Semiconductor memory
a technology of memory and semiconductors, applied in the direction of transistors, solid-state devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of increasing power consumption, difficult to lower power consumption, increasing power consumption, etc., and achieve the improvement of the performance of each transistor, the improvement of various performance of the sram, and the increase of surplus leak current
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
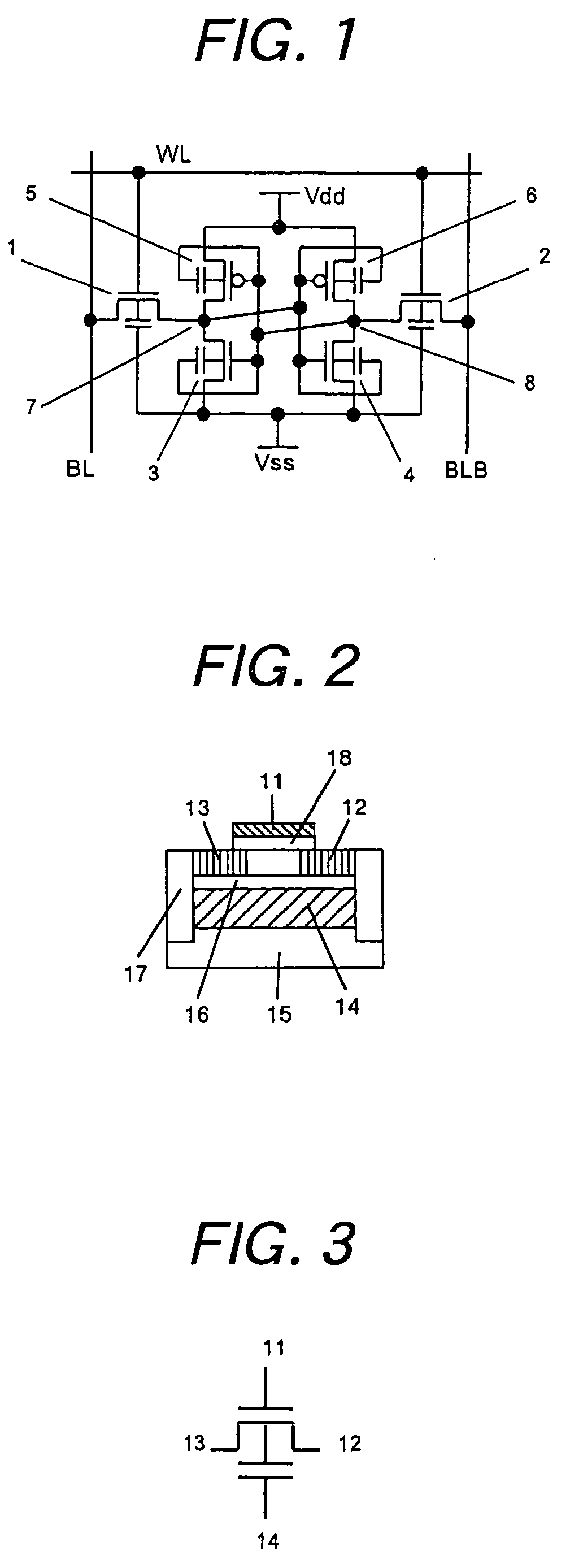
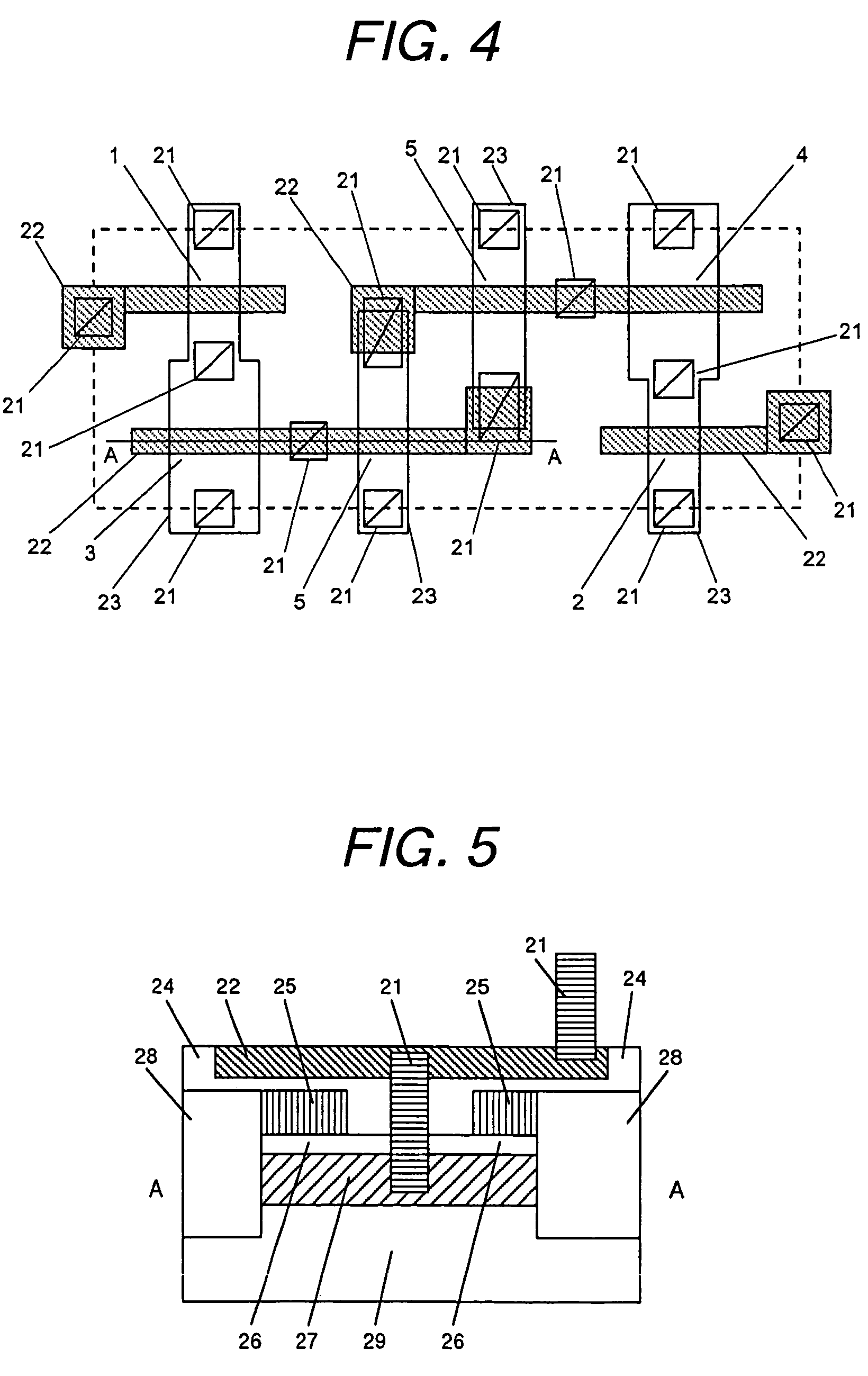
[0047]FIG. 1 is a circuit diagram showing a SRAM memory cell according to the present invention. In FIG. 1, symbols BL and BLB each indicate a bit line, WL indicates a word line, Vdd indicates a power line, and Vss indicates a ground potential line. Further reference numerals 1 and 2 each indicate a transfer transistor for access to a memory cell, 3 and 4 each indicate a driver transistor for driving a storage node for maintaining therein data for the memory cell, 5 and 6 each indicate a load transistor for supplying an electric charge for maintaining data in the memory cell, and 7 and 8 each indicate a storage node for storing data. For instance, Vdd is at an electric potential of 1.2 V, and the ground potential line Vss is at an electric potential of 0 V. FIG. 2 is a general block diagram showing a cross section of a transistor used in the circuit shown in FIG. 1. In FIG. 2, reference numeral 11 indicates a gate, 12 a drain, 13 a source, 14 a well layer under a BOX layer, 15 a sup...
