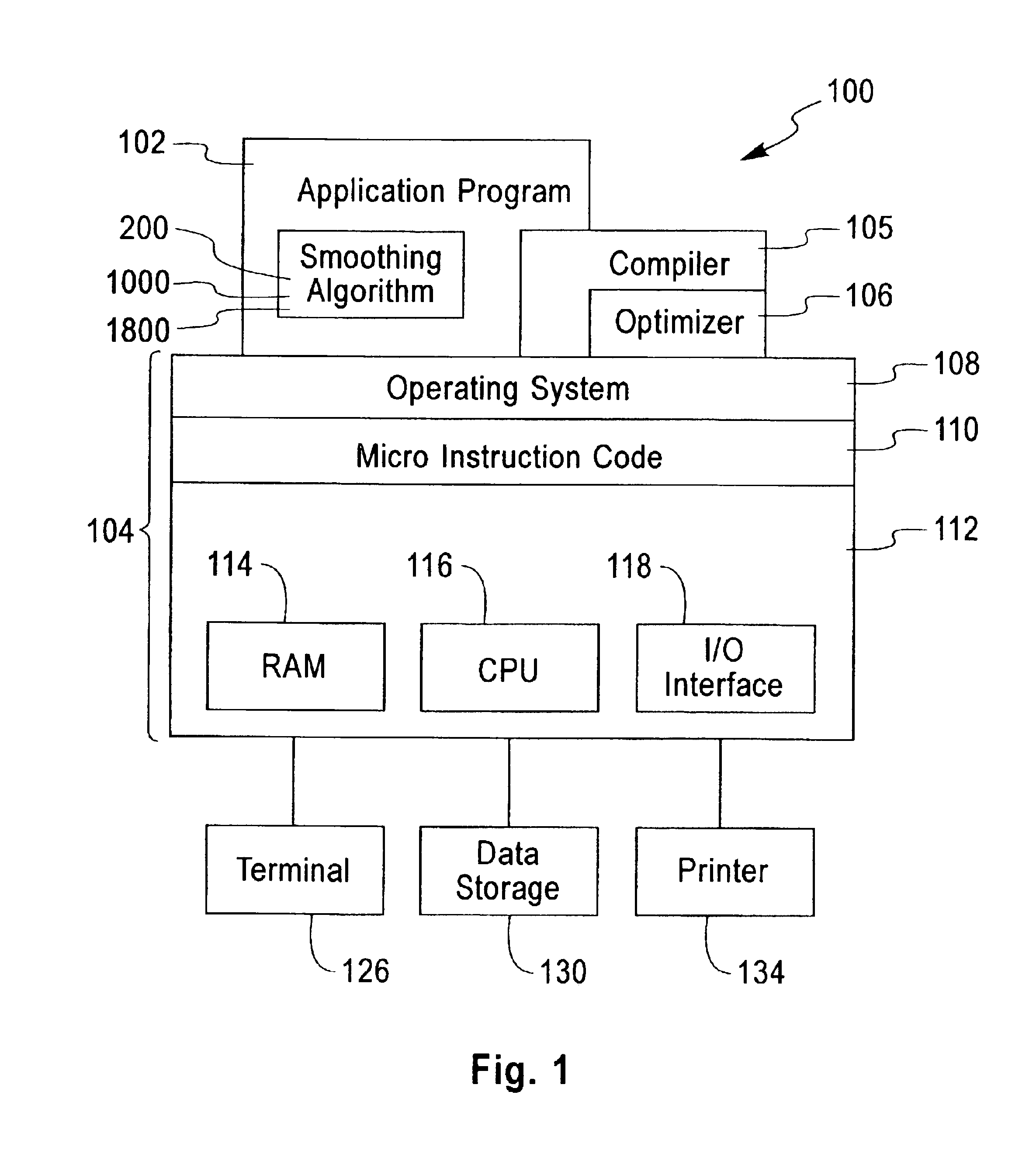
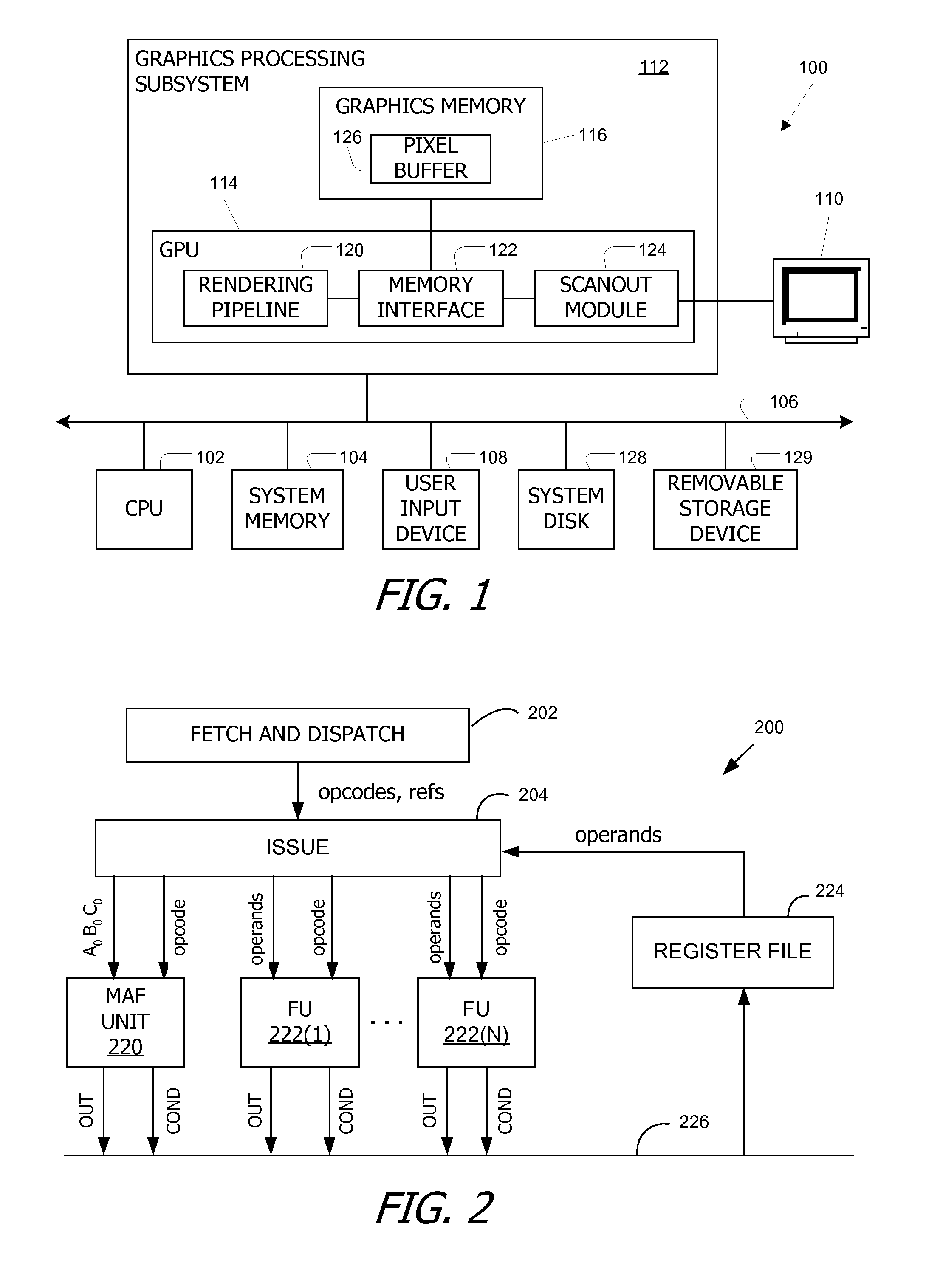
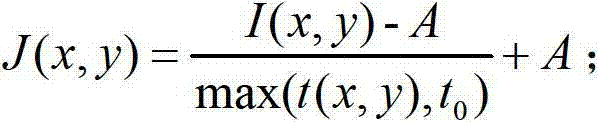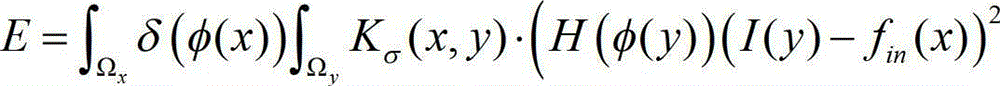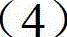