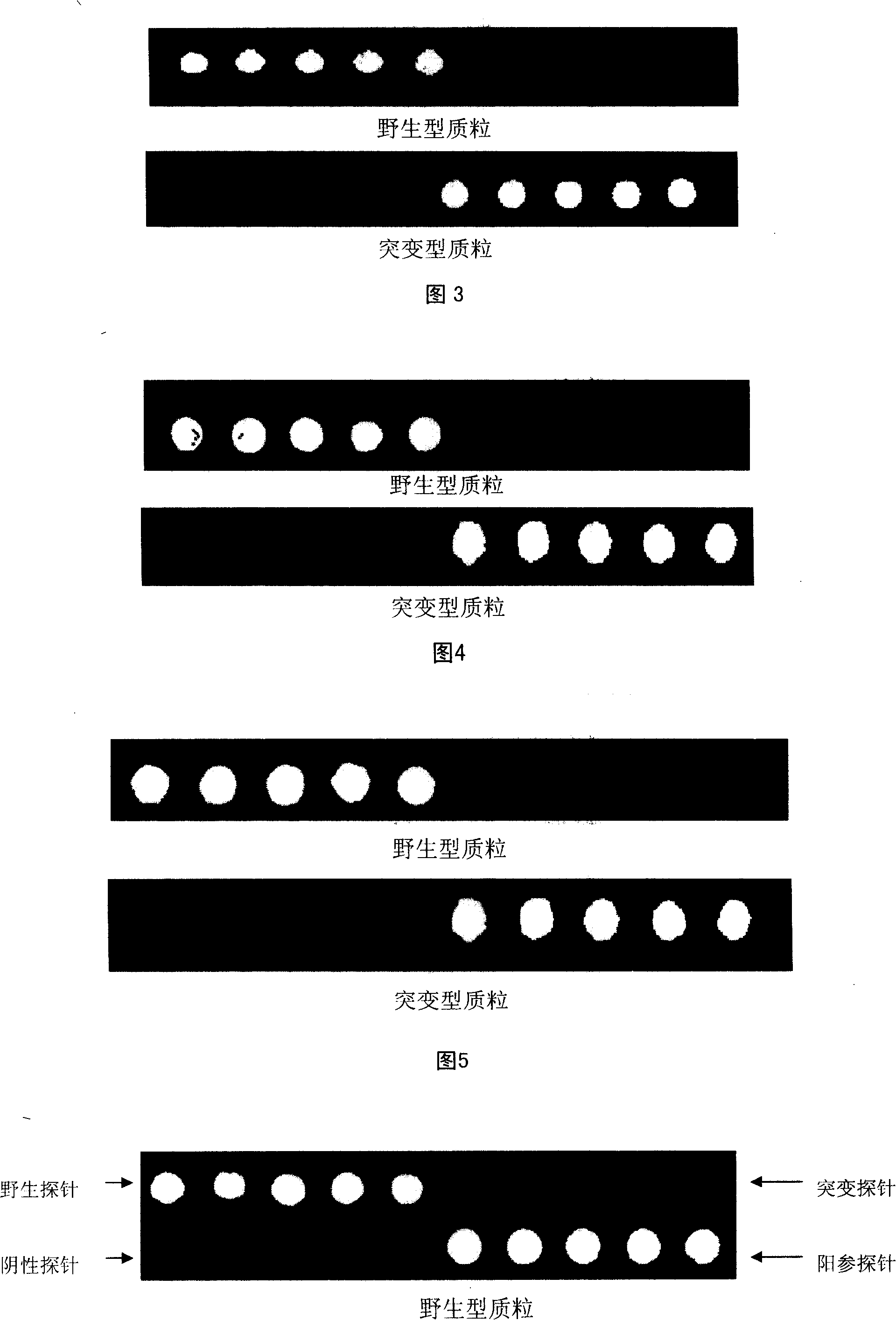
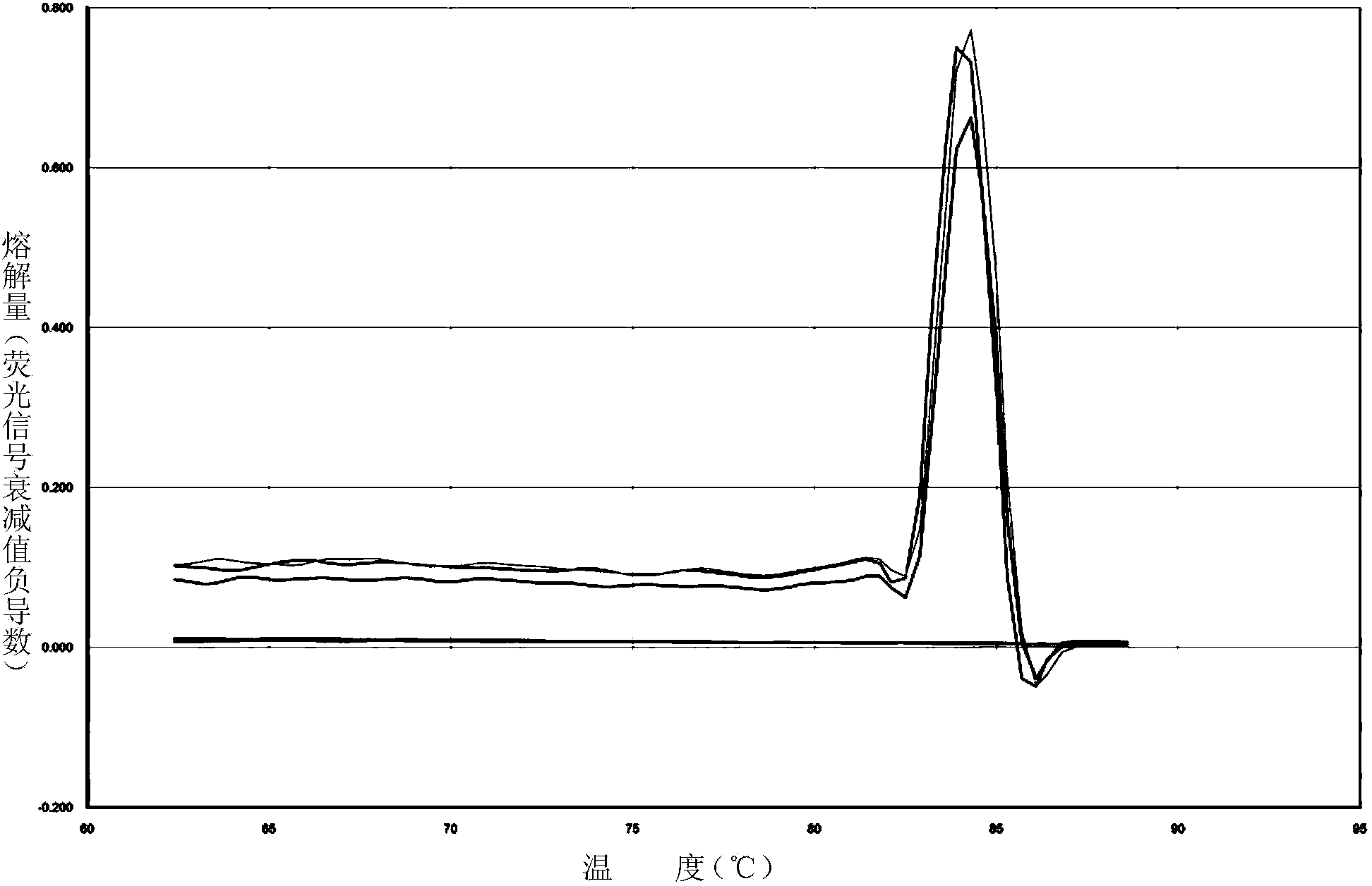
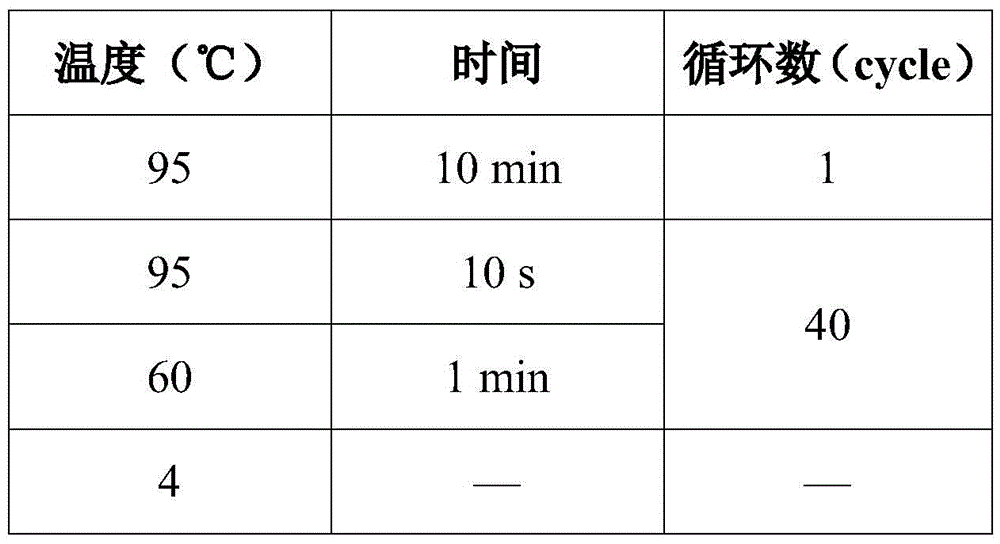
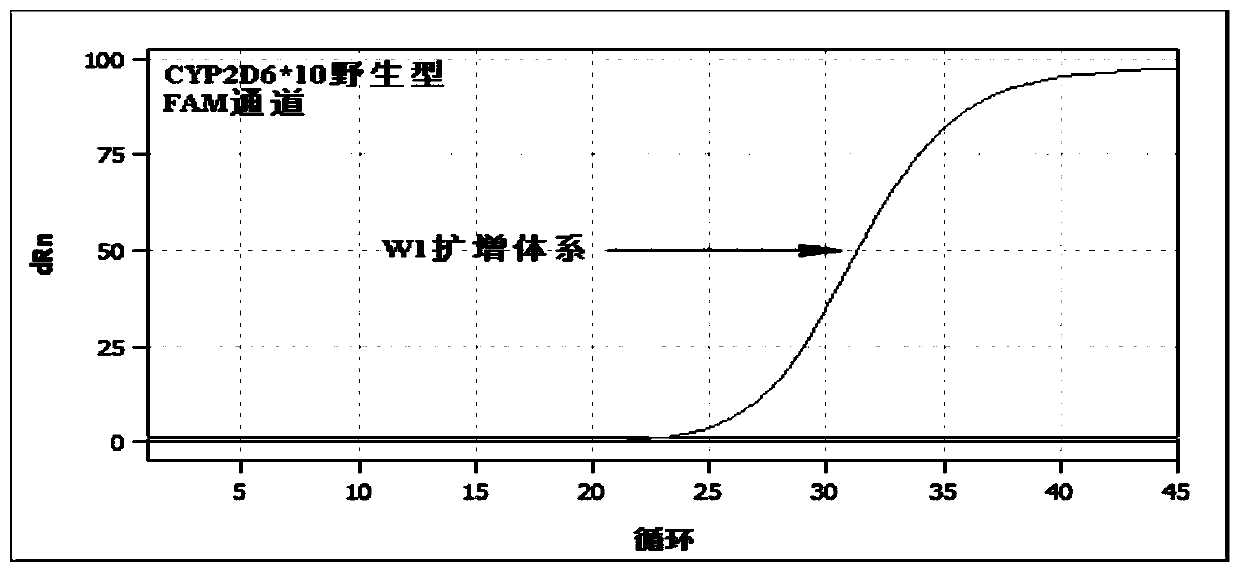
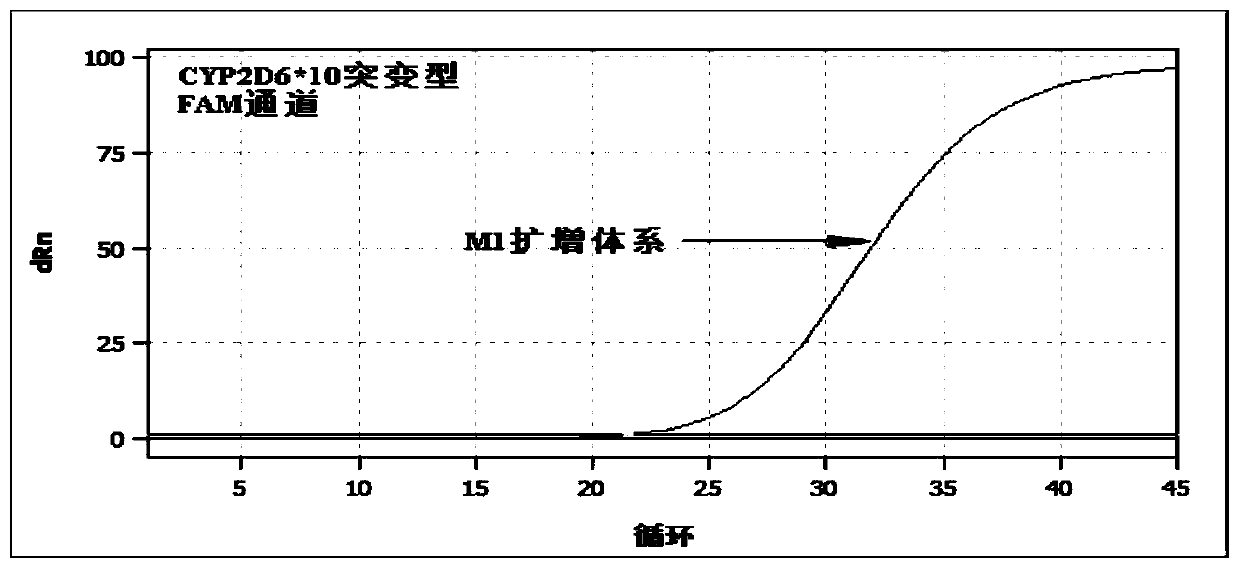
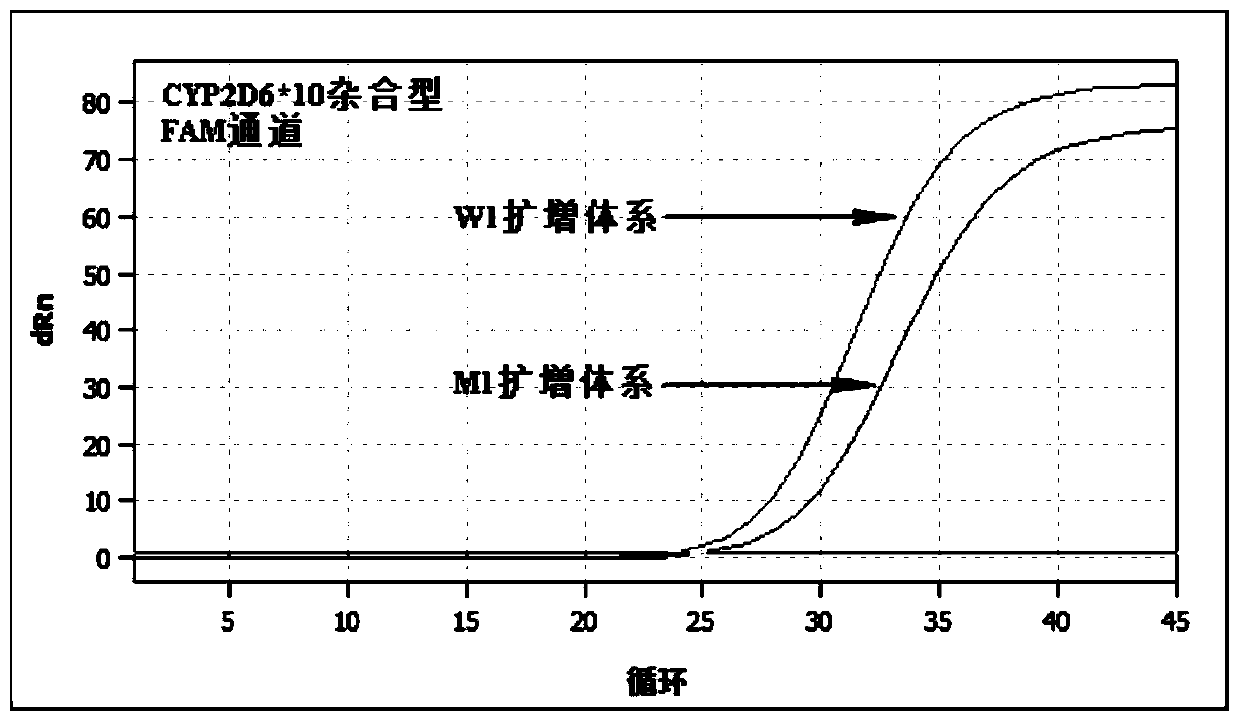
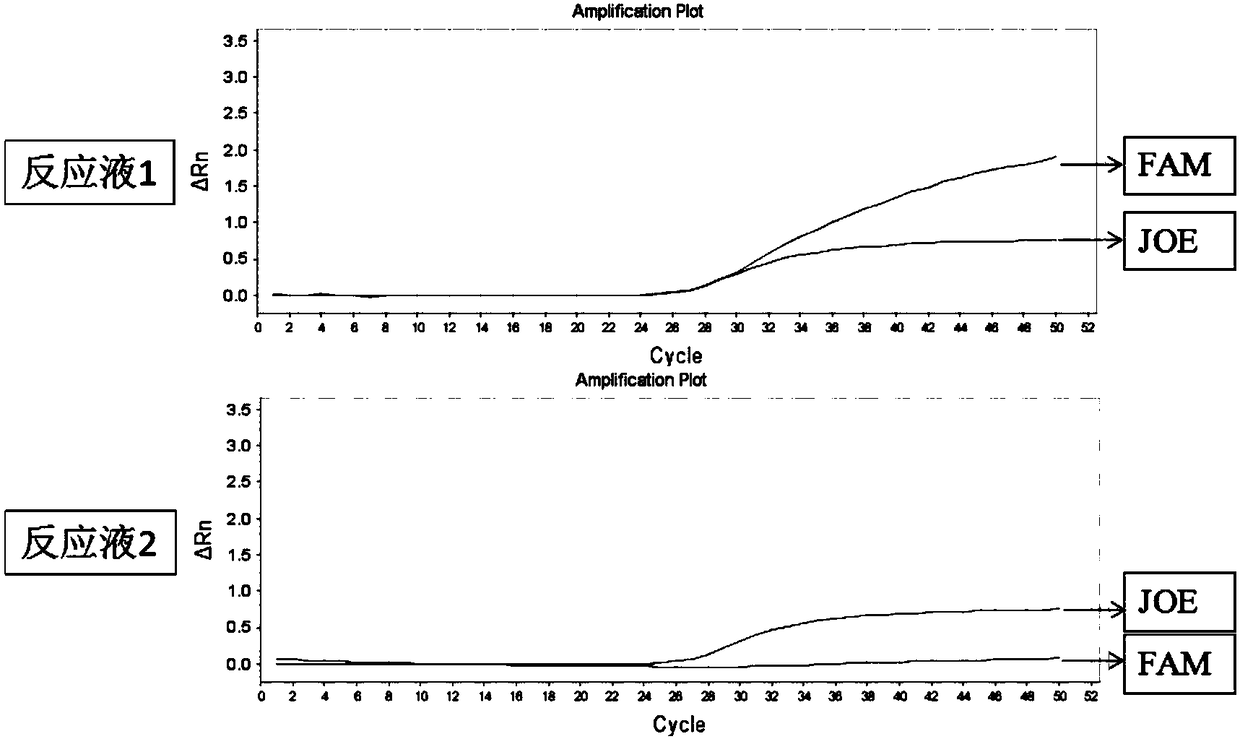
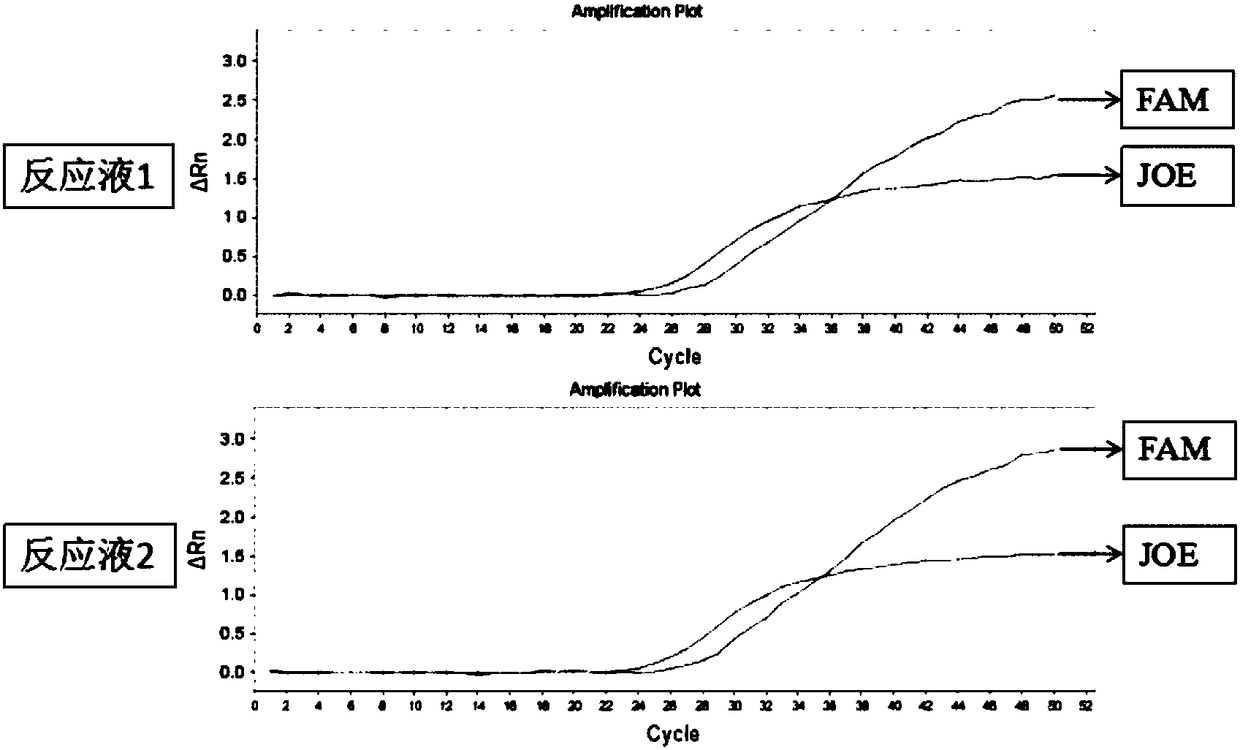
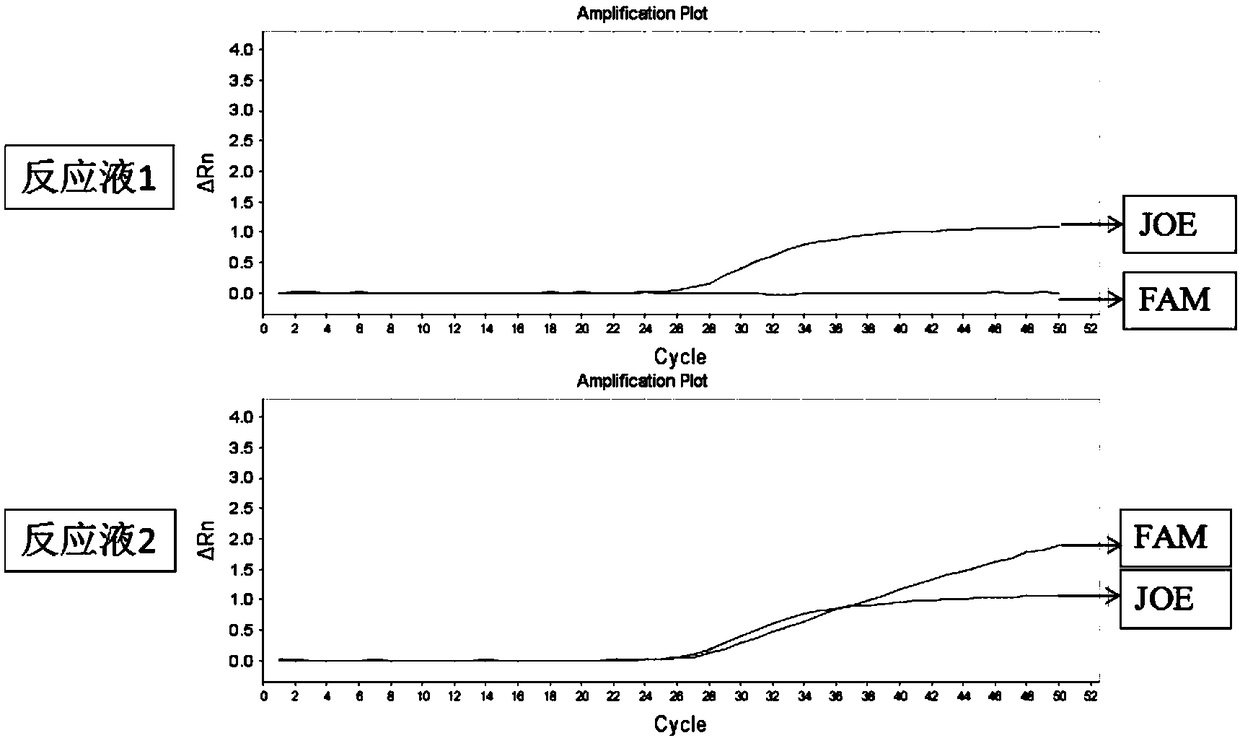
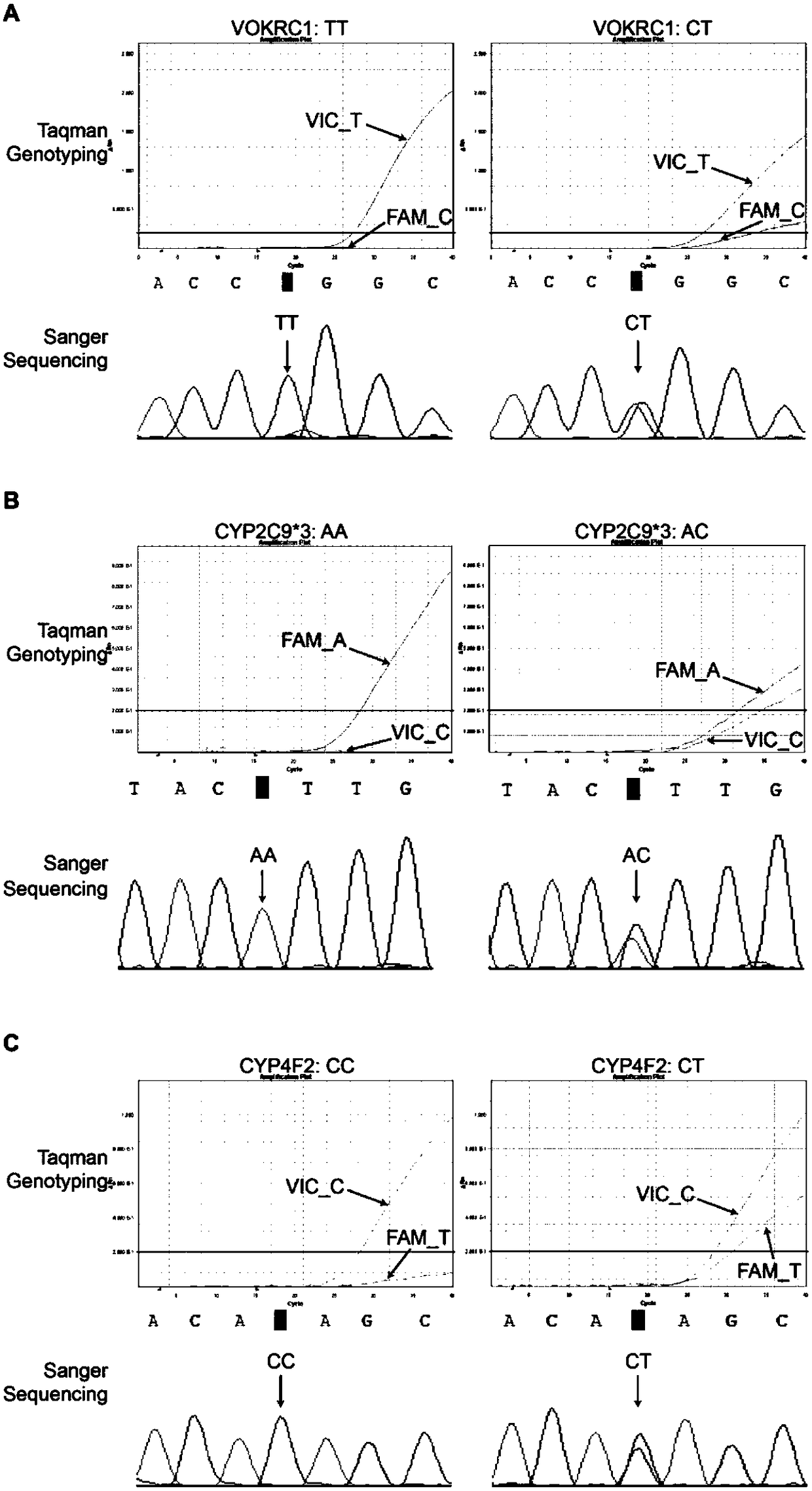
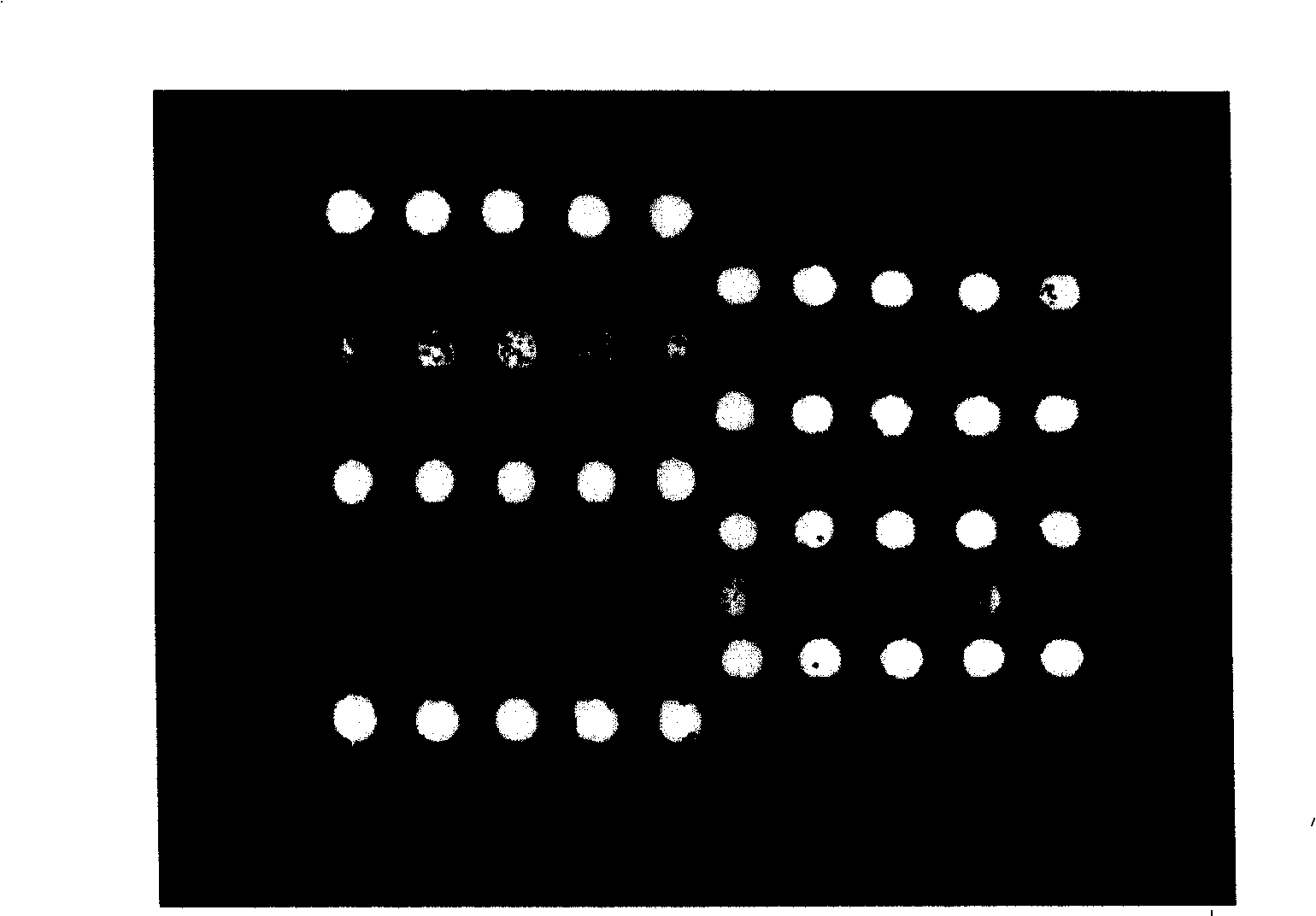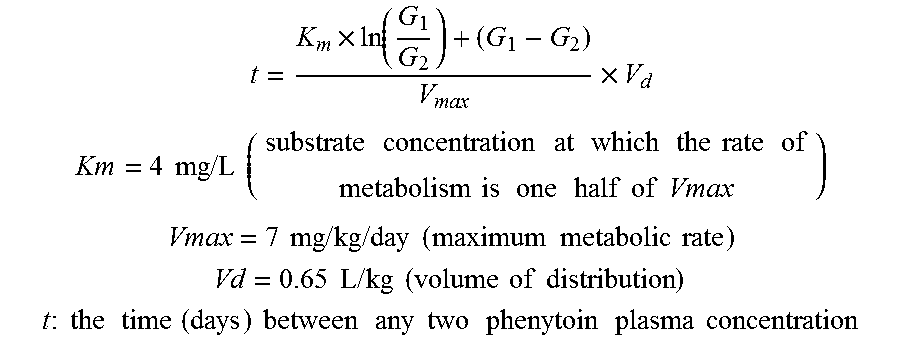Patents
Literature
