Patents
Literature
266results about "Details involving antialiasing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
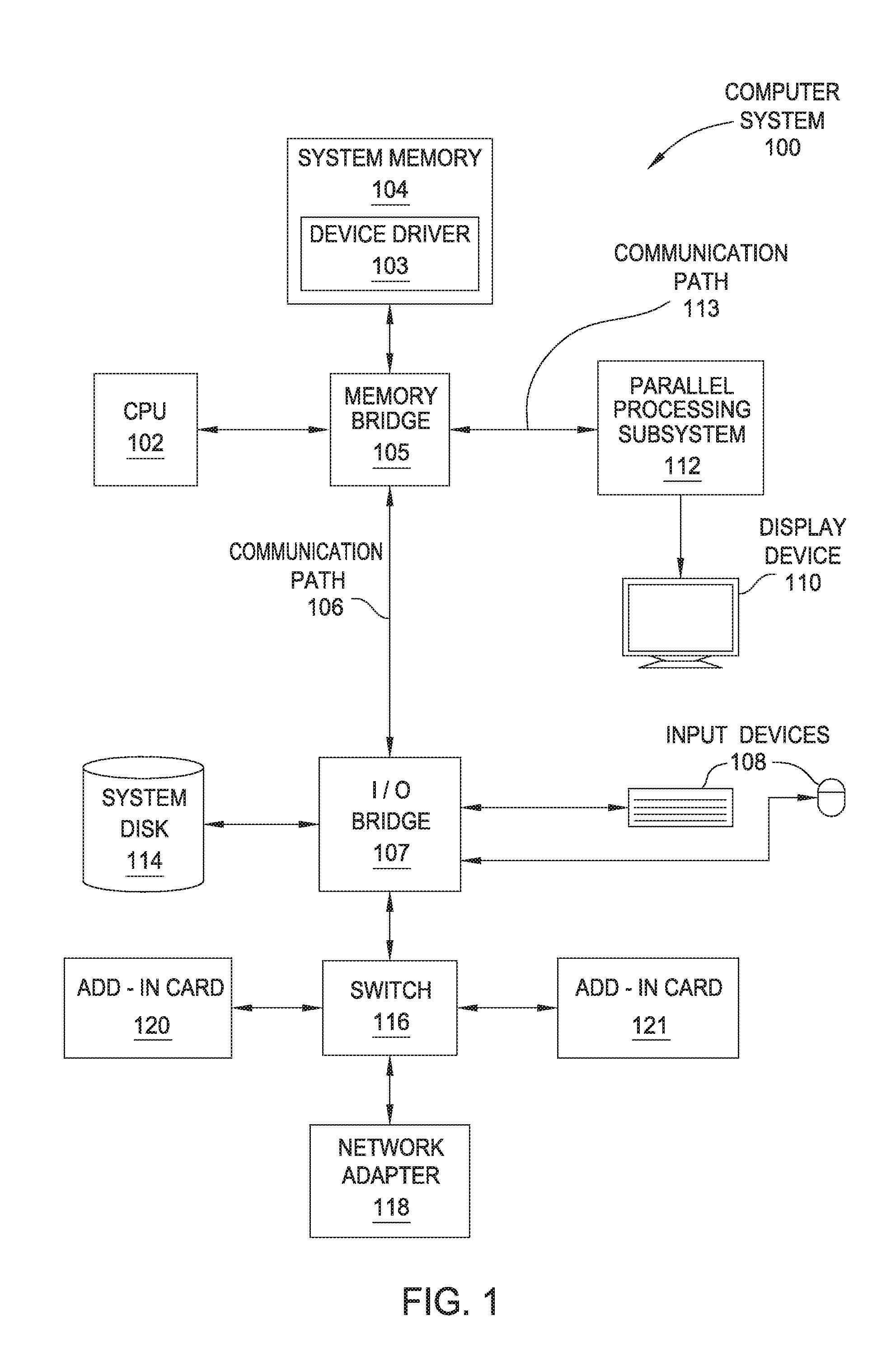
Methods, systems, and programming for computer display of images, text, and/or digital content
InactiveUS7222306B2Reduce the amount requiredImprove clarityDrawing from basic elementsDigital data information retrievalDigital contentDisplay device
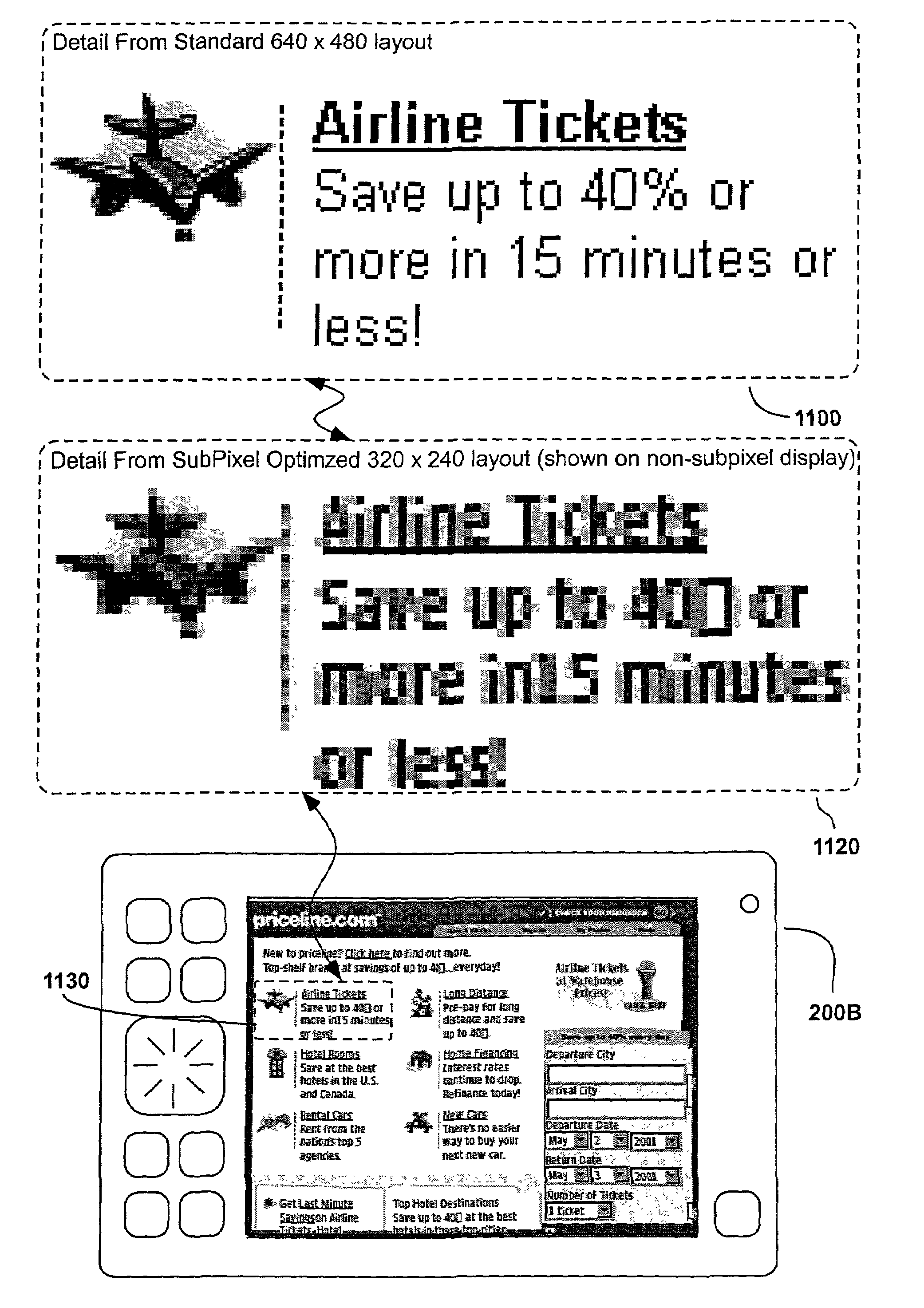
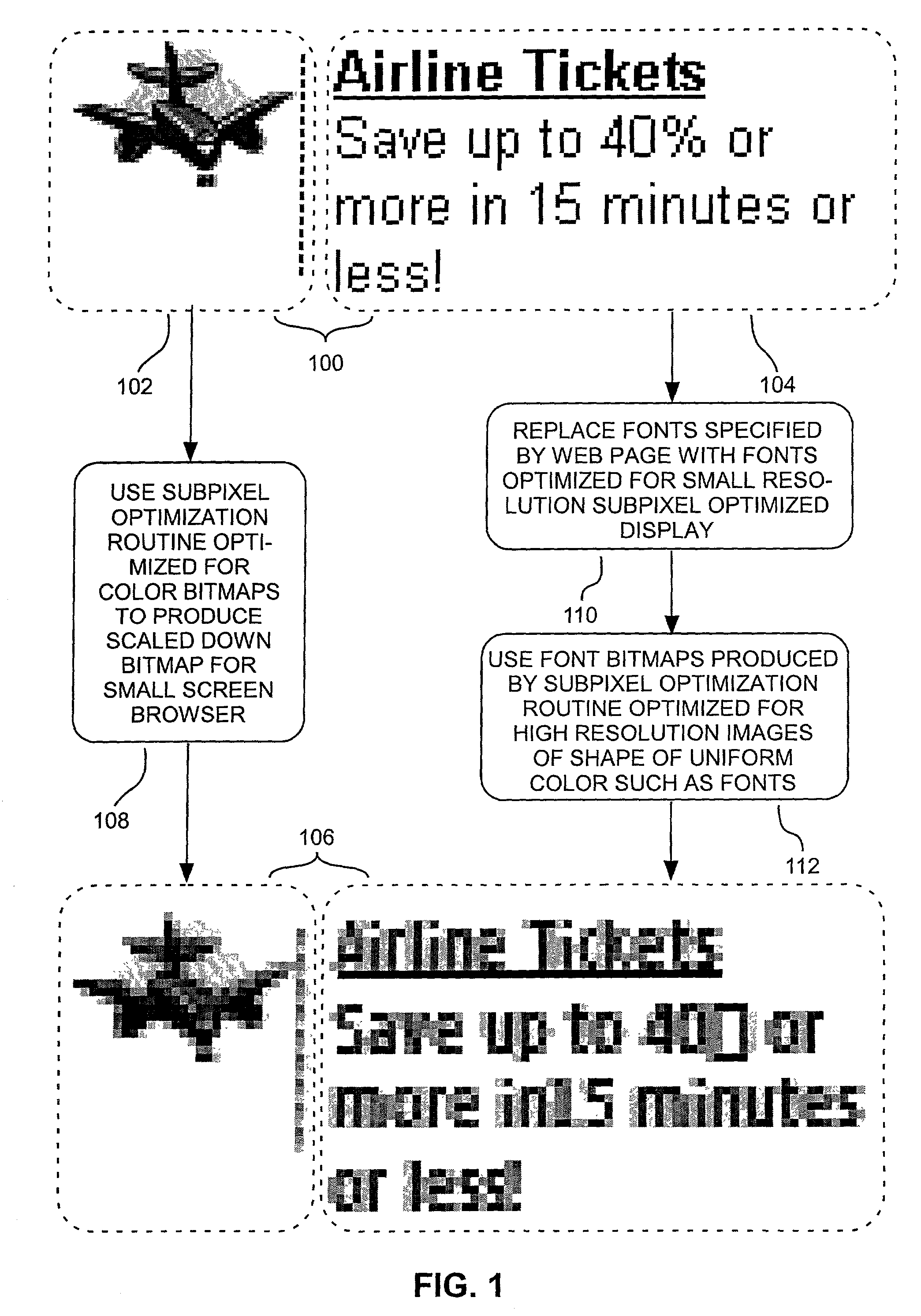
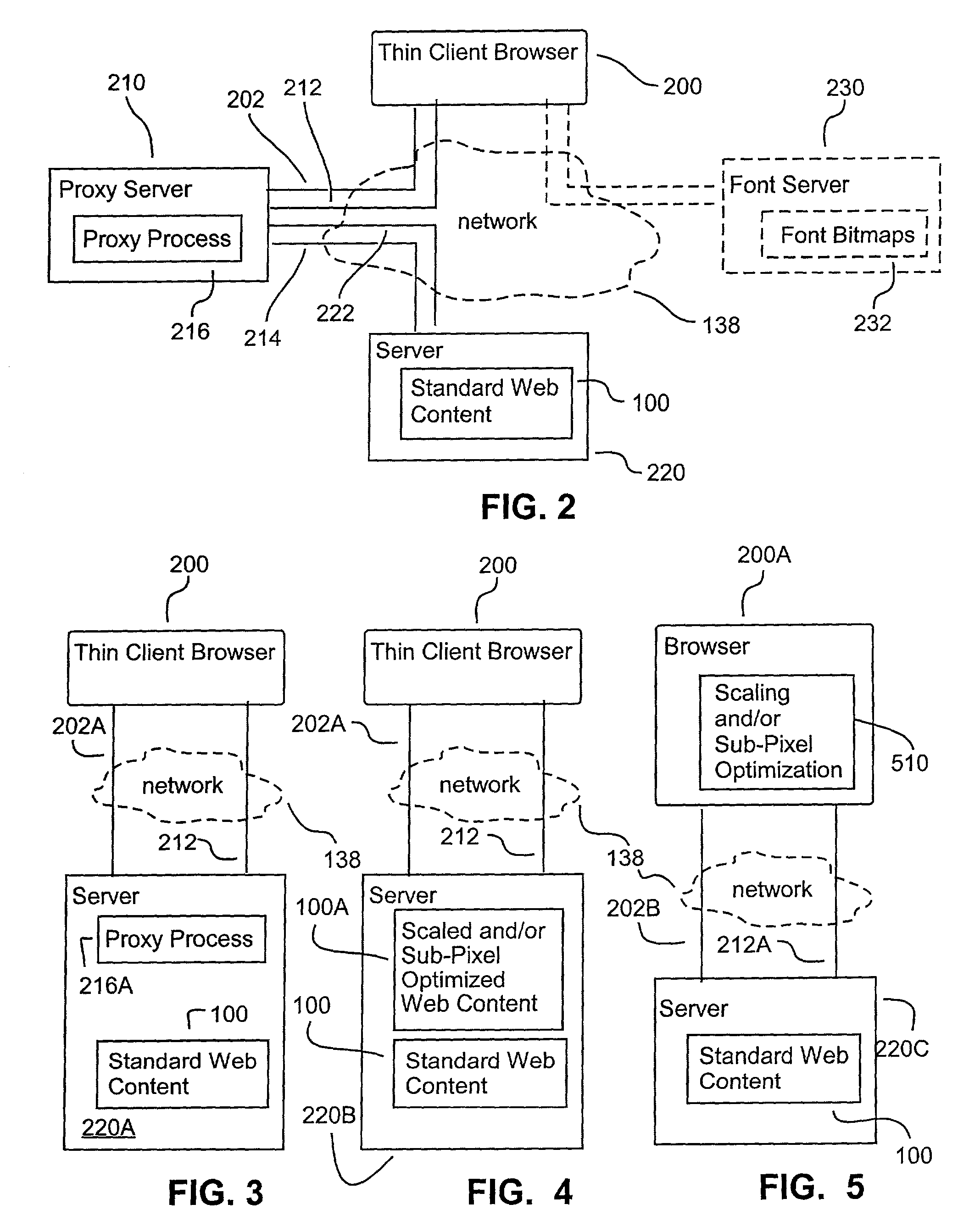
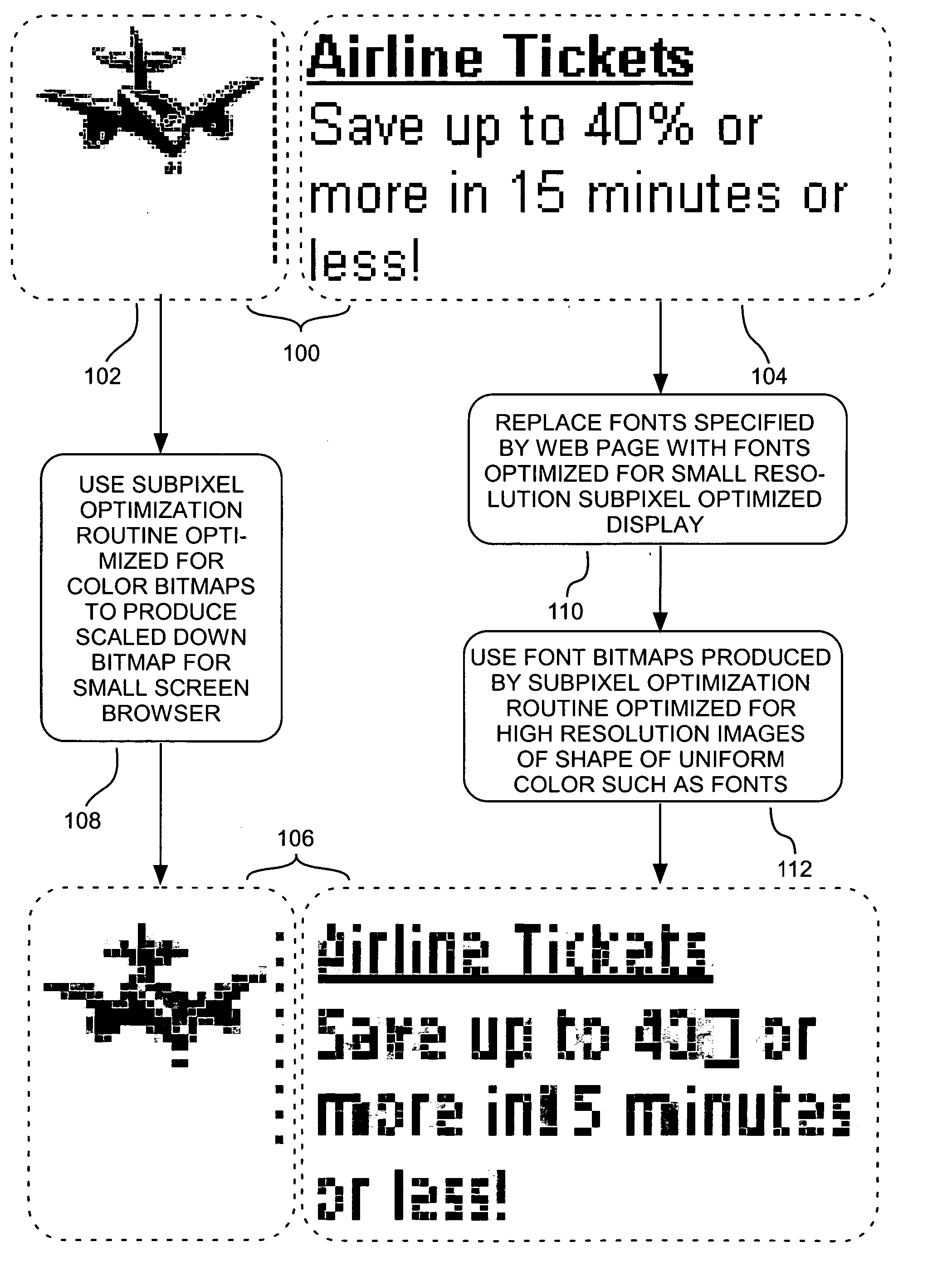
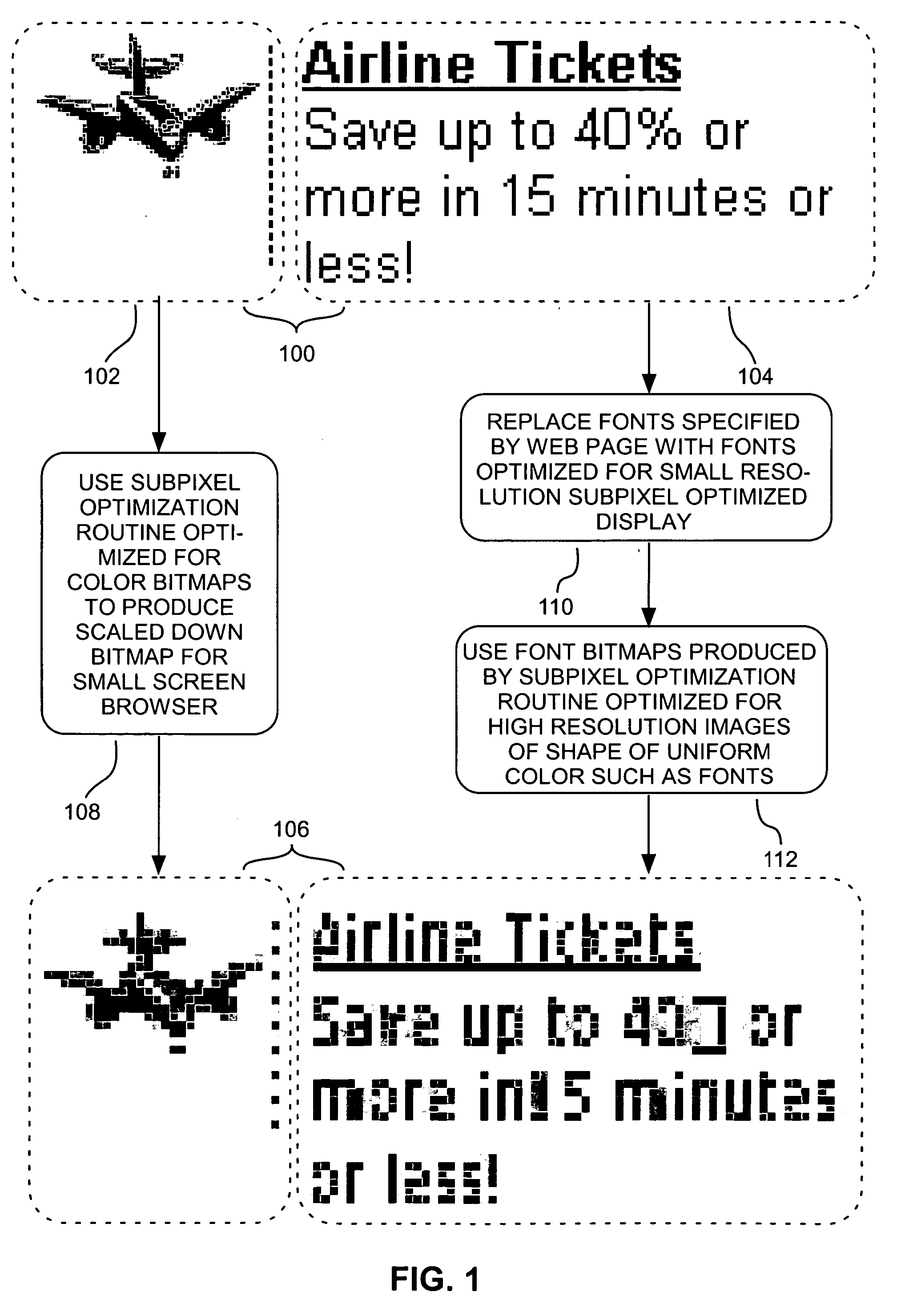
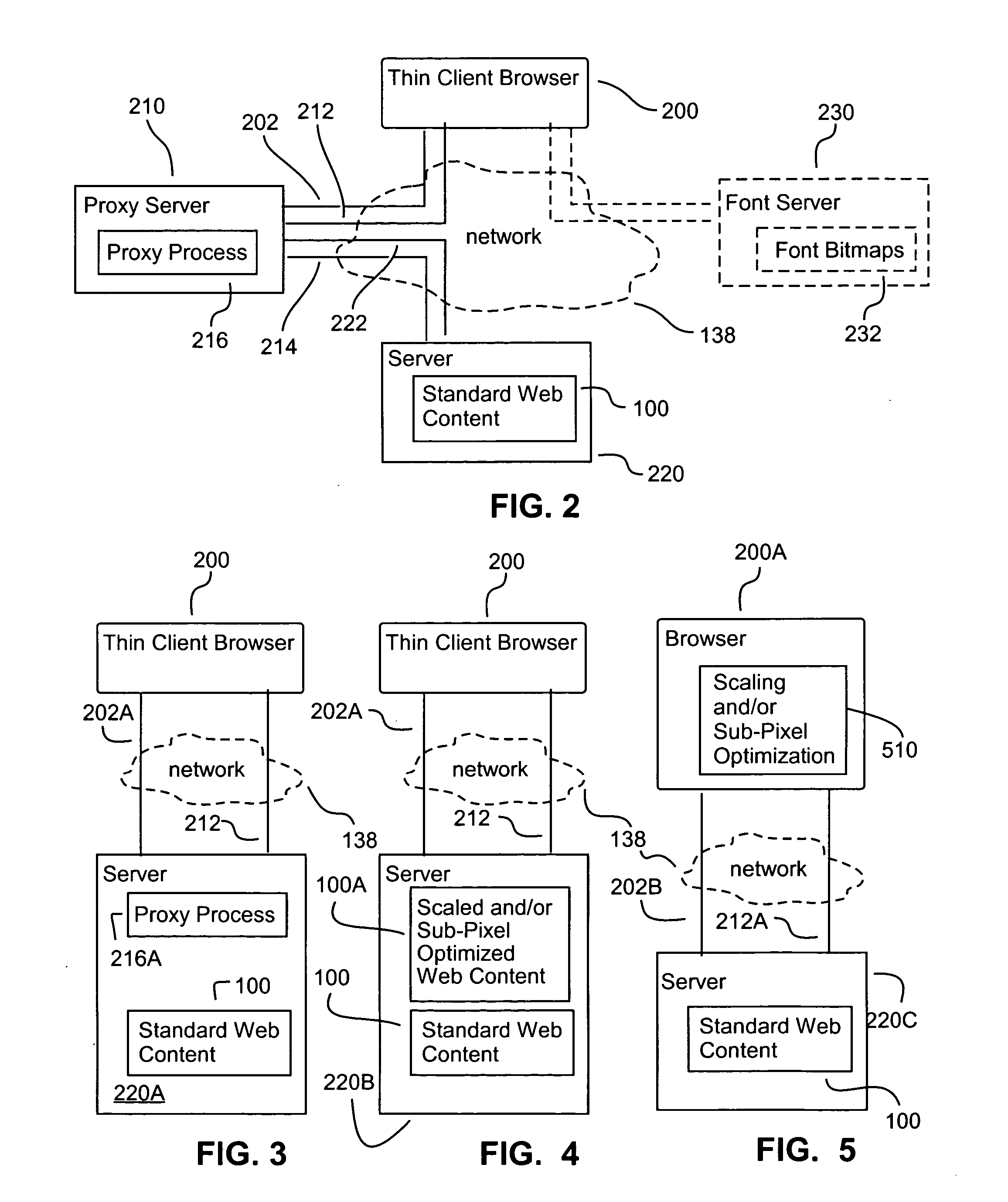
A bitmap of a shape, such as a font, can be subpixel optimized by producing for each of a display's subpixels a coverage value representing the percent of its area covered by the shape being represented and by distributing, to prevent color imbalance, an amount of a given subpixel's coverage value to nearby subpixels of different colors as a function of the percent of the given subpixel's coverage value that causes color imbalance. Web pages can be displayed with scaled-down and subpixel optimized images. A given layout of a Web page can be displayed at each of at least two different selected scale factors, with the font bitmaps used to represent characters in the display at each scale factor having their shape and pixel alignment selected to improve readability for the particular pixel size at which they are displayed at each such scale factor.
