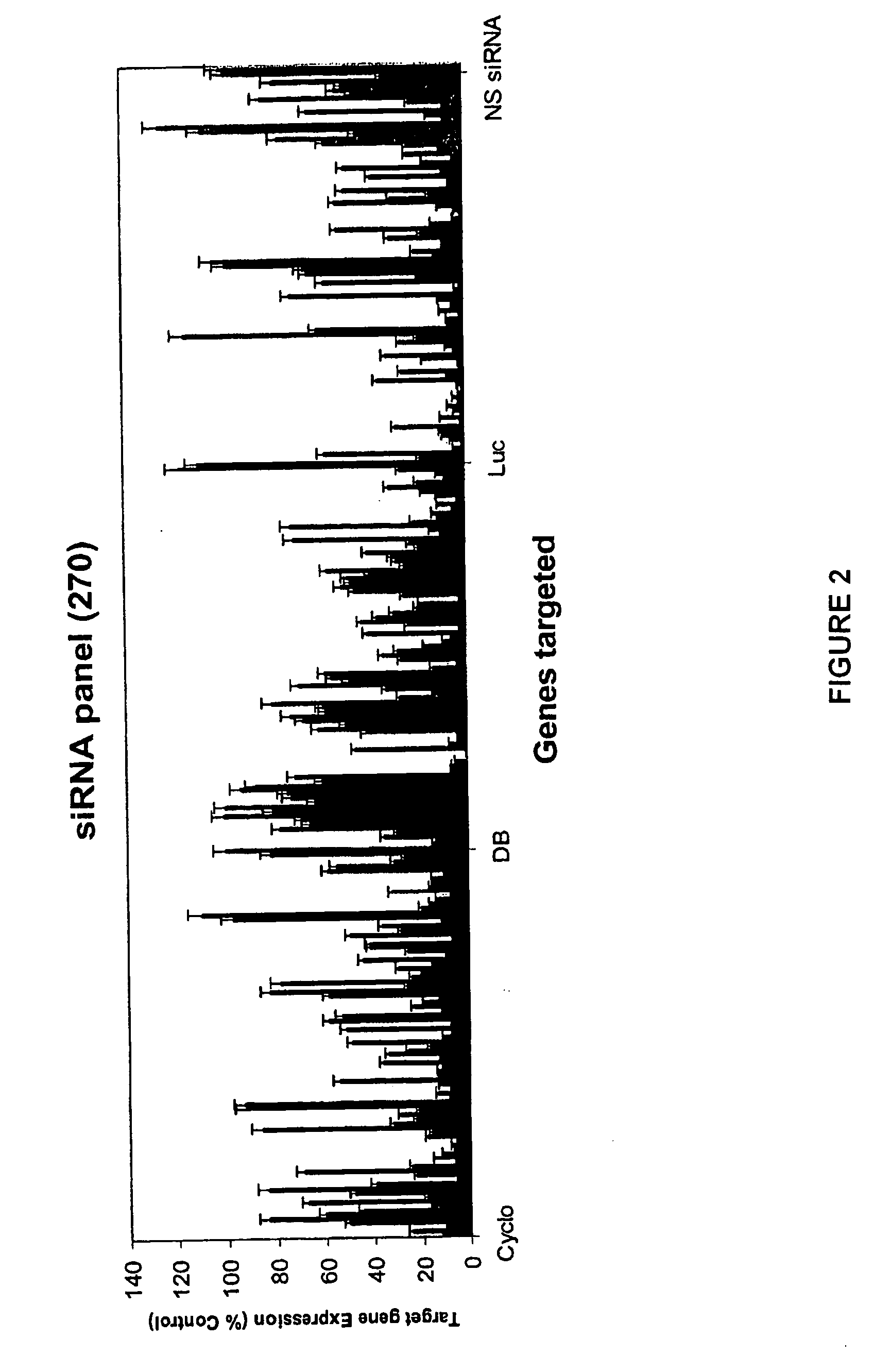
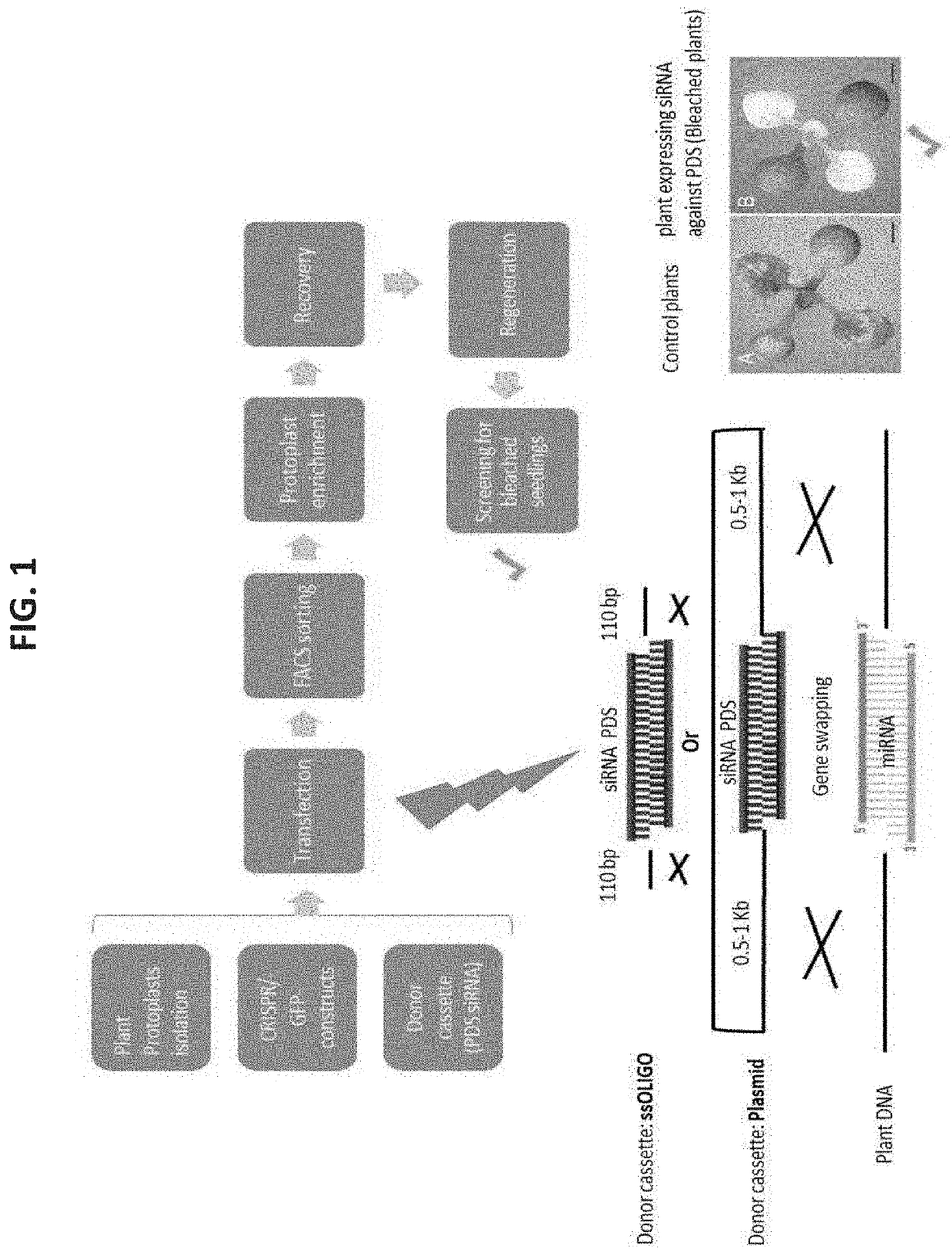
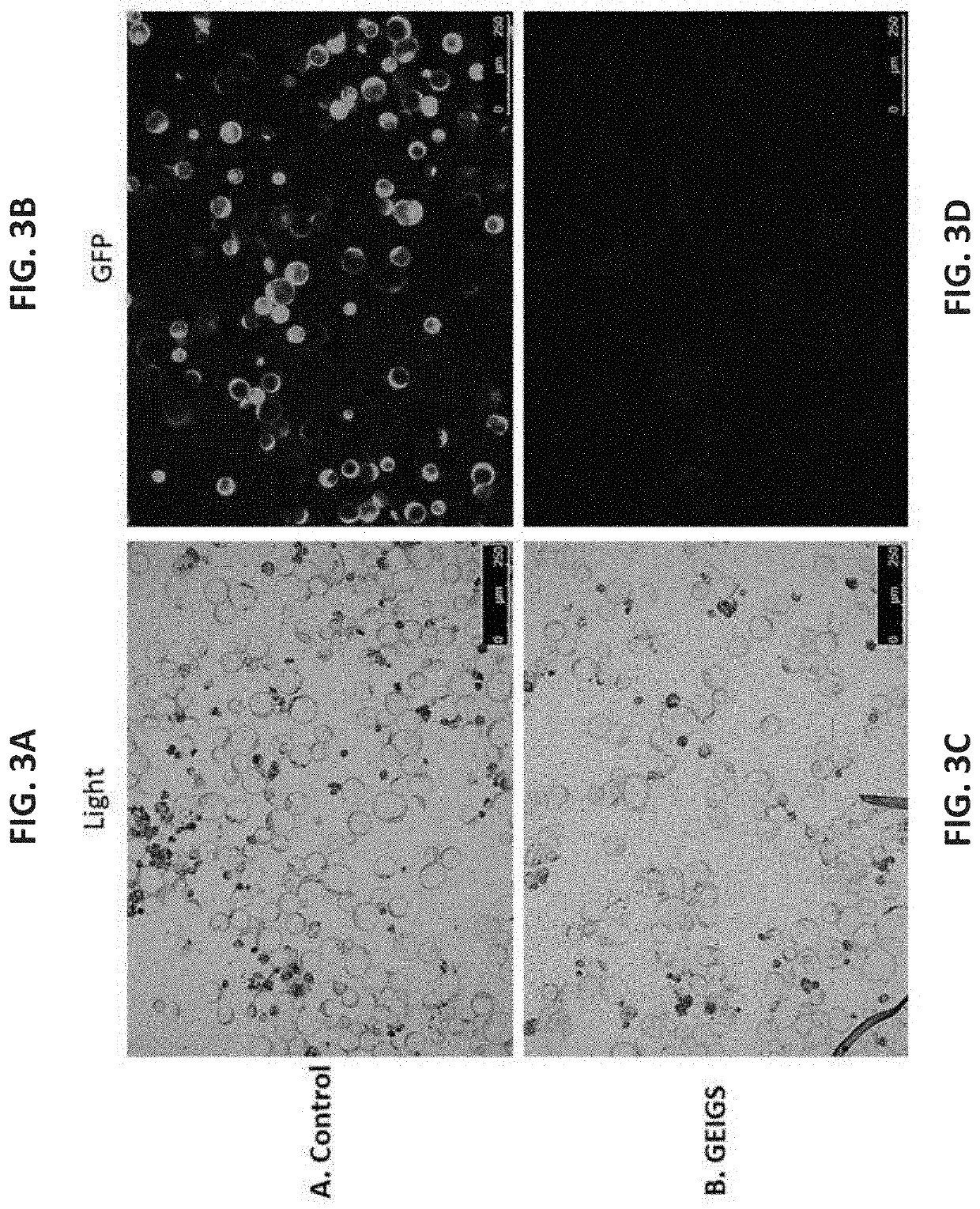
Patents
Literature
169 results about "Silent gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
They do code for proteins, but the cell silences or activates certain genes as a way of controlling protein production. When the gene is silent it is not expressed but this can be reversed, and is usually controlled by transcription factors. Silent gene is actually not a very formally defined term.
Methods and compositions for selecting siRNA of improved functionality
InactiveUS20050255487A1Improve efficiencyGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGene silencingSilencing gene
Efficient sequence specific gene silencing is possible through the use of siRNA technology. By selecting particular siRNAs by rational design, one can maximize the generation of an effective gene silencing reagent, as well as methods for silencing genes. Methods, compositions, and kits generated through rational design of siRNAs are disclosed.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
Modified siRNA molecules and uses thereof
ActiveUS20070135372A1Decrease immunostimulatory propertyImmunostimulatory activity of siRNA can be abolishedOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesLipid formationLipid particle
The present invention provides chemically modified siRNA molecules and methods of using such siRNA molecules to silence target gene expression. Advantageously, the modified siRNA of the present invention is less immunostimulatory than its corresponding unmodified siRNA sequence and retains RNAi activity against the target sequence. The present invention also provides nucleic acid-lipid particles comprising a modified siRNA, a cationic lipid, and a non-cationic lipid, which can further comprise a conjugated lipid that inhibits aggregation of particles. The present invention further provides methods of silencing gene expression by administering a modified siRNA to a mammalian subject. Methods for identifying and / or modifying an siRNA having immunostimulatory properties are also provided.
