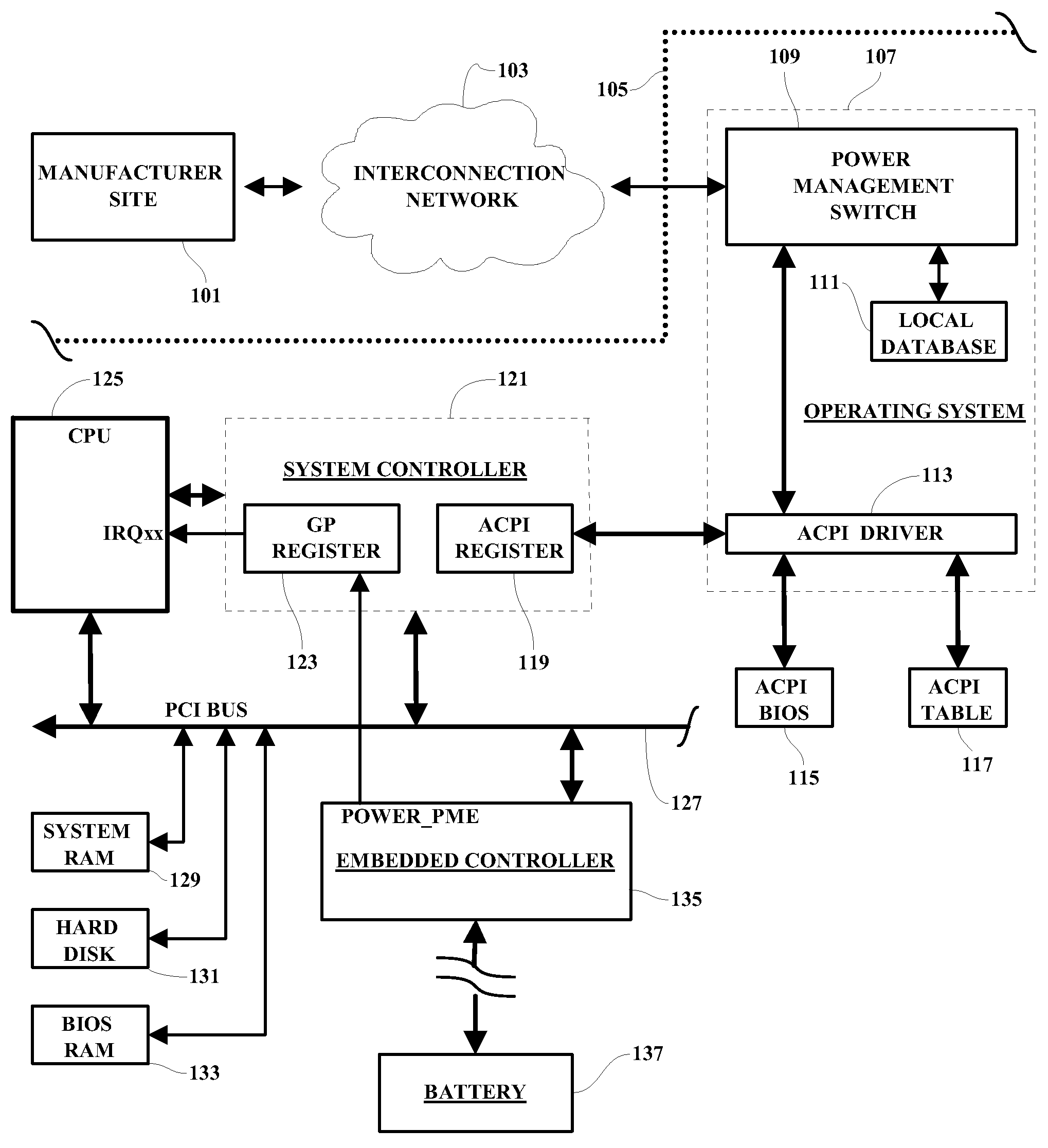
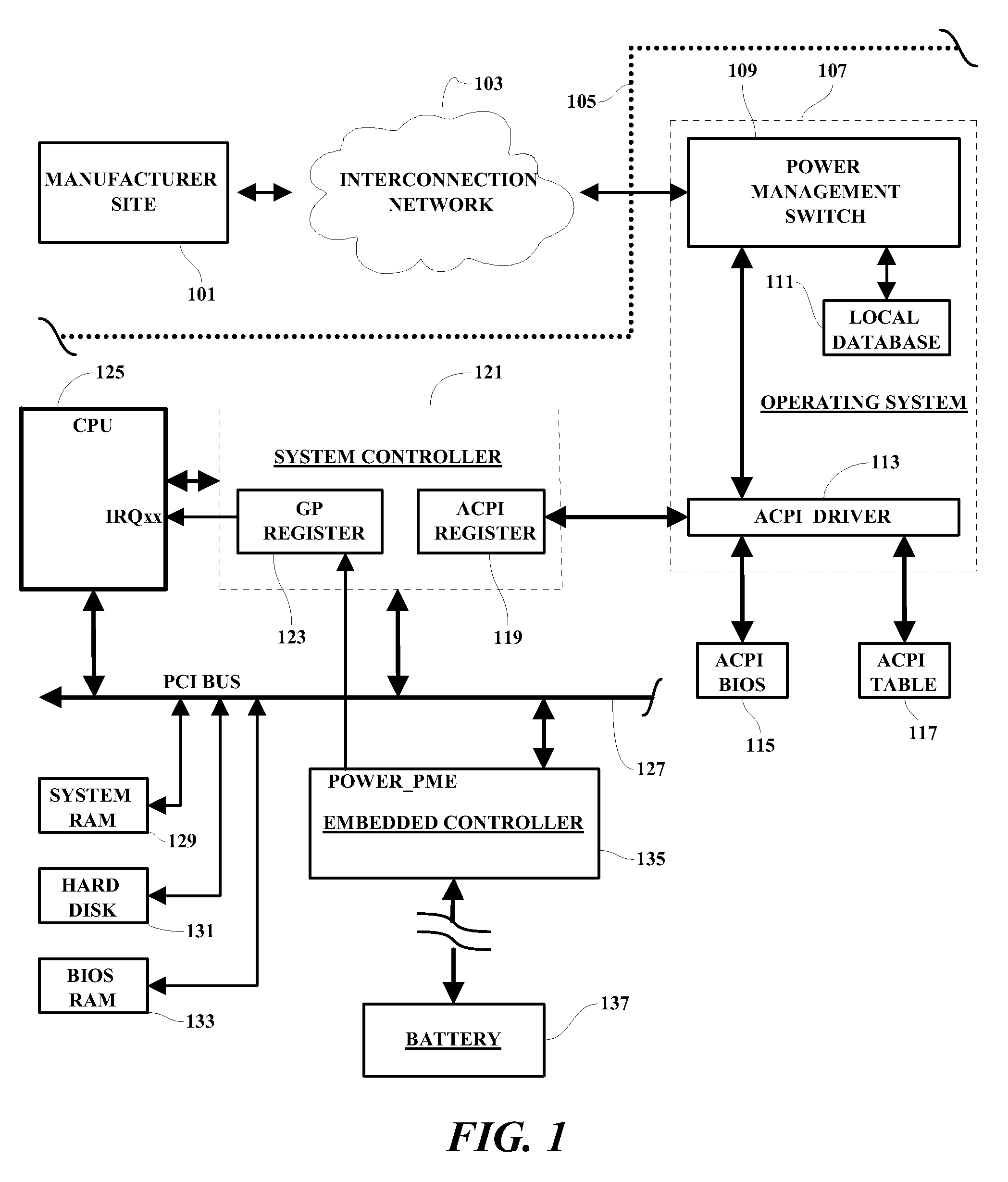
Patents
Literature
1154results about "Charge maintainance charging/discharging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multipurpose, universal Converter with battery control and real-time Power Factor Correction.
InactiveUS20130049471A1Fast feedbackAvoid distortionEnergy industryAc-dc network circuit arrangementsTotal harmonic distortionSmart grid
The Electric Power Converter has the qualifications for an uninterruptable power supply, battery management, energy conversion, micro-grid formation, Power Factor Correction including Total Harmonic Distortion correction in real time. Uninterruptable power supply's use is for always-on, real-time, all-time, reduced distortion with functions of load reduction and management during peak load events. The Electric Power Converter as well has the ability to provide maintenance for most types of batteries including charging and discharge regiments to increase the overall lifetime of a battery, the maintenance, incorporating restorative functions that can refurbish dead batteries or can further increase the overall efficiency and useful function of weaker / aged / defective batteries. Energy conversion capabilities allow for the conversion of AC or DC to AC or DC with high efficiency and ability to actively vary the frequency in accordance to the required parameters. The Electric Power Converter is able to establish and sustain a micro-grid with multiple and varying sources of power generation and load conditions. The Electric Power Converter is achieving dynamic, real-time, interactive Power Factor Correction (PFC) function with advanced voltage harmonic distortion correction with a high efficiency ratio. The Electric Power converter is designed to function with the emerging Smart Grid technologies and provide an overall higher level of operating efficiency and higher quality of electrical power.
Owner:3DFS L L C
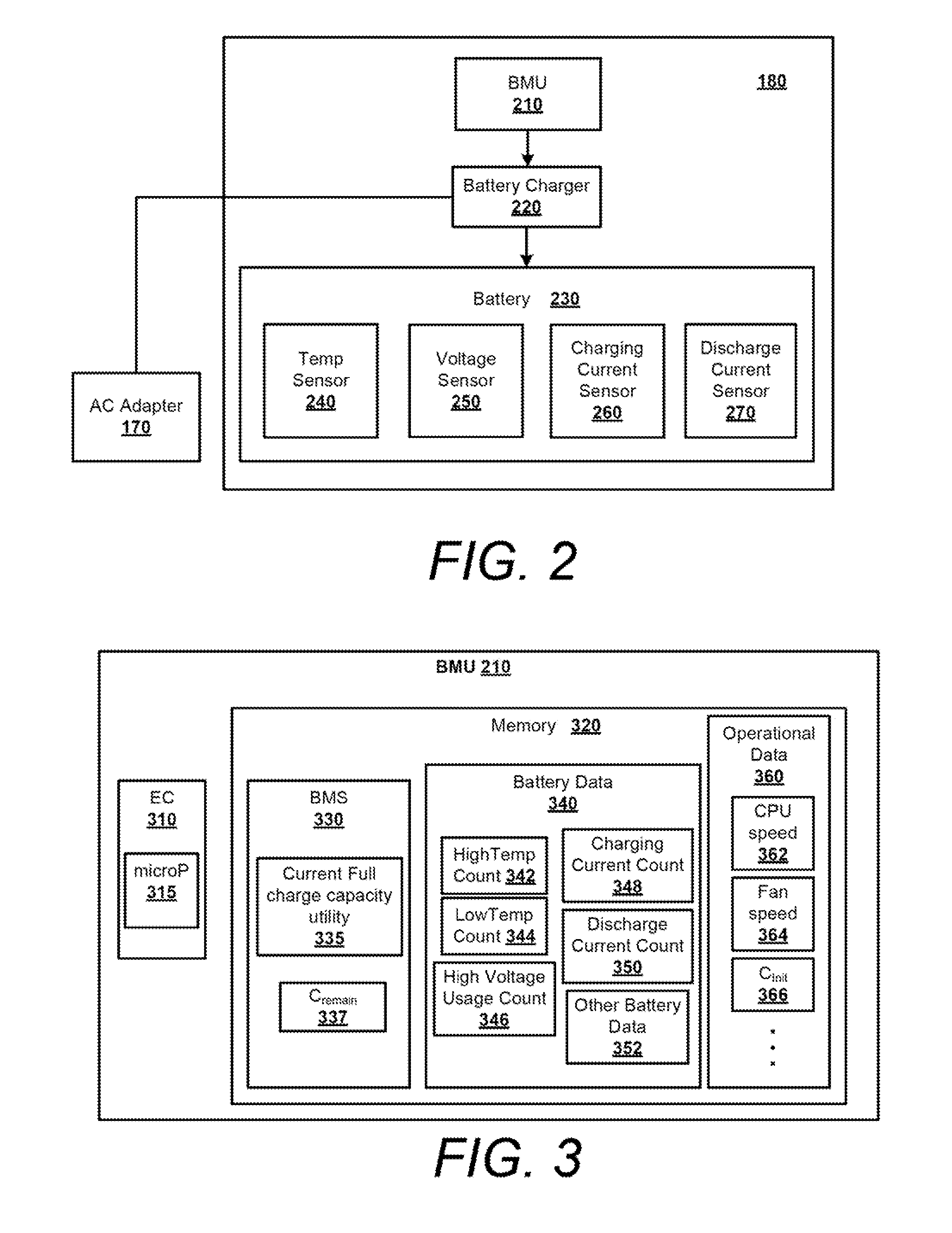
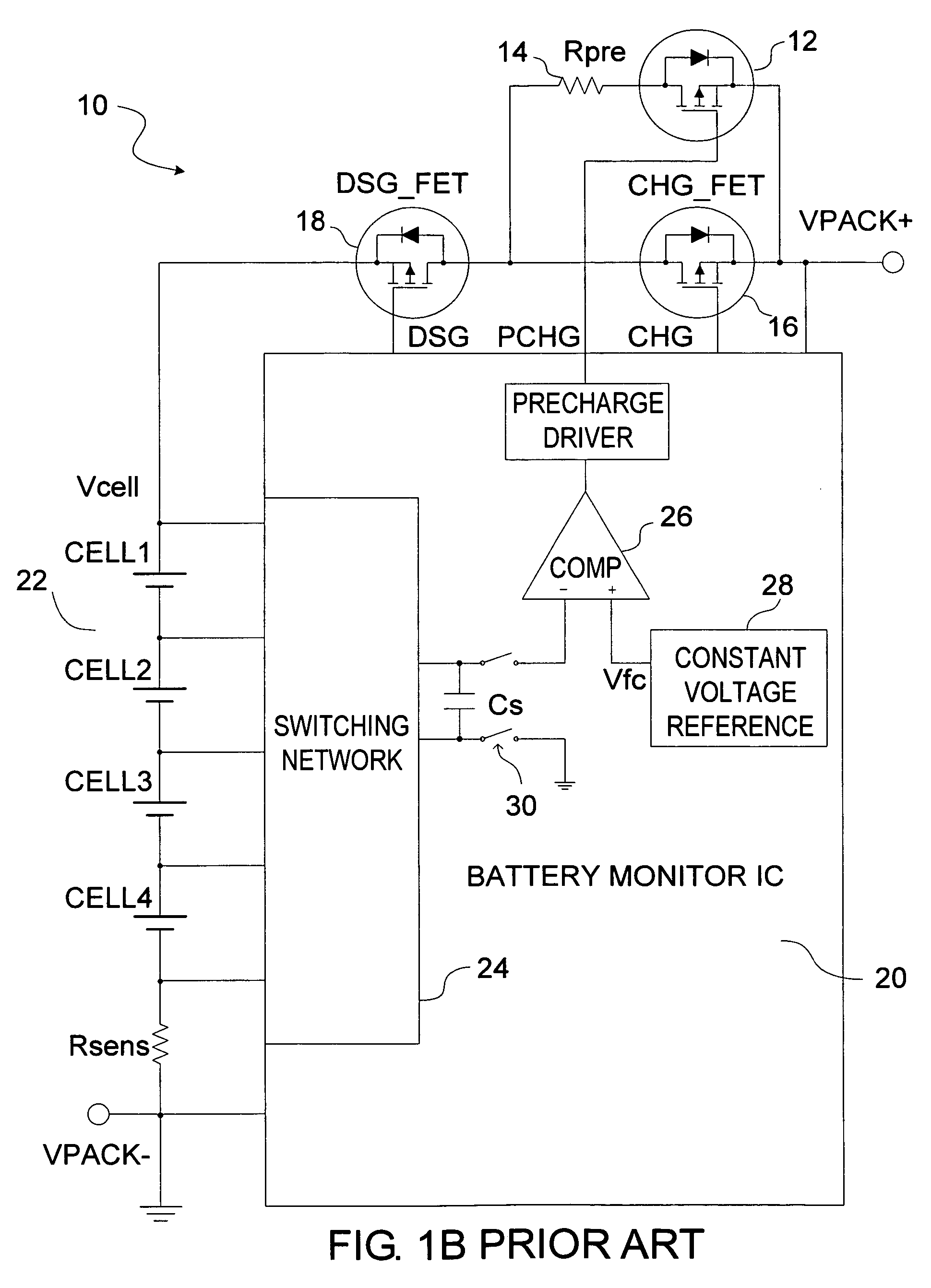
Battery pack having memory
InactiveUS6271643B1Decreasing the turn on potentialWide flexibilityCircuit monitoring/indicationVolume/mass flow measurementCharge currentElectrical battery
In an exemplary embodiment, a method of charging a battery includes supplying a charging current to the battery and measuring one or more battery parameters. The battery parameters may be, for example, temperature, voltage and / or charging current. The battery parameter measured is used to determine a charging current set point. The set point may be selected from a number of different set points stored in memory, where each set point corresponds to a respective battery parameter range. If the charging current being supplied to the battery is different from the charging current set point determined the charging current is adjusted to match the set point. This process is repeated for each of a plurality of time periods (e.g., sampling periods) during charging of the battery.