44 results about "CYP2C9*3" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
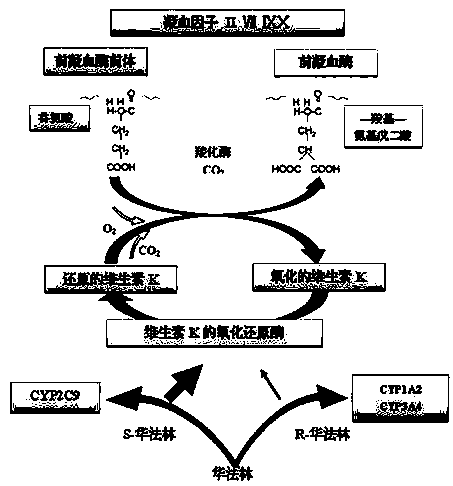
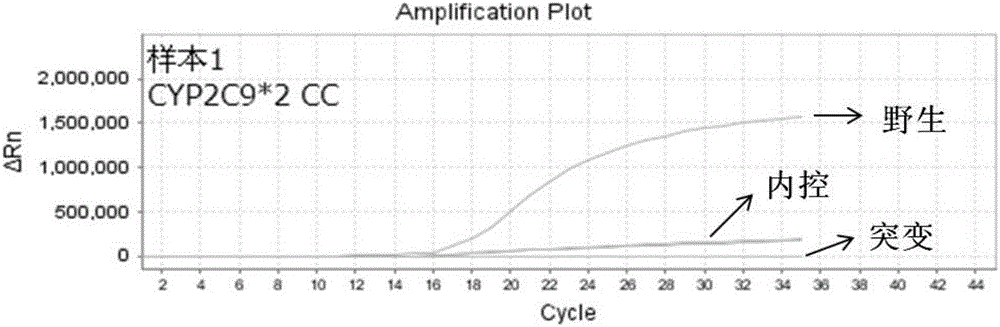
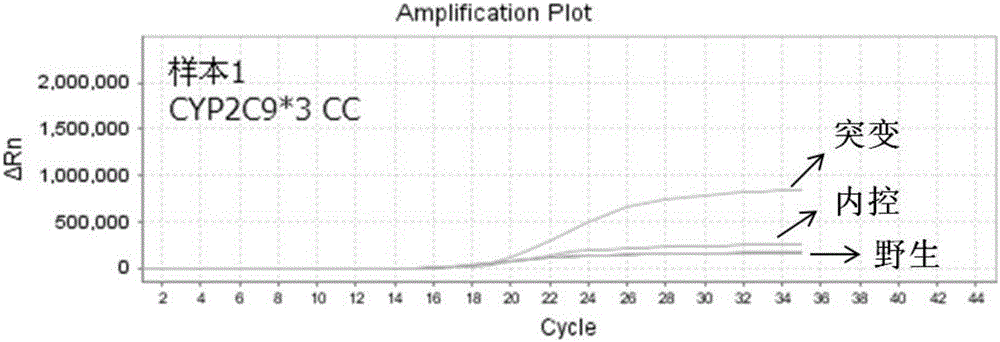
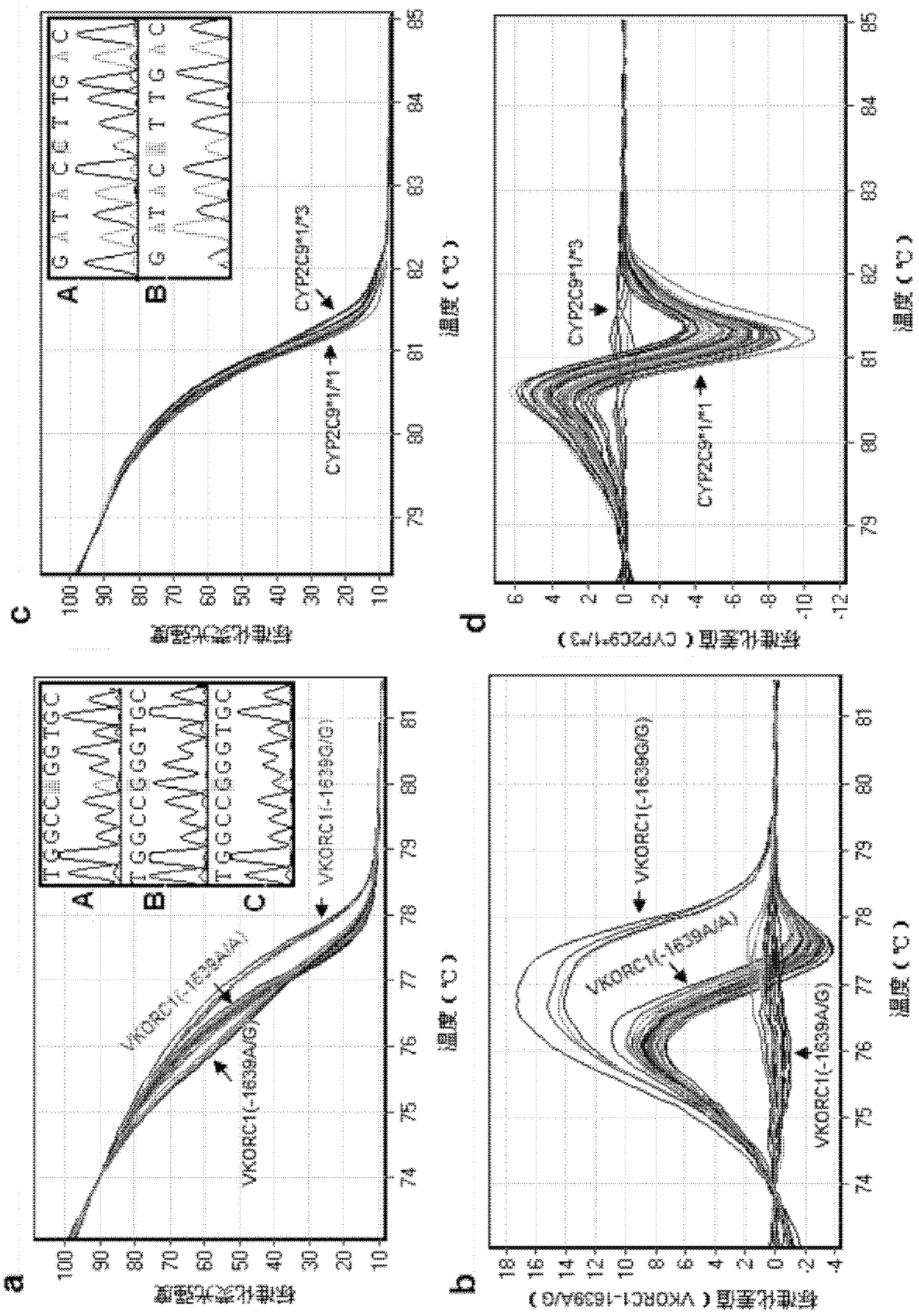
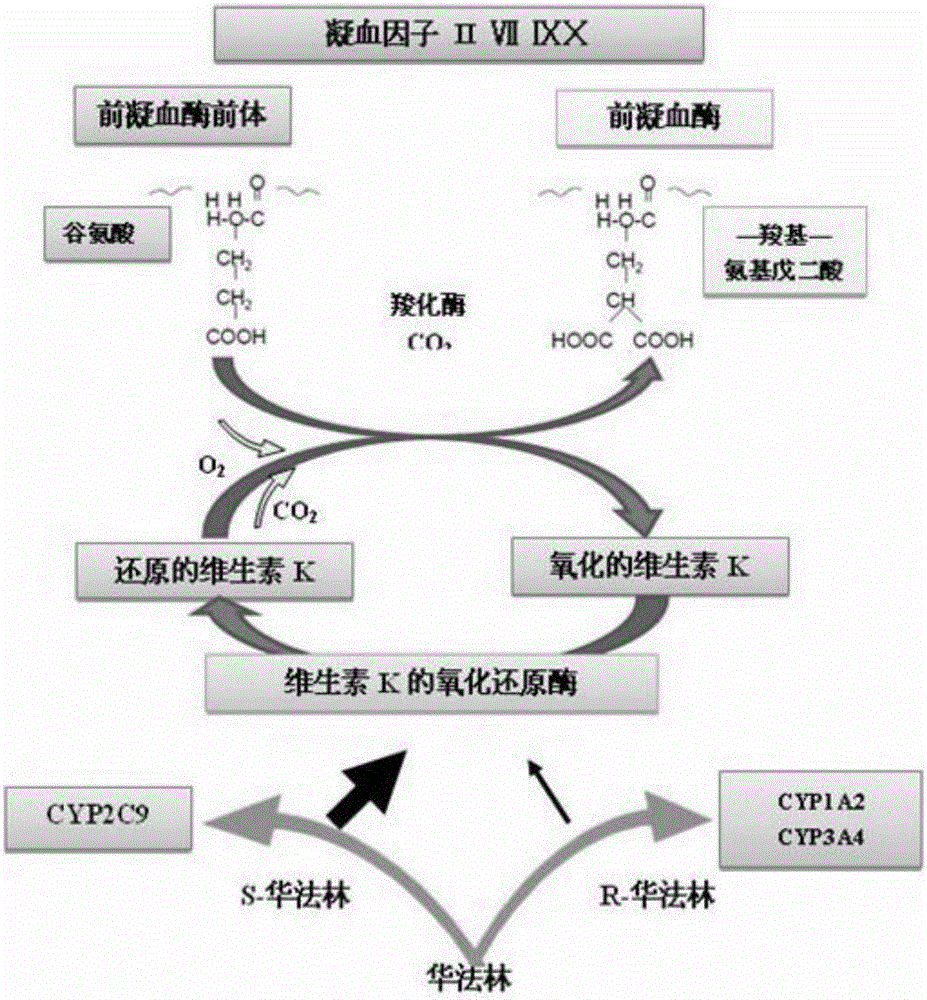
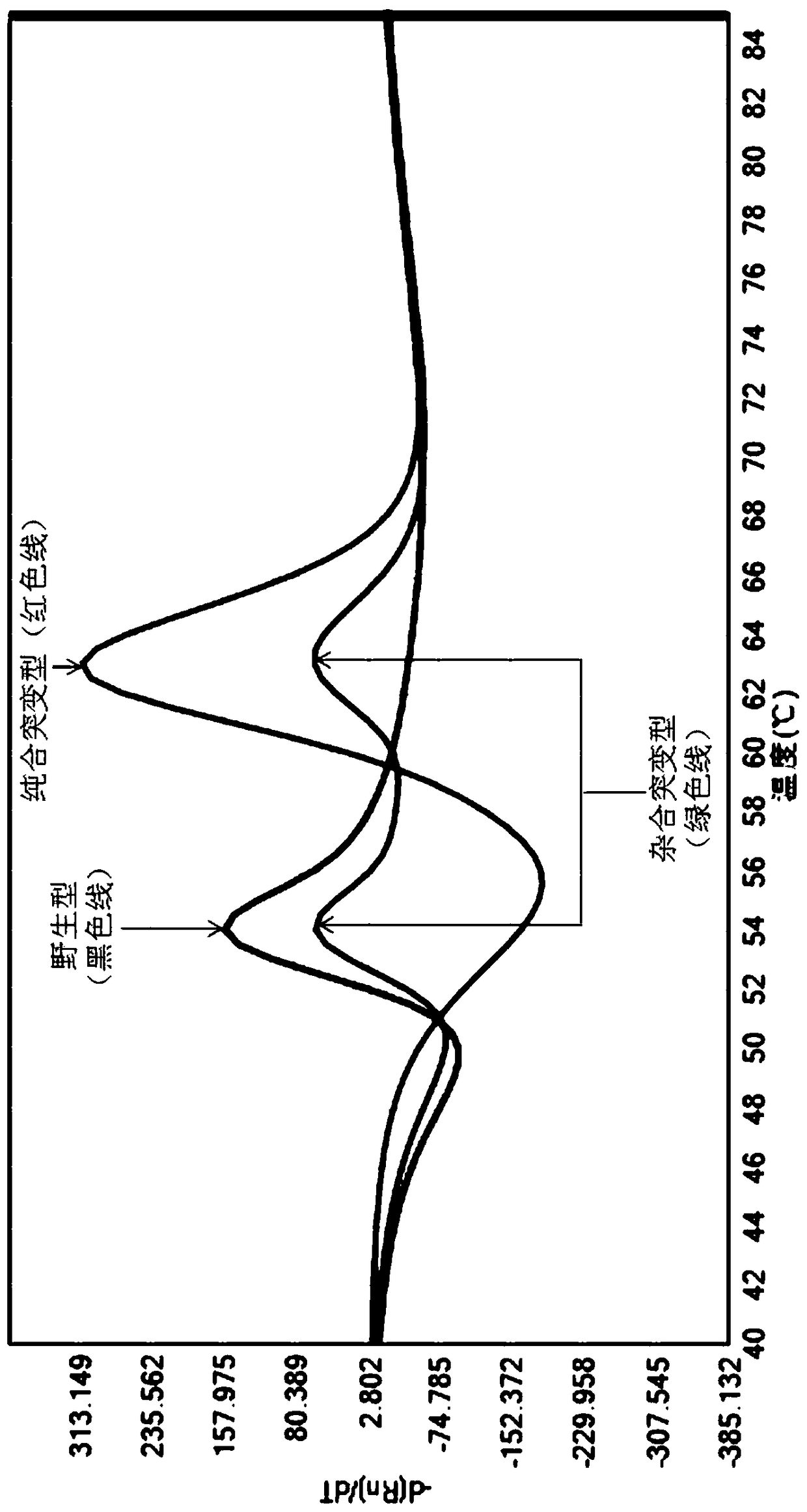
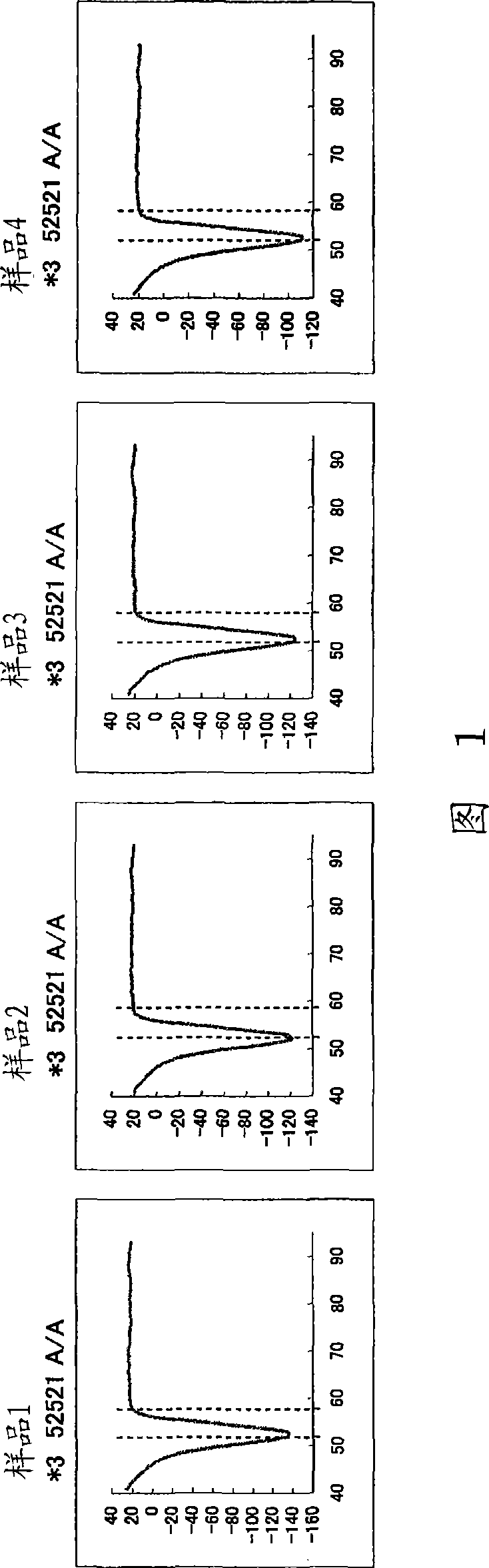
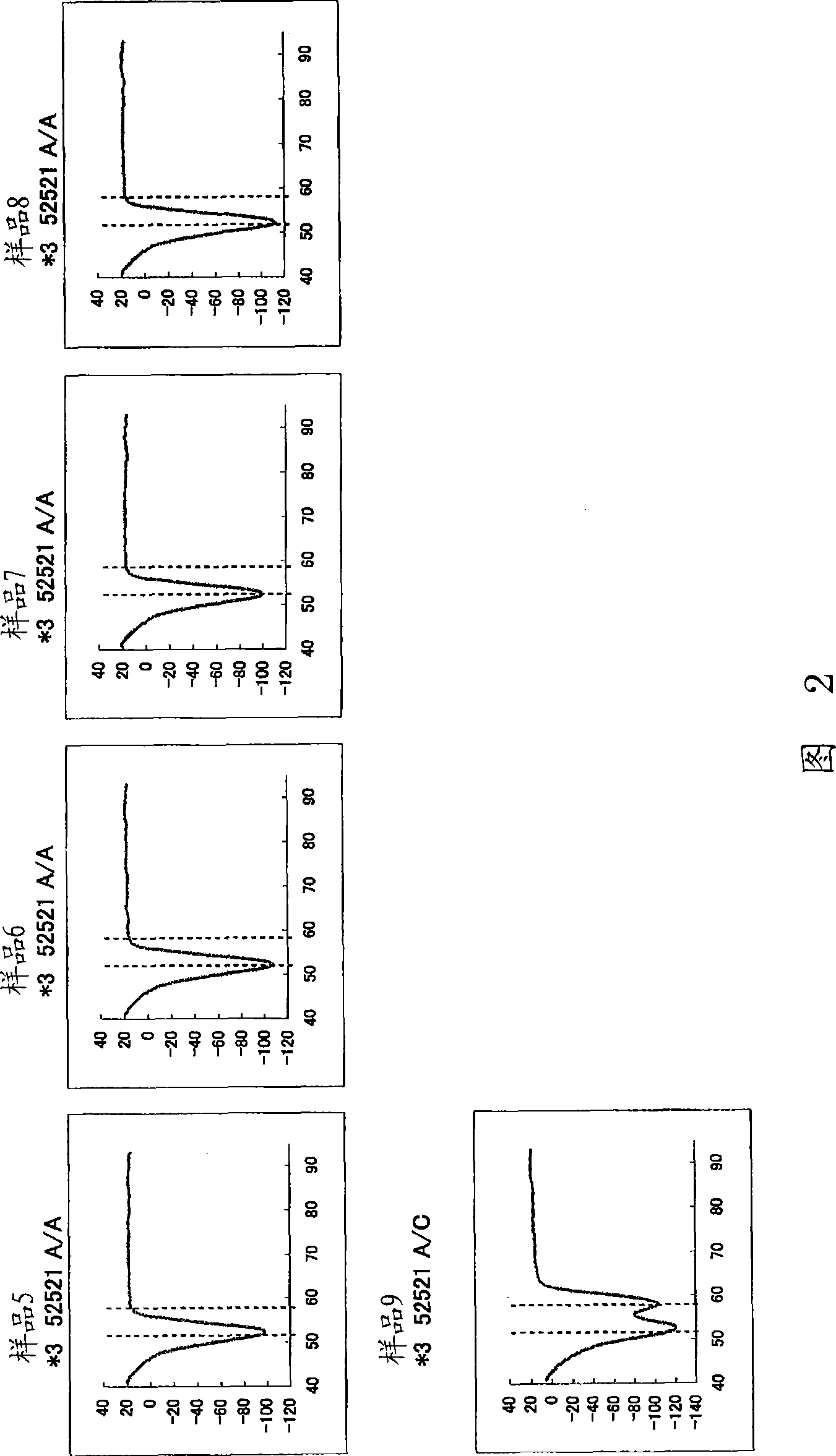
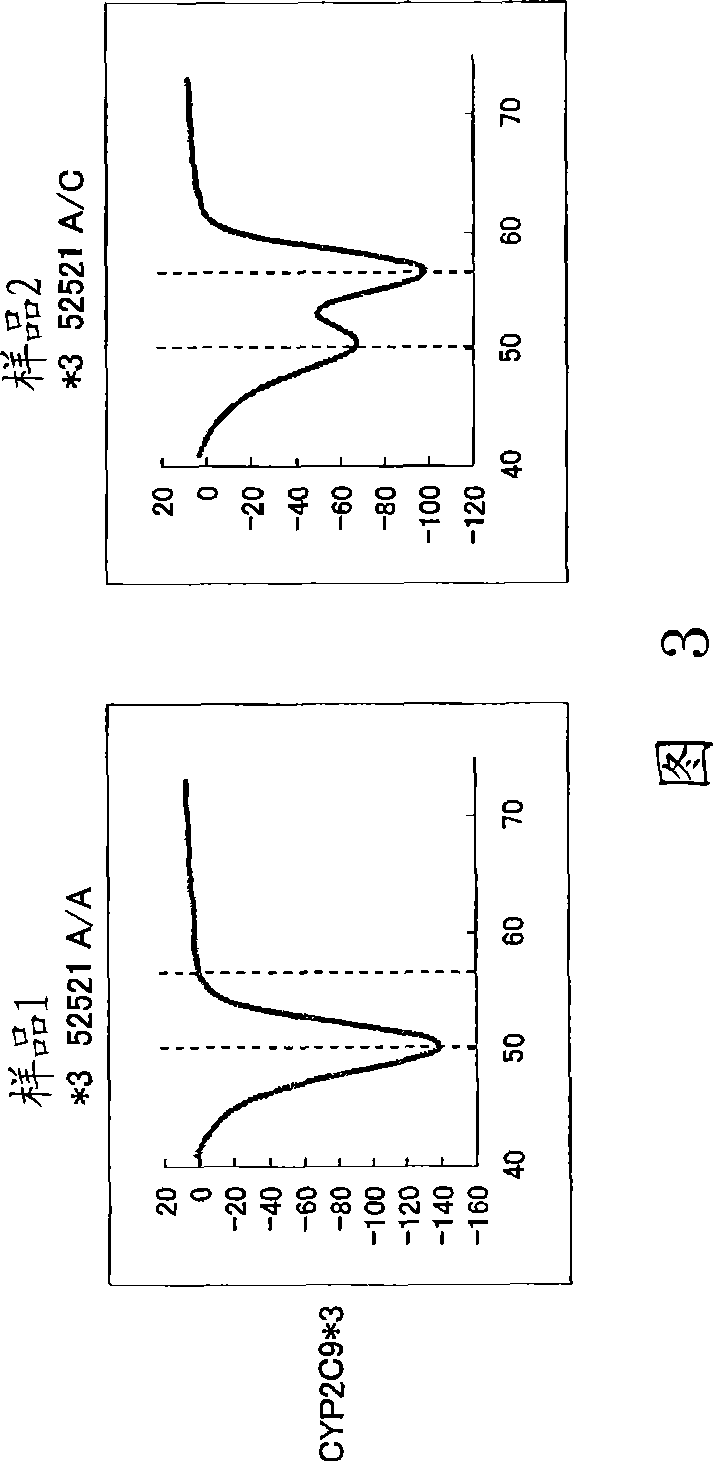
Cytochrome P450 2C9 (CYP2C9), a member of the CYP2C enzyme subfamily, ranks amongst the most important drug metabolizing enzymes in humans. Human CYP2C9 has been shown to exhibit genetic polymorphism. In addition to the wild-type protein CYP2C9*1, at least 32 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) have been reported within the coding region of the CYP2C9 gene producing the variant allozymes. CYP2C9*3 is one of them. CYP2C9*3 reflects an Ile359-Leu (I359L) change in the amino acid sequence, and have reduced catalytic activity compared with the wild type (CYP2C9*1).