embodiment 2
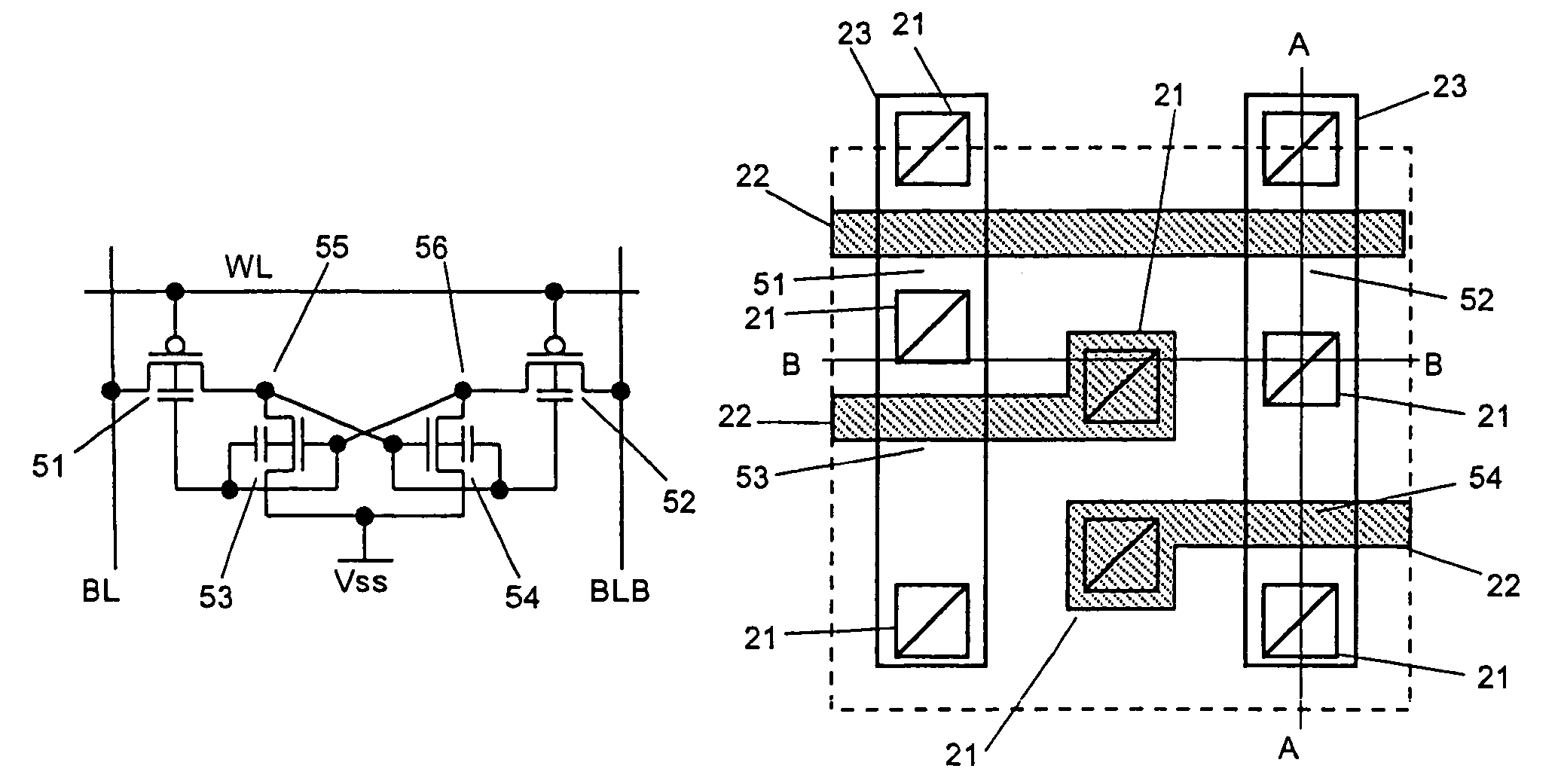
[0055]FIG. 7 shows layout of a SRAM memory cell according to the present invention. In descriptions of the following embodiments, the same reference numerals are used for the same components as those in Embodiment 1, and a description is made only of different components. The circuit configuration of this memory cell at the transistor level is the same as that shown in FIG. 1. The layout of the memory cell shown in FIG. 7 is different from that shown in FIG. 4 only in that a back gate contact for the driver transistor as well as for the load transistor is formed below a contact for connecting the gate node to the metal layer. With this configuration, the contact formed between a driver transistor and a load transistor in the conventional technology is not necessary, so that an area of the memory cell can be reduced. In particular, when a memory cell is formed of a bulk CMOS transistor, it is necessary to separate a well for a driver transistor from that for a load transistor, so tha...
embodiment 3
[0057]FIG. 9 shows layout of a SRAM memory cell according to the present invention. A circuit diagram of the memory cell shown in FIG. 9 at the transistor level is the same as that shown in FIG. 1. The memory cell shown in FIG. 9 is different from that shown in FIG. 1 only in that a gate width (W-size) of the driver transistor is the same as that of the transfer transistor. In the SRAM memory cell, as described in Embodiment 1, it is generally necessary, for the purpose of preventing an electric potential of a storage node at the “L” level from rising, that conductance of the driver transistor is larger than that of the transfer transistor. In a memory cell using a bulk CMOS transistor, the conductance is generally adjusted by controlling the W-size. The W-size of the driver transistor is set to a value about 1.5 times larger as compared to that of the transfer transistor. In this embodiment, the conductance when a back gate of the driver transistor is connected to the gate and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com