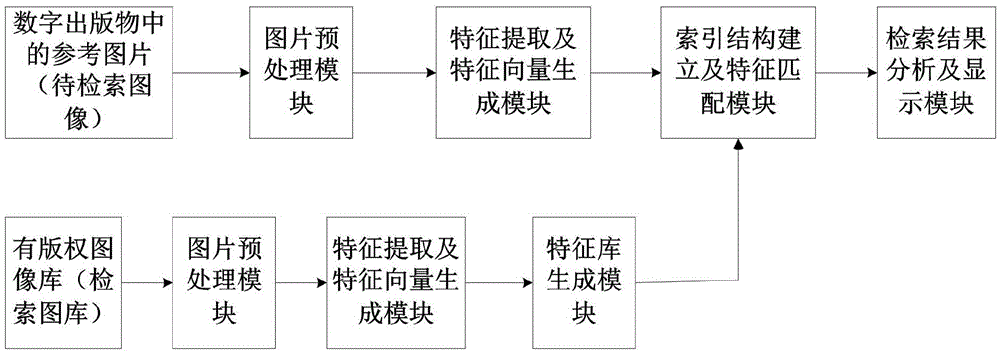
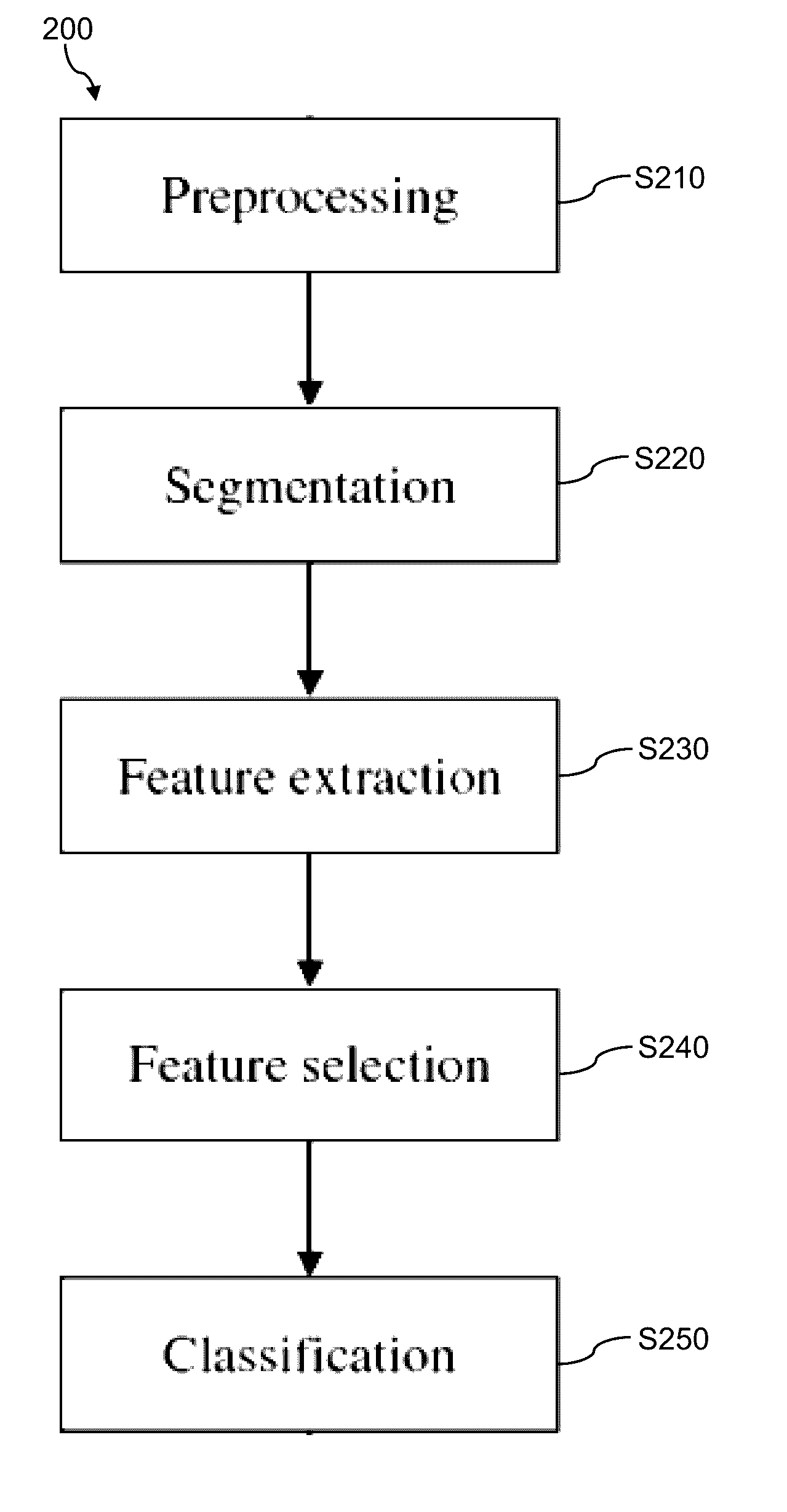
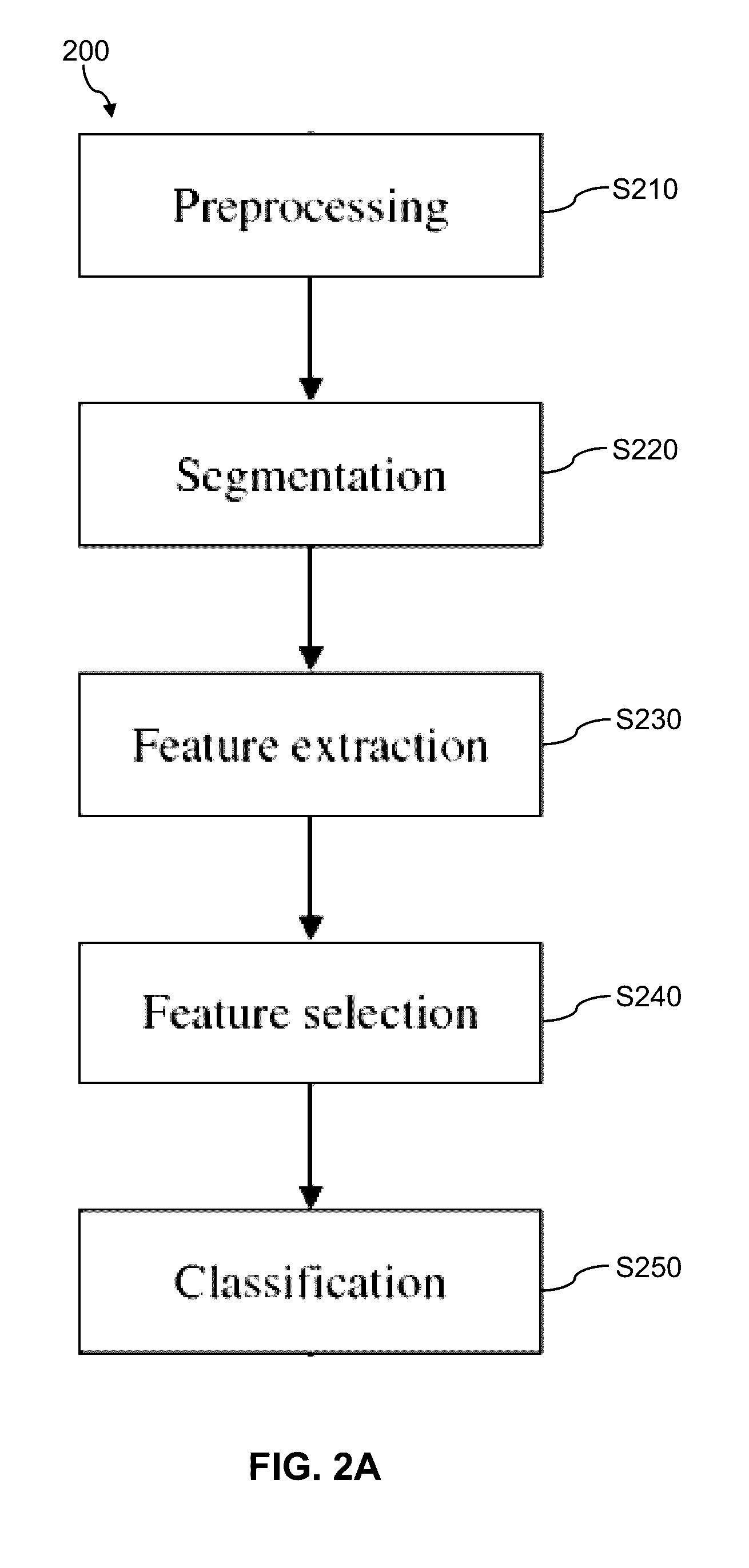
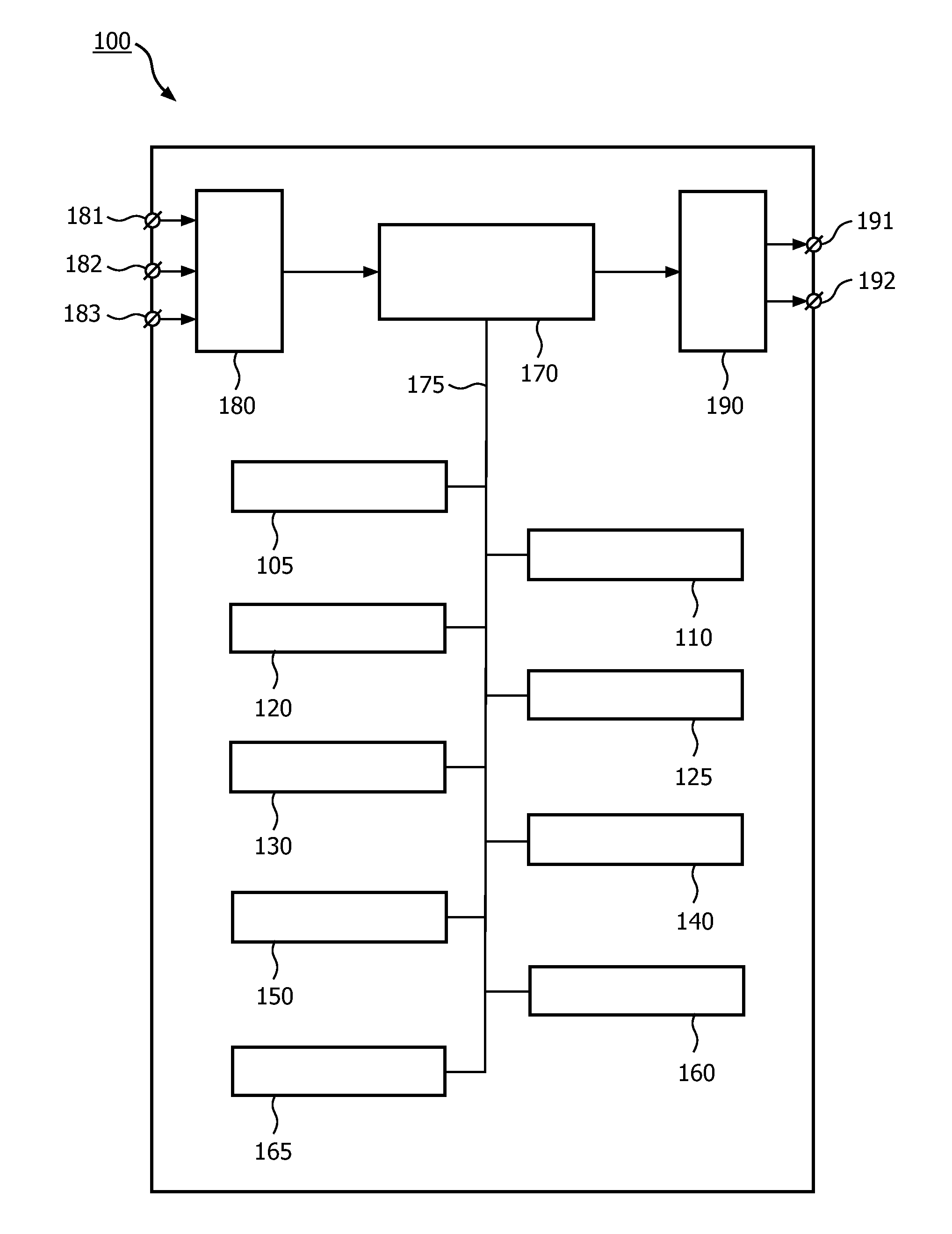
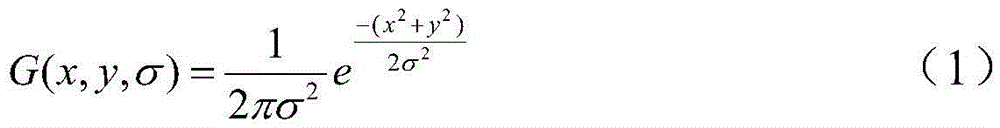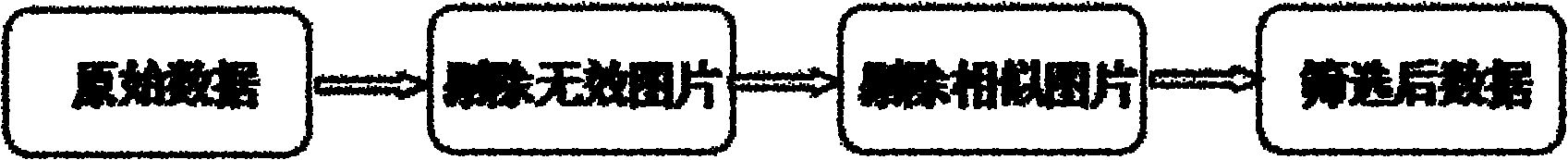Patents
Literature
63 results about "Content base image retrieval" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
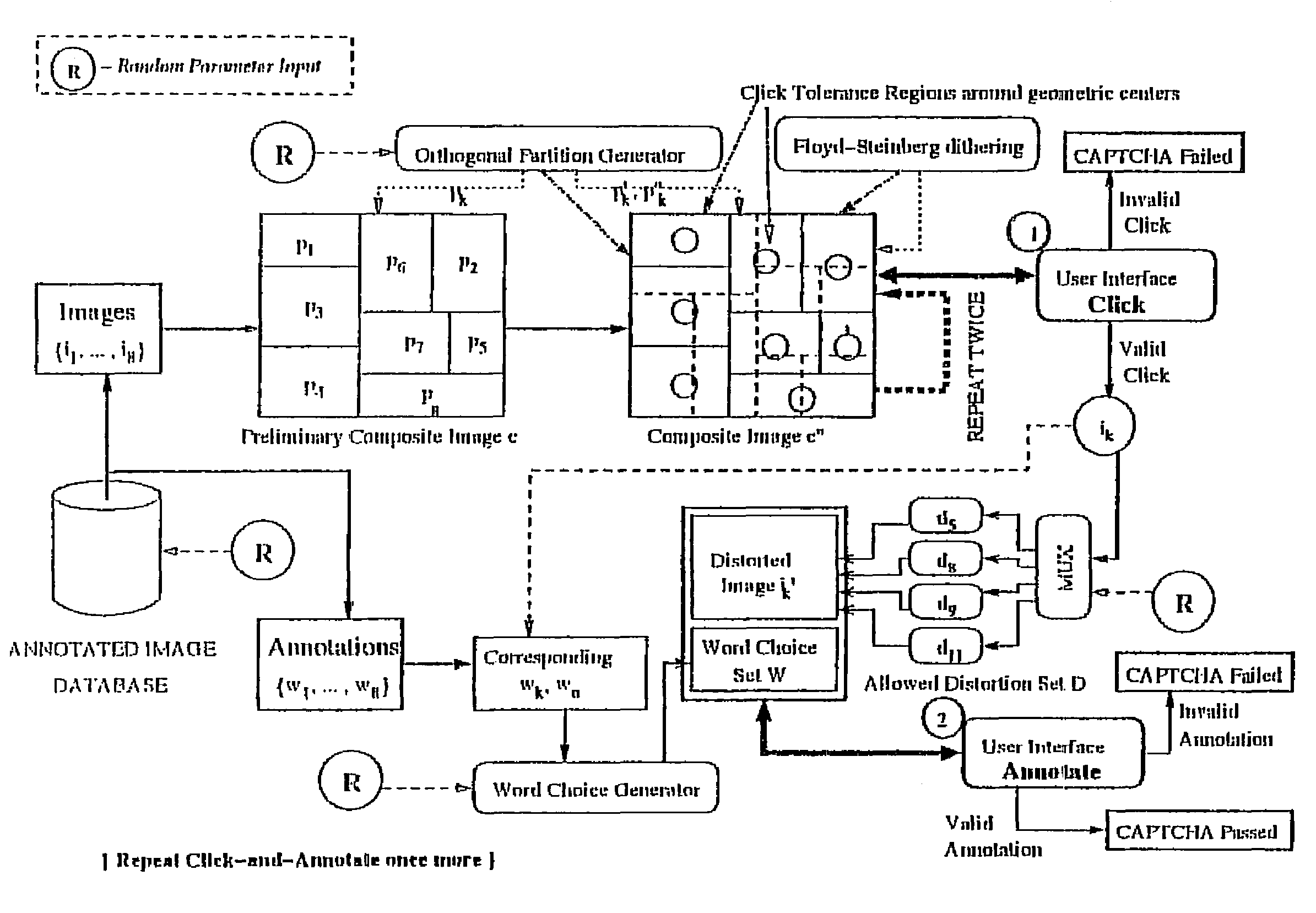
Image-based CAPTCHA generation system
InactiveUS7929805B2Digital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionHigh resistanceAmbiguity
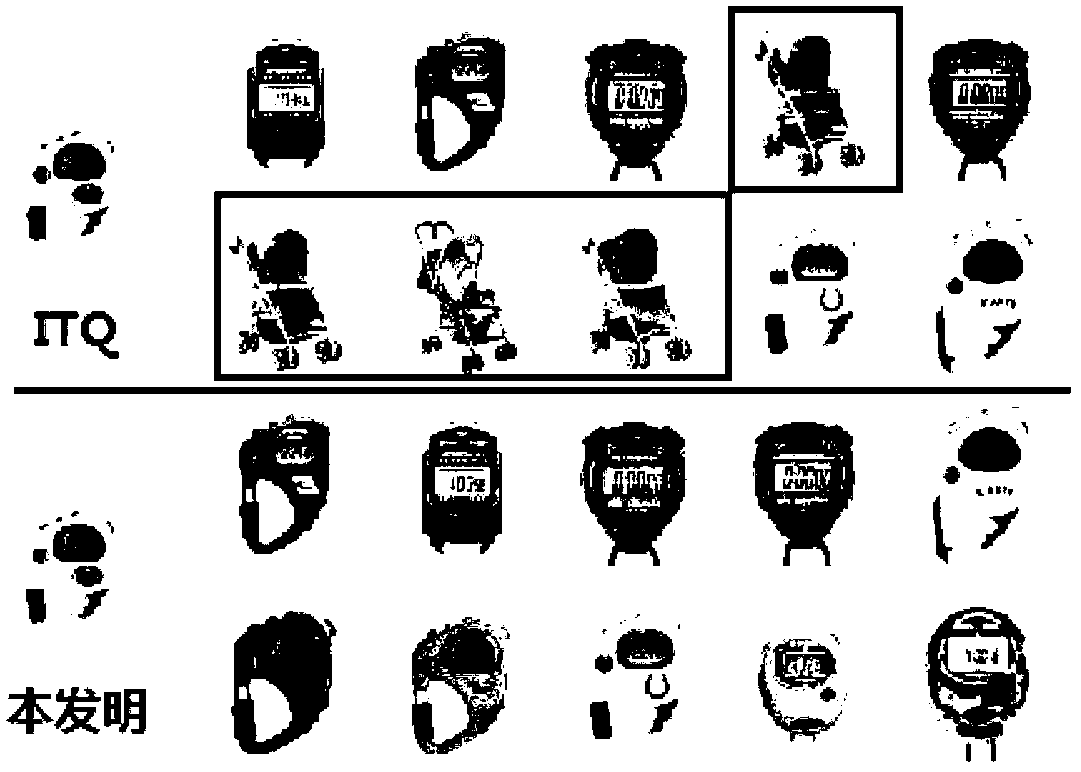
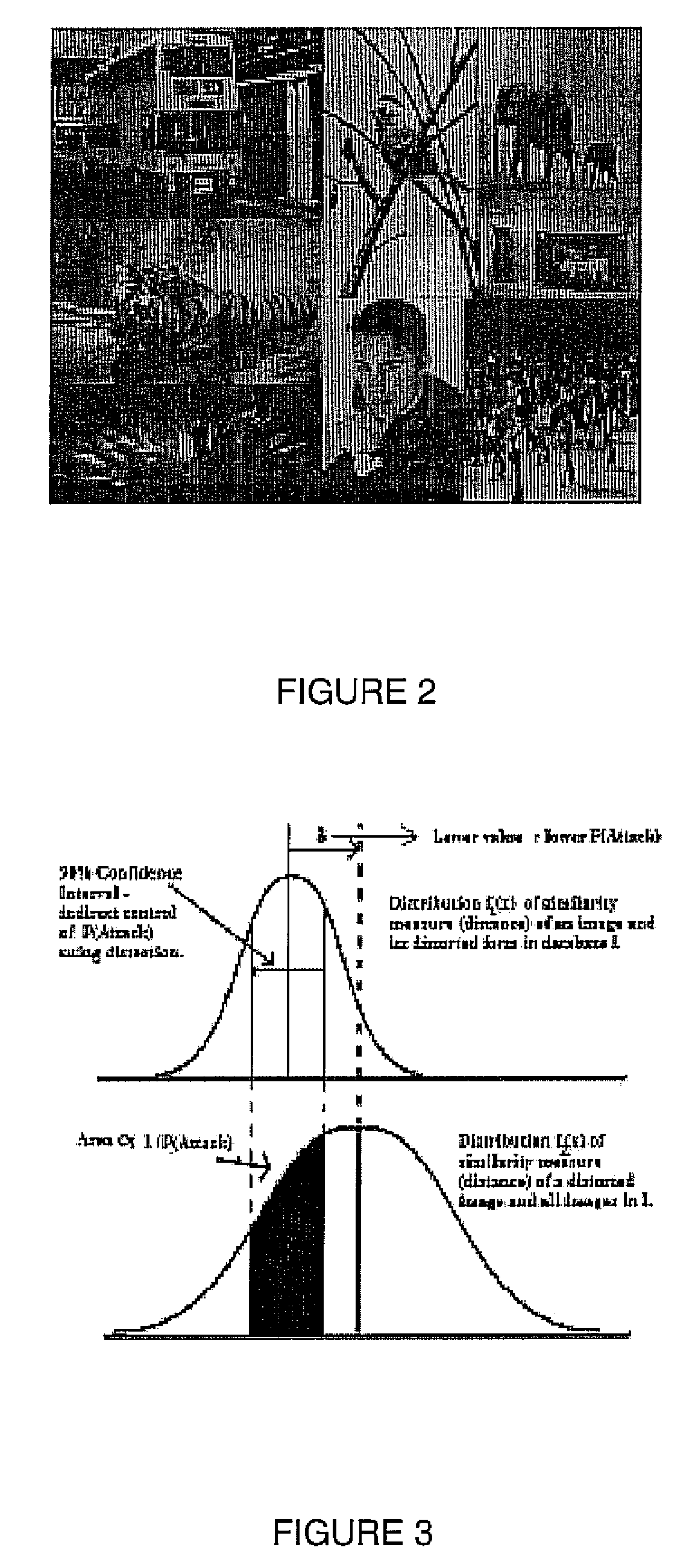
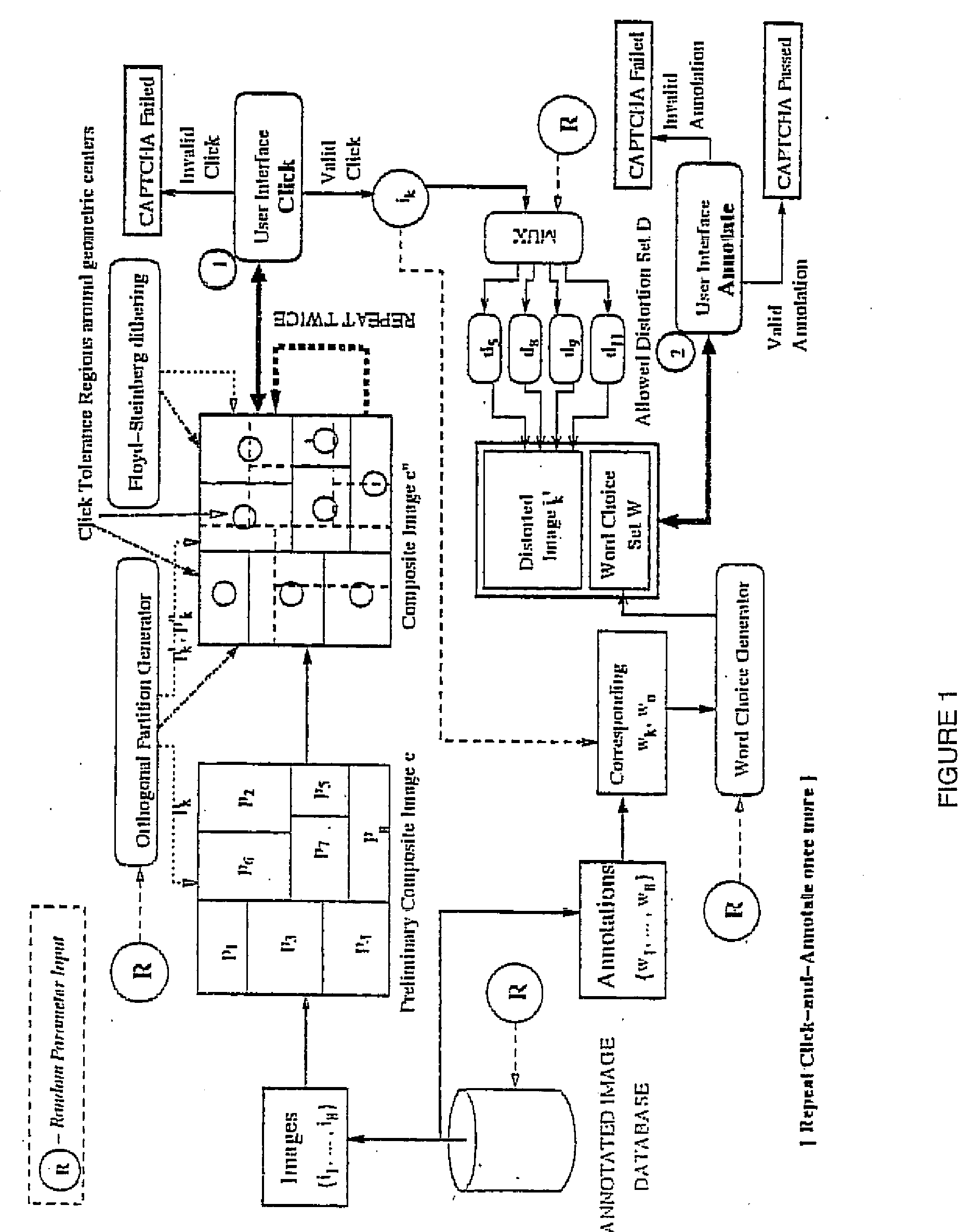
In a system and method for the generation of attack-resistant, user-friendly, image-based CAPTCHAs (Completely Automated Public test to Tell Computers and Humans Apart), controlled distortions are applied to randomly chosen images and presented to a user for annotation from a given list of words. An image is presented that contains multiple connected but independent images with the borders between them distorted or otherwise visually obfuscated in a way that a computer cannot distinguish the borders and a user selects near the center of one of the images. The distortions are performed in a way that satisfies the incongruous requirements of low perceptual degradation and high resistance to attack by content-based image retrieval systems. Word choices are carefully generated to avoid ambiguity as well as to avoid attacks based on the choices themselves.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
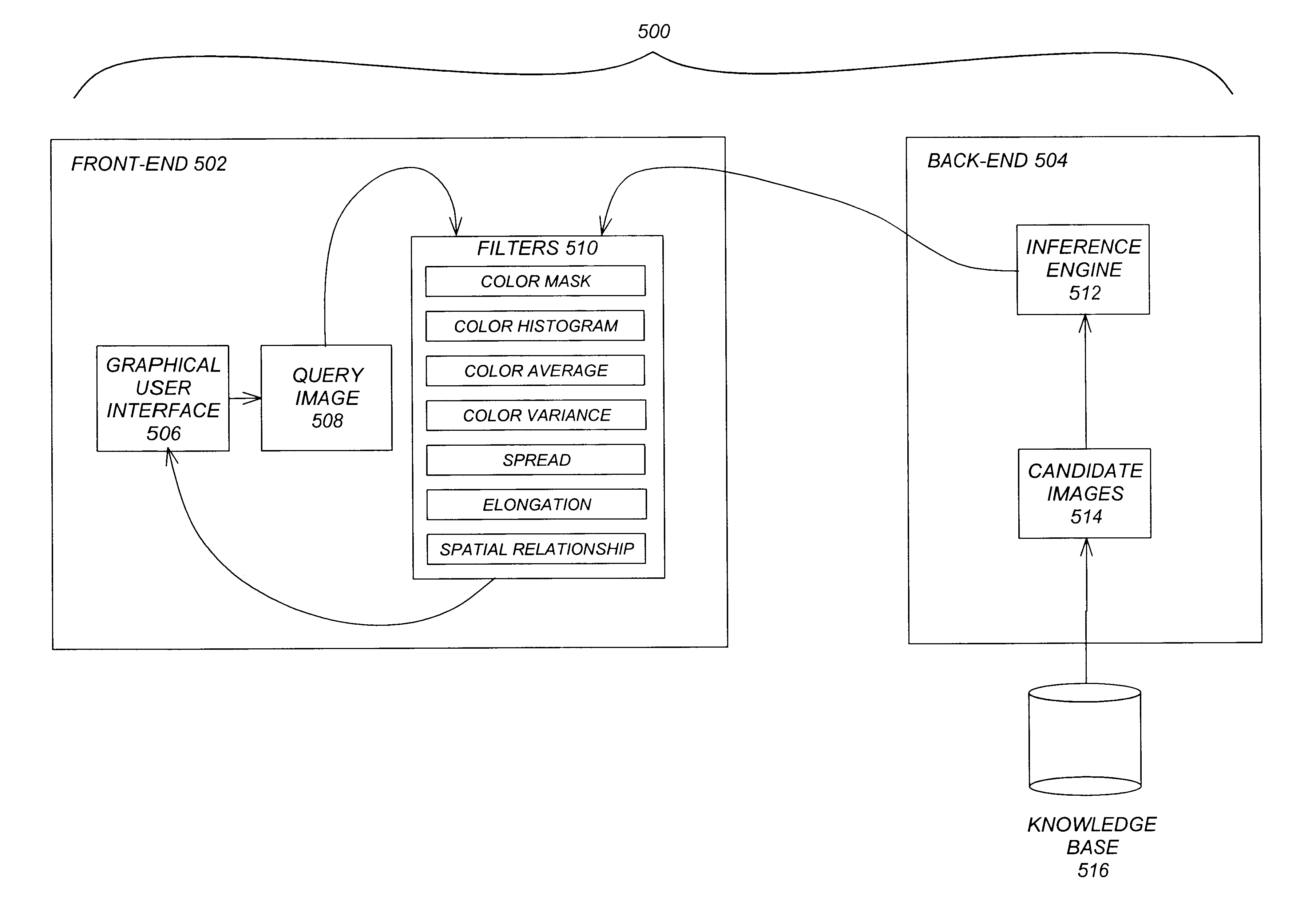
Perception-based image retrieval
InactiveUS6865302B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalAverage filterPattern perception
A content-based image retrieval (CBIR) system has a front-end that includes a pipeline of one or more dynamically-constructed filters for measuring perceptual similarities between a query image and one or more candidate images retrieved from a back-end comprised of a knowledge base accessed by an inference engine. The images include at least one color set having a set of properties including a number of pixels each having at least one color, a culture color associated with the color set, a mean and variance of the color set, a moment invariant, and a centroid. The filters analyze and compare the set of properties of the query image to the set of properties of the candidate images. Various filters are used, including: a Color Mask filter that identifies identical culture colors in the images, a Color Histogram filter that identifies a distribution of colors in the images, a Color Average filter that performs a similarity comparison on the average of the color sets of the images, a Color Variance filter that performs a similarity comparison on the variances of the color sets of the images, a Spread filter that identifies a spatial concentration of a color in the images, an Elongation filter that identifies a shape of a color in the images, and a Spatial Relationship filter that identifies a spatial relationship between the color sets in the images.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Semi-automatic annotation of multimedia objects
InactiveUS20050010553A1Strengthen associationWeakening associationData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsSemi automaticDigital image
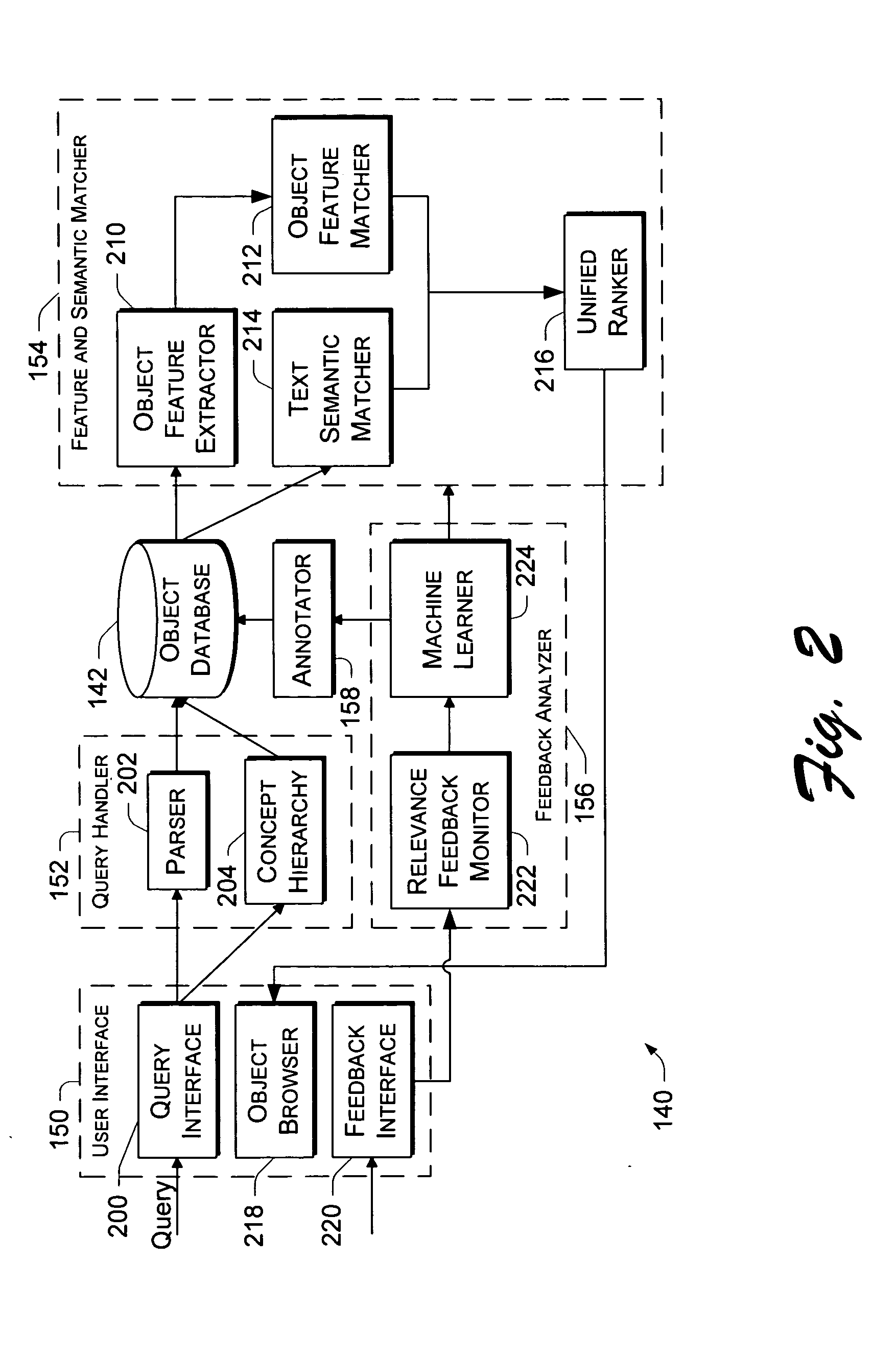
