Patents
Literature
86results about How to "Assist in operation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
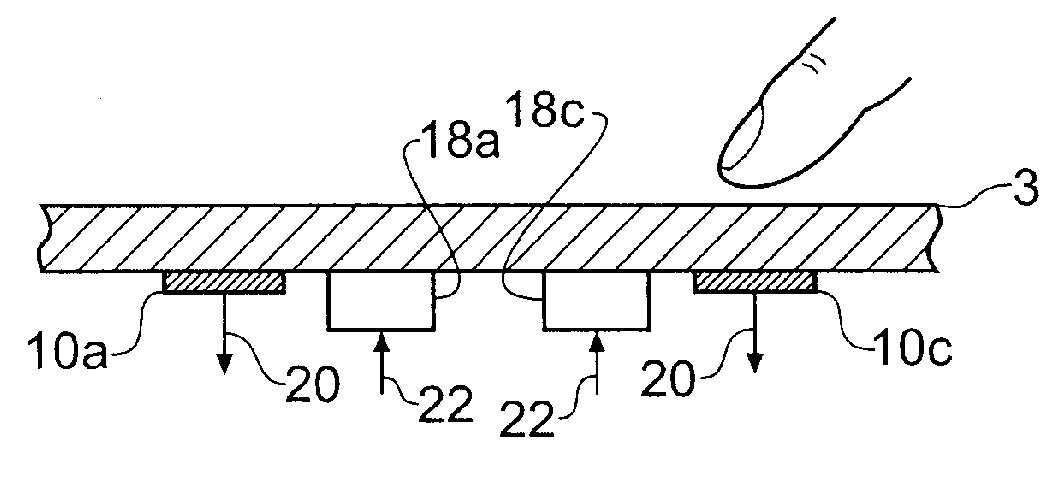
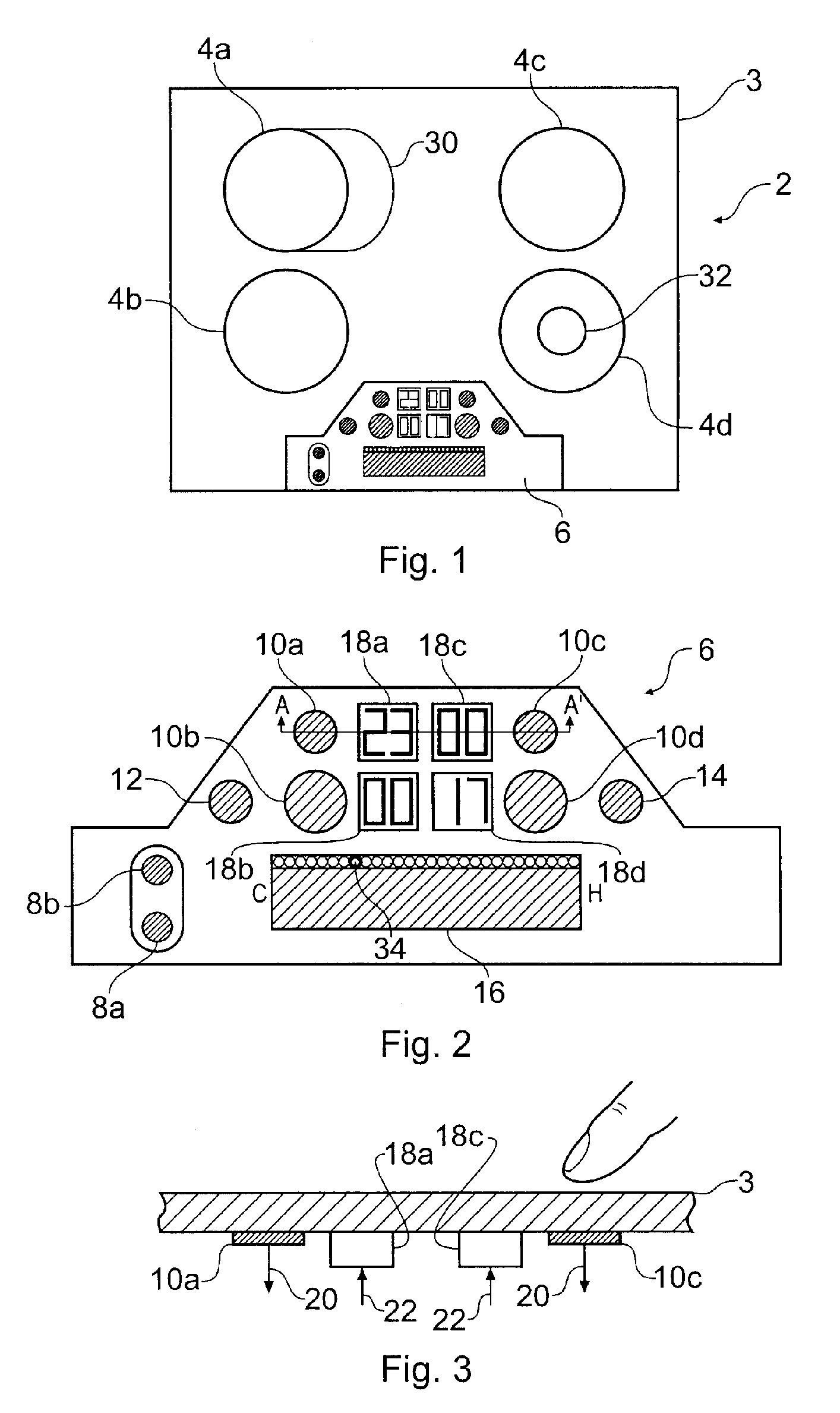
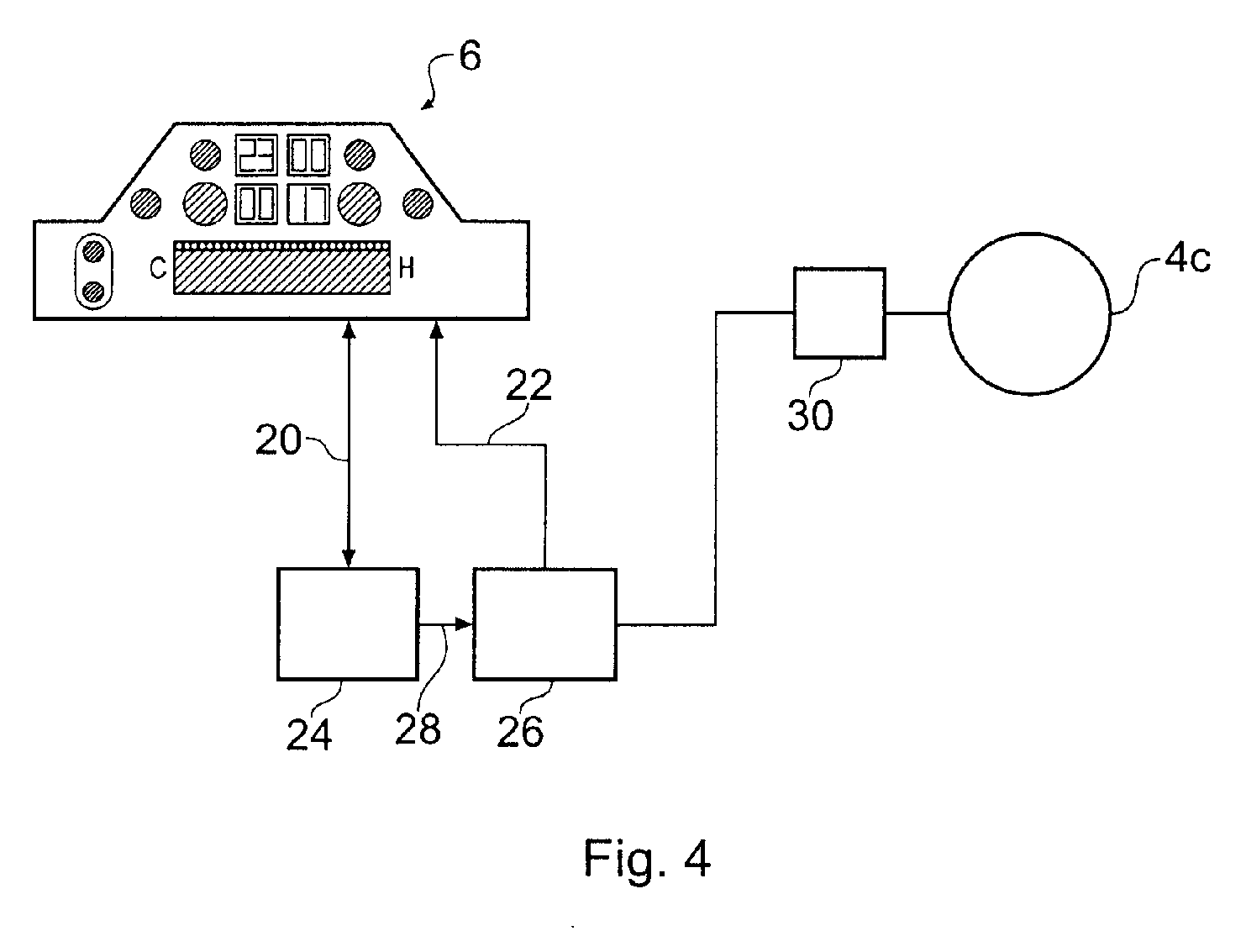
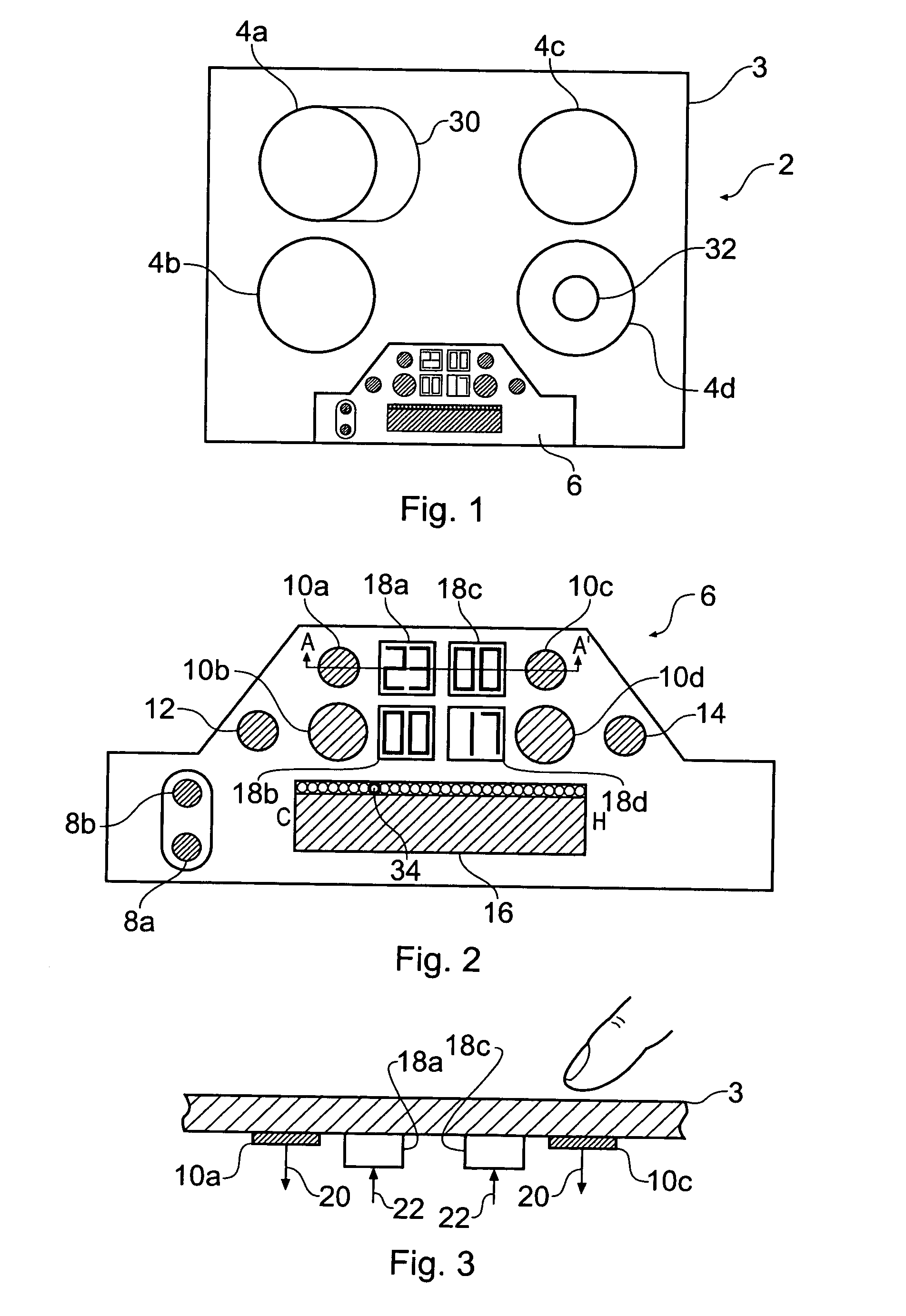
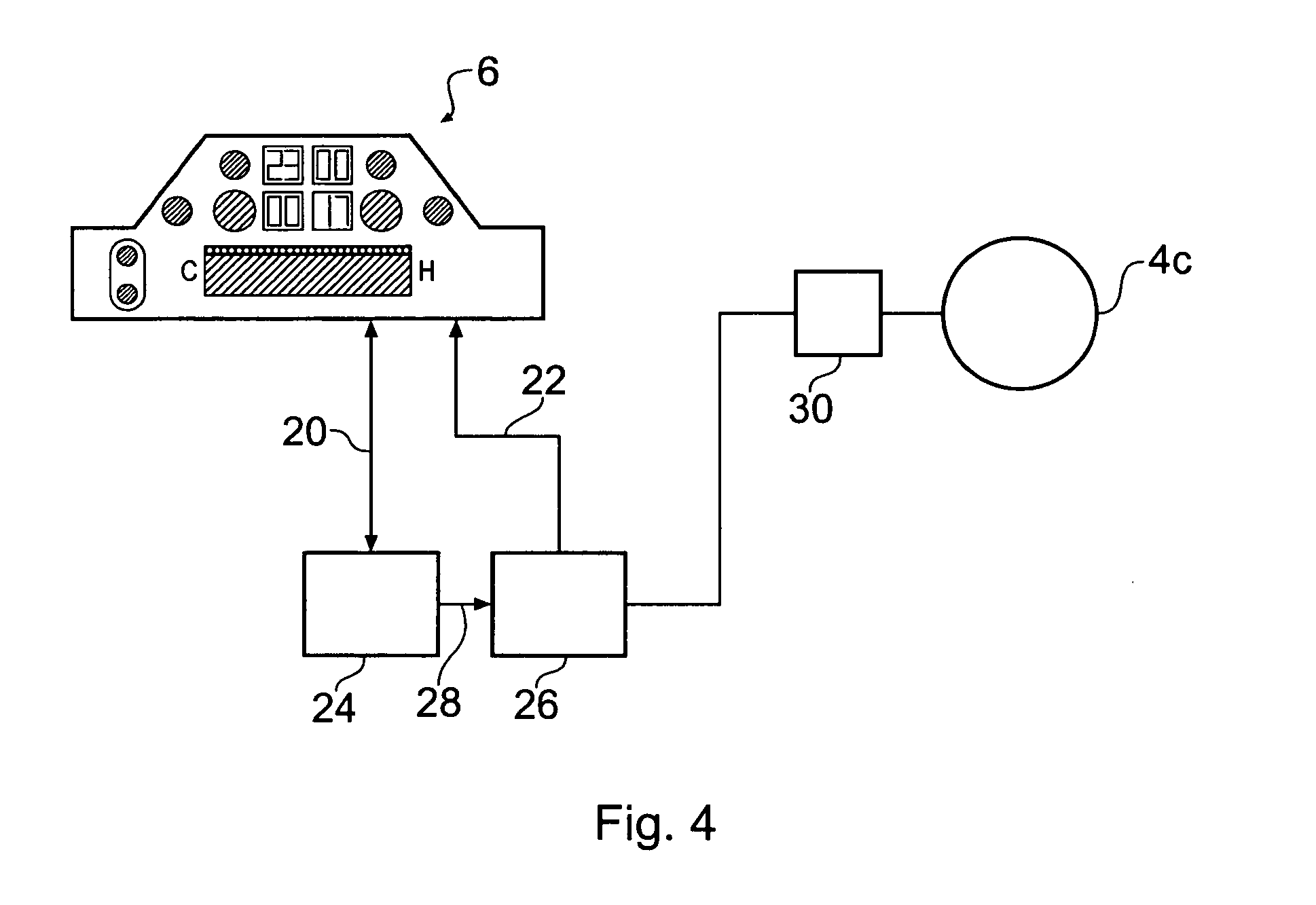
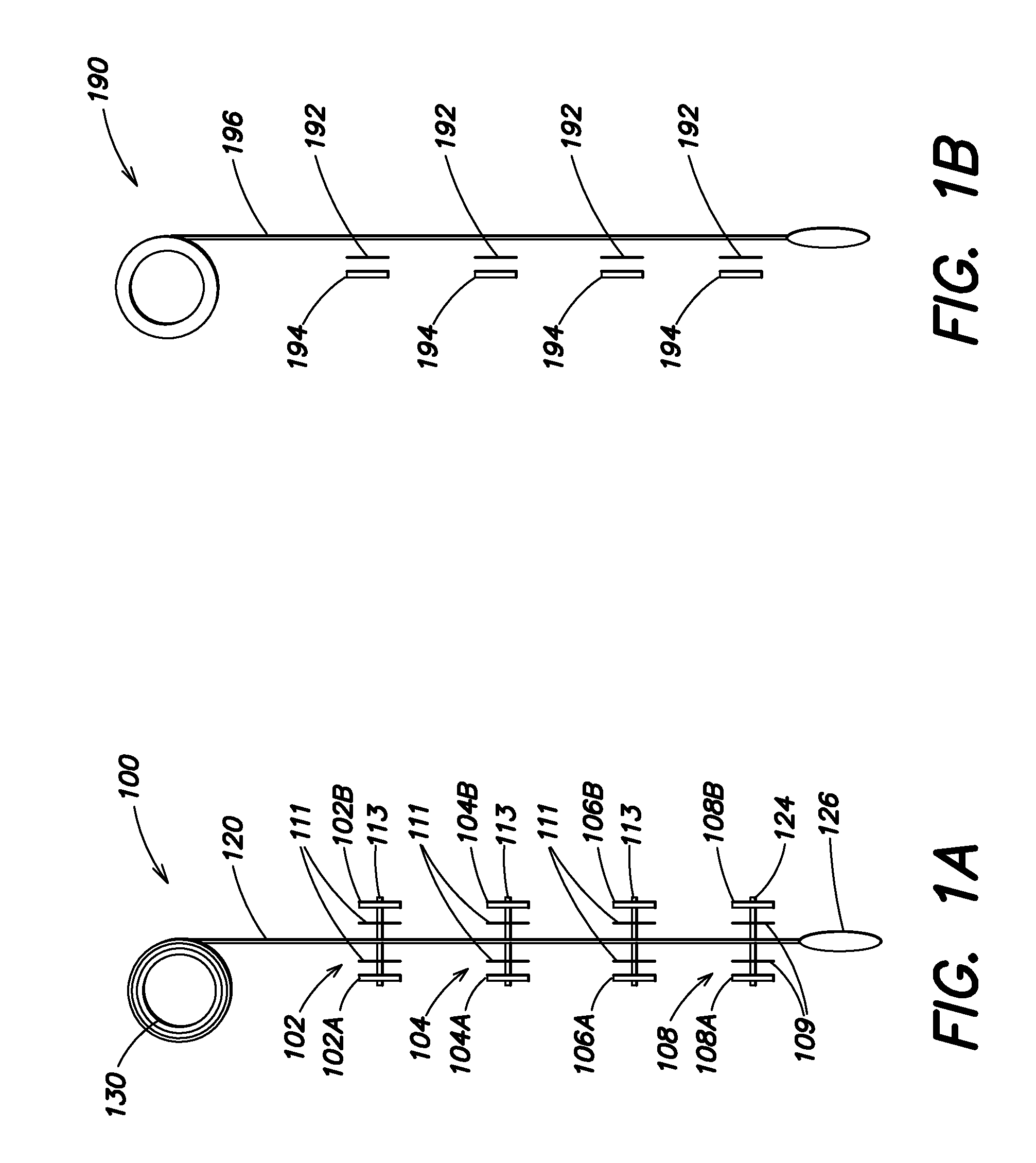
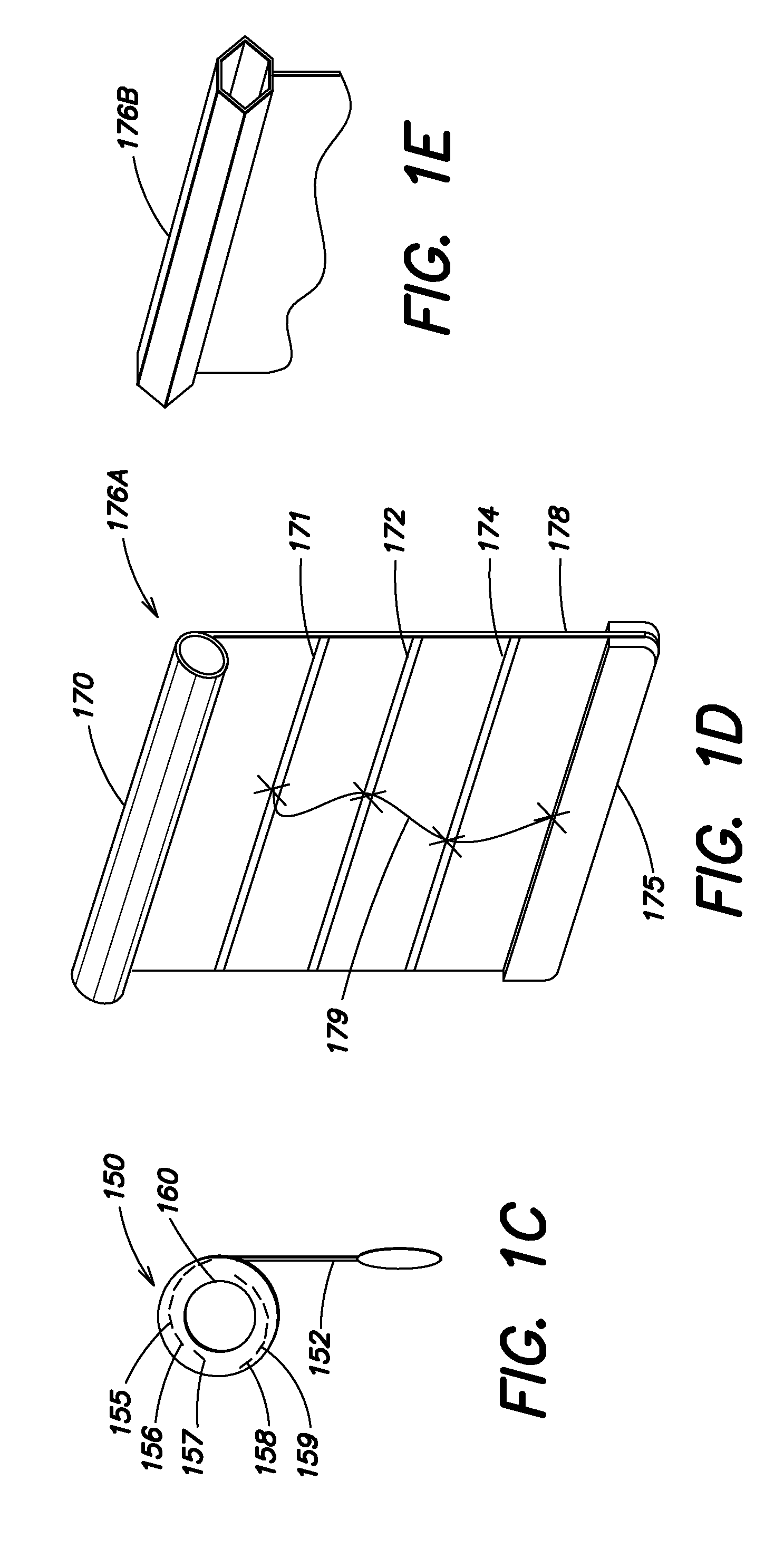
Touch Sensitive Control Panel
ActiveUS20060038793A1Reduce chanceSafer applianceInput/output for user-computer interactionElectric signal transmission systemsProximity sensorBiological activation
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Touch sensitive control panel
InactiveUS20050078027A1SaferReduce chanceElectric signal transmission systemsDomestic stoves or rangesProximity sensorBiological activation
An apparatus for controlling functions of an appliance is described having a touch-sensitive control panel resistant to accidental activation. The touch-sensitive panel has a plurality of proximity sensor areas which may be selected by a user wishing to activate associated functions of the appliance. Driver circuitry coupled to the sensor areas is operable to output detection signals to a controller in response to a user selecting ones of the sensor areas. The controller is configured to activate functions of the appliance in response to these detection signals. For one or more functions of the appliance, for example a switching on function, the controller is configured to only activate the function when a user makes a pre-determined combination of at least two selections from the plurality of sensor areas. This reduces the chances of potentially dangerous functions being activated inadvertently and can further help a designer to provide an intuitive and uncluttered appearance to the control panel.
Owner:PHILIPP HARALD
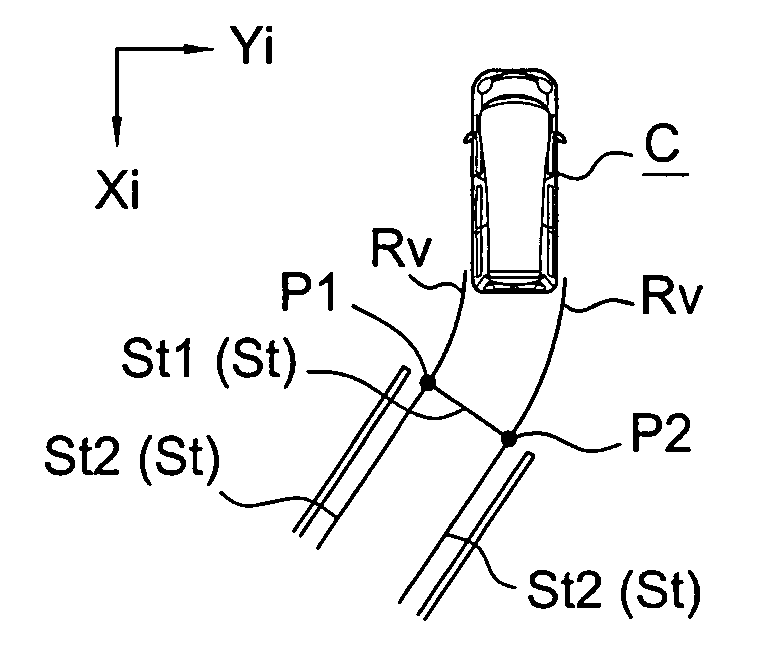
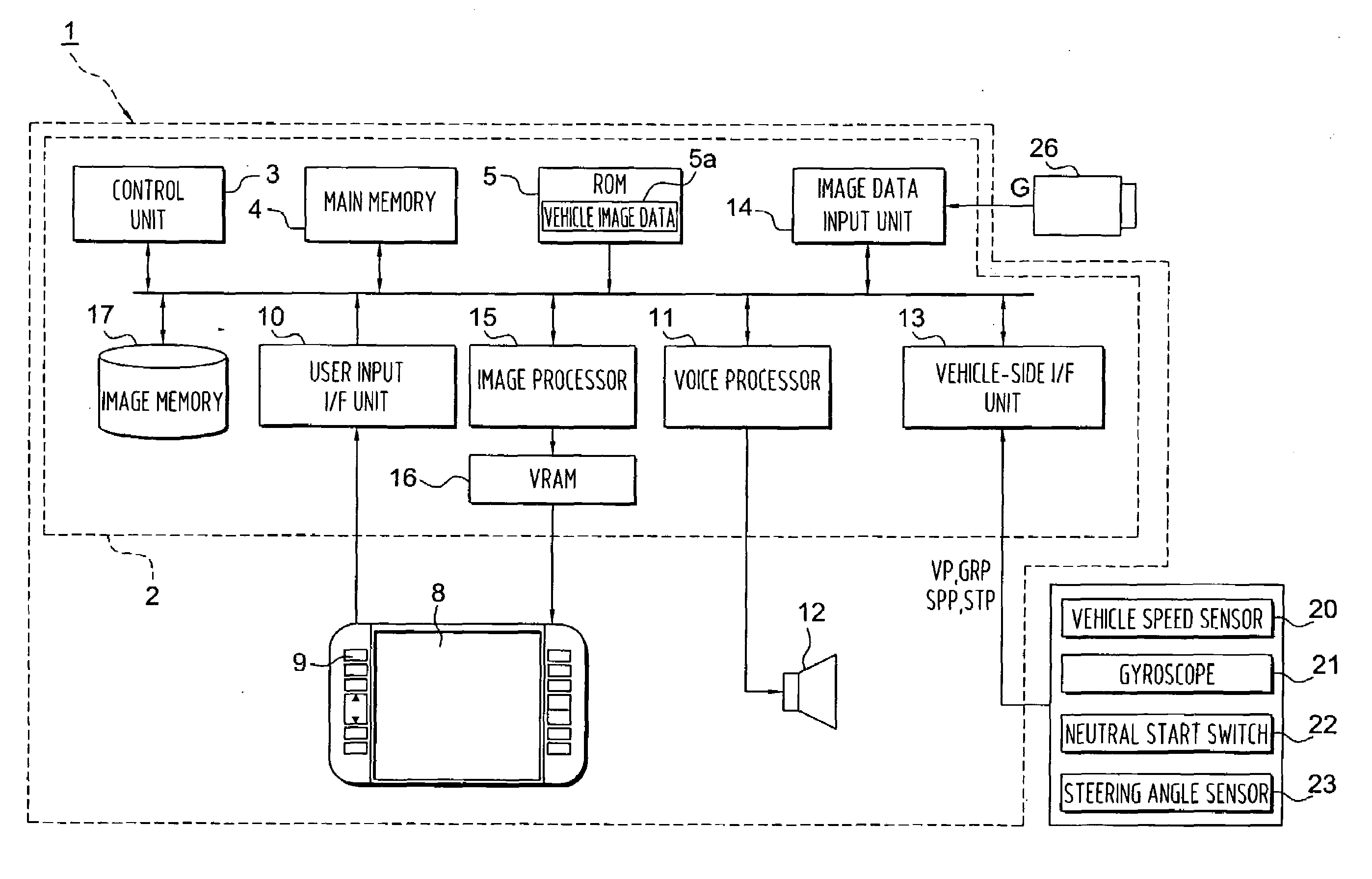
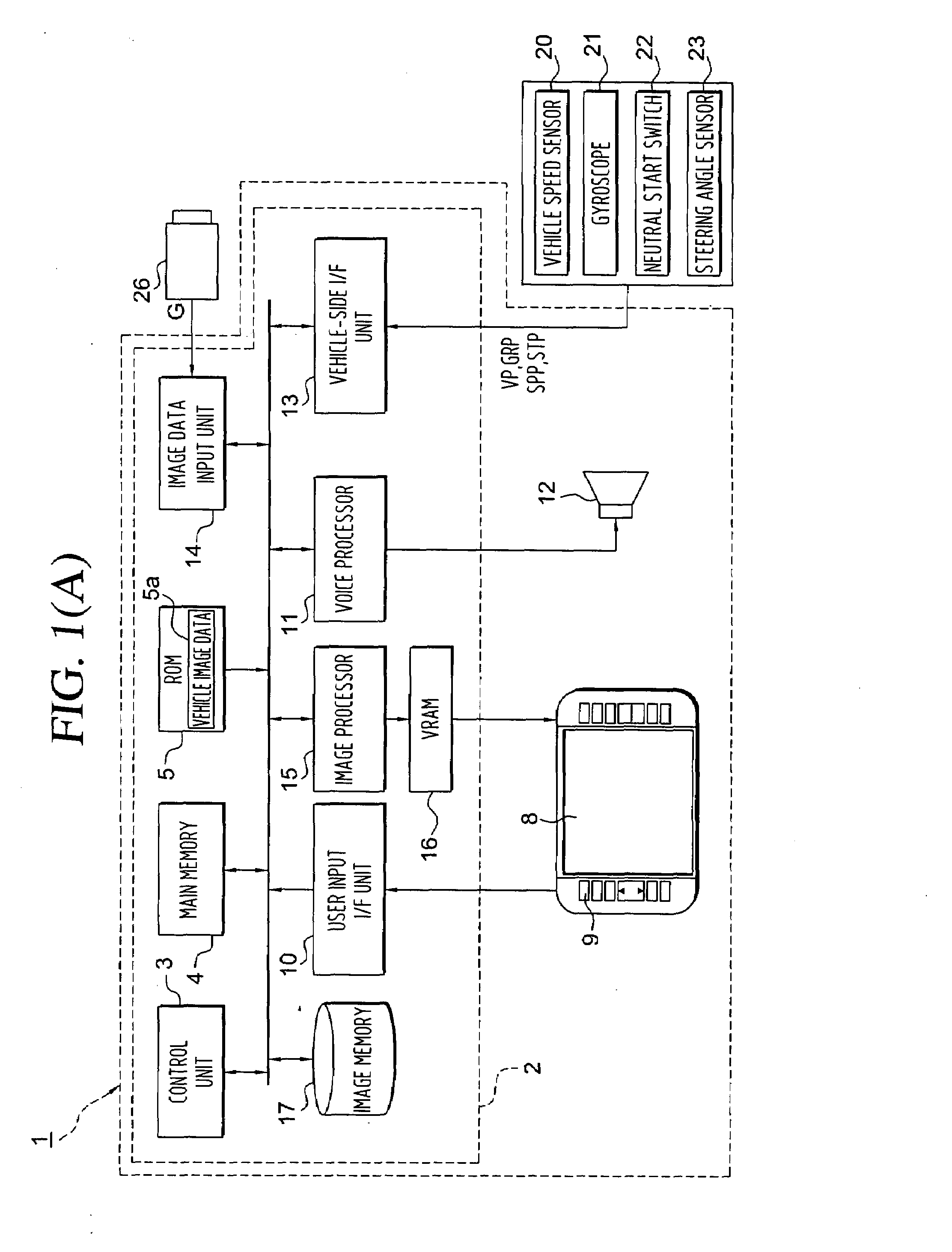
Parking assist method and parking assist apparatus
InactiveUS7969326B2High levelAssist in operationDetection of traffic movementIndication of parksing free spacesSteering angleEngineering
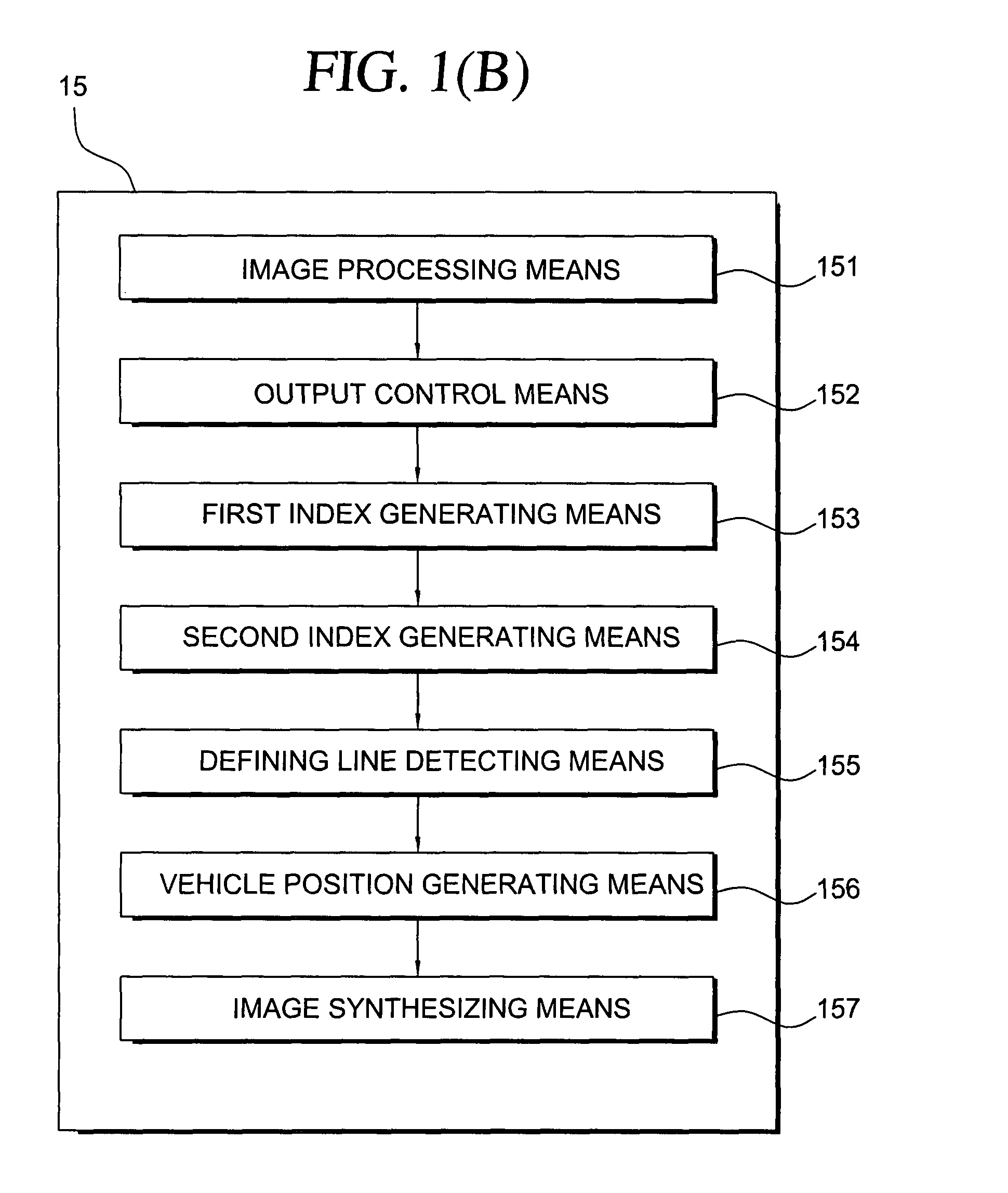
A parking assist apparatus outputs display of a synthesized image of the periphery of a vehicle as a bird's-eye view image, and superimposes, on the synthesized image, turning guide lines based on the current steering angle of the vehicle and straight driving guide lines, along which the vehicle drives in a straight line after turning in accordance with the turning guide lines.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Air conditioner device with trailing electrode
InactiveUS20050000793A1Increase air velocityEasy to collectMechanical apparatusLighting and heating apparatusParticulatesEmissivity
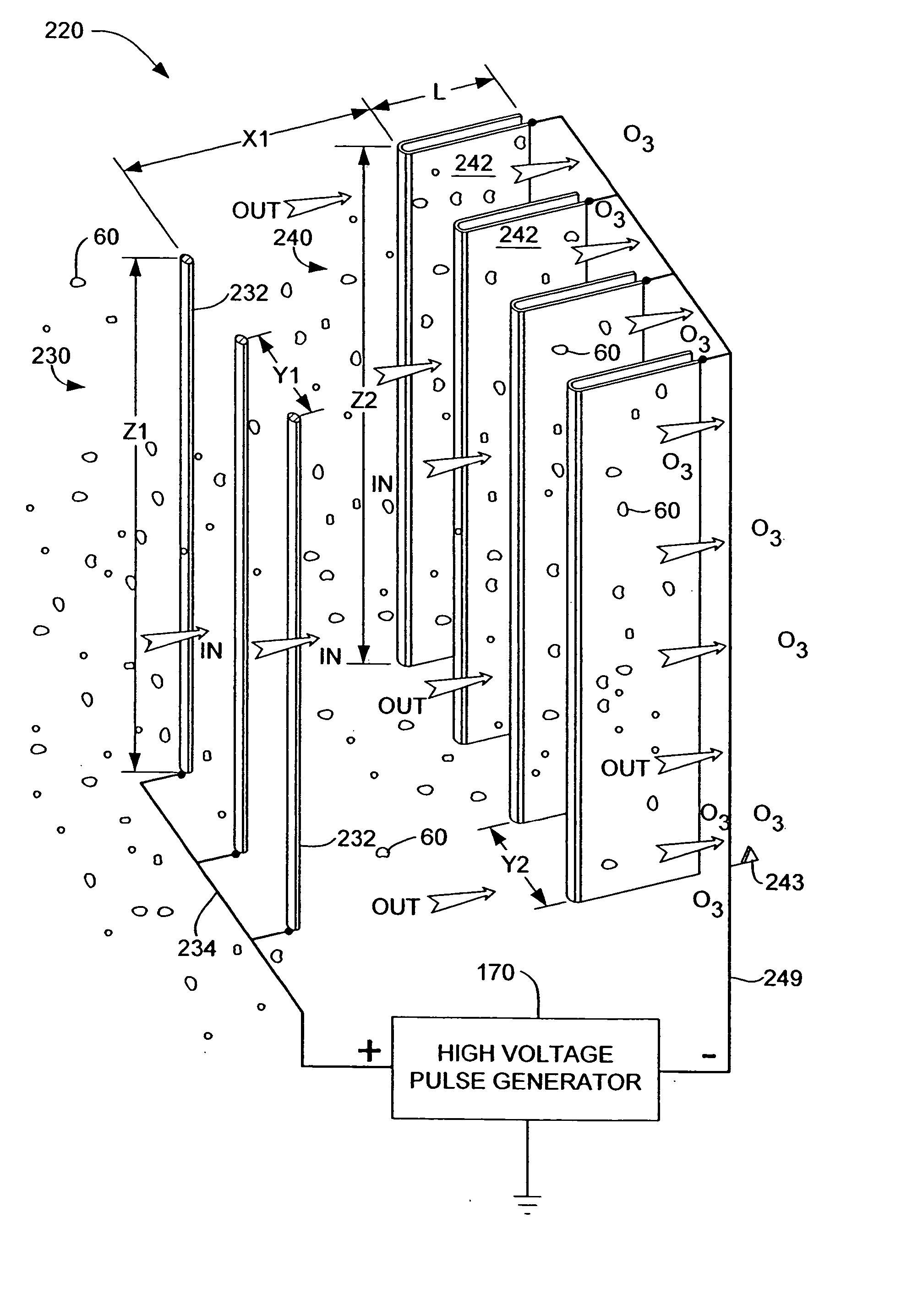
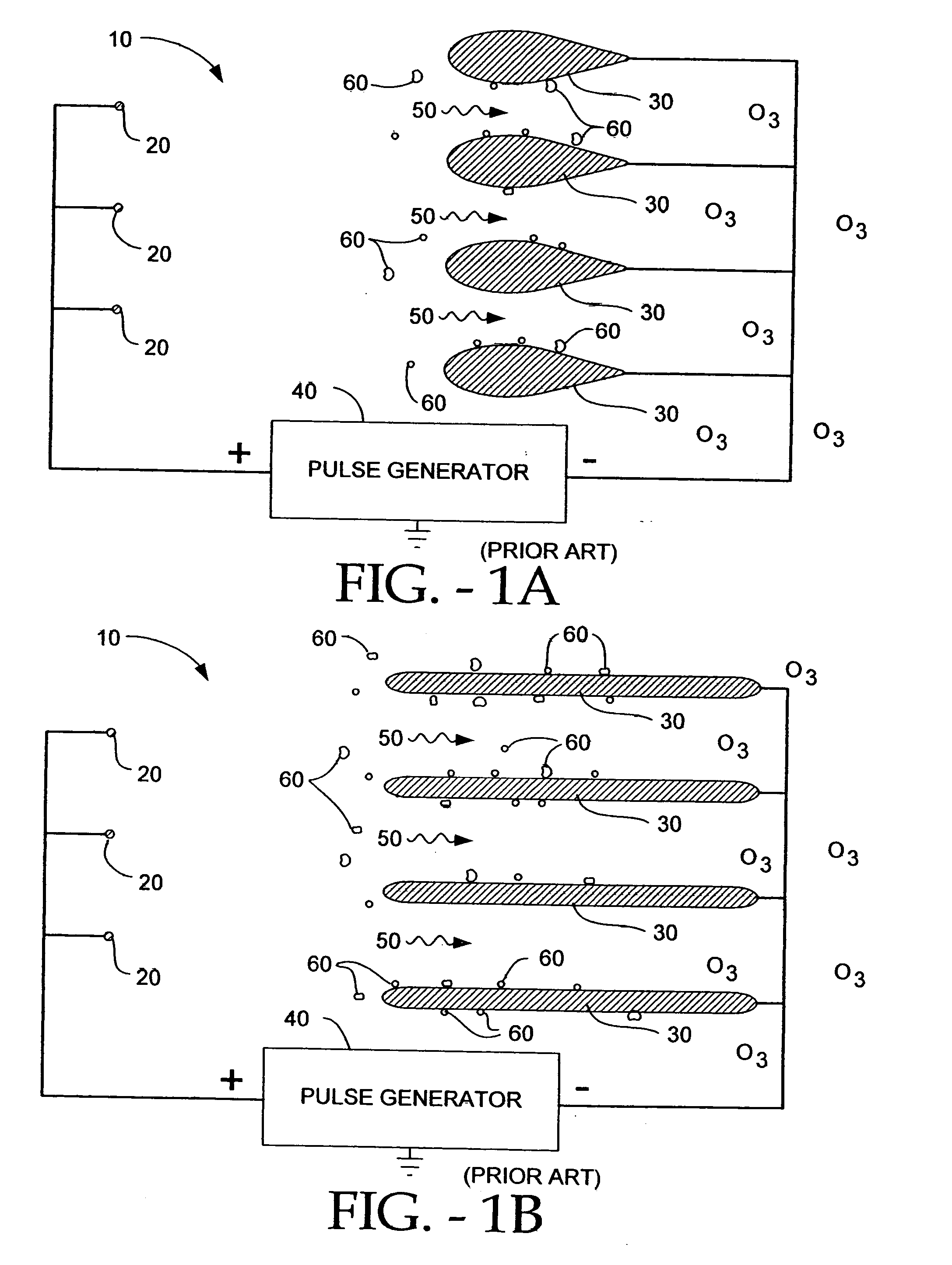
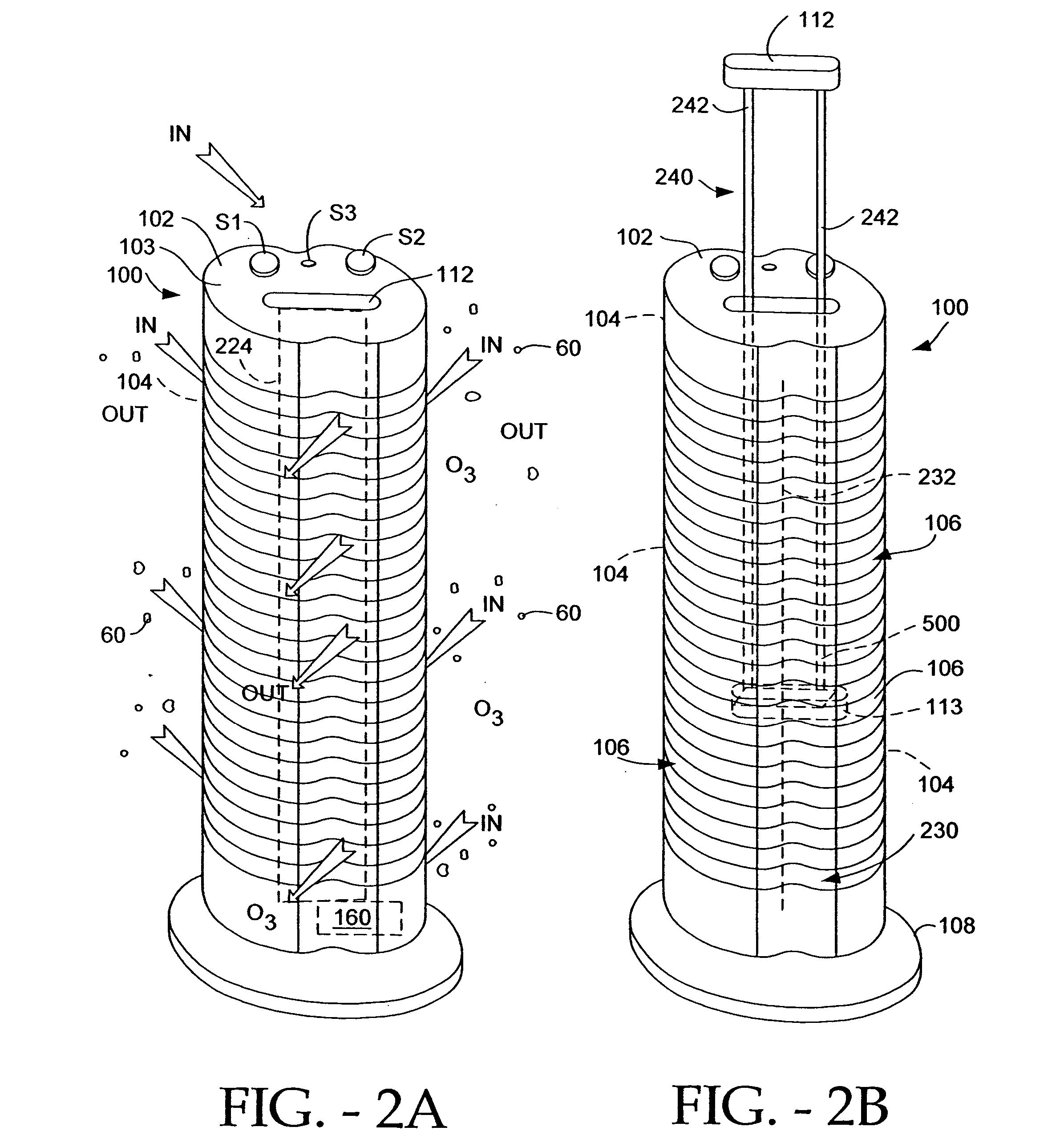
An electro-kinetic air conditioner for removing particulates from the air creates an airflow using no moving parts. The conditioner includes an ion generator that has an electrode assembly including a first array of emitter electrodes, a second array of collector electrodes, and a high voltage generator. Preferably, a third or leading or focus electrode is located upstream of the first array of emitter electrodes, and / or a trailing electrode is located downstream of the second array of collector electrodes. The device can also include an interstitial electrode located between collector electrodes, an enhanced collector electrode with an integrally formed trailing end, and an enhanced emitter electrode with an enhanced length in order to increase emissitivity.