Owner:UNOVA
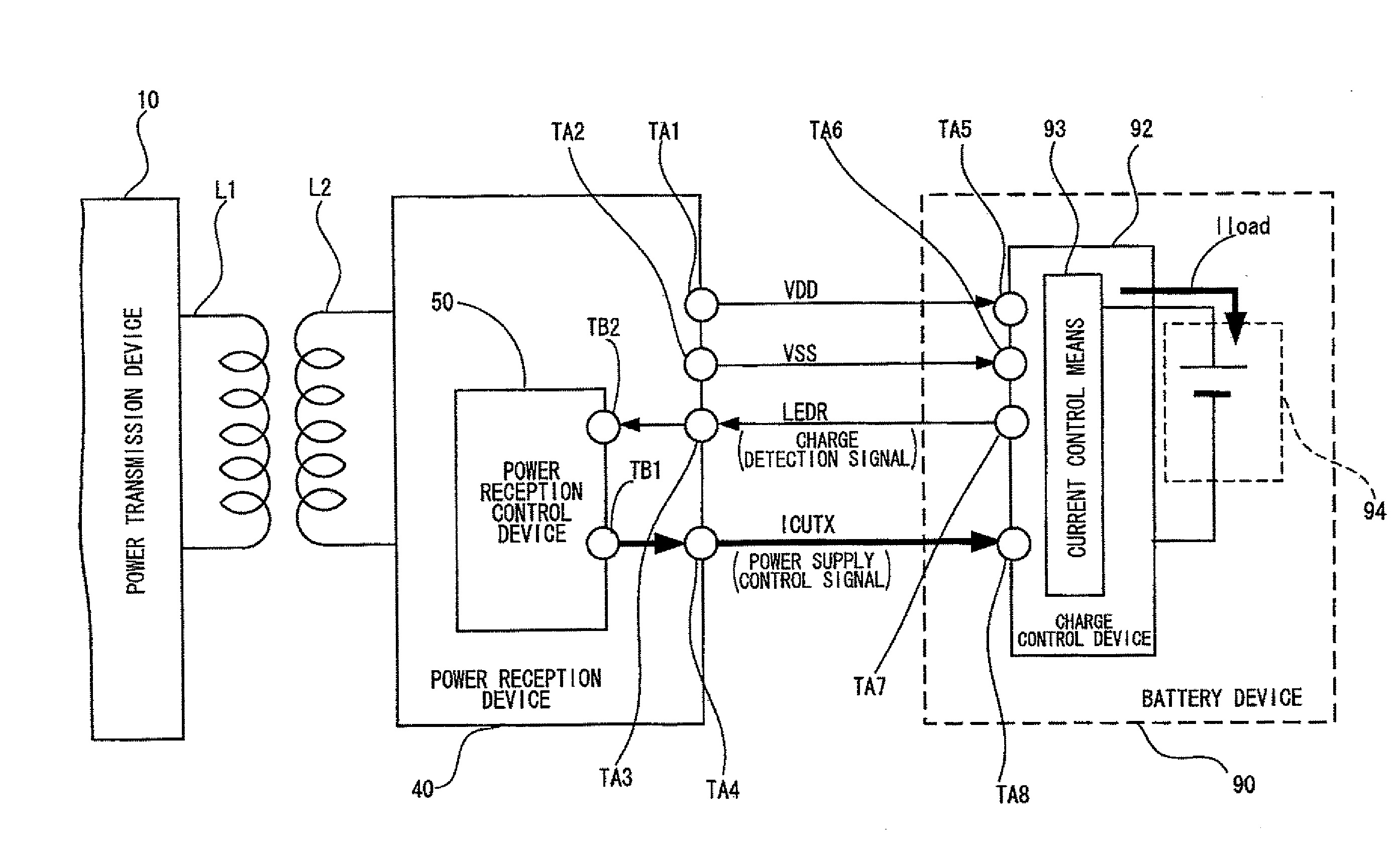
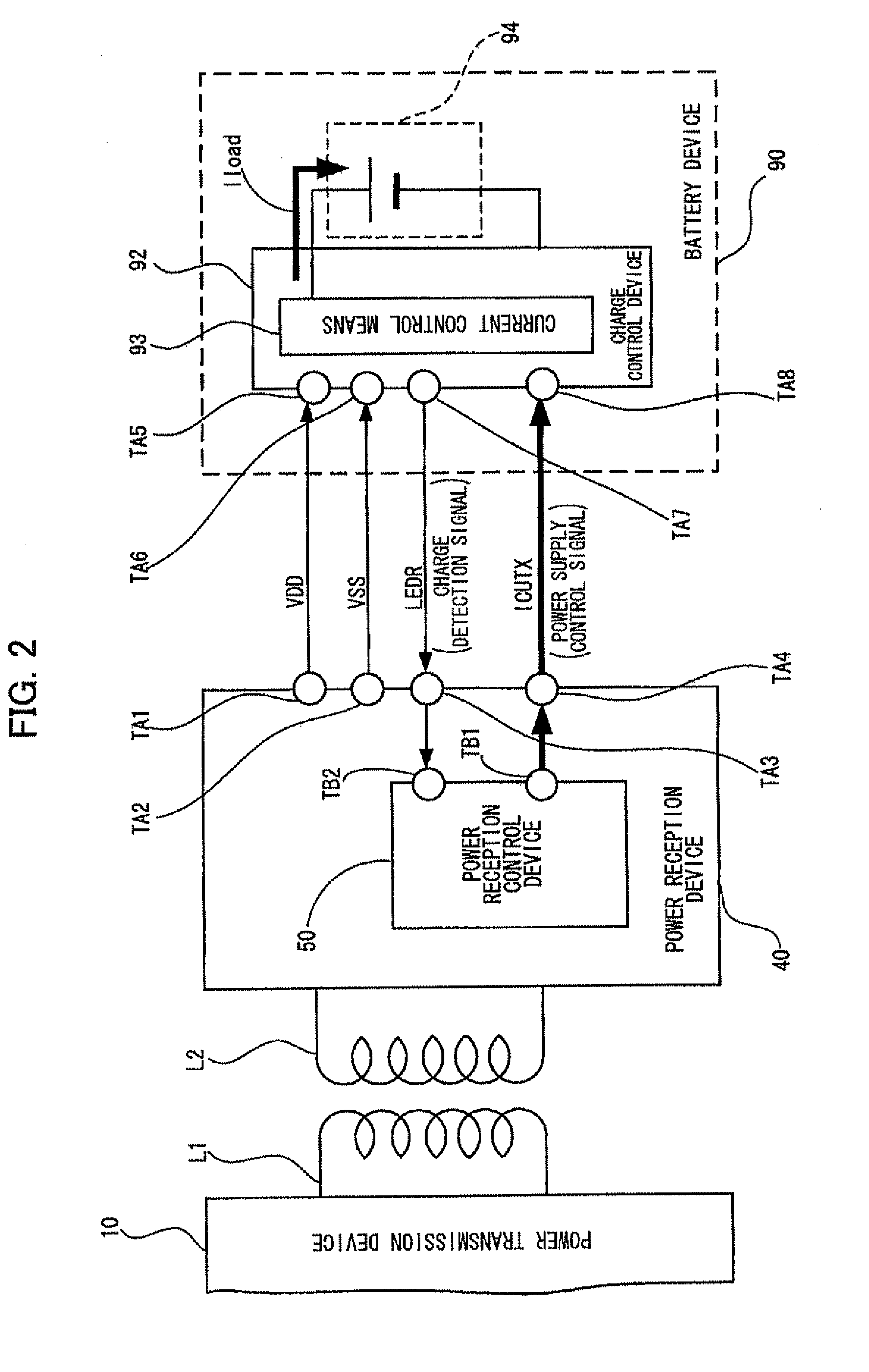
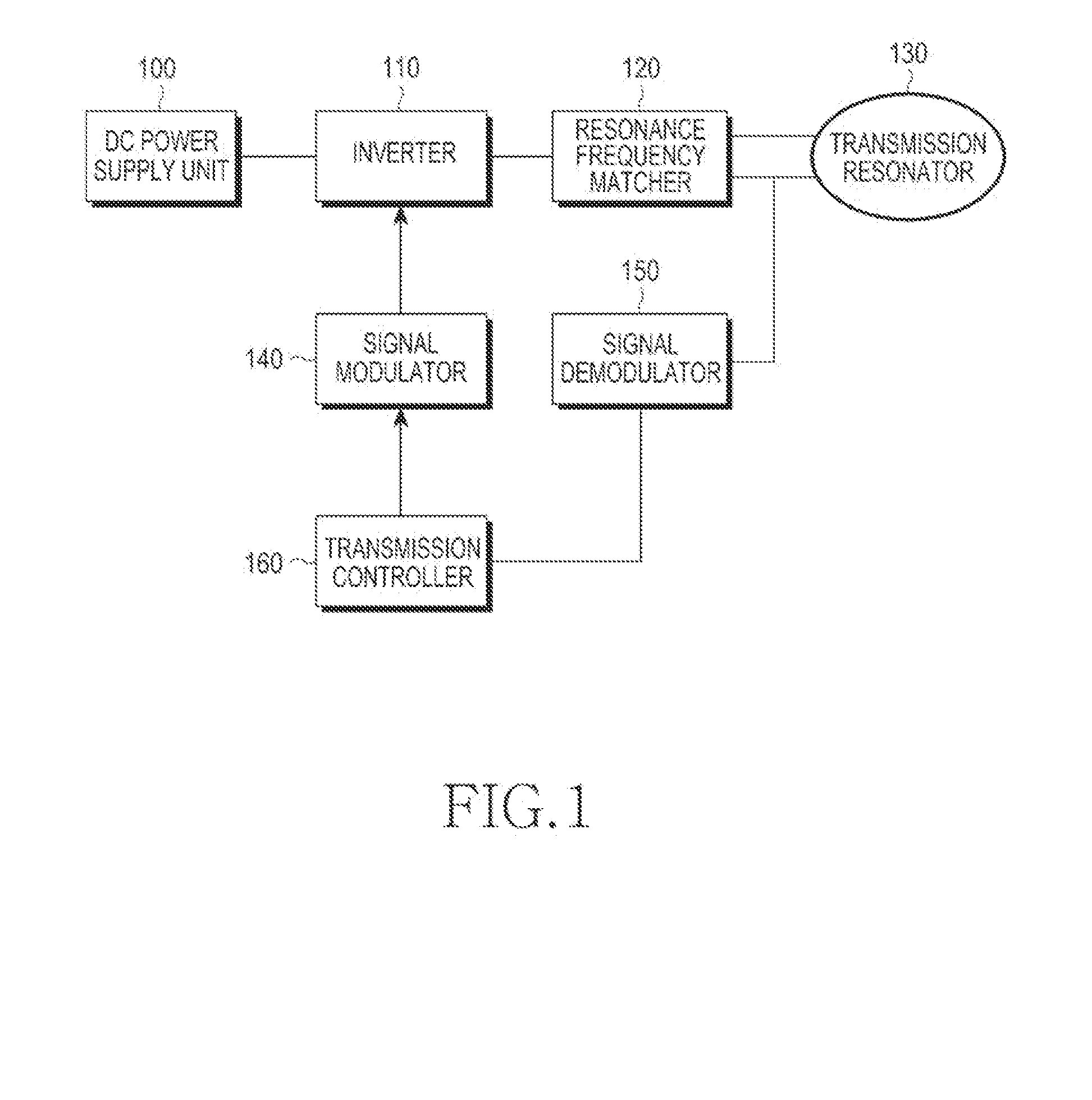
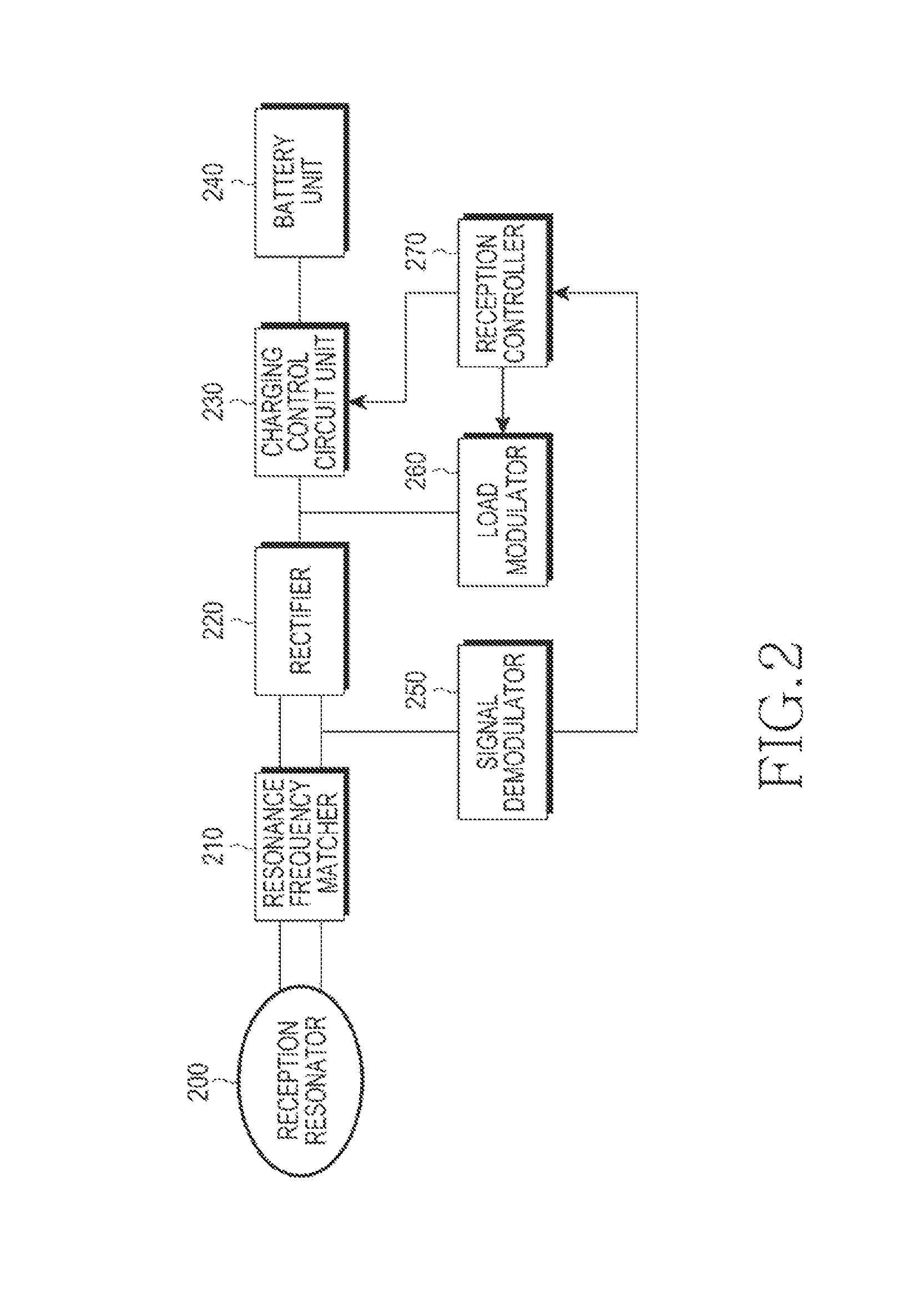
Power reception control device, power reception device, non-contact power transmission system, charge control device, battery device, and electronic instrument
ActiveUS20090021219A1Circuit authenticationNear-field transmissionElectric power transmissionTransport system
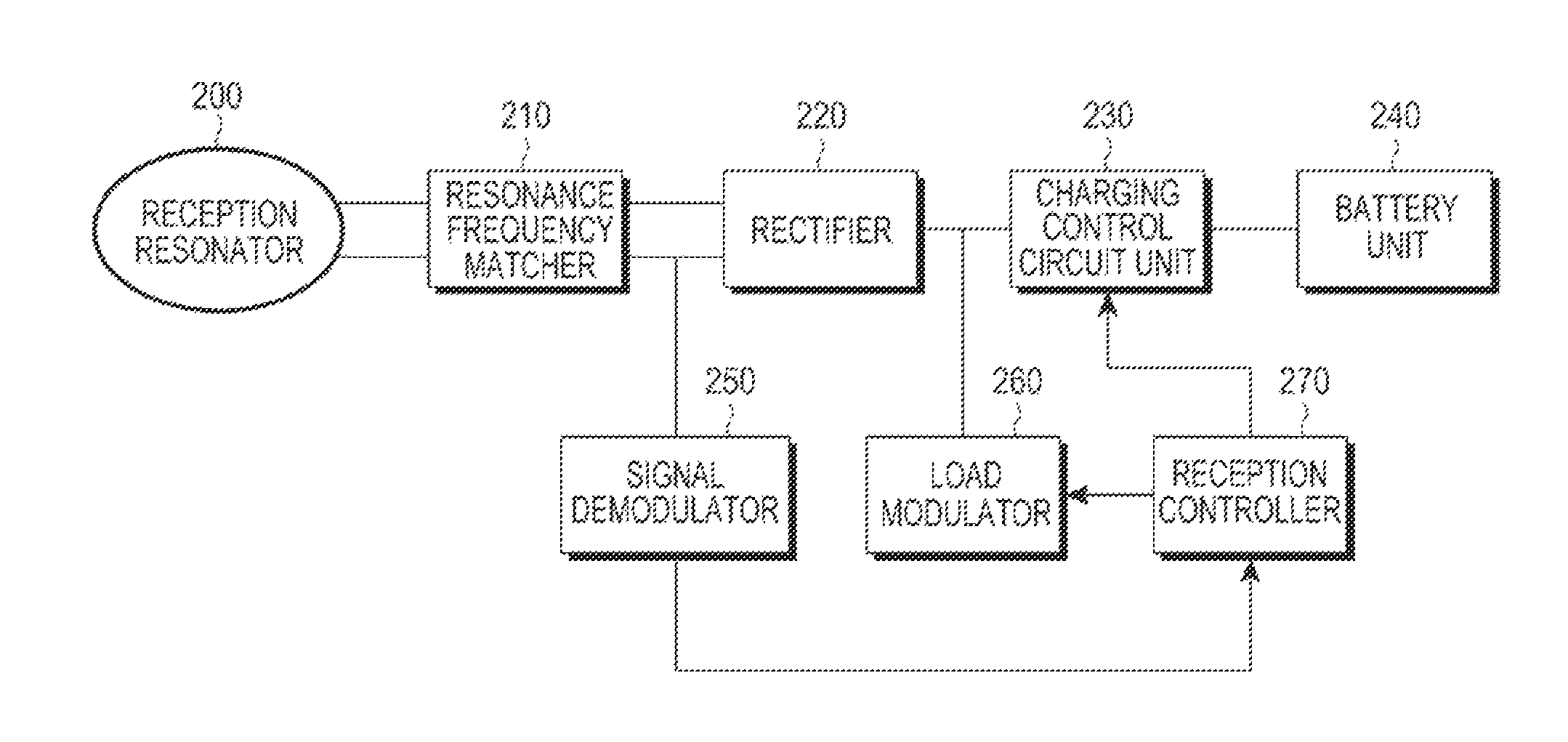
A power reception control device provided in a power reception device of a non-contact power transmission system includes a power-reception-side control circuit that controls an operation of the power reception device, and a power supply control signal output terminal that supplies a power supply control signal to a charge control device, the power supply control signal controlling power supply to a battery. The power-reception-side control circuit controls a timing at which the power supply control signal (ICUTX) is output from the power supply control signal output terminal. The operation of the charge control device is compulsorily controlled using the power supply control signal (ICUTX).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
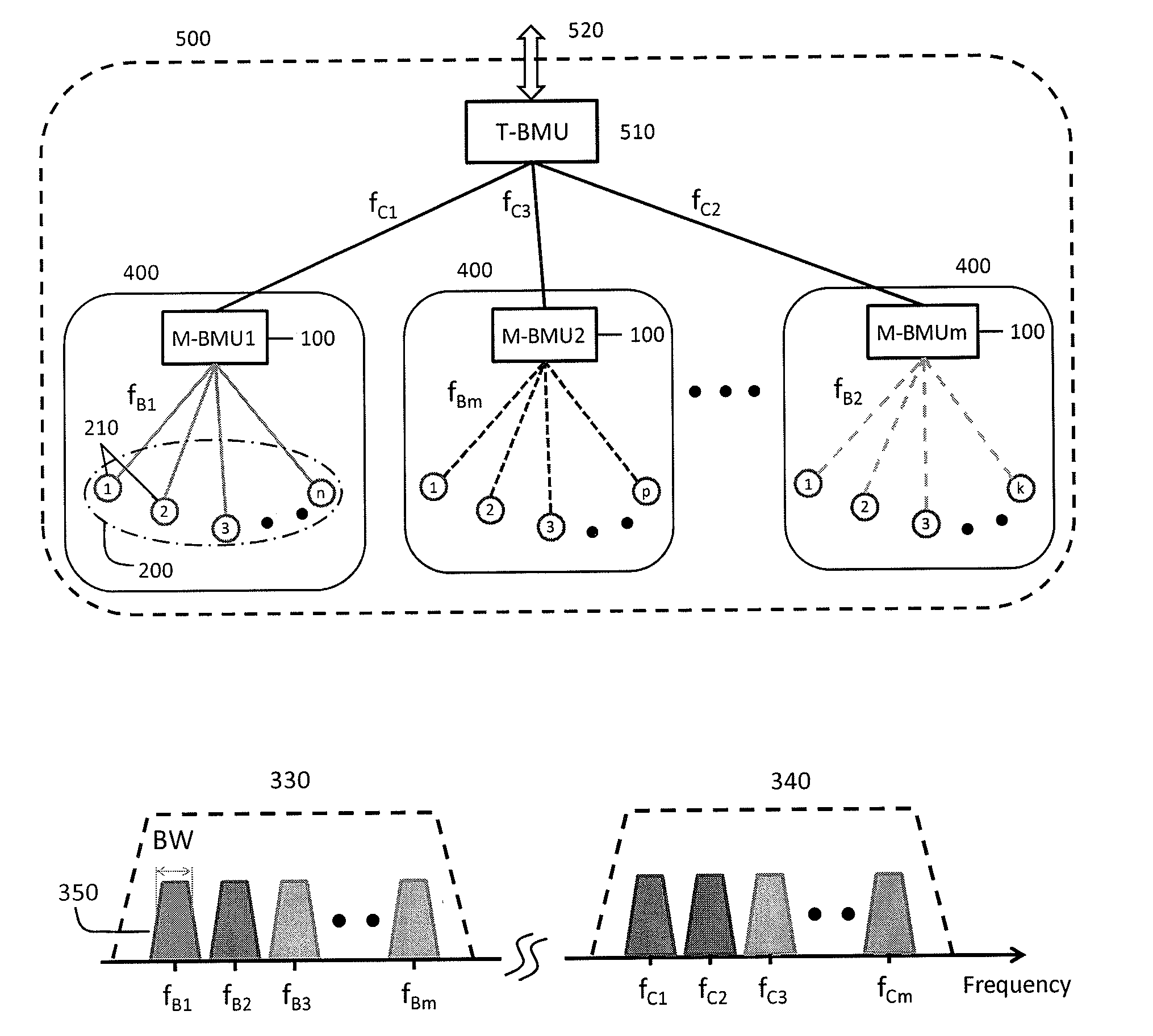
Wireless Battery Area Network For A Smart Battery Management System
ActiveUS20130271072A1Provide scalabilityAccurate configurationCircuit monitoring/indicationCharge equalisation circuitArea networkManagement unit
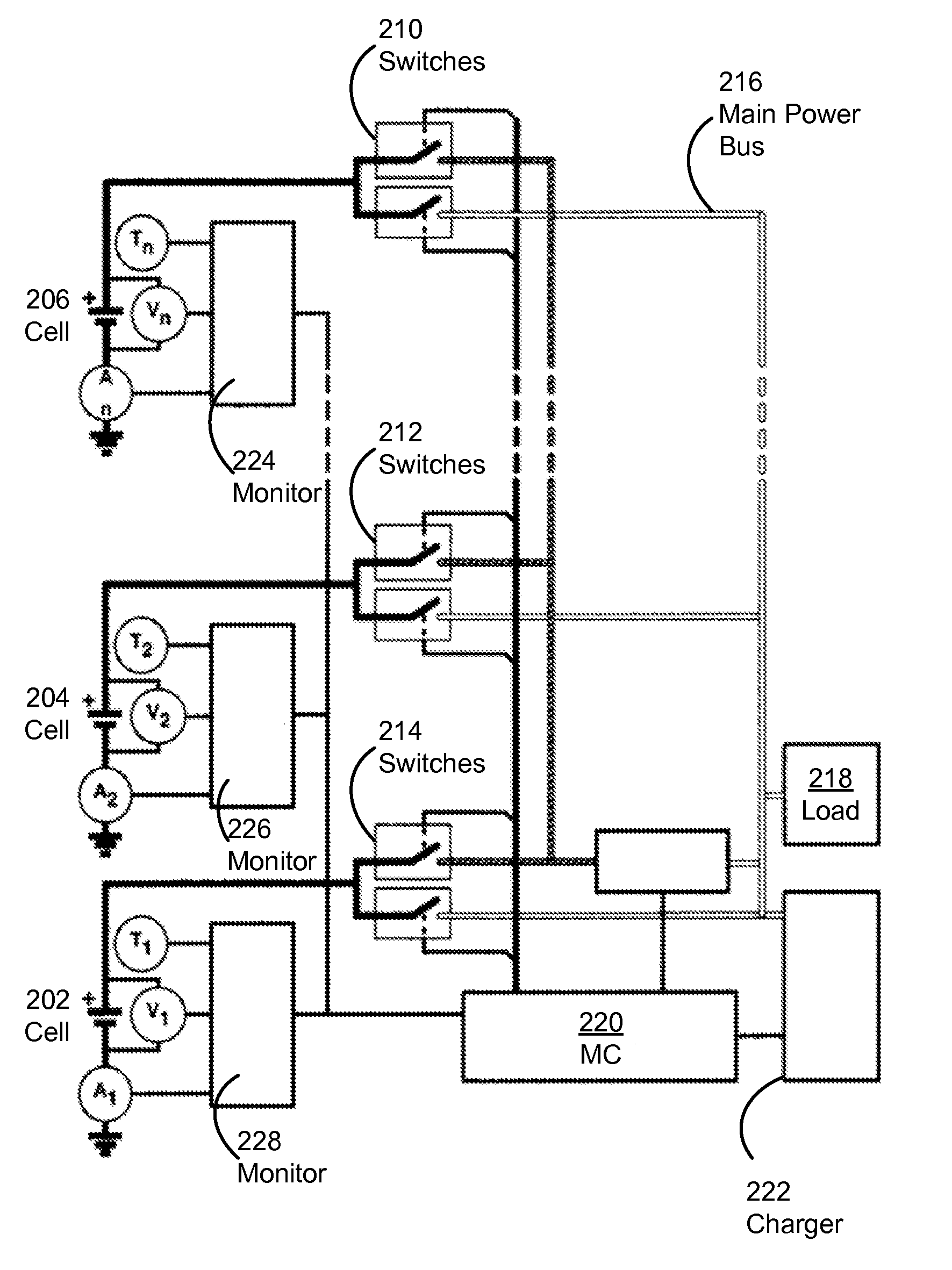
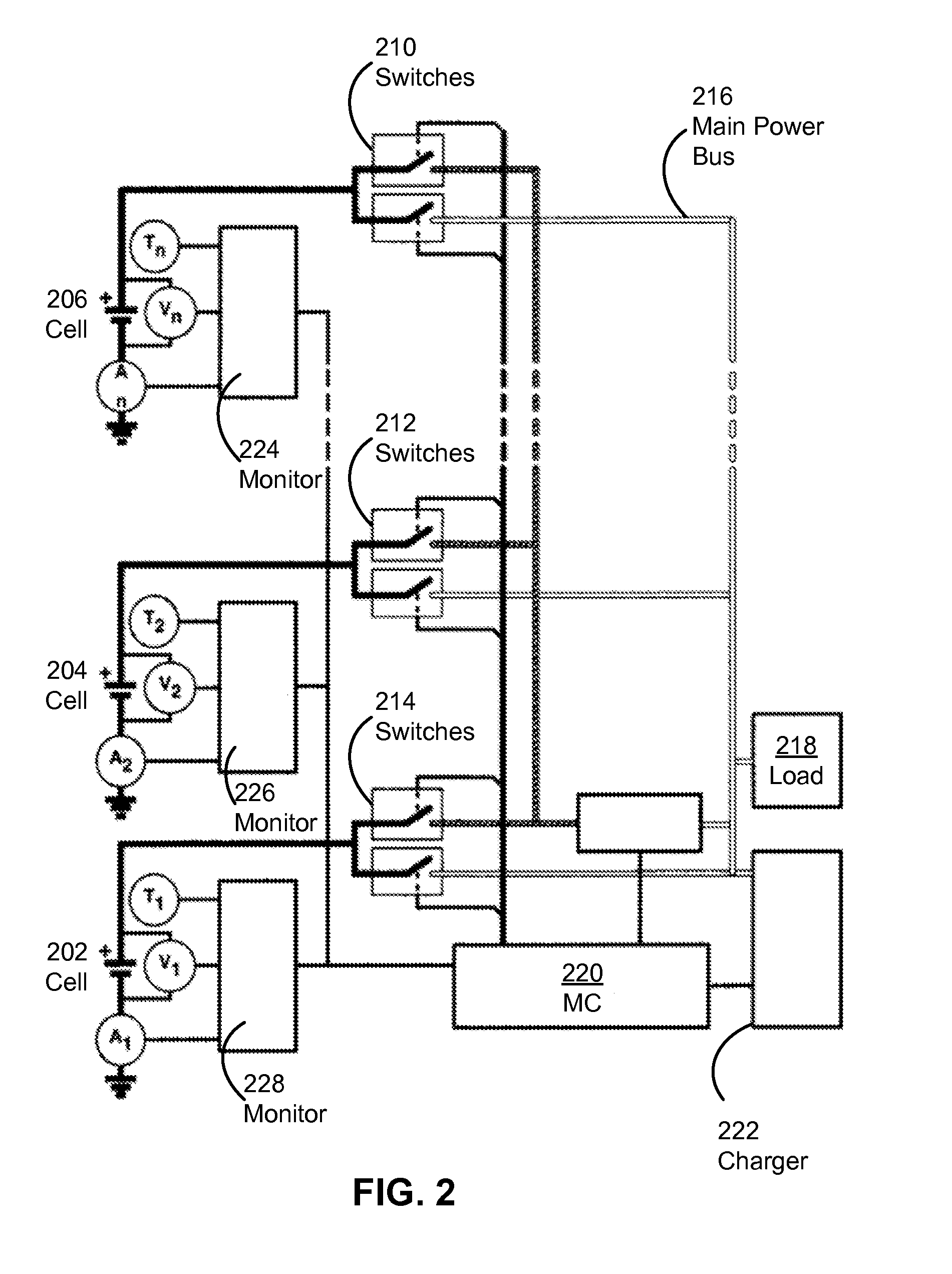
A Wireless battery area network permits the wirelessly monitoring and controlling of individual batteries within large-scale battery applications. The system automatically configures its wireless nodes in the network and provides for the linking of a plurality of batteries (10) to a master battery management unit (M-BMU) (100) by establishing a wireless battery area network within a battery pack that include slave units (S-BMU) (210). The entire system may also be controlled by a top level battery management unit (T-BMU) (510). The system and method allows for the monitoring of voltage, current, temperature, or impedance of individual batteries and for the balancing or bypassing of a battery.
Owner:NAVITAS SOLUTIONS
Fast charger for high capacity batteries
InactiveUS20050046387A1Reduce heatMinimise currentCircuit monitoring/indicationDifferent batteries chargingFast chargingHertz
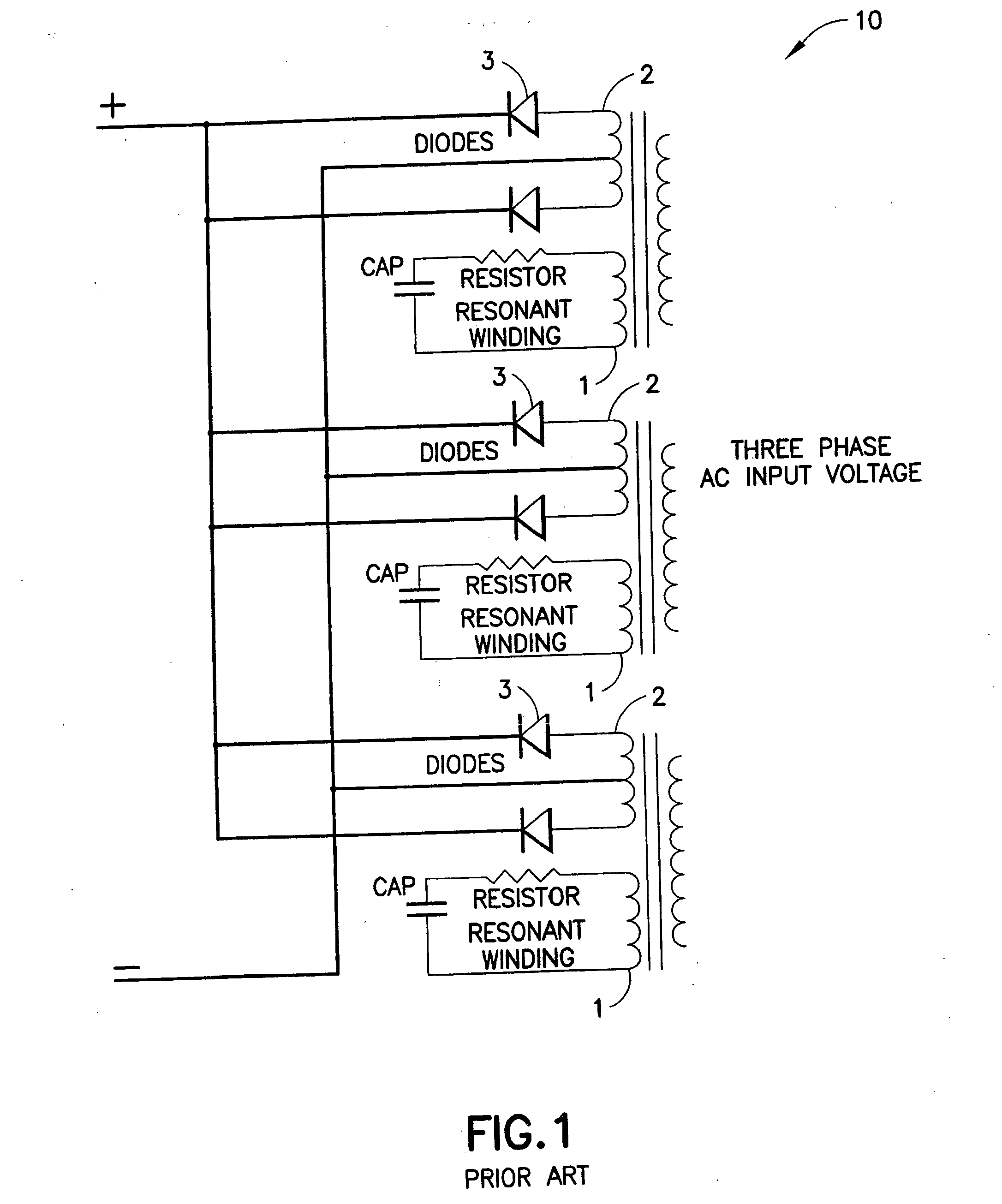
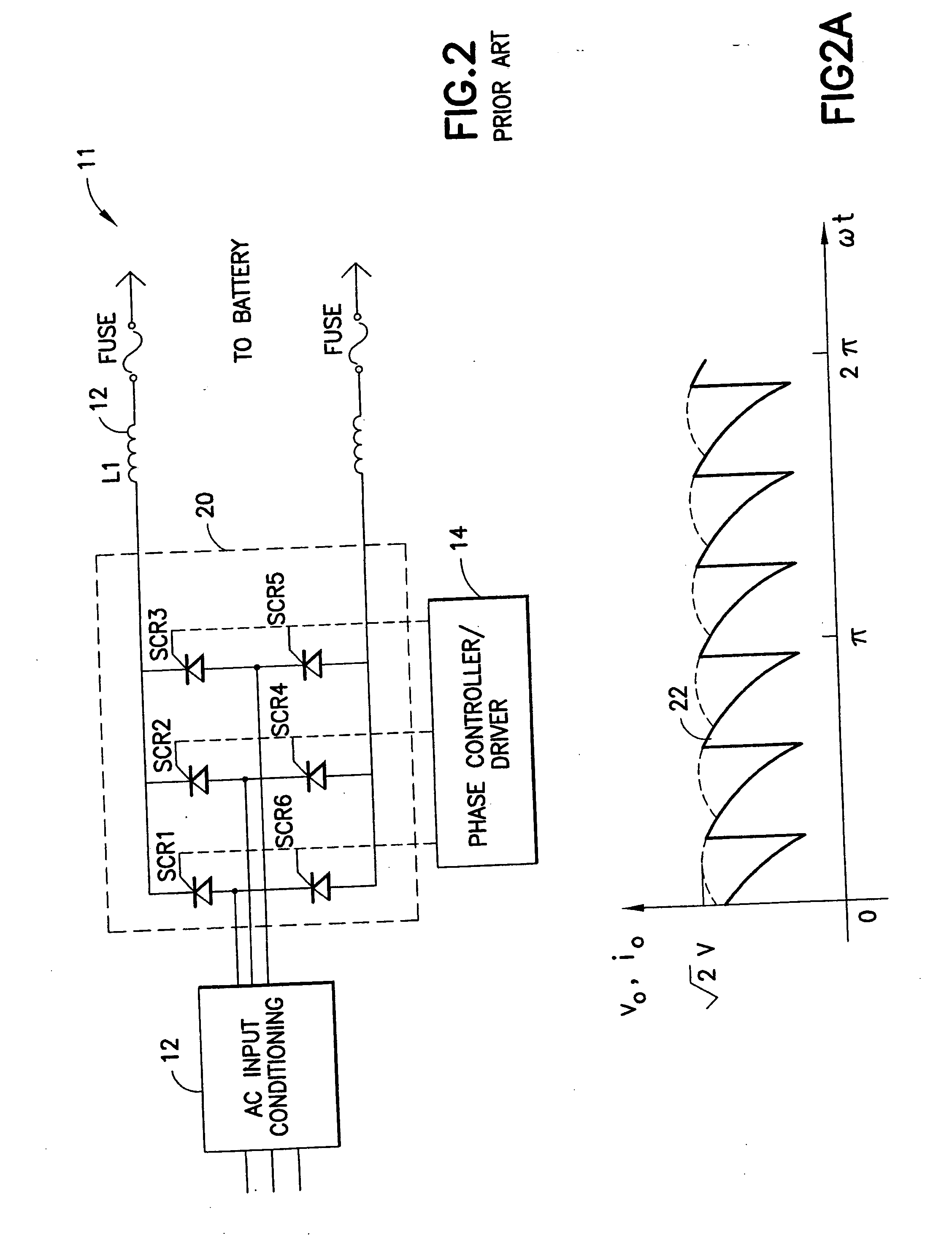
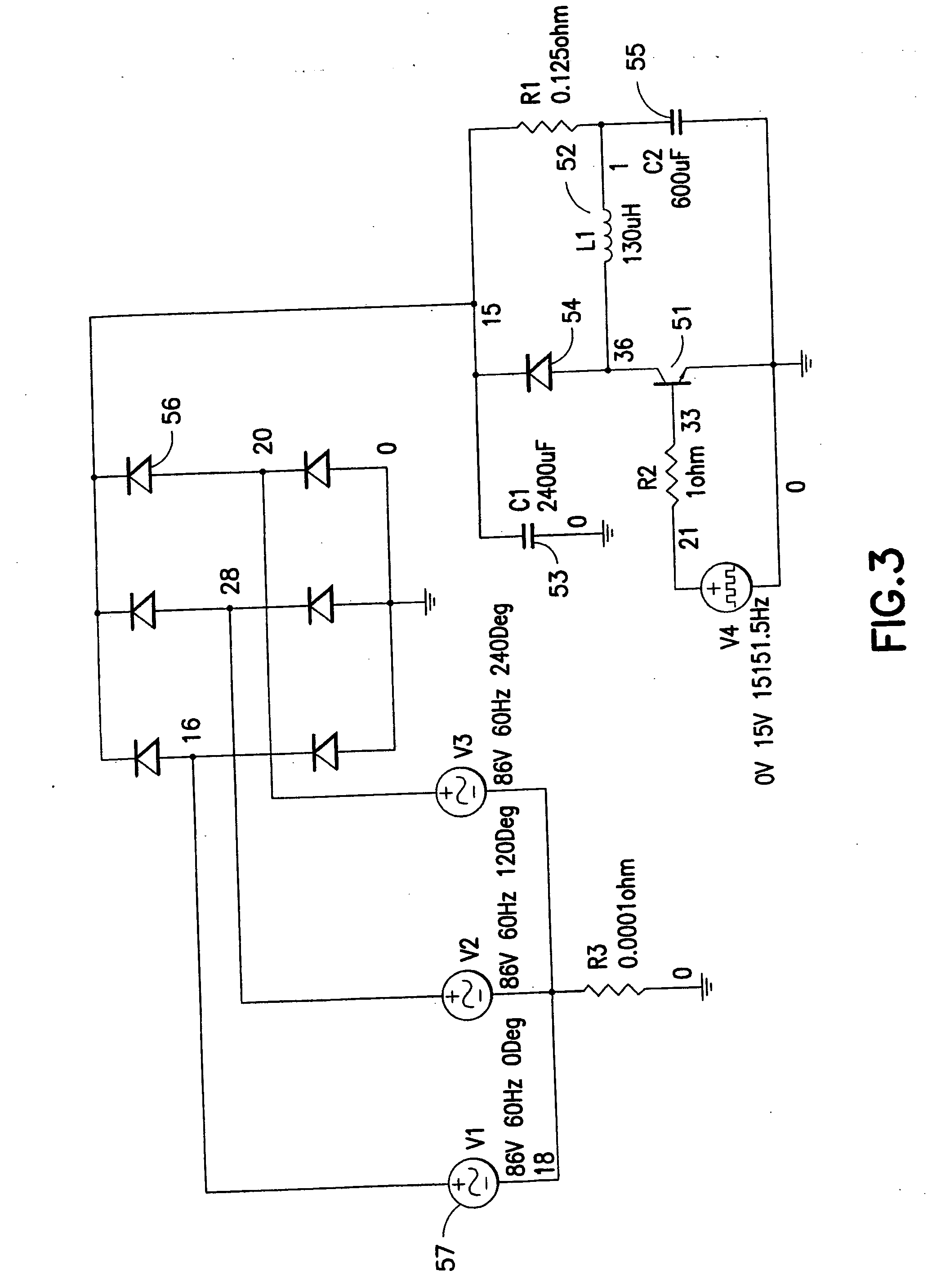
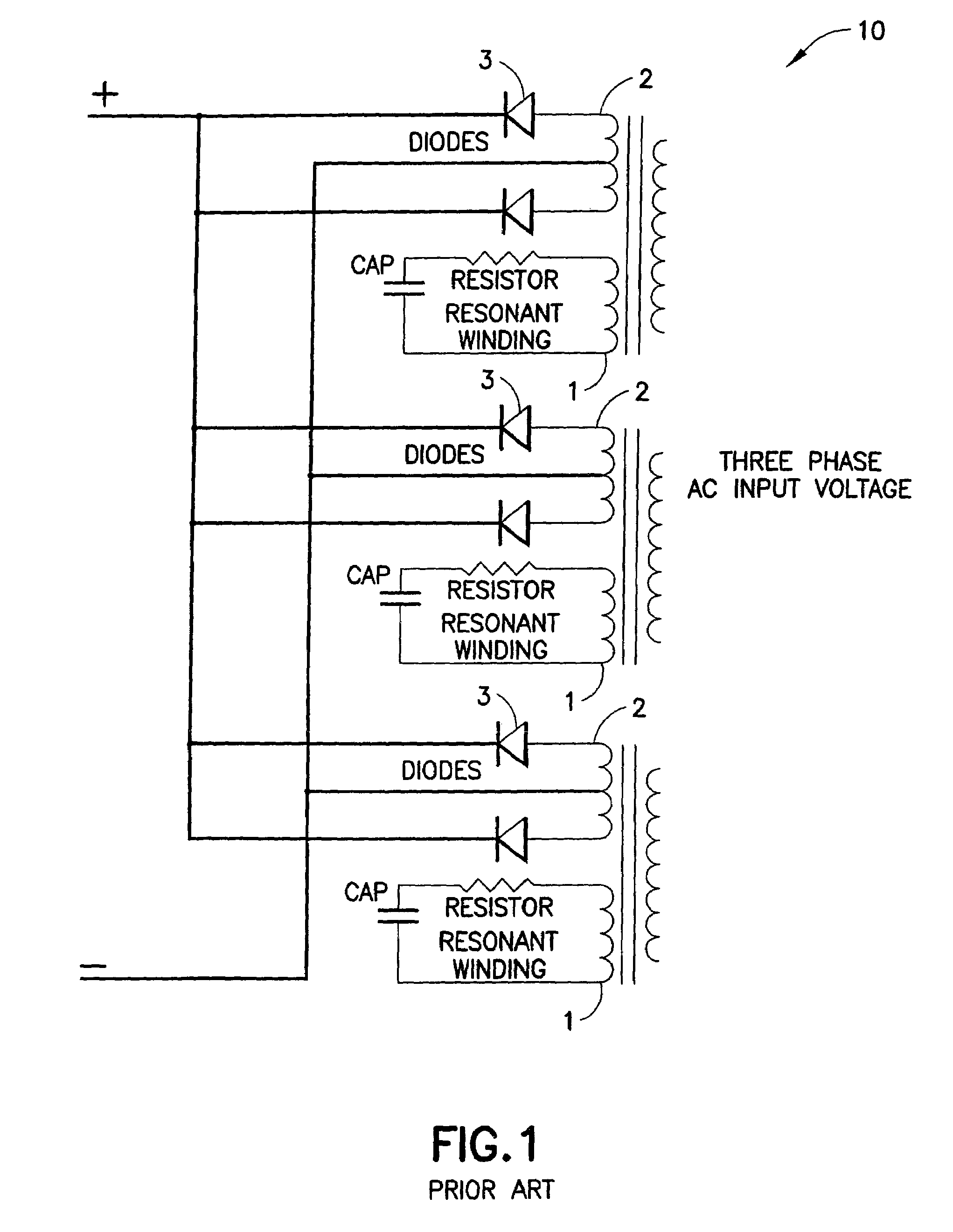
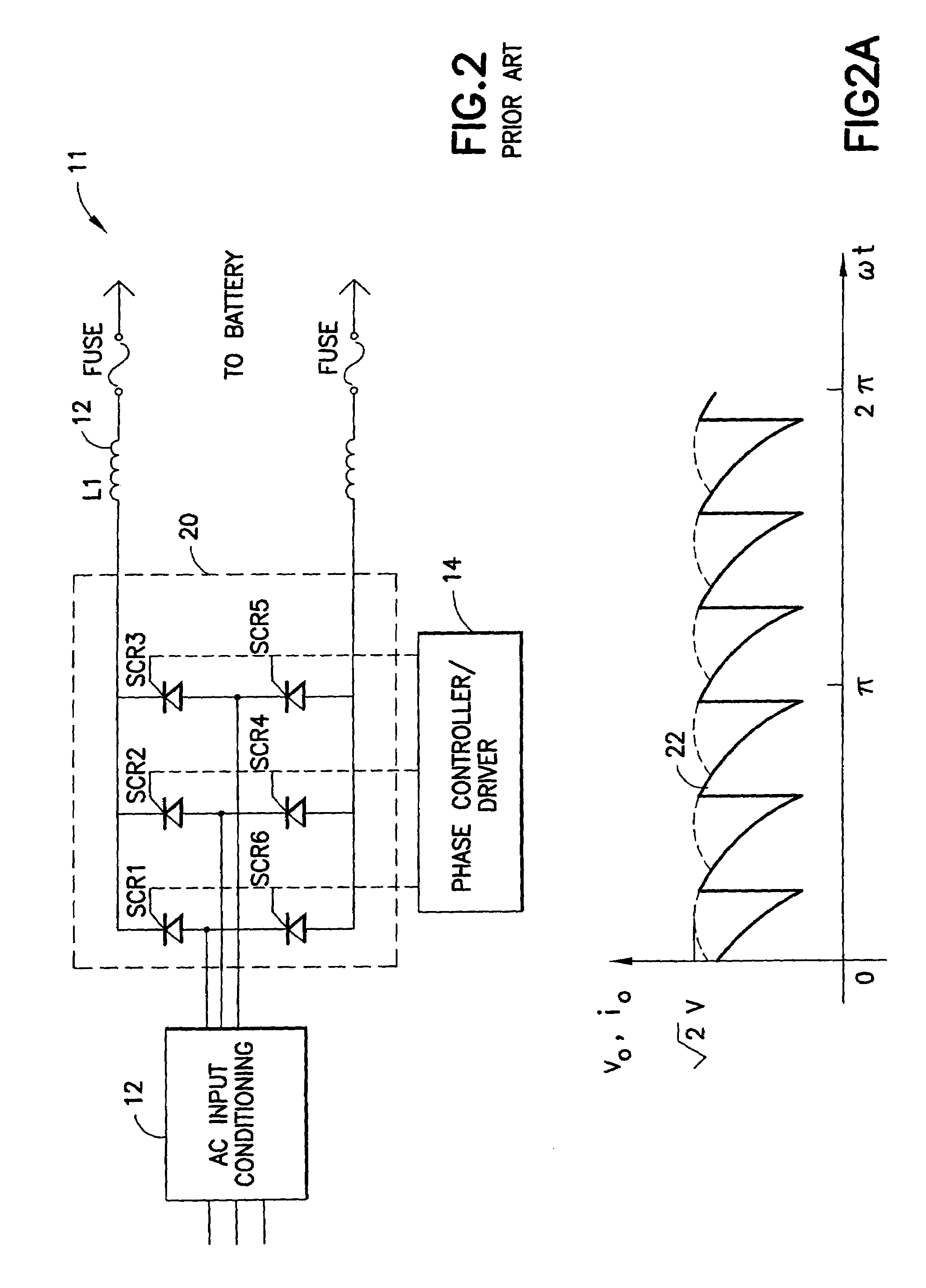
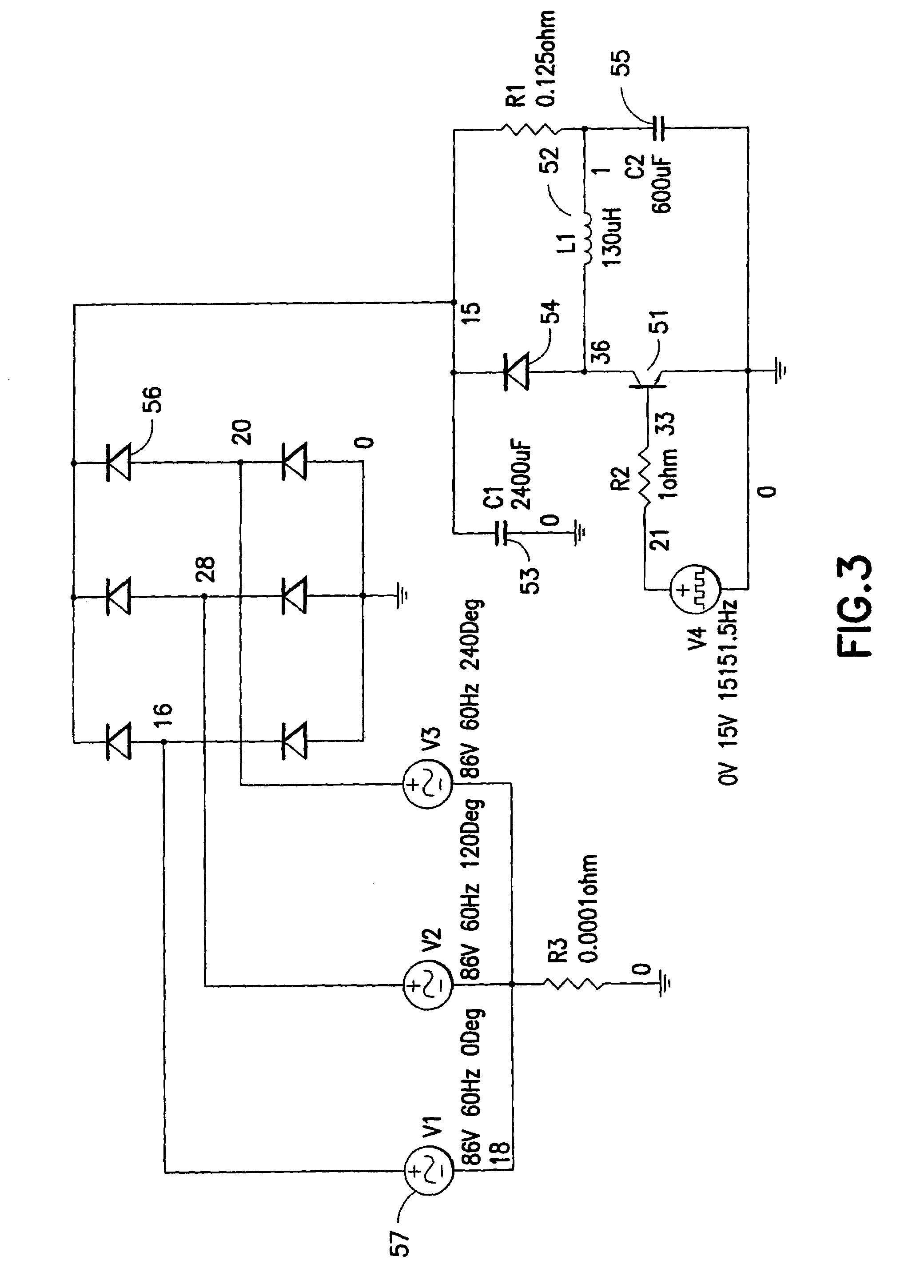