A multimedia object retrieval and annotation system integrates an annotation process with object retrieval and relevance feedback processes. The annotation process annotates multimedia objects, such as digital images, with semantically relevant keywords. The annotation process is performed in background, hidden from the user, as the user conducts normal searches. The annotation process is “semi-automatic” in that it utilizes both keyword-based information retrieval and content-based image retrieval techniques to automatically search for multimedia objects, and then encourages users to provide feedback on the retrieved objects. The user identifies objects as either relevant or irrelevant to the query keywords and based on this feedback, the system automatically annotates the objects with semantically relevant keywords and / or updates associations between the keywords and objects. As the retrieval-feedback-annotation cycle is repeated, the annotation coverage and accuracy of future searches continues to improve.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
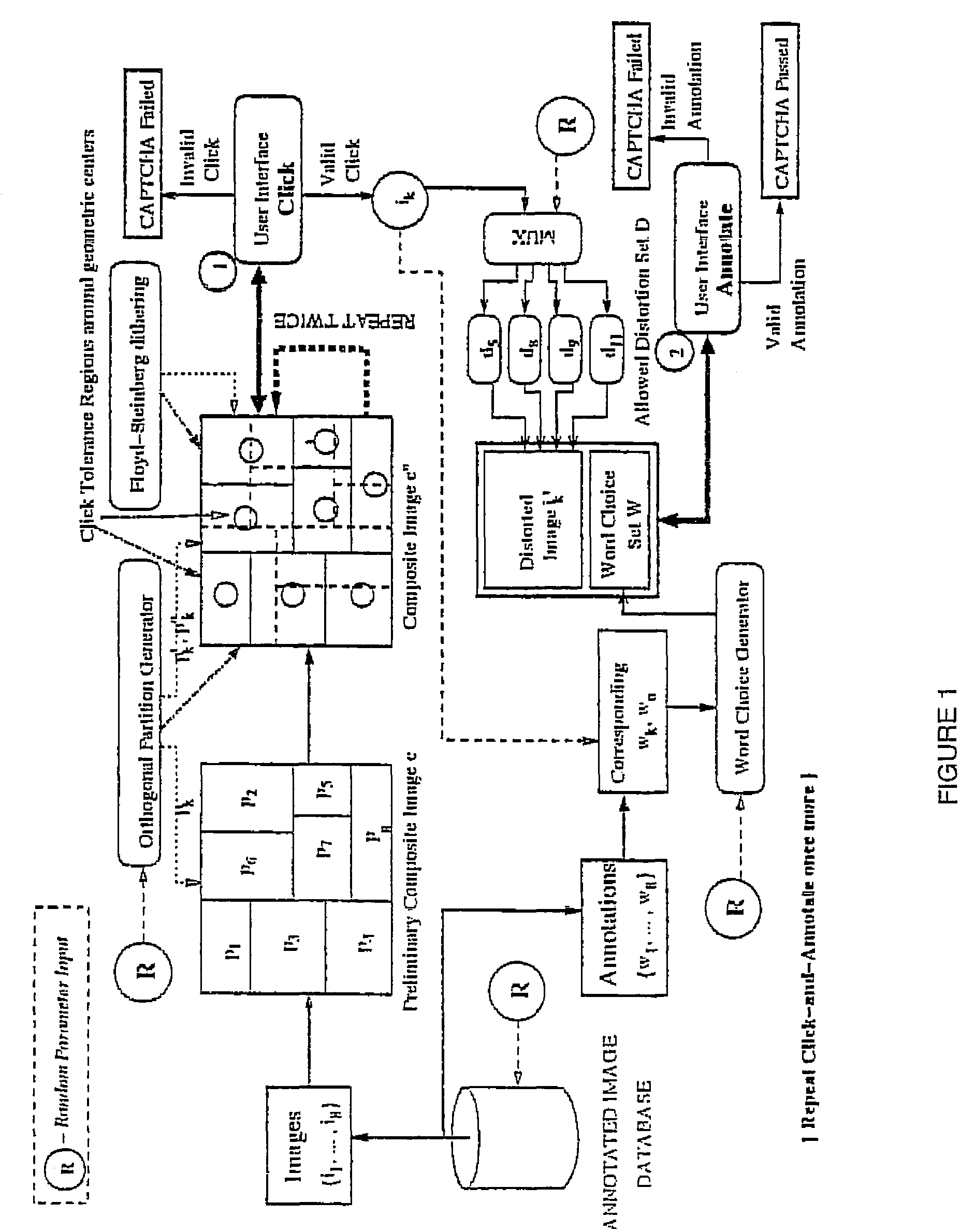
Image-based captcha generation system
InactiveUS20070201745A1Avoid ambiguityIncrease resistanceDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionHigh resistanceAmbiguity
In a system and method for the generation of attack-resistant, user-friendly, image-based CAPTCHAs (Completely Automated Public test to Tell Computers and Humans Apart), controlled distortions are applied to randomly chosen images and presented to a user for annotation from a given list of words. An image is presented that contains multiple connected but independent images with the borders between them distorted or otherwise visually obfuscated in a way that a computer cannot distinguish the borders and a user selects near the center of one of the images The distortions are performed in a way that satisfies the incongruous requirements of low perceptual degradation and high resistance to attack by content-based image retrieval systems. Word choices are carefully generated to avoid ambiguity as well as to avoid attacks based on the choices themselves.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
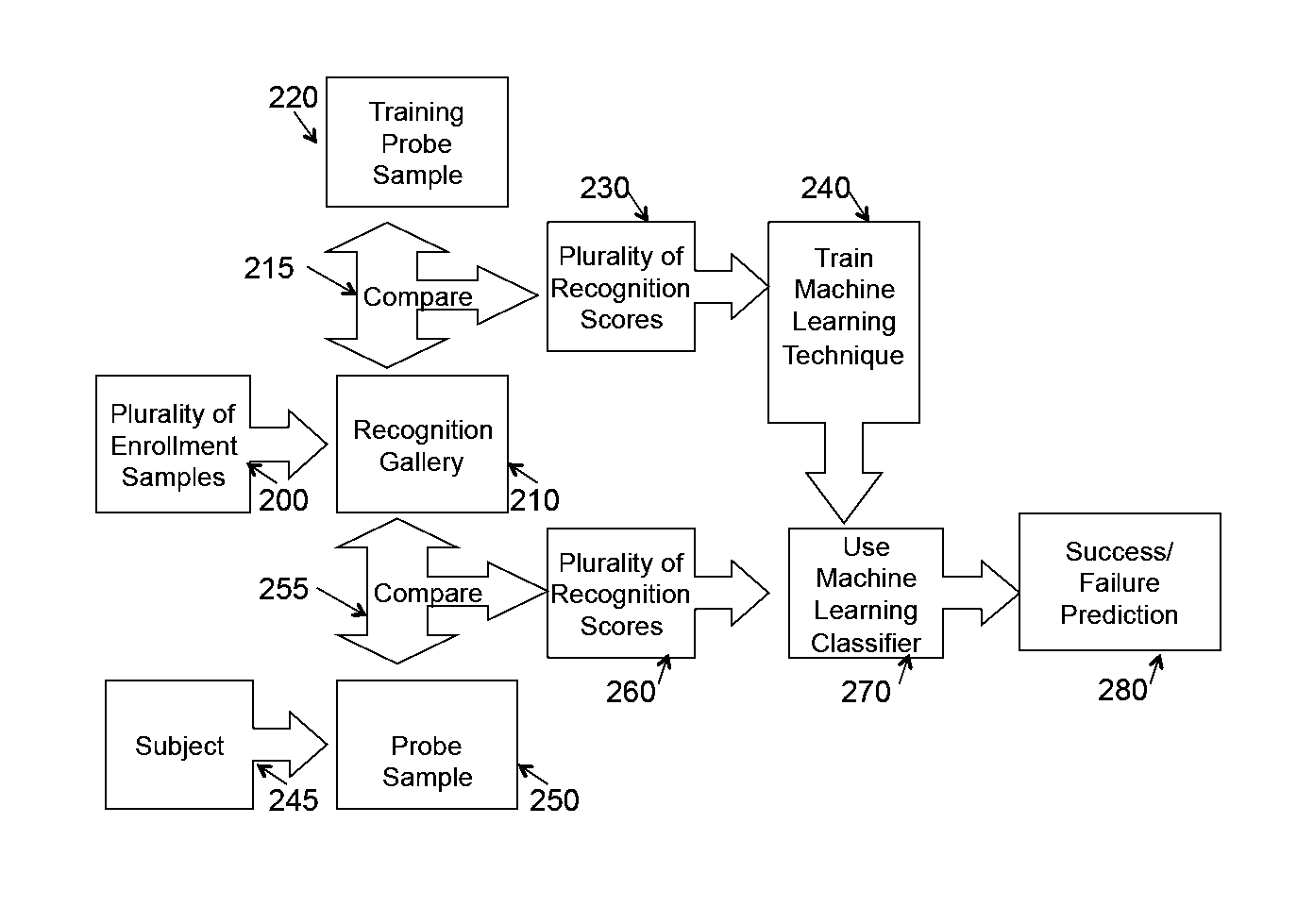
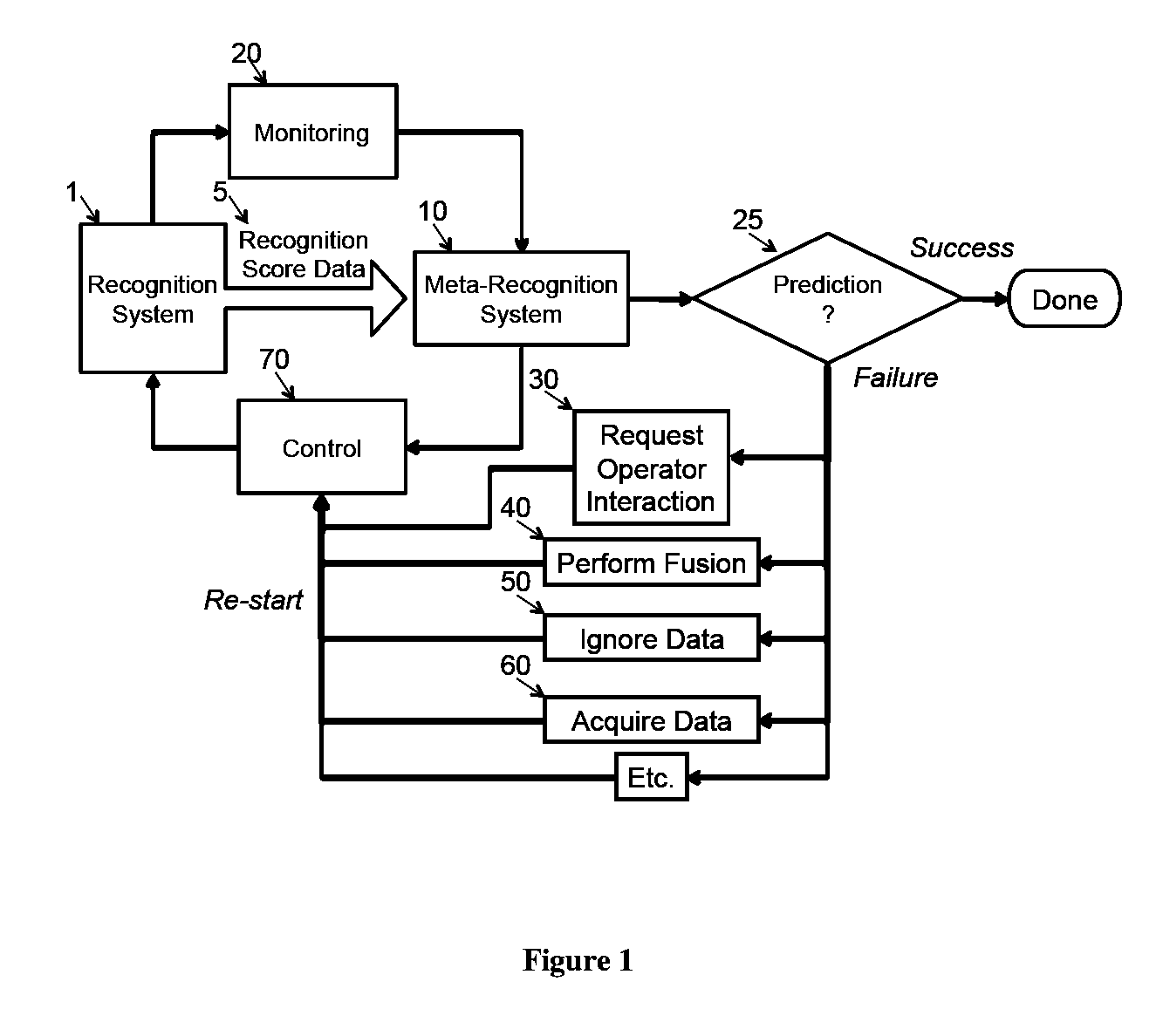
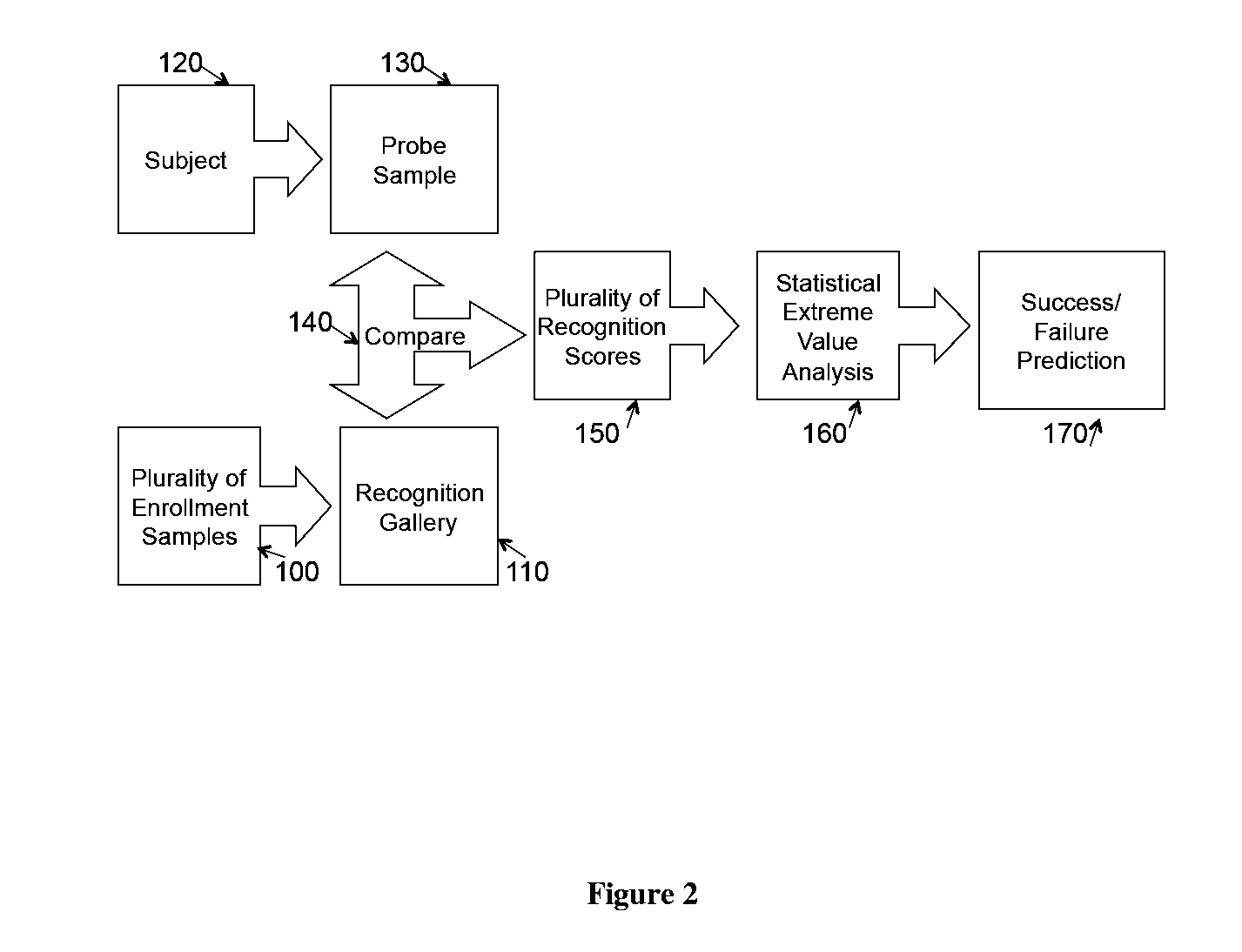
System and appartus for failure prediction and fusion in classification and recognition
InactiveUS20110106734A1Error detection/correctionDigital computer detailsLearning methodsComputer science
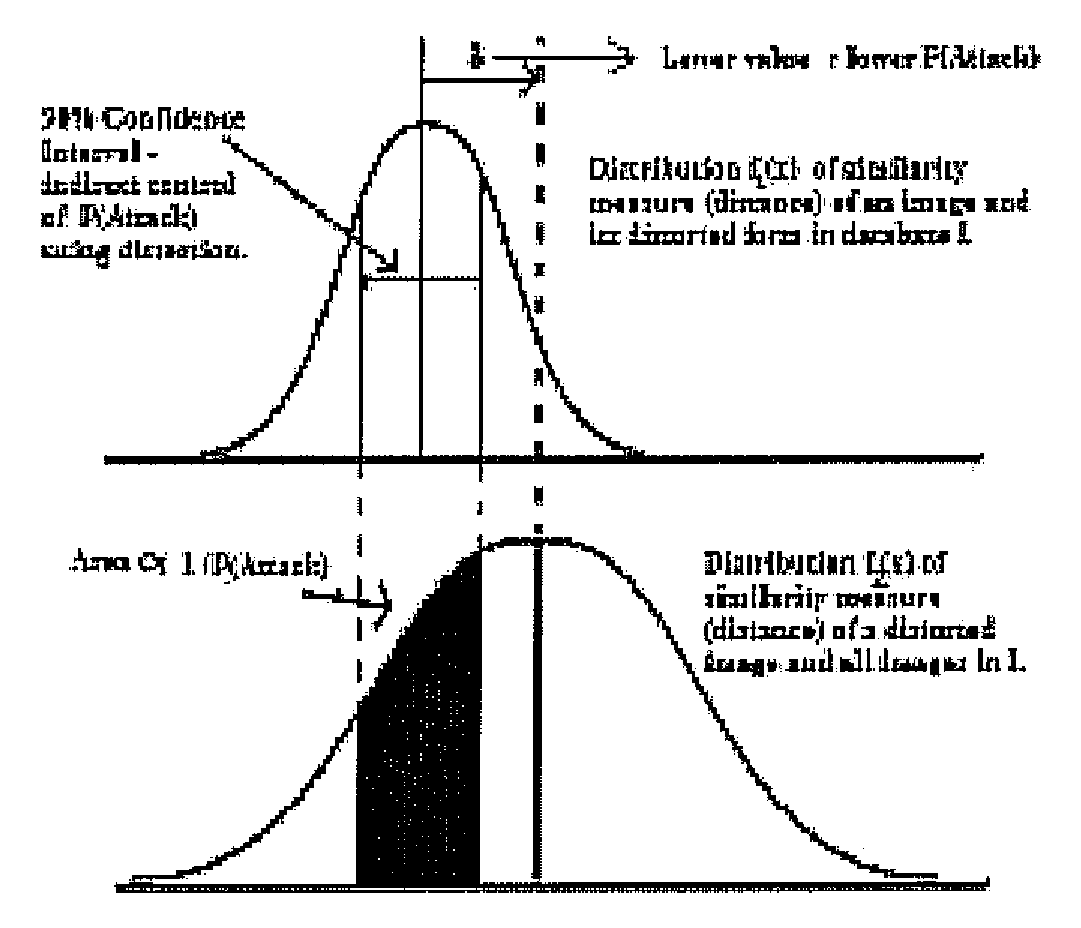
The present invention relates to pattern recognition and classification, more particularly, to a system and method for meta-recognition which can to predict success / failure for a variety of different recognition and classification applications. In the present invention, we define a new approach based on statistical extreme value theory and show its theoretical basis for predicting success / failure based on recognition or similarity scores. By fitting the tails of similarity or distance scores to an extreme value distribution, we are able to build a predictor that significantly outperforms random chance. The proposed system is effective for a variety of different recognition applications, including, but not limited to, face recognition, fingerprint recognition, object categorization and recognition, and content-based image retrieval system. One embodiment includes adapting machine learning approach to address meta-recognition based fusion at multiple levels, and provide an empirical justification for the advantages of these fusion element. This invention provides a new score normalization that is suitable for multi-algorithm fusion for recognition and classification enhancement.
