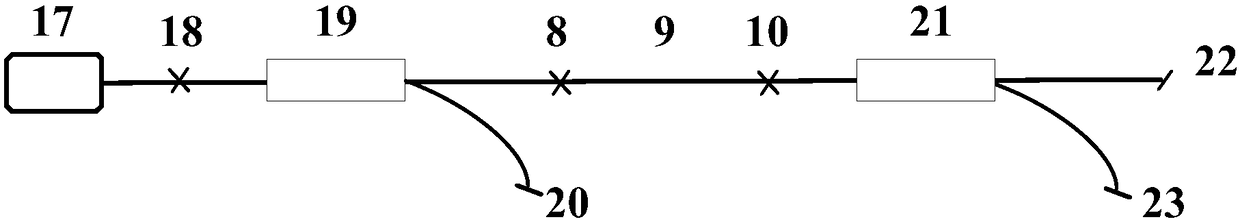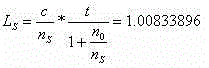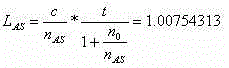Patents
Literature
38 results about "Stokes wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In fluid dynamics, a Stokes wave is a non-linear and periodic surface wave on an inviscid fluid layer of constant mean depth. This type of modelling has its origins in the mid 19th century when Sir George Stokes – using a perturbation series approach, now known as the Stokes expansion – obtained approximate solutions for non-linear wave motion.
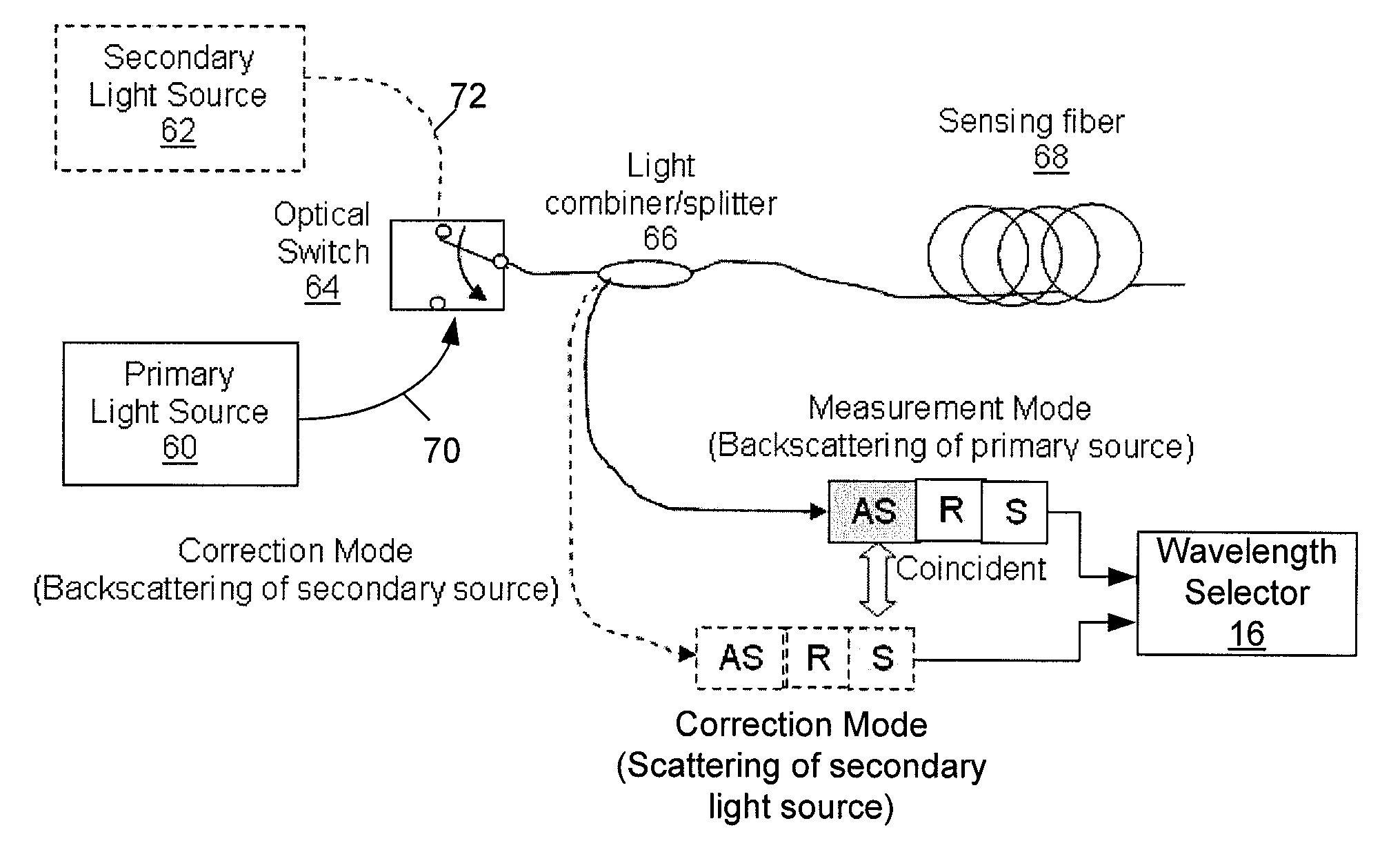
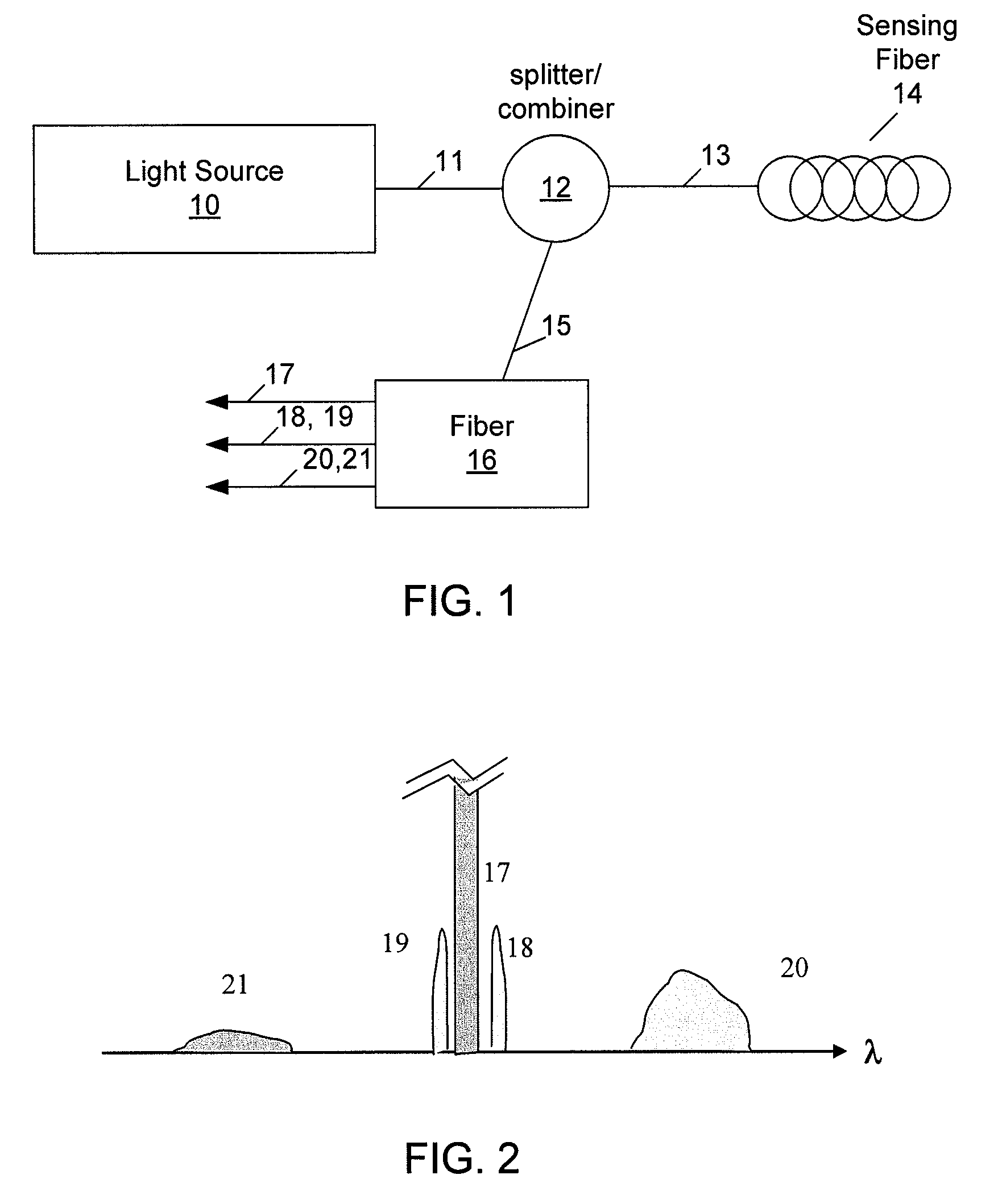
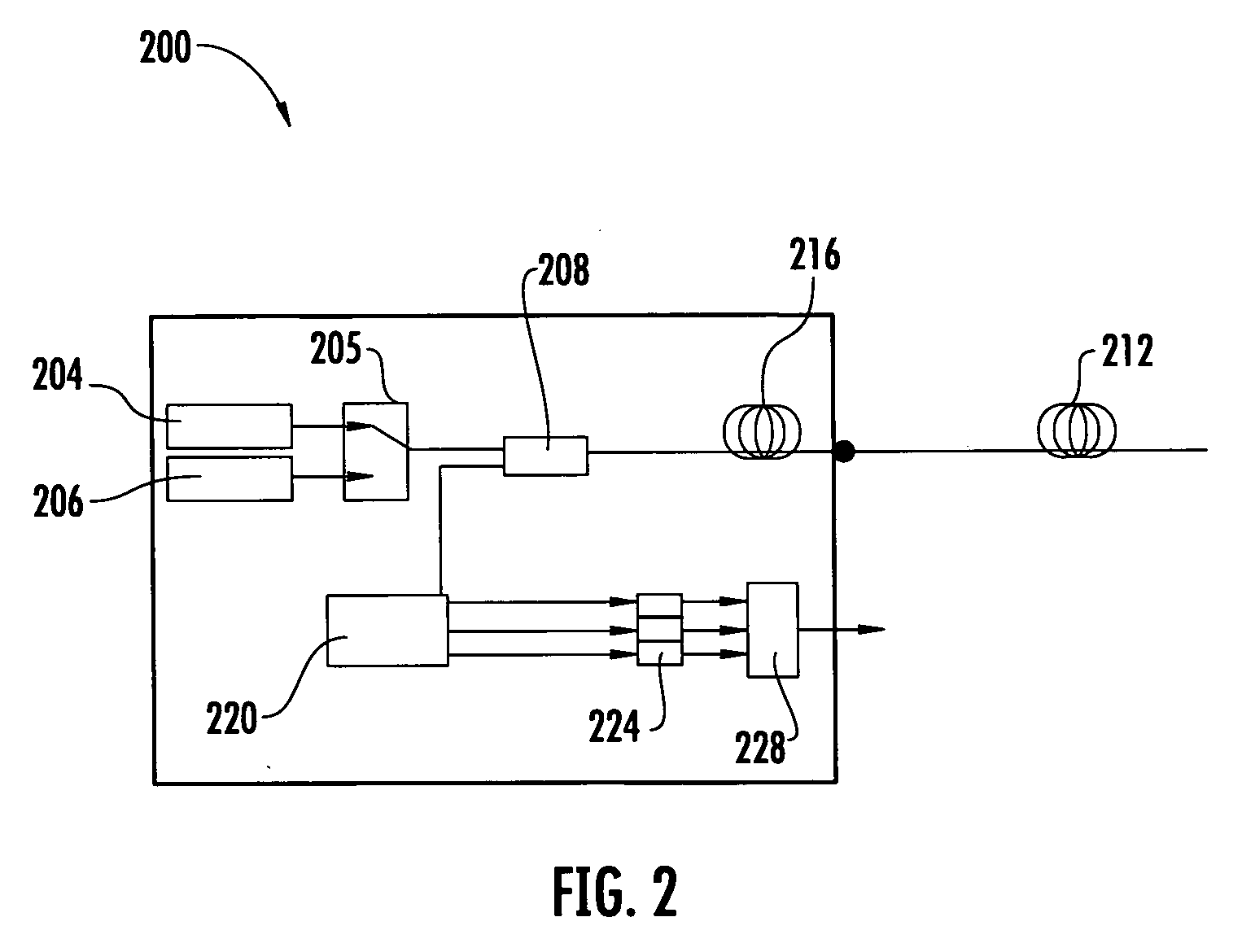
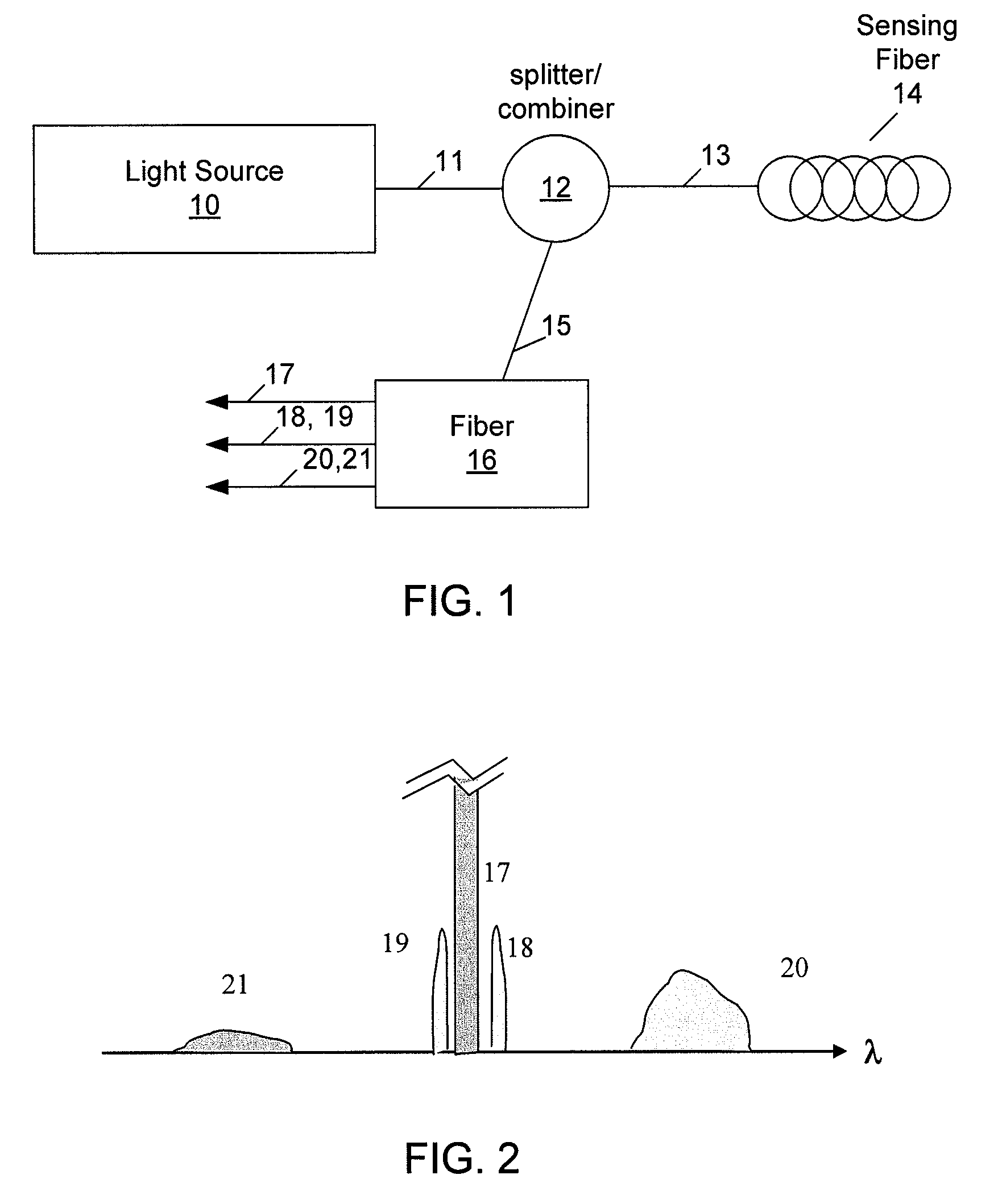
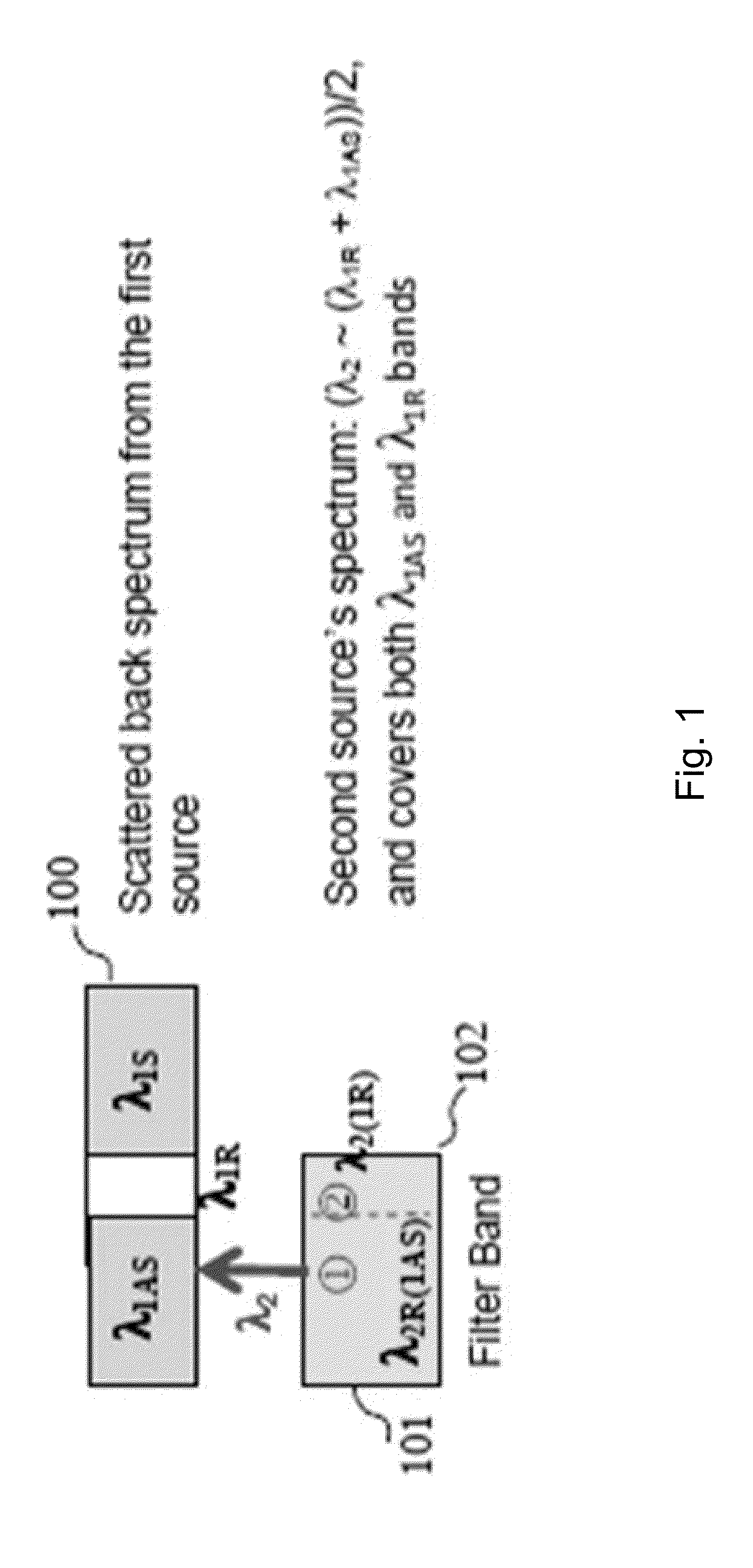
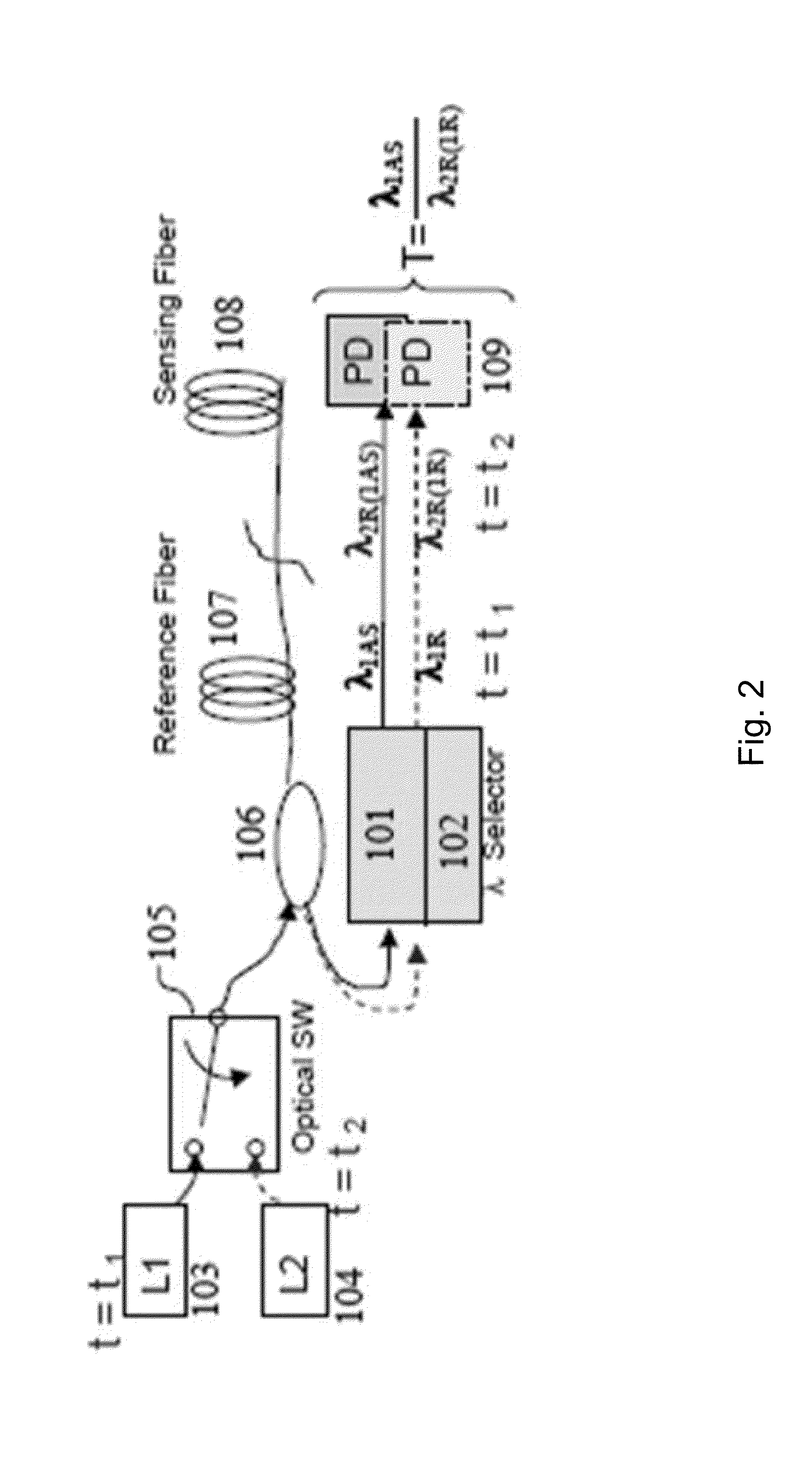
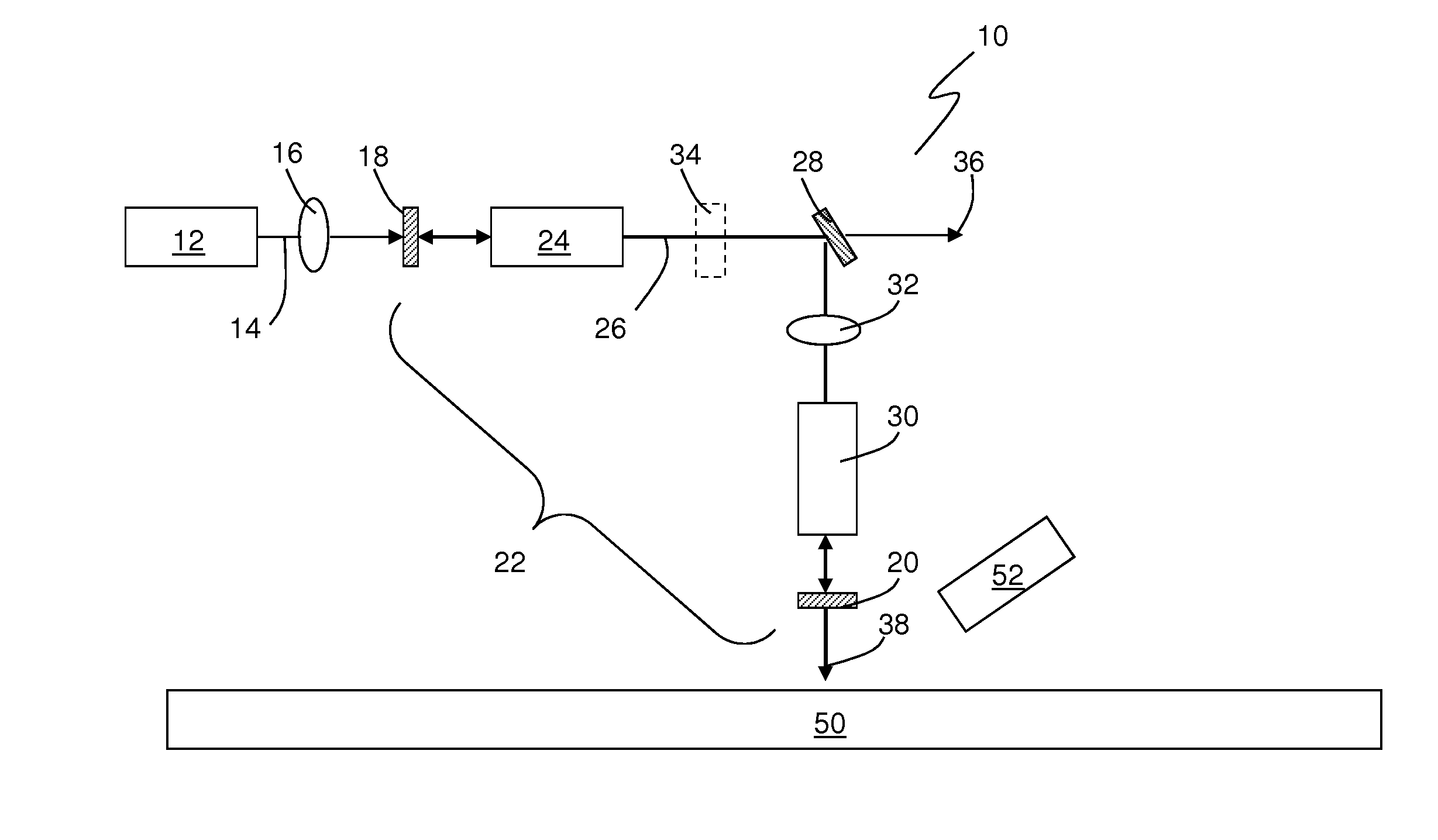
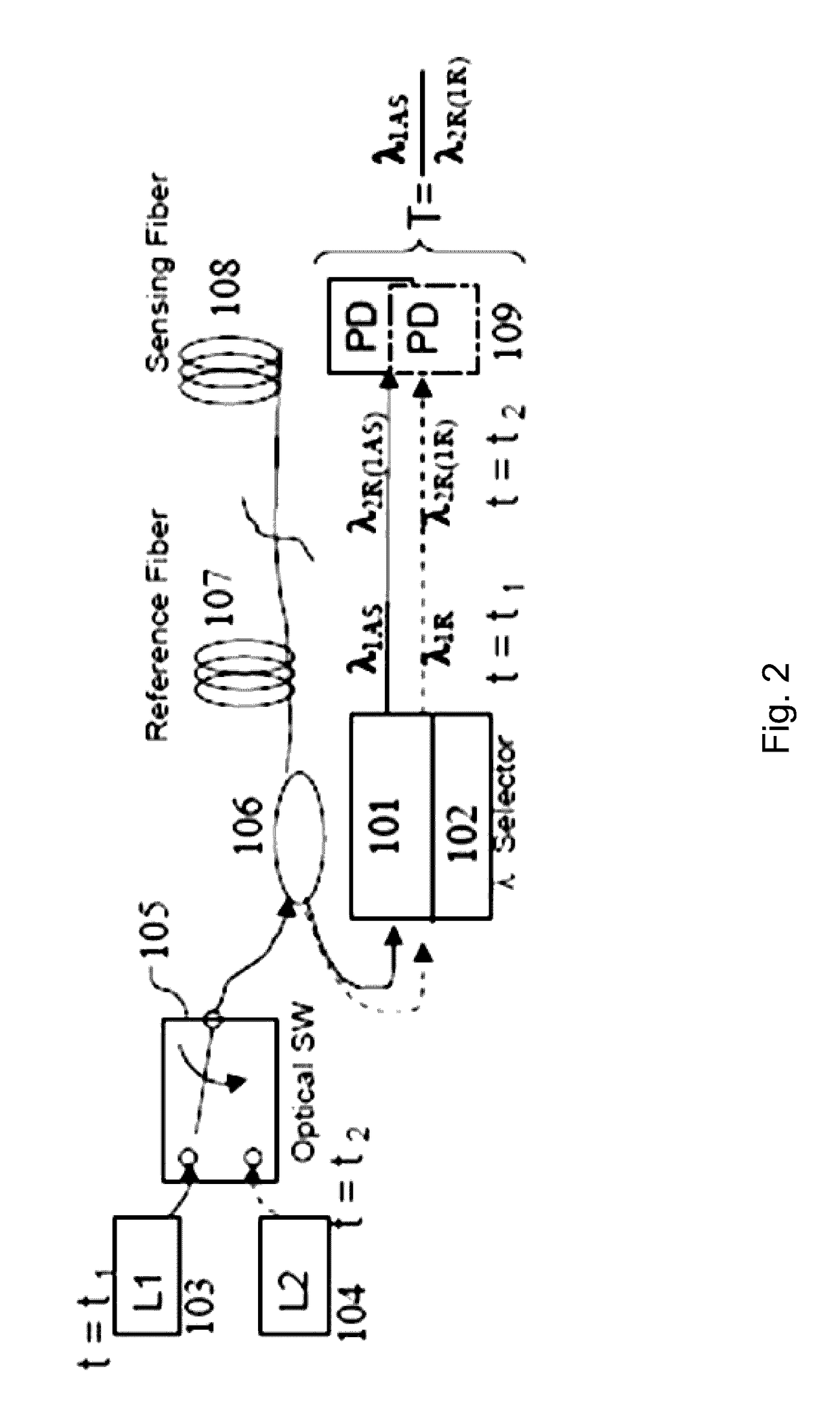
Methods and apparatus for dual source calibration for distributed temperature systems
InactiveUS20070223556A1Accurate temperature profileAccurate profileRadiation pyrometryWeather/light/corrosion resistanceFiberWave band
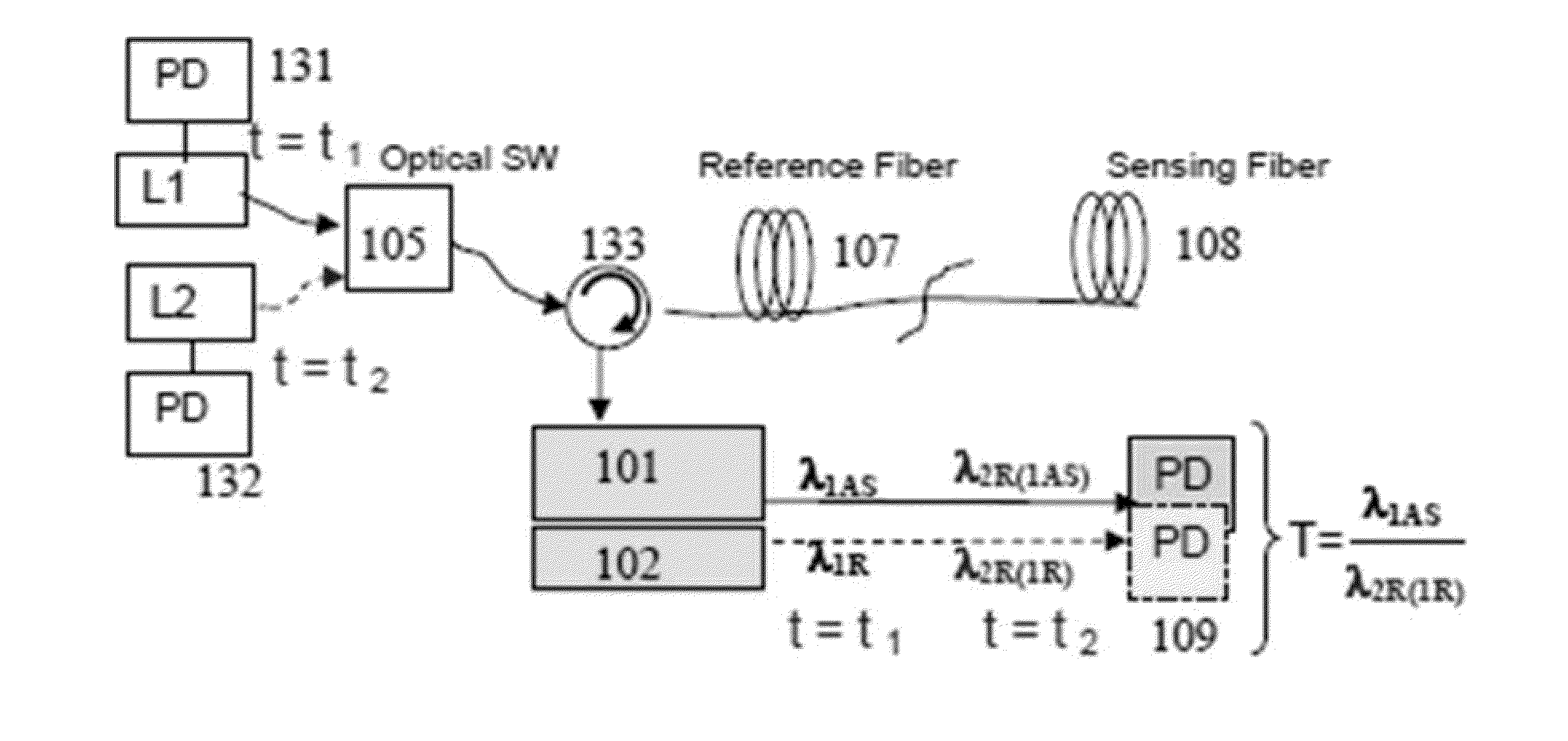
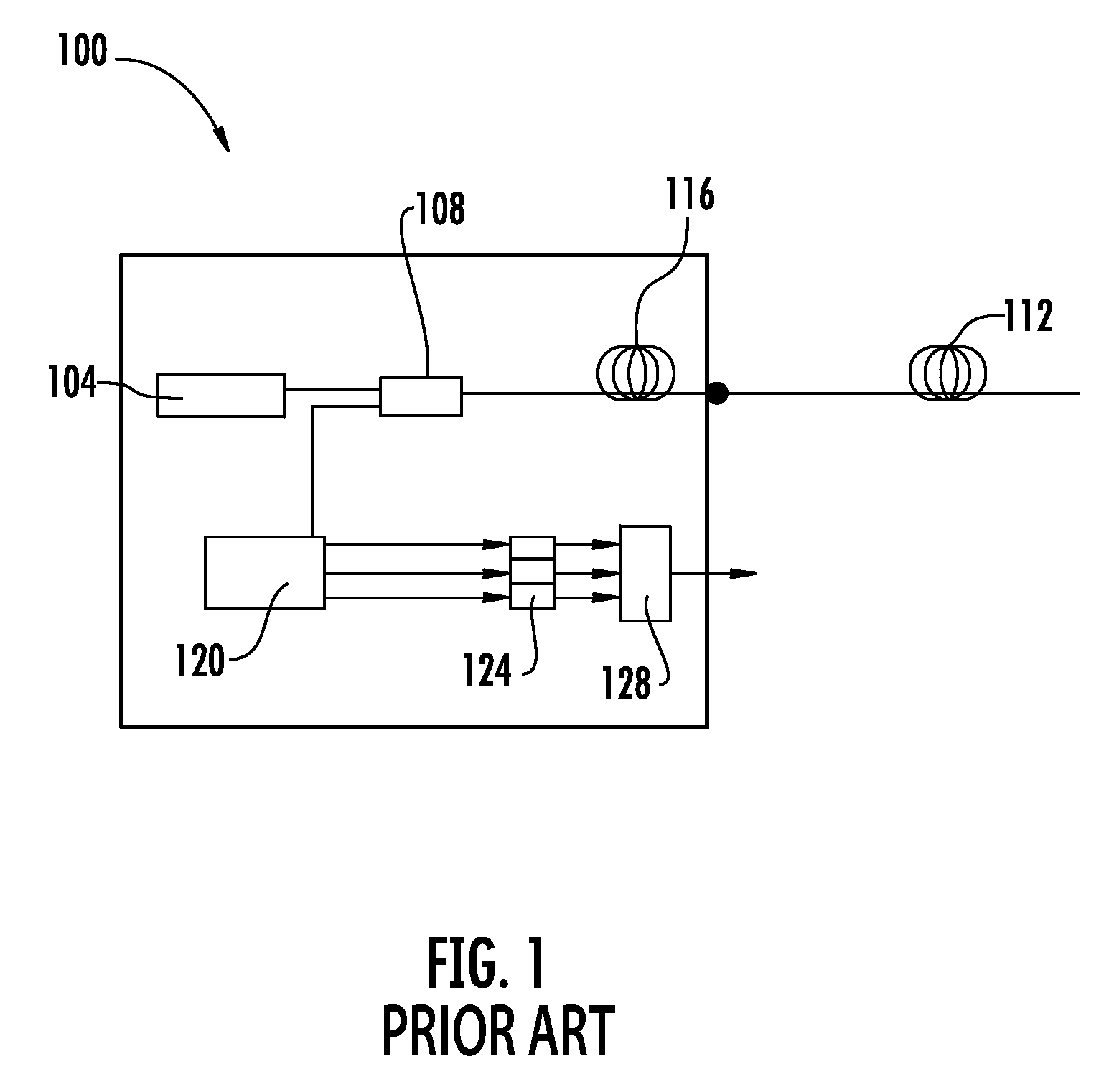
Systems and methods for calibrating a temperature sensing system are disclosed. In one respect, a dual light source configuration may be provided. A first light source may illuminate a sensing fiber and an anti-Stokes band may be detected. A second light source may illuminate a sensing fiber and a Stokes band may be detected, where the Stokes band is substantially similar to the anti-Stokes band of the first light source. A ratio between the anti-Stokes and Stokes band may be used to calibrate a temperature sensing system.