Owner:BITSTREAM INC
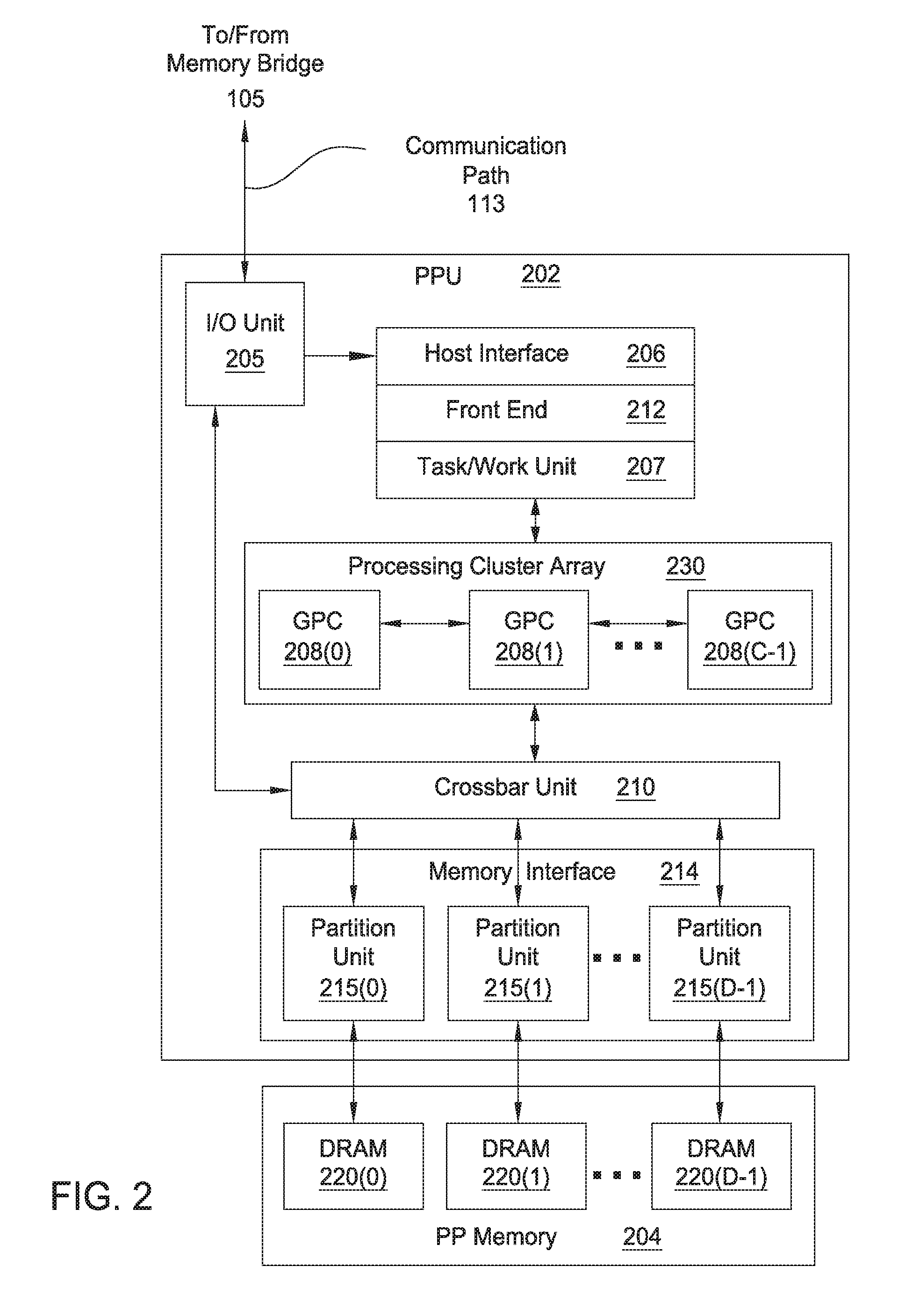
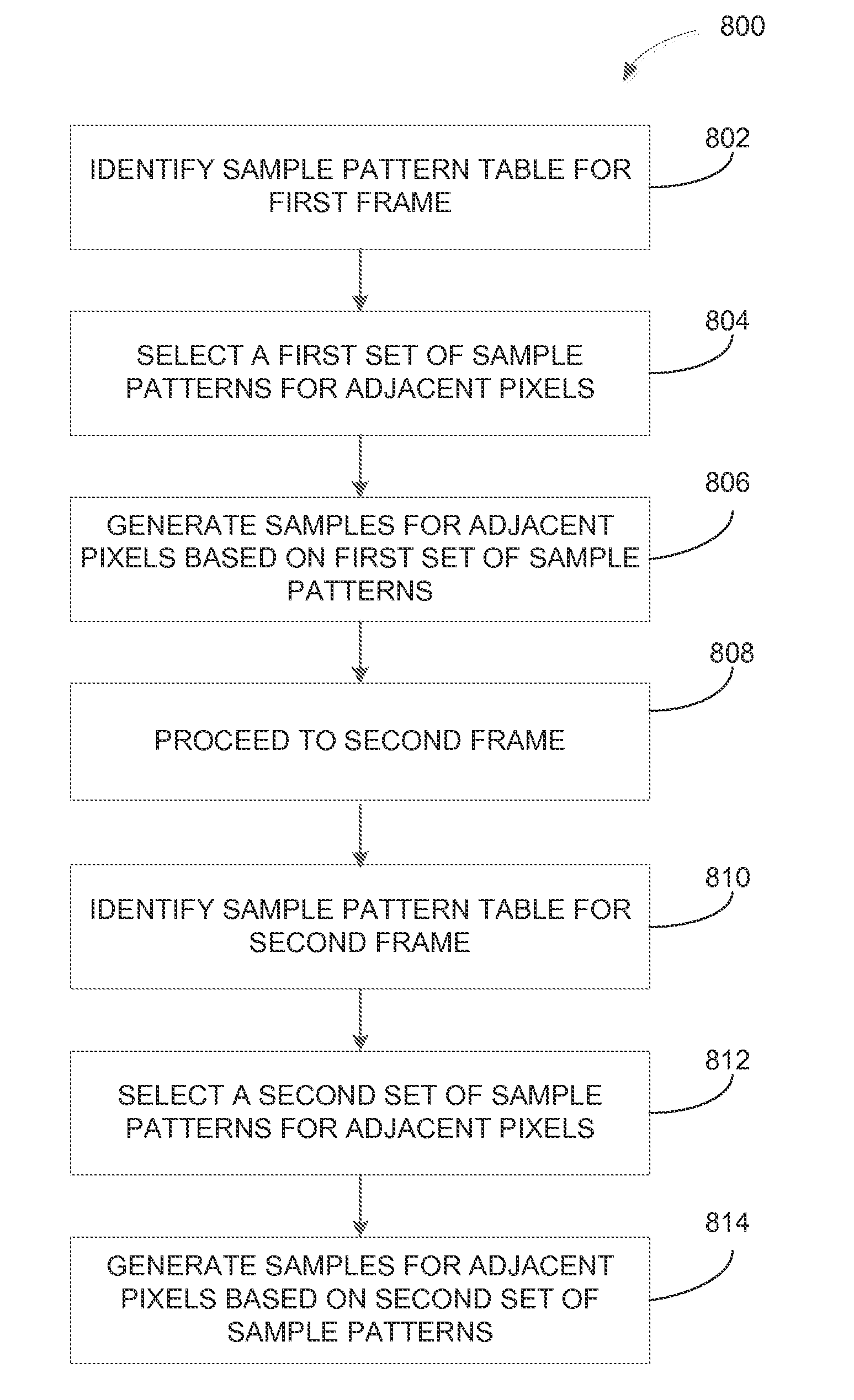
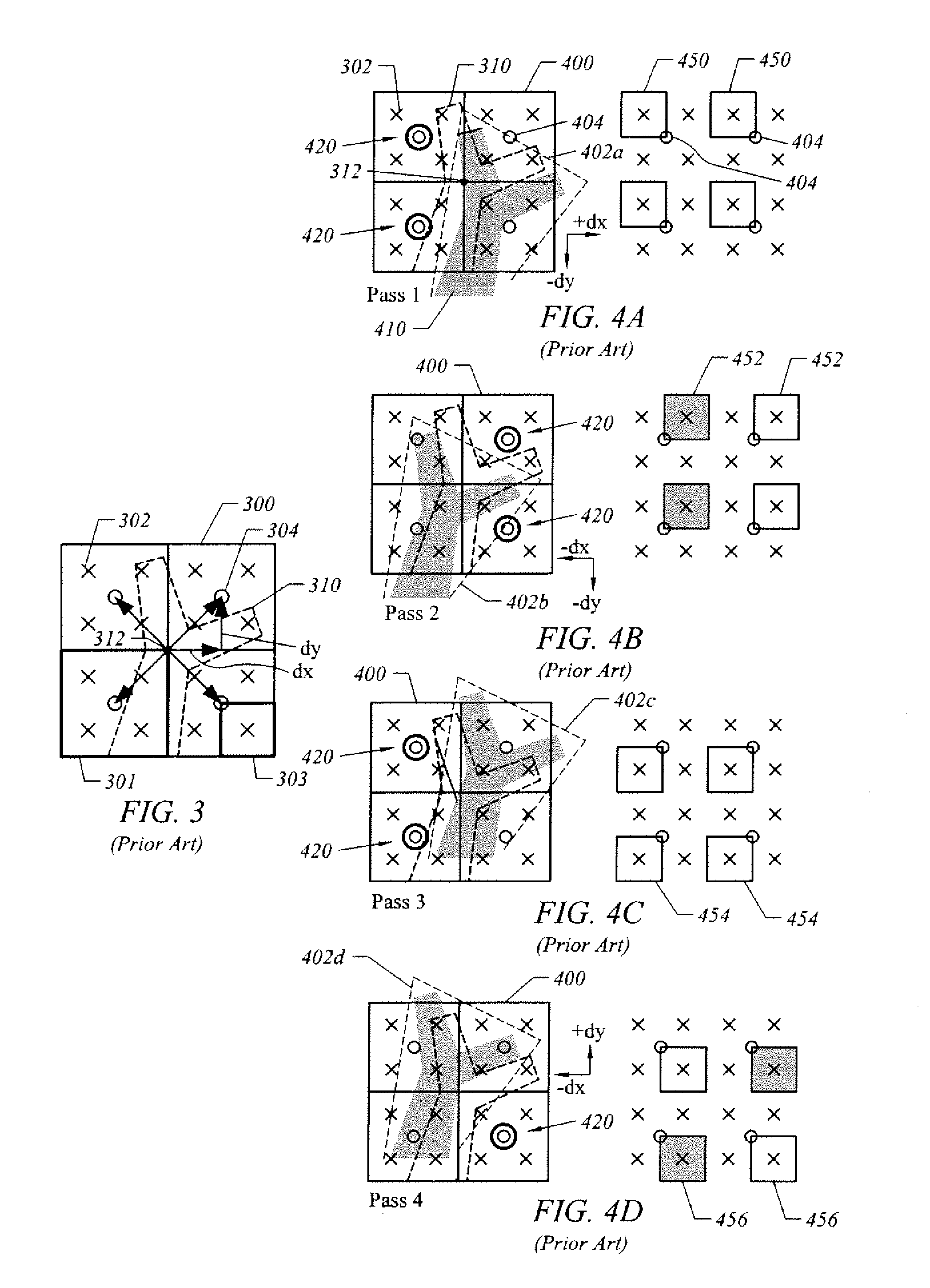
Enhanced Anti-aliasing by varying sample patterns spatially and/or temporally
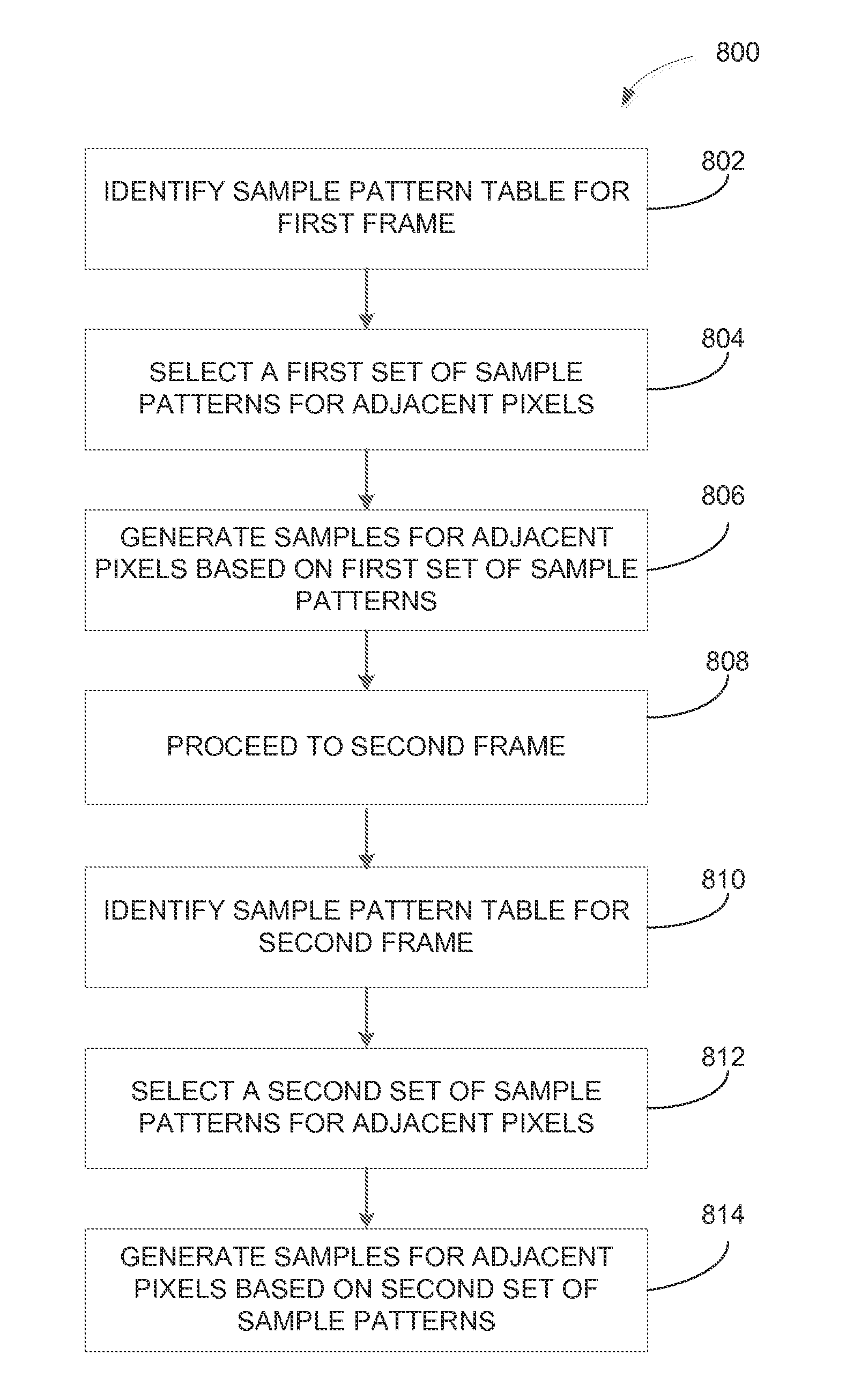
A raster unit is configured to generate different sample patterns for adjacent pixels within a given frame. In addition, the raster unit may adjust the sample patterns between frames. The raster unit includes an index unit that selects a sample pattern table for use with a current frame. For a given pixel, the index unit extracts a sample pattern from the selected sample pattern table. The extracted sample pattern is used to generate coverage information for the pixel. The coverage information for all pixels is then used to generate an image. The resultant image may then be filtered to reduce or remove artifacts induced by the changing of sample locations.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Enhanced Anti-aliasing by varying sample patterns spatially and/or temporally
ActiveUS20160071242A1Quality improvementImage enhancementDetails involving antialiasingComputer visionComputer graphics (images)
A raster unit is configured to generate different sample patterns for adjacent pixels within a given frame. In addition, the raster unit may adjust the sample patterns between frames. The raster unit includes an index unit that selects a sample pattern table for use with a current frame. For a given pixel, the index unit extracts a sample pattern from the selected sample pattern table. The extracted sample pattern is used to generate coverage information for the pixel. The coverage information for all pixels is then used to generate an image. The resultant image may then be filtered to reduce or remove artifacts induced by the changing of sample locations.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
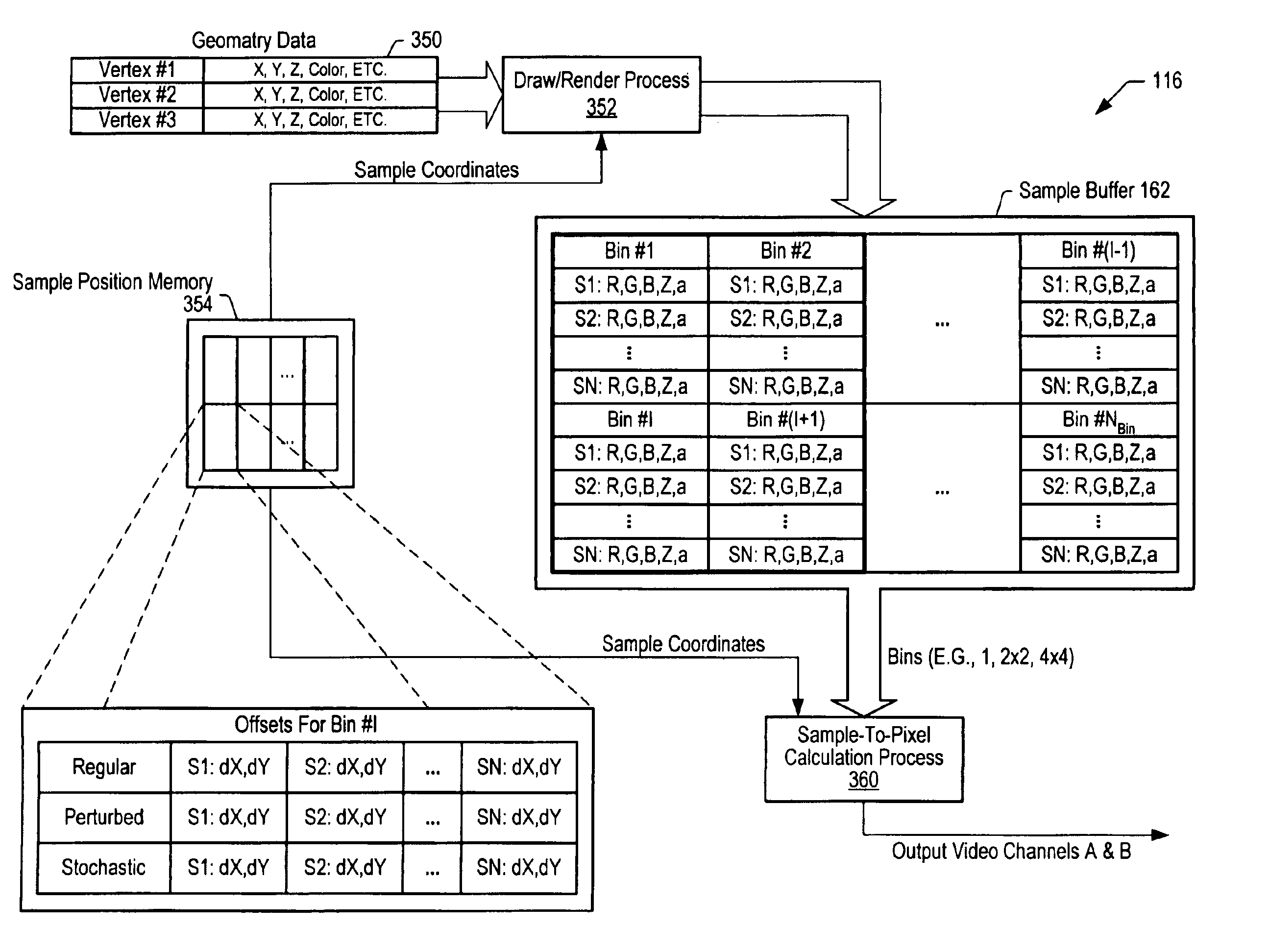
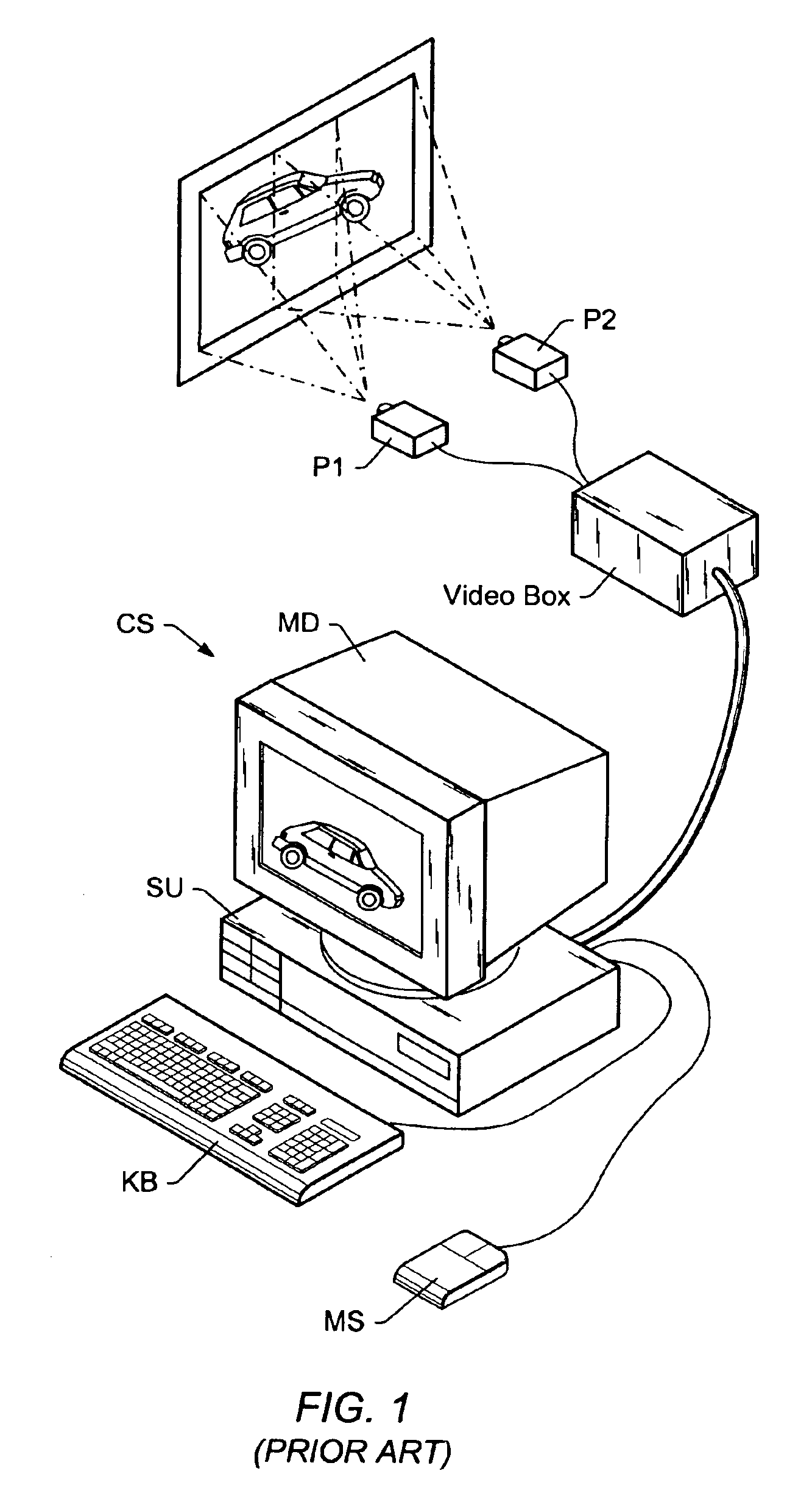
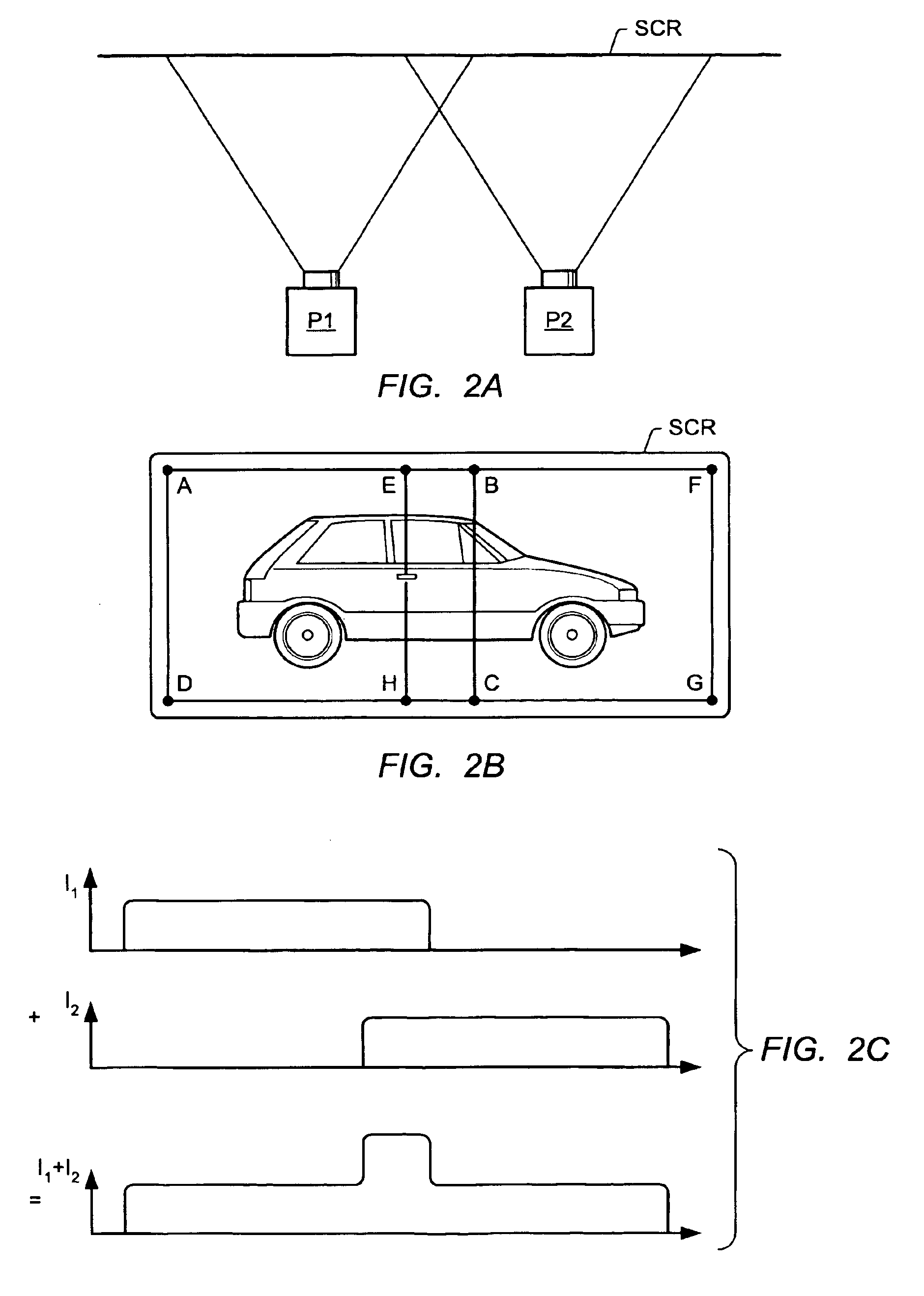
Compensating for the chromatic distortion of displayed images
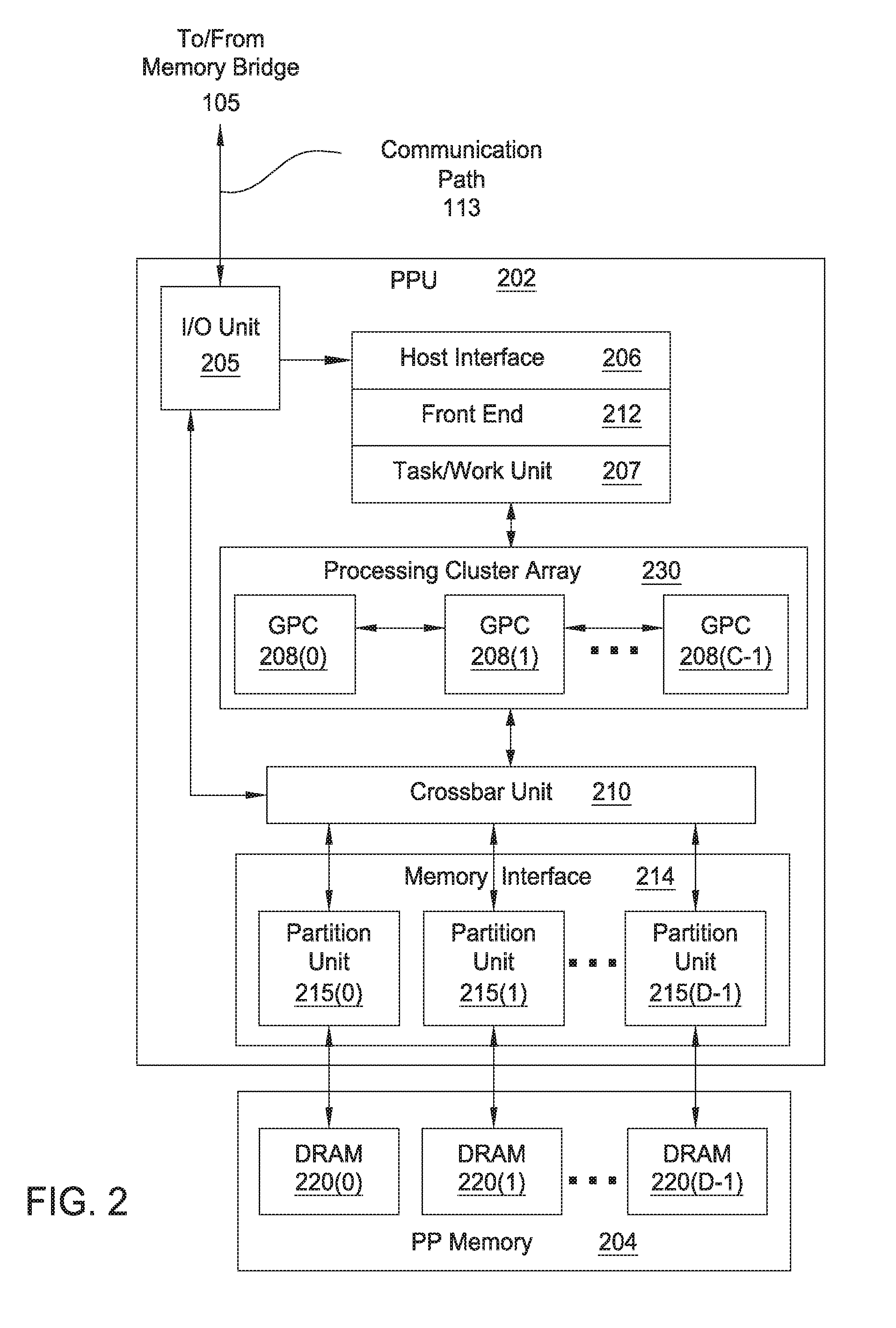
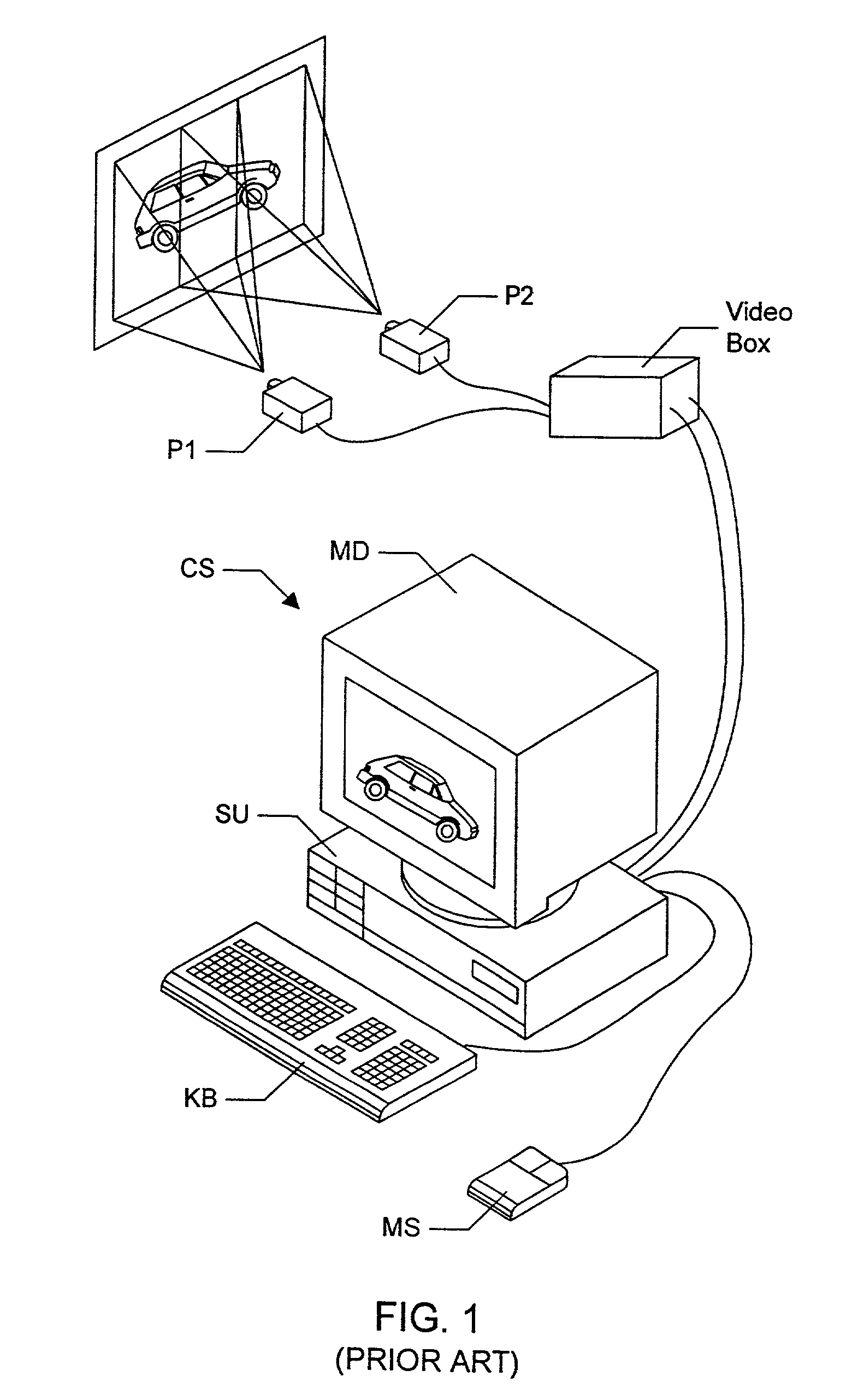
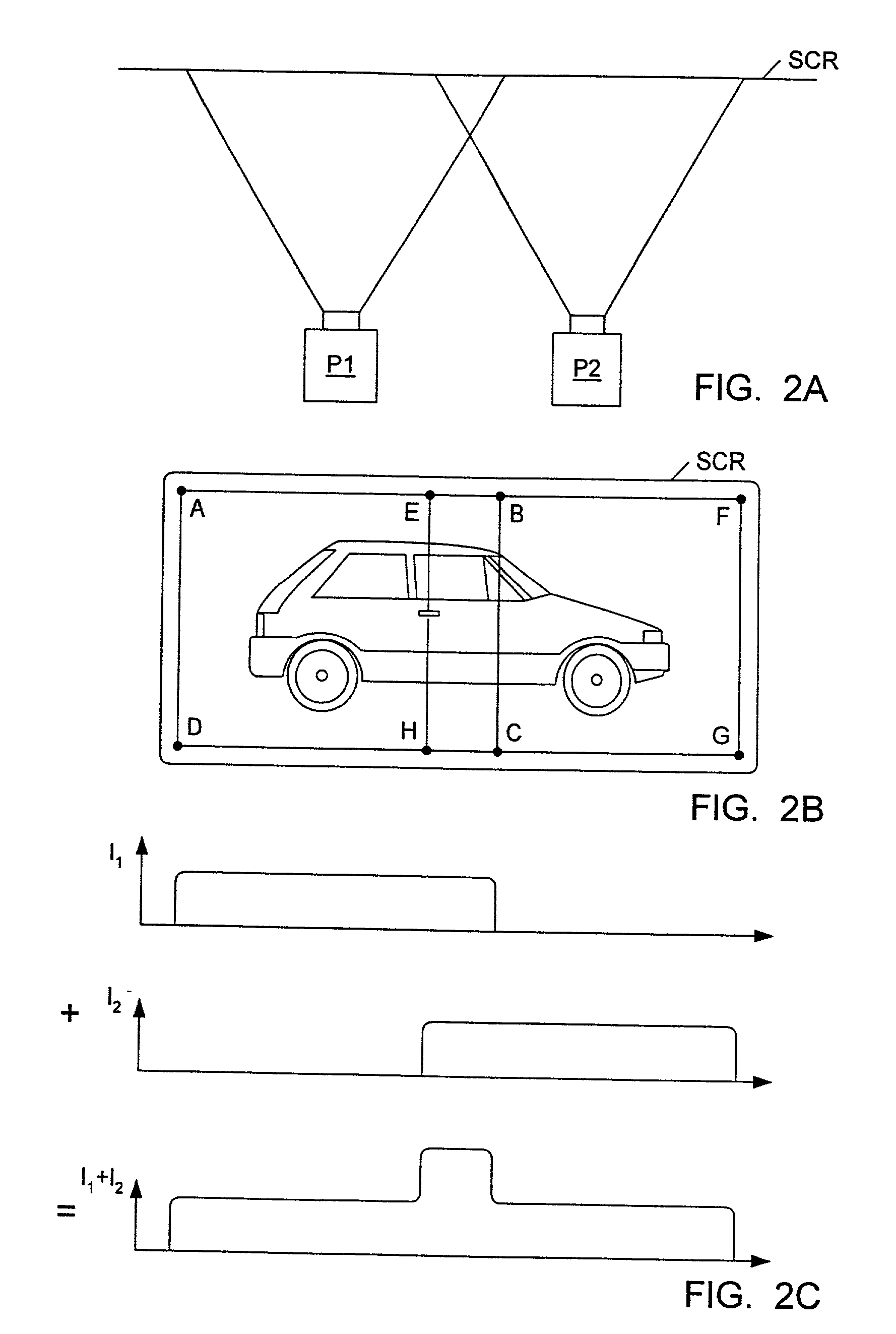
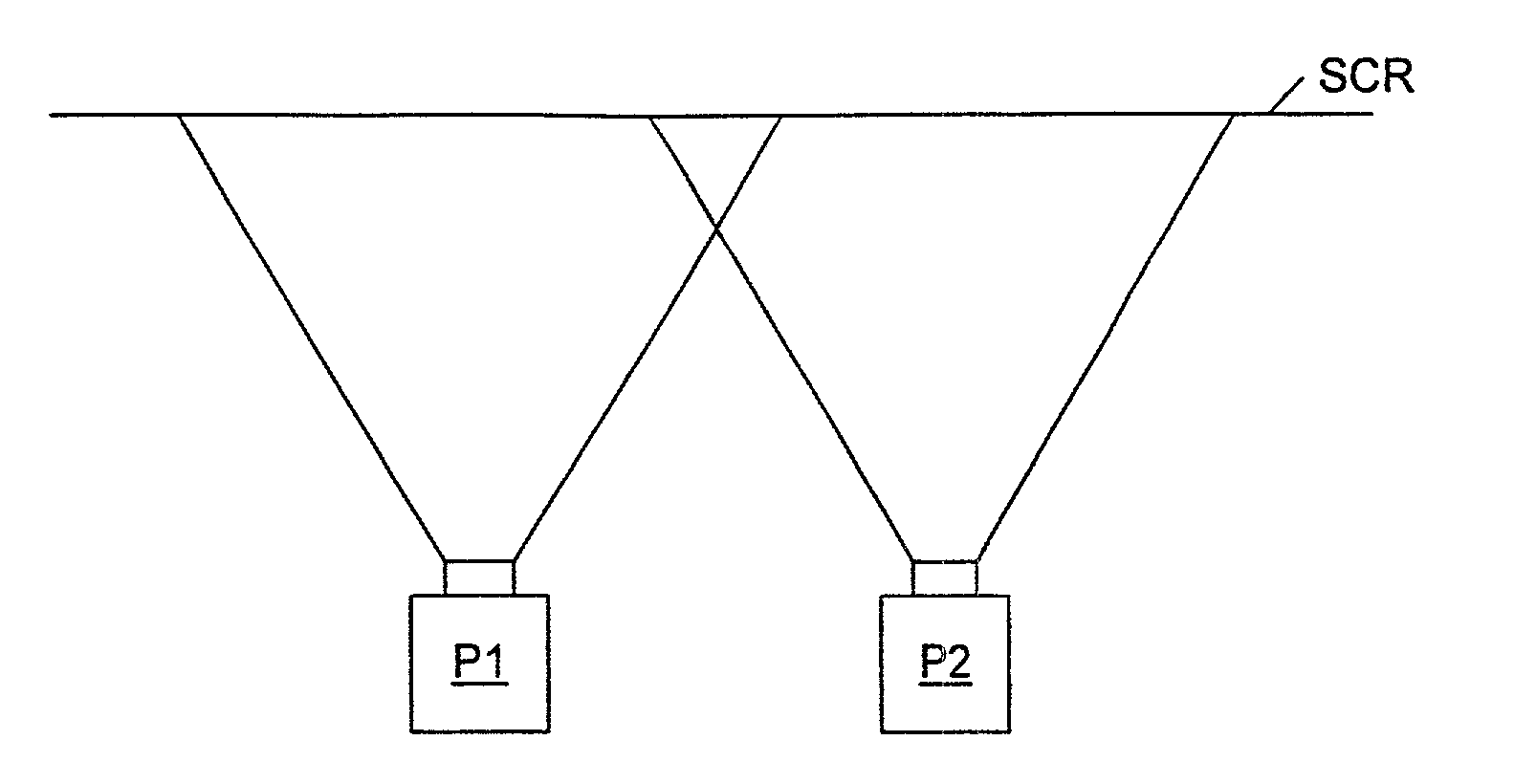
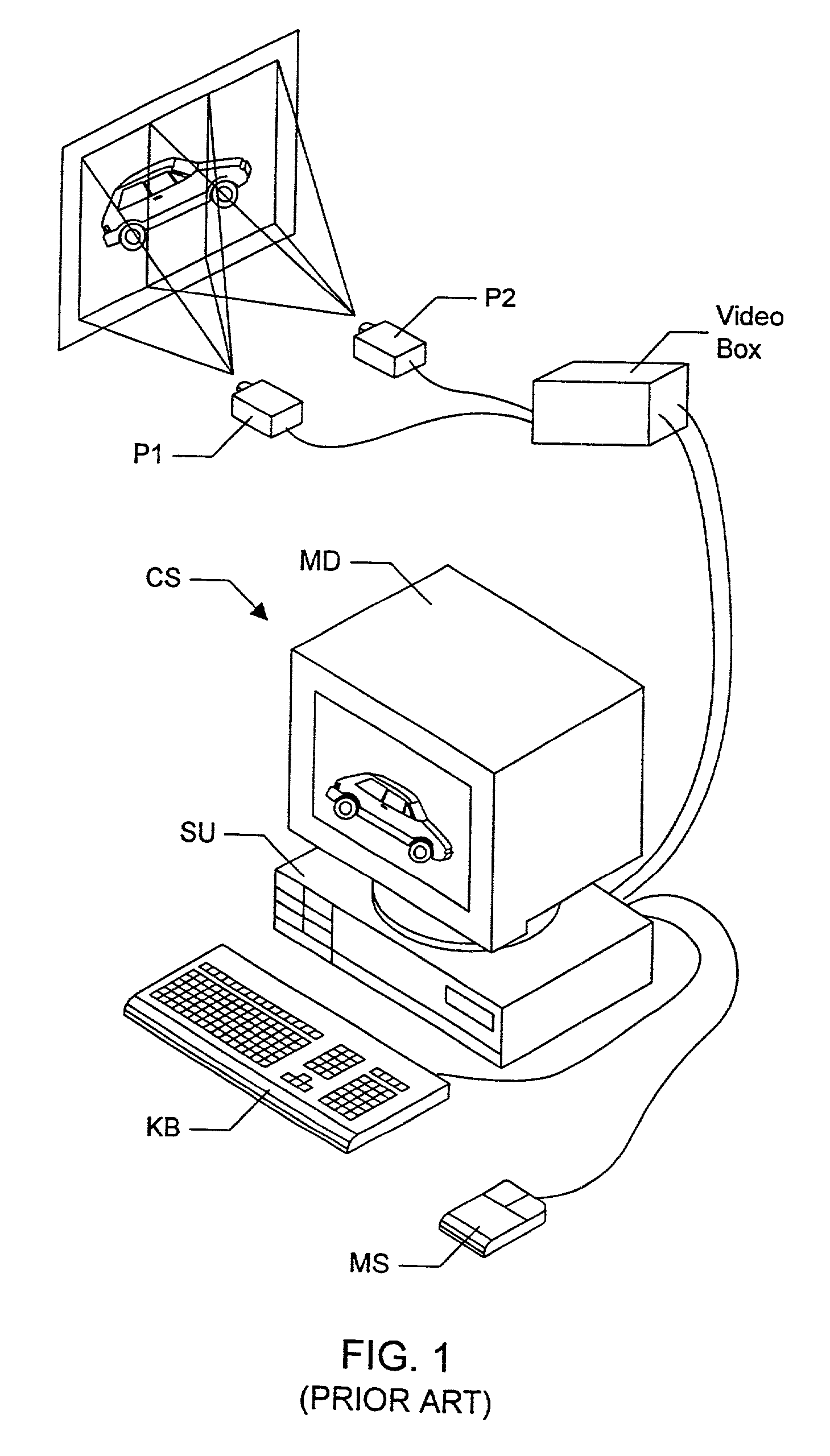
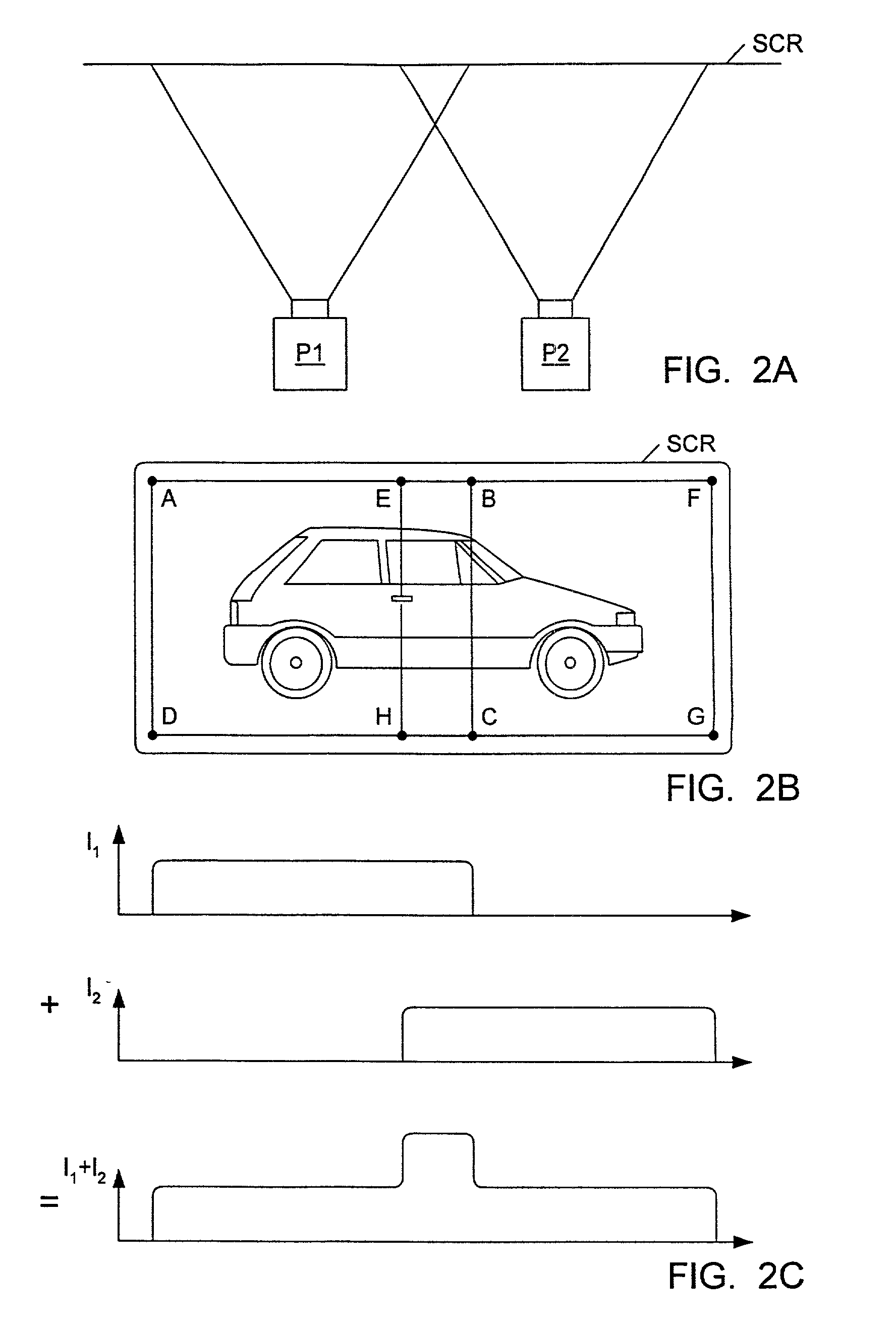
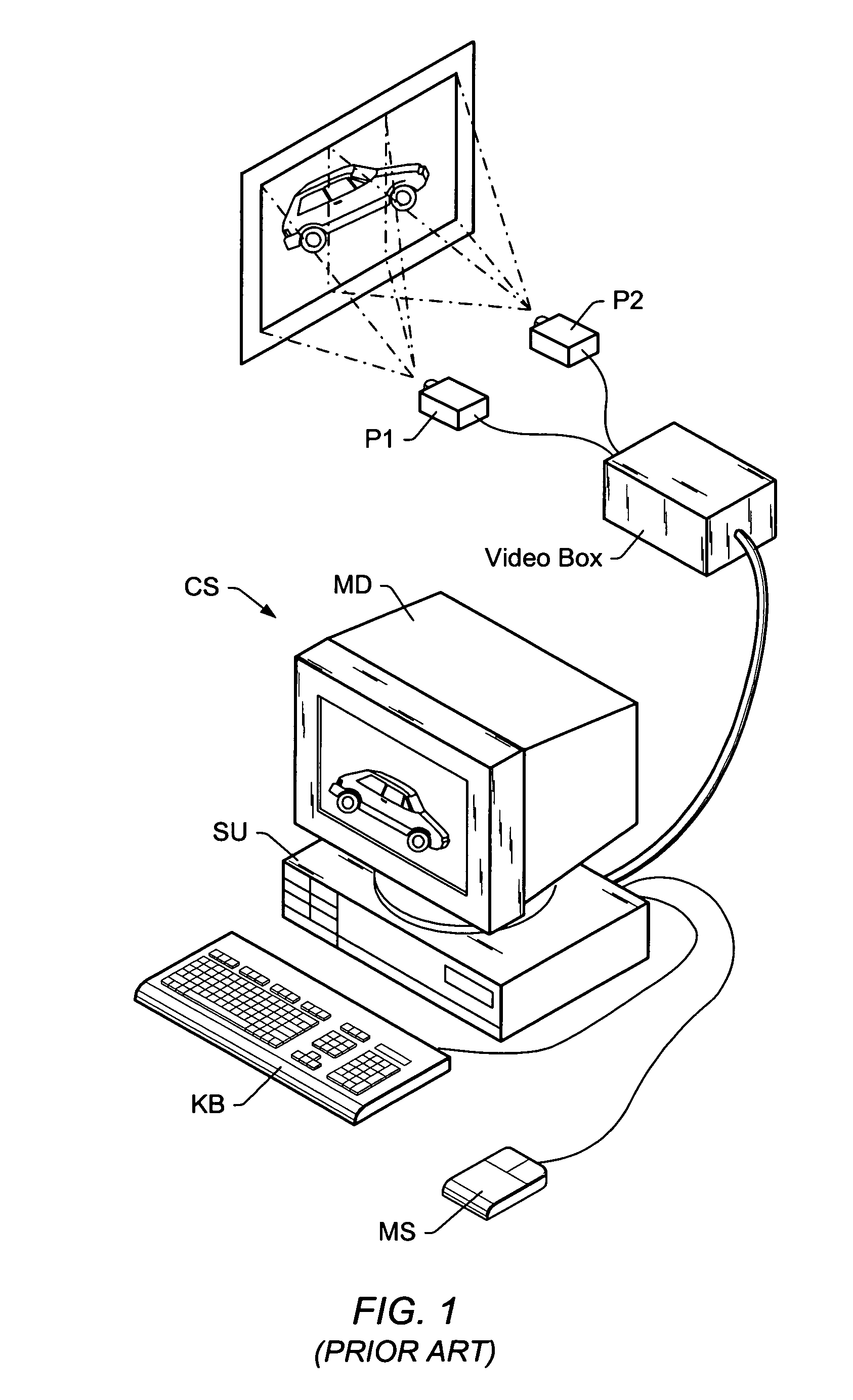
A graphics system comprises pixel calculation units and a sample buffer which stores a two-dimensional field of samples. Each pixel calculation unit selects positions in the two-dimensional field at which pixel values (e.g. red, green, blue) are computed. The pixel computation positions are selected to compensate for image distortions introduced by a display device and / or display surface. Non-uniformities in a viewer's perceived intensity distribution from a display surface (e.g. hot spots, overlap brightness) are corrected by appropriately scaling pixel values prior to transmission to display devices. Two or more sets of pixel calculation units driving two or more display devices adjust their respective pixel computation centers to align the edges of two or more displayed images. Physical barriers prevent light spillage at the interface between any two of the display images. Separate pixel computation positions may be used for distinct colors to compensate for color distortions.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
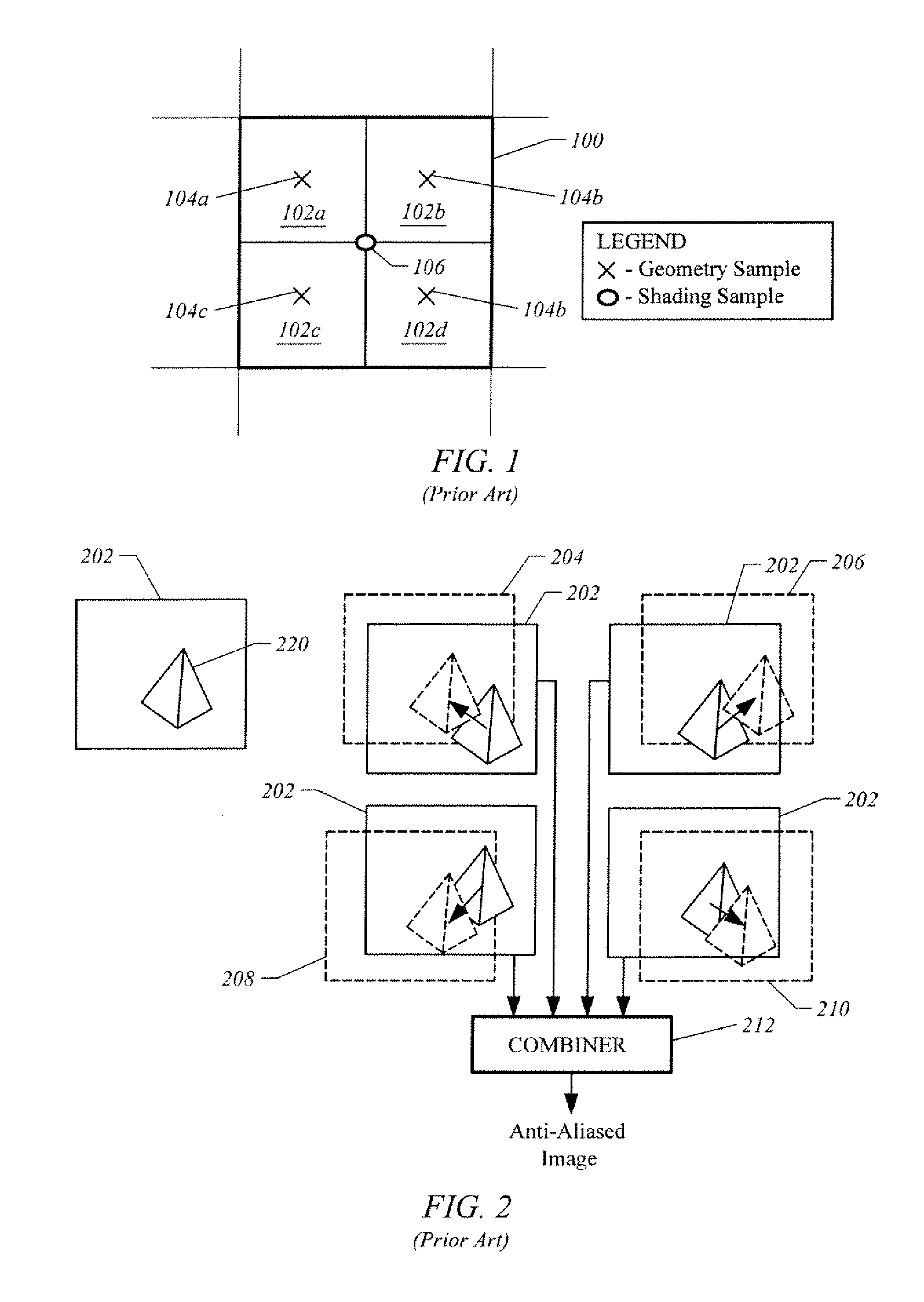
Antialiased imaging with improved pixel supersampling
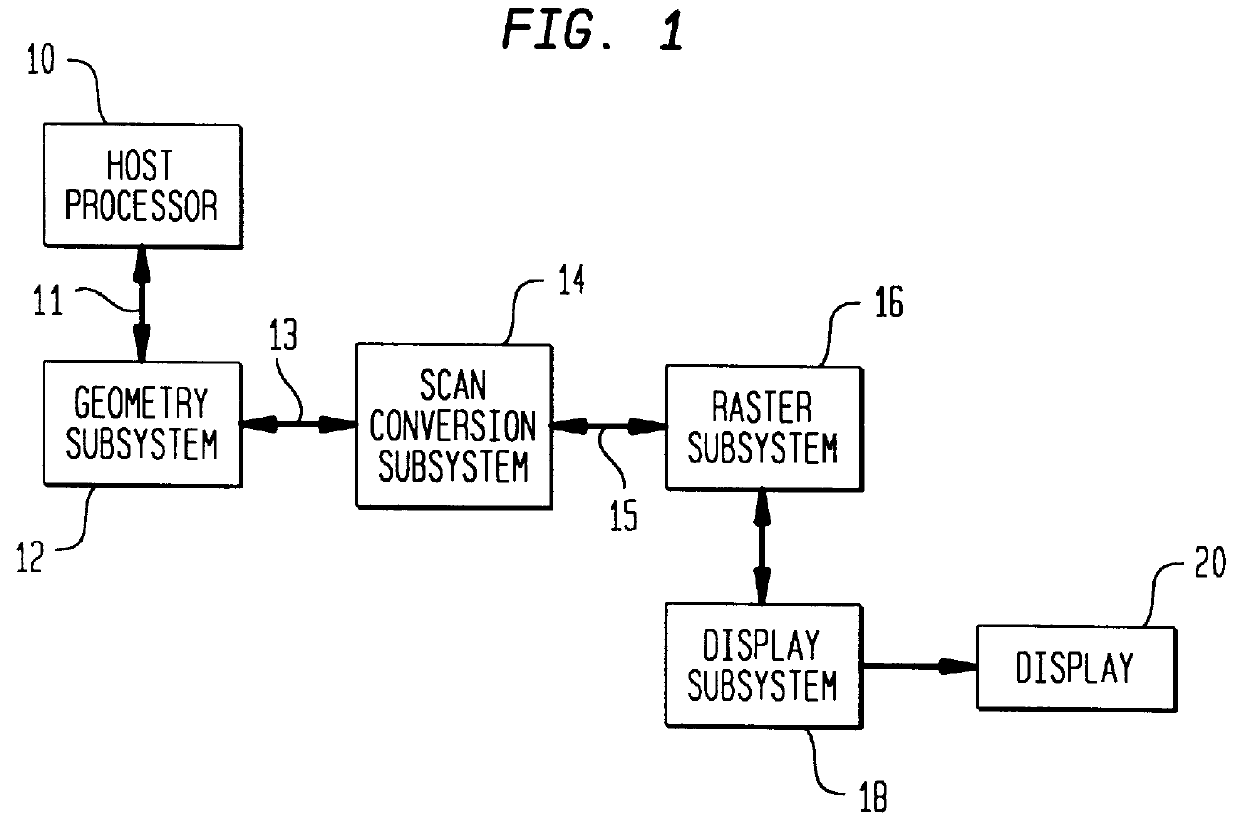
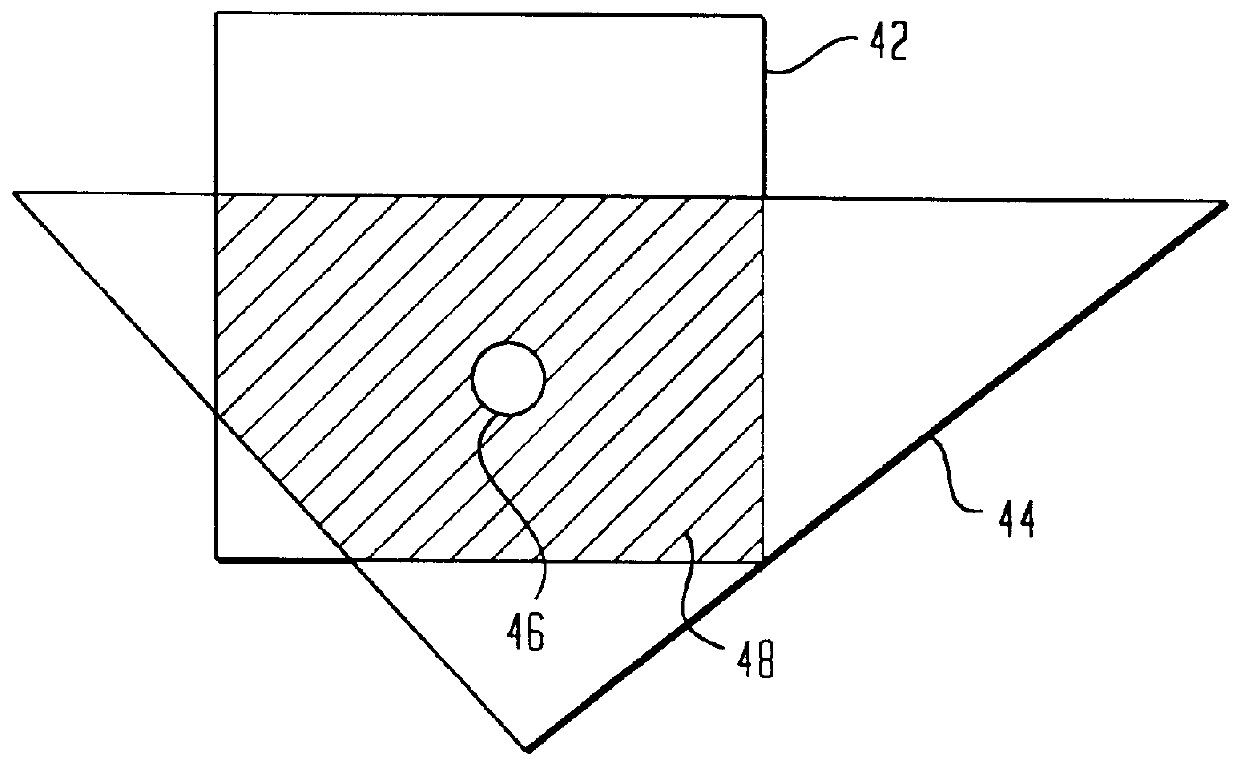
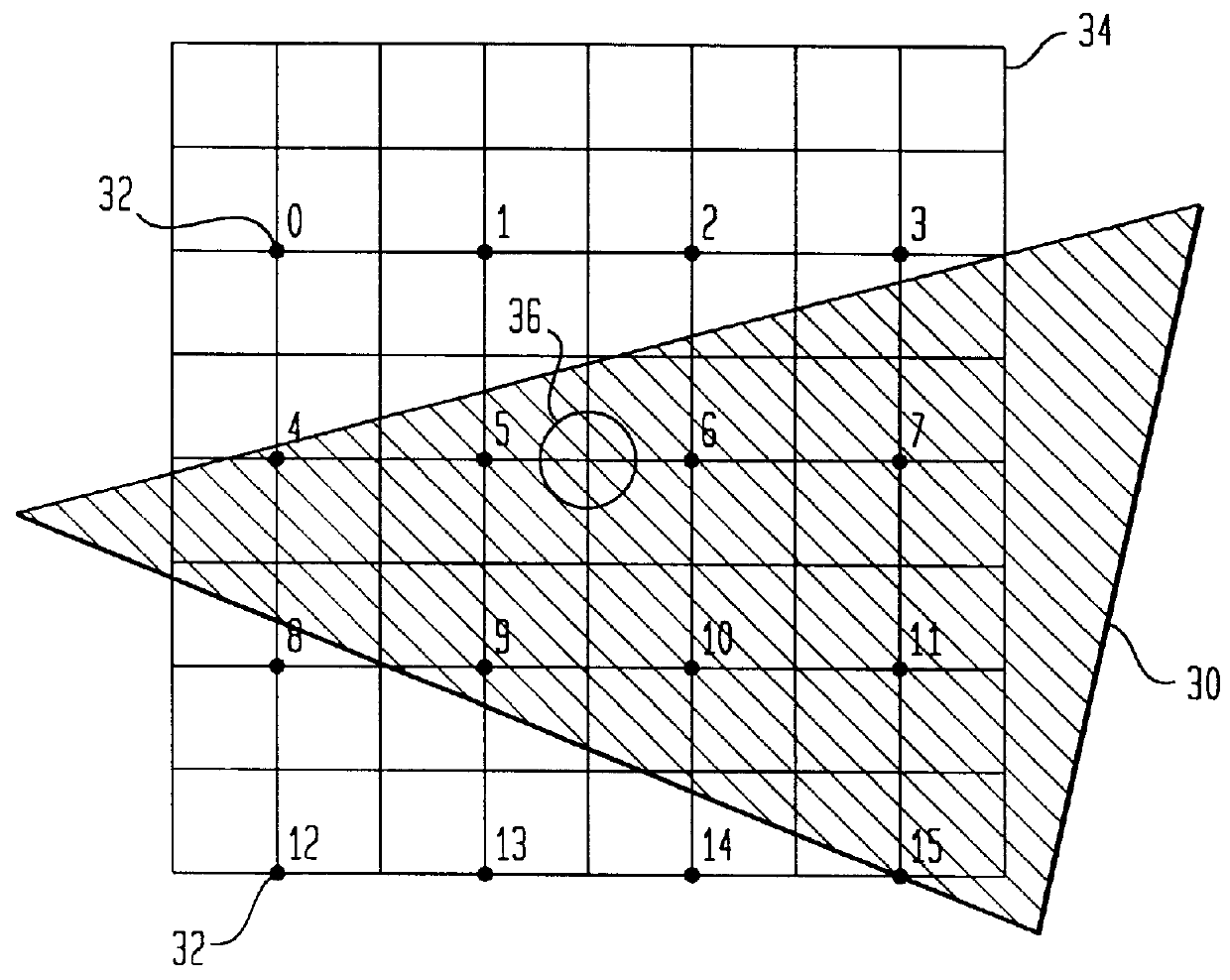
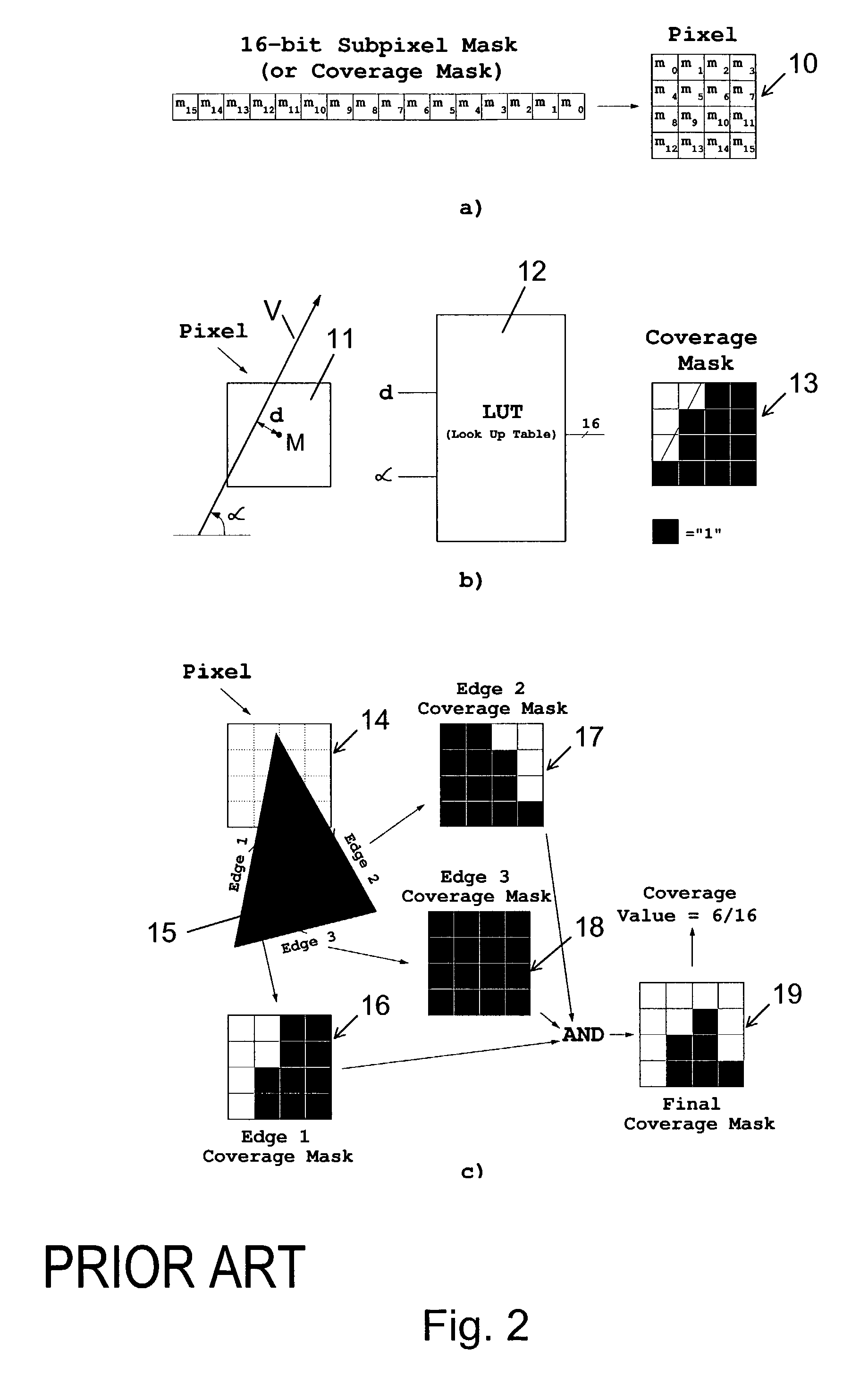
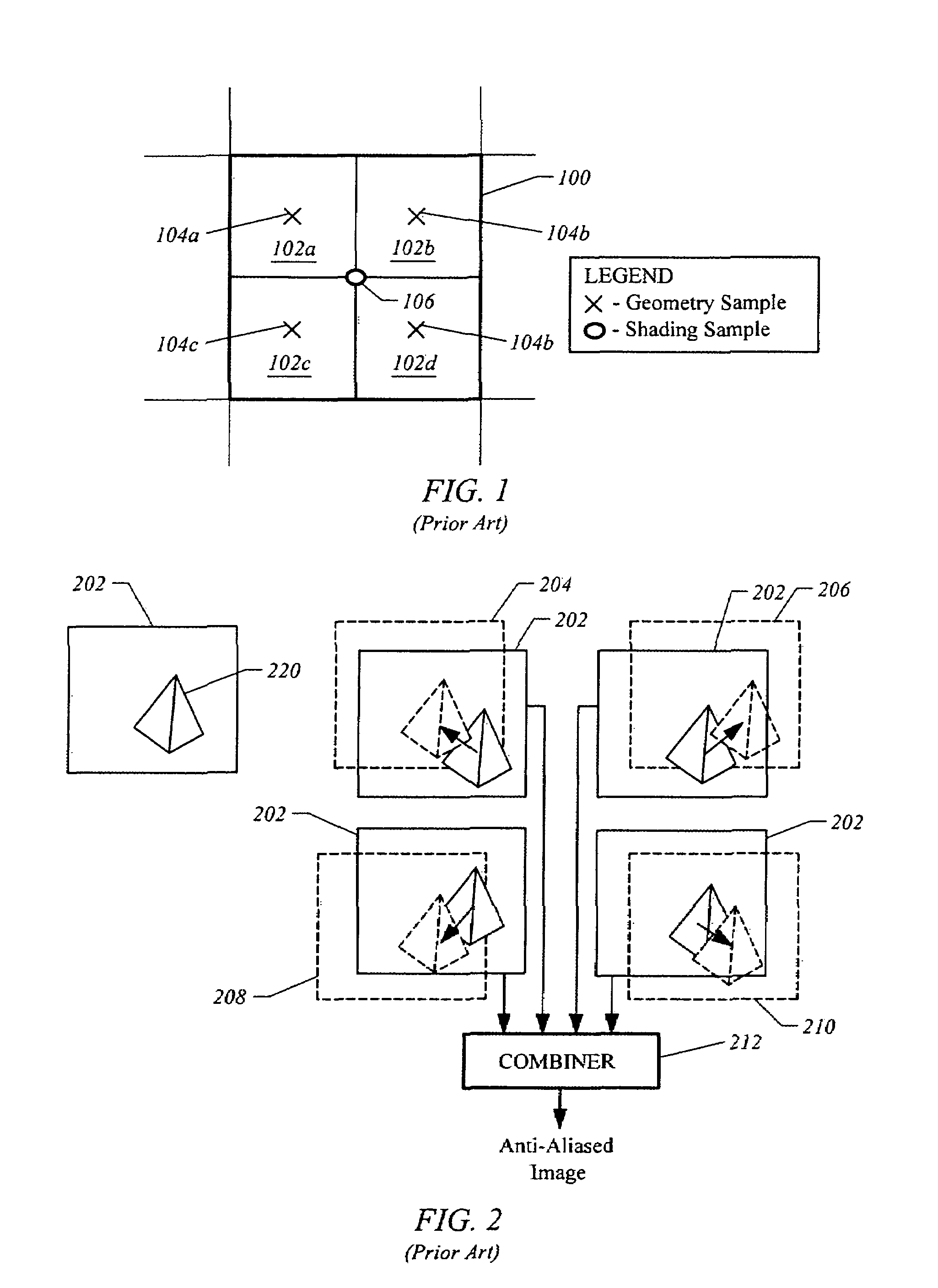