Owner:BOULT TERRANCE +2
Image retrieval method based on image classification
InactiveCN102402621AHigh speedWith scalingCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsContent base image retrievalSimilarity distance
The invention relates to an image retrieval method based on image classification and aims to solve the problem of lower retrieval speed by the conventional method. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, determining the class number of images in the image classification and a training image set; secondly, extracting the content characteristics of the training image set for classifier training to obtain a classifier; thirdly, inputting an image to be retrieved, extracting the content characteristics of the image to be retrieved as the input of the classifier to obtain a retrieval image set which corresponds to the class, and extracting the content characteristics of each image in the retrieval image set; and finally, according to the obtained content characteristics, acquiring similarity distances of the image to be retrieved and each image in the retrieval image set by using a similarity calculation algorithm, sorting the distances to obtain N images which are nearest to the image to be retrieved, and outputting the N images. The image retrieval method based on the image classification has the advantage that: by combining an image classification technology and the conventional content-based image retrieval method, an image retrieval speed is greatly improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for the reduction of image content redundancy in large image libraries
InactiveUS20070260639A1Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsFeature vectorDigital image
A method of increasing information content for content-based image retrieval (CBIR) systems includes the steps of providing a CBIR database, the database having an index for a plurality of stored digital images using a plurality of feature vectors, the feature vectors corresponding to distinct descriptive characteristics of the images. A visual similarity parameter value is calculated based on a degree of visual similarity between features vectors of an incoming image being considered for entry into the database and feature vectors associated with a most similar of the stored images. Based on said visual similarity parameter value it is determined whether to store or how long to store the feature vectors associated with the incoming image in the database.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
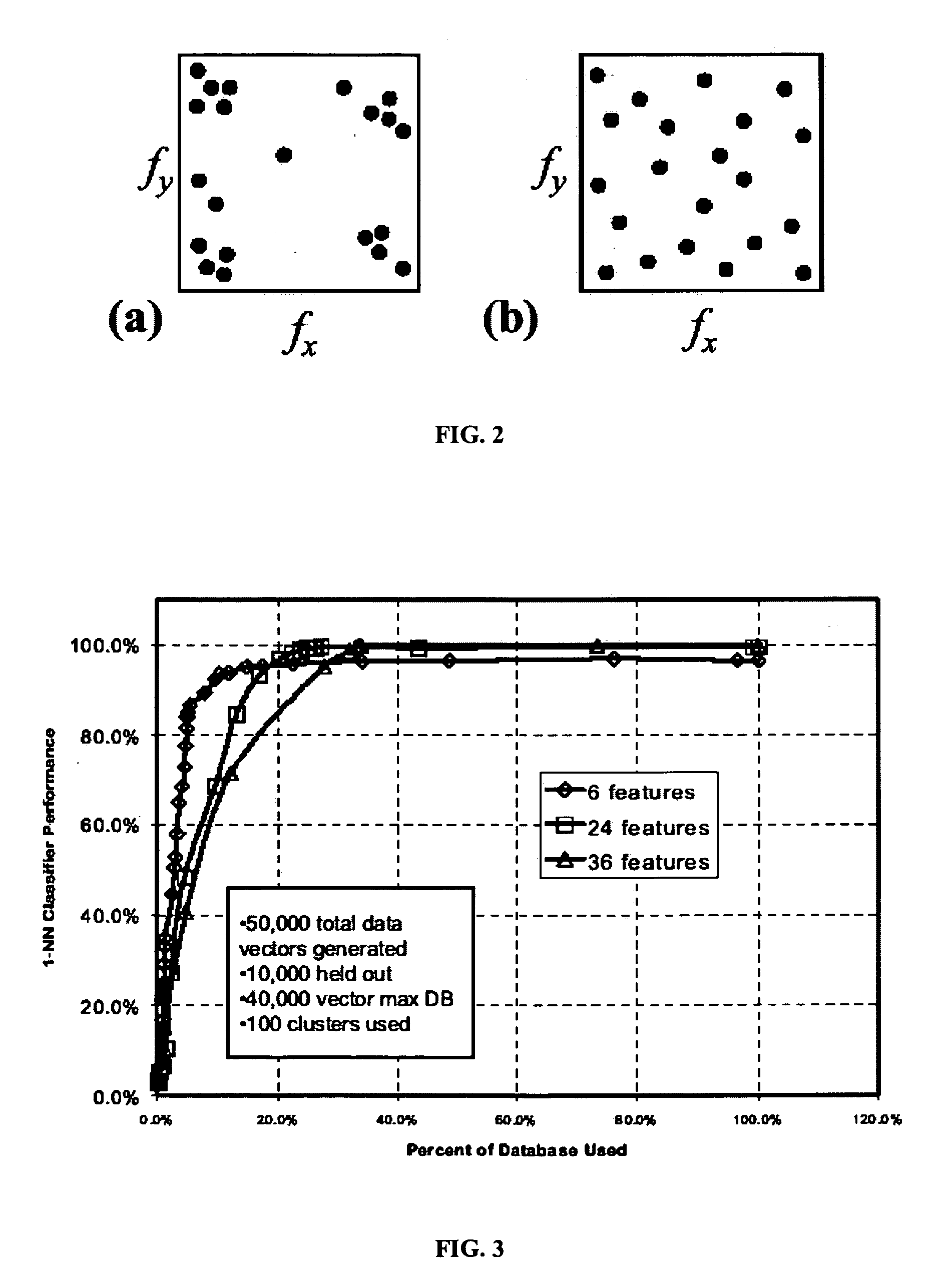
Automatic indexing of digital image archives for content-based, context-sensitive searching
InactiveUS7689544B2Decision supportHigh precisionPicture changing apparatusData processing applicationsAcquired characteristicFeature extraction algorithm
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
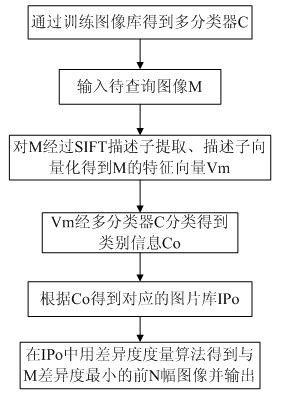
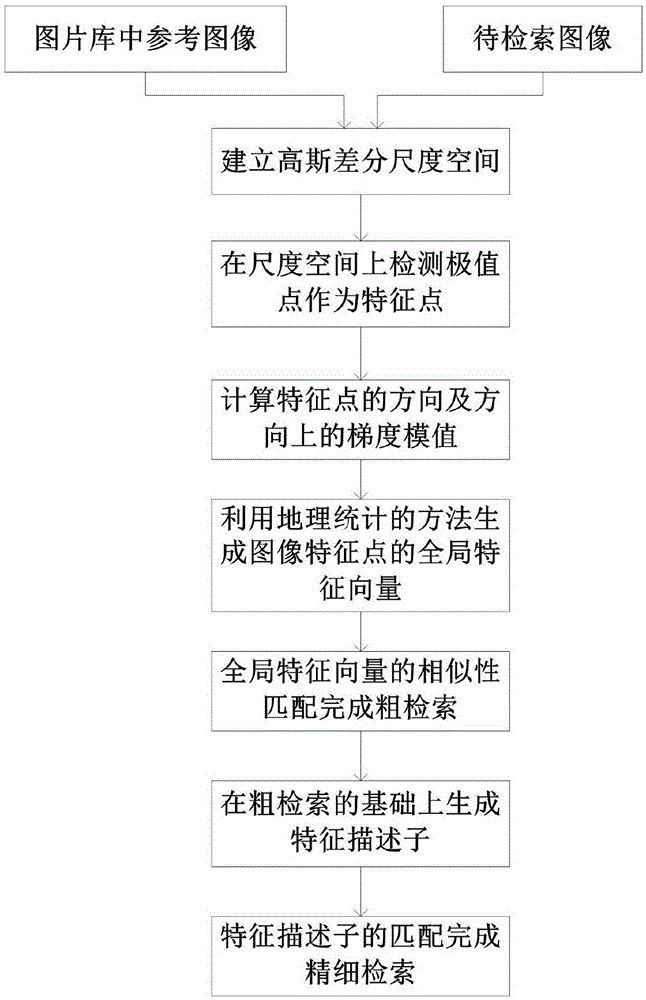
Efficient image retrieval method based on improved SIFT (scale invariant feature transform) feature
ActiveCN105550381AApplicable Image Infringement Review RequirementsSpecial data processing applicationsFeature vectorImaging processing
The invention discloses an efficient image retrieval method based on an improved SIFT (scale invariant feature transform) feature, relates to the field of image processing and computer vision and belongs to a content-based image retrieval method. The method comprises the steps of establishing a gauss difference scale space, taking scale space detection extreme points as feature points, calculating the direction of the feature points and gradient module values in the direction, generating a global feature vector of the image feature points through a geographical statistical method, conducting global feature vector similarity matching to finish rough retrieval, generating feature descriptors on the basis of rough retrieval, and conducting feature descriptor matching to finish accurate retrieval. The novel image retrieval method is superior to a traditional SIFT algorithm, and is more suitable for requirements of image infringement examination in digital prints than an existing retrieval algorithm.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
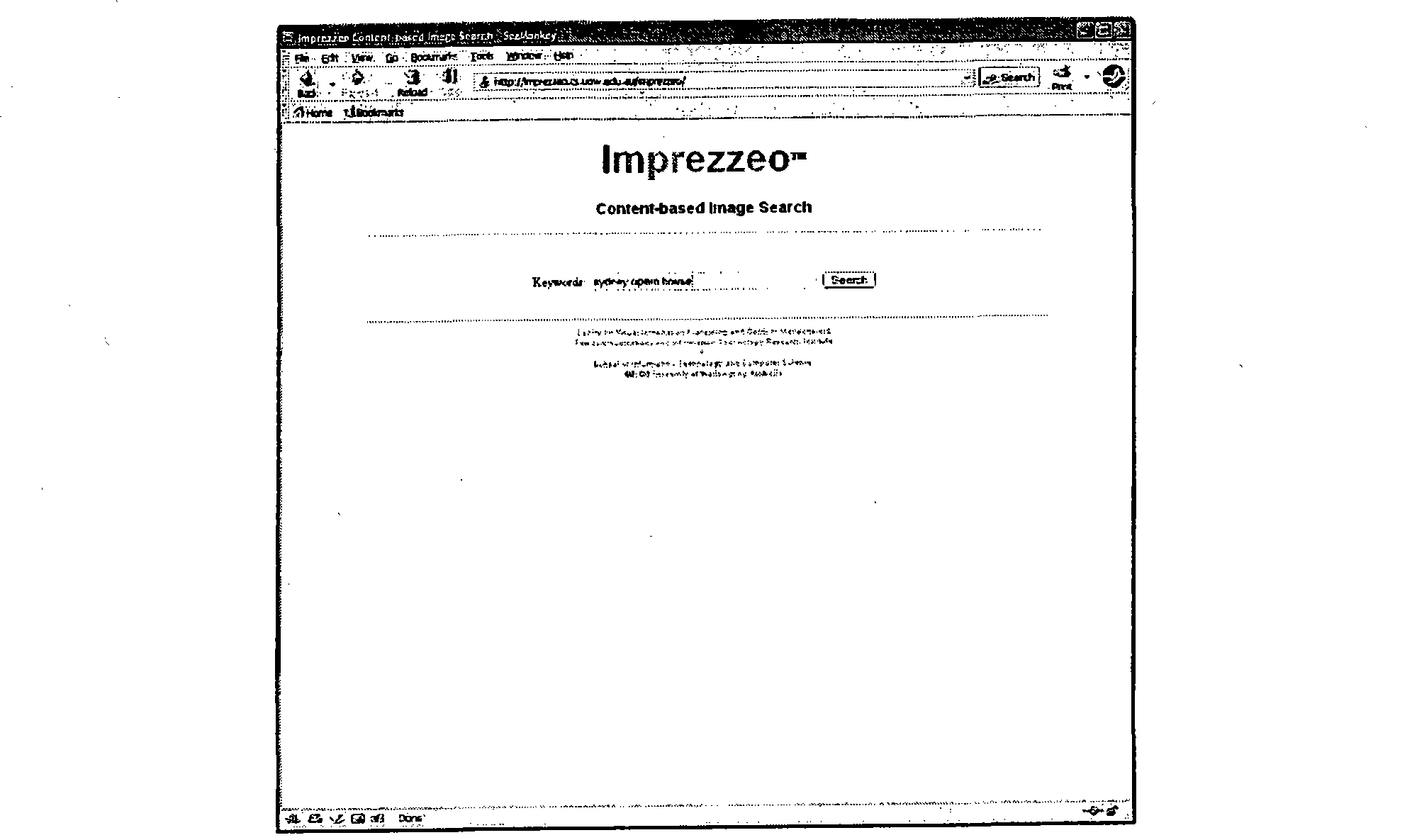
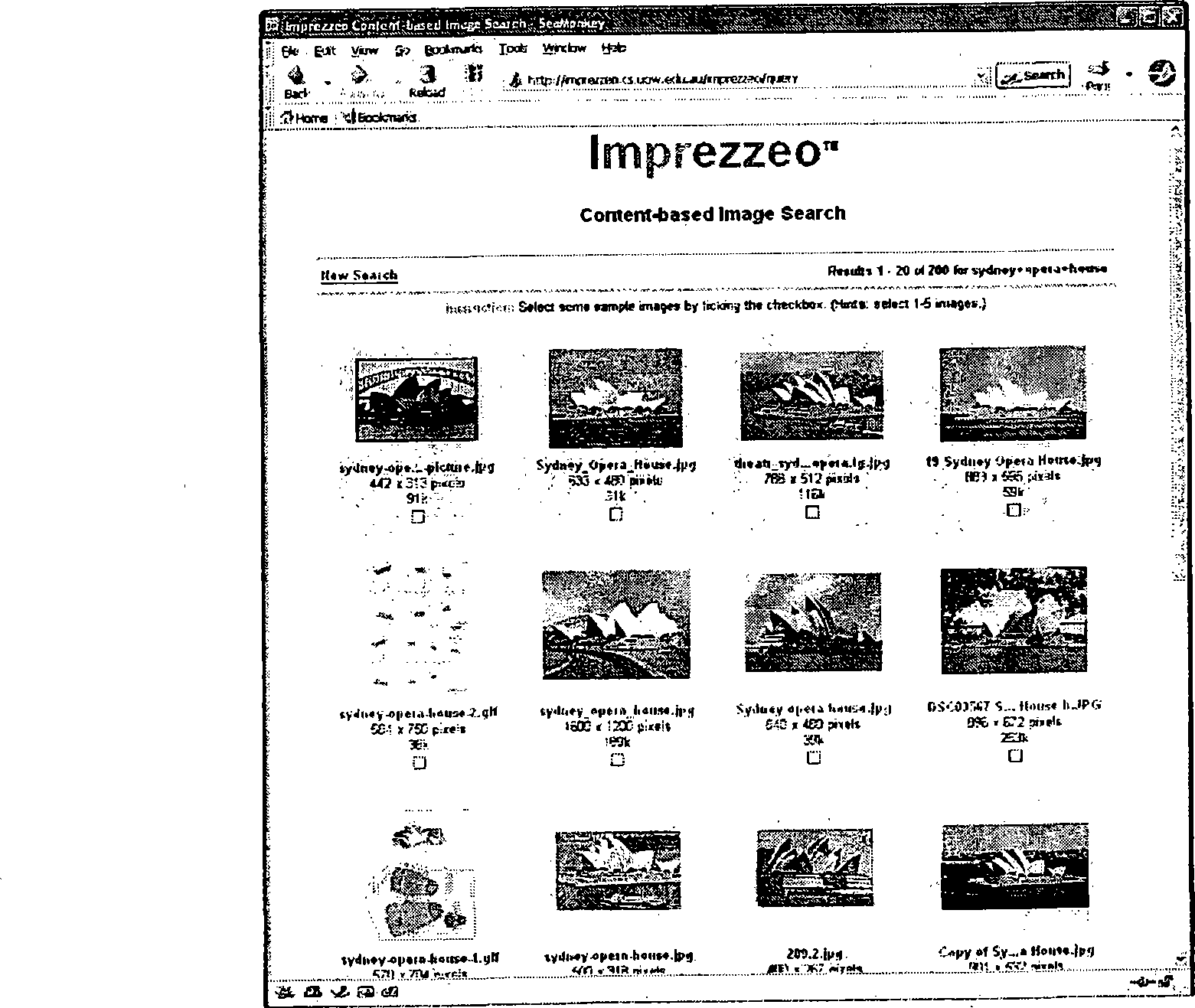
Band weighted colour histograms for image retrieval
InactiveUS20110200251A1Improve accuracyDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionImage segmentationMethod of images
A method of image retrieval from a target image collection, including segmenting a query image into two or more bands, obtaining weighted colour histogram vectors for the two or more bands in the query image, and obtaining weighted colour histogram vectors for two or more bands in a target image. A distance measurement is determined between the query image and the target image using the weighted colour histogram vectors from corresponding bands in the query image and the target image. Bands in an image can be groups, strips, sections, regions, or the like, and can be linear bands, rectangular bands, circular bands, or the like. The bands are preferably, though not necessarily, concentric or otherwise aligned and any number of bands can be utilised. Also, content based image retrieval is provided that incorporates use of varying photo composition in different regions as a technique for improving accuracy of retrieval.
