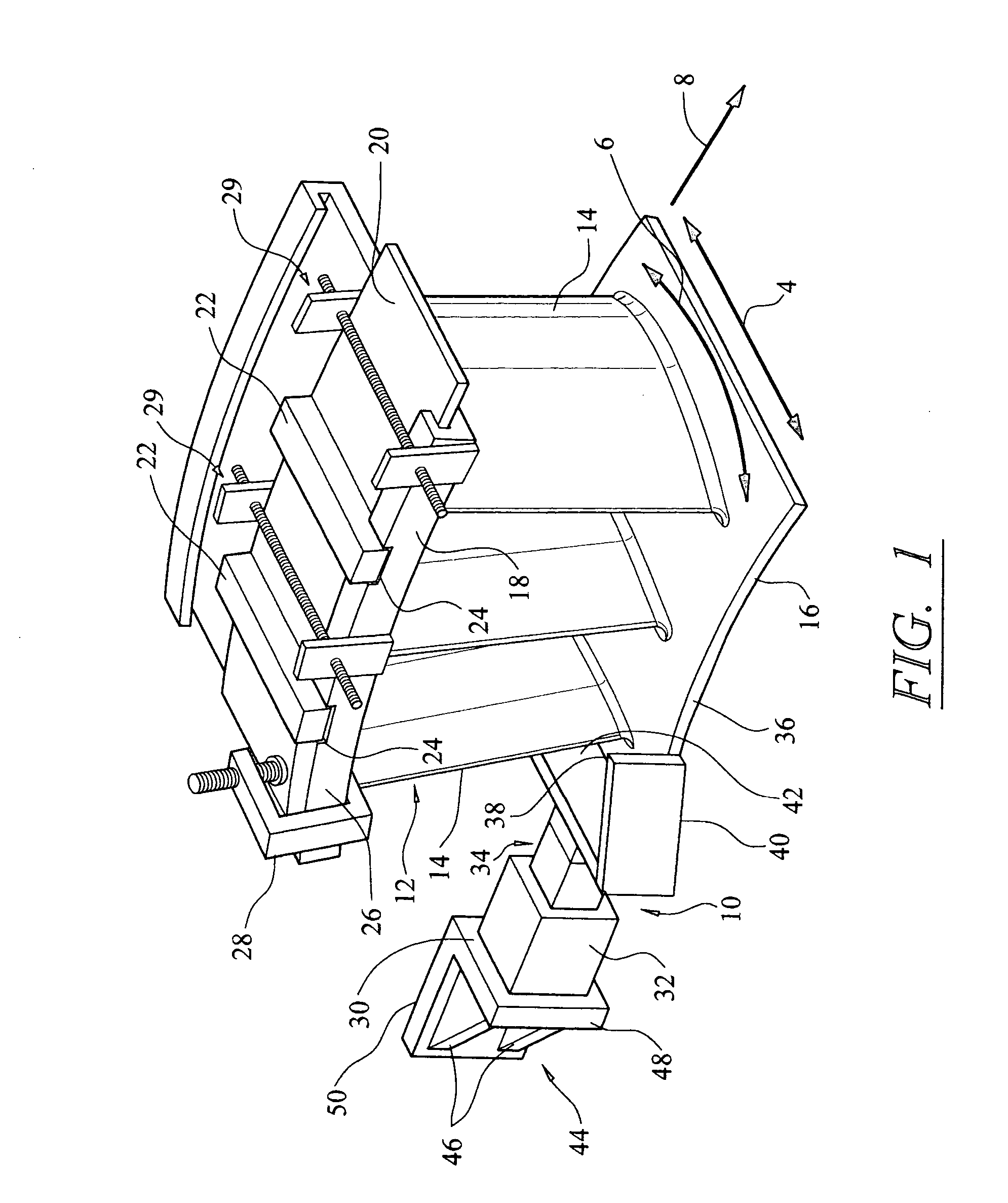
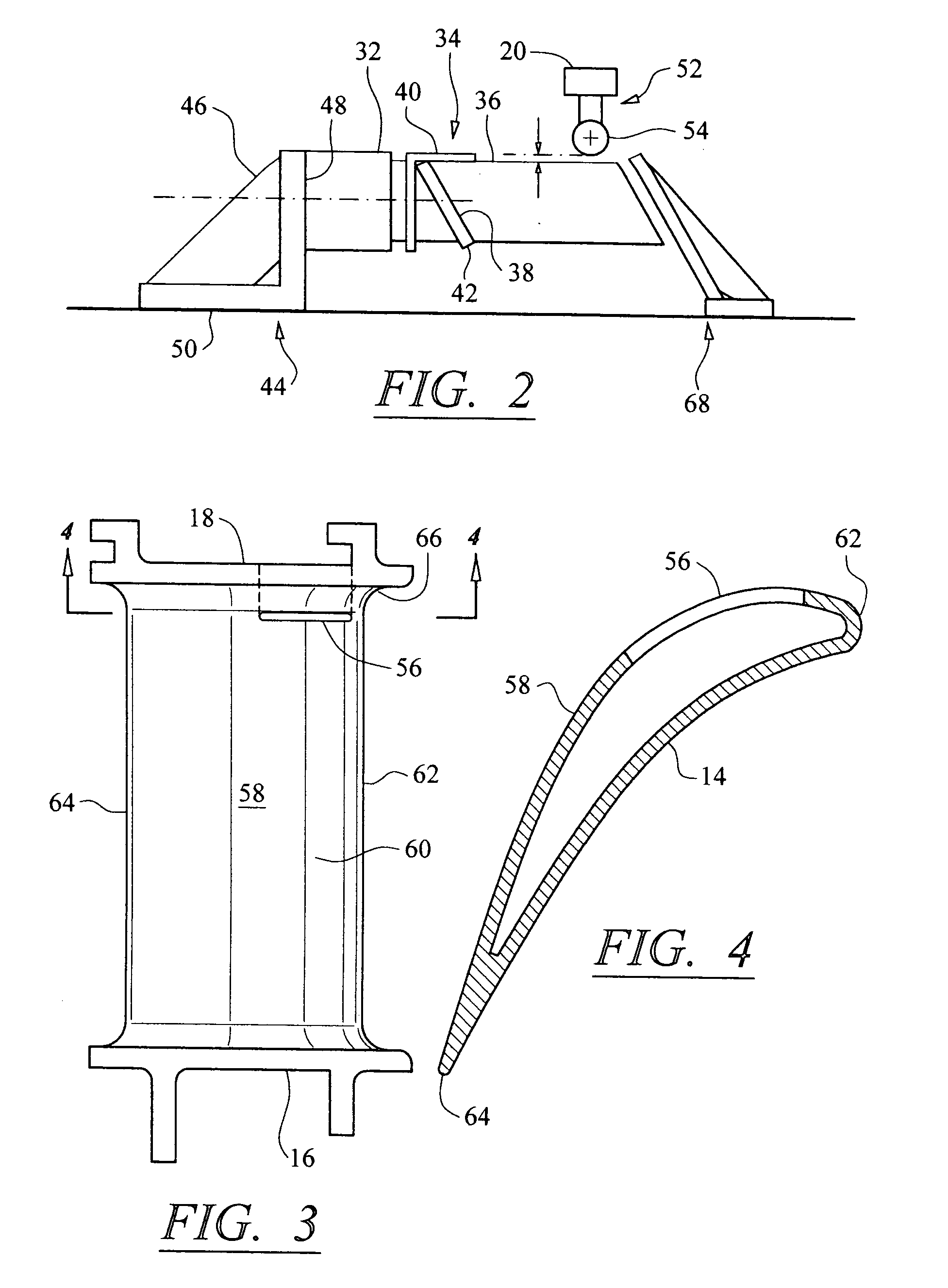
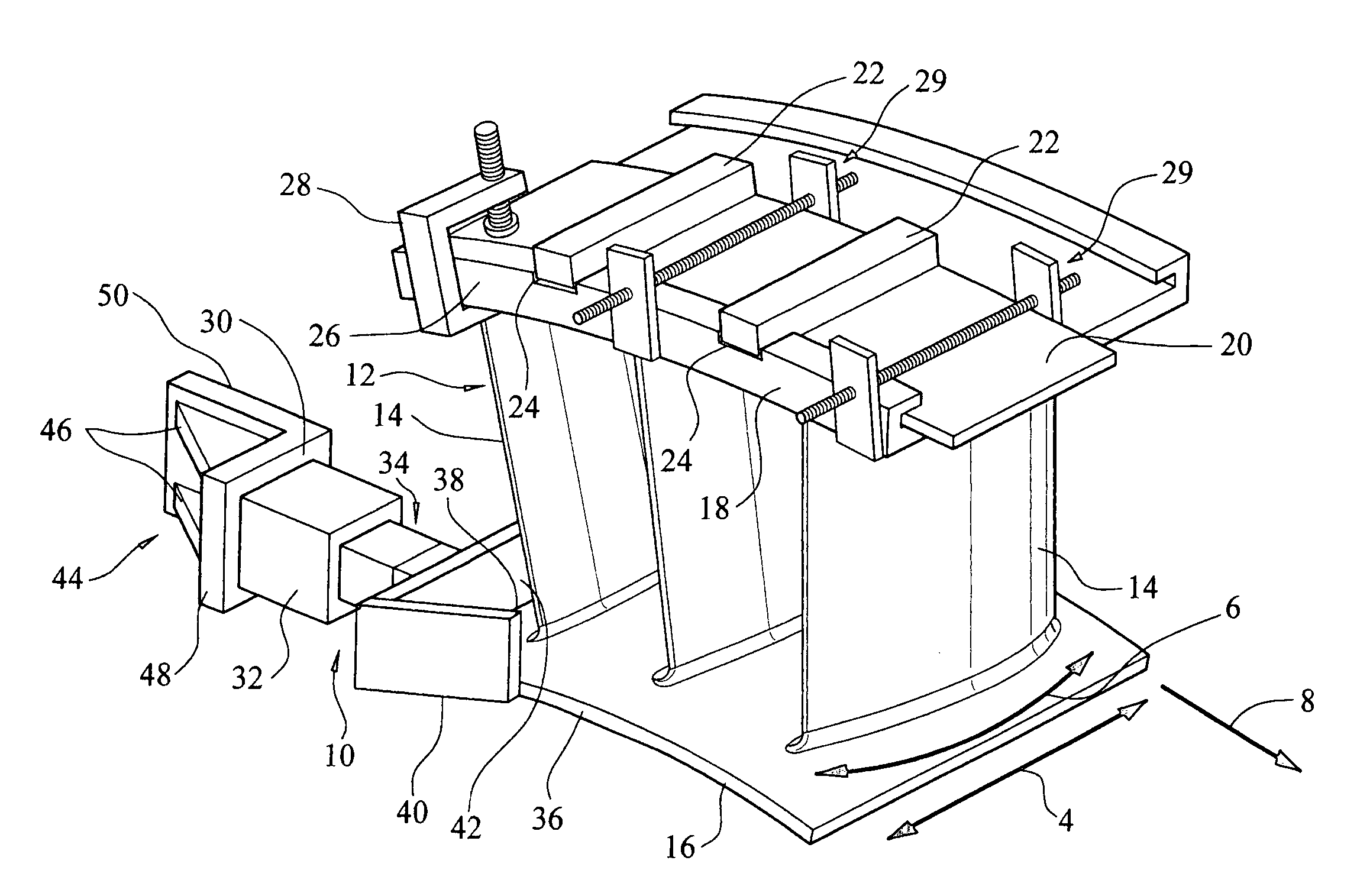
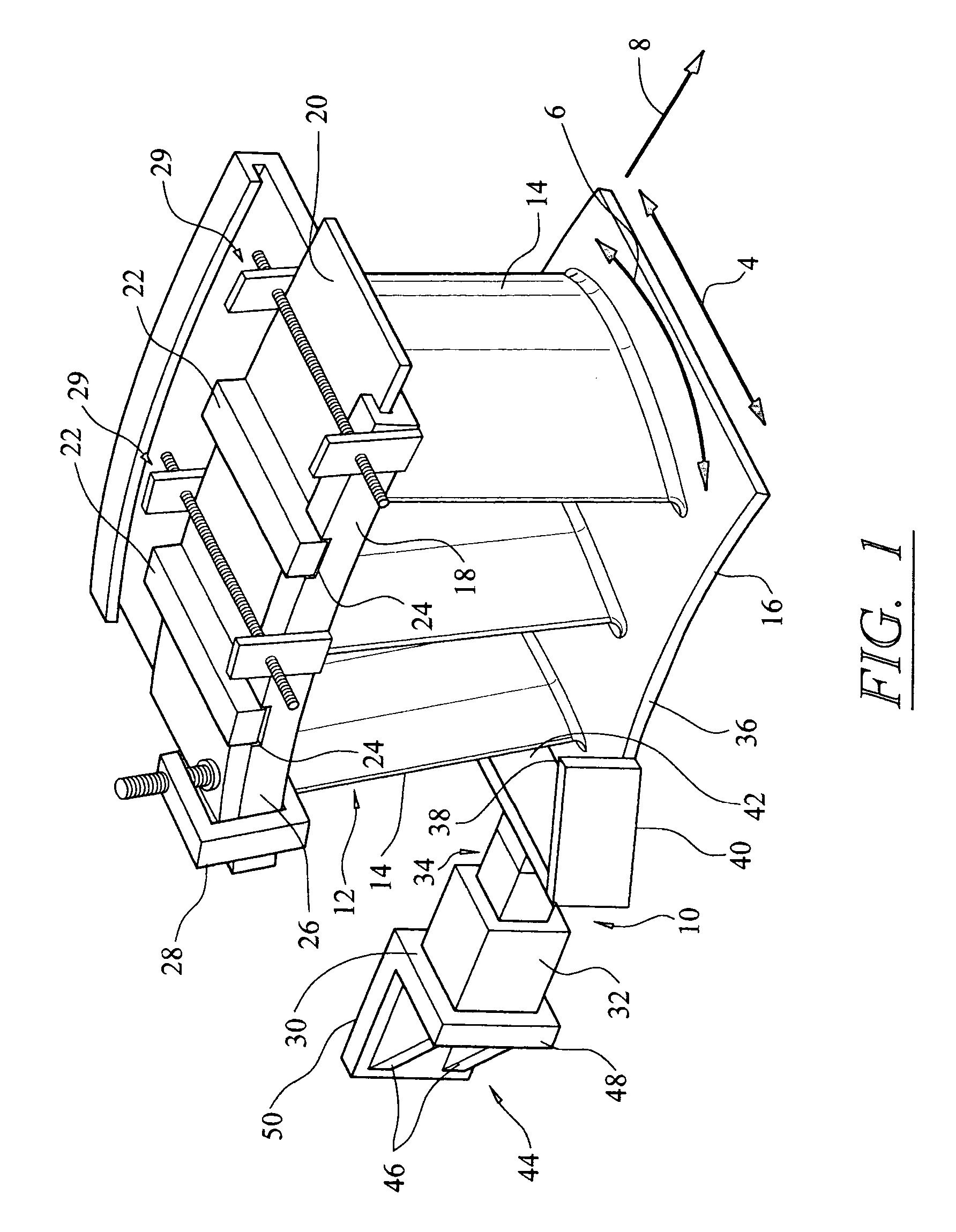
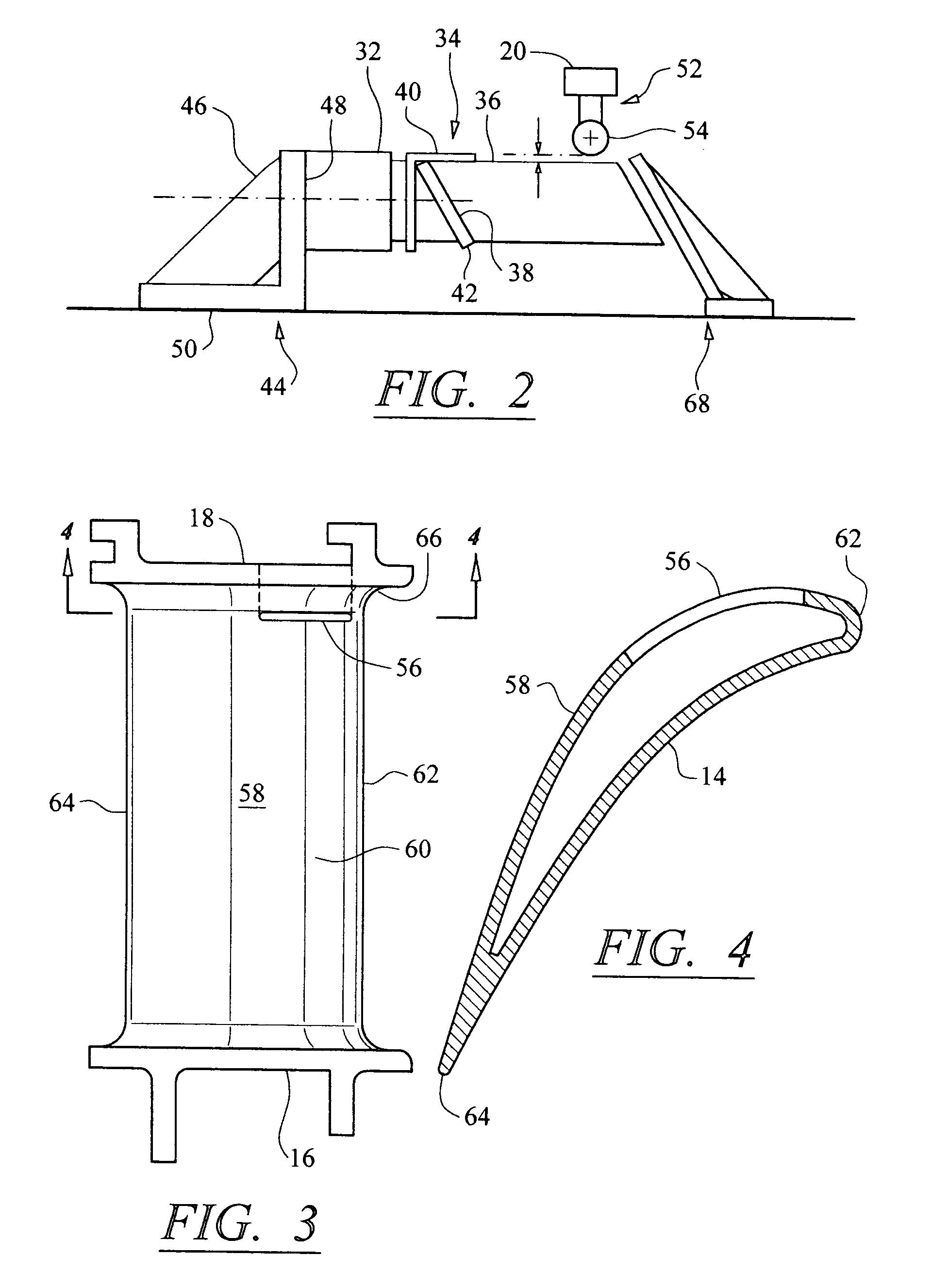
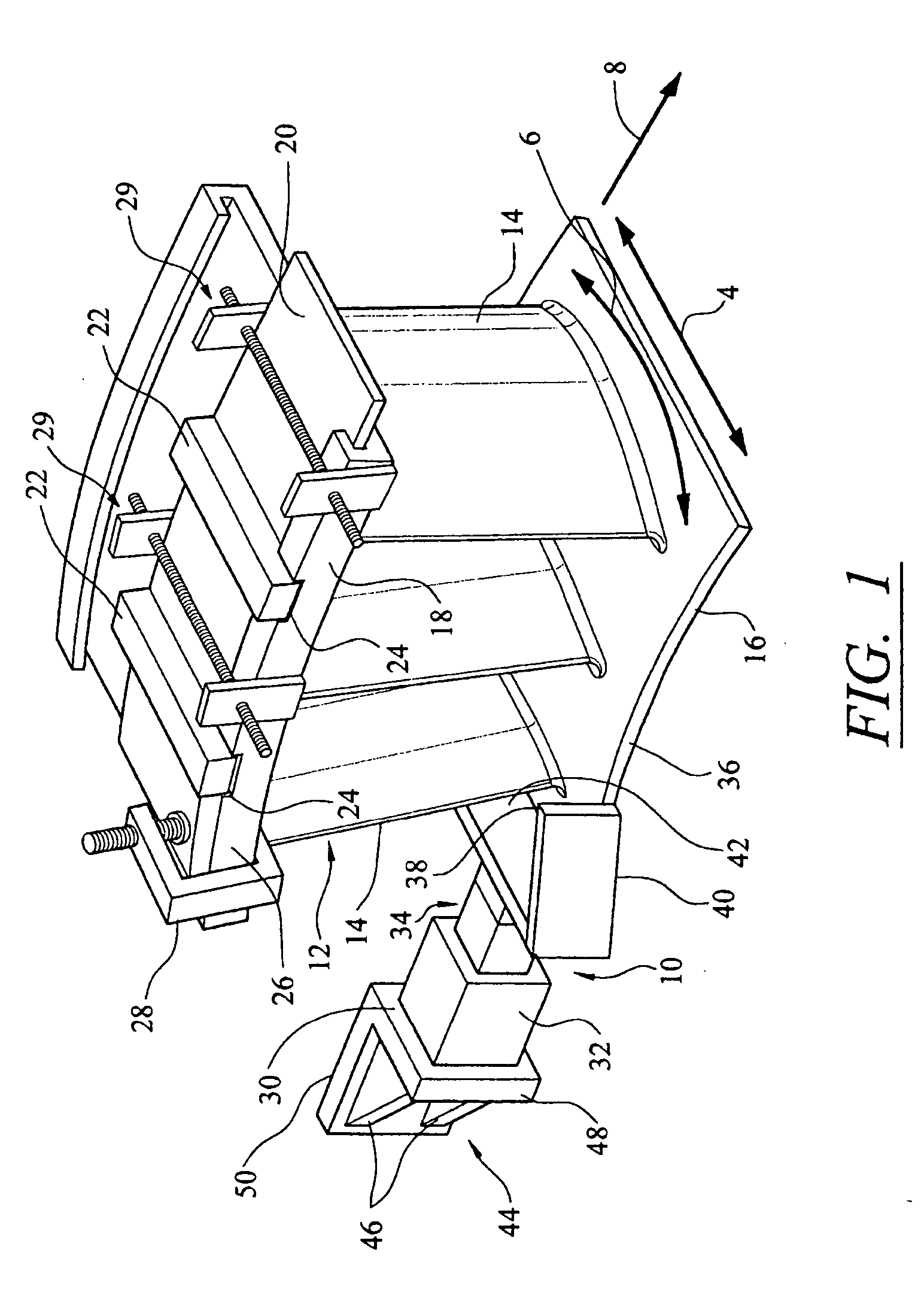