Owner:SENSORTRAN
System and method for resolution enhancement of a distributed sensor
ActiveUS20050213869A1Reduce resolutionForce measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberLine width
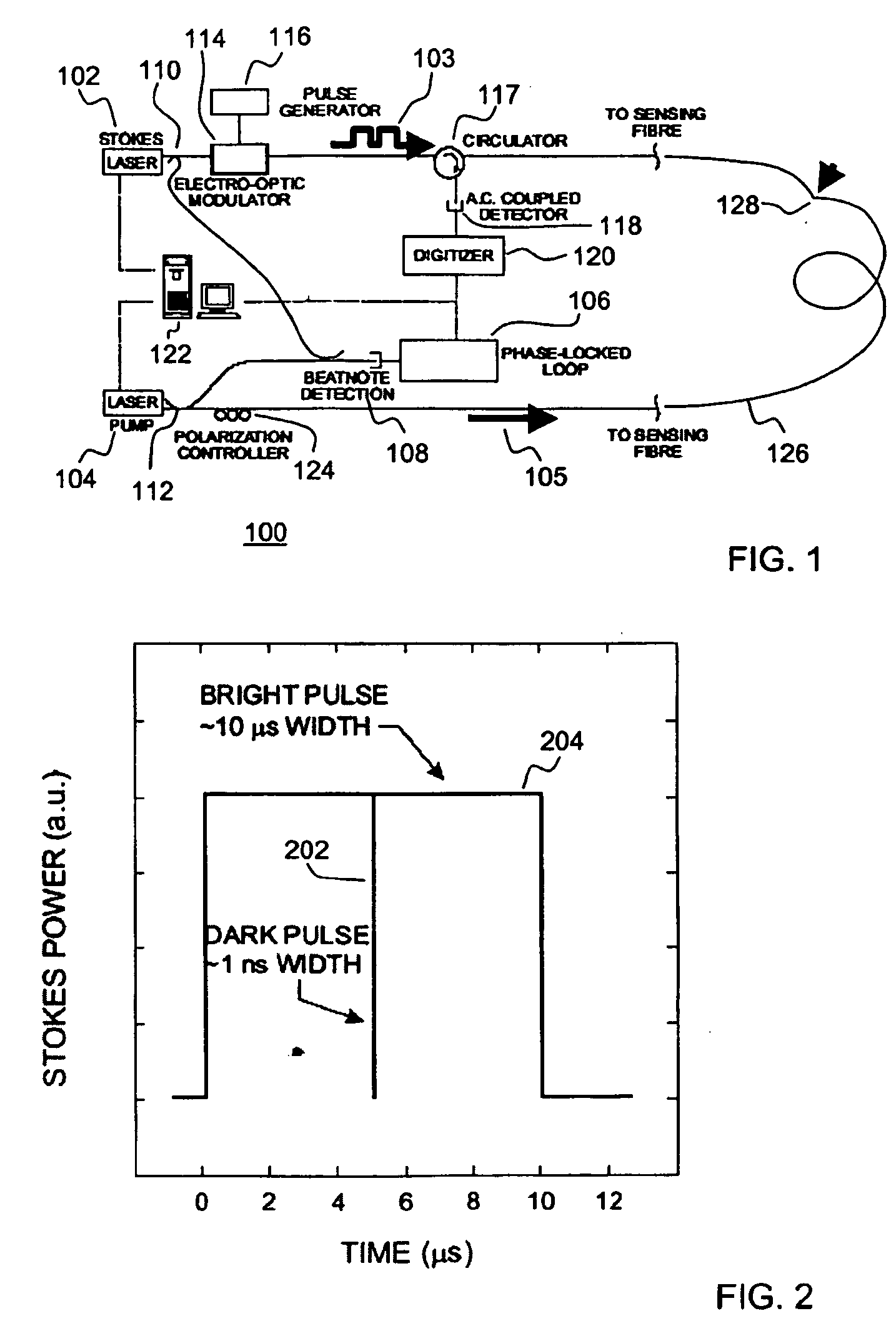
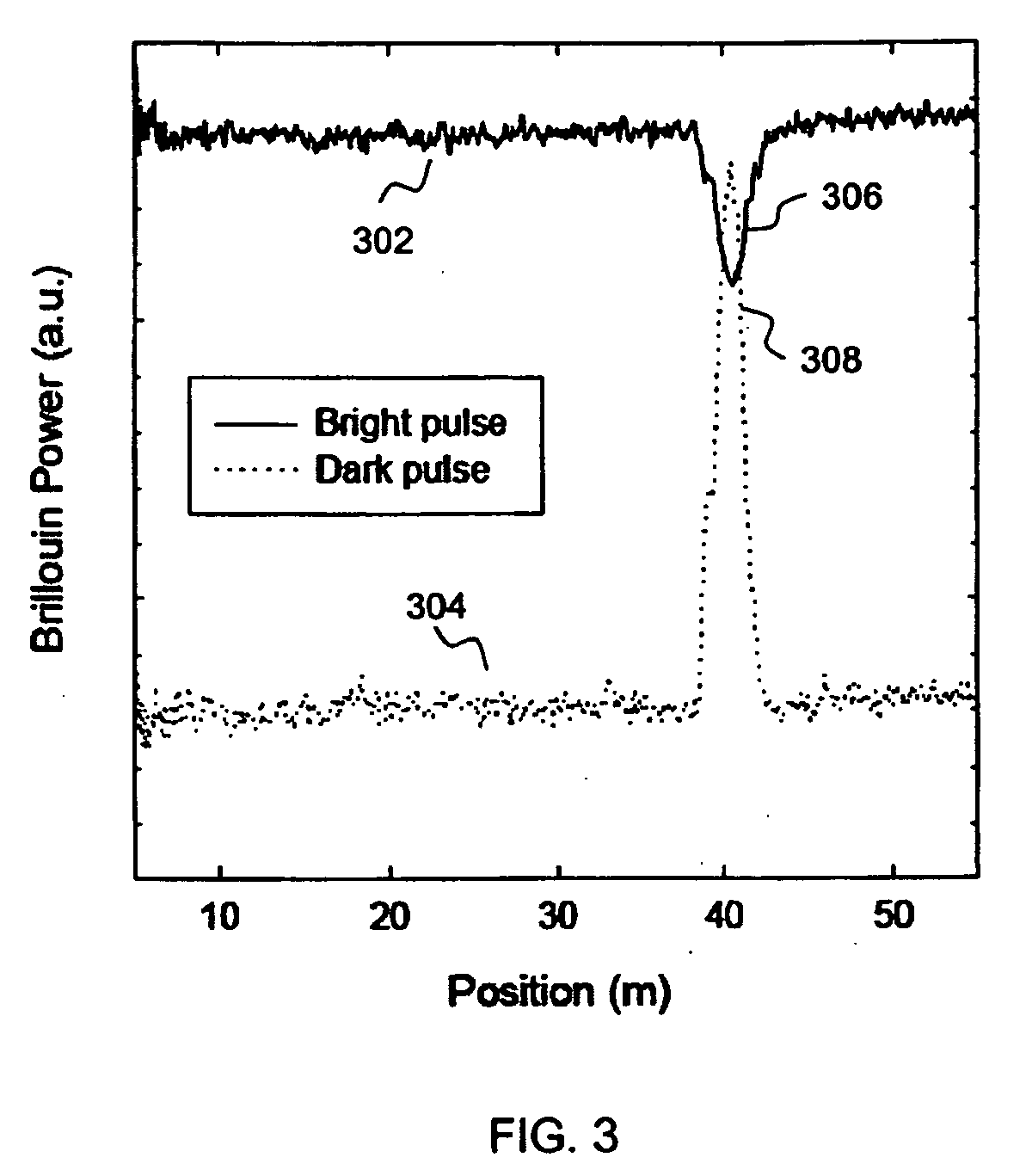
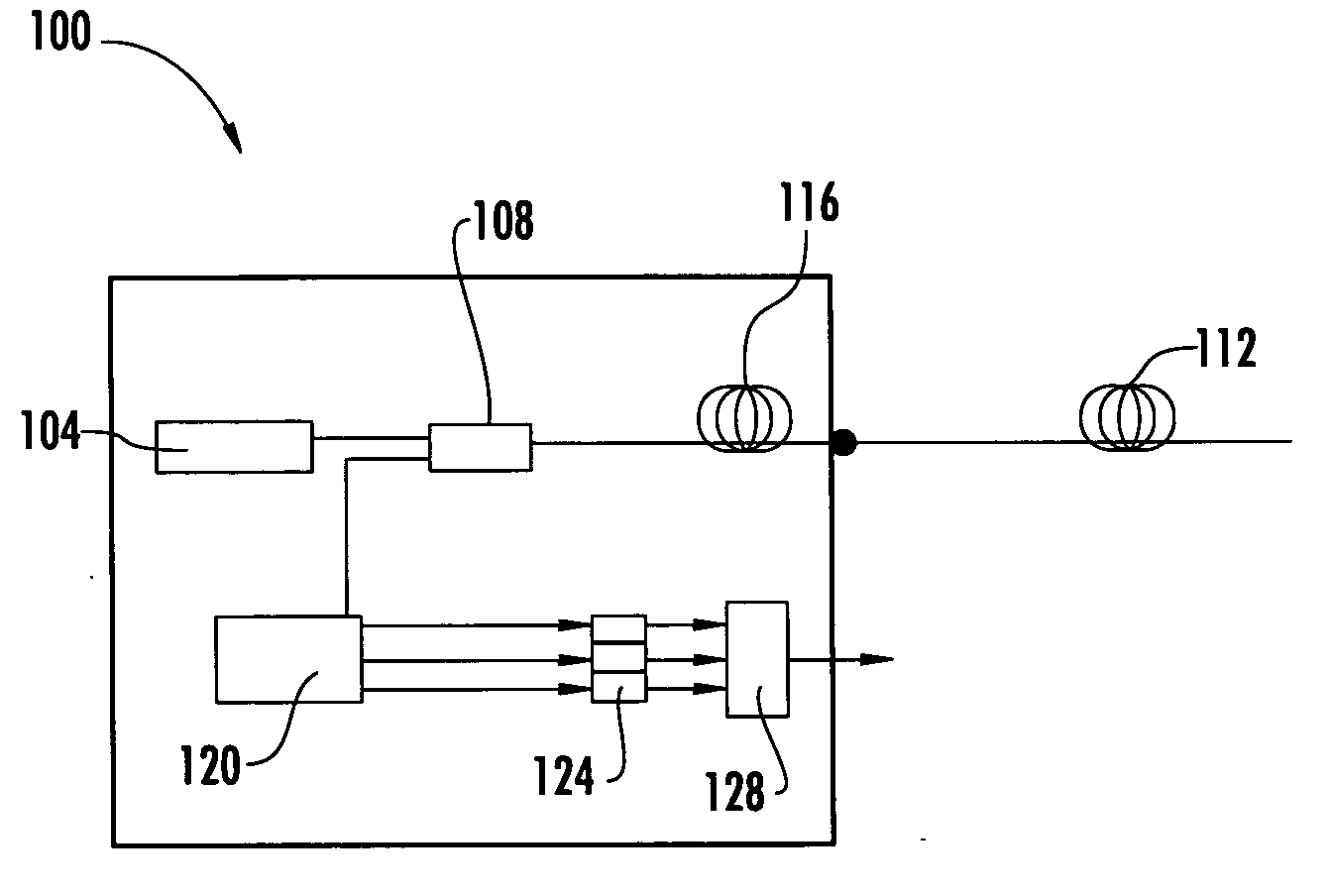
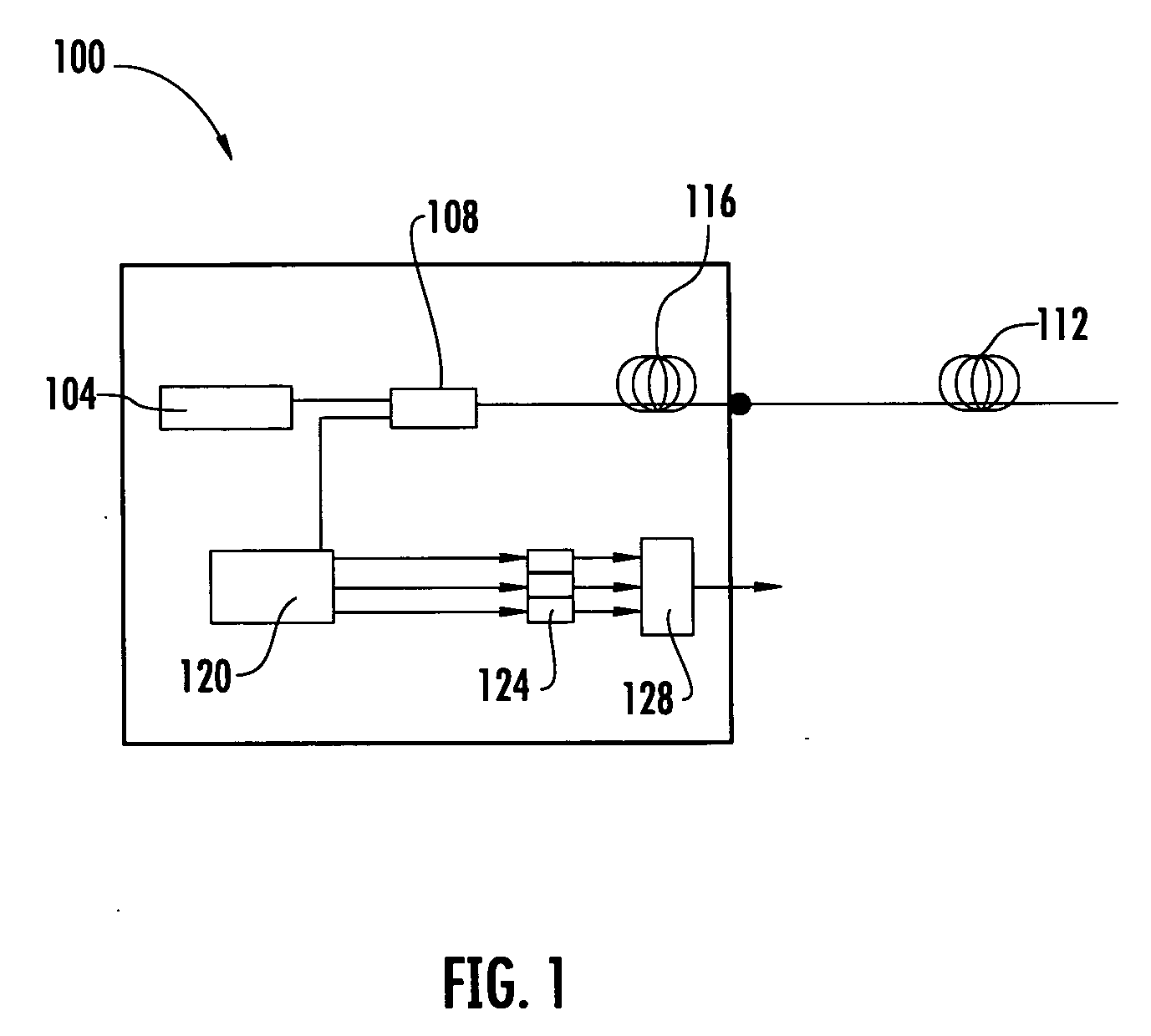
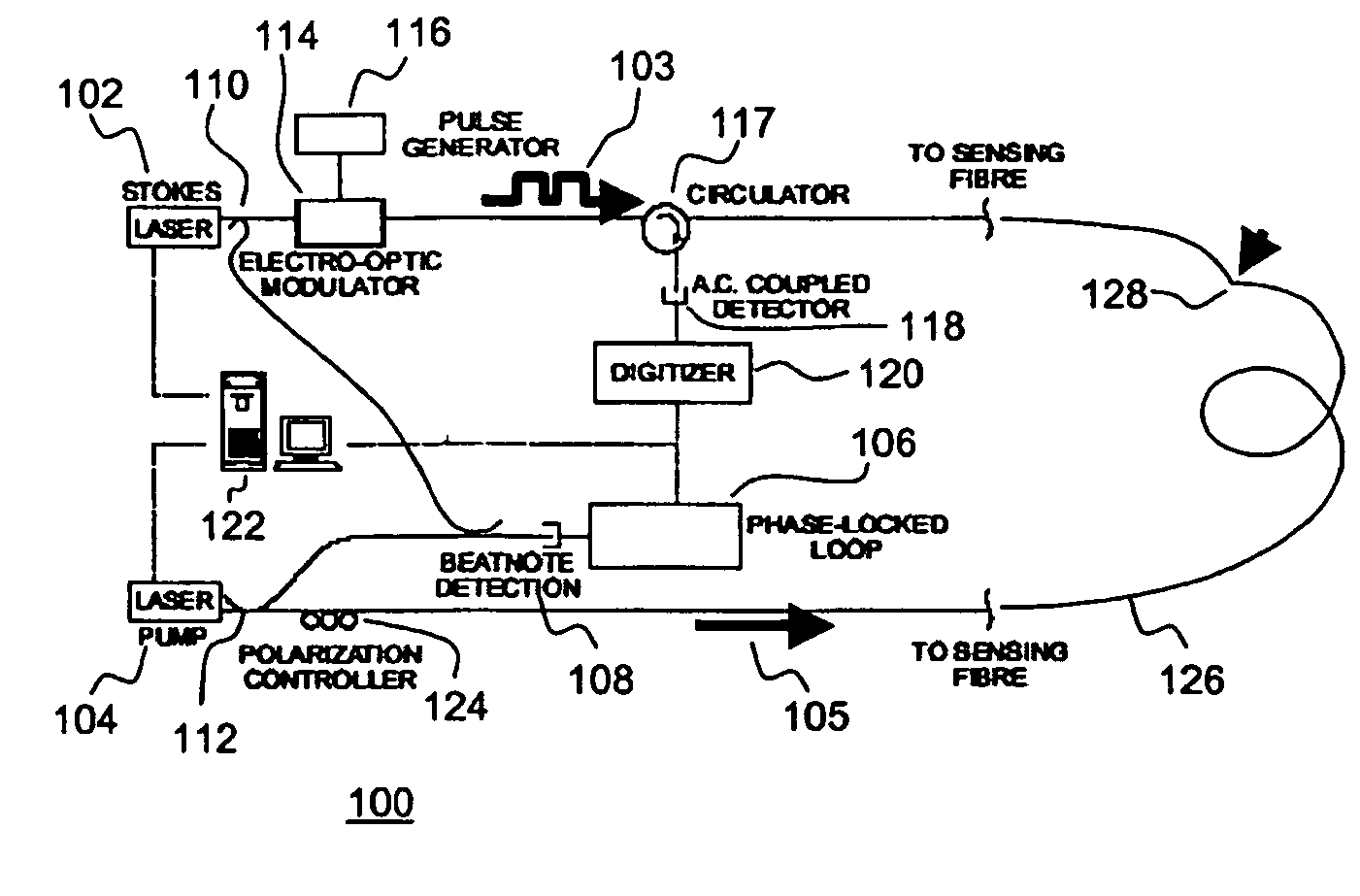
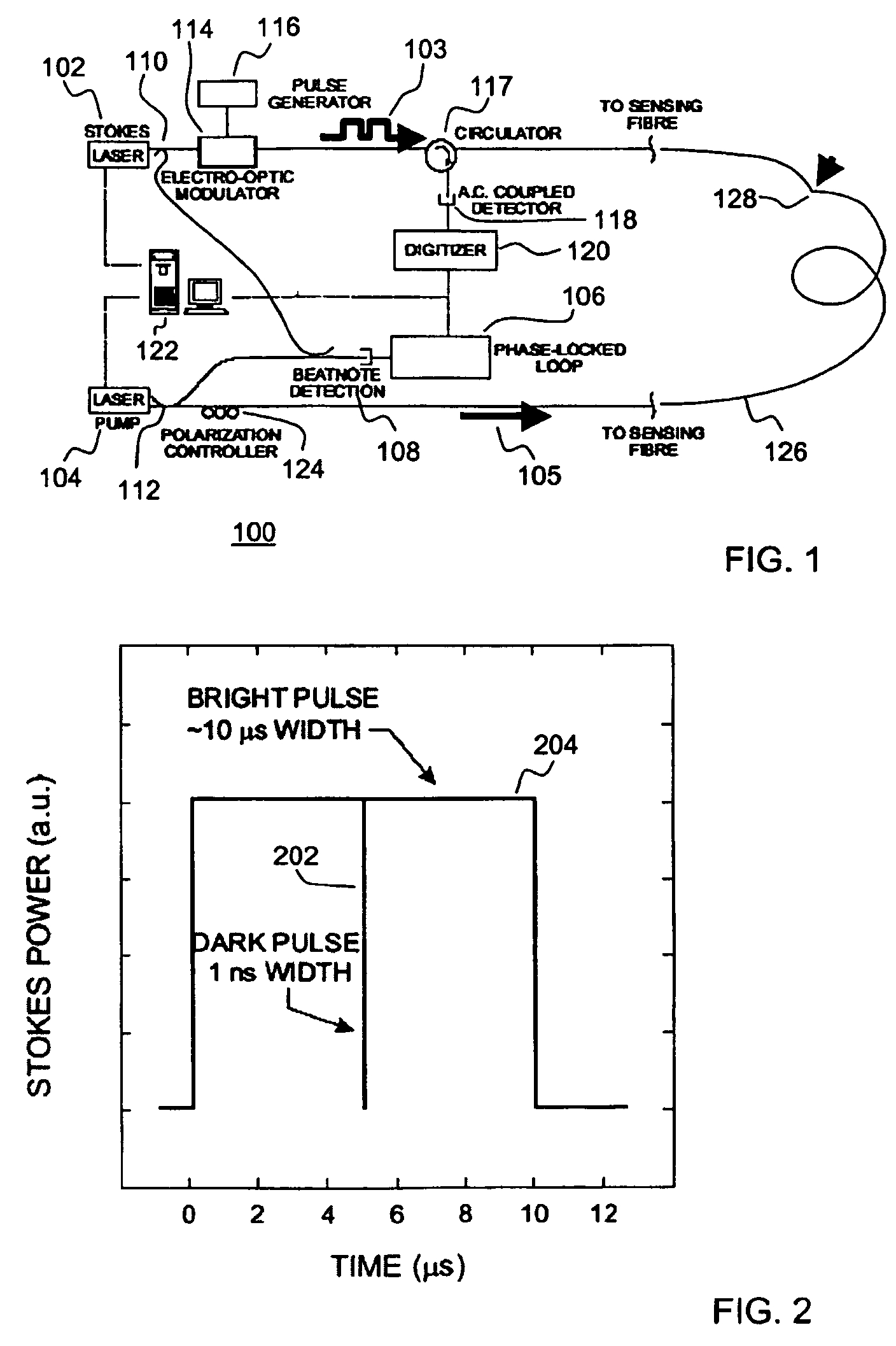
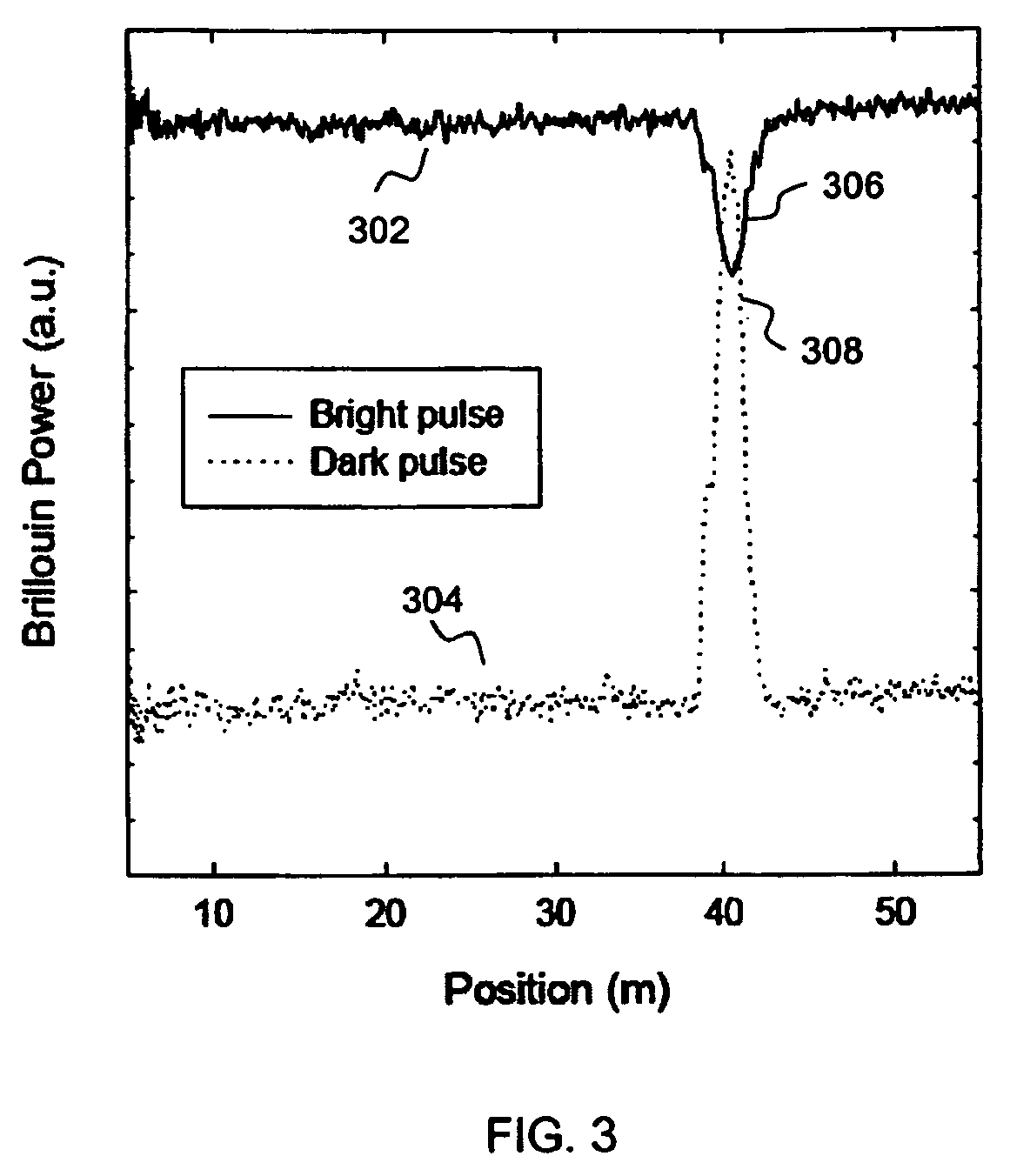
A Brillouin Optical Time-Domain Analysis (BOTDA) distributed sensor system and method use a continuous wave (cw) Stokes wave interrupted with a dark pulse for improved spatial resolution. The cw Stokes wave causes a continuous depletion of the pump wave. The dark pulse causes the depletion to stop for the duration of the pulse. Brillouin interactions are measured during the dark pulse. Very narrow dark pulses can be used because sufficient Stokes wave energy is maintained. The system produces a stronger time-domain signal and narrower linewidth Brillouin spectra than traditional techniques using a bright Stokes pulse. Narrower measurement pulses can be used leading to improved spatial resolution. A quasi-cw Stokes wave can be used to reduce the effect of stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) in long measurement fibers. The system can be used for distributed strain or temperature measurements.