Owner:THE SHARPER IMAGE
Parking assist method and parking assist apparatus
InactiveUS20070273554A1Easily understoodHigh levelDetection of traffic movementIndication of parksing free spacesEngineeringSteering angle
A parking assist apparatus outputs display of a synthesized image of the periphery of a vehicle as a bird's-eye view image, and superimposes, on the synthesized image, turning guide lines based on the current steering angle of the vehicle and straight driving guide lines, along which the vehicle drives in a straight line after turning in accordance with the turning guide lines.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
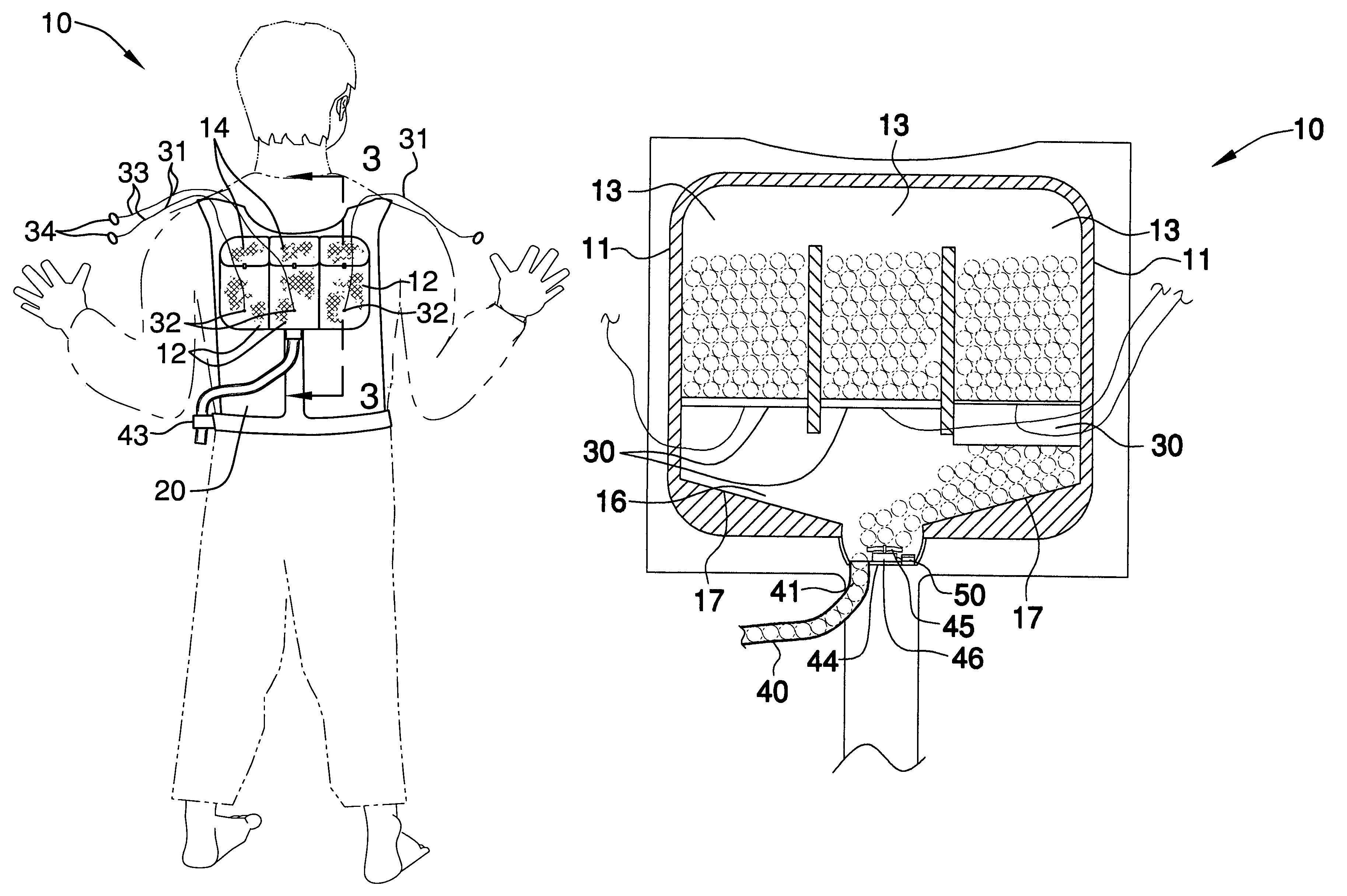
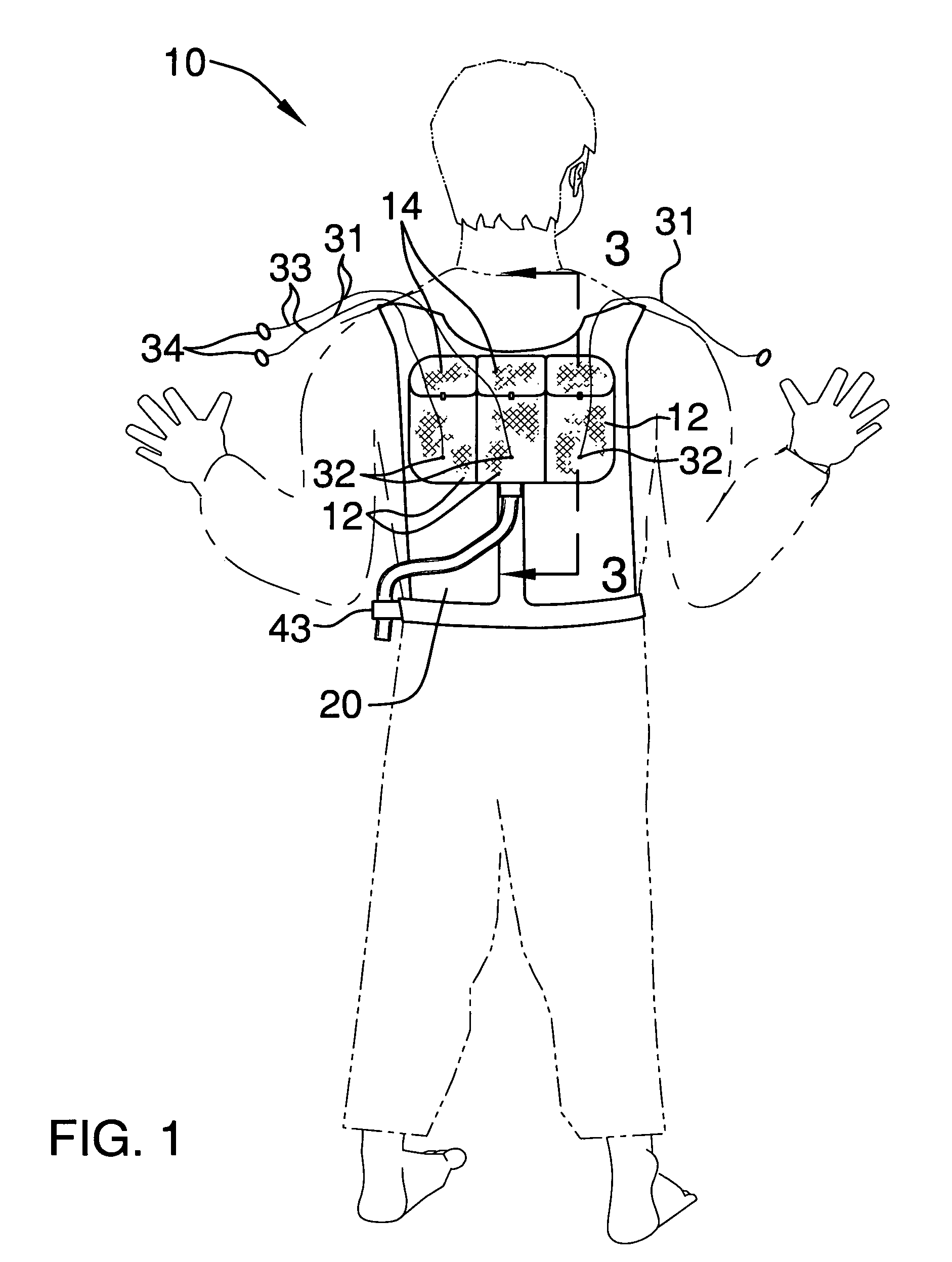
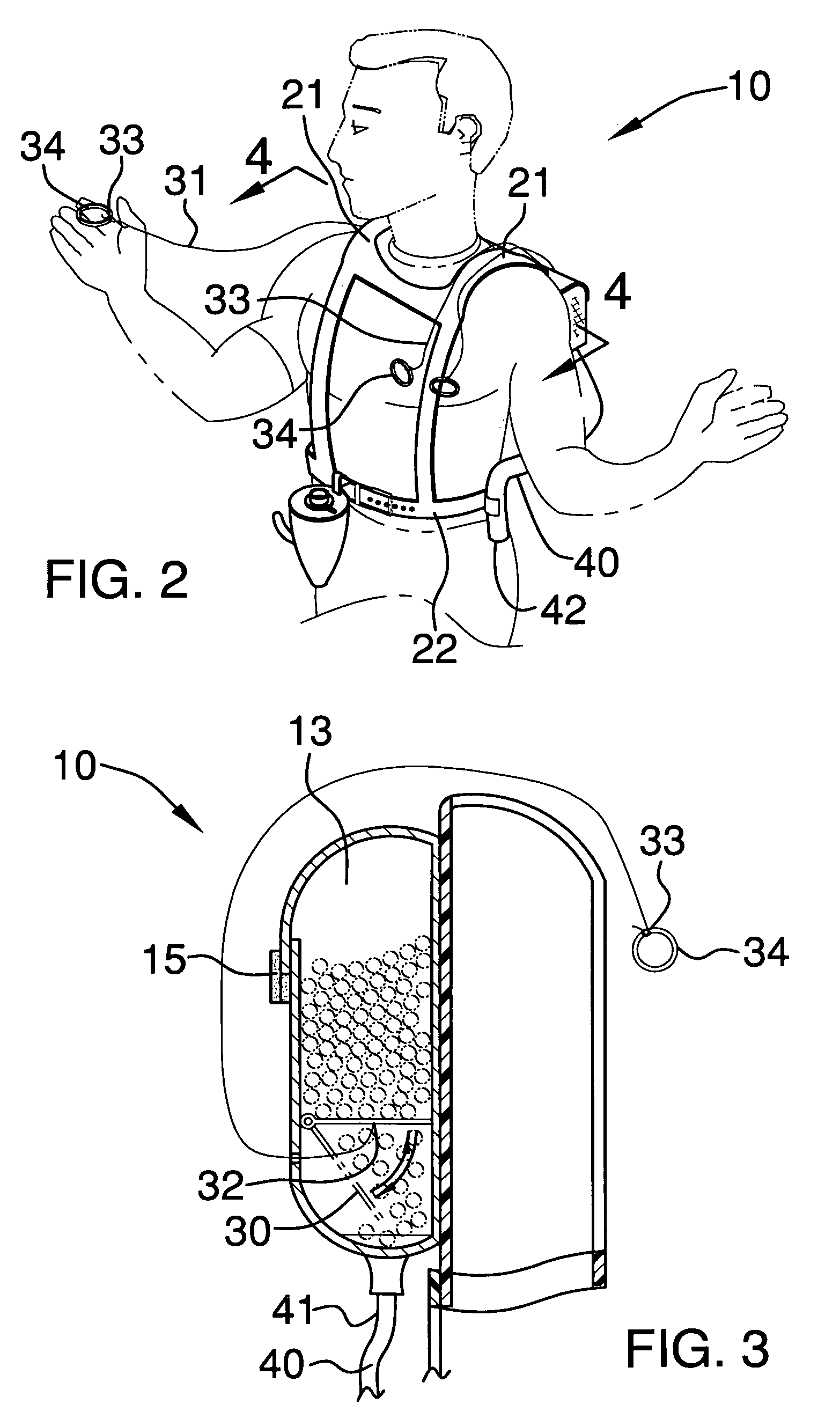
Paintball backpack
InactiveUS6981493B1Assist in operationTravelling carriersAmmunition loadingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A paintball backpack includes a housing including a plurality of isolated compartments having open top end portions. The compartments include a plurality of releasable flap portions connected adjacent the top end portions. The housing further has a lower cavity provided with an outlet positioned substantially medially thereof. The lower cavity is disposed subjacent the compartments and has a bottom surface sloping downwardly and inwardly towards the outlet. The backpack further includes a harness including a plurality of shoulder portions adjacent the flap portions of the housing and extending about a user's torso and a belt section integral therewith. The backpack further includes a mechanism for selectively moving paintballs from the top end portions to the lower cavity and a mechanism for dispensing paintballs outwardly and away from the lower cavity wherein the paintballs are projected from the housing at a predetermined velocity.
Owner:POTERACKE CHARLES J
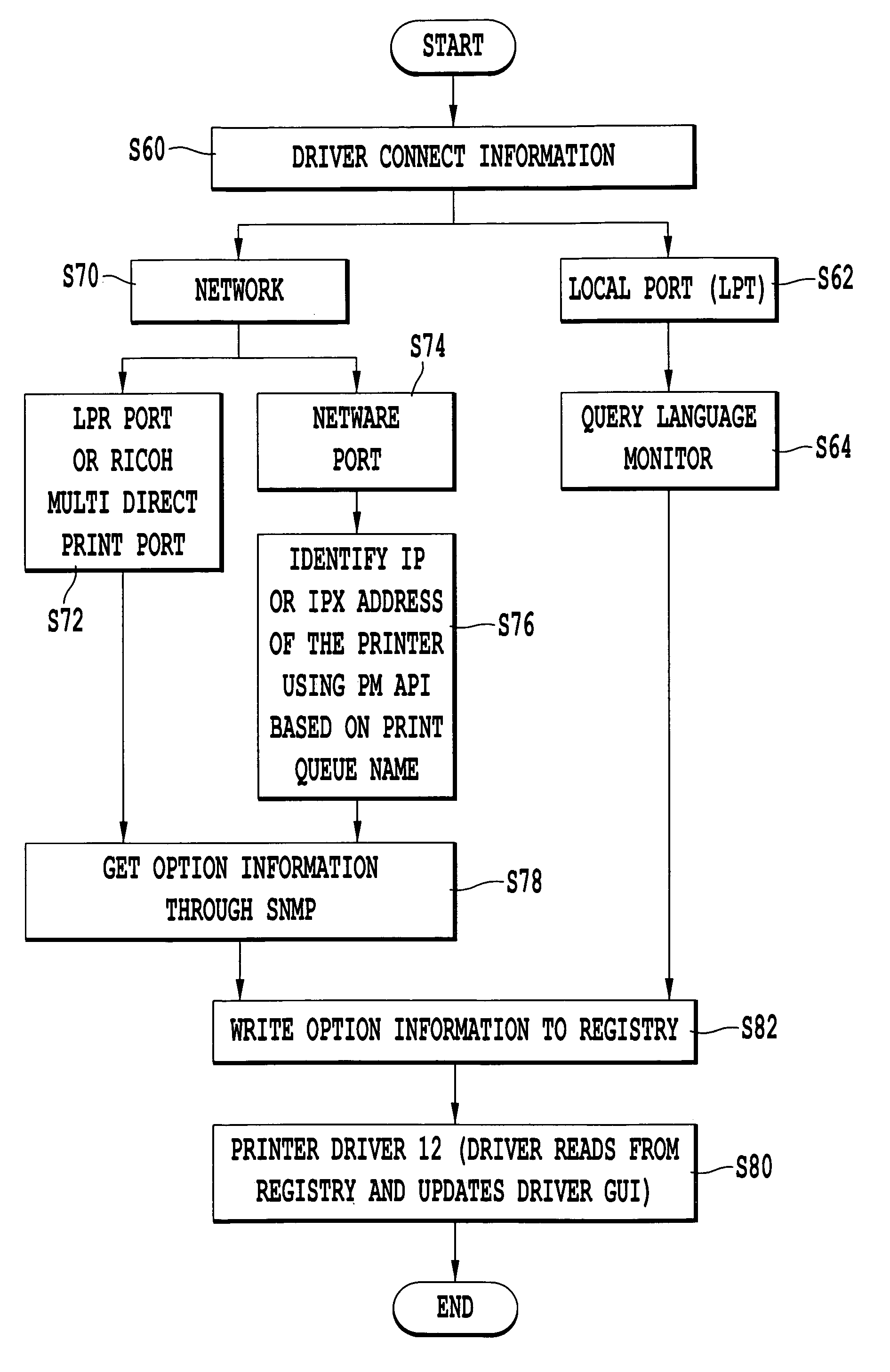
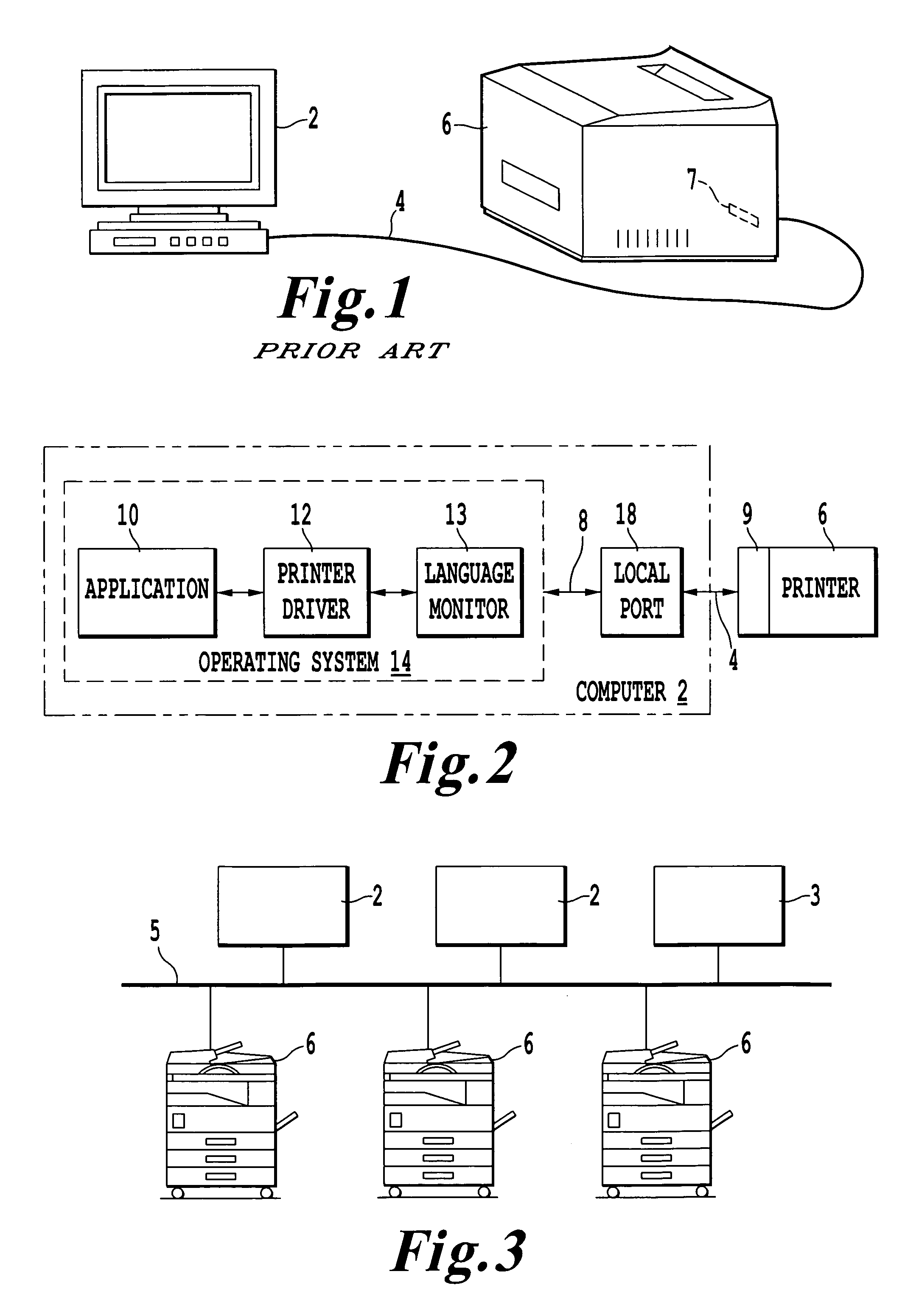
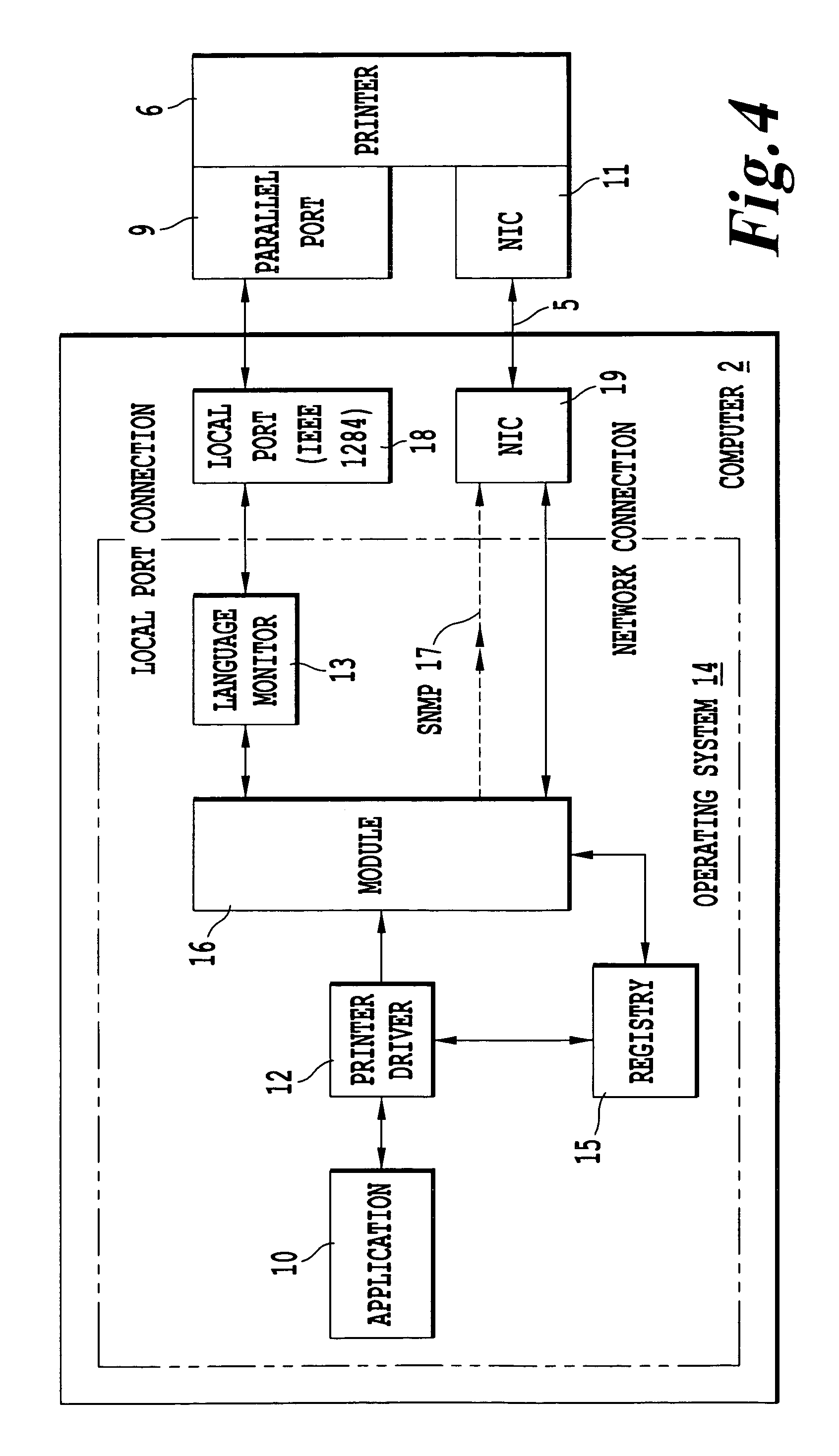
Method of configuring a computer to include the available options of a printer
InactiveUS7143150B1Assist in operationDigital computer detailsData resettingComputer printingNetwork connection
A method of configuring a computer connected to a printer via a network by transmitting commands, such as SNMP commands, to the printer in order to retrieve the available options of the printer. In response to the transmitted commands, the printer transmits its available options to the computer, and the printer driver resident on the computer is then updated without manually selecting individual printer options to include the retrieved options. The present invention also provides a computer program product and corresponding GUI to configure a computer to include the available printer options. The GUI according to the present invention includes a plurality of pop-up menus having various display controls to operate the computer program, and is updated by the printer driver to reflect the available printer options.