A highly efficient fast charger for high capacity batteries and methods for fast charging high capacity batteries. The fast charger preferably comprises a rectified AC input of single or preferably three phases, with an optional power factor corrected input, minimally filtered with high frequency, high ripple current capacitors, which is switched with a power switching circuit in the “buck” configuration into an inductor / capacitor output filter. Metallized film capacitors are employed, to minimize the rectified 360 Hertz AC component filtering while providing transient switch protection and ripple current requirements for the buck regulator, to provide a high current fast charger with substantially improved power factor. High power, high frequency switching with minimized output filter size provides a highly filtered DC output. The fast charger is adapted to be constructed in a modular design for simple maintenance.
Owner:AKER WADE POWER TECH
High voltage battery formation protocols and control of charging and discharging for desirable long term cycling performance
ActiveUS20110236751A1Increase capacityHybrid vehiclesFinal product manufactureElectrical batteryLow voltage
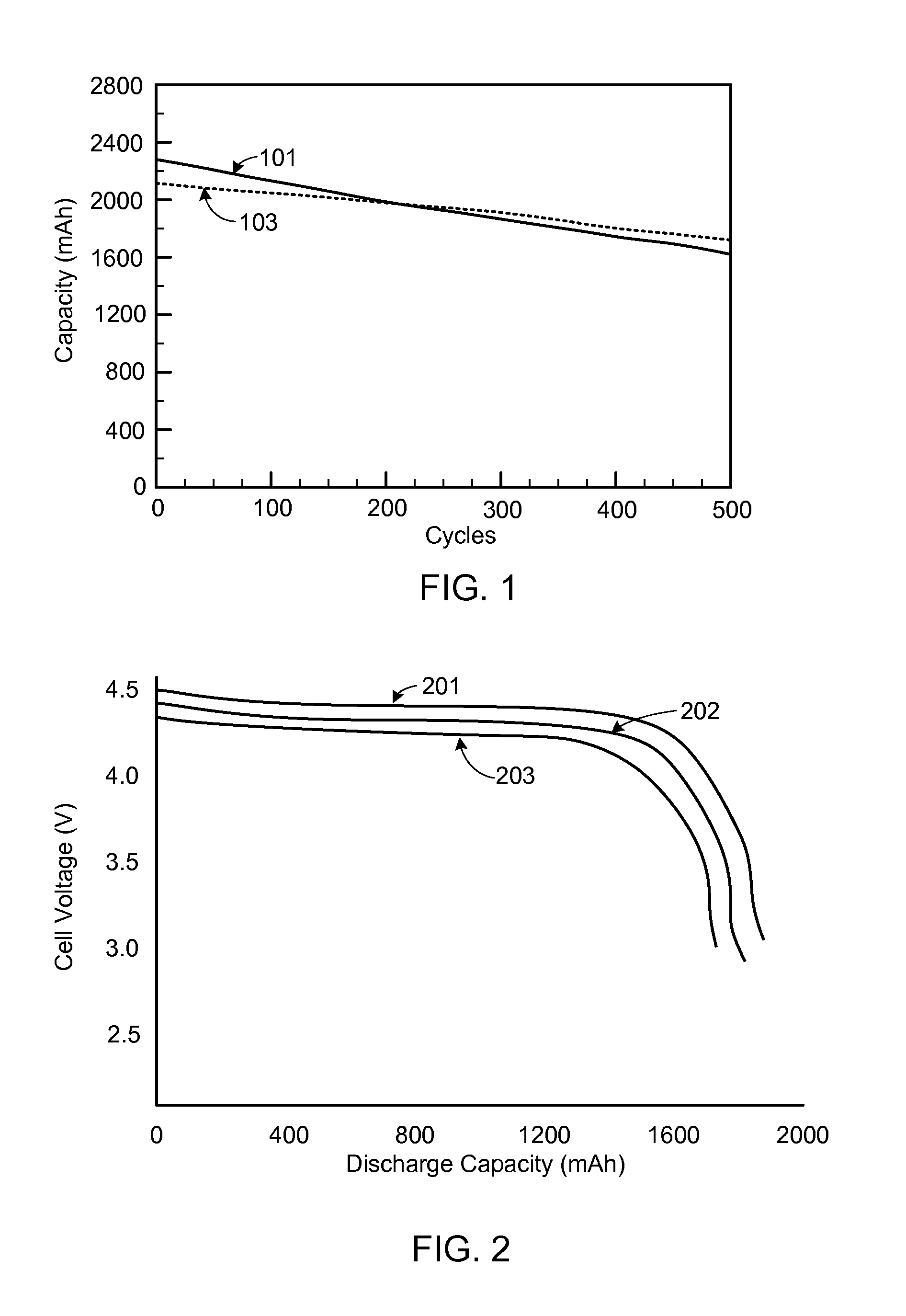
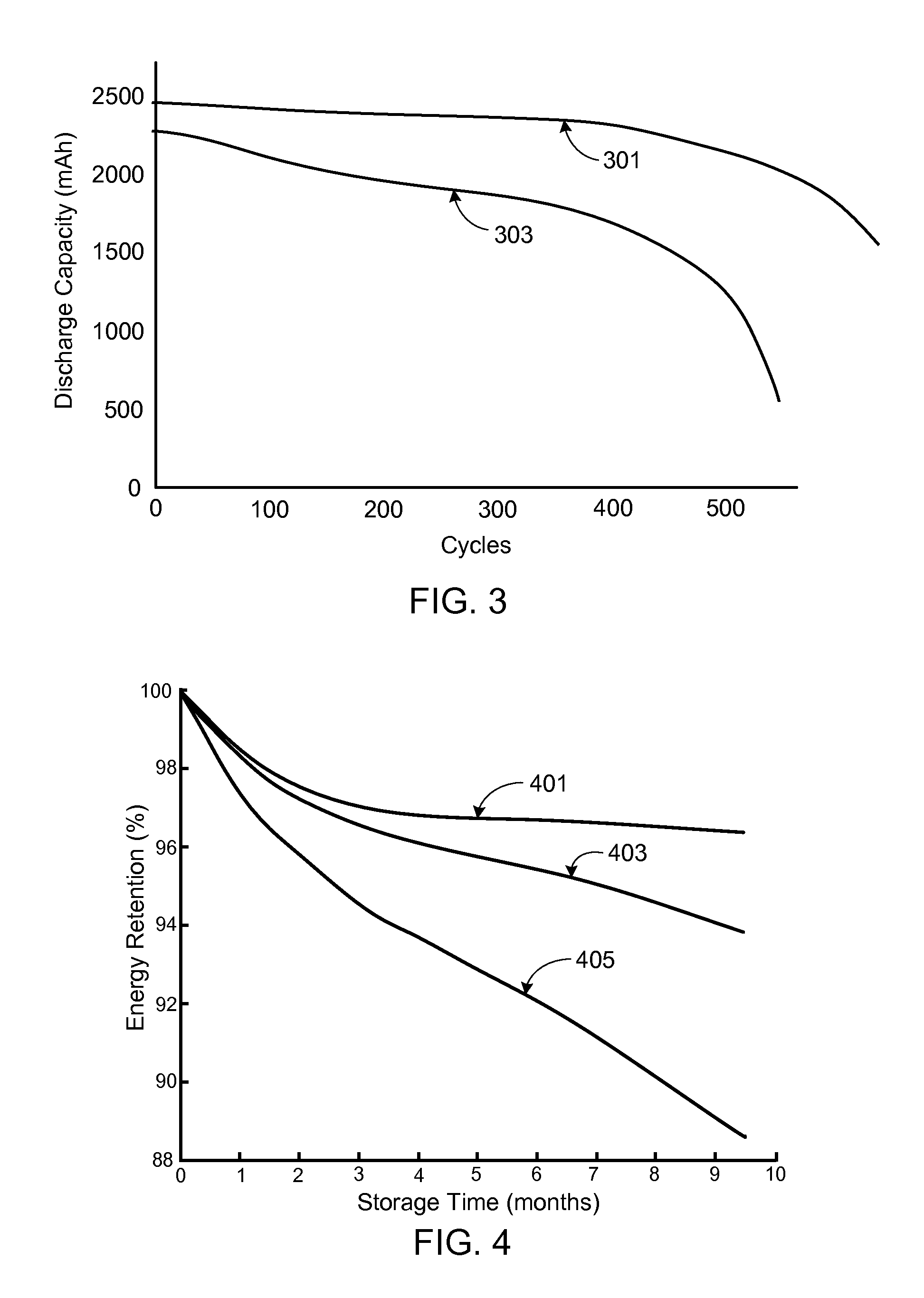
Improved cycling of high voltage lithium ion batteries is accomplished through the use of a formation step that seems to form a more stable structure for subsequent cycling and through the improved management of the charge-discharge cycling. In particular, the formation charge for the battery can be performed at a lower voltage prior to full activation of the battery through a charge to the specified operational voltage of the battery. With respect to management of the charging and discharging of the battery, it has been discovered that for the lithium rich high voltage compositions of interest that a deeper discharge can preserve the cycling capacity at a greater number of cycles. Battery management can be designed to exploit the improved cycling capacity obtained with deeper discharges of the battery.
Owner:IONBLOX INC
Battery charger apparatus
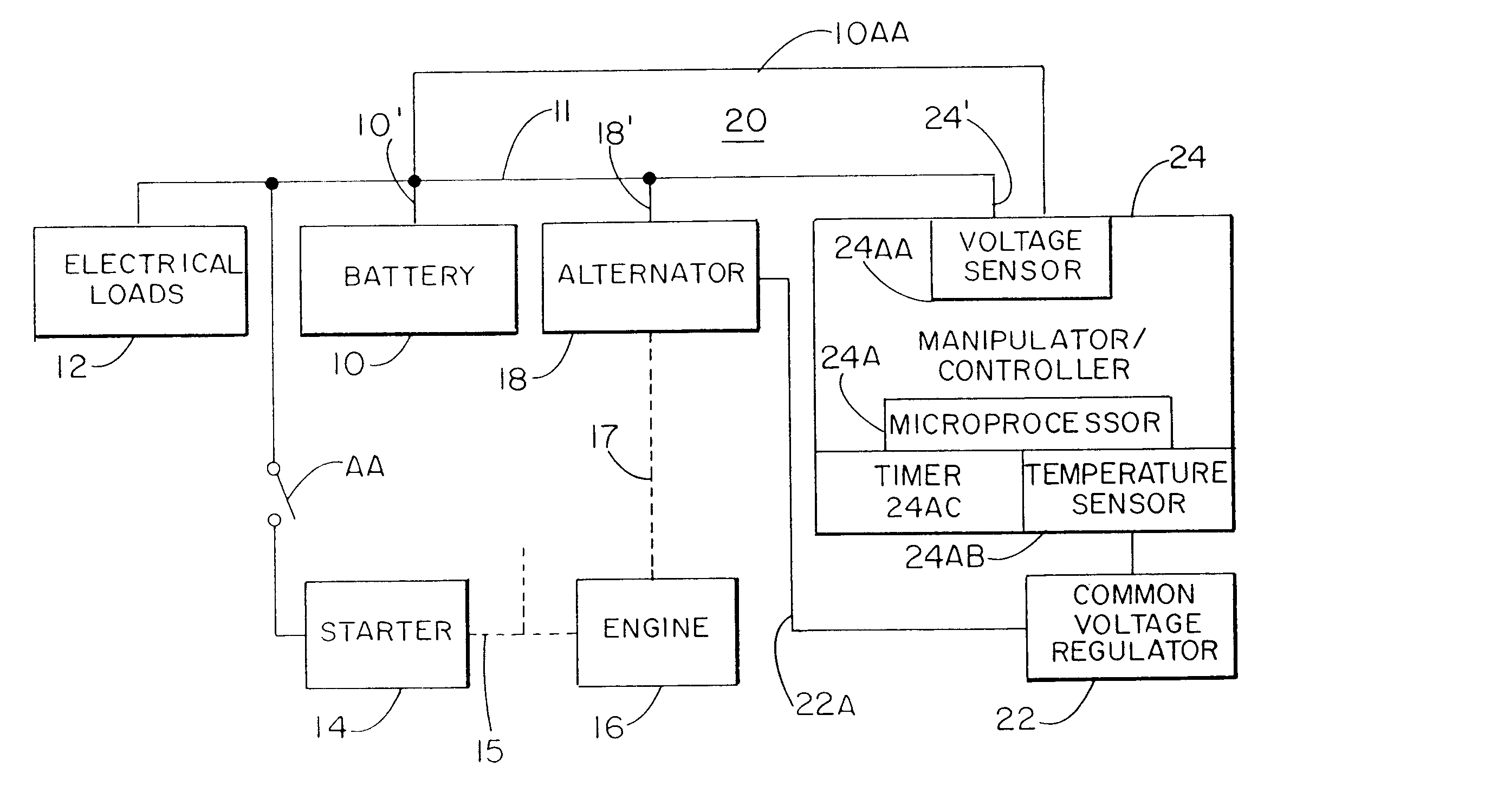
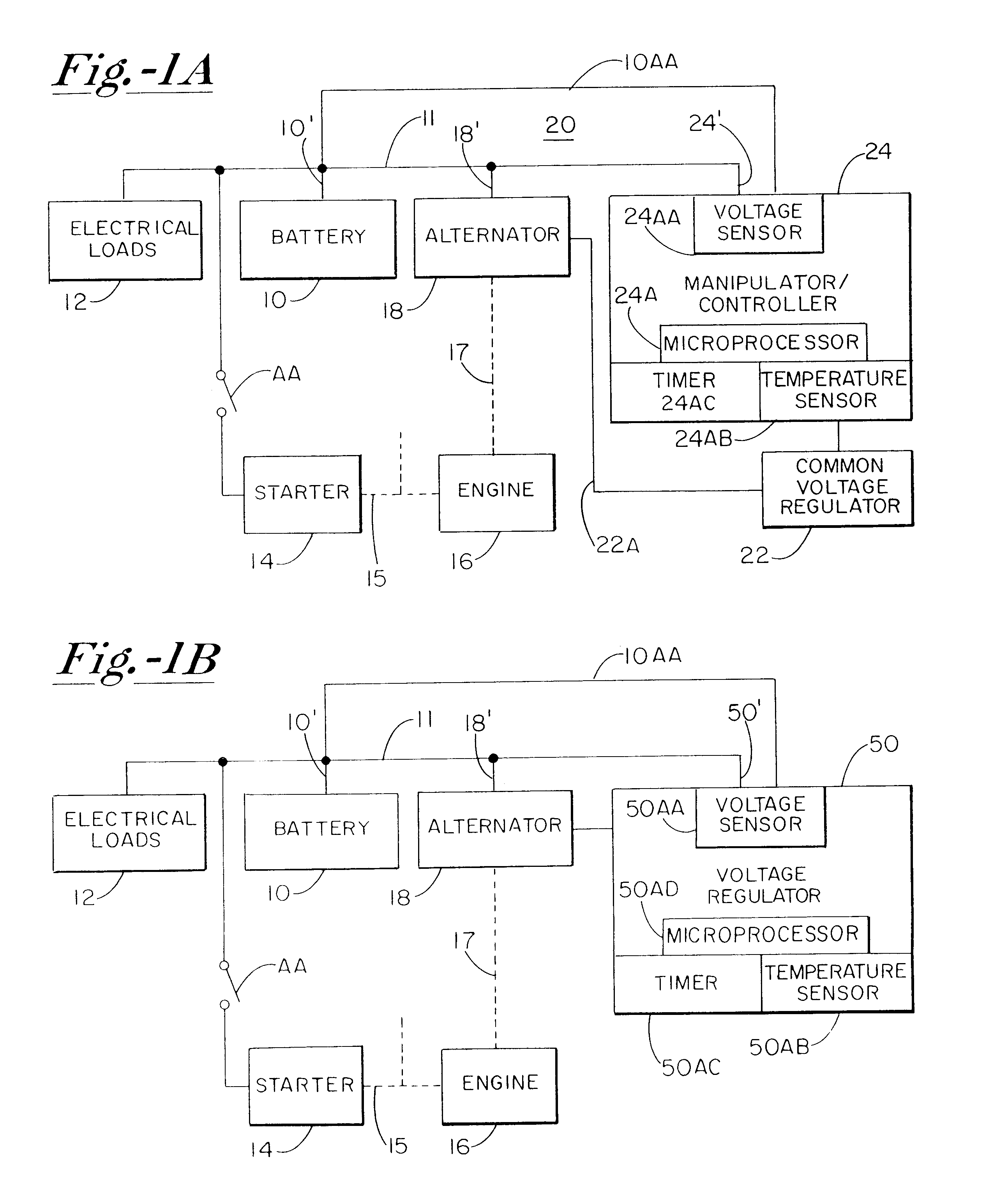
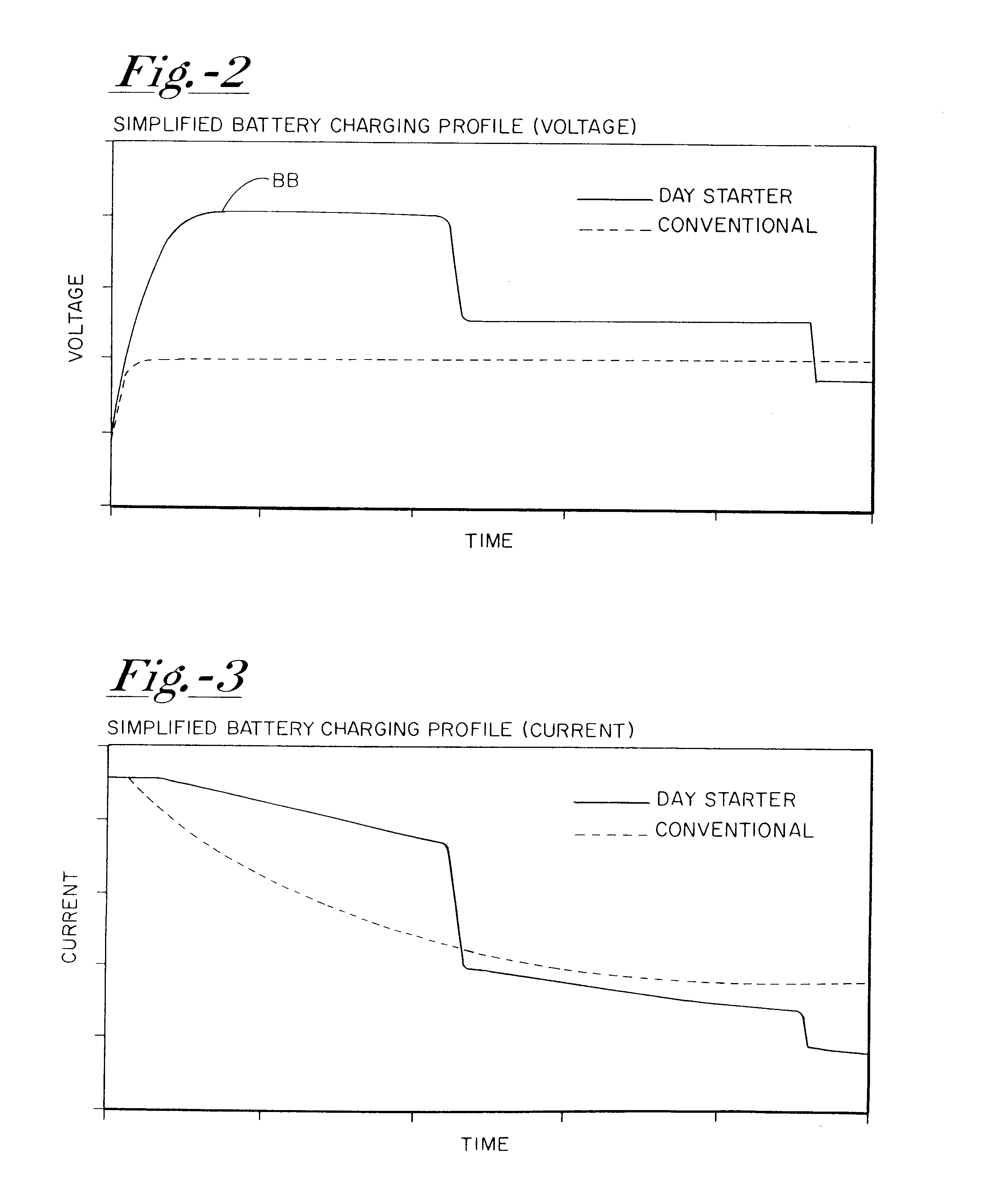
InactiveUS6515456B1Improve economyProlong lifeElectric powerCharge maintainance charging/dischargingBattery state of chargeAlternator
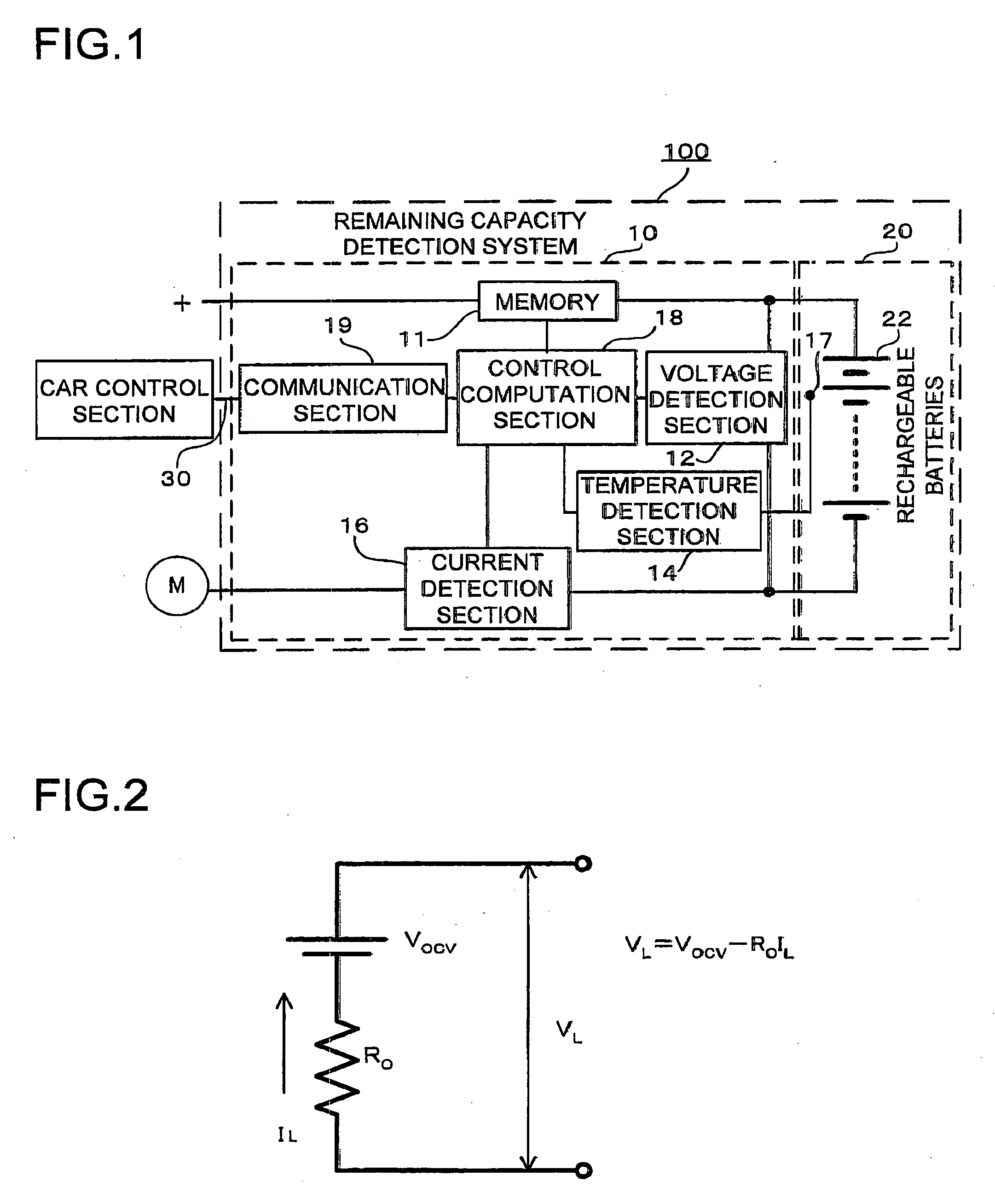
A system for actively controlling the charging profile of a battery uses a software-based alternator control unit to control the charging voltage. The system optimizes battery and alternator life. The system, on a dynamic basis, uses battery open-circuit voltage (OCV) to estimate battery state-of-charge (SOC). Also, the charging current of the battery is periodically estimated; this, after processing, provides an estimated SOC of the battery.