Owner:ARBUTUS BIOPHARMA CORPORAT ION
Functional and hyperfunctional siRNA
ActiveUS20050246794A1Improve efficiencyGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSilent geneGene silencing
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
Functional and hyperfunctional siRNA directed against Bcl-2
InactiveUS20050245475A1Improve efficiencyGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSilencing geneCancer research
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
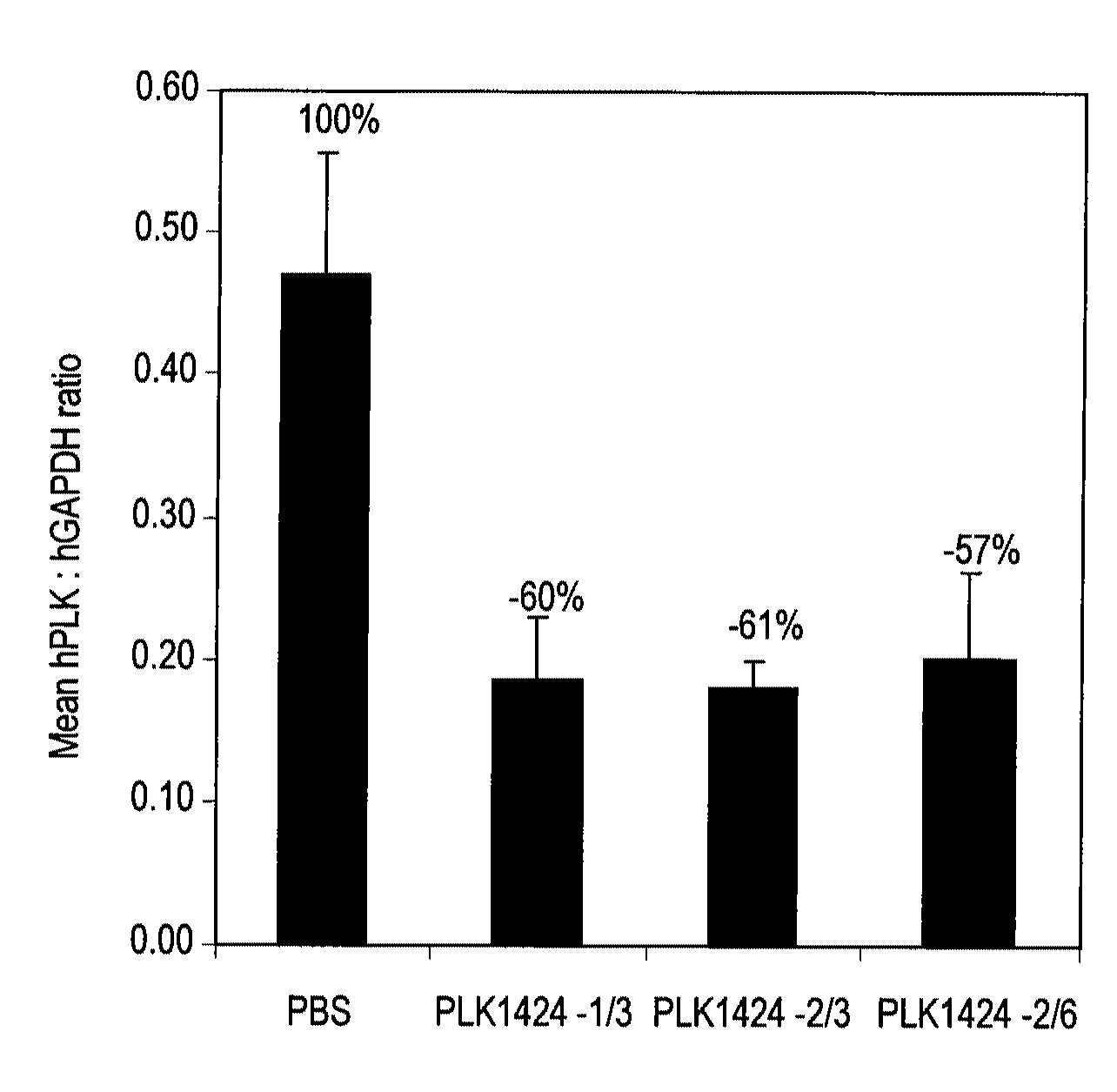
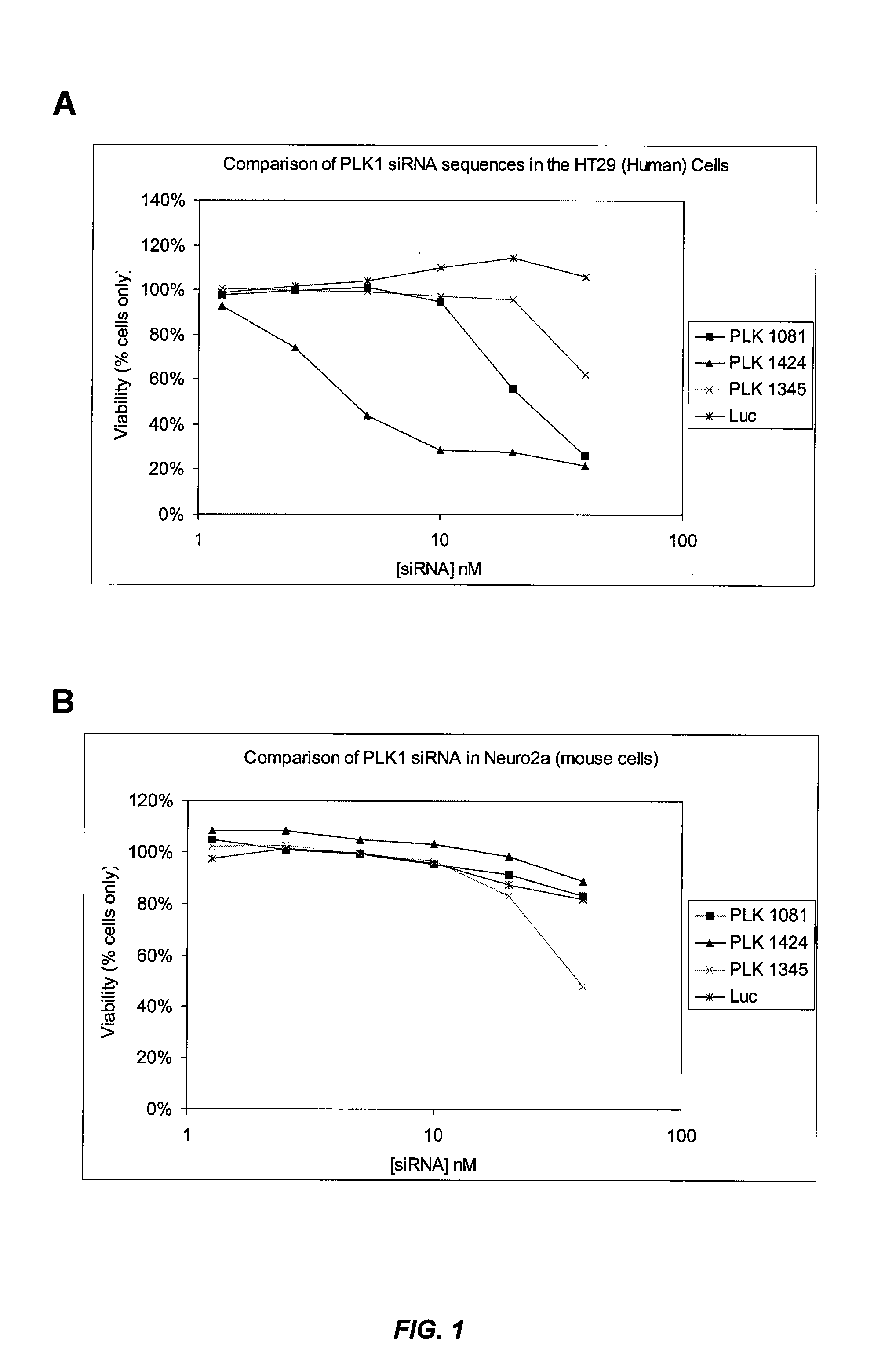
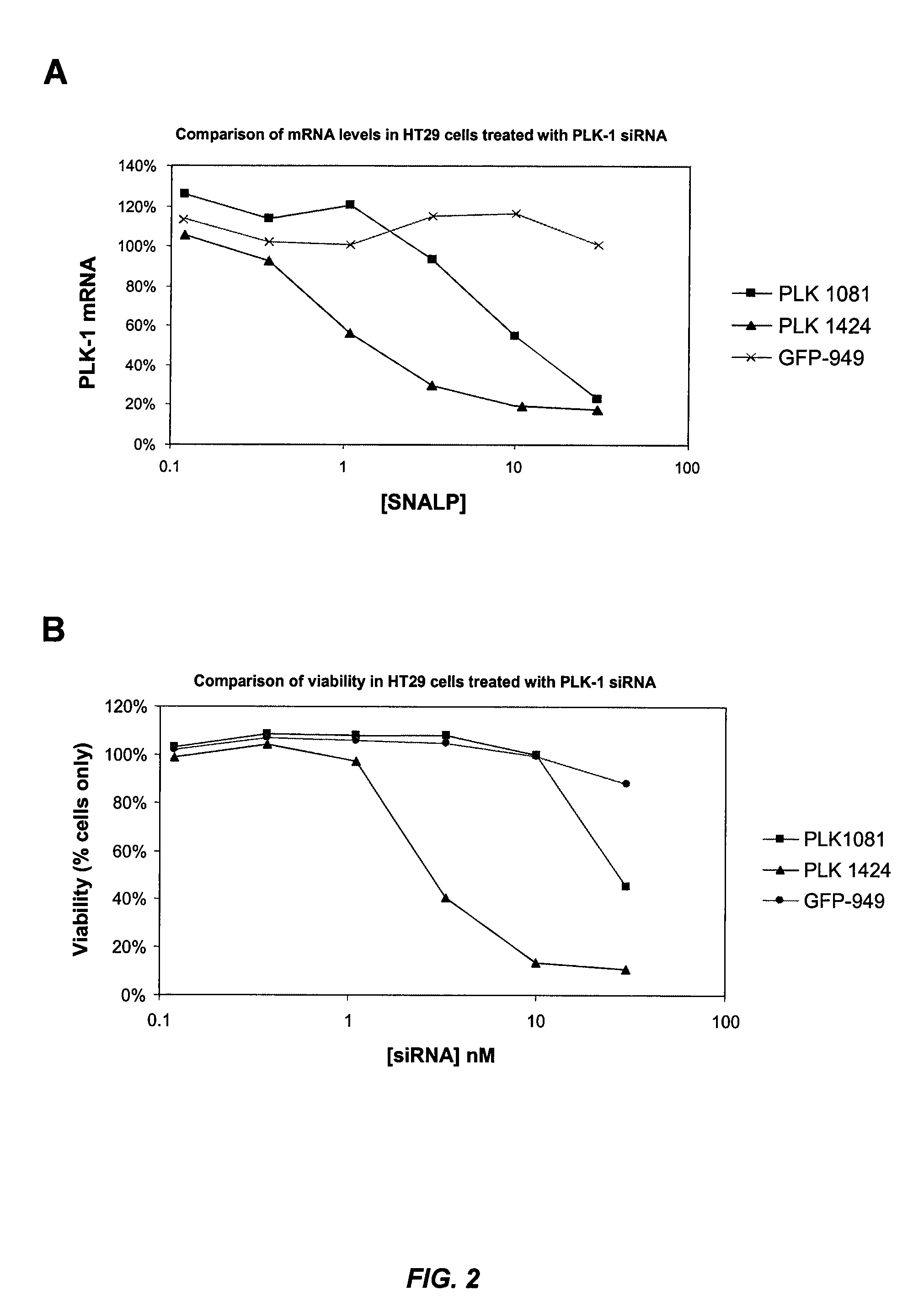
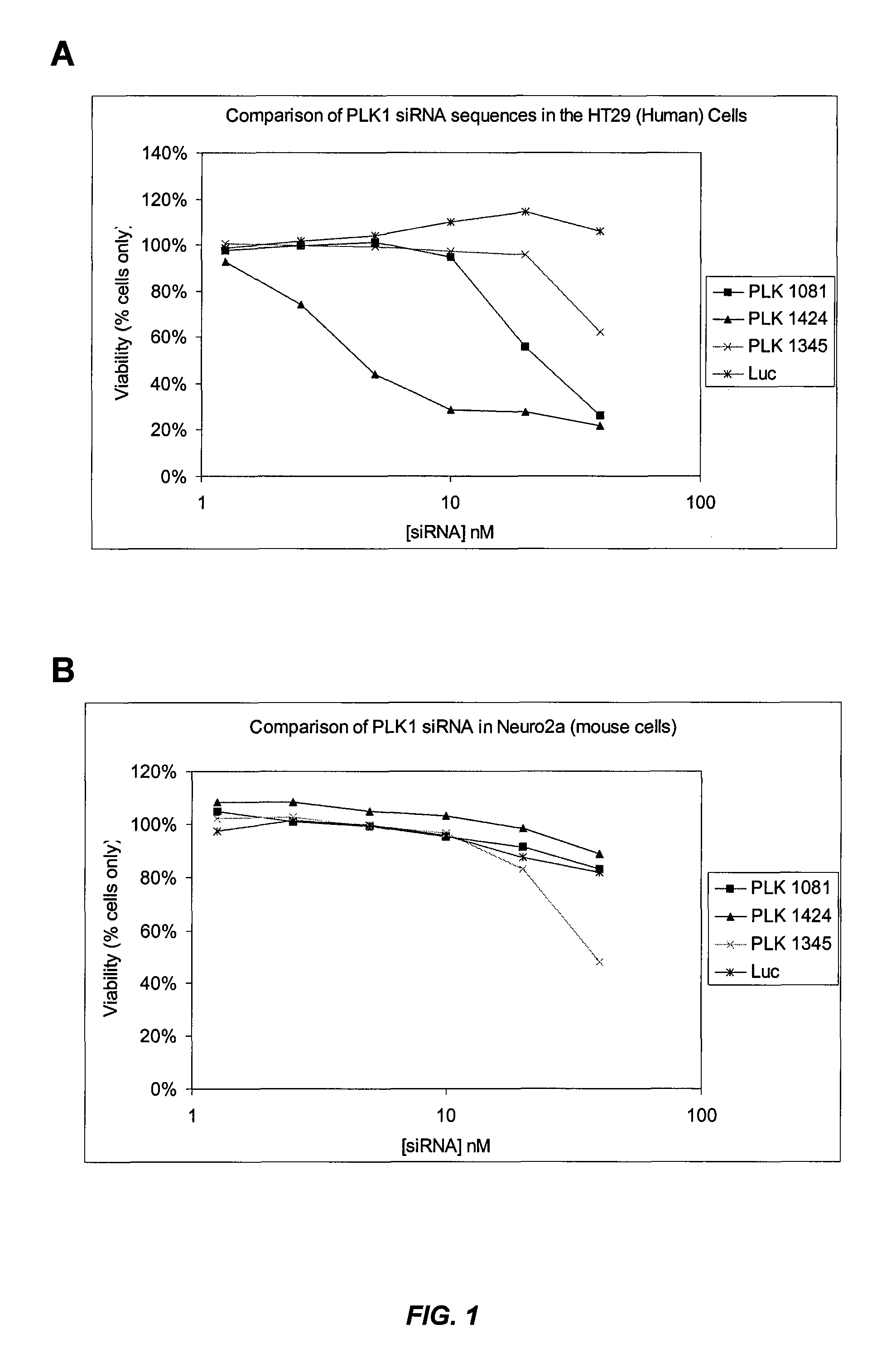
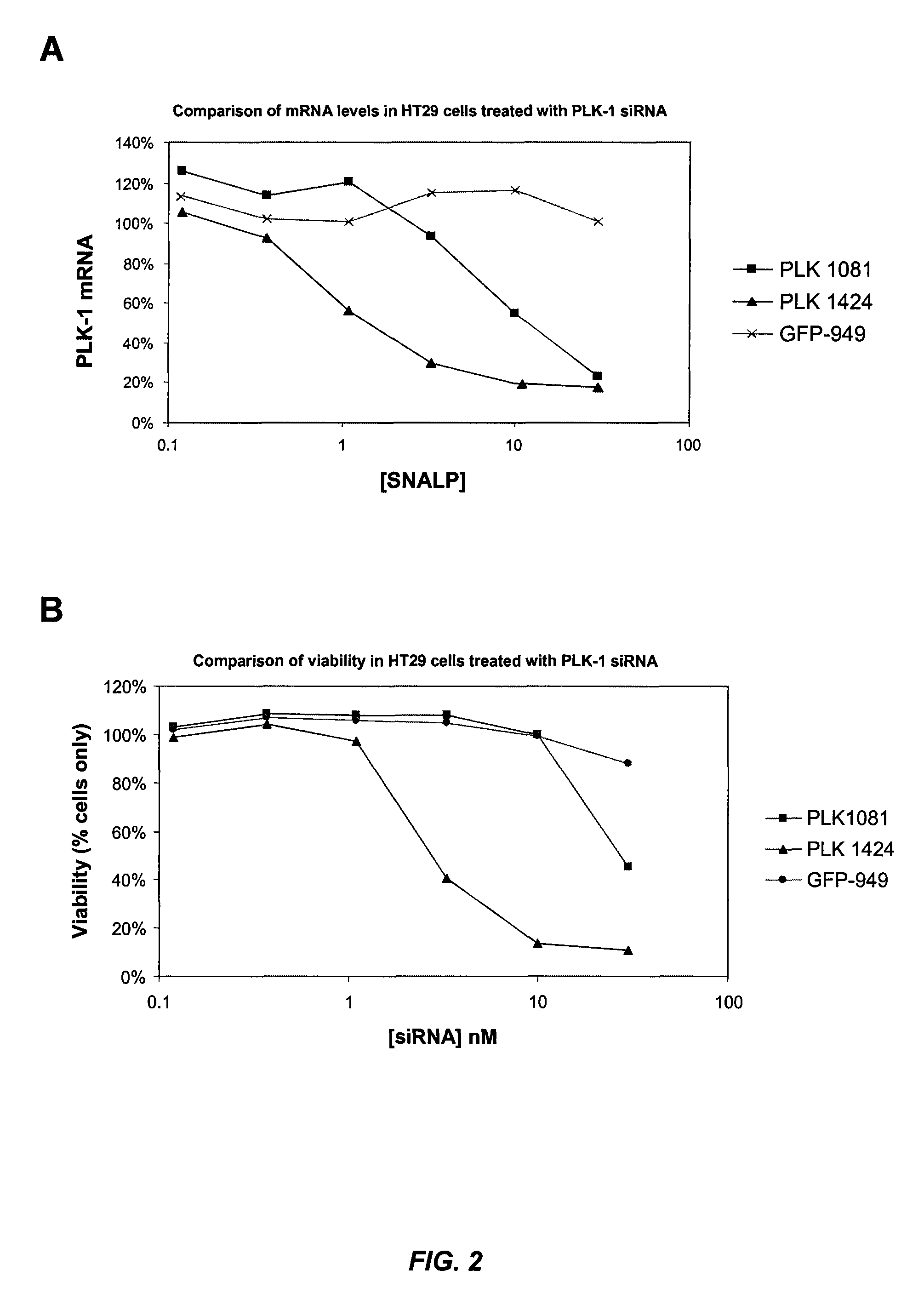
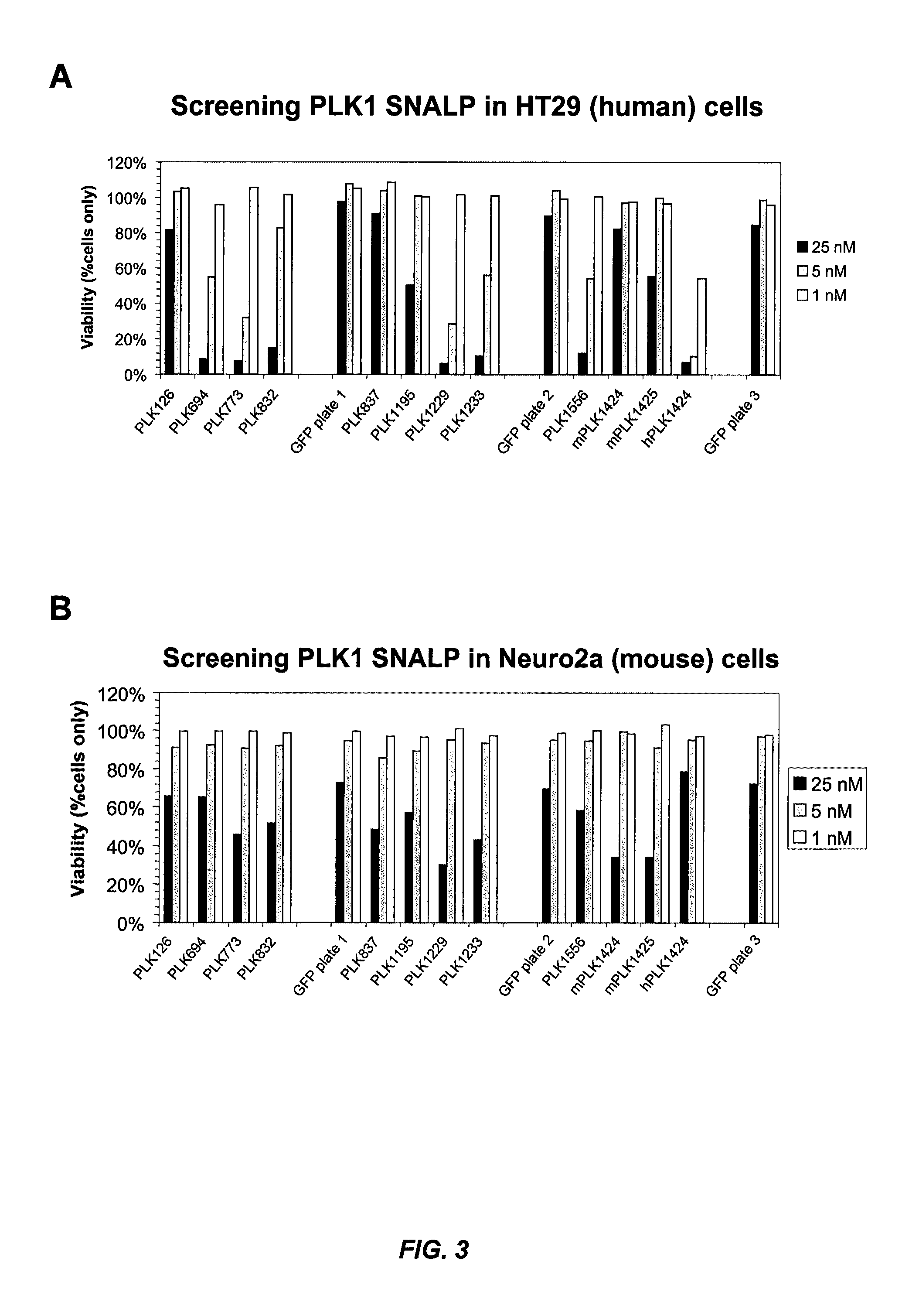
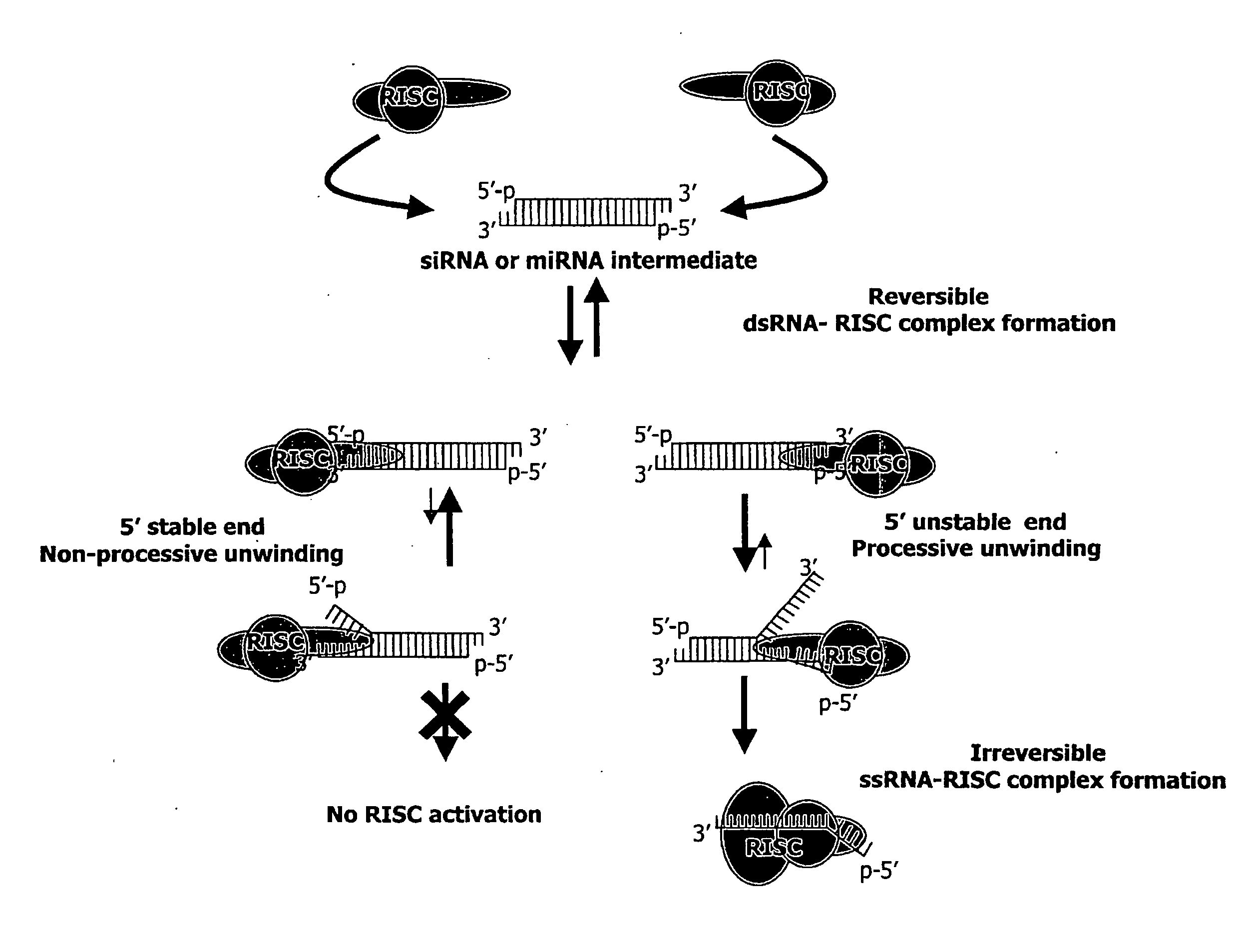
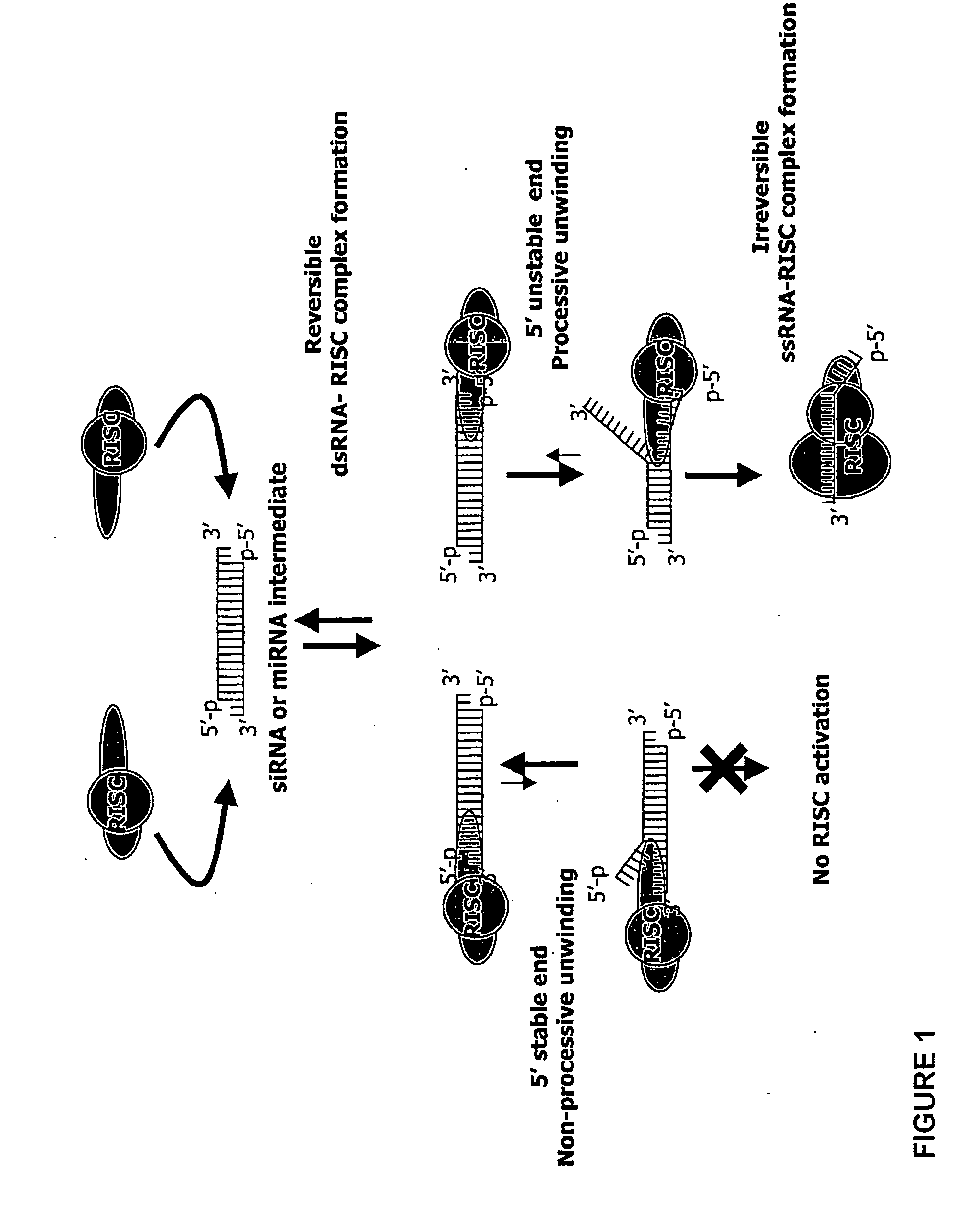
Silencing of polo-like kinase expression using interfering RNA
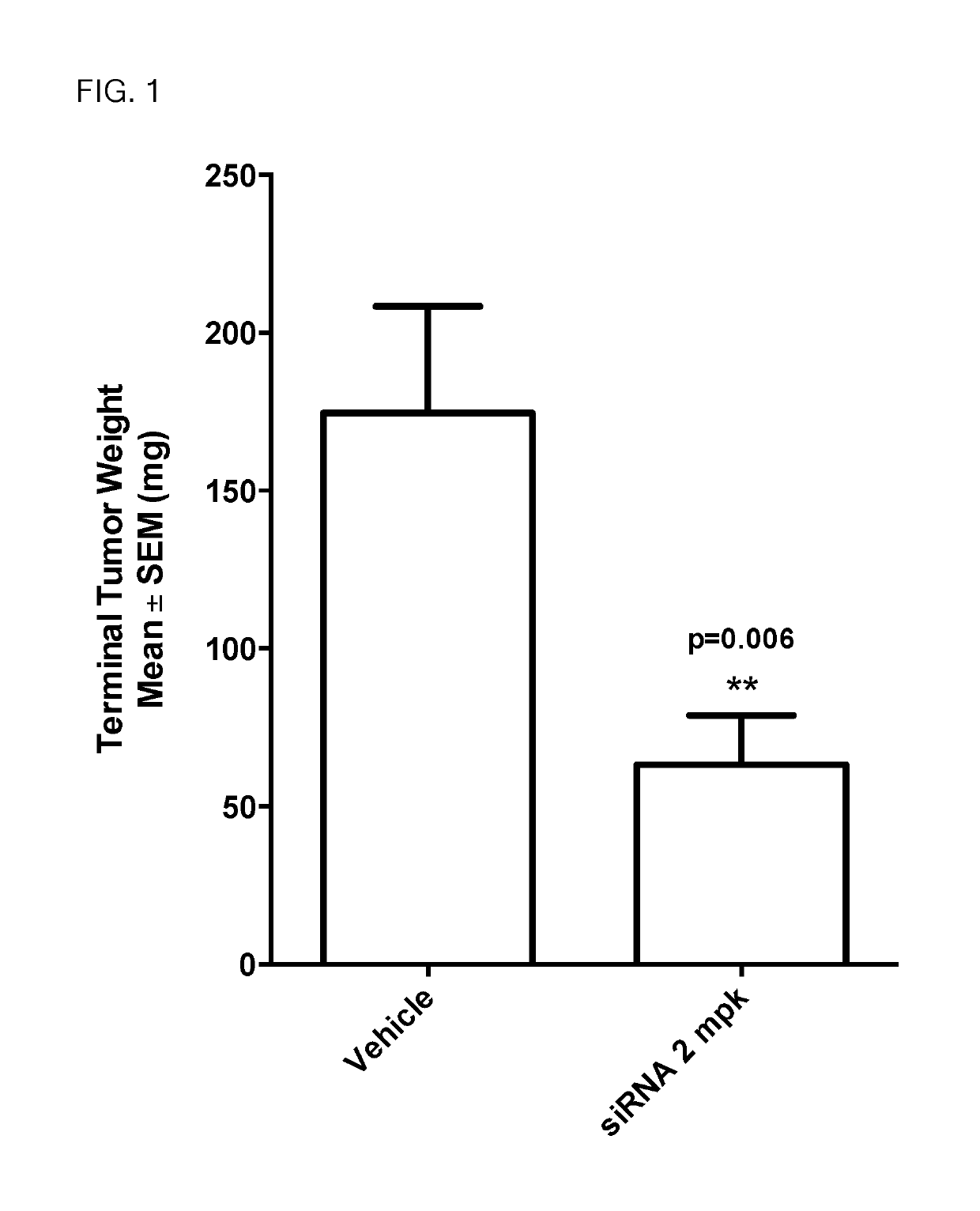
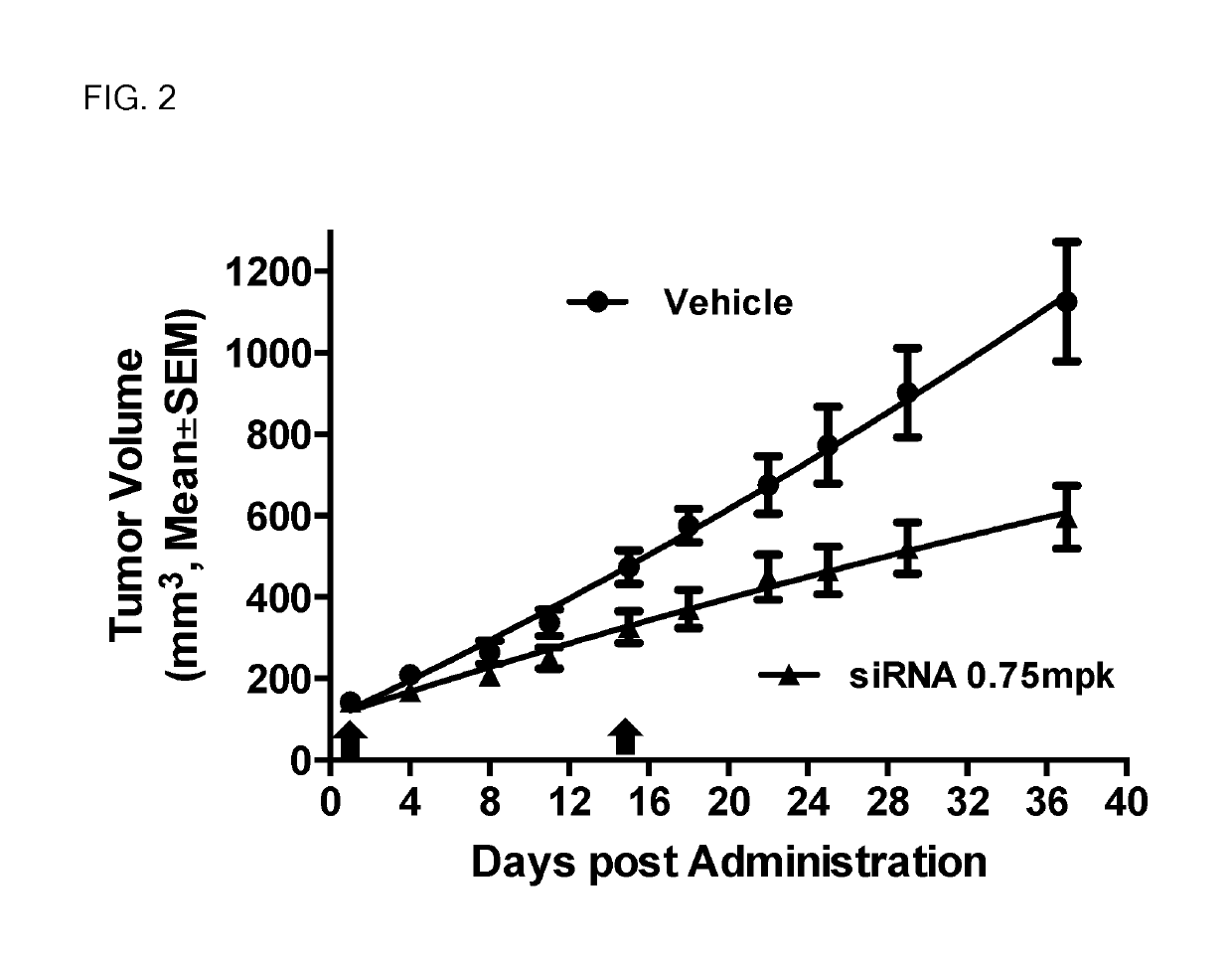
The present invention provides compositions comprising interfering RNA (e.g., siRNA, aiRNA, miRNA) that target polo-like kinase 1 (PLK-1) expression and methods of using such compositions to silence PLK-1 expression. More particularly, the present invention provides unmodified and chemically modified interfering RNA molecules which silence PLK-1 expression and methods of use thereof. The present invention also provides serum-stable nucleic acid-lipid particles (e.g., SNALP) comprising an interfering RNA molecule described herein, a cationic lipid, and a non-cationic lipid, which can further comprise a conjugated lipid that inhibits aggregation of particles. The present invention further provides methods of silencing PLK-1 gene expression by administering an interfering RNA molecule described herein to a mammalian subject. The present invention additionally provides methods of identifying and / or modifying PLK-1 interfering RNA having immunostimulatory properties. Methods for sensitizing a cell such as a cancer cell to the effects of a chemotherapy drug comprising sequentially delivering PLK-1 interfering RNA followed by the chemotherapy drug are also provided.