Owner:RICOH KK
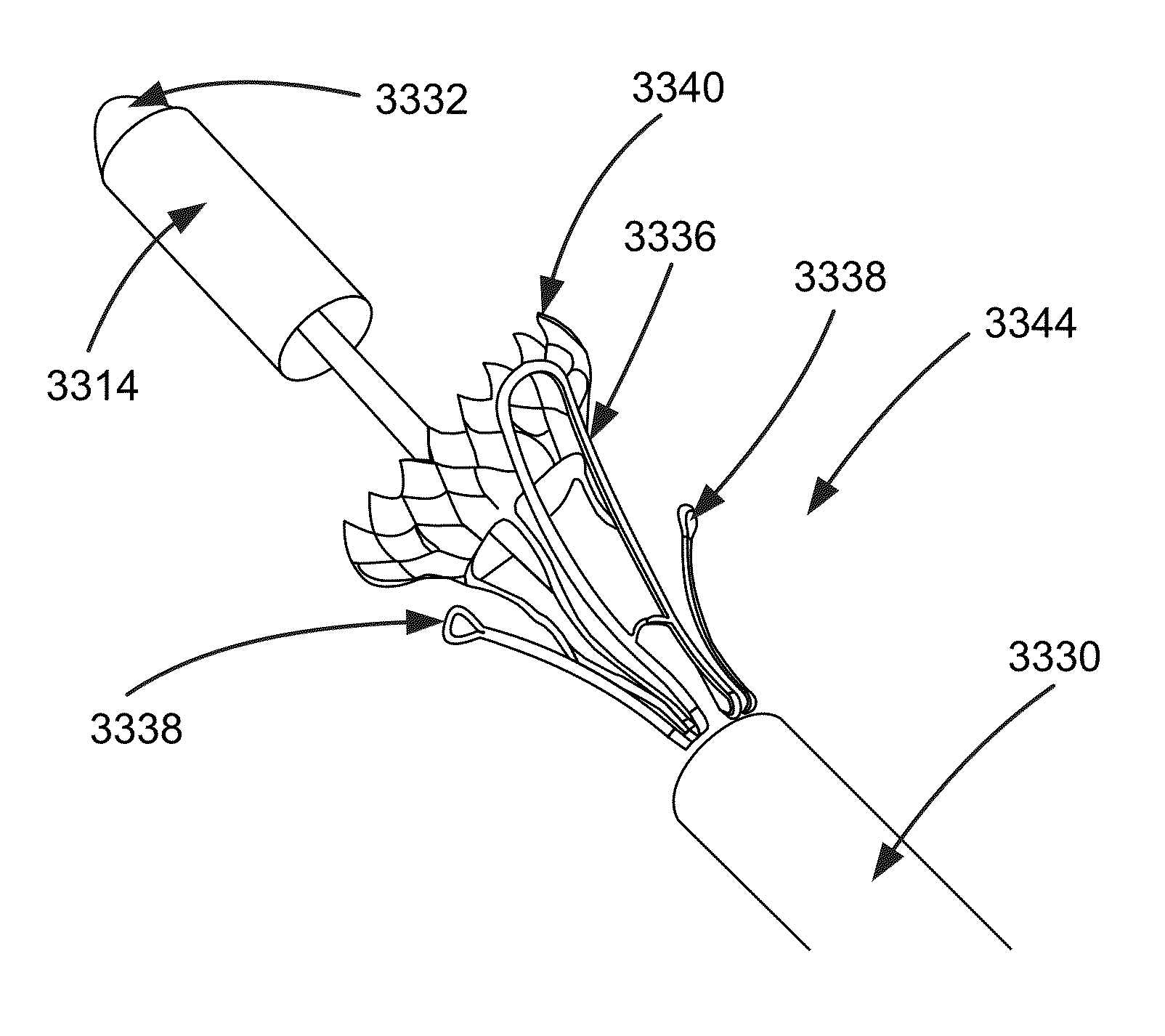
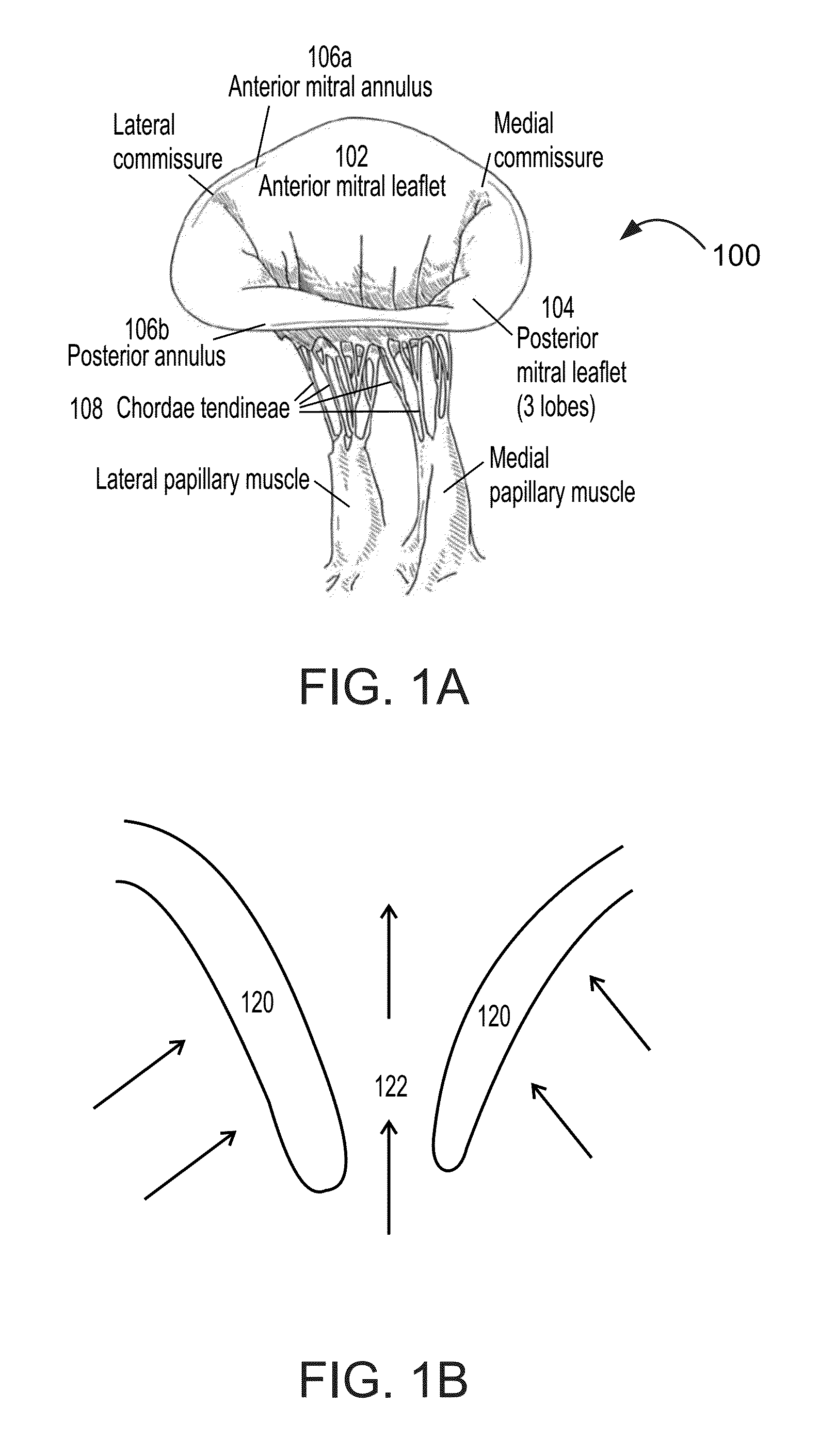
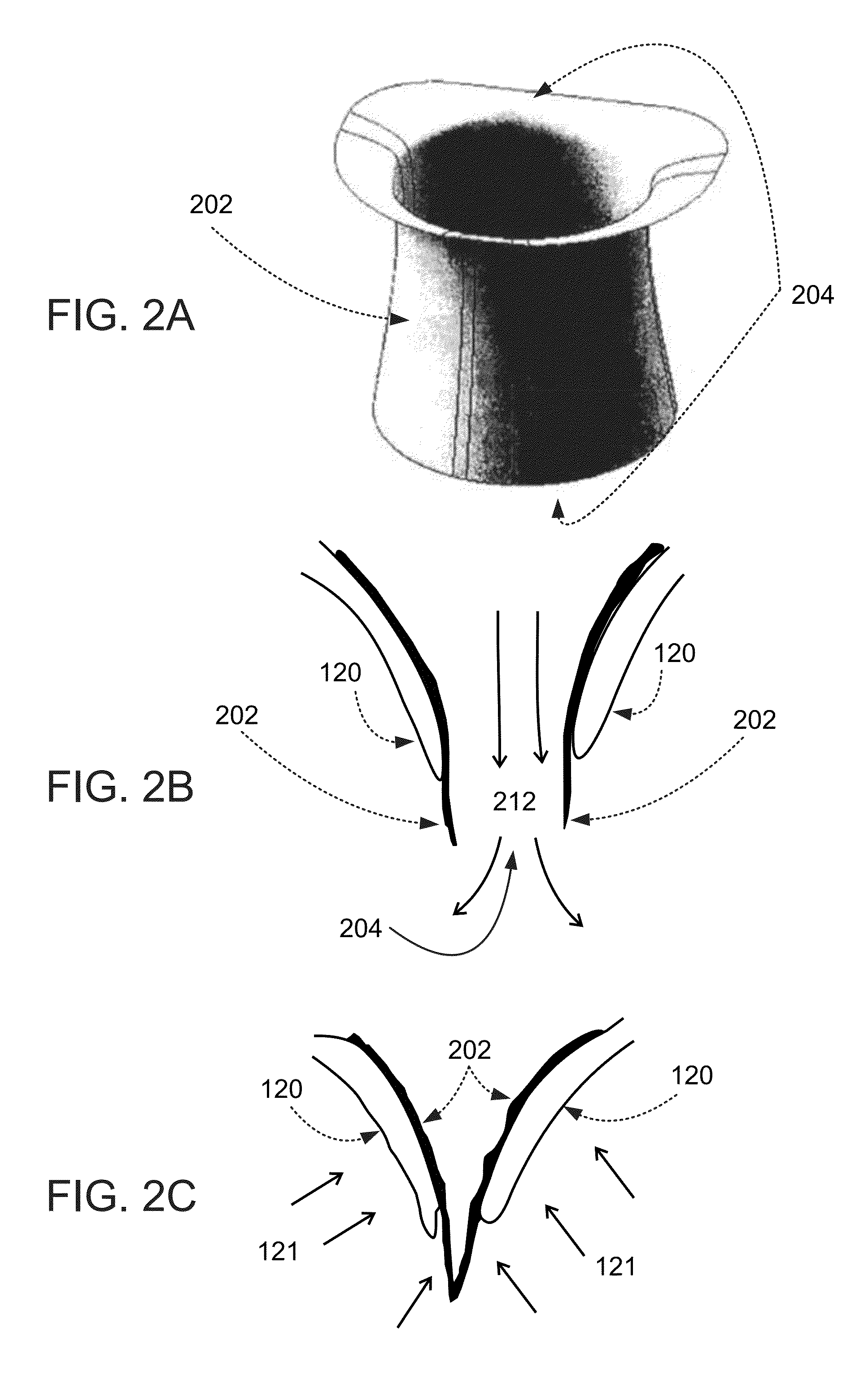
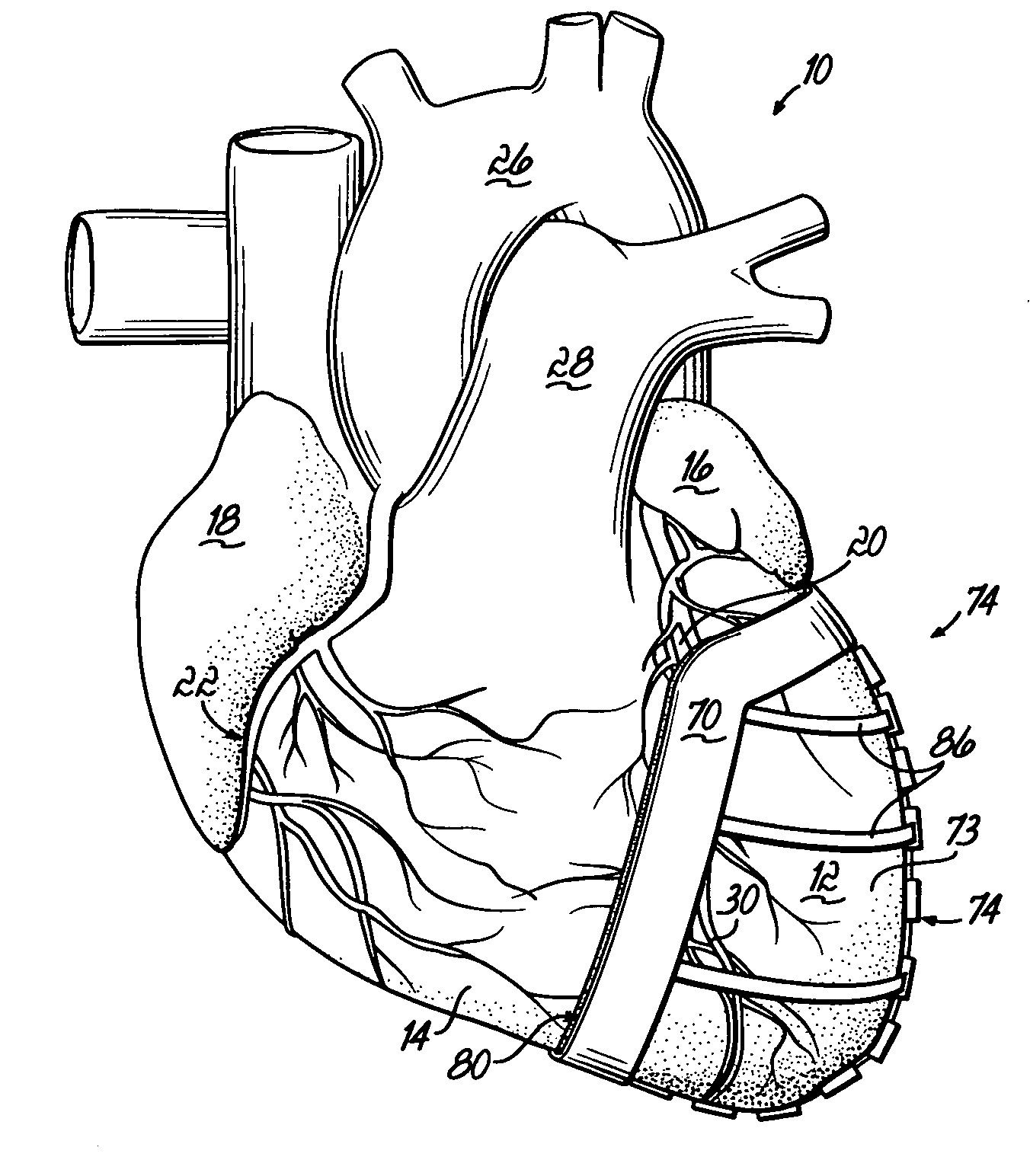
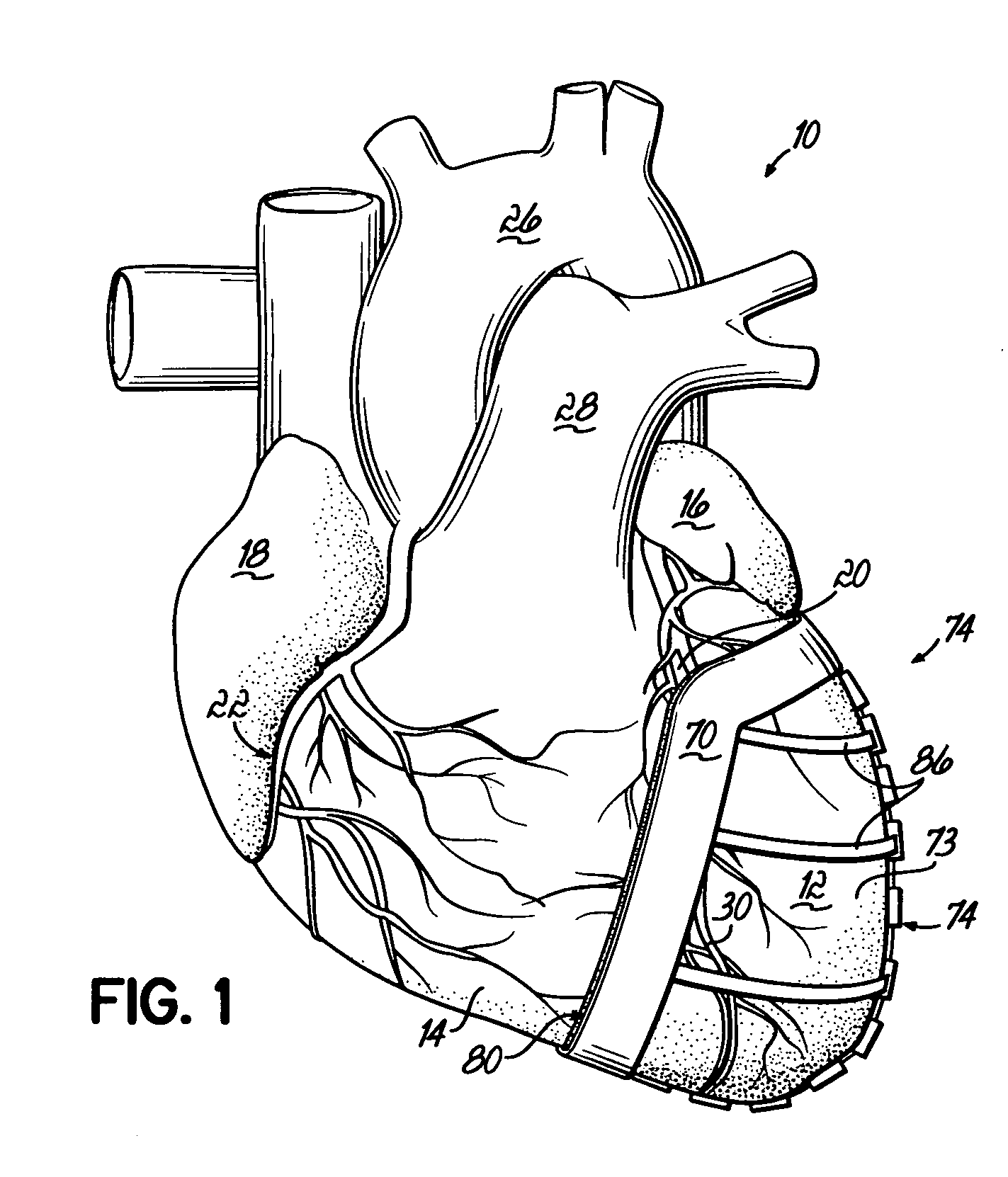
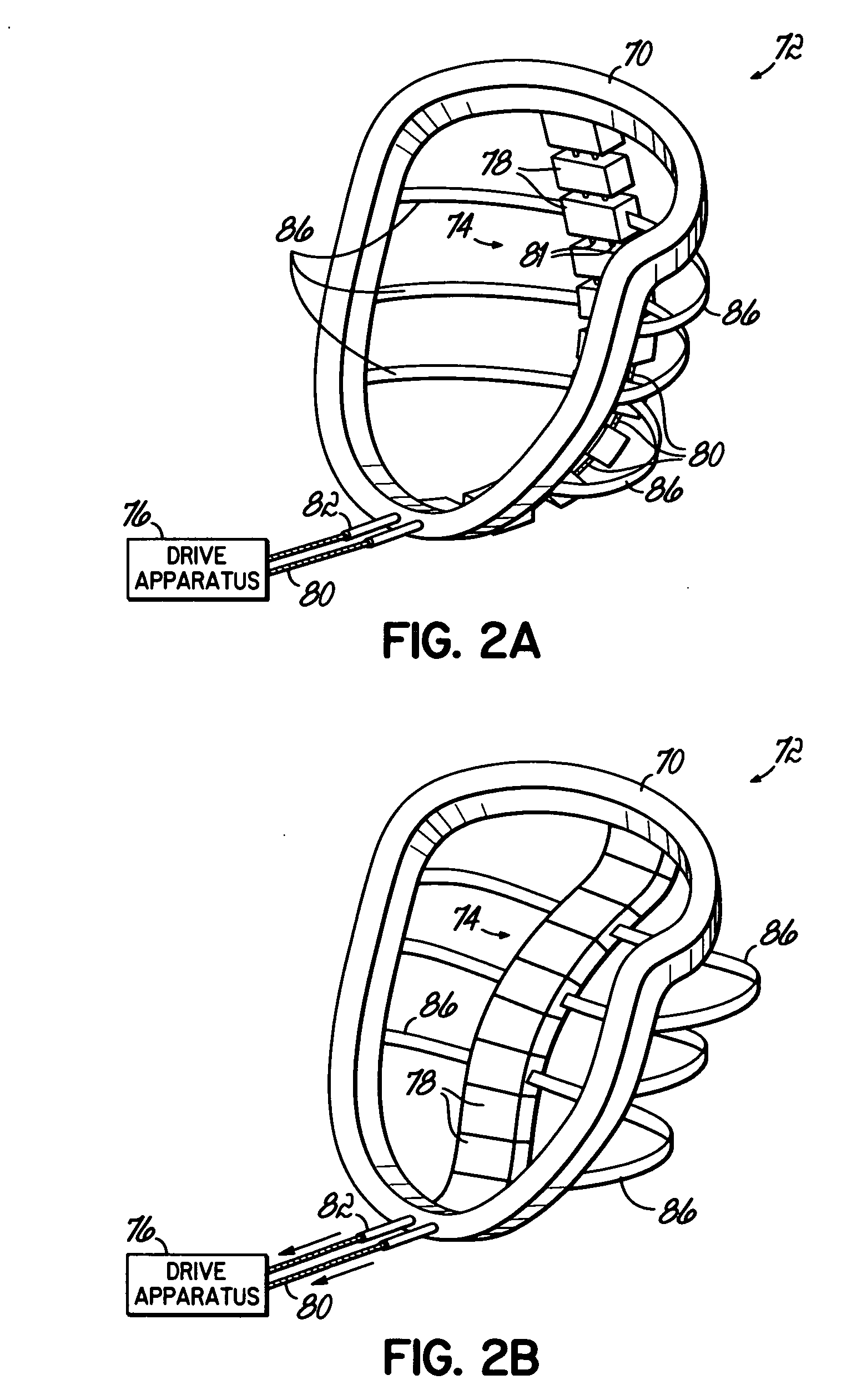
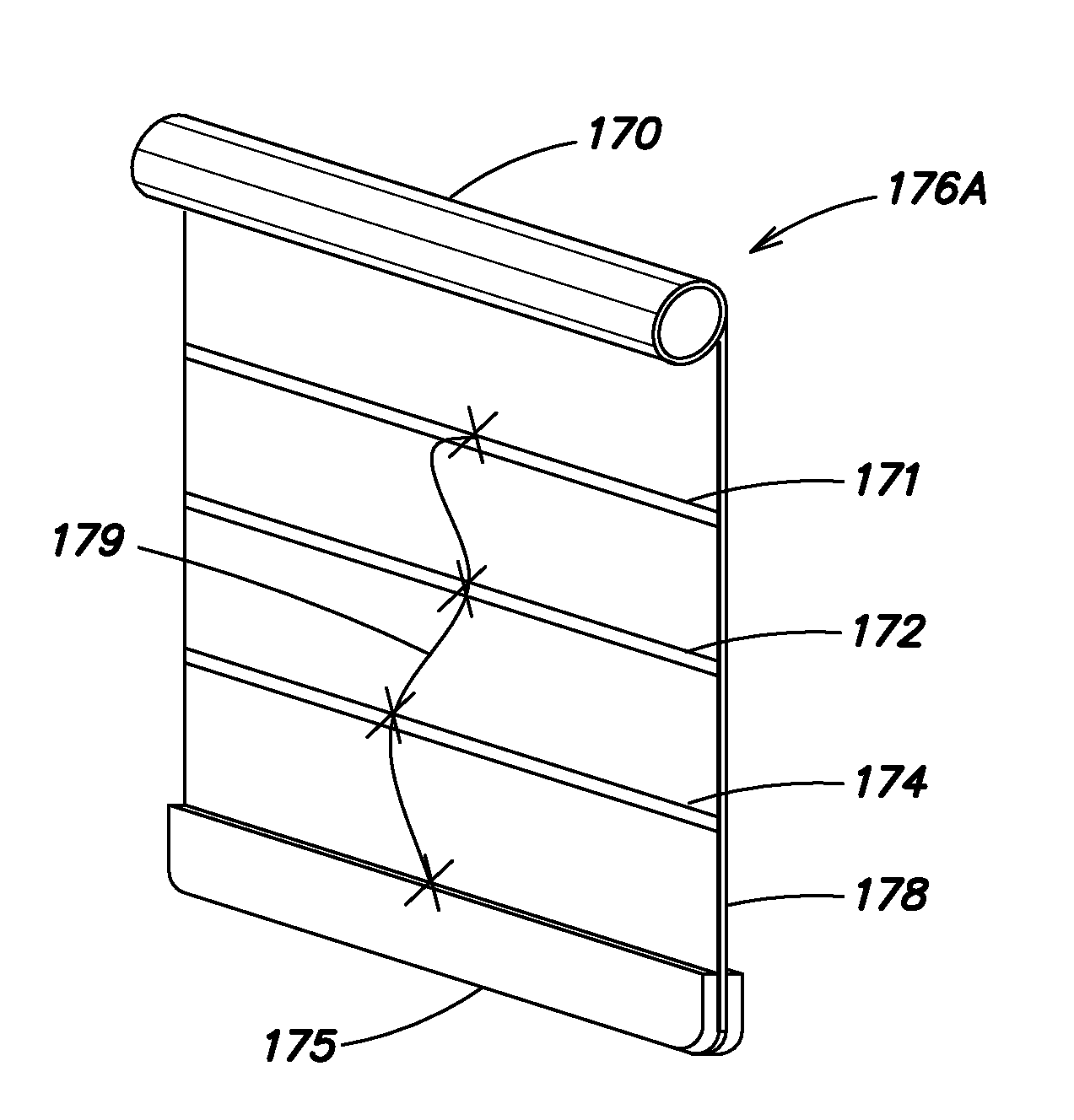
Heart valve assistive prosthesis
A device for placing in a cardiac valve to assist operation of natural cardiac valve leaflets, the device including a frame for anchoring the device, configured to be placed upstream of the cardiac annulus and shaped to prevent the frame from shifting downstream of the cardiac valve annulus, and at least one anchor extension attached to the frame, the anchor extension configured to extend through the leaflets of the cardiac valve at commissures of the cardiac valve and behind the natural leaflets, preventing the anchor extensions from shifting back from the downstream side of the annulus to the upstream side of the annulus. Related apparatus and methods are also described.
Owner:MITRASSIST MEDICAL
Method of and system for non-uniform image enhancement
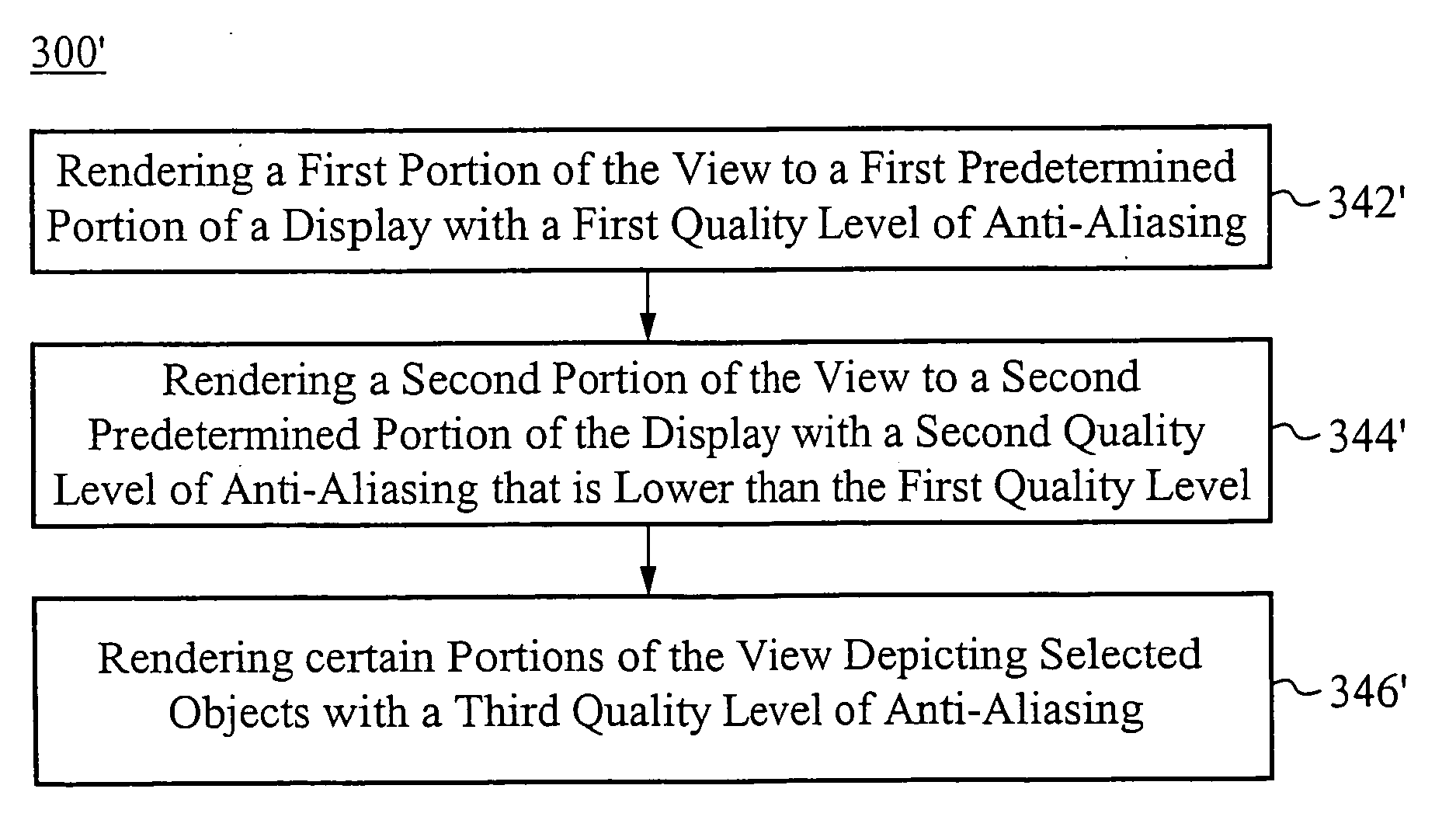
ActiveUS20070229503A1Assist in operationDetails involving antialiasingCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsAnti-aliasing
Methods of rendering a view of a scene include steps that specify quality levels of anti-aliasing and texture filtering for predetermined regions of a display, or selected objects within the scene, or both. Methods of processing data for display include steps adapted to process portions of the image according to selected or predetermined anti-aliasing and texture filtering quality levels. Graphics processing equipment includes hardware or software adapted to perform non-uniform anti-aliasing of images according to specified criteria.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Thin film device and a method of providing thermal assistance therein
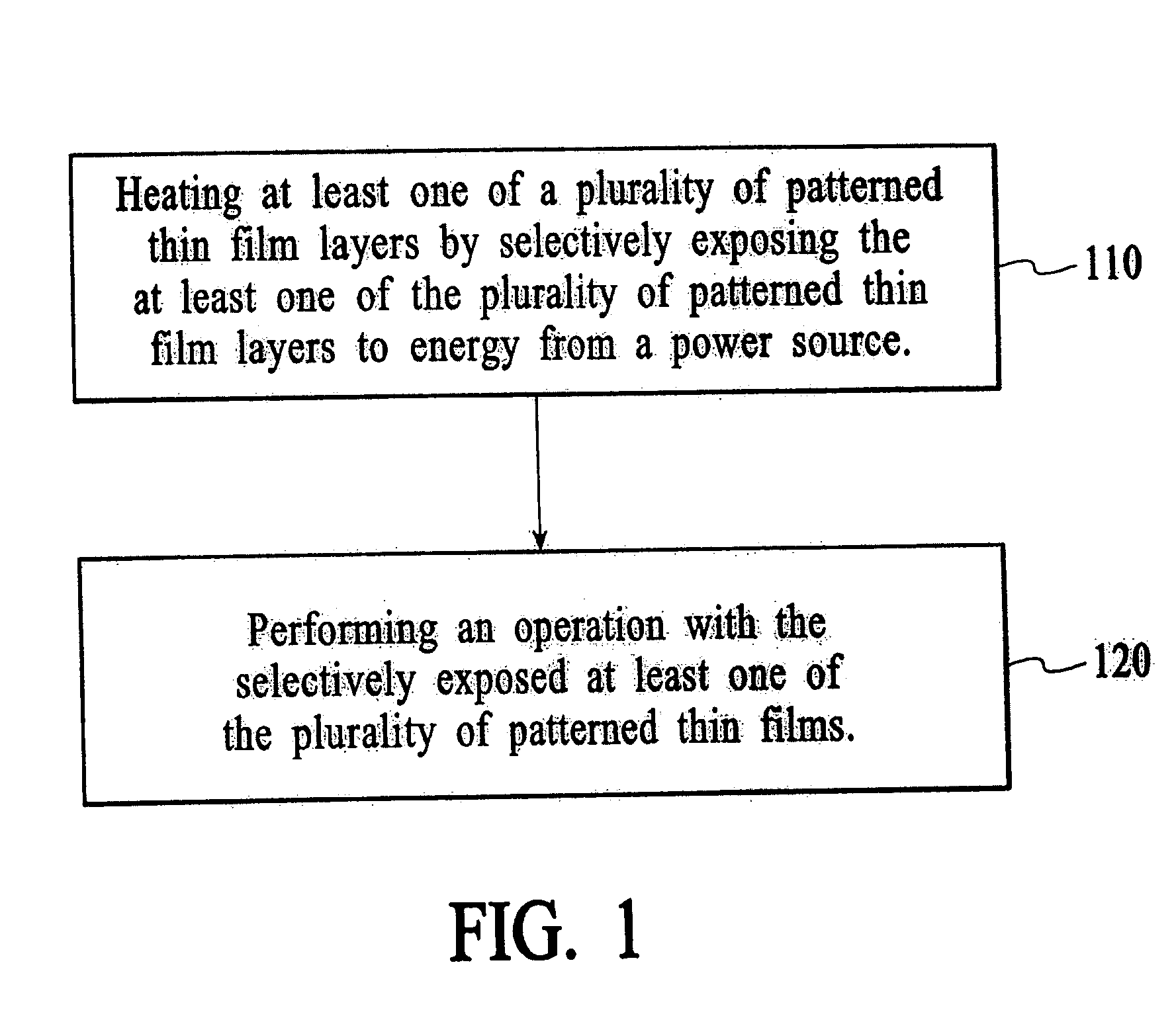
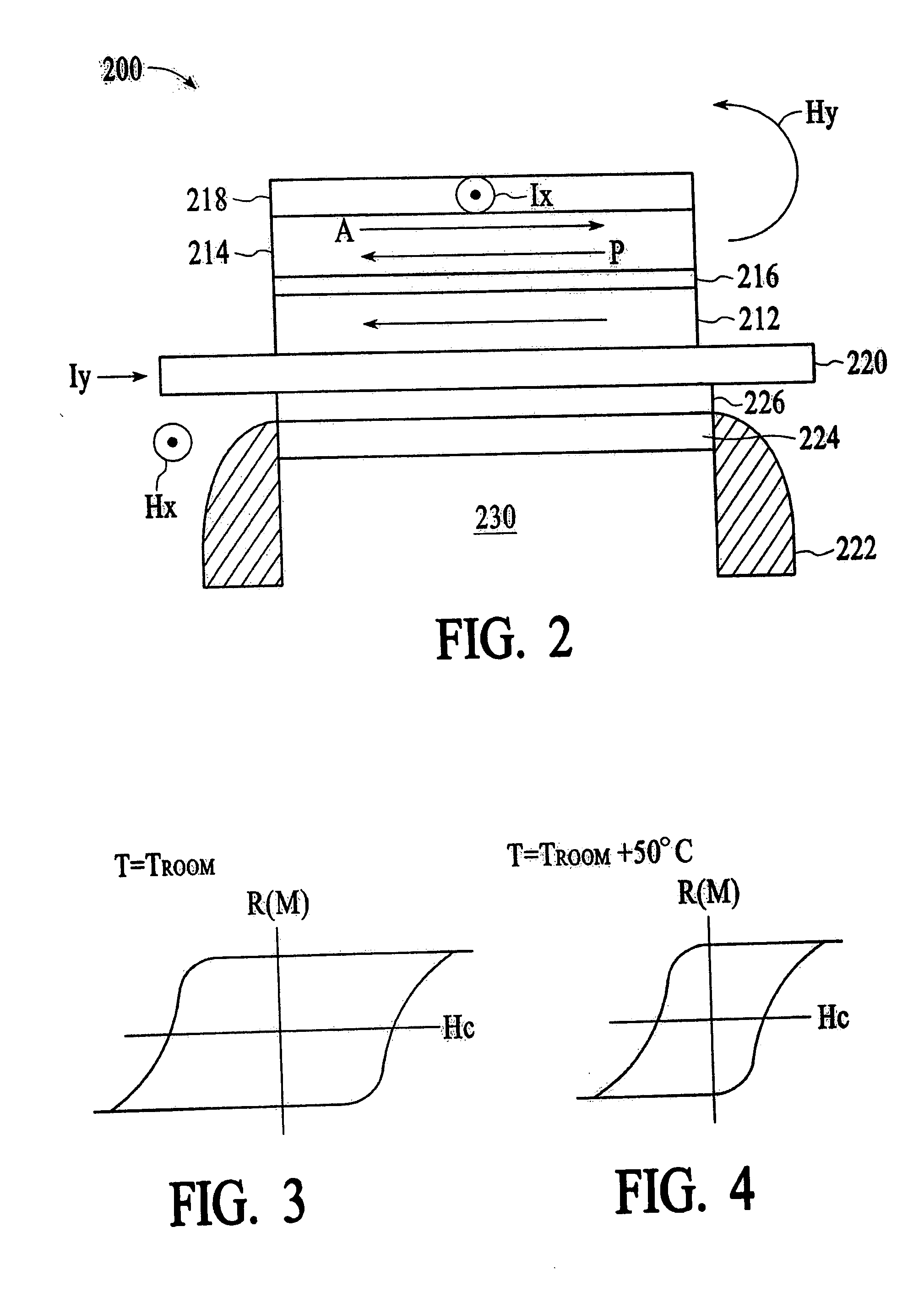
ActiveUS20050104146A1Improve accuracyImprove performanceMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesSupply energyEnergy analysis
A thin film device and a method of providing thermal assistance therein is disclosed. Accordingly, a heater material is utilized to thermally assist in the operation of the thin film device. By utilizing a heater material to thermally assist in the operation of the thin film device, a substantial improvement in the accuracy and performance of the thin film device is achieved. A first aspect of the present invention is a thin film device. The thin film device includes at least one patterned thin film layer, a heater material coupled to the at least one patterned thin film layer for providing thermal assistance to the at least one of the patterned thin film layers and a conductor coupled to the heater material for supplying energy to the heater material.