Patents
Literature
626 results about "Magnetic axis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
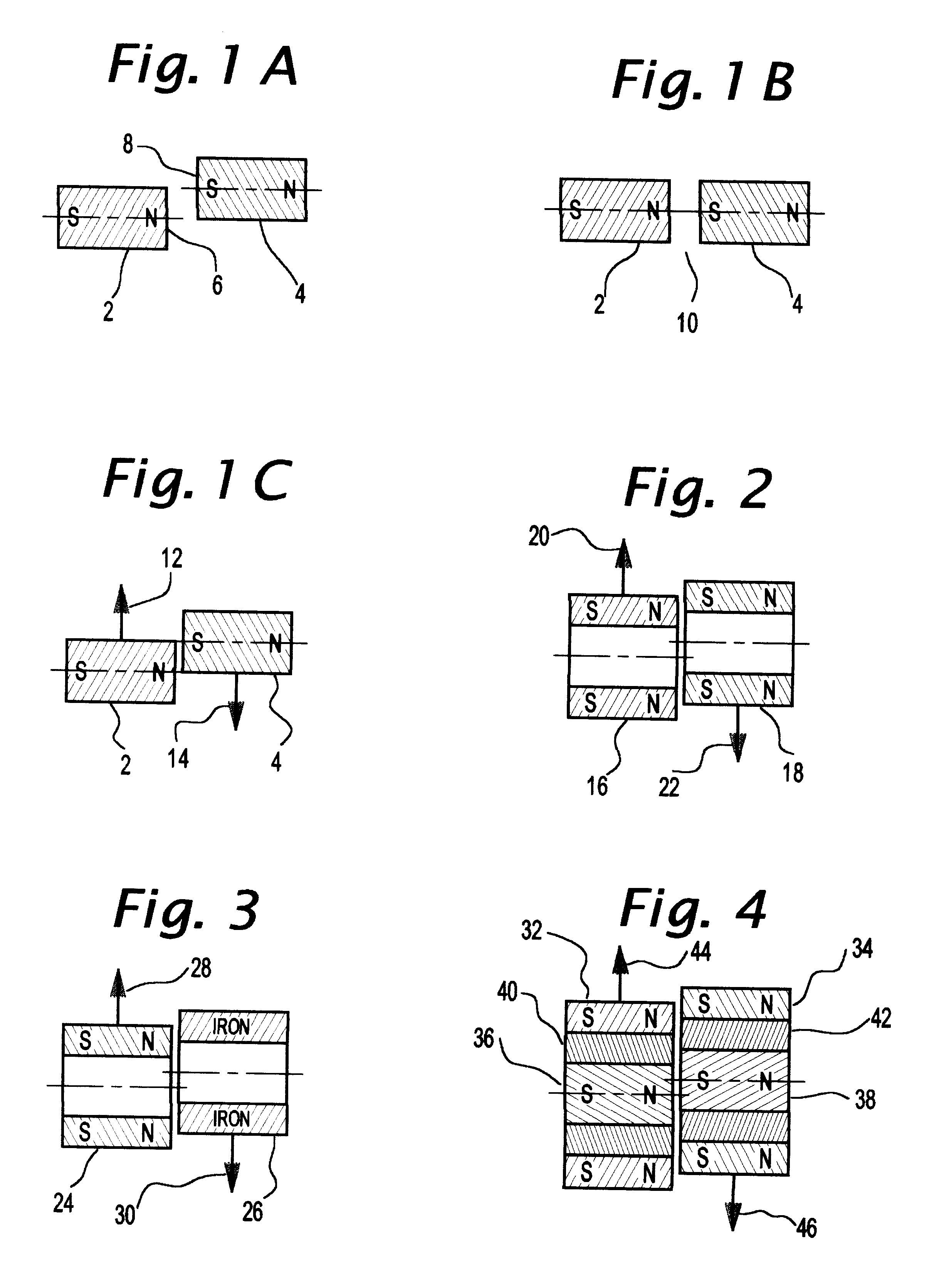
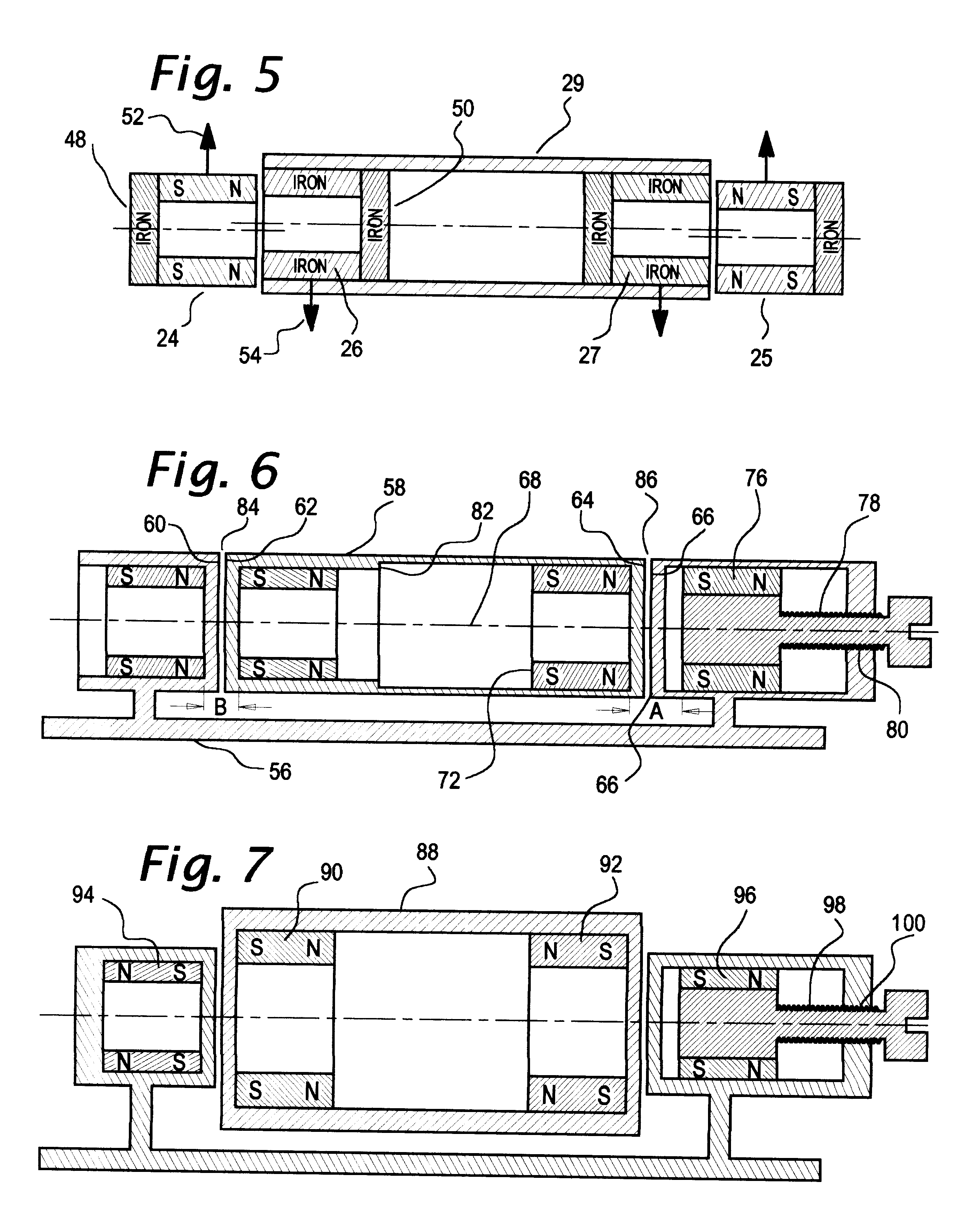
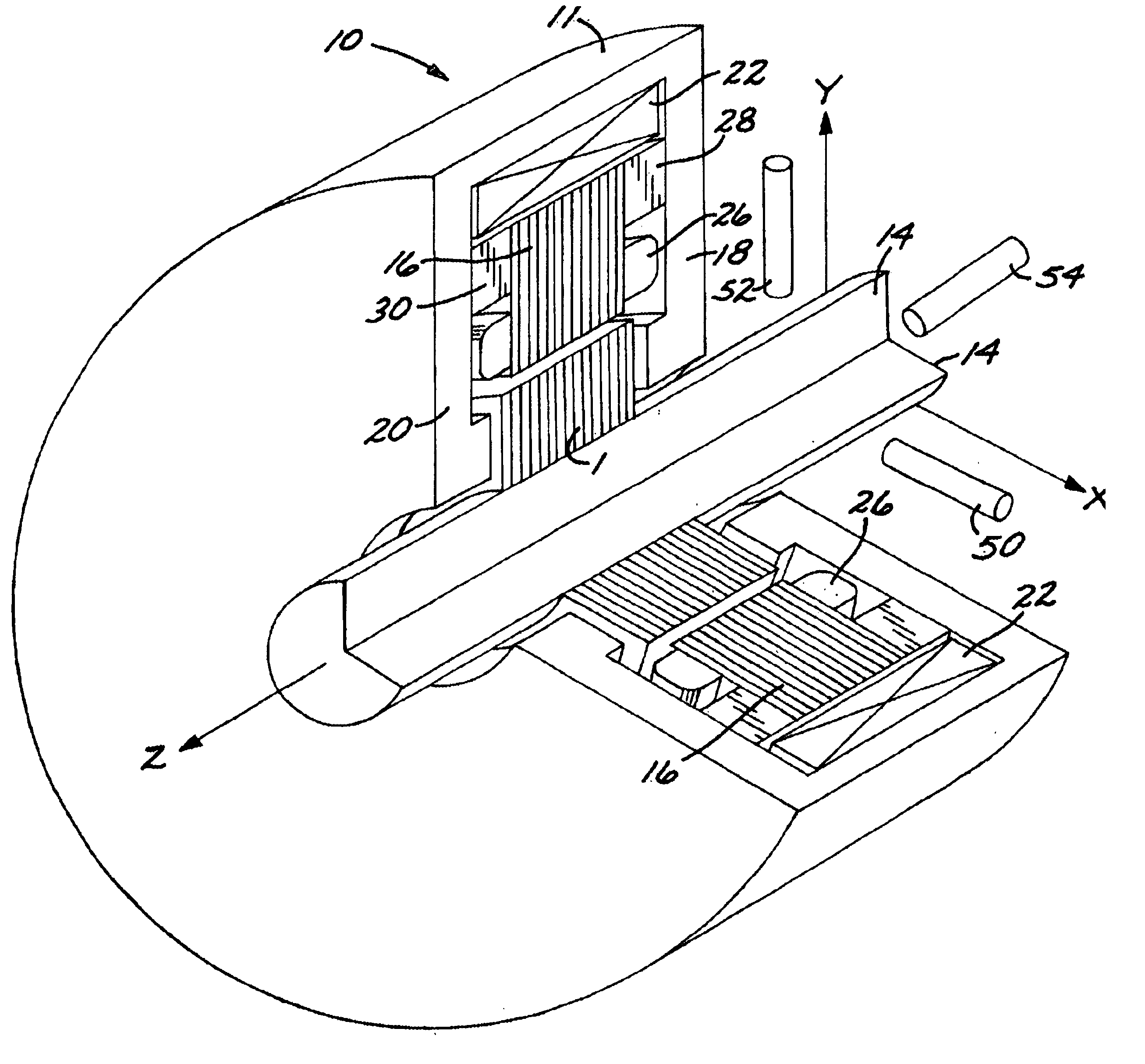
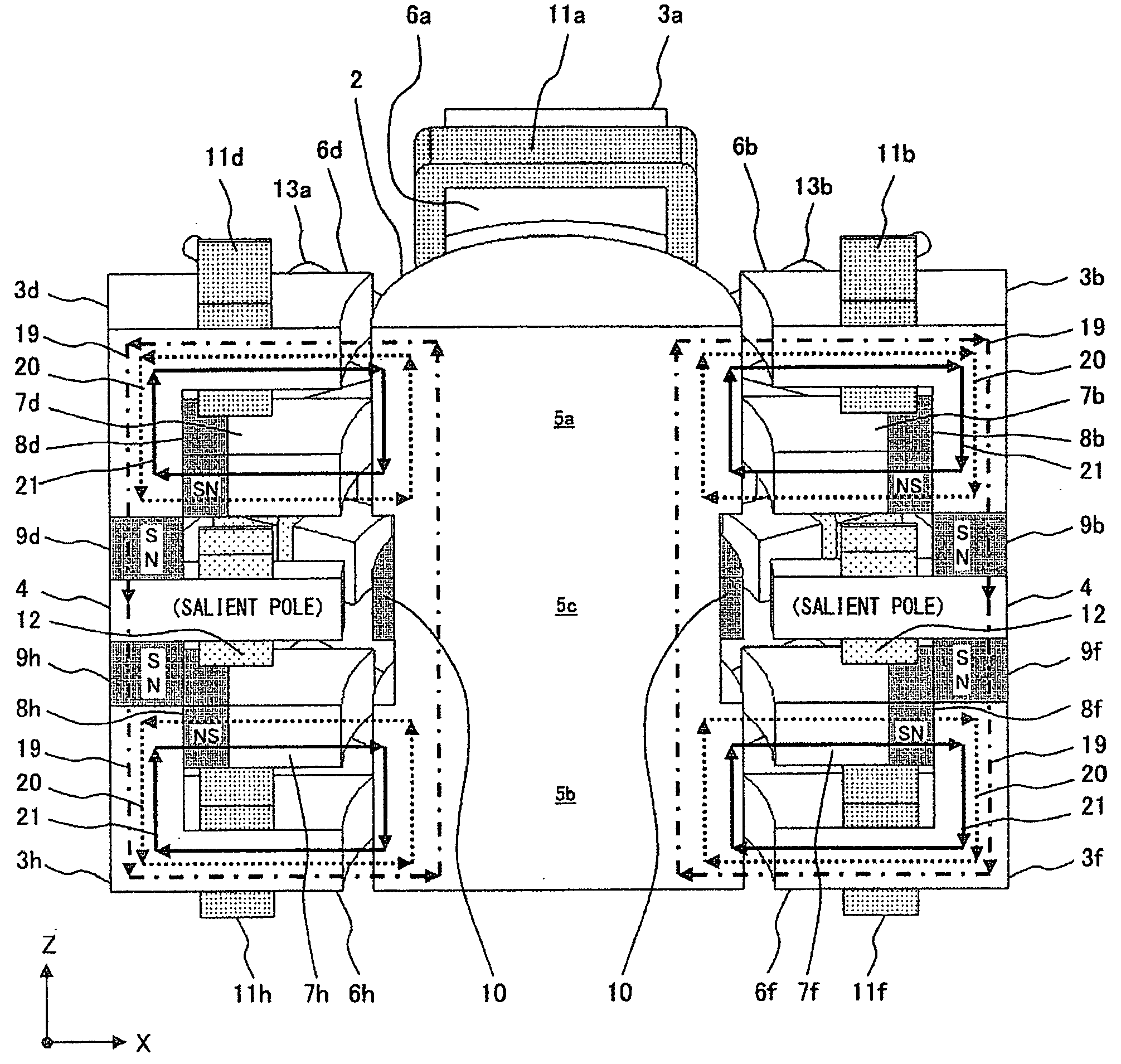
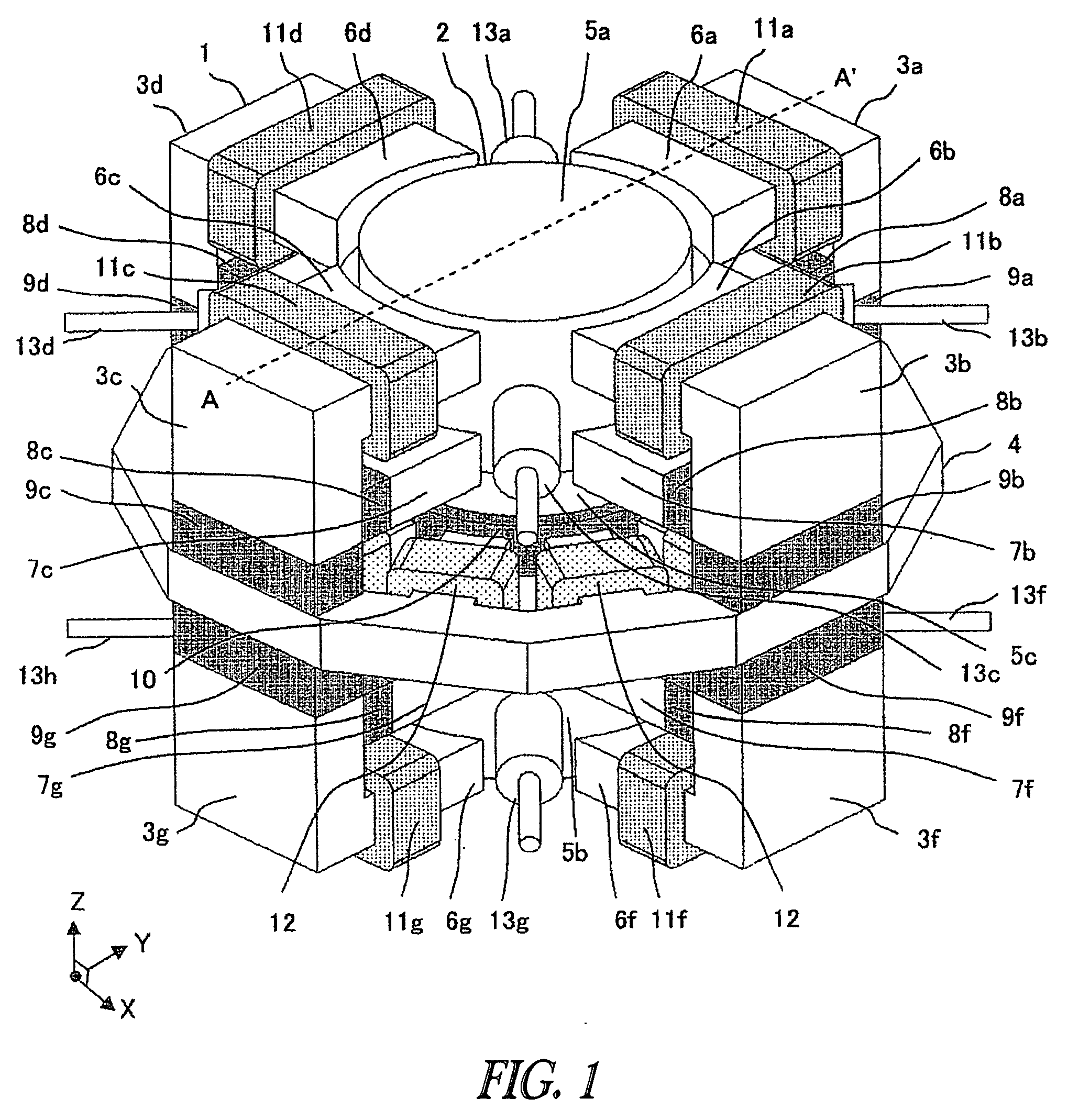
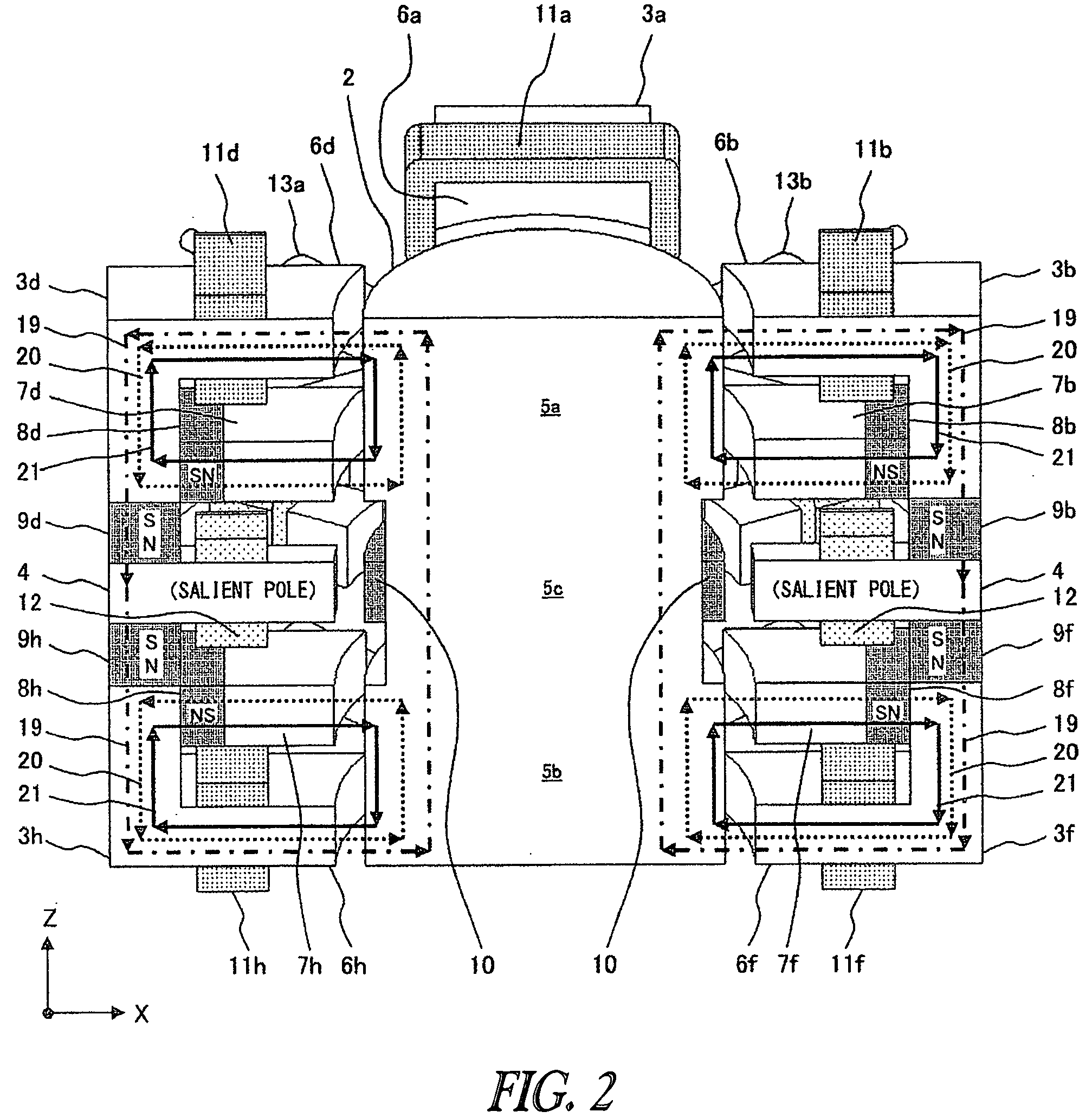
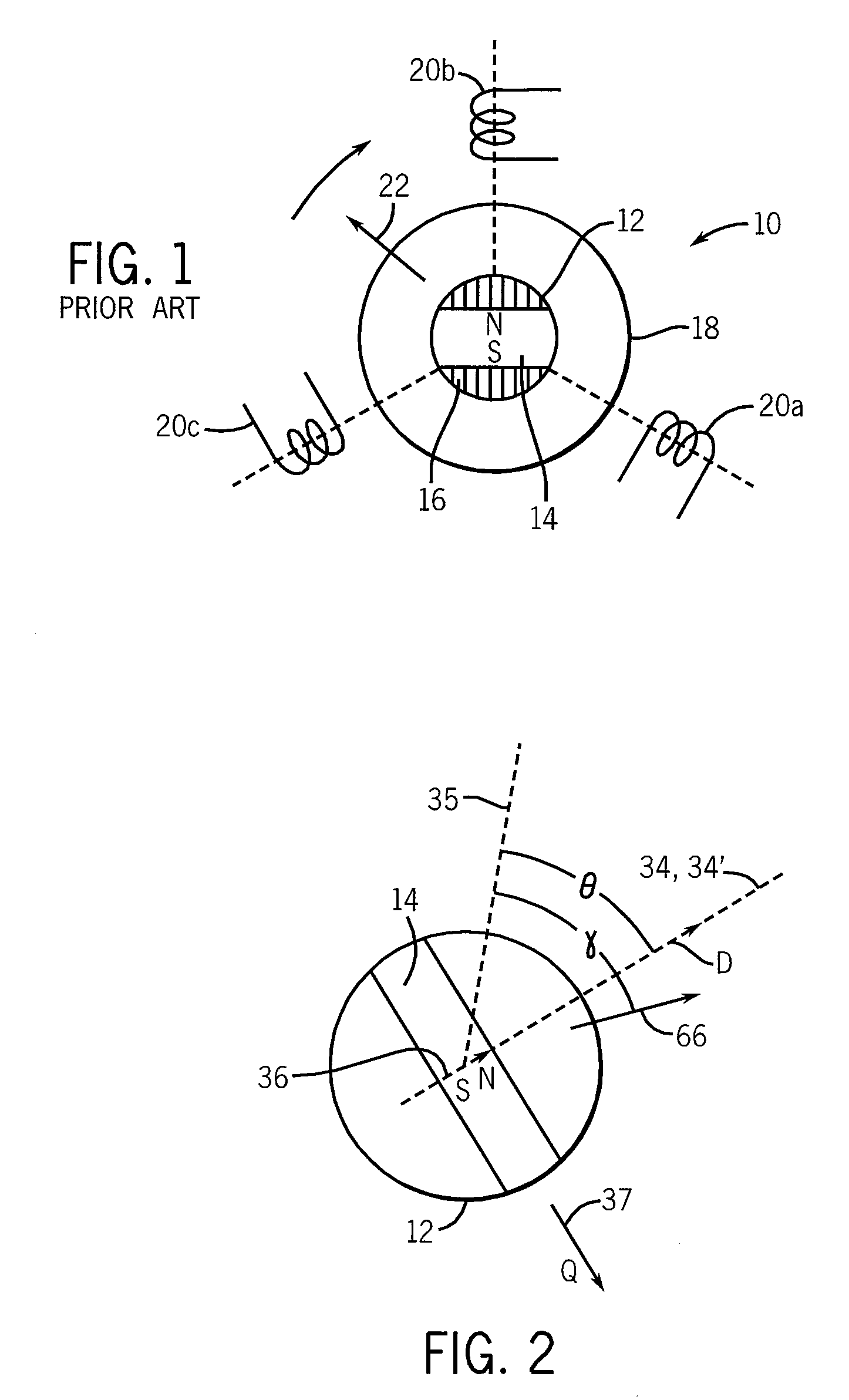
Magnetic axis. [mag′ned·ik ′ak·səs] (electromagnetism) A line through the center of a magnet such that the torque exerted on the magnet by a magnetic field in the direction of this line equals 0. (plasma physics)
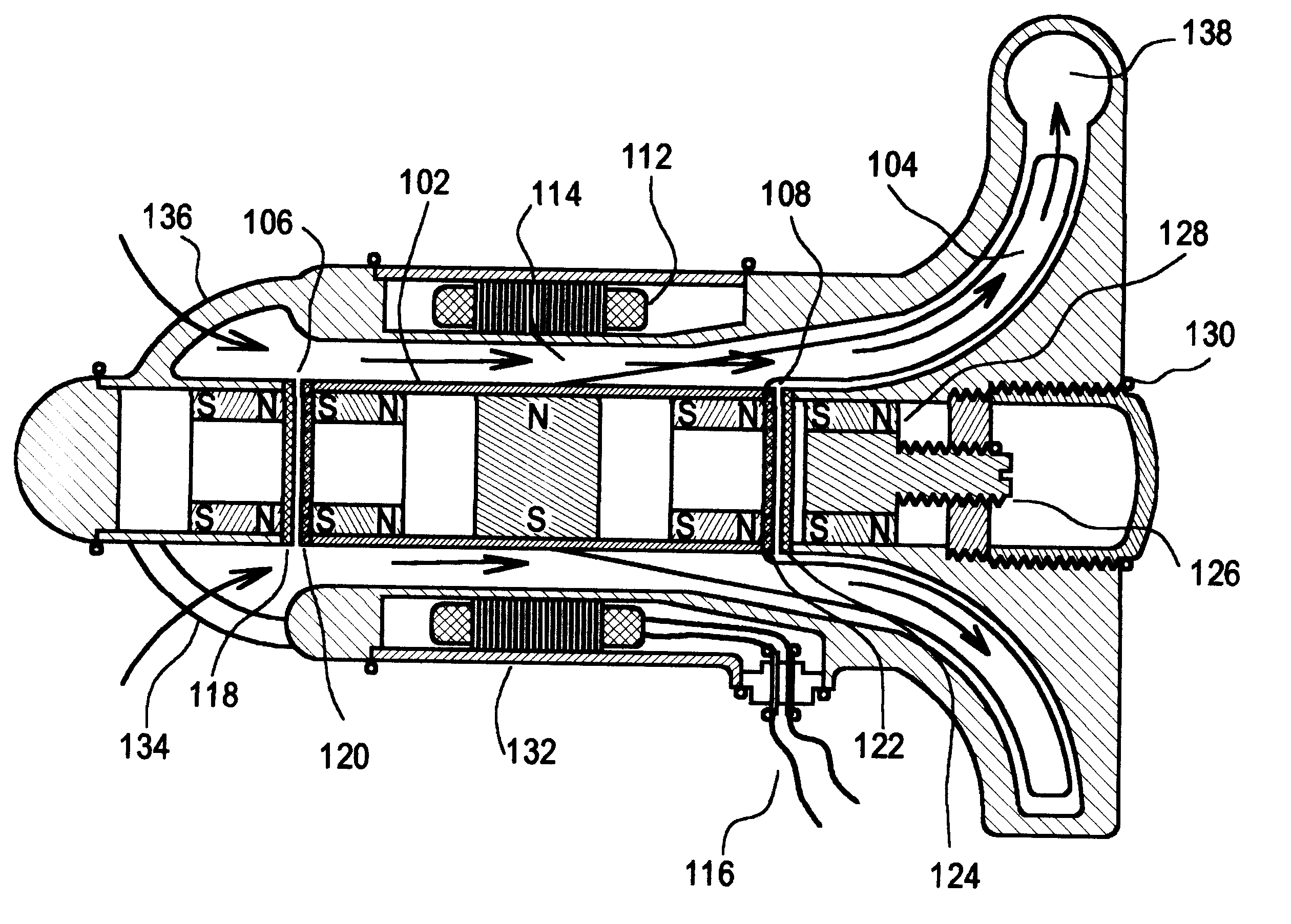
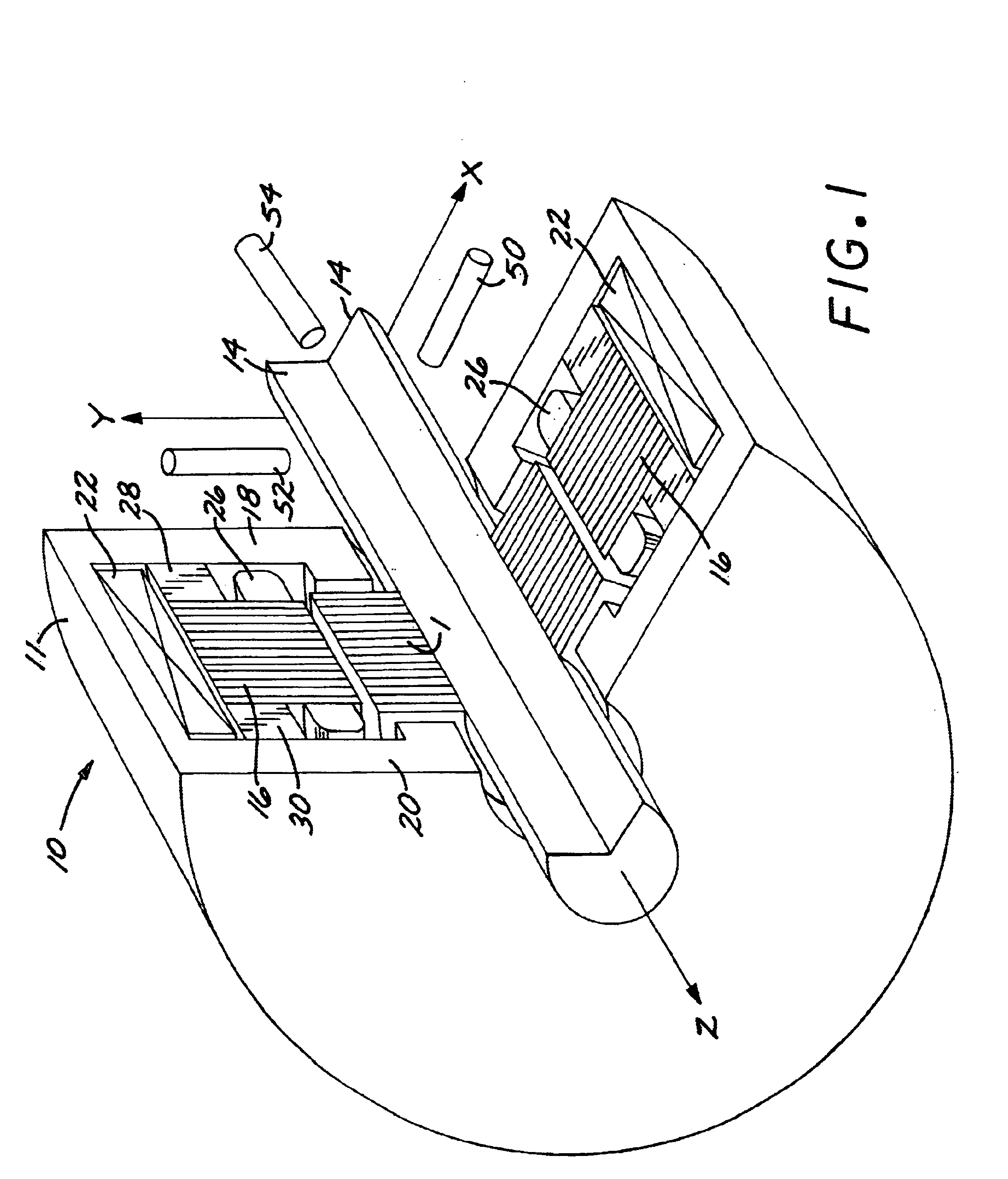
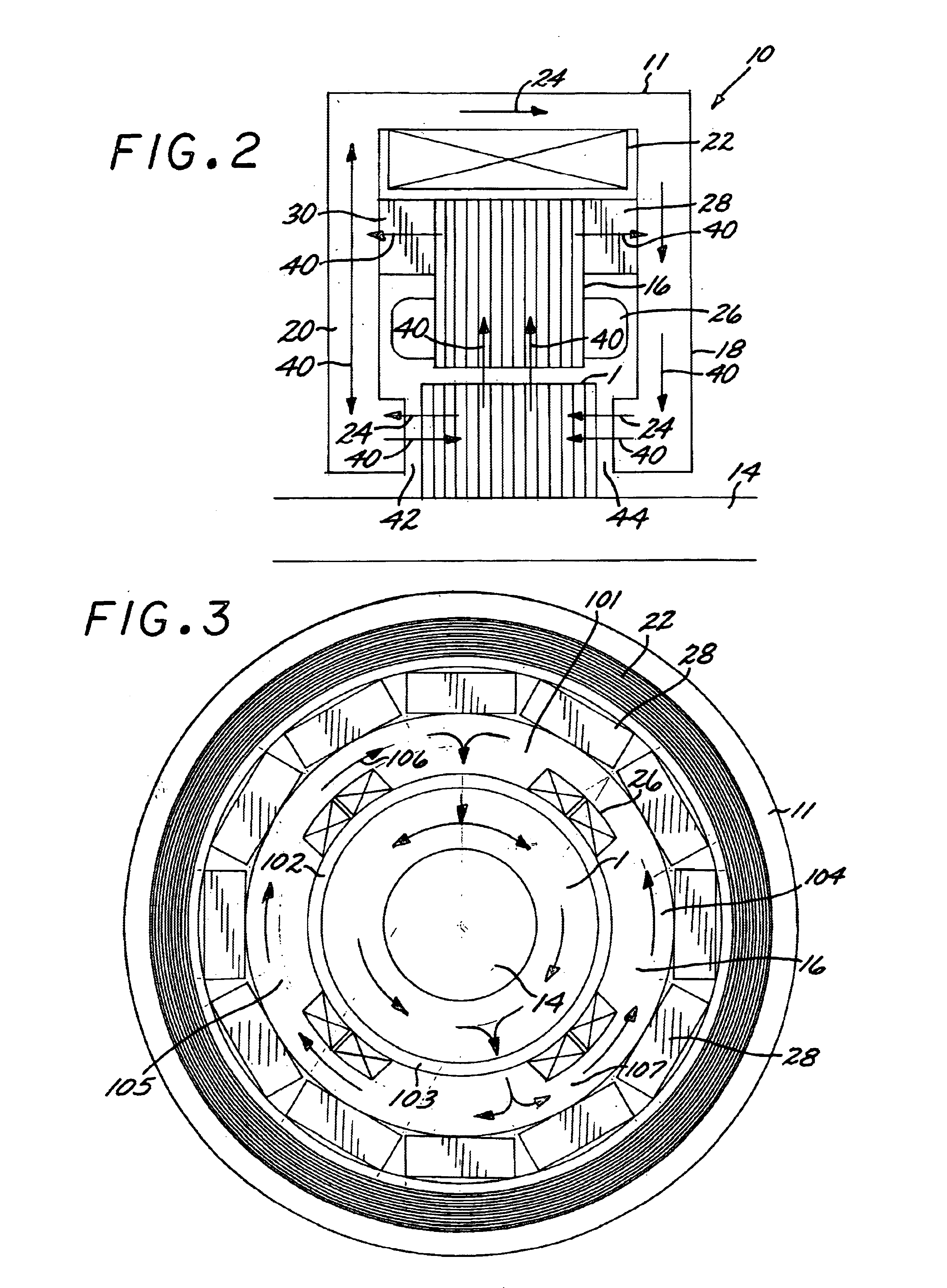
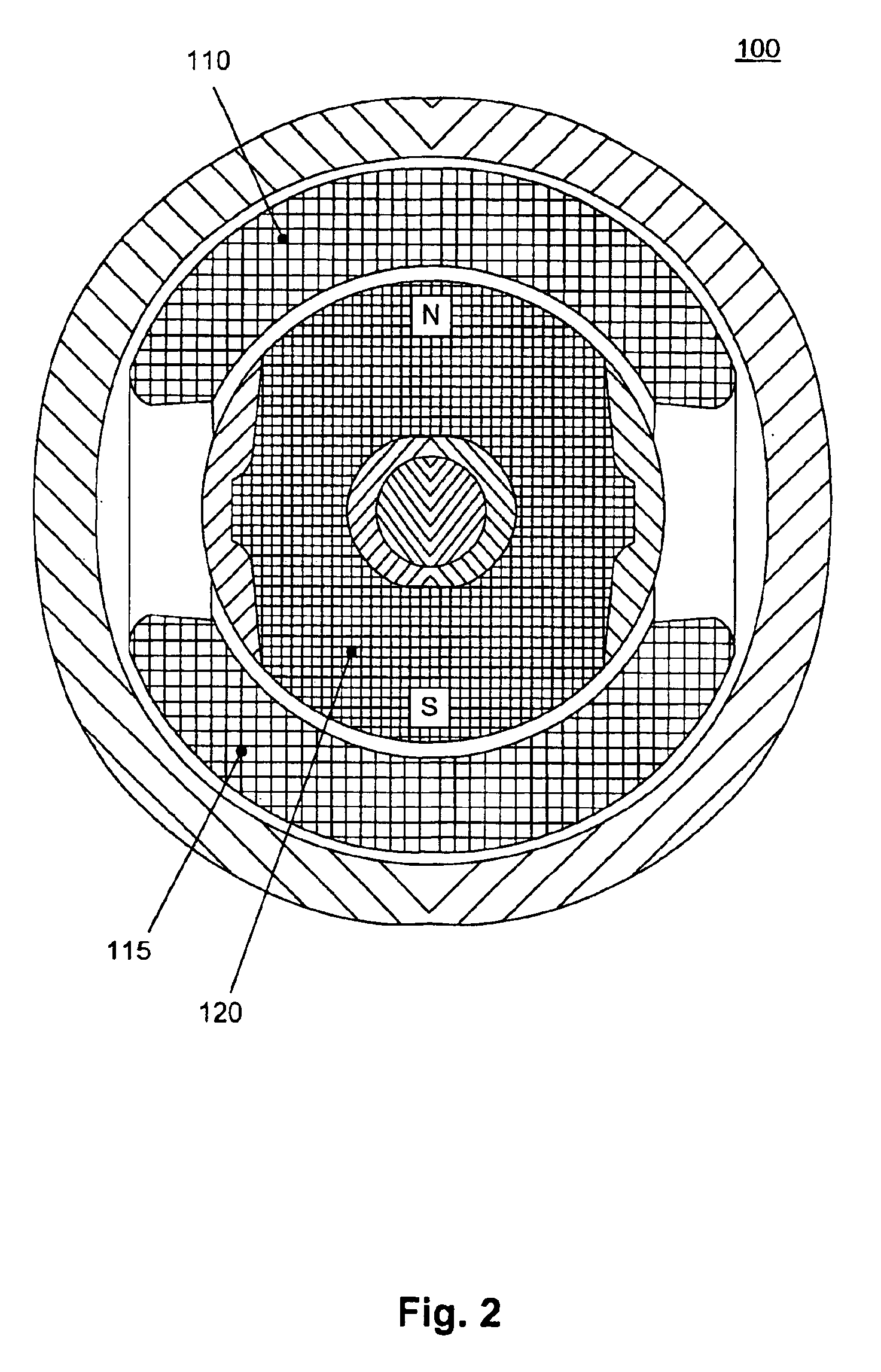
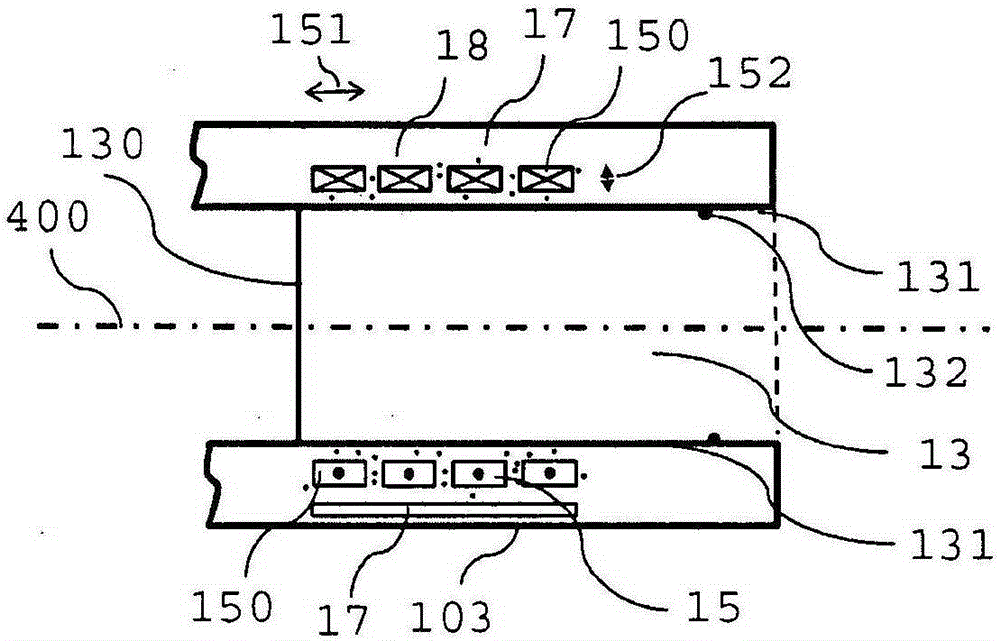
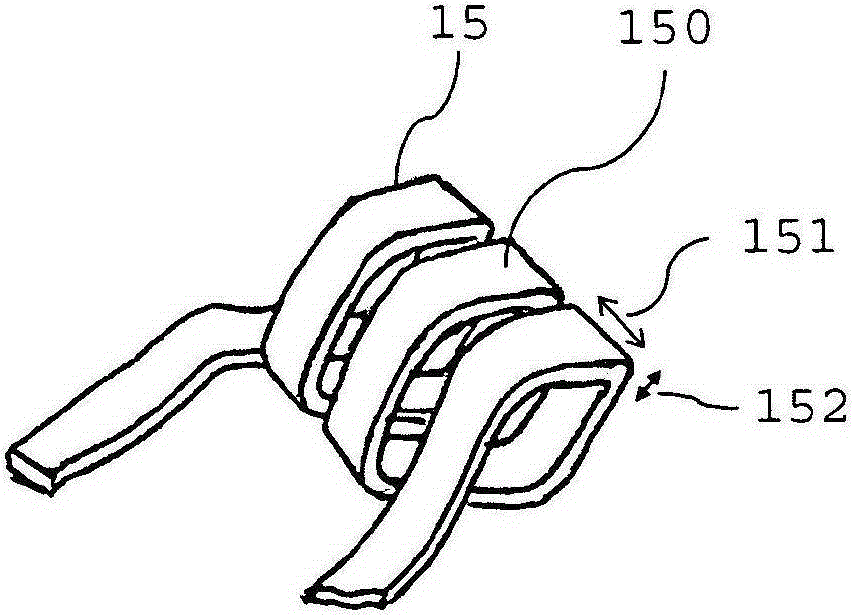
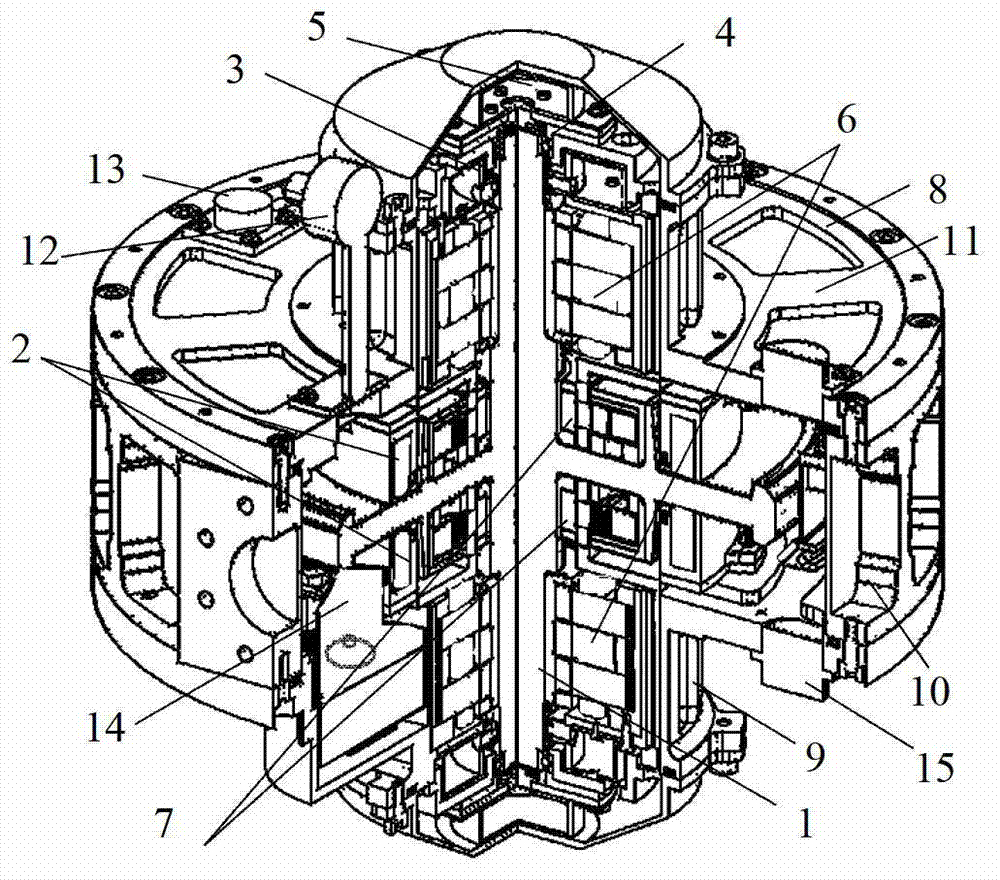
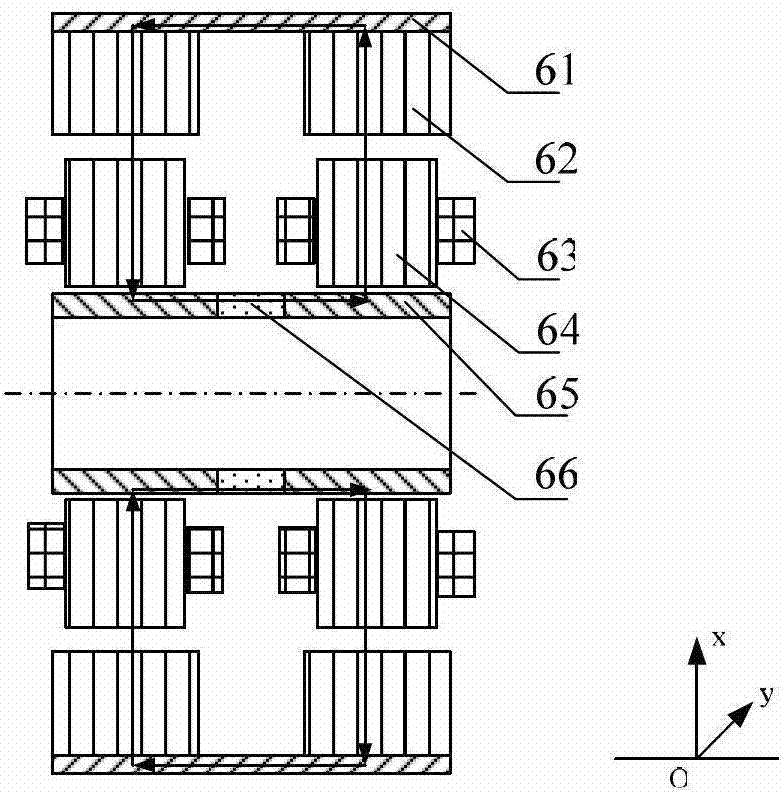
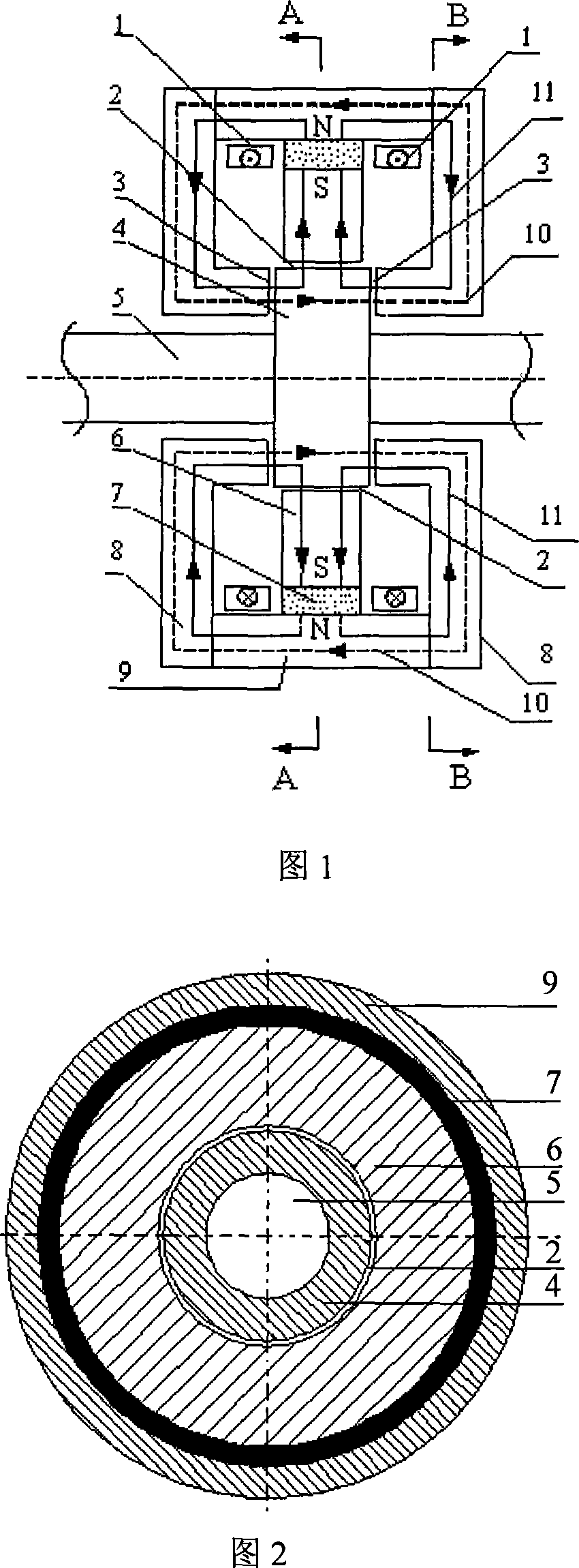
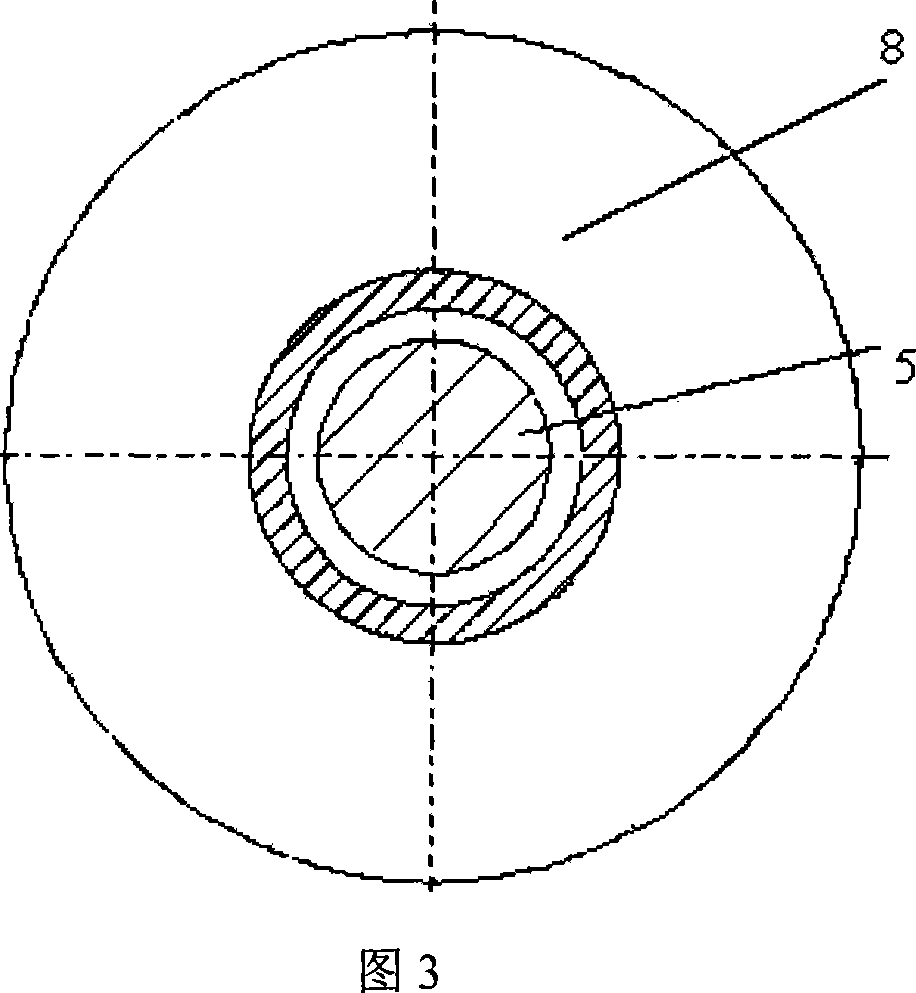
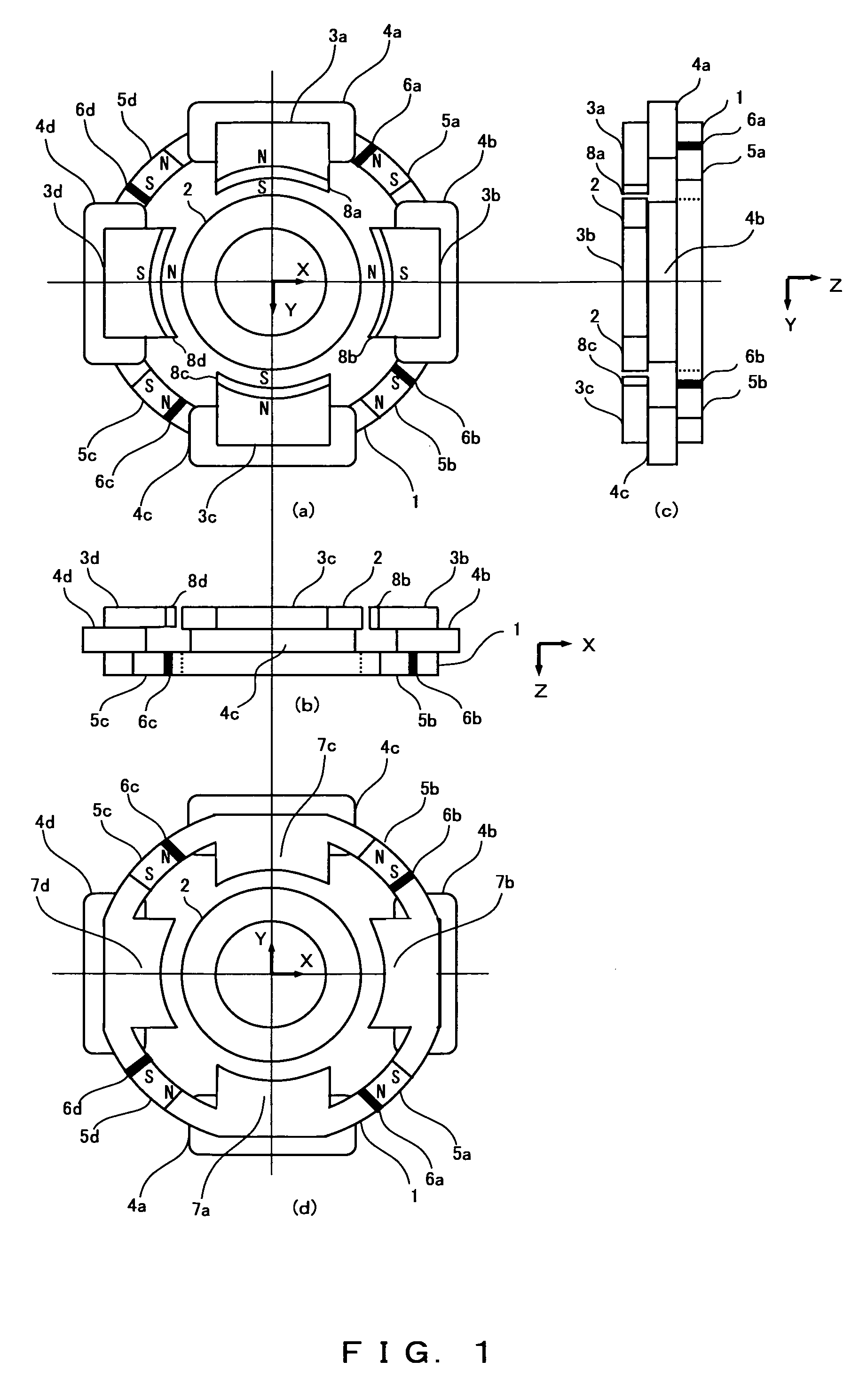
Axial force null position magnetic bearing and rotary blood pumps which use them
InactiveUS6227820B1Improve radial stiffnessSimple designPump componentsSurgeryAxial-flow pumpMagnetic tension force
A generally cylindrical rotor very closely confined between two rigid thrust bearing surfaces is radially suspended by an array of attracting or repelling magnets or by a combination of permanent magnets and ring shaped members composed of ferromagnetic material. The geometry permits very small spacing between magnetic components to achieve high radial stiffness. High magnetic axial forces exerted between the rotor and stationary component on one end of the rotor are counter-balanced by equal and opposite forces at the other end of the rotor. Precise positioning of the rotor in the location where the opposing axial magnetic forces counterballance each other yields a net magnetic axial force on the rotor of near zero, hence the reference to this as the null position. Wear resistant mechanical thrust bearings confine the rotor axially to maintain this position during rotatioin. Precisely balance the magnetic axial forces in the proper geometry with relation to the mechanical thrust bearings. Blood pumps utilizing this type of bearing are disclosed, including both axial flow pump and centrifugal flow pump configurations with high flow washing of the junction of the rotating and stationary parts to prevent thrombus accumulation.
