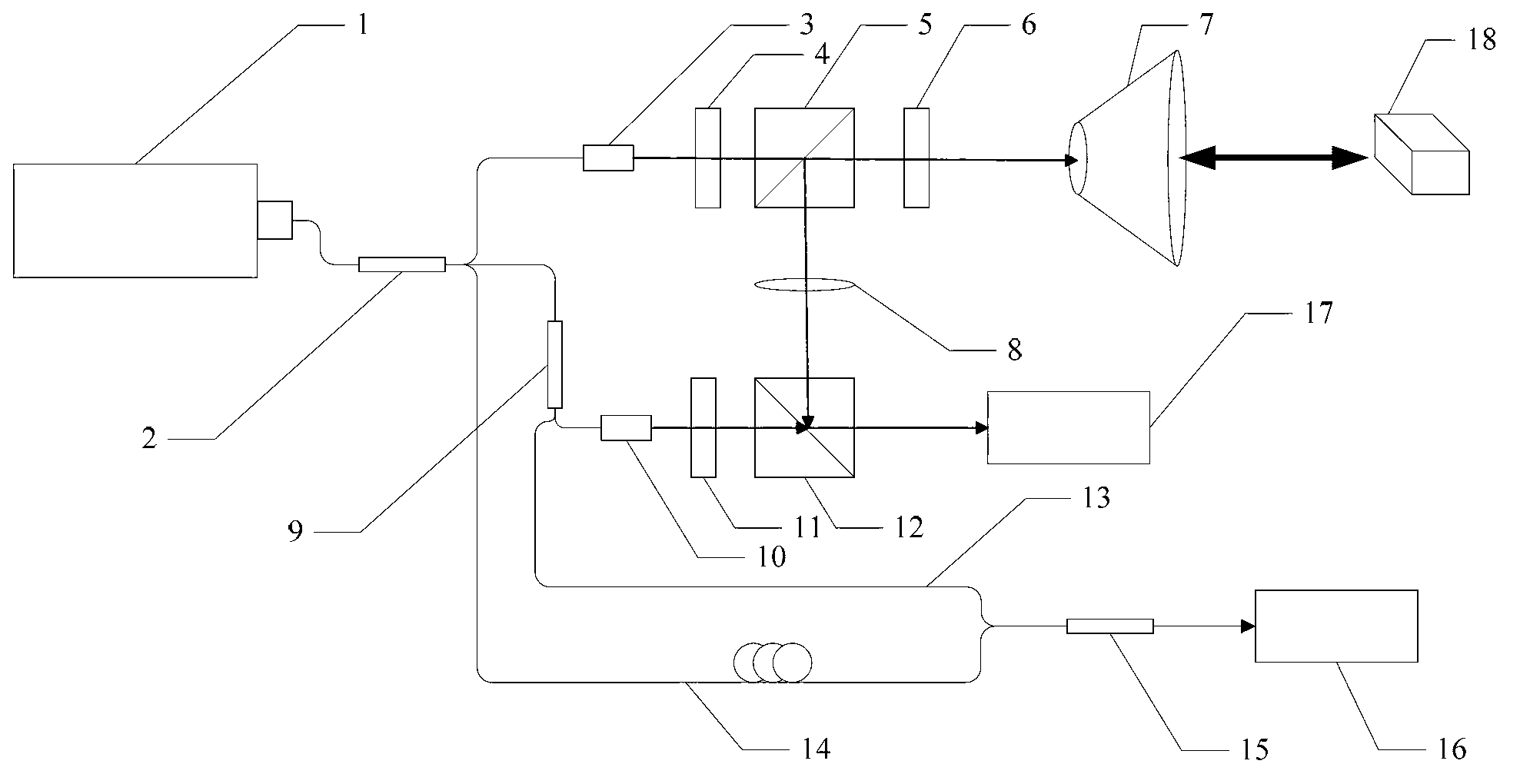Patents
Literature
145 results about "Radar frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
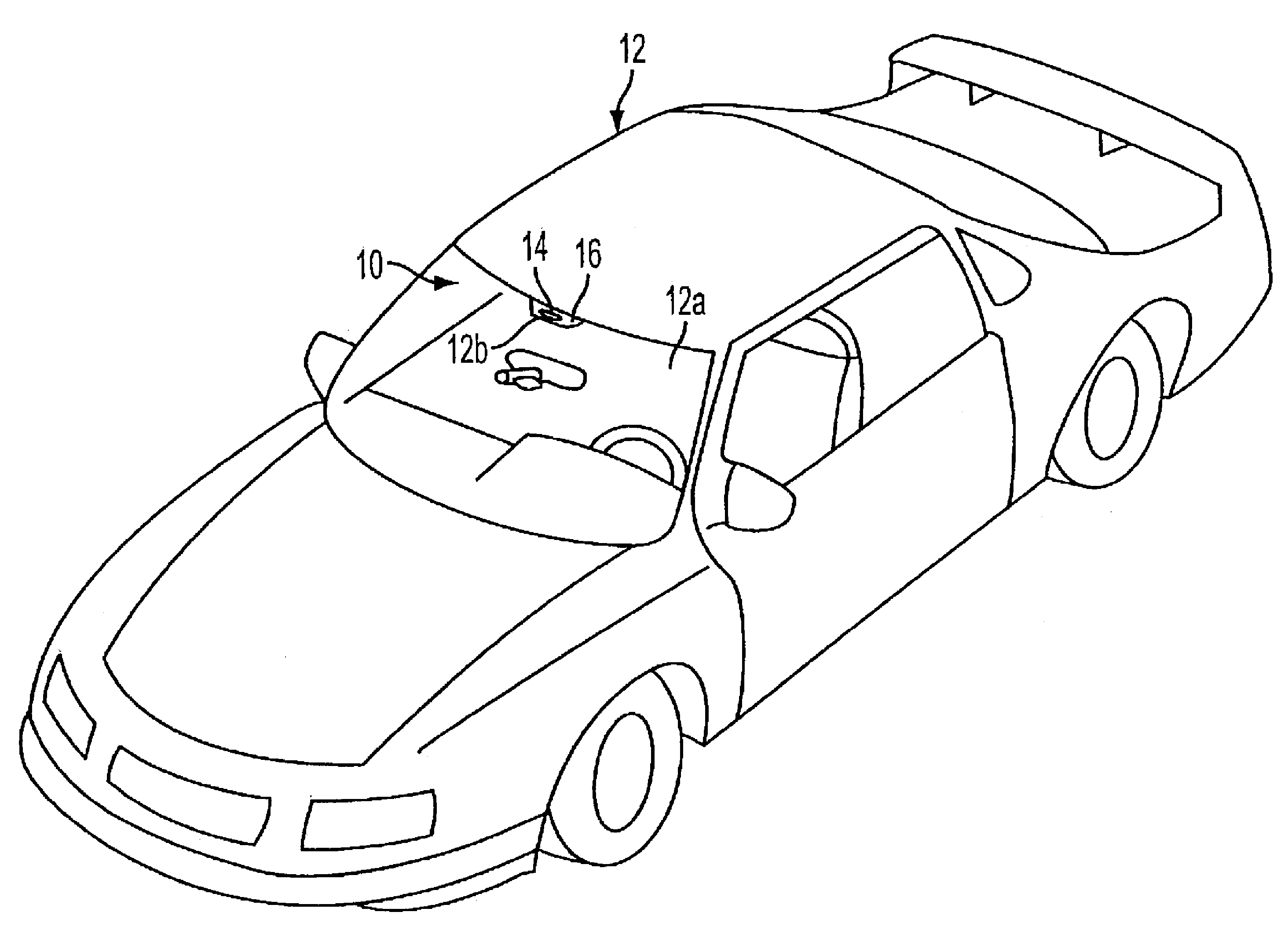
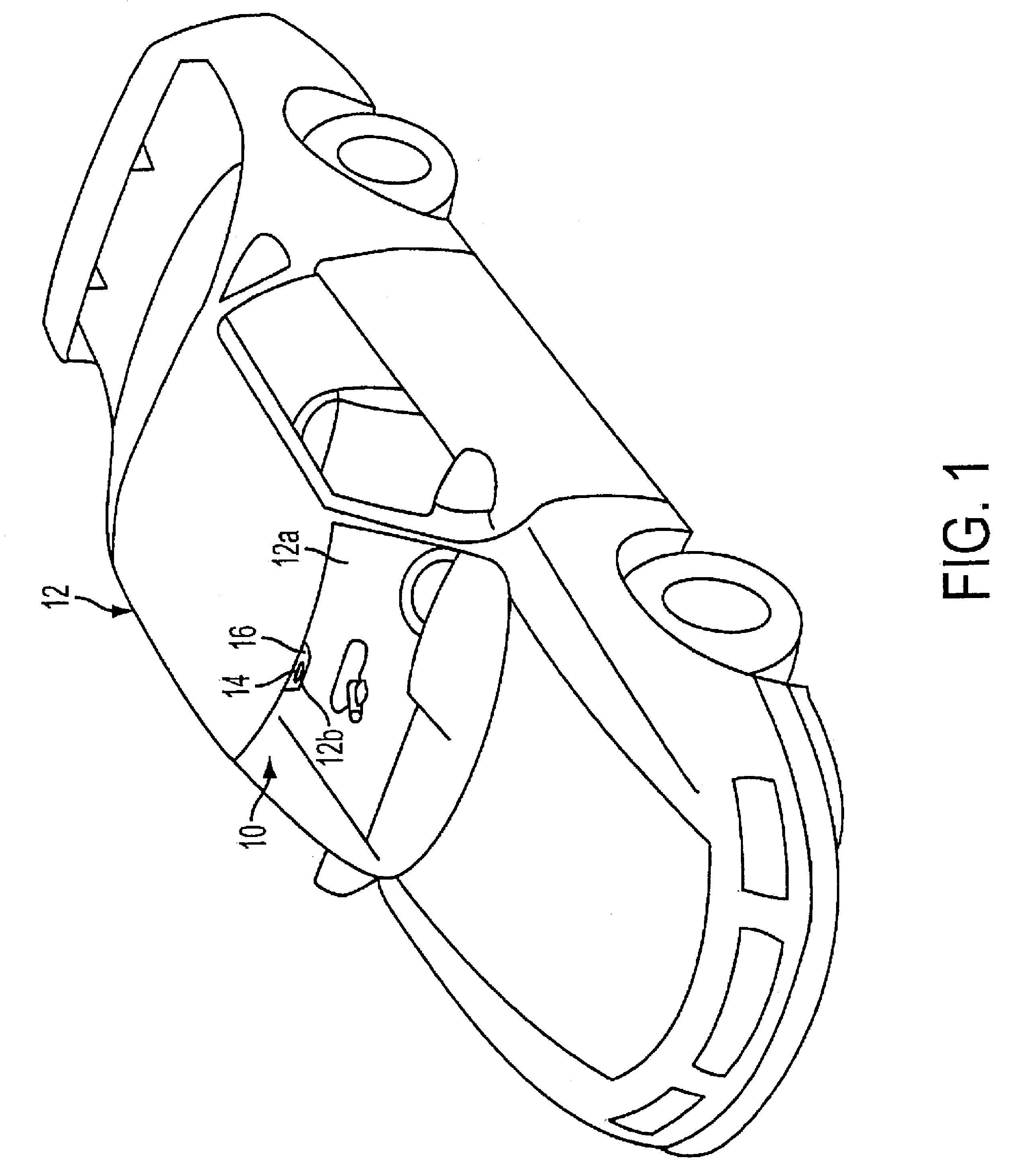
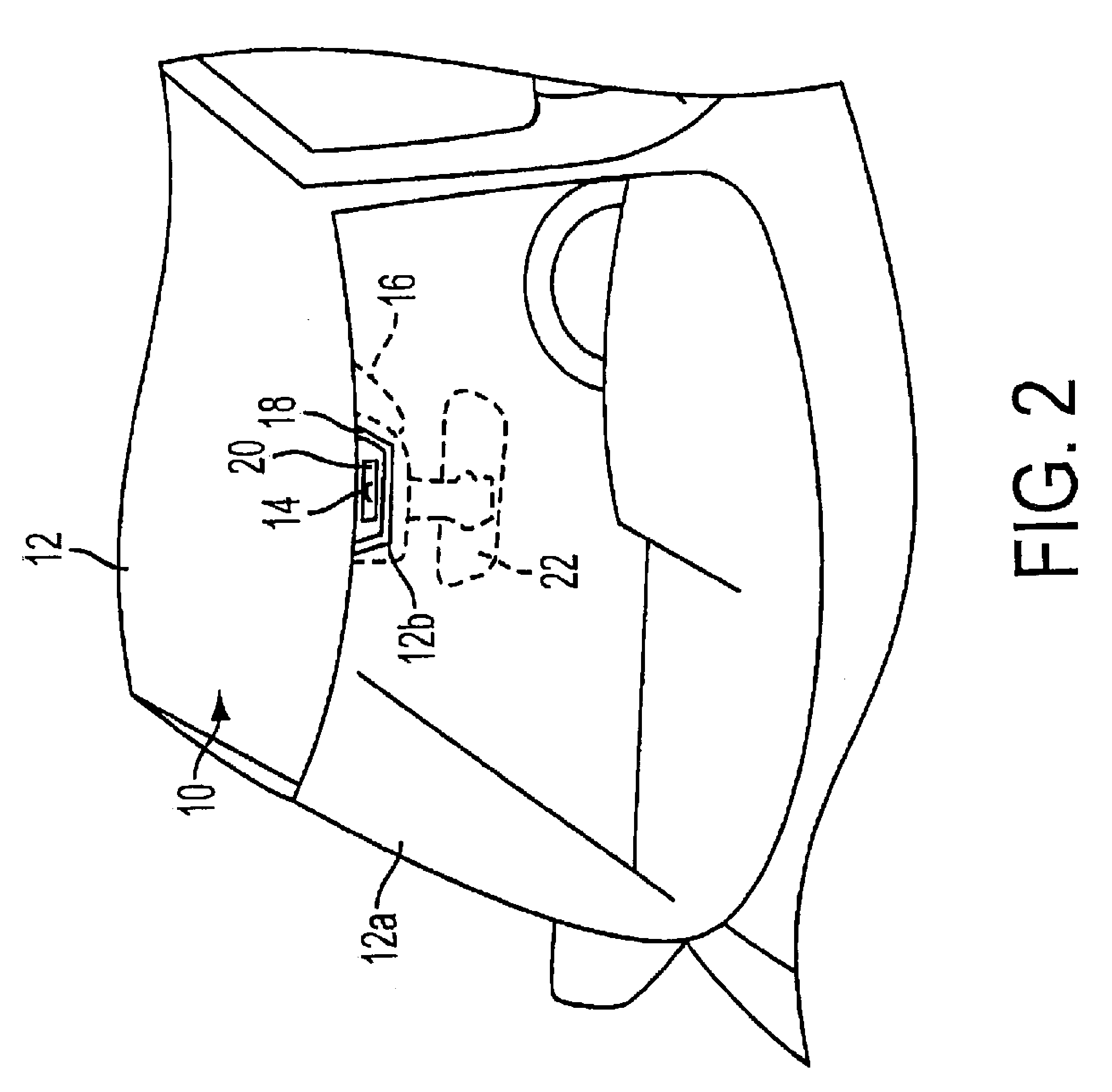
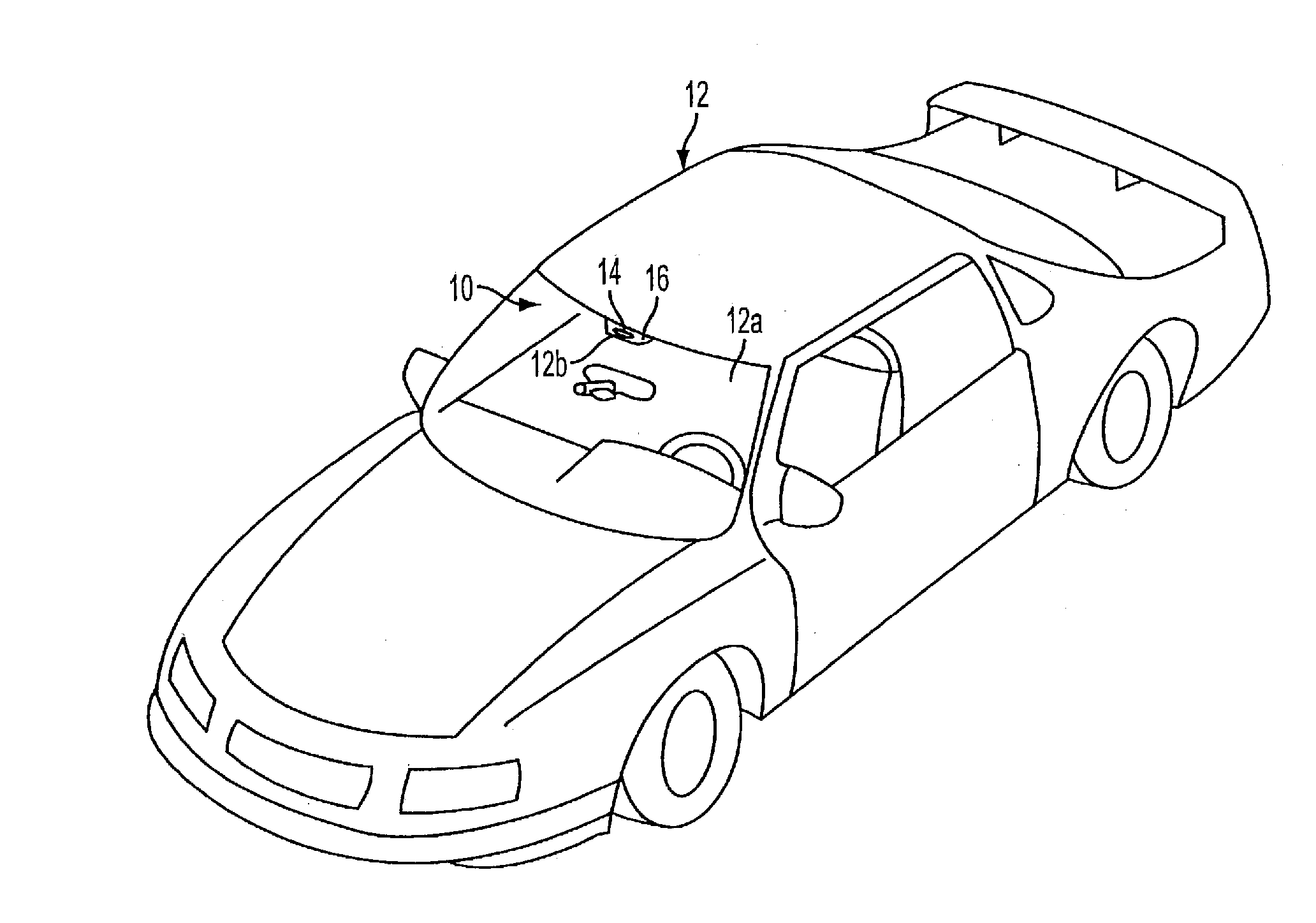
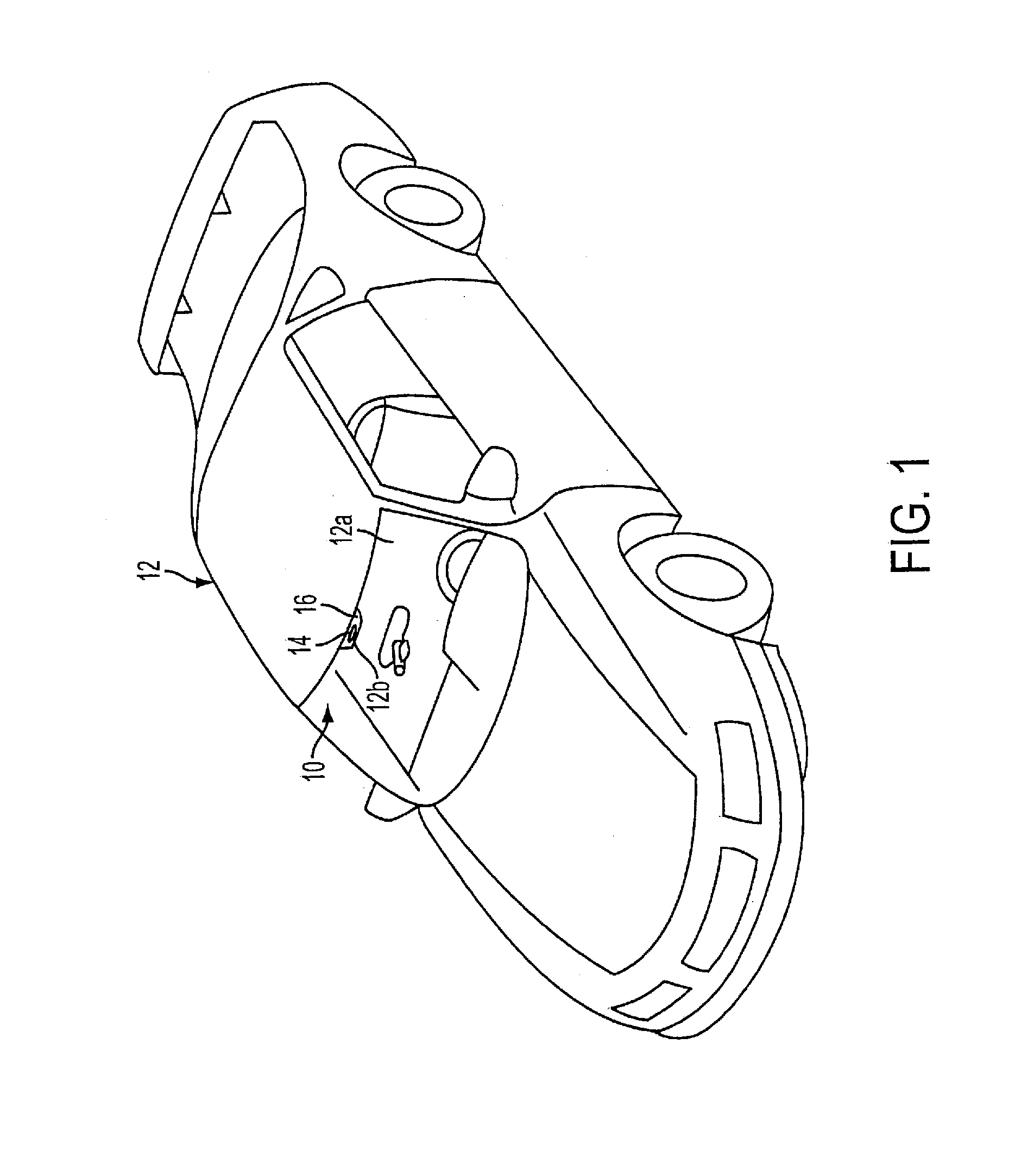
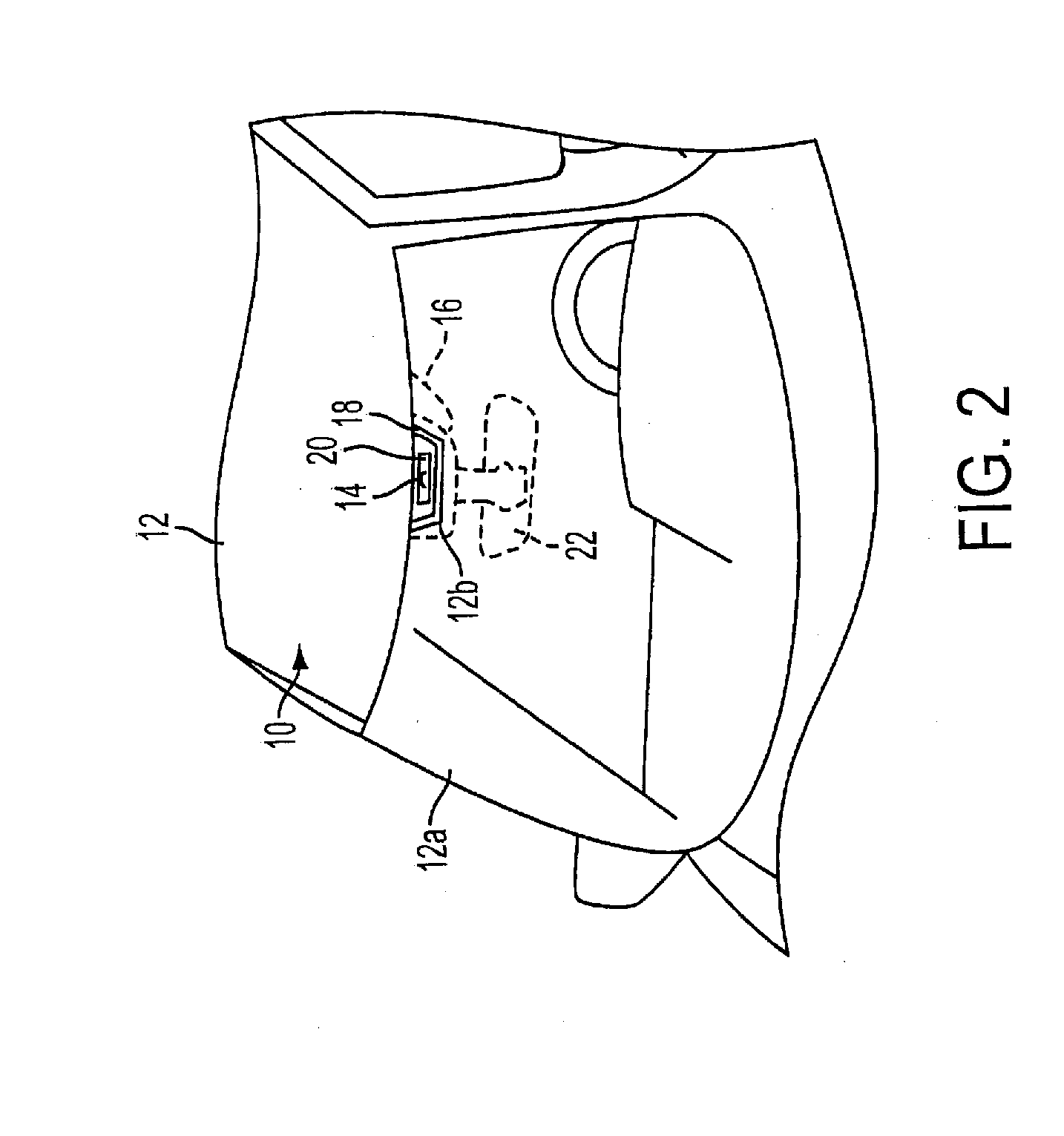
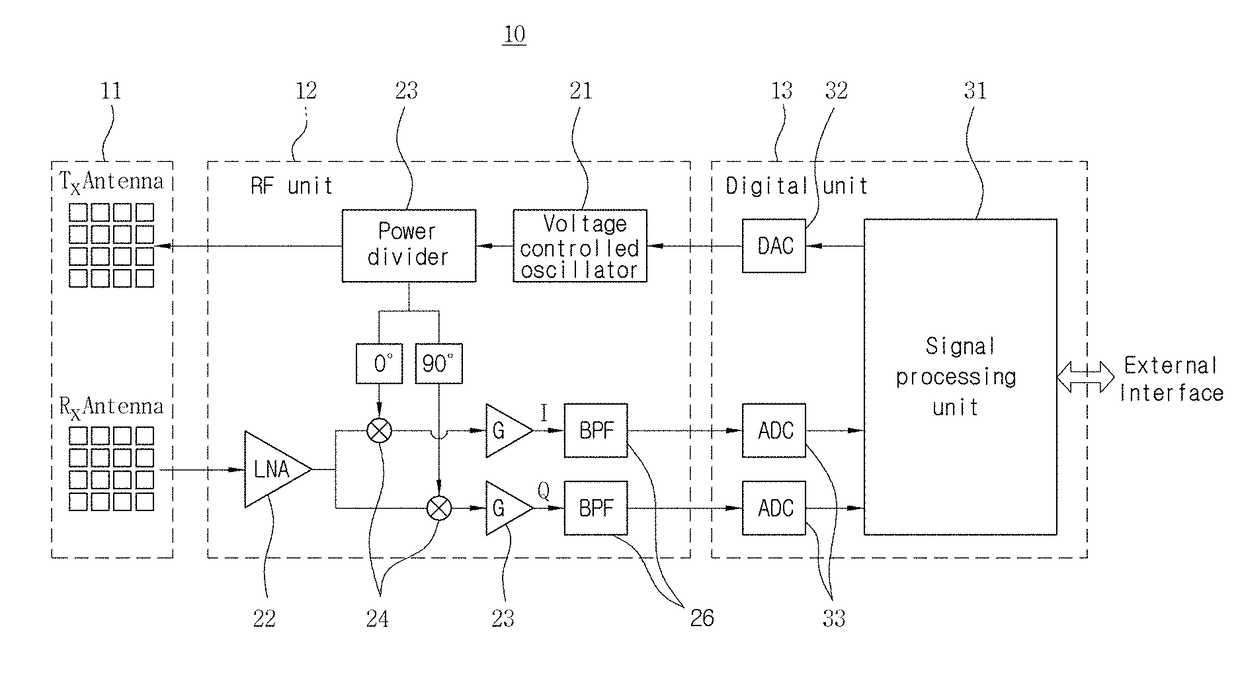
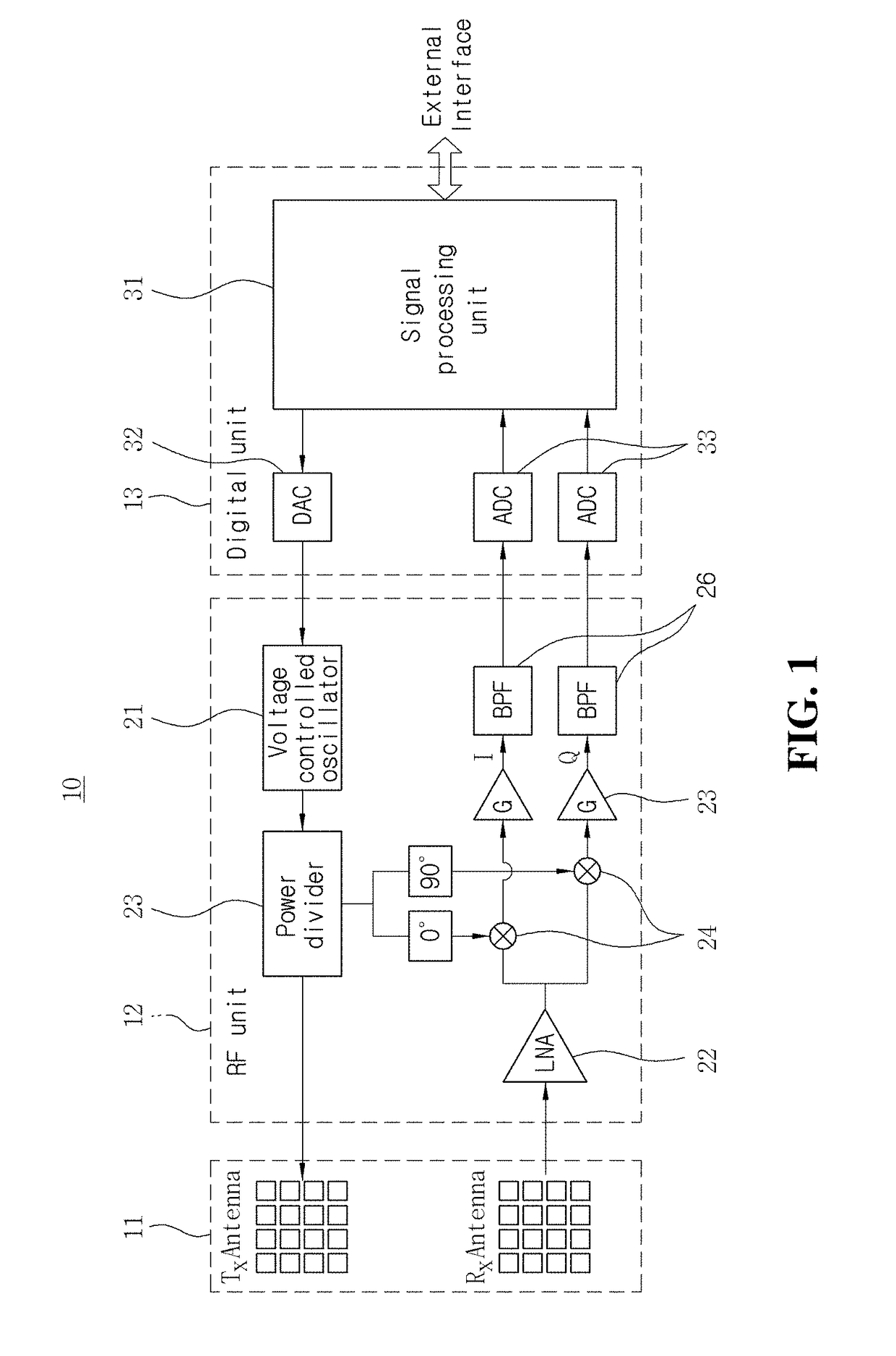
Radar sensing system for vehicle
ActiveUS8013780B2Enhancing interrogationSpeed up the processRoad vehicles traffic controlAutomatic initiationsElectromagnetic radiationElectrical and Electronics engineering
A radar sensing system for a vehicle includes a radar sensor device, a cover panel and a control. The radar sensor device is disposed at a pocket established at an upper edge of the vehicle windshield and having a forward transmitting and receiving direction that is not through the windshield. The cover panel is disposed at the radar sensor device and is substantially sealed at the vehicle windshield at or near the pocket at the upper edge of the vehicle windshield. The cover panel has a material that is substantially transmissive to radar frequency electromagnetic radiation waves. The radar sensor device emits radar frequency electromagnetic radiation waves that transmit through the cover panel. The control is responsive to an output of the radar sensor device.