Owner:DARKPULSE TECH INC
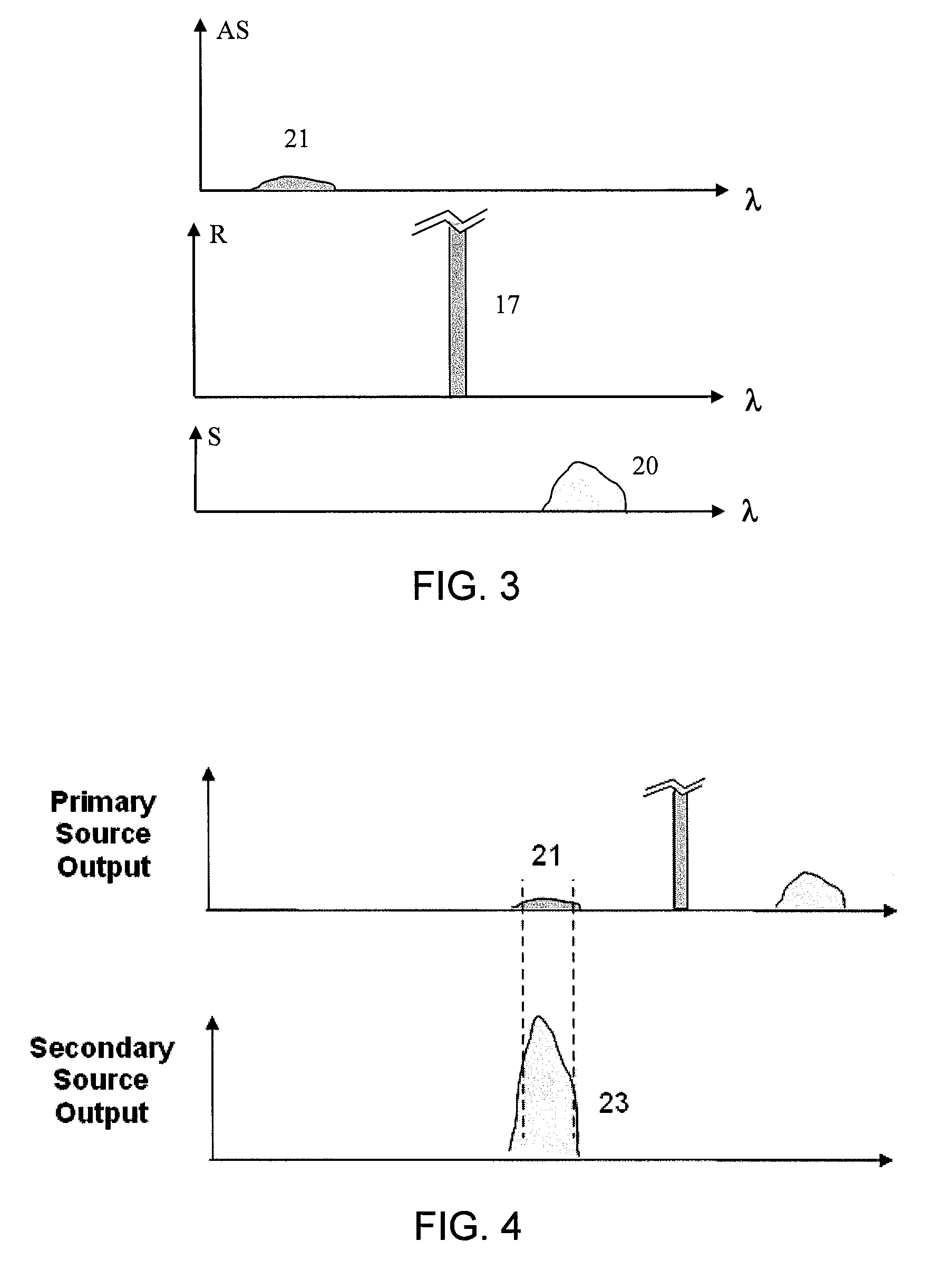
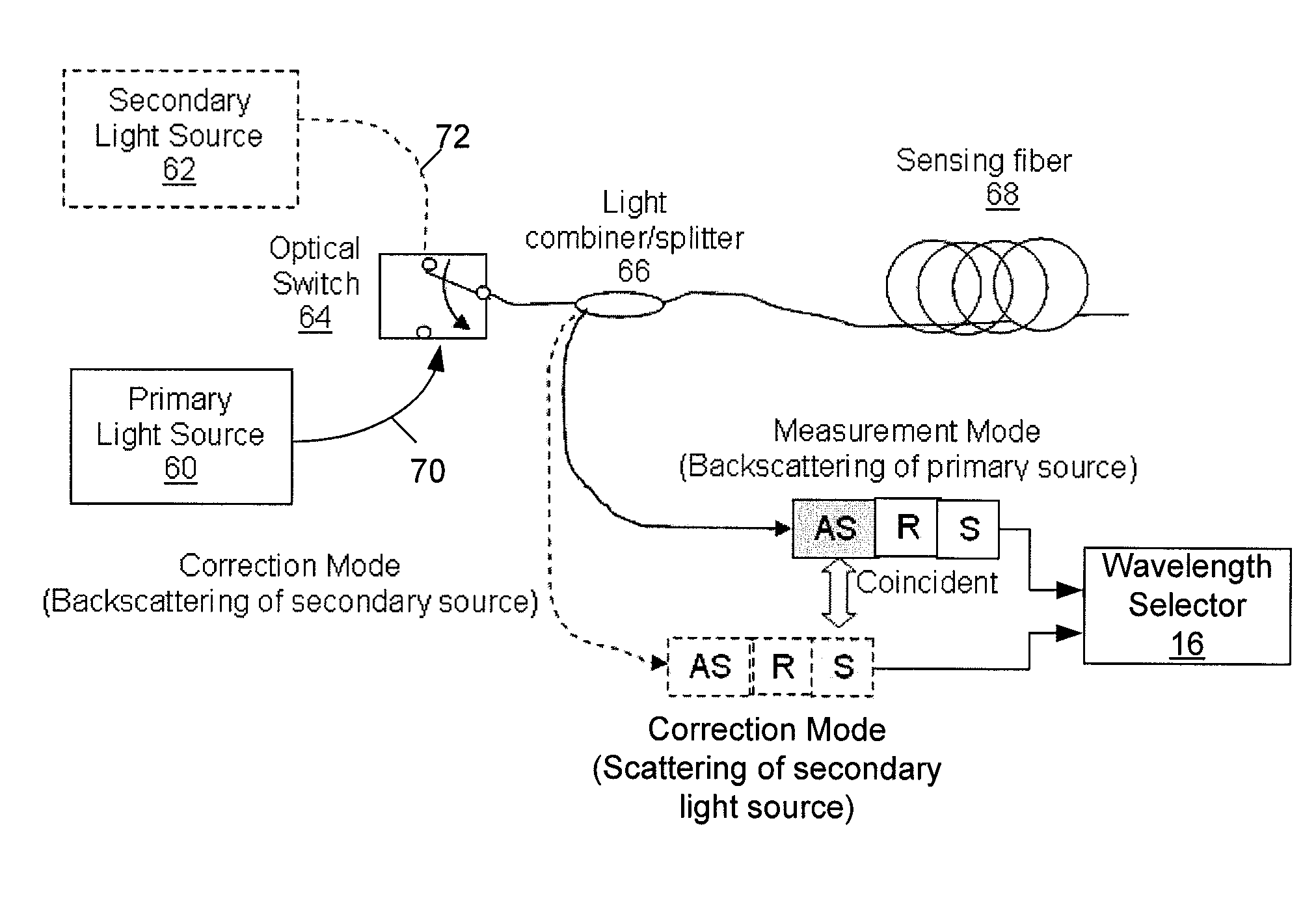
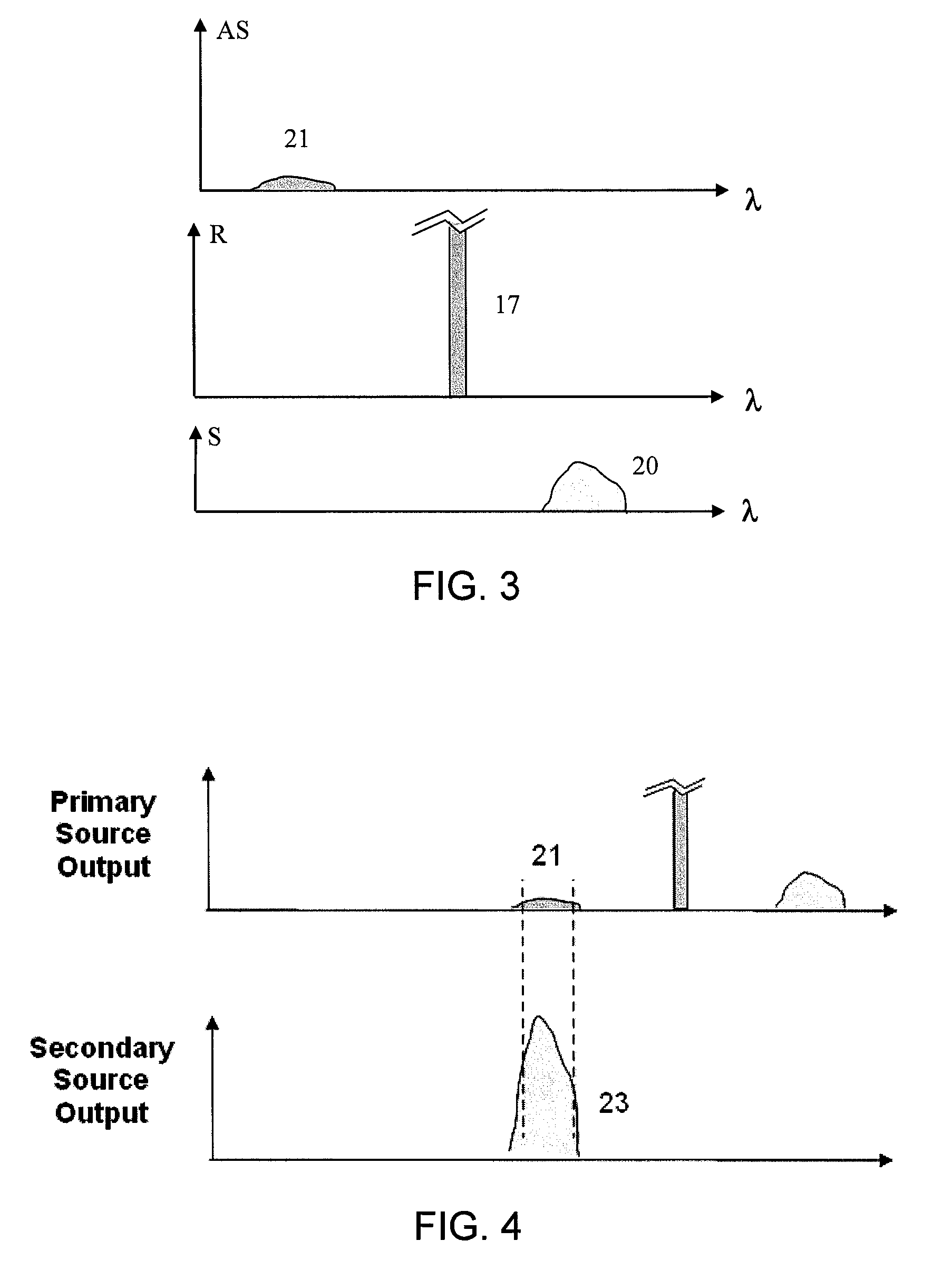
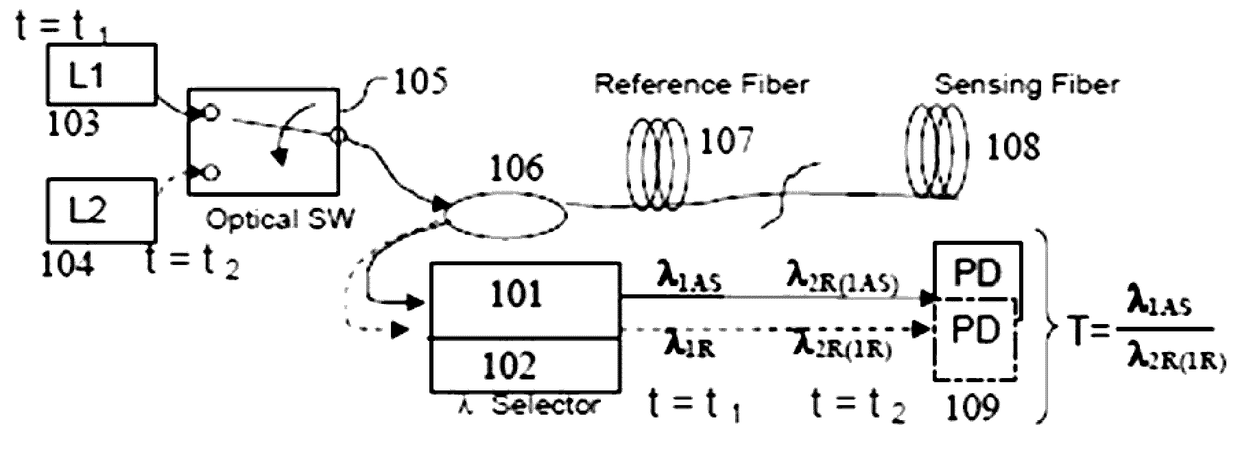
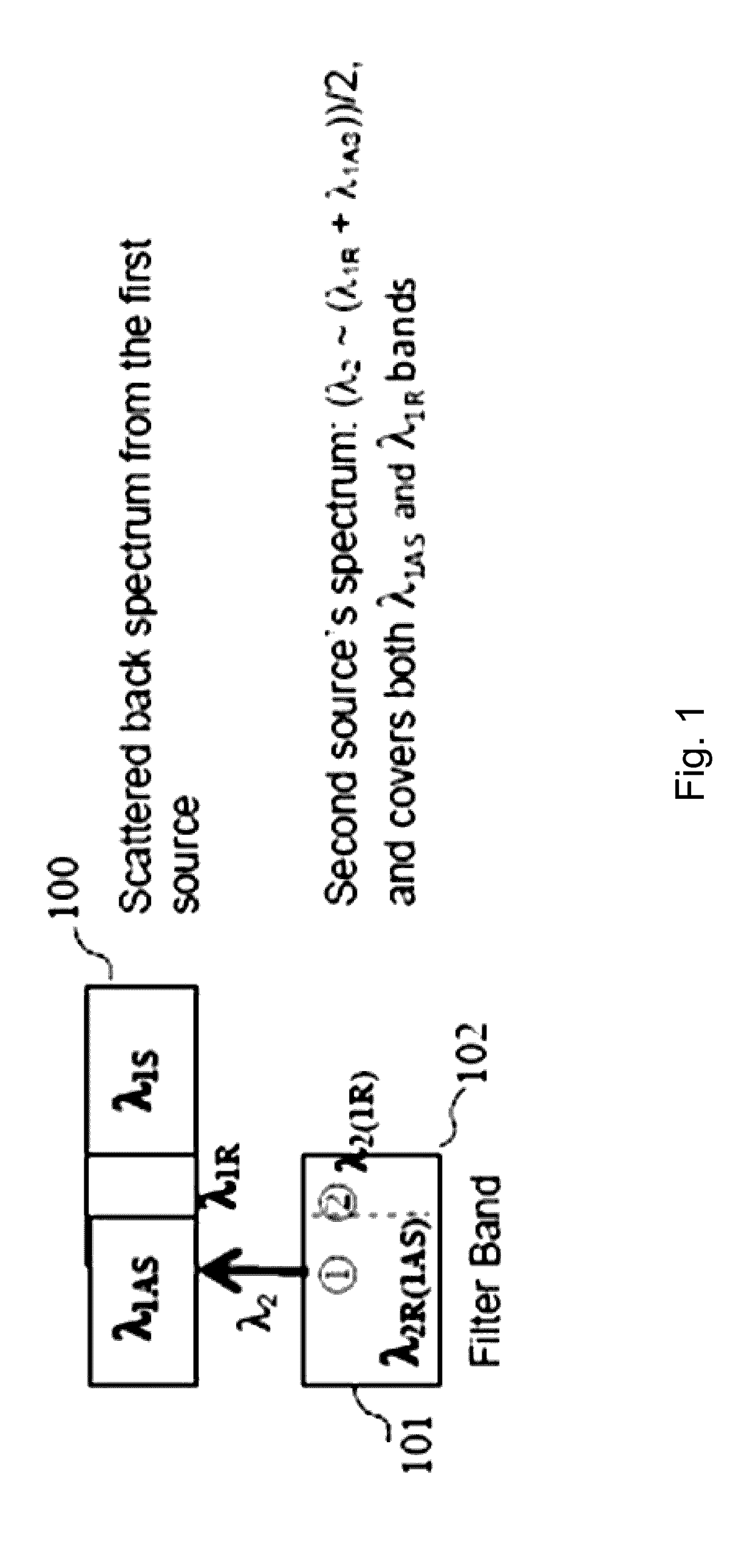
Dual source auto-correction in distributed temperature systems
ActiveUS20100128756A1Accurate methodAccurate temperature monitoringRadiation pyrometryThermometers using physical/chemical changesFiberUltrasound attenuation
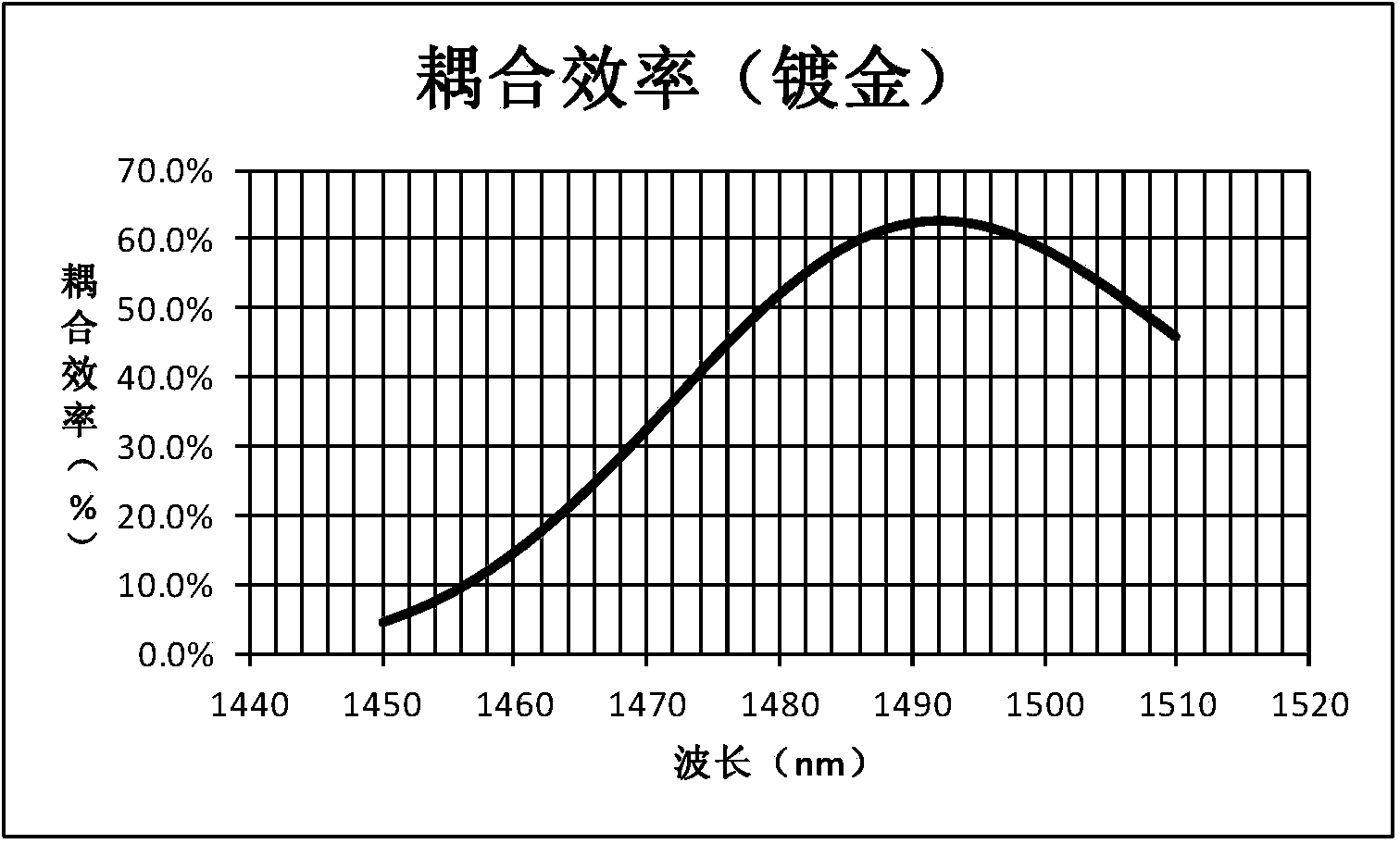
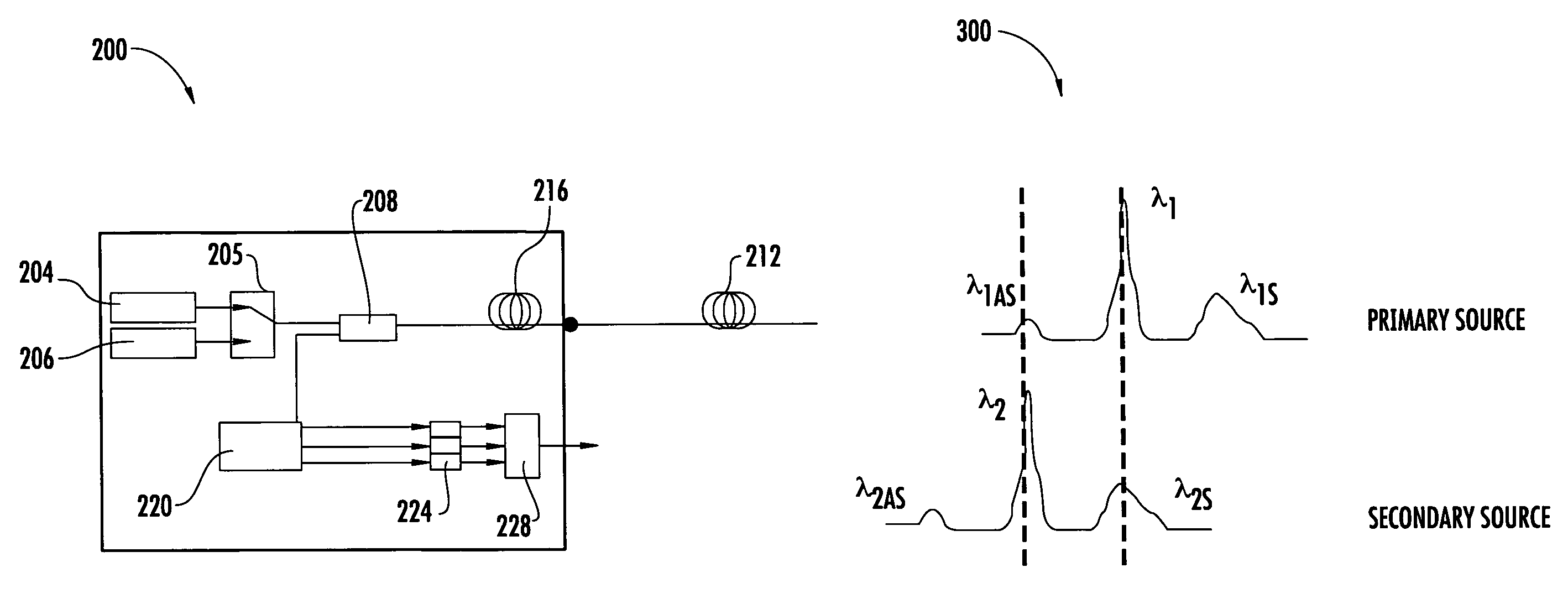
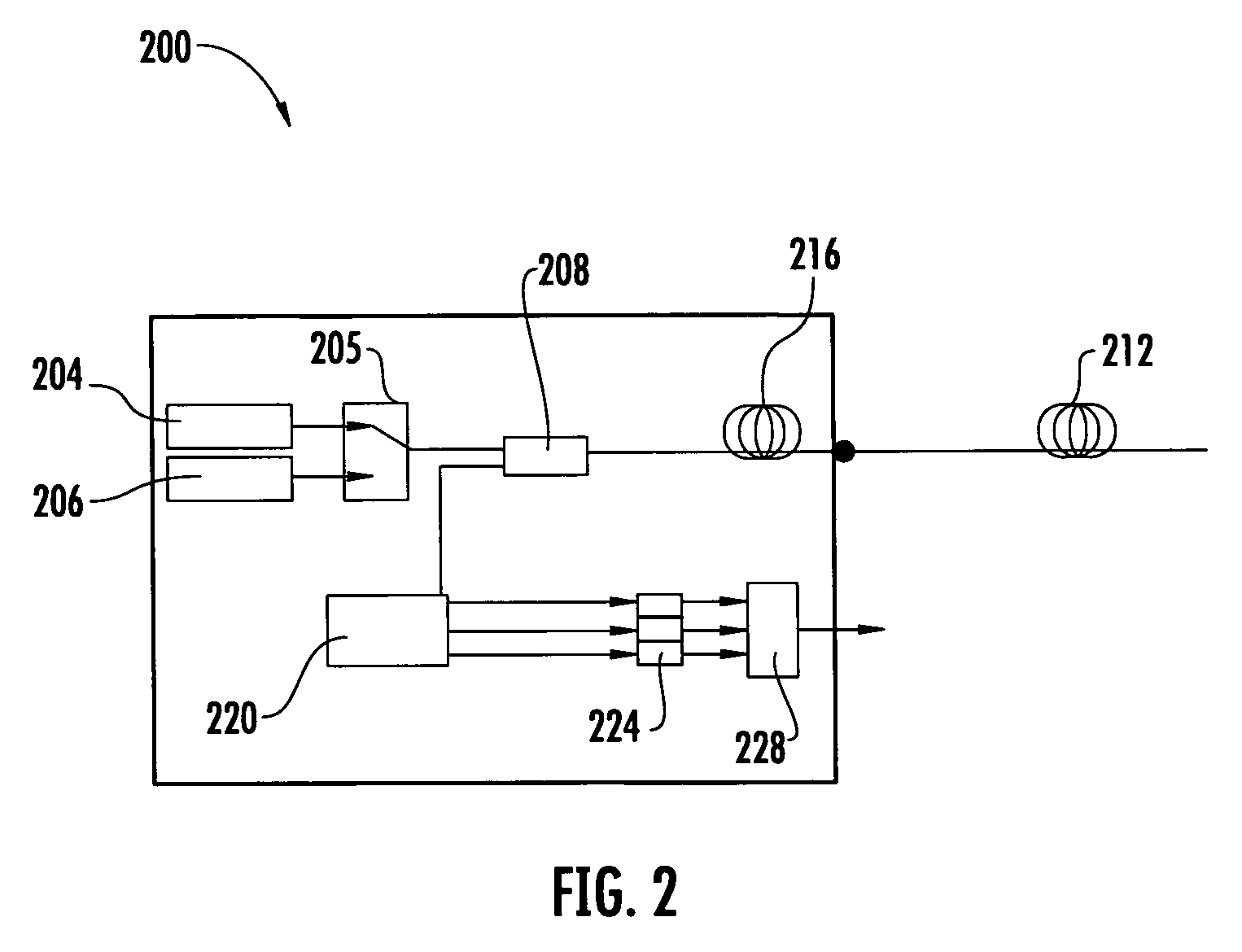
An automatic and continuous method is presented to improve the accuracy of fiber optic distributed temperature measurements derived from Raman back scatterings utilizing two light sources with different wavelengths, by choosing the wavelengths of the two sources so the primary source's return anti-Stokes component overlaps with the incident wavelength of the secondary light source thereby canceling out the non-identical attenuations generated by the wavelength differences between Stokes and anti-Stokes bands.