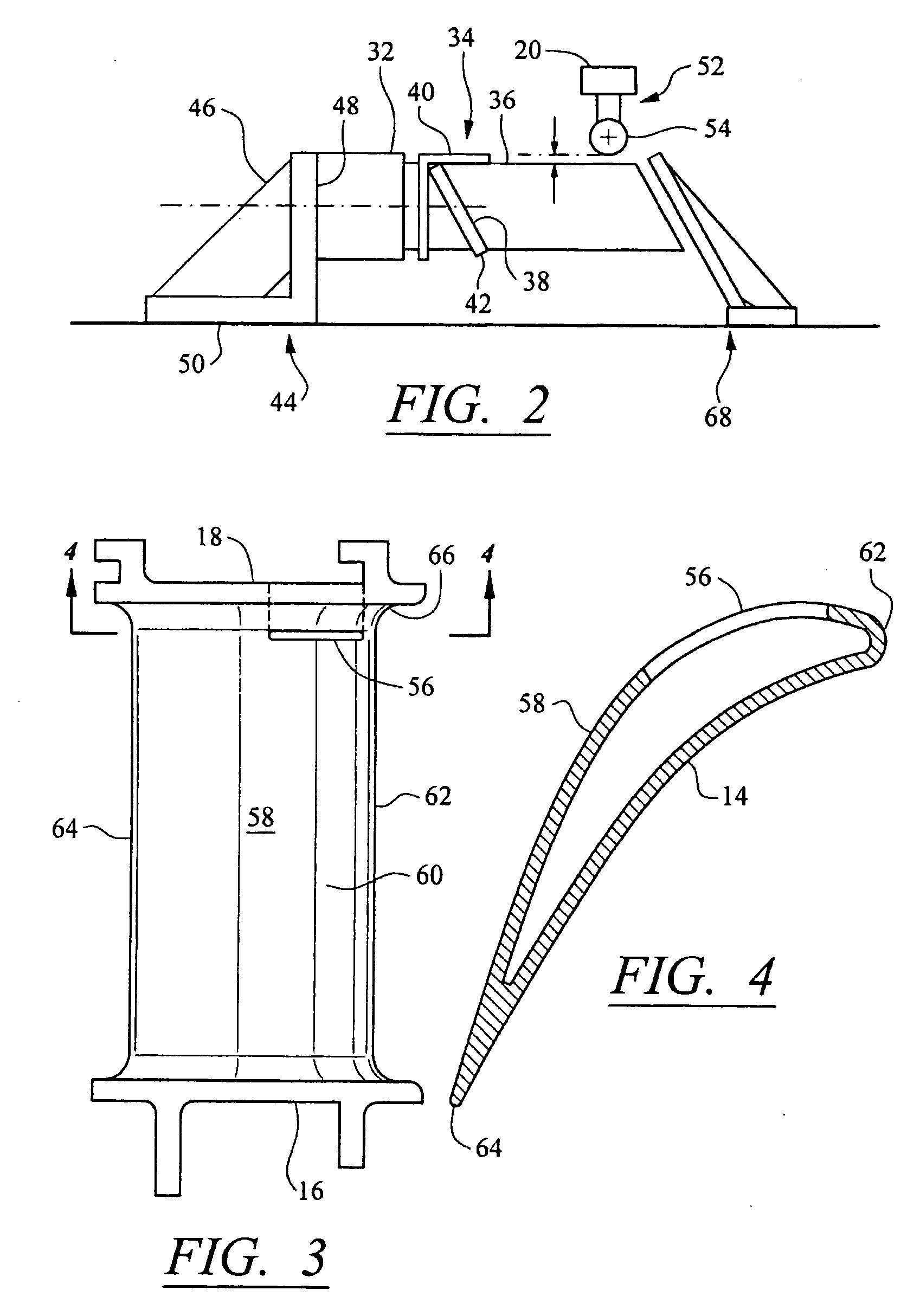
Turbine vane airfoil reconfiguration system
InactiveUS20070084048A1Improve distortionRemove distortion effectsBlade accessoriesMachines/enginesTurbine blade
A system and method for reconfiguring an airfoil of a turbine vane segment. In at least one embodiment, the system may be used to straighten an airfoil of a turbine vane segment to remove lean, twist, or racking, or any combination thereof. The airfoil may be straightened by applying a load to an inner shroud in a direction that is generally tangential to an outer shroud of the turbine vane segment. Orifices may be cut into the airfoil suction side, inboard of the outer shroud, to facilitate the straightening process. The orifices may be sealed upon completion of the process.
