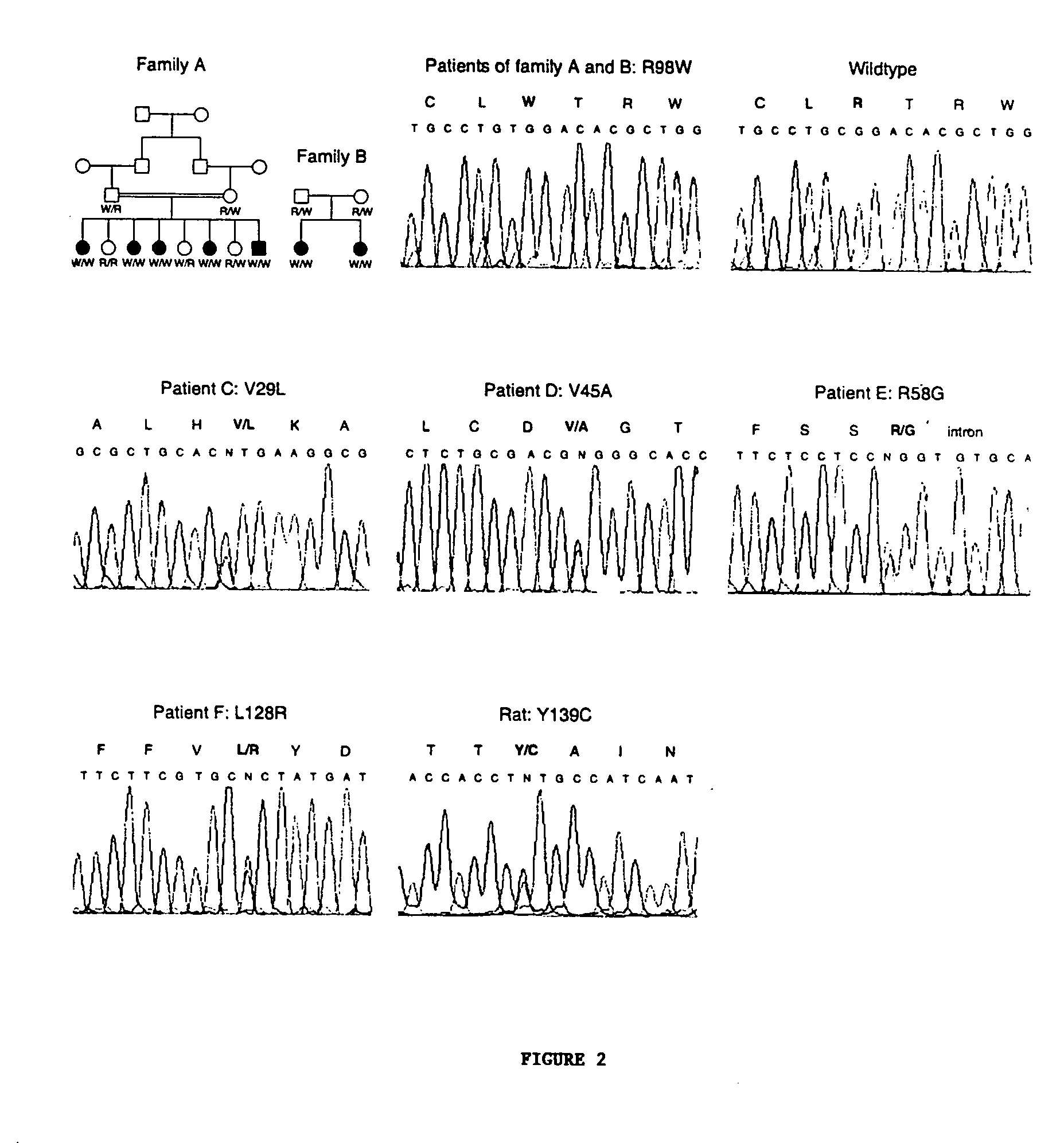
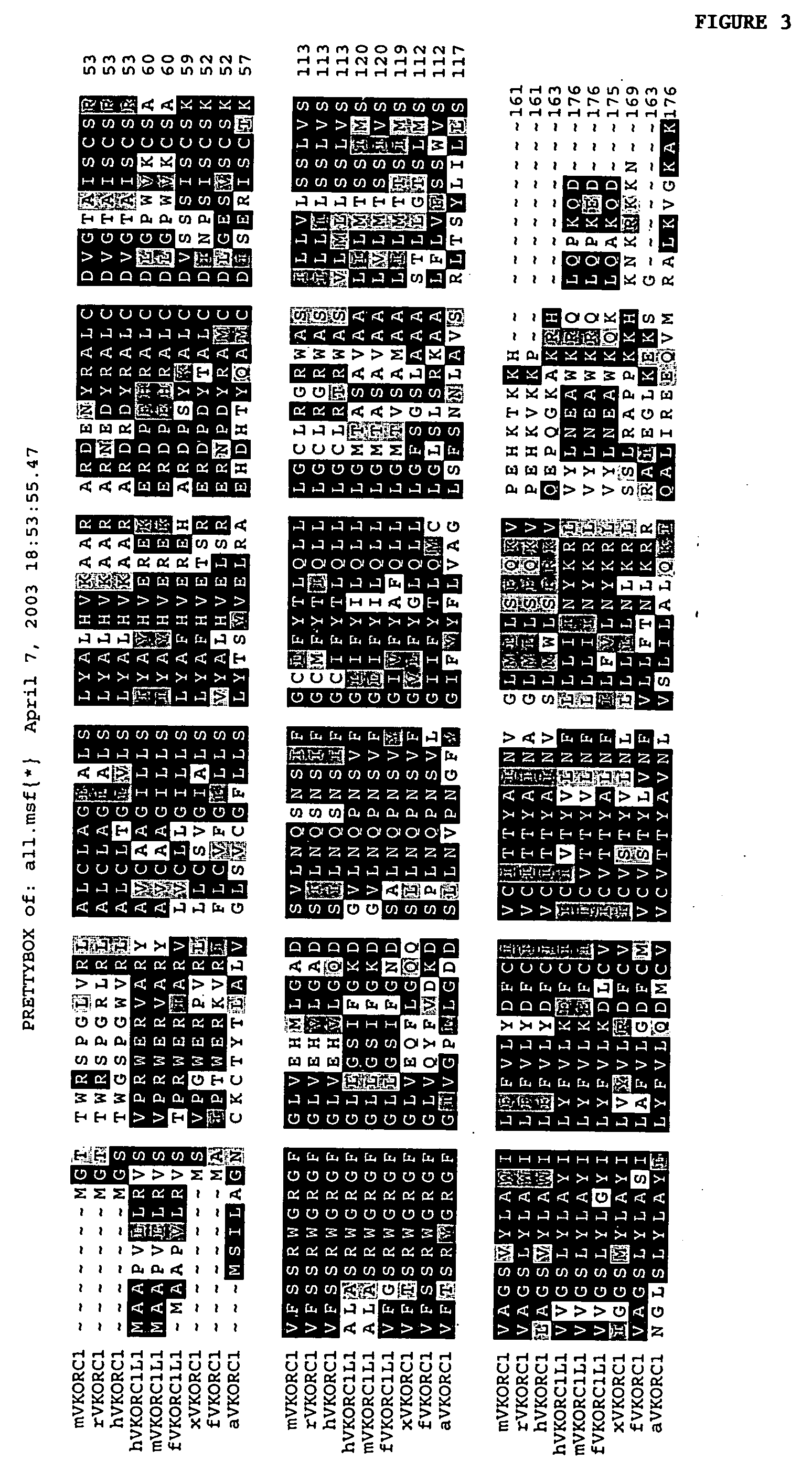
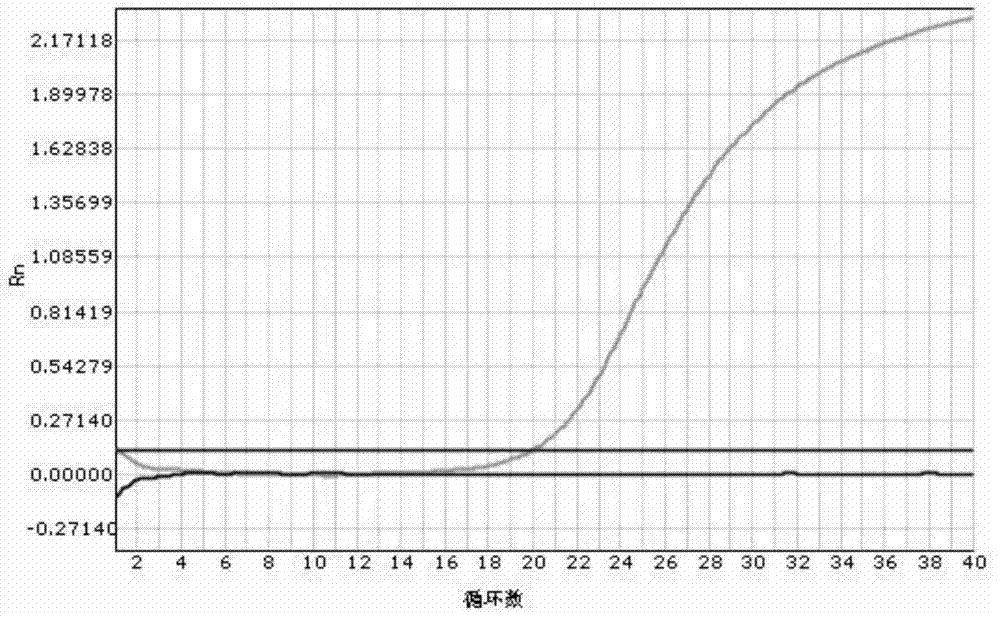
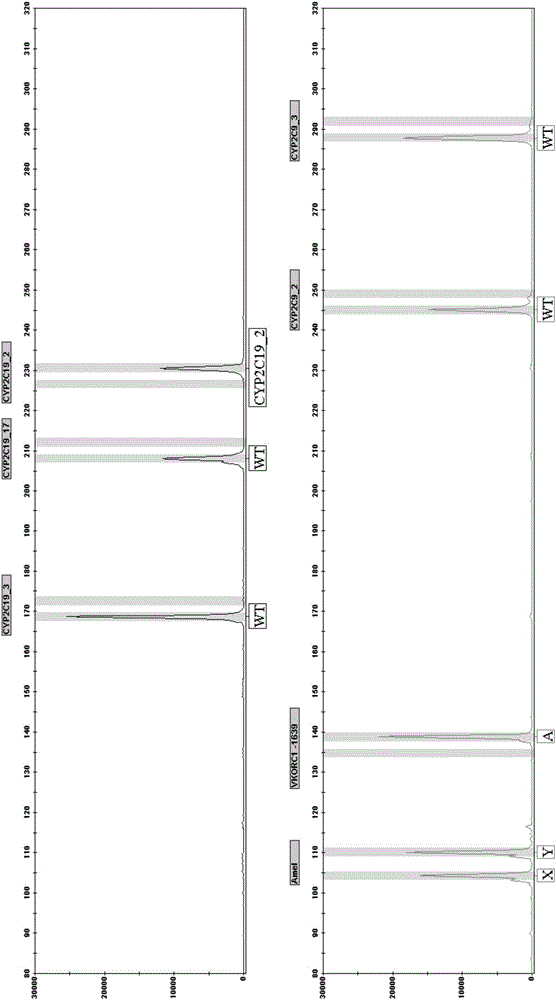
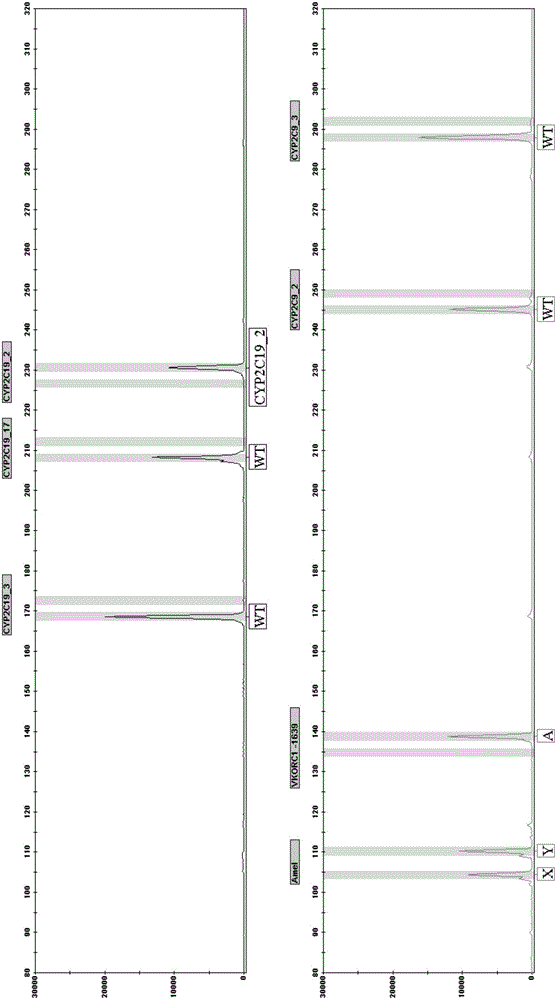
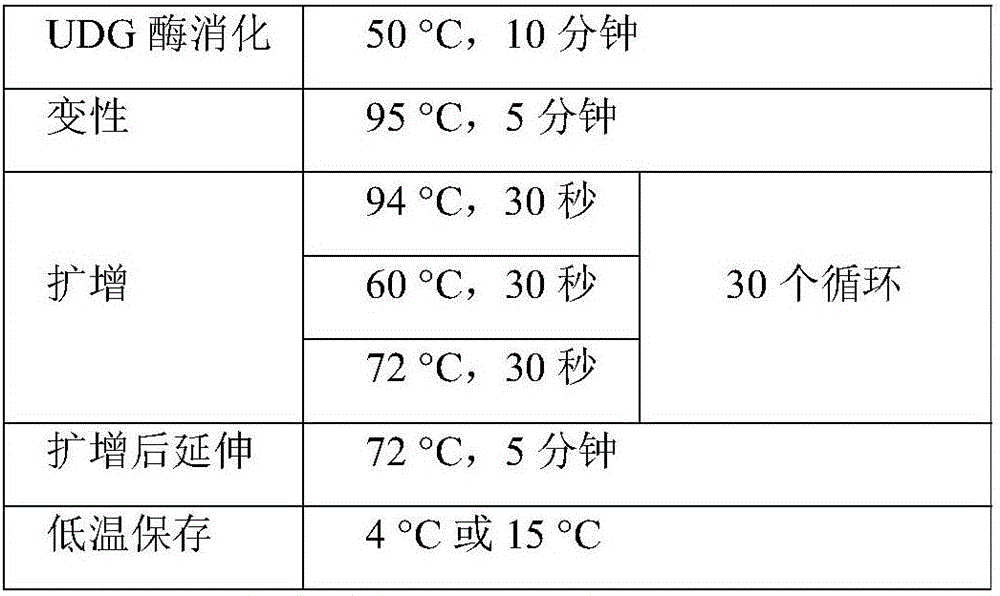
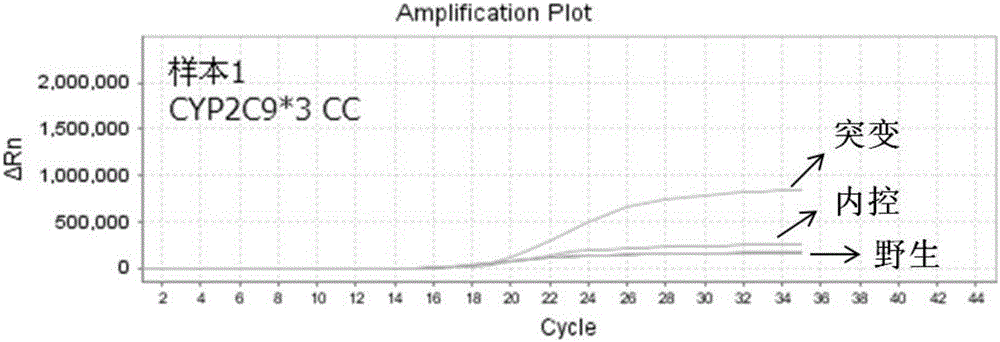
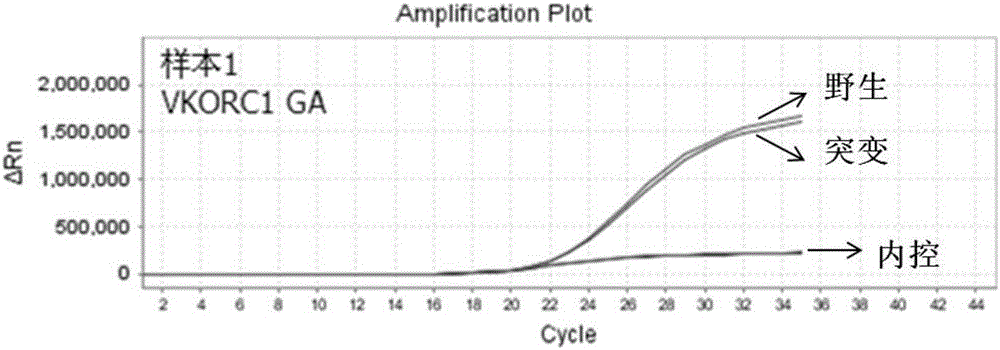
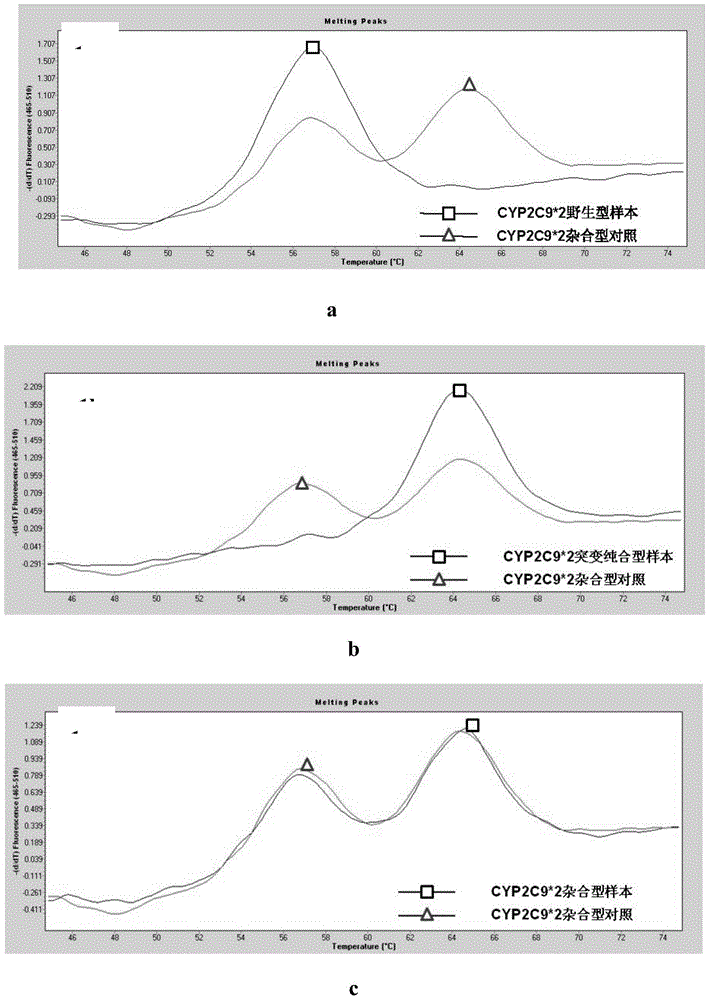
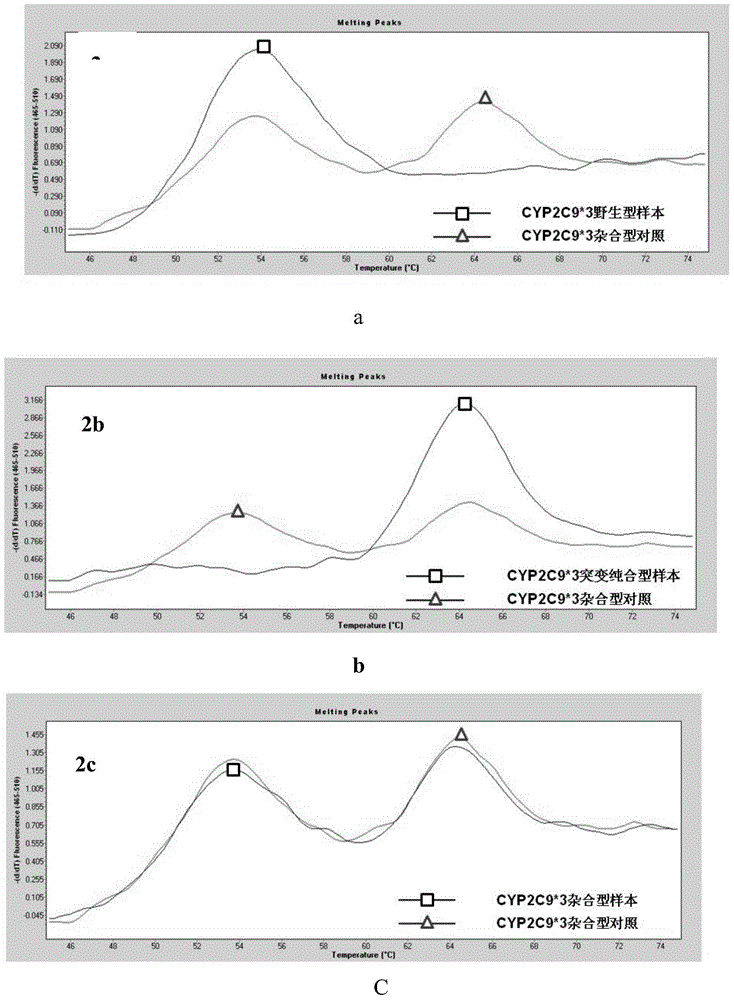
