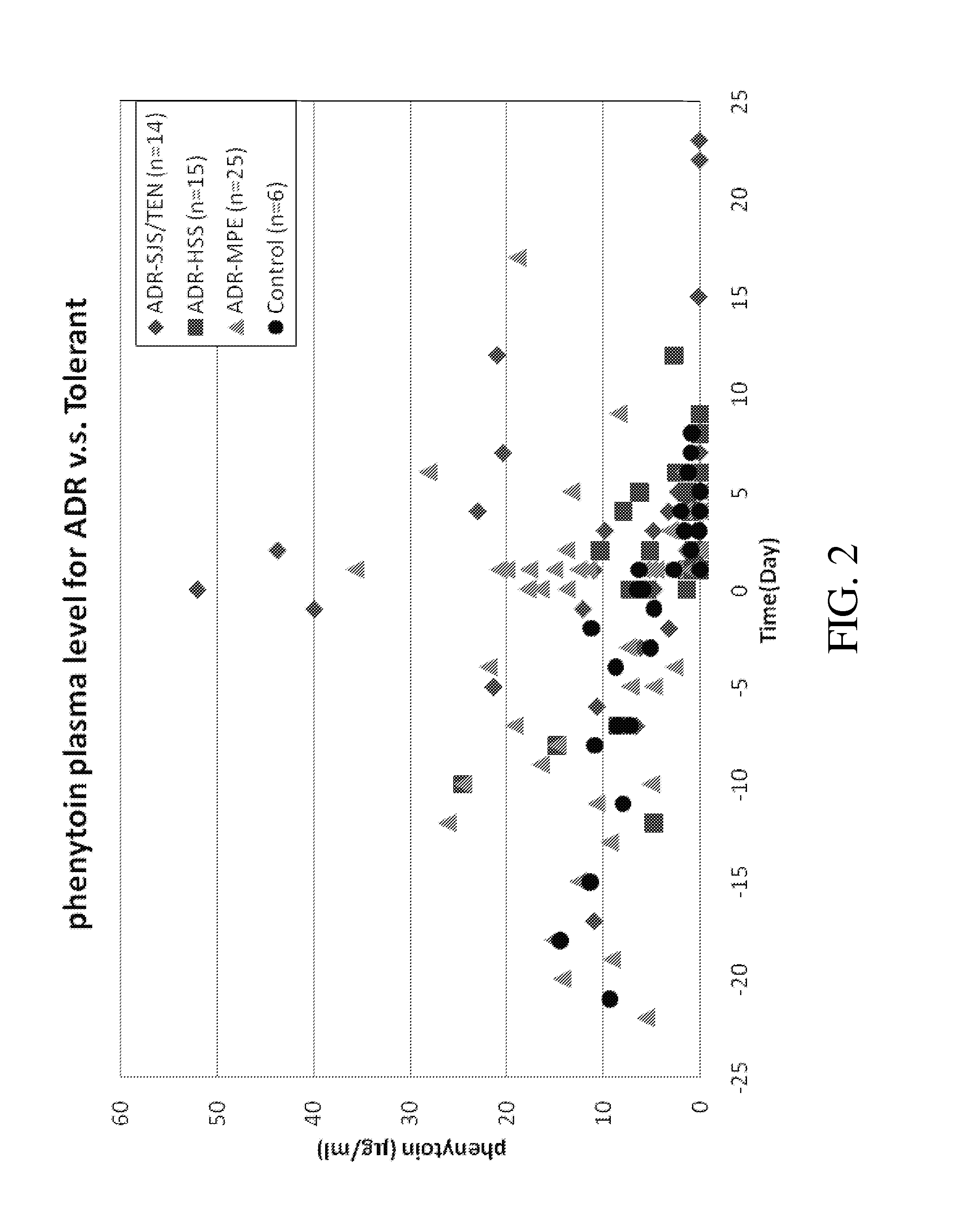
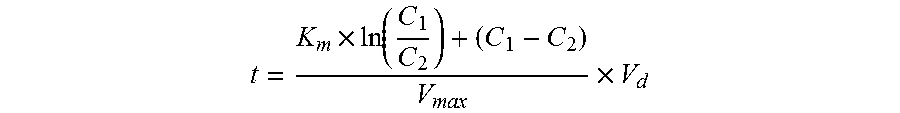Risk assessment for phenytoin-induced adverse drug reactions
a risk assessment and drug technology, applied in the field of risk assessment of adverse drug reactions in response to phenytoin, can solve the problems of delayed clearance and severe cutaneous adverse reactions of phenytoin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Variants on CYP2C Genes and Phenytoin-Related SCAR
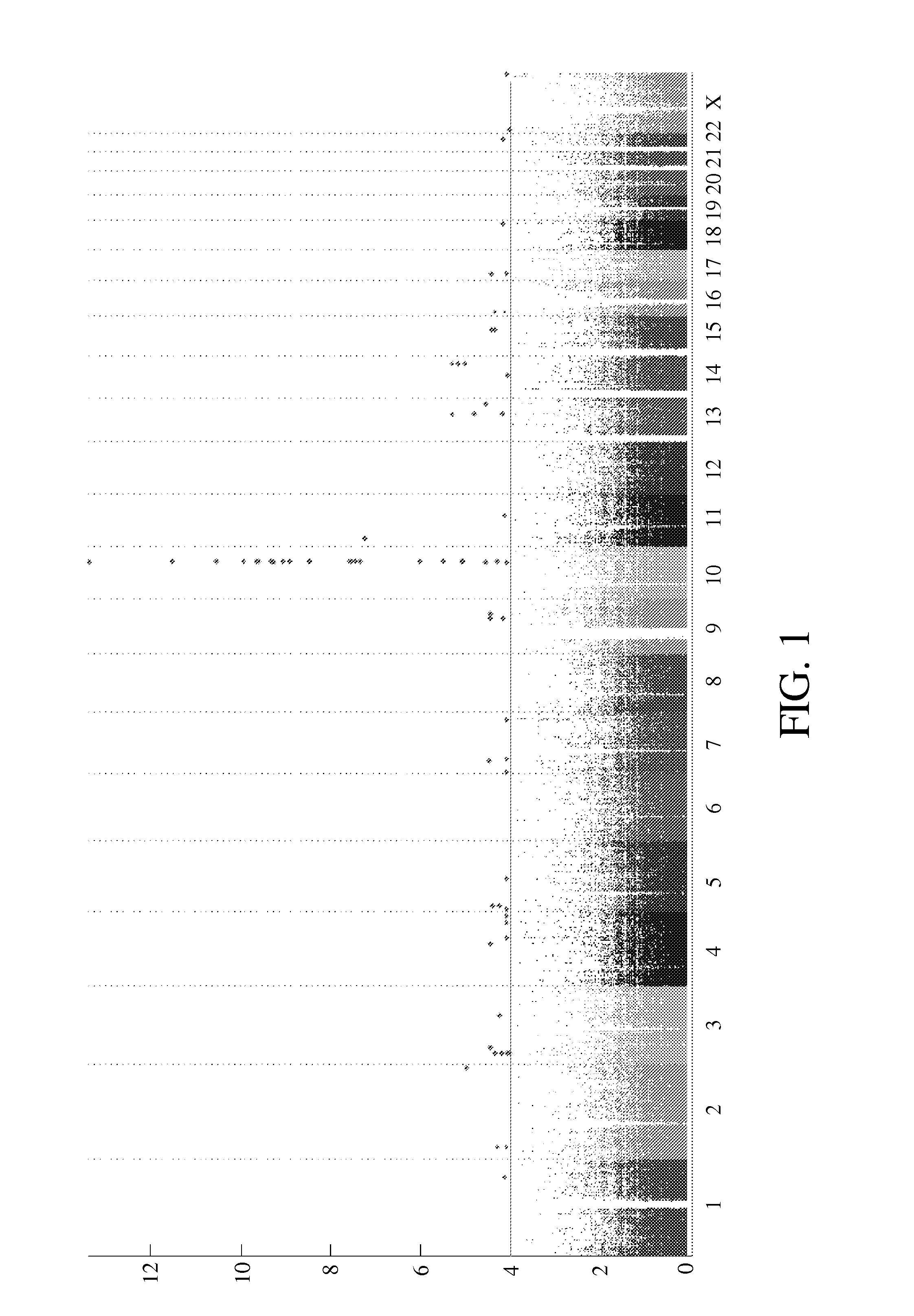
[0050]In the cohort of 168 individuals with phenytoin-related ADRs, 90 cases were diagnosed to have S] S / TEN / DRESS, and 78 individuals had milder cutaneous adverse drug reactions (erythema multiform, maculopapular rash or fixed drug eruption). The control group consisted of 198 subjects. By using genome wide association study (Affymetrix 6.0) of 58 phenytoin-induced SCARs (including SJS, TEN, and DRESS) and 198 population controls, it is found that the most significant SNPs were in chromosome 10 (see FIG. 1) of the CYP2C region, such as rs17110192, rs7896133 on CYP2C18; rs17110321, rs9332093, rs9332245 on CYP2C9; rs3758581, rs2860905, rs4086116 on CYP2C19 and