Patents
Literature
50 results about "Sweep rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
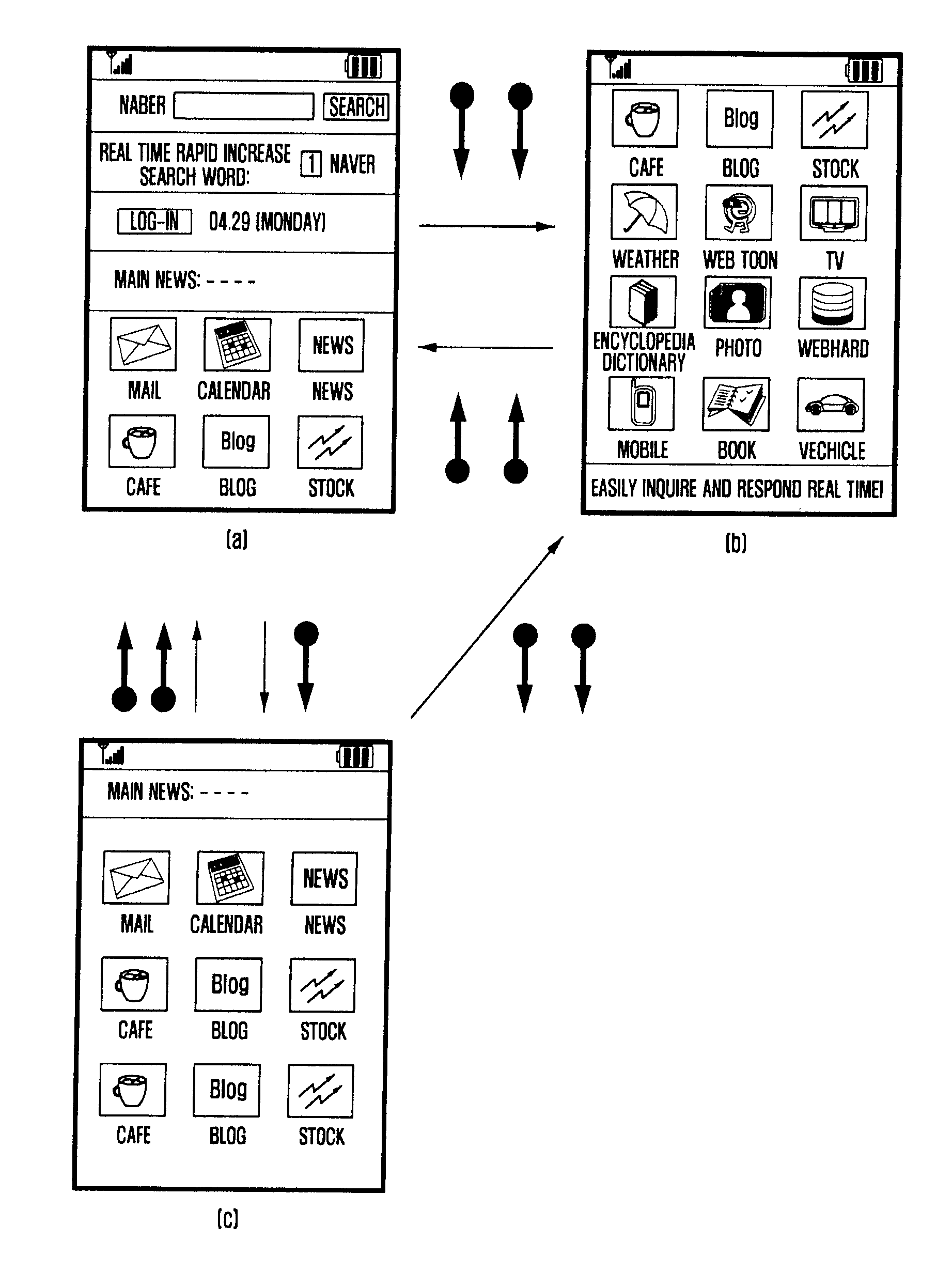
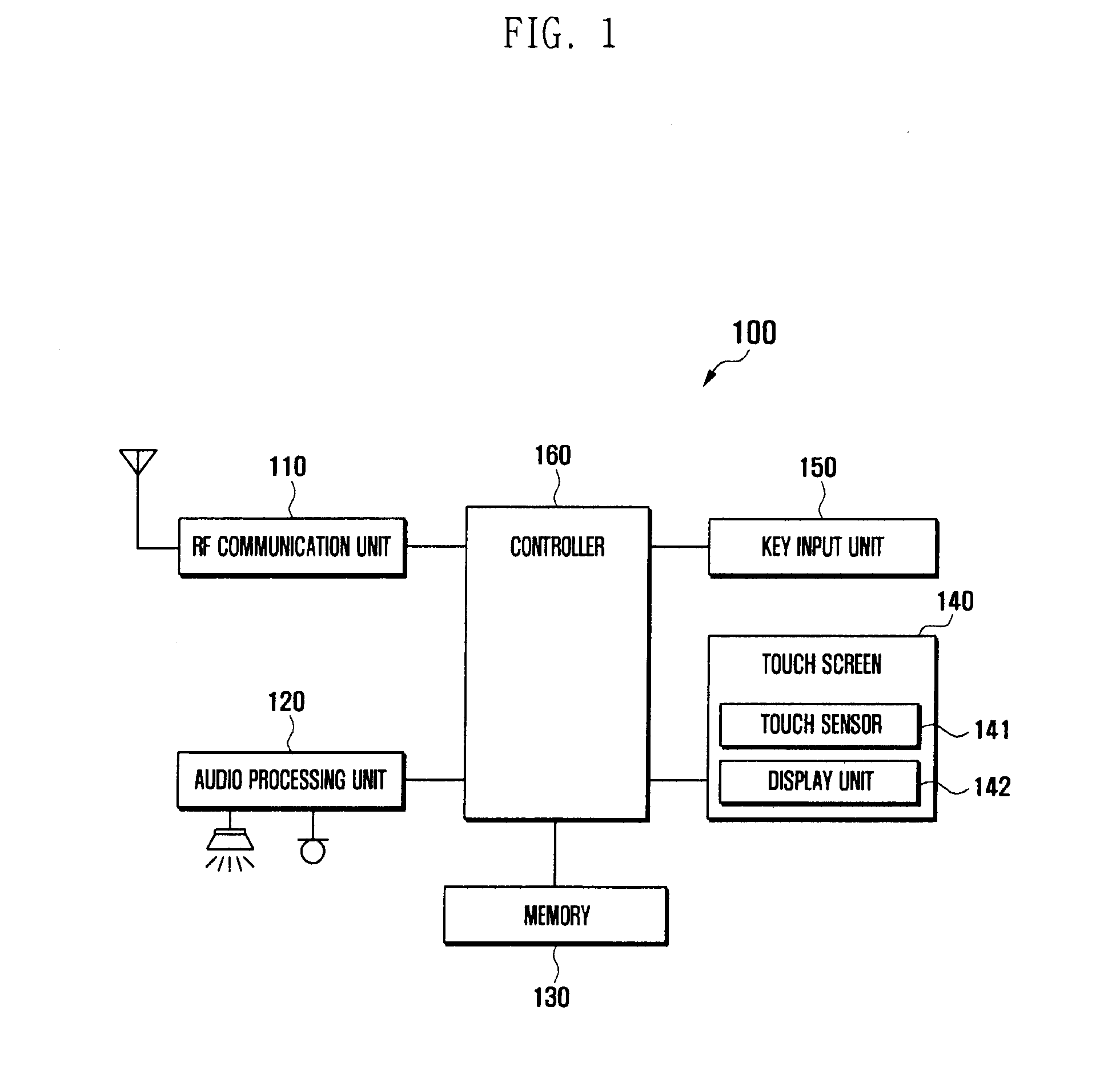
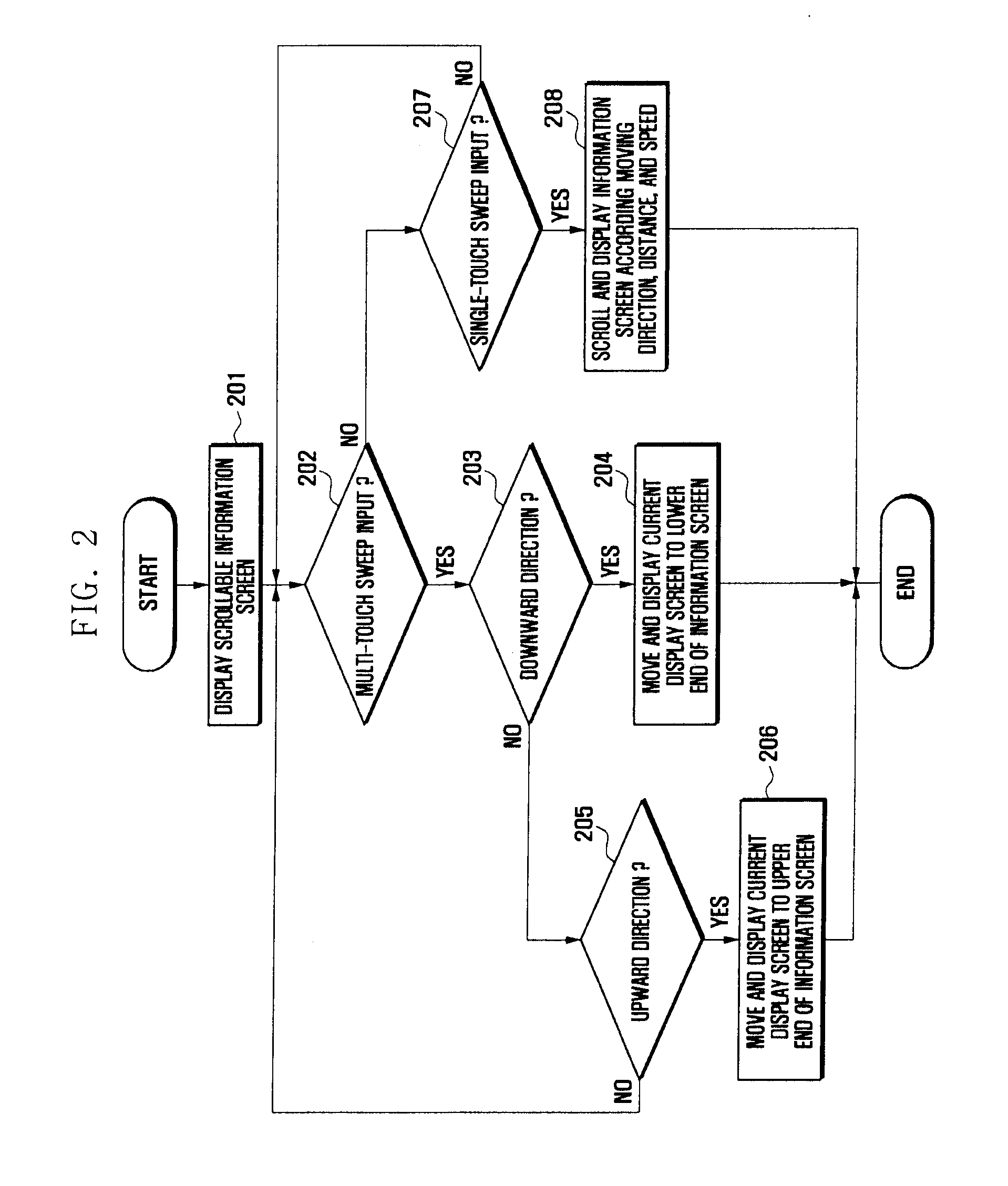
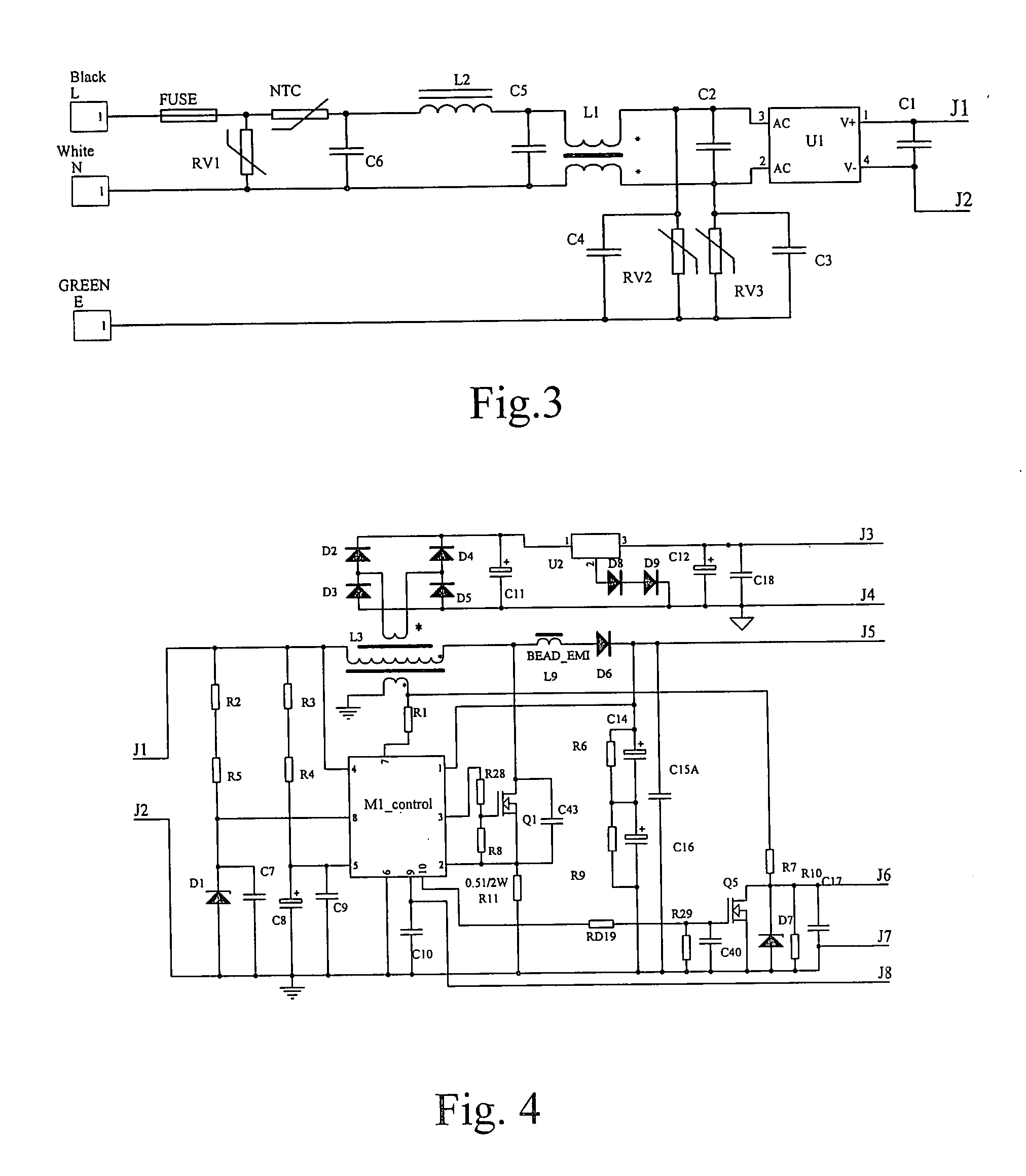
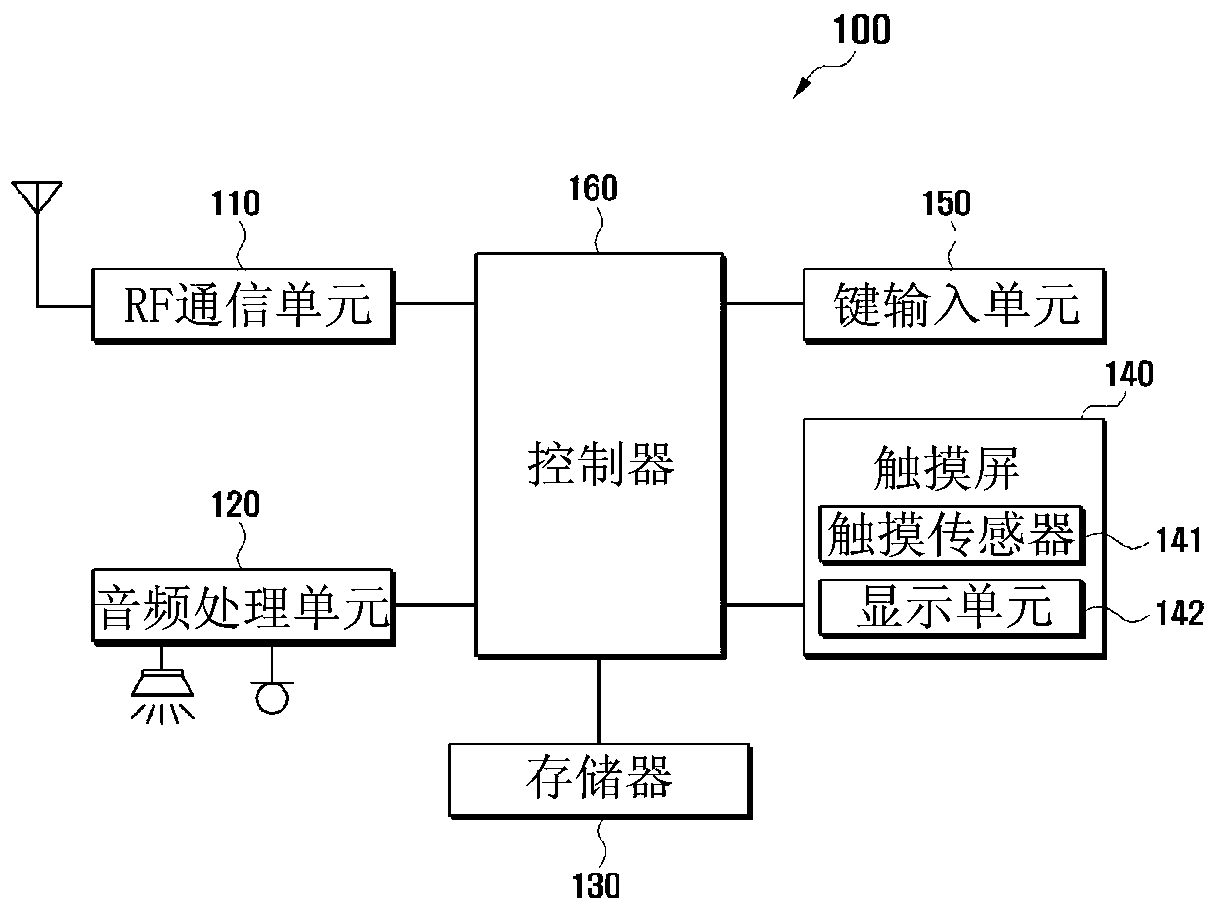
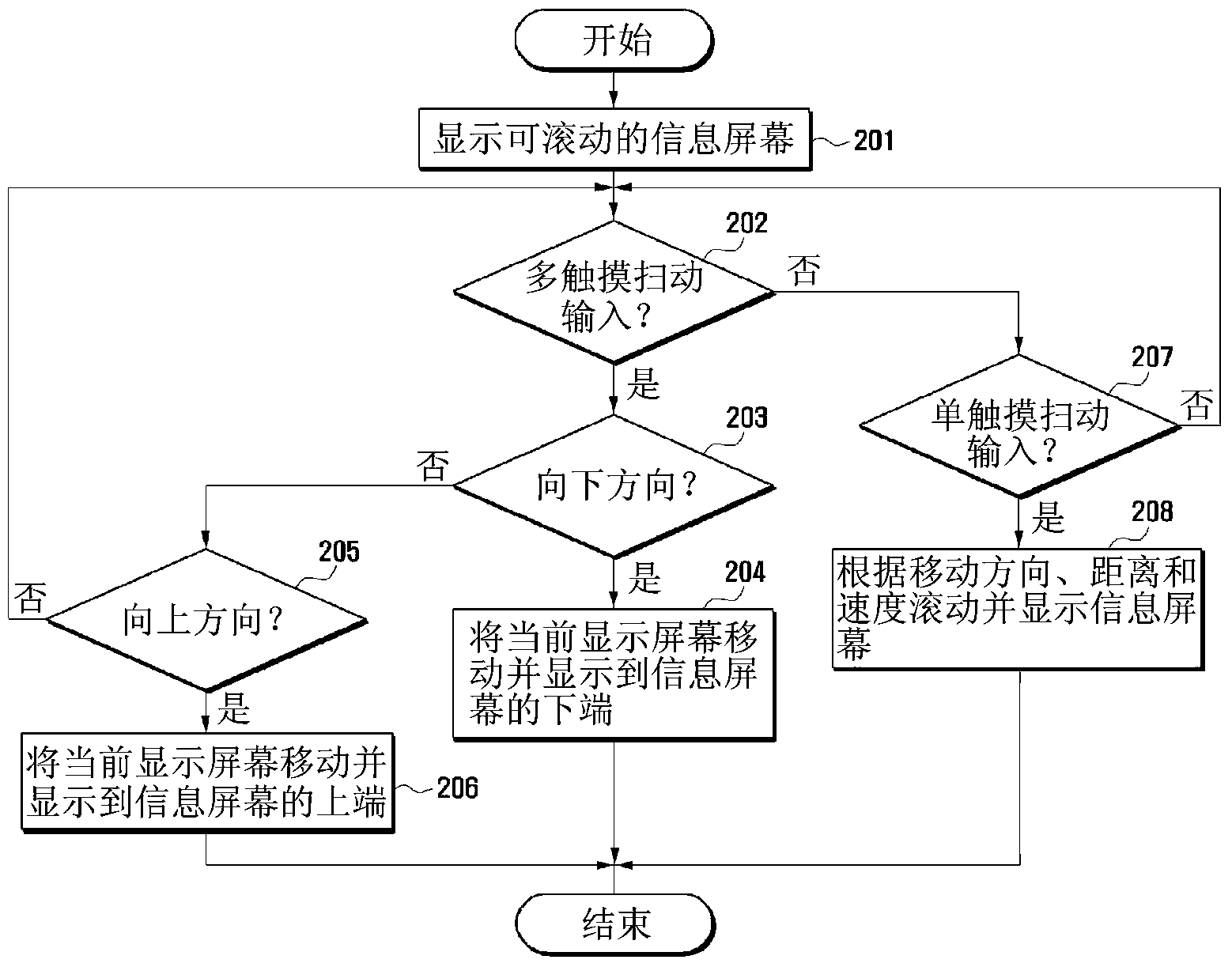
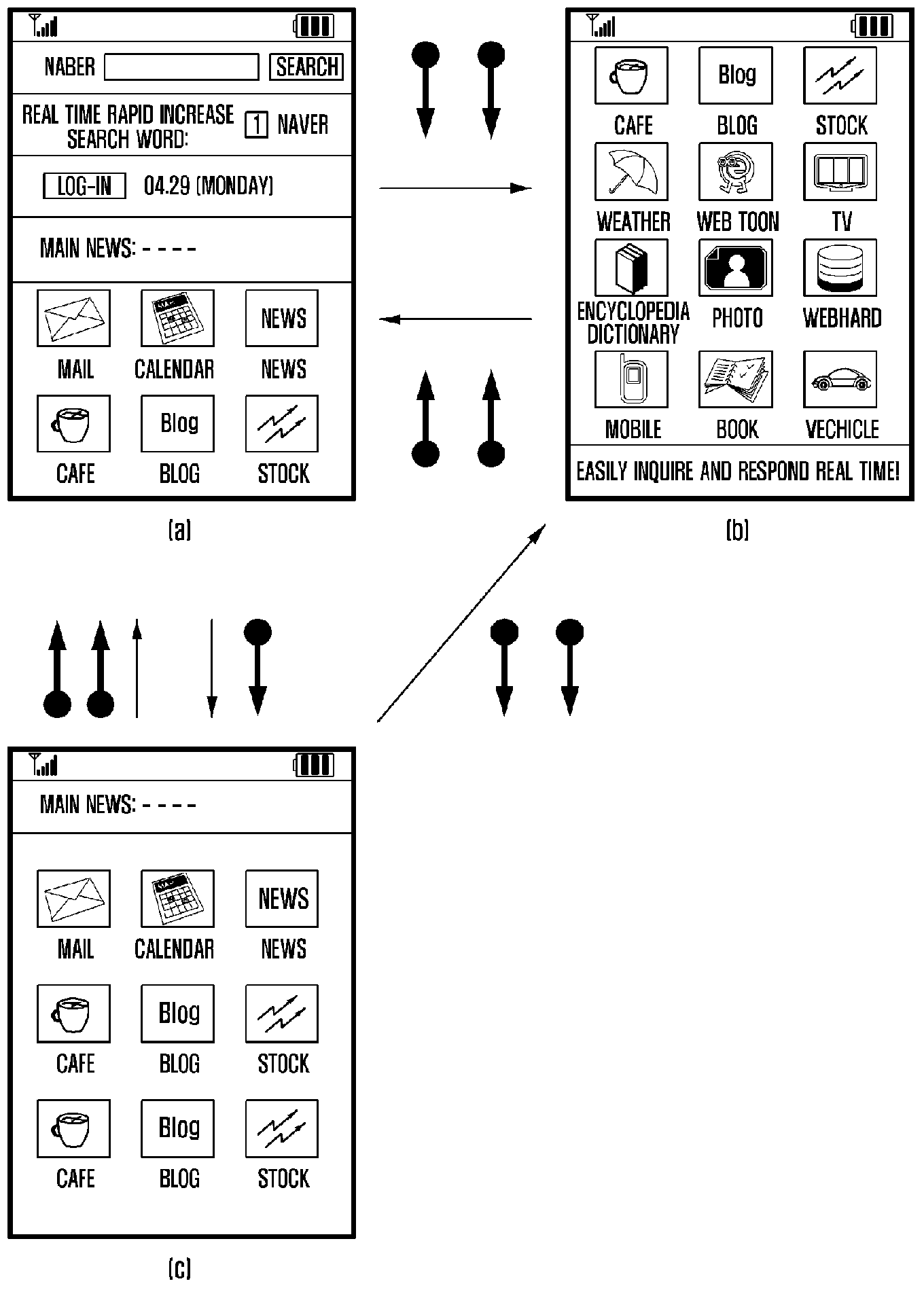
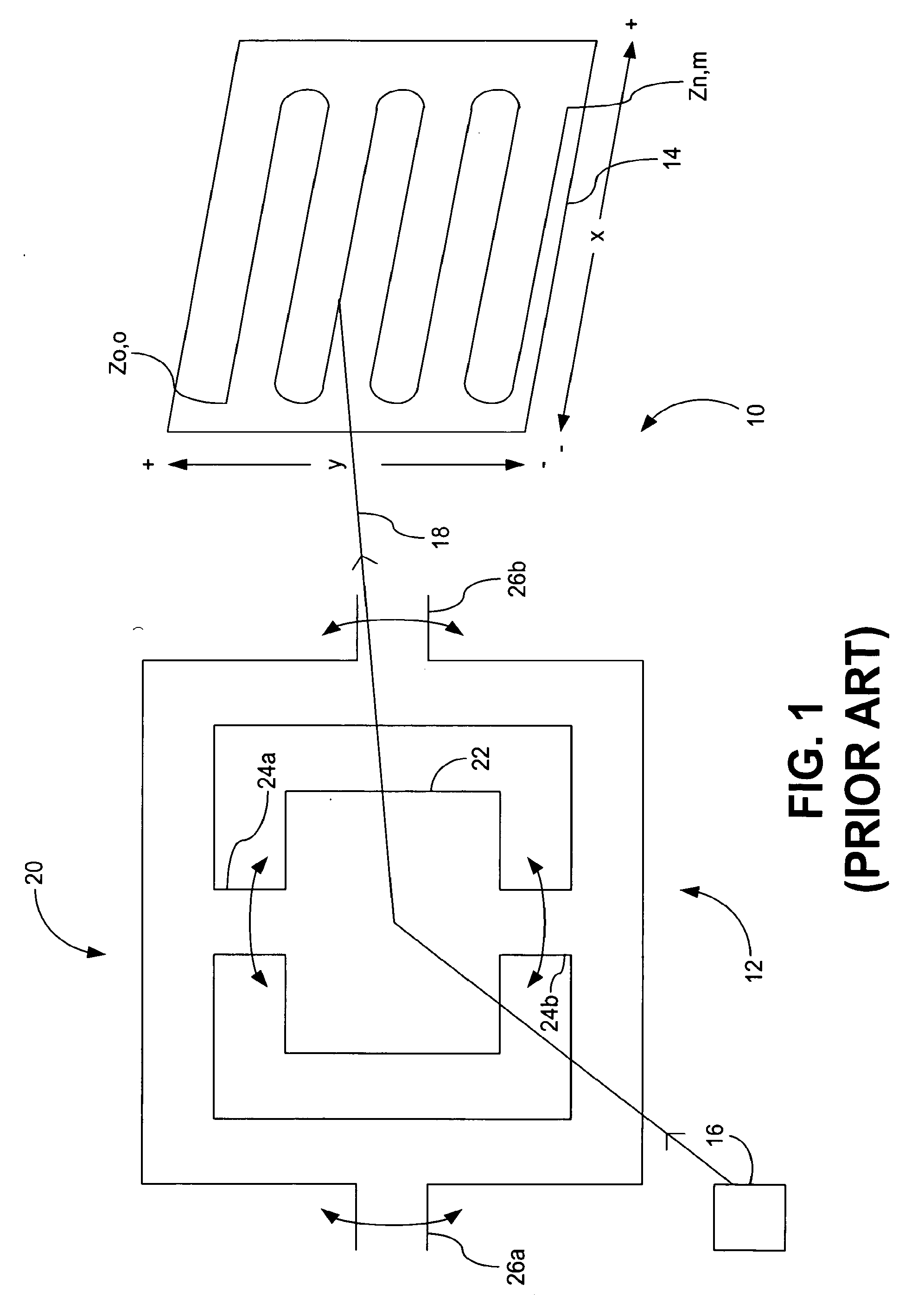
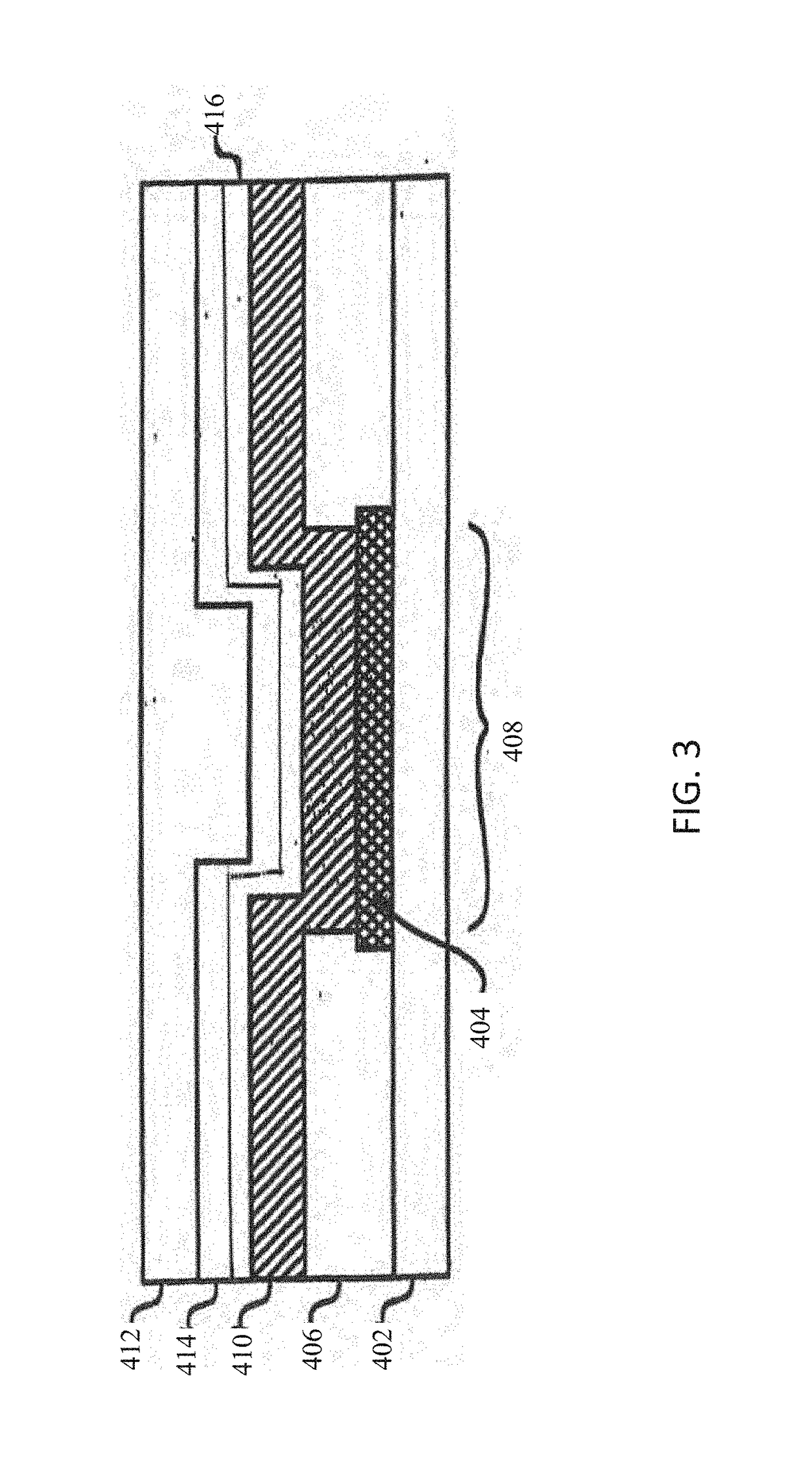
Method and apparatus for controlling touch screen in mobile terminal responsive to multi-touch inputs
InactiveUS20120096393A1Improve user convenienceScroll fastTransmissionInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringTouchscreen
A mobile terminal and method for controlling a touch screen thereof are provided, wherein multi-point touch inputs such as a multi-point sweep input and / or a multi-point double tap input are sensed by a controller, and in response to a multi-point sweep, a display screen can be scrolled at a faster rate relative to a scroll in response to sensing a single point sweep, thus enabling a user to rapidly scroll to desired portions of an information screen using e.g., a two finger sweep, and to scroll slower using a single finger sweep at the same sweep rate and during a photo album application, scrolling to other photos in response to a multi-touch input is possible while in a zoomed-in state, while panning is carried out responsive to a single point touch input.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
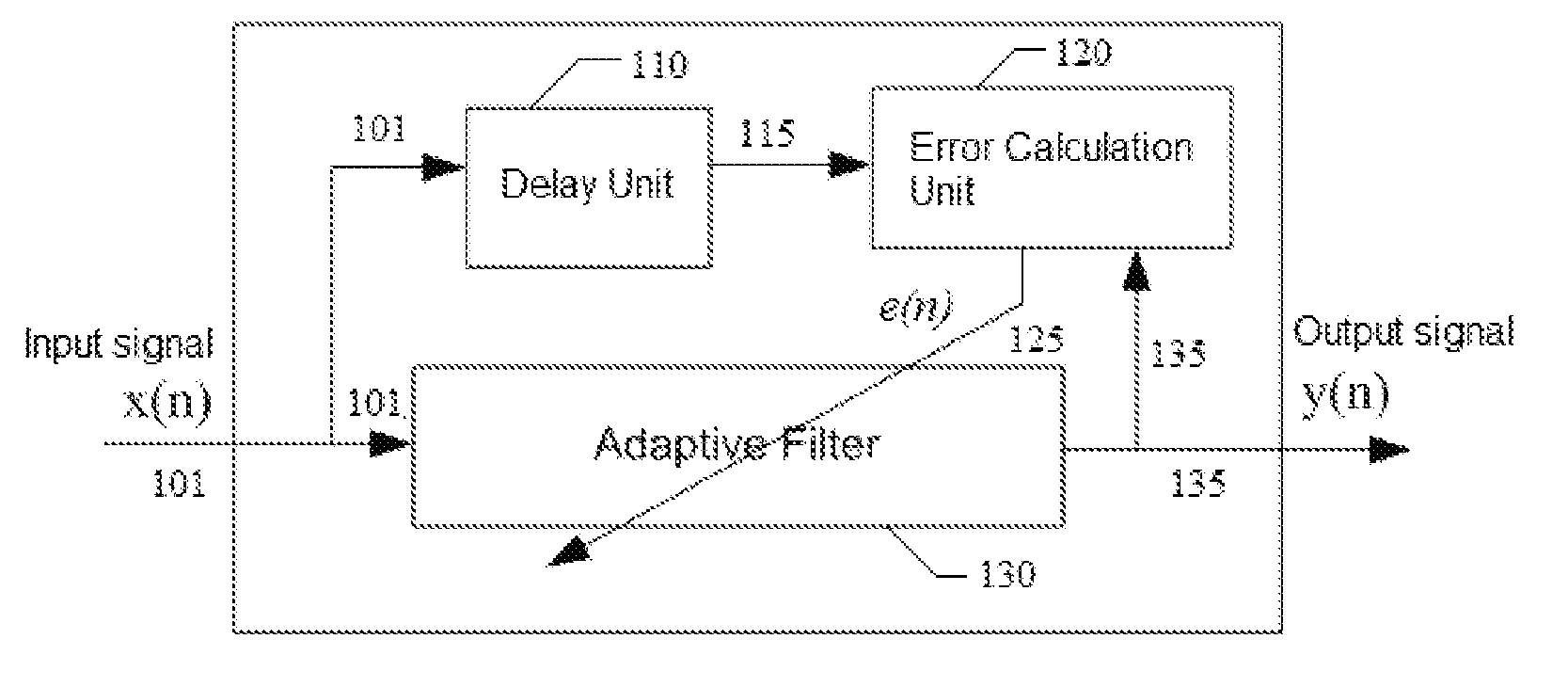
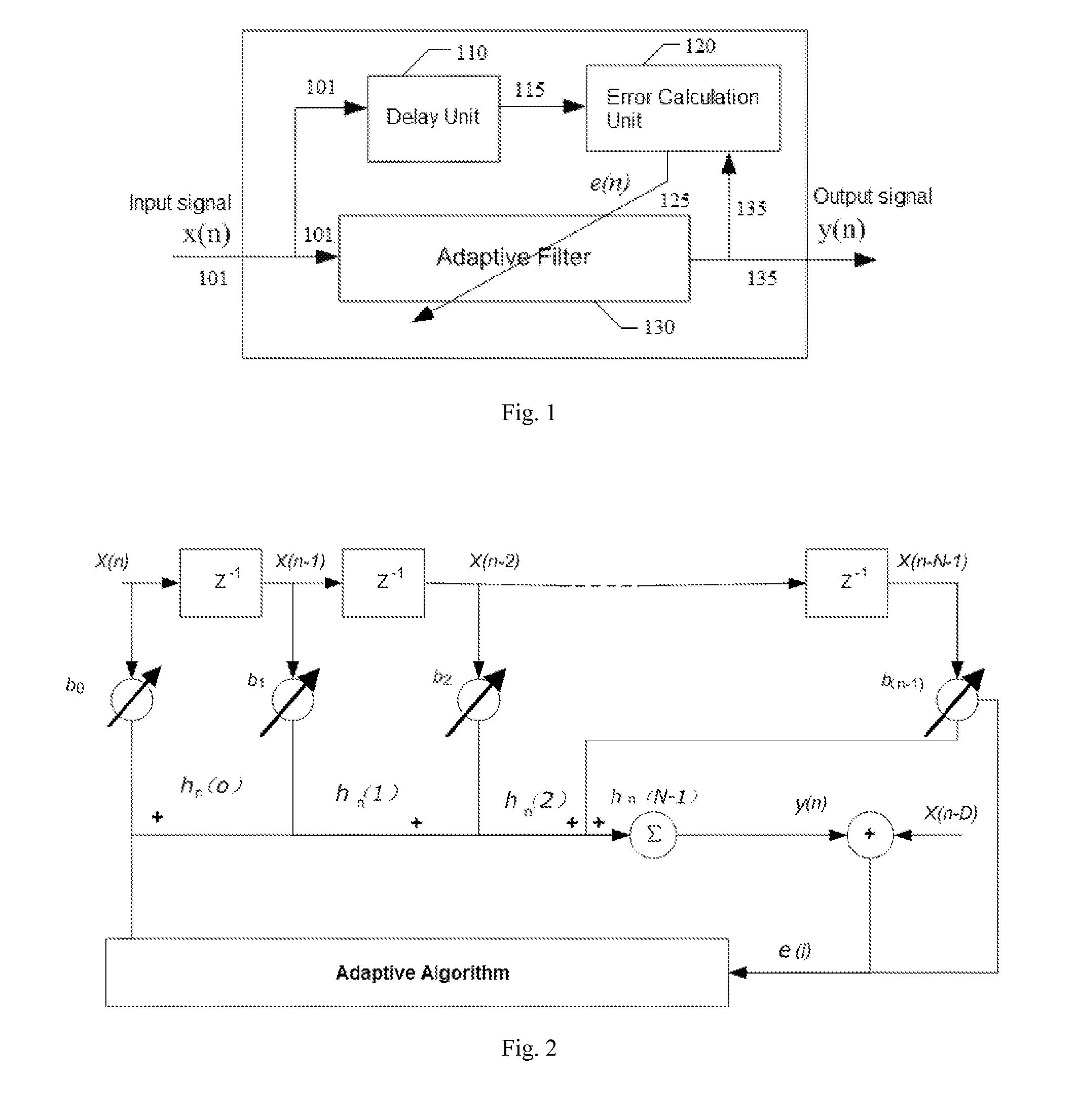
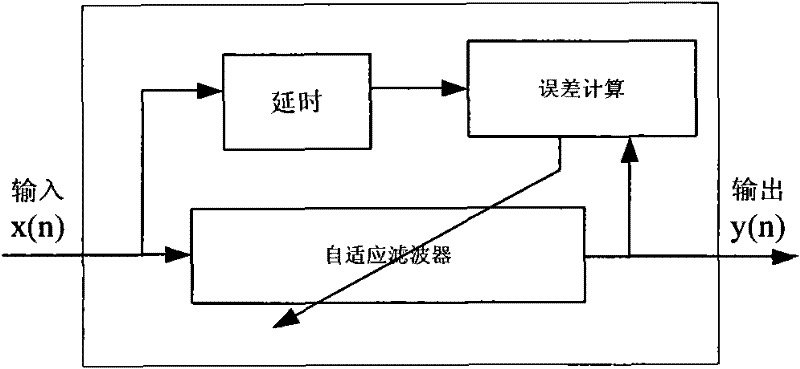
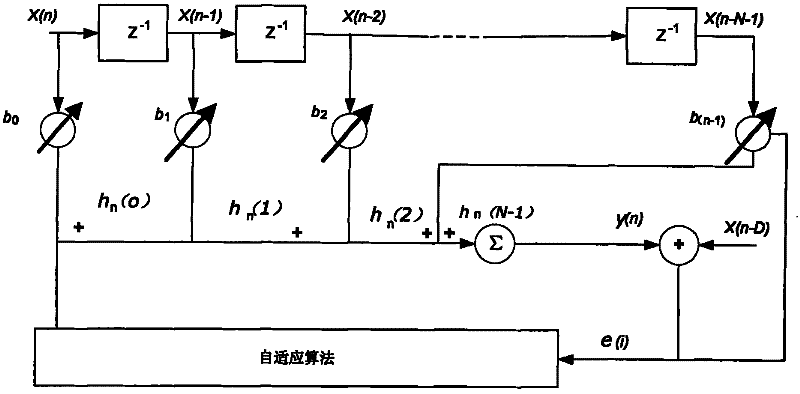
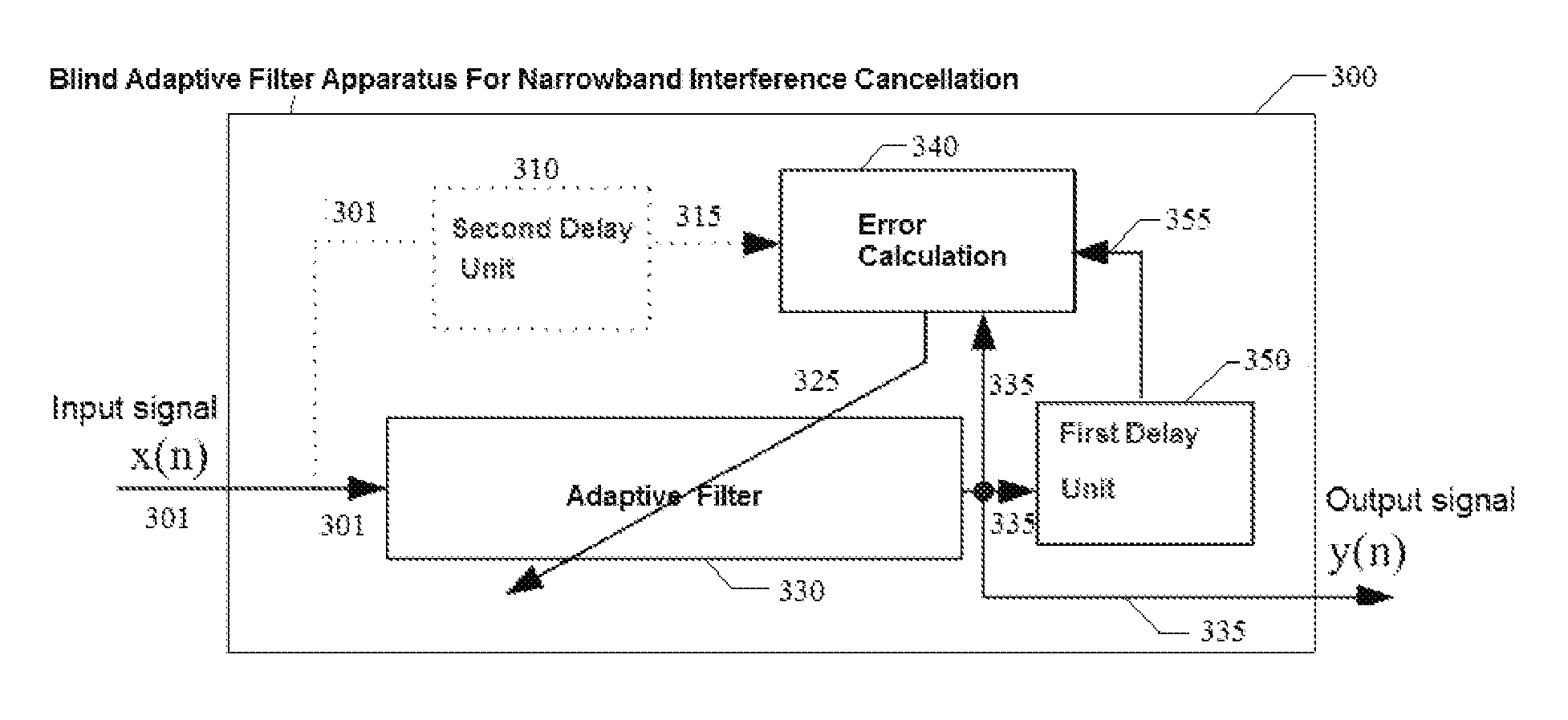
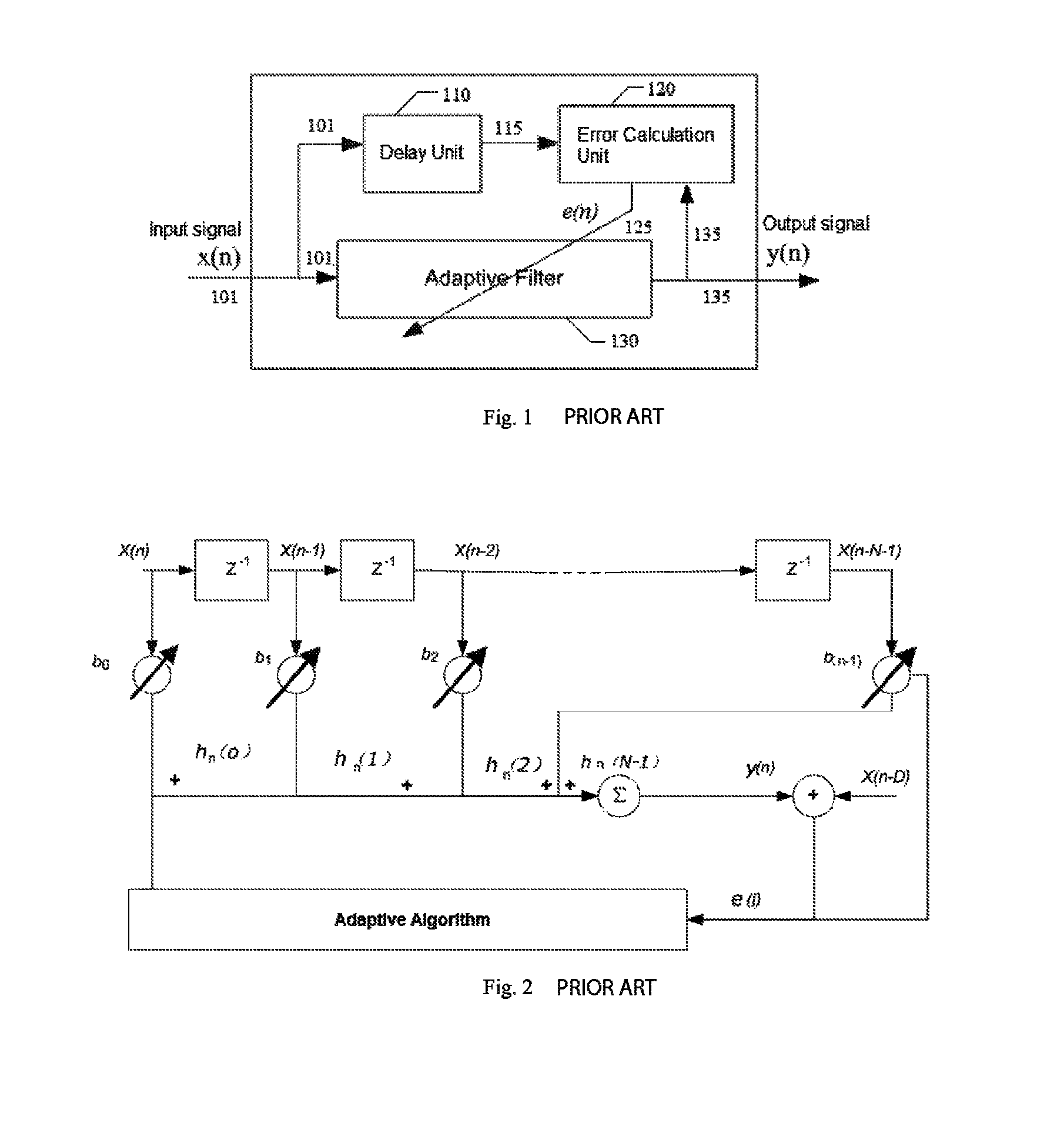
Blind adaptive filter for narrowband interference cancellation
ActiveUS20110305306A1Wide applicationError preventionDigital adaptive filtersSelf adaptiveSweep rate