An image processing system is described that receives polygonal image data at the direction of a processor and develops antialiased image data for display on a raster scanned display. In particular, the image system includes a scan convertor for converting the polygonal image data into pixel data, which includes pixel screen coordinates and at least one color value for each polygon covered pixel of the pixel data and a supersample coverage mask indicating an extent of polygon coverage within each polygon covered pixel. The image system also includes a raster system having at least one image processor for receiving the pixel data for each pixel, for developing a region mask based on the supersample coverage mask, and for storing the color value in association with the region mask as anitialiased display data in an image memory in communication with the image processor based on the pixel screen coordinates. The region mask indicates one or more, geographical regions of supersamples within each pixel covered by one or more polygons and indicates a color value stored in the image memory to be assigned to the supersamples in a region. This requires only a single color value for supersamples within a region of a covered pixel to be stored in the image memory. The image system can also be configured to develop and store Z-values, alpha values, stencil values, and texture values for each pixel for storage in the image memory in association with the region mask.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Matching the edges of multiple overlapping screen images
A graphics system comprises pixel calculation units and a sample buffer which stores a two-dimensional field of samples. Each pixel calculation unit selects positions in the two-dimensional field at which pixel values (e.g. red, green, blue) are computed. The pixel computation positions are selected to compensate for image distortions introduced by a display device and / or display surface. Non-uniformities in a viewer's perceived intensity distribution from a display surface (e.g. hot spots, overlap brightness) are corrected by appropriately scaling pixel values prior to transmission to display devices. Two or more sets of pixel calculation units driving two or more display devices adjust their respective pixel computation centers to align the edges of two or more displayed images. Physical barriers prevent light spillage at the interface between any two of the display images. Separate pixel computation positions may be used for distinct colors to compensate for color distortions.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Matching the edges of multiple overlapping screen images
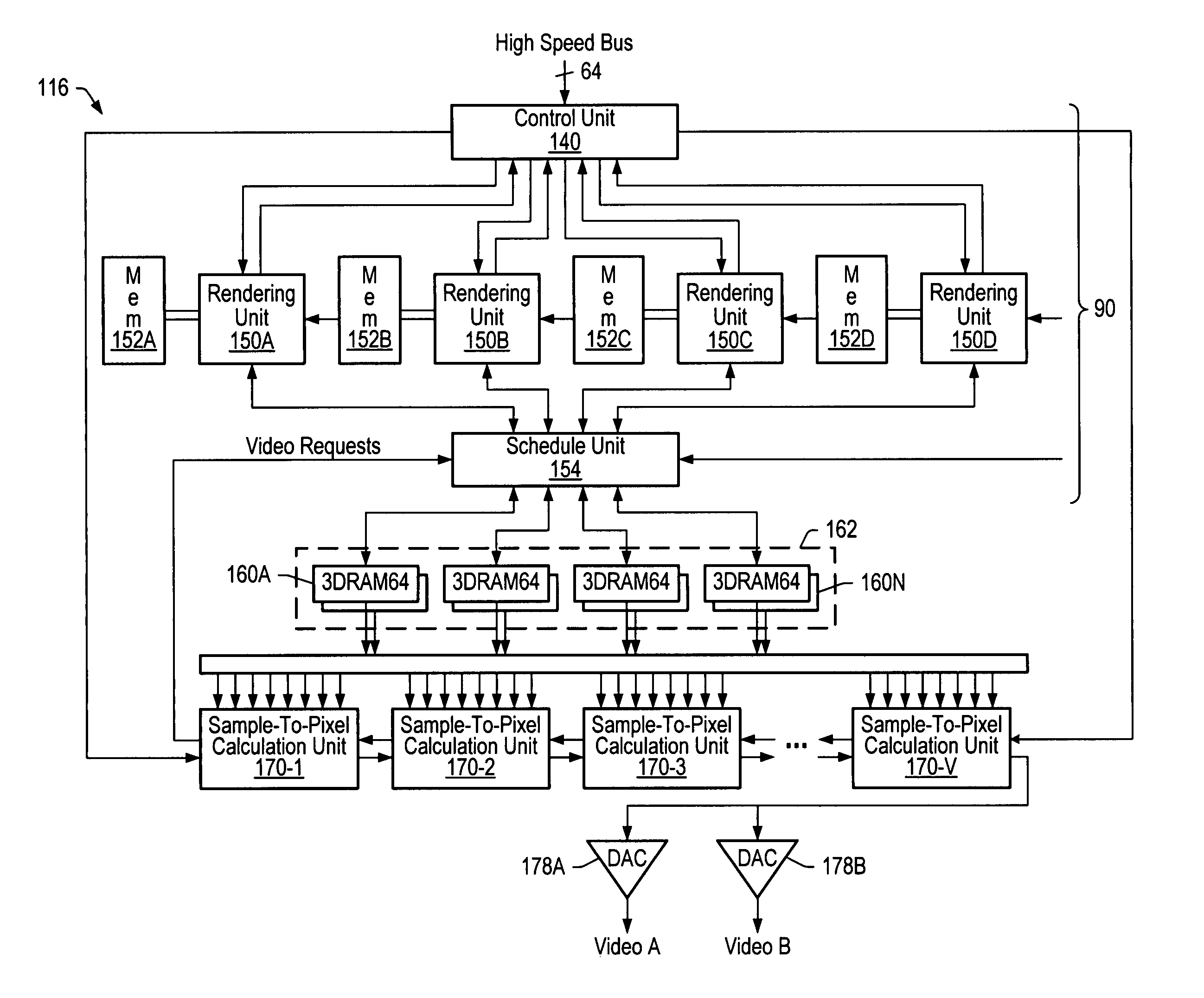
InactiveUS7079157B2Large latency of a frame buffer may be avoidedSignificant latencyImage enhancementImage analysisGraphicsGraphic system
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Image processing apparatus and method of same
InactiveUS20050068333A1Drop in drawing speedAccurate anti-aliasingDetails involving antialiasing2D-image generationImaging processingAnti-aliasing
An image processing apparatus capable of realizing accurate anti-aliasing with a small memory, without being affected by the order of drawing, and without inducing a drop in the drawing speed, including an anti-aliasing system obtaining edge information from an image after drawing, determining a processing content necessary for the anti-aliasing, and performing the determined processing. Specifically, either of the information of a z-buffer and the information of the normal vector at each pixel obtained at the time of drawing, or both information, is scanned or by the information of normal vectors restored from the information of the z-buffer is used, a state machine for holding the state and a counter for measuring the continuity of an edge are prescribed, the value of which pixel adjacent in which direction to each pixel on each edge and what kind of ratio to use for blending are determined, and the determined values are used for blending. This is performed successively until the pixel values are updated.
