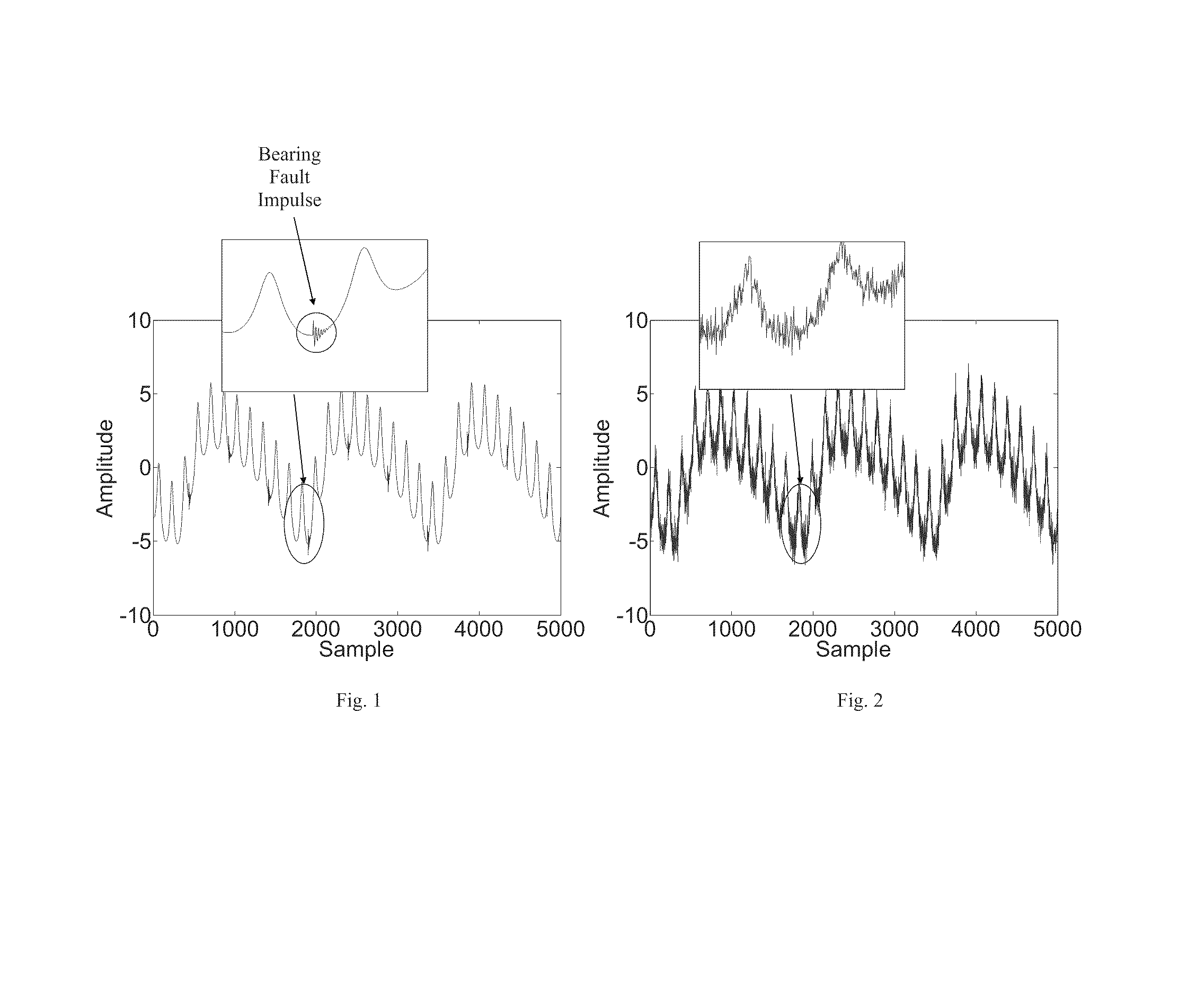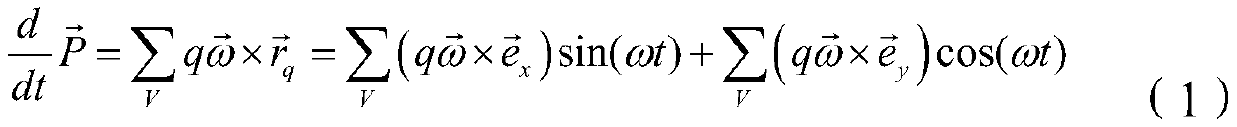Patents
Literature
182 results about "Frequency demodulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
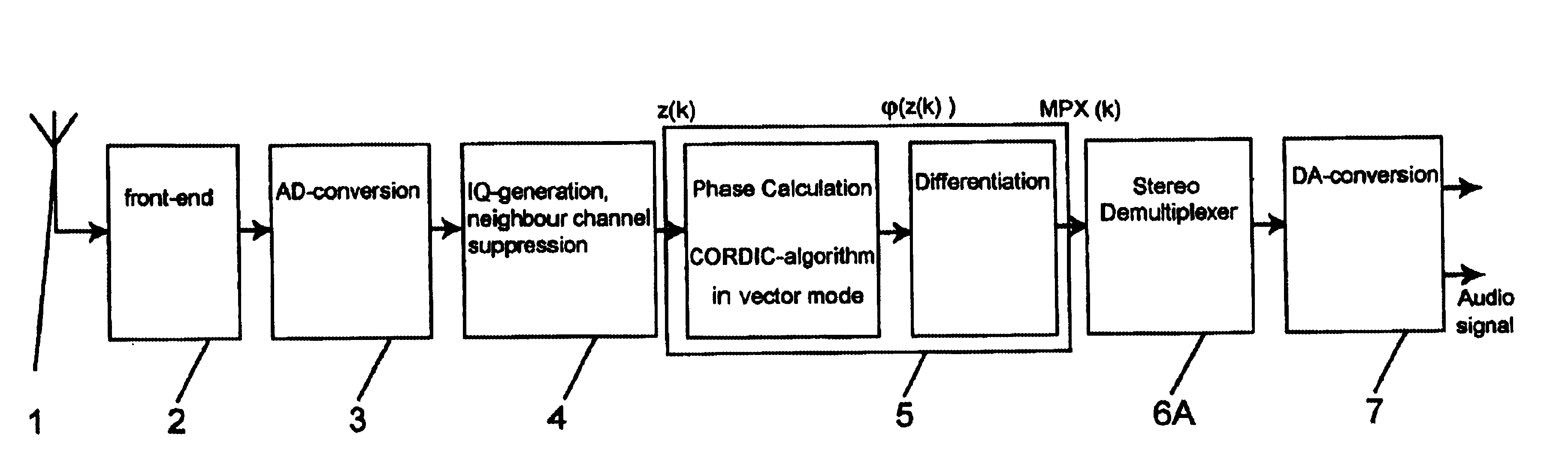
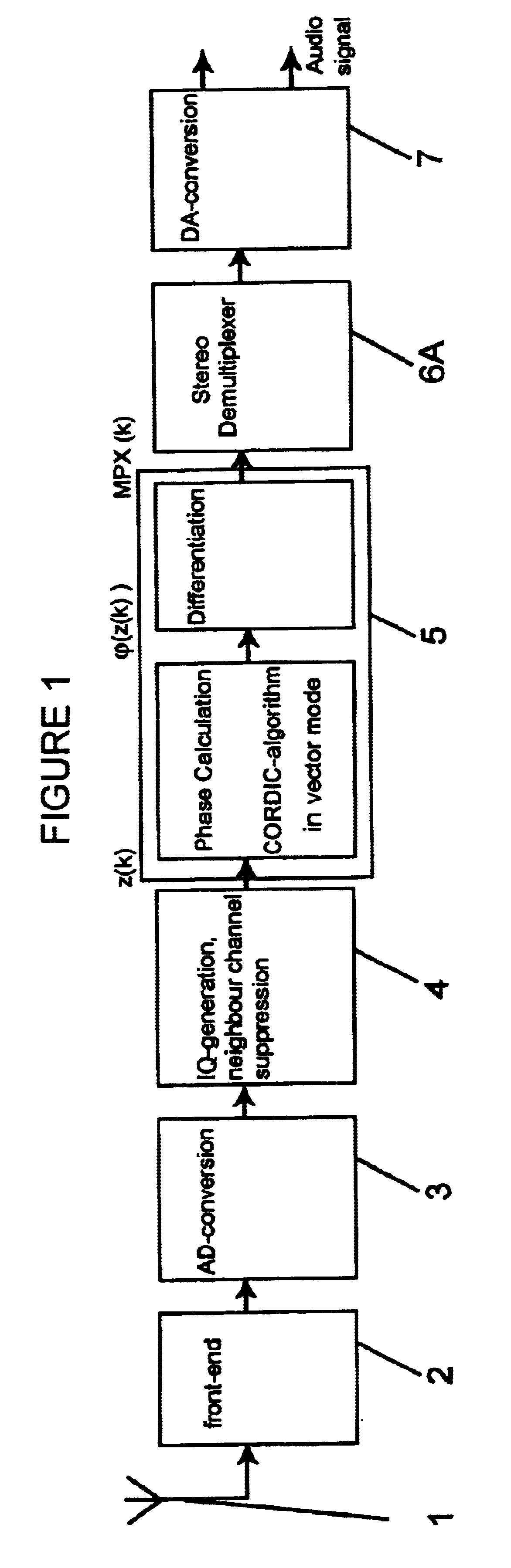
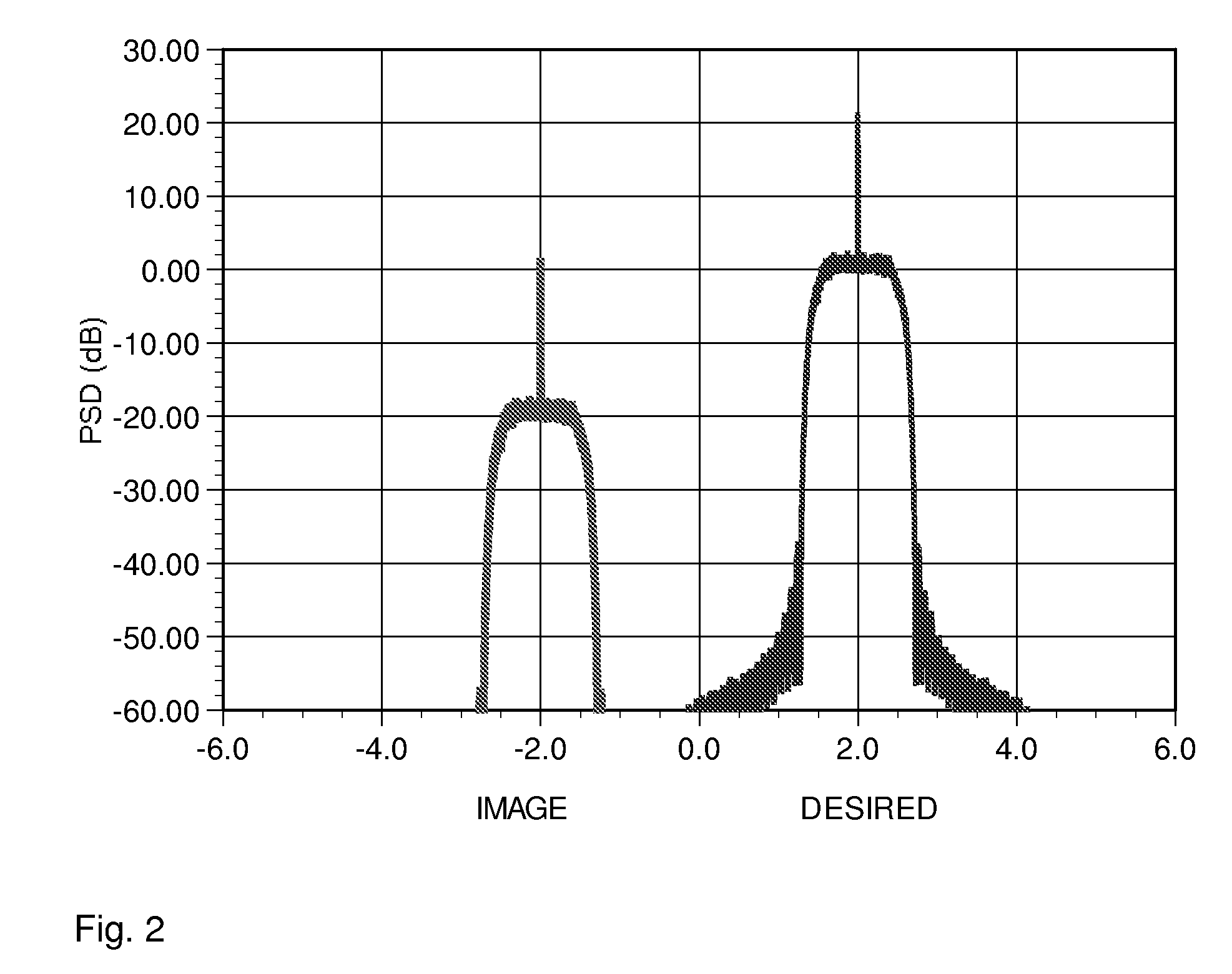
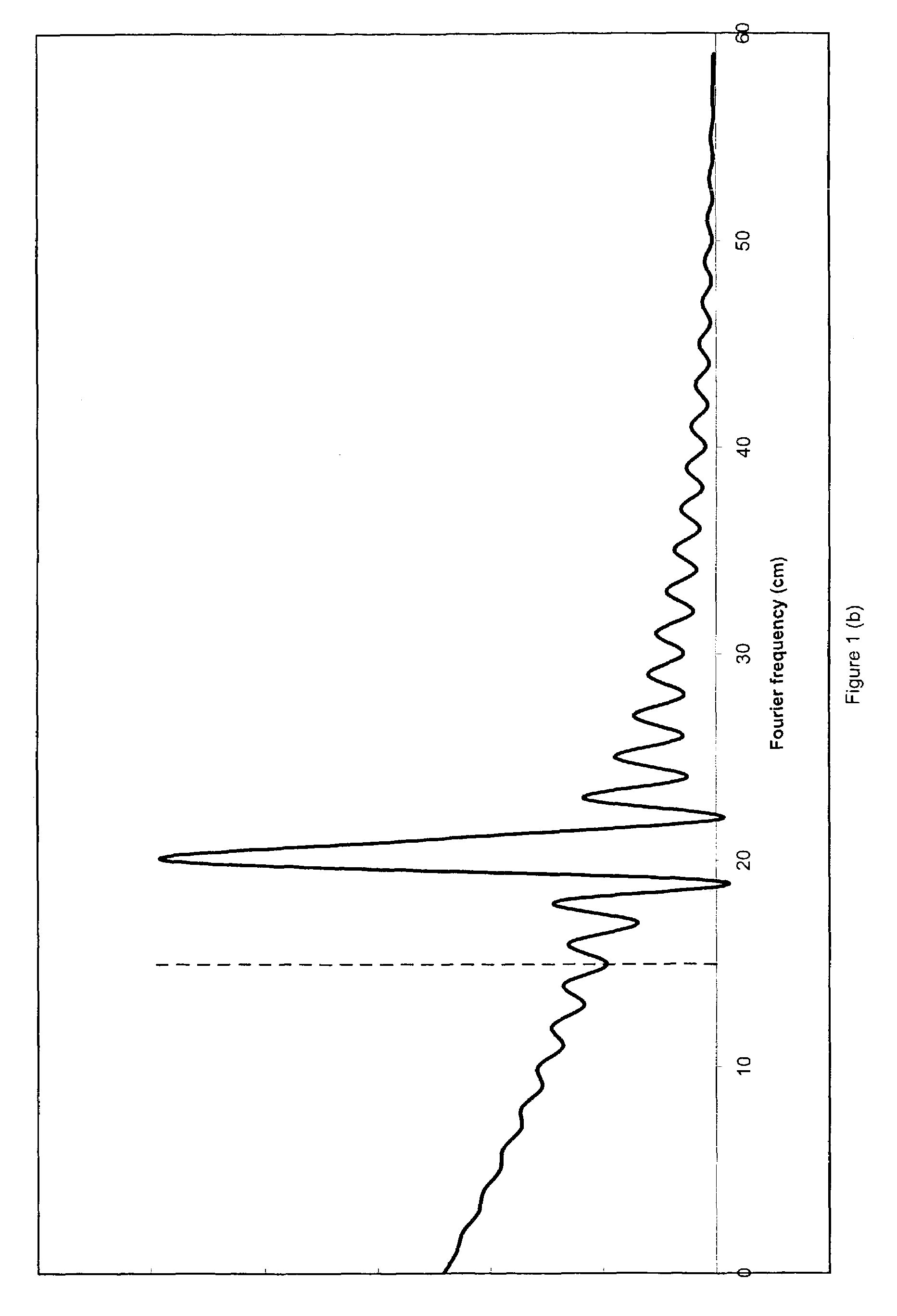
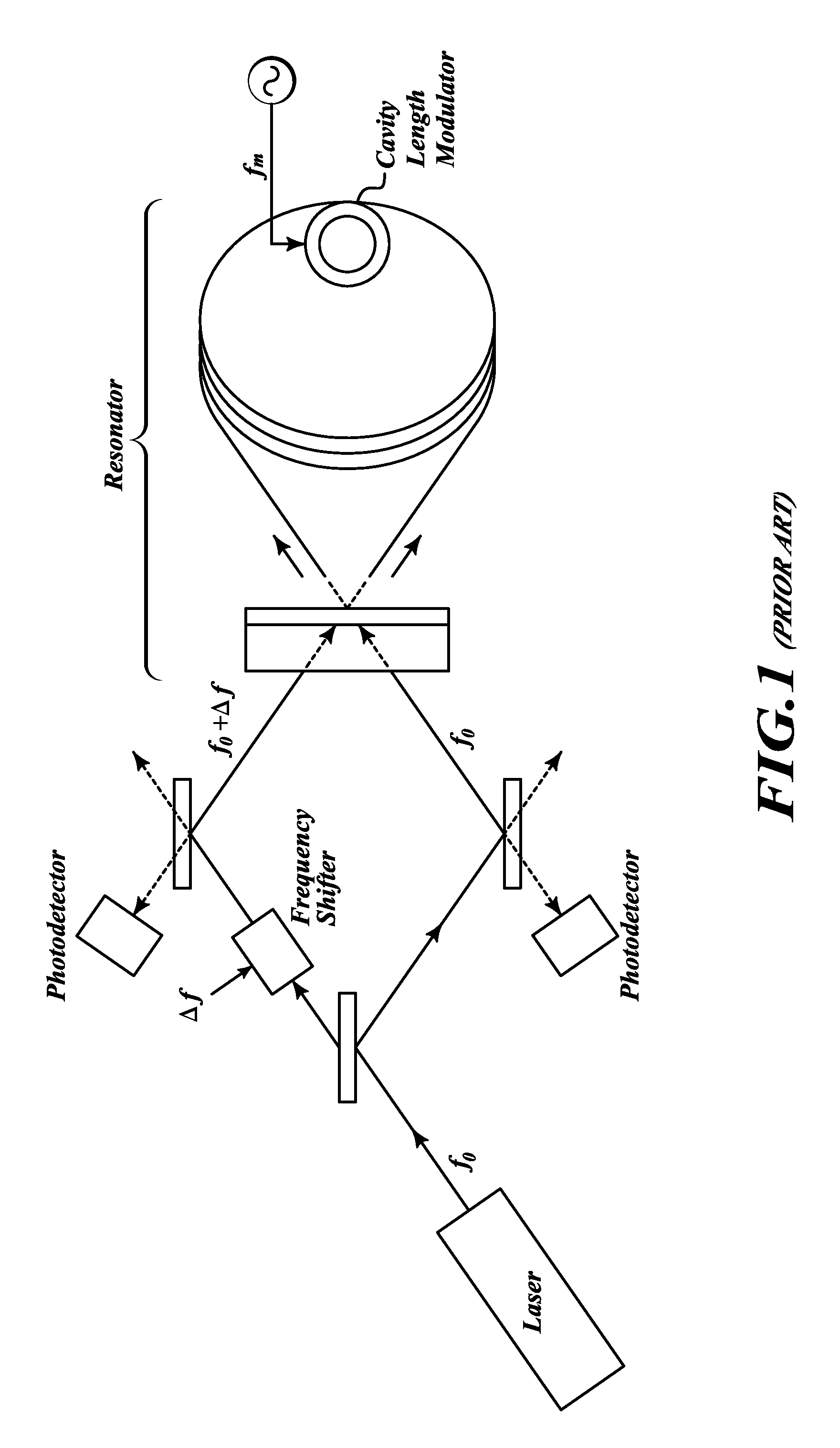
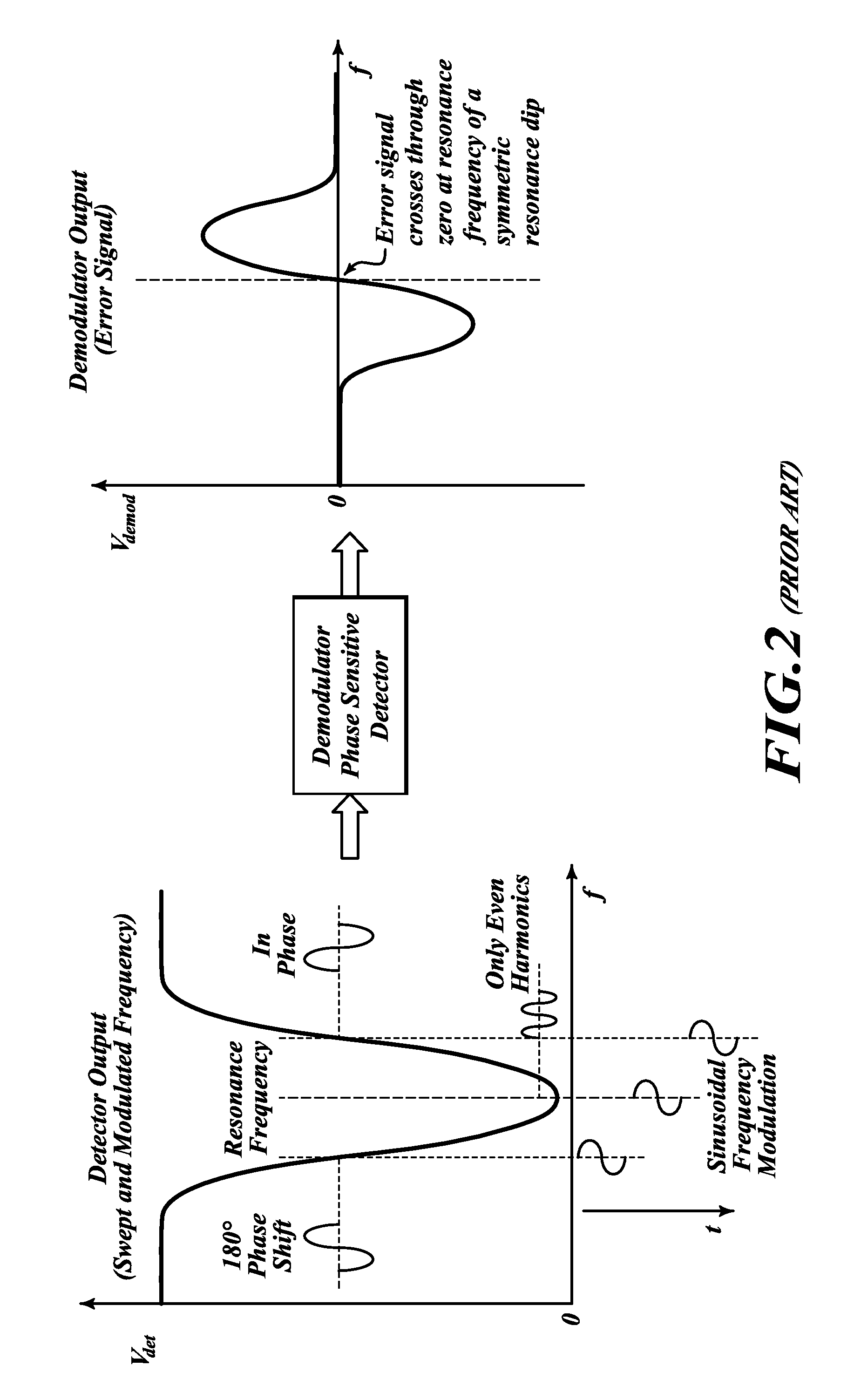
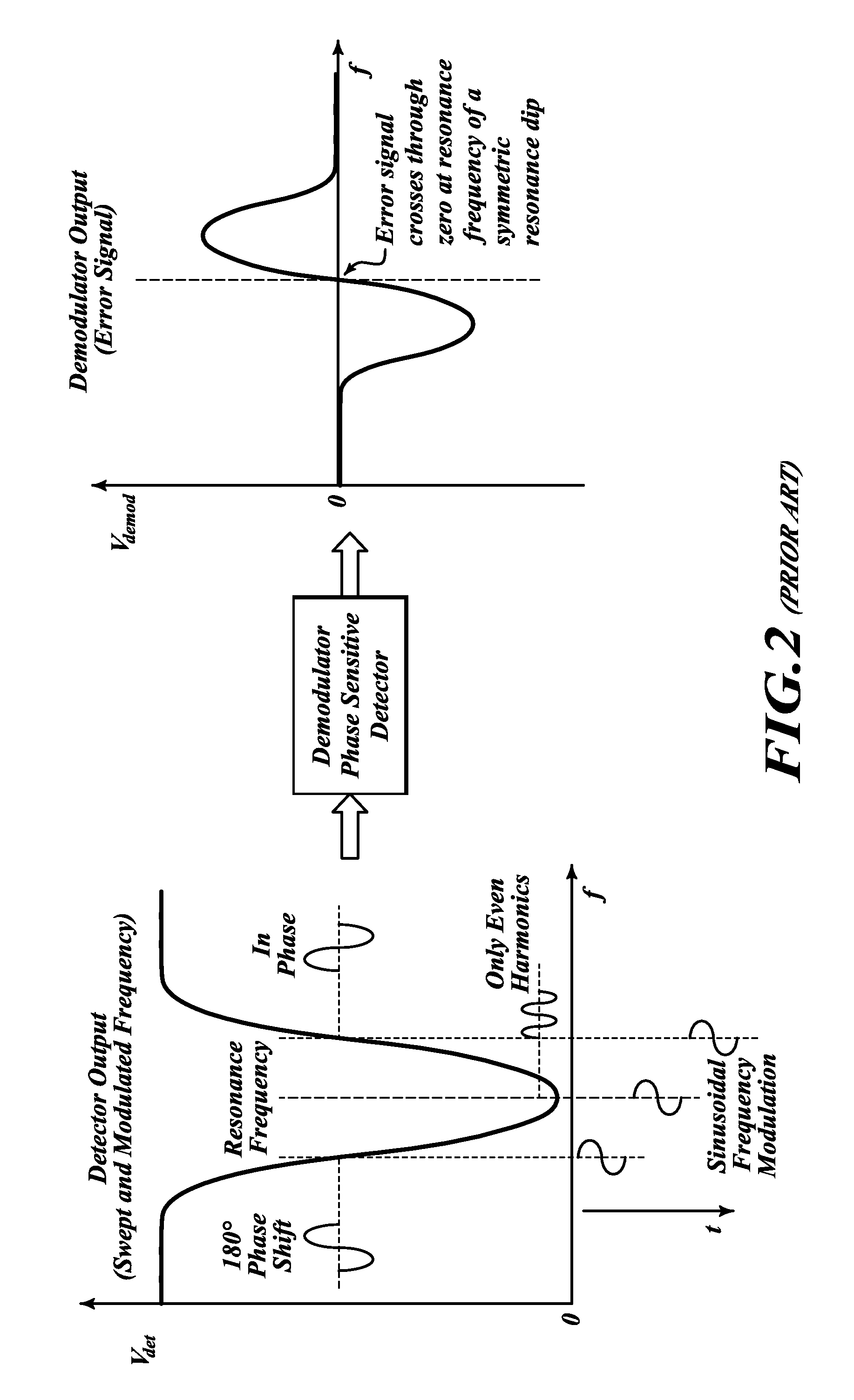
Frequency demodulation or detection can be obtained directly by using the PLL circuit. When the centre frequency of the PLL is selected or designed at the FM carrier frequency, the filtered or output voltage in the circuit shown in figure, is obviously the desired demodulated voltage, that varies in magnitude in proportion to the signal frequency.