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
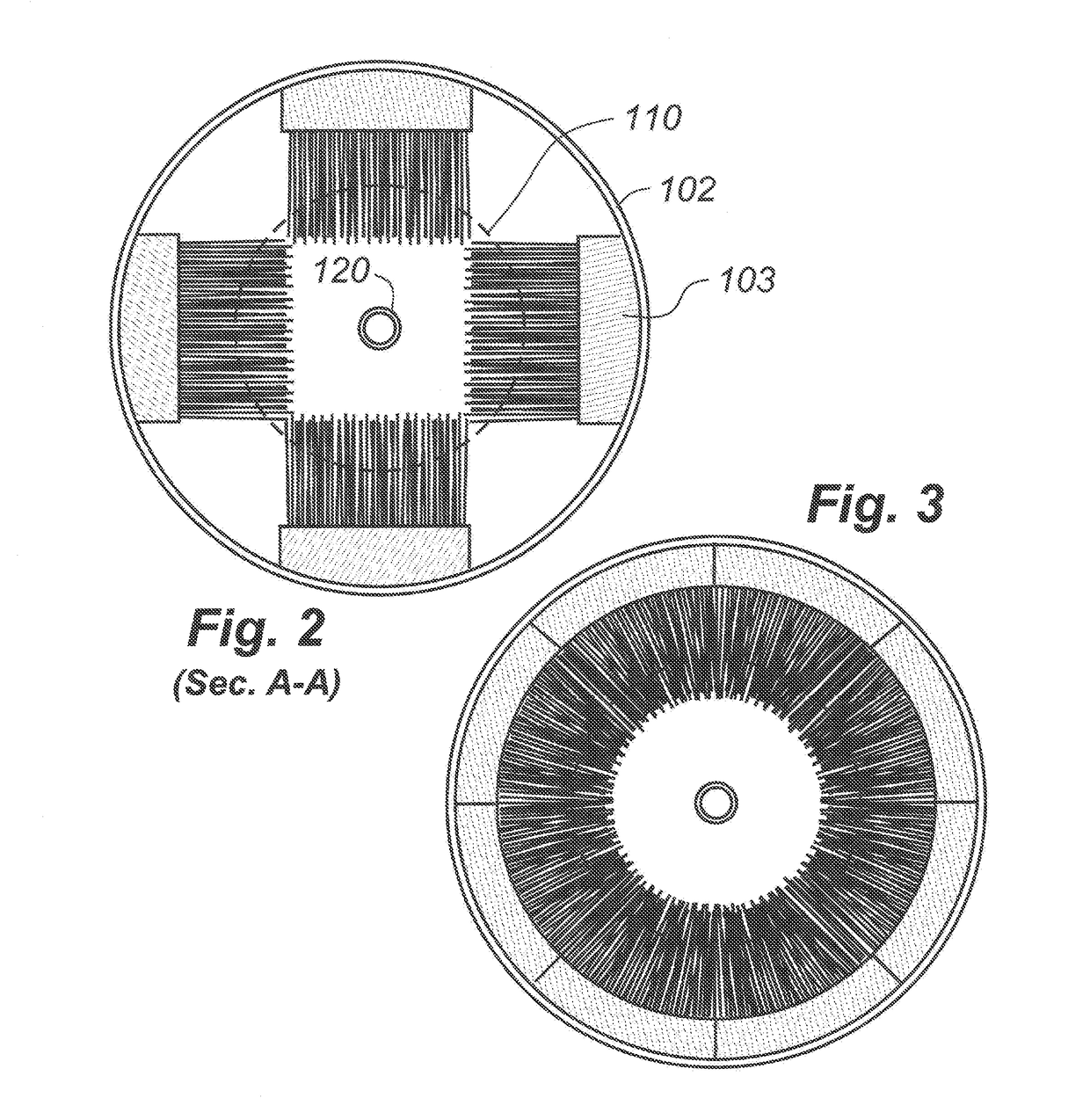
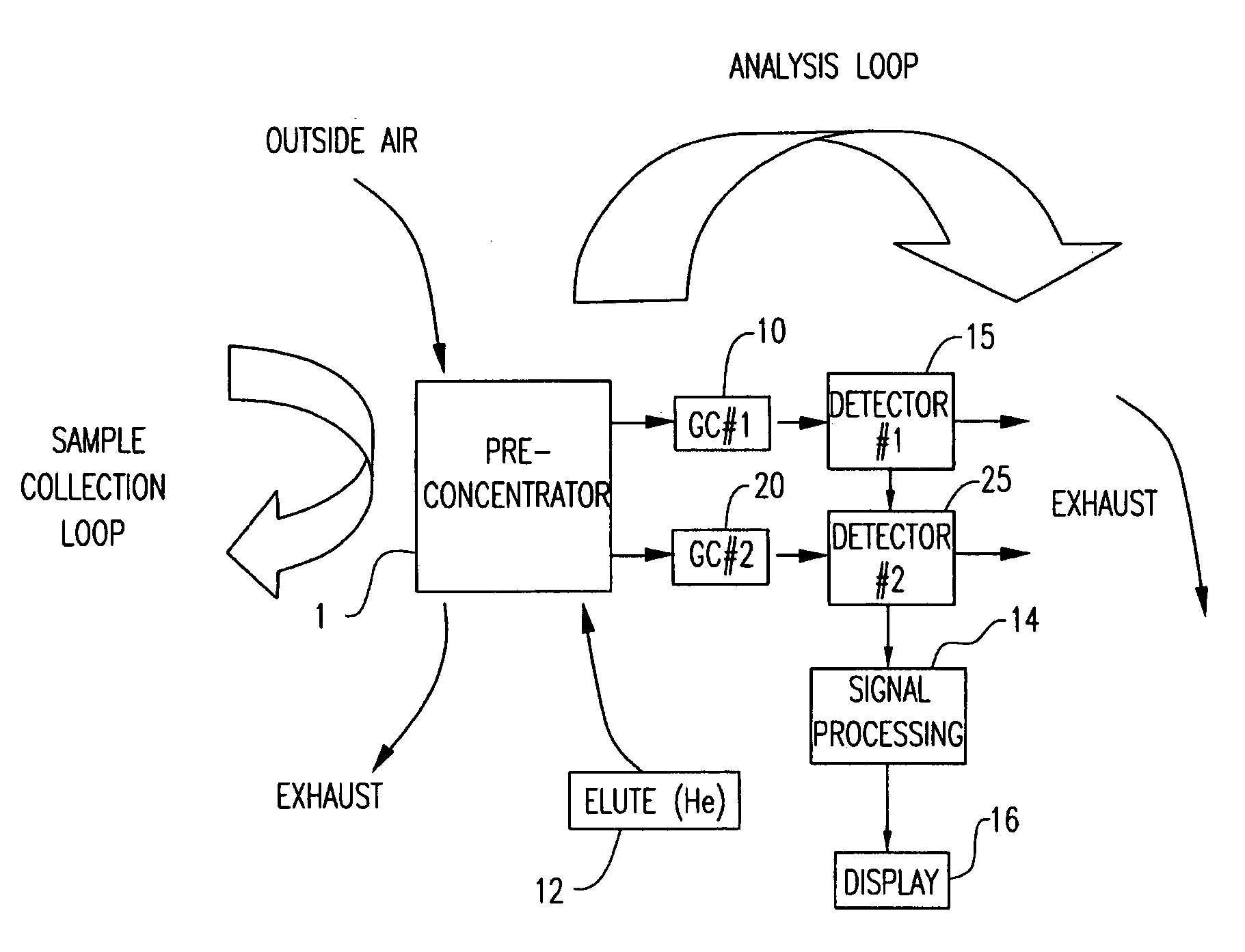
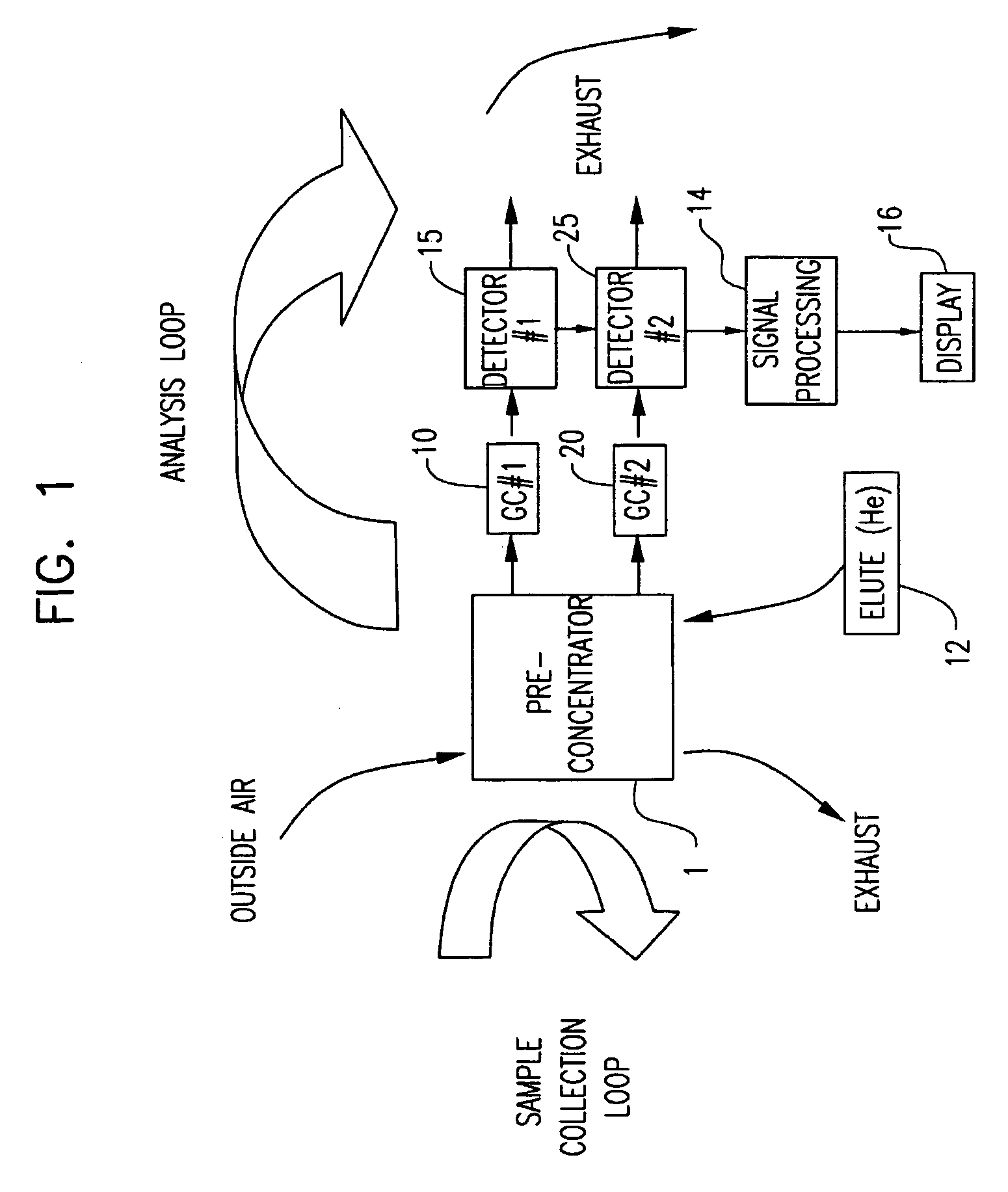
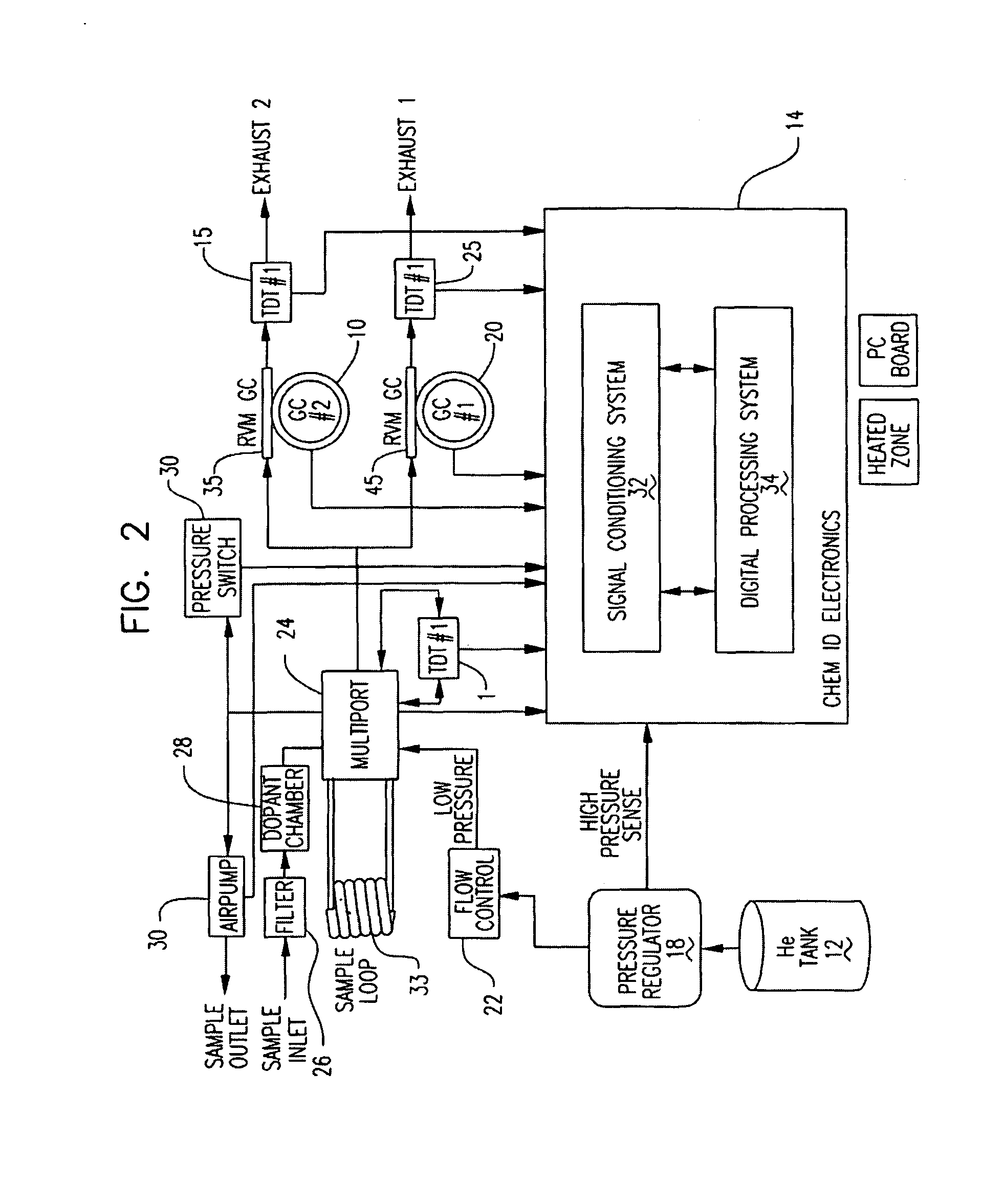
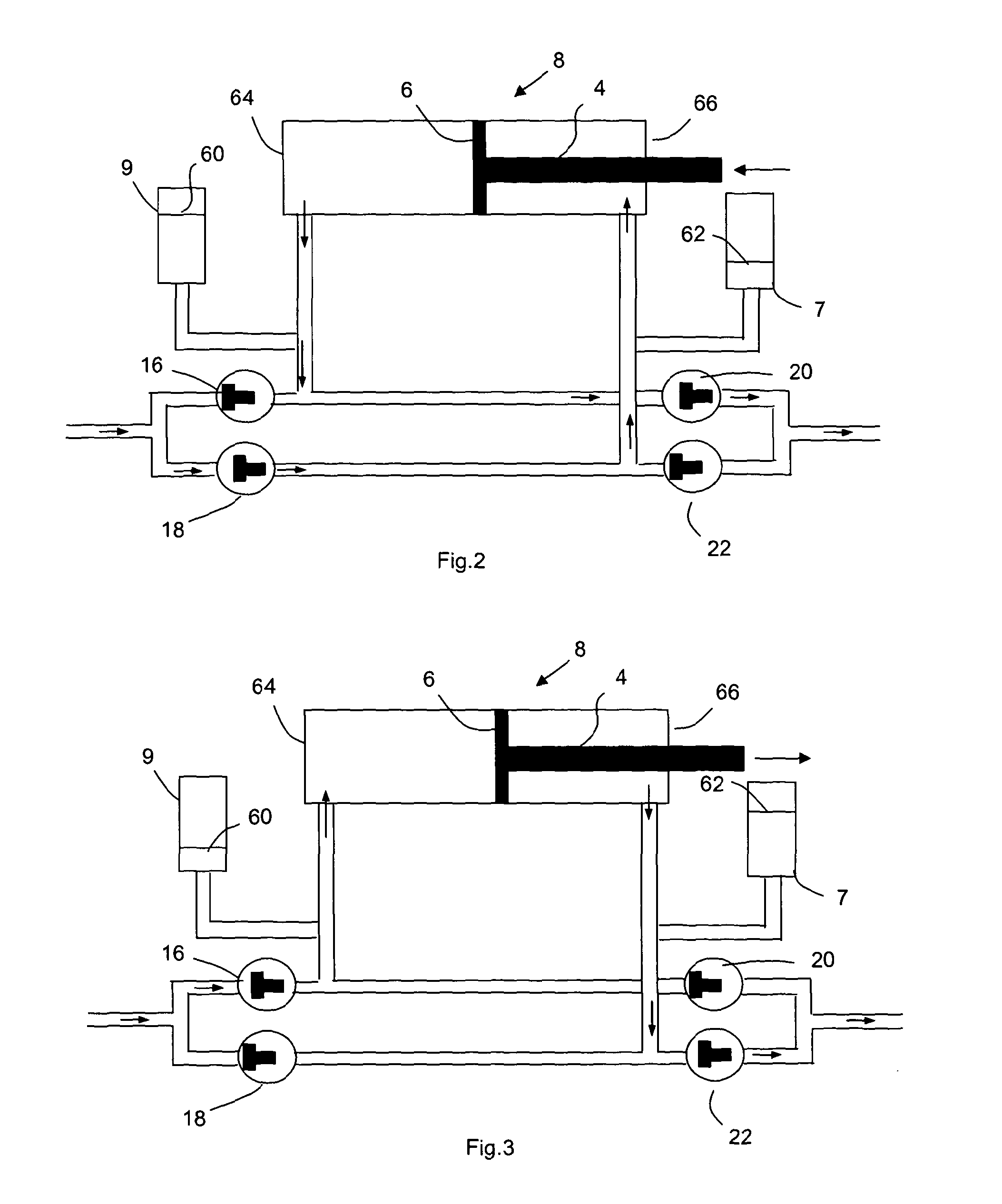
Multi-dimensional portable gas chromatograph system
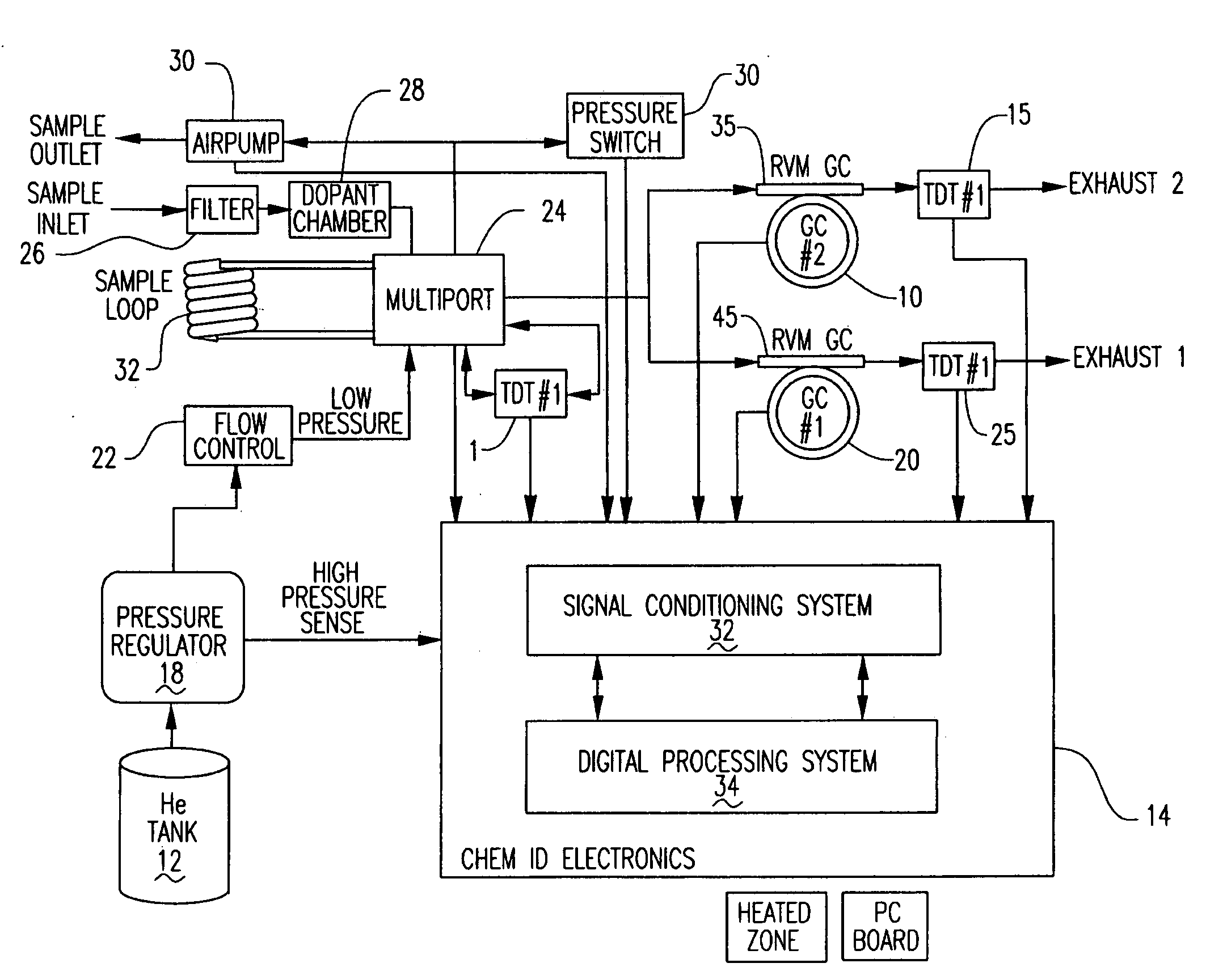
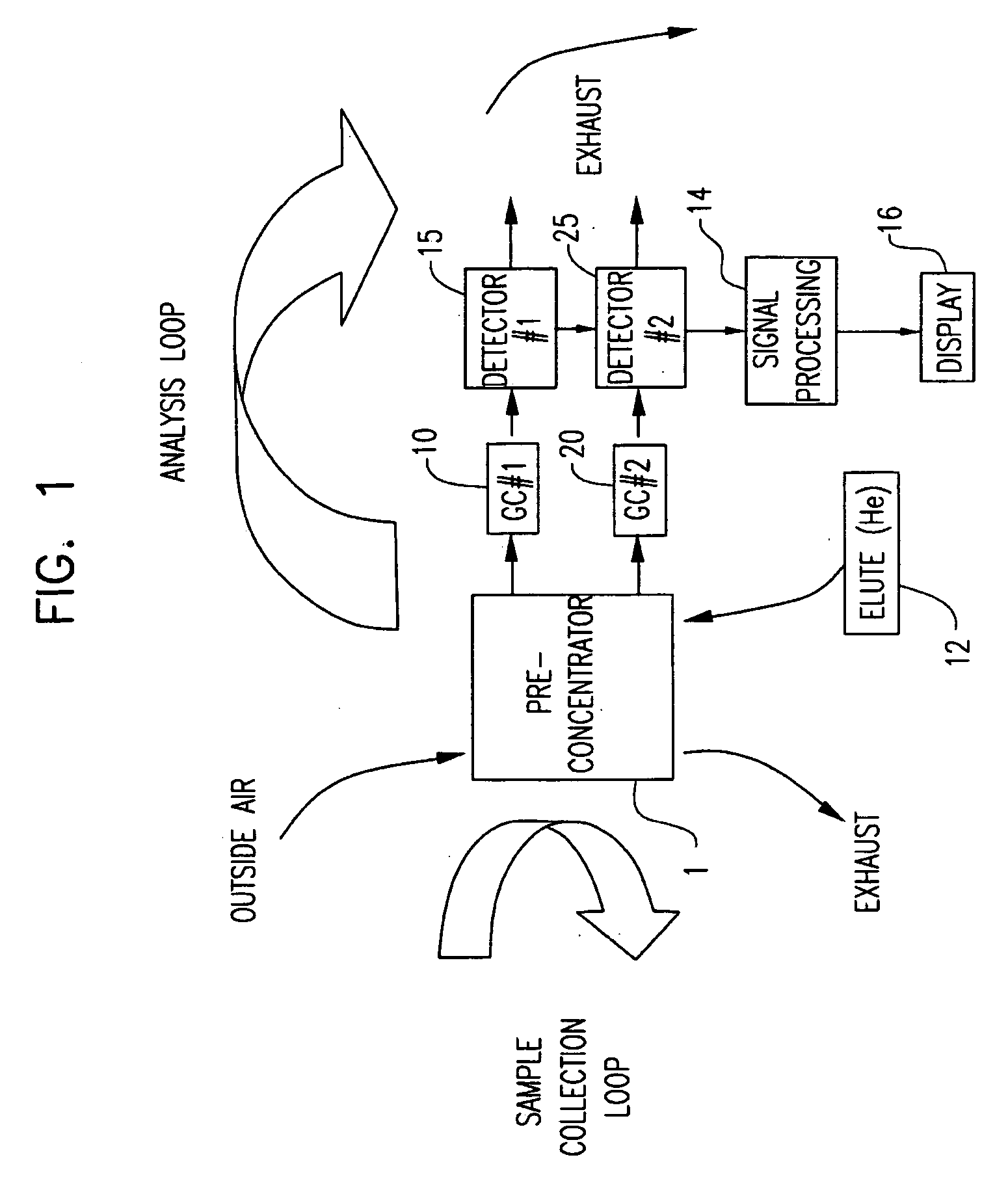
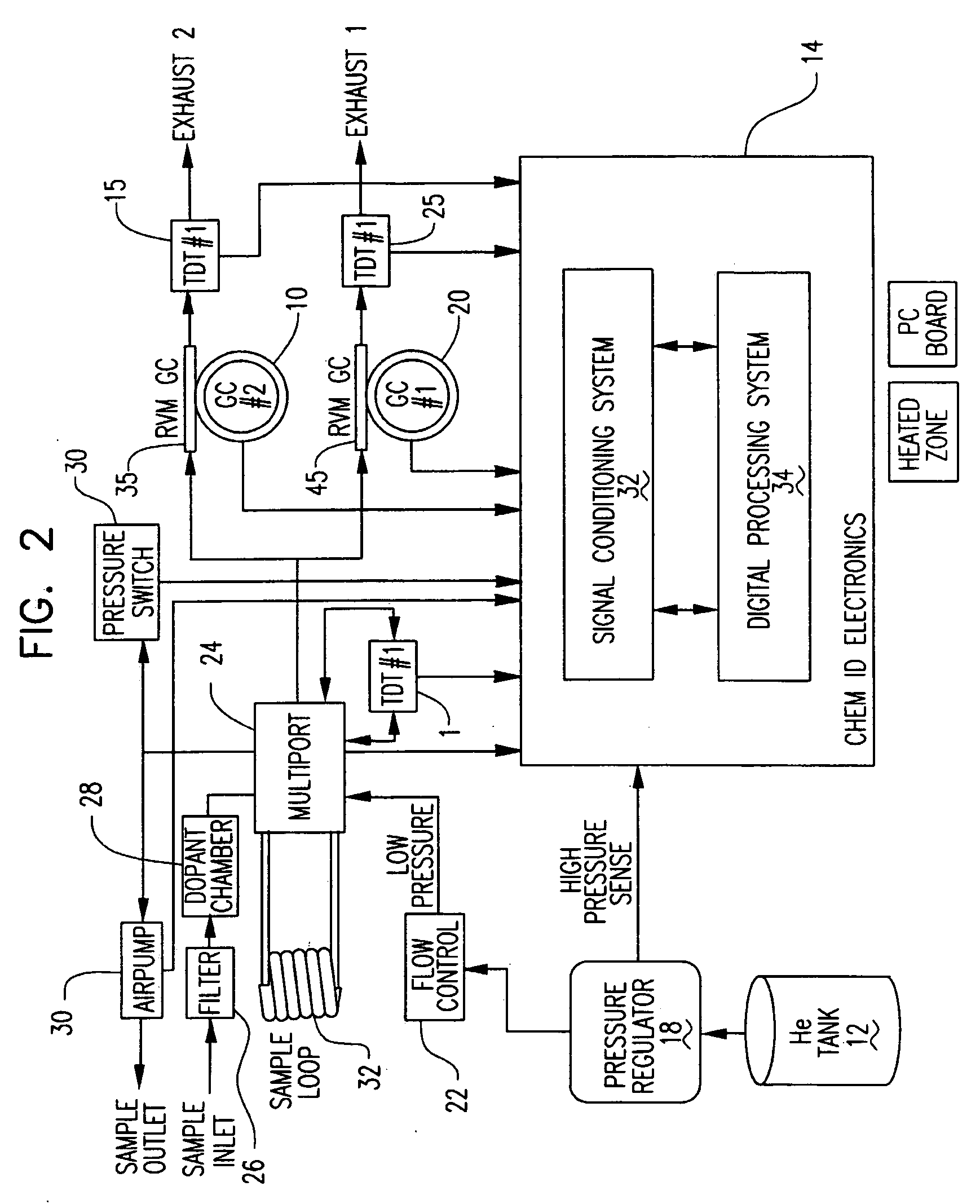
ActiveUS20070266858A1Reduce pressureAssist in operationSamplingComponent separationGas liquid chromatographicEngineering
A portable multi-dimensional gas chromatograph, the gas chromatograph including a carrier gas container, a regulator fluidly connected to the carrier gas container, a dopant chamber containing a reference chemical, at least one pre-concentrator which is fluidly connected to the regulator and the dopant chamber, a first separation column fluidly connected to the at least one pre-concentrator, a second separation column fluidly connected to the at least one pre-concentrator, a first detector fluidly connected to the first separation column, and a second detector fluidly connected to the second separation column.
Owner:LUDLUM MEASUREMENTS
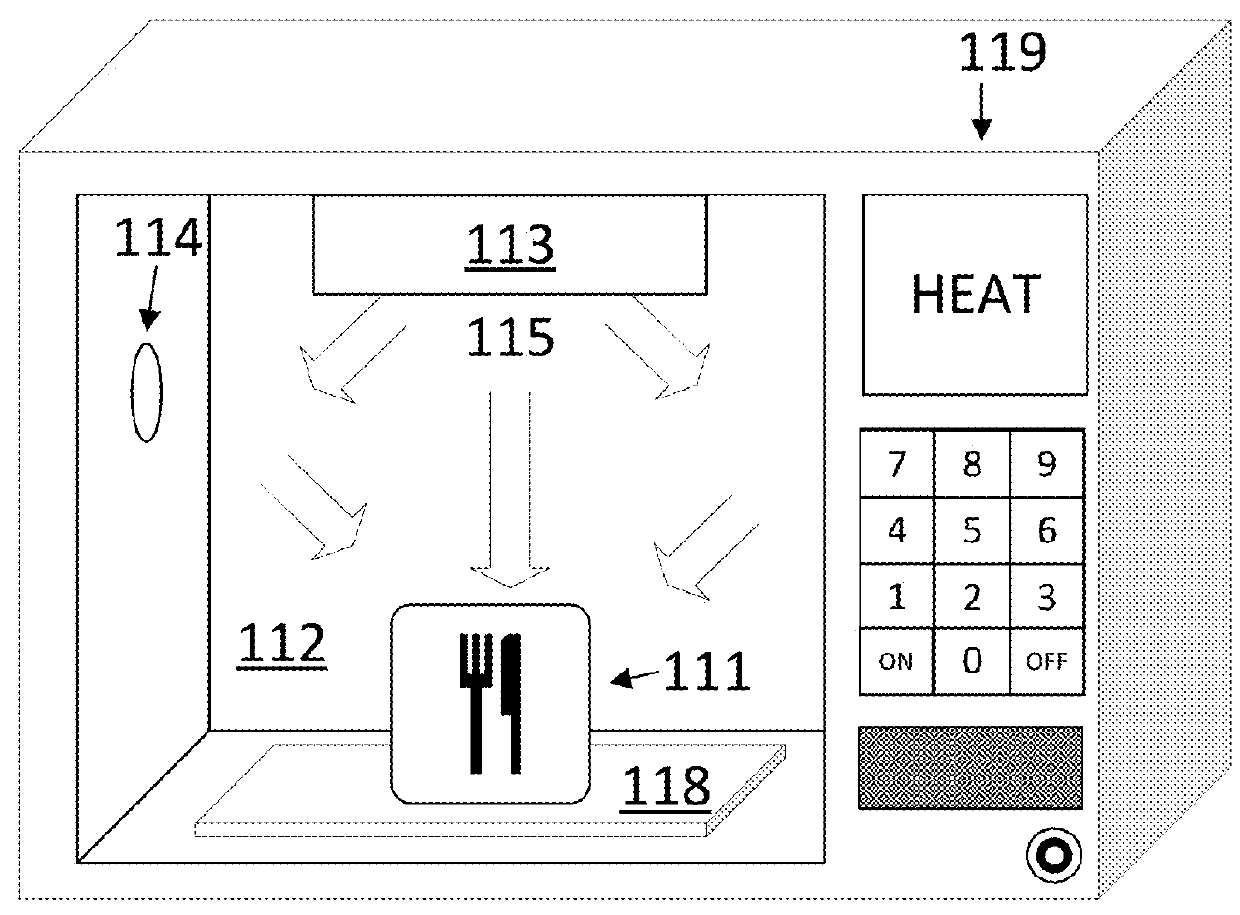
Electronic oven with infrared evaluative control
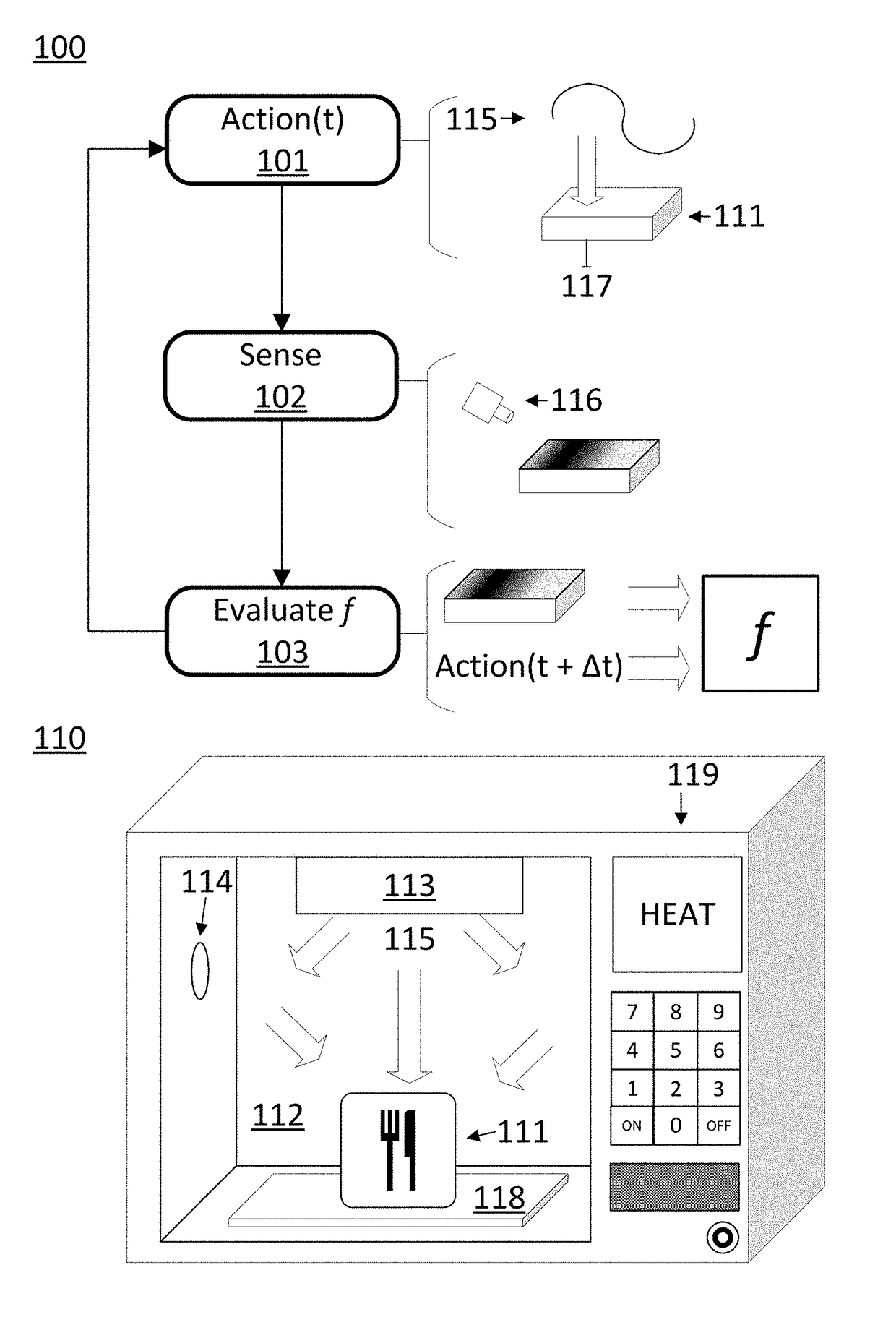
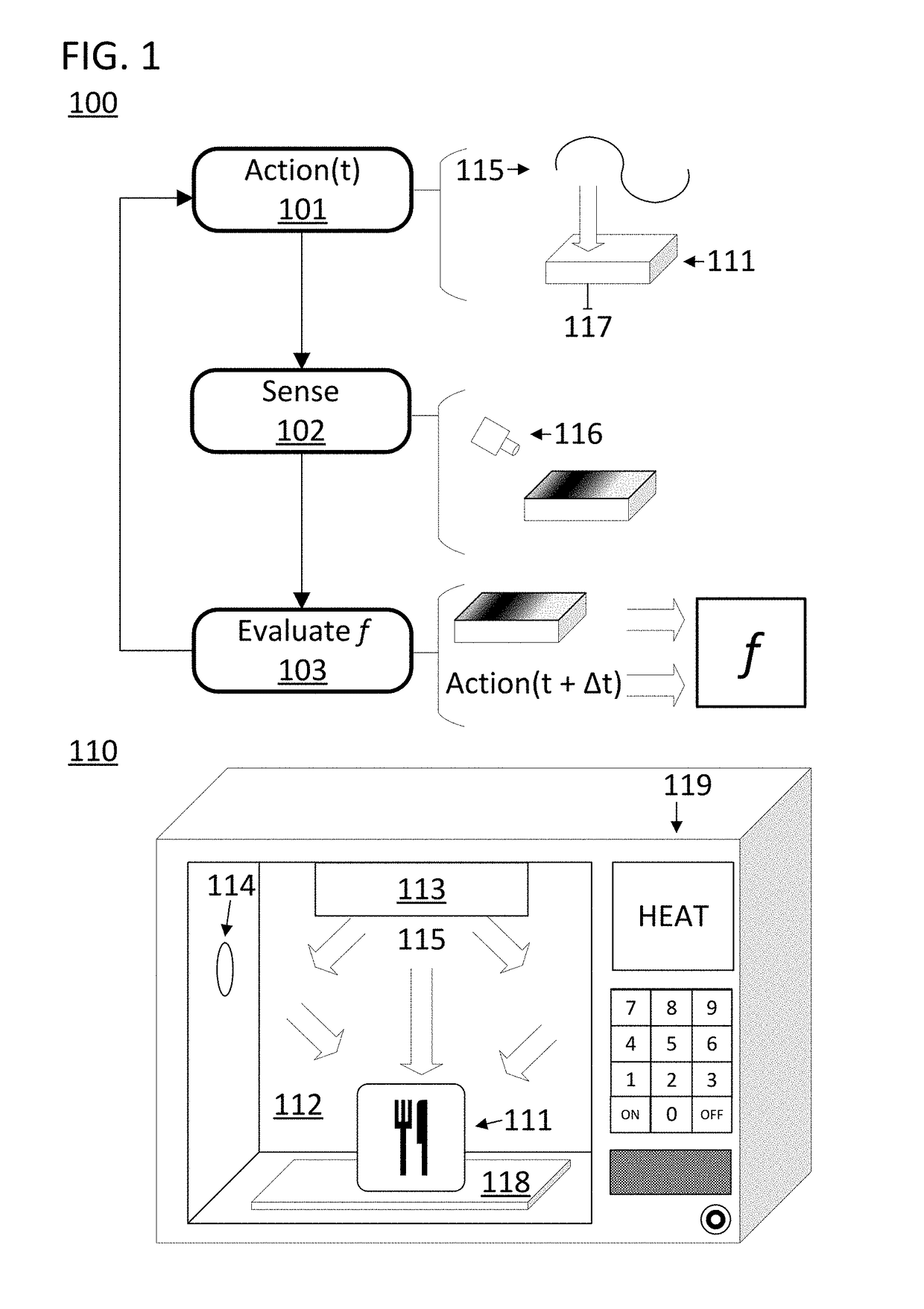
ActiveUS20170290095A1Reliable heatingImprove accuracyDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusControl systemProcess engineering
A disclosed computer-implemented method for heating an item in a chamber of an electronic oven towards a target state includes heating the item with a set of applications of energy to the chamber while the electronic oven is in a respective set of configurations. The set of applications of energy and respective set of configurations define a respective set of variable distributions of energy in the chamber. The method also includes sensing sensor data that defines a respective set of responses by the item to the set of applications of energy. The method also includes generating a plan to heat the item in the chamber. The plan is generated by a control system of the electronic oven and uses the sensor data.