Owner:MAGNA ELECTRONICS INC
Radar Sensing System for Vehicle
ActiveUS20100001897A1Enhancing interrogationSpeed up the processRoad vehicles traffic controlDigital data processing detailsEngineeringElectromagnetic radiation
A radar sensing system for a vehicle includes a radar sensor device, a cover panel and a control. The radar sensor device is disposed at a pocket established at an upper edge of the vehicle windshield and having a forward transmitting and receiving direction that is not through the windshield. The cover panel is disposed at the radar sensor device and is substantially sealed at the vehicle windshield at or near the pocket at the upper edge of the vehicle windshield. The cover panel has a material that is substantially transmissive to radar frequency electromagnetic radiation waves. The radar sensor device emits radar frequency electromagnetic radiation waves that transmit through the cover panel. The control is responsive to an output of the radar sensor device.
Owner:MAGNA ELECTRONICS
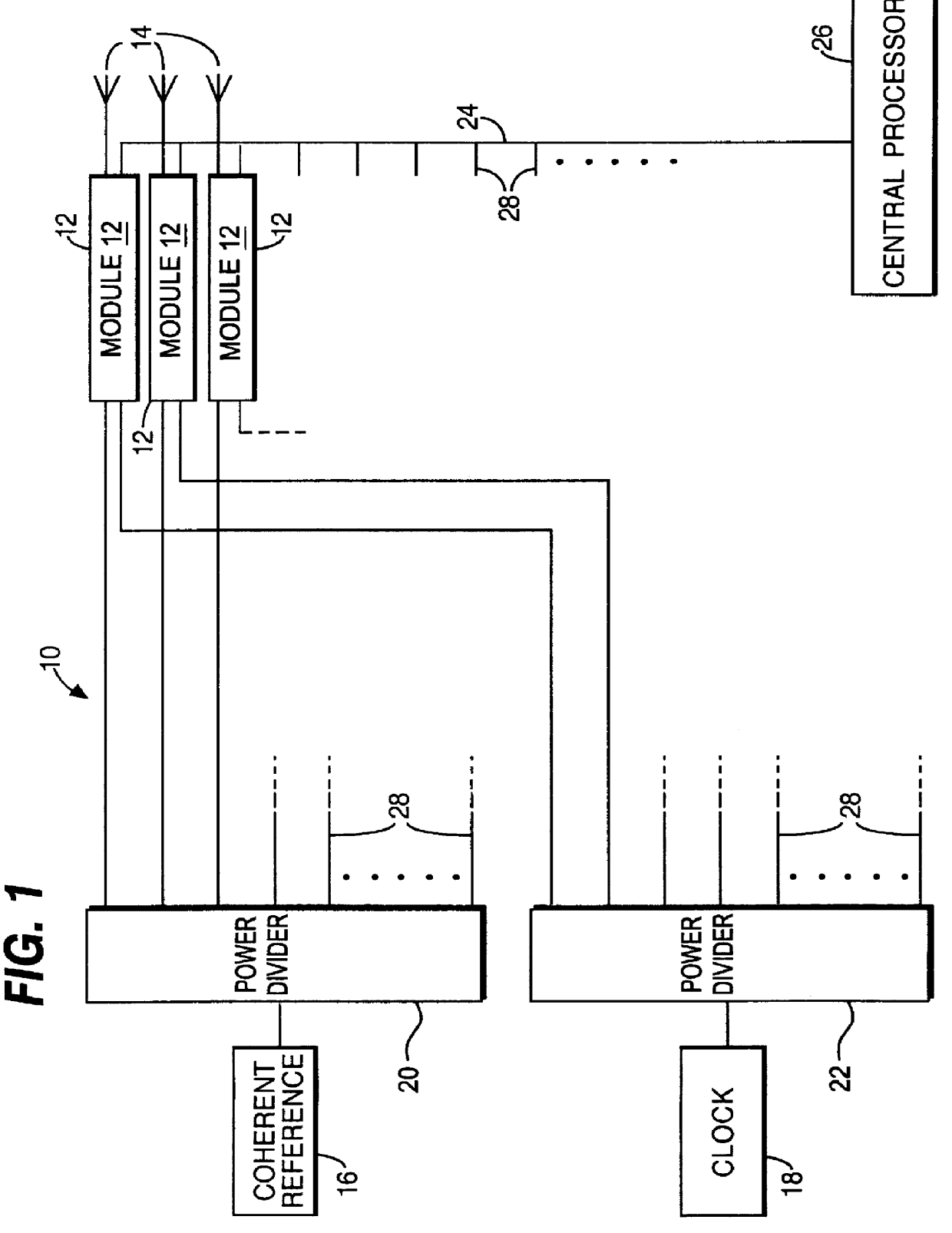
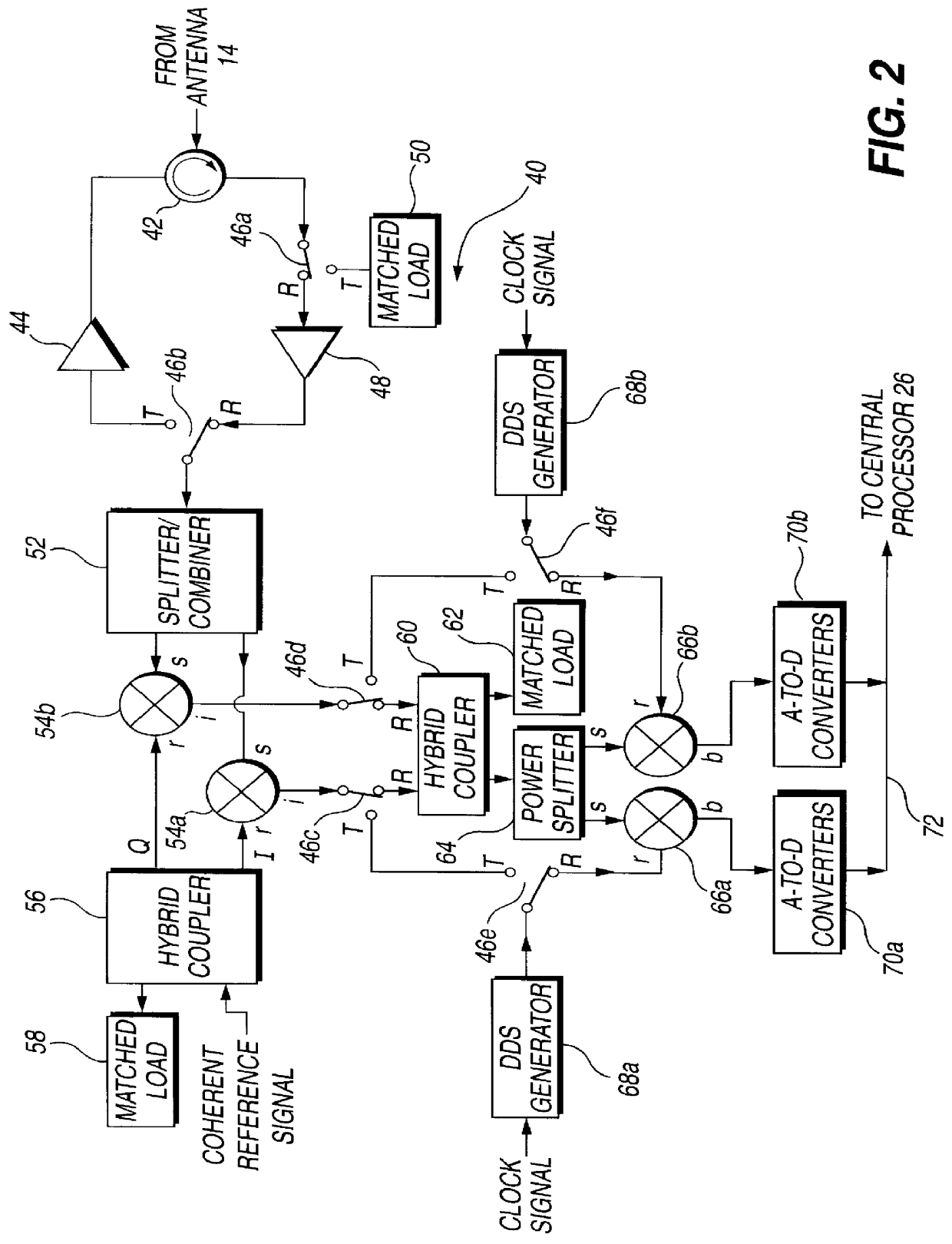
Circuit module for a phased array radar
InactiveUS6054948ALow costReduce the amount requiredMultiplex system selection arrangementsModular arraysLocal oscillator signalIntermediate frequency
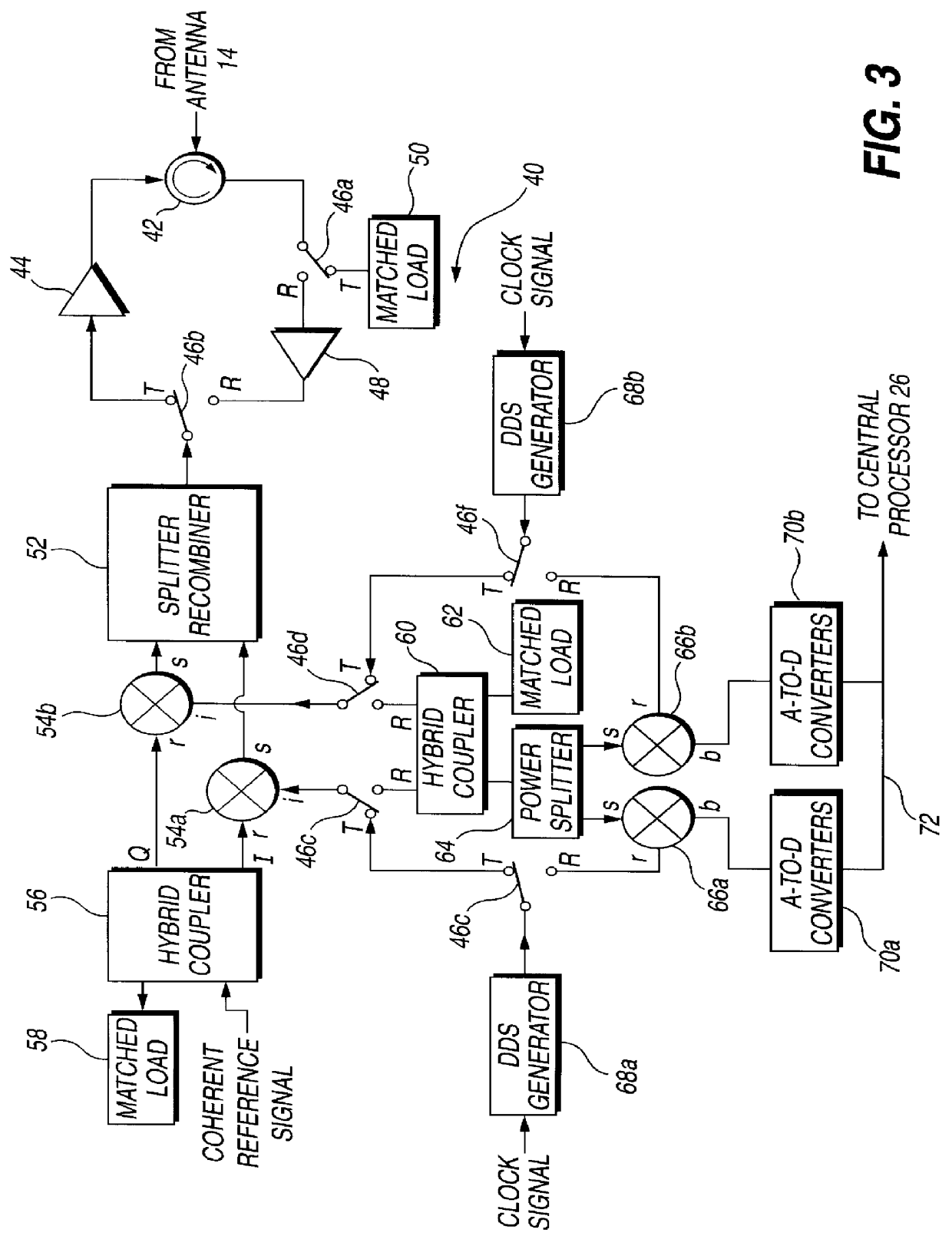
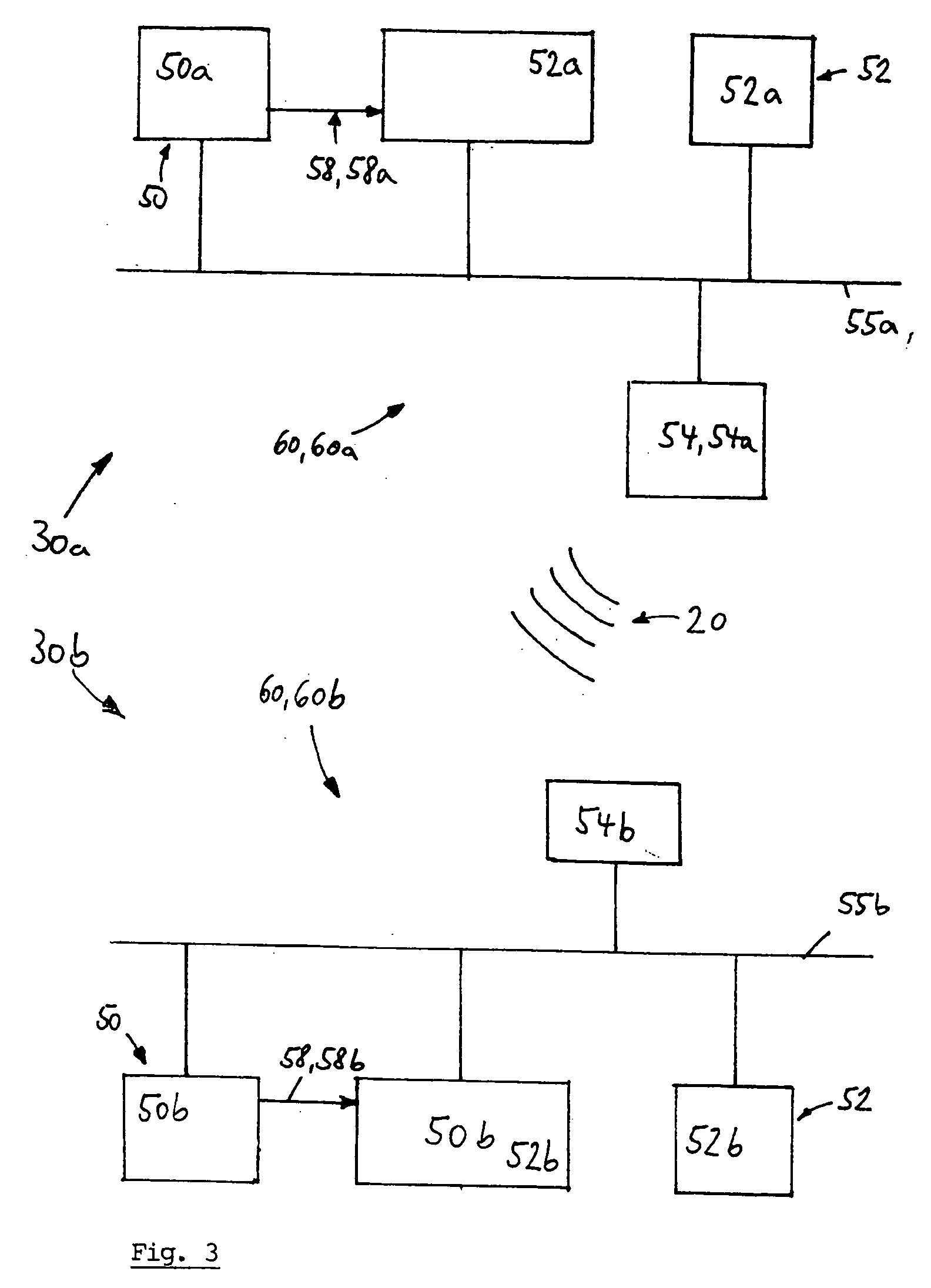
PCT No. PCT / GB95 / 01607 Sec. 371 Date Dec. 10, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Dec. 10, 1997 PCT Filed Jul. 7, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 03367 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 30, 1997A circuit module for a phased array radar (10) incorporates radar frequency (RF) mixers (54a, 54b) connected to an RF splitter / combiner (52) and to in-phase and quadrature RF reference signals. The RF mixers (54a, 54b) are also connected to intermediate frequency (IF) processing circuitry (60 to 68) providing for phase control of RF signals and IF reference signals. In transmission mode, the RF mixer (54a, 54b) receive phase-controlled, digitally synthesised IF signals from clock-activated generators (68a, 68b). Their outputs are combined at the RF splitter / combiner (52) to provide single sideband upconversion of the phase-controlled IF signals. In reception mode, the RF splitter / combiner (52) and the RF mixers (54a, 54b) act as an image rejection mixer circuit in which the phase-controlled IF signals are local oscillator signals. Beamforming is carried out by computer control of the IF phase together with, in the case of reception, analogue or digital summation of output signals from an array of modules (12).
Owner:RAYMARINE BELGIUM
Multi-station HF FMCW radar frequency sharing with GPS time modulation multiplexing
InactiveUS20030025629A1No performance lossMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesPosition fixationTime informationDigital data
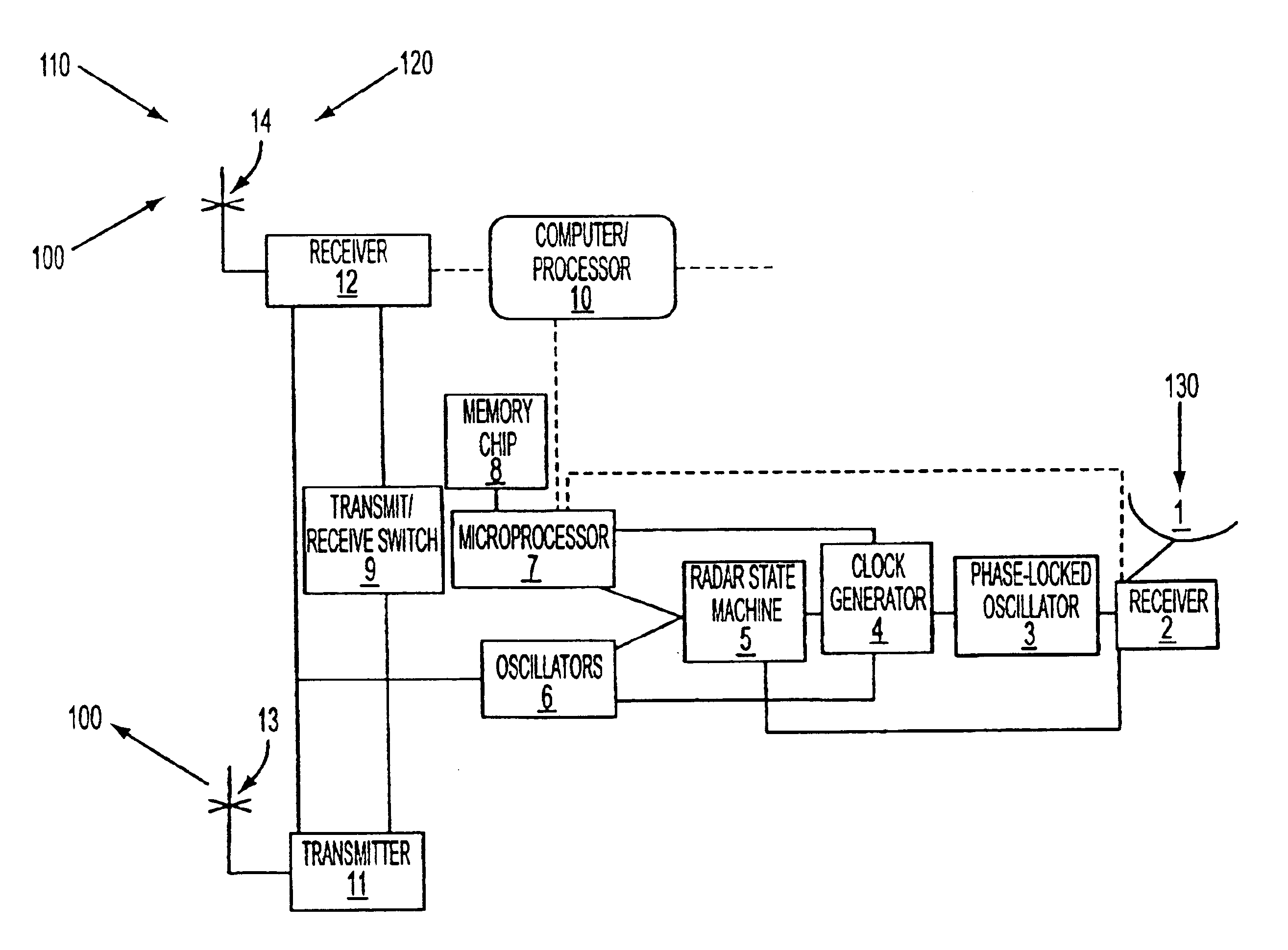
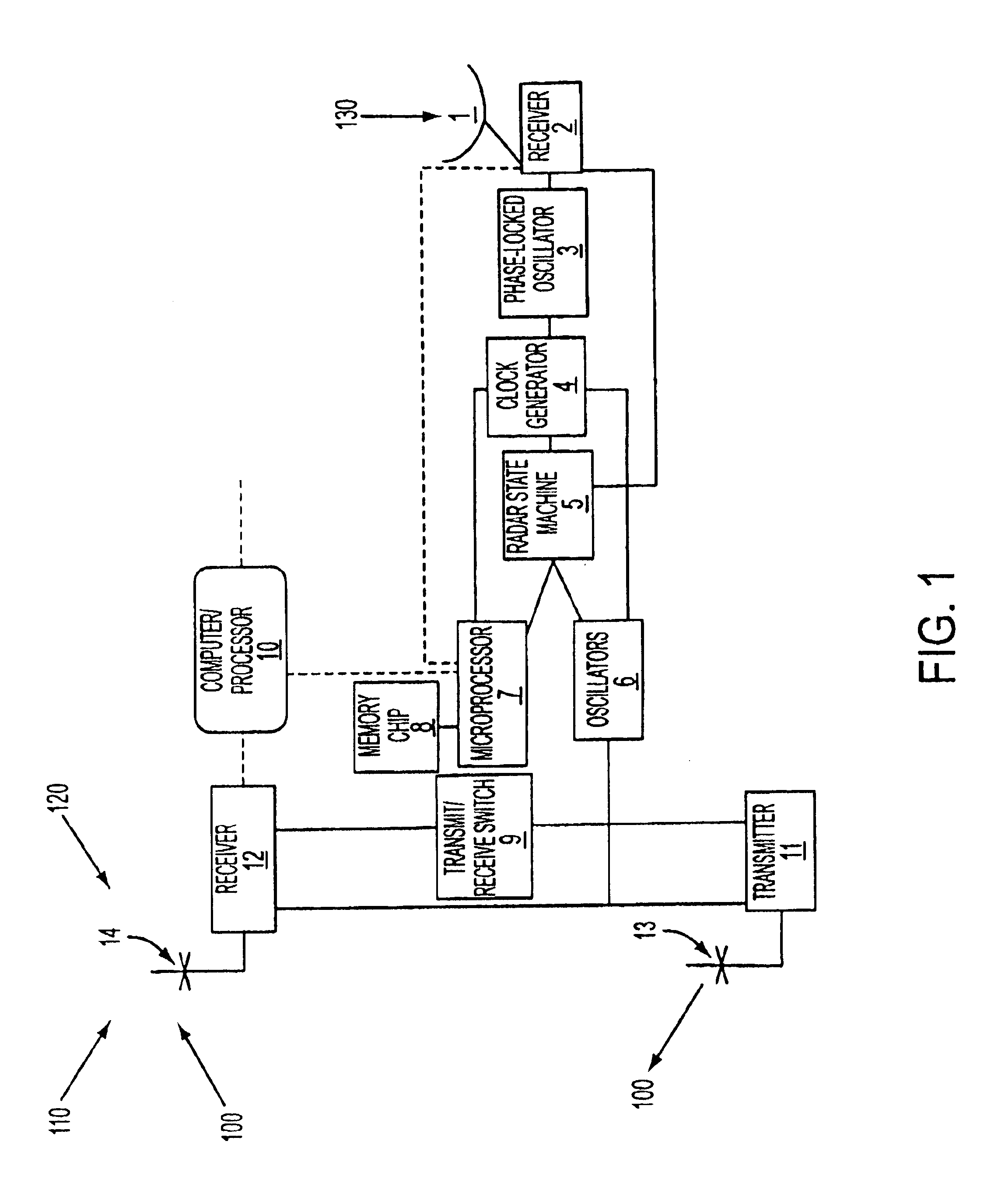
Systems and methods are described for HF radar frequency sharing with GPS time modulation multiplexing. A method is provided that includes generating clock signals from the time information contained in a GPS signal. Radio frequency signals are transmitted and received in a sequence whose start times are dictated by the clock signals. The clock signals also control the modulation of the radio frequency signals. The radio frequency signals are modulated by using a sweep modulation. An apparatus to implement the method includes a GPS receiver, a state machine, a clock generator, a microprocessor, a memory chip, a signal synthesizer, and a digital data output device. The GPS receiver extracts time information from GPS signals. The state machine controls radar functions versus time. The microprocessor performs modulation multiplexing on radar signals.