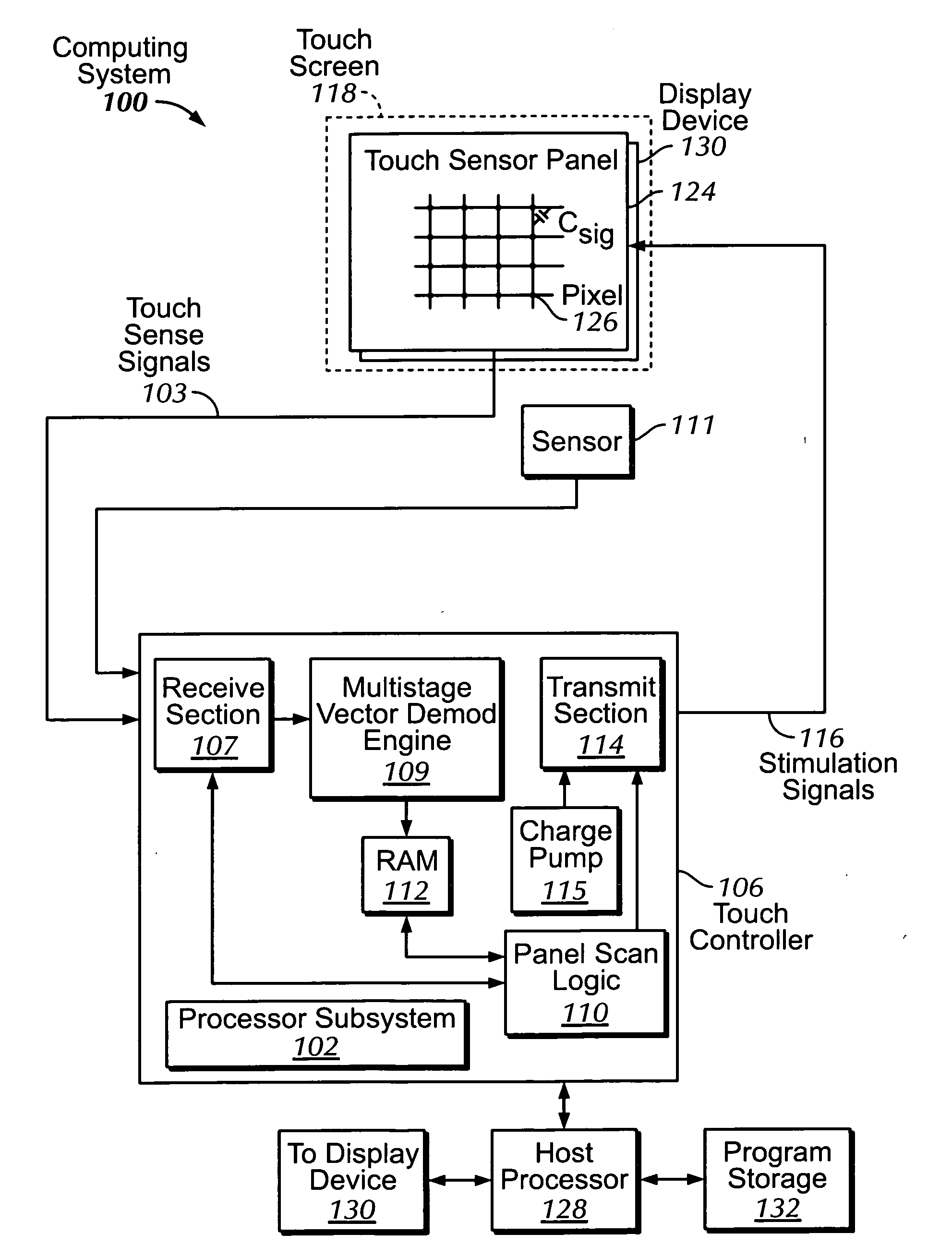
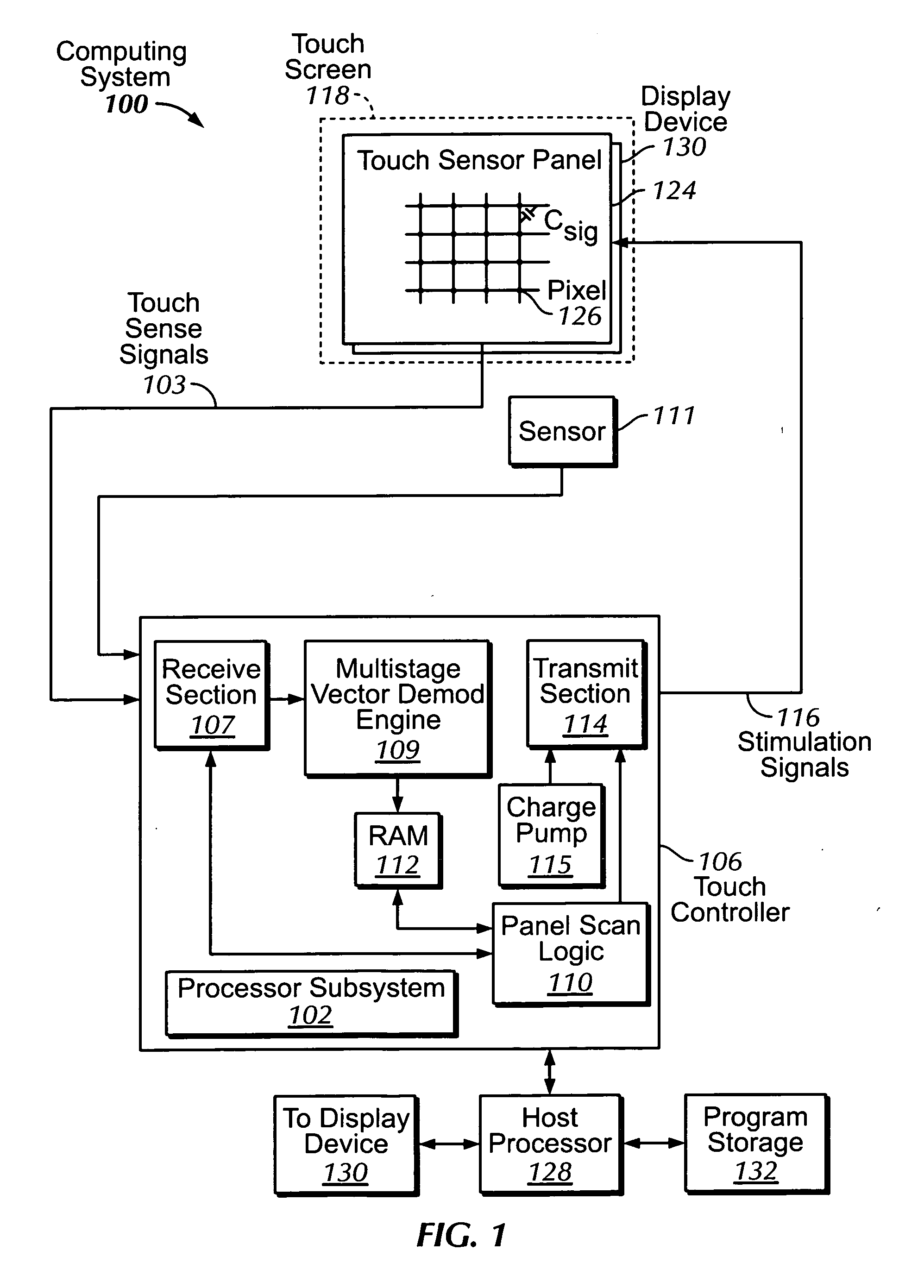
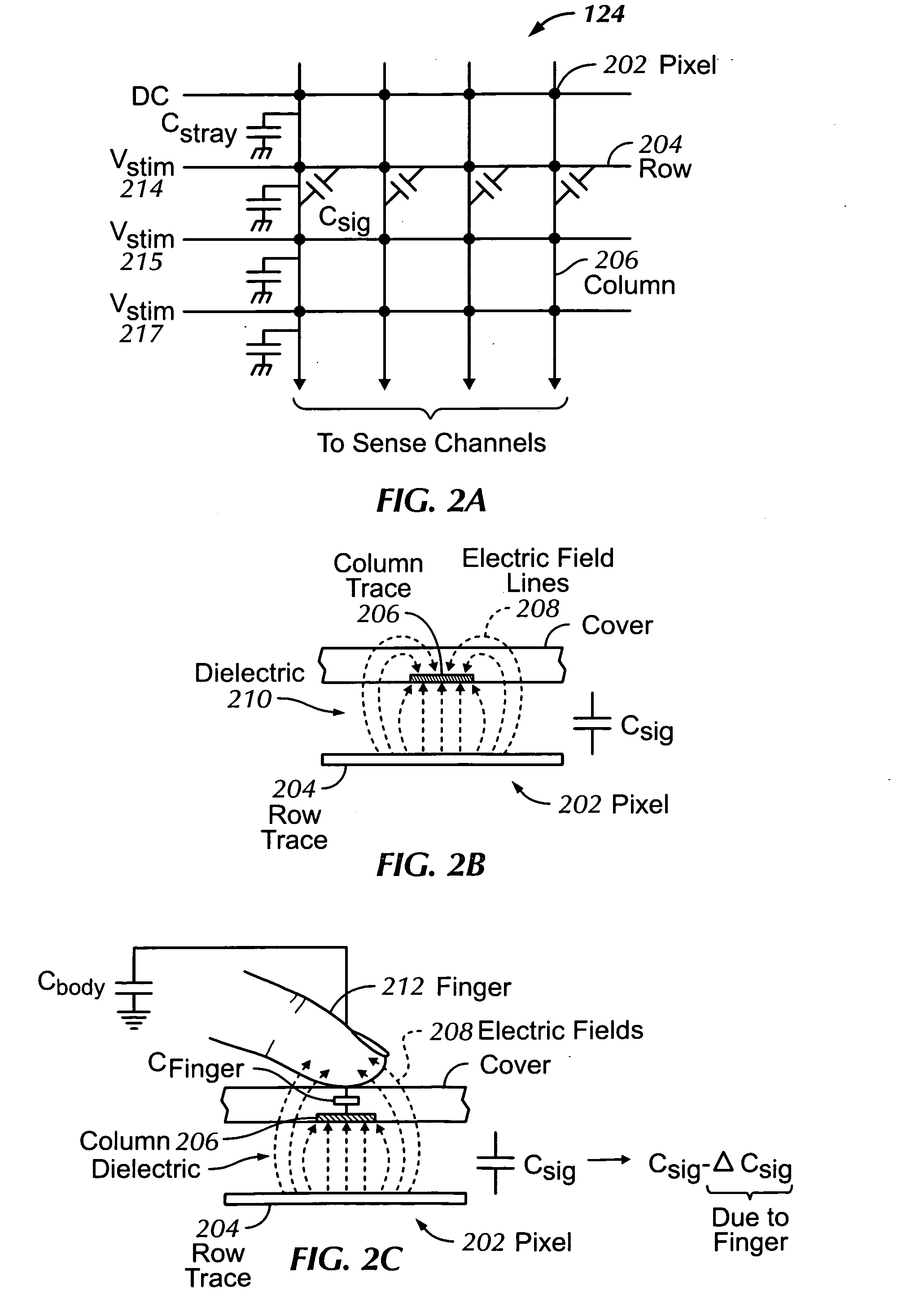
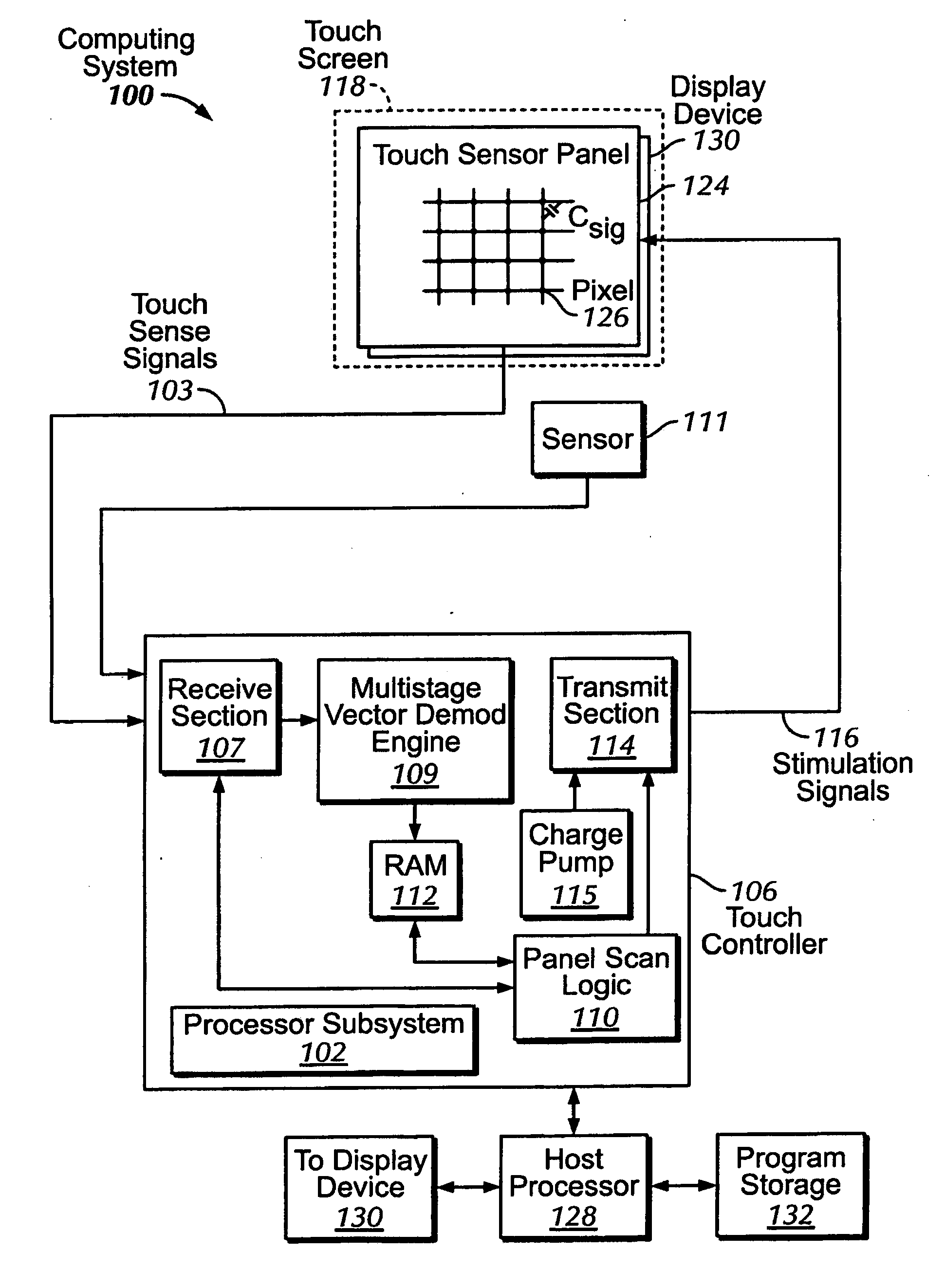
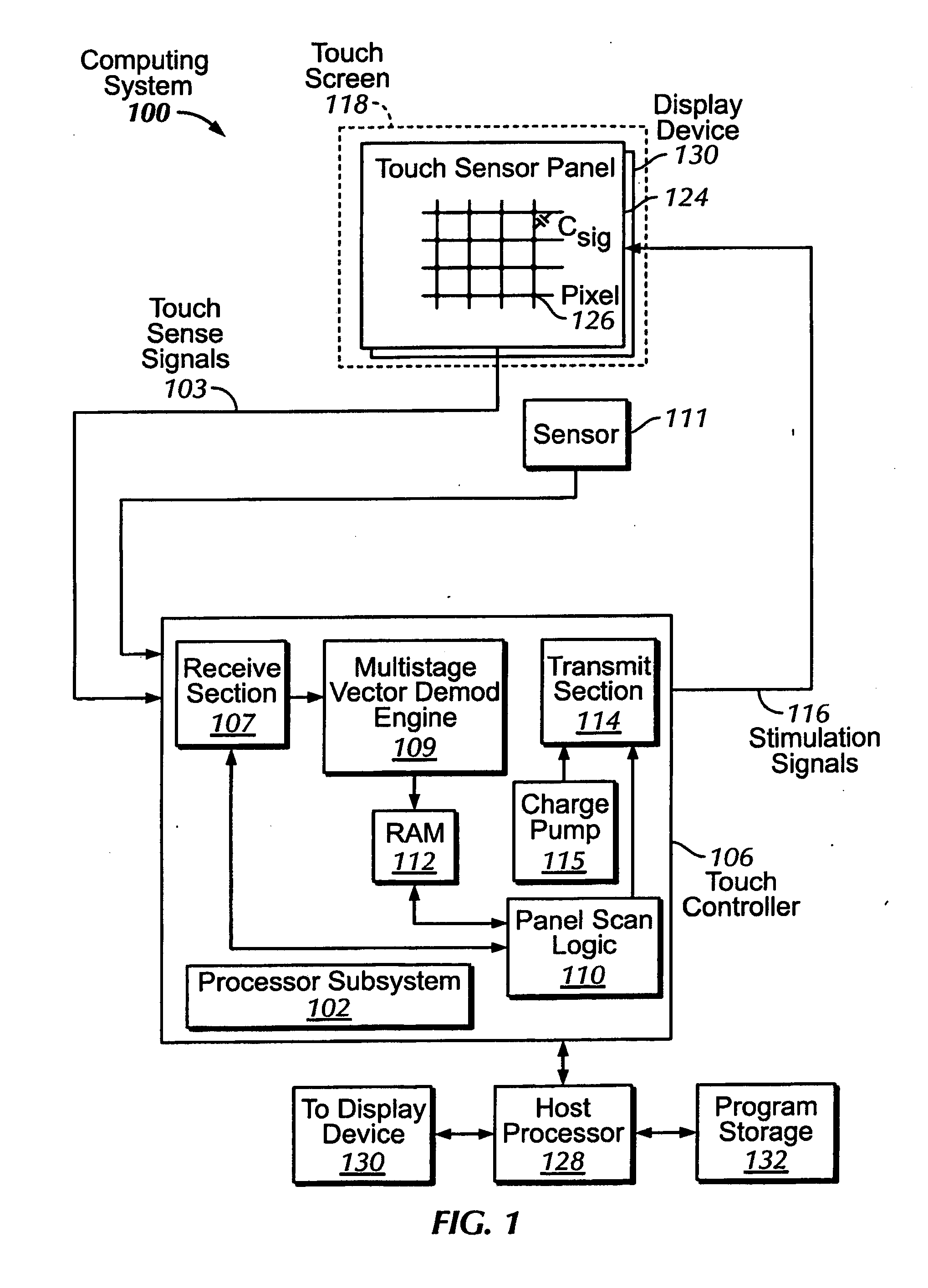
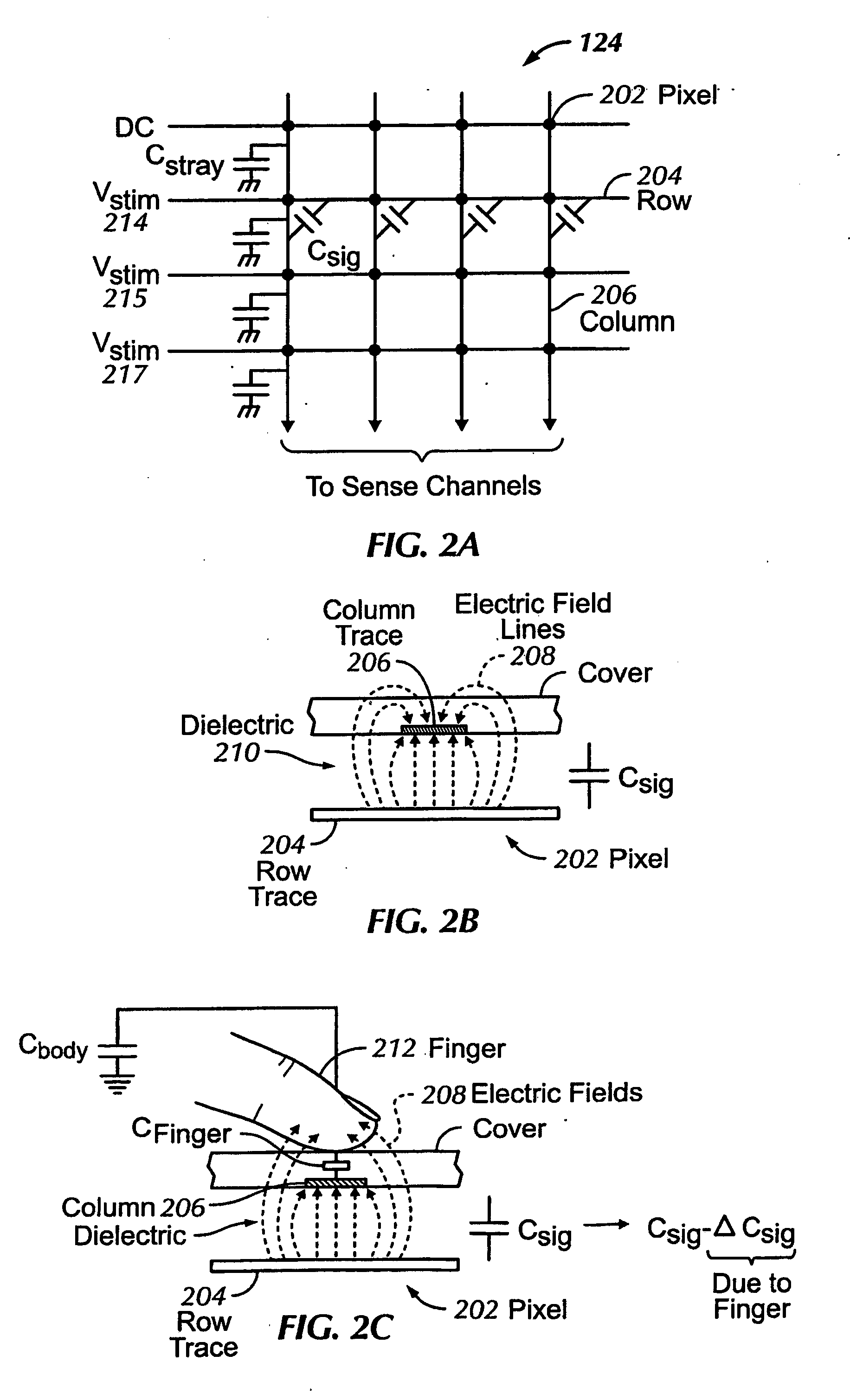
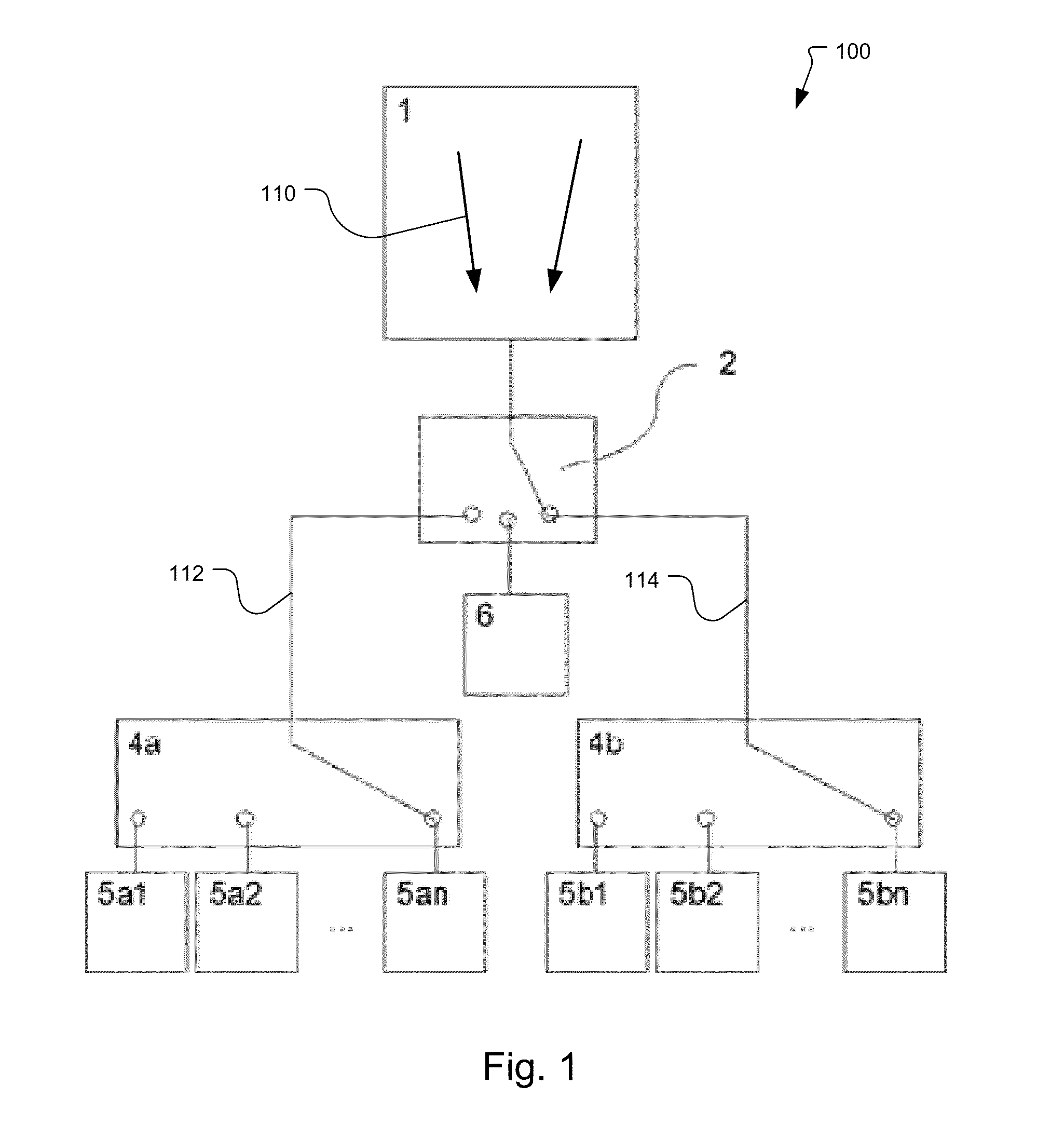
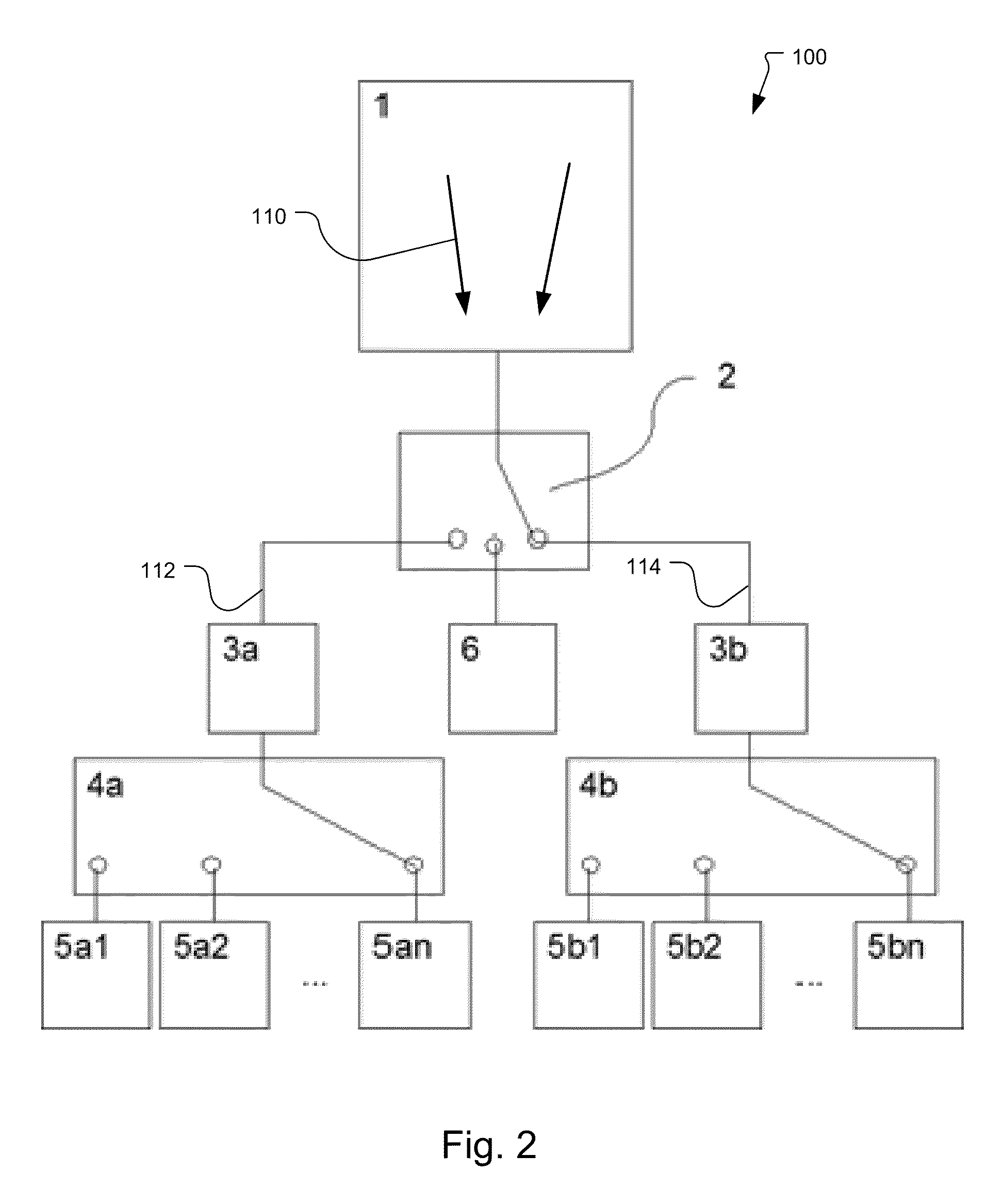
Single-chip multi-stimulus sensor controller
ActiveUS20100059295A1Transmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsSingle chipFrequency demodulation
A multi-stimulus controller for a multi-touch sensor is formed on a single integrated circuit (single-chip). The multi-stimulus controller includes a transmit oscillator, a transmit signal section that generates a plurality of drive signals based on a frequency of the transmit oscillator, a plurality of transmit channels that transmit the drive signals simultaneously to drive the multi-touch sensor, a receive channel that receives a sense signal resulting from the driving of the multi-touch sensor, a receive oscillator, and a demodulation section that demodulates the received sense signal based on a frequency of the receive oscillator to obtain sensing results, the demodulation section including a demodulator and a vector operator.
Owner:APPLE INC
Broadcast receiver
InactiveUS6640093B1Realize cost reductionLow costTelevision system detailsError preventionEngineeringDigital control
A receiver for broadcast signals, e.g. DAB, FM, DVB, and digital or analog short-wave RF broadcast signals according to the present invention includes a polyfunctional circuit (5) that can be switched into three modes and performs the digital frequency demodulation which is needed for the reception of a frequency modulated signal in a first mode A, a digital frequency adjustment of the receiver in case of the reception of a digital or analog modulated broadcast signal like DAB, DVB, DRM or AM in a second mode B and the digital frequency adjustment and the digital gain control of the receiver which is needed in case of the reception of a digitally modulated broadcast signal like DAB, DVB, DRM in a third mode C. Depending on the needed functionality not all of these modes need to be realized. Nevertheless, the same hardware will be used for different purposes although the circuit is realized with an optimized amount of hardware to realize an efficient receiver.