Owner:ARBUTUS BIOPHARMA CORPORAT ION
siRNA targeting cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (p27, Kip1) (CDKN1B)
InactiveUS7612196B2Improve efficiencyGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSilent geneGene silencing
Efficient sequence specific gene silencing is possible through the use of siRNA technology. By selecting particular siRNAs by rational design, one can maximize the generation of an effective gene silencing reagent, as well as methods for silencing genes. Methods, compositions, and kits generated through rational design of siRNAs are disclosed including those directed to nucleotide sequences for CDKN1B.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
Compositions for reduced lignin content in sorghum and improving cell wall digestibility, and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20150291969A1Reduces and silence expressionSuppressing and silencing expressionOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationSorghumCell wall
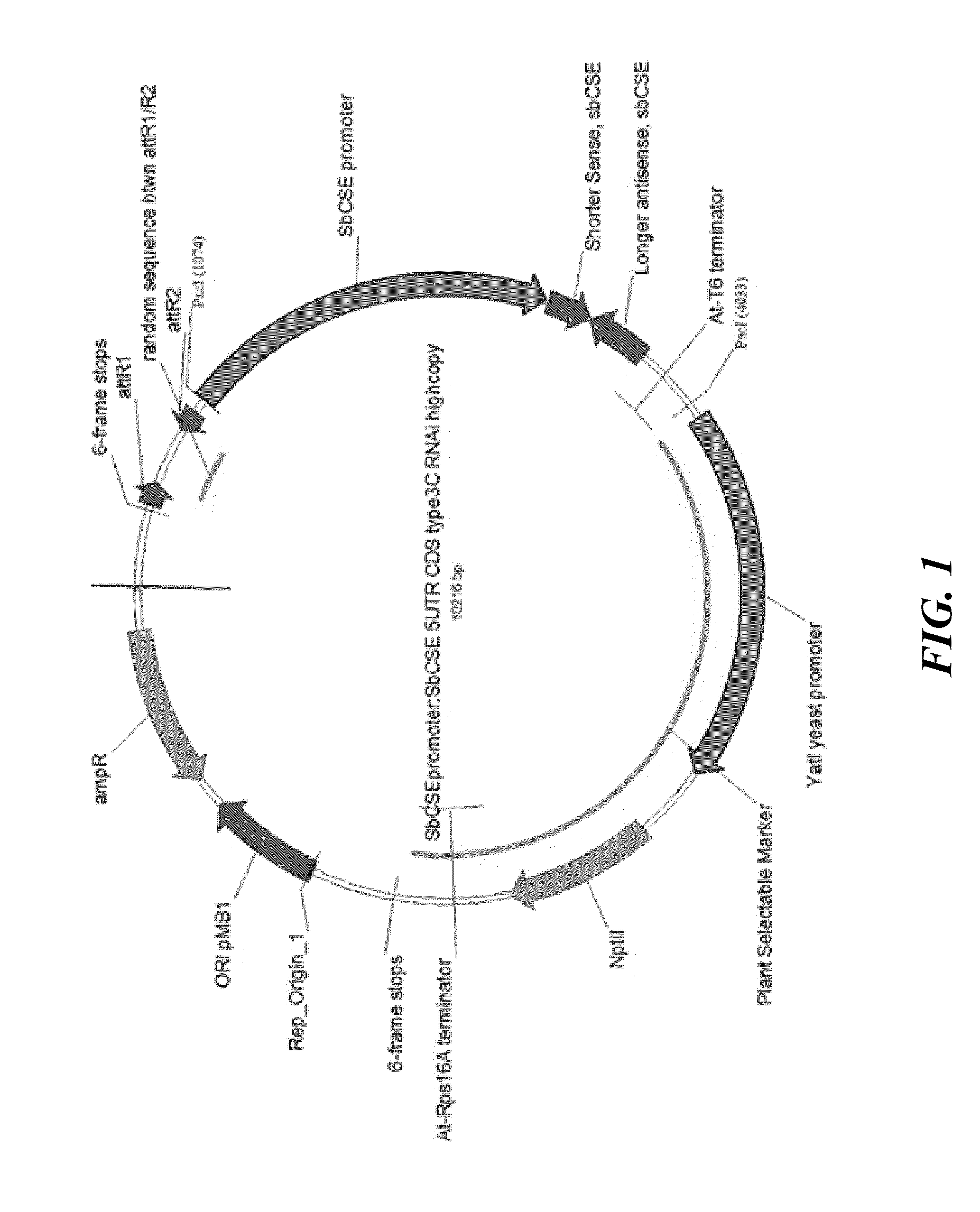
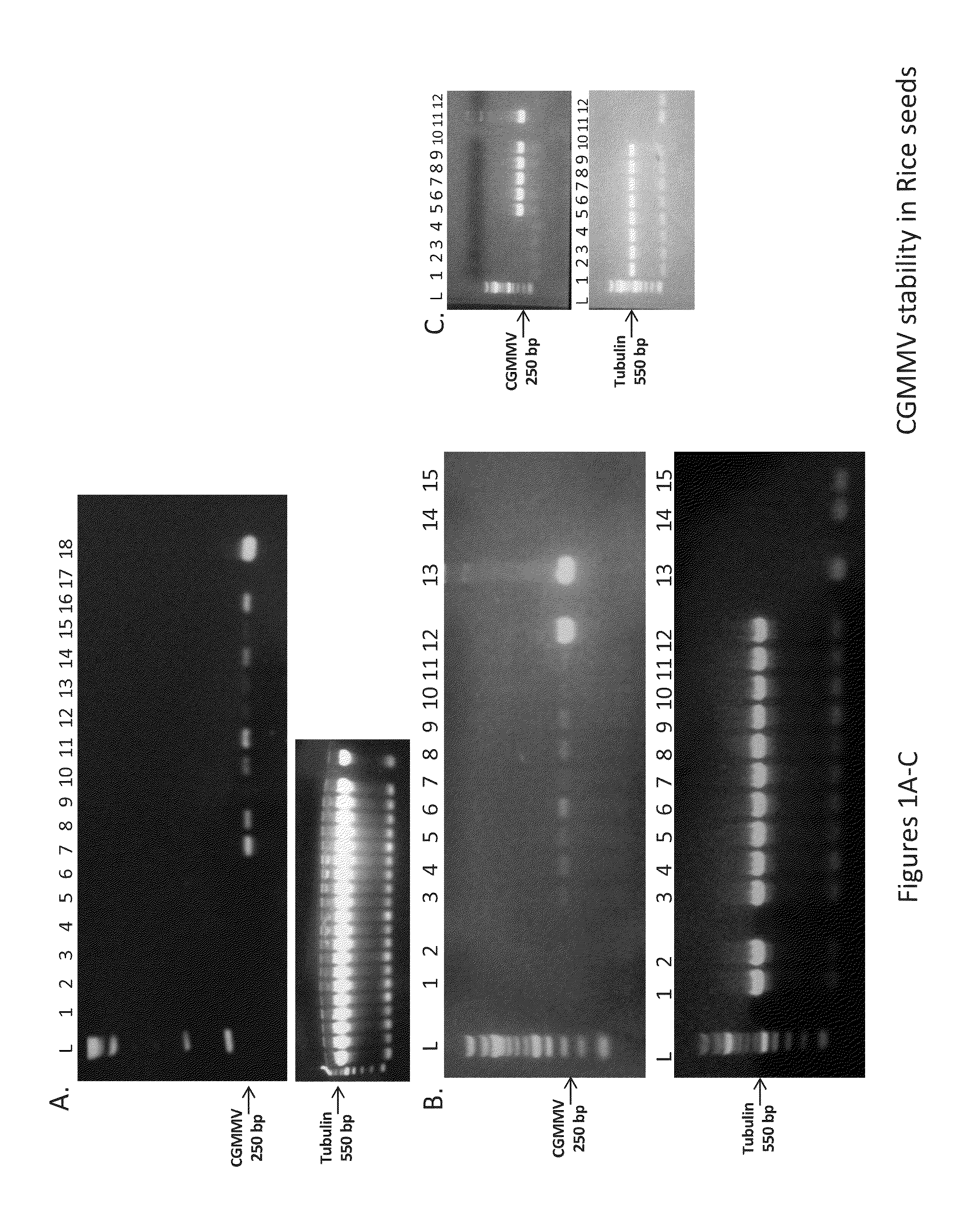
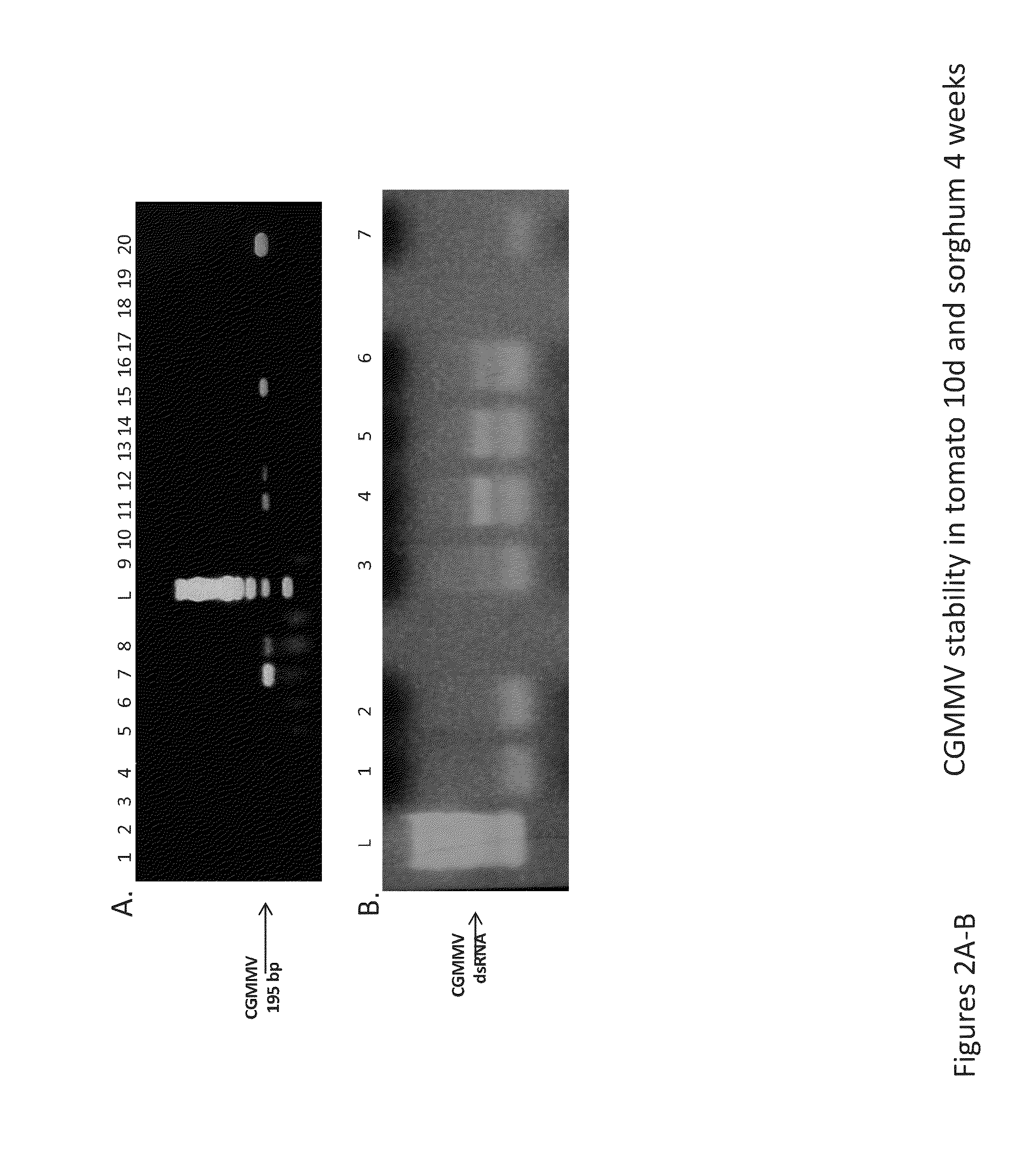
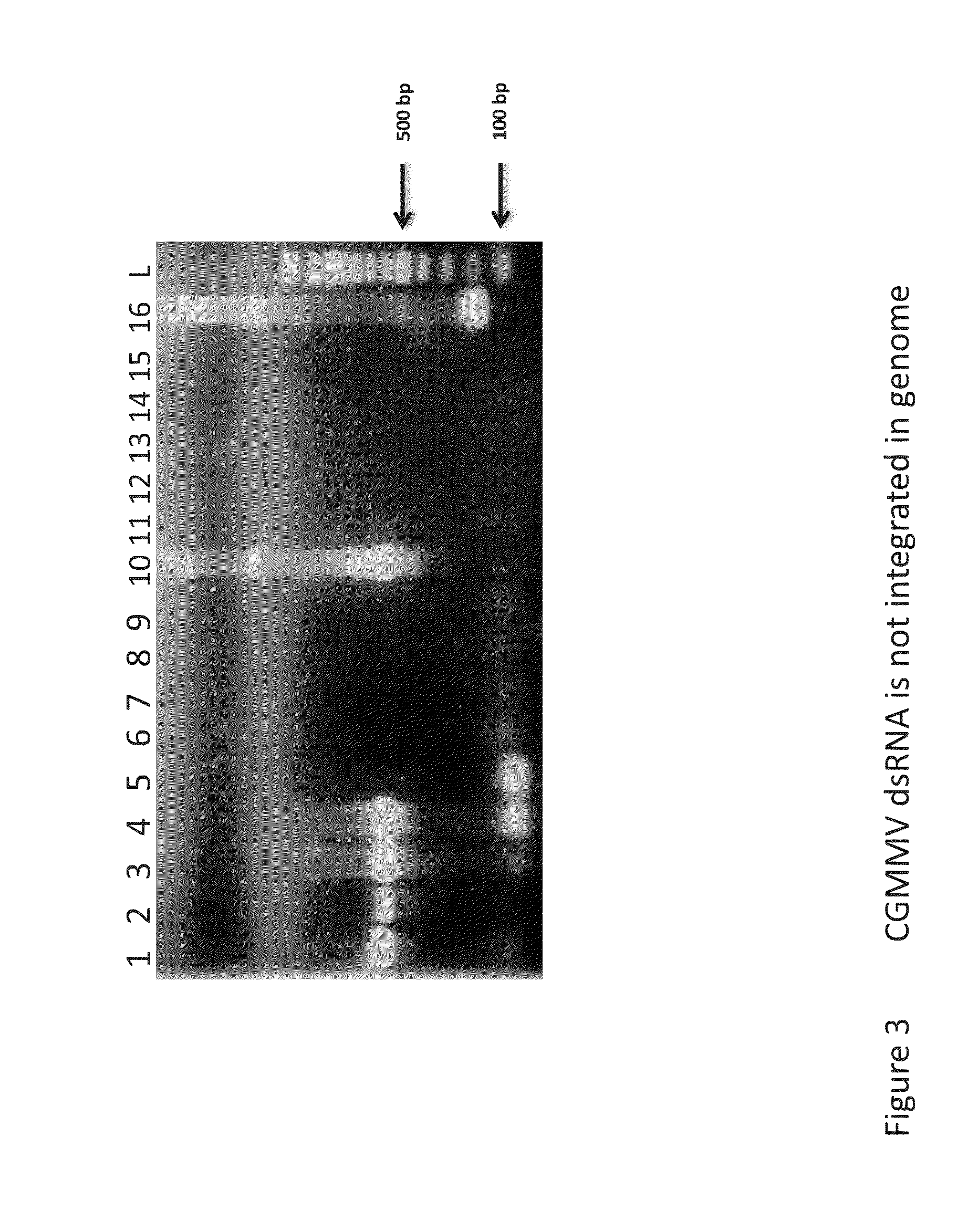
RNAi vectors comprising a fragment of the SbCSE polynucleotide sequence and transgenic plants, e.g. transgenic sorghum plants, comprising said RNAi vectors are described. Aspects of the technology are further directed to methods of using the RNAi vectors of the present technology to silence SbCSE gene expression or activity in a transgenic plant, such as a transgenic sorghum plant. Silencing the SbCSE gene leads to reduced lignin content in a transgenic plant.
Owner:CHROMATIN
Compositions and methods for silencing gene expression
InactiveUS20130318657A1Climate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologySilencing gene
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
siRNA targeting protein kinase N-3 (PKN-3)
ActiveUS7635770B2Improve efficiencyGood curative effectSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsProtein targetSilent gene
Efficient sequence specific gene silencing is possible through the use of siRNA technology. By selecting particular siRNAs by rational design, one can maximize the generation of an effective gene silencing reagent, as well as methods for silencing genes. Methods, compositions, and kits generated through rational design of siRNAs are disclosed including those directed to PKN-3.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
Methods and compositions for gene silencing
InactiveUS20070130653A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesDevelopmental stageHeterologous
Methods and compositions are provided for reducing the level of expression of a target polynucleotide in an organism. The methods and compositions selectively silence the target polynucleotide through the expression of a chimeric polynucleotide comprising the target for a sRNA (the trigger sequence) operably linked to a sequence corresponding to all or part of the gene or genes to be silenced. In this manner, the final target of silencing is an endogenous gene in the organism in which the chimeric polynucleotide is expressed. In a further embodiment, the miRNA target is that of a heterologous miRNA or siRNA, the latter of which is coexpressed in the cells at the appropriate developmental stage to provide silencing of the final target when and where desired. In a further embodiment, the final target may be a gene in a second organism, such as a plant pest, that feeds upon the organism containing the chimeric gene or genes. Compositions further comprise vectors, seeds, grain, cells, and organisms, including plants and plant cells, comprising the chimeric polynucleotide of the invention.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
Nucleic acid compounds for inhibiting erbb gene expression and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080287383A1Thermal stability is maximizedOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSilent geneRNA - Ribonucleic acid
The present disclosure provides meroduplex ribonucleic acid molecules (mdRNA) capable of decreasing or silencing ERBB gene expression. An mdRNA of this disclosure comprises at least three strands that combine to form at least two non-overlapping double-stranded regions separated by a nick or gap wherein one strand is complementary to an ERBB mRNA. In addition, the meroduplex may have at least one uridine substituted with a 5-methyluridine, a nucleoside replaced with a locked nucleic acid, or optionally other modifications, and any combination thereof. Also provided are methods of decreasing expression of an ERBB gene in a cell or in a subject to treat an ERBB-related disease.
Owner:MARINA BIOTECH INC
siRNA targeting v-myc myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog (MYC)
InactiveUS7951935B2Improve efficiencyGood curative effectSugar derivativesActivity regulationViral OncogeneSilent gene
Efficient sequence specific gene silencing is possible through the use of siRNA technology. By selecting particular siRNAs by rational design, one can maximize the generation of an effective gene silencing reagent, as well as methods for silencing genes. Methods, compositions, and kits generated through rational design of siRNAs are disclosed including those directed to MYC.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
Method for evoking differentiation of mesenchyma stem cell and fat stem cell into neurons and special culture medium thereof
ActiveCN101117625ANervous system cellsVector-based foreign material introductionMesenchymal stem cellSilent gene
