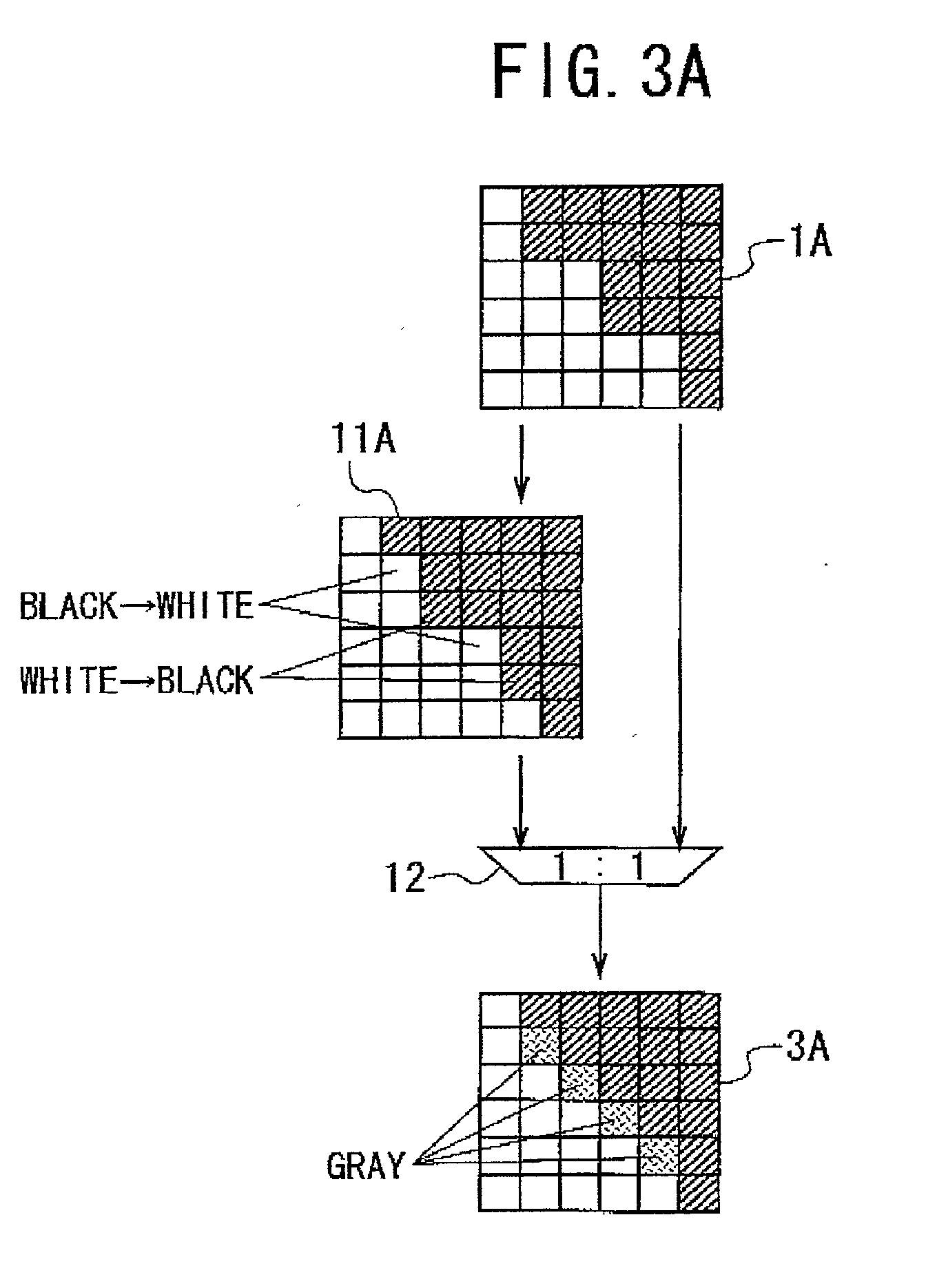
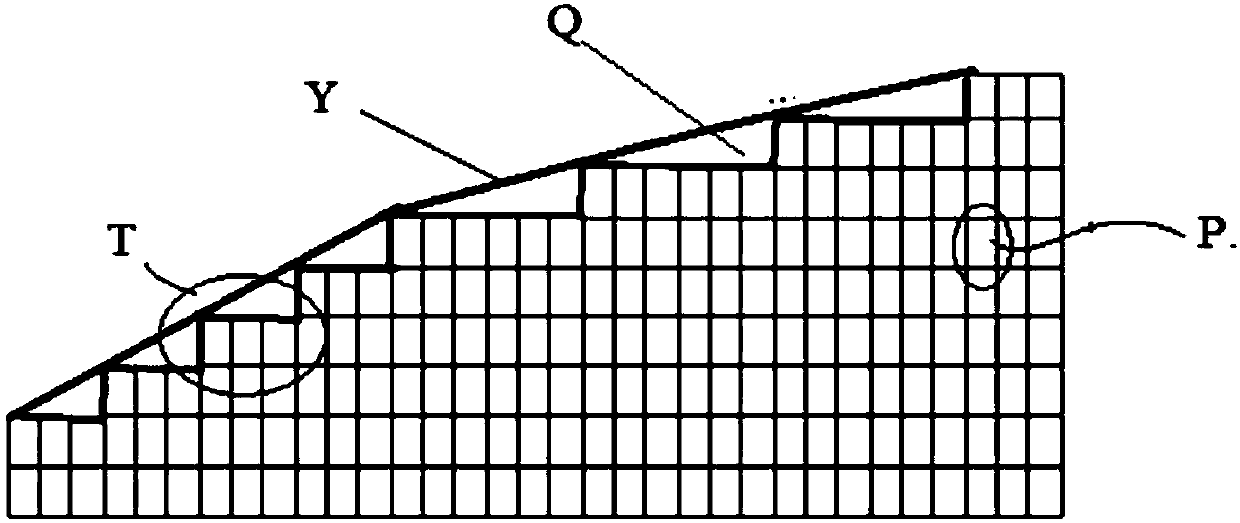
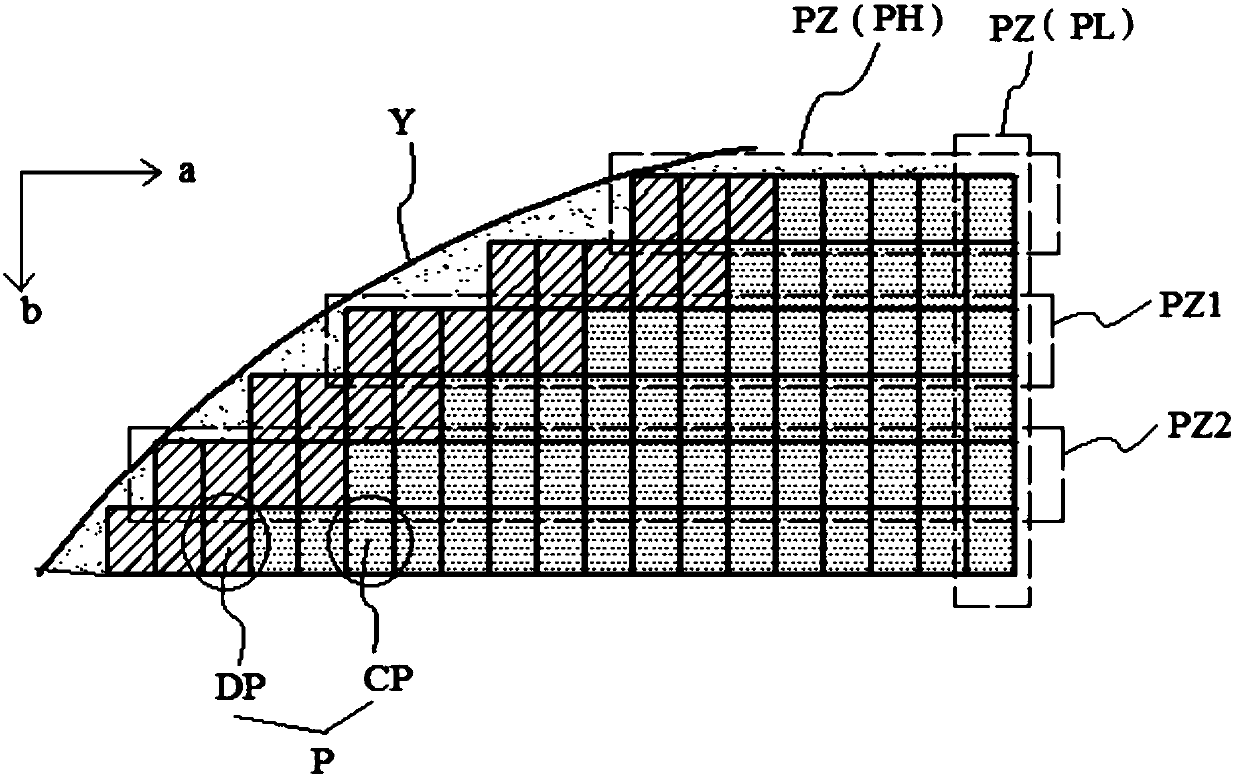
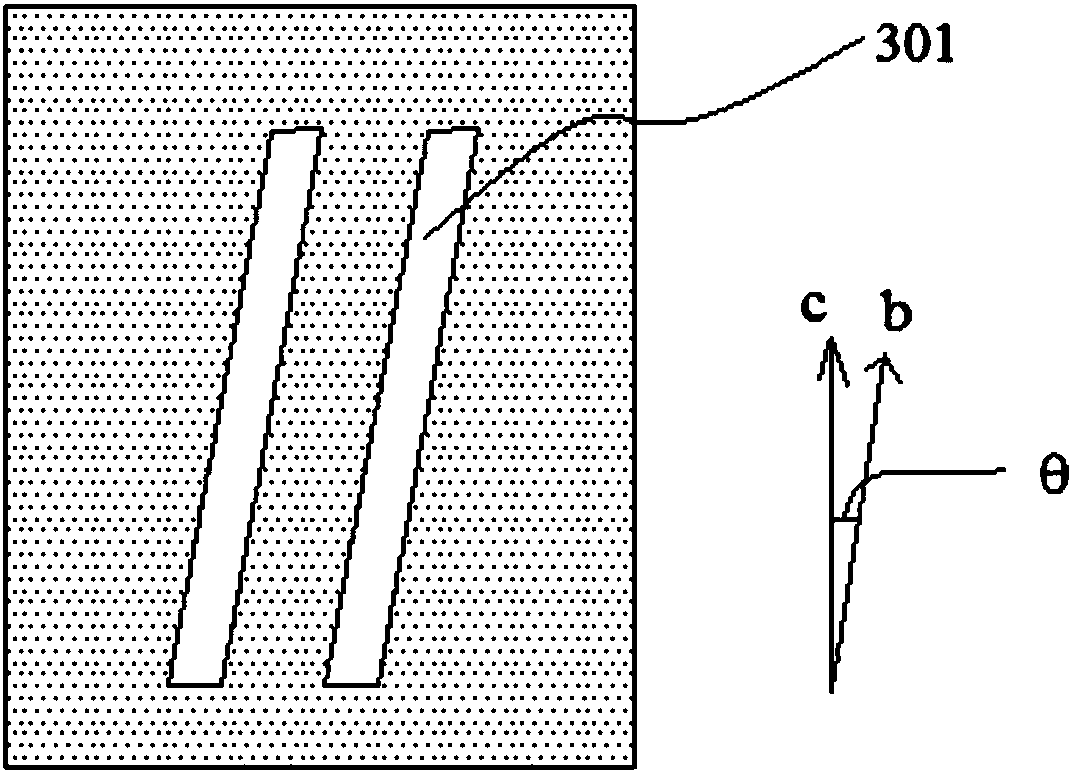
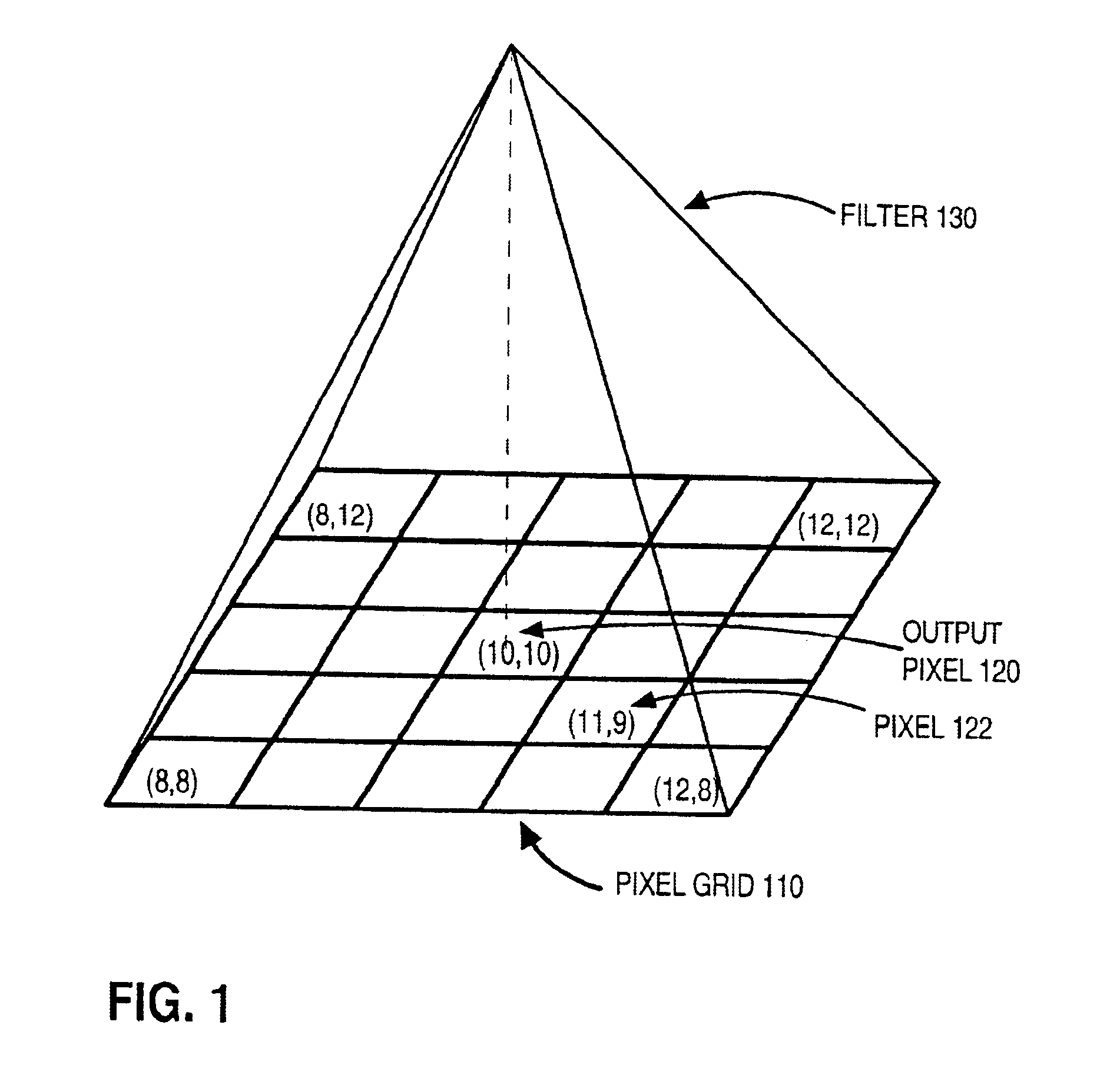
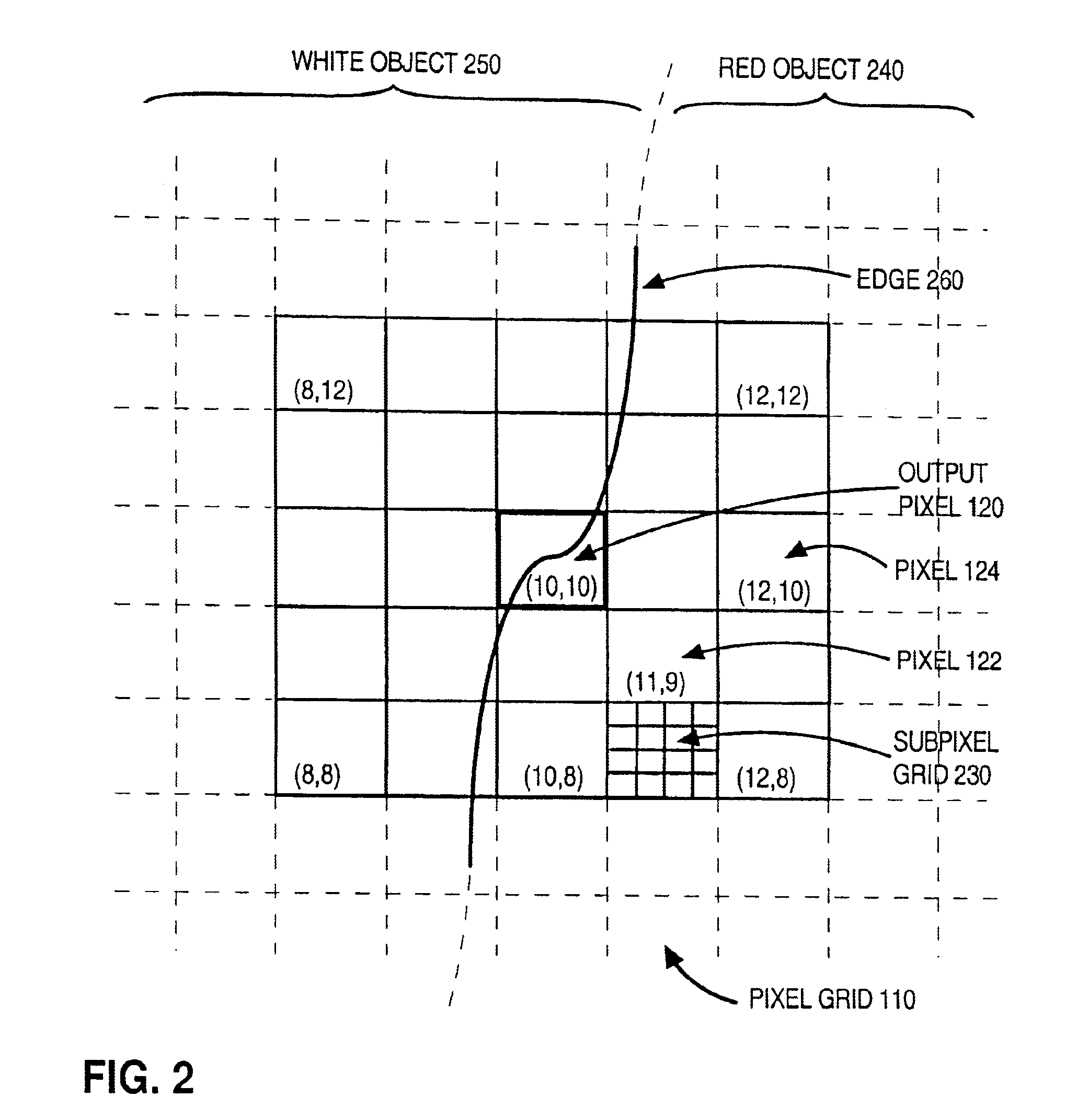
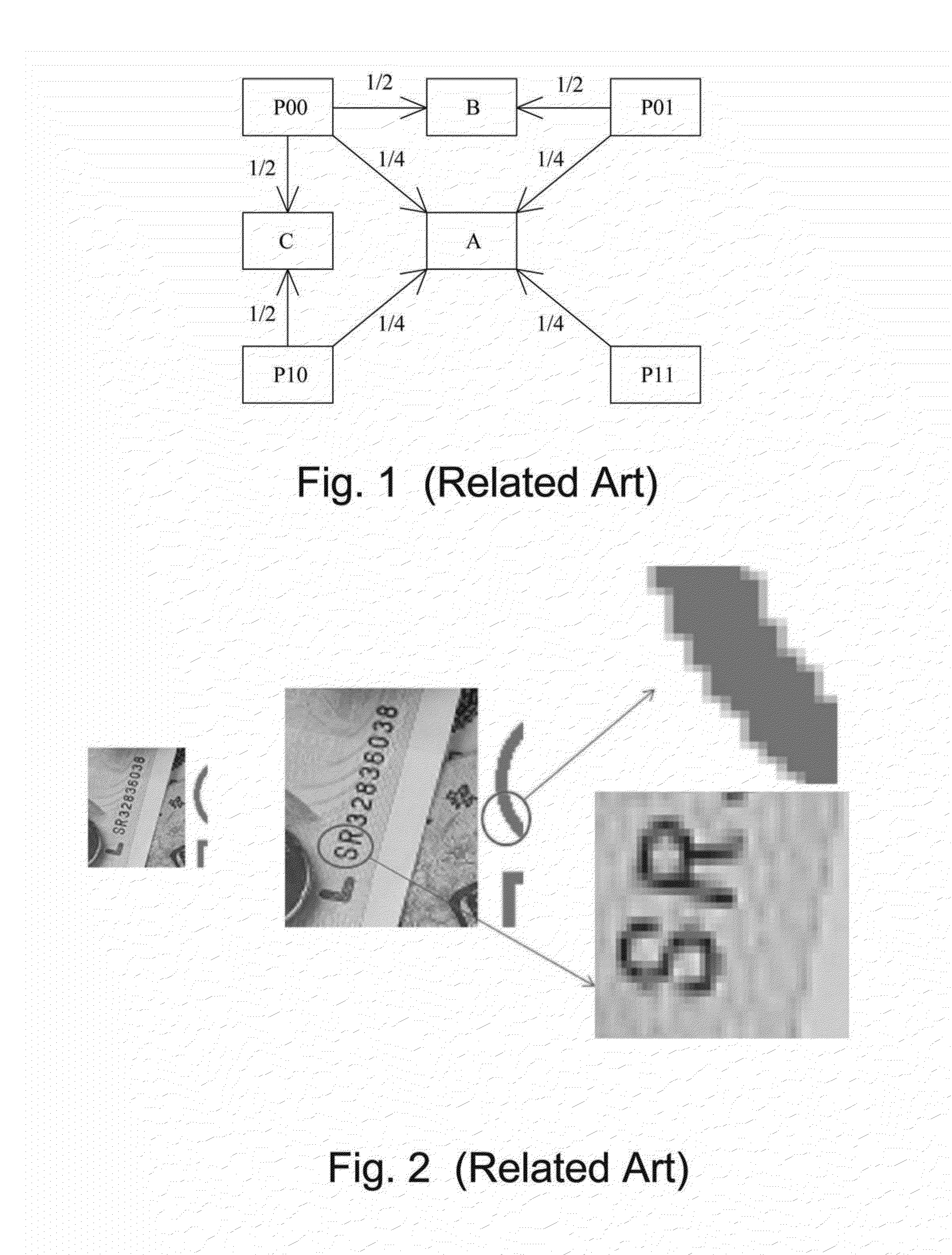
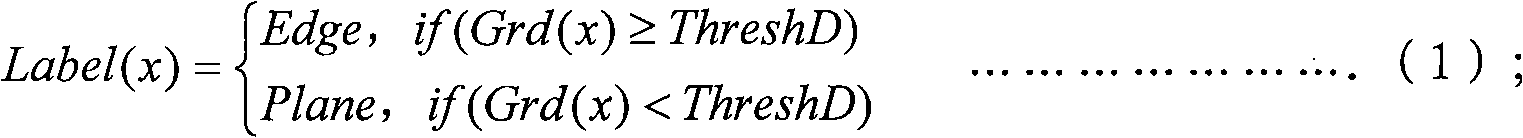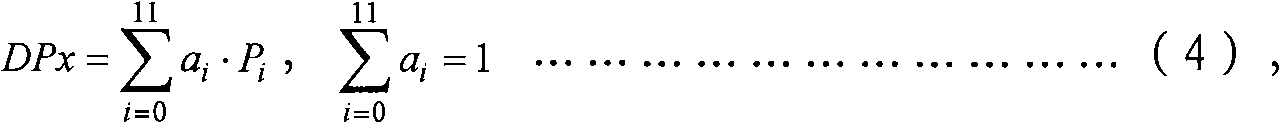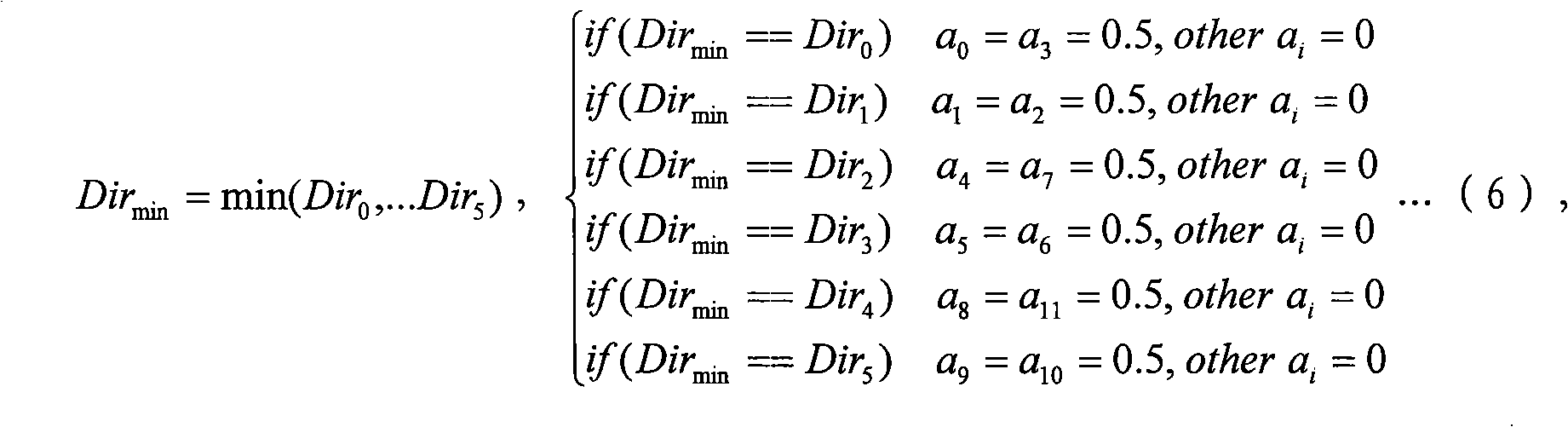Patents
Literature
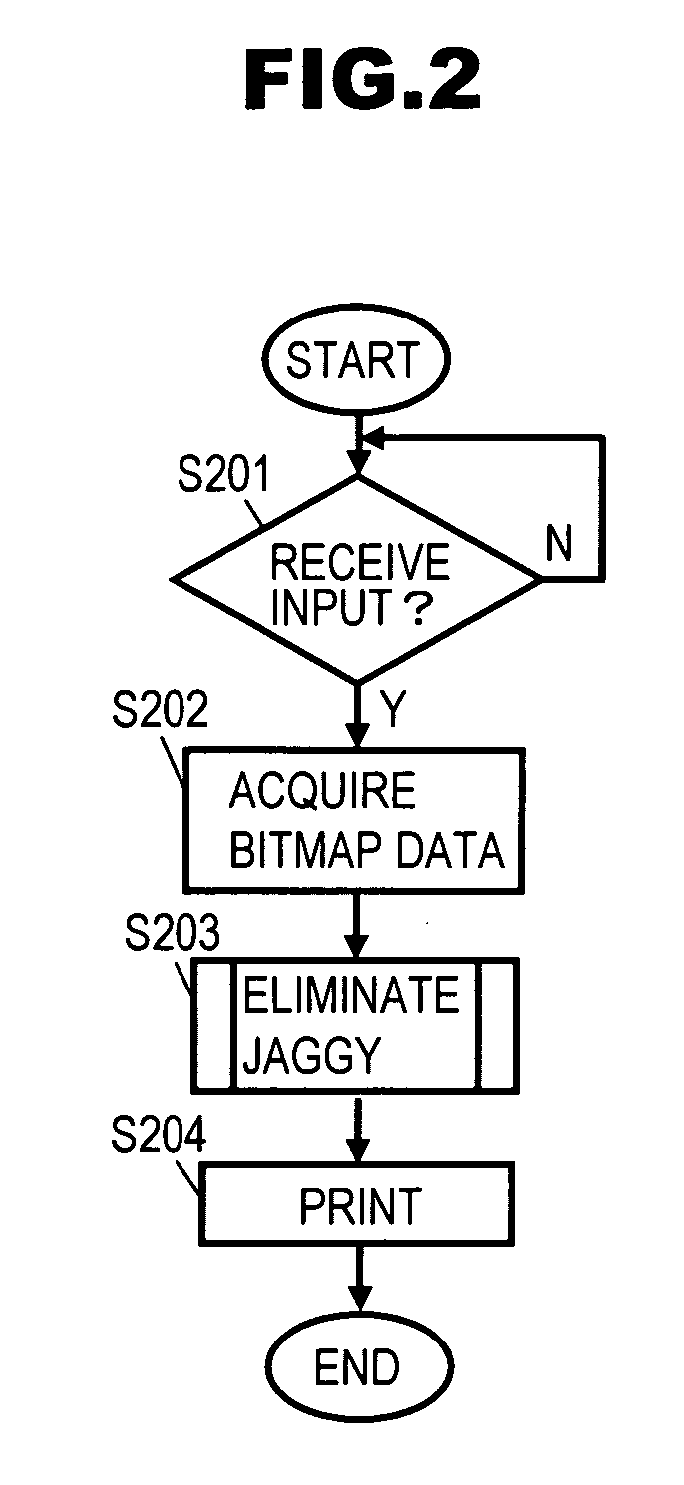
127 results about "Jaggies" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
"Jaggies" is the informal name for artifacts in raster images, most frequently from aliasing, which in turn is often caused by non-linear mixing effects producing high-frequency components, or missing or poor anti-aliasing filtering prior to sampling.