The present invention relates to a blind adaptive filter for narrowband interference cancellation, which includes an adaptive filter, a delay unit coupled to the adaptive filter for generating a delayed signal with a predetermined delay length from the output signal of the adaptive filter, and an error calculation unit coupled to the adaptive filter and the delay unit. The error calculation unit compares the output signal from the adaptive filter and the delayed signal from the delay unit to extract error information, and feedback the first error information to the adaptive filter. The first error information is formed of a transfer function including a number of coefficients, and used to adjust the adaptive filter and remove interference in the next input signal. The disclosed technique is also applicable in wideband receivers, as well as resisting multiple strong narrowband interferences having a frequency sweep rate of tens of milliseconds.
Owner:MONTAGE TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
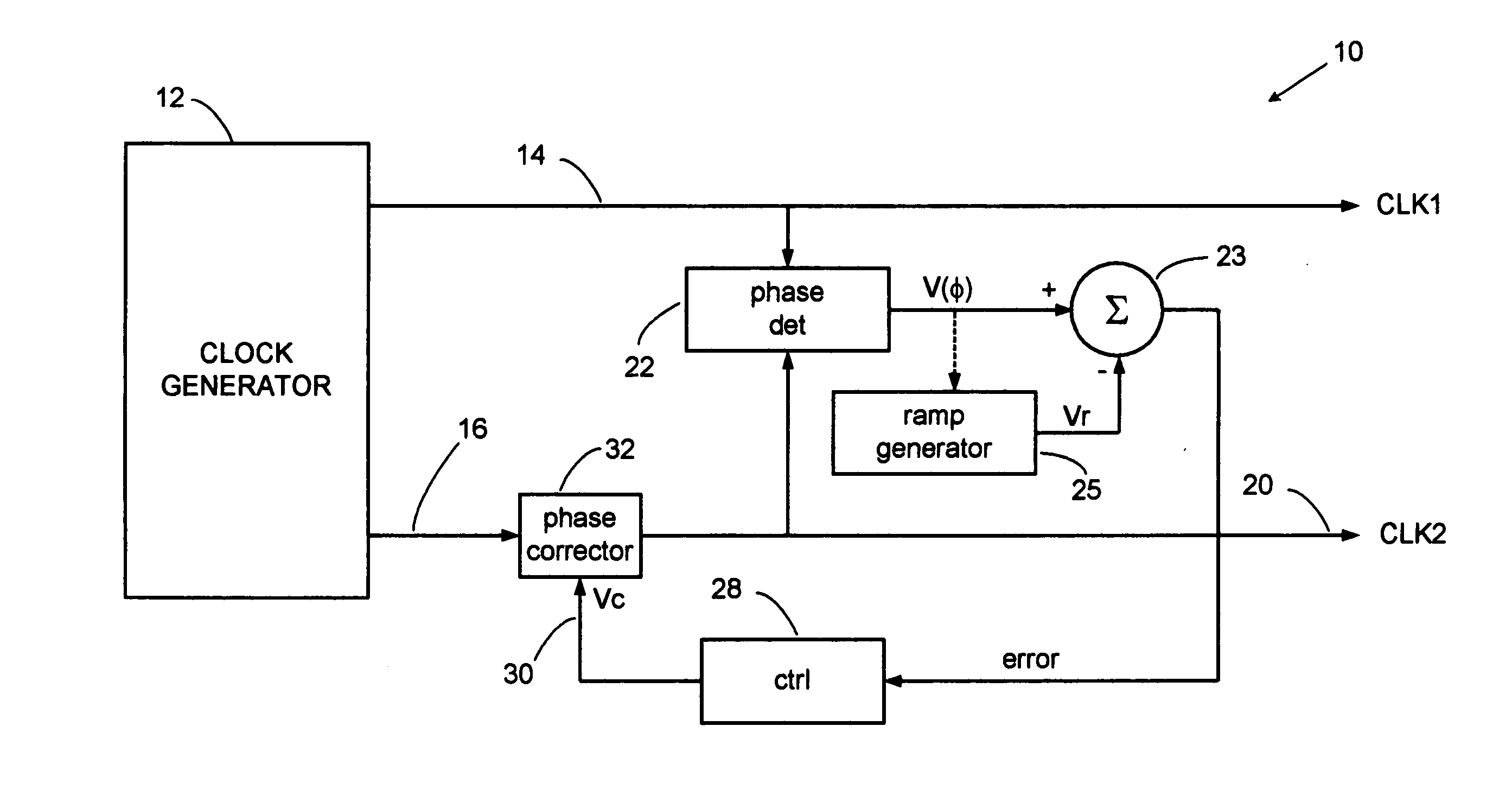
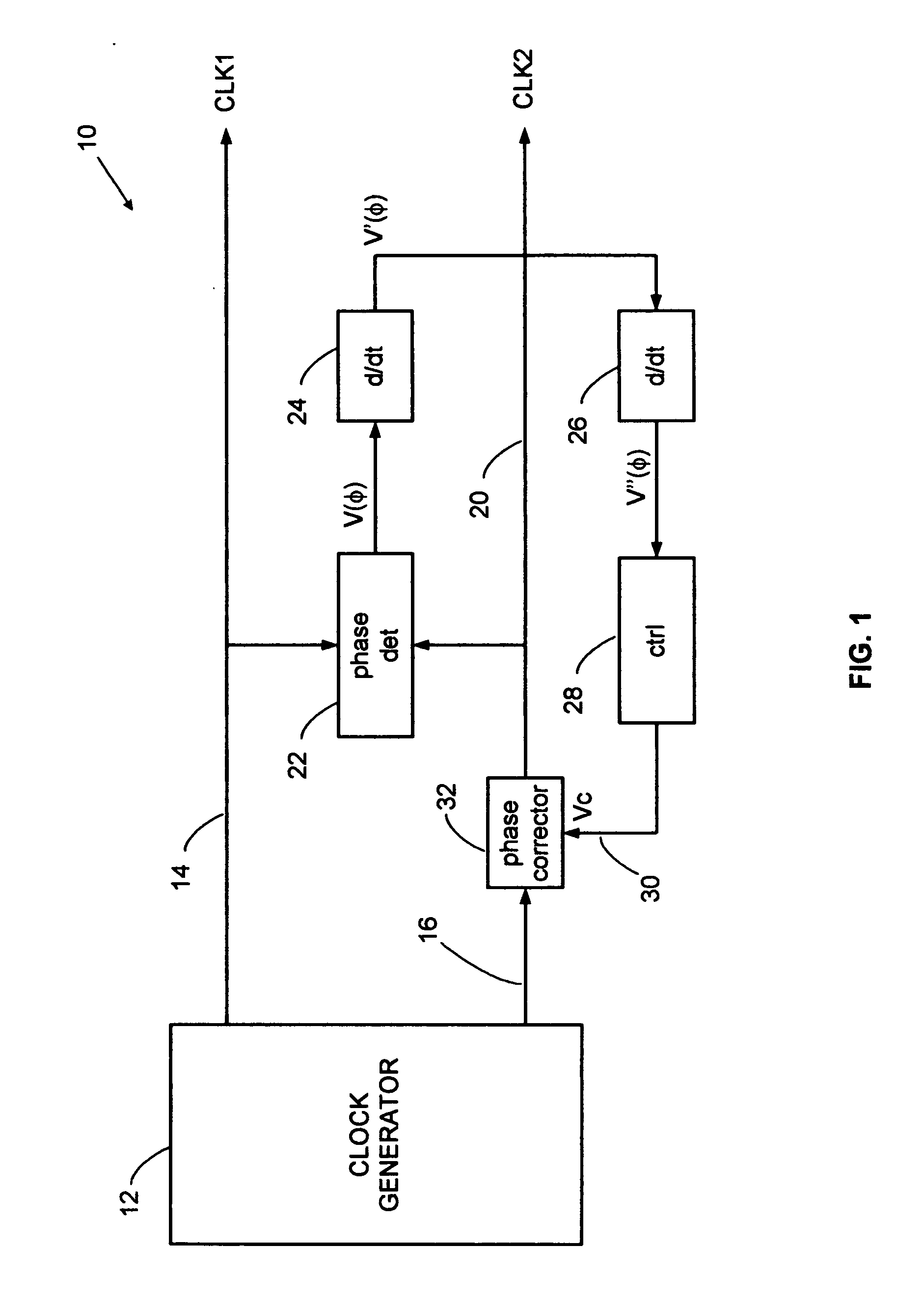
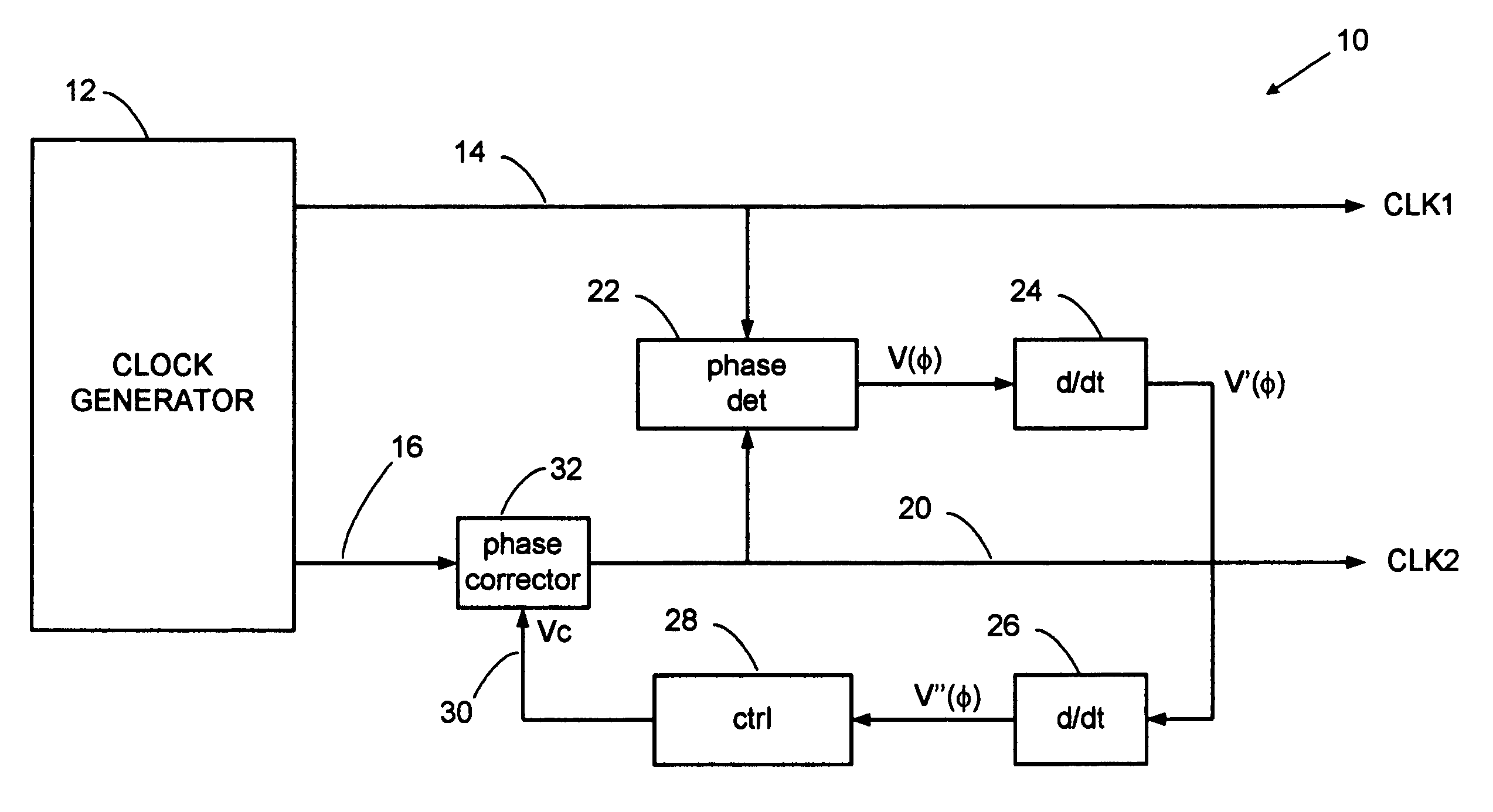
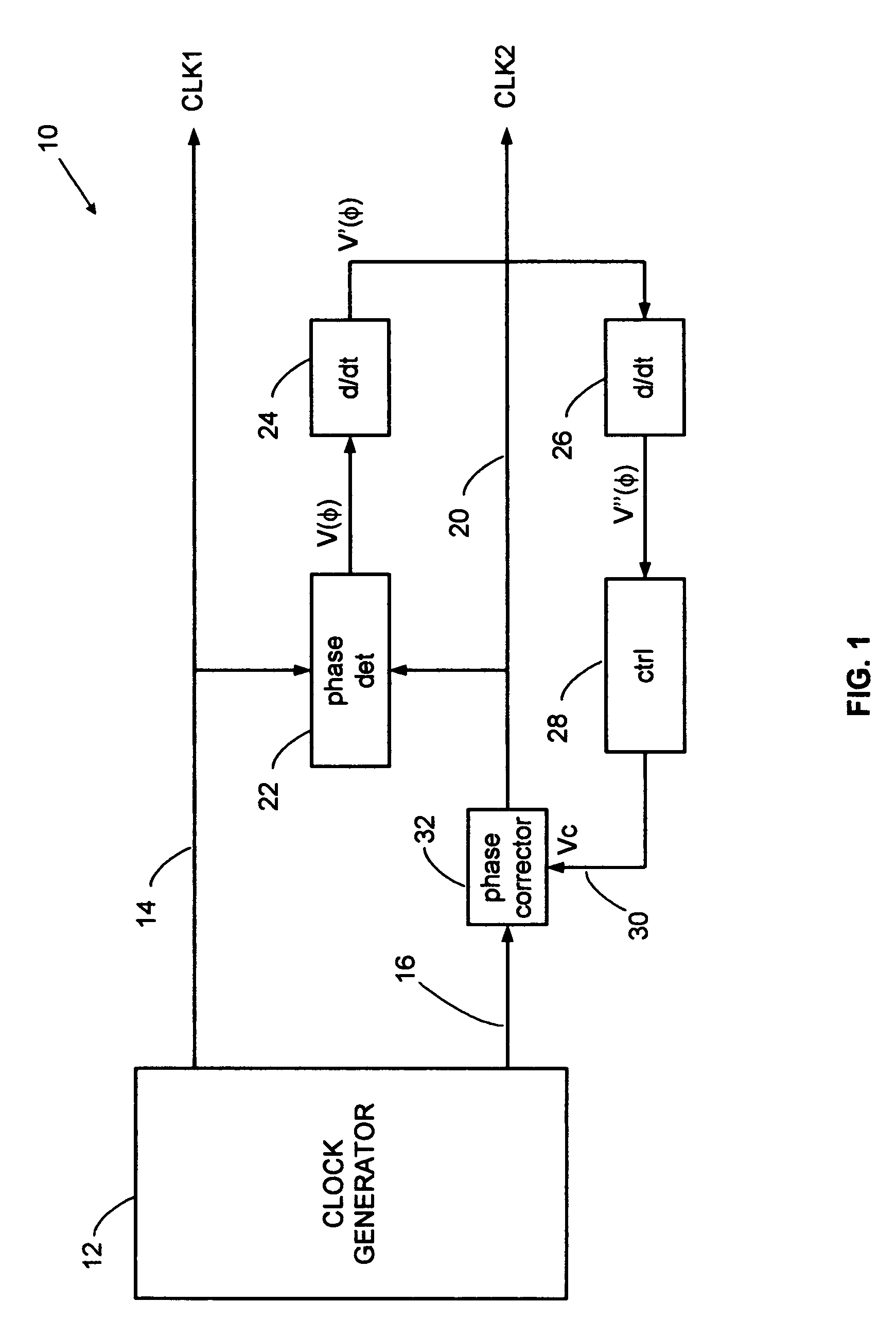
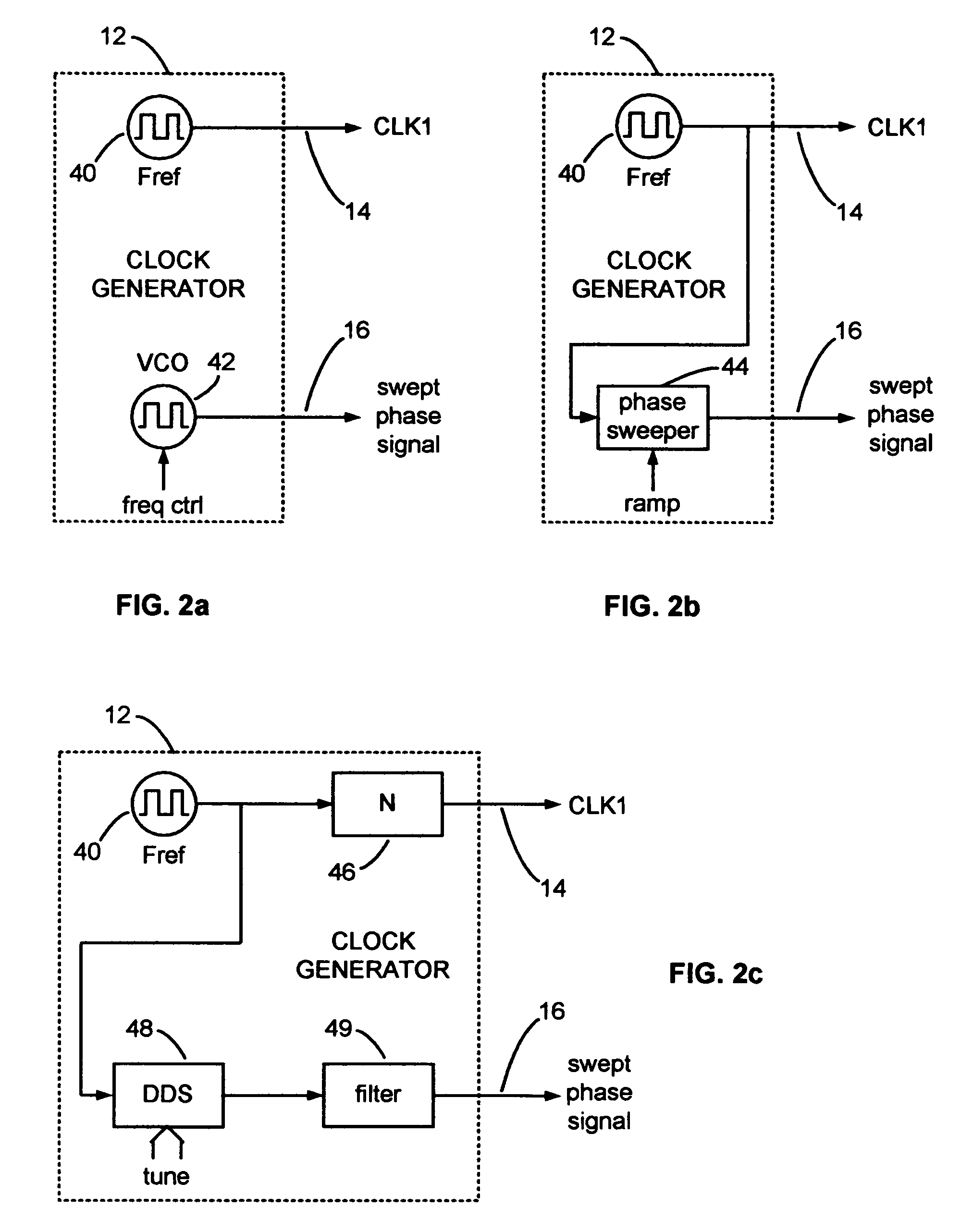
Error corrector for radar timing systems
InactiveUS20070210955A1Reduce biasOvercome limitationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase correctionRadar
A feedback loop corrects timing errors by reducing deviations from a constant radar sweep rate. Errors are detected and fed back to a phase corrector in a high gain feedback system. A precision radar rangefinder can be implemented with a direct digital synthesizer (DDS) that includes feedback error correction for reducing range errors by, for example, 100 times, or to 0.1 mm. An error-corrected DDS swept timing system can enable a new generation of highly flexible, repeatable and accurate radar, laser and guided wave rangefinders.