Owner:CODAR OCEAN SENSORS LTD
Multi-station HF FMCW radar frequency sharing with GPS time modulation multiplexing
InactiveUS6856276B2Multi-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesPosition fixationTime informationDigital data
Systems and methods are described for HF radar frequency sharing with GPS time modulation multiplexing. A method is provided that includes generating clock signals from the time information contained in a GPS signal. Radio frequency signals are transmitted and received in a sequence whose start times are dictated by the clock signals. The clock signals also control the modulation of the radio frequency signals. The radio frequency signals are modulated by using a sweep modulation. An apparatus to implement the method includes a GPS receiver, a state machine, a clock generator, a microprocessor, a memory chip, a signal synthesizer, and a digital data output device. The GPS receiver extracts time information from GPS signals. The state machine controls radar functions versus time. The microprocessor performs modulation multiplexing on radar signals.
Owner:CODAR OCEAN SENSORS LTD
Modular generation method for multi-waveform radar signal
InactiveCN102073032AVersatileImprove compatibilityWave based measurement systemsData acquisitionEngineering
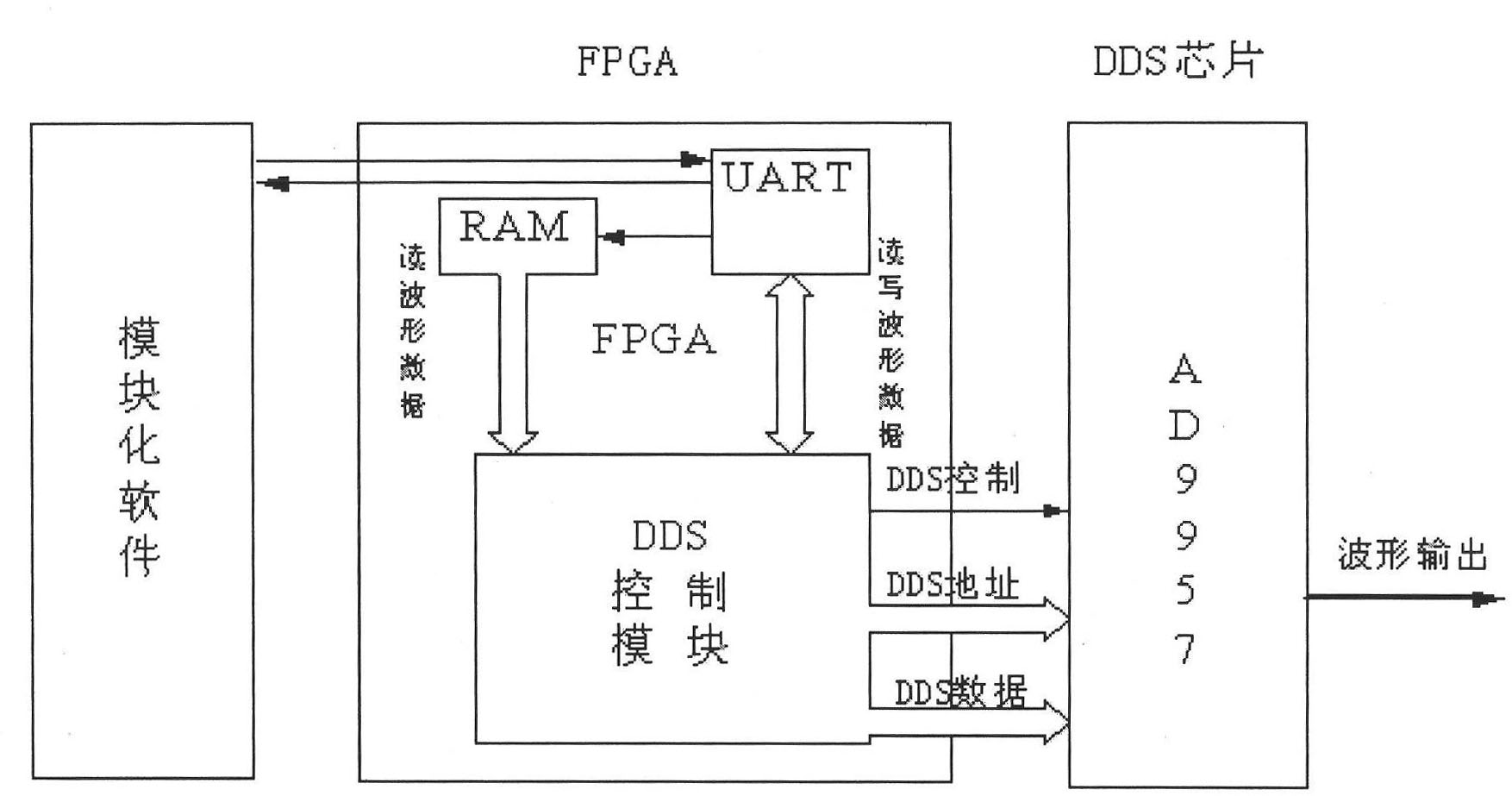
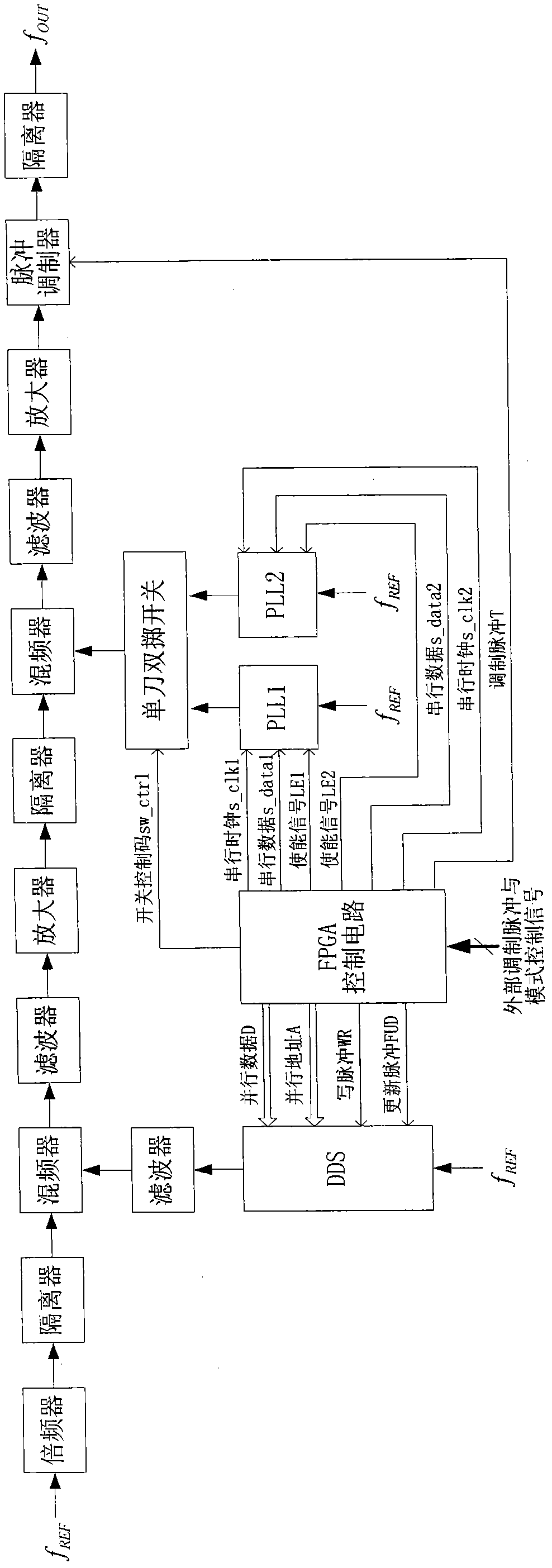
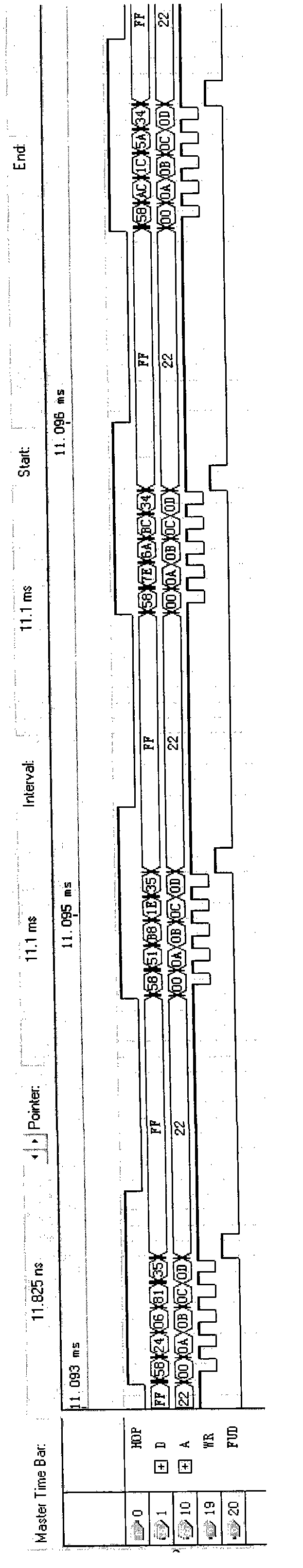
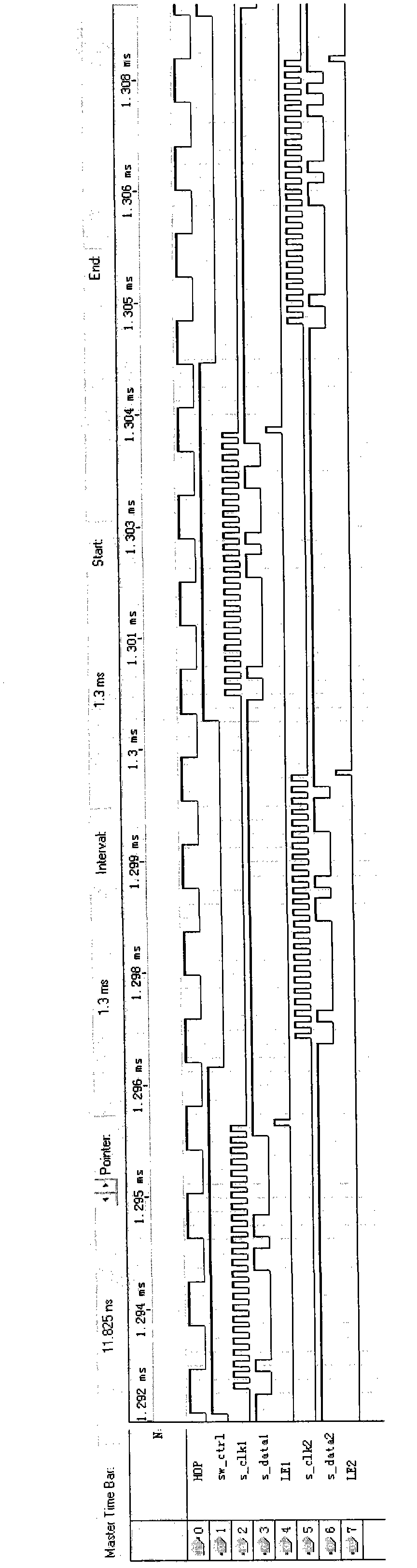
The invention relates to a modular generation method for a multi-waveform radar signal, which belongs to the technical field of radar frequency synthesis and is applied to the design of a direct digital frequency synthesis (DDS)-based frequency synthesizer. A multi-waveform radar signal module consists of modular software, a field programmable gate array (FPGA) and DDS chips. The modular software comprises a man-machine interactive interface and a modular serial port timing module, wherein the man-machine interactive interface performs relevant operation and storage of control parameters and waveform data of the DDS chips and performs data communication with the FPGA; and the modular serial port timing module generates modular serial port control timing which is suitable for the DDS series chips and completes data acquisition and updating by computer communication. The FPGA is provided with a random-access memory (RAM), a universal asynchronous receiver / transmitter (UART) and a DDS control module, and realizes the functions of data communication with a computer and the storage of the control parameters and waveform data of the DDS chips and DDS chip control. The DDS chips output various signals set by the parameters under the control of the FPGA. The modular software developed by the method configures different DDS chips, so various radar signals of point frequency, linear frequency modulation, nonlinear frequency modulation and phase encoding can be generated, and the software supports on-line programming and the real-time updating of the control parameters and waveform data of the DDS chips.
Owner:中国兵器工业第二〇六研究所
Composite frequency-selective-surface invisible radome
InactiveCN102882002AReduce processing difficultyDoes not affect normal work scanningRadiating element housingsWaveguide type devicesScattering cross-sectionMicrowave
The invention discloses a composite frequency-selective-surface invisible radome and relates to the technical field of microwaves. The composite frequency-selective-surface invisible radome solves the problems that an existing radome is streamline in shape and cannot be spread to a plane, random preparation of an FFS (frequency selective surface) on the radome is difficult in process implementation, and FFS passband transmittance is low as incident angles of electromagnetic waves on the FFS are large. The composite frequency-selective-surface invisible radome is prepared by embedding an inner Y-ring-unit frequency-selective-surface conical cover into an outer radome by the aid of special laminating equipment. The composite frequency-selective-surface invisible radome has a band-pass filtering characteristic within a specific radar frequency range and good passband characteristics, is capable of efficiently transmitting through the working frequency range electromagnetic waves, reflects the out-of-band detection electromagnetic waves to a vast space according to the radome shape and reduces backward radar cross section so that invisibility of the radome is achieved. The composite frequency-selective-surface invisible radome can be used for invisibility of radomes of guided missiles and airplanes.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and system for emitter localisation
InactiveUS7579989B2Reduce computing costControl rateDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationLight beamEngineering
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
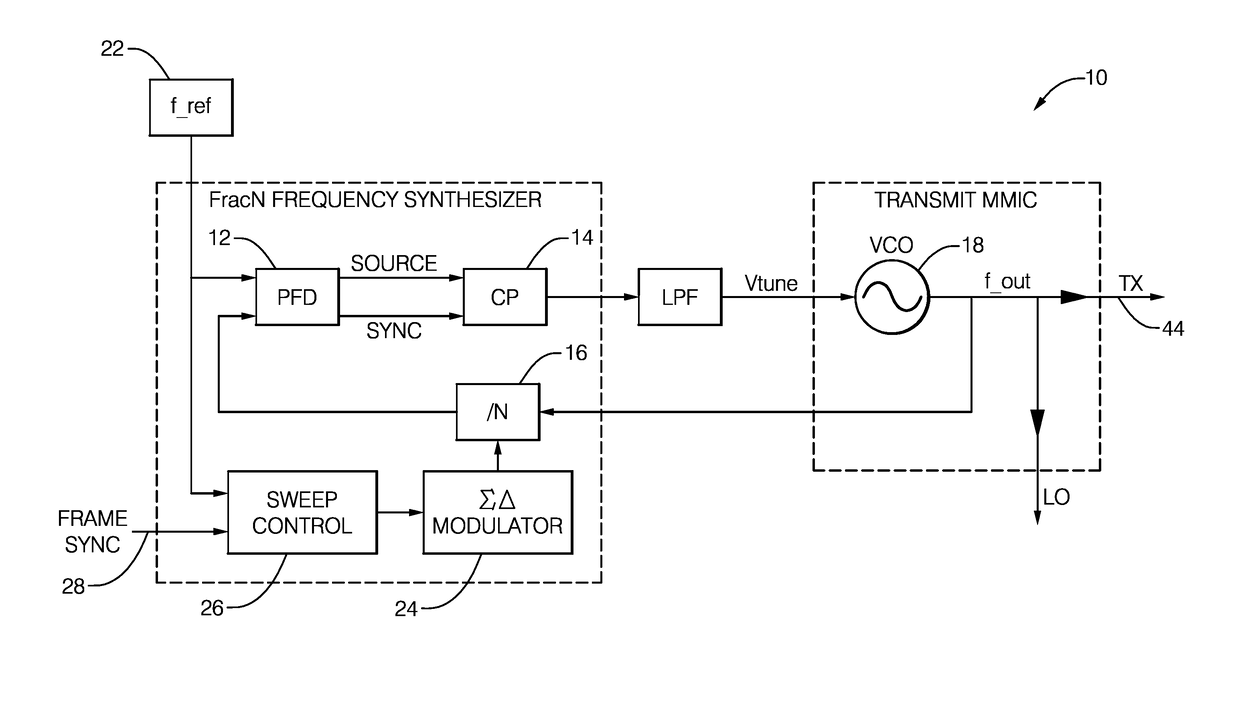
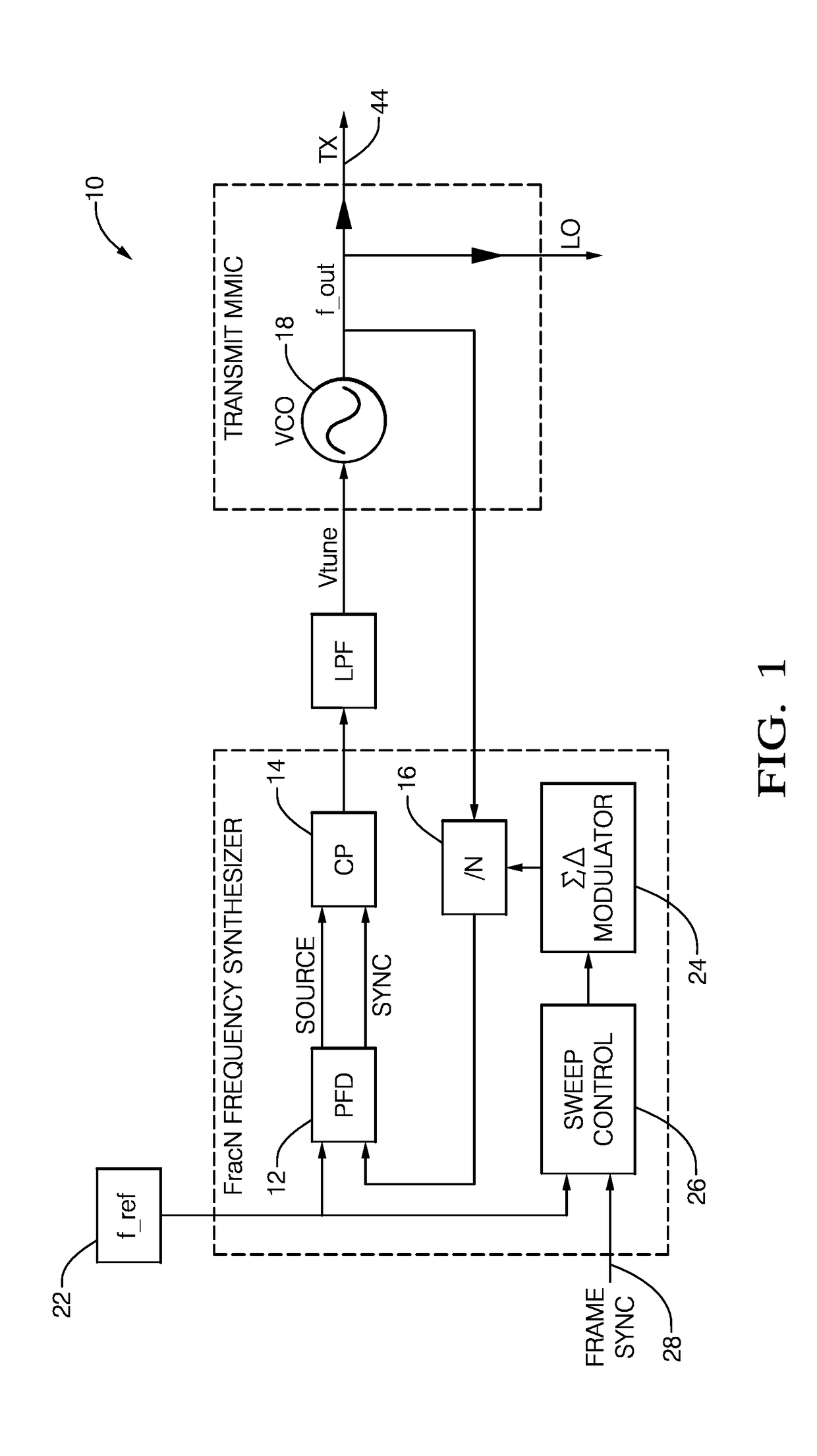
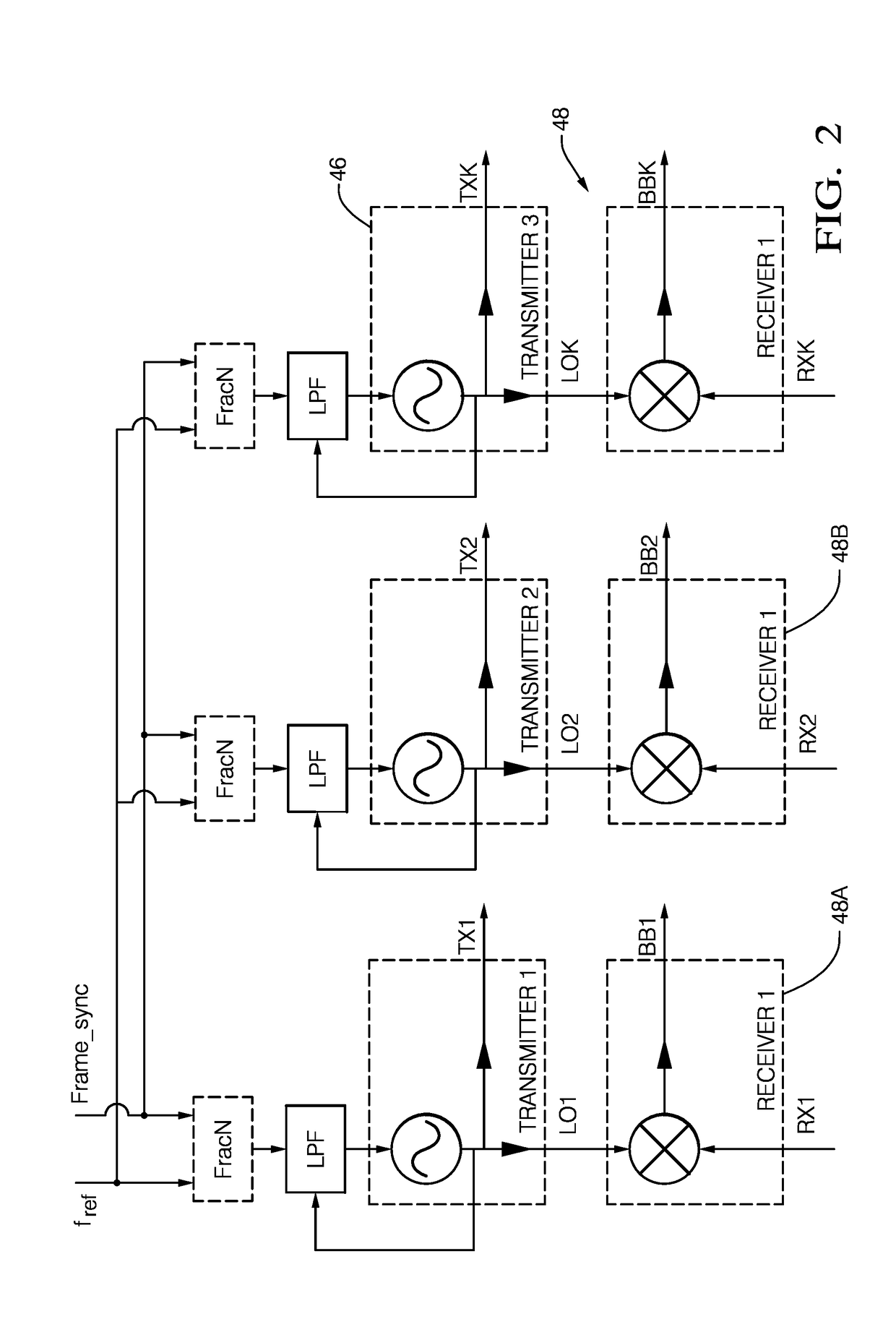
Bi-static radar system
A bi-static radar system configured for coherent detection of a radar-signal includes a plurality of radar-transceivers, a controller, and a communications device. The plurality of radar-transceivers is characterized as physically spaced apart with respect to each other. The controller is in communication with the each of the radar-transceivers and is configured to coherently operate each of the radar-transceivers. The communications device communicates both a reference-clock signal and a frame-sync signal from the controller to each of the plurality of radar-transceivers whereby the plurality of radar-transceivers operate coherently. Alternatively, the system may include a reference-signal generator, a transmitter, and a plurality of receivers. The reference-signal generator generates a reference-signal characterized by a reference-frequency proportional to a fraction of a radar-frequency of a radar-signal transmitted. The transmitter generates the radar-signal at the radar-frequency based on the reference-signal. The plurality of receivers operates coherently to detect the radar-signal based on the reference-signal.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Method and system for emitter localisation
InactiveUS20050052315A1Improve accuracyReduce computing costDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationLight beamEngineering
Process and system for the location of emitters in the radar frequency range on the basis of cross position-finding by at least two flying platforms with, in each case, at least one passive HF sensor for ascertaining the geometrical and electronic properties of the emitter beams, whereby the flying platforms mutually exchange data for describing the geometrical and electronic properties of the emitter beams, and whereby from the plurality of the position-finding beams' possible intersection points, which arise from the emitter surveying operation, use is made, in order to determine the emitter position, of those intersection points at which the electronic properties of the intersecting emitter beams are identical.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
Software channelized coherent frequency-agile radar receiver and receiving method
ActiveCN104849700AExtended viewing distanceExtended Frequency PointsWave based measurement systemsFrequency changerIntermediate frequency