Owner:SONY INT (EURO) GMBH
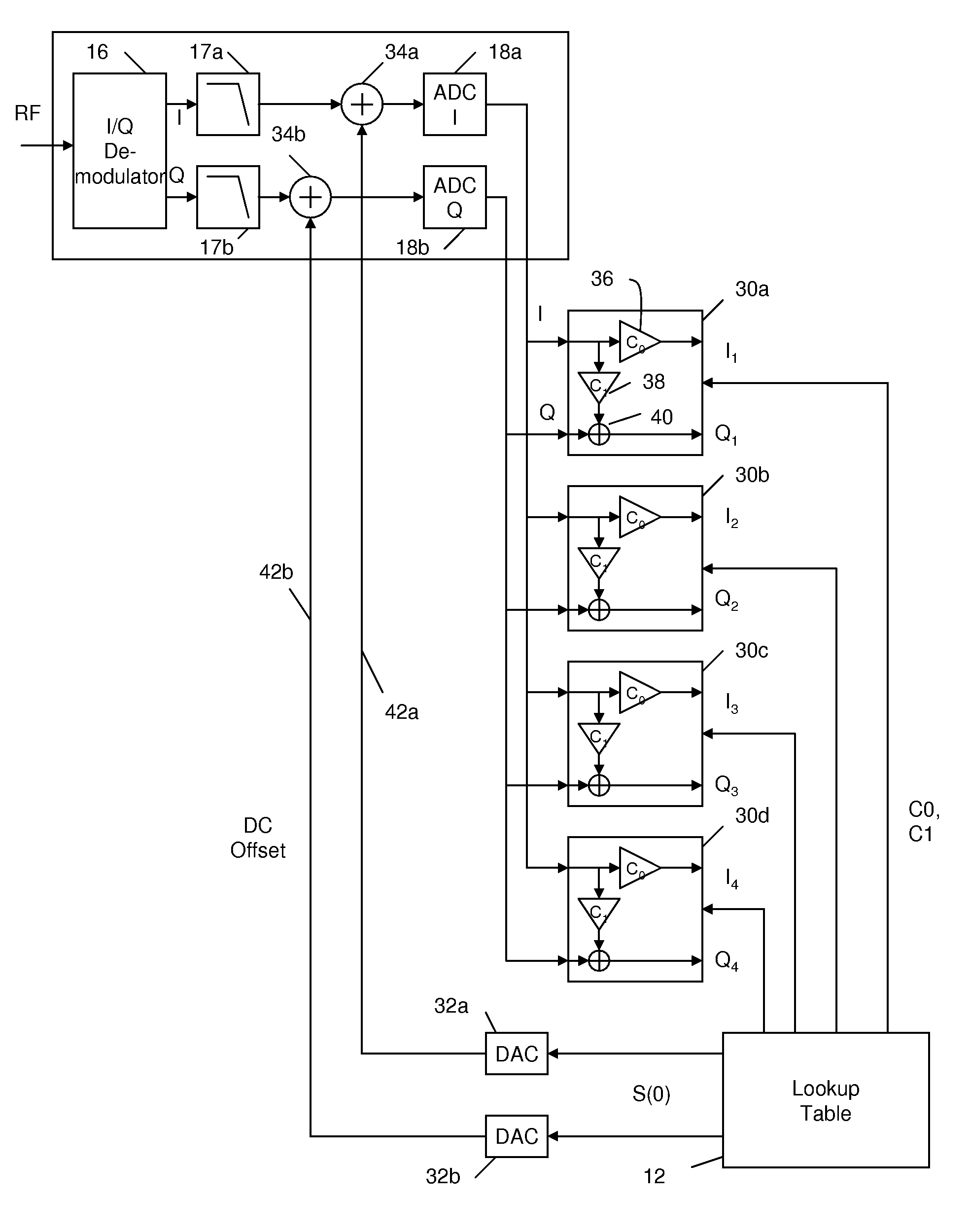
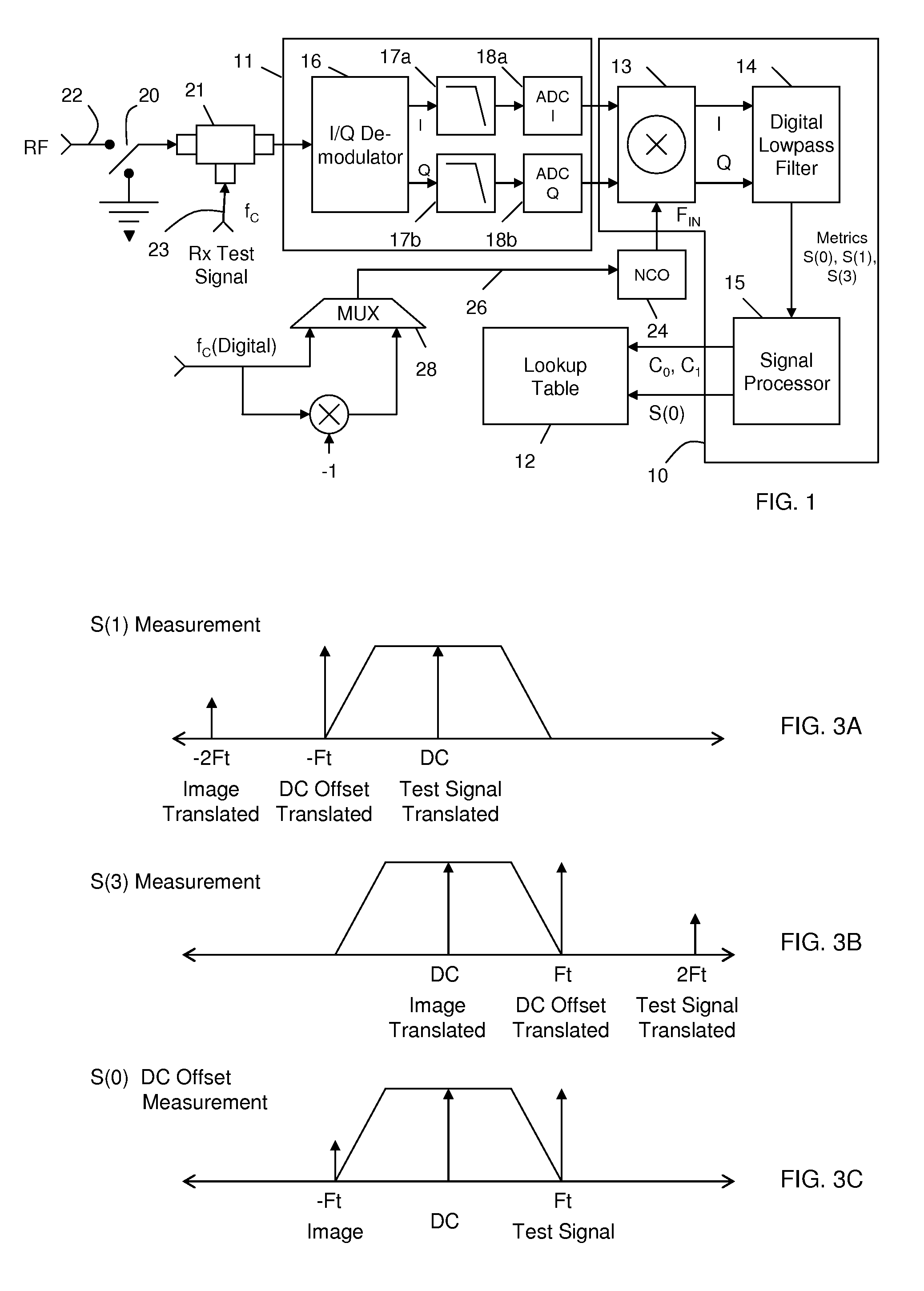
Receiver and transmitter calibration to compensate for frequency dependent I/Q imbalance
A receiver, which is adapted for demodulating signal carriers at variable frequencies to provide received signals at a plurality of different received frequencies, is calibrated to compensate for a frequency-dependent imbalance in the amplitude and / or the quadrature phase of analog in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) received-signal components that have passed through receiver circuit paths that may cause such imbalance. I-channel and Q-channel Rx-correction coefficients for each of a plurality of different calibration frequencies are estimated and stored in a lookup table. Rx-correction coefficients for a calibration frequency or frequencies that are the same as or closest to the received frequency or frequencies are accessed from the lookup table and combined with digital I and Q components of received signals that have been provided by analog-to-digital conversion of analog I and Q components of received signals that have passed through the imbalance-causing receiver circuit paths upon demodulation at the received frequency.
Owner:L 3 COMM TITAN CORP +1
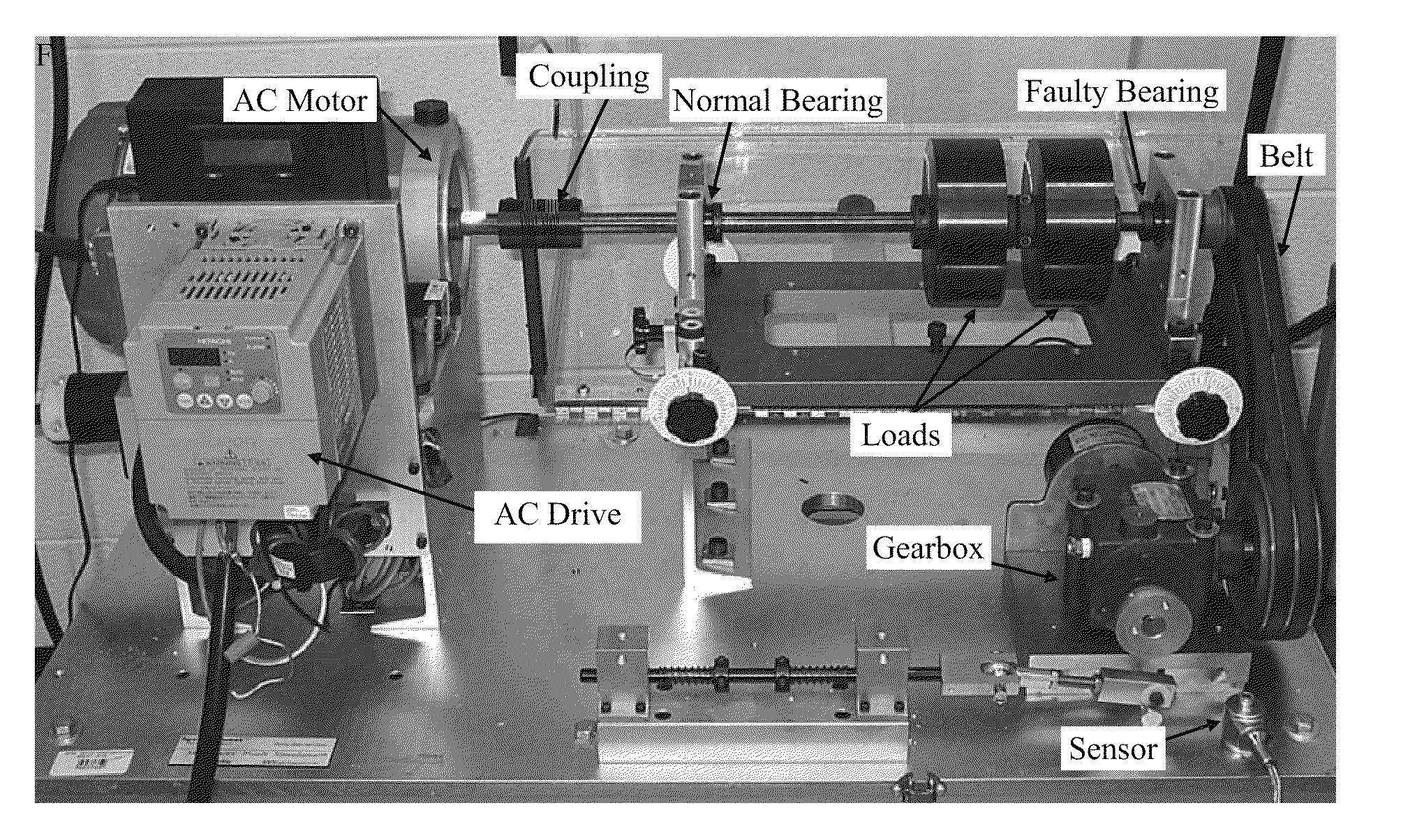
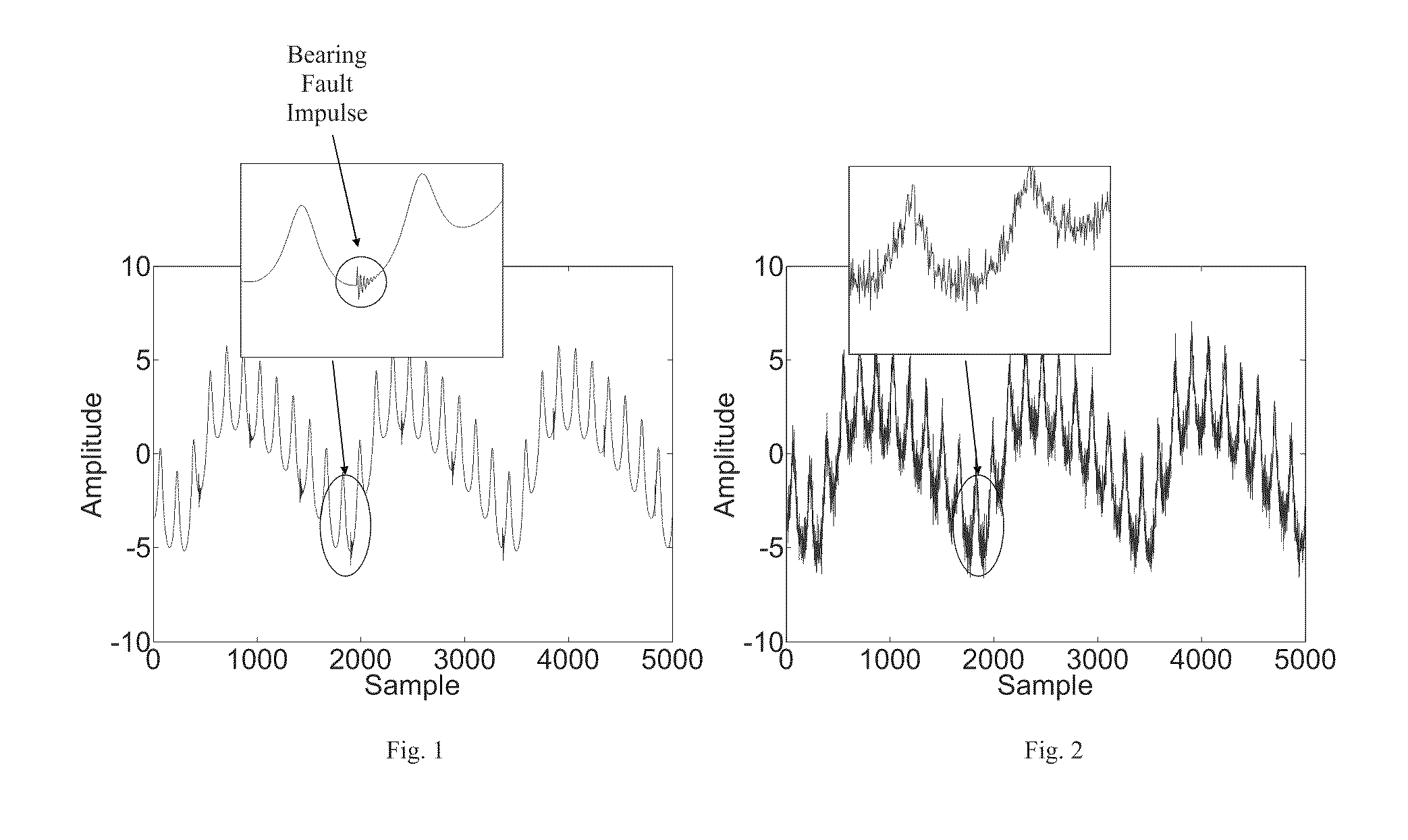
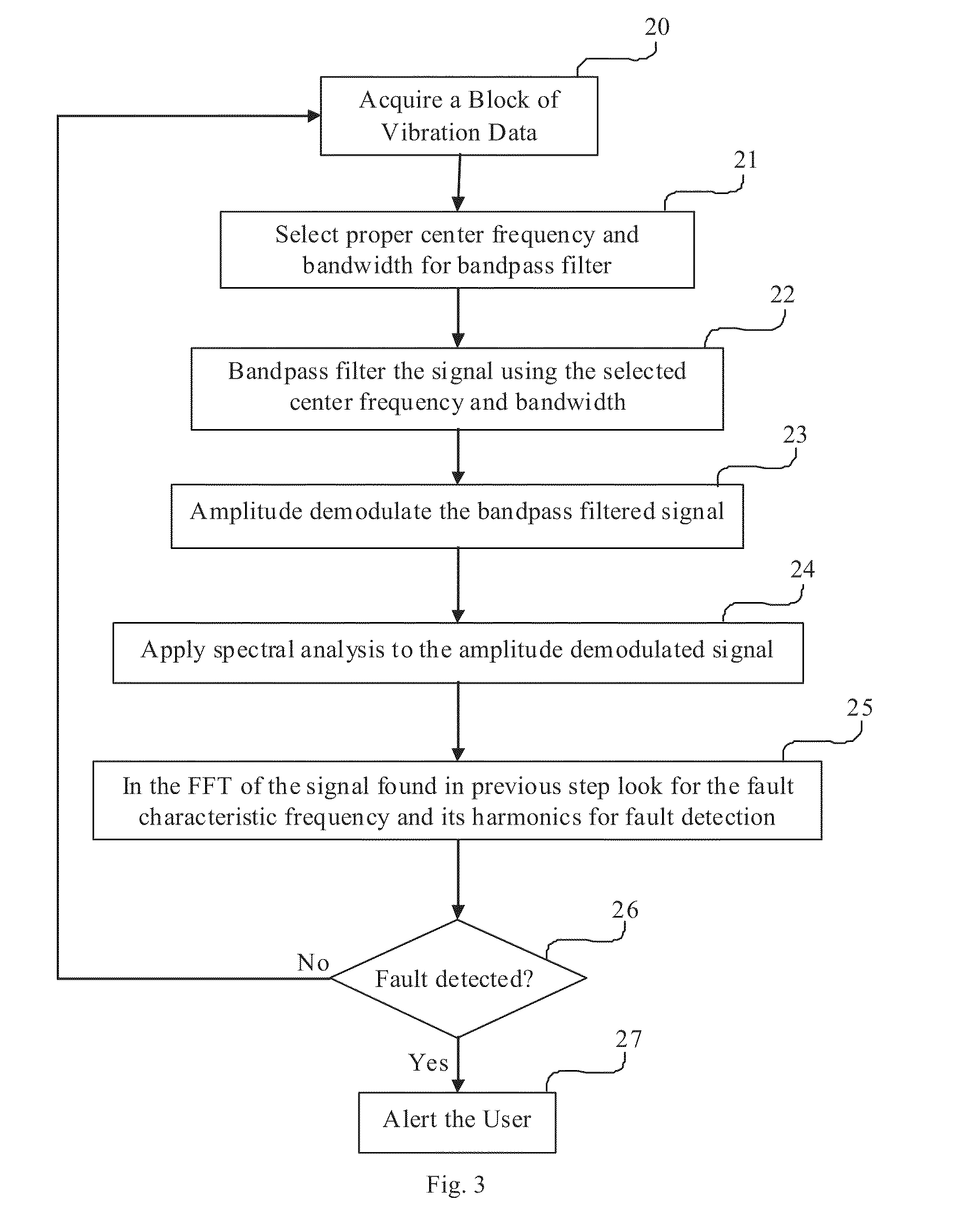
Parameter independent detection of rotating machinery faults
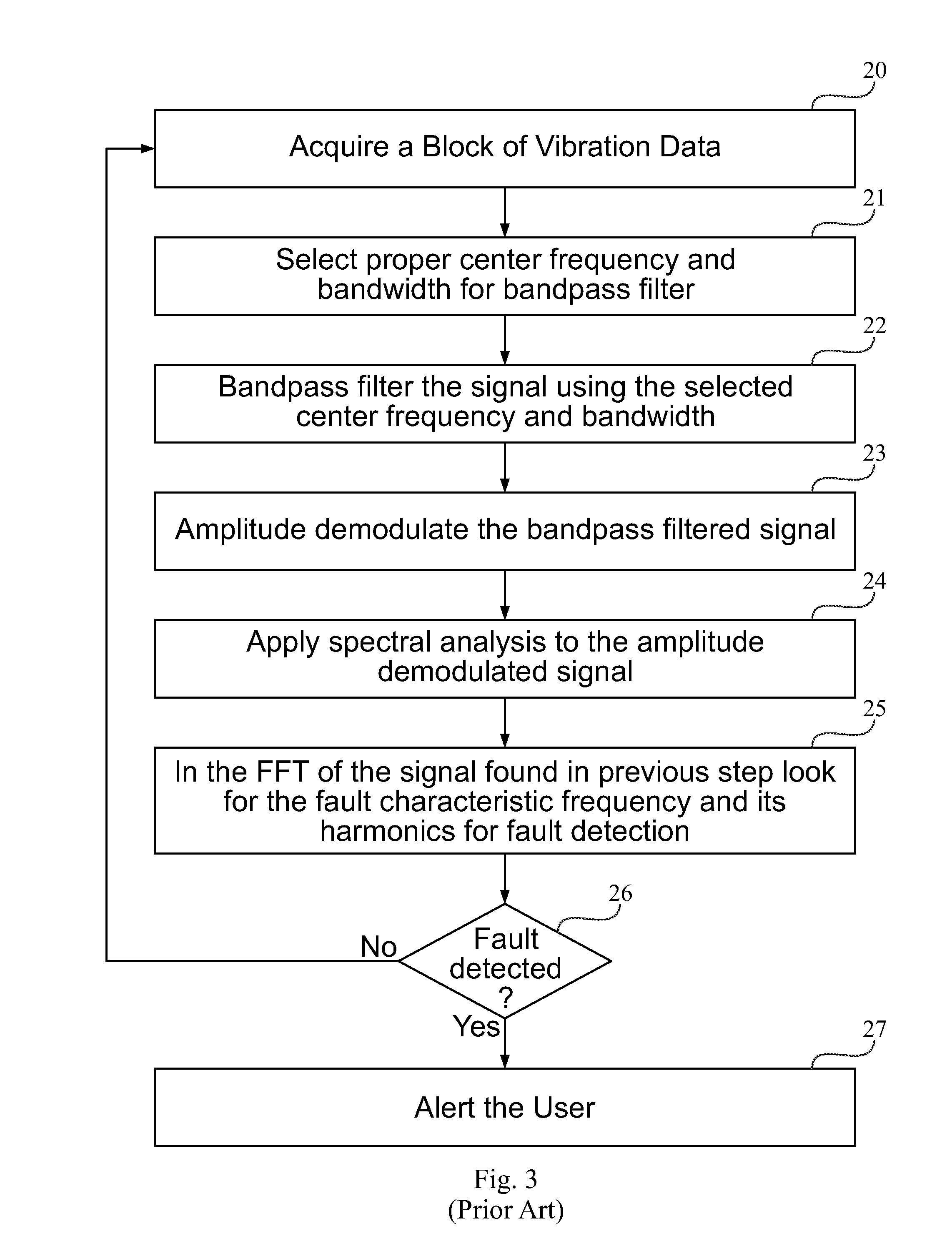
InactiveUS20100139403A1Efficient implementationVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingMechanical componentsAmplitude demodulation
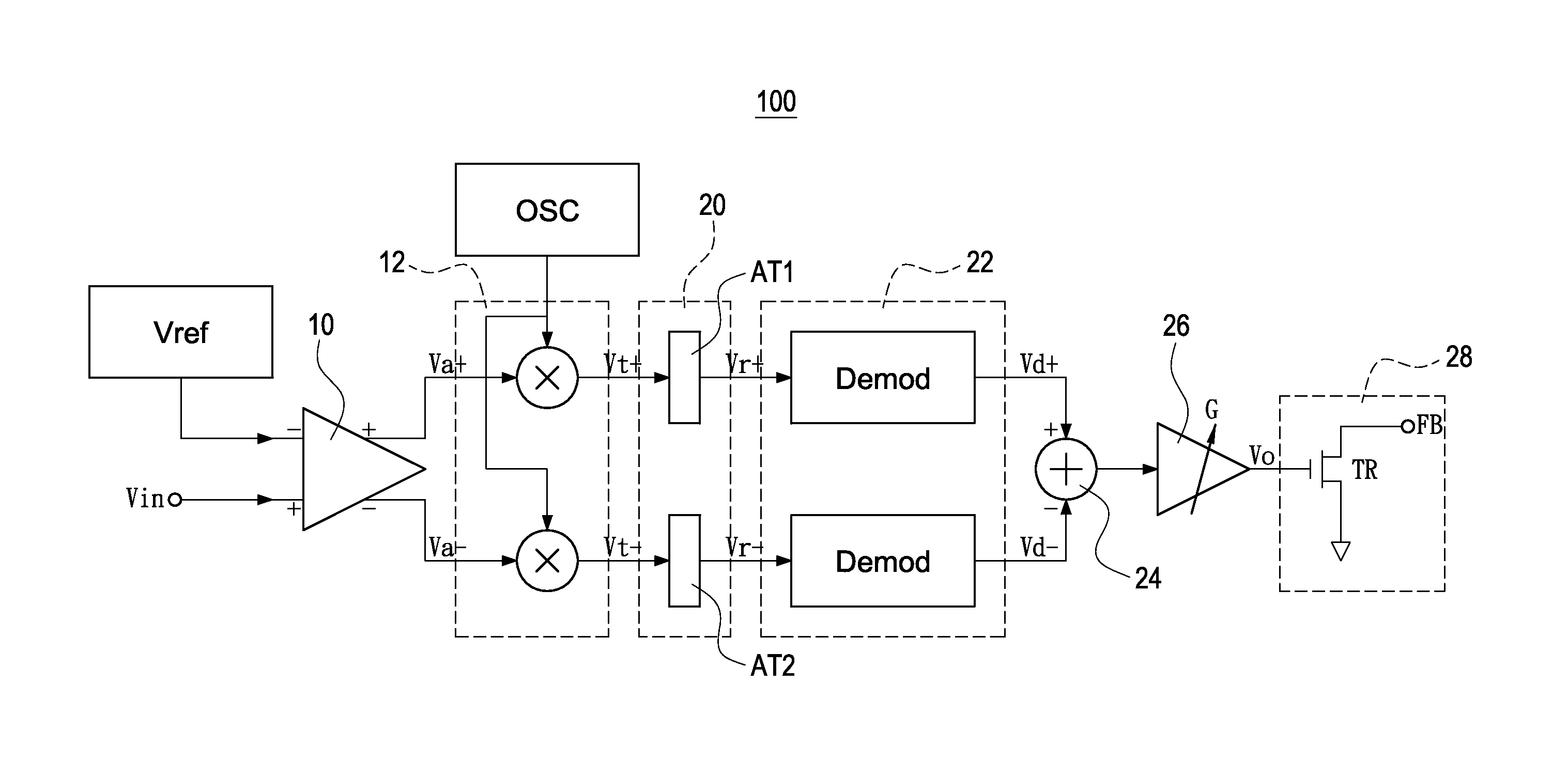
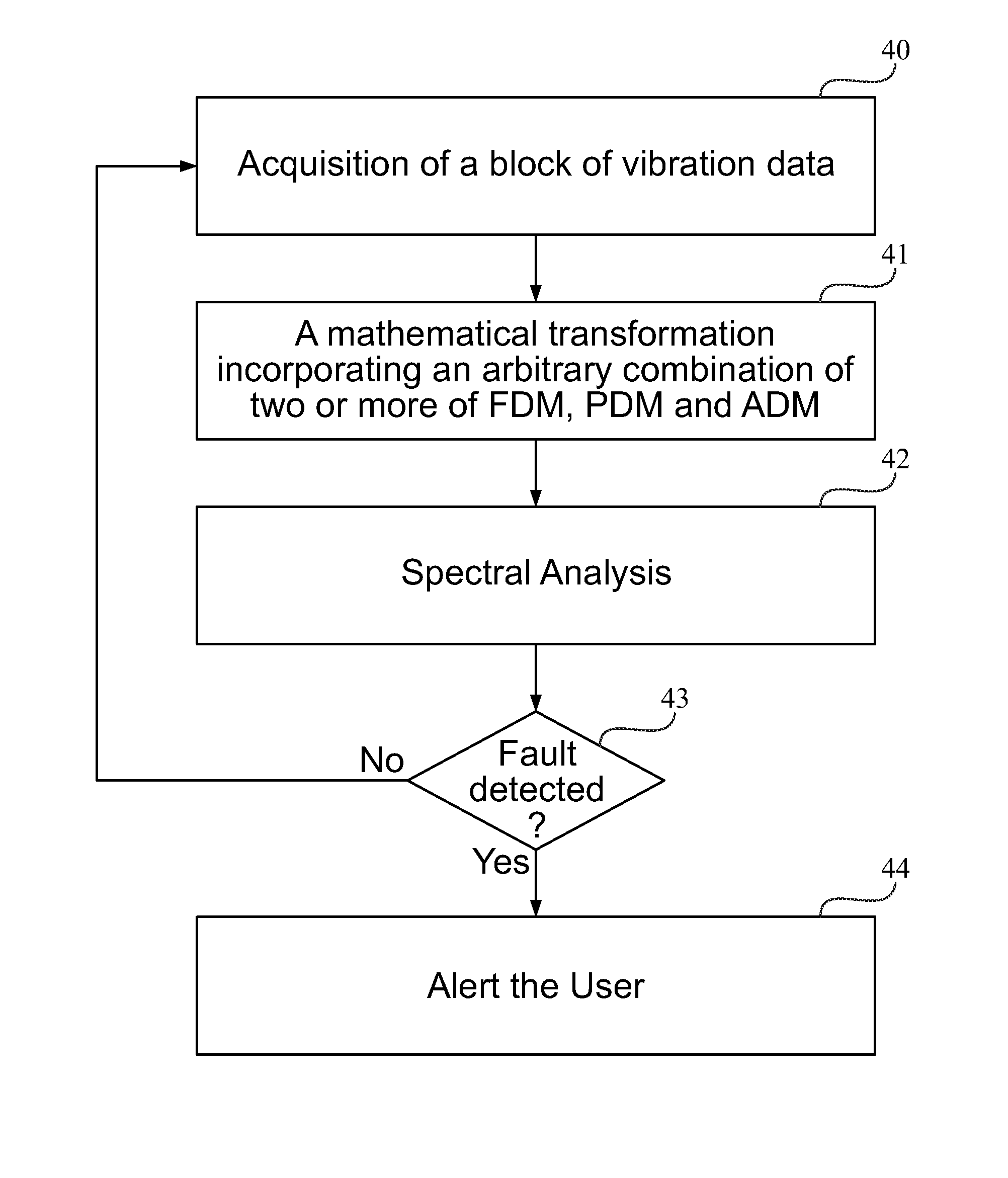
A parameter-free method to analyze sensor signals incorporates two or more of frequency demodulation, amplitude demodulation and phase demodulation of the raw signal data. The resulting signal is transformed to a frequency domain, and target fault characteristics from the demodulated signal are identified. The method is used to detect faults in bearings, gears and other mechanical components.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA
Microwave frequency measuring method based on optical power detection and device thereof
InactiveCN101567723AReduce complexityLow costTransmission monitoringElectromagnetic transmissionContinuous lightCarrier signal
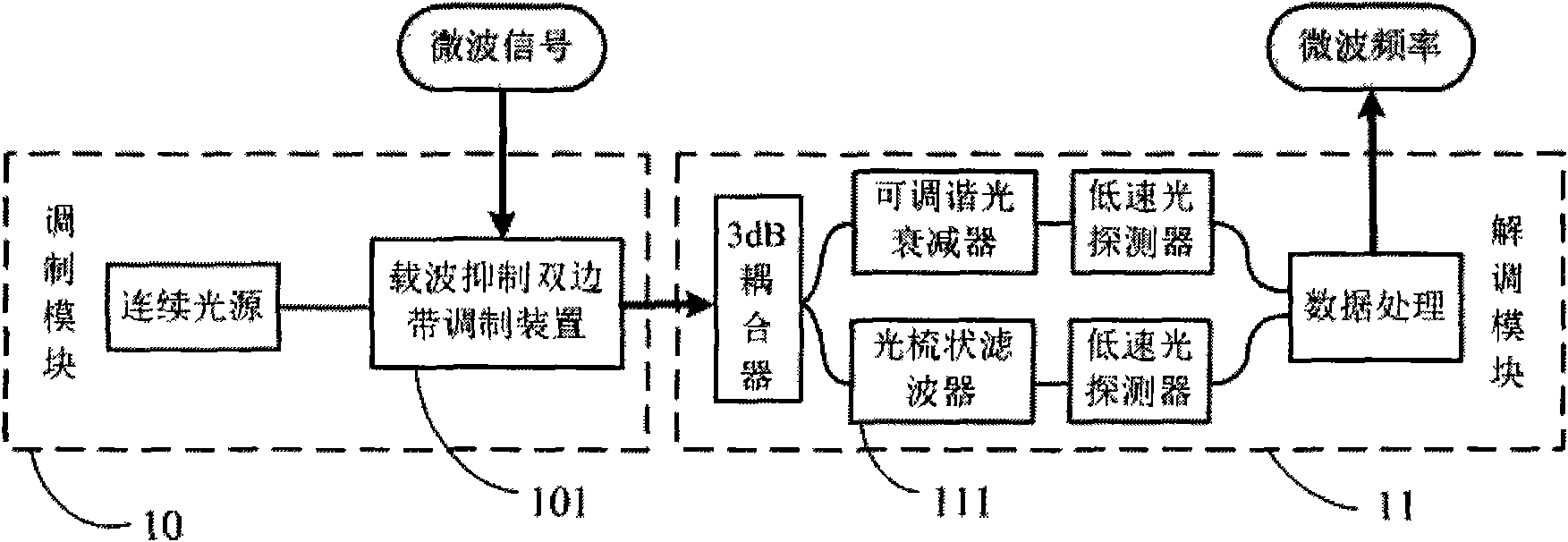
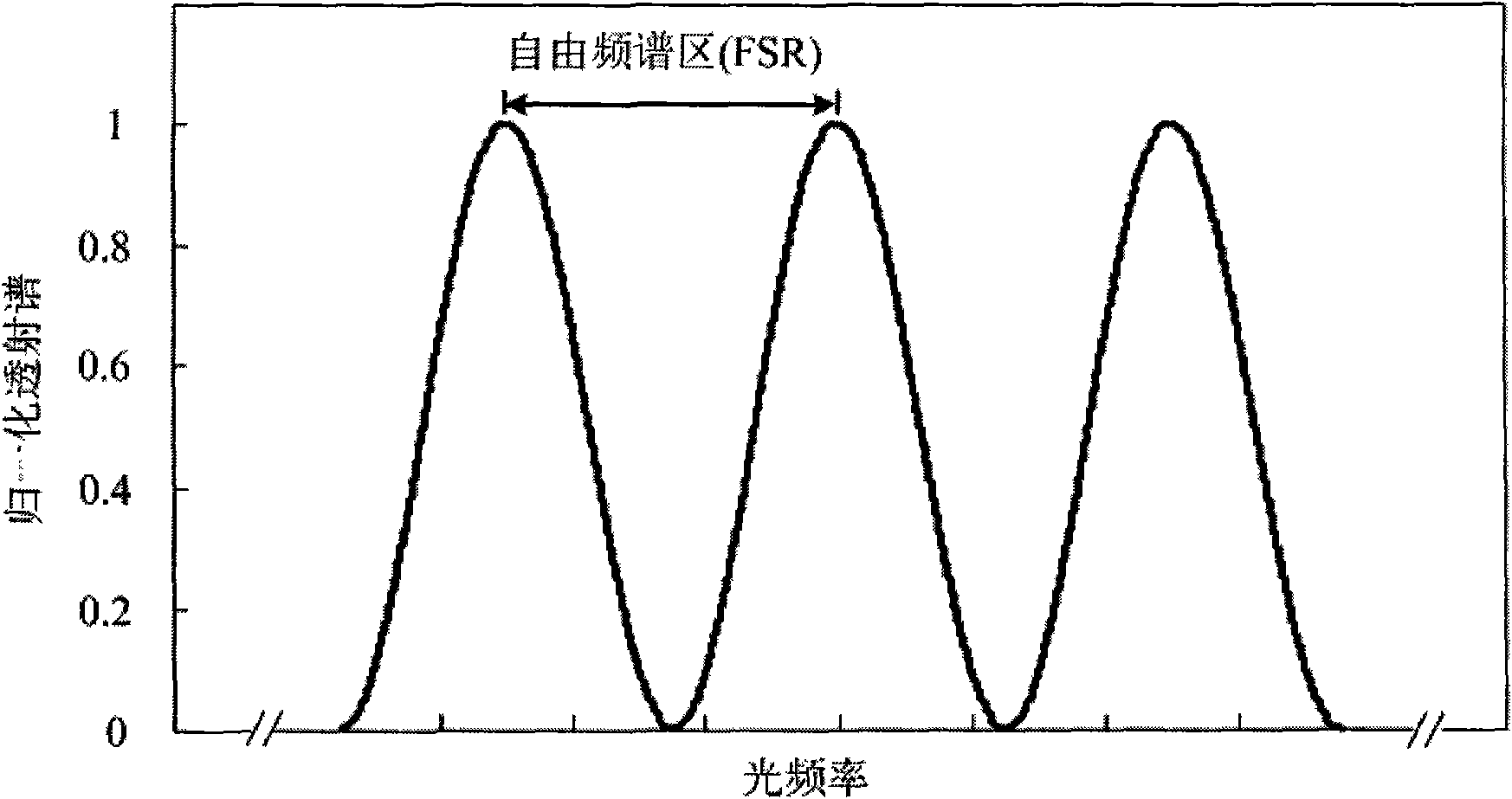
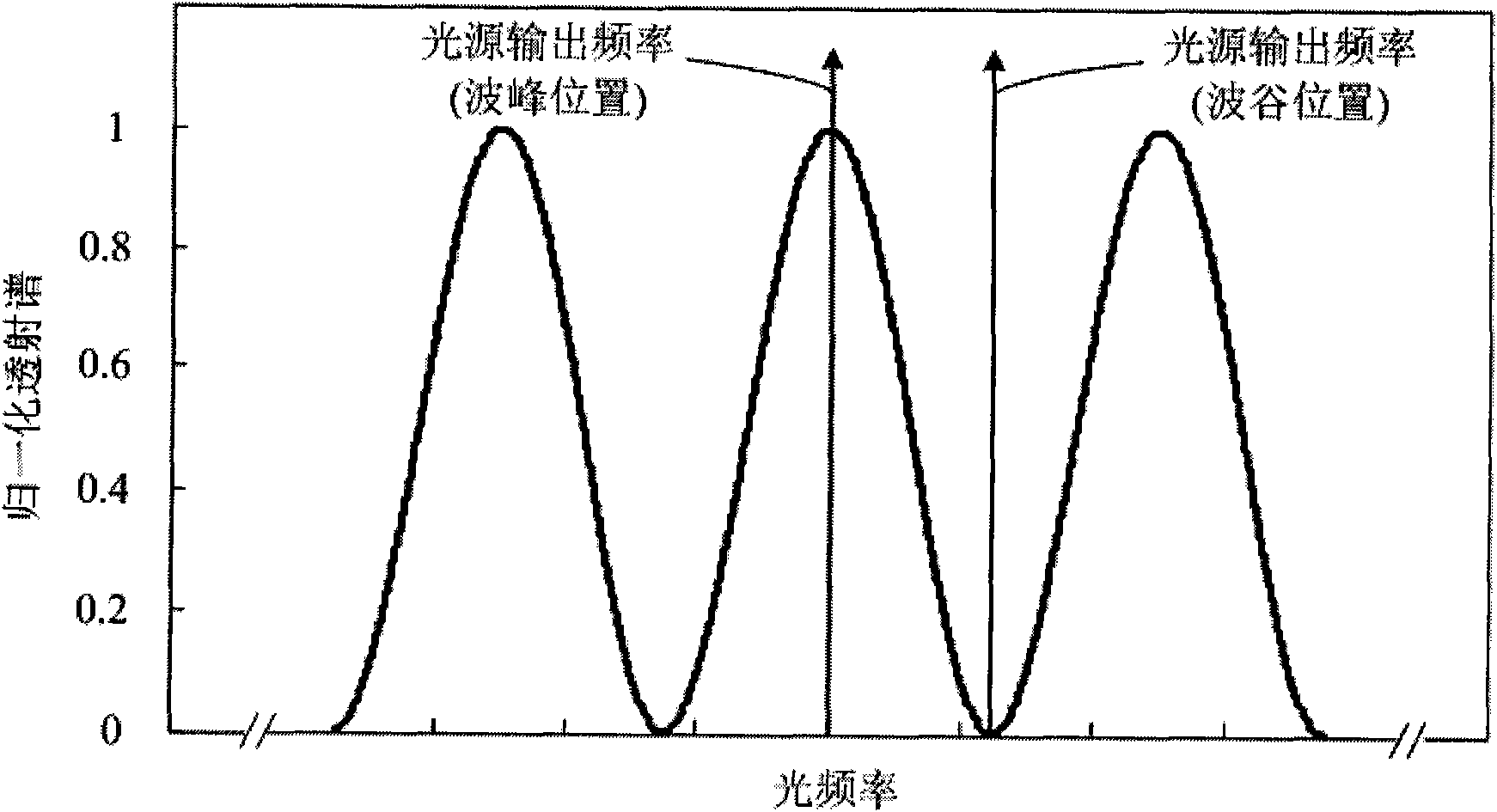