Owner:JARVIK ROBERT
Method and apparatus for providing three axis magnetic bearing having permanent magnets mounted on radial pole stack
InactiveUS6727617B2Effective and inexpensive techniqueHighly linear magnetic biasMechanical energy handlingBearingsAxial displacementAudio power amplifier
An improved magnetic bearing that uses permanent magnets to provide the bias flux. The magnetic circuits generating the control flux and bias fluxes are substantially non-coincident but share the same path over some portions that include radial and axial airgaps allowing for a low reluctance and an efficient path for the electromagnetic flux. The flux paths of the permanent magnets are completely defined with minimized airgaps for achieving higher forces and efficiency and very low control currents that produce extremely large forces. A single coil and amplifier for the axial force control and two coils with one associated amplifier for each radial axis of control provides simplicity and cost effectiveness. A single thrust disk is provided that is reacted against for both radial and the axial displacement. The permanent magnets used in the present invention are first fabricated and axially magnetized as segments or as continuous rings prior to being mounted on the sides of the rotor pole, providing an effective and inexpensive technique of manufacturing magnetic bearings.
Owner:CALNETIX TECH +1
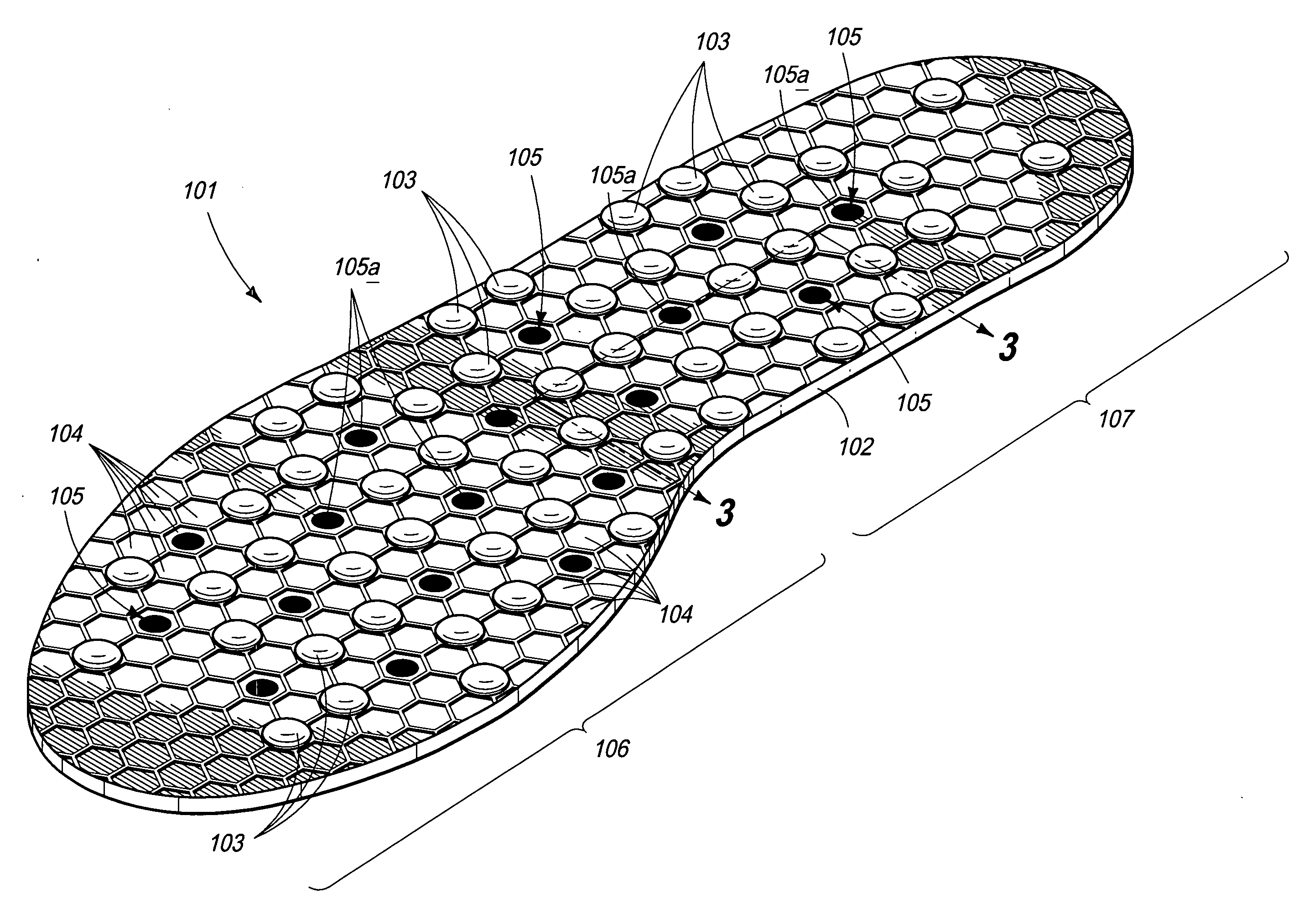
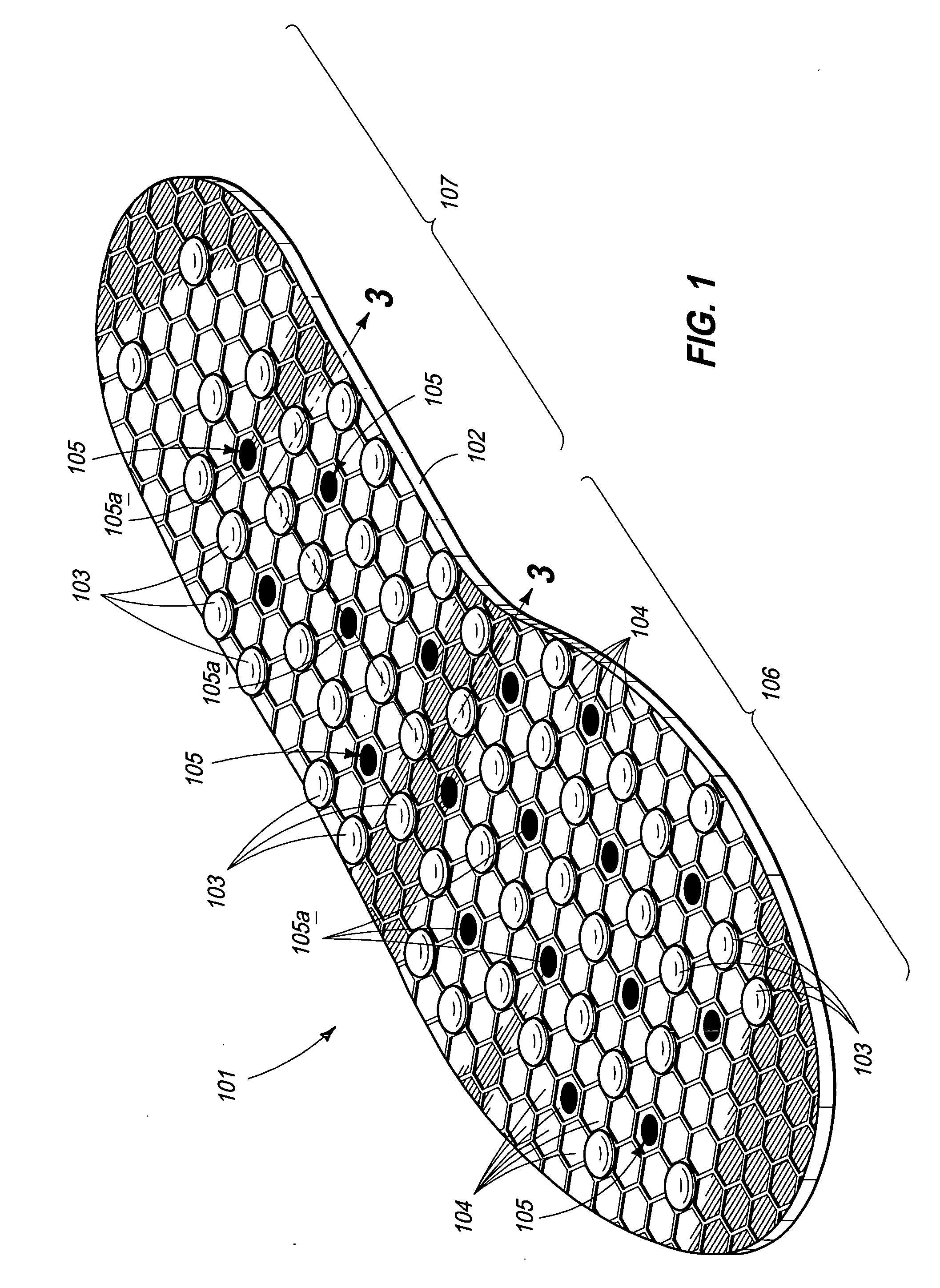
Shoe sole system providing a negative ion environment
This invention includes embodiments which disclose a shoe sole base system wherein there are a plurality of magnets embedded within a shoe base and a plurality of spheres containing tourmaline, also embedded within the shoe base. In further embodiments, the angle of the magnetic axis of each of the plurality of magnets to other magnets in the plurality of magnets is random in both two and in three dimensions and / or the spheres containing tourmaline may emit negative ions and / or far infrared rays.
Owner:U S WAX & POLYMER +1
Method and apparatus for providing three axis magnetic bearing having permanent magnets mounted on radial pole stack