Owner:SENSORTRAN
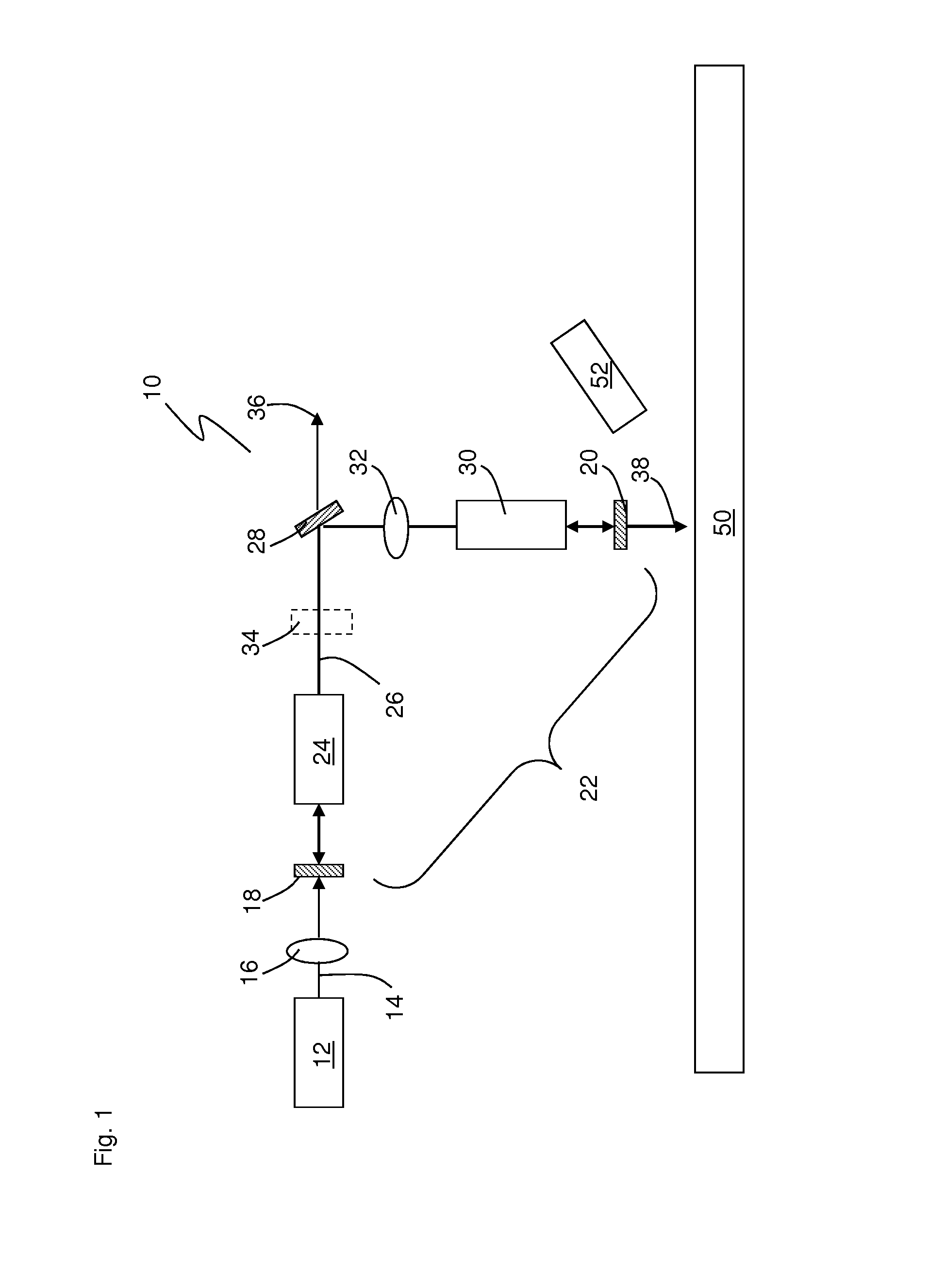
Methods and apparatus for dual source calibration for distributed temperature systems
InactiveUS7628531B2Accurate profileRadiation pyrometryWeather/light/corrosion resistanceFiberWave band
Systems and methods for calibrating a temperature sensing system are disclosed. In one respect, a dual light source configuration may be provided. A first light source may illuminate a sensing fiber and an anti-Stokes band may be detected. A second light source may illuminate a sensing fiber and a Stokes band may be detected, where the Stokes band is substantially similar to the anti-Stokes band of the first light source. A ratio between the anti-Stokes and Stokes band may be used to calibrate a temperature sensing system.
Owner:SENSORTRAN
System and method for resolution enhancement of a distributed sensor
ActiveUS7245790B2Reduce resolutionForce measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberLine width
Owner:DARKPULSE TECH INC
Method and apparatus for auto-correcting the distributed temperature sensing system
InactiveUS20140233600A1Reliable and accurate temperature calculationCalculation is accurate and reliableThermometers using physical/chemical changesThermometer testing/calibrationFiberOptoelectronics
System and method for correcting the potential errors occurring in a fiber optic temperature measurement system are disclosed. In one respect, a dual light sources configuration is provided. The primary light source may illuminate a sensing fiber, and an Anti-Stokes band may be detected. The secondary light source may illuminate a sensing fiber, and a Rayleigh band may be detected, where the Rayleigh band is substantially wide enough to cover the Anti-Stokes band of the primary light source. A ratio between these Anti-Stokes and the Rayleigh bands may be used to measure the temperature and undesired errors due to the perturbations falling on the sensing fiber is continuously corrected.
Owner:LEE CHUNG
Anti-Strokes Raman fiber laser achieving multi-wavelength output
ActiveCN103151682AImprove the scattering effectVariable wavelengthLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionContinuous lightGrating
The invention discloses an anti-Strokes Raman fiber laser achieving multi-wavelength output and aims at providing a laser of which an output wavelength is adjustable and the output wavelength is smaller than a pump wavelength. The fiber laser is composed of a pulse light source, a continuous light source, a wavelength division multiplexer, a high raster, an optical fiber, a low raster and a filter. The central wavelength of the output light of the pulse light source is located at n stage Raman Strokes wavelength of the obtained light wavelength, the output light wavelength of the continuous light source is located at a first stage Raman Strokes wavelength of the output light wavelength of the pulse light source, a zero-dispersion wavelength of the optical fiber is located near the output light wavelength of the pulse light source, the central wavelength of the high raster and the central wavelength of the low raster are equal to the obtained laser wavelength, the input arm working wavelength of the wavelength division multiplexer is respectively equal to the central wavelength of the pulse light source and the central wavelength of the continuous light source, and the central wavelength of the filter is equal to the obtained light wavelength. The anti-Strokes Raman fiber laser is simple in structure, adjustable in the light wavelength and can output a laser shorter than the pump wavelength.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Cascaded cavity silicon raman laser with electrical modulation, switching, and active mode locking capability
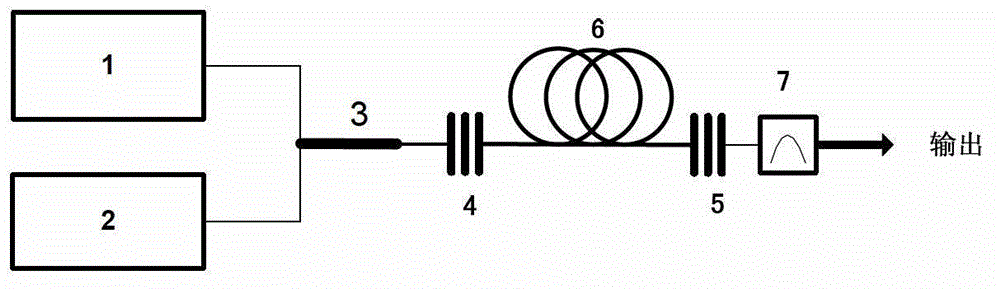
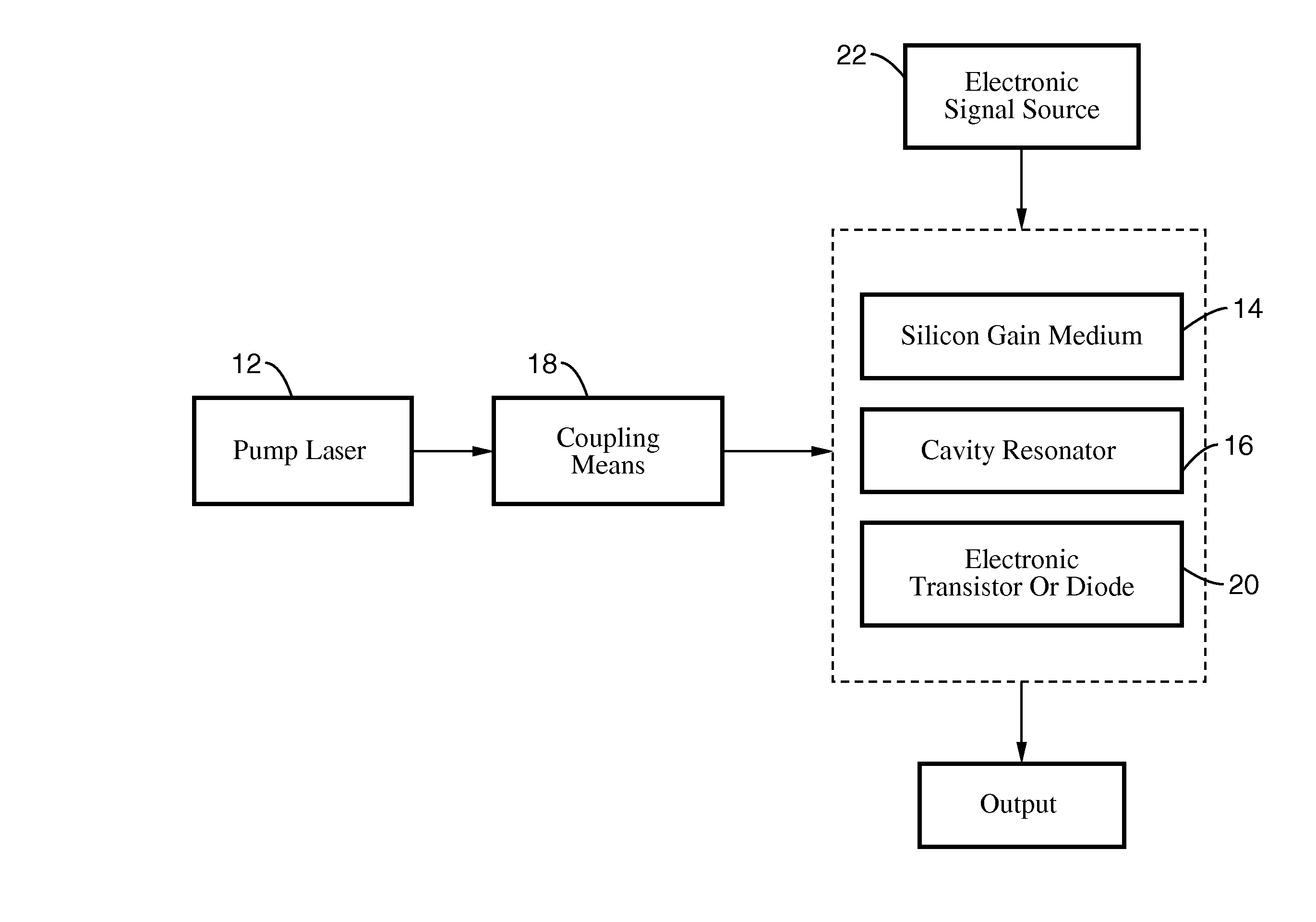
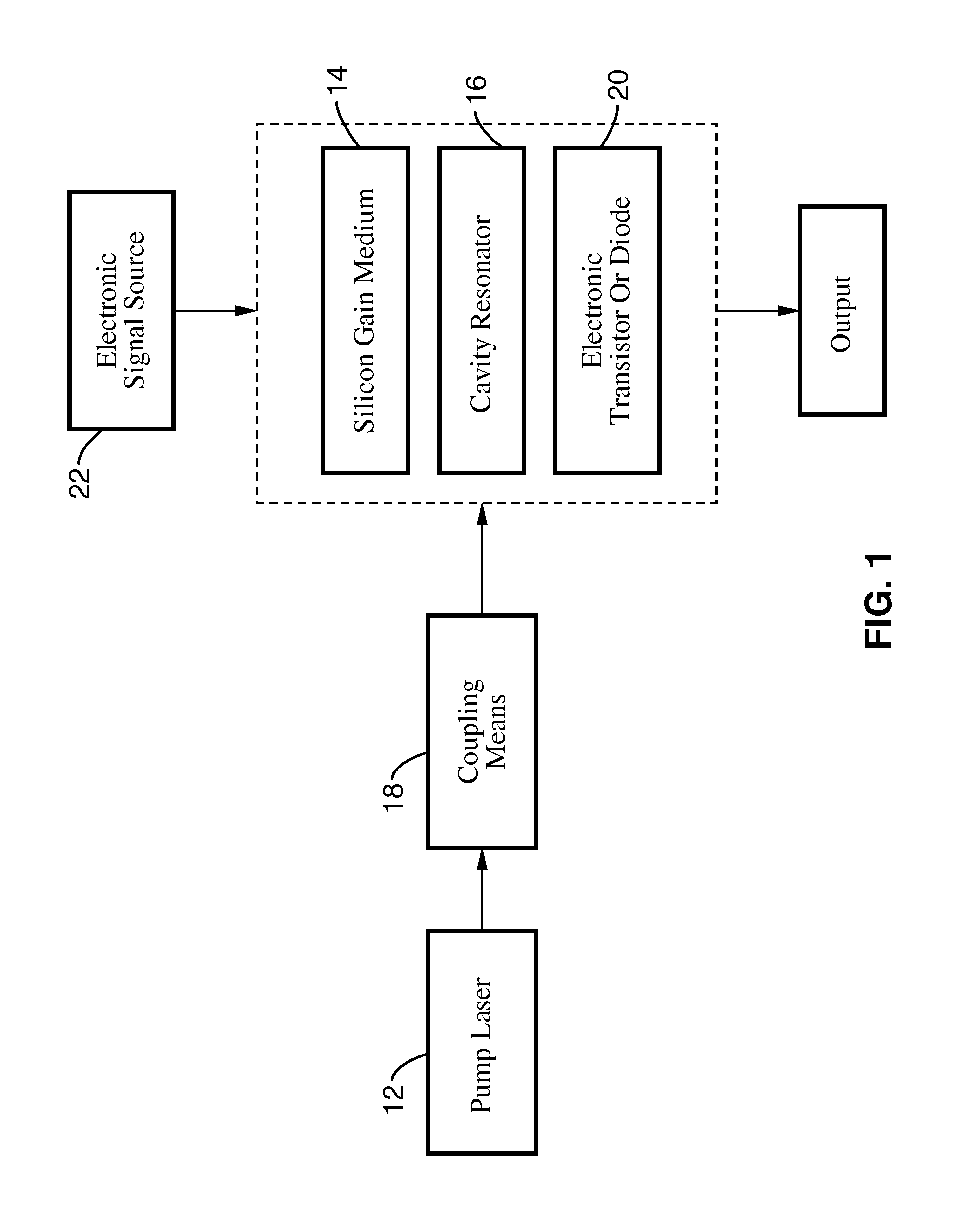
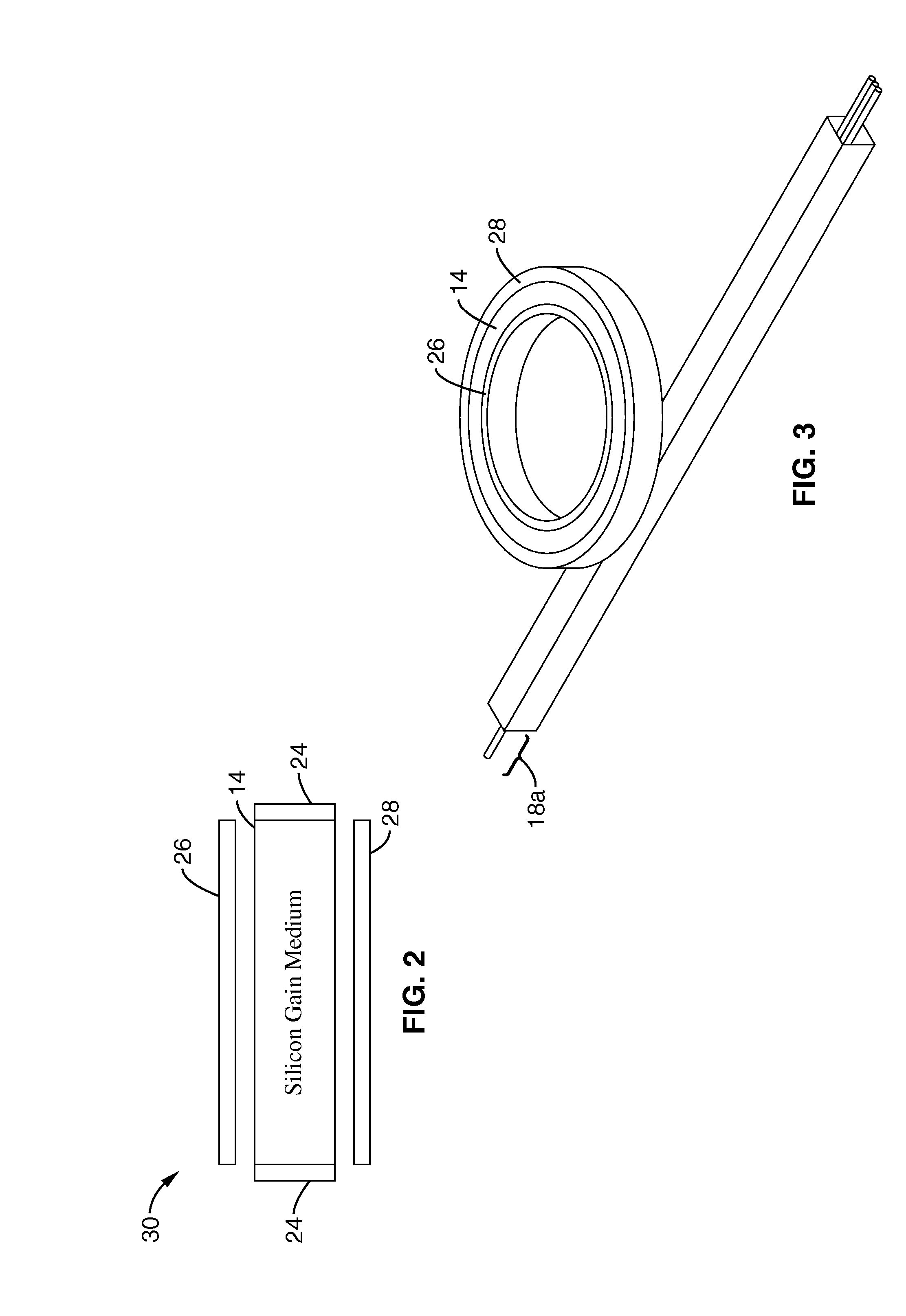
A silicon Raman laser that can be electrically switched or modulated and which demonstrates active mode-locking capabilities. The laser can be used with a more traditional glass fiber cavity, or can be fabricated on a single chip with a cavity, or a cascaded cavity, in which the chip fabrication is compatible with widely used silicon chip fabrication methods. The laser can be tuned by adjusting a source pump laser to produce specific output and operates at room temperature. Output is present in the near- and mid-infrared frequency range, and the laser can simultaneously produce output at the Stokes and at the anti-Stokes wavelengths.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Systems and Methods for Cascaded Raman Lasing at High Power Levels