Owner:MIXON
Electronic cigarette device
InactiveUS8973587B2Firmly connectedSimple connection structureMedical devicesTobacco pipesElectrical batteryElectronic cigarette
Owner:HUIZHOU KIMREE TECH
Method and system for selectively charging a battery
InactiveUS20060103355A1Maximizing available charging current parameterMinimize power consumptionElectric powerCharge maintainance charging/dischargingCharge currentCoupling
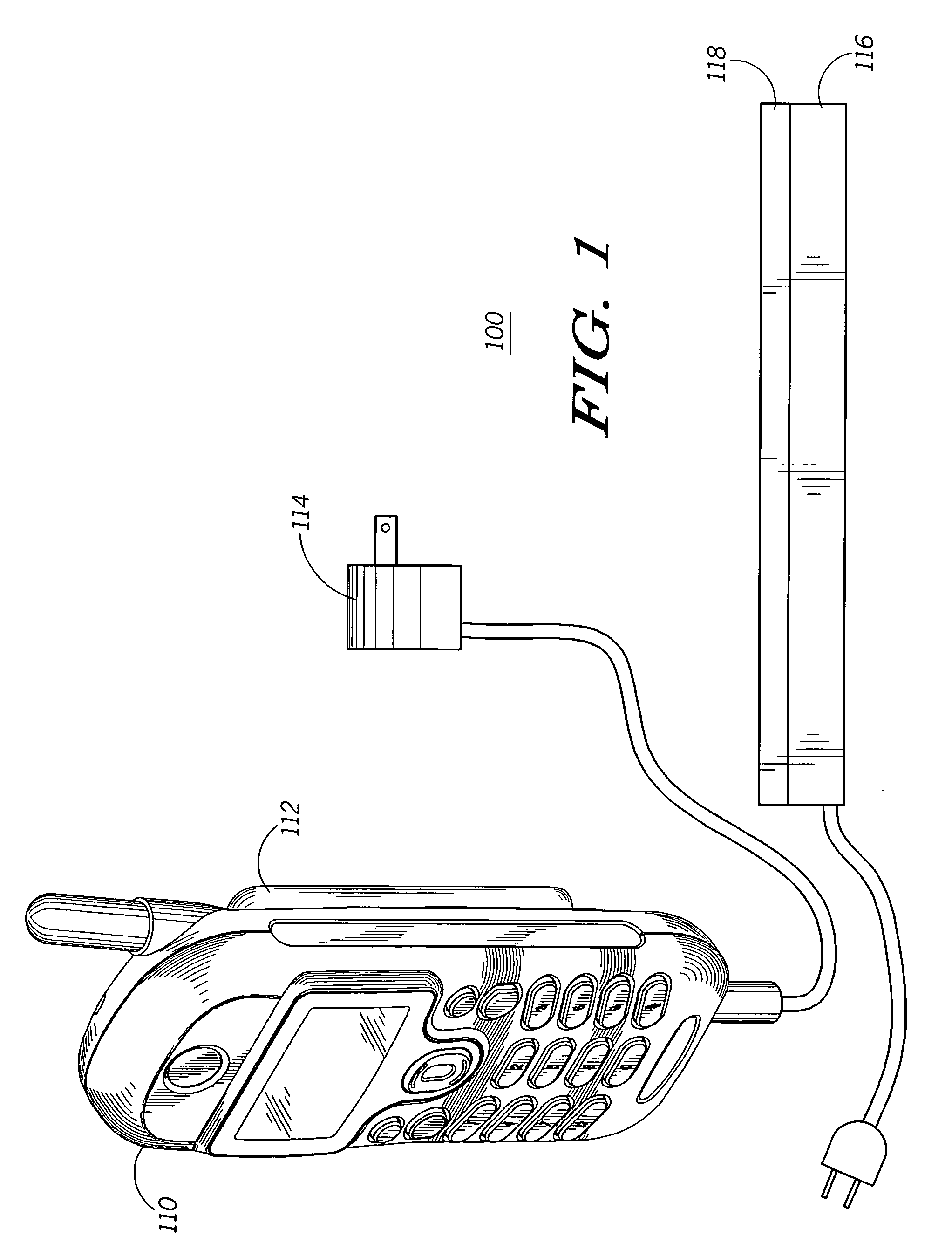
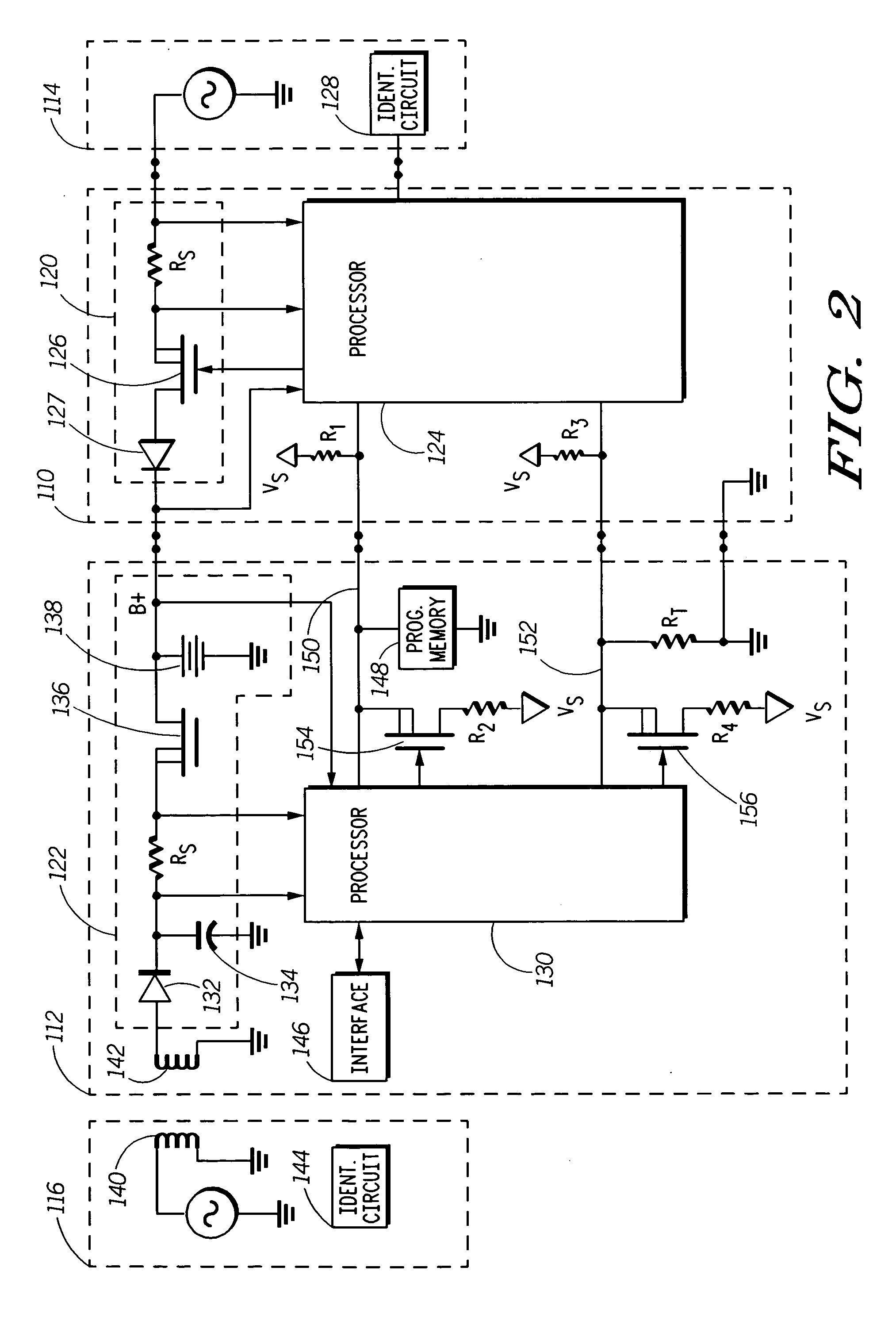
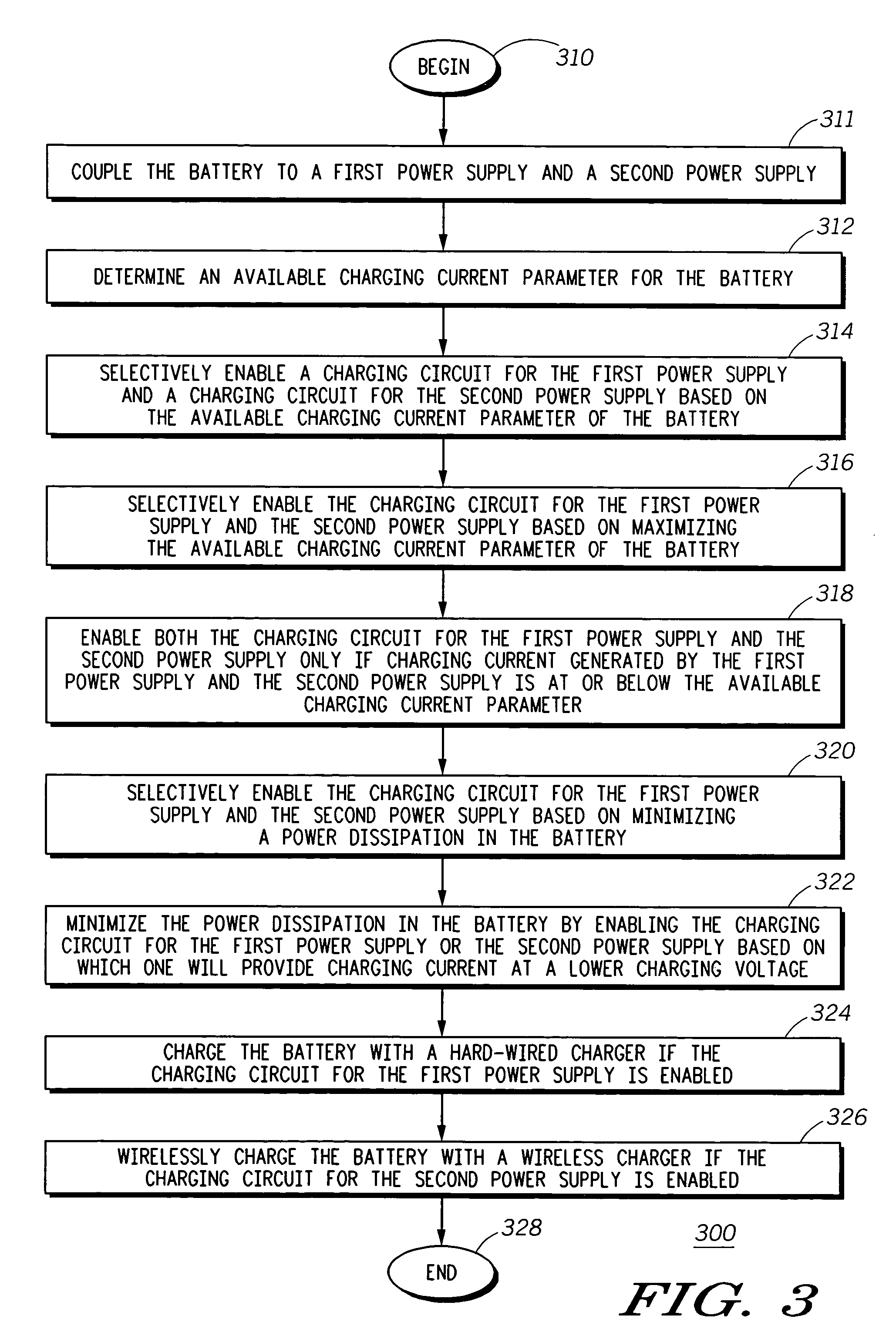
The invention concerns a method (300) and system (100) for selectively charging a battery (112). In one arrangement, the method can include the steps of coupling (311) the battery to a first power supply (114), coupling (311) the battery to a second power supply (116), determining (312) an available charging current parameter for the battery and selectively enabling (314) a charging circuit (120) for the first power supply and a charging circuit (122) for the second power supply based on the available charging current parameter of the battery. The selectively enabling process can be based on maximizing (316) an available charging current of the battery and minimizing (320) a power dissipation of the battery. As an example, the first power supply can be a hard-wired charger (114), and the second power supply can be a wireless charger (116).
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Method of controlling rechargeable battery power and a power source apparatus
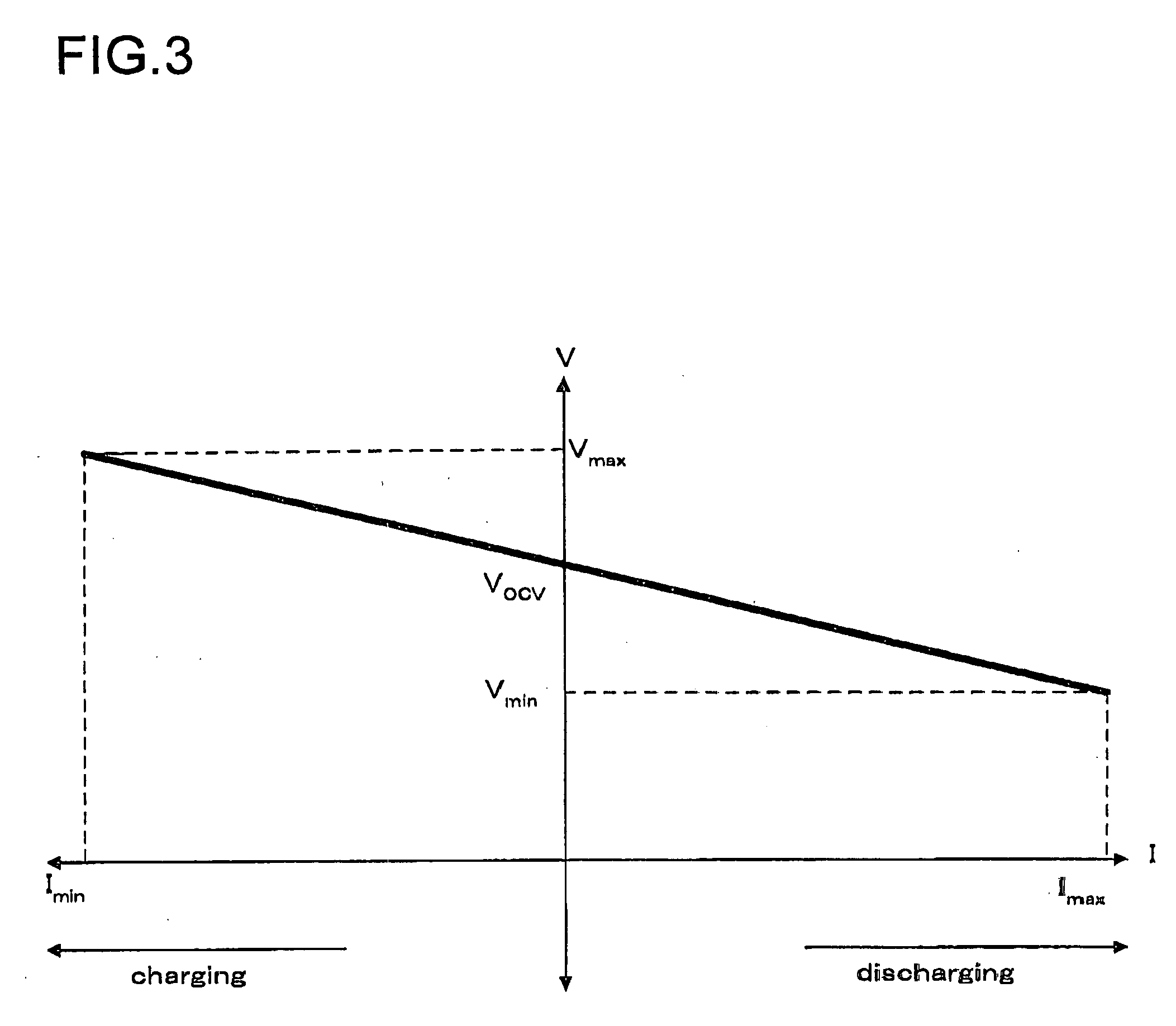
InactiveUS20060087291A1Appropriate settingAvoid excessive dischargeCharging stationsSecondary cells charging/dischargingBattery chargeMemory effect
The method of controlling rechargeable battery power is a method that includes limiting the amount of usable power during rechargeable battery charging and discharging, determining a rechargeable battery current-voltage characteristic function based on rechargeable battery charging and discharging current flow and voltage, finding a limiting discharging current Imax and / or a limiting charging current Imin from a prescribed minimum voltage Vmin to prevent over-discharging and / or a prescribed maximum voltage Vmax to prevent over-charging and their intersection with the current-voltage characteristic function, and controlling current such that discharging current greater than or equal to Imax and / or charging current less than or equal to Imin does not flow through the rechargeable batteries. In this fashion, the amount of usable power can be limited considering factors such as the memory effect, and the rechargeable battery can be used to its maximum capability within the range of safe operation.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Conditional battery charging system
ActiveUS7570015B2Extend your lifeExtend battery lifeSecondary cells charging/dischargingElectric powerBattery chargeElectrical and Electronics engineering
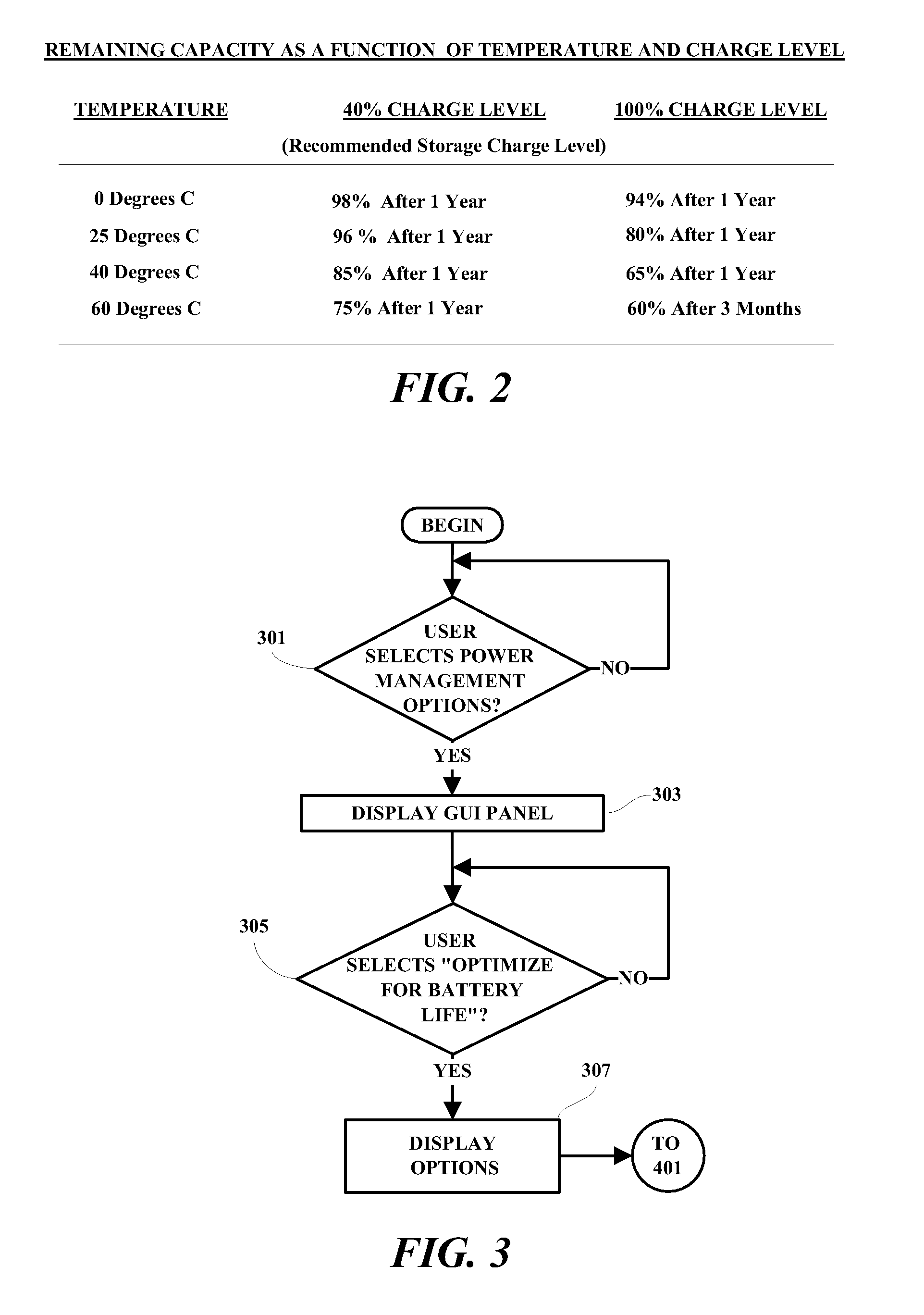
A method and system are provided in which a charging process for rechargeable batteries is controlled in accordance with selected predetermined variable conditions. In an exemplary embodiment, a user is enabled to select the predetermined conditions under which the charging of a battery is suspended until such conditions have changed. Such conditions include, for example, physical location of the battery being charged and / or the time and / or date when the battery is being charged. A user GUI is provided to enable a user to input selected times and / or dates and / or locations when the device containing the battery is likely to be away from a charging source and needs to be fully charged, and / or selected times and / or dates and / or locations when the device is likely to have access to a power source and the battery is enabled to be charged only to a storage level.