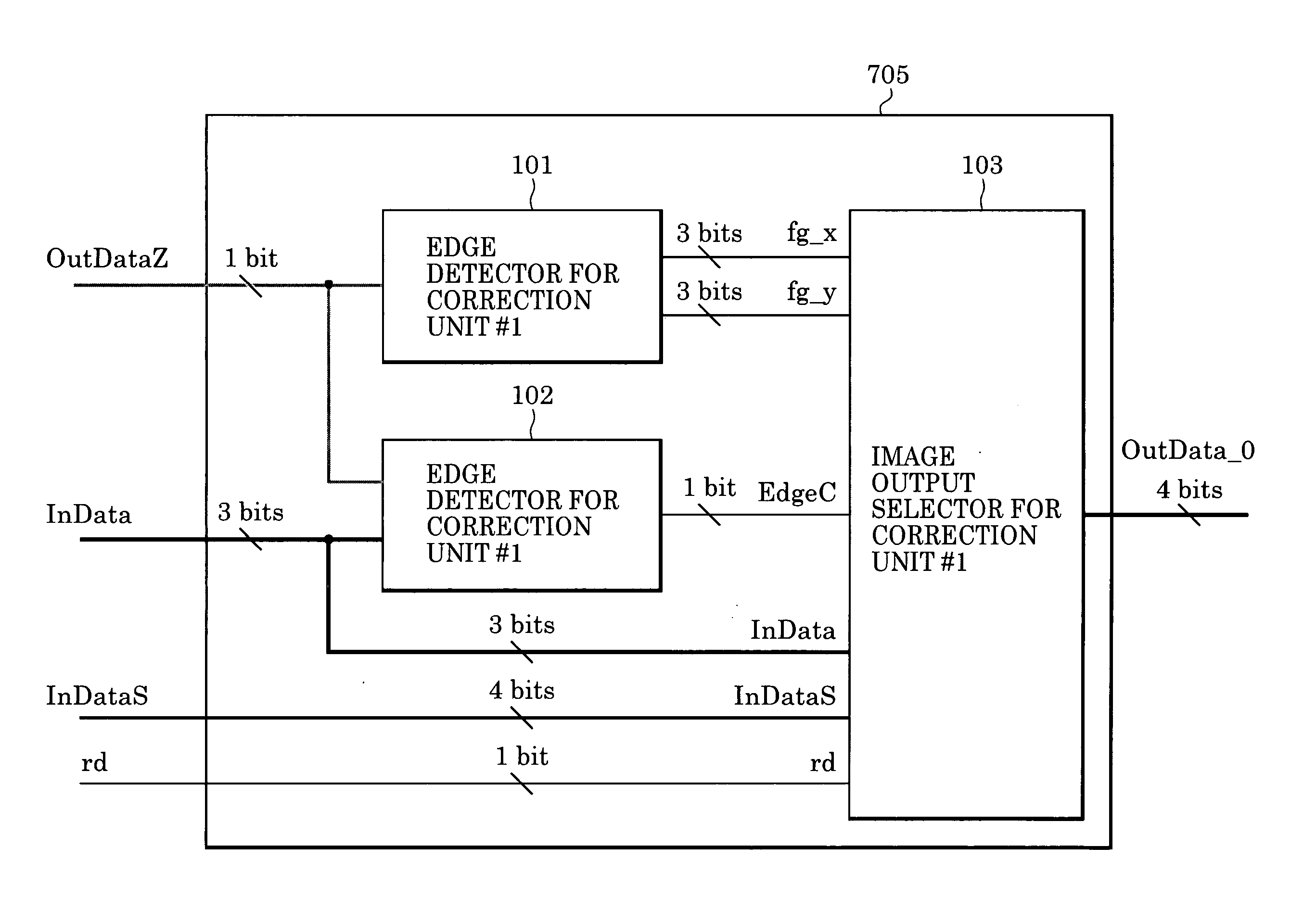
Method and apparatus for anti-aliasing in a graphics system
InactiveUS6999100B1Low costHigh cost-effectiveImage enhancementCathode-ray tube indicatorsInterlaced videoAnti-aliasing
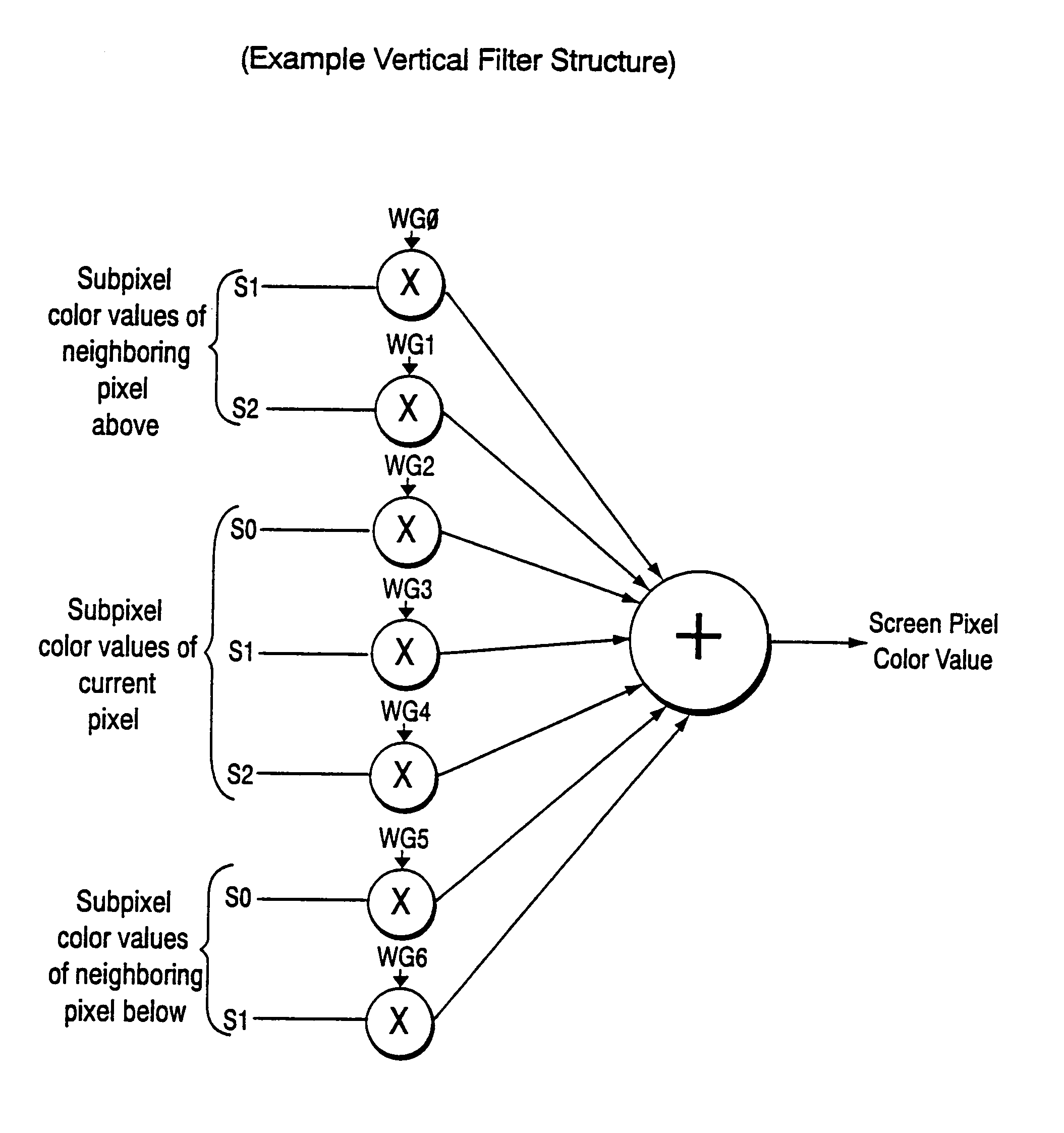
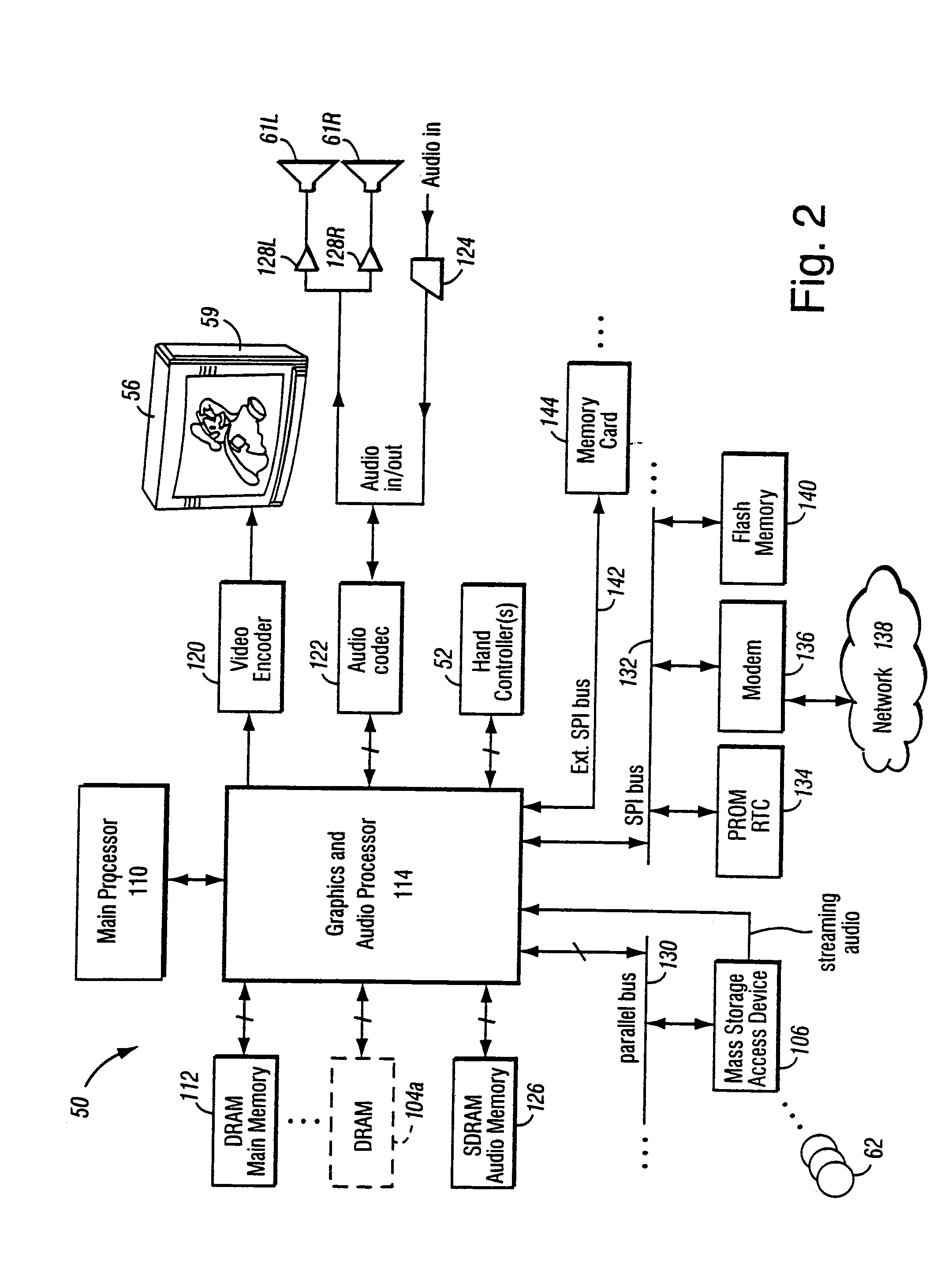
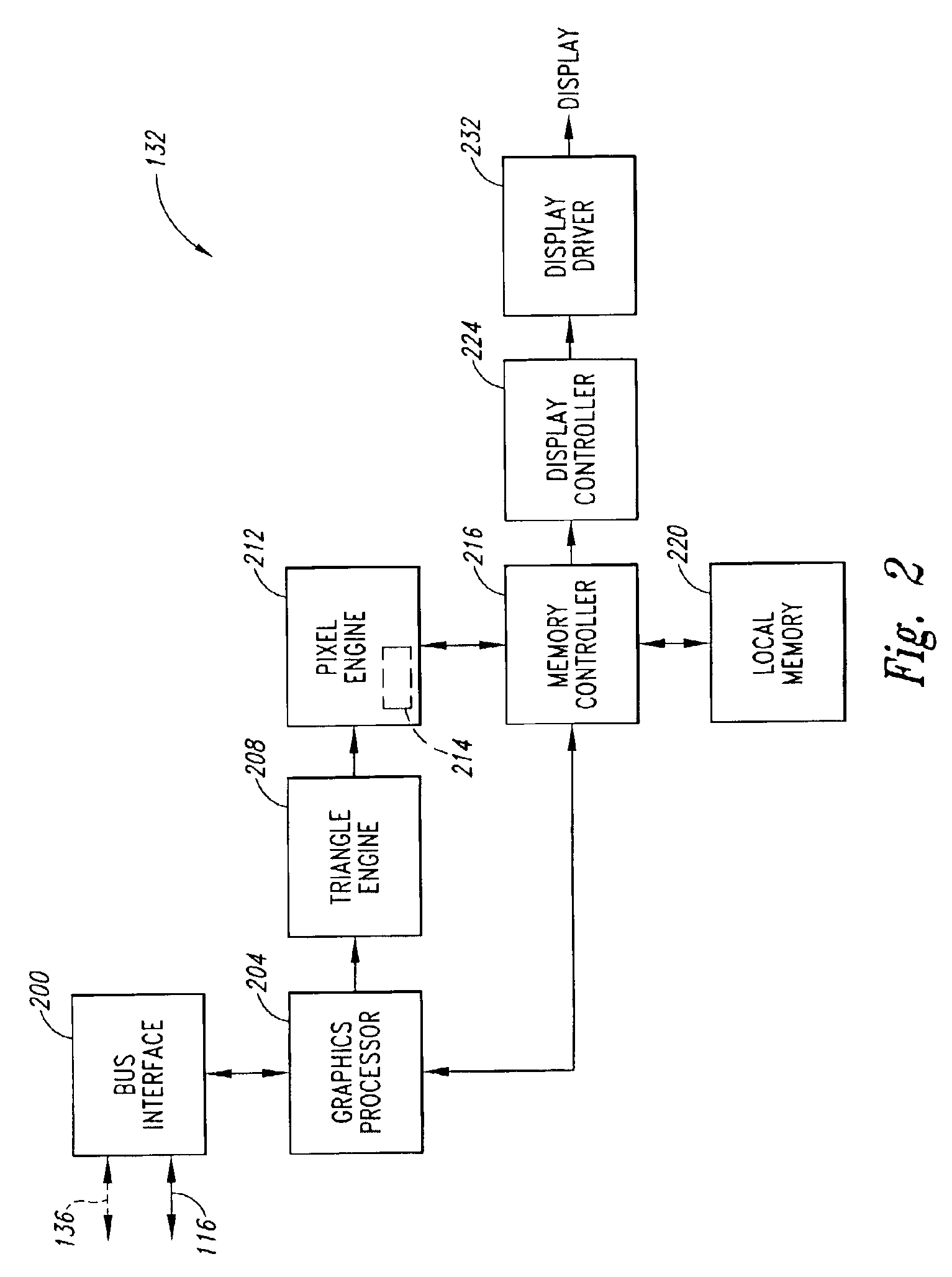
A graphics system including a custom graphics and audio processor produces exciting 2D and 3D graphics and surround sound. The system includes a graphics and audio processor including a 3D graphics pipeline and an audio digital signal processor. The system achieves highly efficient full-scene anti-aliasing by implementing a programmable-location super-sampling arrangement and using a selectable-weight vertical-pixel support area blending filter. For a 2×2 pixel group (quad), the locations of three samples within each super-sampled pixel are individually selectable. A twelve-bit multi-sample coverage mask is used to determine which of twelve samples within a pixel quad are enabled based on the portions of each pixel occupied by a primitive fragment and any pre-computed z-buffering. Each super-sampled pixel is filtered during a copy-out operation from a local memory to an external frame buffer using a pixel blending filter arrangement that combines seven samples from three vertically arranged pixels. Three samples are taken from the current pixel, two samples are taken from a pixel immediately above the current pixel and two samples are taken from a pixel immediately below the current pixel. A weighted average is then computed based on the enabled samples to determine the final color for the pixel. The weight coefficients used in the blending filter are also individually programmable. De-flickering of thin one-pixel tall horizontal lines for interlaced video displays is also accomplished by using the pixel blending filter to blend color samples from pixels in alternate scan lines.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
Antialiased imaging with improved pixel supersampling
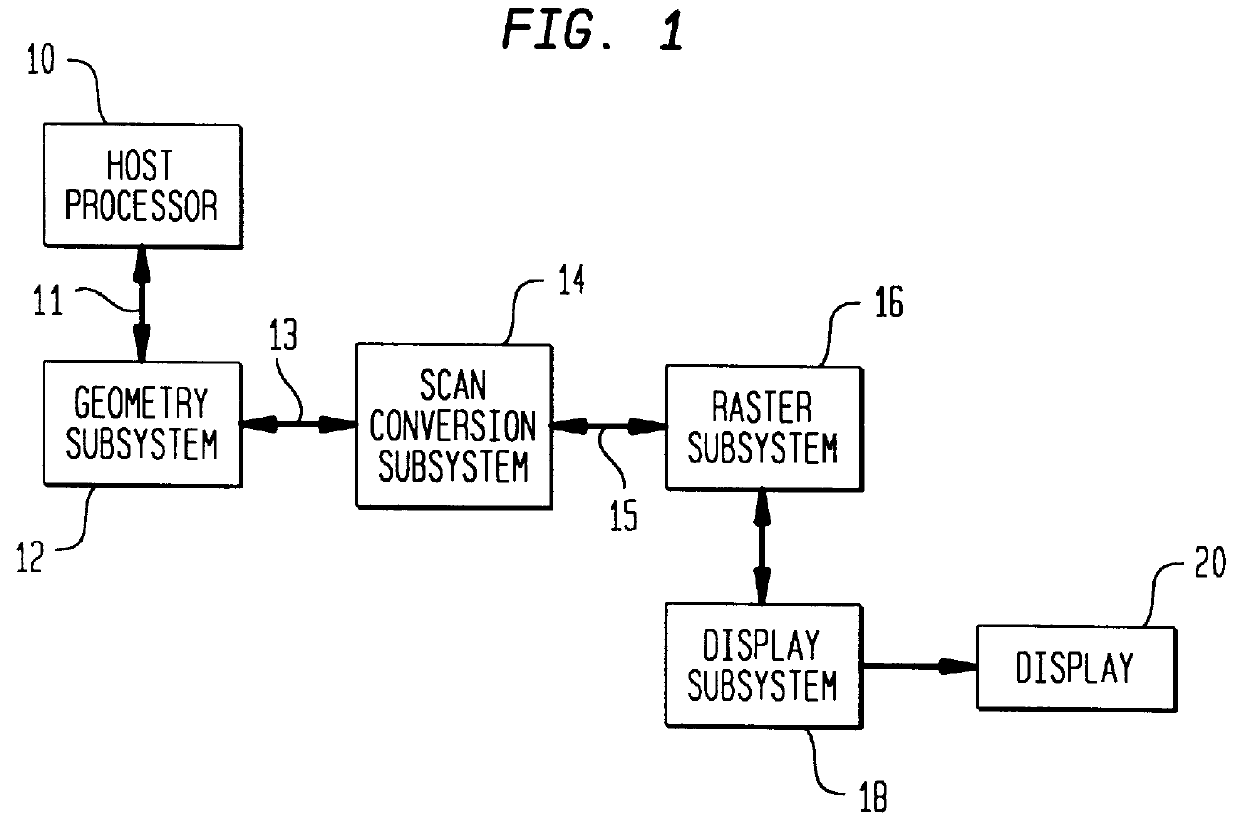
An image processing system is described that receives polygonal image data at the direction of a processor and develops antialiased image data for display on a raster scanned display. In particular, the image system includes a scan convertor for converting the polygonal image data into pixel data, which includes pixel screen coordinates and at least one color value for each polygon covered pixel of the pixel data and a supersample coverage mask indicating an extent of polygon coverage within each polygon covered pixel. The image system also includes a raster system having at least one image processor for receiving the pixel data for each pixel, for developing a region mask based on the supersample coverage mask, and for storing the color value in association with the region mask as anitialiased display data in an image memory in communication with the image processor based on the pixel screen coordinates. The region mask indicates one or more, geographical regions of supersamples within each pixel covered by one or more polygons and indicates a color value stored in the image memory to be assigned to the supersamples in a region. This requires only a single color value for supersamples within a region of a covered pixel to be stored in the image memory. The image system can also be configured to develop and store Z-values, alpha values, stencil values, and texture values for each pixel for storage in the image memory in association with the region mask.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Image processing method for direction dependent low pass filtering
InactiveUS7016549B1Without losing fine structure of imageTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImaging processingJaggies
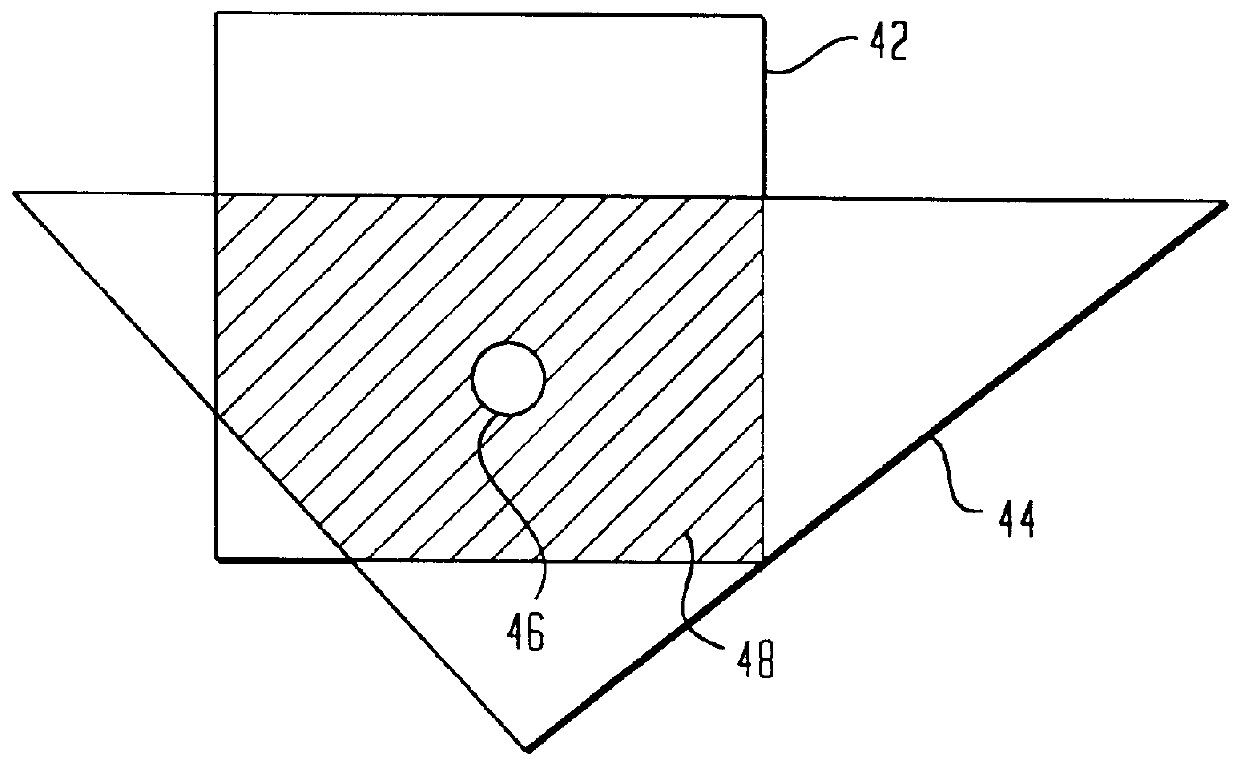
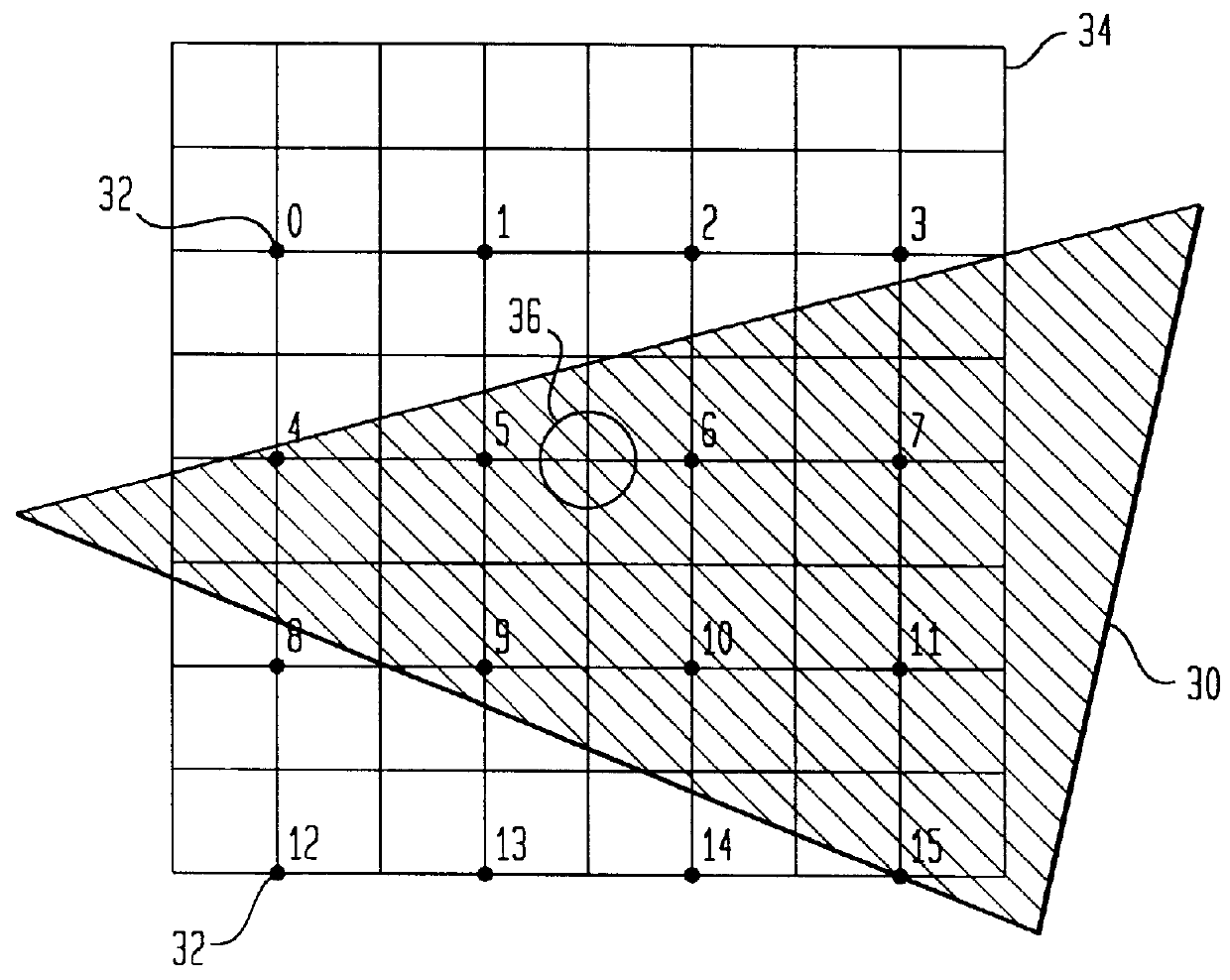
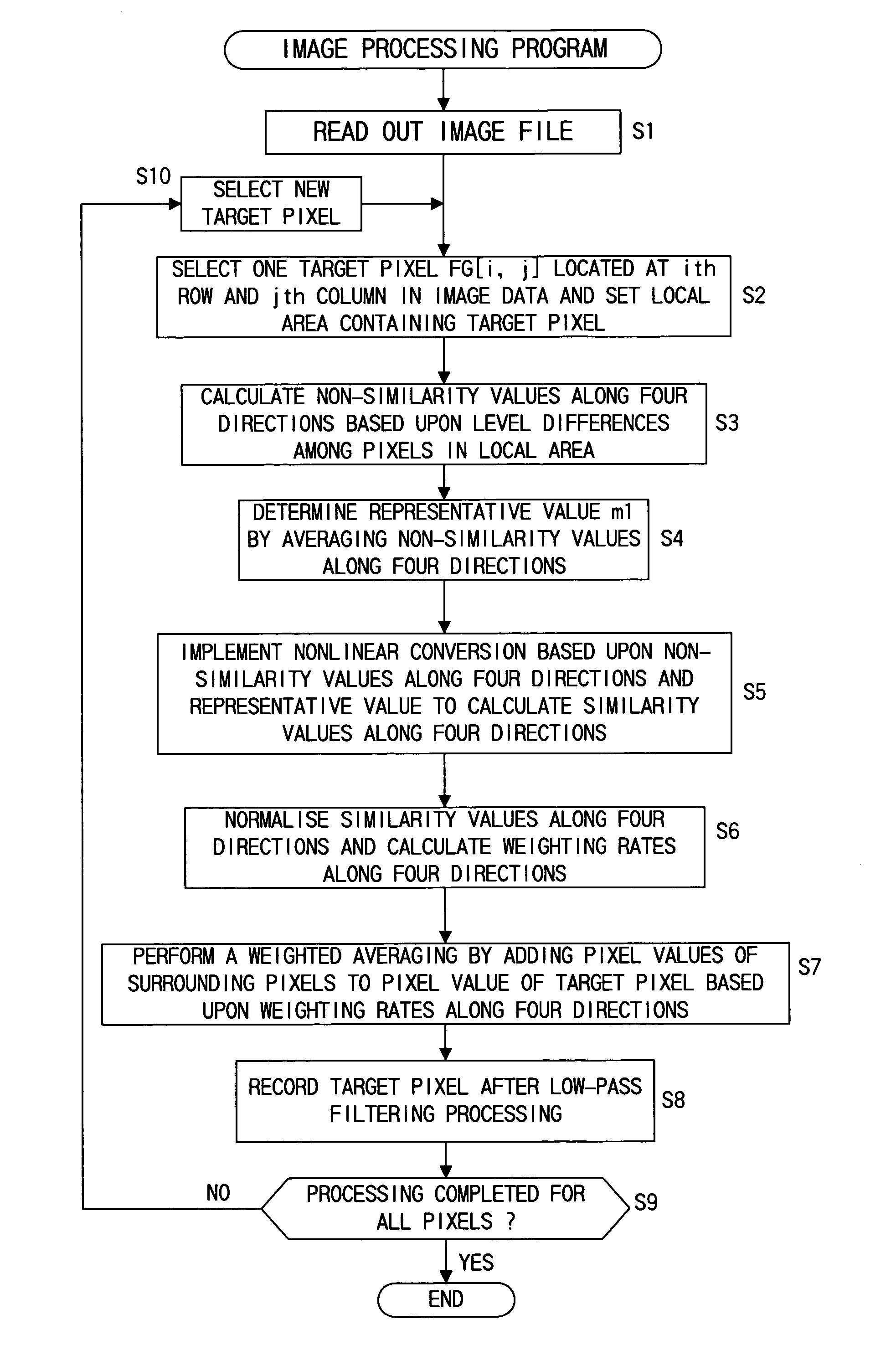
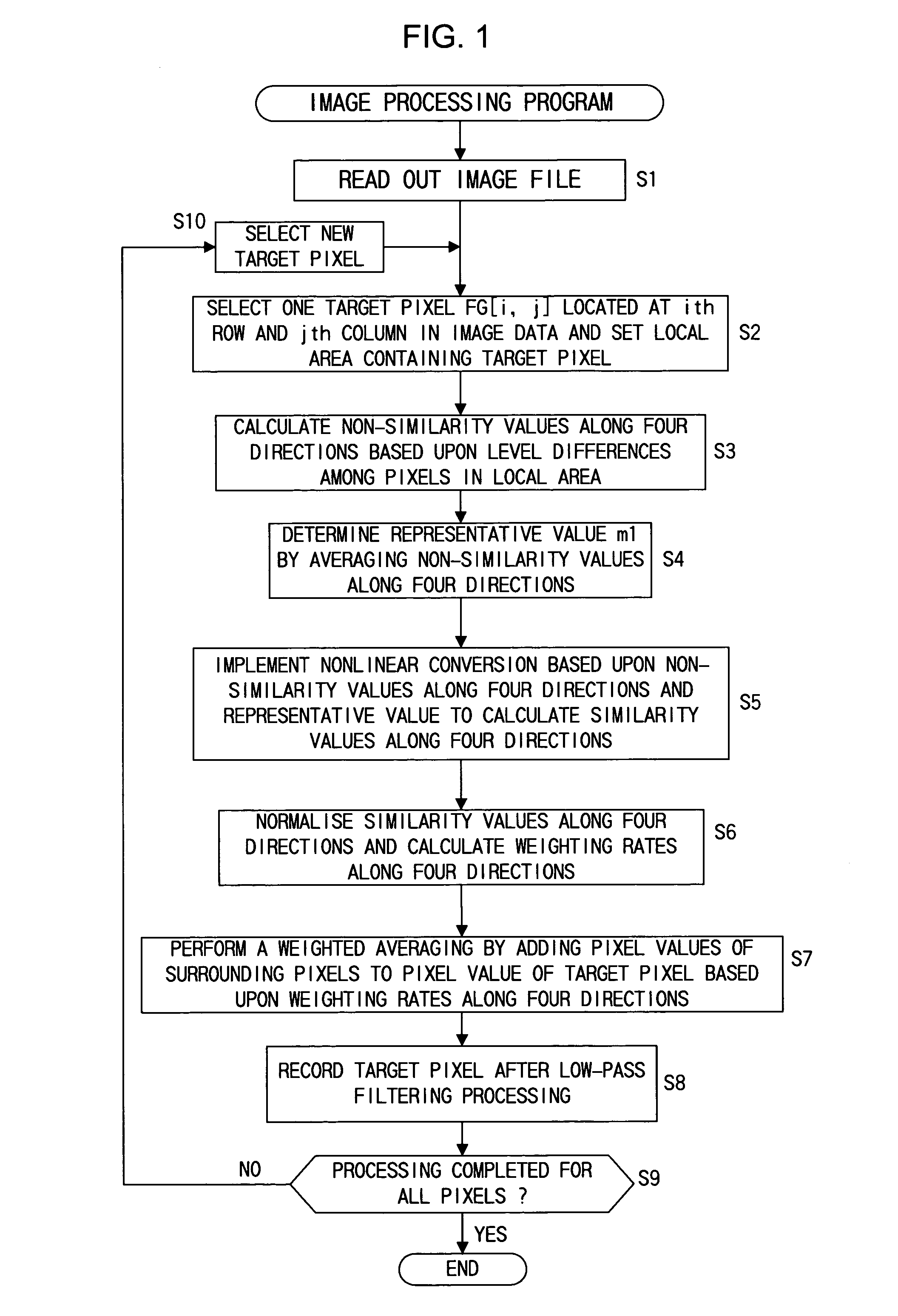
First similarity values along at least four directions are ascertained within a local area containing a target pixel and weighted averaging is performed by adding the pixel values of pixels around the target pixel value to the pixel value of the target pixel, adding weight along a direction having a small first similarity value (along a direction manifesting a high degree of similarity). By incorporating the pixel value level differences among a plurality of pixels on adjacent lines extending adjacent to the target pixel into the first similarity values, it becomes possible to effectively remove jaggies that are difficult to eliminate in the prior art. Furthermore, by making a judgment on degrees of similarity by incorporating color information such as characteristics differences among different color pixels, a more accurate judgment can be made with regard to the image structure to enable very accurate direction-dependent low-pass filtering.