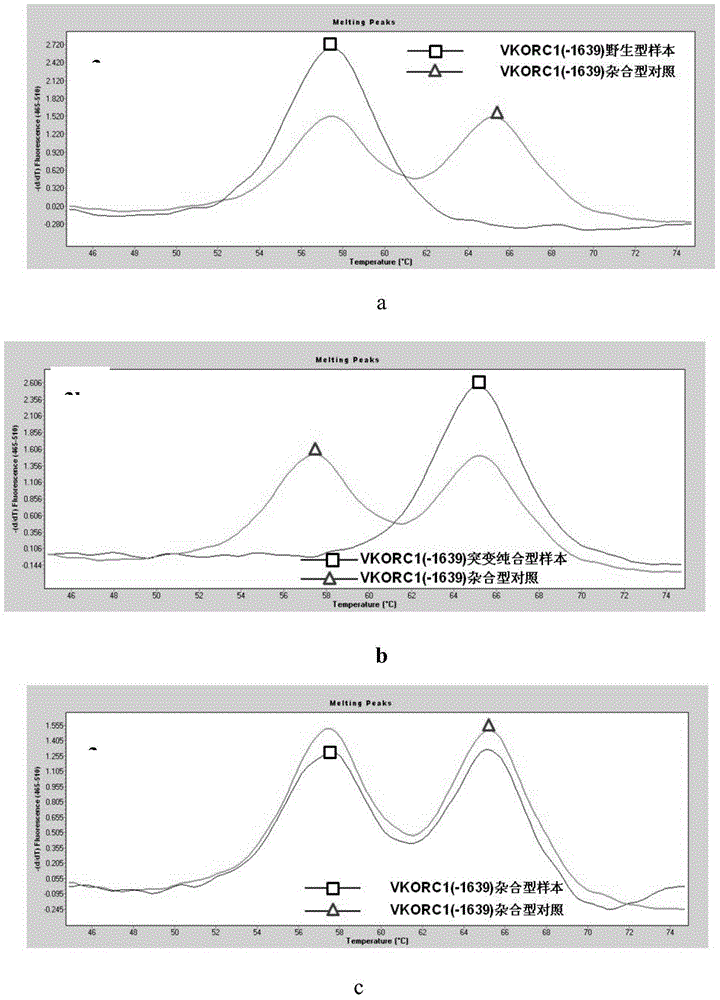
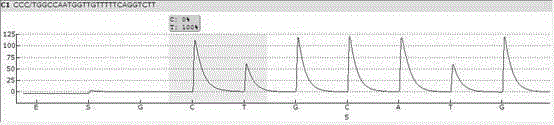
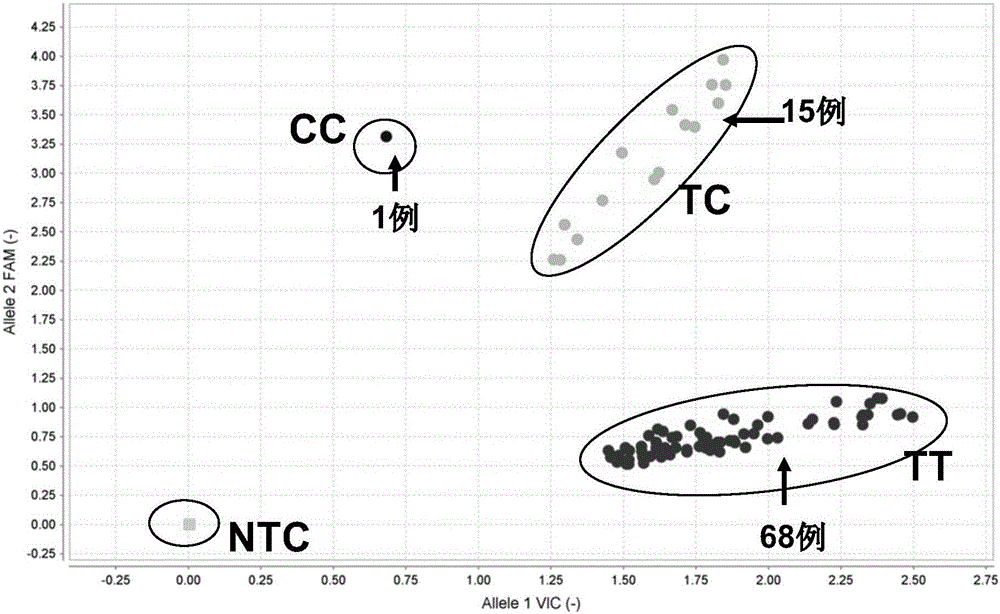
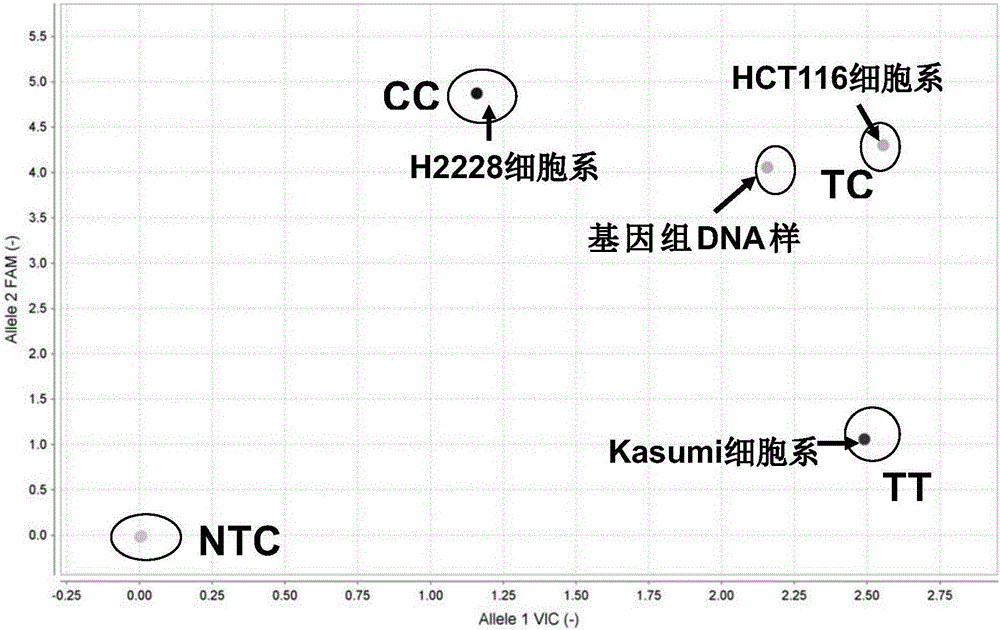
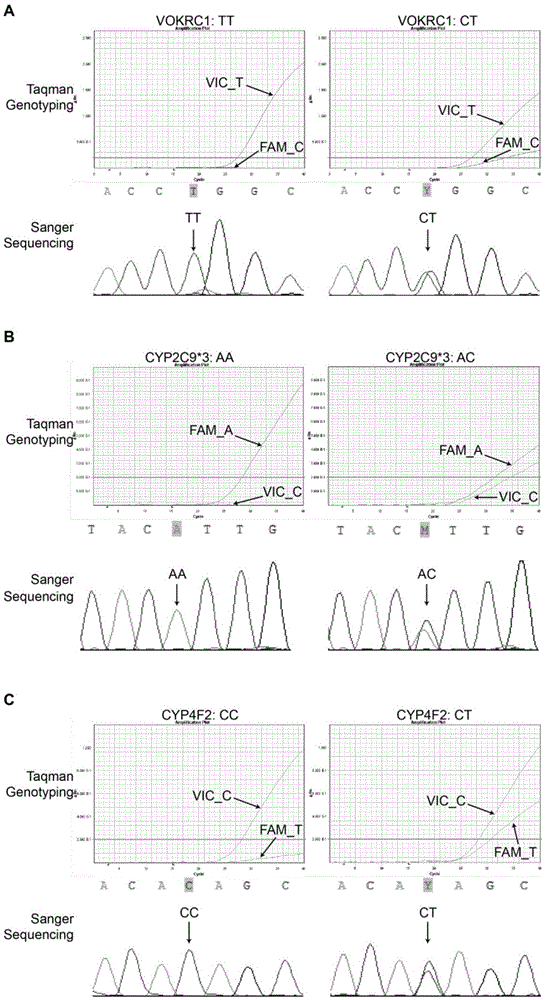
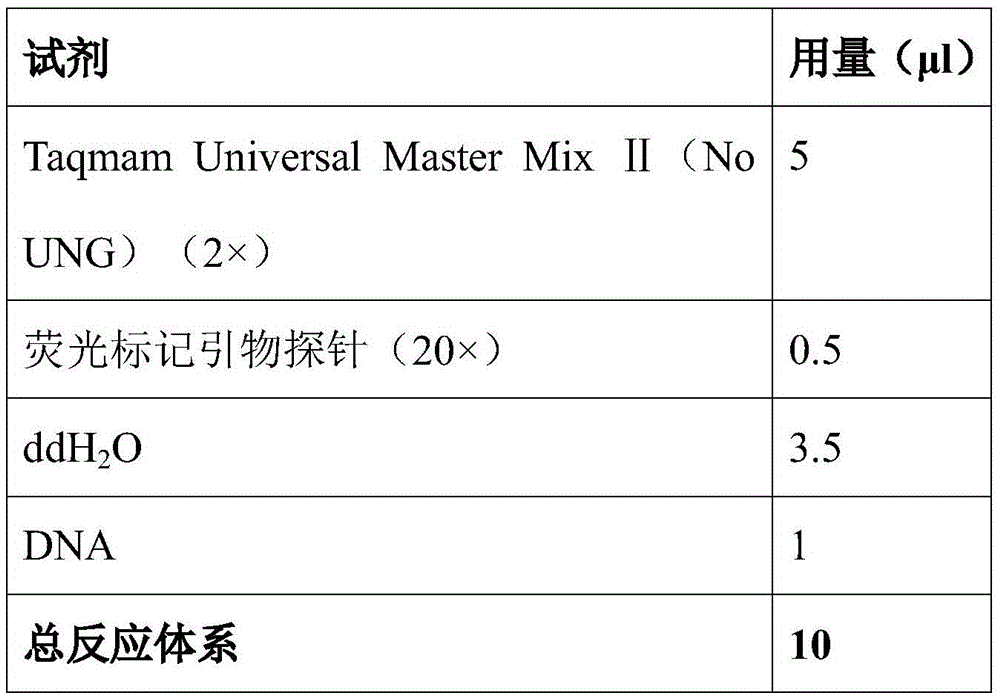
Patents
Literature
56 results about "VKORC1" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
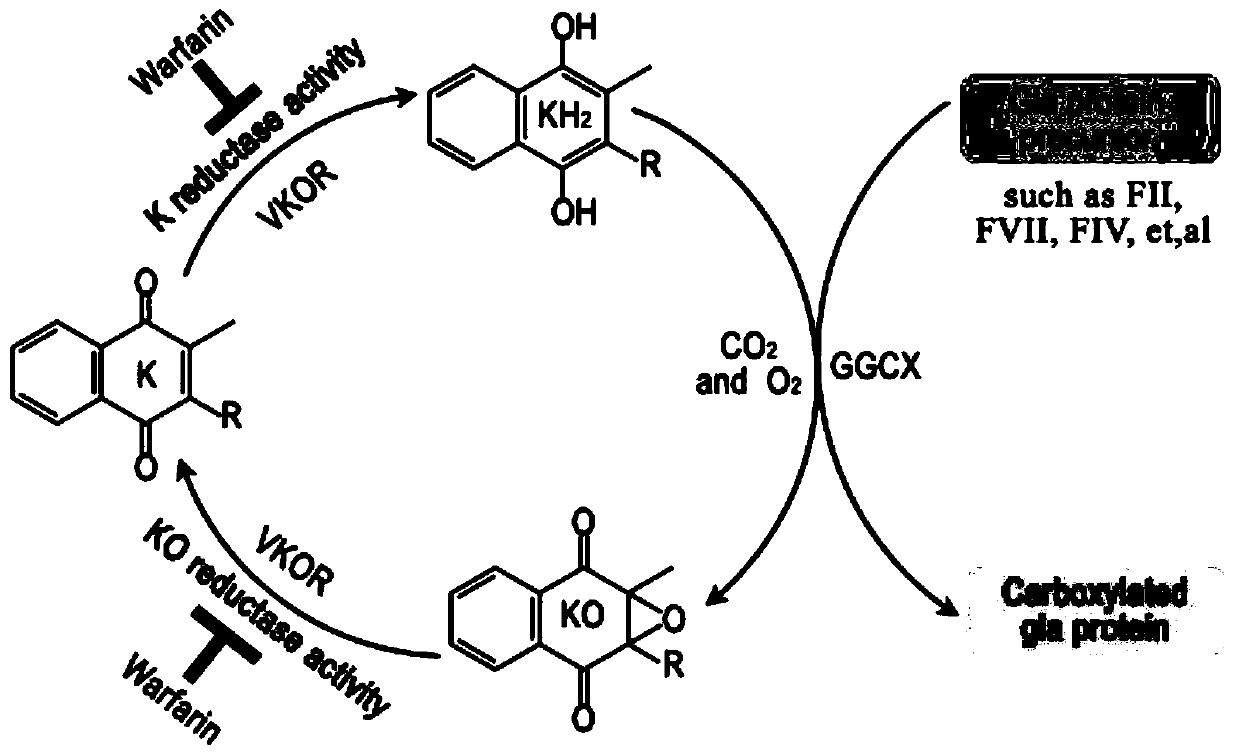