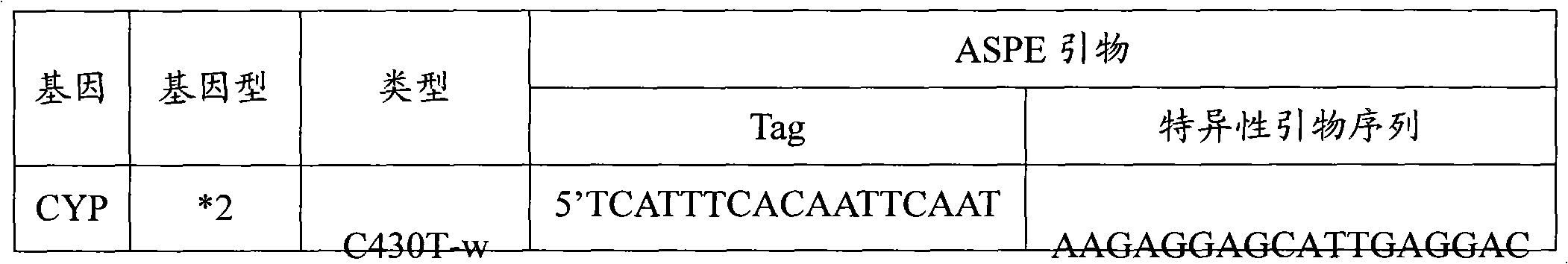
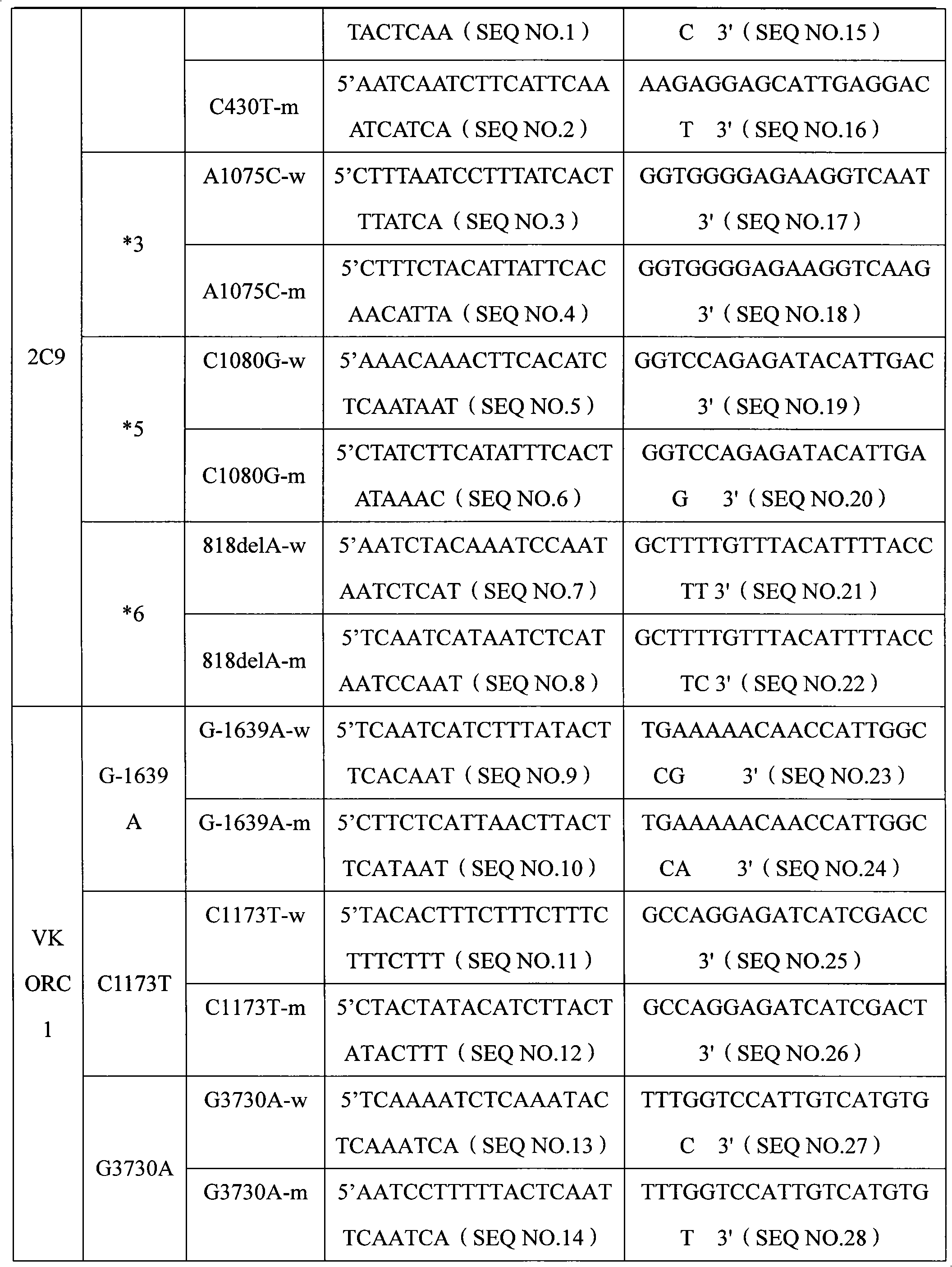
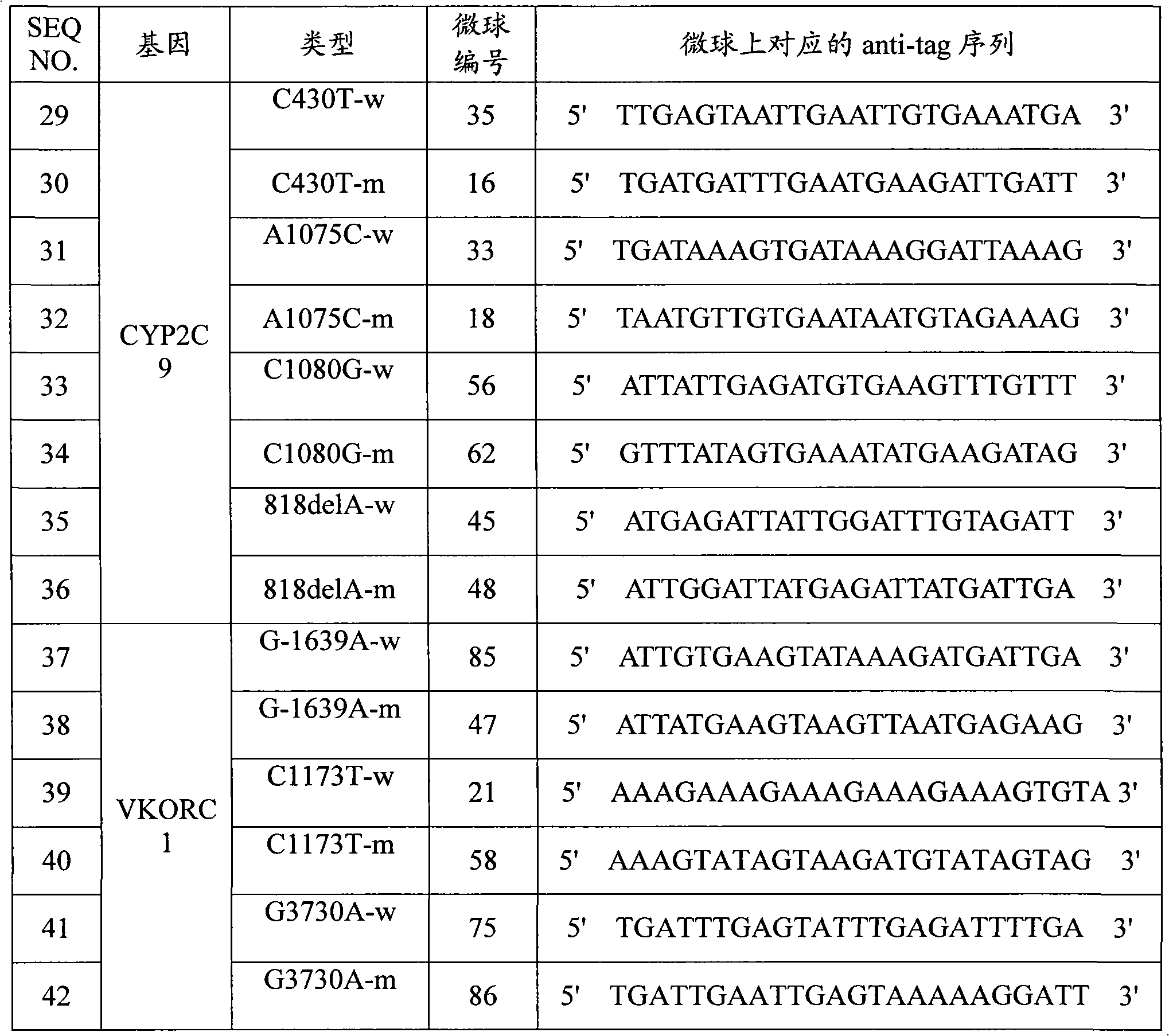
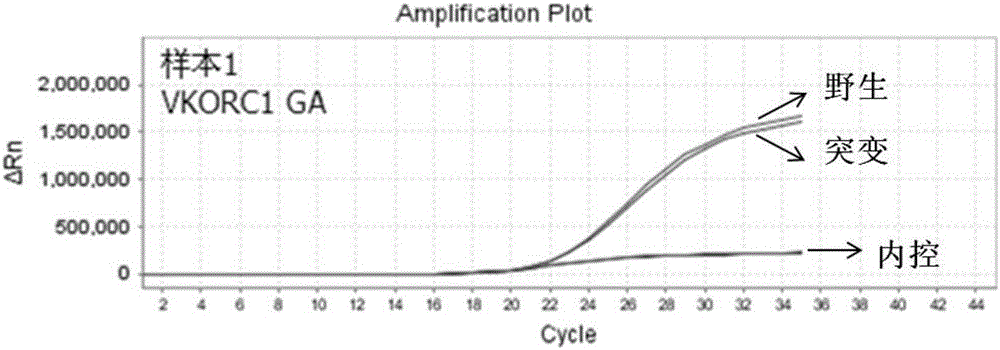
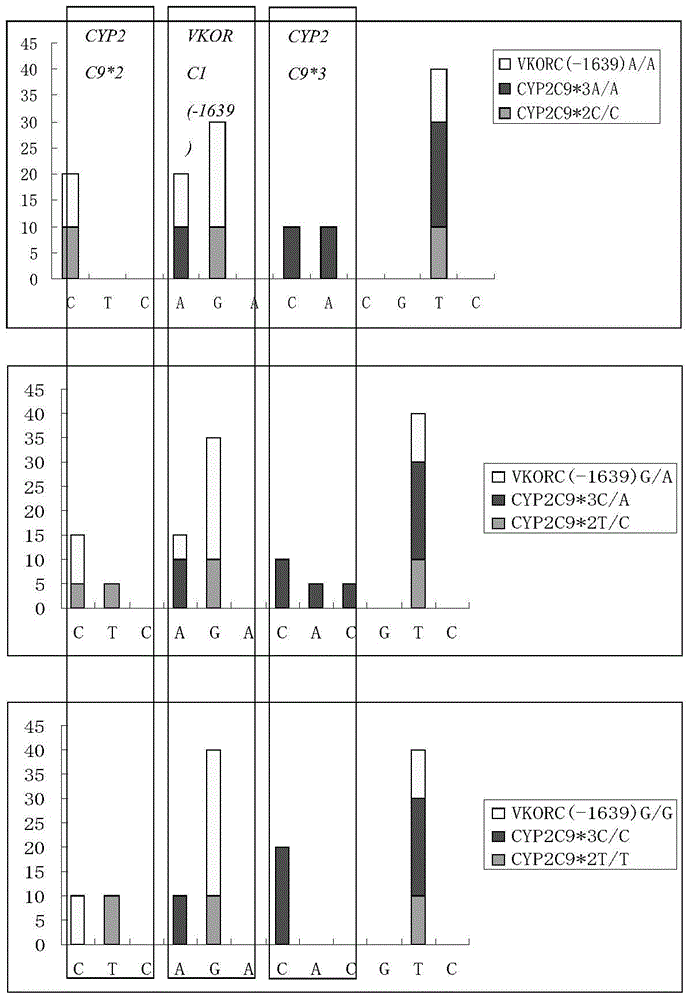
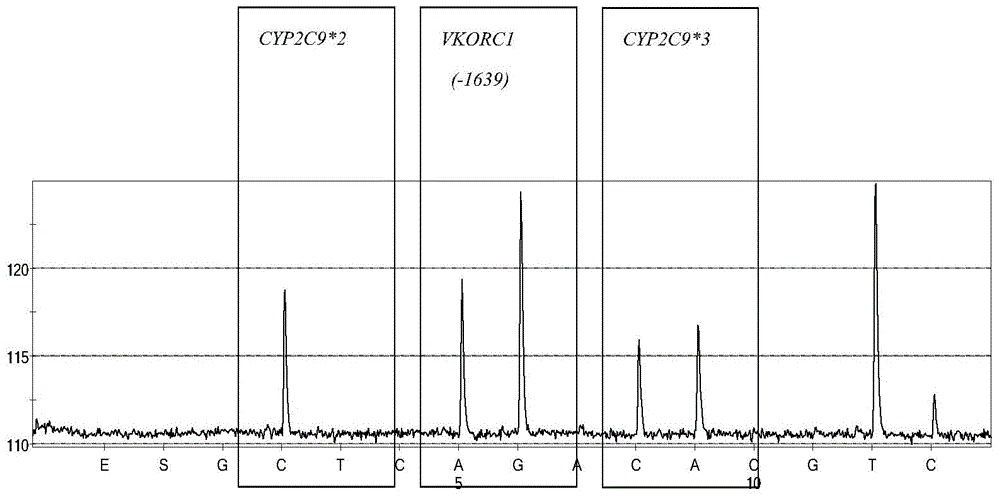
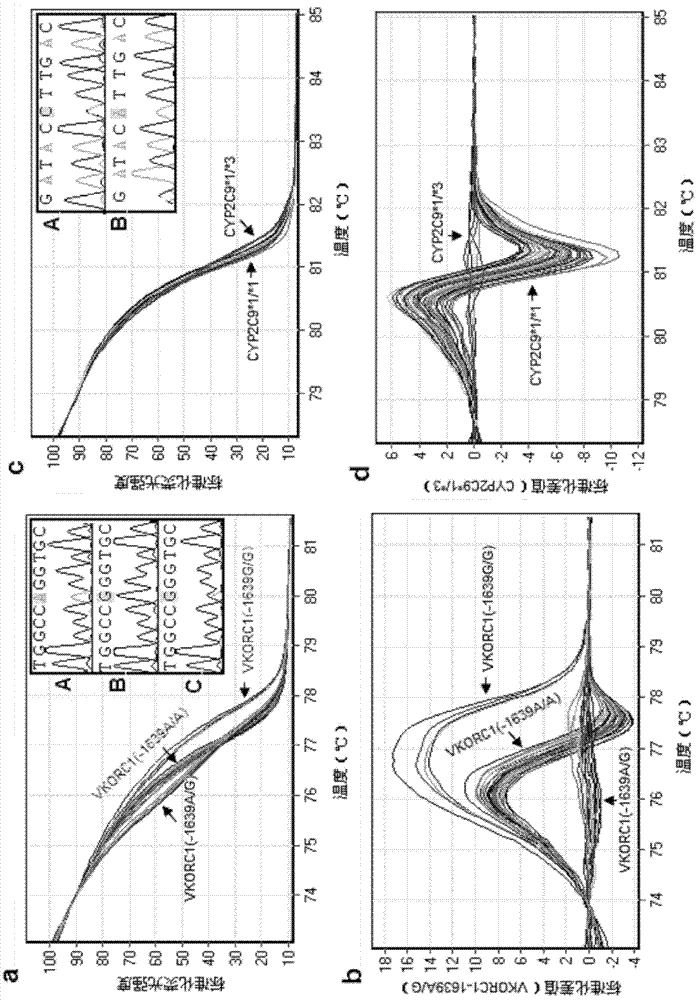
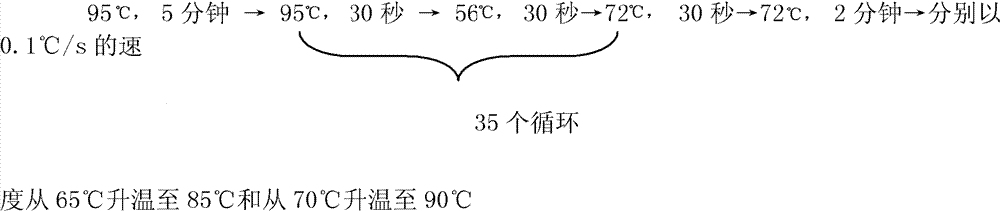
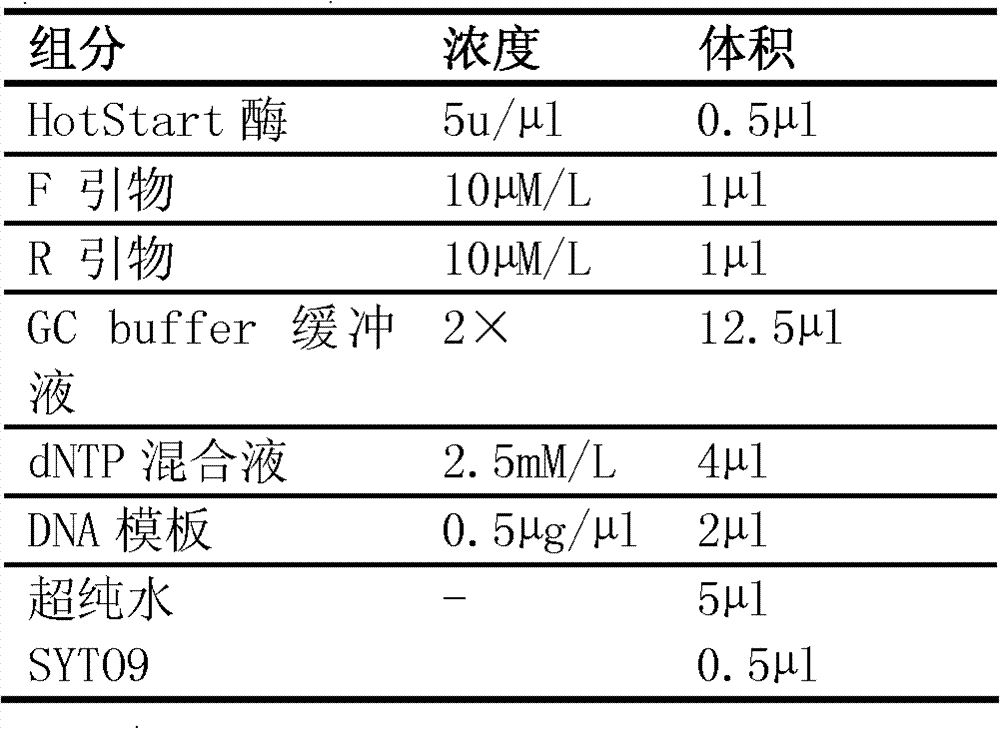
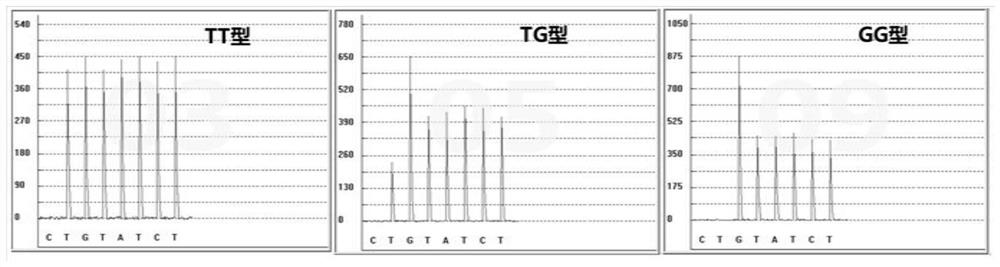
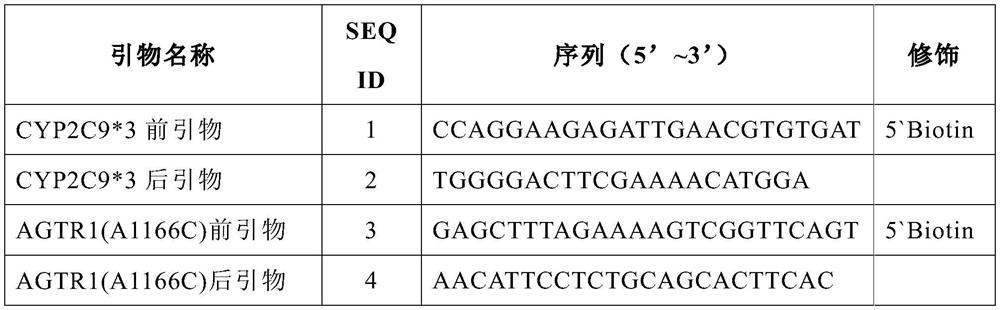
Specific primer, liquid-phase chip and method for SNP detection of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genes
ActiveCN101824466AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImplement parallel detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVKORC1Microsphere
The invention discloses a specific primer, a liquid-phase chip and a method for SNP detection of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genes. The liquid-phase chip comprises wild-type and mutable-type ASPE primer pairs and microspheres coated by a specific anti-tag sequence respectively, which are designed respectively aiming at each type of mutable loci, primers used for amplifying a CYP2C9 gene target sequence having CYP2C9*2, CYP2C9*3, CYP2C9*5 and CYP2C9*6SNP loci, and / or primers used for amplifying a VKORC1 gene target sequence having G1639A, G1173T and G3730A SNP loci. The liquid phase chip of the invention has a quite good signal-noise ratio, and the cross reaction does not happen between a designed probe and the anti-tag sequence basically; the ASPE primer designed by the invention has quite good specificity, and can accurately differentiate various types of mutable loci; and the detection method has the advantages that: a few steps are adopted, 7 types of SNP loci can be detected in one step, the operation is convenient, a lot of uncertain factors existing in a process of repeated operations can be avoided, and the detection accuracy is greatly improved.
