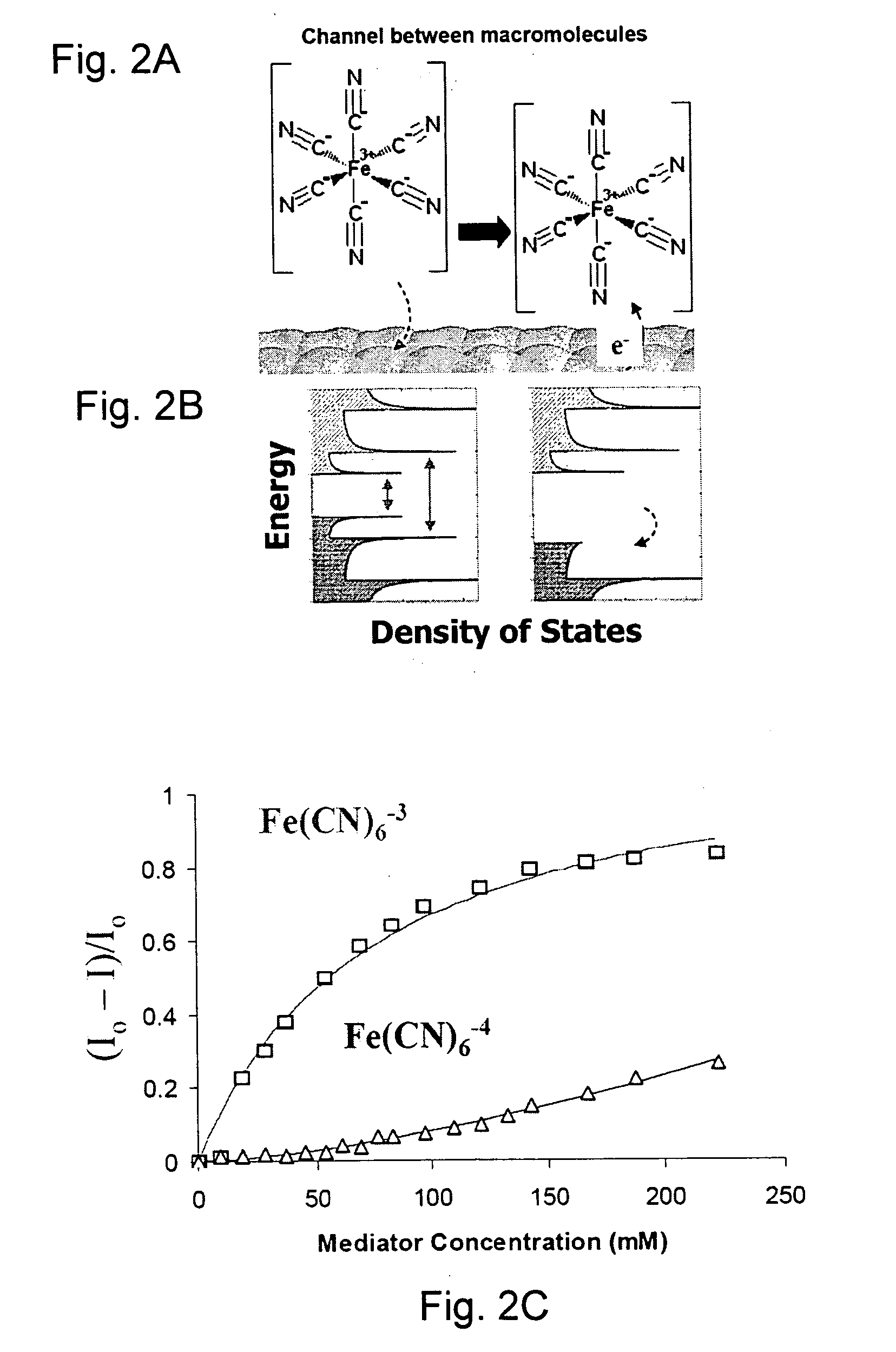
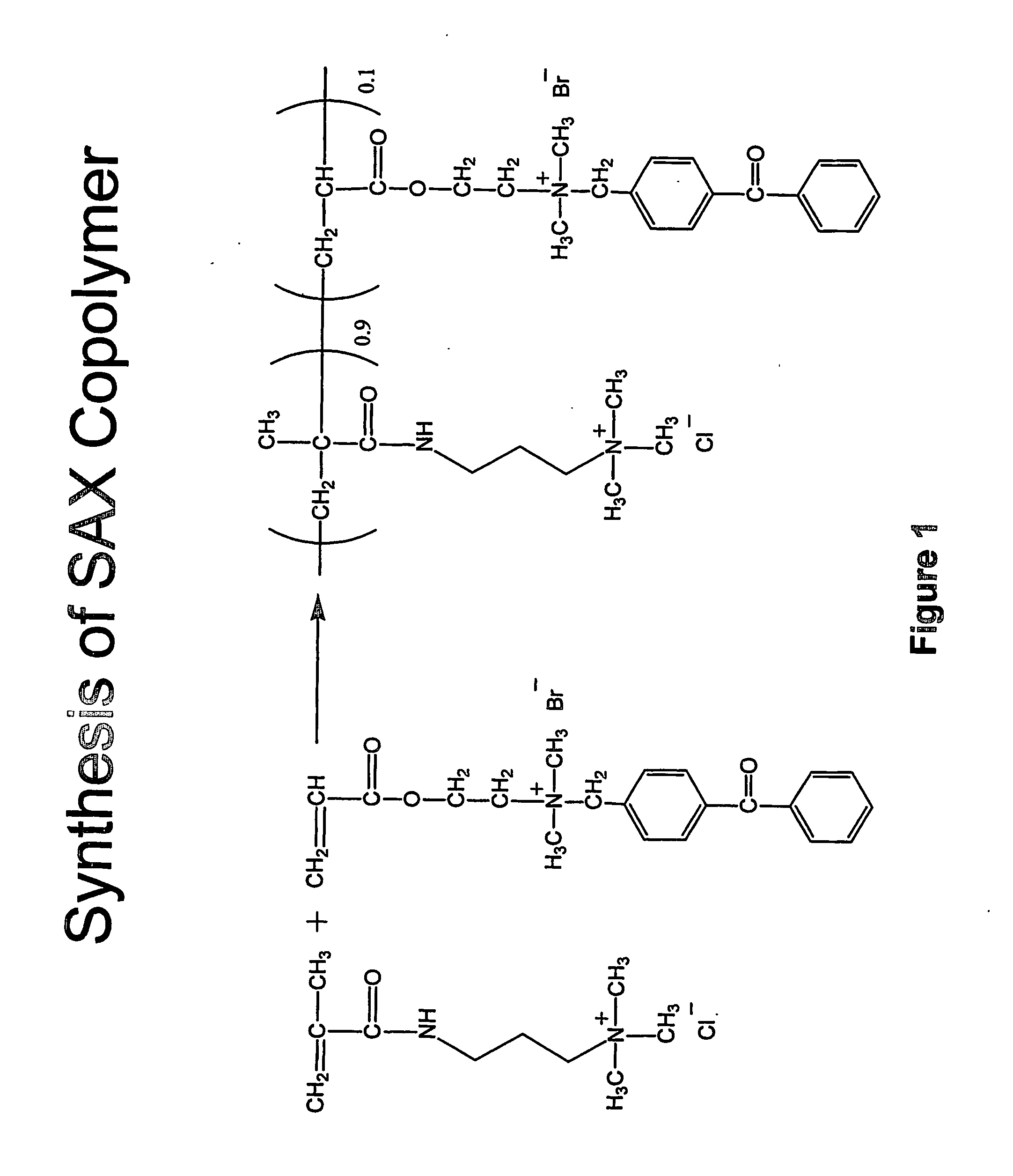
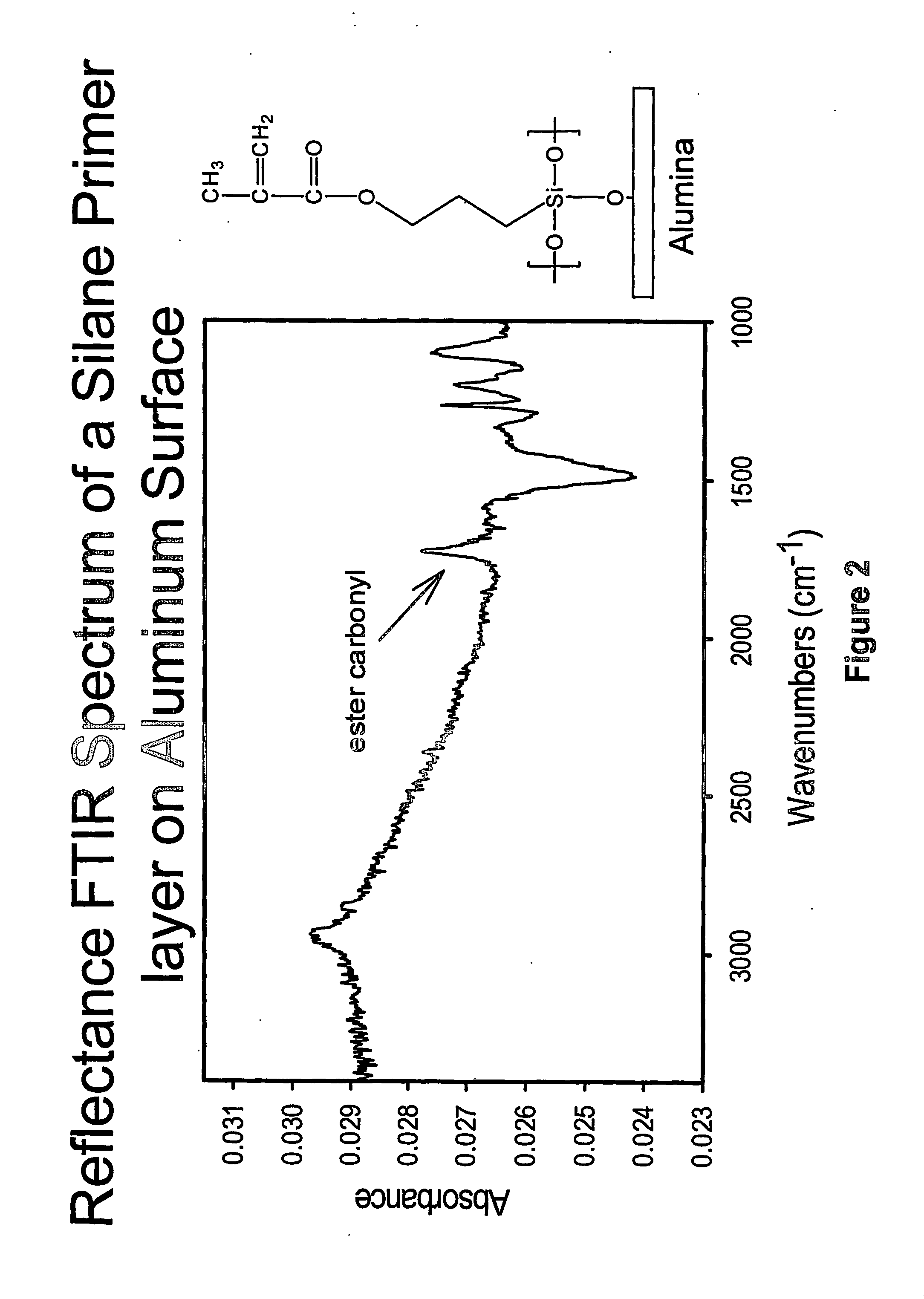
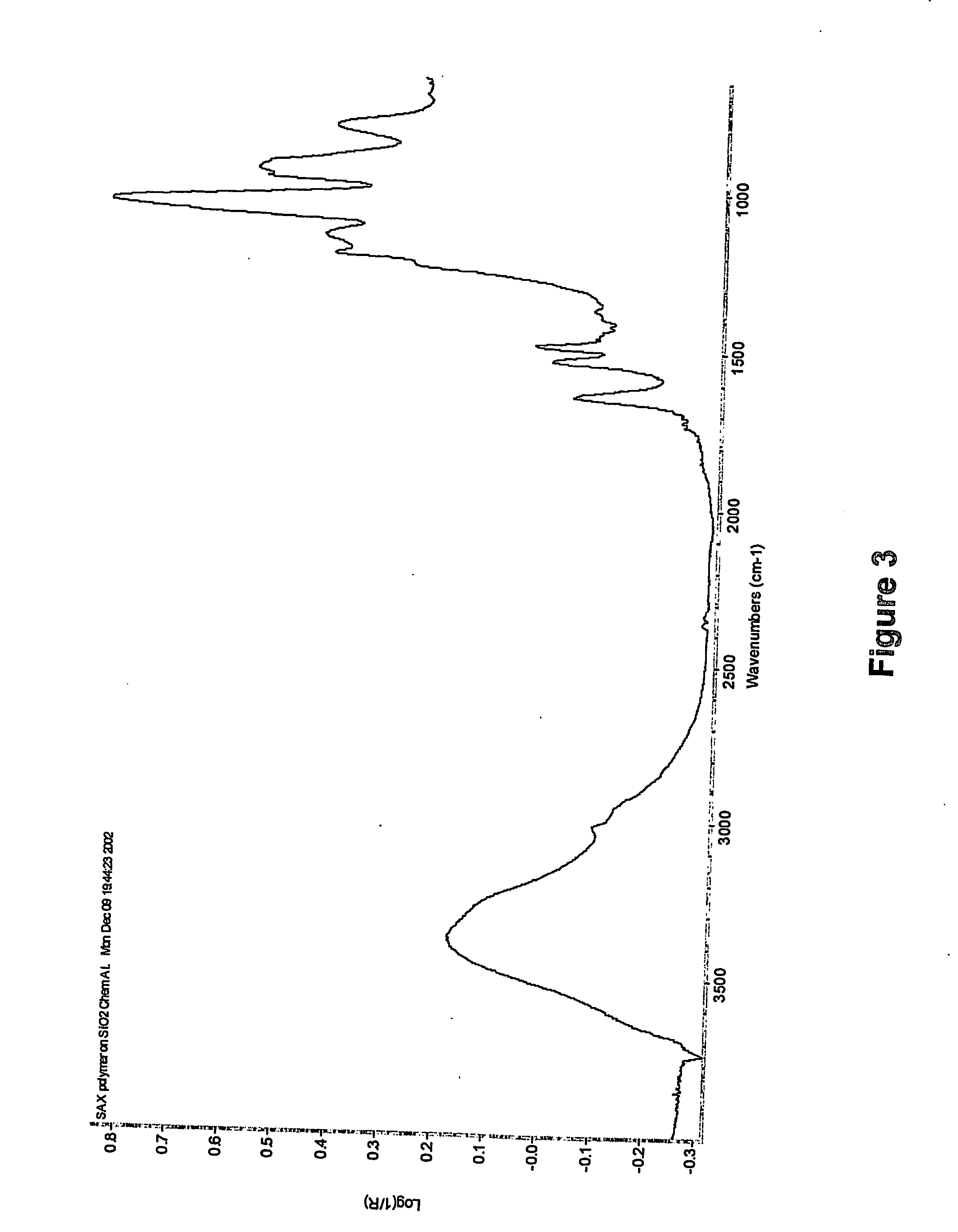
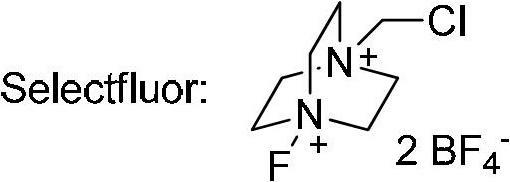Patents
Literature
434 results about "Chemoselectivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
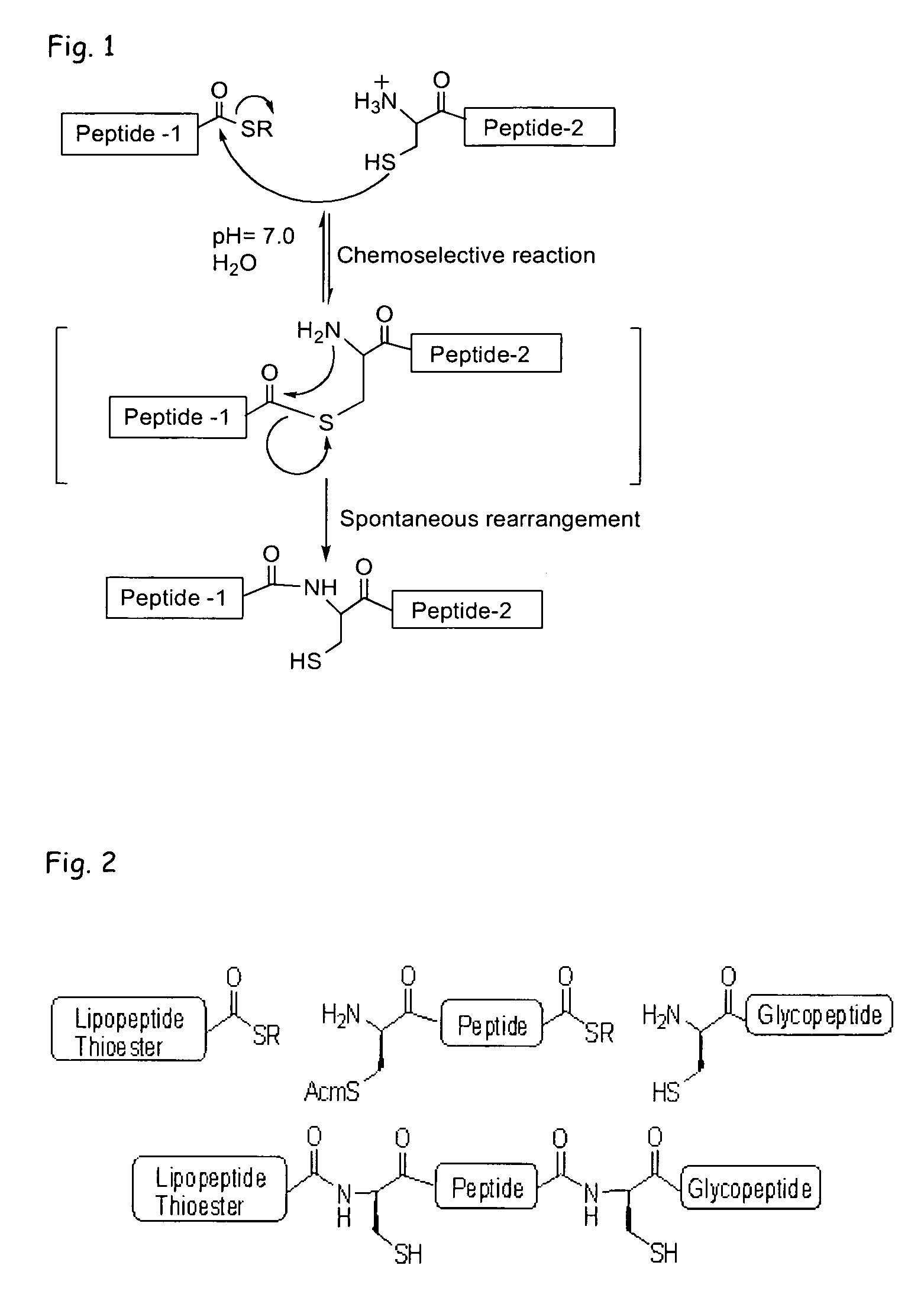
Chemoselectivity is the preferential outcome of a chemical reaction over a set of possible alternative reactions. In another definition, chemoselectivity refers to the selective reactivity of one functional group in the presence of others; often this process in convoluted and protecting groups are on the molecular connectivity alone. Such predictions based on connectivity are generally considered plausible, but the physical outcome of the actual reaction is ultimately dependent on a number of factors that are practically impossible to predict to any useful accuracy (solvent, atomic orbitals, etc.).
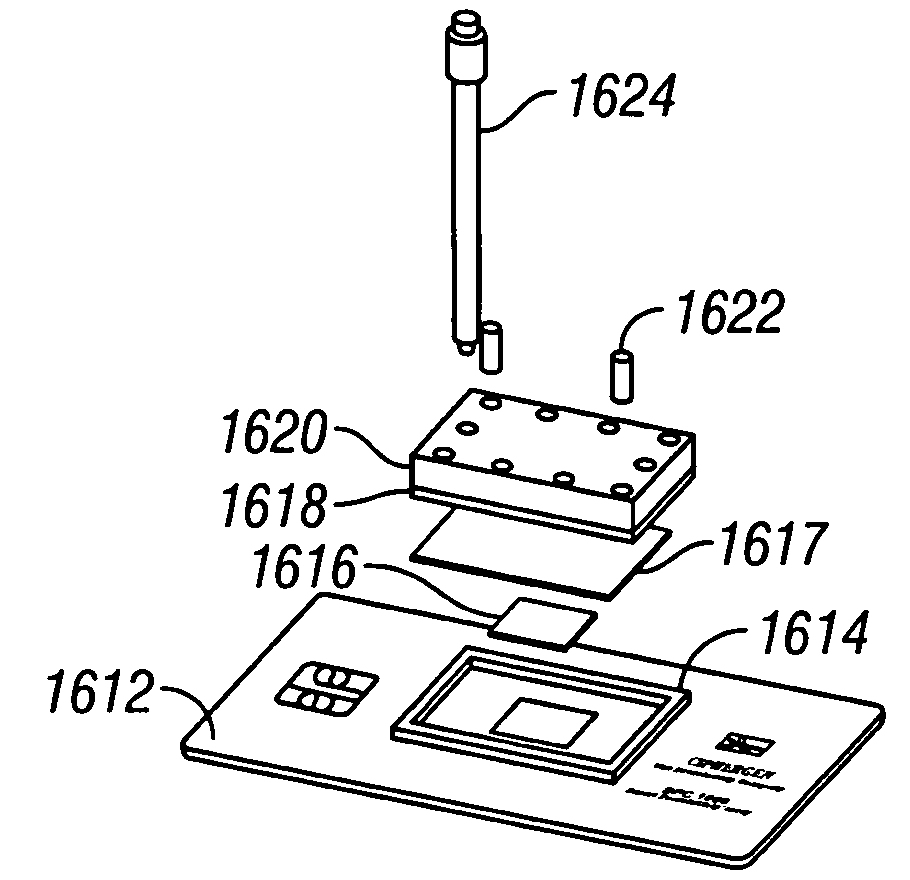
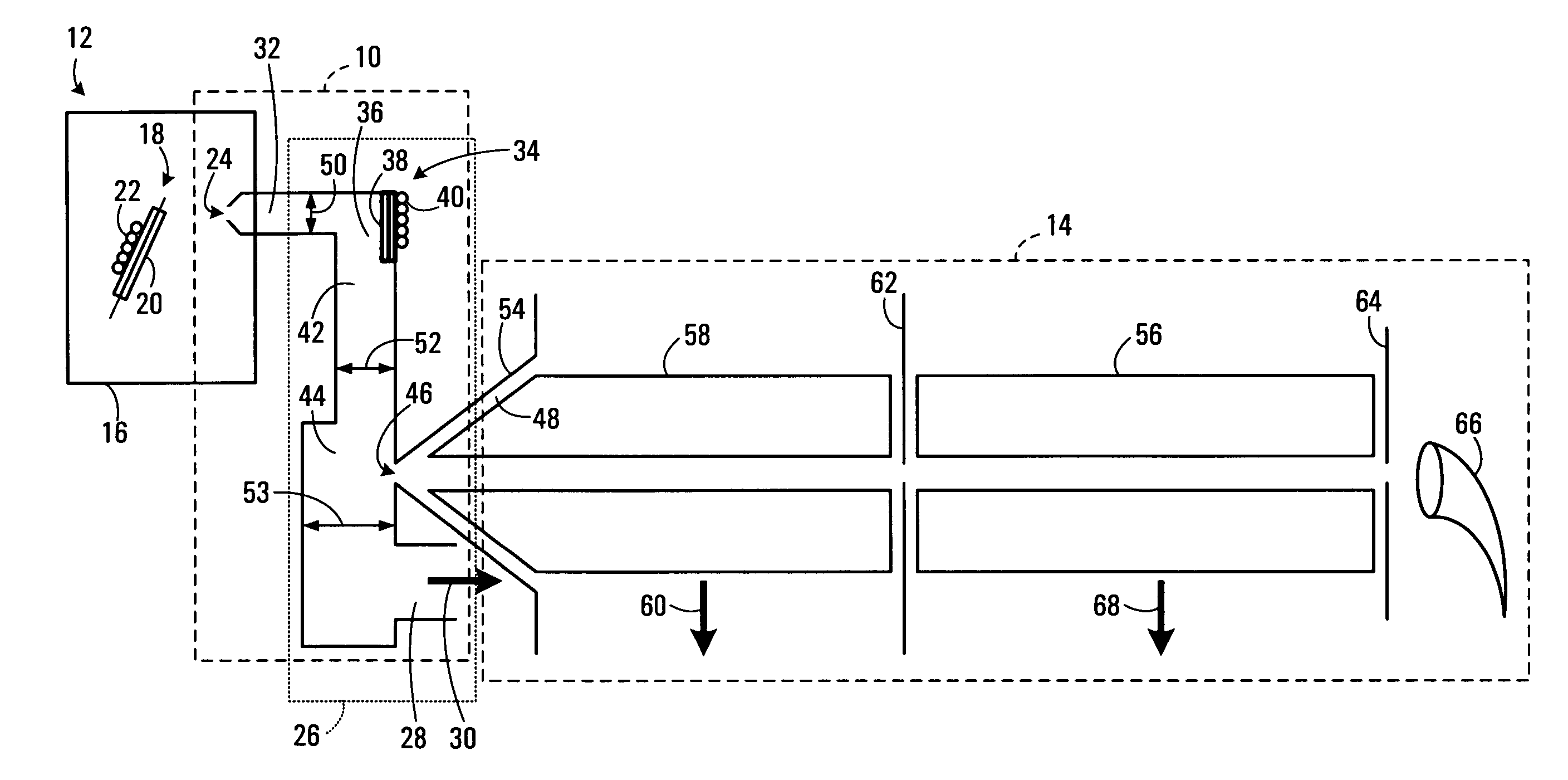
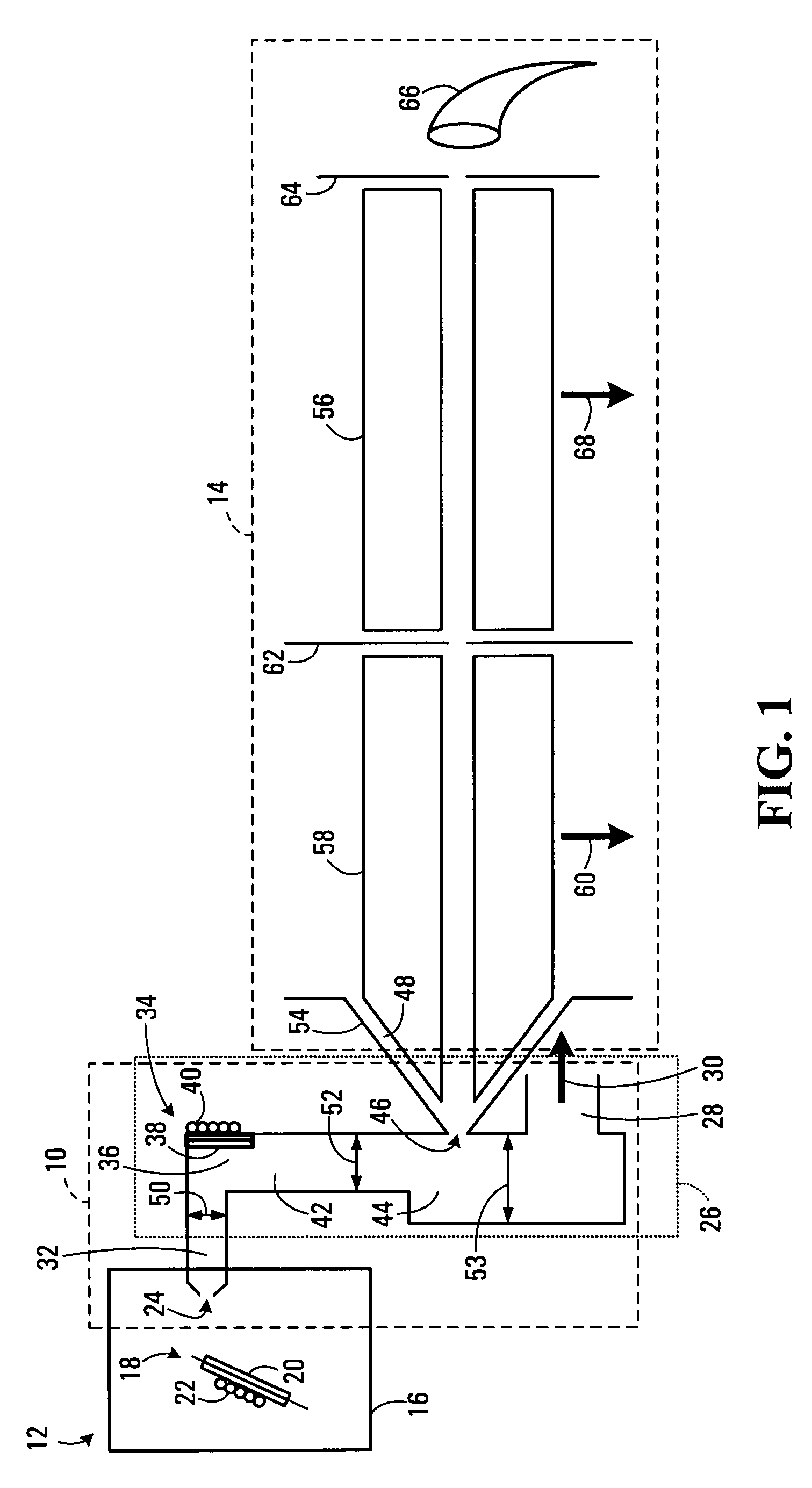
Apparatus for microfluidic processing and reading of biochip arrays
InactiveUS7046357B2Improve performanceParticle separator tubesBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsAnalyteAnalysis tools
A method and a device for detecting an analyte, including a substrate having a chemically selective surface; and a fluidic system disposed on the substrate, the manifold having at least one fluid path in communication with at least a discrete region of the surface, wherein the one fluid path and the discrete region together define a contained sample region on the surface. The fluidic system has a removable portion, wherein the removal of the removable portion of the fluidic system renders the discrete region directly interrogatable by a surface-based analytical tool.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
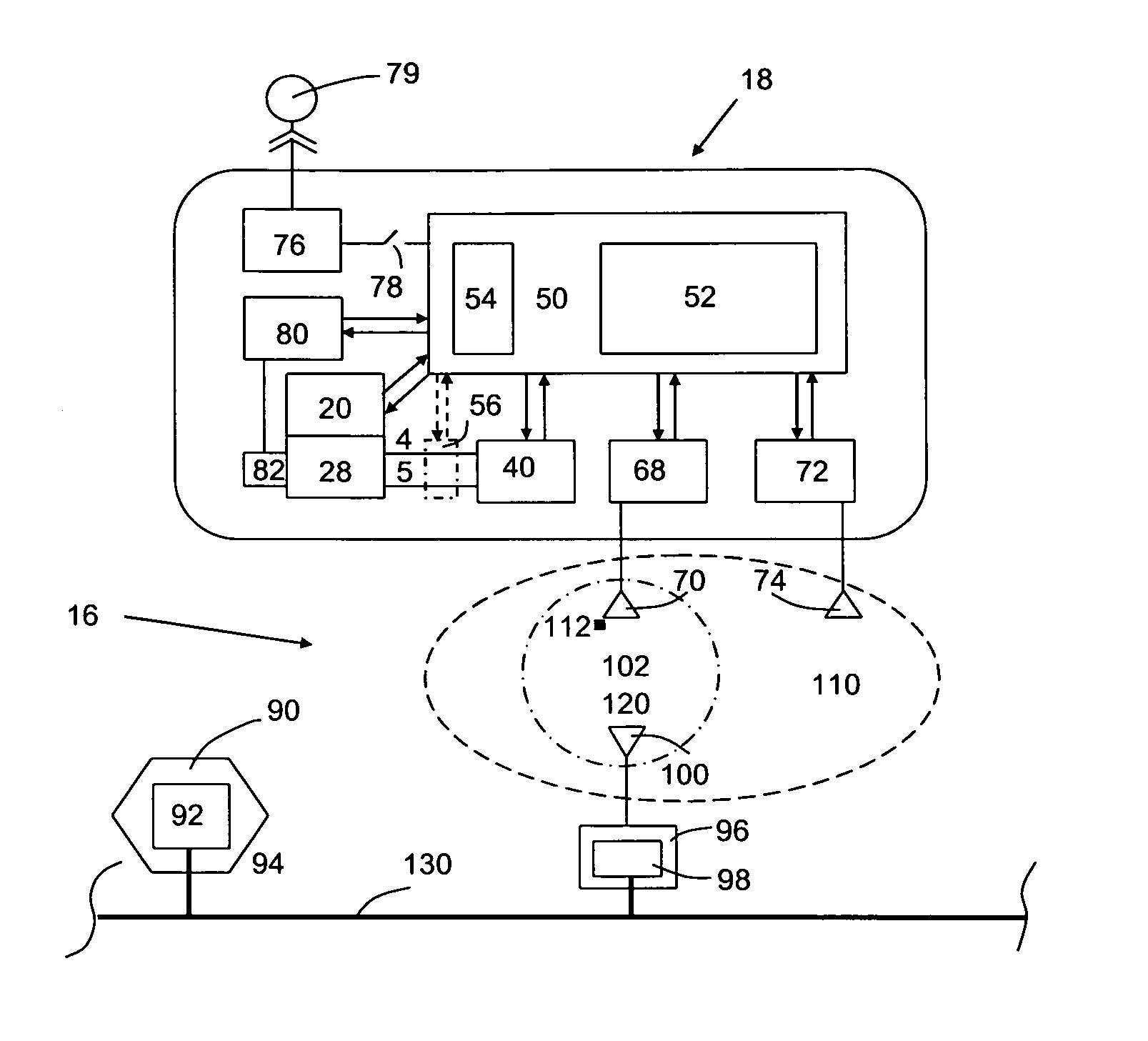
Sensor instrument system including method for detecting analytes in fluids
ActiveUS8449824B2Novel and uniqueSimple designLaboratory glasswaresNanosensorsTransceiverHydrogen selectivity
A sensor instrument system for detecting and identifying analytes in fluids of a region contains a local sensor instrument and remote central station. The instrument includes a core technology employing a single sensor having two electrodes operated by an electrical frequency sweeping to generate two sets of patterned electrical information from a single measurement, a data transmission module and a GPS receiver module. The central station connects to a network means connected to a plurality of local receiving sites equipped with including the respective transceivers, so that the local analyte electrical information and geographic position information transmitted by the instrument can be wirelessly and remotely received and processed by the central station. The core technology further includes a reference sensor for eliminating background influence, a temperature programming to control adsorption and desorption of analytes, and usage of all kinds of adsorbent materials having chemical selectivities including the hydrogen selectivity to enhance detection and identification of analytes in fluids.
