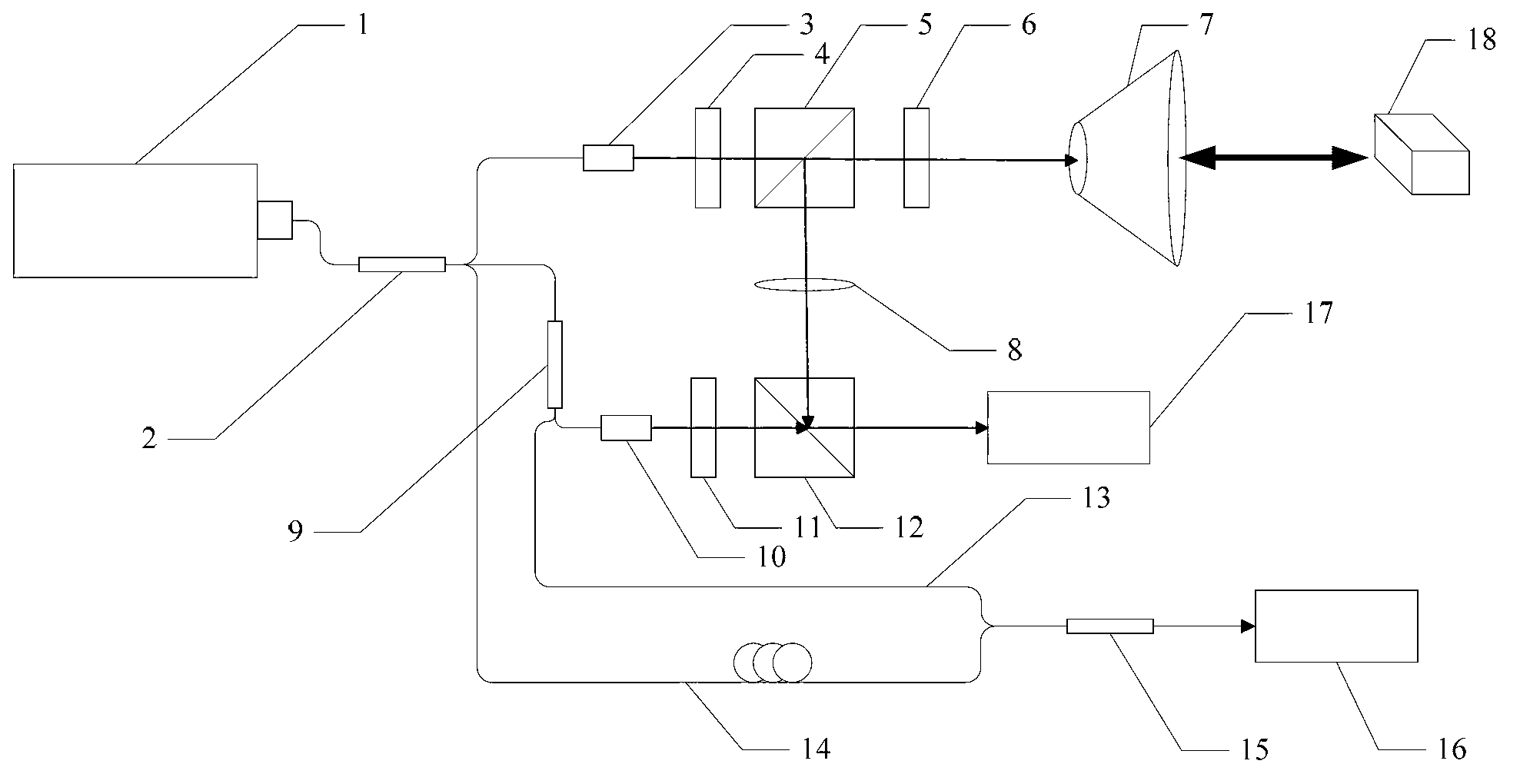Non-linear correction method for LFMCW (linear frequency modulated continuous wave) laser radar frequency modulation based on optical fiber sampling technology
A nonlinear correction and lidar technology, applied in the field of nonlinear correction, can solve problems such as inability to perform nonlinear correction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0022] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 and Figure 8 Describe this embodiment, the nonlinear correction method of LFMCW laser radar frequency modulation based on optical fiber sampling technology described in this embodiment, the LFMCW laser radar is an LFMCW laser radar with a correction