Owner:SUREXAM BIO TECH
Gene chip for detection of hyperpiesis individual medicine correlated gene mutation and uses thereof
InactiveCN101343658AAccurate detectionSensitive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementGNB3CYP2C9*3
The invention relates to a gene chip used for detecting gene mutation relating to a high blood pressure personalized medicine. The gene chip for detecting the gene mutation relating to high blood pressure personalized medicine comprises a solid phase support, a gene probe (an oligonueleotide probe) fixed in the solid phase support sequentially and a PCR primer used for amplifying the mutated gene fragment in the sample; the gene probe (the oligonueleotide probe) and the PCR primer are designed aiming at one or two points of the gene mutation in ACE (I / D) and CYP3A5*3 and / or two or more points as follows: CYP2C9*3, CYP2C9*13, AGTR1(A1166C), CYP2D6*10, ADRB1(C1165G), TSC(C1784T), ADRB3(T727C), SCNN1G_rs5729, SCNN1G_rs5723, ENOSA_rs1799983 and GNB3(C825T). The invention provides the gene chip and applications thereof for conveniently, quickly and systematically detecting the gene mutation relating to high blood pressure personalized medicine so as to determine drug reactions.
Owner:湖南宏灏基因生物科技有限公司
Multiplex PCR combined pyrosequencing kit used for guiding individualized medication of warfarin and detection method thereof
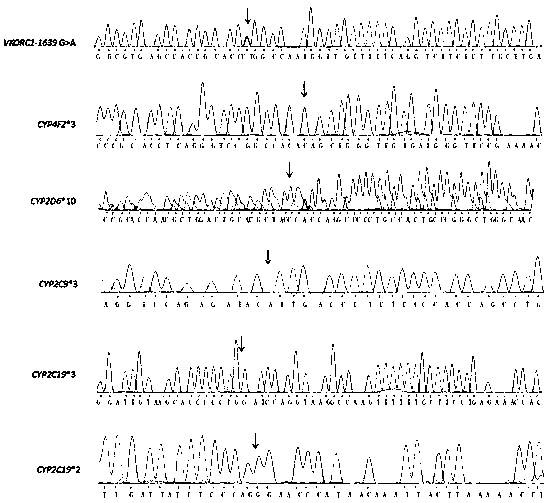
The invention provides a multiplex PCR combined pyrosequencing kit used for guiding individualized medication of warfarin and a detection method thereof, relating to warfarin. The kit comprises a whole blood genome DNA extraction reagent, multiplex PCR amplification primers, a multiplex PCR amplification reagent, a single-stranded DNA separating and purifying reagent, pyrosequencing primers, a pyrosequencing reagent and a kit body. The detection method comprises the following steps: extraction of human whole blood genome DNA; multiplex PCR amplification; separation and purification of a single-stranded DNA sample; and pyrosequencing and result analysis. According to the invention, main factors influencing difference of individual dosage of warfarin, i.e., important gene polymorphic sites of VKORC1 and CYP2C9, specifically being VKORC1-1639G>A, CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3, are detected so as to guide individualized dosage of warfarin in treatment of patients needing to take warfarin, thereby achieving the purpose of reduction in side effects.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL XIAMEN UNIV +1
Primer and probe composition for detecting polymorphism of human CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genes, kit and application
ActiveCN108570498AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceMicrobiology
The invention discloses a primer and probe composition for detecting polymorphism of human CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genes, a kit and application. The primer and probe composition comprises three pairs of specific primers for amplifying CYP2C9*2, CYP2C9*3 and VKORC1 sites, and three specific fluorescent probes. The primers and the probes, disclosed by the invention, have high sensitivity, strong specificity and strong anti-interference capability; a manner combining an asymmetric PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification and fluorescent probe melting curve analysis technologies is used for detecting the gene polymorphism; different gene types can be effectively distinguished according to the quantity and Tm value of a melting peak; a result is convenient, clear and objective to judge and read.Single-tube sampling can be used for simultaneously detecting 6 mutation types of 3 gene sites; the primer and probe composition is simple and convenient to operate and the detection efficiency is improved; a large batch of samples can be detected and clinical operation is facilitated.
Owner:SHANDONG VIGENE BIOSCI
Hypertension gene polymorphism fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) solubility curve detecting kit and application thereof
PendingCN109457024AEasy to operateShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSolubilityRibonucleoside
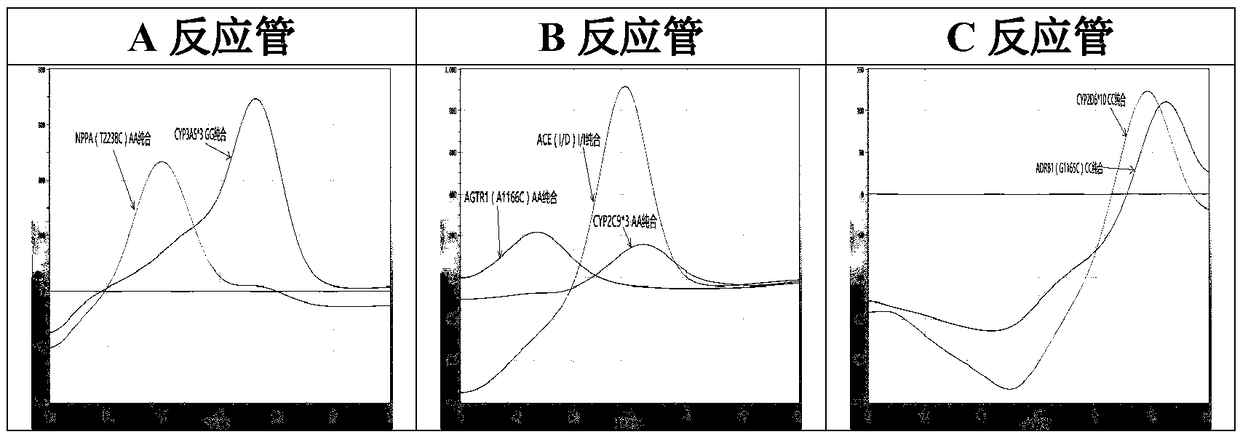
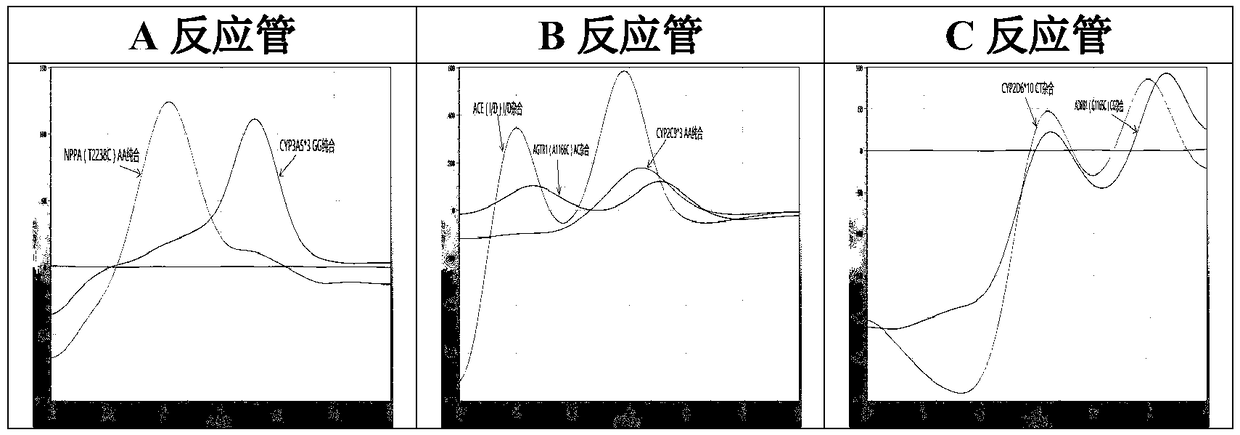
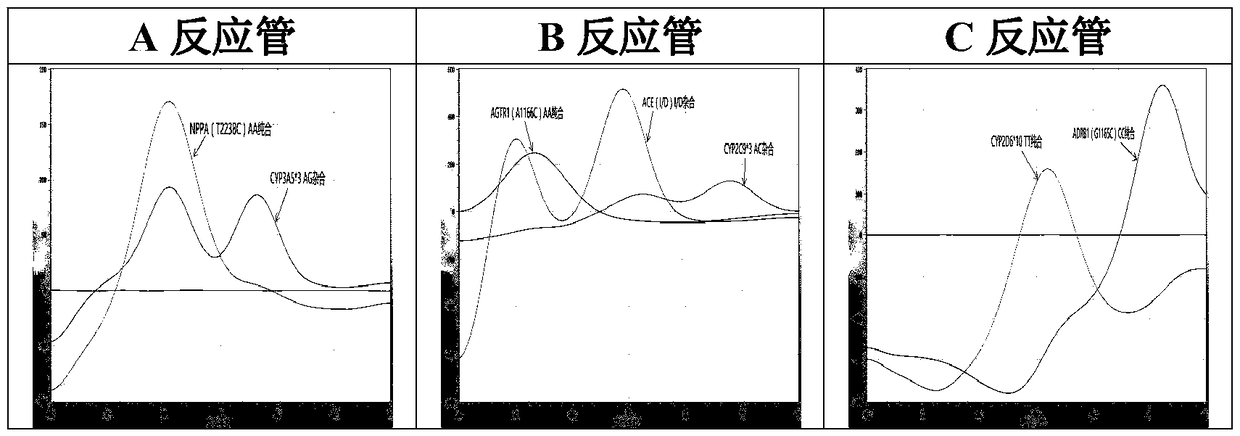
The invention relates to a hypertension gene polymorphism fluorescent PCR solubility curve detecting kit and application thereof, and a hypertension medication gene multiple-PCR solubility curve detecting method. The hypertension gene polymorphism fluorescent PCR solubility curve detecting kit mainly comprises a primer combination, a probe combination, and PCR reaction agents such thermally activated polymerases, PCR buffer solution and dNTPs (deoxy-ribonucleoside triphosphates) and involves polymorphism detection of 7 hypertension-related genes including CYP2D6*10, CYP2C9*3, ADRB1(1165G)C), AGTR1(1166A)C), CYP3A5*3, NPPA(T2338C) and ACE(I / D); the three reaction agents are applied to perform PCR amplification and solubility analysis to determine the related polymorphism of the 7 genes to guide clinical customized application of 5 majors types of hypertension drugs. The hypertension gene polymorphism fluorescent PCR solubility curve detecting kit can easily complete detection through 3reaction tubes, and meanwhile, save a nucleic acid extraction process, simplify operation steps and achieve a simple interpretation method.
Owner:众福健康科技(杭州)有限公司
Kit and method for detecting gene polymorphism related to warfarin personalized medication by pyro sequencing method
InactiveCN102676666AQuick analysisAccurate analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementVKORC1Nucleotide
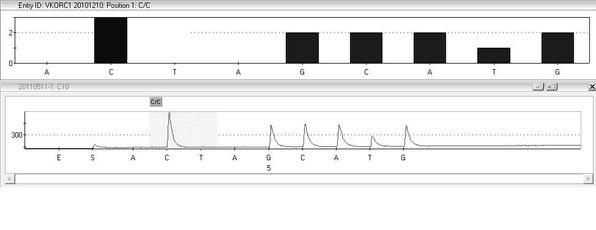
The invention discloses a kit and a method for detecting the gene polymorphism related to warfarin personalized medication by a pyro sequencing method. The kit is used for typing genes related to the warfarin medication, and the single nucleotide polymorphism of VKORC1-1639 G>A (rs9923231) and CYP2C9*31075A>C(rs1057910) is involved; and the kit comprises primers shown as SEQ ID NO.3-8. By the kit, VKORC1-1639G>A and CYP2C9*3 1075A>C can be detected accurately and quickly in high flux, so that the safe, reasonable and effective personalized administration of the warfarin medication is realized.
Owner:周宏灏
Kit for rapidly detecting warfarin individualized medication related gene SNP sites, and its detection method
The invention relates to a kit for rapidly detecting warfarin individualized medication related gene SNP sites, and its detection method, and belongs to a genetic detection technology in the clinic detection technique of the biomedical field. The genetic typing of two polymorphic sites comprising CYP2C9*3(1061A / C) and VKORC1(-1639G / A) is rapidly and accurately carried out through human peripheral blood DNA drawing, specific PCR amplification by a Taq man probe and fluorescence signal analysis. The invention provides primers, probes and kits which are used for detecting the polymorphic sites, a use of the primers and the probes in the preparation of the kits, and a use of the determination of the warfarin application amount of a patient according to the detection results of the polymorphic sites. The determination use can effectively reduce the generation of the warfarin application amount related adverse events and prevent thrombotic diseases. The detection method can be used for the auxiliary diagnosis and treatment of various patients needing warfarin clinically.
Owner:丁虎 +1
Primer group and test kit for detecting polymorphism of related genes of hypertensive drugs
The invention discloses a primer group and a test kit for detecting the polymorphism of related genes of hypertensive drugs. The primer group is characterized by containing the following primers: CYP2D6*10-F, CYP2D6*10-R, ADRB1-F, ADRB1-R, AGTR1-F, AGTR1-R, ACE-F, ACE-R, CYP2C9*3-F and CYP2C9*3-R. The genes of CYP2C9*3, ADRB1 (1165G is greater than C), AGTR1 (1166A is greater than C), CYP2D6*10 and ACBL (I / D) disclosed by the invention are proved to be closely related to the efficacy of common drugs for treating hypertension; in addition, the rational and safety use of drugs for hypertension patients can be guided according to detection results of polymorphism site of the genes.
Owner:SHANGHAI PERSONAL BIOTECH
Primer pair for detecting CYP2C9 genetic typing through pyrosequencing method and kit
InactiveCN105368826AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleic acid detectionBiotin
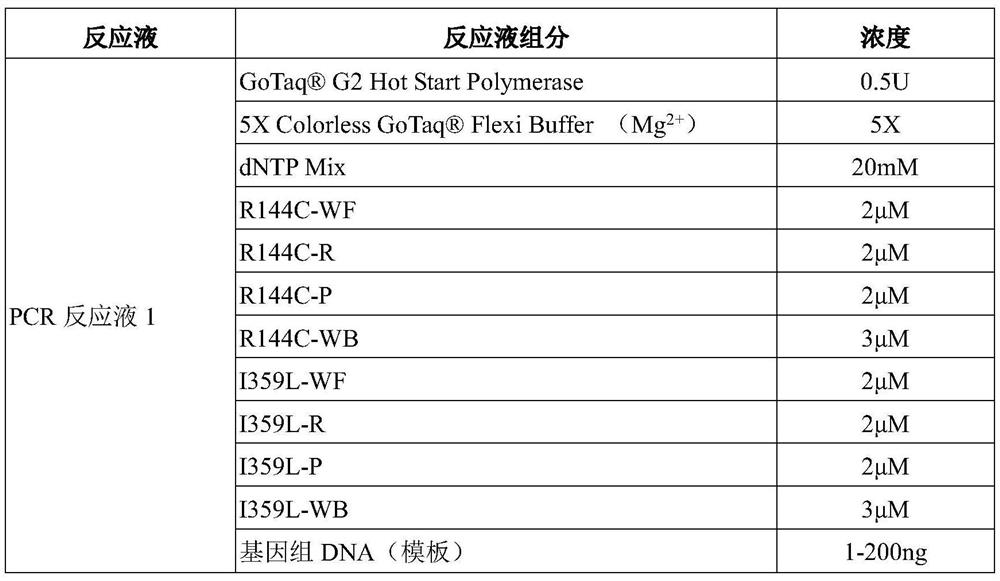
The invention relates to a primer pair for detecting CYP2C9 genetic typing through a pyrosequencing method and a kit, and belongs to the technical field of in vitro nucleic acid detection. The primer pair comprises a CYP2C9*2 forward amplification primer, a CYP2C9*2 reverse amplification primer, a CYP2C9*2 sequencing primer, a CYP2C9*3 forward amplification primer, a CYP2C9*3 reverse amplification primer and a CYP2C9*3 sequencing primer. Biotin labeling is conducted at the 5' end of the CYP2C9*2 forward amplification primer and the 5' end of the CYP2C9*3 reverse amplification primer. The kit comprises the amplification primers, a PCR reaction solution 1, a PCR reaction solution 2, the sequencing primers, uracil DNA glycosylase and Taq polymerase. The kit has the advantages of being accurate in detection result, high in specificity, short in detection period, easy to operate and capable of effectively meeting the clinical examination requirement.
Owner:CHANGSHA 3G BIOTECH
Primer, probe and kit for detecting gene polymorphism of CYP2C9 and VKORC1
InactiveCN106399560AAccurate detectionHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVKORC1Hazardous substance
The invention discloses a primer, a probe and a kit for detecting gene polymorphism of CYP2C9 and VKORC1. The primer comprises a gene detection specificity primer sequence of three loci YP2C9*2, CYP2C9*3 and VKORC1 and a probe sequence (SEQ ID NO.1-12). An ARMS primer is used to differentiate field and mutant genes, so that the primer has the advantages of high sensitivity and high specificity and is suitable for various sample types and high in detection result accuracy. In addition, the ARMS primer is quick and simple to synthesize, low in synthesis cost and better in amplification effect, and production cost can be lowered effectively. The kit is high in detection speed and quite convenient, and the whole detection process only takes 90 minutes. The whole kit does not contain toxic and harmful substances, thereby being harmless to operating personnel and environment and suitable for wide application in clinic detection and the like.