The invention discloses a microwave frequency measuring method based on optical power detection and a device thereof, which conducts real-time measurement on microwave frequency by adopting a system consisting of an electro-optical modulating module and a frequency demodulating module. A continuous microwave signal is loaded on a continuous light source in the modulating module in the modulating manner of carrier suppressed small signals, and only generates two plus or minus 1 stage optical margin strips; the modulated optical signal is divided into two paths, wherein one path is injected into a comb-like filter with sine-function transmission spectrum while the other path is injected into a tunable optical attenuator; the output optical power of the two paths are detected and compared with each other and the microwave frequency is obtained from the demodulation of power ratio. The invention lowers the complexity and cost of the system, eliminates the influence of fluctuation of output power of the light source on the measurement of the frequency and enlarges the measuring frequency band of frequency linear demodulation.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Single-chip multi-stimulus sensor controller
ActiveUS20120019467A1Transmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsFrequency demodulationSingle chip
A multi-stimulus controller for a multi-touch sensor is formed on a single integrated circuit (single-chip). The multi-stimulus controller includes a transmit oscillator, a transmit signal section that generates a plurality of drive signals based on a frequency of the transmit oscillator, a plurality of transmit channels that transmit the drive signals simultaneously to drive the multi-touch sensor, a receive channel that receives a sense signal resulting from the driving of the multi-touch sensor, a receive oscillator, and a demodulation section that demodulates the received sense signal based on a frequency of the receive oscillator to obtain sensing results, the demodulation section including a demodulator and a vector operator.
Owner:APPLE INC
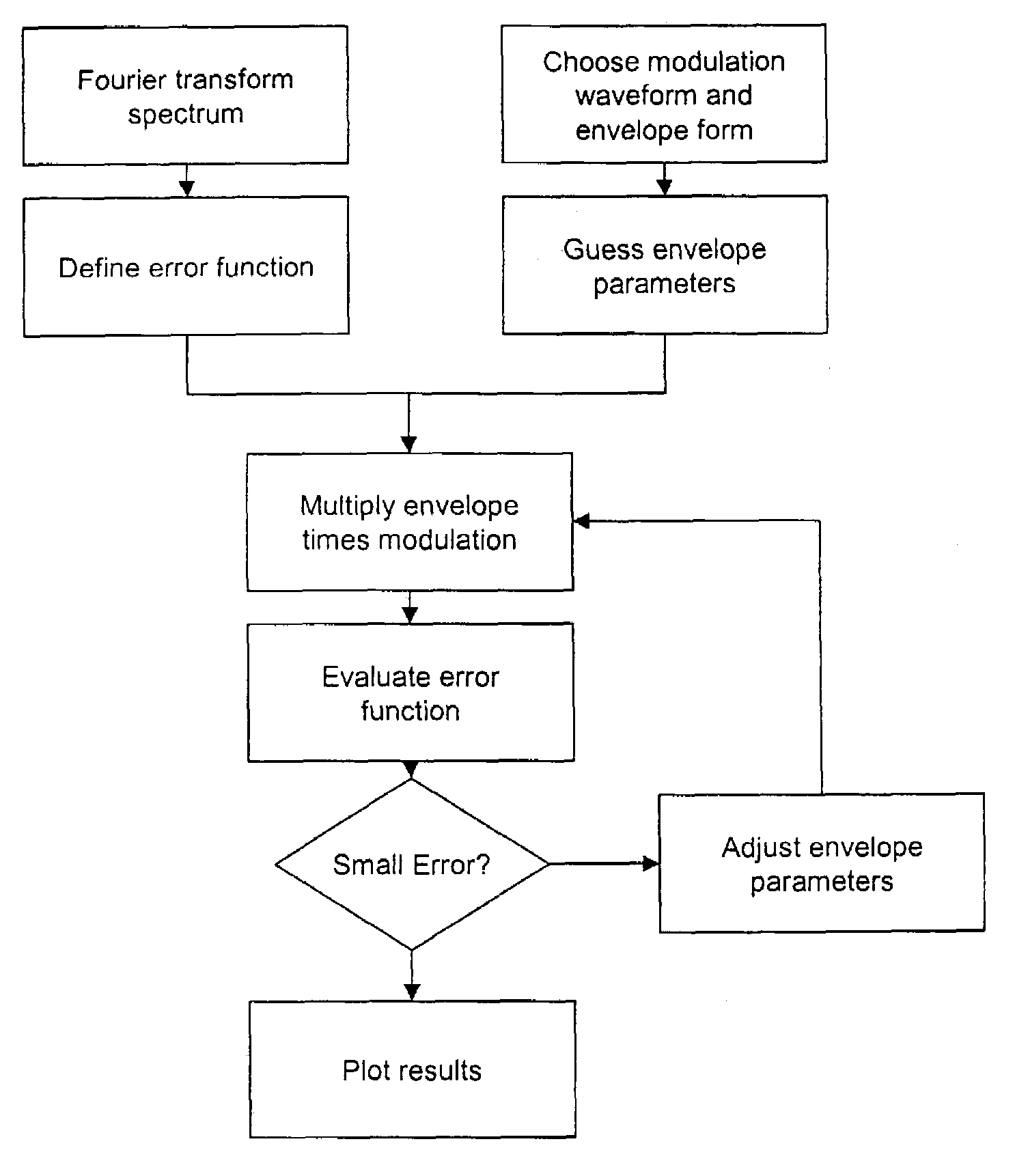
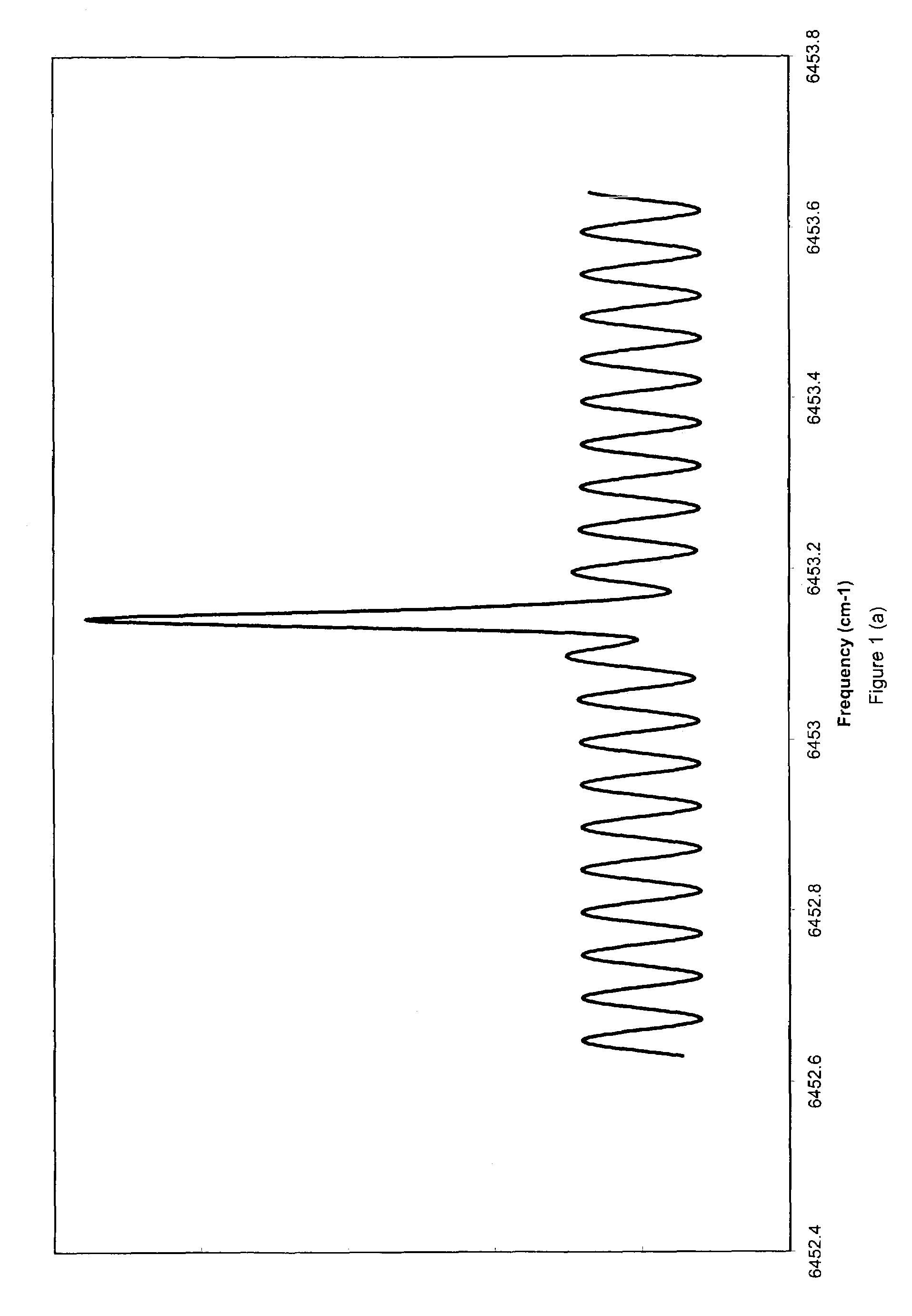
Envelope functions for modulation spectroscopy
InactiveUS6940599B1Minimize the differencePermit sensitive detectionRadiation pyrometryOptical rangefindersPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
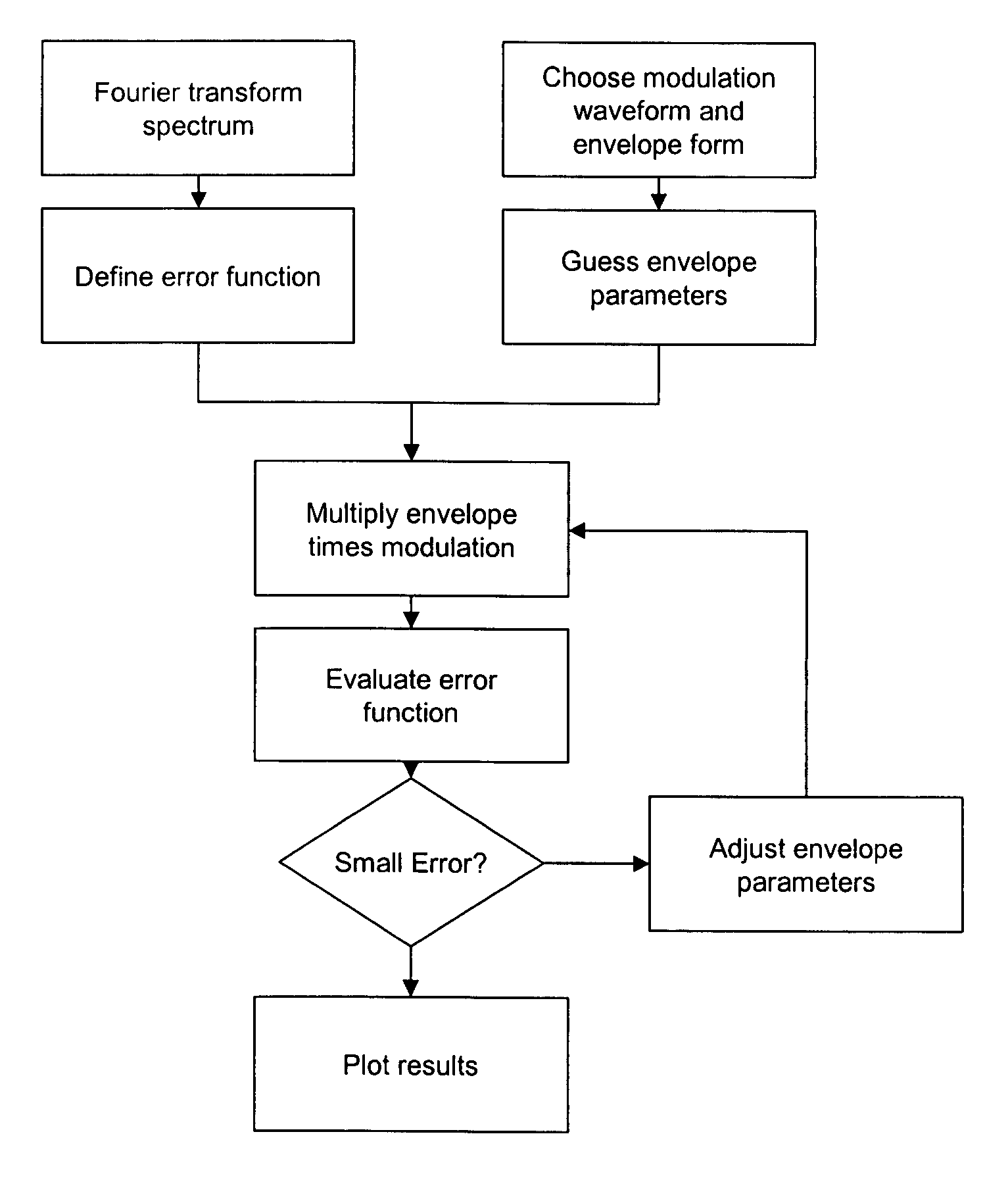
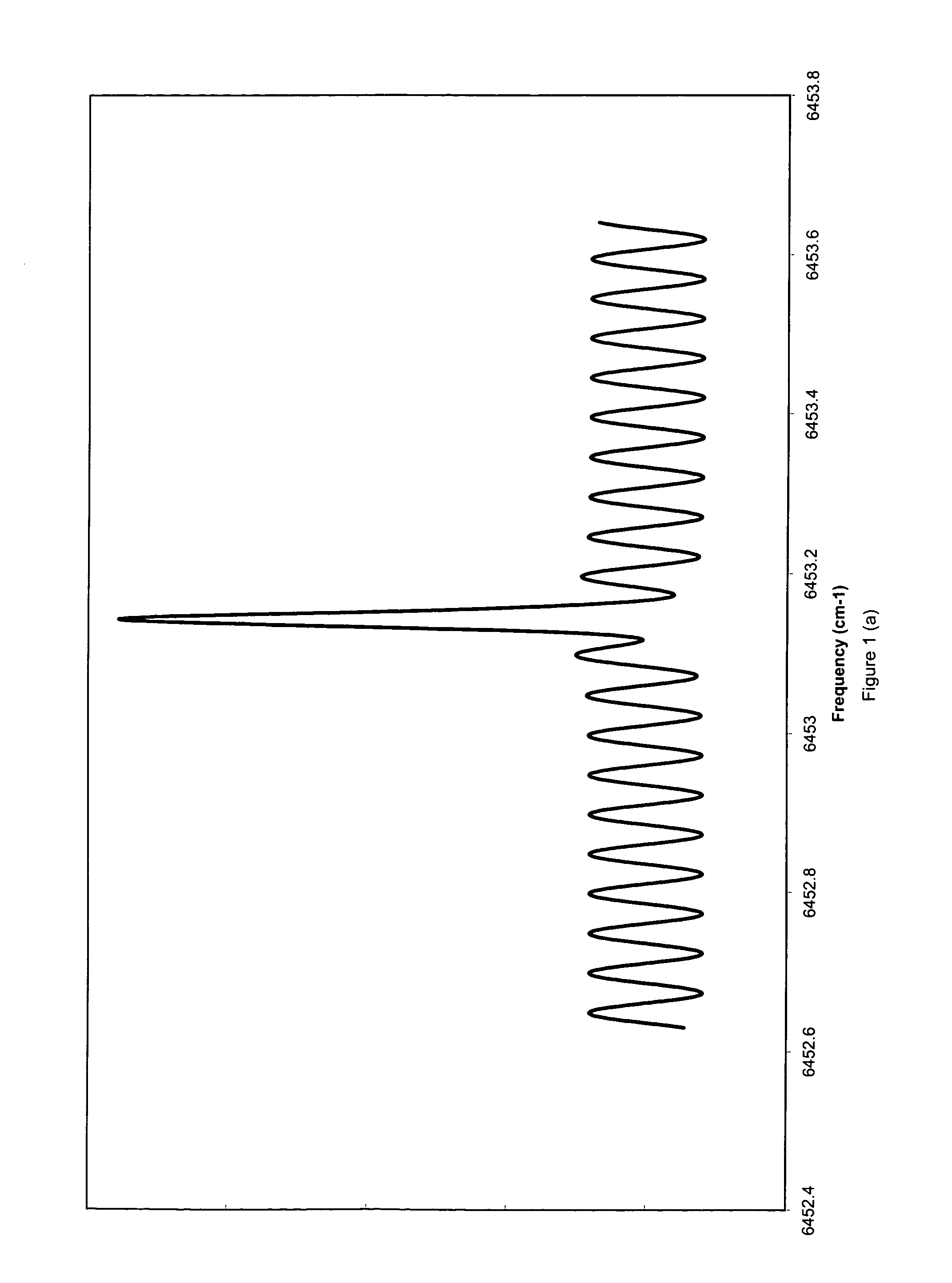
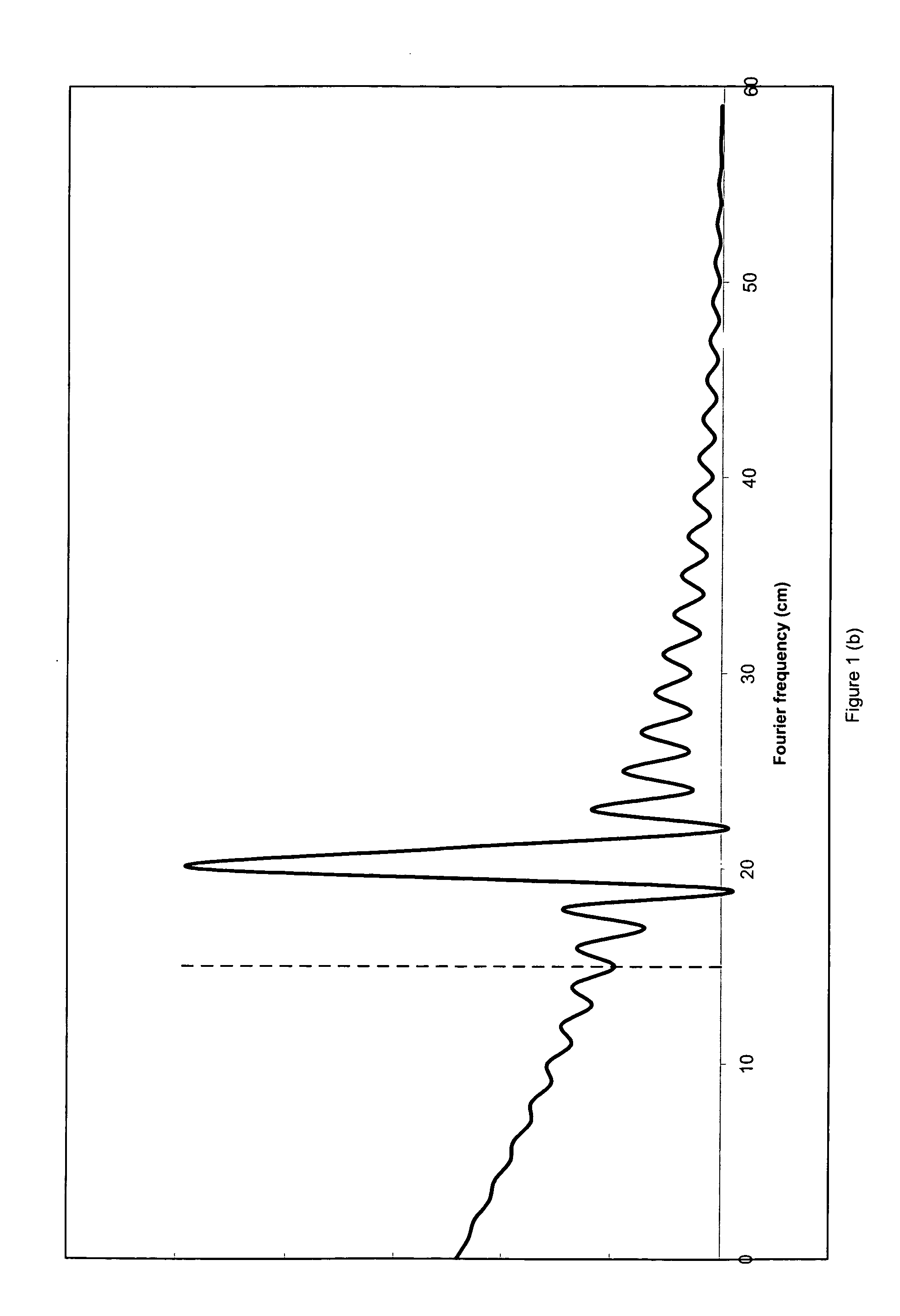
A spectrometer and spectrometry method comprising modulating a light source with a carrier waveform multiplied by an envelope function, directing light from the light source through a sample region and to a photodetector, and demodulating current from the photodetector at a reference frequency. Also a method for computing a modulation waveform comprising specifying a target detection efficiency in a Fourier space, computing a response of a waveform that comprises a carrier wave multiplied by an envelope function, and modifying the envelope function using nonlinear optimization means to minimize a difference between the computed response and a predetermined target gain spectrum.