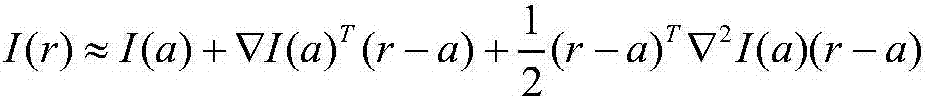Patents
Literature
63 results about "Anisotropic filtering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
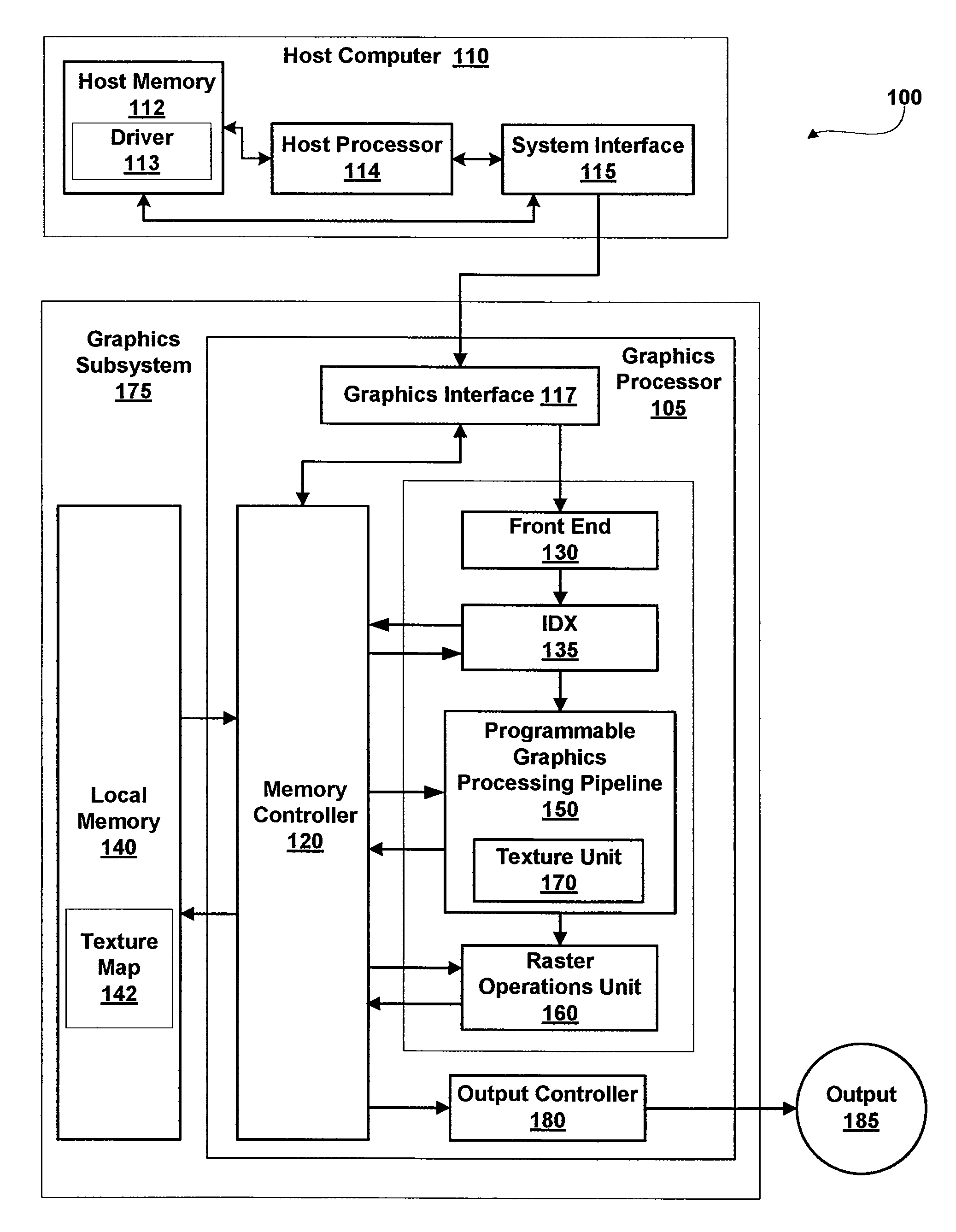
