Wave trough control circuit and wave trough control method
A technology for controlling circuits and wave troughs, which is applied in the direction of control/regulation systems, electrical components, and adjustment of electrical variables, etc., can solve problems such as difficult design of EMI circuits, large output ripples, and large range of operating frequency changes of switching tubes. Effect of Design and Optimization, Elimination of Output Ripple, Reduction of Full Load Operating Frequency Range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
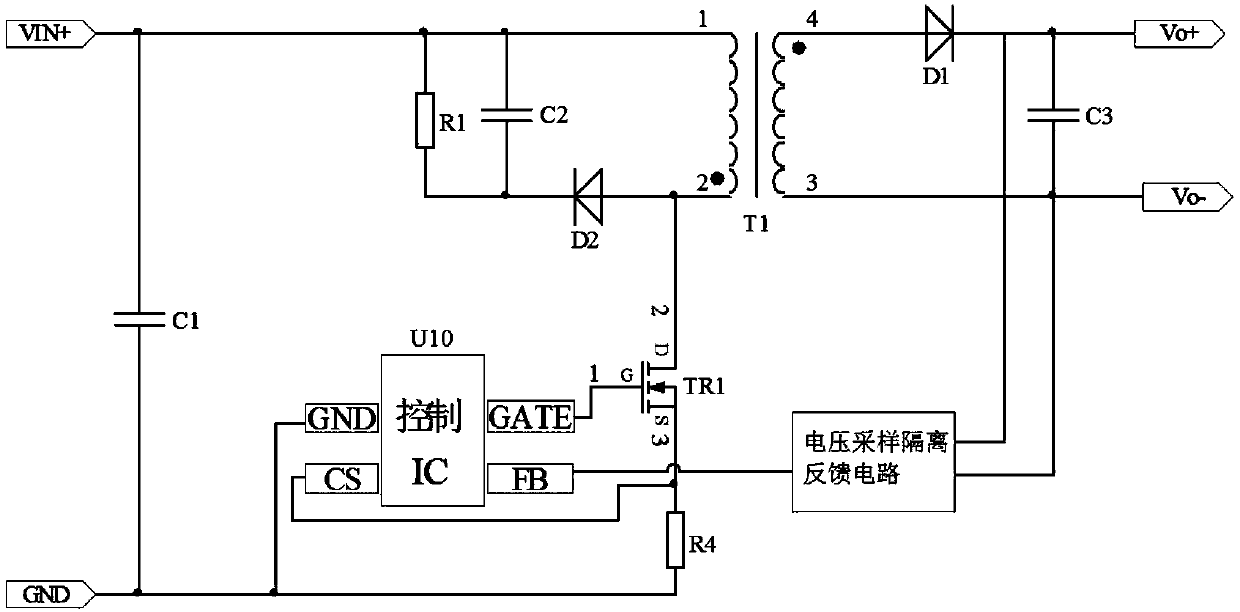
[0036] Figure 4 It is the circuit schematic diagram of the flyback converter of the present invention. The flyback converter includes a transformer T1, a primary side circuit, a secondary side circuit and a control circuit. The primary side circuit includes a filter capacitor C1, a main power circuit, a clamping circuit, and a current sampling circuit. And the voltage divider circuit, the main power circuit is formed by connecting the primary winding of the transformer T1 and the main switching tube TR1 (the main switching tube is a MOS tube, which may also be referred to as MOS tube TR1 below). The clamping module is formed by connecting a resistor R1, a capacitor C2 and a diode D2. The current sampling circuit is formed by connecting resistor R4. The