Patents
Literature
168 results about "Hardware register" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
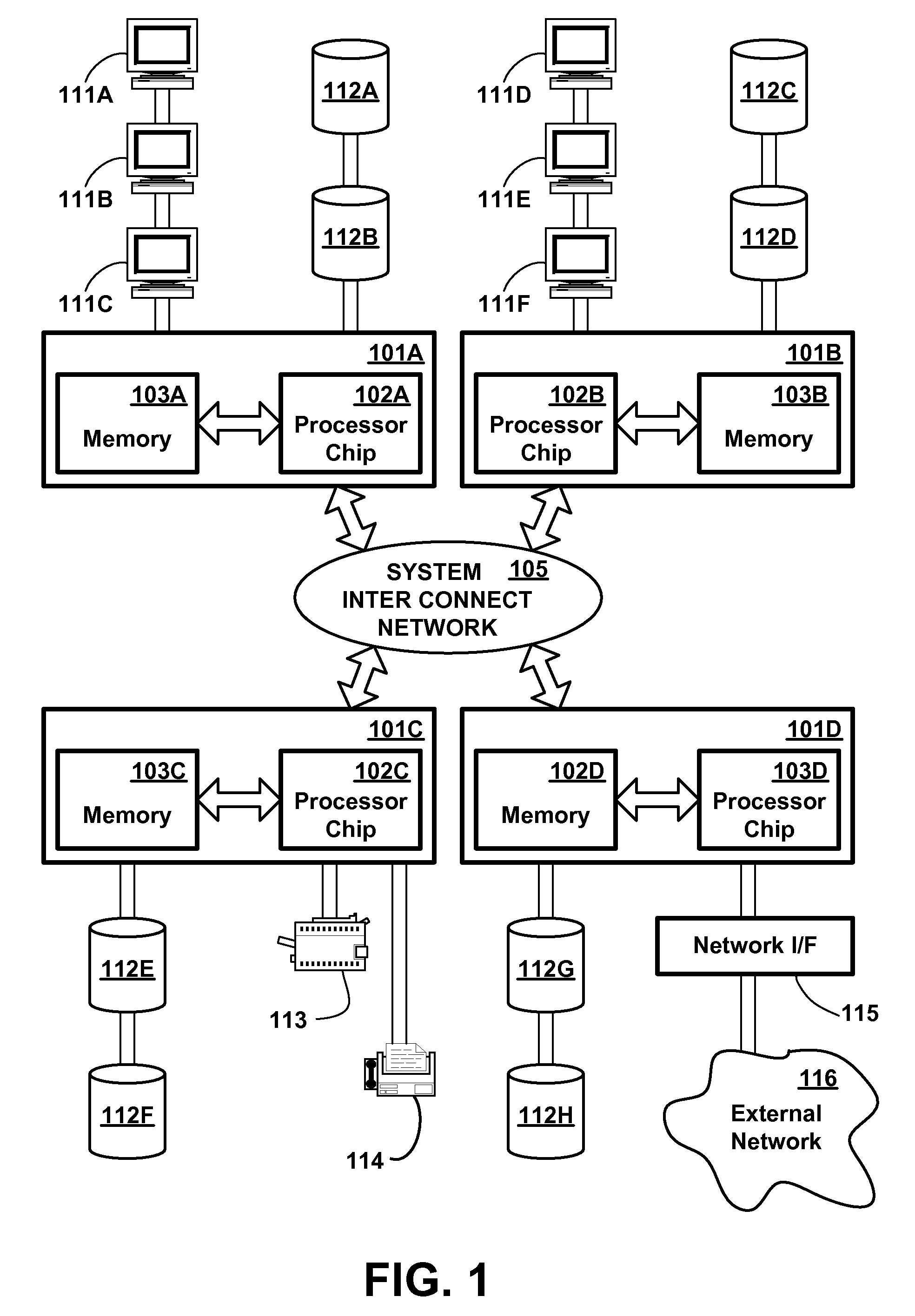
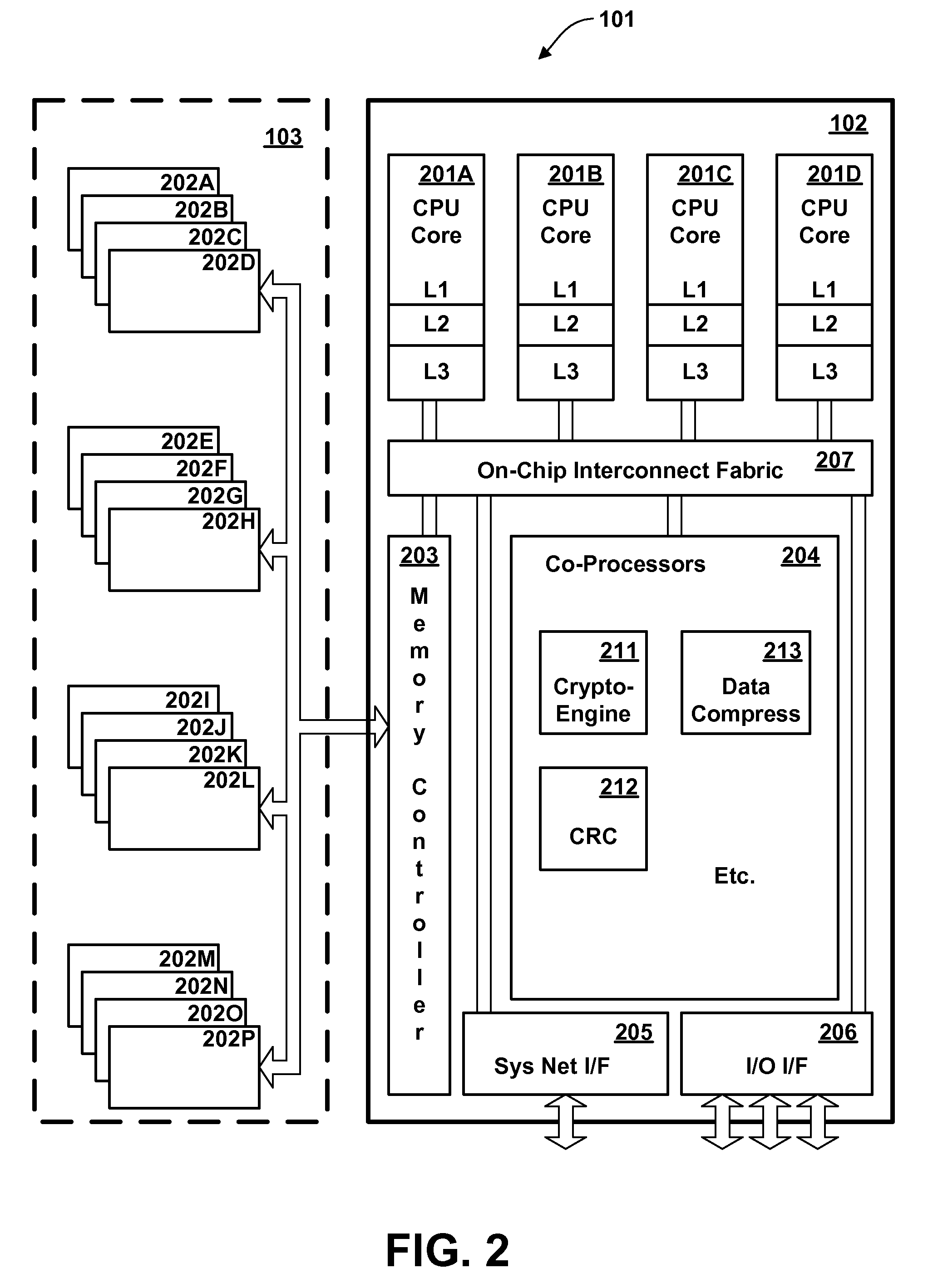
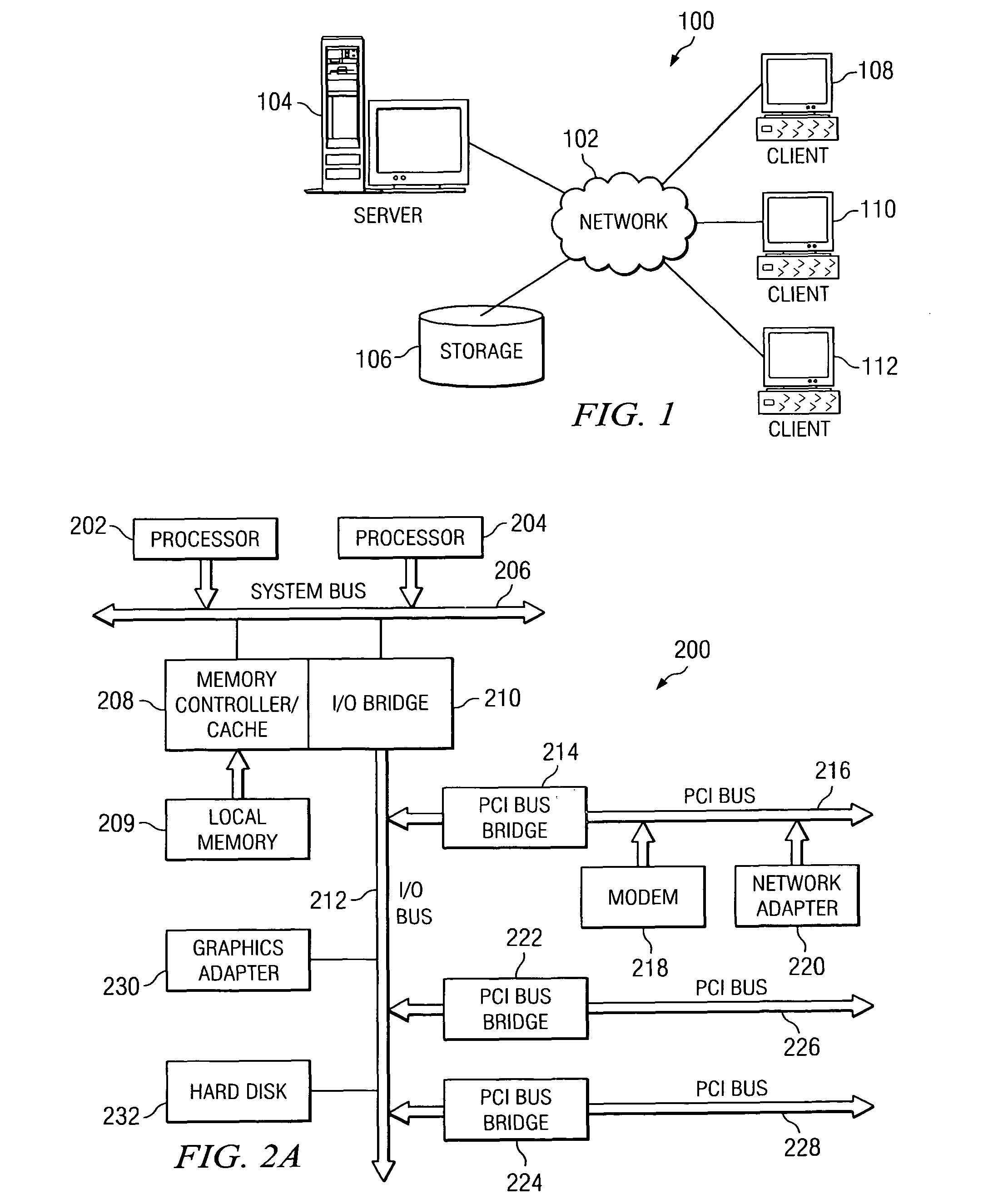
In digital electronics, especially computing, hardware registers are circuits typically composed of flip flops, often with many characteristics similar to memory, such as...
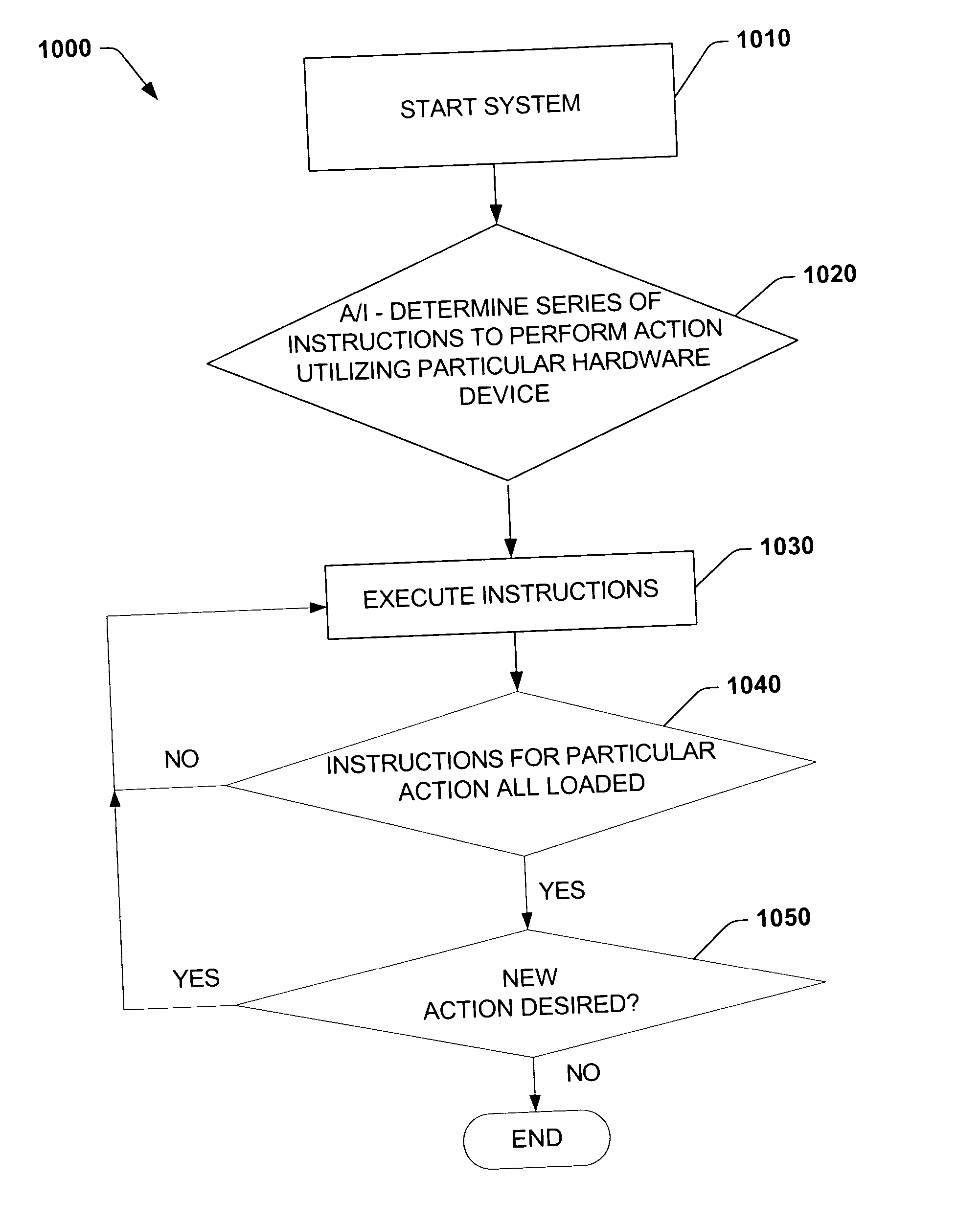
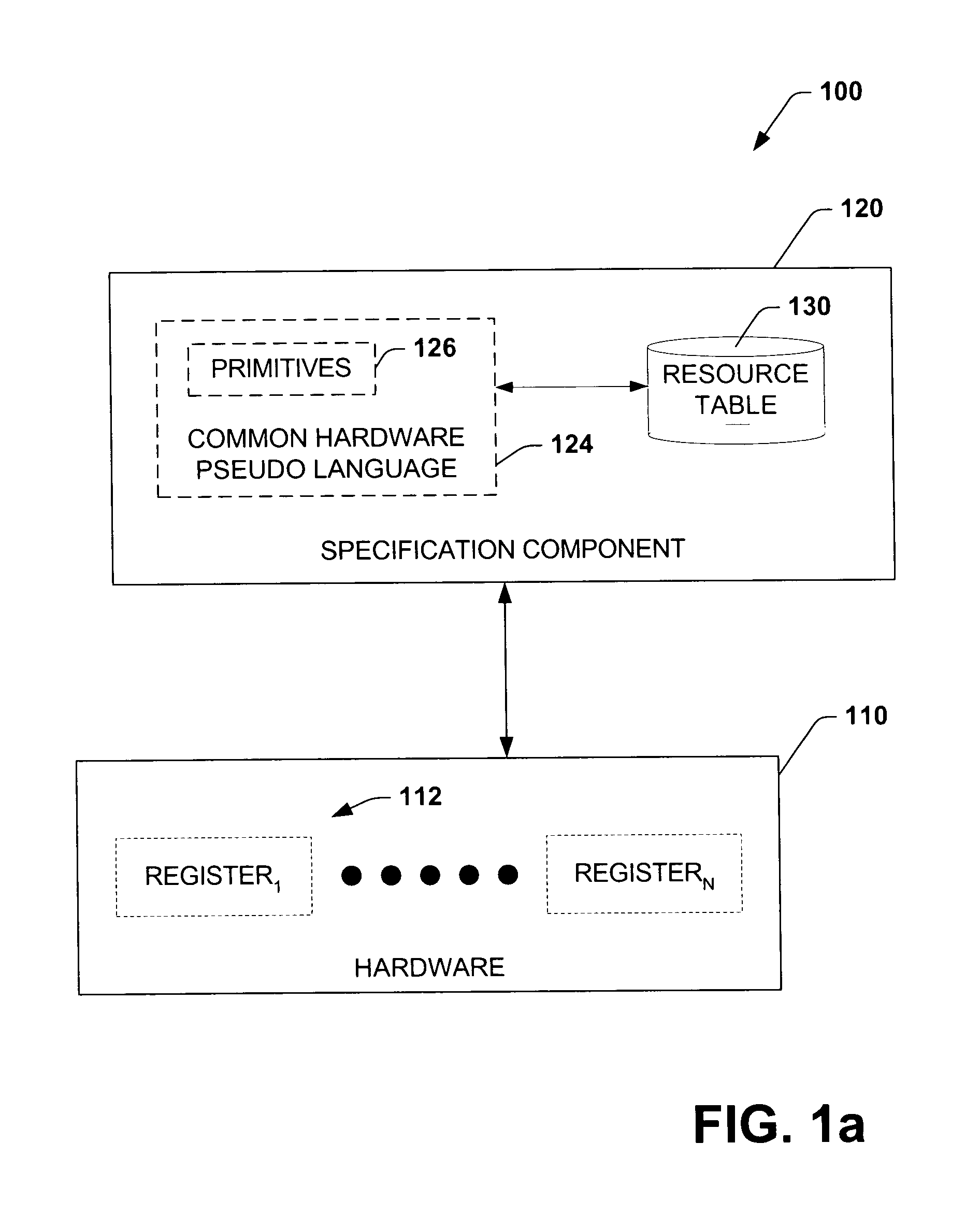
Language for performing high level actions using hardware registers
InactiveUS20050060525A1Easy to useDigital computer detailsProgram loading/initiatingComputer hardwareHuman language
A system and method that utilizes a common hardware register pseudo-language are disclosed. The present invention employs a common platform to specify hardware functionality and to execute hardware action(s). Hardware actions can be effectuated by performing a series of instructions, which comprise hardware register primitives and resources utilized by the primitives. The hardware register primitives are operations defined according to the common hardware register pseudo-language. The series of instructions can be loaded prior to boot or during initialization.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
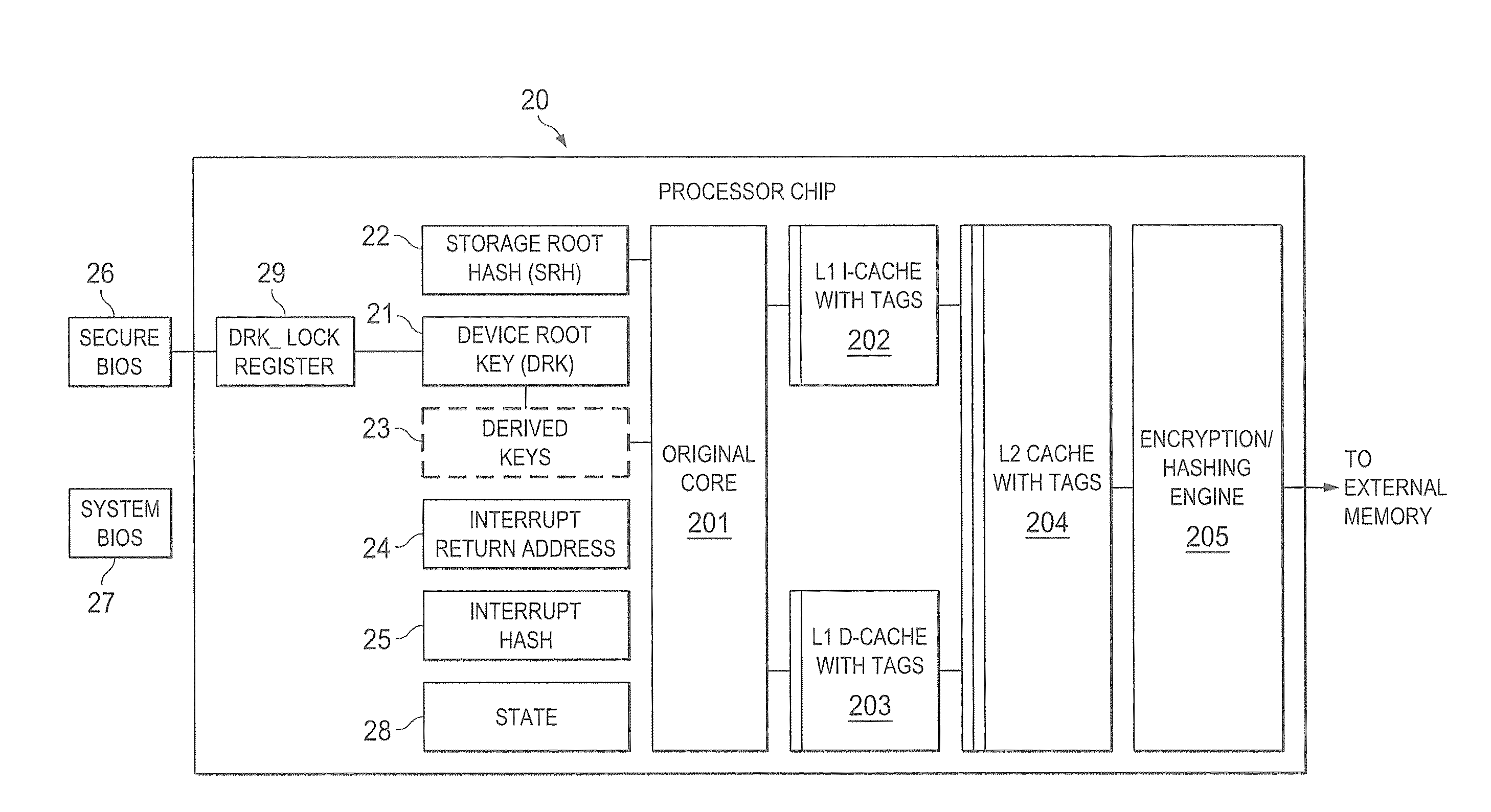
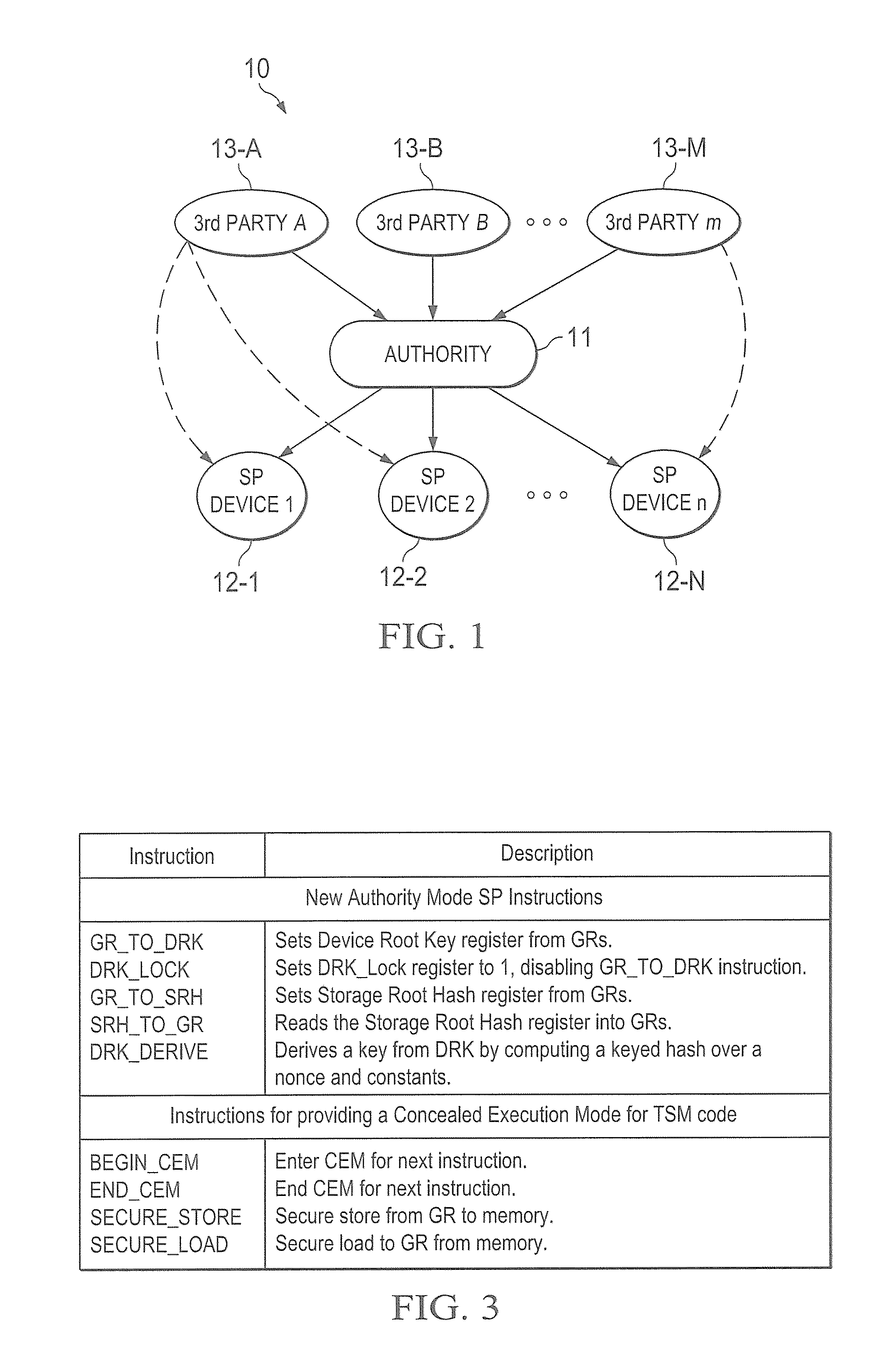
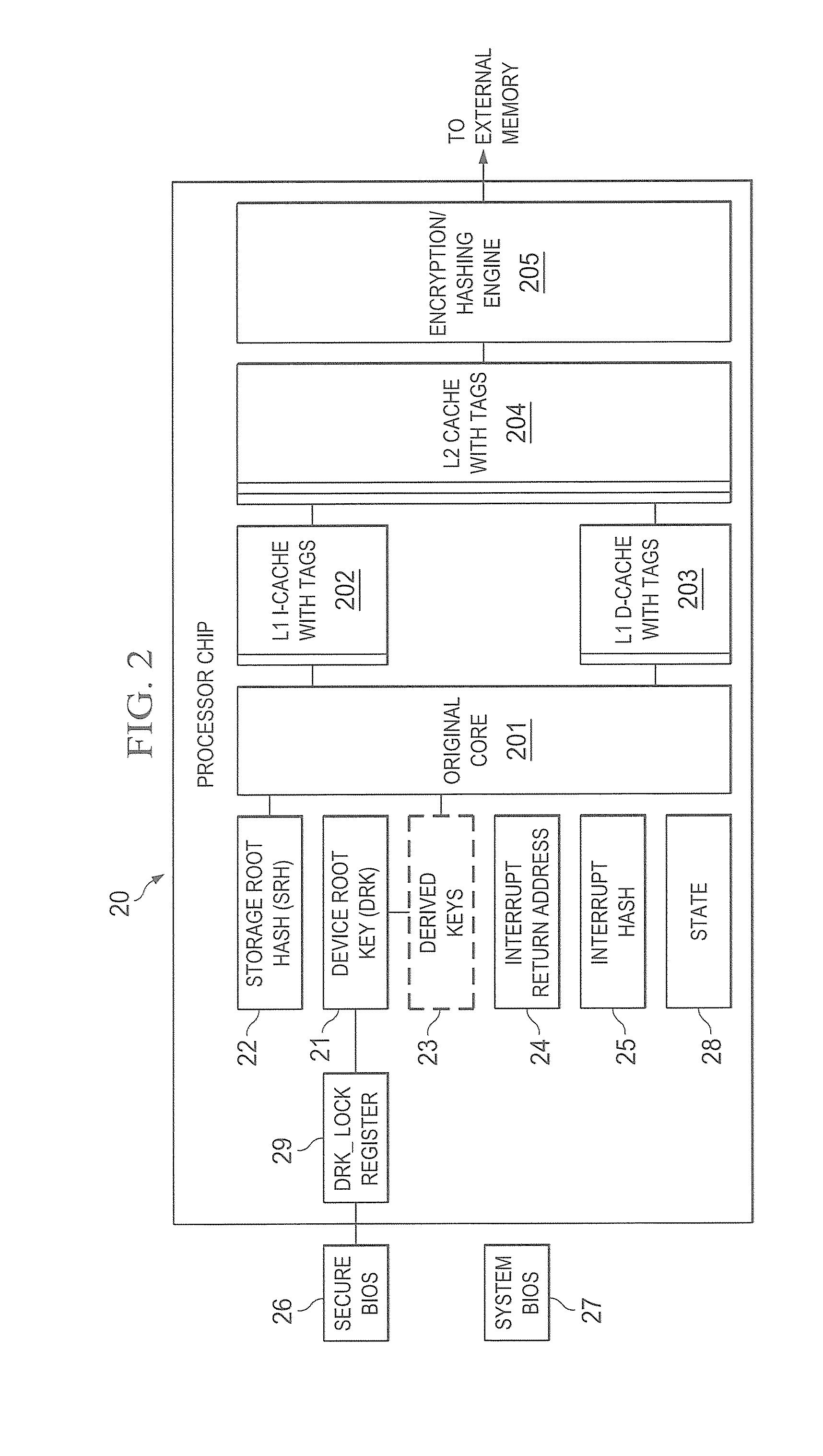
Hardware trust anchors in sp-enabled processors
ActiveUS20100042824A1User identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsOperational systemConfidentiality
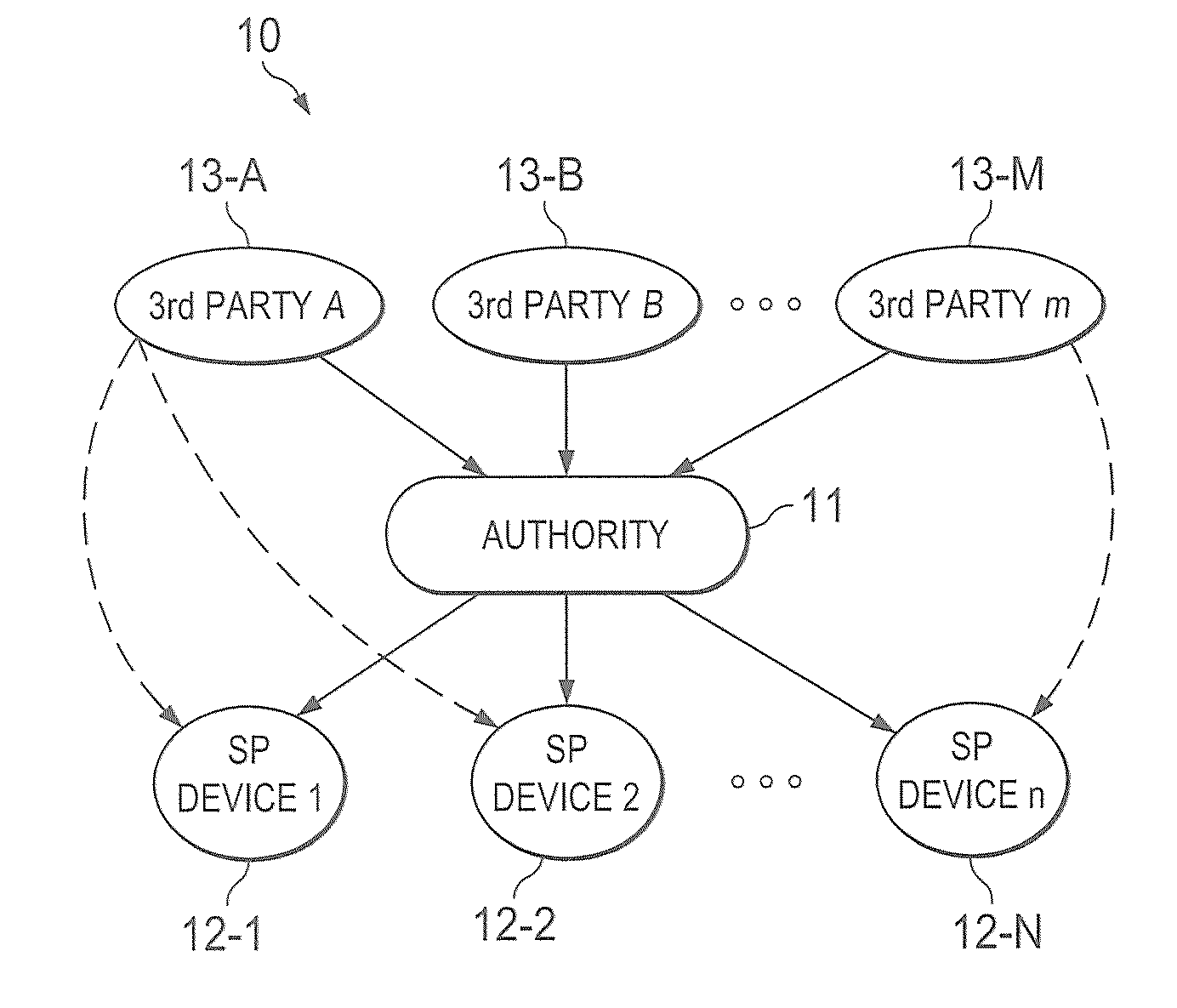
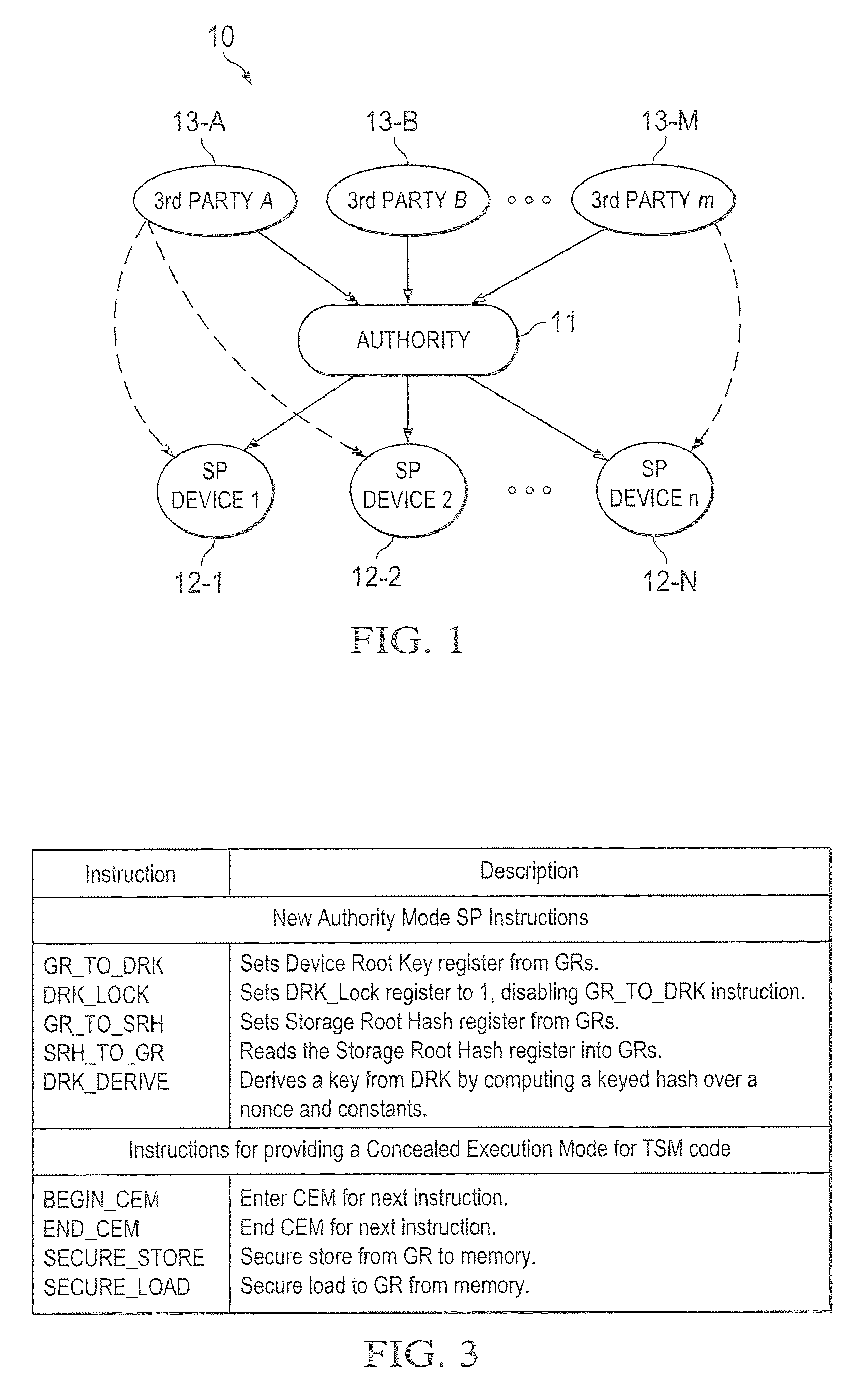
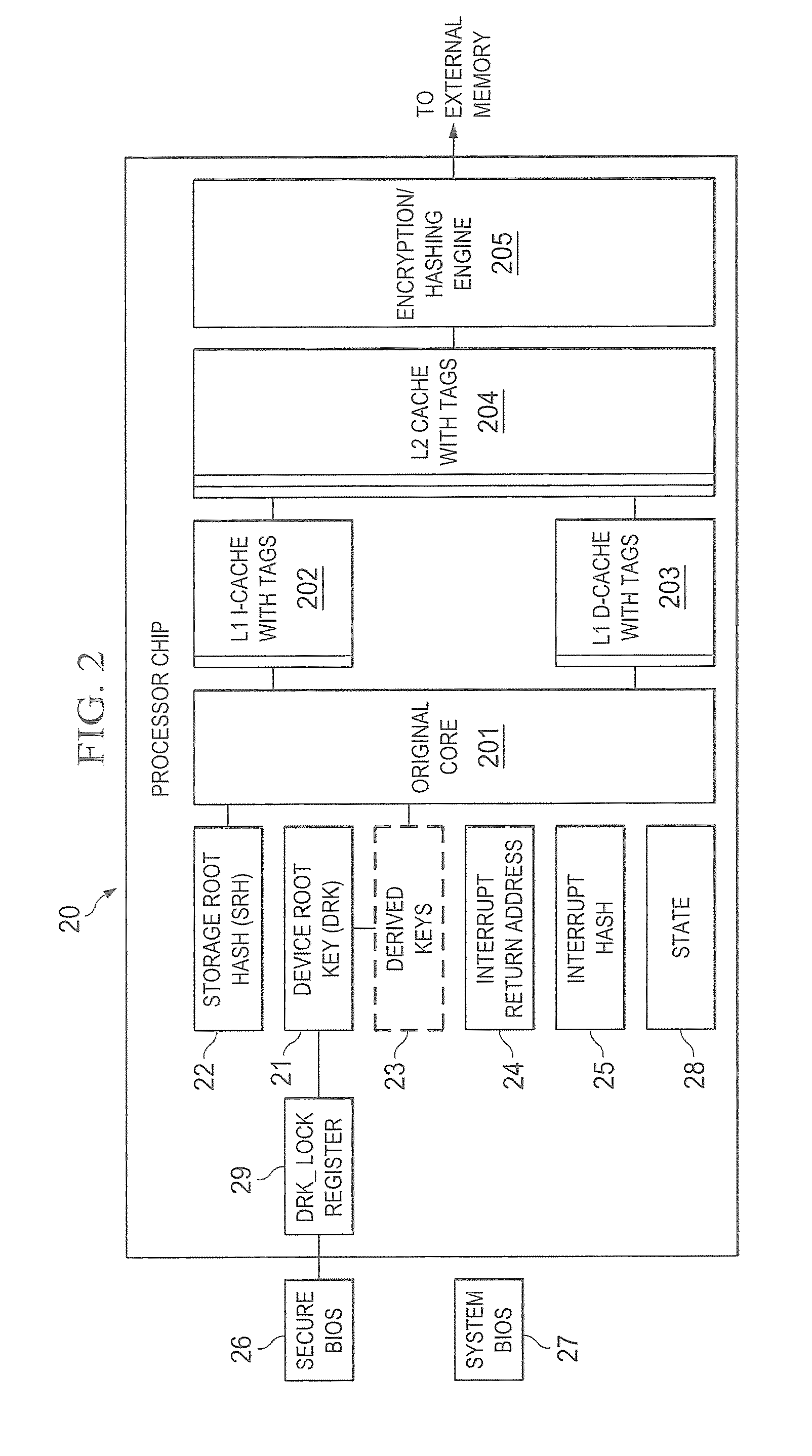
A trust system and method is disclosed for use in computing devices, particularly portable devices, in which a central Authority shares secrets and sensitive data with users of the respective devices. The central Authority maintains control over how and when shared secrets and data are used. In one embodiment, the secrets and data are protected by hardware-rooted encryption and cryptographic hashing, and can be stored securely in untrusted storage. The problem of transient trust and revocation of data is reduced to that of secure key management and keeping a runtime check of the integrity of the secure storage areas containing these keys (and other secrets). These hardware-protected keys and other secrets can further protect the confidentiality and / or integrity of any amount of other information of arbitrary size (e.g., files, programs, data) by the use of strong encryption and / or keyed-hashing, respectively. In addition to secrets the Authority owns, the system provides access to third party secrets from the computing devices. In one embodiment, the hardware-rooted encryption and hashing each use a single hardware register fabricated as part of the computing device's processor or System-on-Chip (SoC) and protected from external probing. The secret data