Owner:THE MARKOV CORP
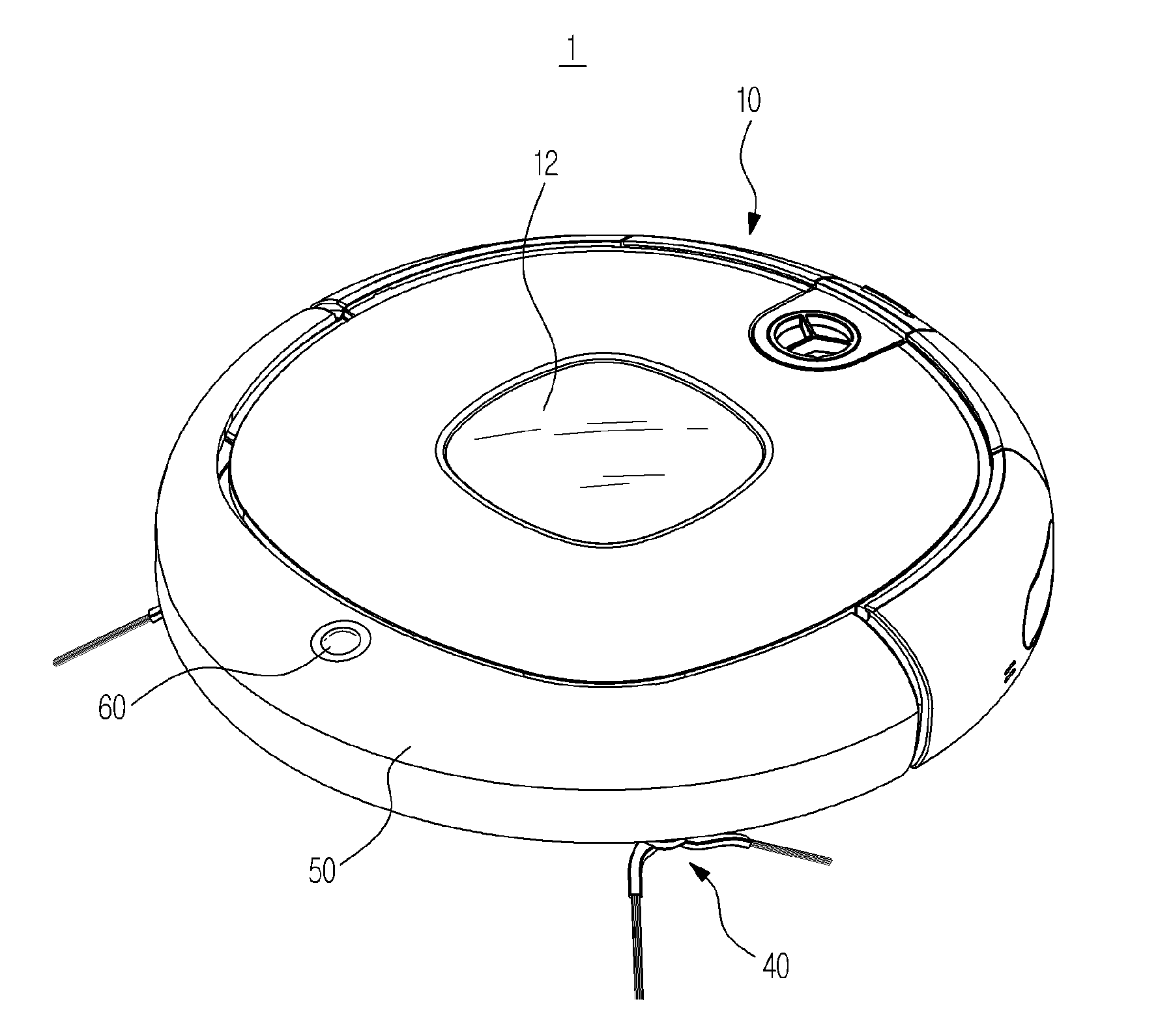
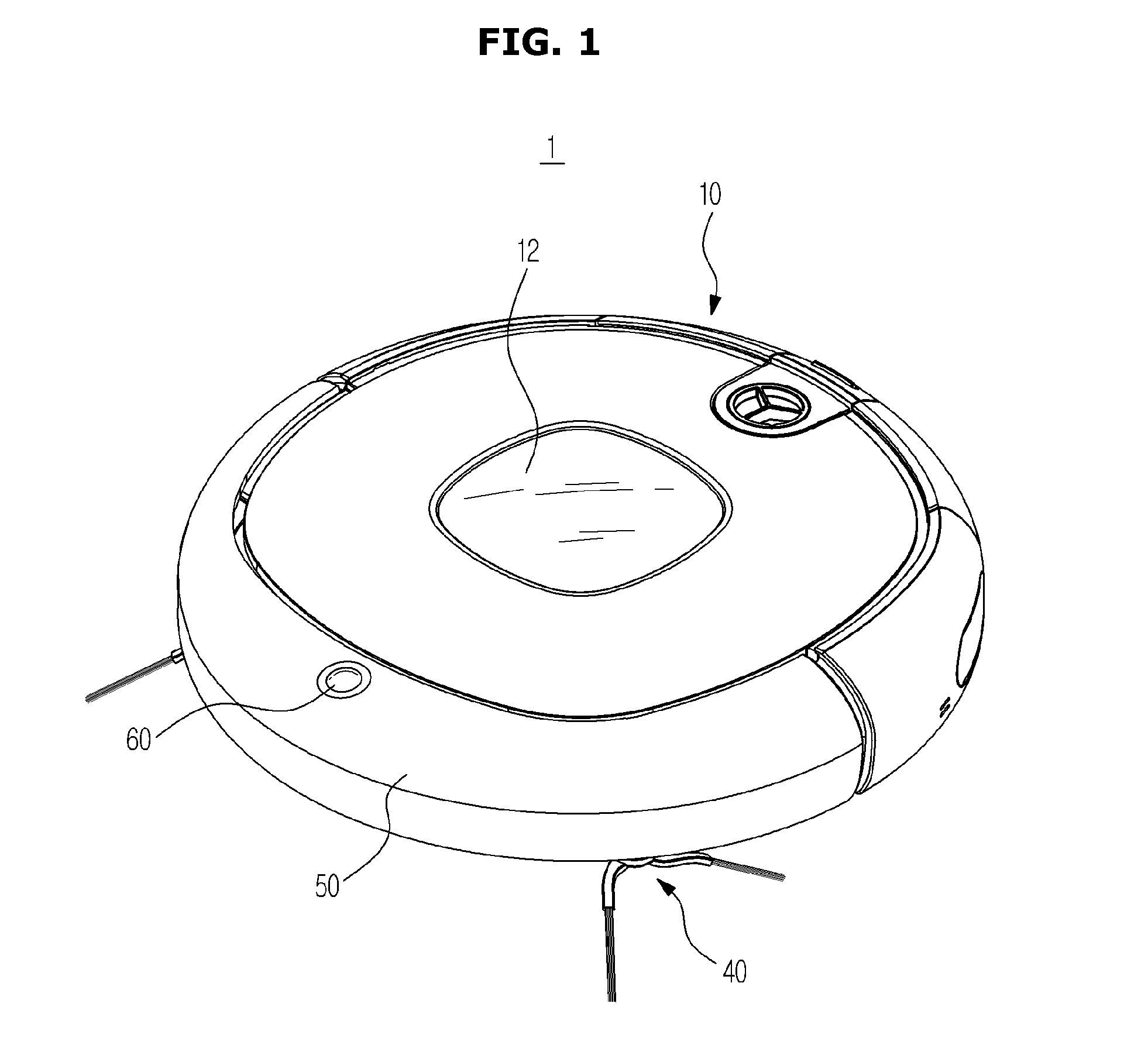
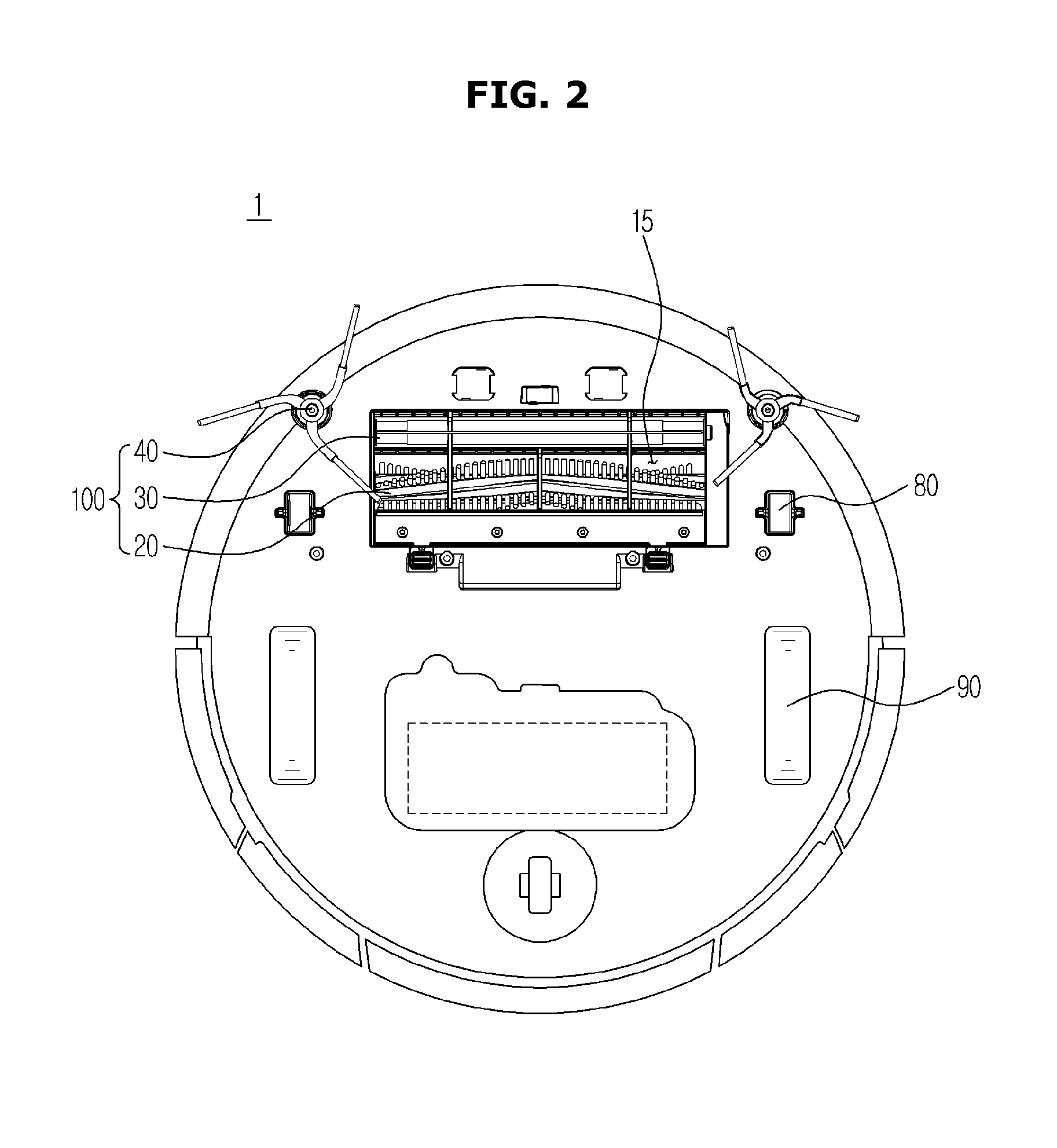
Robot cleaner
ActiveUS20150223653A1Assist in operationCarpet cleanersFloor cleanersEngineeringMechanical engineering
A robot cleaner drives various brushes using a single motor. The robot cleaner includes a main body having a suction port, a main brush rotatably disposed in the suction port, an auxiliary brush rotatably disposed adjacent to the main brush and at least one side brush rotatably installed to move dust to the suction port, wherein the main brush, the auxiliary brush, and the at least one side brush are driven by a single motor in an interlocking fashion.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
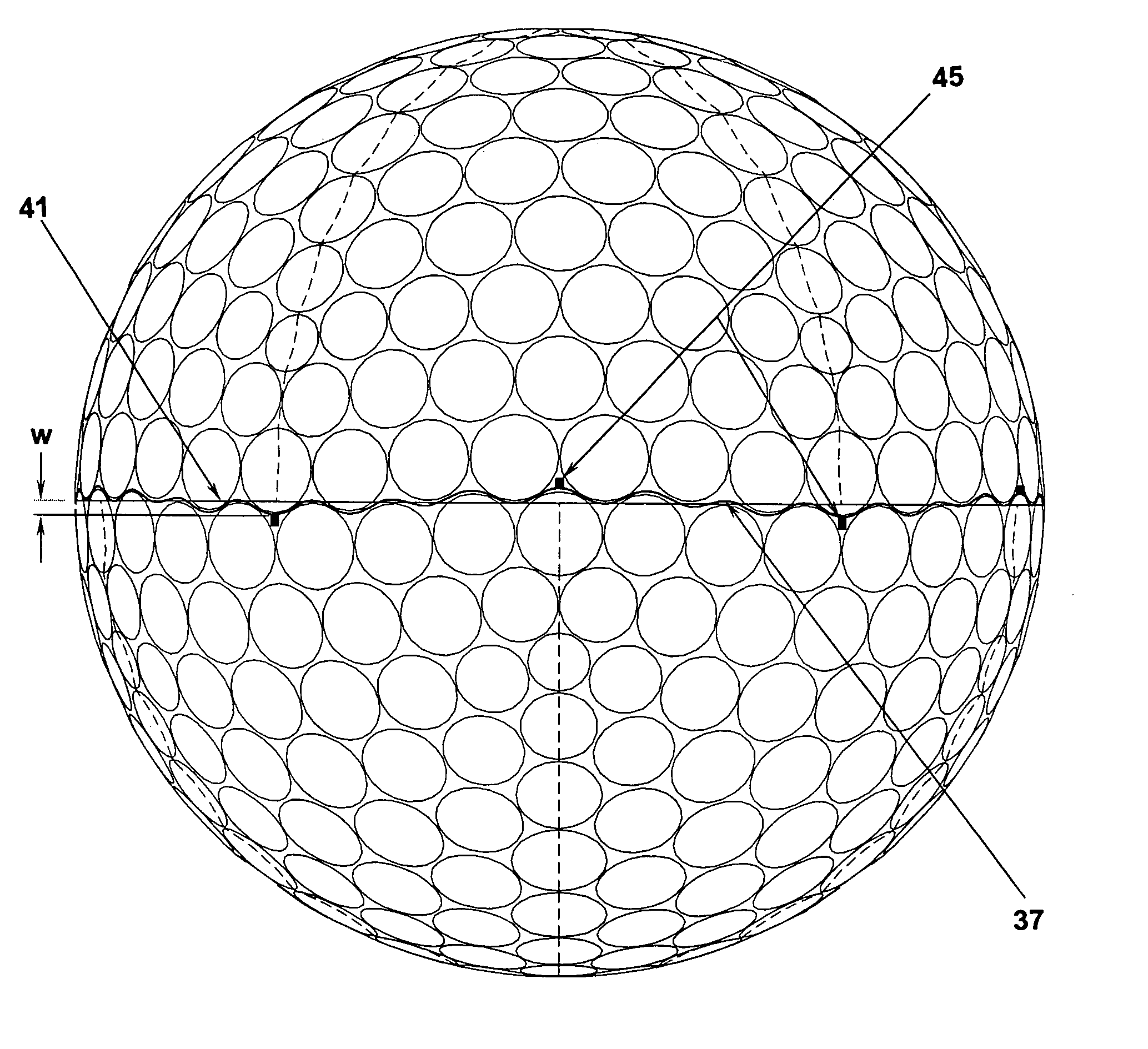
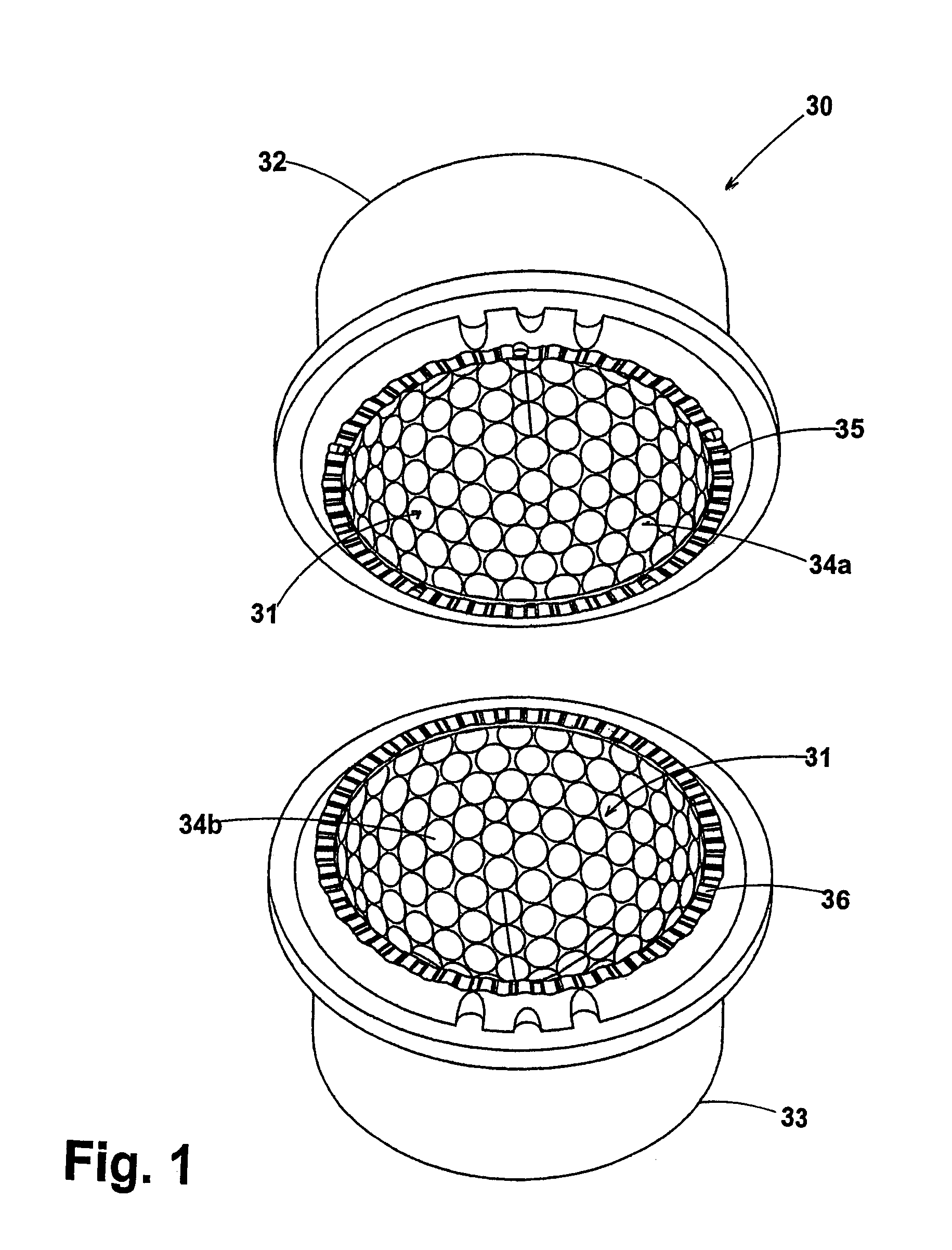
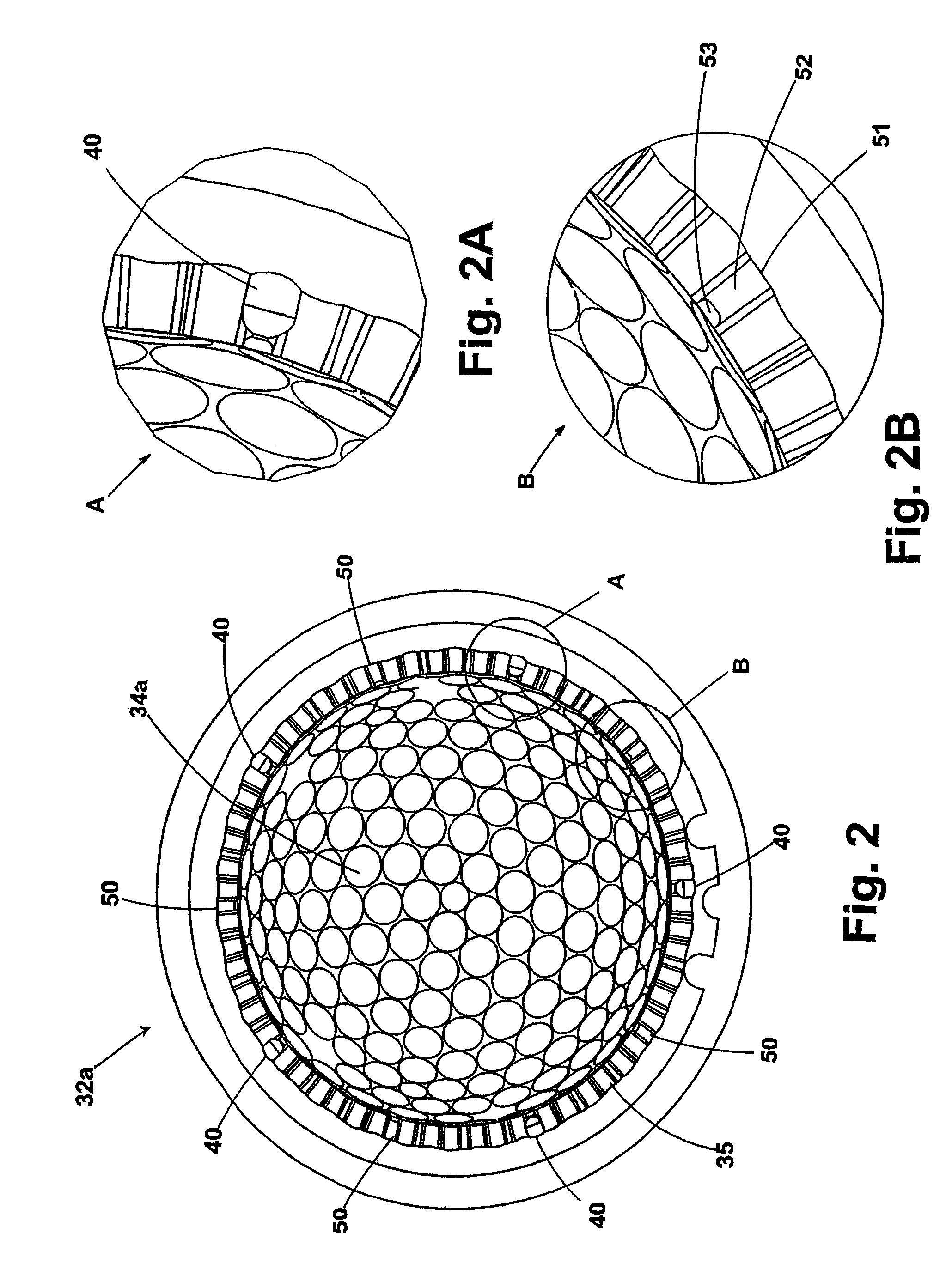
Golf ball
ActiveUS7431670B2Minimizing mold flashAssist in operationFrequency-division multiplexGolf ballsNumerical controlWave shape
A golf ball that is formed by a mold developed from a computerized modeling system such as CAD or CAE in combination with a CNC machine tool which superimposes a short waveform, or multiple waveforms, onto a longer base waveform to create a non-planar parting line that is functionally dependent on the underlying dimple geometry. The non-planar parting line is comprised of a plurality of peaks and valleys that are offset from the dimple perimeters, as not to bisect any dimple edge. Also, dimples on one side of the parting line interdigitate with dimples on the other side to form a more uniform distribution of dimples over the entire golf ball surface. Still further, the non-planar parting line has a amplitude which is less than 0.02 inch from an axis substantially coincident with the equator of the ball and the length of the parting line is less than 110 percent of the length of a curve defined by the circumference of the equator. Located at a plurality of sites on the non-planar parting line and offset from the equator are tabs which are formed on the ball to aid in the finishing operation wherein flash is removed from the ball parting line. The tabs are created by true sprues (vents) and false sprues on the parting surfaces of the ball mold halves.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
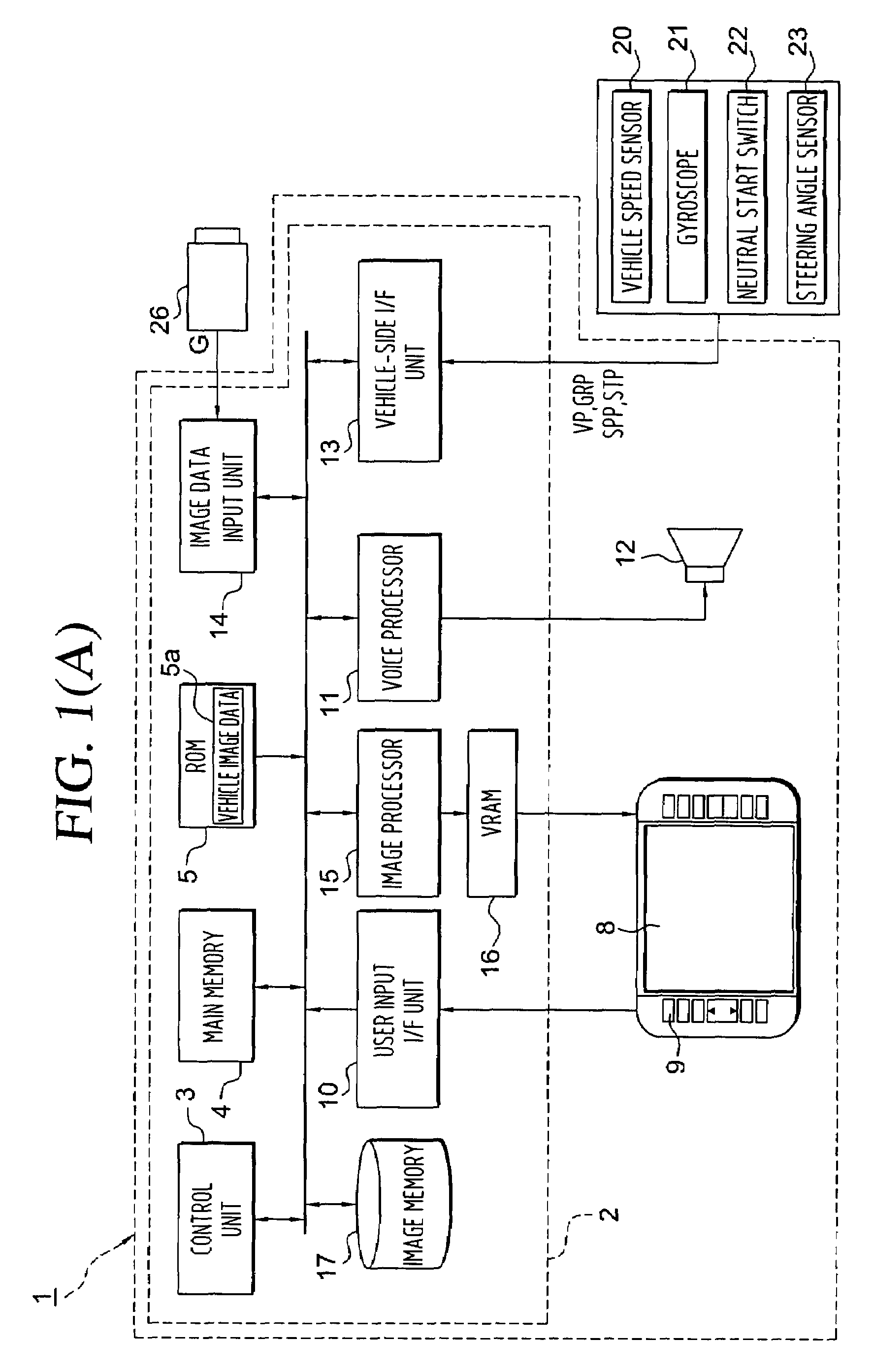
Driving support control apparatus for vehicle
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Electric power steering apparatus
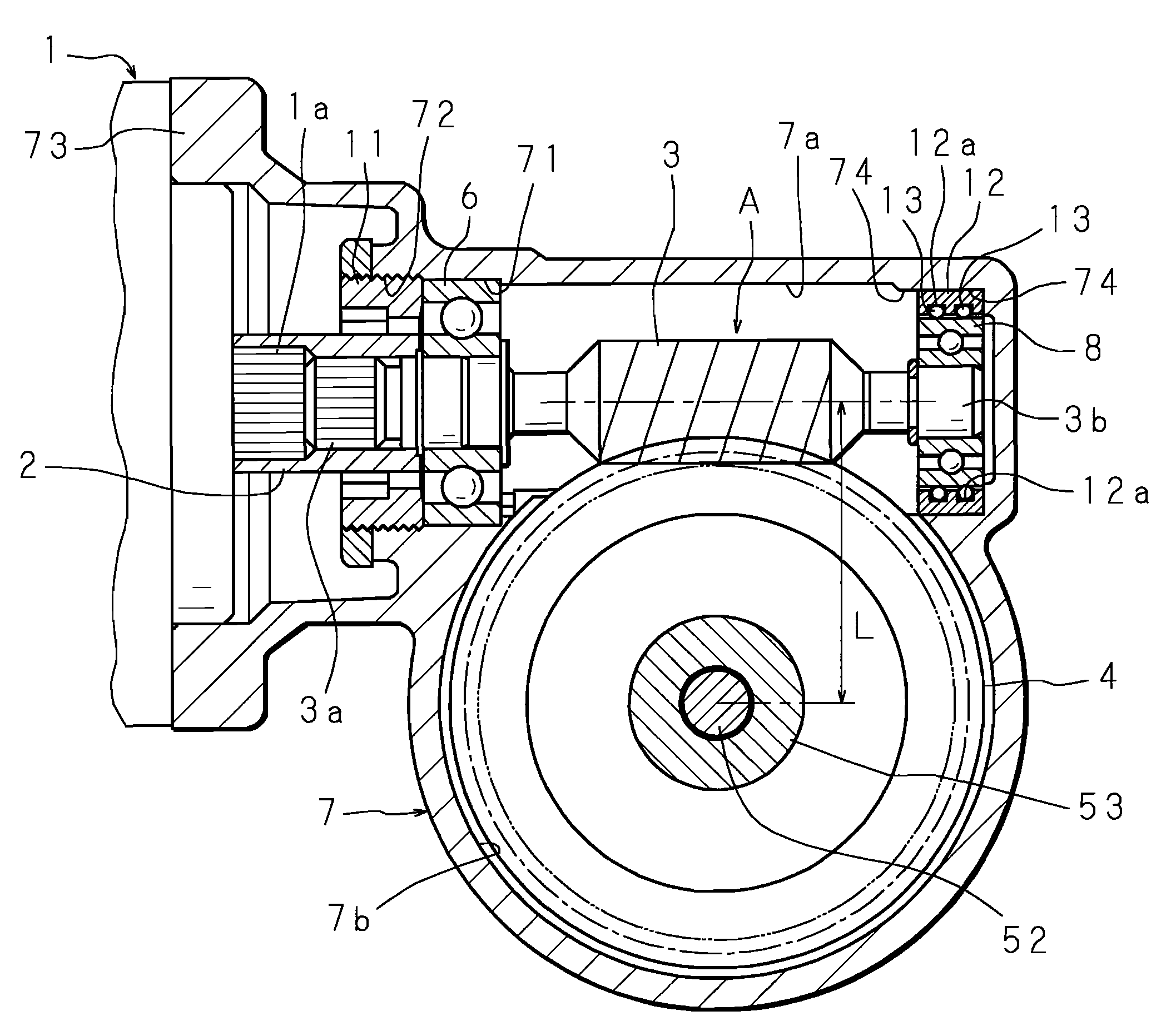
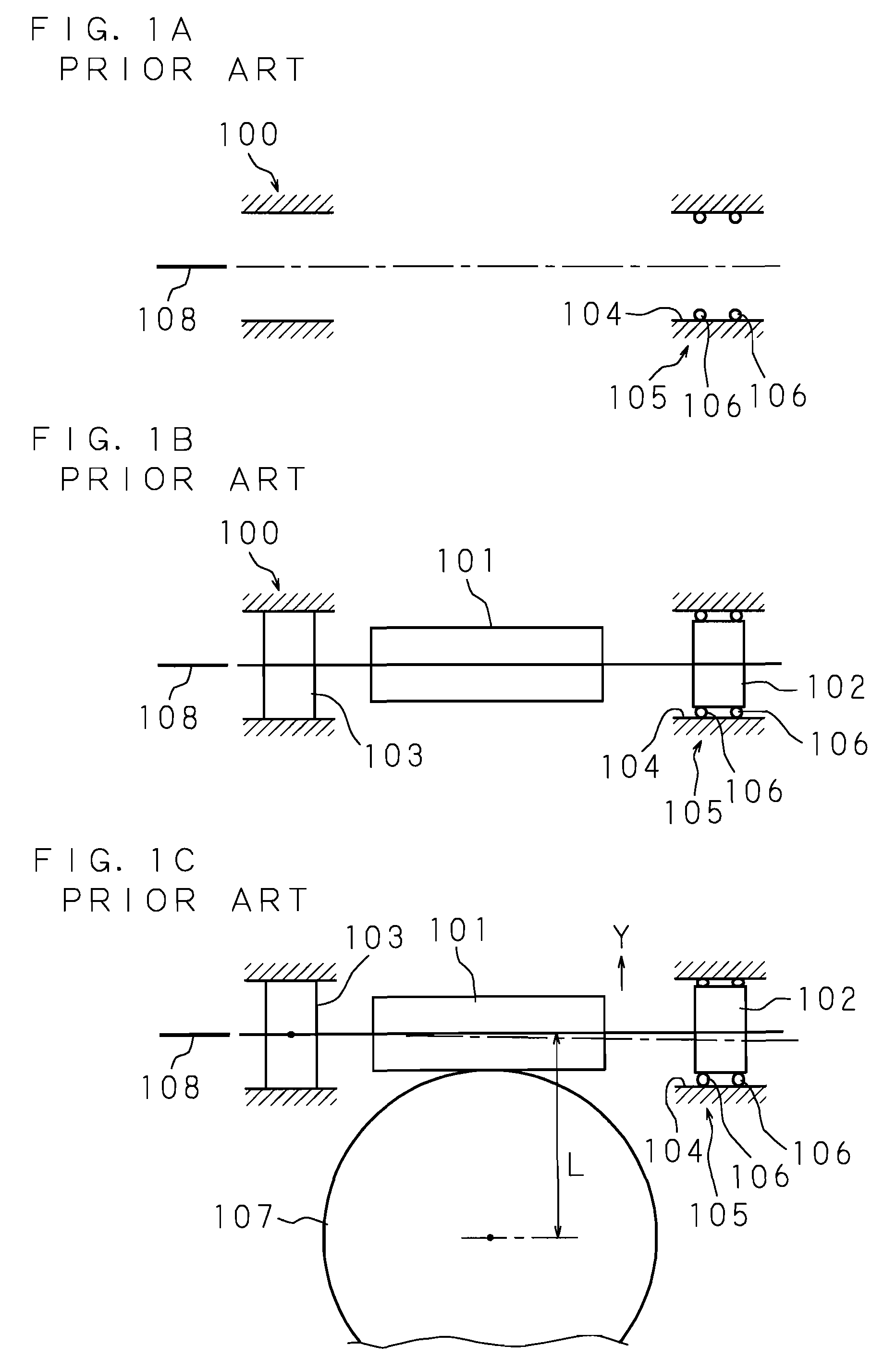
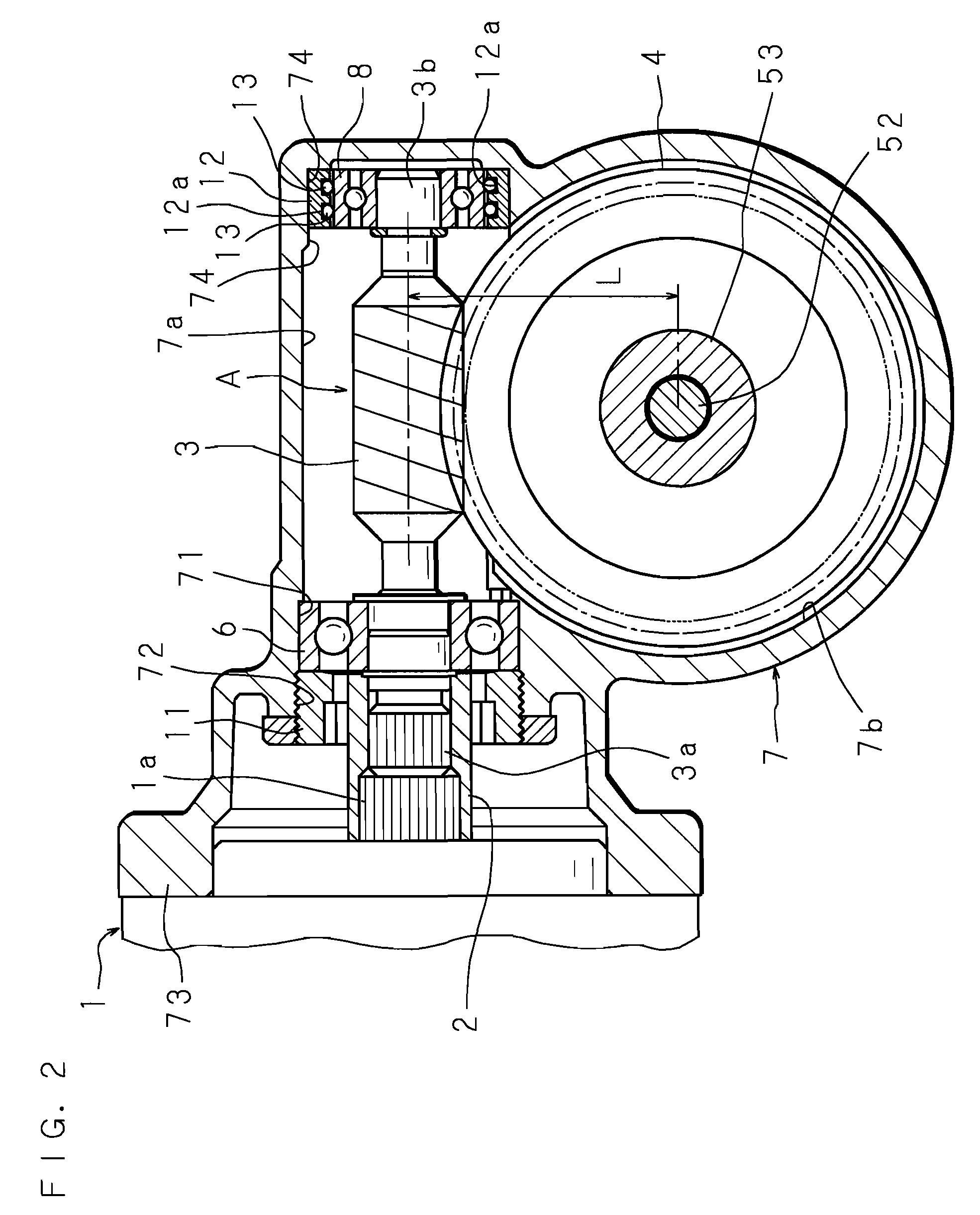
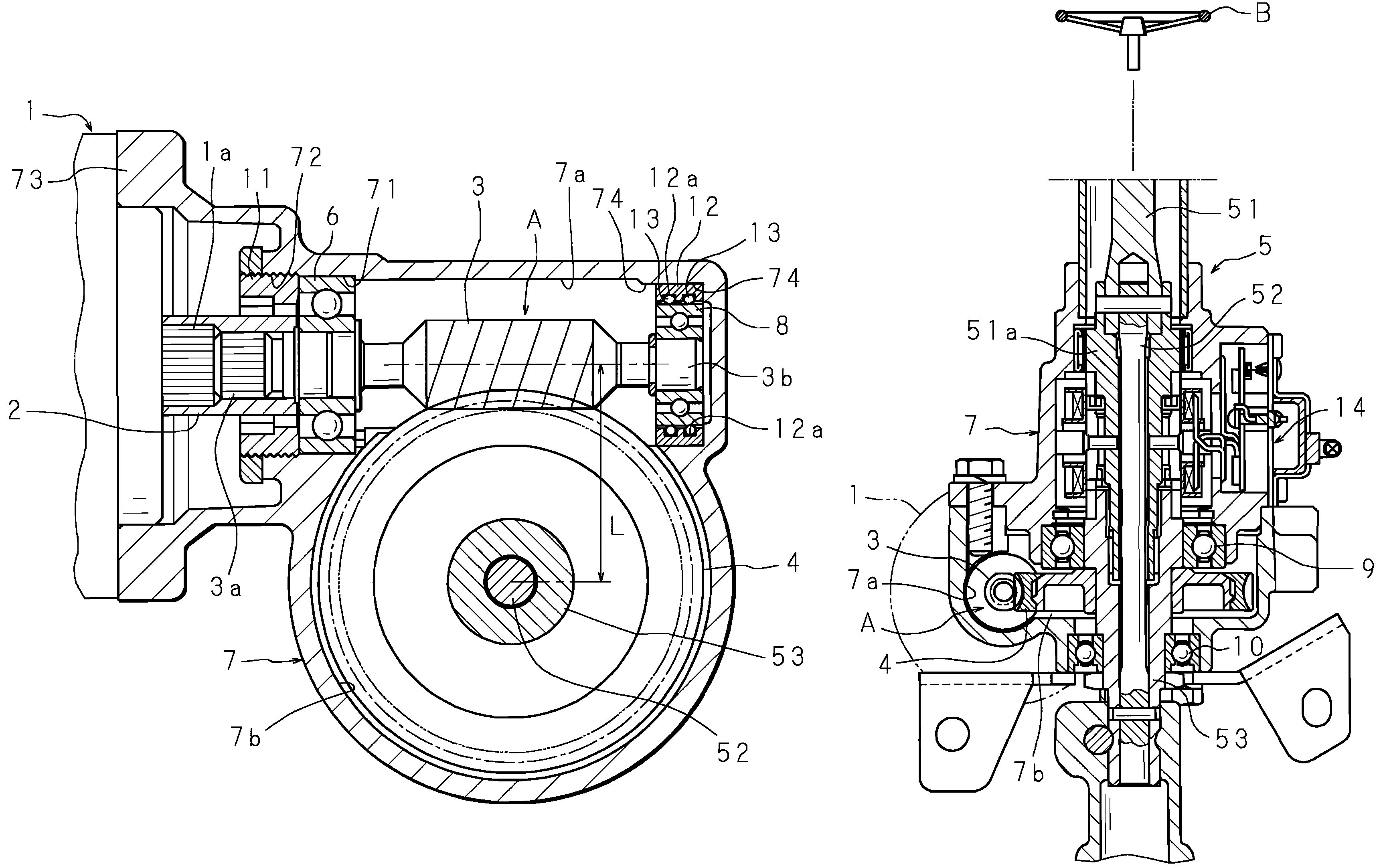
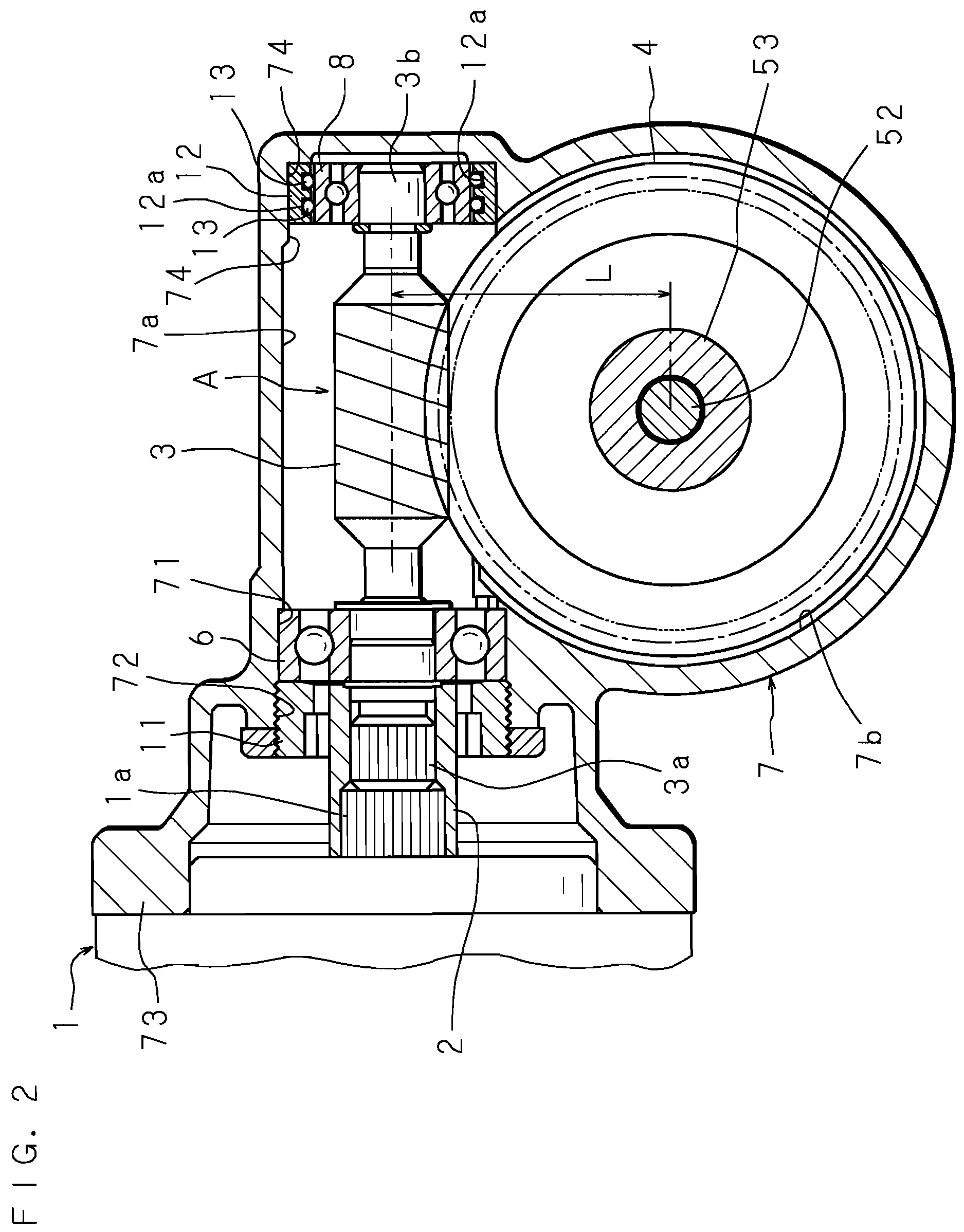