The present invention discloses a method for inducing mesenchymal stem cell to divide into nerve cell and the special culture medium. The culture medium is DMEM culture medium of cattle fetus blood serum which the volume and the thickness percent ratio is 8 to 12 percent. The method is provided with steps as follows: firstly, a small disturbing RNA which restrains the express of limited silent gene of a nerve cell is composed or an intervention carrier of carrying a small disturbing RNA coding gene with restraining the express of limited silent gene of a nerve cell is composed; secondly, the small disturbing RNA which restrains the express of limited silent gene of a nerve cell or the intervention carrier of carrying a small disturbing RNA coding gene with restraining the express of limited silent gene of a nerve cell is transformed or transfected into mesenchymal stem cell or fat stem cell, then the recombined mesenchymal stem cell or the recombined fat stem cell is positioned in the culture medium induced by nerve cell, and cultivated under the temperature of 36 to 38 DEG C, thereby getting nerve cell. The prevent invention can play an important role in the medical field, and has wide applied prospect.
Owner:FIELD OPERATION BLOOD TRANSFUSION INST OF PLA SCI ACAD OF MILITARY
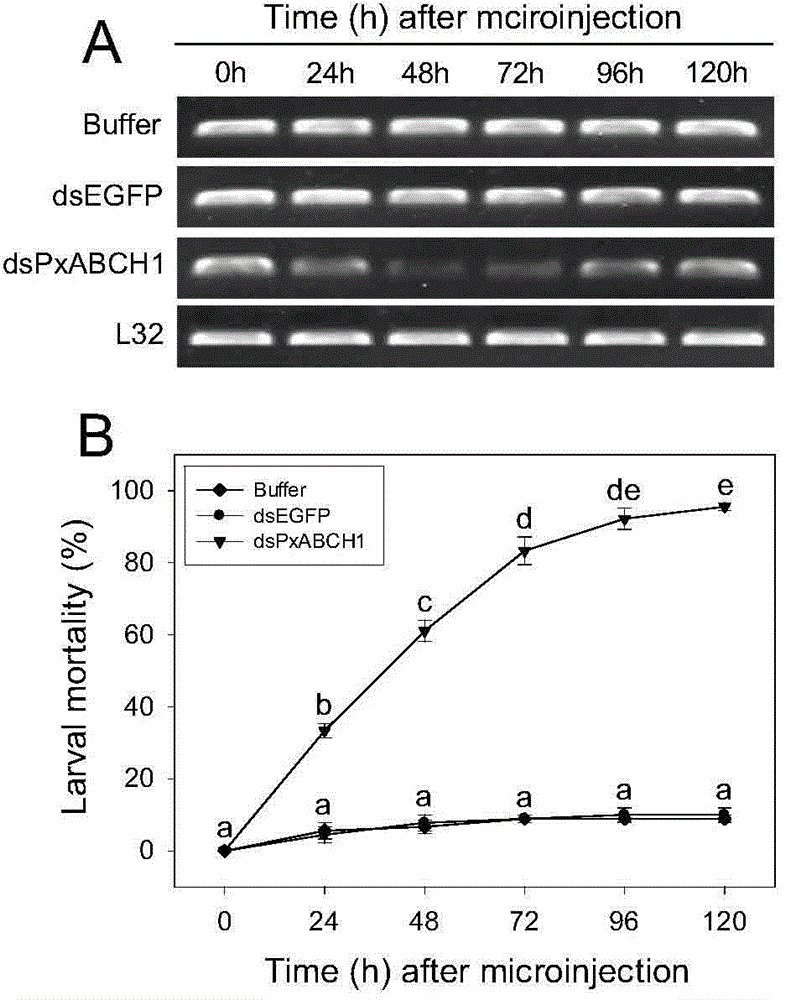
ABC transportprotein gene ABCH1 and application of specific dsRNA of ABCH1 in prevention and control of diamond back moth and Bt resistance treatment
The invention relates to an ABC transportprotein gene ABCH1 and an application of the specific dsRNA of ABCH1 in the prevention and control of diamond back moth and Bt resistance treatment. The invention discloses an insect ABC transportprotein gene and an application of an encoding gene ABCH1 and the double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) of the insect ABC transportprotein gene, and the insect ABC transportprotein gene can specifically silence ABCH1 gene so that Bt Cry1Ac insecticidal protein-sensitive and resistant diamond back moth dies. The gene full-length nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 and is used for encoding the protein as shown in the SEQ ID NO. 2. The invention also discloses ABCH1 gene specific fragments which are used for synthesis of dsRNA; after dsRNA is injected into the Bt Cry1Ac insecticidal protein-sensitive and resistant early 3-year-old diamond back moth larvae body cavity, the diamond back moth slowly develops during the growing process, which results in the death of the diamond back moth in larva and pupa stages. The invention provides a novel target for the prevention and control of field pests and Bt resistance treatment based on RNA interference and thus has good application prospects.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Compositions and methods for silencing ebola virus gene expression
InactiveUS20110201667A1Improve effectivenessHigh activitySsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsEbola virusSilent gene
The present invention provides compositions comprising therapeutic nucleic acids (e.g., interfering RNA such as siRNA) that target Ebola virus (EBOV) gene expression and methods of using such compositions to silence EBOV gene expression. More particularly, the invention provides unmodified and chemically modified interfering RNA which silence EBOV gene expression and methods of use thereof, e.g., for preventing or treating EBOV infections caused by one or more EBOV species such as Zaire EBOV. The invention also provides serum-stable nucleic acid-lipid particles comprising one or more interfering RNA molecules, a cationic lipid, and a non-cationic lipid, which can further comprise a conjugated lipid that inhibits aggregation of particles. Methods of silencing EBOV gene expression by administering one or more interfering RNA molecules to a mammalian subject are also provided.
Owner:GEISBERT THOMAS W +6
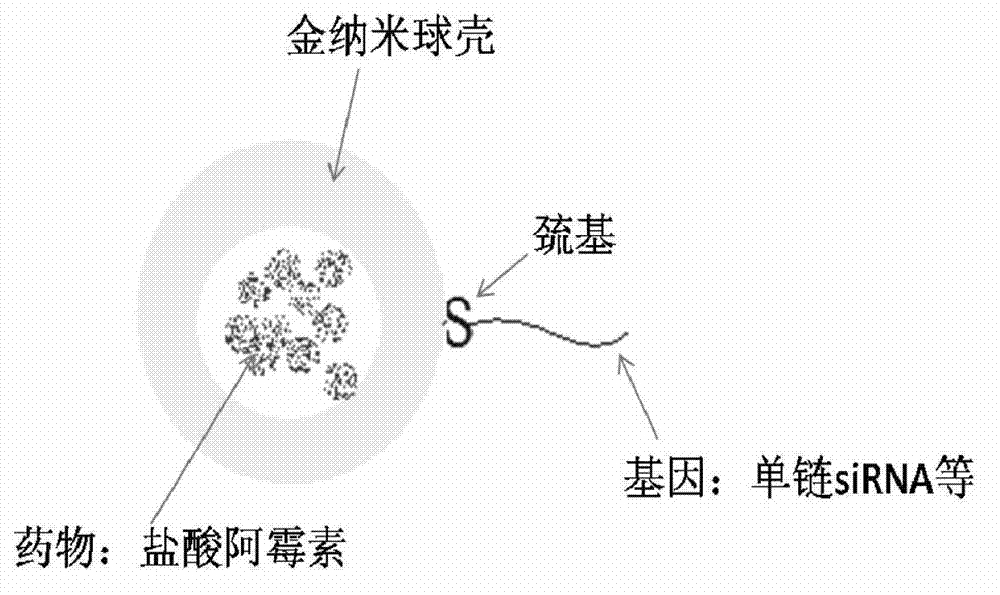
Gene drug co-carrier system using cation liposome to establish gold nano-spherical shell and preparation method
InactiveCN102805873AOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCarrier systemPhospholipid
The invention relates to a gene drug co-carrier system using cation liposome to establish a gold nano-spherical shell and a preparation method. The method comprises: using phosphatides such as DPPC, MPPC and DPPE-PEG and the derivatives thereof to form the cation liposome via membrane extrusion; carrying the hydrophilic drug hydrochloric acid adriacin into the liposome in the forming process; forming the drug-carried cation liposome; adding chlorauric acid solution into cation liposome solution; adsorbing on the surface of the cation liposome; adding ascorbic acid solution for reduction; forming the gold nano-spherical shell structure; reducing sulfhydryl out of the single chain of green fluorescent protein silent gene with a disulfide bond, grafting onto the surface of the gold nano-spherical shell; and forming the gene drug co-carrier system. The gold nano-spherical shell has low toxicity and unique optical properties. The gene drug co-carrier system using cation liposome to establish the gold nano-spherical shell can provide carrier for the co-treatment of drugs and genes, can select light to illuminate the gold nano-spherical shell, and utilize light-heat conversion property to realize the co-release of the drugs and genes.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for silencing IFNARI gene in DF-1 cell line
ActiveCN104694576AReduce manufacturing costSolve the insufficient amount of antigenFermentationPlant genotype modificationGene expressionTiter
The invention discloses a method for silencing an IFNARI gene in a DF-1 cell line. The method includes the steps that according to the IFNARI gene, multiple pieces of siRNA of an RNA interference target spot sequence are designed, and the siRNA knocking down IFNARI gene expression at the mRNA level is screened out; a lentiviral vector containing an IFNARI RNAi gene is built; by means of the lentiviral vector, the IFNARI RNAi gene is mediated into the DF-1 cell line to silence IFNARI gene expression, and the proliferation titer of an avian influenza virus in the DF-1 cell line is improved. The method can increase the antigen amount of the avian influenza virus in the DF-1 cell line by 5-10 times, the production cost of a vaccine is greatly reduced, the problems that the vaccine is insufficient in antigen amount and high in production cost can be solved, and the research and development process of an avian influenza bioreactor cell culture technology is promoted.