Owner:IMPREZZEO
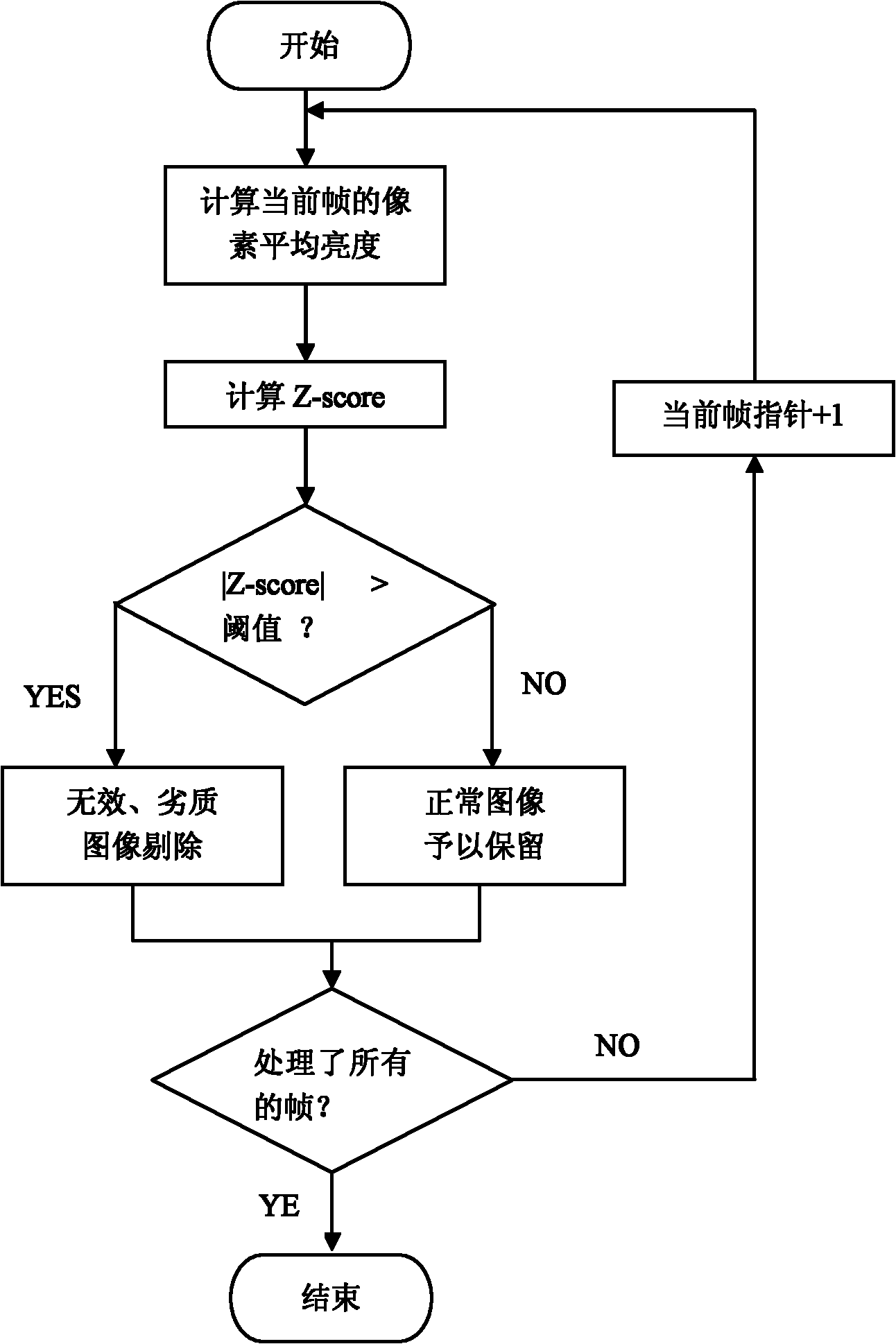
Automatic eliminating method for redundant image data of capsule endoscope
InactiveCN102096917ANo data reductionEasy to calculateImage analysisSurgeryNormalized mutual informationSkew normal distribution
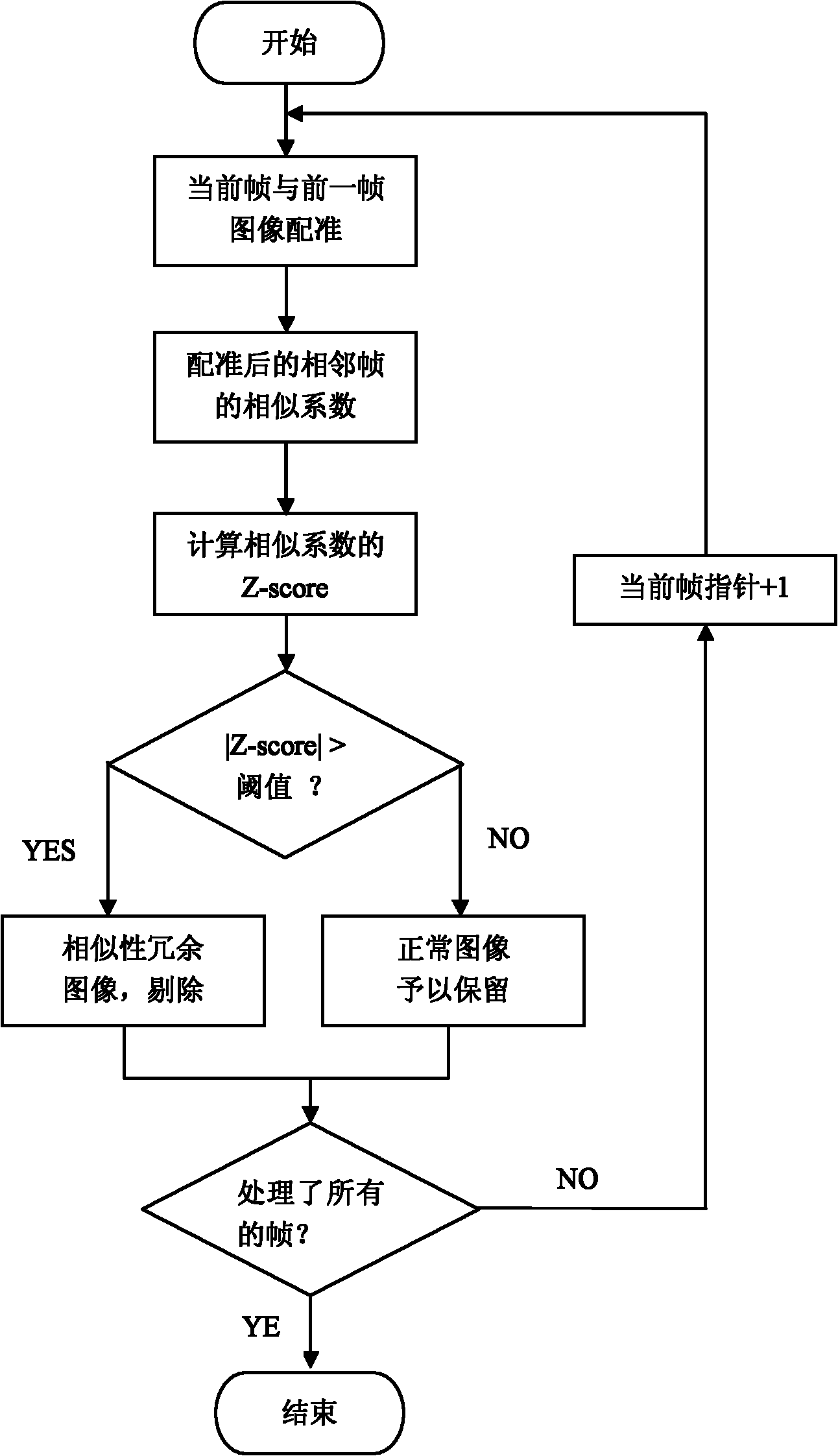
The invention discloses an automatic eliminating method for redundant image data of a capsule endoscope, and the method comprises the following steps: firstly, selecting a normal image sample to obtain the mean value and variance of the average gray distribution of image pixels, computing the average gray value of the pixels of each frame of the image in picture data to be judged, judging whether the image is an image with abnormal exposure according to the characteristic of the standard normal distribution, and eliminating the image with the abnormal exposure; then, supposing that the normalized related coefficient or normalized mutual information quantity between every two adjacent frames of the images is submitted to the normal distribution; evaluating the mean value and the variance from an image sample to be processed; rigidly registering the images which are adjacent to the image to be processed; and judging whether the contents of the two adjacent frames of the images are highly repeated according to the characteristic of the standard normal distribution, and delimiting the repeated images. The method is performed before the content-based image retrieval is carried out, so that the searching efficiency can be preferably improved, the interference can be eliminated as much as possible, and the film reading time can be shortened, therefore, the diagnosis efficiency of a doctor is improved.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Network image retrieval method based on semantic analysis
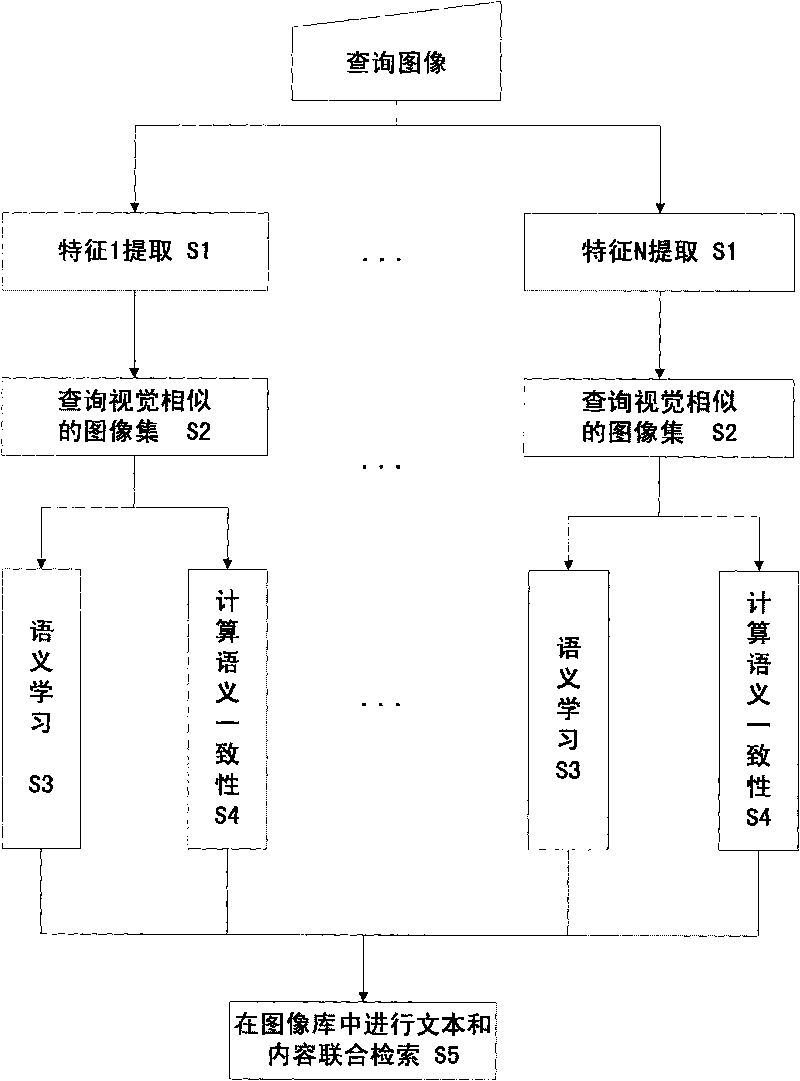
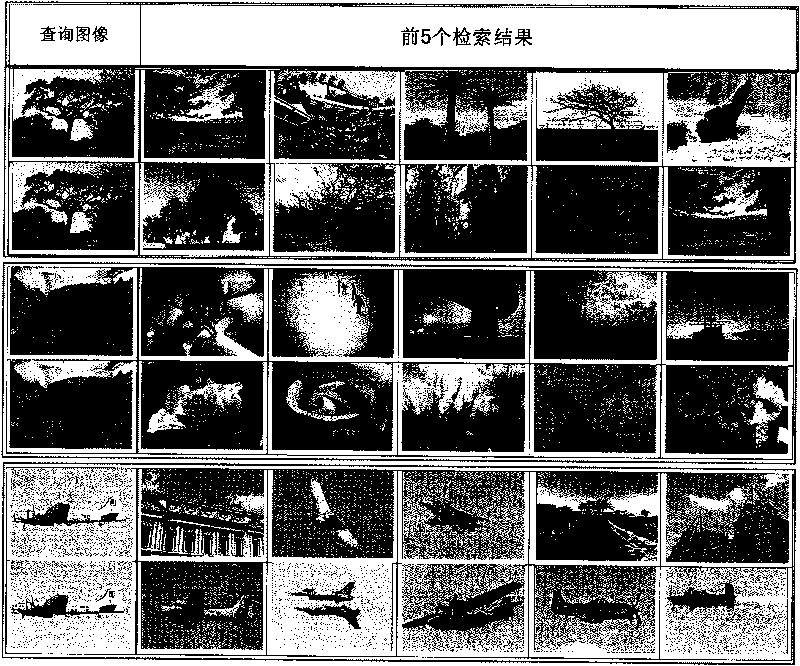
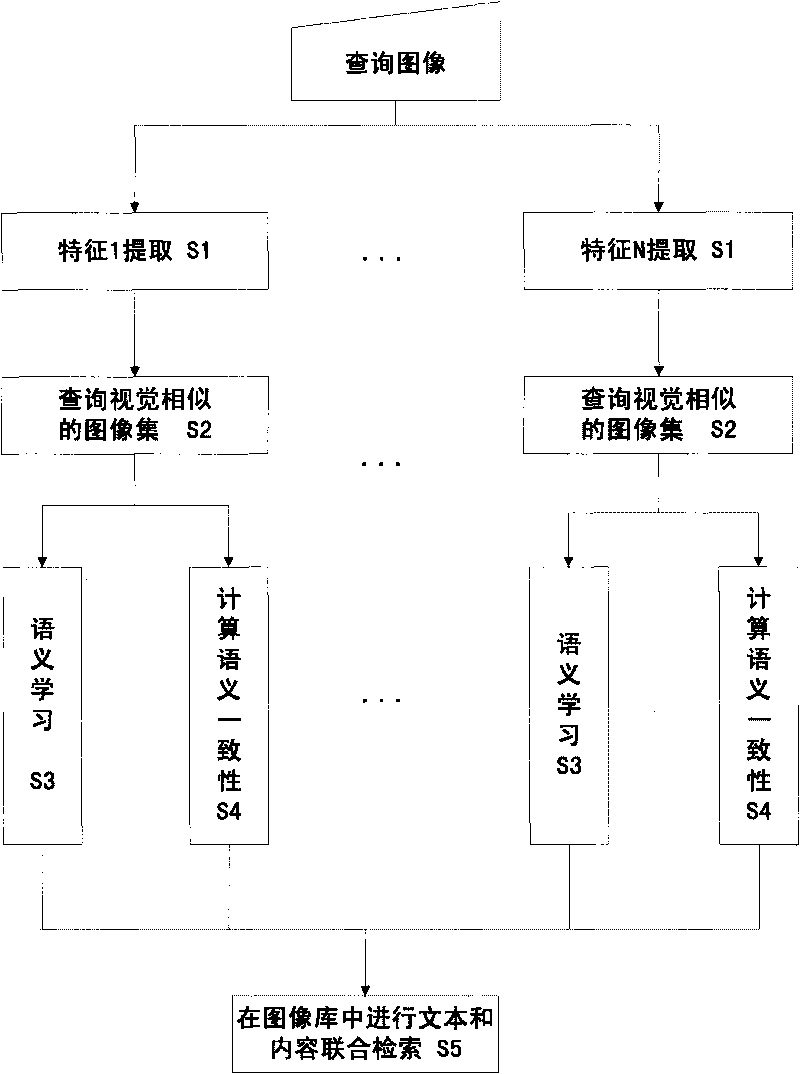
InactiveCN101751447AMeet search requirementsImprove consistencySpecial data processing applicationsImage extractionImage query
The invention relates to a network image retrieval method based on semantic analysis, which is used for extracting low-level features. Content-based image retrieval is performed on each type of feature to find out a visually-similar network image set. The related text information is used for semantic learning corresponding to each image in the network image set corresponding to each image in the network image set to obtain the semantic expression for the image query. The semantic consistency of the retrieval image set corresponding to various features on the text information is judged, the semantic consistency is used to measure the description capacities of various features, to endow the description capacities with different degree s of confidence. The semantics and semantic consistency of the image query are adopted to perform text-based image retrieval in the image base to obtain the semantic relevance of each image in the image base and the image query; the low-level features are adopted to perform content-based image retrieval on the image base to obtain the visual relevance of the each image in the image base and the image query; the semantics is fused with visual relevance through a linear function to ensure the image for the user to have both semantic and visual relevance.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
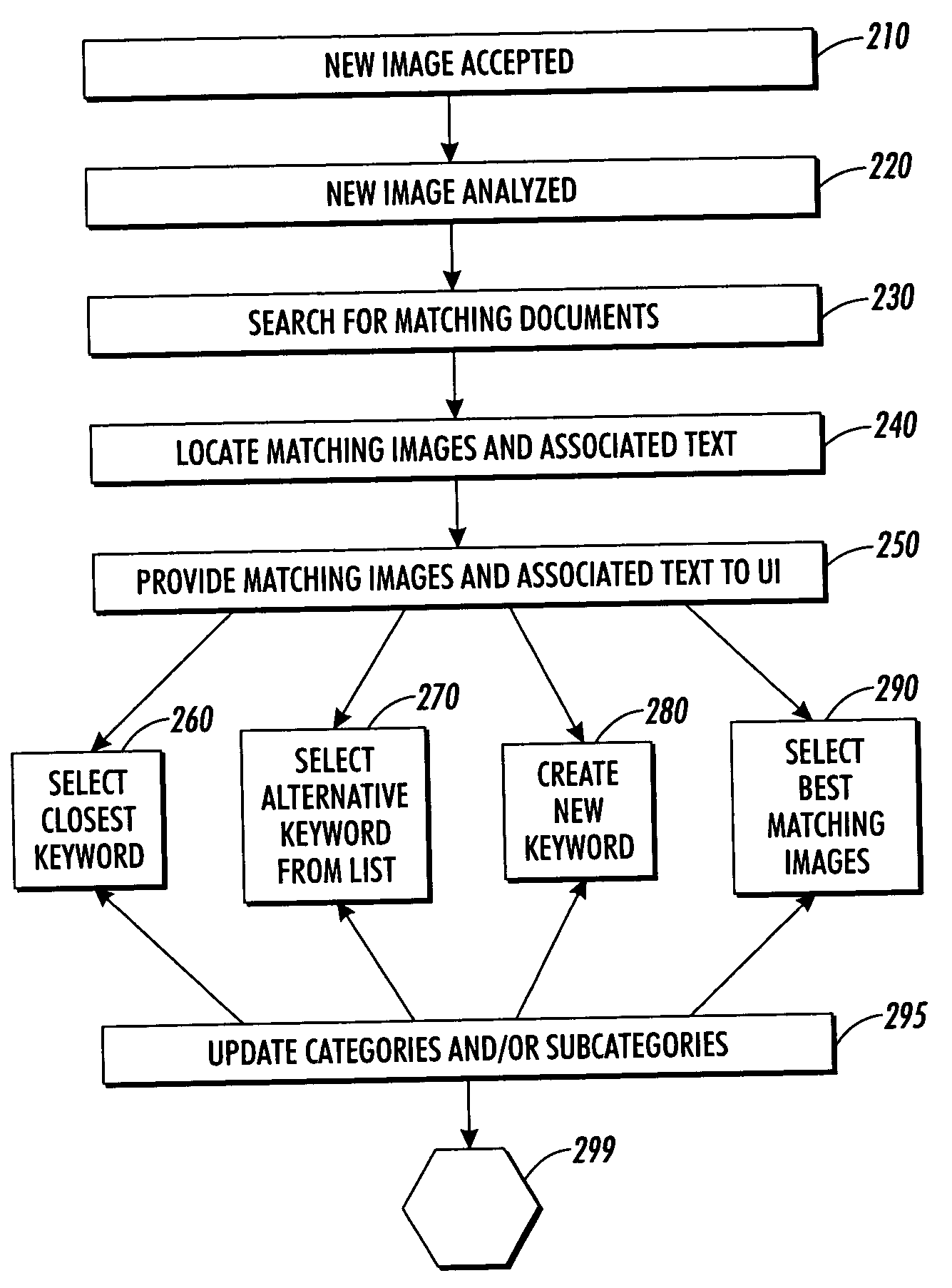
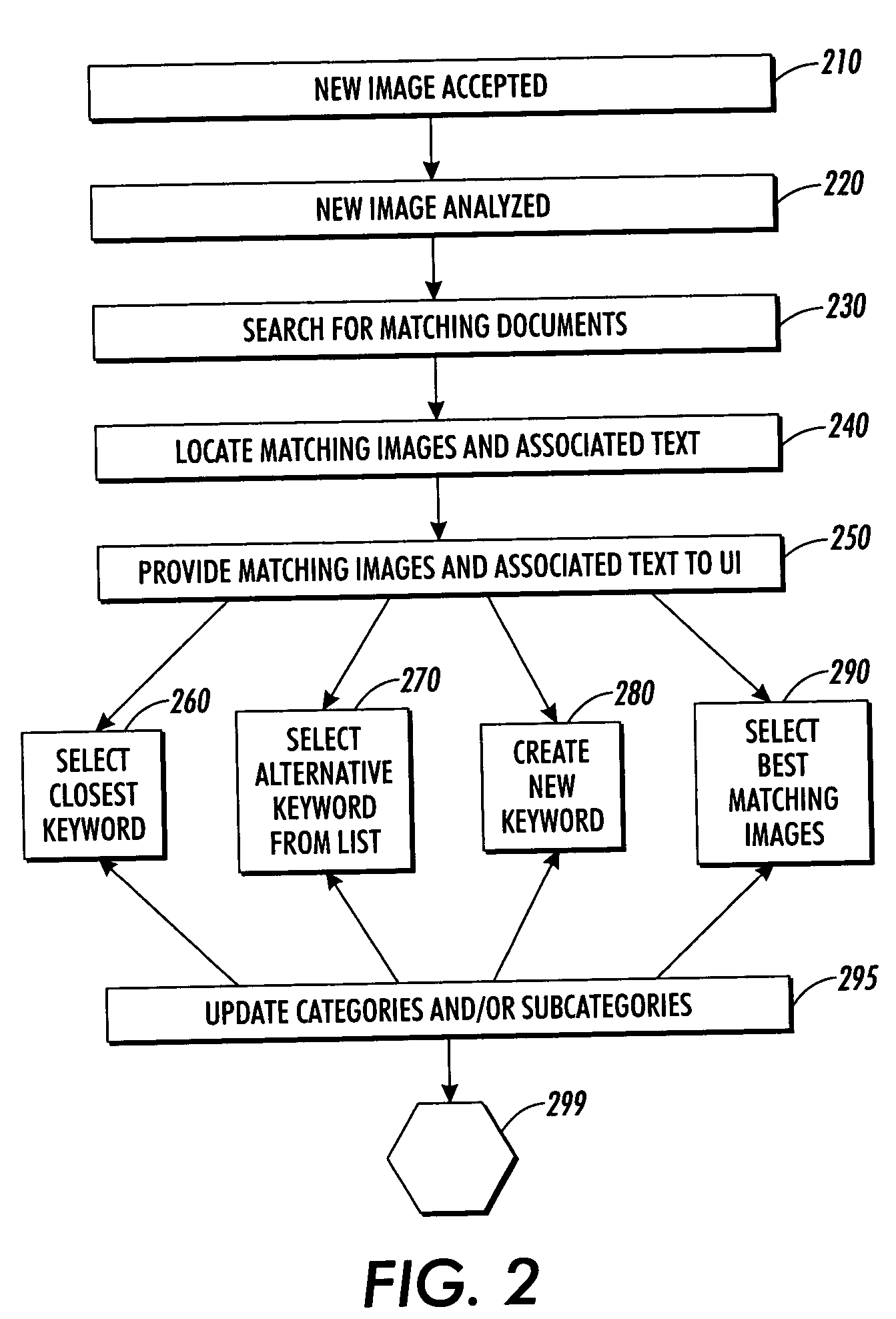
Methods and systems for attaching keywords to images based on database statistics
InactiveUS20050091232A1Accelerated programDigital data processing detailsMetadata still image retrievalStatistical analysisSystem usage
Methods and systems for adding identifying keywords to images stored within a database. A new image is compared to other images stored in a database using content based image retrieval methods. A user is automatically offered a set of keywords associated with stored images that most closely match the new image based on the comparison. The user can accept keywords contained in the offer or enter alternative keywords for the new image. A system can include a database adapted for storing images, a content based image retrieval module for providing text-associated image archiving, image management and image retrieval capabilities, database statistics module for providing statistical analysis regarding the number and type of images and metadata stored in the database, and a user interface (UI) adapted for providing user intervention during image archiving and further enables user acceptance of system suggestions, user selection of system suggestions, and enables user entry of user-provided keywords for association with images.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method for the reduction of image content redundancy in large image databases
InactiveUS7672976B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalFeature vectorDigital image
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
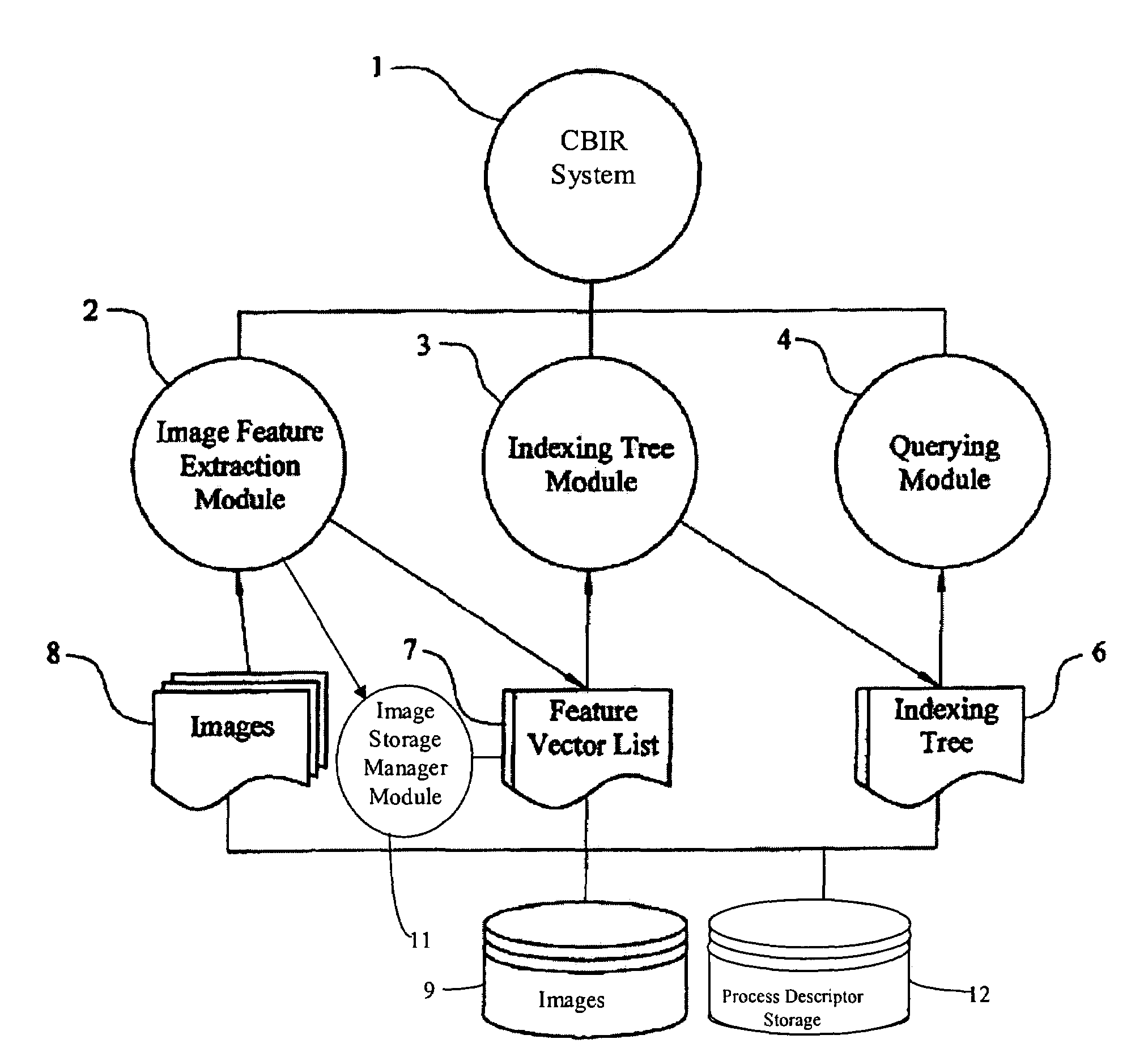
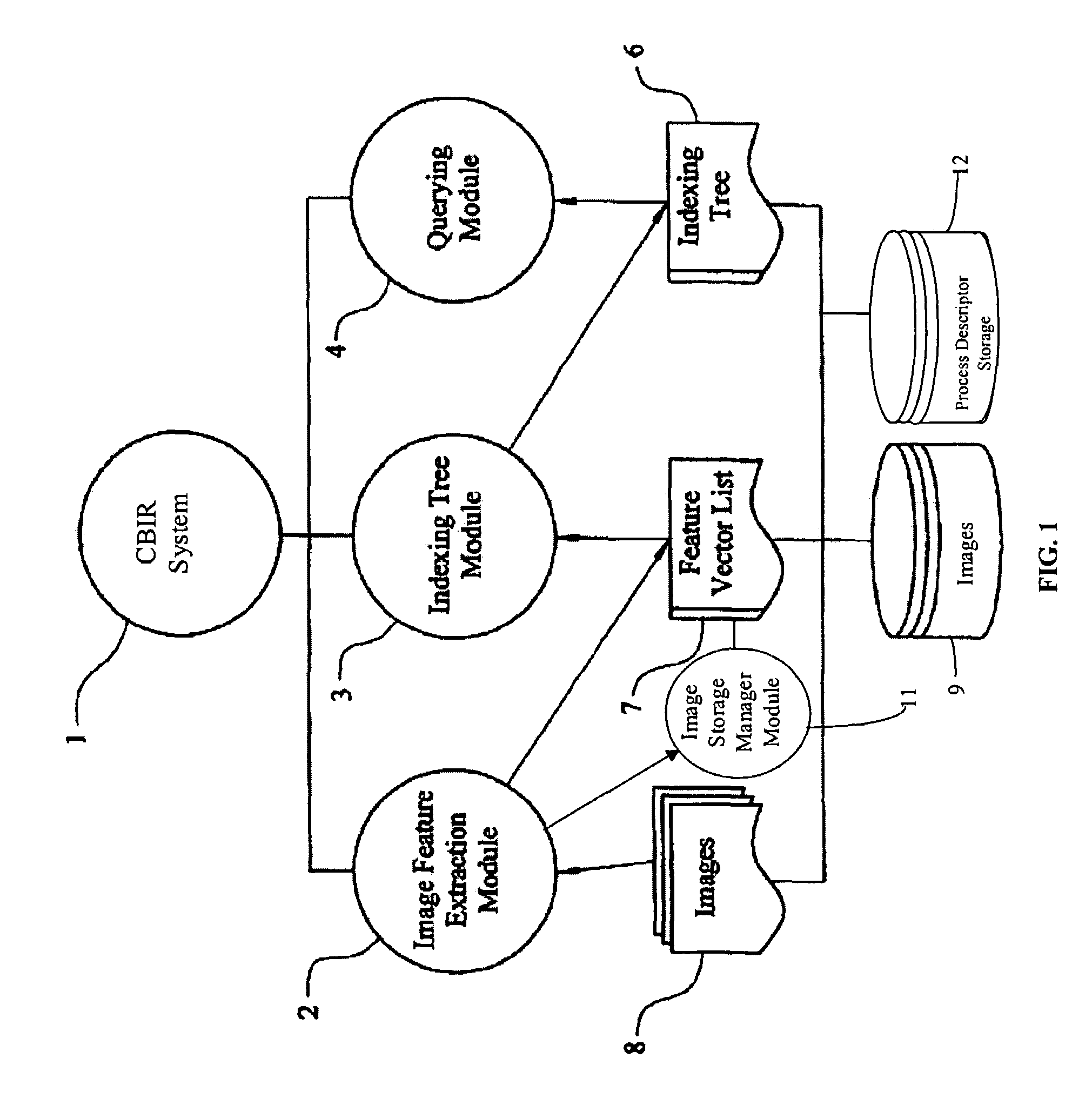
Content based image retrieval system, computer program product, and method of use
InactiveUS20090125487A1Poorly framed contourDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsContent base image retrievalComputer program
The present invention relates to a method and system for searching a target image in a data repository. A user may search a collection of images and retrieve images based upon the image content of a target or query image. The system may apply a combination of pre-processing techniques and image search techniques to provide matches for the target or query image.