Owner:CHROMALLOY GAS TURBINE
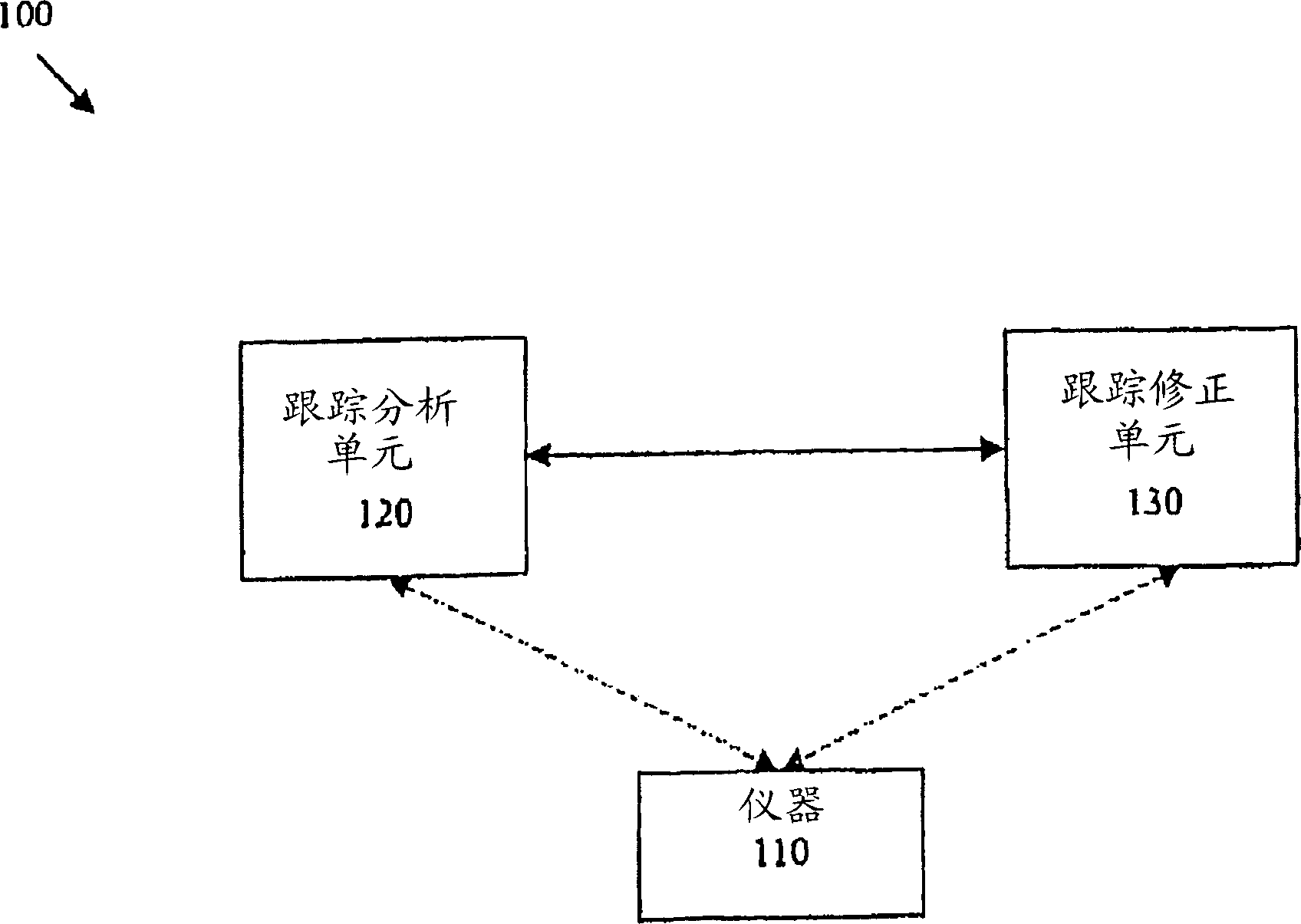
System and method for distortion reduction in an electromagnetic tracker
InactiveCN1901835ARemove distortion effectsCompensation for Distortion EffectsPosition fixationUsing electrical meansSonificationMedical treatment
The present invention provides a system (100) and method (200) for distortion analysis and reduction in an electromagnetic (EM) tracker. The EM tracker may employ coils as receivers and transmitters. Certain embodiments of the system (100) include a tracking analysis unit (120) for analyzing a tracking behavior of an instrument (110) and a tracking modification unit (130) for compensating for the tracking behavior of the instrument (110). Such an instrument (110) is, for example, a medical instrument, such as a drill, a catheter, a scalpel or a scope. These instruments and their surroundings often include metal components. Positioning an EM navigation device, such as a receiver or a transmitter, on the instrument (110) may cause a distortion in the magnetic field which affects the tracking and tracking accuracy. Uses outside medical applications are foreseen, as are tracking systems other than EM tracking systems, such as ultrasound or inertial position.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Improved power transmission line lightning stroke double-end traveling wave positioning method
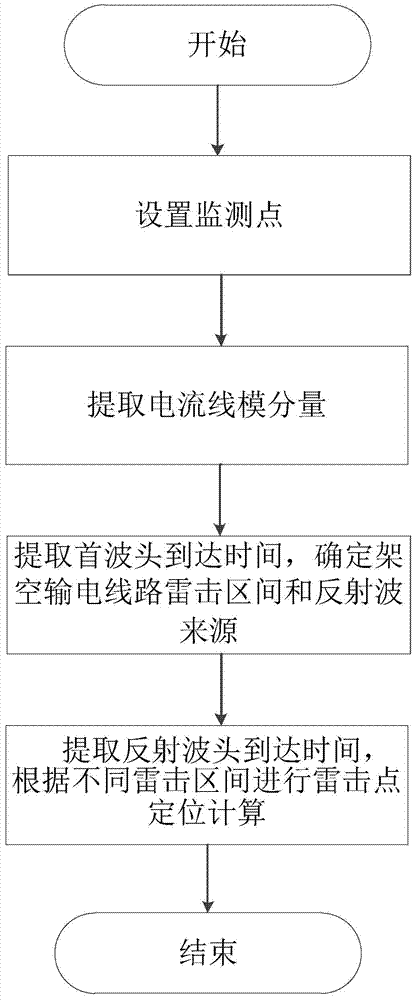
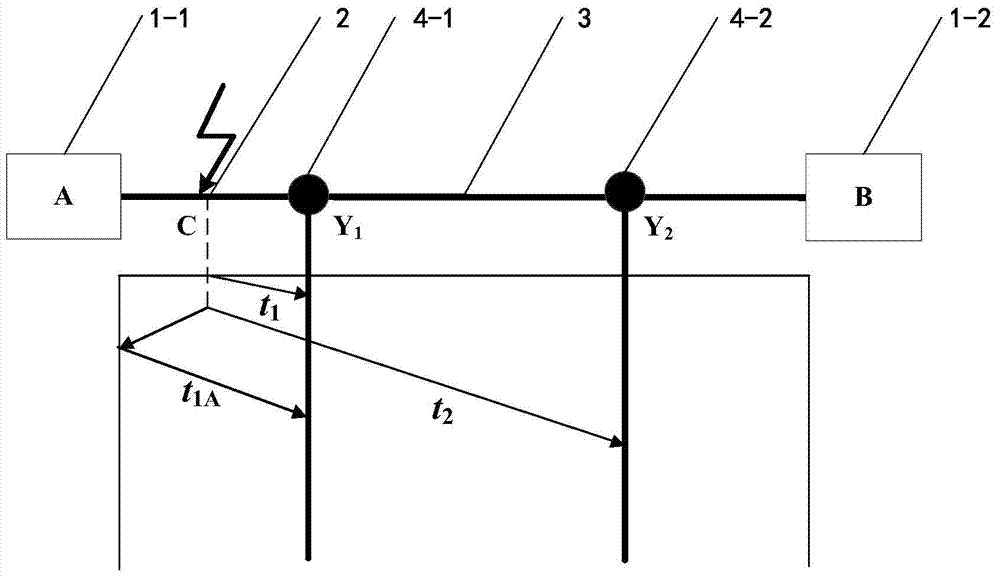
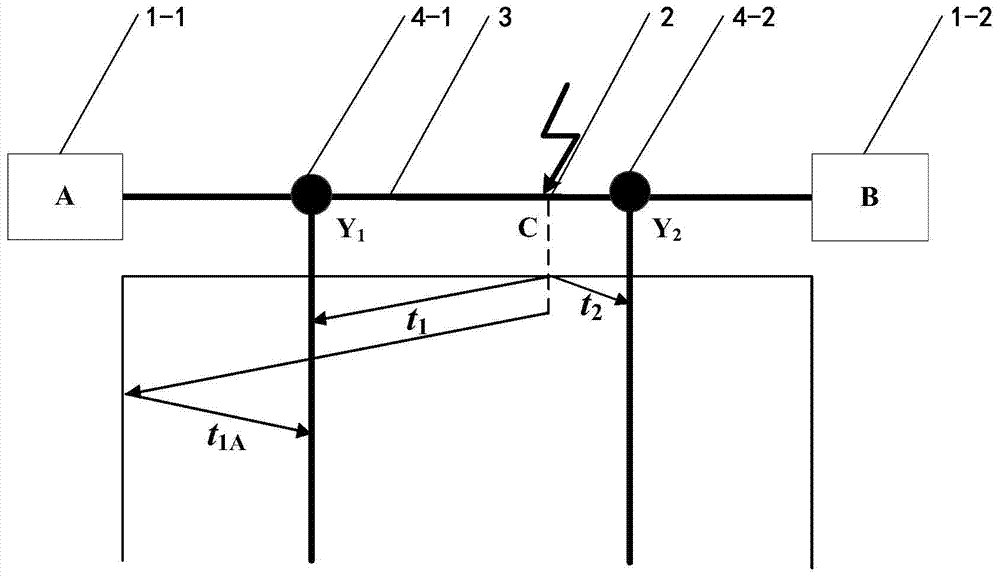
ActiveCN103499772AImprove the positioning accuracy of lightning strikesComplete recordFault locationLightning strokesReflected waves
The invention provides an improved power transmission line lightning stroke double-end traveling wave positioning method, and relates to an overhead transmission line lightning stroke fault positioning calculation method. A computer is utilized, through program, the lightning stroke fault point position on an overhead transmission line is determined through setting monitoring points, extracting current line model components, extracting the first wave head reaching time, determining the overhead transmission line lightning stroke interval and reflecting wave sources, extending the reflecting wave head reaching time and carrying out lightning stroke point positioning calculation according to different lightning stroke intervals. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics that simplicity and feasibility are realized, the positioning precision is high, the positioning efficiency is high, the practicability is high, the lightning stroke fault points on the overhead transmission line can be fast and accurately judged, the popularization and the application are convenient, and the like. The method provided by the invention can be widely applied to the lightning positioning calculation of the overhead transmission line, and is particularly suitable for the lightning positioning calculation of the high-voltage overhead transmission line with the voltage being 110kV and higher.