Owner:NIKON CORP
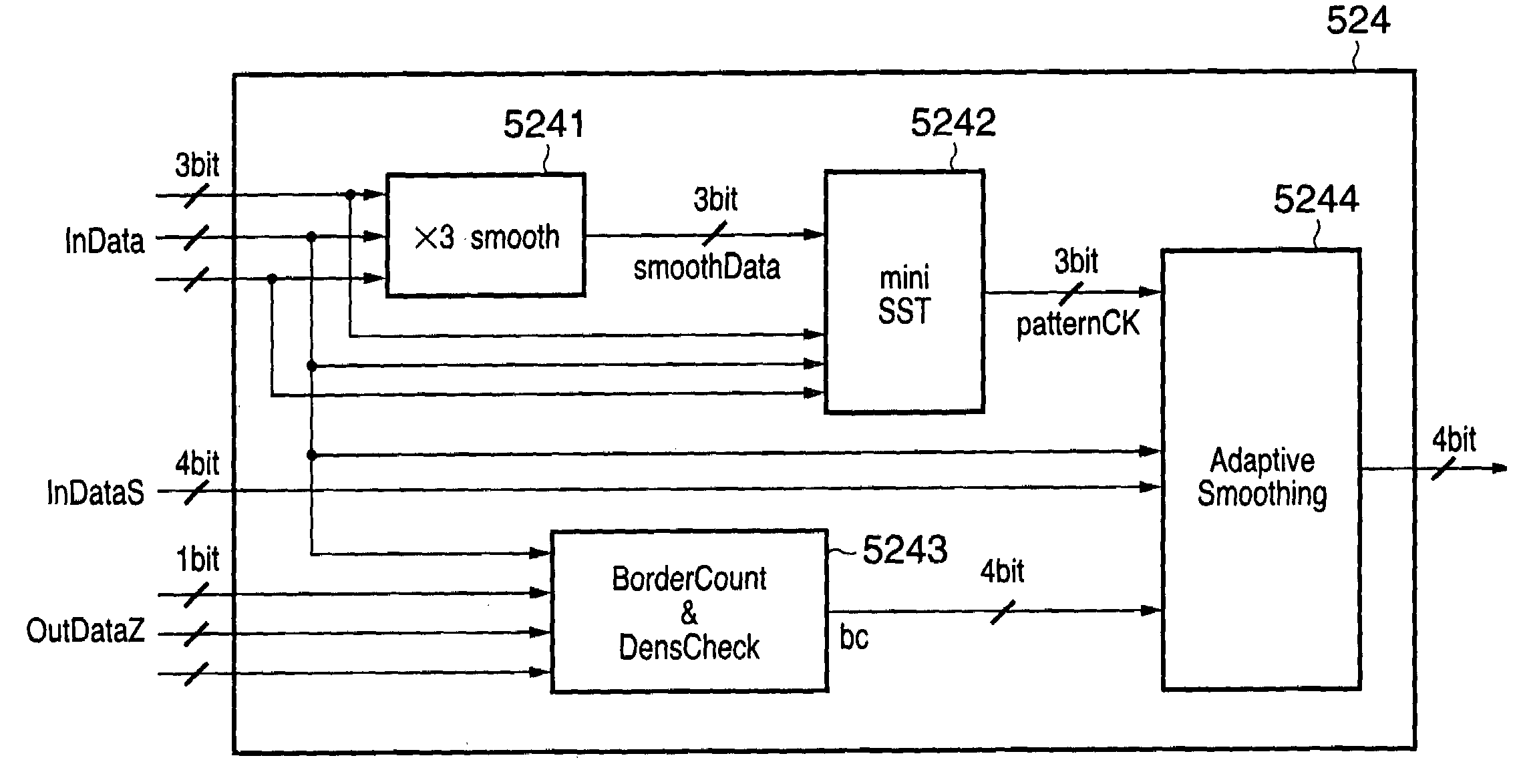
Selective super-sampling/adaptive anti-aliasing of complex 3D data
InactiveUS20050179698A1Avoid it happening againReduce trafficGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsJaggies
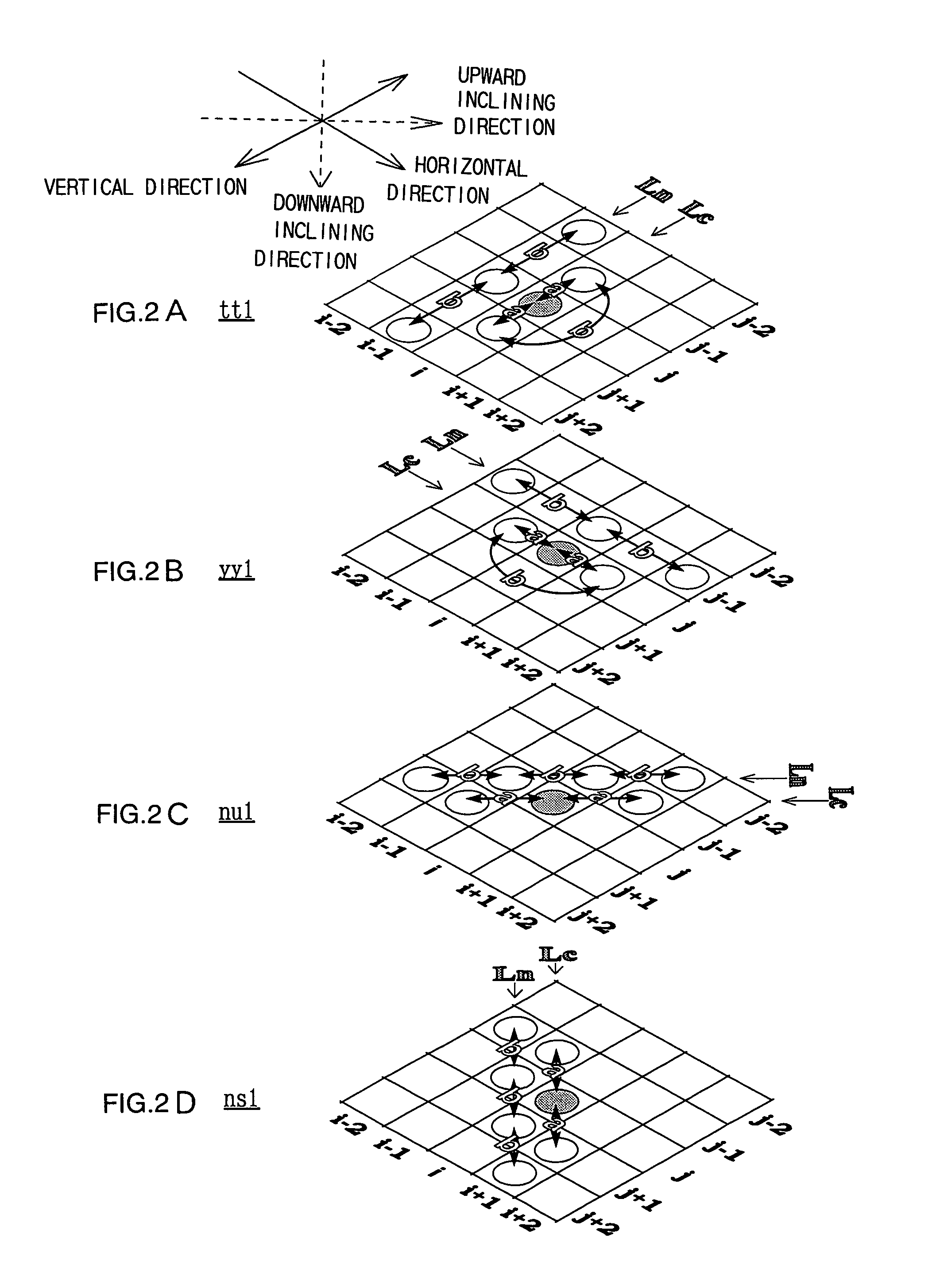
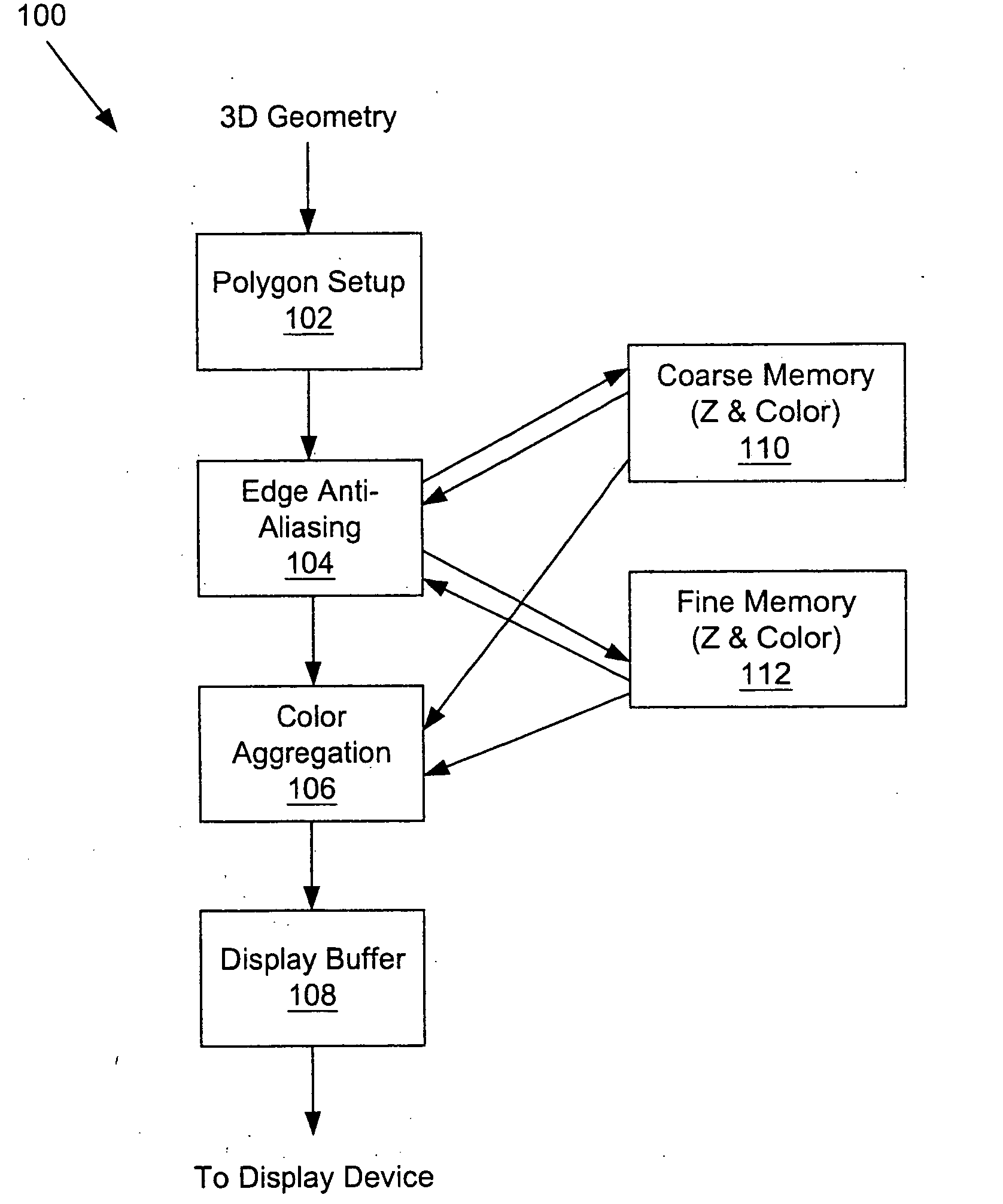
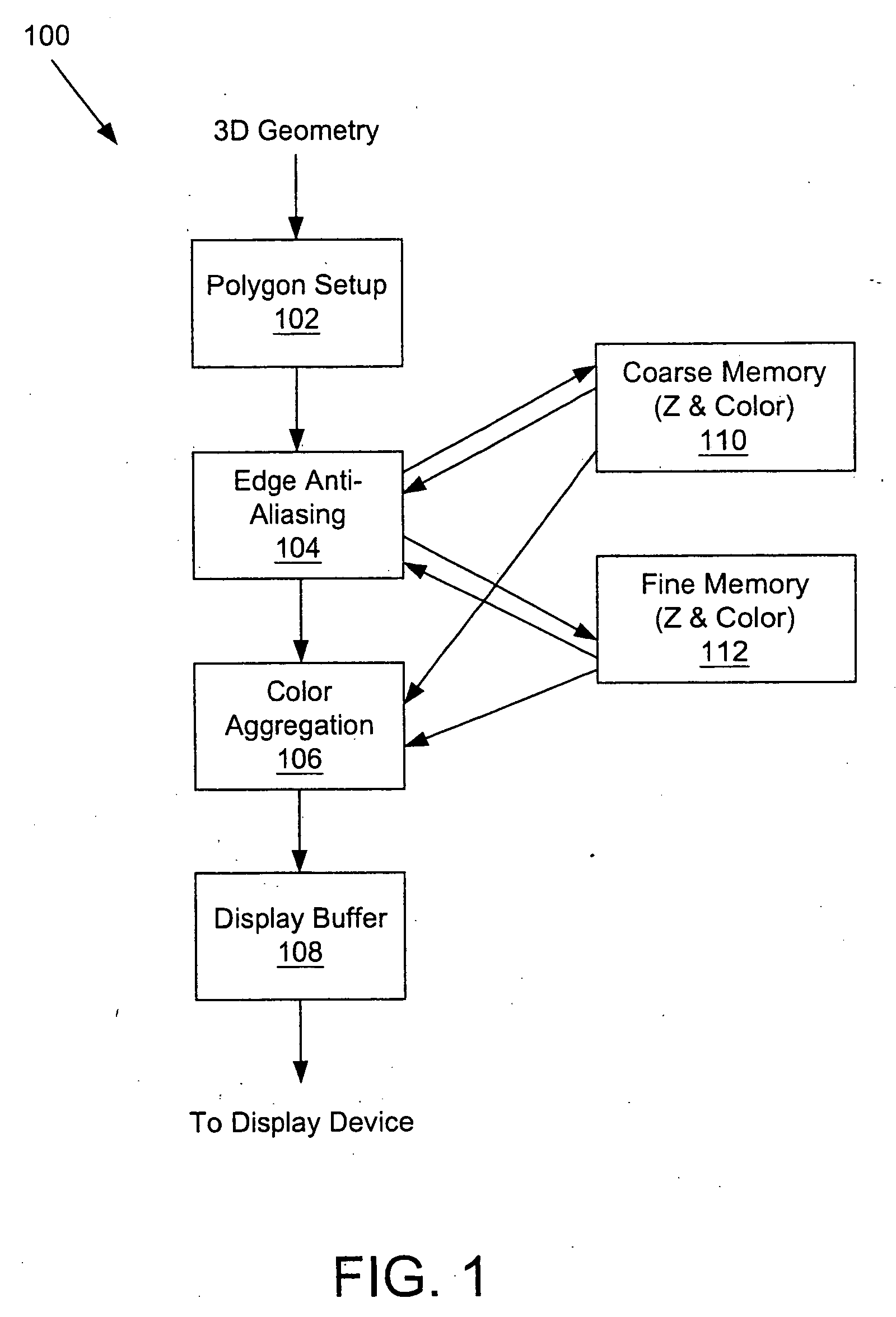
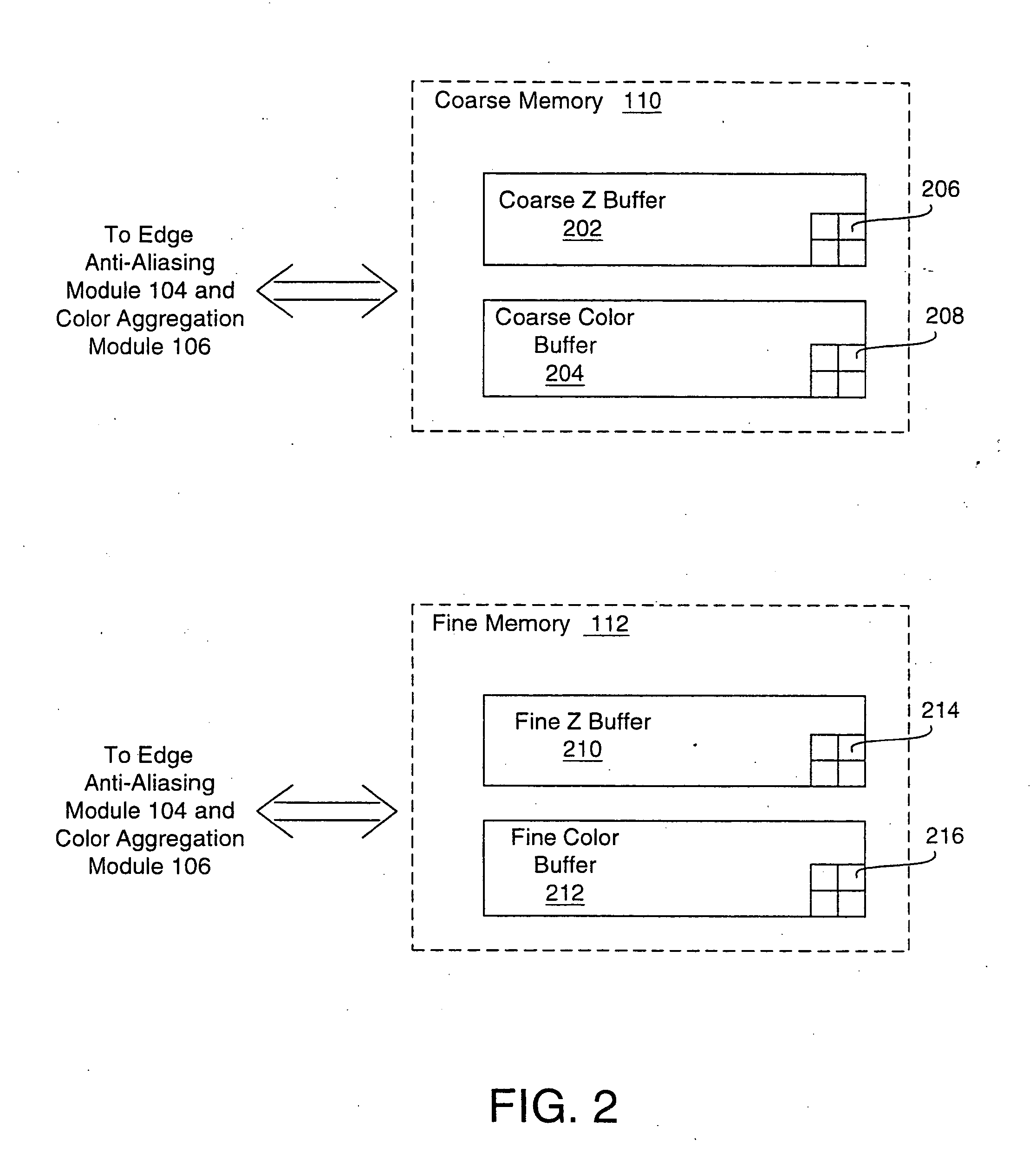
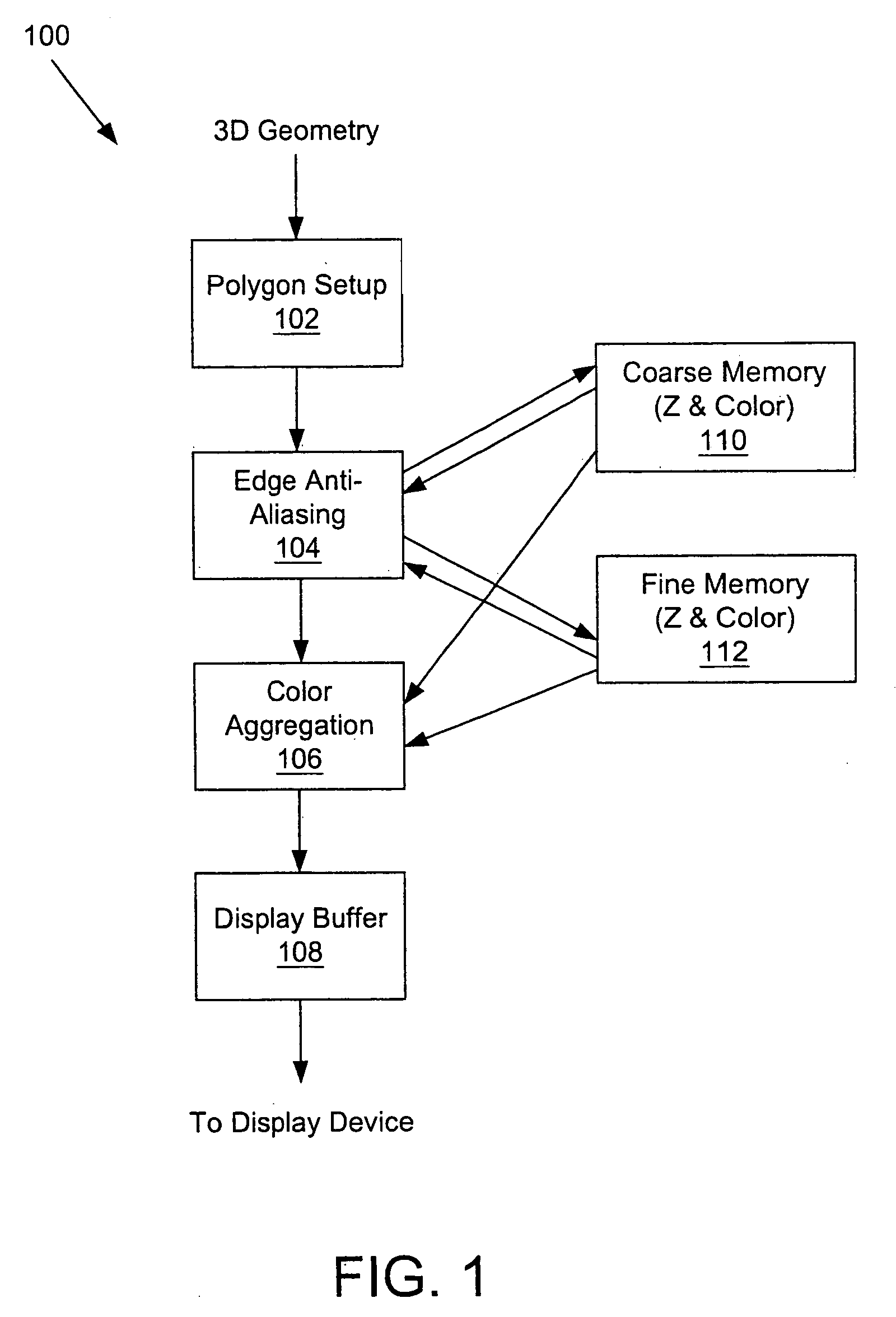
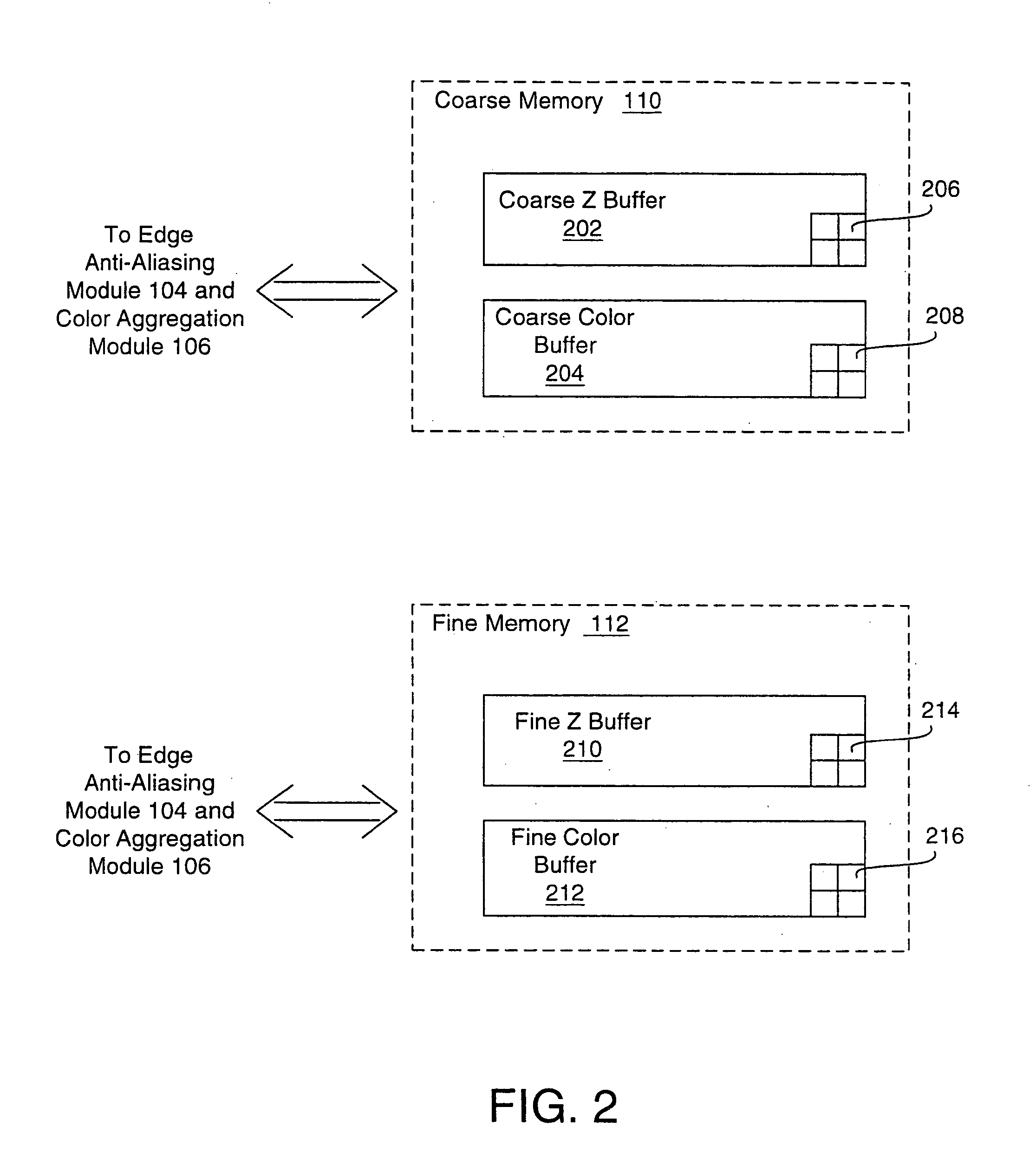
A system and method is provided for preventing the occurrence of aliasing at the edges of polygons in 3D graphics. The system may detect both polygon geometric edges and Z edges due to intersection of multiple polygons. In one embodiment, the system includes an edge anti-aliasing module configured to selectively super-sample edge portions of primitives. The system further includes a coarse memory for storing information of pixels that are not super-sampled and a fine memory for storing information of pixels that are super-sampled by the edge anti-aliasing module.
Owner:S3 GRAPHICS
Image and video amplification method and relevant image processing device
ActiveCN101815157AStrong contrastSmall distortionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsJaggiesImaging processing
The invention relates to an image and video amplification method and a relevant image processing device. The method comprises a preprocessing module and a composite amplification module, wherein the preprocessing module is used for executing high-pass filtering processing to an input image to extract the high-frequency part of the input image and is used for executing image decomposition processing to the input image to decompose the input image into smooth areas and marginal areas; and the composite amplification module is used for conducting amplification processing to the original input image and the smooth areas through simple interpolation operation and is used for conducting amplification processing to the marginal areas and the high-frequency part through both complex interpolationoperation and simple interpolation operation. By adopting the method, the amplification results of the original input image, the smooth areas, the marginal areas and the high-frequency part can be fused, i.e. an output image with features of saw tooth resistance, clear-cut margin, rich detail, high contrast and the like can be output according to a preset amplification scale under the circumstance that the operation workload is small, the complexity is low and the speed is high.