Owner:PLATINUM SOLUTIONS
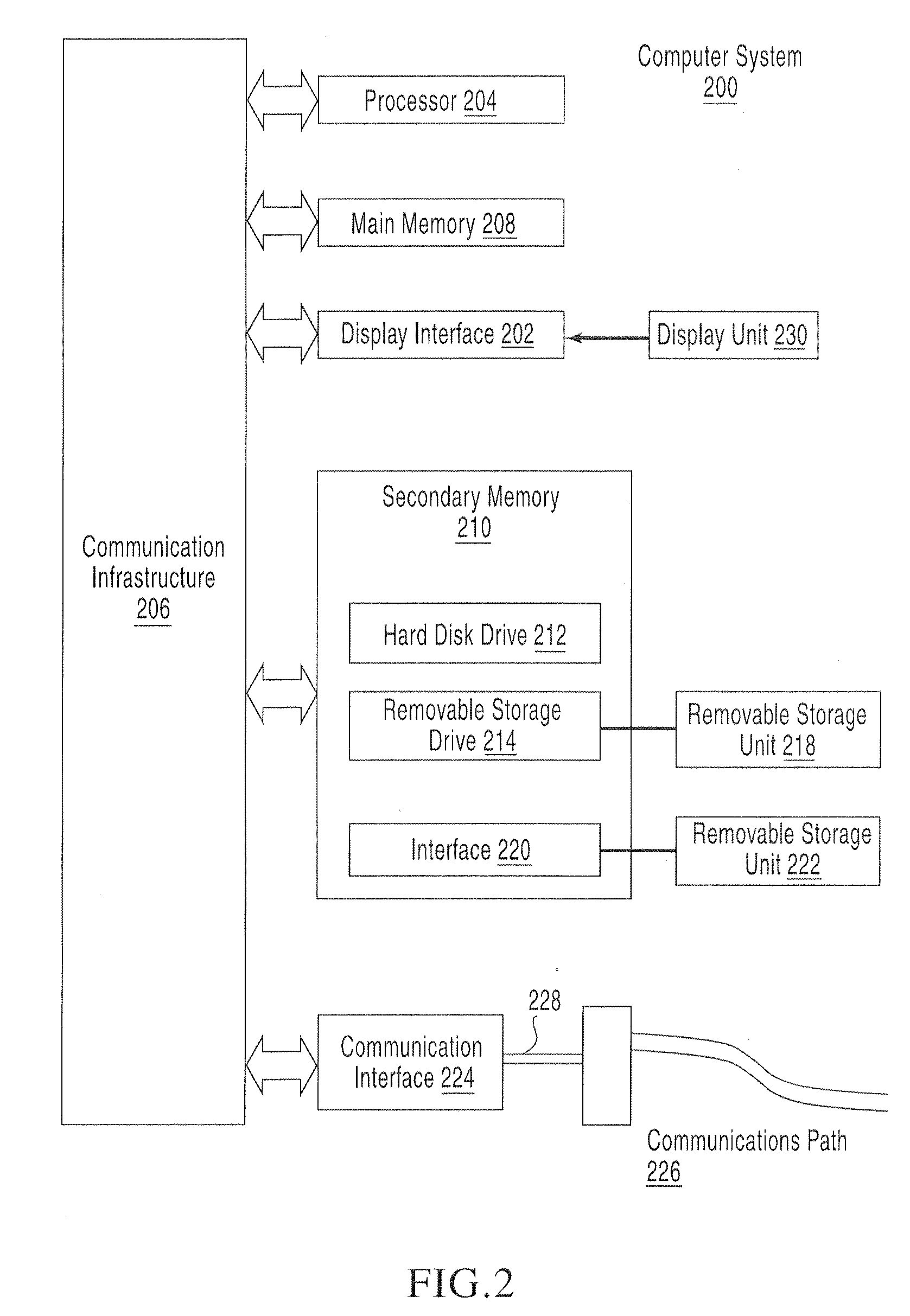
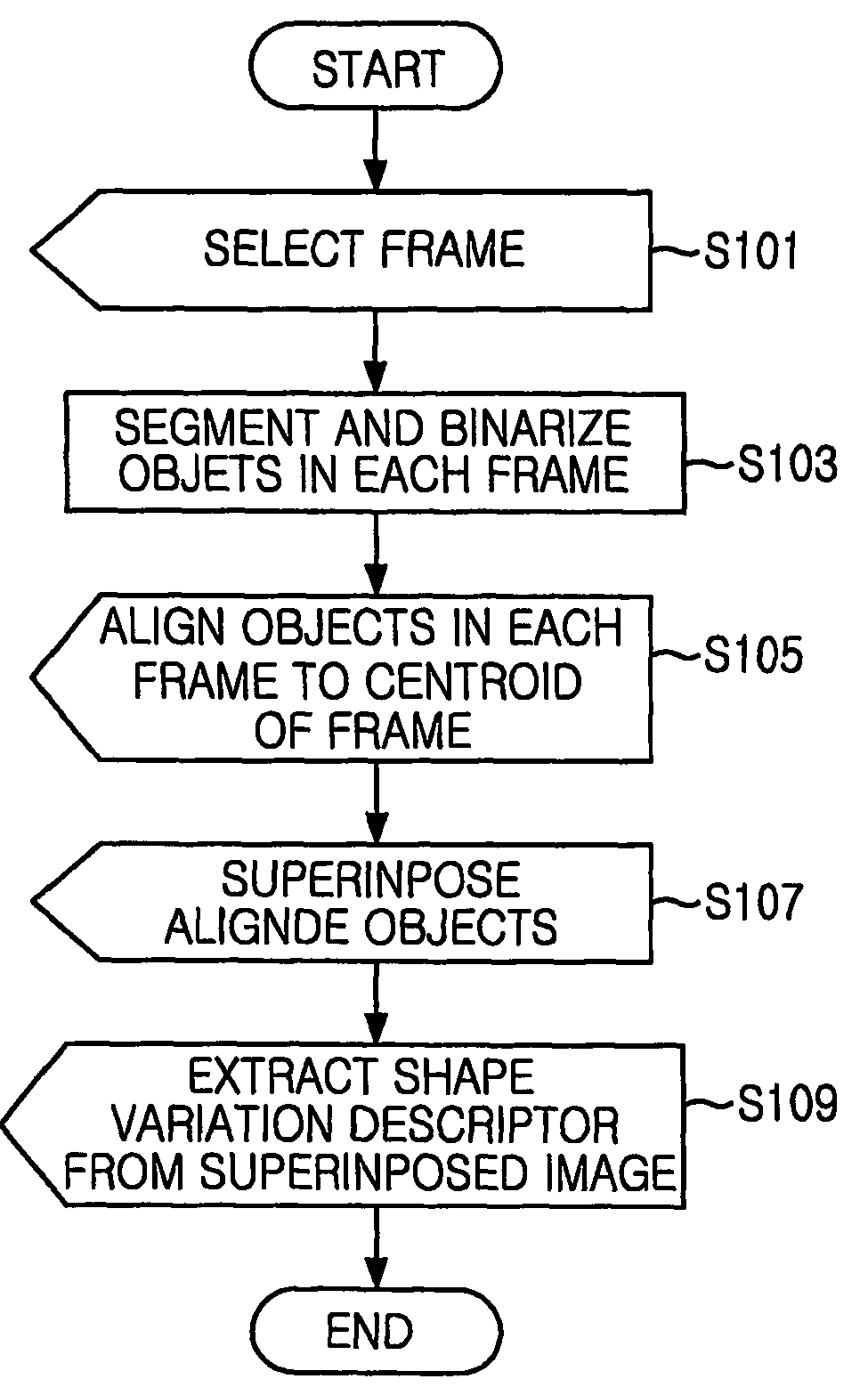
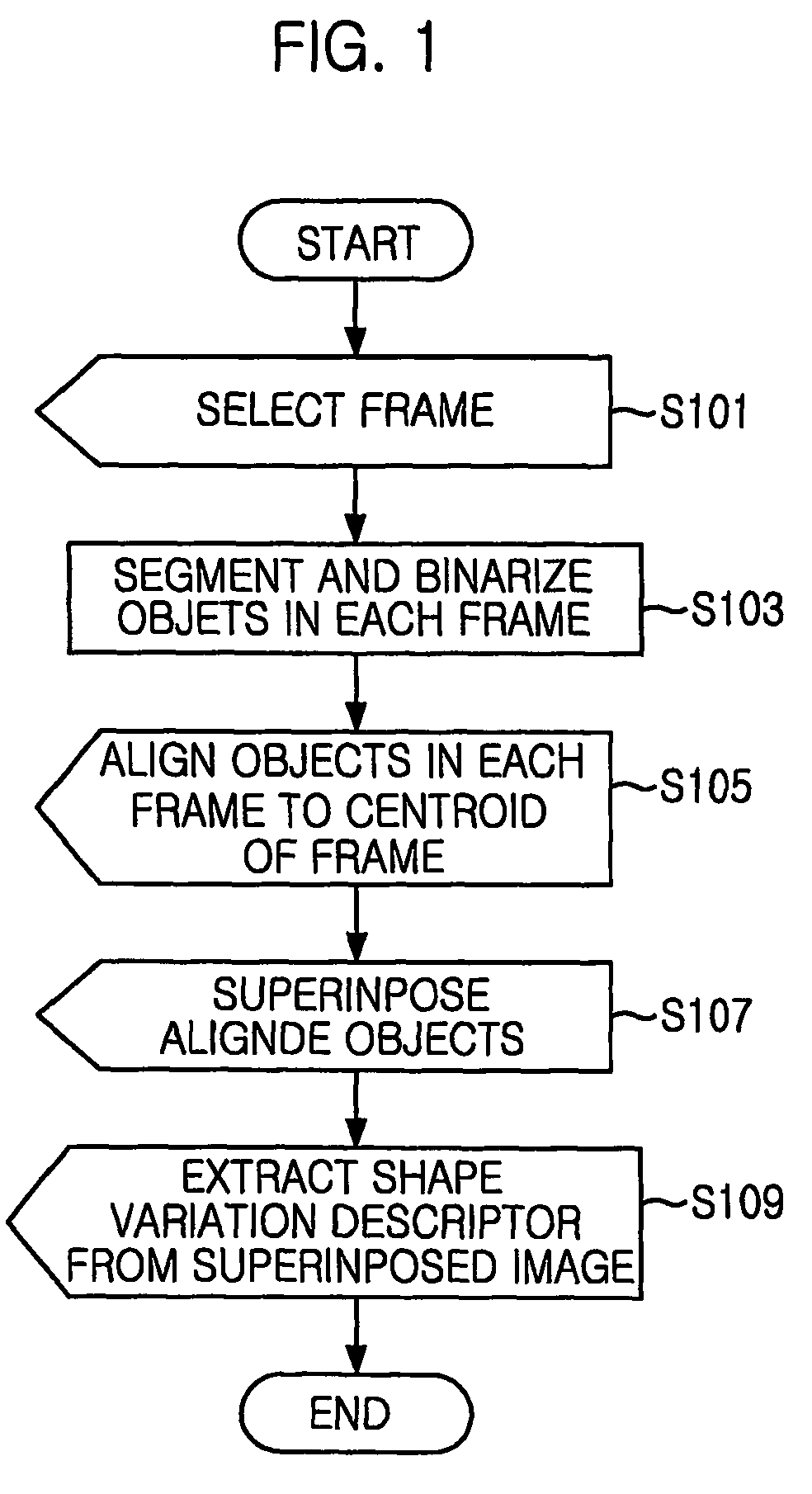
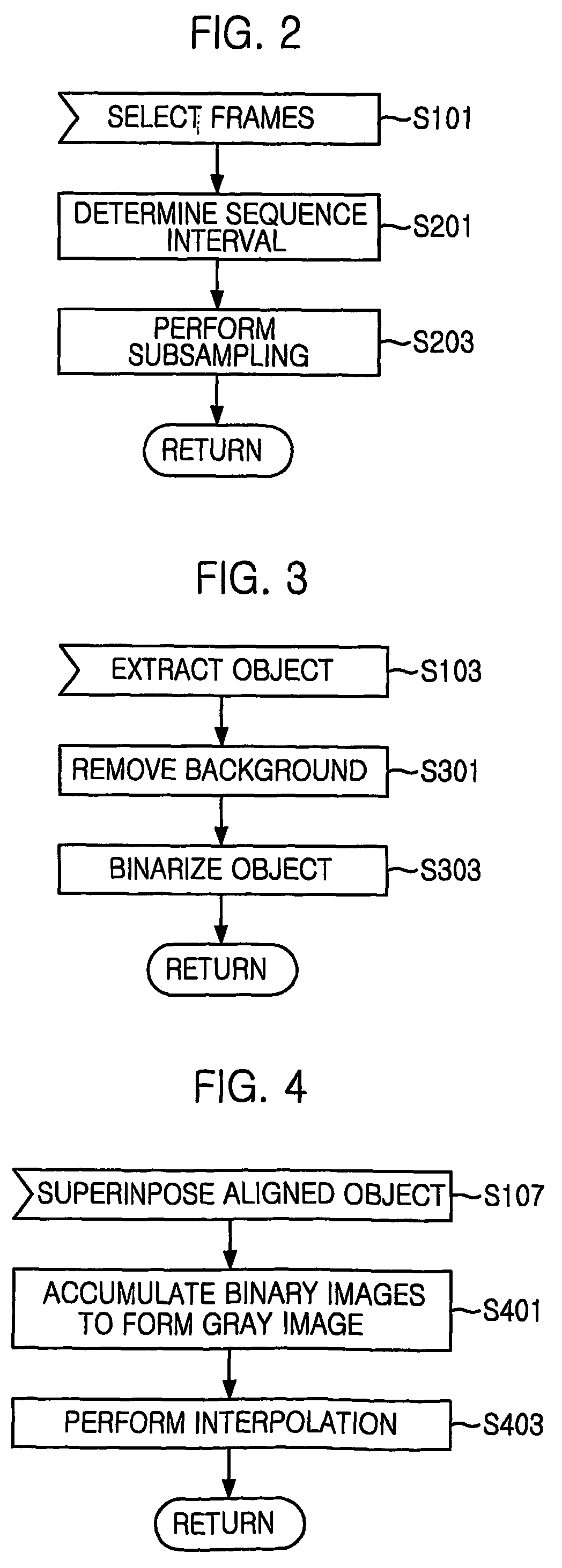
Method of extracting shape variation descriptor for retrieving image sequence
ActiveUS7212671B2Increase weightAccurate captureData processing applicationsImage analysisContent base image retrievalImage sequence
A method for extracting a shape variation descriptor from image sequence data for content-based image retrieval is disclosed. The method for extracting the shape variation descriptor from image sequence data for content-based image retrieval, image sequence data representing variation of object through a plurality of frames, the method includes the steps of creating a frame including variation information and shape information by accumulating the plurality of frames, the centroid of object regions in each frame aligned; and extracting shape descriptor from the frame.
Owner:KT CORP +1
Method for fuzzy logic rule based multimedia information retrival with text and perceptual features
InactiveUS7065521B2Data processing applicationsMetadata multimedia retrievalDocument preparationMachine learning
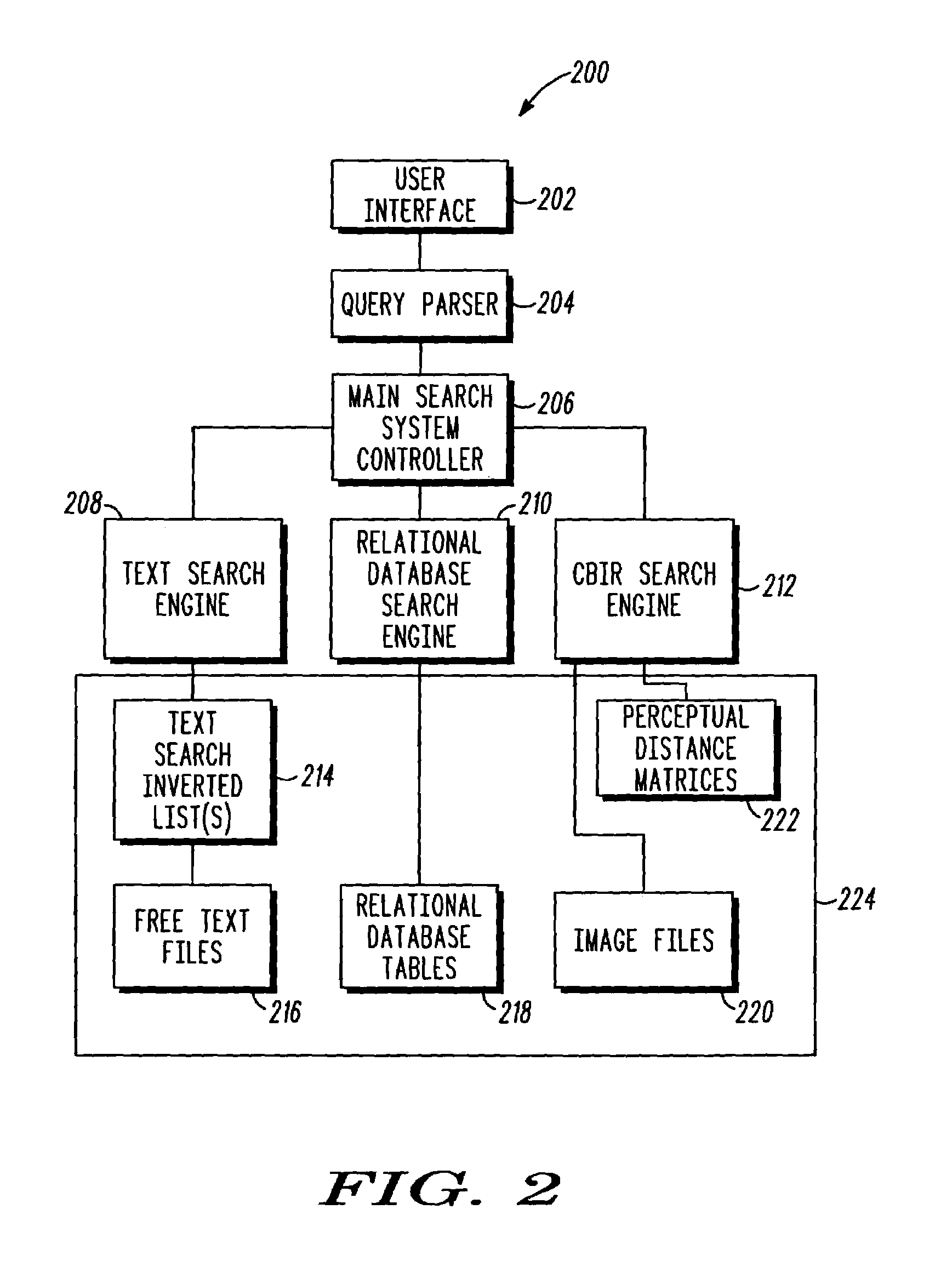
A search system (200) for a database (224) including records having a multiple disparate types of media is provided. The search system supports queries, that include different types of search criteria, including content based retrieval search criteria. A fuzzy logic method (400) is provided for effectively combining the results of different types of search criteria. The fuzzy logic method also allows confidence levels entered by the user for search criteria to be considered in combining results. Retrieval relevance values for documents for at least some search criteria are used in the fuzzy logic method. For content based image retrieval searches, the retrieval relevance values are computed by mapping a distance between quantitative characterizations of a search basis image, and other images into a finite range.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
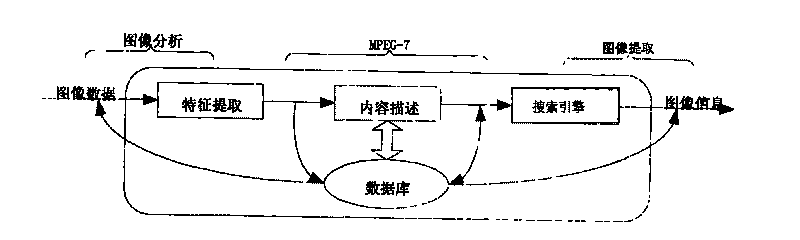
MPEG-7-based image retrieving system
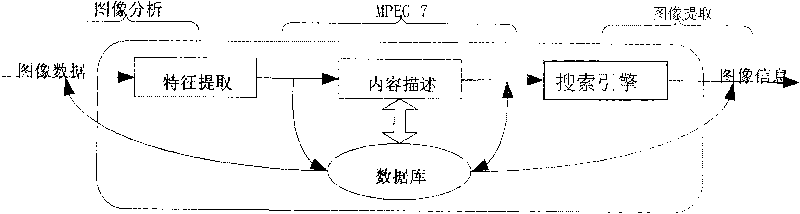
InactiveCN101739397AEfficient retrievalGood retrieval effectSpecial data processing applicationsTrademarkVisual perception
The invention discloses an MPEG-7-based image retrieving system, which mainly comprises three key techniques, namely, characteristic extraction, content description and searching engine. The MPEG-7-based image retrieving system comprises (1) content-based image retrieval CBIR, (2) a multimedia content description interface MPEG-7 and (3) a database model and management. Specifically, the MPEG-7-based image retrieving system comprises a characteristic extraction module, a retrieval module, an output module and a query module, and realizes network function-oriented image content-based query, so that a user can quickly and effectively retrieve image resources. A descriptor specified by an MPEG-7 standard is improved so as to obtain remarkable retrieval effect and perform combined query on different visual characteristics, such as colors, textures and shapes. The image retrieving system is developed for digital libraries, medical application and trademark retrieval application, and an algorithm is optimized according to the MPEG-7 standard, so that the MPEG-7-based image retrieving system reaches a leading domestic level in terms of algorithm study and application. The MPEG-7-based image retrieving system has the characteristics of clear technical direction, smooth development and relatively stronger maturity.