rs7899038, rs1592037, rs1934952, rs11572139, rs6583967 on CYP2C8 (see Table 1). The other SNPs which located nearby CYP2C loci, such as rs2274222, rs11188183, rs7921561, rs10882544, rs7084271, rs644437, rs12769577, rs617848, rs10882551, rs585381, rs648638, rs664093, rs12262878, ...
example 2
HLA Alleles and Phenytoin-Related SCAR
[0056]The HLA susceptibility of phenytoin-related cutaneous adverse reactions was analyzed due to the presence of immunological characteristics in the disease. Specific oligonucleotide primers and probes were used to identify the HLA-A, HLA-B and HLA-DRB1 genotype of phenytoin-ADRs patients and tolerant controls. The results indicated that HLA-A*0207, HLA-A*2402, HLA-B*1301, HLA-B*1502, HLA-B*4001, HLA-B*4609, HLA-B*5101, HLA-DRB1*1001 or HLA-DRB1*1502 were significantly associated with phenytoin-induced ADRs (SJS / TEN, DRESS, or MPE) (see Table 4 to 6). The data shows that HLA-B*1301 allele significantly increased frequencies among patients with phenytoin-ADRs compared to the tolerant controls. There were 15 SJS / TEN patients (28.3%) and 12 DRESS patients (46.2%) carried HLA-B*1301, while only 14 tolerant patients (11.9%) carried this genotype (SJS / TEN vs. tolerant controls: P=0.001, OR=3.8 (1.7-8.5); DRESS vs. tolerant controls: P=2×10−4, OR=6.4...
example 3
Combination of CYP2C and HLA Alleles for Predicting Phenytoin-SCAR
[0059]We designed kits which consisted reagents and oligonucleotide primers and probes for detecting the presence of the risk alleles selected from a panel, comprising rs1057910 (CYP2C9*3), rs3758581, and HLA-B*1502, HLA-B*1301, and HLA-B*5101. The detection of both CYP2C alleles and HLA alleles further improved the sensitivity of test for phenytoin-related SCAR. For example, the sensitivity of a CYP2C genetic test which detects the presence of either rs1057910 or rs3758581, could be improved with the inclusion of HLA-B*15:02 allele in the testing panel, in which the sensitivity will be 55.93%, and the specificity of 90.77%, positive predictive value (PPV) of 77.33%, and negative predictive value (NPV) of 81.94% for predicting phenytoin-SJS / TEN. Furthermore, adding HLA-B*1301 and HLA-B*5101 to CYP2C (rs1057910 / rs3758581) genetic screening improved the sensitivity to 67.27% for all types of phenytoin-SCAR, including SJ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| enzyme activity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com