is protected while in the device even during operating system malfunctions and becomes non-accessible from storage according to various rules, one of the rules being the passage of a certain time period. The use of the keys (or other secrets) can be bound to security policies that cannot be separated from the keys (or other secrets). The Authority is also able to establish remote trust and secure communications to the devices after deployment in the field using a special tamper-resistant hardware register in the device, to enable, disable or update the keys or secrets stored securely by the device.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV +1
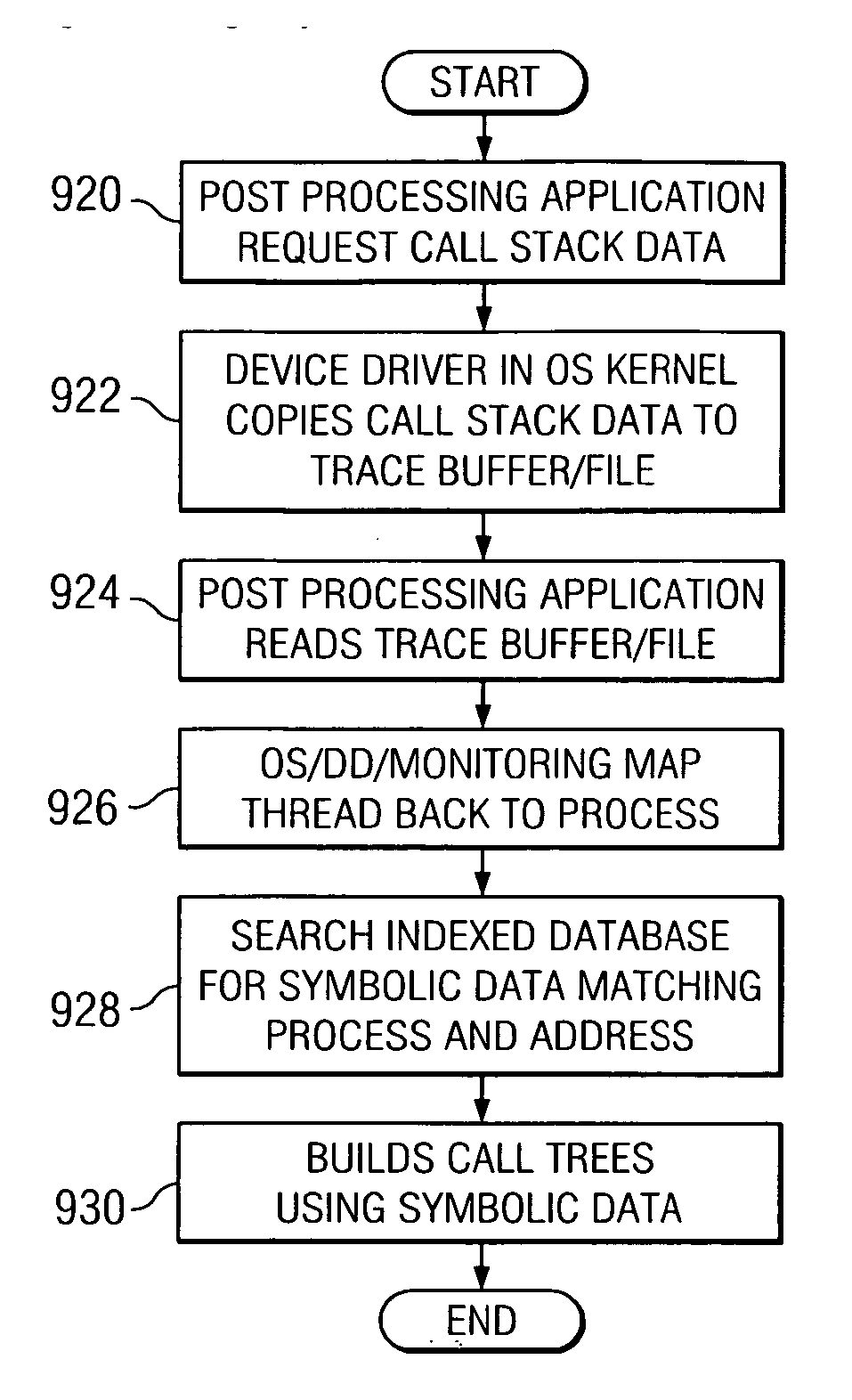
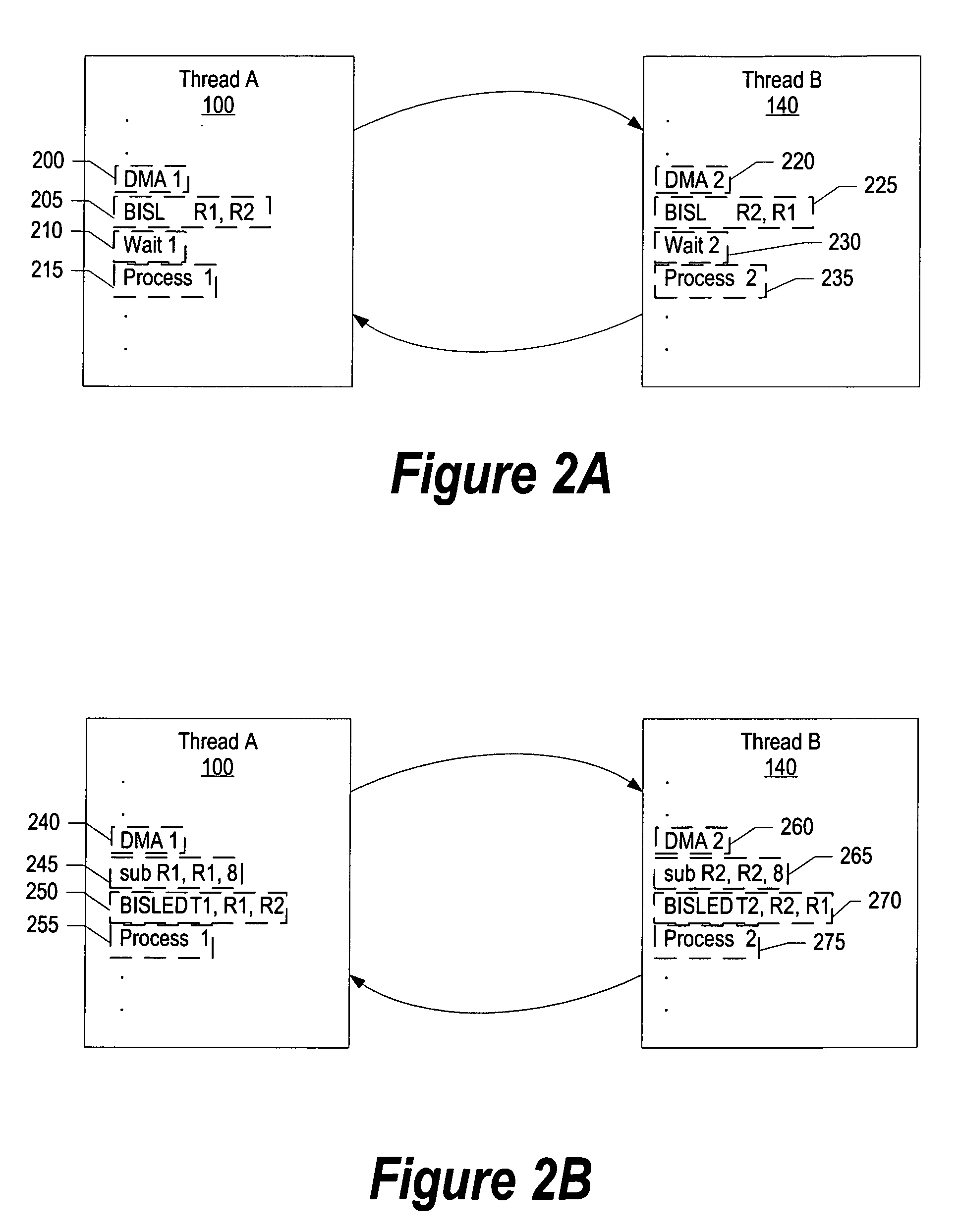
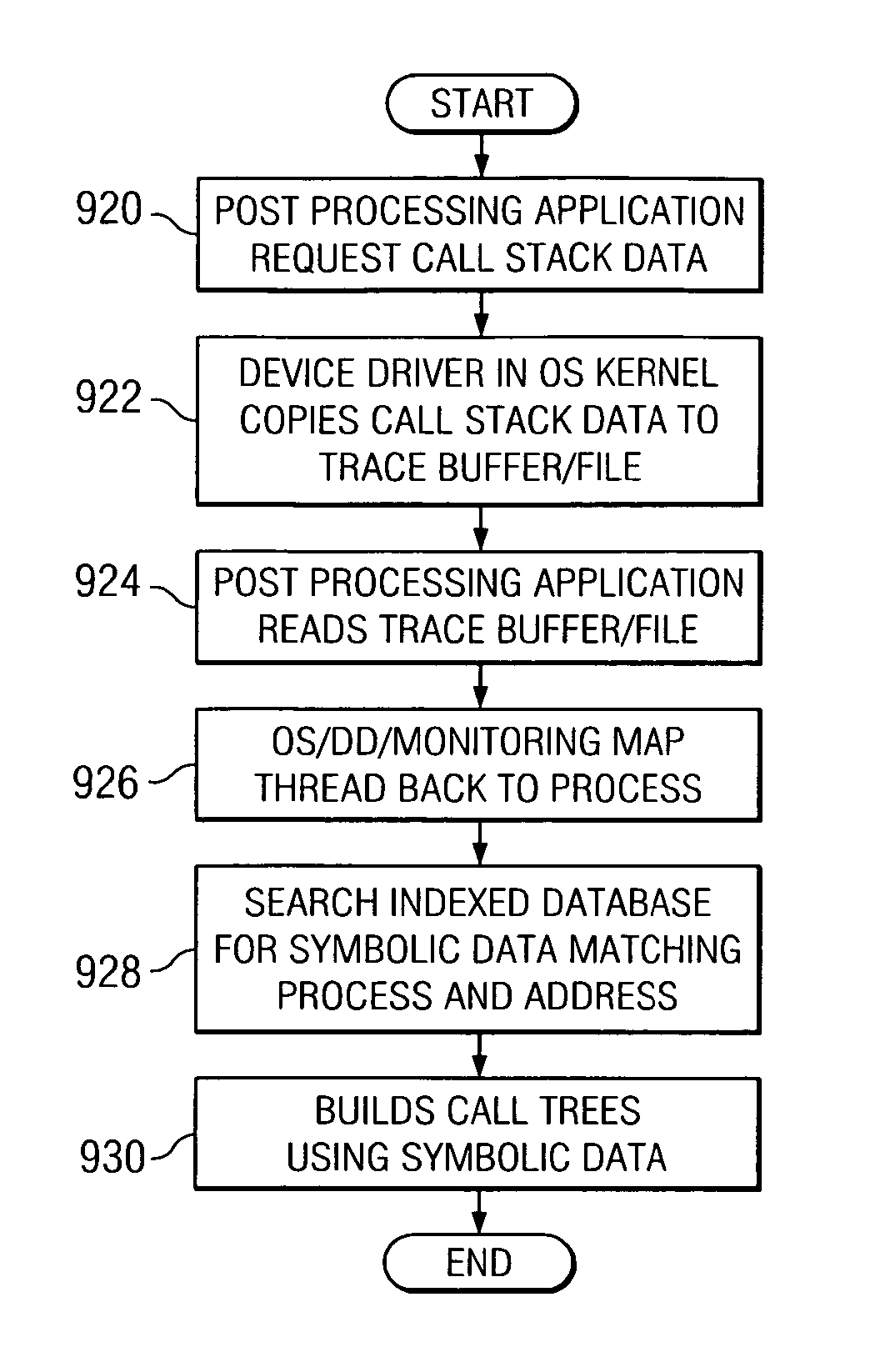
Method and apparatus for determining computer program flows autonomically using hardware assisted thread stack tracking and cataloged symbolic data
InactiveUS20050210454A1Error detection/correctionDigital computer detailsCall stackOperational system
A method, apparatus, and computer instructions for determining computer flows autonomically using hardware assisted thread stack and cataloged symbolic data. When a new thread is spawned during execution of a computer program, new thread work area is allocated by the operating system in memory for storage of call stack information for the new thread. Hardware registers are set with values corresponding to the new thread work area. Upon context switch, values of the registers are saved in a context save area for future restoration. When call stack data is post-processed, the operating system or a device driver copies call stack data from the thread work areas to a consolidated buffer and each thread is mapped to a process. Symbolic data may be obtained based on the process identifier and address of the method / routine that was called / returned in the thread. Corresponding program flow is determined using retrieved symbolic data and call stack data.
Owner:IBM CORP
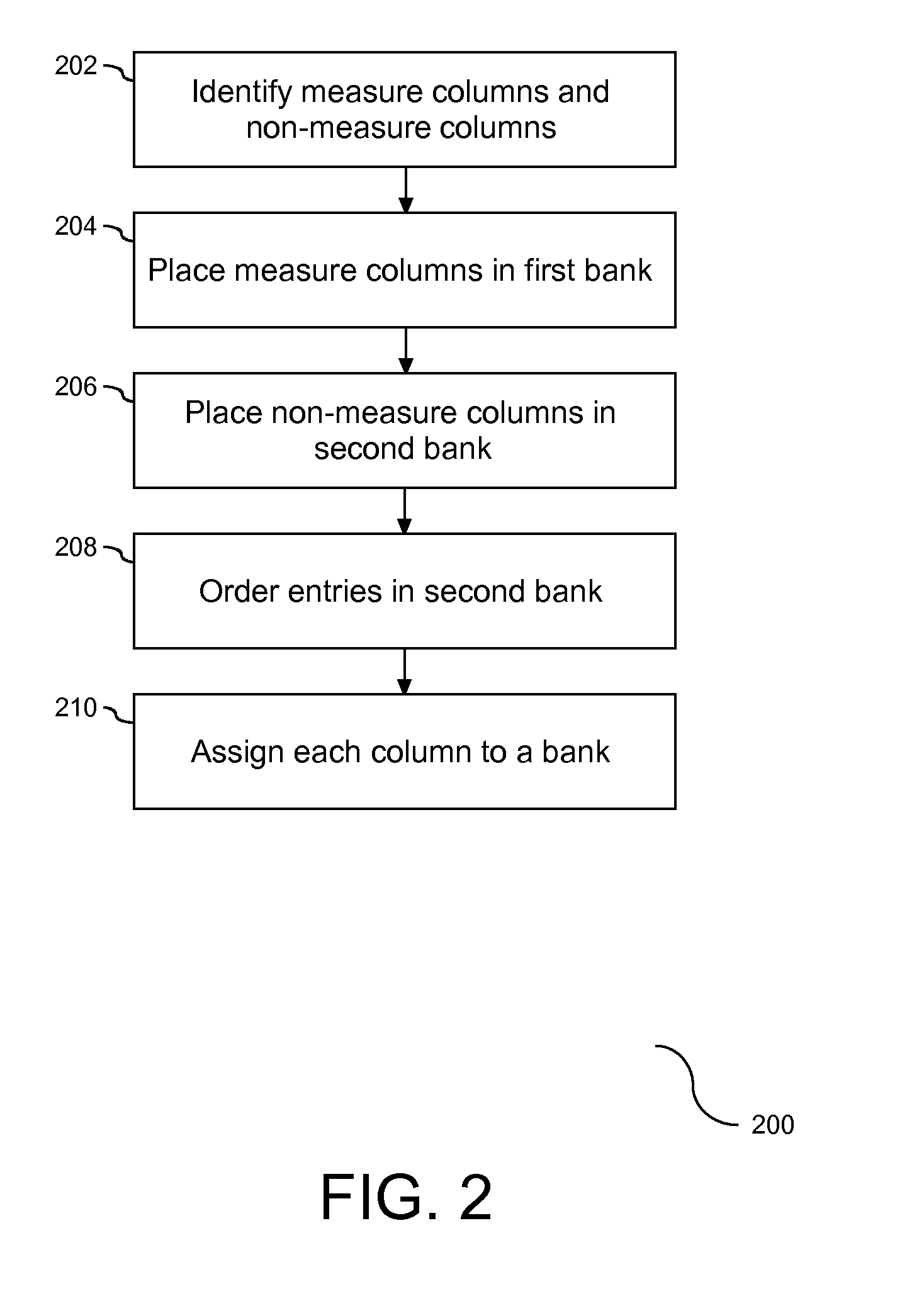
Method for Laying Out Fields in a Database in a Hybrid of Row-Wise and Column-Wise Ordering
ActiveUS20100042587A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsProcessor registerData mining
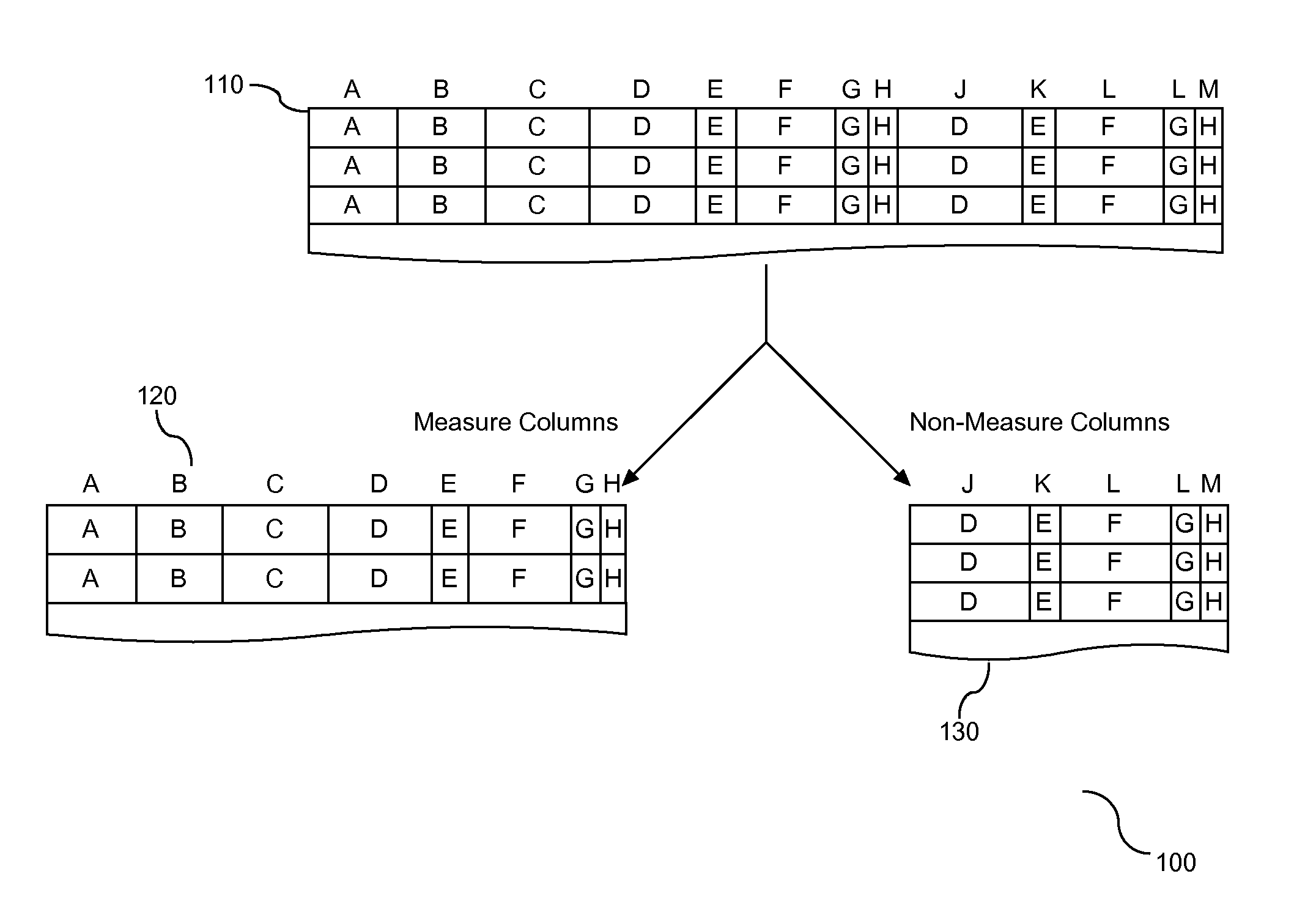
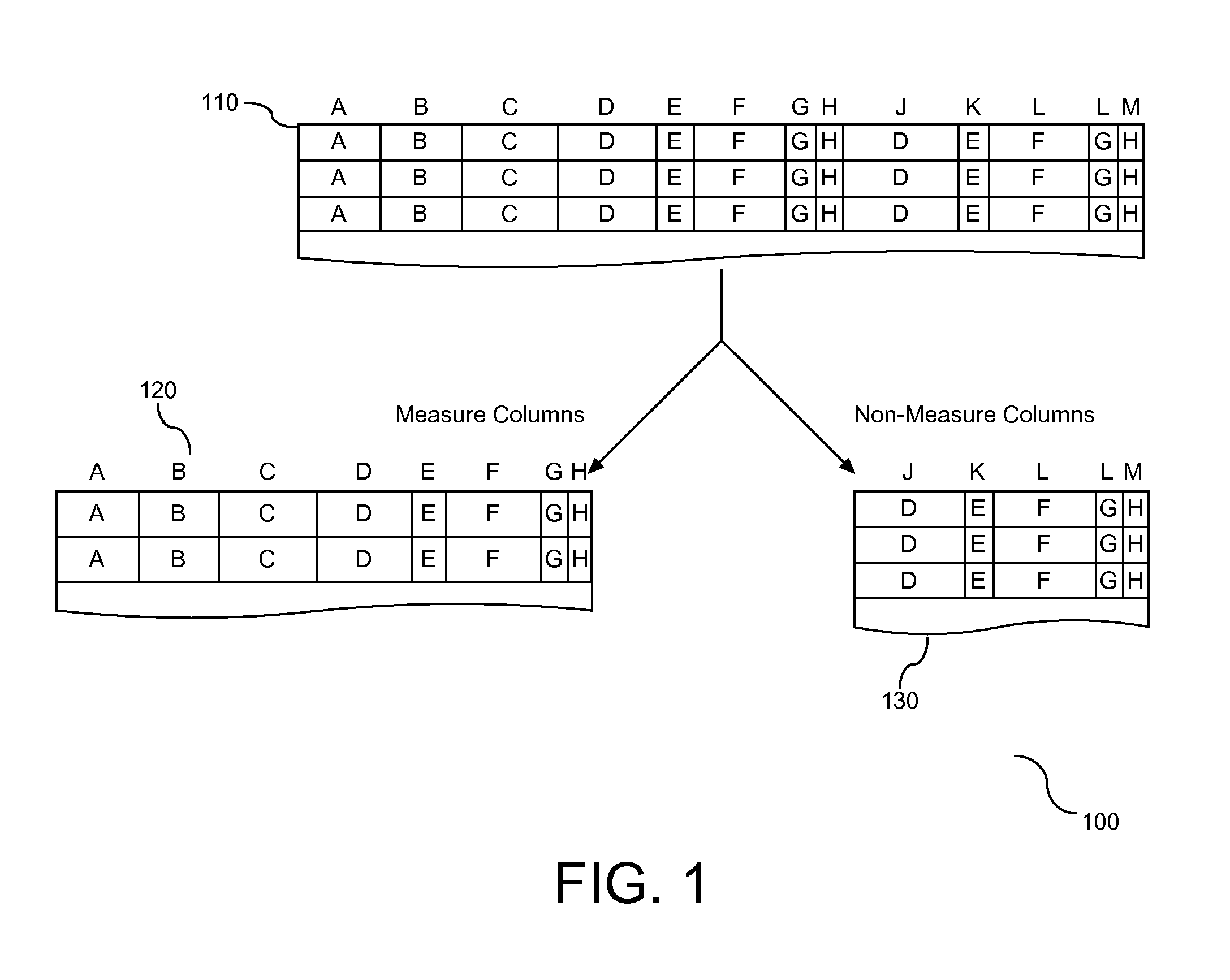
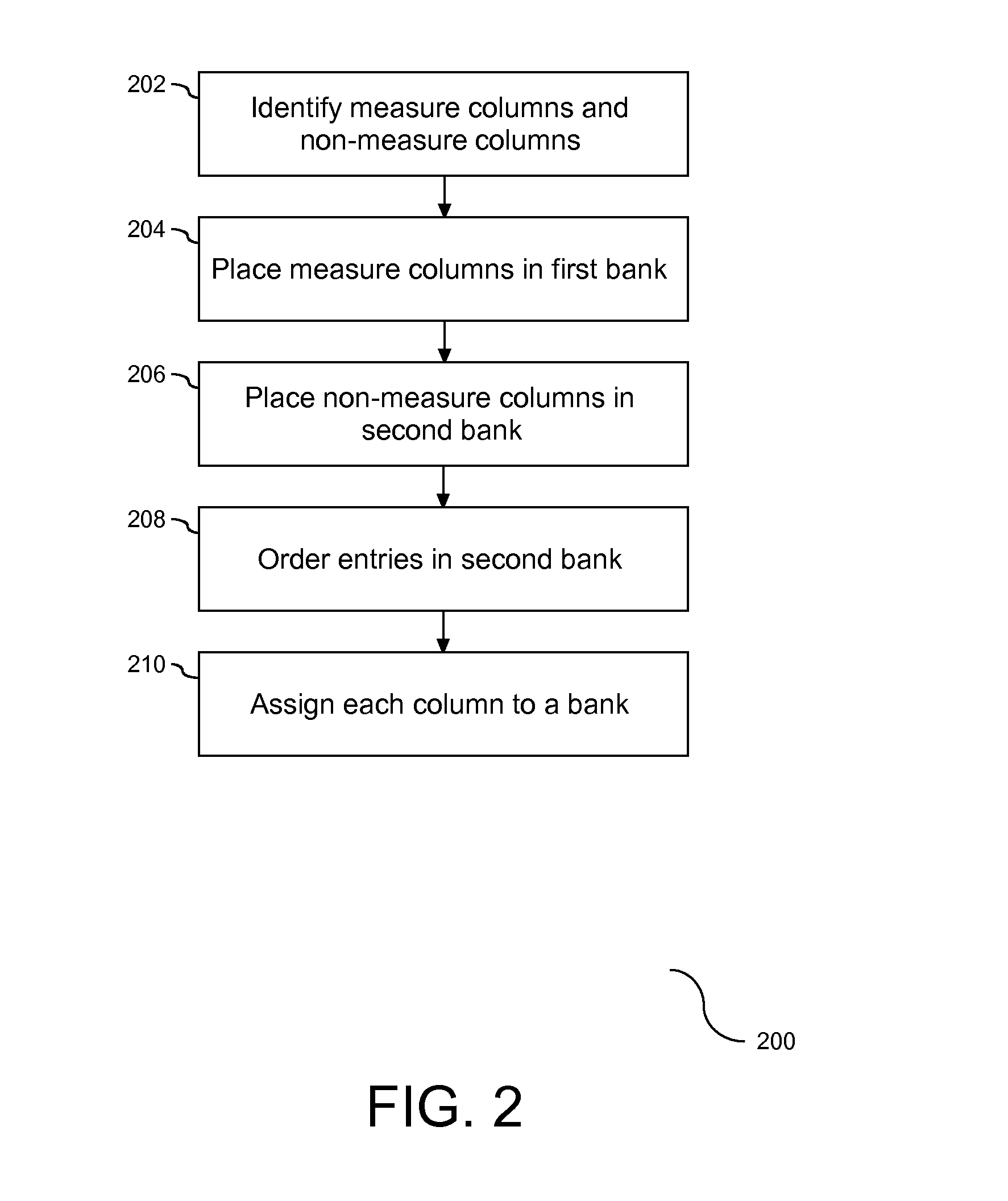
A method, system, and article are provided for employment of a hybrid layout of representation of data objects in computer memory. Columns of the database are separated based upon a classification of the columns. A vertical partition in the form of a bank is provided to receive an assignment of one or more data objects identified in the columns. Each bank is sized to be a divisor of a size of an associated hardware register. Assignment of data objects to banks organizes the data in a manner that support efficient query processing that mitigates the quantity of banks required to respond to the query.