Owner:POULTRY INST SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
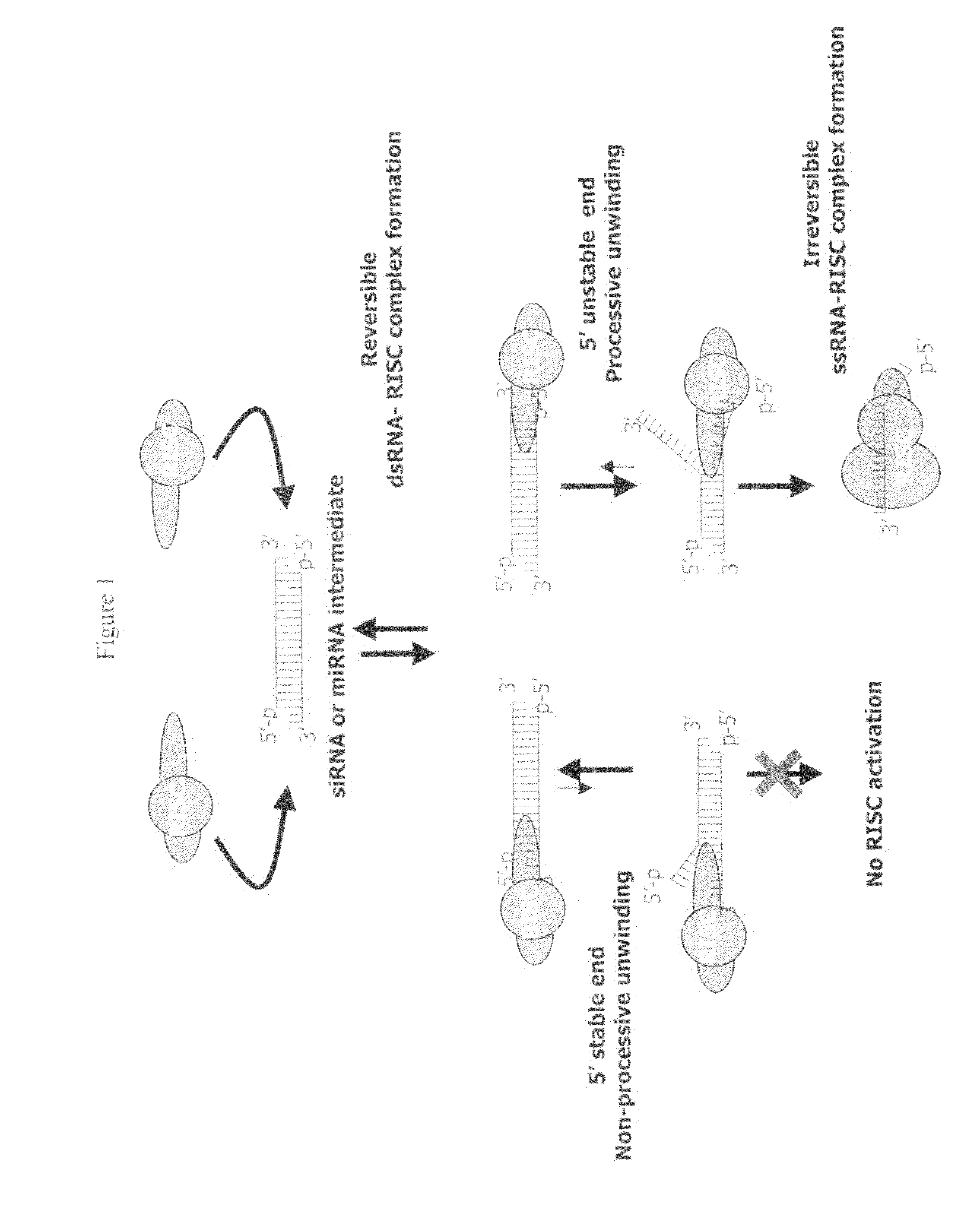
Double stranded RNA structures and constructs, and methods for generating and using the same
InactiveUS20090258930A1Improve efficiencyPrevent gene silencingOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseaseNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to novel double stranded RNA (dsRNA) structures and dsRNA expression constructs, methods for generating them, and methods of utilizing them for silencing genes. Desirably, these methods specifically inhibit the expression of one or more target genes in a cell or animal (e.g., a mammal such as a human) without inducing toxicity. These methods can be used to prevent or treat a disease or infection by silencing a gene associated with the disease or infection. The invention also provides methods for identifying nucleic acid sequences that modulate a detectable phenotype, such as the function of a cell, the expression of a gene, or the biological activity of a target polypeptide.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
Application of protein arginine methyl transferase 5 in cell detection and treatment of leukemia
InactiveCN1908187AHigh sensitivityThe detection method is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsArginineTumor therapy
Owner:BEIJING CHILDRENS HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV +1
siRNA targeting tumor protein 53 (P53)
ActiveUS20100048425A1Improve efficiencyGood curative effectSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesSilent geneGene silencing
Efficient sequence specific gene silencing is possible through the use of siRNA technology. By selecting particular siRNAs by rational design, one can maximize the generation of an effective gene silencing reagent, as well as methods for silencing genes. Methods, compositions, and kits generated through rational design of siRNAs are disclosed.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
Silencing of polo-like kinase expression using interfering RNA
The present invention provides compositions comprising interfering RNA (e.g., siRNA, aiRNA, miRNA) that target polo-like kinase 1 (PLK-1) expression and methods of using such compositions to silence PLK-1 expression. More particularly, the present invention provides unmodified and chemically modified interfering RNA molecules which silence PLK-1 expression and methods of use thereof. The present invention also provides serum-stable nucleic acid-lipid particles (e.g., SNALP) comprising an interfering RNA molecule described herein, a cationic lipid, and a non-cationic lipid, which can further comprise a conjugated lipid that inhibits aggregation of particles. The present invention further provides methods of silencing PLK-1 gene expression by administering an interfering RNA molecule described herein to a mammalian subject. The present invention additionally provides methods of identifying and / or modifying PLK-1 interfering RNA having immunostimulatory properties. Methods for sensitizing a cell such as a cancer cell to the effects of a chemotherapy drug comprising sequentially delivering PLK-1 interfering RNA followed by the chemotherapy drug are also provided.
Owner:ARBUTUS BIOPHARMA CORPORAT ION
siRNA targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 1
InactiveUS20070128641A1Improve efficiencyGood curative effectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHypoxia-inducible factorsSilencing gene
Efficient sequence specific gene silencing is possible through the use of siRNA technology. By selecting particular siRNAs by rational design, one can maximize the generation of an effective gene silencing reagent, as well as methods for silencing genes. Methods, compositions, and kits generated through rational design of siRNAs are disclosed.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
Modifying the specificity of plant non-coding RNA molecules for silencing gene expression