Owner:SOUTHWEST SCI
Permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor position observer for random frequency high-frequency square wave voltage injection
InactiveCN106849804ANoise reduction effectEasy to useElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlControl systemPermanent magnet synchronous motor
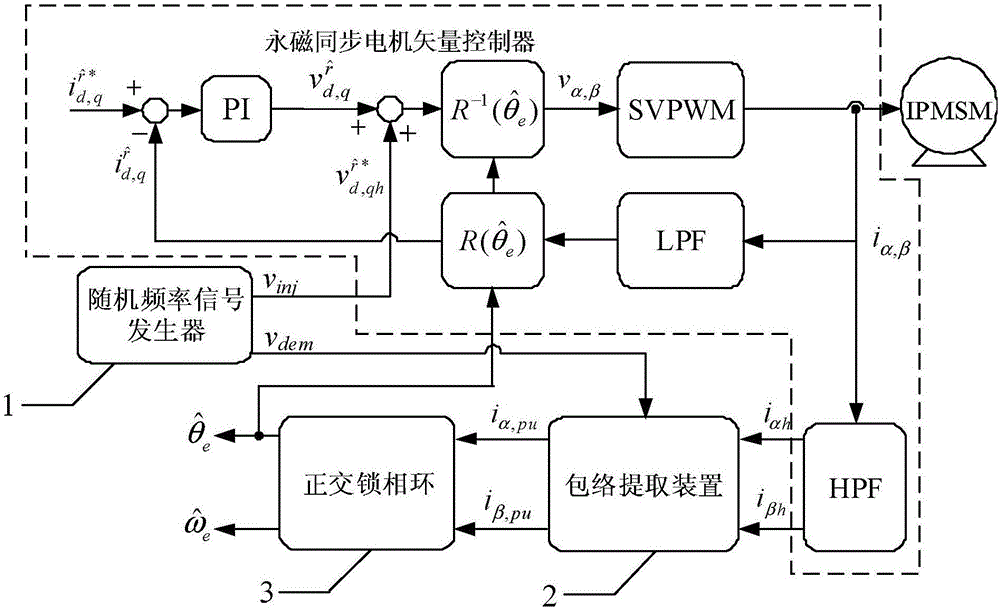
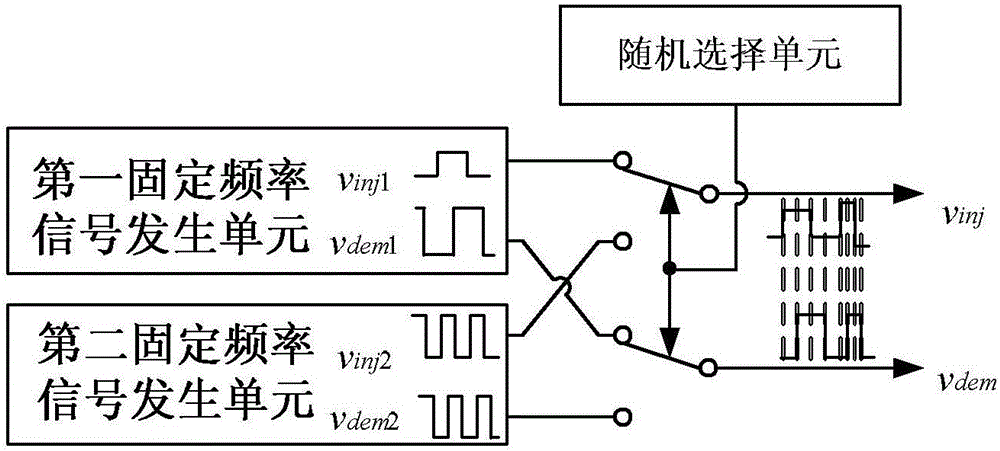
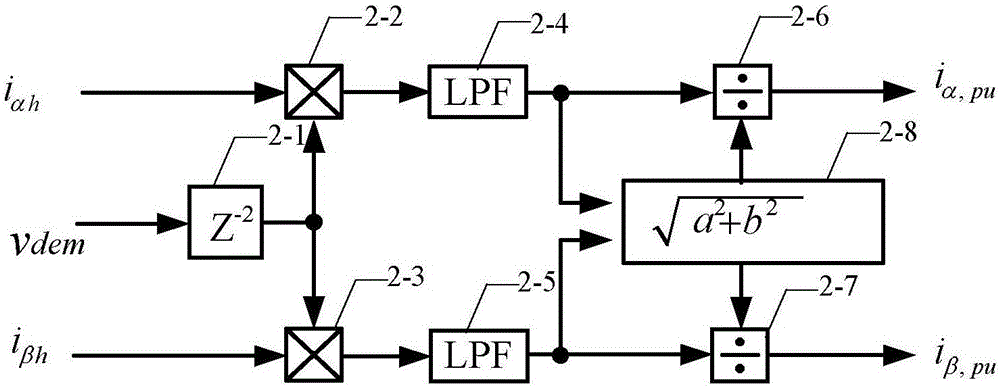
In order to solve the problem of noise generated in the sensorless control of the existing built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor based on the high frequency signal injection method, a permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor position observer with random frequency high frequency square wave voltage injection is provided, which belongs to the motor control field. The present invention includes: a random frequency signal generator for generating a random frequency injection signal v with the same frequency and phase quadrature inj and a random frequency demodulated signal v dem ; Envelope extraction means for demodulating signal v according to random frequency dem , to extract the α-axis high-frequency current i αh and β-axis high-frequency current i βh The envelope line of the α-axis high-frequency current envelope signal i is obtained α,pu and β-axis high-frequency current envelope signal i β,pu ; Quadrature phase-locked loop 3, used for the high-frequency current envelope signal i according to the α-axis α,pu and β-axis high-frequency current envelope signal i β,pu , to estimate the position of the rotor. The invention can be widely applied to the control system of the built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor, does not need additional hardware, and has obvious effects of reducing noise.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Fiber laser static-state strain beat frequency demodulation system based on single-sideband frequency sweep modulation
ActiveCN105091776AStatic strain beat frequency demodulation highSolve complexityUsing optical meansFrequency stabilizationLaser light
The invention discloses a fiber laser static-state strain beat frequency demodulation system based on single-sideband frequency sweep modulation. The system comprises a pumped source, a coupler, a first wavelength division multiplexer, a second wavelength division multiplexer, a first polarization controller, a second polarization controller, a sensing fiber laser, a reference fiber laser, a first isolator, a second isolator, a first beam combiner, a second beam combiner, a first broadband photoelectric detector, a second broadband photoelectric detector, a control processor, a narrow linewidth laser light source, a third isolator, a third polarization controller, a third beam combiner, a suppressed carrier single-sideband modulator, a fourth beam combiner, a frequency sweep signal generator, a phase modulator, a radio frequency signal generator, a frequency stabilization source and a photoelectric detector. The system provided by the invention realizes high-precision static-state strain measurement of the fiber lasers and solves the problems of incapacity of realizing high-precision static-state strain measurement, influences exerted by tunable laser frequency sweep non-linearity on demodulation precision, and the like by use of a conventional fiber laser demodulation technology.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
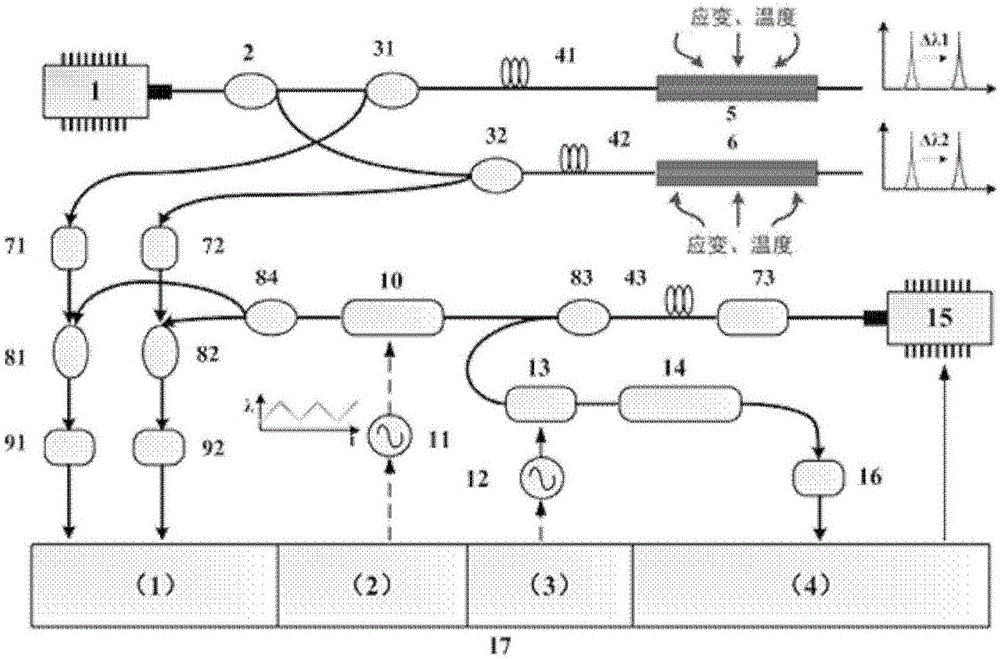
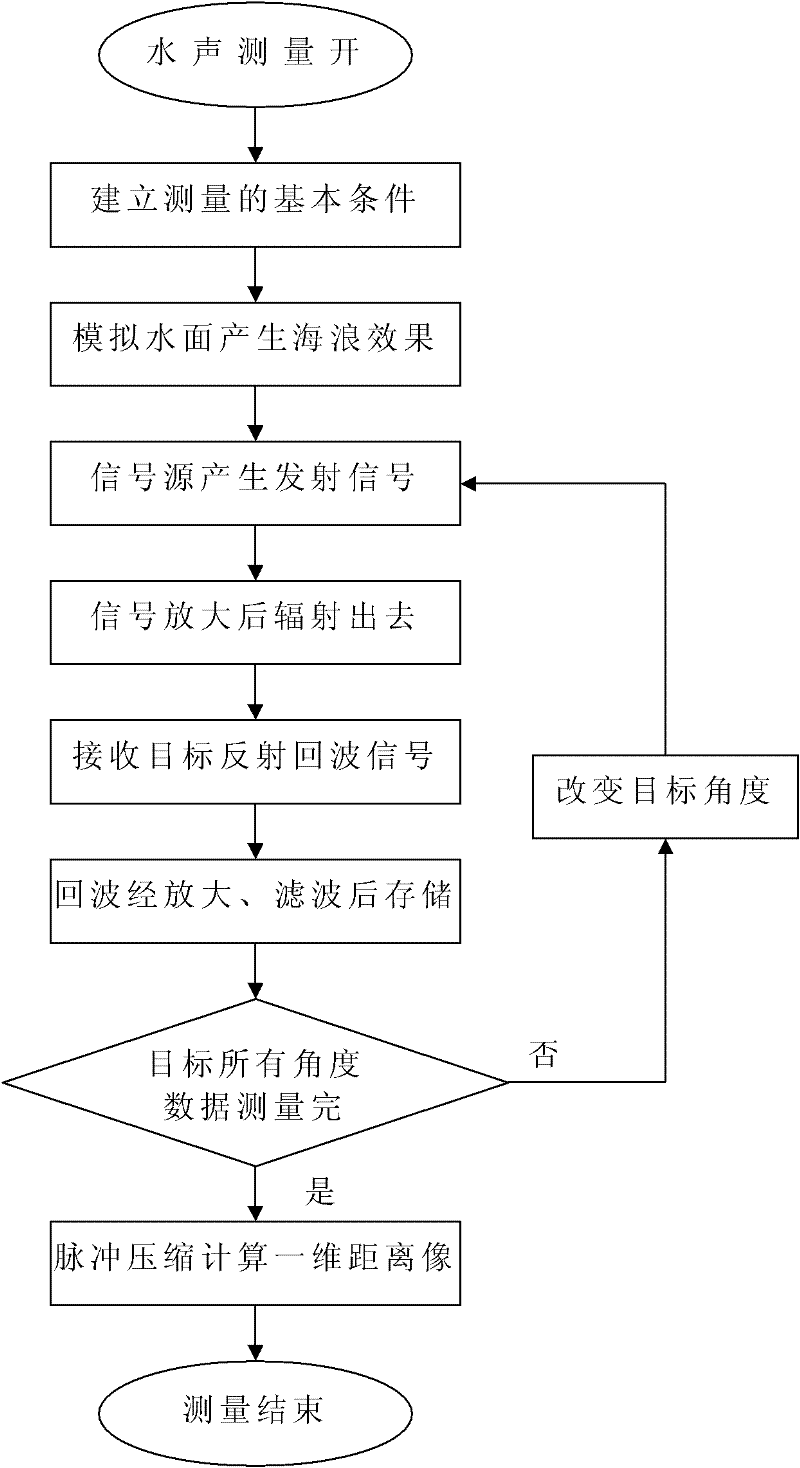
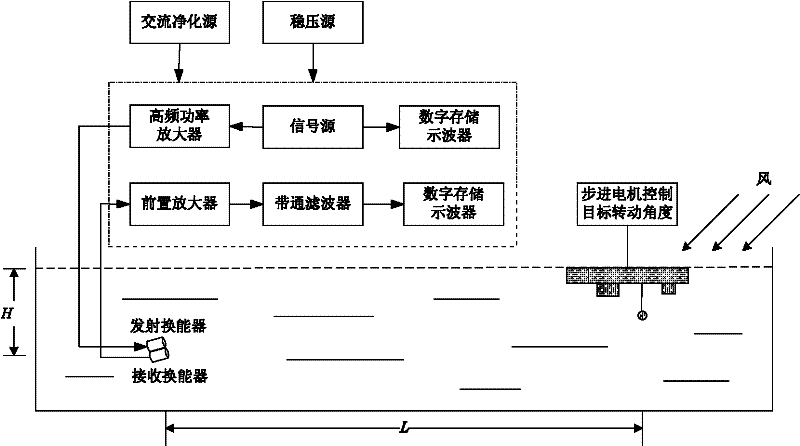
Underwater acoustic measurement method for scattering properties of ship target broadband radar
The invention discloses an underwater acoustic measurement method for scattering properties of a ship target broadband radar, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: firstly, inversely arranging a scaled model of a measured ship target in an anechoic tank, regulating basic conditions of a measurement device and a modeling test, simulating irregular sea waves at an interface between the scaled model of the ship target and water, amplifying a linear frequency demodulation signal generated by a signal source and radiating the amplified frequency demodulation signal in a sonic signal manner, amplifying and filtering an echo output signal reflected by the scaled model and then storing, then acquiring a plurality of groups of echo signal data on each rotating angle and then storing; and finally, processing the echo signals of the scaled model of the measured ship target on different rotating angles by adopting a pulse compression technology to obtain one-dimensional distance image data of the measured ship target. The invention overcomes the defects of rigorous requirements on measurement equipment and environment and incapability of measuring sea-surface target characteristics in the prior art, and has the advantages of flexibility in the measurement method, low cost, easiness in realization and the like.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
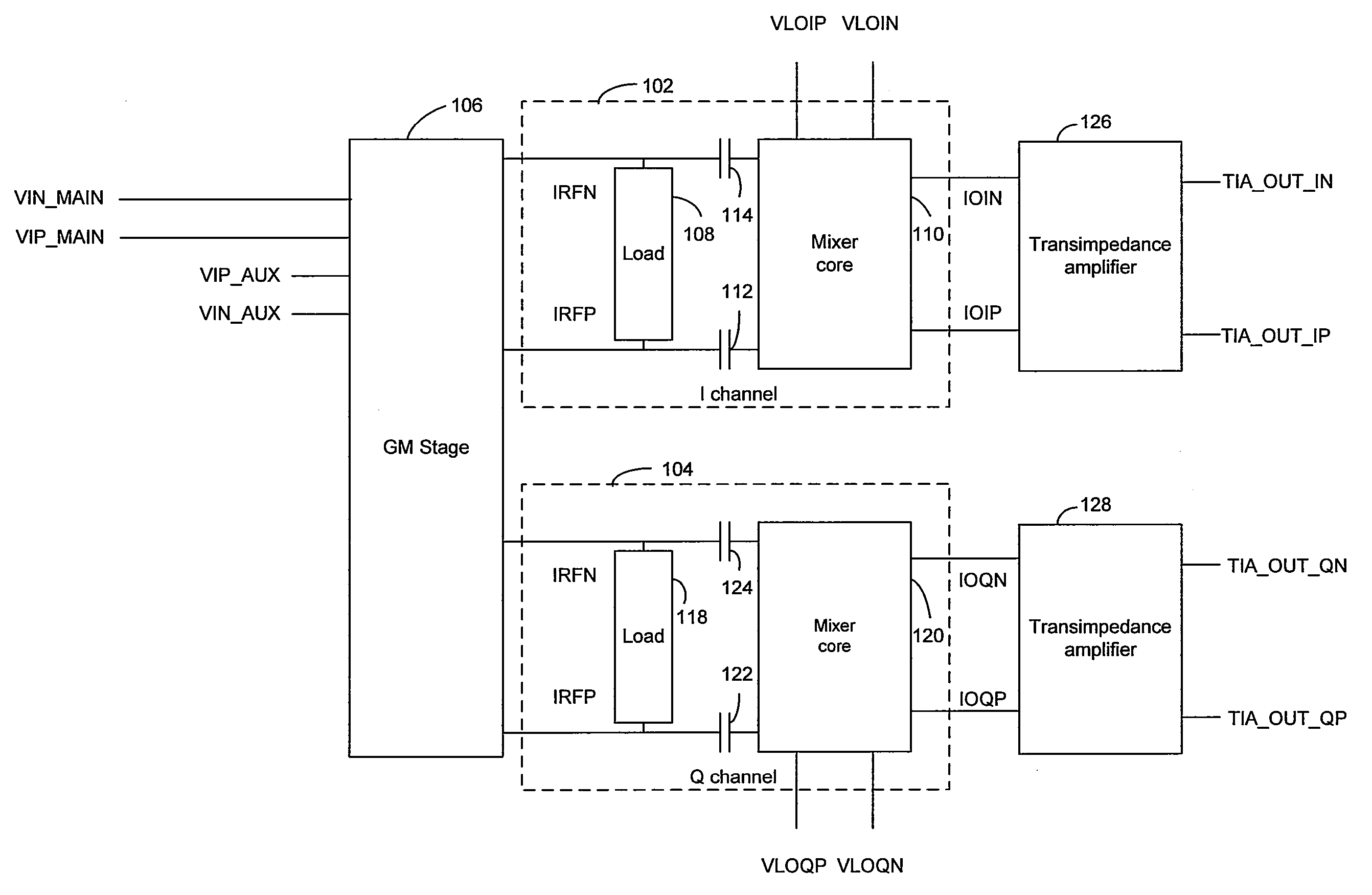
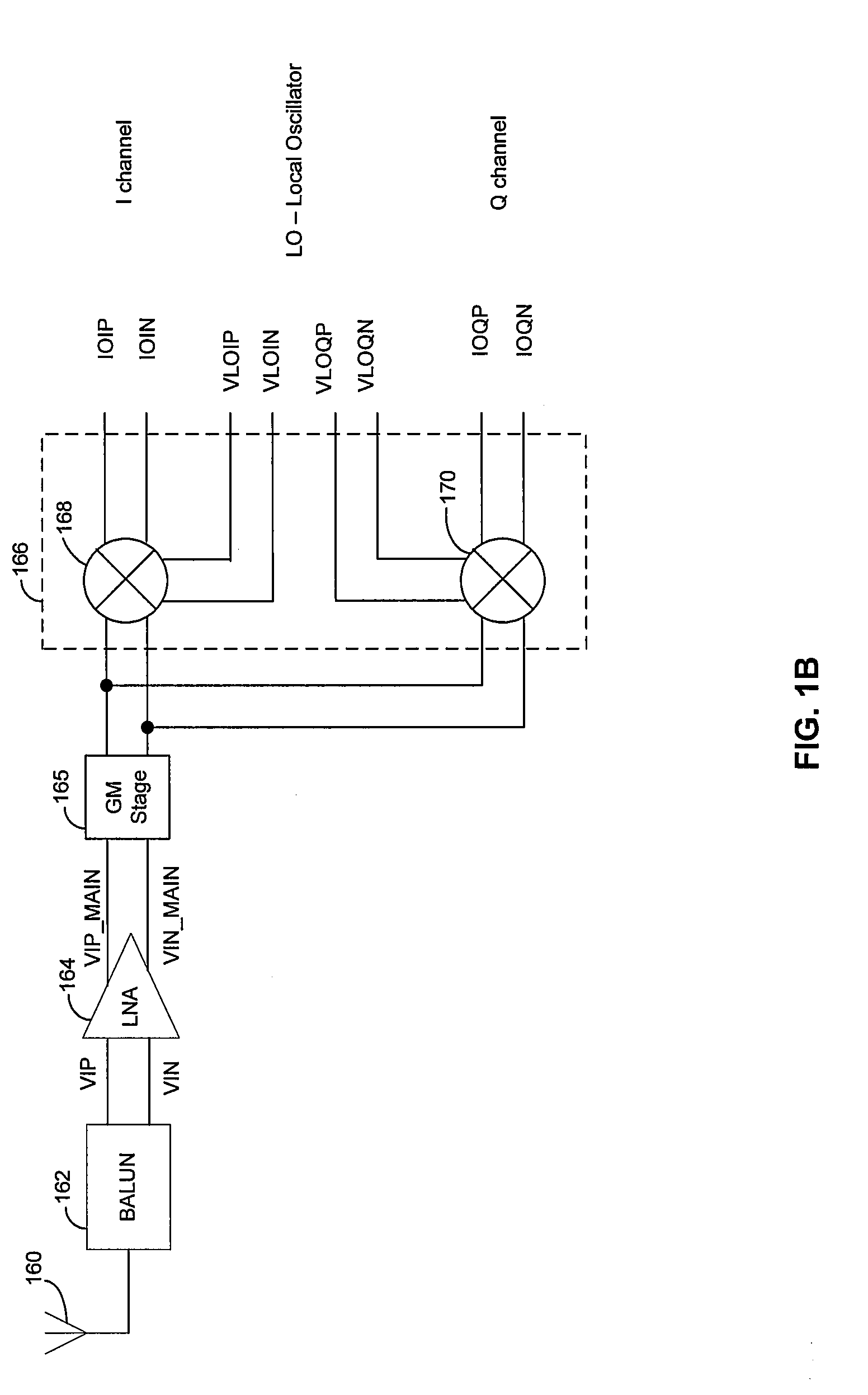
Method and system for a shared gm-stage between in-phase and quadrature channels
InactiveUS20080139162A1Frequency-modulated carrier systemsComputing operation arrangementsUltrasound attenuationFrequency mixer
Aspects of a method and system for a shared GM-stage between in-phase and quadrature channels may include processing an in-phase (I) component signal for the I channel and a quadrature (Q) component signal for the Q channel via one or more shared transconductance stages in a frequency demodulator. The I channel may be isolated from the Q channel and the Q channel may be isolated from the I channel using isolation resistors. The values of the isolation resistors may be selected so as to balance the isolation and signal attenuation. A folding circuit, comprising active devices, may isolate the I channel from the Q channel. A generated voltage may be utilized to bias the folding circuit. An oscillator for the I channel may be isolated from a mixer for the Q channel and an oscillator for the Q channel may be isolated from a mixer for the I channel.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
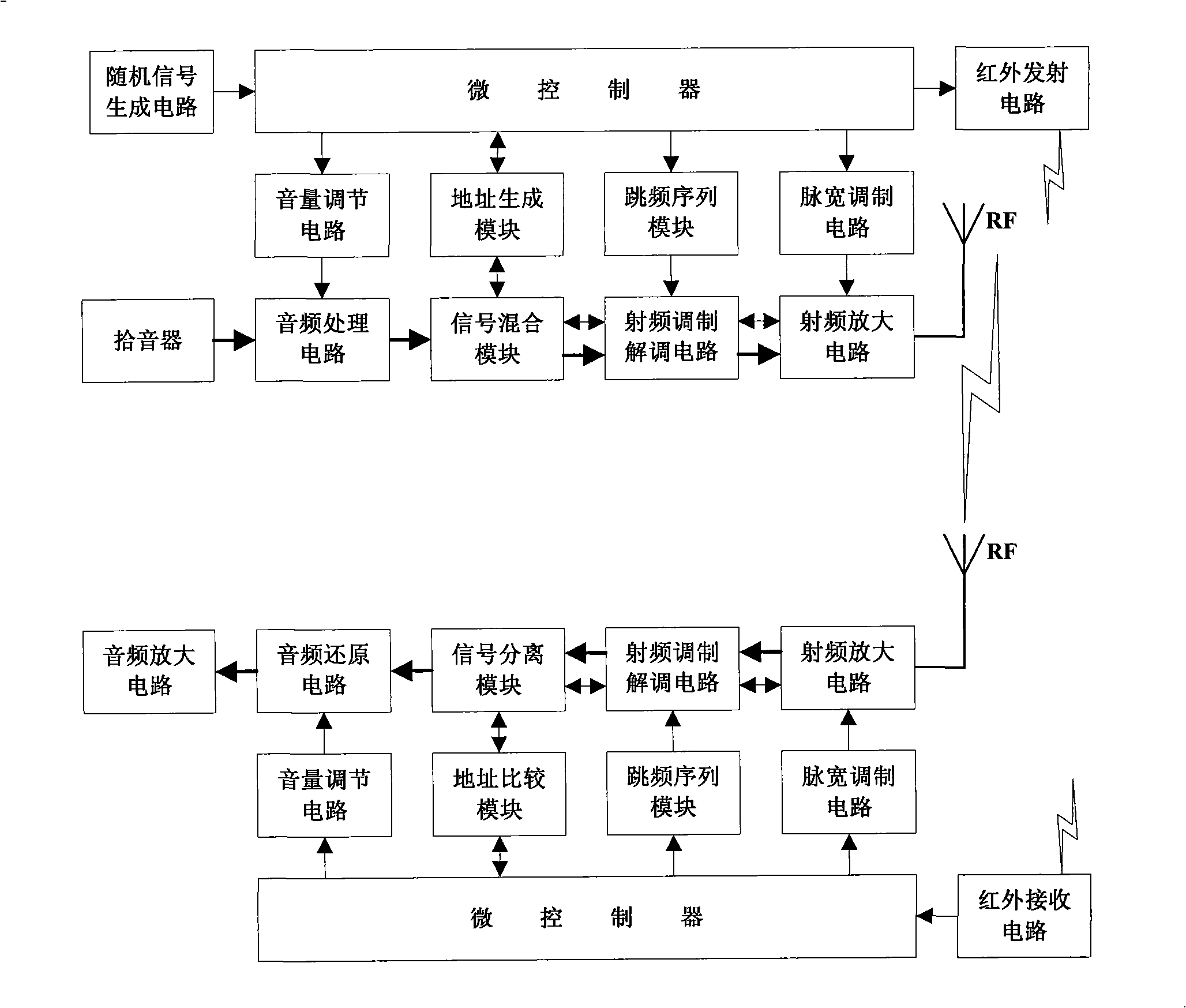
Random addressing self-adapting frequency-hopping wireless microphone and receiving machine thereof
InactiveCN101309088ANear-field systems using receiversElectric megaphonesWireless microphoneShortest distance
Disclosed are a randomly addressing adaptive frequency-hopping wireless transmitter and the receiver thereof, which belong to short distance wireless communication audio-frequency transmitting and receiving device, and solve the discretional matching problem of the wireless transmitter and receiver and the inconvenience during the manufacturing of the manufactures. The transmitter of the invention includes a micro controller, a microphone, a volume tuning circuit, an audio signal process circuit, a signal mixing module, a frequency hopping sequence module, a radio frequency modulation and demodulation circuit and a radio frequency amplifying circuit; the transmitter also includes a random signal generation circuit, an address generation module and a pulse width modulation circuit. The receiver of the invention includes a radio frequency amplifying circuit, a radio frequency modulation and demodulation circuit, a frequency hopping sequence module, a signal separation module, audio signal recovery circuit, a volume tuning circuit, a micro controller and an audio amplifying circuit; the receiver also includes a pulse width modulation circuit and an address comparison module. The randomly addressing adaptive frequency-hopping wireless transmitter and the receiver of the invention realize the discretional matching of the transmitter and the receiver in large scale application without interference with other transmitters; meanwhile, the randomly addressing adaptive frequency-hopping wireless transmitter and the receiver of the invention bring convenience in manufacturing the same model wireless transmitter and receiver.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
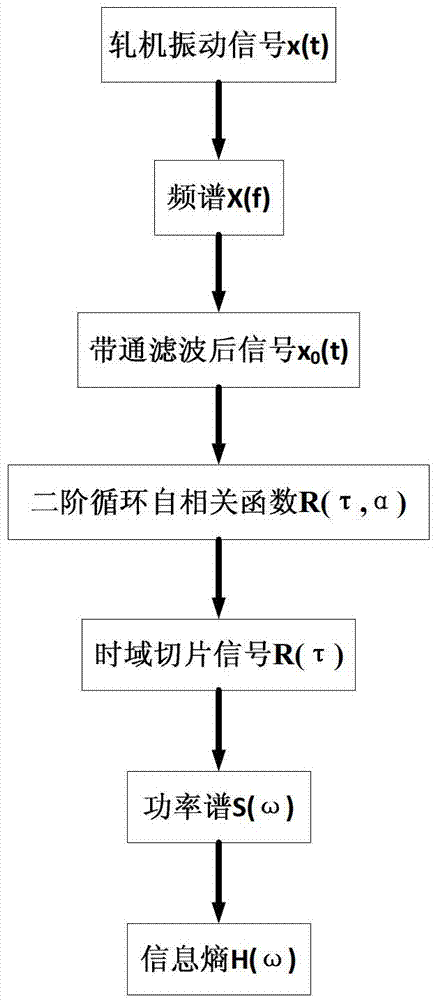
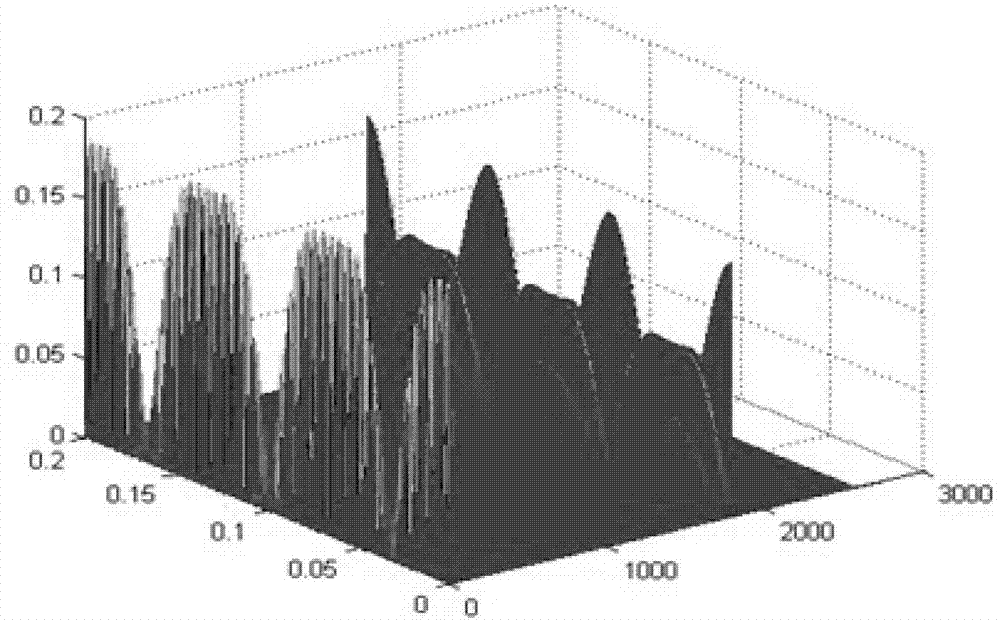
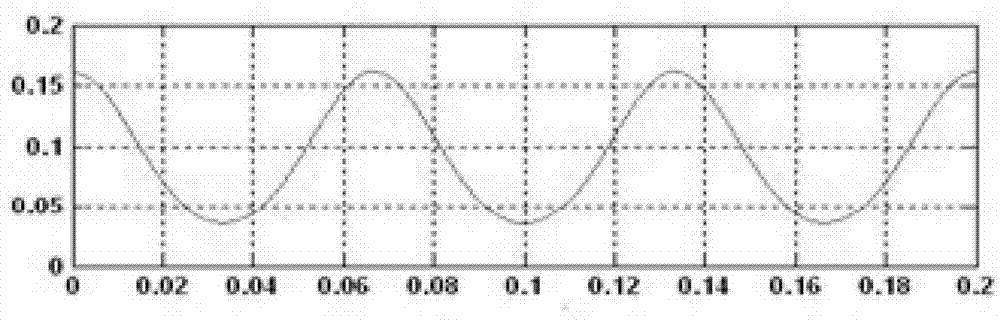
Fault feature extraction method and fault feature recognition method of vibration signal of rolling mill chatter mark
ActiveCN103115668ADemodulation is validImprove accuracySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementTime domainCyclic autocorrelation function
The invention provides a fault feature extraction method and a fault feature recognition method of a vibration signal of a rolling mill chatter mark, and belongs to the field of rolling mill fault monitoring. The fault feature extraction method analyzes the vibration signal of the chatter mark via autocorrelation demodulation based on a second-order cycle, so unstable vibration signal of chatter mark is processed through frequency demodulation, a demodulated second-order cycle autocorrelation function is sliced according to time domain, and modulation information of the chatter mark vibration signal is kept completely. Therefore, accuracy of fault feature extraction of the vibration signal of the chatter mark is improved. The fault feature recognition method recognizes whether the rolling mill faults exist or not by the form of power spectrum information entropy, influence of rolling mill speed fluctuation needs not to be considered, and the recognition method is simple and accurate.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Rfog modulation error correction
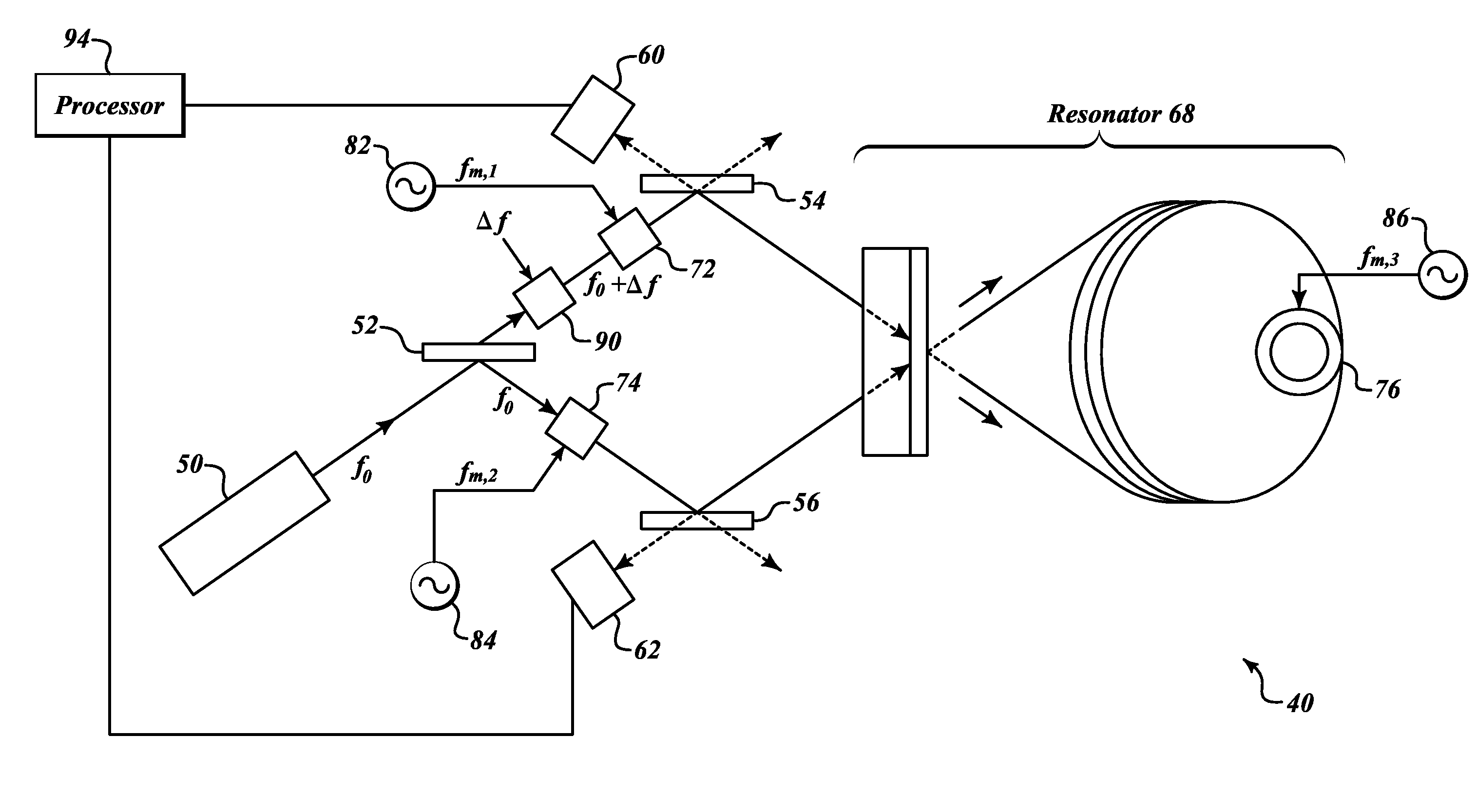
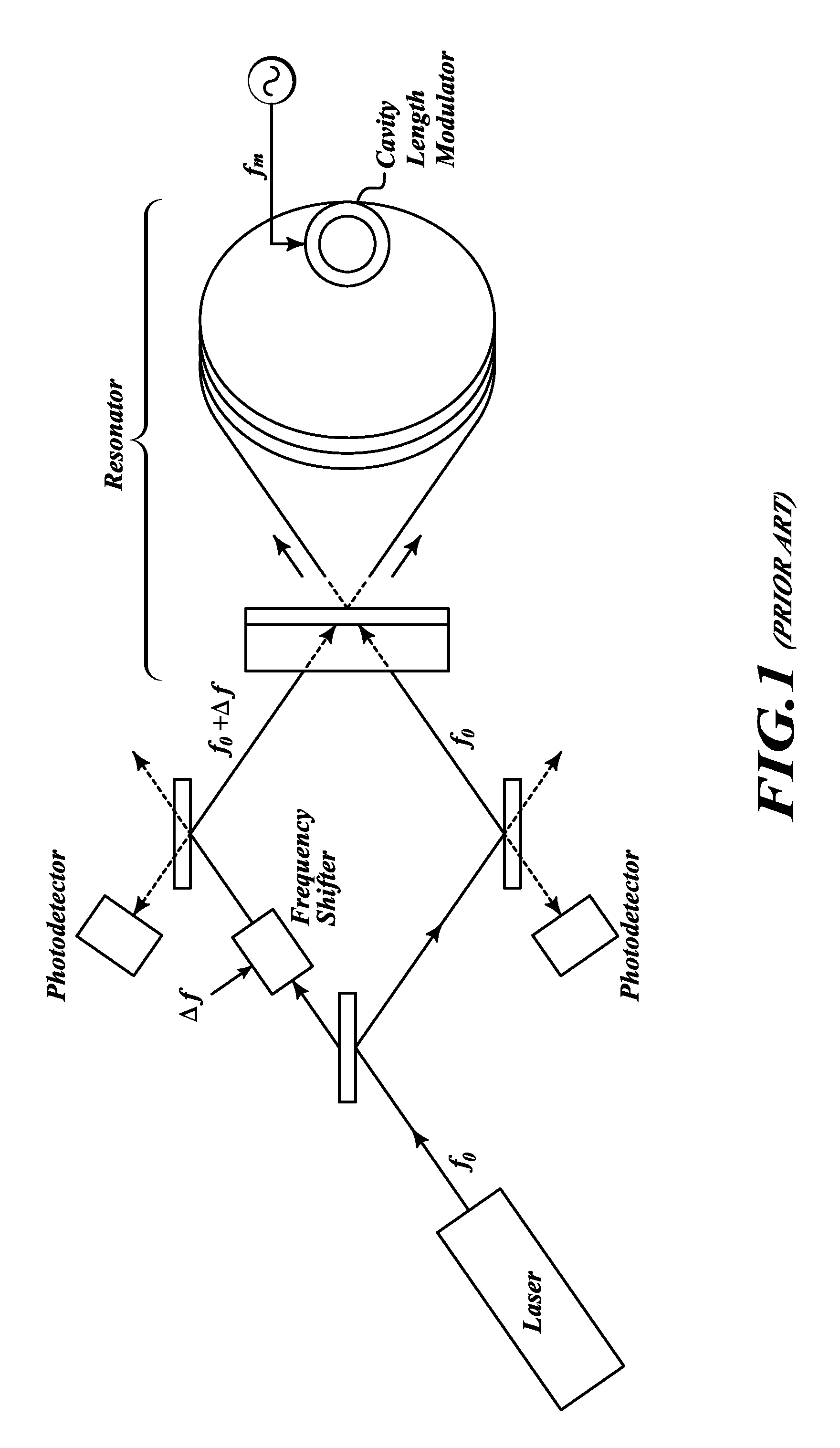
ActiveUS20100002239A1Speed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersHarmonicLight beam