Owner:IBM CORP
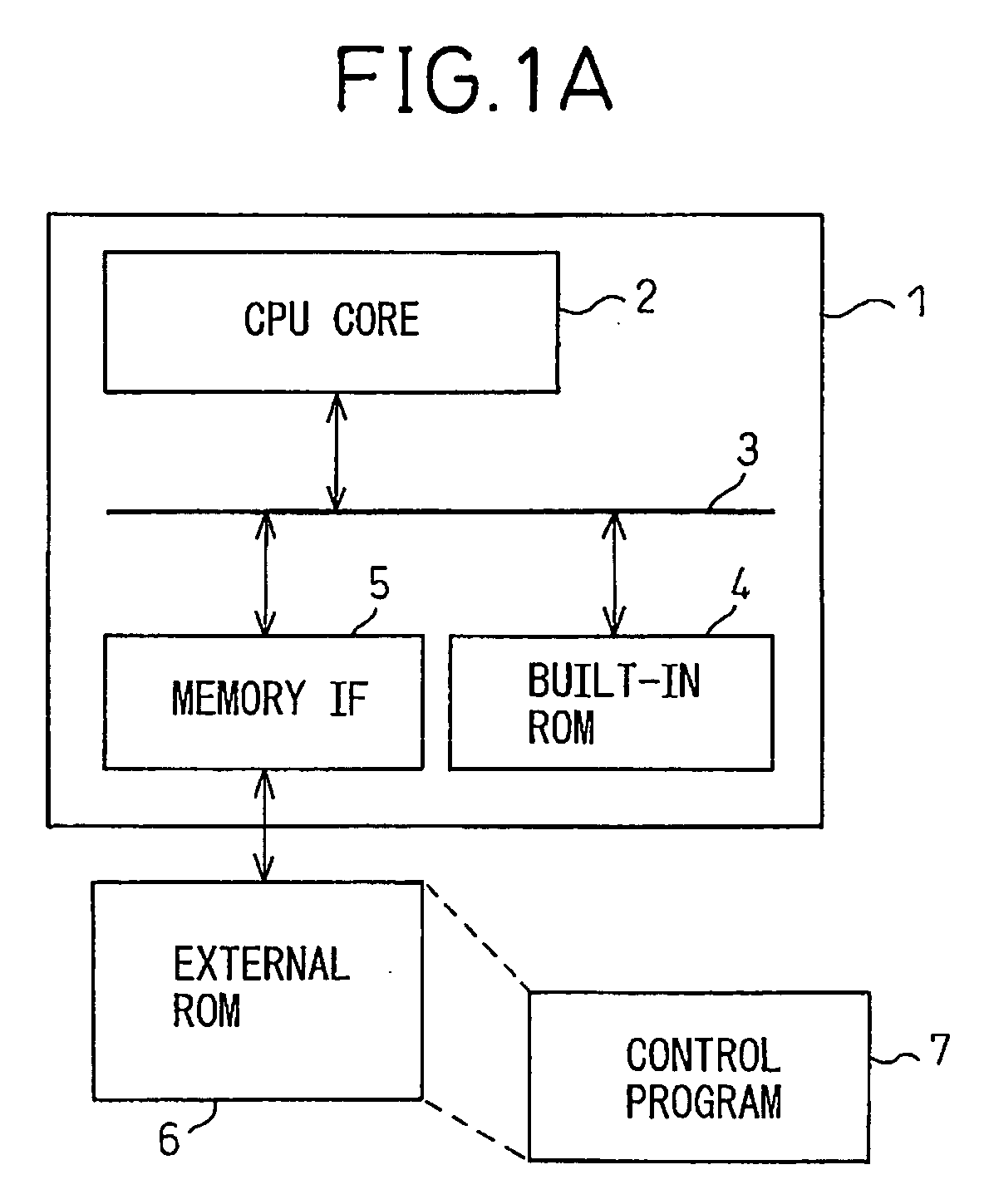
Secure processor system without need for manufacturer and user to know encryption information of each other
InactiveUS20080205651A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationProcessor registerSecure cryptoprocessor
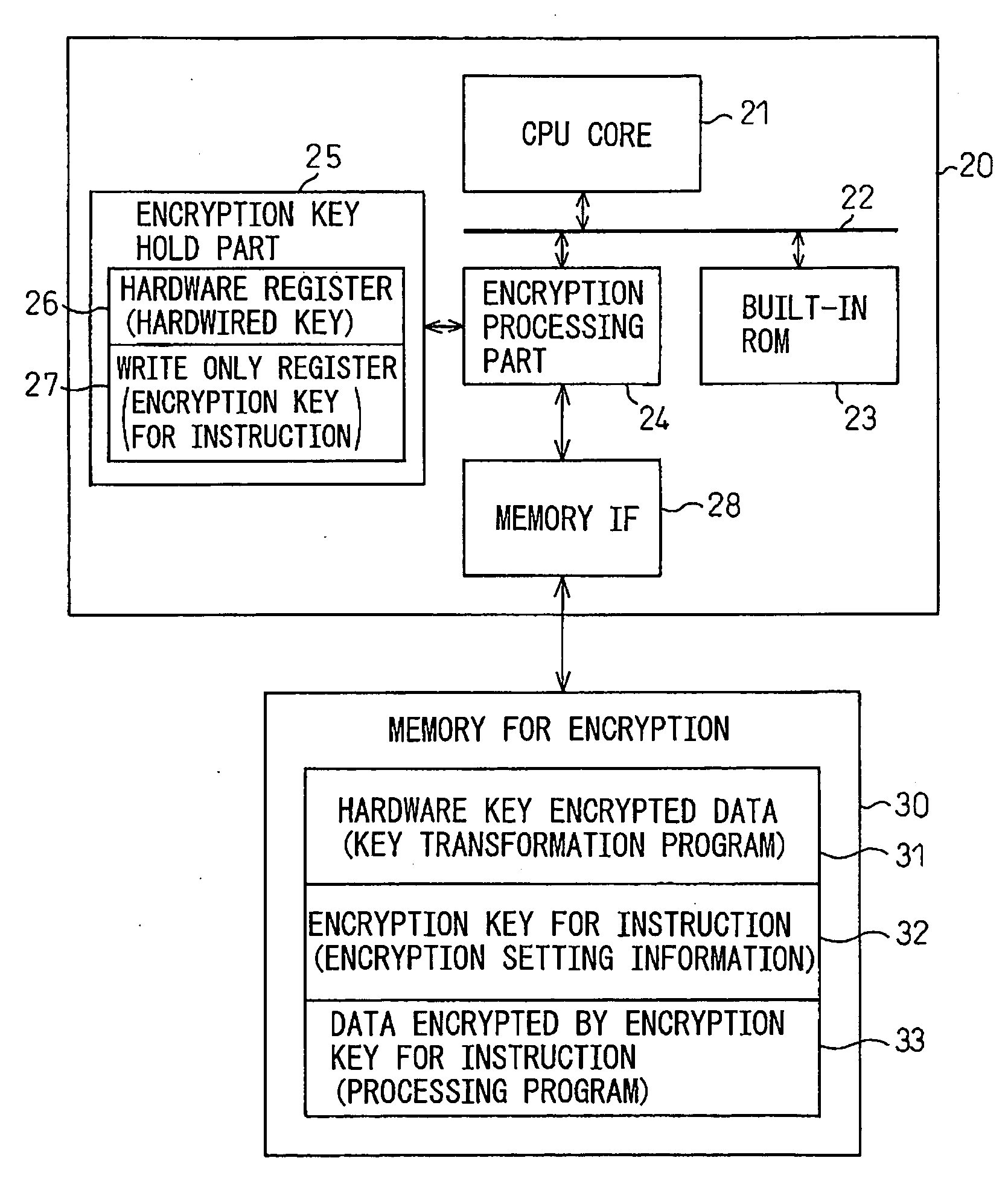
A secure processor system capable of improving the security of processor processing by the addition of minimum modules without the need for a manufacturer and a user to know encryption information of each other has been disclosed. The secure processor system includes a secure processor having a CPU core that executes a instruction code, an encryption key hold part that holds a processor key, and an encryption processing part that encrypts or decrypts data input / output to / from the core with a processor key and a memory, and the encryption key hold part includes a hardware register that holds a hardwired encryption key, a write only register that stores an encryption key for instruction to be input and holds the stored encryption key for instruction so that it cannot be read, and the encryption key hold part outputs a hardware encryption key as a processor key at the time of activation and outputs a command encryption key as a processor key after a encryption key for instruction is written.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
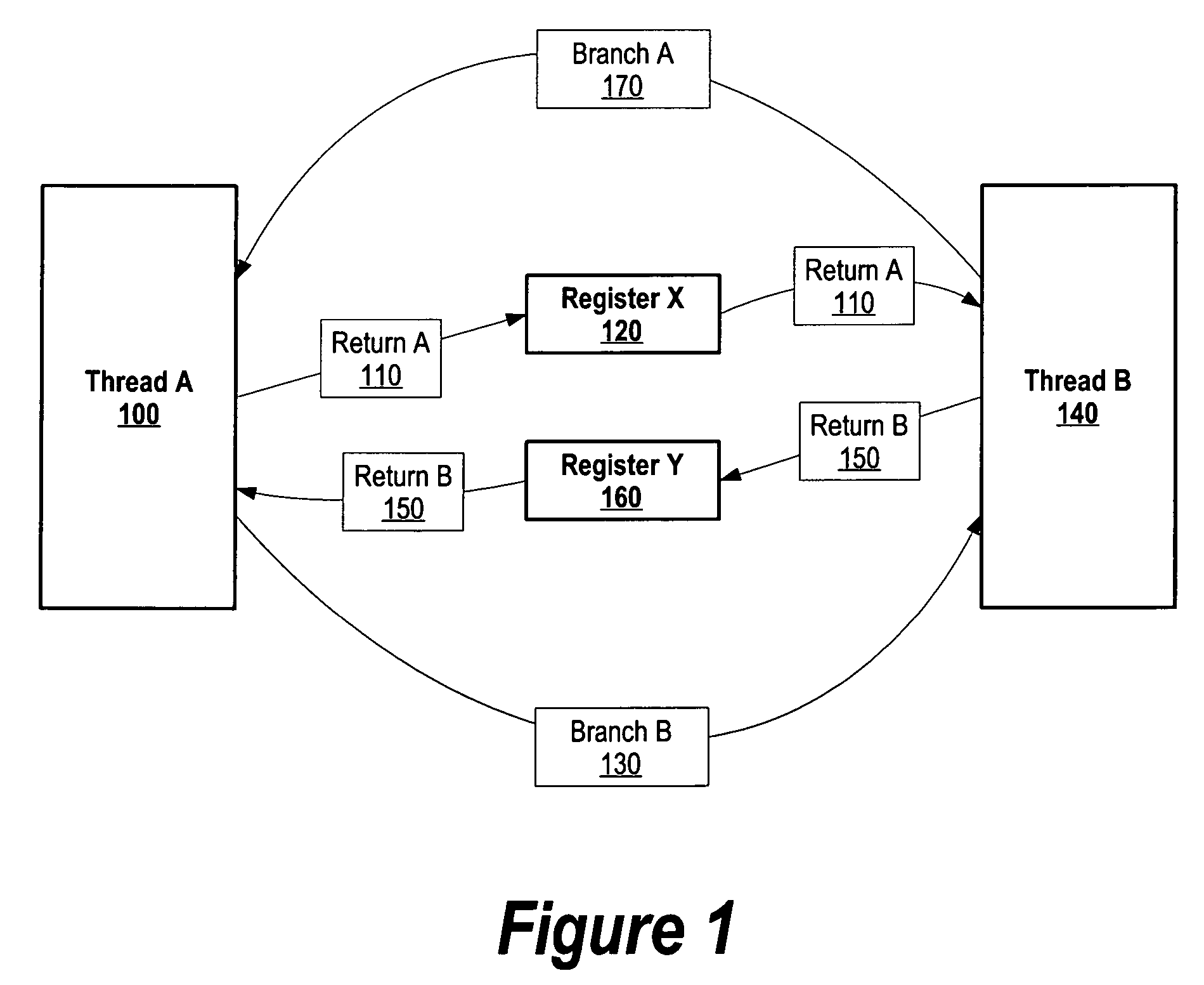
System and method for partitioning processor resources based on memory usage
A system and method for partitioning processor resources based on memory usage is provided. A compiler determines the extent to which a process is memory-bound and accordingly divides the process into a number of threads. When a first thread encounters a prolonged instruction, the compiler inserts a conditional branch to a second thread. When the second thread encounters a prolonged instruction, a conditional branch to a third thread is executed. This continues until the last thread conditionally branches back to the first thread. An indirect segmented register file is used so that the “return to” and “branch to” logical registers within each thread are the same (e.g., R1 and R2) for each thread. These logical registers are mapped to hardware registers that store actual addresses. The indirect mapping is altered to bypass completed threads. When the last thread completes it may signal an external process.
Owner:IBM CORP
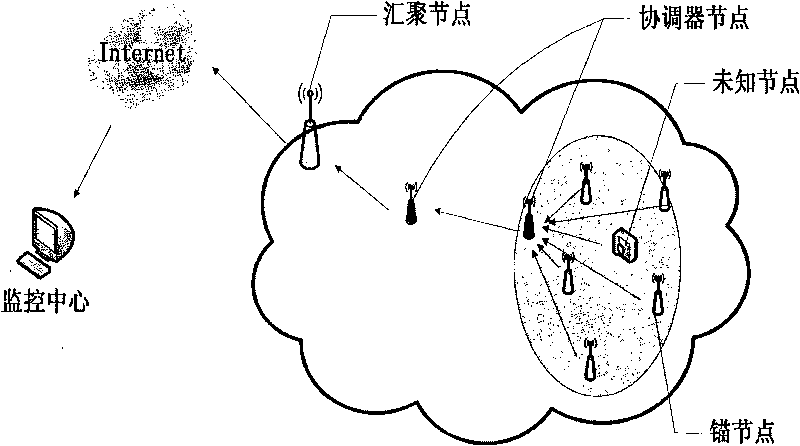
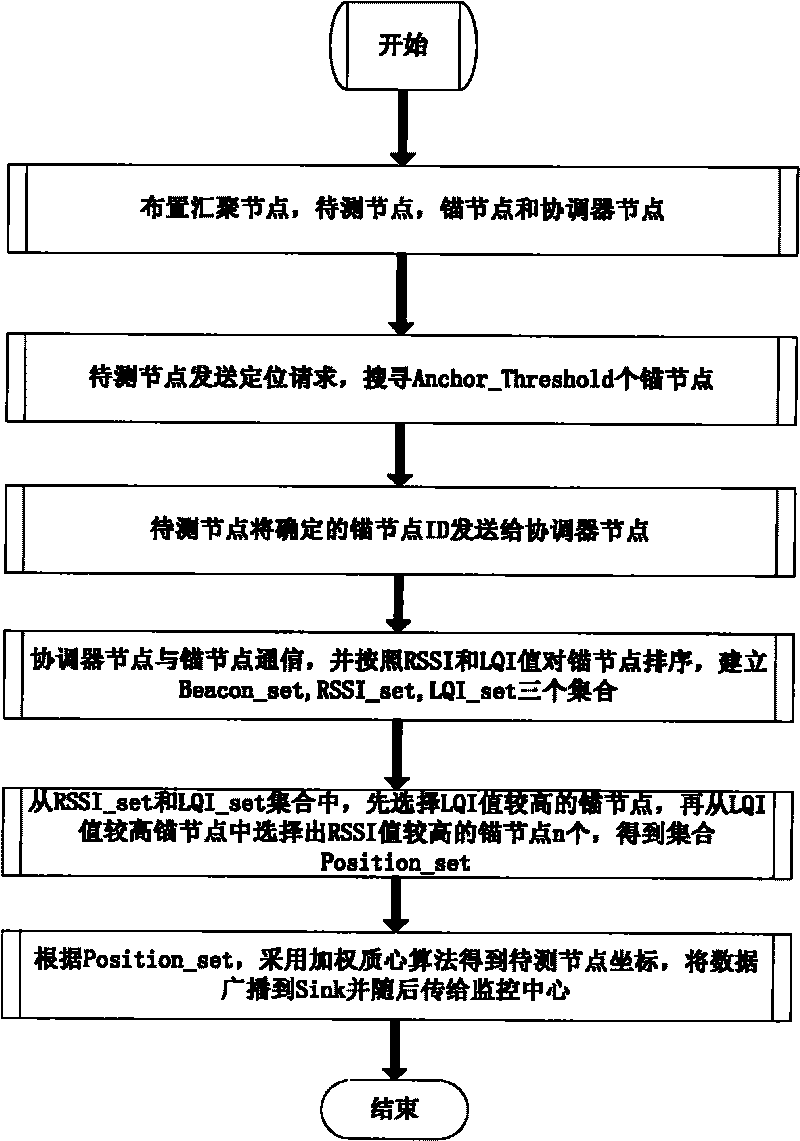
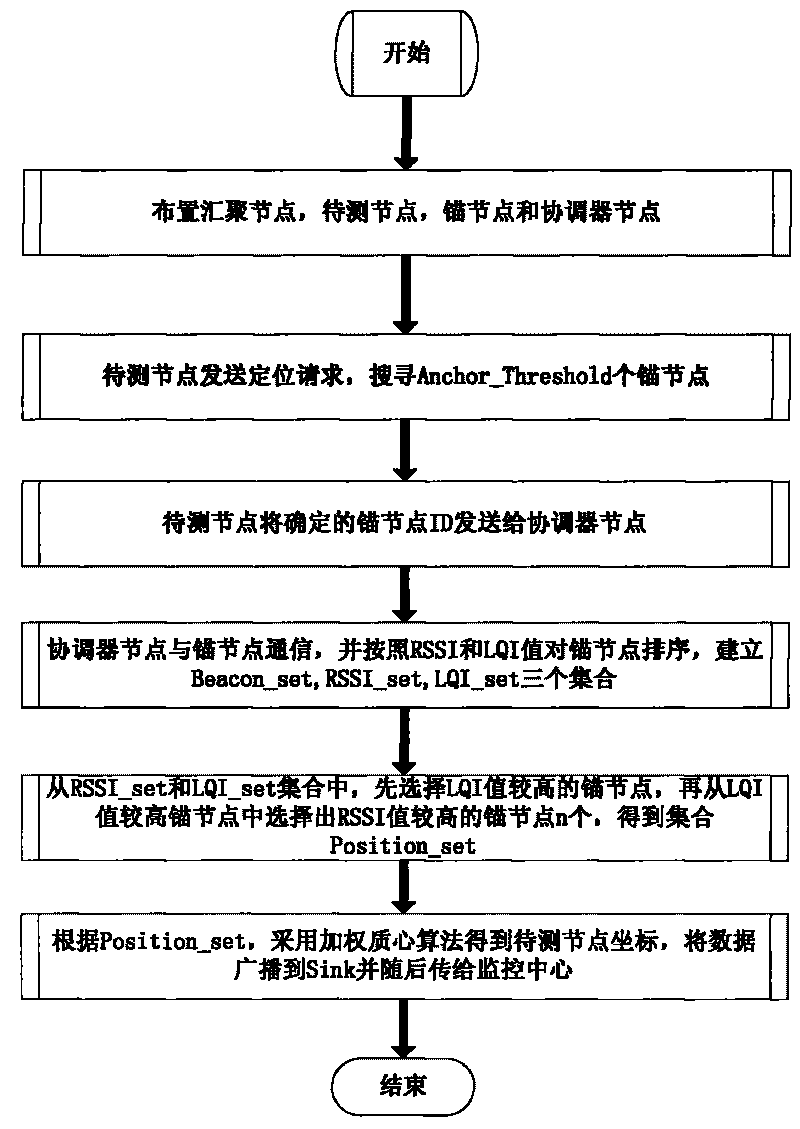
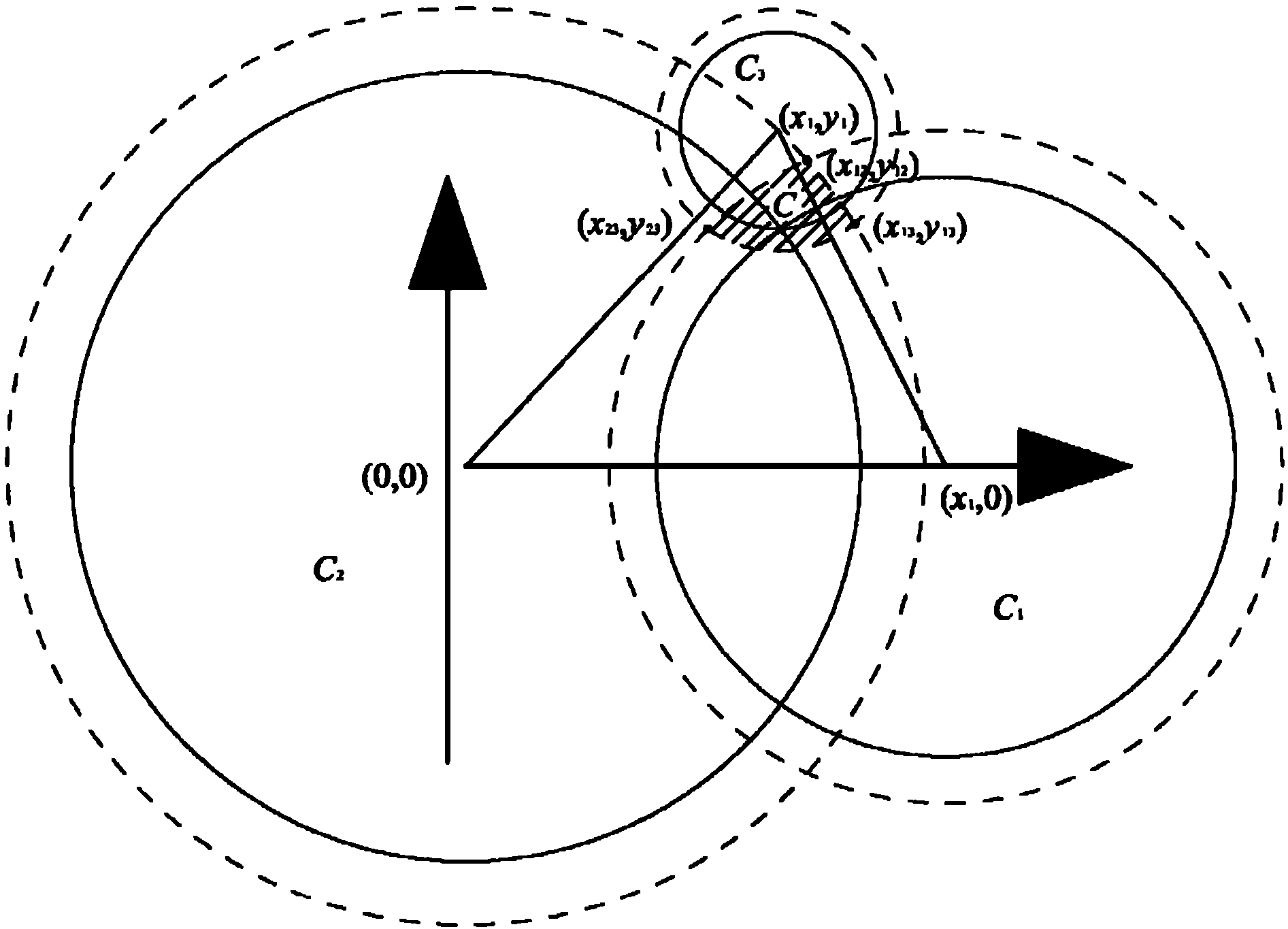
Positioning method of weighted wireless sensor network nodes based on RSSI and LQI
InactiveCN101715232AEasy to implementSave hardware resourcesNetwork topologiesComputation complexityRound complexity
The invention relates to a positioning method of weighted wireless sensor network nodes based on an RSSI and an LQI, which is characterized in that (1) the parameters of the RSSI and the LQI, which can be acquired easily from a hardware register, are used for positioning, thus the method can be realized easily and has few required hardware resources; (2) an LQI ranging model obtained by fitting experimental data is combined with an RSSI ranging model to select anchor nodes; and (3) an RSSI value and an LQI value which pass through an average filter are weighted and combined, an improved weighted centroid algorithm is used for estimating the positions of nodes to be detected, the data is broadcasted to cluster nodes, and then, the data is uploaded to a monitoring centre through a wired network. The positioning method of invention has the advantages of high positioning accuracy without being influenced by the environment easily, easy implementation of hardware, lower cost and smaller computation complexity.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Improved weighting trilateral positioning method based on RSSI (received signal strength indicator) in wireless sensor network
InactiveCN102158956AEasy to implementSave hardware resourcesTransmission monitoringWireless communicationWireless mesh networkProcessor register
The invention provides an improved weighting trilateral positioning method based on RSSI (received signal strength indicator) in a wireless sensor network and relates to the field of node self-positioning in the wireless sensor network. The method is used for solving the problem that a bigger positioning error is easily caused by the using of the traditional method which cannot meet the indoor positioning requirement in real life because the traditional method is limited by the factors such as signal multipath transmission, sight distance, low coordinate calculation precision, and the like. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: starting an unknown node positioning function and guiding an unknown node to send out a message; after receiving the message from the unknown node by an anchor node, calculating RSSI and storing in a hardware register; sending the ID number, RSSI value and position information (Xi, Yi) (i is equal to 1,2,...), which are distributed to the anchor node, to the unknown node by the anchor node; sequencing the anchor node according to the size of the received RSSI, and choosing N anchor nodes having big RSSI for self-positioning, wherein N is more than or equal to 3; according to the information of N anchor nodes, confirming the weighted value by the using of the trilateral positioning method; and using a weighting algorithm to calculate the coordinate of the unknown node. The method provided by the invention is used for weighting the coordinate information by utilizing the weighting principle.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
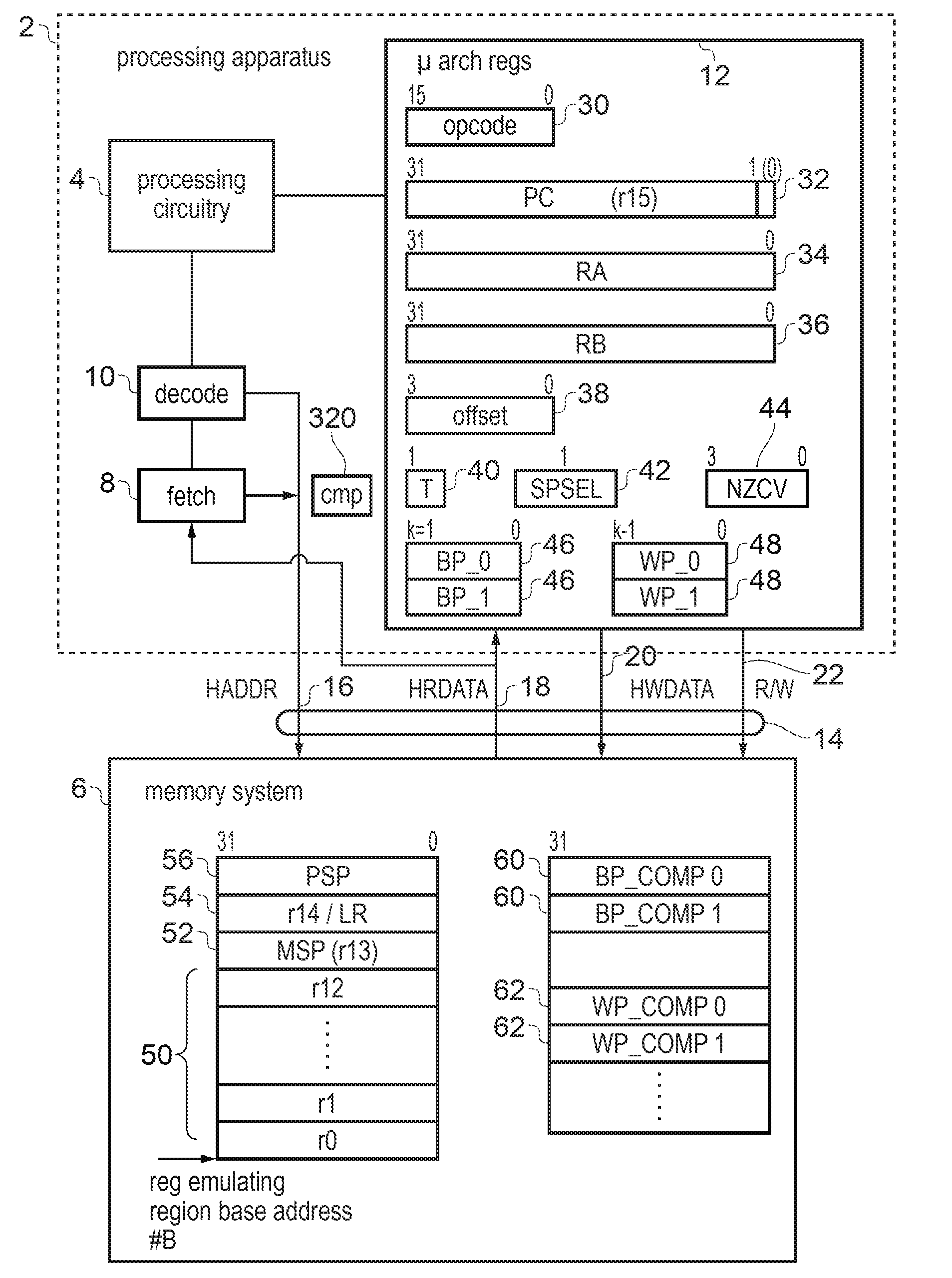
Apparatus with reduced hardware register set
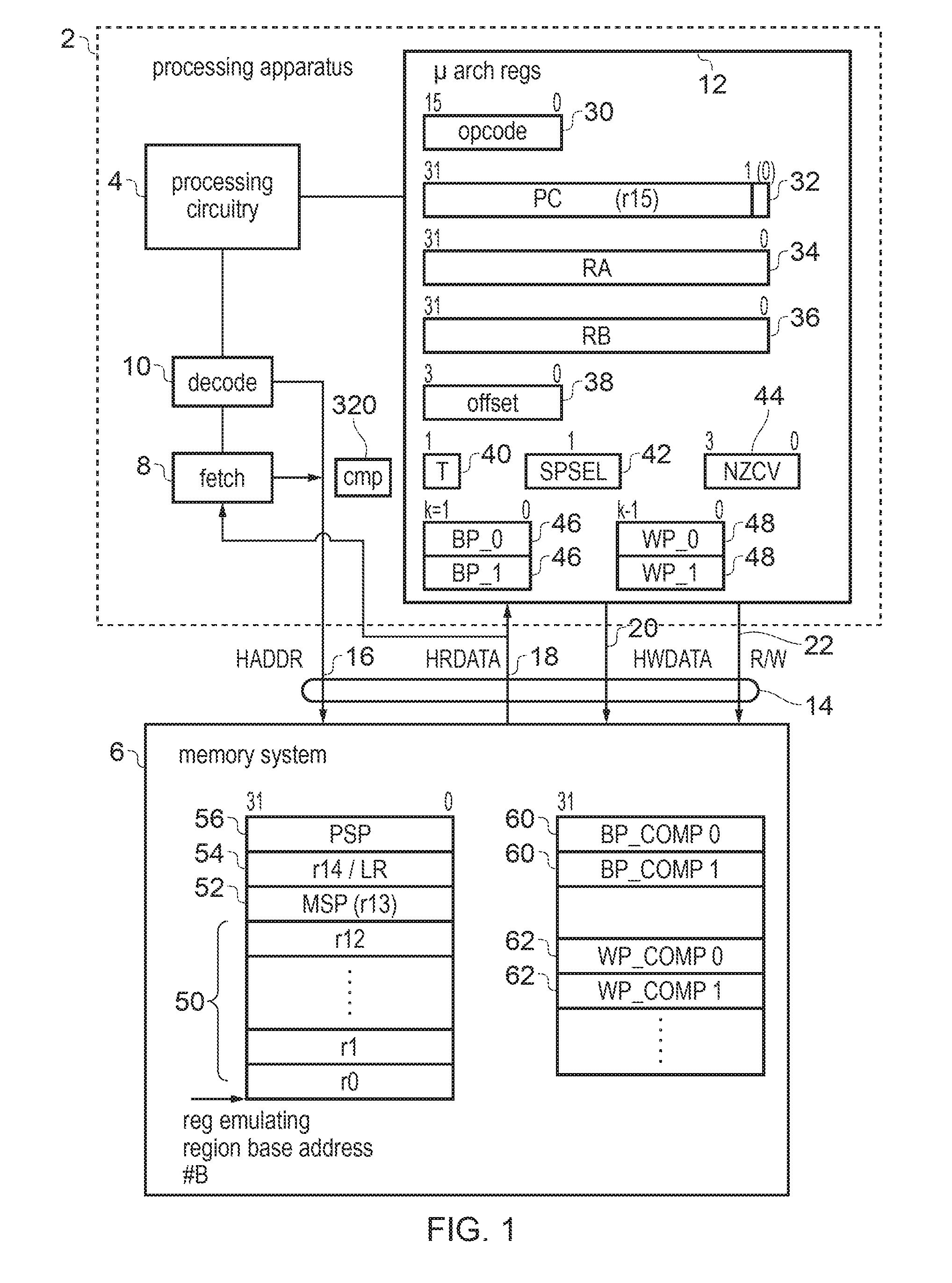
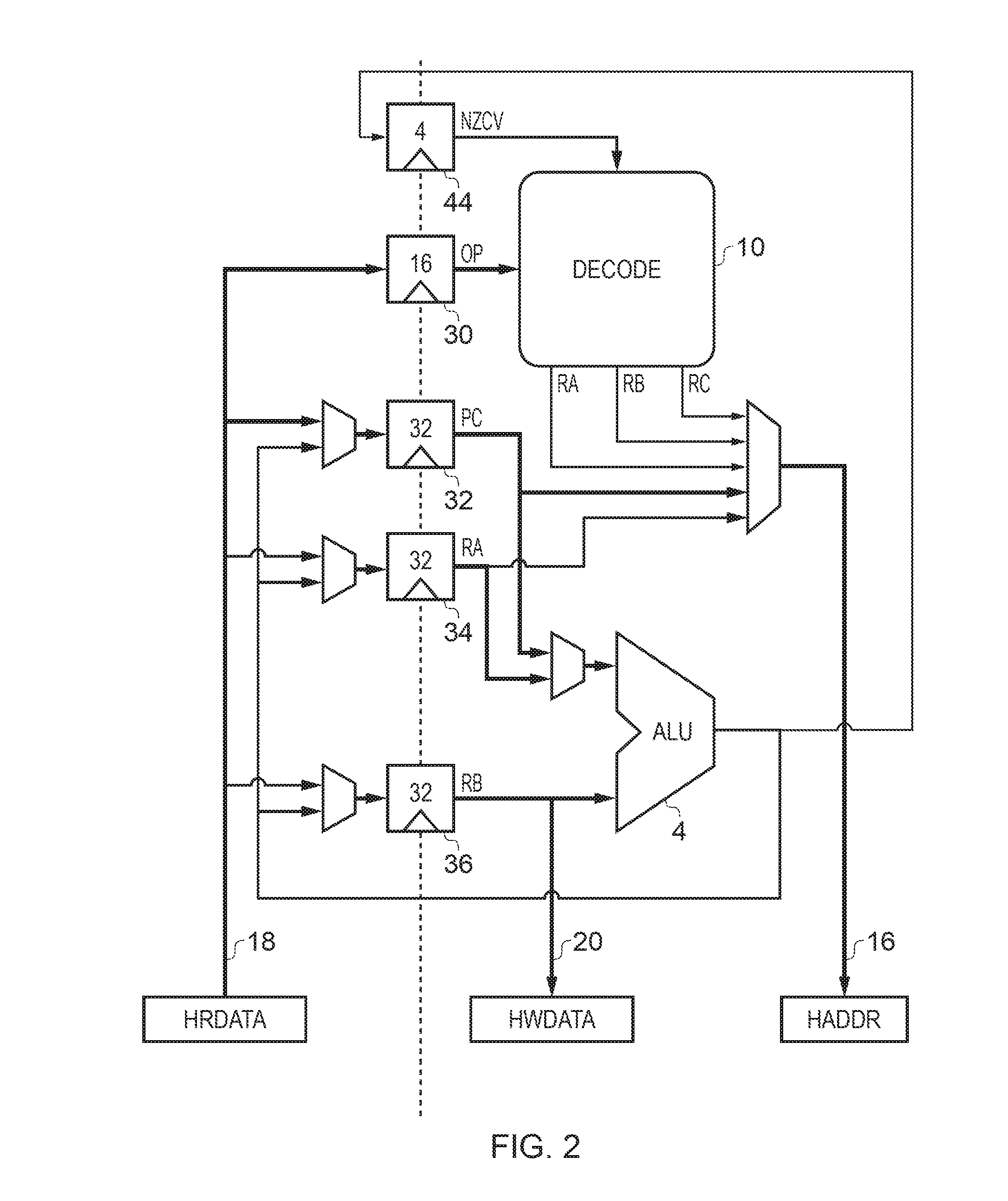
InactiveUS20170031685A1Register arrangementsConcurrent instruction executionProgram instructionParallel computing
An apparatus comprises processing circuitry for processing program instructions according to a predetermined architecture defining a number of architectural registers accessible in response to the program instructions. A set of hardware registers is provided in hardware. A storage capacity of the set of hardware registers is insufficient for storing all the data associated with the architectural registers of the pre-determined architecture. Control circuitry is responsive to the program instructions to transfer data between the hardware registers and at least one register emulating memory location in memory for storing data corresponding to the architectural registers of the architecture.