Owner:新疆亚泰信息技术有限公司
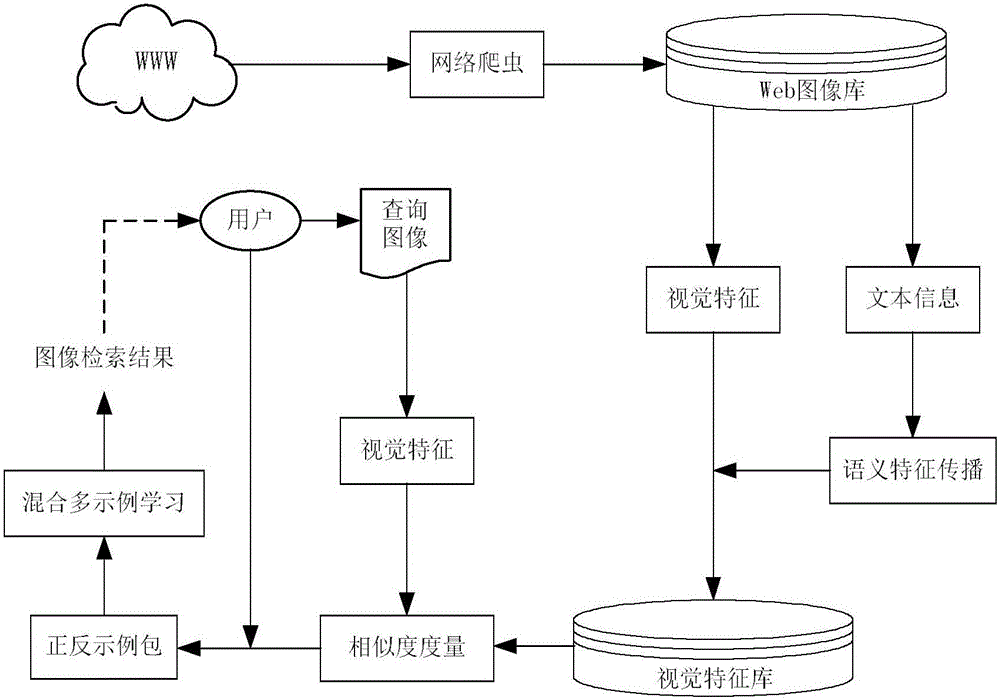
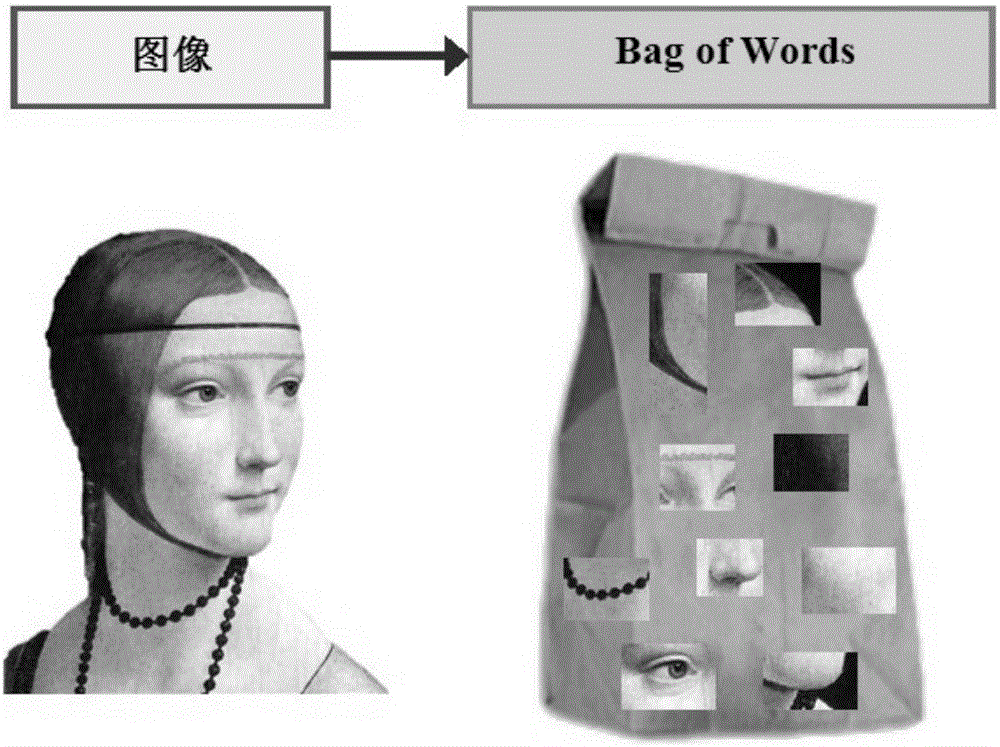
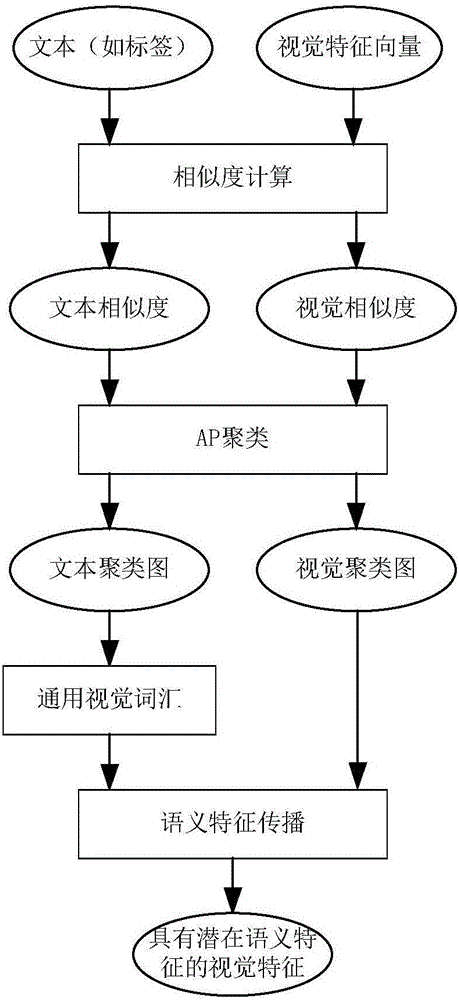
Semantic propagation and mixed multi-instance learning-based Web image retrieval method
ActiveCN106202256AReduce Extraction ComplexityImprove classification performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsSmall sampleThe Internet
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing and particularly provides a semantic propagation and mixed multi-instance learning-based Web image retrieval method. Web image retrieval is performed by combining visual characteristics of images with text information. The method comprises the steps of representing the images as BoW models first, then clustering the images according to visual similarity and text similarity, and propagating semantic characteristics of the images into visual eigenvectors of the images through universal visual vocabularies in a text class; and in a related feedback stage, introducing a mixed multi-instance learning algorithm, thereby solving the small sample problem in an actual retrieval process. Compared with a conventional CBIR (Content Based Image Retrieval) frame, the retrieval method has the advantages that the semantic characteristics of the images are propagated to the visual characteristics by utilizing the text information of the internet images in a cross-modal mode, and semi-supervised learning is introduced in related feedback based on multi-instance learning to cope with the small sample problem, so that a semantic gap can be effectively reduced and the Web image retrieval performance can be improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
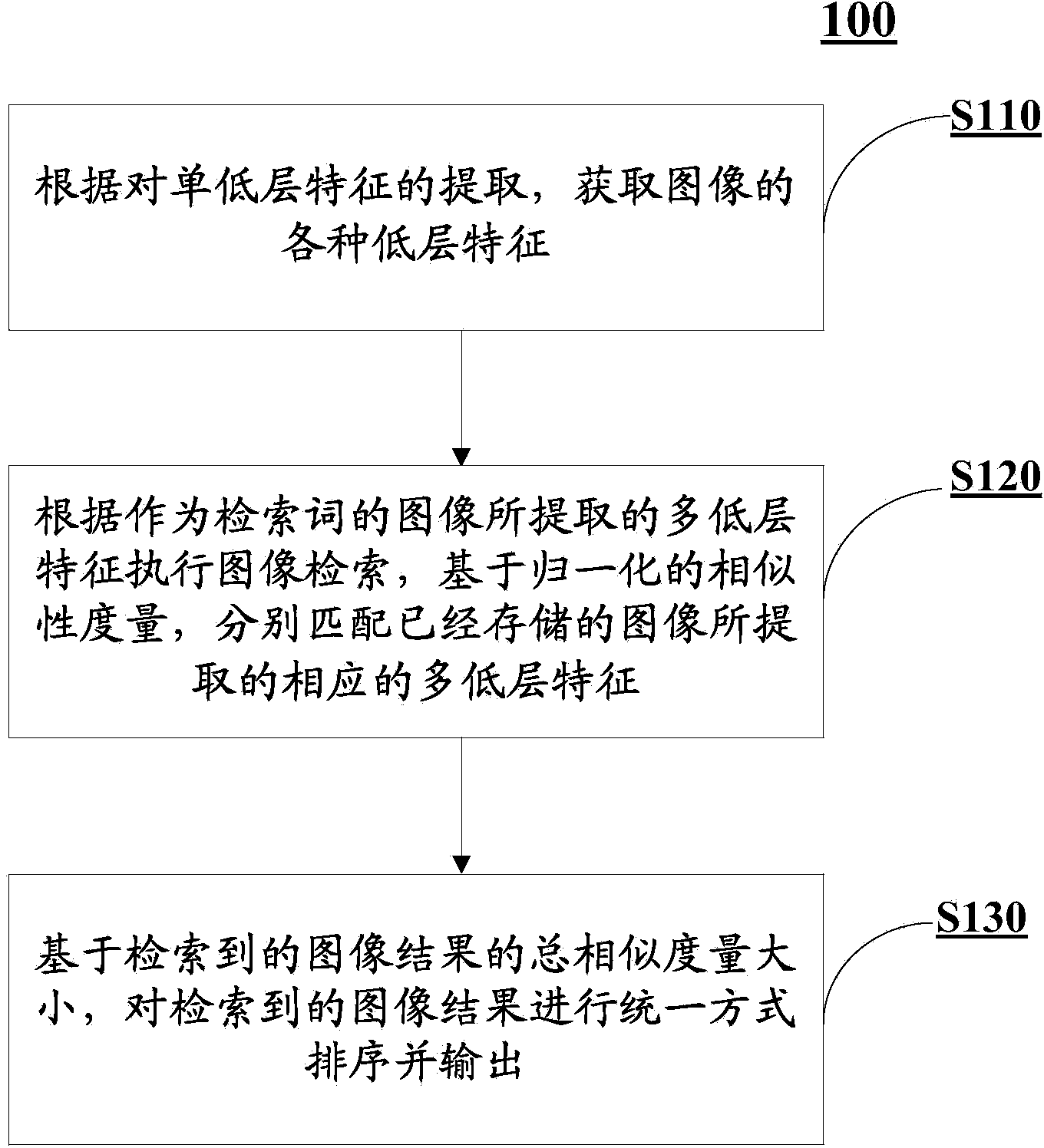
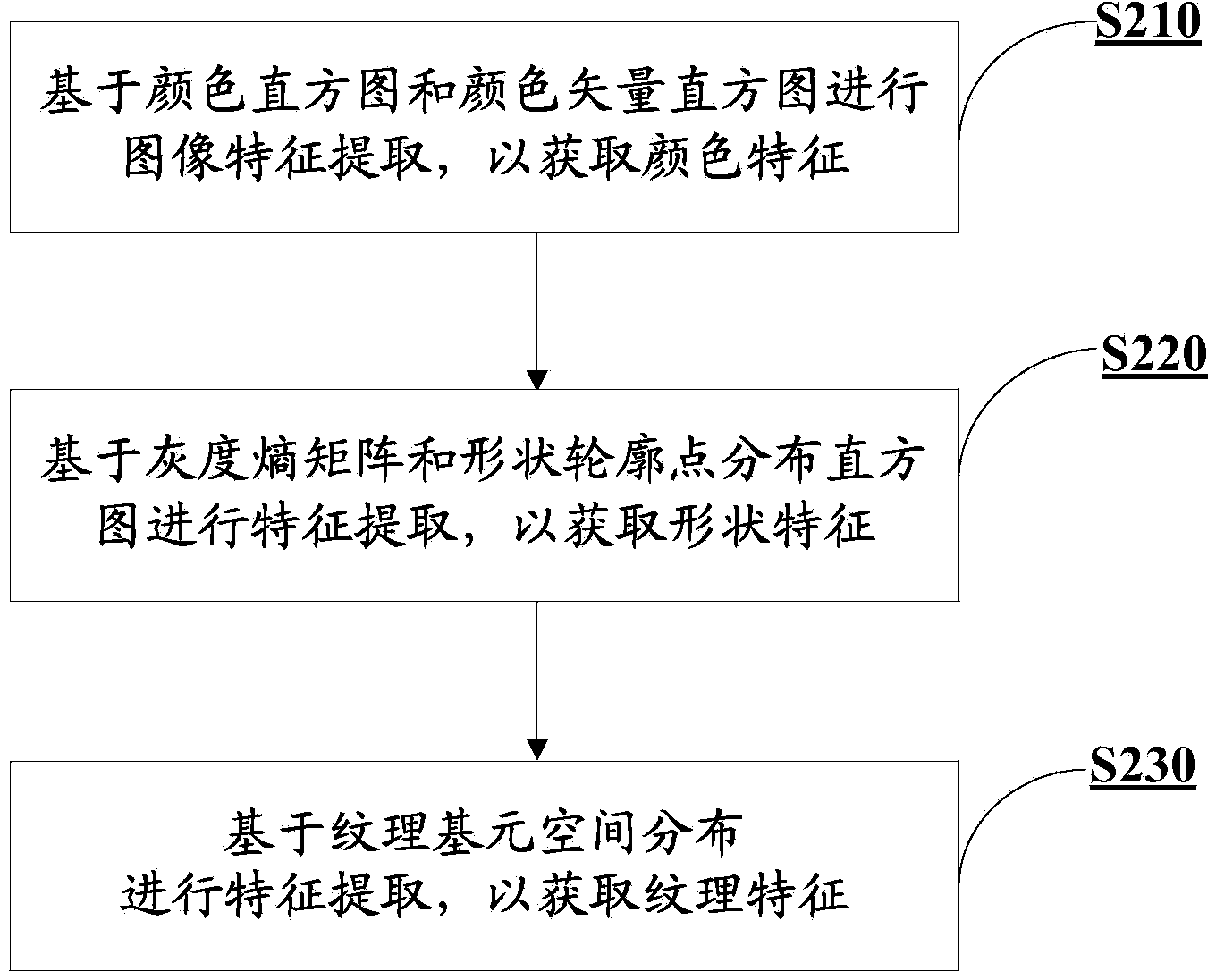
Multi-feature content-based image retrieval method and system
InactiveCN104298775AMeet search requirementsMeet actual needsCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsMulti aspectSimilarity measure
The invention provides a multi-feature content-based image retrieval method and system. The multi-feature content-based image retrieval method comprises the steps that according to various single low-layer features of images which are obtained through extraction and serve as retrieval terms, image retrieval is executed on the basis of normalization similarity measurements according to the various single low-layer features so that corresponding single low-layer features of various stored images can be matched with the obtained single low-layer features respectively; image results obtained through retrieval are ordered in a unified mode and output on the basis of total similarity measurements of the image results obtained through retrieval. In this way, the effect that in the content-based image retrieval process, combination of multiple low-layer features is optimized in the linear weighting mode of unifying the similarity measurements of all the low-layer features is achieved, the recall factor and the pertinency factor are increased, and multi-aspect actual requirements of users for content-based image retrieval are better met.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
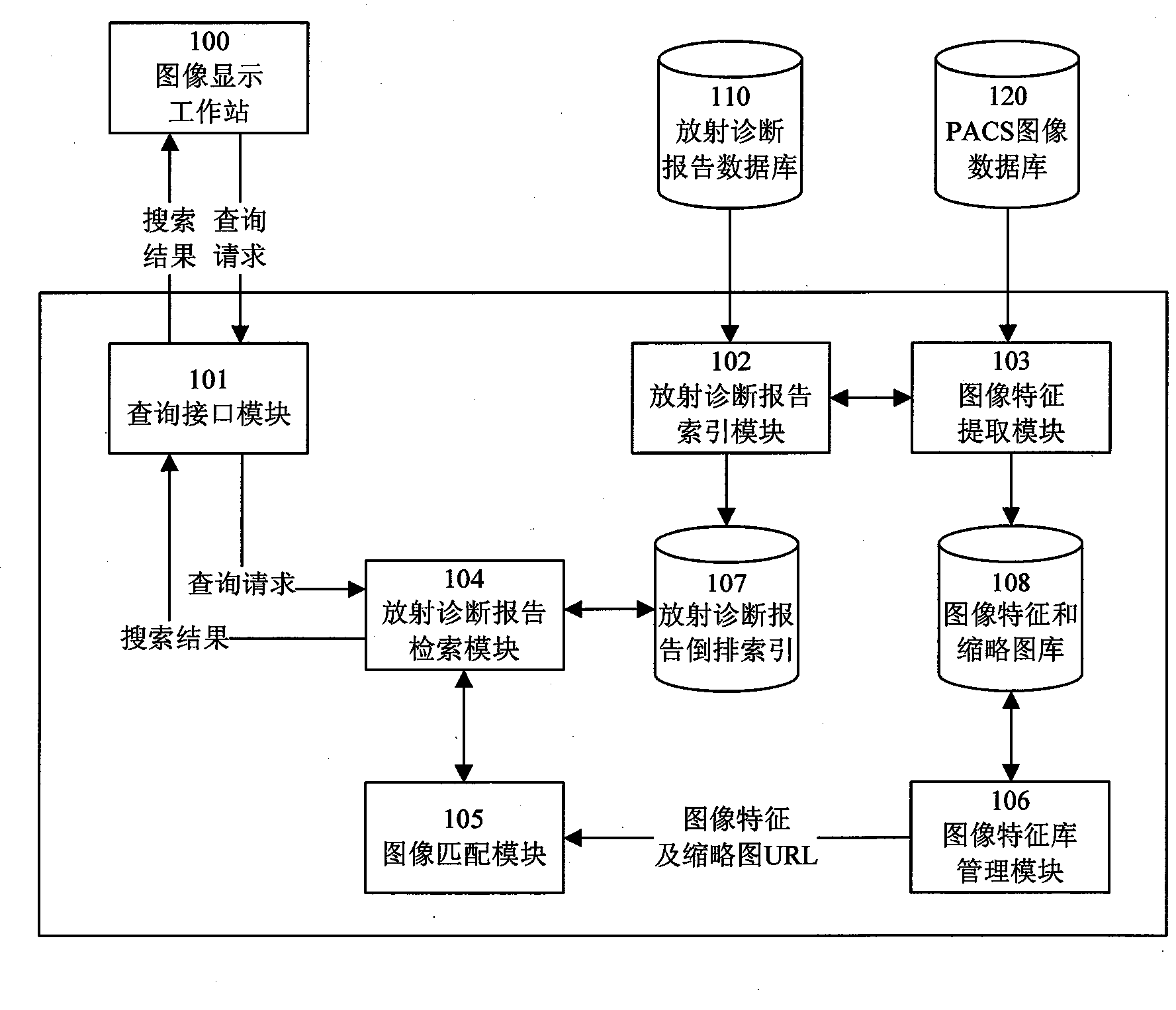
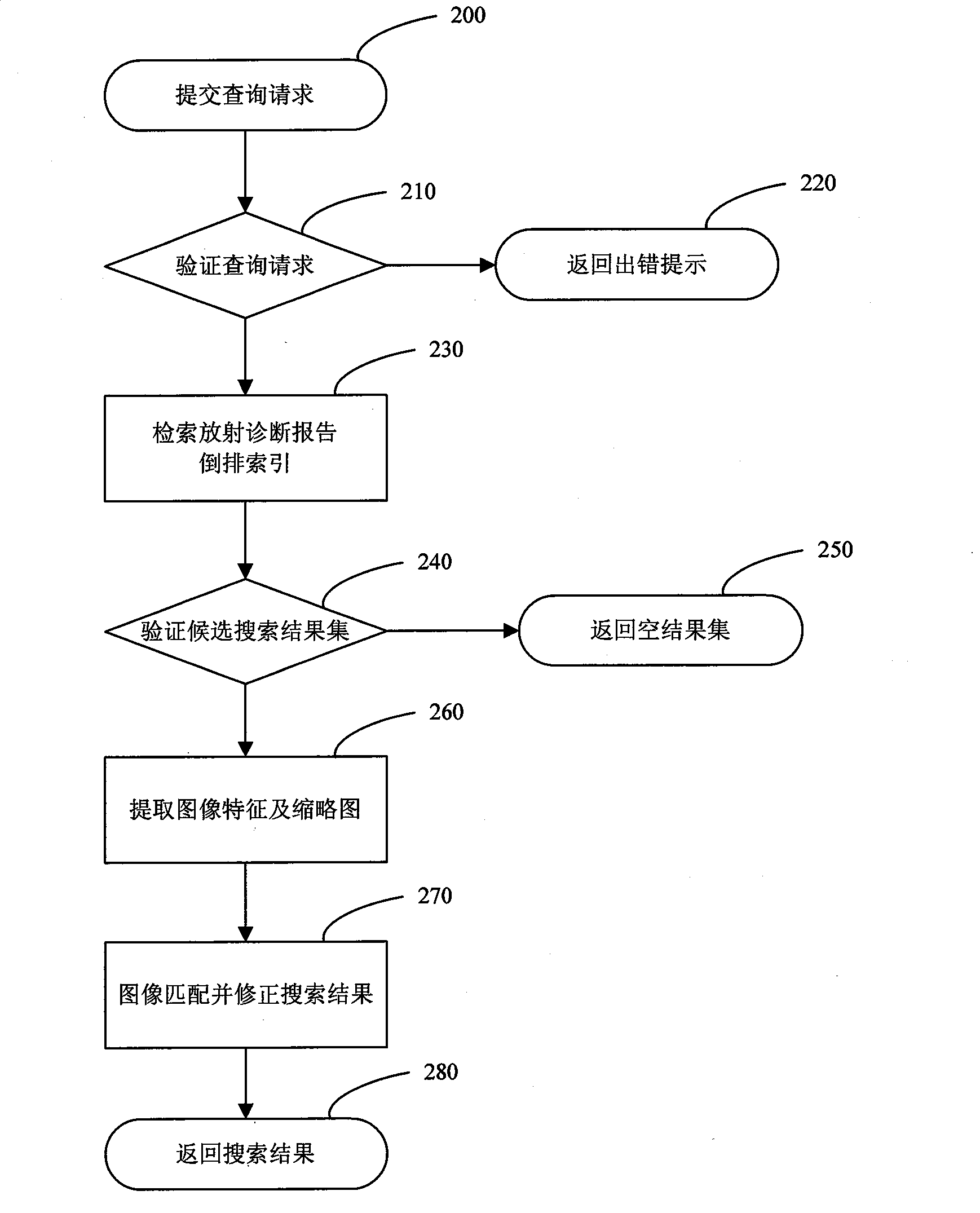
Search method and system facing to radiation image in PACS database based on content
InactiveCN101441658AReduce in quantityImprove performanceSpecial data processing applicationsSemantic gapReverse index
The invention discloses a content-based retrieval method and a content-based retrieval system facing radiographs in a PACS database. The content-based retrieval to the radiographs is realized by associating a radiodiagnosis report in a radio information system with the radiographs in the PACS database, establishing the reverse index of the radiodiagnosis report and a feature index library of the radiographs, and then using a two-phase search algorithm. The retrieval method, by effectively integrating text retrieval technology and content-based image retrieval technology, overcomes the defect that the prior content-based image retrieval technology is not suitable for large-scale image databases, alleviates the semantic gap in the prior content-based image retrieval technology to a certain extent, and has high application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Perception-based image retrieval
InactiveUS20010046332A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalAverage filterPattern perception
A content-based image retrieval (CBIR) system has a front-end that includes a pipeline of one or more dynamically-constructed filters for measuring perceptual similarities between a query image and one or more candidate images retrieved from a back-end comprised of a knowledge base accessed by an inference engine. The images include at least one color set having a set of properties including a number of pixels each having at least one color, a culture color associated with the color set, a mean and variance of the color set, a moment invariant, and a centroid. The filters analyze and compare the set of properties of the query image to the set of properties of the candidate images. Various filters are used, including: a Color Mask filter that identifies identical culture colors in the images, a Color Histogram filter that identifies a distribution of colors in the images, a Color Average filter that performs a similarity comparison on the average of the color sets of the images, a Color Variance filter that performs a similarity comparison on the variances of the color sets of the images, a Spread filter that identifies a spatial concentration of a color in the images, an Elongation filter that identifies a shape of a color in the images, and a Spatial Relationship filter that identifies a spatial relationship between the color sets in the images.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
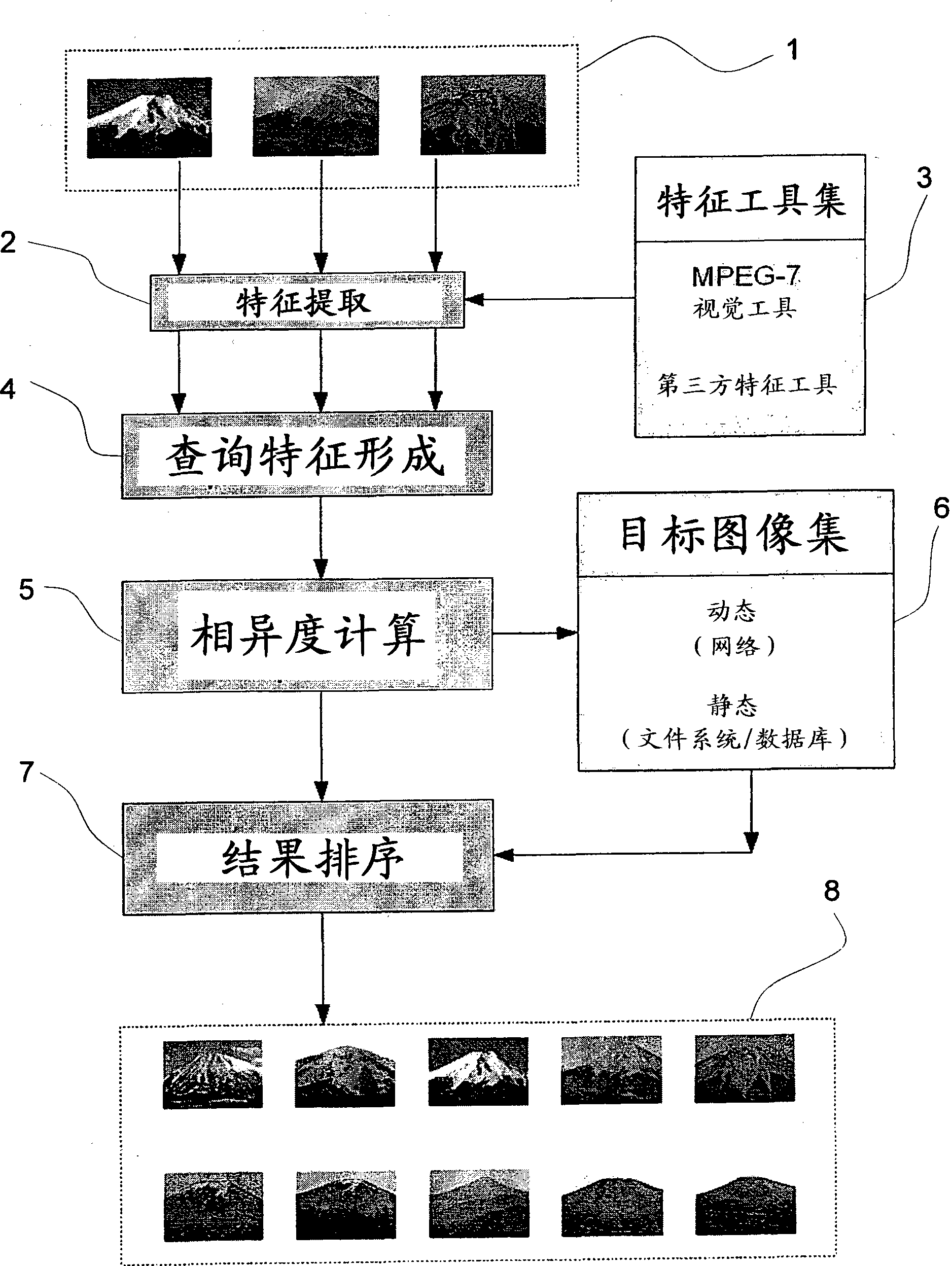
Optimising content based image retrieval
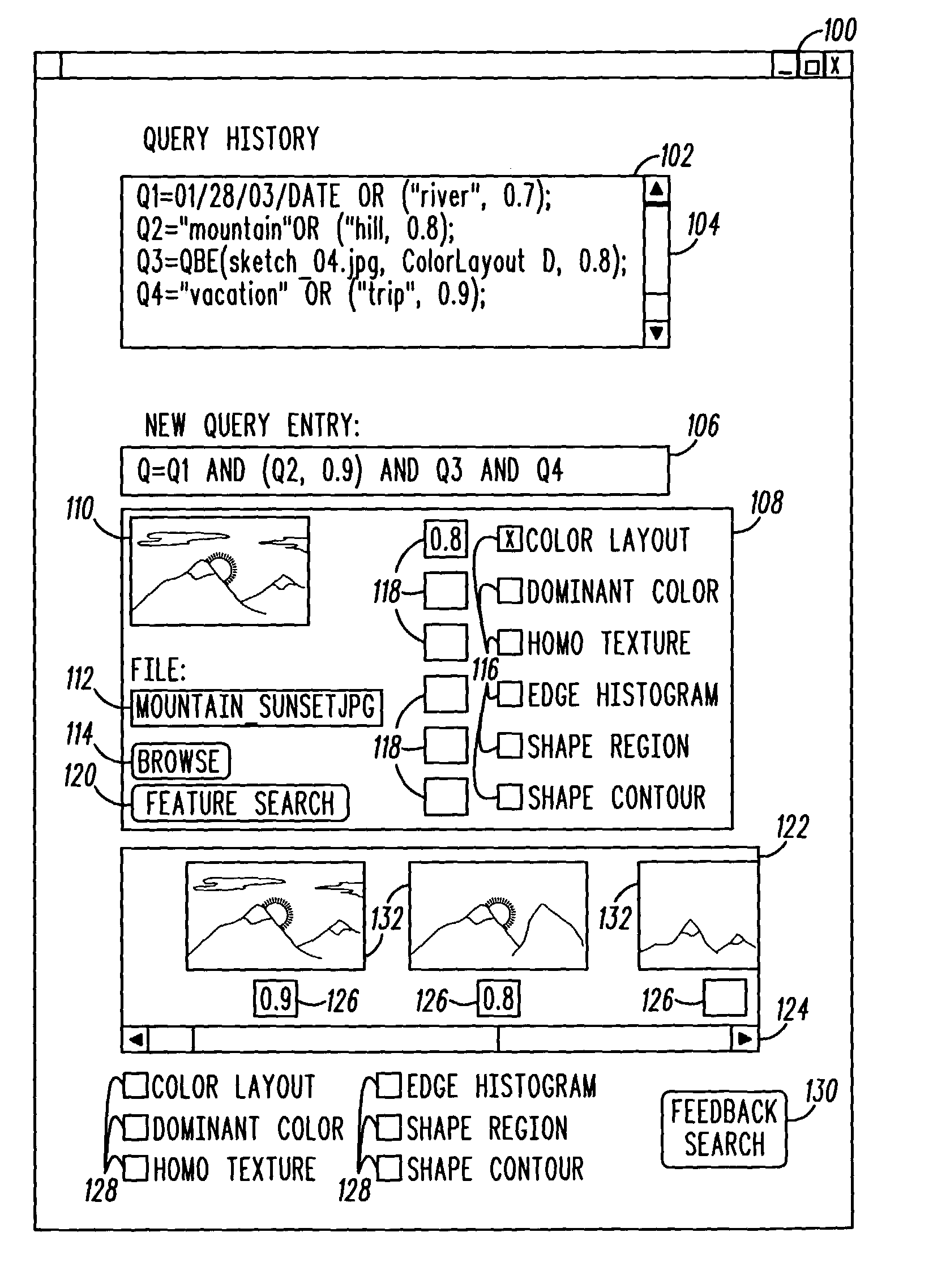
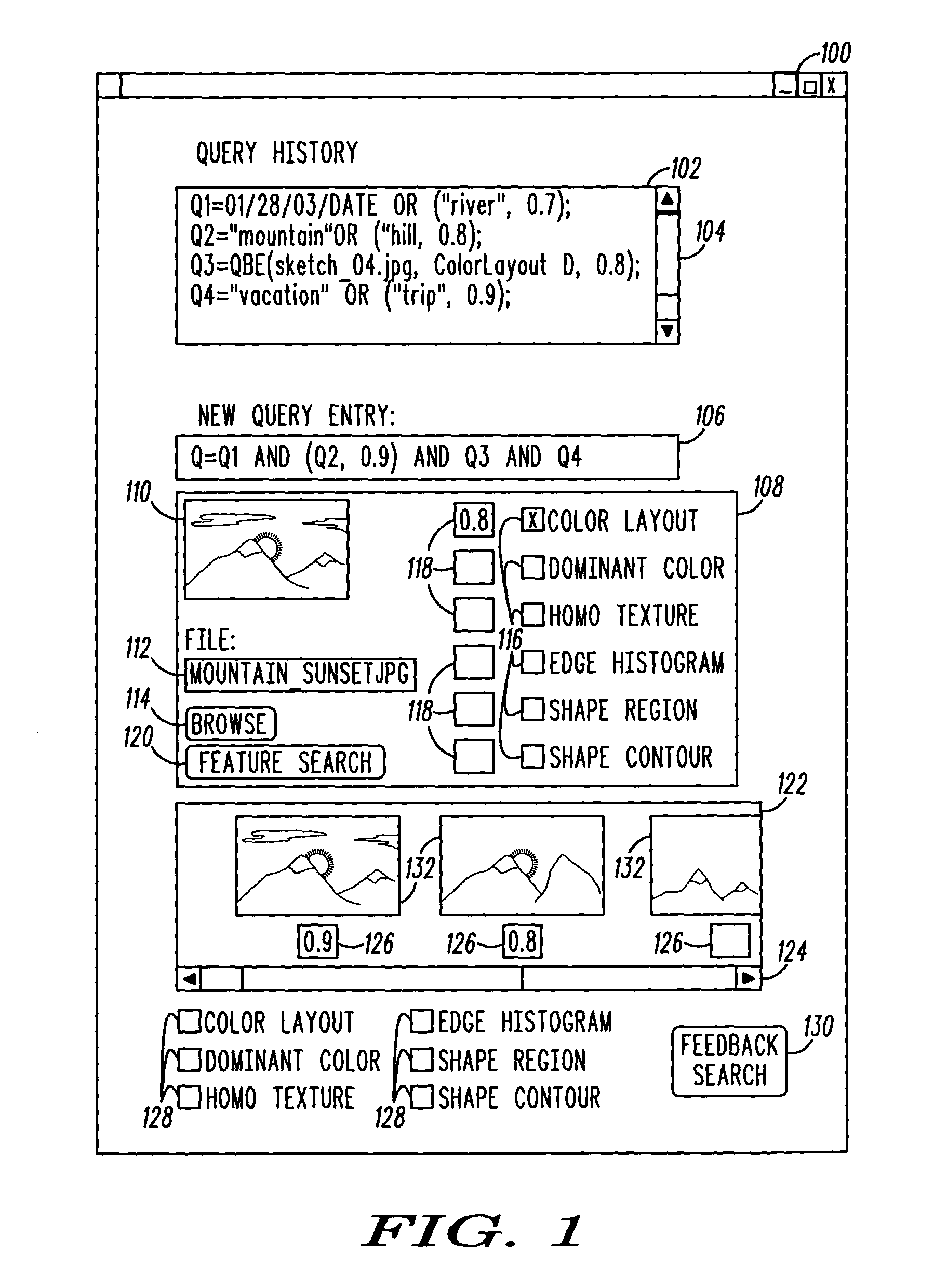
InactiveUS20110202543A1High similarityDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFeature setResult set
A method, processing system and computer program product for optimising a search of a collection of images. In one aspect, the method includes iteratively performing, in a processing system, steps of comparing a test search result set for a search query to a user defined expected search result set for the search query, wherein the search query includes a query feature set of a search image, each feature being associated with a weight; and adjusting one or more weights of the query feature set according to the results of the comparison to improve the similarity between the test and expected search result sets, thereby optimising a future image search of the collection of images.
Owner:IMPREZZEO