InactiveUS20070205039A1Reduce the amount of backlashConvenience to workSpringsBall bearingsElectric power steeringGear wheel
An electric power steering apparatus includes a worm interlockedly connected to an output shaft of an electric motor, a first and a second bearing each supporting the respective side of the worm in a housing, and a gear wheel meshed with the worm. The housing includes a fitting bore in which the first bearing supporting a side of the worm closer to the electric motor is to be fitted, and an annular retaining portion located at a position corresponding to the second bearing and eccentrically oriented with respect to the center (axial center) of the fitting bore in a direction that shortens a distance L between the center of rotation of the worm and that of the gear wheel, and the annular retaining portion retains a coil spring around an outer circumference of the second bearing.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Electronic oven with infrared evaluative control
ActiveUS20180098381A1Function be alteredProcedure be alteredDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusControl systemEngineering
A disclosed computer-implemented method for heating an item in a chamber of an electronic oven towards a target state includes heating the item with a set of applications of energy to the chamber while the electronic oven is in a respective set of configurations. The set of applications of energy and respective set of configurations define a respective set of variable distributions of energy in the chamber. The method also includes sensing sensor data that defines a respective set of responses by the item to the set of applications of energy. The method also includes generating a plan to heat the item in the chamber. The plan is generated by a control system of the electronic oven and uses the sensor data.
Owner:THE MARKOV CORP
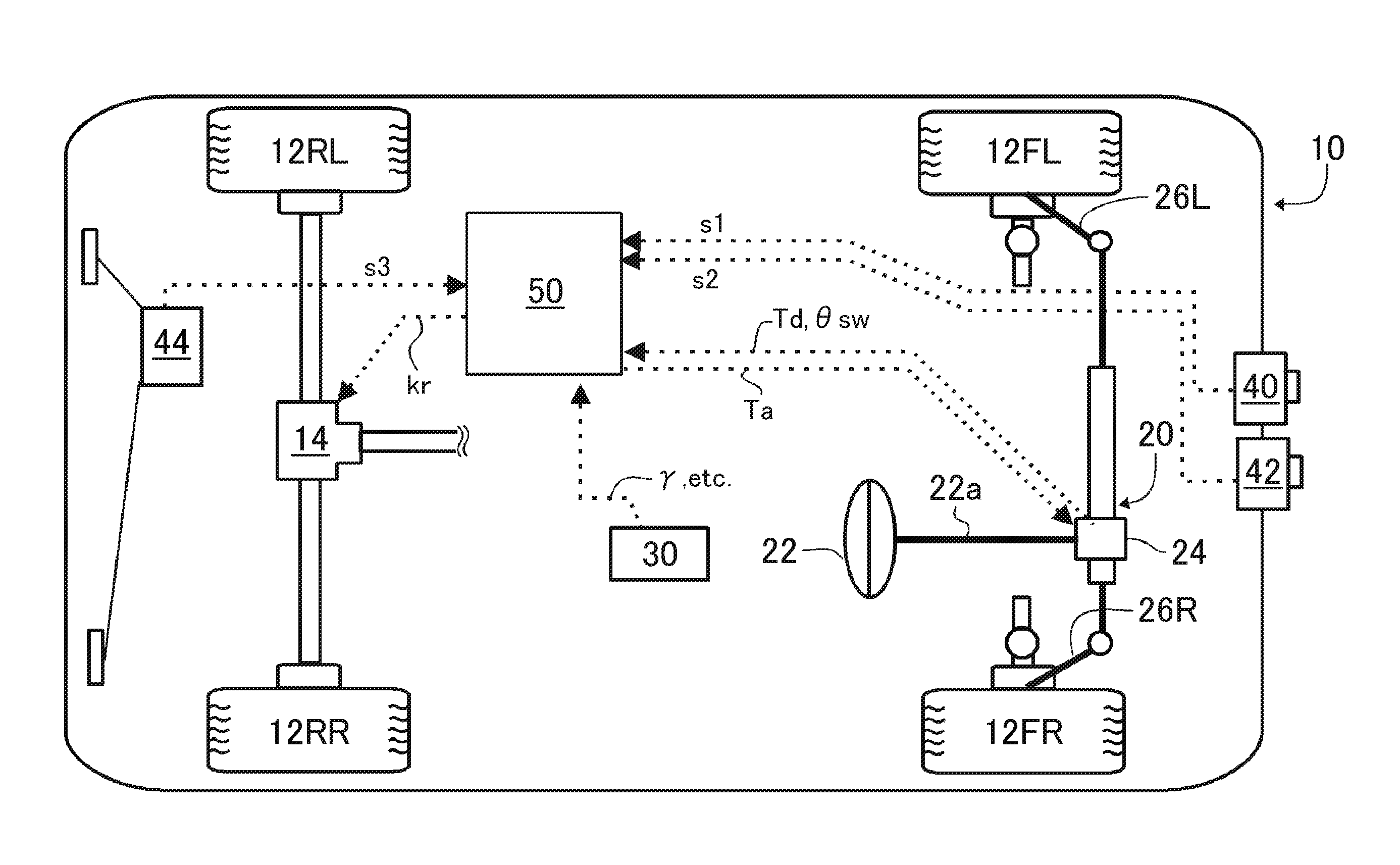
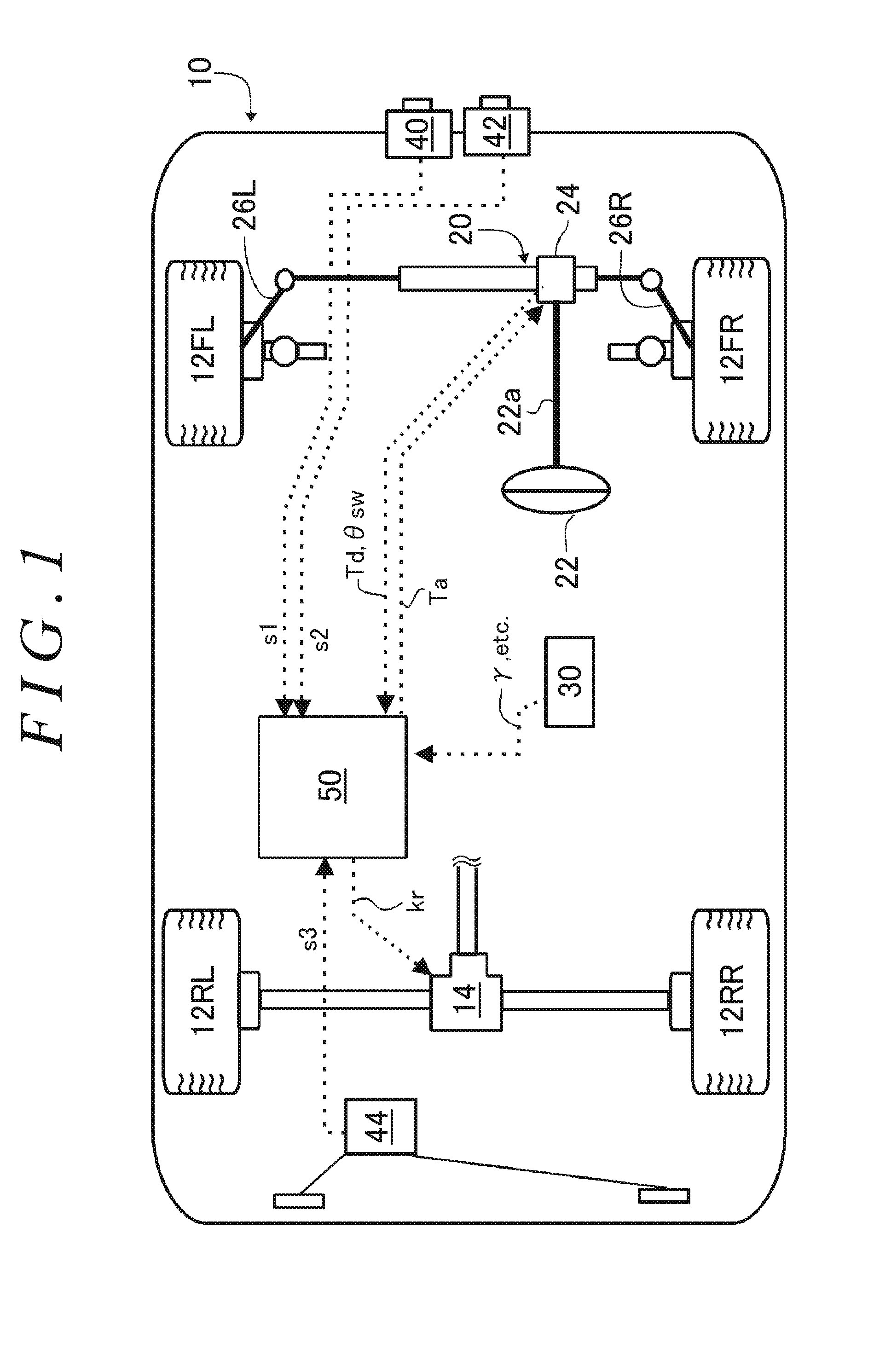
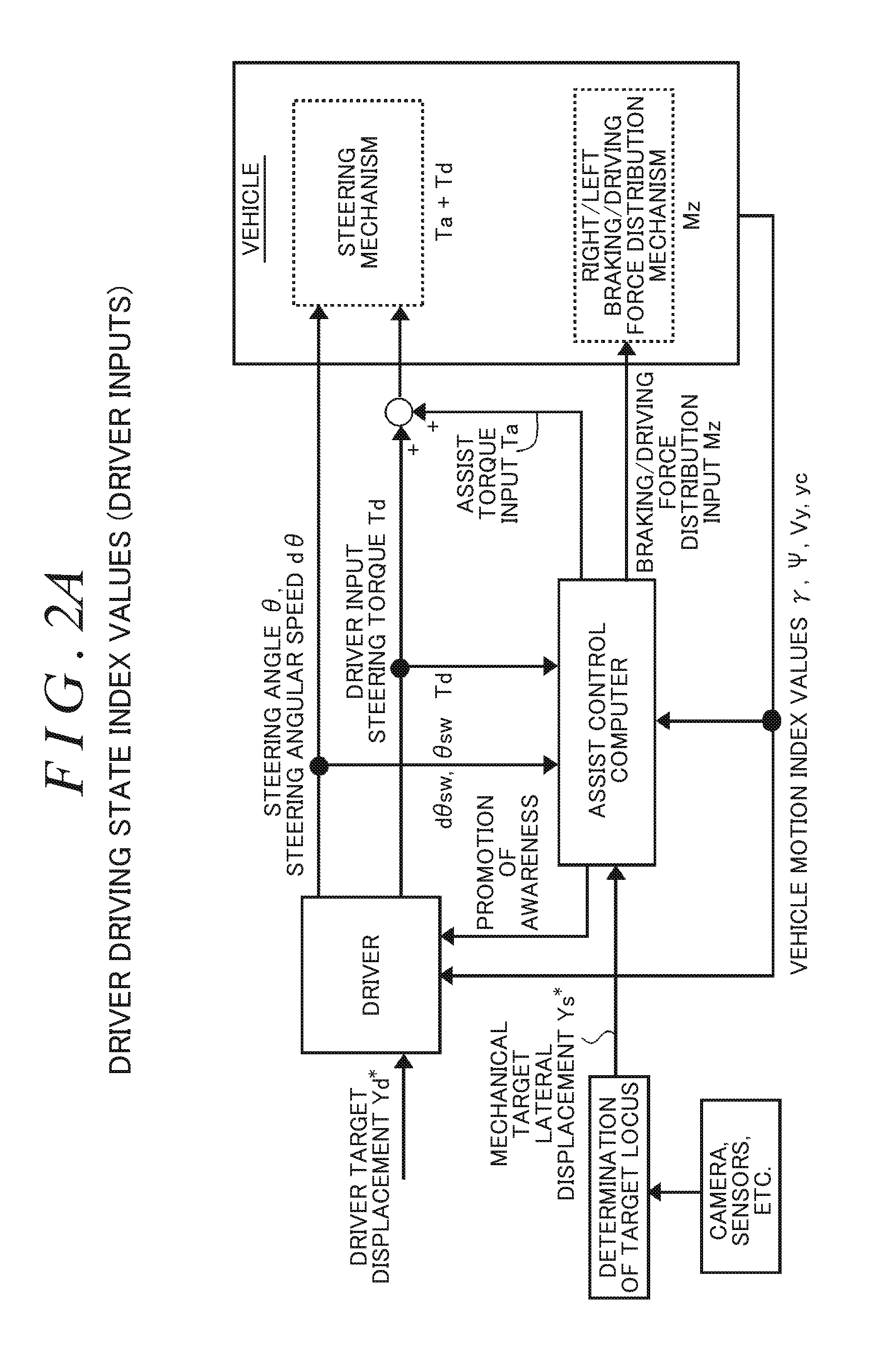
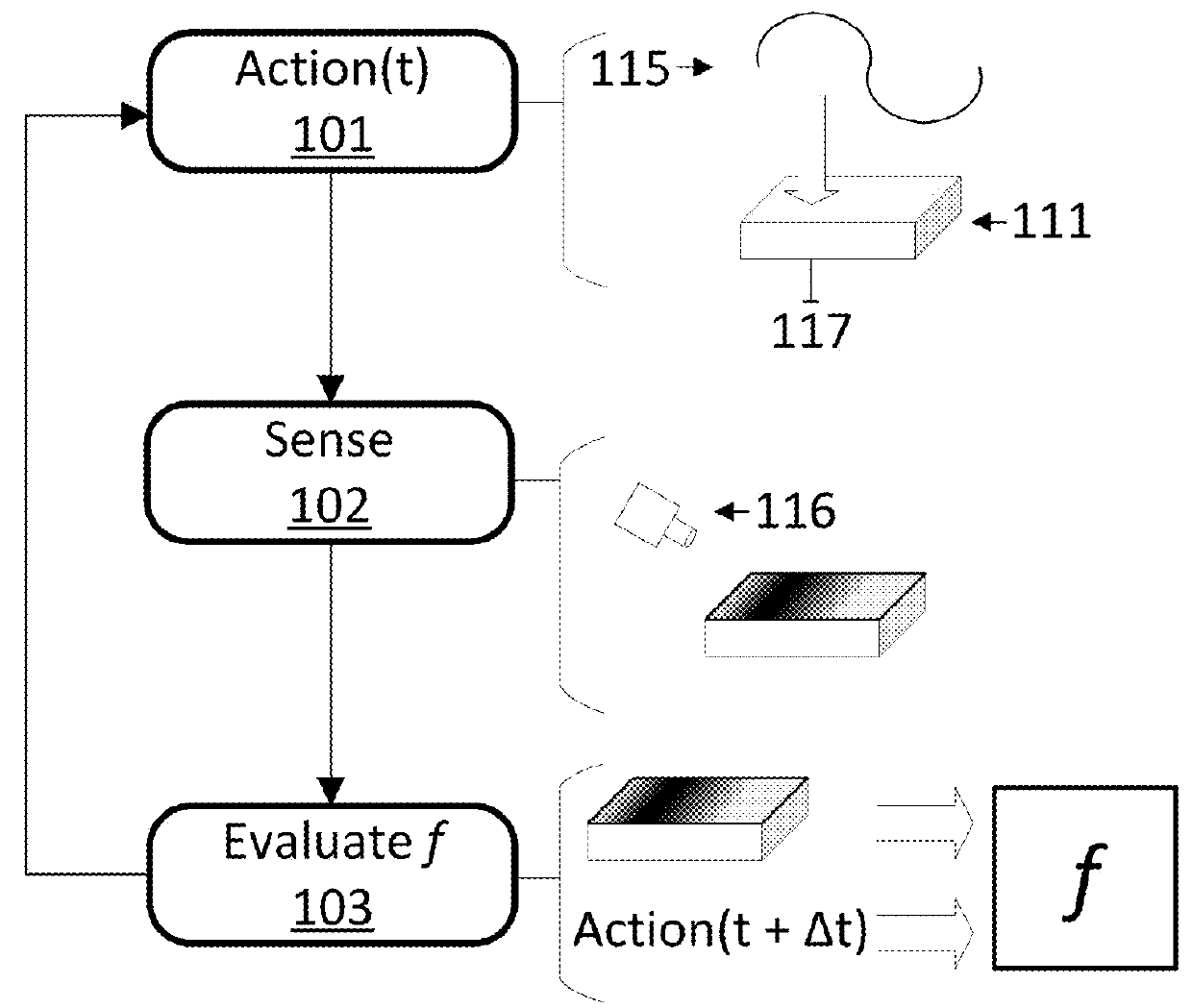
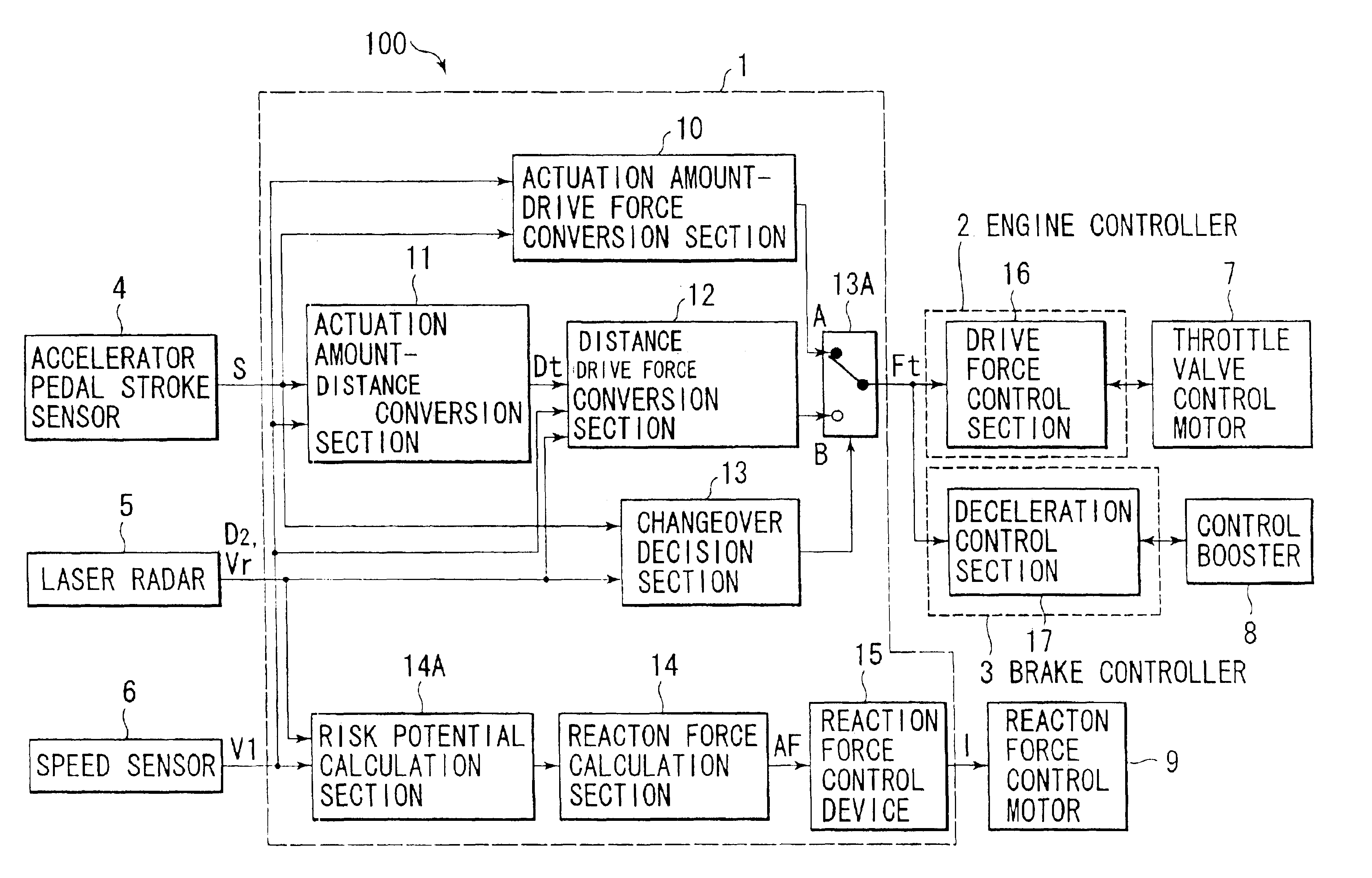
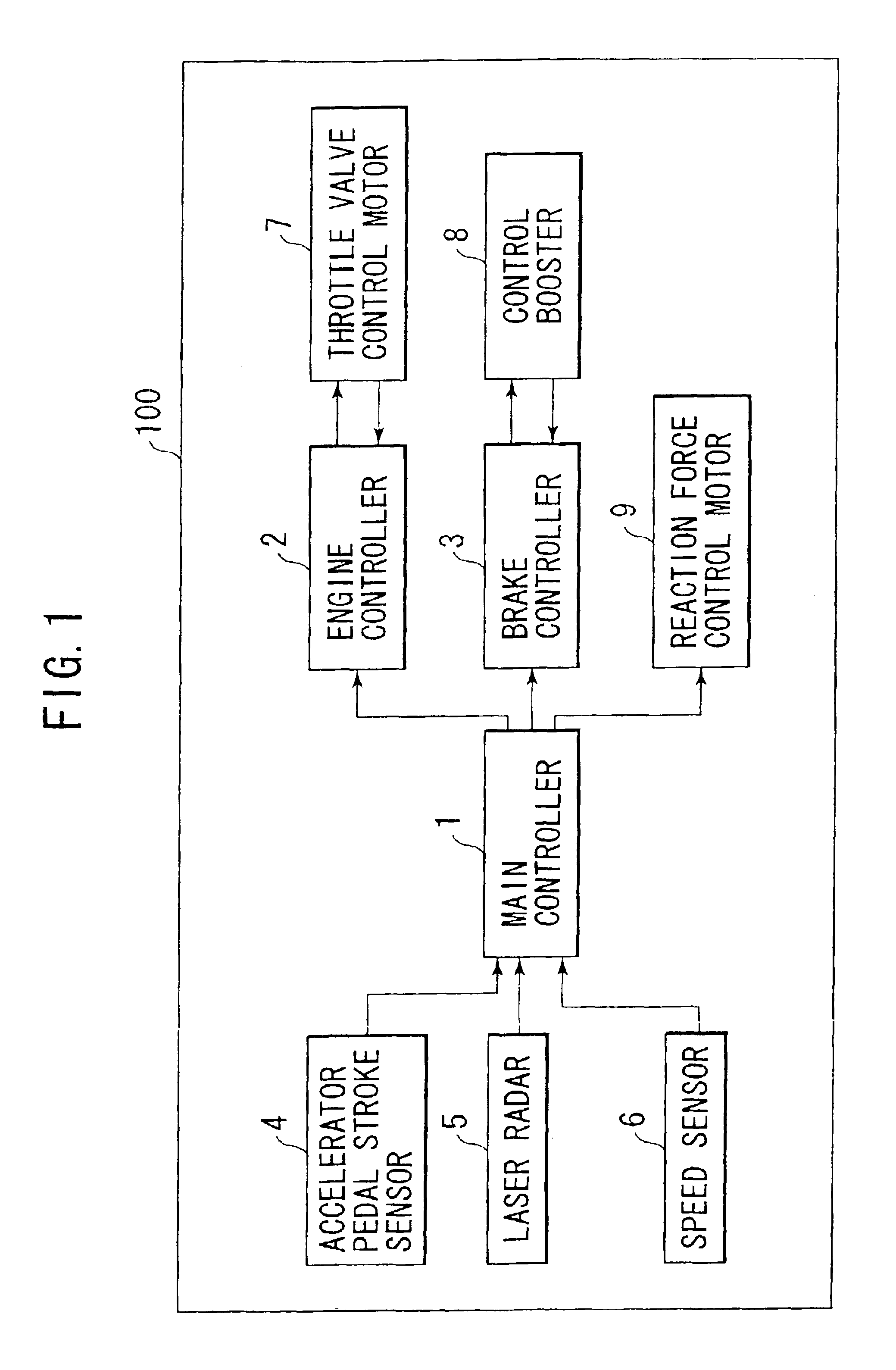
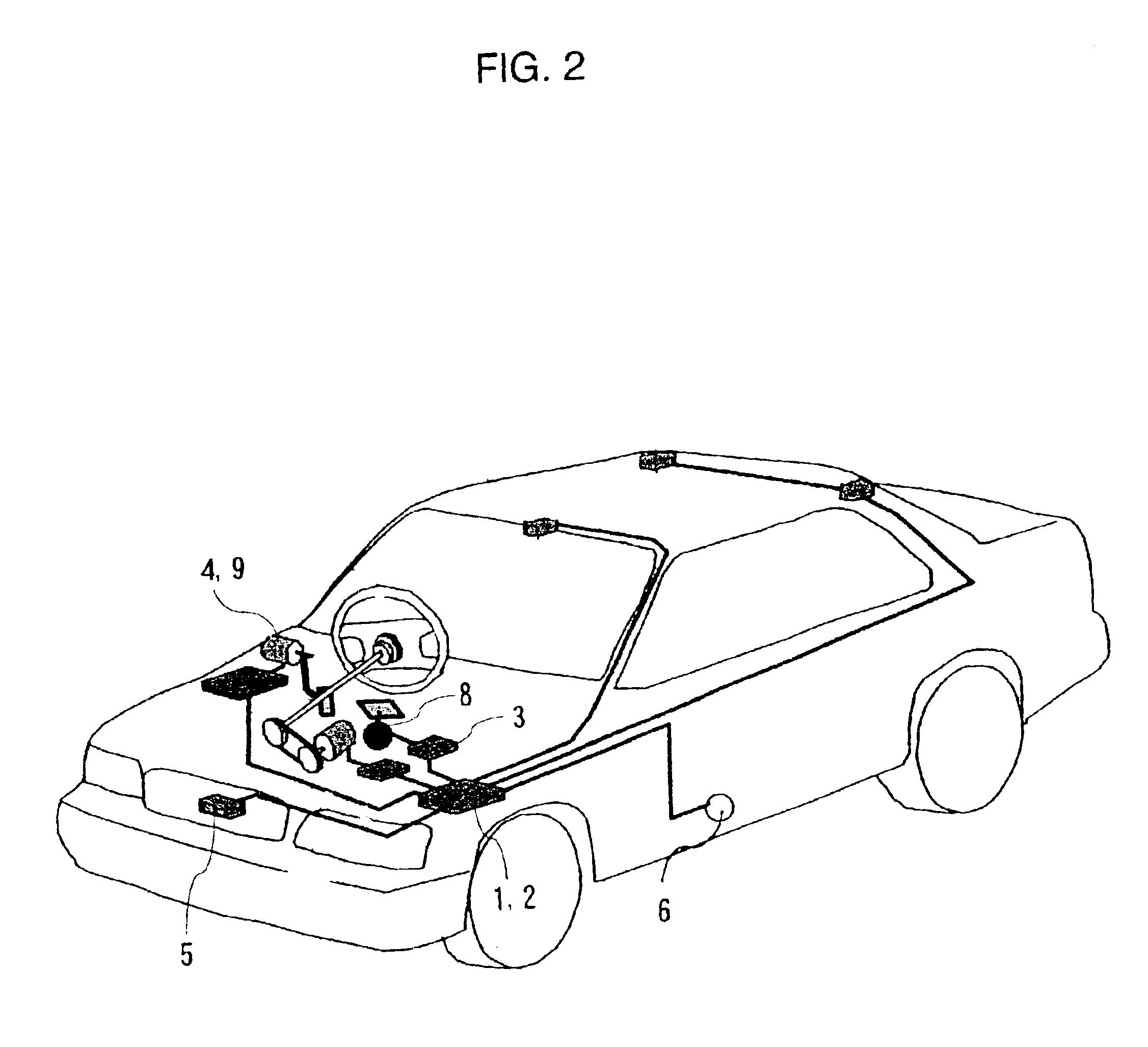
Driving assist system for vehicle
InactiveUS6917872B2Assist in operationVehicle fittingsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringVehicle driving
A vehicle driving assist system comprises a traveling situation detection device that detects a vehicle condition and a traveling environment around a subject vehicle; a risk potential calculation device that calculates a risk potential around the subject vehicle based upon detection results of the traveling situation detection device; an accelerator pedal reaction force control device that controls an actuation