ActiveUS20200248196A1Improve stress resistanceIncrease productionHydrolasesClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyPlant cell
A method of modifying a gene encoding or processed into a non-coding RNA molecule having no RNA silencing activity in a plant cell is disclosed. The method comprising introducing into the plant cell a DNA editing agent conferring a silencing specificity of the non-coding RNA molecule towards a target RNA of interest. A method of modifying a gene encoding or processed into a RNA silencing molecule in a plant cell is also disclosed. The method comprising introducing into the plant cell a DNA editing agent which redirects the silencing specificity of the non-coding RNA molecule towards a target RNA of interest. Plant cells, plant seeds, plants, and methods of generating plants are also disclosed.
Owner:TROPIC BIOSCI UK LTD
Screening system for modulators of her2 mediated transcription and her2 modulators identified thereby
InactiveUS20050123896A1Easy to addImprove stabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAbnormal tissue growthMammal
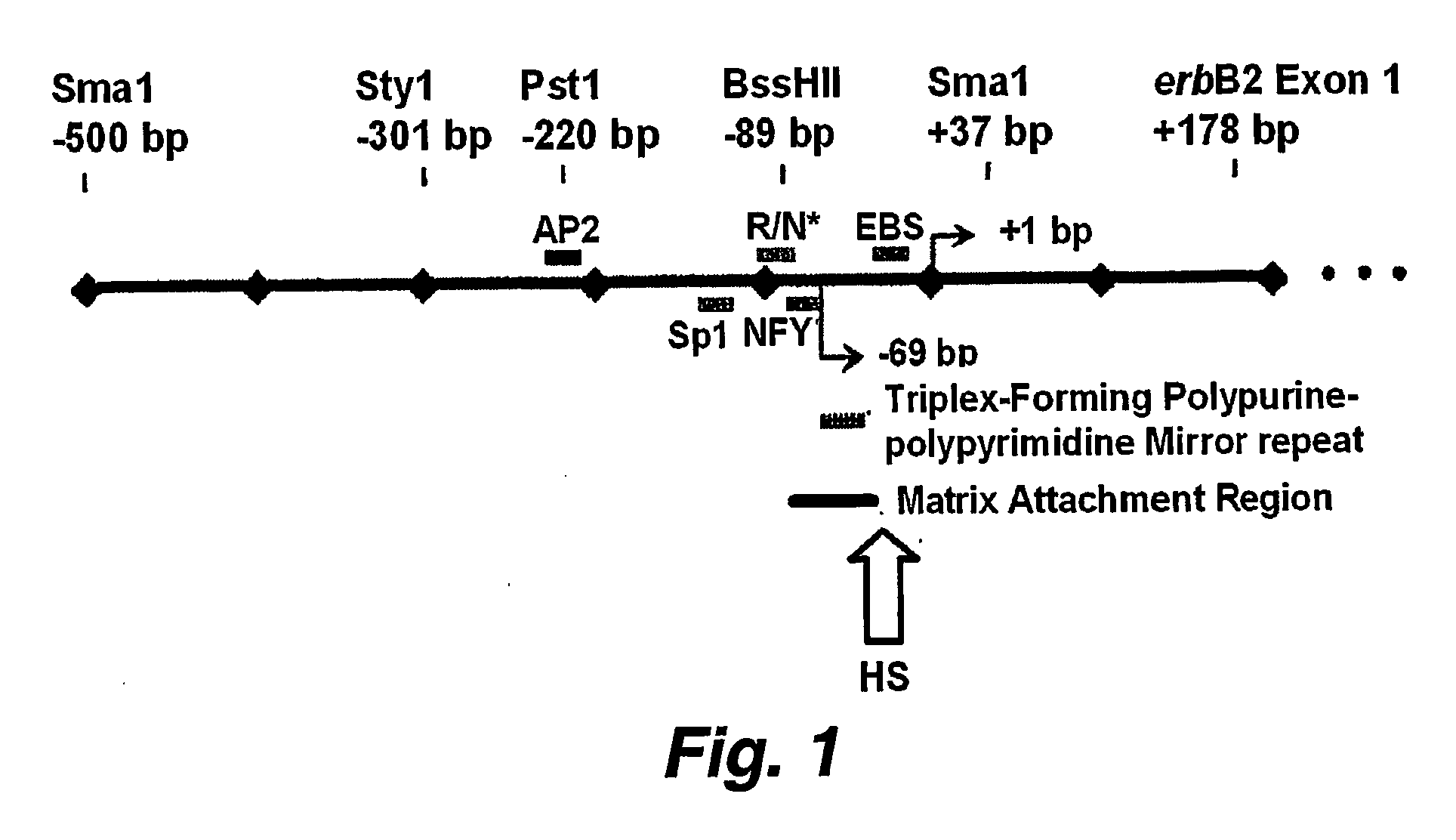
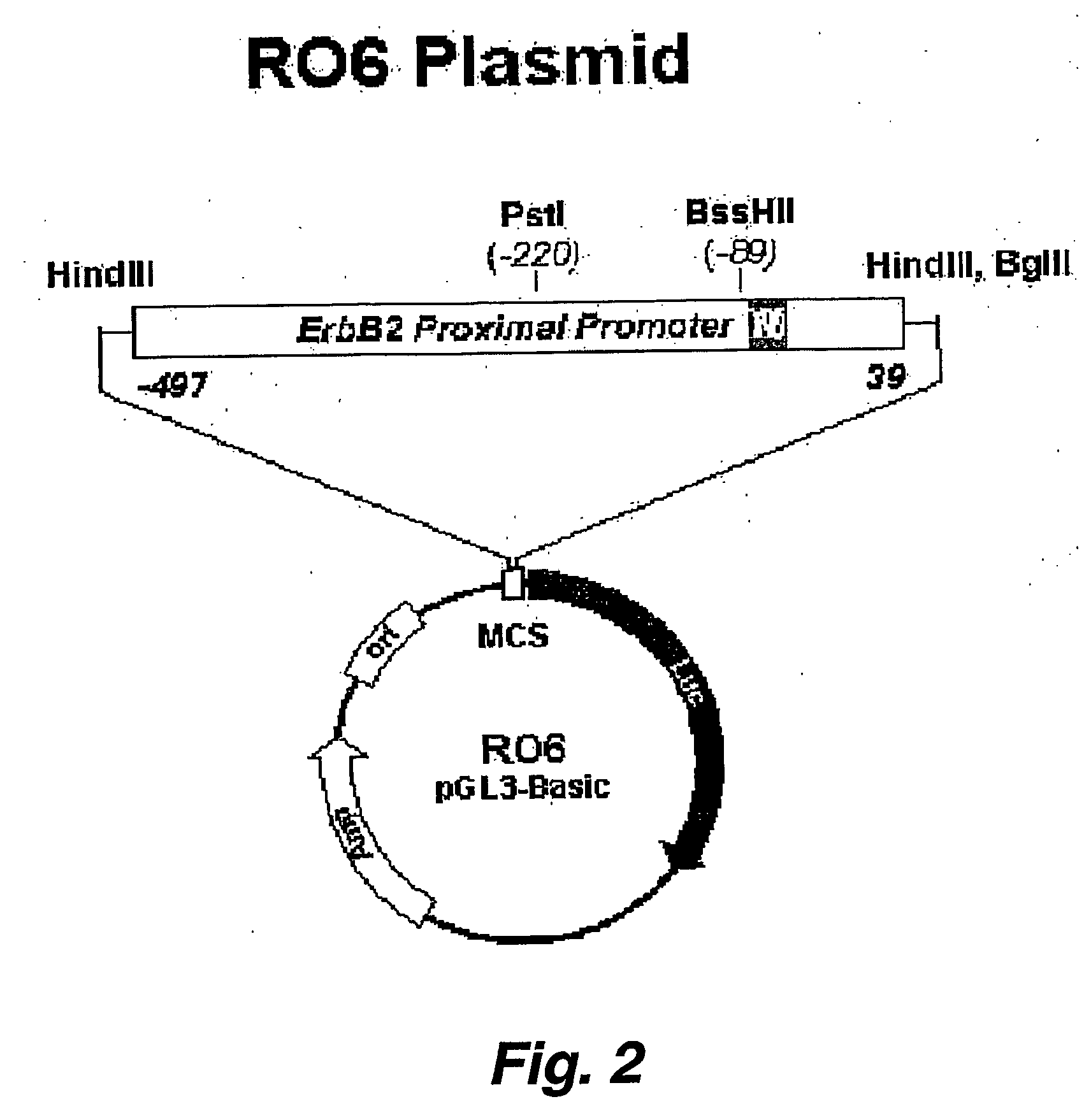
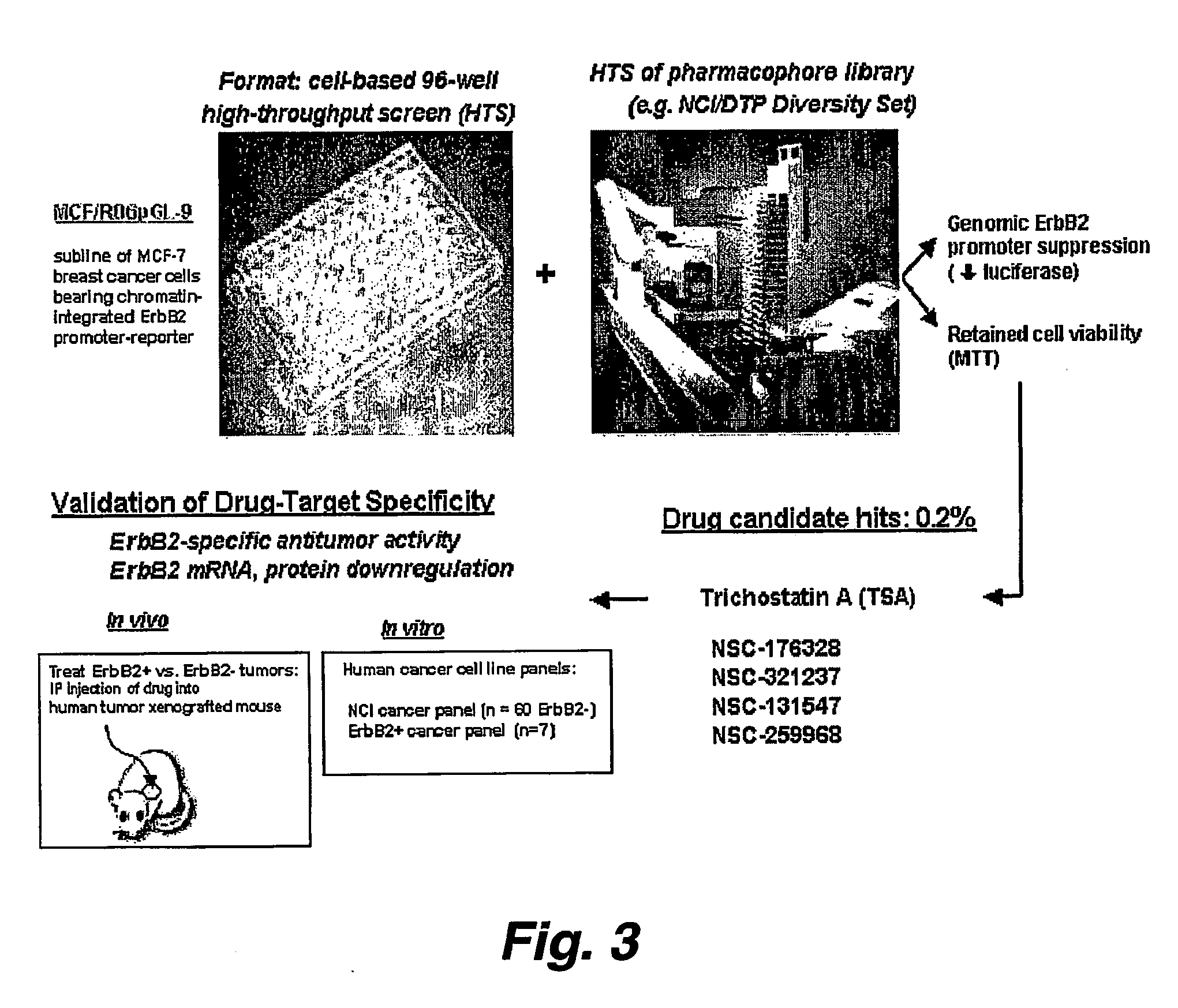
This invention pertains to the development of a screening system to identify (screen for) HER2 promoter silencing agents. Such agents are expected to be of therapeutic value in the treatment of cancers characterized by HER2 amplification / upregulation. In addition, this invention pertains to the discovery that histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors like sodium butyrate and trichostatin A (TSA), in a time and dose dependent fashion can silence gnomical.ly integrated and / or amplified / overexpressing promoters, such as that driving the HER2 / ErbB2 / neu oncogene, resulting in inhibition of gene products including transcripts and protein, and subsequent production of tumor / cell growth inhibition, apoptosis and / or differentiation. In another embodiment, this invention provides novel SNPs associated with the coding region of the ErbB2. proto-oncogene. The SNPs are indicators for altered risk, for developing ErbB2-positive cancer in a mammal
Owner:THE BUCK INST FOR RES ON AGING
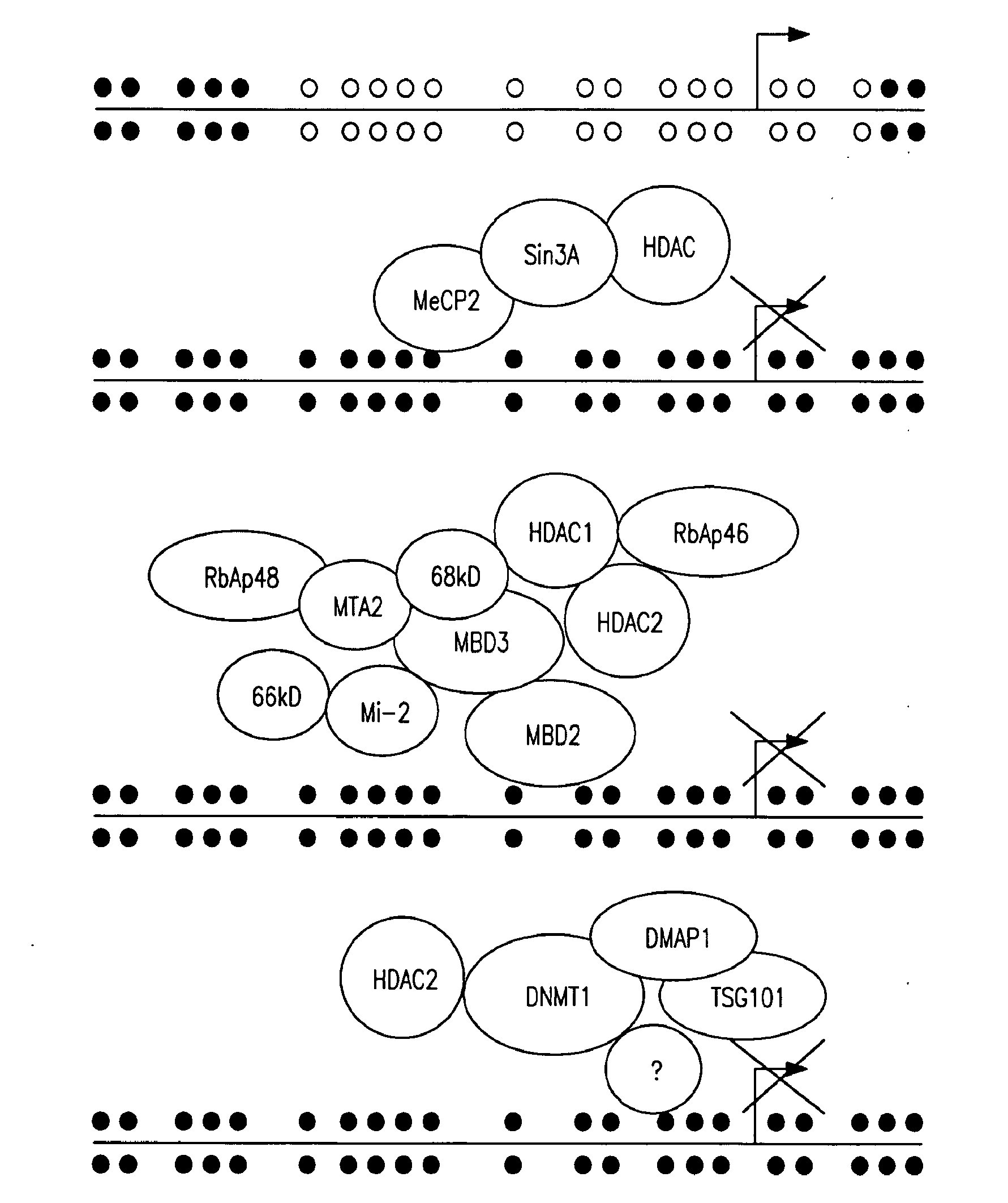
Agents for Reversing Epigenetic Silencing of Genes
ActiveUS20100093768A1Increase transcriptionPreventing and treating cancerCompound screeningBiocideSickle cell anemiaGenomic DNA
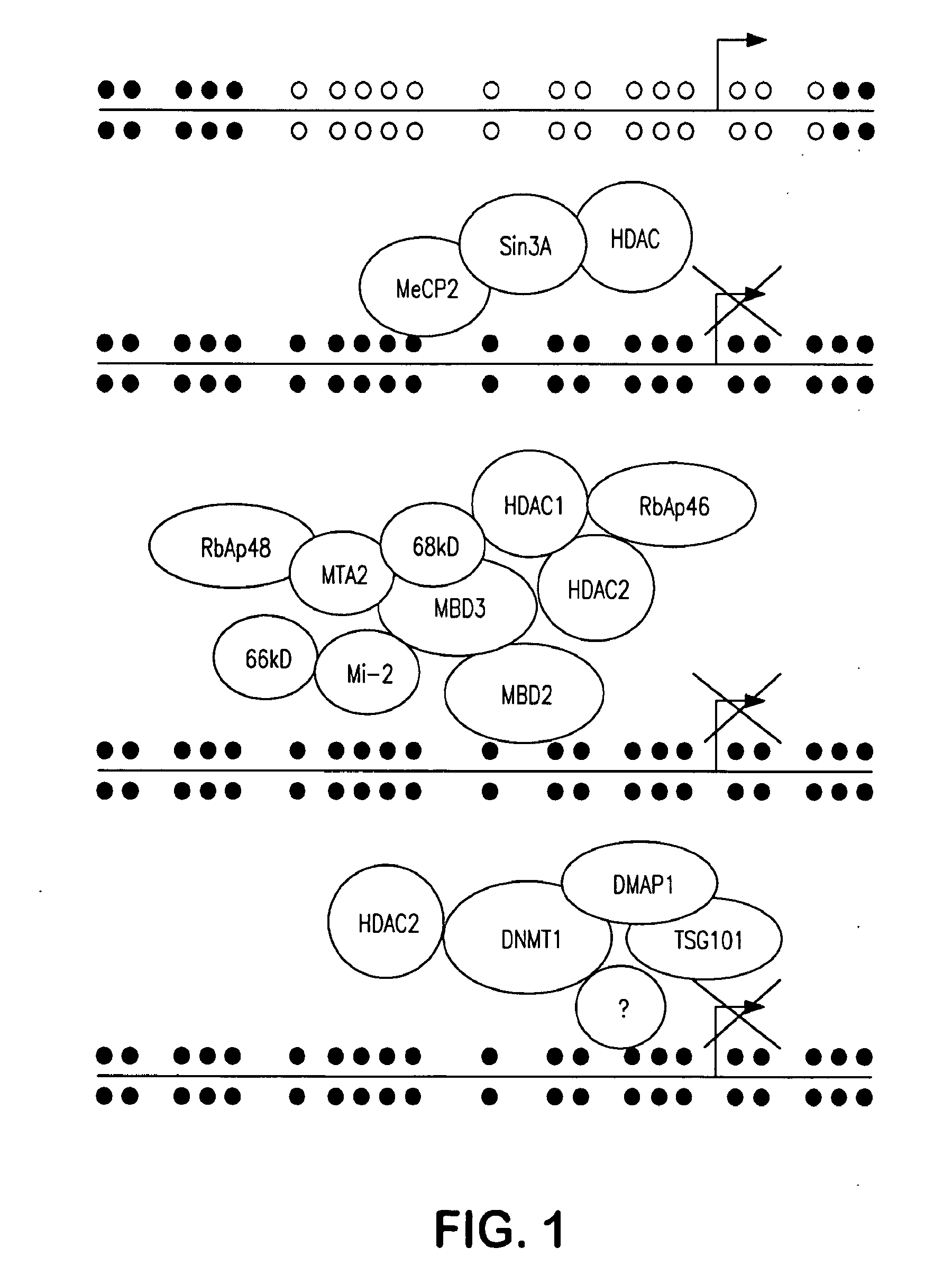
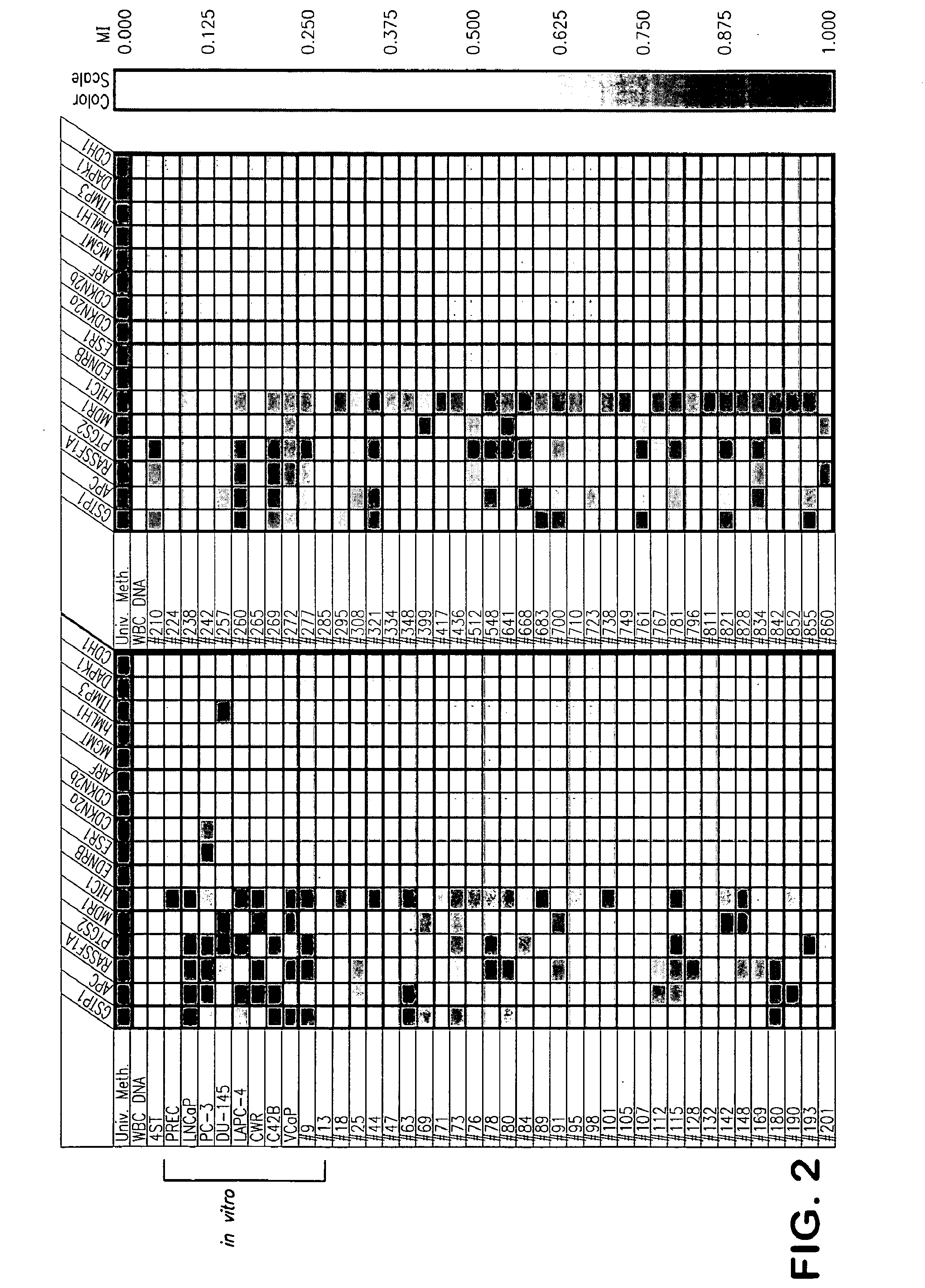
The present invention provides methods for discovering agents that are effective in reversing epigenetic silencing by inhibiting the interaction of methyl-binding (MBD) proteins with methylated genomic DNA. Also provided are methods for reactivating silenced genes having CpG island hypermethylation along with methods for treatment and prevention of diseases, such as cancer and sickle cell anemia, by administering an agent that modulates methyl-binding domain (MBD) protein-mediated transcriptional repression, thereby increasing gene transcription to prevent or treat disease. Additionally, compounds identified by the present invention useful for treatment and prevention of diseases, such as cancer and sickle cell anemia, are provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
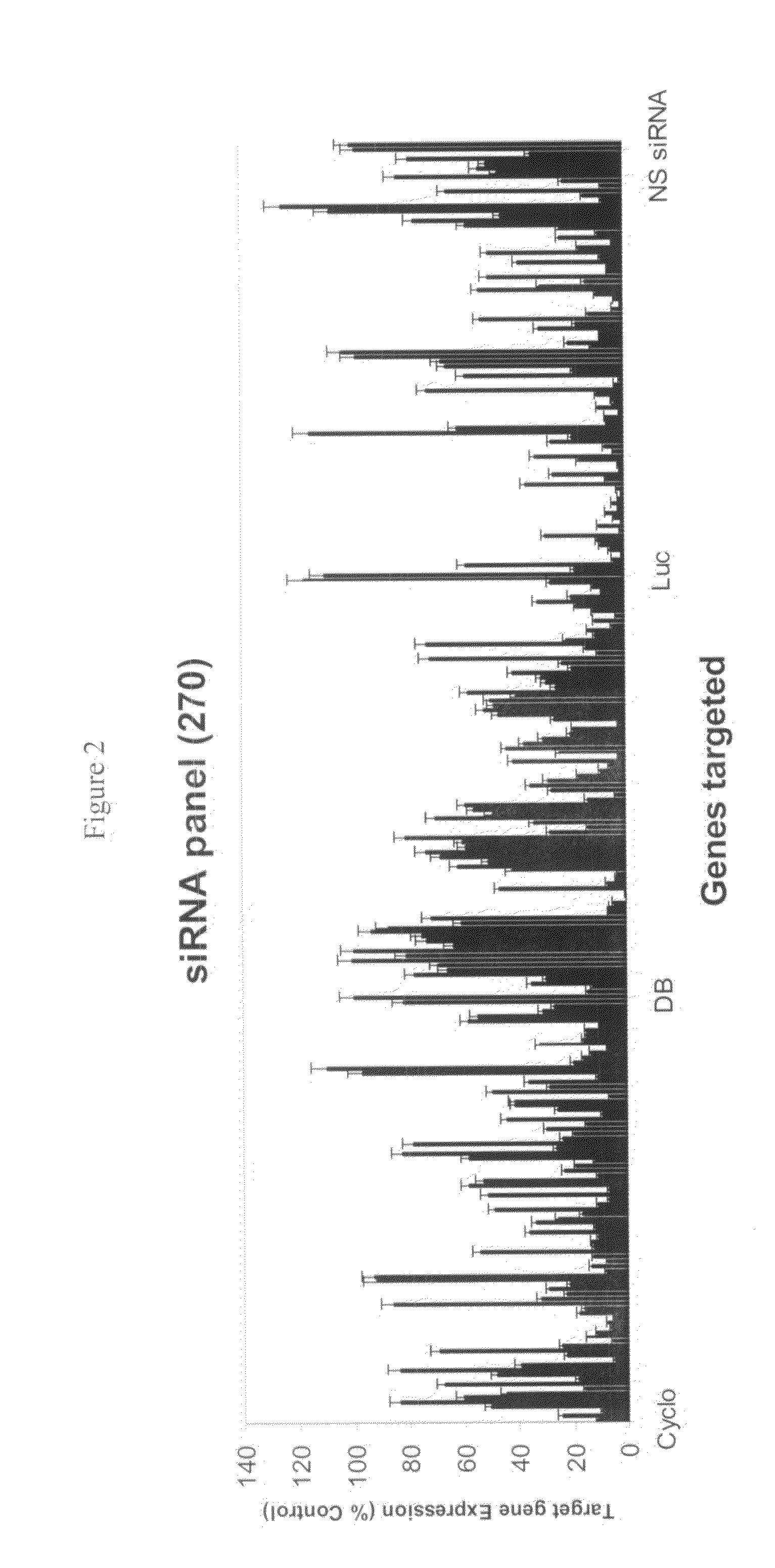
siRNA structures for high activity and reduced off target
ActiveUS10358647B2High activityReduced off target actionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseaseNucleotide
This invention provides compounds, compositions and methods for modulating the expression of target genes using RNA interference. RNAi structures and molecules of this invention can be used for modulating or silencing the expression of genes, with high levels of RNAi activity and reduced off target actions. Advantageous structures include siRNAs targeted to any gene having one or more 2′-deoxy nucleotides located in the seed region. The RNA interference molecules can be used in methods for preventing or treating diseases.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
