Method of down-chain power control in packet switching cellular system
A downlink and power control technology, applied in the field of downlink power control, can solve problems such as strong cooperative channel interference, unreliable uplink connection, inability to comply with transmission delay or other quality objectives, and achieve high data rate, prevention of uncertainty, and risk reduction effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] Figures 1, 2, 3a, 3b and 4 have been discussed above as appropriate.
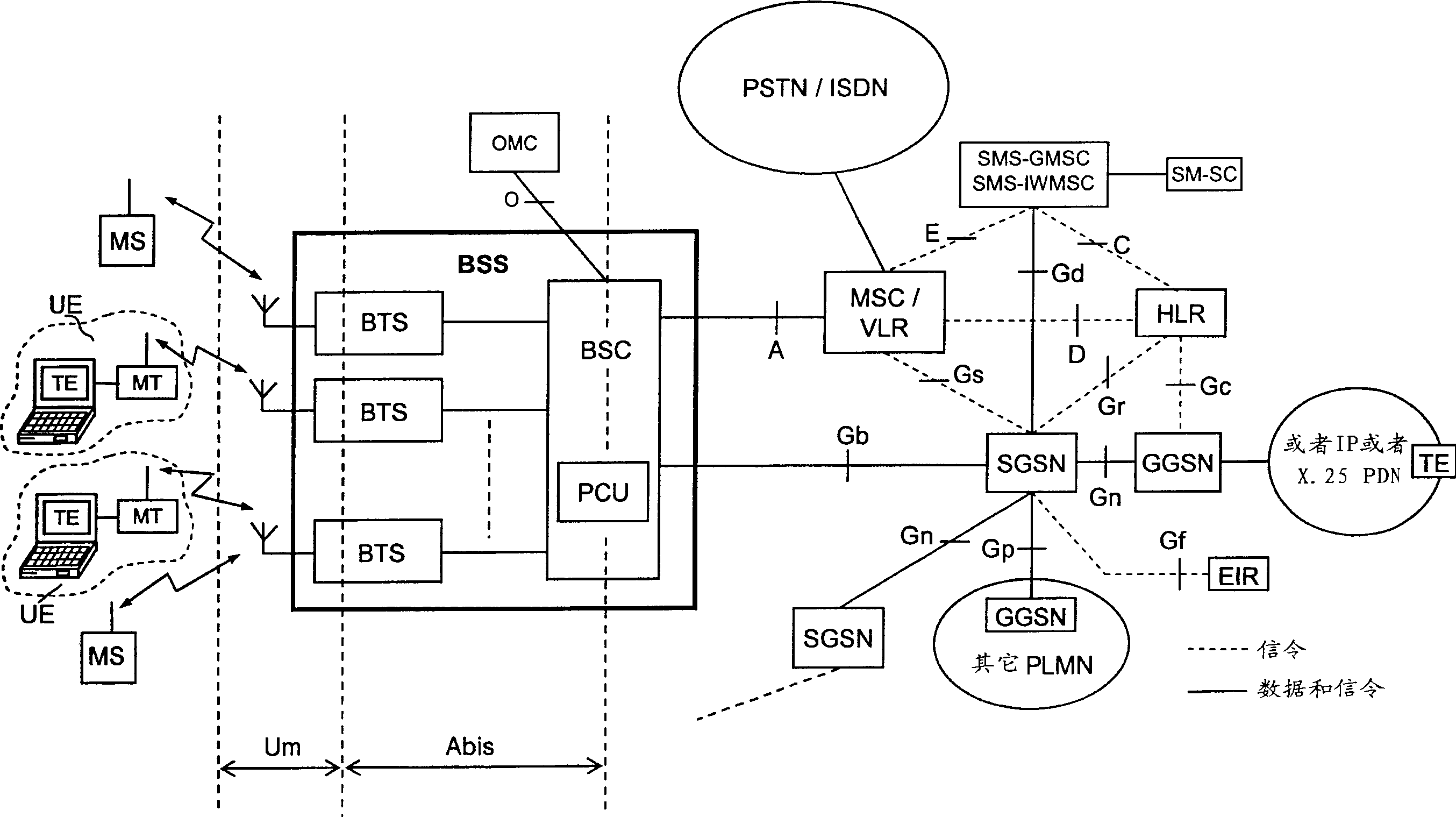
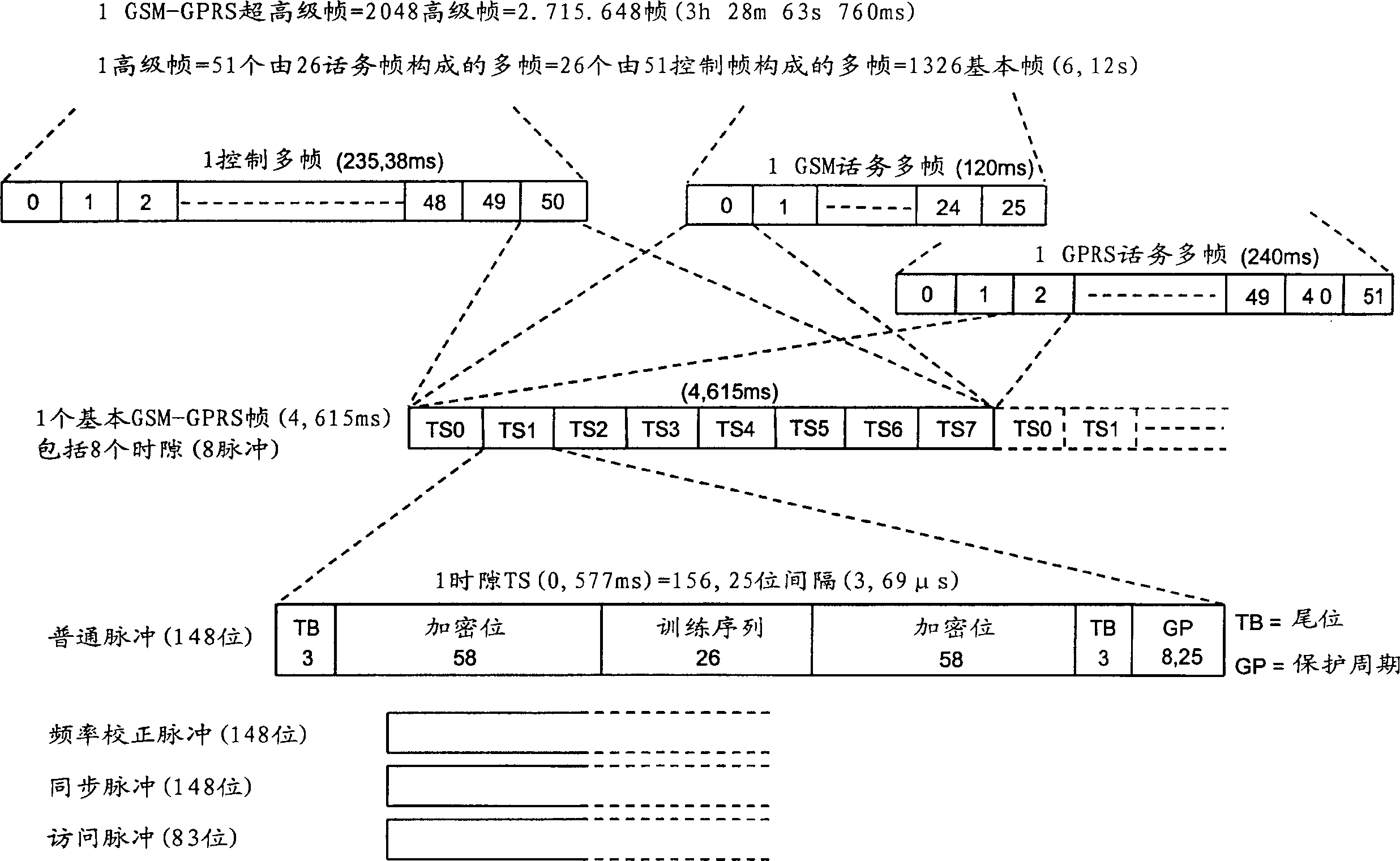
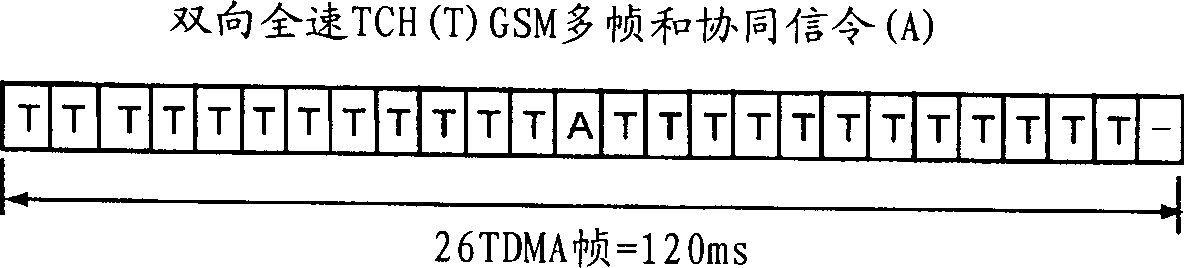
[0029]Figure 5 is a block diagram illustrating a base transceiver station (BTS) incorporated into the present invention by implementing more reliable transmission of USF flags. The BTS station of Fig. 5 comprises both through BTS control processor and RAM (BTS CONTROL PROCESSOR & RAM) block control transmitting section (TRANSMITTING SECTION) and receiving section (RECEIVING SECTION), and this BTS control processor and RAM block also control the two Part of the shared frequency synthesizer and forwarding (FrequencySynthesizer&Hopping) unit. These two parts and the BTS control processor and RAM block are connected to the A-Bis interface functional block for receiving / outputting one or more 2Mb carrying PCU frames from or to the BSC block (Fig. 1) / s PCM stream (link). The branching unit (BRANCHING UNIT) between the antenna and the two BTS parts includes a duplex filter that transmits the global RF ou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com