Owner:HANGZHOU ARCVIDEO TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
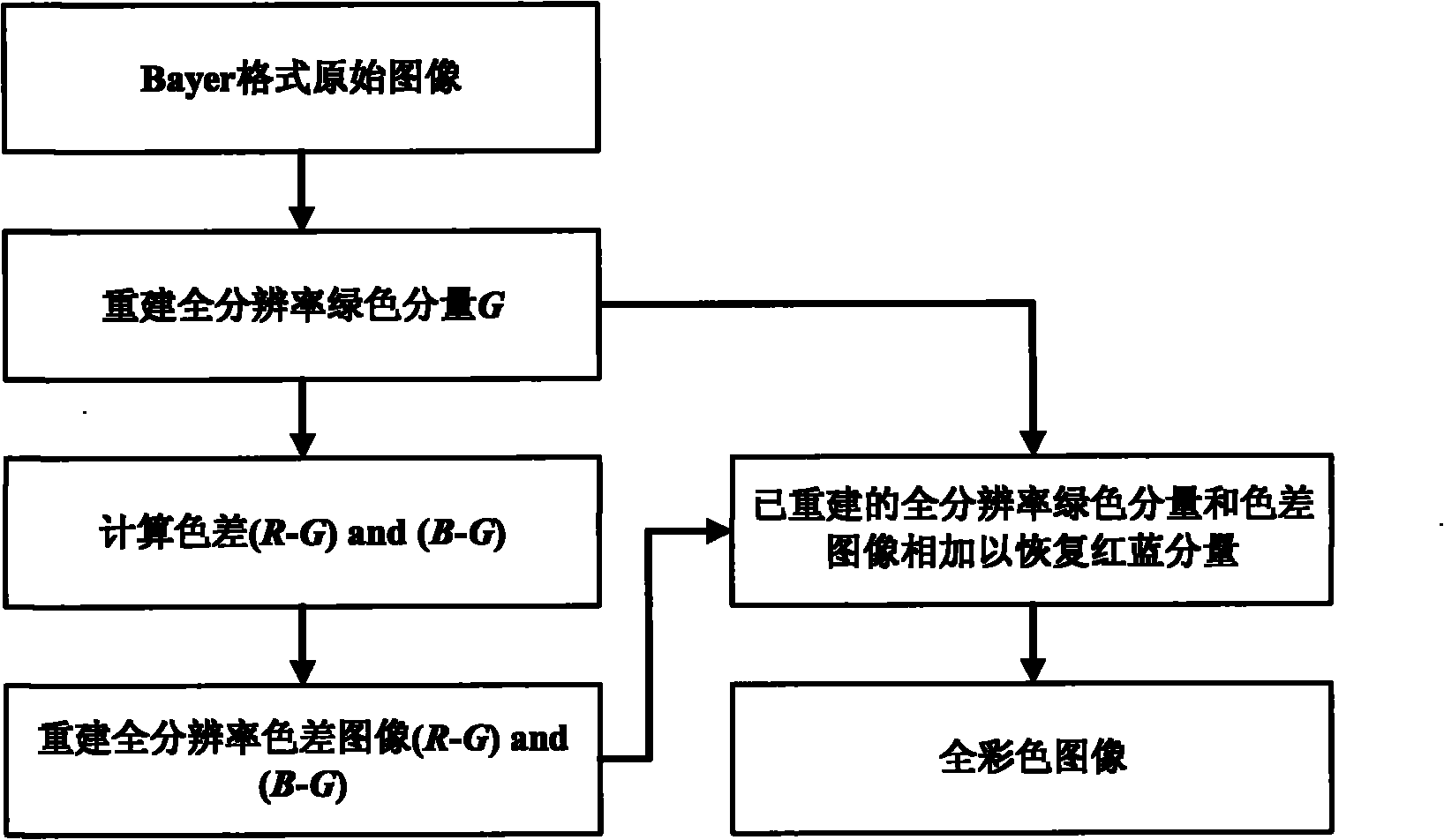
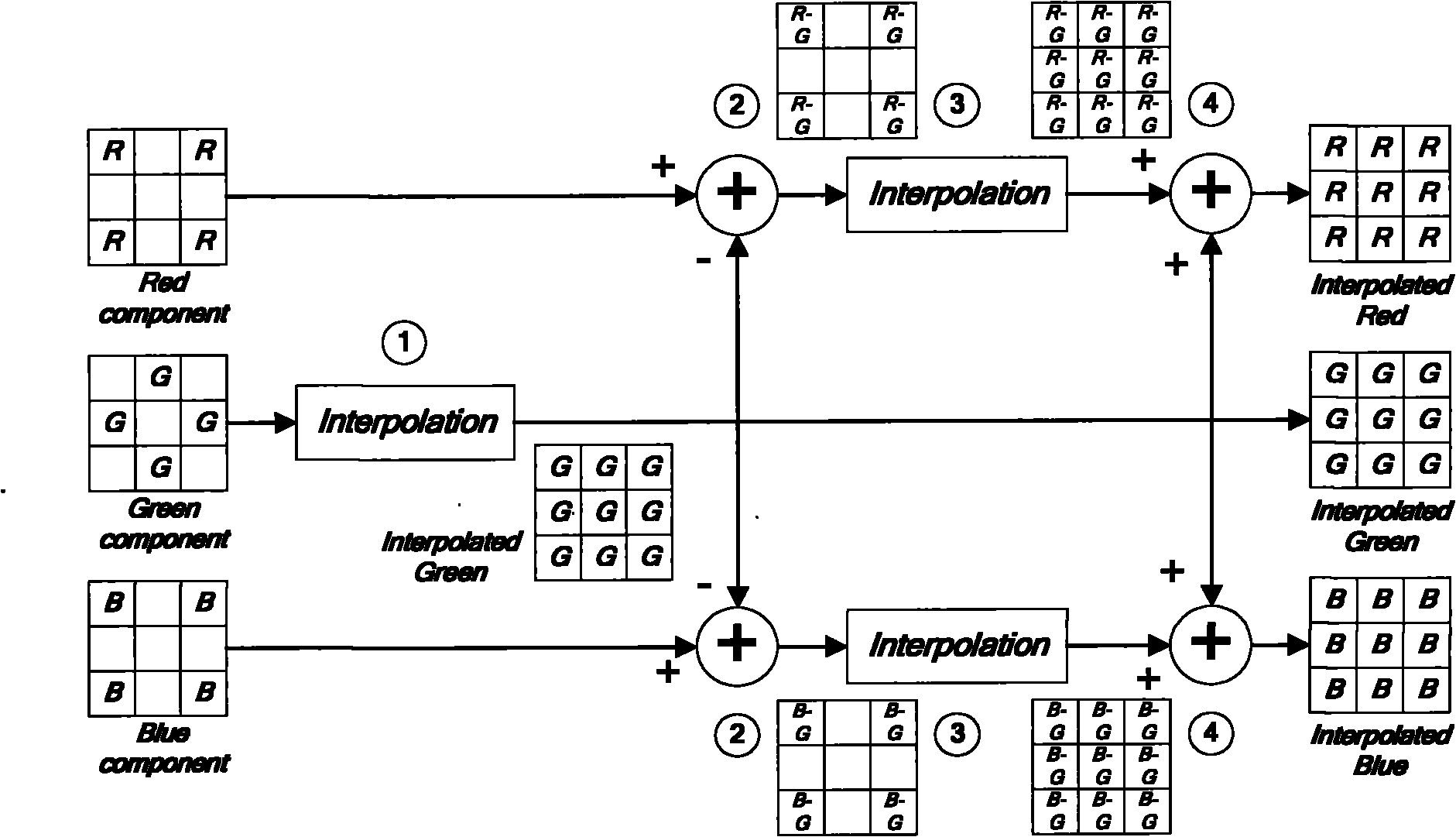
Green component and color difference space-based Bayer format color interpolation method
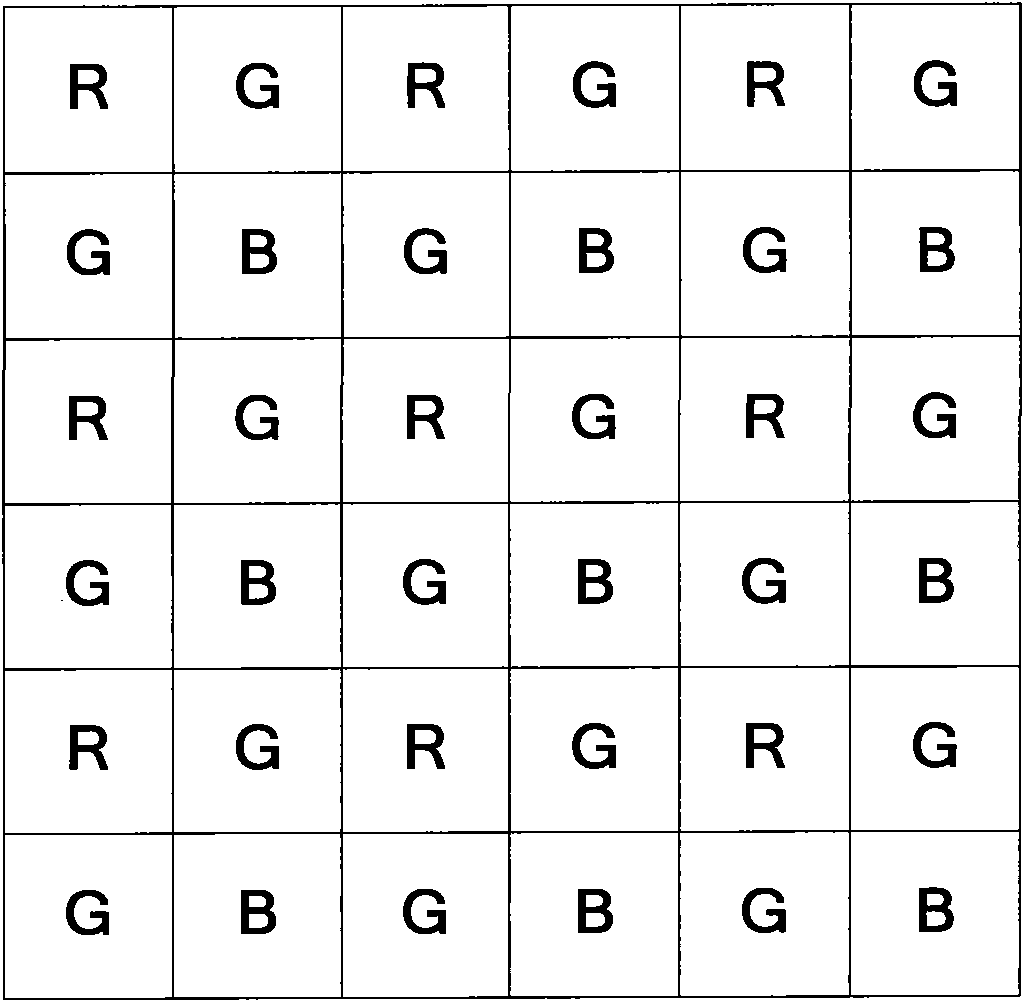
InactiveCN101917629AReduce operational complexityImprove peak signal-to-noise ratioBrightness and chrominance signal processing circuitsPicture signal generatorsJaggiesImage resolution
The invention relates to a green component and color difference space-based Bayer format color interpolation method. Two main errors which are jaggies and pseudo colors respectively exist in the conventional color interpolation methods. In the method, in a full-color image recovery process, color recovery is realized by adopting a combined way of interpolating green components, red components and blue components in steps; and the method comprises the reconstruction of the full-resolution green components G, the calculation of pixel point color differences R-G or B-G comprising the red or blue components, the reconstruction of full-resolution color difference images R-G and B-G, and the recovery of the red components R and the blue components B by the addition of the reconstructed full-resolution green components and the reconstructed color difference images. The method of the invention has the advantages of effectively solving the problem that the images have blurry edges and unsharp detail textures, reducing the color distortion of the images, preventing color mutation and improving color smoothness.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
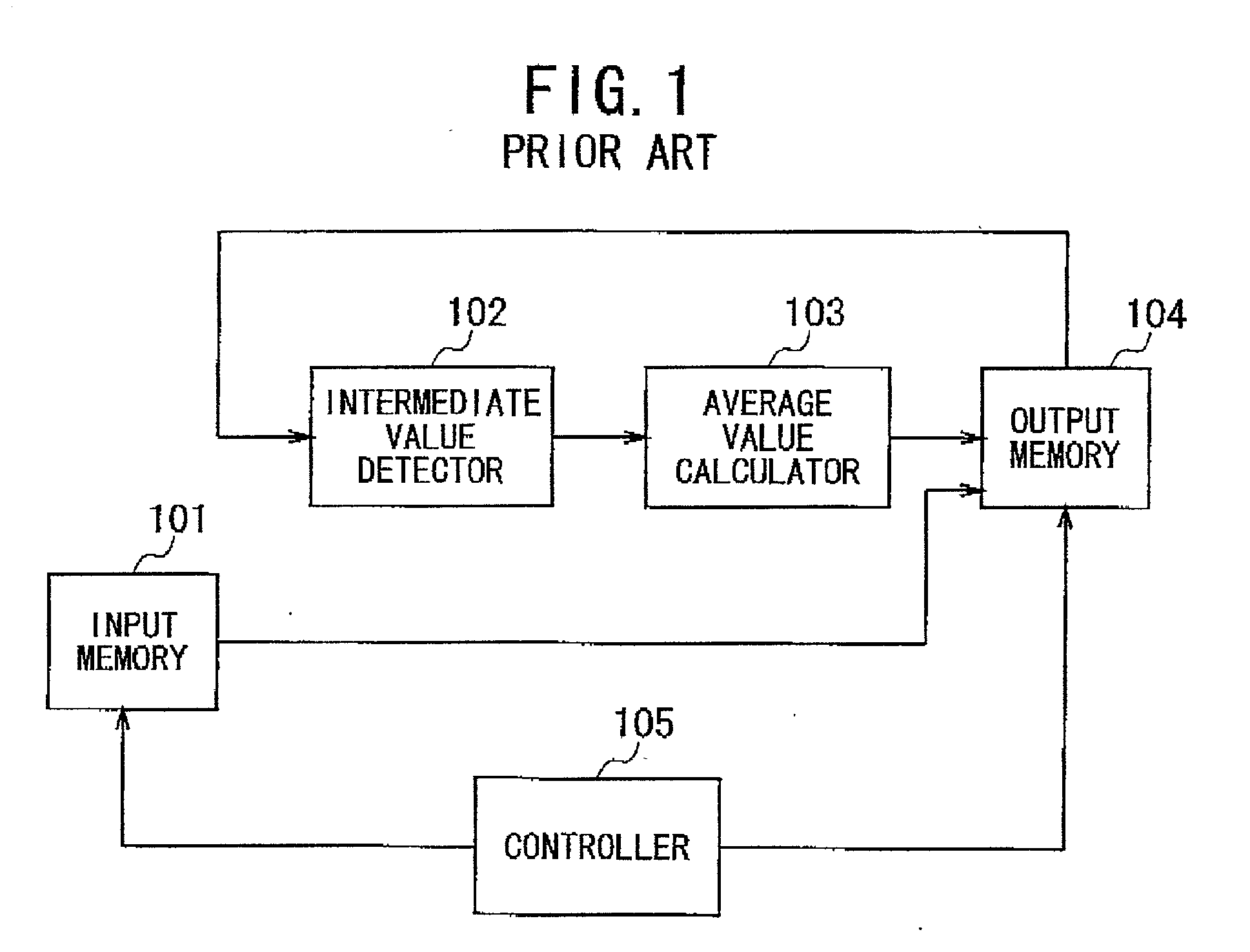
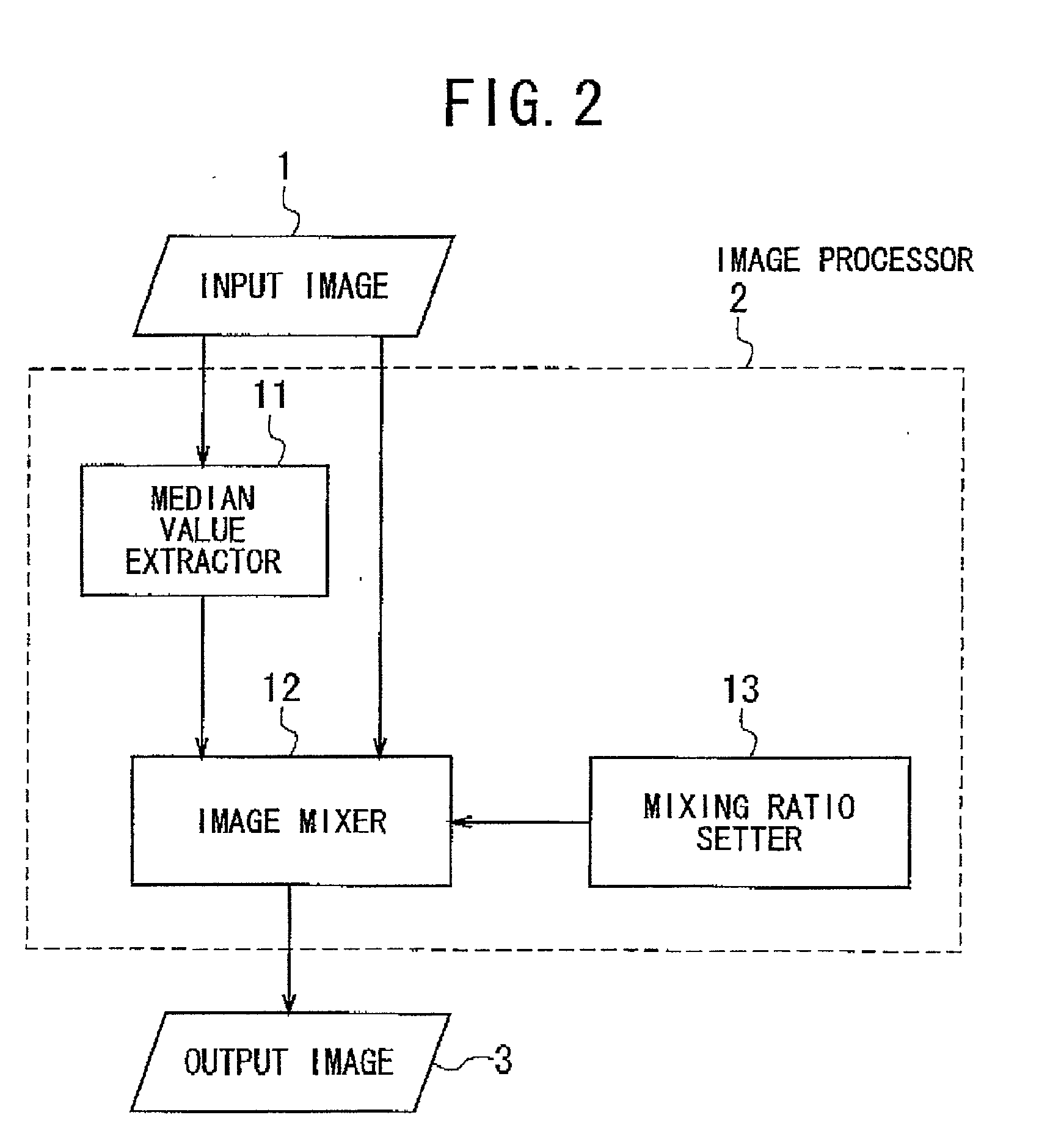
Image processing method and system for interpolation of resolution
An image processing method is provided, which makes it possible to enlarge an input or original image in such a way as to suppress or eliminate jaggies at the contours in the image, and which is applicable to a dot-matrix type display device with a fixed resolution. In the step (a) a local area is defined in an input image. The local area includes a target pixel and neighboring pixels surrounding the target pixel. In the step (b), a filtering operation is applied to the target pixel and the neighboring pixels in the local area while all the pixels in the local area are successively assigned to the target pixel, thereby outputting a filtered image. In the step (c), the filtered image and the input image are mixed together at a specific mixing ratio, thereby forming an output image. In the step (b), the median or average value is preferably used for forming the filtered image.
Owner:NEC CORP
Special-shaped display panel and display device
The invention discloses a special-shaped display panel and a display device. A display area of the special-shaped display panel has a special-shaped boundary, the display panel includes low-luminancepixels and conventional pixels, and the conventional pixels are arranged away from the special-shaped boundary; multiple pixels form multiple pixel rows and multiple pixel lines, the pixel rows or thepixel lines comprise pixel groups, the pixel groups comprise the first pixel groups and the second pixel groups, the number of pixels adjacent to the special-shaped boundary in the first pixel groupsis larger than that of pixels adjacent to the special-shaped boundary in the second pixel groups, and the number of low-luminance pixels in the first pixel groups is larger than that of low-luminancepixels in the second pixel groups; each pixel comprises at least three sub-pixels, electrodes are arranged in the sub-pixels, and each electrode is provided with at least one slit; in the same pixelgroup, in the direction from the special-shaped boundary to the display area, the angles and / or numbers of slits in the electrodes of the sub-pixels in the low-luminance pixels are gradually increased. By means of the special-shaped display panel and the display device, the phenomenon of jaggies in a special-shaped display panel is relieved.
Owner:XIAMEN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS
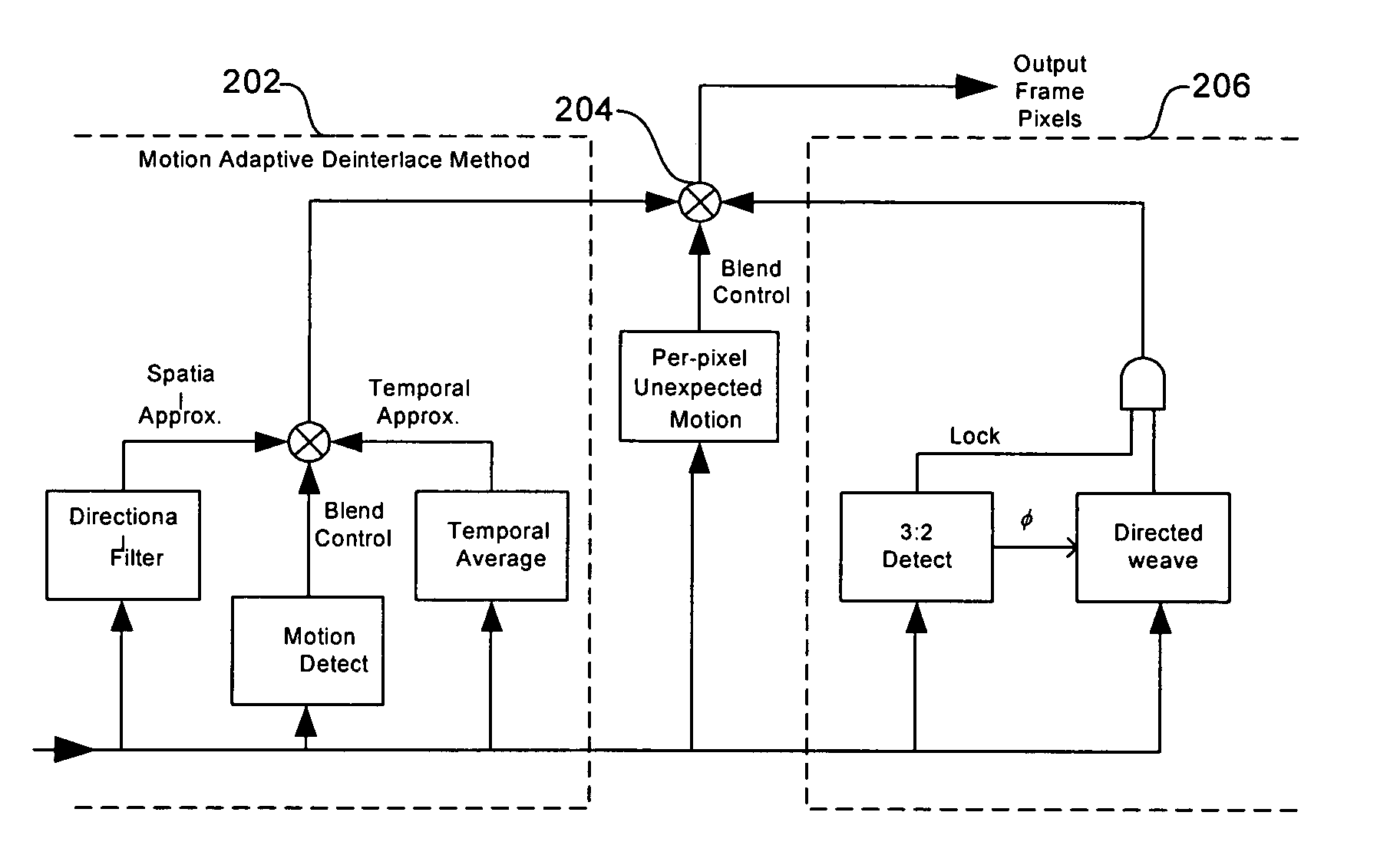
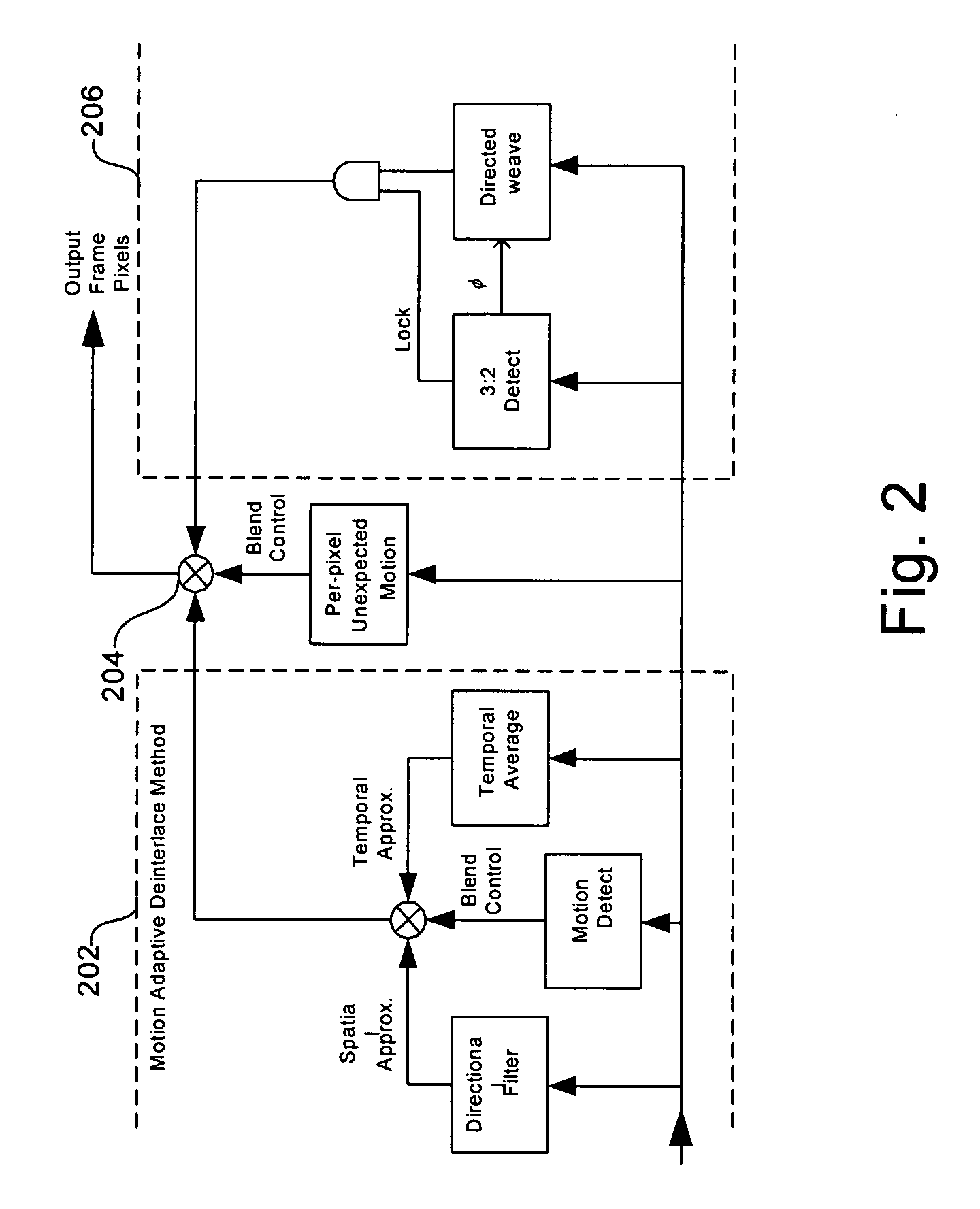
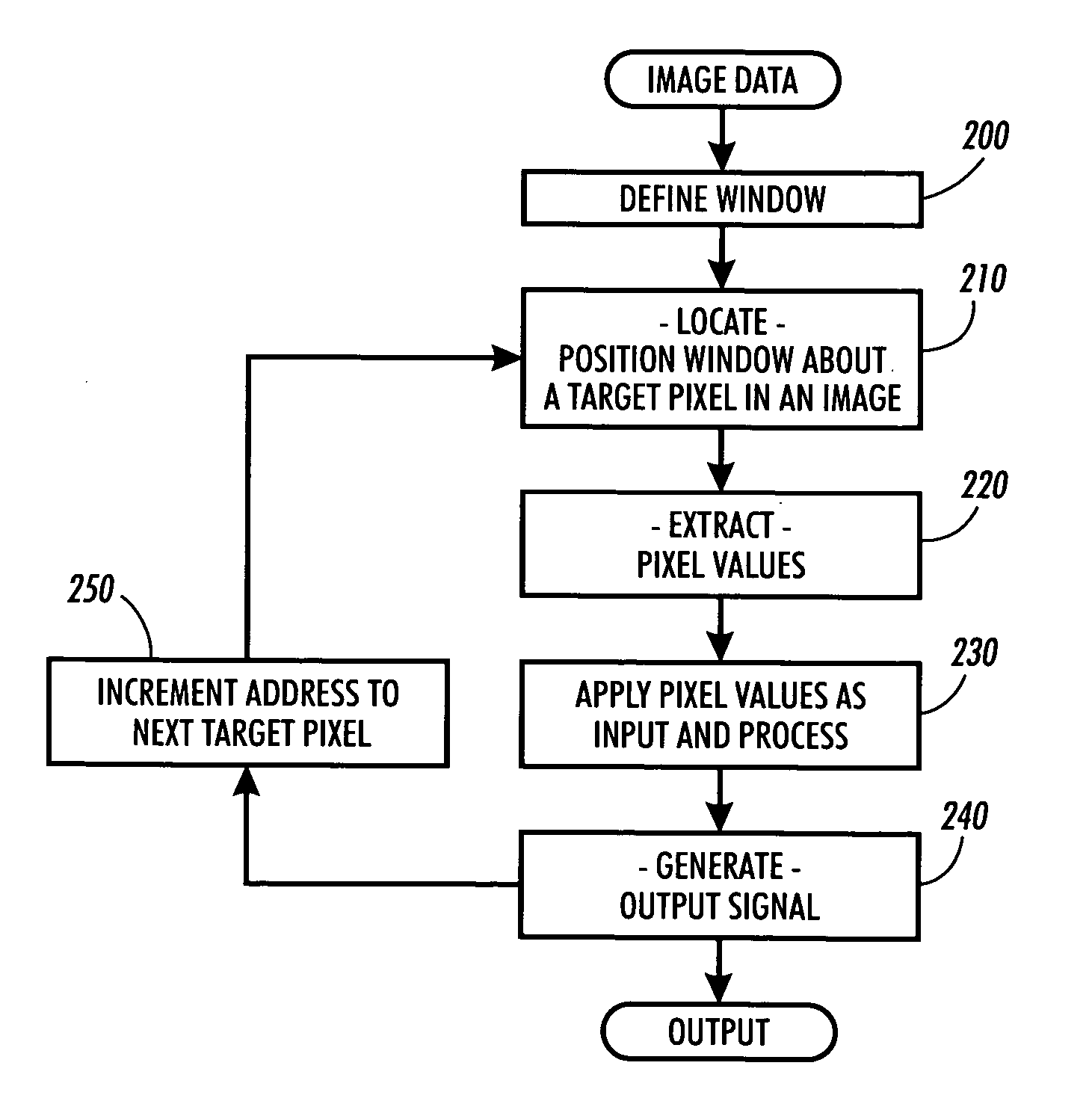
Method and system for reducing the appearance of jaggies when deinterlacing moving edges
InactiveUS20070070244A1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsJaggiesInterlaced video
A method and system for reducing the appearance of jaggies when deinterlacing moving edges in a video processing system are provided. The method may comprise detecting the direction of an angled edge in an interlaced video image to determine a filtering direction to be used for approximating absent pixels in deinterlacing the interlaced video. In detecting the direction of the angled edge, a group of windows of different sizes may be used to look at the edge, where a missing pixel is the center of each of the windows. Detecting the direction of the edge, and therefore the direction of filtering, may comprise: determining the angle associated with the edge, determining the strength of the edge, examining the pixels surrounding the absent pixel, and adjusting the first angle measure and the second angle measure based on the pattern of the surrounding pixels.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Corner sharpening of text and line art in a super resolution anti-aliasing image path
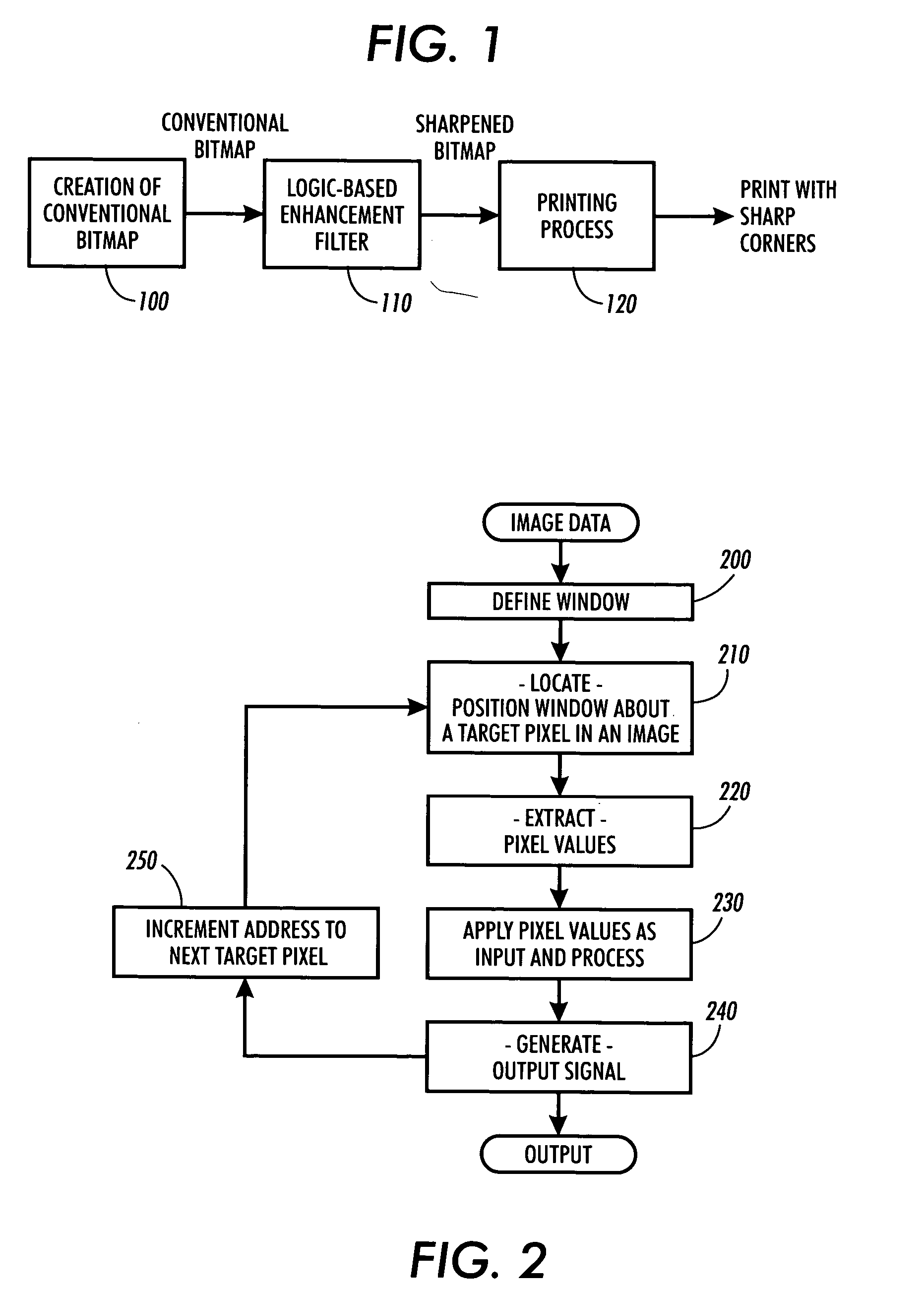
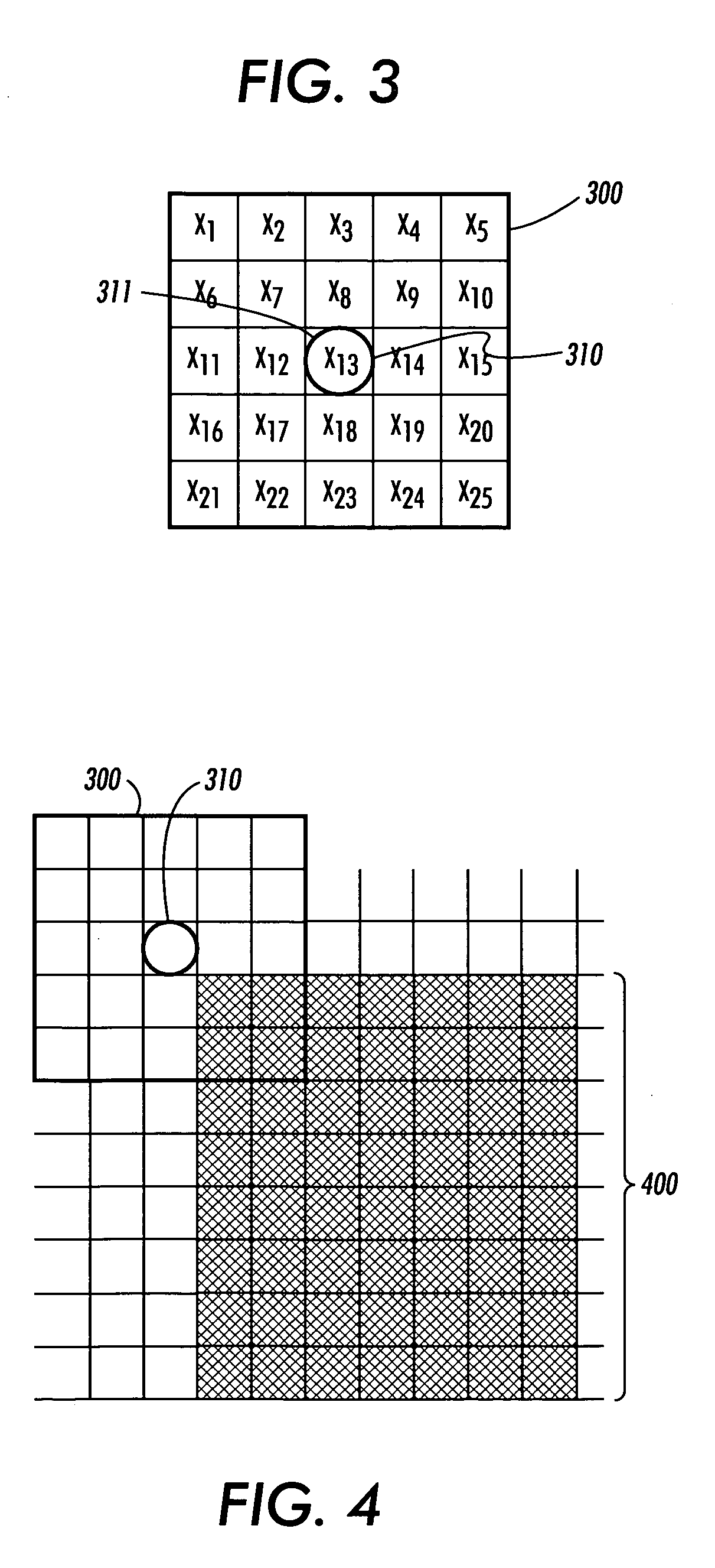
ActiveUS20050129328A1Enhancing contour fidelityEnhances resolution and qualityImage enhancementImage analysisAnti-aliasingJaggies
A method for sharpening the corners of digital image data within an anti-aliasing image path so as to overcome corner rounding when displayed or printed. The method comprises stepping a window across the image data and comparing that windowed data to templates or performing Boolean logic and arithmetic operations on the image data. Upon determining a match or a corner detection, pixel values are substituted in the identified pixel locations to achieve a clustering of the substituted pixel values about the corner structure producing a corner-enhanced digital image. Filtering and sampling are then performed according to an anti-alias operation to the corner-enhanced image to produce an anti-aliased corner enhanced image. The data substitution will achieve a localized clustering or “ear” of toner / ink, or in the alternative for inside corners the localized clustered absence of toner / ink. The result of this clustering is a sharpening of the corners so that they display or print as intended by the bitmap.