Owner:YUN NAN ELECTRIC TEST & RES INST GRP CO LTD ELECTRIC INST +1
Monocular vision robot rapid tracking method based on road correction
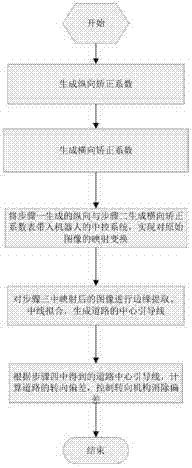
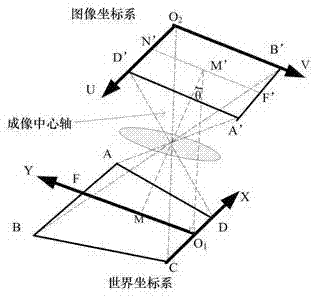
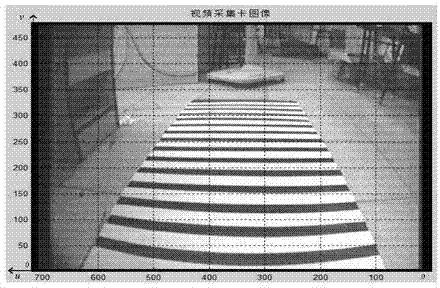
InactiveCN104123535AFast real-time correctionRemove distortion effectsImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionControl mannerSimulation
The invention discloses a monocular vision robot rapid tracking method based on road correction, and belongs to the field of monocular vision robot path recognition. The basic idea of the method comprises building a correction mapping table for an original road image in longitudinal and transverse directions so as to achieve correction on the road image of a monocular vision robot; and on the above basis, automatic tracking travel of the robot is achieved by adopting a deviation control manner. On the above basis, the robot travels by tracking the road, physical information such as actual road curvature and curvature can be accurately obtained, and influence of road image distortion on control and operation of the robot is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNION UNIVERSITY
Carrier phase synchronization system for improved amplitude modulation and television broadcast reception
InactiveUS7587017B2Remove distortion effectsCarrier regulationBroadcast transmission systemsPhase controlRadio frequency
Systems and methods are described for carrier phase synchronization for improved AM and TV broadcast reception. A method includes synchronizing the phase of a carrier frequency of a broadcast signal with the phase of a remote reference frequency. An apparatus includes a receiver to detect the phase of a reference signal; a phase comparator coupled to the reference signal-phase receiver; a voltage controlled oscillator coupled to the phase comparator; and a phase-controlled radio frequency output coupled to the voltage controlled oscillator.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Servo-actuated machine vision apparatus and dynamic tracking range finding method
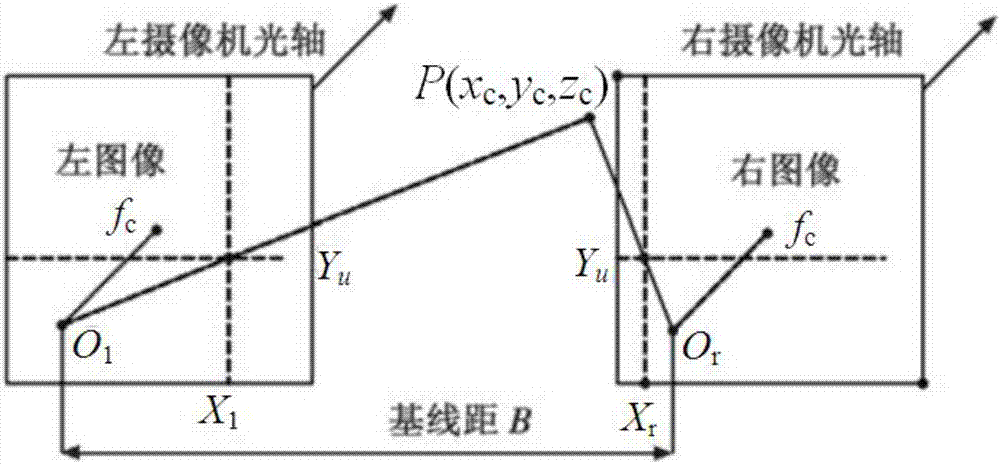
The invention discloses a servo-actuated machine vision apparatus and a dynamic tracking range finding method. The servo-actuated machine vision apparatus includes a vision system, a servo driving and control system and a host computer task control system, wherein the vision system is formed by lenses, a cameras, an image processing board card and software; and the servo driving and control system is formed by a support, a decelerator, a servo motor, a rotary encoder and a servo controller. The dynamic tracking range finding method is characterized by rotating two cameras which are away from each other by certain distance through servo driving so as to enable the target to approach the optical axis of each camera; measuring the included angle between the optical axis and the baseline through the rotary encoder; and then obtaining the target distance and position through simple geometrical operation, and improving the measuring accuracy through zooming of the lens. The dynamic tracking range finding method can achieve the aim of quick tracking and high accuracy range finding without a complicated characteristic point coupling process. The camera lens of the servo-actuated machine vision apparatus can perform optical focusing randomly to amplify and clarify the target image, and can improve the tracking and range finding accuracy.
Owner:CISDI ENG CO LTD +1
Turbine vane airfoil reconfiguration system
InactiveUS7503113B2Improve distortionRemove distortion effectsBlade accessoriesMachines/enginesTurbine blade
A system and method for reconfiguring an airfoil of a turbine vane segment. In at least one embodiment, the system may be used to straighten an airfoil of a turbine vane segment to remove lean, twist, or racking, or any combination thereof. The airfoil may be straightened by applying a load to an inner shroud in a direction that is generally tangential to an outer shroud of the turbine vane segment. Orifices may be cut into the airfoil suction side, inboard of the outer shroud, to facilitate the straightening process. The orifices may be sealed upon completion of the process.
Owner:CHROMALLOY GAS TURBINE
Method and apparatus to estimate wireless base station signal quality over the air
ActiveUS20090264080A1Remove distortion effectsRemove distortionFrequency-division multiplexTransmission monitoringSignal qualitySignal on
The quality of the signal from a base station is measured and adjusted for distortion due to multipath and due to signals from neighboring co-channel base stations. The signal quality is measured conventionally by determining Rho or EVM and then Rho or EVM are adjusted. To adjust the signal the process includes the steps of: (a) sampling a received CDMA base station signal in a particular frequency channel, calculating the total received power to provide a reference value for subsequent normalization; (b) demodulating the received signal and constructing an ideal reference signal; (c) correlating between the ideal reference signal and received signal to determine a Rho value, or calculating the ratio of the difference between ideal and received signal to the ideal signal to obtain EVM; (d) performing a self cross correlation to separate signals from the sampled received signal on different delay paths, and determining a multipath power value x as a total power of signals on non-dominant ones of the delay paths; (e) performing a code correlation pilot scan of the sampled signal to determine strengths of signals from neighboring co-channel base stations; (f) summing the power levels of the neighboring co-channel base station signals to provide a total pilot pollution power y; and (g) calculating an adjusted Rho or EVM by removing x and y from the total received power.