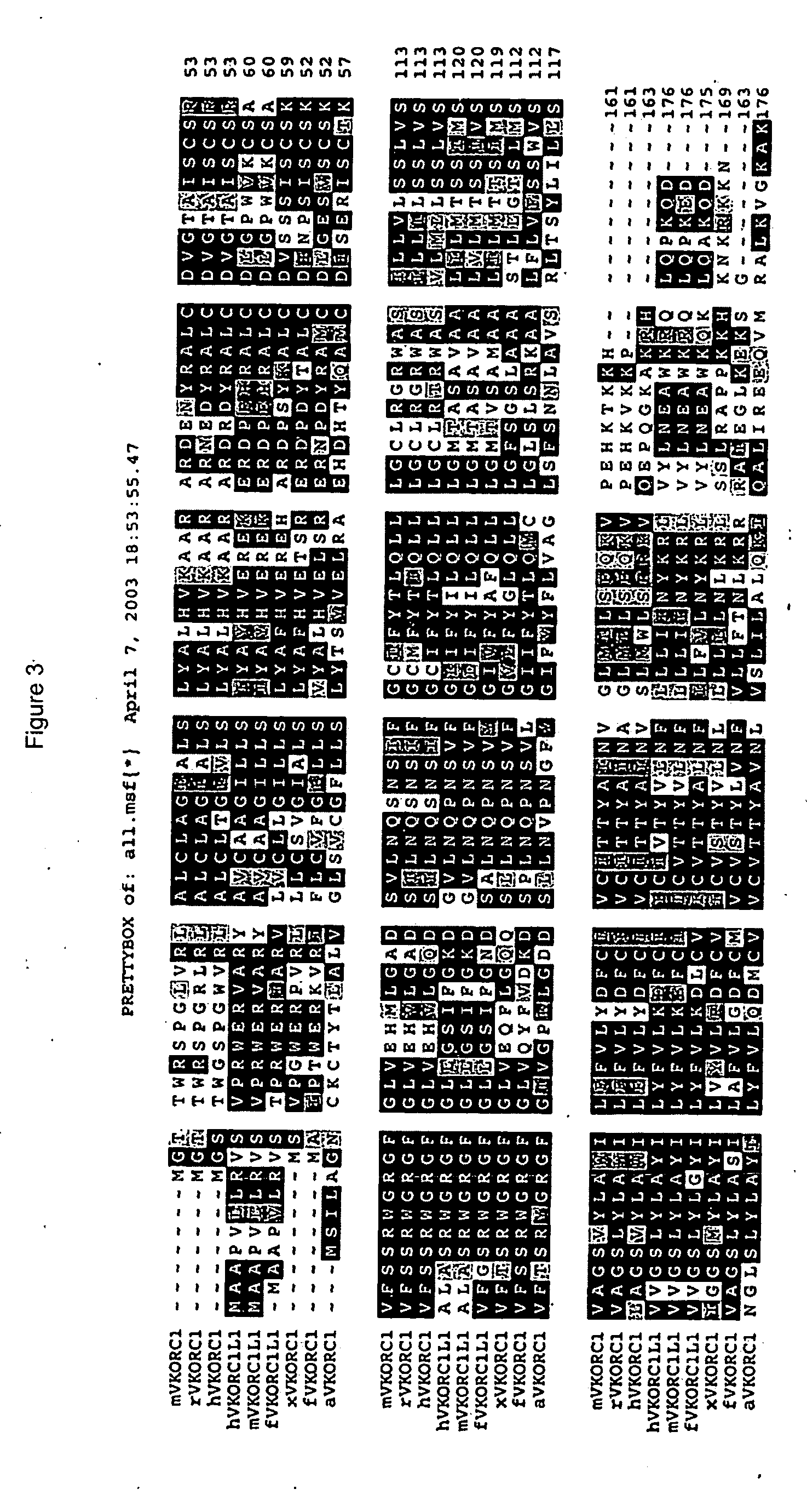
The human gene VKORC1 encodes for the enzyme, Vitamin K epOxide Reductase Complex (VKORC) subunit 1. This enzymatic protein complex is responsible for reducing vitamin K 2,3-epoxide to its active form, which is important for effective clotting. In humans, mutations in this gene can be associated with deficiencies in vitamin-K-dependent clotting factors.