Owner:ARM LTD
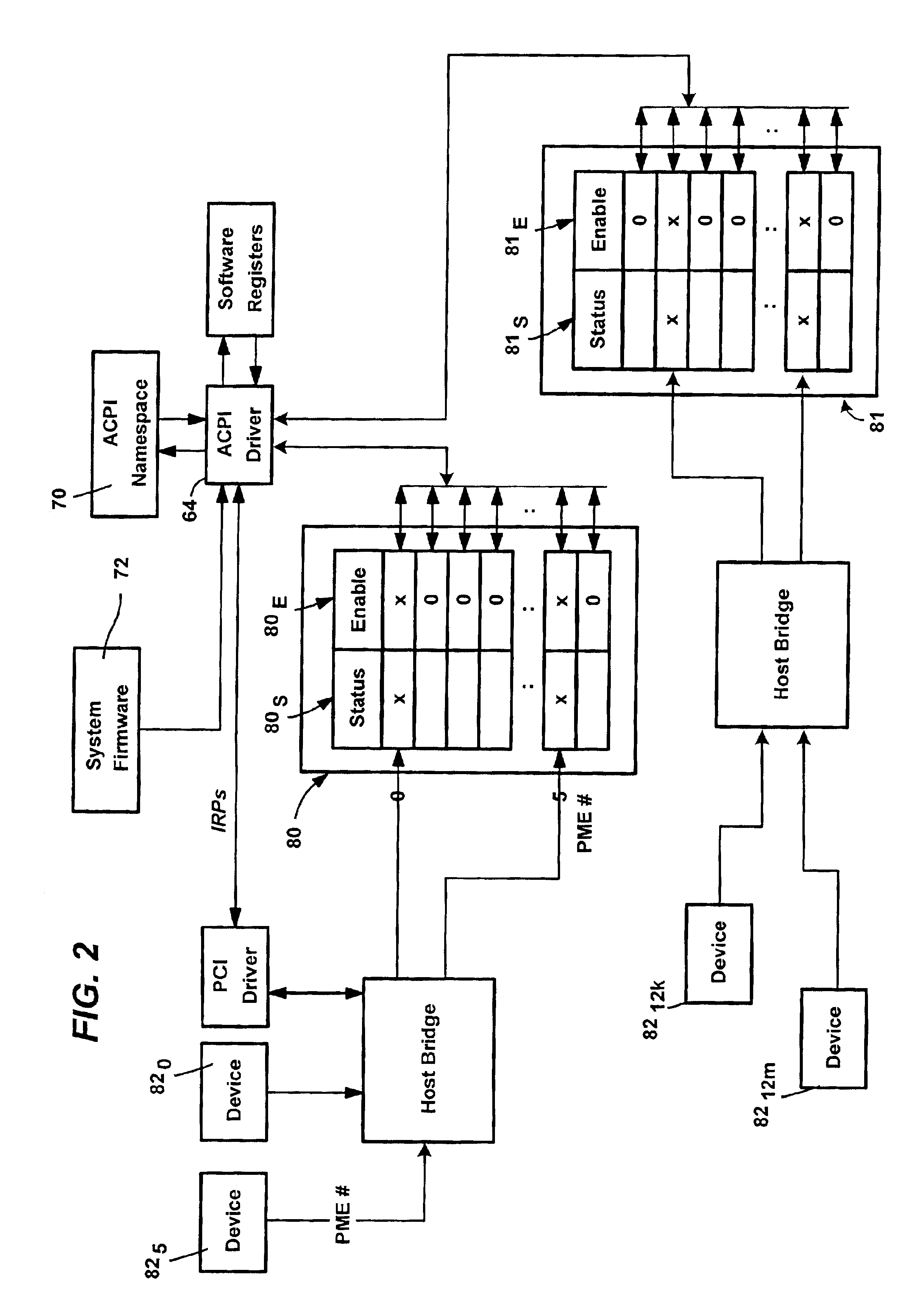
Preventing general purpose event interrupt storms in a computer system
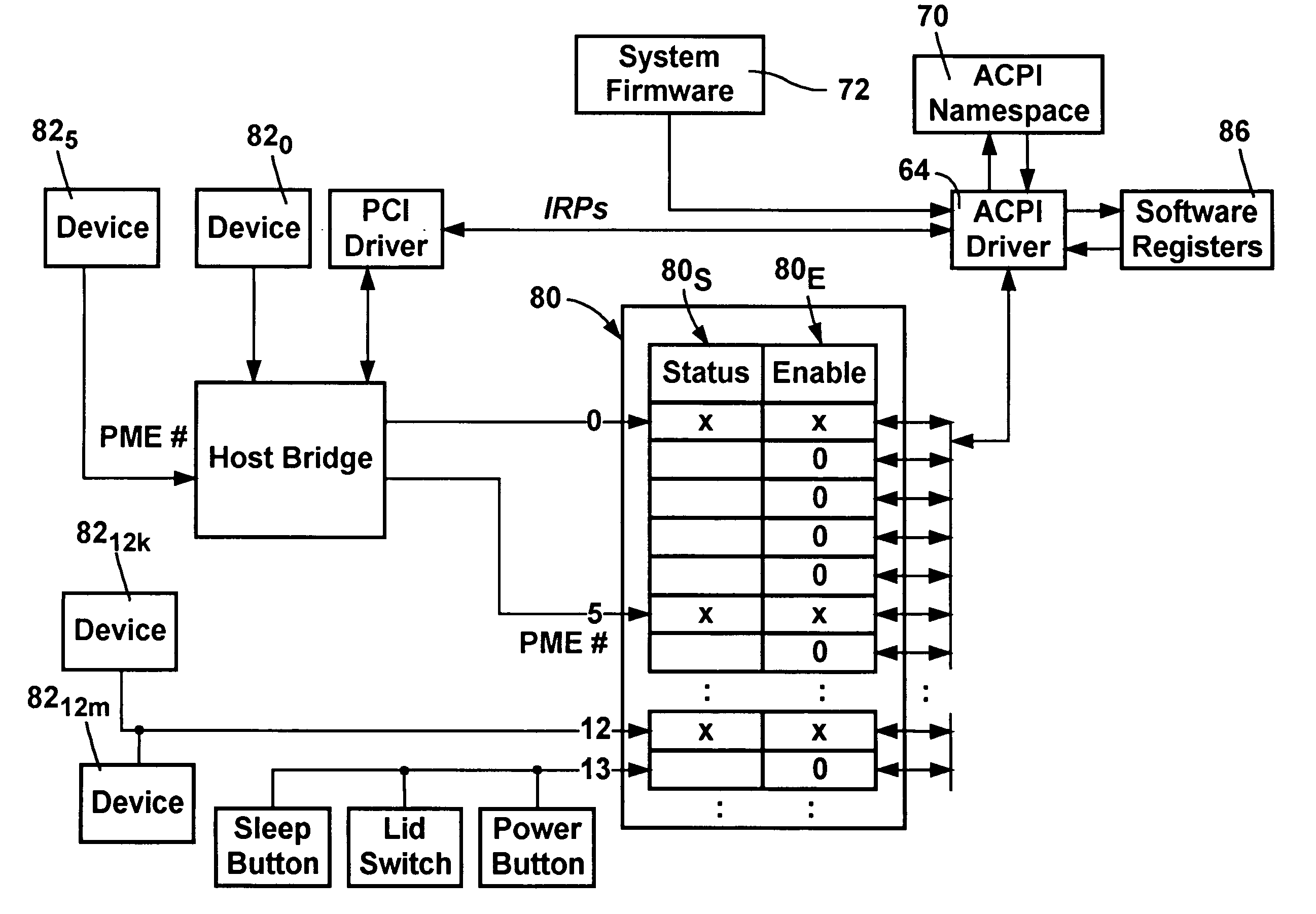
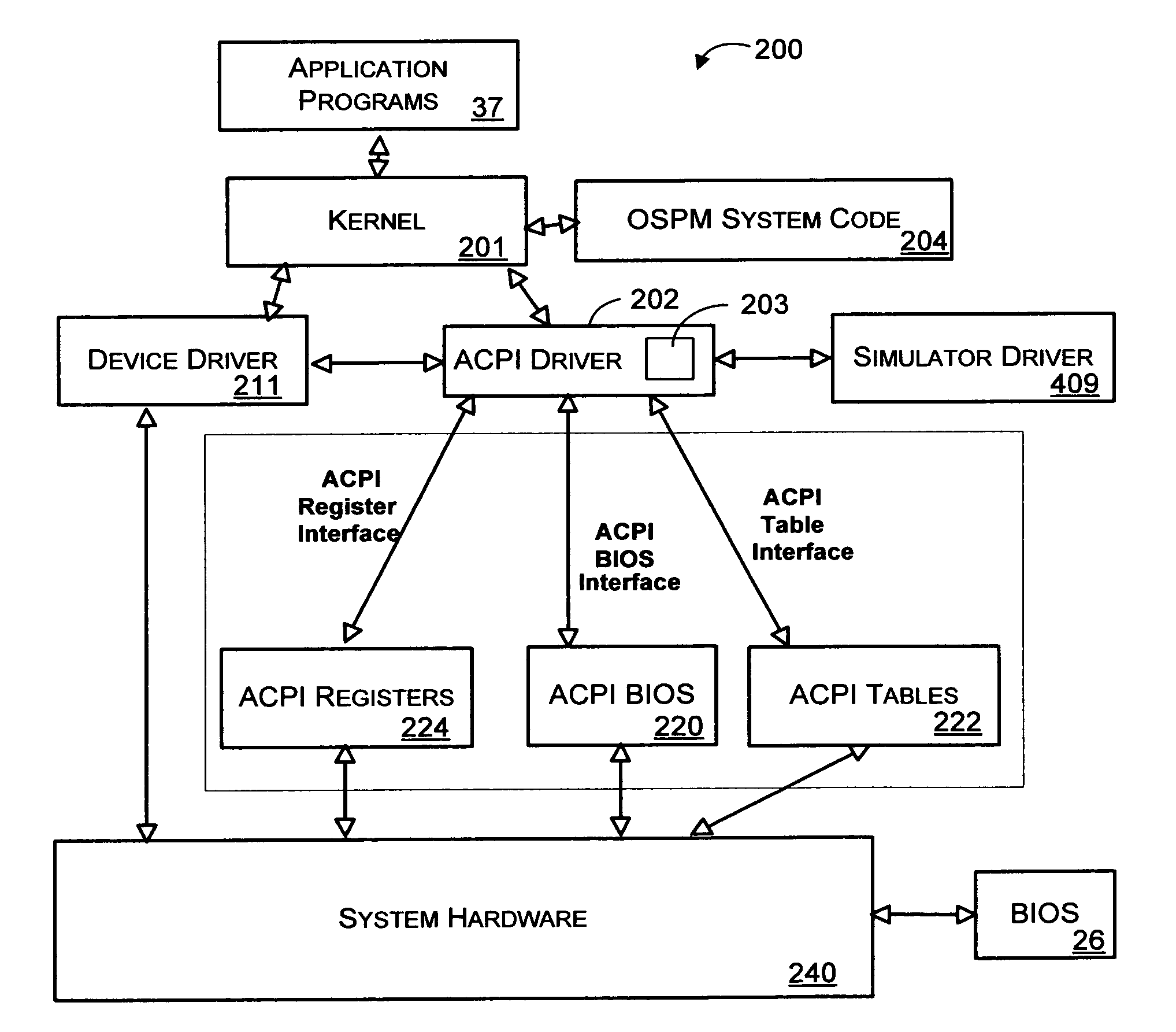
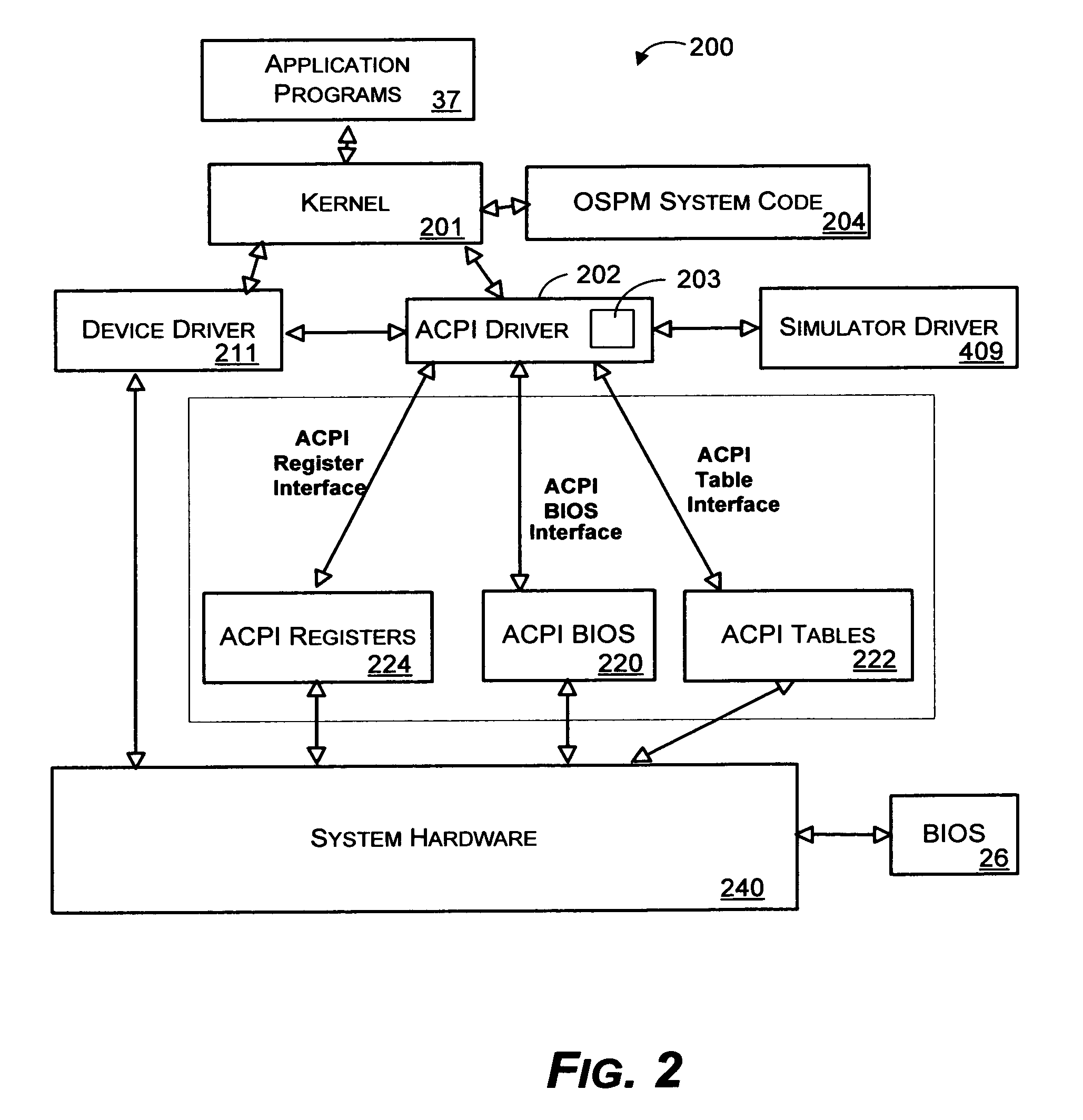
InactiveUS6931553B1Management intelligenceProgram initiation/switchingVolume/mass flow measurementGeneral purposeOperational system
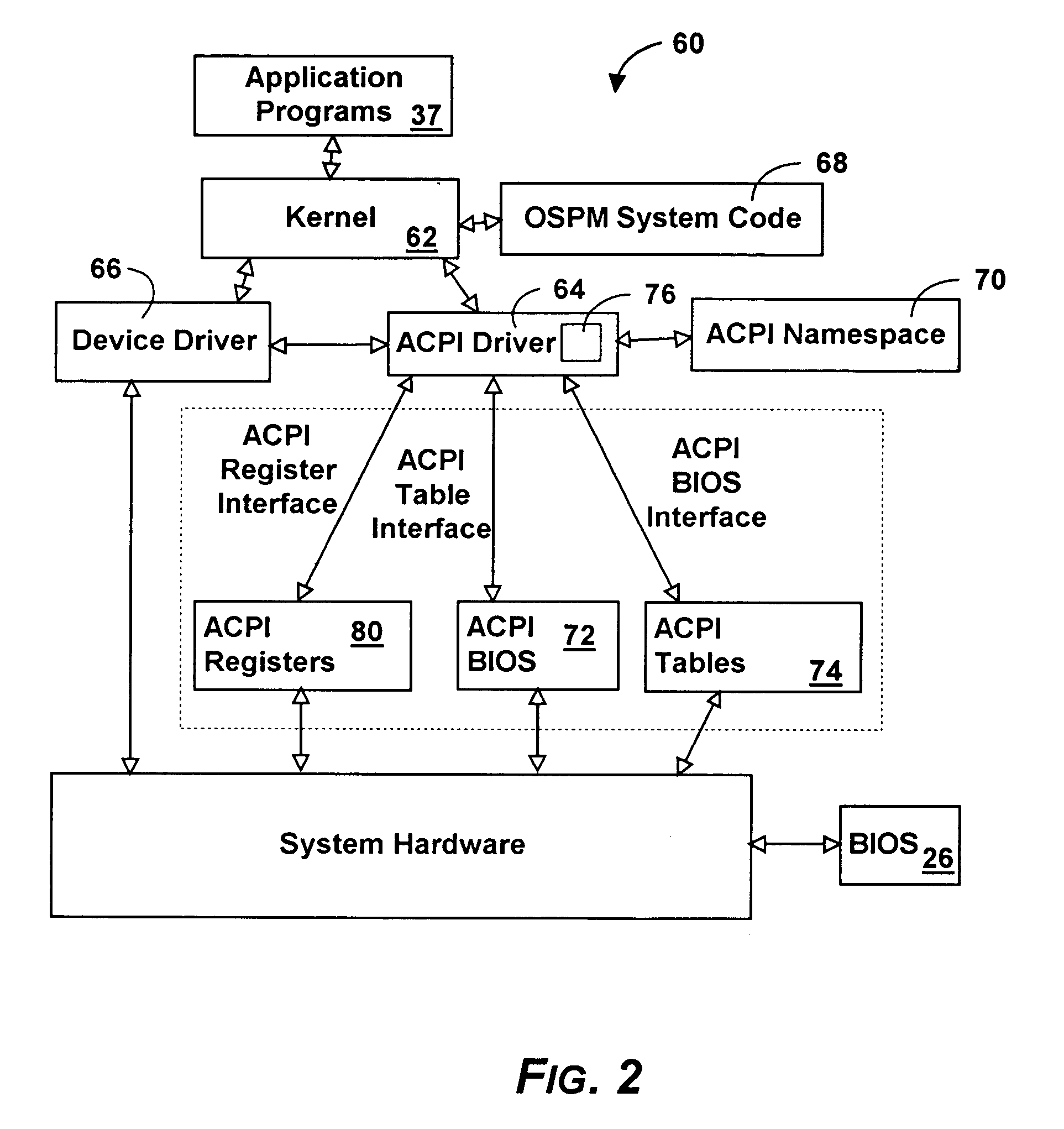
A method and system for selectively enabling wake events in software of a computer system to overcome problems arising when hardware devices fail to clear a wake signal. The operating system manages wake events, and also distinguishes between events that are exclusively wake events, exclusively run-time events, and shared wake and run-time events. At boot time, the ACPI driver examines system tables provided by firmware to determine which GPEs are associated with wake-up events, either exclusively or shared with run-time events. These wake event associations are tracked and managed differently from events received on other hardware register pins. When the operating system receives events in a GPE Status hardware register that is enabled in a counterpart Enable register, the operating system runs an associated GPE method. When the GPE method has completed, the operating system selectively determines whether the event needs to be re-enabled.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Prioritization for conflict arbitration in transactional memory management
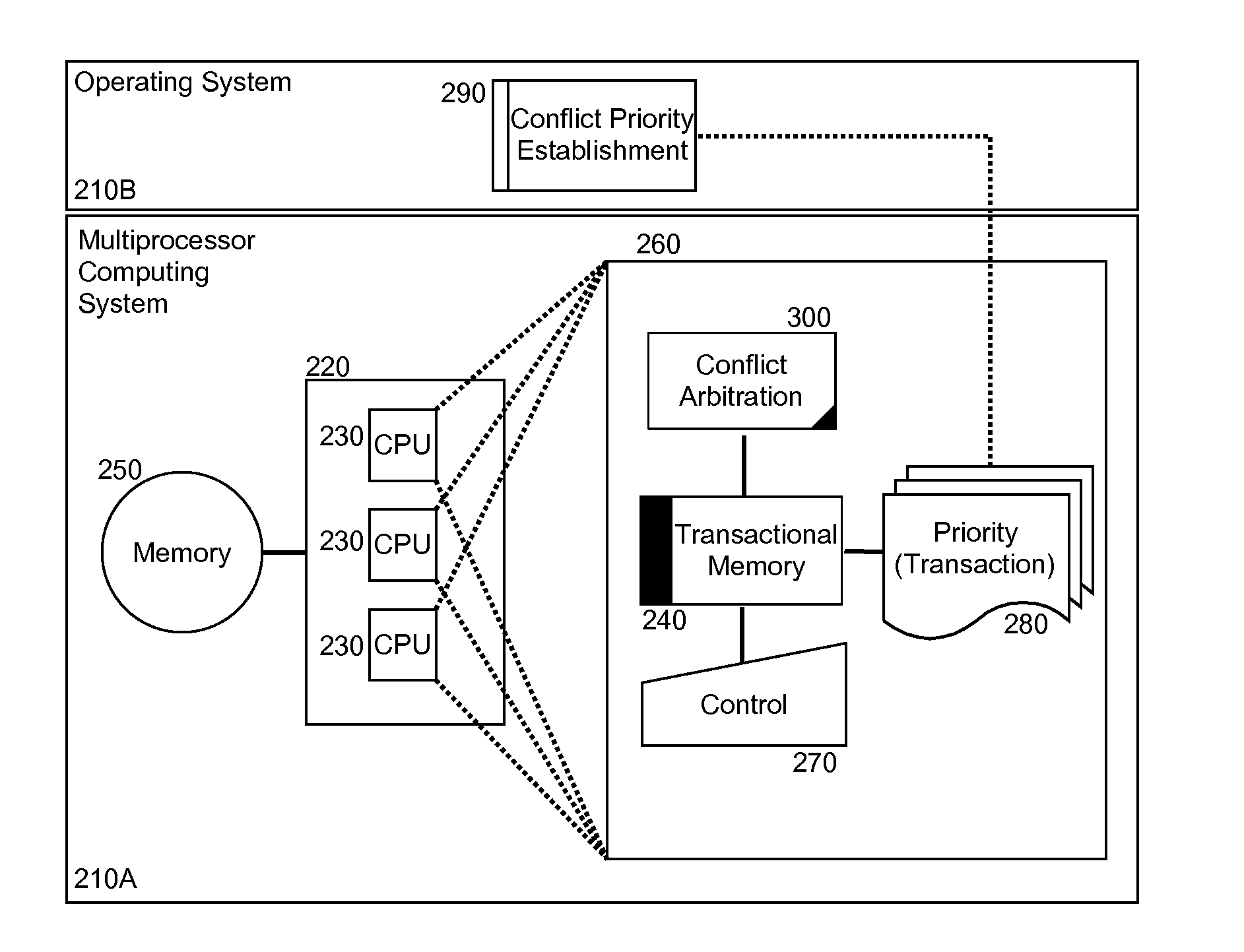
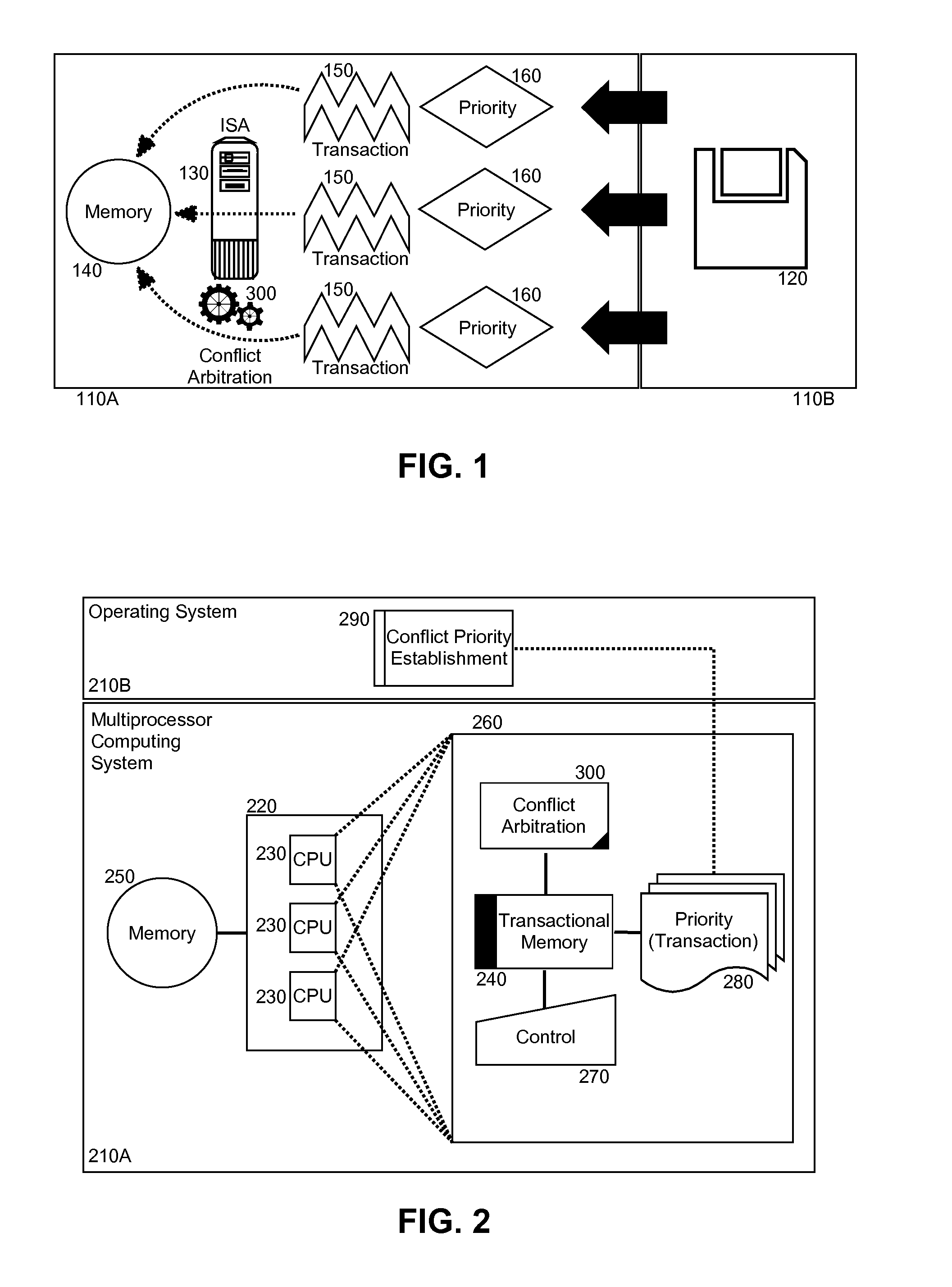
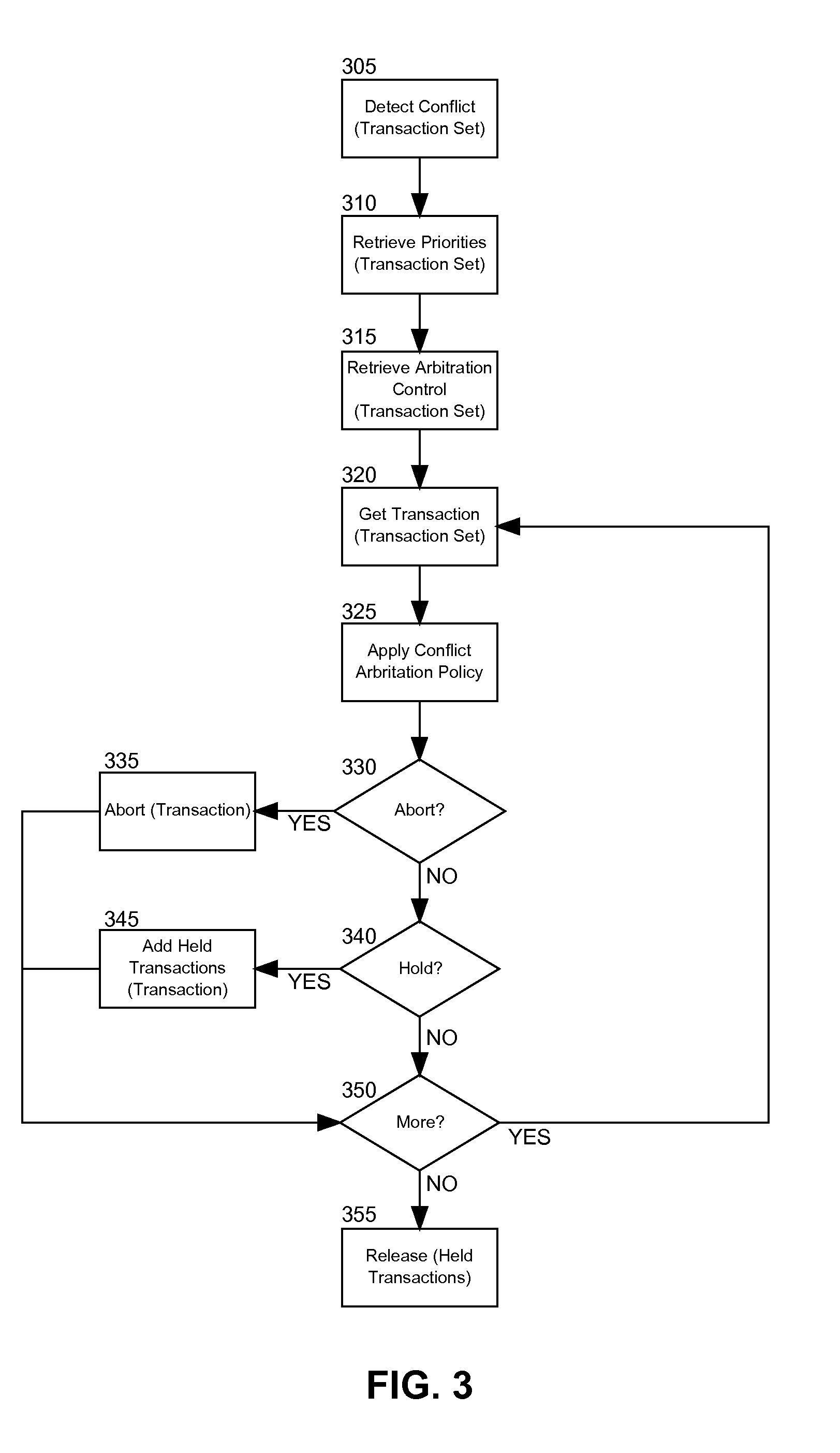
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method, system and computer program product for software prioritization of concurrent transactions for embedded conflict arbitration in transactional memory management. In an embodiment of the invention, a method for software prioritization of concurrent transactions for embedded conflict arbitration in transactional memory management can include setting different hardware registers with different priority values for correspondingly different transactions in a transactional memory system configured for transactional memory management according to respective priority values specified by priority assignment logic in external software support for the system. The method also can include detecting a conflict amongst the transactions in the system. Finally, the method can include applying conflict arbitration within the system based upon the priority values specified by the priority assignment logic in the external software support for the system.