InactiveUS20030155829A1Effective and inexpensive techniqueHighly linear magnetic biasMechanical energy handlingBearingsAxial displacementMagnetic bearing
An improved magnetic bearing that uses permanent magnets to provide the bias flux. The magnetic circuits generating the control flux and bias fluxes are substantially non-coincident but share the same path over some portions that include radial and axial airgaps allowing for a low reluctance and an efficient path for the electromagnetic flux. The flux paths of the permanent magnets are completely defined with minimized airgaps for achieving higher forces and efficiency and very low control currents that produce extremely large forces. A single coil and amplifier for the axial force control and two coils with one associated amplifier for each radial axis of control provides simplicity and cost effectiveness. A single thrust disk is provided that is reacted against for both radial and the axial displacement. The permanent magnets used in the present invention are first fabricated and axially magnetized as segments or as continuous rings prior to being mounted on the sides of the rotor pole, providing an effective and inexpensive technique of manufacturing magnetic bearings.
Owner:CALNETIX TECH +1
Magnetic levitation motor and pump
A magnetic levitation motor including a stator having magnetic bearing units and a motor unit, and a rotor provided to the stator. And the occurrence of an eddy current at a magnetic bearing is suppressed and the rotation loss of the rotor can be reduced, and also to provide a pump using such the magnetic levitation motor.
Owner:IWAKI
NFC Card Sensitive to Eddy Currents
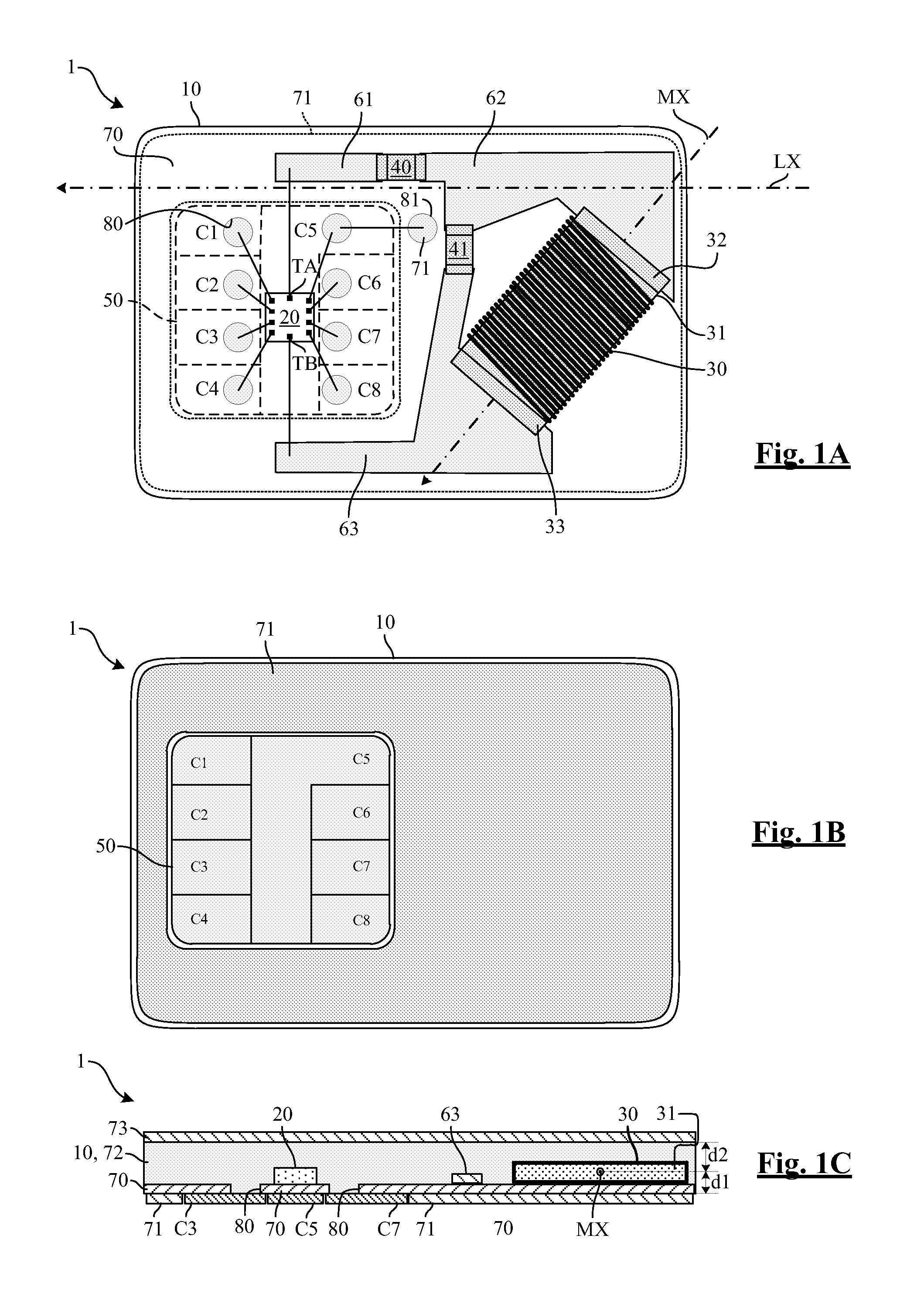
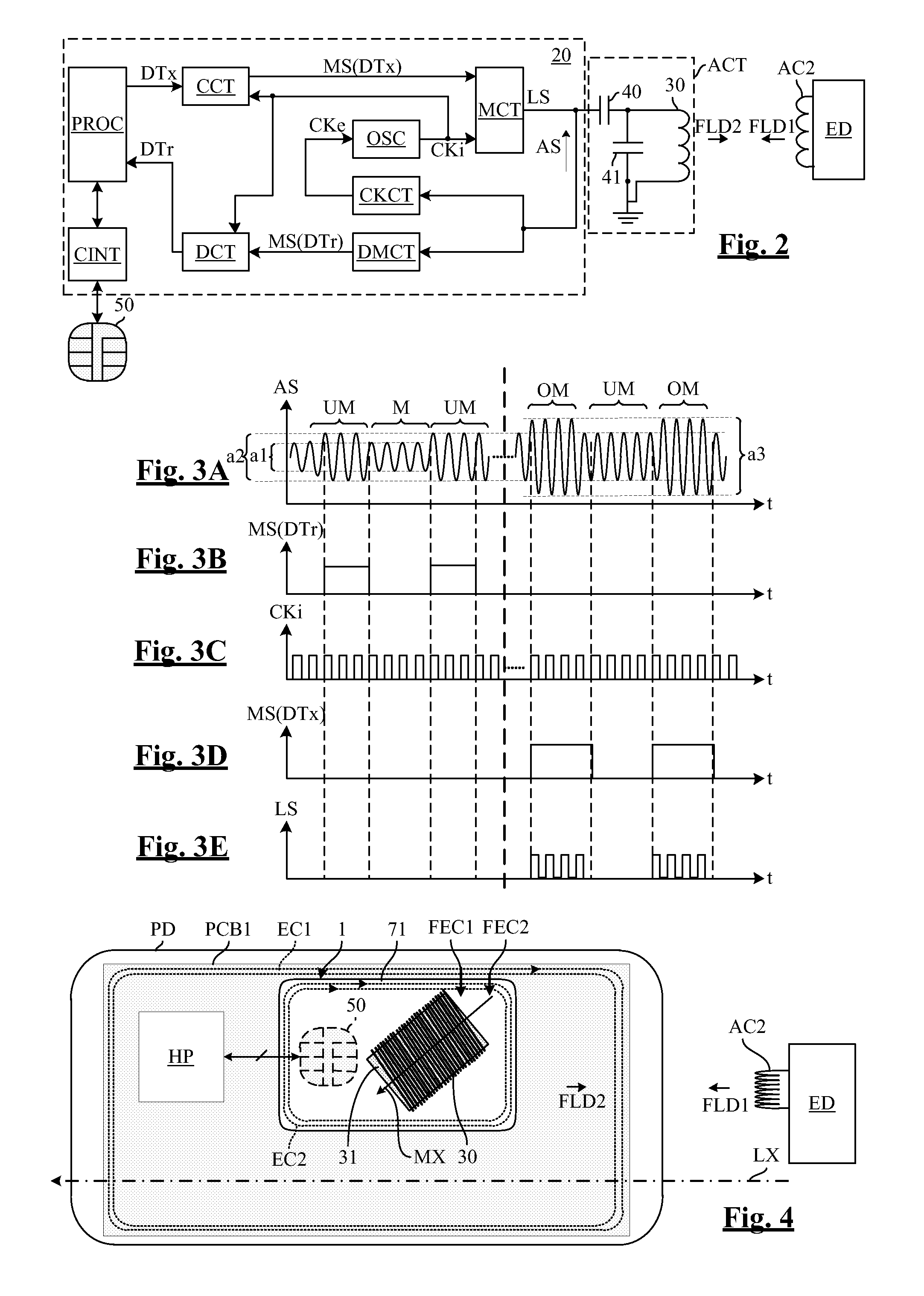
ActiveUS20120071090A1Increase maximum communication distanceReduce impactNear-field transmissionRecord carriers used with machinesEddy currentMagnetic axis
An NFC card includes an antenna circuit including an antenna coil having at least one magnetic axis, and at least one integrated circuit linked to the antenna circuit. The magnetic axis of the antenna coil is substantially parallel to the plane of the card, and is at an angle of 45°±25° with respect to a longitudinal axis LX of the card. Embodiments of the invention are applicable in particular to SIM-NFC card and SD-NFC cards.