Owner:武汉海吉力生物科技有限公司
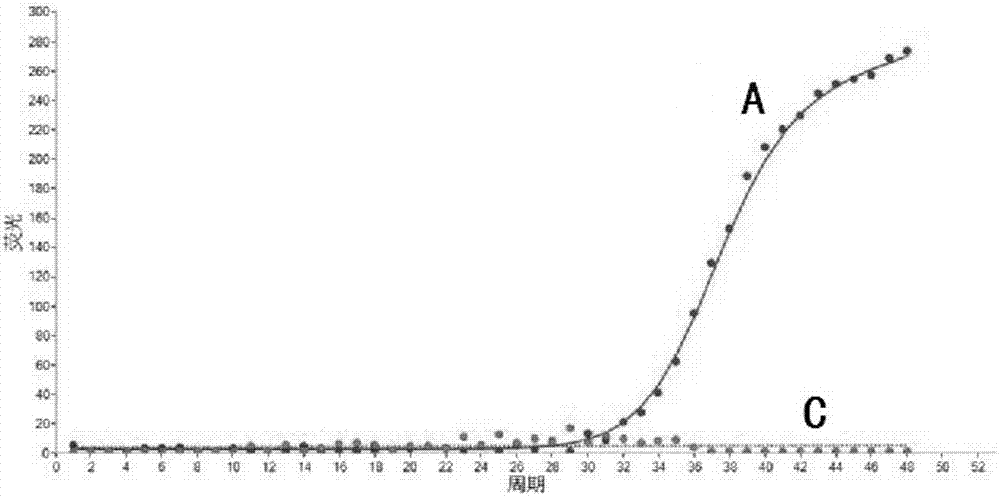
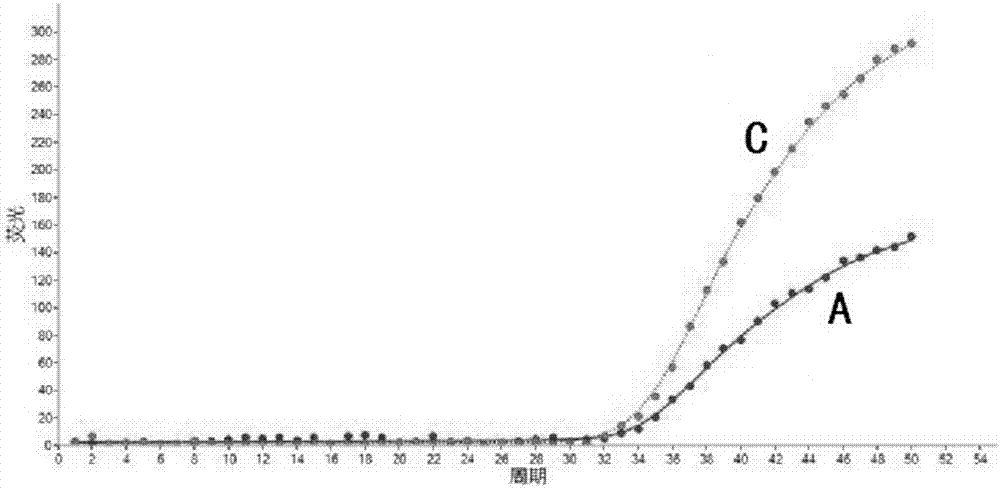
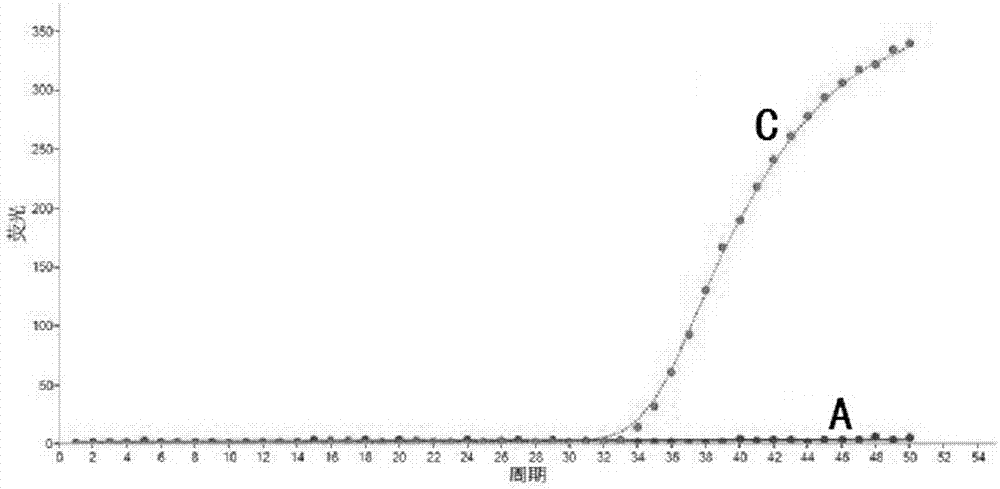
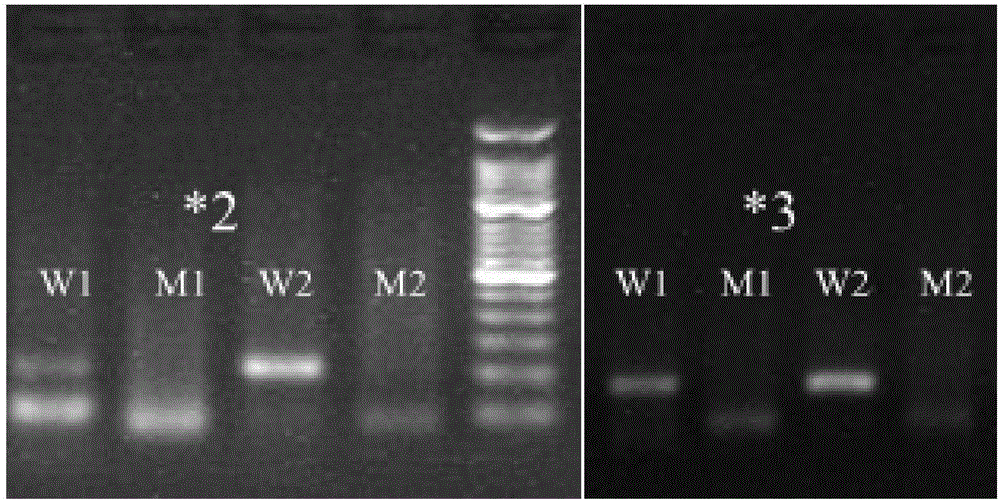
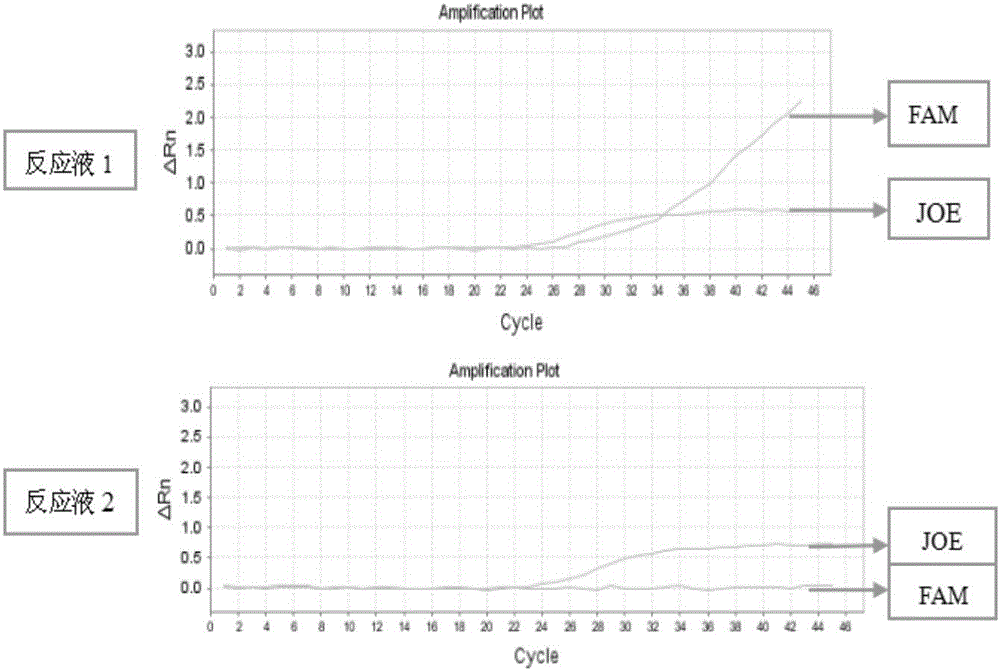
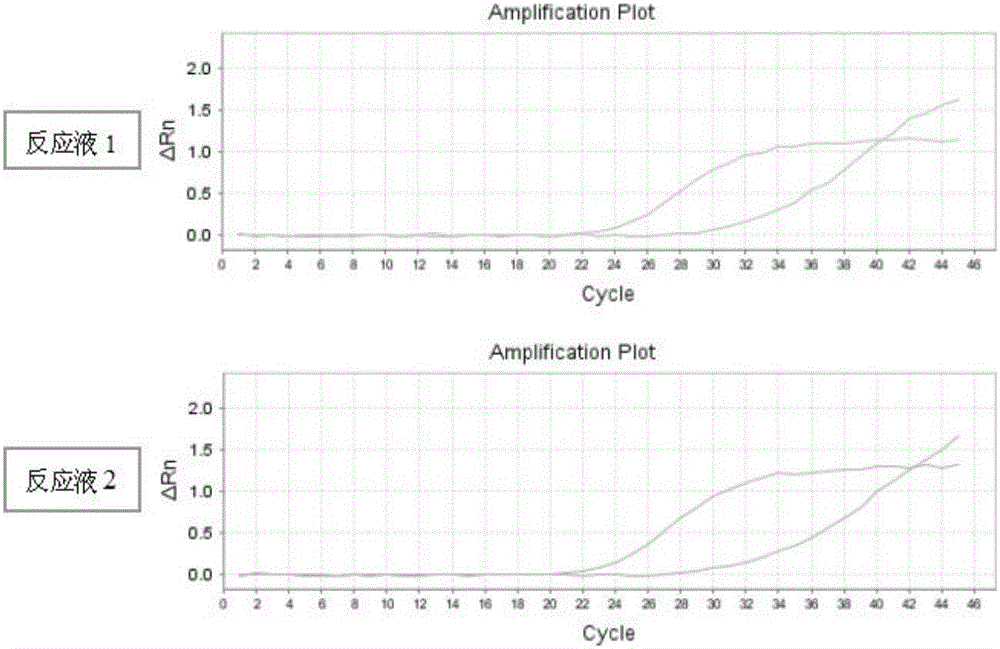
Primer, molecular beacon and kit for rapidly detecting CYP2C9*3 gene polymorphism and detection method of CYP2C9*3 gene polymorphism
InactiveCN107227371AEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerPolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a kit for rapidly detecting CYP2C9*3 gene polymorphism. The kit comprises a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) reaction mixing solution which comprises the following raw materials by final concentration: 0.05-0.12 U / microliter of DNA polymerase, 0.2 mM of dNTPs, 1 X of 5 X PCR buffering solution, 1.5-3.5 mM of MgCl2, 0.0005-0.015% (w / v) of lauryl sodium sulfate, 0.001-0.03% (w / v) of polyethylene glycol octylphenol ether, 0.5-1 micron of a forward primer, 0.5-1 micron of a reverse primer, 0.5-1 micron of a mutant molecular beacon, and 0.5-1 micron of a wild type molecular beacon; and the PCR reaction mixing solution is used for detecting cell samples. The primer, a Taqman-MGB probe and the kit for rapidly detecting the CYP2C9*3 gene polymorphism and the detection method of the CYP2C9*3 gene polymorphism are simple to operate, free from pollution, and rapid to detect.
Owner:重庆京因生物科技有限责任公司
Detection kit for guiding warfarin dosage with high precision and detection method thereof
InactiveCN106350599ASafe and reasonable to useStable INR valueMicrobiological testing/measurementWarfarinVKORC1
The invention provides a detection kit for guiding warfarin dosage with high precision. The kit comprises amplification primers containing VKORC1 (1639G / A), CYP4F2(V433M), GGCX rs11676382, CYP2C9*2, CYP2C9*3, CYP2C9*5 and CYP2CP*6, a PCR reagent and a RFLP reagent. The invention also provides a detection method of the kit. According to the invention, the optimal dosage of warfarin of a patient can be accurately predicated, so as to assist doctors in using warfarin more reasonably and safely, thus reaching the steady INR value as far as possible, reducing the risks of bleeding and thrombus in the early stage of administration, and improving the treatment effect.
Owner:成都睿杰森生物科技有限公司
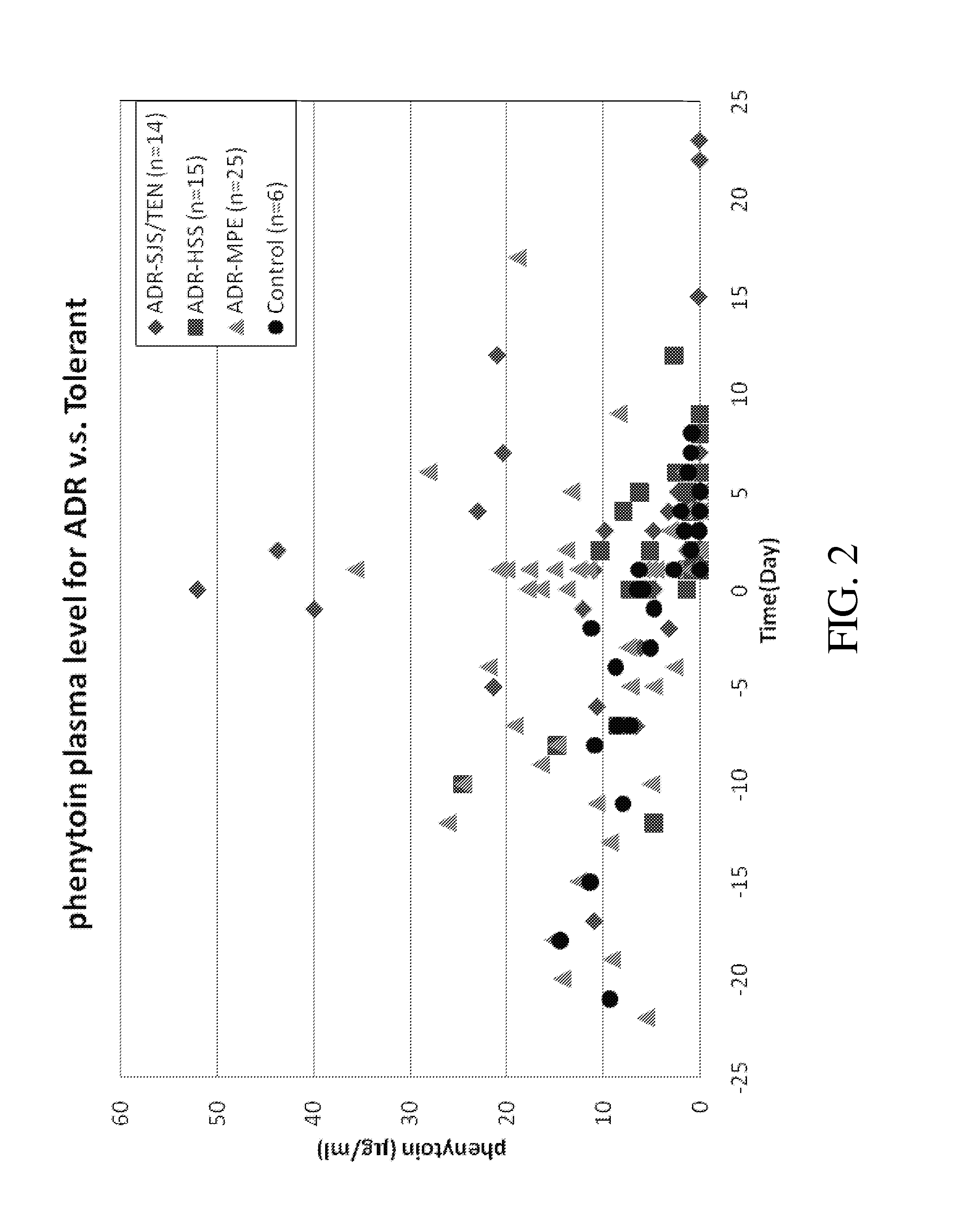
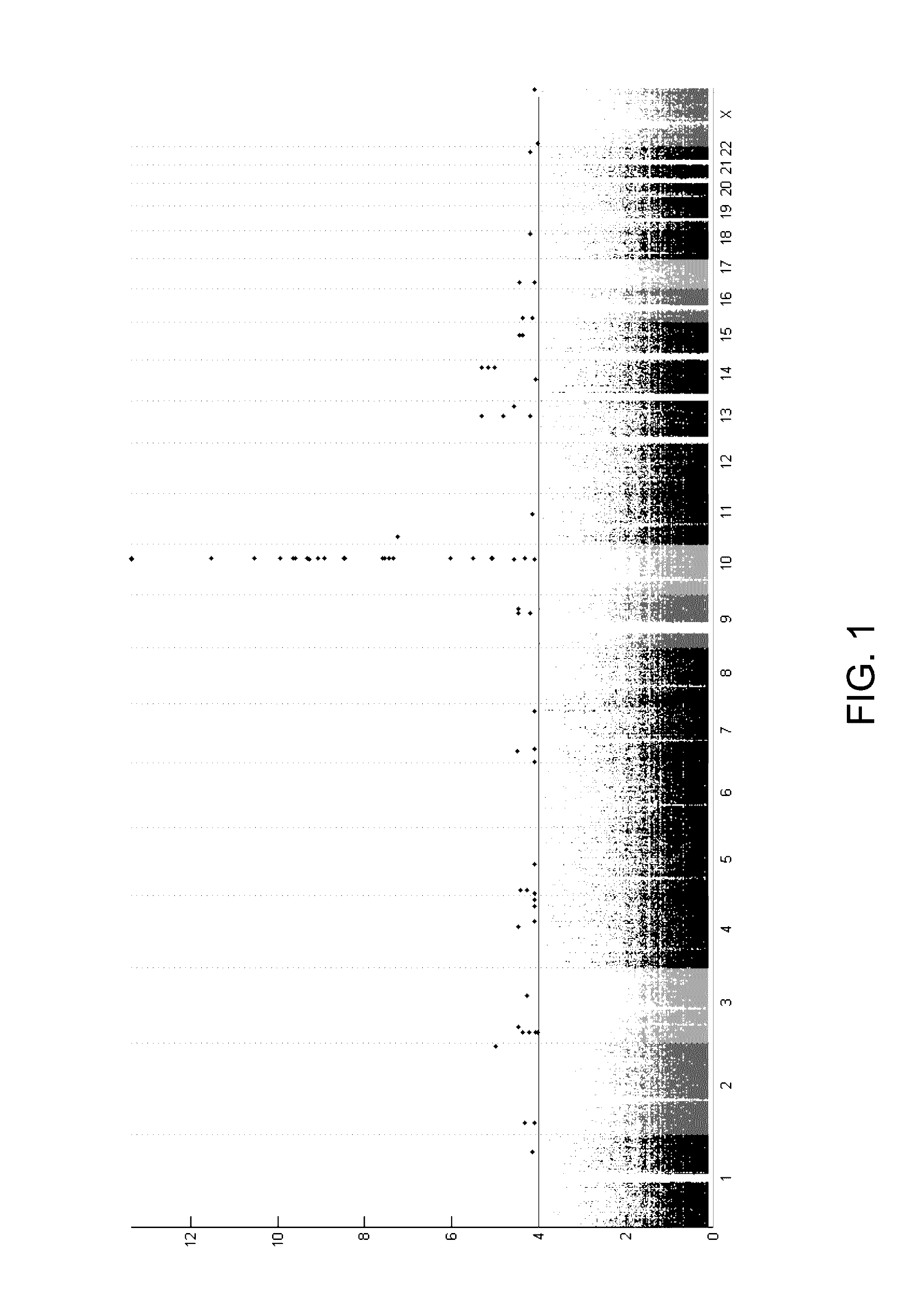
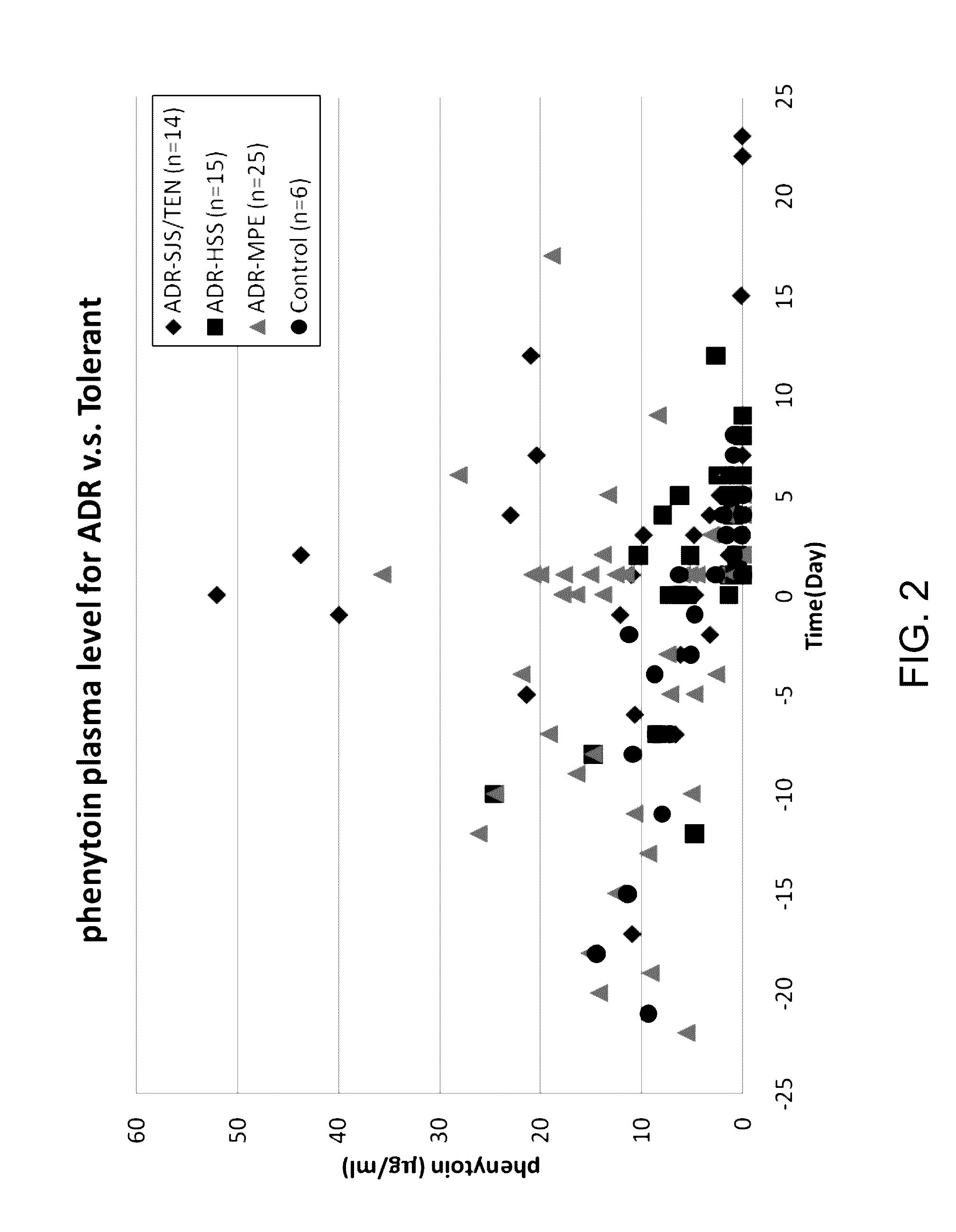
Risk assessment for phenytoin-induced adverse drug reactions
InactiveUS20150225788A1Predict riskNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementHLA-BCvd risk
A method of predicting the risk of a patient for developing phenytoin-induced adverse drug reactions (ADRs), including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), or drug reactions with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) is disclosed. Genetic polymorphisms of CYP2C genes (including rs1057910 (CYP2C9*3) and rs3758581 on CYP2C19), and HLA alleles (including HLA-B*1502, HLA-B*1301, and HLA-B*5101) can predict adverse reactions caused by phenytoin or fosphenytoin. Accordingly, the present invention provides a kit to assess the risk of a patient for developing adverse reactions in response to phenytoin-related drugs, which comprises the determination of the presence of a specific allele selected from the group consisting of rs1057910 (CYP2C9*3), rs3758581 on CYP2C19, HLA-B*1502, HLA-B*1301, and HLA-B*5101, wherein the presence of at least one allele is indicative of a risk for the adverse drug reactions.