Owner:SONY CORP
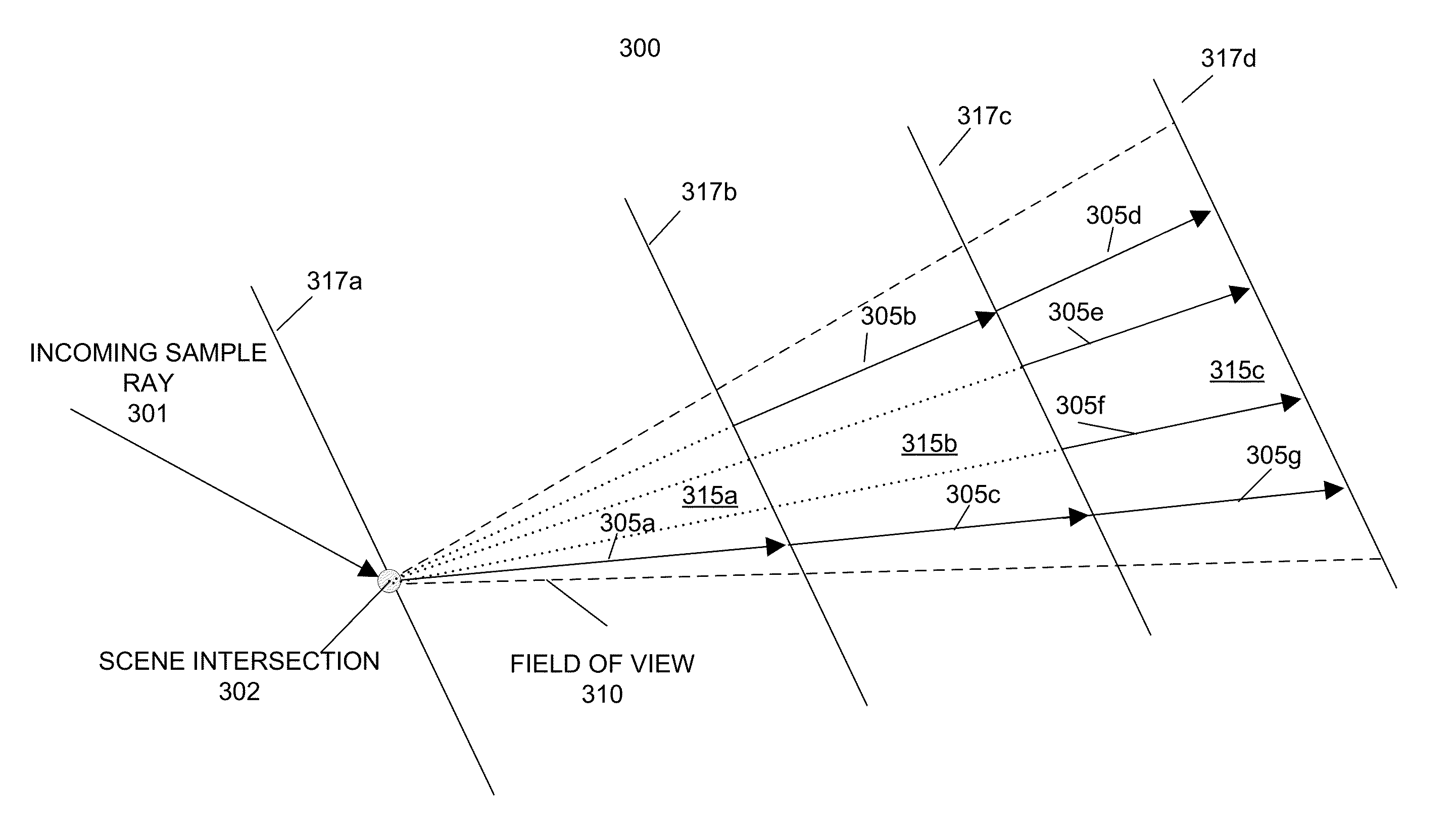
Adaptive depth of field sampling
ActiveUS8493383B1Increase the number ofDetails involving antialiasingCathode-ray tube indicatorsDepth of fieldSelf adaptive
Adaptive sampling alleviates aliasing by partitioning the field of view of an image sample point into depth regions. Portions of the scene are sampled within a depth region using sample rays. If a sample ray is not completely occluded in the depth region, corresponding sample rays are evaluated in adjacent depth regions. Sample rays can be recursively evaluated in further depth regions until all the subsamples intersect opaque objects or a depth limit or transparency threshold is reached. The value of an image sample point is the weighted combination of sample rays. The number of sample rays in each depth region may increase monotonically with distance along a line of sight from an image sample point for effects such as reflection, refraction, and illumination. The number of sample rays in each depth region may increase monotonically with distance from a focal plane for effects such as depth of field.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
Graphics system configured to perform distortion correction
A graphics system comprises pixel calculation units and a sample buffer which stores a two-dimensional field of samples. Each pixel calculation unit selects positions in the two-dimensional field at which pixel values (e.g. red, green, blue) are computed. The pixel computation positions are selected to compensate for image distortions introduced by a display device and / or display surface. Non-uniformities in a viewer's perceived intensity distribution from a display surface (e.g. hot spots, overlap brightness) are corrected by appropriately scaling pixel values prior to transmission to display devices. Two or more sets of pixel calculation units driving two or more display devices adjust their respective pixel computation centers to align the edges of two or more displayed images. Physical barriers prevent light spillage at the interface between any two of the display images. Separate pixel computation positions may be used for distinct colors to compensate for color distortions.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
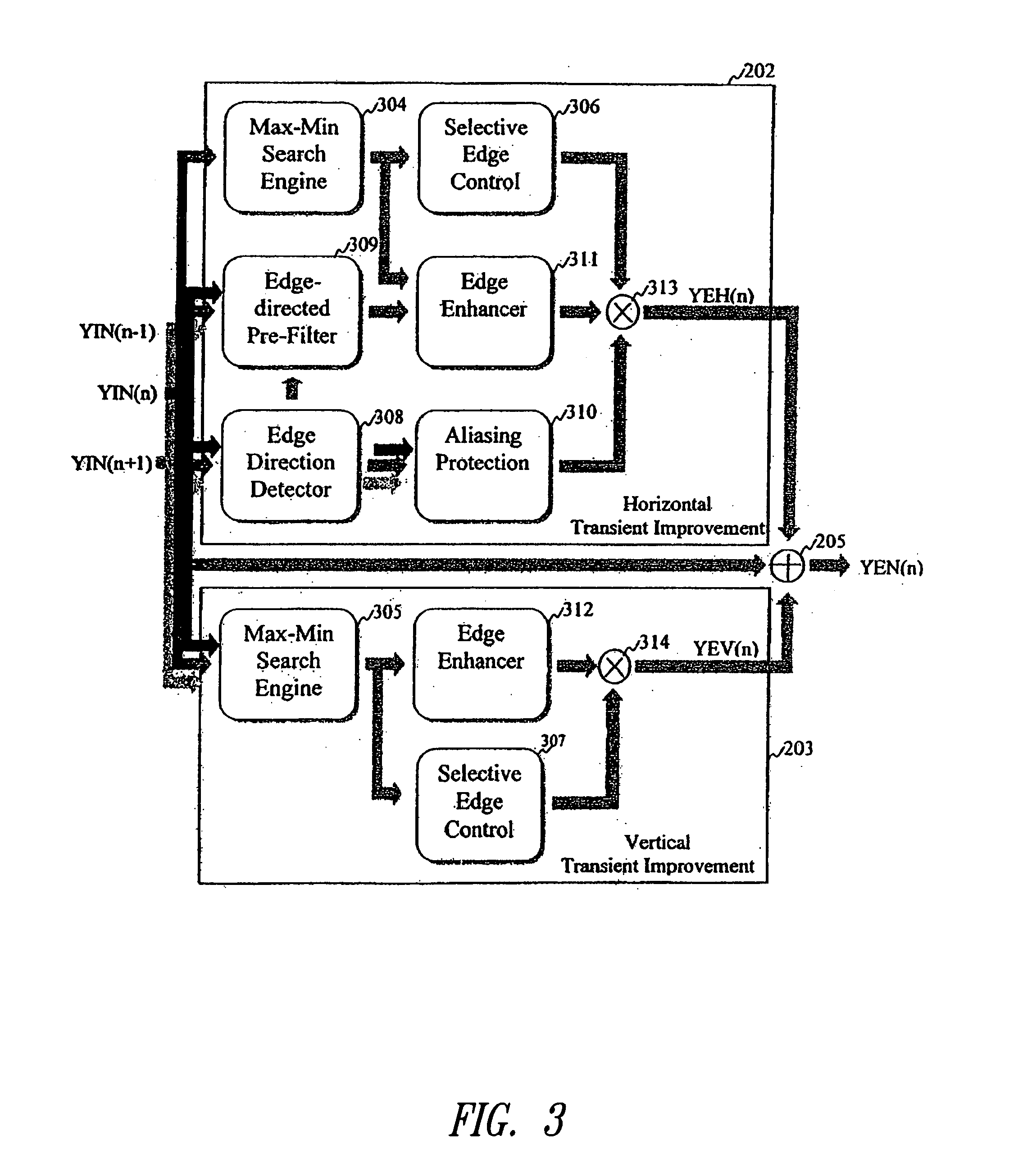
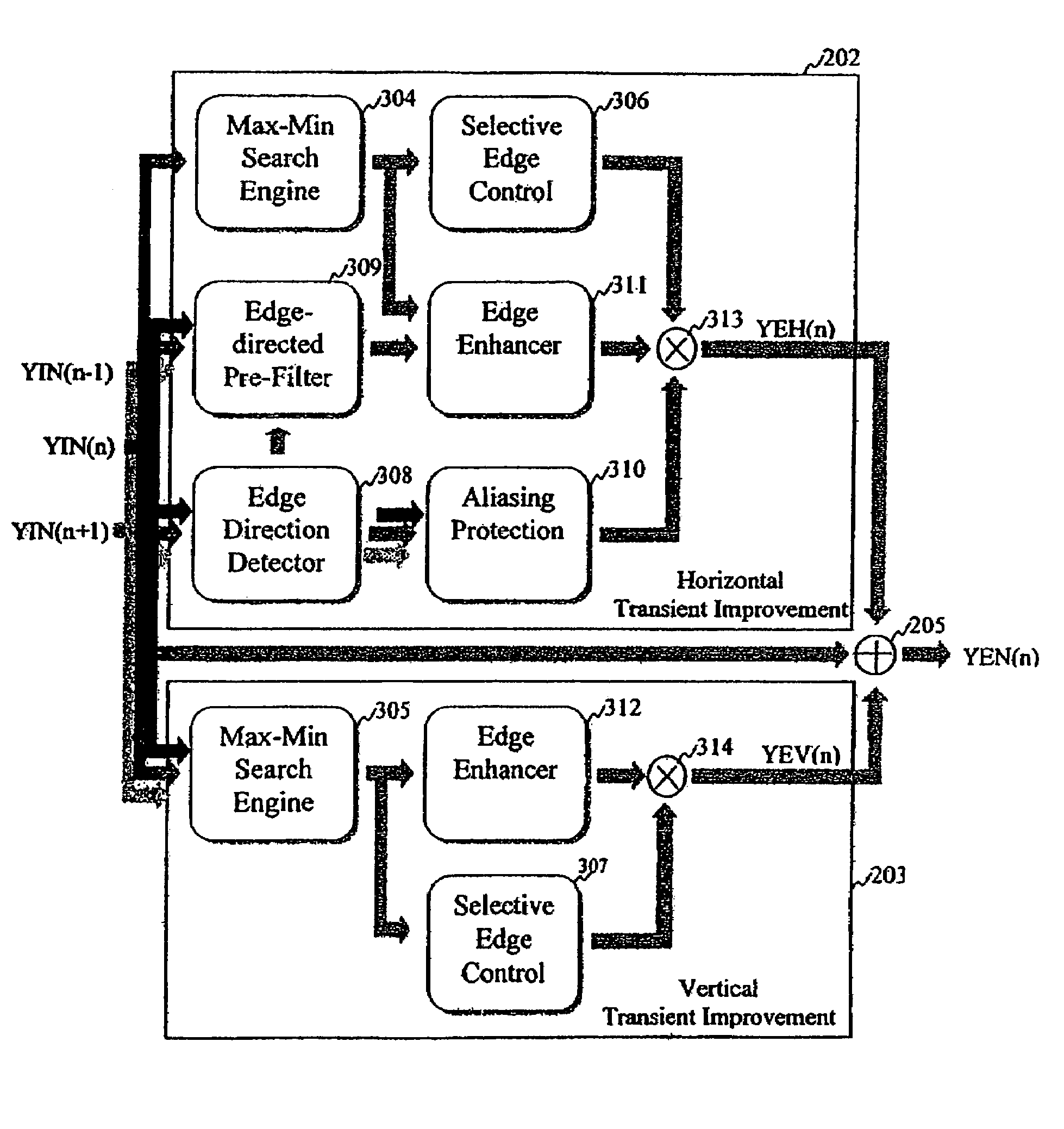
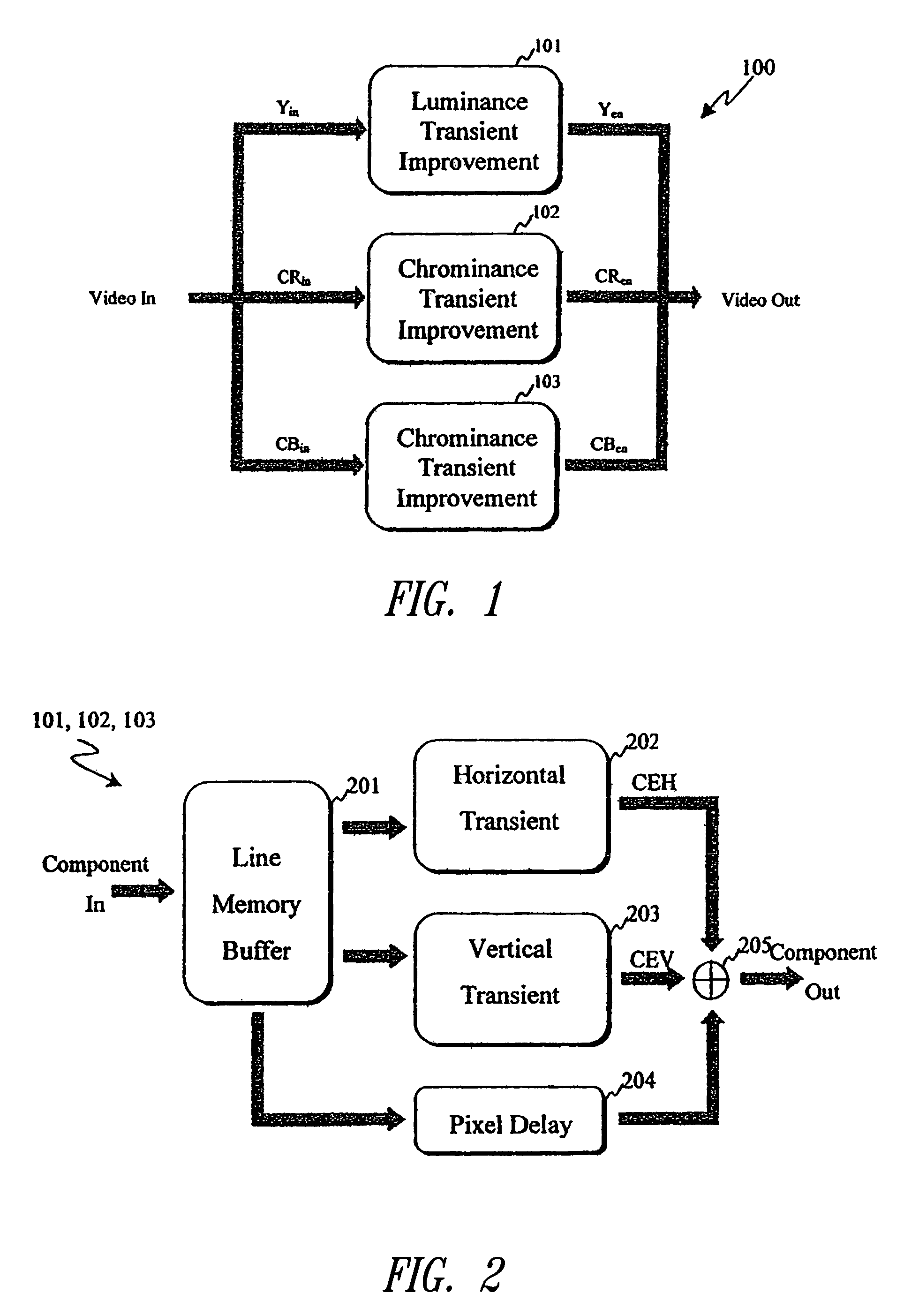
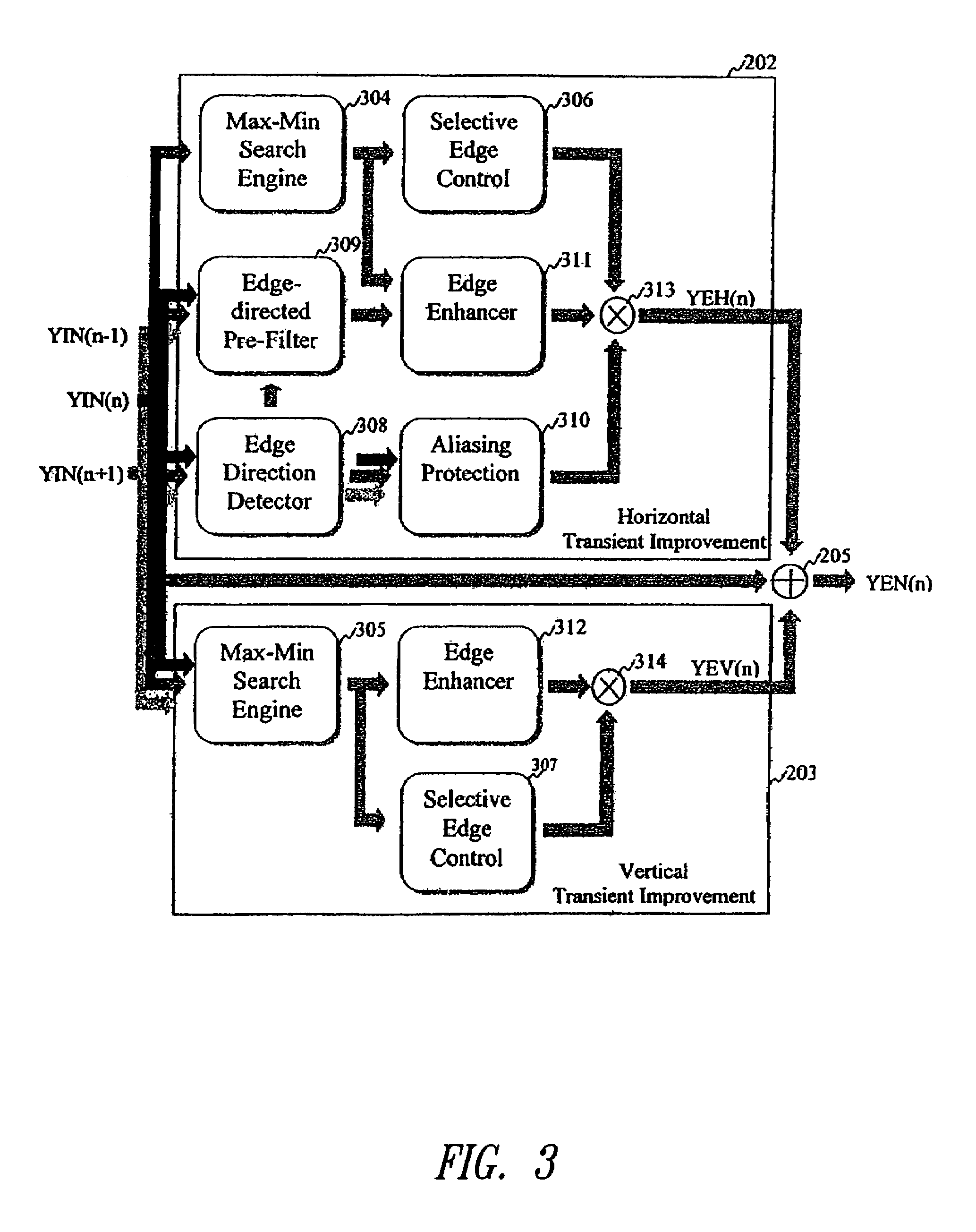
Edge enhancement process and system
InactiveUS20050008251A1Avoid problemsImprove visibilityImage enhancementImage analysisVisibilityVertical edge
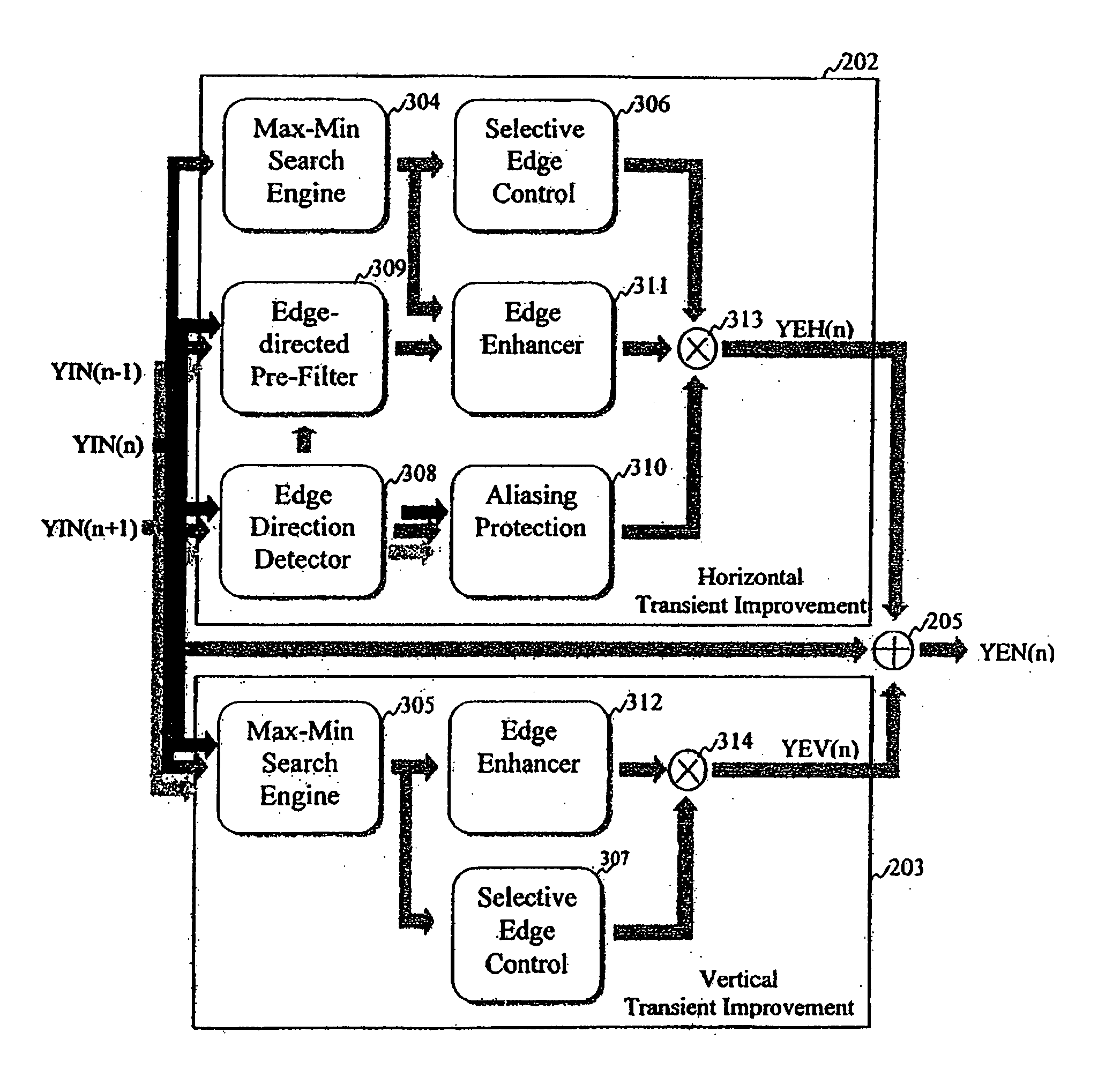
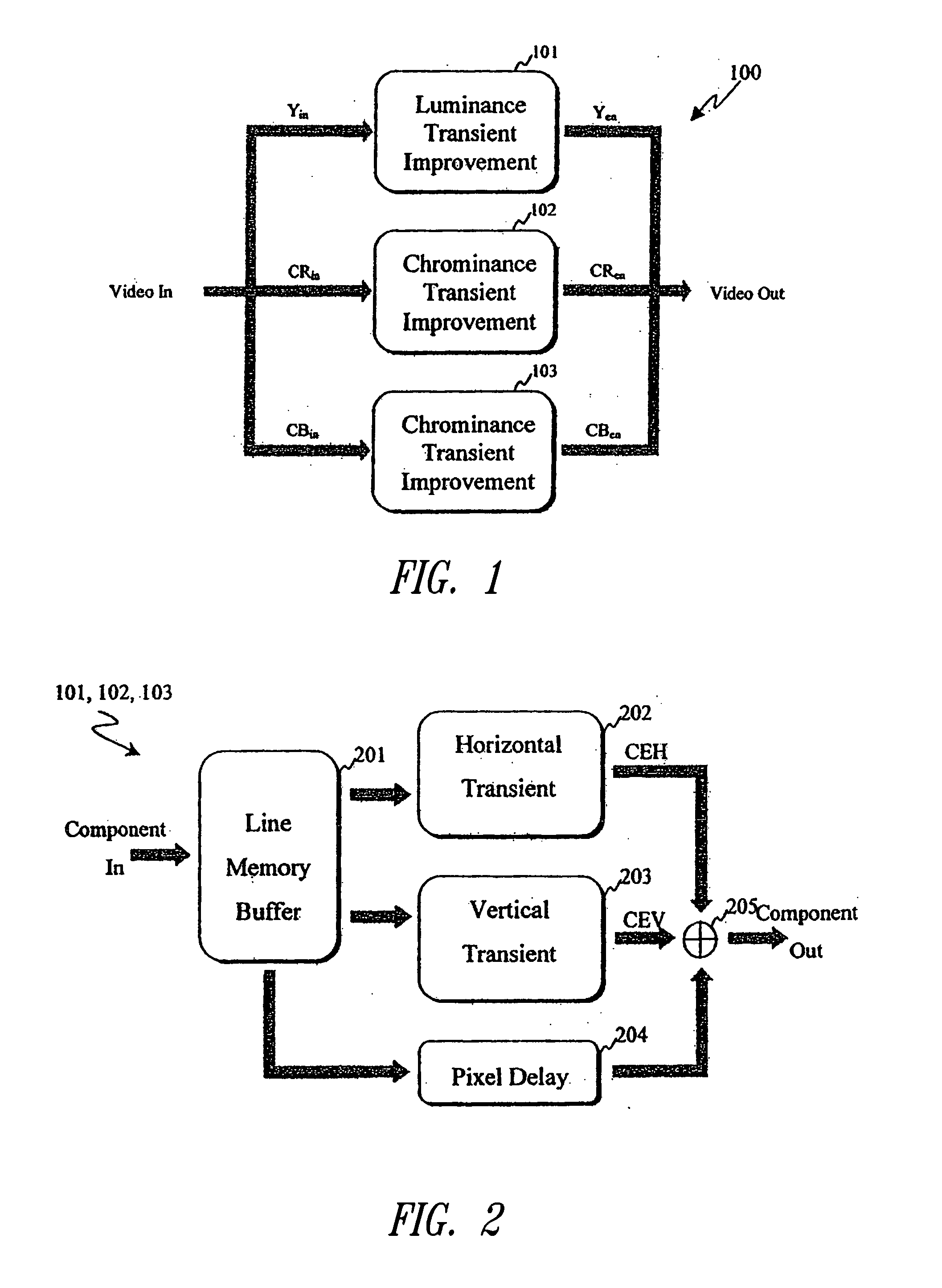
An edge enhancement system, including a selective edge controller for determining one or more properties of an edge of image data, and for generating one or more weighting factors on the basis of properties of the edge; and a scaling module for scaling an edge enhancement signal by the weighting factors to control the degree of edge enhancement. The image data may represent a still or moving (i.e., video) image. A max-min search circuit determines maximum and minimum turning points closest to the center of the data processing window and that are located on opposing sides of the window, to determine values and locations of maximum and minimum pixels of the edge. An edge-directed pre-filtering circuit reduces the amplification of edge fuzziness by smoothing close the edges vertical prior to enhancement. An aliasing protection circuit reduces the visibility of saw-tooth defects on predominantly horizontal diagonal edges.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
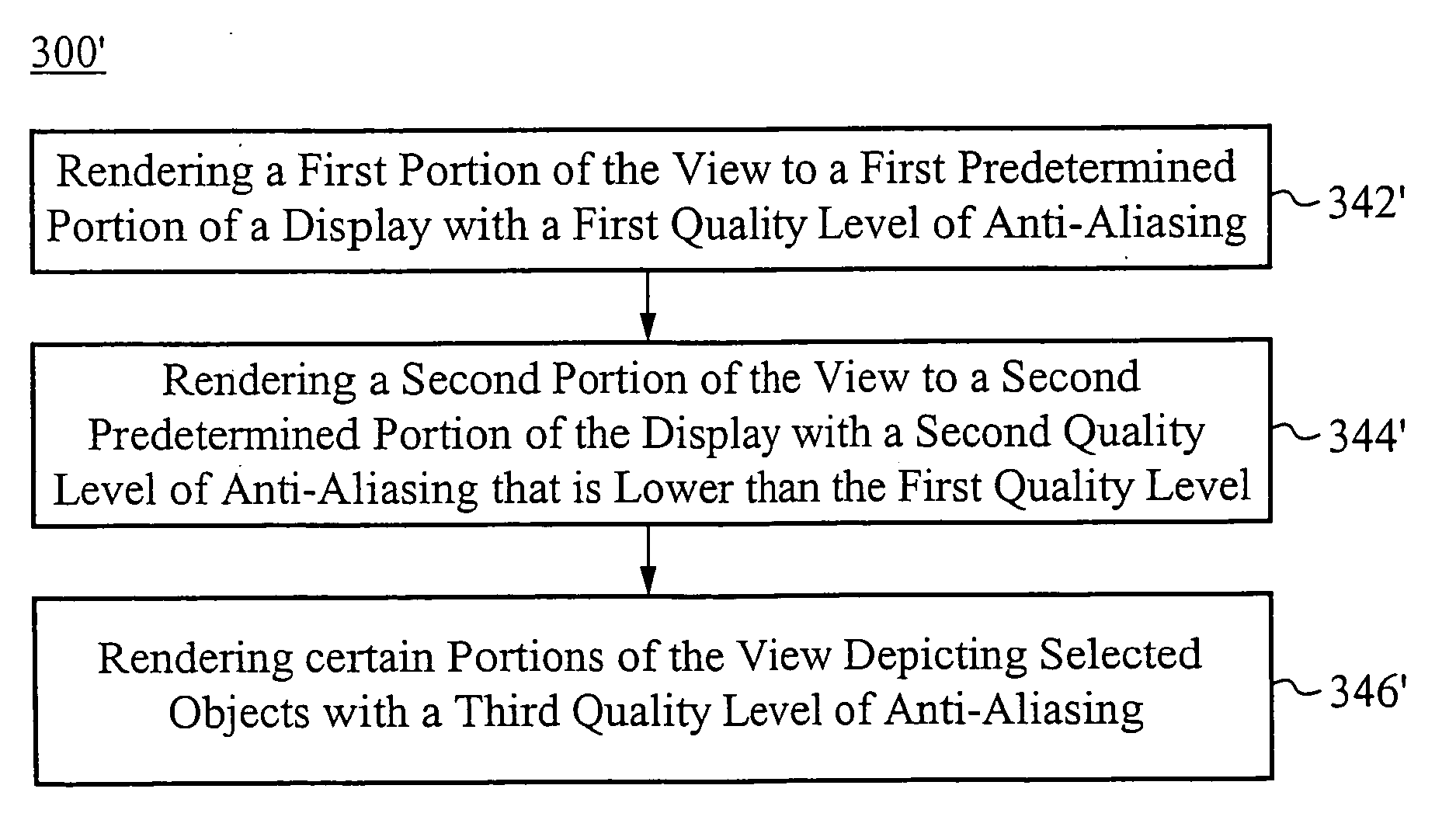
Method of and system for non-uniform image enhancement
ActiveUS20070229503A1Assist in operationDetails involving antialiasingCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsAnti-aliasing
Methods of rendering a view of a scene include steps that specify quality levels of anti-aliasing and texture filtering for predetermined regions of a display, or selected objects within the scene, or both. Methods of processing data for display include steps adapted to process portions of the image according to selected or predetermined anti-aliasing and texture filtering quality levels. Graphics processing equipment includes hardware or software adapted to perform non-uniform anti-aliasing of images according to specified criteria.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
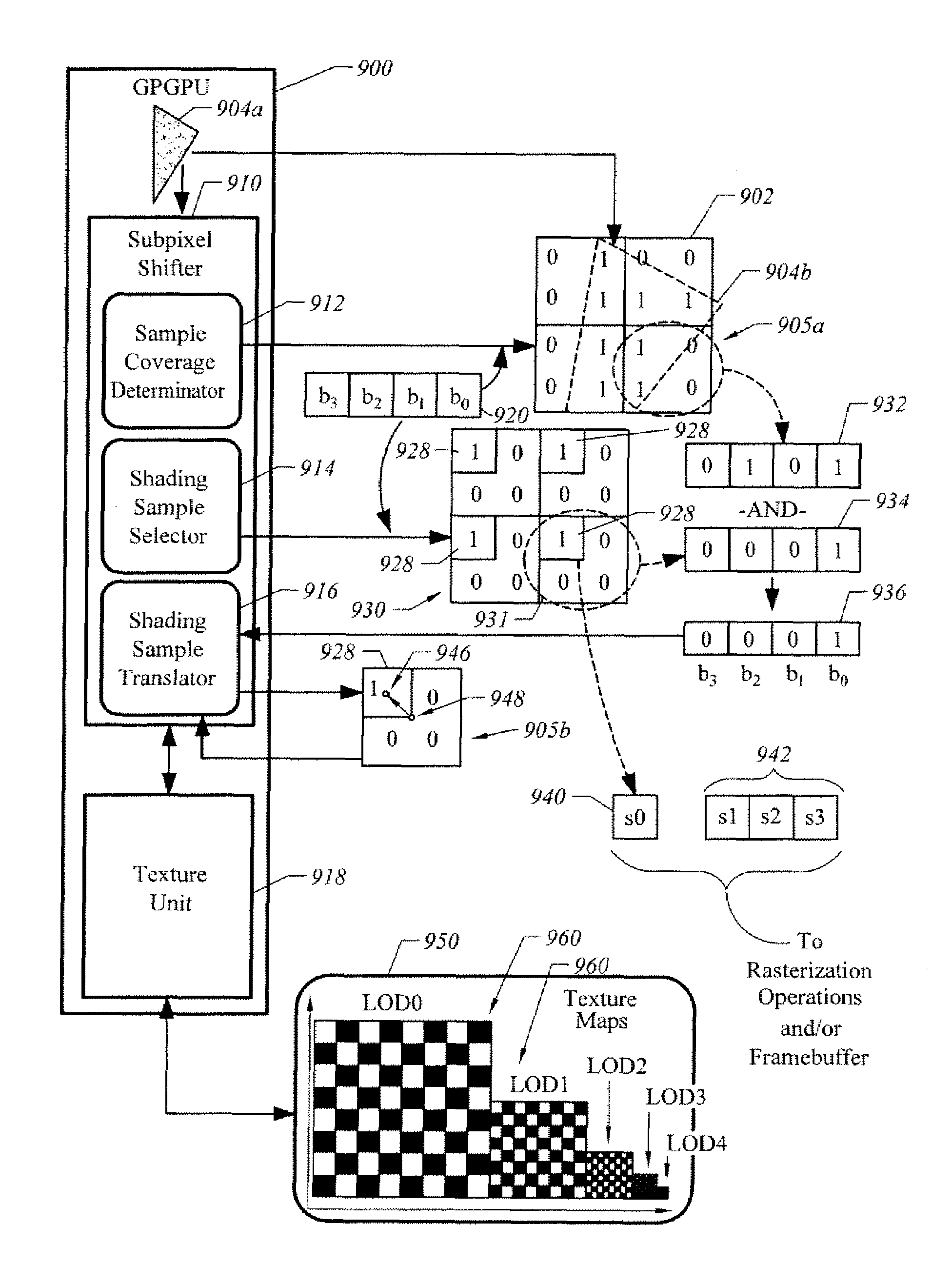
Graphical processing system, graphical pipeline and method for implementing subpixel shifting to anti-alias texture