Owner:VERIMATRIX INC
Energy storage device of magnetic suspension flywheel
InactiveCN102437675AReduce the burden onImprove reliabilityMechanical energy handlingMagnetic holding devicesMagnetic bearingEngineering
The invention discloses an energy storage device of magnetic suspension flywheel, comprising an energy storing and converting part, a magnetic suspension supporting part and an auxiliary part, wherein the energy storing and converting part includes a flywheel, a rotor of the motor / generator and a stator part; the magnetic suspension supporting part comprises a radial magnetic bearing, an axial magnetic bearing, an axial sensor, a radial sensor and a protection bearing; the auxiliary part includes a shell and a mounting shaft; the radial magnetic bearing is a radial mixed conical magnetic bearing; the suction disk of each axial magnetic bearing is respectively installed on two side wheel surfaces of the flywheel; the radial mixed conical magnetic bearing and the axial magnetic bearing are non-mechanically contacted magnetic suspension bearings; the mounting shafts of the energy storing and converting part, the magnetic suspension supporting part and the auxiliary part are sealed in the shell of the auxiliary part; the inside of the shell is in vacuum state. The invention has the characteristics of compact structure, high specific energy density and discharge depth, long service life, low power consumption and stable performance without pollution.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
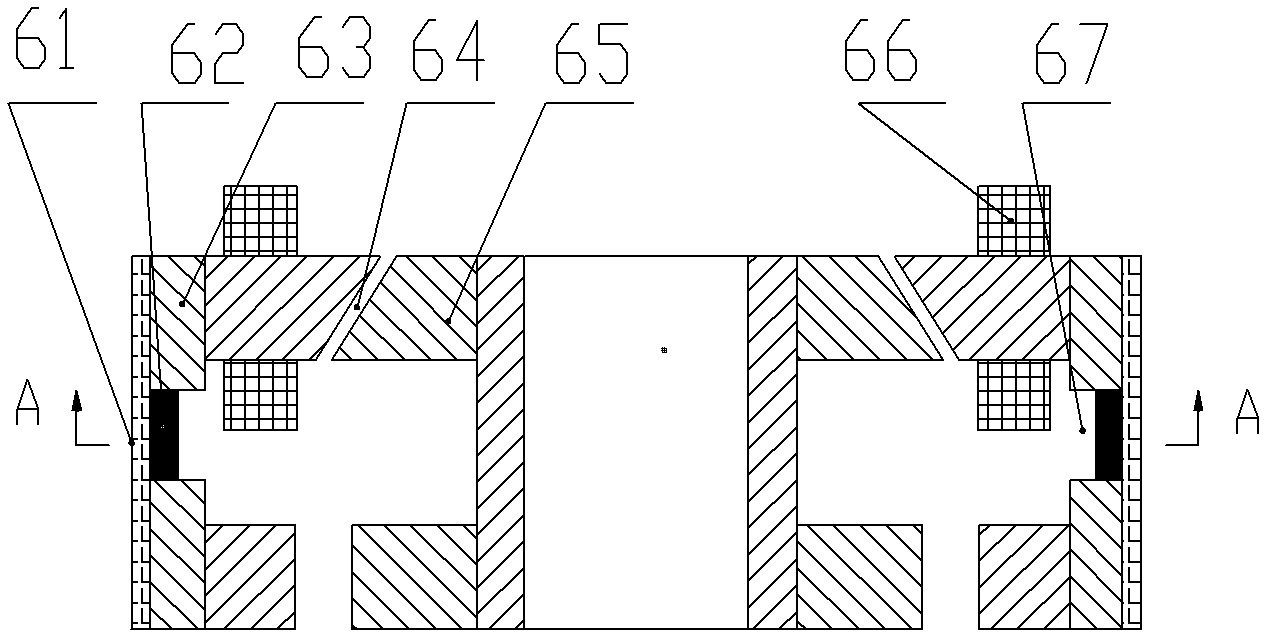
Low power consumption permanent magnet biased axial magnetic bearing
InactiveCN1648479AEliminate bias excitation currentReduce copper consumptionBearingsMagnetic bearingElectric machine
An axial magnetic bearing consists of a bearing body, an exciting coil, a permanent magnet, a magnetizer ring and an exciting gap. The permanent magnet contacting closely to the bearing body produces magnetic fields in different polarities separately in the inner and outer gaps; the exciting coil wound onto the bearing body generates the exciting magnetic flux; and the magnetizer ring contacting closely to the permanent magnet forms exciting gap between the magnetizer ring and the bearing body for providing the magnetic flux the exciting coil generates with magnetic path. The axial magnetic bearings of the present invention are used in pair in machine and the corresponding parts are made of magnetic permeable material. The present invention has the advantages of low magnetic reluctance, low exciting cut, low power consumption, small size, light weight, easy manufacture, etc. and may be used as the no-contact support for rotating part in machine.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Control magnetic bearing device
InactiveUS7053582B2Low costSmall sizeAC motor controlTemperatue controlDriver circuitMagnetic bearing
Owner:KOYO SEIKO CO LTD
Method and apparatus for automatically identifying electrical parameters in a sensor-less pmsm
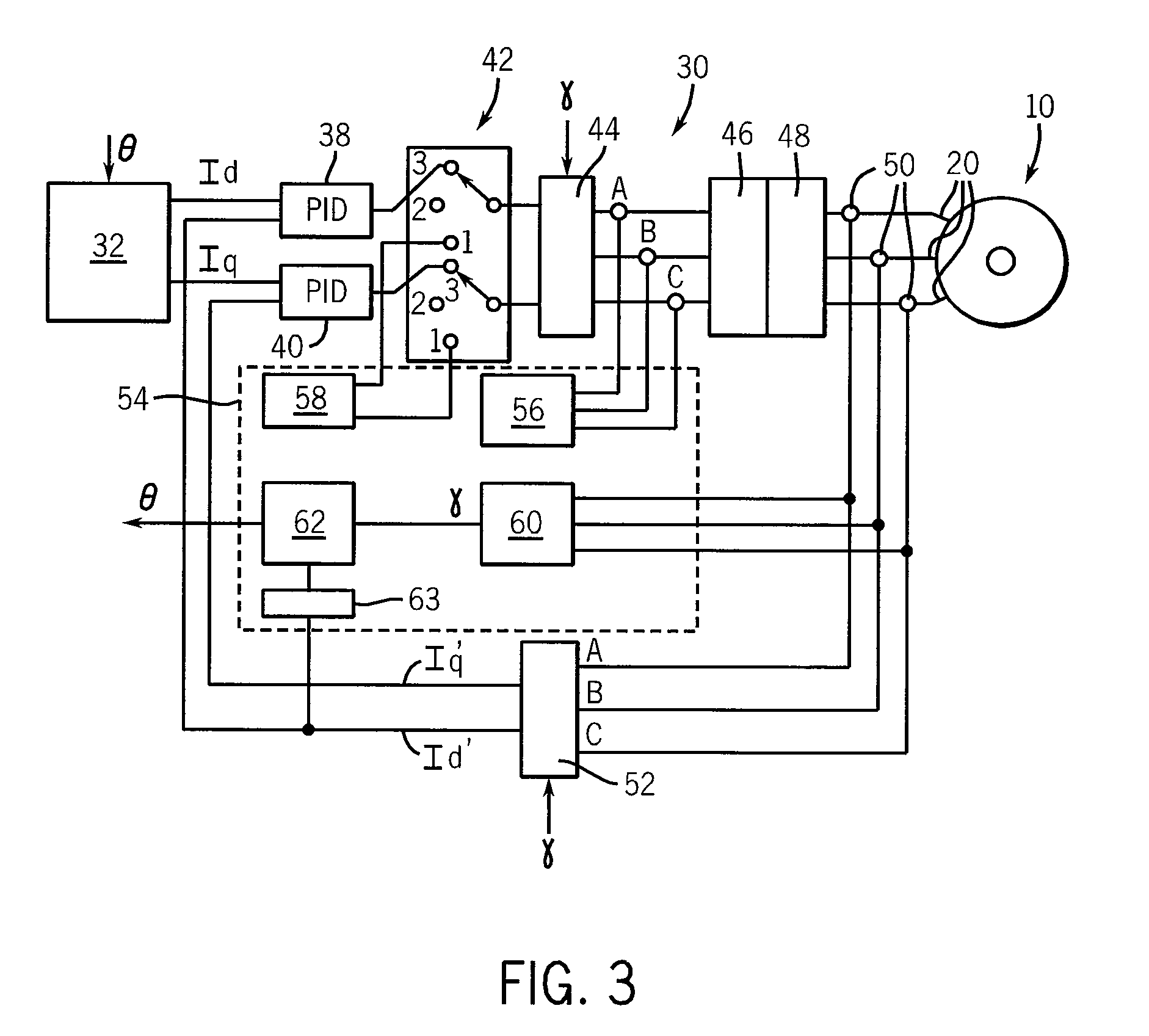
ActiveUS20100060210A1Effective parameter estimationAccurately model saturation effectElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersElectricityPermanent magnet synchronous machine
A method and apparatus for determining electrical parameters for commissioning a sensor-less permanent magnet synchronous machine uses knowledge of the rotor position to apply balanced pulses along the rotor magnet axis and perpendicular to the rotor magnet axis allowing measurement of q- and d-inductance at multiple current levels without substantial rotor movement.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Alternating current axially oscillating motor
InactiveUS6891287B2Avoid problemsMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlElectric machineAlternating current
An alternating current motor may include a rotor configured to rotate about a longitudinal axis, the rotor comprising a diametrically magnetized permanent magnet. Furthermore, the alternating current motor may include stationary coils having a magnetic axis substantially perpendicular to the rotor's longitudinal axis, the stationary coils adapted to the rotor's outer periphery and being substantially coaxial with the rotor's longitudinal axis. In addition, the alternating current motor may include a stator adapted to the stationary coils' outer periphery and being substantially coaxial with the rotor's longitudinal axis, wherein the diametrically magnetized permanent magnet is configured to cause the rotor's oscillation angle to vary no more than 30% between the rotor's oscillation angle at a beginning value of a frequency range of an alternating current in the stationary coil and the rotor's oscillation angle at an ending value of the frequency range of the alternating current in the stationary coil.
Owner:SWISS HEALTHCARE SOLUTIONS SARL +1
Low-consumption permanent-magnet offset external rotor radial magnetic bearing
InactiveCN1644940AReduce copper consumptionNo lossShaftsRotary machine partsMagnetic bearingInner loop
A low power consuming eternal magnetic external rotor magnetic axletree comprises outer magnetic loop, eternal magnet, iron stators, magnetism irritation loop, inner magnetic loop, iron stators and air clearance. On each side of X and Y axes, each two iron stators constitute eight magnetic pole in four directions. On each magnetic pole enwind magnetism irritation loop, outside of the iron rotors is the outer magnetic loop, inside the iron rotors are the iron stators, where between the rotors and stators leave air clearance. The inner magnetic loop fix inside of the iron stator. The eternal magnet locates between two inner magnetic loops. The two inner loops link with two iron stators to make a magnetic circle.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
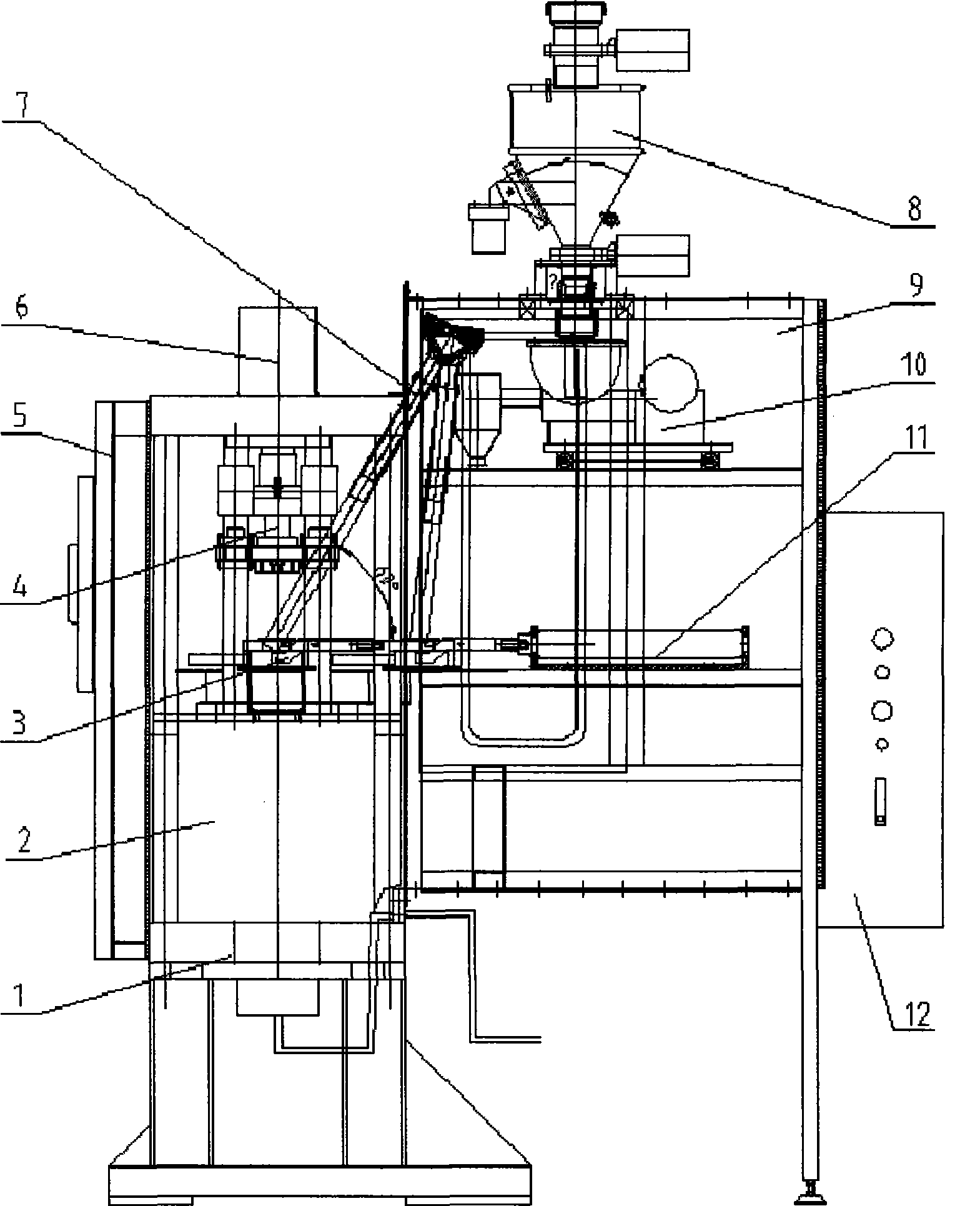
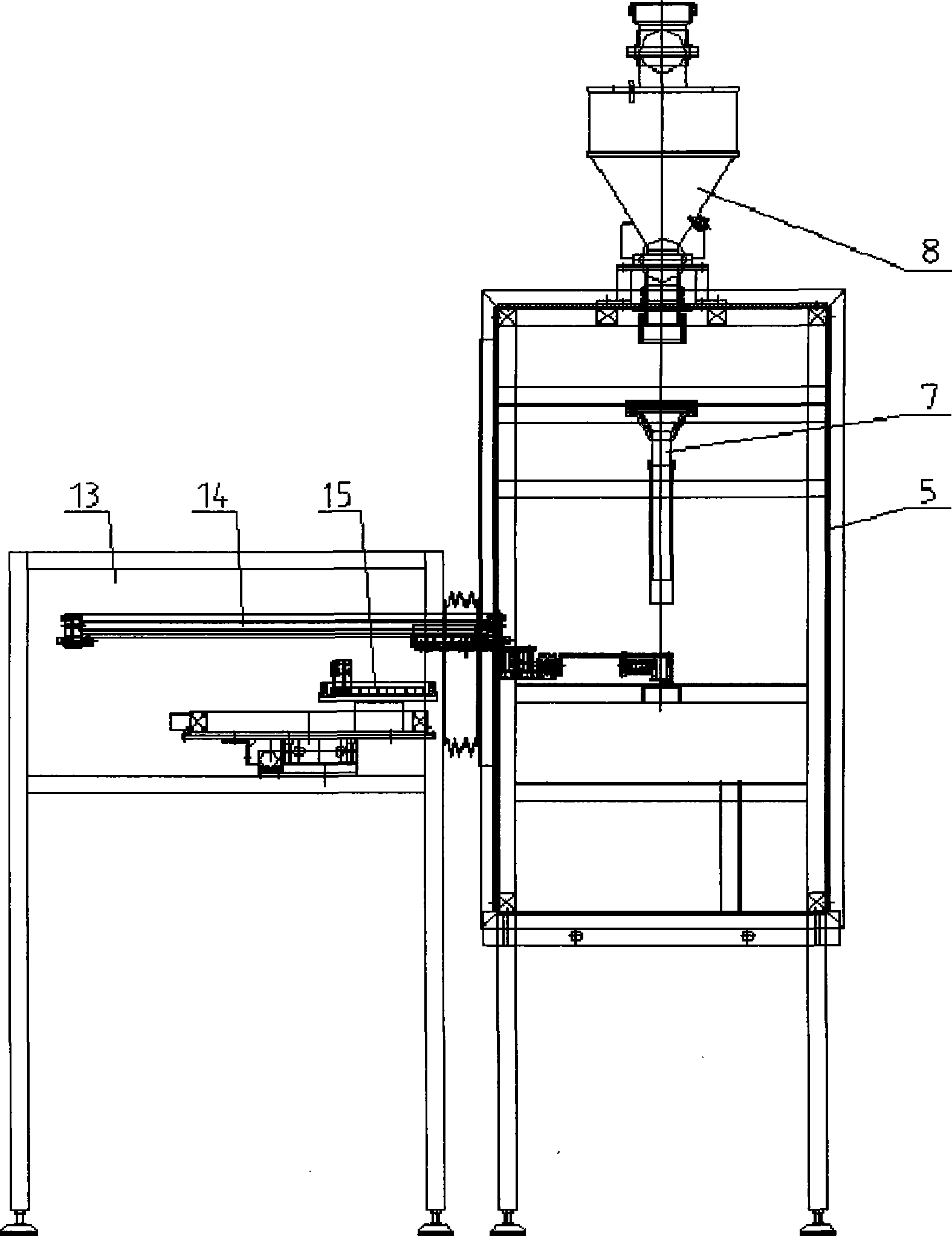
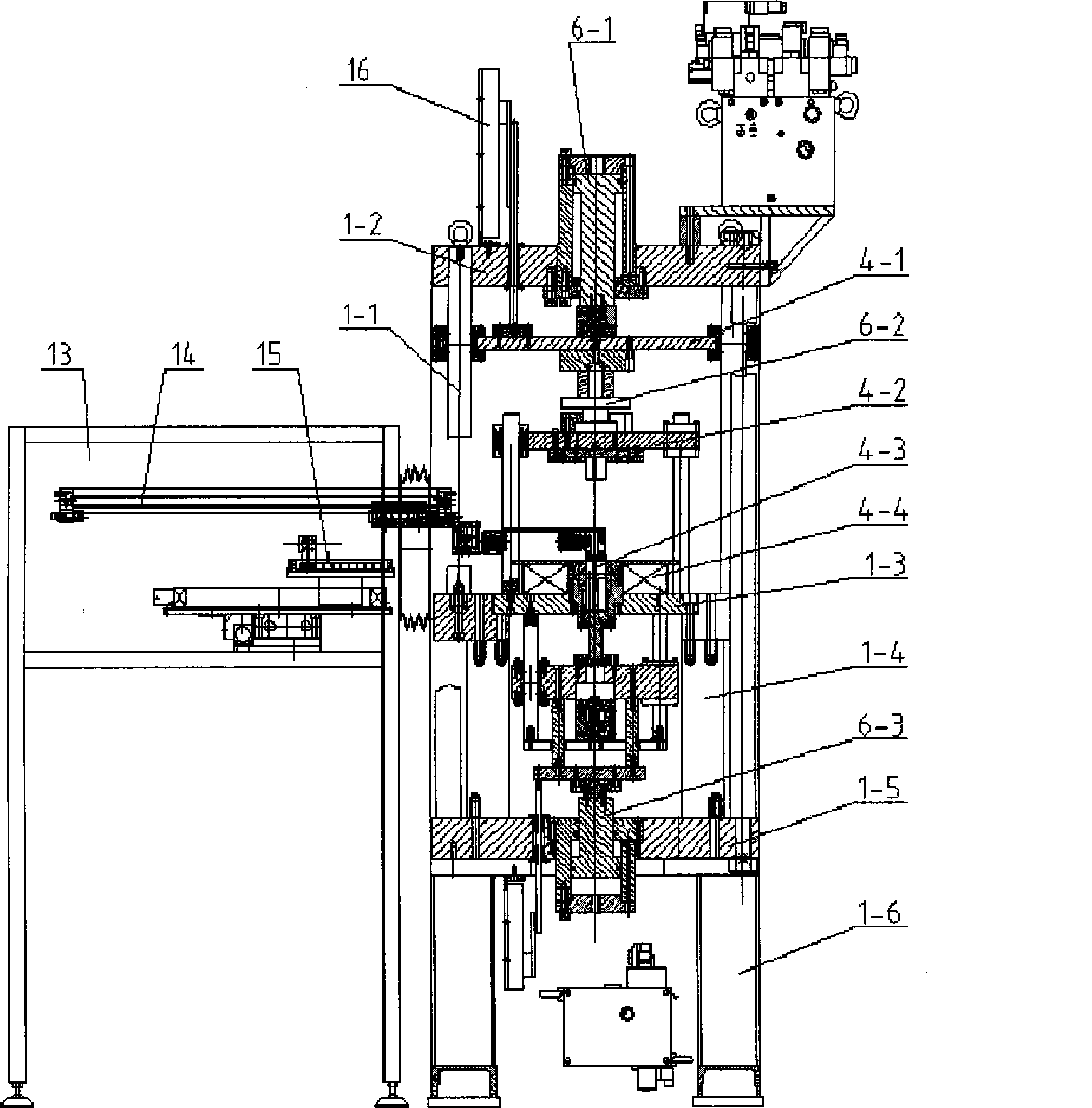
Oil press for automatically moulding rare-earth magnetic powder
The invention relates to an automatic forming oil-hydraulic press for rare earth magnetic powder, and belongs to the technical field of high-quality rare earth permanent magnet mechatronic processing equipment. The automatic forming oil-hydraulic press for the rare earth magnetic powder consists of a feeding system, a forming and pressing system, a material taking system and an electrical control system, wherein body frames of the feeding system, the forming and pressing system and the material taking system are connected with each other in the shape of Chinese character 'pin'; a shell of the automatic forming oil-hydraulic press is sealed by transparent organic glass materials; and the inside of the automatic forming oil-hydraulic press is mutually communicated and provided with an oxygen content detector, so that the processing operation process of the rare earth magnetic powder can be performed in a completely hermetic inert protective gas environment. The automatic forming oil-hydraulic press has the advantages of automatic powder supply of the feeding system, a magnetic (field) oriental coil in a die component of the forming and pressing system, automatic die lubrication, leftover removal and a completely automatic PLC control system with a low oxygen concentration, and guarantees uniaxial orientation of the height of a magnetic axis of the rare earth magnetic powder and full automation, high accuracy, high reliability and high product quality in the whole pressing production process.