Owner:MCEWAN TECH
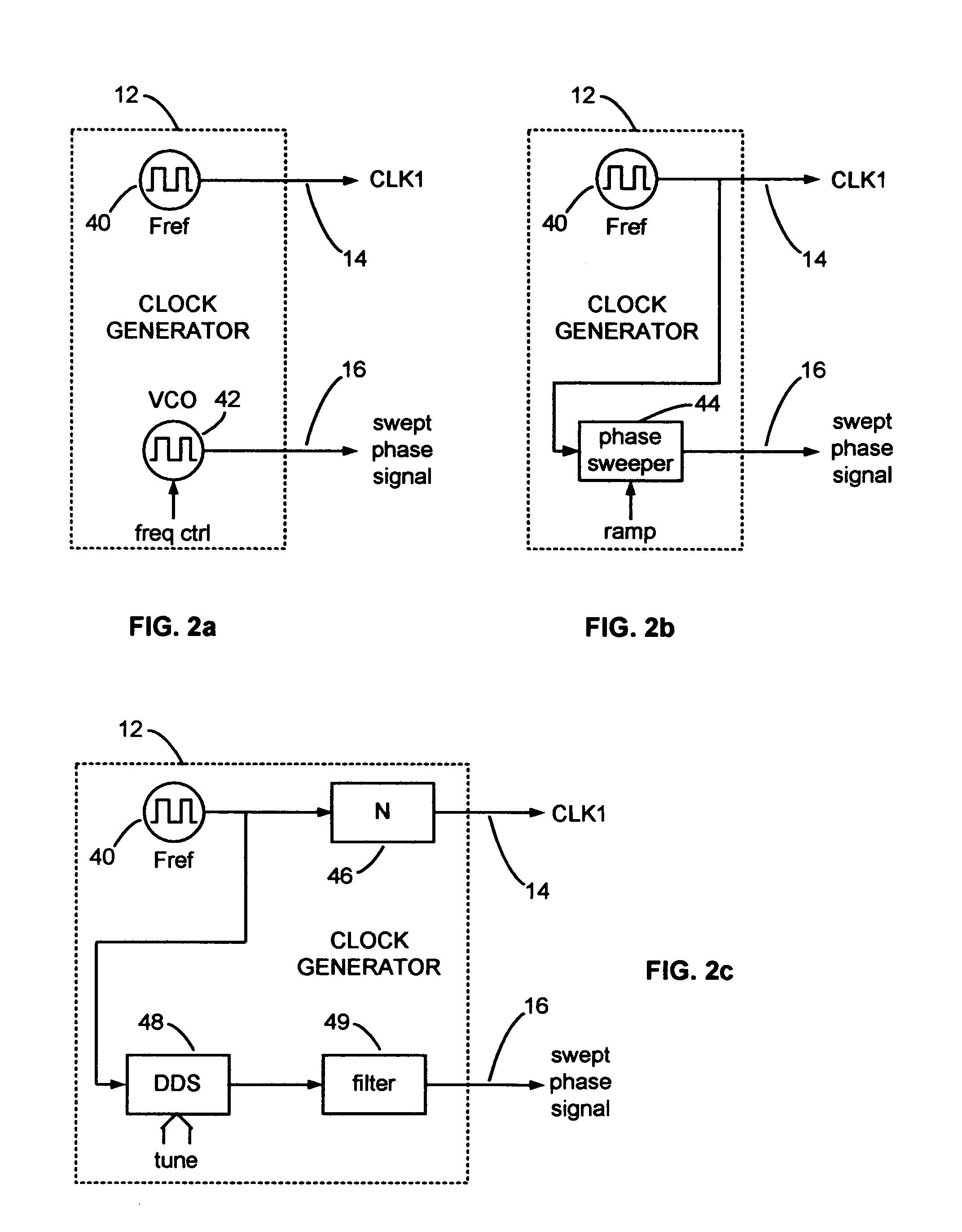
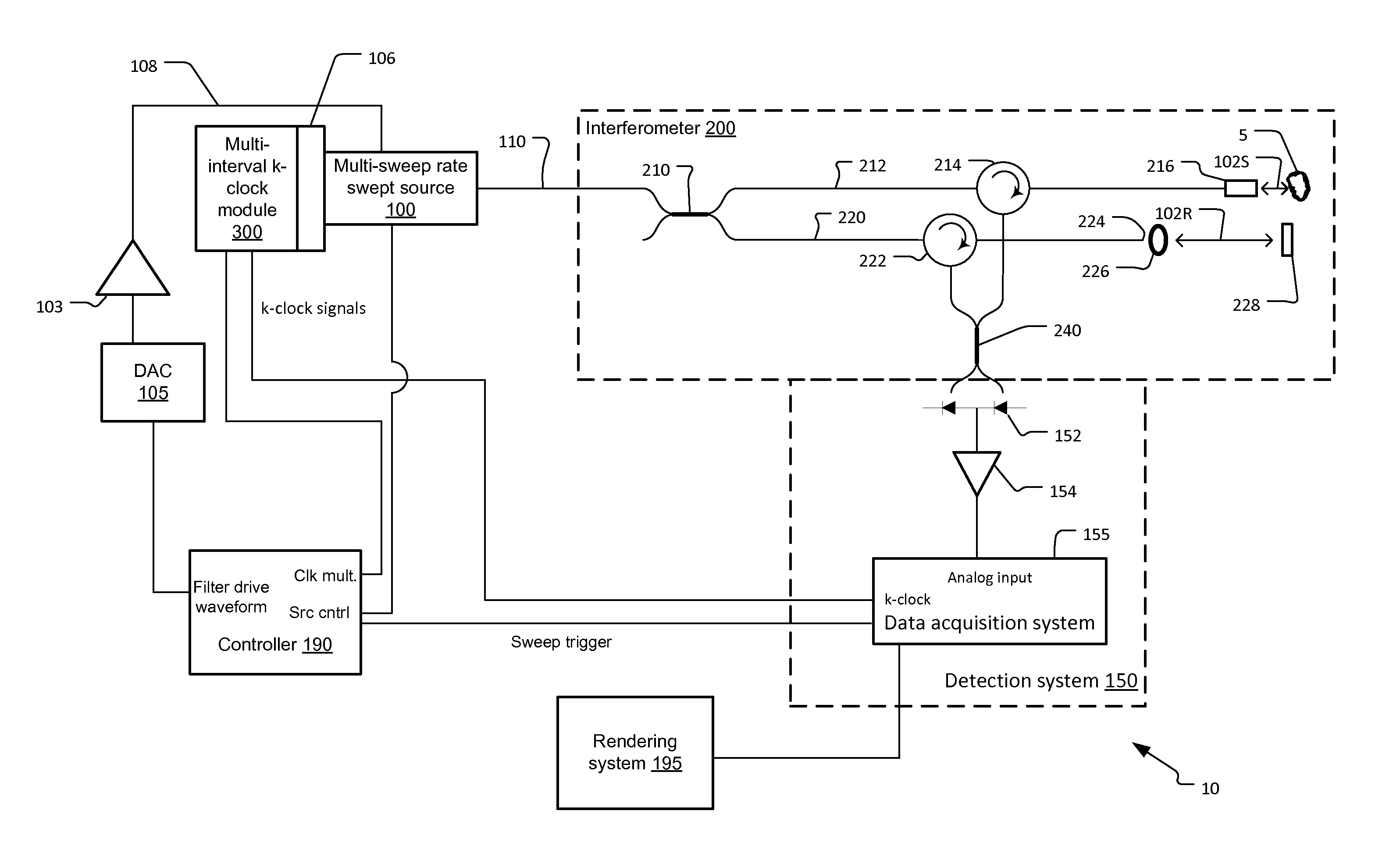
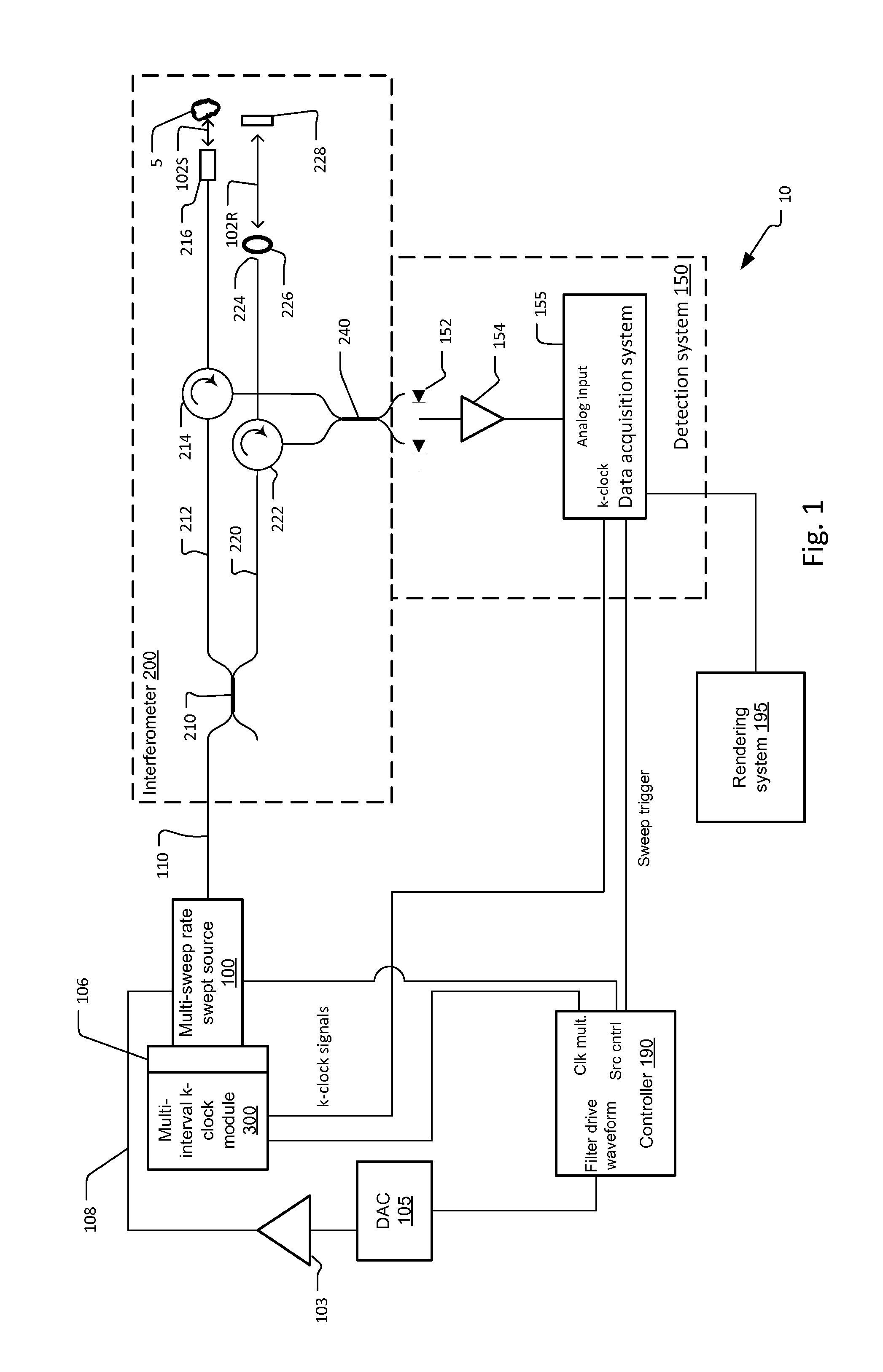
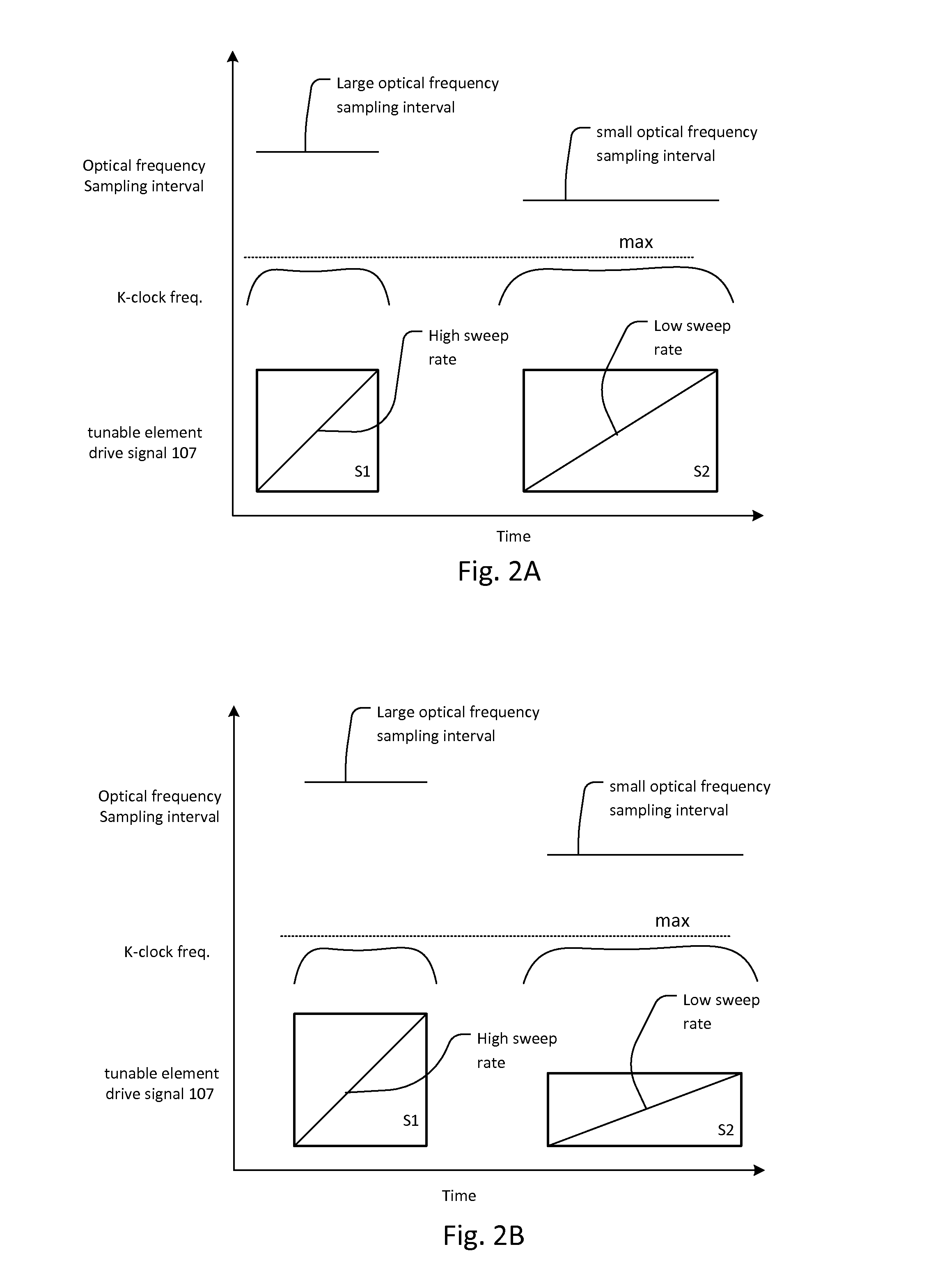
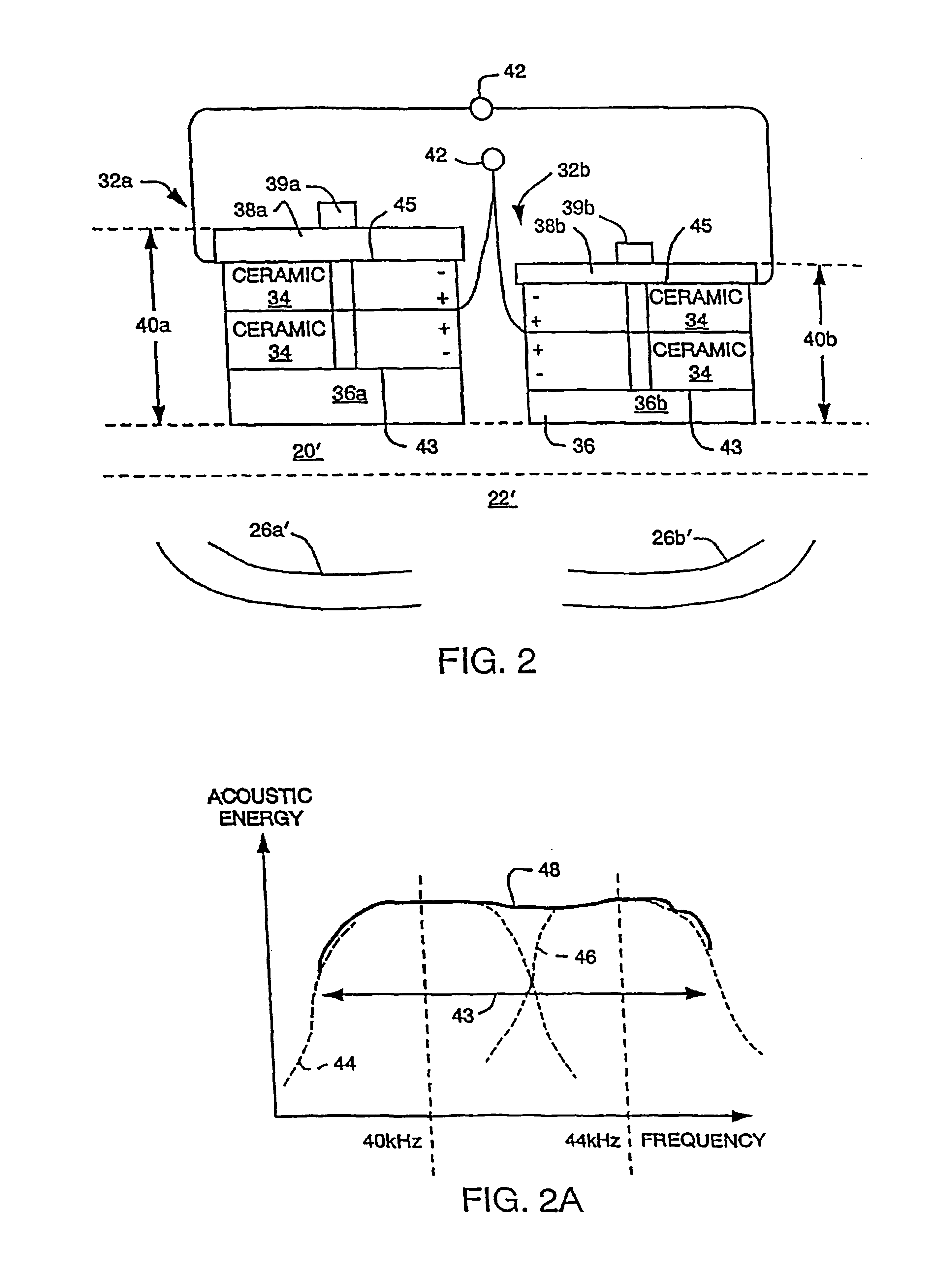
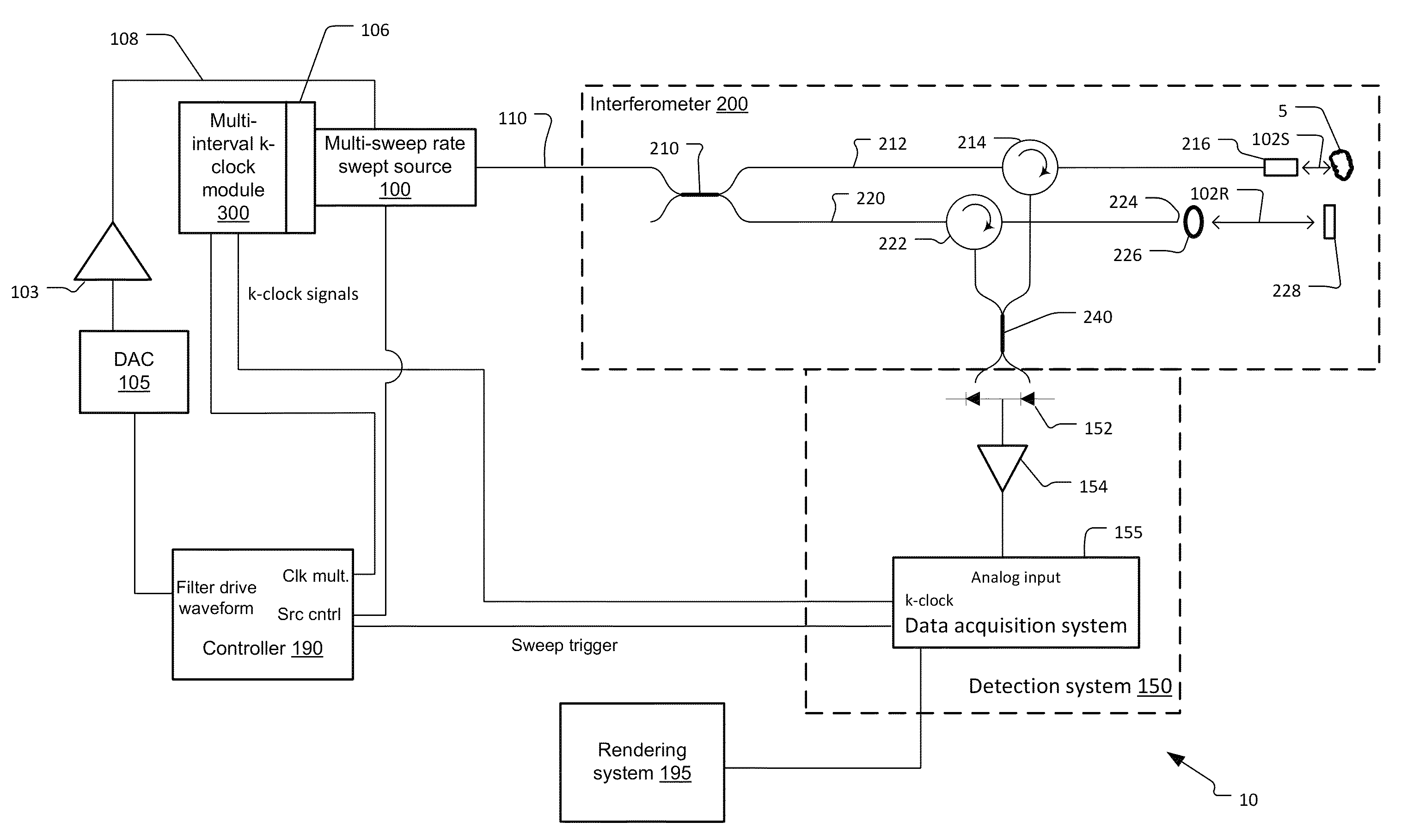
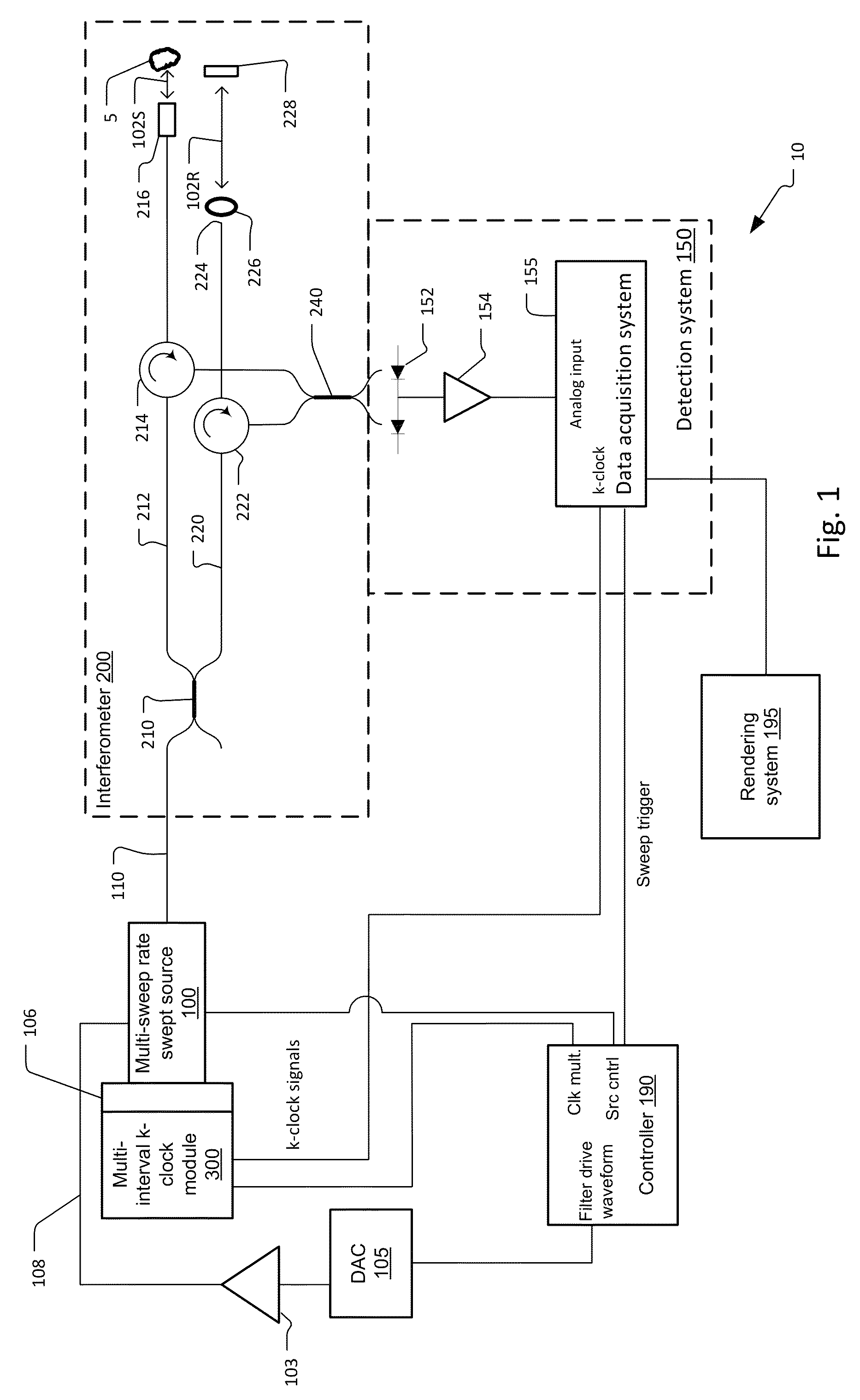
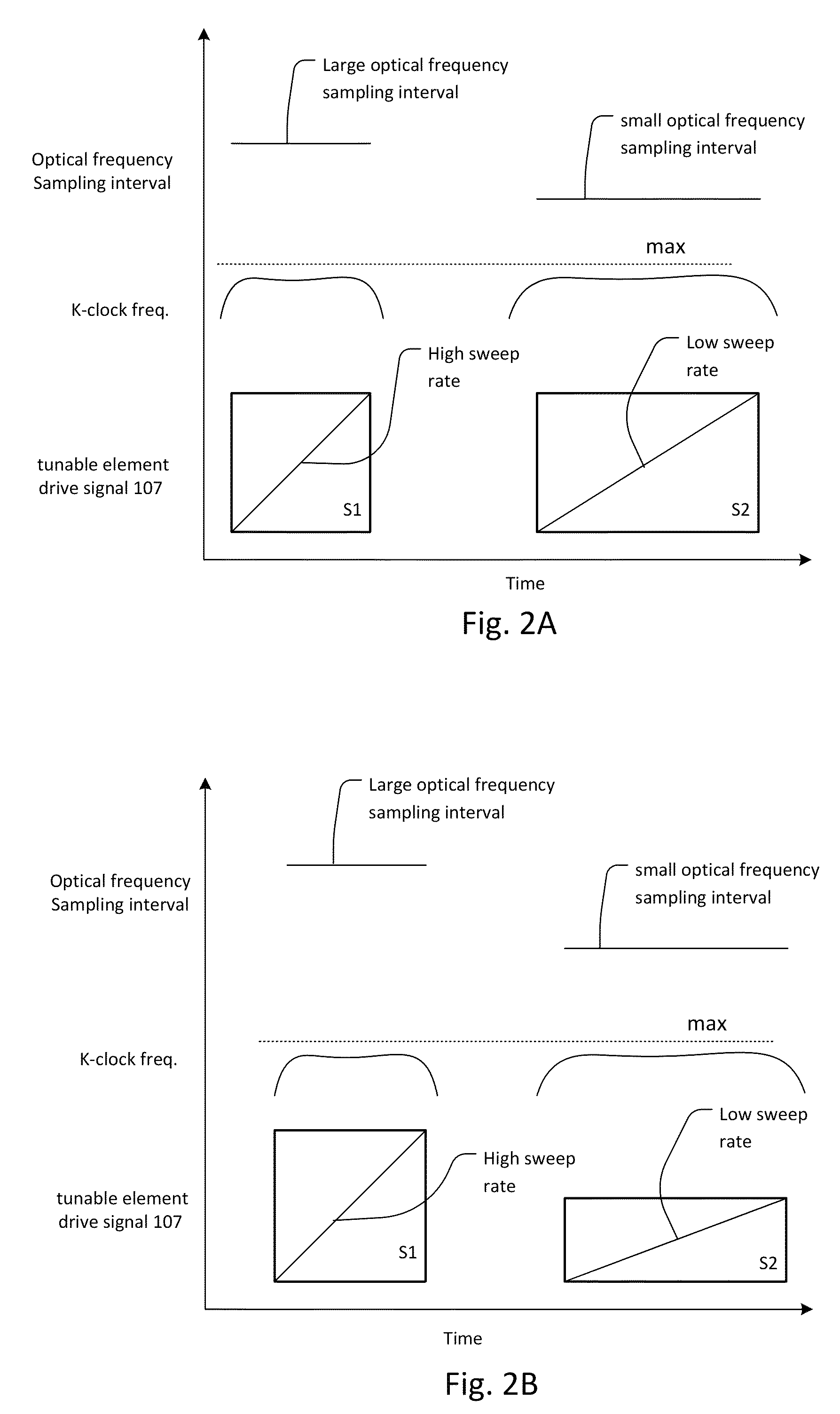
Multi-speed OCT swept source with optimized k-clock
An optical coherence tomography system utilizes an optical swept source that frequency scans at least two different sweep rates. In this way, the system can perform large depth scans of the sample and then the same system can perform shorter depth high precision scans, in one specific example. In order to optimally use the analog to digital converter that samples the interference signal, the system further samples the interference signals at different optical frequency sampling intervals depending upon the selected sweep rates of the optical swept source. This allows the system to adapt to different sweep rates in an optimal fashion.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
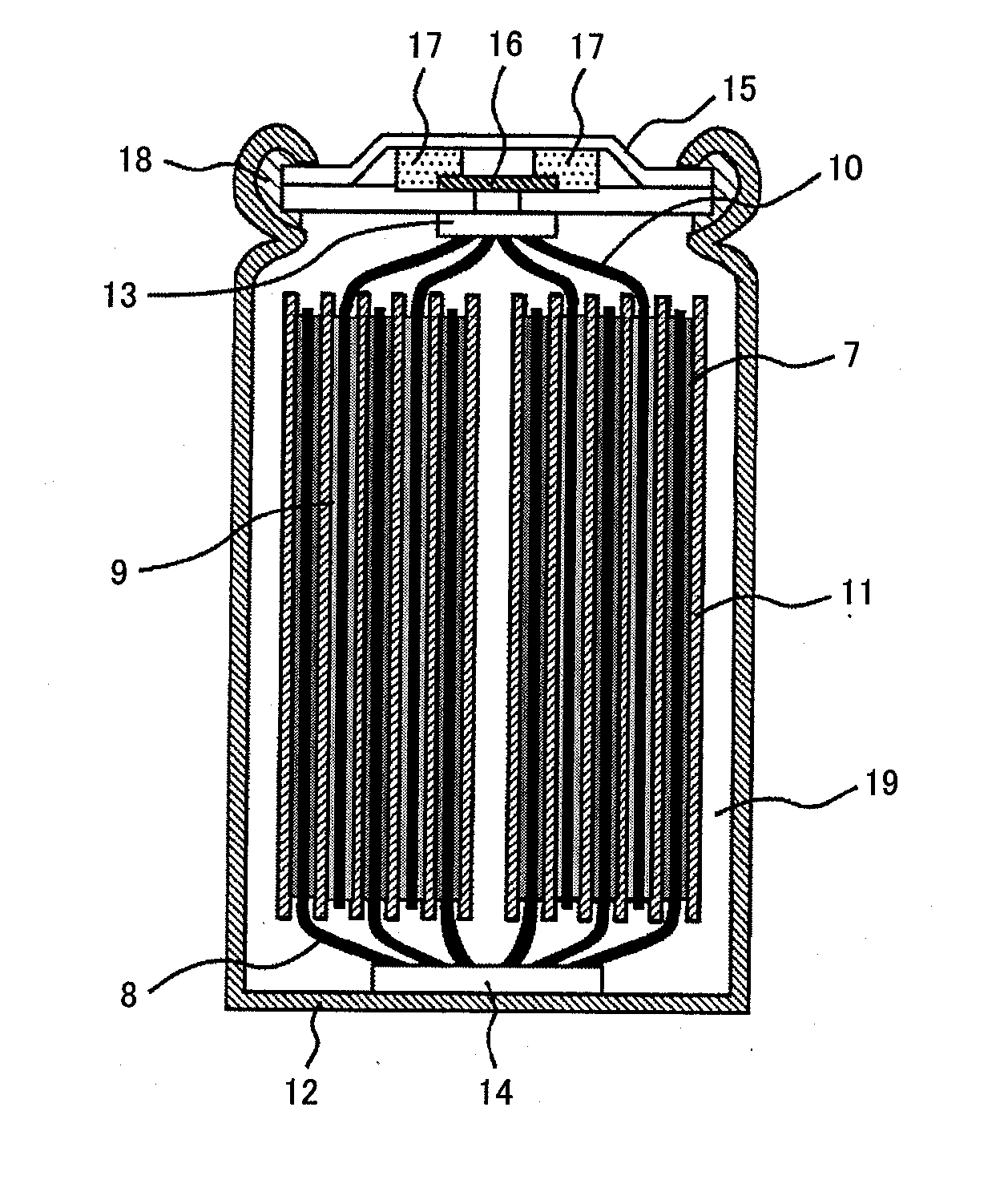
Lithium-ion secondary battery
InactiveUS20120100436A1Solution to short lifeIncrease battery outputCell electrodesOrganic electrolyte cellsSolventCarbonate
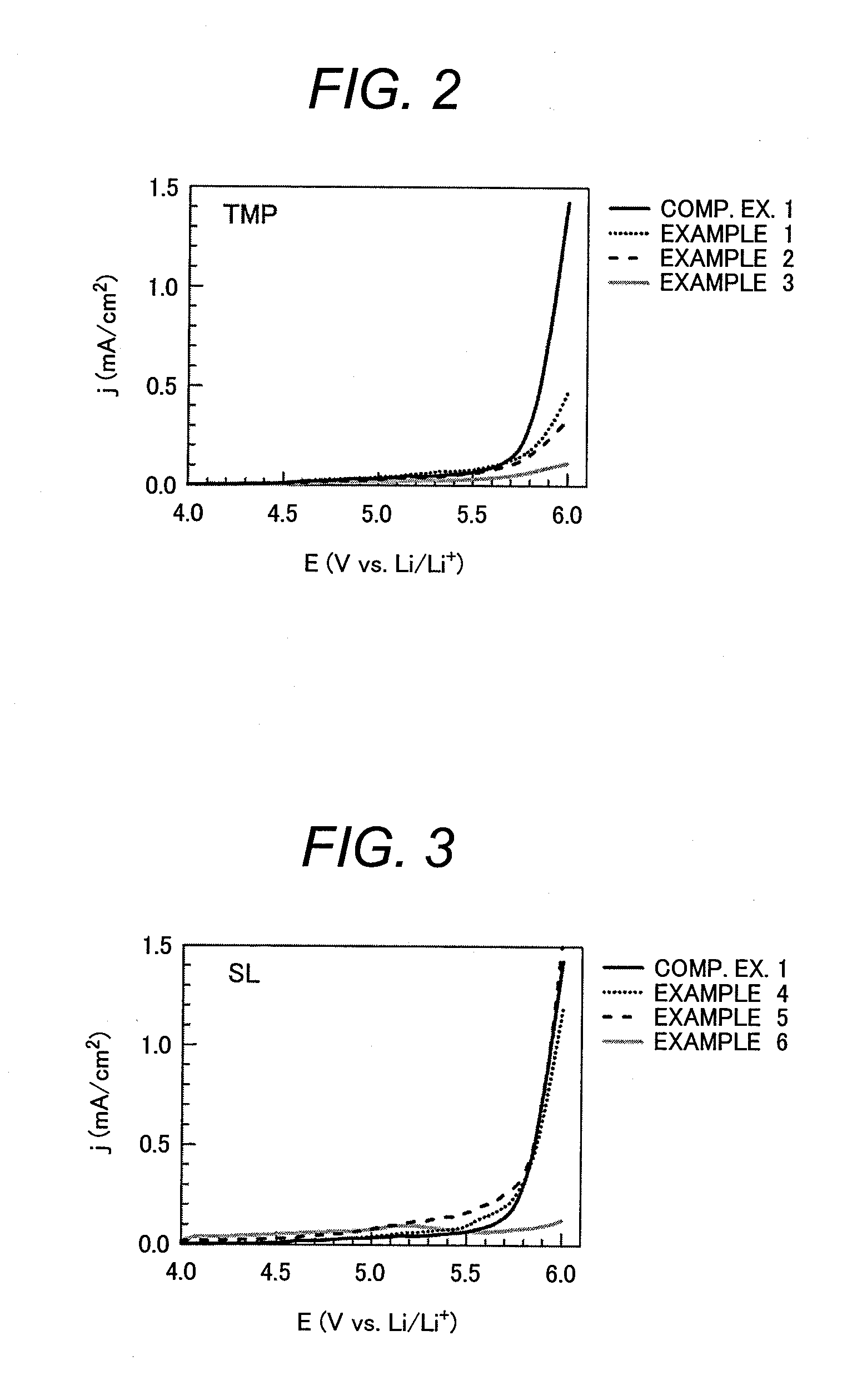
Disclosed is a lithium-ion secondary battery which includes a carbonaceous material in an anodic active material mix, and a cyclic carbonate and a chain carbonate both in an electrolytic solution. The solvent contains an additive which is a substance having a LUMO energy determined through molecular orbital calculation of lower than the LUMO energy of ethylene carbonate determined through molecular orbital calculation and having a HOMO energy lower than the HOMO energy of vinylene carbonate determined through molecular orbital calculation, the electrolytic solution contains LiPF6 or LiBF4 as an electrolyte, and the electrolytic solution shows a reduction-reaction current of −0.05 mA / cm2 (provided that a reaction current on the reducing side be negative) or less at a potential lower than 1 V and shows an oxidation-reaction current of 0.5 mA / cm2 (provided that a reaction current on the oxidizing side be positive) or more at a potential higher than 5.7 V in an LSV measurement at a potential sweep rate of 1 mV / s using a glassy-carbon disk electrode as a working electrode, a platinum electrode as a counter electrode, and a lithium electrode as a reference electrode.
