Boost unit Z-source inverter
A source inverter and inverter bridge technology, applied in the field of power electronic converters, can solve the problems of small turn ratio, high-frequency transformer boost volume, large weight loss, etc., and achieve high boost characteristics and wide input voltage range , the effect of high conversion efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
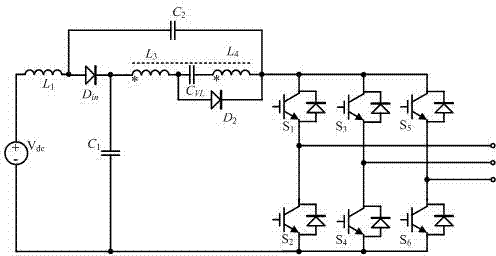
[0032] Such as figure 1 The Z-source inverter of the boost unit includes a Z-source structure, a boost unit and an inverter bridge. The input terminal of the Z-source inverter of the boost unit is connected to a DC voltage source, and the output terminal is connected to a filter inductor and a filter capacitor. In this embodiment, the second inductor in the conventional Z-source structure is replaced by a boost unit.
[0033] Specifically, the Z source structure provided by this embodiment includes: DC voltage source V dc , the first inductance L 1 , boost unit, first capacitor C 1 , the second capacitance C 2 and the first power diode D in ; Among them: the first inductance L 1 One end of the DC voltage source is connected to the positive pole, and the first inductor L 1 The other end of the first power diode D in the anode and the second capacitor C 2 One end of the connection; the first power diode D in The cathode is connected to one end of the boost unit and the ...
Embodiment 2
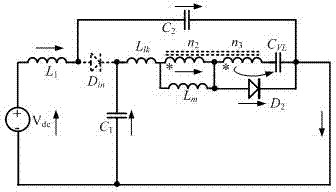
[0058] Such as Figure 8 The boost unit Z-source inverter shown is another embodiment provided by the present invention, which includes a Z-source structure, a boost unit and an inverter bridge. The Z-source structure includes two sets of capacitors, two sets of inductors, a boost unit and a power diode connected across the midpoint of the two sets of inductors and capacitors. The above boost unit includes a coupling inductor, a capacitor and a power diode. The coupled inductor includes a first winding and a second winding, and the output voltage gain is determined by setting the turn ratio of the second winding to the first winding. In this embodiment, the second inductor in the conventional Z-source structure is replaced by a boost unit.
[0059] Specifically, the Z source structure provided by this embodiment includes: DC voltage source V dc , the first inductance L 1 , boost unit, first capacitor C 1 , the second capacitance C 2 and the first power diode D in ; Amon...
Embodiment 3
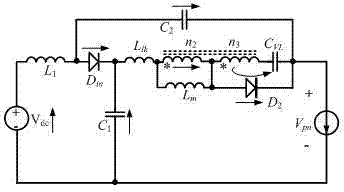
[0064] Such as Figure 9 The boost unit Z-source inverter shown includes a Z-source structure, a boost unit and an inverter bridge. The Z source structure includes two sets of capacitors, two sets of inductors, a boost unit, a DC voltage source connected across the midpoint of the two sets of inductors and capacitors, and a power diode. The boost unit includes a coupled inductor, a capacitor, and a power diode. The coupled inductor includes a first winding and a second winding. The output voltage gain is determined by setting the turn ratio of the second winding to the first winding.
[0065] Specifically, the Z source structure provided by this embodiment includes: DC voltage source V dc , the first inductance L 1 , the second inductance L 2 , the first capacitance C 1 , the second capacitance C 2 and the first power diode D in ; Among them: the first inductance L 1 One end of the first capacitor C 1 One end of the inverter bridge is connected to the negative end, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com