optical path, which includes an interferometric optical path and a correction optical path, The interferometric optical path includes a tuning laser 1, a first coupler 2, a first collimating mirror 3, a first glass slide 4, a first polarizing beam splitter 5, a second glass slide 6, a collimating beam expander 7, a focusing A lens 8, a second coupler 9, a second collimating mirror 10, a third glass slide 11, a second polarization beam splitter 12 and a second detector 17, and the correction optical path includes a first optical fiber 13, a second optical fiber 14, The third coupler 15 and the first detector 16,
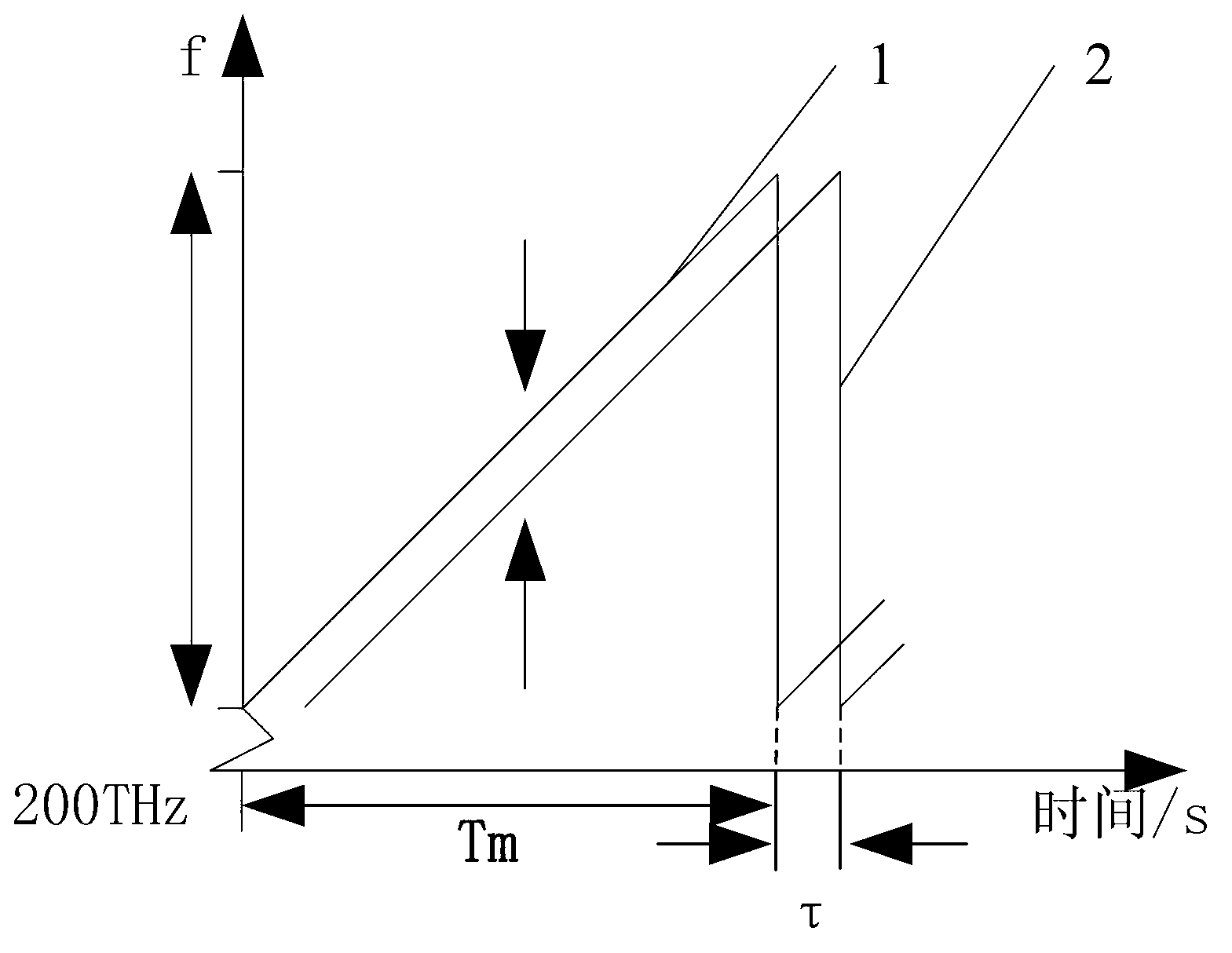
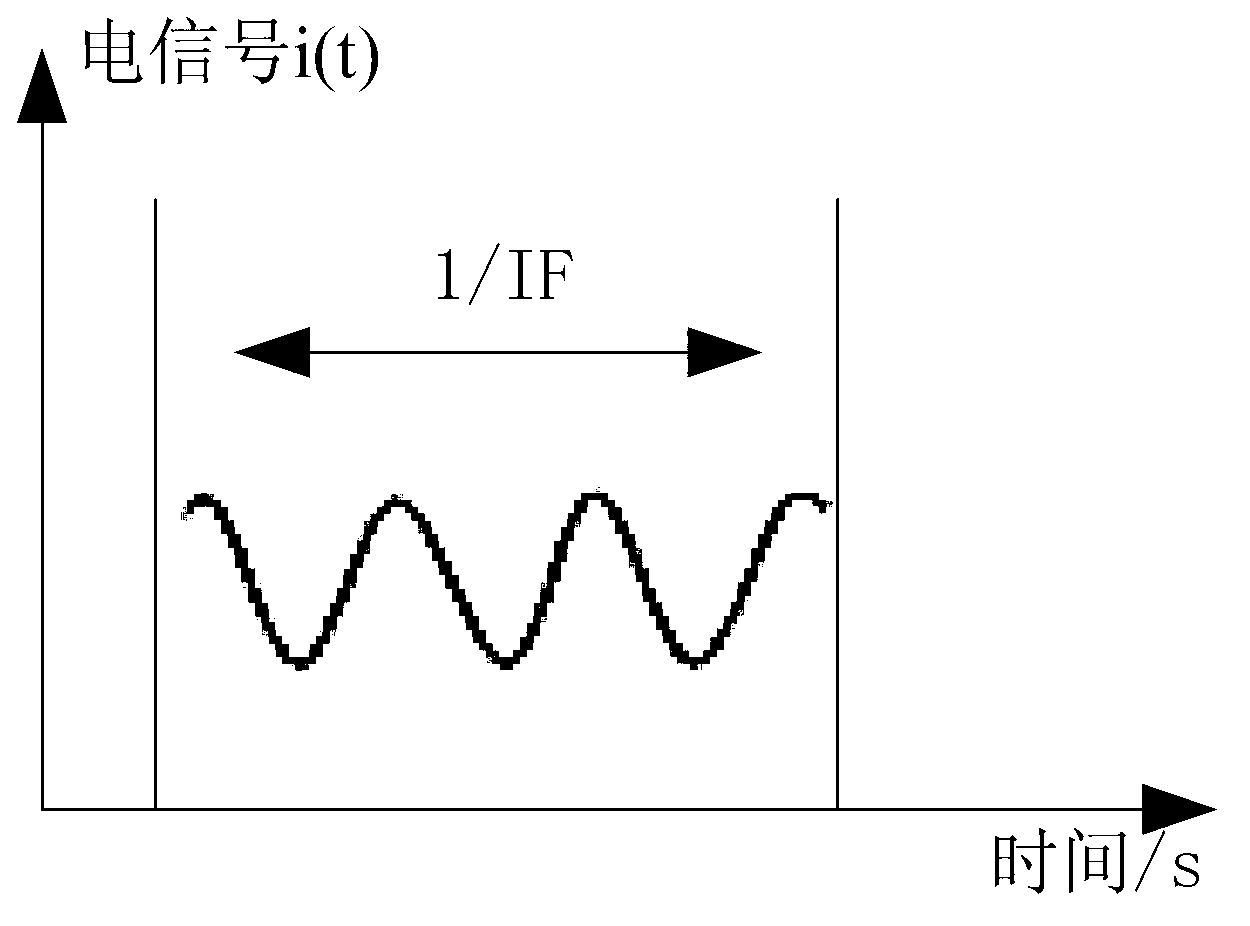
[0023] The linear continuous frequency-modulated laser lig...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0032] Embodiment 2: This embodiment is a further limitation of the non-linear correction method for LFMCW lidar frequency modulation based on fiber sampling technology described in Embodiment 1, and the tuned laser 1 is a 1550nm tuned laser.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0033] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is a further limitation of the non-linear correction method of LFMCW laser radar frequency modulation based on fiber sampling technology described in Embodiment 1, and the first coupler 2 is a 1×3 coupler.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com