ActiveUS7456846B1Reduce aliasingReduce textureDetails involving antialiasingCathode-ray tube indicatorsGeneral purposeGraphics
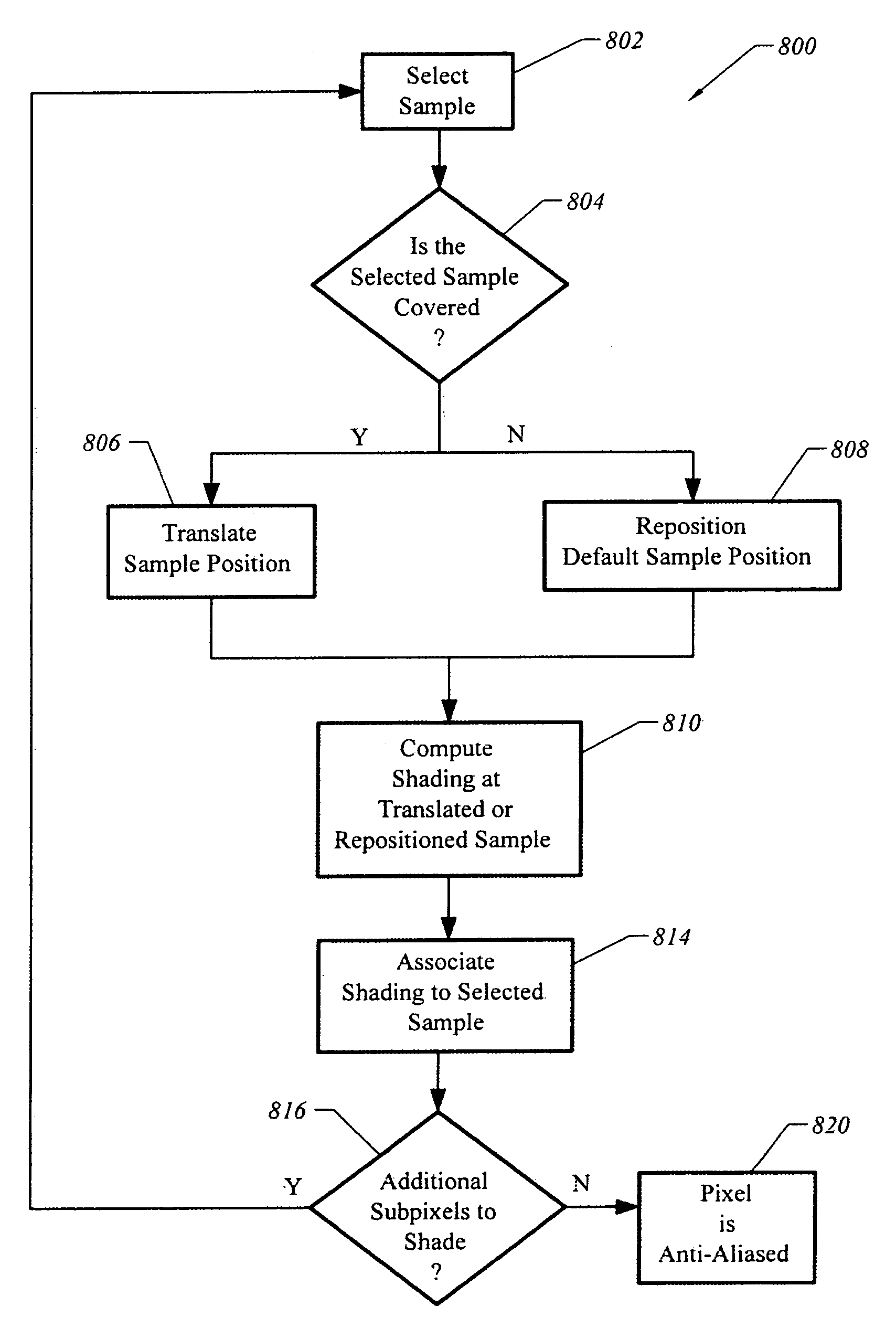
A system, apparatus, and method are disclosed for modifying positions of sample positions for selectably oversampling pixels to anti-alias non-geometric portions of computer-generated images, such as texture, at least in part, by shifting shading sample positions relative to a frame of reference. There is generally no relative motion between the geometries and the coverage sample positions. In one embodiment, an apparatus, such as a graphics pipeline and / or a general purpose graphics processing unit, anti-aliases geometries of a computer-generated object. The apparatus includes at least a texture unit and a pipeline front end unit to determine geometry coverage and a subpixel shifter to shift shading sample positions relative to the frame of reference. The apparatus can receive subpixel shifting masks to select subsets of shading sample positions. Each of the shading sample positions is shifted to a coverage sample position to reduce level of detail (“LOD”) artifacts.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Graphics system configured to perform distortion correction
InactiveUS6940529B2Large latency of a frame buffer may be avoidedSignificant latencyImage enhancementDetails involving antialiasingGraphicsGraphic system
A graphics system comprises pixel calculation units and a sample buffer which stores a two-dimensional field of samples. Each pixel calculation unit selects positions in the two-dimensional field at which pixel values (e.g. red, green, blue) are computed. The pixel computation positions are selected to compensate for image distortions introduced by a display device and / or display surface. Non-uniformities in a viewer's perceived intensity distribution from a display surface (e.g. hot spots, overlap brightness) are corrected by appropriately scaling pixel values prior to transmission to display devices. Two or more sets of pixel calculation units driving two or more display devices adjust their respective pixel computation centers to align the edges of two or more displayed images. Physical barriers prevent light spillage at the interface between any two of the display images. Separate pixel computation positions may be used for distinct colors to compensate for color distortions.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
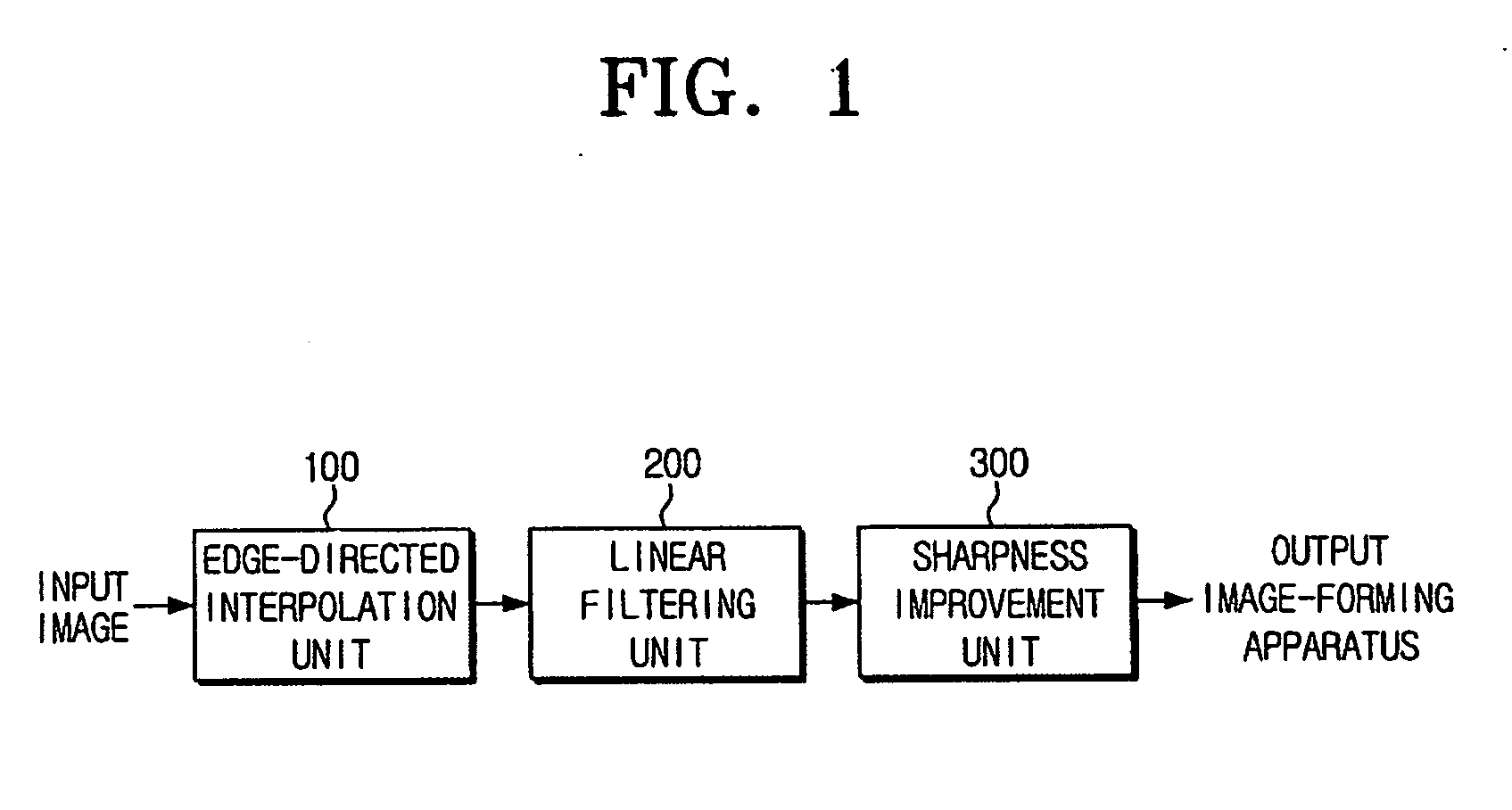
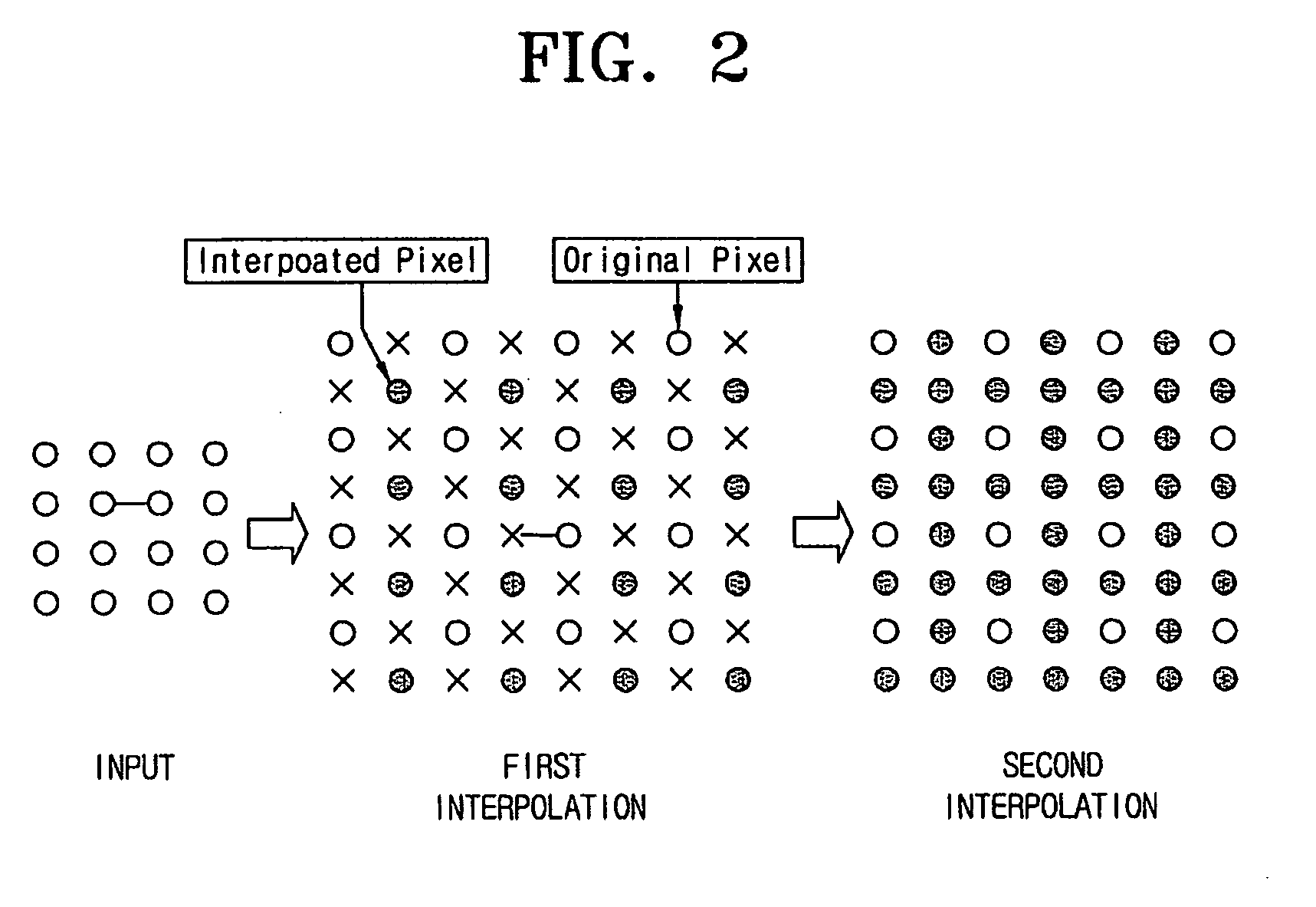
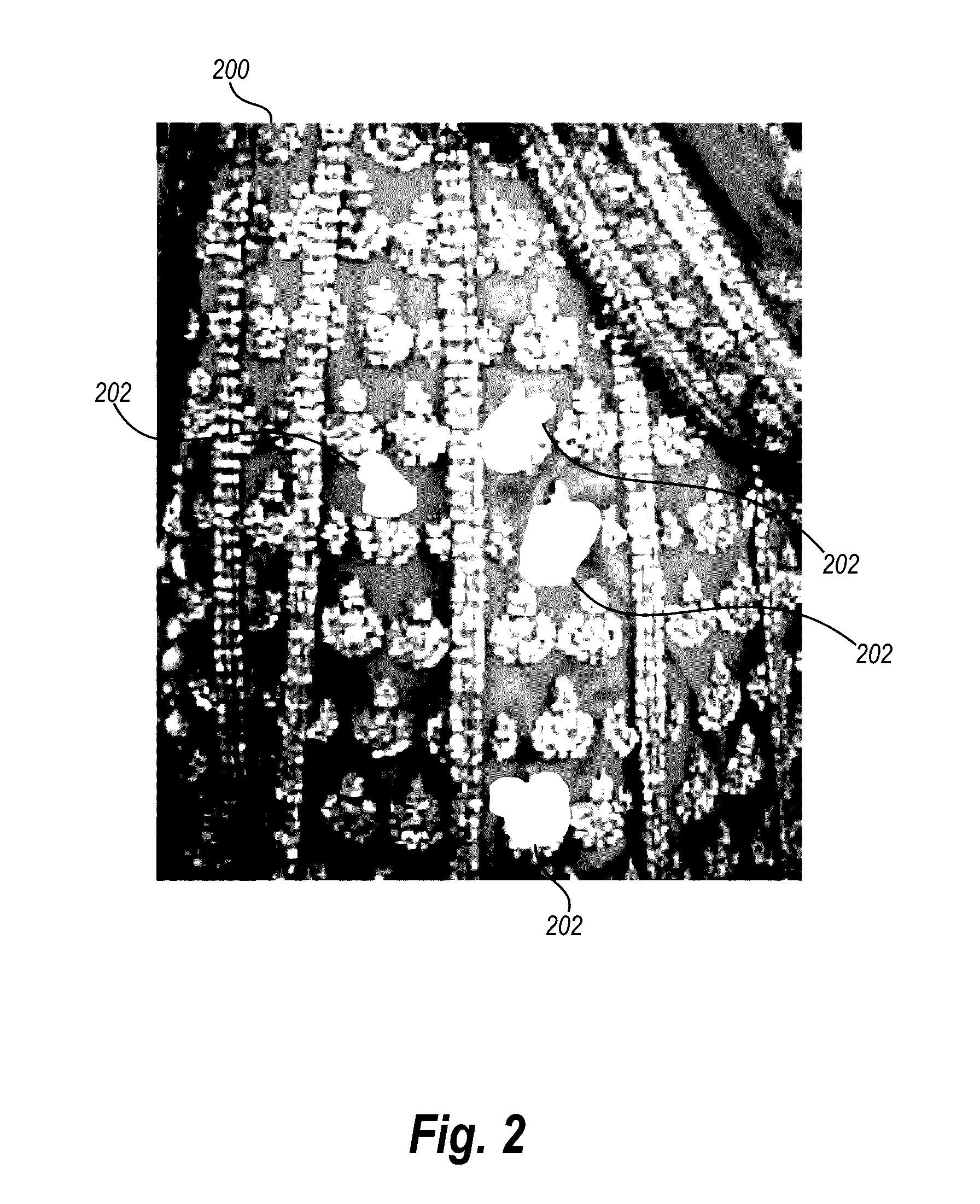
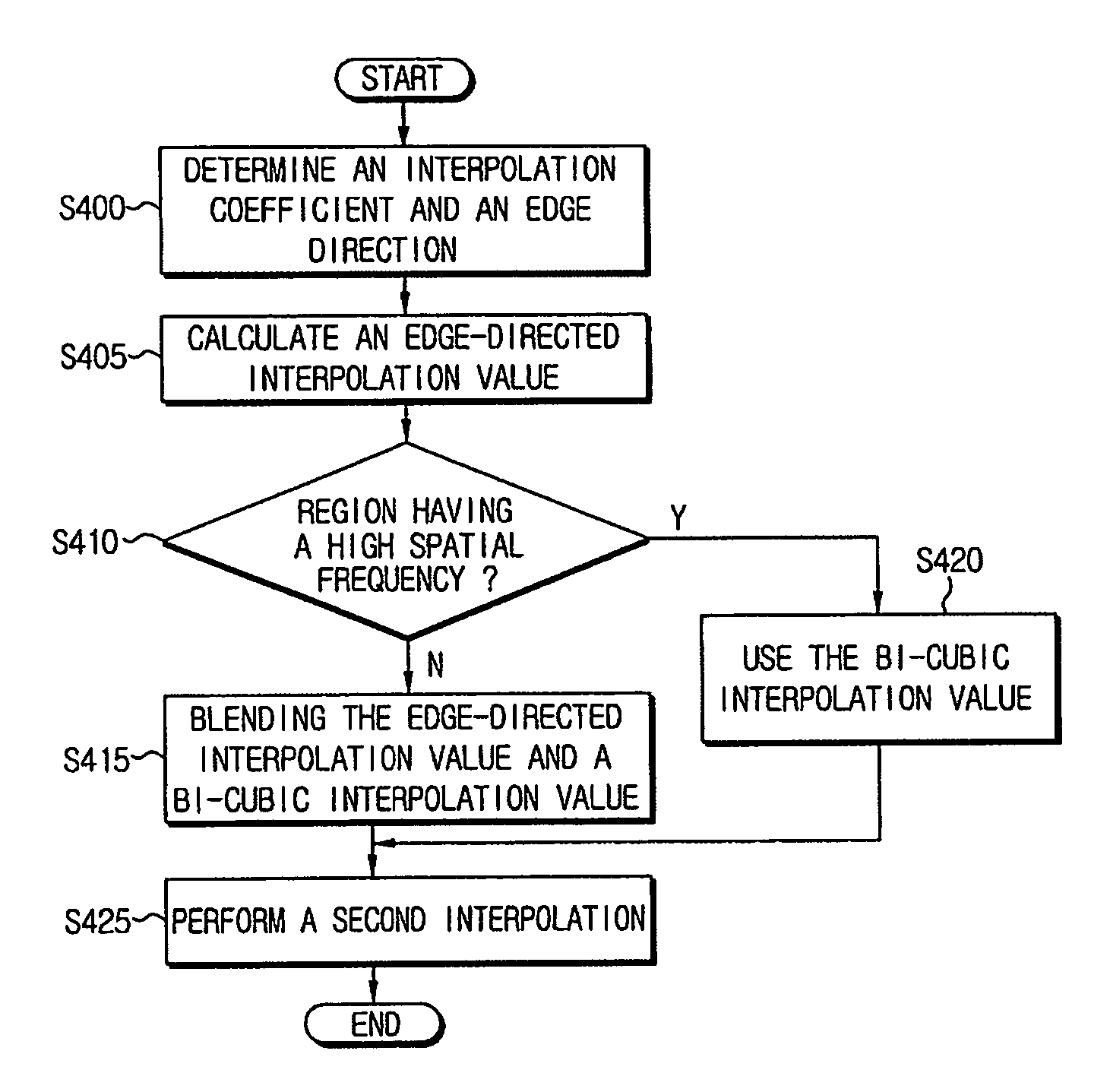
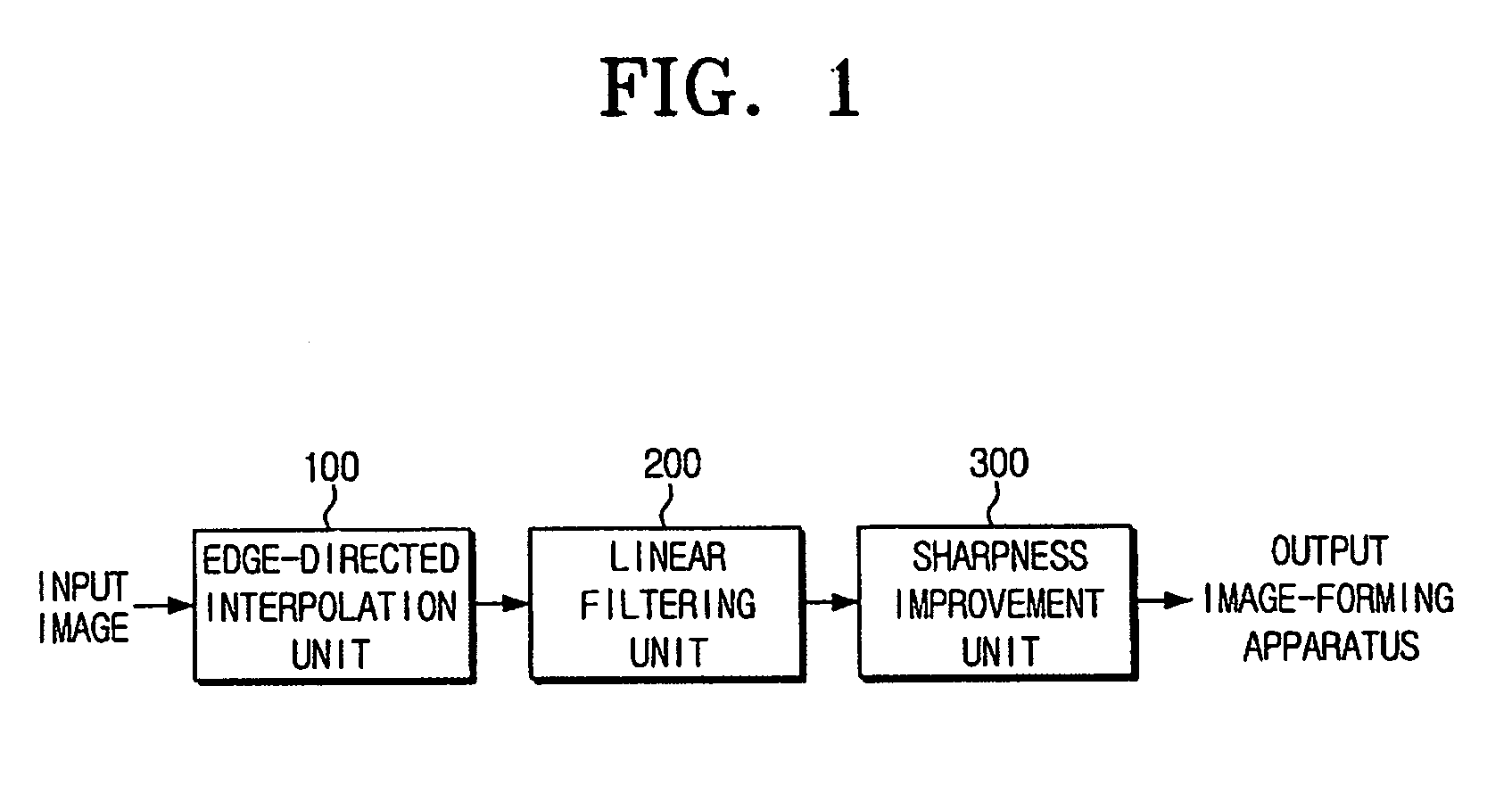
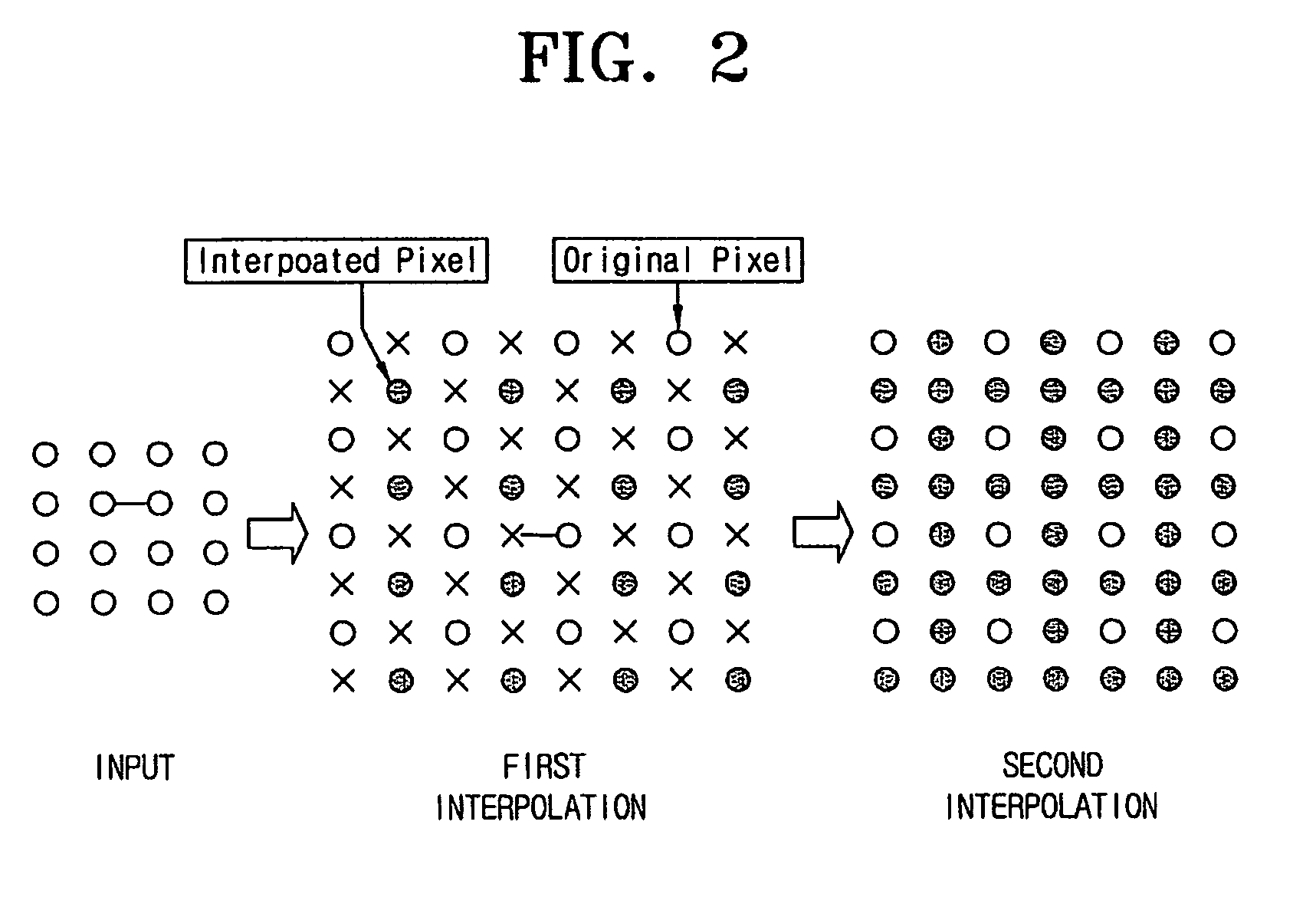
Resolution-converting apparatus and method
ActiveUS20060033936A1Eliminating occurrence of quality-degradingImprove clarityImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersPattern recognitionIntermediate image
The resolution-converting method comprises steps of applying an edge-directed interpolation to an input image and producing an intermediate image; converting a sampling rate with respect to the intermediate image and producing an output image having a predetermined resolution; and improving sharpness of the produced output image. The present invention prevents image-quality degradation factors that can occur in the conventional resolution-converting method as well as obtains an output image having a resolution of a desired size.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Edge enhancement process and system
InactiveUS7406208B2Efficiency problemReduce generationImage enhancementDetails involving antialiasingVisibilityVertical edge
An edge enhancement system, including a selective edge controller for determining one or more properties of an edge of image data, and for generating one or more weighting factors on the basis of properties of the edge; and a scaling module for scaling an edge enhancement signal by the weighting factors to control the degree of edge enhancement. The image data may represent a still or moving (i.e., video) image. A max-min search circuit determines maximum and minimum turning points closest to the center of the data processing window and that are located on opposing sides of the window, to determine values and locations of maximum and minimum pixels of the edge. An edge-directed pre-filtering circuit reduces the amplification of edge fuzziness by smoothing close the edges vertical prior to enhancement. An aliasing protection circuit reduces the visibility of saw-tooth defects on predominantly horizontal diagonal edges.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
Determining a coverage mask for a pixel