Owner:CHANG GUNG MEDICAL FOUND CHANG GUNG MEMORIAL HOSPITAL AT KEELUNG
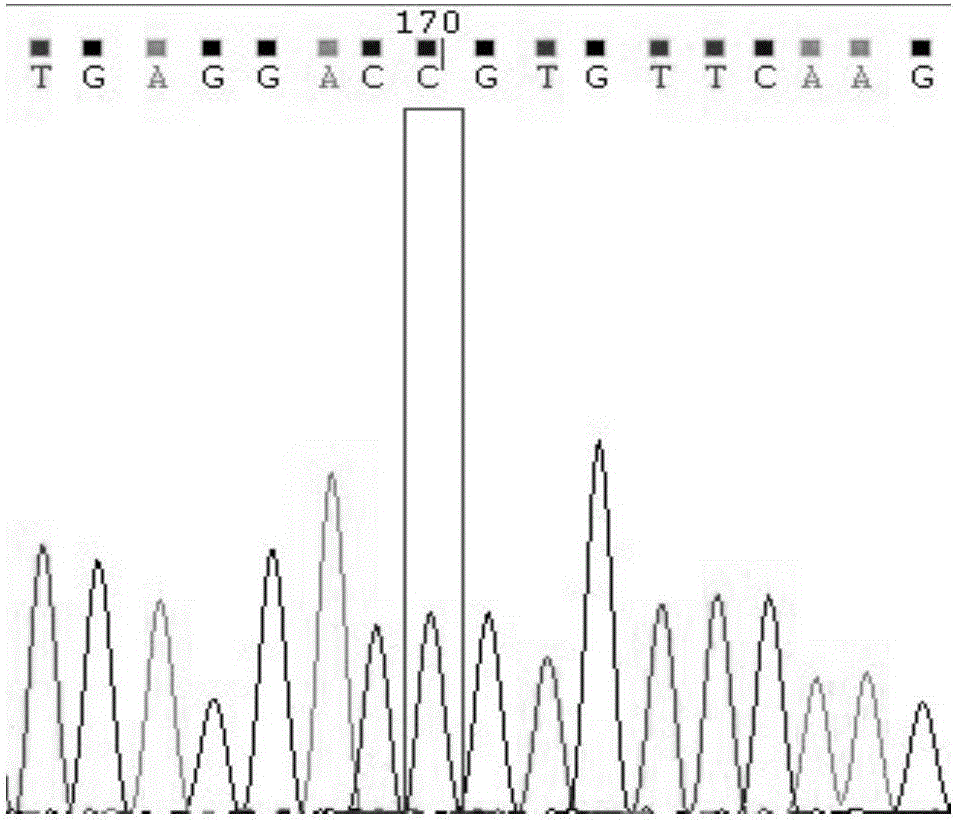
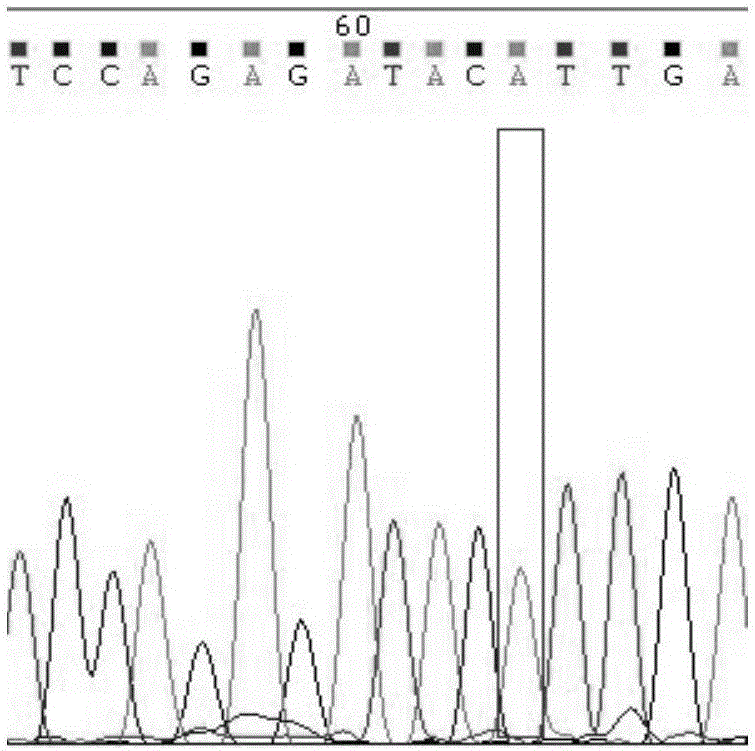
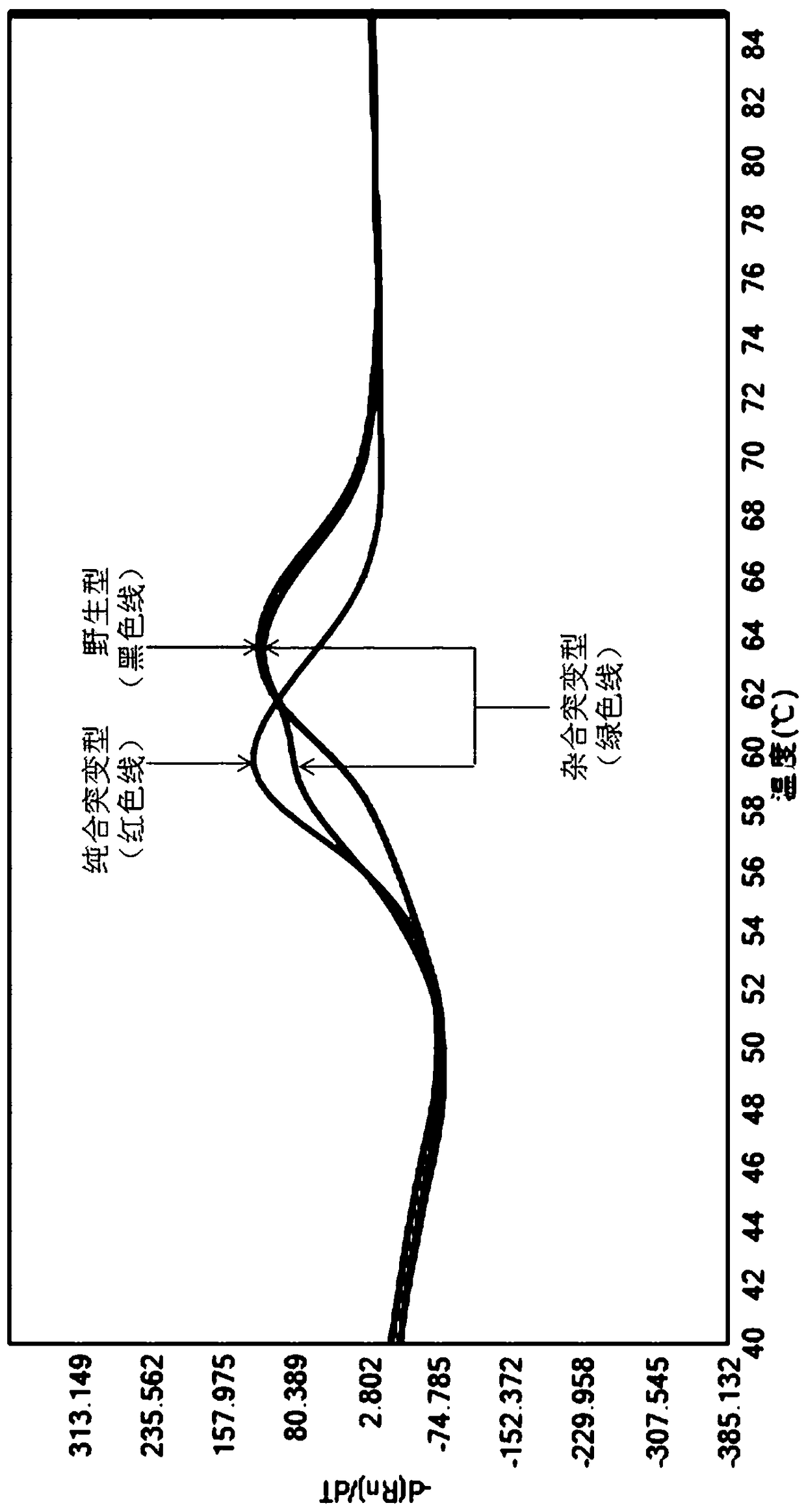
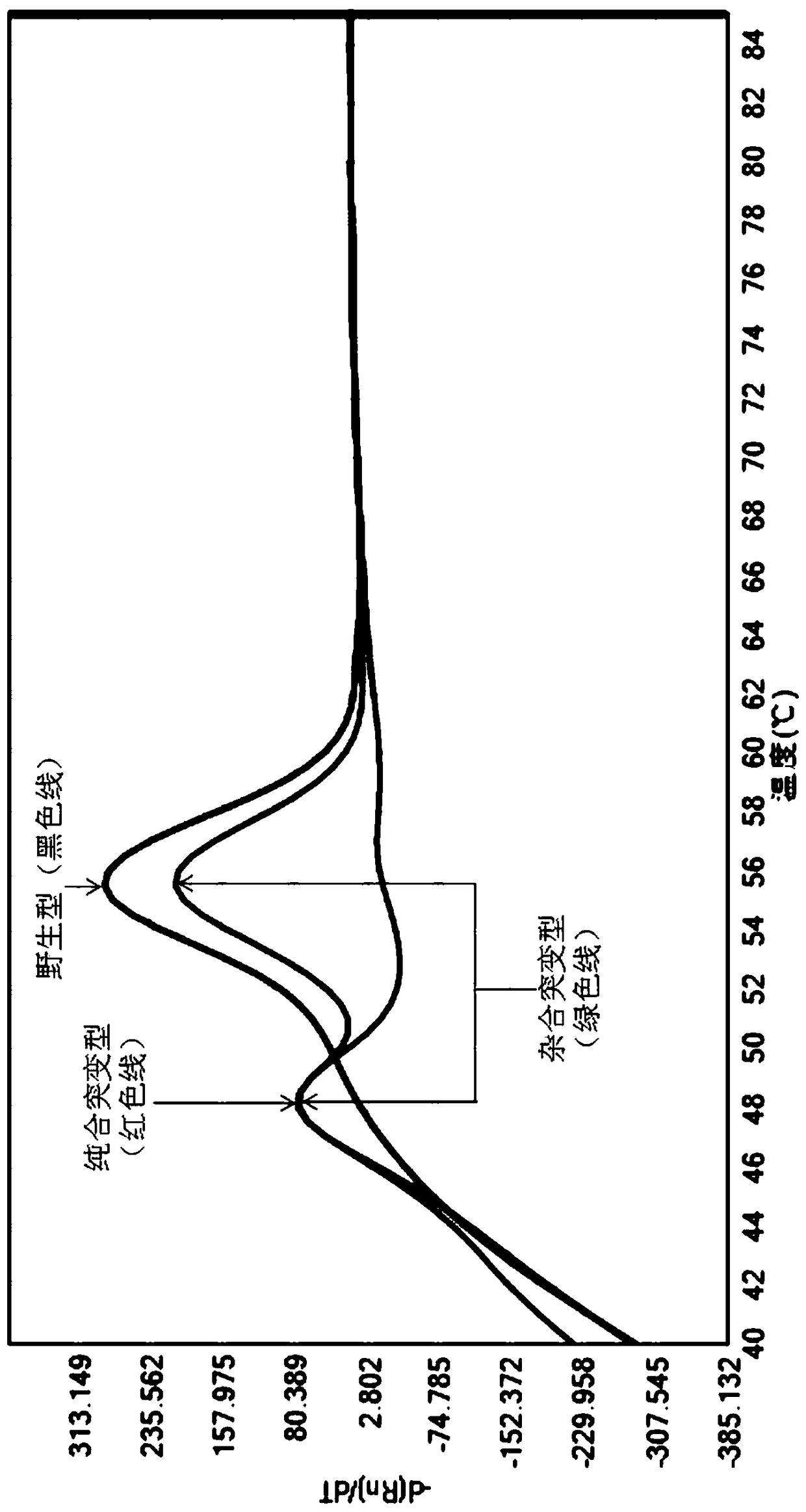
Detection method for CYP2C9*3 gene polymorphism, as well as nucleic acid probe and kit for method
InactiveCN104561301AQuick and easy analysisEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerBase J
The invention discloses a detecting probe for CYP2C9*3 gene polymorphism. The nucleotide sequences of the detecting probe are selected from a sequence 1 and a sequence 2; a fluorescent group and a quenching group are respectively arranged at the ends (5'and 3'); the peak values of the wavelengths of the florescent light emitted from the fluorescent group are at different positions. Preferably, the quenching group is selected from MGB and BHQ2; preferably, the fluorescent group is selected from FAM, VIC, JOE, HEX, CY3, NED, TAMRA, ROX, TEXAS RED, CY5 and the like. The invention further discloses a primer pair used for gene amplification; the primer pair comprises a forward primer and a reverse primer; the forward primer is an oligonucleotide which consists of base sequences of a sequence 3; the reverse primer is an oligonucleotide which consists of base sequences of a sequence 4. The invention further discloses a kit which contains the primers and the probe, and a detecting method for the CYP2C9*3 gene polymorphism.
Owner:FUWAI HOSPITAL OF CARDIOVASCULAR DESEASE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Quick genotyping method for guiding Warfarin utilization starting dose and kit
ActiveCN102605076AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseGenotyping
The invention discloses a quick genotyping method for guiding Warfarin utilization starting dose and a kit and belongs to the gene detection technology in clinical detection technology in the biomedicine field. According to the quick genotyping method, the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of a host cell gene group is extracted, and the gene types of CYP2C9*3(1061 A / C) and VKORCI (-1639 G / A) of a subject are measured. The CYP2C9 *3(1061 A / C) and VKORCI (-1639 G / A) genes have a nucleic acid sequence site shown as SEQ ID 1, wherein the site is one of the two most main sites associated with Warfarin metabolism. The invention provides the quick and accurate genotyping method and the associated kit. The method is quick and simple in operation, and low in cost, can be applied to prevention, auxiliary diagnosis and treatment on thrombotic associated diseases, and is conveniently popularized and used in basic medical institutions.