Owner:SUN YIZHONG
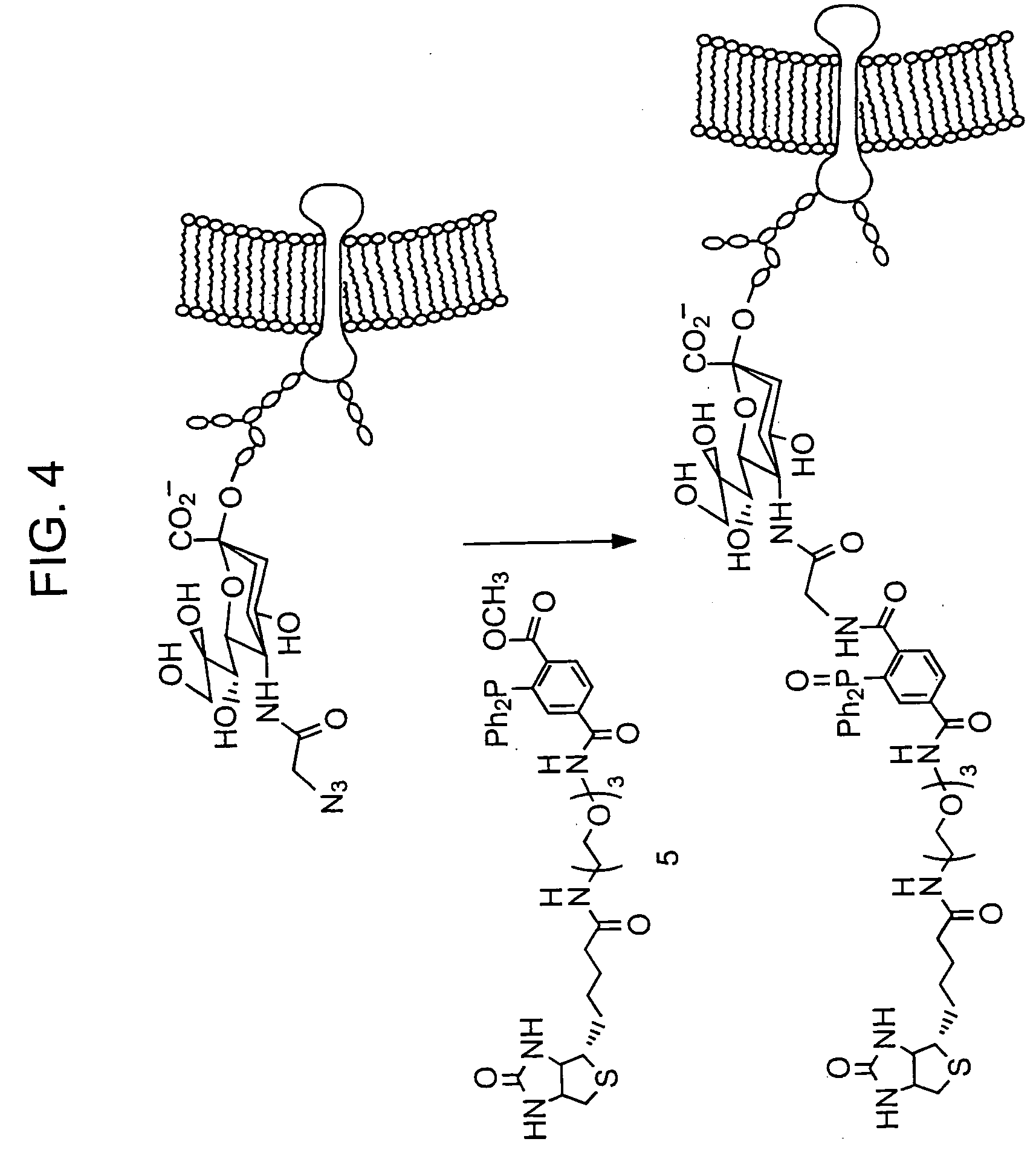
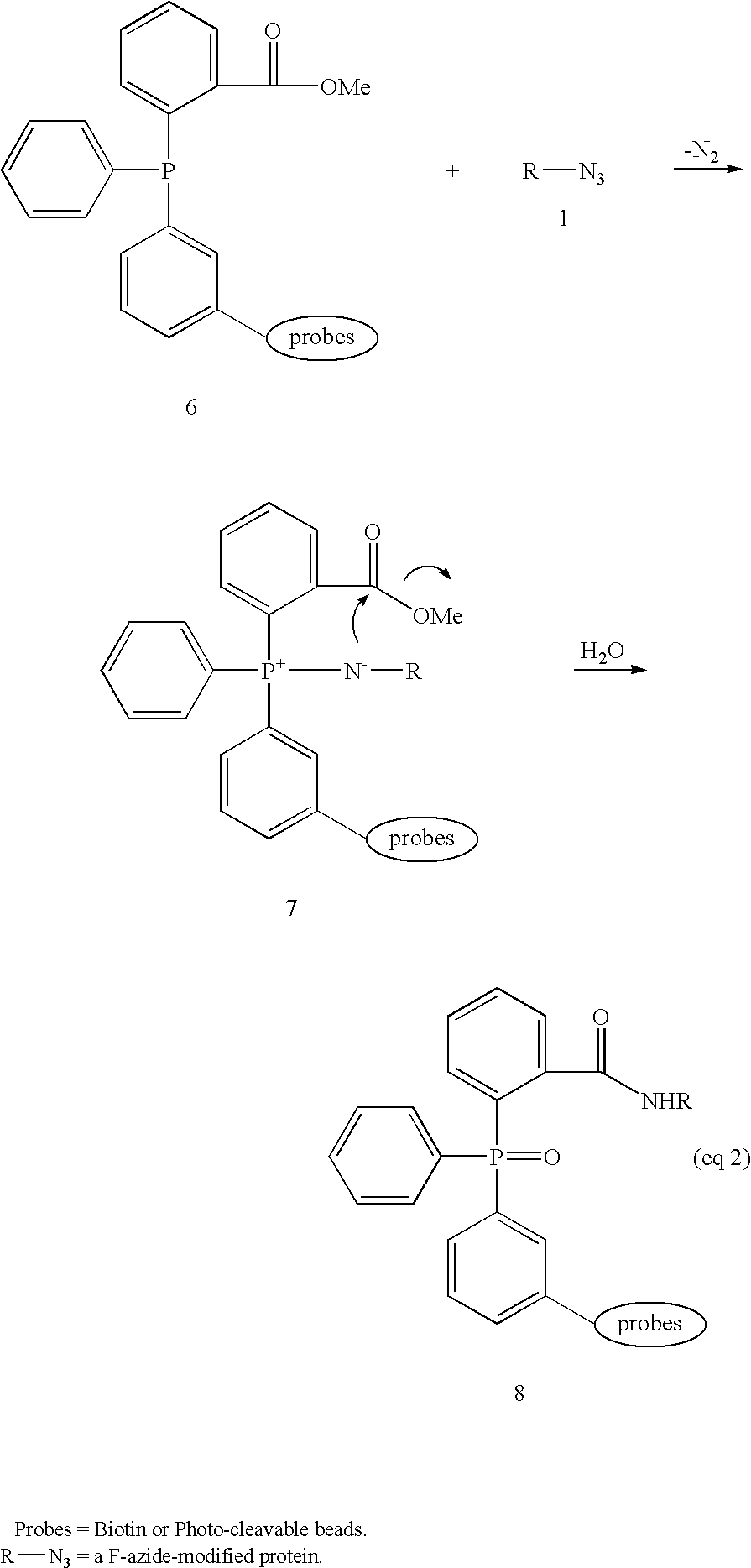
Chemoselective ligation
InactiveUS20050148032A1Esterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesIn vivoChemoselective ligation
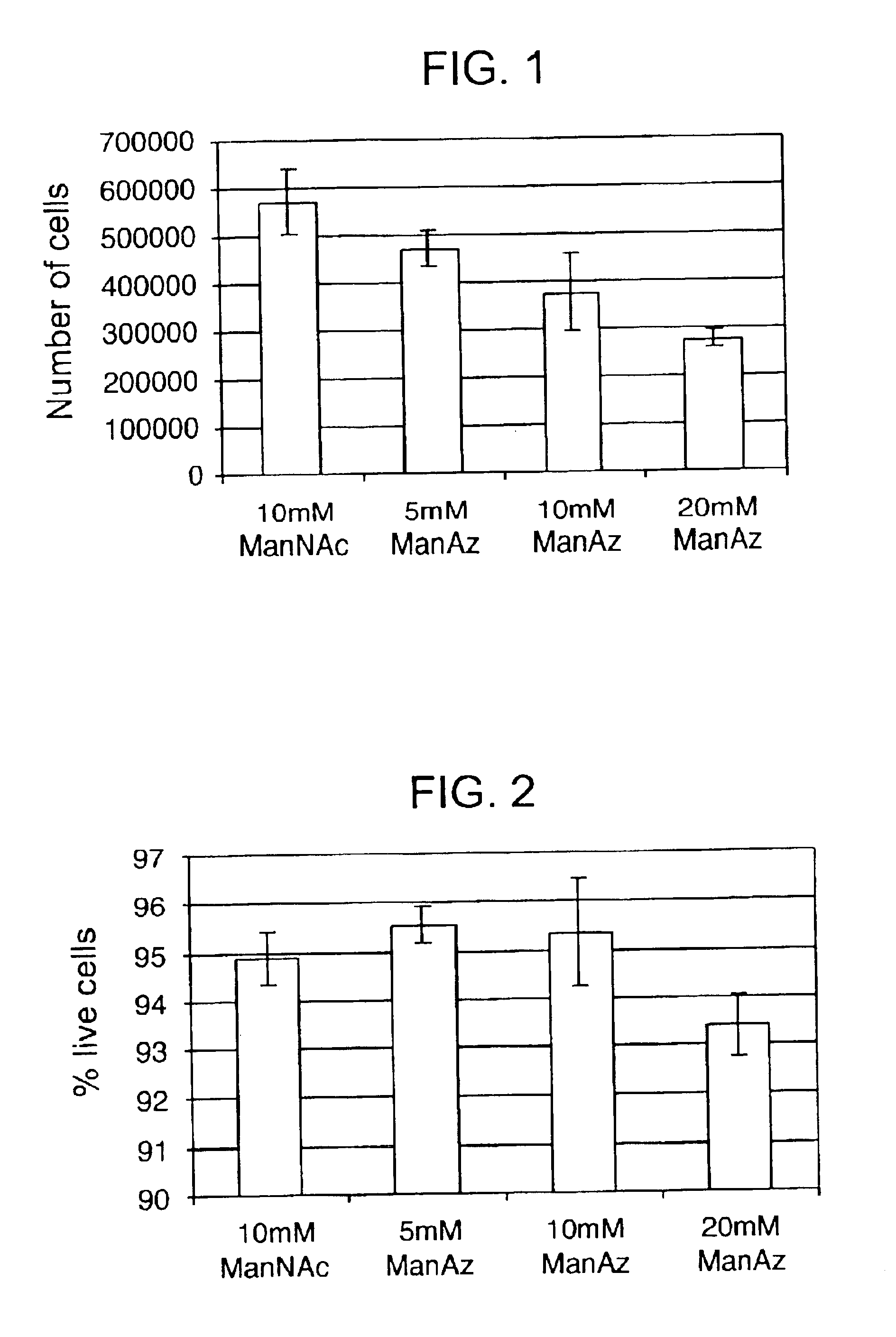
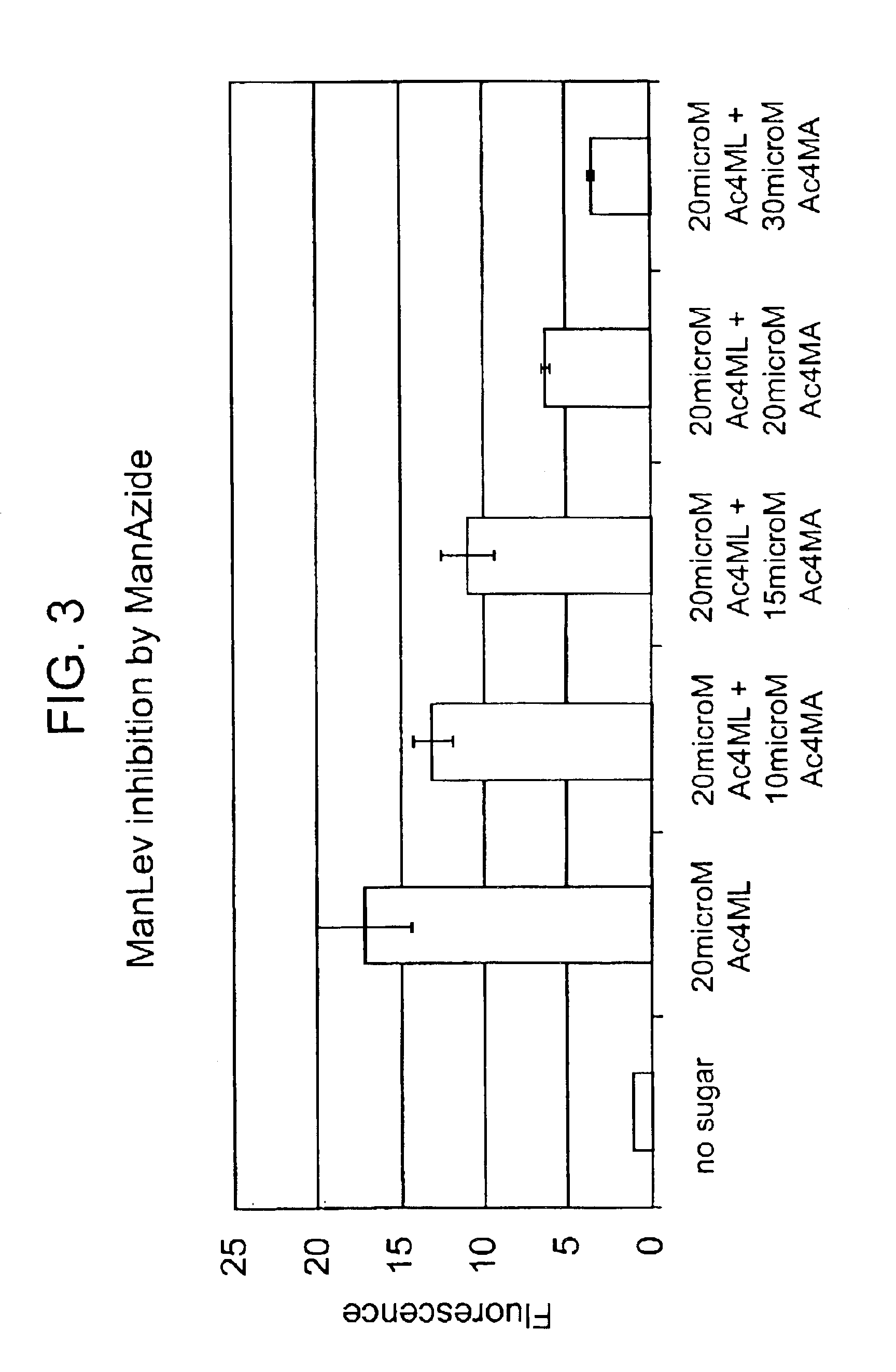
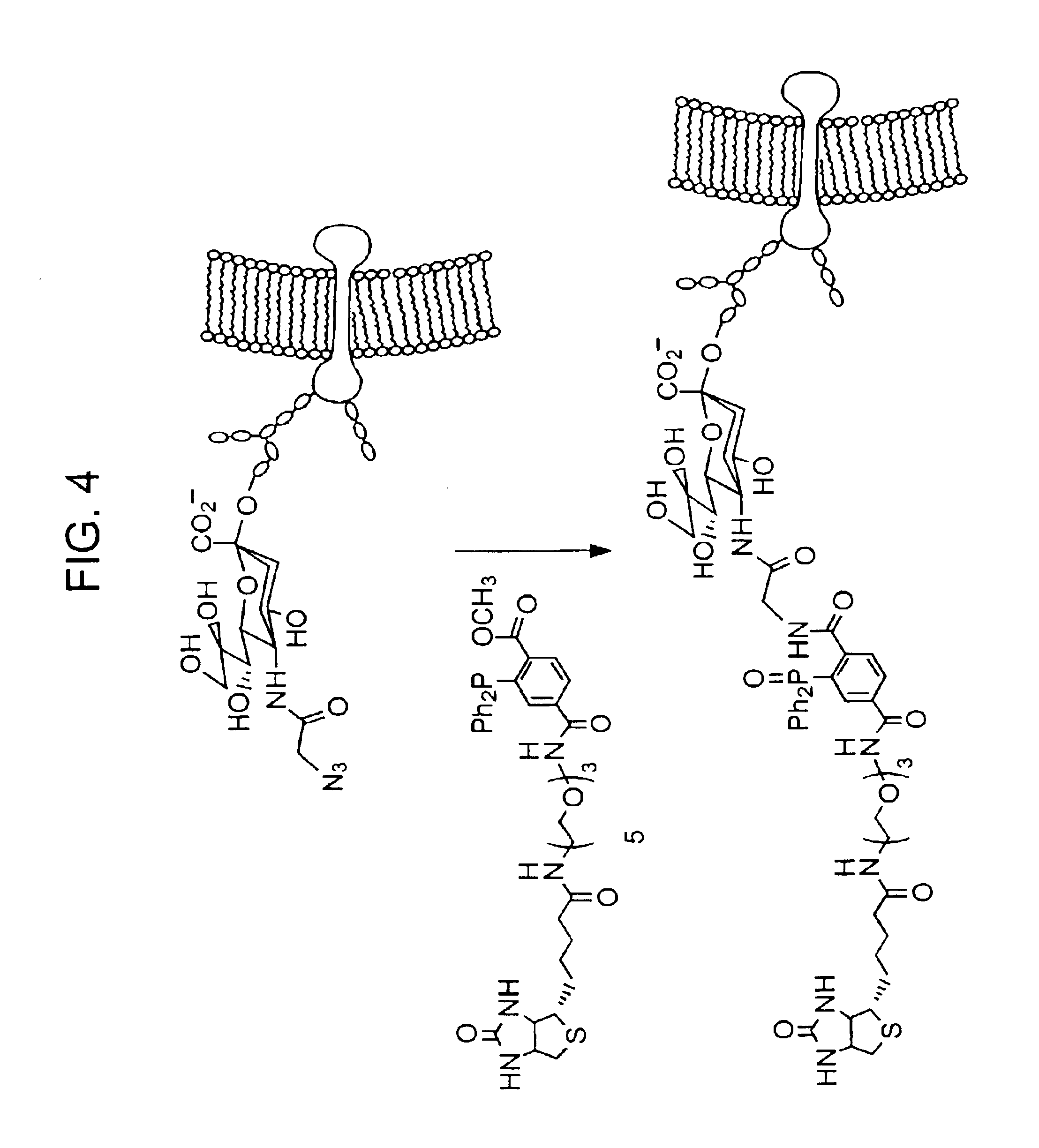
The present invention features a chemoselective ligation reaction that can be carried out under physiological conditions. In general, the invention involves condensation of a specifically engineered phosphine, which can provide for formation of an amide bond between the two reactive partners resulting in a final product comprising a phosphine moiety, or which can be engineered to comprise a cleavable linker so that a substituent of the phosphine is transferred to the azide, releasing an oxidized phosphine byproduct and producing a native amide bond in the final product. The selectivity of the reaction and its compatibility with aqueous environments provides for its application in vivo (e.g., on the cell surface or intracellularly) and in vitro (e.g., synthesis of peptides and other polymers, production of modified (e.g., labeled) amino acids).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
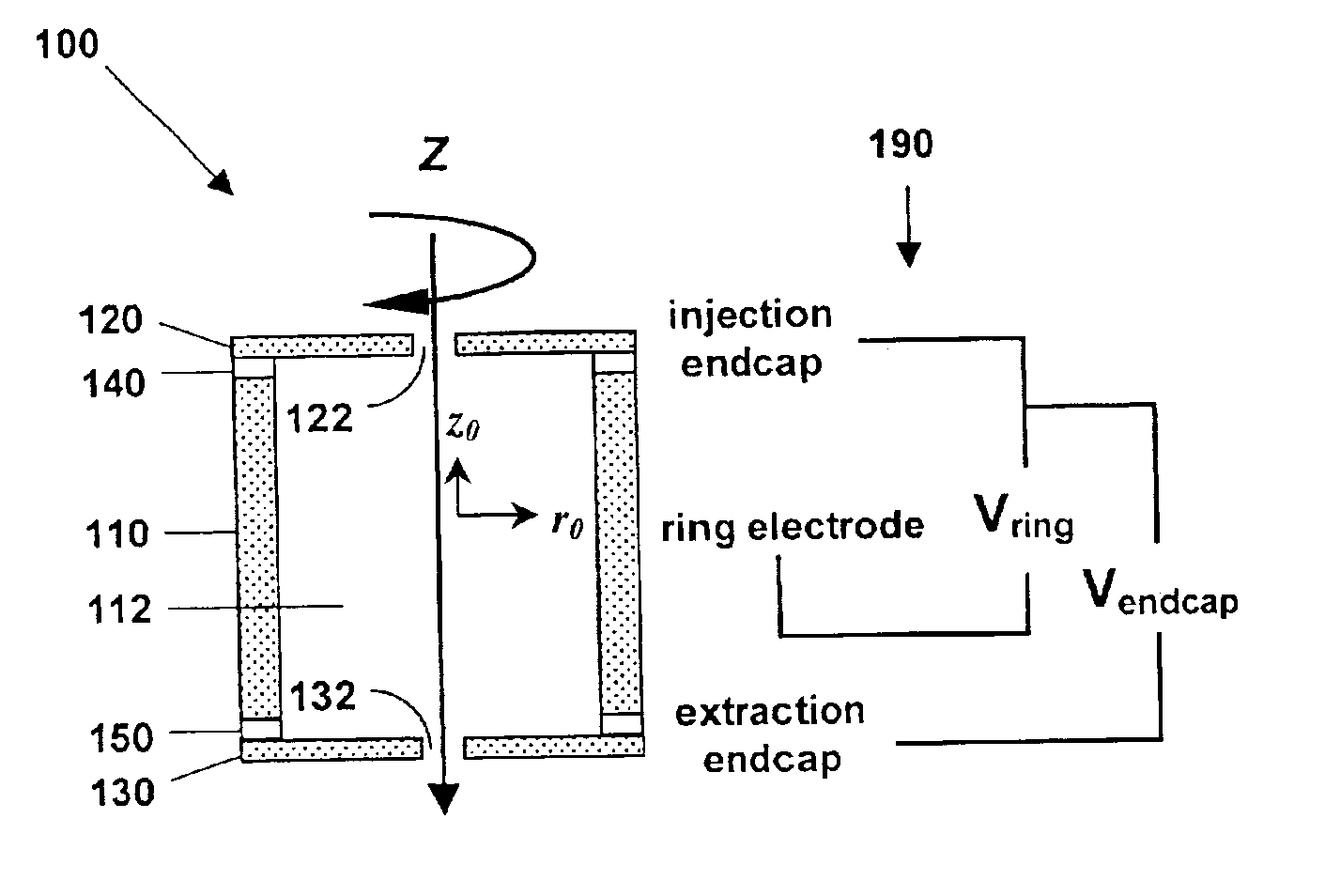
Microfabricated cylindrical ion trap
InactiveUS6870158B1Stability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationManufacturing cost reductionHigh pressure
A microscale cylindrical ion trap, having an inner radius of order one micron, can be fabricated using surface micromachining techniques and materials known to the integrated circuits manufacturing and microelectromechanical systems industries. Micromachining methods enable batch fabrication, reduced manufacturing costs, dimensional and positional precision, and monolithic integration of massive arrays of ion traps with microscale ion generation and detection devices. Massive arraying enables the microscale cylindrical ion trap to retain the resolution, sensitivity, and mass range advantages necessary for high chemical selectivity. The microscale CIT has a reduced ion mean free path, allowing operation at higher pressures with less expensive and less bulky vacuum pumping system, and with lower battery power than conventional- and miniature-sized ion traps. The reduced electrode voltage enables integration of the microscale cylindrical ion trap with on-chip integrated circuit-based rf operation and detection electronics (i.e., cell phone electronics). Therefore, the full performance advantages of microscale cylindrical ion traps can be realized in truly field portable, handheld microanalysis systems.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Chemoselective ligation