reaction force which is generated for an accelerator pedal based upon the risk potential which has been calculated by the risk potential calculation device; an actuation amount detection device that detects an actuation amount of the accelerator pedal; and a vehicle distance control device that controls a distance between the subject vehicle and a preceding vehicle present in front of the subject vehicle based upon the accelerator pedal actuation amount which is detected by the actuation amount detection device.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
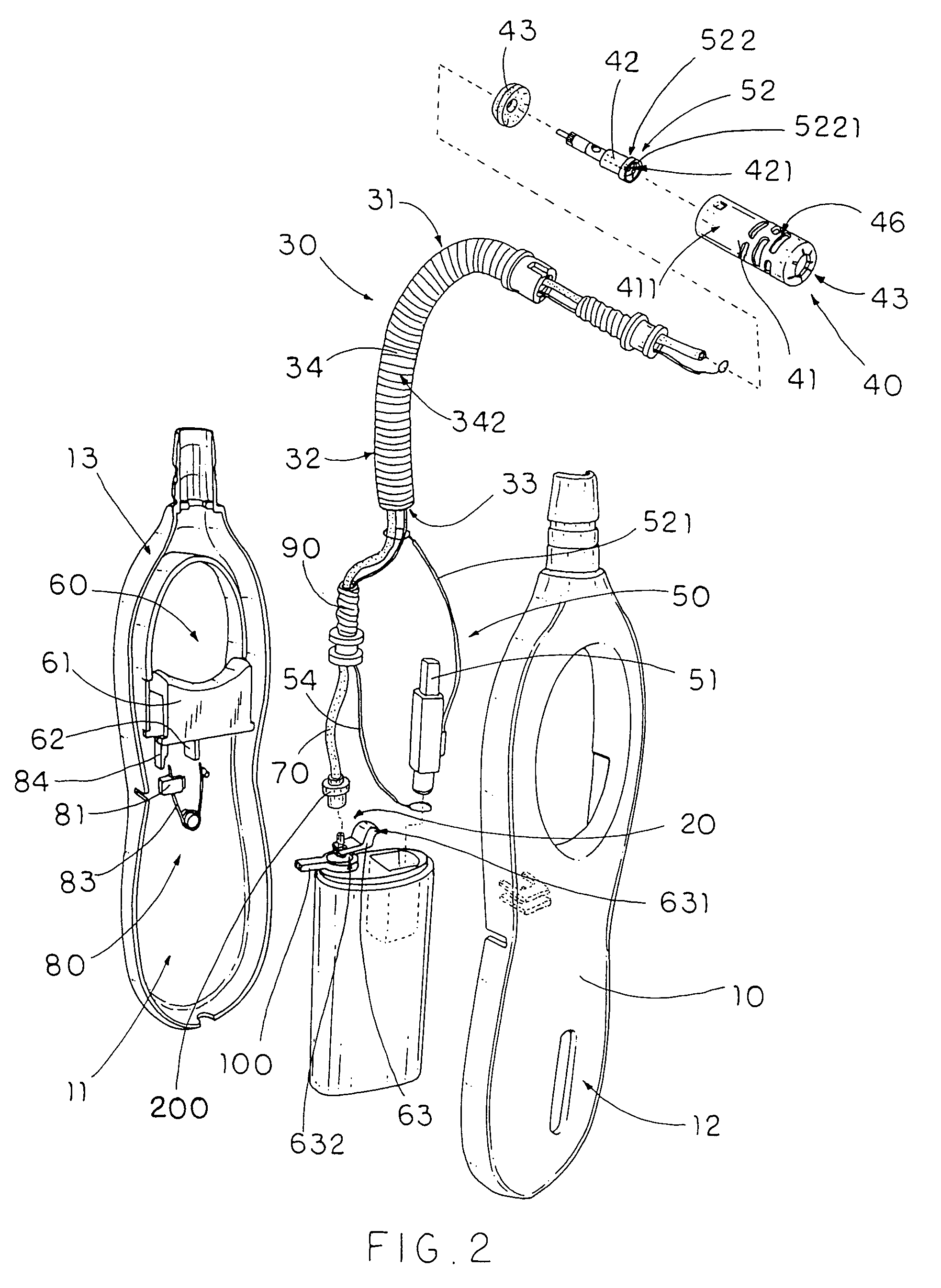
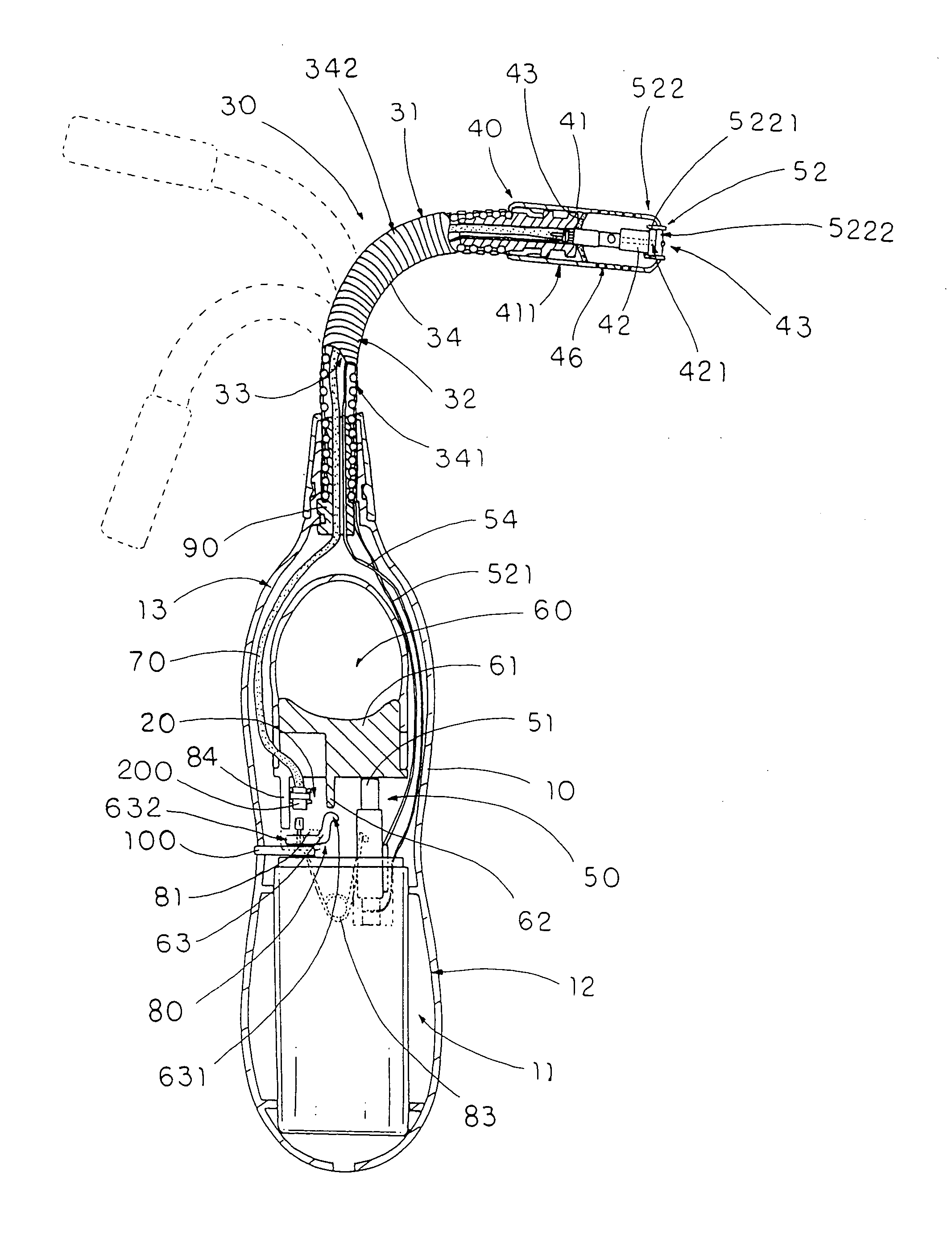
Utility lighter
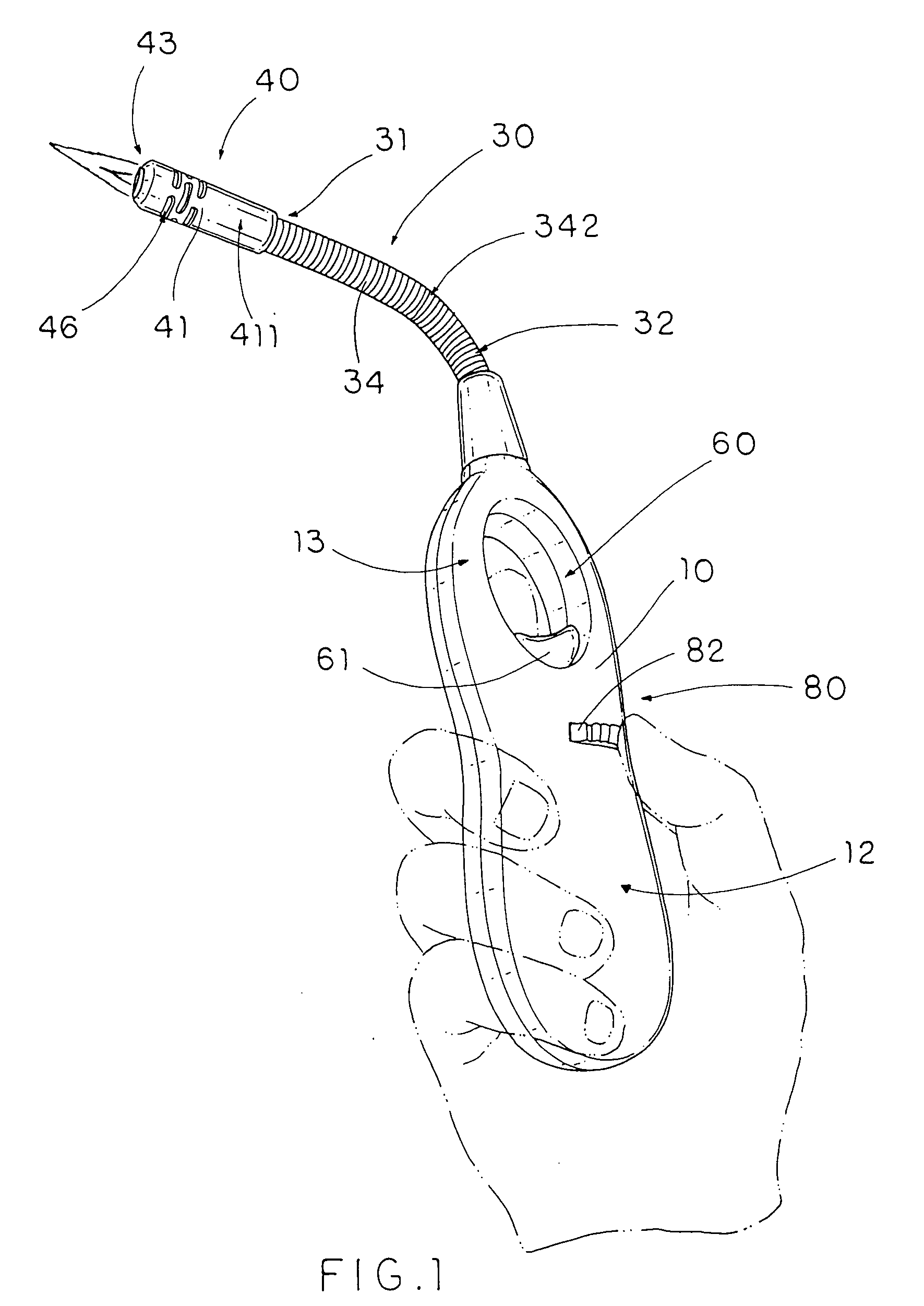
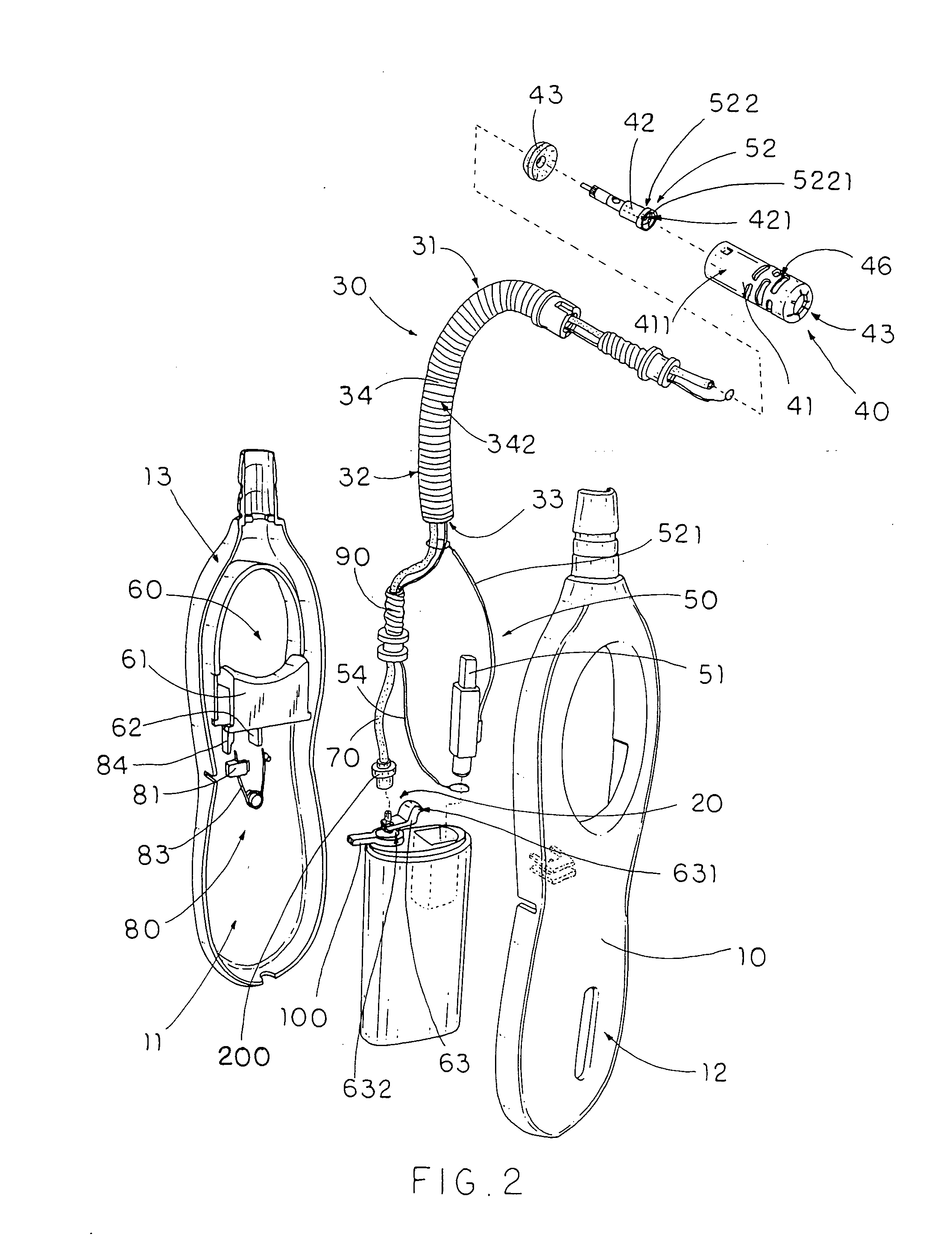
InactiveUS7563094B2Assist in operationAvoid accidental ignitionIncandescent ignitionFuel lightersEngineeringTorch
A utility lighter includes a handle casing, a gas releasing valve, a bendable extension arm, a torch nozzle, a piezoelectric unit and an actuation device. The bendable extension arm has an upper end and a lower end extended from the handle casing, wherein the extension arm has a deformable receiving channel which is extended from the lower end to the upper end and is adapted to be curved when the extension arm is selectively bent between the upper end and the lower end. The torch nozzle is provided at the upper end of the extension arm to communicate with the gas releasing valve through the receiving channel for releasing the gas through the torch nozzle when the actuation device is actuated to depress the piezoelectric unit. The result is that a torch flame is generated at the torch nozzle at a distance from the handle casing.
Owner:YANG JOHN
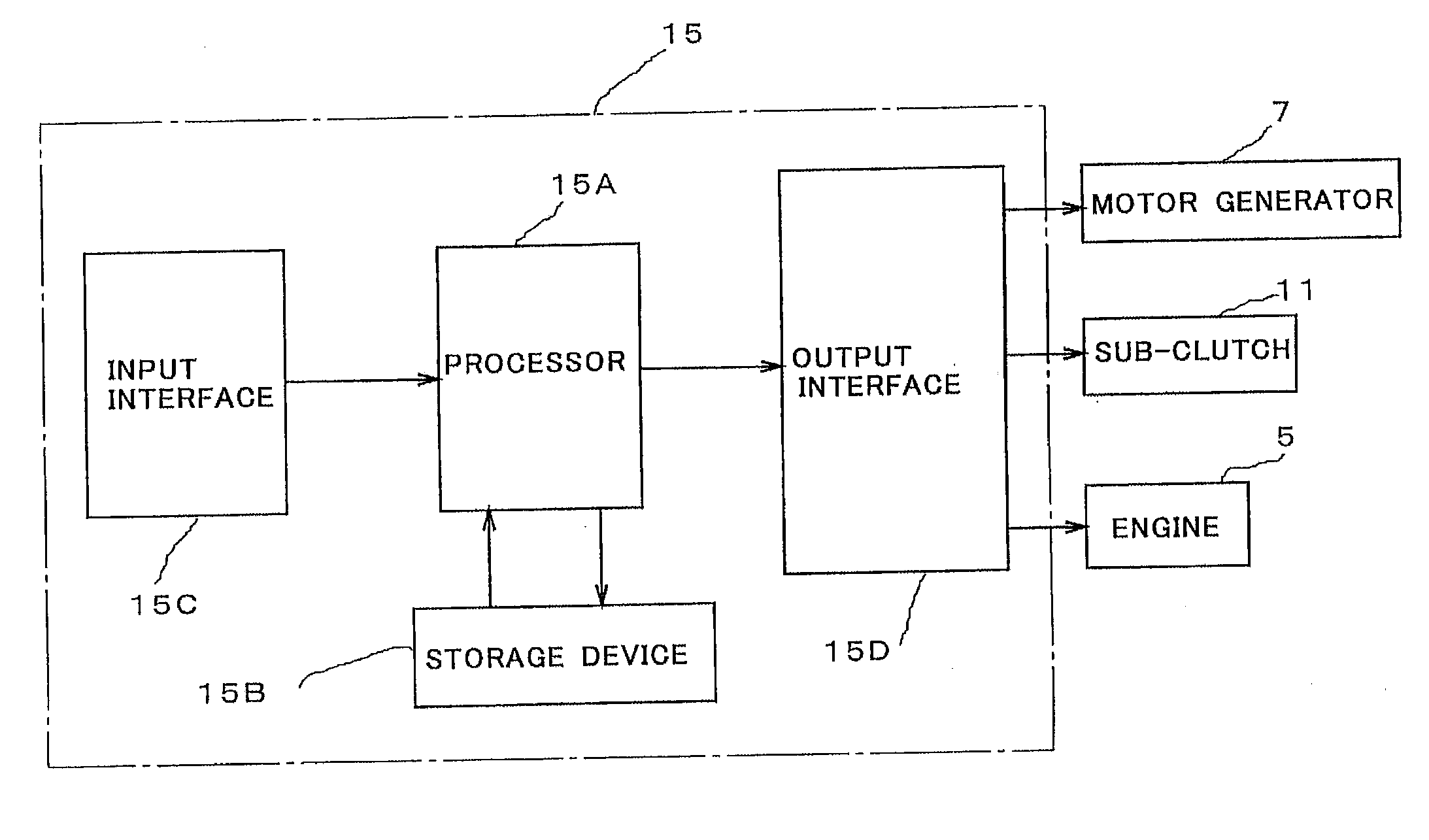
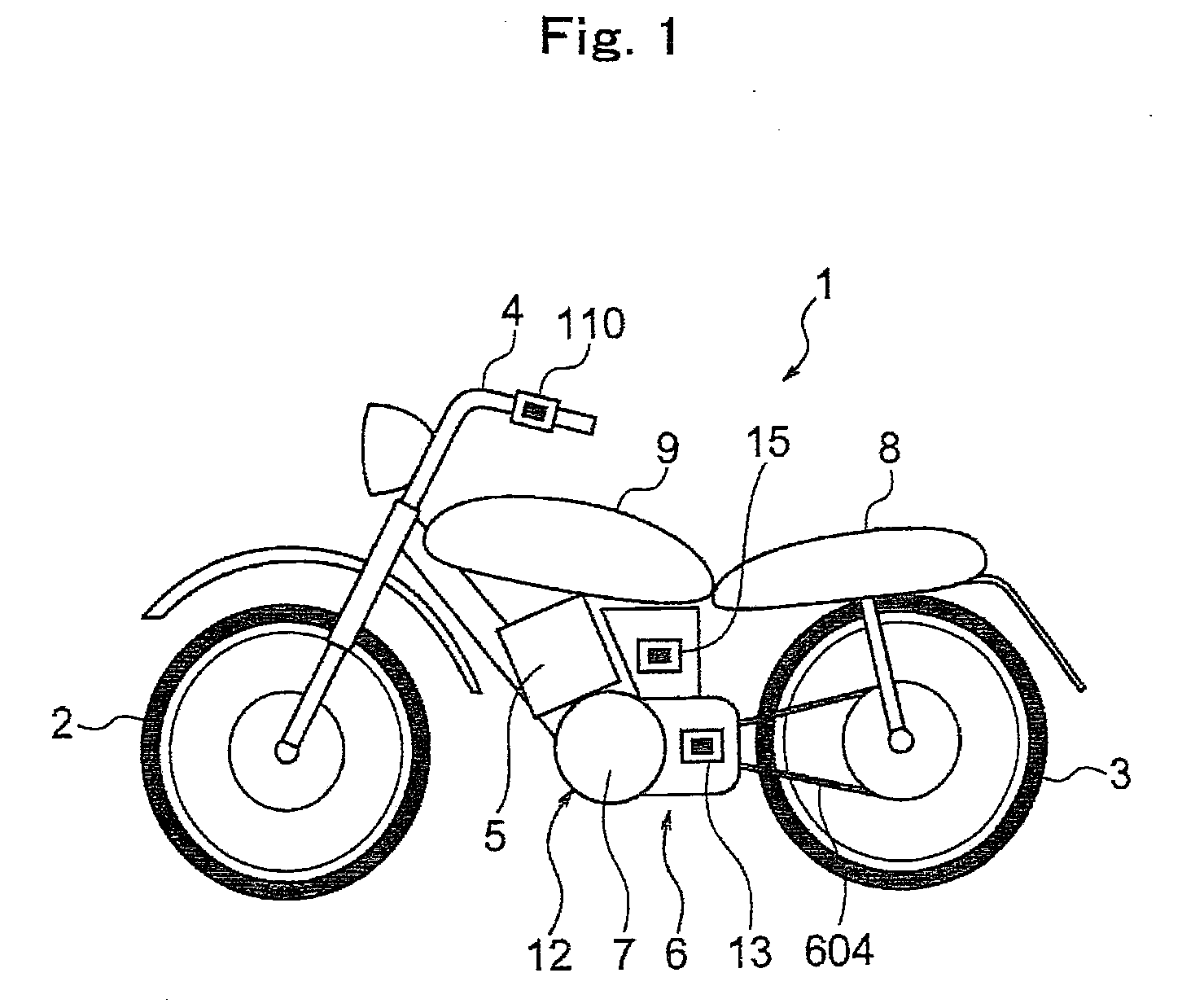
Motorcycle
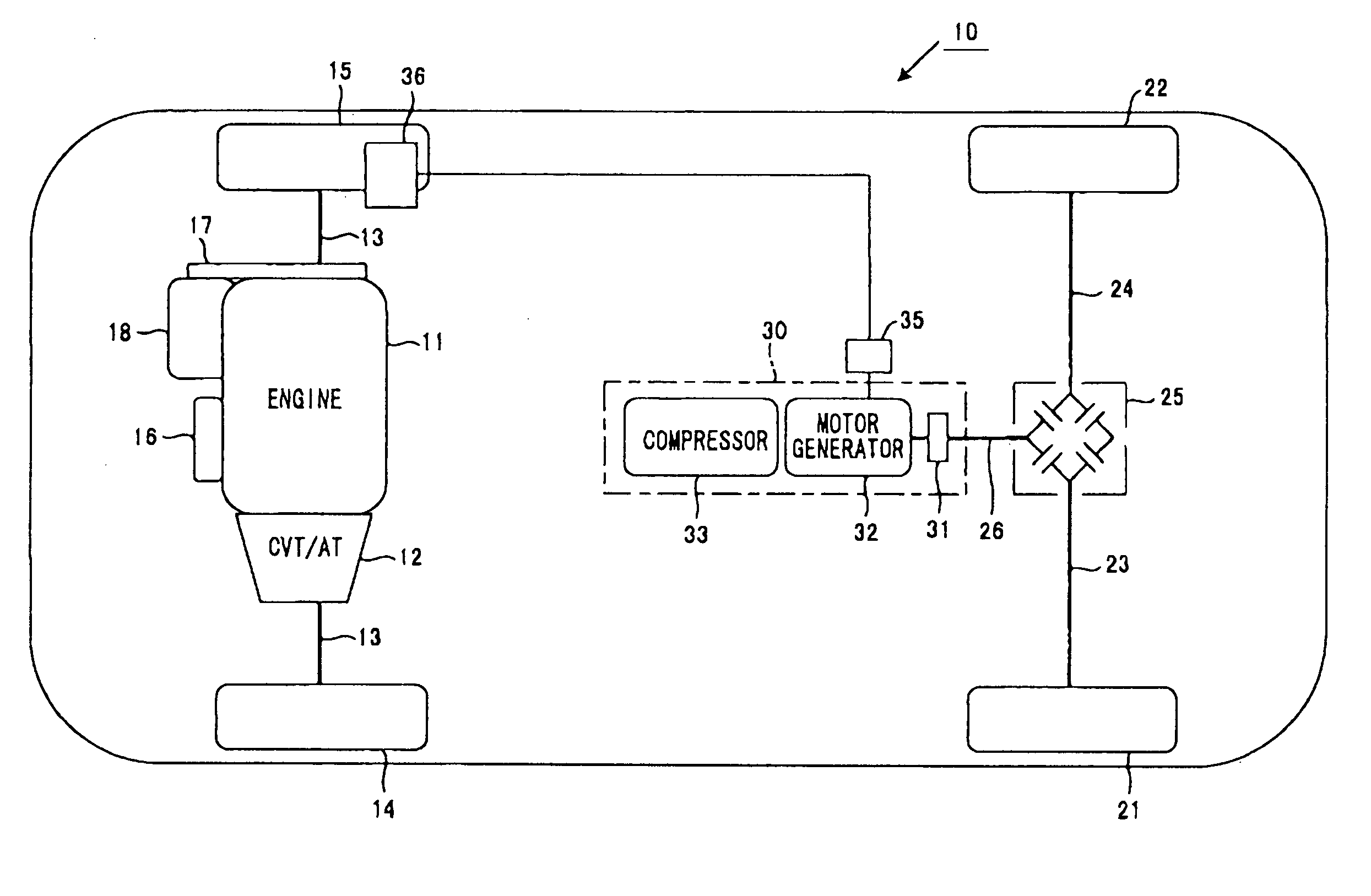
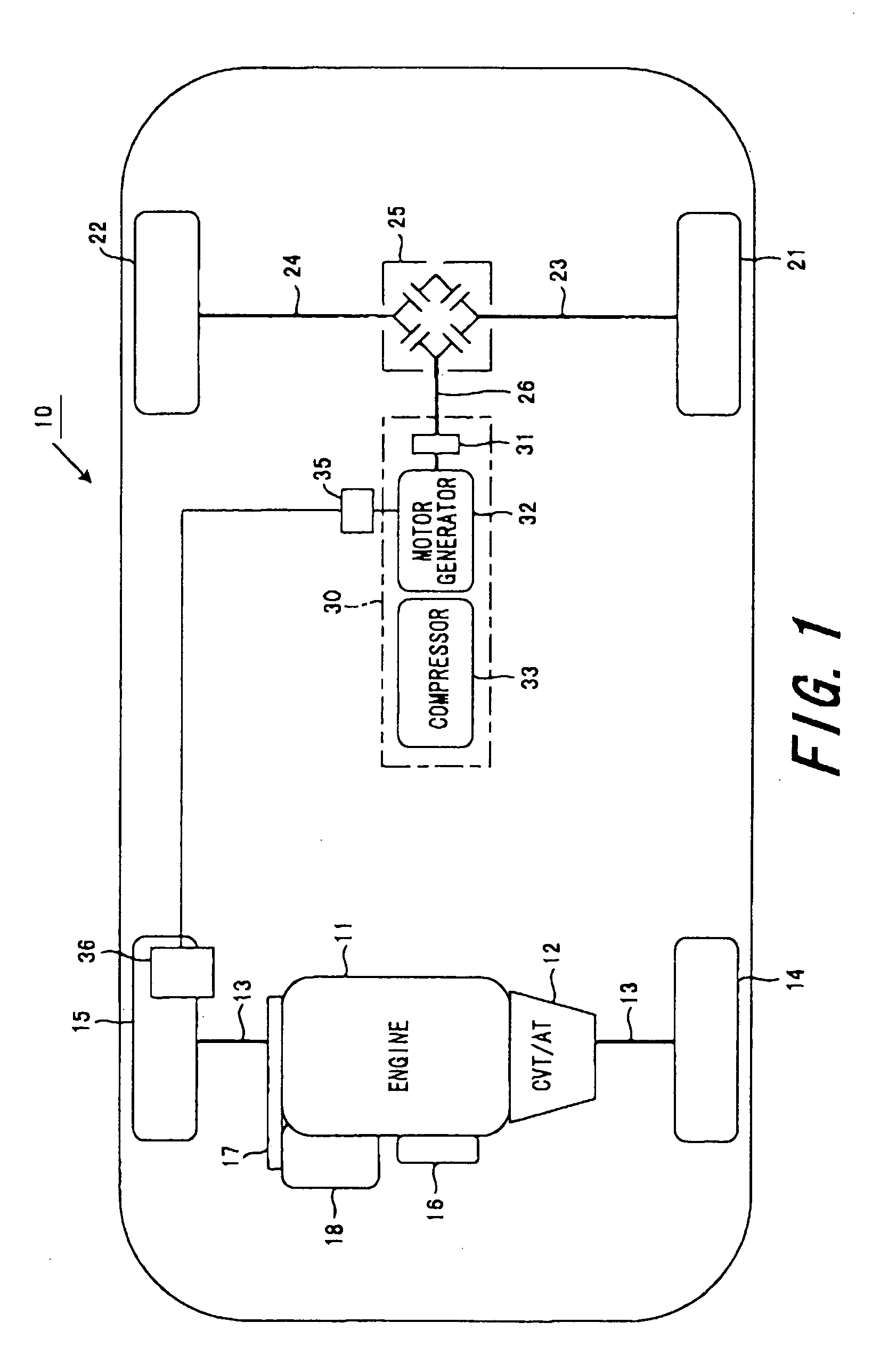
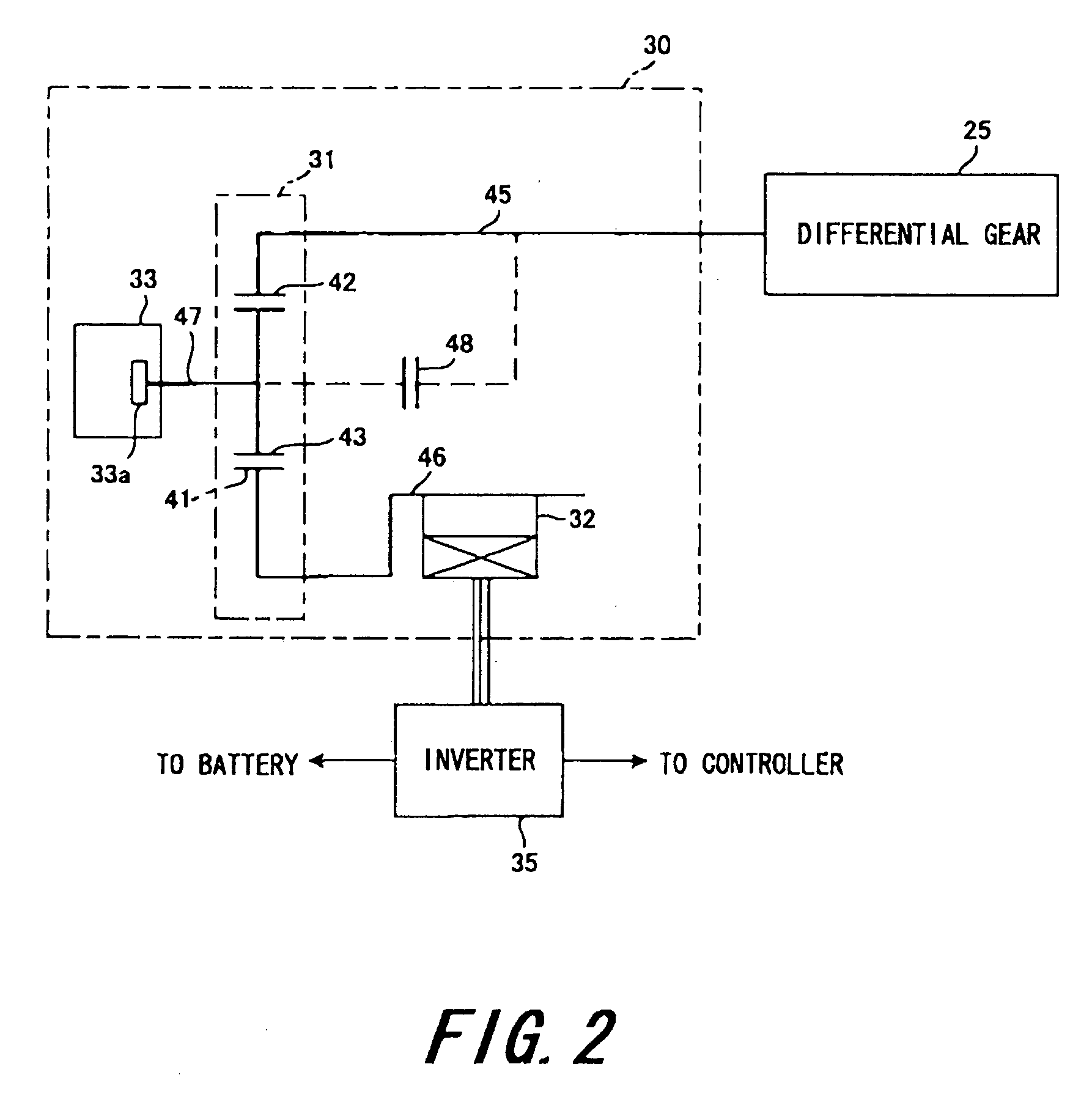
InactiveUS20110040434A1Easy to controlRunning speedDigital data processing detailsPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingDrive wheelControl theory
A motorcycle that transmits a rotation of an engine to a driving wheel via a power transmission device having a main clutch comprises a sub-clutch inserted between the power transmission device and an output shaft of the engine and a motor generator having a rotating shaft coupled to the power transmission device and is comprised so that the rotating shaft of the motor generator is coupled to the engine via the sub-clutch and to the driving wheel via the main clutch, and the motorcycle can be moved backward by turning off the sub-clutch and transmitting a rotation of the motor generator to the driving wheel via the main clutch.