Owner:珠海赛乐奇医学检验有限公司
Primer set capable of synchronously detecting related gene polymorphism of anticoagulant drug and application
InactiveCN107904302AGuaranteed reliabilityAmplification program reductionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVKORC1Anticoagulant drug
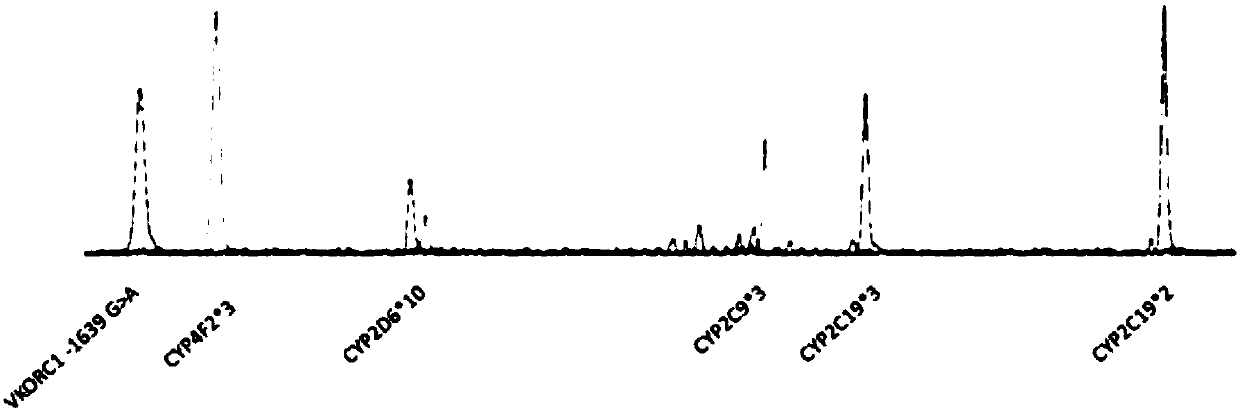
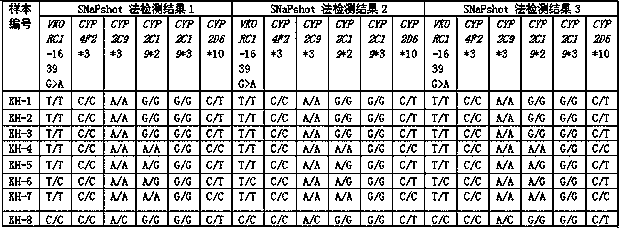
The invention discloses a primer set capable of synchronously detecting related gene polymorphism of an anticoagulant drug. The primer set comprises a PCR amplification primer and a SNaPshot PCR primer; the detected sites include VKORC1-1639>A, CYP4F2*3, CYP2C9*3, CYP2C19*2, CYP2C19*3 and CYP2D6*10. Compared with a general method for individually amplifying a plurality of sites, the primer used for detecting has the advantages that the amplification processes are decreased, and the amplification cost is reduced; ,moreover, the high sensitivity, the high accuracy and the high precision can be ensured, the method reliability is ensured, and a doctor can accurately select drugs for patients and reasonably adjust the dosage of the drug.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Primer-probe combination and kit for detecting associated genotyping of warfarin medication
InactiveCN105648082AType is convenient and easyGuaranteed non-invasive diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWarfarinSide effect
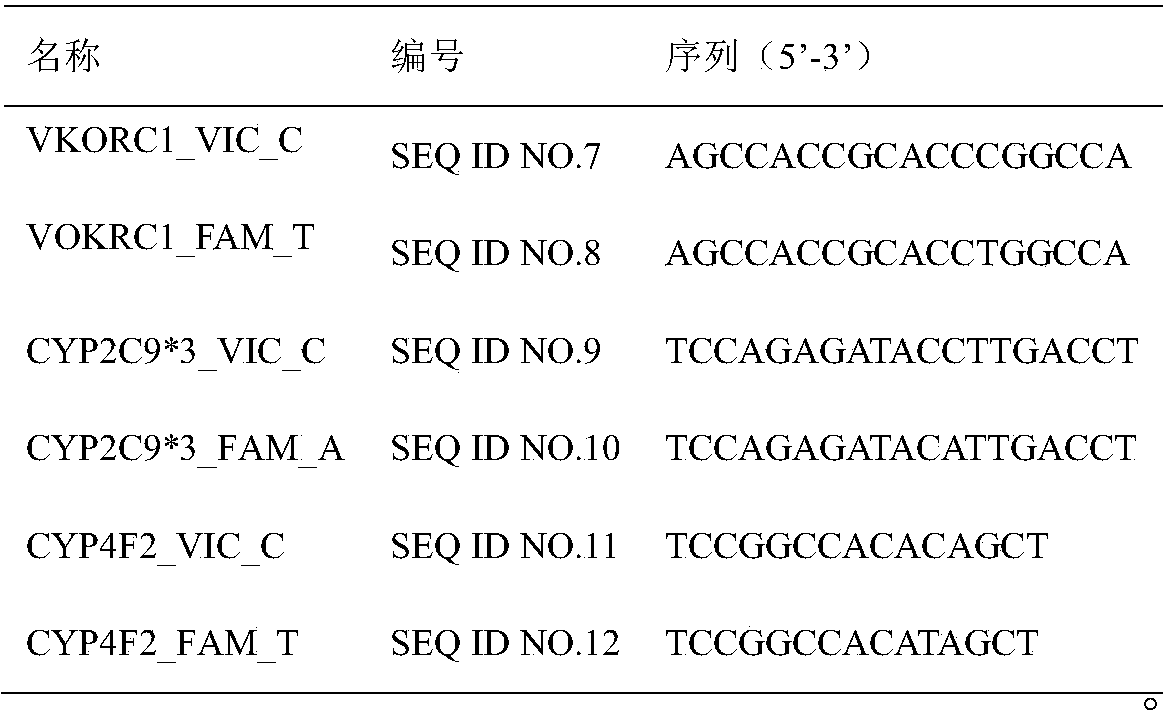
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and relates to a primer-probe combination and a kit for detecting associated genotyping of warfarin medication. The invention provides primers and probes for detecting associated genotyping of warfarin medication. The sequences of the primers are shown as SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.6, and the sequences of the probes are shown as SEQ ID NO.7-SEQ ID NO.12. The primer-probe combination and the kit for detecting associated genotyping of warfarin medication have the advantages that development and application of the gene detection kit are guided through warfarin medication, typing of the three genes of CYP2C9*3, CYP4F2 and VKORC1 is facilitated and easily achieved, and noninvasive diagnosis is guaranteed to enable clinicians to master patient heredity conditions rapidly and accurately, decrease medical accident incidence caused by inappropriate medicine dose greatly, reduce medication side effect and lay the foundation for improvement on clinical treatment effect; since only about 2 hours is needed for detection of every sample, high detection speed is achieved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU TCM HOSPITAL
Kit for detecting polymorphism of hypertension medication related genes
The invention relates to the technical field of in vitro diagnosis, in particular to a kit for detecting polymorphism of human CYP2D6, CYP2C9, ADRB1, AGTR1, ACE genes by a multiple fluorescent PCR method. The kit is used to detect CYP2D6*10, CYP2C9*3, ADRB1 (1165G > C), AGTR1 (1166A > C), ACE (I / D) polymorphism sites. The primer and the probe have high sensitivity and high specificity, and can accurately detect genomic DNA as low as 0.1 ng / <mu>L. The kit is easy to operate, and can cooperate with an automated instrument for detection.
Owner:AUTOBIO DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Risk assessment for phenytoin-induced adverse drug reactions
ActiveUS20170022561A1Predict riskMicrobiological testing/measurementFosphenytoinDrug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms
A method of predicting the risk of a patient for developing phenytoin-induced adverse drug reactions (ADRs), including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), or drug reactions with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) is disclosed. Genetic polymorphisms of CYP2C genes (including rs1057910 (CYP2C9*3) and rs3758581 on CYP2C19), and HLA alleles (including HLA-B*1502, HLA-B*1301, and HLA-B*5101) can predict adverse reactions caused by phenytoin or fosphenytoin. Accordingly, the present invention provides a kit to assess the risk of a patient for developing adverse reactions in response to phenytoin-related drugs, which comprises the determination of the presence of a specific allele selected from the group consisting of rs1057910 (CYP2C9*3), rs3758581 on CYP2C19, HLA-B*1502, HLA-B*1301, and HLA-B*5101, wherein the presence of at least one allele is indicative of a risk for the adverse drug reactions.
Owner:CHANG GUNG MEDICAL FOUND CHANG GUNG MEMORIAL HOSPITAL AT KEELUNG +1
Kit for rapid detection of polymorphism of Warfarin metabolic enzyme gene by virtue of pyrosequencing method and application of kit
InactiveCN105886606AQuick analysisAccurate analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideMetabolic enzymes
The invention discloses a kit for rapid detection of polymorphism of a Warfarin metabolic enzyme gene by virtue of a pyrosequencing method. The kit consists of three pairs of specific amplification primers and three sequencing primers; the three pairs of specific amplification primers include two genes, namely a CYP2CP gene and a VOKRC1 gene, wherein the CYP2CP gene contains two pairs of primers; the three sequencing primers specifically relate to three single nucleotide polymorphisms, namely CYP2C9*2, CYP2C9*3 and VKORC1 (-1693); and the nucleotide sequences are as shown in SEQ ID NO.1-9. The detection method disclosed by the invention is not only high in sensitivity, but also direct in result, and simpler, rapider and more accurate in interpretation; the kit is capable of achieving accurate, rapid and high-throughput detection of the Warfarin metabolic enzyme gene; and the kit is relatively high in popularization and application values in personalized medicine.
Owner:CHANGSHA DIAN MEDICAL SCI INSPECTION CO LTD
ARMS primer for detecting CYP2C9 gene polymorphism
InactiveCN106399552AAvoid nearby areasStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGeneticsCYP2C9*3
The invention discloses an ARMS primer for detecting CYP2C9 gene polymorphism. Aiming at sequence changes in every SNP of CYPC2C9*2(rs1799853, C430T, Arg144Cys) and CYP2C9*3(rs1057910, A1075C, Ile359Leu), the specificity ARMS primer and shared primers are designed. Mismatched base group (base group is marked with underline) is introduced to the second or third place of the 3' terminal end of the specificity ARMS primer so as to enlarge efficiency gap generating when specificity ARMS primer 3' terminal base are complementary and are not complementary to the SNP locus base on the DNA template, thus sharply improving specificity and accuracy of the detection.
Owner:SHANGHAI PERSONAL BIOTECH
Quick genotyping method for guiding Warfarin utilization starting dose and kit
ActiveCN102605076BHigh sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseNucleic acid sequencing
The invention discloses a quick genotyping method for guiding Warfarin utilization starting dose and a kit and belongs to the gene detection technology in clinical detection technology in the biomedicine field. According to the quick genotyping method, the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of a host cell gene group is extracted, and the gene types of CYP2C9*3(1061 A / C) and VKORCI (-1639 G / A) of a subject are measured. The CYP2C9 *3(1061 A / C) and VKORCI (-1639 G / A) genes have a nucleic acid sequence site shown as SEQ ID 1, wherein the site is one of the two most main sites associated with Warfarin metabolism. The invention provides the quick and accurate genotyping method and the associated kit. The method is quick and simple in operation, and low in cost, can be applied to prevention, auxiliary diagnosis and treatment on thrombotic associated diseases, and is conveniently popularized and used in basic medical institutions.
Owner:珠海赛乐奇医学检验有限公司
Gene detection kit for administration of angiotensin II receptor inhibitors as well as detection method and application of gene detection kit
PendingCN113249463AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMultiplexCarboxyl radical
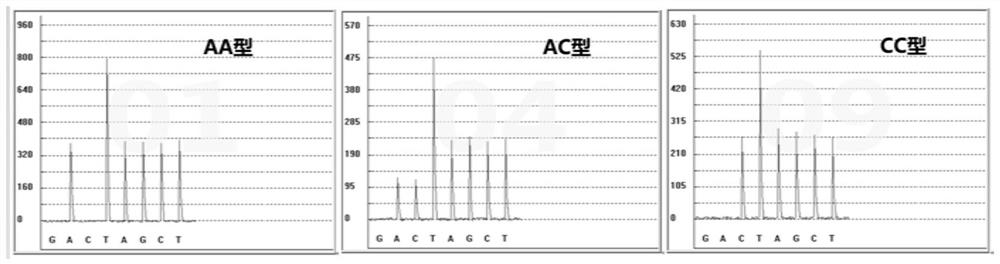
The invention discloses a gene detection kit for administration of angiotensin II receptor inhibitors. Specific amplification primers and sequencing primers are designed for the polymorphic angiotensin II receptor inhibitors of two genes CYP2C9 * 3 and AGTR1 (A1166C); and the kit comprises the following components of an amplification reaction solution, a CYP2C9 * 3 sequencing primer, an AGTR1 (A1166C) sequencing primer and a positive control. According to the kit, gene polymorphism related to administration of the angiotensin II receptor inhibitors is detected by using a combination of asymmetric multiplex PCR amplification and an optimized pyrosequencing technology, the kit can simultaneously detect gene polymorphism of the CYP2C9 * 3 and the AGTR1 (A1166C), the sequencing primer is a compound of carboxyl modifier agarose gel and an amino-labeled DNA sequence, the kit can be used as a sequencing primer and a capture probe, the gene polymorphism can be rapidly and accurately detected, a result is conveniently and clearly interpreted, the administration of the angiotensin II receptor inhibitors can be guided from the gene level, and a gene-oriented suggestion can be provided for clinical personalized administration.
Owner:湖南菲思特精准医疗科技有限公司
CYP2C9 genotype detecting primer-probe set and kit
InactiveCN106350587AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPositive controlControl substances
The invention relates to a CYP2C9 genotype detecting primer-probe set. The primer-probe set comprises primers and a probe of CYP2C9*2, primers and a probe of CYP2C9*3 and primers and a probe of internally-controlled GAPDH. The invention further relates to a CYP2C9 genotype detecting kit. The kit comprises a PCR reaction solution 1, a PCR reaction solution 2, a PCR reaction solution 3, a PCR reaction solution 4, a positive control substance and a blank control substance. The kit provided by the invention has high sensitivity up to one ten thousandth and the minimum detection limit of only 1-2 copies, and is especially applicable to detection of low-content mutant samples (such as serum or plasma); compared with a sequencing method, the invention has the advantages as follows: results obtained in the invention can be observed in real time, gel electrophoresis detection on a product is not required, the risks in contaminating the PCR product are effectively reduced through completely-closed operation, and the detection speed is high; therefore, the primer-probe set and the kit are suitable for high-throughput sample detection.
Owner:CHANGSHA 3G BIOTECH
Warfarin medication gene detection kit and use method thereof
InactiveCN111690736AEasy to detectEnables polygenic variant analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementVKORC1Medicine
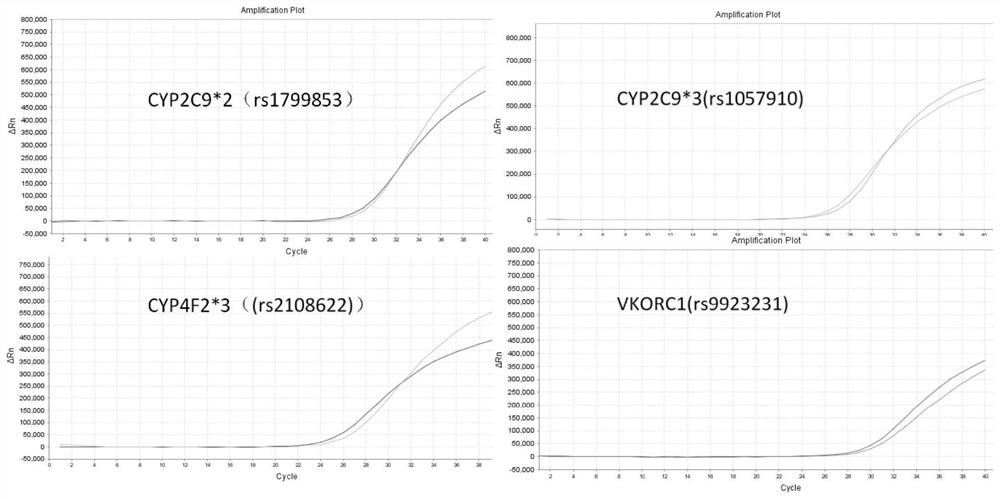
The invention provides a warfarin medication gene detection kit. The warfarin medication gene detection kit comprises a primer pair used for detecting polymorphism of to-be-detected loci of CYP2C9 * 2, CYP2C9 * 3, CYP4F2 * 3 and VKORC1 genes, probes, an inhibitor, a PCR reaction liquid, a positive quality control product and a negative quality control product; and the to-be-detected loci are at least one of an rs1799853 locus of CYP2C9 * 2 (430C>T) gene, an rs1057910 locus of CYP2C9 * 3 (1075A>C) gene, an rs2108622 locus of the CYP4F2 * 3 (1297G>A) gene and an rs9923231 locusof the VKORC1 (-1639G>A) gene. The invention also provides a use method of the warfarin medication gene detection kit. The problems of high sample treatment requirement, long detection period, complex operation, high cost, low specificity and the like during gene polymorphism are solved.
Owner:重庆浦洛通基因医学研究院有限公司
Self-assembled label-free magnetic nano CYP2C9 * 3 gene probe and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111926006ALow priceStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCYP2C9*3Gene probe
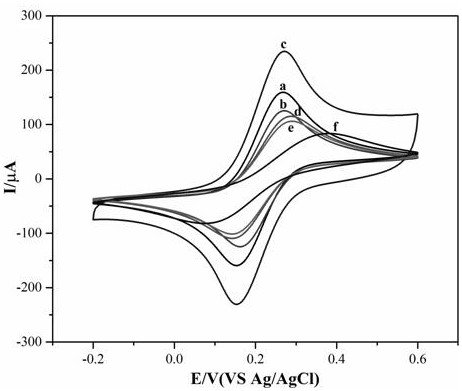
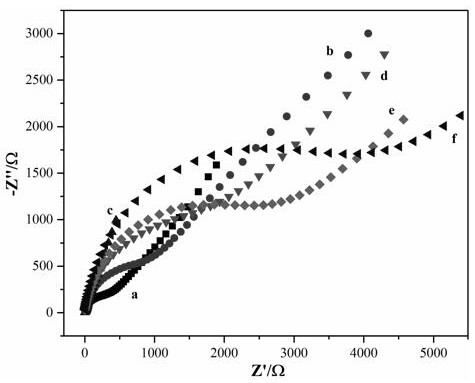
The invention provides a self-assembled label-free magnetic nano CYP2C9 * 3 gene probe and a preparation method thereof. The probe is a Fe3O4 / Fe2O3(at)Au-PNA / MCH / DNA nano CYP2C9 * 3 gene probe. The linear range of the detectable concentration of the probe is 1 pM-1 mu M, the peak current range is 55-89 mu A, the detection limit is 0.95 pM (S / N = 3), and the quantification limit is 3.18 pM (S / N = 10). The nano DNA probe prepared by the invention is simple and rapid to operate, strong in specificity, short in detection period, low in required equipment price and strong in applicability.
Owner:GUODIAN SCI & TECH RES INST +2
Primer group for detecting polymorphism of human cytochrome P450 related gene, kit and detection method
InactiveCN108841948AStrong specificityRelieve painMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationA-DNACYP3A5
The invention discloses a primer group for detecting polymorphism of a human cytochrome P450 related gene. The primer group comprises specific primers and probes aiming at gene sites of CYP2C19*2, CYP2C19*3, CYP3A4*18, CYP2C9*3, CYP2D6*10 and CYP3A5*3. The invention further relates to a kit for detecting polymorphism sites of the human cytochrome P450 related gene. The kit comprises PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) reaction liquid freeze-dried powder (PCR buffer, dNTPs, MgCl2, UNG enzyme, Taq enzyme and trehalose) with the primers and the probes. The invention further relates to a method for detecting polymorphism sites of the human cytochrome P450 related gene. By adopting the method, a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) extraction procedure is avoided, micro whole-blood amplification is directlyimplemented, a small amount of blood is used, and patients can be relieved from pain; the time and the labor can be saved, and in addition, economic expense can be greatly reduced.
Owner:XIAMEN WIZ BIOTECH CO LTD
Primer set for amplification of CYP2C9 gene, reagent for amplification of CYP2C9 gene comprising the same, and use of the same
InactiveCN101443448APolymorphism is simplePolymorphic shorteningMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerNucleotide sequencing
Disclosed is a primer set for amplifying a region in CYP2C9 gene that contains a detection target site having CYP2C9*3 therein by a gene amplification method, which enables to amplify the region specifically. A pair of primer set is used, which comprises a forward primer comprising a nucleotide sequence depicted in SEQ ID NO:4 and a reverse primer comprising a nucleotide sequence depicted in SEQ ID NO:17. The primer set enables to amplify a region containing a site having a polymorphism CYP2C9*3 occurring in CYP2C9 gene in a specific manner and with a high degree of efficiency.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Primer pairs and kit for detecting warfarin medication related gene polymorphism
InactiveCN108277269AEasy to handleHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWarfarinReference genes
The invention relates to primer pairs and a kit for detecting warfarin medication related gene polymorphism, and belongs to the technical field of in vitro nucleic acid detection, wherein the primer pair comprises amplification primers respectively for alleles such as VKORC1-1639, CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3, and GAPDH internal reference gene, and the kit comprises PCR reaction solutions containing theamplification primers. According to the present invention, the kit has high sensitivity and is suitable for the detection of low-content mutation samples, wherein the sensitivity can be up to 1 / 10000,and the minimum detection limit is only 1-2 copies; compared to the sequencing method, the method of the present invention has the following advantages that the detection result can be real-timely observed, the product does not require gel electrophoresis detection, and the completely closed tube operation is performed so as to effectively reduce the risk of PCR product contamination; and the kitfurther has the fast detection speed, and is suitable for high-throughput sample detection.
Owner:CHANGSHA 3G BIOTECH
A primer probe combination and kit for detecting genotyping related to warfarin medication
InactiveCN105648082BType is convenient and easyGuaranteed non-invasive diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWarfarinSide effect
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and relates to a primer-probe combination and a kit for detecting associated genotyping of warfarin medication. The invention provides primers and probes for detecting associated genotyping of warfarin medication. The sequences of the primers are shown as SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.6, and the sequences of the probes are shown as SEQ ID NO.7-SEQ ID NO.12. The primer-probe combination and the kit for detecting associated genotyping of warfarin medication have the advantages that development and application of the gene detection kit are guided through warfarin medication, typing of the three genes of CYP2C9*3, CYP4F2 and VKORC1 is facilitated and easily achieved, and noninvasive diagnosis is guaranteed to enable clinicians to master patient heredity conditions rapidly and accurately, decrease medical accident incidence caused by inappropriate medicine dose greatly, reduce medication side effect and lay the foundation for improvement on clinical treatment effect; since only about 2 hours is needed for detection of every sample, high detection speed is achieved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU TCM HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com