Owner:HITACHI VEHICLE ENERGY
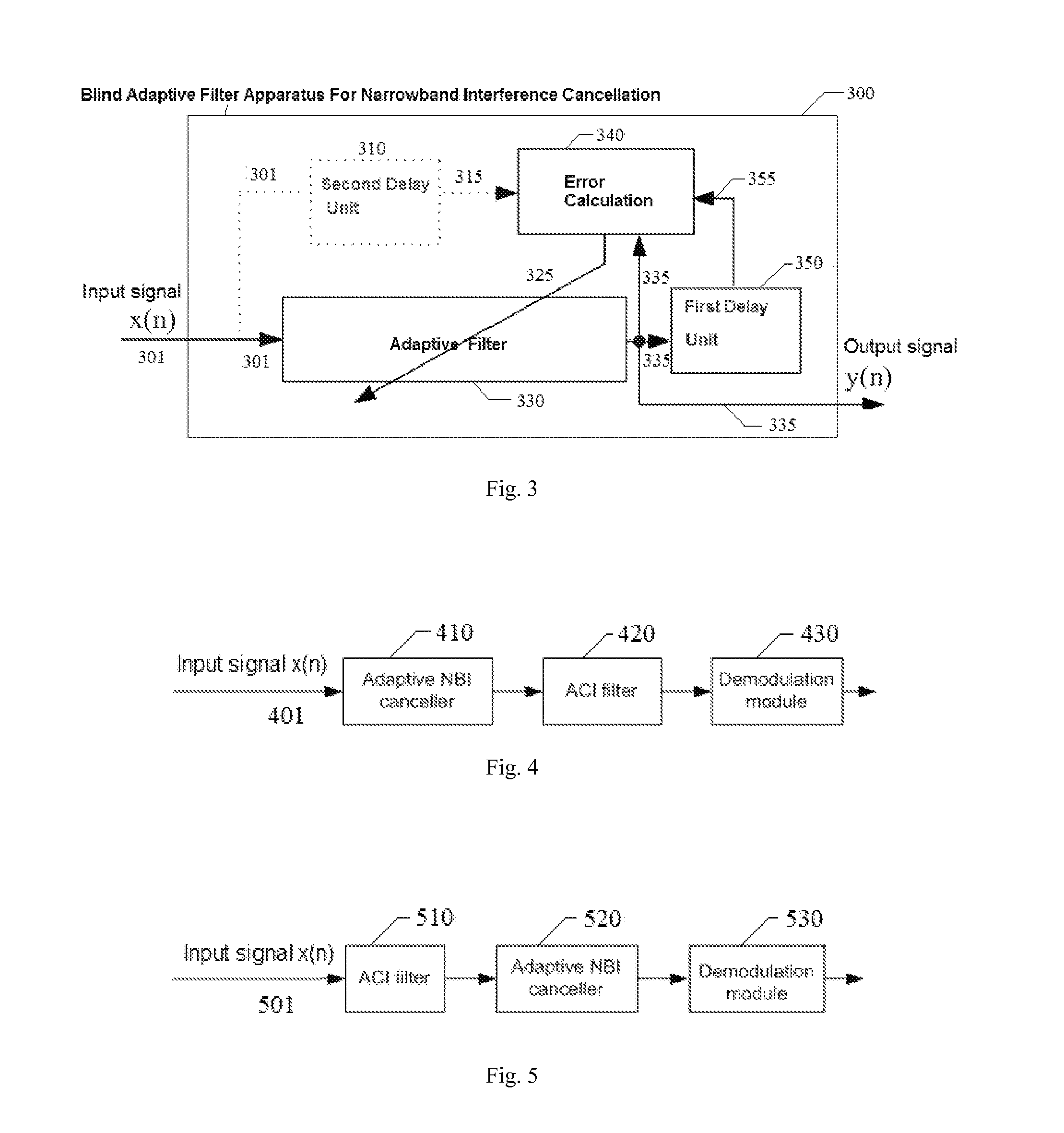
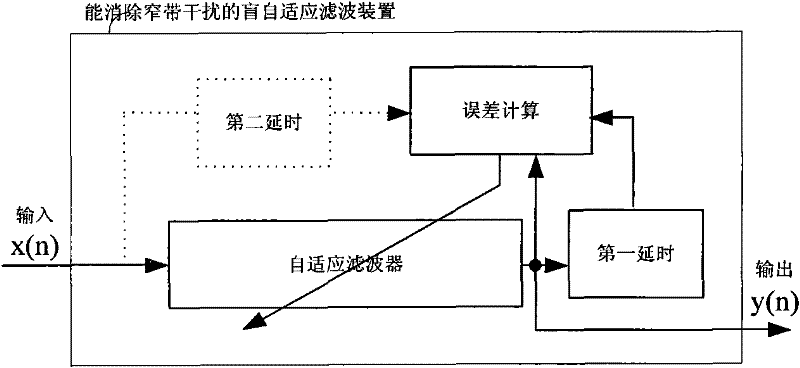
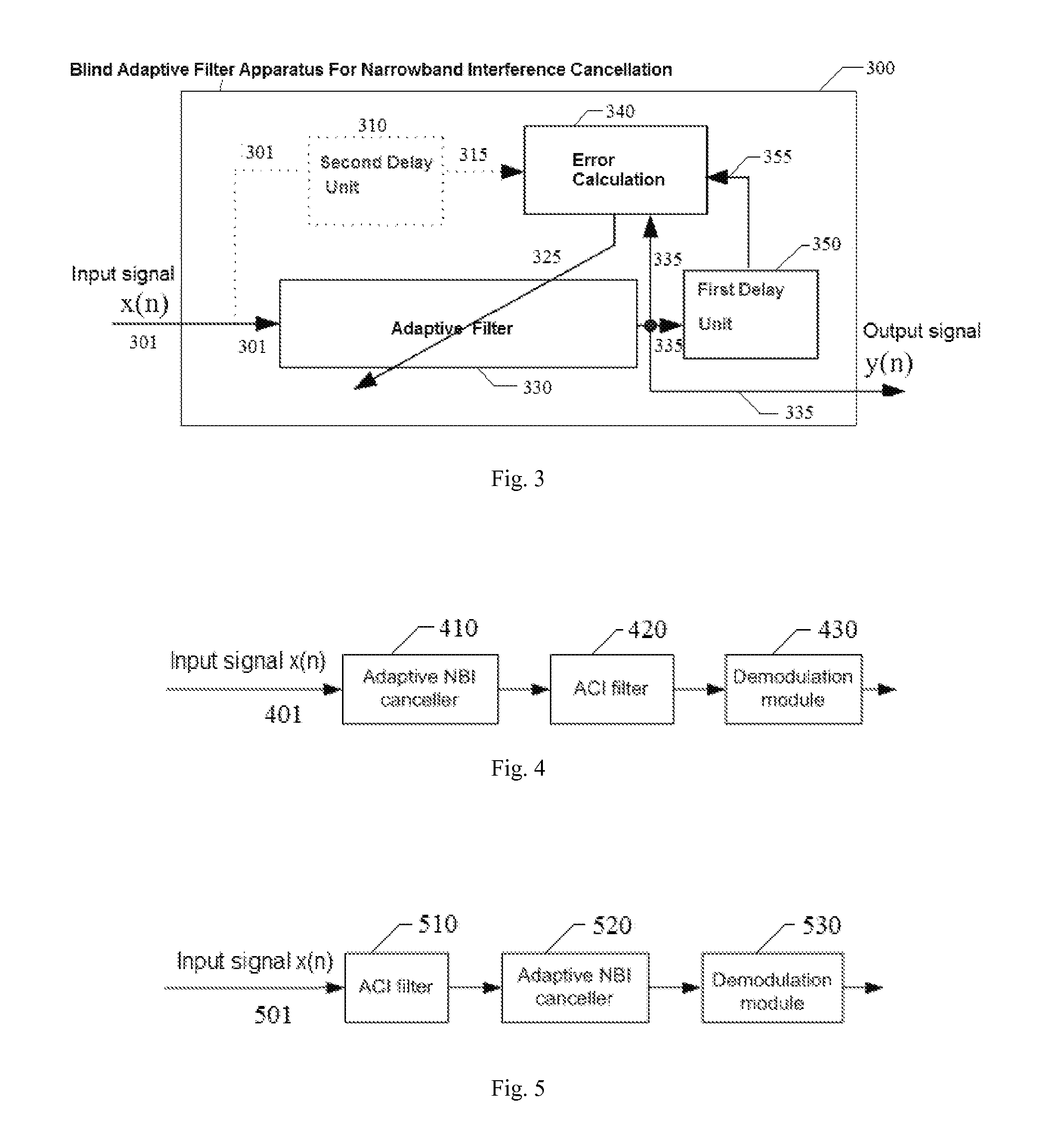
Blind adaptive filtering device capable of eliminating narrowband interference and its application
ActiveCN102281044AEliminate effectiveAdaptive networkTransmissionAdaptive filterBroadband transmission
A blind self-adaptive filtering method, an apparatus and a broadband transmission system for eliminating narrowband interference are provided. The self-adaptive filtering apparatus includes: a self-adaptive filter, for filtering the current input signal and then outputting it, a first delay unit, for delaying the signal output from the self-adaptive filter with a first time delay length, and an error calculation unit, for implementing correlation operation on the signal output from the self-adaptive filter and the delay signal of the output signal to obtain error information. The self-adaptive filter adjusts the filter parameter according to the feedback error information to eliminate the interference in the latter input signal. As applying the output signal to implement correlation operation with the delay signal of the output signal, thus, the apparatus is used widely, for example, it can be applicable to broadband receiver, it also can be applicable to the case that there are a plurality of strong narrowband interferences, and it also can counteract a plurality of strong narrowband interferences whose swept rate is decades of milliseconds.
Owner:MONTAGE SEMICON SHANGHAI CO LTD
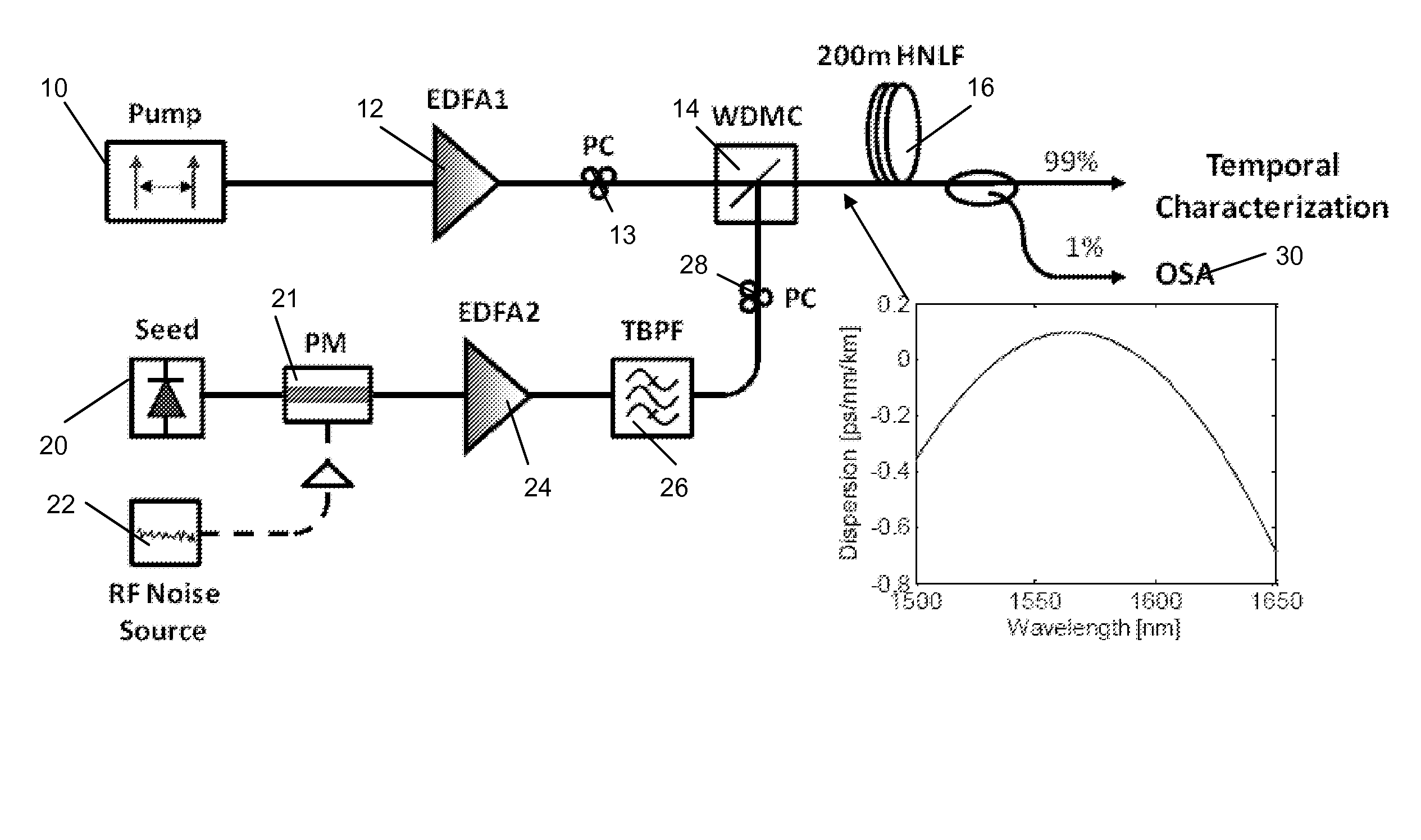
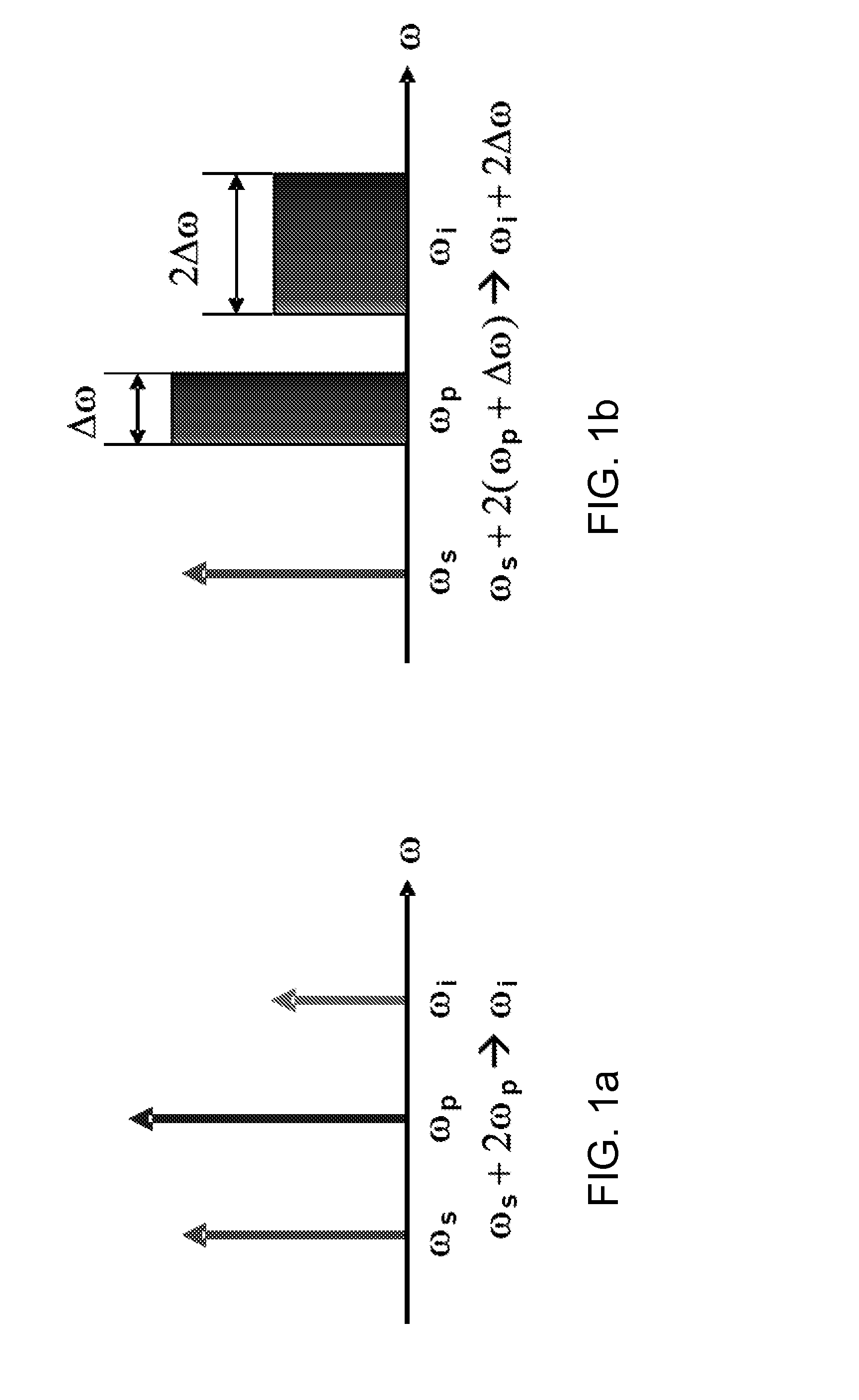
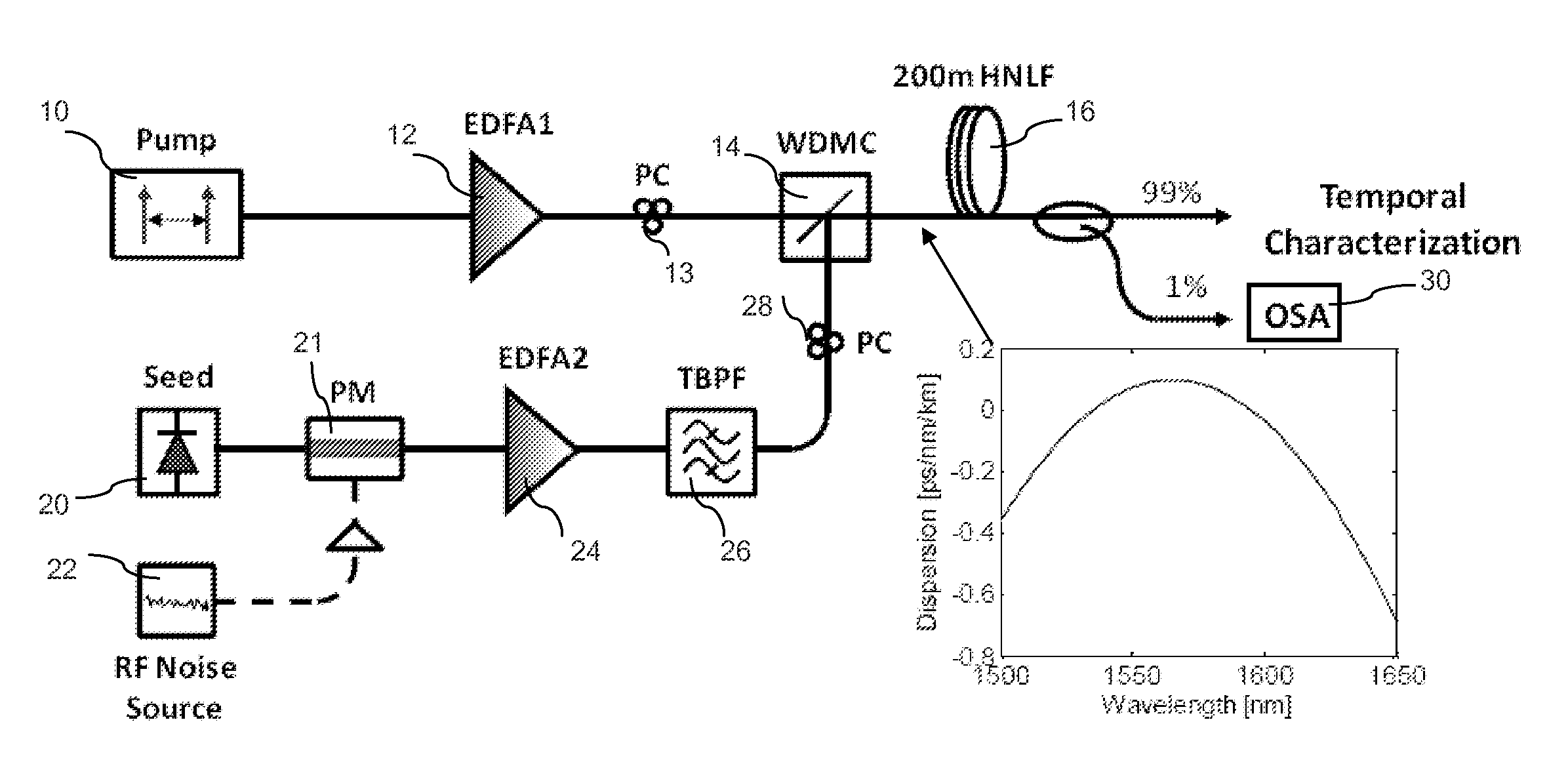
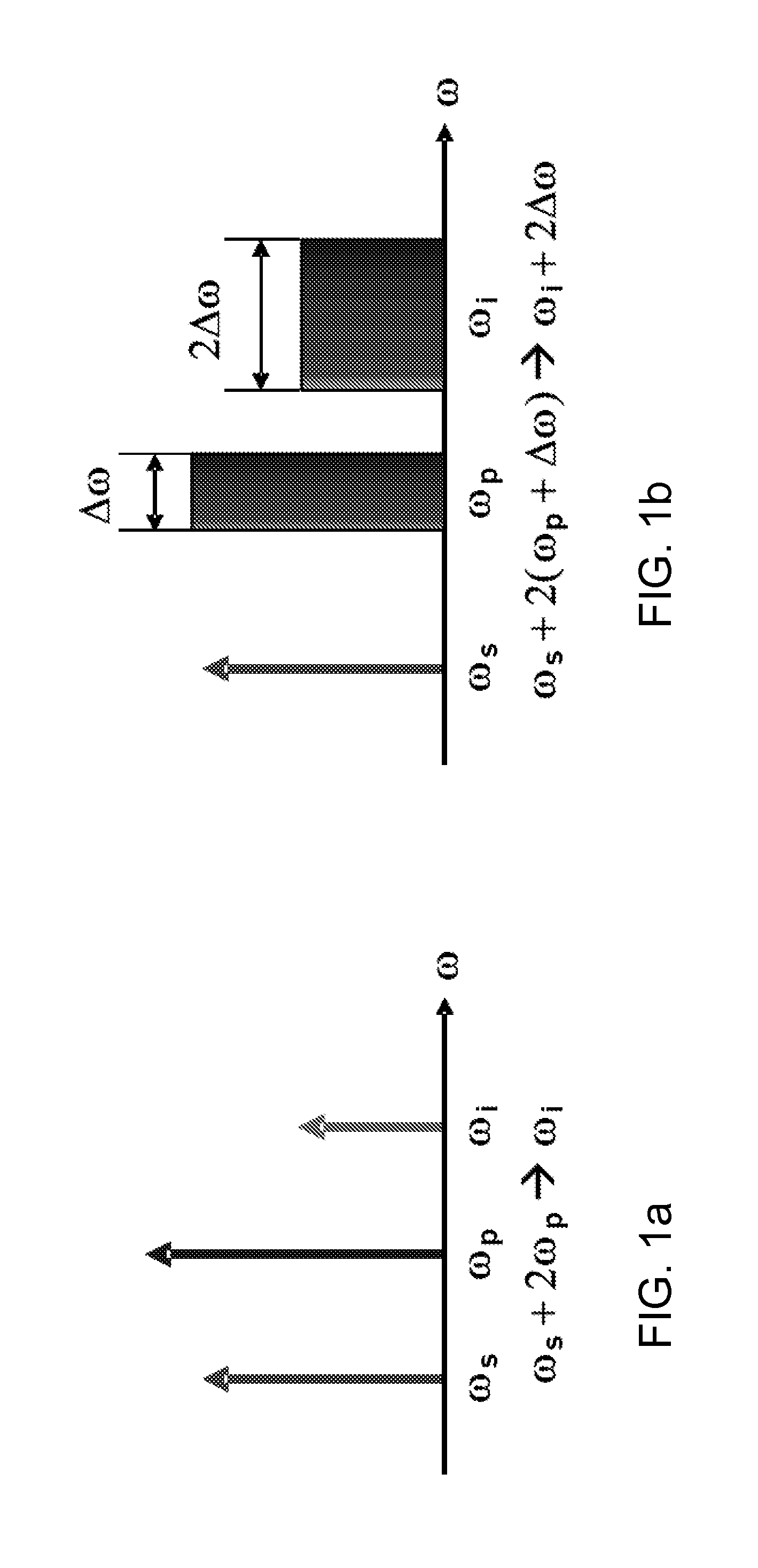
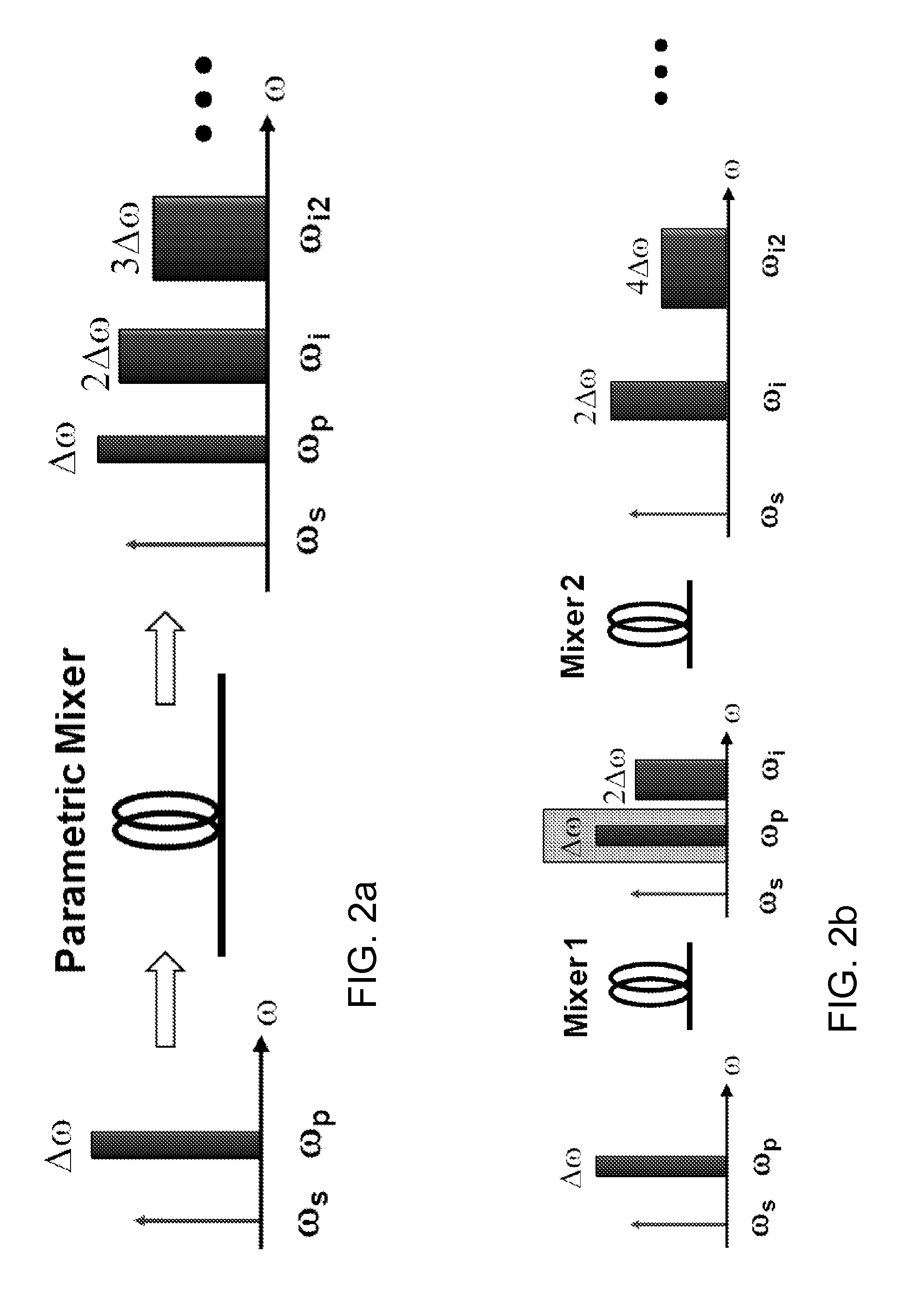
Method and device for fast tuning of optical sources
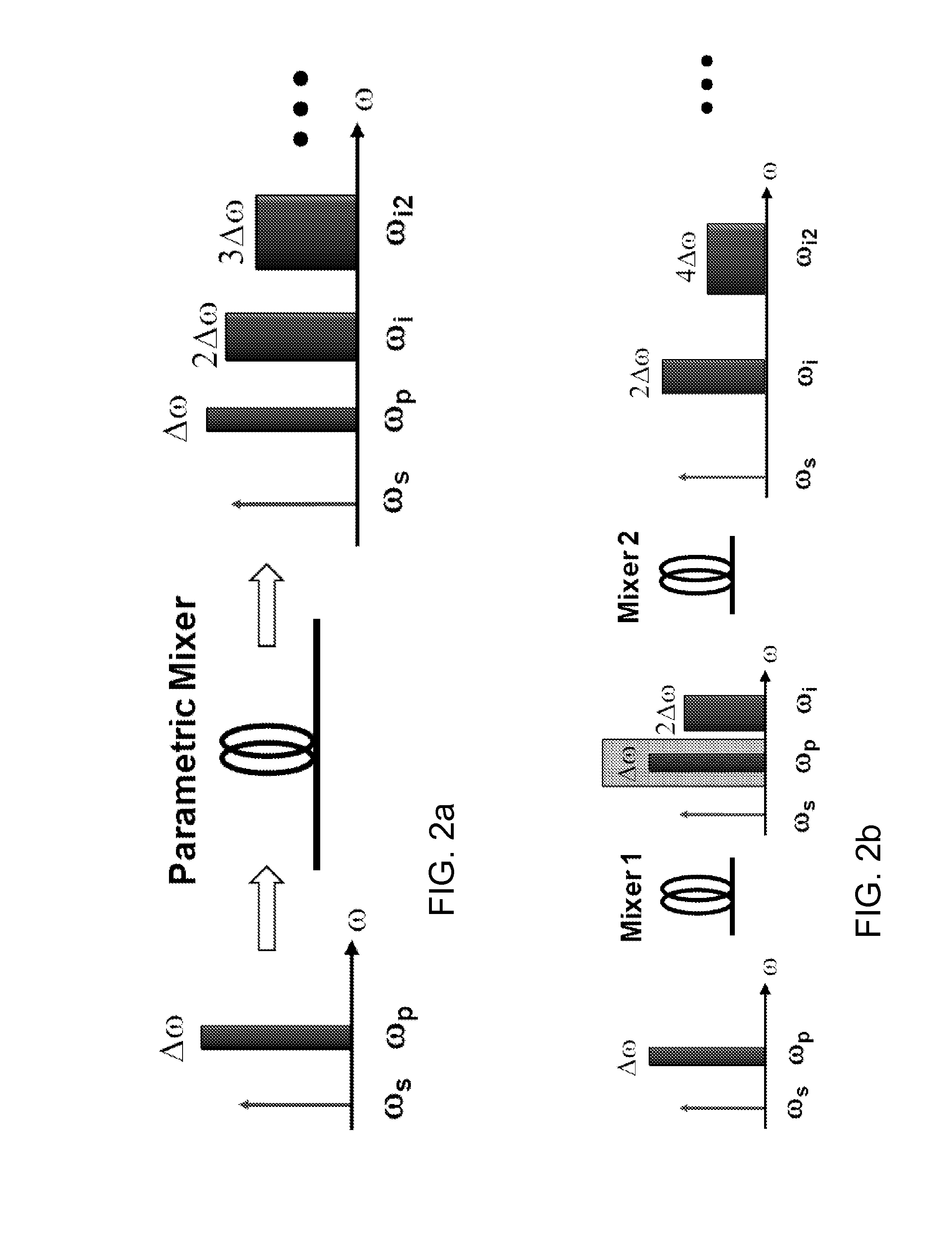
ActiveUS20130223459A1Improve performanceFOM of a one pump mixer can be further enhancedLaser detailsNon-linear opticsFrequency mixerEngineering
A method and device are provided for fast, continuous tuning of an optical source. A first pump signal with a first pump frequency is input into a mixer along with a first seed signal having a first seed frequency. Within the mixer, the first pump signal and the first seed signal generate at least one idler having an idler frequency defined as two times the pump frequency minus the seed frequency. Shifting the pump signal across a frequency range at a sweep rate causes the idler frequency to be shifted by two times the frequency range at two times the sweep rate. The shifted at least one idler is mixed with the shifted pump signal to generate a first mix product that has two times the sweep rate and frequency range of the pump signal.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Error corrector for radar timing systems
InactiveUS7446699B2Reduce biasOvercome limitationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase correctionRadar
A feedback loop corrects timing errors by reducing deviations from a constant radar sweep rate. Errors are detected and fed back to a phase corrector in a high gain feedback system. A precision radar rangefinder can be implemented with a direct digital synthesizer (DDS) that includes feedback error correction for reducing range errors by, for example, 100 times, or to 0.1 mm. An error-corrected DDS swept timing system can enable a new generation of highly flexible, repeatable and accurate radar, laser and guided wave rangefinders.