Owner:IBM CORP
Hardware trust anchors in SP-enabled processors
ActiveUS9317708B2Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationOperational systemConfidentiality
A trust system and method is disclosed for use in computing devices, particularly portable devices, in which a central Authority shares secrets and sensitive data with users of the respective devices. The central Authority maintains control over how and when shared secrets and data are used. In one embodiment, the secrets and data are protected by hardware-rooted encryption and cryptographic hashing, and can be stored securely in untrusted storage. The problem of transient trust and revocation of data is reduced to that of secure key management and keeping a runtime check of the integrity of the secure storage areas containing these keys (and other secrets). These hardware-protected keys and other secrets can further protect the confidentiality and / or integrity of any amount of other information of arbitrary size (e.g., files, programs, data) by the use of strong encryption and / or keyed-hashing, respectively. In addition to secrets the Authority owns, the system provides access to third party secrets from the computing devices. In one embodiment, the hardware-rooted encryption and hashing each use a single hardware register fabricated as part of the computing device's processor or System-on-Chip (SoC) and protected from external probing. The secret data is protected while in the device even during operating system malfunctions and becomes non-accessible from storage according to various rules, one of the rules being the passage of a certain time period. The use of the keys (or other secrets) can be bound to security policies that cannot be separated from the keys (or other secrets). The Authority is also able to establish remote trust and secure communications to the devices after deployment in the field using a special tamper-resistant hardware register in the device, to enable, disable or update the keys or secrets stored securely by the device.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV +1
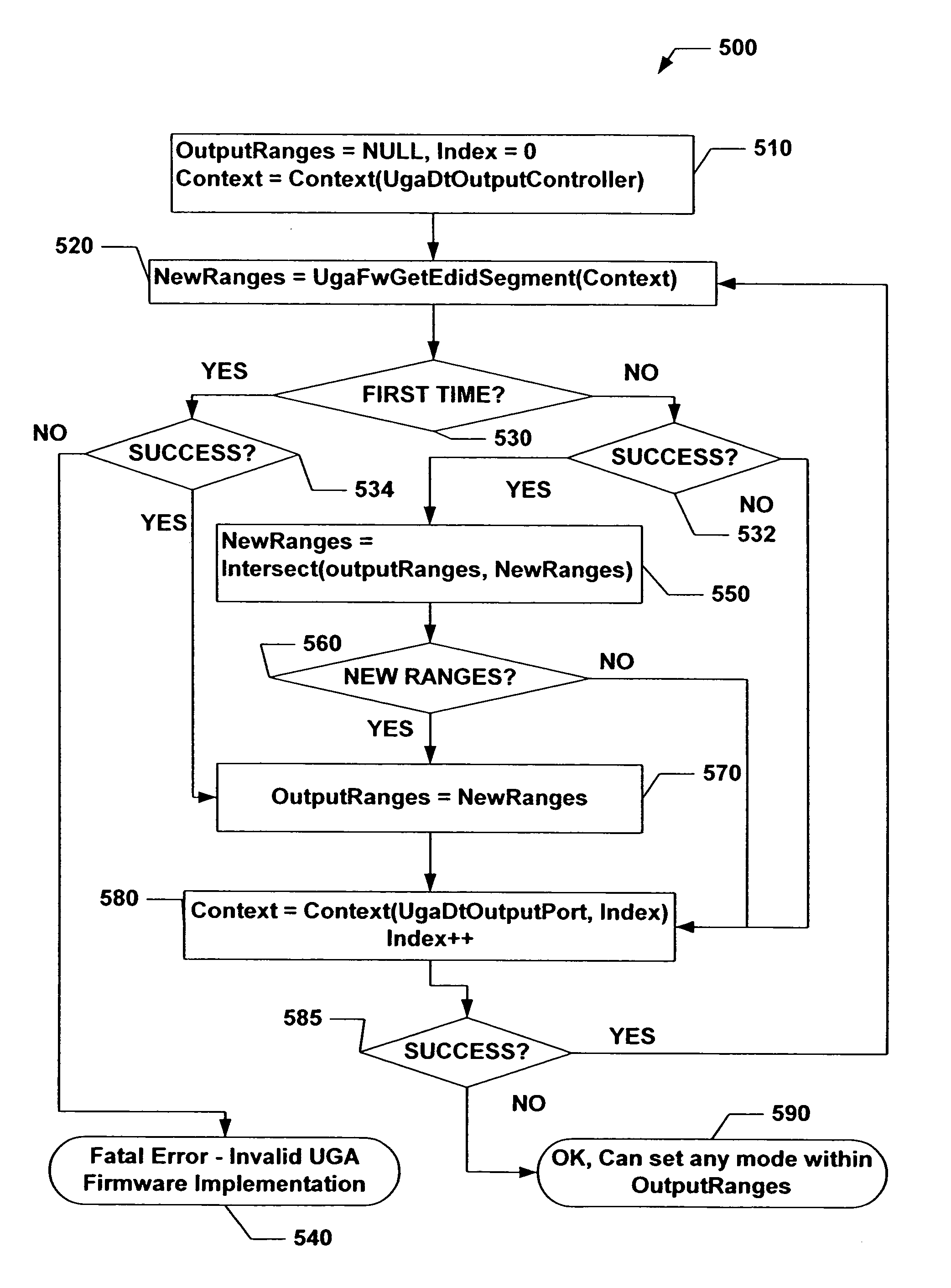
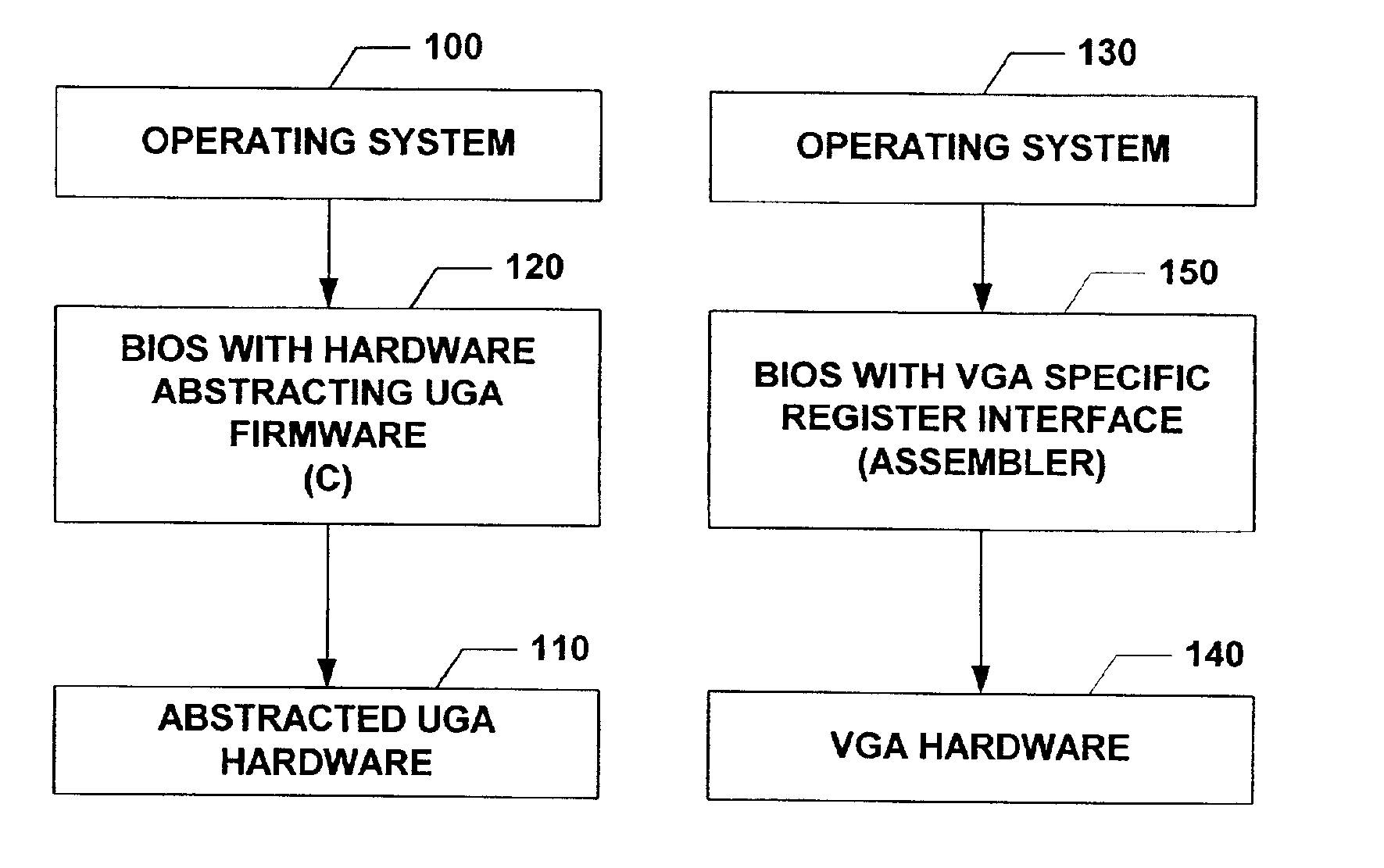
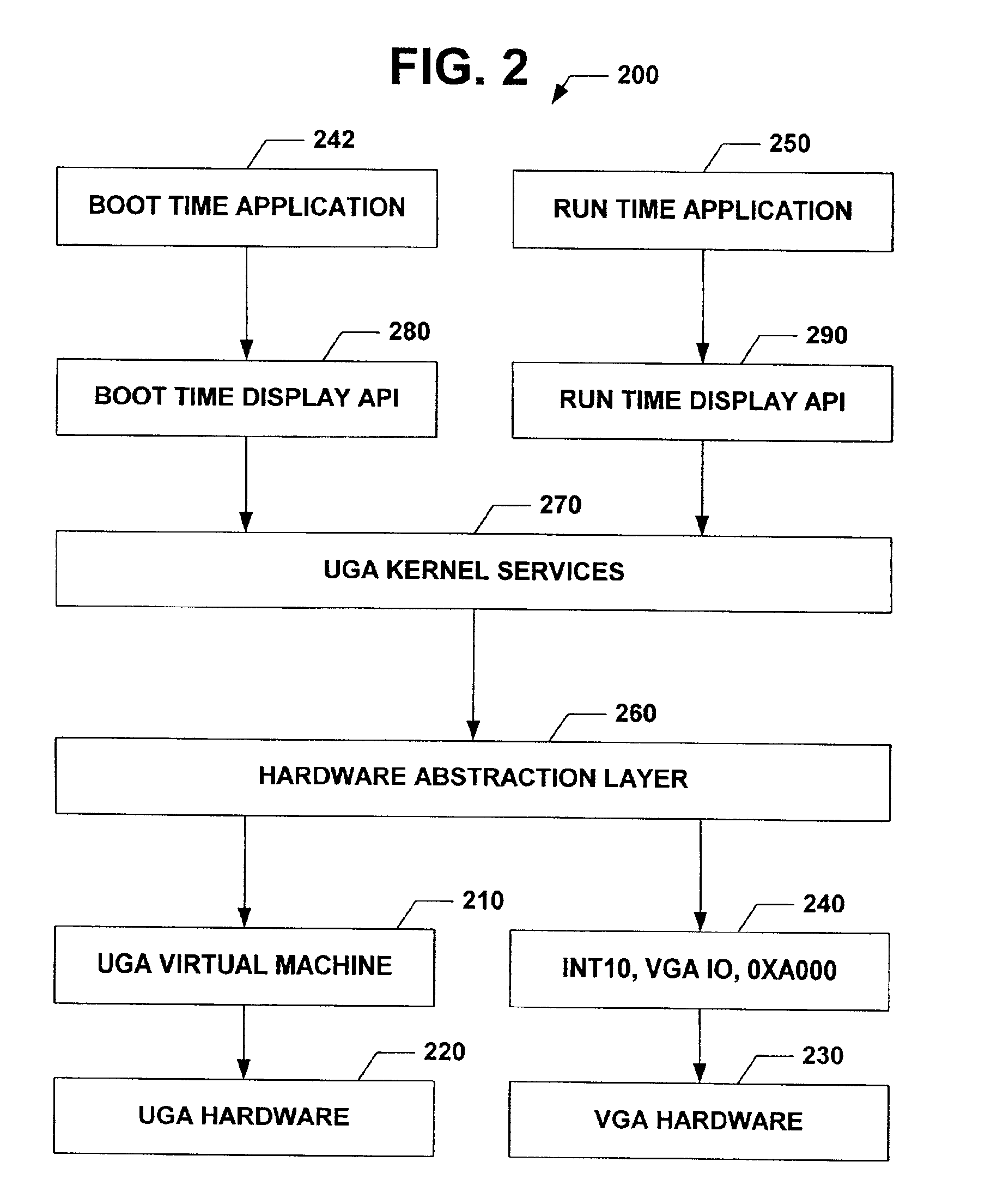
Universal graphic adapter for interfacing with hardware and means for determining previous output ranges of other devices and current device intial ranges
InactiveUS7257650B2Easy to updateQuality improvementDigital computer detailsData resettingProcessor registerAssembly language
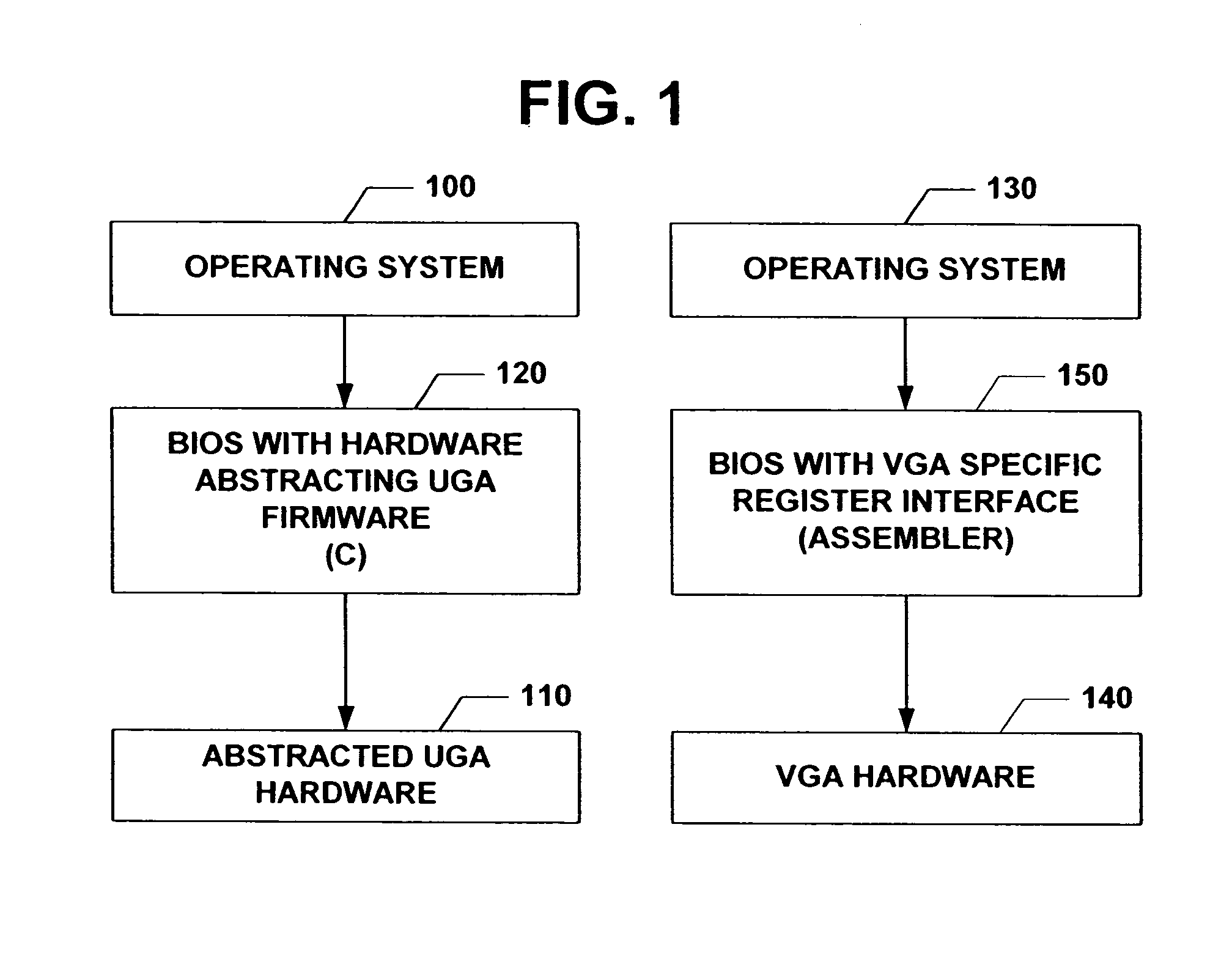
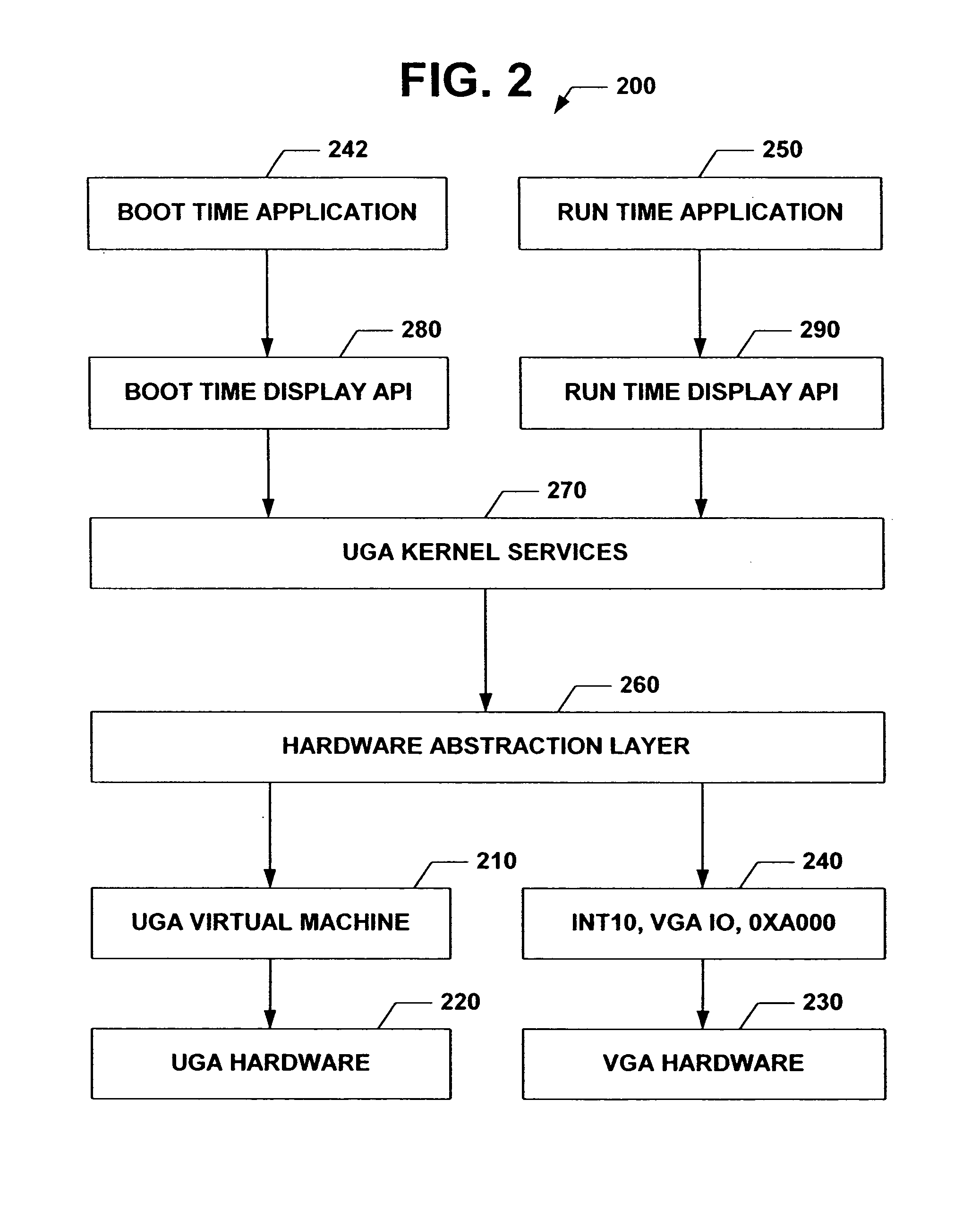
The subject invention relates to a Universal Graphics Adapter (UGA) that is a hardware-independent design that encapsulates and abstracts low-level graphics hardware in a standard manner through firmware. UGA is a firmware standard, intended to wrap existing or planned hardware, including VGA. UGA does not require the use of real-mode assembly language, direct hardware register, or frame buffer access to program, thus providing advantages over conventional systems. UGA supports basic drawing operations, continuous display modes, and power management. As a firmware-based standard, UGA facilitates updating a system to support both evolving and new hardware features.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
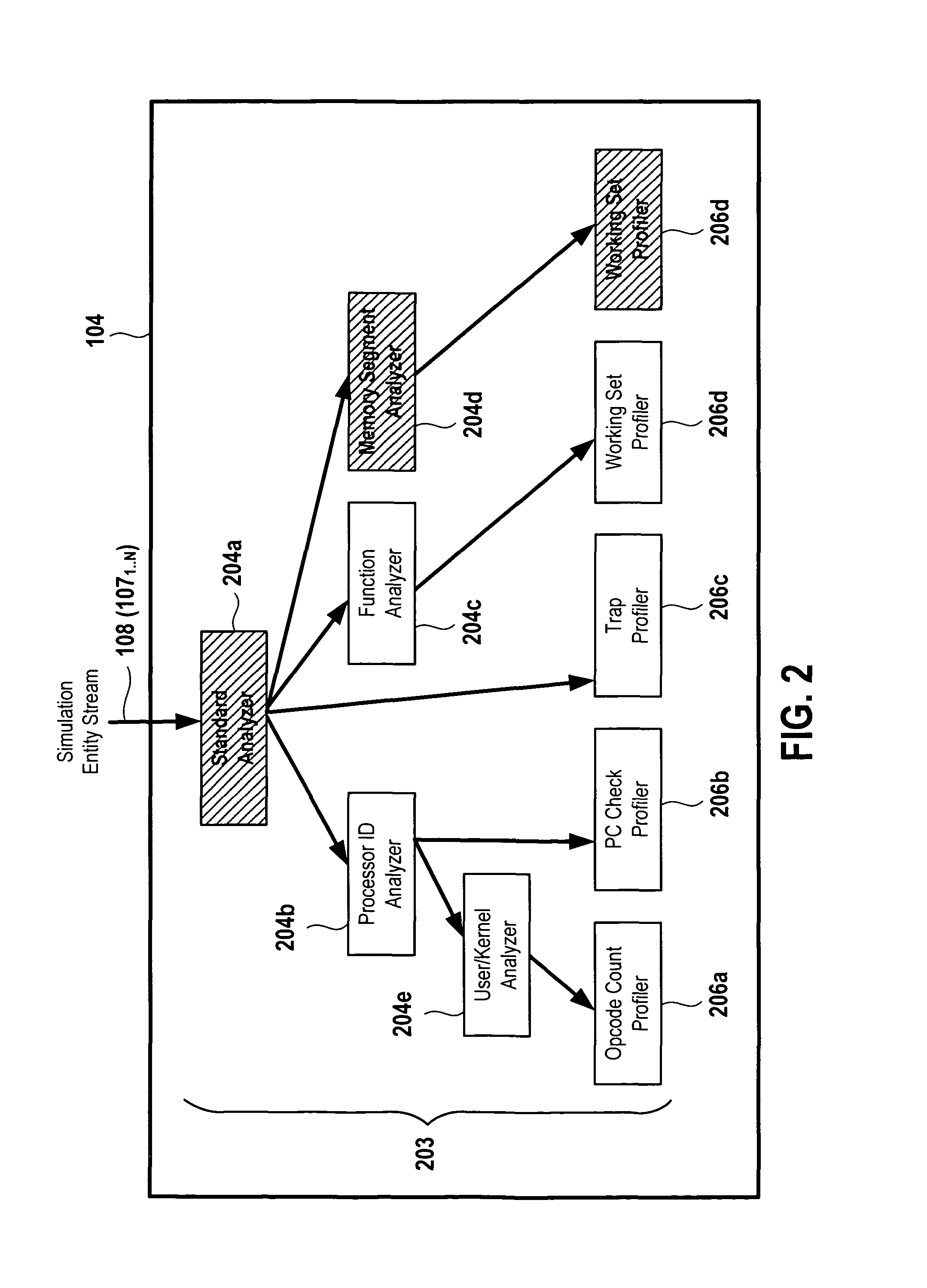
System for application level analysis of hardware simulations
ActiveUS8229726B1CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationProcessor registerSoftware analytics
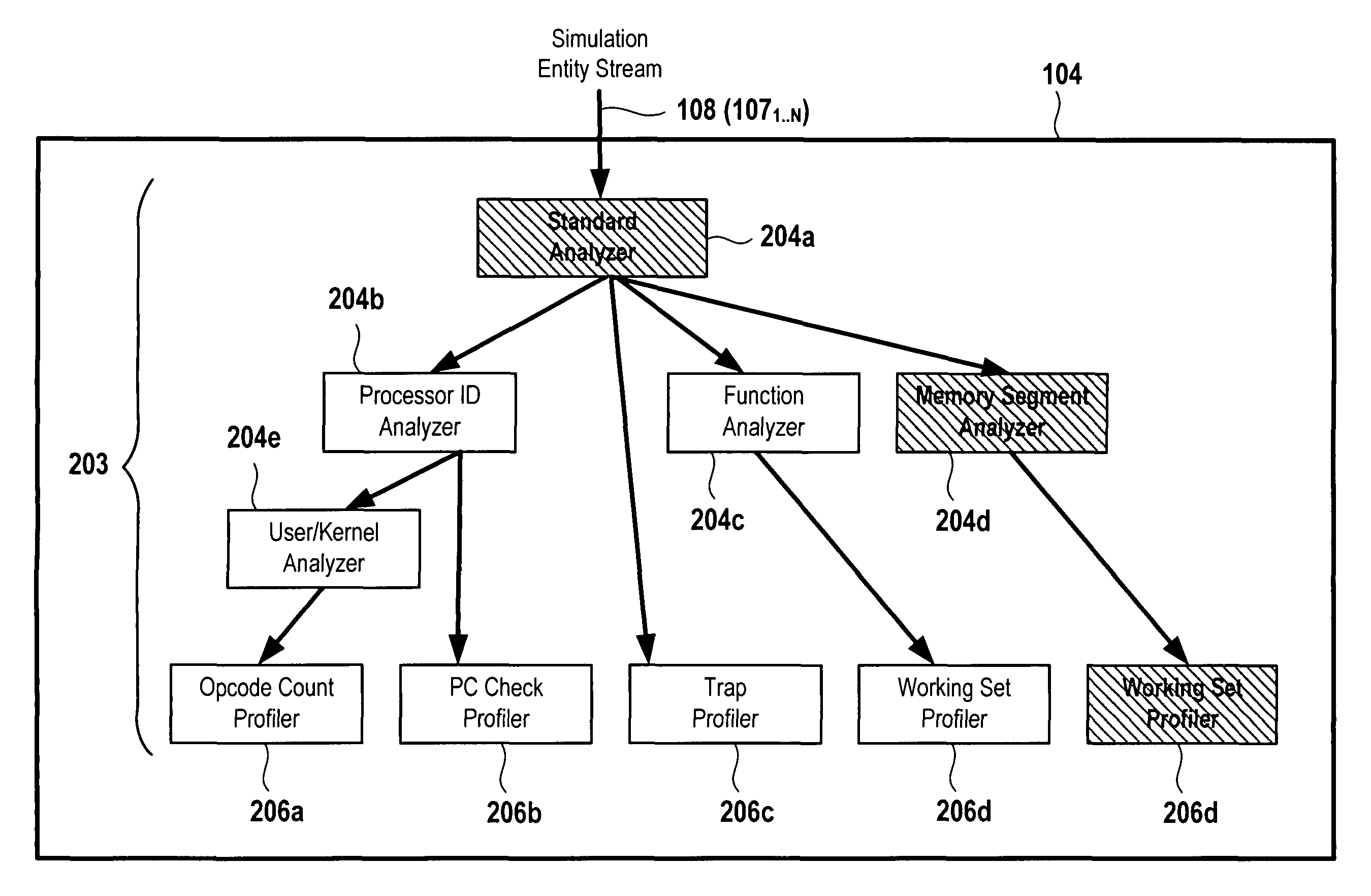
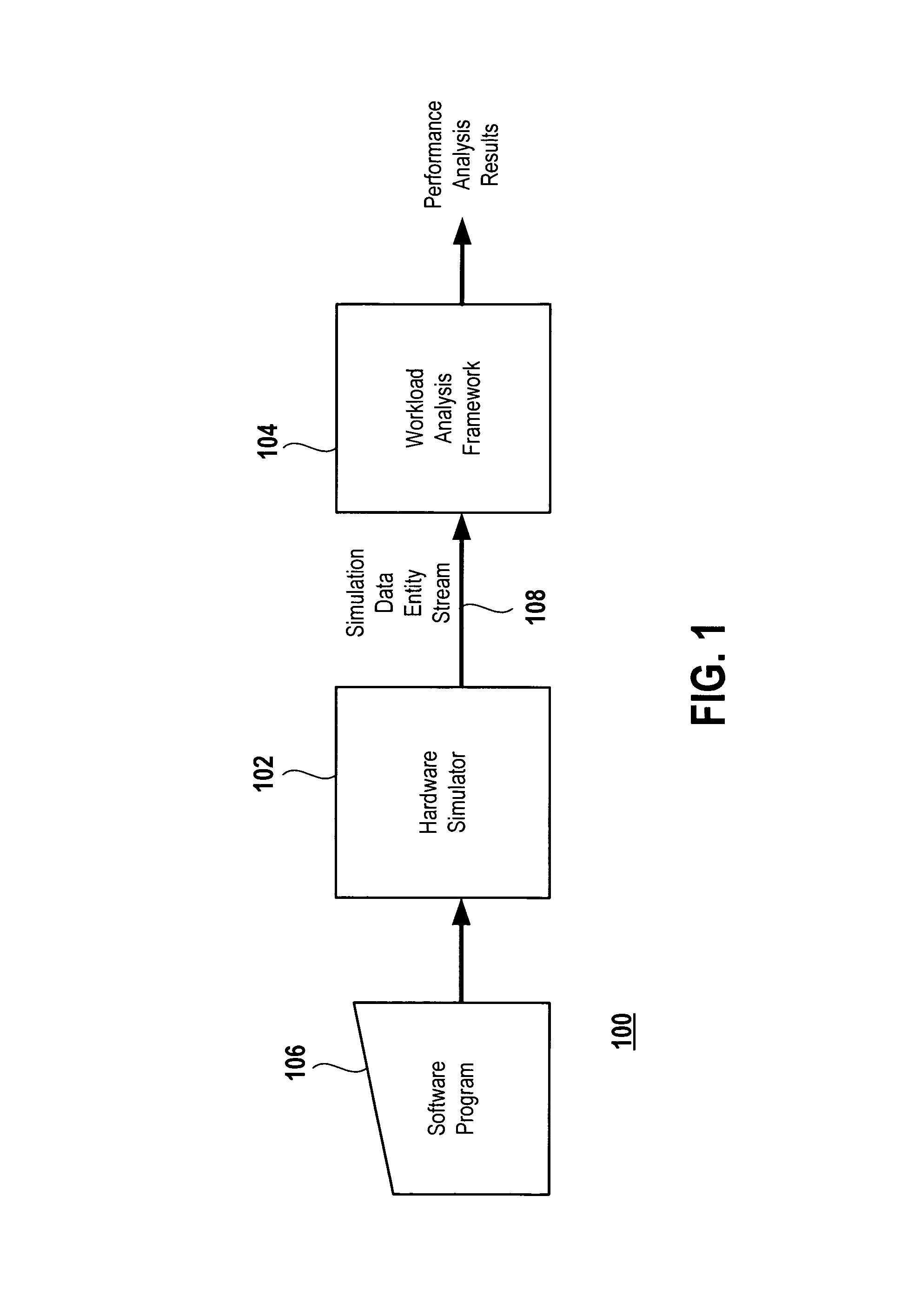
An object-oriented software analysis framework is provided for enabling software engineers and hardware engineers to gain insight into the behavior of software applications on emerging hardware platforms even before the hardware is fabricated. In this analysis framework, simulation data containing instruction, address and / or hardware register information is sent to interchangeable and parameterizable analyzer and profiler modules that decode the data and perform analysis of the data according to each module's respective analysis function. This detailed analysis is performed by constructing a tree of such modules through which the data travels and is classified and analyzed or filtered at each level of the tree. Each node of the tree is represented by an analyzer or a profiler module that performs sub-analysis based on the analysis performed by its parent such that at the end of a hardware simulation, each node, starting at the root, recursively calls on its children to dump their analysis, resulting in a categorized performance report.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