Self-adaptation Hash rearrangement method for image retrieval
InactiveCN103226585AGeneralNo added computational complexitySpecial data processing applicationsFeature vectorComputation complexity
The invention belongs to the technical field of image retrieval, and relates to a self-adaptation Hash rearrangement method for image retrieval, in particular to an image Hash method for carrying out content-based image retrieval. The method adopts the mapping and then sequencing Hash rearrangement method, and comprises the following steps: high-dimensional visual feature vectors of images in a training library are abstracted, a proper Hash method is selected to map the high-dimensional visual feature vectors into Hash codes, and specific class weight vectors are generated for each class of images; the hamming distance between the Hash codes of the retrieved images and the Hash codes in the training library is calculated, and retrieval results are returned in an ascending order; and according to the retrieval results, the self-adaptation weight vectors of the retrieved images are calculated, the hamming distance is weighted by utilizing the structures of the self-adaptation weight vectors of the retrieved images, the returned images are rearranged by utilizing the weighted hamming distance, and more accurate retrieval results are obtained. The self-adaptation Hash rearrangement method calculates specific weights according to the retrieved images, has universality, and remarkably improves the retrieval effect without increase of calculation complexity.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method, system and computer program product for breast density classification using parts-based local features
InactiveUS20160314579A1Improve accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPrincipal component analysisClassification methods
An automated content-based image retrieval method, a system and a computer program product for the classification of breast density from mammographic imagery. Raw digital mammogram images taken of patients are initially pre-processed to remove noise and enhance contrast, then subjected to pectoral muscle segmentation to produce region of interest (ROI) images. The ROI images are then decomposed using non-negative matrix factorization (NMF), where a non-negative sparsity constraint and reconstruction quality measures are imposed on the extracted and retained first few NMF factors. Based on the retained NMF factors, kernel matrix-based support vector machines classify the mammogram images binomially or multinomially to breast density categories. Methods of assessing and comparing the NMF-based breast classification method to principal component analysis or PCA-based methods are also described, and the NMF-based method is found to achieve higher classification accuracy and better handling of invariance in the digital mammogram images because of its parts-based factorization.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
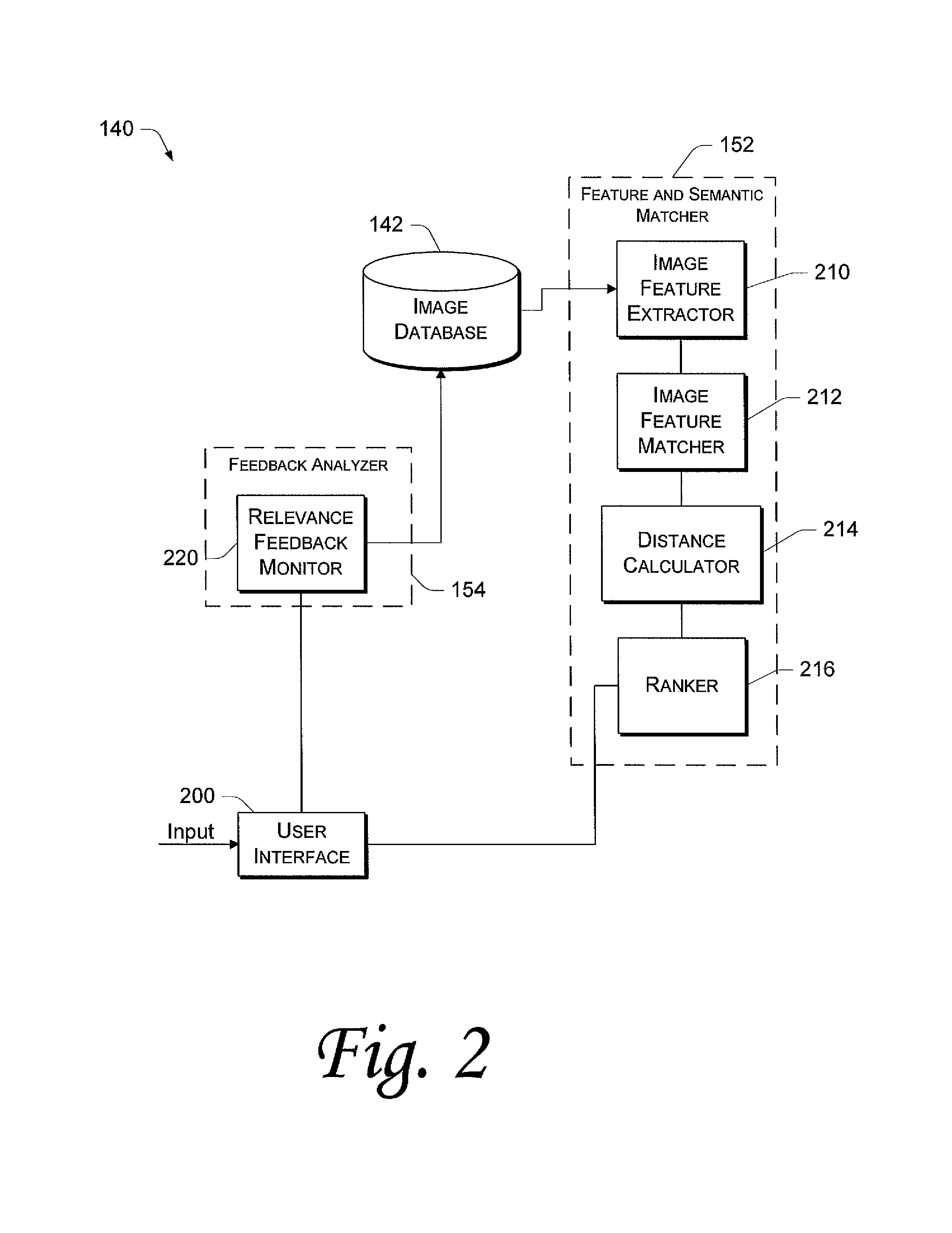
Visualization of relevance for content-based image retrieval
InactiveUS20120158717A1Promptly compareStill image data retrievalDigital data processing detailsCorrelation functionContent base image retrieval
The invention relates to a system (100) for retrieving an image from the storage of images, the system comprising: a retrieval unit (110) for retrieving an image from the storage of images, on the basis of similarity of images from the storage of images o a query image, wherein the similarity is defined by means of a similarity function; a relevance unit (120) for computing images t relevance of a first portion of the retrieved image to a respective first portion of the query image and of a second portion of the retrieved image to a respective second portion of the query image; and a visualization unit (130) for visualizing the relevance of the first and second portion of the retrieved image to the respective first and second portion of the query image. The relevance of the first and second portion of the retrieved image to the respective first and second portion of the query image may be computed using a first and second relevance function. The computed values of the relevance may be visualized, e.g. using a color coding and coloring the first and second portion of each retrieved image. The colored portions are easy to see and analyze. Thus, the system of the invention facilitates visualizing and comparing retrieved images with respect to each other as well as with the query image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
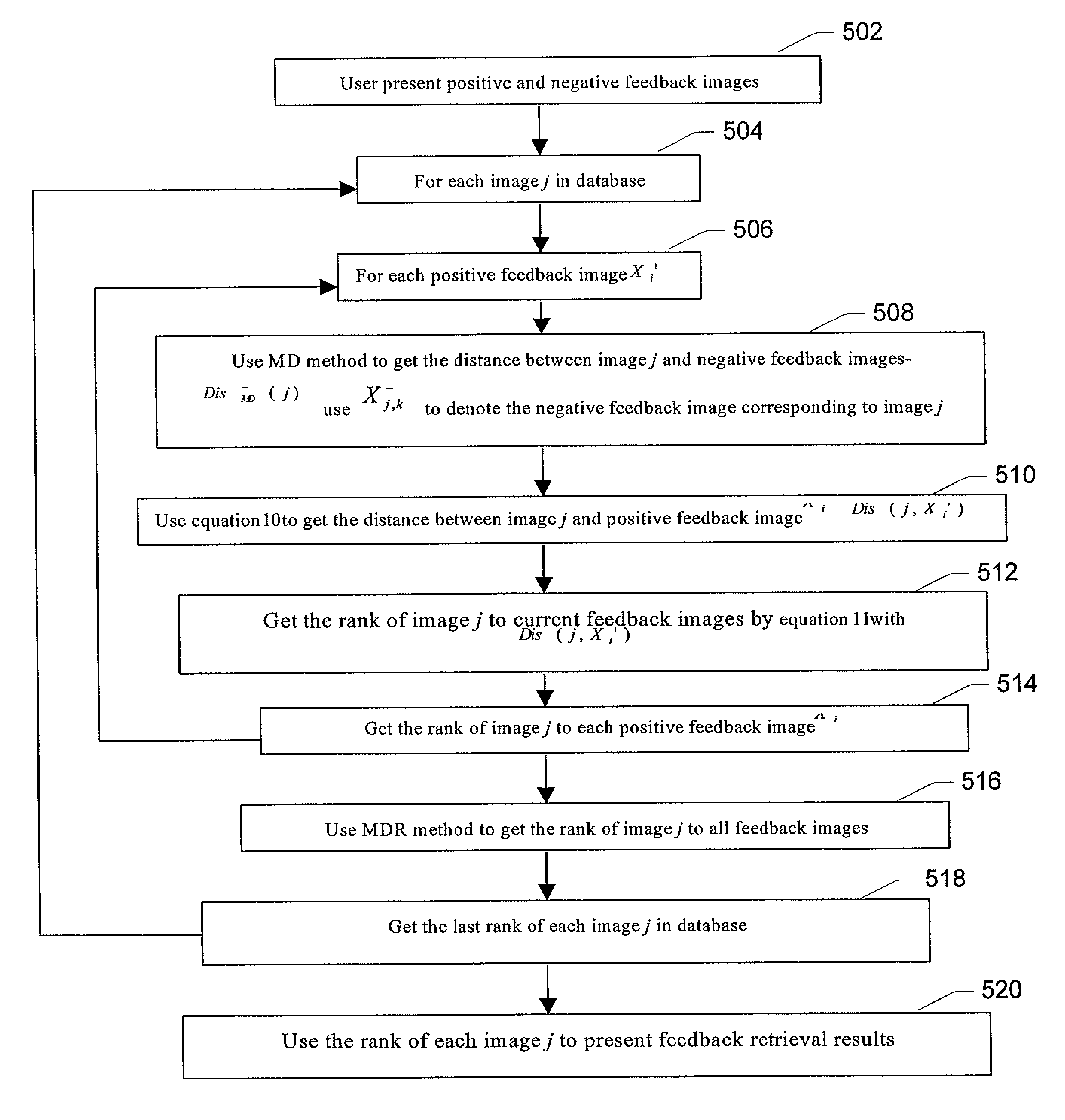
Relevance maximizing, iteration minimizing, relevance-feedback, content-based image retrieval (CBIR)
InactiveUS7546293B2Minimize the numberMaximizing resulting relevanceData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalNegative feedbackUsability
An implementation of a technology, described herein, for relevance-feedback, content-based image retrieval minimizes the number of iterations for user feedback regarding the semantic relevance of exemplary images while maximizing the resulting relevance of each iteration. One technique for accomplishing this is to use a Bayesian classifier to treat positive and negative feedback examples with different strategies. In addition, query refinement techniques are applied to pinpoint the users' intended queries with respect to their feedbacks. These techniques further enhance the accuracy and usability of relevance feedback. This abstract itself is not intended to limit the scope of this patent. The scope of the present invention is pointed out in the appending claims.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
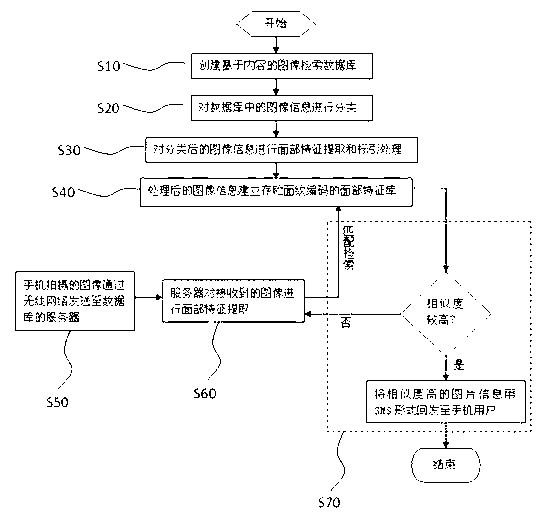
Face recognition method used for mobile terminal
InactiveCN103258190AImprove organizational structureImprove recognition rateCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging FeatureComputer terminal
The invention relates to a face recognition method used for a mobile terminal. First, a content-based image retrieval data bank is built first, then image information in the data bank is classified, facial feature extraction and indexing processing are carried on the classified image information, a facial feature library storing facial line codes is built for the processed image information, an image taken by a mobile phone user is sent to a server of the data bank through a wireless network, the server extracts the facial features of the received image, finally carries out matching retrieval in the feature library, and sends image information with high similarity back to the mobile phone user in the mode of the SMS to carry out identity verification. Due to the fact that the matching retrieval is carried out on the classified image features, the rate of recognition is promoted, and the matching speed is greatly promoted.