Owner:KOKUSAN DENKI CO LTD
Power train system for vehicle
InactiveUS20060047398A1Easy to operateReduce pressureHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsDrive wheelCoupling
A power train system for a vehicle is disclosed, in which the vehicle is provided with front wheels and rear wheels, one of which are main drive wheels and the other of which are subsidiary drive wheels. The system comprises a first power source arranged to power the main drive wheels and a second power source arranged to power the subsidiary drive wheels. The system further comprises a wheel coupling shaft mechanically coupled with the subsidiary drive wheels and a power distribution device mechanically coupled with the wheel coupling shaft and the second power source to perform power distributions to and from the wheel coupling shaft.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Utility lighter
InactiveUS20080171295A1Assist in operationAvoid accidental ignitionIncandescent ignitionFuel lightersTorchEngineering
A utility lighter includes a handle casing, a gas releasing valve, a bendable extension arm, a torch nozzle, a piezoelectric unit and an actuation device. The bendable extension arm has an upper end and a lower end extended from the handle casing, wherein the extension arm has a deformable receiving channel which is extended from the lower end to the upper end and is adapted to be curved when the extension arm is selectively bent between the upper end and the lower end. The torch nozzle is provided at the upper end of the extension arm to communicate with the gas releasing valve through the receiving channel for releasing the gas through the torch nozzle when the actuation device is actuated to depress the piezoelectric unit. The result is that a torch flame is generated at the torch nozzle at a distance from the handle casing.
Owner:YANG JOHN
Manually operated bearing cleaning apparatus
A simple but effective manually operated bearing cleaning apparatus comprises a container adapted to receive a solvent. One or more brushes mounted on the inner sidewall of the container have bristles oriented generally toward a centerline of the container, while leaving a central opening enabling a bearing to pass therethrough. A telescoping sleeve including a lower sleeve with a lower end, and an upper sleeve with an upper end is configured to receive a bearing to be cleaned between upper and lower retainers on the upper sleeve. A coupling is provided between the lower end of the lower sleeve and the inner bottom surface of the container, whereby a user moves the upper sleeve in an up-and-down motion, forcing the bearing through the central opening of the bristles, thereby cleaning the bearing in the solvent.
Owner:LANCASTER CHRISTOPHER NEIL
Multi-dimensional portable gas chromatograph system
ActiveUS7735352B2Reduce pressureAssist in operationSamplingComponent separationEngineeringMulti dimensional
A portable multi-dimensional gas chromatograph, the gas chromatograph including a carrier gas container, a regulator fluidly connected to the carrier gas container, a dopant chamber containing a reference chemical, at least one pre-concentrator which is fluidly connected to the regulator and the dopant chamber, a first separation column fluidly connected to the at least one pre-concentrator, a second separation column fluidly connected to the at least one pre-concentrator, a first detector fluidly connected to the first separation column, and a second detector fluidly connected to the second separation column.
Owner:LUDLUM MEASUREMENTS
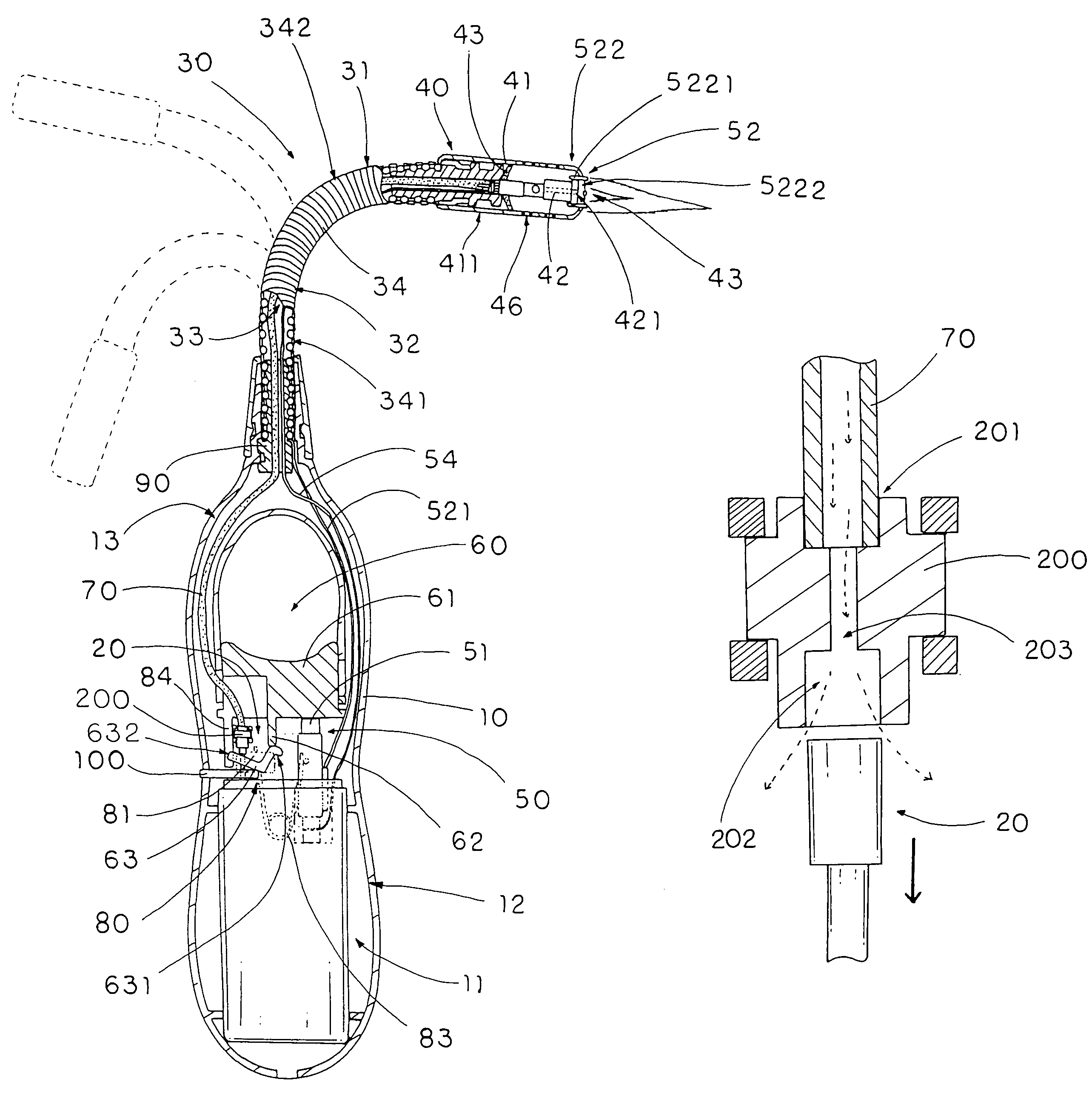
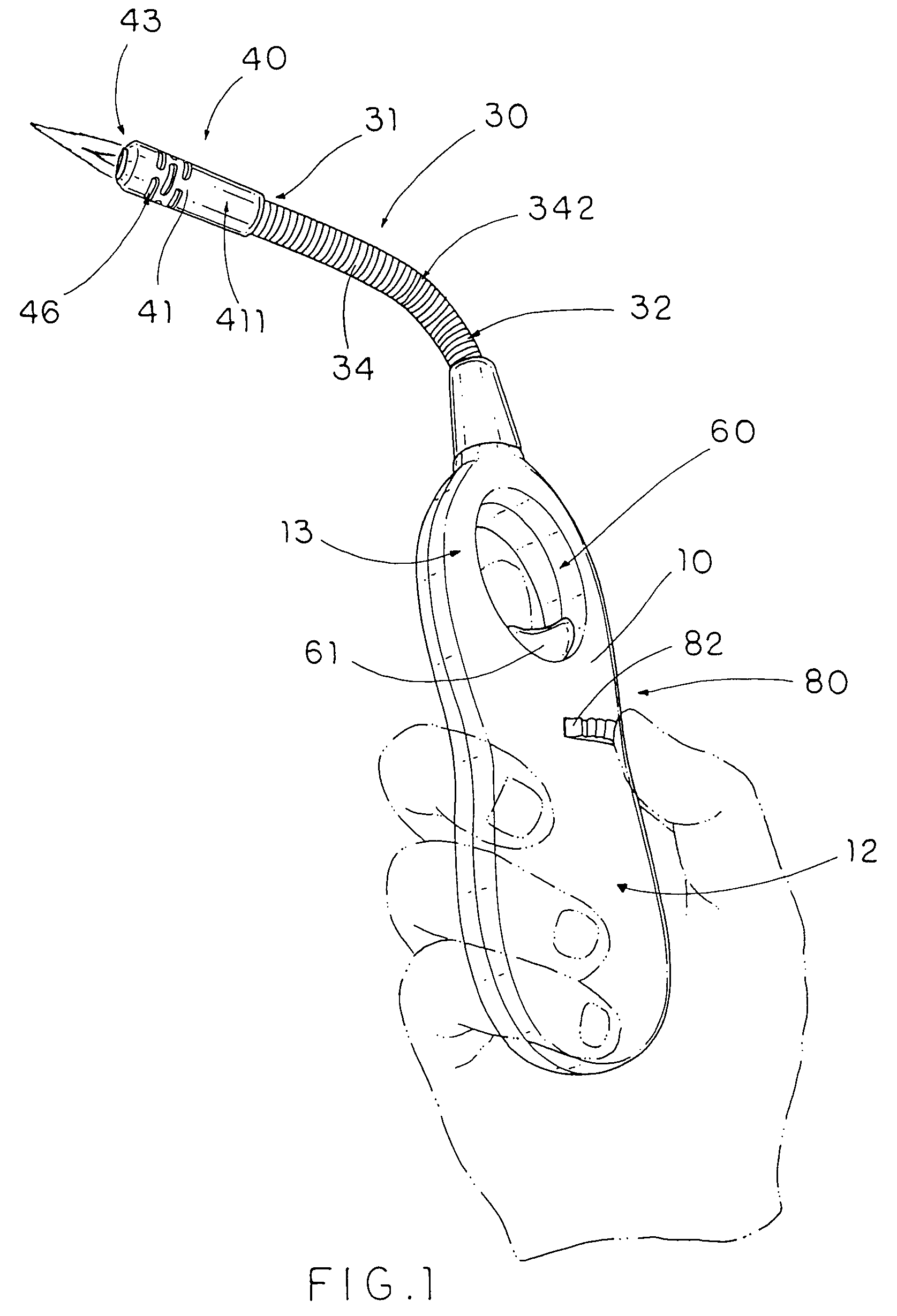
Heart wall actuation system for the natural heart with shape limiting elements
InactiveUS20050250976A1Avoid strainAssist in operationHeart valvesIntravenous devicesHeart wallEngineering
An actuation system for assisting the operation of the natural heart includes an actuator element adapted to be positioned proximate a portion of a heart wall. The actuator element is operable for acting on the heart wall portion to effect a change in the shape of the heart. A shape-limiting element is configured for being positioned proximate a heart wall. The shape-limiting element is operable for flexing to assume a curvature no greater than a predetermined curvature when the heart wall is acted upon and maintaining that predetermined curvature to control the shape of the actuated heart.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI +1
Architectural apparatus and method
ActiveUS20110094689A1Minimize overlapEasy to operateScreensCurtain suspension devicesAdhesiveEngineering
According to one aspect, there is provided a curtain assembly including a curtain and a plurality of rails. The curtain can be used to cover a variety of openings. The plurality of rails can be attached to and disposed horizontally on the curtain to provide rigidity to the curtain when in an open position (covering the opening). The plurality of rails can be made of two main sections, a first and a second coupled to opposite sides of the curtain. The second section can be configured to provide the lateral stability to the curtain, permitting the first section to be made of almost any material. Typically both sections are metal. The first section can also include folded over portions which wrap around the edges of the curtain. The folded over to portions provide for attachment and also insure no sharp edges exist on the exterior sides of the curtain. The plurality of rails can be bonded to the curtain using an adhesive. The curtain can include prepared bonding surface to receive the rails. Both can be spaced to minimize overlap between the plurality of rails when the curtain is in a recessed position (wound around a roller).
Owner:DWARKA RAJIVA
Wave energy conversion apparatus and method
InactiveUS20120187689A1Simple and efficientSimple designFluid couplingsEngine fuctionsEngineeringPower extraction
A wave energy conversion apparatus comprises:-a mechanical element arranged in operation to move repeatedly in a cycle in response to wave motion, wherein the speed of the mechanical element varies between a maximum and a minimum during each cycle; power extraction means arranged to extract energy from the movement of the mechanical element; and movement assistance means arranged to assist the movement, in response to the wave motion, of the mechanical element, during at least one part of the cycle during which the speed of movement of the mechanical element is substantially equal to the minimum for that cycle, wherein the power extraction means comprises a fluid pressurisation system that is arranged so that in operation fluid in the fluid pressurisation system is pressurised in response to movement of the mechanical element, the fluid pressurisation system comprises a one-way valve for transferring pressurised fluid from the fluid pressurisation system and the movement assistance means is located upstream of the one-way valve.
Owner:AQUAMARINE POWER
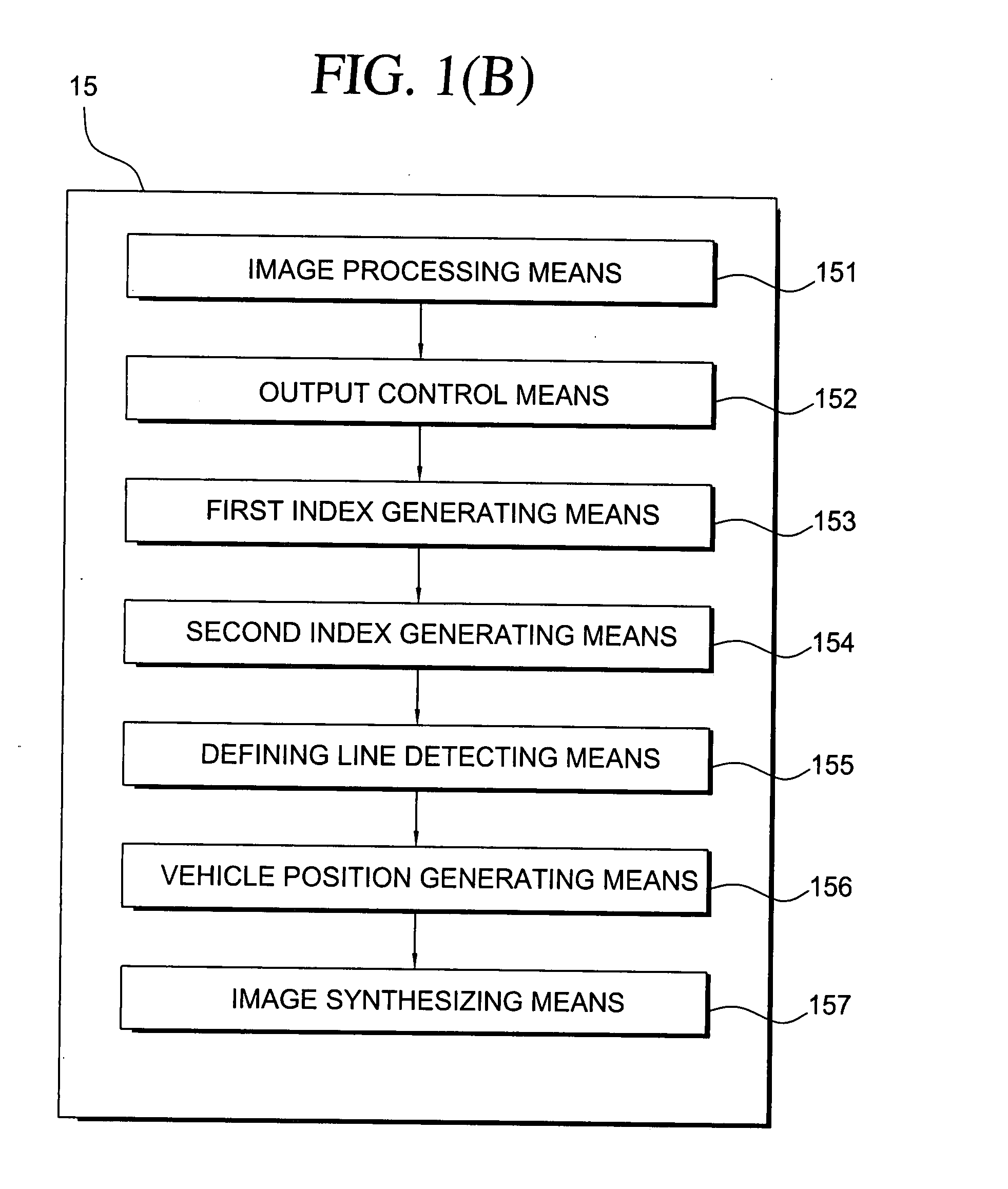
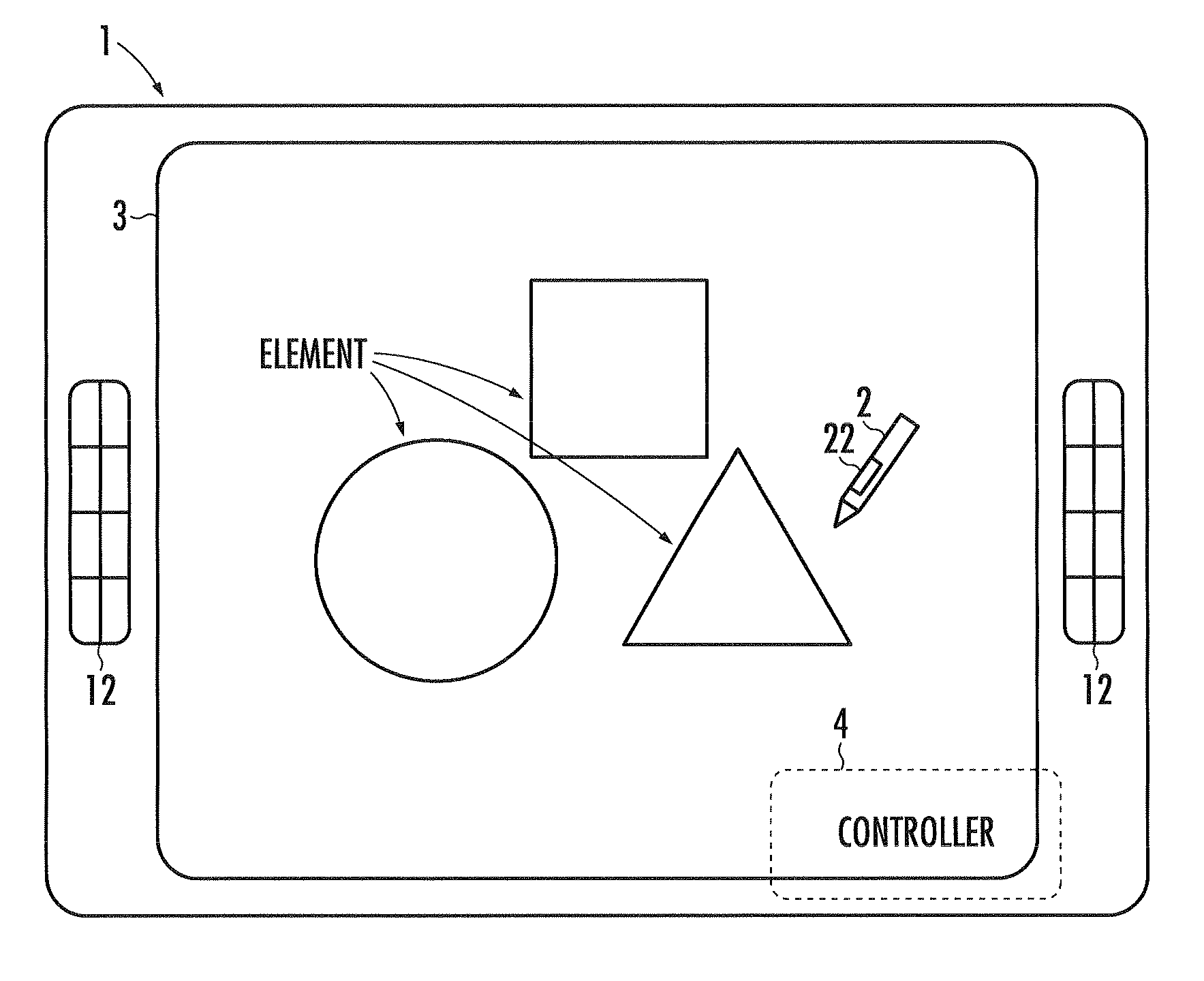
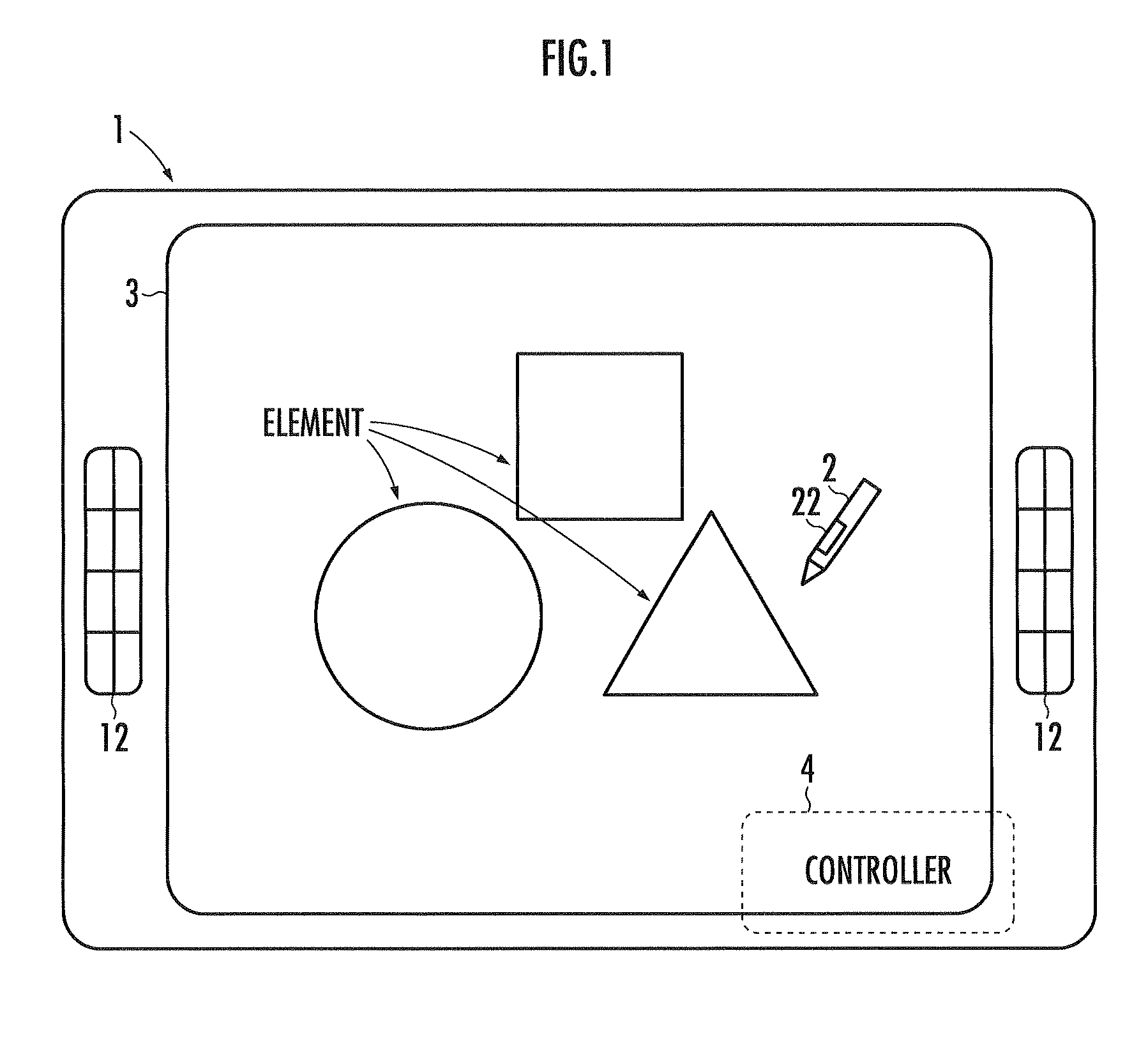
Drawing assist device, drawing assist program, and drawing assist method
ActiveUS20100309115A1Assist in operationImprove efficiencyCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingAssisted procedureComputer science
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Vehicle steering apparatus
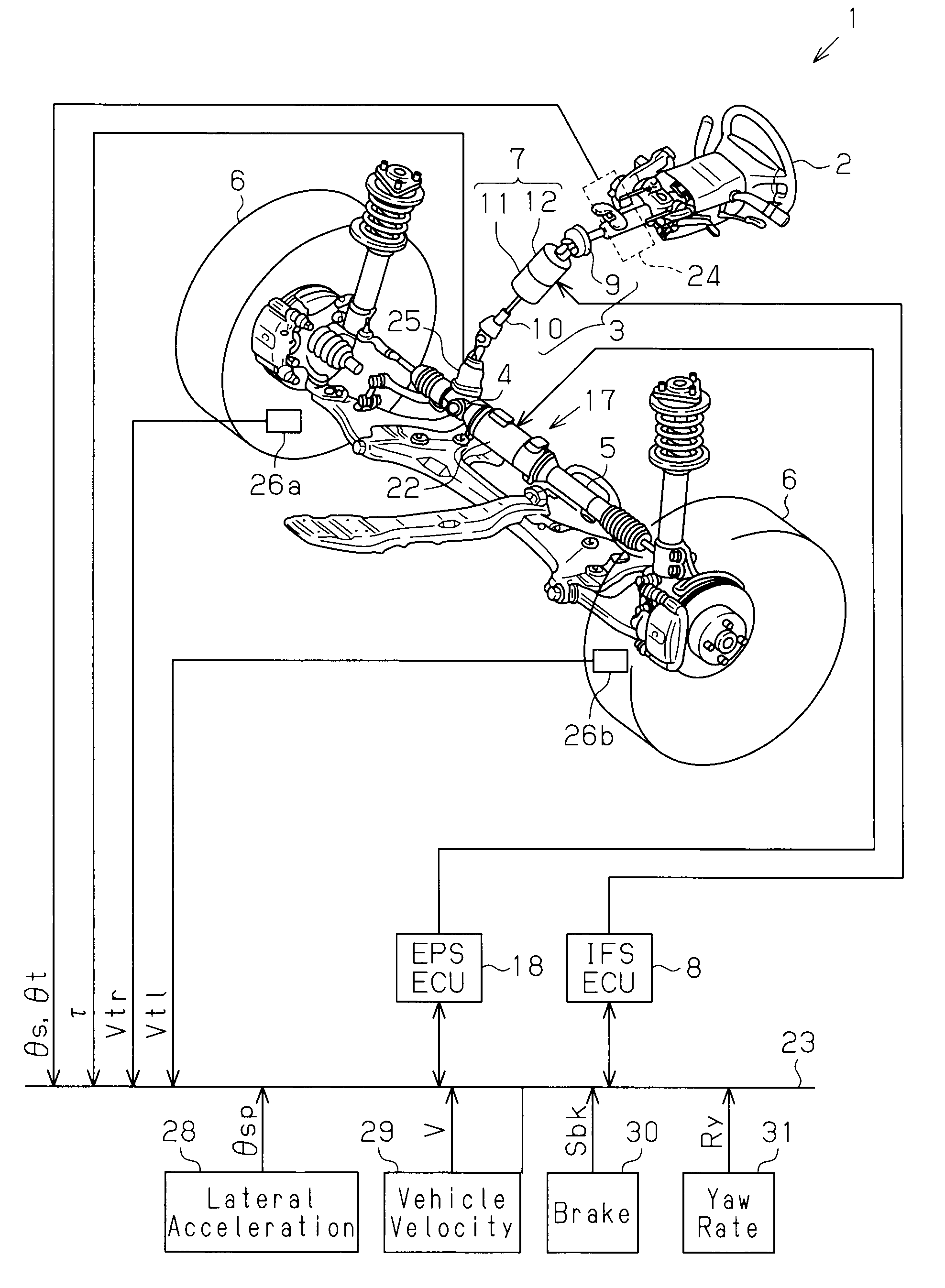
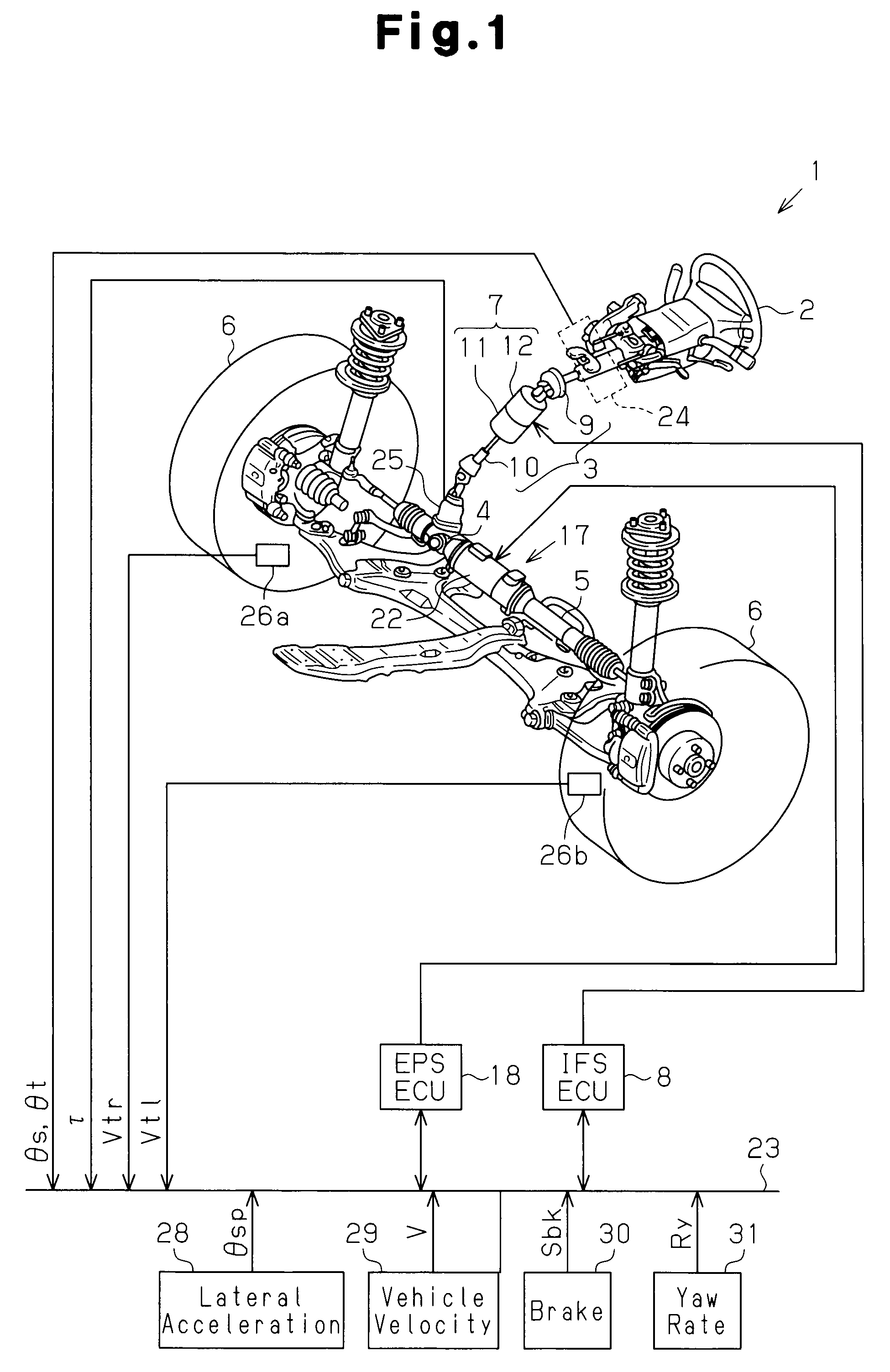
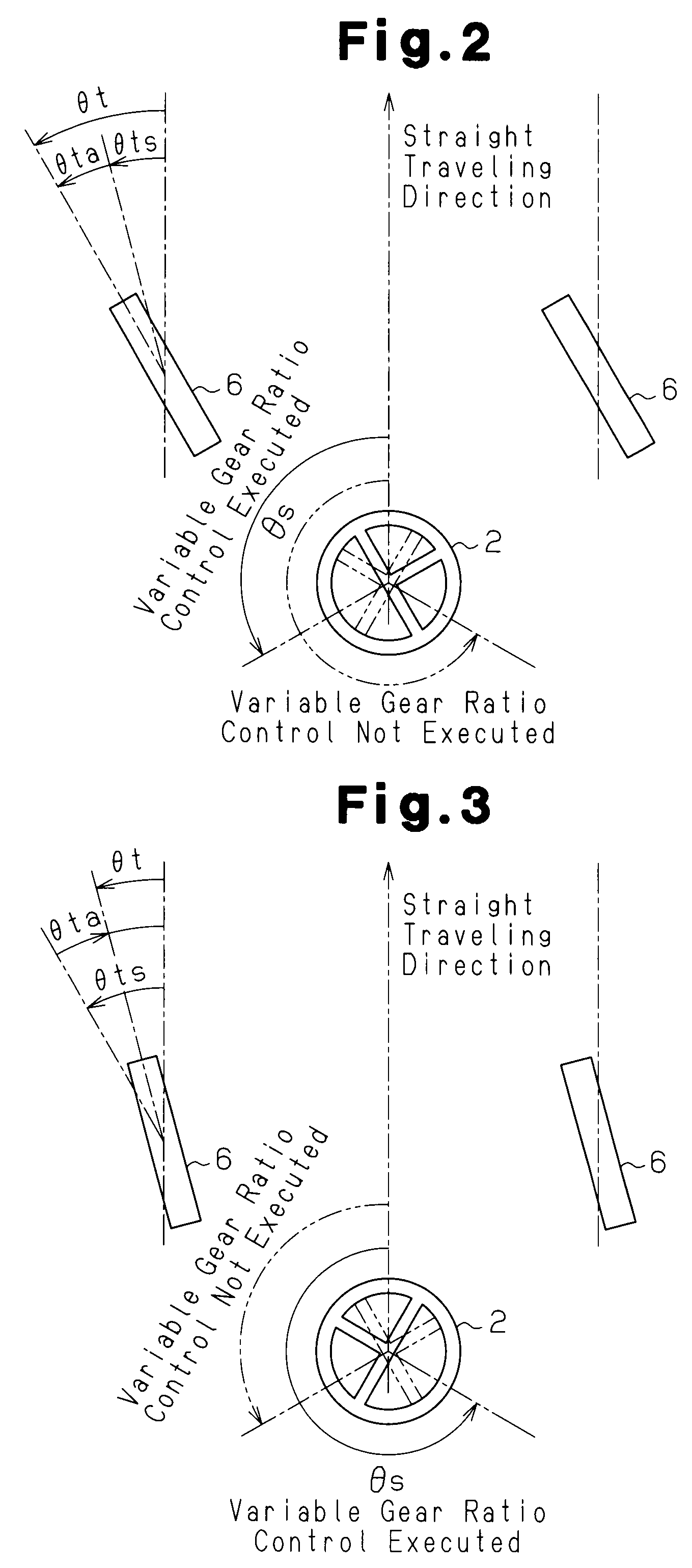
InactiveUS20090026003A1Favorable steering feelingSolve the stability is not highSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsMicrocomputerActuator
A vehicle steering apparatus 1 includes an EPS actuator 17 and an EPS ECU 18 that controls the EPS actuator 17. The EPS actuator 17 applies an assist force that assists a steering operation. A microcomputer 43 of the EPS ECU 18 determines whether the currently executed oversteer control (OS control) is being intensified or converged. In the OS control intensification state, in which the vehicle stability is low, the microcomputer 43 reduces a damper compensation current command Idp* (Idp**), which is a damper compensation component for attenuating a steering wheel turning speed ωs.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Electric power steering apparatus
InactiveUS7523805B2Reduce the amount requiredConvenience to workSpringsBall bearingsElectric power steeringGear wheel
An electric power steering apparatus includes a worm interlockedly connected to an output shaft of an electric motor, a first and a second bearing each supporting the respective side of the worm in a housing, and a gear wheel meshed with the worm. The housing includes a fitting bore in which the first bearing supporting a side of the worm closer to the electric motor is to be fitted, and an annular retaining portion located at a position corresponding to the second bearing and eccentrically oriented with respect to the center (axial center) of the fitting bore in a direction that shortens a distance L between the center of rotation of the worm and that of the gear wheel, and the annular retaining portion retains a coil spring around an outer circumference of the second bearing.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com