Owner:MCEWAN TECH
Interferometric optical fibre sensor system and method of interrogation
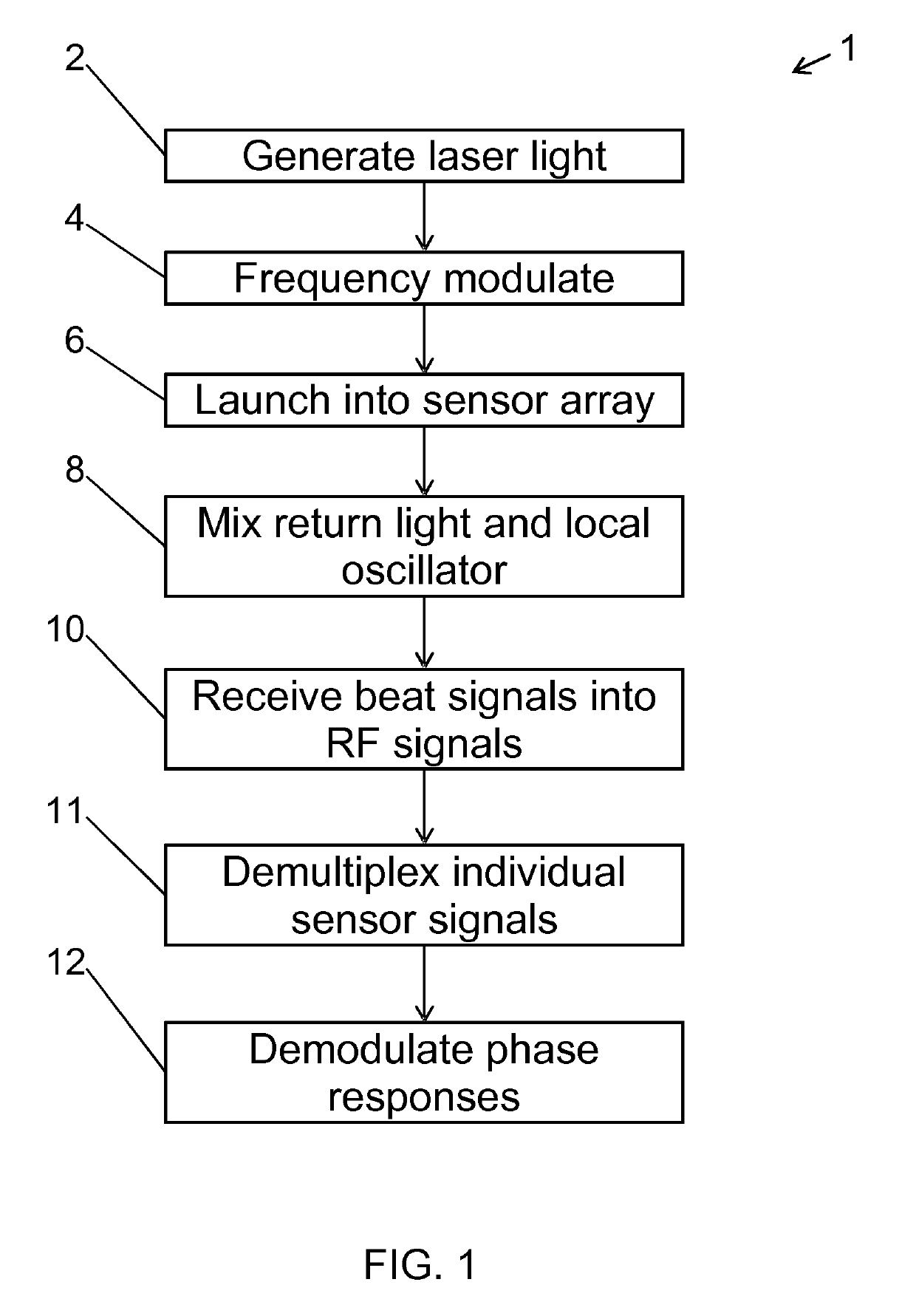
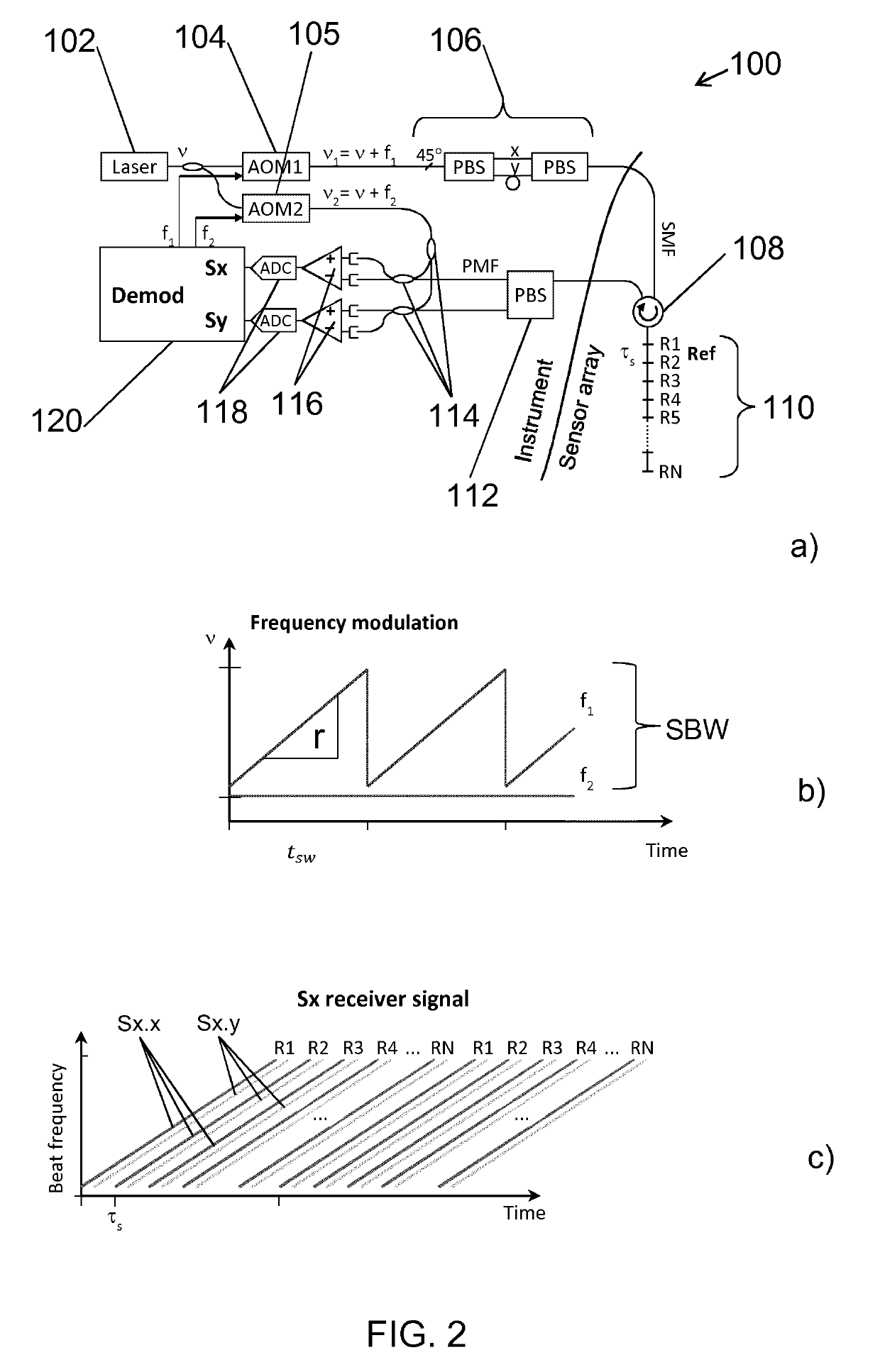
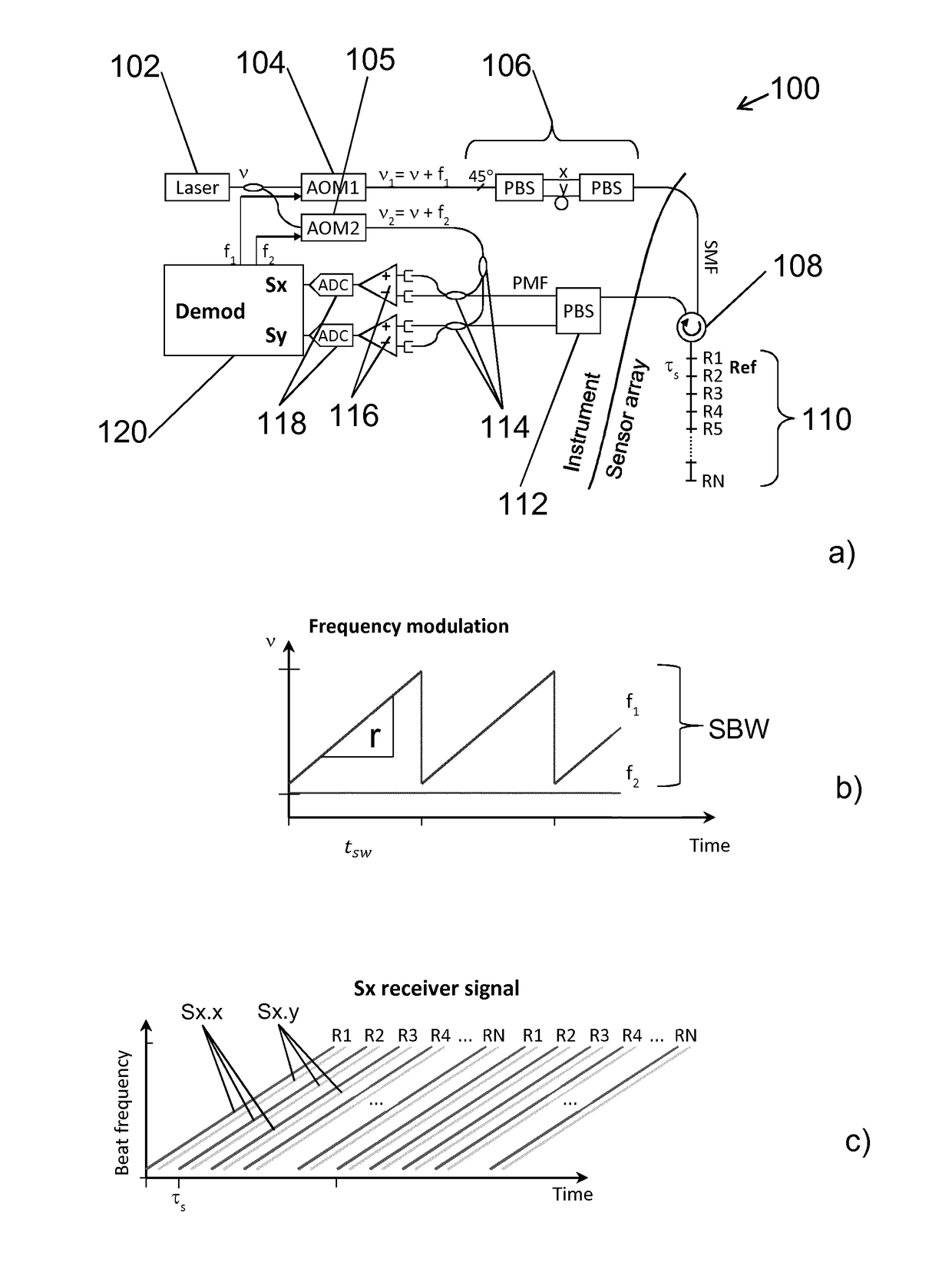
ActiveUS10247581B2High resolutionLarge dynamic rangeInterferometersUsing optical meansSensor arrayLocal oscillator signal
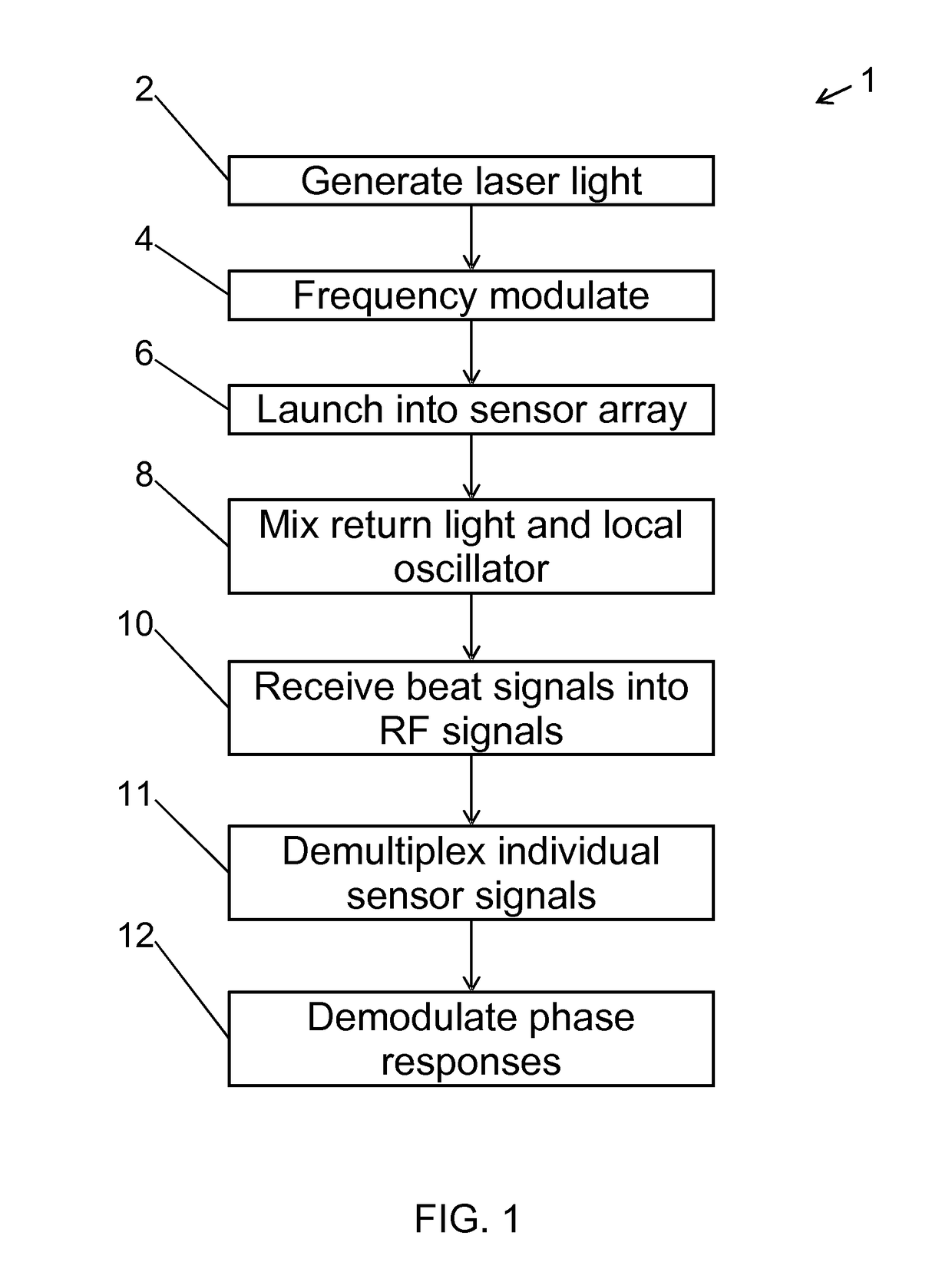
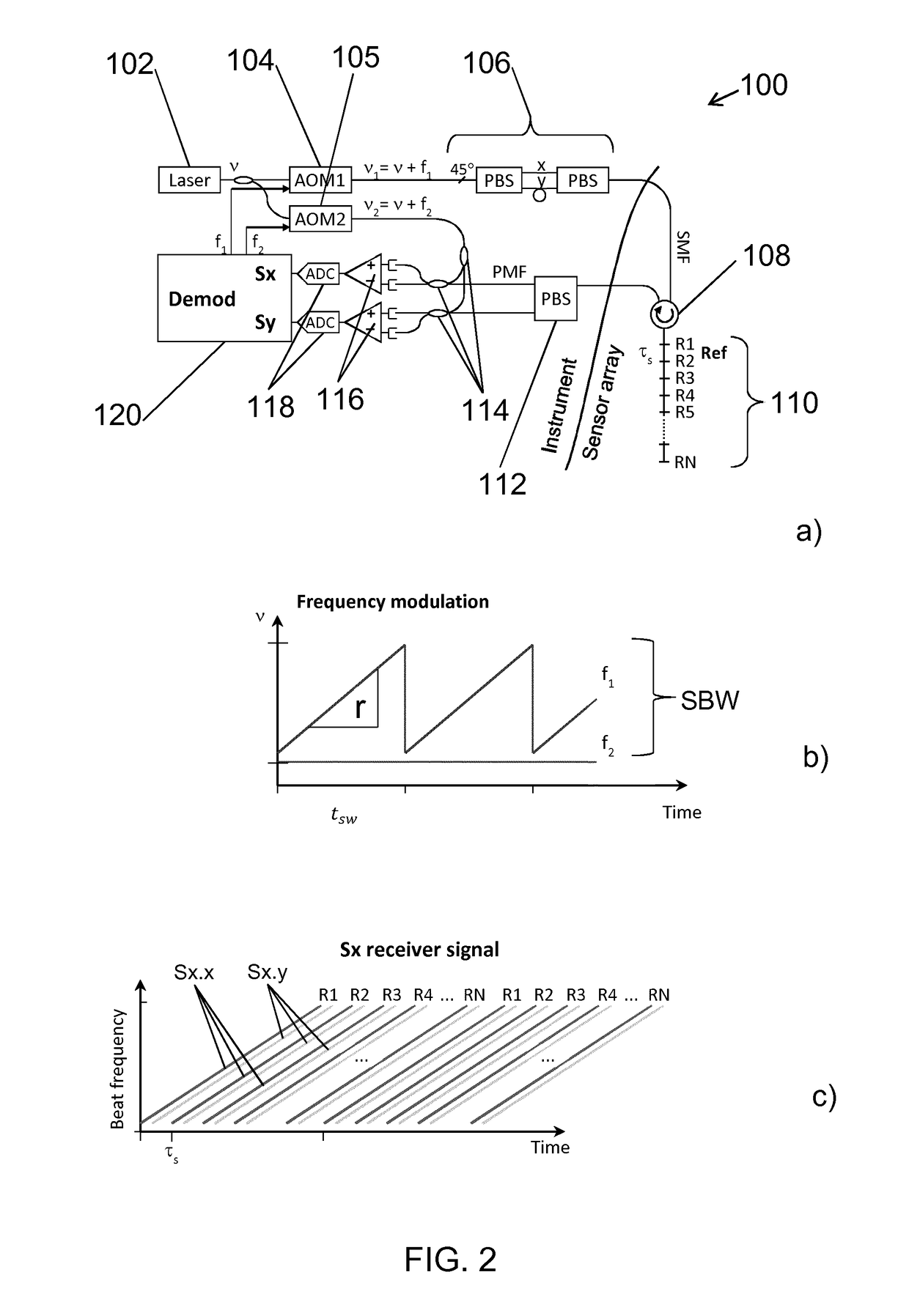
The invention relates to a method of interrogating an interferometric optical fiber sensor system including a laser source configured to generate interrogation light and a sensor array with at least a first reflector and a second reflector. The method includes continuously and repeatedly frequency sweeping the interrogation light from the laser source within a sweep bandwidth (SWB) over a sweep duration (tsw) with a substantially constant sweep rate r=SBW / tsw to produce a swept interrogation light signal, launching the swept interrogation light signal into the sensor array, detecting reflected signals being returned from the sensor array by each of the reflectors, respectively, wherein detection includes mixing a return light signal from the sensor array with a local oscillator signal onto an optical receiver to produce an electrical radio frequency signal, demultiplexing the electrical radio frequency signal into a first signal channel and a second signal channel, corresponding to the first and second reflector, respectively, demodulating each of the first and second signal channel into a first phase response from the first reflector and a second phase response from the second reflector, and subtracting the first phase response from the second phase response to obtain a sensor phase signal.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
Systems and methods for controlling motion of detectors having moving detector heads
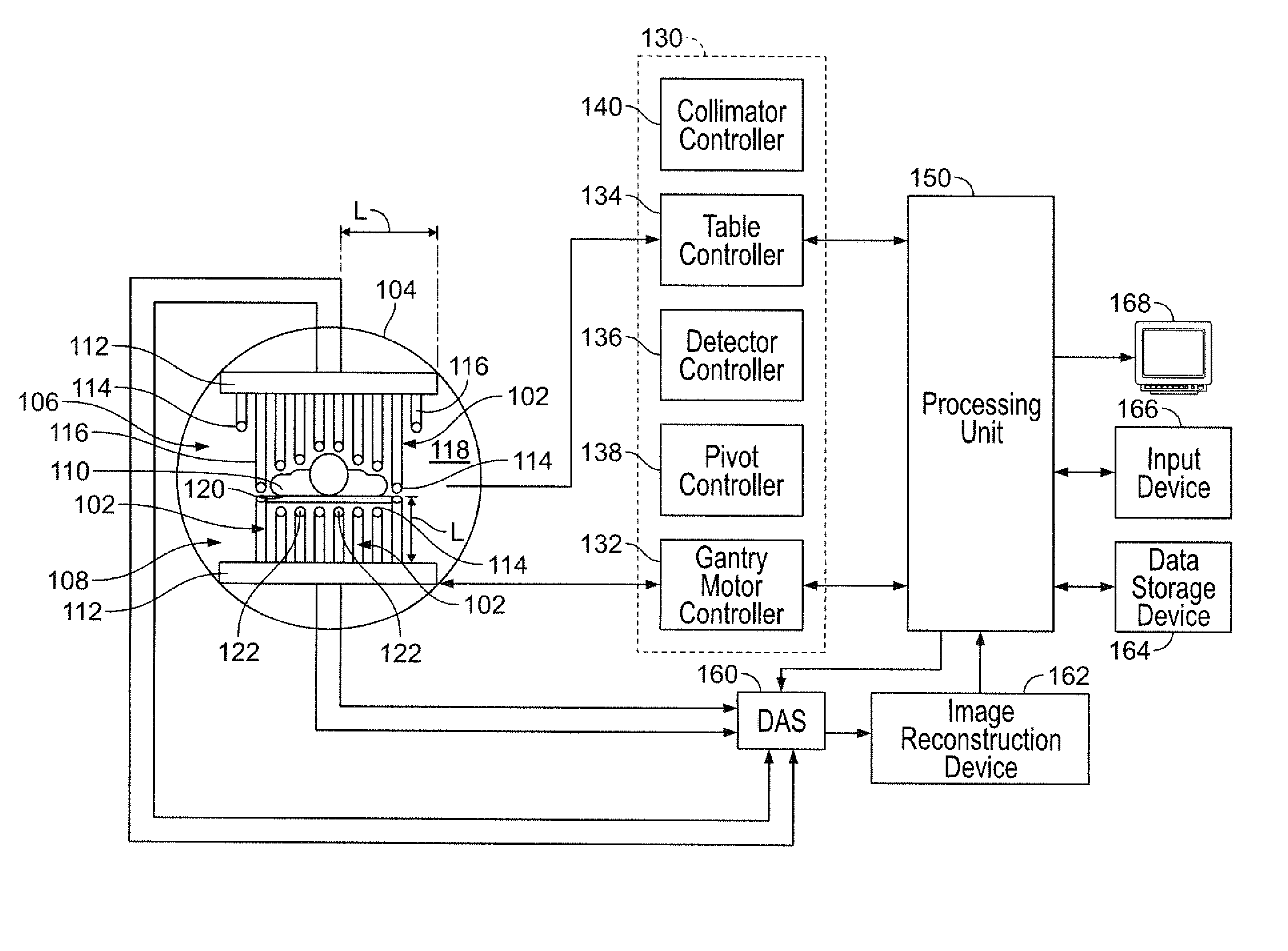
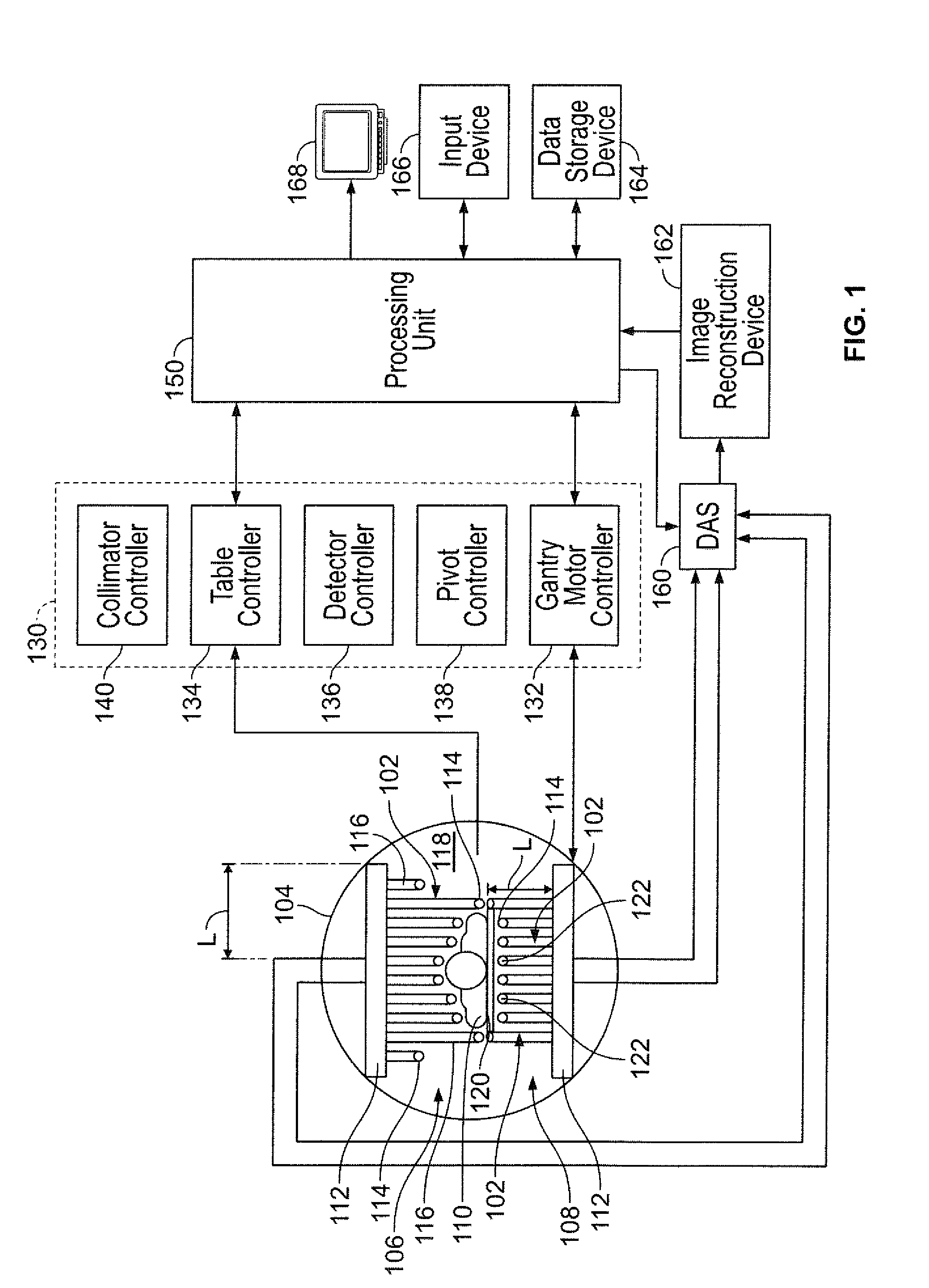
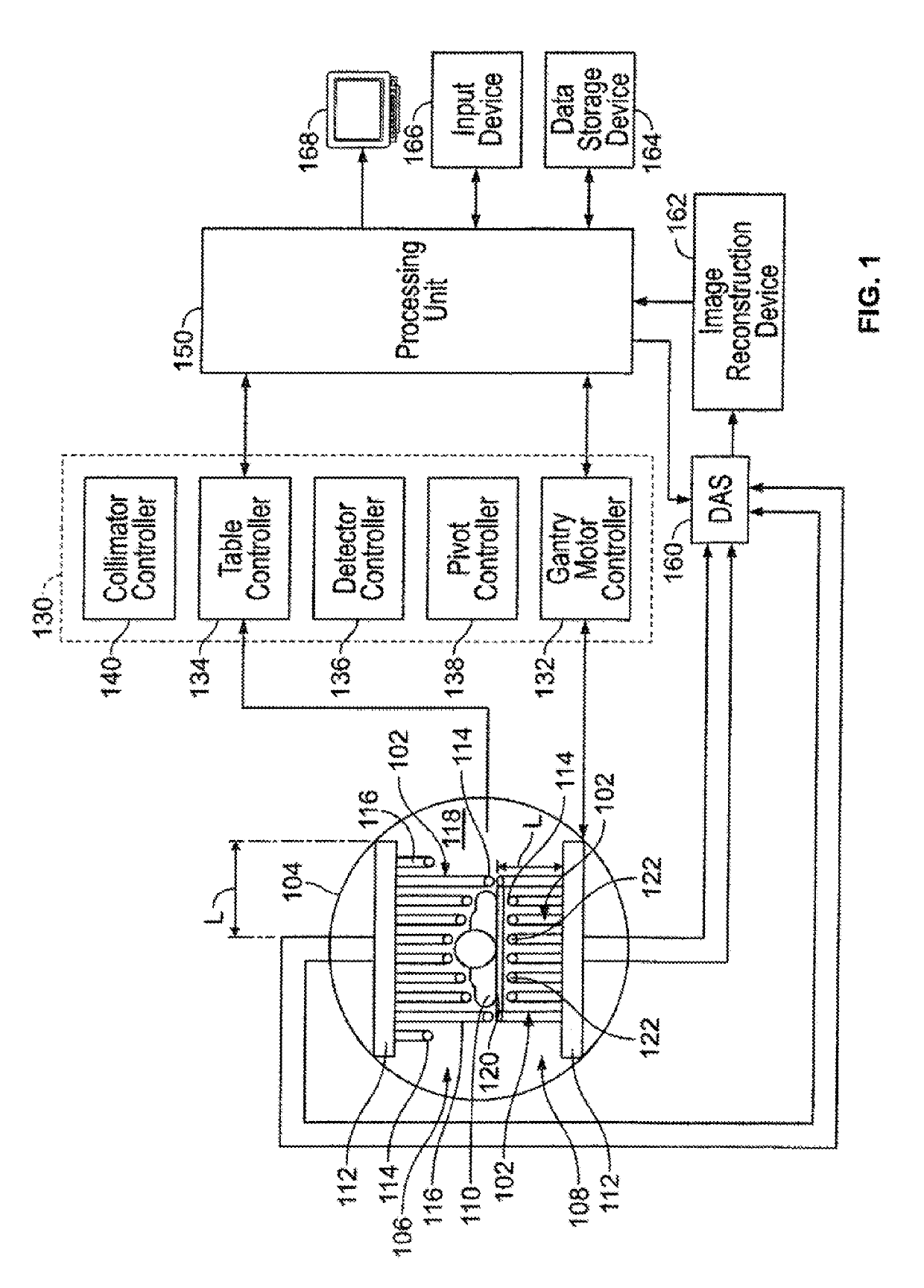
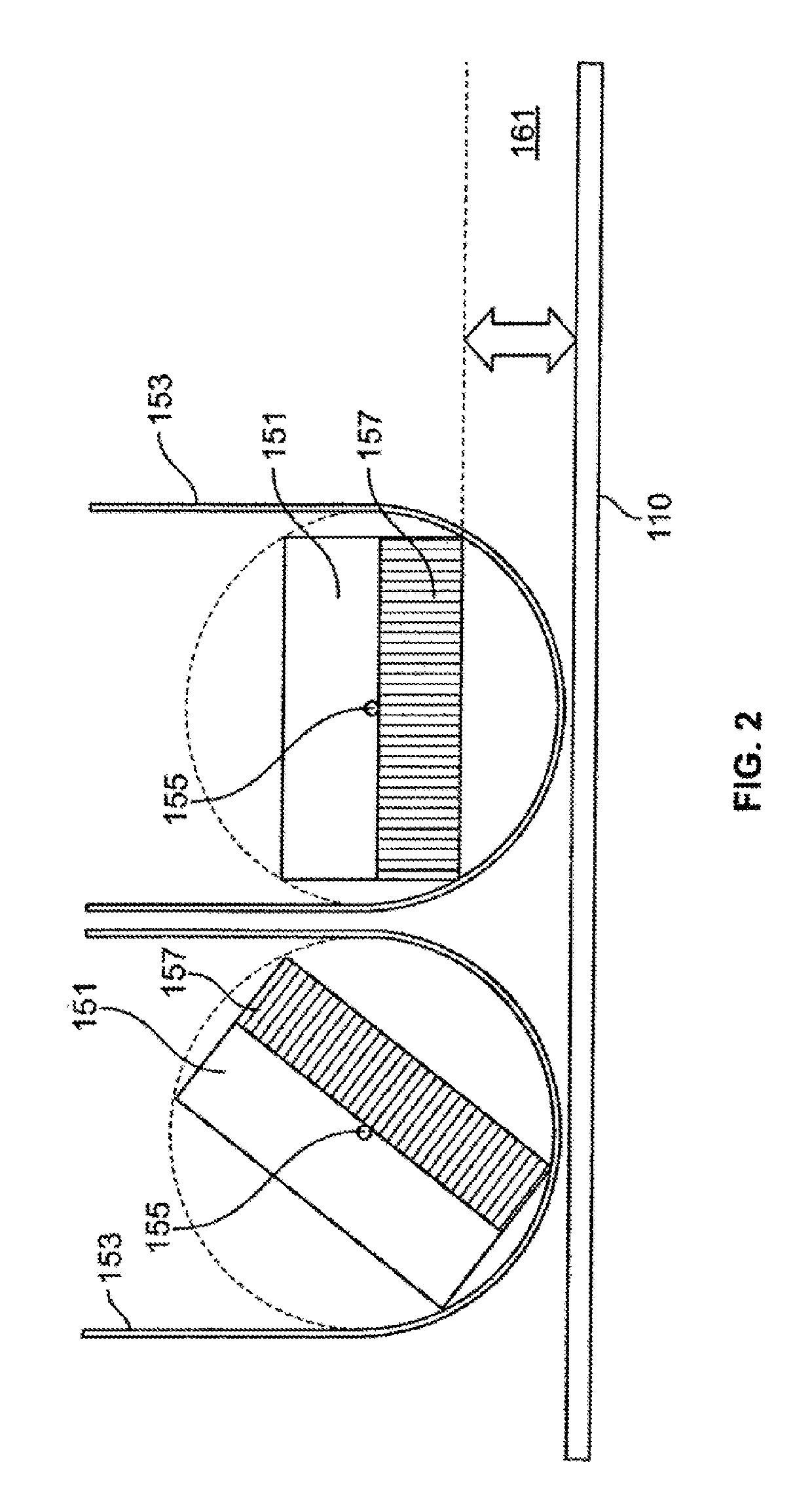
ActiveUS20150094571A1Reduce image resolutionA large amountRadiation diagnostic device controlComputerised tomographsComputer scienceField of view
An imaging system is provided including a gantry, a detector unit mounted to the gantry, at least one processing unit, and a controller. The at least one processing unit is configured to obtain object information corresponding to an object, and to automatically determine at least one first portion of the object and at least one second portion of the object. The controller is configured to control a rotational movement of the detector unit. The detector unit is rotatable at a sweep rate over a range of view of the object to be imaged, and the controller is configured to rotate the detector unit at an uneven sweep rate. The uneven sweep rate varies during the rotation from the, wherein a larger amount of scanning information is obtained for the at least one first portion than for the at least one second portion.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST ISRAEL
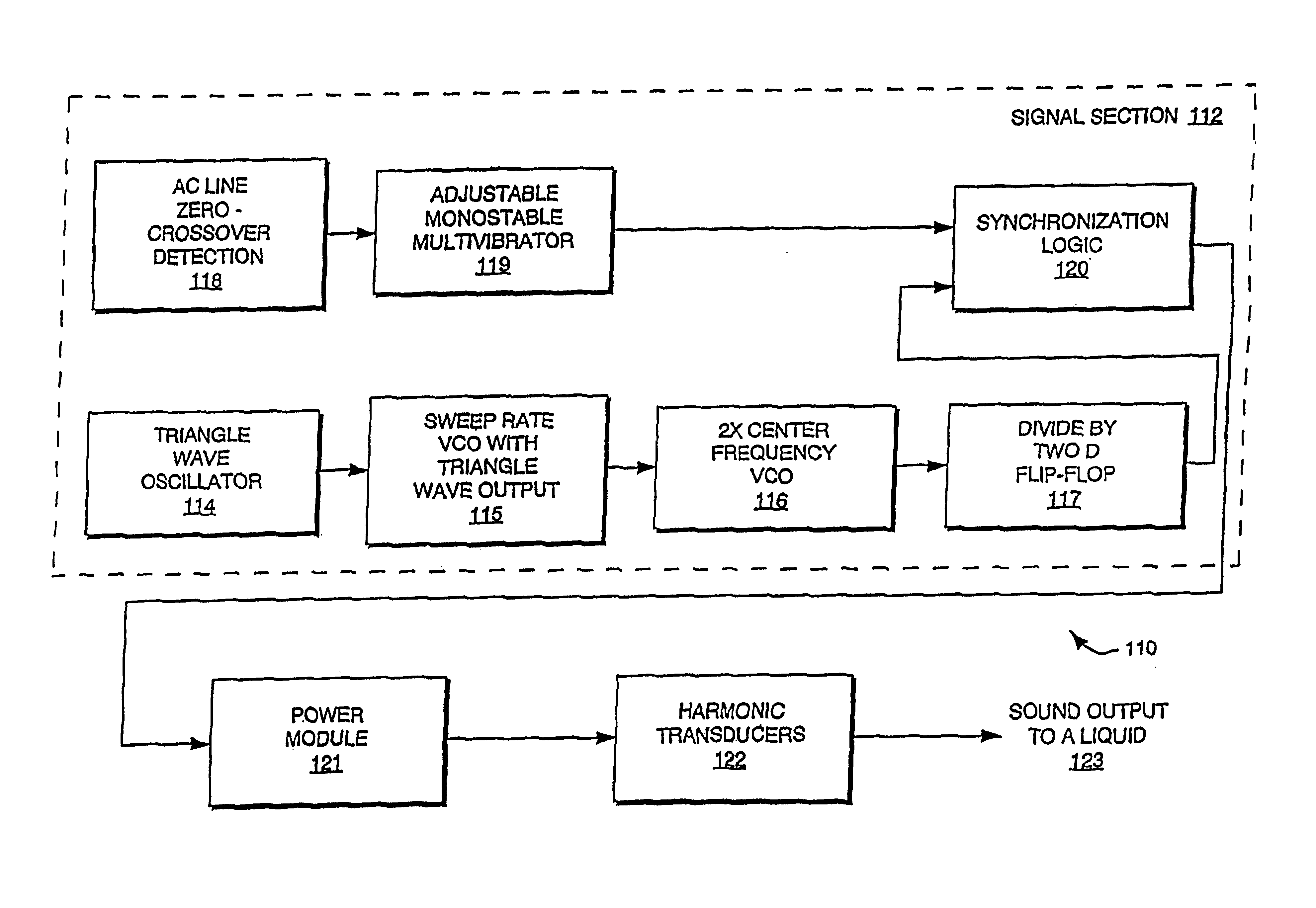
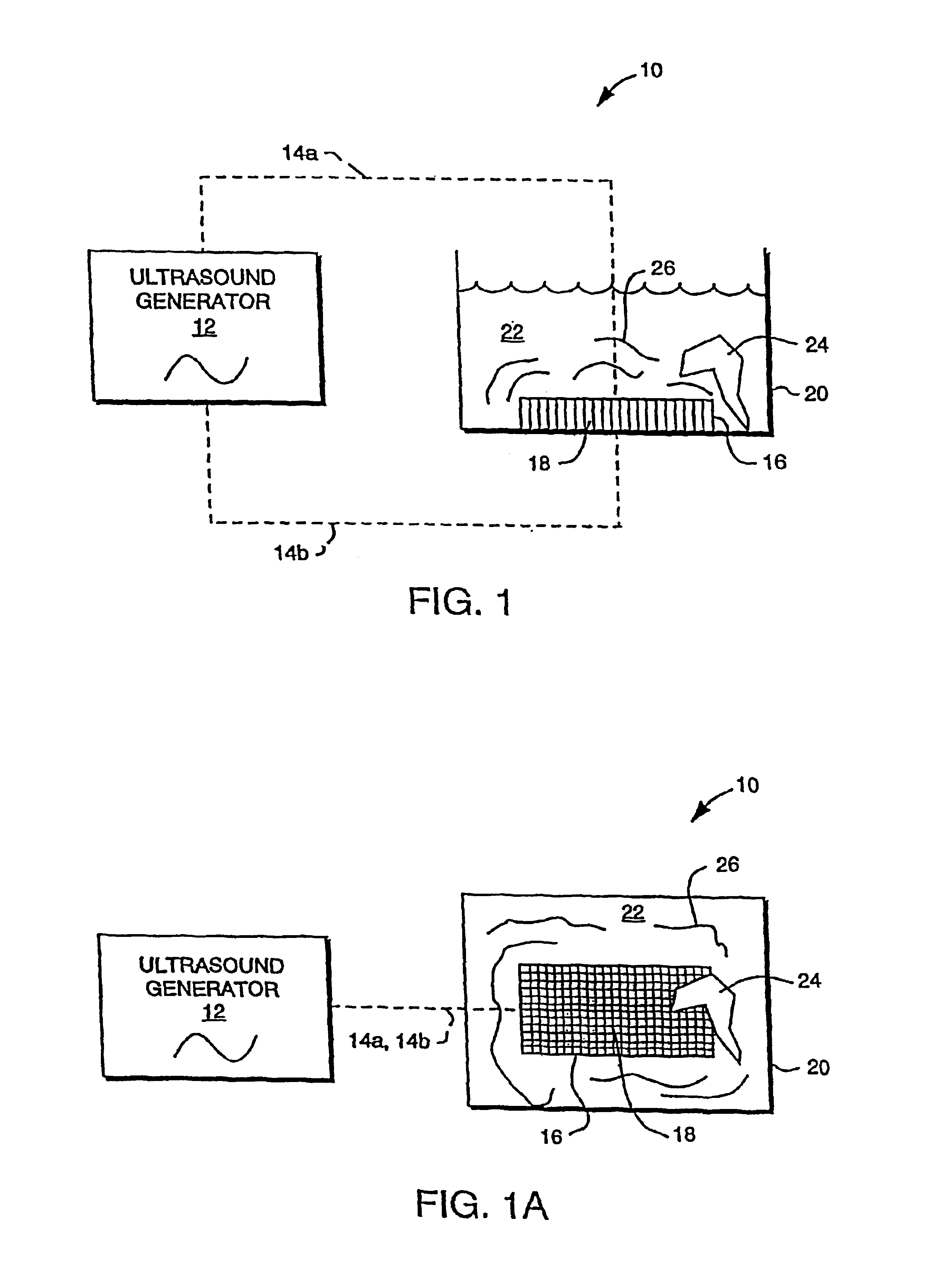
Apparatus and methods for cleaning and/or processing delicate parts
InactiveUS6946773B2Reduces or eliminates low frequency beat resonancesReduce frequencyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesHollow article cleaningUltrasonic sensorCavitation
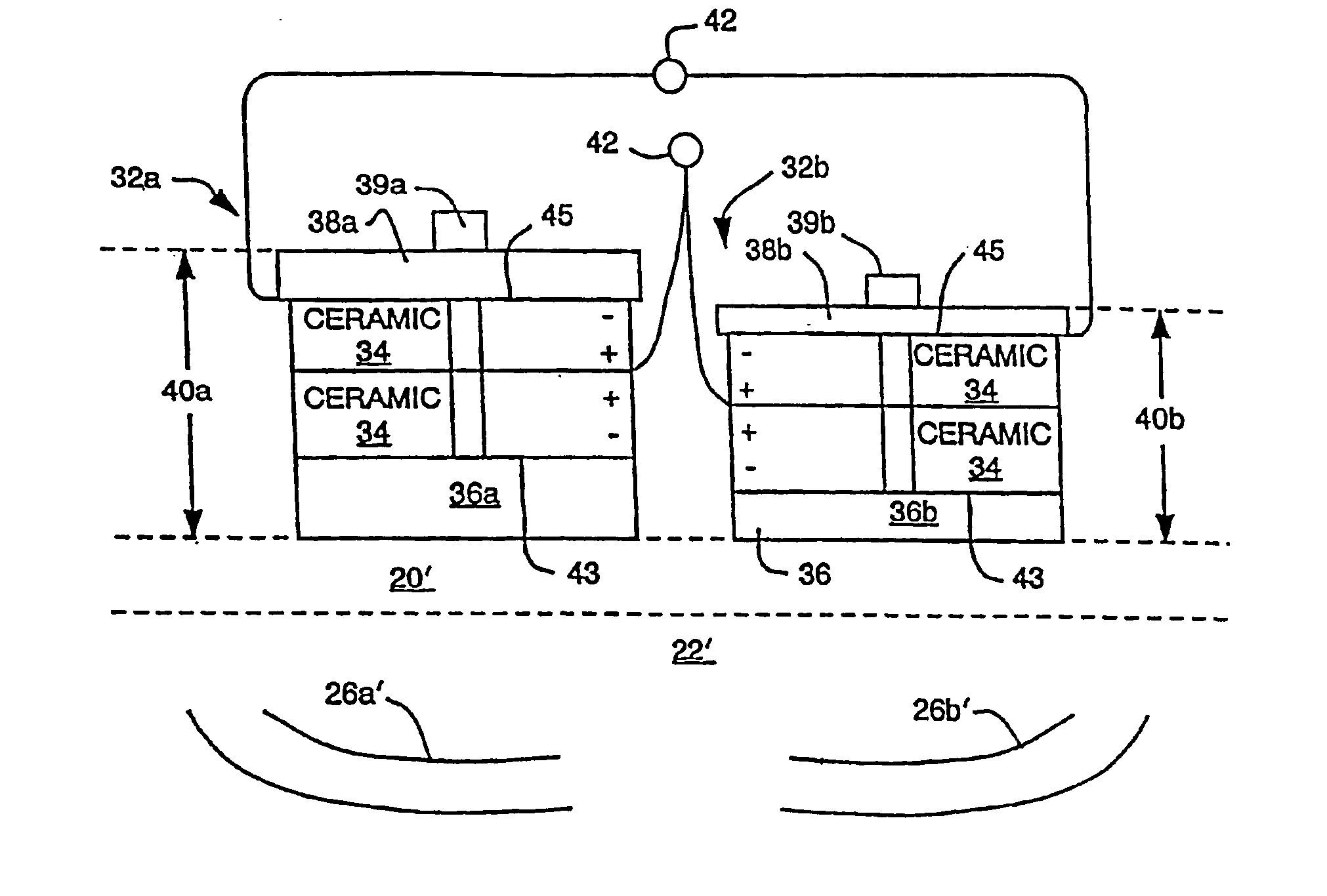
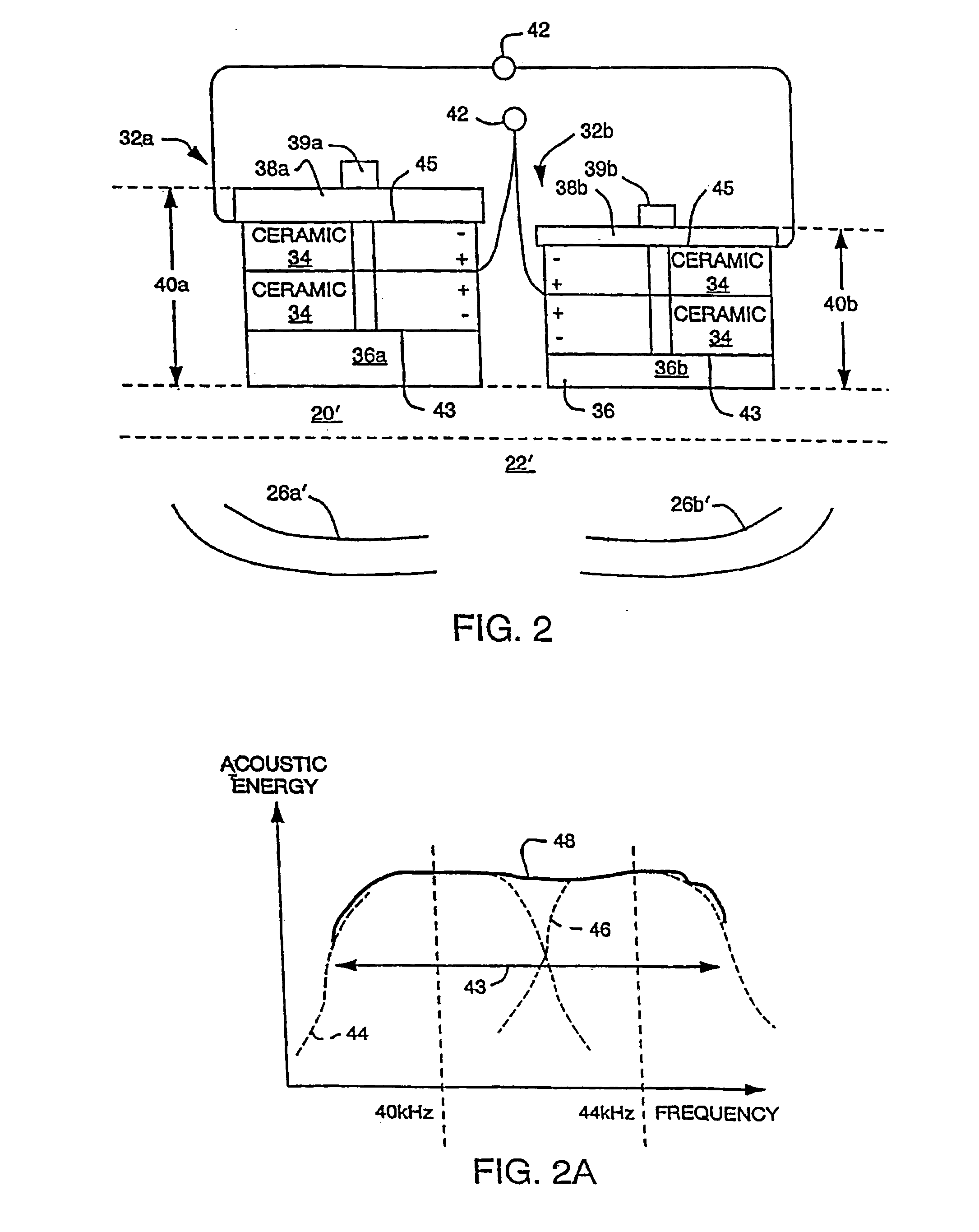
The invention utilizes harmonics of certain clamped ultrasound transducers to generate ultrasound within the liquid of an ultrasonic tank and in a frequency range of between about 100 khz to 350 khz (i.e., “microsonic” frequencies). The application of microsonic frequencies to liquid preferably occurs simultaneously with a sweeping of the microsonic frequency within the transducer's harmonic bandwidth to reduce or eliminate (a) standing waves within the liquid, (b) other resonances, (c) high energy cavitation implosion, and (d) non-uniform sound fields, each of which is undesirable for cleaning and / or processing of semiconductor wafers and other delicate parts. The invention can also drive ultrasonic transducers such that the frequency of applied energy has a sweep rate within the ultrasonic bandwidth of the transducers; and that sweep rate is also varied so that the sweep rate is substantially non-constant during operation.
Owner:PUSKAS WILLIAM L
Multi-speed OCT swept source with optimized k-clock
ActiveUS9243885B2Short depthEasy to useUsing optical meansAnalog-to-digital converterOptical scanning
An optical coherence tomography system utilizes an optical swept source that frequency scans at least two different sweep rates. In this way, the system can perform large depth scans of the sample and then the same system can perform shorter depth high precision scans, in one specific example. In order to optimally use the analog to digital converter that samples the interference signal, the system further samples the interference signals at different optical frequency sampling intervals depending upon the selected sweep rates of the optical swept source. This allows the system to adapt to different sweep rates in an optimal fashion.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Apparatus and methods for cleaning and/or processing delicate parts
InactiveUS6914364B2Reduce harmReduces or eliminates low frequency beat resonancesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMechanical vibrations separationCavitationSonification
The invention utilizes harmonics of certain clamped ultrasound transducers to generate ultrasound within the liquid of an ultrasonic tank and in a frequency range of between about 100 khz to 350 khz (i.e., “microsonic” frequencies). The application of microsonic frequencies to liquid preferably occurs simultaneously with a sweeping of the microsonic frequency within the transducer's harmonic bandwidth to reduce or eliminate (a) standing waves within the liquid, (b) other resonances, (c) high energy cavitation implosion, and (d) non-uniform sound fields, each of which is undesirable for cleaning and / or processing of semiconductor wafers and other delicate parts. The invention can also drive ultrasonic transducers such that the frequency of applied energy has a sweep rate within the ultrasonic bandwidth of the transducers; and that sweep rate is also varied so that the sweep rate is substantially non-constant during operation. This reduces or eliminates resonances which are created by transducers operating with a single sweep rate. An ultrasound generator of the invention sometimes utilizes amplitude modulation (AM), and the AM frequency is swept over time so as to reduce resonances. AM control is preferably provided by selecting