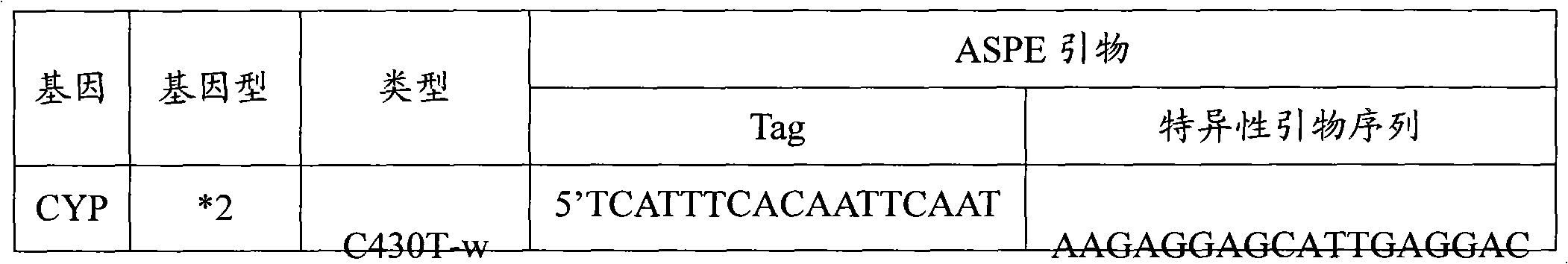
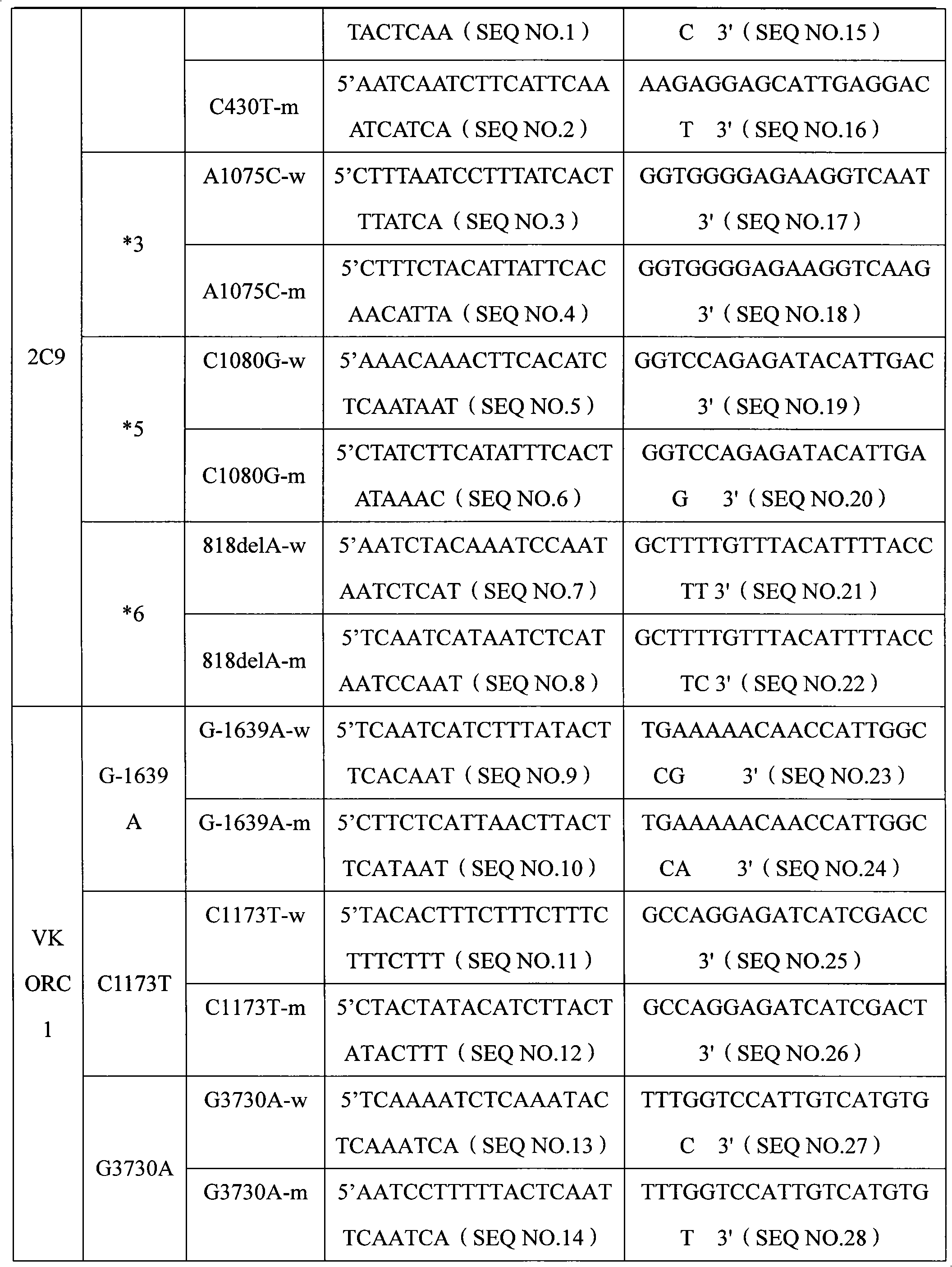
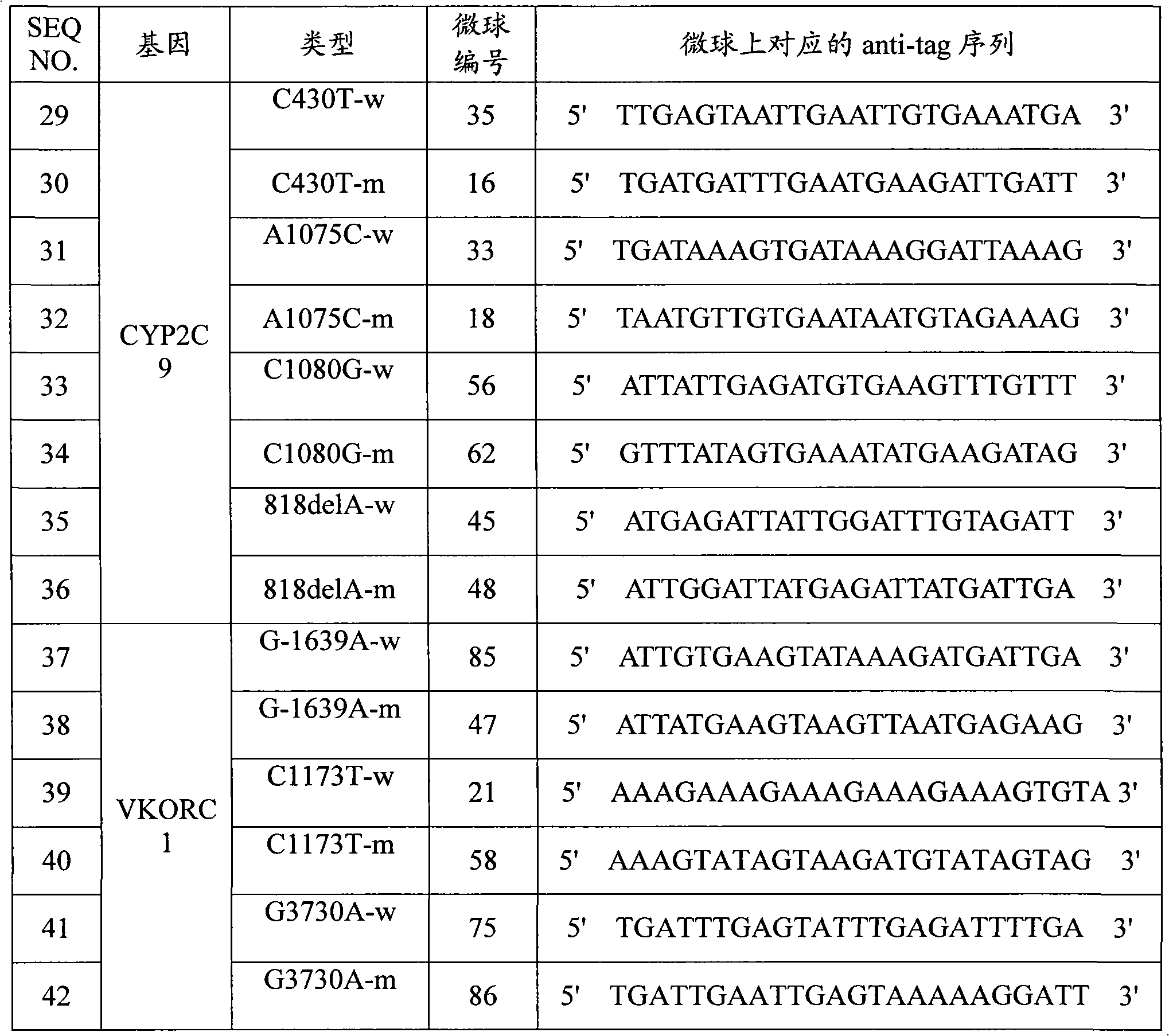
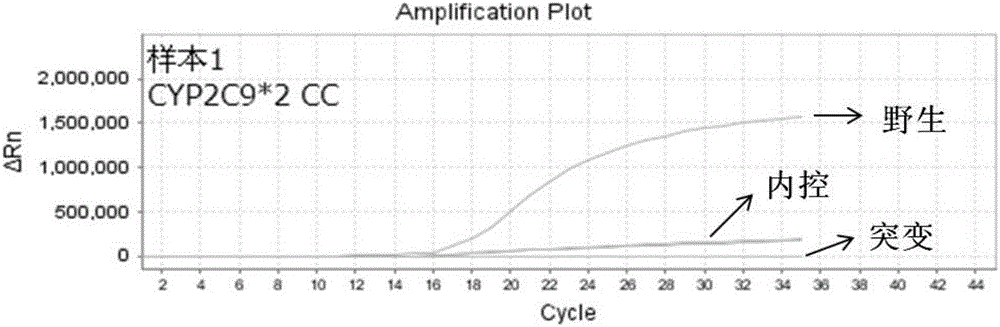
Specific primer, liquid-phase chip and method for SNP detection of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genes
ActiveCN101824466AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImplement parallel detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVKORC1Microsphere
The invention discloses a specific primer, a liquid-phase chip and a method for SNP detection of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genes. The liquid-phase chip comprises wild-type and mutable-type ASPE primer pairs and microspheres coated by a specific anti-tag sequence respectively, which are designed respectively aiming at each type of mutable loci, primers used for amplifying a CYP2C9 gene target sequence having CYP2C9*2, CYP2C9*3, CYP2C9*5 and CYP2C9*6SNP loci, and / or primers used for amplifying a VKORC1 gene target sequence having G1639A, G1173T and G3730A SNP loci. The liquid phase chip of the invention has a quite good signal-noise ratio, and the cross reaction does not happen between a designed probe and the anti-tag sequence basically; the ASPE primer designed by the invention has quite good specificity, and can accurately differentiate various types of mutable loci; and the detection method has the advantages that: a few steps are adopted, 7 types of SNP loci can be detected in one step, the operation is convenient, a lot of uncertain factors existing in a process of repeated operations can be avoided, and the detection accuracy is greatly improved.
Owner:SUREXAM BIO TECH
Vitamin K epoxide recycling polypeptide VKORC1, a therapeutic target of coumarin and their derivatives
The invention relates to a novel polypeptide vitamin K epoxide recycling polypeptide (VKORC1) as a target for coumarin and its derivatives. The invention further provides methods for identifying coumarin derivatives, and also claims VKORC1 polypeptides and VKORC1 nucleic acids containing a sequence abnormality associated with a VKORC1 associated deficiency such as warfarin resistance, wherein the VKORC1 polypeptides and VKORC1 nucleic acids can be used for diagnosing these deficiencies. Moreover, the invention relates to methods for identifying coumarin derivatives usable in pest control of rodents.
Owner:BAXALTA GMBH
Recombinant co-expression of vitamin K epoxide reductase subunit 1 to improve vitamin K dependent protein expression
InactiveUS20060194284A1Improve productivityFibrinogenMammal material medical ingredientsVKORC1Host organism
The present invention relates to a host organism containing recombinant nucleic acids coding for the vitamin K reductase complex subunit 1 (VKORC1) and recombinant nucleic acids coding for a vitamin K dependent (VKD) protein, wherein both the recombinant VKORC1 and the recombinant VKD protein are expressed in said host organism. Further, the present invention relates to a cell culture system comprising cells which contain said recombinant nucleic acids and to methods for improving the productivity of recombinant VKD protein expression in a host organism being cultured in suitable systems.
Owner:BAXALTA GMBH
Primer and probe composition for detecting polymorphism of human CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genes, kit and application
ActiveCN108570498AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceMicrobiology
The invention discloses a primer and probe composition for detecting polymorphism of human CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genes, a kit and application. The primer and probe composition comprises three pairs of specific primers for amplifying CYP2C9*2, CYP2C9*3 and VKORC1 sites, and three specific fluorescent probes. The primers and the probes, disclosed by the invention, have high sensitivity, strong specificity and strong anti-interference capability; a manner combining an asymmetric PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification and fluorescent probe melting curve analysis technologies is used for detecting the gene polymorphism; different gene types can be effectively distinguished according to the quantity and Tm value of a melting peak; a result is convenient, clear and objective to judge and read.Single-tube sampling can be used for simultaneously detecting 6 mutation types of 3 gene sites; the primer and probe composition is simple and convenient to operate and the detection efficiency is improved; a large batch of samples can be detected and clinical operation is facilitated.
Owner:SHANDONG VIGENE BIOSCI
Warfarin individual anticoagulant pharmacogenomics detection kit suitable for Chinese population
The invention provides a warfarin individual anticoagulant pharmacogenomics detection kit suitable for Chinese population, which mainly comprises CYP2C9, VKORC1 and CYP4F2 related gene-type amplification primers, CYP2C9, VKORC1 and CYP4F2 related gene-type sequencing primers, a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) reagent and a sequencing reagent. The warfarin individual anticoagulant pharmacogenomicsdetection kit suitable for the Chinese population also can comprise a specification used for explaining a warfarin pharmacogenomics dose prediction model suitable for the Chinese population or / and a computer readable storage medium recording the warfarin pharmacogenomics dose prediction model suitable for the Chinese population. The warfarin pharmacogenomics detection kit provided by the invention is simple in preparation and is convenient in use. By adopting the kit, the warfarin anticoagulant therapy dose of Chinese patient population can be accurately estimated through detecting warfarin pharmacogenomics indexes, integrating clinical environmental factors and utilizing warfarin pharmacogenomics dose prediction model software suitable for the Chinese population, which is established by the invention.
Owner:尹彤
Kit for detecting SNP locus of gene associated with individualized medication of warfarin and PCR amplification method thereof
ActiveCN101899519AStrong specificityReduce the binding forceMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerDisease
The invention provides a kit for detecting SNP locus of a gene associated with individualized medication of warfarin and a PCR amplification method thereof. The kit comprises two forward primers and a reverse primer used for detecting SNP locus of a gene VKORC1(-1639G / A) and / or two forward primers and a reverse primer used for detecting SNP locus of a gene CYP2C9(1075A / C). The kit of the invention can realize the high-efficiency and high-pass detection of the SNP loci of VKORC1(-1639G / A) and CYP2C9(1075A / C), so that the quantized control on the amount of warfarin is achieved; furthermore, the method plays a certain role in prevention of thrombotic diseases, choice of anticoagulants, research and development of new anticoagulants and prognosis of thrombotic diseases.