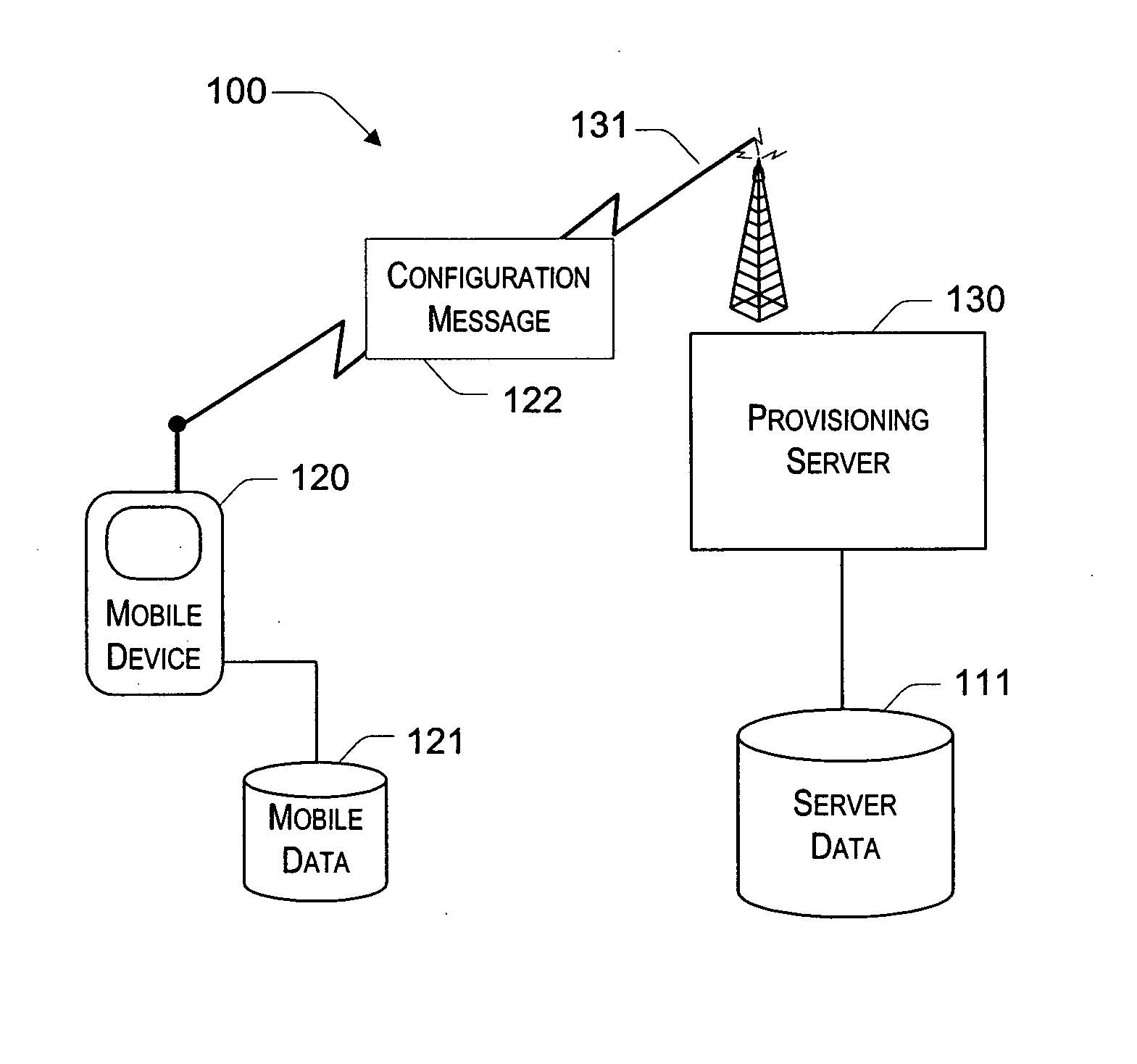
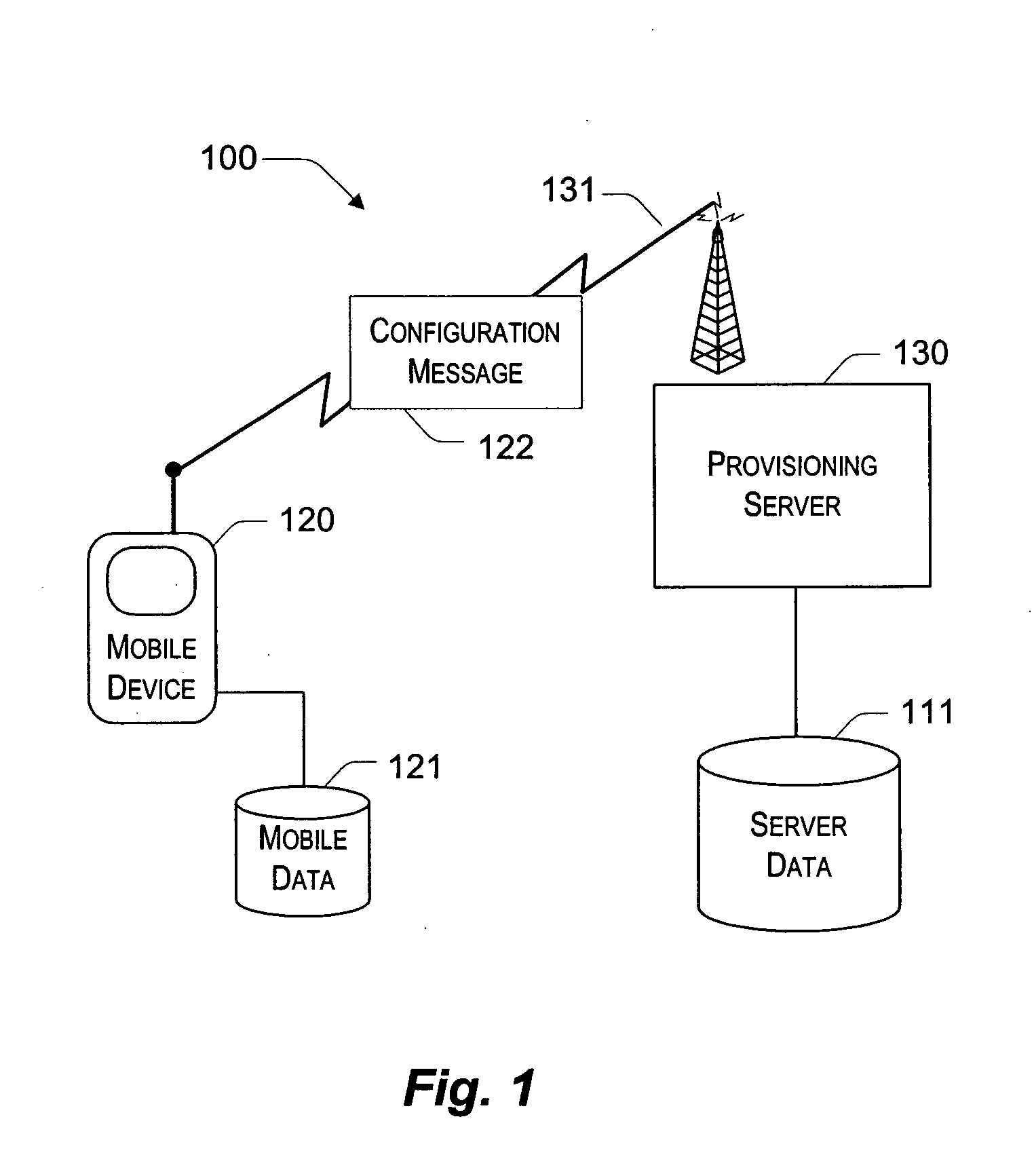
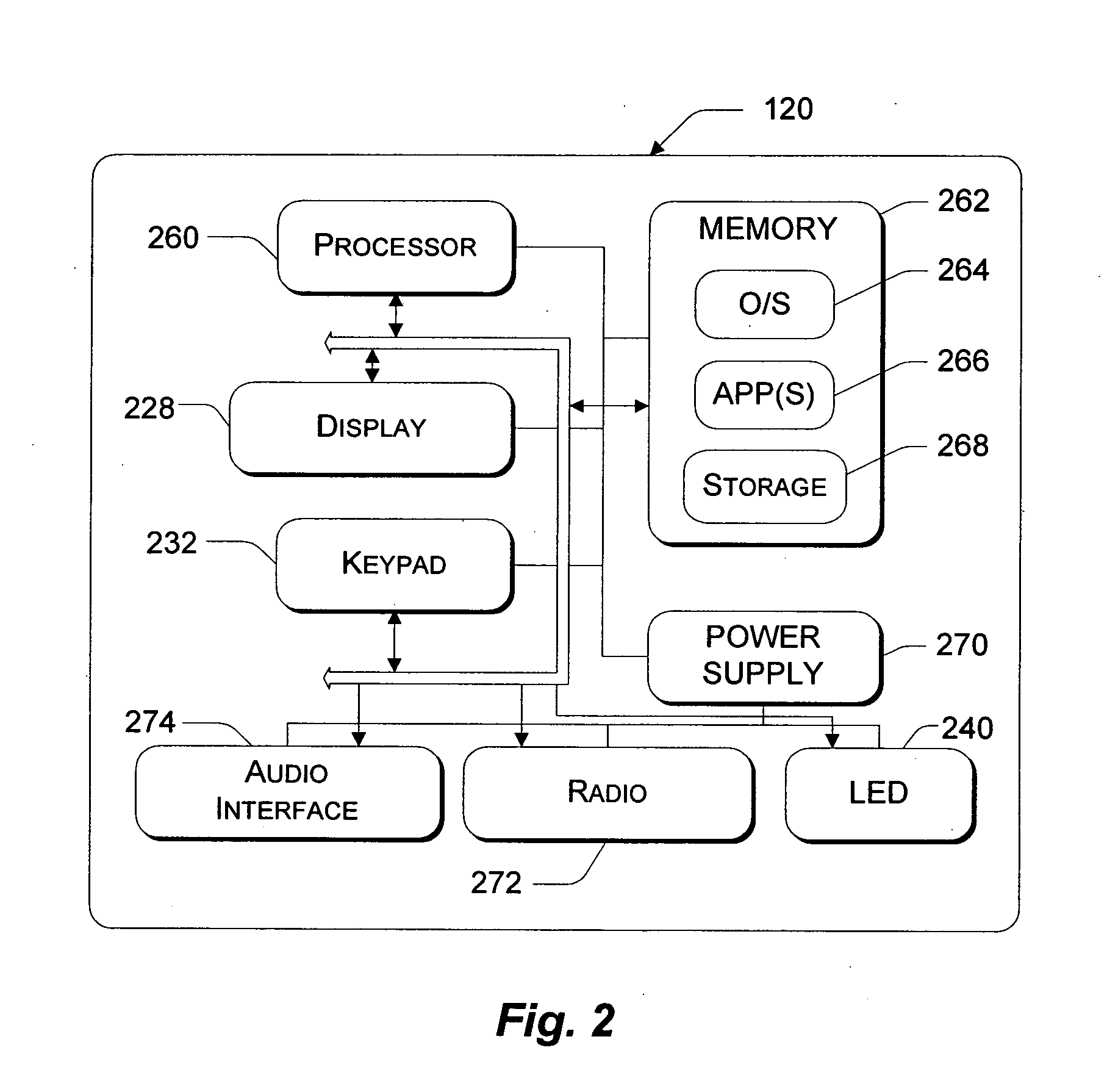
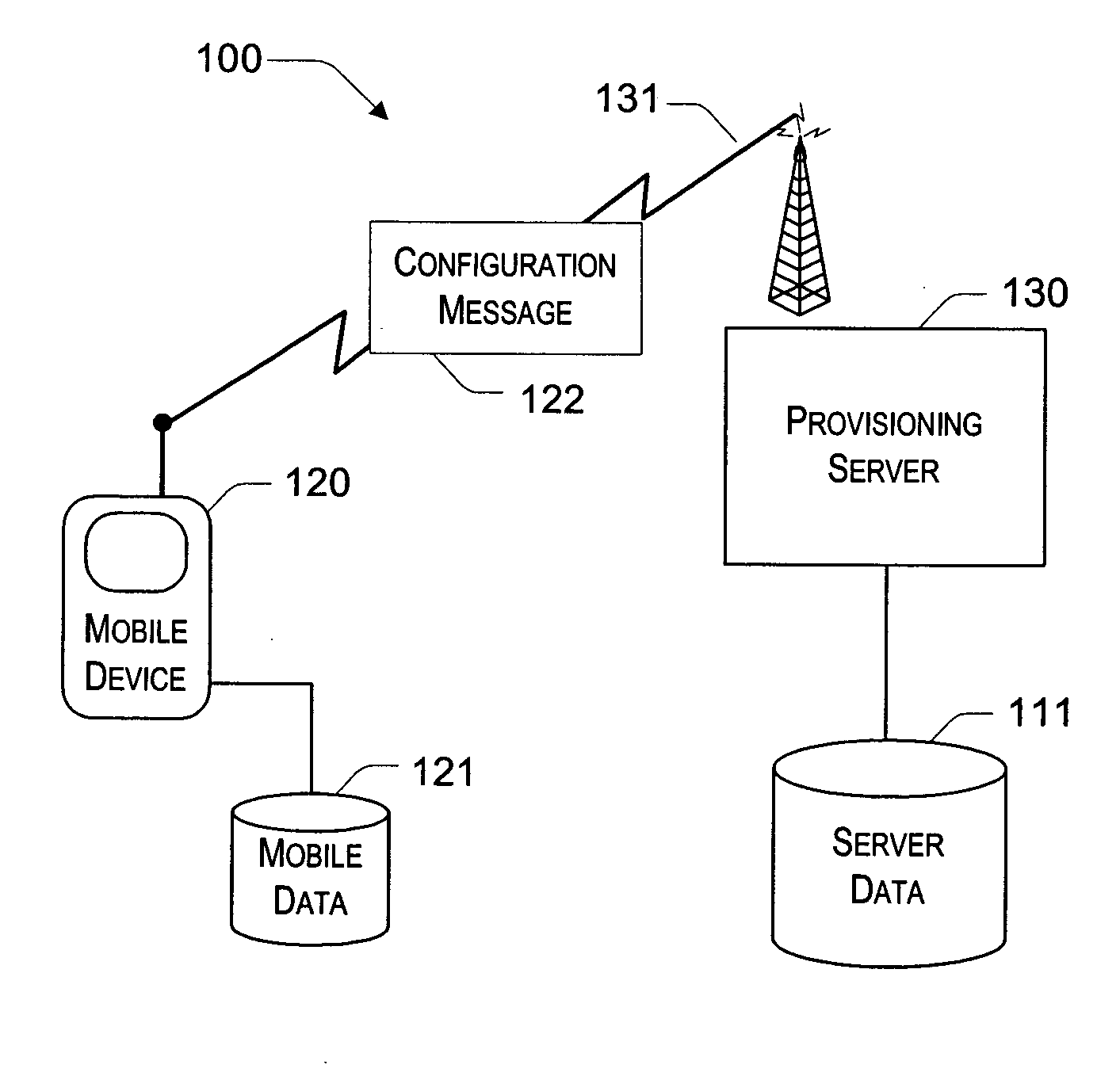
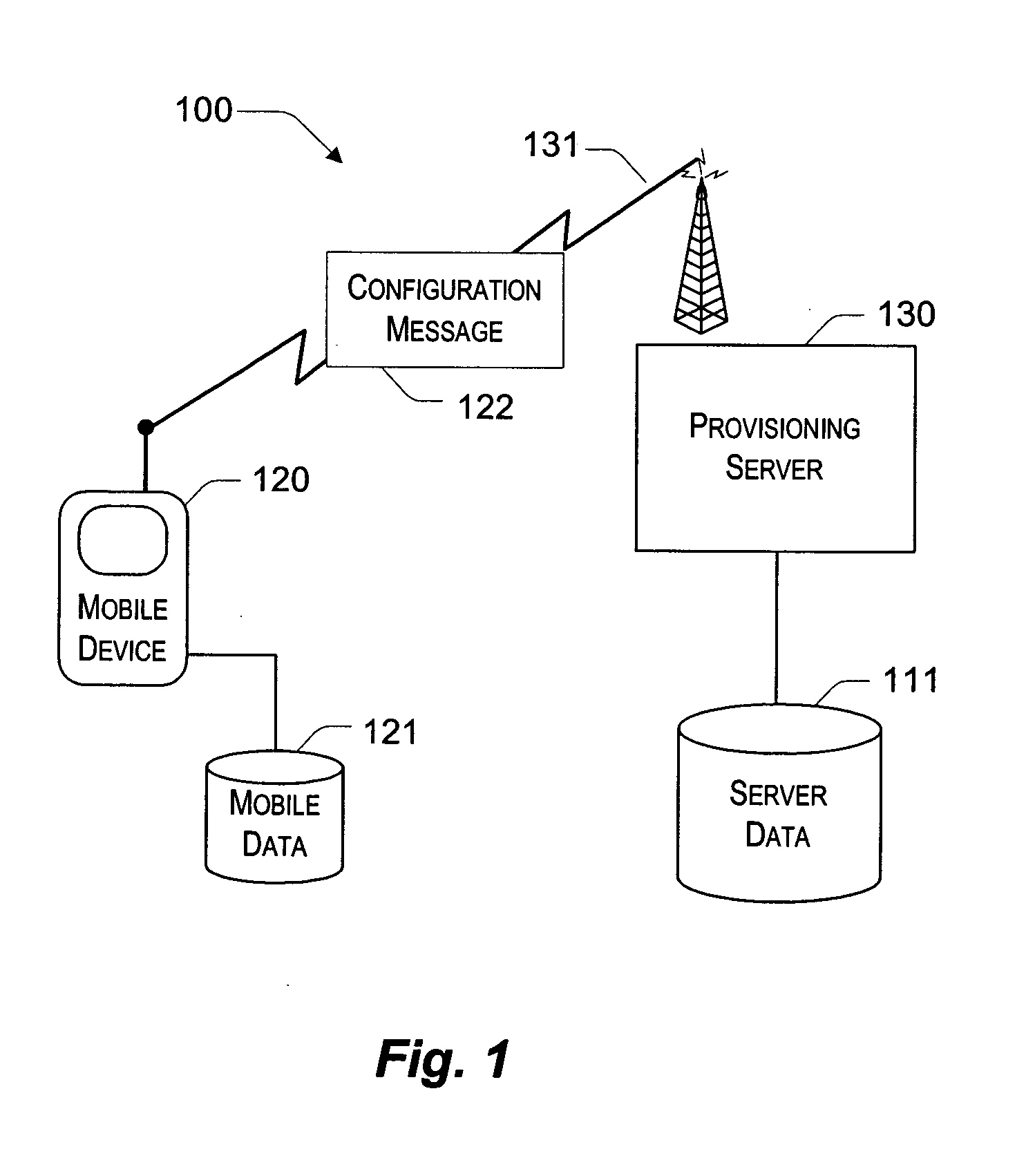
System and method for continuously provisioning a mobile device
InactiveUS20050190764A1Completely successfulNetwork traffic/resource managementDigital computer detailsDocument formatExtensible markup
Described is a provisioning system for receiving configuration changes to and queries of settings on a mobile device. One implementation includes a router component and a configuration manager component. The router component is responsible for receiving messages delivered to the mobile device and parsing the messages into requests for information. The messages may be delivered in document format, such as in the eXtensible Markup Language (XML) format. The requests may take the form of a request to respond with existing configuration settings, or to set certain configuration settings on the mobile device. The router component is also responsible for authenticating and decrypting the messages. Once properly authenticated and decrypted, the router component passes the message to the configuration manager component. The configuration manager component is responsible for determining what configuration settings are affected by the message and for processing the requests within the message. For example, the configuration manager component may process a request to query a configuration setting by retrieving the requested information from a hardware register or a software registry. The configuration manager component may implement one or more configuration service providers to perform the actual request processing. The configuration manager component may additionally compose a response document to return in the event that a response has been requested in the message. In one implementation, the response may be created by modifying the original message received and returning that message to the router component.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for simulating hardware components in a configuration and power management system
InactiveUS6980944B1Analogue computers for electric apparatusCAD circuit designProcessor registerSimulation
A mechanism for simulating the existence of hardware in a configuration and power management system is described. In one aspect, a simulator interfaces with the configuration and power management system to generate simulated events. In another aspect, accesses to hardware registers are simulated by registering the simulator with the configuration and power management system to handle accesses to a simulated hardware device. A component within the configuration and power management system may define the simulated hardware device such that accesses to the simulated hardware device occur with respect to a defined I / O space.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
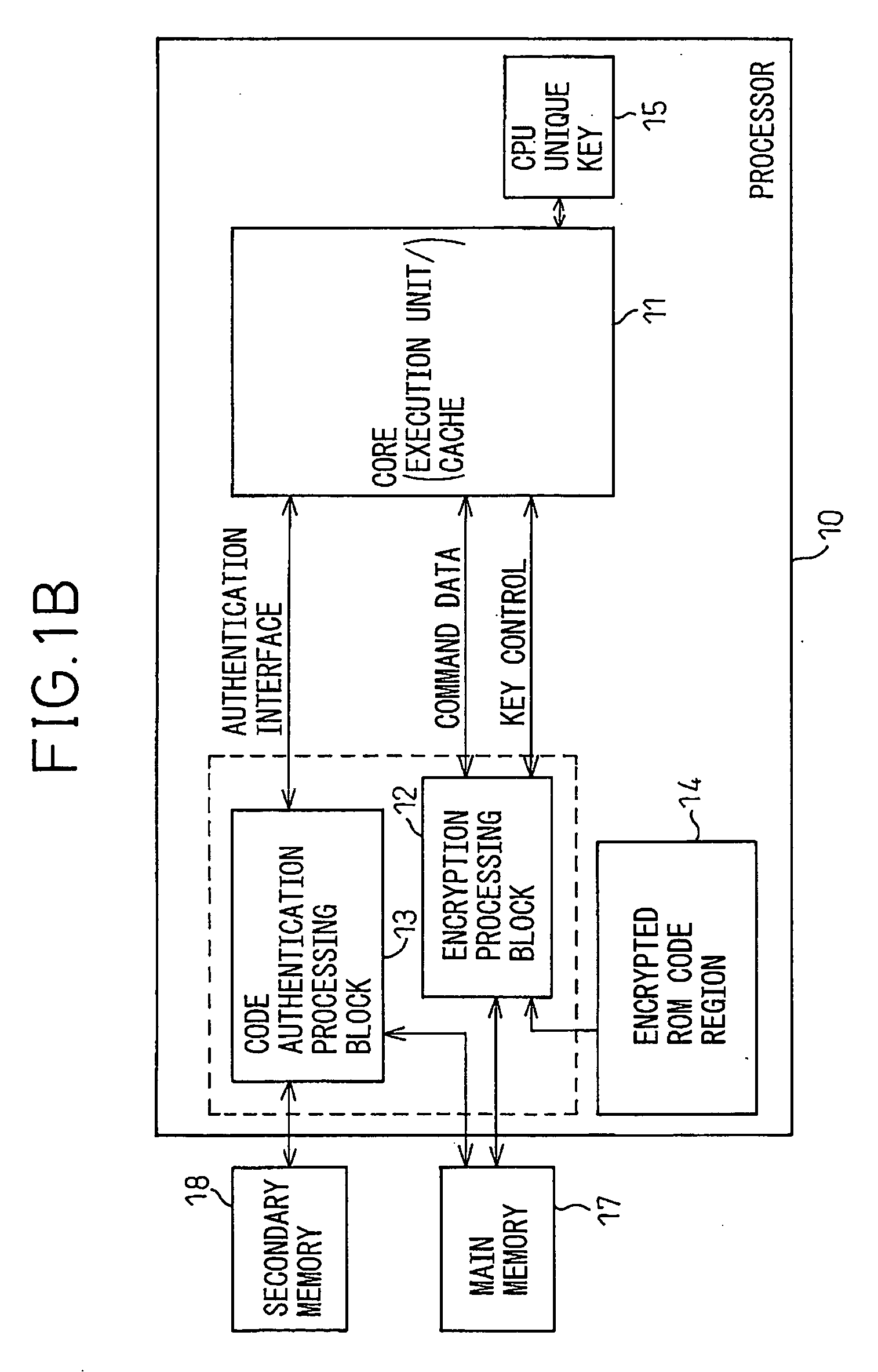
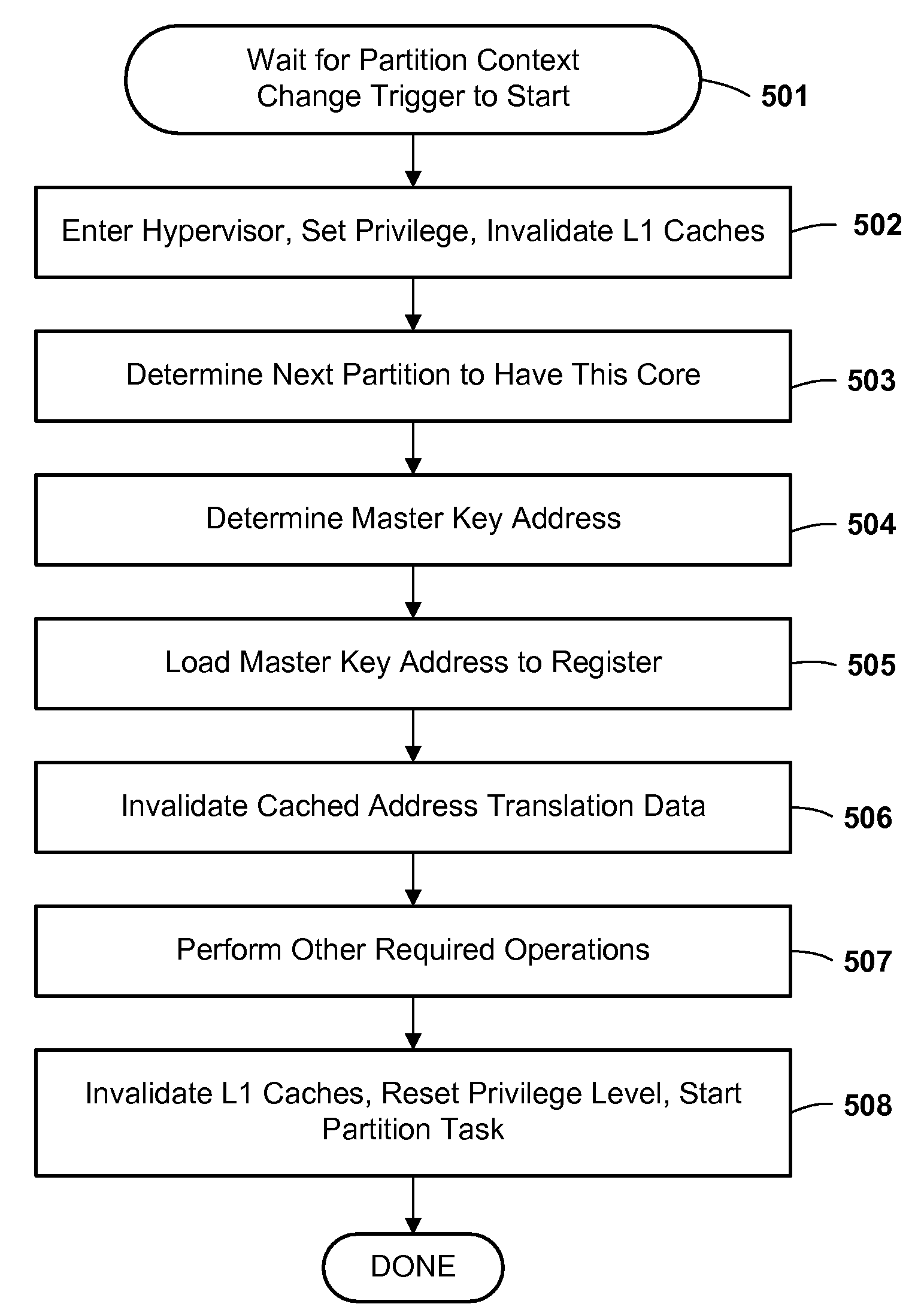
Method and Apparatus for Protecting Encryption Keys in a Logically Partitioned Computer System Environment
InactiveUS20090214040A1Avoid callingProtective layerKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwareMemory address
In a logically partitioned computer system, a partition manager maintains and controls master encryption keys for the different partitions. Preferably, processes executing within a partition have no direct access to real memory, addresses in the partition's memory space being mapped to real memory by the partition manager. The partition manager maintains master keys at real memory addresses inaccessible to processes executing in the partitions. Preferably, a special hardware register stores a pointer to the current key, and is read only by a hardware crypto-engine to encrypt / decrypt data. The crypto-engine returns the encrypted / decrypted data, but does not output the key itself or its location.