a portion of the rectified power line frequency. In applications which utilize multiple generators, multiple transducers, and one or more tanks, simultaneously, the invention synchronizes the operation of the generators to a common FM signal to reduce beat frequencies between generators. Each such generator can also be adjusted, through AM, to control the process characteristics within the associated tank. Two or more transducers are sometimes used by the invention, in combination, to broaden the overall bandwidth of acoustical energy applied to the liquid around the primary frequency or one of the harmonics. The bandwidths of the transducers are made to overlap such that an attached generator can drive the transducers, in combination, to deliver ultrasound to the liquid in a broader bandwidth. In a single chamber ultrasound system, two or more generators, each operating or optimized to generate a different range of frequencies, are connected to a multiplexer; and the desired frequency range is selected, and hence the right generator, according to the cavitation implosion energy that is desired within the tank chemistry.
Owner:PUSKAS WILLIAM L
Oscillation device
To provide an oscillation device having a long oscillation wavelength in which wavelength variable width is relatively broad and wavelength sweep rate is relatively high. An oscillation device includes a gain medium having a gain with respect to an electromagnetic wave to be oscillated, cavity structures for resonating the electromagnetic wave, and energy injection means and for injecting pumping energy into the gain medium. The gain medium is sandwiched between a first negative permittivity medium and a second magnetic permittivity medium each of which real part of permittivity with respect to the electromagnetic wave is negative. Electric field application means is provided for at least one of the first negative permittivity medium and the second negative permittivity medium to apply an electric field for changing a depletion region formed at a boundary part with the gain medium.
Owner:CANON KK
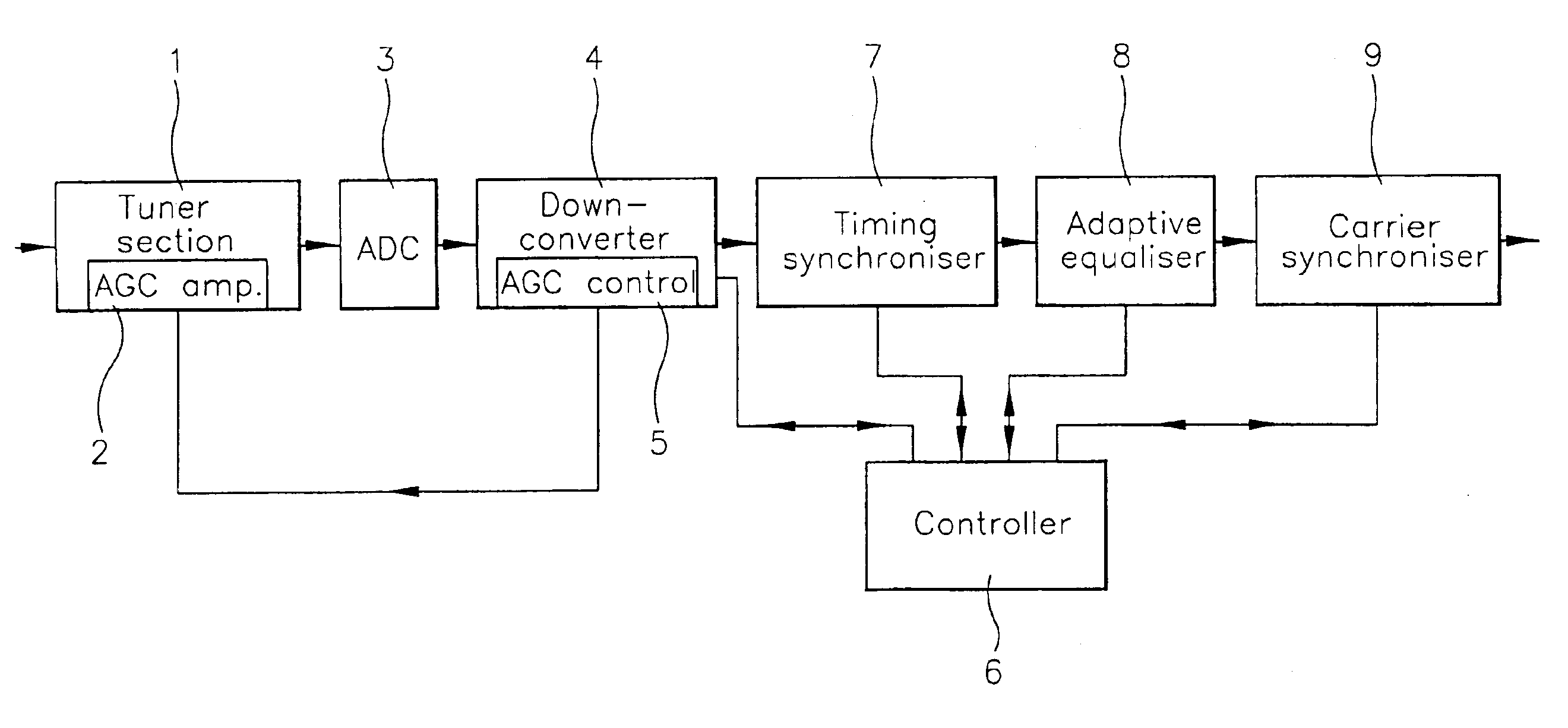
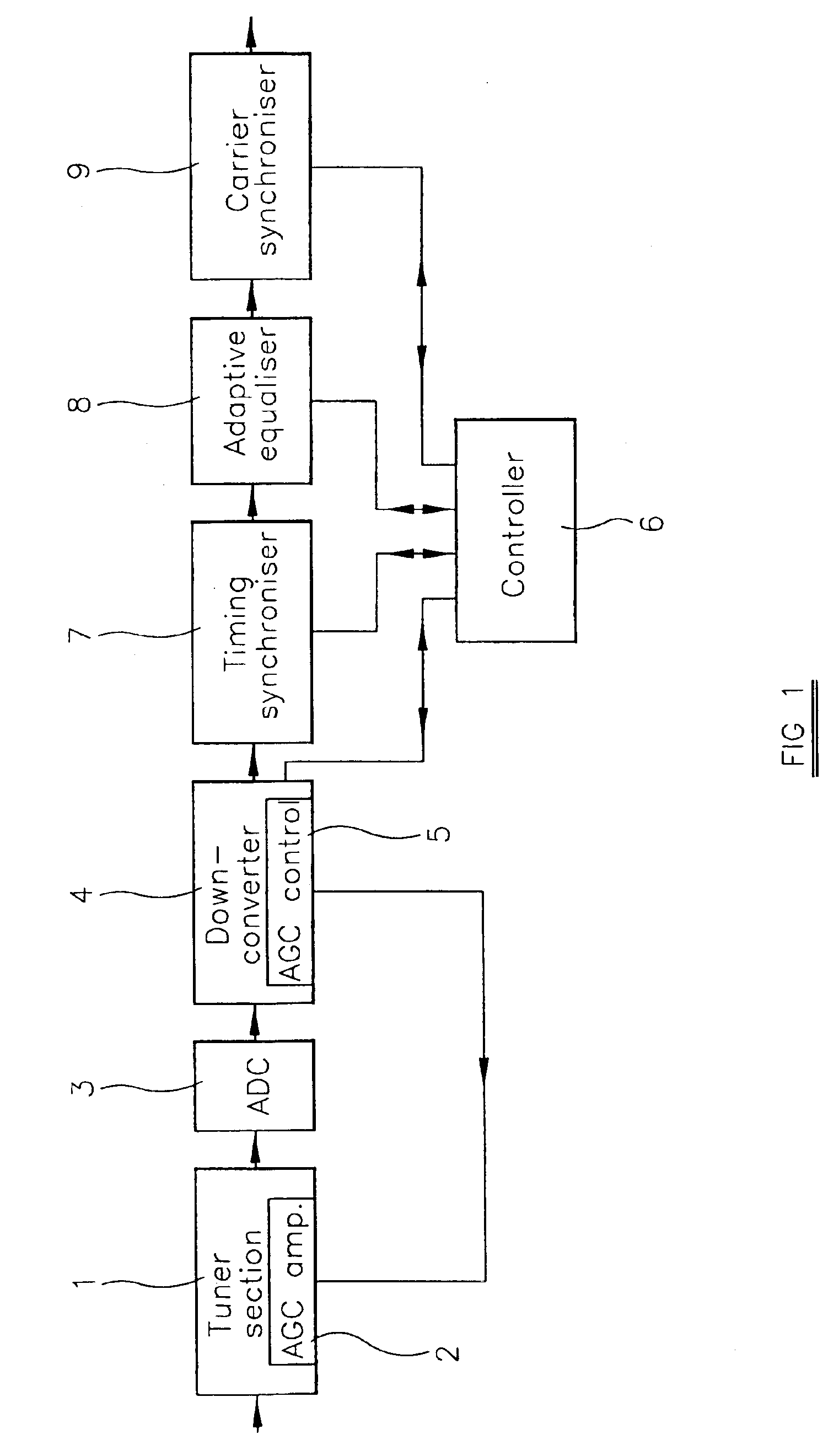
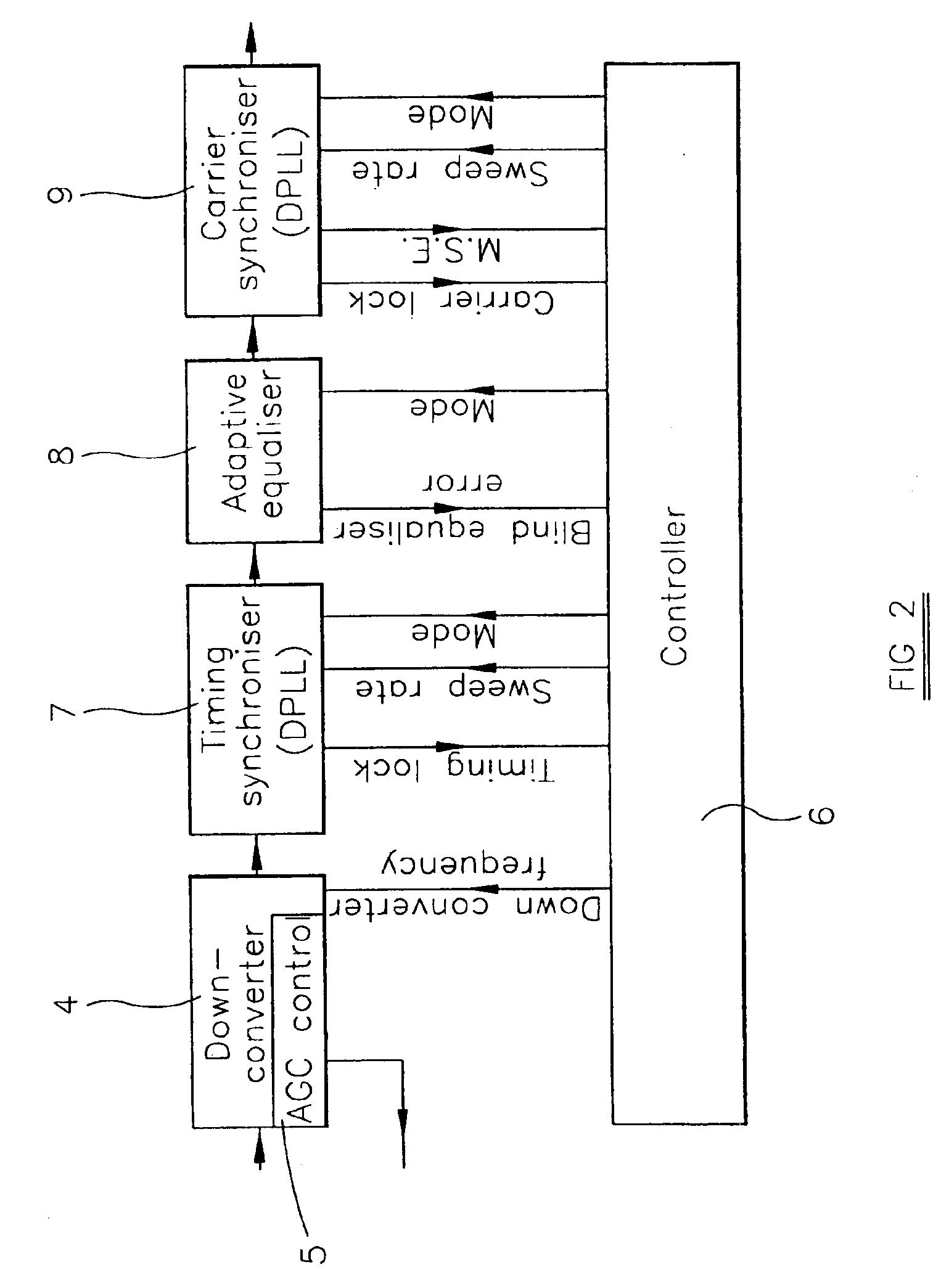
Quadrature amplitude modulation demodulator and receiver
InactiveUS6879646B2Rapidly and reliably locking onto incoming QAM signalPoor signal to noise ratioReceiver initialisationPulse automatic controlHigh rateModem device
A QAM demodulator comprises a timing synchronizer whose output is supplied via an adaptive equalizer to a carrier synchronizer, all of which are controlled by a controller. The timing synchronizer resamples the incoming signal in the digital domain with a sampling period which, during an acquisition mode, sweeps between limit values at different rates. The controller begins an acquisition cycle at the highest rate and monotonically lowers the sweep rate until timing lock is achieved. The sampling rate is then fixed at the correct value. Similarly, the controller sweeps the local oscillator of a phase locked loop in the carrier synchronizer initially at a highest rate and at progressively lower rates until the carrier synchronizer locks to the phase of the incoming signal.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Organo-electronic functional material and use thereof
The invention provides an organo-electronic functional material comprising a tris(arylamino)benzene represented by the general formula (I)wherein A and B are each a group represented by the general formula (II)in which R is an alkyl group of 1-6 carbons or a cycloalkyl group of 5 or 6 carbon atoms and n is 0, 1, 2 or 3, and A and B may be the same or different from each other, and exhibiting a cyclic voltamogram in which a deviation of peak current of cyclic curves as measured 50 times at a sweep rate of 20 mV / s falls within ±10% of the average of peak current.The organo-electronic functional material has an opto-electronic exchanging function, a reversible oxidation-reduction property and a high glass transition temperature, and can form amorphous film in itself. In addition, it is stable and exhibits only slight variation of peak current in repeated oxidation-reduction process so that it is suitable for use as, for example, a hole transporting material among others in various electronic devices including an organic electroluminescence element.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CHEMICAL CO LTD
Activated carbon for supercapacitor and preparation method and application of activated carbon
InactiveCN108751192AHigh specific capacitanceWell-developed pore structureCarbon compoundsHybrid capacitor electrodesCapacitanceBiological activation
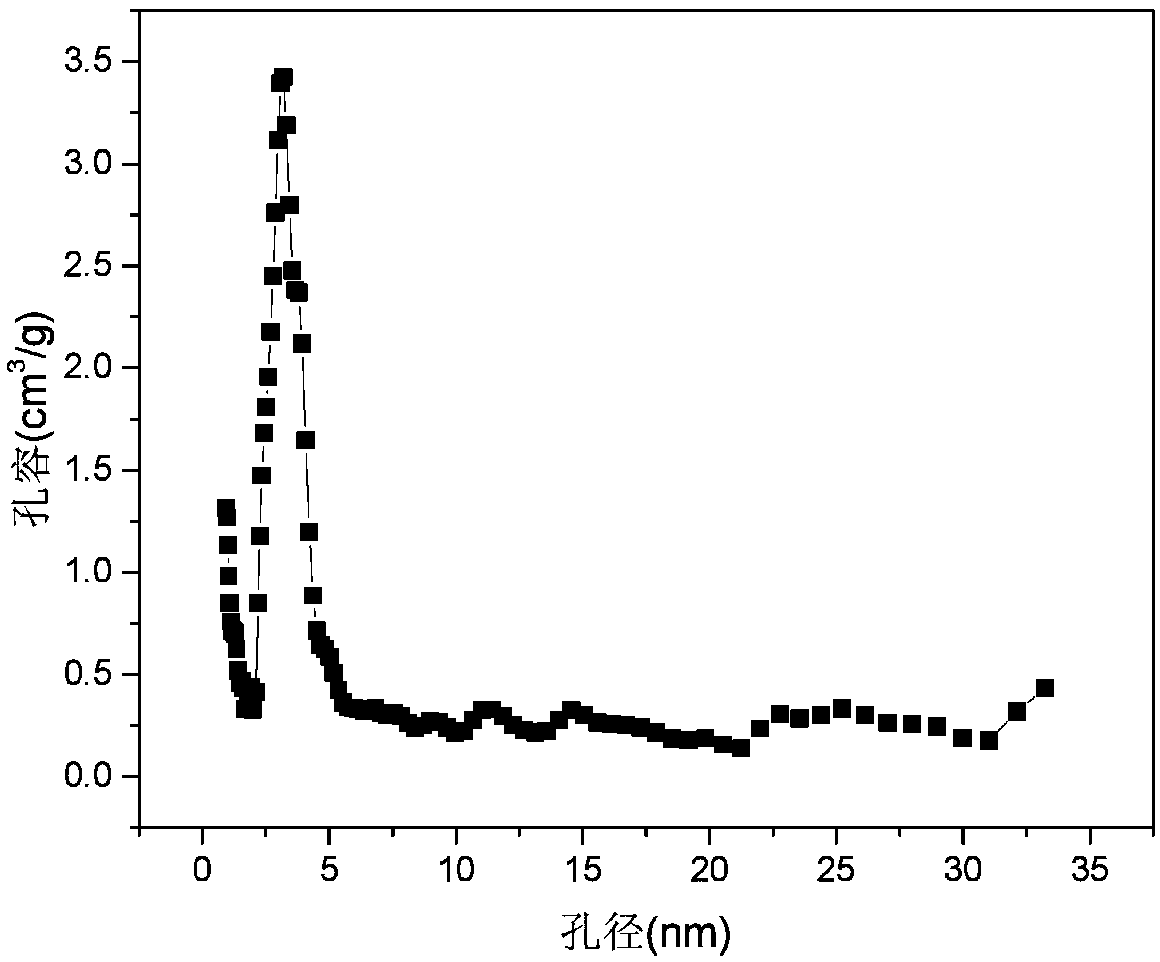
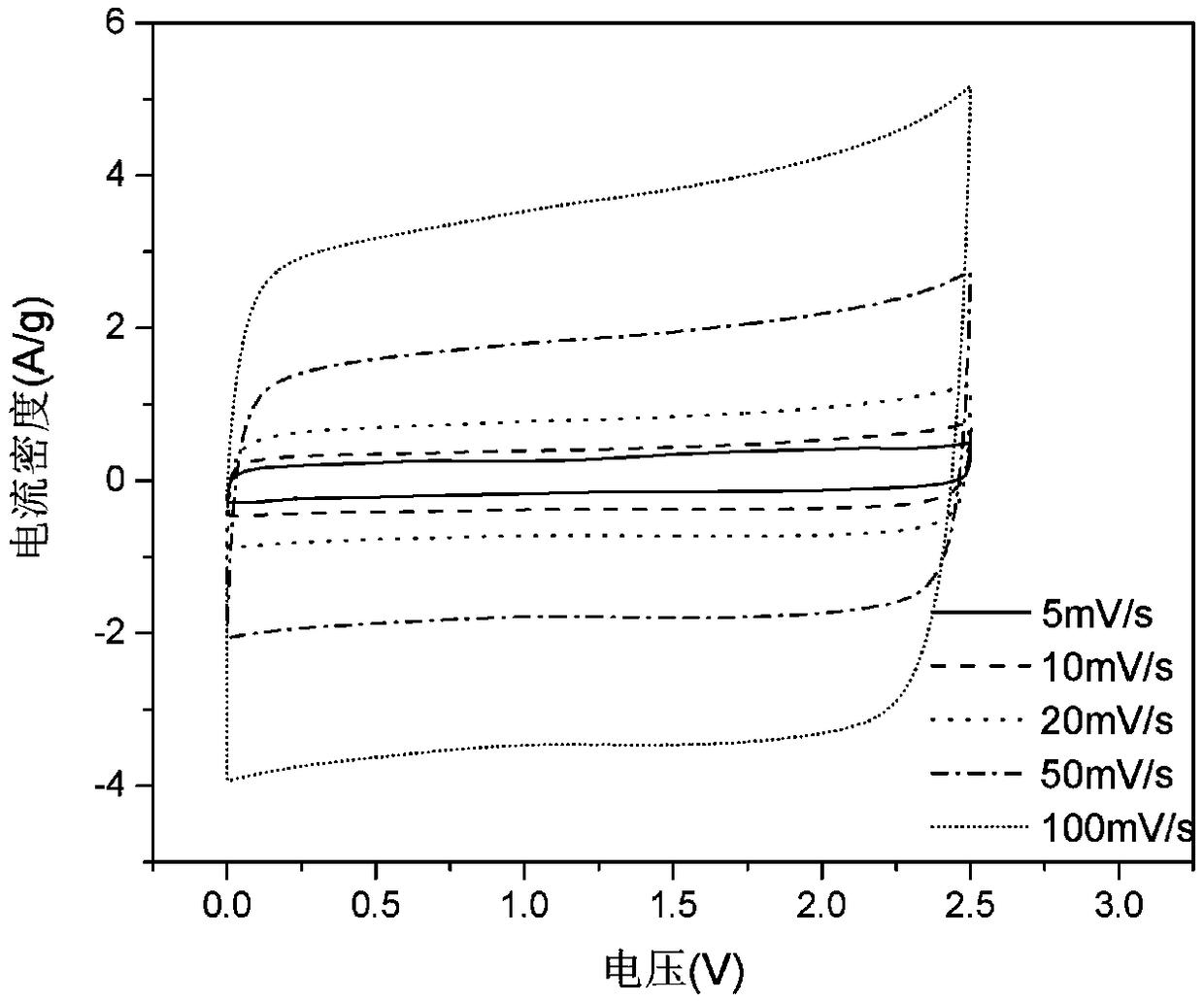
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of activated carbon materials and particularly relates to activated carbon for a supercapacitor and a preparation method and application ofactivated carbon. Different activators are used for performing gas activation on carbonized materials twice, the carbonized materials are activated into activated carbon with mesoporous and microporous structures, a large-area space is provided for charge storage, and a rapid transport channel is also provided for electrolyte ions, so that increase of the specific capacitance of the supercapacitoris facilitated. Results of the embodiment show that when activated carbon obtained by the method is used as an electrode material of the supercapacitor, a 2 mol / L of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate / acetonitrile solution is used as an electrolyte, and when the sweep rate is 5 mV / s, the specific capacitance of the supercapacitor reaches 110-186 F / g.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
High efficiency electronic ballast for metal halide lamp
InactiveUS20070222398A1Reduce probabilityStable areaElectric light circuit arrangementGas discharge lamp usageEngineeringLamp current
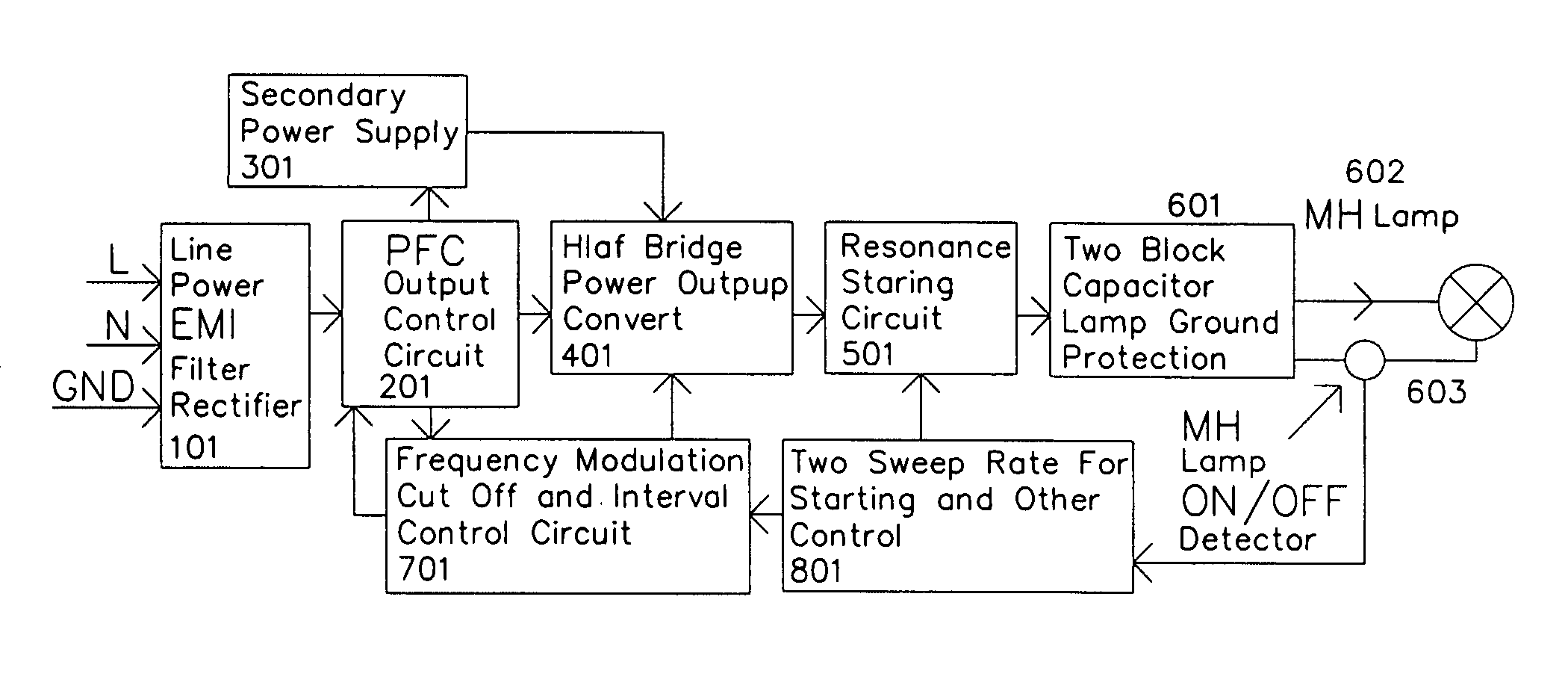
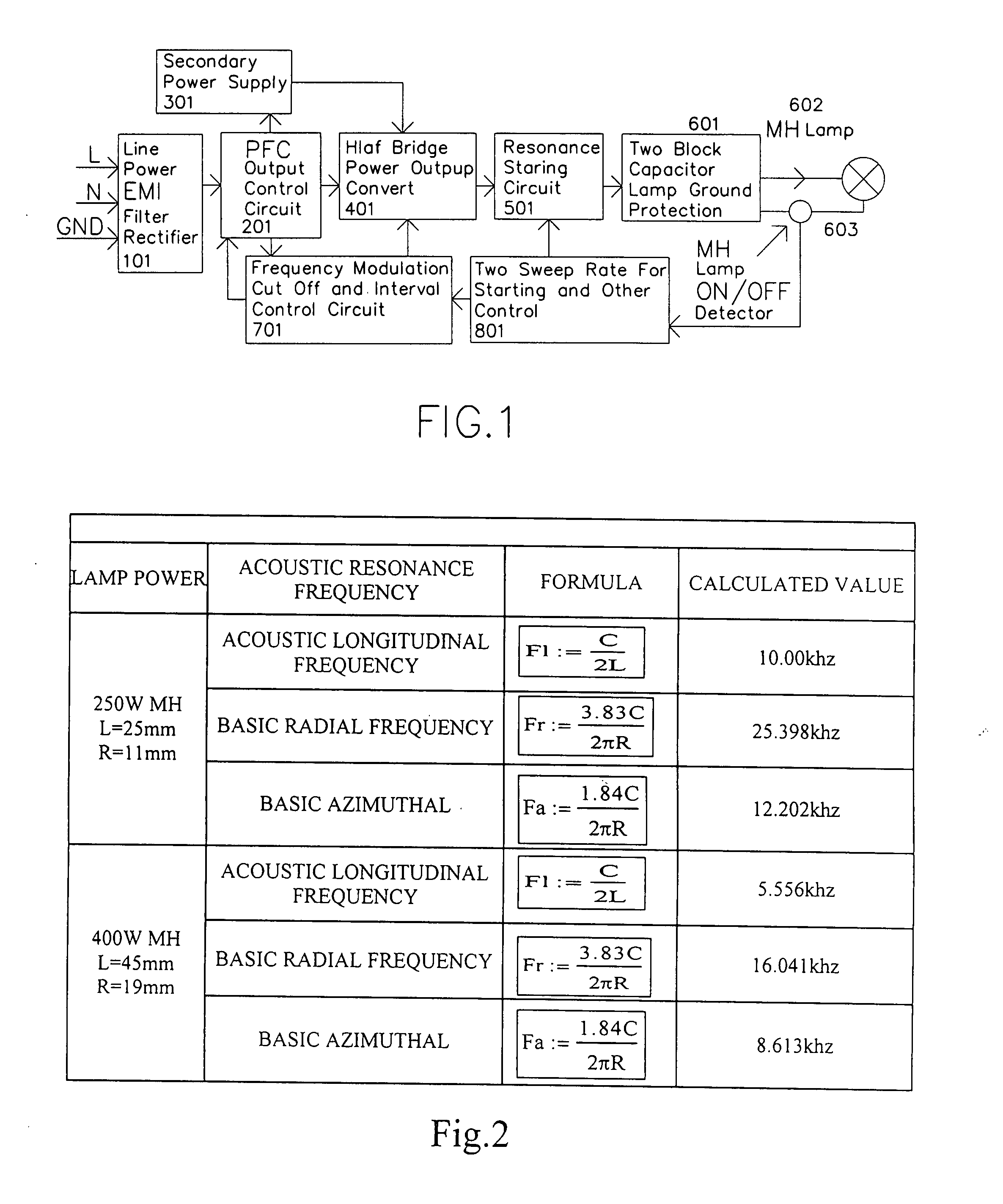
A high efficiency electronic ballast for large power metal halide lamp includes a power input circuit, a power factor correction circuit, a secondary power supply, a control circuit, a half bridge power converter, a resonant starting circuit, and lamp current on / off detector. The half bridge power converter has two DC block output capacitor to protect the converter when the output is shorted to ground. The operation frequency of the converter is chosen in the weak area of the acoustic resonant to avoid the acoustic resonant in the lamp. The control circuit adds a method for deep frequency and amplitude modulation and delay control function to the converter. For fine sweep pass through the output resonance point for igniting high voltage, two sweep rate control circuits are added. The metal halide lamp can be operated with very stable from starting to normal operation with high electronic ballast system efficiency.