Owner:ATREUS LABS LLC
Fast-charging method and mobile terminal
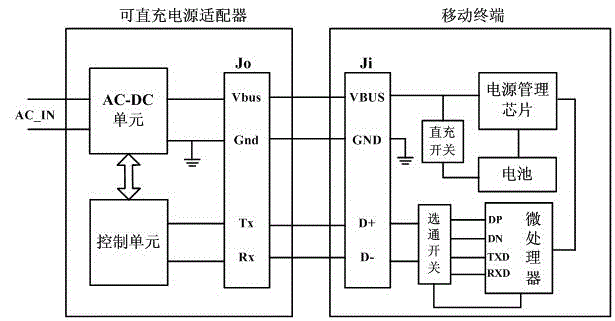
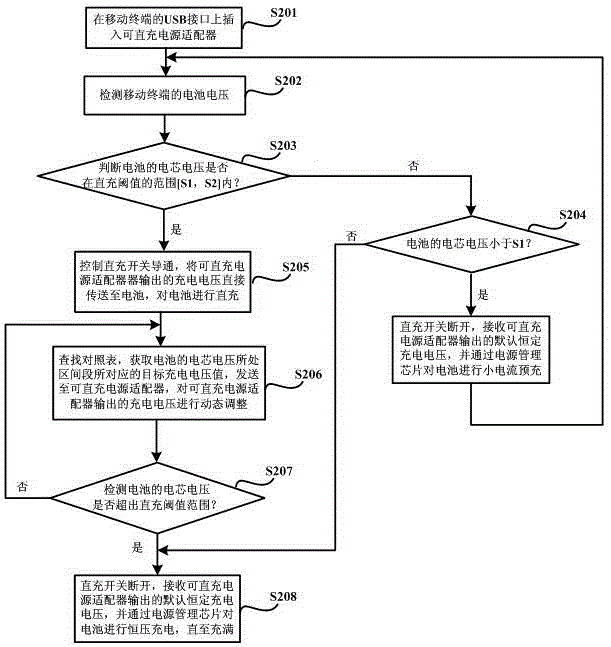
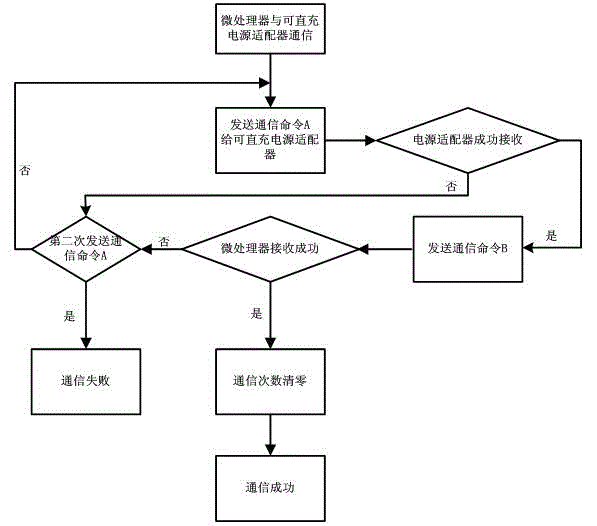
ActiveCN104967199AShorten the timeFast chargingElectric powerCharge maintainance charging/dischargingCharge currentFast charging
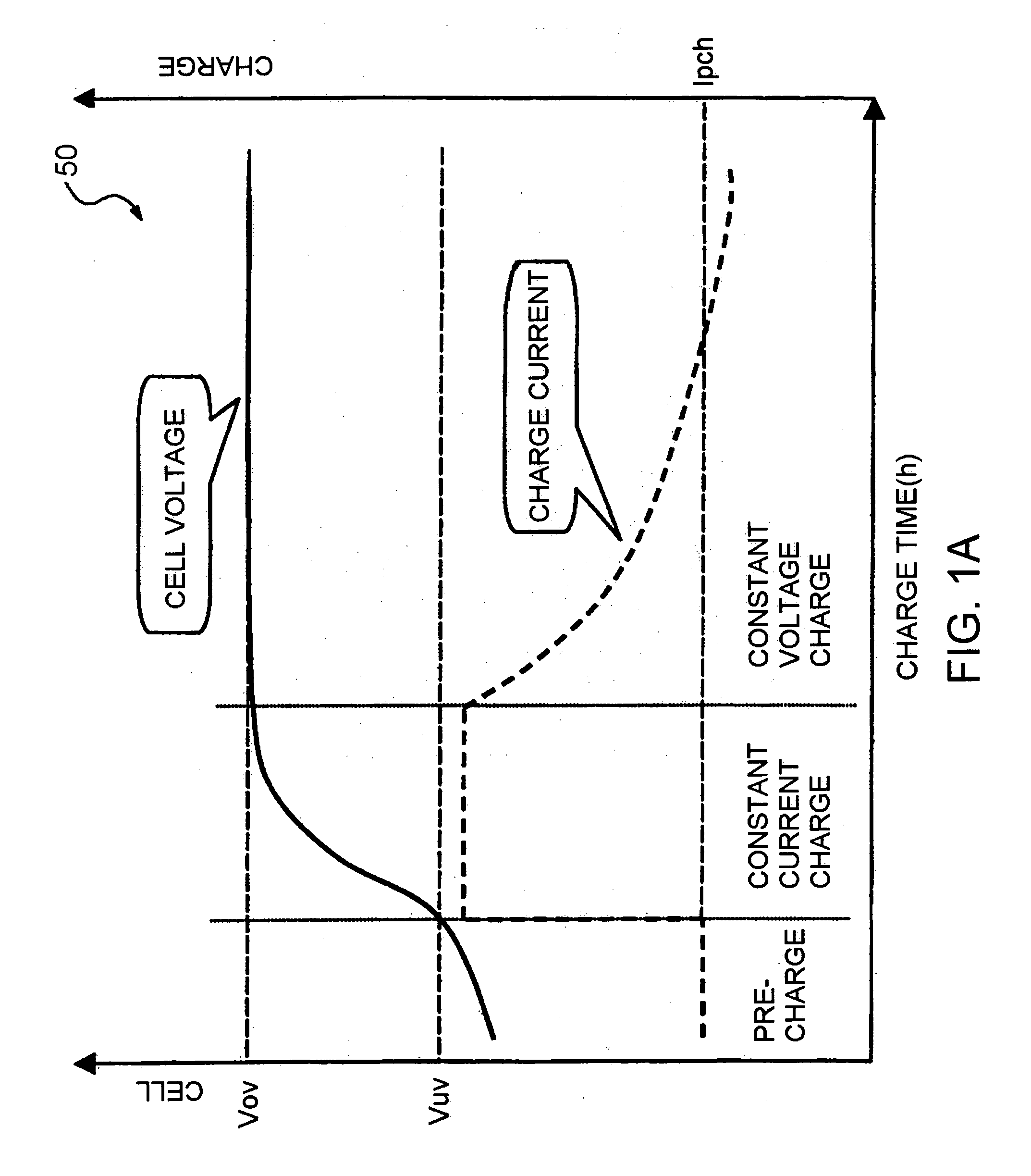
The invention discloses a fast-charging method and a mobile terminal. The fast-charging method is provided based on the power adapter of which output voltage dynamic is adjustable. The voltage of the battery-core of a battery is divided into multiple sections, then a sectional-type constant-current charging way is adopted, the value of the charging voltage output through the power adapter is adjusted dynamically according to the located sections of the battery-core voltage of the battery inside the mobile terminal in the charging process, and the battery is charged directly through the charging voltage output through the power adapter, so that the charging current is improved greatly, thereby the charging speed of the battery is accelerated, the single-time charging time needed by the movable terminal is shortened, the influence of the situation that the mobile terminal needs to be charged frequently for a long time on daily use of a user is lowered, and the customer-using satisfaction degree in promoted to a large extent.
Owner:QINGDAO HISENSE MOBILE COMM TECH CO LTD
Managing Cycle and Runtime in Batteries for Portable Electronic Devices
InactiveUS20130257382A1Prolong lifeIncrease ratingsSecondary cells charging/dischargingElectric powerResting timeUser input
The disclosed embodiments provide a system that manages use of a battery in a portable electronic device. The system includes a monitoring mechanism that monitors one or more battery-usage parameters of the battery during use of the battery with the portable electronic device. The battery-usage parameters may include a battery age, a resting time, a swell rate, a temperature, a cell balance, a voltage, a current, usage data about how the battery has been cycled, and / or user input. The system also includes a management apparatus that adjusts a charge-termination voltage or a discharge-termination voltage of the battery based on the battery-usage parameters to manage a cycle life of the battery, the swell rate, and / or a runtime of the battery.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and system for charging a fleet of batteries
InactiveUS20120133337A1Energy balanceEfficient and durable usePayment architectureVehicular energy storageBattery chargeElectrical battery
In a method for charging a fleet of batteries (110) from a power grid (100), a fleet charge schedule (301) is determined and thereafter individual battery charge schedules are dynamically optimized. The fleet charge schedule (301) for the entire fleet (110) is determined optimizing an energy portfolio balance of an energy portfolio manager. Thereafter, battery charge schedules for individual batteries (111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118) in the fleet (110) are dynamically optimized such that the battery charge schedules in aggregation realize the fleet charge schedule (301). The battery charge schedules are dynamically optimized in consideration of at least technical specifications of assets in the battery fleet and user constraints of the battery users.
Owner:RESTORE
System and method for optimizing use of a battery
A battery optimization system and method for regulating and discharging a battery so as to optimize the use of the battery in accordance with the user's preference is provided. The battery optimization system includes a power source, a charging / discharging station connecting the battery with the power source, and a controller in communication with the charging / discharging station. The battery optimization system further includes an input operable to provide the user's preferences. The controller is also in communication with the battery and is operable to process battery and power source information along with user input to calculate an optimal charging / discharging cycle. The charging / discharging cycle is configured to charge or discharge the battery so as to optimize the use of the battery based upon the end user's preference. For instance, the calculated optimal charging / discharging cycle may be based upon the user's desire to maximize the life of the battery, or to charge the battery as inexpensively as possible.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD
Electronic Cigarette Device
InactiveUS20140053857A1Firmly connectedEasy to operateTobacco pipesMedical devicesElectronic cigaretteEngineering
This invention relates to an electronic cigarette device, including an electronic cigarette and an electronic cigarette charger, the electronic cigarette charger forming a first magnetic portion, the electronic cigarette correspondingly forming a second magnetic portion mutually magnetically adsorbed with the first magnetic portion. The electronic cigarette charger forms a first connector, and the first connector comprises a first seat, a first electrode pole disposed at a middle portion of the first seat and a first insulating sleeve disposed between the first seat and the first electrode pole to insulate the first seat and the first electrode pole. The electronic cigarette forms an electronic cigarette battery therein, and the electronic cigarette at an end thereof forms a second connector connected with the electronic cigarette battery and the first connector of the electronic cigarette charger. The electronic cigarette device is convenient to put / take the electronic cigarette into / out of the electronic cigarette charger.
Owner:HUIZHOU KIMREE TECH
Control system of secondary battery and hybrid vehicle equipped with the same
ActiveUS20100033132A1Rapid deteriorationPreventing overchargeHybrid vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesElectrical batteryEngineering
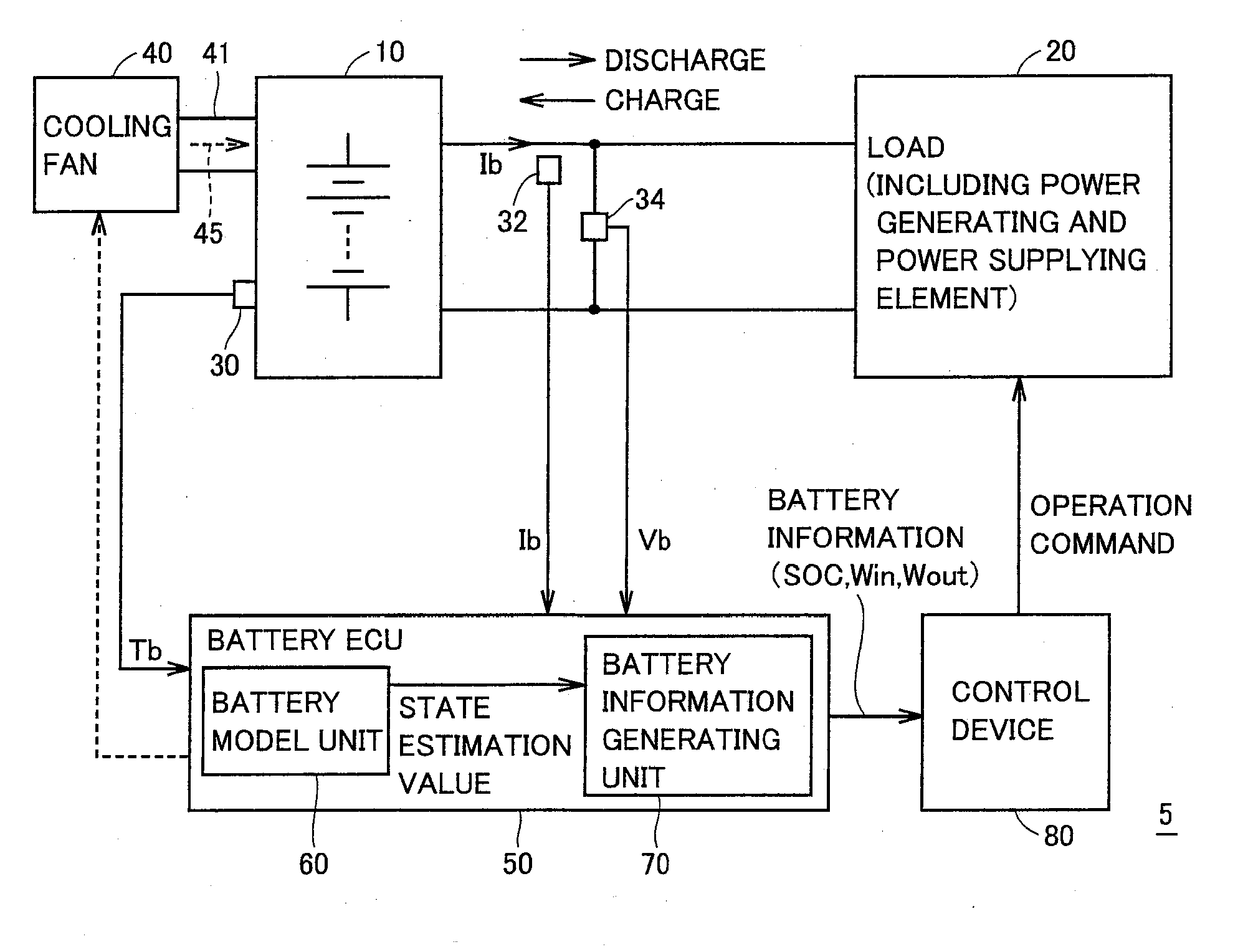
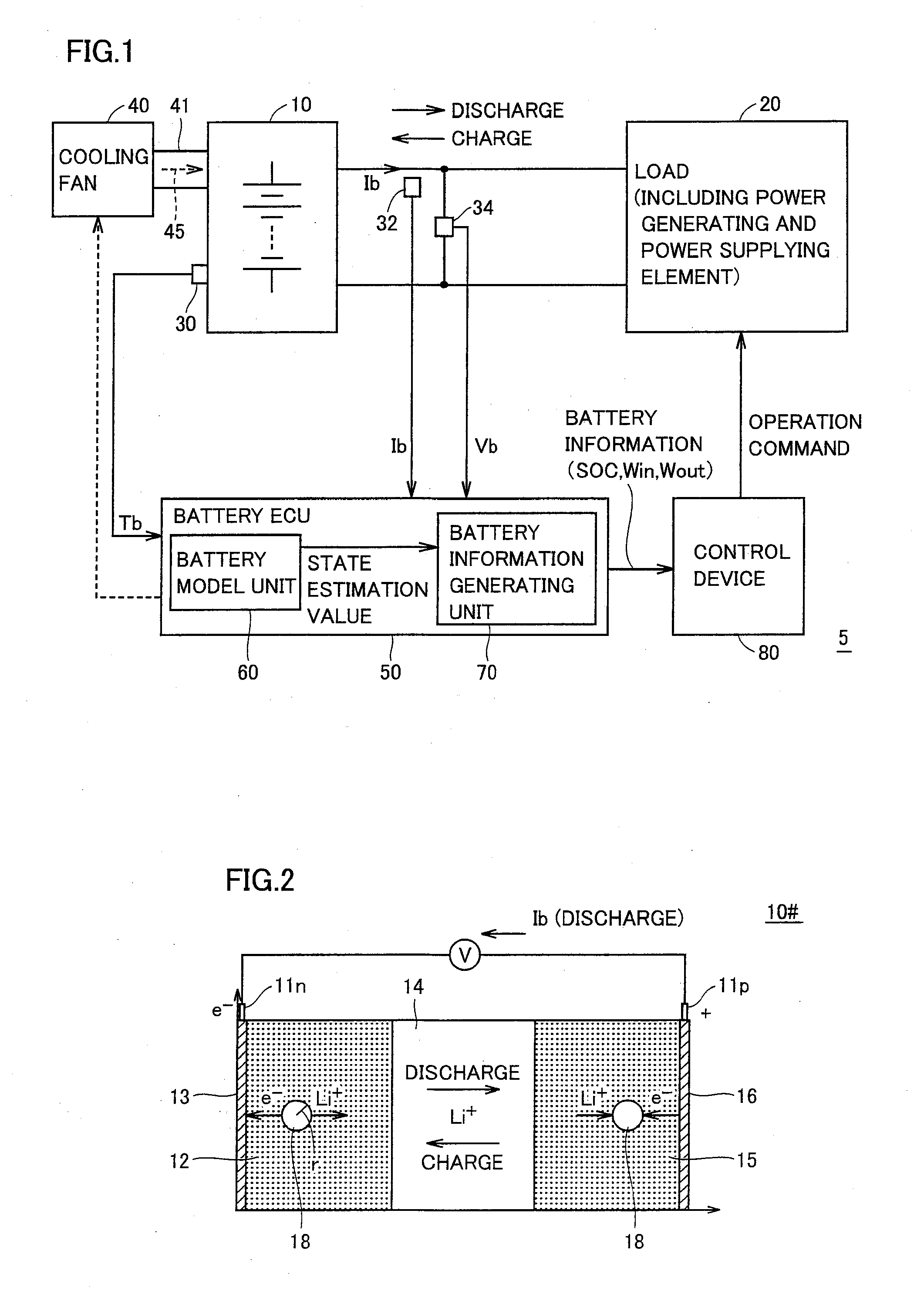
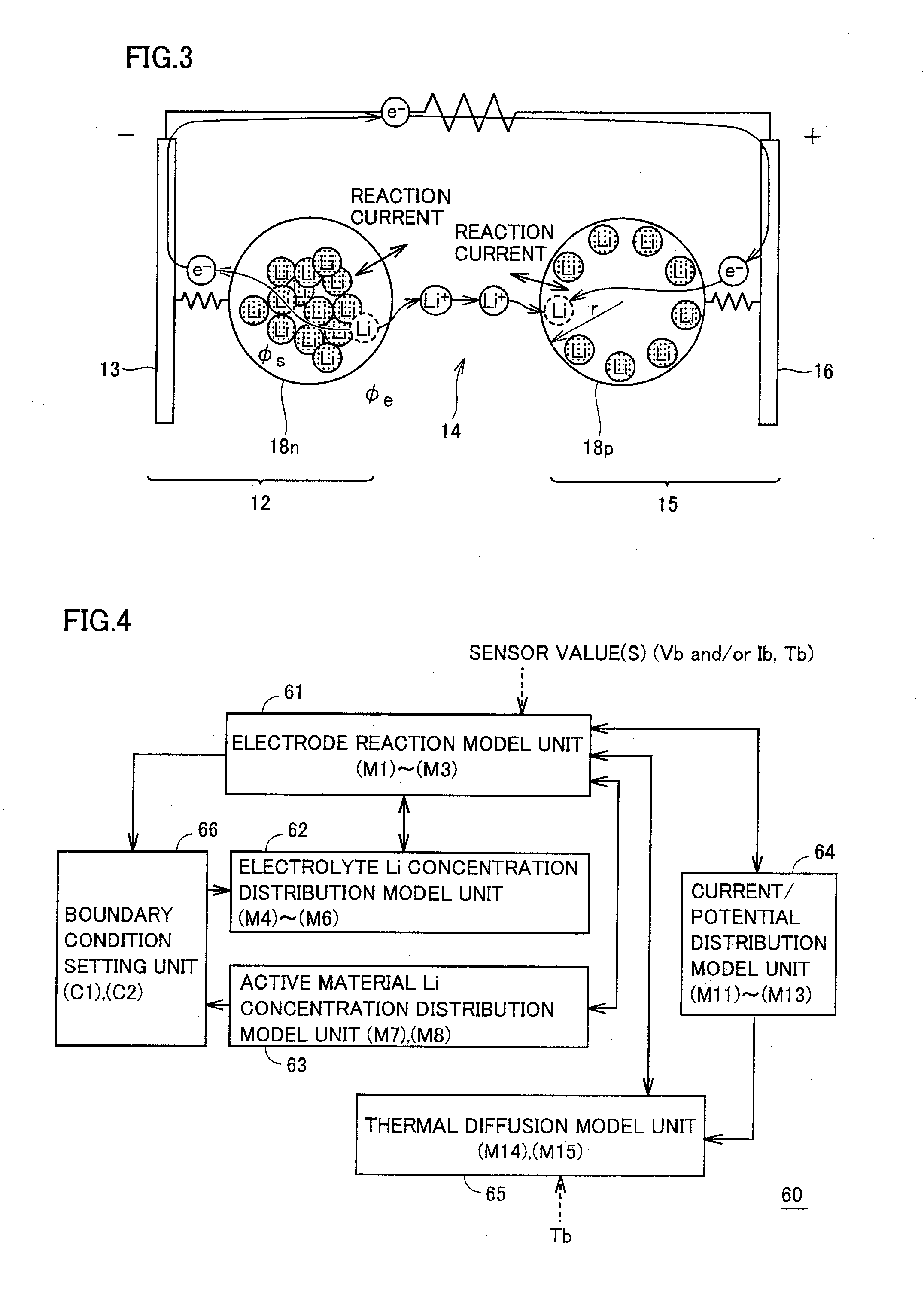
A battery model unit includes an electrode reaction model unit based on the Butler_Volmer equation, an electrolyte lithium concentration distribution model unit analyzing a lithium ion concentration distribution in an electrolyte solution by a diffusion equation, an active material lithium concentration distribution model unit analyzing an ion concentration distribution in a solid state of an active material by a diffusion equation, a current / potential distribution model unit for obtaining a potential distribution according to the charge conservation law, a thermal diffusion model unit and a boundary condition setting unit. The boundary condition setting unit (66) sets a boundary condition at an electrode interface such that a reacting weight at the electrode interface is not determined by a difference in material concentration between positions but a deviation from an electrochemically balanced state causes a change with time in lithium concentration at the interface and thus a (time-based) drive power for material transportation. Thereby, an appropriate charge / discharge control can be performed based on the battery model having the appropriately set battery condition.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Electric Vehicle Battery Lifetime Optimization Operational Mode
ActiveUS20130221928A1Electric powerVehicular energy storageAutomotive batteryElectric-vehicle battery
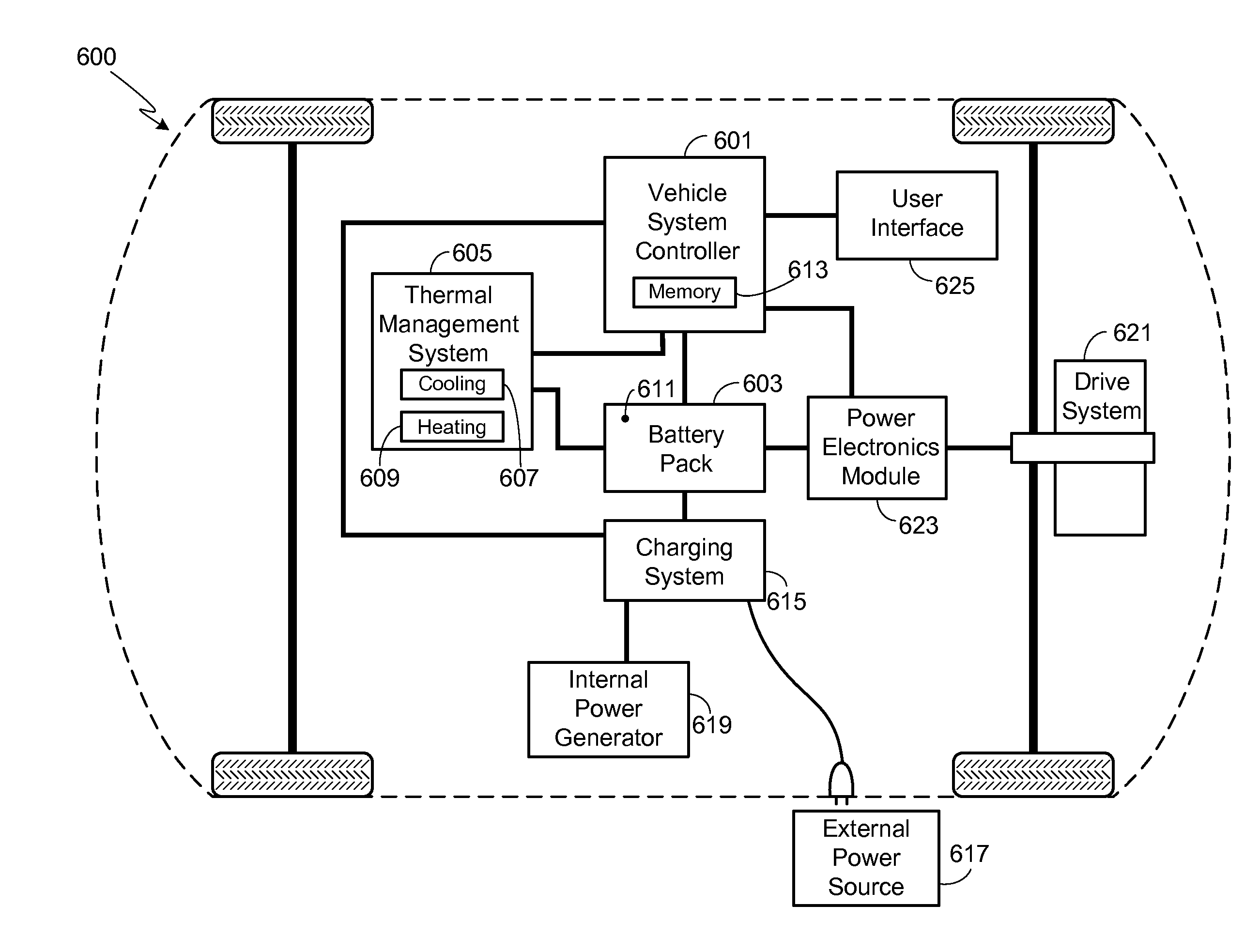
A method of setting the operational mode of an electric vehicle is provided, where the operational mode is selected from a plurality of operational modes that include at least a Battery Life mode and a Standard mode, wherein the Battery Life mode is configured to select operating and charging parameters that emphasize battery health and battery life over vehicle range and / or vehicle performance. The system includes a thermal management system for maintaining the vehicle's battery pack to within any of a plurality of temperature ranges, and a charging system for charging the vehicle's battery pack to any of a plurality of minimum and maximum SOC levels and at any of a plurality of charging rates.