Owner:IBM CORP
Universal graphic adapter for interfacing with hardware and means for encapsulating and abstracting details of the hardware
InactiveUS6907482B2Easy to updateQuality improvementDigital computer detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsProcessor registerAssembly language
The subject invention relates to a Universal Graphics Adapter (UGA) that is a hardware-independent design that encapsulates and abstracts low-level graphics hardware in a standard manner through firmware. UGA is a firmware standard, intended to wrap existing or planned hardware, including VGA. UGA does not require the use of real-mode assembly language, direct hardware register, or frame buffer access to program, thus providing advantages over conventional systems. UGA supports basic drawing operations, continuous display modes, and power management. As a firmware-based standard, UGA facilitates updating a system to support both evolving and new hardware features.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
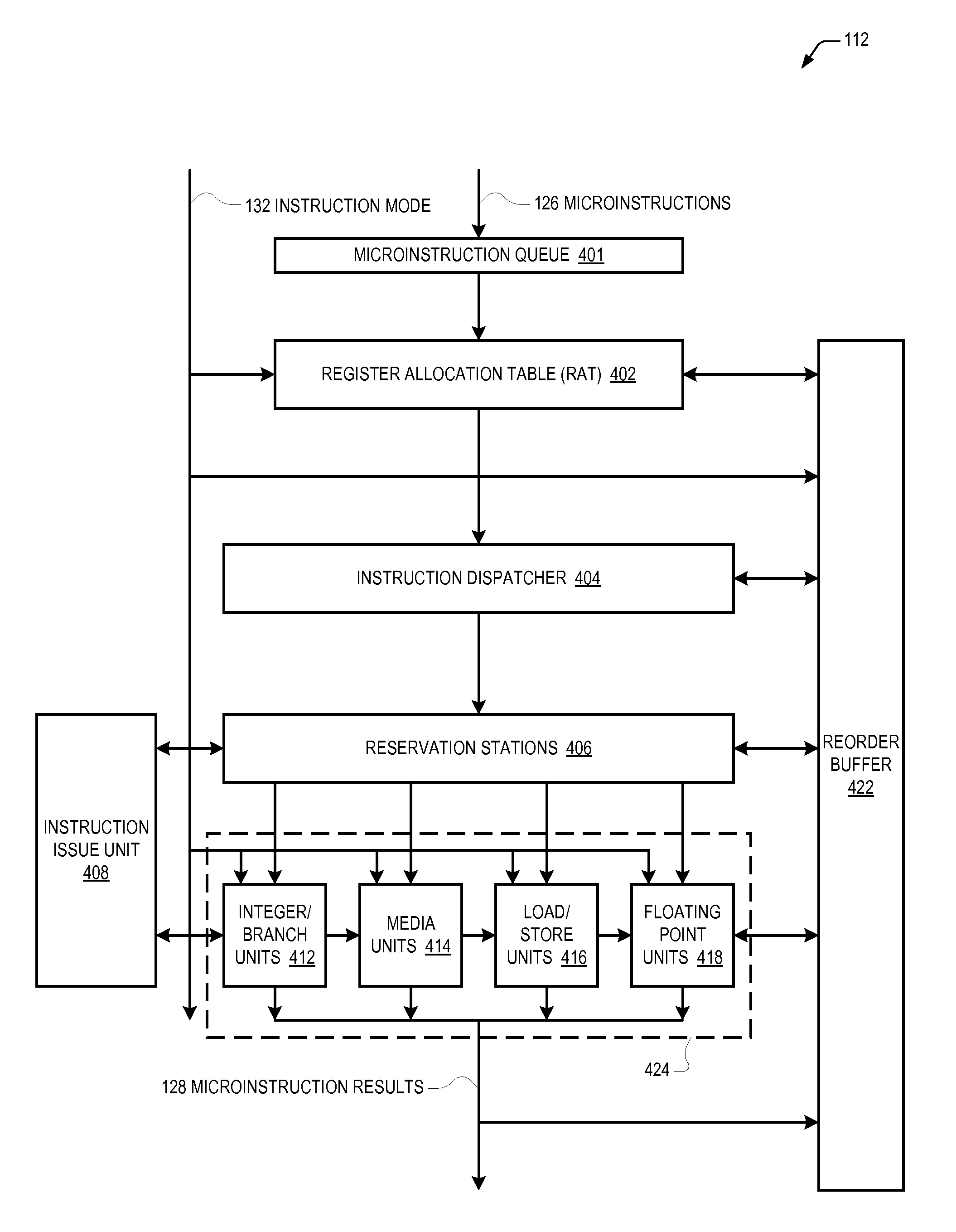
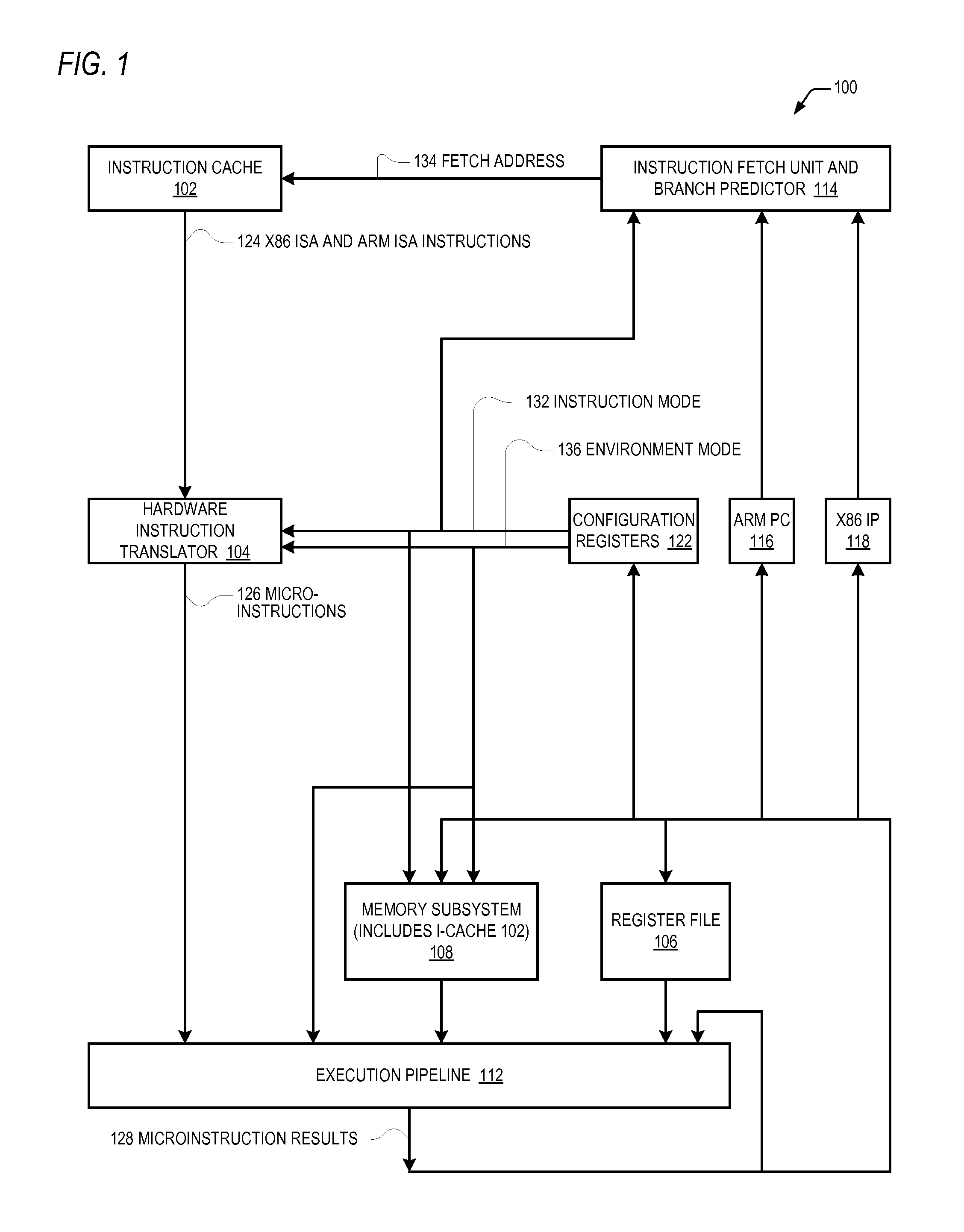
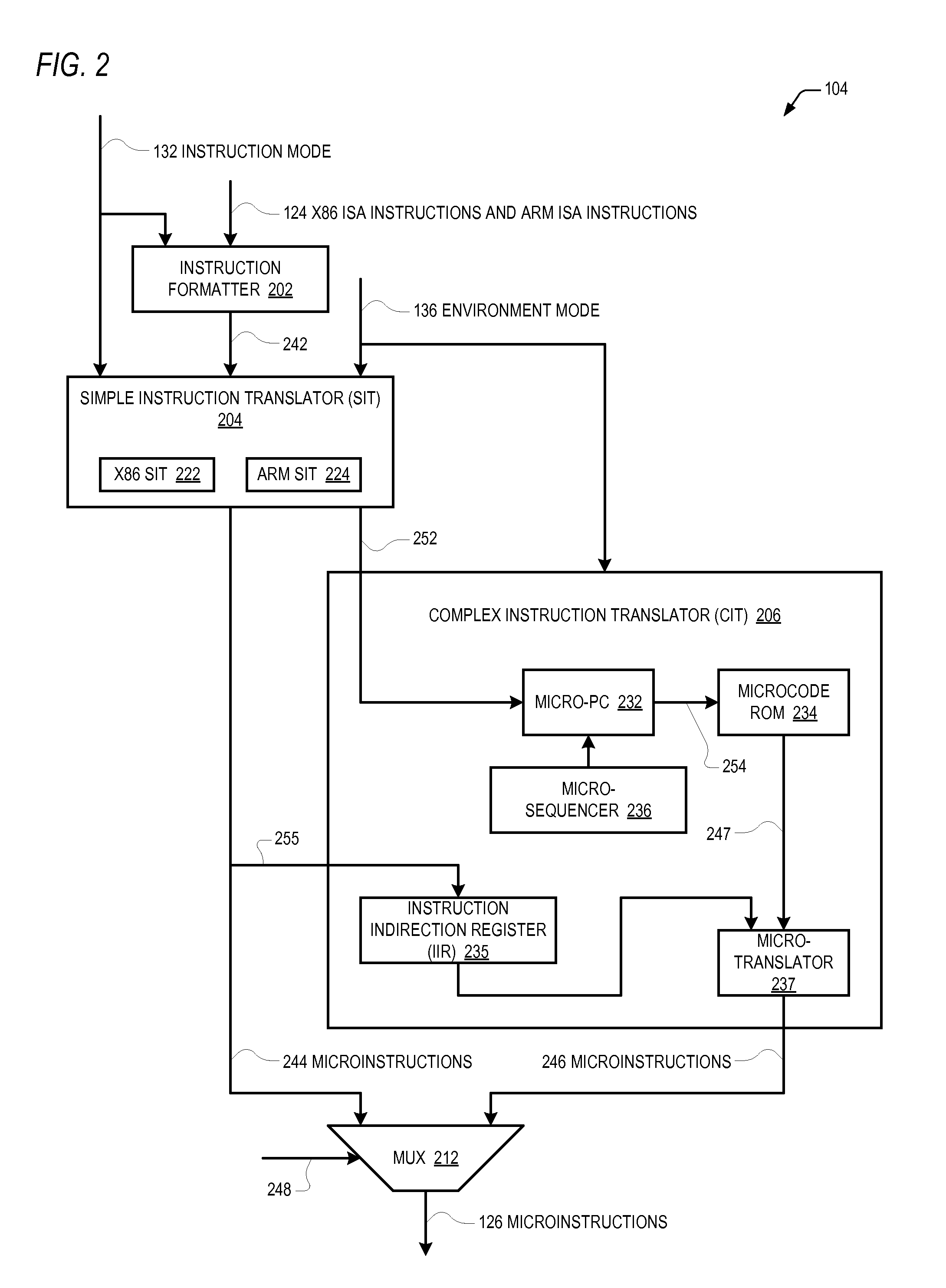
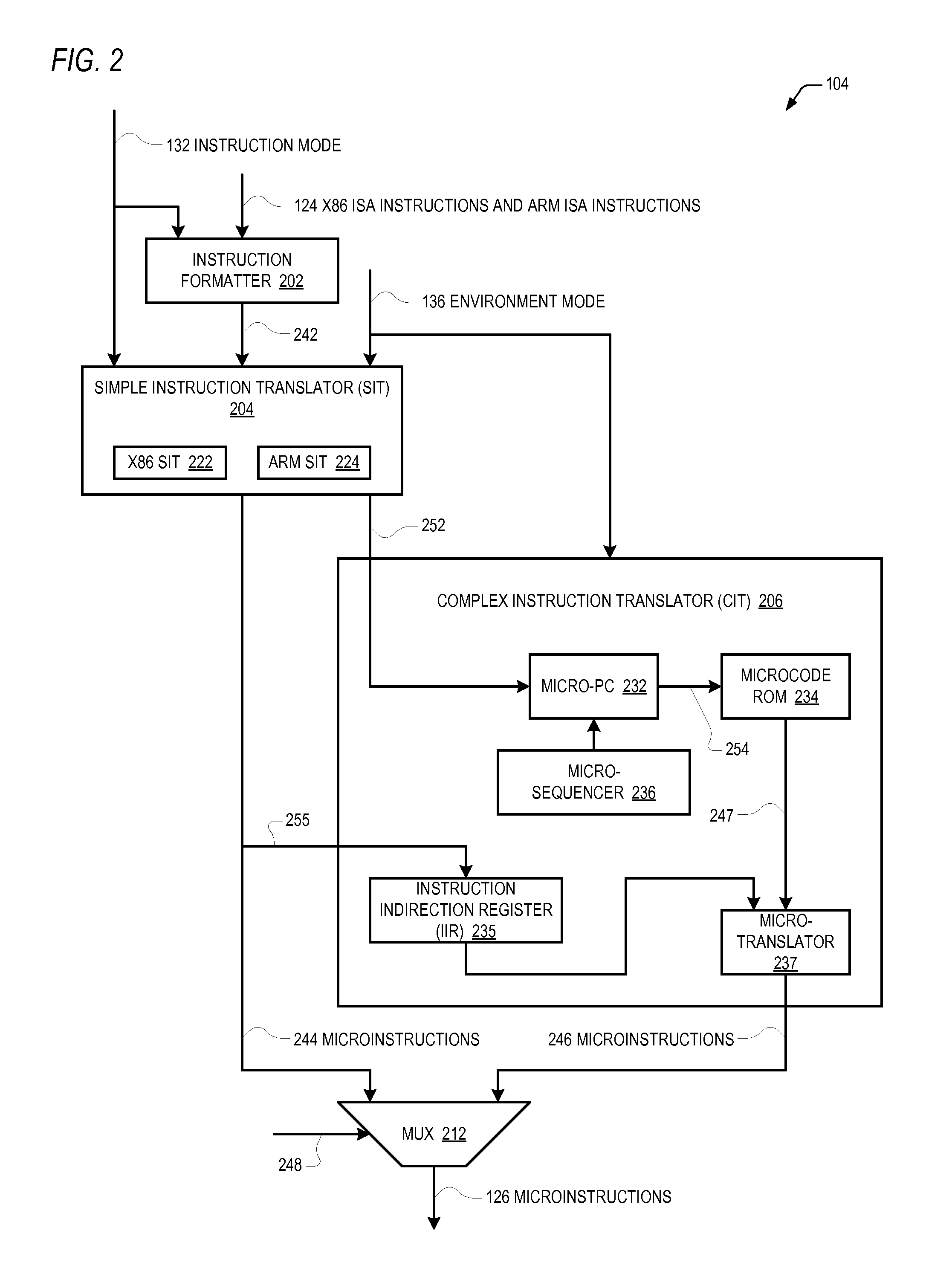
Microprocessor that makes 64-bit general purpose registers available in msr address space while operating in non-64-bit mode
A microprocessor includes hardware registers that instantiate the IA-32 Architecture EDX and EAX GPRs and hardware registers that instantiate the Intel 64 Architecture R8-R15 GPRs. The microprocessor associates with each of the R8-R15 GPRs a respective unique MSR address. In response to an IA-32 Architecture RDMSR instruction that specifies the respective unique MSR address of one of the R8-R15 GPRs, the microprocessor reads the contents of the hardware register that instantiates the specified one of the R8-R15 GPRs into the hardware registers that instantiate the EDX:EAX registers. In response to an IA-32 Architecture WRMSR instruction that specifies the respective unique MSR address of one of the R8-R15 GPRs, the microprocessor writes into the hardware register that instantiates the specified one of the R8-R15 GPRs the contents of the hardware registers that instantiate the EDX:EAX registers. The microprocessor does so even when operating in non-64-modes.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Deterministic microcontroller with configurable input/output interface
ActiveUS20060168429A1Minimal interventionDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsMicrocontrollerData acquisition
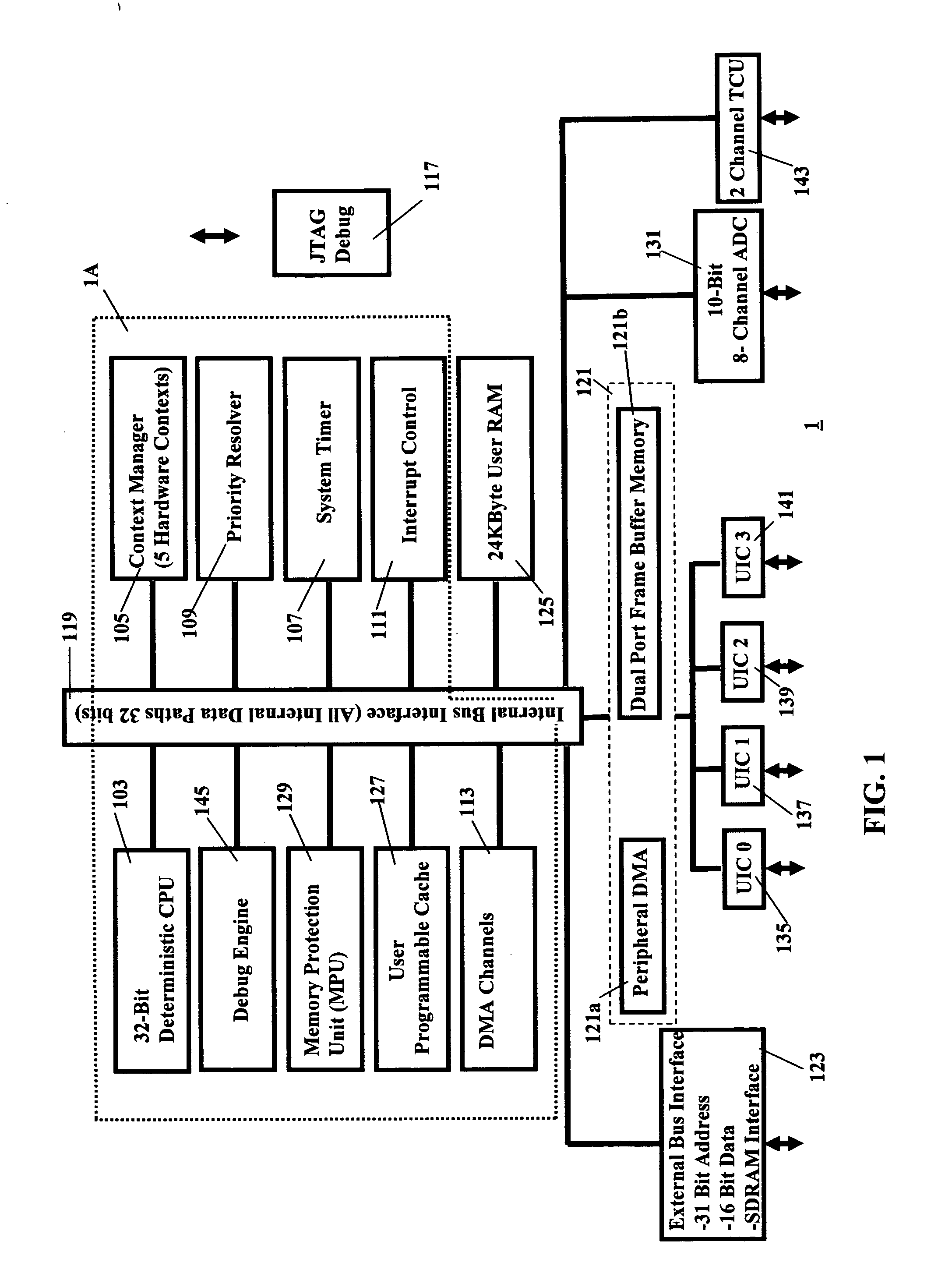
A deterministic microcontroller includes a plurality of blocks of cache memories formed on the same integrated circuit as the microprocessor unit. A corresponding plurality of hardware contexts for the microcontroller is provided by the plurality of sets of hardware registers. A context manager controls the selection of the hardware registers such that contexts are changed within one bus cycle and a plurality of hardware contexts are provided. The deterministic microcontroller includes a configurable input / output interface that is programmable to handle any one of a plurality of interfaces that embedded applications might have, including communication protocols and bus interfaces, data acquisition from multiple sensors and actuators, and controls of various motors.
Owner:INNOVASIC
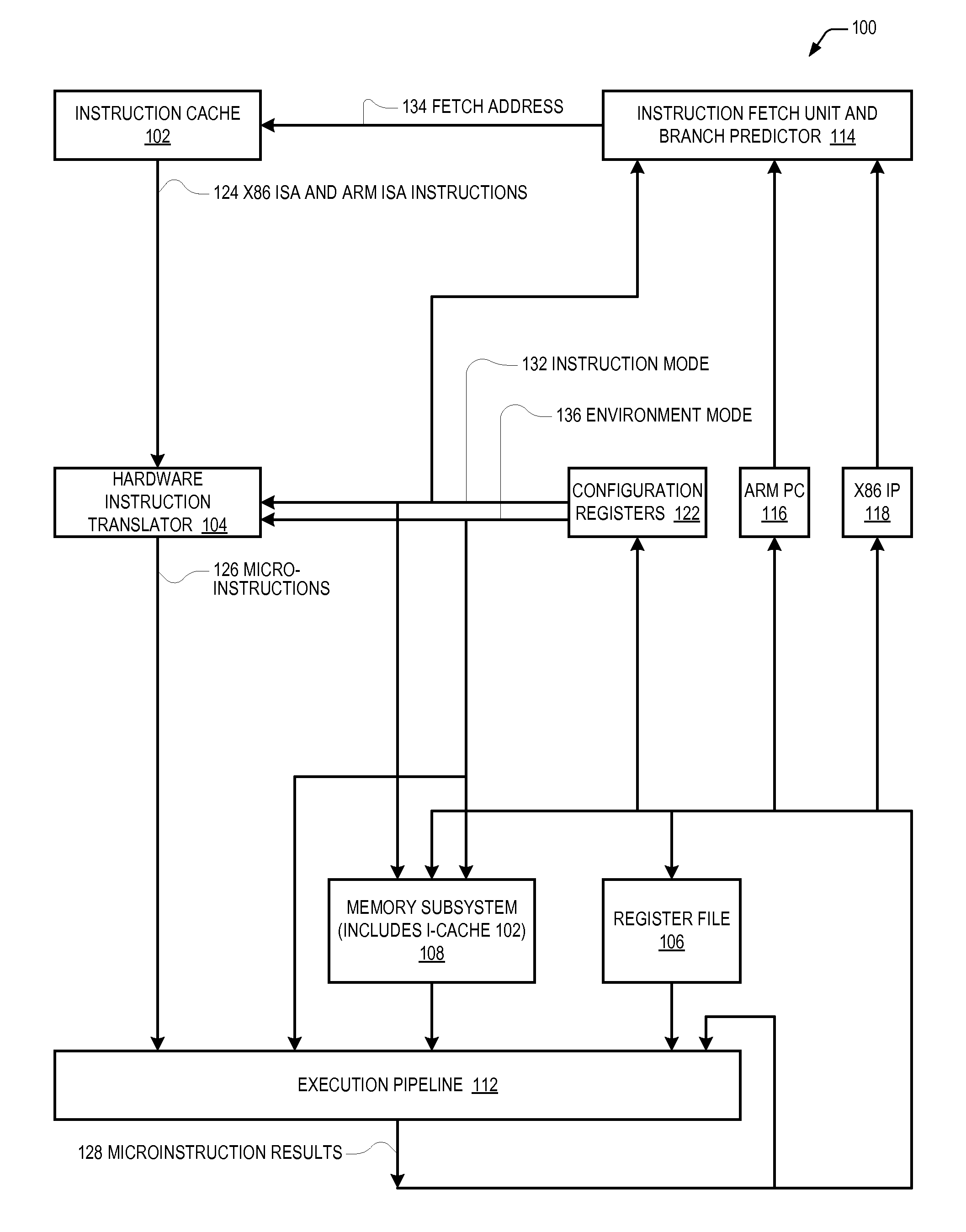
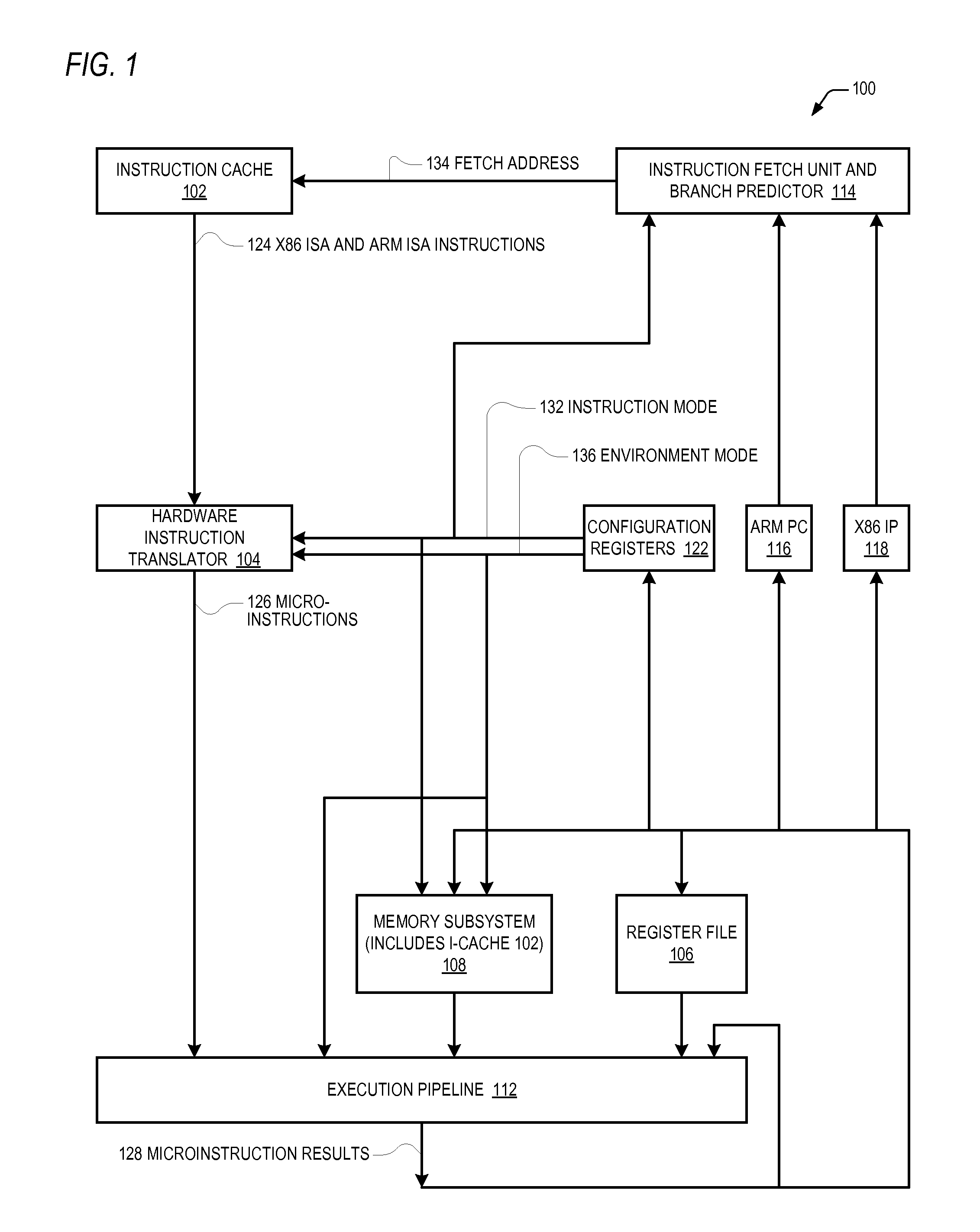
Microprocessor that enables arm isa program to access 64-bit general purpose registers written by x86 isa program
A microprocessor includes hardware registers that instantiate the Intel 64 Architecture R8-R15 GPRs. The microprocessor associates with each of the R8-R15 GPRs a respective unique MSR address. The microprocessor also includes hardware registers that instantiate the ARM Architecture GPRs. In response to an ARM MRRC instruction that specifies the respective unique MSR address of one of the R8-R15 GPRs, the microprocessor reads the contents of the hardware register that instantiates the specified one of the R8-R15 GPRs into the hardware registers that instantiate two of the ARM GPRs registers. In response to an ARM MCRR instruction that specifies the respective unique MSR address of one of the R8-R15 GPRs, the microprocessor writes into the hardware register that instantiates the specified one of the R8-R15 GPRs the contents of the hardware registers that instantiate two of the ARM Architecture GPRs registers. The hardware registers may be shared by the two Architectures.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Method for laying out fields in a database in a hybrid of row-wise and column-wise ordering
ActiveUS8099440B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsProcessor registerData mining
A method, system, and article are provided for employment of a hybrid layout of representation of data objects in computer memory. Columns of the database are separated based upon a classification of the columns. A vertical partition in the form of a bank is provided to receive an assignment of one or more data objects identified in the columns. Each bank is sized to be a divisor of a size of an associated hardware register. Assignment of data objects to banks organizes the data in a manner that support efficient query processing that mitigates the quantity of banks required to respond to the query.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
System and method for adding hardware registers to a power management and configuration system
InactiveUS6907474B2Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsGeneral purposeMemory map
A system for adding multiple GPE blocks (in addition to the system / root GPE block device) to a computing system by creating a device entry in the ACPI namespace, and using a _CRS object to describe the system resources consumed by the device is described. The GPE block device may then access associated hardware devices through a well known mechanism (either I / O or Memory Mapped accesses). By creating additional GPE block devices within the ACPI namespace, general purpose events may be delivered using more traditional hardware interrupt mechanisms than with existing systems (e.g., wiring GPE blocks together). Moreover, by putting GPE block devices in the ACPI namespace, hardware components having hardware registers may be “hot plugged” to the computing system.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
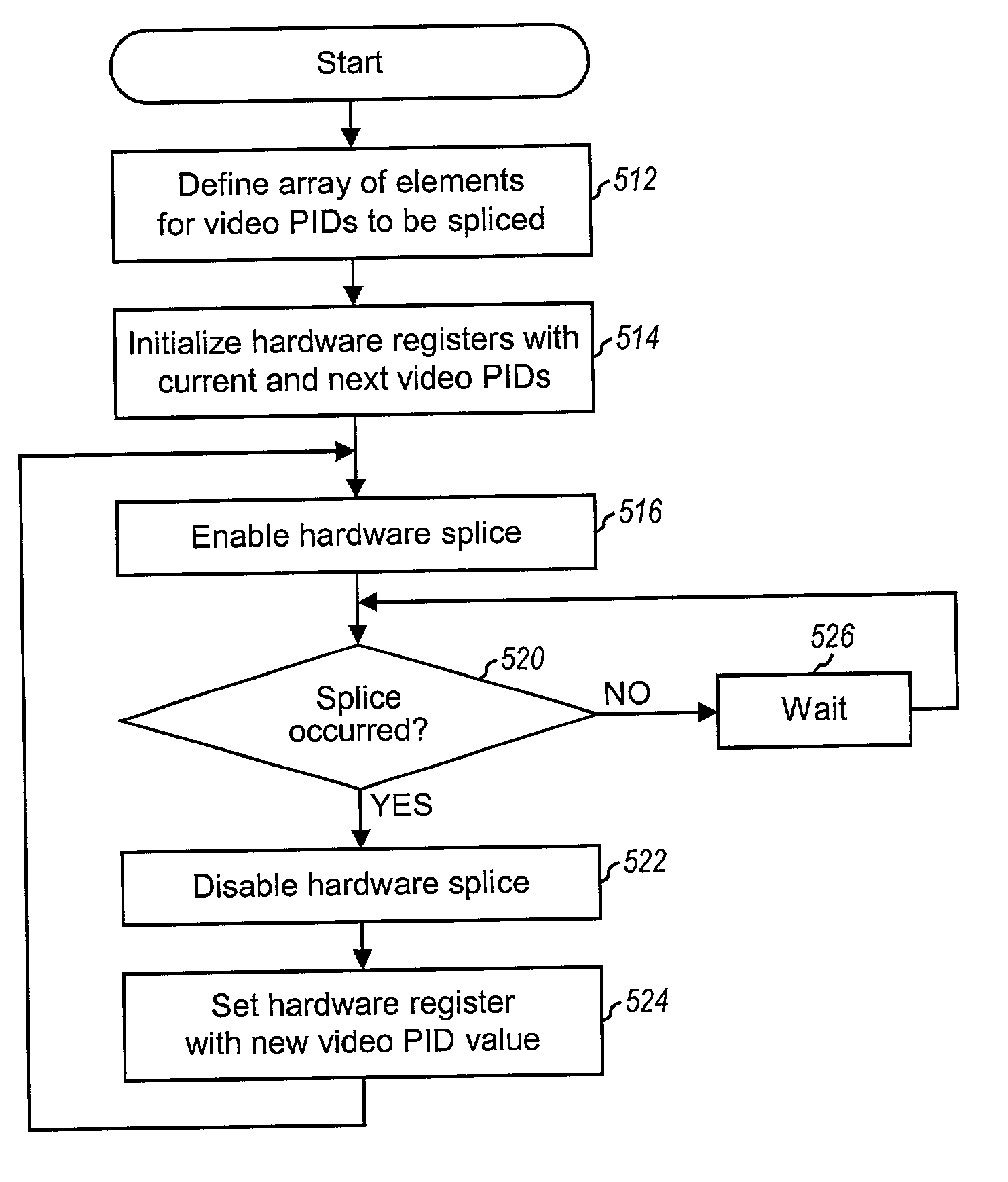
Method and apparatus for performing sub-picture level splicing based on interrupts
ActiveUS7174084B2Eliminate needTelevision system detailsRecording carrier detailsProcessor registerEmbedded system
Techniques to effectuate splicing at sub-picture level. In one aspect, splicing is effectuated via an interrupt generated after each splice has occurred. The interrupt may be generated by either the hardware designated to perform splicing or other peripheral hardware. The interrupt may be provided to a controller, which then performs the necessary processing to effectuate the next splice (e.g., load a new PID value for the next splice into the hardware register). The interrupts required for splicing may be generated in various manners, and typically depends on the specific design of the splicing and / or peripheral hardware. In one simple design, the splicing hardware generates an interrupt after each splice. Other mechanisms may also be used to generate the interrupt. For example, (e.g., scrambled audio) packets may be inserted into a transport stream and used to cause the hardware to generate an interrupt each time the packet is detected.