Owner:FUJIAN JUAN KUANG YAMING ELECTRIC
Method and apparatus for controlling touch screen in mobile terminal responsive to multi-touch inputs
InactiveCN103181089ATransmissionInput/output processes for data processingComputer terminalTouchscreen
A mobile terminal and method for controlling a touch screen thereof are provided, wherein multi-point touch inputs such as a multi-point sweep input and / or a multi-point double tap input are sensed by a controller, and in response to a multi-point sweep, a display screen can be scrolled at a faster rate relative to a scroll in response to sensing a single point sweep, thus enabling a user to rapidly scroll to desired portions of an information screen using e.g., a two finger sweep, and to scroll slower using a single finger sweep at the same sweep rate and during a photo album application, scrolling to other photos in response to a multi-touch input is possible while in a zoomed-in state, while panning is carried out responsive to a single point touch input.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for the ply-by-ply machining of a component made of composite material, by applying energy
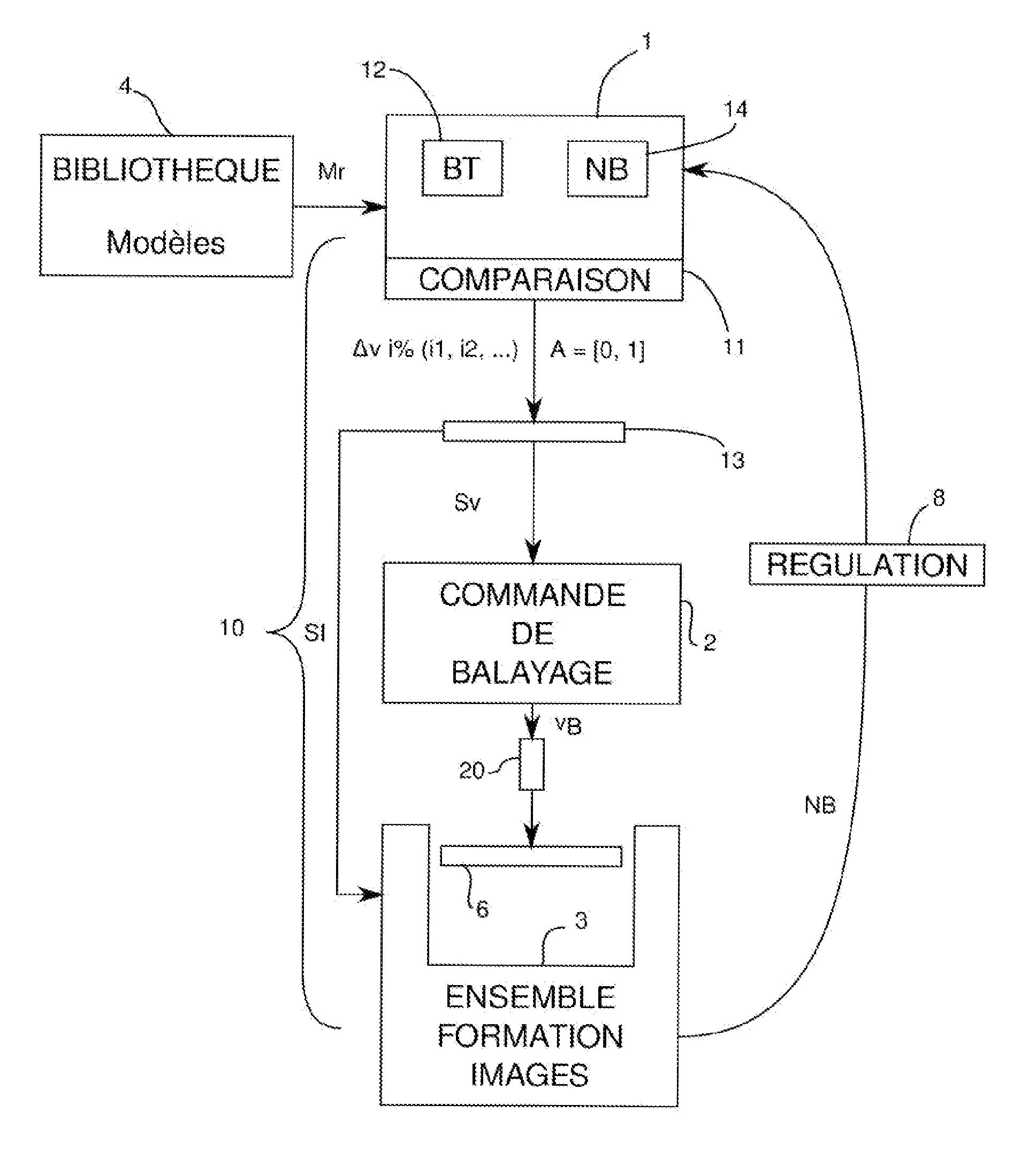
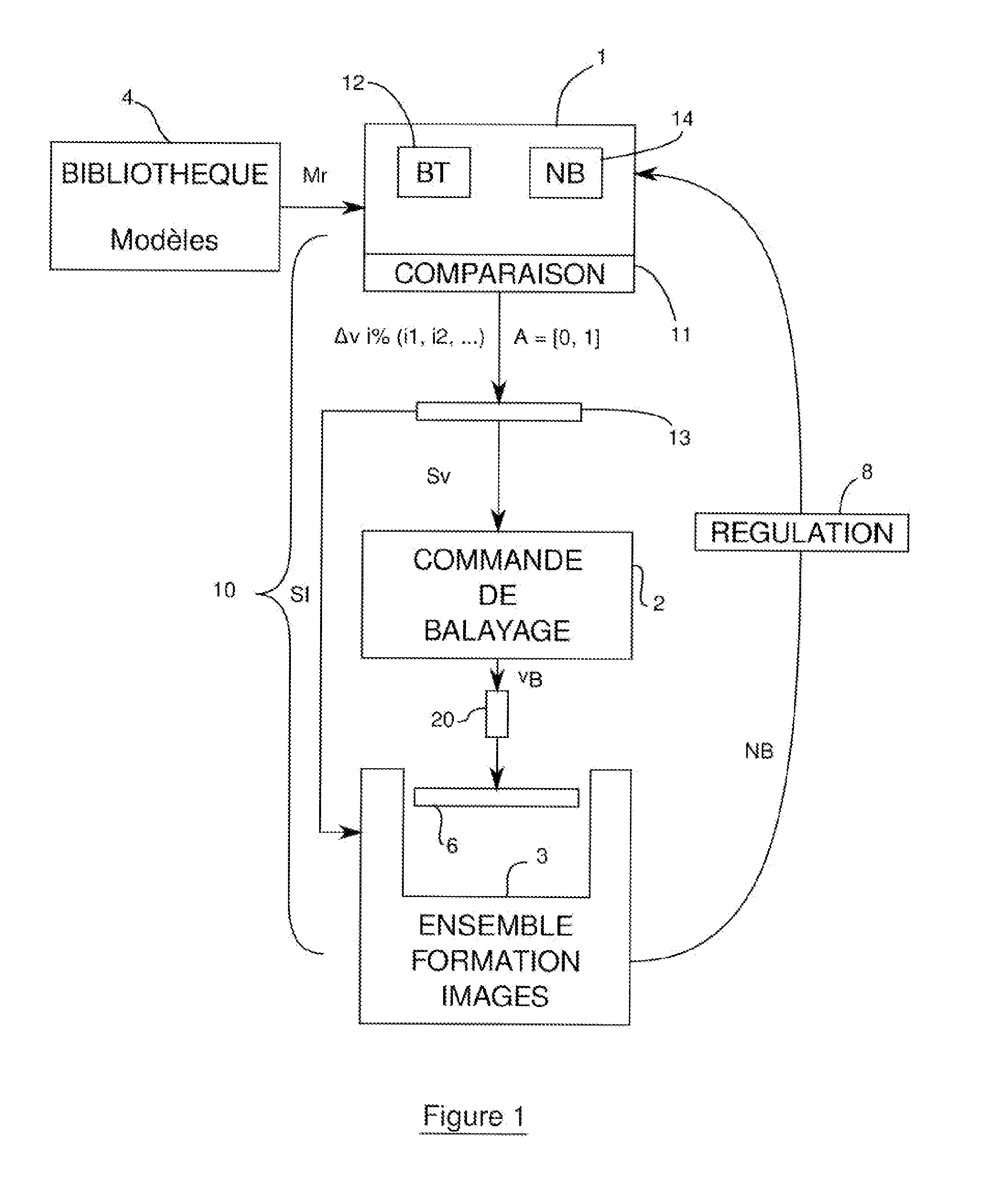
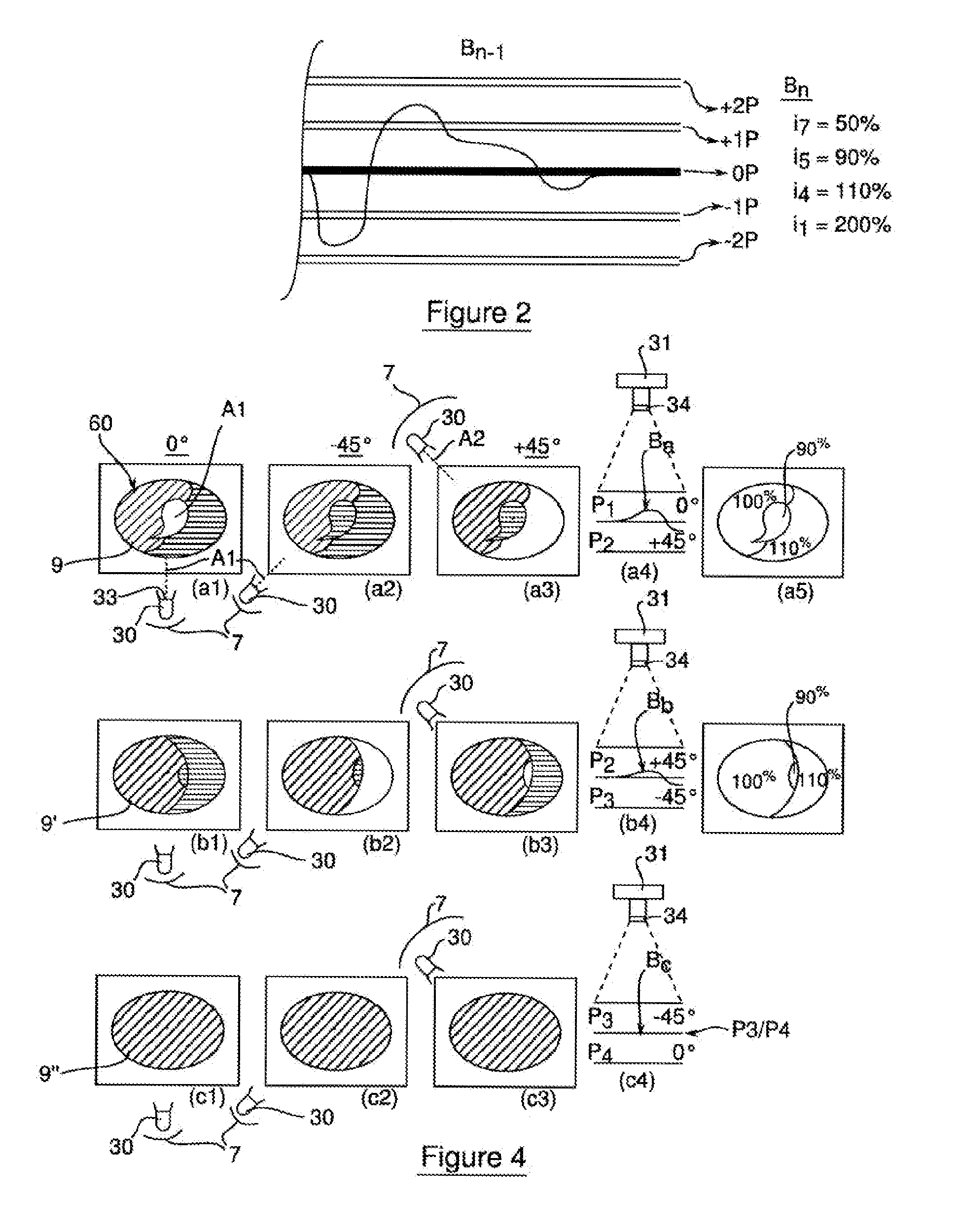
ActiveUS20150099422A1Constant ply machiningAdaptability of amountInvestigating composite materialsAbrasive blasting machinesImage formationProcessing element
The invention relates to machine a component made of composite material in order to eliminate singularities, defects or damage to the component using a method that is repeatable and adaptable. To do this, it is proposed that the defects and their type be identified by image processing of the surface of the component and that the local machining rates at which the plies are machined be regulated at the function of this identification. According to one embodiment, a system (10) for the ply-by-ply machining of defects of a component made of composite material includes a numerical data processing unit (1) combined with a sweep control (2) that commands the sweep of a high-pressure water jet machine (20), and an image formation assembly (3) including an image capturing device (30, 31) connected with the numerical processing unit (1). The processing unit (1) includes regulating devices (11, 13) indexing local sweep rates, by convergence of brightness levels (NB) from the successive sweeps, these being formed by the image capturing assembly (3) toward making the brightness uniform according to a model (Mr) correlating brightness to ply state typology identification (BT) that can be supplied by a library (4). The correlation data (BT) and brightness levels (NB) are stored in memory modules (12, 14) of the processing unit (1).
Owner:JEDO TECH
Interferometric optical fibre sensor system and method of interrogation
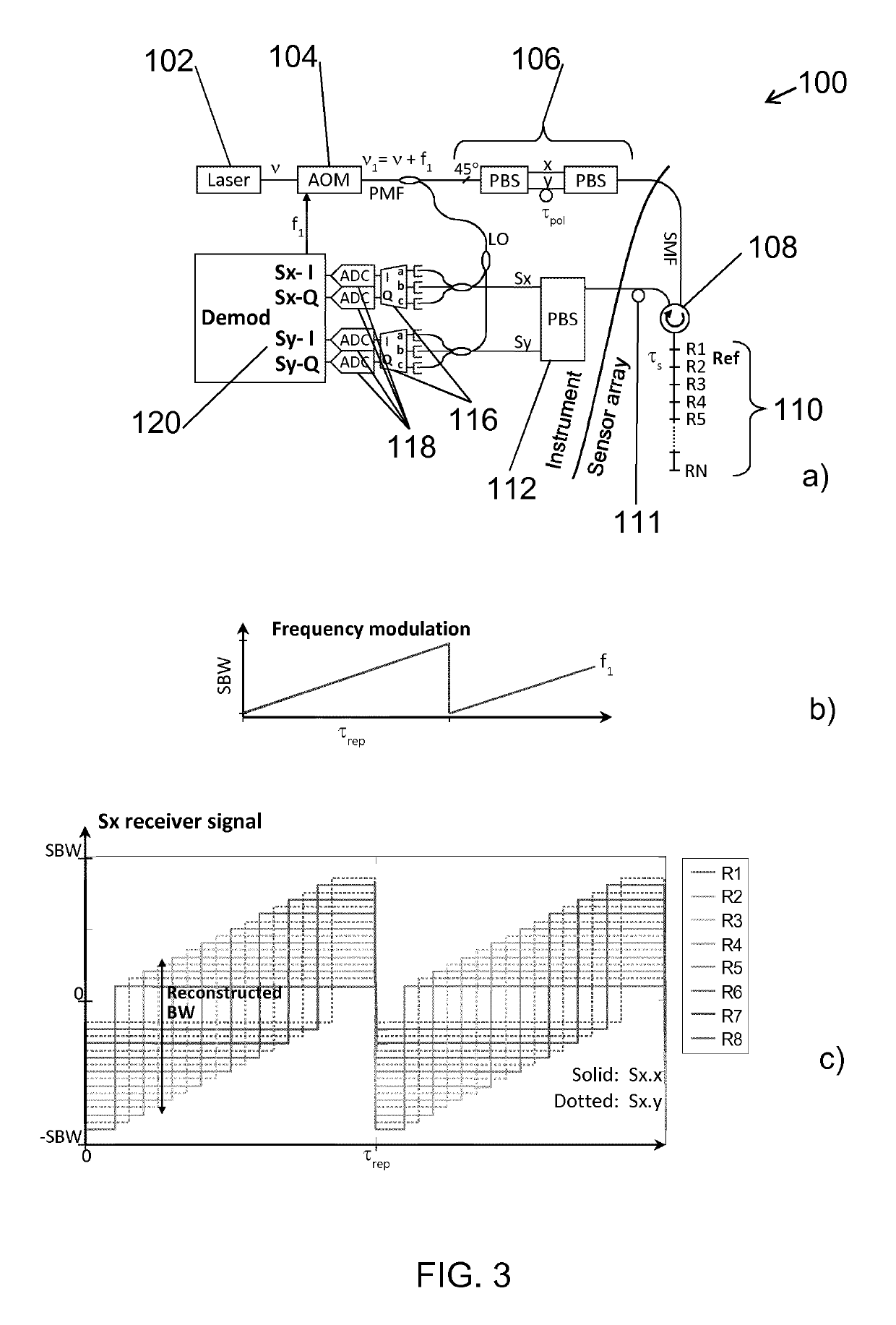
ActiveUS20180188077A1High resolutionLarge dynamic rangeInterferometersUsing optical meansSensor arrayLocal oscillator signal
The invention relates to a method of interrogating an interferometric optical fibre sensor system including a laser source configured to generate interrogation light and a sensor array with at least a first reflector and a second reflector. The method includes continuously and repeatedly frequency sweeping the interrogation light from the laser source within a sweep bandwidth (SWB) over a sweep duration (tsw) with a substantially constant sweep rate r=SBW / tsw to produce a swept interrogation light signal, launching the swept interrogation light signal is launched into the sensor array, detecting reflected signals being returned from the sensor array by each of the reflectors, respectively, wherein detection includes mixing a return light signal from the sensor array with a local oscillator signal onto an optical receiver to produce an electrical radio frequency signal, demultiplexing the electrical radio frequency signal into a first signal channel and a second signal channel, corresponding to the first and second reflector, respectively, demodulating each of the first and second signal channel into a first phase response from the first reflector and a second phase response from the second reflector, and subtracting the first phase response from the second phase response to obtain a sensor phase signal.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
Oscillation device
InactiveUS20100164636A1High speed information communicationEffective applicationRadiation pyrometrySolid masersPermittivityLength wave
To provide an oscillation device having a long oscillation wavelength in which wavelength variable width is relatively broad and wavelength sweep rate is relatively high. An oscillation device includes a gain medium having a gain with respect to an electromagnetic wave to be oscillated, cavity structures for resonating the electromagnetic wave, and energy injection means and for injecting pumping energy into the gain medium. The gain medium is sandwiched between a first negative permittivity medium and a second magnetic permittivity medium each of which real part of permittivity with respect to the electromagnetic wave is negative. Electric field application means is provided for at least one of the first negative permittivity medium and the second negative permittivity medium to apply an electric field for changing a depletion region formed at a boundary part with the gain medium.
Owner:CANON KK
Systems and methods for controlling motion of detectors having moving detector heads
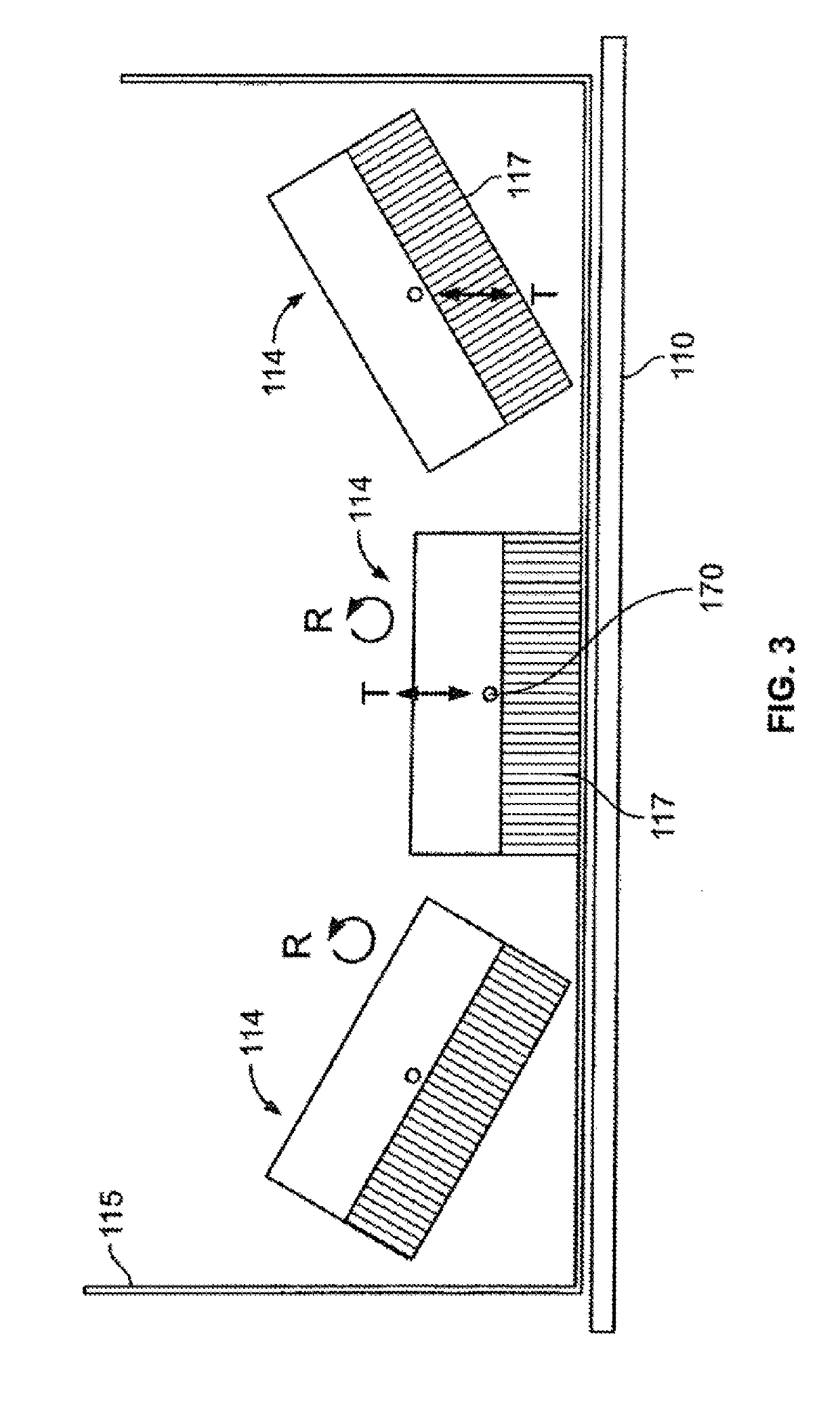
ActiveUS20190223816A1Radiation diagnostic device controlComputerised tomographsComputer visionSweep rate
An imaging system is provided that includes a gantry, at least five detector units mounted to the gantry, a corresponding collimator for each of the detector units, at least one processing unit, and a controller. Each collimator has septa defining plural bores for each pixel of at least some of a plurality of pixels of the detector unit. A corresponding interior septum of the collimator is disposed above an internal portion of a corresponding pixel of the at least some of the plurality of pixels. The at least one processing unit is configured to obtain object information corresponding to the object to be imaged. The controller is configured to control an independent rotational movement of each the detector units used to acquire scanning information by detecting emissions from the object, wherein the controller rotates each of the detector units at a corresponding sweep rate.