Owner:QIANDONG RARE EARTH GRP
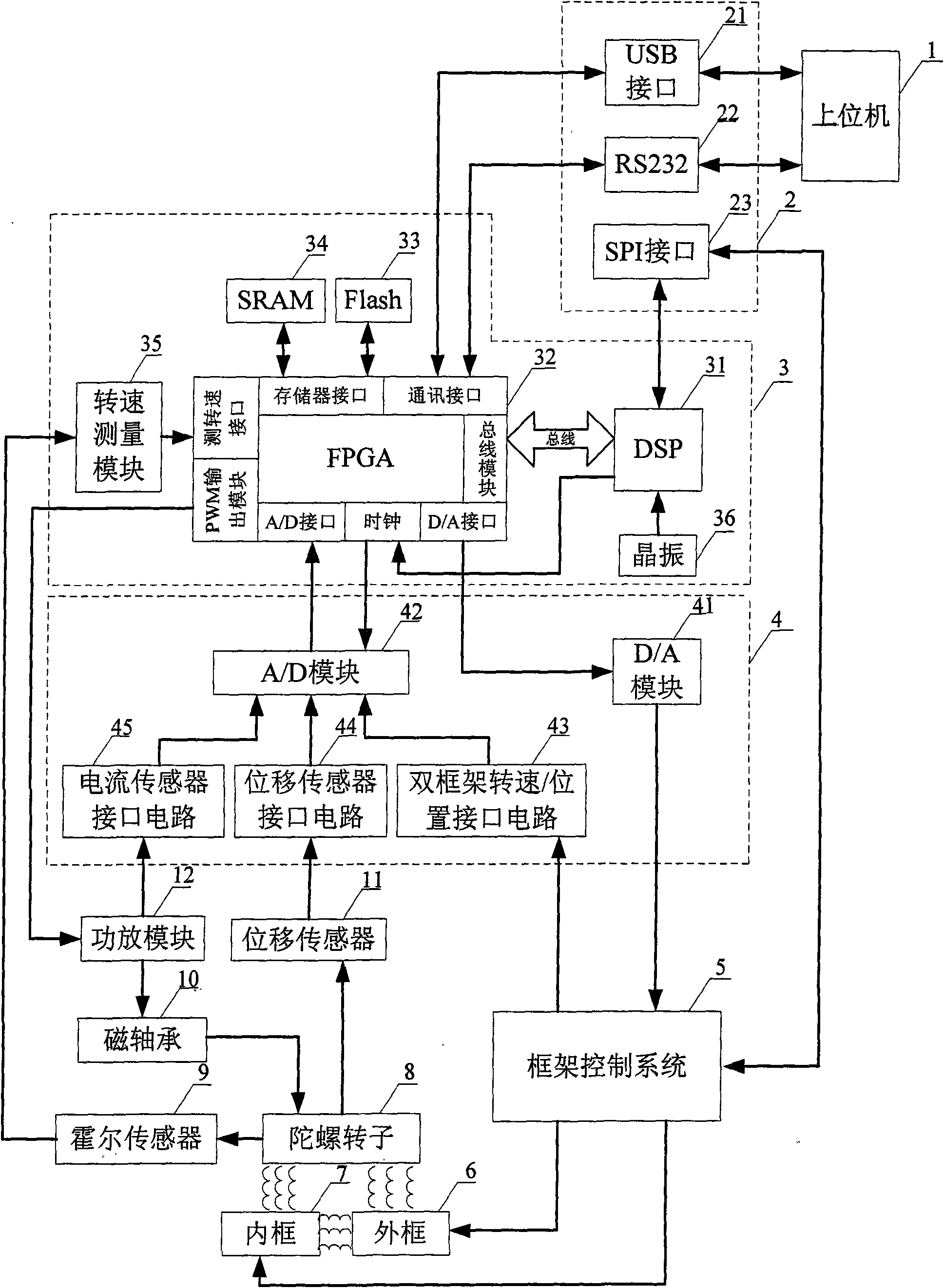
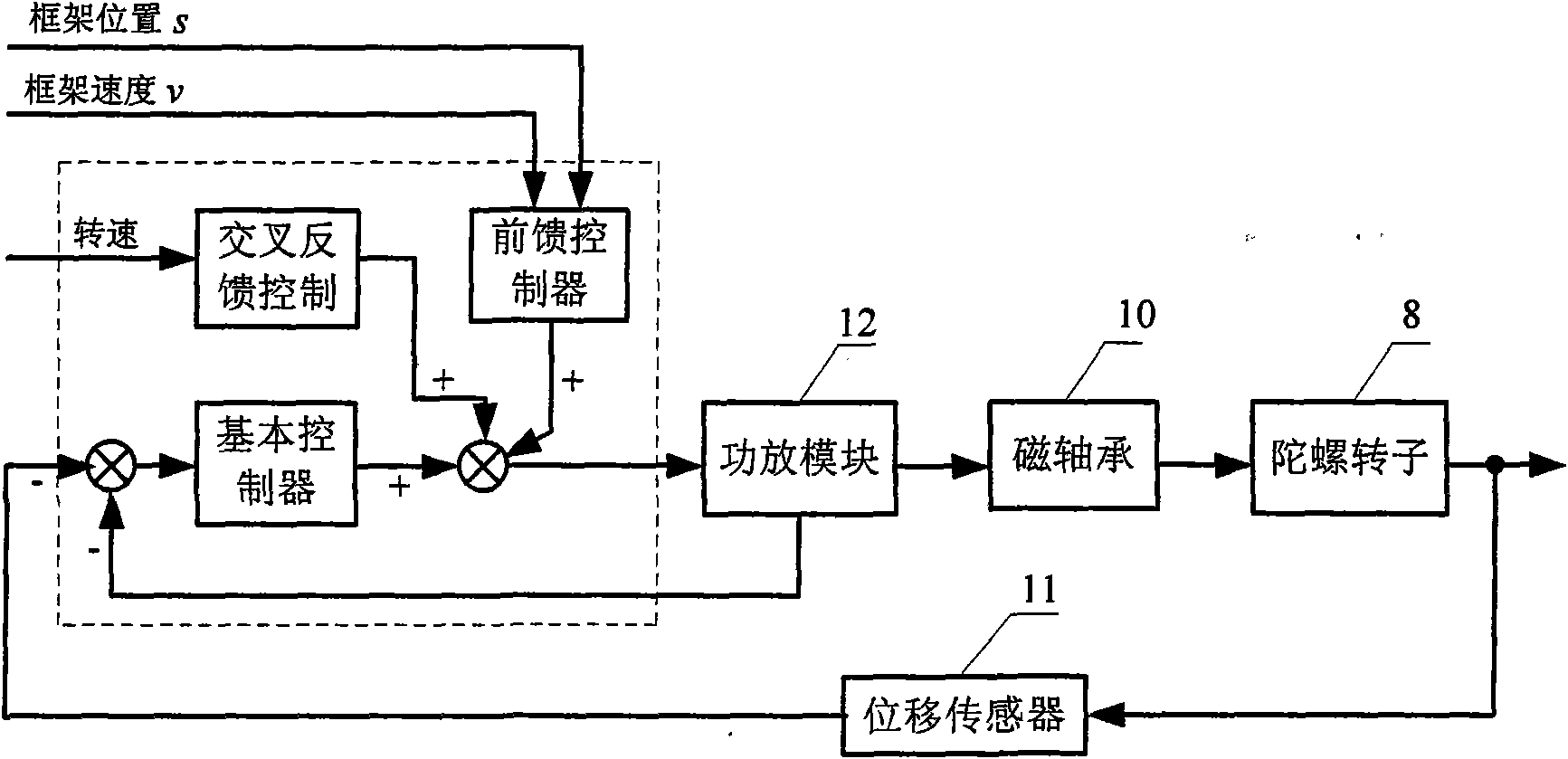
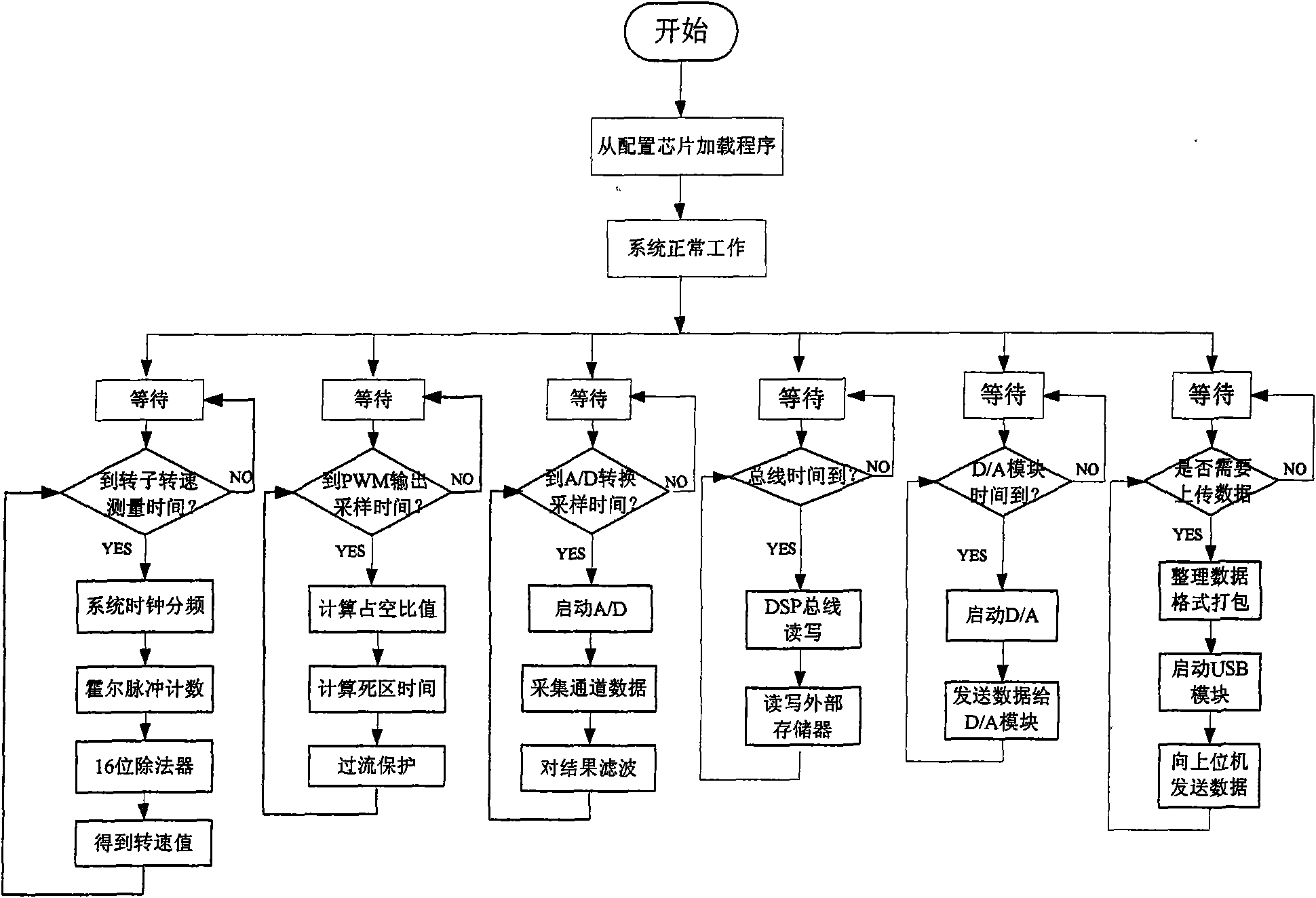
Integrating double-framework magnetically suspended control moment gyroscope (MSCMG) magnetic bearing control system
InactiveCN101599670AImplement extensionsRealize the isolation functionMechanical energy handlingBearingsMagnetic bearingGyroscope
The invention is an integrating double-framework magnetically suspended control moment gyroscope (MSCMG) magnetic bearing control system, comprising a control circuit, a collecting circuit and a communication interface; wherein, the control circuit comprises a FPGA module, a DSP module and the like; the collecting circuit consists of current, a displacement sensor interface circuit, a double-framework revolution / position interface circuit, an A / D module, and a D / A module; the communication interface comprises a USB interface, RS232 and an SPI interface; the control circuit in the system is used for receiving gyroscope rotor signal processed by the collecting circuit, controlling the stable suspension thereof, transmitting the controlled variable to an upper computer through the communication interface, and realizing on-line monitoring on the suspended gyroscope rotor, data collecting and on-line modification for the controlled variable under the control of the upper computer. The system provided in the invention has the advantages of effectively communicating an inner framework and an outer framework rotational signals under the control of high precision, realizing the integrating design of the control system and the measurement and control system, and satisfying the requirements of speed and precision for the data collecting and the on-line monitoring.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
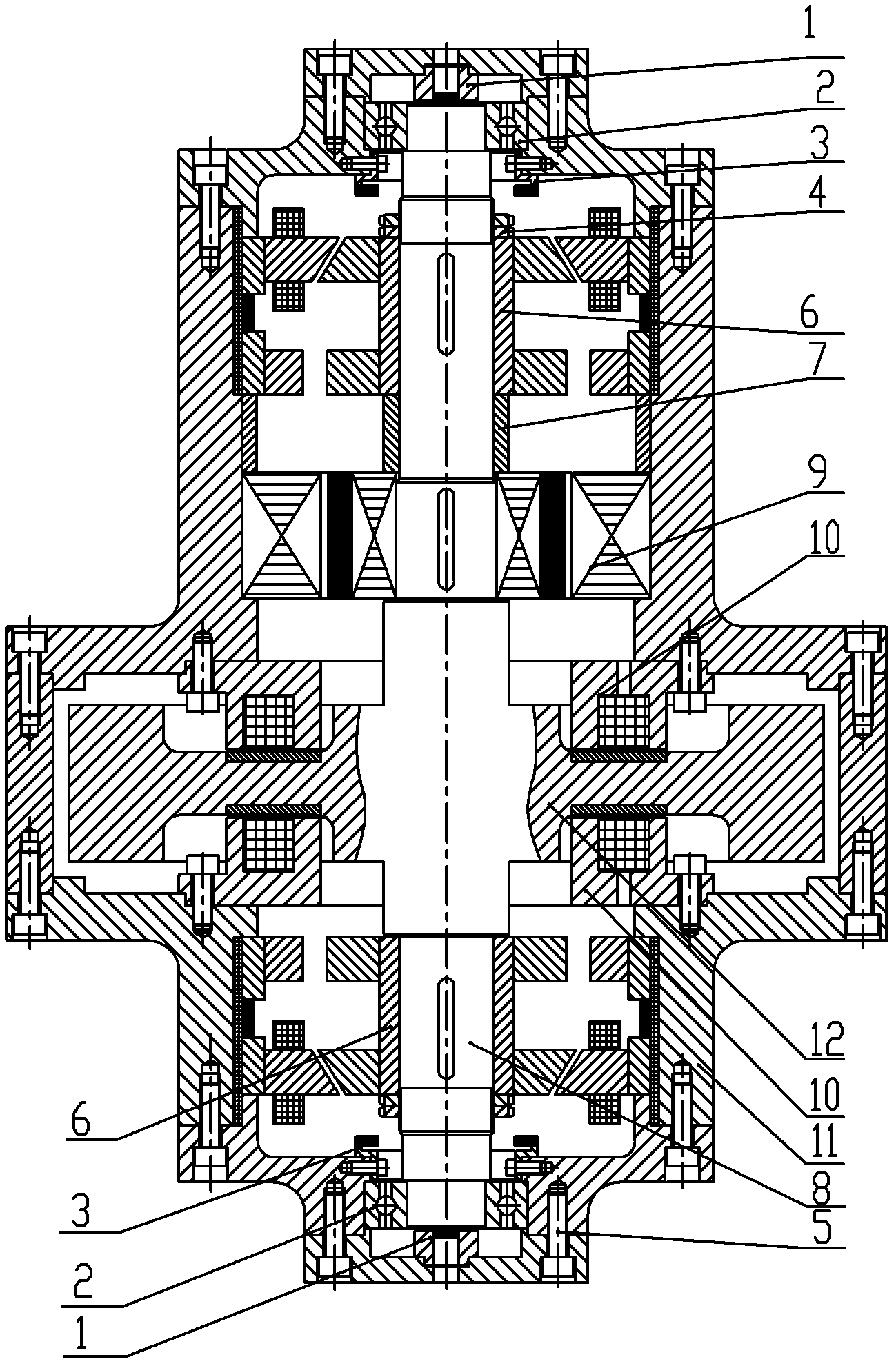
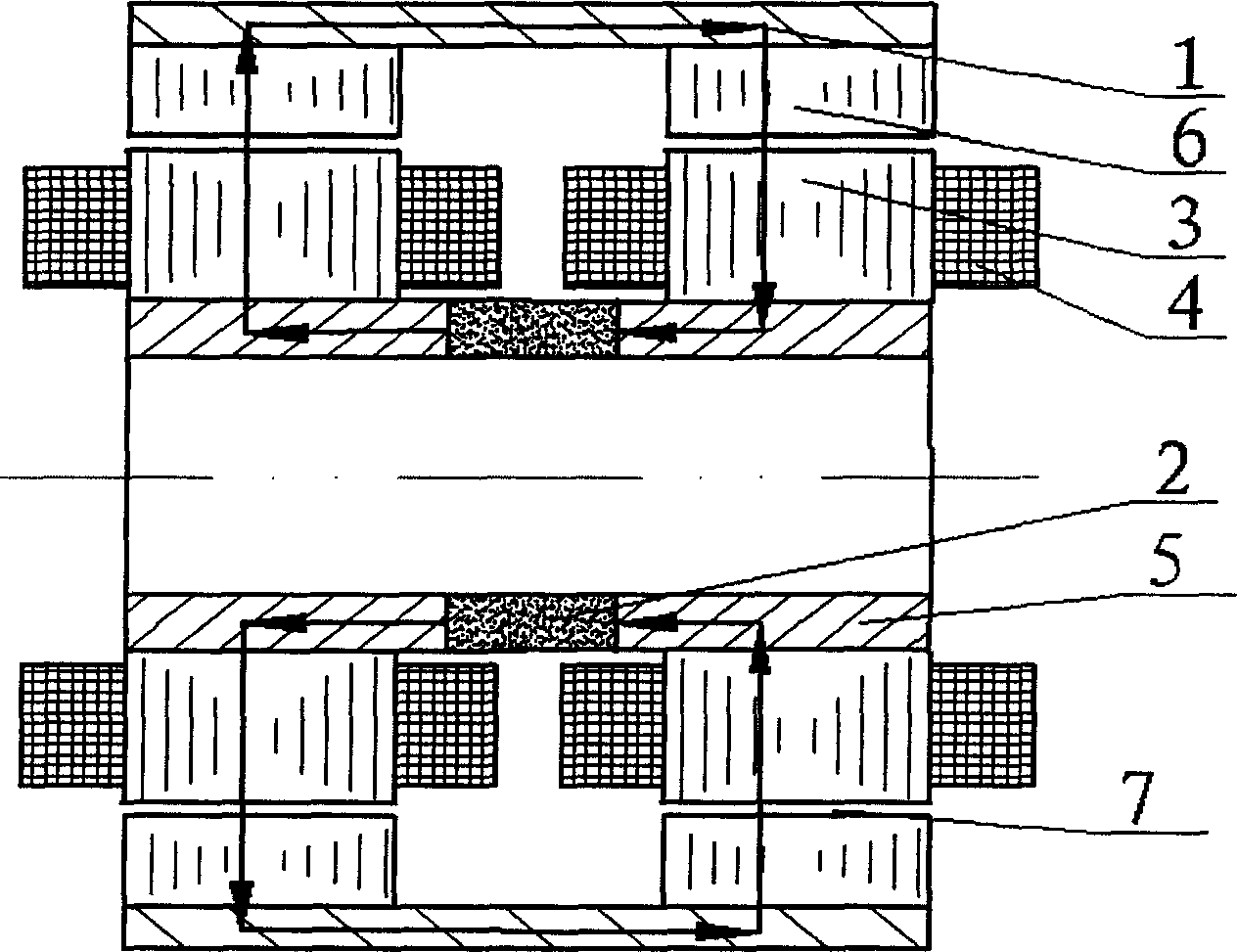
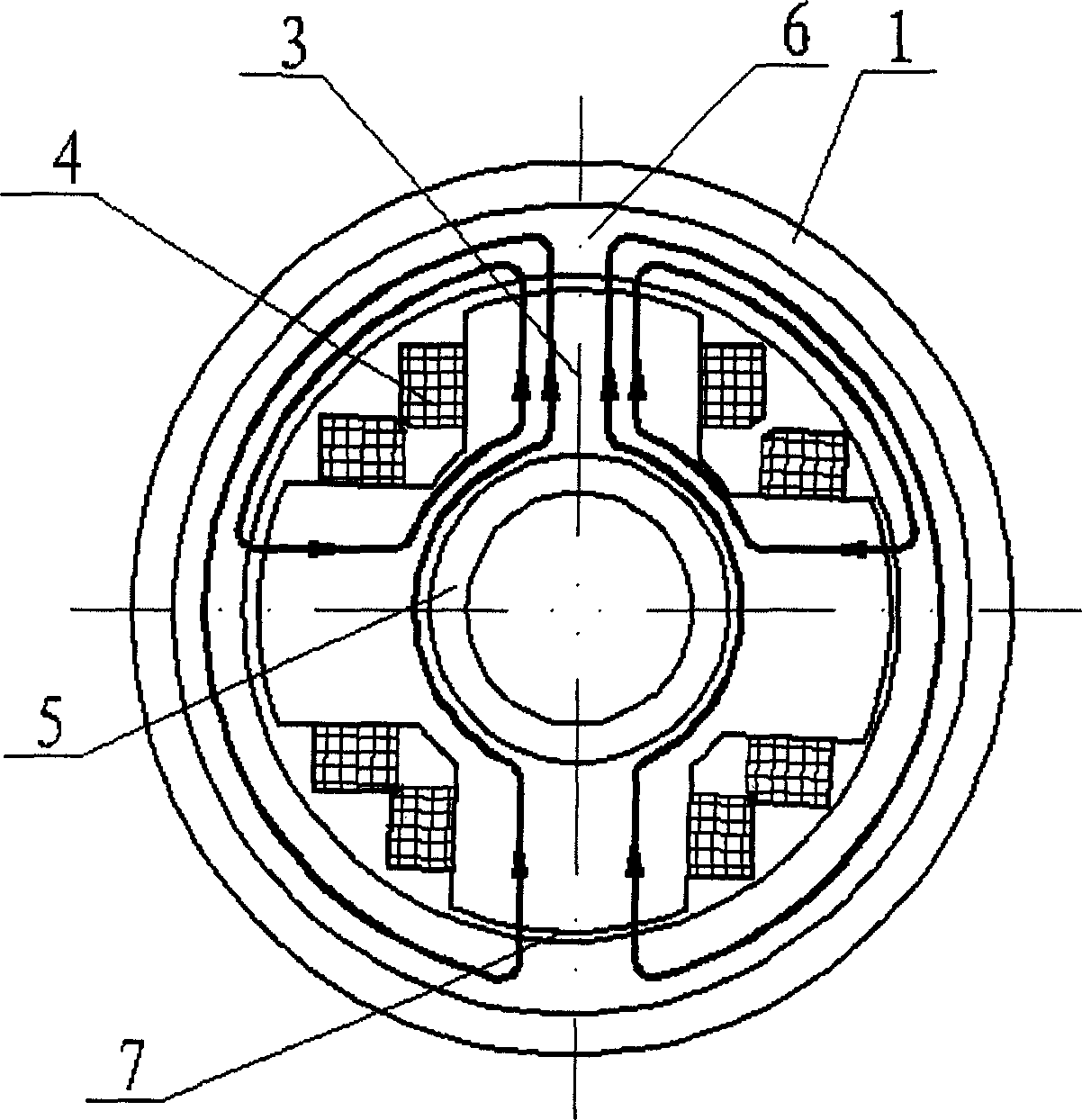
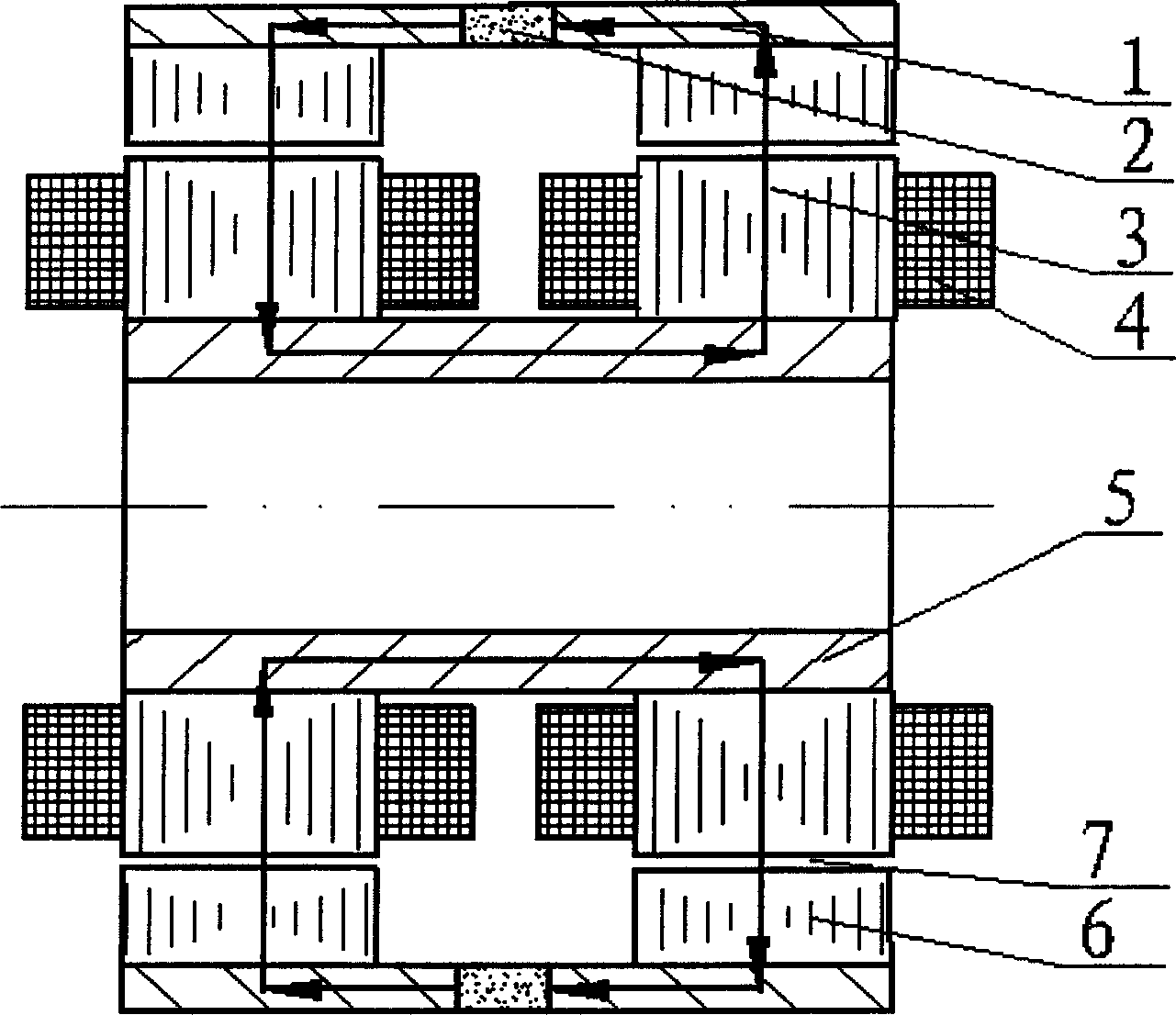
Permanent-magnetic biased axial radial magnetic bearing
The permanently magnetic biased axial and radial magnetic bearing as one mixed magnetic bearing includes one axial stator, one axial control winding, two radial magnetized ring permanent magnets, two radial stator with three poles, one radial control winding, and one rotor with jacketed iron core. The permanently magnetic biased axial and radial magnetic bearing has one static bias magnetic field established with two radial magnetized ring permanent magnets, one closed magnetic path formed with one external axial magnetic pole iron core, one rotor iron core and one radial stator, one axial suspension controlled by the axial superposed magnetic flux, and one two freedom suspension controlled by the radial superposed magnetic flux. The present invention has simple structure, high critical rotation speed, low power consumption, and broad application foreground in energy storing flywheel, air conditioner compressor and other high speed application fields.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
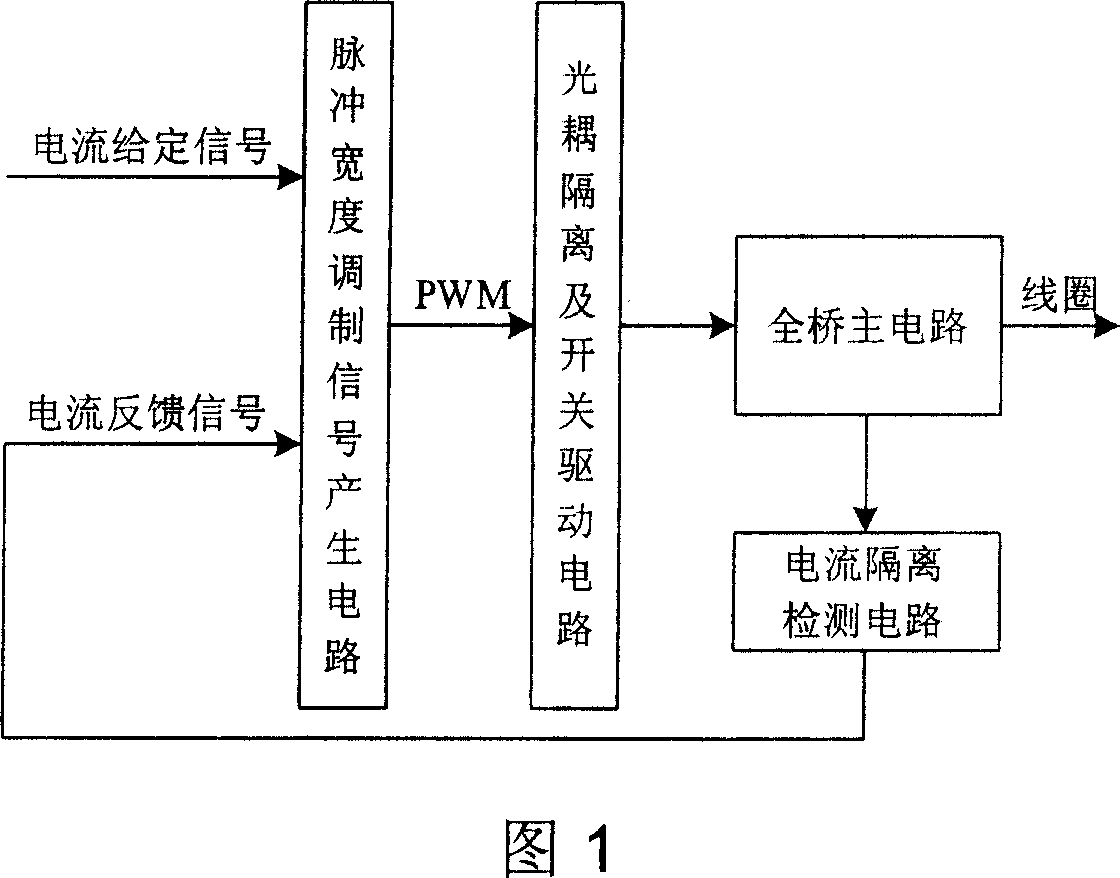
Digital switch power amplifier for magnetic suspension flywheel magnetic bearing system
ActiveCN1949642AReduce power consumptionHighly integratedDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationMagnetic bearingFull bridge
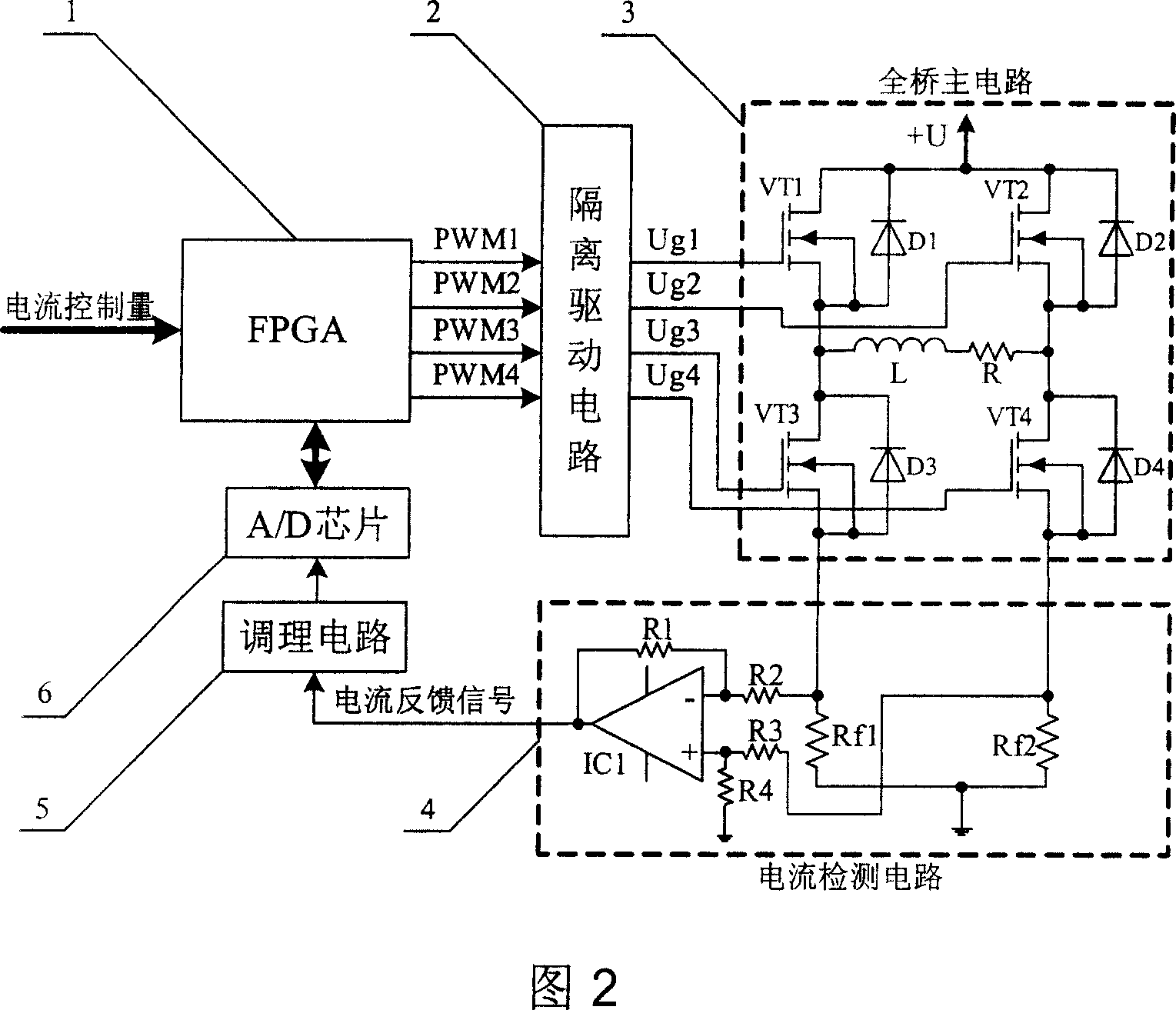
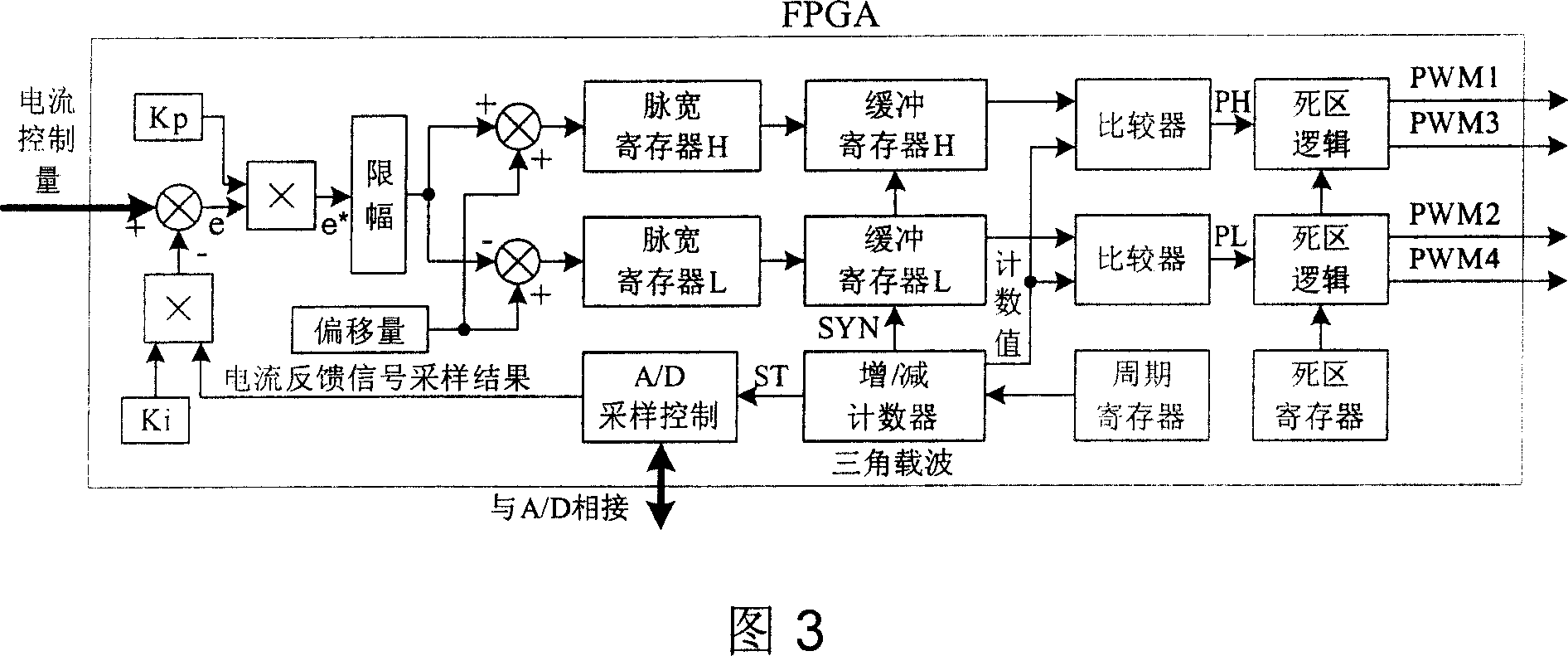
The invention is a digital switching power amplifier for magnetic bearing system of magnetic suspension flywheel, a device for actively controlling the current in the magnetic bearing coil, mainly comprising FPGA, isolated driving circuits, full-bridge main circuit, current detection circuit, conditioning circuit, A / D chip and overcurrent detection circuit. And the digital switch power amplifier makes PWM modulation by the error signal formed by the FPGA according to the given digital control quantity and sampling result of current feedback signal, directly control ON and OFF of power switches in the full bridge main circuit by the ready- modulated PWM signals through the isolated driving circuits, so as to achieve the purpose of controlling the current in the magnetic bearing coil. And the invention has advantages of simple structure and high reliability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Dual-feeding mixed excitation axial magnetic field magento motor
InactiveCN1808846AWide range of amplitude variationRealize decoupling regulationMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machineMagnetic poles
This invention relates to double mixture excitation axis field motor, which comprises One retardant left and right rotors on both sides, wherein, the rotor magnetic electrode is divided into inner and outer rings by isolation area with outer ring as iron electrode, inner ring as electrode alternating permanent part; two rotor iron core outside gear is fixed with magnetic field control coil fixed by motor main coil set. This invention adjusts the motor gas gap size by alternating magnetic control coil set to alternate inductance potensation size.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Embedded Symmetric Multiple Axis Antenna System With Isolation Among The Multiple Axes
InactiveUS20150318624A1Minimize cross-couplingLarge isolationLoop antennas with ferromagnetic corePosition fixationCouplingAntenna element