Owner:XEROX CORP
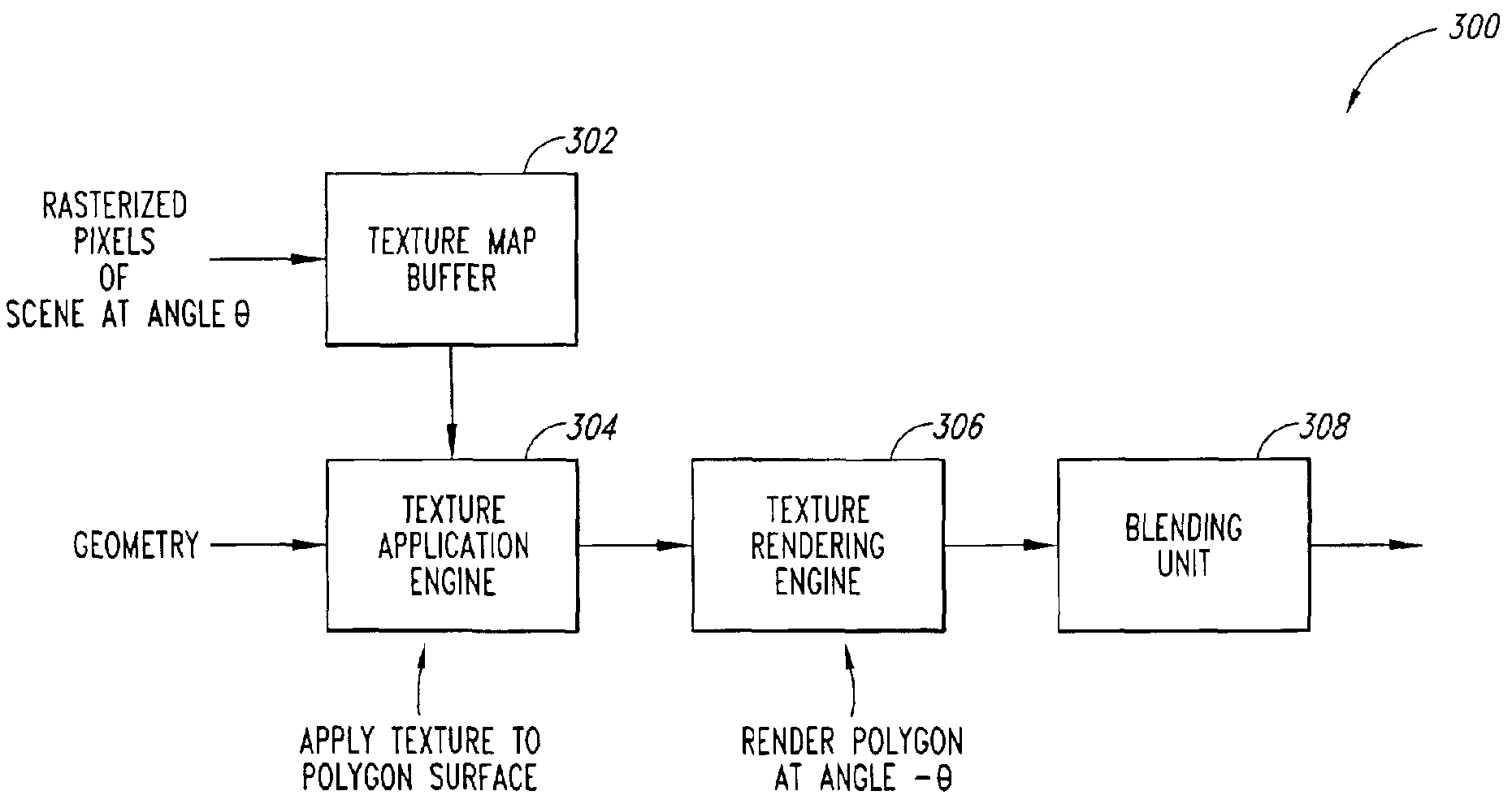
Full-scene anti-aliasing method and system
InactiveUS6922199B2Minimizing aliasingPrecise positioningCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingAnti-aliasingJaggies
A method and system for performing full-scene anti-aliasing for an image through a technique of rotating and unrotating rasterization of a scene and rendering a resulting image. A scene is rasterized at a first angle relative to a first coordinate system to generate a plurality of pixels, which are then applied to a polygon surface that is rendered at a second angle equal to the inverse of the first angle. Thus, the resulting image is re-oriented with respect to the first coordinate system.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Image processing apparatus and image processing method
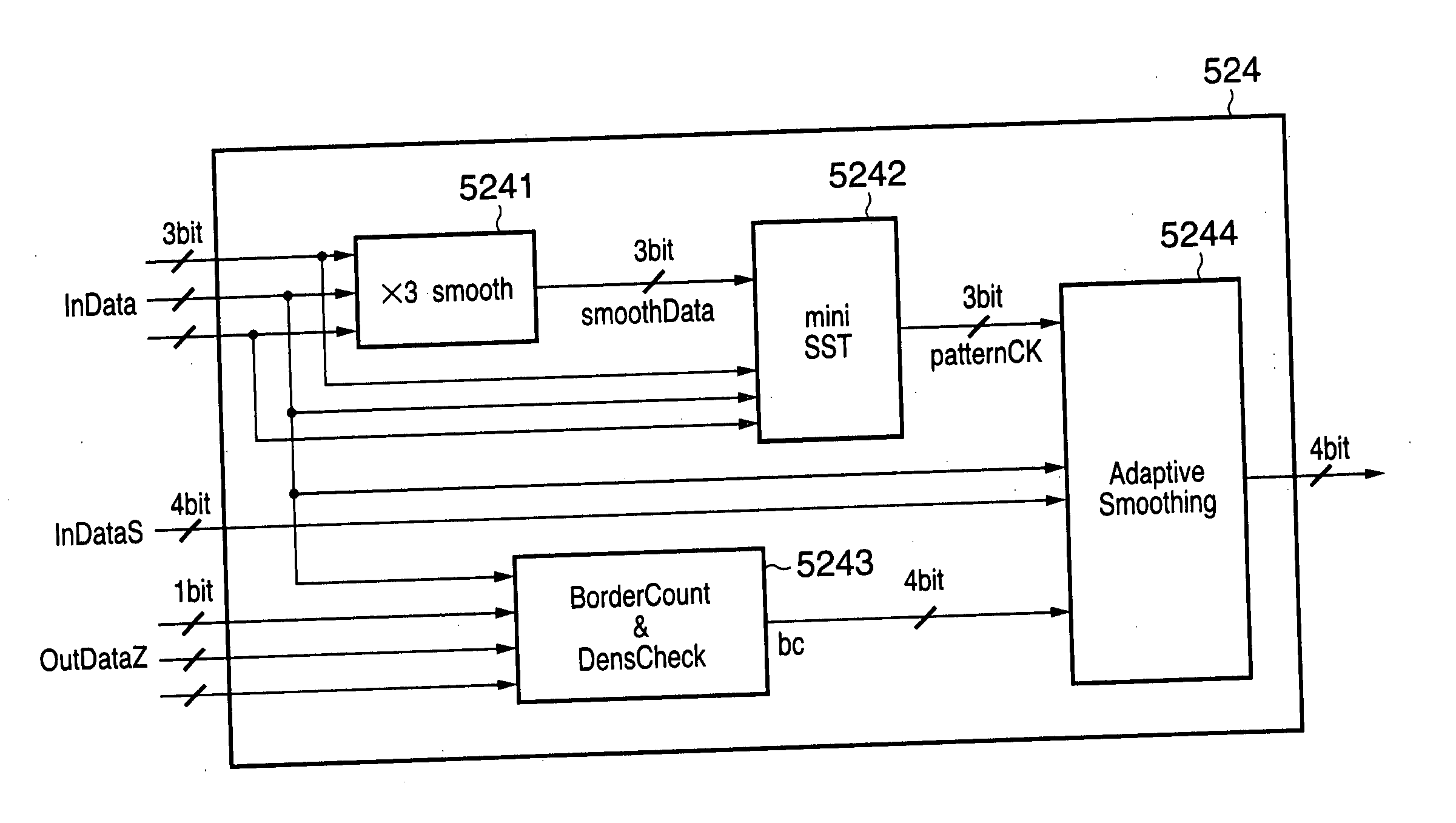
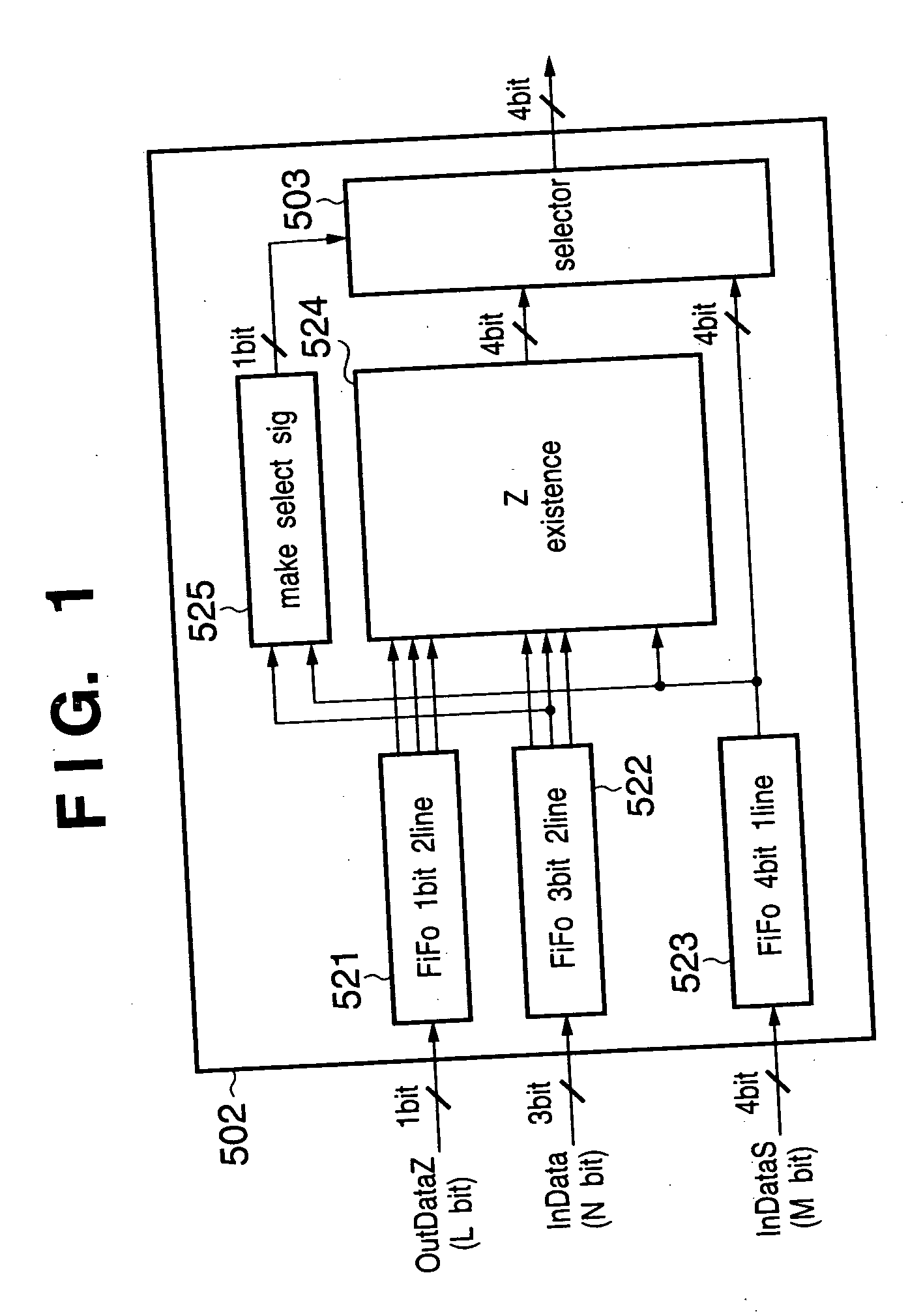
ActiveUS20060092475A1Suppress jaggiesConvenient ArrangementImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersPattern recognitionHigh density
To suppress jaggies in second image data on the basis of first image data, the second image data obtained by executing halftoning processing for the first image data, and attribute data representing an attribute of each pixel contained in the first image data, a judgment signal indicating whether to execute smoothing processing is output on the basis of the attribute data. Edge correction data is generated from the first image data by executing smoothing processing in accordance with the judgment signal. The pixel data of the second image data is compared with the pixel data of the edge correction data. The pixel data having a higher density is output. Jaggies generated by halftoning processing can be suppressed with a simple arrangement at a low cost.
Owner:CANON KK
Image processing apparatus and image processing method
InactiveCN101867682ASolve the problem of adding correction data at the boundaryPrevent smoothingPictoral communicationImaging processingJaggies
The invention provides an image processing apparatus and an image processing method. For reducing jaggies in second image data based on first image data, the second image data obtained by performing digital halftoning on each image signal of the first image data, and attribute data indicating the attribute of each pixel in the first image data, a determination signal indicating whether or not to perform smoothing processing is output based on the first image data, edge correction data for the smoothing processing is generated from the first image data, and whether or not to perform edge correction processing that uses the edge correction data is selected according to the determination signal and the attribute data. Moreover, the second image data and the edge correction data are compared for each image signal so as to output either one thereof according to the comparison result.
Owner:CANON KK
Image pickup apparatus and image pickup apparatus control method, and program
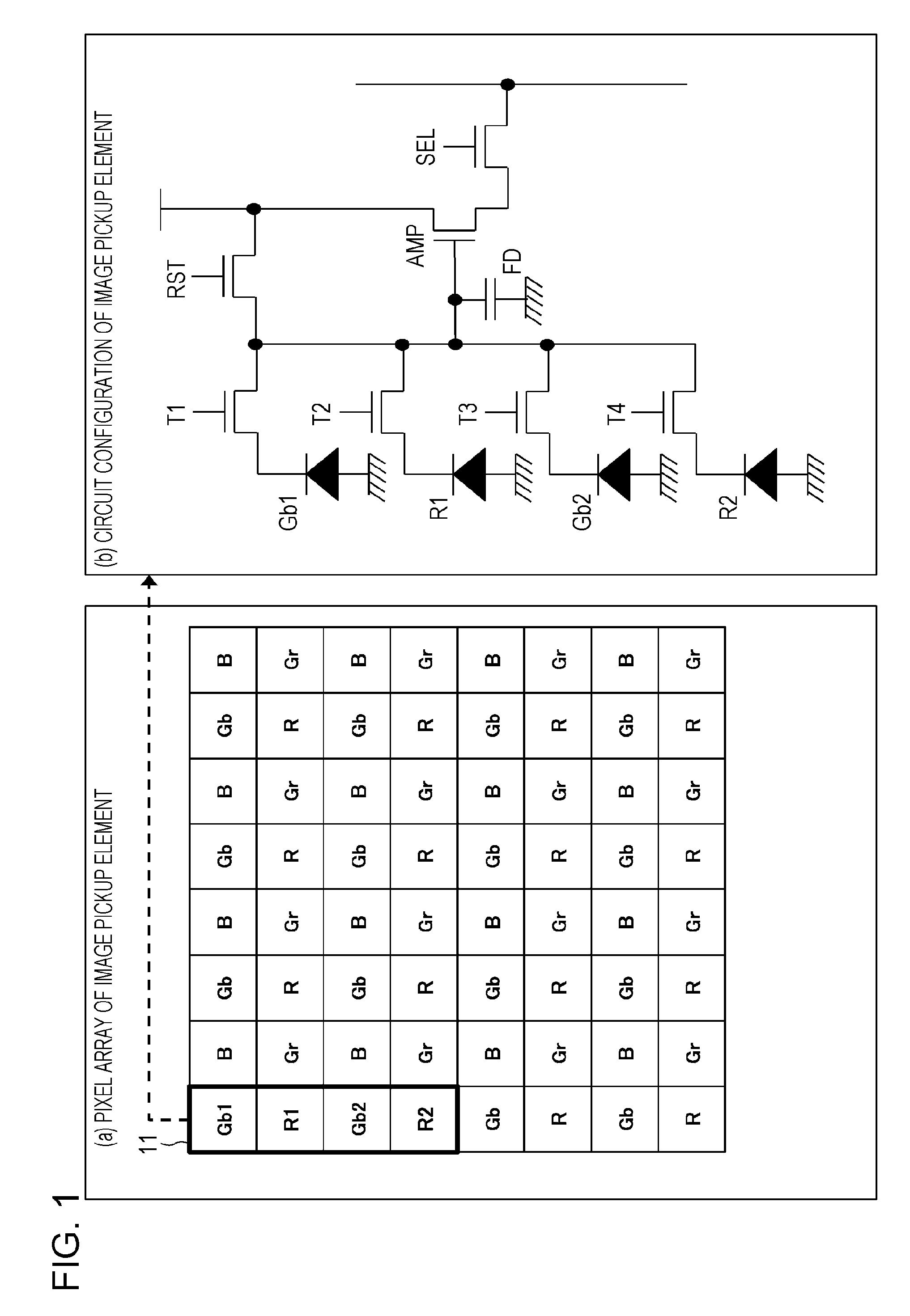
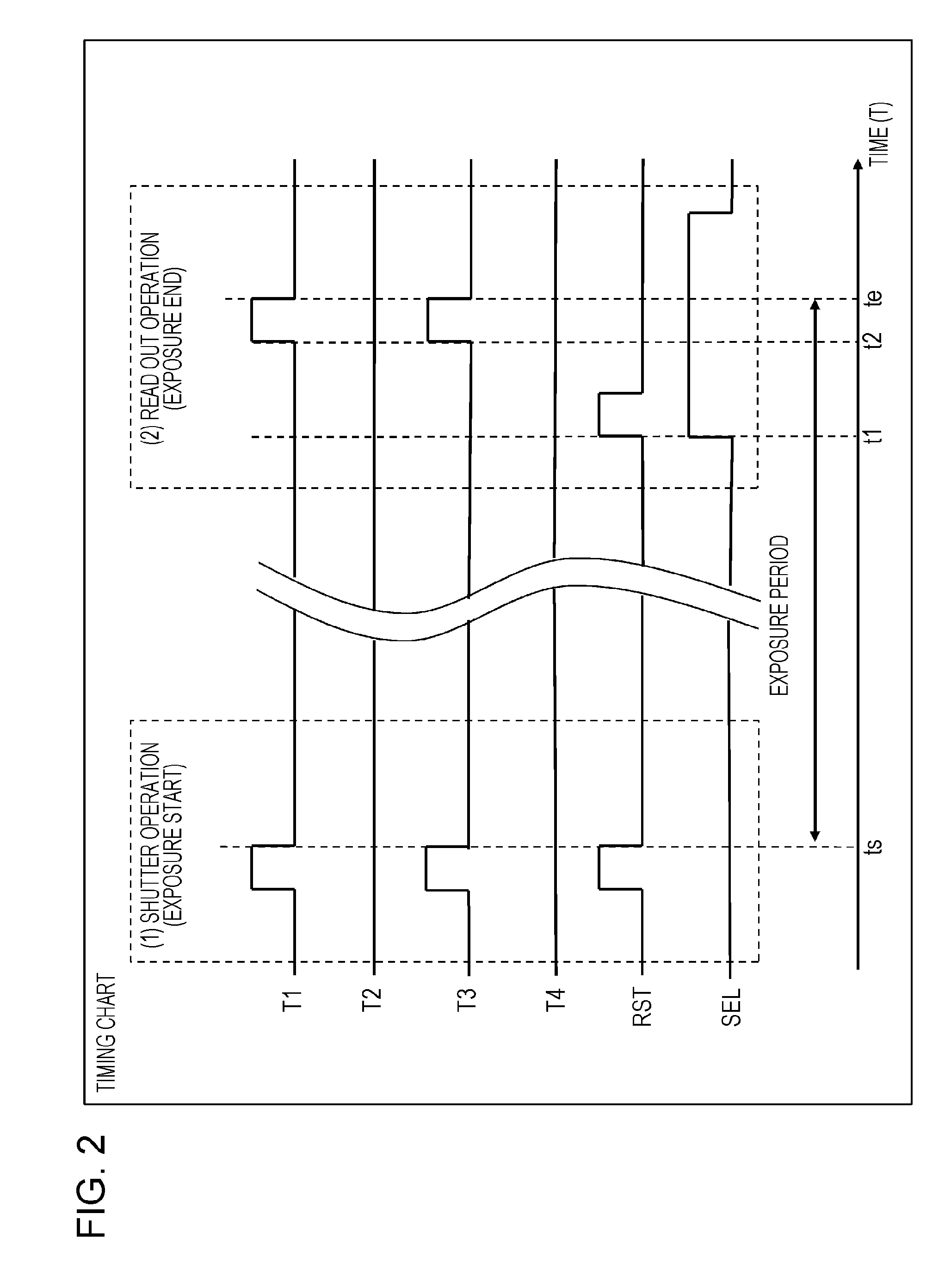
ActiveUS20130010153A1Evenly arrangedQuality improvementTelevision system detailsSolid-state device signal generatorsJaggiesGravity center
To provide an apparatus and method for realizing a processing with which a pixel gravity center control can be conducted when a pixel number reduction image is generated in an image pickup apparatus. A pixel unit configured to output a pixel addition signal obtained by adding output pixel signals from pixels having different sensitivities to each other and a pixel information synthesis unit configured to execute a weighted addition processing of multiplying plural pixel addition signals output from the pixel unit by a previously set gain and calculate a configuration pixel value of a pixel number reduction image where a total number of pixels is lower than a number of pixels of the pixel unit are provided. A control on gravity center positions for respective pixels constituting the pixel number reduction image is executed through the pixel addition signal generation processing by the pixel unit and the weighted addition processing by the pixel information synthesis unit. For example, a gravity center position control to evenly arrange the gravity center positions for the respective pixels constituting the pixel number reduction image in the pixel unit is executed. Through this processing, it is possible to generate a high quality image in which a generation of jaggies or the like is suppressed.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
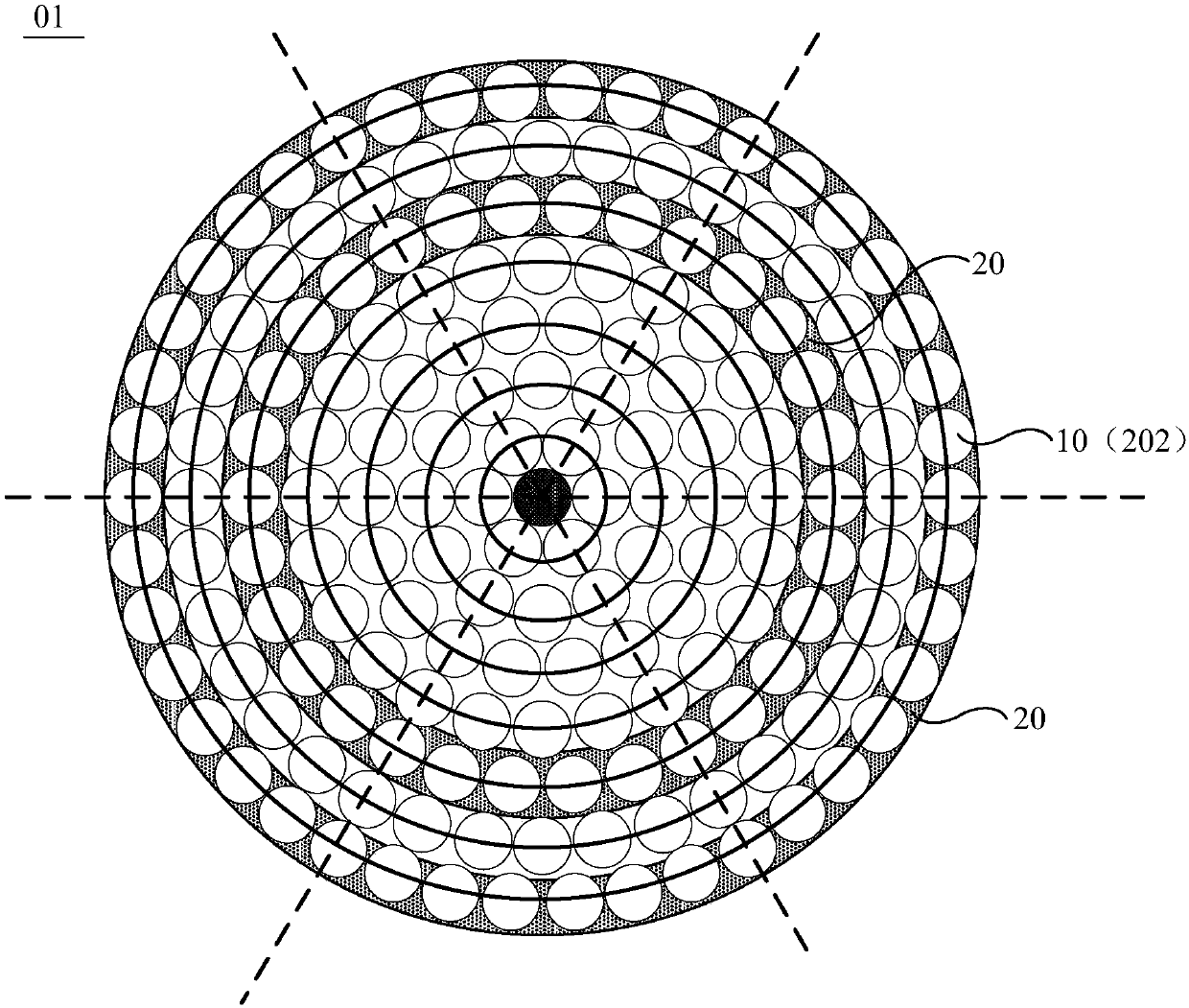
Pixel structure, display panel and display device
ActiveCN107589600AReduce jaggednessDecreased acuityStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsJaggiesDisplay device
The embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of display, and provides a pixel structure, a display panel and a display device for weakening jaggies at the periphery of a display area. The pixel structure comprises multiple circular pixels; the circular pixels include one center pixel and multiple peripheral pixels; the peripheral pixels form multiple first pixel groups; multipleperipheral pixels in each first pixel group are distributed on the same circumference with the center pixel as the circle center; in the direction away from the center pixel, the radii of the circumferences where the peripheral pixels in different first pixel groups are distributed are gradually increased. The pixel structure is used for displaying images.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
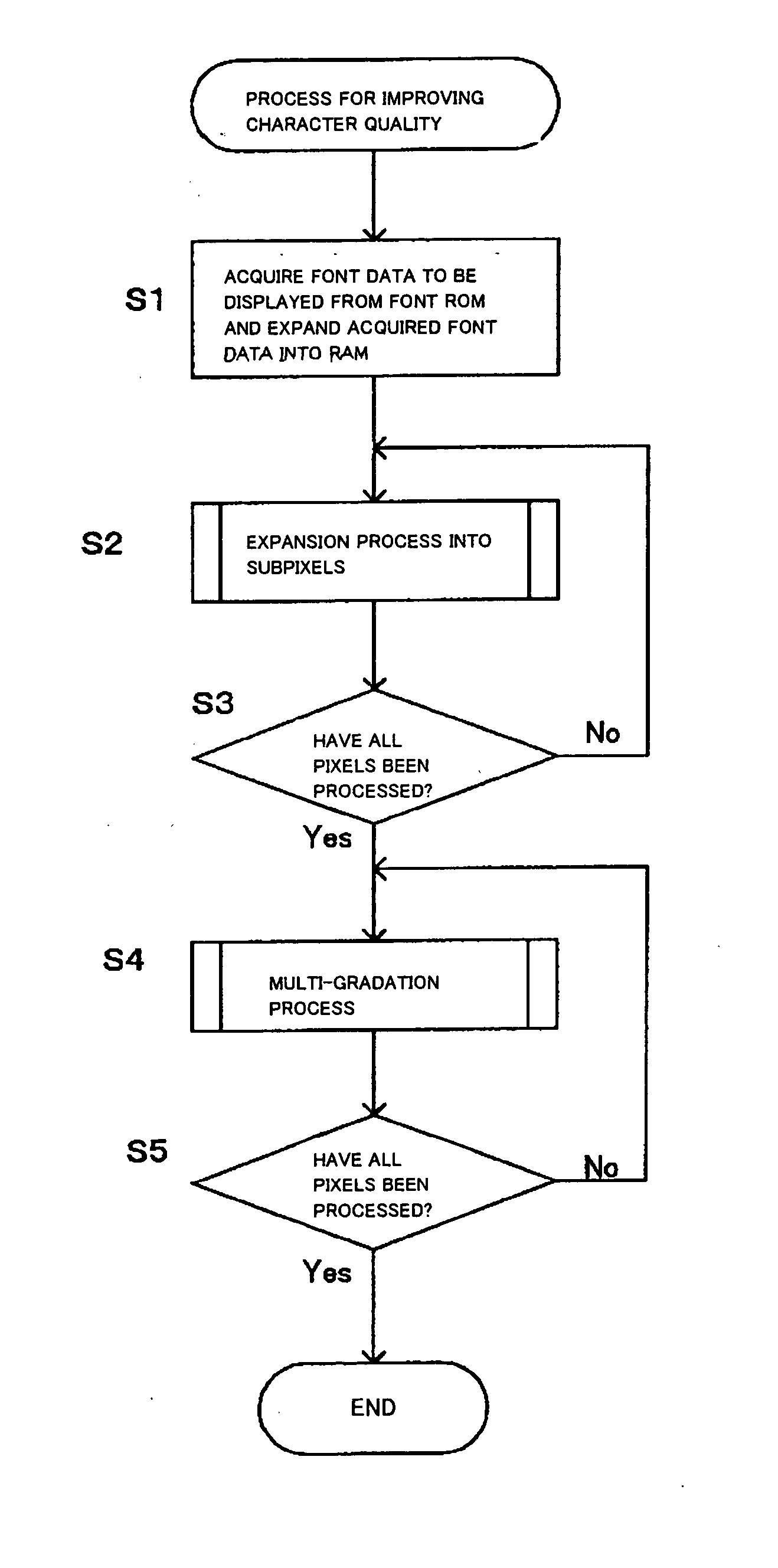
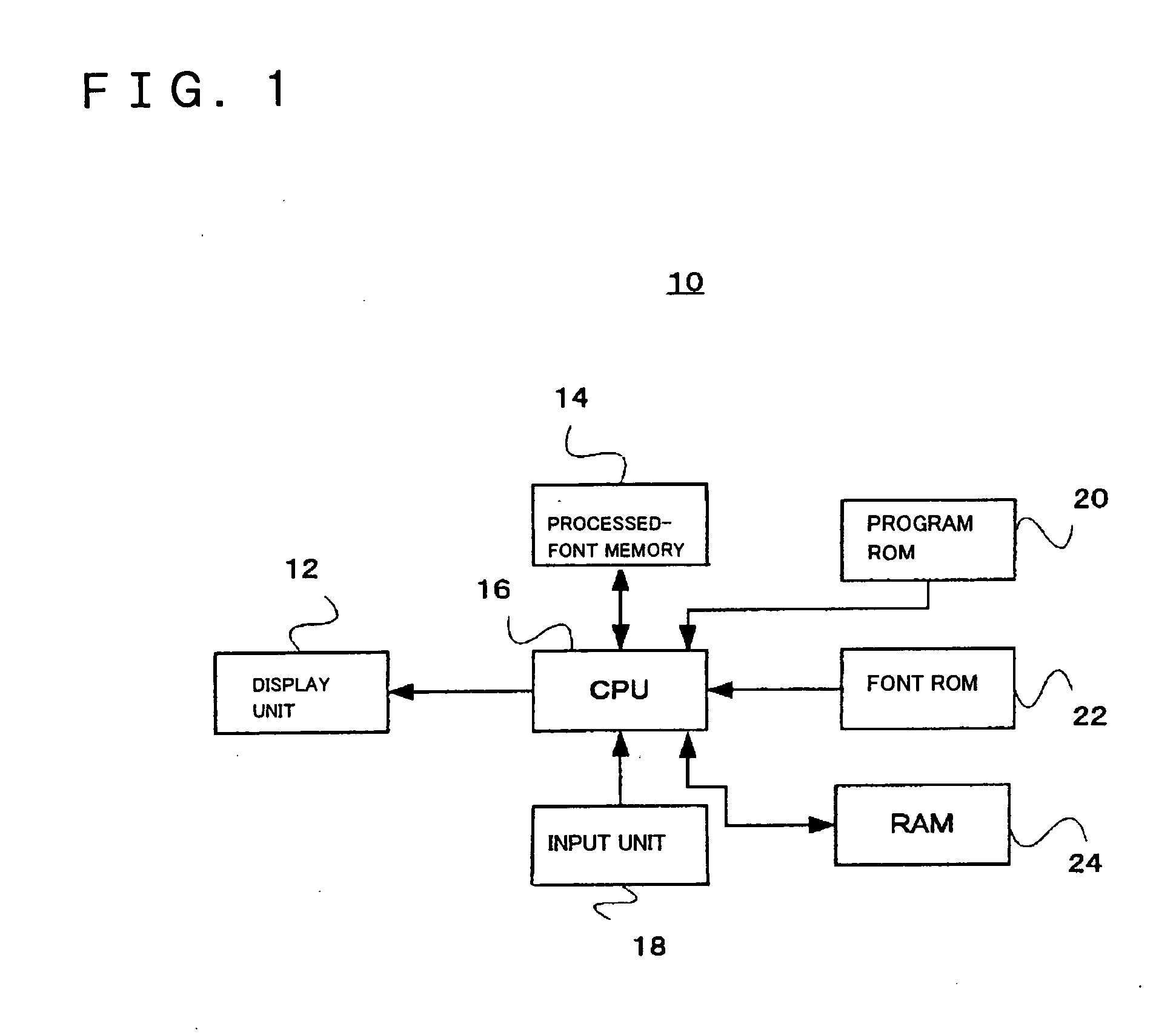
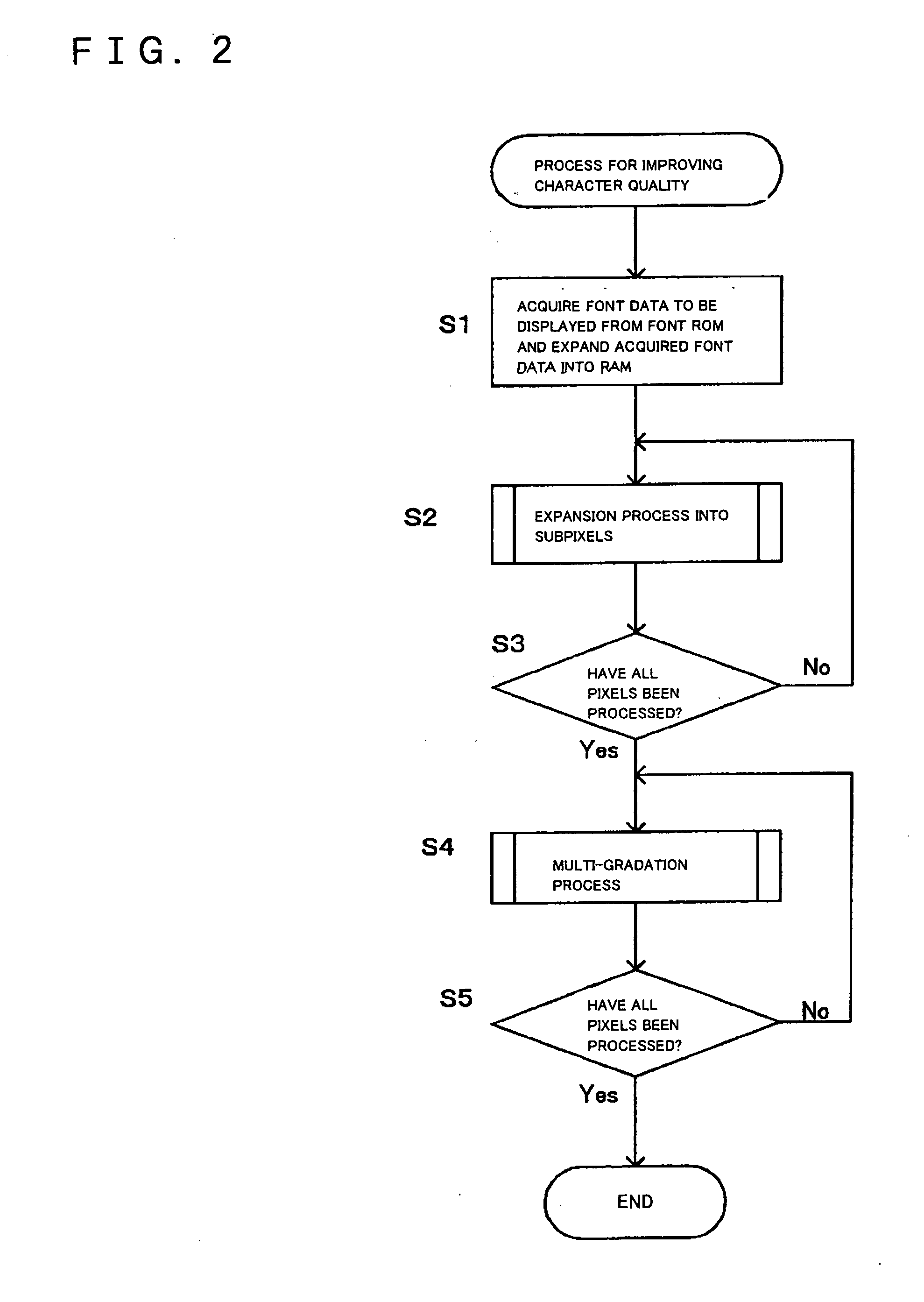
Font processor, terminal device, font processing method, and font processing program
InactiveUS20050162427A1Improve display quality2D-image generationCathode-ray tube indicatorsJaggiesPattern matching
The invention provides a font processor that is able to display bitmap fonts used in a mobile phone, a PDA, or the like with a small amount of computation and with high quality. A font processor of the present invention can acquire predetermined data of the bitmap fonts and analyzes the pixel arrangement of the acquired font data by pattern matching. The font processor then generates subpixel fonts that have data in subpixels constituting the pixel of the font data in accordance with the pixel arrangement. A subpixel is an element constituting a pixel. A collection of three subpixels, that is, R (red), G (green), and B (blue) subpixels, generally constitutes one pixel. Analyzing the pixel arrangement and generating the subpixel fonts that are collections of data in subpixels increase the apparent resolution of the font data. Accordingly, finer lines can be drawn and jaggies occurring in diagonal lines of the font data in pixels can be reduced. Performing the processing described above by pattern matching requires only a small amount of computation.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Single-pass image resampling system and method with anisotropic filtering
ActiveUS7064770B2Conservation valueImage enhancementGeometric image transformationJaggiesImaging quality
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
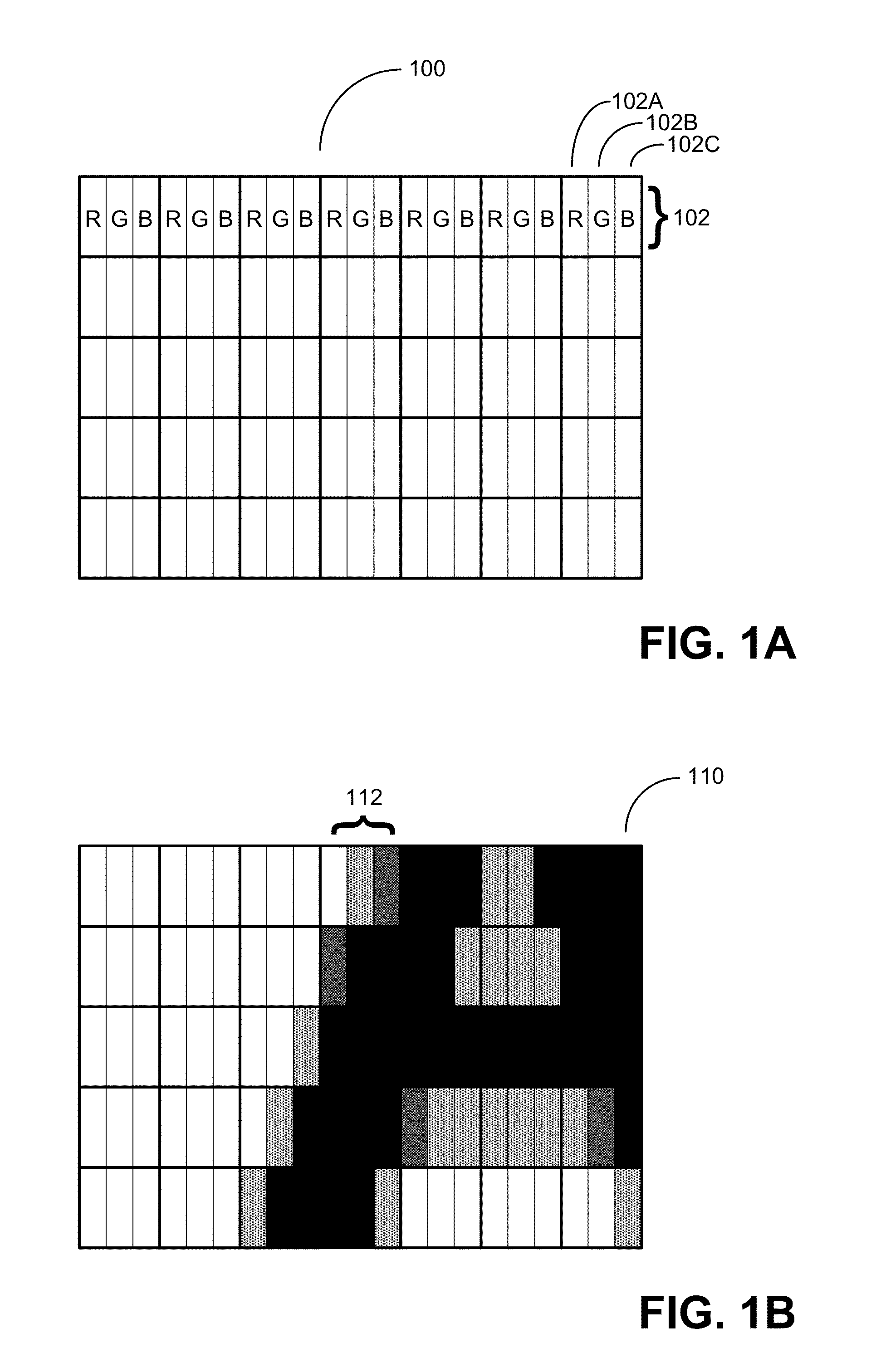
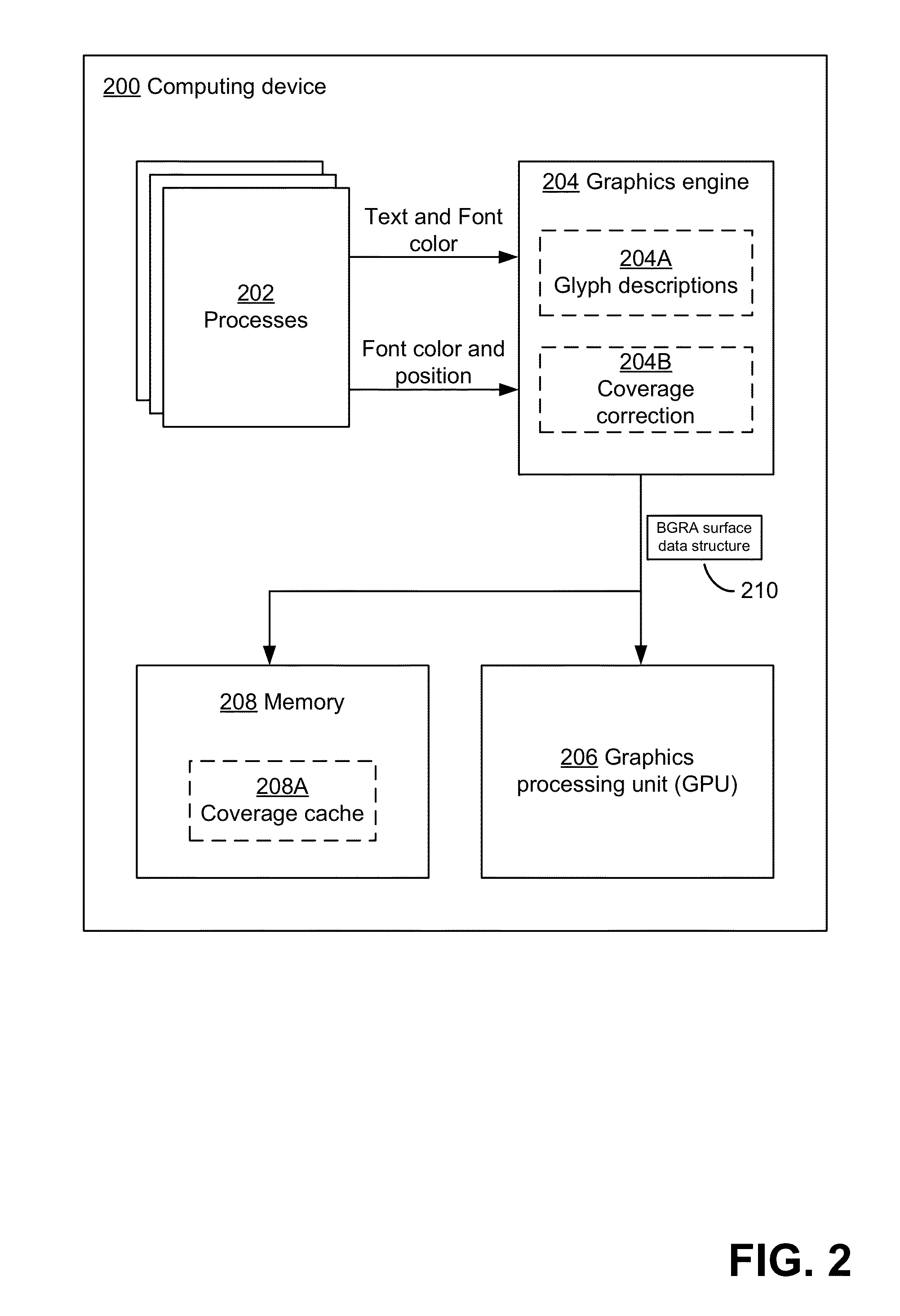
Caching coverage values for rendering text using Anti-aliasing techniques
ActiveUS20130088505A1Improve display qualityEasy to cacheDetails involving antialiasing2D-image generationGraphicsJaggies
Techniques for calculating sub-pixel coverage values for text to be displayed, so as to enable caching of the sub-pixel coverage values. The sub-pixel coverage values may enable a linear combination of color information for the text with color information for one or more other, overlapping display elements for calculating composite color values to be used in controlling a display. Such composite color values to be used in controlling sub-pixels of a display may be calculated, in some embodiments, without performing a gamma correction process. Also described are techniques for retrieving cached sub-pixel coverage values and combining the values with color information for text and for other, overlapping display elements to calculate composite color values for sub-pixels of a display. At least one graphics processing unit (GPU) may be configured to perform operations using the sub-pixel coverage information and to calculate the composite color values for the sub-pixels.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
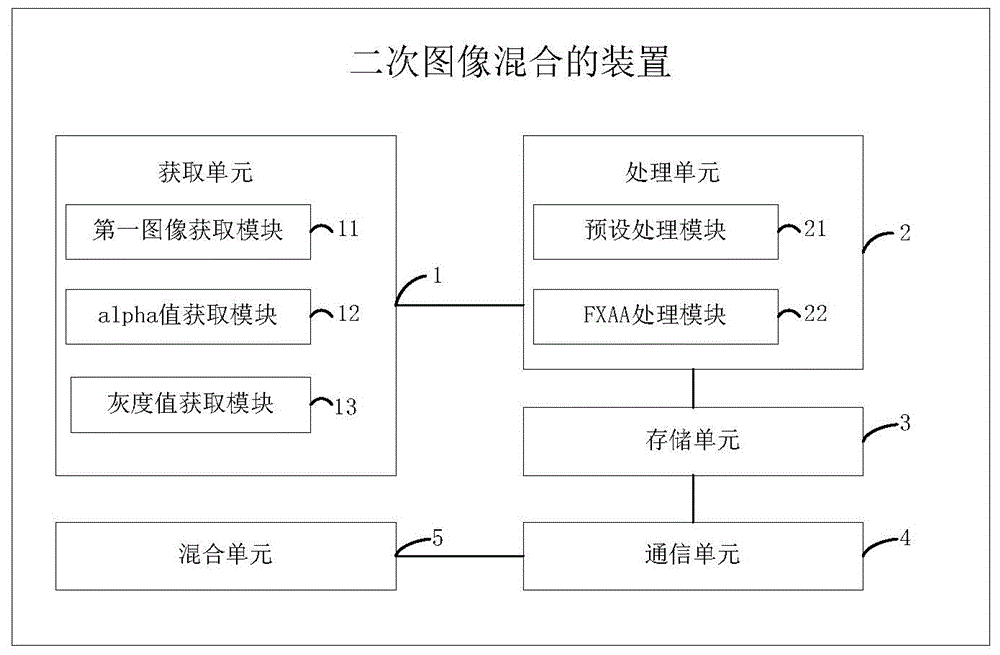
Secondary image mixing method and apparatus
The invention provides a secondary image mixing method and a secondary image mixing apparatus. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a first image from a first process; acquiring alpha value information and gray value information from the first image; performing a first preset processing on the alpha value information and a second preset processing on the gray value information, and storing the processed alpha value information and the processed gray value information into different channels of a texture map; performing FXAA processing on the texture map and a second image, and acquiring the RGB information of the second image and the alpha value information of the texture map according to the processing result to obtain a third image; inputting the third image into a second process and mixing the third image and a fourth image in the second process according to the alpha value information. By the method, the third image and the fourth image in the second process can be mixed well, and the phenomenon of jaggies occurring when the image is imported from one process to another process is greatly reduced, so that the user experience is enhanced.