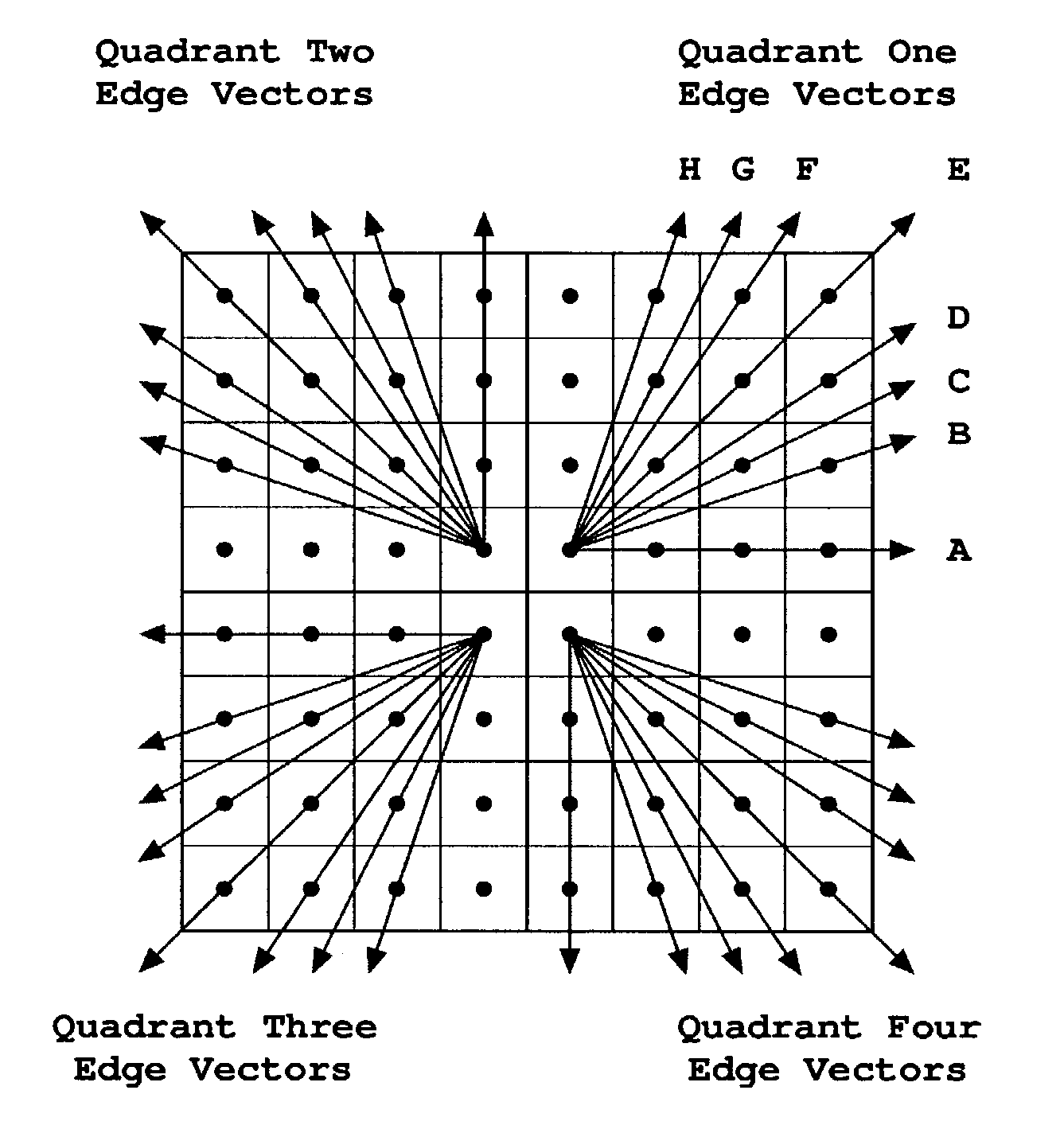
InactiveUS7006110B2Reduce storage spaceSufficiently smoothDetails involving antialiasingImage analysisFour quadrantsGeometric primitive
The invention relates to a method, a device, a system and a software program product for determining for a pixel a coverage mask reflecting an orientation and possibly a distance from the pixel center of an original edge vector. The pixel is to be employed for displaying at least a part of a geometric primitive on a display, and the original edge vector represents an oriented edge of the geometric primitive. The method comprises as a first step determining one of four quadrants of a Cartesian coordinate system to which the original edge vector belongs due to its orientation. The original edge vector is then transposed into a predetermined one of the four quadrants. Next, a stored coverage mask is fetched, which is associated at least indirectly to the transposed edge vector. Finally, the fetched coverage mask is transformed to the quadrant to which the original edge vector belongs.
Owner:RPX CORP
Methods, systems, and programming for producing and displaying subpixel-optimized images and digital content including such images
InactiveUS20050062758A1Reduce color imbalanceSuitable displayDigital data information retrievalDetails involving antialiasingDigital contentLuminosity
The invention relates to methods, systems, and programming for producing and displaying subpixel-optimized images and digital content including such images. Some embodiments access digital content represented by a mark-up language and display it with its images scaled down in a subpixel-optimized manner in a format dictated by the mark-up language. Some embodiments produce subpixel-optimized images by calculating the luminosity of a subpixel in such an image as a function of the length of a plurality of coverage lines within a window in a source image corresponding to the subpixel that is covered by source image pixels having the subpixel's color. Some embodiments calculate the luminosity of a subpixel in a subpixel-optimized image as a function both of the average luminosity of pixels in the subpixel's source image window and as a function of any color balancing distribution between resulting subpixel luminosities necessary to reduce color imbala
Owner:MARLBOROUGH SOFTWARE DEV HLDG
System, apparatus and method for subpixel shifting of sample positions to anti-alias computer-generated images
ActiveUS7369140B1Reduce computational overheadComputational resources can be preservedDetails involving antialiasingDrawing from basic elementsPattern recognitionGeometric primitive
A system, apparatus, and method are disclosed for modifying positions of sample positions for selectably oversampling pixels to anti-alias non-geometric portions of computer-generated images, such as texture, at least in part, by translating (e.g., shifting) shading sample positions relative to a frame of reference in which there is no relative motion between the geometries and the coverage sample positions. In one embodiment, an exemplary method determines whether a coverage sample position is covered by a geometric primitive. The method includes translating a shading sample position from an original shading sample position to the coverage sample position. This generally occurs if the geometry covers the coverage sample position to form a covered coverage sample position. Further, the method samples a shading value at the covered coverage sample positions for the pixel portion to anti-alias, for example, texture to reduce level of detail (“LOD”) artifacts.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
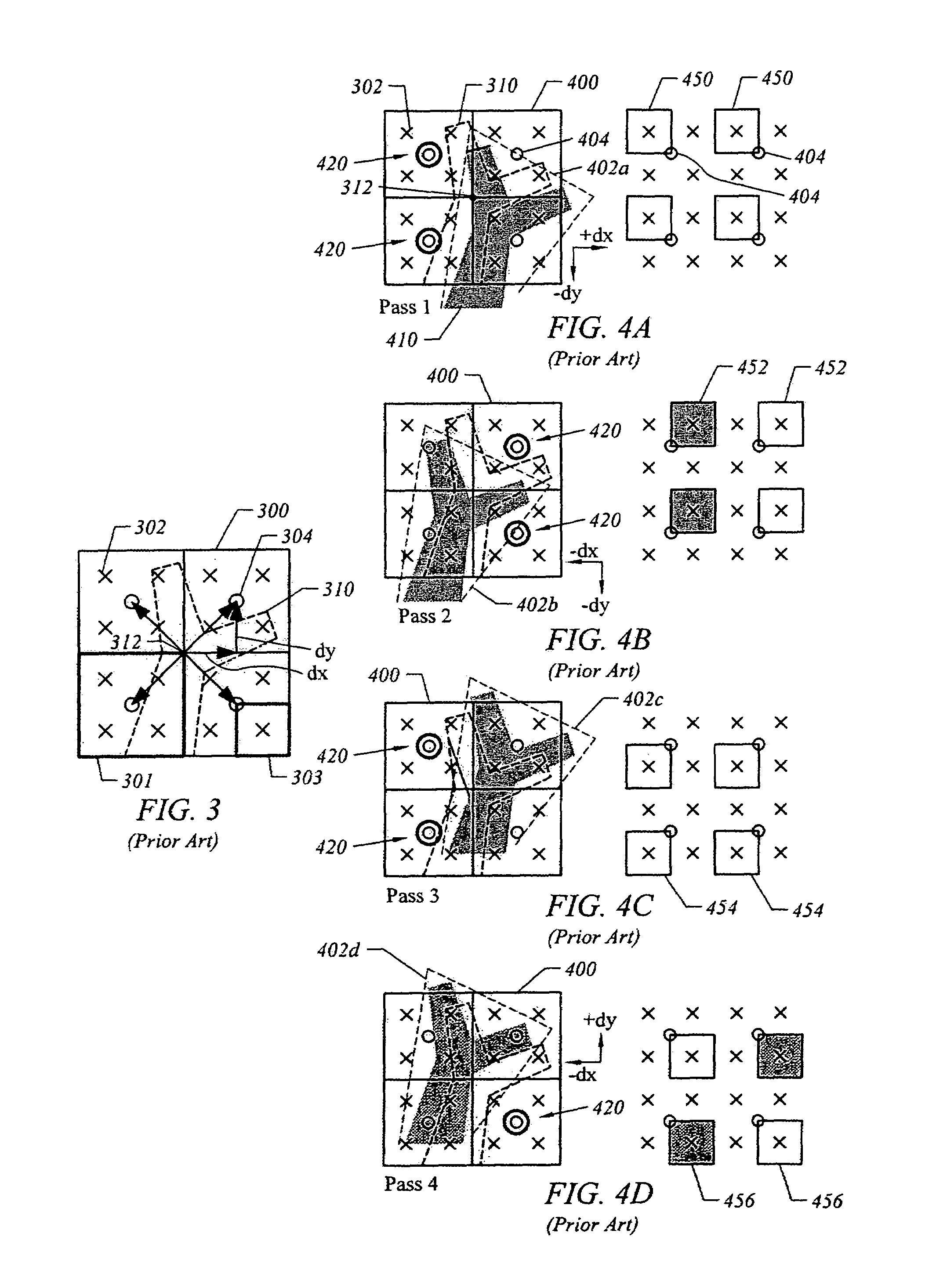
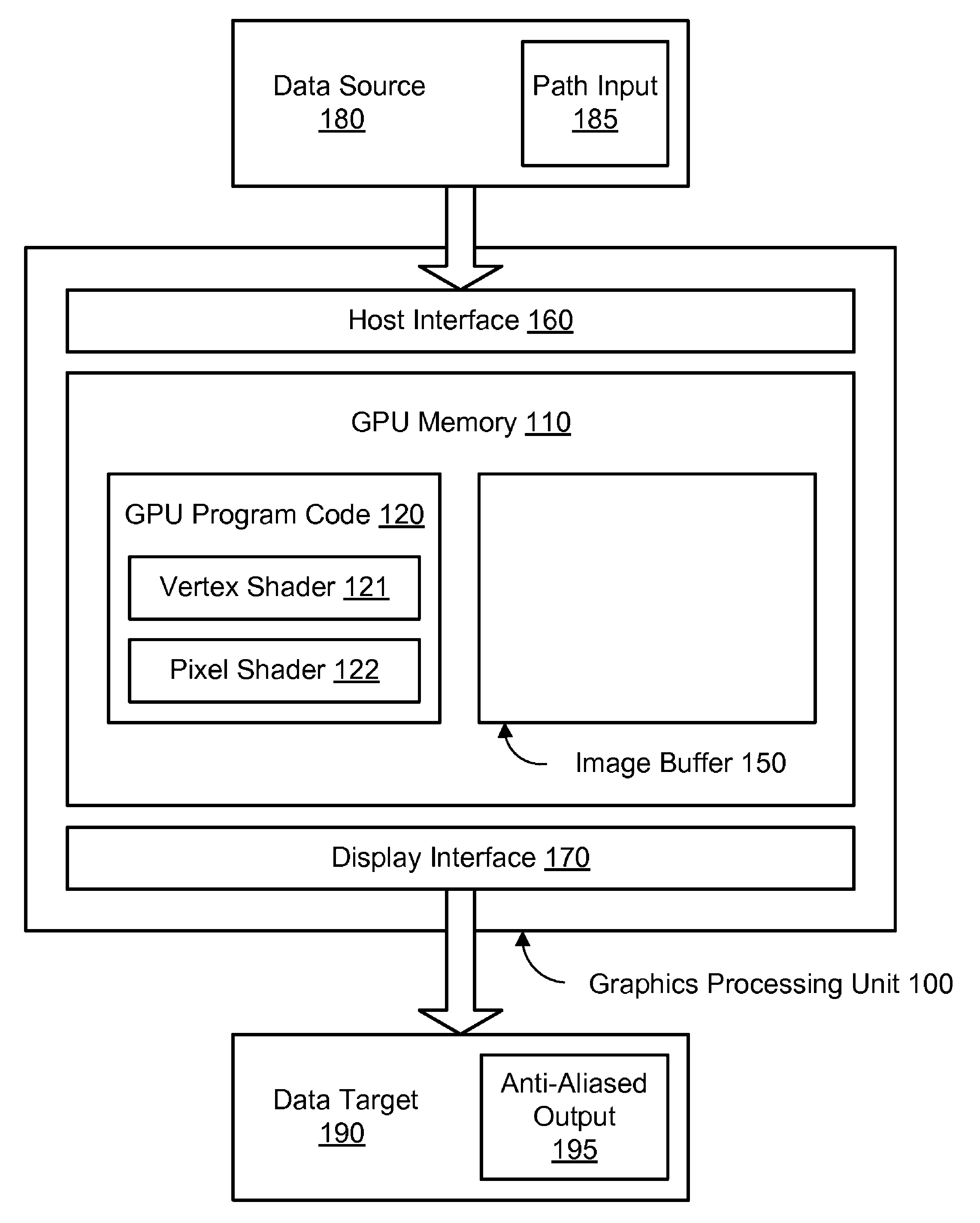
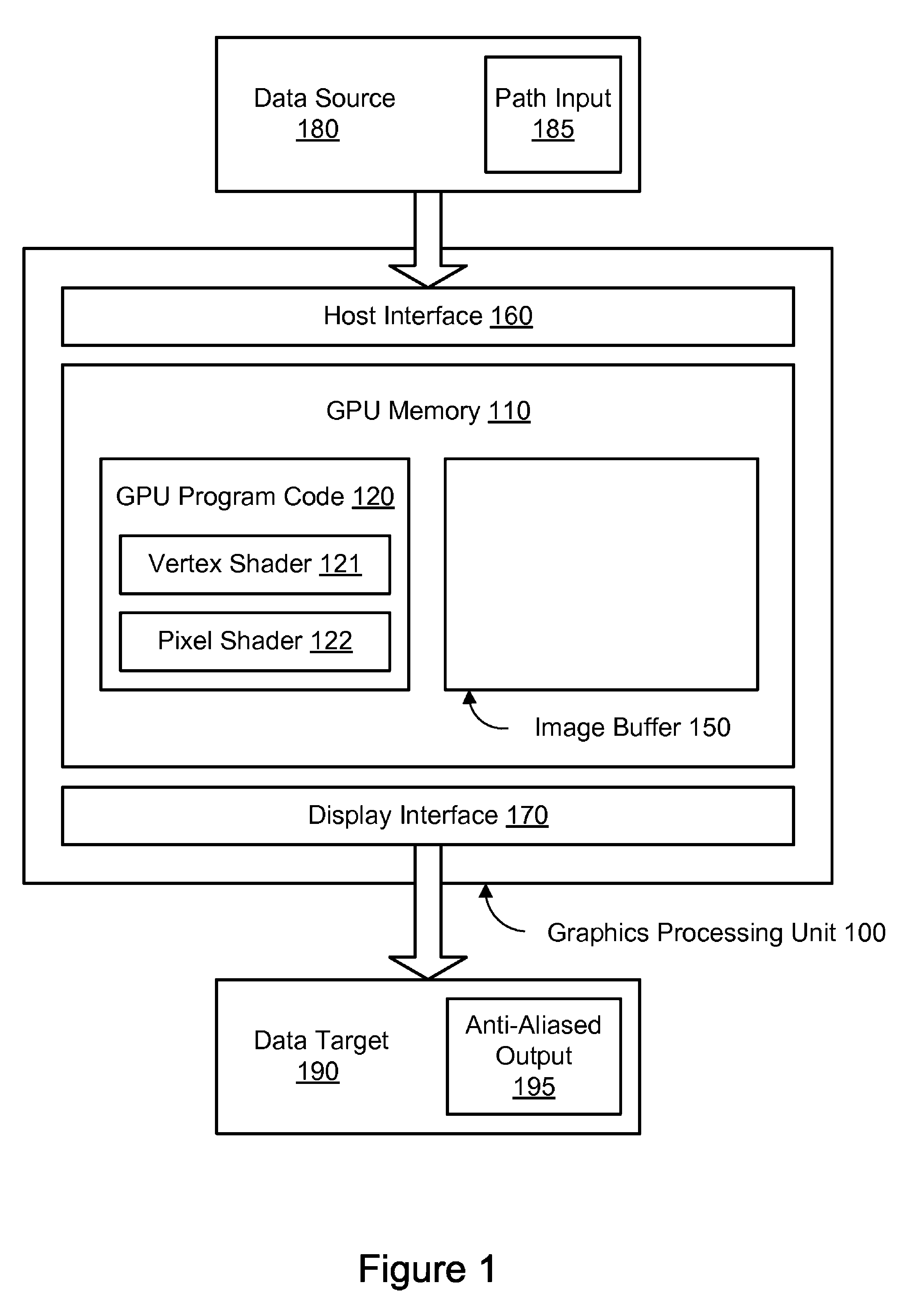
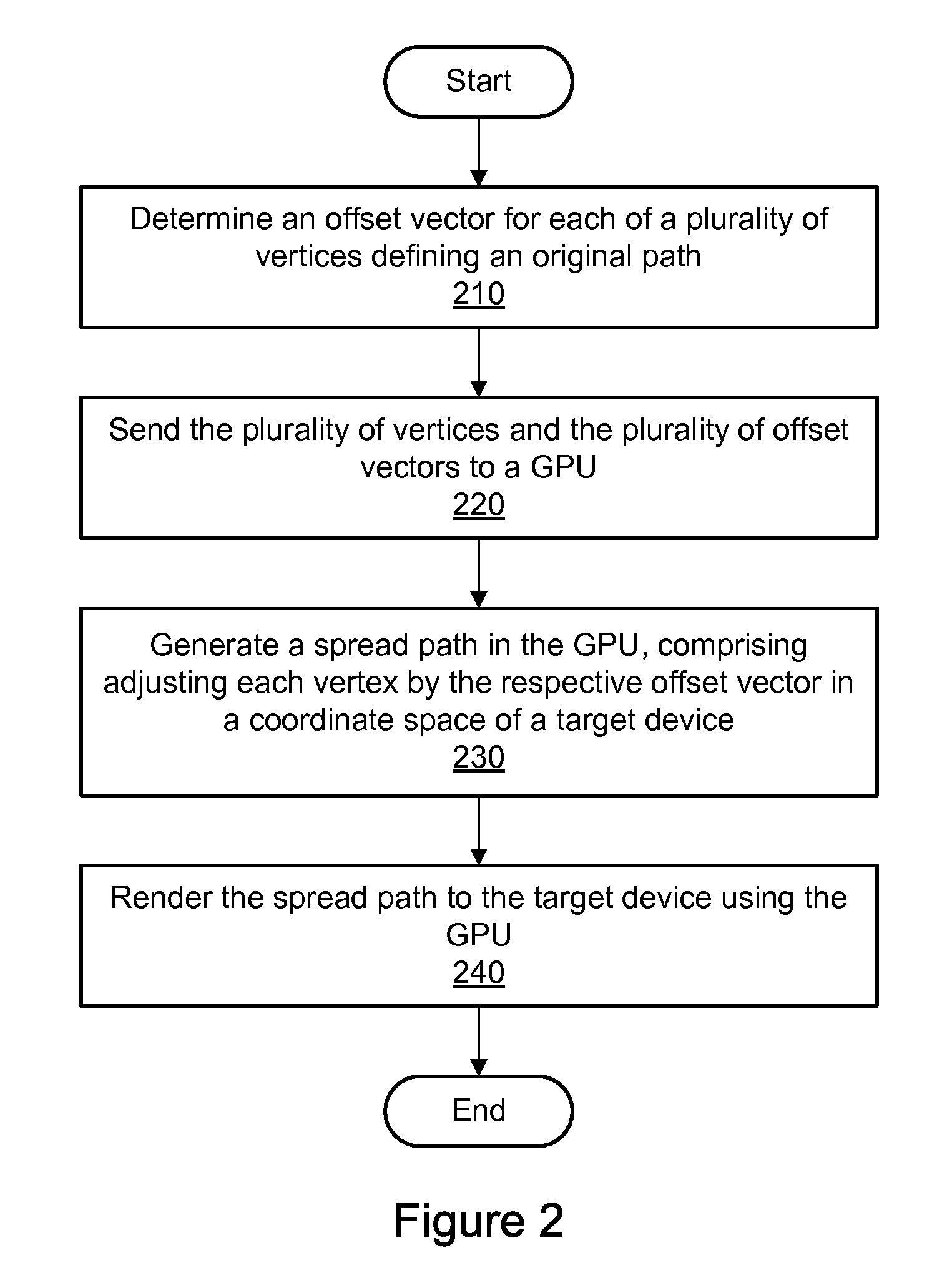
Dynamic tessellation spreading for resolution-independent GPU anti-aliasing and rendering
ActiveUS8044955B1Improve performanceDetails involving antialiasing2D-image generationGraphicsAnti-aliasing
A method, system, and computer-readable storage medium are disclosed for dynamic tessellation spreading. In one embodiment, an offset vector may be determined for each of a plurality of vertices, wherein the plurality of vertices define an original path. The plurality of vertices and the plurality of offset vectors may be sent to a graphics processing unit (GPU). A spread path may be generated in the GPU, wherein generating the spread path comprises adjusting each vertex by the respective offset vector in a coordinate space of a target device. The spread path may be rendered to the target device using the GPU.