The present disclosure pertains to a rotationally triply symmetric three axis magnetic antenna system having substantial isolation among the three axes, including a three axis skew orthogonal magnetic antenna system and device utilizing the antenna system. The antenna system comprising three substantially identical magnetic antenna elements disposed symmetrically about a reference point such that the magnetic axes from the three antenna elements are orthogonal to one another in direction and do not intersect one another. The three antenna elements are positioned in a substantial cross coupling null from one another to minimize cross coupling. The arrangement yields packaging efficiency for compact electronic devices. A 1, 1, diameter embodiment is disclosed. A location system utilizing the antenna system is disclosed. Methods for producing the antenna are disclosed. A moldable triple coil holder for the antenna system is described.
Owner:GAN CORP
Measurement of torsional dynamics of rotating shafts using magnetostrictive sensors
InactiveUS7131339B2Low-cost and long-termWork measurementTorque measurementContact methodEngineering
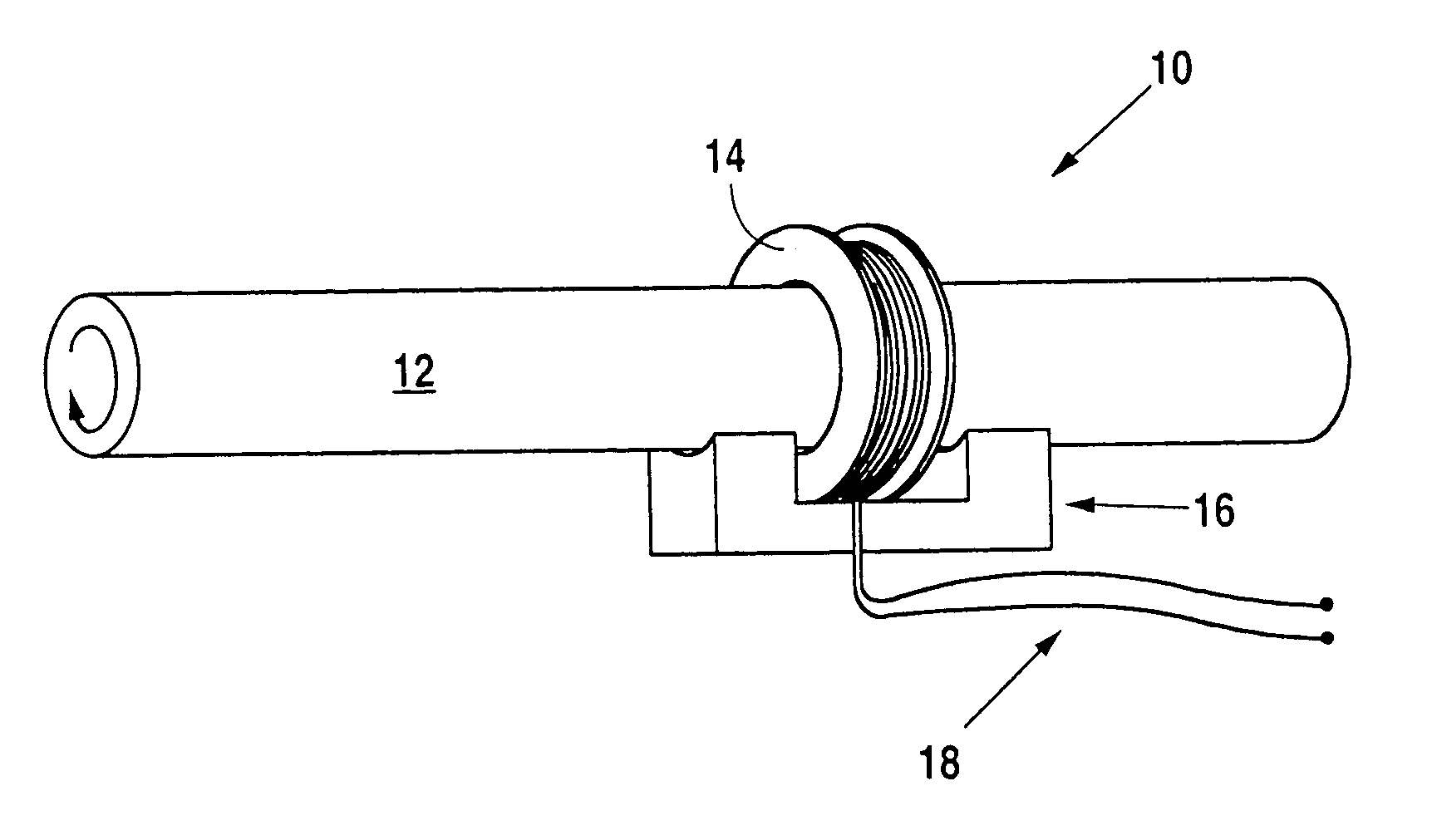
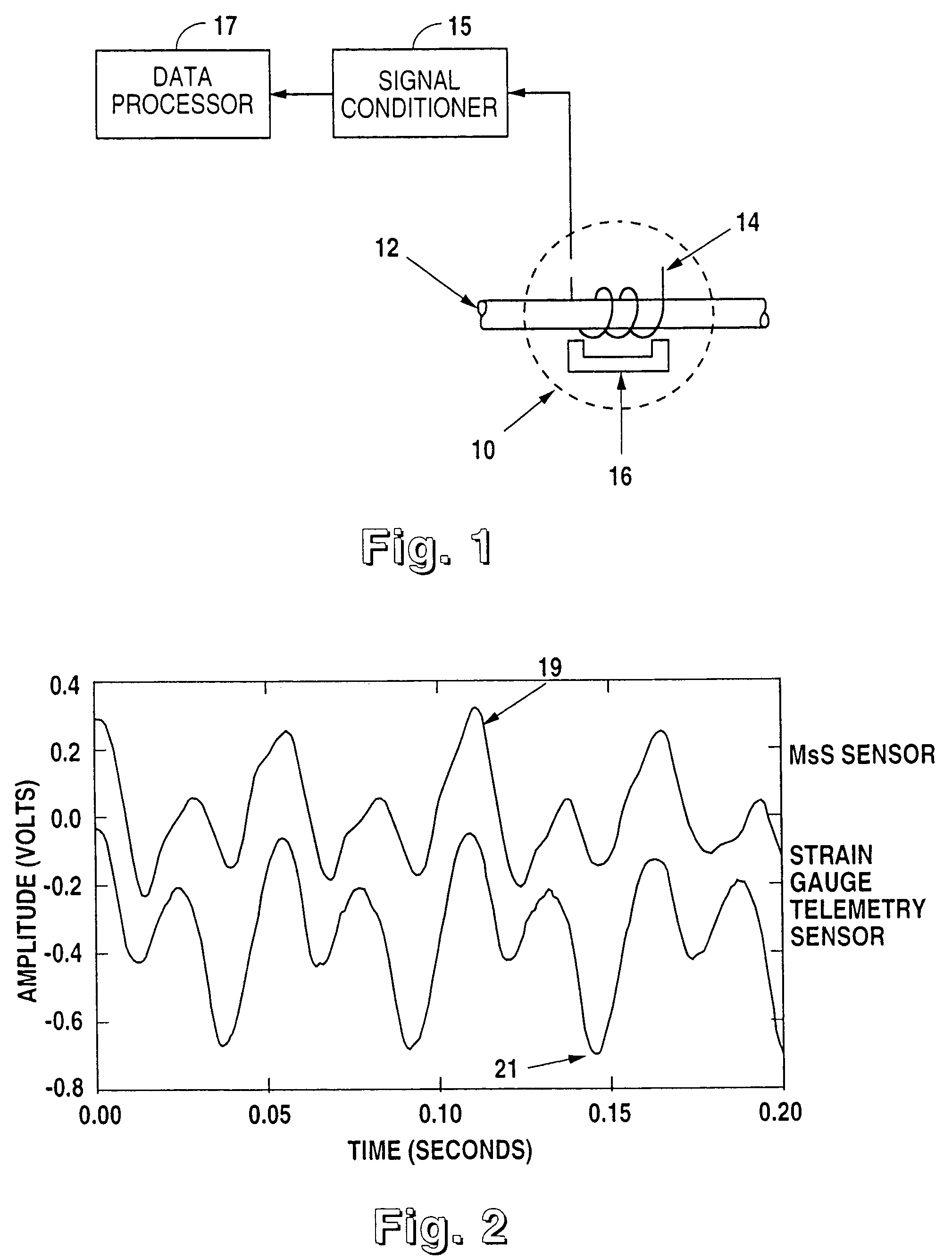
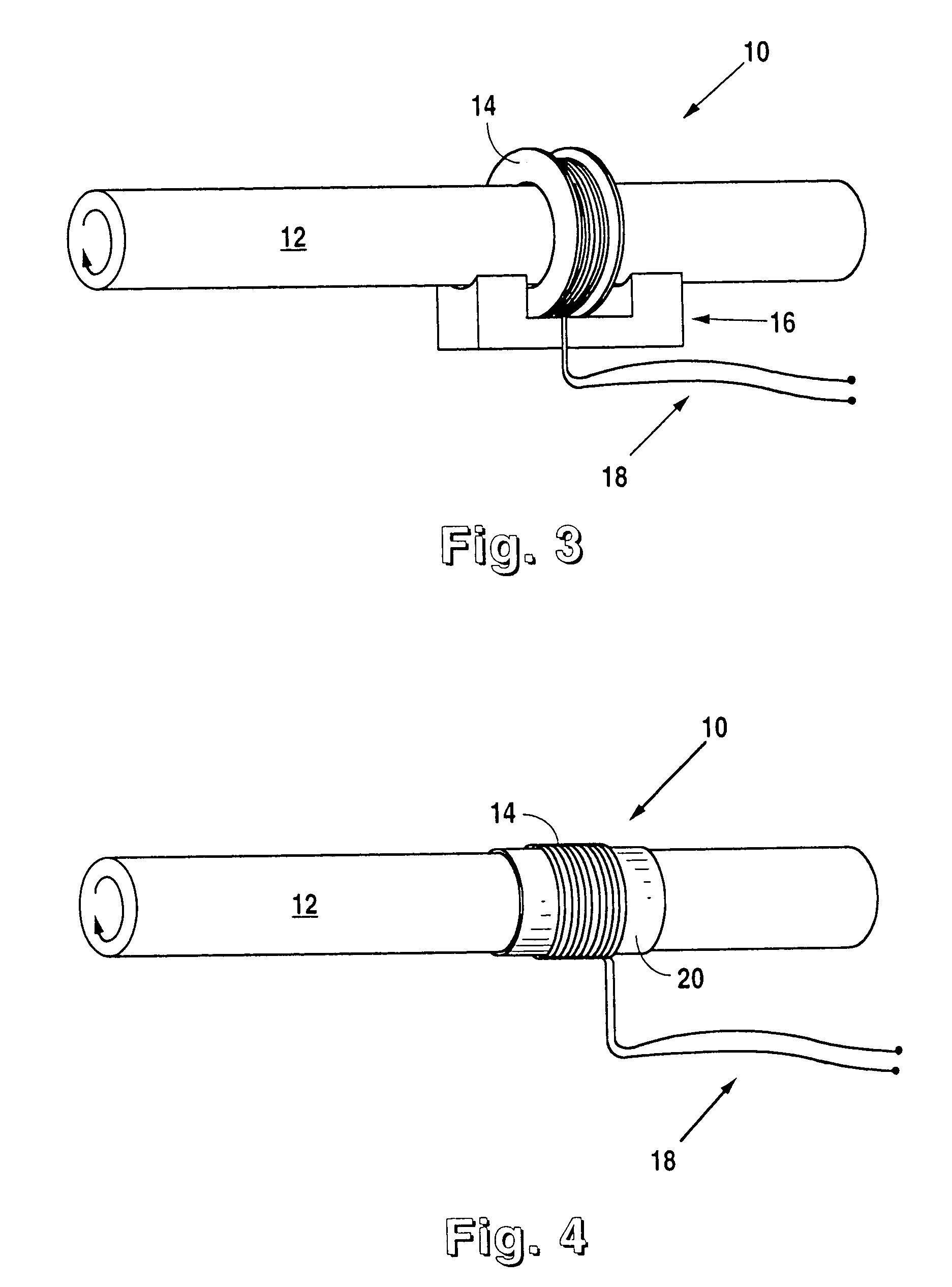
A device and method for the non-contact measurement of dynamic torsion in a rotating shaft using magnetostrictive sensors (MsS). The monitoring and detection system have specially configured magnetostrictive signal detectors that include inductive pickup coils, in which signals corresponding to localized shaft torques are induced. The non-contact method for measuring dynamic torques includes fixing a ferromagnetic strip to a ferromagnetic or non-ferromagnetic shaft and inducing a circumferential residual magnetization therein. An MsS in the form of either an encircling coil positioned around the shaft on a cylindrical substrate, or a partially encircling coil positioned on a flexible substrate and wrapped partially about the shaft.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Inductive heating device and system for aerosol generation
The inductive heating device (1) for aerosol-generation comprises a device housing comprising a cavity (13) having an internal surface for receiving at least a portion of an aerosol-forming insert (2) comprising an aerosol-forming substrate and a susceptor. The device housing further comprises an induction coil (15) having a magnetic axis, the induction coil (15) being arranged such as to surround at least a portion of the cavity (13). The device (1) yet further comprises a power source (11) connected to the induction coil (15) and configured to provide a high frequency current to the induction coil (15). Therein, a wire material forming the induction coil has a cross-section comprising a main portion, the main portion having a longitudinal extension in a direction of the magnetic axis and a lateral extension perpendicular to the magnetic axis, which longitudinal extension is longer than the lateral extension of the main portion.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS PROD SA
Five-freedom active magnetic bearing type dual-axis angular rate gyroscope
ActiveCN103196436ASmall drift rateAvoid disturbance torqueRotary gyroscopesAxial displacementGyroscope
The invention discloses a five-freedom active magnetic bearing type dual-axis angular rate gyroscope. The five-freedom active magnetic bearing type dual-axis angular rate gyroscope consists of rotors, a radial magnetic bearing, an axial magnetic bearing, a protection bearing, a radial displacement sensor, an axial displacement sensor, a driving motor, gyroscope cases and a circuit system. By using position feedback information of the rotors of the radial sensor and the axial sensor relative to the gyroscope cases, the circuit system regulates the coil winding current of the radial magnetic bearing and the axial magnetic bearing in real time, so that the five-freedom fully-active suspension of the rotors is realized, and the rotors are driven by the driving motor to rotate at a high speed so as to generate an angular momentum. When the attitude of an external rotor is changed, the coil winding current is correspondingly changed, and the magnitude of external input angular rate is calculated according to a linear relationship between the coil winding current and the input angular rate. The five-freedom active magnetic bearing type dual-axis angular rate gyroscope is applicable to the field of high-accuracy angular rate measurement application, and has the characteristics of small zero offset, low output noise, high resolution and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
NFC Card for Handheld Device
ActiveUS20120071088A1Improve overall senseReduce impactNear-field transmissionRecord carriers used with machinesHand held devicesMagnetic axis
An NFC card includes an antenna circuit including an antenna coil having at least one magnetic axis, and at least one integrated circuit linked to the antenna circuit. The magnetic axis of the antenna coil is substantially parallel to at least one side of the card, and the card further includes at least one electrically conductive screen extending near the antenna coil, which does not cross the magnetic axis. The card does not include any magnetically permeable material between the at least one conductive screen and the antenna coil. Embodiments of the invention are applicable in particular to SIM-NFC card and SD-NFC cards.