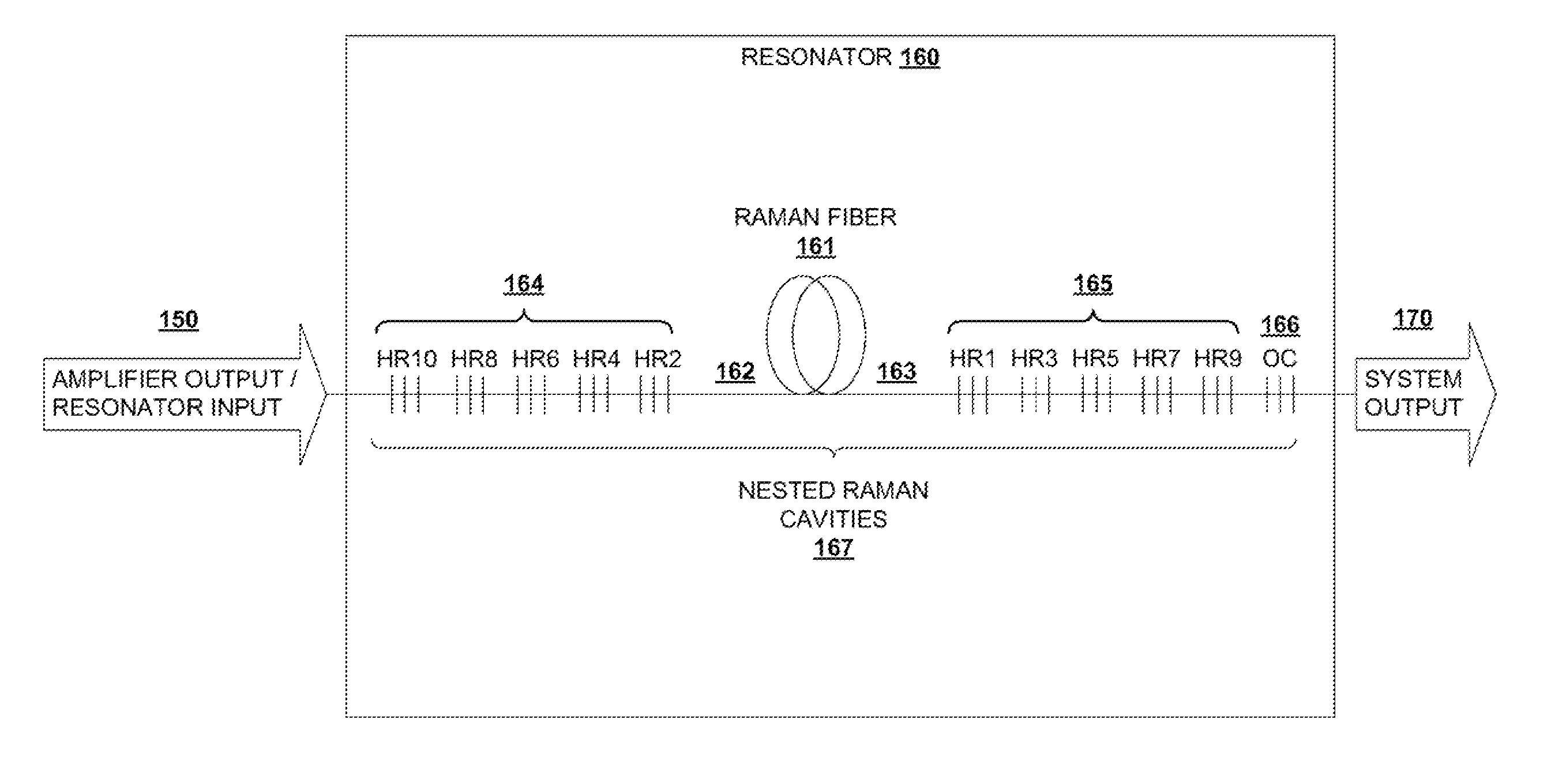
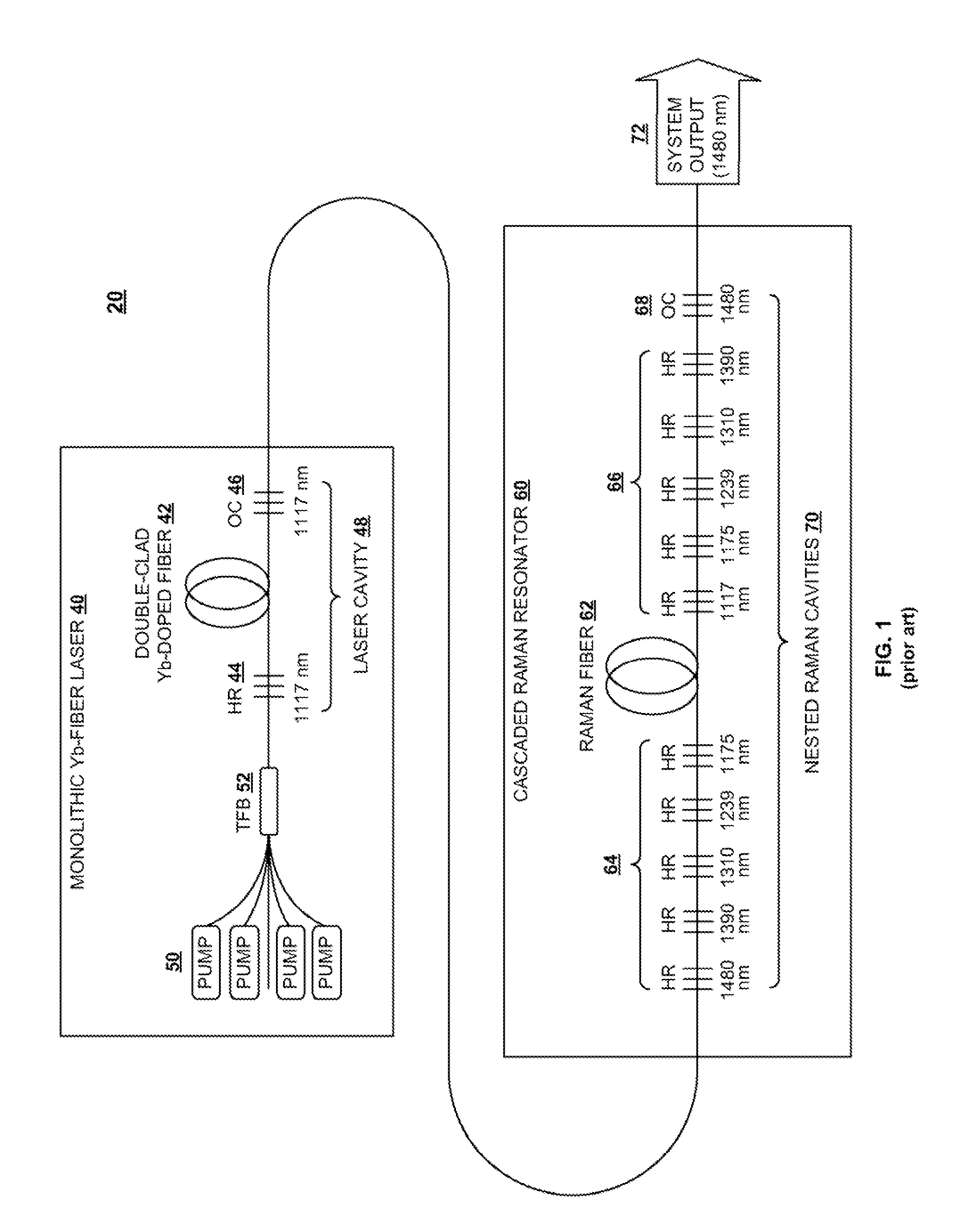
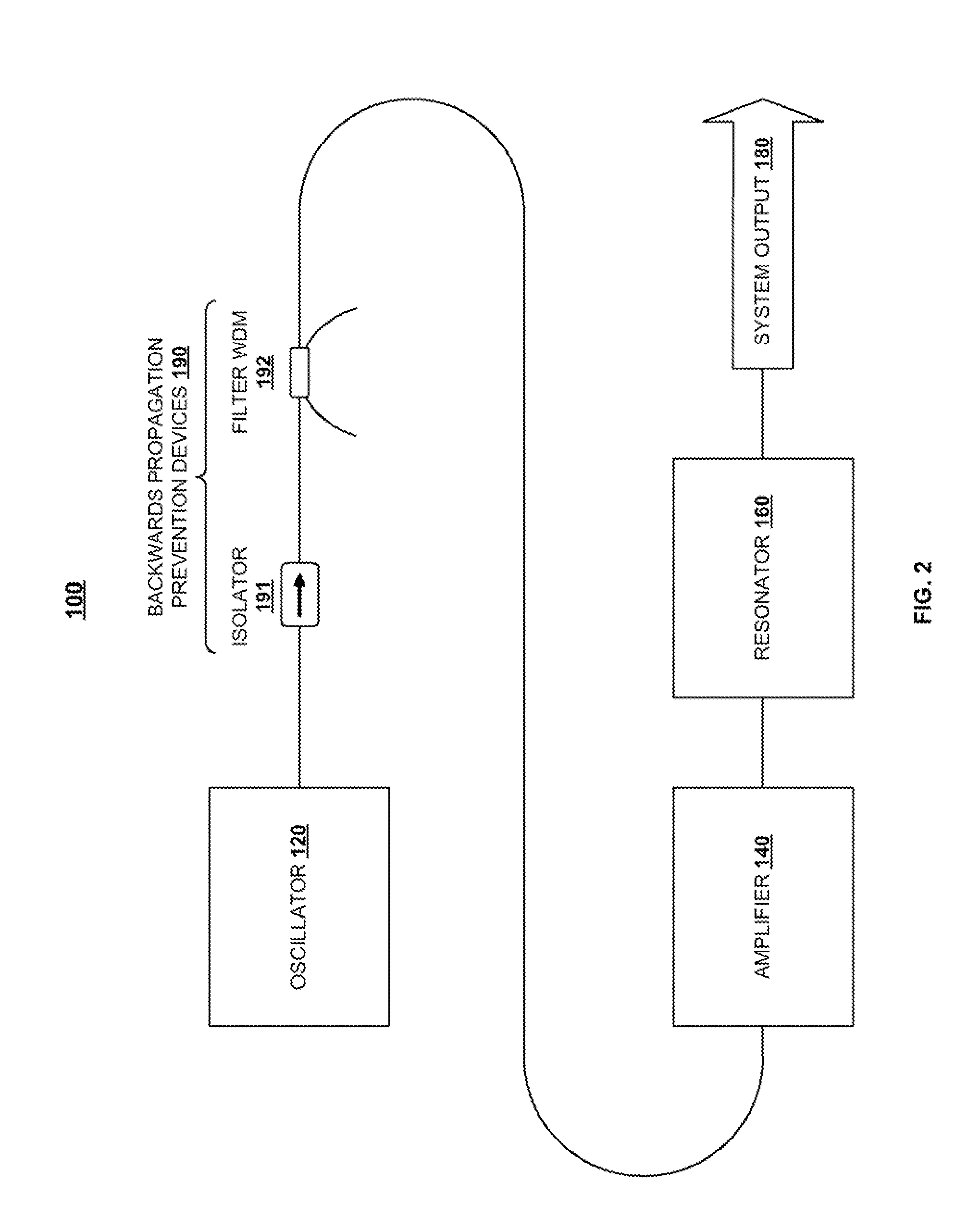
ActiveUS20100284060A1Prevent backward propagation of lightLaser using scattering effectsFibre transmissionFiberAudio power amplifier
In a light amplification system, a fiber-based oscillator, amplifier, and cascaded Raman resonator are coupled together in series. The oscillator output is provided as an input into the amplifier, the amplifier output is provided as a pumping input into the cascaded Raman resonator, and the cascaded Raman resonator provides as an output single-mode radiation at a target wavelength. A loss element is connected between the oscillator and amplifier, whereby the oscillator is optically isolated from the amplifier and cascaded Raman resonator. A filter is coupled between the isolator and the amplifier for filtering out backward-propagating Stokes wavelengths generated in the cascaded Raman resonator. The oscillator is operable within a first power level range, and the amplifier and cascaded Raman resonator are operable within a second power level range exceeding the first power level range.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Multi-wavelength Brillouin fiber laser based optical fiber temperature sensor
ActiveCN104390723AHigh precision temperature measurementHigh temperature sensitivityThermometers using physical/chemical changesSpectrum analyzerLine width
A multi-wavelength Brillouin fiber laser based optical fiber temperature sensor which is formed according to an optical fiber Brillouin gain effect, an er-doped optical fiber amplifying effect, a multi-level Brillouin scattering temperature effect and a heterodyning beat frequency demodulation principle comprises a narrow line width single frequency laser, an optical branching device, a polarization controller, an opto-isolator, an optical circulator, a single-mode sensing fiber, an er-doped optical fiber amplifier, an er-doped optical fiber being not pumped, a high-speed photoelectric detector and a frequency analyzer. The multi-wavelength Brillouin fiber laser based optical fiber temperature sensor has the advantages of being many in the number of wavelengths, narrow in line width, fixed in wavelength interval and stable in output. The multi-wavelength Brillouin fiber laser based optical fiber temperature sensor achieves heterodyning best frequency demodulating detection of a high-order stokes wave and high-accuracy high-sensitivity temperature measuring with the single-mode optical fiber which provides gain for the fiber laser being served as a temperature sending detect unit.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Multi-wavelength light source based on stimulated raman scattering effect
ActiveCN104270202ACompact structureReduce power consumptionLaser detailsElectromagnetic transmittersGratingFiltration
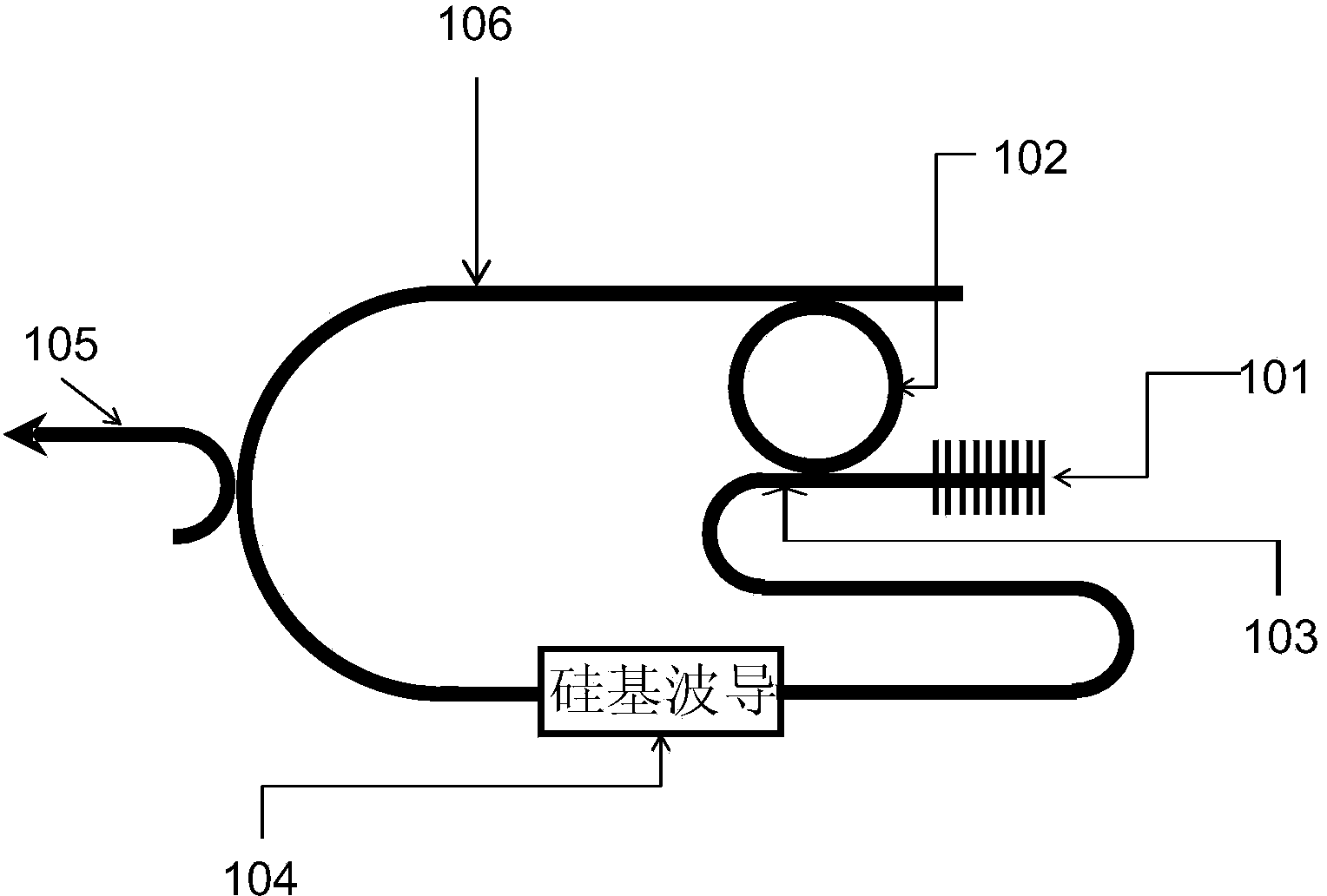
The invention discloses a multi-wavelength light source based on the stimulated raman scattering effect. The multi-wavelength light source comprises an optical grating coupler, a silicon-based annulet filter, a silicon-based waveguide and an output coupling waveguide. The silicon-based annulet filter is an Add-Drop type and comprises a silicon-based annulet, a first straight waveguide and a second straight waveguide. The pump light is input into the first straight waveguide through the optical grating coupler, the pump light is coupled to the silicon-based annulet filter through the first straight waveguide, the needed-wavelength light obtained through filtration enters the silicon-based waveguide, the stimulated raman scattering is carried out through the silicon-based waveguide to generate a one-level stokes wave input into the second straight waveguide, one part of the one-level stokes wave is coupled to the output coupling waveguide through the second straight waveguide, equal-interval and multi-wavelength lasers are output, and the rest of the one-level stokes wave is coupled to the silicon-based annulet filter to be input into the silicon-based annulet again. The multi-wavelength light source with fixed wavelength intervals is achieved through the free spectrum range of the silicon-based annulet and the stimulated raman scattering of the silicon-based waveguide, and the multi-wavelength light source has the advantages of being compact in structure, low in power consumption and the like, and is suitable for optical communication systems.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