Owner:GE PRECISION HEALTHCARE LLC
Arrangement and a method relating to phase locking
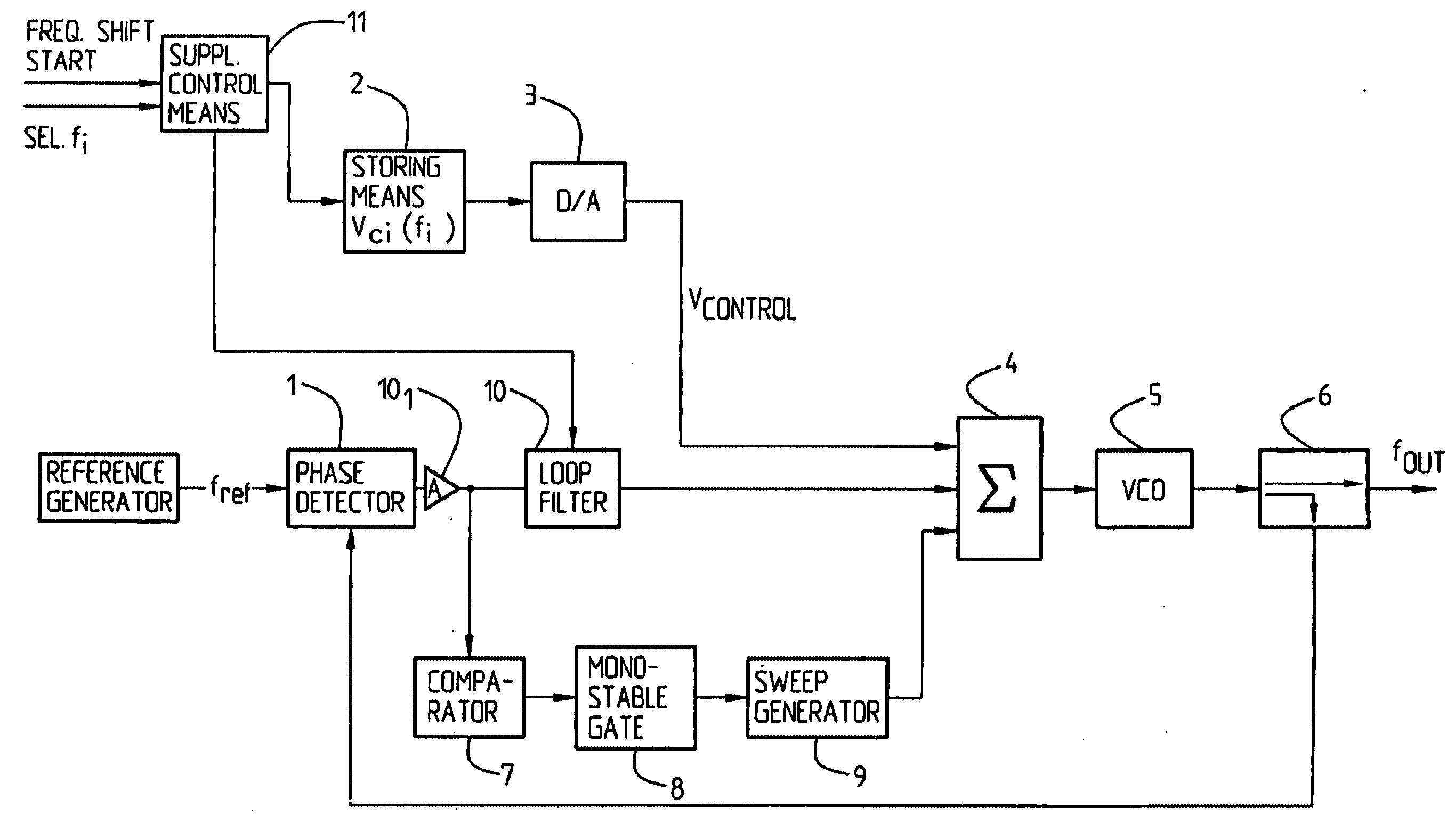
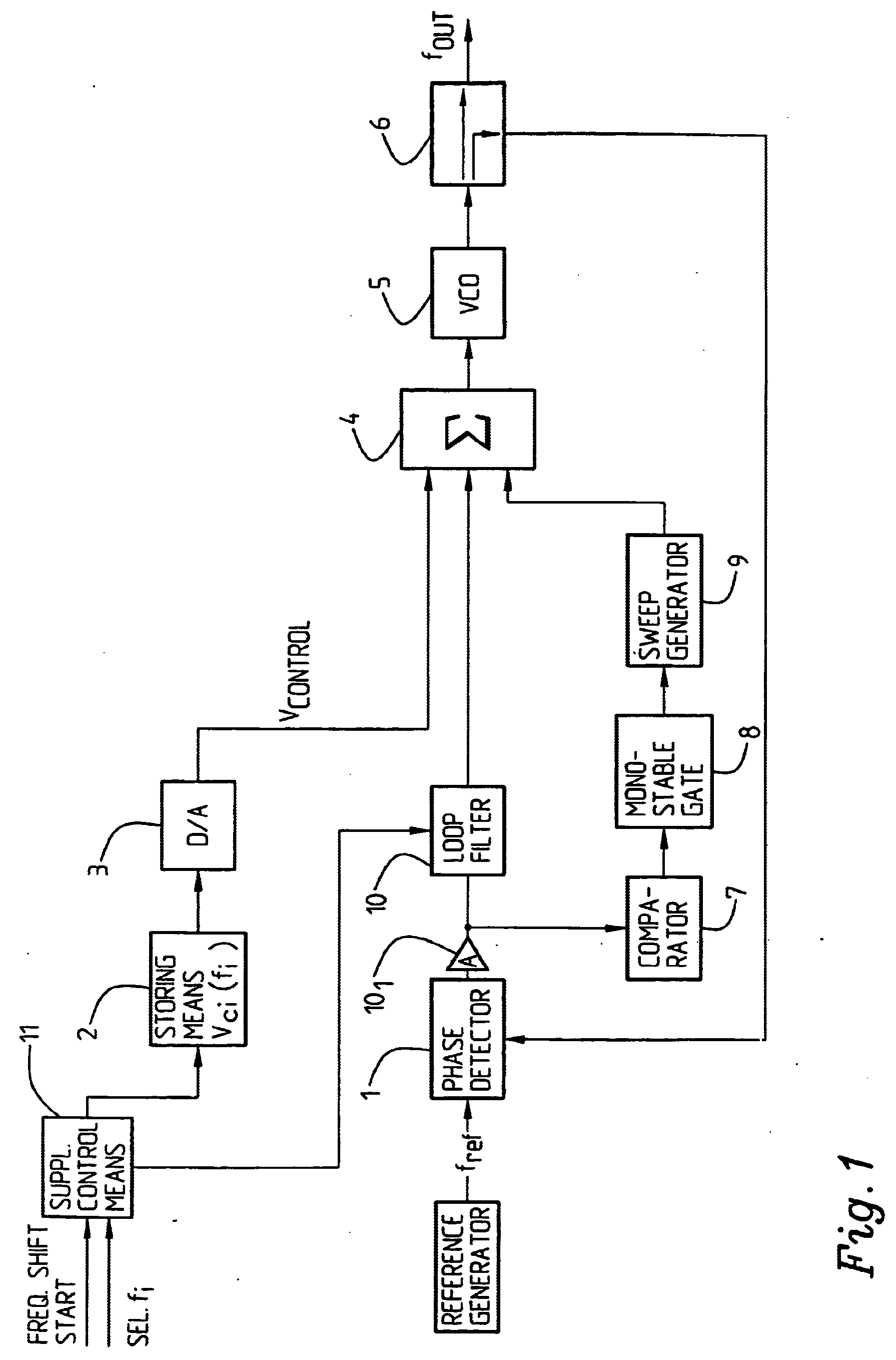
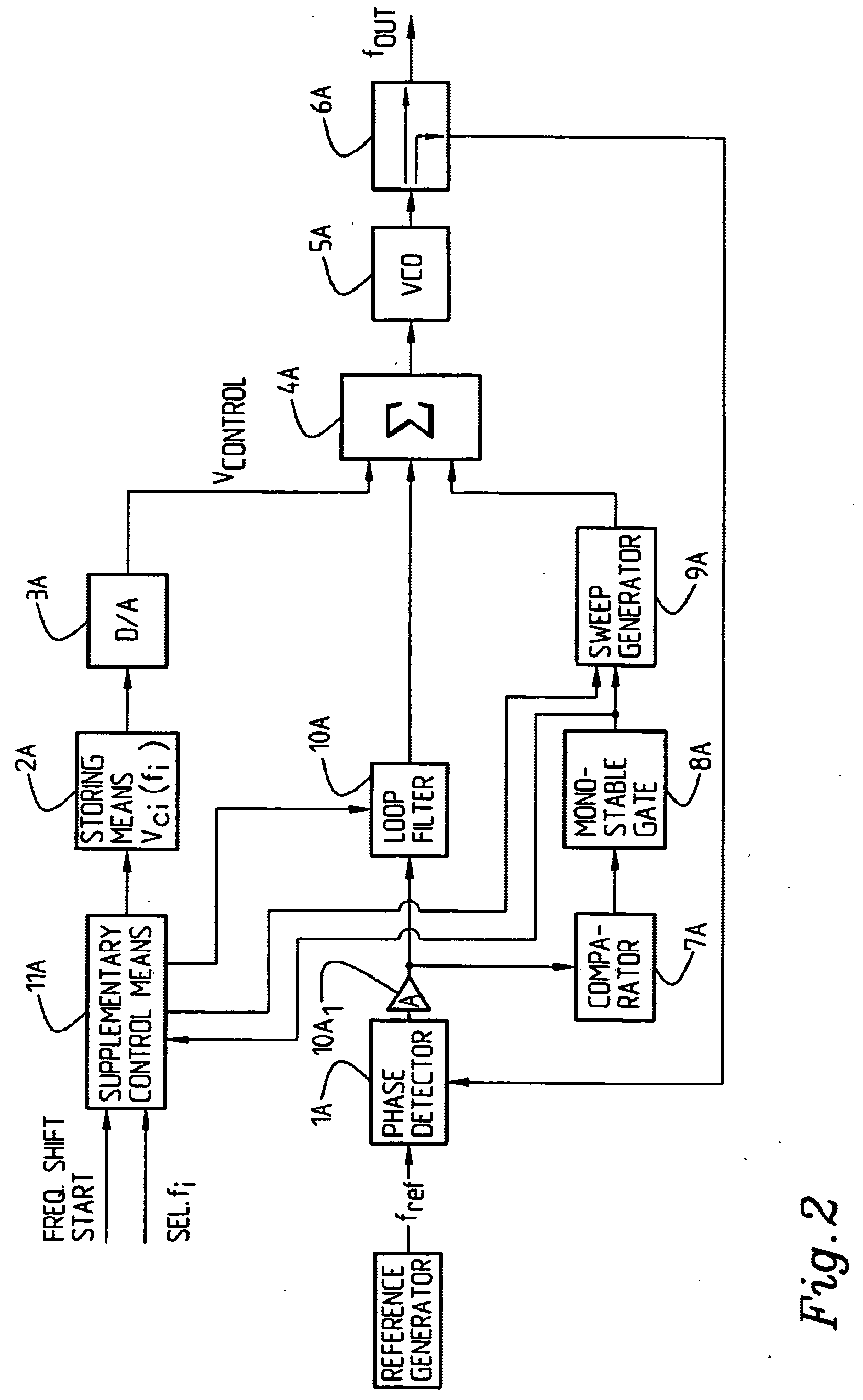
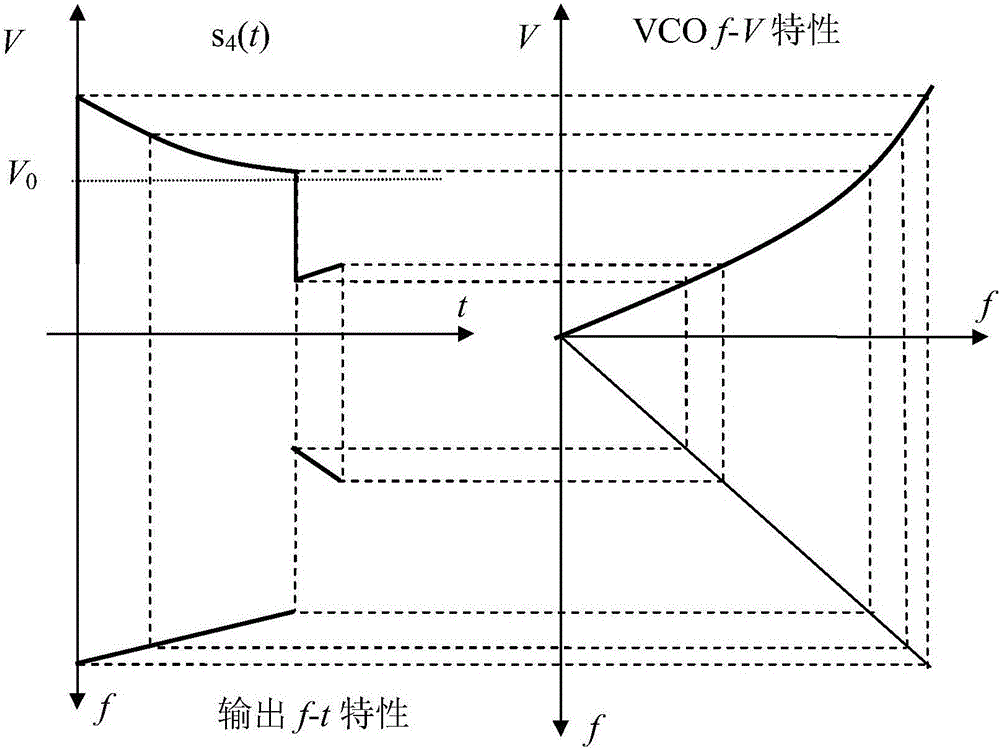
The present invention relates to an arrangement for phase locking of a Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) to a selected frequency harmonic among a number of predetermined or available frequencies (harmonics), comprising a reference generator for generating a reference frequency, a phase lock loop (1; 101; 10, 4, 5, 6, 9) for producing an output signal in response to the input reference frequency, said phase lock loop comprising (enclosing) a phase detector (1), a loop filter (10), said VCO (5), adding means (4) and a power splitter (6). The arrangement also includes a sweep generator (9). It further comprises or is associated with storing means 82) for storing information about, for each selectable or available frequency harmonic, a first (coarse) control voltage providing a VCO frequency output which is lower / higher than, and differs from the selected frequency (harmonic) by a given value (Δf1). That the sweep generator (9) adds (superimposes) a controllable sweep voltage to / on the first control voltage at least until a varying, second frequency difference (Δfc) between the output VCO frequency and the selected frequency harmonic reaches a given value. Monitoring / detecting means are provided for detecting the varying, second frequency difference (Δfc) between the selected frequency harmonic and the VCO output frequency, and sweep generator control means are provided for reducing the sweep rate until the VCO is phase locked to the selected frequency harmonic.
Owner:HIGHBRIDGE PRINCIPAL STRATEGIES LLC AS COLLATERAL AGENT
Apparatus and Method for Interpolating the Intensities of Scanned Pixels from Source Pixels
InactiveUS20090213040A1Reduce error in beam positionReduce in quantityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsHarmonicLight beam
A scan assembly of an image generator sweeps an image beam in a first dimension at a first rate and bi-directionally in a second dimension at a slower rate. Sweeping the beam bi-directionally in the vertical dimension (generally the dimension of the lower sweep rate) can reduce the scanning power by eliminating the flyback period, and, where the scan assembly includes a mechanical reflector, can reduce the error in the beam position without a feedback loop by reducing the number of harmonics in the vertical sweep function. Furthermore, because the image beam is “on” longer due to the elimination of the flyback period, the scanned image is often brighter for a given beam intensity. The scan assembly may also sweep the image beam non-linearly in the vertical dimension, and this sweep may be bi-directional or uni-directional. Sweeping the beam non-linearly can also reduce the error in the beam position by reducing the number of harmonics in the vertical sweep function.
Owner:MICROVISION
Novel sensor initialization methods for faster body sensor response
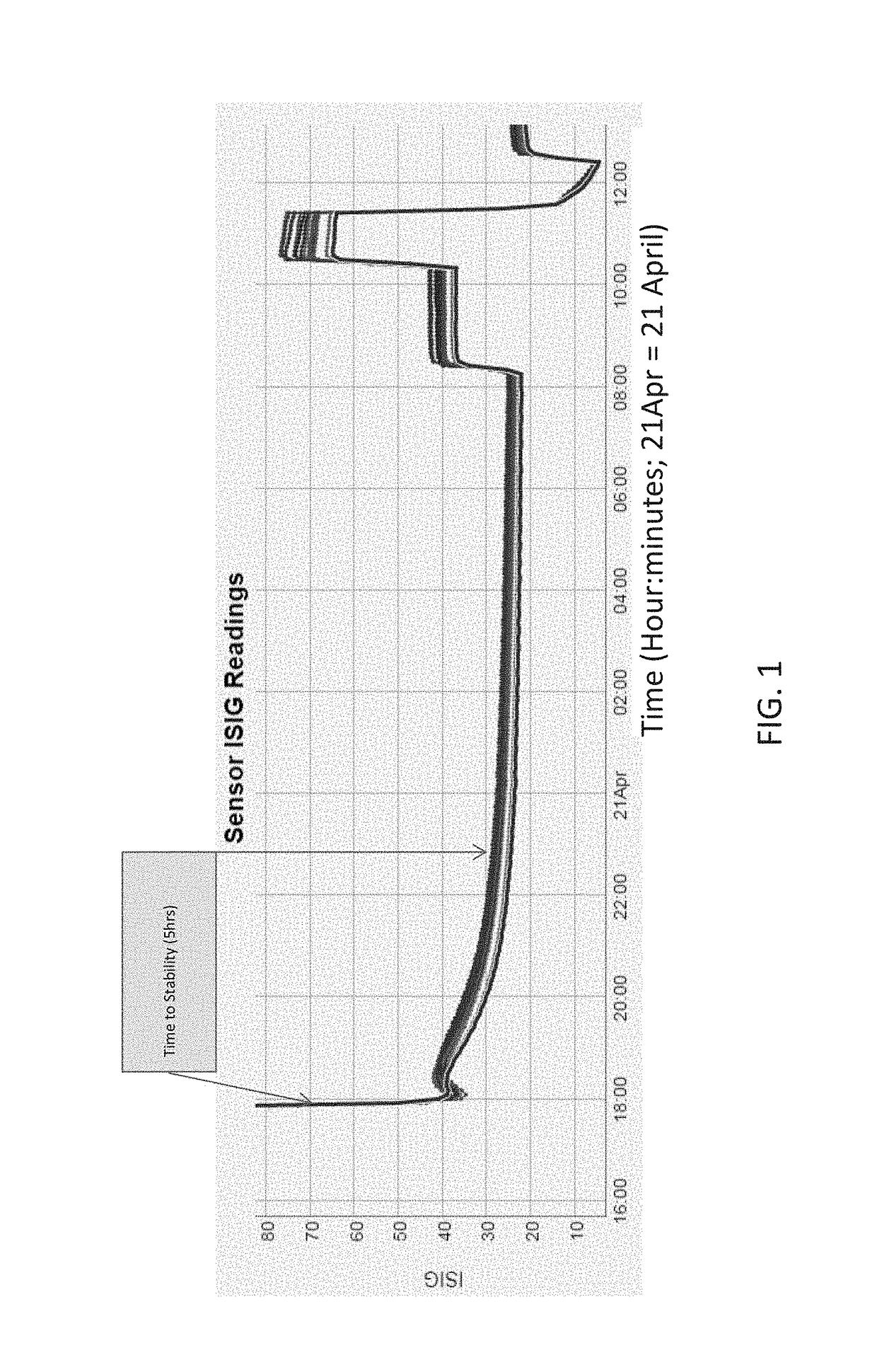
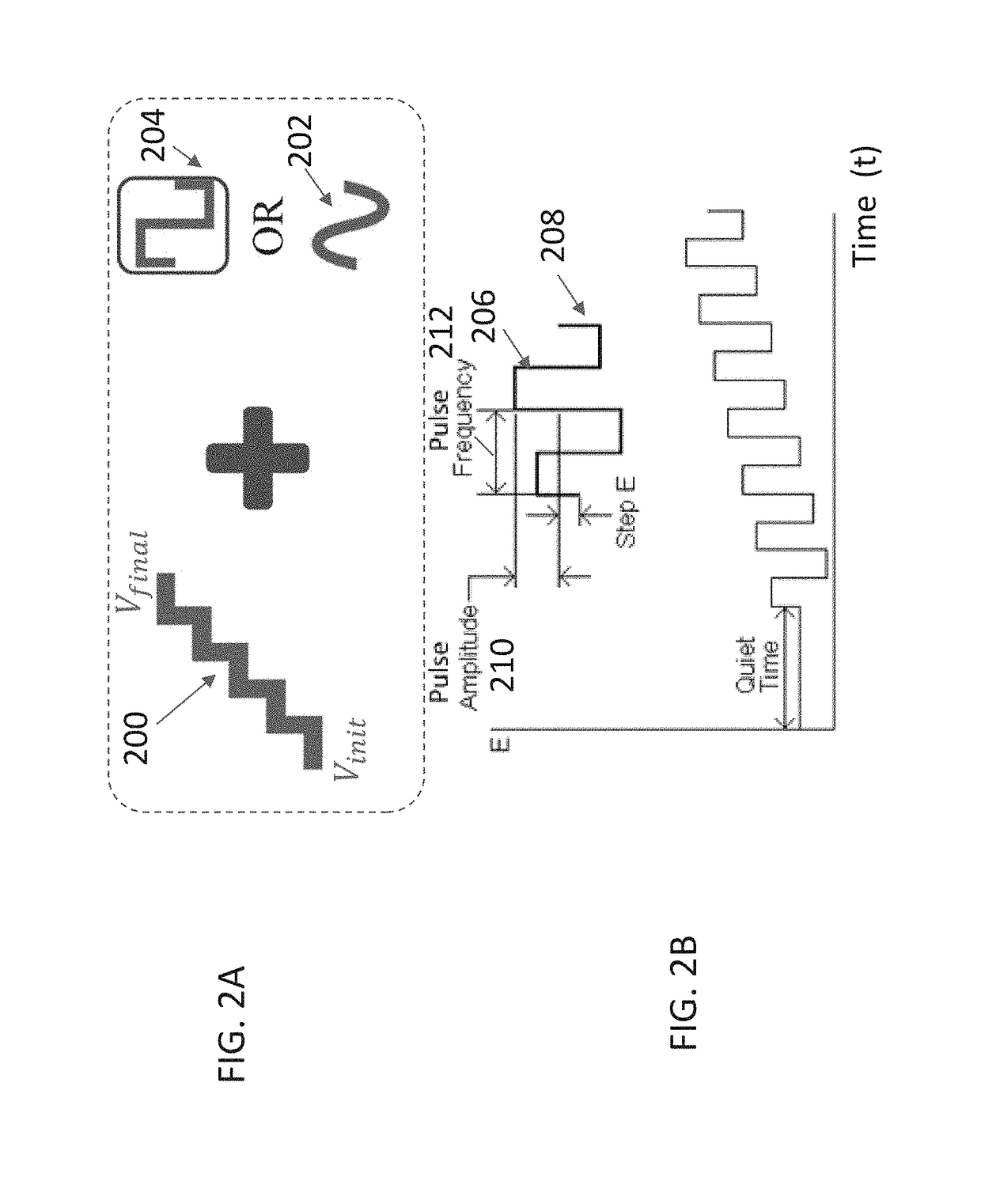
ActiveUS20190000358A1Low time to electrical current stabilityImprove performanceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCatheterVoltage pulseEngineering
A method of initializing a sensor with a voltage sequence including a ramped voltage combined with a biphasic voltage pulse. The initialization scheme results in faster in-vitro sensor run-in and stabilization times. In various examples, the in-vitro sensor stabilization time is reduced from 200 minutes to 40-55 minutes (a reduction by a factor of least 5 as compared to a non-initialized sensor). In addition, staircase voltage initialization is implemented adaptively so that the voltage step size and sweep rates are changed depending on the state of the sensor (characterized by ISIG magnitude). As a result, individual sensors can be initialized in a customized manner rather than by using a general hardwired and harsh initialization scheme.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
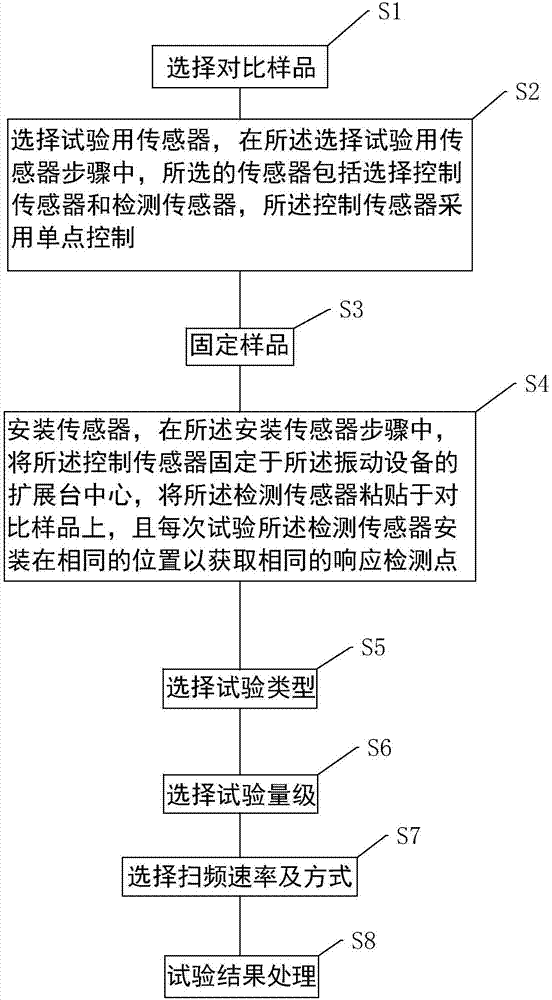
Vibration equipment confirmation method
InactiveCN107356386AGuarantee authenticityGuaranteed reliabilityVibration testingEngineeringInter-laboratory
The invention discloses a vibration equipment confirmation method comprising the following steps of selecting contrast samples, selecting sensors used for the test, fixing the samples, installing the sensors, selecting the test type, selecting the test magnitude, selecting the test video range, selecting the frequency sweep rate and mode and processing the test result. In the step of selecting the sensors used for the test, the selected sensors include a control sensor and a detection sensor, wherein the control sensor adopts single-point control. In the step of installing the sensors, the control sensor is fixed at the extension table center of vibration equipment, the detection sensor is adhered on the contrast samples, and the detection sensor is installed at the same position in each time of test. The method can be used for guiding inter-laboratory and intra-laboratory vibration capacity comparison, and the same response detection points are sampled in comparison so that the test data are ensured to be real and reliable, the vibration equipment is enabled to be accurately confirmed, and the method also has the advantages of being simple and practicable and convenient to operate.
Owner:GOERTEK INC
Blind adaptive filter for narrowband interference cancellation
The present invention relates to a blind adaptive filter for narrowband interference cancellation, which includes an adaptive filter, a delay unit coupled to the adaptive filter for generating a delayed signal with a predetermined delay length from the output signal of the adaptive filter, and an error calculation unit coupled to the adaptive filter and the delay unit. The error calculation unit compares the output signal from the adaptive filter and the delayed signal from the delay unit to extract error information, and feedback the first error information to the adaptive filter. The first error information is formed of a transfer function including a number of coefficients, and used to adjust the adaptive filter and remove interference in the next input signal. The disclosed technique is also applicable in wideband receivers, as well as resisting multiple strong narrowband interferences having a frequency sweep rate of tens of milliseconds.
Owner:MONTAGE TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
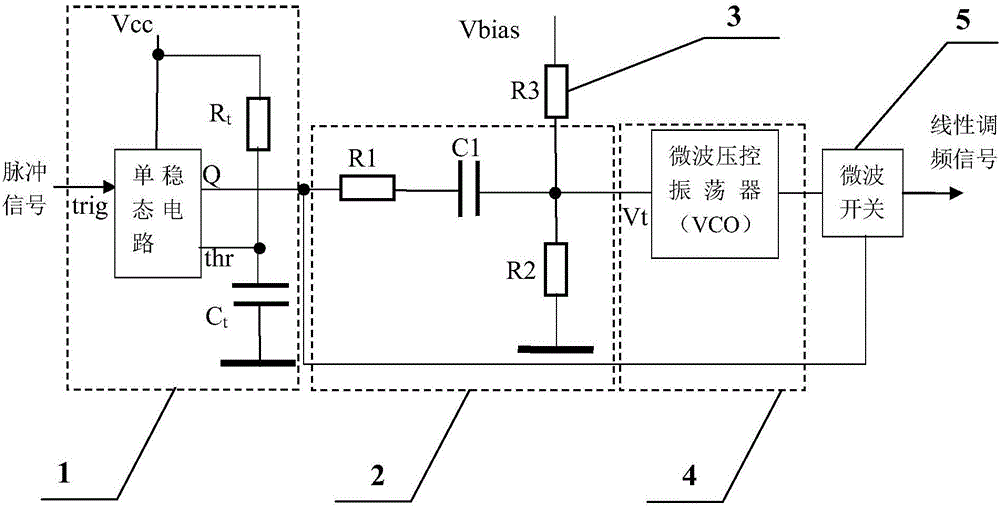
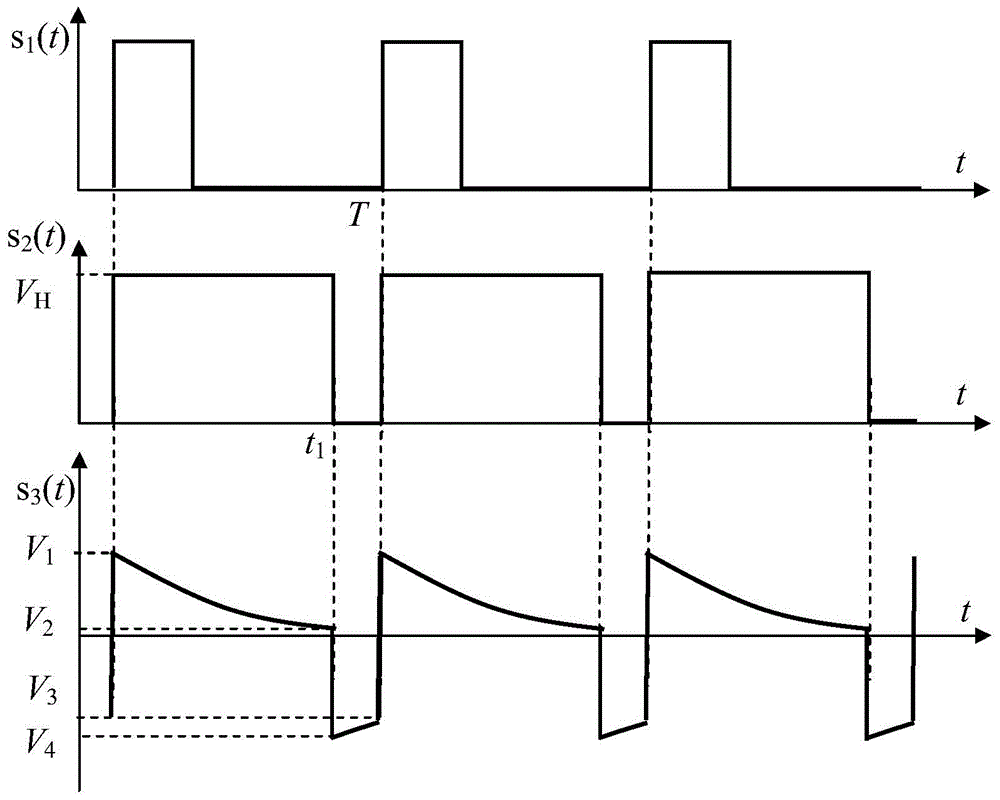
Microwave vco direct modulation high linear frequency modulation signal generating circuit
ActiveCN104079269BSweep Linear Accuracy ImprovementReduce ranging errorPulse shapingIntermediate frequencyMicrowave oscillators
A microwave VCO directly modulates a high linear FM signal generating circuit proposed by the present invention, aiming to provide a frequency-modulation continuous-wave radar intermediate frequency with second-order or higher frequency sweep linear accuracy, unlimited sweep rate, and capable of suppressing cross-mixing A microwave chirp signal generation circuit for spurious signals. The present invention is realized through the following technical solutions: the monostable pulse shaping circuit shapes the input periodic pulse signal used to trigger the frequency sweep signal into a pulse signal with a pulse width equal to the frequency sweep time in one cycle, and generates nonlinearity through the C-R differential circuit Ramp down sawtooth voltage signal, superimposed on the DC bias voltage V 0 Above, a frequency-sweeping control voltage signal that compensates with the nonlinear tuning voltage-frequency characteristic of the microwave VCO (4) is formed to control the oscillation frequency of the microwave VCO to change linearly with time. The pulse signal generated by the shaping controls the microwave switch to gate the output of the microwave VCO, and suppresses the interference of the intermediate frequency stray signal generated by the close-range strong echo to the radar.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Method and device for fast tuning of optical sources
ActiveUS8879588B2Improve performanceFOM of a one pump mixer can be further enhancedLaser arrangementsNon-linear opticsFrequency mixerEngineering
A method and device are provided for fast, continuous tuning of an optical source. A first pump signal with a first pump frequency is input into a mixer along with a first seed signal having a first seed frequency. Within the mixer, the first pump signal and the first seed signal generate at least one idler having an idler frequency defined as two times the pump frequency minus the seed frequency. Shifting the pump signal across a frequency range at a sweep rate causes the idler frequency to be shifted by two times the frequency range at two times the sweep rate. The shifted at least one idler is mixed with the shifted pump signal to generate a first mix product that has two times the sweep rate and frequency range of the pump signal.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com