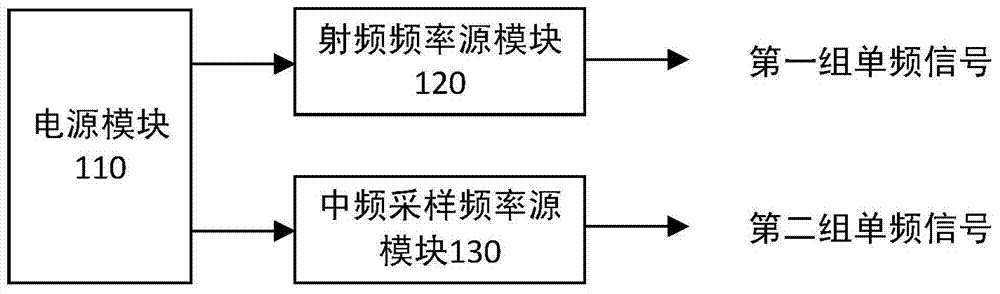
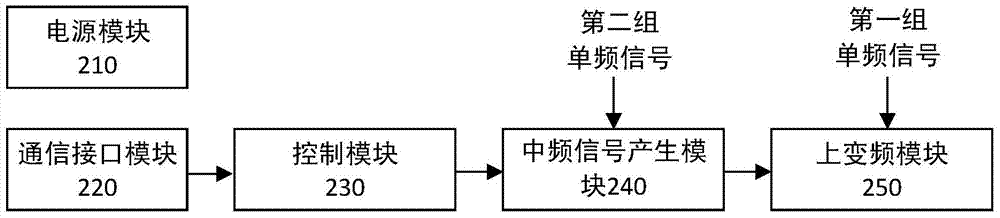
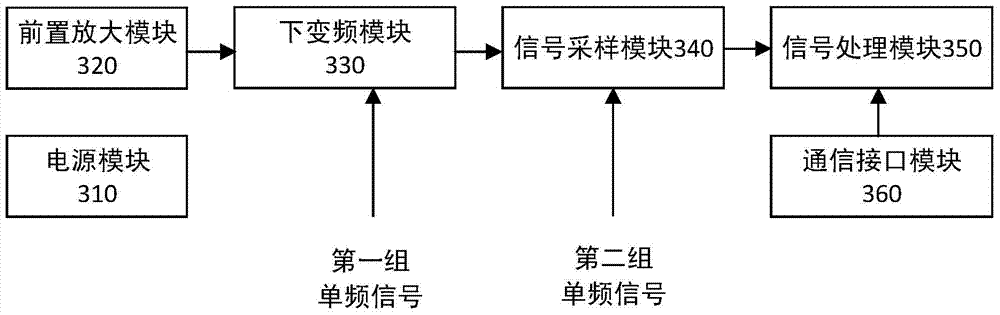
The invention discloses a software channelized coherent frequency-agile radar receiver and a receiving method. The software channelized coherent frequency-agile radar receiver includes a local frequency oscillator module which generates a first group of single-frequency signals of a fixed frequency and a second group of single-frequency signals of a fixed frequency, a waveform generation and up-converter module which selects base band waveform required by a radar and generates corresponding intermediate-frequency waveform according to the base band waveform, and performs up conversion on the intermediate-frequency waveform to radar radio frequency, and amplifies the radar radio frequency and transmits radar radio frequency signals, and a signal acquisition and down-converter module which receives the radar radio frequency signals and performs down-conversion on the radar radio frequency signals to intermediate frequency, and amplifies the radar radio frequency signals and then performs digital sampling, and performs digital down-conversion on the radar radio frequency signals, and demodulates the signals in to the base band the digital domain. The invention also discloses a software channelized coherent frequency-agile radar receiving method. The software channelized coherent frequency-agile radar receiver and receiving method of the invention can greatly increase radar frequency-agile frequency points under the premise that no equipment is increased; and the software channelized coherent frequency-agile radar receiver and receiving method of the invention have the advantages of excellent coherent performance, multi-frequency point simultaneous receiving and wide observation distance range.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Operation period underground pipeline pipe diameter measuring method based on ground penetrating radar
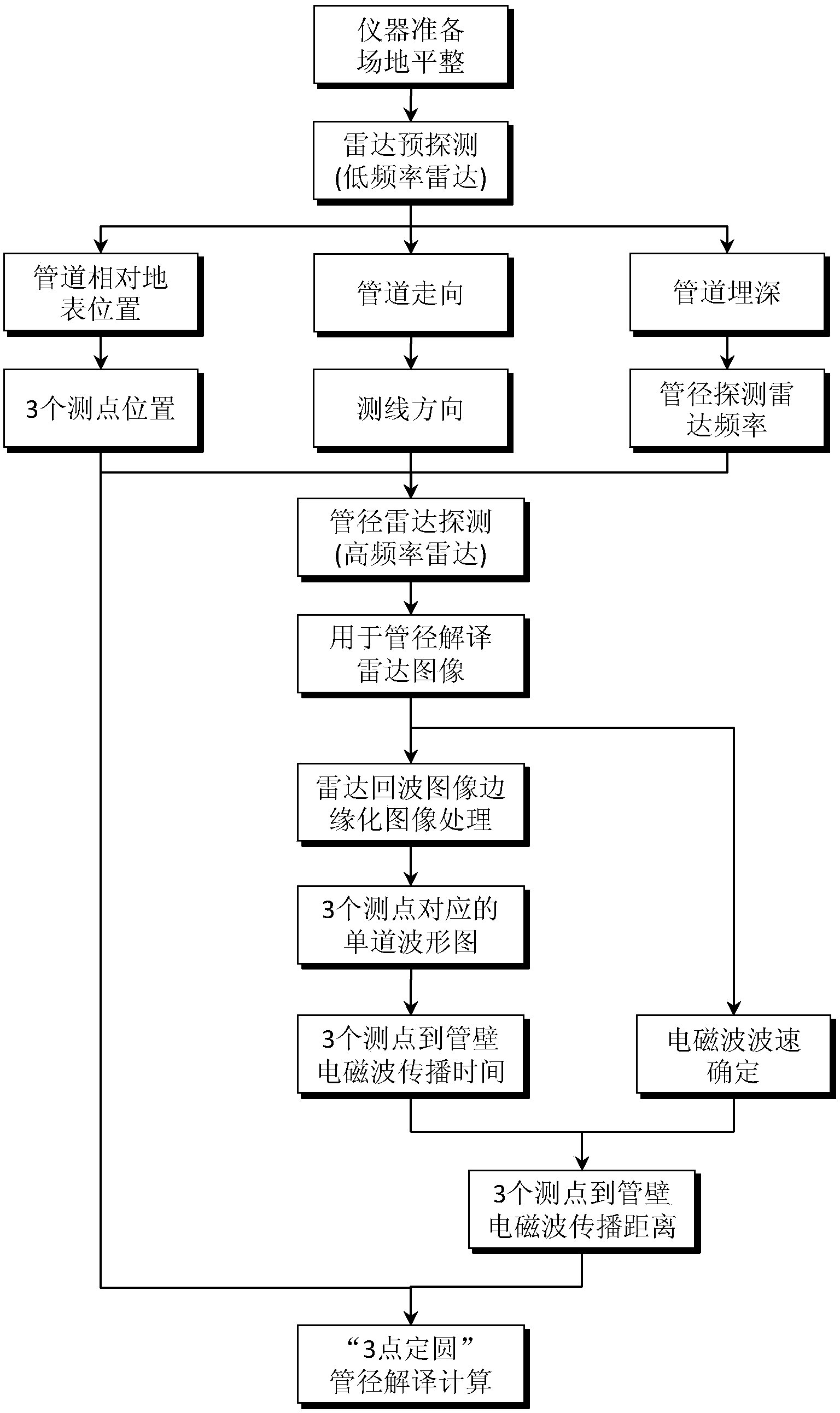
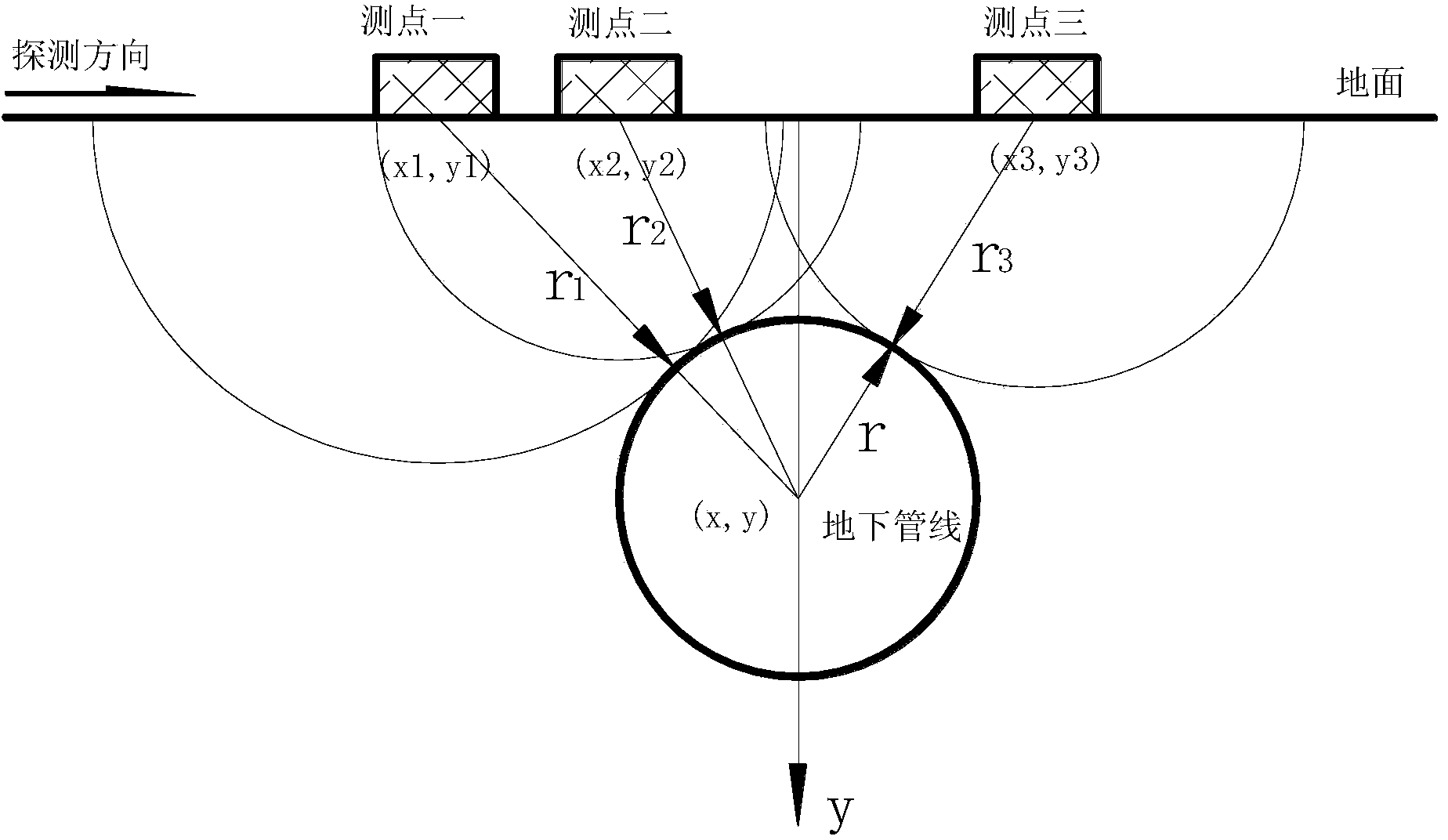
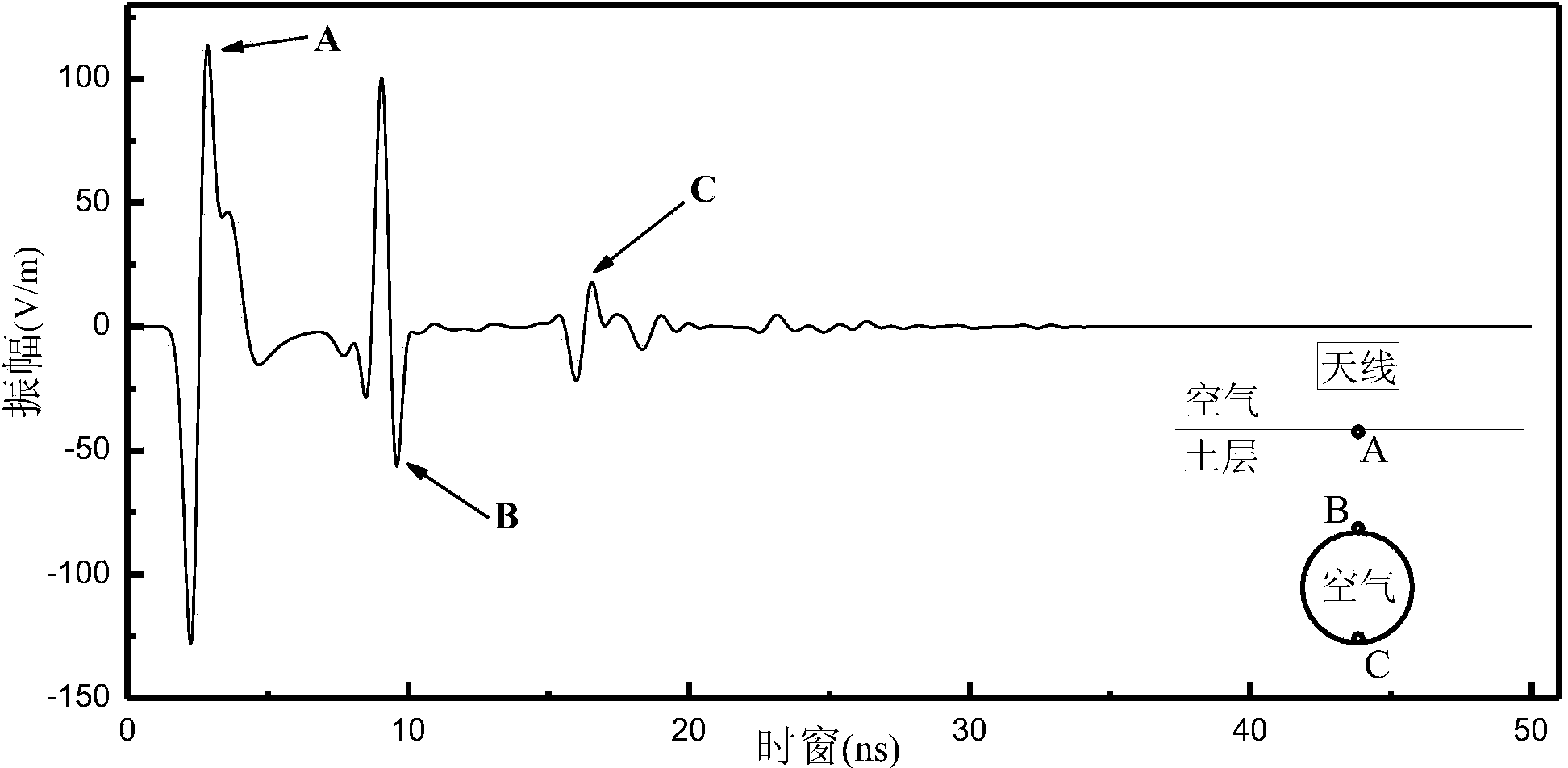
InactiveCN103675922ASolve the difficulty of accurate positioningAvoid destructionDetection using electromagnetic wavesImage denoisingDielectric
The invention provides an operation period underground pipeline pipe diameter measuring method based on a ground penetrating radar. The principle is that a ground penetrating radar electromagnetic wave reflection mechanism and a pipeline special circular shape are used for achieving underground pipeline pipe diameter detecting and interpreting under the non-excavation and non-disturbance situation when an operation period pipeline of an underground pipeline is filled with lossy dielectric. The implementation steps are that (1) on the basis that underground pipeline trend, burial depth, corresponding earth surface positions and proper radar frequency spectrum parameters are determined, ground penetrating radar detecting is carried out, and radar images of three measuring points in a radar measuring line direction above the pipeline are obtained by measuring; (2) on the basis of radar image denoising processing, electromagnetic wave single-track oscillographs corresponding to the coordinates of the three measuring points are extracted; (3) electromagnetic wave transmission time from the three measuring points to a pipe wall is determined through a single-track wave curve peak-valley value; (4) on the basis that field electromagnetic wave speed is determined, the transmission distance between the three measuring points and the pipe wall is obtained; and (5) the coordinates of the three measuring points and the electromagnetic wave transmission distance between the three measuring points and the pipe wall are used for computing the pipeline pipe diameter.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for generating stepped frequency signals based on combination of direct digital synthesis (DDS) and ping-pong phase locked loop
InactiveCN102185608AImprove combat skill indicatorsTechnical indicators leapWave based measurement systemsPulse automatic controlPhase noiseEngineering
The invention discloses a method for generating stepped frequency signals based on the combination of direct digital synthesis (DDS) and a ping-pong phase locked loop. DDS has the advantages of high narrowband application performance and capability of easily realizing extremely small frequency step, and the phase locked loop has the advantages of easily realizing broadband application and ensuring high comprehensive performance particularly in broadband great-step application. In the method, advantage complementarity between the DDS and the phase locked loop is utilized, a ping-pong phase locked loop is formed by combining two identical phase locked loops and a microwave single-pole double-throw switch, frequency synthesis is performed by combining the DDS and the ping-pong phase locked loop, the DDS is used for synthesizing narrowband small-step signals, the ping-pong phase locked loop is used for synthesizing broadband great-step signals, and the broadband great-step signal and the narrowband small-step signals are combined together in a frequency shifting way, thereby generating broadband radar stepped frequency signals with low phase noise, low stray, small step and frequency agility. Therefore, tactical and technical indexes of a radar frequency synthesizer are greatly increased, and qualitative leaps in technical indexes of the radar stepped frequency signals are achieved.
Owner:中国兵器工业第二0六研究所
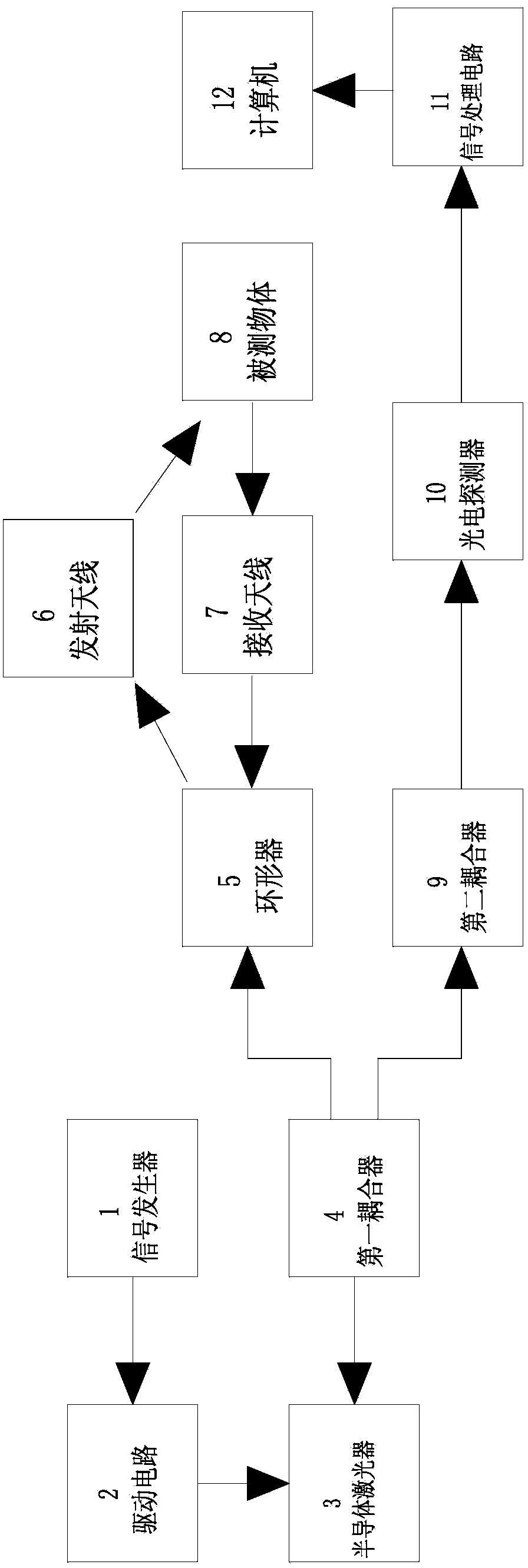
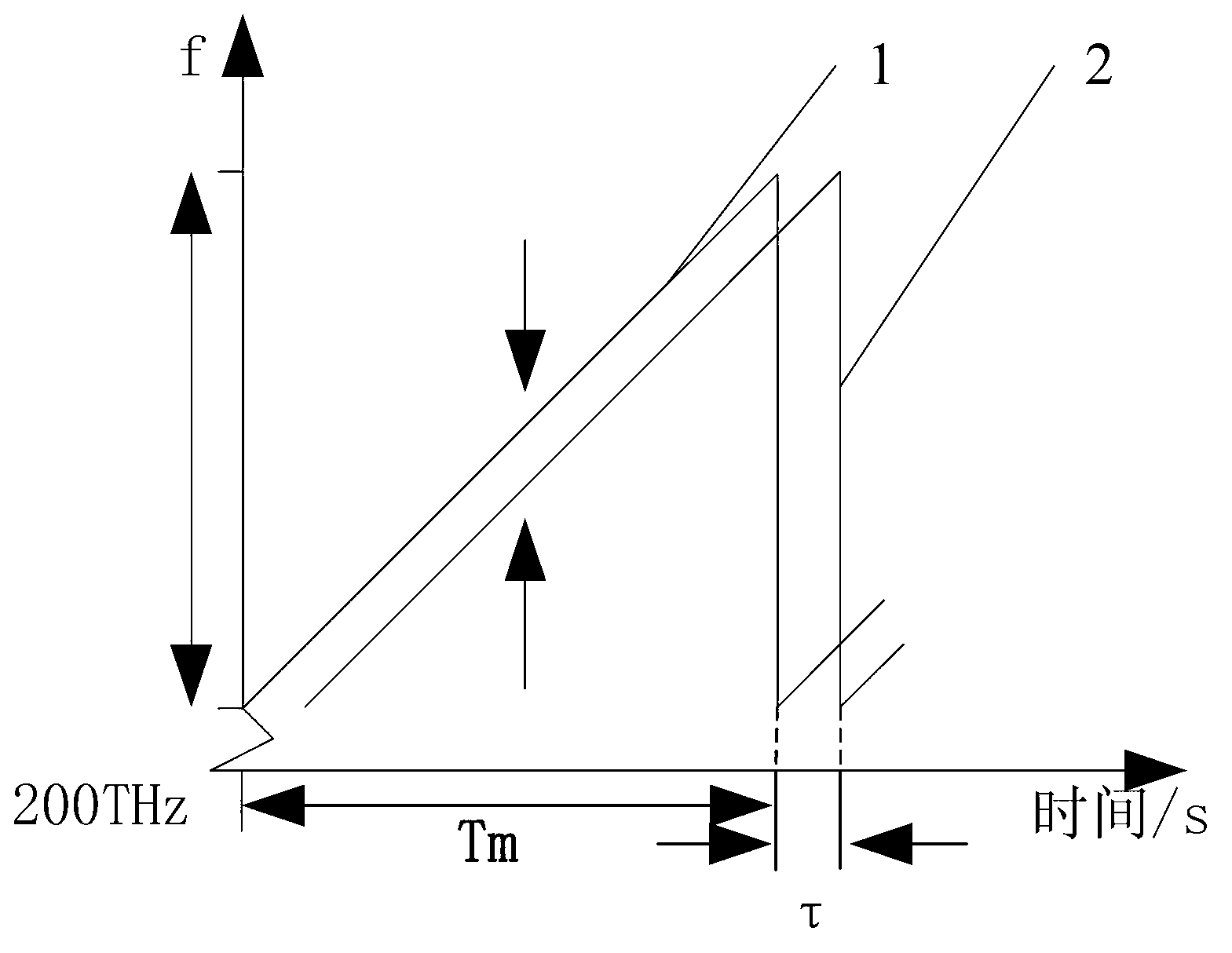
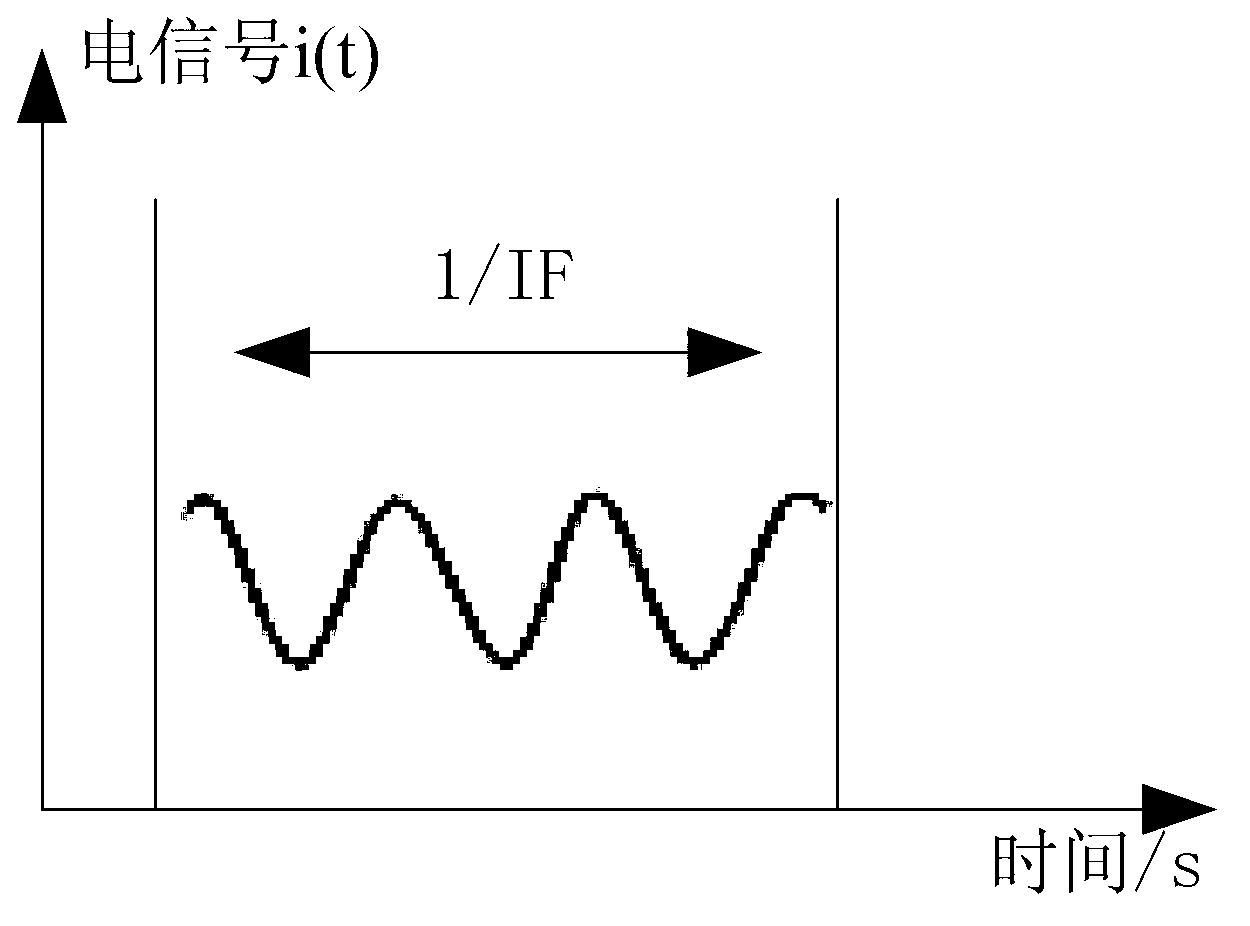
Frequency modulated continuous wave laser radar frequency modulation nonlinear response coefficient measuring method and device
The invention provides a frequency modulated continuous wave laser radar frequency modulation nonlinear response coefficient measuring method. According to the method, a signal generator generates sawtooth wave frequency-modulated signals, inputs the sawtooth wave frequency-modulated signals into a driving circuit and drives a laser to work, modulation signal light output by the laser is divided into two paths through a first coupler, one path of light is emitted to a measured object through a circulator, return light returned by the measured object is received by the circulator, the return light and the other path of light are coupled through a second coupler, light output by the second coupler is received by a photoelectric detector, obtained beat frequency signals are processed through a signal processing circuit, difference frequency is obtained through processing of computer software and a nonlinear frequency modulation coefficient is worked out. The frequency modulated continuous wave laser radar frequency modulation nonlinear response coefficient measuring method can be used for accurately measuring the nonlinear coefficient, provides key parameters for frequency modulation nonlinear rectification for a system, and has great significance for improving the frequency modulation linearity of frequency modulated continuous wave laser radar range radar, and the accuracy of measurement of the speed and distance of the system .