Owner:FUJIAN TQ DIGITAL
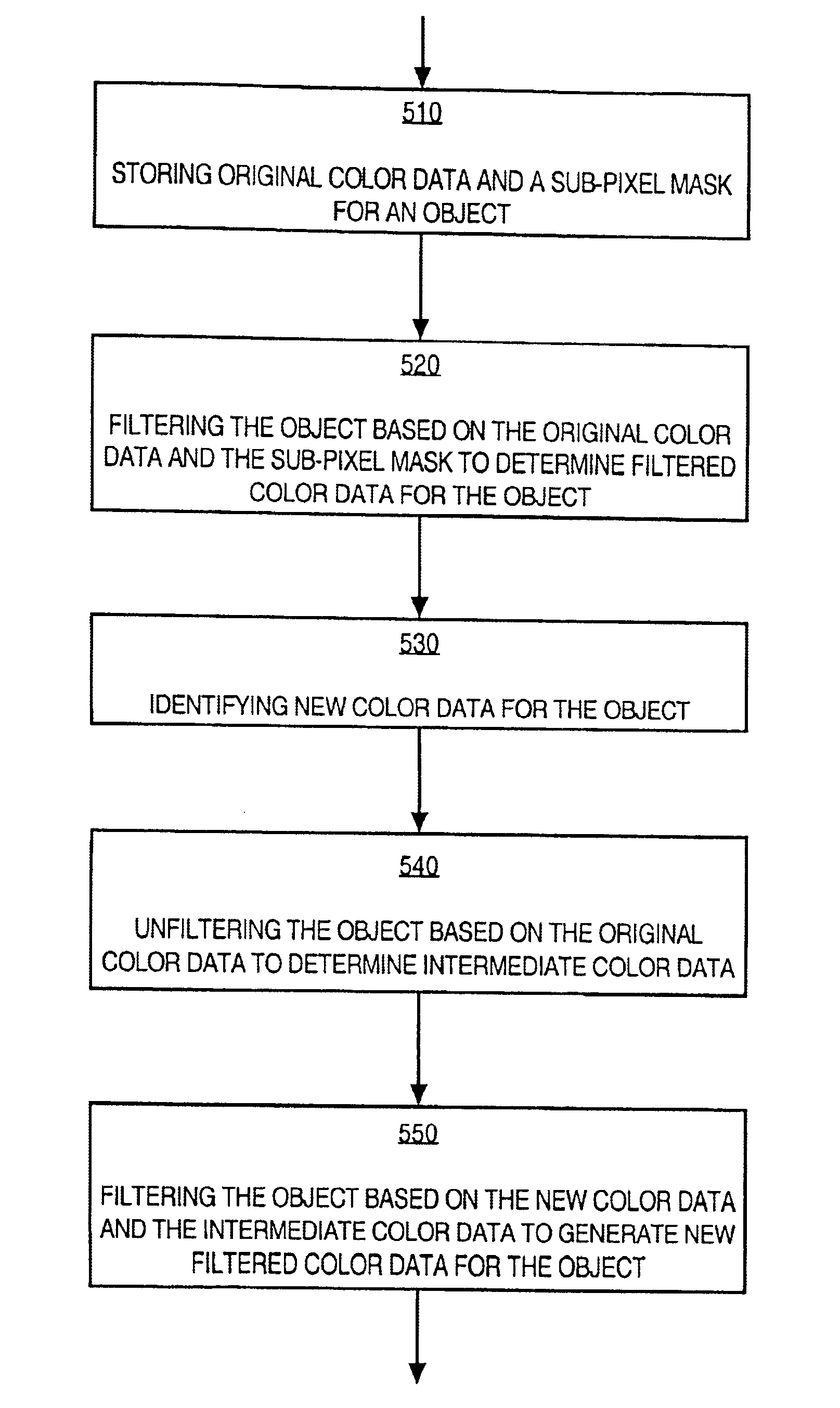
Incremental update of graphical images when using anti-aliasing techniques
An approach for incrementally updating graphical images when using anti-aliasing techniques is disclosed. Data for an original color is stored, and an image is filtered based on the original color. A new color for an image portion less than the entire image is identified. The new color is used with the old color to re-filter the image portion. The re-filtering may be performed by a two-step approach in which the image portion is filtered using the negative of the original color and then the image portion is filtered using the new color. The re-filtering may be performed by a one-step approach in which the portion of the image is filtered using the difference between the new color and the old color. The appearance of a halo around the portion of the image that would otherwise occur when filtering based on only the new color is thereby avoided.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
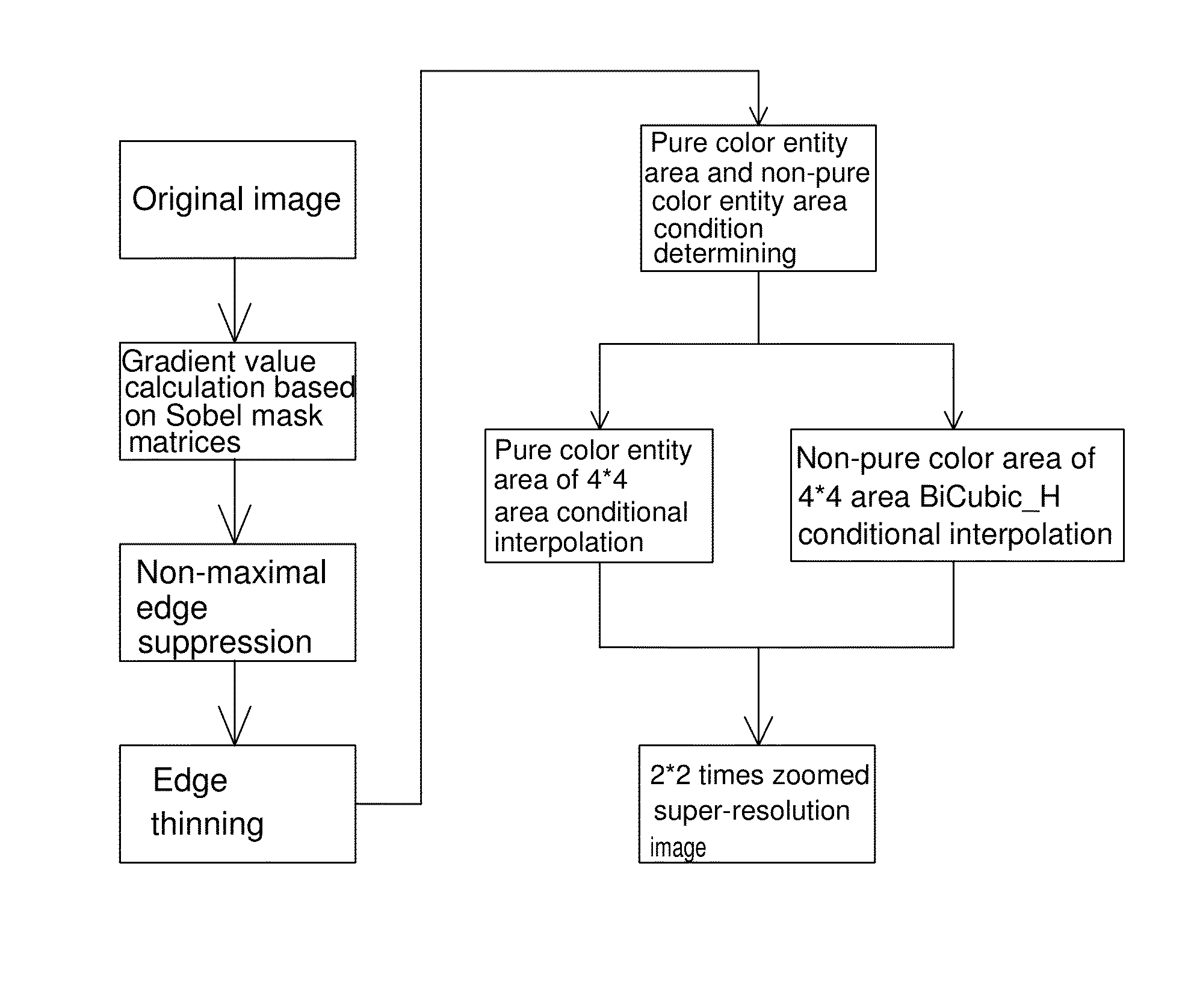
Super-resolution reconstructing method for enhancing smoothness and sharpness of video image
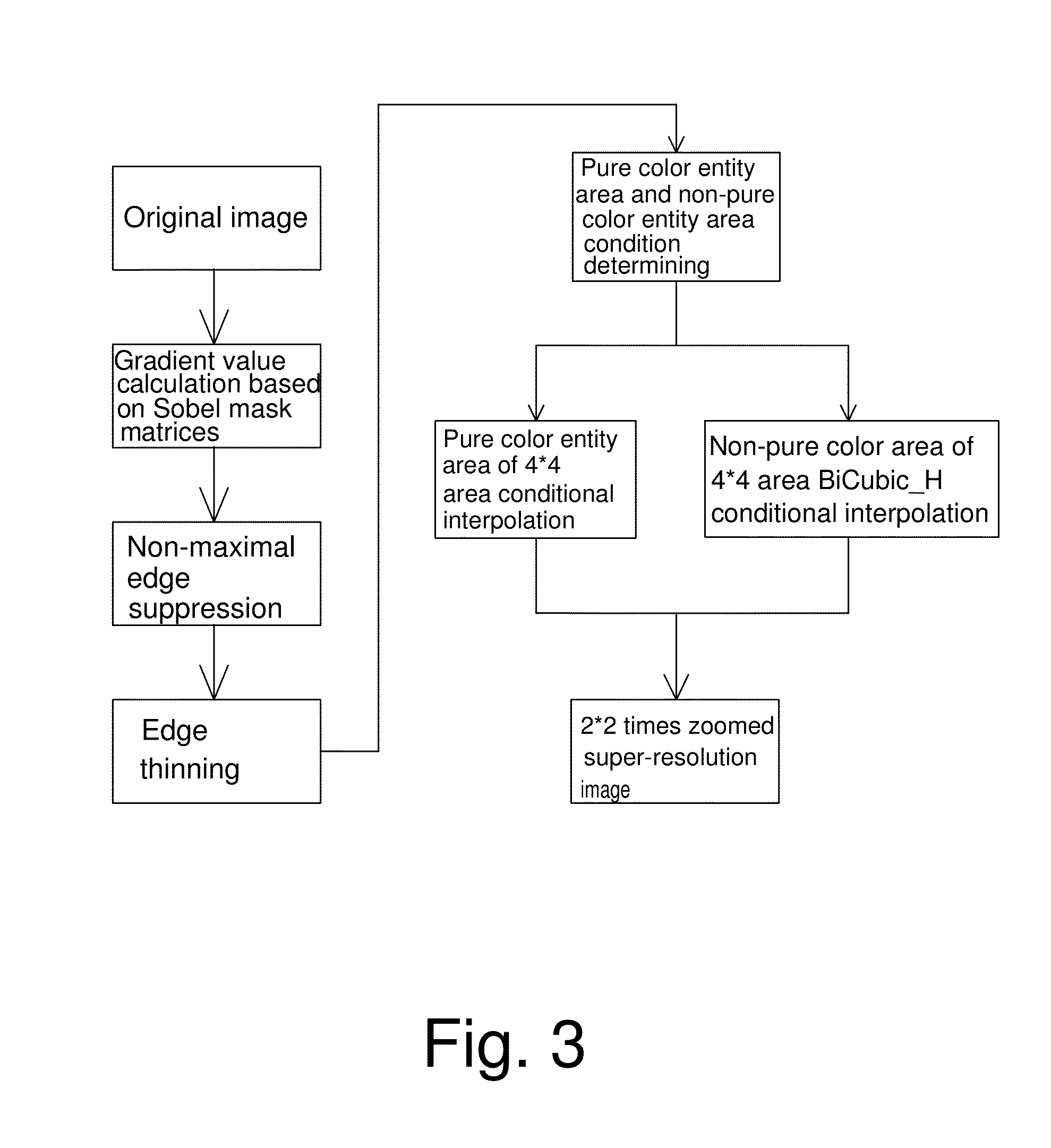
A super-resolution reconstructing method includes: providing an original image including multiple original image pixel points arranged in an array; performing edge detecting on the original image by Canny_H method and considering pixel edge information of 4*4 area image range; performing 2*2 times interpolation zooming to edge pixel points and determining a type of the 4*4 area image as pure color entity area or non-pure color entity area according to the pixel edge information; performing a conditional interpolation individually on pure color entity area and non-pure color entity area; and obtaining a pixel 2*2 times interpolation zoomed super-resolution image. In pure color entity area, interpolation is performed according to edge information of 4*4 area image range to maintain border sharpness of pure color entity area and reduce jaggies. In non-pure color entity area, BiCubic_H interpolation is performed to enhance smoothness and sharpness of image.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
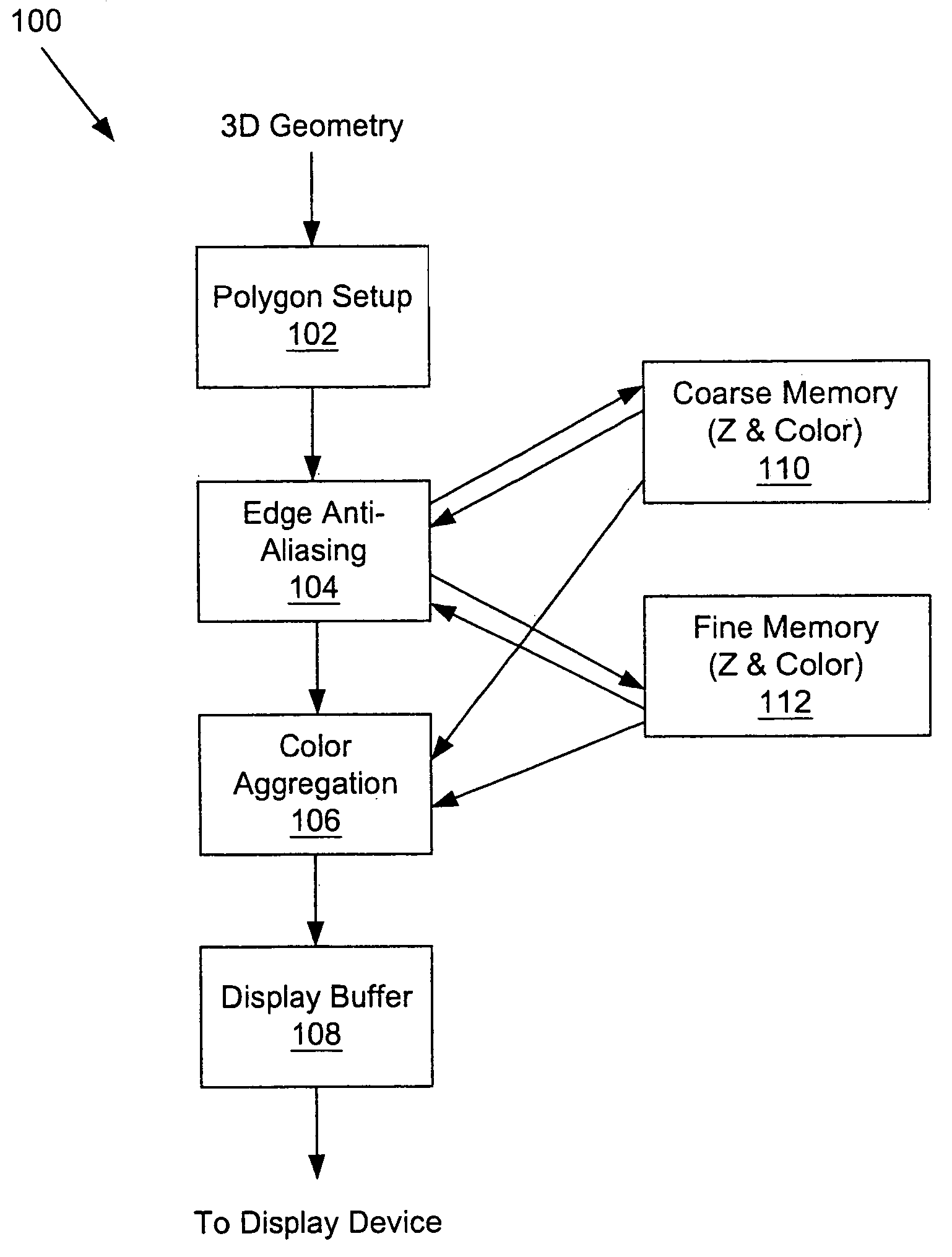
System and method for multi-sampling primitives to reduce aliasing
A method and system for performing multi-sample, antialiased rendering of images by performing multi-sample antialiasing at the primitive level. Geometric primitives used to represent a graphics environment are set-up, and then shifted by a sub-pixel offset and rendered to generate values for pixels of an intermediate image. The shifting and rendering is repeated for the geometric primitive, each time generating values for pixels of another intermediate image. The values for the pixels of the intermediate images are combined to produce values for the respective pixels of the resulting image.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Image processing apparatus and image processing method for suppressing jaggies in the edge portions of image
ActiveUS7706021B2Suppress jaggiesConvenient ArrangementImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersPattern recognitionImaging processing
To suppress jaggies in second image data on the basis of first image data, the second image data obtained by executing halftoning processing for the first image data, and attribute data representing an attribute of each pixel contained in the first image data, a judgment signal indicating whether to execute smoothing processing is output on the basis of the attribute data. Edge correction data is generated from the first image data by executing smoothing processing in accordance with the judgment signal. The pixel data of the second image data is compared with the pixel data of the edge correction data. The pixel data having a higher density is output. Jaggies generated by halftoning processing can be suppressed with a simple arrangement at a low cost.
Owner:CANON KK
Selective super-sampling/adaptive anti-aliasing of complex 3D data
InactiveUS7095421B2Avoid it happening againReduce trafficGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsJaggies
A system and method is provided for preventing the occurrence of aliasing at the edges of polygons in 3D graphics. The system may detect both polygon geometric edges and Z edges due to intersection of multiple polygons. In one embodiment, the system includes an edge anti-aliasing module configured to selectively super-sample edge portions of primitives. The system further includes a coarse memory for storing information of pixels that are not super-sampled and a fine memory for storing information of pixels that are super-sampled by the edge anti-aliasing module.
Owner:S3 GRAPHICS
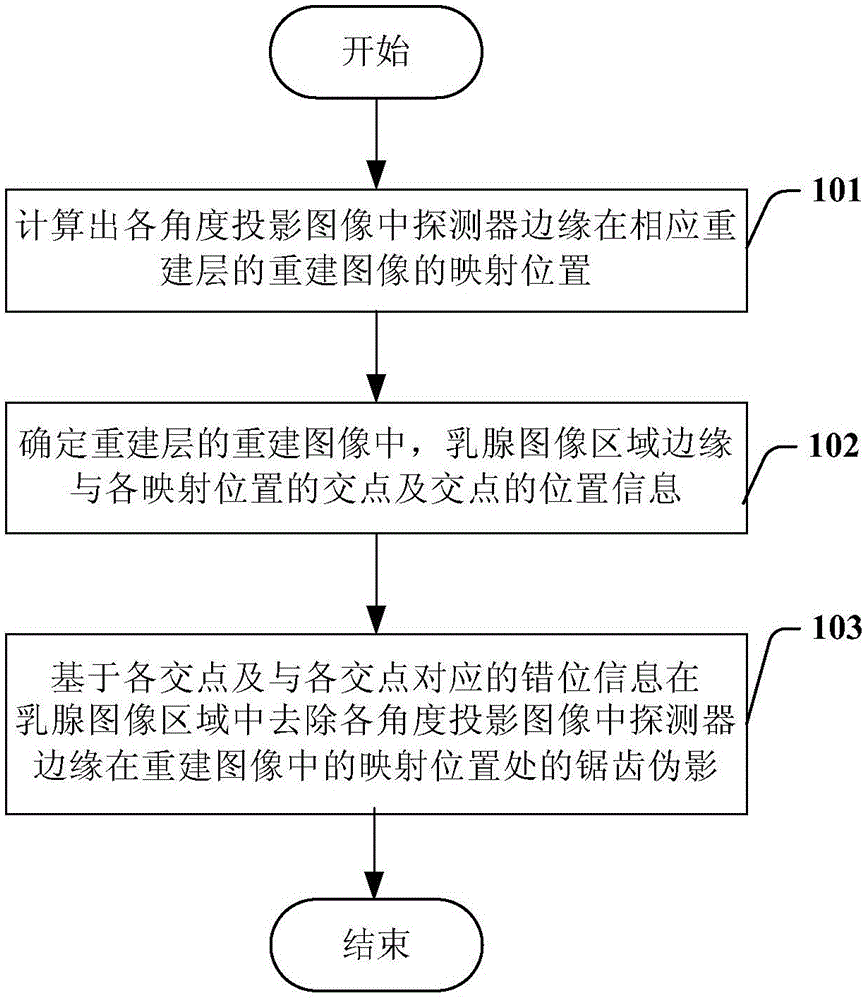
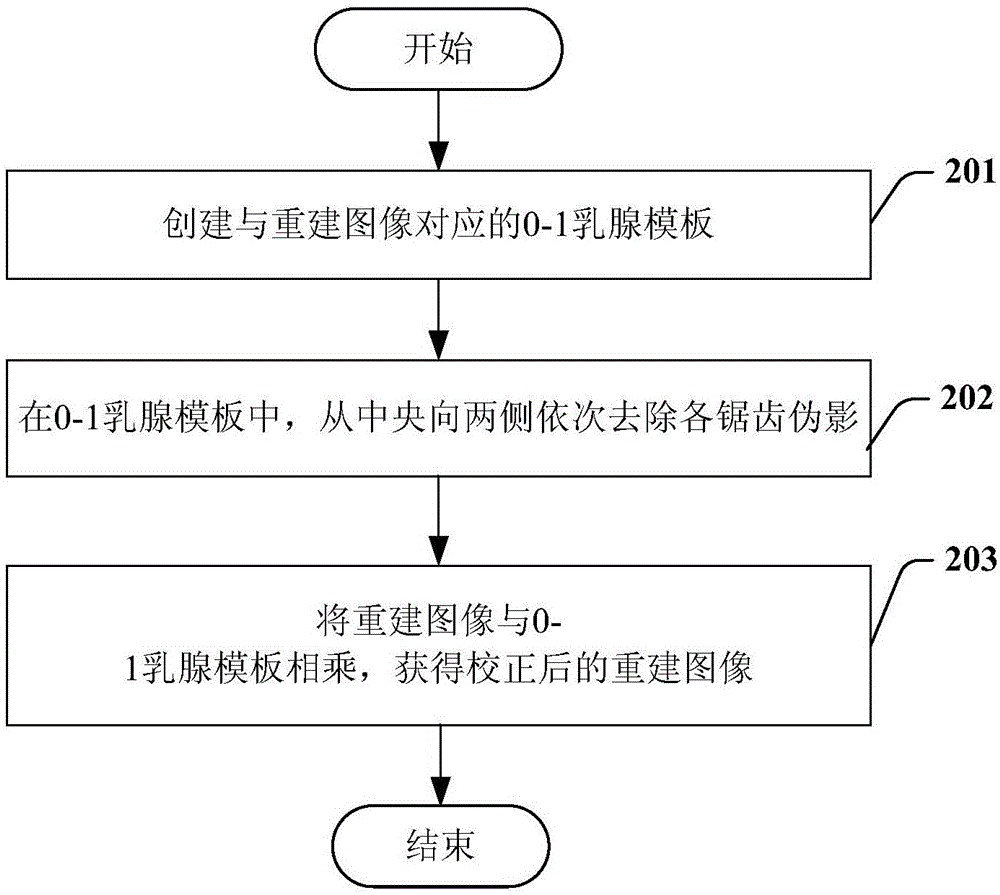
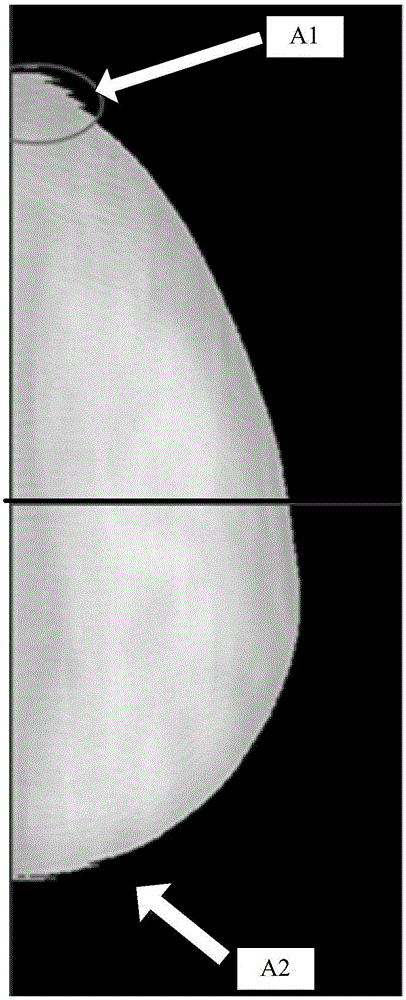
Correction method and device for sawtooth artifacts in digital breast mammary tomographic reconstruction
ActiveCN105078492AQuality improvementImage analysisRadiation diagnosticsJaggiesIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention provides a correction method and a correction device for sawtooth artifacts in digital breast mammary tomographic reconstruction. The method comprises the following steps: calculating the mapping positions of the edges of a detector in reconstruction images of corresponding reconstruction layers in projected images in various angles; determining the intersection points of the edges of the mammary image region and the mapping positions and the position information of the intersection points in the reconstruction images of the reconstruction layers; and based on the intersection points and malposition information corresponding to the intersection points, removing the sawtooth artifacts of the edges of the detector in the mapping position of the reconstruction images in the projected images in various angles in the mammary image region, wherein the malposition information corresponding to the intersection points refers to the shift of the sharp end of the sawtooth artifacts corresponding to the intersection points relative to the intersection points in the horizontal direction.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
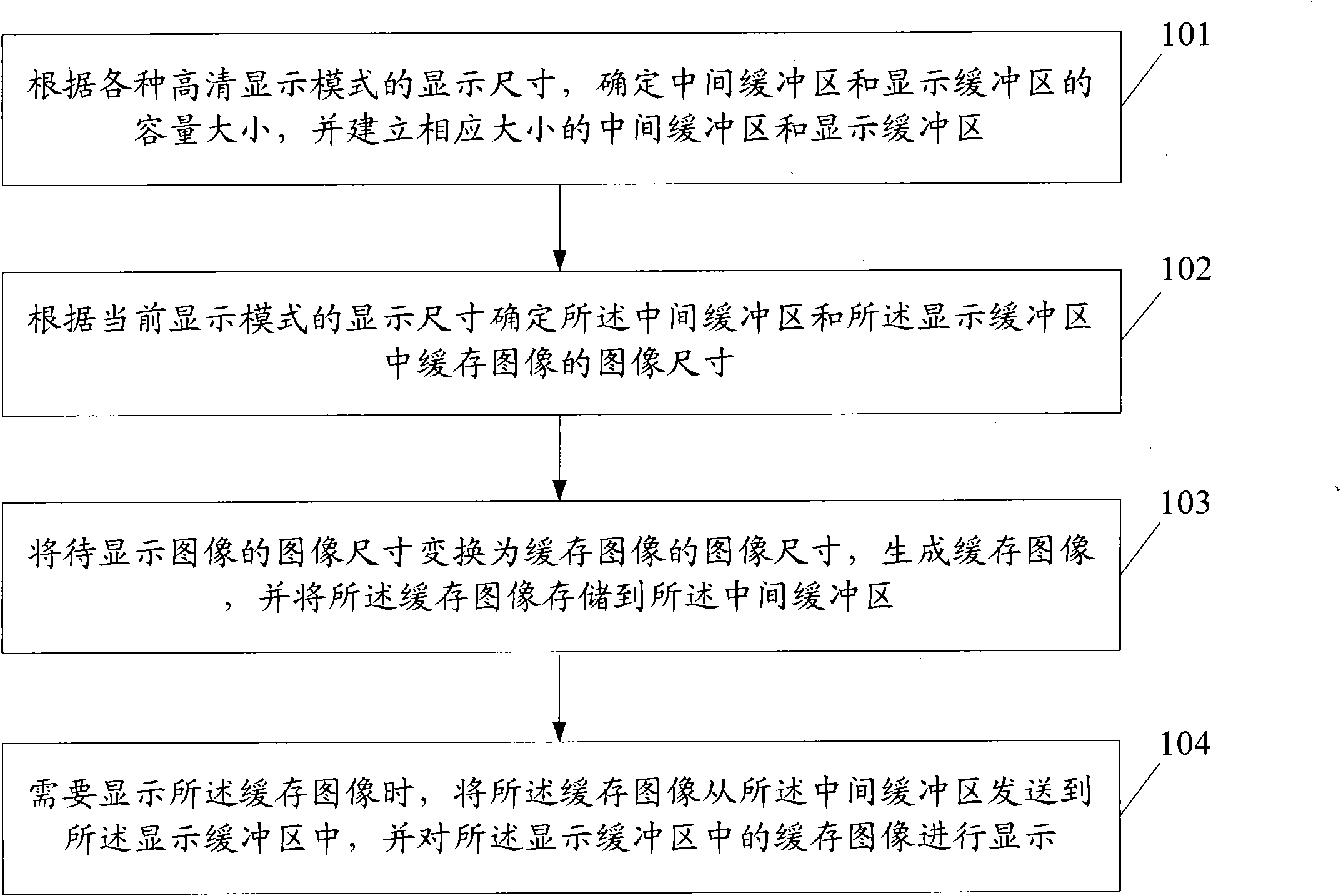
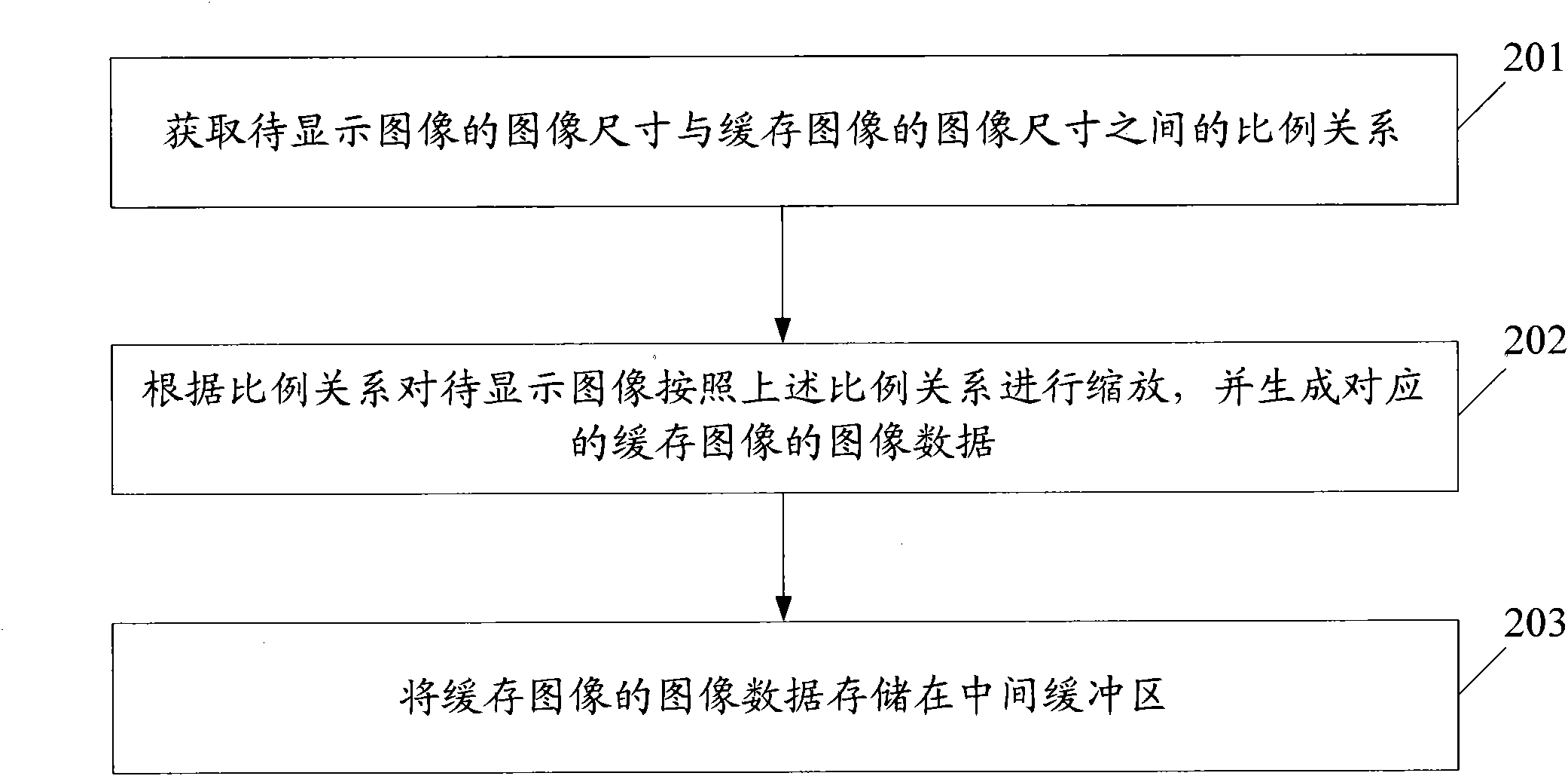
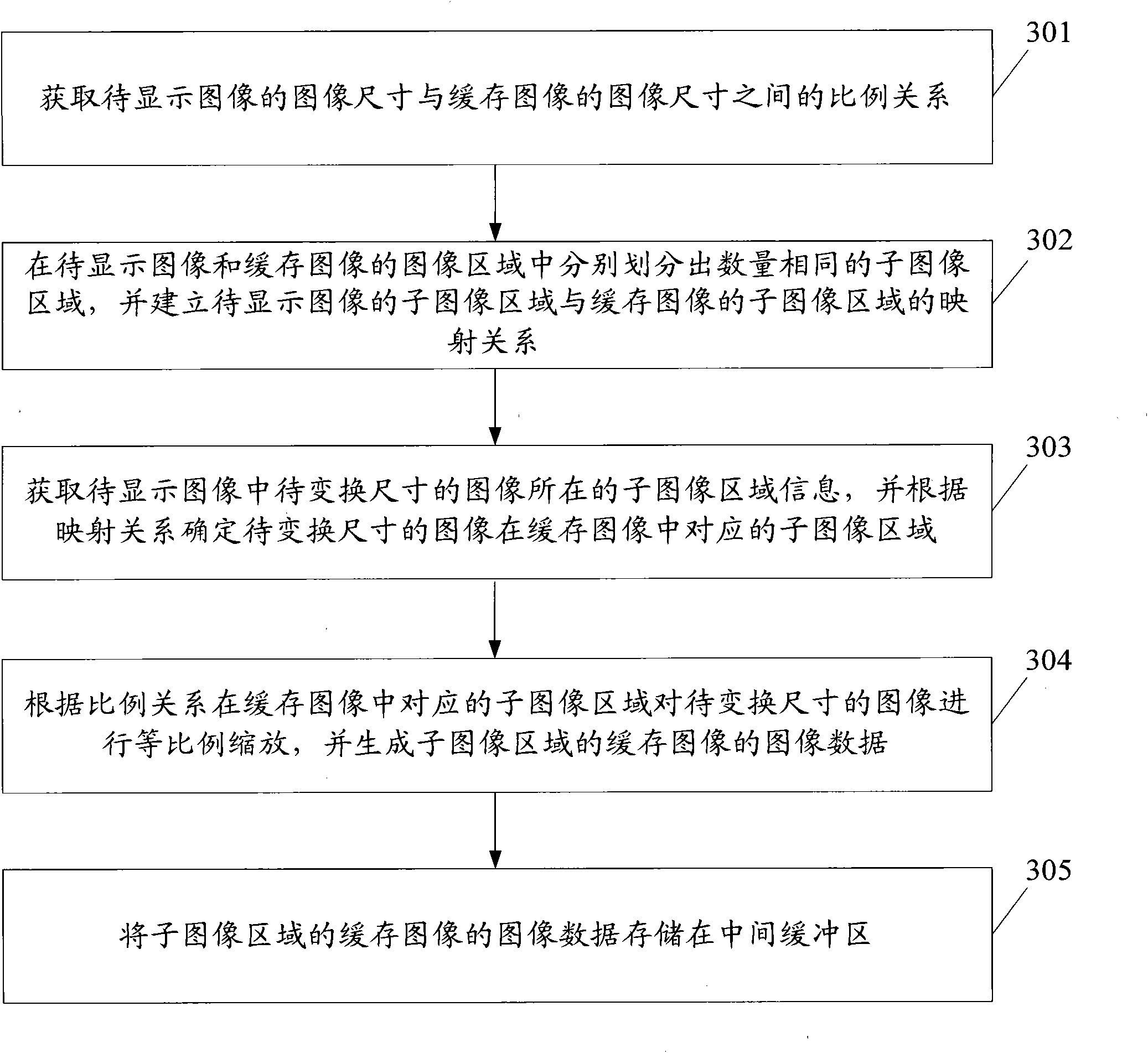
High-definition image sawtooth-prevention method, device and digital television receiving terminal
InactiveCN101778226AImprove display speedSave memoryTelevision system detailsImage enhancementJaggiesOperating system
The invention provides a high-definition image sawtooth-prevention method, which comprises the following steps: the capacity of a middle cache area and a display cache area is determined according to the display size of different high-definition display modes, the middle cache area and the display cache area with corresponding size are established, the size of the cache image in the middle cache area and the display cache area is determined according to the display size of the present display mode, the image size of the image to be displayed is changed to the image size of the cache image so as to generate a cache image, the cache image is stored into the middle cache area, when the cache image is required to be displayed, the cache image is sent from the middle cache area to the display cache area, and the cache image in the display cache area is displayed. The invention also provides a high-definition image sawtooth-prevention device and a digital television receiving terminal. By implementing the embodiment, the display speed of the high-definition image can be improved, while the high-definition image sawtooth prevention is realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN COSHIP ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Image processing apparatus and image processing method
A smoothing process is performed on image data to obtain improved image quality. Output image data is switched among image data subjected to smoothing, image data subjected to second bit conversion, and image data subjected to pseudo halftone representation process. In this manner, jaggies at edges can be smoothed even in multilevel image data subjected to image forming process such as screen processing. Smoothing for image data with degraded image quality due to, for example, lossy compression such as JPEG compression can also be achieved. Furthermore, degradation in image quality that occurs when a conventional smoothing process is applied to image data subjected to particular image processing can be avoided.