Owner:COX COMMUNICATIONS
Method and apparatus for determining computer program flows autonomically using hardware assisted thread stack tracking and cataloged symbolic data
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
System and method for continuously provisioning a mobile device
InactiveUS20060193321A1Completely successfulNetwork traffic/resource managementDigital computer detailsDocument formatExtensible markup
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
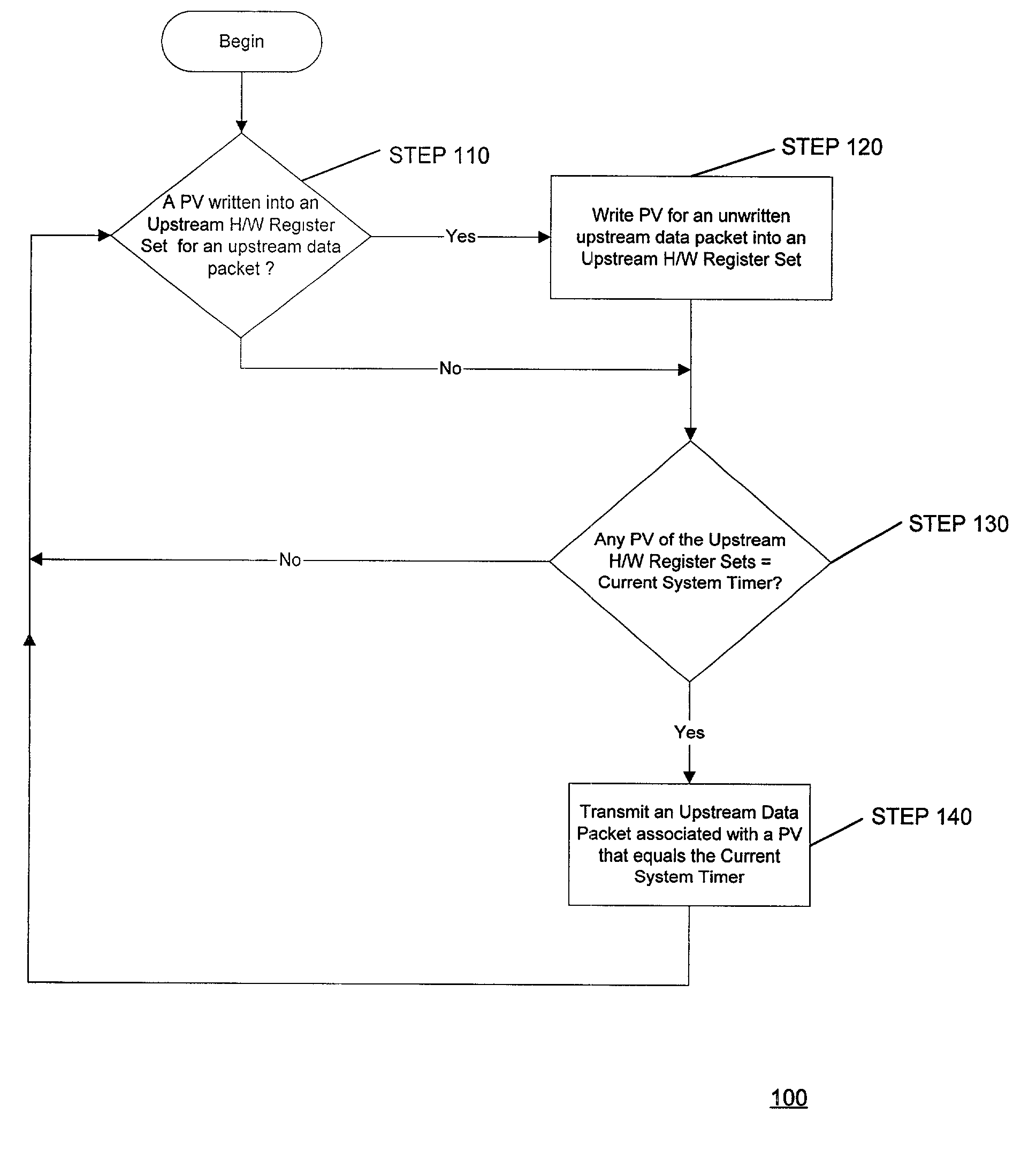
Method and apparatus for scheduling upsteam data packets in a broadband communication system
InactiveUS7016376B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationClock timeCommunications system
A method and apparatus for scheduling upstream data packets in a communication system is described. The present inventive method obtains a priority value (PV) for an upstream data packet and compares (using hardware registers) the PV of a queued upstream data packet to a current system timer. In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, the current system timer comprises the current clock time of the communication system. When a PV equals the current system timer, the method transmits the upstream data packet associated with the PV to the CMTS via the upstream transmission path.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
System and method for dynamically selecting storage instruction performance scheme
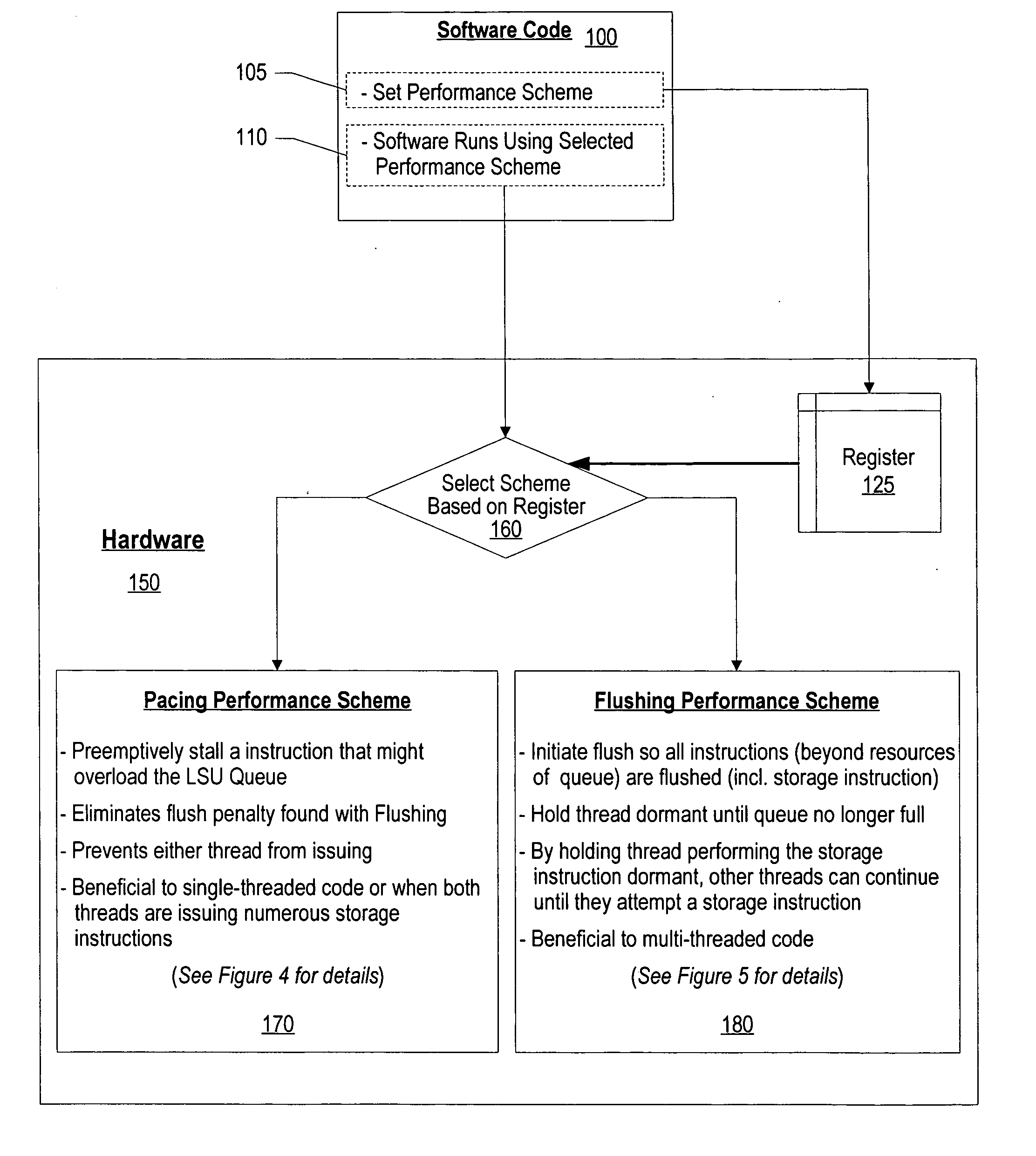
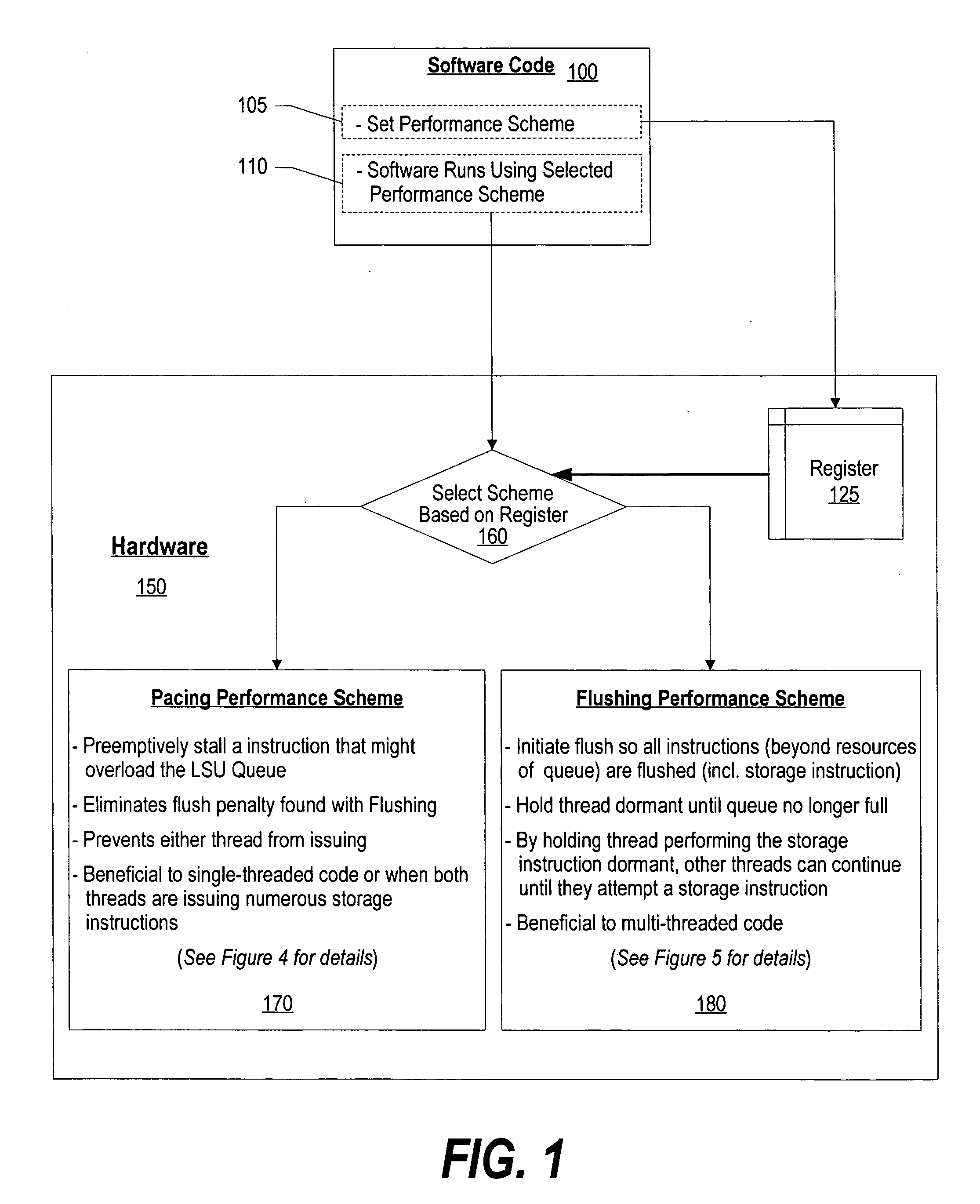
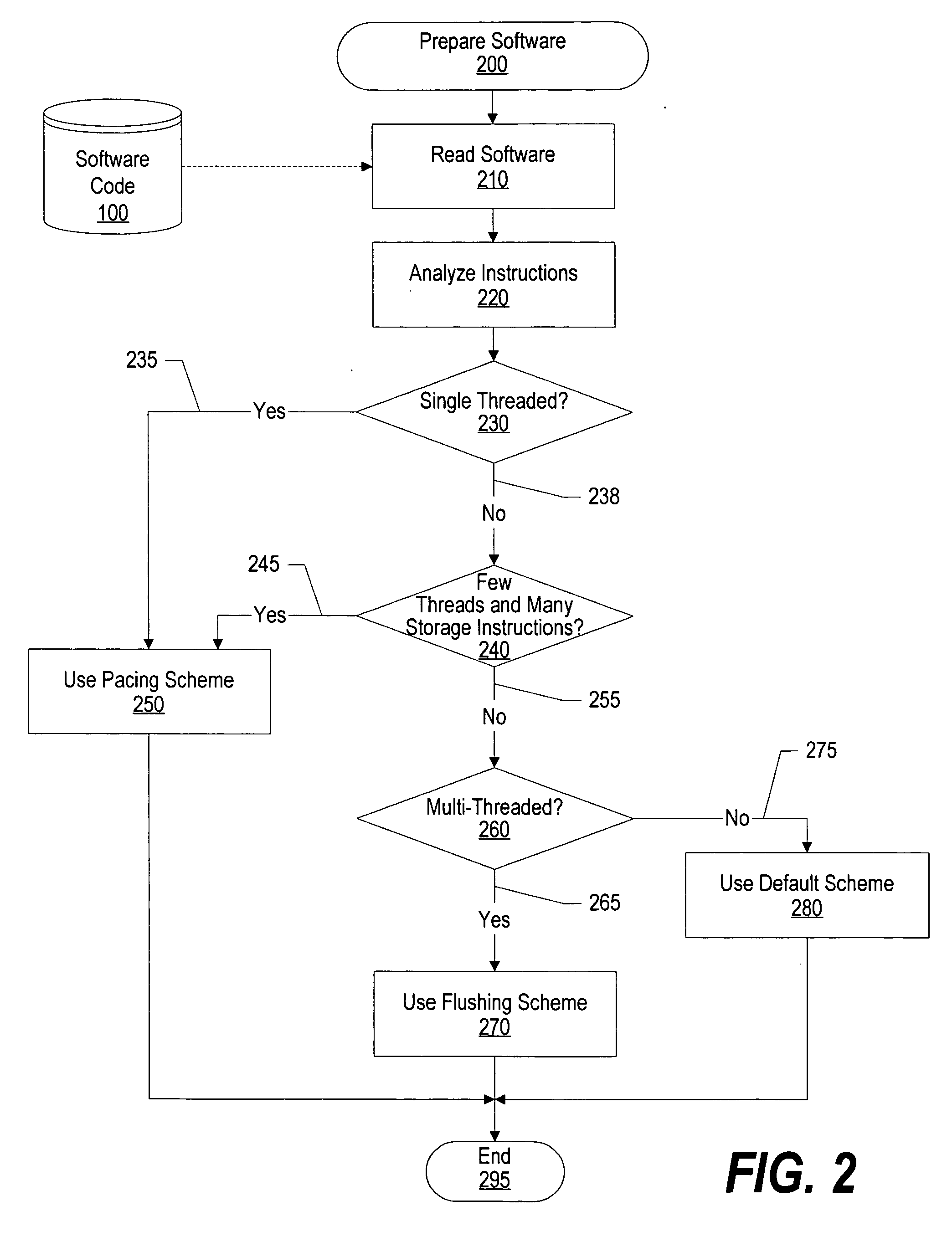
InactiveUS20070118726A1Eliminates flush penaltyAvoid issuingProgram control using stored programsLink editingParallel computingComputer science
A system and method for dynamic switching between performance schemes is presented. The software program uses an instruction to indicate whether a pacing performance scheme or a flushing performance scheme is to be used. The selection by the software program is stored in a hardware register that the processor uses to determine whether the pacing or flushing performance scheme is used. After setting the performance scheme, subsequent instructions of the software program will be executed using the selected performance scheme. The pacing performance scheme preemptively stalls an instruction that might overload the queue that stores instructions for the Load / Store Unit (LSU). The flushing performance scheme flushes instructions when the LSU storage queue is overloaded and holds the thread that caused the overflow dormant until the queue is no longer full.
Owner:MACHINES CORP INT BUSINESS
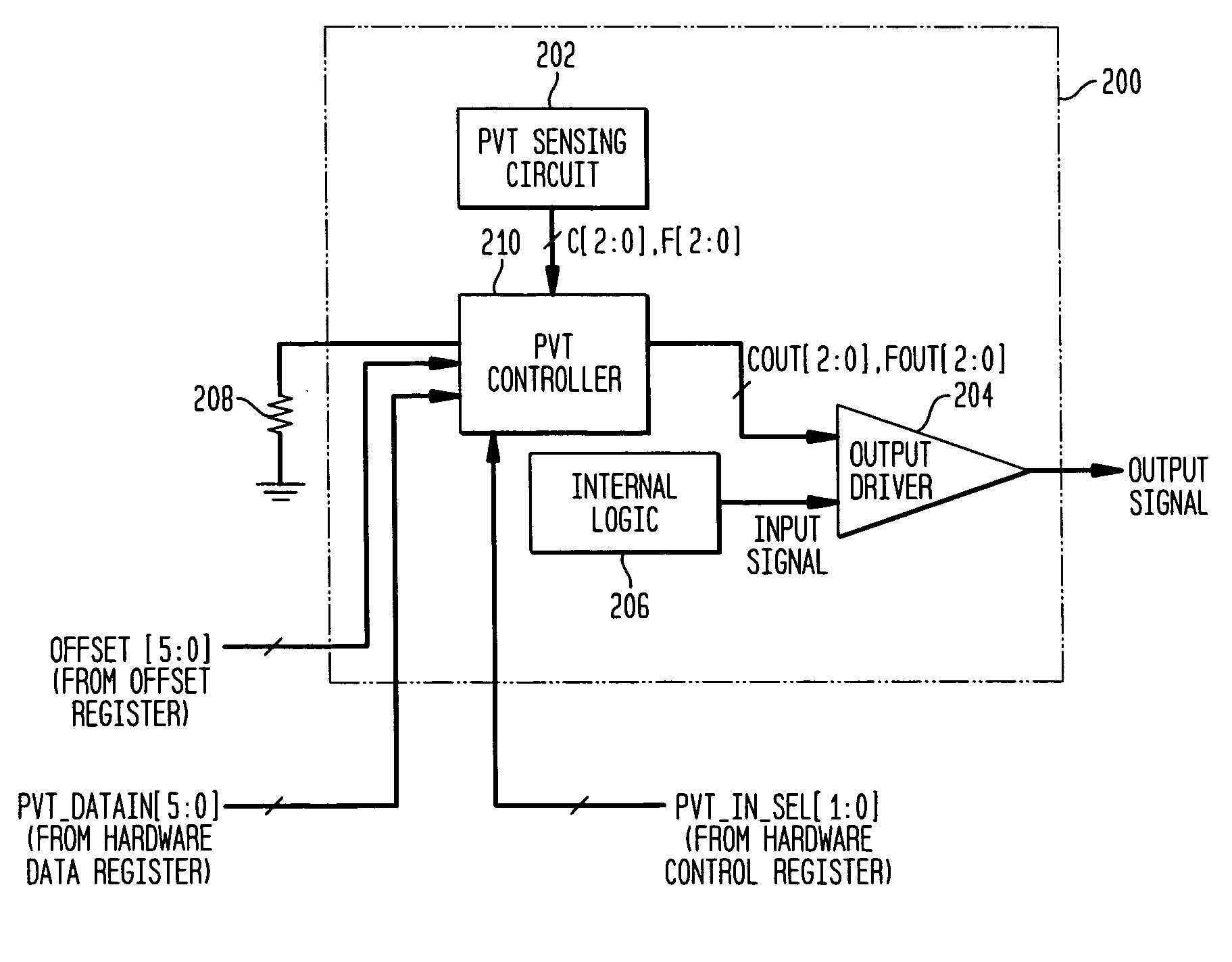
Adjusting settings of an I/O circuit for process, voltage, and/or temperature variations
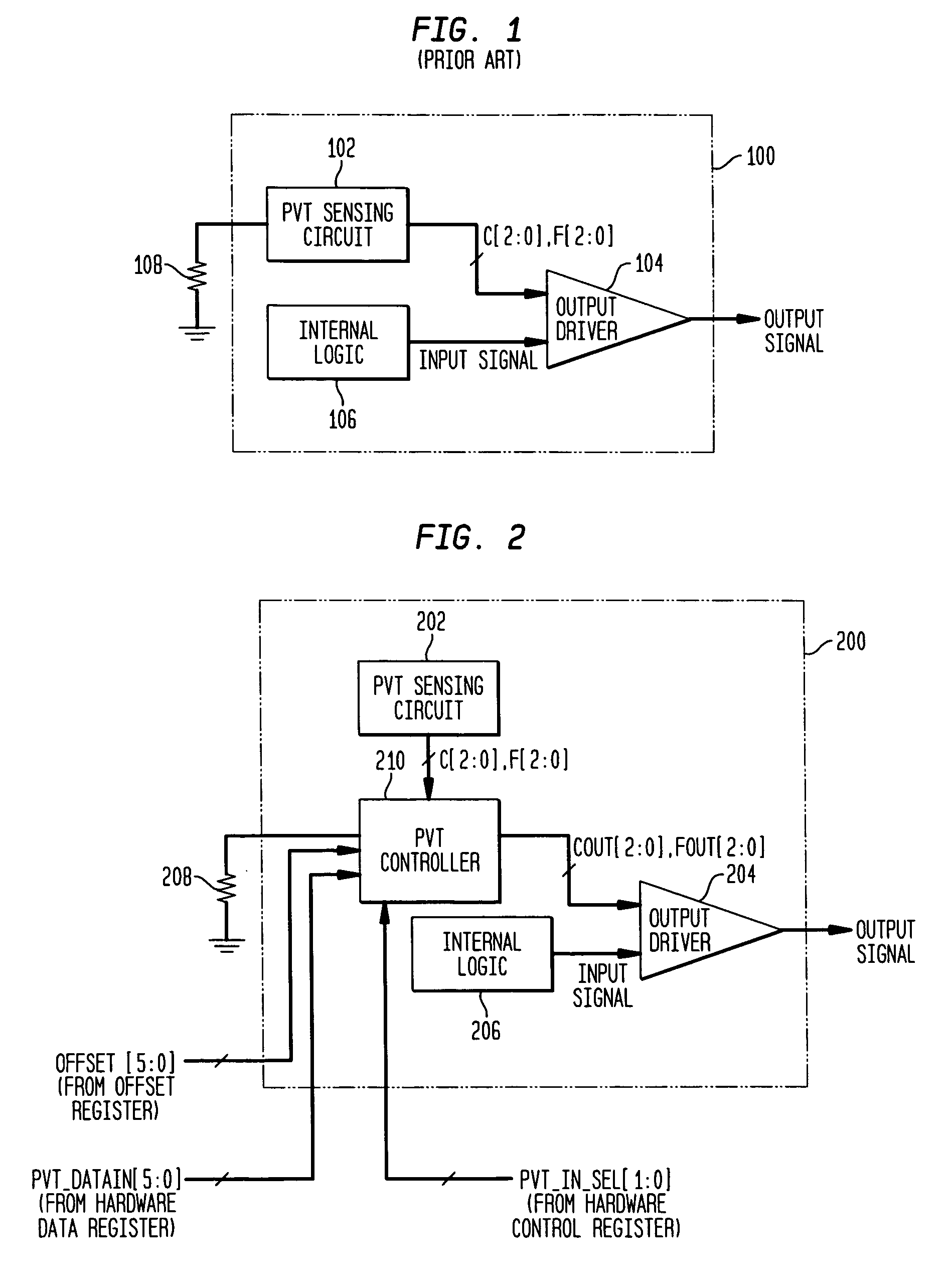
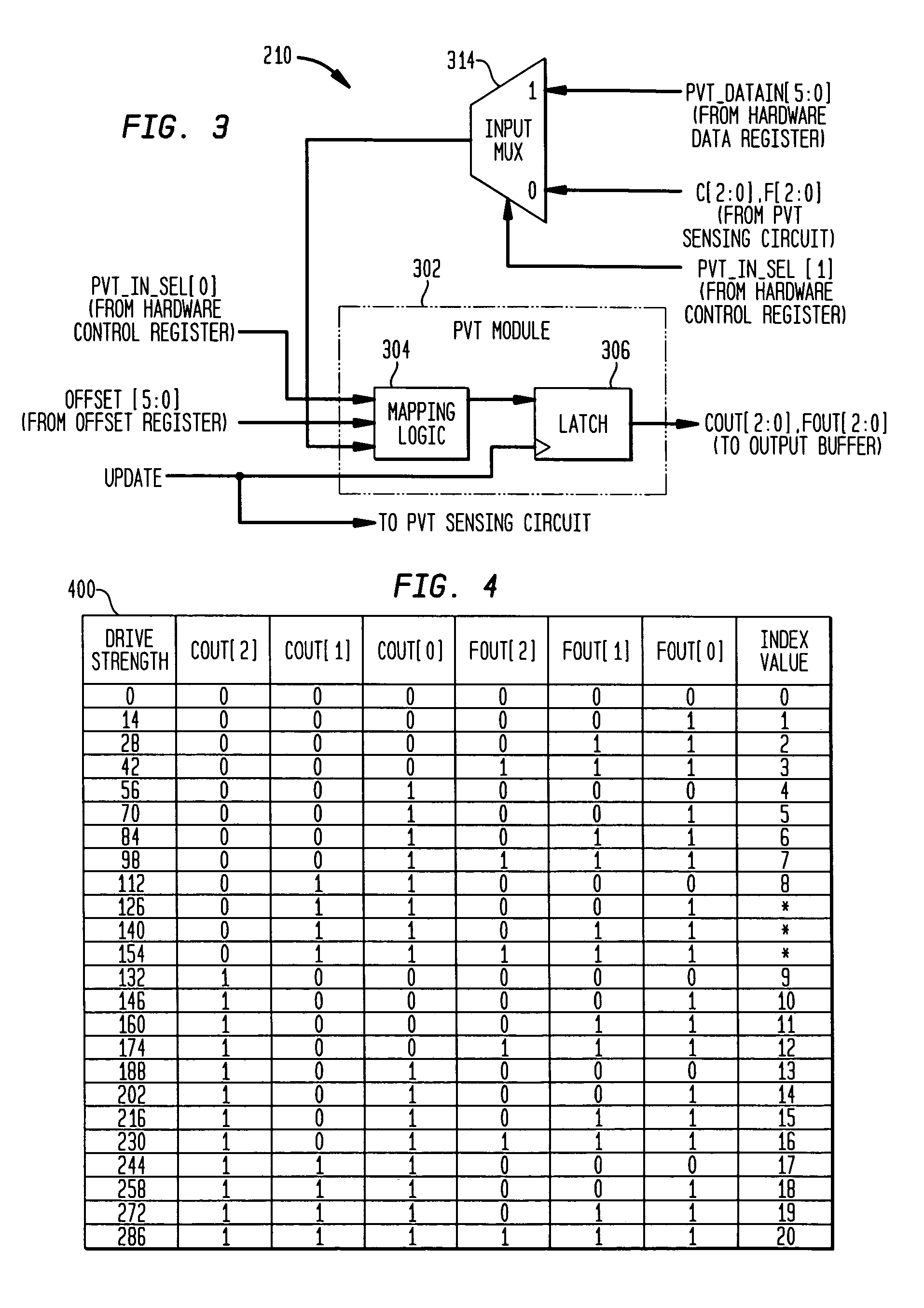
A control circuit and method for controlling the electrical characteristics of an input / output (I / O) circuit such as an output driver to account for variations in fabrication process, supply voltage, and / or temperature (PVT) conditions includes a PVT controller having appropriate control logic to permit PVT compensation to be observed, tested, and selectively adjusted. The PVT controller permits selection between PVT sensing circuit-provided control signals and control signals stored in a hardware register for controlling drive strength. The PVT controller further provides the capability to offset the selected drive strength by a fixed amount and select whether or not the offset is applied and permits full testability and observability of the selected control signal, an offset value applied thereto, and the resulting output signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
A method for hardware drive program of intelligent loading mobile phone
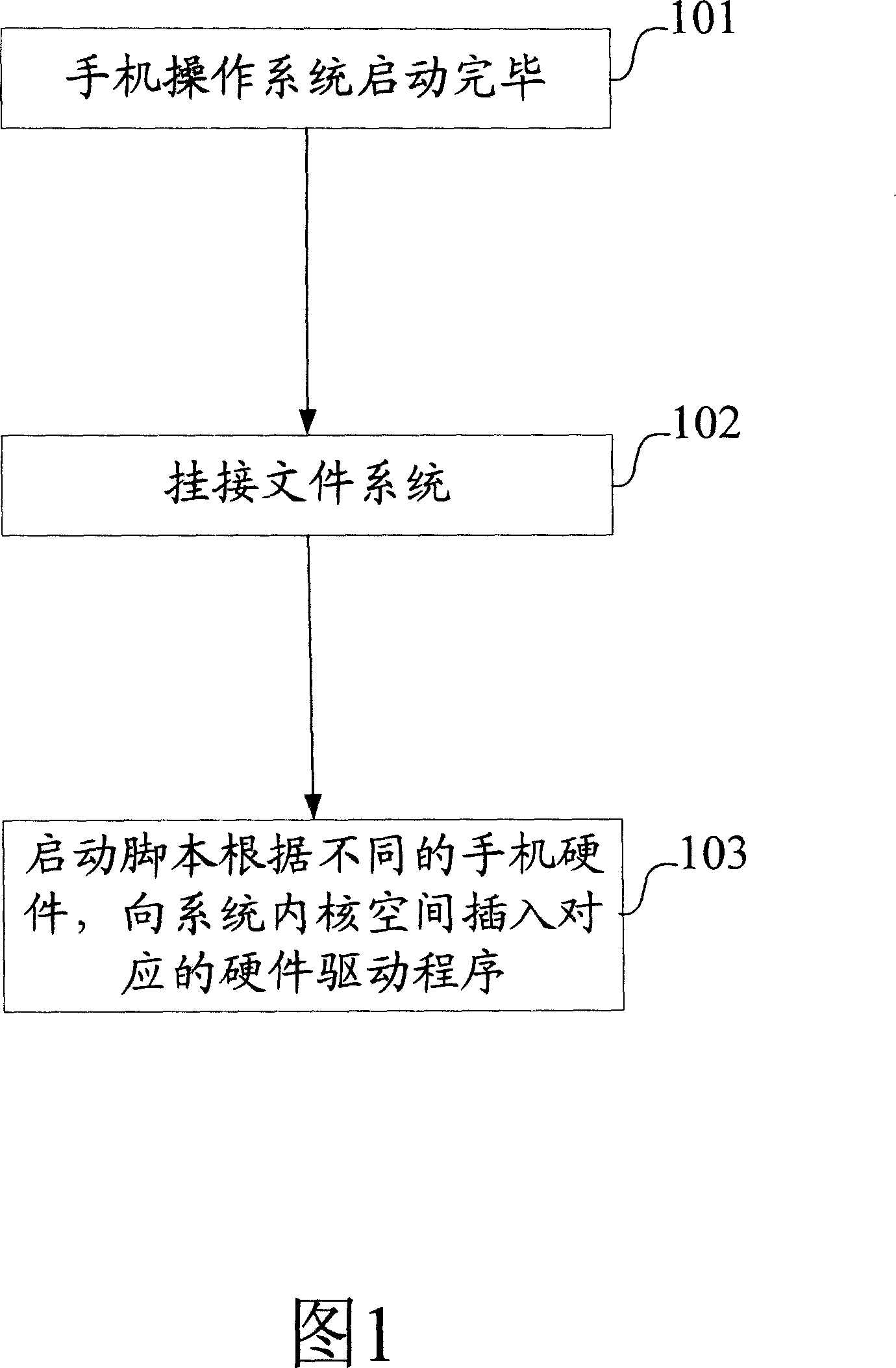
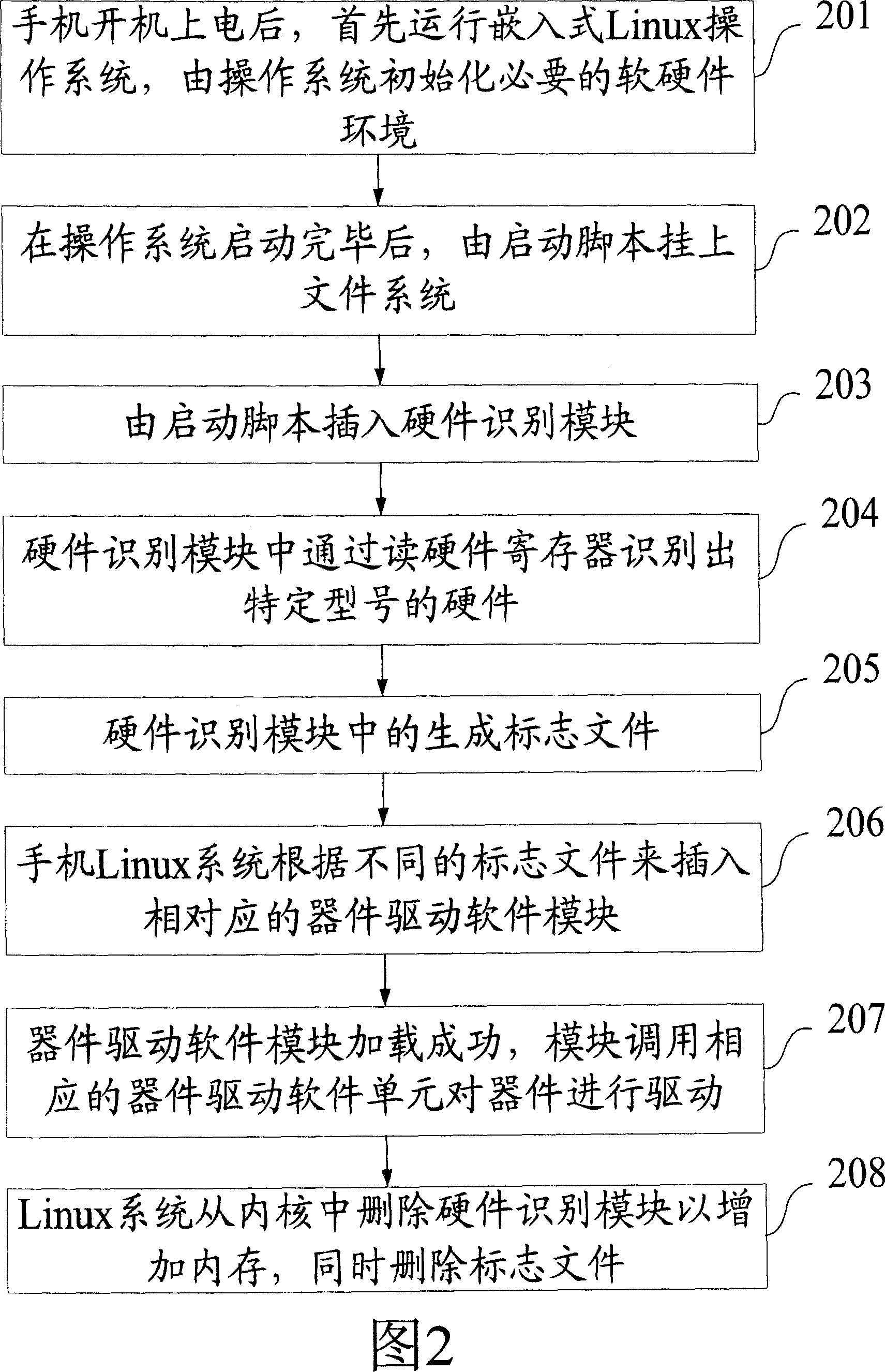
InactiveCN1964526AOvercome the problem of limited storage space resourcesEasy loadingRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSubstation equipmentOperational systemProcessor register
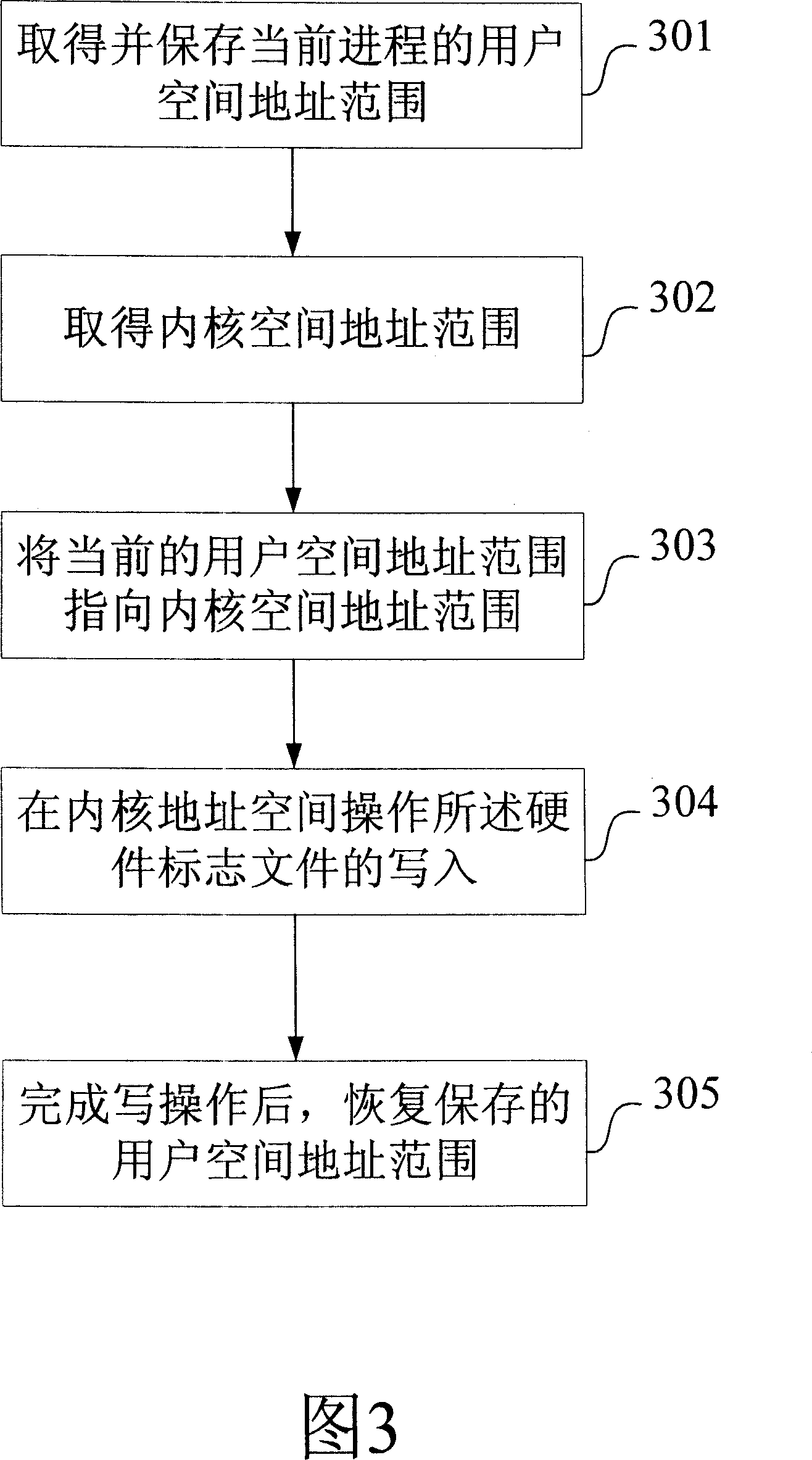
The provided intelligent loading method for mobilephone hardware driver comprises: inserting a hardware recognition module into OS kernel to read hardware register and recognize hardware type, generating hardware mark file; then inserting hardware driver into OS kernel. This invention overcomes defect in prior art, saves cost, and convenient to expand and update.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com