Owner:TESLA INC
Power storage device control system, power storage system, and electrical appliance
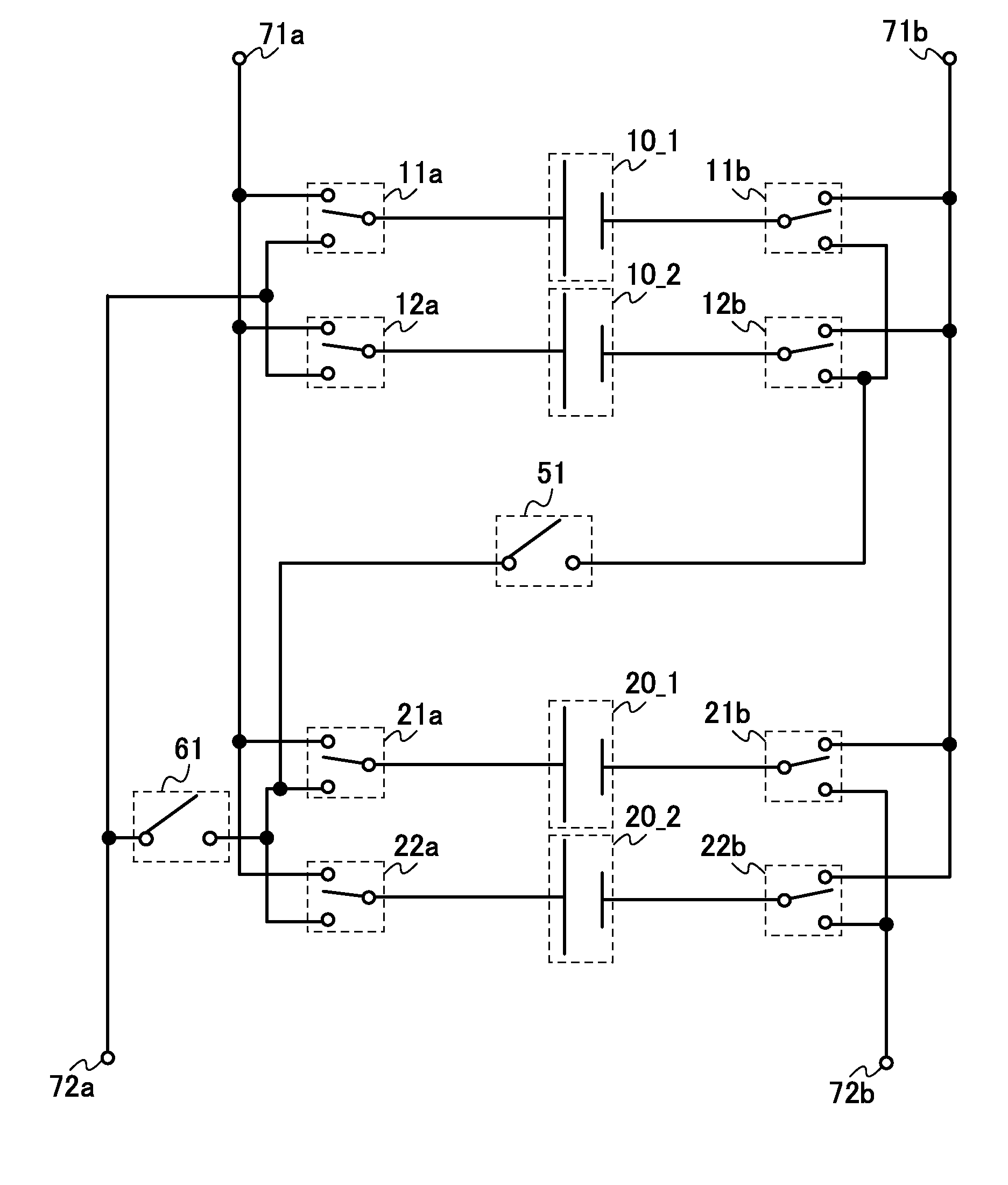
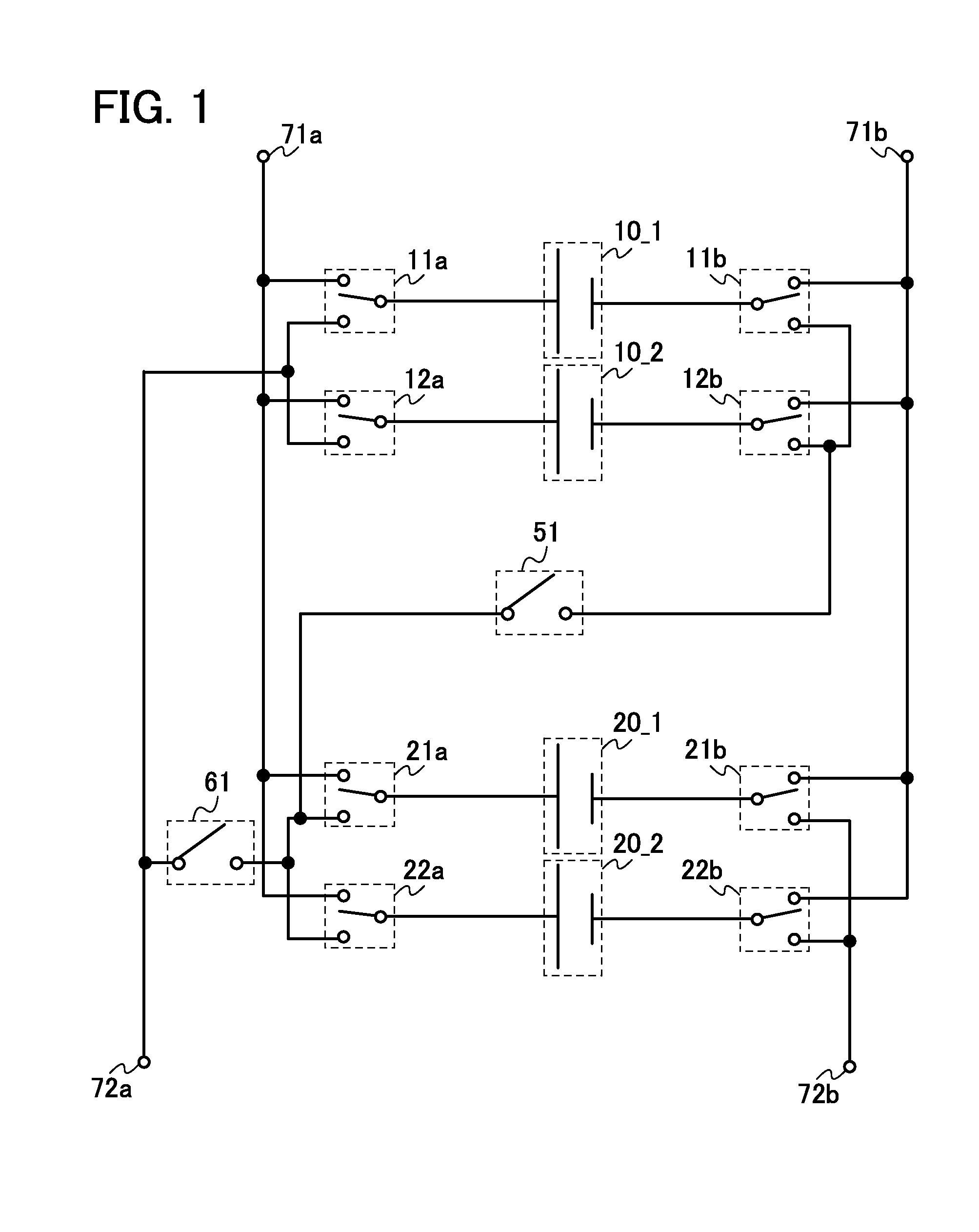
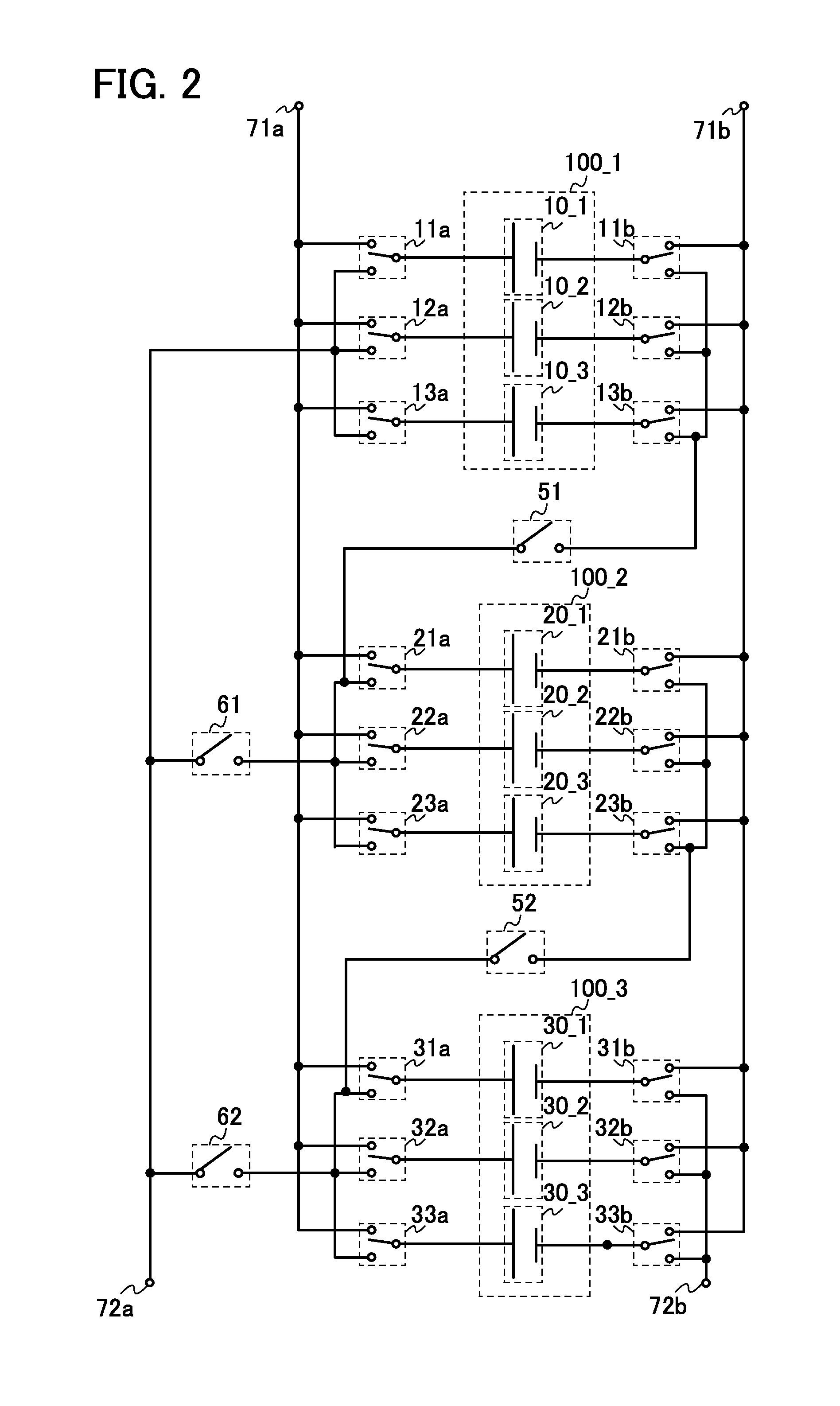
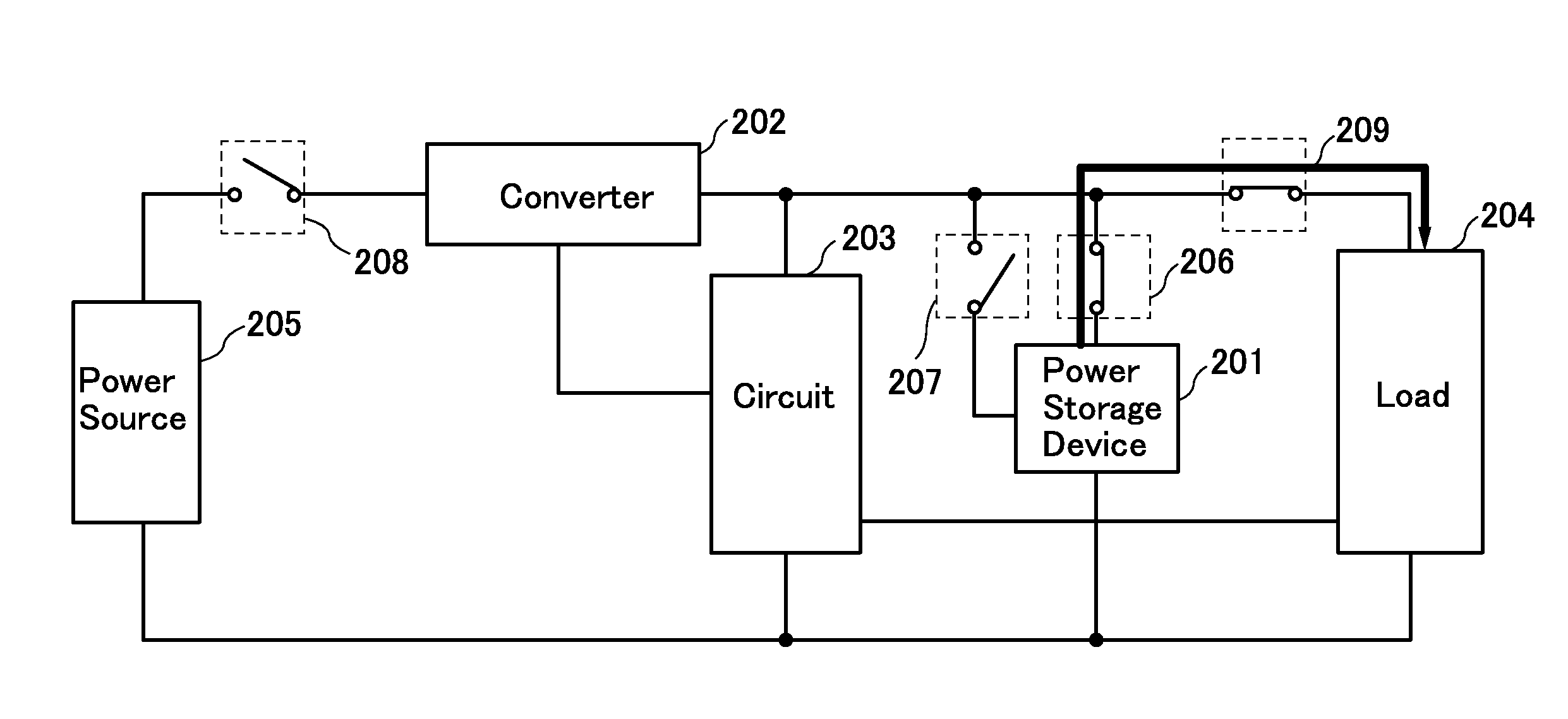
ActiveUS20140184162A1Reduce deteriorationLow powerPrimary cell to battery groupingCell electrodesControl signalControl system
Deterioration of a power storage device is reduced. Switches that control the connections of a plurality of power storage devices separately are provided. The switches are controlled with a plurality of control signals, so as to switch between charge and discharge of each of the power storage devices or between serial connection and parallel connection of the plurality of power storage devices. Further, a semiconductor circuit having a function of carrying out arithmetic is provided for the power storage devices, so that a control system of the power storage devices or a power storage system is constructed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Power Supply Device, Control Method of Power Supply Device, and Motor Vehicle Equipped with Power Supply Device
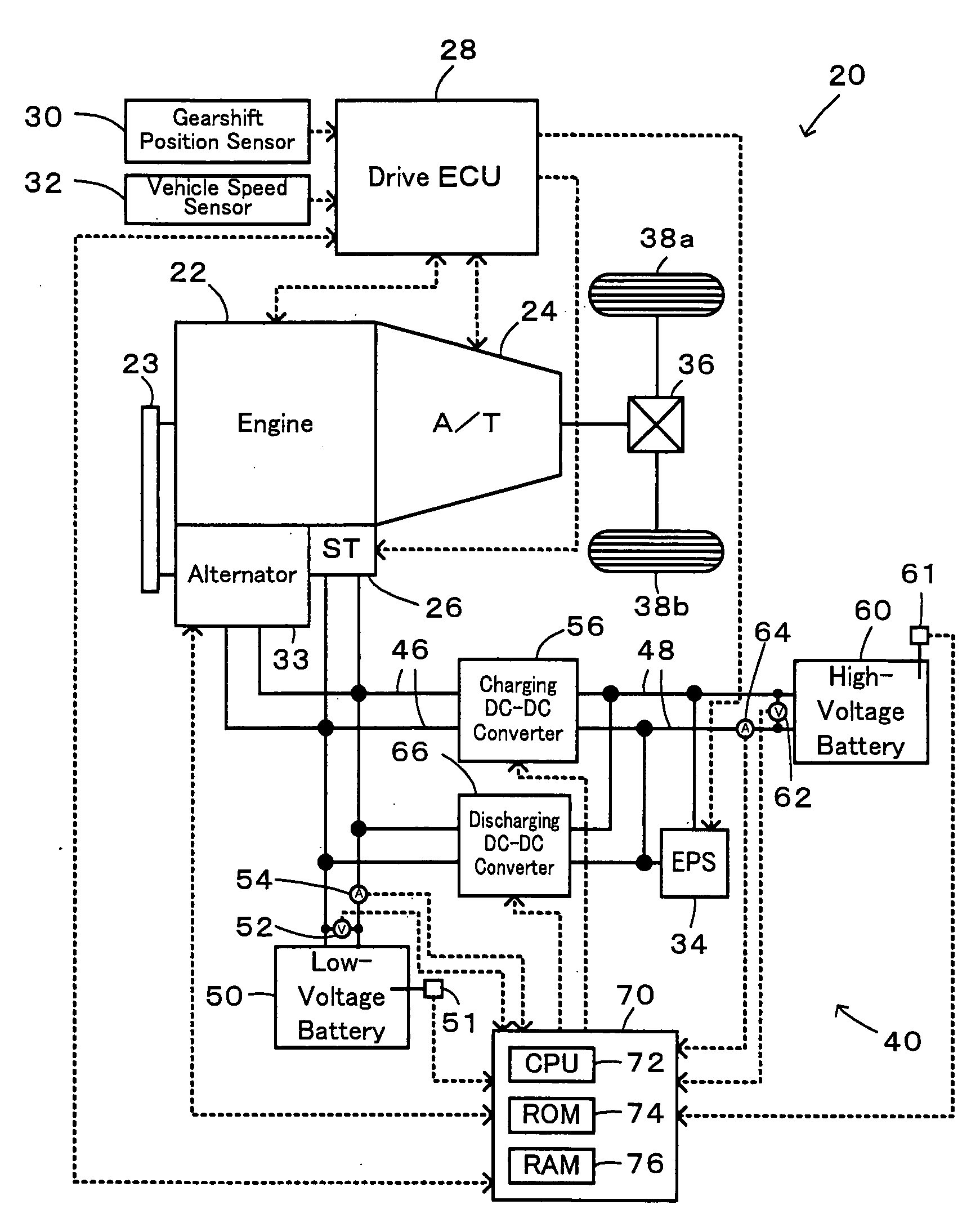
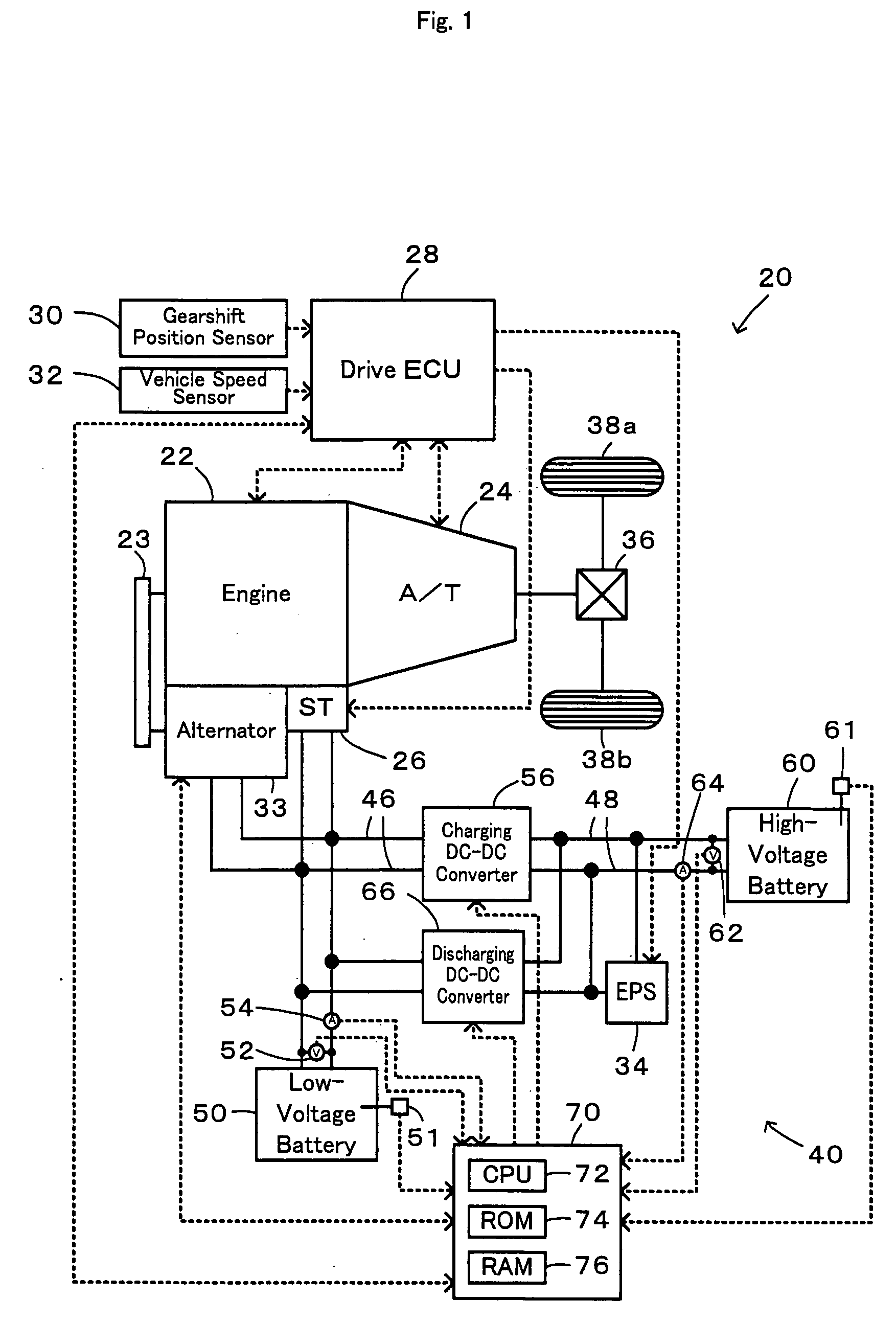
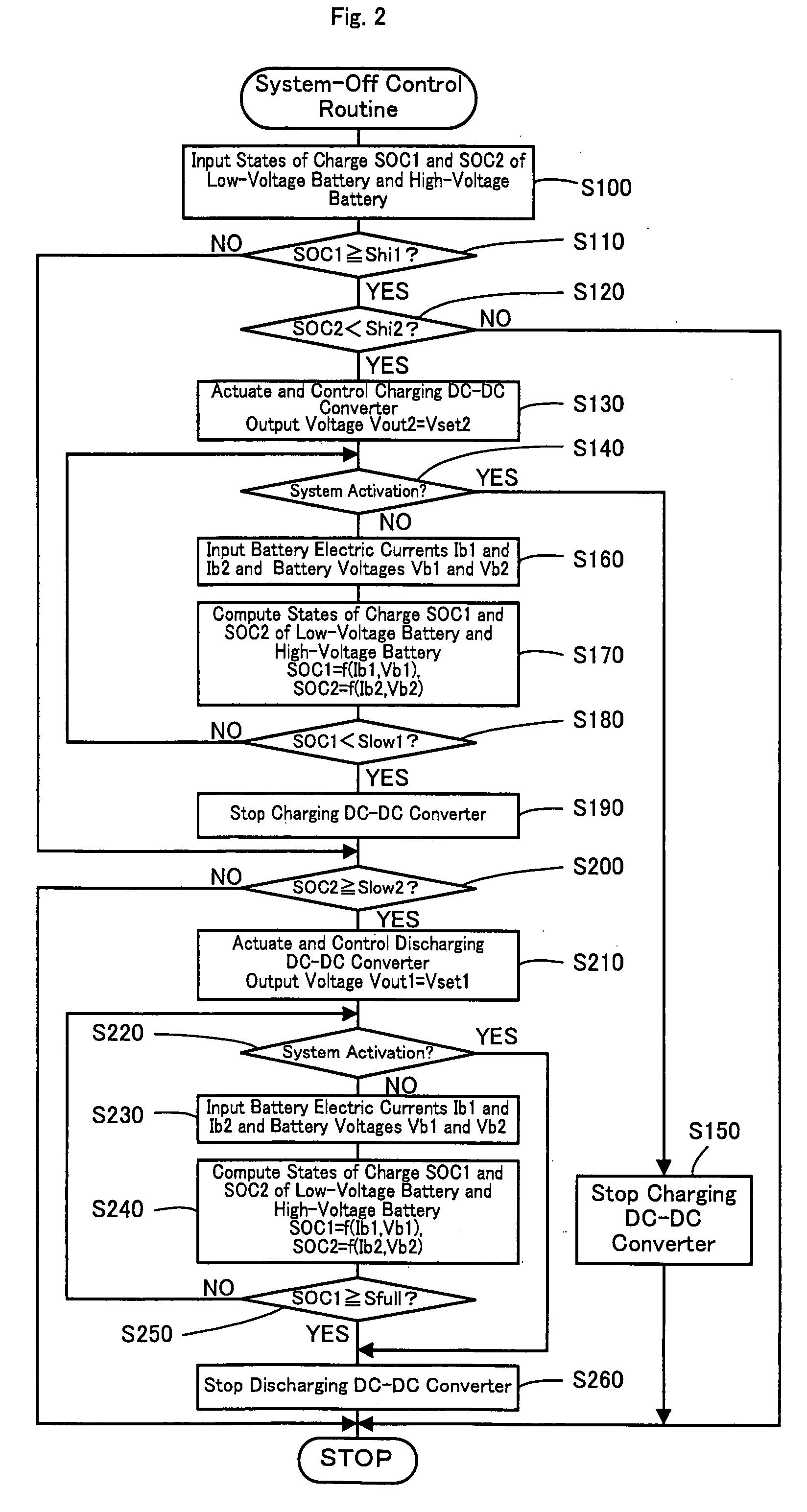
InactiveUS20090015193A1Favorable state of chargeSufficient supplyHybrid vehiclesVehicle sub-unit featuresLow voltageElectrical battery
In a power supply device of the invention, when the state of charge SOC1 of a low-voltage battery is lower than a discharging reference value Shi1 below a full charge level and when the state of charge SOC2 of a high-voltage battery is not lower than a discharging reference value Slow2 at a system-off time, the low-voltage battery is charged close to its full charge level with the electric power supplied from the high-voltage battery. The lead acid battery used for the low-voltage battery has the high potential for deterioration in the continuously low state of charge SOC. The lithium secondary battery used for the high-voltage battery has the high potential for deterioration in the continuously high state of charge SOC. The charge of the low-voltage battery in combination with the discharge of the high-voltage battery enables both the low-voltage battery and the high-voltage battery to have respective favorable states of charge with little potentials for deterioration. The technique of the invention thus effectively prevents quick deterioration of both the low-voltage battery and the high-voltage battery.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Fast charger for high capacity batteries
InactiveUS7301308B2Reduce heatMinimise currentCircuit monitoring/indicationDifferent batteries chargingFast chargingEngineering
A highly efficient fast charger for high capacity batteries and methods for fast charging high capacity batteries. The fast charger preferably comprises a rectified AC input of single or preferably three phases, with an optional power factor corrected input, minimally filtered with high frequency, high ripple current capacitors, which is switched with a power switching circuit in the “buck” configuration into an inductor / capacitor output filter. Metallized film capacitors are employed, to minimize the rectified 360 Hertz AC component filtering while providing transient switch protection and ripple current requirements for the buck regulator, to provide a high current fast charger with substantially improved power factor. High power, high frequency switching with minimized output filter size provides a highly filtered DC output. The fast charger is adapted to be constructed in a modular design for simple maintenance.