The present invention features a chemoselective ligation reaction that can be carried out under physiological conditions. In general, the invention involves condensation of a specifically engineered phosphine, which can provide for formation of an amide bond between the two reactive partners resulting in a final product comprising a phosphine moiety, or which can be engineered to comprise a cleavable linker so that a substituent of the phosphine is transferred to the azide, releasing an oxidized phosphine byproduct and producing a native amide bond in the final product. The selectivity of the reaction and its compatibility with aqueous environments provides for its application in vivo (e.g., on the cell surface or intracellularly) and in vitro (e.g., synthesis of peptides and other polymers, production of modified (e.g., labeled) amino acids).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Fabrication of conductive/non-conductive nanocomposites by laser evaporation
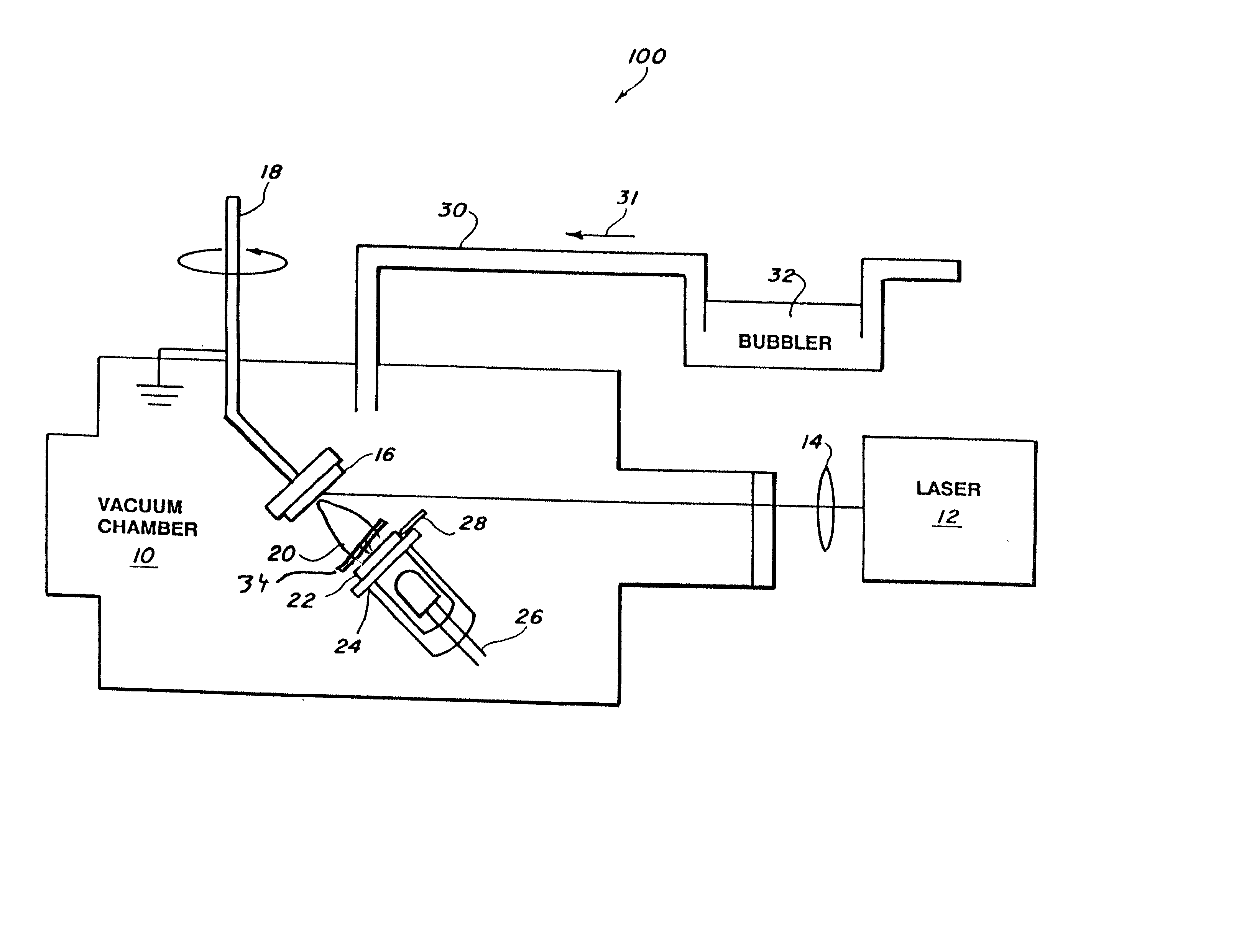
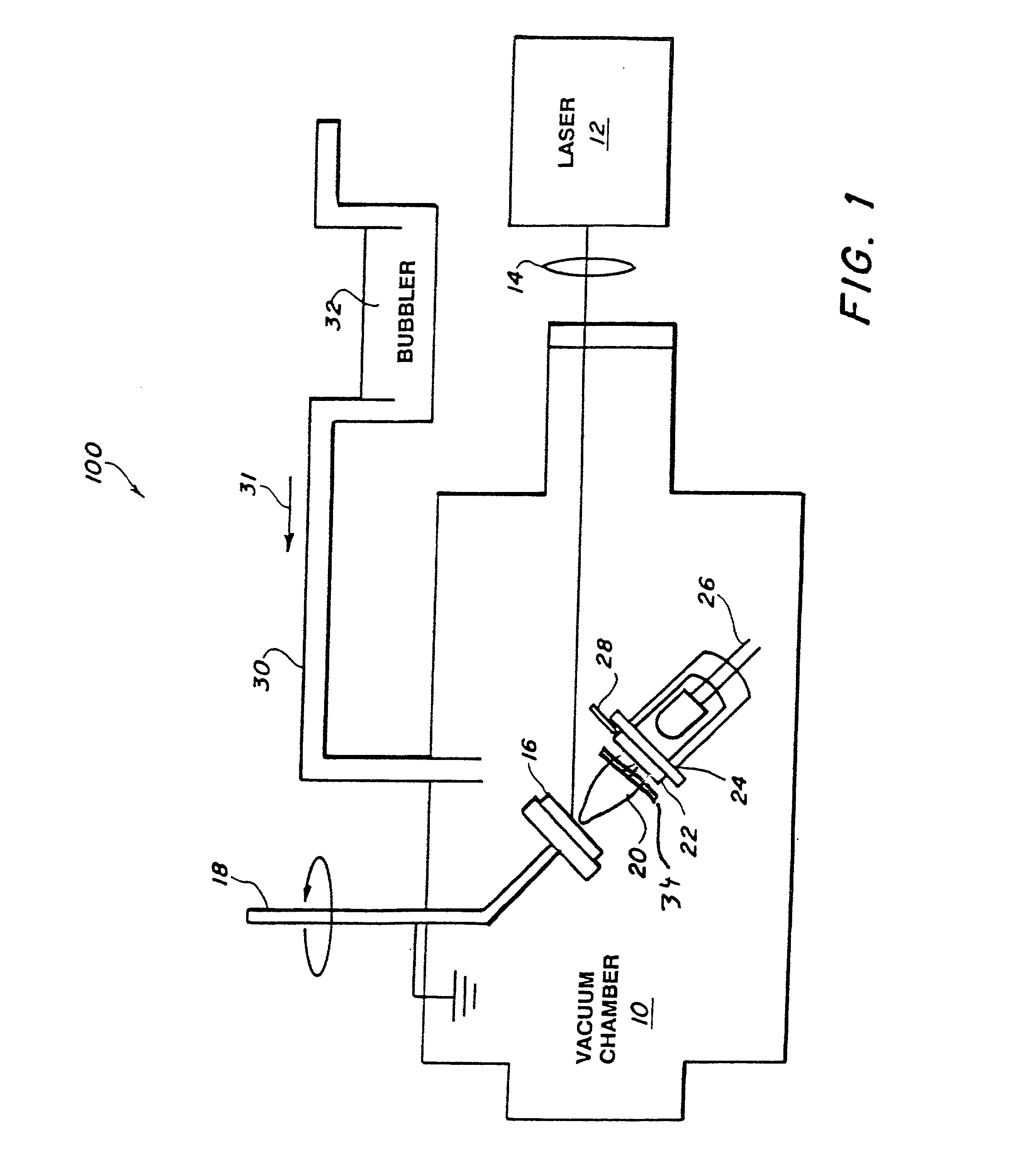
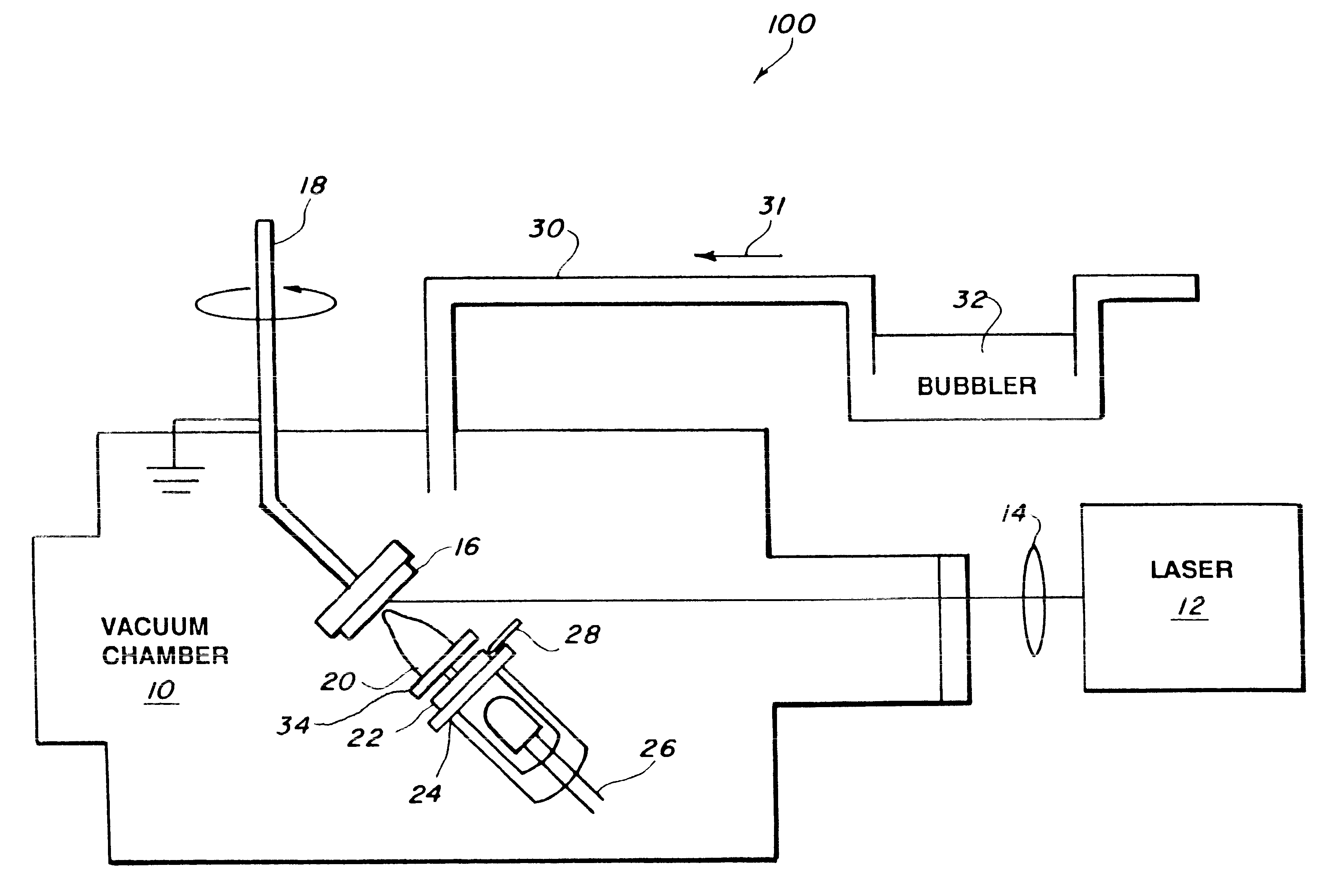
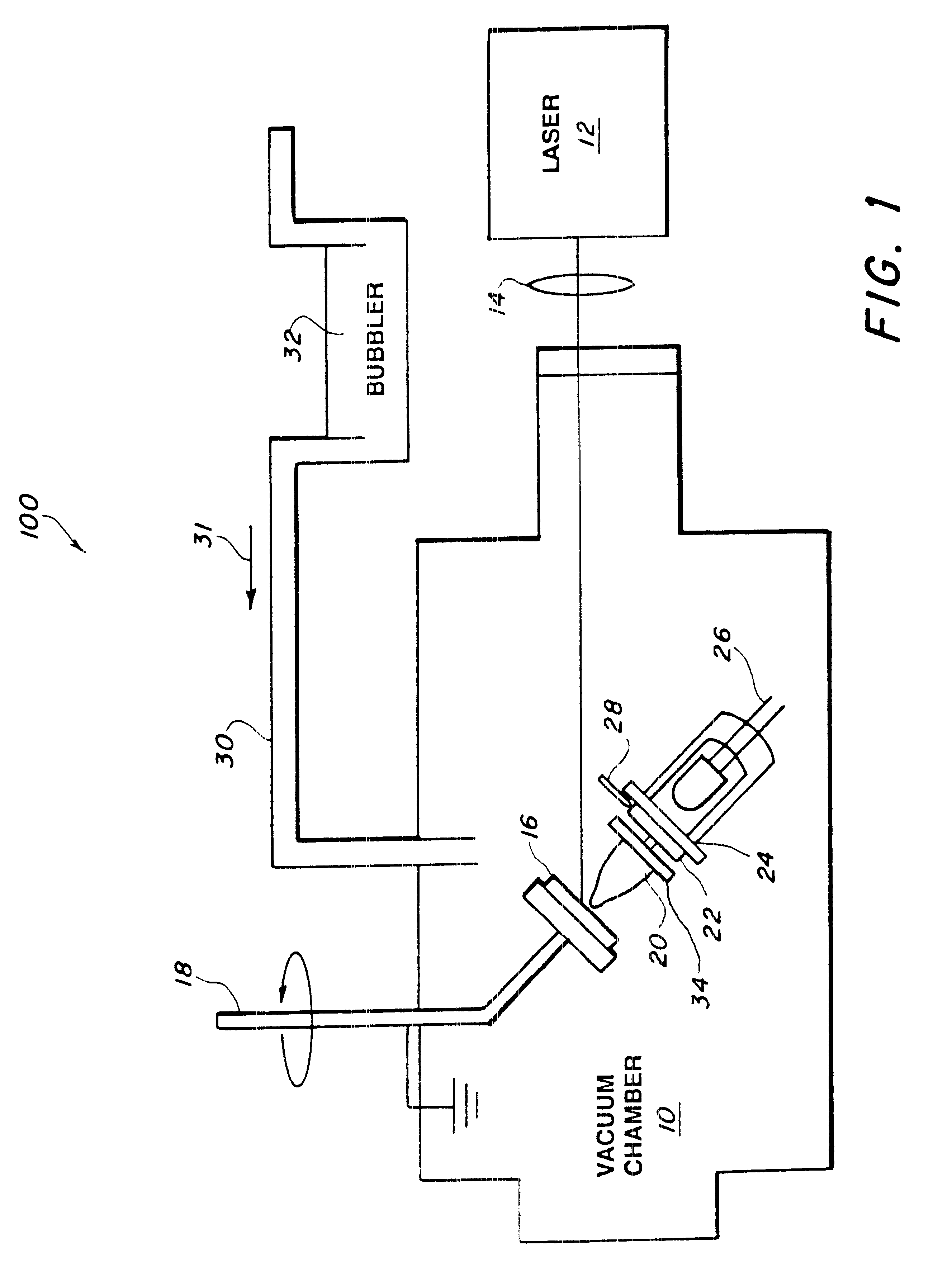
A composite layer of a sorbent, chemoselective, non-electrically-conducting polymer and nano-particles of an electrically conducting material dispersed throughout the polymer is formed on a substrate by pulsed laser deposition, matrix assisted pulsed laser evaporation or matrix assisted pulsed laser evaporation direct writing.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
High surface density covalent immobilization of oligonucleotide monolayers
InactiveUS6159695AIncrease surface densityHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologySilanesHigh surface
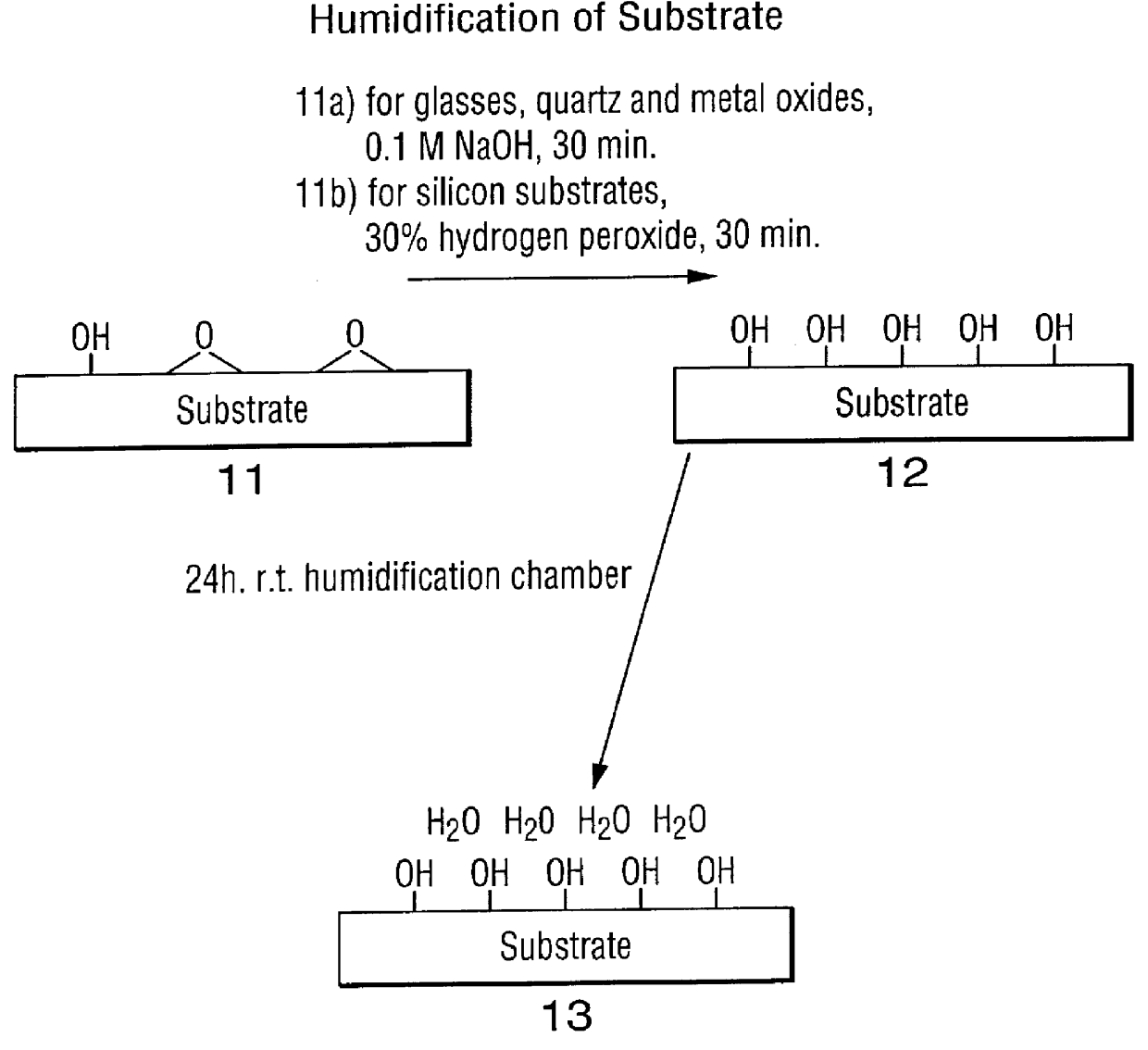
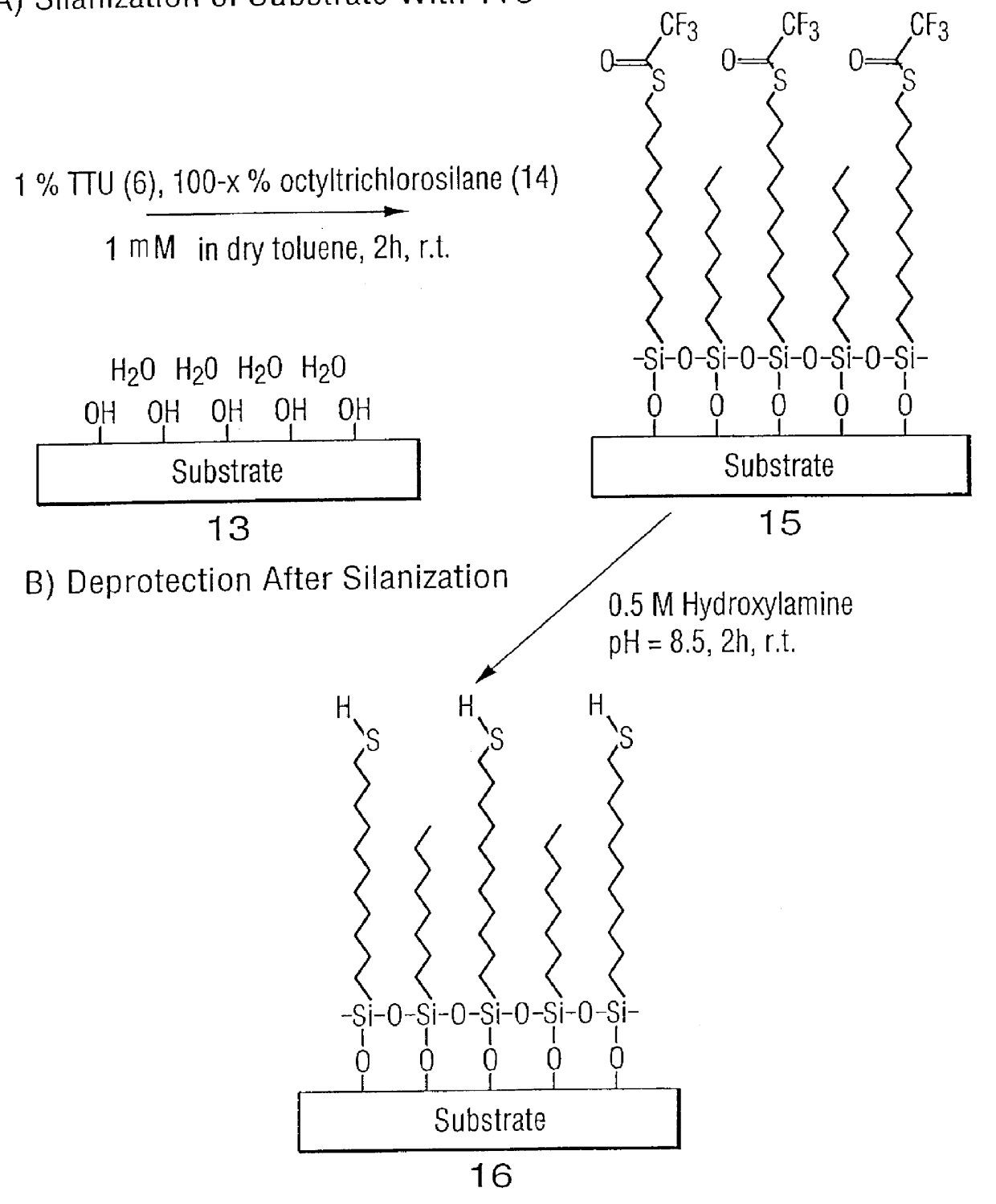
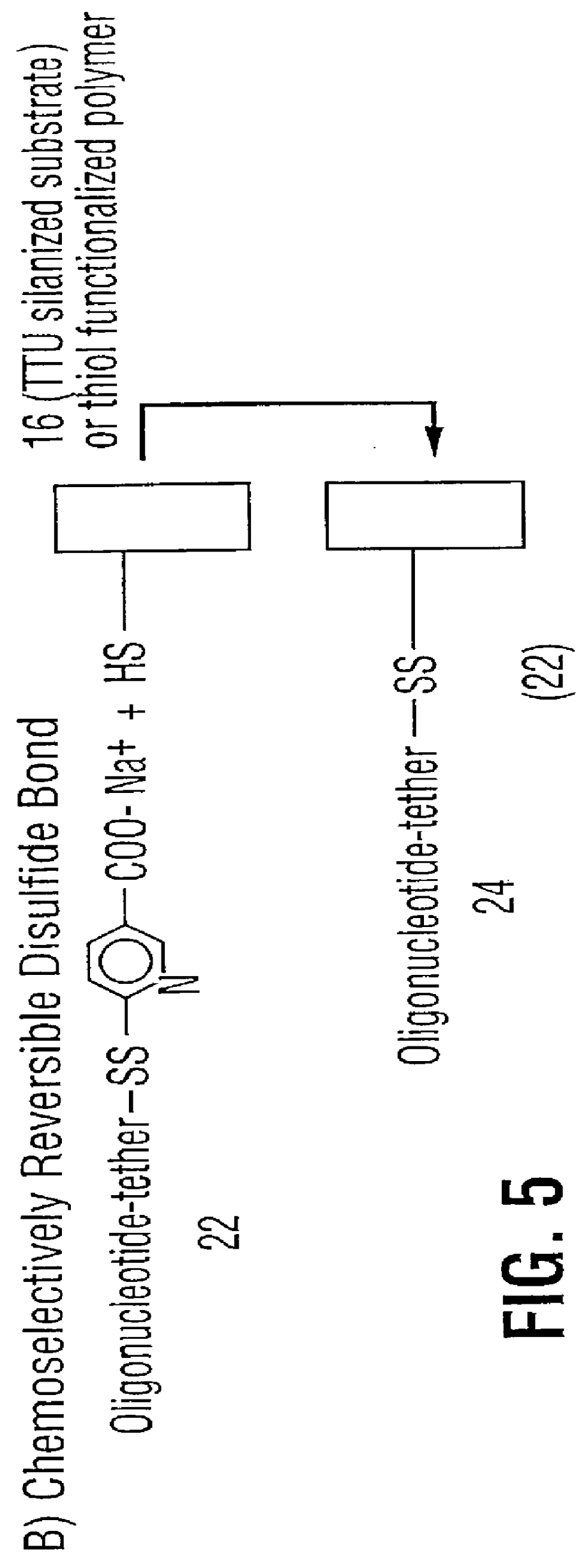
Oligonucleotides and other biomolecules are immobilized in high density on solid substrates through covalent forces using either a permanent thioether bond, or a chemoselectively reversible disulfide bond to a surface thiol. Substrates which have hydroxyl groups on their surfaces can be first silanized with a trichlorosilane containing 2-20 carbon atoms in its hydrocarbon backbone, terminating in a protected thiol group. The oligonucleotides or other biomolecules are first connected to a tether consisting of a hydrocarbon or polyether chain of 2-20 units in length which terminates in a thiol group. This thiol may be further modified with a halobenzylic-bifunctional water soluble reagent which allows the conjugate to be immobilized onto the surface thiol group by a permanent thioether bond. Alternatively, the oligonucleotide-tether-thiol group can be converted to a pyridyldisulfide functionality which attaches to the surface thiol by a chemoselectively reversible disulfide bond. The permanently bound oligonucleotides are immobilized in high density compared to other types of thiol functionalized silane surface and to the avidin-biotin method.