Owner:VERIMATRIX INC
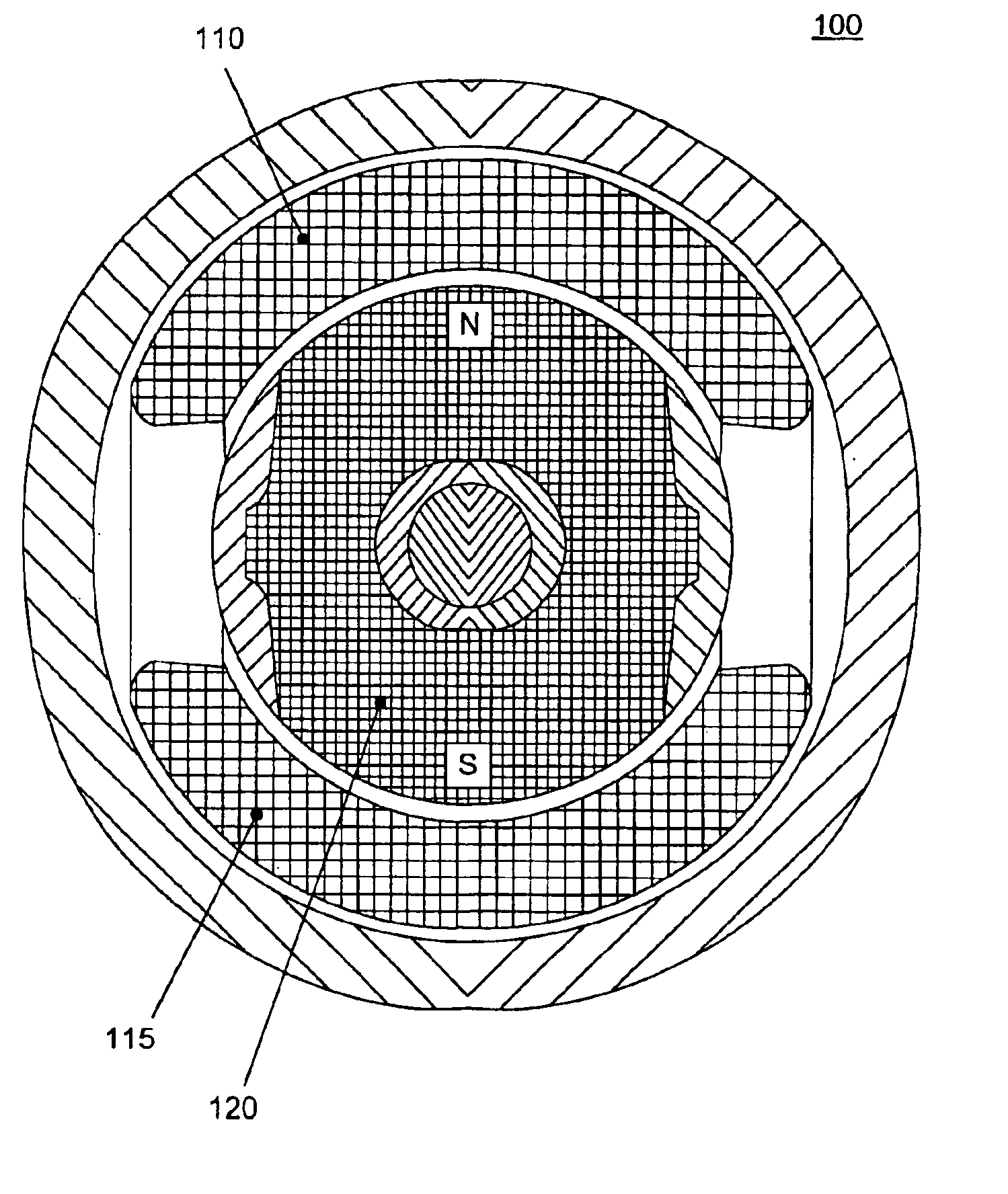
Permanent magnet bias-magnetic axial mixed magnetic bearing
The invention is a permanent magnet biasing axial mixed magnetic bearing, relating to the technical field of electromechanical engineering, comprising axial control coils, rotor, rotating shaft, stator, permanent magnet, axial stator discs, and axial stator cylinder, where two axial control coils are connected in series and respectively arranged between two axial stator discs and arranged inside and close to the axial stator cylinder; the rotor is jacketed on the rotating shaft; radial stator and permanent are arranged inside the axial stator cylinder and a radial gap is formed between the radial stator and the rotor; two axial gaps are formed between two axial stator discs and the rotor; the two axial stator discs, axial stator cylinder, two axial gaps and rotor compose a complete control flux circuit; the permanent magnet is inserted between the axial stator cylinder and the radial rotor, and forms permanent magnet biasing magnetic circuit path together with the radial gap and the rotor through the two axial gaps, respectively. And the invention need not install a large axial suction disc on the rotating shaft, largely reducing moment of inertia of the rotor, and the structure is simple, and it is easy to install.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
MRI shoulder coil
A MRI quadrature coil for imaging a human shoulder has a first coil shaped to conform to the top of the shoulder and a second coil adapted to encircle the shoulder. The second coil has a magnetic axis generally orthogonal to that of the first coil.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
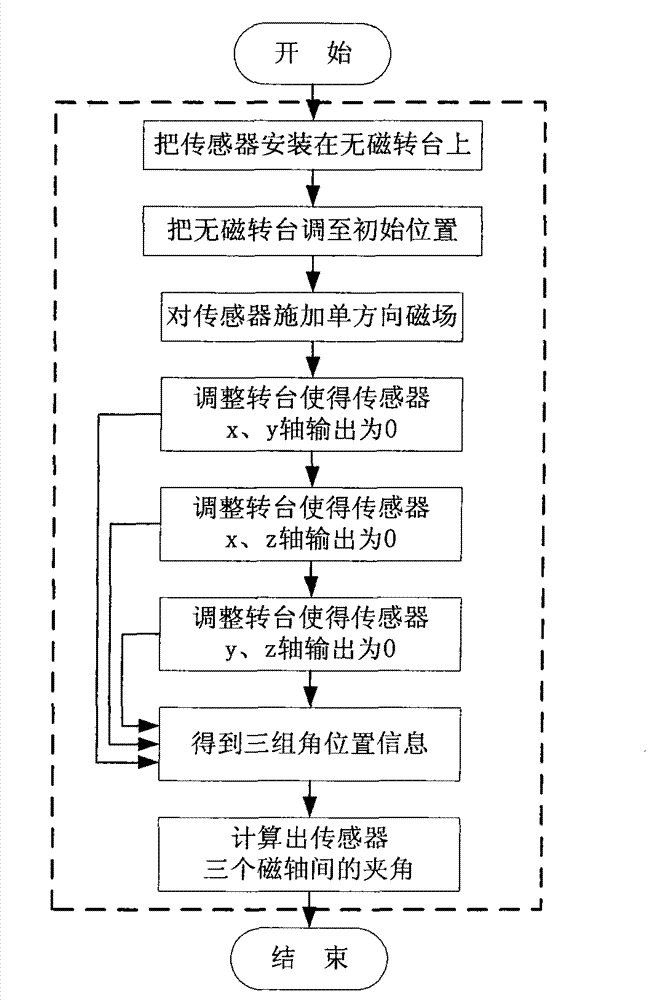
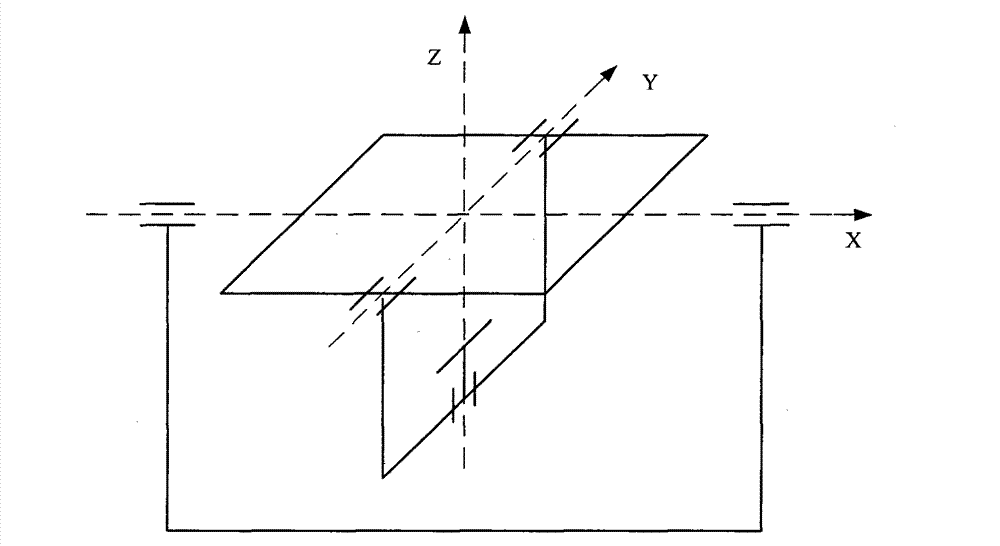
Method for calibrating verticality of magnetic shaft of three-shaft magnetic sensor
ActiveCN102853760ANo measurement errorNo errorUsing electrical meansMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsCalibration resultMagnetic axis
The invention discloses a method for calibrating verticality of a magnetic shaft of a three-shaft magnetic sensor. A three-dimensional magnetic field generator and a nonmagnetic rotary table are adopted, the three-dimensional magnetic field generator and the nonmagnetic rotary table are arranged at first; the magnetic sensor which needs to be calibrated is fixed on the rotary table; a large magnetic field ranging from top to bottom is generated by the magnetic field generator, so that a numeric value measured by the sensor is not zero; the zero position of the rotary table is marked, the angle values of three shafts of the rotary table are recorded, and three shafts of the rotary table are rotated, so that the outputs of a shaft m and a shaft n of the sensor are zero and the angle values of the three shafts of the rotary table are recorded; the three shafts of the rotary table are rotated again, so that the outputs of a shaft m and a shaft n of the sensor are zero and the angle values of the three shafts of the rotary table are recorded; transformation relation between each shaft m, n and p of a coordinate O and each shaft x3y3z3 of the coordinate O3 can be obtained by calculating multiple recorded angle values so as to obtain a calibration result. The method is simple and feasible, high in accuracy and small in errors.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
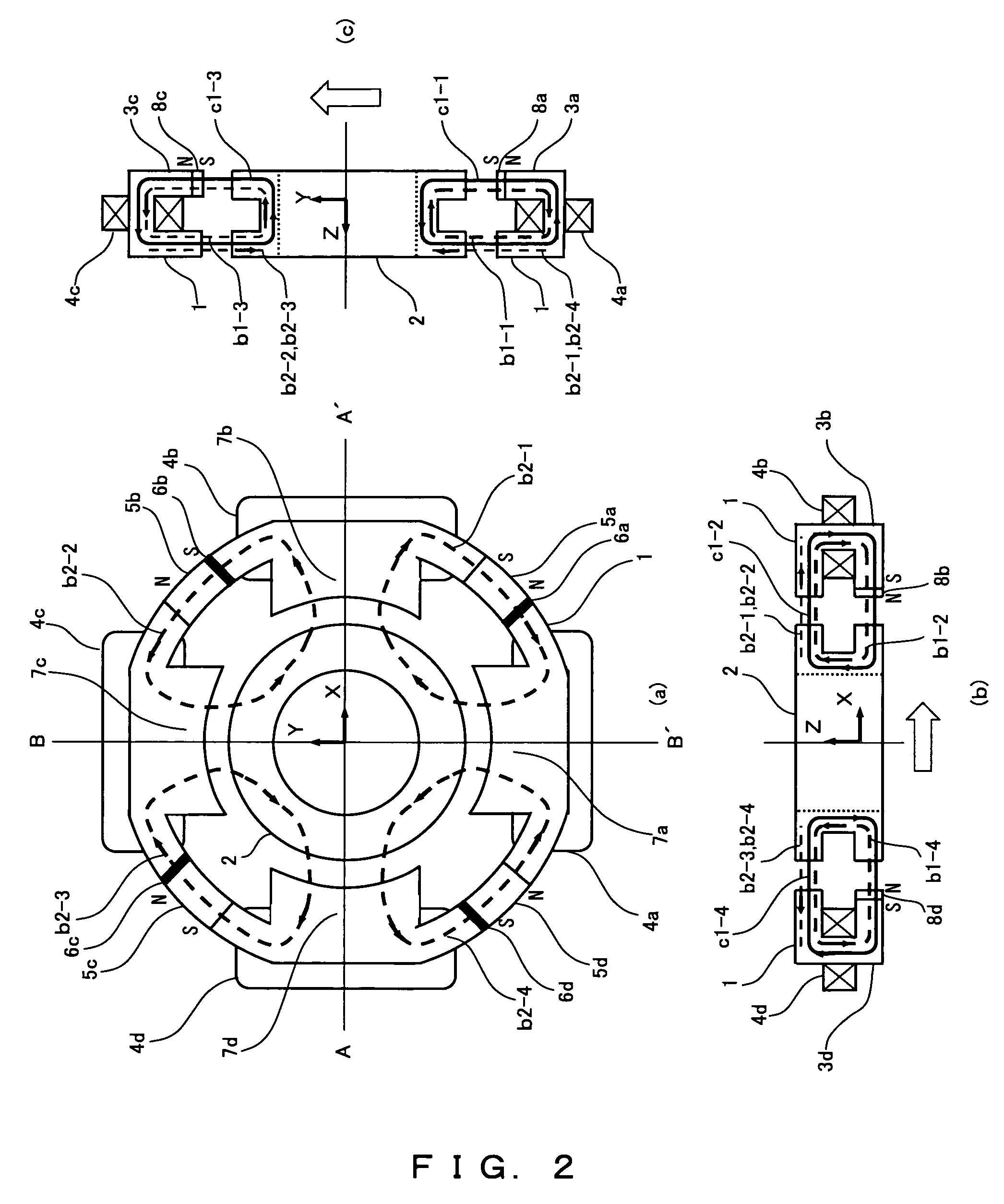
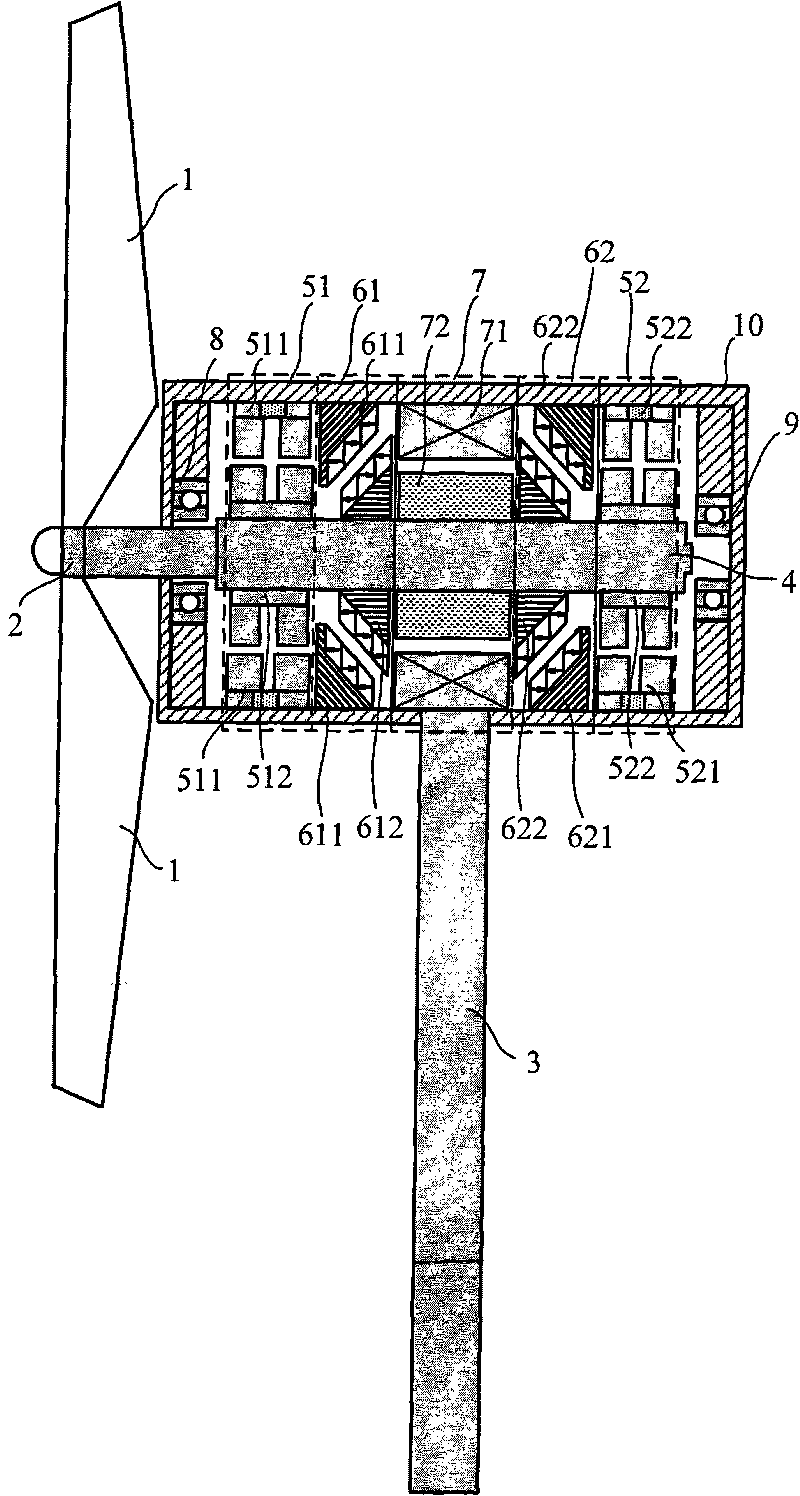
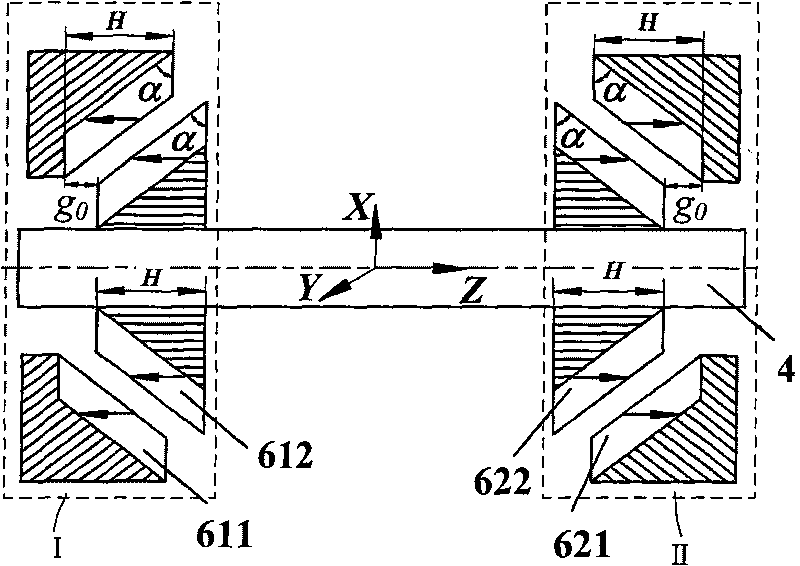
Vertical shaft maglev wind power generator
ActiveCN101761454ALow start wind speedExtend working hoursShaftsMachines/enginesMagnetic bearingMagnetic poles
A vertical shaft maglev wind power generator is composed of vanes, a rotary shaft, a power generator, a radial magnetic bearing, an axial TDOF magnetic bearing, an upper protection bearing, a lower protection bearing, an upper protection bearing retainer ring and a lower protection bearing retainer ring; the rotational part and the stationary part of the fan are not in mechanical contact, the mechanical friction in the fan is completely eliminated and the FDOF levitation of the fan rotor is realized. The axial magnetic bearing of the fan supplies gravity offset through 4 stator magnetic poles and the effect of a suction disc and performs axial translation and two radial rotational DOF control on the rotor; and the radial magnetic bearing finishes the two radial translation control of the fan rotor. The invention has reasonable layout of the components, completely eliminates the friction problem of the vertical shaft fan bearing, greatly reduces the starting wind speed of the wind power generator and improves the wind energy utilization rate.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Signal transfer method and apparatus