Owner:SUZHOU KUANGYUAN MOLECULAR BIOTECH
Kit for quickly detecting polymorphism of human VKORC1 and CYP2CP genes and using method of kit
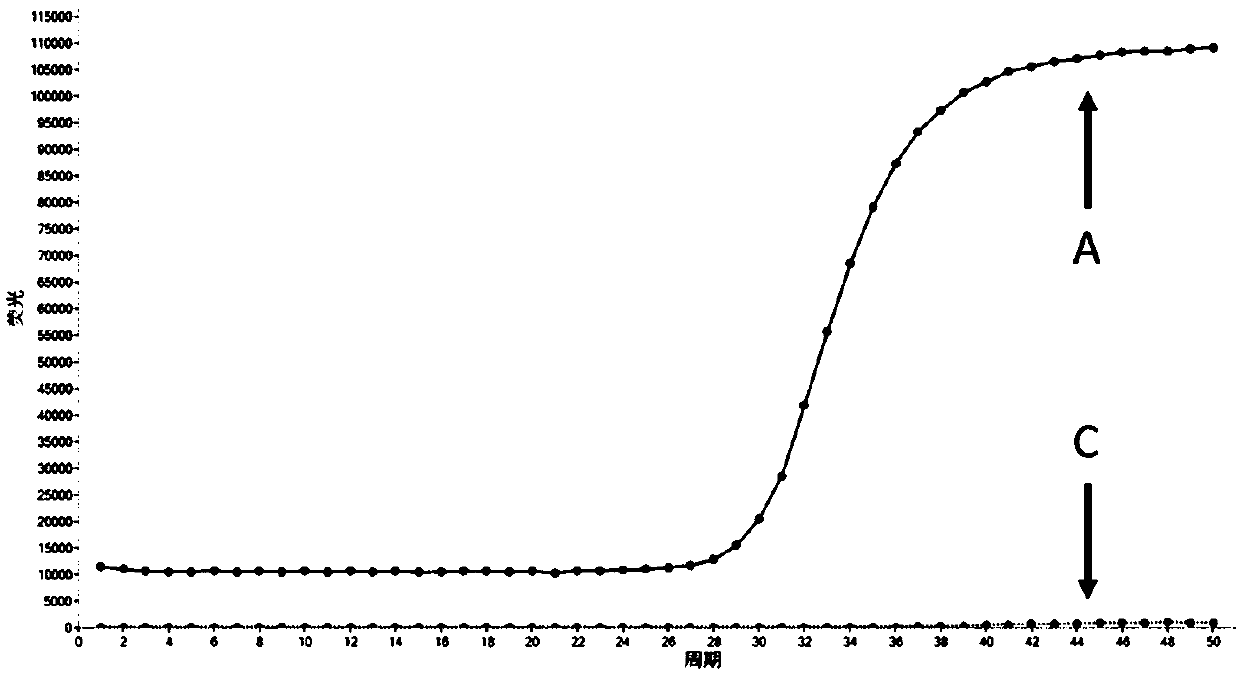
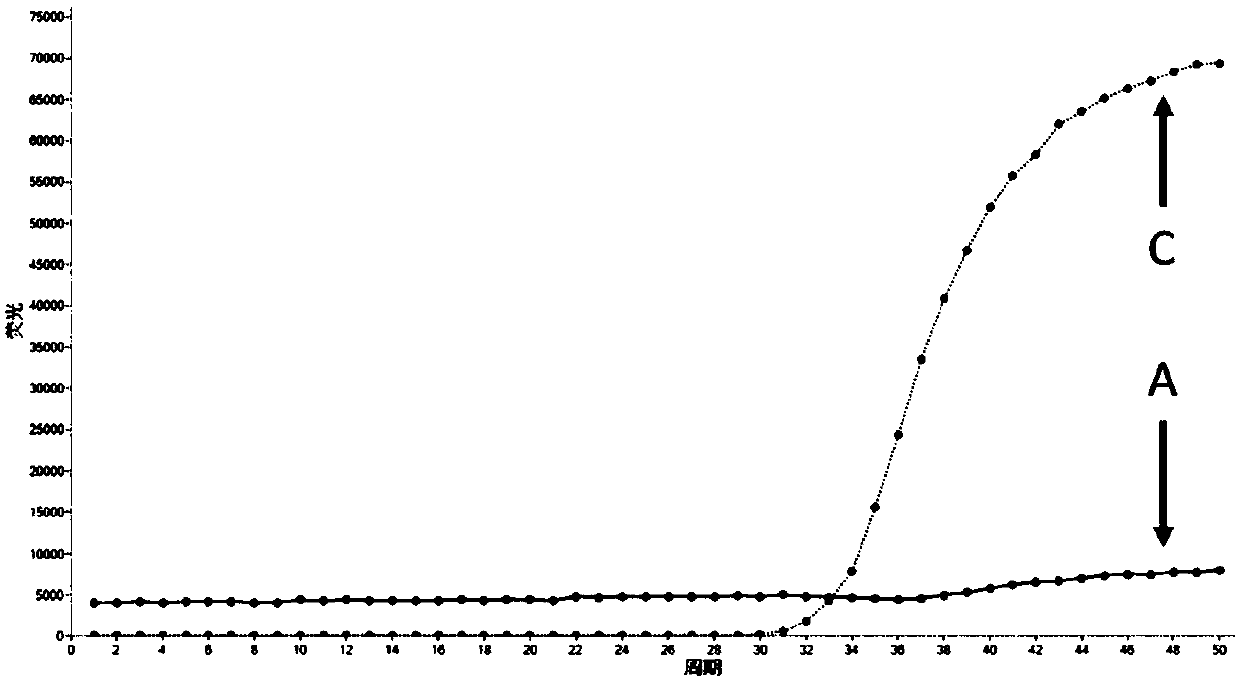
ActiveCN104293920ANo human errorLow false positiveMicrobiological testing/measurementVKORC1Fluorescence
The invention belongs to the gene detecting technology in the clinical detecting technology in the bio-medical field and particularly relates to a kit for quickly detecting polymorphism of human VKORC1 and CYP2CP genes and a using method of the kit. The kit comprises three pairs of primers, three probes, six PNA sequences, 1 pair of beta-Actin interior label primers and one interior label probe, further comprises Mg<2+> PCR (polymerase chain reaction) buffer liquor, a dNTP mixture, Tag enzyme and ddH2O. The kit disclosed by the invention can be used for performing qualitative detection on polymorphic sites of the VKORC1 and CYP2C9 genes, performing two-tube PNA-PCR fluorescent amplification reaction according to an SNP site and performing result judgment according to the condition whether a two-tube fluorescent curve is formed or not without producing manual errors, so that the false positive rate and the false negative rate are low. The kit disclosed by the invention can easily realize high-flux detection and is capable of satisfying clinical use very well.
Owner:WUHAN HEALTHCHART BIOLOGICAL TECH
CYP2C19, CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotyping multiplex amplification system and detection kit
InactiveCN105861739AHigh detection sensitivityImprove detection resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerNucleotide
The invention discloses a CYP2C19, CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotyping multiplex amplification system and detection kit. The amplification system comprises two forward primers and a reverse fluorescent primer of six SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) respectively and can simultaneously amplify the six SNPs. The system is characterized by achieving one-tube amplification of three SNPs on the gene CYP2C19, two SNPs on the gene CYP2C9 and one SNP on the gene VKORC1 through multiple PCR (polymerase chain reaction). In particular, the amplification system can achieve direct amplification of blood and blood spot samples and dispenses with the step of extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). The amplification system can integrate the UDG-dUTP antipollution measure and can effectively prevent product pollution. The detection system is comprehensive in site detection, is simple and convenient to operate, has high specificity, high sensitivity and strong reliability, is low in cost and has the capacity of mass detection.
Owner:BEIJING MICROREAD GENE TECH
Human CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genetic polymorphism detection kit
InactiveCN105177116AEasy to detectAccurate Typing DetectionMicrobiological testing/measurementVKORC1Internal standard
The present invention provides a human CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genetic polymorphism detection kit. The kit includes a PCR buffer, dNTP, MgCl2, 2 groups of specific primers, 2 groups of specific probes, an internal standard system, HotStart Taq enzyme and UNG enzyme. The detection kit for detecting CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genetic polymorphism has the advantages of high specificity, high sensitivity, easy and fast operation, high-throughput, security, and objective interpretation of the results.
Owner:WUHAN YZY MEDICAL SCI & TECH
Kit and method for detecting gene polymorphism related to warfarin personalized medication by pyro sequencing method
InactiveCN102676666AQuick analysisAccurate analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementVKORC1Nucleotide
The invention discloses a kit and a method for detecting the gene polymorphism related to warfarin personalized medication by a pyro sequencing method. The kit is used for typing genes related to the warfarin medication, and the single nucleotide polymorphism of VKORC1-1639 G>A (rs9923231) and CYP2C9*31075A>C(rs1057910) is involved; and the kit comprises primers shown as SEQ ID NO.3-8. By the kit, VKORC1-1639G>A and CYP2C9*3 1075A>C can be detected accurately and quickly in high flux, so that the safe, reasonable and effective personalized administration of the warfarin medication is realized.
Owner:周宏灏
Kit for rapidly detecting warfarin individualized medication related gene SNP sites, and its detection method
The invention relates to a kit for rapidly detecting warfarin individualized medication related gene SNP sites, and its detection method, and belongs to a genetic detection technology in the clinic detection technique of the biomedical field. The genetic typing of two polymorphic sites comprising CYP2C9*3(1061A / C) and VKORC1(-1639G / A) is rapidly and accurately carried out through human peripheral blood DNA drawing, specific PCR amplification by a Taq man probe and fluorescence signal analysis. The invention provides primers, probes and kits which are used for detecting the polymorphic sites, a use of the primers and the probes in the preparation of the kits, and a use of the determination of the warfarin application amount of a patient according to the detection results of the polymorphic sites. The determination use can effectively reduce the generation of the warfarin application amount related adverse events and prevent thrombotic diseases. The detection method can be used for the auxiliary diagnosis and treatment of various patients needing warfarin clinically.
Owner:丁虎 +1
Kit for detecting polymorphism of VKORC1 and CYP2C9 genes
ActiveCN102329885AHigh detection sensitivityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWarfarinVKORC1
The invention provides a kit for quickly detecting polymorphism of VKORC1 and CYP2C9 genes. The kit is used for guiding the dosage of clinical warfarin. The kit comprises three pairs of primers shown as SEQ ID No.1-6, and can also further comprise one or more of the following reagents: polymerase chain reaction (PCR) reaction liquid, negative control, positive control, PCR sequencing reaction liquid and human peripheral blood genome extraction reagent. The kit is used for detecting the polymorphism of the VKORC1 and CYP2C9 genes by adopting a gene sequencing method with relatively high sensitivity and specificity, the specificity and the sensitivity of the detection result of the kit are remarkably improved, and the kit provides a brand-new, quick, simple and convenient gene diagnosis technology for clinically improving the safety and the validity of warfarin application.
Owner:李艳 +1
Method and system for extraction and normalization of relationships via ontology induction
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Primer, probe and kit for detecting gene polymorphism of CYP2C9 and VKORC1
InactiveCN106399560AAccurate detectionHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVKORC1Hazardous substance
The invention discloses a primer, a probe and a kit for detecting gene polymorphism of CYP2C9 and VKORC1. The primer comprises a gene detection specificity primer sequence of three loci YP2C9*2, CYP2C9*3 and VKORC1 and a probe sequence (SEQ ID NO.1-12). An ARMS primer is used to differentiate field and mutant genes, so that the primer has the advantages of high sensitivity and high specificity and is suitable for various sample types and high in detection result accuracy. In addition, the ARMS primer is quick and simple to synthesize, low in synthesis cost and better in amplification effect, and production cost can be lowered effectively. The kit is high in detection speed and quite convenient, and the whole detection process only takes 90 minutes. The whole kit does not contain toxic and harmful substances, thereby being harmless to operating personnel and environment and suitable for wide application in clinic detection and the like.
Owner:武汉海吉力生物科技有限公司
Detection kit for guiding warfarin dosage with high precision and detection method thereof
InactiveCN106350599ASafe and reasonable to useStable INR valueMicrobiological testing/measurementWarfarinVKORC1
The invention provides a detection kit for guiding warfarin dosage with high precision. The kit comprises amplification primers containing VKORC1 (1639G / A), CYP4F2(V433M), GGCX rs11676382, CYP2C9*2, CYP2C9*3, CYP2C9*5 and CYP2CP*6, a PCR reagent and a RFLP reagent. The invention also provides a detection method of the kit. According to the invention, the optimal dosage of warfarin of a patient can be accurately predicated, so as to assist doctors in using warfarin more reasonably and safely, thus reaching the steady INR value as far as possible, reducing the risks of bleeding and thrombus in the early stage of administration, and improving the treatment effect.
Owner:成都睿杰森生物科技有限公司
Probes and kit for detecting human CYP2C9 (Cytochrome P450 2C9) and VKORC1 (Vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1) gene polymorphism
InactiveCN104404163AWide detection rangeImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVKORC1Fluorescence
The invention discloses a kit for detecting human CYP2C9 (Cytochrome P450 2C9) and / or VKORC1 (Vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1) gene polymorphism. The kit comprises a fluorescence detection probe I represented as SEQ ID NO:3, a fluorescence detection probe II represented as SEQ ID NO:6 and / or a fluorescence detection probe III represented as SEQ ID NO:9, wherein the fluorescence detection probe I comprises an amplimer for C43oT site of a CYP2C9 gene as well as a base; the fluorescence detection probe II comprises an amplimer for A1075C site of the CYP2C9 gene as well as a base; and the fluorescence detection probe III comprises an amplimer for G-1639A site of a VKORC1 gene as well as a base. Specific primers, fluorescence detection probes and an optimized detection system are adopted, the three gene types can be detected separately or synchronously, the detection linearity is wide, a 25 mu L detection system can detect 2ng-600ng human genomic DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), the accuracy is high, and the detection result is completely consistent with that of the Sanger sequencing method.
Owner:HELIXGEN GUANGZHOU
Primer pair and kit for detecting VKORC1 (vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1) genotyping by pyrosequencing
InactiveCN105154569AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVKORC1Biotin
The invention relates to a primer pair and kit for detecting VKORC1 (vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1) genotyping by pyrosequencing, belonging to the technical field of in vitro nucleic acid detection. The primer pair comprises VKORC1 G1639A and VKORC1 C1173T forward amplification primers, VKORC1 G1639A and VKORC1 C1173T reverse amplification primers and VKORC1 G1639A and VKORC1 C1173T sequencing primers, wherein 5' terminals of the VKORC1 G1639A forward amplification primer and the VKORC1 C1173T reverse amplification primer are respectively subjected to biotin labelling. The kit comprises the amplification primers, a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) liquid 1, a PCR liquid 2, the sequencing primers, uracil DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)glycosylase and Taq polymerase. The kit provided by the invention has the advantages of accurate detection results, high specificity, short detection period, simplicity in operation, capability of effectively meeting the requirements of clinical examination, capability of monitoring the reaction process in real time, short reaction time, sequencing of PCR products on a pyrosequencing instrument after the PCR products are simply treated, high throughput sample detection and higher sensitivity than gold standard methods, namely capillary electrophoresis sequencing methods.