Owner:SENSORCHEM INT
Fabrication of conductive/non-conductive nanocomposites by laser evaporation
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
Sensor instrument system including method for detecting analytes in fluids
ActiveUS20090261987A1Improves analyte detectionEasy to identifyElectric signal transmission systemsLaboratory glasswaresTransceiverDesorption
A sensor instrument system for detecting and identifying analytes in fluids of a region comprising a local sensor instrument and remote central station. The instrument is comprised of a core technology employing a single sensor having two electrodes operated by an electrical frequency sweeping to generate two sets of patterned electrical information from a single measurement, a data transmission module and a GPS receiver module. The central station connects to a network means connected to a plurality of local receiving sites equipped with including the respective transceivers, so that the local analyte electrical information and geographic position information transmitted by the instrument can be wirelessly and remotely received and processed by the central station. The core technology is further comprised of a reference sensor for eliminating background influence, a temperature programming to control adsorption and desorption of analytes, and usage of all kinds of adsorbent materials having chemical selectivity including the hydrogen selectivity to enhance detection and identification of analytes in fluids.
Owner:SUN YIZHONG
Optical MEMS Chemical Sensor Array
ActiveUS20100238454A1High selectivityIncrease flexibilityMaterial analysis using immobilised reagentsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSensor arrayWaveguide
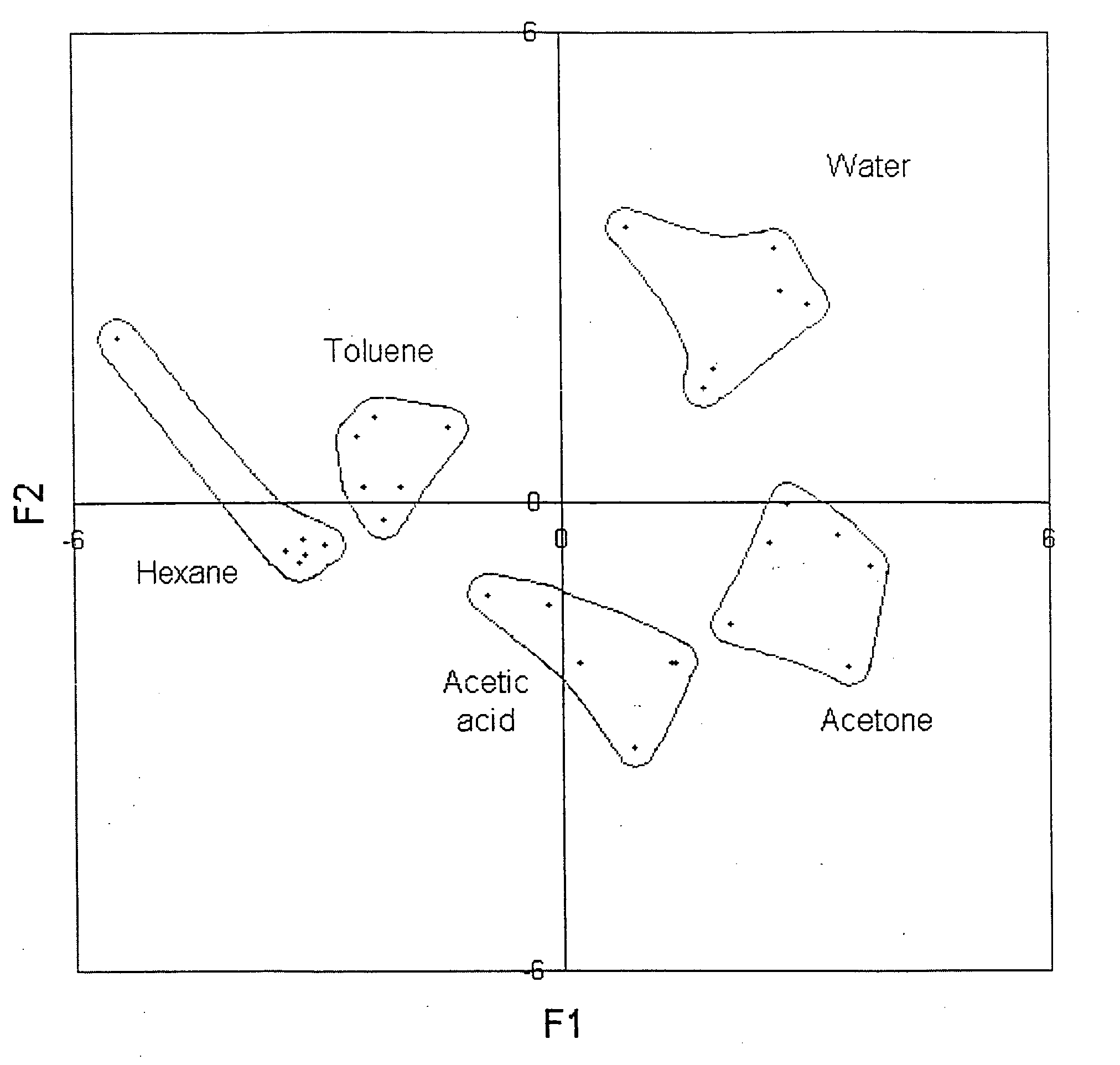
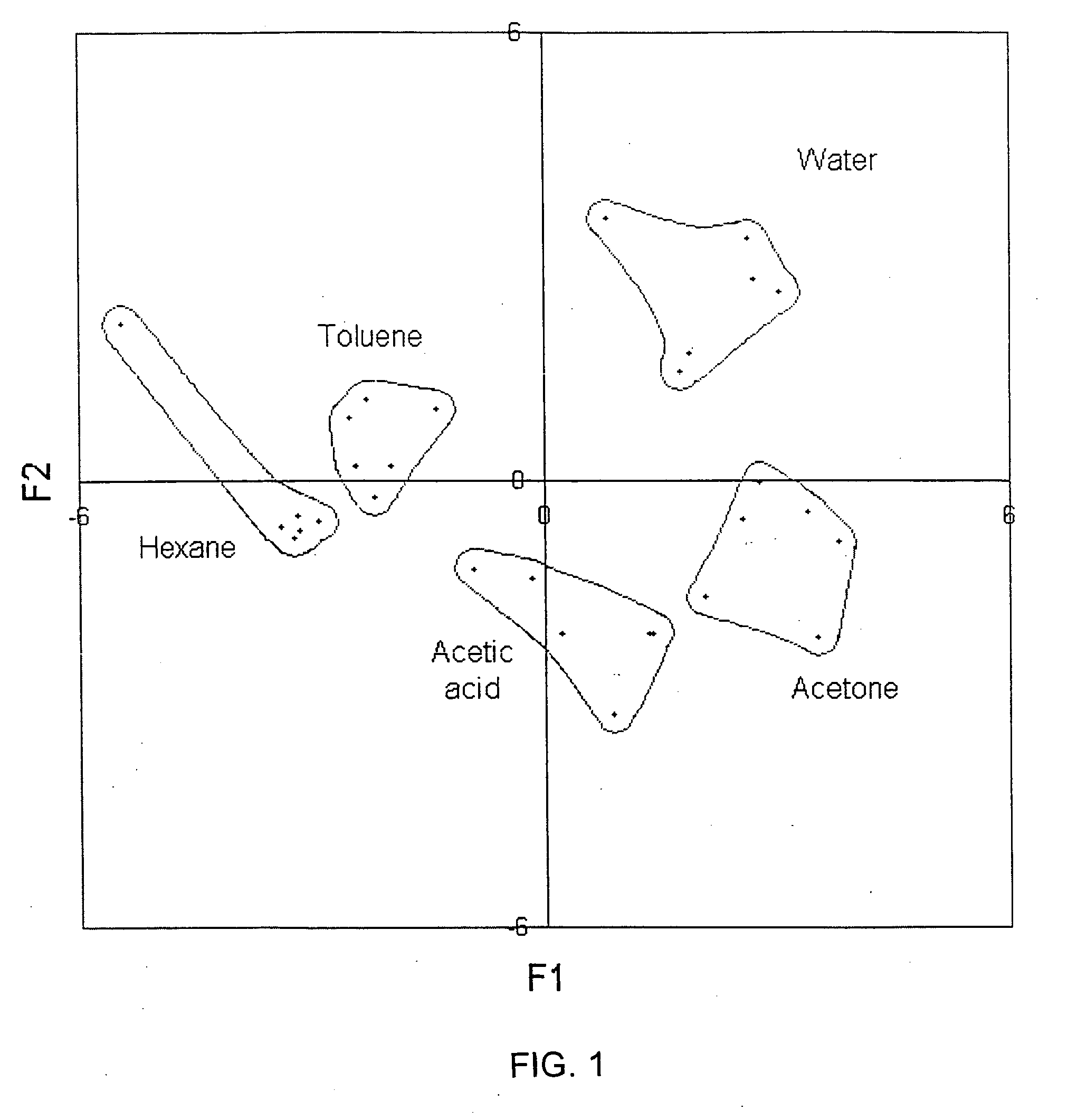
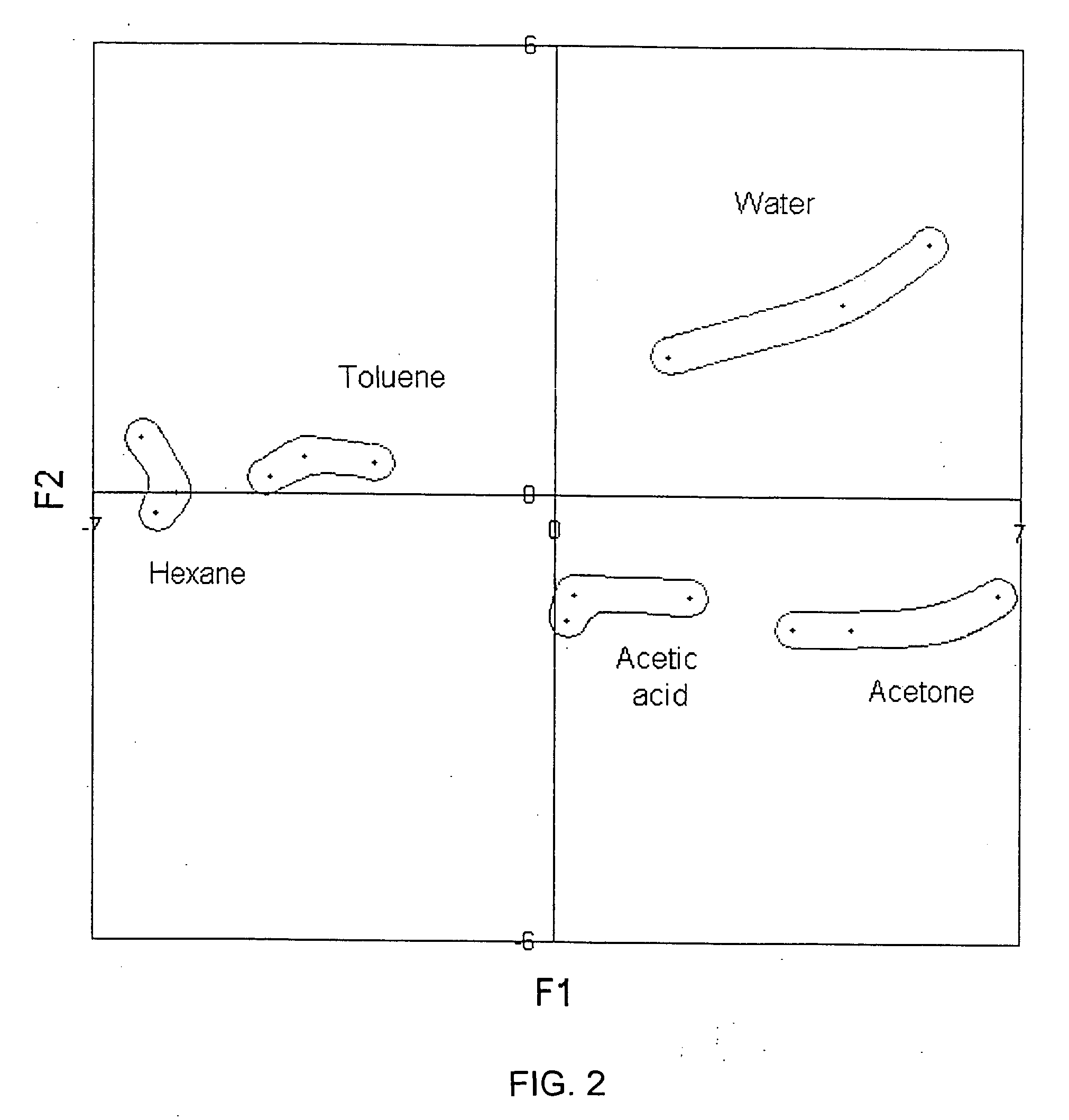
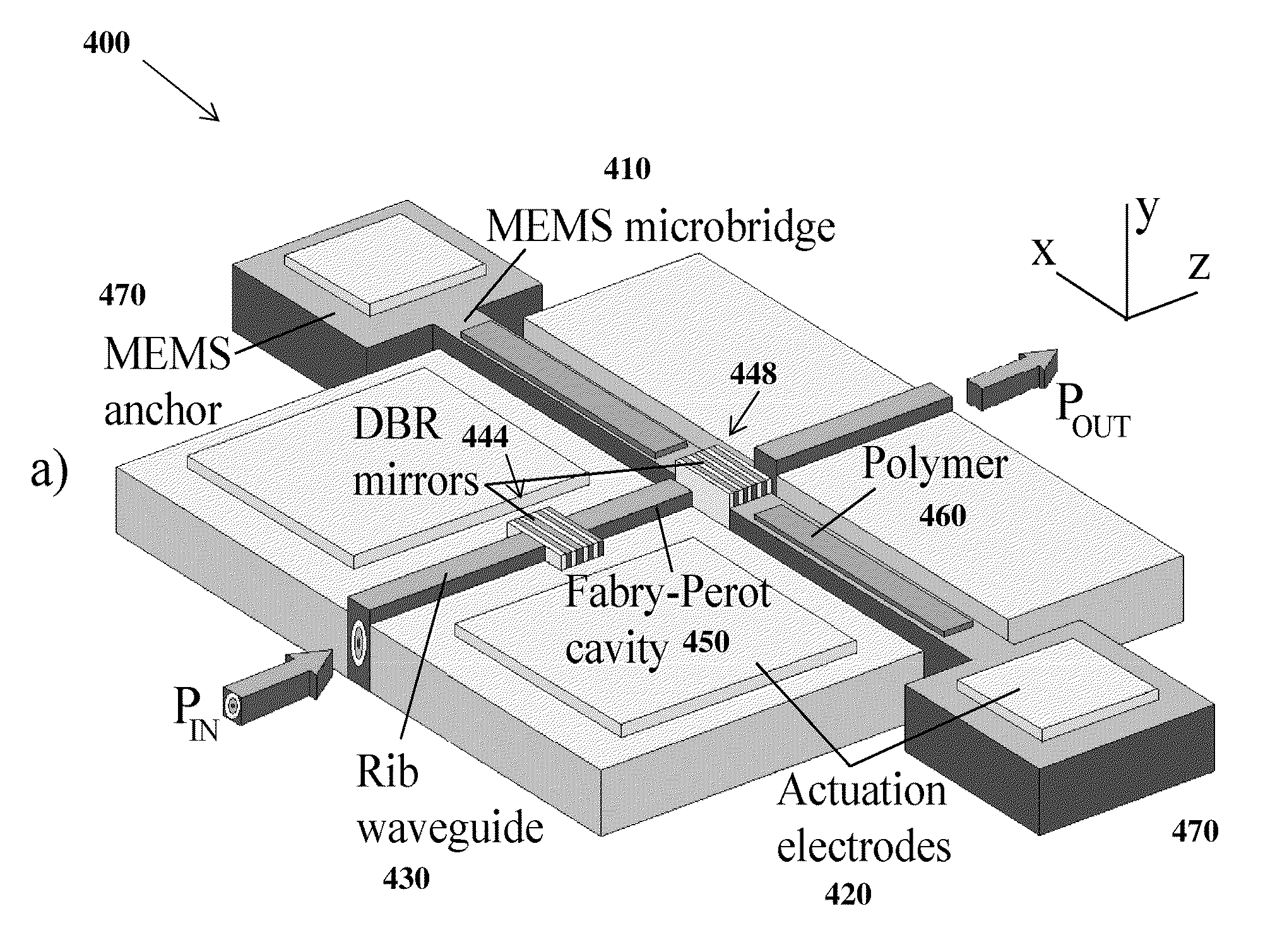
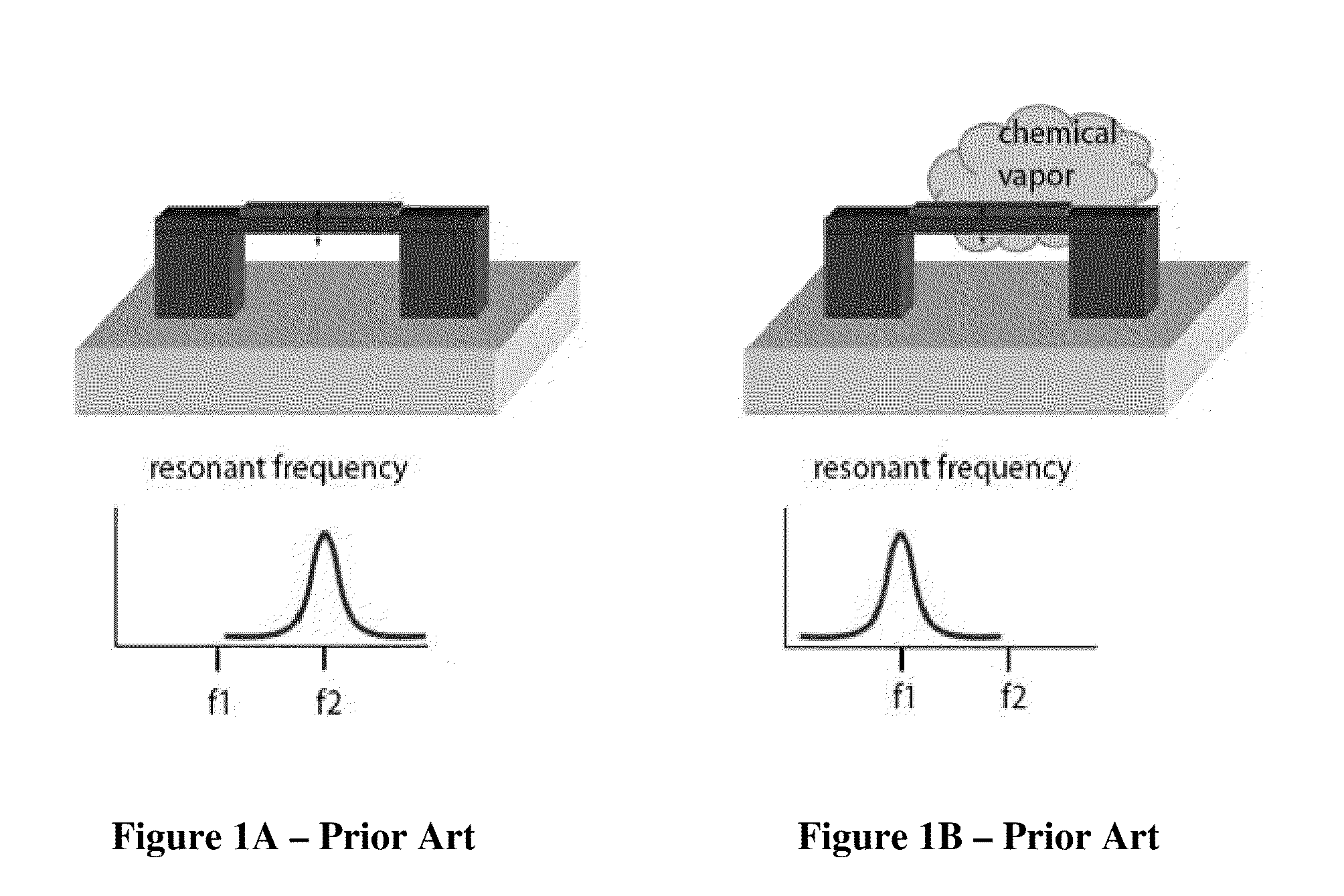
A change in mass of a microbridge in a mass sensor can be sensed by applying a time-varying amplitude modulated electrostatic force to excite the microbridge into resonance at the frequency of amplitude modulation. An optical energy is then transmitted at a wavelength close to a resonant wavelength of a Fabry-Perot microcavity, which is formed by etching a movable reflective mirror into a region of the microbridge and by etching a fixed reflective minor in a region spaced apart from the microbridge. The two mirrors are interconnected by an optical waveguide. The movable mirror and fixed mirror reflect the optical energy to a receiver, and a change in the Fabry-Perot microcavity's reflectivity is interferometrically determined. The change in reflectivity indicates a change in the microbridge's resonant frequency due to increased mass of the microbridge resulting from sorption of a target chemical by a layer of chemoselective material deposited on the microbridge.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
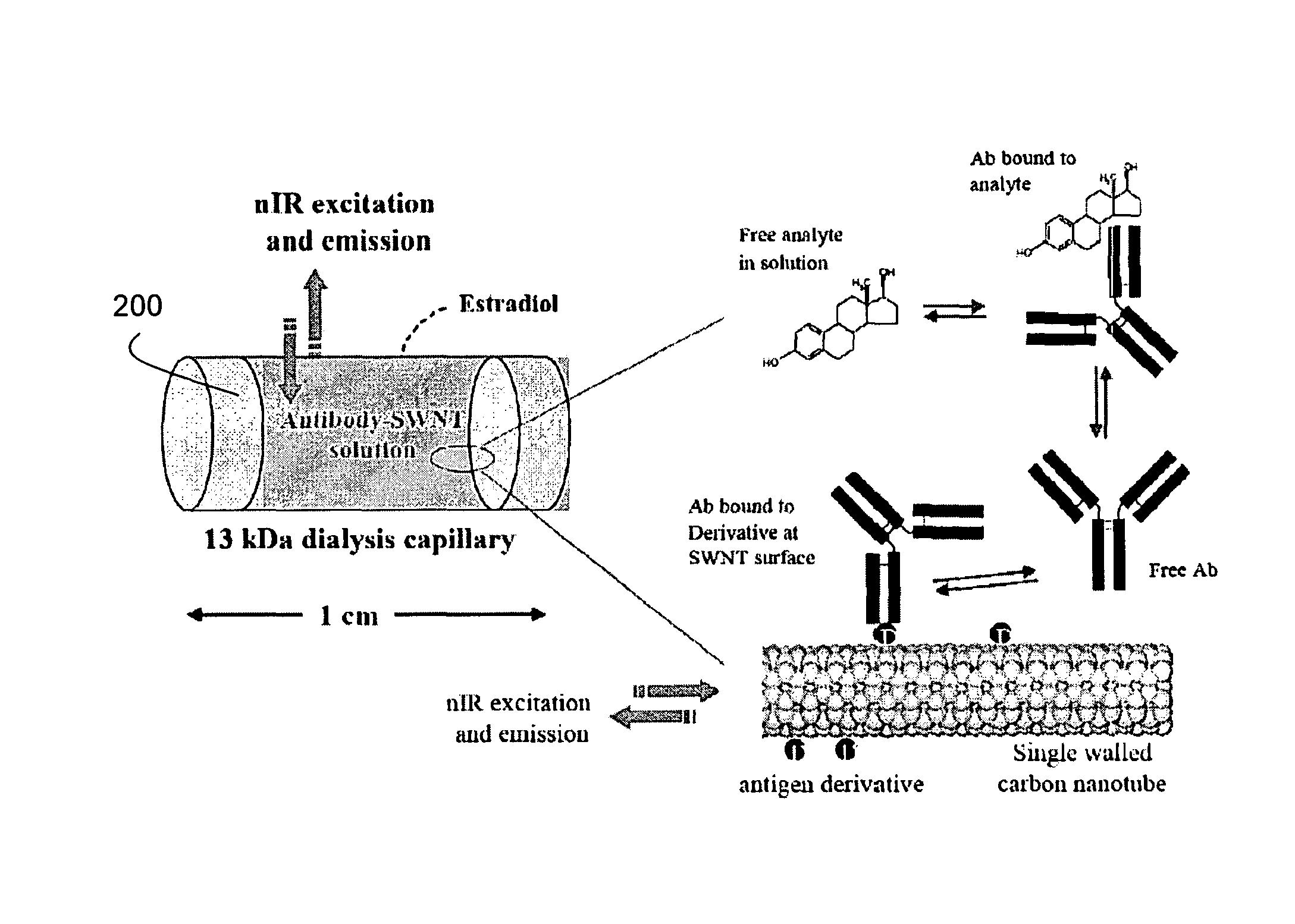
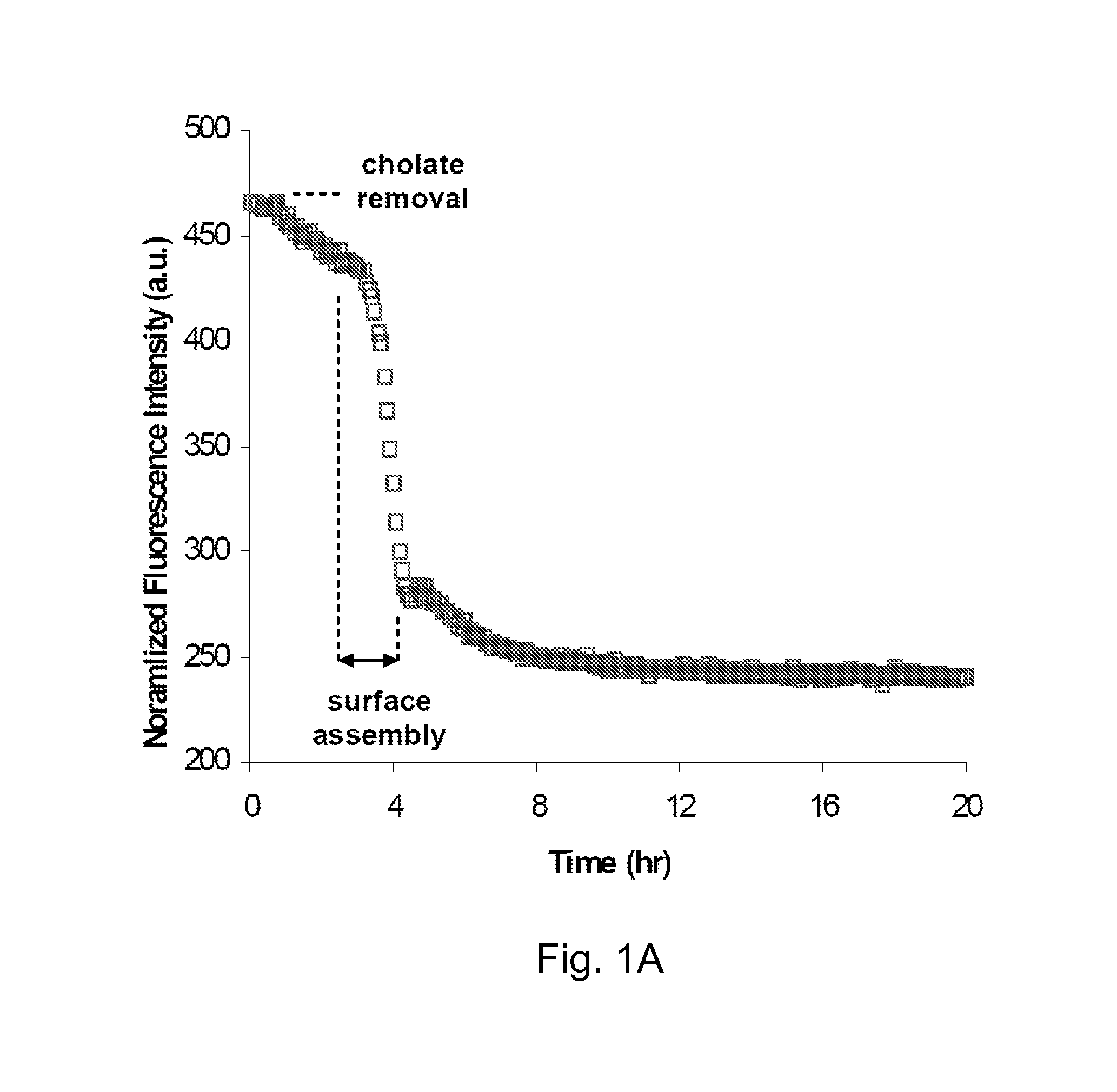
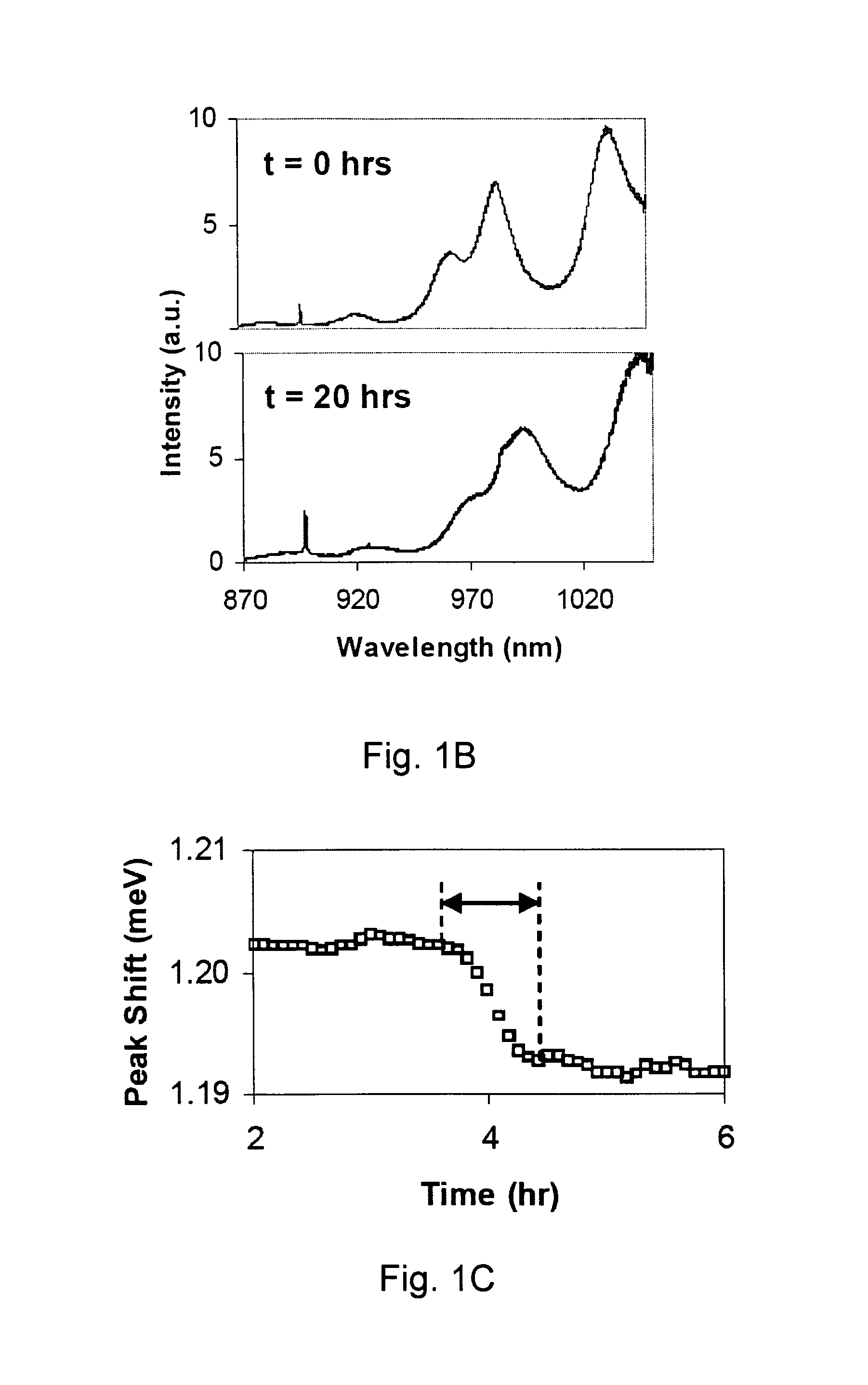
Sensors employing single-walled carbon nanotubes
ActiveUS20070292896A1Facilitate selective reactionFacilitate ligand-receptor binding or antigen-antibody (Material nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteBiopolymer
Sensing compositions, sensing element, sensing systems and sensing devices for the detection and / or quantitation of one or more analytes, Compositions comprising carbon nanotubes in which the carbon nanotubes retain their ability to luminesce and in which that luminescence is rendered selectively sensitive to the presence of an analyte. Compositions comprising individually dispersed carbon nanotubes, which are electronically isolated from other carbon nanotubes, yet which are associated with chemical selective species, such as polymers, particularly biological polymers, for example proteins, which can interact selectively with, or more specifically selectivity bind to, an analyte of interest. Chemically selective species bind, preferably non-covalently, to the carbon nanotube and function to provide for analyte selectivity. Chemically selective species include polymers to which one or more chemically selective groups are covalently attached. Chemically selective polymers include, for example, proteins and polysaccharides.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Photocrosslinked hydrogel surface coatings
InactiveUS20070082019A1Fast curing timeHigh binding capacityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteMass spectrometry