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Radar device and frequency interference cancellation method thereof
ActiveUS20180003799A1Degrading transmitted signalReduce signaling processing loadLine-faulsts/interference reductionTransmission noise suppressionControl signalTime changes
The present invention relates to a radar device and a frequency interference cancellation method thereof, and arranges a configuration comprising: an antenna unit for transmitting a radar transmission signal to a periphery and receiving a signal reflected from a target; an RF unit for generating the transmission signal, converting frequencies of a transmission signal and a reception signal, and amplifying a reception signal; a signal processing unit for generating a control signal to generate the transmission signal and cancelling frequency interference from a reception signal of the RF unit; and a control unit for generating radar detection information by using an output signal of the signal processing unit, and tracking information by accumulating the radar detection information. The present invention enables real time changing of a hopping pattern according to a radar frequency interference environment, thereby achieving operation of the hopping pattern adaptively optimized to the frequency interference environment.
Owner:DIGITAL EDGE
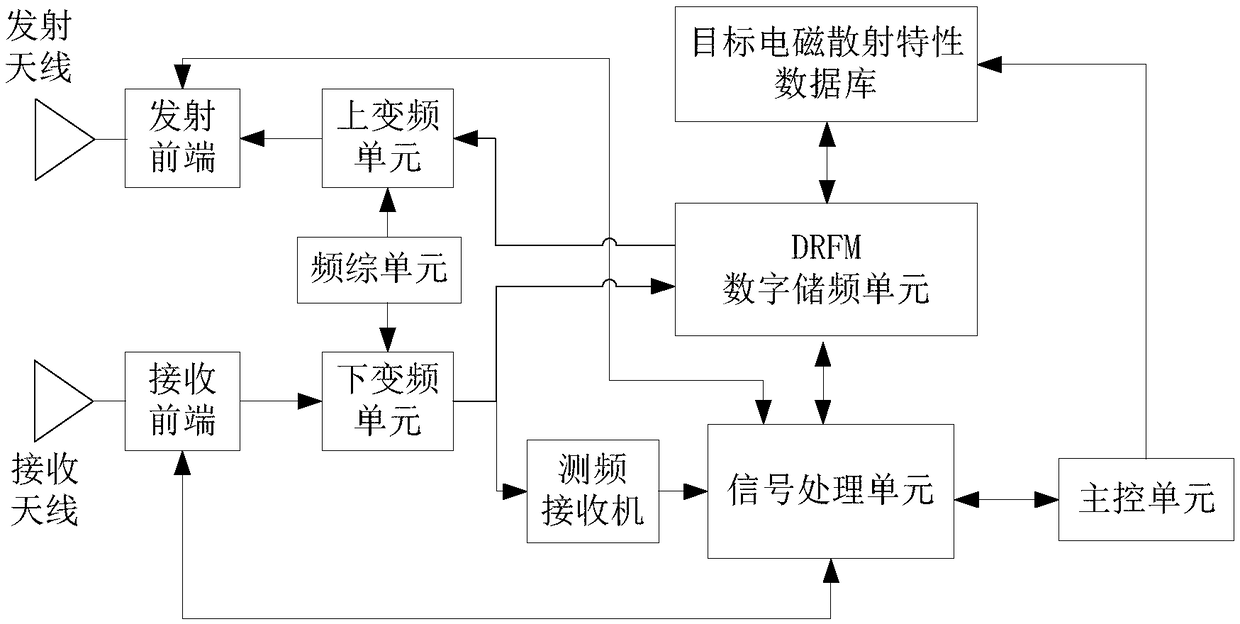
Radar target echo simulation system based on electromagnetic scattering model, and simulation method thereof
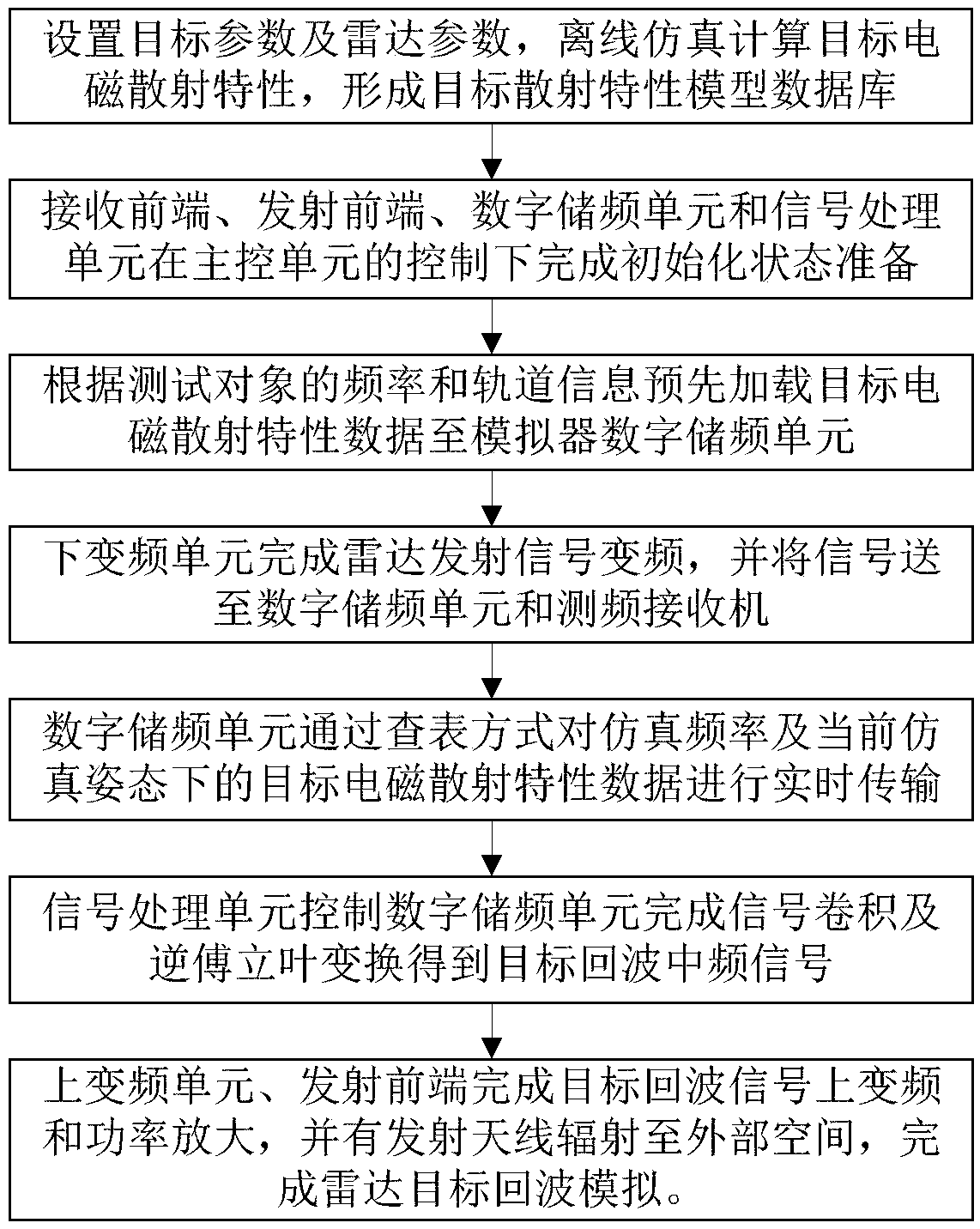
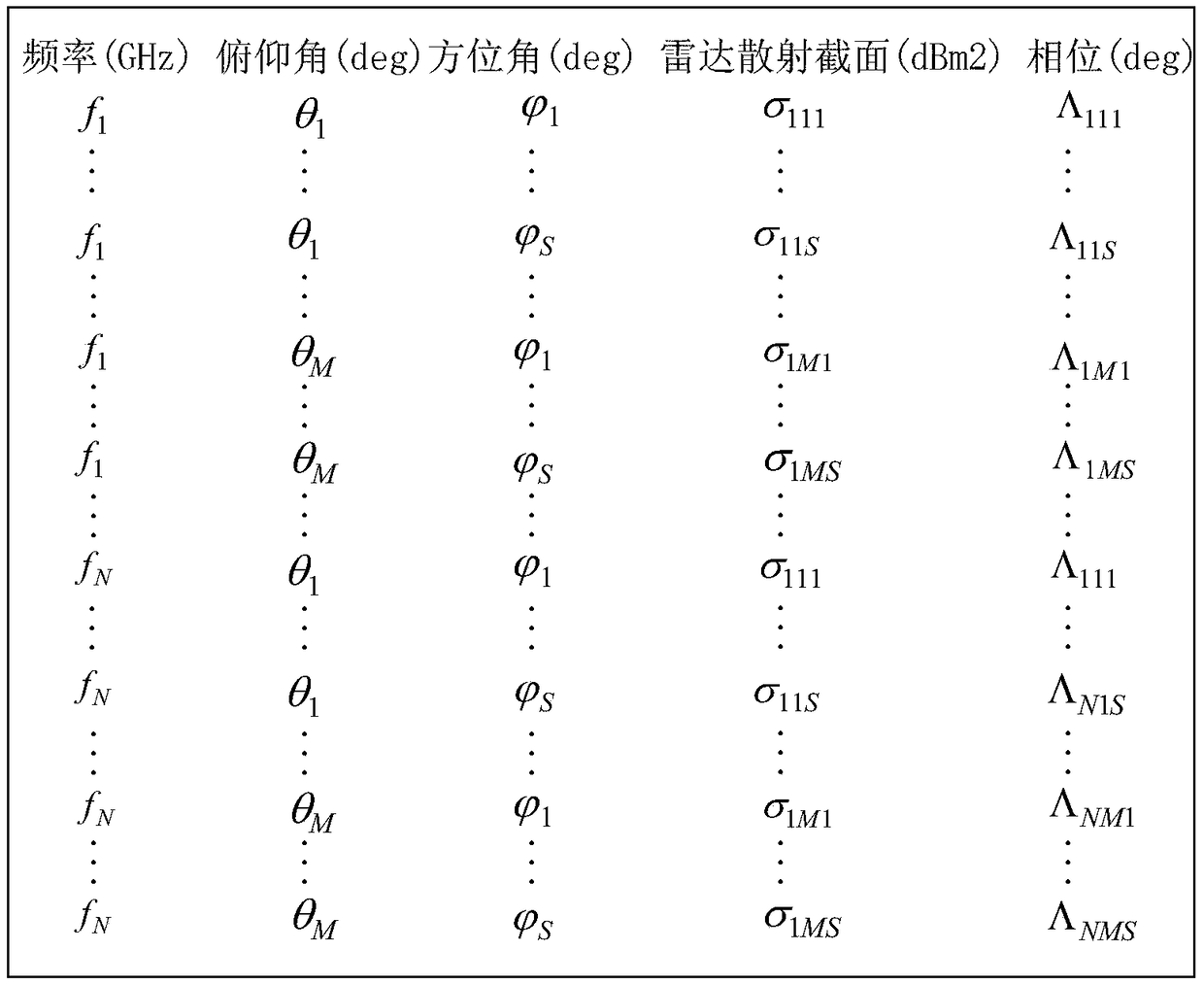
ActiveCN109239684AIncrease credibilitySolve the problem that the target echo simulation is not realisticWave based measurement systemsFourier transform on finite groupsElectromagnetic field
The invention discloses a radar target echo simulation system based on an electromagnetic scattering model, and a simulation method thereof. The simulation method comprises the following steps: utilizing electromagnetic field simulation software, taking a precise three-dimensional geometric model of the radar target as input, setting radar frequency, space angle and like parameters, and computingradar target electromagnetic scattering characteristics through offline simulation; generating target electromagnetic scattering characteristic data under different frequencies and different space angles, and forming a scattering model database; when performing the radar target echo simulation, preloading the target electromagnetic scattering characteristic data to a simulator digital radio frequency memory unit (DRFM) according to the frequency and the orbit information of the radar test, wherein the DRFM performs real-time transmission on the target electromagnetic characteristic data underthe simulation frequency and the current simulation attitude through a table look-up way, and a signal processing unit controls the DRFM to accomplish frequency domain convolution of a radar emissionsignal and the target scattering characteristic data, and performs inverse Fourier transform processing on a convolution result to obtain a target time domain echo.
Owner:NO 8511 RES INST OF CASIC
Radar Unit, Integrated Circuit and Methods for Detecting and Mitigating Mutual Interference