Owner:CHANGSHA 3G BIOTECH
Primer set capable of synchronously detecting related gene polymorphism of anticoagulant drug and application
InactiveCN107904302AGuaranteed reliabilityAmplification program reductionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVKORC1Anticoagulant drug
The invention discloses a primer set capable of synchronously detecting related gene polymorphism of an anticoagulant drug. The primer set comprises a PCR amplification primer and a SNaPshot PCR primer; the detected sites include VKORC1-1639>A, CYP4F2*3, CYP2C9*3, CYP2C19*2, CYP2C19*3 and CYP2D6*10. Compared with a general method for individually amplifying a plurality of sites, the primer used for detecting has the advantages that the amplification processes are decreased, and the amplification cost is reduced; ,moreover, the high sensitivity, the high accuracy and the high precision can be ensured, the method reliability is ensured, and a doctor can accurately select drugs for patients and reasonably adjust the dosage of the drug.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Primer and method for simultaneously detecting VKORC1 and CYP2C9 gene polymorphisms
InactiveCN104988223AStrong specificityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVKORC1Specific detection
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological detection, and provides a primer for simultaneously detecting VKORC1 and CYP2C9 gene polymorphisms. The primer comprises a PCR amplification primer and a SNaPshot PCR primer. The primer can achieve specific detection on VKORC1 and CYP2C9 gene polymorphisms, causes no cross reaction and is good in accuracy.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KINGMED DIAGNOSTICS CENT +1
Primers, probes, kit and method for testing human VKORC1 and CYP2C9 gene polymorphisms
InactiveCN106702005AReduce signal strengthStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVKORC1Microbiology
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and discloses a primer and probe combination for testing human VKORC1 and CYP2C9 gene polymorphisms, a kit containing the primer and probe combination and a fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method for testing human VKORC1 and CYP2C9 gene polymorphisms by adopting the primer and probe combination. The invention, which is based on the TaqMan fluorescent PCR technique, is simple, efficient and highly sensitive. In addition, by reasonably matching primers with probes, the interaction between the primers, the interaction between the primers and the probes and the interaction between the probes are effectively prevented, thus reducing testing errors. When used for testing human VKORC1 and CYP2C9 gene polymorphisms, the primers, the probes and the kit which are provided by the invention have the advantages of high sensitivity, high specificity, easiness, quickness and safety in operation, simple and visual result judgment and the like, and can directly use a blood sample or a dried blood spot sample as a template.
Owner:SHENZHEN TISSUEBANK PRECISION MEDICINE CO LTD +3
Primer-probe combination and kit for detecting associated genotyping of warfarin medication
InactiveCN105648082AType is convenient and easyGuaranteed non-invasive diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWarfarinSide effect
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and relates to a primer-probe combination and a kit for detecting associated genotyping of warfarin medication. The invention provides primers and probes for detecting associated genotyping of warfarin medication. The sequences of the primers are shown as SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.6, and the sequences of the probes are shown as SEQ ID NO.7-SEQ ID NO.12. The primer-probe combination and the kit for detecting associated genotyping of warfarin medication have the advantages that development and application of the gene detection kit are guided through warfarin medication, typing of the three genes of CYP2C9*3, CYP4F2 and VKORC1 is facilitated and easily achieved, and noninvasive diagnosis is guaranteed to enable clinicians to master patient heredity conditions rapidly and accurately, decrease medical accident incidence caused by inappropriate medicine dose greatly, reduce medication side effect and lay the foundation for improvement on clinical treatment effect; since only about 2 hours is needed for detection of every sample, high detection speed is achieved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU TCM HOSPITAL
Use of a Factor Xa Inhibitor for Treating and Preventing Bleeding Events And Related Disorders in Patients Having Sensitivity to Vitamin K Antagonists Used As Anticoagulants
InactiveUS20150272935A1Reduce riskIncreased riskBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementVKORC1Thrombus
The invention provides methods of treating or preventing bleeding events or over-anticoagulation in a subject in need thereof who is identified as having sensitivity to a vitamin K antagonist such as warfarin by administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of an FXa inhibitor, which can be a direct or indirect FXa inhibitor, or a warfarin or VKA alternative drug or compound. The direct FXa inhibitor can be the small molecule edoxaban p-toluenesulfonate monohydrate, edoxaban, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt and / or hydrate thereof. In aspects, the subject is identified as having one or more genetic polymorphisms in genes CYP2C9 and / or VKORC1 resulting in loss of function, reduction in function, or aberrant function of these genes and / or their protein products, and sensitivity to warfarin. The invention provides methods of administering an FXa inhibitor or warfarin alternative to safely and effectively reduce, prevent, reduce the risk of, prevent the recurrence of, or prevent the risk of recurrence of, conditions such as embolism, thrombosis, thromboembolism, etc. in a subject who is in need of anticoagulant therapy and who is identified as having one or more genetic polymorphisms resulting in warfarin sensitivity.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
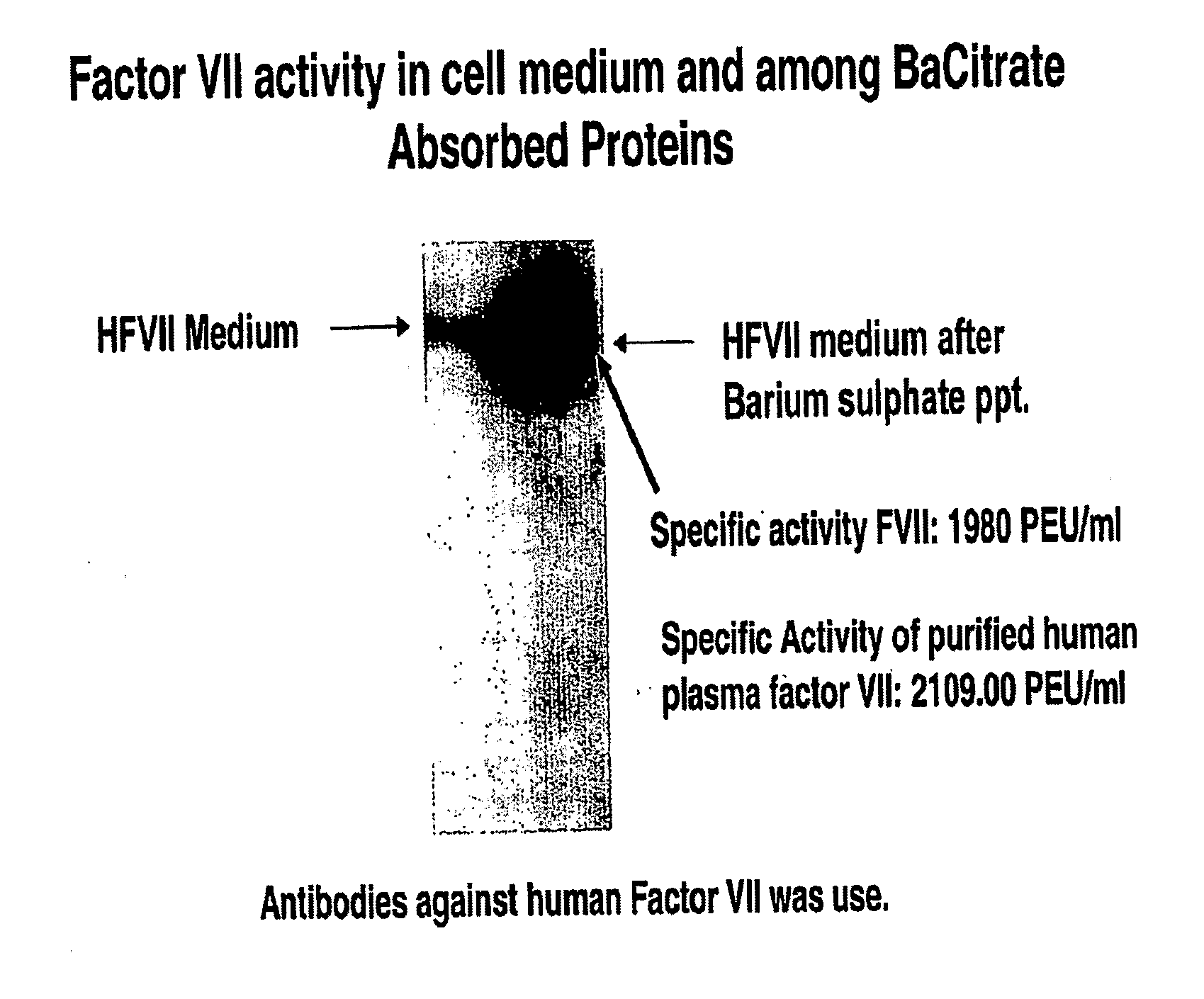
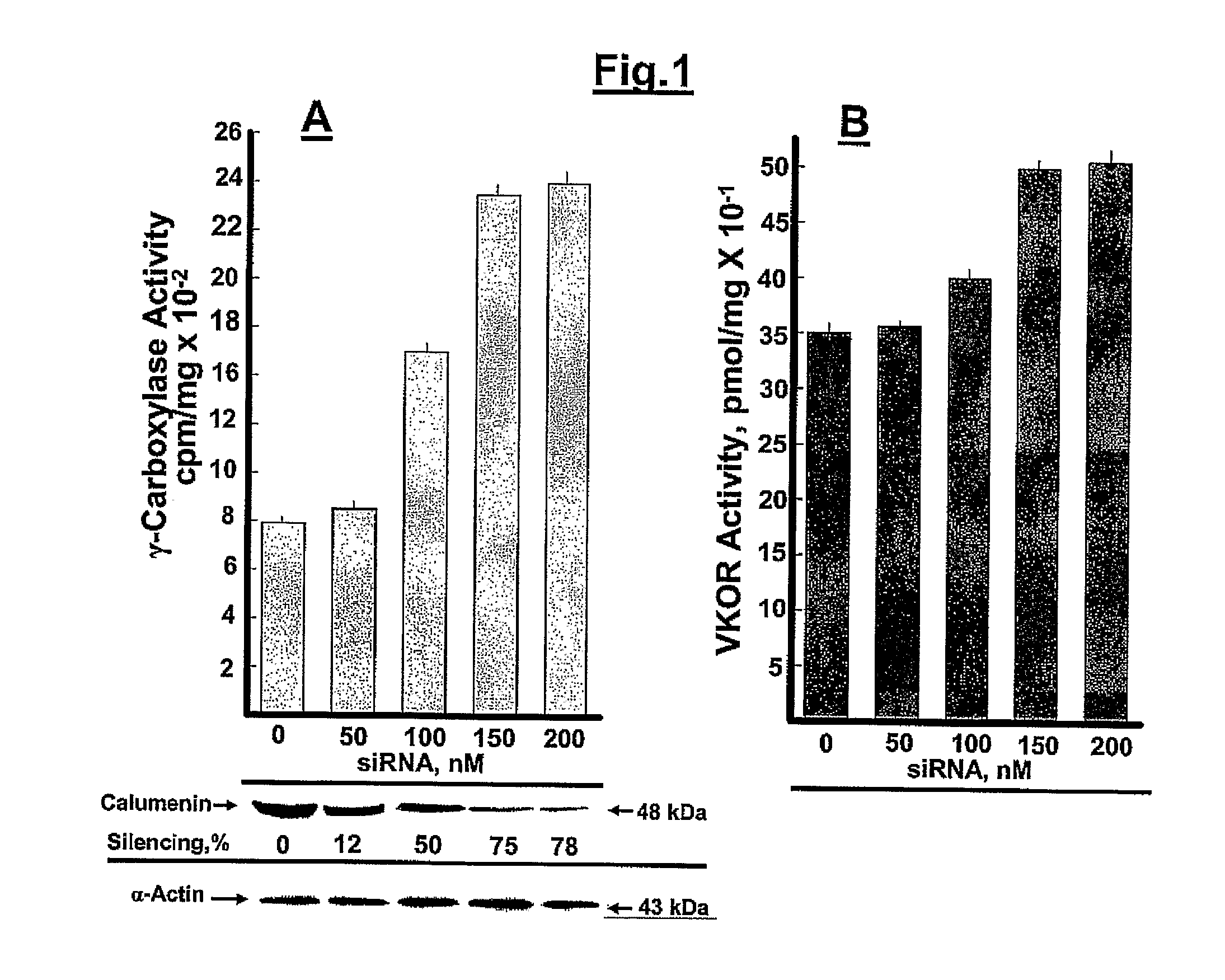
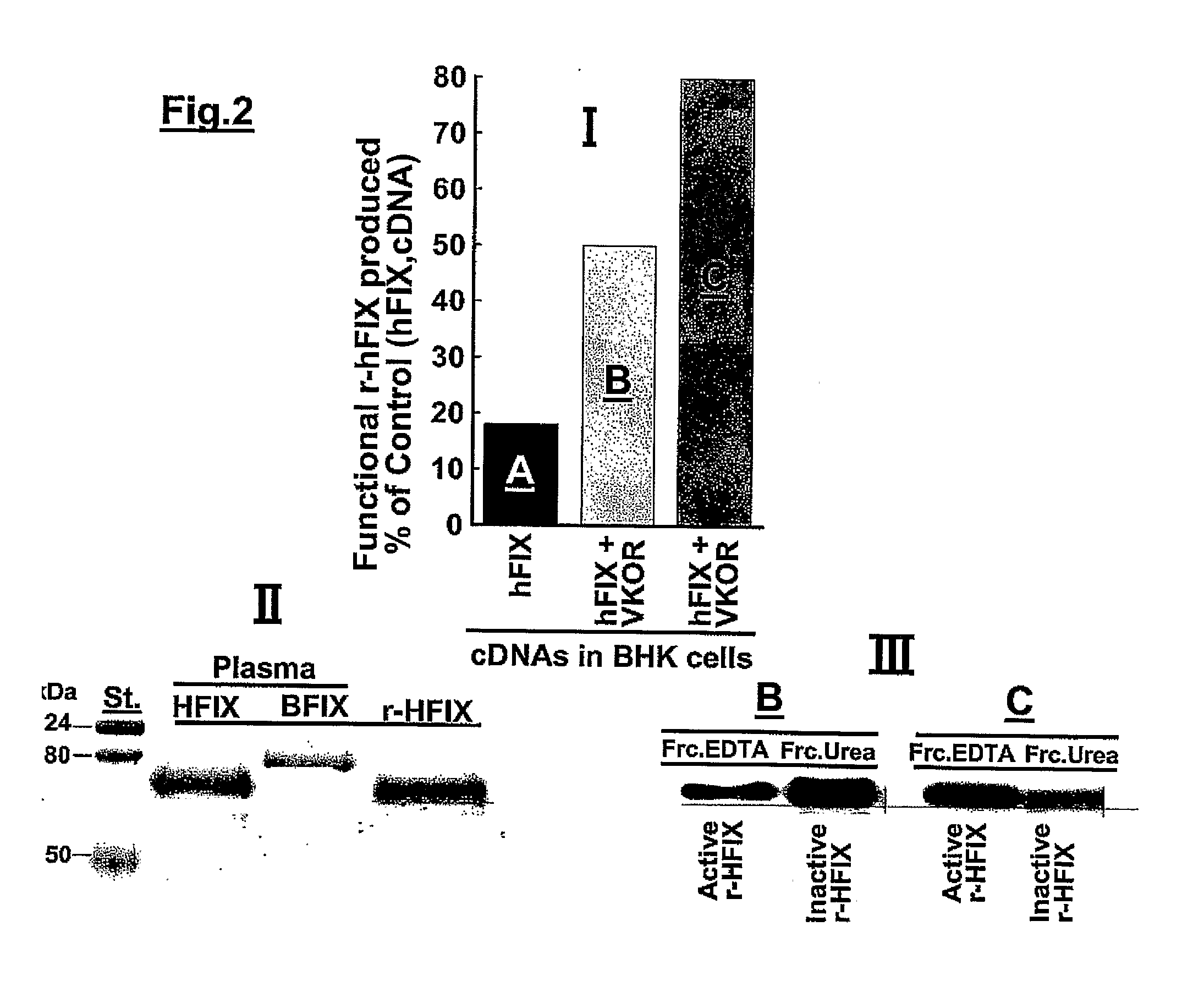
Compositions and Methods for Increasing Production of Recombinant Gamma-Carboxylated Proteins
InactiveUS20100331255A1Increase productionHigh yieldPeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationVKORC1Genetic engineering
Methods and cell lines for overexpressing functional gamma-carboxylated proteins are disclosed by way of genetically engineered cell lines which over-express VKORC1. Also disclosed is the antisense inhibition of expression of calumenin in conjunction with overexpression of VKORC1 which also increases expression of functional gamma-carboxylated proteins. Gamma-carboxylated proteins of interest may include blood coagulation factors such as human clotting factors IX and VII.