Owner:AKER WADE POWER TECH
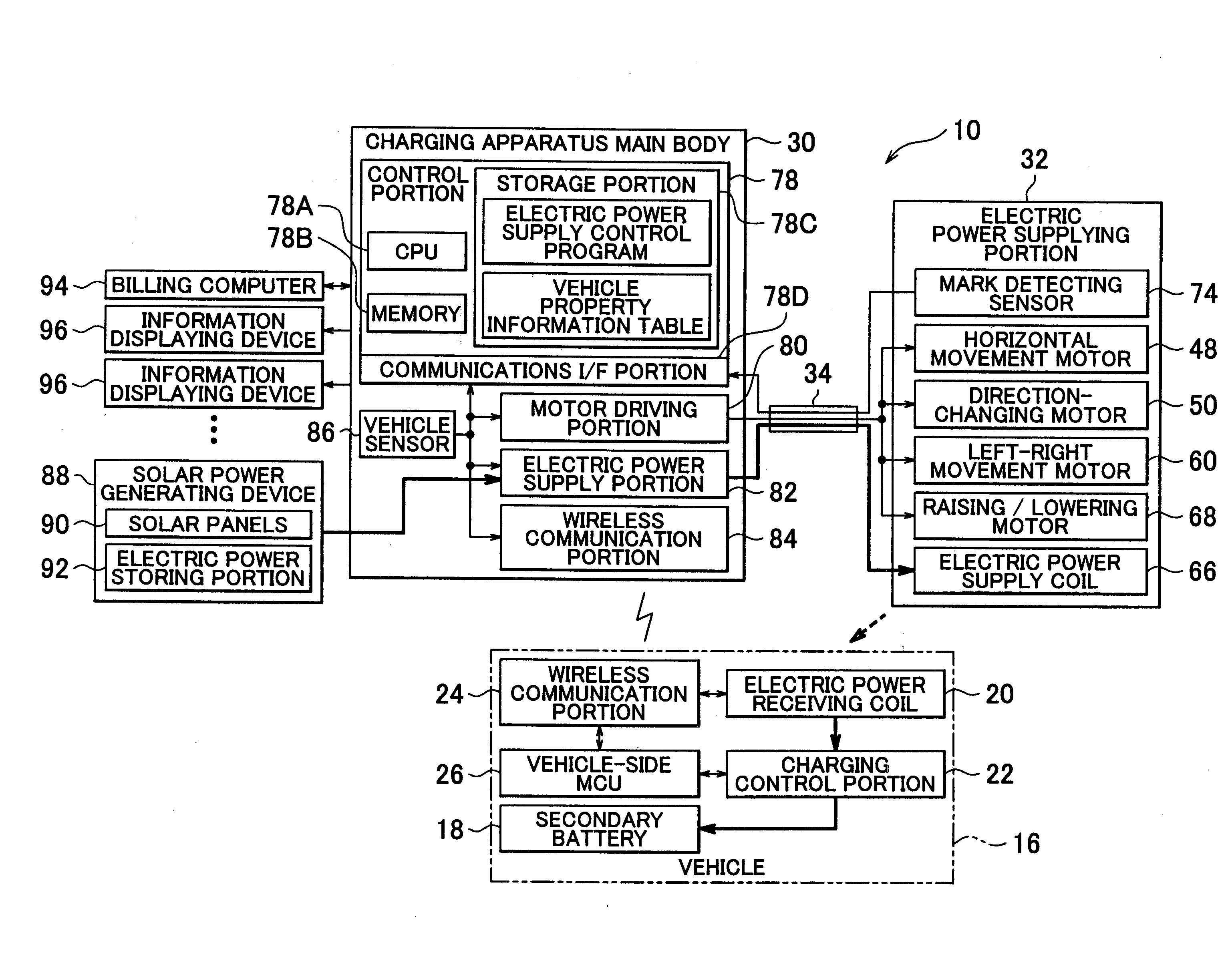
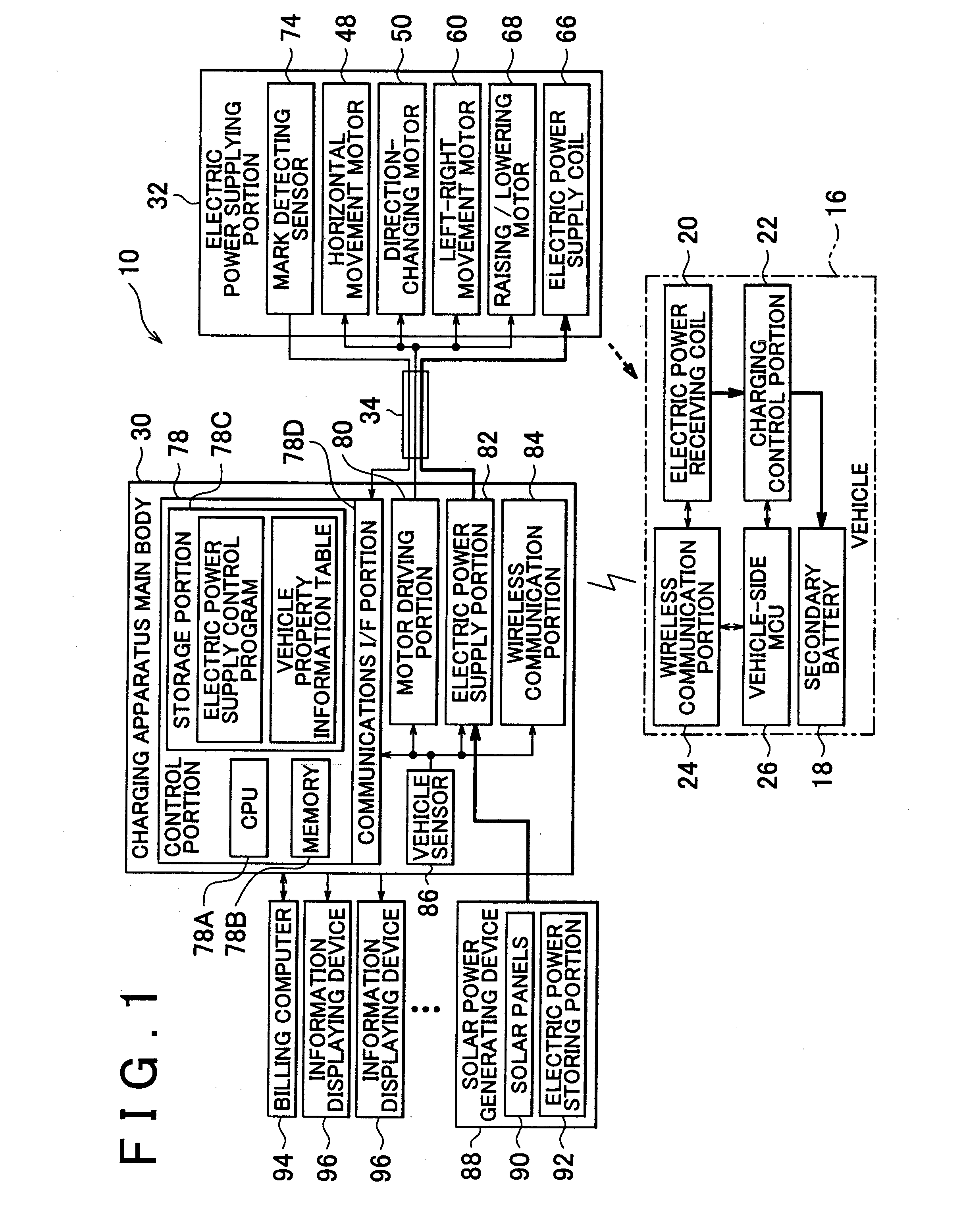
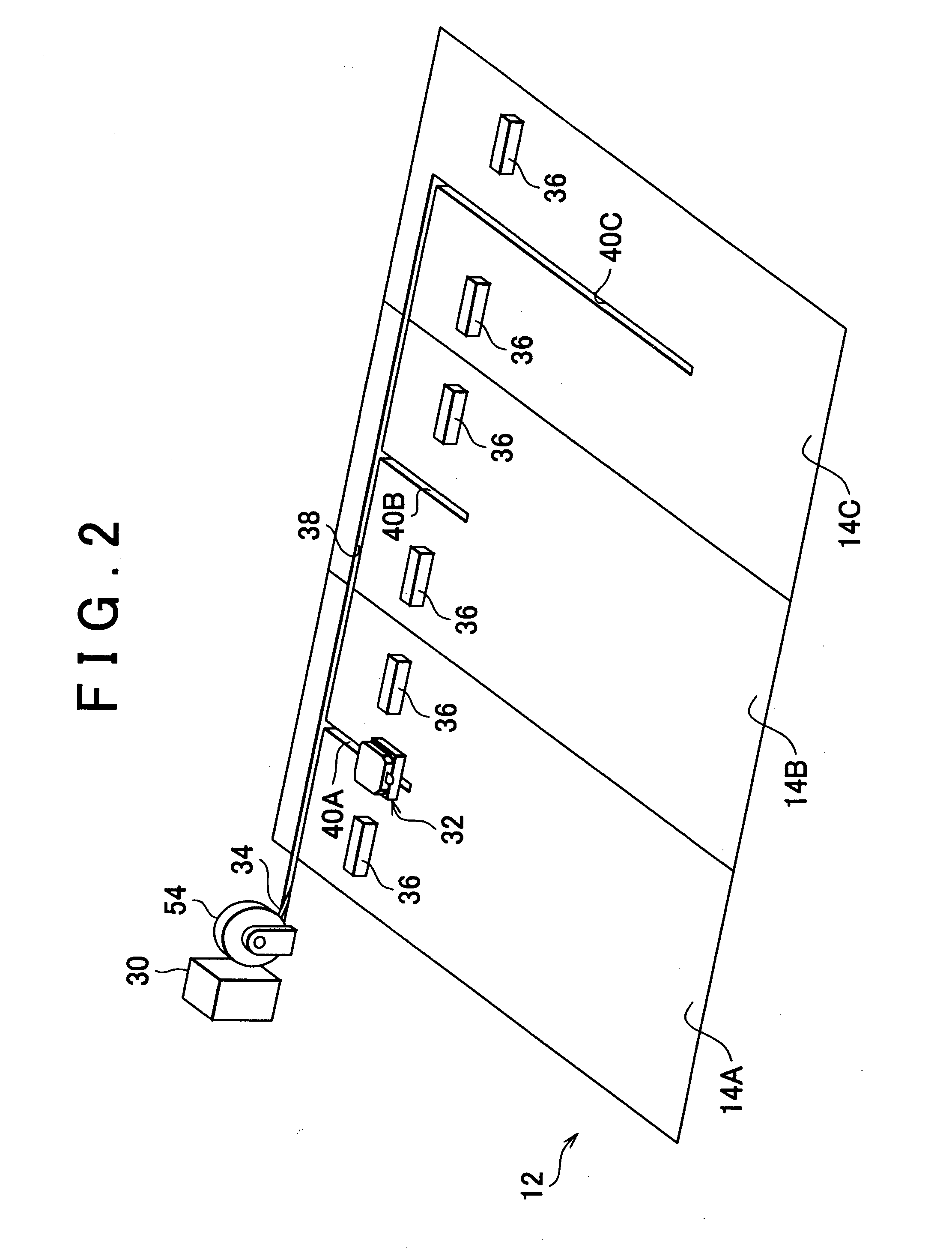
Charging apparatus
InactiveUS20130076296A1Complete chargingReduce the amount requiredCharging stationsElectric devicesElectric power systemTransverse groove
A charging apparatus charges a secondary battery of a vehicle by moving an electric power supplying portion along a transverse groove and a longitudinal groove to a position that enables electric power to be supplied to a parked vehicle, and then supplying electric power to the vehicle from the electric power supplying portion, each time a vehicle is parked in a parking space of a parking lot, when the parked vehicle is an authorized vehicle and a state of charge of the secondary battery is equal to or less than a predetermined value.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
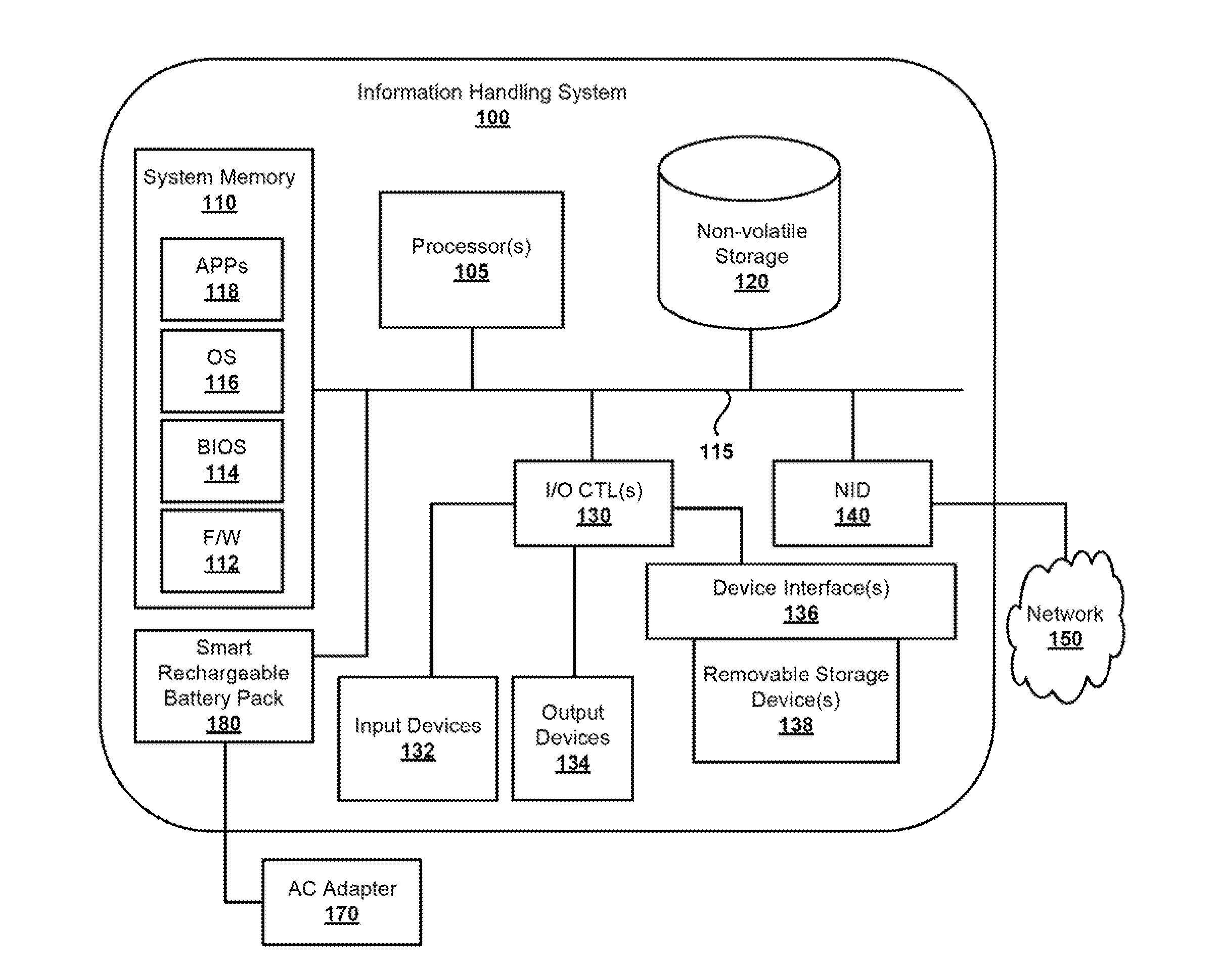
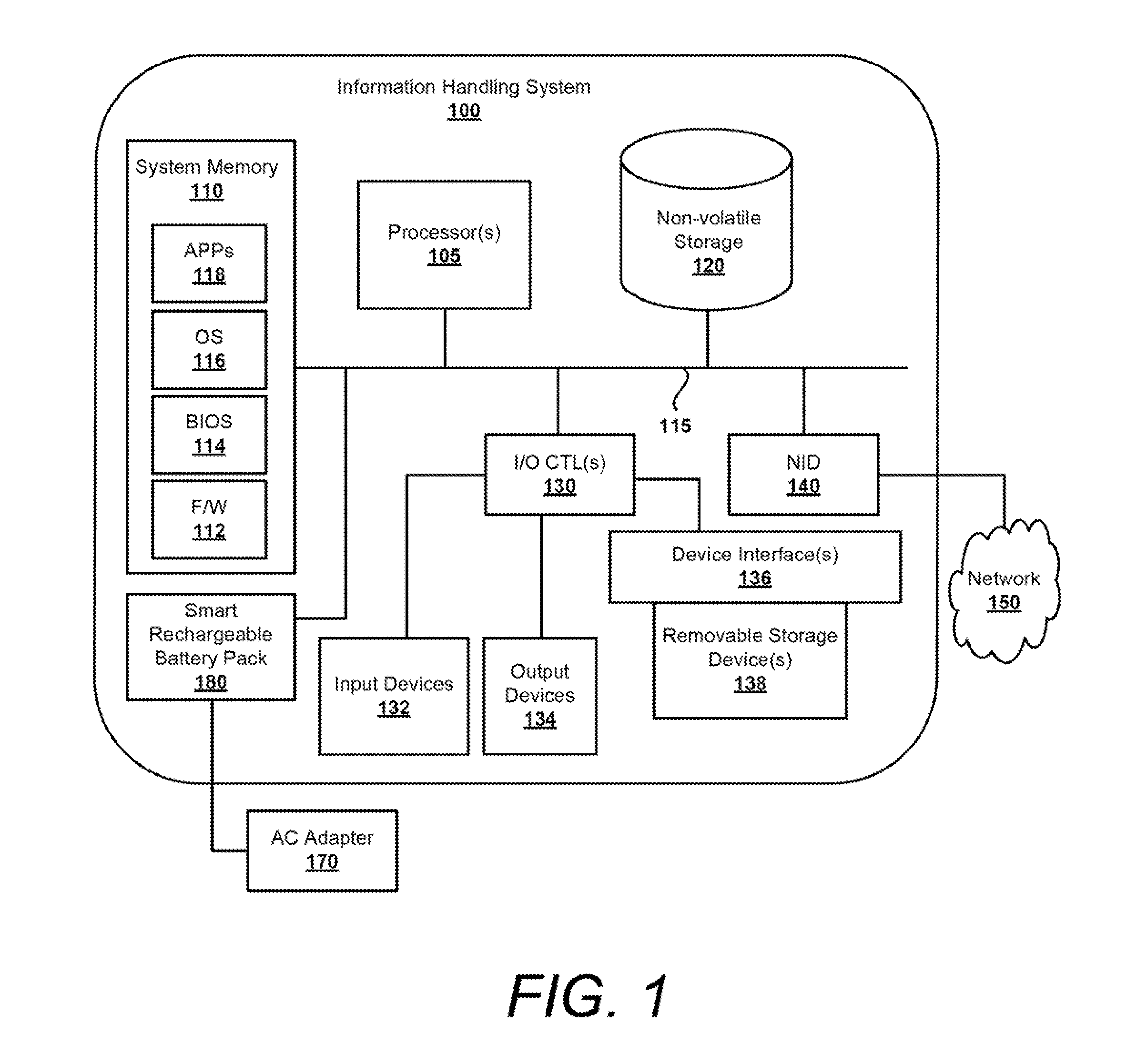
Mitigating premature wear out of a rechargeable battery
ActiveUS20140217958A1Rate of decrease in fullReduce degradation rateElectrical testingElectric powerRechargeable cellInformation handling system
A computer-implemented method and information handling system manage a rate of decreasing full capacity of a rechargeable battery by using a projected / target rate of decreasing charge capacity for the battery. The method includes determining an actual rate of decreasing charge capacity of the battery, comparing the actual rate of decreasing charge capacity to the projected / target rate of decreasing charge capacity to determine whether the actual rate of decreasing charge capacity is greater than the projected rate of decreasing charge capacity, and if the actual rate of decreasing charge capacity is greater than the projected / target rate of decreasing charge capacity, modifying one or more variable parameters to slow down the actual rate of decreasing charge capacity of the battery such that the actual rate of decreasing charge capacity remains within a range of the projected / target rate of decreasing charge capacity, and charging and discharging the battery using the modified parameters.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
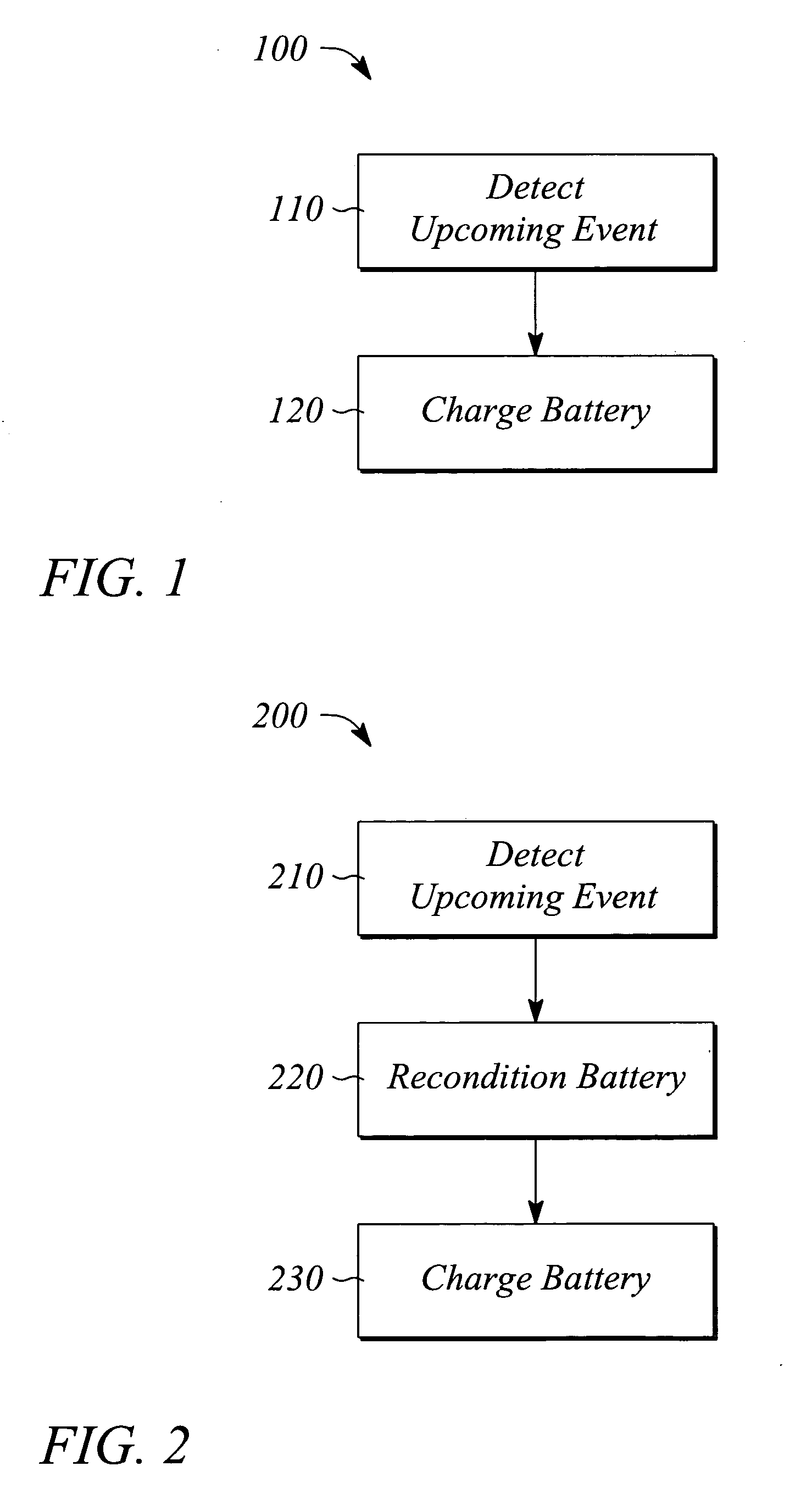
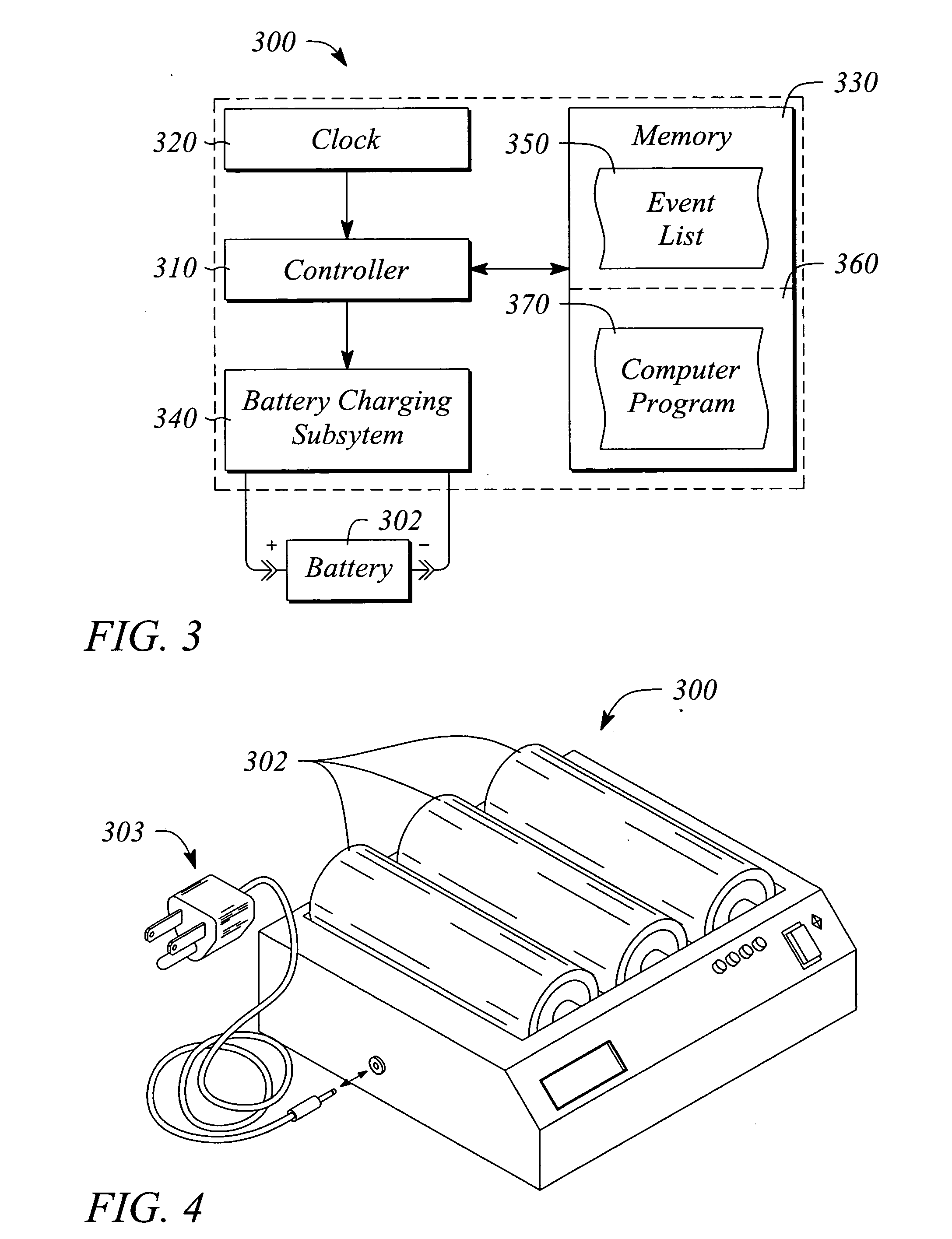
Event-driven battery charging and reconditioning
InactiveUS20050248313A1Secondary cells charging/dischargingElectric powerBattery chargeElectronic systems
Event-driven battery charging charges or reconditions and charges a rechargeable battery in response to a detected upcoming event. An upcoming event is a member of a list of events stored in computer-readable memory. Each member has respective occurrence information. The upcoming event is detected when a current date or date and time corresponds to the occurrence information for a respective event in the list. A battery charger includes the list of events stored in the memory, a clock, a battery charging subsystem and a controller that controls the battery charging subsystem. A battery-powered device includes the list of events stored in the memory, a clock, a battery charging subsystem, a controller, and a computer program stored in the memory and executed by the controller. The computer program includes instructions that implement detecting an upcoming event and charging the battery in situ when the upcoming event is detected.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
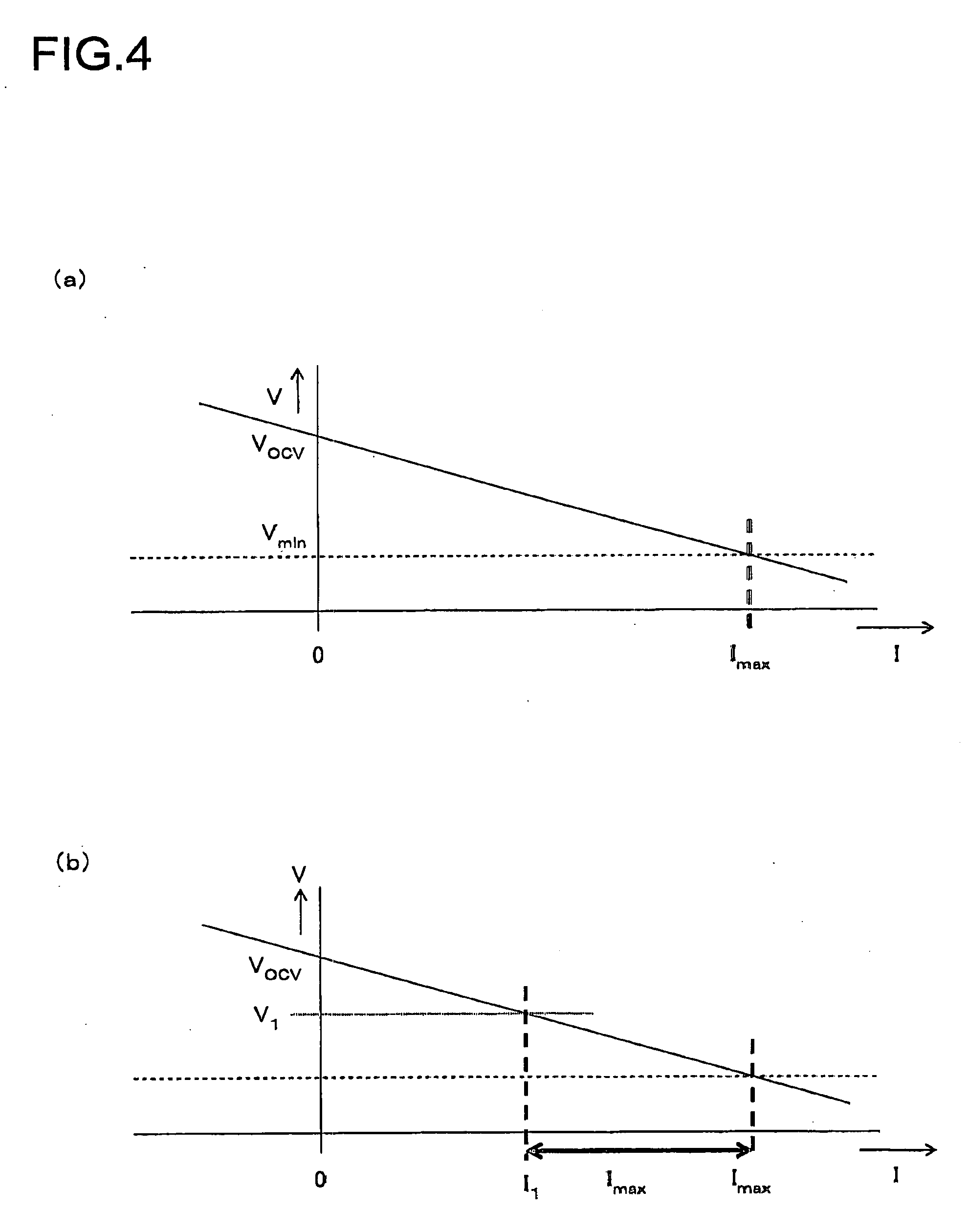
Charge/Discharge Control Device and Charge/Discharge Control Method for Power Storage Device, and Electric-Powered Vehicle
InactiveUS20090266631A1Suppress chargingAccurate settingSecondary cells charging/dischargingPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingLower limitElectrical resistance and conductance
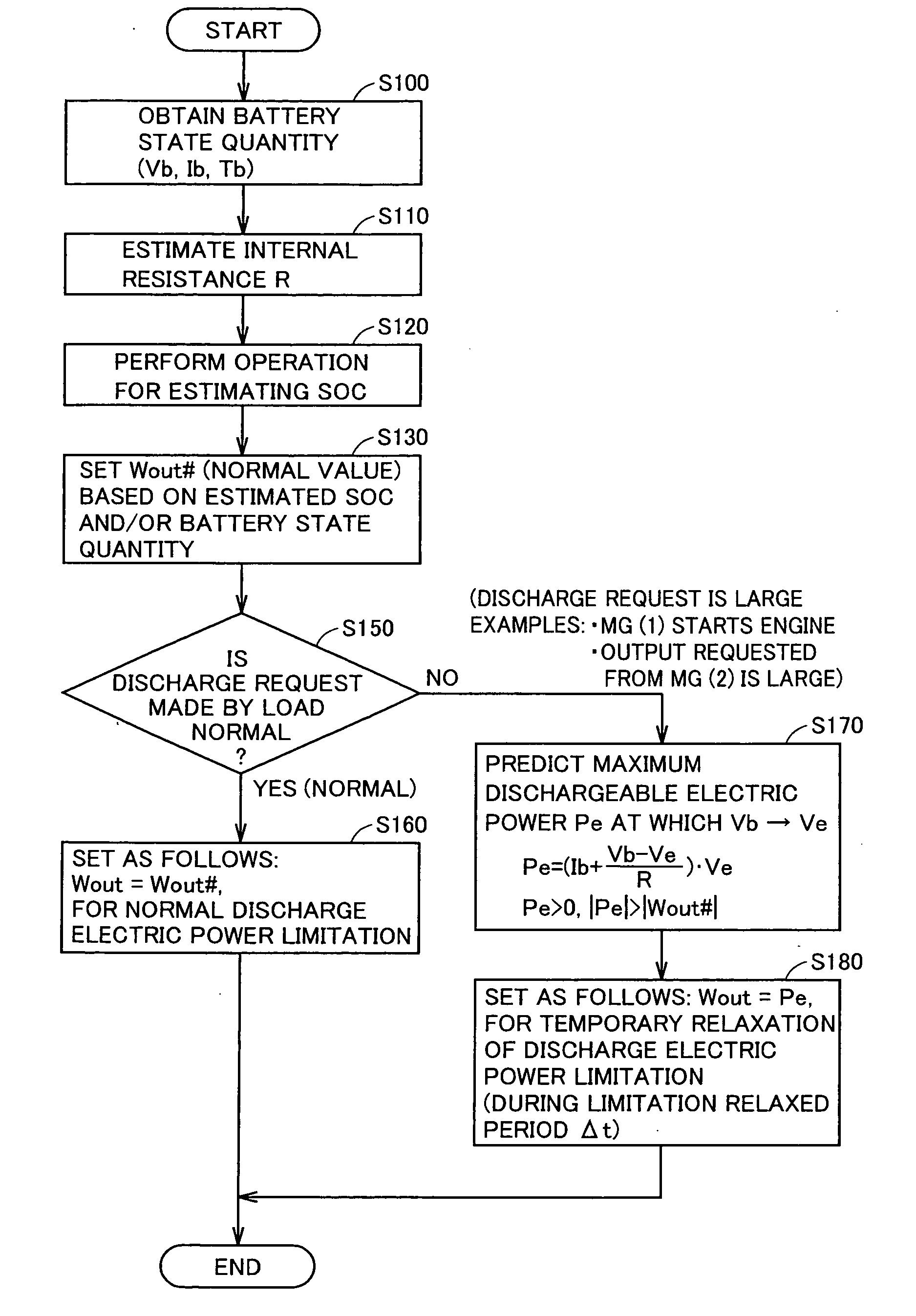
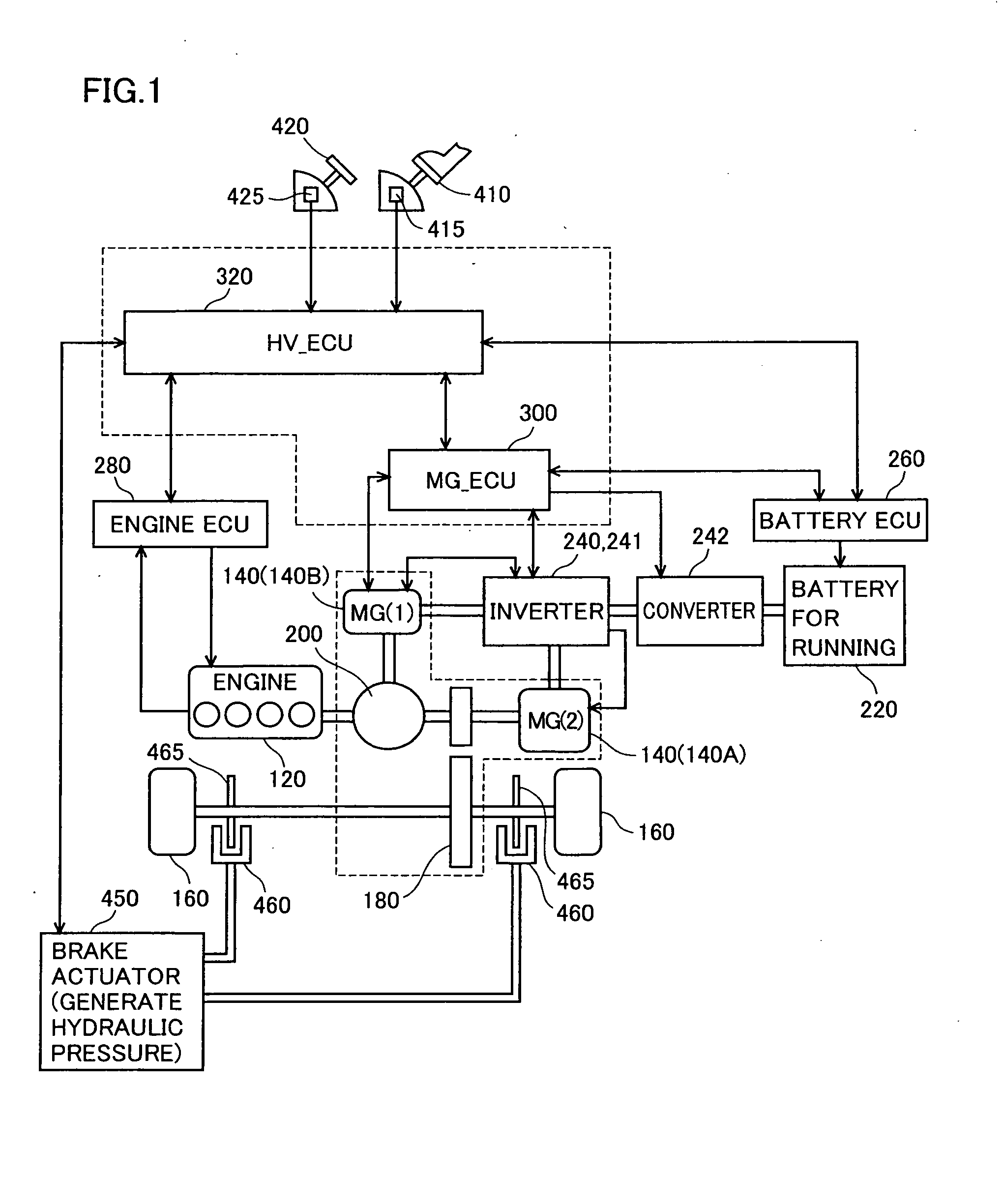
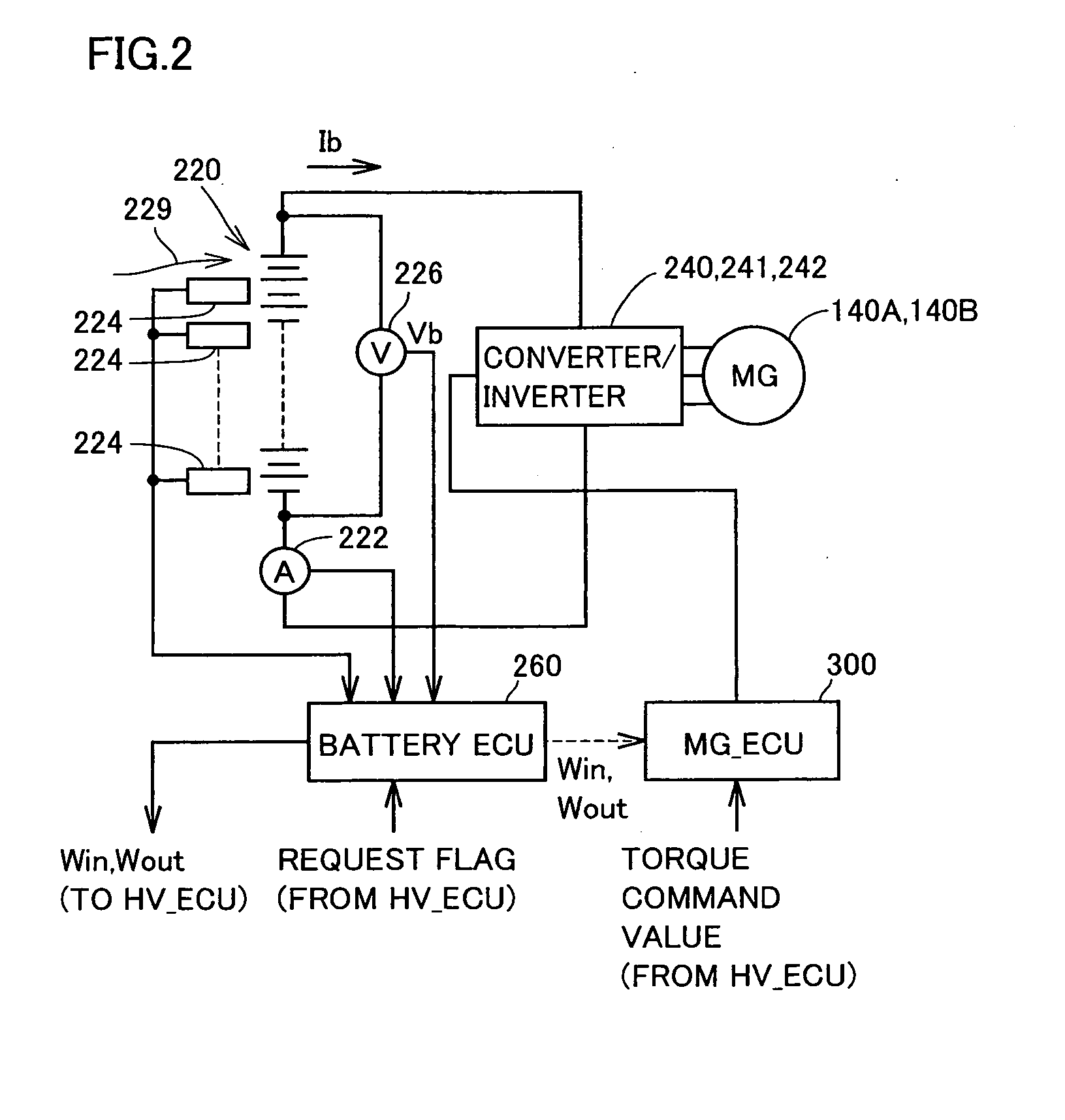
A maximum dischargeable current Idmax obtained when electric power output from a battery is increased from a battery current Ib and a battery voltage Vb at present under internal resistance R at present (an operating point 510) until the battery voltage reaches a lower limit voltage Ve (an operating point 520), is shown as follows: Idmax=Ib+(Vb−Ve) / R. Therefore, in accordance with multiplication of the lower limit voltage Ve and the maximum dischargeable current Idmax, it is possible to predict maximum dischargeable electric power at which the battery voltage does not become lower than the lower limit voltage even if discharge limitation is temporarily relaxed, as a relative value with respect to the battery voltage and the battery current at present. When the discharge electric power limitation for the battery (the power storage device) is temporarily relaxed in accordance with a discharge request made by a load, a discharge electric power permissible value is set to correspond to the maximum dischargeable electric power, such that the output voltage of the power storage device does not fall outside a controlled voltage range from the lower limit voltage to an upper limit voltage.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Apparatus and method for controlling charging power of wireless power receiver