A radar unit (400) for detecting an existence of interference is described that includes: a millimetre wave (mmVV) transceiver (Tx / Rx) circuit configured to radiate a transmit radar signal and receive an echo signal thereof; a mixed analog and baseband circuit operably coupled to the mmW Tx / Rx circuit; and a signal processor circuit (452) operably coupled to the mixed analog and baseband circuit. An interference detection unit (448) is operably coupled to the mmW Tx / Rx circuit and configured to: monitor a whole or a portion of a radar frequency band supported by the radar unit and identify, from a received interference signal, an arrival direction of the identified interference and a level of interference and output an interference detected signal; and wherein the signal processor circuit (452) is configured to analyse the interference detected signal and quantify a response to the detection of an arrival direction and a level of received interference.
Owner:NXP BV
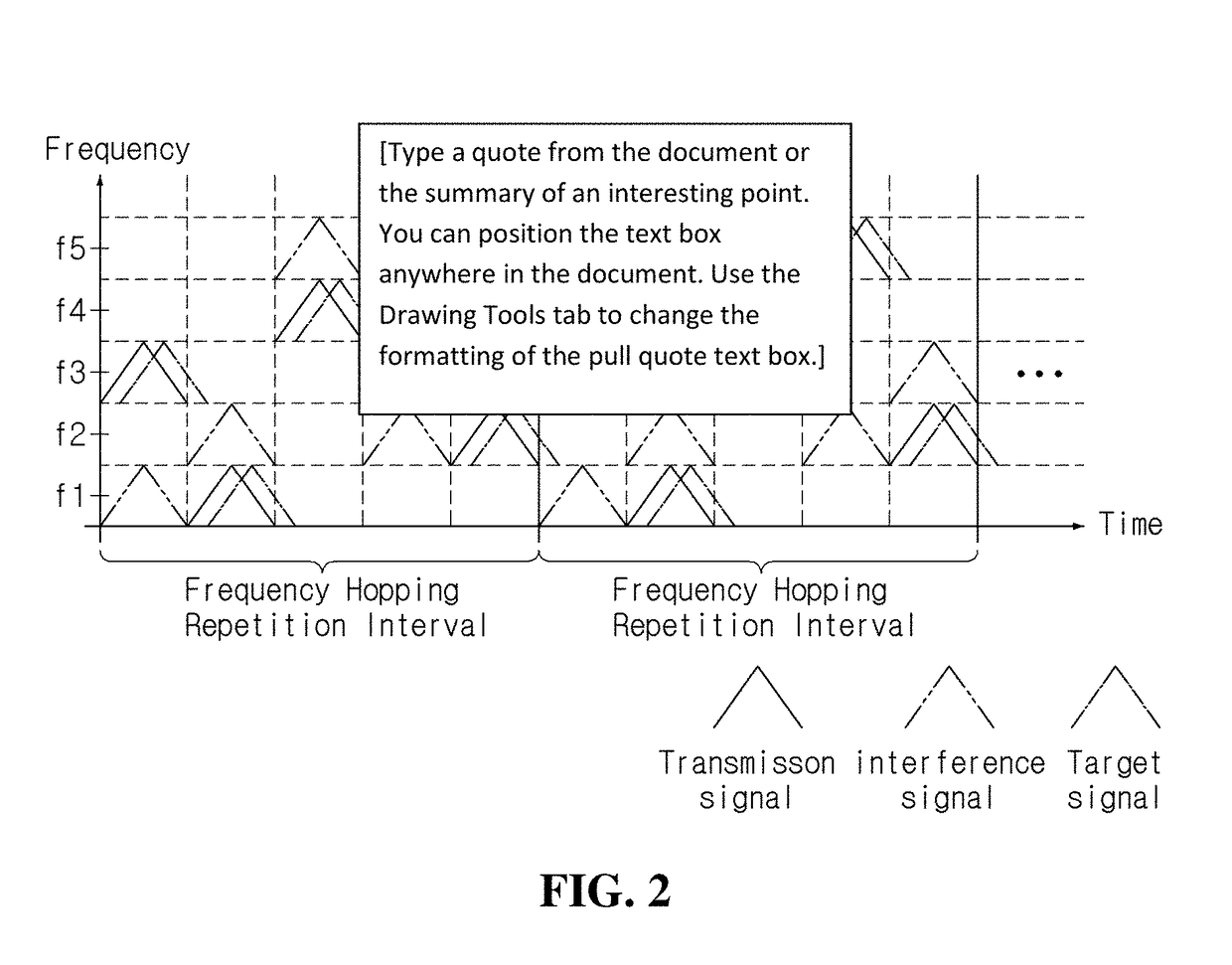
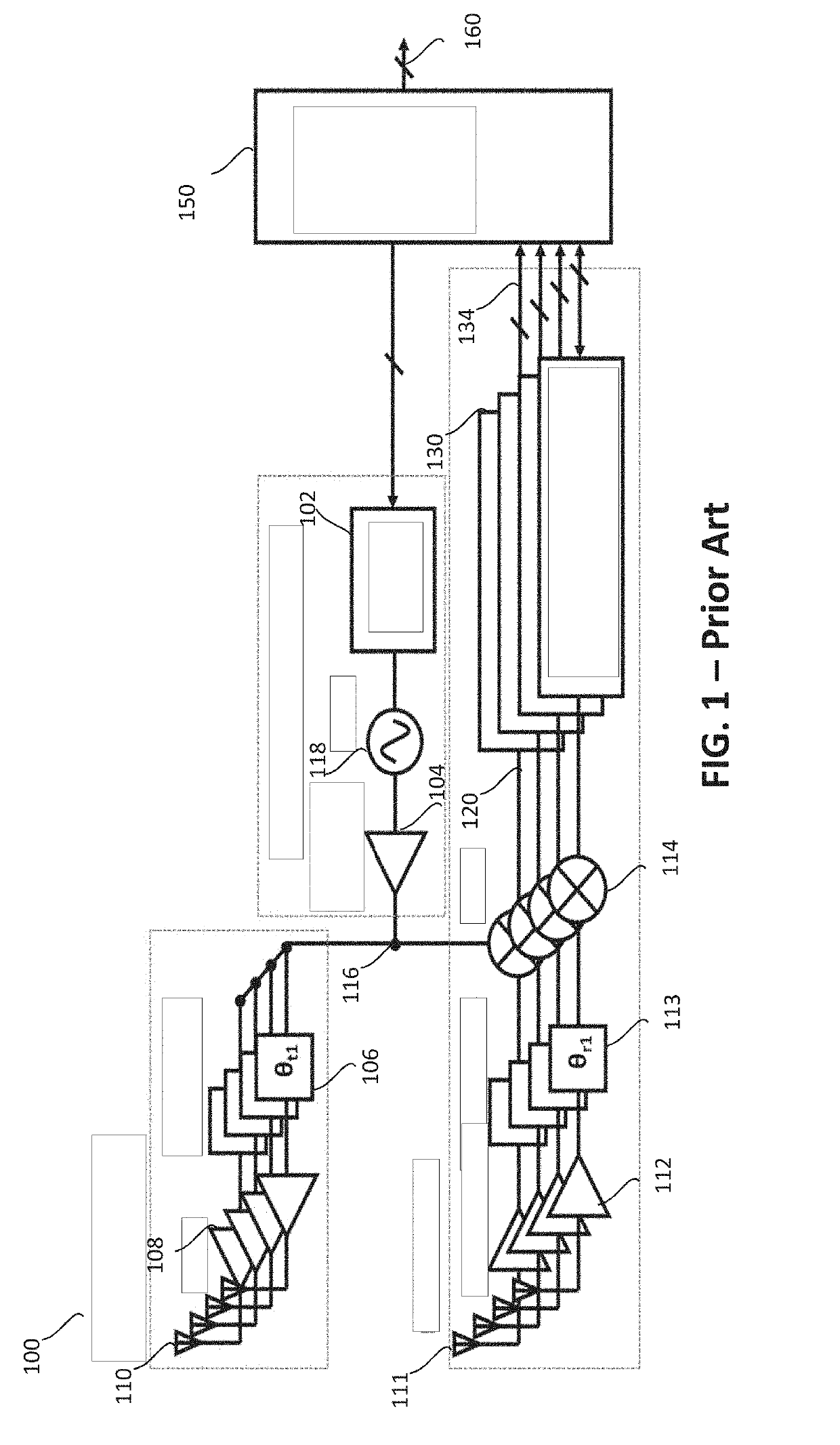
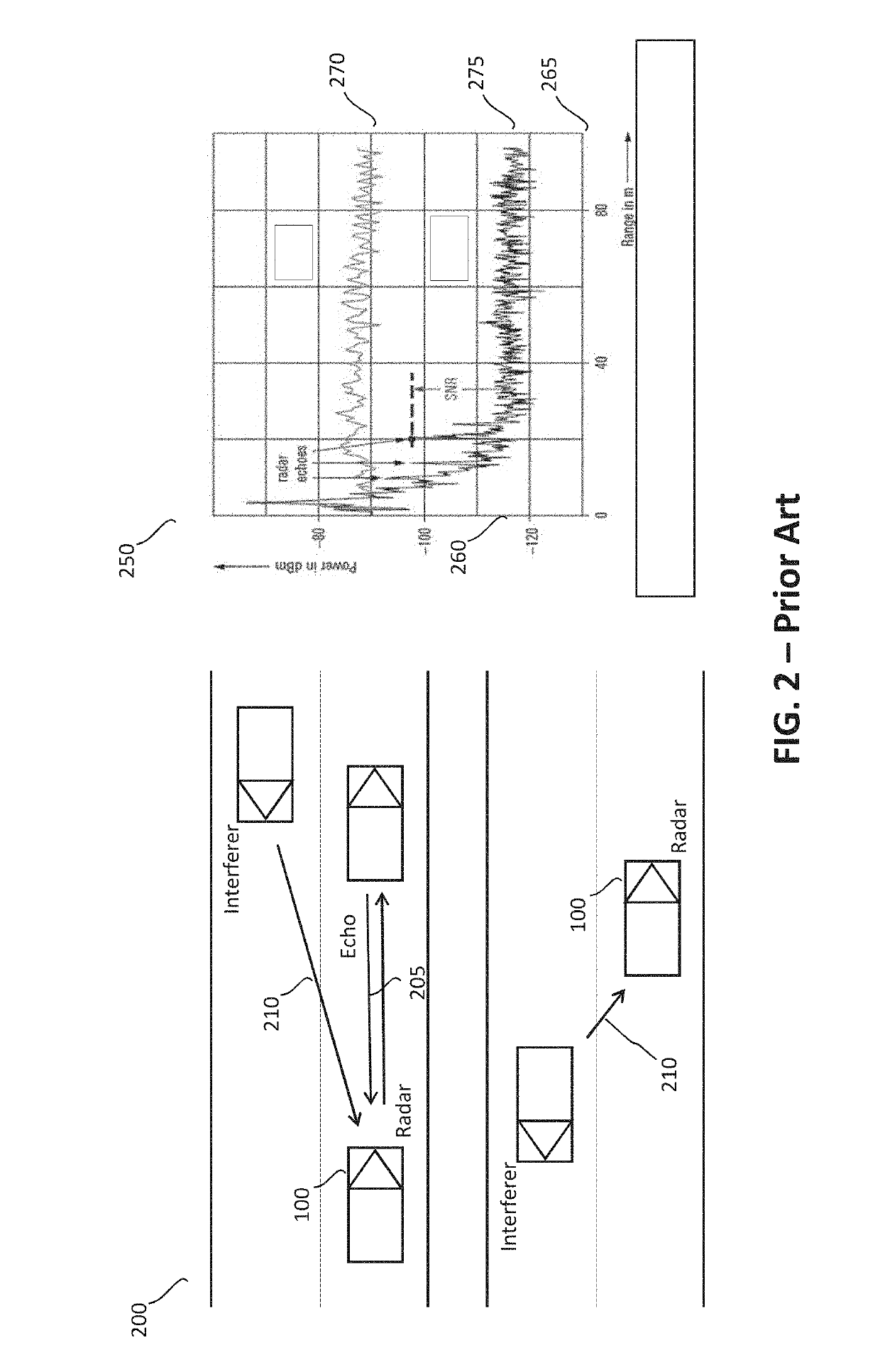
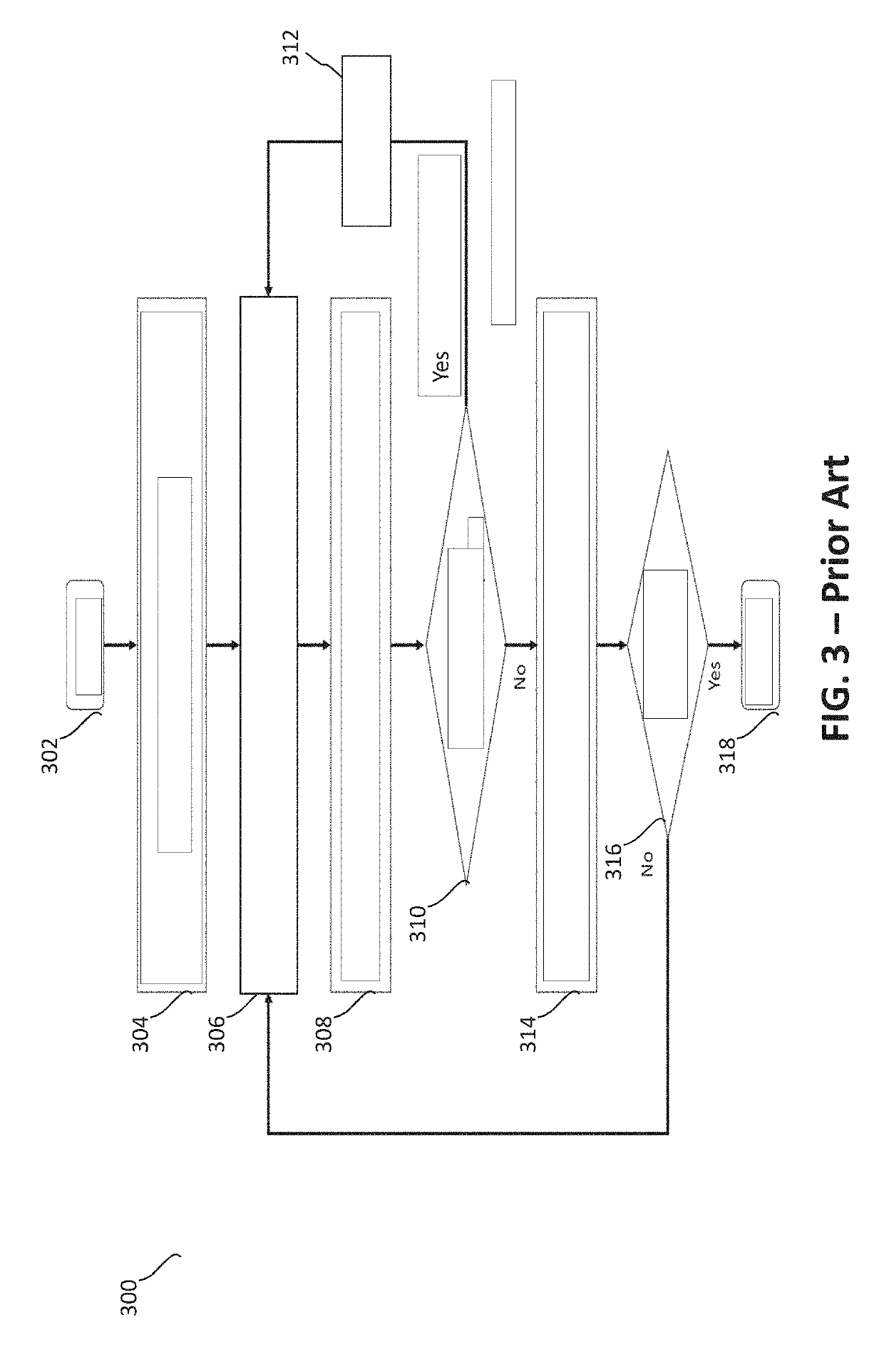
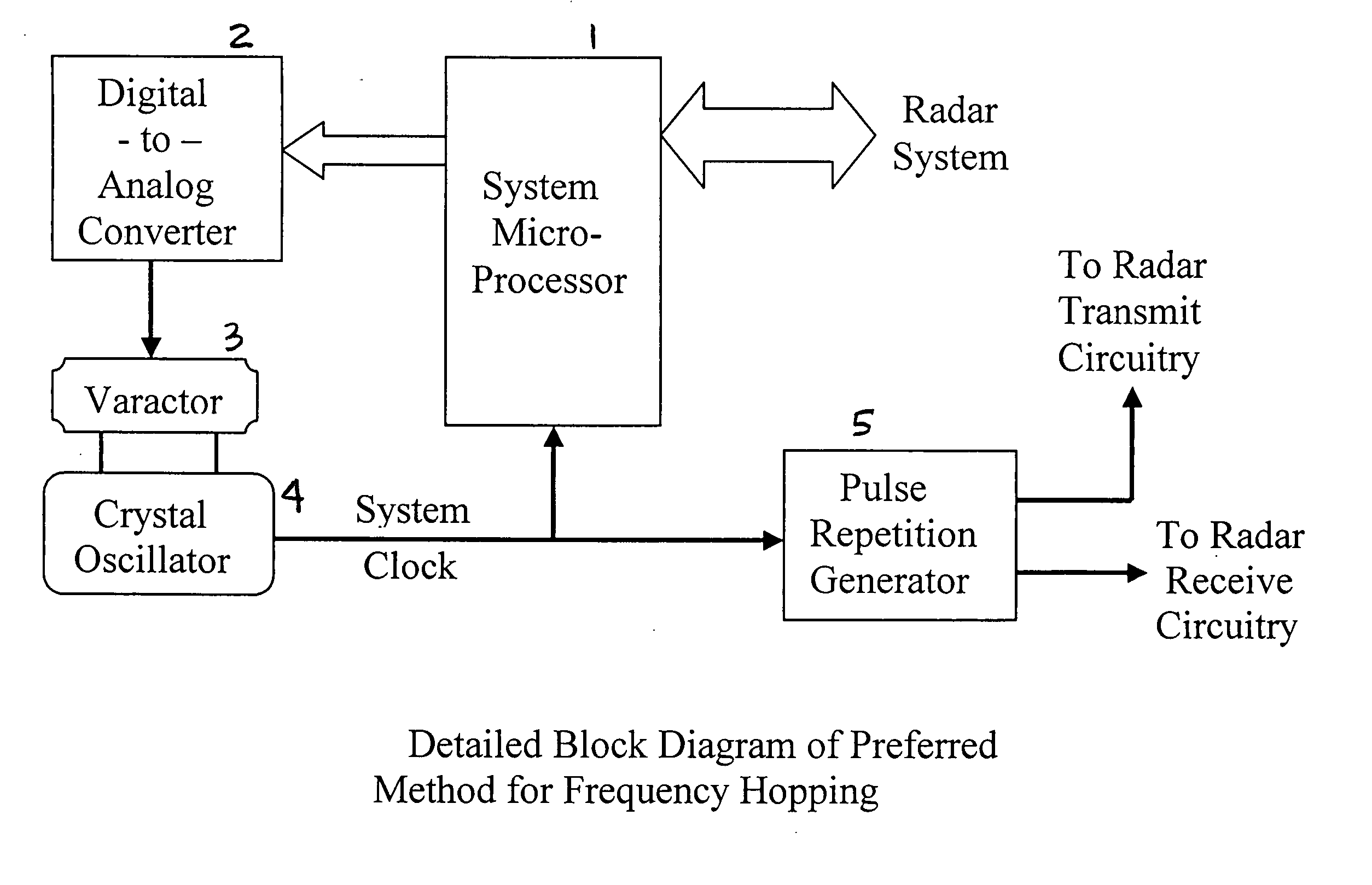
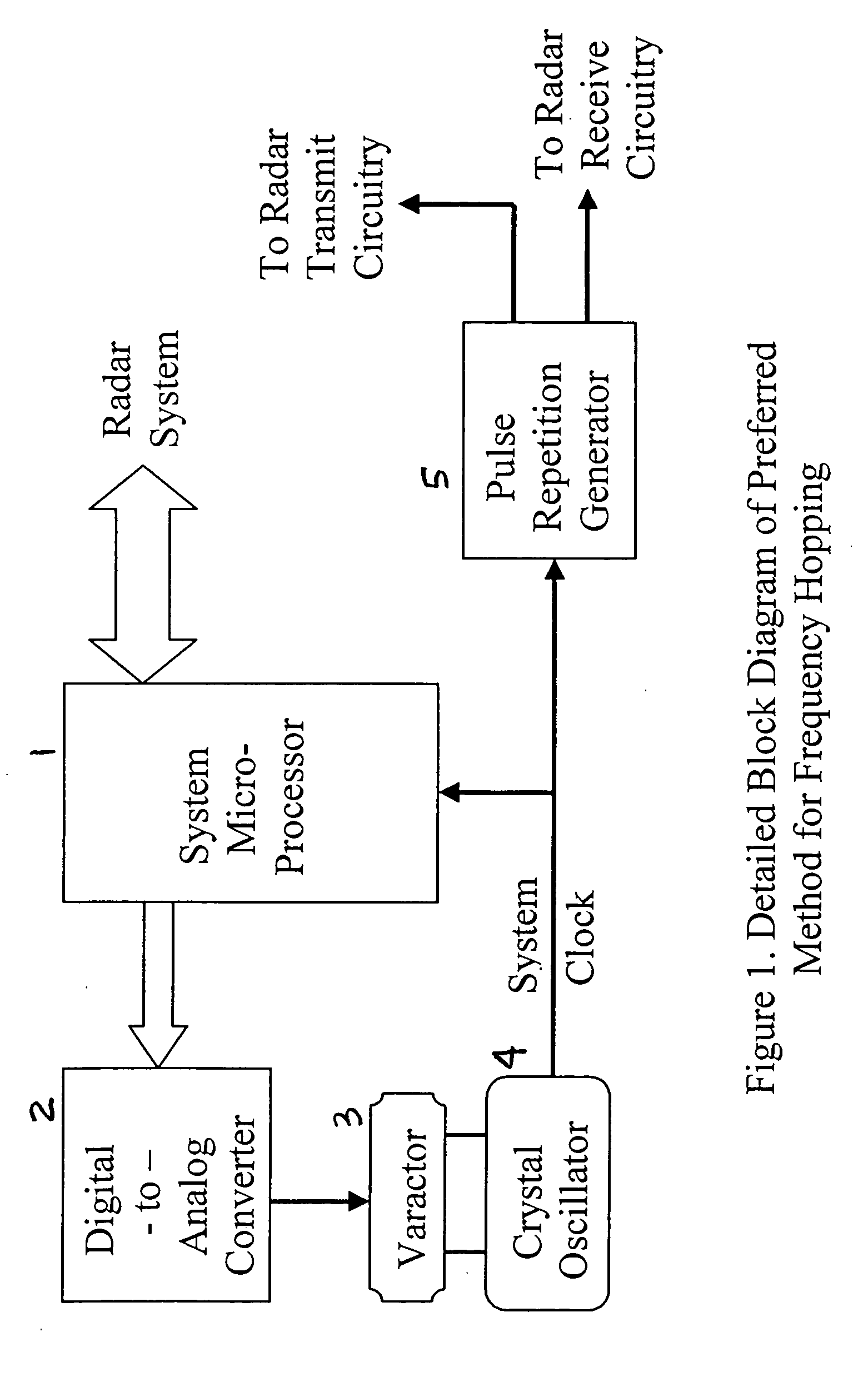
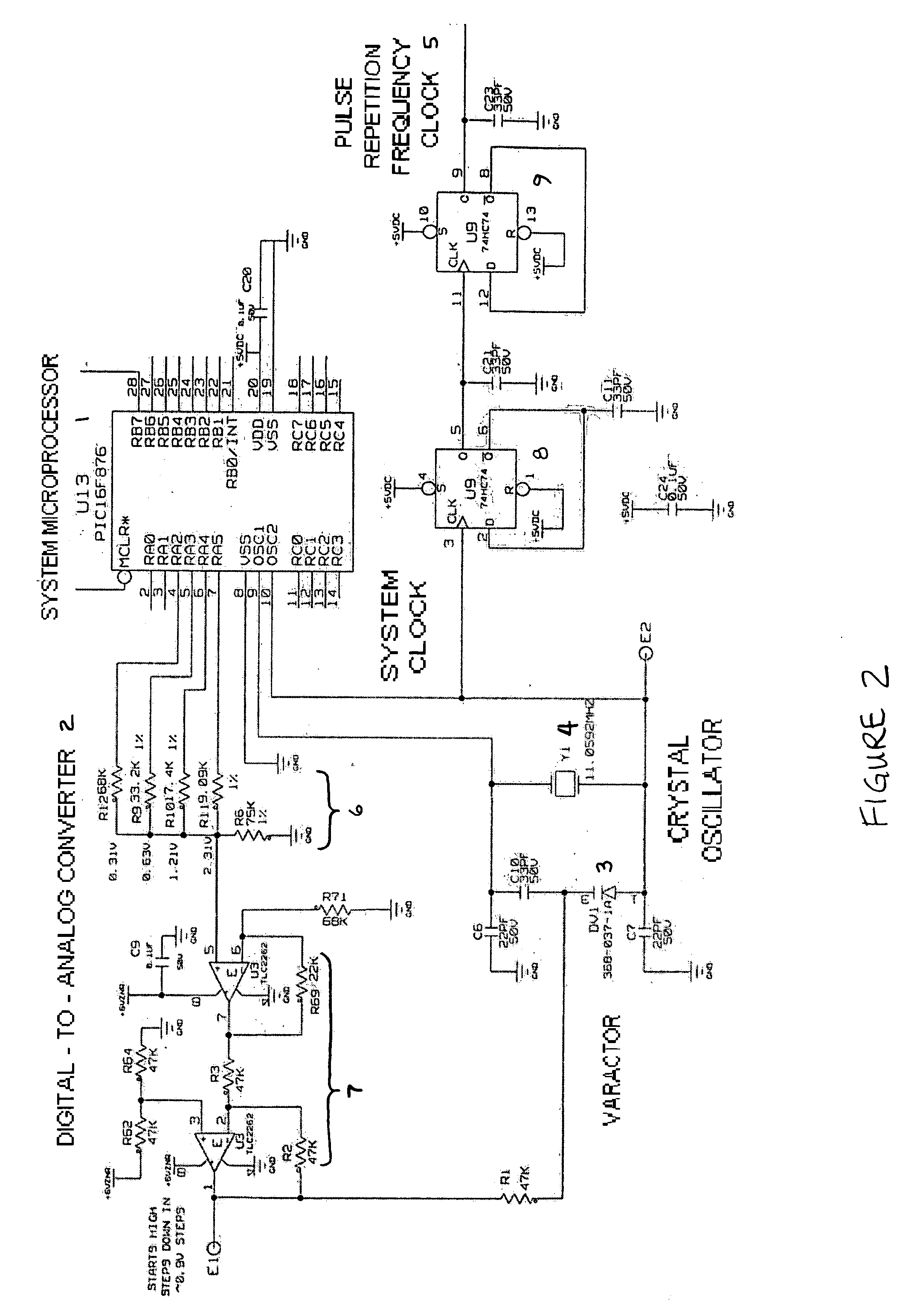
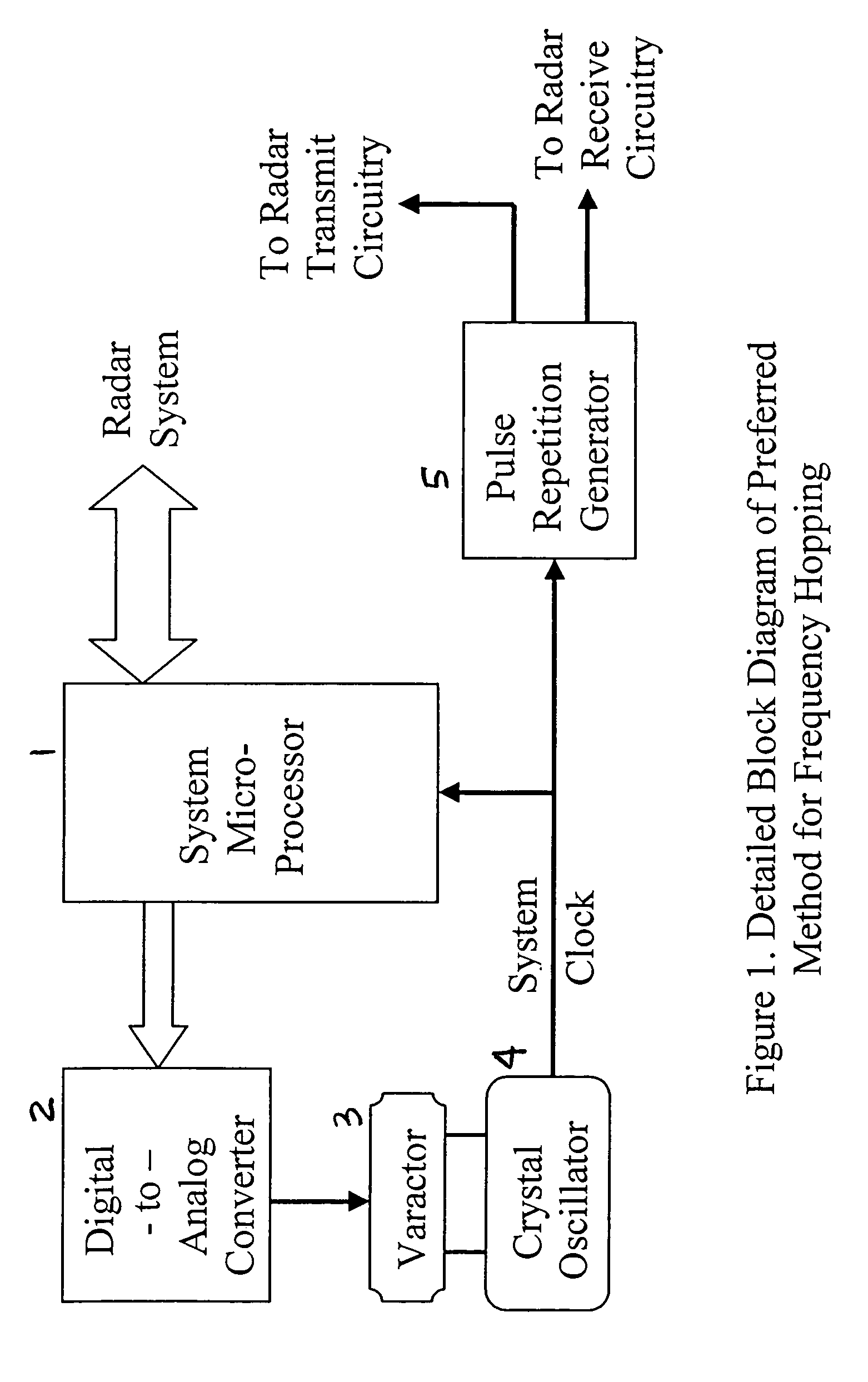
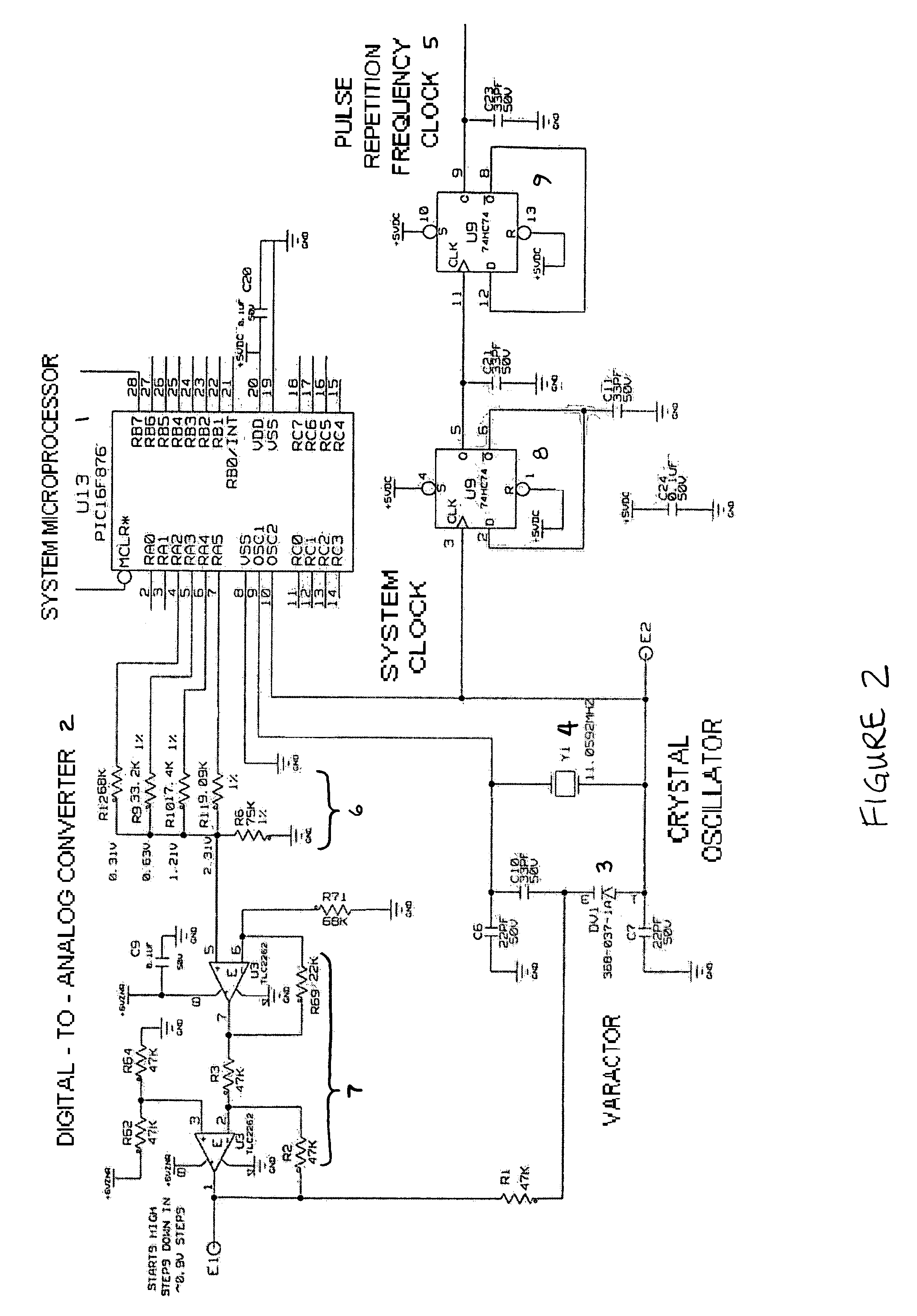
Radar frequency hopping
ActiveUS20050104765A1Avoiding extended reception of interfering signalMaximize receiver sensitivityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionUltra-widebandTime domain
Apparatus and methods for adjusting or “hopping” the center frequency or the pulse repetition frequency of a radar system improve the co-locatability of multiple radars commonly located in a region. In a Time Domain Downconversion (TDDC) or Ultra-Wideband (UWB) radar system having a display update period between range sweeps, the preferred device comprises a frequency variable oscillator for adjusting the radar's internal timing reference frequency during a plurality of the display update periods. Radar frequency hopping methods and apparatus may result in improvements in interference immunity compared to other interference reduction techniques and may achieve cost reduction. In frequency hopping radar, if an actual target is present, the receiver waveform will repeat at the newly adjusted center frequency. Confirmation of a target is realized as an ongoing reflection and not interference.
Owner:PRECO ELECTRONICS
Radar sensor for use with automobiles
InactiveUS7268732B2Improve directionalityDecreased wavelengthSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesPulse radiationAcoustics
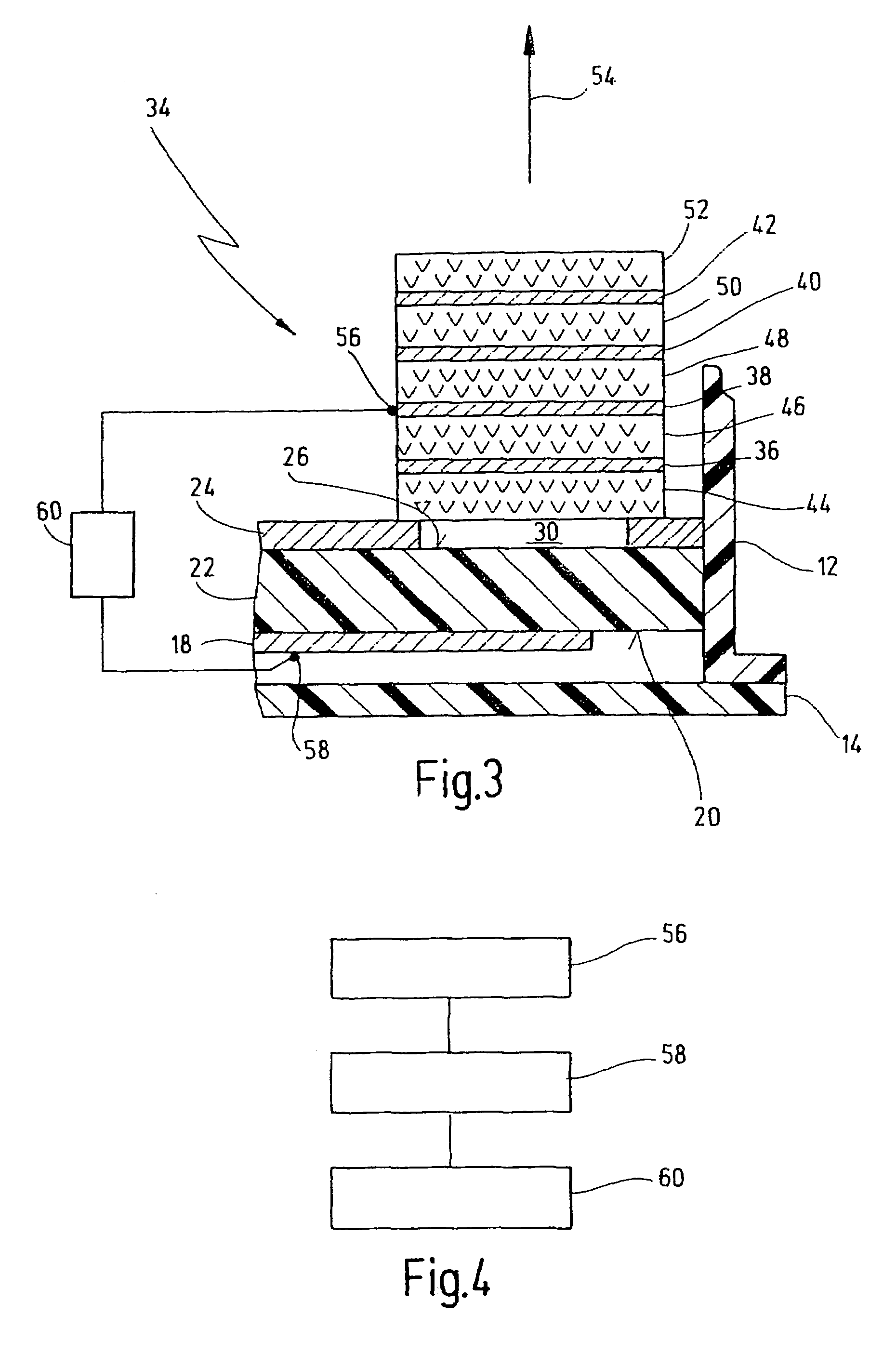
The invention relates to a radar sensor (10) for use with automobiles. Said radar sensor emits pulsed radiation. The radar sensor is characterized in that it comprises an antenna with at least one layer-structured block (34) consisting of metal layers (36, 38, 40, 42) which are arranged according to the Yagi principle and which are respectively separated from each other by a dielectric intermediary layer (46, 48, 50). At least one of the metal layers (36, 38, 40, 42) is excited by a supply system (18) with a radar frequency.