secondary circuit is composed of the secondary winding of the transformer T1, the diode D1, and the capacitor C3. The control circuit is composed of a control chip U1 and a voltage sampling isolation feedback circuit. The con...
Embodiment 2
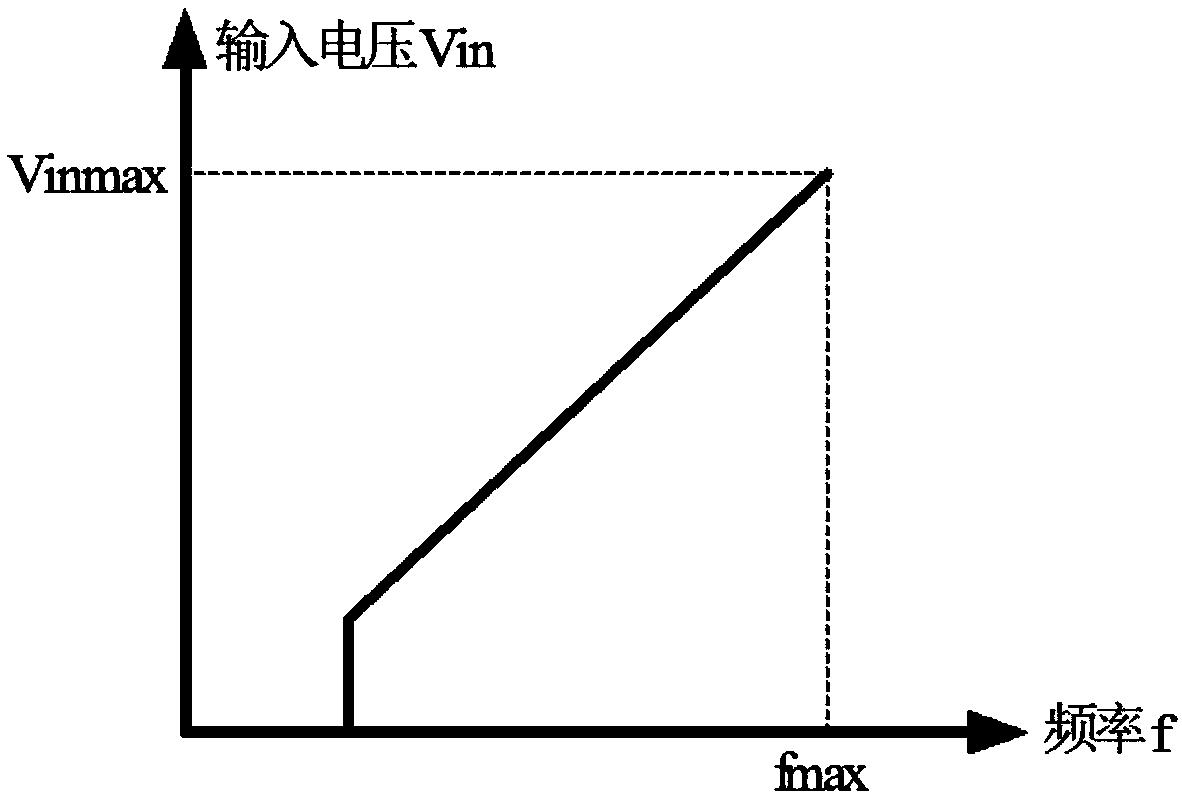
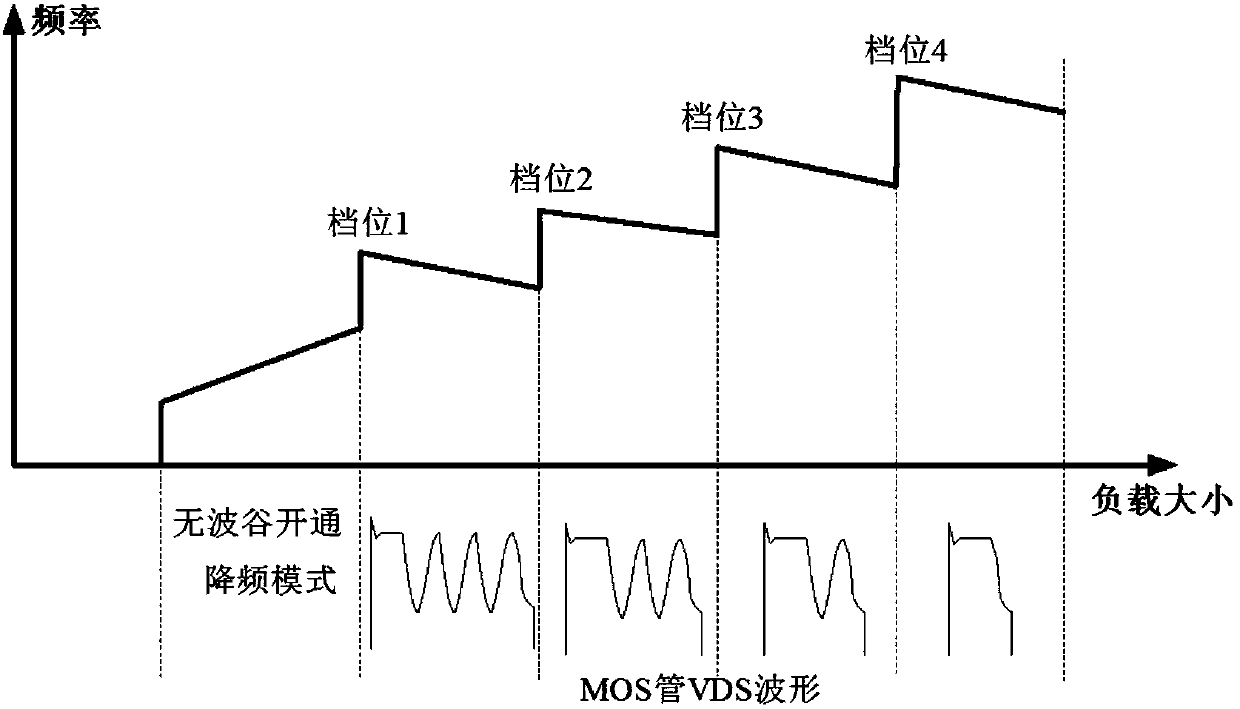
[0047] Figure 8 It is the circuit schematic diagram of the valley control circuit of the second embodiment of the present invention applied in the flyback converter. Compared with the first embodiment, the main MOS transistor TR1 of the flyback converter and the resistor R4 of the current sampling circuit are used in the second embodiment It is integrated into the chip of the control chip U1', which simplifies the peripheral parameters. The control chip U1' includes UVP pins, GND pins, DRIN pins and FB pins. The UVP pins are input voltage detection pins, which are used to detect the gears of the input voltage to determine which valleys to open and do Undervoltage protection; the GND pin is the reference ground pin of the chip; the DRIN pin is the drain pin of the switch tube, which is used to sample the waveform of the drain of the built-in MOS transistor TR1, and provide it to the valley control circuit to count the number of valleys ; and as the drain terminal of the built...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com