A hydrogel layer is applied to a substrate advantageously when the layer is formed in situ, using a polymeric or copolymeric precursor that includes, respectively, monomer subunits that have a photocrosslinkable functionality and monomer subunits that have a chemically selective functionality for binding a biomolecular analyte, such as a protein. A hydrogel-coated substrate thus obtained is particularly useful as a probe for mass spectroscopic analysis, including SELDI analysis. Hydrogel particles also can be used for SELDI analysis.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
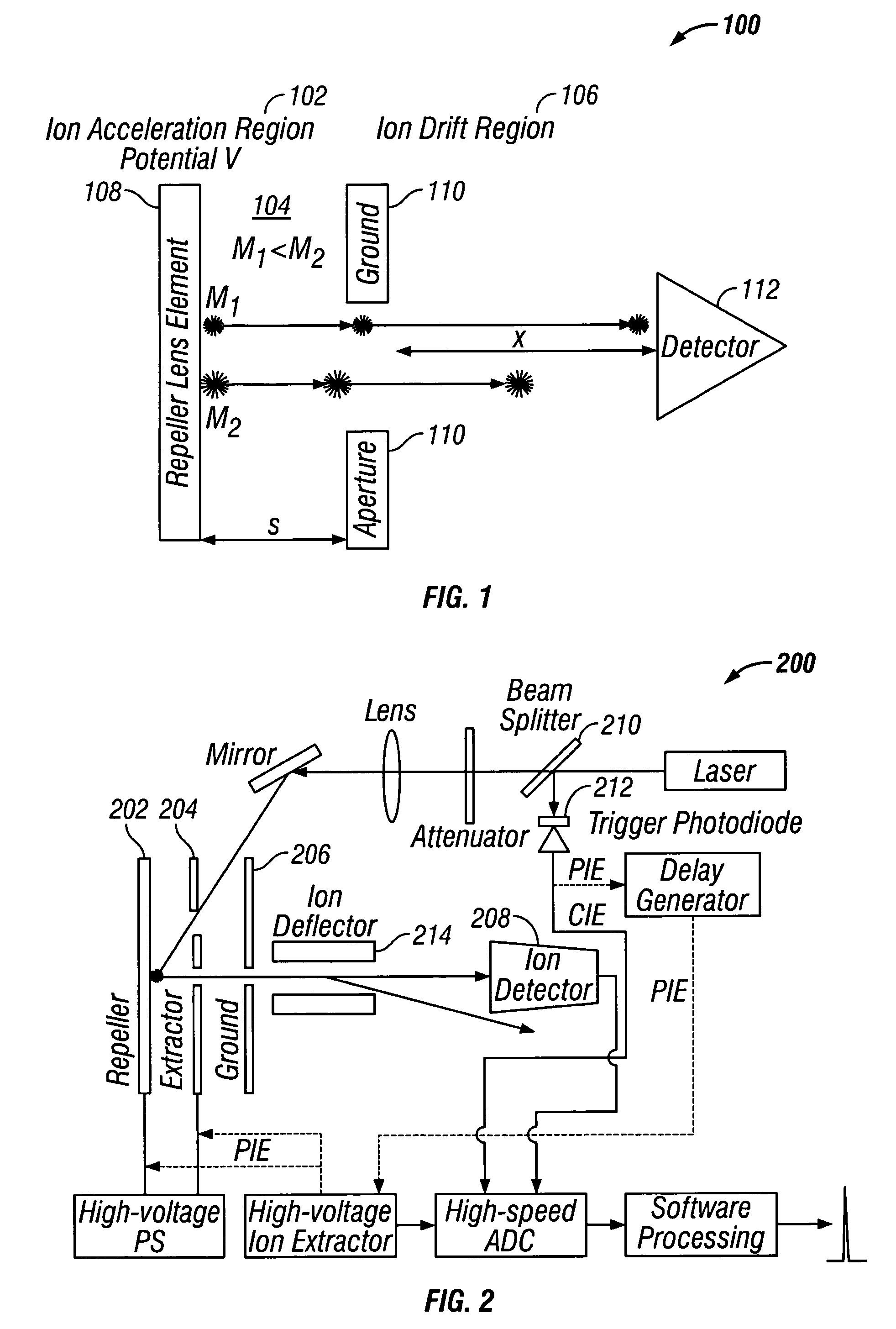
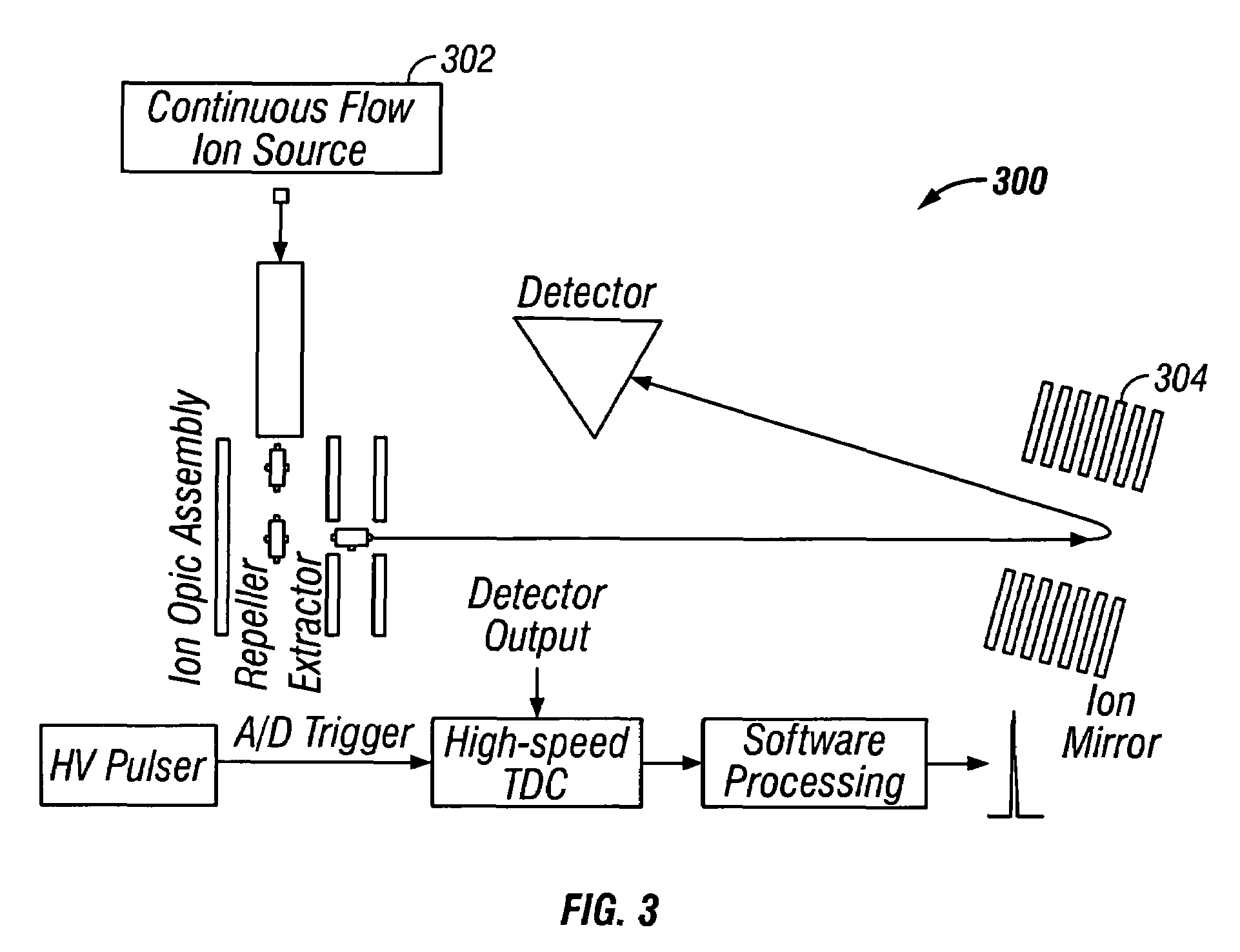
Mass spectrometer interface
ActiveUS7091477B2Improve concentrationPromote liberationStability-of-path spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionThermal energyMass analyzer
A mass spectrometer interface, having improved sensitivity and reduced chemical background, is disclosed. The mass spectrometer interface provides improved desolvation, chemical selectivity and ion transport. A flow of partially solvated ions is transported along a tortuous path into a region of disturbance of flow, where ions and neutral molecules collide and mix. Thermal energy is applied to the region of disturbance to promote liberation of at least some of the ionized particles from any attached impurities, thereby increasing the concentration of the ionized particles having the characteristic m / z ratios in the flow. Molecular reactions and low pressure ionization methods can also be performed for selective removal or enhancement of particular ions.
Owner:PERKINELMER SCI CANADA ULC
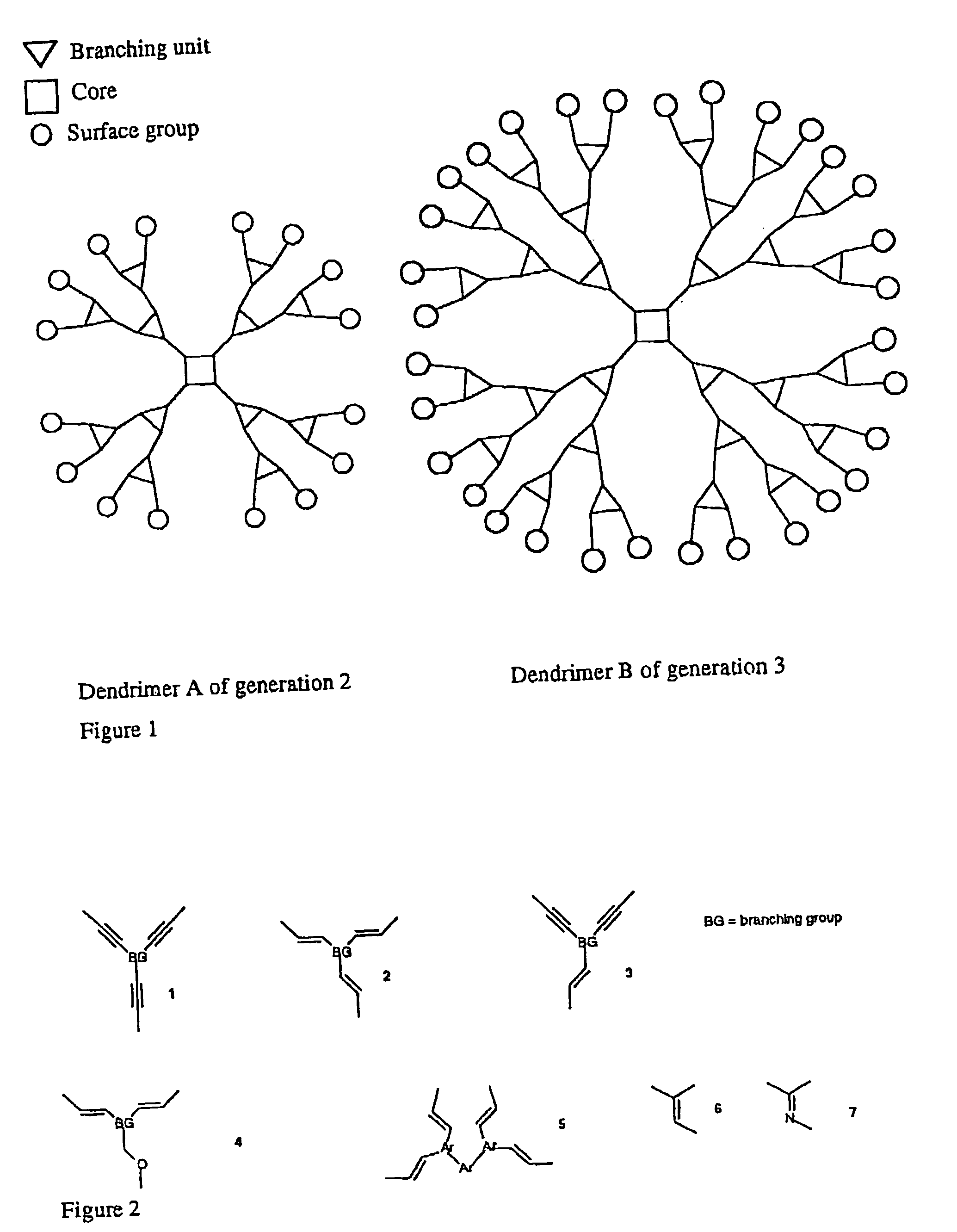
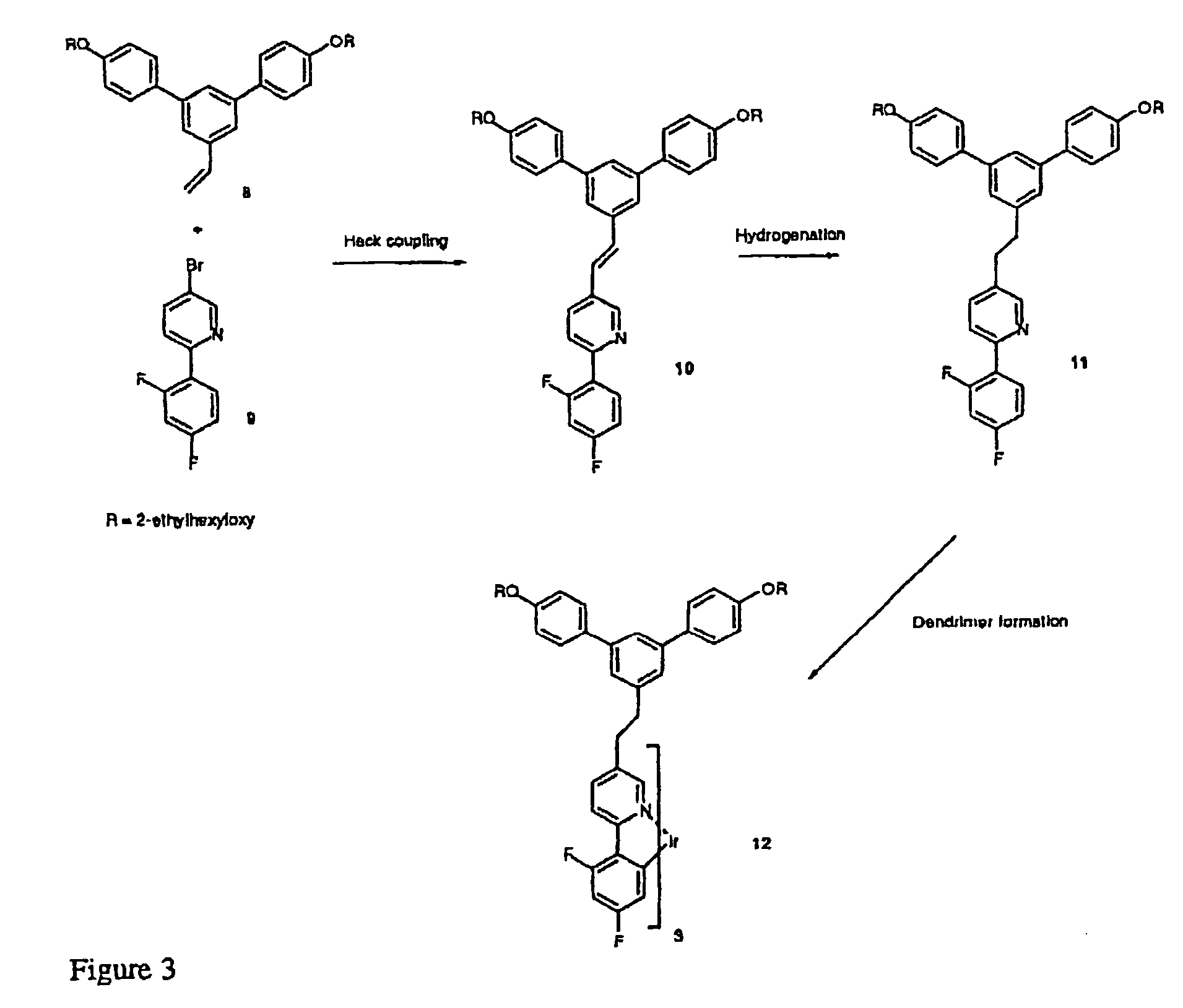
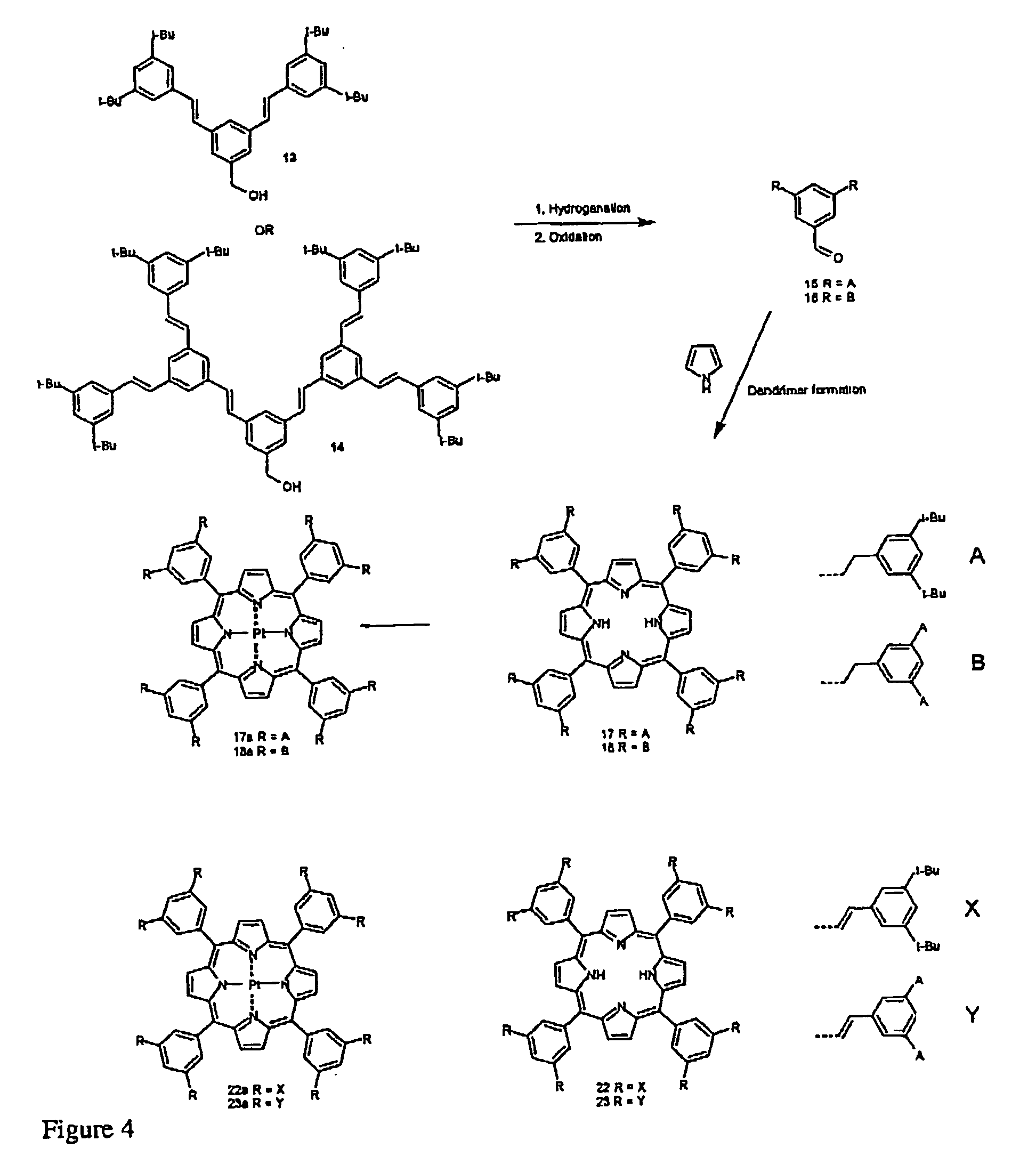
Reactive dendrimers
A process for modifying at least one dendron that is intended to form part of a dendrimer is disclosed. One reacts at least one reactable unsaturated group in a chemoselective manner to form a less unsaturated group. Also disclosed is a process for modifying dendrimers in a similar manner.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE DISPLAY TECH LTD +1
Methods and compositions for tagging via azido substrates
InactiveUS7070941B2Immobilised enzymesOrganic active ingredientsBiotin-streptavidin complexProtein insertion
The invention provides methods and compositions for azide tagging of biomolecules. In one embodiment of the invention, proteins are tagged by metabolic incorporation of prenylated azido-analog substrates. Examples of such analogs are azido farnesyl diphosphate and azido farnesyl alcohol. The azido moiety in the resulting modified proteins provides an affinity tag, which can be chemoselectively captured by an azide-specific conjugation reaction, such as the Staudinger reaction, using a phosphine capture reagent. When the capture agent is biotinylated, the resulting conjugates can be detected and affinity-purified by streptavidin-linked- HRP and streptavidin-conjugated agarose beads, respectively. The invention allows detection and isolation of proteins with high yield, high specificity, and low contamination without harsh treatment of proteins.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
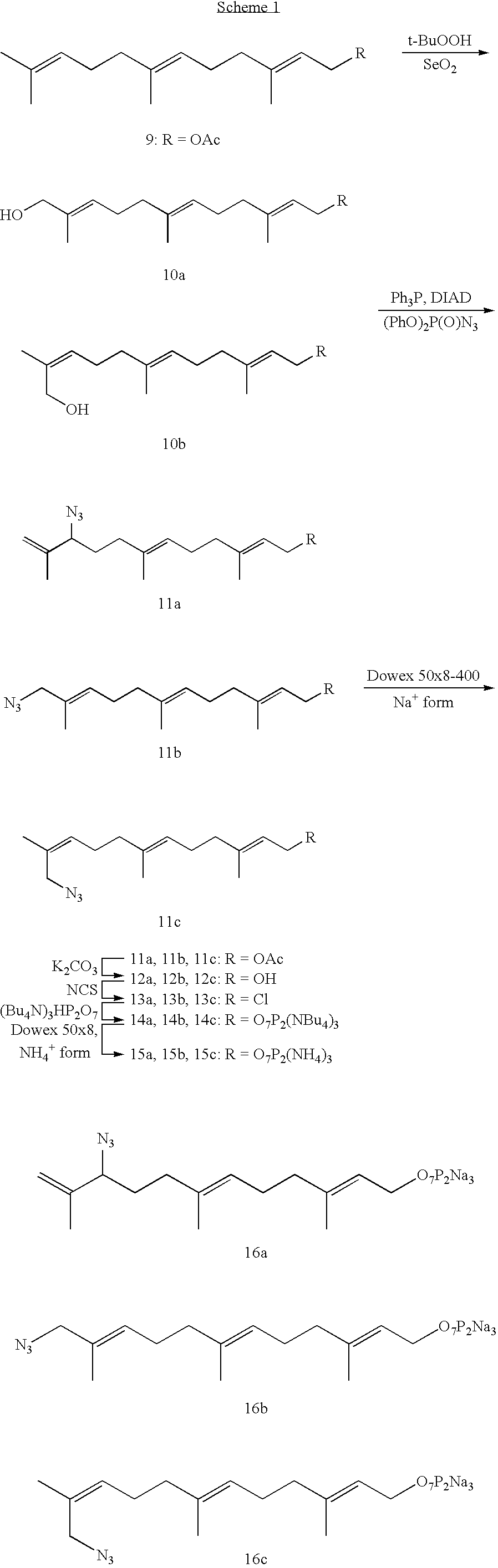
Hierarchical assembly of interconnects for molecular electronics
InactiveUS20050156157A1Well representedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsNanowireNanoparticle
A hierarchical assembly methodology can interconnect individual two- and / or three-terminal molecules with other nanoelements (nanoparticles, nanowires, etc.) to form solution-based suspensions of nanoscale assemblies. The nanoassemblies can then undergo chemical-selective alignment and attachment to nanopatterned silicon and / or other surfaces for interconnection and / or measurement.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Liposome-mediated ligation
InactiveUS20090196916A1Easy to implementSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsLiposomeChemoselective ligation
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
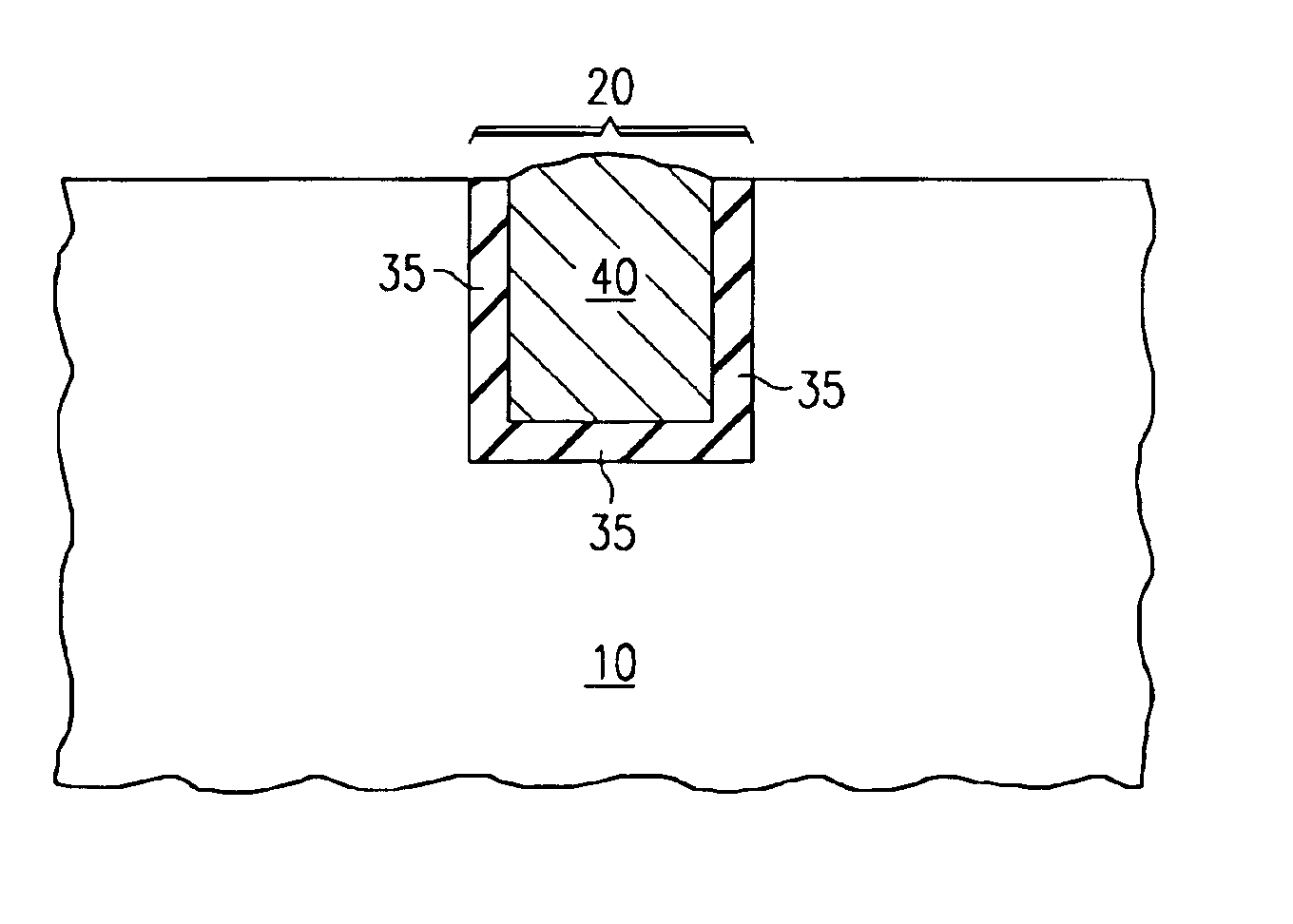
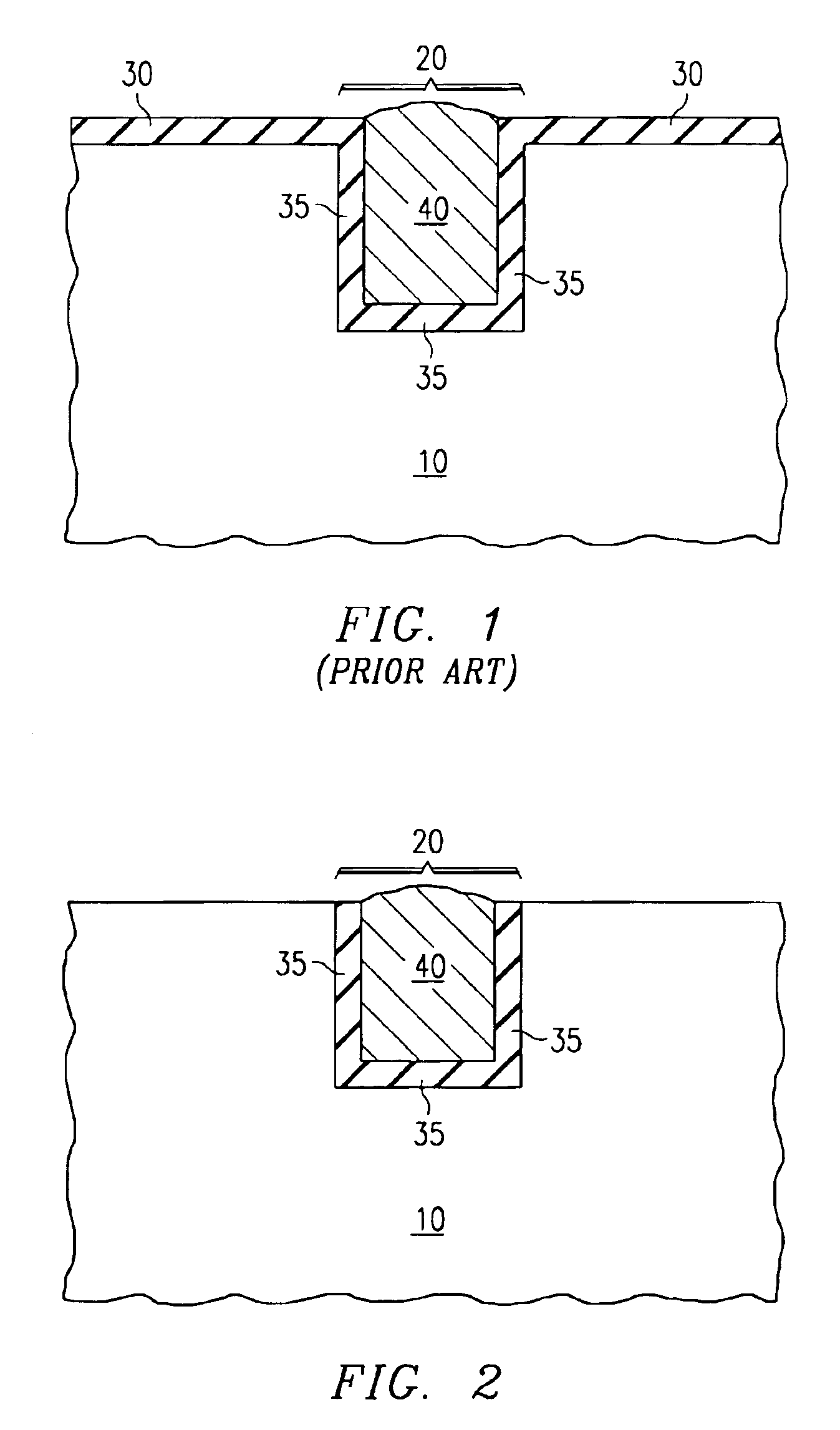
Selective dry etching of tantalum and tantalum nitride
The invention describes a method for the selective dry etching of tantalum and tantalum nitride films. Tantalum nitride layers (30) are often used in semiconductor manufacturing. The semiconductor substrate is exposed to a reducing plasma chemistry which passivates any exposed copper (40). The tantalum nitride films are selectively removed using an oxidizing plasma chemistry.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Sensor instrument system including method for detecting analytes in fluids
ActiveCN101581685ADetectableTo achieve the purpose of identificationMaterial resistanceTransceiverDesorption