Dual source auto-correction in distributed temperature systems
ActiveUS8496376B2Radiation pyrometryThermometers using physical/chemical changesFiberUltrasound attenuation
An automatic and continuous method is presented to improve the accuracy of fiber optic distributed temperature measurements derived from Raman back scatterings utilizing two light sources with different wavelengths, by choosing the wavelengths of the two sources so the primary source's return anti-Stokes component overlaps with the incident wavelength of the secondary light source thereby canceling out the non-identical attenuations generated by the wavelength differences between Stokes and anti-Stokes bands.
Owner:SENSORTRAN
Optical fiber Brillouin laser for bi-directional dual wavelength lasing
ActiveCN101483315ASimple structureImprove performanceLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionLine widthLasing wavelength
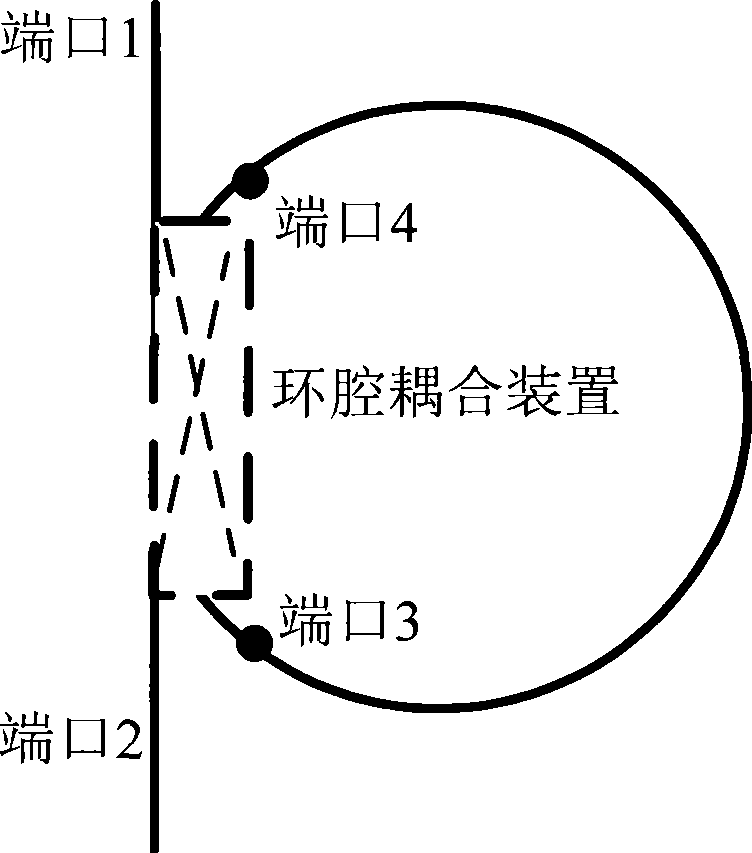
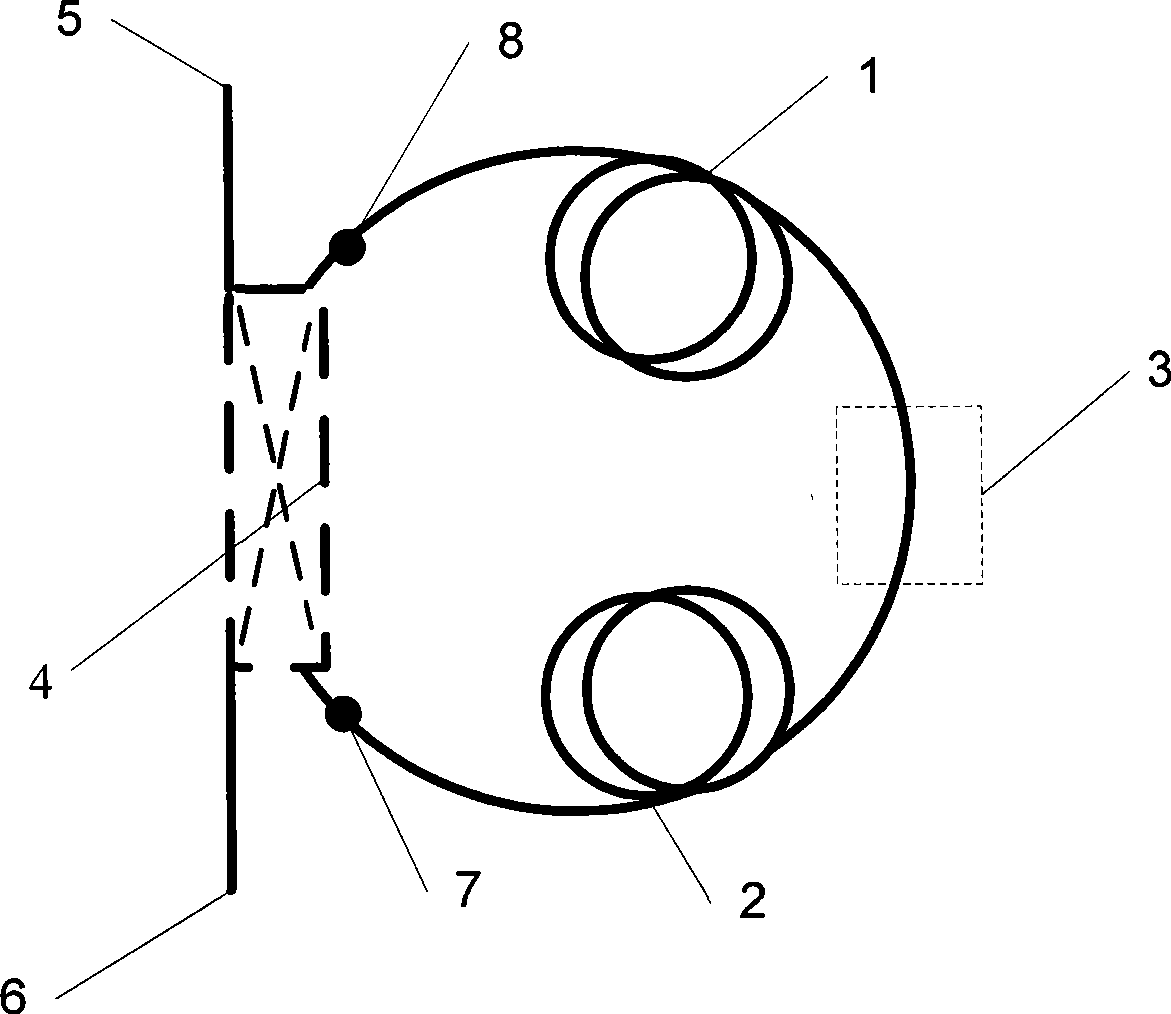
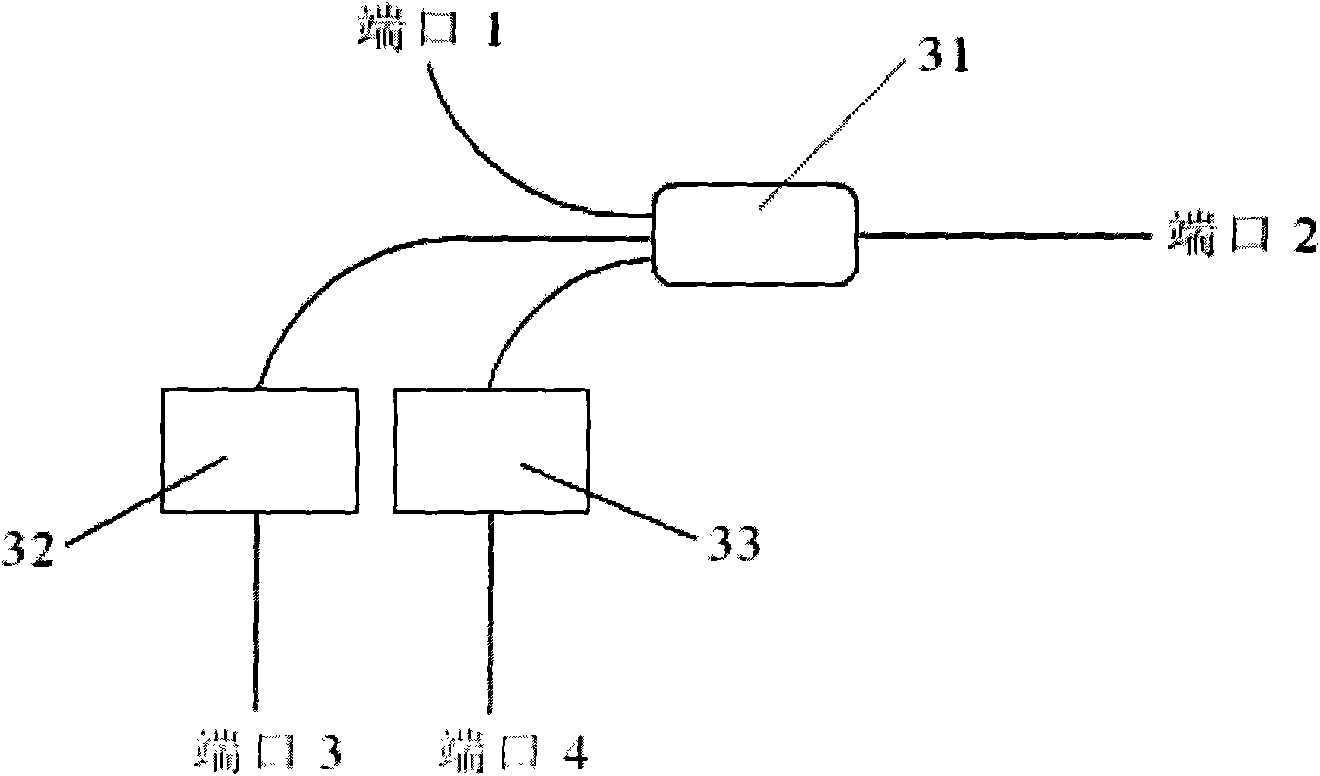
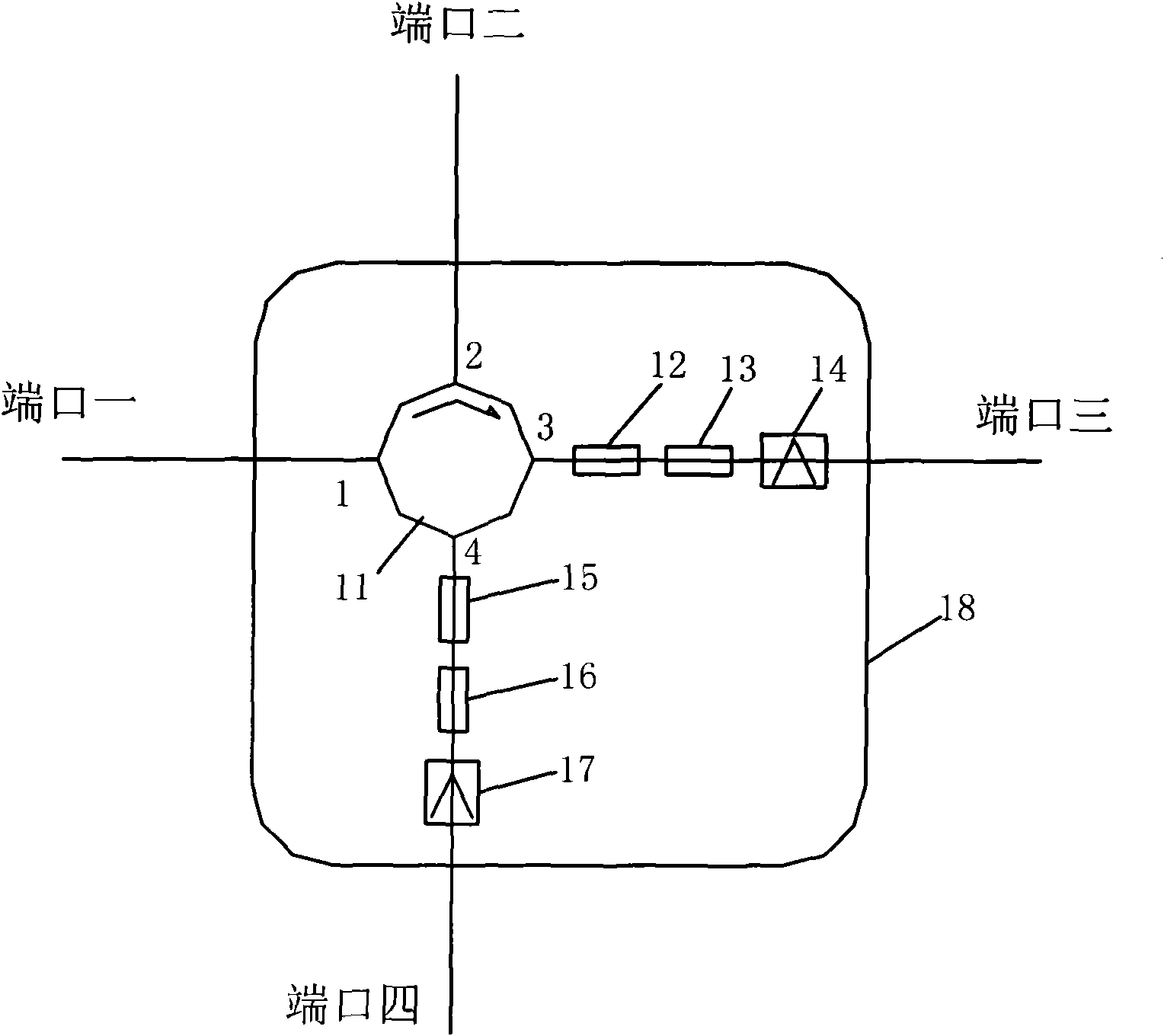
The present invention relates to technical field of optical fiber sensing. The present invention provides a bi-directional dual wavelength simultaneous lasing brillouin fiber laser, wherein the laser comprises a first optical fiber 1, a lumped loss component 3, a second optical fiber 2 and a coupling device 4, wherein the coupling device 4 is provided with a first terminal port 5, a second terminal port 6, a third terminal port 7 and a fourth terminal port 8; all components constitute a mixed ring cavity; the two pieces of optical fiber are provided with different brillouin frequency excursion characteristic; two narrow line-width lasers with same wavelength are injected into the ring cavity by the first and second terminal port of the coupling device 4; two lasing brillouin Stokes waves are generated in clockwise and anti-clockwise direction respectively and output from the first and the second terminal port respectively so as to realize bi-directional lasing, and only one lasing wavelength in each lasing direction.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
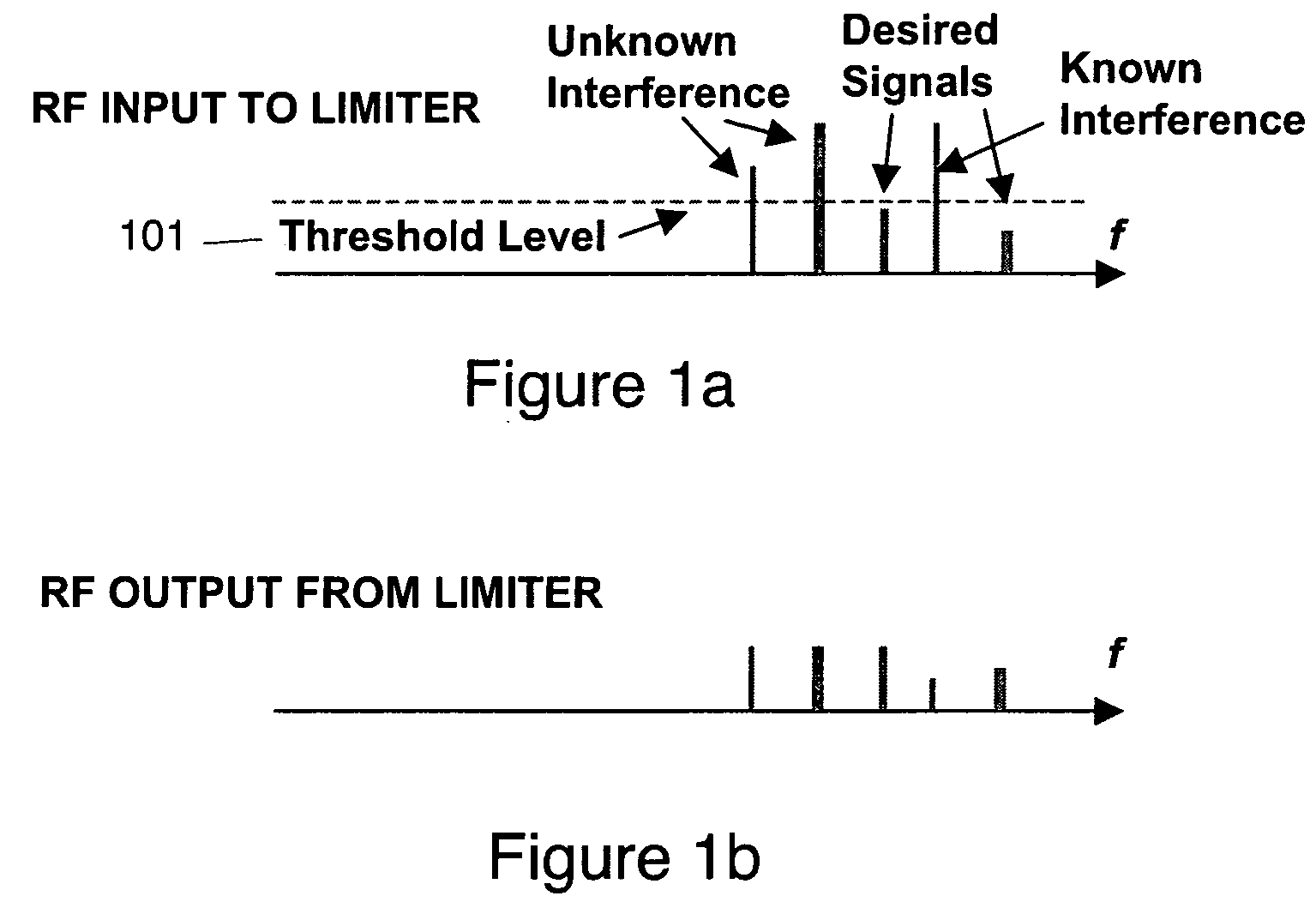
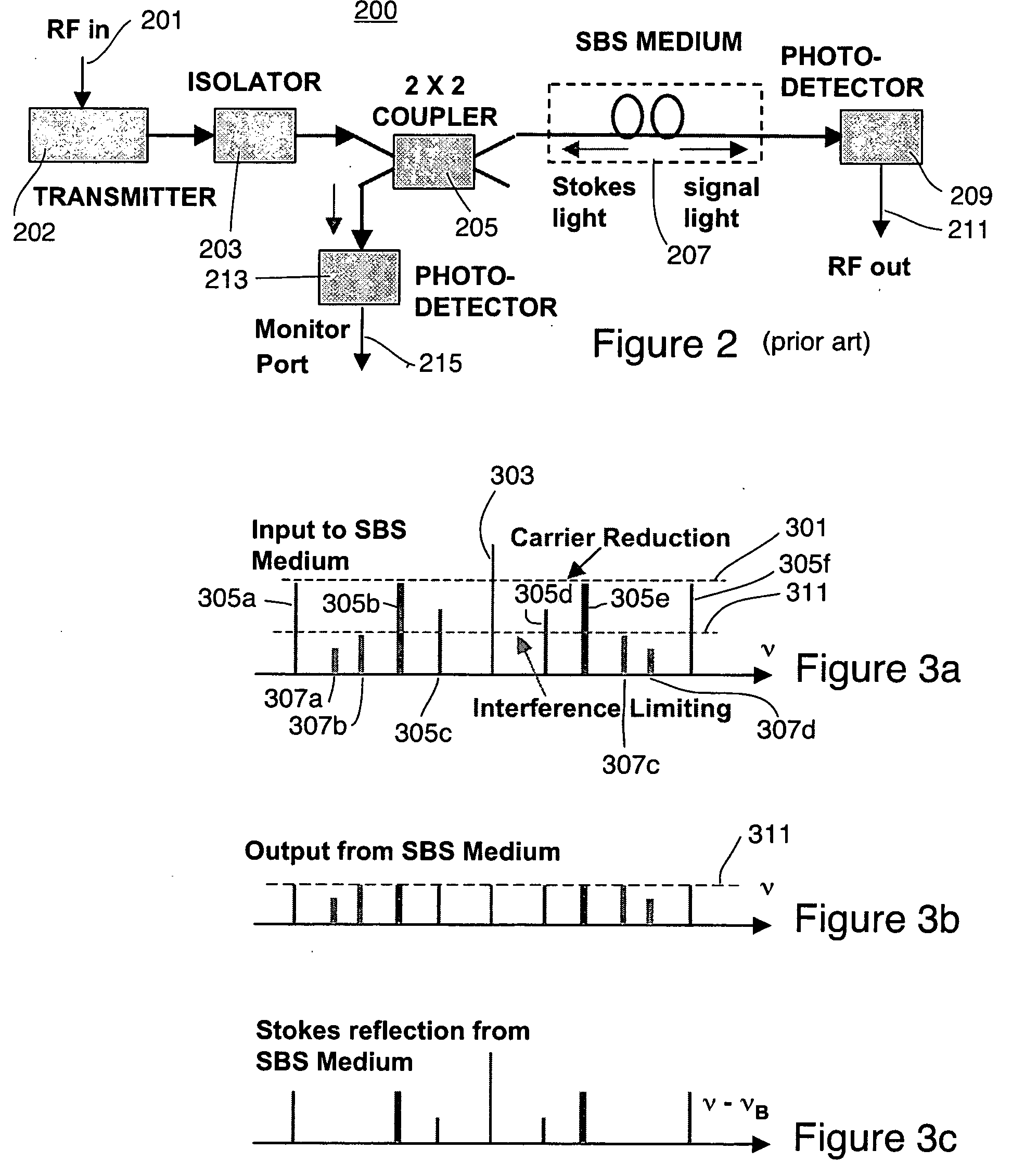
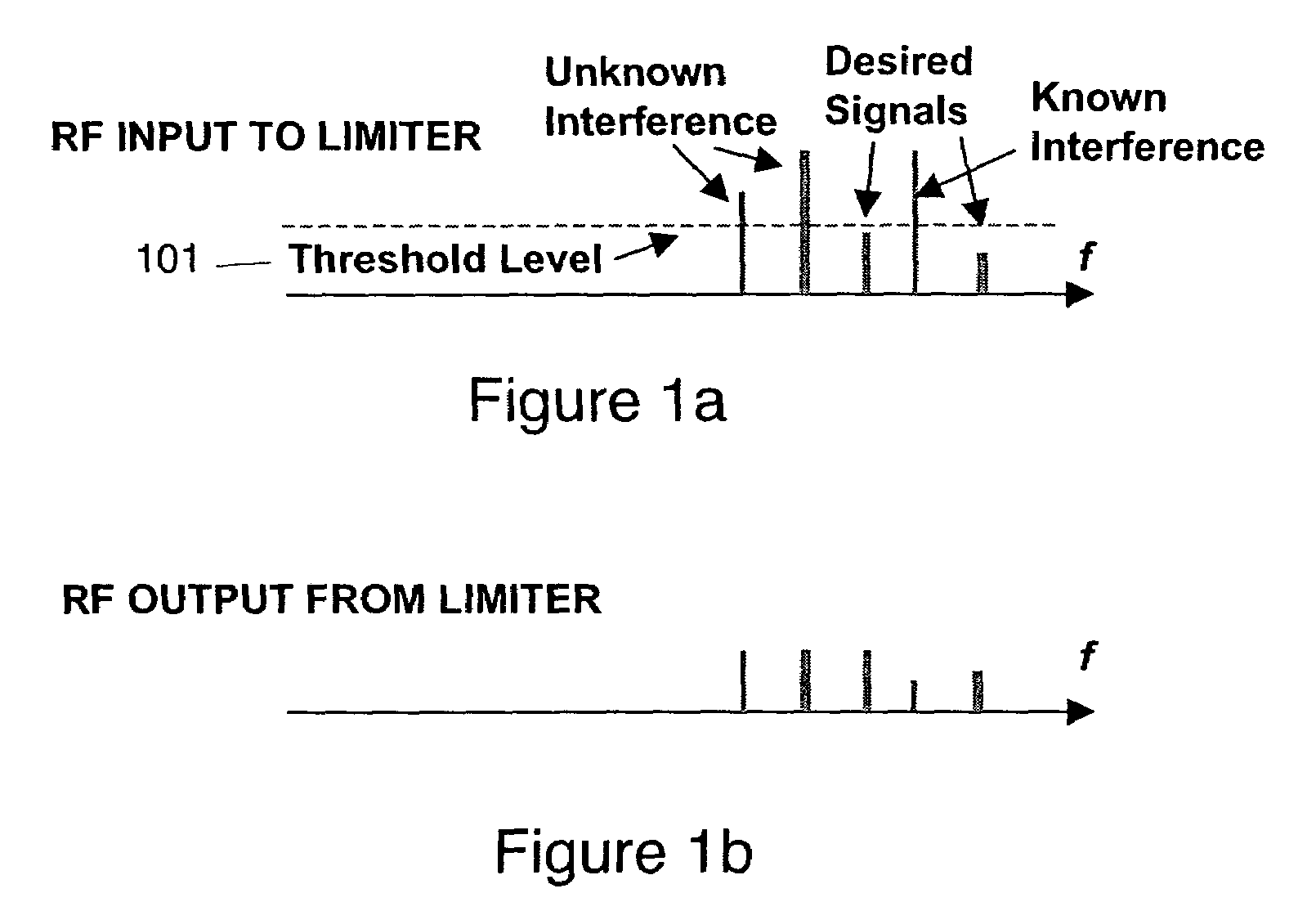
Self-adapting limiter
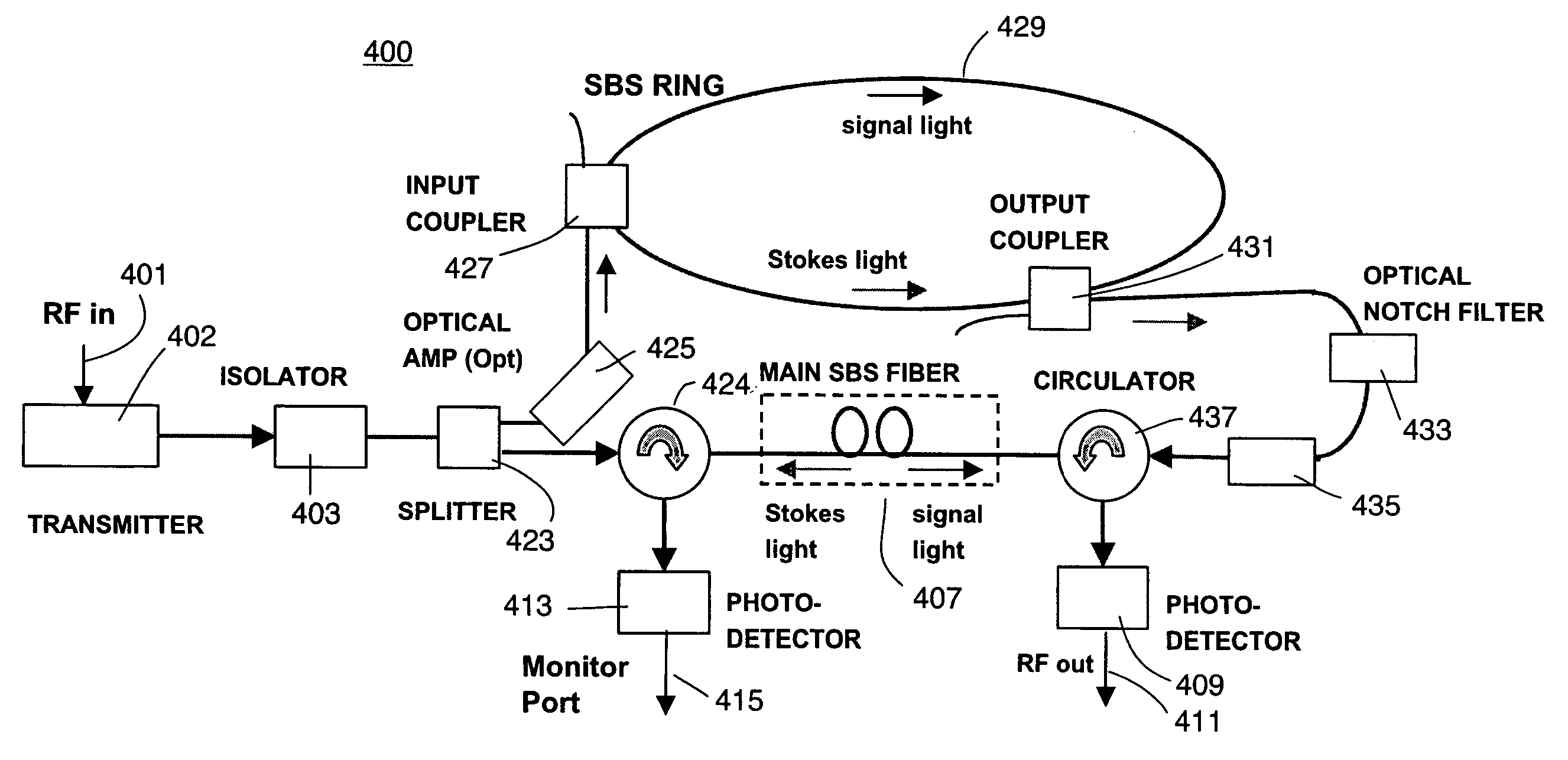
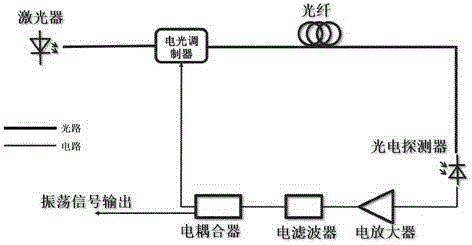
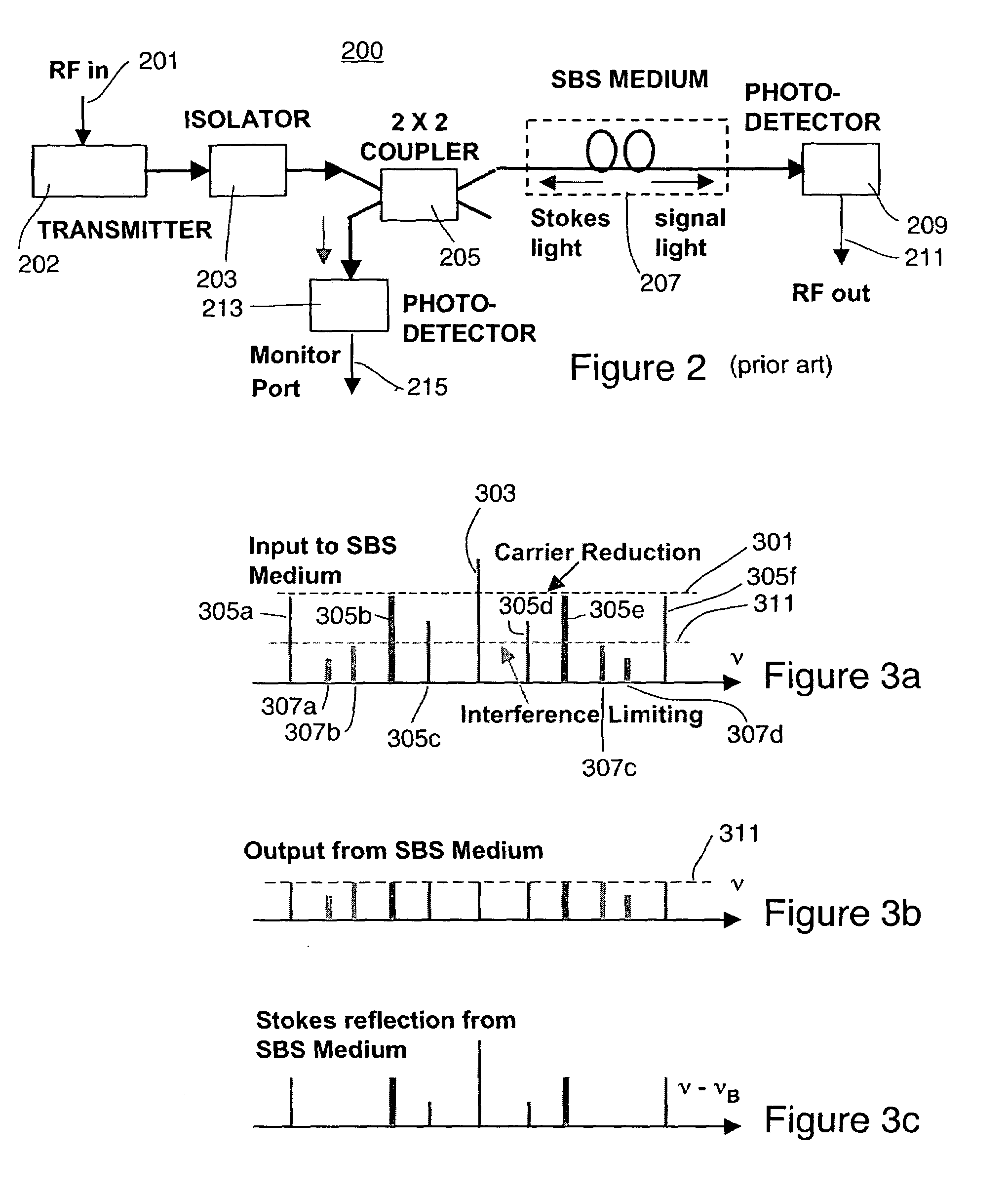
InactiveUS20060165336A1Reduce the amount requiredShorten the lengthLaser detailsWave based measurement systemsSelf adaptiveStokes wave
A limiter for limiting selected frequency components by generating Stokes waves in a stimulated Brillouin scattering medium. The generated Stokes waves create a seed that is provided to another stimulated Brillouin scattering medium. The seed selecting the undesired frequency components to be attenuated.
Owner:HRL LAB
Wavelength division multiplexer
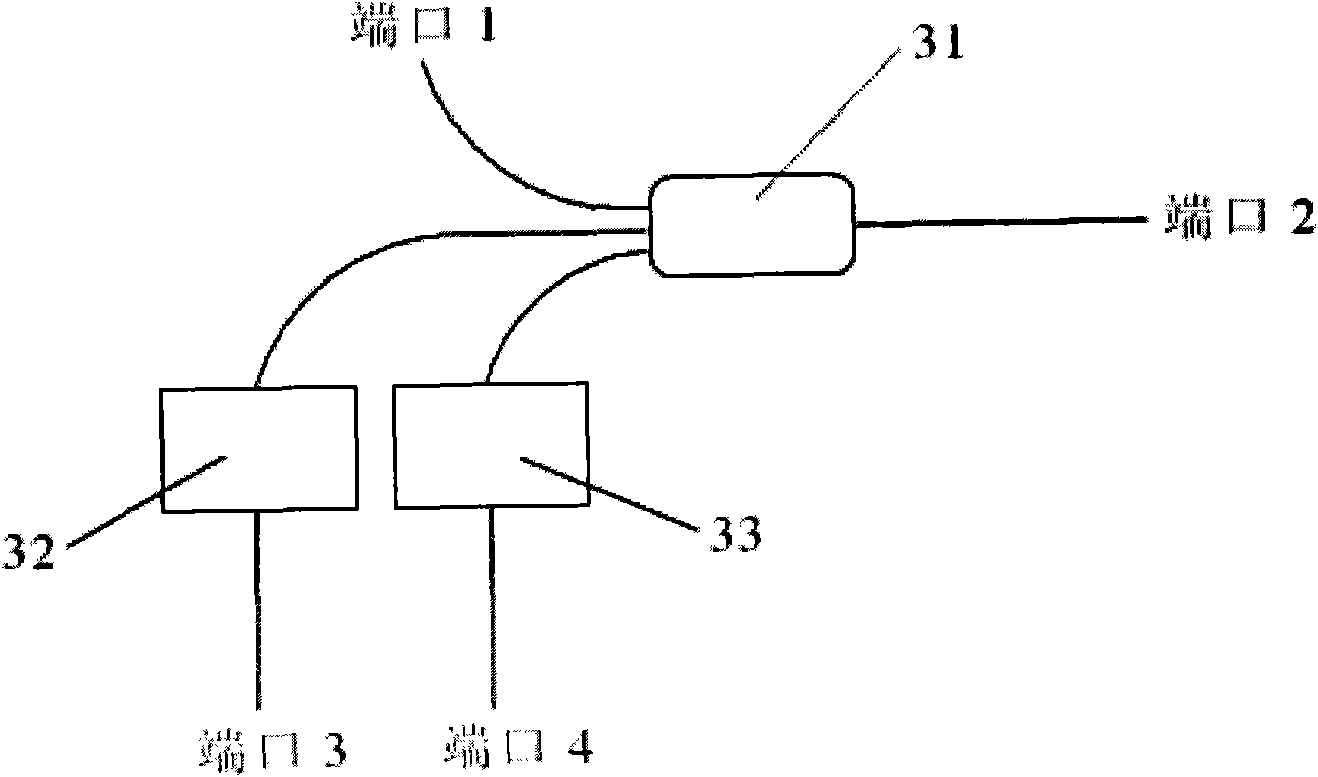
InactiveCN102081197AThermometers using physical/chemical changesOptical light guidesMultiplexerImage resolution
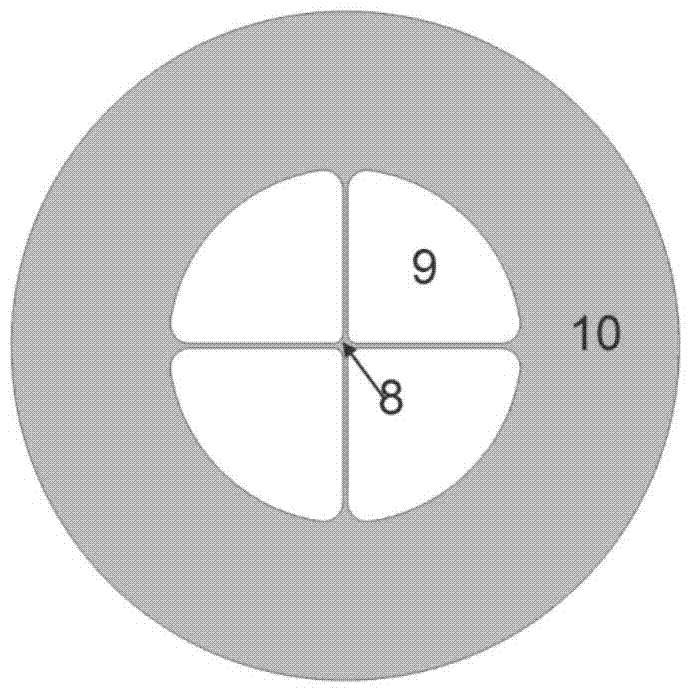
The invention discloses a wavelength division multiplexer, which belongs to the field of optical fiber sensor, and comprises four ports arranged on a shell, and two double-fiber collimators, two single-fiber collimators and four wavelength division multiplexing filters, which are arranged in the shell, wherein the two double-fiber collimators are connected by one of the respective tail fibers of the two double-fiber collimators, and the other respective tail fibers of the two double-fiber collimator are connected to the two ports among the four ports; the tail fibers of the two single-fiber collimators are connected to the rest two ports among the four ports respectively; two anti-stokes-wavelength wavelength division multiplexing filters among the four wavelength division multiplexing filters are spaced and arranged at an included angle between a double-fiber collimator and a single-fiber collimator; and the other two anti-stokes-wavelength wavelength division multiplexing filters are spaced and arranged at an included angle between the other double-fiber collimator and the other single-fiber collimator. The insulation degree of the device is high, and the device can be formed into a distributed optical fiber temperature sensor and can improve the temperature resolution of a system.