Systems and methods for performing modulation error correction. An example system applies common phase / frequency modulation to first and second laser beams, a first intensity modulation to the first modulated beam, and a second intensity modulation to the second modulated beam. Signals outputted are demodulated according to the frequency of the common phase / frequency modulation. Then the first of these demodulated signals is demodulated based on the frequency of the intensity modulation of the first beam, and the second of these demodulated signals is demodulated based on the frequency of the intensity modulation of the second beam. Then, rate of rotation is determined based on demodulated signals. Frequencies of the intensity modulations are unequal and not harmonically related, and intensity modulation encodes each light beam with a unique signature.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
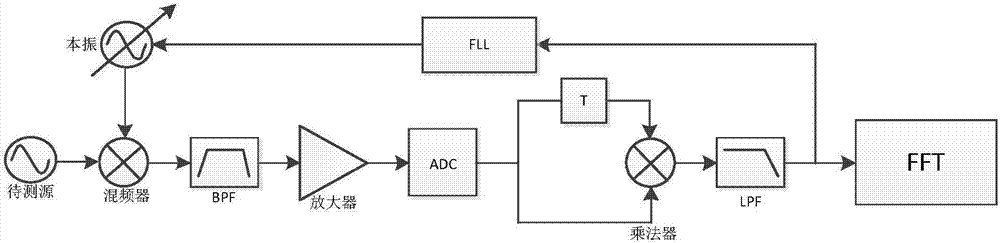
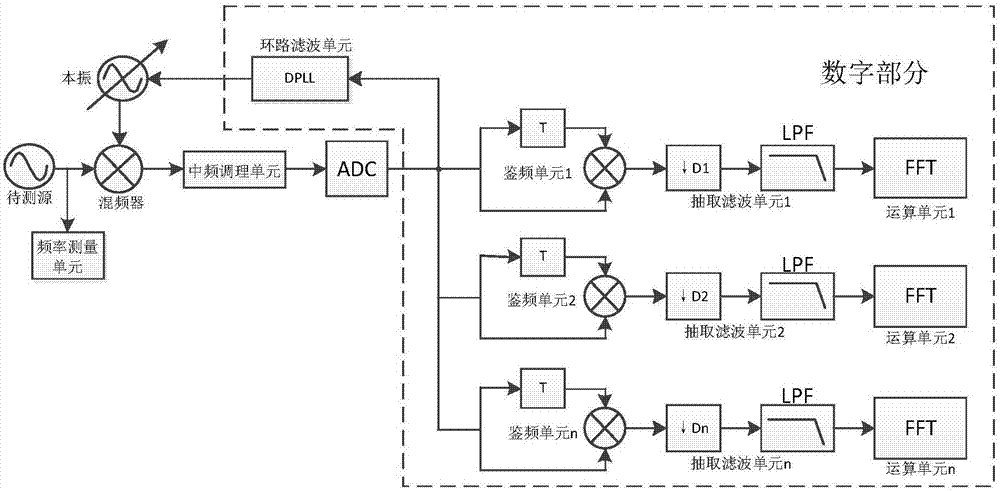
Digital frequency demodulation phase noise measuring device and method
InactiveCN107966620AMeet the requirements of phase noise testingTake advantage of real-time processing capabilitiesNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementPhase noiseIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a digital frequency demodulation phase noise measuring device and method and belongs to the electronic measurement technology field. A digital phase-locked loop is utilized torealize carrier frequency tracking and phase locking of a to-be-measured source, an intermediate frequency amplifying unit is utilized to realize adaptive adjustment, an original digital frequency demodulation unit is utilized to extract noise, and plural average of the frequency domain is utilized to improve the phase noise measurement sensitivity of a system. The method is advantaged in that when phase noise measurement can be realized through the frequency demodulation method, compatibility of frequency offset and sensitivity indexes is analyzed, and the better near-end phase noise measurement sensitivity can be realized; the realization scheme is simple, system configuration is concise, the technology is relatively mature, realization cost is low, and the cost performance advantage isrealized to a certain degree.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Combined time frequency distribution and compression sensing radar frequency smeared spectrum interference method
ActiveCN105891789AClear conceptSuppression of Spectrum Dispersion (SMSP) Interfering SignalsWave based measurement systemsFrequency spectrumTarget signal
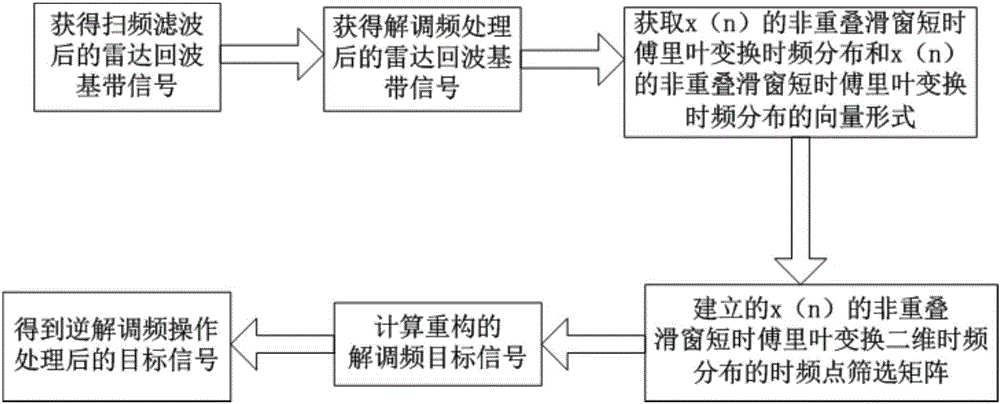
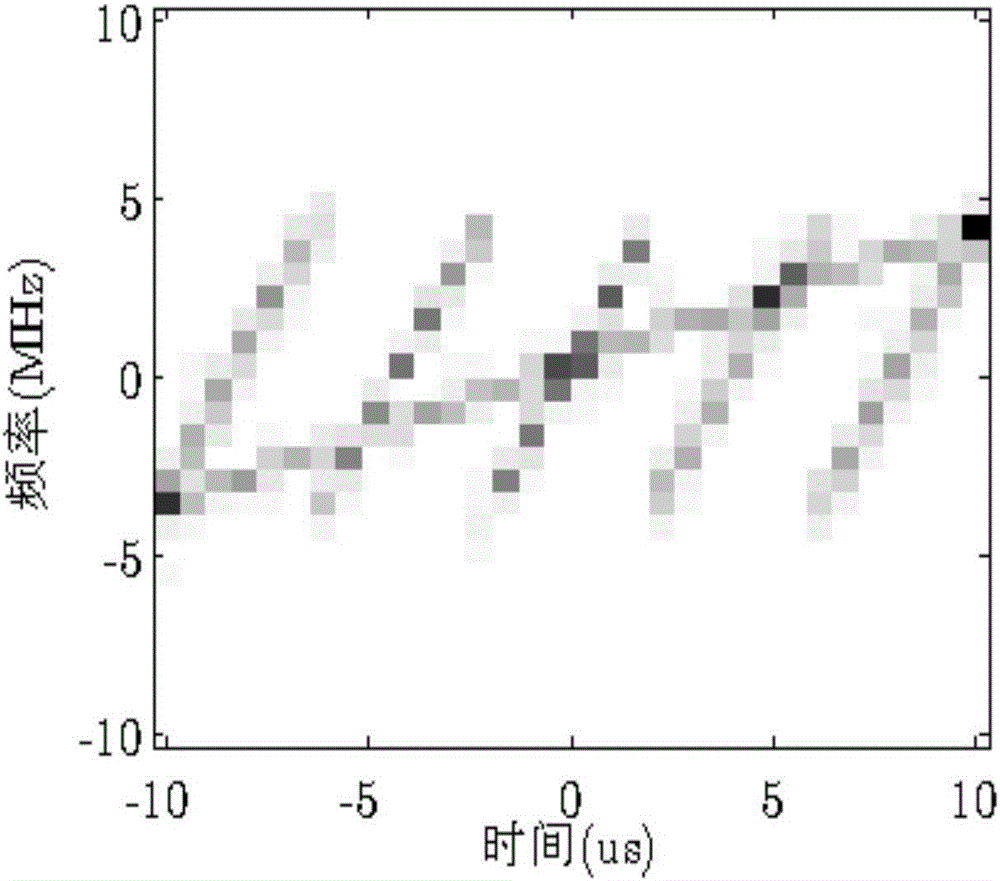
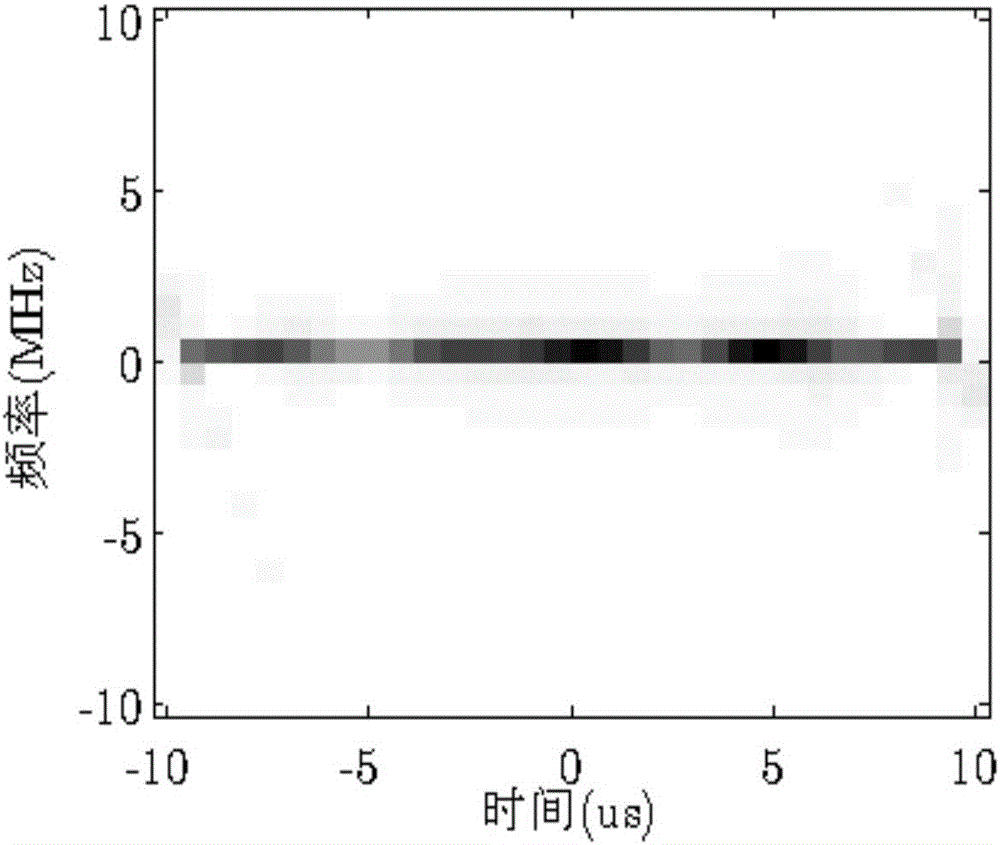
The invention discloses a combined time frequency distribution and compression sensing radar frequency smeared spectrum interference method. The method includes obtaining radar echo signals and conducting down conversion processing to obtain the radar echo baseband signal s, conducting u domain frequency sweep filtering and frequency demodulation to obtain radar eco baseband signal x after frequency demodulation, setting the discrete time sequence x(n) of x, sequentially calculating the vector form Xi<^> of the non-overlapping slide window short time Fourier Transform time frequency distribution of the Xi<^> and Xi<^> of x (n), establishing the linear relation between the Xi<^> and x, setting the time-frequency point screening threshold, screening the time-frequency points contained in the Xi<^> to sequentially obtain the time-frequency points retained in the Xi<^> and a time-frequency point screening matrix Psi<^> of the Xi<^>, setting the vector form of Xi<^> after time-frequency points screening as Xi<^> bar and obtaining the linear relation among the Xi<^> bar, Psi<^> bar and Xi<^>, setting the x frequency spectrum as X, further establishing the linear relation between the Xi<^> bar and X, conducting reconstruction and inverse Fourier transform for X to obtain a reconstructed frequency demodulation target signal X<^>, and conducting inverse frequency demodulation for the X<^> to obtain the target signal after inverse frequency demodulation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Isolated feedback system for power converters
InactiveUS20110286243A1Eliminate the effects ofEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionTransformerCarrier signal
An isolated feedback system for power converters includes an error amplifier for receiving an input voltage to output an error signal; a modulator circuit to modulate the error signal with a carrier signal; an acoustic transformer unit, one end of the acoustic transformer connected to the modulator circuit, where a frequency of the carrier signal is away from resonant frequencies of the acoustic transformer; and a demodulation circuit connected to the other end of the acoustic transformer and receiving the modulated signal.
Owner:NEOENERGY MICROELECTRONICS
Parameter independent detection of rotating machinery faults
InactiveUS8544331B2Efficient implementationVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingMechanical componentsAmplitude demodulation
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA
RFOG modulation error correction
ActiveUS7855789B2Sagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsHarmonicLight beam
Systems and methods for performing modulation error correction. An example system applies common phase / frequency modulation to first and second laser beams, a first intensity modulation to the first modulated beam, and a second intensity modulation to the second modulated beam. Signals outputted are demodulated according to the frequency of the common phase / frequency modulation. Then the first of these demodulated signals is demodulated based on the frequency of the intensity modulation of the first beam, and the second of these demodulated signals is demodulated based on the frequency of the intensity modulation of the second beam. Then, rate of rotation is determined based on demodulated signals. Frequencies of the intensity modulations are unequal and not harmonically related, and intensity modulation encodes each light beam with a unique signature.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Underwater acoustic detection device based on photoelectric oscillator
ActiveCN108731789AHigh precisionImprove response rateSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansFiber gratingsSound pressure
The invention provides an underwater acoustic detection device based on a photoelectric oscillator. The device comprises a laser light source circuit, a photoelectric oscillation loop and a frequencydemodulation circuit. The device enables a phase-shifted fiber grating or a fiber grating F-P cavity interferometer to be embedded into a microwave photon filter, and uses an elastic cylinder to convert external acoustic wave changes into fiber grating stress or pressure changes, thereby enabling wavelength changes to be converted into the changes in the center frequency of the microwave photon filter, and enabling the frequency of the output microwave signal of the photoelectric oscillator to change. The underwater sound field detection is completed by analyzing the frequency changes by the digital signal demodulation technology. Compared to a conventional fiber optic hydrophone device, the device provided by the invention has higher accuracy, demodulation speed and signal to noise ratio,and a large dynamic range. The technical contents involved mainly include the microwave photon filter making technology, the multi-frequency photoelectric oscillation technology, the scalar sound pressure and three-dimensional sound field measurement technology, the signal demodulation technology, the packaging technology and the array multiplexing technology.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Envelope functions for modulation spectroscopy
InactiveUS7230711B1Minimize the differencePermit sensitive detectionRadiation pyrometryOptical rangefindersPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A spectrometer and spectrometry method comprising modulating a light source with a carrier waveform multiplied by an envelope function, directing light from the light source through a sample region and to a photodetector, and demodulating current from the photodetector at a reference frequency. Also a method for computing a modulation waveform comprising specifying a target detection efficiency in a Fourier space, computing a response of a waveform that comprises a carrier wave multiplied by an envelope function, and modifying the envelope function using nonlinear optimization means to minimize a difference between the computed response and a predetermined target detection efficiency.
Owner:SOUTHWEST SCI
Method and apparatus for generating absolute time in pregroove data
InactiveUS20050226114A1Generate accuratelyFilamentary/web record carriersRecord information storageCompact discOriginal data
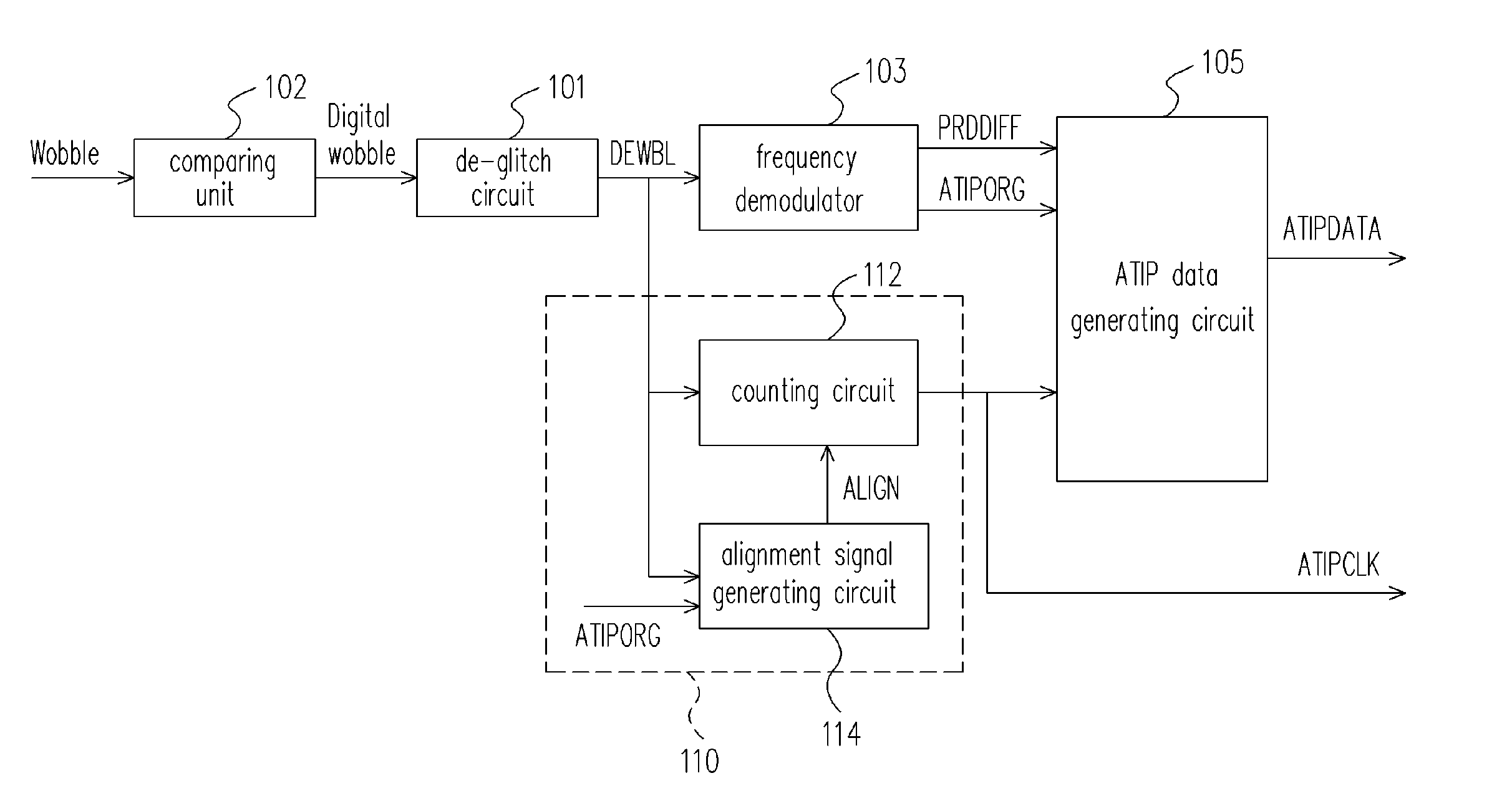
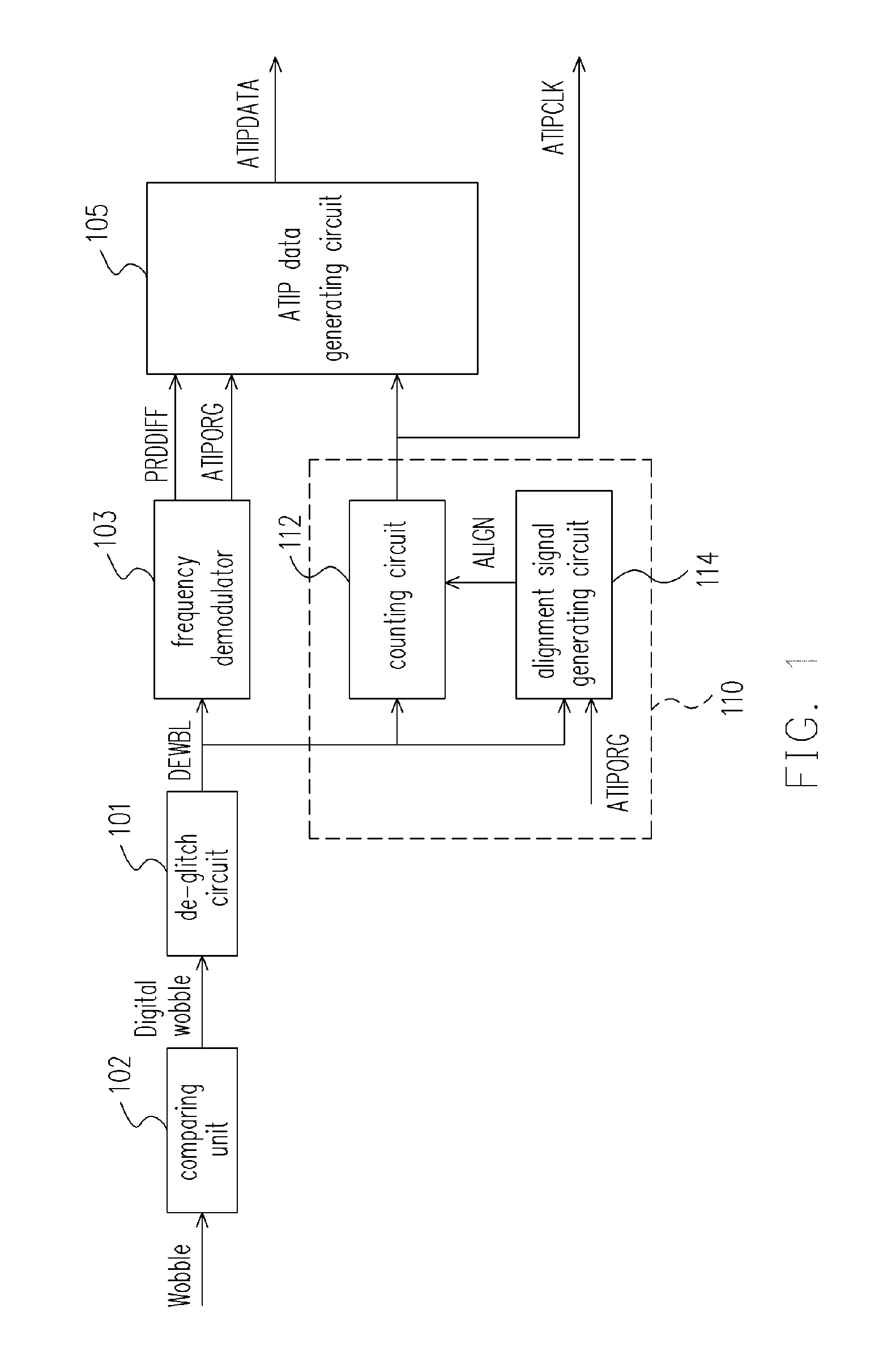
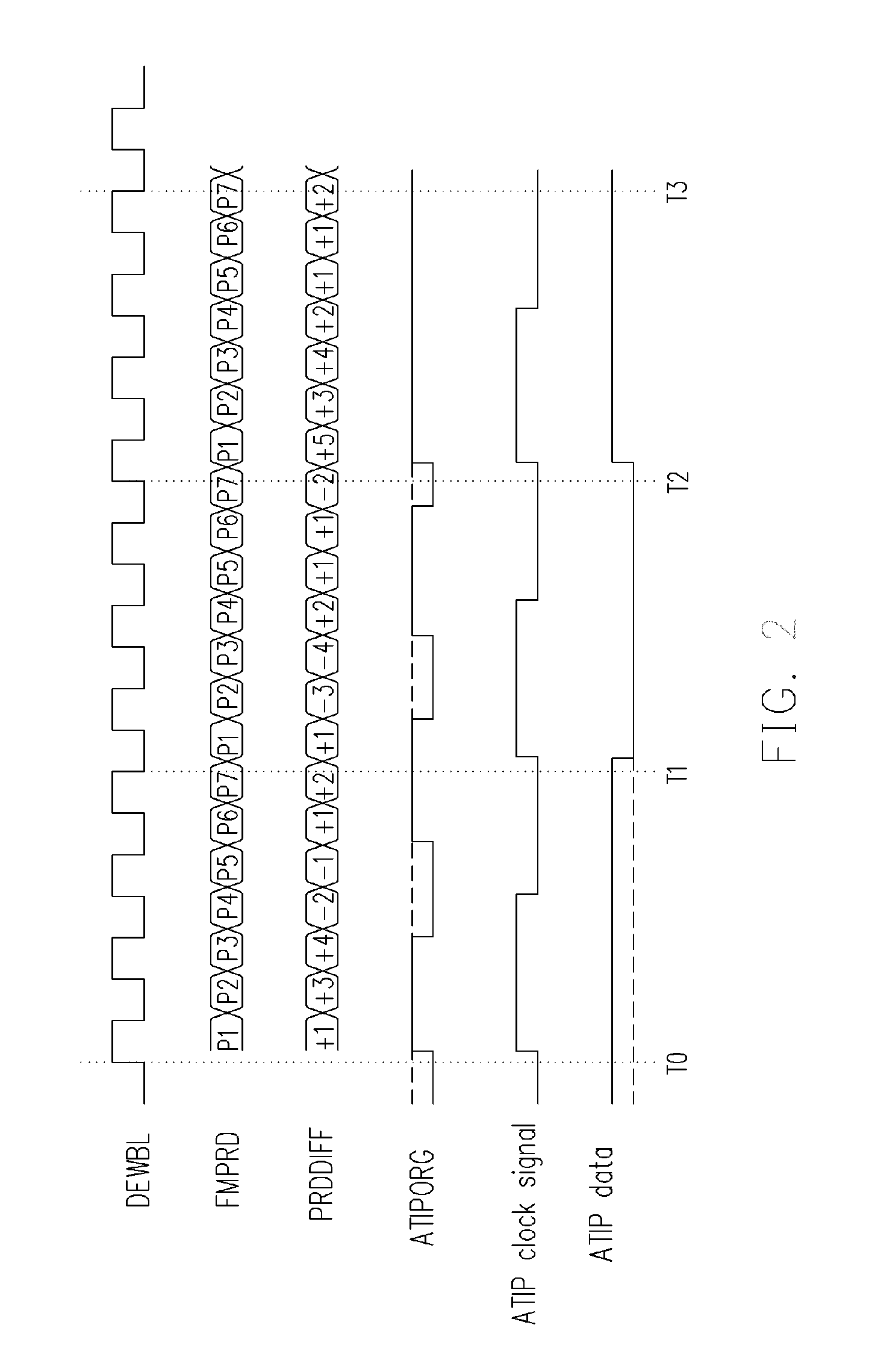
An apparatus and a method for generating an ATIP data are provided. The apparatus, based on a wobble signal generated by reading a re-writable compact disc, generates an ATIP data; the apparatus includes: a frequency demodulator for demodulating the wobble signal to generate an original ATIP data signal; an ATIP clock generating circuit for generating an ATIP clock signal based on the wobble signal; and a data generating circuit, coupled to the frequency demodulator and the ATIP clock generating circuit, for generating the ATIP data based on the number of the original ATIP data signal at a first logic level during one period of the ATIP clock signal. This apparatus uses the number of the original ATIP data signal at a first logic level during one period of the ATIP clock signal and the bi-phase rule to precisely generate the ATIP data.