InactiveUS7907130B2Reduce decreaseElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersEnergy transferConductor Coil
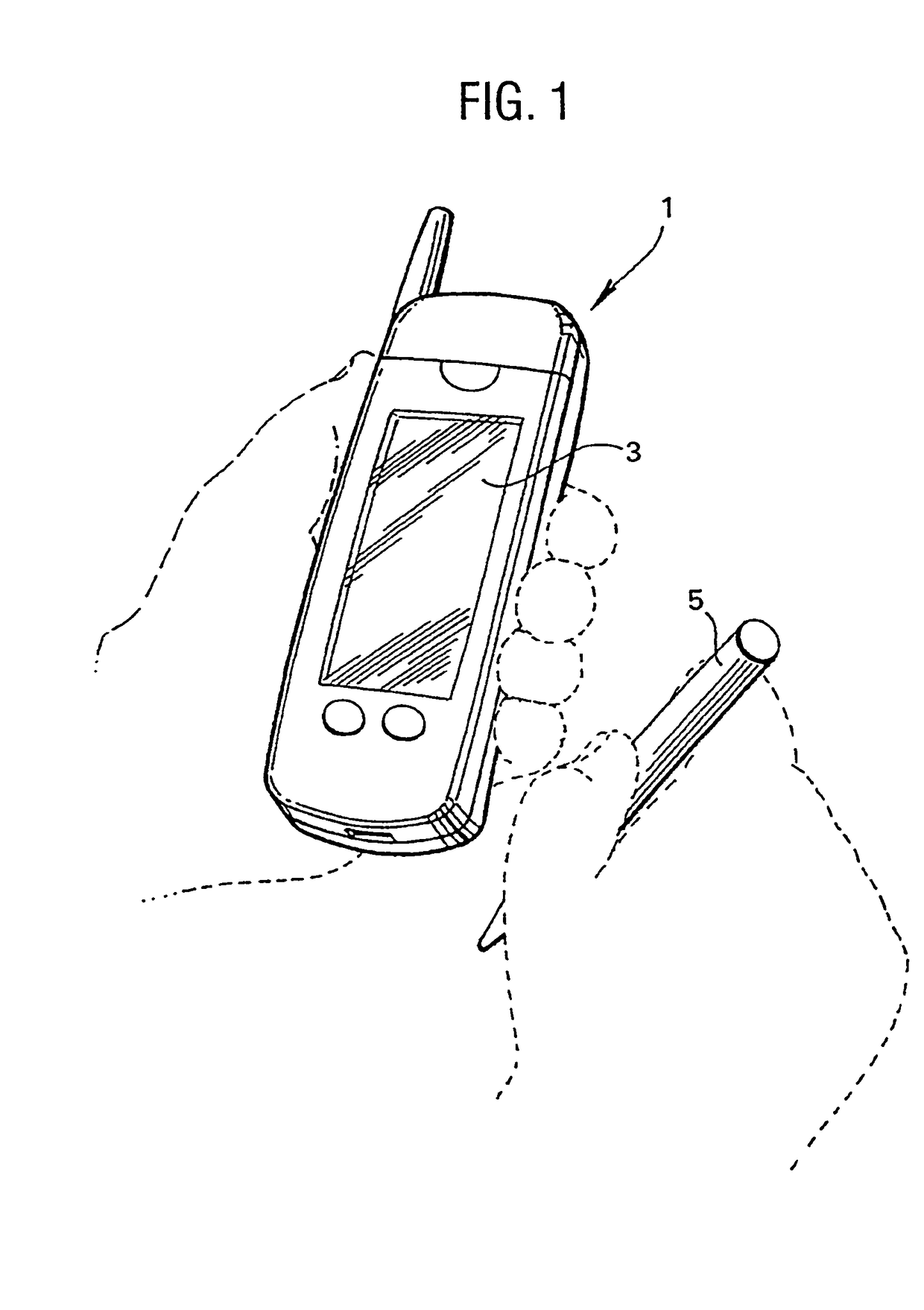
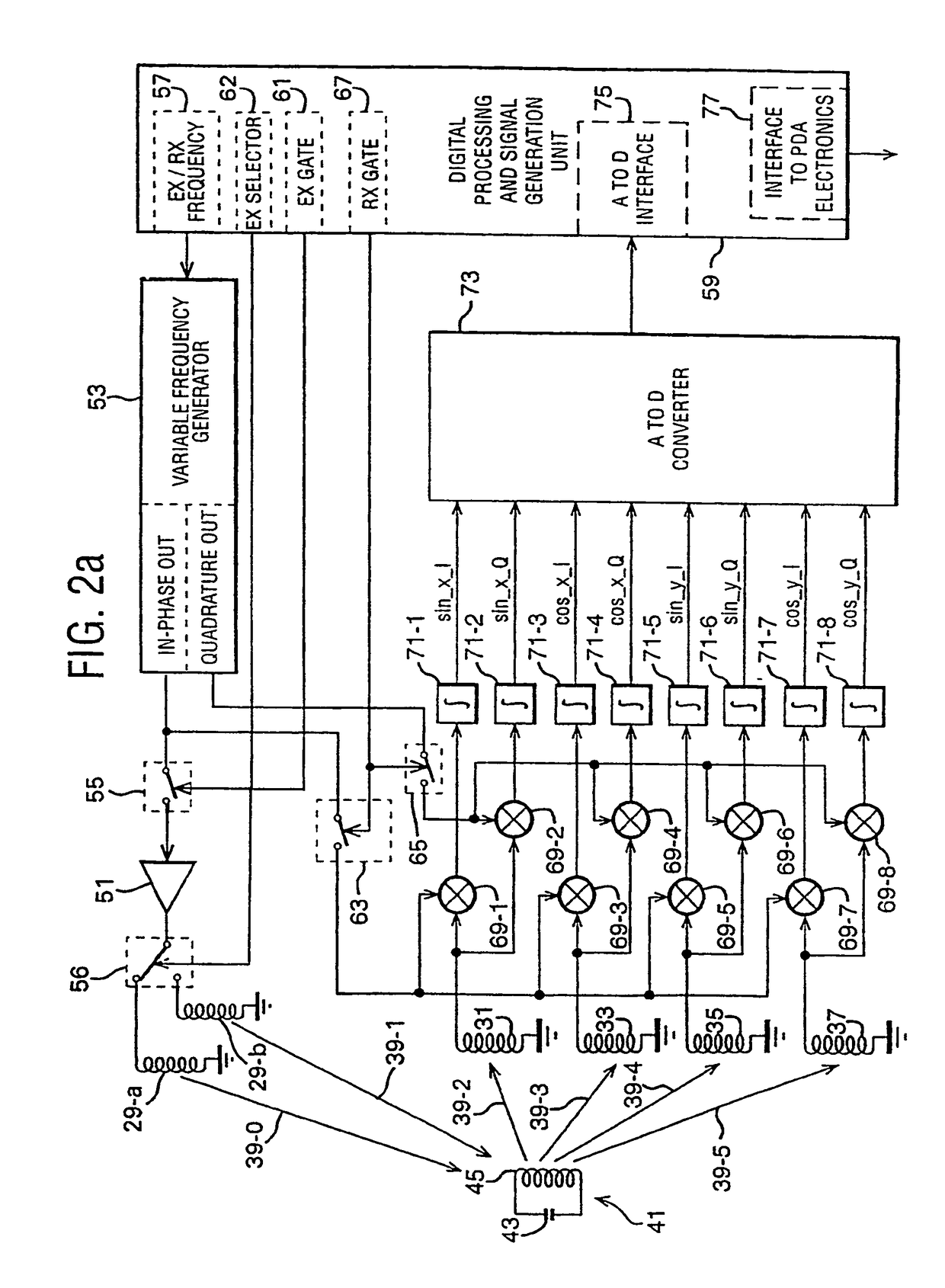
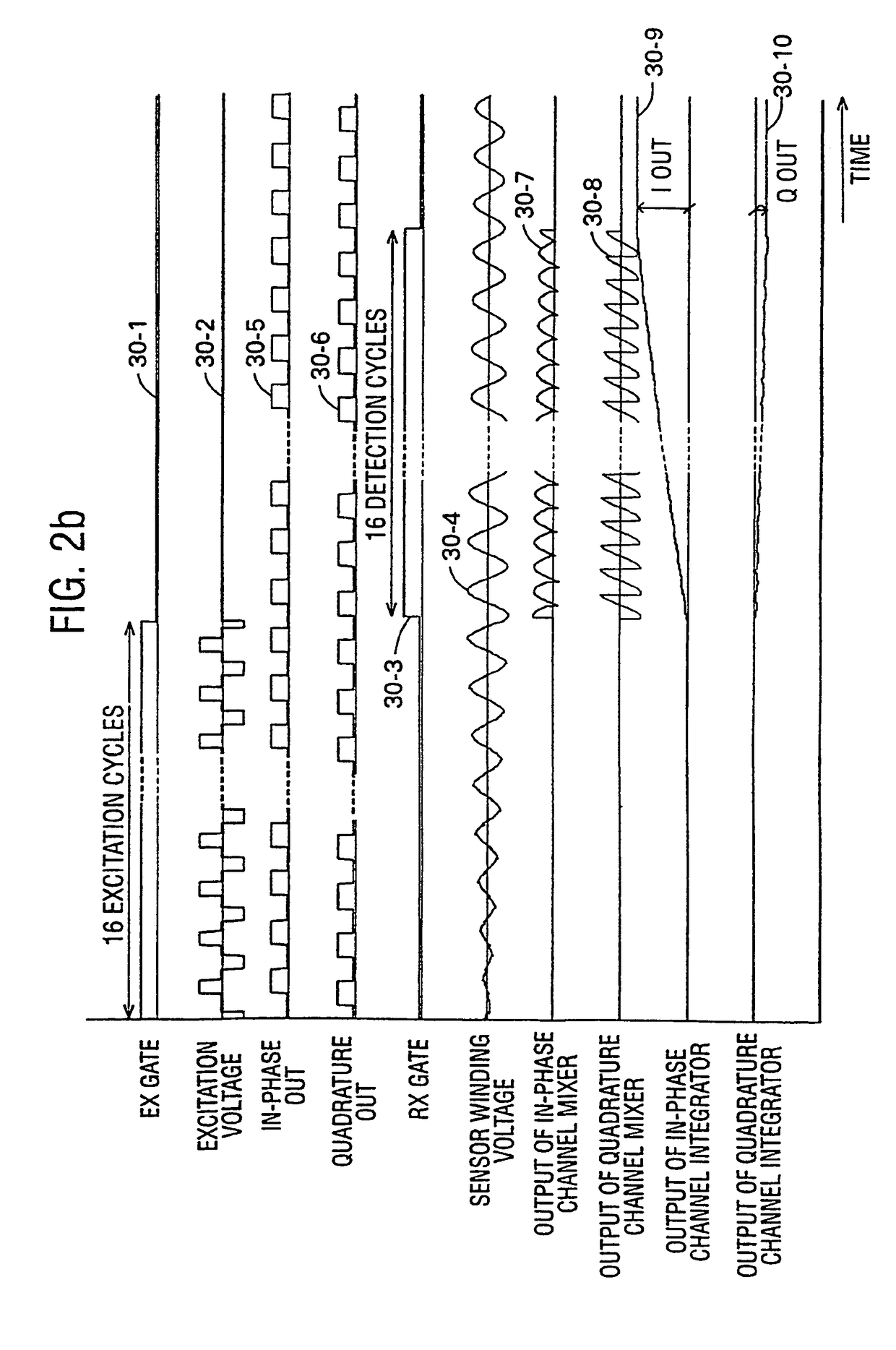
An x-y digitising system is described which operates with a resonant stylus. The x-y digitising system includes an excitation winding for energising the resonant stylus and a number of sensor windings for receiving a signal re-radiated by the resonant stylus when energised. At least one of the excitation winding and the sensor winding is arranged to have its effective magnetic axis non-othogonal to the working area of the x-y digitising system. With this arrangement, improved energy transfer between the x-y digitising system and the resonant stylus can be achieved and / or improved position measurement accuracy can be obtained.
Owner:SINNAPTIX
Instantaneous power floating frame controller
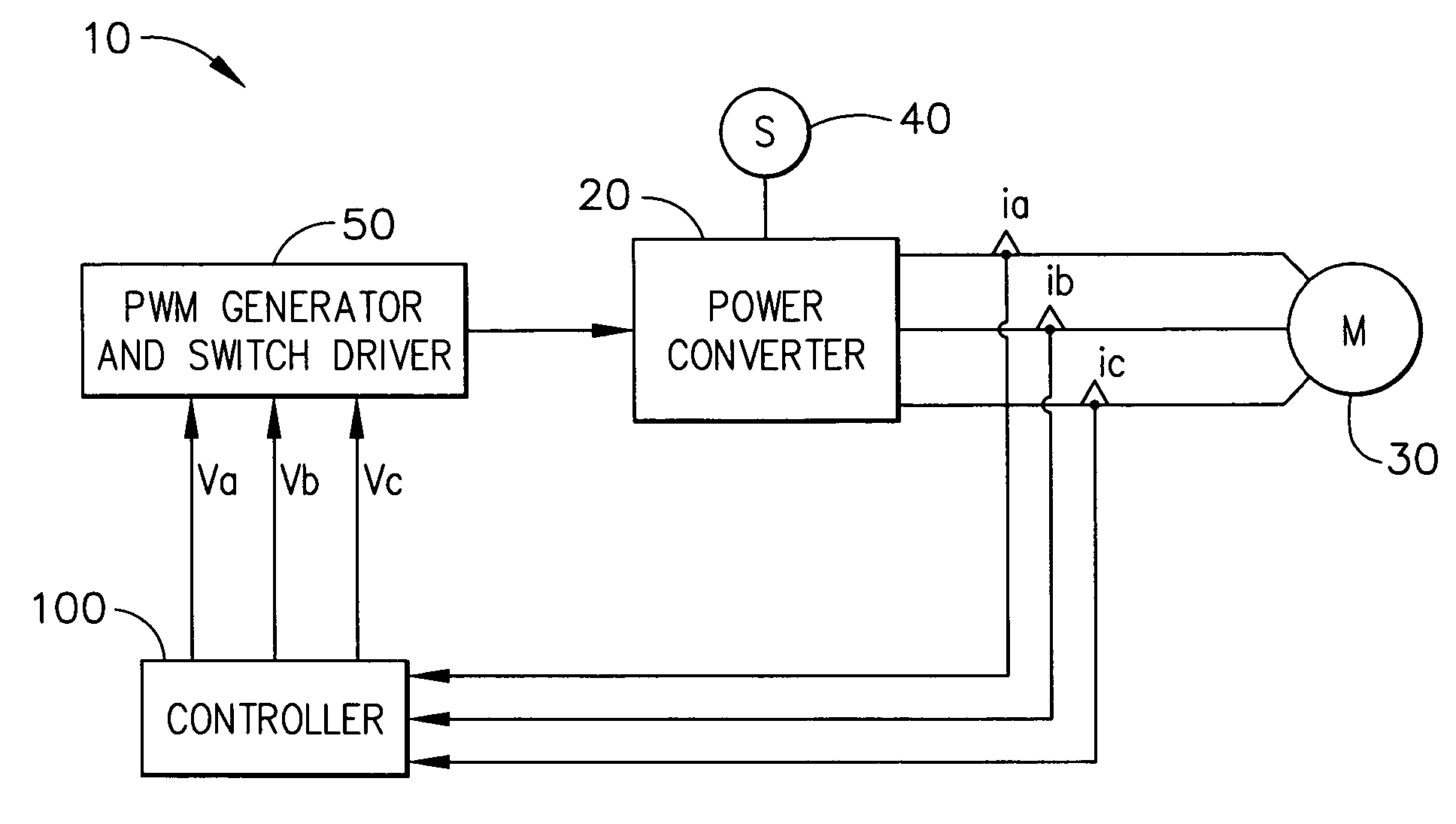
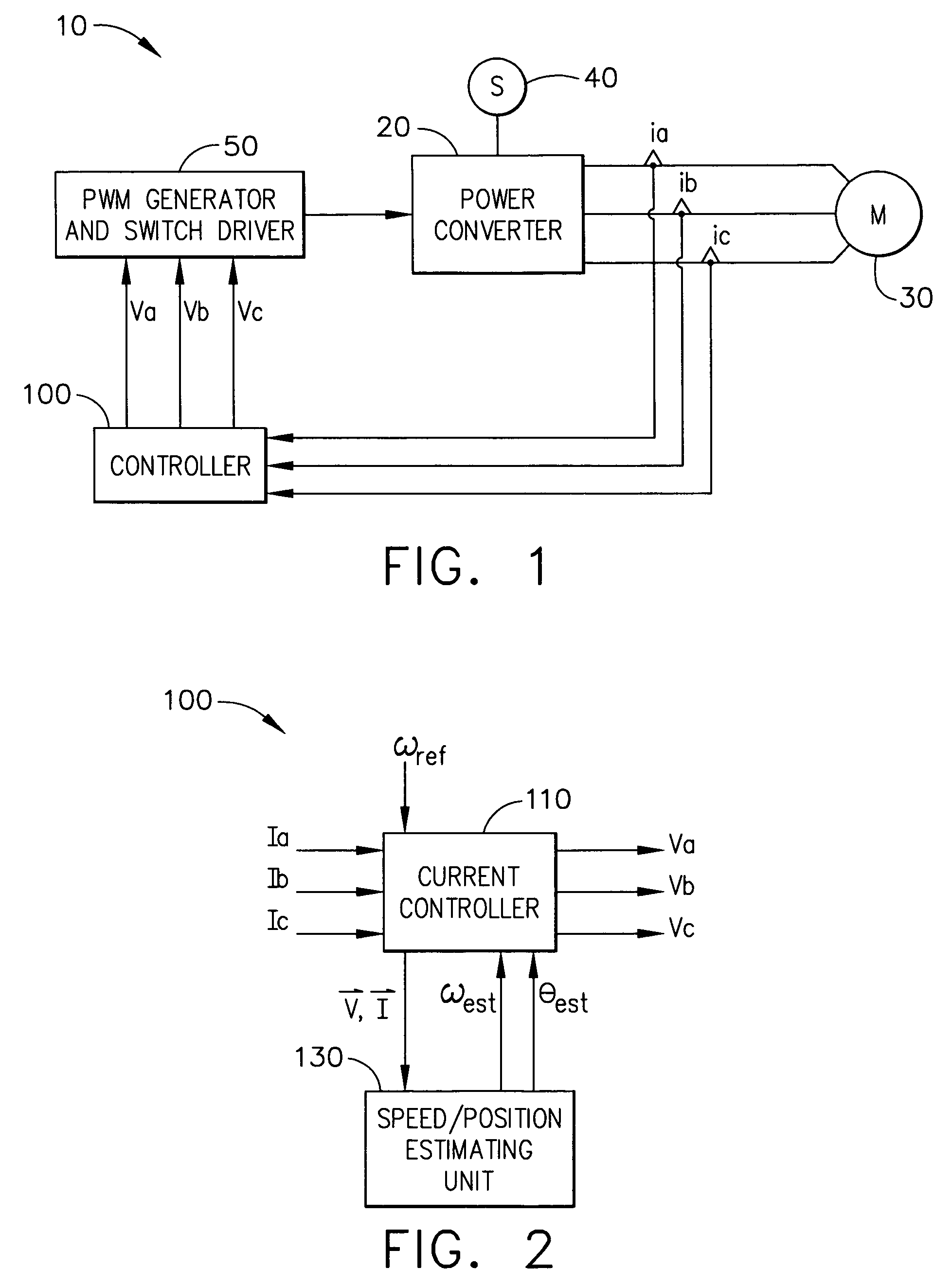
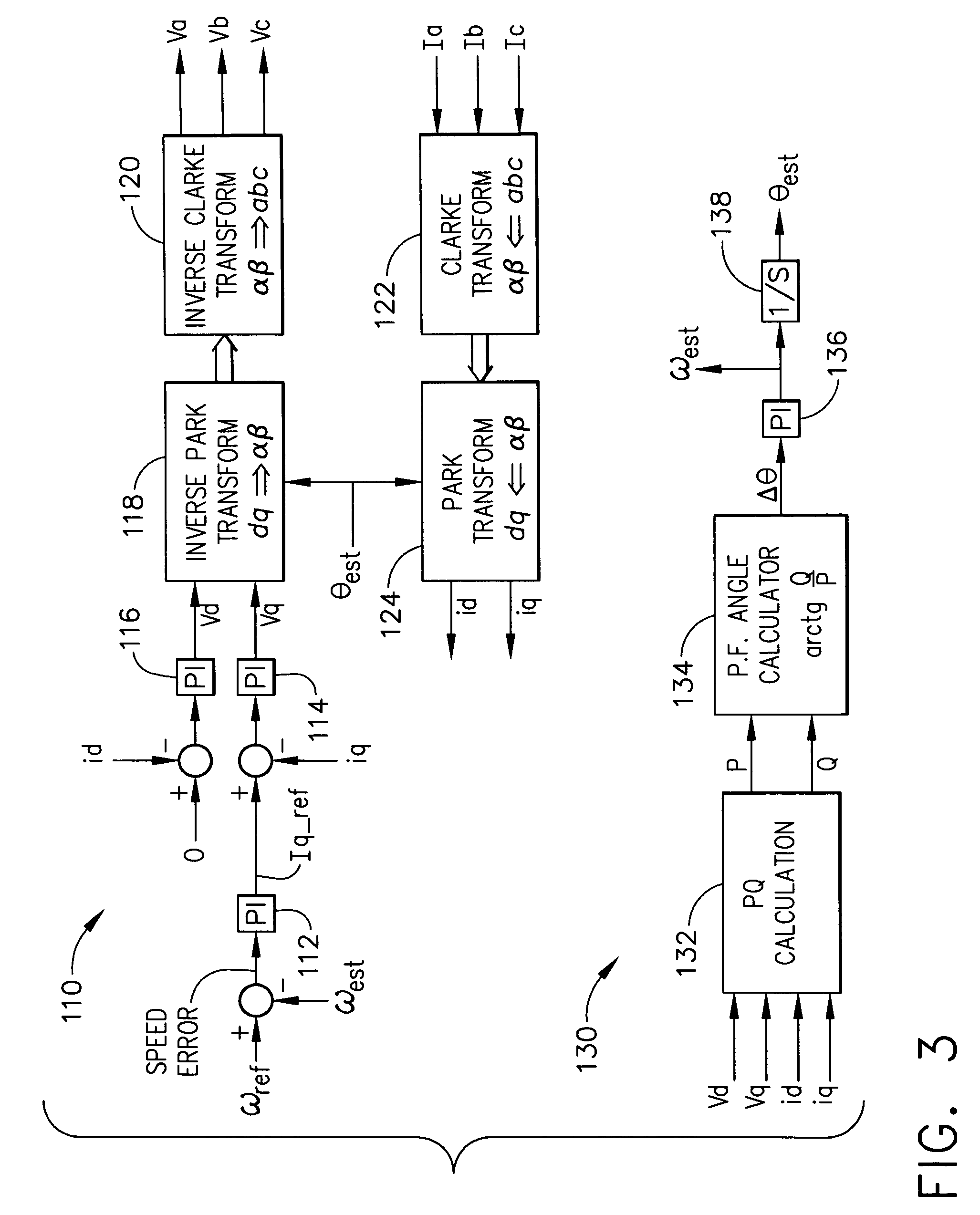
The present invention relates to a method of controlling a power converter (20) of a synchronous machine system (10), the method comprising sampling phase-current values between the power converter (20) and the synchronous machine (30); selecting a reference frame; regulating a current vector to align with the selected reference frame, the selected reference frame having a direct-axis component and a quadrature-axis component; estimating rotor speed and position as a function of instantaneous power; adjusting the selected reference frame, based on estimated rotor position, to synchronize the selected reference frame with a magnetic axis of the rotor, thereby generating a synchronized floating frame; and applying the synchronized floating frame to control the power converter (20). The present invention also related to a power converter controlling apparatus (100) for controlling a power converter (20) of a synchronous machine system (10) without use of a machine position sensor.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Hybrid magnetic bearing
ActiveUS7683514B2Highly controllableIncrease stiffnessSynchronous generatorsWindingsMagnetic bearingMagnetic axis
In a hybrid magnetic bearing, the electromagnet has a core wound with a control coil and has a main pole and a commutating pole with a commutating pole permanent magnet provided approximately parallel to each other at predetermined intervals in a protruding condition radially or axially to the rotor. In the magnetic bearing provided radially, two electromagnets are placed oppositely to each other across the rotor in an approximately horizontal position, and the rotor is arranged so as to have a predetermined gap with the main pole and the commutating pole, and the permanent magnet is provided between the adjacent electromagnets. In the magnetic bearing provided axially, two electromagnets are placed in parallel in an approximately horizontal position, and the rotor is arranged so as to have a predetermined gap with the main pole and the commutating pole, and the permanent magnet is provided between the adjacent electromagnets.
Owner:IWAKI
Horizontal shaft magnetic suspension wind driven generator
InactiveCN101701573ARealize full suspension operationReduce maintenanceShaftsWind motor combinationsWind drivenMagnetic bearing
The invention relates to a horizontal shaft magnetic suspension wind driven generator, comprising a stationery part and a rotating part; the stationery part comprises a radial magnetic bearing stator part, an axial magnetic bearing stator part, a generator stator part, a front protective bearing, a rear protective bearing, a stator shell and a blower tower; the rotating part comprises a blade, a hub, a rotating shaft, a radial magnetic bearing rotor part, an axial magnetic bearing rotor part and a generator rotor part; an axial magnetic bearing is composed of a permanent magnet without a control system, a radial magnetic bearing is a permanent magnet bias magnetic bearing, the permanent magnet provides bias flux density, and control force is adjusted by current; the blower rotor realizes five-freedom-degree stable suspension, can completely eliminate the mechanical friction of the rotating part and the stationery part, reduce starting resisting moment and starting wind velocity of the blower and improve the wind energy utilization rate. All components of the invention have rational and compact layout, the maintenance of the blower can be reduced and the service life is prolonged.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com