A sensor instrument system and a method for detecting and identifying analytes in fluids of a region comprising a local sensor instrument and remote central station are disclosed. The instrument is comprised of a core technology employing a single sensor having two electrodes operated by an electrical frequency sweeping to generate two sets of patterned electrical information from a single measurement, a data transmission module and a GPS receiver module. The central station connects to a network means connected to a plurality of local receiving sites equipped with including the respective transceivers, so that the local analyte electrical information and geographic position information transmitted by the instrument can be wirelessly and remotely received and processed by the central station. The core technology is further comprised of a reference sensor for eliminating background influence, a temperature programming to control adsorption and desorption of analytes, and usage of all kinds of adsorbent materials having chemical selectivity including the hydrogen selectivity to enhance detection and identification of analytes in fluids.
Owner:孙一慧 +1
Sensors employing single-walled carbon nanotubes
ActiveUS8765488B2Facilitate selective reactionFacilitate ligand-receptor binding or antigen-antibody (Material nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteBiopolymer
Sensing compositions, sensing element, sensing systems and sensing devices for the detection and / or quantitation of one or more analytes, Compositions comprising carbon nanotubes in which the carbon nanotubes retain their ability to luminesce and in which that luminescence is rendered selectively sensitive to the presence of an analyte. Compositions comprising individually dispersed carbon nanotubes, which are electronically isolated from other carbon nanotubes, yet which are associated with chemical selective species, such as polymers, particularly biological polymers, for example proteins, which can interact selectively with, or more specifically selectivity bind to, an analyte of interest. Chemically selective species bind, preferably non-covalently, to the carbon nanotube and function to provide for analyte selectivity. Chemically selective species include polymers to which one or more chemically selective groups are covalently attached. Chemically selective polymers include, for example, proteins and polysaccharides.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
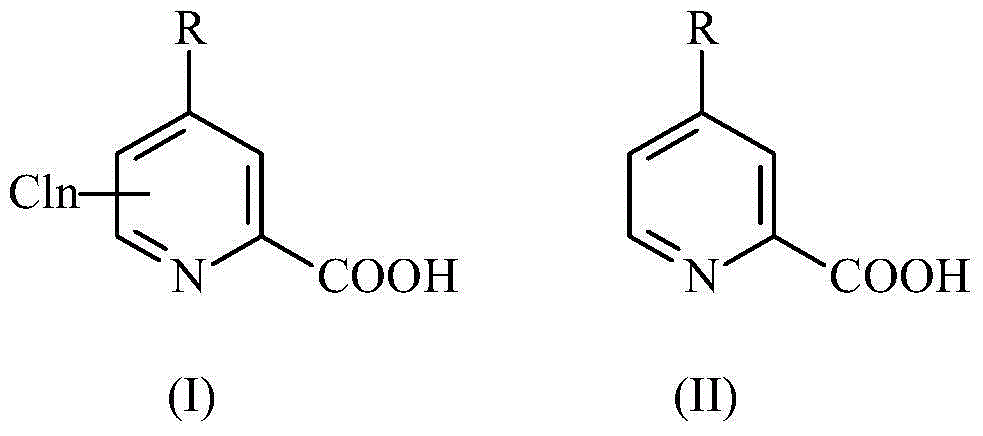
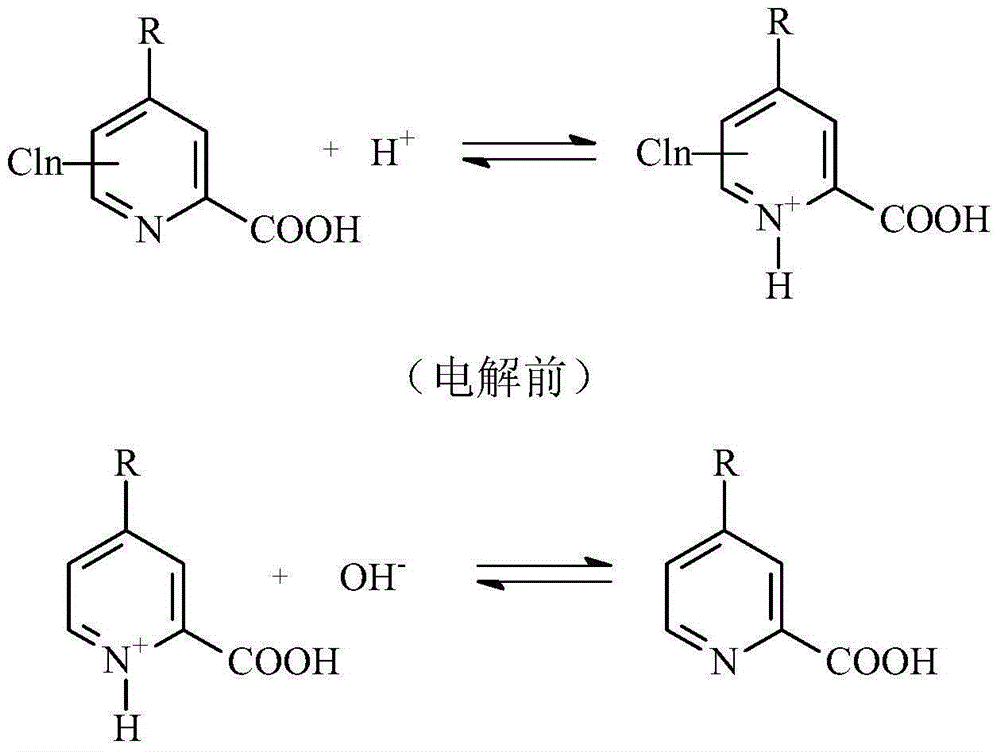
Method for preparing picolinic acid through electro-catalysis selective dechloridation of chloropicolinicacid
ActiveCN104988531AIncrease added valueSolve processing problemsElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic organic productionSupporting electrolyteElectrolysis
Owner:菏泽建数智能科技有限公司
Chemical sensor made of nano particle/dendrite composite material
InactiveCN1402000AIncreased sensitivityShort response timeOther chemical processesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorCross-linkDendrimer
Owner:SONY INT (EURO) GMBH +1
Decarboxylation and fluorination method for carboxylic acid
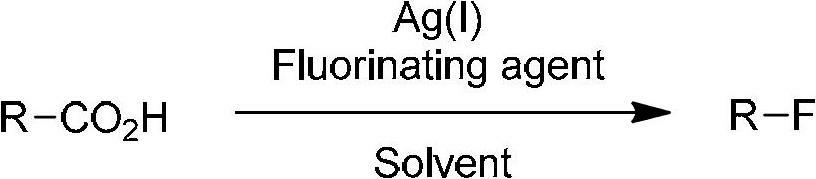
ActiveCN102675015AOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationCarbon–fluorine bondRoom temperature
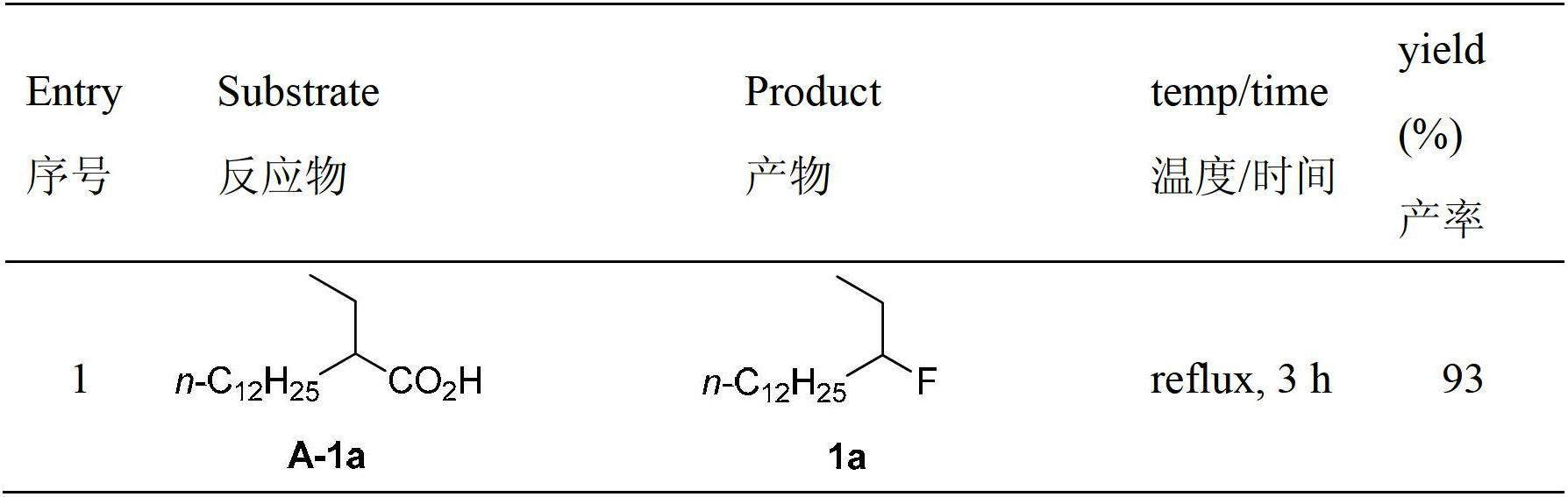
The invention relates to a decarboxylation and fluorination method for carboxylic acid. According to the method, fatty acid RCOOH, monovalent silver salt catalyst and fluorinated reagent Selectfluor or hexafluorophosphate derivative thereof are reacted in a solvent at the temperature of between room temperature and 80 DEG C to obtain RF; and by adopting the method, the carboxylic acid is efficiently converted into corresponding decarboxylated and fluorinated product in an aqueous phase. The method is mild in reaction conditions and easy to operate, has good chemical selectivity and functional group compatibility, and is a very practical sp<3> carbon-fluorine bond synthesizing method.
Owner:上海睿瓦科技有限公司
Portable breath volatile organic compounds analyzer and corresponding unit
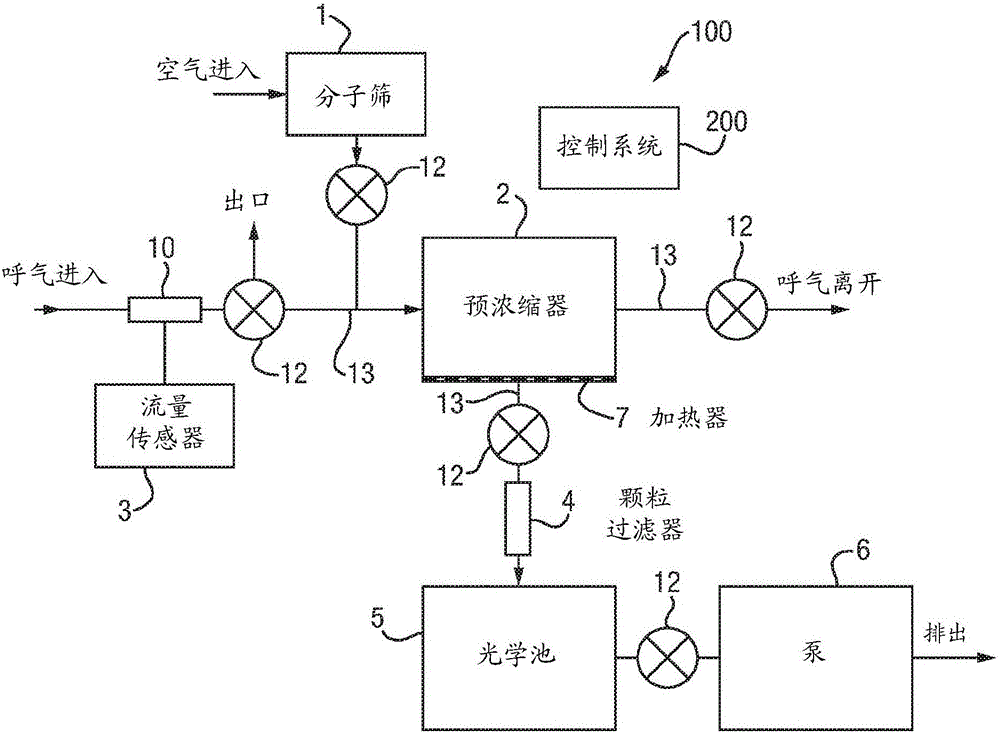
InactiveCN104995511AWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationKetoneBlood ketone level
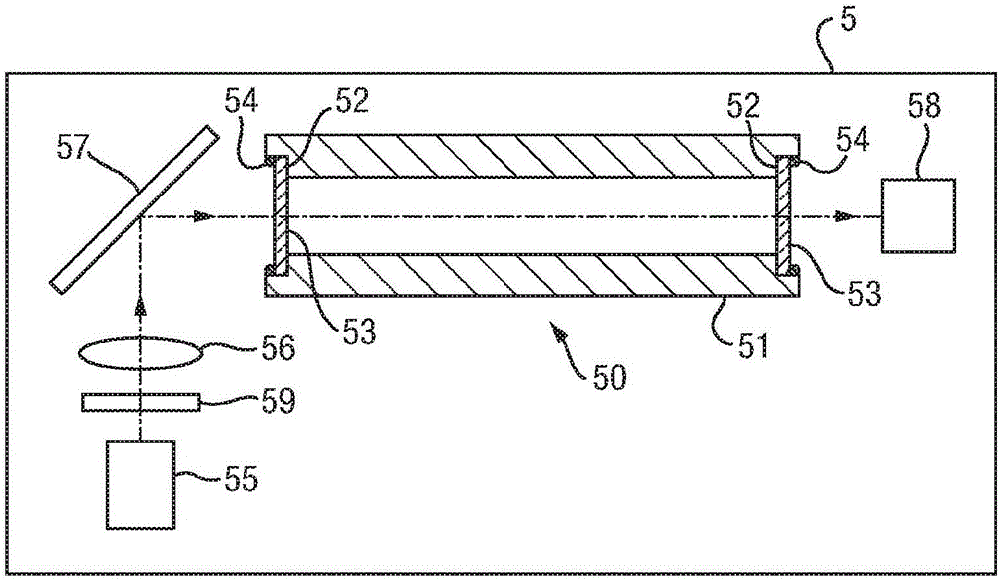
A compact, portable or handheld device for measurement of breath VOCs such as acetone is described, which incorporates a flow measurement sensor, a mini preconcentrator unit and an spectroscopy unit, such as a cavity-enhanced absorption spectrometer. The preconcentrator includes a chemically selective material to trap VOCs, which is supported on a metal foam. The apparatus is suitable for measuring sub ppm levels of breath VOCs such as acetone and for tracking blood ketone levels.
