Smooth nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control method suitable for control system with relative degree of 1
A non-singular terminal and control system technology, applied in the field of smooth non-singular terminal sliding mode control, can solve the problems of chattering controller, unable to output continuous and smooth control signal, unable to apply control system, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
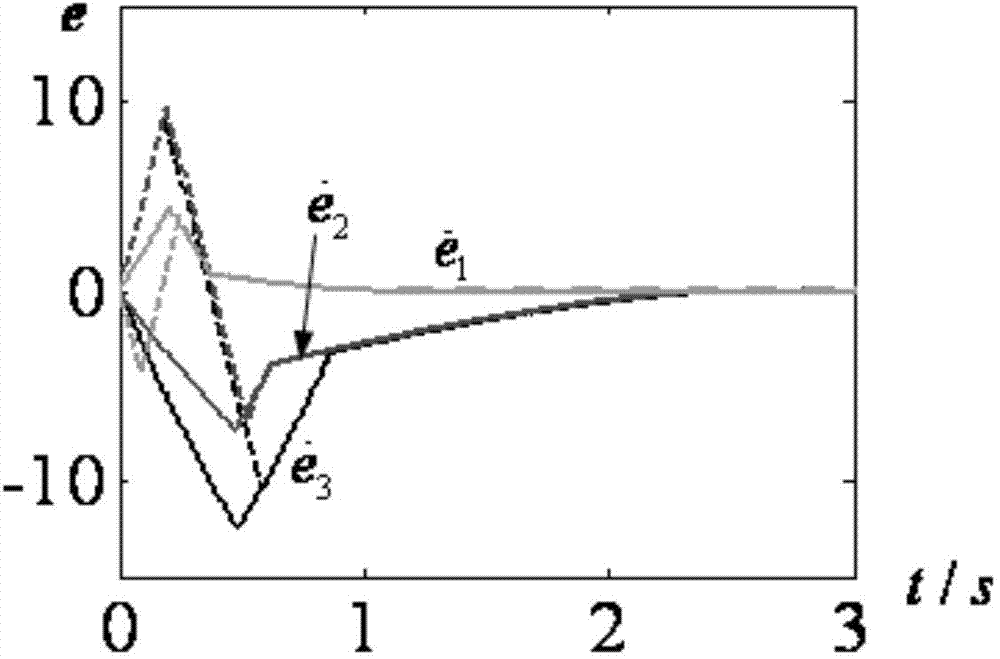
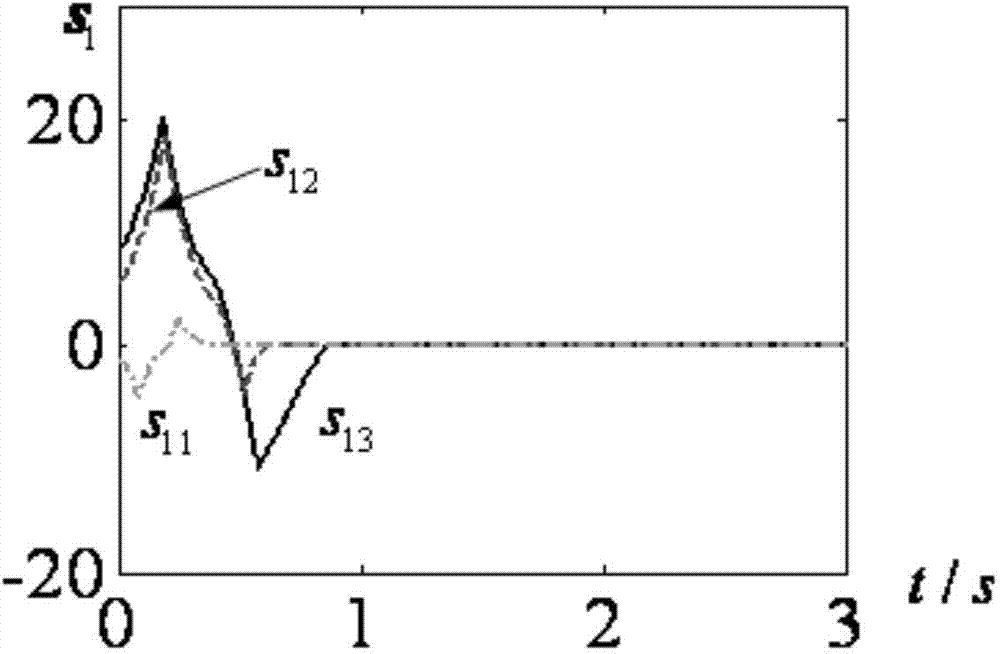
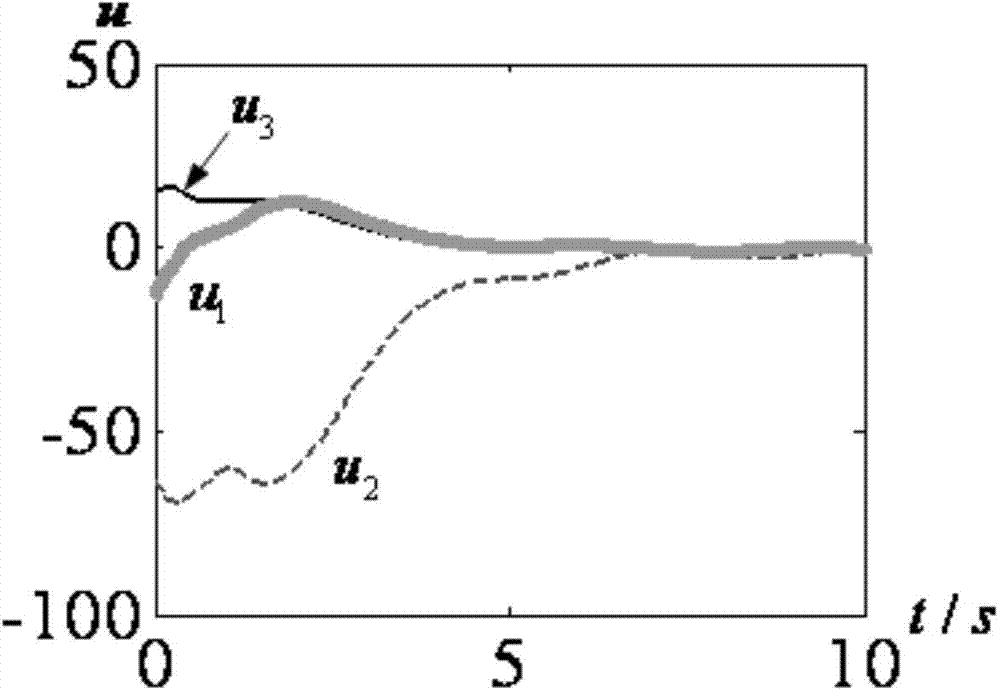
[0049] Specific implementation mode 1: The smooth non-singular terminal sliding mode control method applicable to the relative order 1 control system of this implementation mode, the control method is realized by the following steps:
[0050] Step 1. If the controlled system is a single-input single-output control system A with a relative order of 1: In the formula, Represents the state differential signal of the single-input single-output control system A, x represents the system state of the single-input single-output control system A, u represents the control quantity of the single-input single-output control system A, and t represents the time, then execute the control method of step 2; if The controlled system is a multiple-input multiple-output control system with a relative order of 1: In the formula, Represents the state differential signal of the multiple-input multiple-output control system, x s Indicates the state of the multiple-input multiple-output control...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0082] The difference from the specific embodiment 1 is that this embodiment is applicable to the smooth non-singular terminal sliding mode control method of the relative order 1 control system. In order to make the input and output subsystem 2 track the upper reference model 1 in a limited time, the step 32 in the The design process of the control law u′ of the reference model 1 described in step 5 is specifically as follows:
[0083] First, define the bias variable e=z 1 –ξ, from the input-output subsystem 2 and the reference model 1, the deviation system with a relative order of 1 can be obtained: e · ( t ) = ( ϵ + 1 ) B 1,0 ( I + d ( t ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0099] The difference from Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 is that the smooth non-singular terminal sliding mode control method applicable to the relative order 1 control system of this embodiment, in order to make the reference model 1 converge to zero within a finite time and the deviation described in step 5 After the system converges to zero, the reference model 1 is equivalent to the input-output subsystem 2, and the approximate formula of the deviation system is zero, namely e · ( t ) = ( ϵ + 1 ) B 1,0 u ′ ( t ) - w ′ ( t ) + f m ′ ′ ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com