Owner:VALEO SCHALTER & SENSOREN
Doppler anemometry laser radar radial wind speed real-time correction system
ActiveCN106019303AHigh precisionVerify accuracyFluid speed measurementElectromagnetic wave reradiationGeometric factorData acquisition
The invention discloses a Doppler anemometry laser radar radial wind speed real-time correction system. A very small part of laser is split in the system, and is couple to a self-built controllable atmospheric environment through a polarization coaxial optical path. An atmospheric echo signal in the environment is detected. A Doppler anemometry laser radar frequency discrimination system and a data acquisition system are used to inverse a measurement value in the state. At the same time, most of the laser is emitted to natural atmosphere. The echo signal is used to inverse the radial wind speed of natural atmosphere. The difference between the measurement value and the radial wind speed of natural atmosphere is true radial wind speed. According to the invention, the self-built atmospheric environment is controllable; the polarization coaxial optical path eliminates the influence of geometric factors; the system has a real-time calibration function; and the measurement accuracy of a Doppler anemometry laser radar is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Combined time frequency distribution and compression sensing radar frequency smeared spectrum interference method
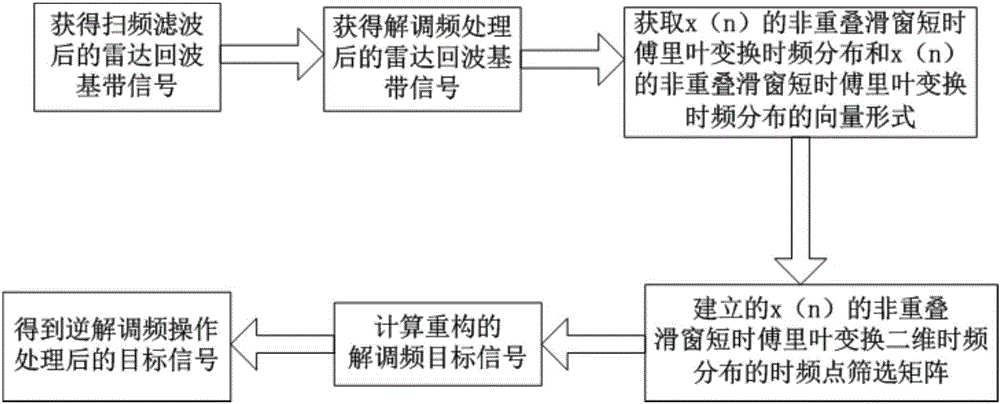
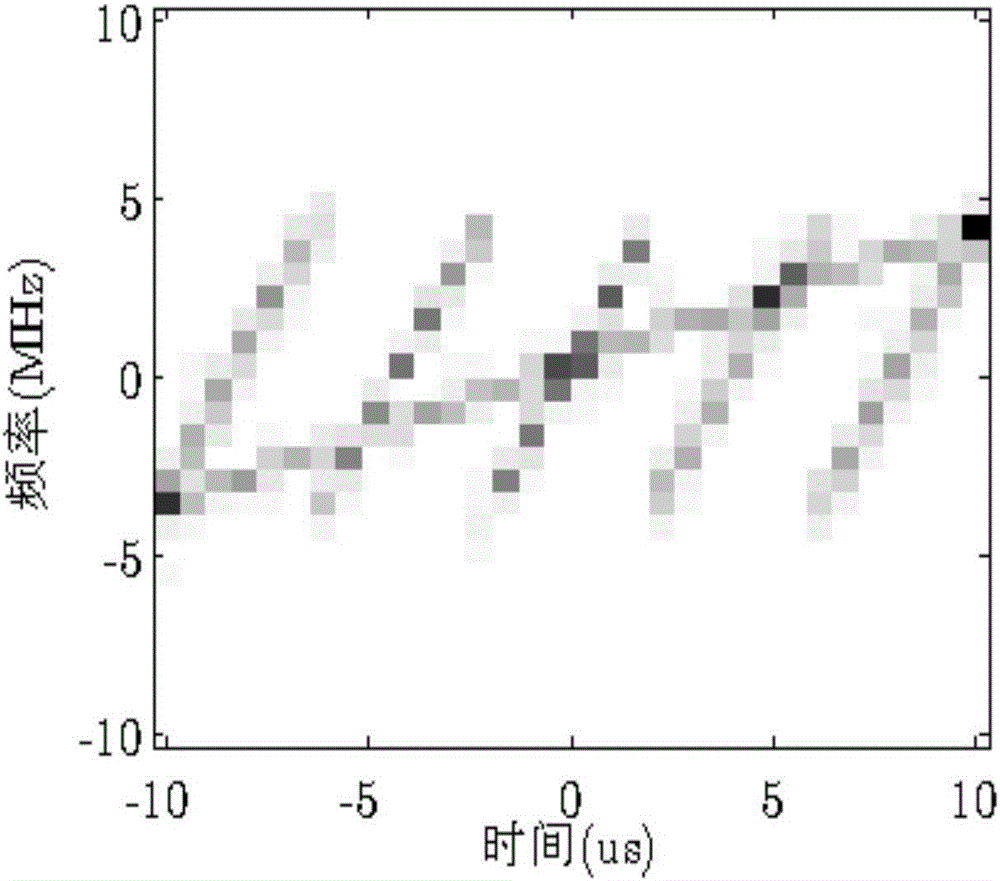
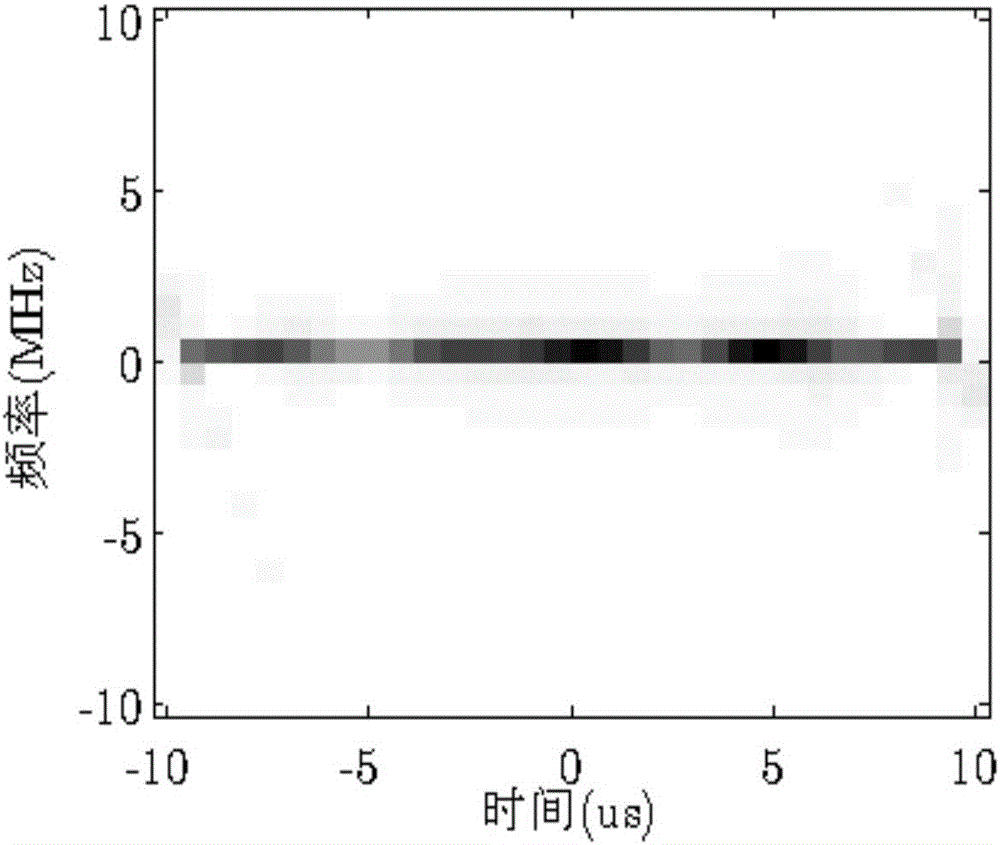
ActiveCN105891789AClear conceptSuppression of Spectrum Dispersion (SMSP) Interfering SignalsWave based measurement systemsFrequency spectrumTarget signal
The invention discloses a combined time frequency distribution and compression sensing radar frequency smeared spectrum interference method. The method includes obtaining radar echo signals and conducting down conversion processing to obtain the radar echo baseband signal s, conducting u domain frequency sweep filtering and frequency demodulation to obtain radar eco baseband signal x after frequency demodulation, setting the discrete time sequence x(n) of x, sequentially calculating the vector form Xi<^> of the non-overlapping slide window short time Fourier Transform time frequency distribution of the Xi<^> and Xi<^> of x (n), establishing the linear relation between the Xi<^> and x, setting the time-frequency point screening threshold, screening the time-frequency points contained in the Xi<^> to sequentially obtain the time-frequency points retained in the Xi<^> and a time-frequency point screening matrix Psi<^> of the Xi<^>, setting the vector form of Xi<^> after time-frequency points screening as Xi<^> bar and obtaining the linear relation among the Xi<^> bar, Psi<^> bar and Xi<^>, setting the x frequency spectrum as X, further establishing the linear relation between the Xi<^> bar and X, conducting reconstruction and inverse Fourier transform for X to obtain a reconstructed frequency demodulation target signal X<^>, and conducting inverse frequency demodulation for the X<^> to obtain the target signal after inverse frequency demodulation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Infrared camouflage paint and preparation method thereof
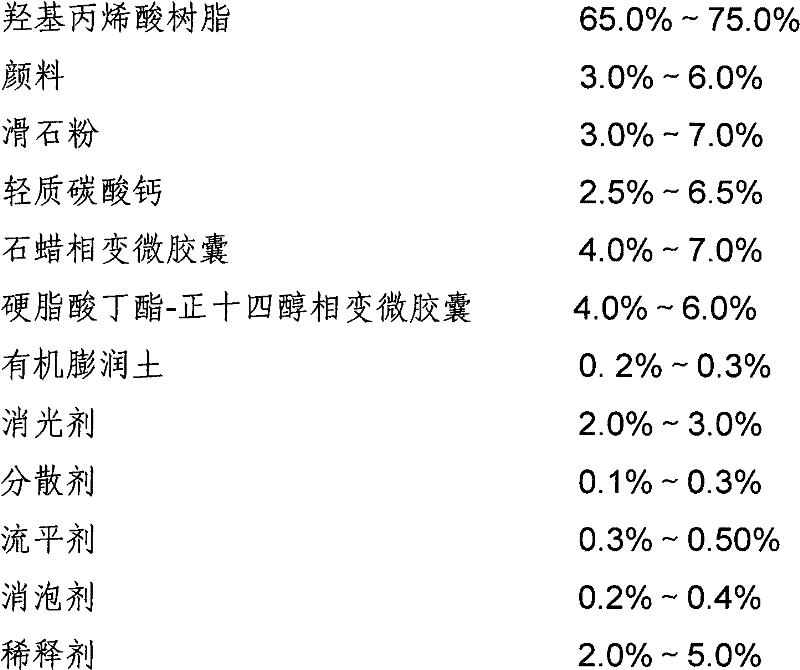
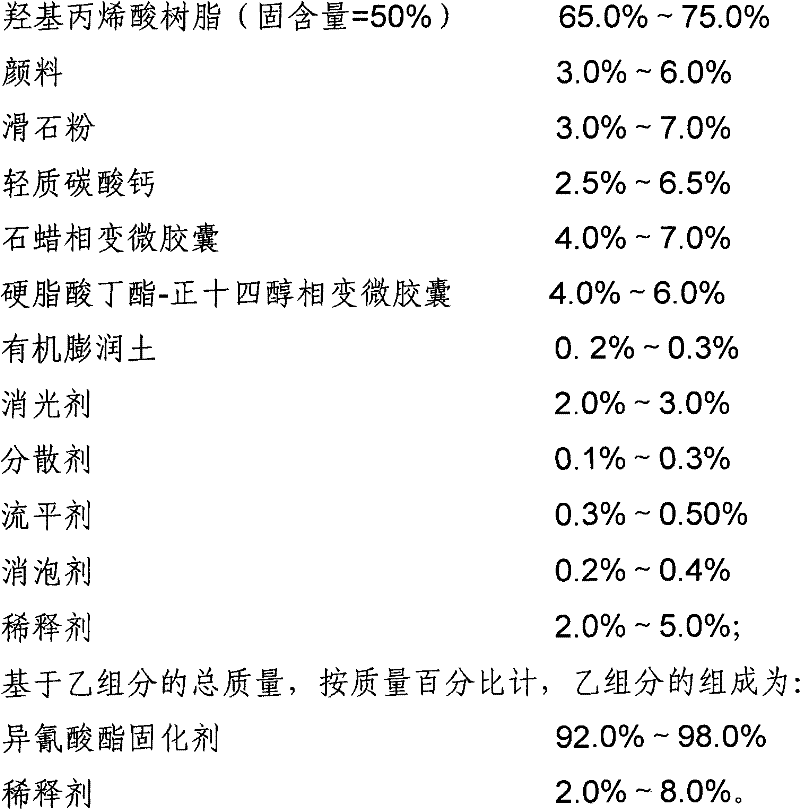
InactiveCN102417771AImprove stabilityImprove heat transfer performanceCoatingsMicroballoon preparationIn situ polymerizationLow emissivity
The invention discloses infrared camouflage paint and a preparation method thereof. The infrared camouflage paint uses three different phase change materials with different phase transition temperature ranges as the core materials and melamine-formaldehyde resin as the wall material; and the in-situ polymerization method is adopted to prepare phase change microcapsules which are used as the temperature controlling material to be added in the infrared camouflage paint, thus the temperature of the target can be regulated, the thermal infrared radiation intensity of the target can be controlled, the aim of infrared camouflage can be achieved and the infrared camouflage requirement of the protected target can be met at about 10-60 DEG C. By adopting the paint, the defects of the low emissivity infrared camouflage material that the paint and the visible light are difficult in compatibility, especially in the radar frequency band, the tolerance of the paint on the pollution is poor, the emissivity can be obviously increased owning to dust and water and the camouflage effect is lowered, can be overcome.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Non-linear correction method for LFMCW (linear frequency modulated continuous wave) laser radar frequency modulation based on optical fiber sampling technology
ActiveCN103176173AEliminate the effects ofSimple structureWave based measurement systemsLight beamContinuous wave
The invention discloses a non-linear correction method for LFMCW (linear frequency modulated continuous wave) laser radar frequency modulation based on an optical fiber sampling technology, and relates to the technical field of LFMCW laser radar frequency modulation and non-linear correction. The method solves the problems that non-linear correction cannot be performed when frequency modulation curve changes are not gradual. Lengths of a first optical fiber and a second optical fiber in a correction optical path are calibrated in advance, the length difference of the first optical fiber and the second optical fiber is the maximum measuring distance of an LFMCW laser radar, namely the measuring range upper limit, a third coupler combines beams of the first optical fiber and the second optical fiber, and correction light is received by a first probe to form a beat frequency signal. After the beat frequency signal is subjected to electrical frequency doubling, beat frequency signals in an interferometry optical path are sampled, and then the sampled signals are subjected to signal processing, so that influences, of frequency modulation non-nonlinearity of a frequency modulation laser, on measuring results are eliminated. The method is suitable for laser radar frequency modulation non-linear correction.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Ultra-high frequency (UHF) radar frequency spectrum shifting method of frequency selective surface (FSS)-based multi-layer reflective modulation plate
InactiveCN107565218ARealize two-phase constant modulus modulationRealize Spectrum ShiftAntennasFrequency spectrumUhf radar
The invention relates to an ultra-high frequency (UHF) radar frequency spectrum shifting method of a frequency selective surface (FSS)-based multi-layer reflective modulation plate, and belongs to thetechnical field of electromagnetic field microwave. By means of electromagnetic characteristic controllability of an electromagnetic metamaterial, an FSS-based three-layer structured reflective modulation plate is designed, dynamic conversion of a transient characteristic impedance state is achieved, so that the electromagnetic characteristic such as margin and phase of a low-frequency radar incident wave and a reflective wave direction are changed, and the problem of frequency spectrum shift of an UHF radar incident wave and receiver signal detection are solved. The three-layer reflective modulation plate is designed on the basis of FSS, conversion between a high-impedance state and a low-impedance state of a surface of an active layer is controlled, and two-phase constant-mode modulation of the radar incident signal is achieved; and meanwhile, based on a transmission line principle, an equivalent circuit of an adjustable reflective modulation plate is designed and has ideal wave absorption capability, and frequency spectrum shift of the UHF frequency radar signal is achieved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Radar frequency hopping
ActiveUS7215278B2Avoiding extended reception of interfering signalMaximize receiver sensitivityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime domainUltra-wideband