Owner:ADOBE INC
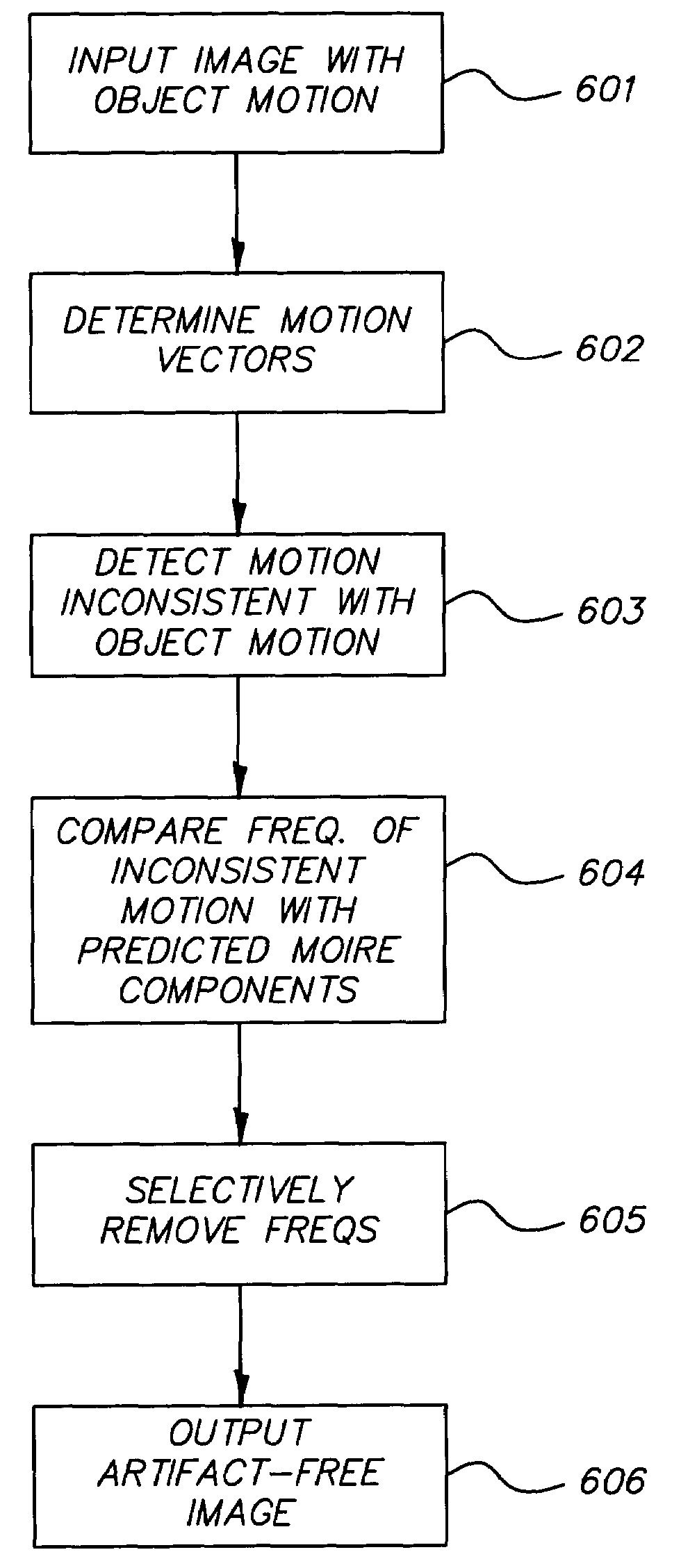
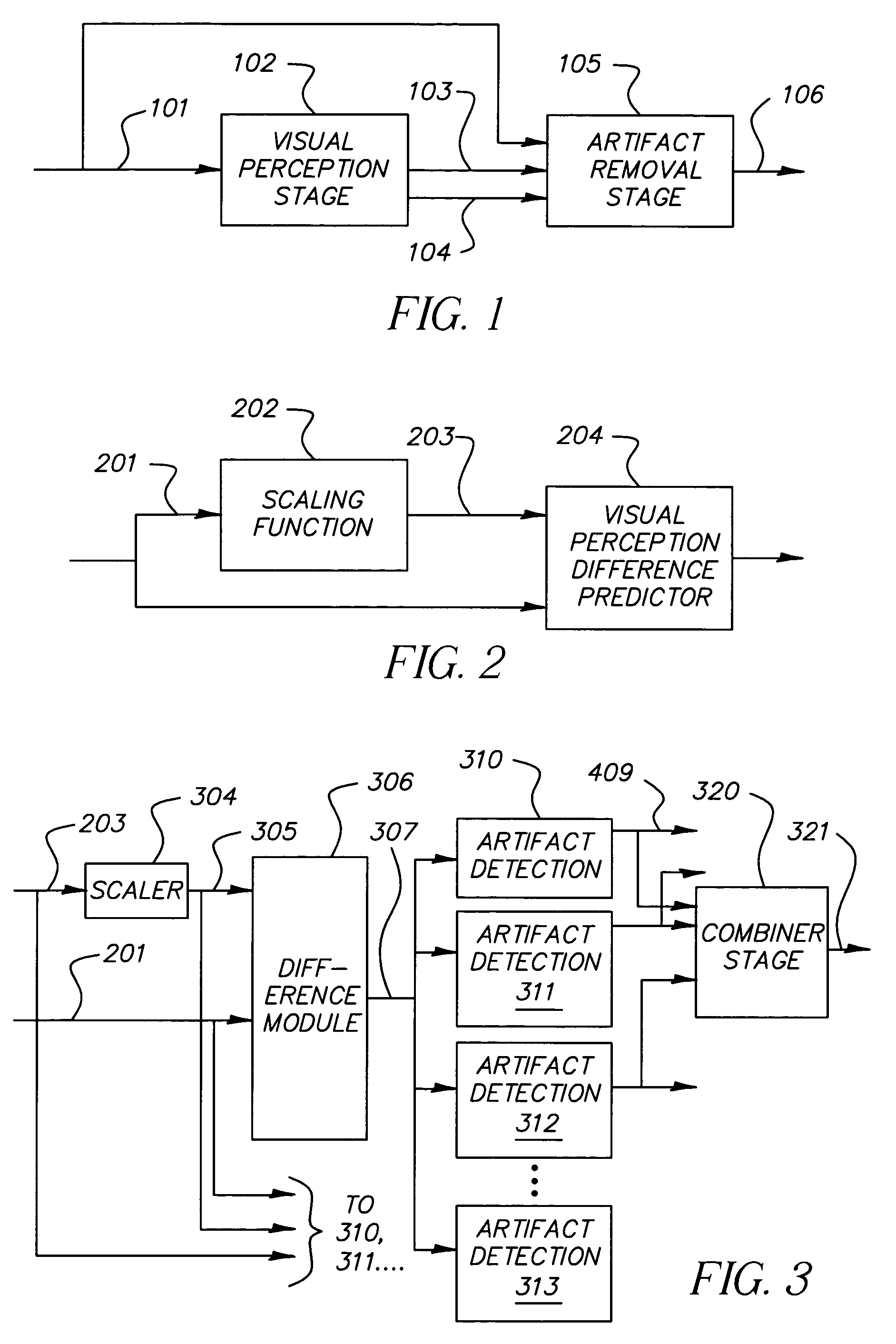
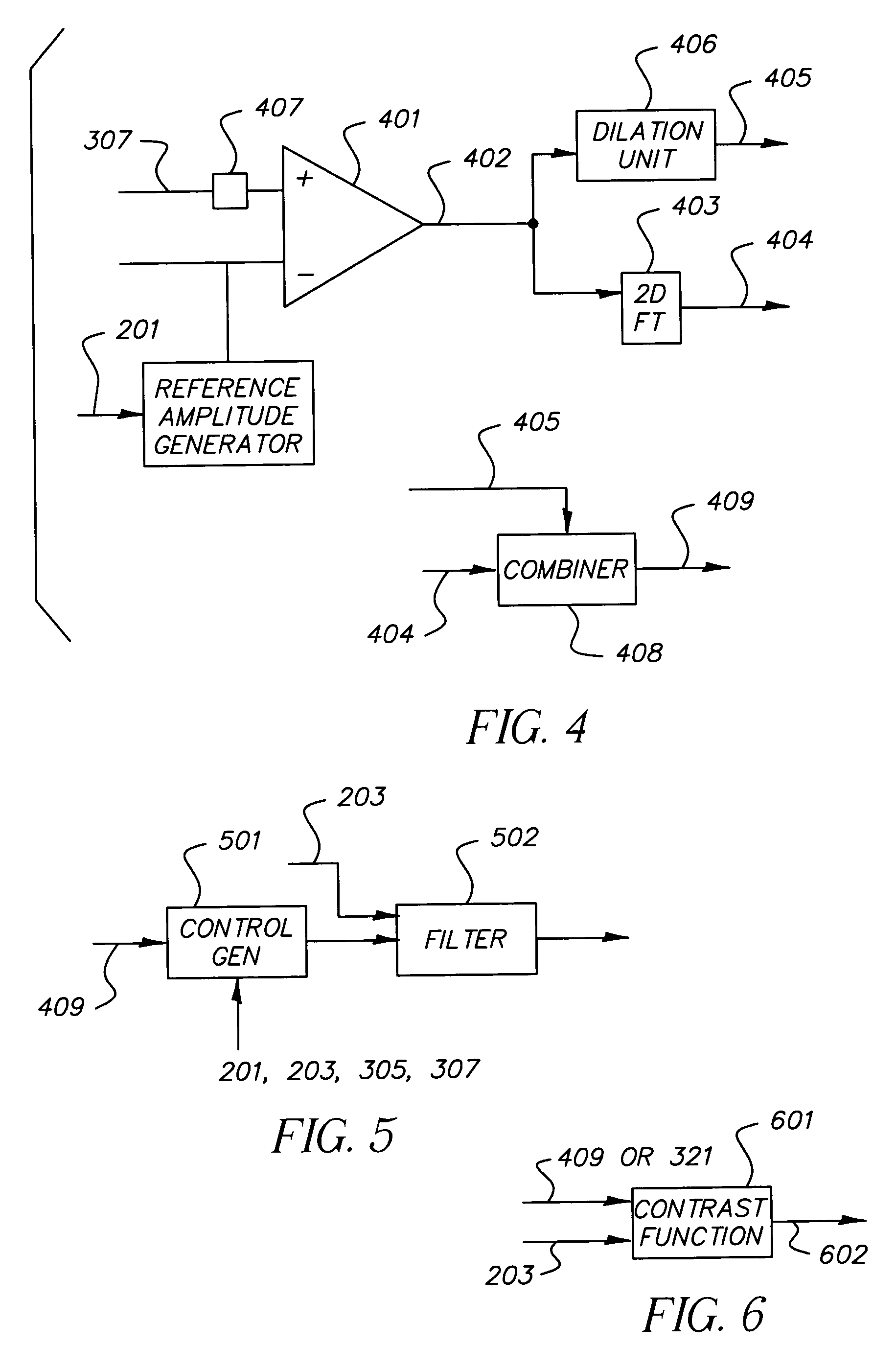
Method and system for automatically reducing aliasing artifacts
InactiveUS7164807B2Improve visibilityReduce artifactsImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionVisibility
Artifacts in an image introduced by sub-Nyquist aliasing are reduced below a visually perceptible level by a method comprising the steps of: providing an input image having sub-Nyquist aliasing artifacts; using a visual perception algorithm to identify the location and characteristics of the sub-Nyquist aliasing artifacts, thereby generating artifact coordinates and parameters; and processing the sub-Nyquist aliasing artifacts by reference to the artifact coordinates and parameters to reduce their visibility, thereby providing an artifact corrected image.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES FUND 83 LLC
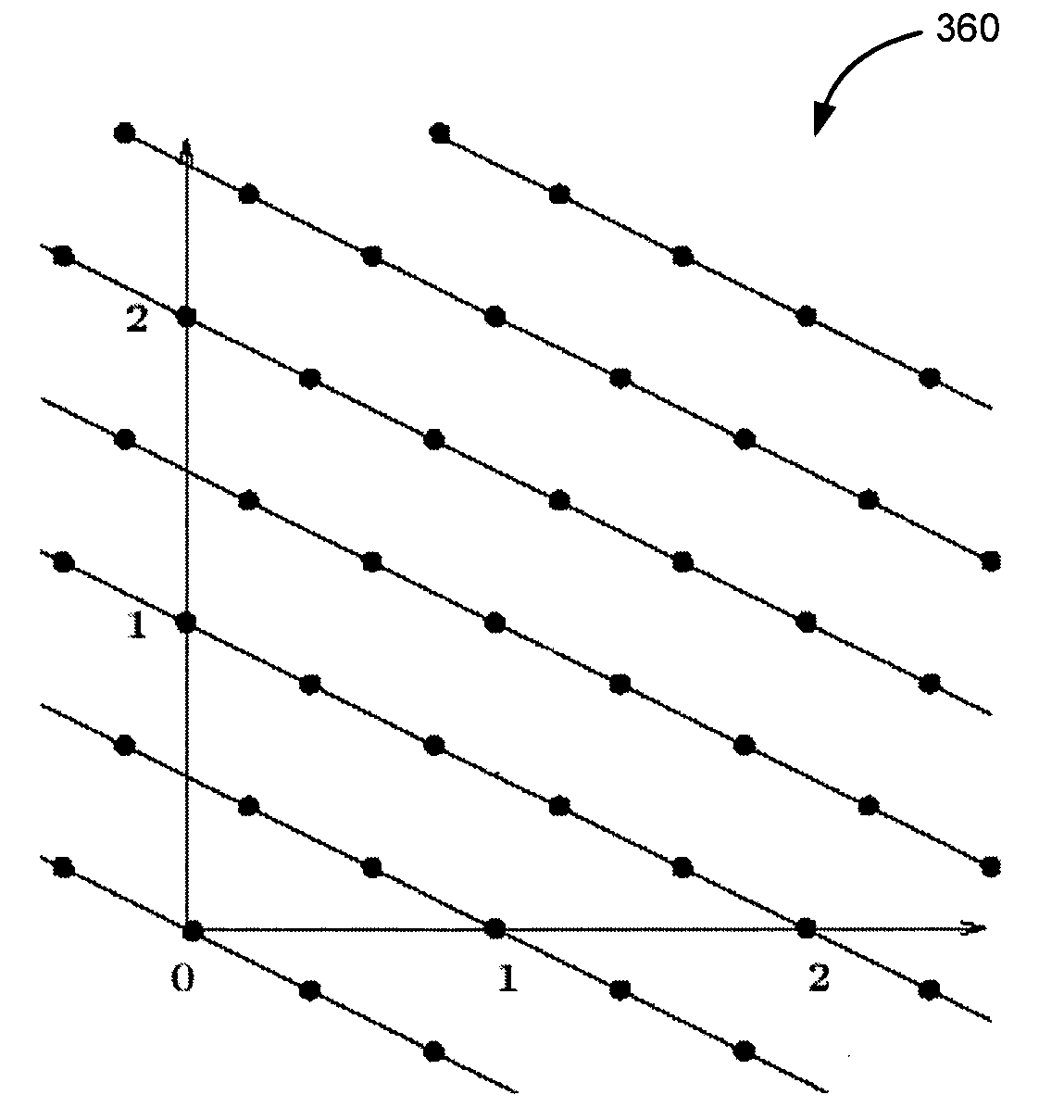
Image synthesis by rank-1 lattices
ActiveUS20070109320A1Details involving antialiasingDrawing from basic elementsAnti-aliasingImaging processing
Systems and techniques are described in which rank-1 lattices are used in computerized image processing, in particular in the context of image synthesis. These include systems and techniques for selection of rank-1 lattices, rasterization on rank-1 lattices, anti-aliasing by rank-1 lattices, and adaptive refinement and filtering by rank-1 lattices.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
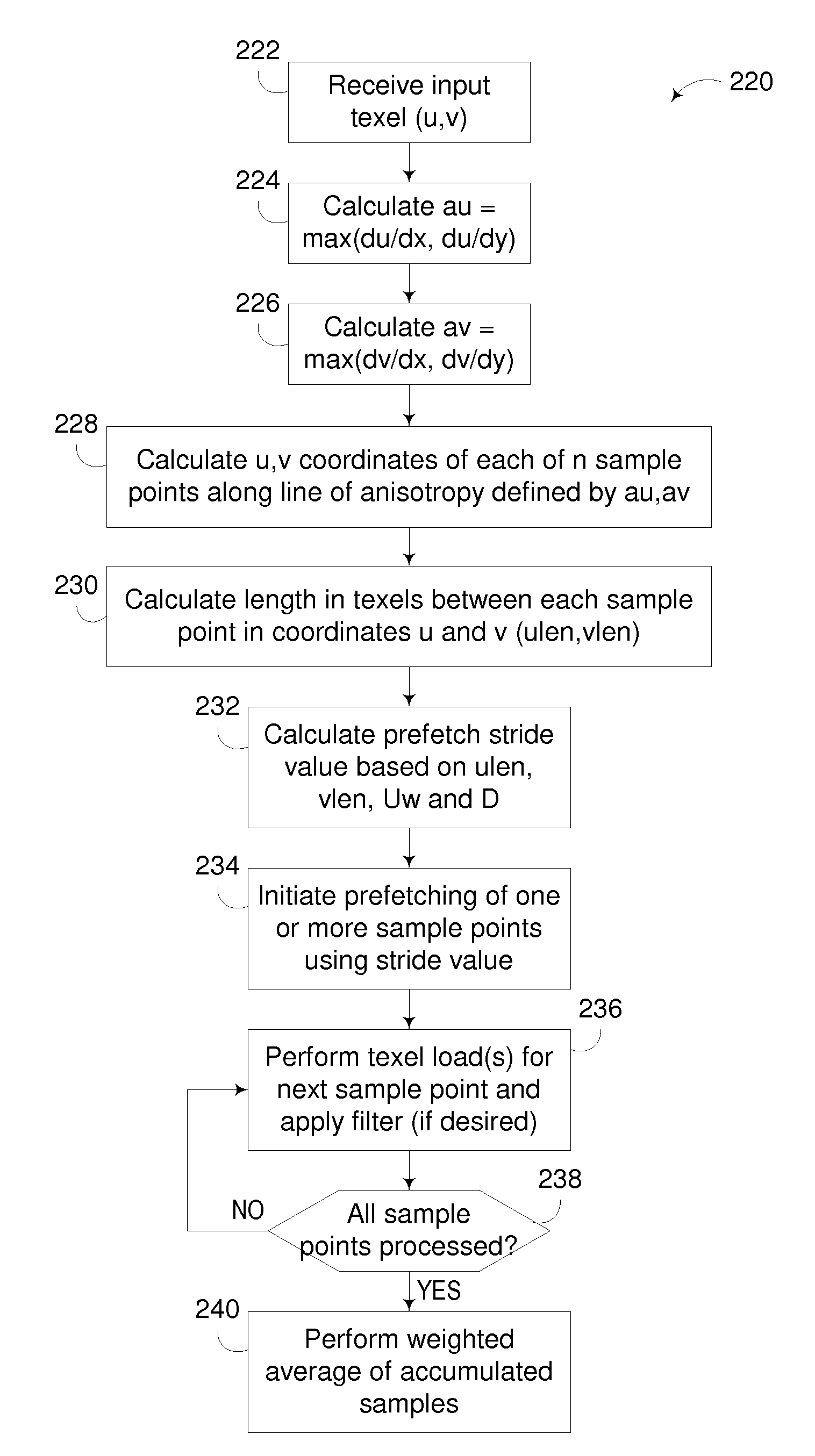
Anisotropic Texture Filtering with Texture Data Prefetching
InactiveUS20090315908A1Details involving antialiasingCharacter and pattern recognitionComputational scienceMemory address
A circuit arrangement and method utilize texture data prefetching to prefetch texture data used by an anisotropic filtering algorithm. In particular, stride-based prefetching may be used to prefetch texture data for use in anisotropic filtering, where the value of the stride, or difference between successive accesses, is based upon a distance in a memory address space between sample points taken along the line of anisotropy used in an anisotropic filtering algorithm.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
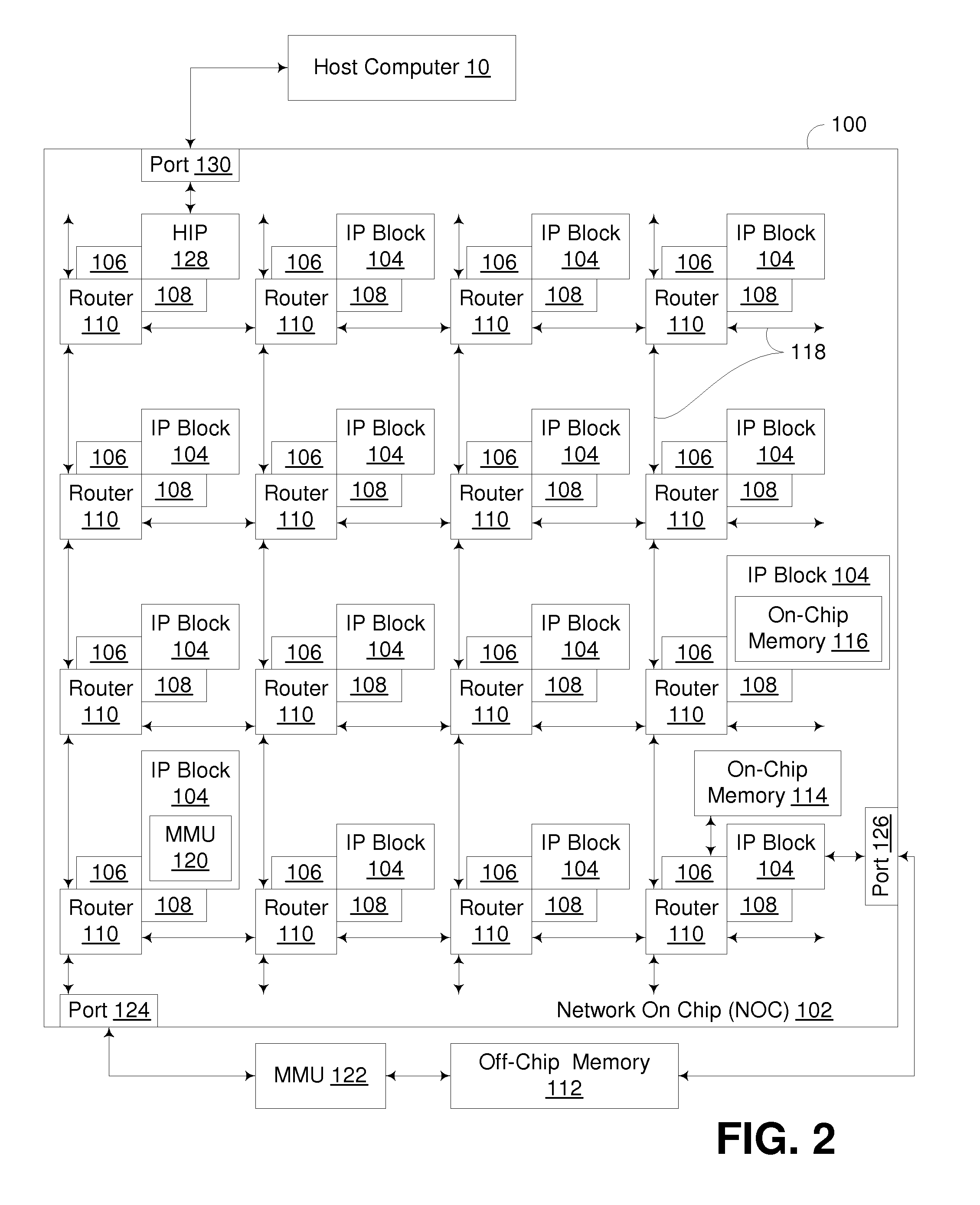
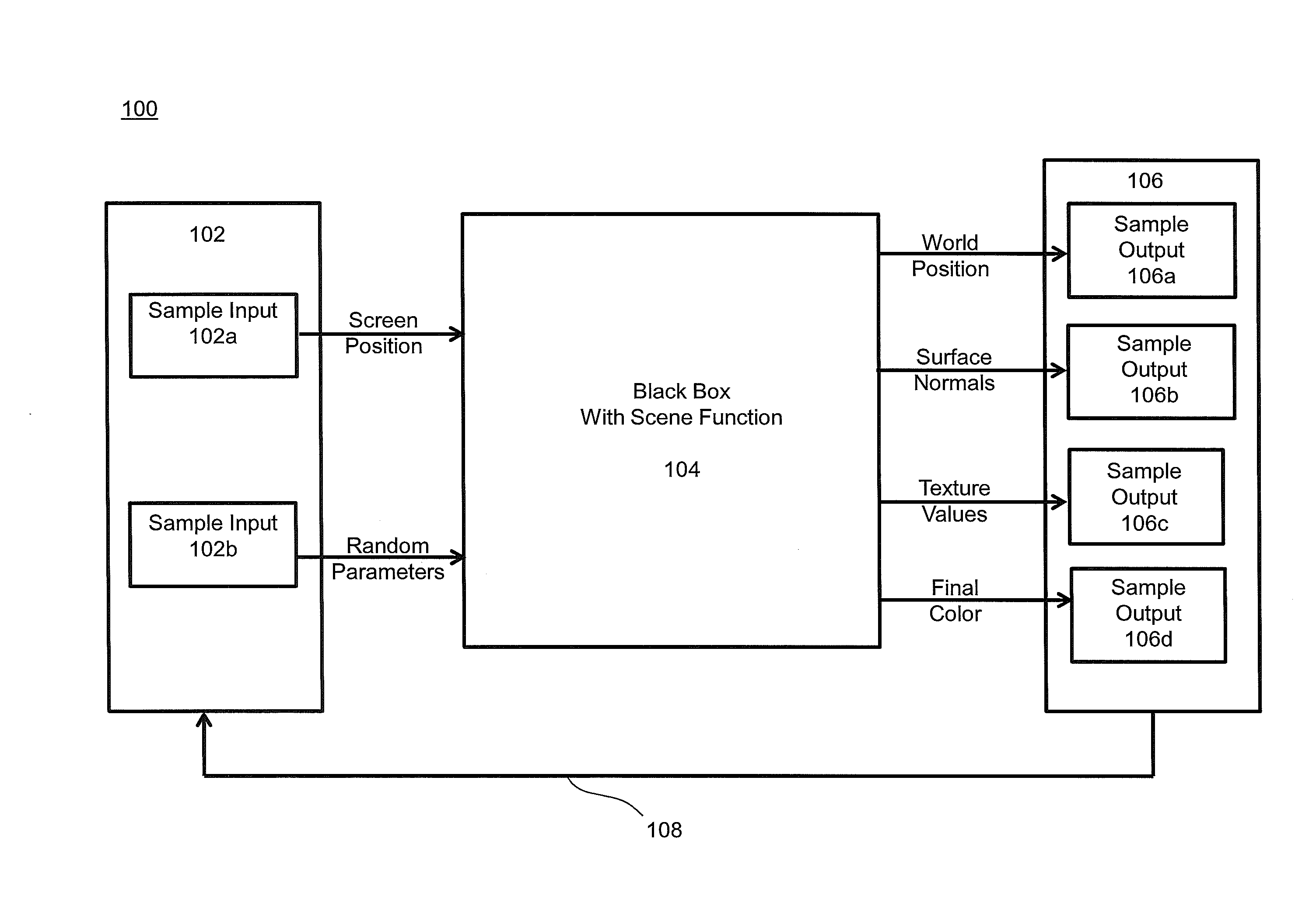
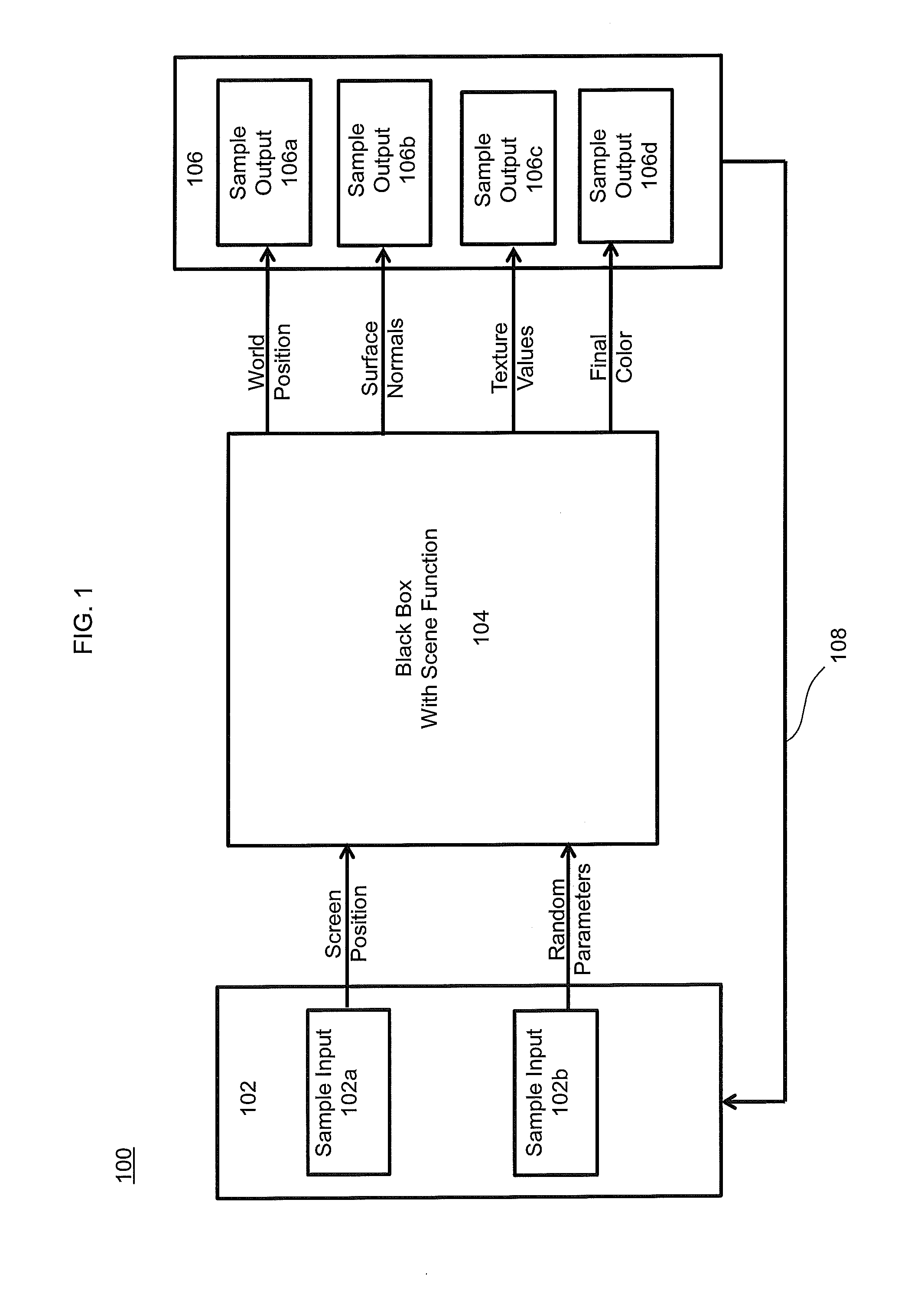
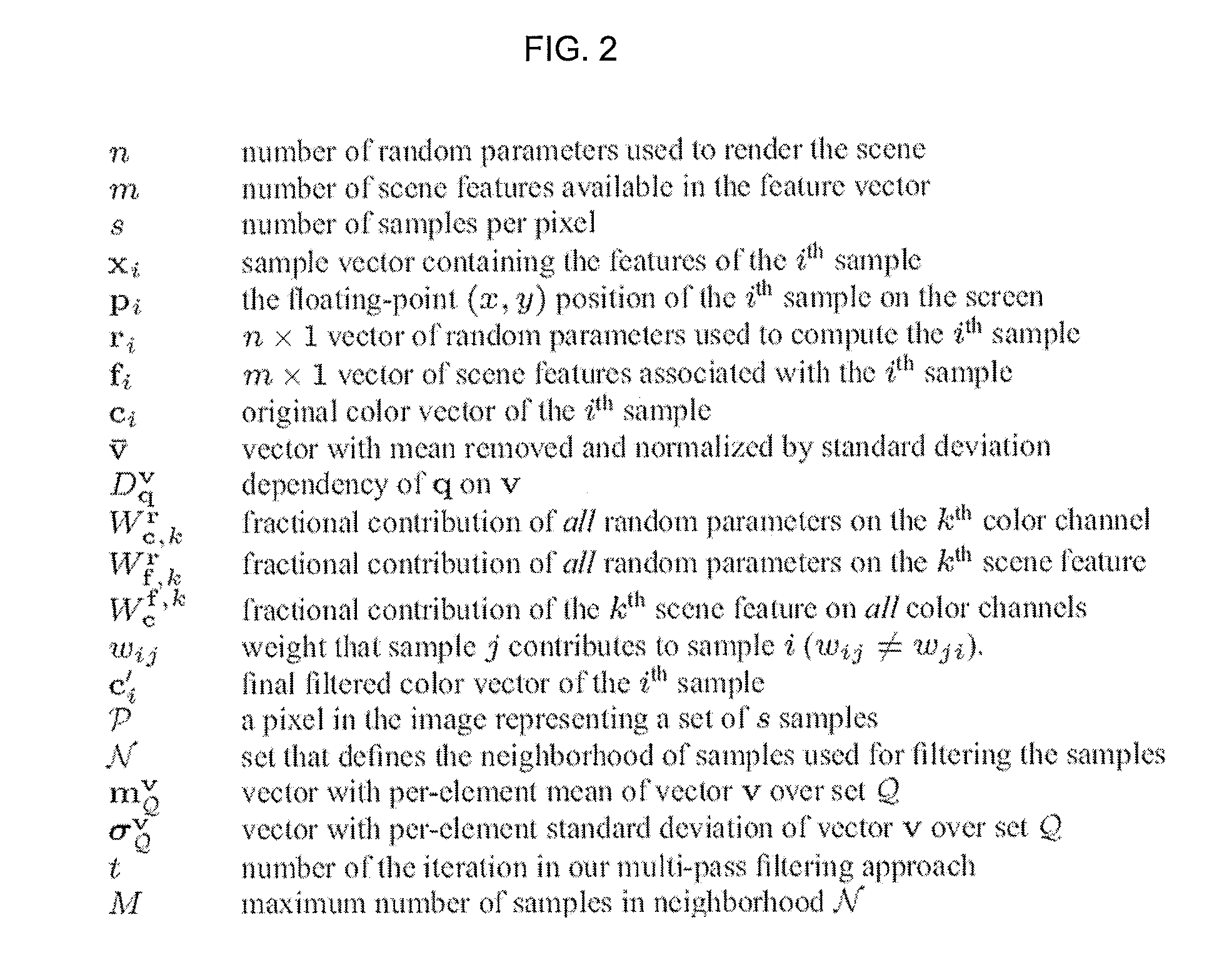
System and methods for random parameter filtering
ActiveUS20140029849A1Cancel noiseWide rangeImage enhancementDetails involving antialiasingBilateral filterMutual information
The invention produces a higher quality image from a rendering system based on a relationship between the output of a rendering system and the parameters used to compute them. Specifically, noise is removed in rendering by estimating the functional dependency between sample features and the random inputs to the system. Mutual information is applied to a local neighborhood of samples in each part of the image. This dependency is then used to reduce the importance of certain scene features in a cross-bilateral filter, which preserves scene detail. The results produced by the invention are computed in a few minutes thereby making it reasonably robust for use in production environments.