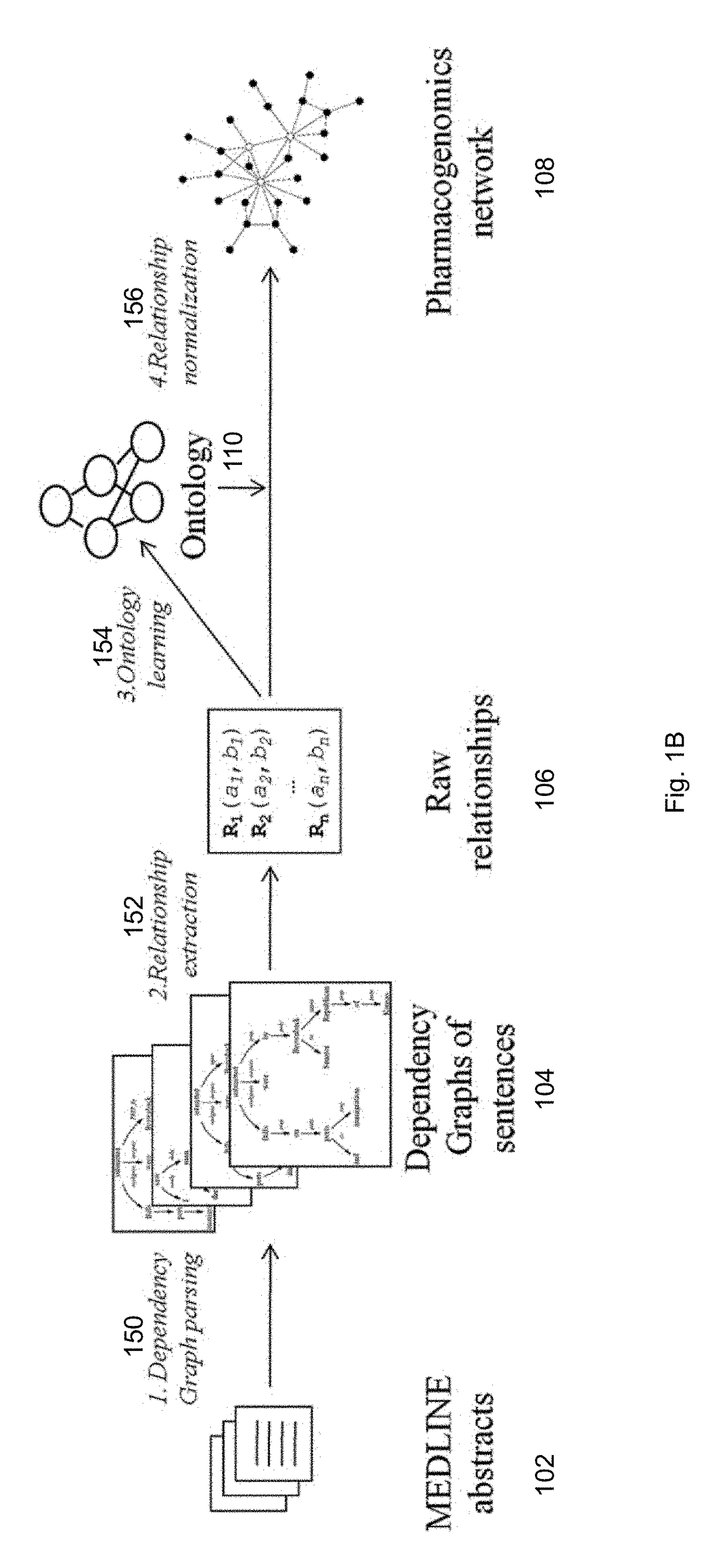
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Screening method and application of small molecular compound for targeted inhibition of vitamin K dependent gamma-glutamyl carboxylase
ActiveCN111239386ARapid High Throughput ScreeningInhibits VKGC activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCarboxysomeVKORC1
The invention discloses a screening method and application of a small molecular compound for targeted inhibition of vitamin K dependent gamma-glutamyl carboxylase, and belongs to the technical field of molecular cell biology and biochemistry. By constructing a vitamin K circulating small molecule inhibitor screening system, a drug small molecule library can be rapidly subjected to high-throughputscreening, and a small molecule compound for targeted inhibition of vitamin K circulation is obtained; furthermore, the inhibition effect of the small molecular compound on the activity of the VKOR protein is detected; and the screened small molecular compound is identified by using a VKORC1 and VKORC1L1 gene double knockout cell line, so as to obtain the small molecular compound for targeted inhibition of vitamin K-dependent gamma-glutamyl carboxylase (VKGC). By adopting the method, a small molecular compound capable of specifically inhibiting vitamin K-dependent gamma-glutamyl carboxylase isscreened for the first time, and the small molecule can be used for researching biochemical characteristics of VKGC protein and has potential application value of being developed into rodenticide andanticoagulant drugs.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Host cell containing vector for expressing functional recombinant human coagulation factor VII and high-level expression method of functional recombinant human coagulation factor VII
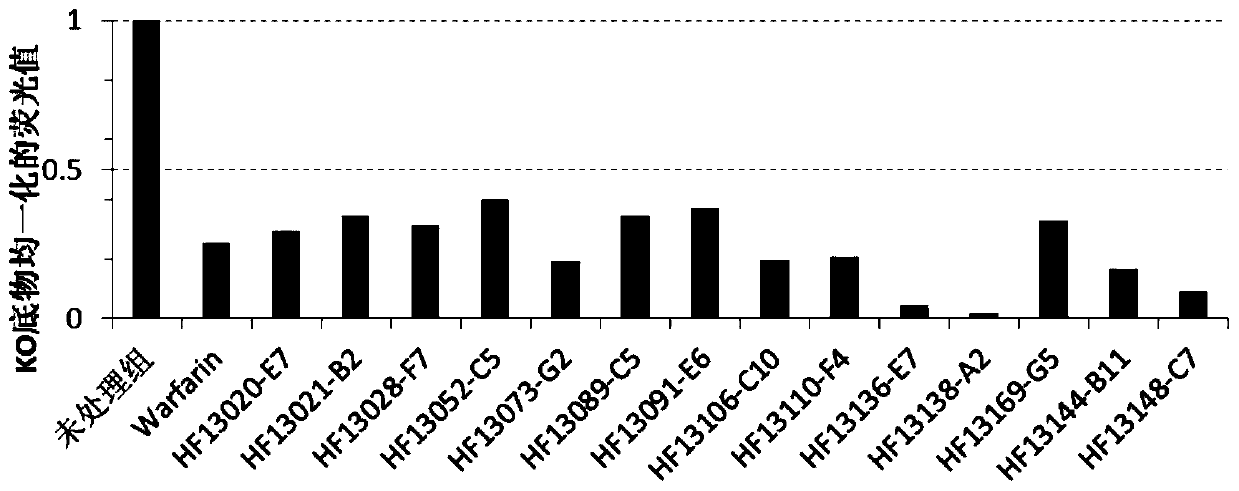
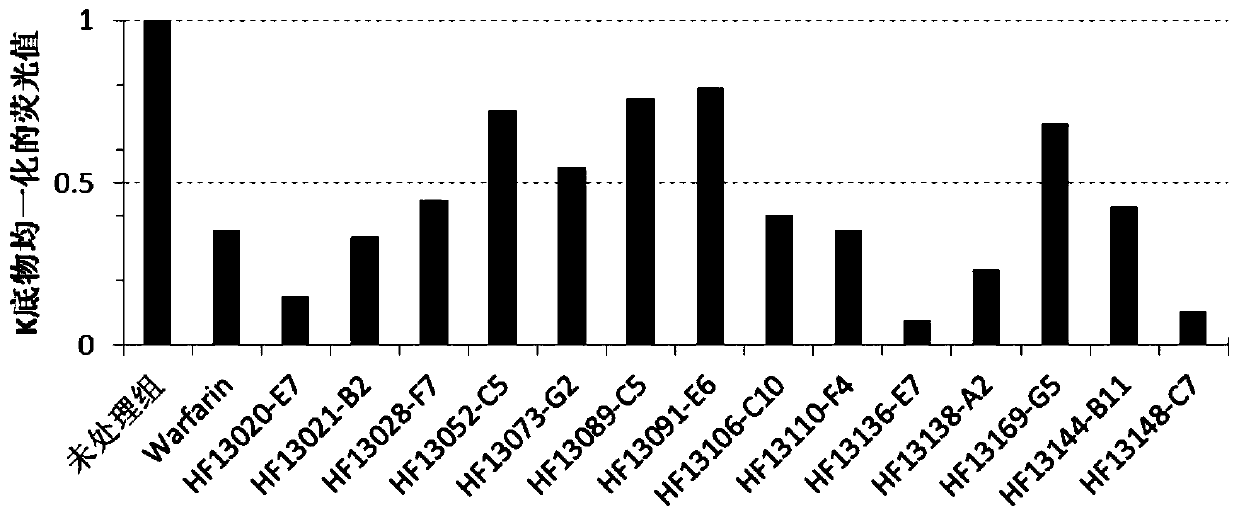
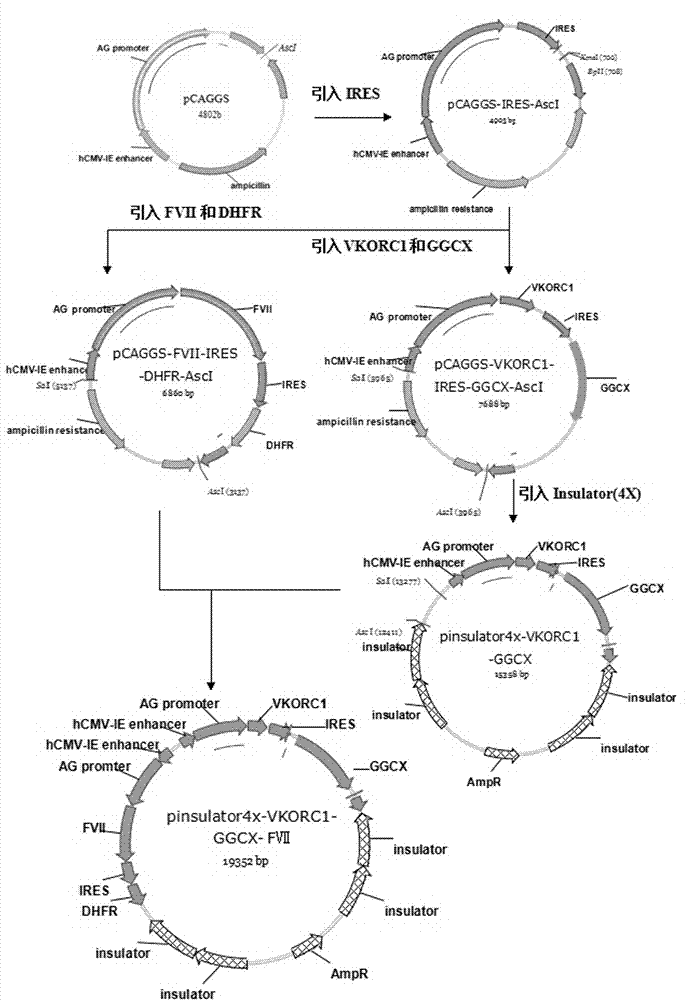
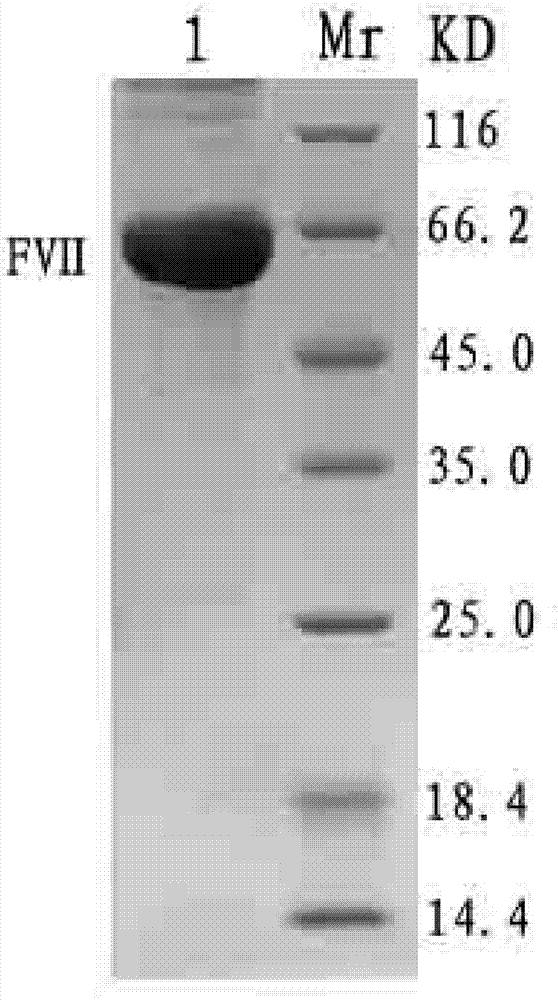
ActiveCN104293737AAvoid interactionImprove expression levelHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionVKORC1High level expression
The invention provides a host cell containing a vector for expressing a functional recombinant human coagulation factor VII and a high-level expression method of the functional recombinant human coagulation factor VII, and aims at establishing an expression vector containing F VII, GGCX and VKORC1 recombinant nucleic acids and improving the g-carboxylation modification of the recombinant F VII by virtue of coordinated expression of the GGCX and the VKORC1. The host cell contains the F VII recombinant nucleic acid (human coagulation factor VII), depending on which the vitamin K is coded, a VKORC1 (mouse vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1) recombinant nucleic acid and a GGCX (mouse g glutamyl carboxylase) recombinant nucleic acid, as well as an insulator (4X) recombinant nucleic acid; the high-level expression method of the functional recombinant human coagulation factor VII comprises the steps of establishing an expression vector, mediating the expression vector into a DHFR deficient CHO animal cell by use of a lipidosome method and screening out positive clones by virtue of a DMEM culture medium, performing serum-free acclimation and culture on the host cell strain, purifying the h FVII recombinant protein by virtue of nickel ion affinity chromatography and performing SDS-PAGE and Westernblot detection, and finally, determining the procoagulant activity of the FVII recombinant protein according to the prothrombin time (PT).