Owner:KINGSHORE NEW RESOURCES ELECTRIC JIANGSU
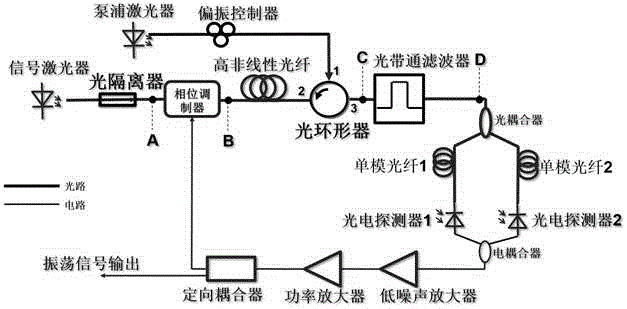
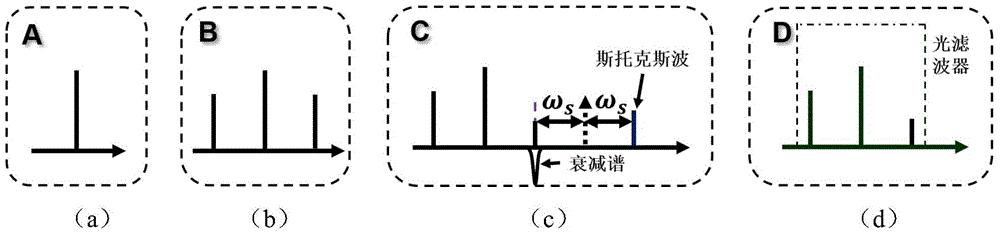
Wide tuning photoelectric hybrid oscillator and microwave signal generation method
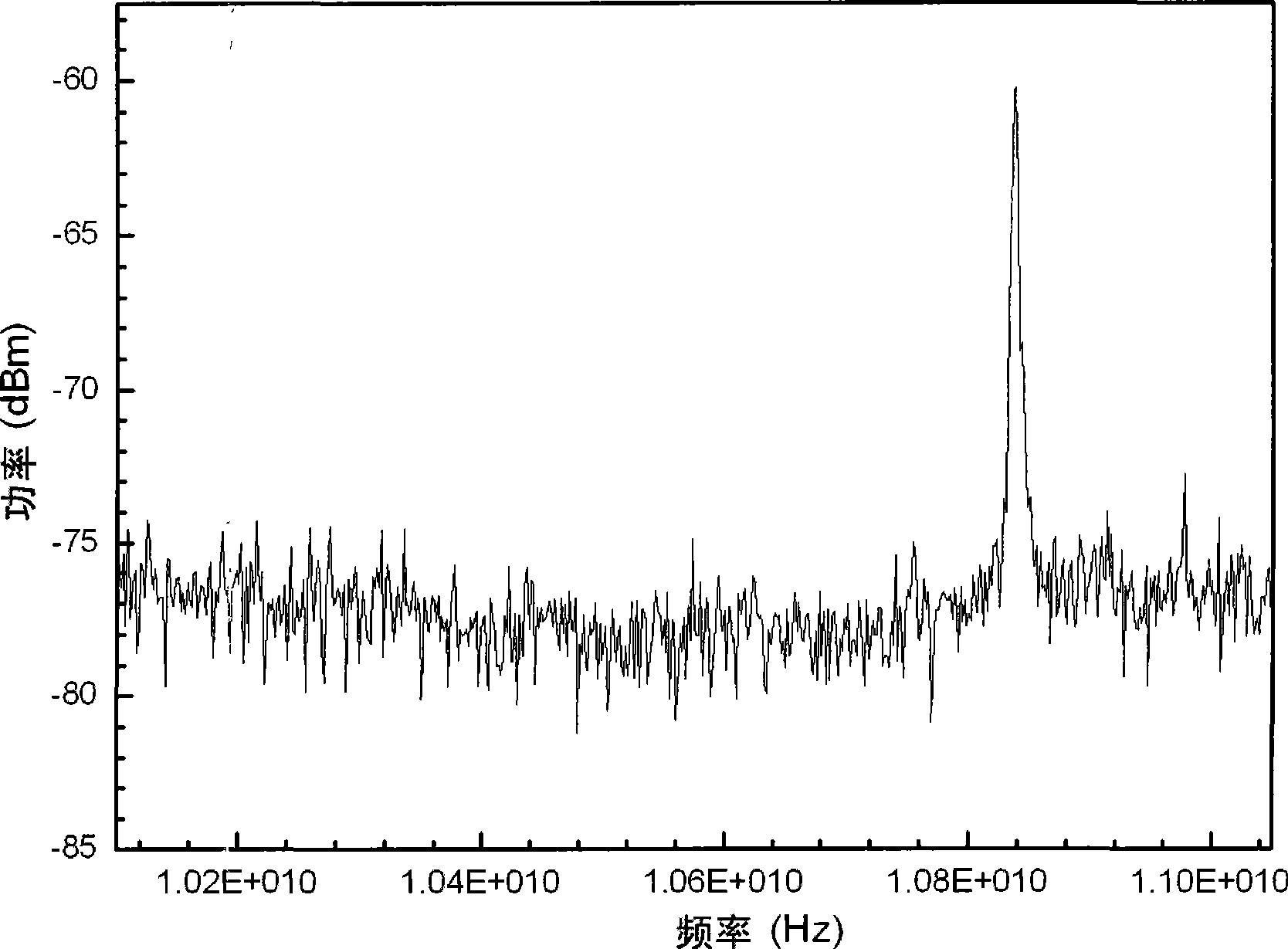
The invention discloses a wide tuning photoelectric hybrid oscillator and a microwave signal generation method. A signal light source output end of the oscillator is connected with an input end of a phase modulator, the input end of the phase modulator is connected with a second port of a light circulator through a non-linear fiber, an output end of a pump light source is connected with a first port of the light circulator through a polarization controller, a third port of the light circulator is connected with a photoelectric conversion link through a light filter, an output end of the photoelectric conversion link is connected with a radio frequency driving end of the phase modulator, another output end of the photoelectric conversion link is taken as a microwave signal output end, wavelength of the pump light source is greater than wavelength of a signal light source, frequency of the signal light source is at least f greater than frequency of the pump light source, the f is Stokes frequency shift, and the light filter is used for filtering Stokes waves generated by the non-linear fiber. The wide tuning photoelectric hybrid oscillator is suitable for generation of wide frequency tuning low phase noise microwave signals, bandwidth of the signals is dozens of MHz, a sub-oscillation mode can be effectively inhibited, and good stability is realized.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Mitigation of stimulated brillouin scattering in electromagnetic waveguides using wavelenght-selective mirrors
InactiveUS20050129362A1Prevent buildupReduce harmful effectsLaser using scattering effectsCoupling light guidesGratingFiber Bragg grating
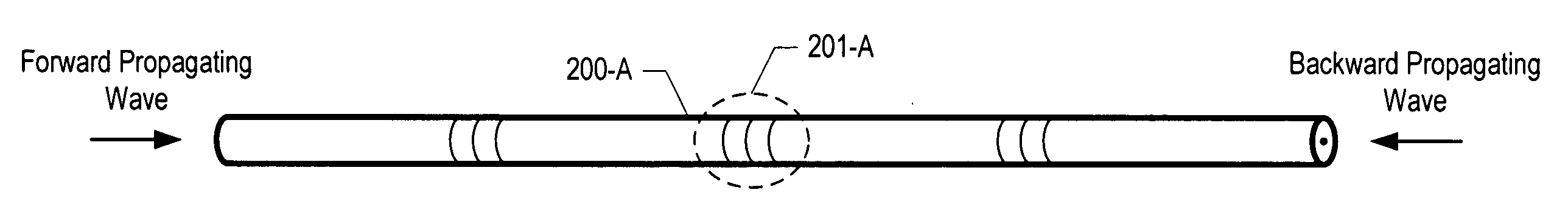
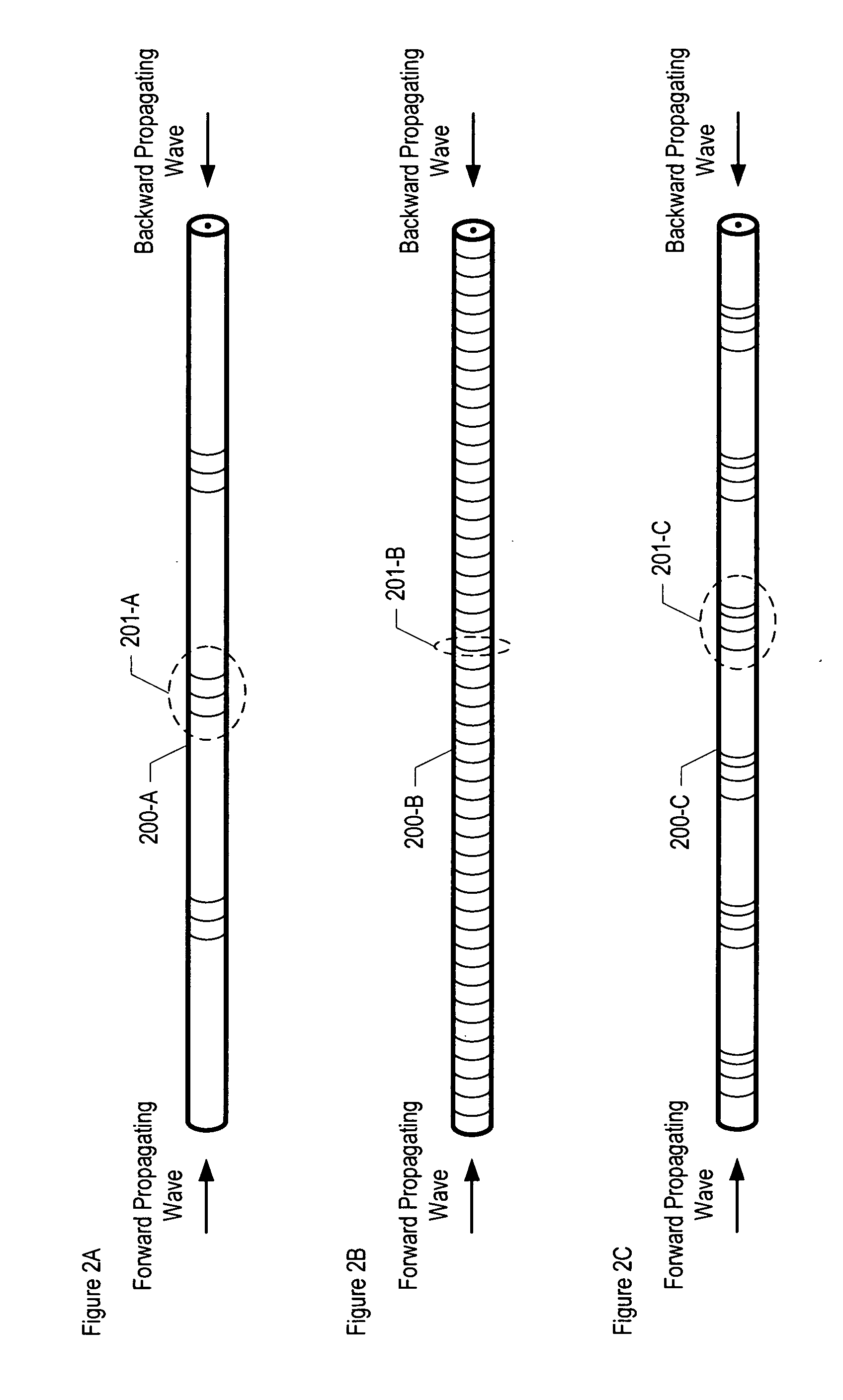
A mechanism for mitigating the effects of Stimulated Brillouin Scattering in electromagnetic waveguides such as optical fibers is disclosed. In particular, the illustrative embodiment of the present invention incorporates a plurality of evenly-spaced wavelength-selective mirrors, such as fiber Bragg gratings, into the waveguide that are designed to convey a forward-propagating incident wave and to reflect the backward-propagating Stokes wave induced by the incident wave. This prevents the build up of the backward-propagating Stokes wave and mitigates the deleterious effects of Stimulated Brillouin Scattering
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
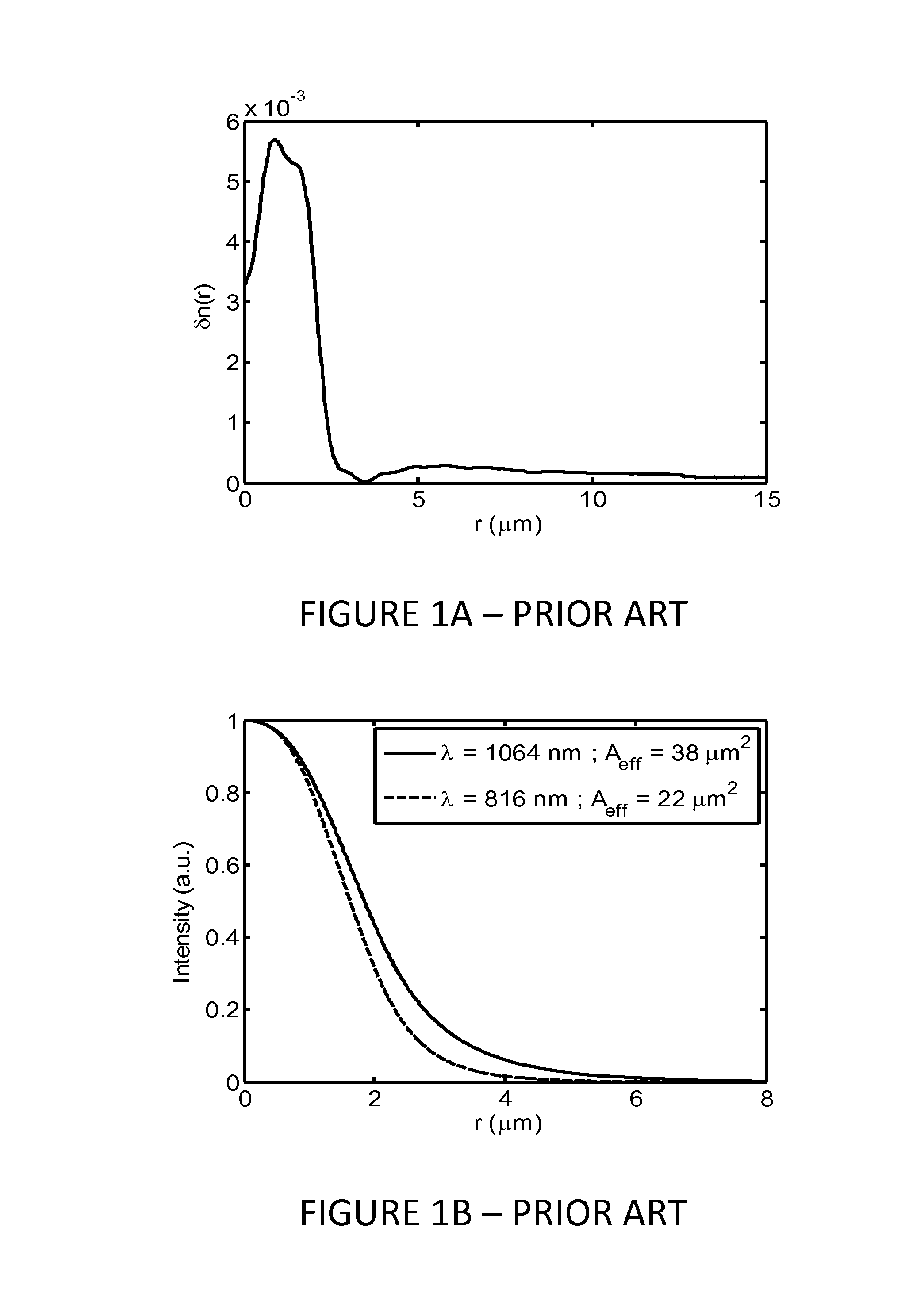
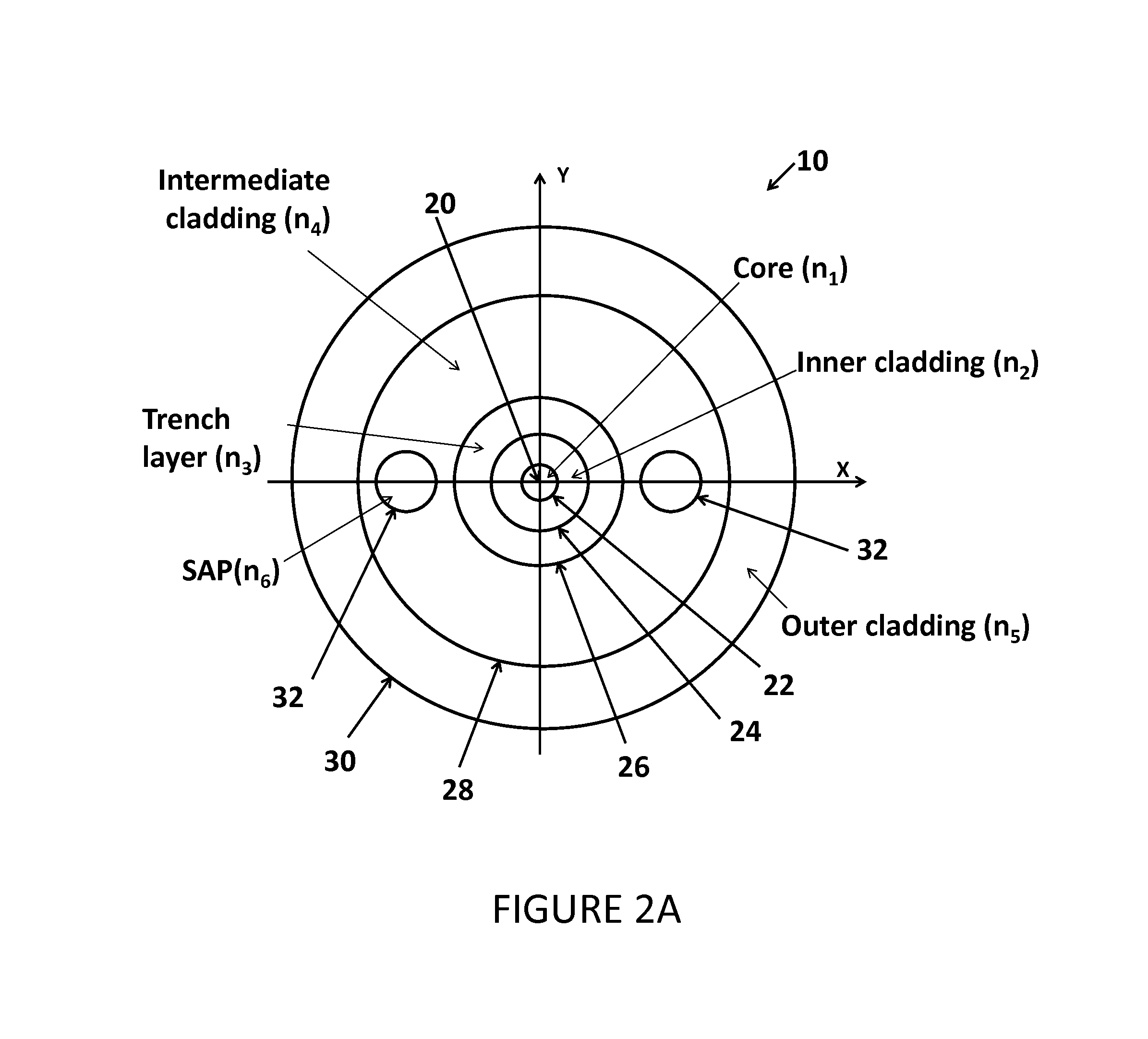
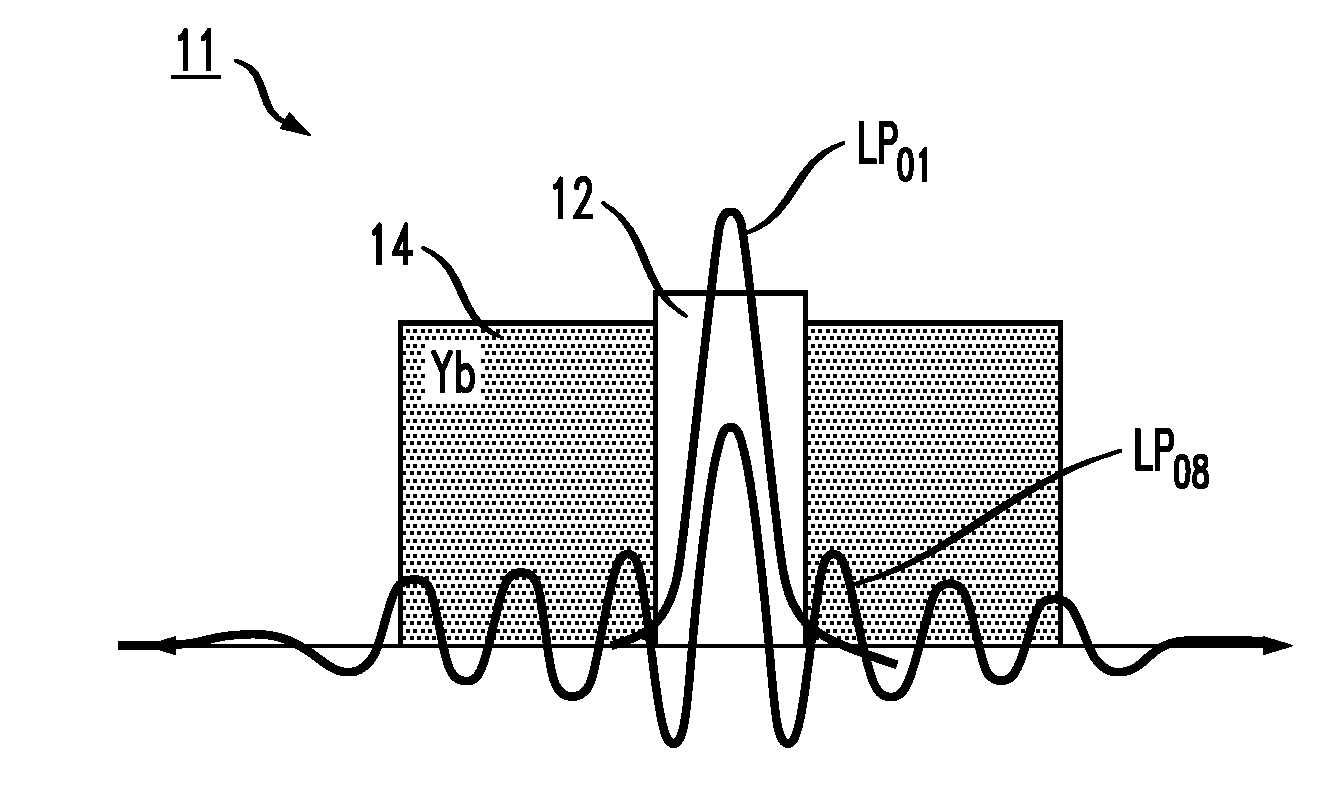
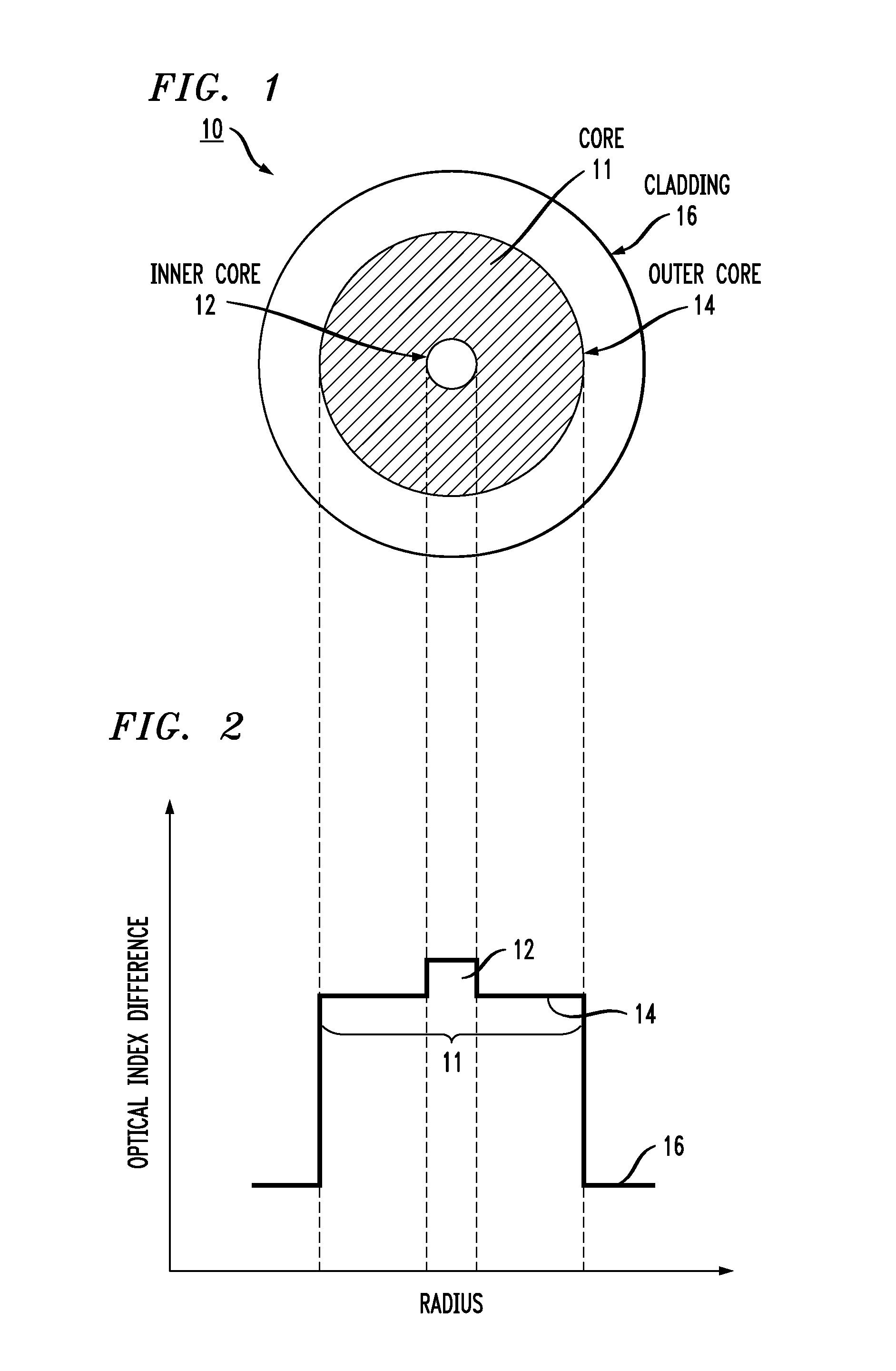
Optical fiber for Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman scattering endoscopes
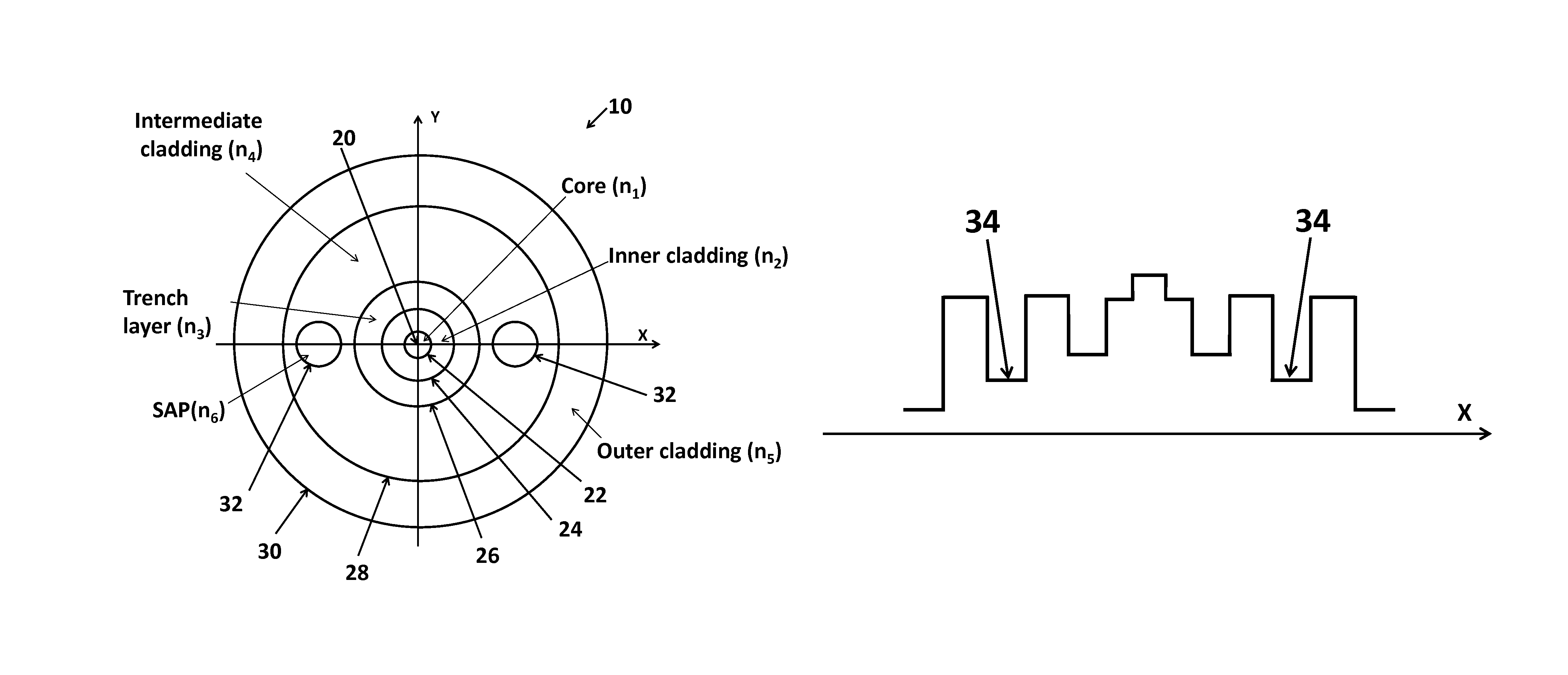
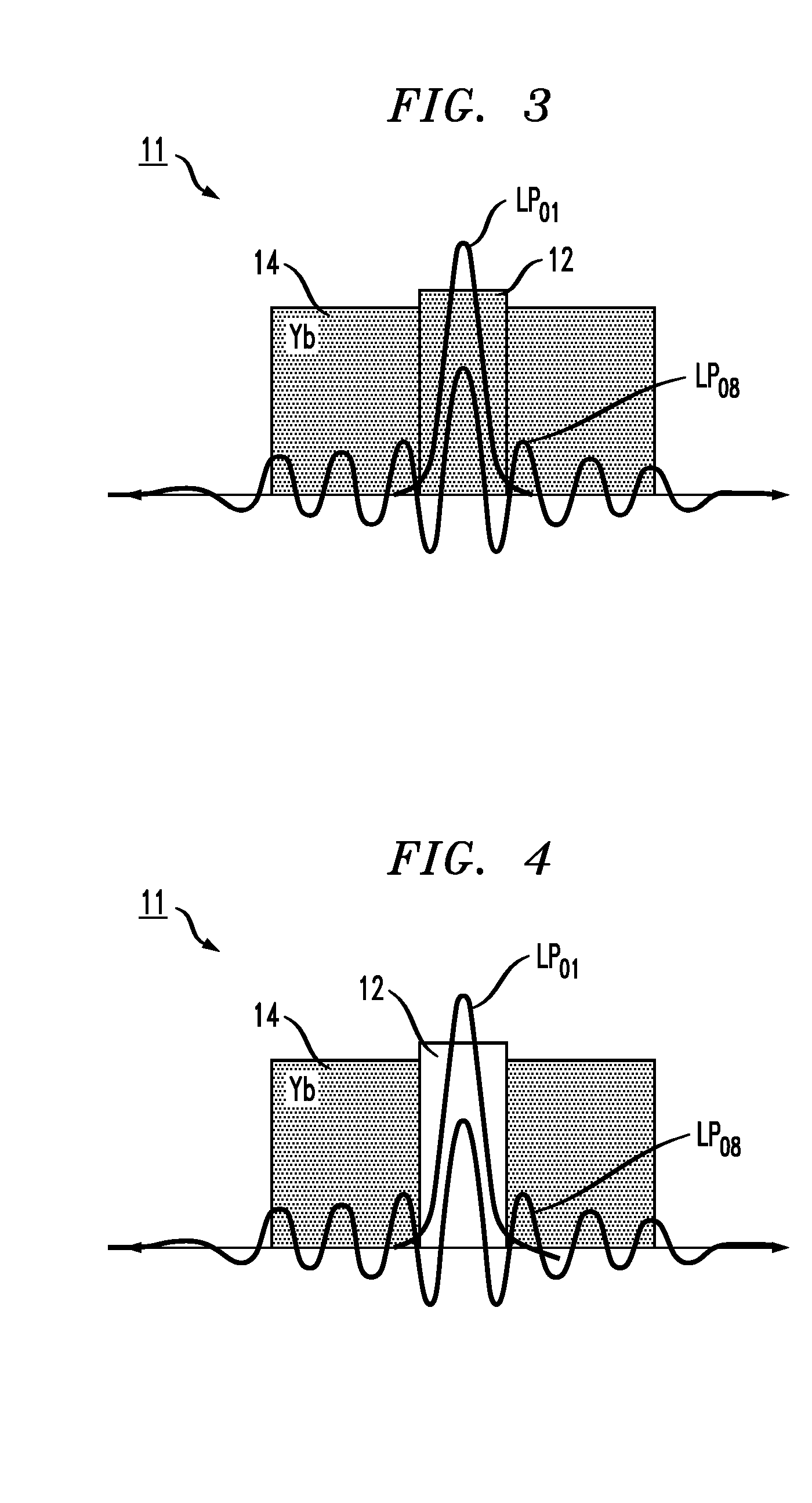
An optical fiber for use in a Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering (CARS) endoscope, comprising a core guiding lightwaves at a pump wavelength and at a Stokes wavelength, the core being single-mode at both wavelengths. The core is surrounded by cladding layers, including an inner cladding layer, a trench cladding layer, an intermediate cladding layer and an outer cladding layer. The refractive index of the trench cladding layer is lower than those of both neighboring cladding layers so as to define a trench in the radial refractive-index profile. The bending losses of the fundamental LP01 mode of the fiber at the Stokes wavelength are limited while maintaining high confinement losses for the higher-order LP11 mode of the fiber at the pump wavelength. The combination of the intermediate and outer cladding layers forms a multimode waveguide for guiding a collected CARS signal generated by an object or medium probed with the endoscope.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Self-adapting limiter
A limiter for limiting selected frequency components by generating Stokes waves in a stimulated Brillouin scattering medium. The generated Stokes waves create a seed that is provided to another stimulated Brillouin scattering medium. The seed selecting the undesired frequency components to be attenuated.