Owner:STC UNM
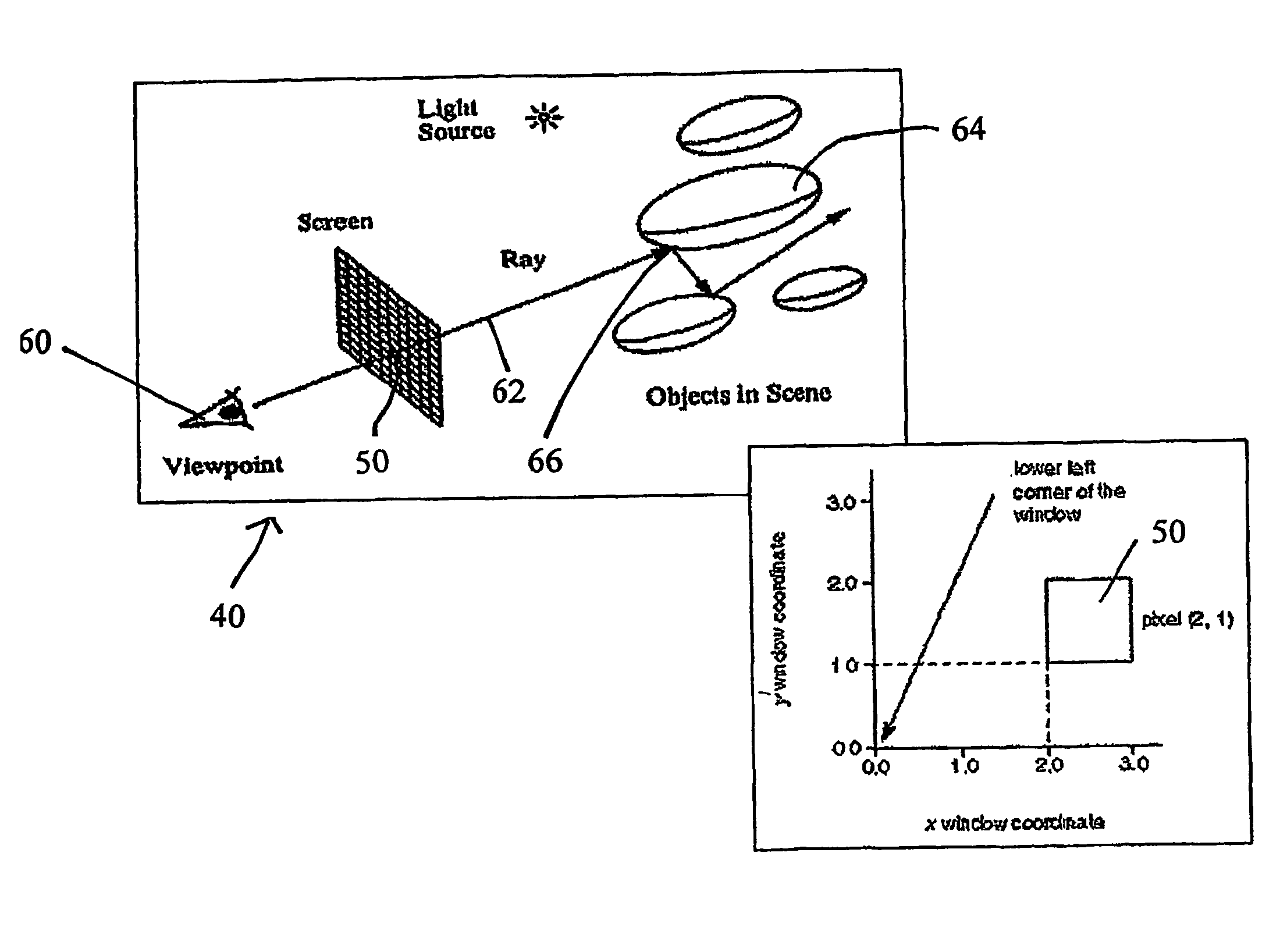
System and method visible surface determination in computer graphics using interval analysis
ActiveUS7250948B2Easy to adjustEliminate aliasingDetails involving antialiasingCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsGeometric primitive
A system (40) is provided for visible surface determination in furtherance of photorealistic rendering in a computer graphics environment. The system includes a scene database (42) and a processor, visual characteristics of objects of an image frame (44) of a scene of the scene database (42) are delimited as geometric primitive. The processor, for executing an interval analysis, to a user degree of certainty, accurately and deterministically ascertains a visible solution set of an area not exceeding a pixel dimension for a pixel of an array of pixels (50) that form said image frame (44).
Owner:SUNFISH STUDIO
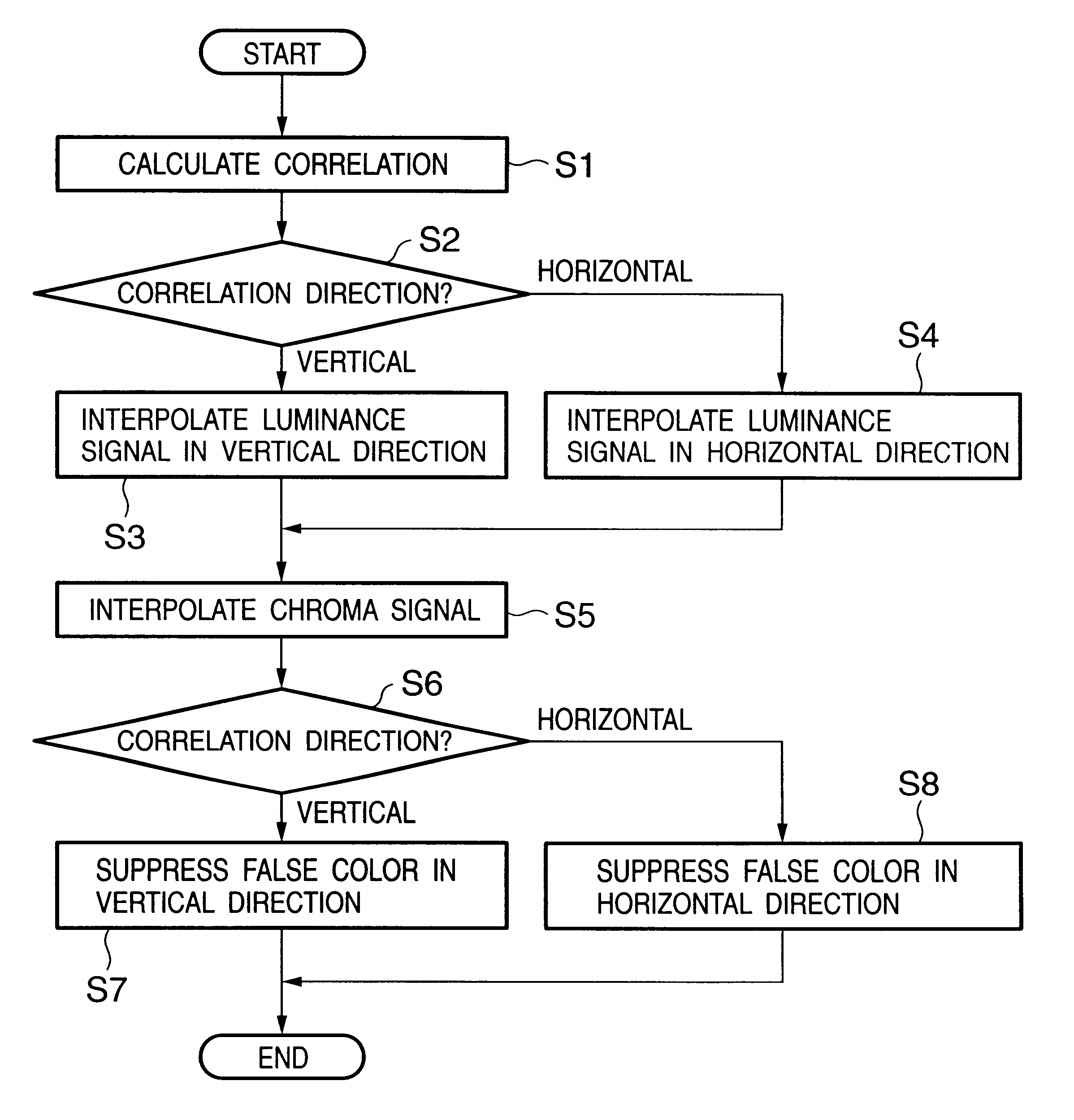
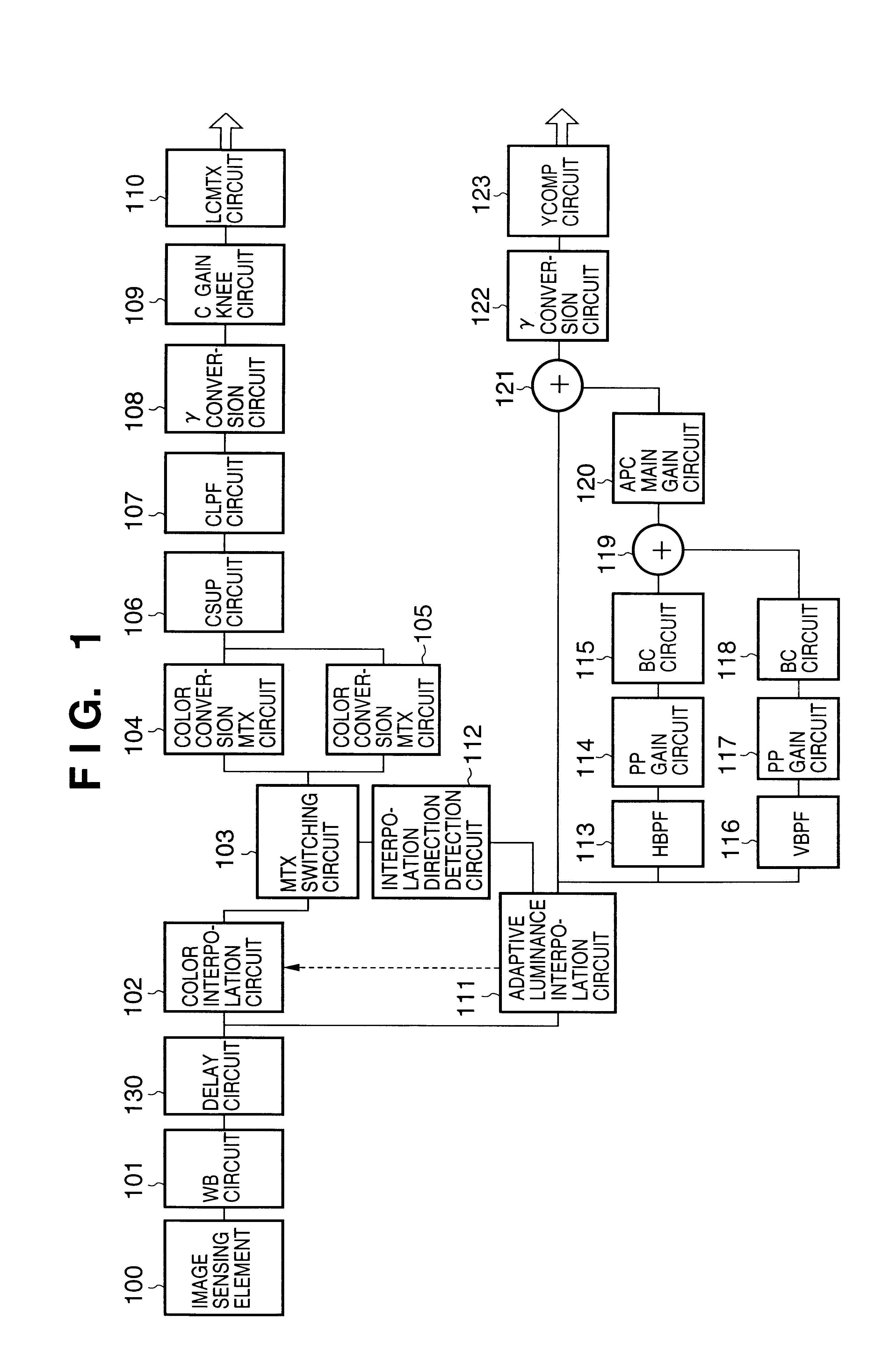
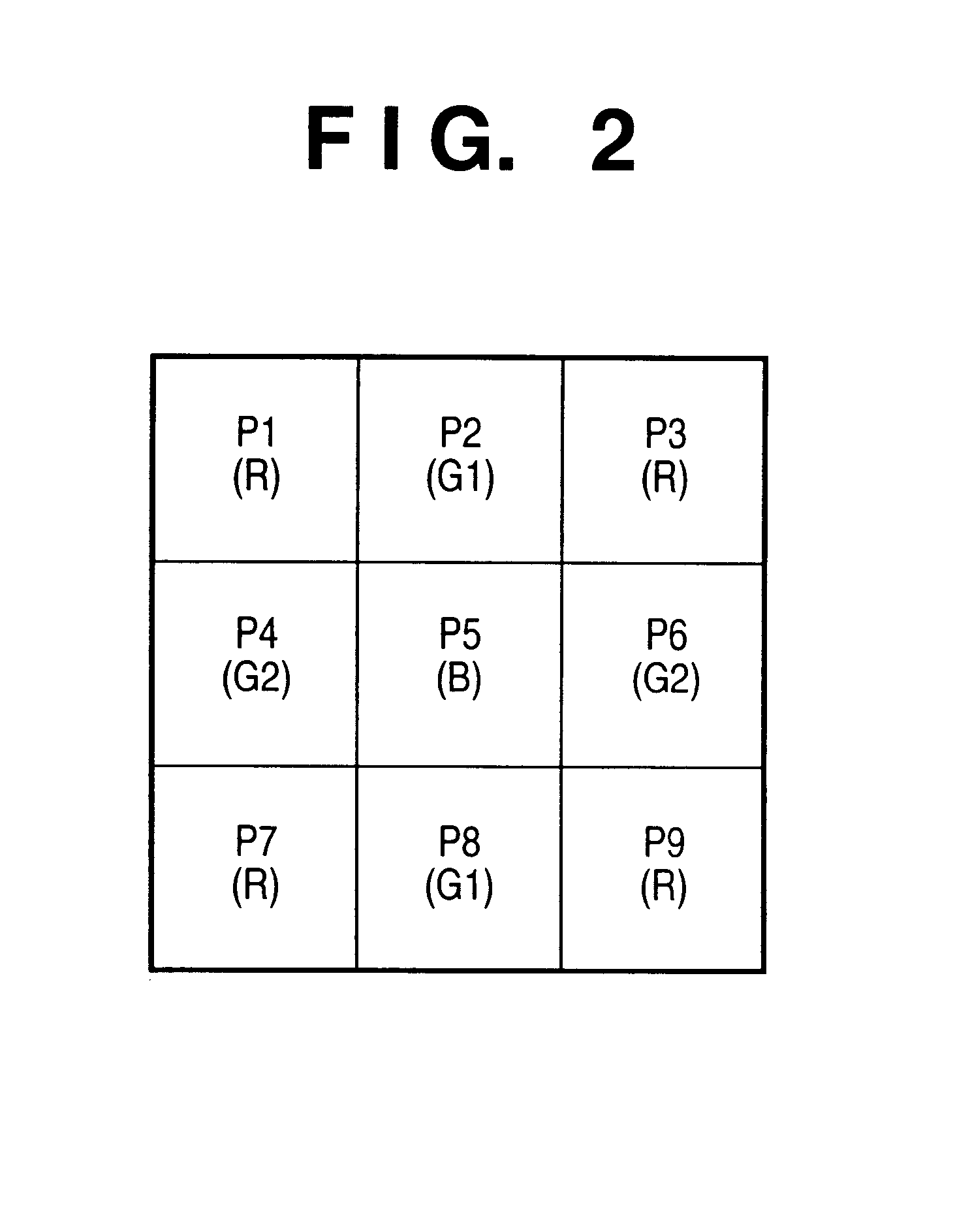
Signal processing apparatus and method for reducing generation of false color by adaptive luminance interpolation
InactiveUS6853748B2Reduce colorWithout decreasing resolutionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionFalse color
Adaptive luminance interpolation processing in a signal processing apparatus for acquiring an image signal from an image sensing element having color filters and processing the image signal is described. An adaptive luminance interpolation circuit determines the correlation of the image signal in the vertical and horizontal directions, and interpolates the luminance signal of the image signal in a direction in which the correlation is higher. The chroma signal of the image signal is interpolated regardless of the correlation direction. The chroma signal is processed by a color conversion matrix circuit for performing signal processing of suppressing a false color in the vertical direction or a color conversion matrix circuit for performing signal processing of suppressing a false color in the horizontal direction, switched by a matrix switching circuit based on the interpolation direction.
Owner:CANON KK
Resolution-converting apparatus and method
ActiveUS7876979B2Eliminating occurrence of quality-degradingImprove clarityImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersIntermediate imageImage resolution
The resolution-converting method comprises steps of applying an edge-directed interpolation to an input image and producing an intermediate image; converting a sampling rate with respect to the intermediate image and producing an output image having a predetermined resolution; and improving sharpness of the produced output image. The present invention prevents image-quality degradation factors that can occur in the conventional resolution-converting method as well as obtains an output image having a resolution of a desired size.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
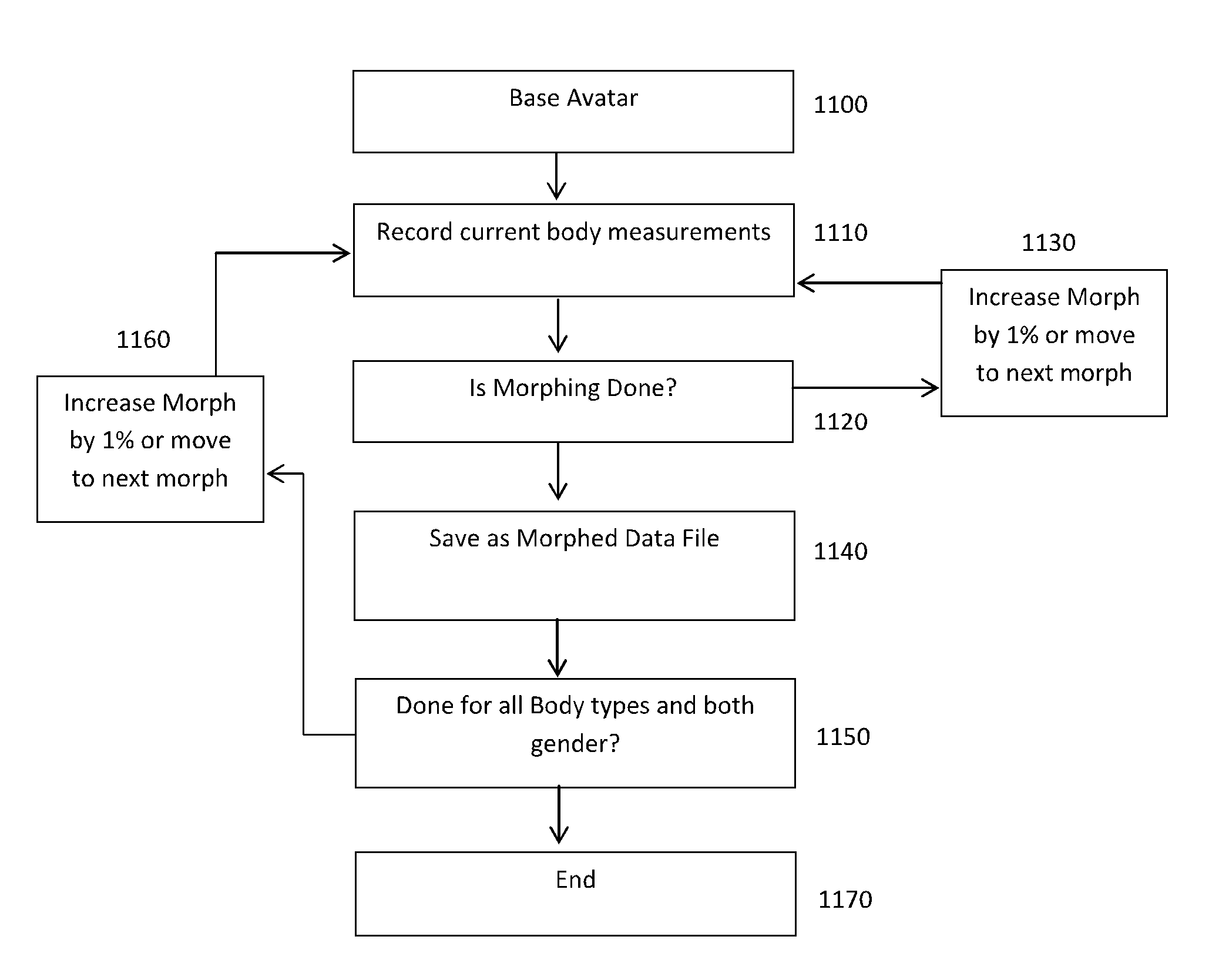
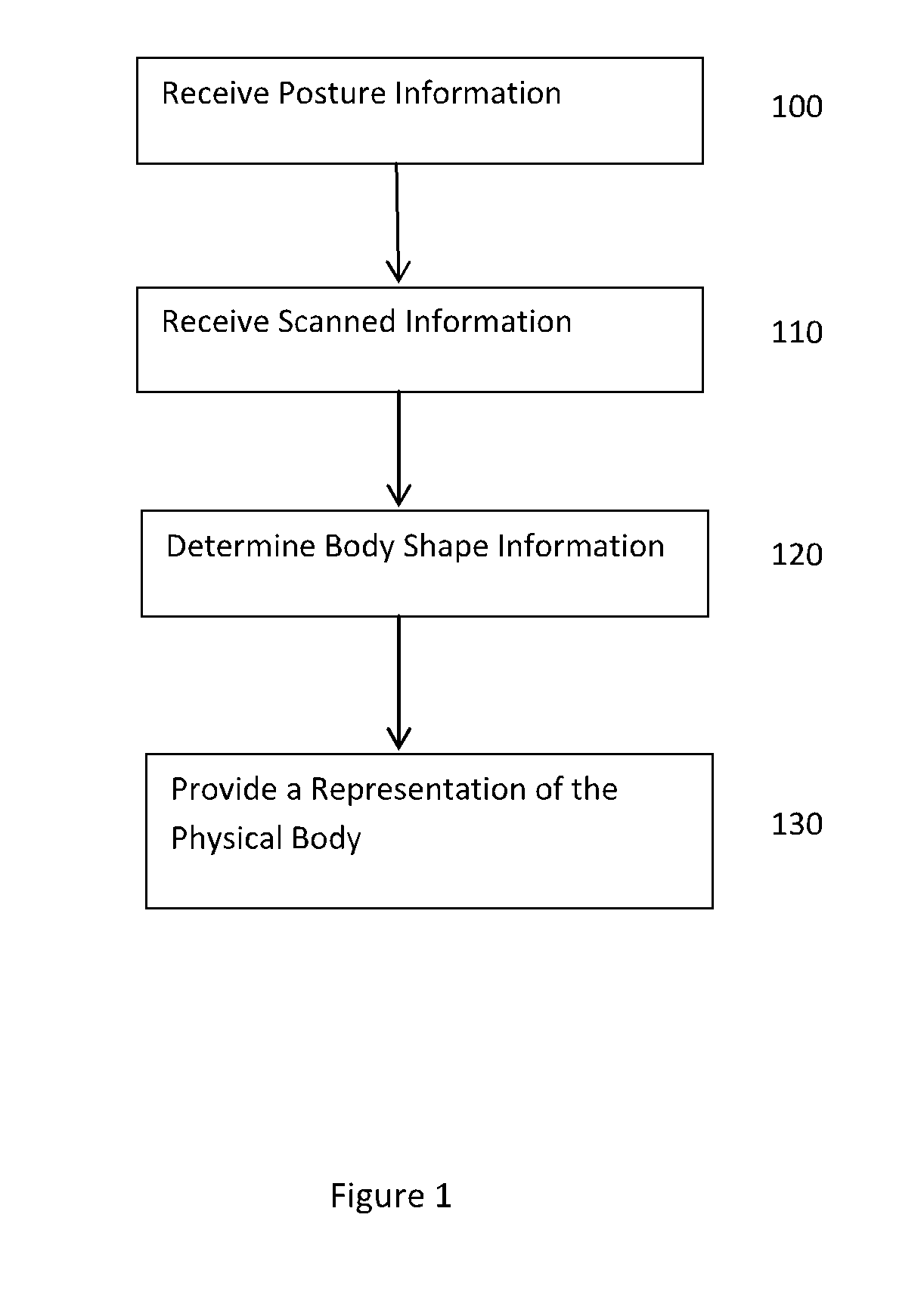
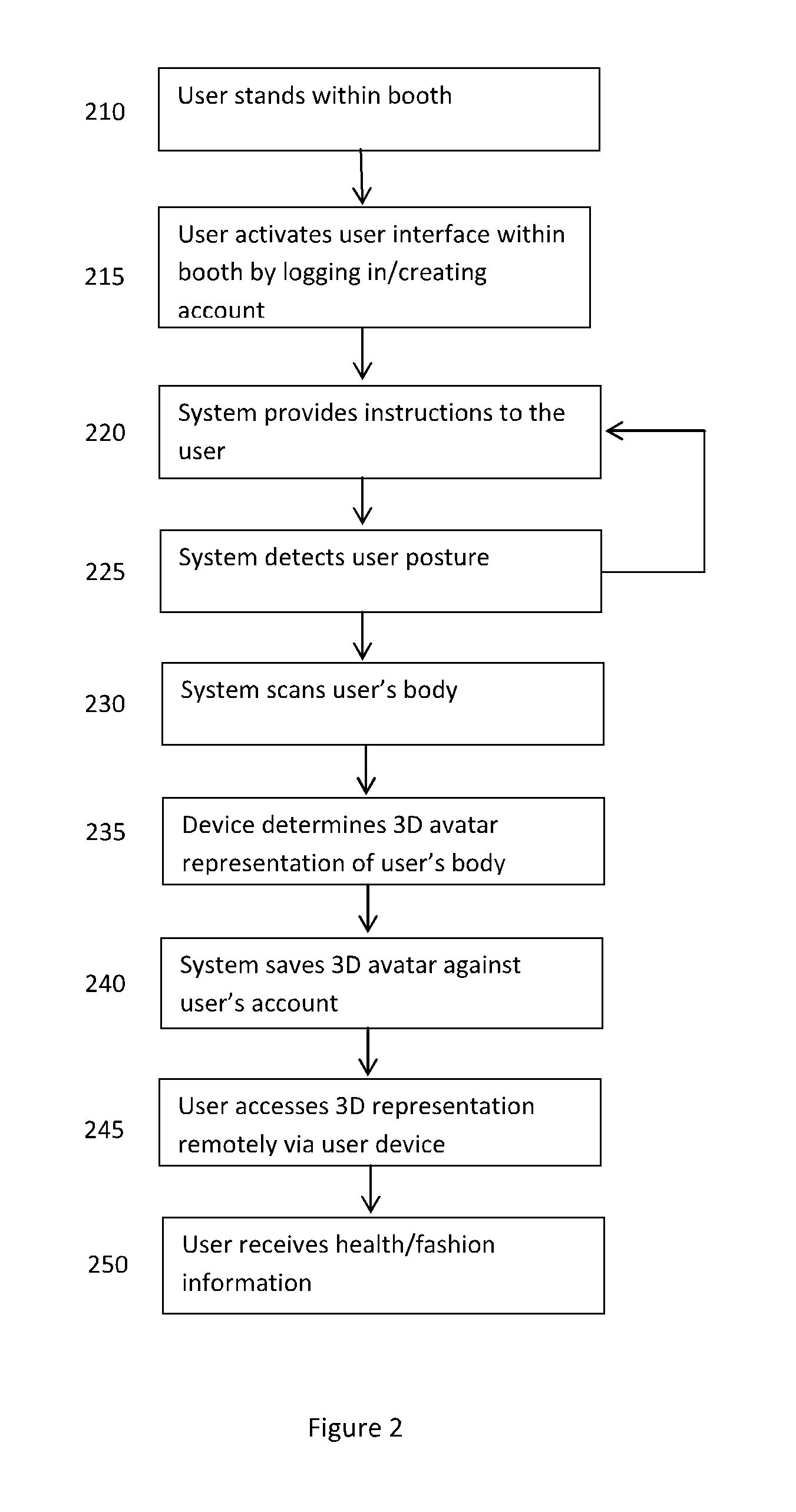
Devices, frameworks and methodologies for enabling user-driven determination of body size and shape information and utilisation of such information across a networked environment
ActiveUS20160093085A1Accurate measurementAccurate representationPhysical therapies and activitiesImage enhancementMorphingBody size
A scanning booth with a user interface. The interface receives user identification or registration data and provides instructional prompts for the user to assume various predefined positions, stances and postures. Image data of each pose is captured using scanning devices in the booth. A three dimensional avatar is generated based on the mapping or morphing of image data to a generic avatar model. Data from the generated model is transmitted to a server where it is stored in a database for later account application in, for example, garment sizing, display or fitting, or health monitoring.
Owner:MPORT
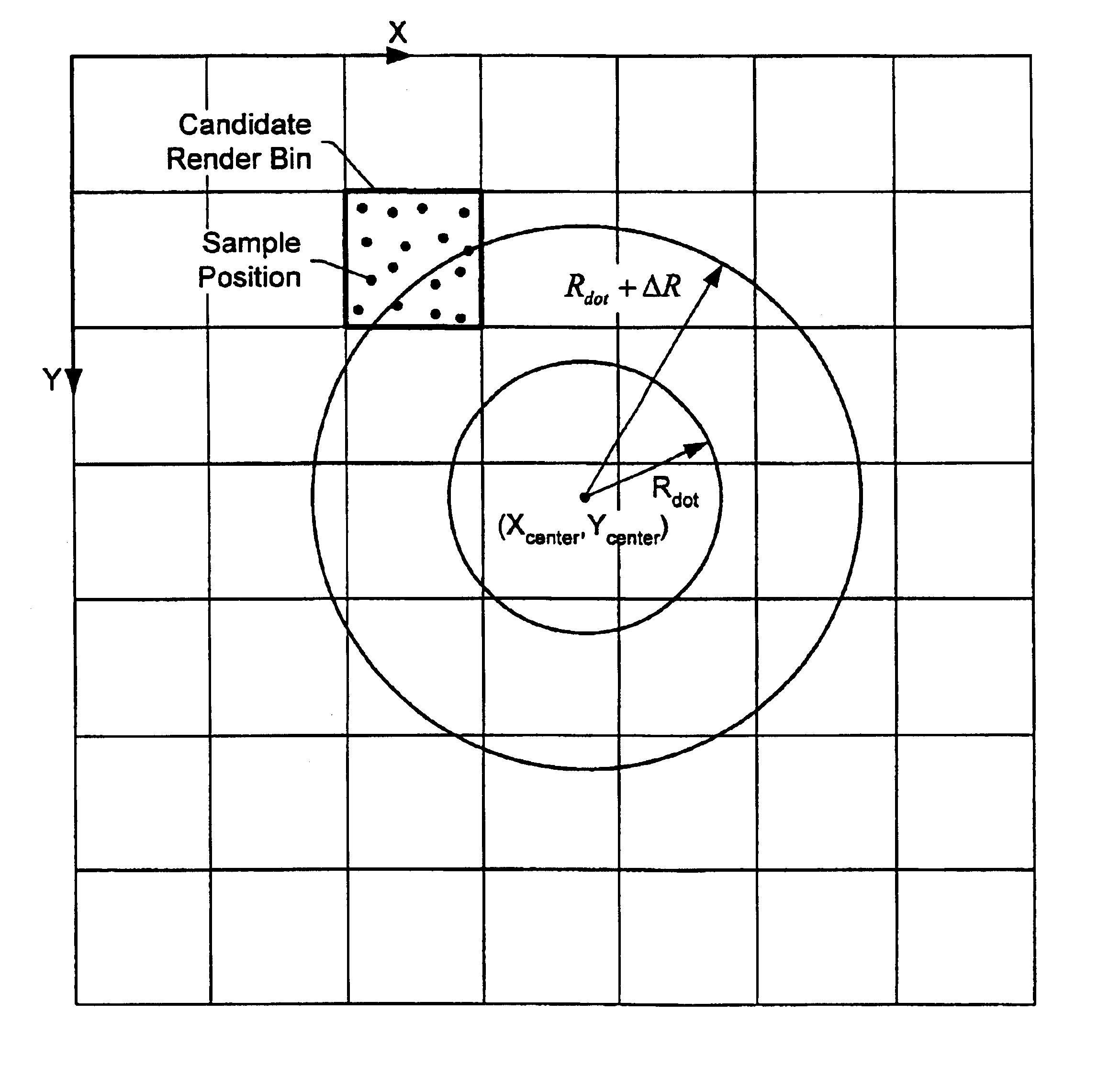
Efficient anti-aliased dot rasterization
InactiveUS6731300B2Details involving antialiasingCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsComputational science
A graphics system may be configured to render anti-aliased dots in terms of samples and to generate pixels by filtering the samples. The pixels are supplied to one or more display devices. The means used to generate the samples may perform the computation of radial distance at positions on a grid in a rendering coordinate space, and interpolate estimates for the radial distances of samples around the dot as needed based on the radii at the grid positions.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com