Owner:山西省博奥特医学检验有限公司
CYP2C9 and VKORC1 gene typing detection reagent kit
InactiveCN105002281AIncrease production capacityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementVKORC1Nucleotide
The invention discloses a CYP2C9 and VKORC1 gene typing detection reagent kit. The CYP2C9 and VKORC1 gene typing detection reagent kit comprises a gene chip and various primers. The gene chip is provided with 4 mutation sites of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genes and nucleotide sequence probes in normal contrast and complementation with the mutation sites, wherein the probes have the sequences shown in SEQ ID Nos. 1-8 or sequences complementary to the sequences shown in SEQ ID Nos. 1-8; the gene chip is further provided with an DNA sequence marked with biotin points, wherein the DNA sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.9. The primers have the sequences shown in SEQ ID Nos. 10-17. The CYP2C9 and VKORC1 gene typing detection reagent kit provides a CYP2C9 and VKORC1 gene typing joint detection platform, can achieve synchronous joint detection, improve detection specificity, lower the cost and shorten detection time, and has great significance in carrying out CYP2C9 and VKORC1 gene detection and mass screening.
Owner:潮州凯普生物化学有限公司
Preparation method of electrochemical sensor for VKORC1-1639G>A gene polymorphism detection
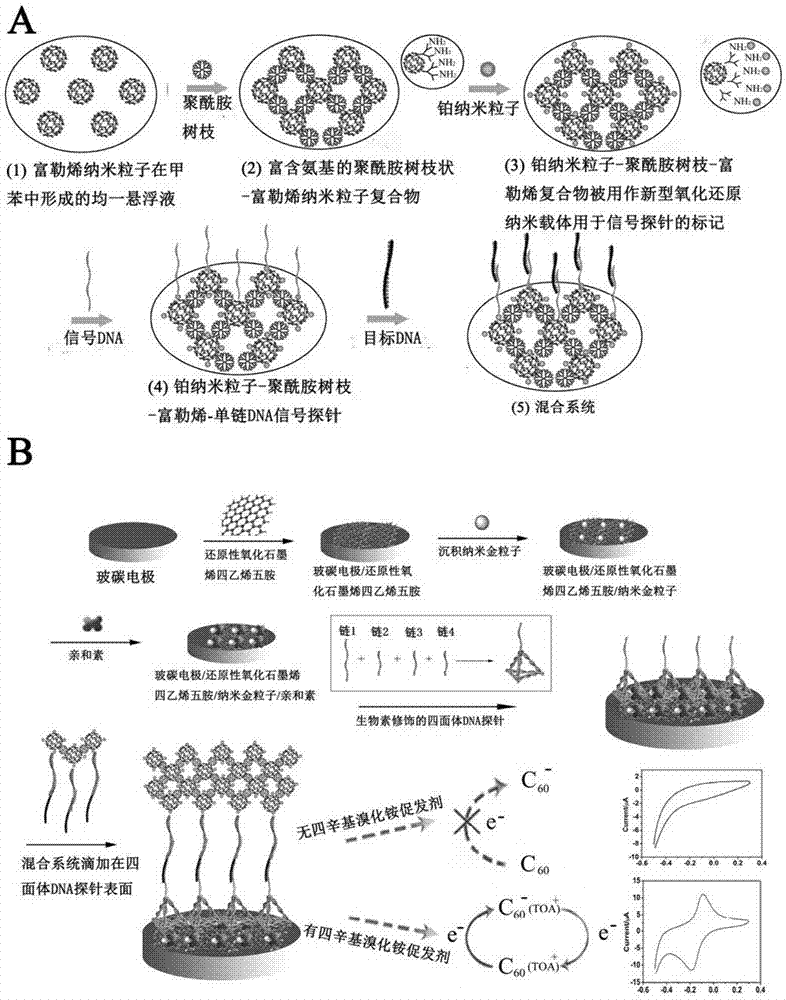
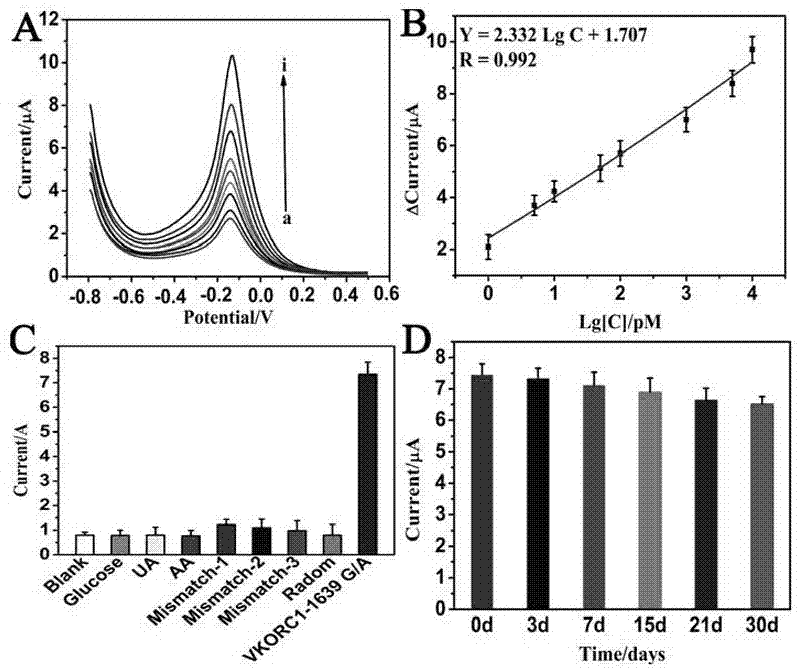
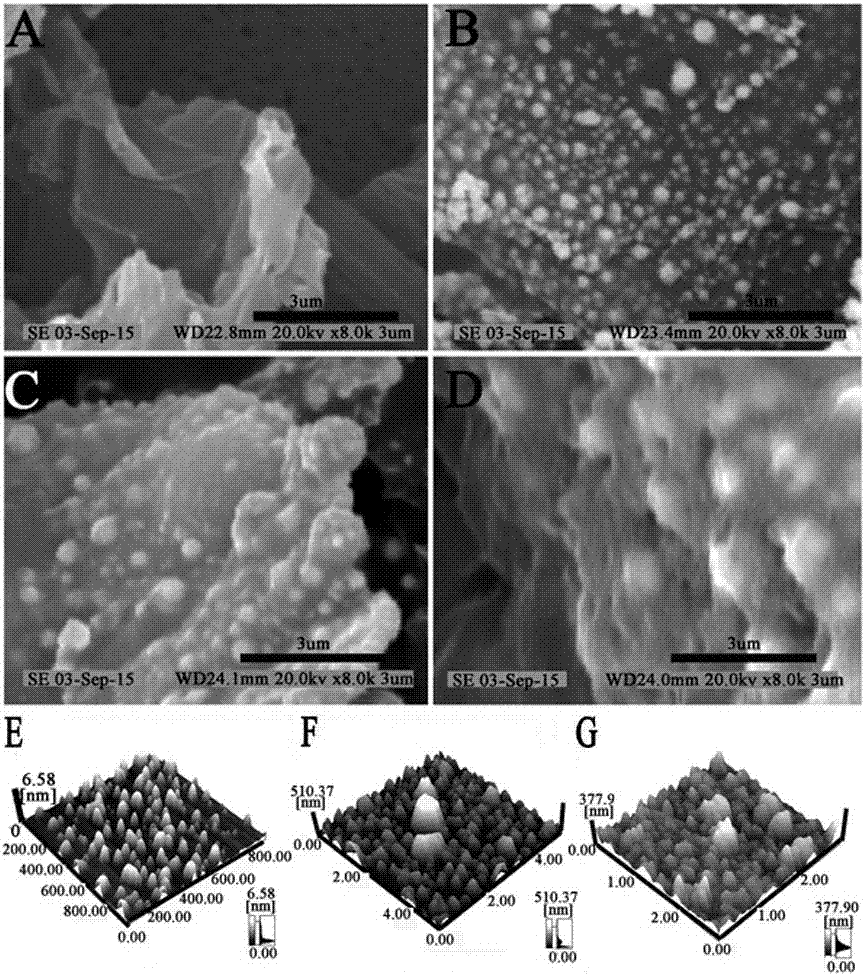
InactiveCN106979964AHigh sensitivityGood biocompatibilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansVKORC1Polyamide
The invention provides a preparation method of an electrochemical sensor for VKORC1-1639G> A gene polymorphism detection, first, amino-modified polyamide dendritic polymer PAMAM is used to process and functionalize hollow nano platinum to obtain a tPNPs-PAMAM composite material, the tPNPs-PAMAM composite material, a single strand DNA signal probe and fullerene nanoparticles are mixed to obtain a redox probe, and by layer by layer self-assembly of reductive graphene oxide tetraethylenepentamine, nano gold and avidin, biotinylated tetrahedral DNA capture probe is fixed, and then the electrochemical sensor for VKORC1-1639G> A gene polymorphism detection is prepared. The electrochemical sensor is successfully used for detection of single base mutation of VKORC1. The electrochemical sensor has the advantages of high sensitivity, strong specificity, rapid detection and convenience. The electrochemical sensor provides a new detection method for warfarin individualized medication.
Owner:SHIYAN TAIHE HOSPITAL
Nucleic acids encoding vitamin K expoxide reductase subunit 1 and vitamin K dependent protein expression and methods of using same
InactiveUS9617523B2Improve productivityPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsVKORC1Host organism
The present invention relates to a host organism containing recombinant nucleic acids coding for the vitamin K reductase complex subunit 1 (VKORC1) and recombinant nucleic acids coding for a vitamin K dependent (VKD) protein, wherein both the recombinant VKORC1 and the recombinant VKD protein are expressed in said host organism. Further, the present invention relates to a cell culture system comprising cells which contain said recombinant nucleic acids and to methods for improving the productivity of recombinant VKD protein expression in a host organism being cultured in suitable systems.
Owner:BAXALTA GMBH
Vitamin K Epoxide Recycling Polypeptide VKORC1, a Therapeutic Target of Coumarin and Their Derivatives
The invention relates to a novel polypeptide vitamin K epoxide recycling polypeptide (VKORC1) as a target for coumarin and its derivatives. The invention further provides methods for identifying coumarin derivatives, and also claims VKORC1 polypeptides and VKORC1 nucleic acids containing a sequence abnormality associated with a VKORC1 associated deficiency such as warfarin resistance, wherein the VKORC1 polypeptides and VKORC1 nucleic acids can be used for diagnosing these deficiencies. Moreover, the invention relates to methods for identifying coumarin derivatives usable in pest control of rodents.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Rapid detection kit for CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotype based on POCT mode
InactiveCN109251976ARealize instant detectionAvoid Medication ErrorsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVKORC1Genomic DNA
The present invention provides a rapid detection kit for CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotypes based on a POCT mode. The kit contains a fluorescent quantitative PCR primer and probe for detecting CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotypes, and a cell lysate, wherein the sequence of the PCR primer is shown as SEQ ID NO.1-2 and SEQ ID NO.5-6, and the sequence of the probe is shown as SEQ ID NO.3-4 and SEQ ID NO.7-8. The kitcan realize real-time detection without DNA purification. A sample can be directly added into a reagent for a PCR reaction, the kit is especially suitable for rapid accurate detection of samples withlow DNA content (such as oral exfoliated cells), and the detection accuracy is 99% or more. The detection sensitivity is high, and the detection limit of genomic DNA as low as 0.125 ng can be accurately detected. The whole detection takes a short time, and a detection result can be obtained within one hour and provides a medicine use basis for a doctor at the first time, thereby reducing the riskof medicine administration.
Owner:重庆京因生物科技有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com