In an apparatus for adjusting charging power of a wireless power receiver, when one or more wireless power receivers require charging, it is determined whether the sum of required charging powers required by the one or more wireless power receivers exceeds maximum supplied power provided by a wireless power transmitter. When a result indicates that the sum exceeds the maximum supplied power, a control operation is performed to adjust the required charging power of each wireless power receiver. Therefore, it is possible to wirelessly charge each wireless power receiver without interruption.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Over voltage transient controller
InactiveUS20050212489A1Eliminate needSecondary cells charging/dischargingElectric powerEngineeringComparator
An over voltage transient controller to protect a rechargeable battery from an over voltage transient condition. The over voltage transient controller may comprise a comparator to compare a first signal with a second signal representative of a reference voltage level and to provide an output signal representative of an over voltage transient condition to a switch if the first signal is greater than or equal to the second signal. The switch is responsive to the output signal to protect the rechargeable battery from the over voltage transient condition. The over voltage transient controller may further comprise a DAC, wherein the second signal is based, at least in part, on an output of the DAC. An apparatus comprising a charge switch and such an over voltage transient controller is also provided.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
Power storage device and charging method thereof
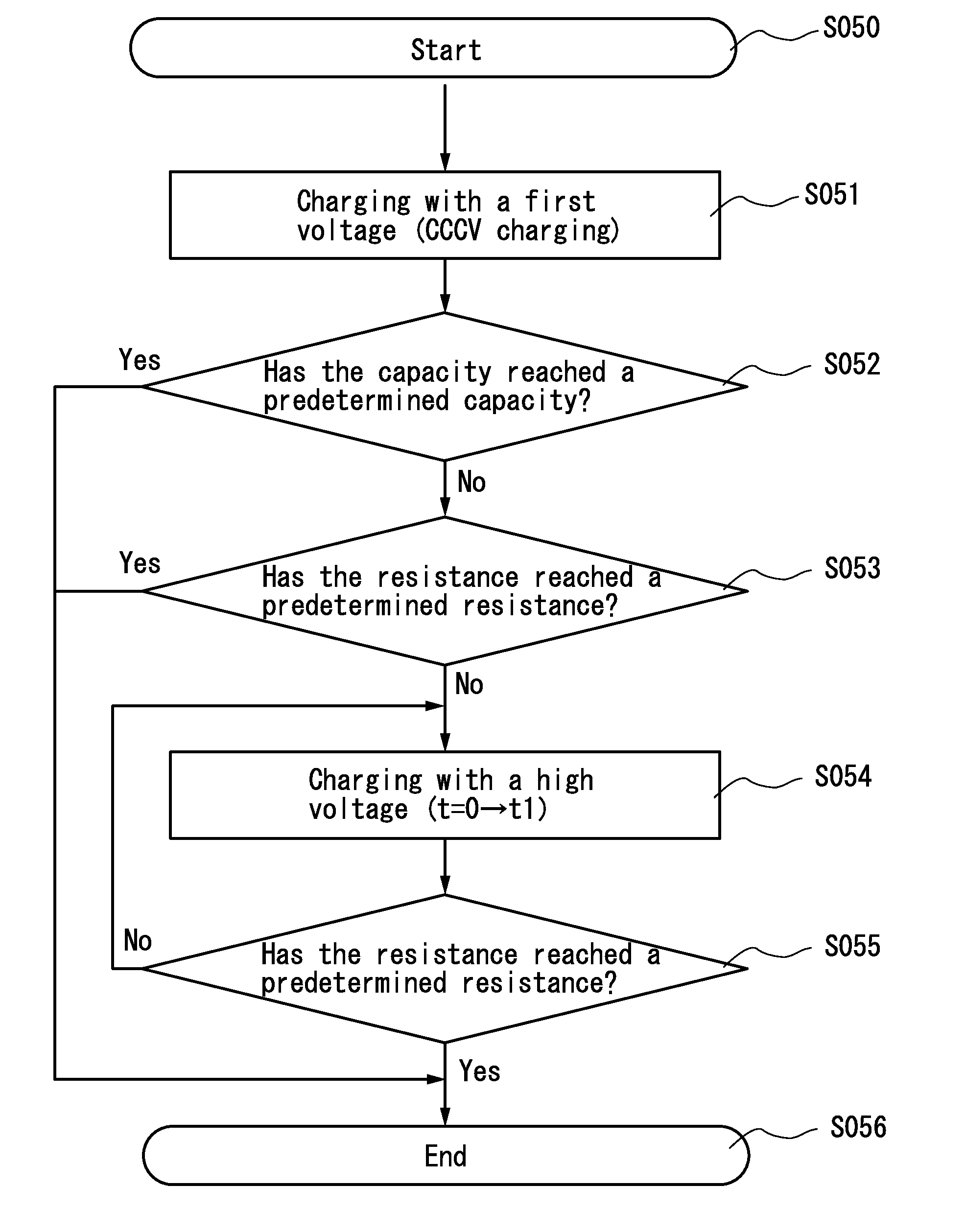
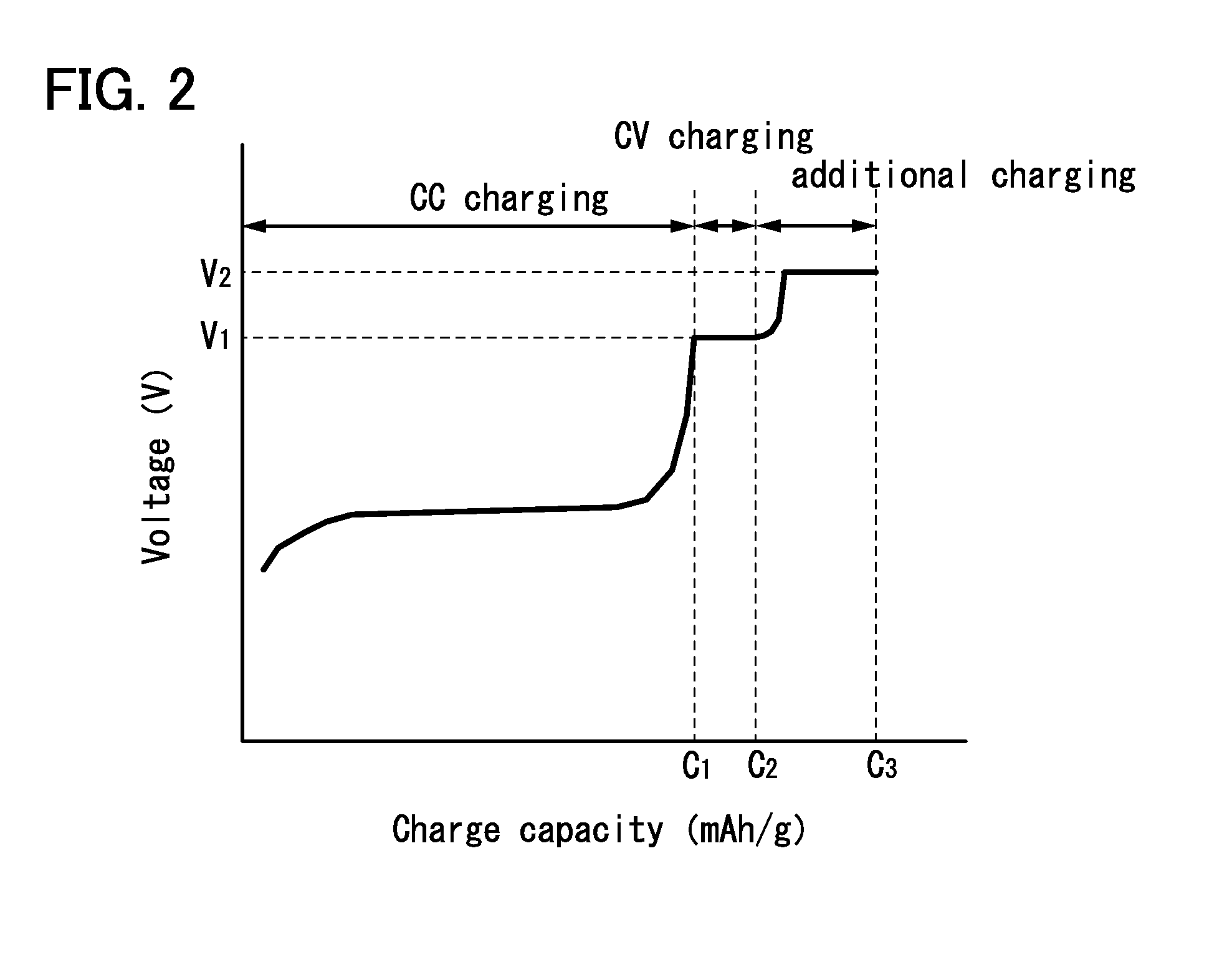
ActiveUS20140184172A1Reduced shutdown currentReduce power consumptionCharging stationsCell electrodesDecompositionEngineering
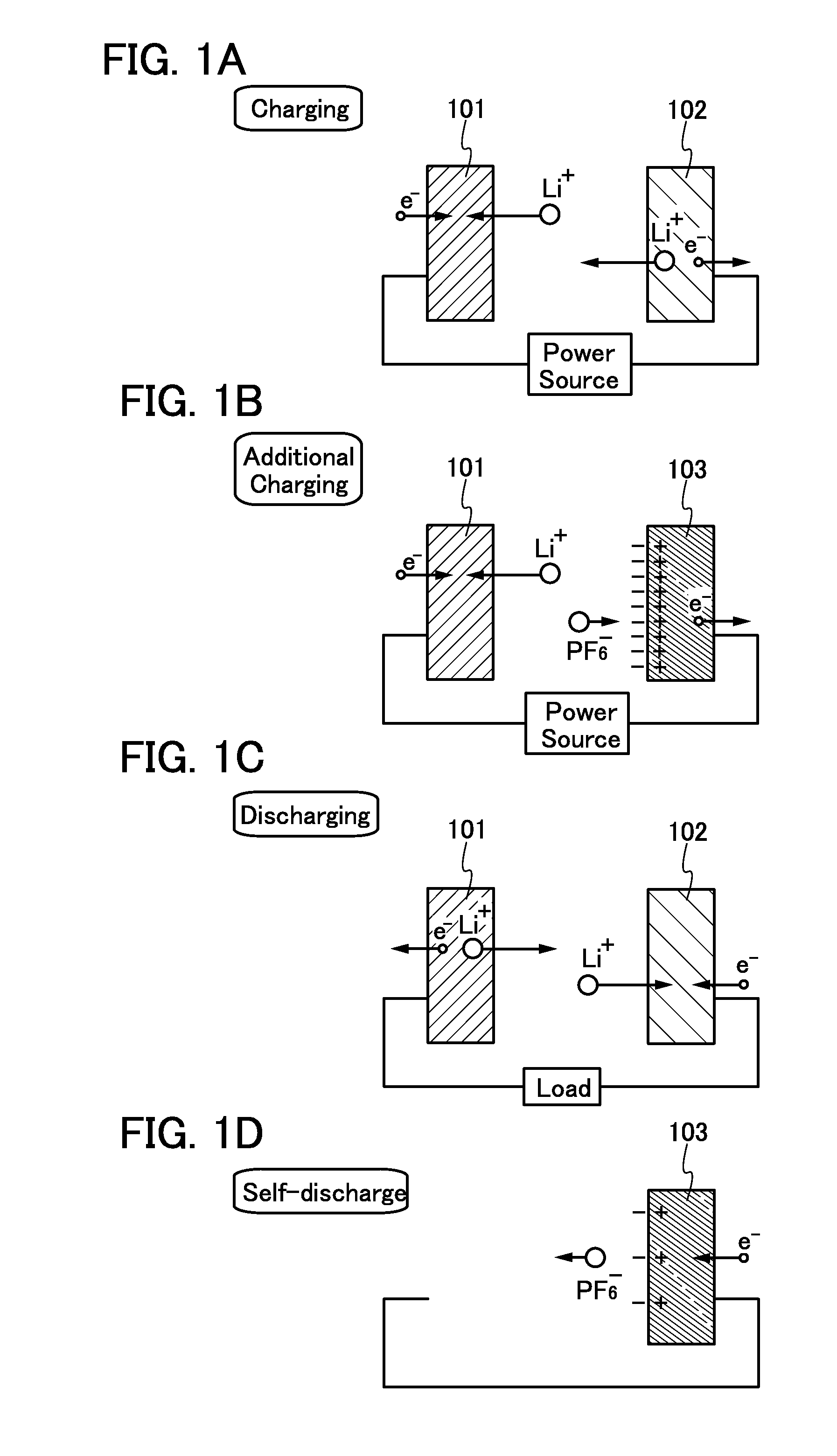
An object is to inhibit a decrease in the capacity of a power storage device or to compensate the capacity, by adjusting or rectifying an imbalance between a positive electrode and a negative electrode, which is caused by decomposition of an electrolyte solution at the negative electrode. Provided is a charging method of a power storage device including a positive electrode using an active material that exhibits two-phase reaction, a negative electrode, and an electrolyte solution. The method includes the steps of, after constant current charging, performing constant voltage charging with a voltage that does not cause decomposition of the electrolyte solution until a charging current becomes lower than or equal to a lower current value limit; and after the constant voltage charging, performing additional charging with a voltage that causes decomposition of the electrolyte solution until a resistance of the power storage device reaches a predetermined resistance.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Power storage device and method for charging the same
ActiveUS20140176076A1Reduce capacityIncrease resistance of positive electrodeFinal product manufactureElectrolyte/reactants regenerationCapacitanceElectric force
A decrease in the capacity of a power storage device is inhibited by adjusting or reducing imbalance in the amount of inserted and extracted carrier ions between positive and negative electrodes, which is caused by decomposition of an electrolyte solution of the negative electrode. Further, the capacity of the power storage device can be restored. Furthermore, impurities in the electrolyte solution can be decomposed with the use of the third electrode. A power storage device including positive and negative electrodes, an electrolyte, and a third electrode is provided. The third electrode has an adequate electrostatic capacitance. The third electrode can include a material with a large surface area. In addition, a method for charging the power storage device including the steps of performing charging by applying a current between the positive and negative electrodes, and performing additional applying a current between the third electrode and the negative electrode is provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
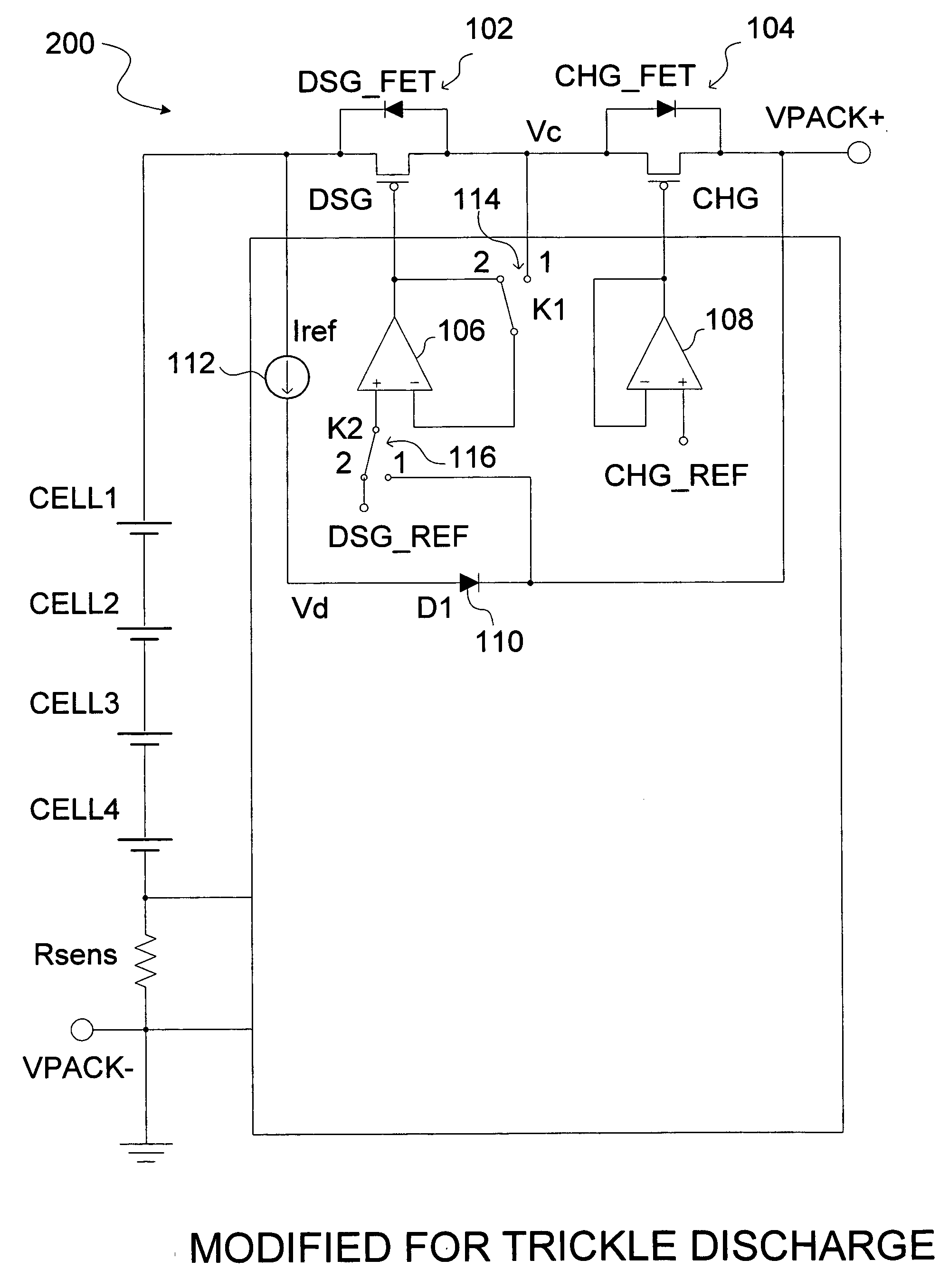
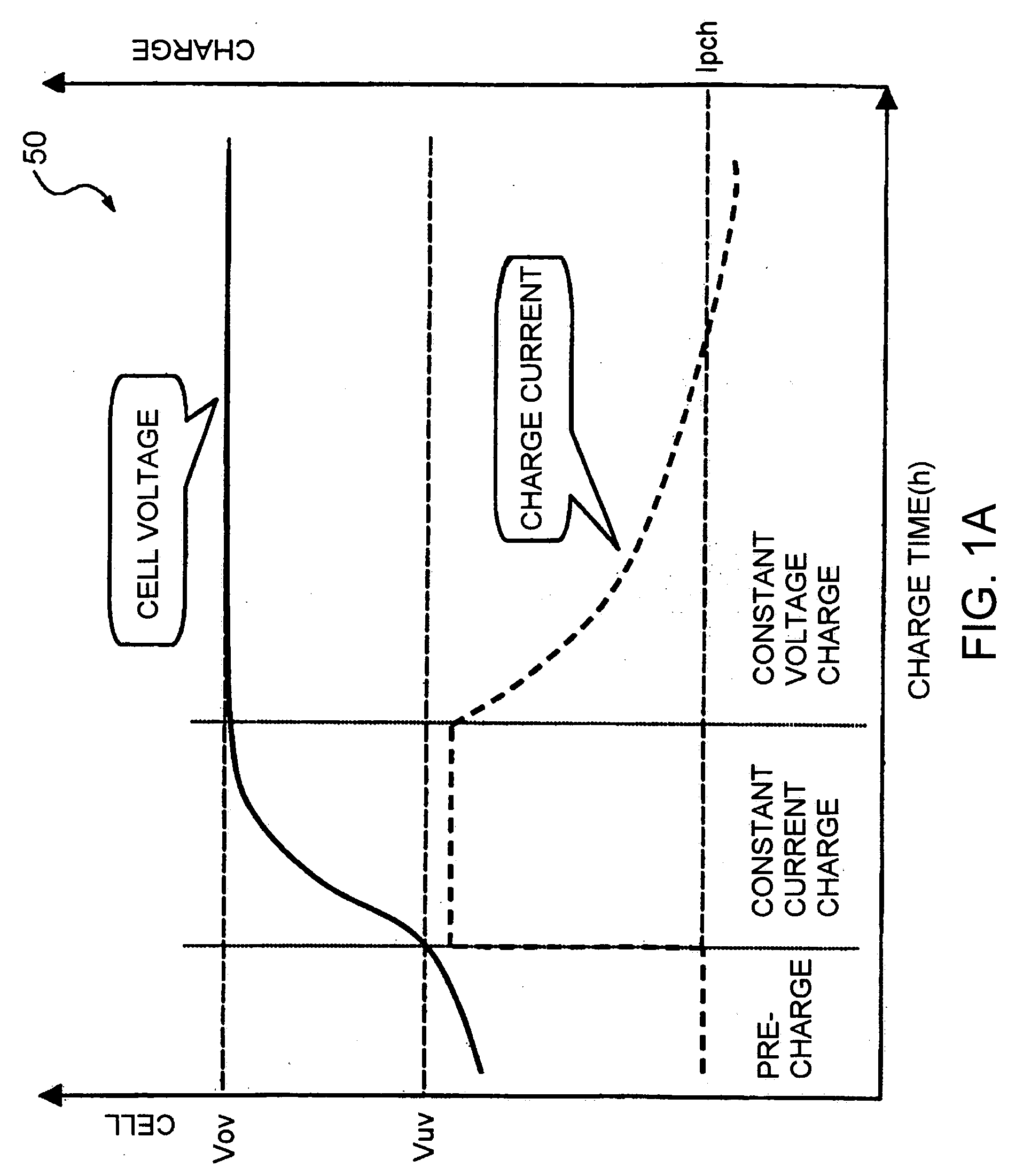
Circuits capable of trickle precharge and/or trickle discharge
ActiveUS20050212484A1Eliminate needSecondary cells charging/dischargingElectric powerBattery chargeControl signal
Battery charging circuitry and systems are provided. One embodiment may include at least one switch having a full conduction state and a controllable conduction state and switch control circuitry capable of sensing a condition. The switch control circuitry may further be capable of generating at least one control signal capable of controlling the conduction state of the switch based on, at least in part, the sensed condition.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
Popular searches
Harmonic reduction arrangement Ac network to reduce harmonics/ripples Emergency power supply arrangements Cells structural combination Current conducting connections Cells with cell condition indications Power supply for data processing Exchanging data charger Battery load switching Passive battery identification
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com