Owner:TIAN HLDG
Carrier tracking device capable of adaptively adjusting parameters
ActiveCN102801671AImprove signal-to-noise ratioHigh Doppler Rate of ChangeModulated-carrier systemsSynchronising arrangementIntegratorCarrier signal
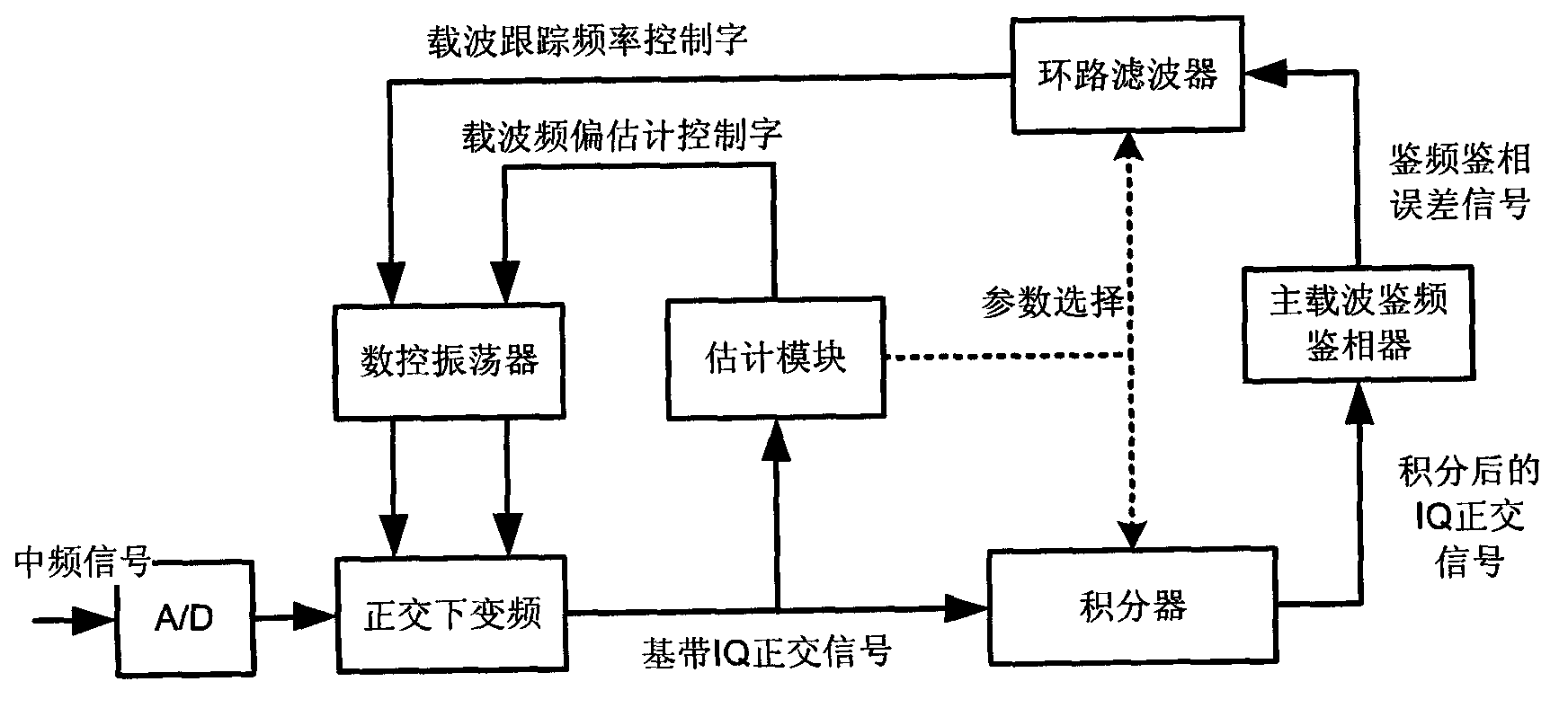
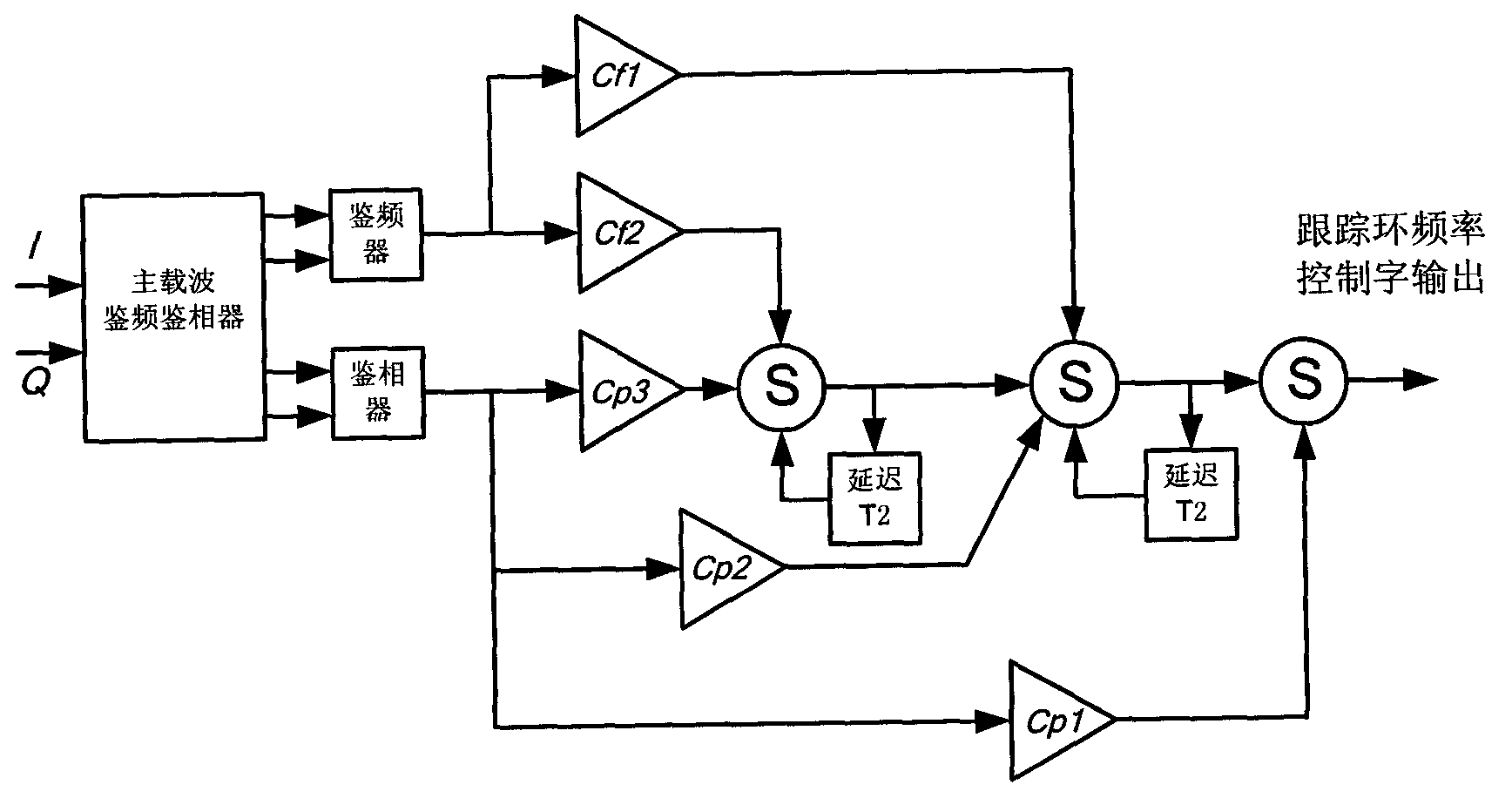
The invention discloses a carrier tracking device capable of adaptively adjusting parameters, comprising an A / D (Analogue / Digital) converter, an orthogonal down convertor, a digital control oscillator, an estimation module, an integrator, a main carrier frequency demodulation and phase demodulation device and a loop filter, wherein an orthogonal down convertor module utilizes a local reference signal to carry out digital down conversion on a sampling signal output by the A / D converter to generate a baseband signal; the digital control oscillator generates the local reference signal according to a carrier frequency offset control word and a carrier tracking frequency control word; the carrier frequency offset control word is generated by the estimation module according to the baseband signal; the carrier tracking frequency control word is generated by the loop filter according to a frequency demodulation and phase demodulation error signal; the main carrier frequency demodulation and phase demodulation device generates the frequency demodulation and phase demodulation error signal according to an integrated signal; and the integrator and the loop filter determine the integrated time and loop filtering parameter according to selected parameters and the selected parameters are determined according to a signal to noise rate of the baseband signal by the estimation module. The carrier tracking device disclosed by the invention can realize the self-adaptive tracking on an upstream carrier signal according to the estimation of the baseband signal of an input signal.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
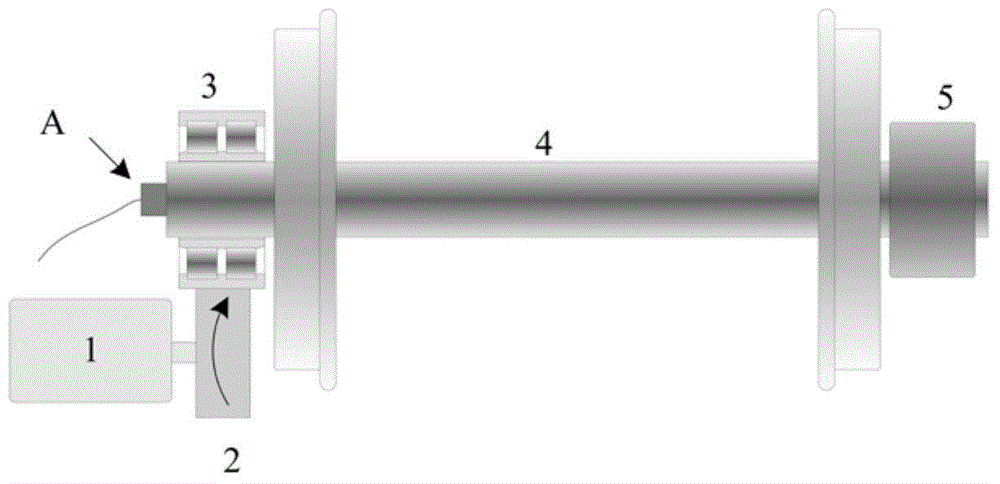
Transmitting system based on rotary mechanical antenna and information loading method
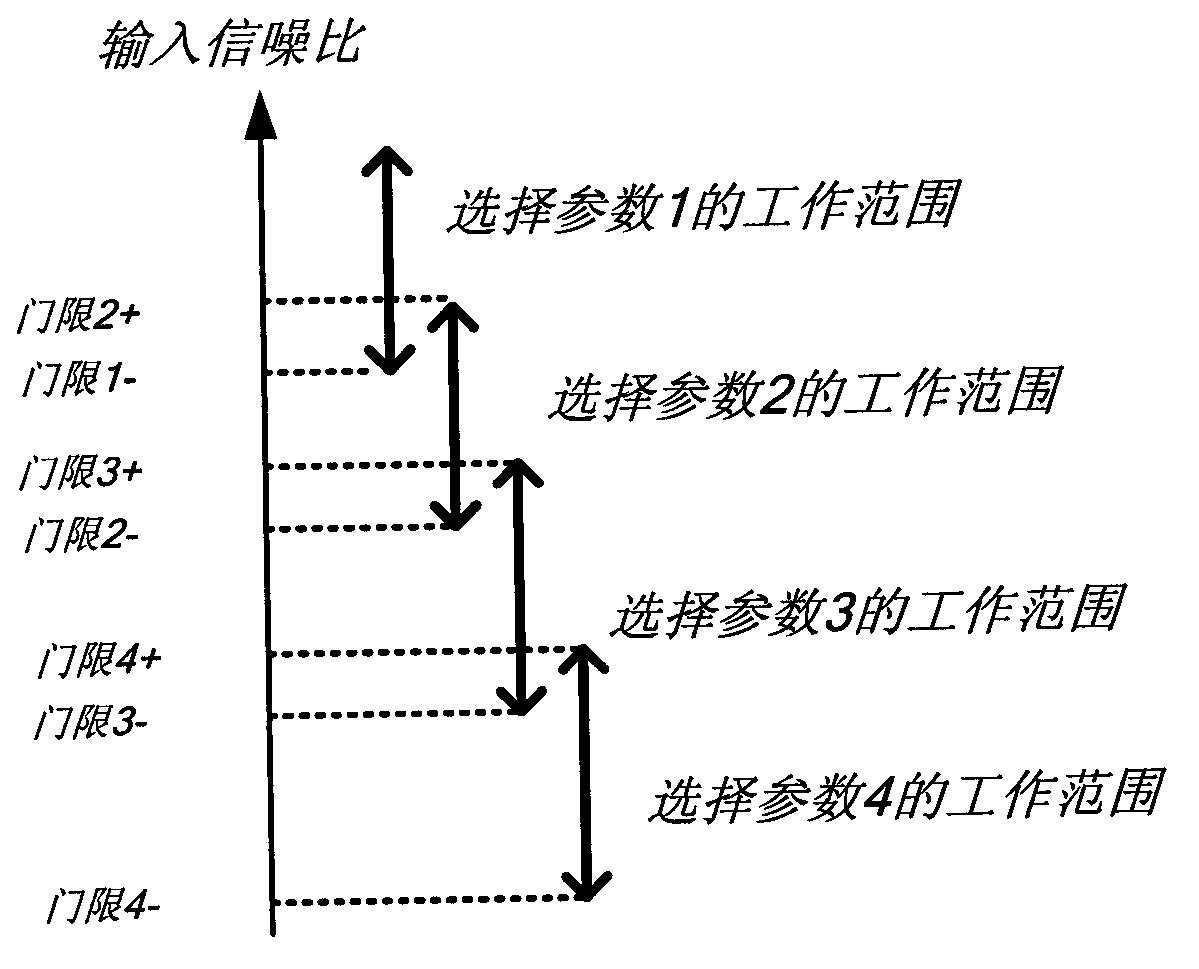
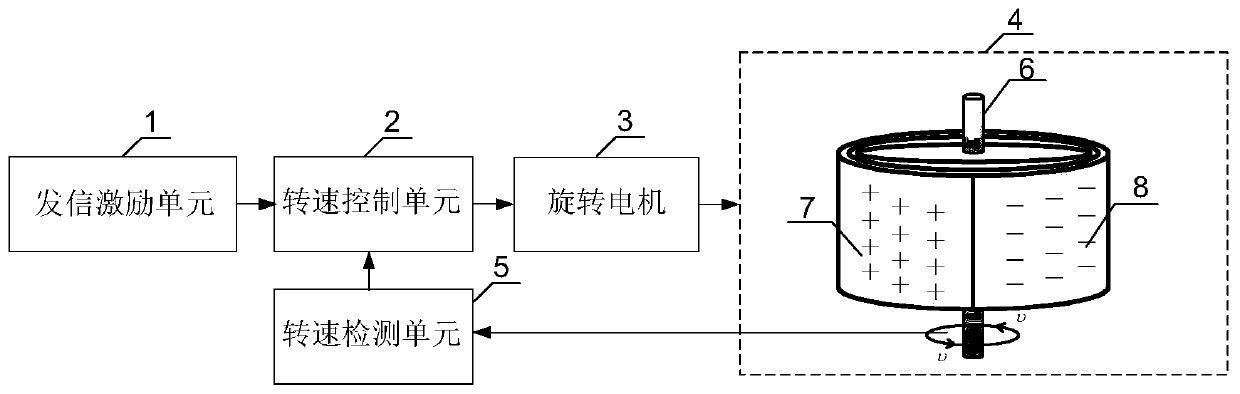
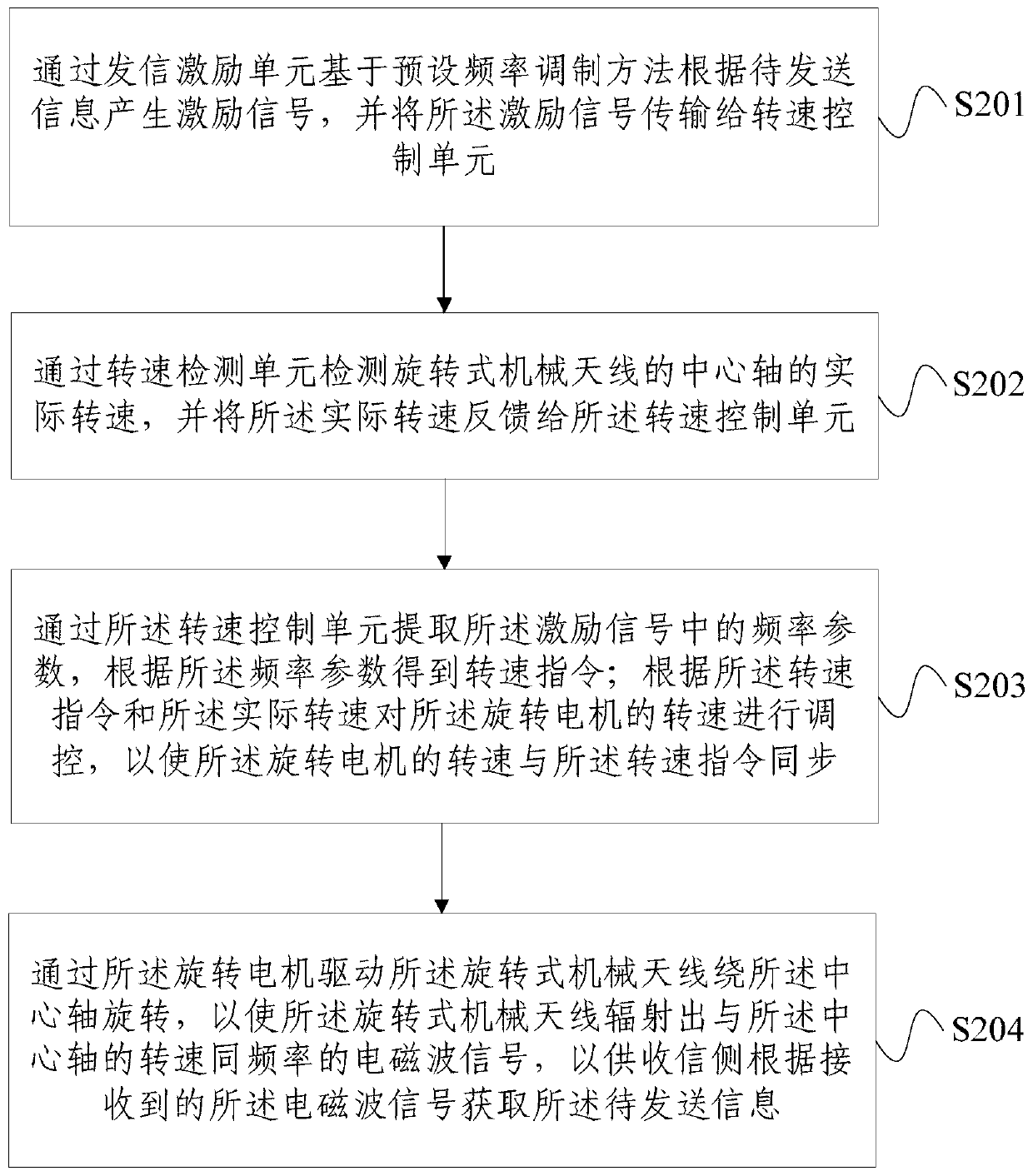
ActiveCN110943953ARealize long-distance communicationRadiating elements structural formsFrequency-modulated carrier systemsElectric machineClosed loop feedback
The invention provides a transmitting system based on a rotary mechanical antenna and an information loading method. The method comprises: information is loaded to a frequency parameter for emitting electromagnetic waves through rotating speed regulation and control according to requirements of a signalling excitation signal; then through rotating speed detection and closed-loop feedback control,regulating and controlling the rotating speed of the rotating motor and the mechanical antenna fixedly connected with the rotating motor, and achieving frequency control of an emitted electromagneticwave; and driving the rotary mechanical antenna by the rotary motor to rotate around the center shaft at a high speed, transmitting electromagnetic waves with the same frequency as the rotating speedto the outside, receiving the transmitted electromagnetic wave signal by a receiving side, receiving information through frequency demodulation, and then achieving low-frequency radio long-distance communication.
Owner:武汉船舶通信研究所
Method of simultaneously performing packet detection, symbol timing acquisition, and carrier frequency offset estimation using multiple correlation detection, and bluetooth apparatus using same
ActiveUS20190028316A1Improve accuracyEnsure reliabilitySynchronisation arrangementMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsCarrier frequency offsetBluetooth
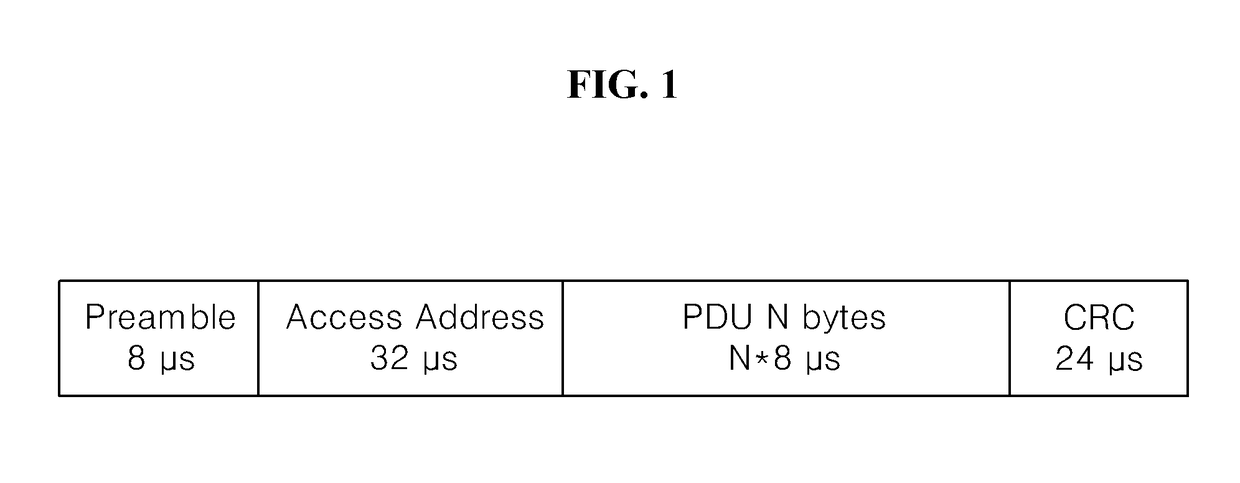
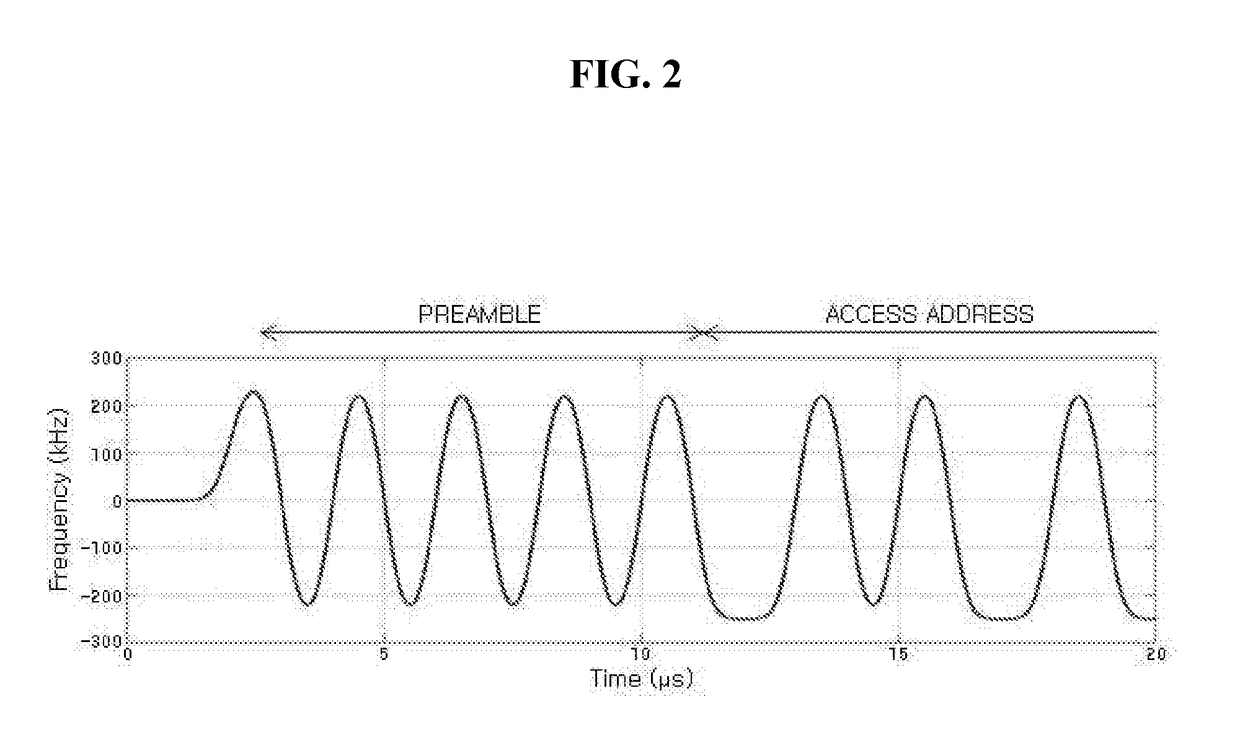
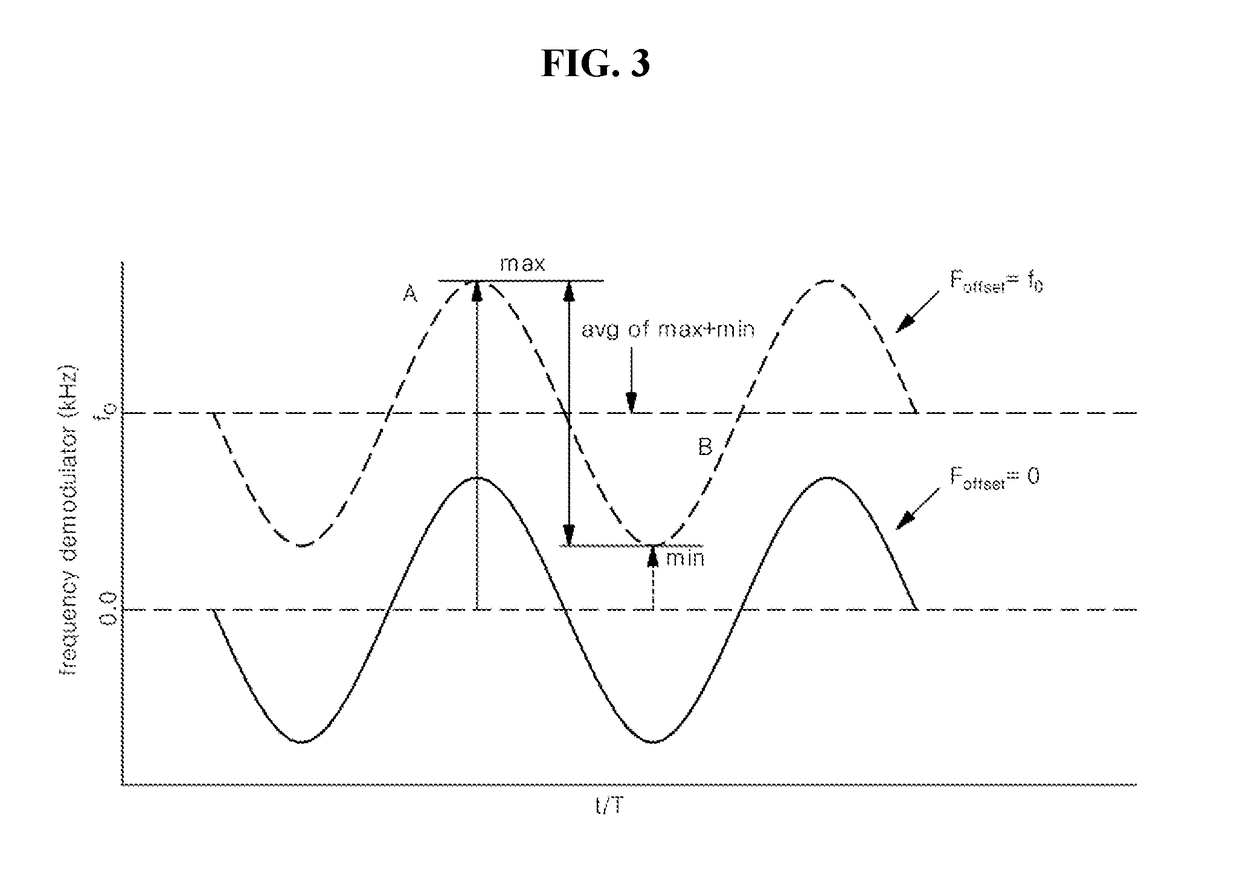
The present invention relates to a method of simultaneously performing packet detection, symbol timing acquisition, and carrier frequency offset estimation in parallel using multiple correlation detection and a Bluetooth apparatus using the same, in which the Bluetooth apparatus receiving a frequency modulated signal includes a frequency demodulating unit converting the received signal into a similar amplitude modulated signal; and multiple correlation detectors generating multiple correlation indices from the converted signal, on a basis of an access address received from a link layer and a plurality of carrier frequency offset search windows. According to the present invention, since packet detection, symbol timing acquisition and carrier frequency offset estimation are simultaneously performed in parallel in the relatively long access address reception interval instead of the short preamble signal reception interval.