Owner:HRL LAB
Wavelength division multiplexing device for distributed optical fiber temperature sensor
InactiveCN102062648ABlock deliveryAccurate temperature distribution signalThermometers using physical/chemical changesDiffraction gratingsRayleigh scatteringGrating
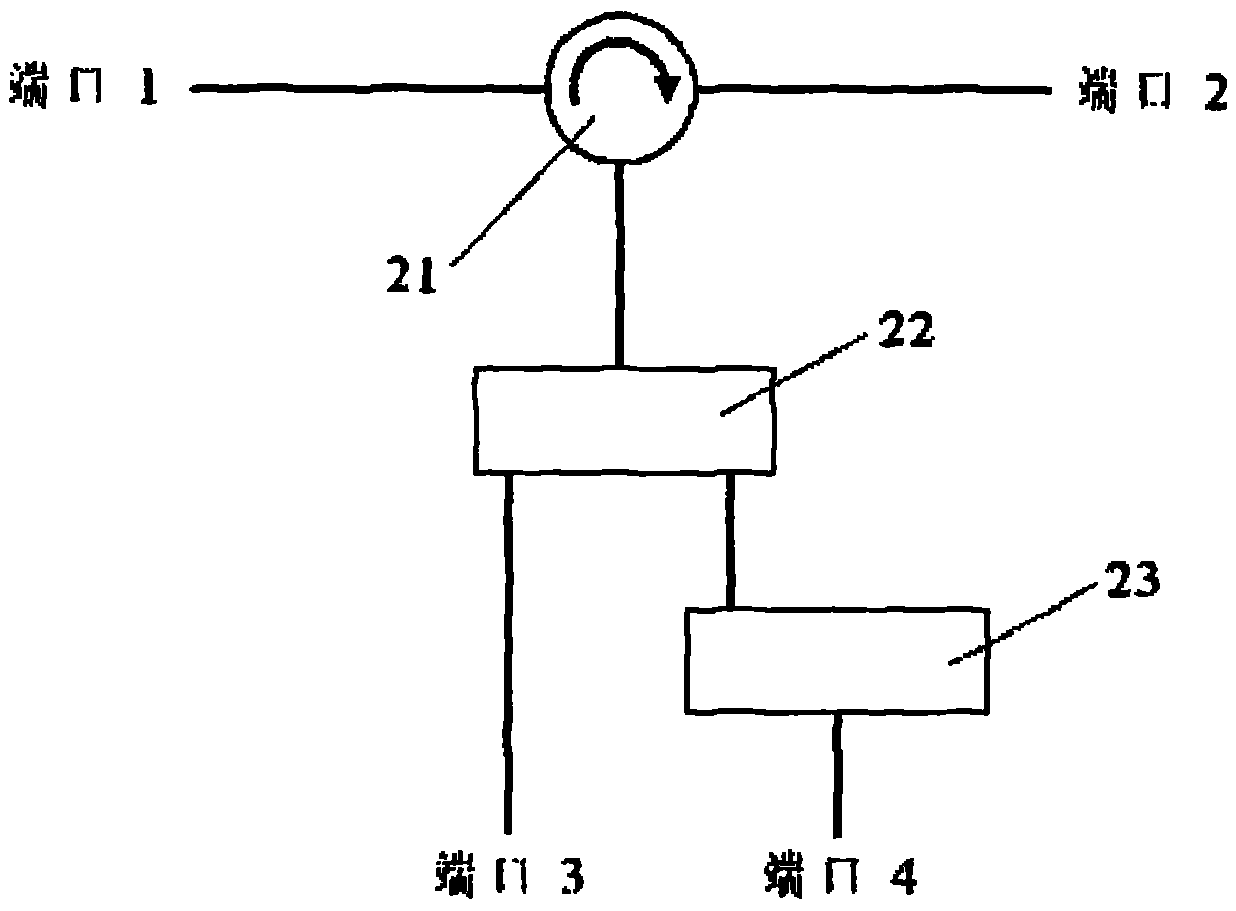
The invention discloses a wavelength division multiplexing device for a distributed optical fiber temperature sensor in the field of optical fiber sensors. The device comprises four ports formed on a shell; an optical circulator with four ports is arranged in the shell; first and second ports of the optical circulator are directly connected to a port 1 and a port 2 on the shell respectively; a fiber Bragg grating with Rayleigh scattering wavelength, a fiber Bragg grating with Stokes wavelength and a band-pass filter with anti-Stokes wavelength are connected in series between a third port of the optical circulator and a port 3 on the shell; the fiber Bragg grating with the Rayleigh scattering wavelength, a fiber Bragg grating with the anti-Stokes wavelength and a band-pass filter with the Stokes wavelength are connected in series between a fourth port of the optical circulator and a port 4 on the shell; and a light path in the optical circulator circulates from the first port to the fourth port step by step. The device can reliably separate anti-Stokes light from Stokes light, the accurate temperature information can be acquired further, and the temperature resolution of the system is improved.
Owner:KINGSHORE NEW RESOURCES ELECTRIC JIANGSU
Continuous wave ultraviolet laser based on stimulated raman scattering
InactiveUS20150063830A1Laser using scattering effectsElectromagnetic transmittersResonant cavityHarmonic
The present application is directed to a laser system using Stimulated Raman Scattering and harmonic conversion to produce a continuous wave ultraviolet wavelength output signal. More specifically, the laser system includes a pump source configured to generate at least one pump signal, a resonant cavity resonant at a Stokes wavelength in optical communication with the pump source, a SRS gain device positioned within the resonant cavity and configured to generate at least one SRS output signal at a Stokes wavelength when pumped with the pump signal, and a harmonic conversion device positioned within the resonant cavity and configured to produce a continuous wave second harmonic output signal of the SRS output signal.
Owner:NEWPORT CORP
Method and apparatus for auto-correcting the distributed temperature sensing system
InactiveUS9645018B2Calculation is accurate and reliableRadiation pyrometryThermometers using physical/chemical changesFiberOptoelectronics
System and method for correcting the potential errors occurring in a fiber optic temperature measurement system are disclosed. In one respect, a dual light sources configuration is provided. The primary light source may illuminate a sensing fiber, and an Anti-Stokes band may be detected. The secondary light source may illuminate a sensing fiber, and a Rayleigh band may be detected, where the Rayleigh band is substantially wide enough to cover the Anti-Stokes band of the primary light source. A ratio between these Anti-Stokes and the Rayleigh bands may be used to measure the temperature and undesired errors due to the perturbations falling on the sensing fiber is continuously corrected.
Owner:LEE CHUNG
Device for generating high-efficiency multi-wavelength ultra-short pulse lasers
InactiveCN103490274ASimple structureOptical resonator shape and constructionStimulate raman scatteringLasing wavelength
The invention provides a device for generating high-efficiency multi-wavelength ultra-short pulse lasers to solve the problem that the self-phase modulation process, the self-focusing process and the multiple-photon dissociation process in the transient stimulated raman scattering process under the ultra-short pulse pumping are seriously influenced, and relates to the technical field of non-linear optical equipment. A raman pool is composed of a stainless steel pipe, a fused quartz incidence window without a coating film, and an exit window without a coating film, and pure hydrogen, methane, deuterium gas and the like or mixed gas formed by mixing the pure hydrogen or the methane or the deuterium with inert gas or mixed gas formed by multiple types of raman media can be filled into the raman pool. More stokes wavelength output can be obtained by mixing working gas media, the magnitude of the output stokes wavelength can be adjusted due to the addition of buffer gas, and dense flint materials are selected as materials of an equilateral dispersing prism. The dispersing prism, a fifth focus lens and laser mode selection pinholes are used in cooperation so that different types of laser wavelength output can be selected and energy measurement can be conducted. The device is suitable for the technical field of non-linear optical equipment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
High order Raman inhibition method based on polarization maintaining optical fiber 45-degree dislocation welding technology
PendingCN108321673ASuppression wavelengthSimple structureLaser using scattering effectsCoupling light guidesRotation functionPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
The invention provides a high order Raman inhibition method based on a polarization maintaining optical fiber 45-degree dislocation welding technology. The method realizes a polarization rotation function through the characteristic that Raman gain is low when pump wave and Stokes wave in a Raman gain spectrum are subjected to cross polarization in an online polarized Raman fiber laser and the 45-degree dislocation welding of polarization maintaining passive optical fiber, so that the polarization directions of pump light and low order Raman light are not changed, and the polarization directionof high order Raman and the pump light are orthometric, and the high order Raman grain is inhibited.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Optical fiber refractive index sensor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN104122227AHigh nonlinear coefficientShorten the lengthPhase-affecting property measurementsCross sensitivityHigh power lasers
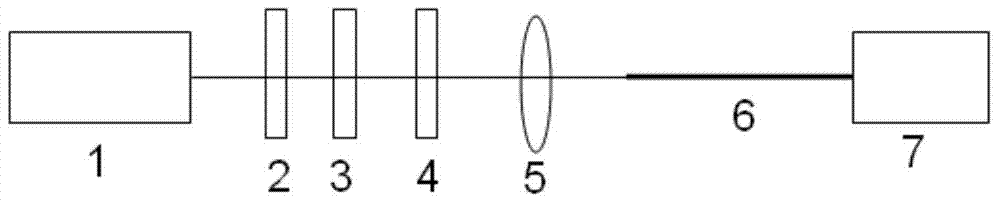
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical fiber sensing and provides a suspended core pohotonic crystal fiber refractive index sensor based on a four-wave mixing effect. The suspended core pohotonic crystal optical fiber refractive index sensor is composed of a high-power laser device, two half wave plates, a polarizer, a coupling lens, a suspended core pohotonic crystal optical fiber and a spectrograph. A covering layer of the suspended core pohotonic crystal optical fiber is provided with a plurality of air holes which are suspended at the periphery of a quartz fiber core through a sub-wavelength quartz arm; the fiber core of the fiber is small and the air holes of the covering layer are large; high nonlinear coefficient of the optical fiber is ensured, the length of the sensing optical fiber is reduced, and the air holes can be conveniently filled with liquid. Furthermore, the invention provides a manufacturing method of the suspended core pohotonic crystal fiber refractive index sensor based on the four-wave mixing effect; a zero dispersion wavelength of the suspended core pohotonic crystal fiber is close to a pumping wavelength so that generated Stokes waves and anti-Stokes waves are very sensitive to optical fiber dispersion and the refractive index sensing with the ultra-high sensitivity can be realized; the sensitivity can reach up to 105nm / RIU (Refractive Index Unit). The temperature crossing sensibility is avoided and the high-precision sensing measurement on reflective index micro-variables of the external environment is realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
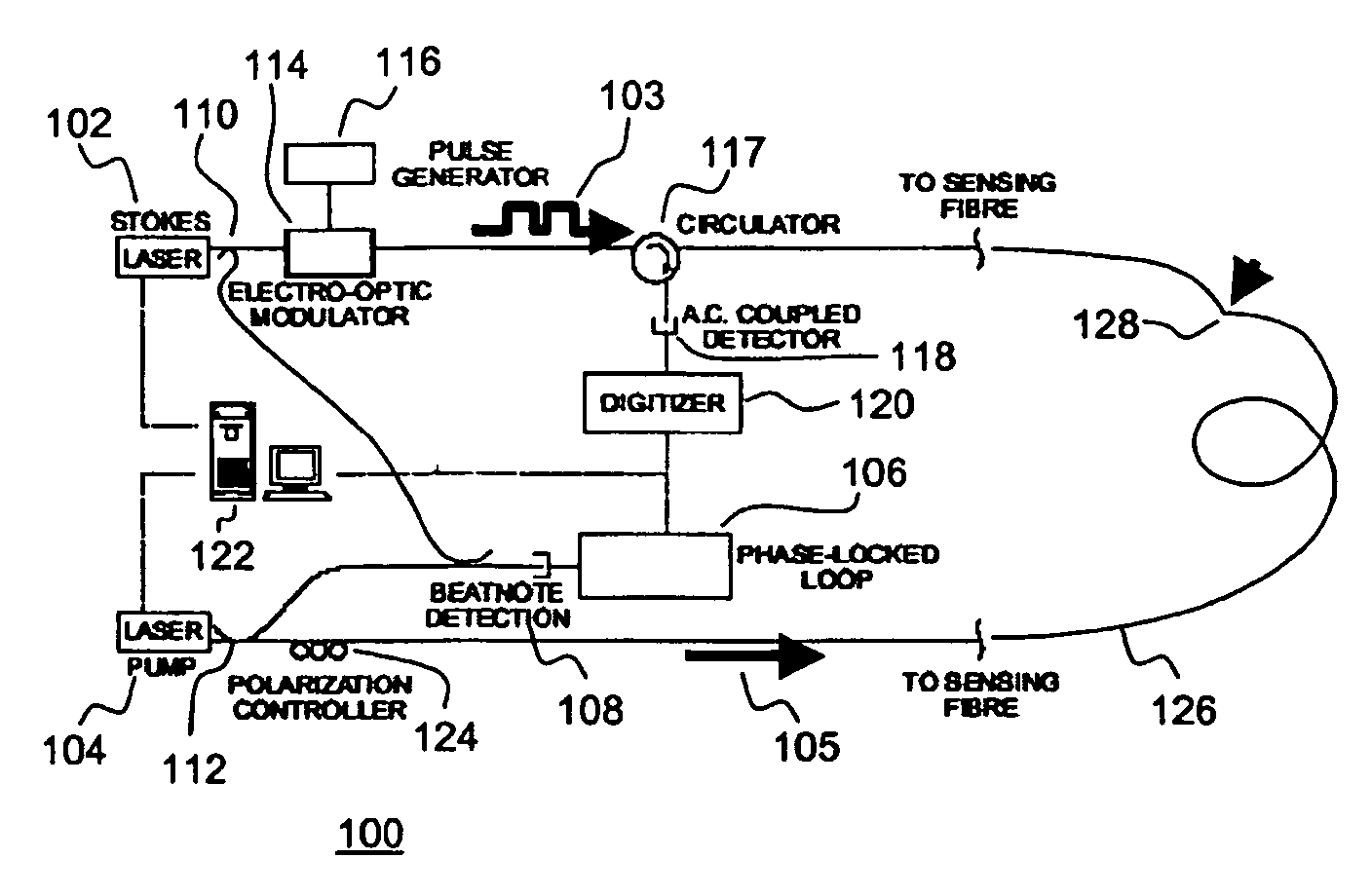
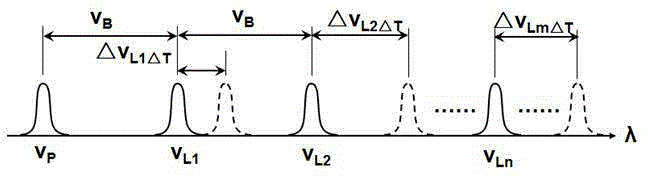
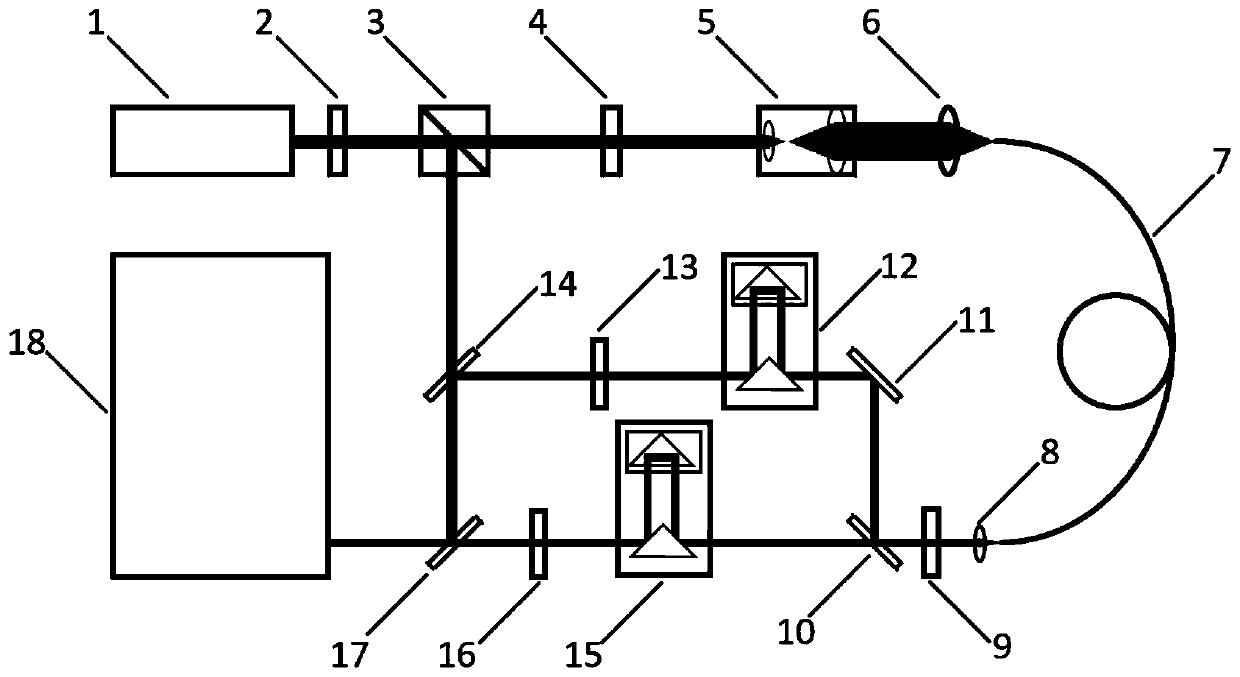
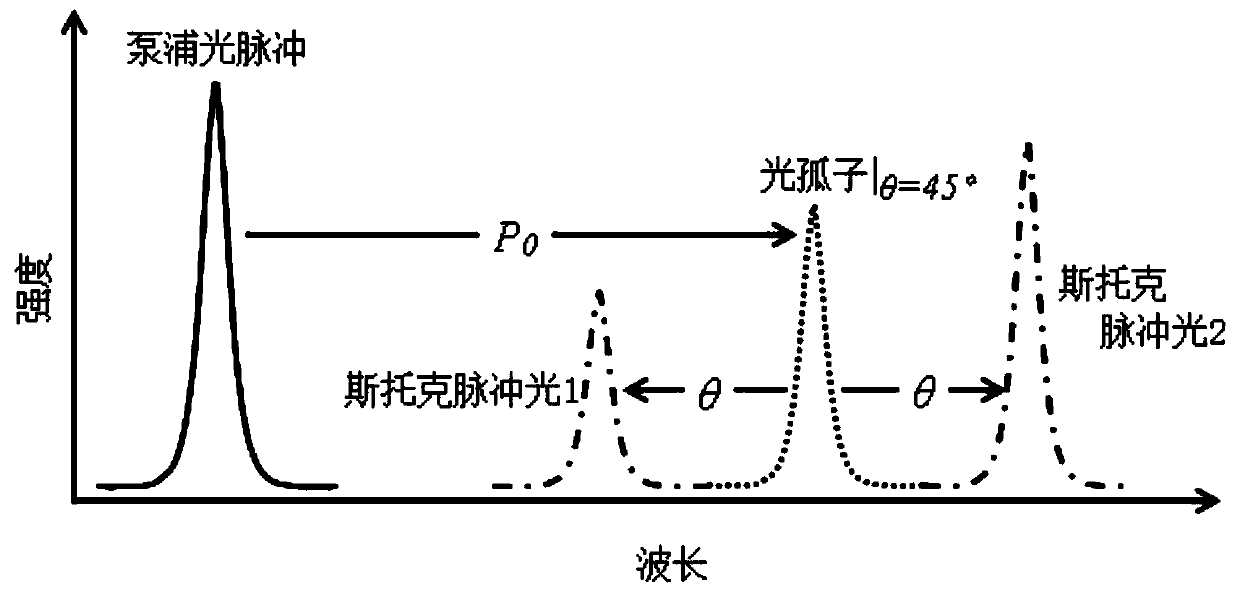
Sensitivity adjustable distributed fiber sensing system based on high-order Stokes waves
ActiveCN105783955AResolve SensitivitySolve the adjustmentConverting sensor output opticallyData acquisitionErbium doping
The invention relates to a sensitivity adjustable distributed fiber sensing system based on high-order Stokes waves, belongs to a distributed fiber sensing system, and solves the problem that the detection sensitivity of a present distributed fiber sensing system is low and cannot be adjusted. The sensitivity adjustable distributed fiber sensing system based on high-order Stokes waves comprises an adjustable single-frequency laser, a semiconductor laser, a phase-locked loop, a first polarization controller, a second polarization controller, an electro-optical modulator, a unidirectional erbium doped fiber amplifier, a light circulator, an adjustable optical filter, a photoelectric detector, data collection card and a resonant cavity; and the resonant cavity further comprises a bidirectional erbium doped fiber amplifier, a first bidirectional optical demultiplexer, a second bidirectional optical demultiplexer and a single-mode sensing fiber. The system of the invention is suitable for the distributed fiber sensing field.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
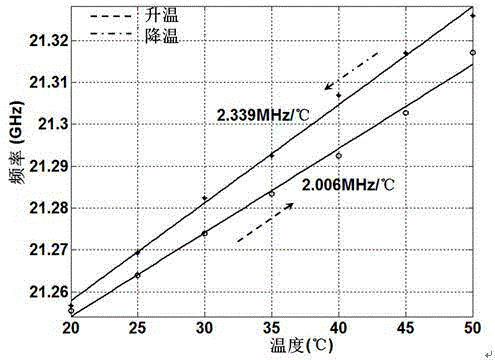
High-precision distributed optical fiber temperature sensing system
The invention discloses a high-precision distributed optical fiber temperature sensing system. According to the system, different sampling rates are set for a data acquisition unit according to the characteristic of different wavelengths of stokes and anti-stokes to ensure that each pair of acquired stokes and anti-stokes data corresponds to a position on an optical fiber; the influence of the different wavelengths of the stokes and the anti-stokes on spatial resolution, positioning precision and temperature precision is eliminated fundamentally; the three key indexes of the system are improved; and the application scope of the distributed optical fiber temperature sensing system is expanded.
Owner:WEIHAI BEIYANG PHOTOELECTRIC INFORMATION TECH
Fully electronically controlled double-Stokes optical wavelength tuning device and method
ActiveCN110186896AEnhanced tuning stabilityImproving the imaging rateRaman scatteringFiberOptical polarization
The invention discloses a fully electronically controlled double-Stokes optical wavelength tuning device, comprising a femtosecond laser (1), an ultrashort pulse power and polarization state adjustment part, a high nonlinear polarization-maintaining pohotonic crystal fiber (7), an optical fiber collimation and beam expanding mirror (8), an optical filter (9), double-Stokes optical pulse delay adjustment part and a CARS microimaging system (18), wherein optical soliton with a wavelength capable of being continuously adjusted within a wide range is generated by the soliton self frequency shifteffect in the high nonlinear polarization-maintaining pohotonic crystal fiber and is used as a Stokes optical pulse, and the ultrashort pulse optical power entering the high nonlinear polarization-maintaining pohotonic crystal fiber and the linear polarization direction are changed by an electronically controlled liquid crystal wave plate and an electronically controlled liquid crystal polarization rotating sheet, so that the independent and flexible adjustment of the wavelengths of the optical solitons of a fast axis and a slow axis can be achieved. The fully electronically controlled double-Stokes optical wavelength tuning device disclosed by the invention enhances the tuning stability of an excitation source of the CARS microimaging system, realizes the independent and flexible adjustment of double-Stokes wavelength, and improves the imaging rate of the CARS microimaging system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Suppression of stimulated brillouin scattering in higher-order-mode optical fiber amplifiers
ActiveUS9356416B2Increase output powerMinimises levelLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingDopantOptical fiber amplifiers
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
High-accuracy distributed optical fiber sensing system based on narrow linewidth high-order Brillouin Stokes wave
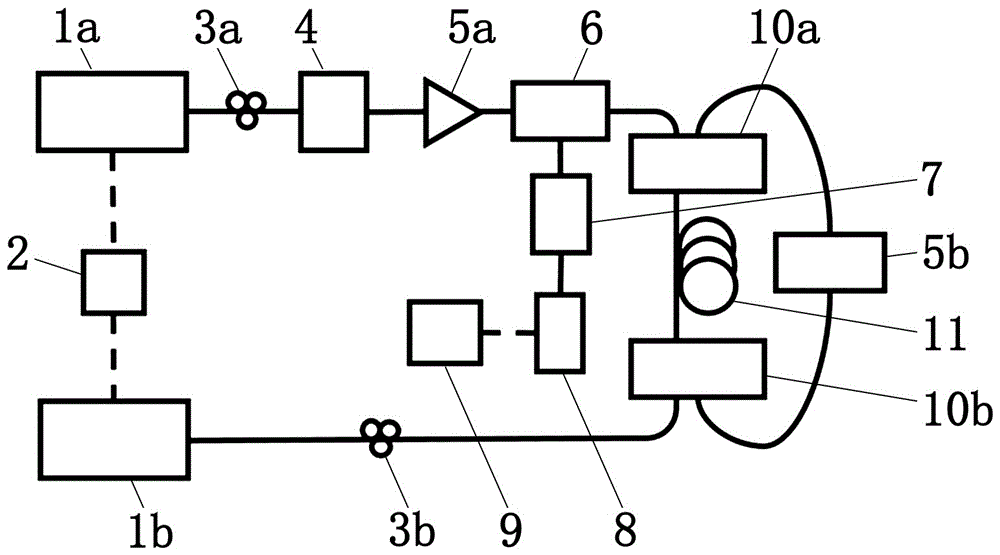
InactiveCN109029515AImprove sensor sensitivityImprove detection accuracyConverting sensor output opticallyLine widthData acquisition
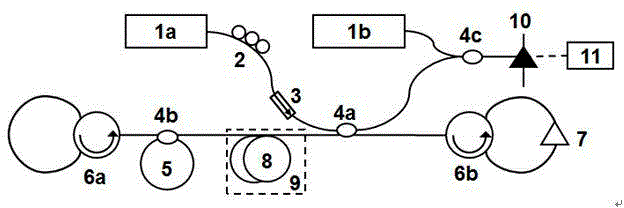
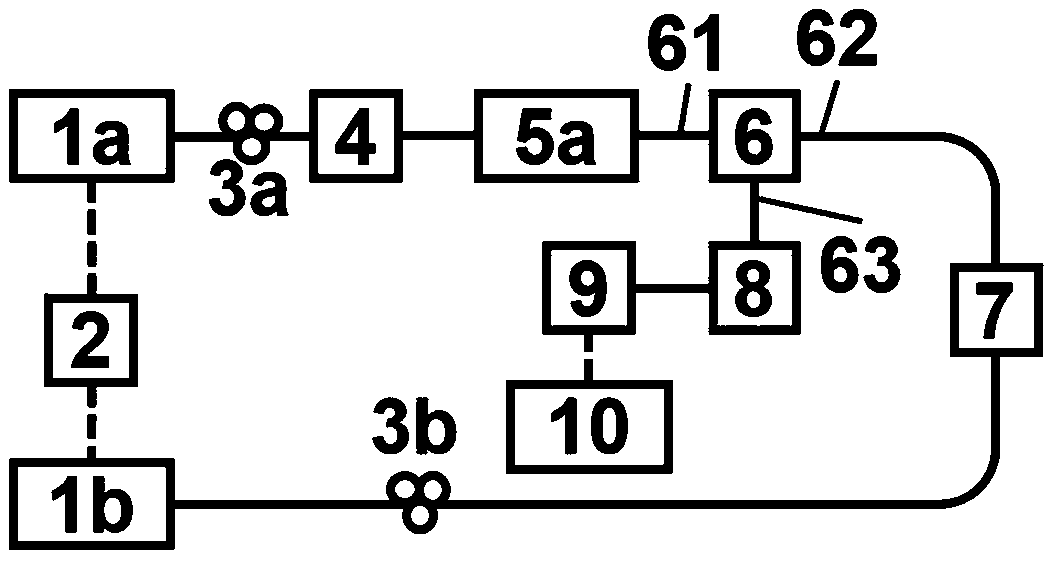
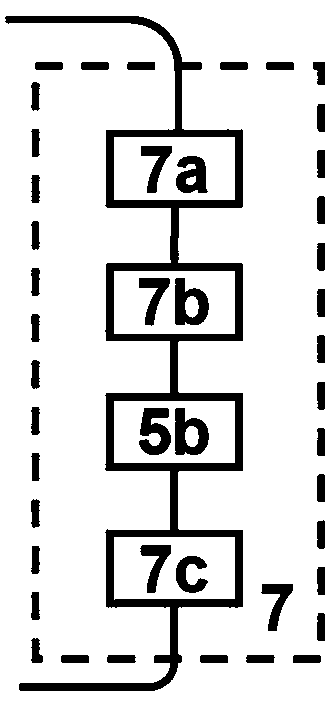
The invention discloses a high-accuracy distributed optical fiber sensing system based on a narrow linewidth high-order Brillouin Stokes wave. The system comprises an adjustable semiconductor laser (1a), a single-frequency semiconductor laser (1b), a frequency locking device (2), a first polarization controller (3a), a second polarization controller (3b), an acousto-optic modulator (4), a one-wayoptical fiber amplifier (5a), a bidirectional optical fiber amplifier (5b), an optical circulator (6), a multi-wavelength narrow linewidth Brillouin optical fiber laser (7), an adjustable optical filter (8), a photoelectric detector (9) and a data collection card (10), wherein the multi-wavelength narrow linewidth Brillouin optical fiber laser (7) consists of an automatic following multi-wavelength narrow-band filter (7a), a sensing optical fiber (7b), a bidirectional Er-doped optical fiber amplifier (5b) and a Faraday polariscope (7c). The system is reasonable in design, the multi-wavelengthnarrow linewidth Brillouin optical fiber laser is used, and a high-order Brillouin Stokes wave frequency shift amount is detected to realize high-accuracy temperature and strain detection.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com