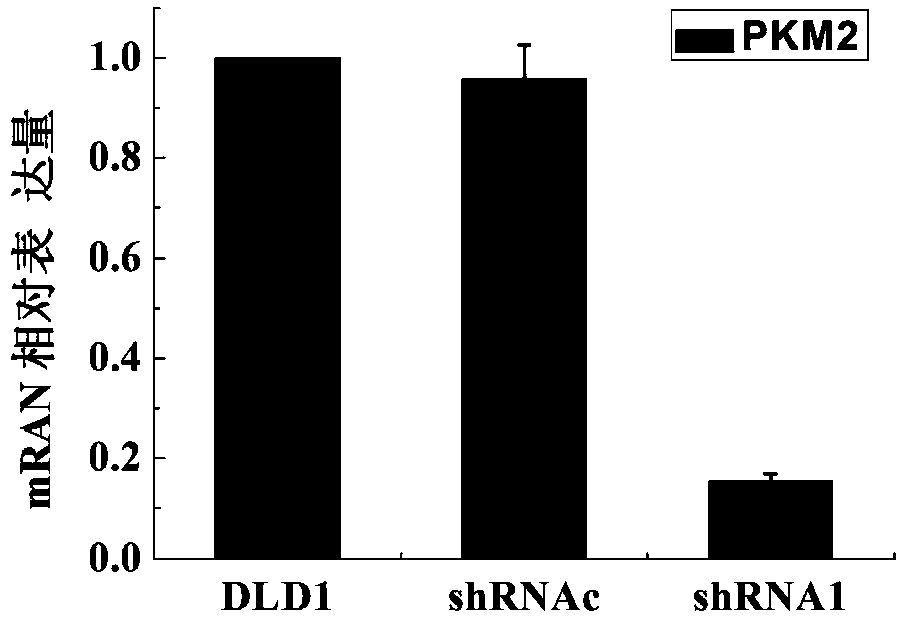
Preparation method and application of colon cancer cell strain expressed by stabilized silent PKM2 gene
InactiveCN103451222AEnhanced inhibitory effectMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor/cancer cellsLentivirusLarge Intestine Cancer
The invention provides a preparation method of a colon cancer cell strain expressed by stabilized silent PKM2 gene. The preparation method comprises the steps of constructing of shRNA lentiviral expression vector of human PKM2 gene, packaging and obtaining of lentivirus, DLD1 colon cancer lentivirus infecting, stabilized cell strain puromycin screening and Real-time PCR, Western blot identification. The experimental results show that the shRNA nucleotide sequence can be successfully inserted into the pLKO.1-puro expression vector, and the inhibitory effect on the expression of PKM2 gene is remarkable, endurable and stable. The prepared cell strain can be used as the experimental material for researching the regulating effect of PKM2 in malignant characteristics such as colon cancer cell energy metabolism, cell proliferation, cell migration and inflammation.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
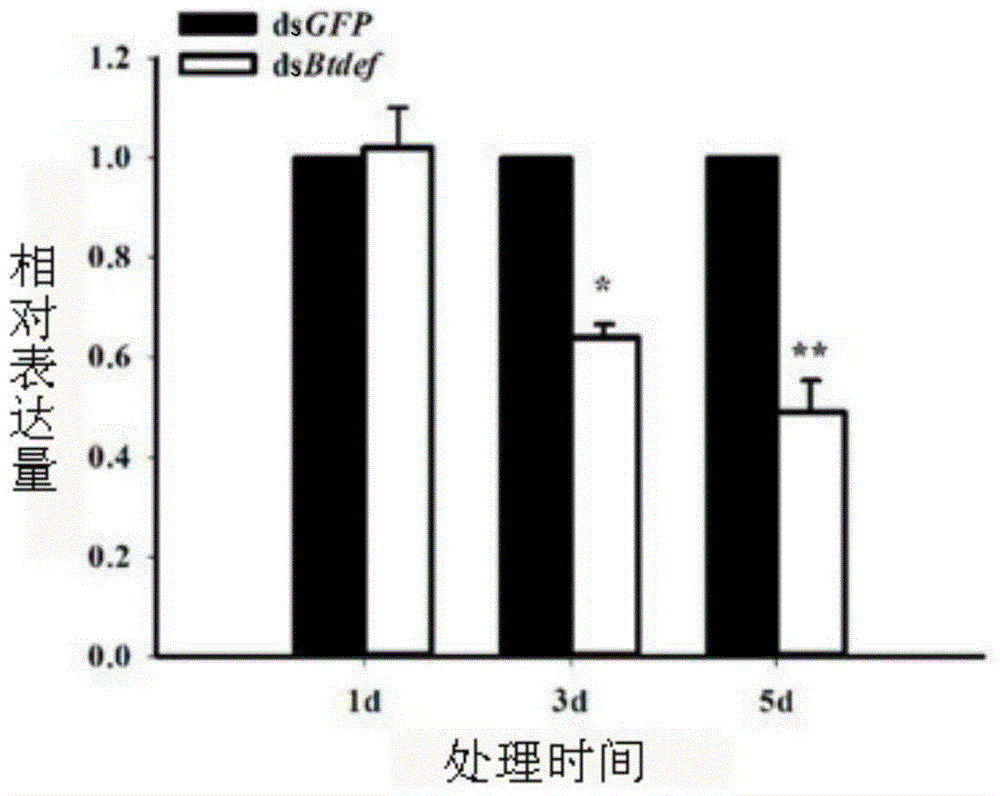
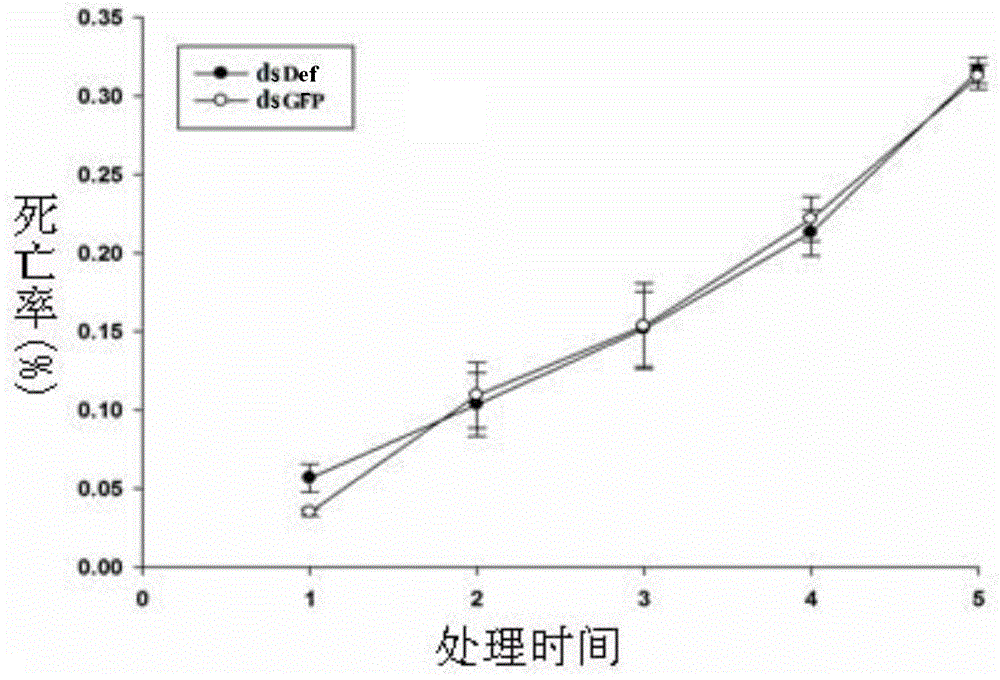
Bemisia tabaci defensin gene segment and dsRNA thereof based on gene silencing technology
InactiveCN104480115AReduce mechanical damageEasy to operateAnimal feeding stuffFermentationNucleotideGene silencing
The invention relates to molecular biology and agricultural biotechnology, and aims to provide a bemisia tabaci defensin gene segment and dsRNA thereof based on the gene silencing technology. The nucleotide sequence of the bemisia tabaci defensin encoding gene segment is as shown in the SEQ ID NO.1. An improved artificial feeding method is adopted to carry out RNAi interference experiment, and compared with an injection method, the improved artificial feeding method has the advantages that mechanical injury of insect bodies can be reduced, operation is convenient, a true sense of natural feeding is realized, and the method can be widely popularized. The dsRNA of the synthesized defensin gene can be used for effectively silencing the defensin gene, has a stable double-stranded structure, is capable of preventing degradation of RNA enzyme, and can be used for laying a foundation for establishing bemisia tabaci gene function researches by utilizing the RNA interference technology and providing a new experimental means for new strategy of insect control.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods and compositions for selecting siRNA of improved functionality
ActiveUS9879266B2Improve efficiencyGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNucleotide sequencingSilencing gene
Efficient sequence specific gene silencing is possible through the use of siRNA technology. Be selecting particular siRNAs by rational design, one can maximize the generation of an effective gene silencing reagent, as well as methods for silencing genes. Methods compositions, and kits generated through rational design of siRNAs are disclosed, including those directed to the nucleotide sequences for HAO1.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
Methods and compositions for selecting siRNA of improved functionality
ActiveUS9839649B2Improve efficiencyGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSilencing geneNucleotide sequencing
Efficient sequence specific gene silencing is possible through the use of siRNA technology. Be selecting particular siRNAs by rational design, one can maximize the generation of an effective gene silencing reagent, as well as methods for silencing genes. Methods compositions, and kits generated through rational design of siRNAs are disclosed, including those directed to the nucleotide sequences for AAT.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com