Owner:SUZHOU FUFENG TECH
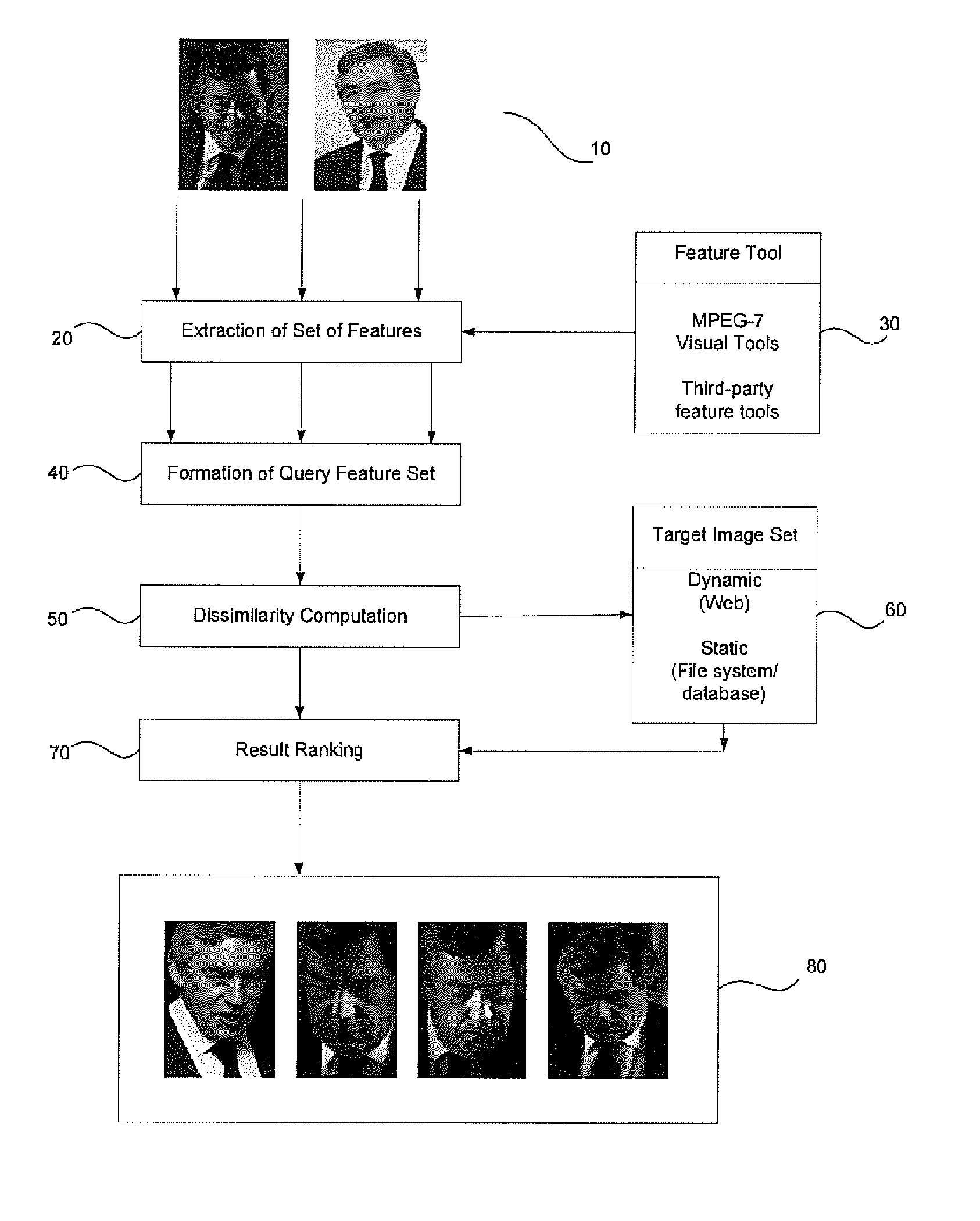
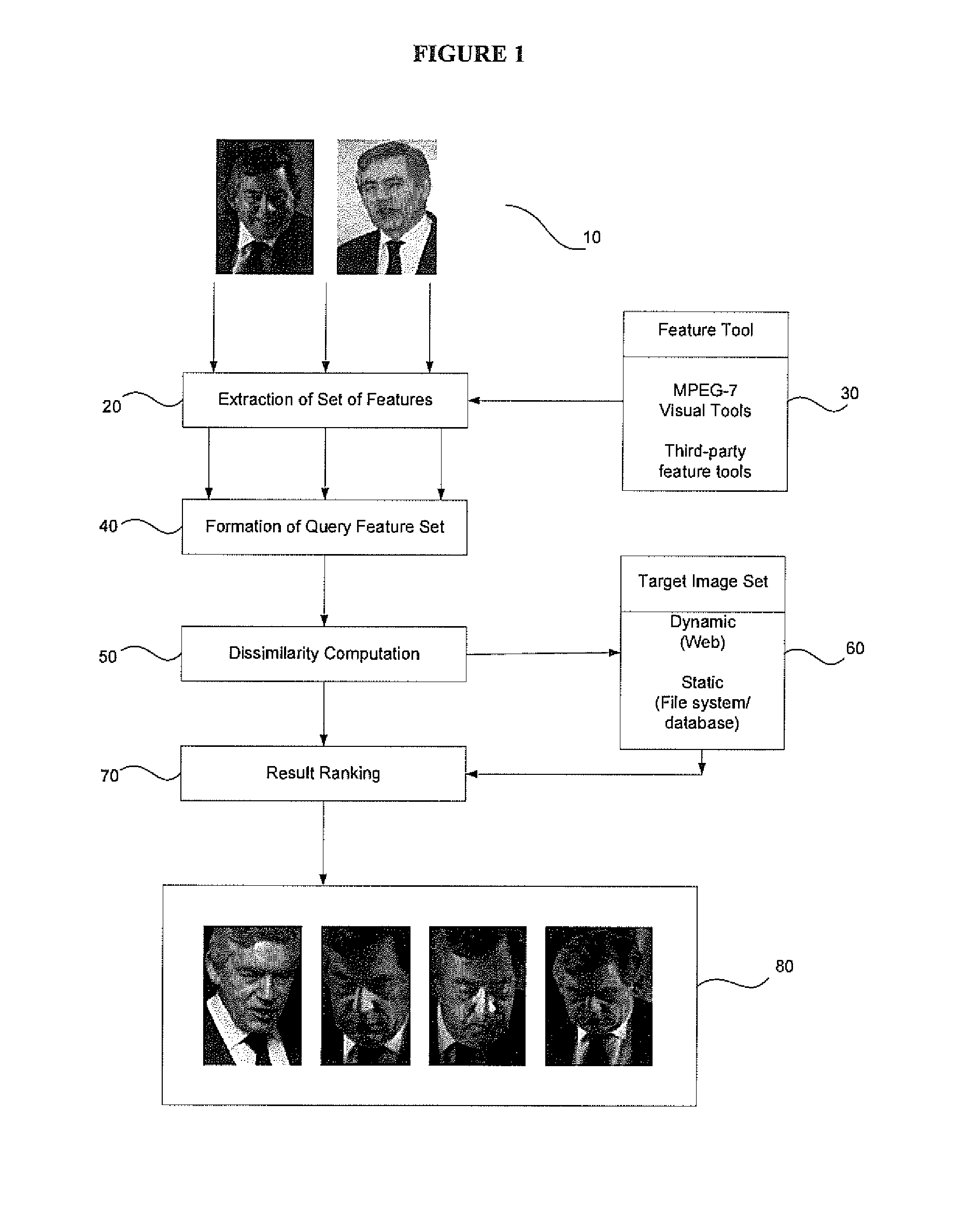
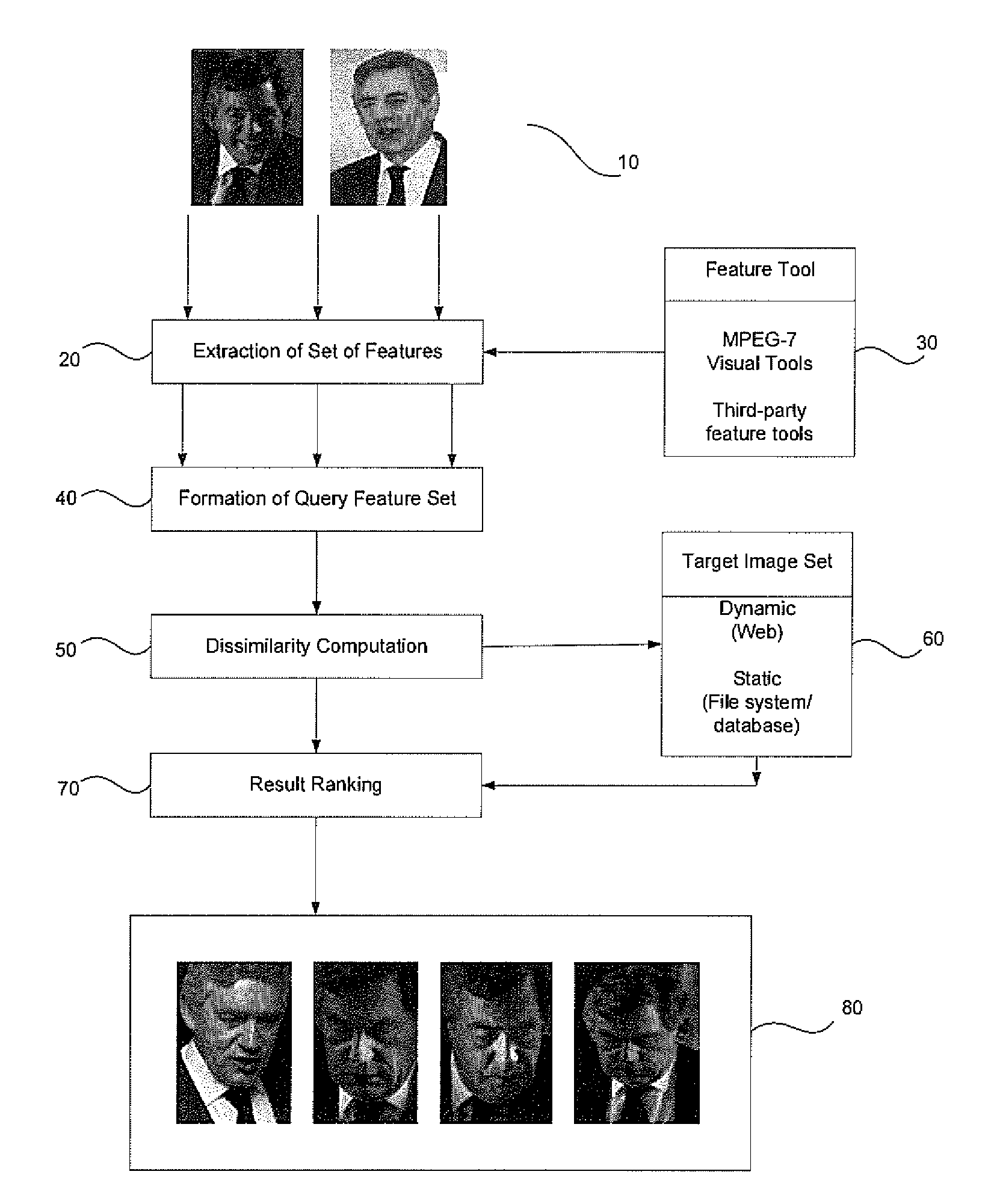
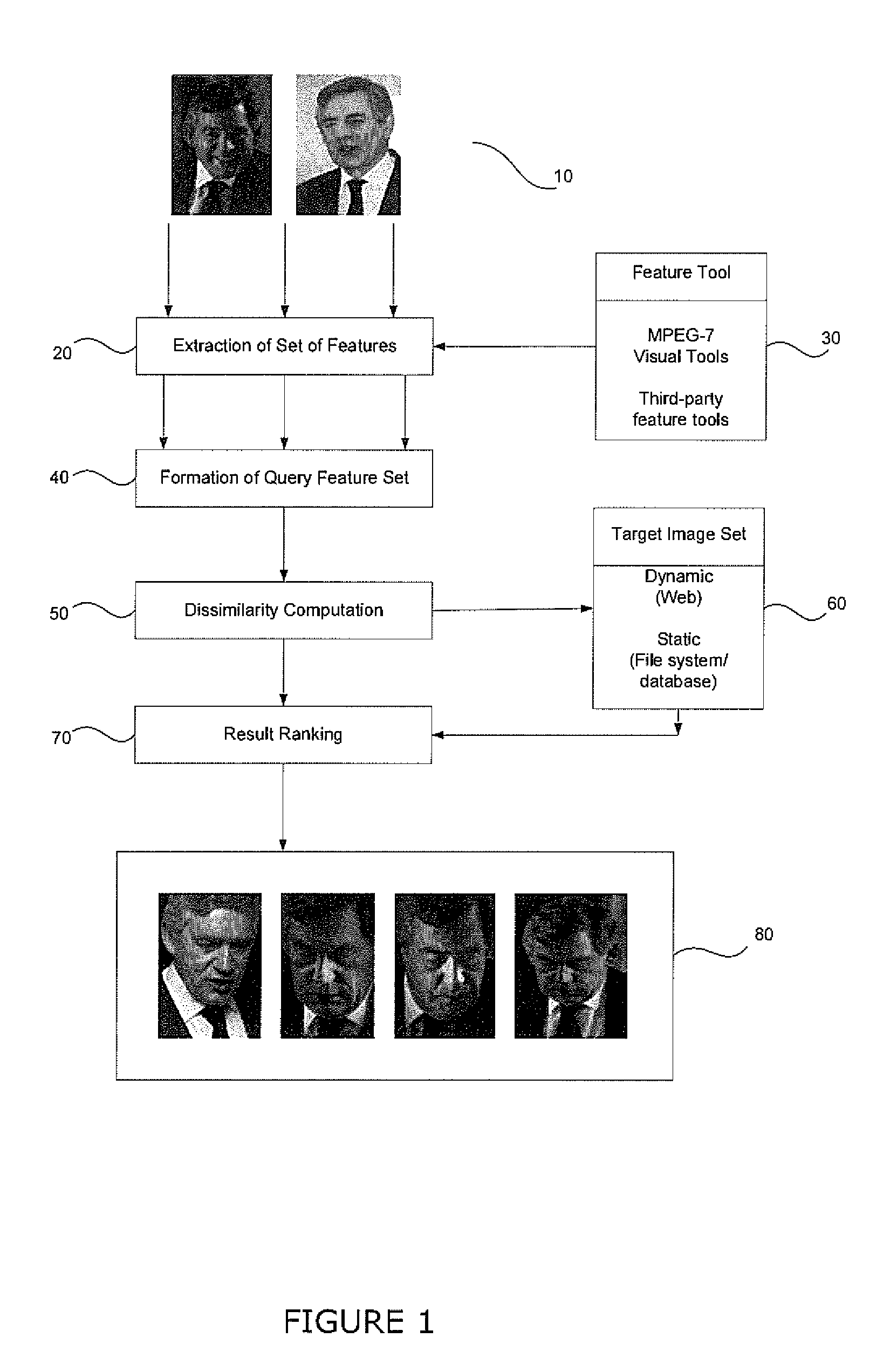
Content based image retrieval
InactiveCN101460947ADigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionContent base image retrieval
A content based image retrieval system that extracts images from a database of images by constructing a query set of features and displaying images that have a minimum dissimilarity metric from images in the database. The dissimilarity metric is a weighted summation of distances between features in the query set and features of the images in the database. The method is useful for image searching such as web-based image retrieval and facial recognition.
Owner:UNIV OF WOLLONGONG
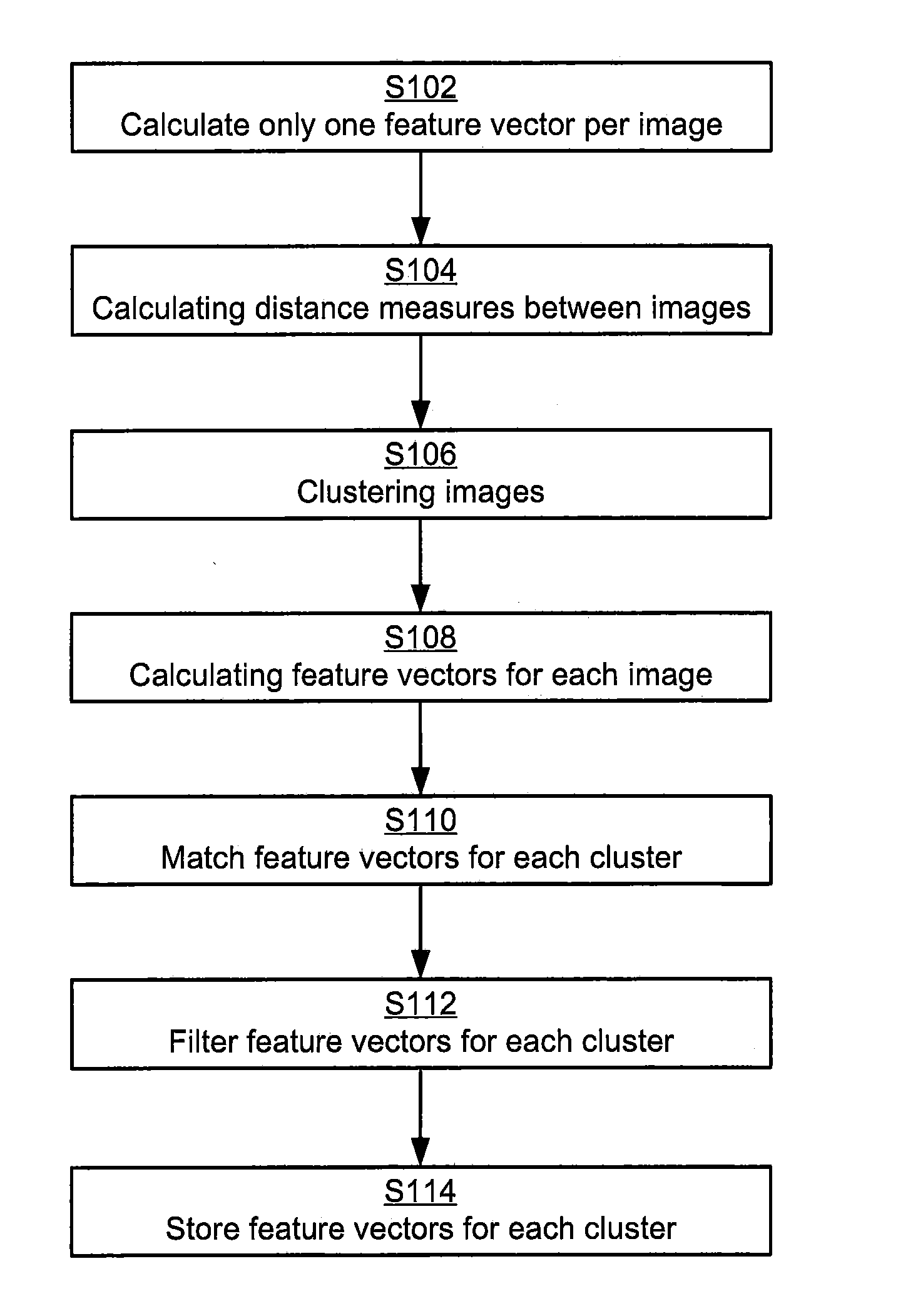
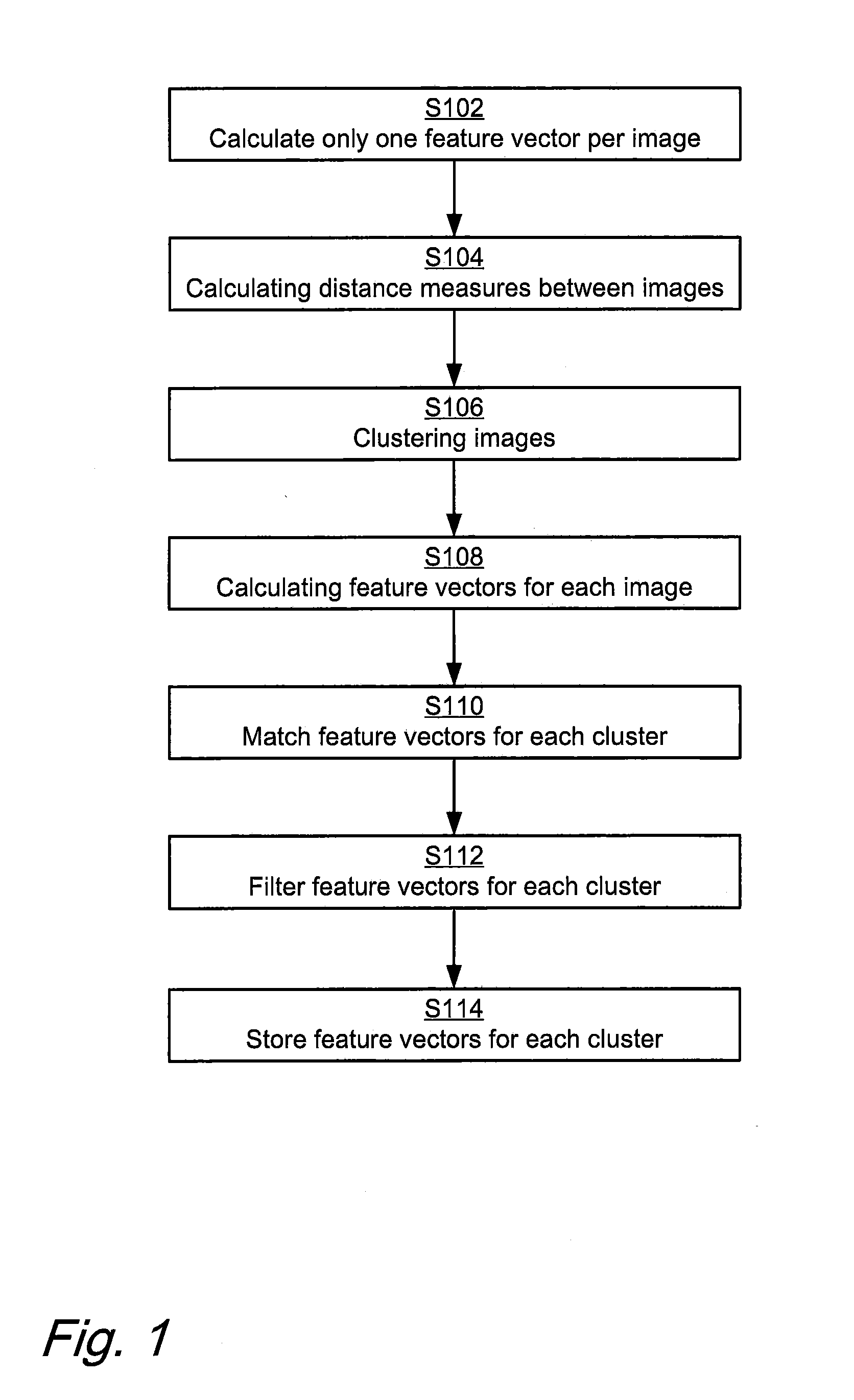
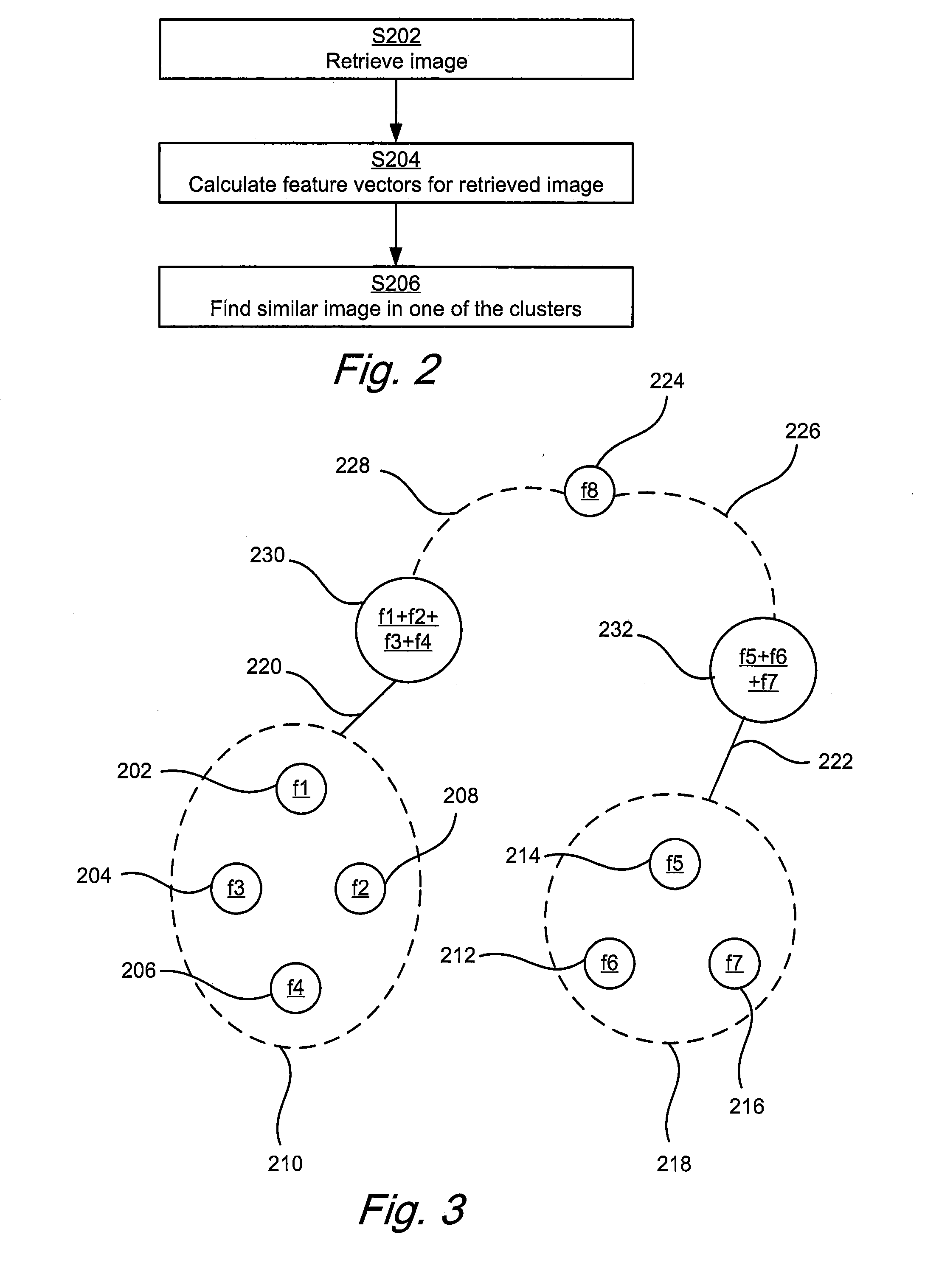
Efficient local feature descriptor filtering
ActiveUS20160232428A1Fast and also accurateQuick and computational efficientCharacter and pattern recognitionStill image data indexingFeature vectorLocal feature descriptor
The present disclosure generally relates to methods and computer program products for searching for a similar image among a plurality of stored images, and in particular to a method and computer program product used in a content based image retrieval system where roughly similar images are clustered and feature vectors for the clustered images are filtered based on a matching frequency for the feature vectors among the images in the cluster.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com