Apparatus and methods for adjusting or “hopping” the center frequency or the pulse repetition frequency of a radar system improve the co-locatability of multiple radars commonly located in a region. In a Time Domain Downconversion (TDDC) or Ultra-Wideband (UWB) radar system having a display update period between range sweeps, the preferred device comprises a frequency variable oscillator for adjusting the radar's internal timing reference frequency during a plurality of the display update periods. Radar frequency hopping methods and apparatus may result in improvements in interference immunity compared to other interference reduction techniques and may achieve cost reduction. In frequency hopping radar, if an actual target is present, the receiver waveform will repeat at the newly adjusted center frequency. Confirmation of a target is realized as an ongoing reflection and not interference.
Owner:PRECO ELECTRONICS
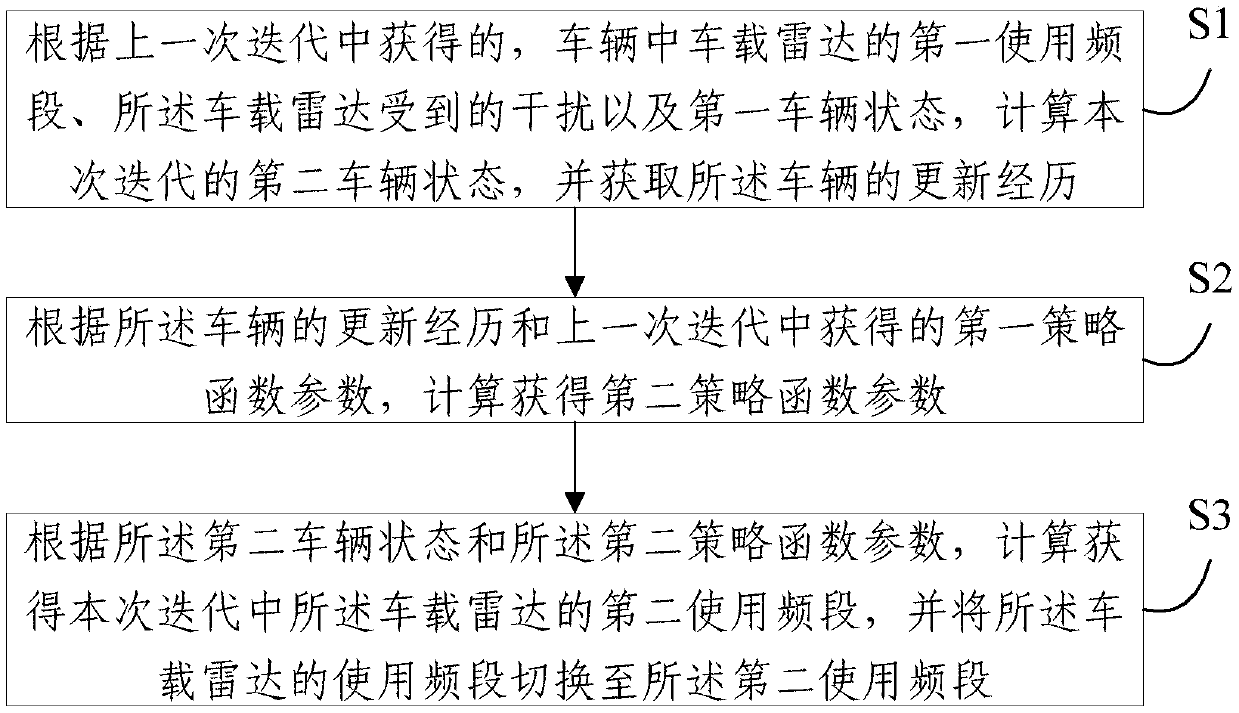
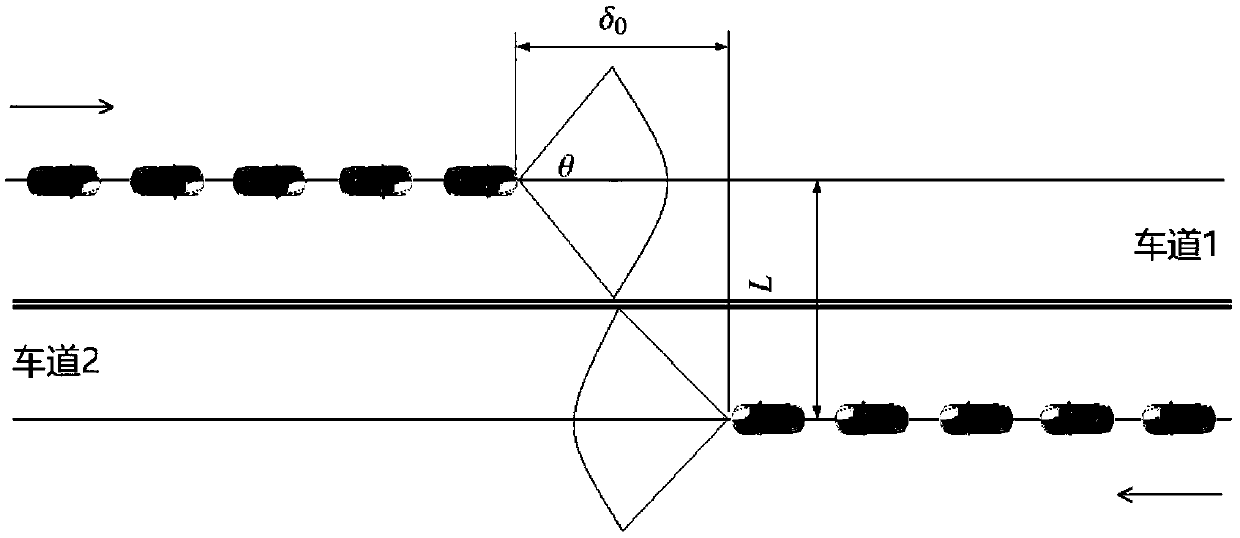
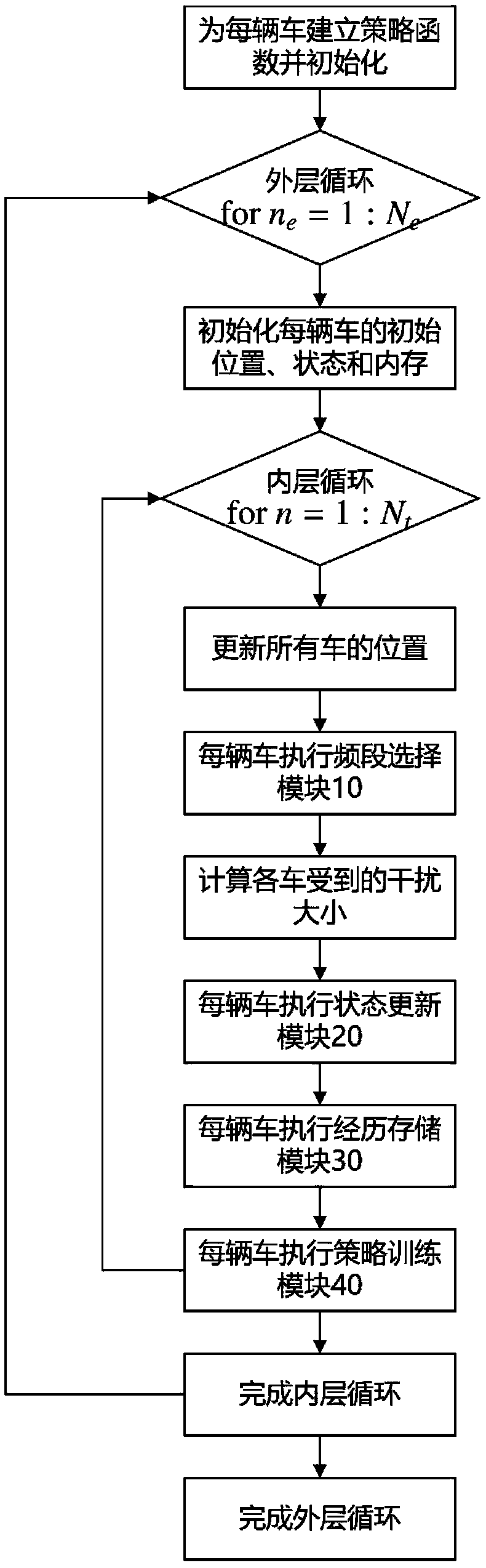
Vehicle-mounted radar frequency band distribution method and system
ActiveCN108710109ARealize distributed controlAvoid interferenceWave based measurement systemsNeural learning methodsFrequency spectrumDistribution method
The embodiment of the invention provides a vehicle-mounted radar frequency band distribution method and system. The method comprises steps of according to last iteration, the first use frequency bandof a vehicle-mounted radar in the vehicle, interference suffered by the vehicle radar and the first vehicle state, calculating a second vehicle state of the iteration this time and acquiring updatinghistory of the vehicle; according to the updating history of the vehicle and a first strategy function parameter acquired in the last iteration, calculating to acquire a second strategy function parameter; and according to the second vehicle state and the second strategy function parameter, calculating to acquire a second use frequency band of the vehicle radar in the iteration this time and switching the use frequency band of the vehicle radar to the second use frequency band. According to the invention, by combining observation of the current environment, distribution of radar resources in the dynamic environment is achieved; each vehicle is allowed to adaptively selects emission frequency band through a frequency band selection strategy according to local information of own observation;distributed control is achieved; interference can be effectively avoided; and the control is quite flexible than centralized control.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
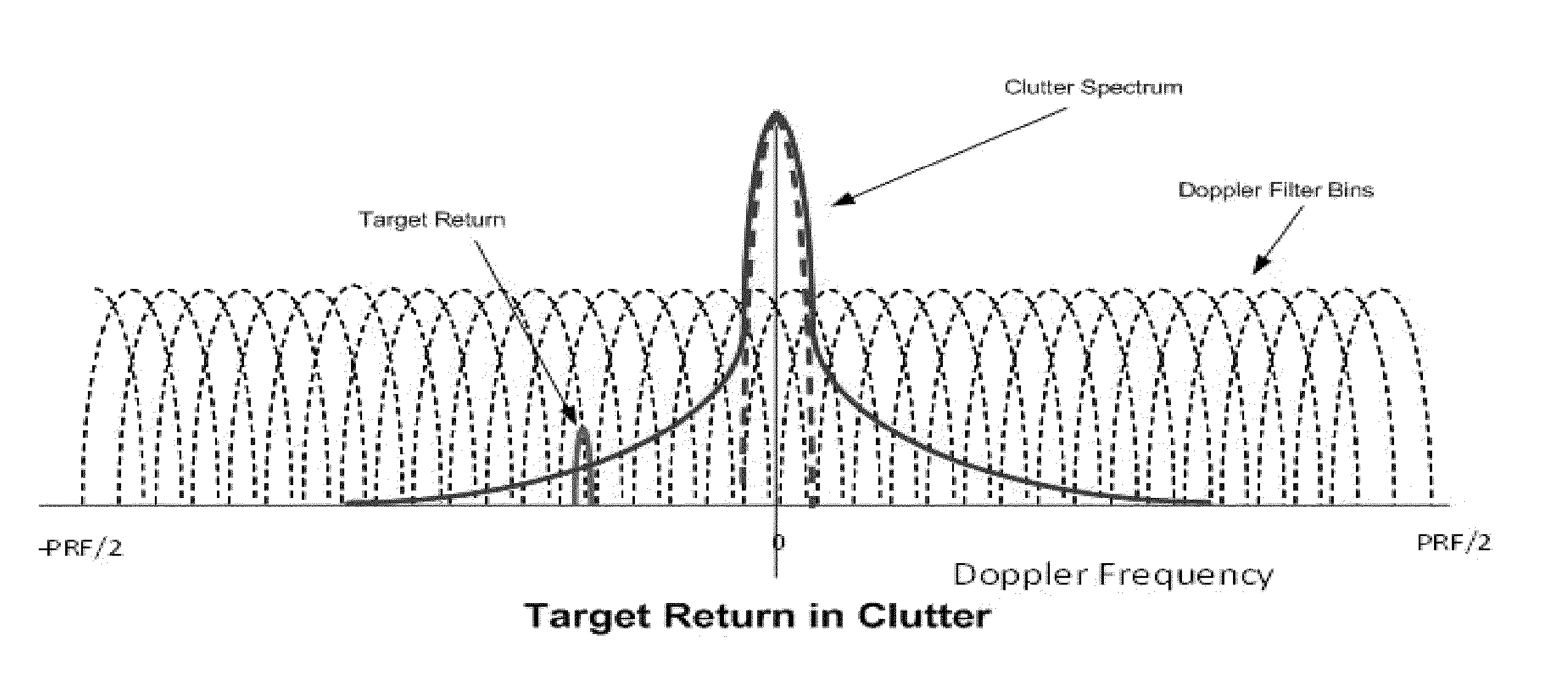
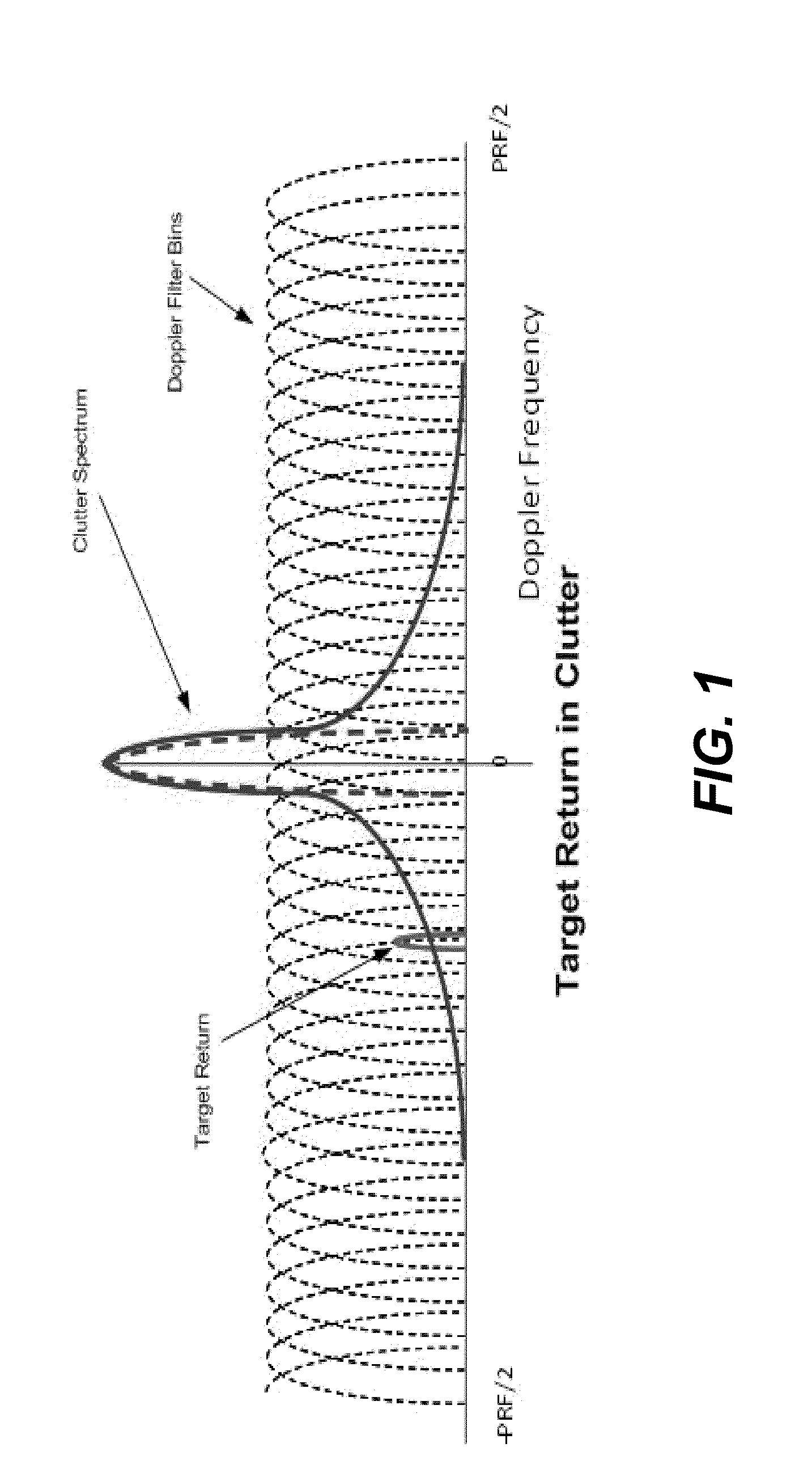
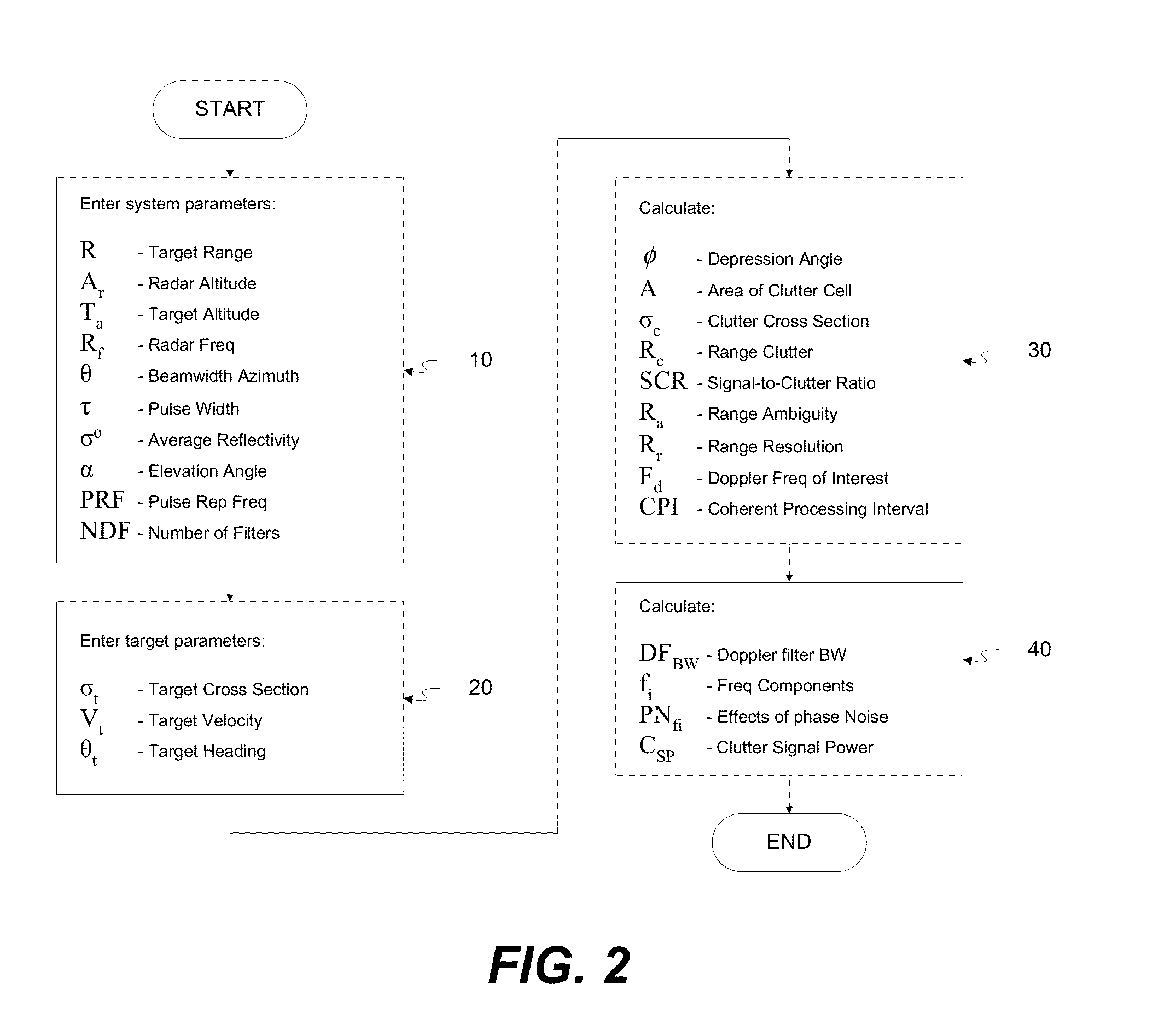
Phase noise simulation model for pulse doppler radar target detection
ActiveUS20160012164A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationPhase noiseRadar systems
Method for generating a model of the effect of phase noise during use of a Doppler radar system including calculating, using a processor, an initial signal-to-clutter ratio (SCR) representing a ratio of power received from echoes from a target by the radar system to power resulting from clutter reflection received by the radar system. The initially calculated SCR is modified as a function of a range ambiguity and range resolution. A Doppler frequency of interest is calculated based on velocity of a target, target heading and radar frequency, along with a Doppler filter bandwidth, frequency components and a measure of clutter signal passing through the Doppler filter of interest by summing products of the phase noise for each frequency by the Doppler filter bandwidth. This measure indicates effectiveness of target detection by the Doppler radar system as a function of distance.
Owner:ADVANCED TESTING TECH
Transceiver system implementation method for implementing digital phase shift and calibration with DDS (Direct Digital Synthesizer) as local oscillator
InactiveCN109031214APhase shifting is simple and feasibleLow priceWave based measurement systemsTransceiverMicrowave
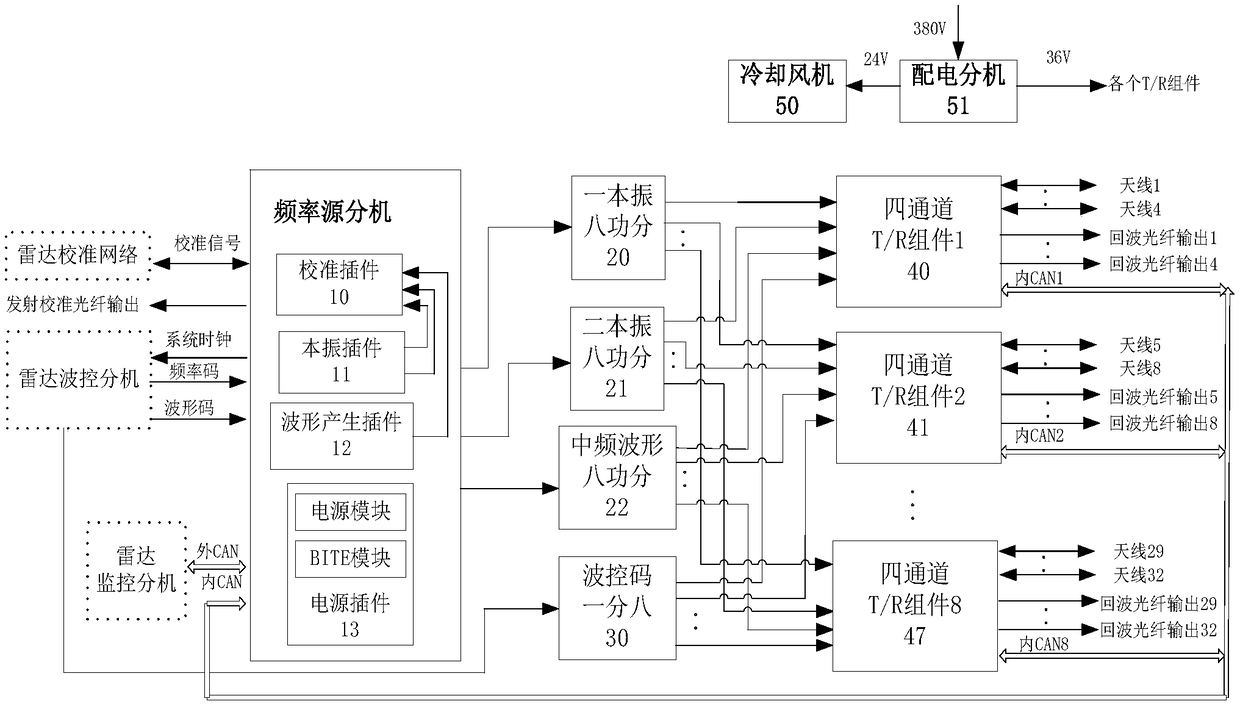
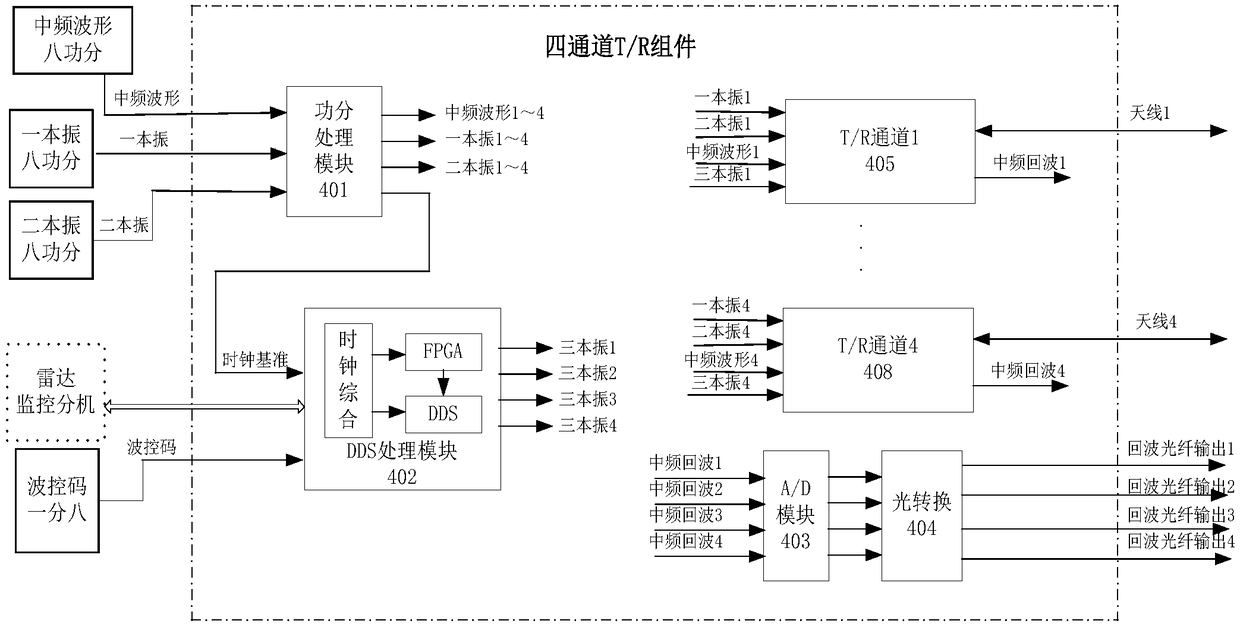
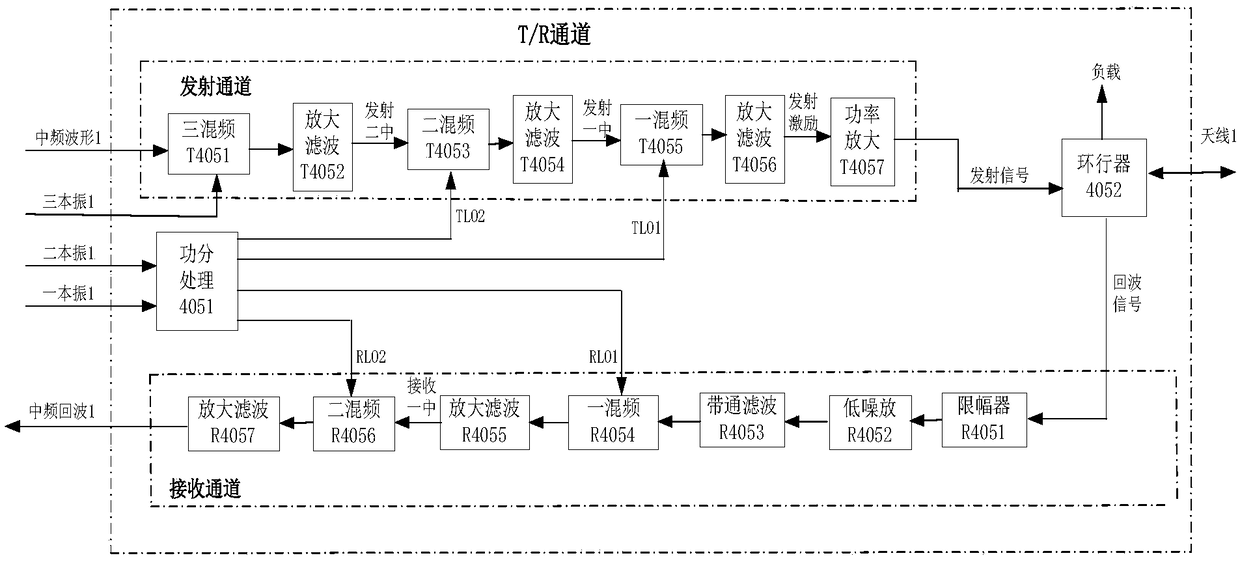
The invention belongs to the field of radar microwave transceiving, and especially relates to a transceiver system implementation method for implementing digital phase shift and calibration with a DDS(Direct Digital Synthesizer) as a local oscillator. The DDS generates four paths of outputs to each path of T / R channel used as a third local oscillator; a waveform generation plug-in of a radar frequency source extension generates an intermediate frequency waveform and then the intermediate frequency waveform is provided to eight four-channel T / R components through an eight-way power divider; afirst local oscillator and a second local oscillator generated by the radar frequency source extension are sent to eight four-channel T / R components through the eight-way power divider; a single DDS processing module can carry out phase shift on four transmitting channels at the same time; and when a radar works in a transmission calibration mode, a calibration plug-in receives and processes signals sent by a calibration network and converts the signals into optical fiber signals to be output. The transceiver system implementation method for implementing the digital phase shift and calibrationwith the DDS as the local oscillator provided by the invention fully utilizes the advantages that DDS phase shift is simple and feasible, large in number of bits, high in precision, lower in price, small in size, multiple in channels and the like, and overcomes the problems that a traditional digital phase shifter is high in price, limited in the number of bits, low in integration level, large inweight and each channel needs a phase shifter.
Owner:WUHAN BINHU ELECTRONICS
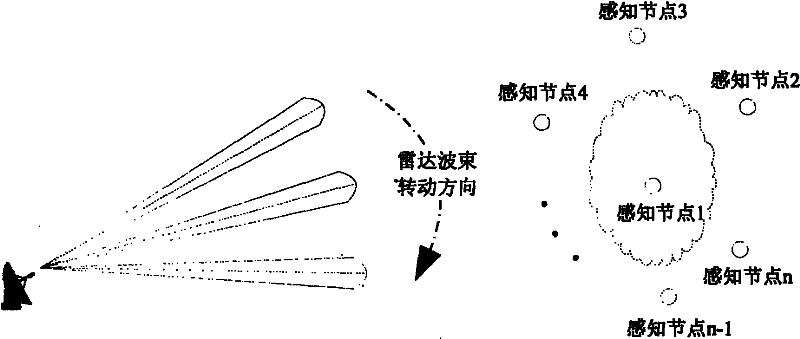
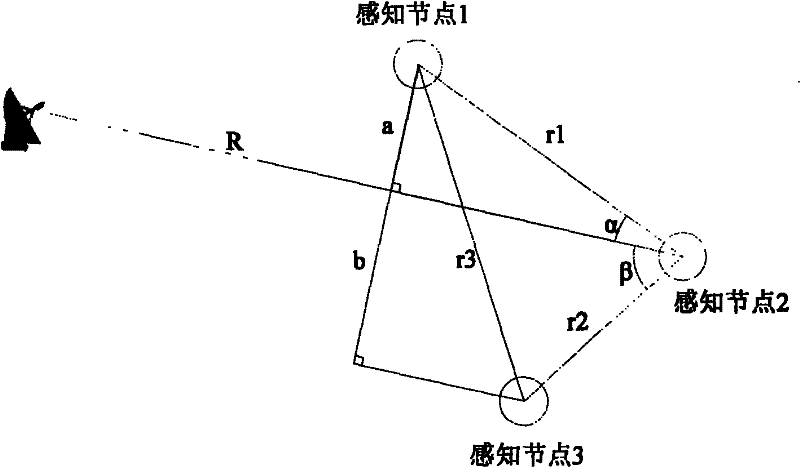
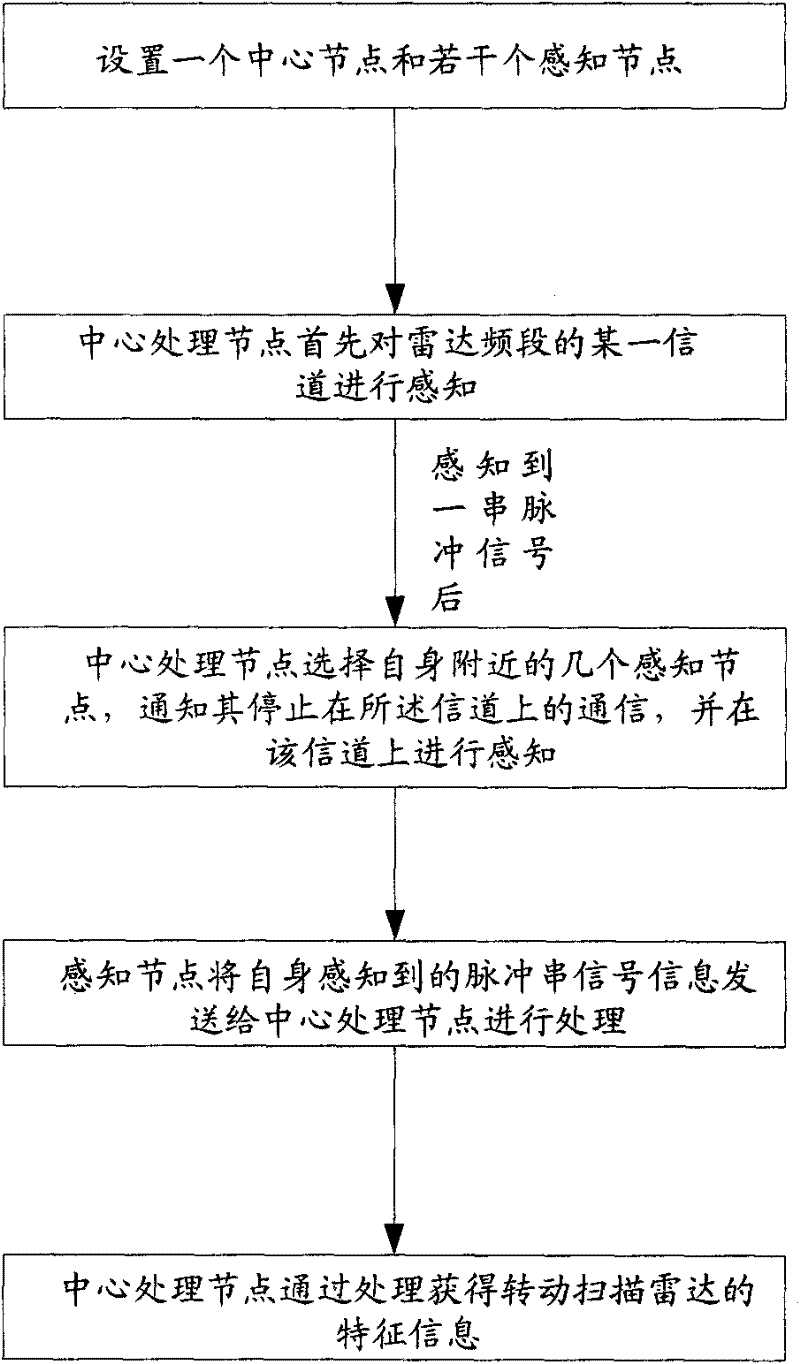
Method for efficiently cooperatively sensing rotation scanning radar signals and system thereof
InactiveCN102223186AReasonable sharingEfficient sharingTransmission monitoringNetwork planningCommunications systemPrior information
The invention discloses a method for efficiently cooperatively sensing rotation scanning radar signals and a system thereof. The method includes the following steps: step 1, a center processing node and several sensing nodes are arranged; step 2, the center processing node selects some sensing nodes to sense a channel of a radar frequency band so as to obtain a sensing result; step 3, the center processing node processes the sensing result so as to obtain characteristic information of the rotation scanning radar. By using the method, the rotation scanning radar can be accurately identified; scanning direction of the rotation scanning radar can be confirmed in less than a scanning period time; corresponding parameters of the sensed radar, such as the scanning cycle, a location and the like, can be further confirmed in less than two scanning period time. Prior information is not needed to be known. Sensing time is short, efficiency is high and reliability is strong. Secondary communication system can reasonably and efficiently share the radar frequency band. Interference on radar radio determination business can be avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS COMM
Broadband automotive radar microstrip patch antenna
ActiveCN109713444AEasy to moveStrong penetrating powerAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip patch antennaIsoetes triquetra
The invention provides a broadband automotive radar microstrip patch antenna. The broadband automotive radar microstrip patch antenna is formed by sequentially connecting a top radiation metal patch layer, an intermediate dielectric substrate and a bottom grounding plate metal patch layer. The top radiation metal patch layer is integrally square. Firstly, a square slot is dug out of an external square patch, and then two or more than two groups of nested patterns with round patches dug out are added into the square slot. Finally, a hexagonal patch with an equilateral triangle dug out is addedinto the center of the nested patterns. The bottom grounding plate metal patch layer is a combination of rectangular patches with different sizes. The frequency band range of the antenna is 22-60 GHz.The relative working bandwidth of the antenna is close to 100%, and the working bandwidth of the antenna completely covers a ka wave band and a U wave band. The working requirement in the radar frequency band range of automobiles is met. Meanwhile the antenna has the advantages of small size, low profile and easy integration. The antenna is suitable for a modern wireless communication system working in above frequency bands.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com