Owner:ANRITSU CO
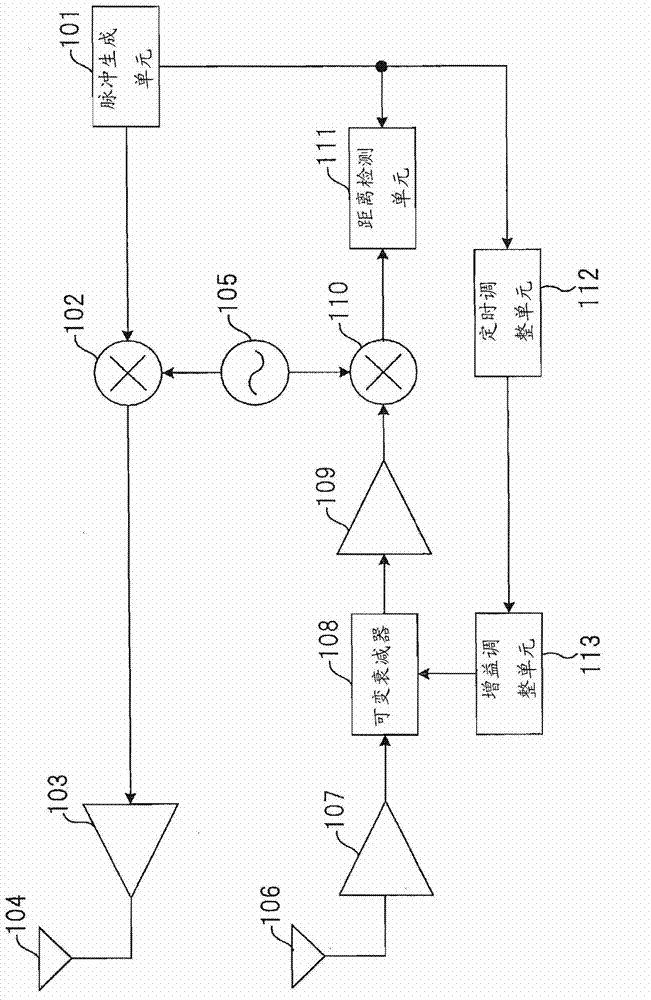
Radar apparatus
ActiveCN103026255AReduce signal distortionImprove deteriorationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDistortionPhysics
The influence of a signal distortion, which occurs when the gain of a reception unit in a radar apparatus is adjusted, is reduced, thereby lessening the degradation of received signals. A pulse signal is generated, as a transport signal, by a pulse generating unit (101), and then repetitively transmitted via an antenna (104) at constant time intervals. A received signal, which is received via an antenna (106) and includes a reflected wave having been reflected by an object, is amplified by an amplifier (107) and then gain-adjusted by a variable attenuator (108). Thereafter, a distance detecting unit (111) detects a received pulse of the reflected wave, thereby calculating the distance from the object. The variable attenuator (108) attenuates the received signal by use of the gain that has been adjusted in accordance with a gain control signal supplied from a gain adjusting unit (113). The gain (attenuation amount) of the variable attenuator (108) is controlled in such a manner that the gain becomes largest just after the transmission of the pulse signal and then becomes smaller as time goes by. The gain adjustment timing at which to change the attenuation amount is made different, on the basis of a gain adjustment timing signal from a timing adjusting unit (112), for each transmission of the pulse signal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
System and method for correcting optical distortions when projecting 2d images onto 2d surfaces
ActiveUS20150124174A1Reduce keystoneReduce optical distortion effectTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsComputer graphics (images)Angular velocity
A system for projecting 2D images, providing a computerized representation of a first, dense, grid of spatial 3D coordinates which respectively correspond to a set of time-points evenly distributed along a time-dimension with constant time-discretization; deriving a dense 2D representation of an image, whose coordinate pairs respectively correspond to said set of time-points; d. Defining a sparse 2D grid of second coordinate pairs, spaced such that distances between any two adjacent coordinate pairs along a row of said sparse 2D grid are constant; and finding, coordinate pairs closest to the second sparser grid to yield a third grid, and a laser controller to control the laser to project a digitally represented image, from said distance, timed to project pixels whose locations respectively correspond to the subset of uniformly distanced positions forming said third grid, thereby to prevent image distortion despite non-uniformity of micro-mirror's angular velocity.
Owner:MARADIN
Method of processing signals and apparatus for signal processing
InactiveUS6570576B1Remove distortion effectsImprove representationColor television with pulse code modulationColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionColor image
An image processing apparatus processes input signal samples representative of at least part of a color video image to produce legal color signal samples. An over sampled version of the input signal samples is produced. A plurality of adjustment factors are generated which, when combined with the input signal samples, have the effect of converting illegal color pixels of the color image into legal color pixels. The over sampled legalized color signal samples are decimated, resulting in a sampling rate corresponding to that of the base input signal samples, by selecting signal samples from the over sampled version of the legalized color signal samples which have not changed with respect to the corresponding input signal samples. If the signal samples have changed, a plurality of the over sampled legalized color signal samples are combined to produce the decimated legalized signal samples; and if neither the base nor the associated extra color signal samples have changed, base legalized color signal samples are selected.
Owner:SONY UK LTD
Method, apparatus and computer program product for mapping and modeling a three dimensional structure
ActiveUS10539676B2Simplify a trajectory pathRemove distortion effectsInstruments for road network navigationCharacter and pattern recognitionDriver/operatorComputer graphics (images)
Embodiments described herein may provide a method for generating a three-dimensional vector model of the interior of a structure. Methods may include: receiving sensor data indicative of a trajectory; receiving sensor data defining structural surfaces within a structure; generating a three-dimensional point cloud from the sensor data defining structural surfaces within the structure; segmenting the three-dimensional point cloud into two or more segments based, at least in part, on the sensor data indicative of trajectory; generating a three-dimensional surface model of an interior of the structure based on the segmented three-dimensional point cloud with semantic recognition and labelling; and providing the three-dimensional surface model of an interior of the structure to an advanced driver assistance system to facilitate autonomous vehicle parking.
Owner:HERE GLOBAL BV
Image pick-up apparatus and image restoration method
InactiveCN1725811AAccurate recoveryRemove distortion effectsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage detectionImage restoration
The present invention provides an image pick-up apparatus and iamge recoery method. The image pick-up apparatus includes an optical system which forms a subject image. An image pick-up unit obtains image data from the subject image formed by the optical system. A vibration detecting unit detects a vibration of the image pick-up apparatus. In an image deterioration information storage unit, information of image deterioration generated by the optical system is stored. An image deterioration correcting unit corrects the image deterioration generated by the optical system with respect to the image data output from the image pick-up unit in accordance with the image deterioration information stored in the image deterioration information storage unit. A vibration restoring unit restores the image deteriorated by the vibration with respect to the image data output from the image deterioration correcting unit in accordance with the vibration detecting signal of the time series.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Turbine vane airfoil reconfiguration method
InactiveUS20070084050A1Facilitating twistingRemove distortion effectsBlade accessoriesMachines/enginesTurbine blade
A method for reconfiguring an airfoil of a turbine vane segment. In at least one embodiment, the method may be used to straighten an airfoil of a turbine vane segment to remove lean, twist, or racking, or any combination thereof. The airfoil may be straightened by heating the airfoil to no more than 750 degrees F. while applying a load to an inner shroud in a direction that is generally tangential to an outer shroud of the turbine vane segment. The load is up to 6000 lbf. Orifices may be cut into the airfoil suction side, inboard of the outer shroud, to facilitate the straightening process. The orifices may be sealed upon completion of the process.
Owner:CHROMALLOY GAS TURBINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com