Owner:ABOV SEMICON
Multi-wavelength Brillouin fiber laser based optical fiber temperature sensor
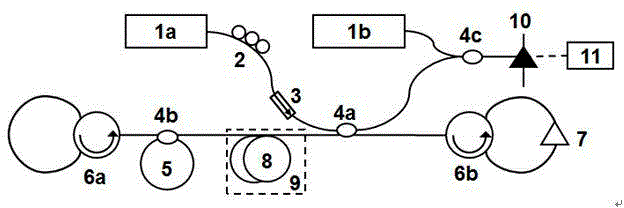
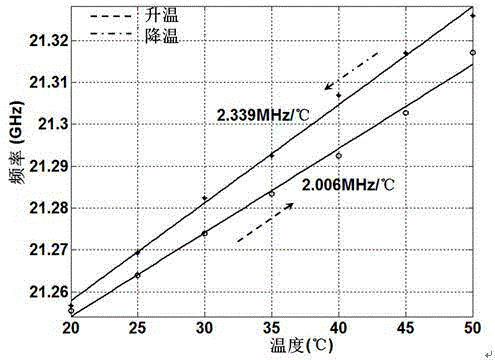
ActiveCN104390723AHigh precision temperature measurementHigh temperature sensitivityThermometers using physical/chemical changesSpectrum analyzerLine width
A multi-wavelength Brillouin fiber laser based optical fiber temperature sensor which is formed according to an optical fiber Brillouin gain effect, an er-doped optical fiber amplifying effect, a multi-level Brillouin scattering temperature effect and a heterodyning beat frequency demodulation principle comprises a narrow line width single frequency laser, an optical branching device, a polarization controller, an opto-isolator, an optical circulator, a single-mode sensing fiber, an er-doped optical fiber amplifier, an er-doped optical fiber being not pumped, a high-speed photoelectric detector and a frequency analyzer. The multi-wavelength Brillouin fiber laser based optical fiber temperature sensor has the advantages of being many in the number of wavelengths, narrow in line width, fixed in wavelength interval and stable in output. The multi-wavelength Brillouin fiber laser based optical fiber temperature sensor achieves heterodyning best frequency demodulating detection of a high-order stokes wave and high-accuracy high-sensitivity temperature measuring with the single-mode optical fiber which provides gain for the fiber laser being served as a temperature sending detect unit.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
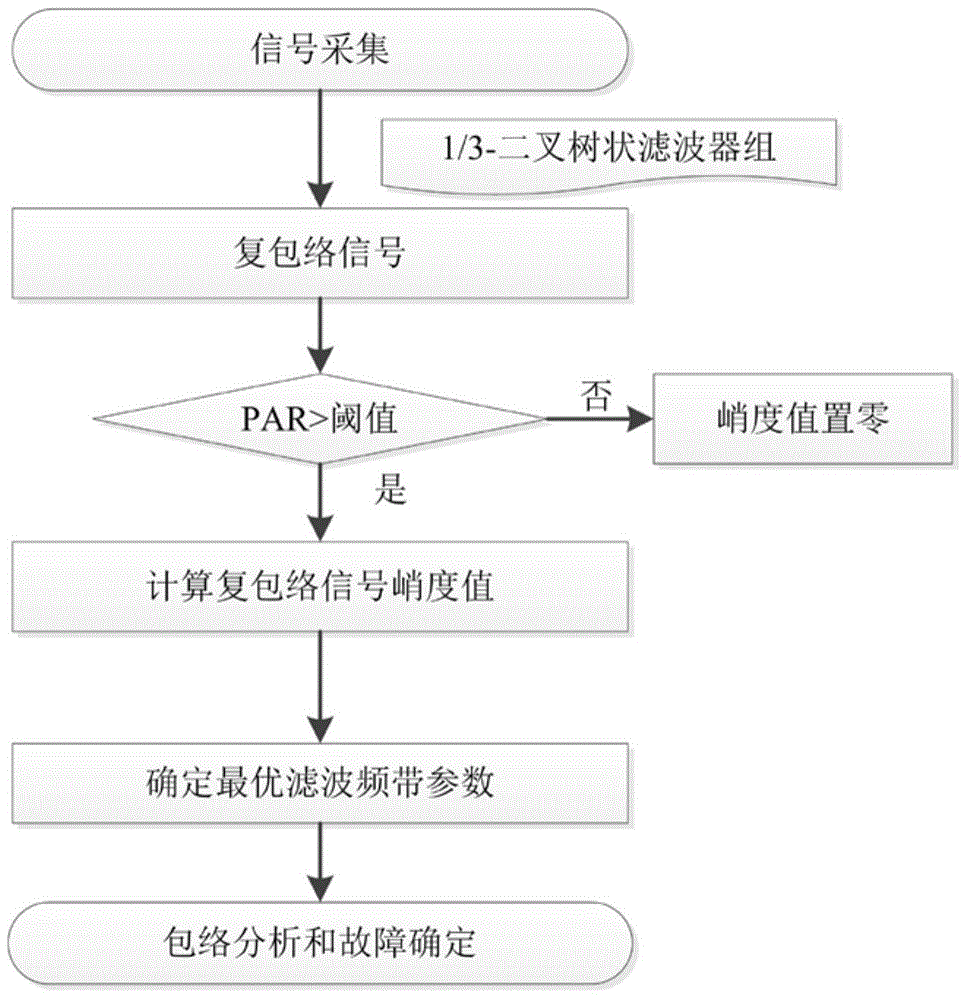
Method for confirming optimal resonance frequency band based on period target
ActiveCN104316323AAvoid interferenceRobustMachine bearings testingFeature extractionFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a method for confirming an optimal resonance frequency band based on a period target, and the method is characterized by adsorbing a vibration acceleration sensor to a tested rolling bearing pedestal to acquire vibration signals, creating a 1 / 3 binary tree filter bank to gain filtered complex envelope signals, calculating the periodical intensity PAR of each envelope signal, clearing the complex envelope signal kurtosis value less than a threshold value, calculating the kurtosis values of the surplus envelop signals, selecting the frequency band corresponding to the greatest-kurtosis complex envelope signal as the optimal resonance frequency band and the frequency spectrum of the envelope signal so as to obtain an envelop spectrum, in comparison with the fault feature frequency corresponding to the fault type in the rolling bearing, finally confirming the fault type of the rolling bearing; the method utilizes the substantive characteristics of the fault stimulation impact to avoid the non-periodic impact to interfere the resonance frequency demodulation band, and the method has robustness and can accommodate the confirmation process of the resonance frequency demodulation band so that fault feature extraction and diagnostic test can be automatically achieved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Gear fault detection method and system of planetary gear box
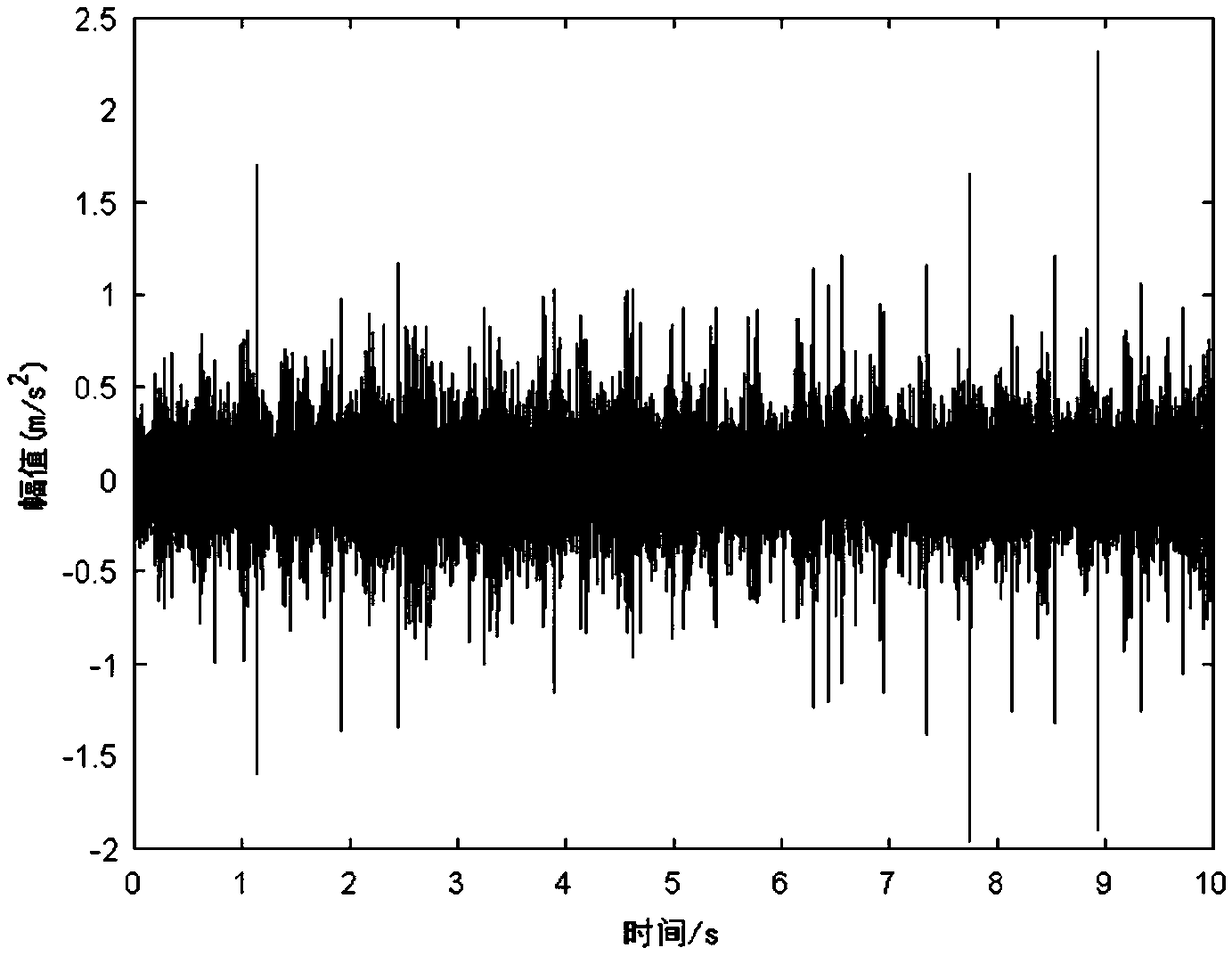
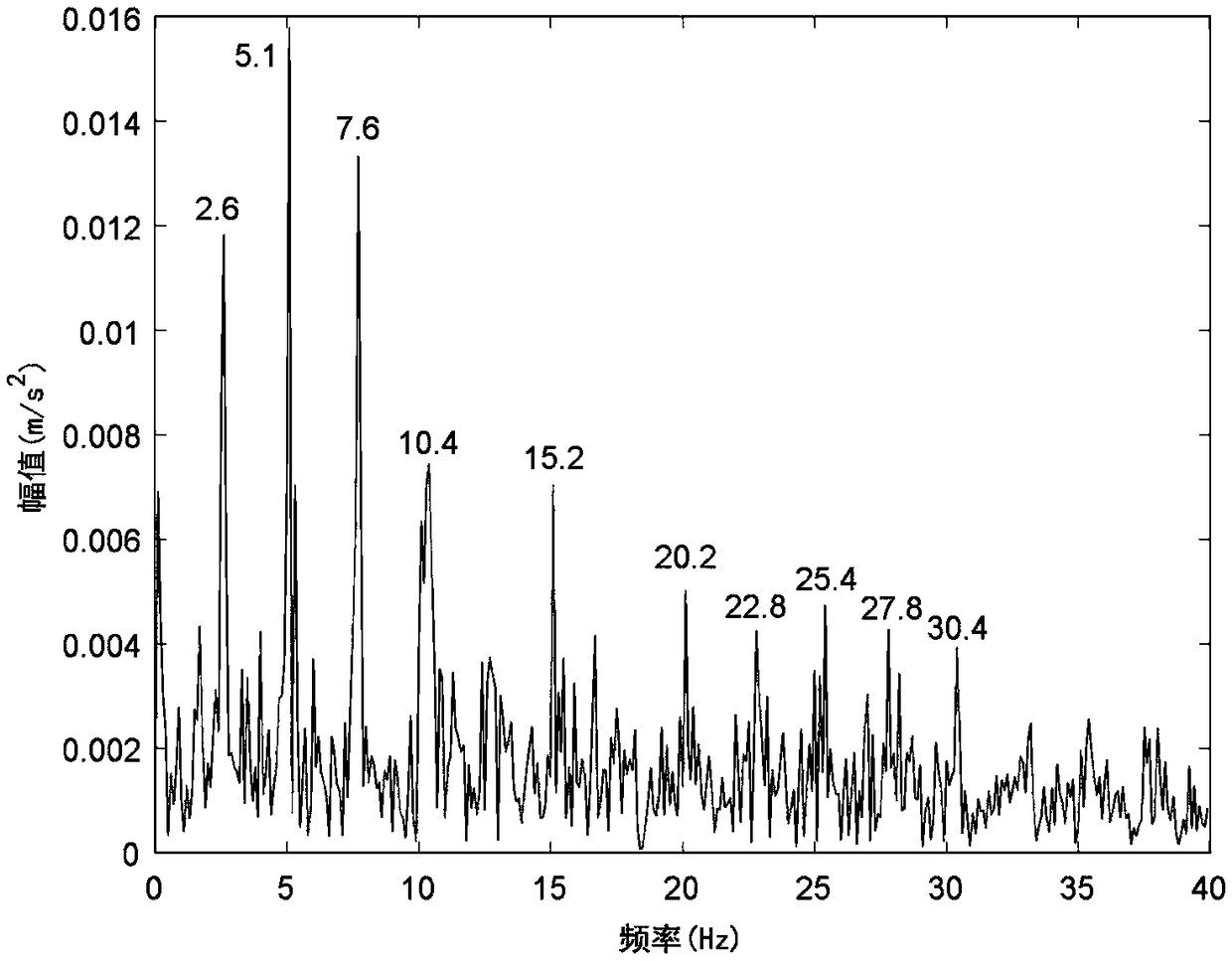
ActiveCN109029987AEffectively judge fault informationReduce lossesMachine gearing/transmission testingFrequency spectrumGear wheel
The embodiment of the invention provides a gear fault detection method and system of a planetary gear box. The method comprises the following steps: performing empirical modal decomposition on an acquired gear vibration signal to obtain multiple intrinsic modal components corresponding to the gear vibration signal; determining the preset amount of target component from all intrinsic modal components, and performing signal recombination of the preset amount of target component to obtain a recombined signal; performing band-pass filtering and Hilbert demodulation on the recombined signal to obtain a feature frequency demodulation spectrum of a gear so as to perform the fault detection on the gear according to the feature frequency demodulation spectrum of the gear. Through the gear fault detection method and system of the planetary gear box provided by the embodiment of the invention, the spectrum feature of the gear fault can be extracted through the empirical modal decomposition and the Hilbert demodulation technology, thereby effectively judging the fault information of the gear, and the corresponding processing can be performed in time according to the fault information so as toreduce the loss on the material resources, the financial resources and the manpower aspects.
Owner:北航(天津武清)智能制造研究院有限公司 +1
Multistage Demodulation Pixel and Method
ActiveUS20110273561A1Reduce Motion ArtifactsImprove performanceTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringFrequency demodulation
A demodulation structure for a n-tap pixel, mainly for 3D time-of-flight (TOF) applications uses a 2-stage switch structure for demodulating a modulated electromagnetic wave. An almost arbitrary number of storage sites per pixel can be implemented enabling an almost arbitrary number of samplings captured during one exposure. It also provides the option to demodulate and integrate different phasing samples according to the different modulation frequencies within the same exposure.
Owner:AMS SENSORS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
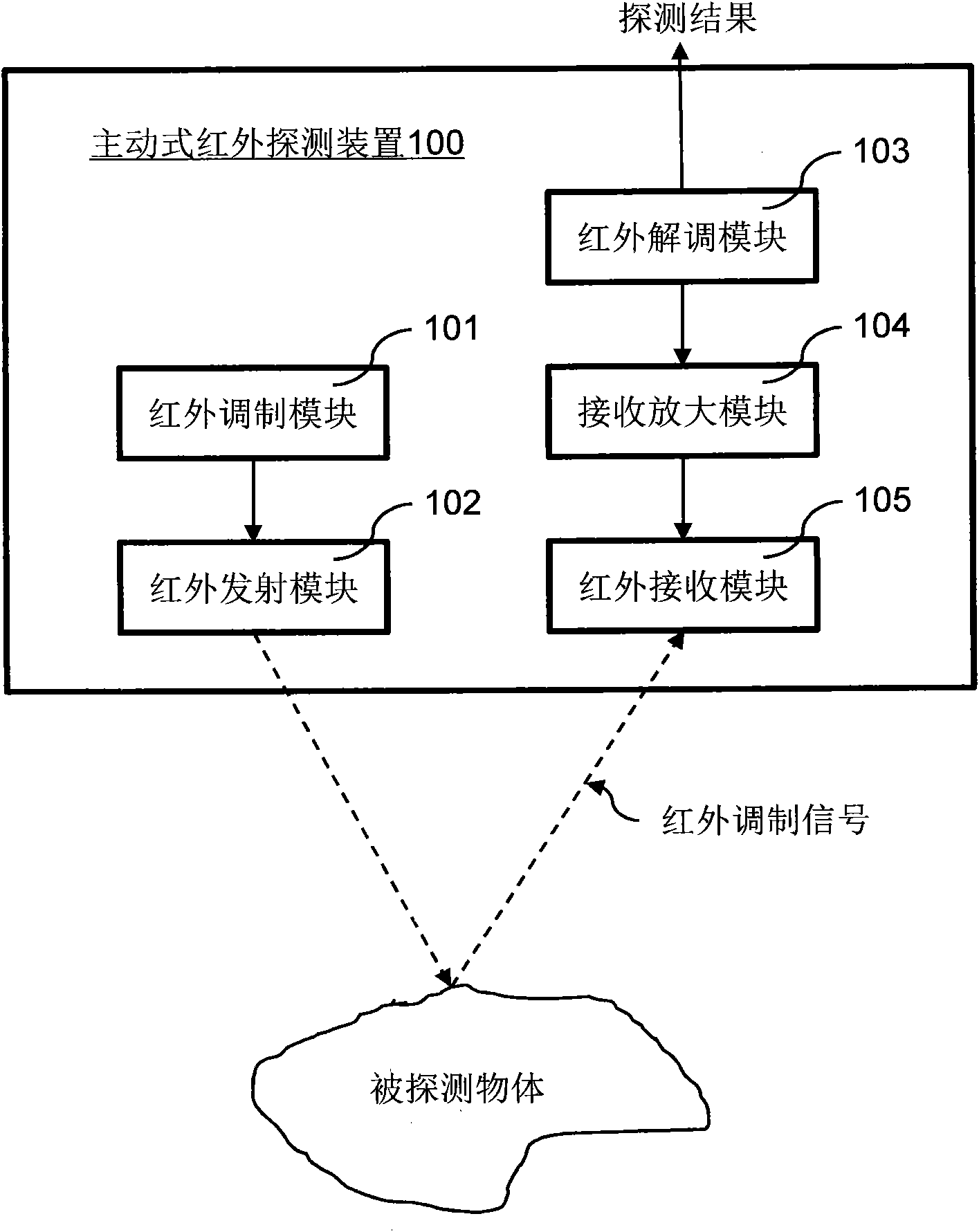
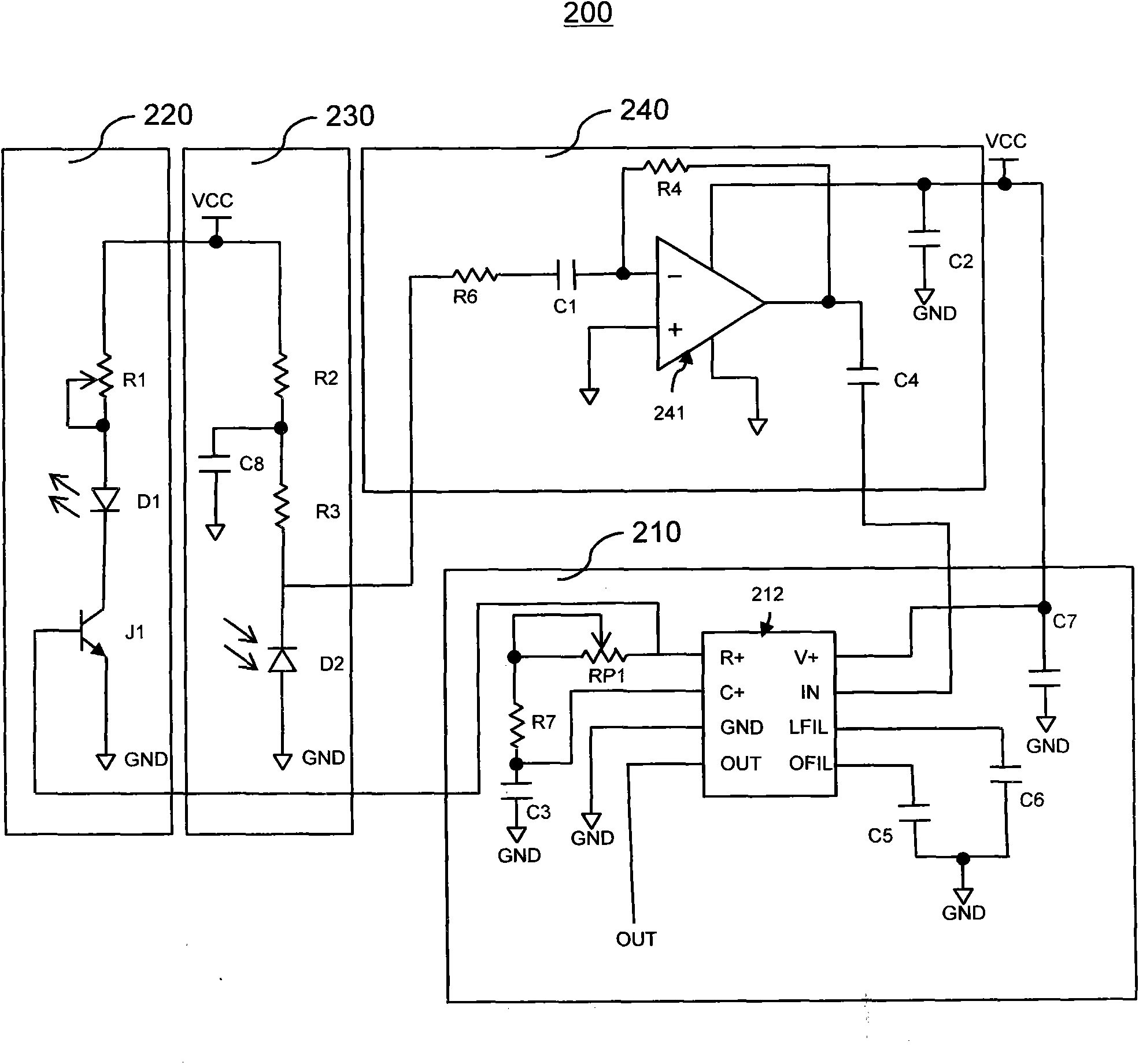
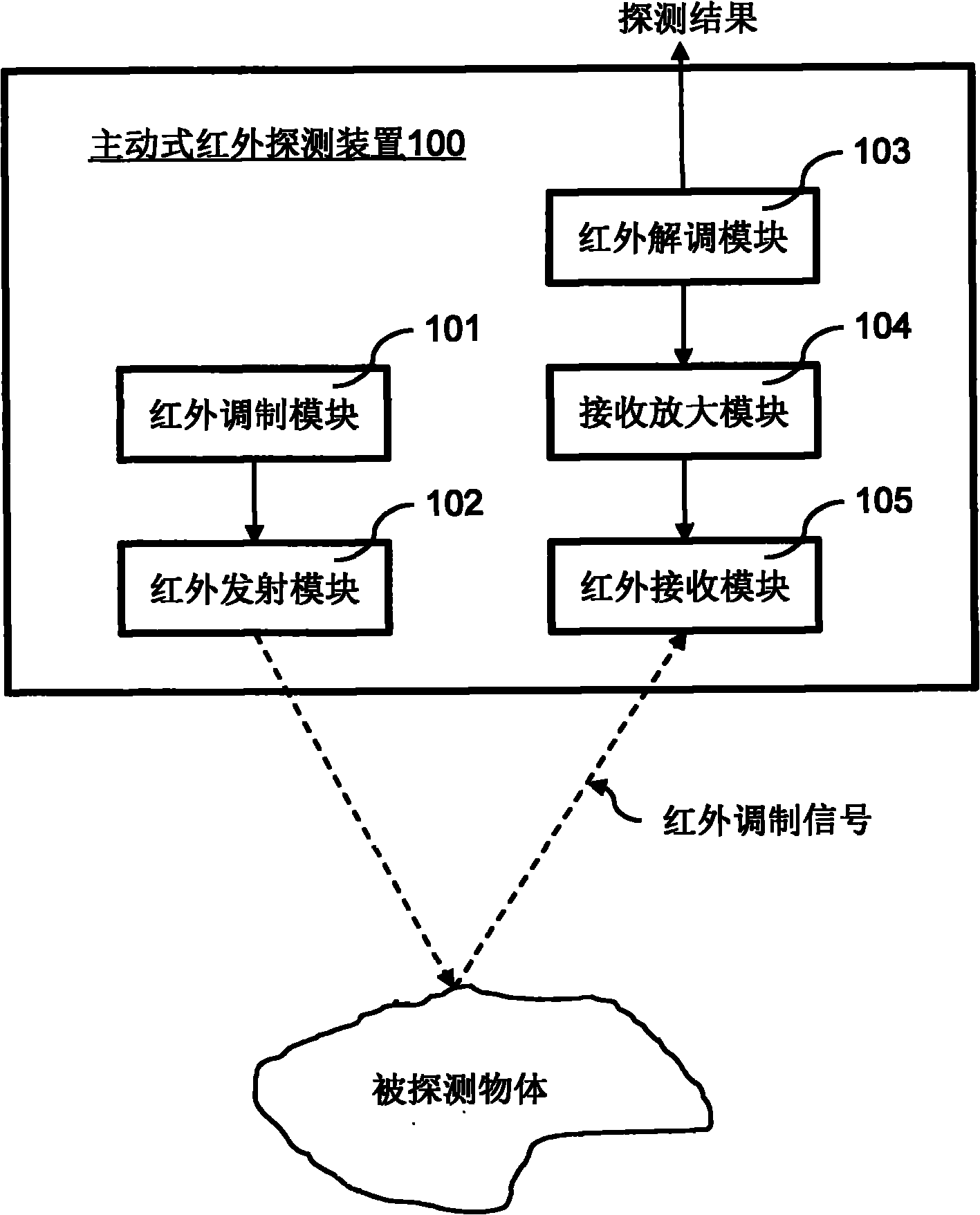
Active infrared detection device
ActiveCN101943762ANo received signalNo situationOptical detectionFrequency demodulationActive infrared
The invention discloses an active infrared detection device. The device comprises an infrared modulating module, an infrared transmission module, an infrared receiving module and an infrared demodulating module, wherein the infrared modulating module modulates an infrared modulating signal according to a preset frequency; the infrared transmission module transmits the infrared modulating signal to detect an object; the infrared receiving module receives the infrared modulating signal reflected by the detected object; and the infrared demodulating module demodulates the infrared modulating signal according to the preset frequency. The active infrared detection device transmits and receives the infrared ray with a 'special mark' by a method for modulating and demodulating the transmitted infrared ray with the same frequency signal, eliminates most infrared jamming caused by environmental factors, and acquires excellent antijamming capacity.
Owner:WUXI ZGMICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com