Owner:OXFORD MEDICAL DIAGNOSTICS LTD
Multisensor array for detection of analytes or mixtures thereof in gas or liquid phase
ActiveUS20130096030A1Solve problemsQuick checkAnalysis using chemical indicatorsOrganic chemistrySensor arrayAnalyte
The present invention relates to a multisensor array for detection of analytes in the gas phase or in the liquid phase, comprising at least two different chemo-selective compounds represented by the general formula (I) wherein the hetero atoms X1-X4 and the substituents R1-R4 are defined in the specification and the dashed bonds represent independently of each other either a single bond or a double bond. Said chemo-selective compounds are capable of individually changing physicochemical properties when exposed to analytes or analyte mixtures and these changes can be detected by a transducer or an array of transducers. The present invention does also relate to the use of at least two different chemo-selective compounds in a sensor array, a method for preparation of such sensor arrays and the use of said sensor arrays. Furthermore the present invention relates to methods for detecting and identifying analytes or mixtures thereof in the gas phase or in the liquid phase.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
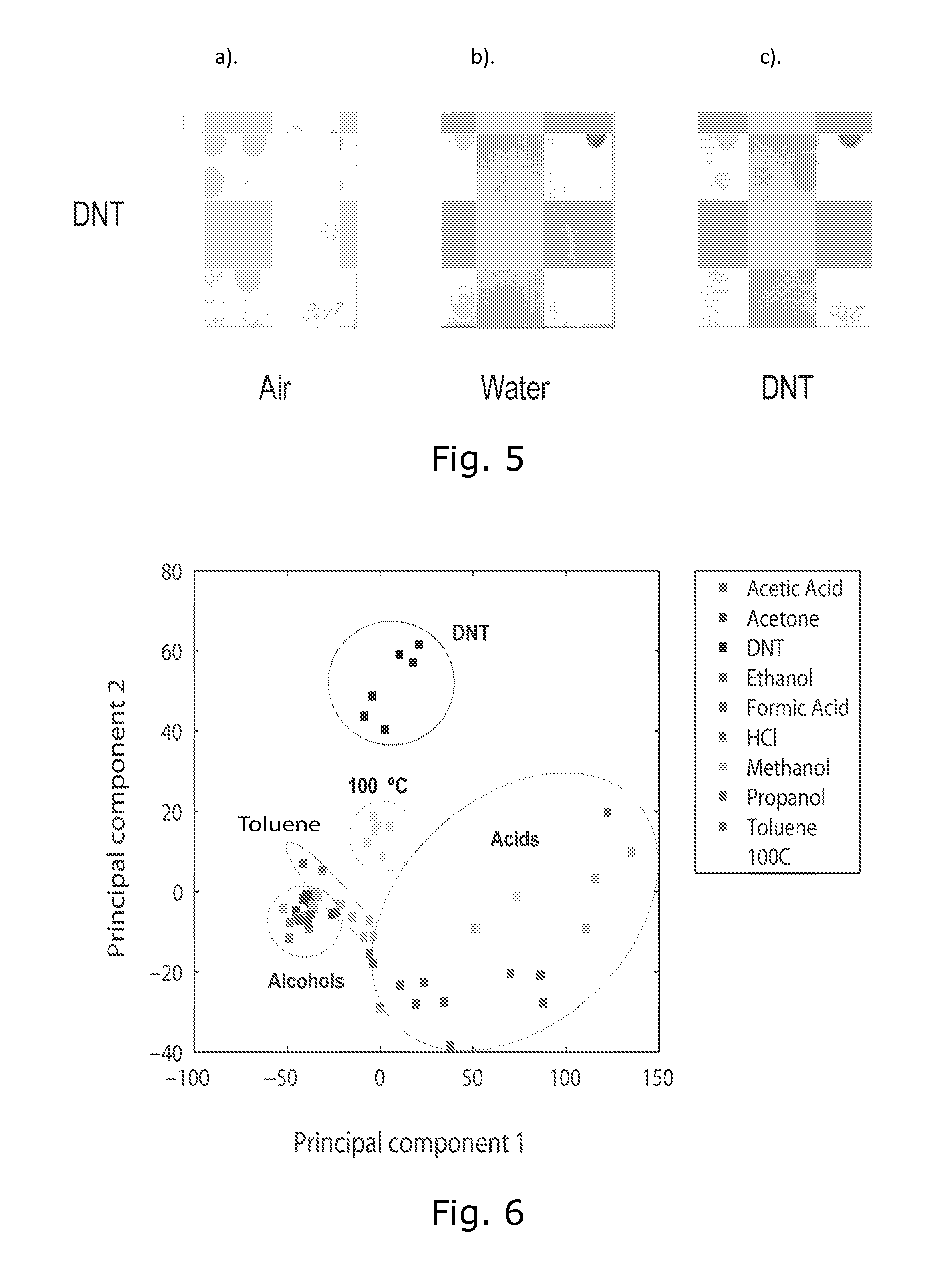
Process for manufacturing a polysaccharide sweetener compound
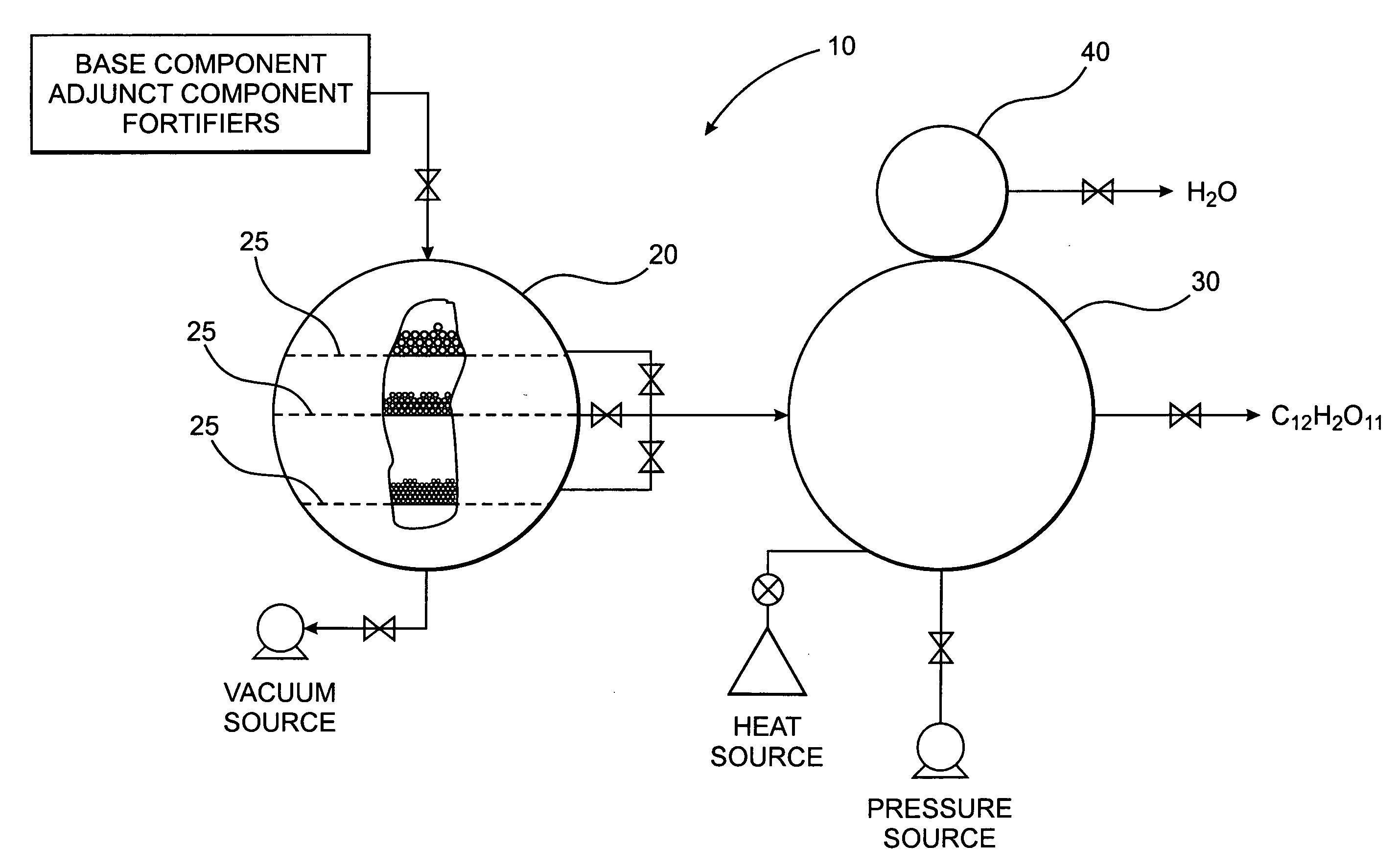
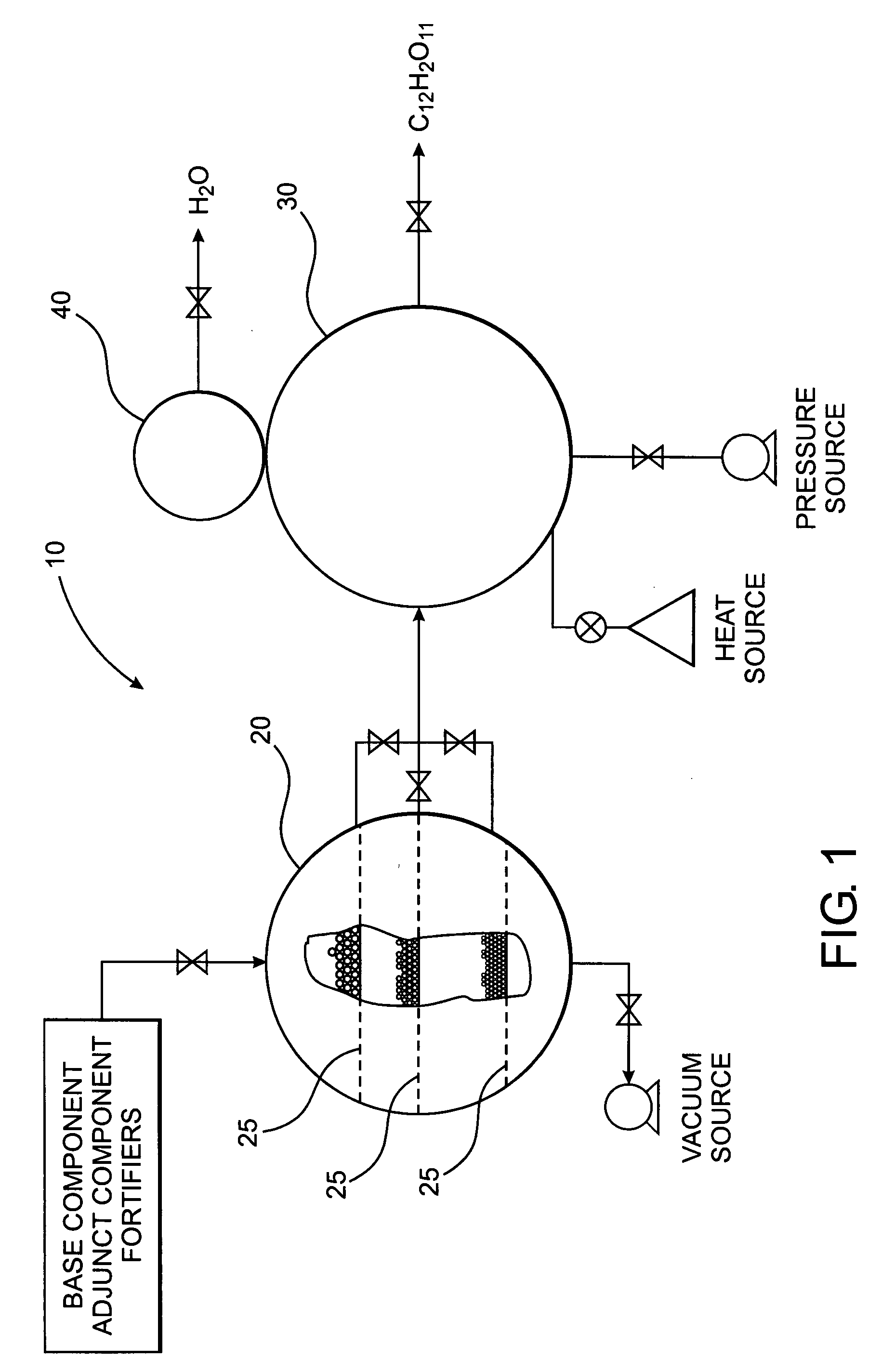
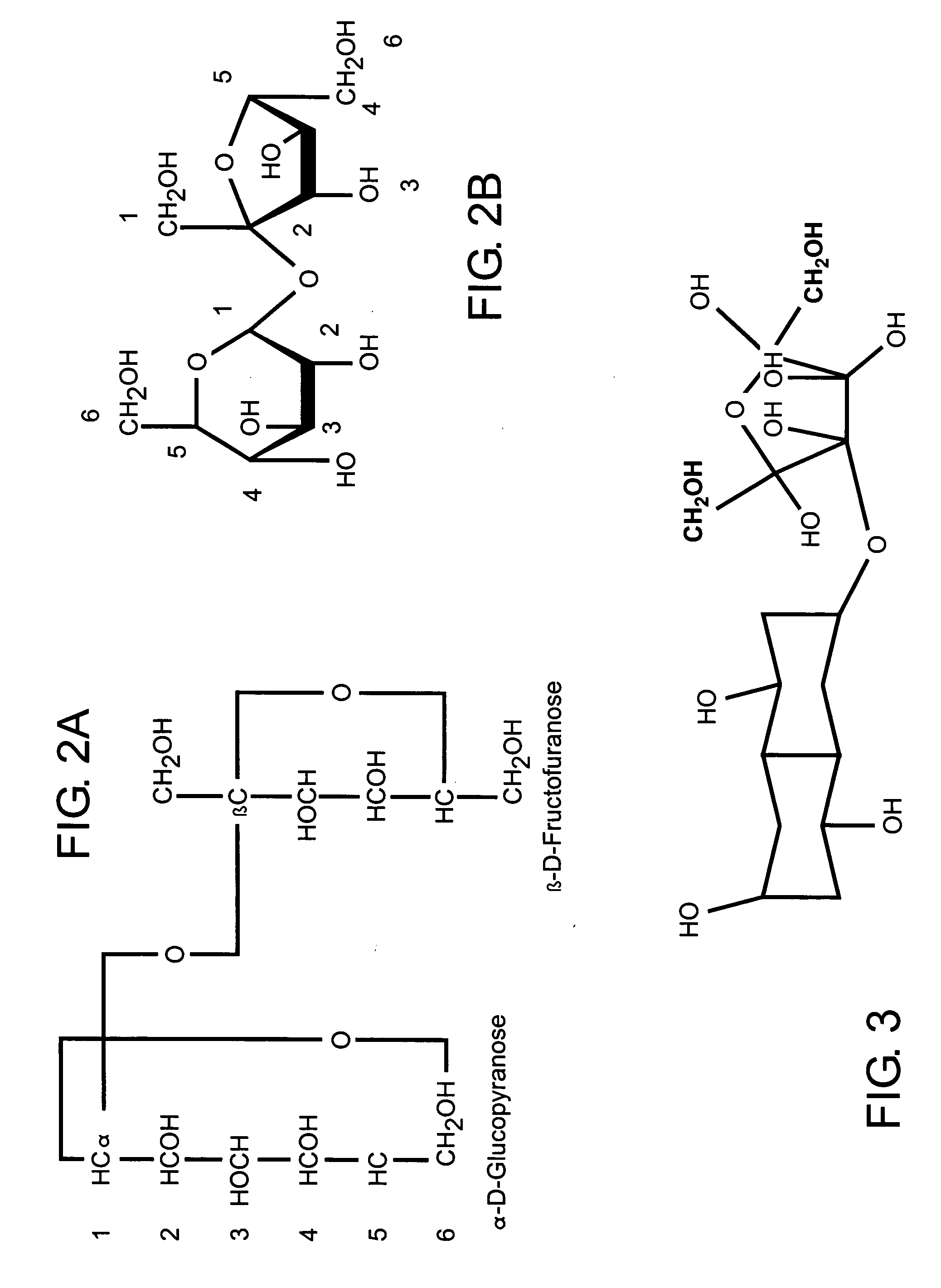
InactiveUS20070077339A1Reduce pressureReduce the temperatureSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationCycloadditionFood processing
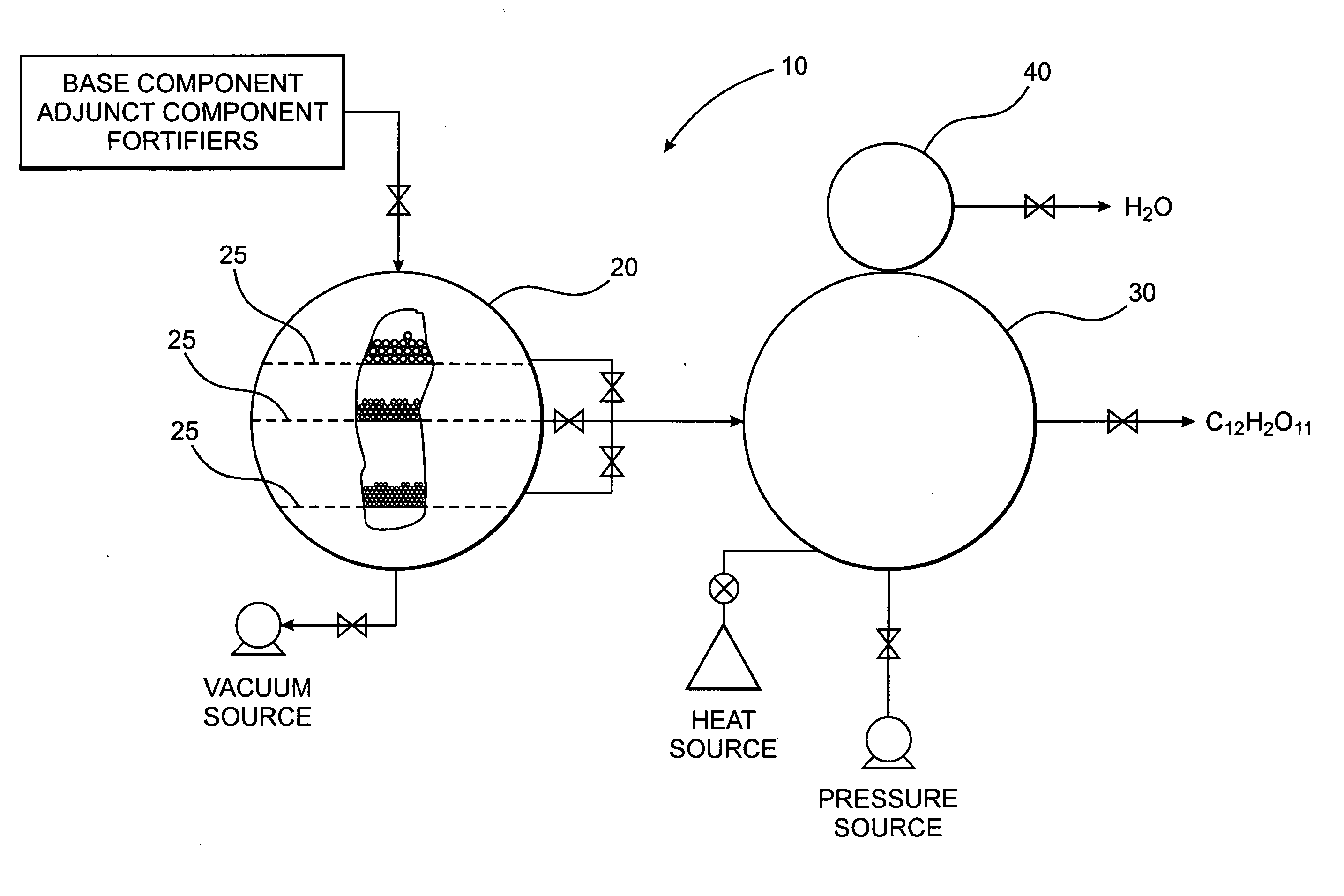
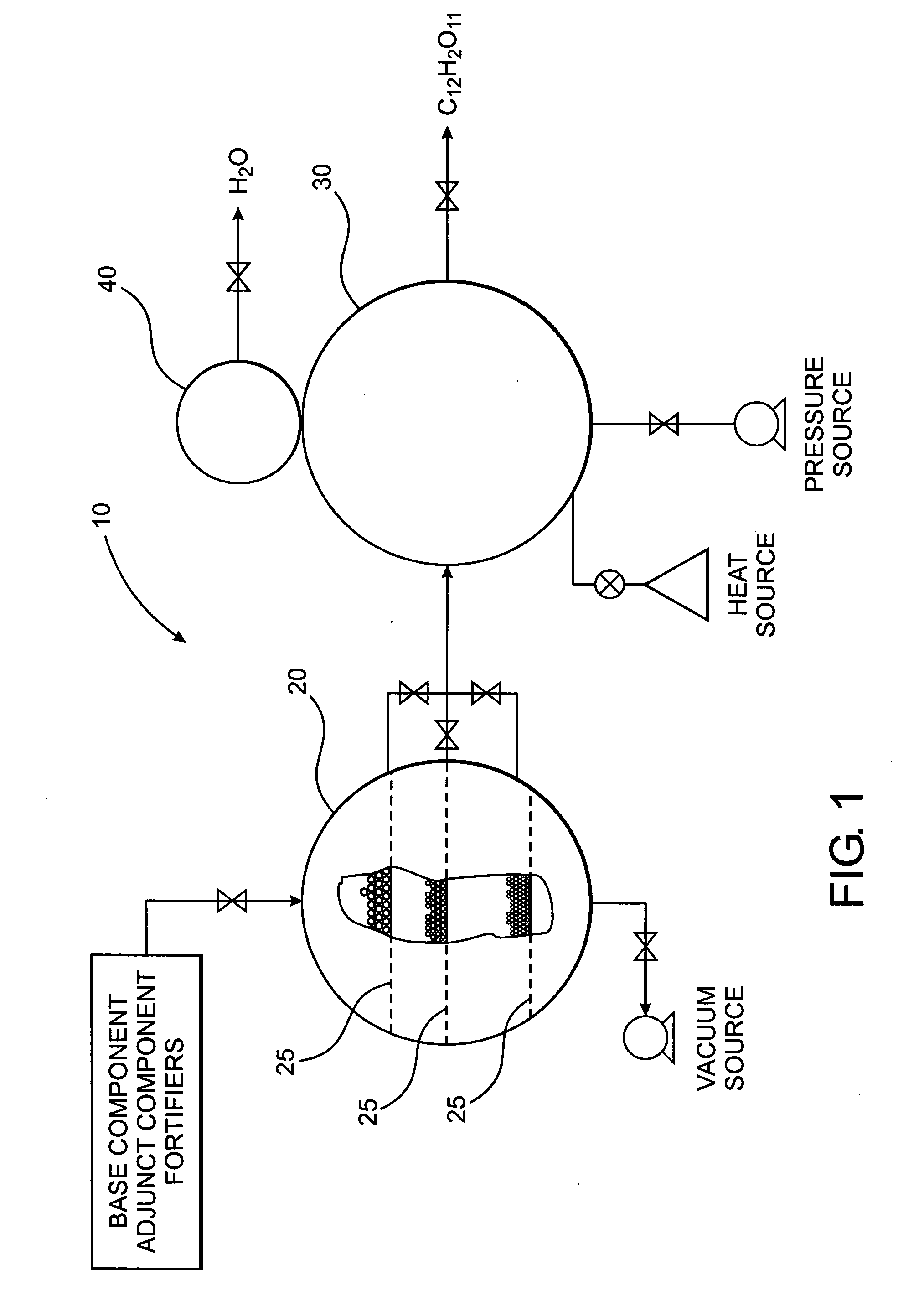
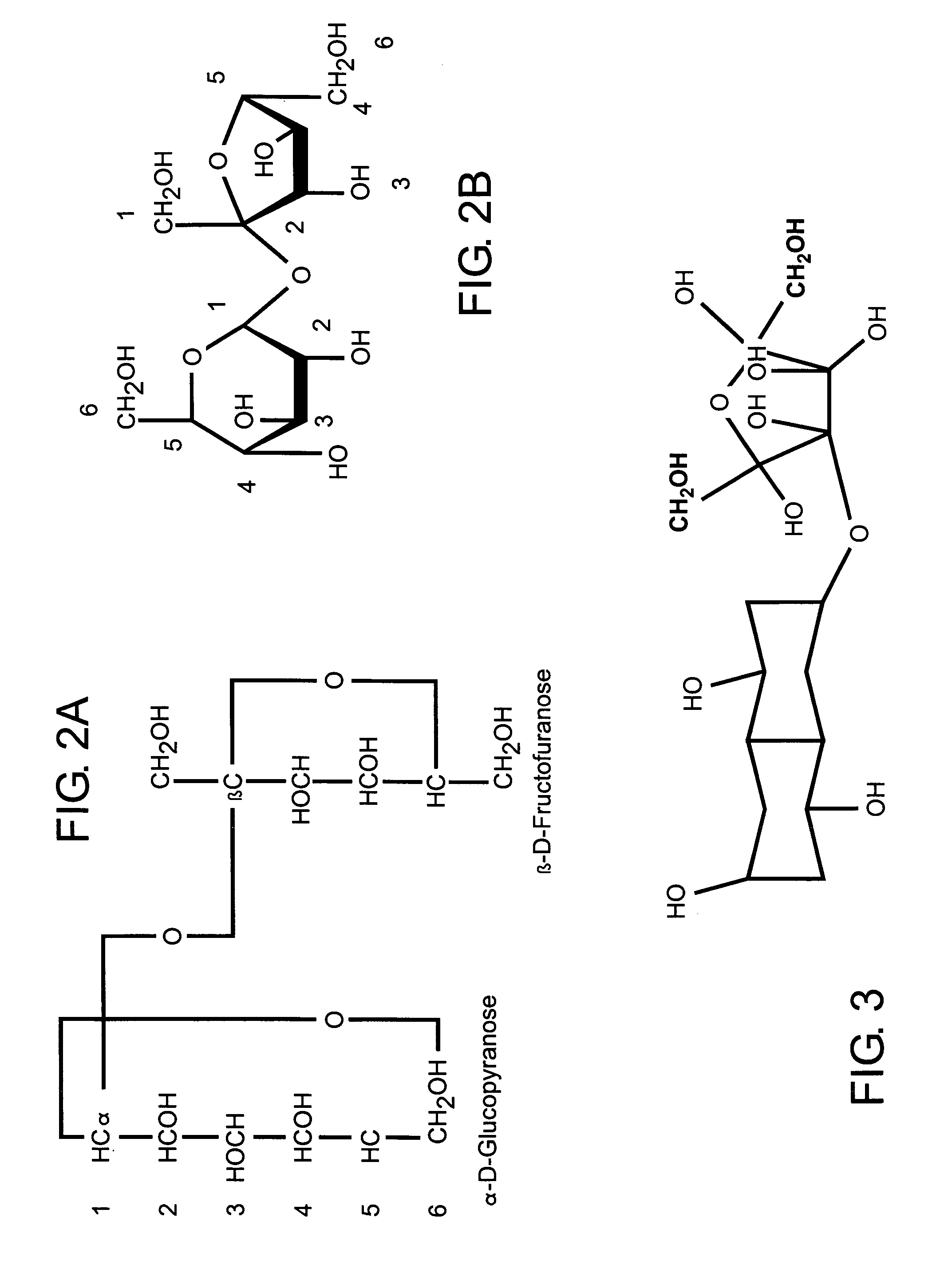
A method of forming a compound such as a polysaccharide sweetener compound is obtained via a process of cycloelimination of a macromolecule, for example, a glycoside, chemoselective promiscuous ligation of a first component constituent such as a constituent disaccharide fraction derived from the macromolecule with a second component such as a base monosaccharide, such as fructose, and cycloaddition of the base monosaccharide with a the constituent disaccharide fraction. Subsequent addition of fortifiers such as vitamins and minerals may be accomplished via baric processing to effect cross-linking or cross-bonding with the polysaccharide sweetener compound. A process for manufacturing polysaccharide sweetener compounds is provided and permits baric, electromagnetic, and thermal processing, at low temperatures, to effect the cycloelimination, chemoselective promiscuous ligation, and cycloaddition reactions. A method for selecting base and adjunct components for the manufacture of a polysaccharide sweetener compound having an equivalent functionality as a natural sweetener and / or derivative thereof as required for a specific food processing application is presented.