Owner:CANON KK
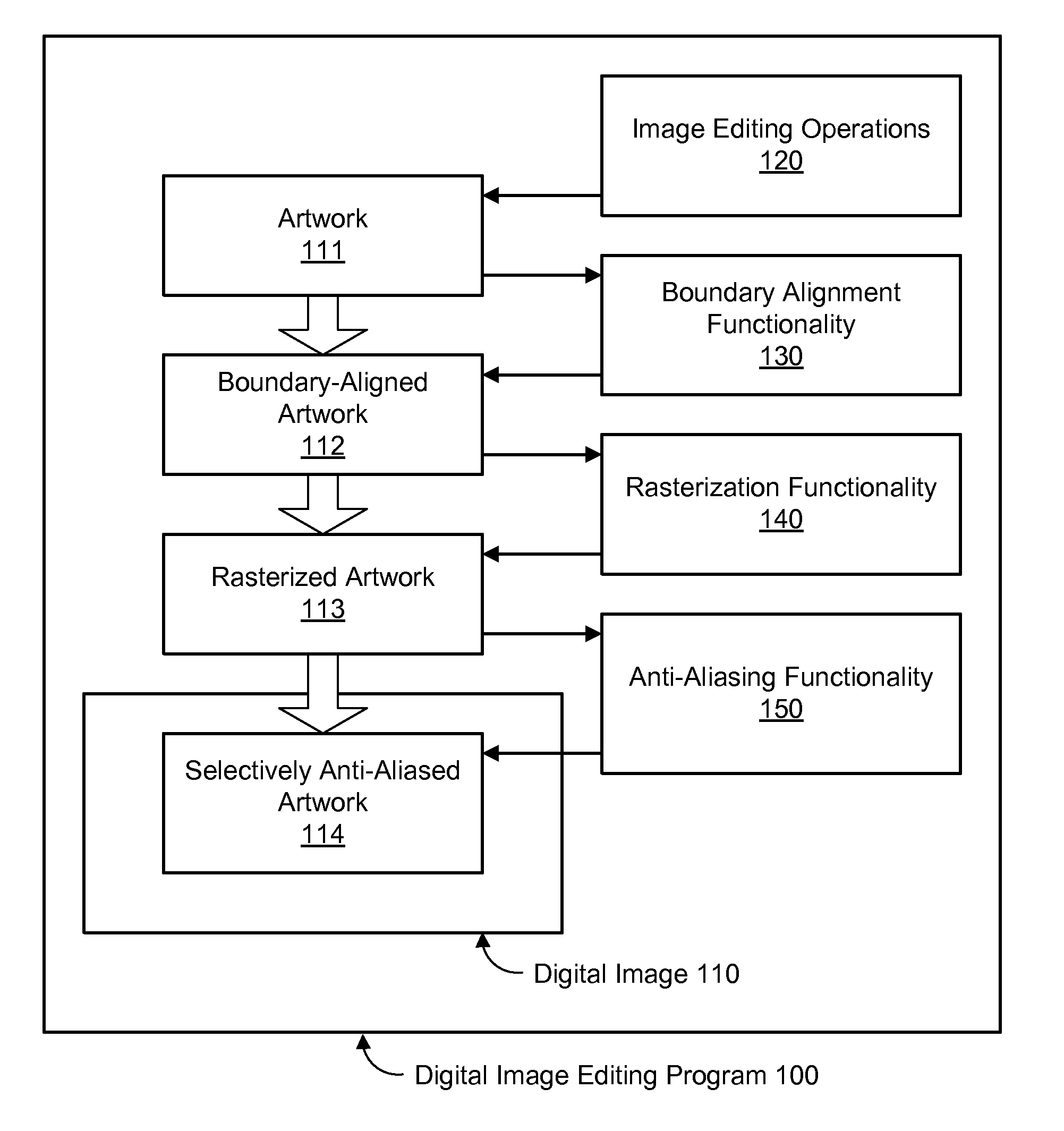
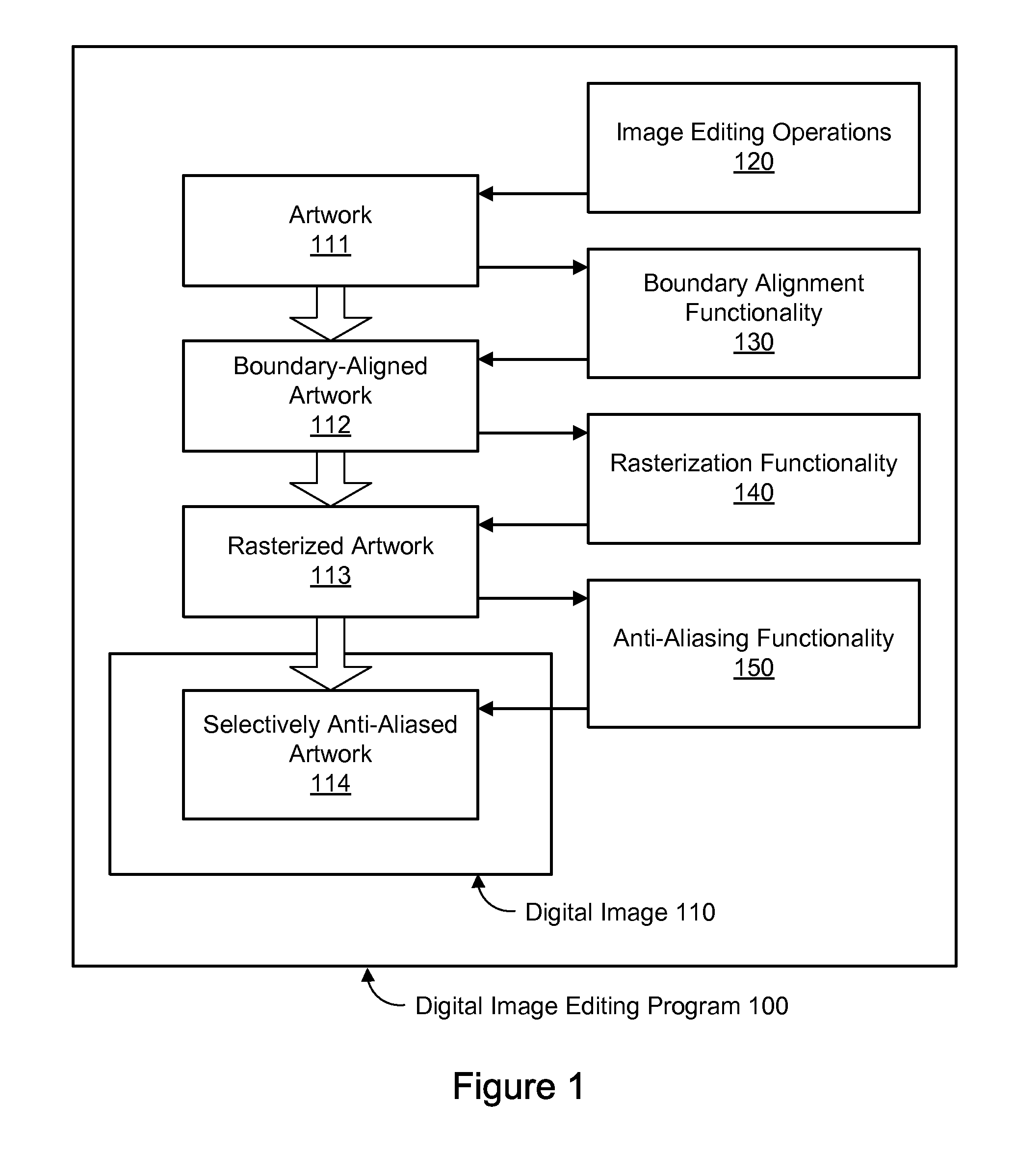
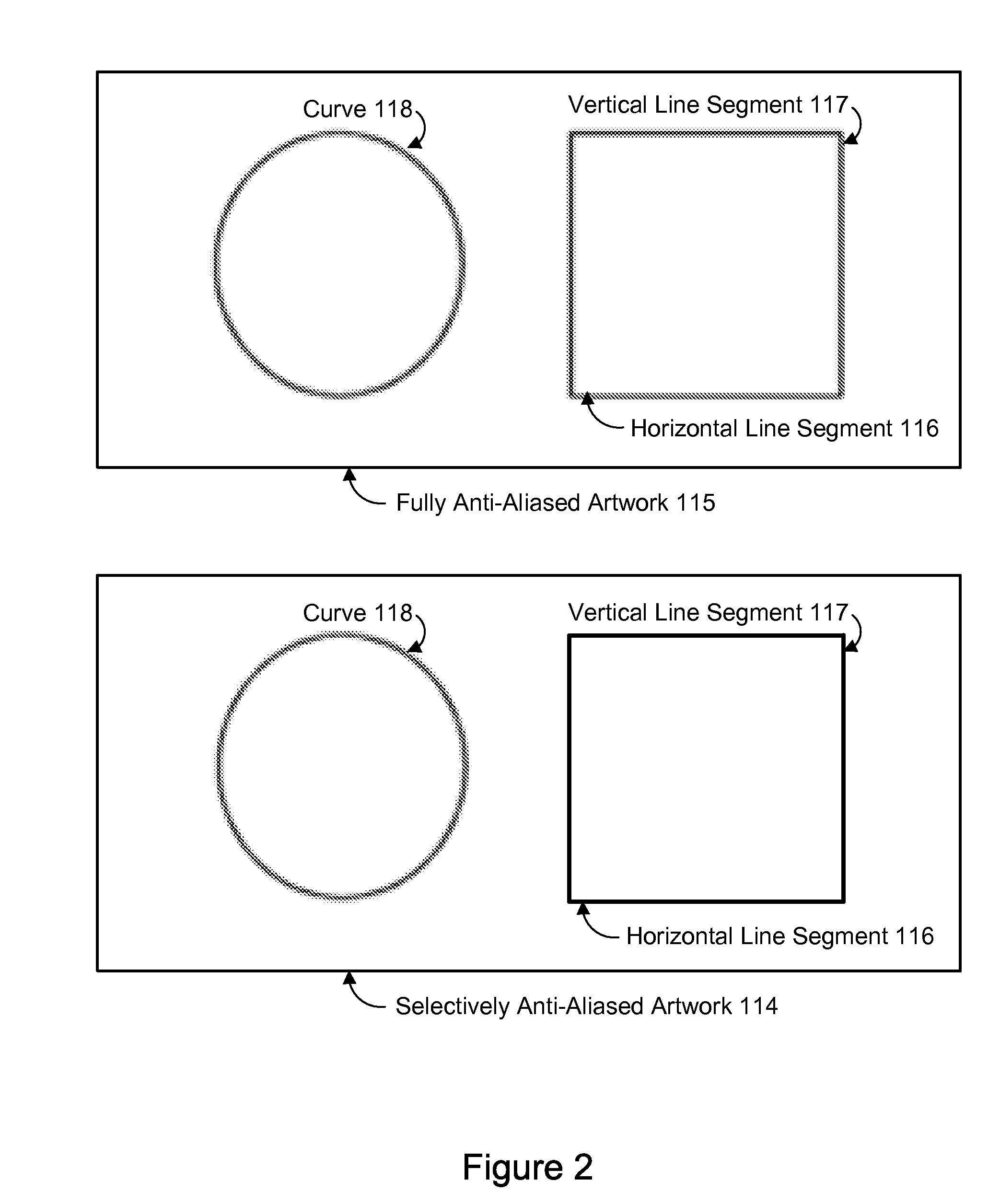
Pixel-Aligned Drawing to Avoid Anti-Aliasing
A method, system, and computer-readable storage medium are disclosed for boundary-aligned anti-aliasing. In one embodiment, artwork input comprising a first set of one or more graphical elements and a second set of one or more graphical elements may be received. The first set may comprise at least one horizontal or vertical line segment. Each graphical element in the first set of one or more graphical elements may be automatically aligned to pixel boundaries based on a pixel resolution of a target imaging device. An anti-aliasing function may be applied to generate a selectively anti-aliased artwork based on the artwork input. Applying the anti-aliasing function may comprise applying anti-aliasing effects to the second set of one or more graphical elements and not to the first set of one or more graphical elements. The selectively anti-aliased artwork may be displayed on the target imaging device.
Owner:ADOBE INC
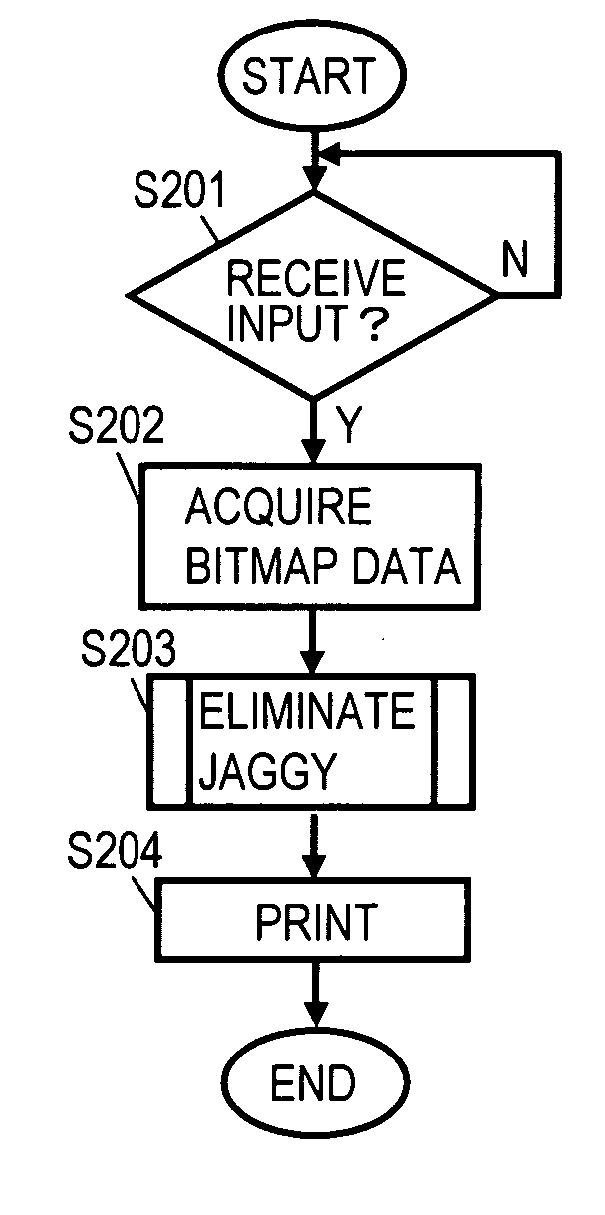
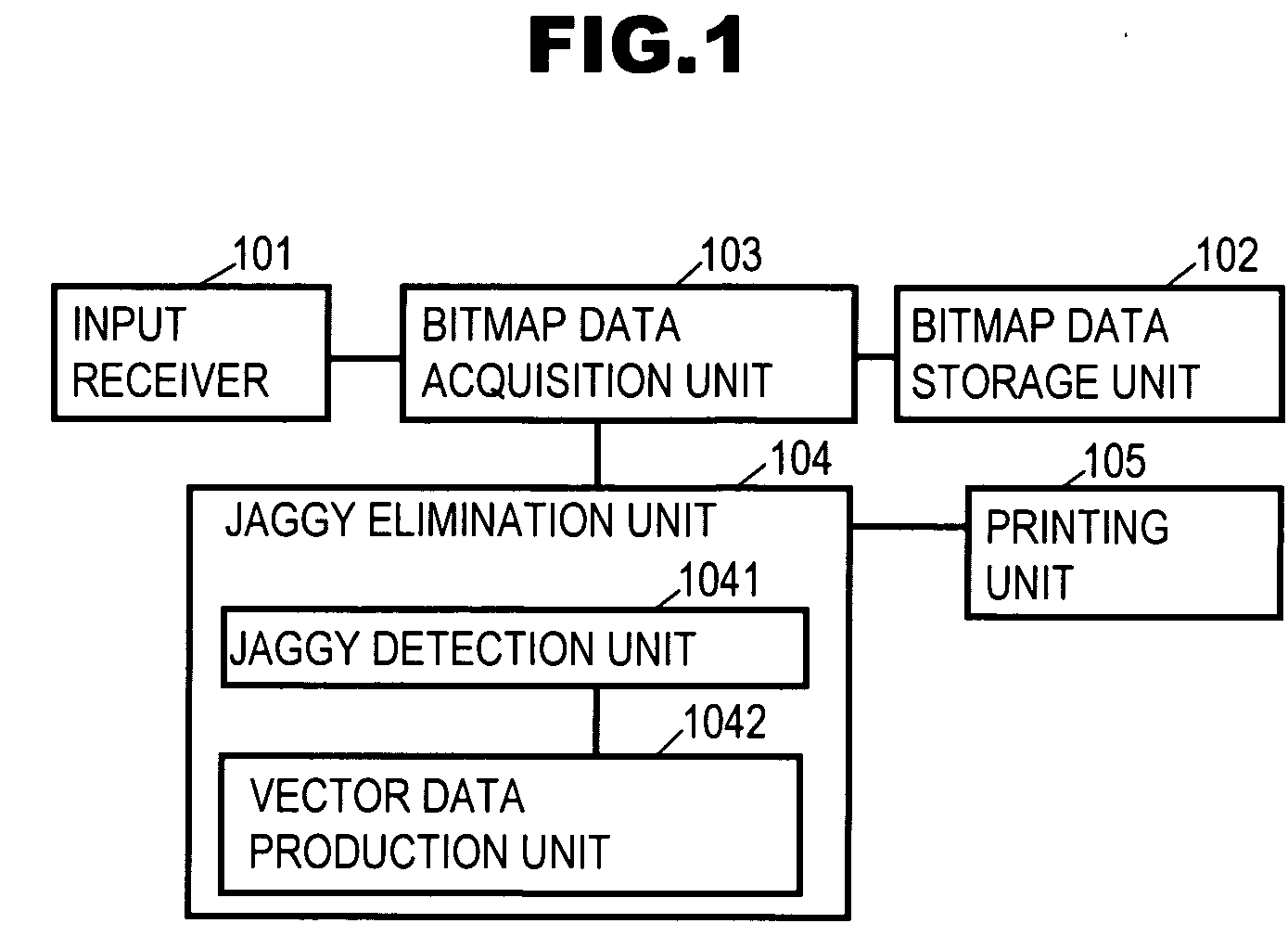
Output apparatus and program thereof
InactiveUS20060119897A1Improve image qualityExclude dataImage enhancementGeometric image transformationJaggiesImaging quality
Output apparatus including a vectorization unit for vectorizing part of bitmap data into first vector data, a data production unit for producing bitmap data after transformation, and an output unit of outputting that bitmap data. The data production unit includes an inverse transformation unit for transforming first coordinate information of a target dot with an inverse function of a certain calculation, and a color determination unit for determining the color of a dot specified by second coordinate information based on the first vector data and the color of a dot on the bitmap data so that the color determined thereby is setup for a dot specified by first coordinate information, and a control unit for enabling the inverse transformation and the color determination to be performed on all dots on the bitmap data to be outputted. Thereby, jaggy-less bitmap data can be outputted without losing its image quality.
Owner:SOFTWARE CRADLE
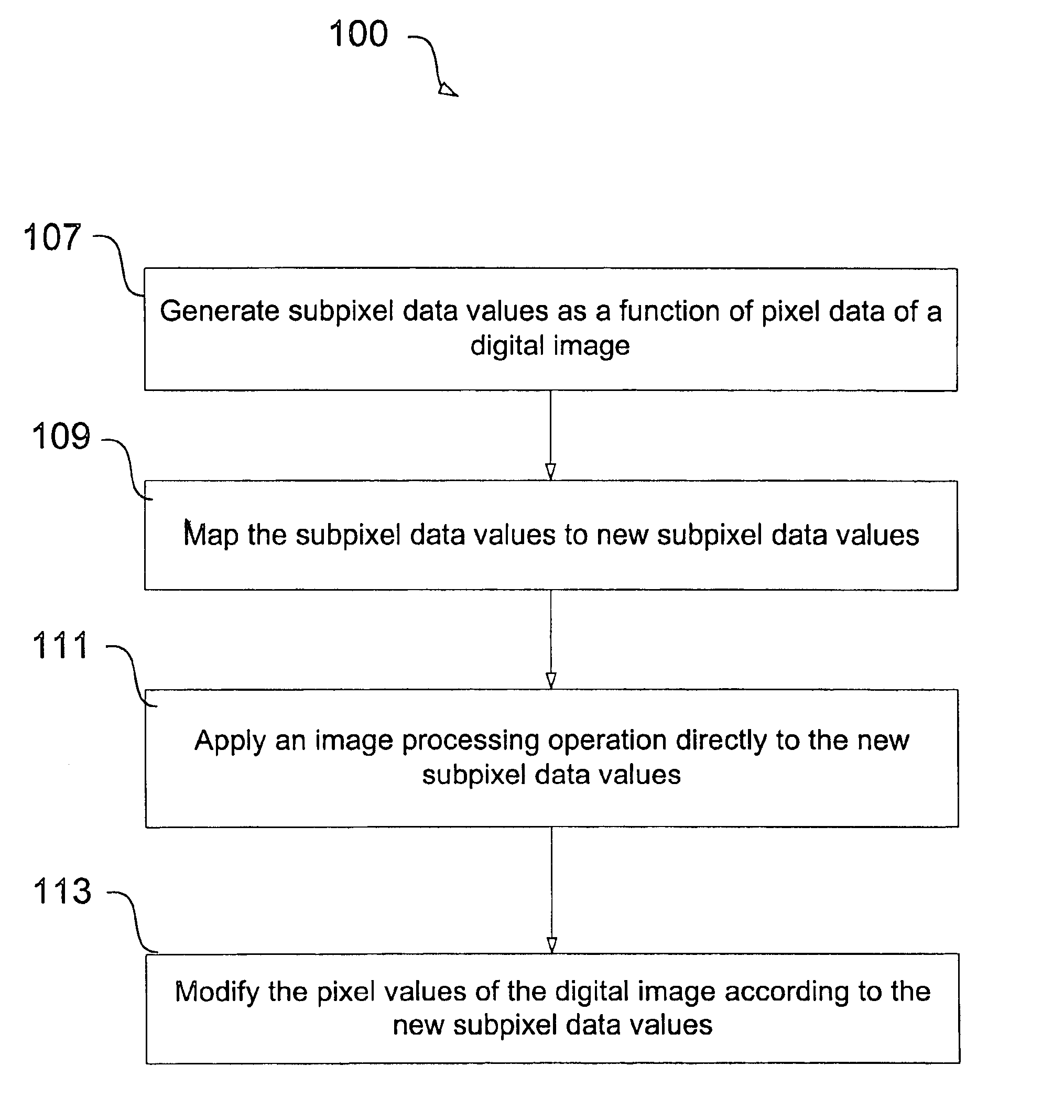
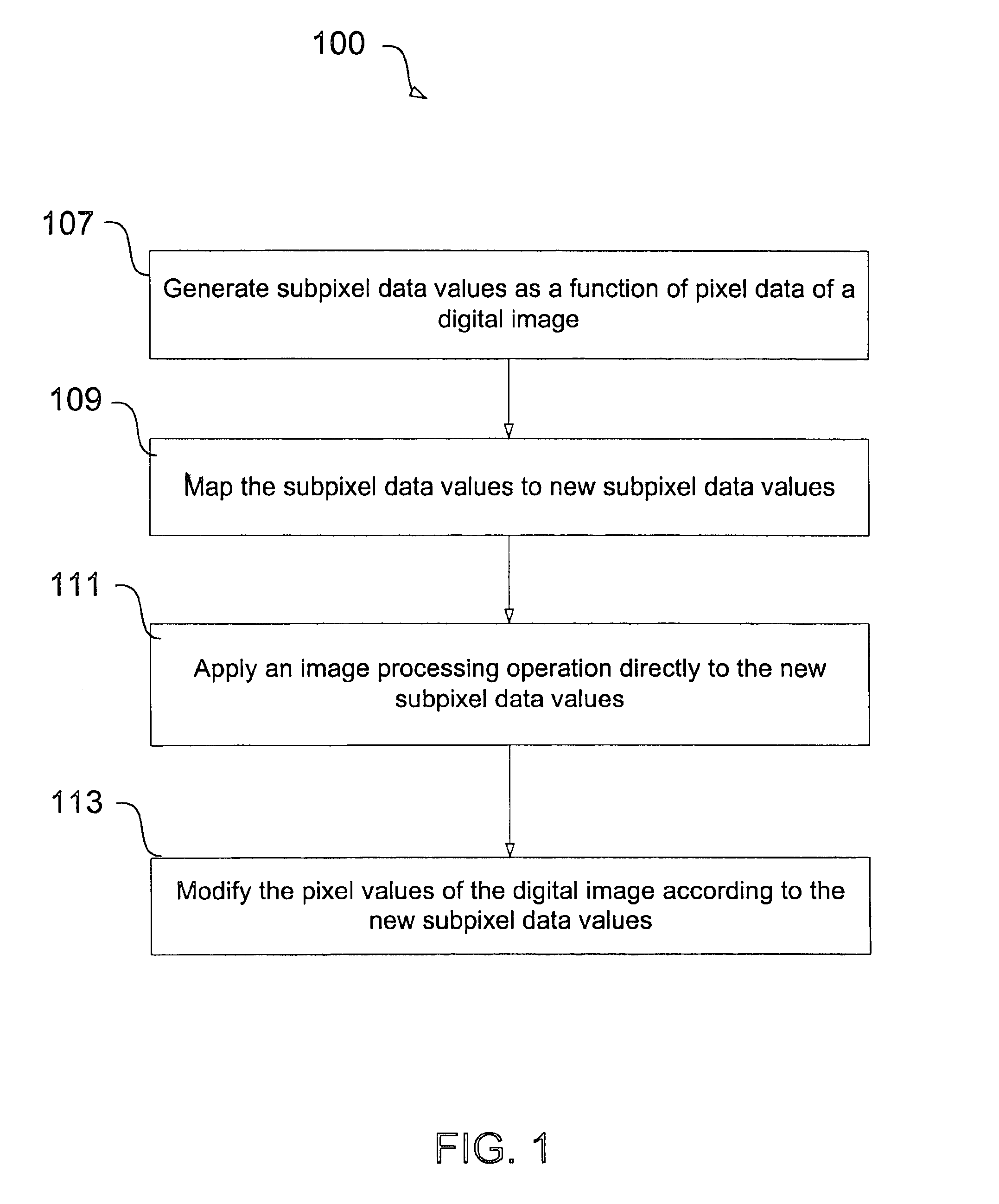
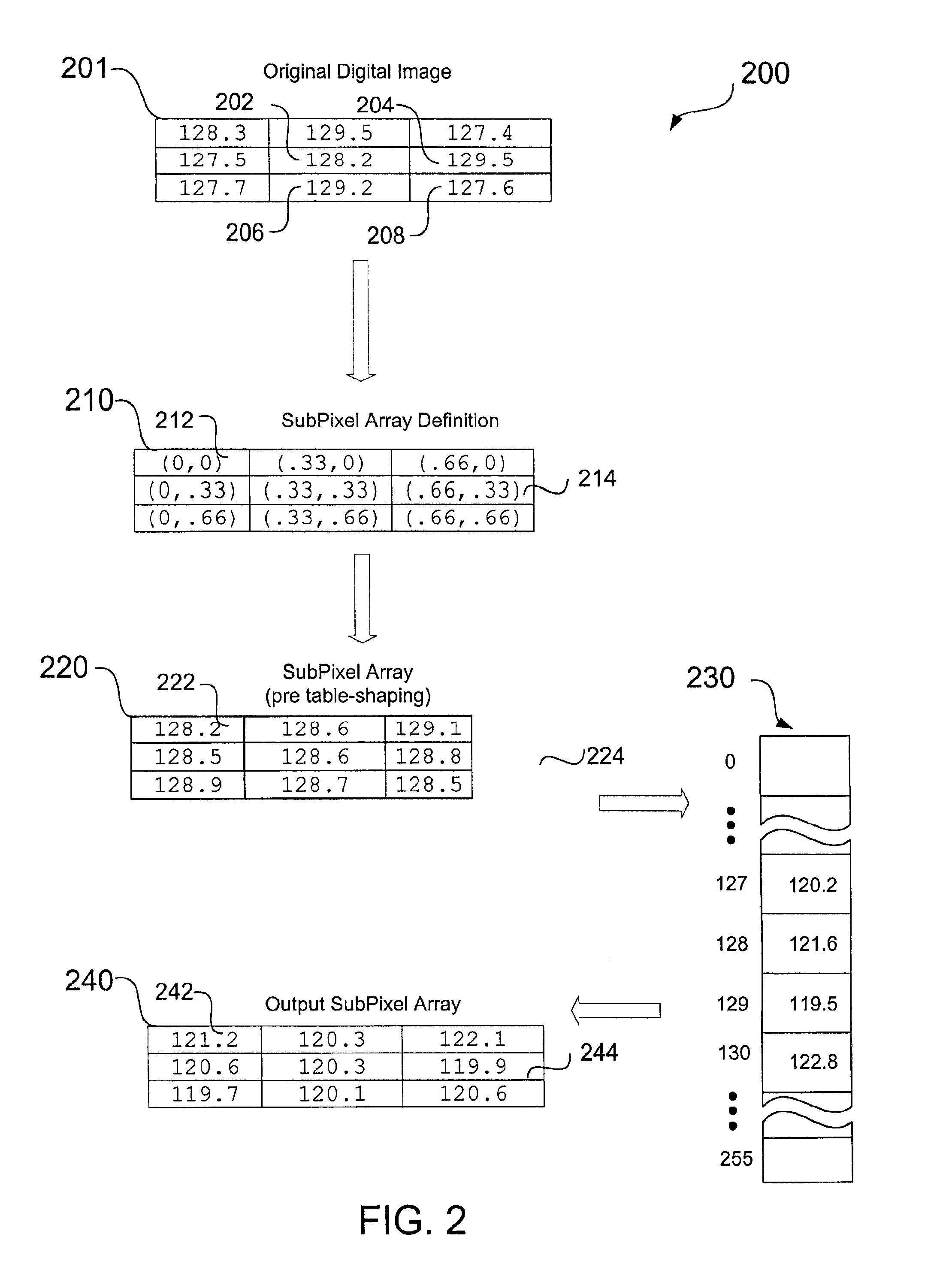
Reducing aliasing artifacts when shaping a digital image
InactiveUS6865301B1Reducing aliasing artifactHigh resolutionImage enhancementDetails involving antialiasingJaggiesImaging processing
A method and apparatus, including a computer program apparatus, implementing techniques for reducing aliasing artifacts when shaping a digital image such as a digital matte. Prior to shaping the image, the computer program generates a set of subpixel data values as a function of the pixels of the digital image. Each subpixel data value has an integer component and a fractional component and represents an interpolation between the corresponding pixel and one or more adjacent pixels. After generating the subpixel data values, the computer program maps the subpixel data values to new subpixel data values. The computer program adjusts the original pixel data according to the new subpixel data values, thereby shaping the image. In one configuration, the computer program applies additional lookup tables or image processing operations, such as image shading, directly to the new subpixel data values before updating the pixel data. In this fashion the computer program applies the operation at a higher resolution than if applied directly to the original pixel data, thereby reducing aliasing artifacts that might otherwise be introduced by shaping the digital image.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com