Owner:QUANTUM FOOD DESIGN
Polysaccharide sweetener compounds, process for manufacture, and method of selecting components for polysaccharide sweetener compounds based on user specific sweetener applications
InactiveUS20070082105A1Reduce pressureFacilitate the processSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationCycloadditionGlycoside formation
A polysaccharide sweetener compound is obtained via a process of cycloelimination of a macromolecule, for example, a glycoside, chemoselective promiscuous ligation of a constituent disaccharide fraction derived from the macromolecule with a base monosaccharide, such as fructose, and cycloaddition of the base monosaccharide with the constituent disaccharide fraction. Subsequent addition of fortifiers such as vitamins and minerals may be accomplished via baric processing to effect cross-linking or cross-bonding with the polysaccharide sweetener compound. A process for manufacturing polysaccharide sweetener compounds is provided and permits baric, electromagnetic, and thermal processing, at low temperatures, to effect the cycloelimination, chemoselective promiscuous ligation, and cycloaddition reactions. A method for selecting base and adjunct components for the manufacture of a polysaccharide sweetener compound having an equivalent functionality as a natural sweetener and / or derivative thereof as required for a specific food processing application is presented.
Owner:QUANTUM FOOD DESIGN
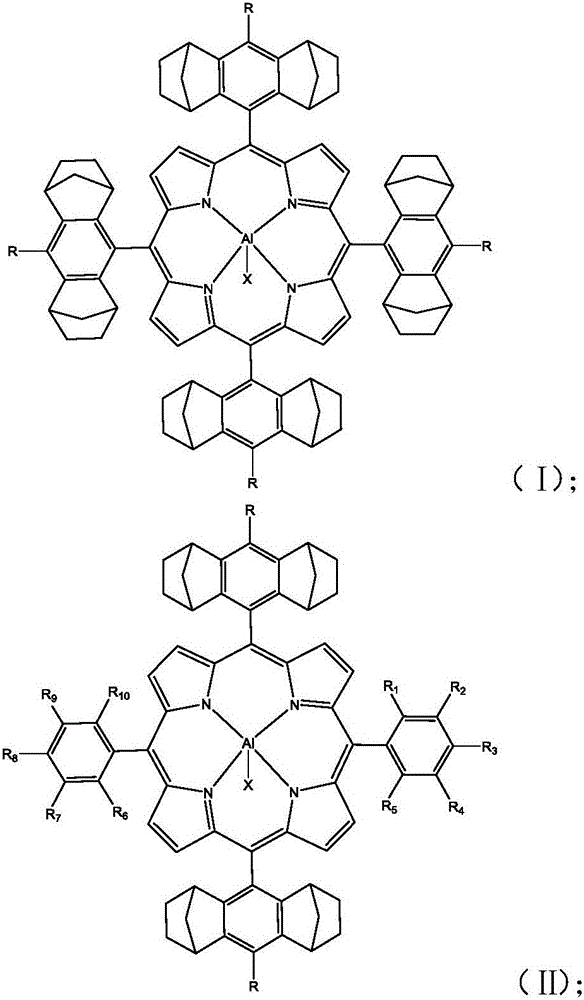
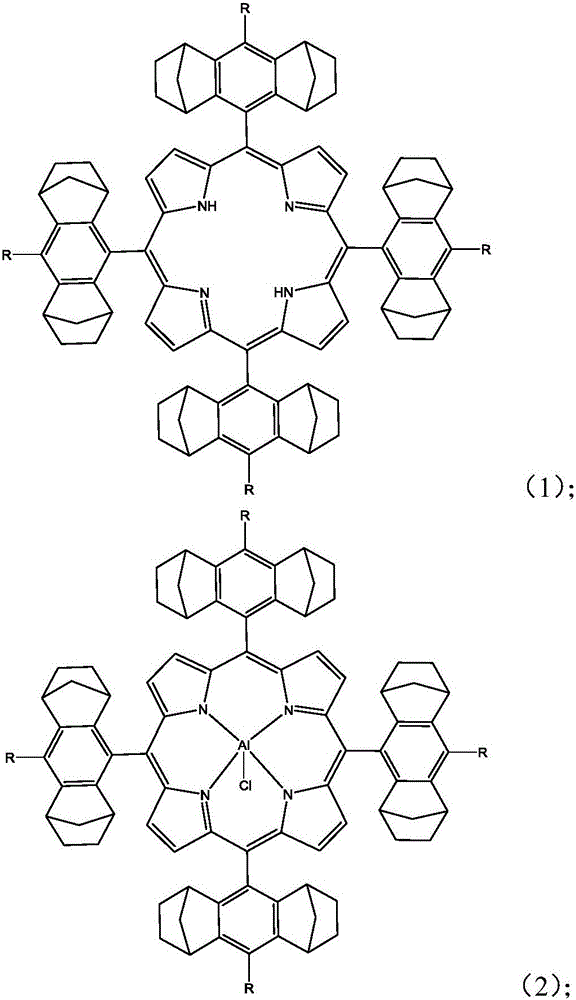
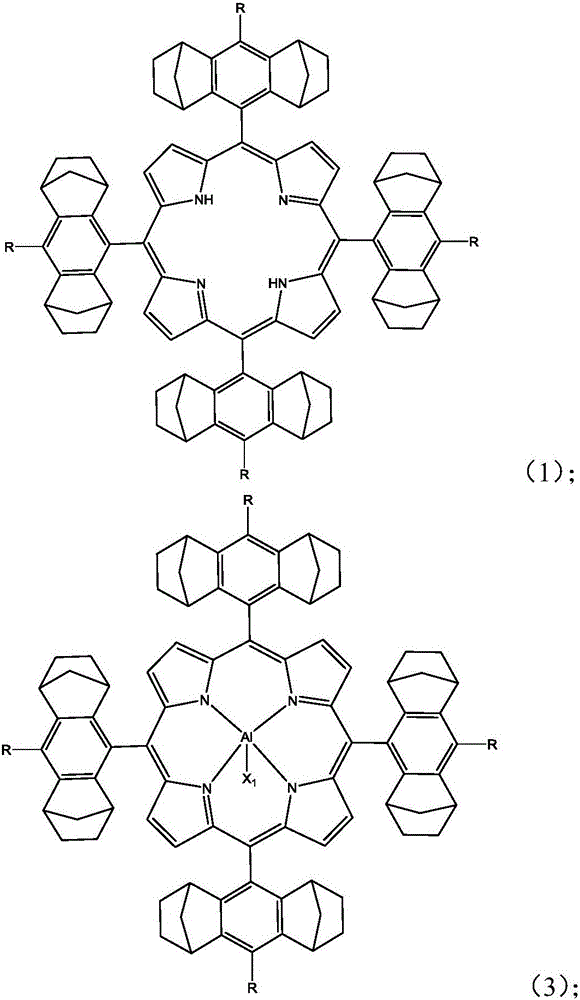
Preparation method of porphyrin aluminum complex and preparation method of polycarbonate
InactiveCN105753894AIncreased polycarbonate unit contentHigh content of polycarbonate unitsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsPorphyrinEther
The invention provides a porphyrin aluminum complex with a structure as shown in a formula (I) or a formula (II), a preparation method of the porphyrin aluminum complex, and a preparation method of polycarbonate. Under the catalysis of a main catalyst and a cocatalyst of the porphyrin aluminum complex provided by the invention, carbon dioxide and epoxide are subjected to copolymerization, so that the polycarbonate is obtained. In a copolymerization process, the porphyrin aluminum complex participates in the reaction process and serves as the main catalyst, the porphyrin aluminum complex has high catalytic activity and particularly has excellent chemistry selectivity (which is greater than 99%), and the polycarbonate with low ether segments and high alternation is prepared.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sensor instrument system including method for detecting analytes in fluids
ActiveCN103293198AReduce manufacturing costOverall small sizeMaterial resistanceDesorptionHydrogen selectivity
A sensor instrument system and a method for detecting and identifying analytes in fluids of a region comprising a local sensor instrument and remote central station are disclosed. The instrument is composed of a core technology employing a single sensor having two electrodes operated by an electrical frequency sweeping to generate two sets of patterned electrical information from a single measurement. The instrument further includes a data transmission module and a GPS receiver module. The central station is connectd with a plurality of local information sites which can wirelessly transmit and receive information in different areas in the region, so that information transmitted by the sensor instrument can be received by the central station through the local sites. The core technology further comprises a reference sensor for eliminating background influence, a temperature programming to control adsorption and desorption of analytes, and usage of all kinds of adsorbent materials having chemical selectivity including the hydrogen selectivity to enhance detection and identification of analytes in fluids.
Owner:孙一慧 +1
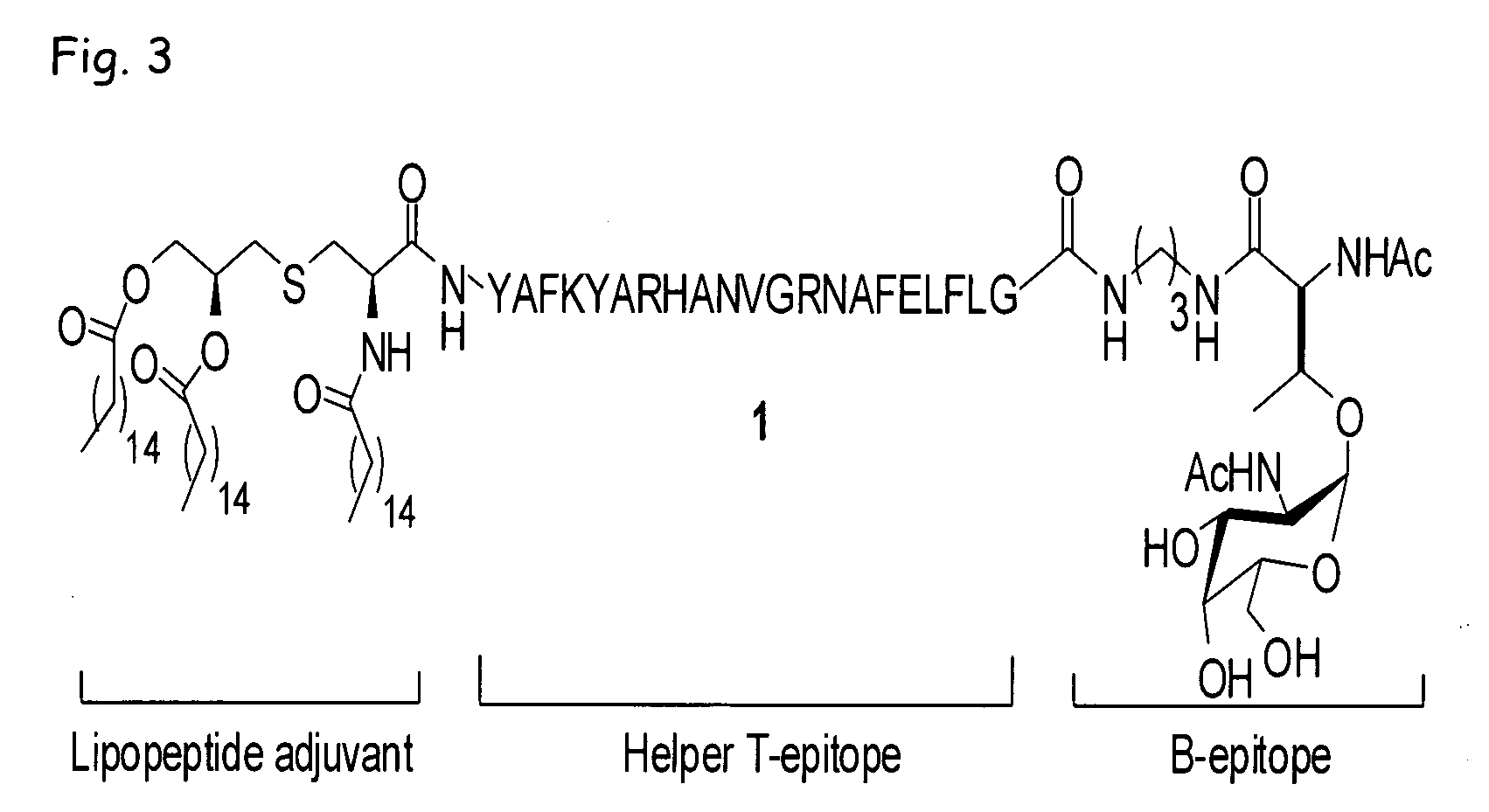
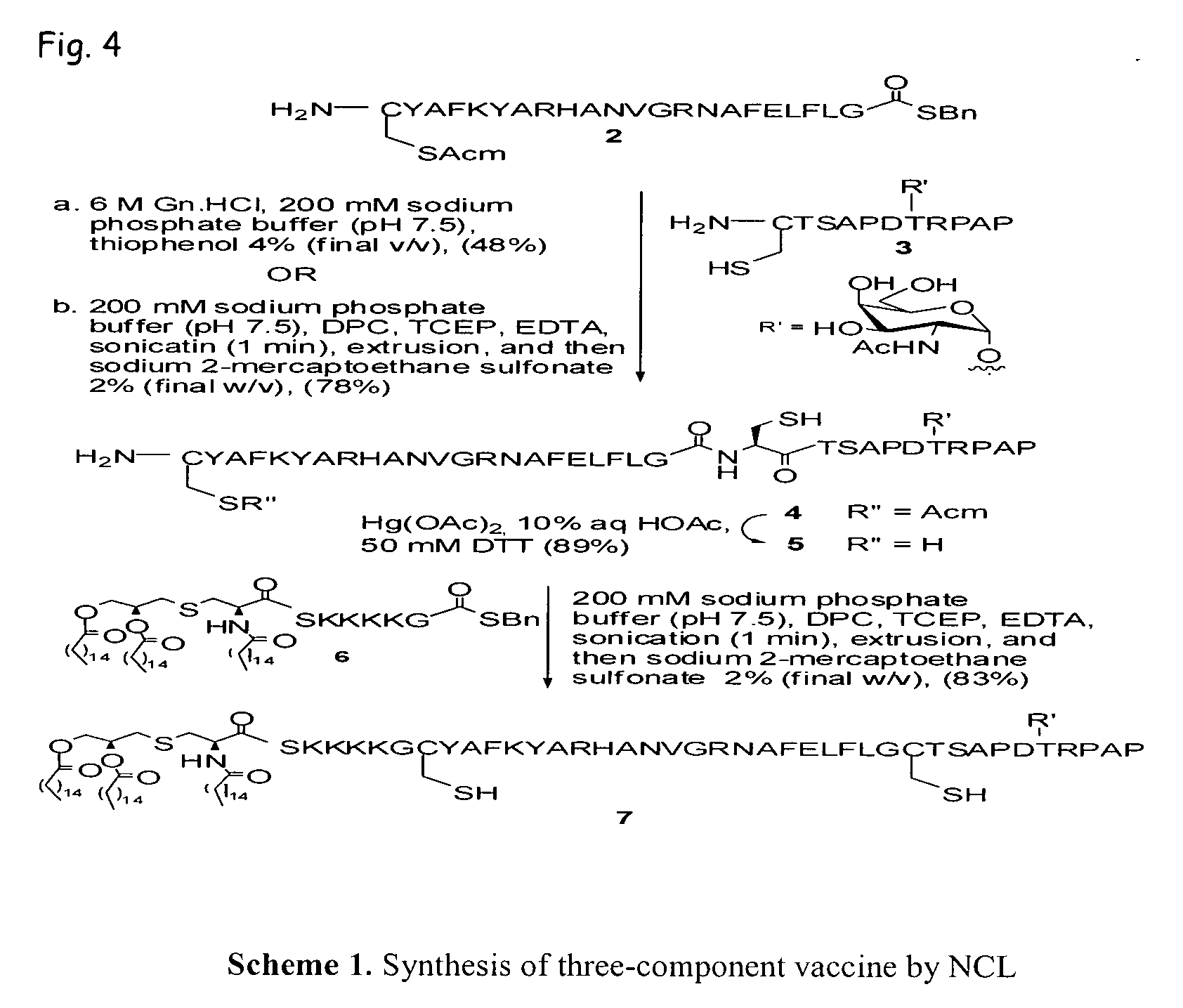
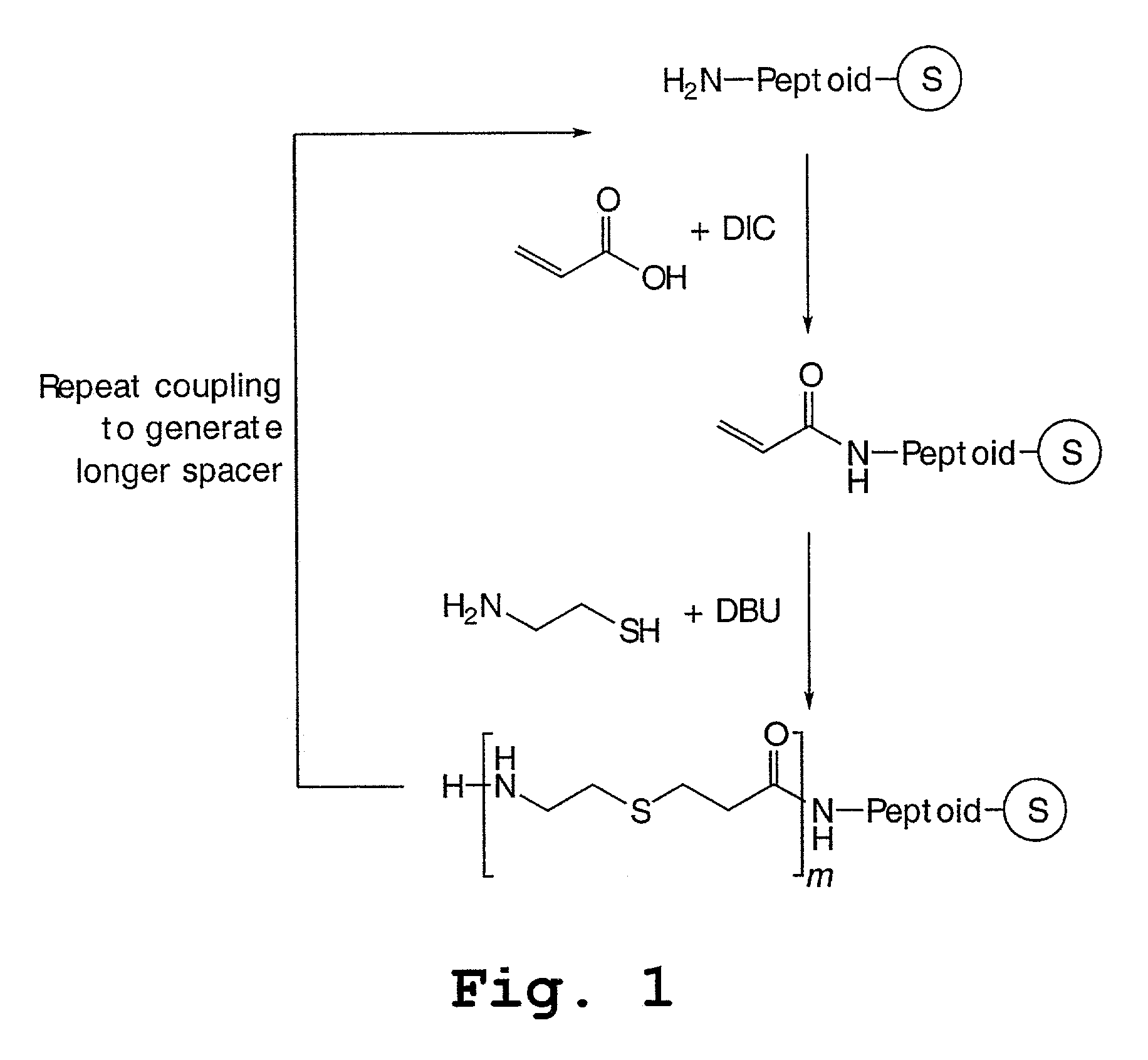
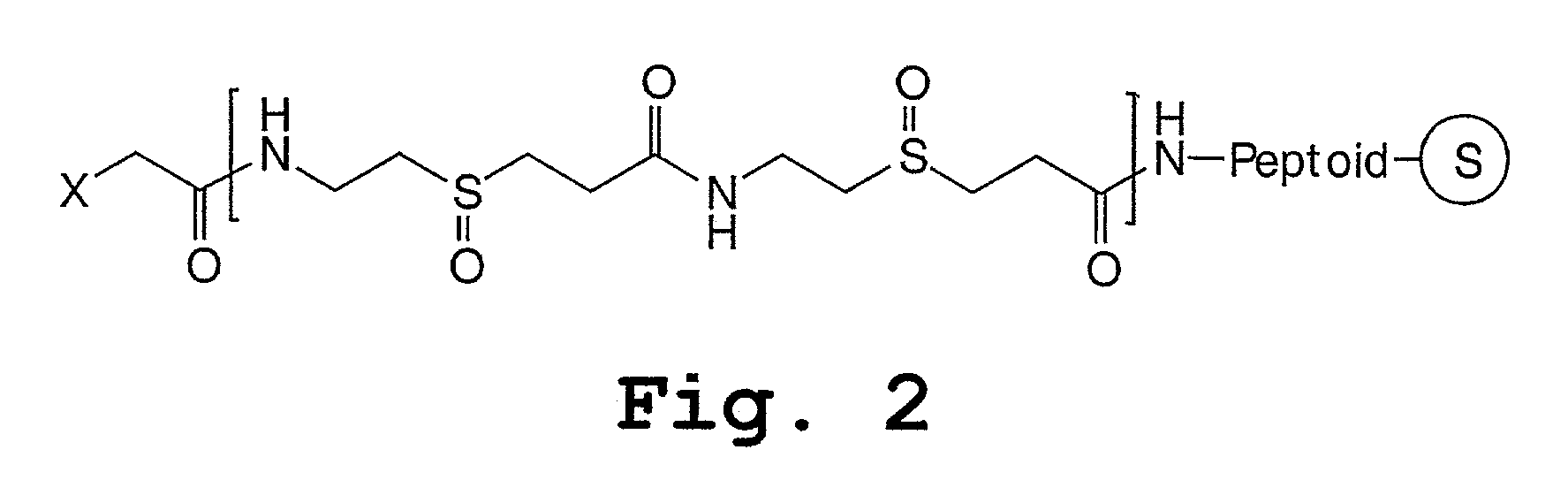
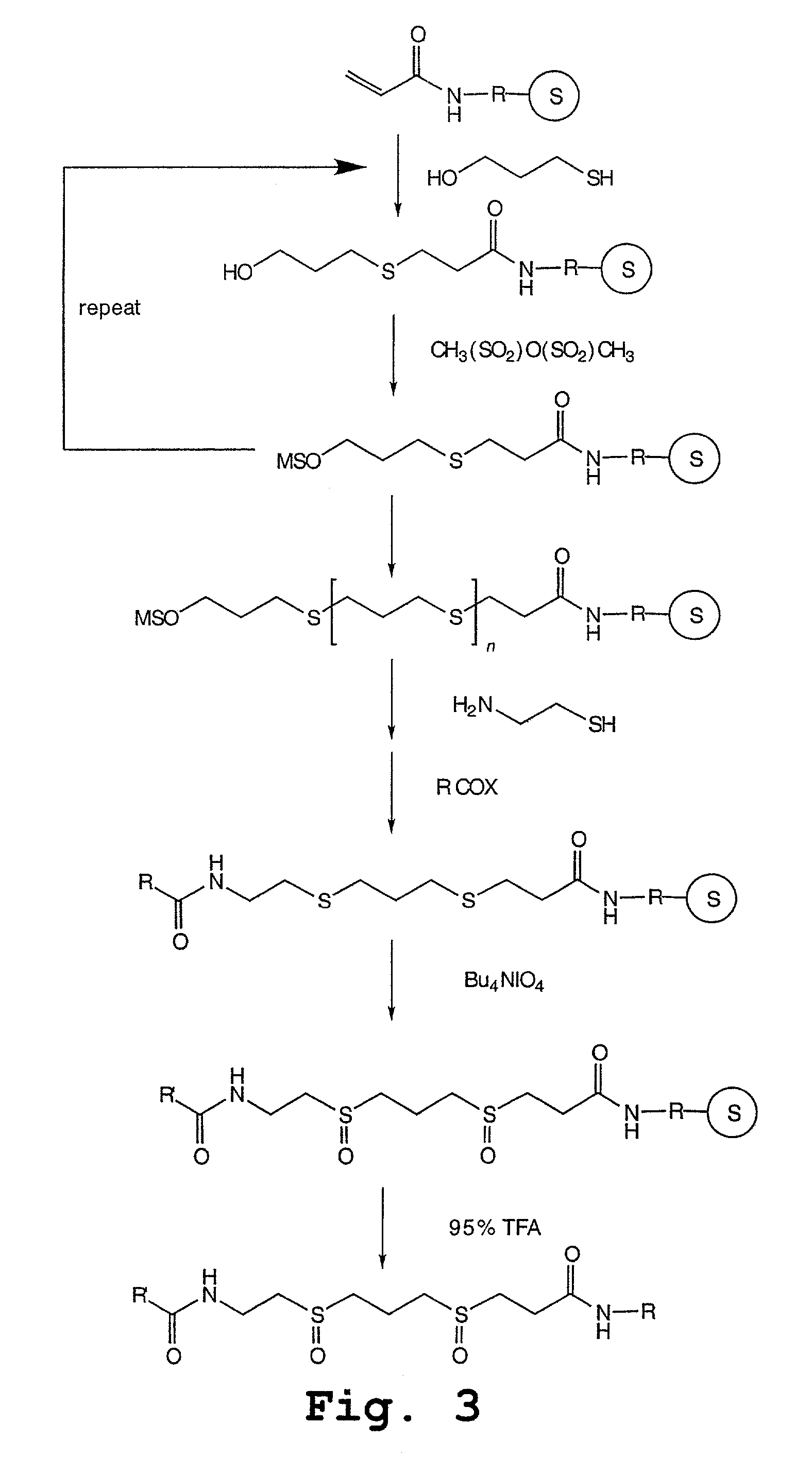
Peptoids incorporating chemoselective functionalities
InactiveUS7030216B2Material nanotechnologySugar derivativesCombinatorial chemistryChemoselective ligation
Molecules having potential biological activity, particularly peptoids, that are conjugated to solid phase supports, spacer groups, and / or ligation moieties, and methods of their preparation, are described. In some instances, the molecules of the invention are made entirely by solid phase synthesis. In other instances, the spacer groups are hydrophilic and compositions containing them, and to solid phase synthesis of varied structure peptoids using chemoselective ligation moieties.
Owner:CHIRON CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com