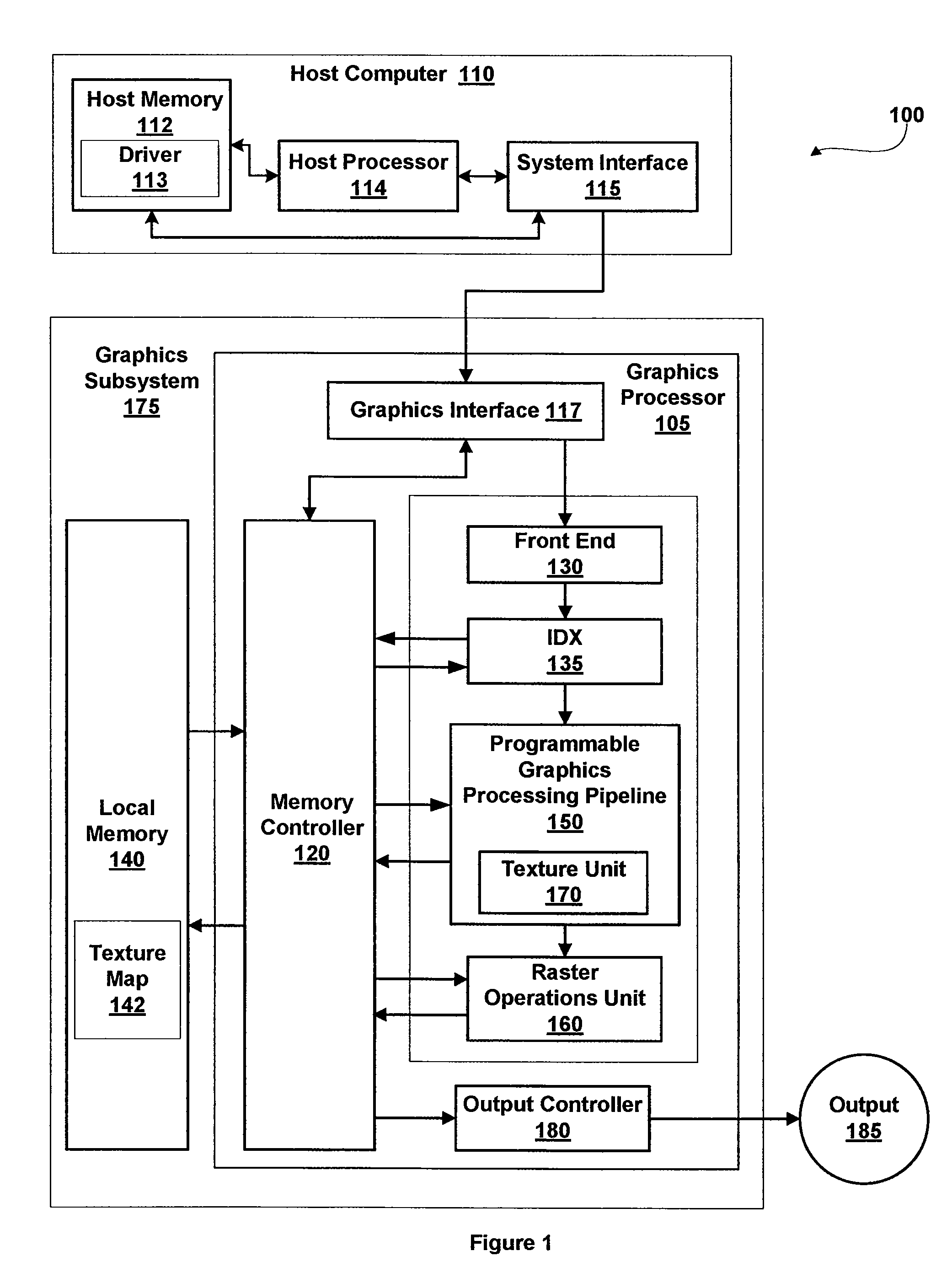
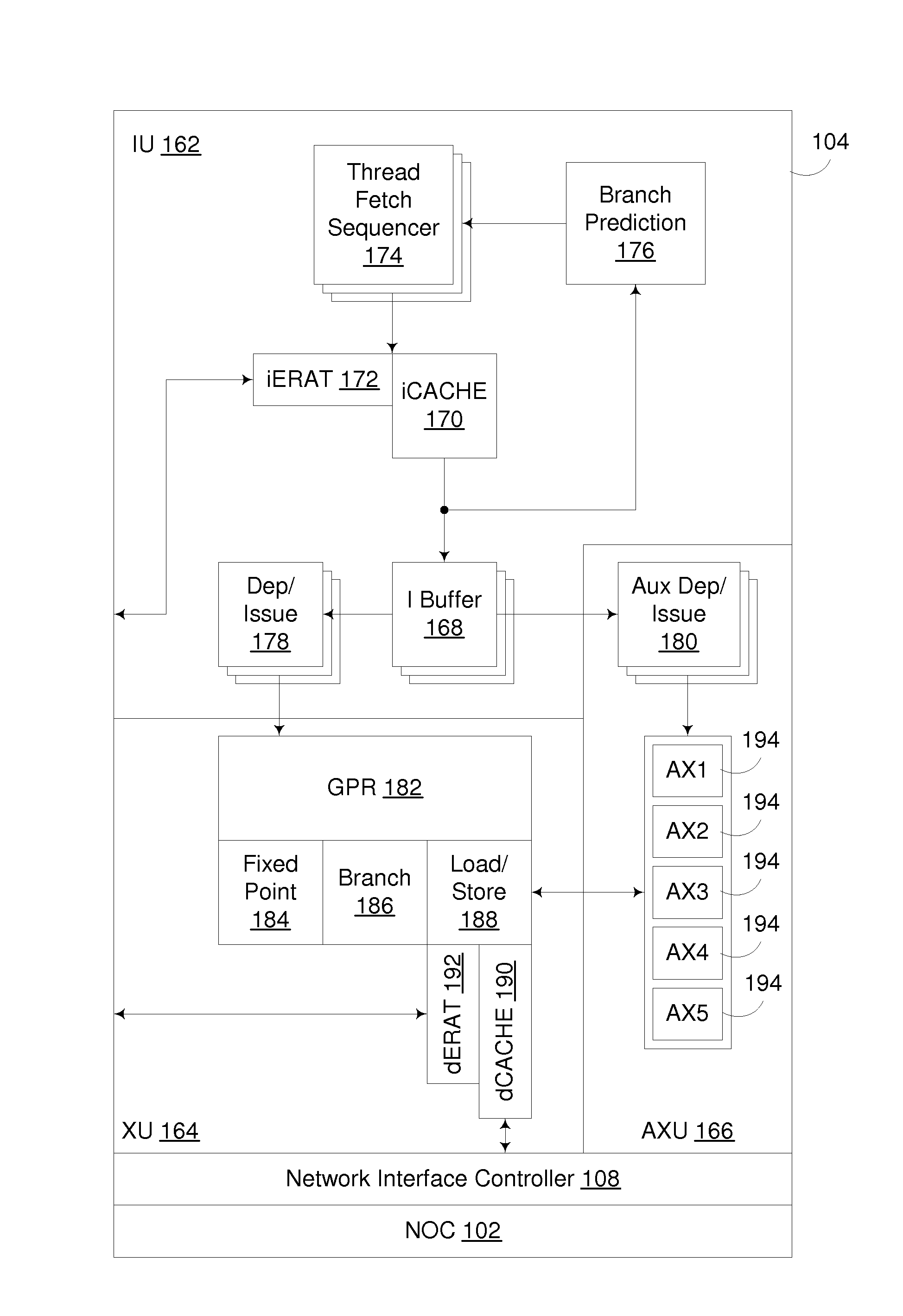
In 3D computer graphics, anisotropic filtering (abbreviated AF) is a method of enhancing the image quality of textures on surfaces of computer graphics that are at oblique viewing angles with respect to the camera where the projection of the texture (not the polygon or other primitive on which it is rendered) appears to be non-orthogonal (thus the origin of the word: "an" for not, "iso" for same, and "tropic" from tropism, relating to direction; anisotropic filtering does not filter the same in every direction).
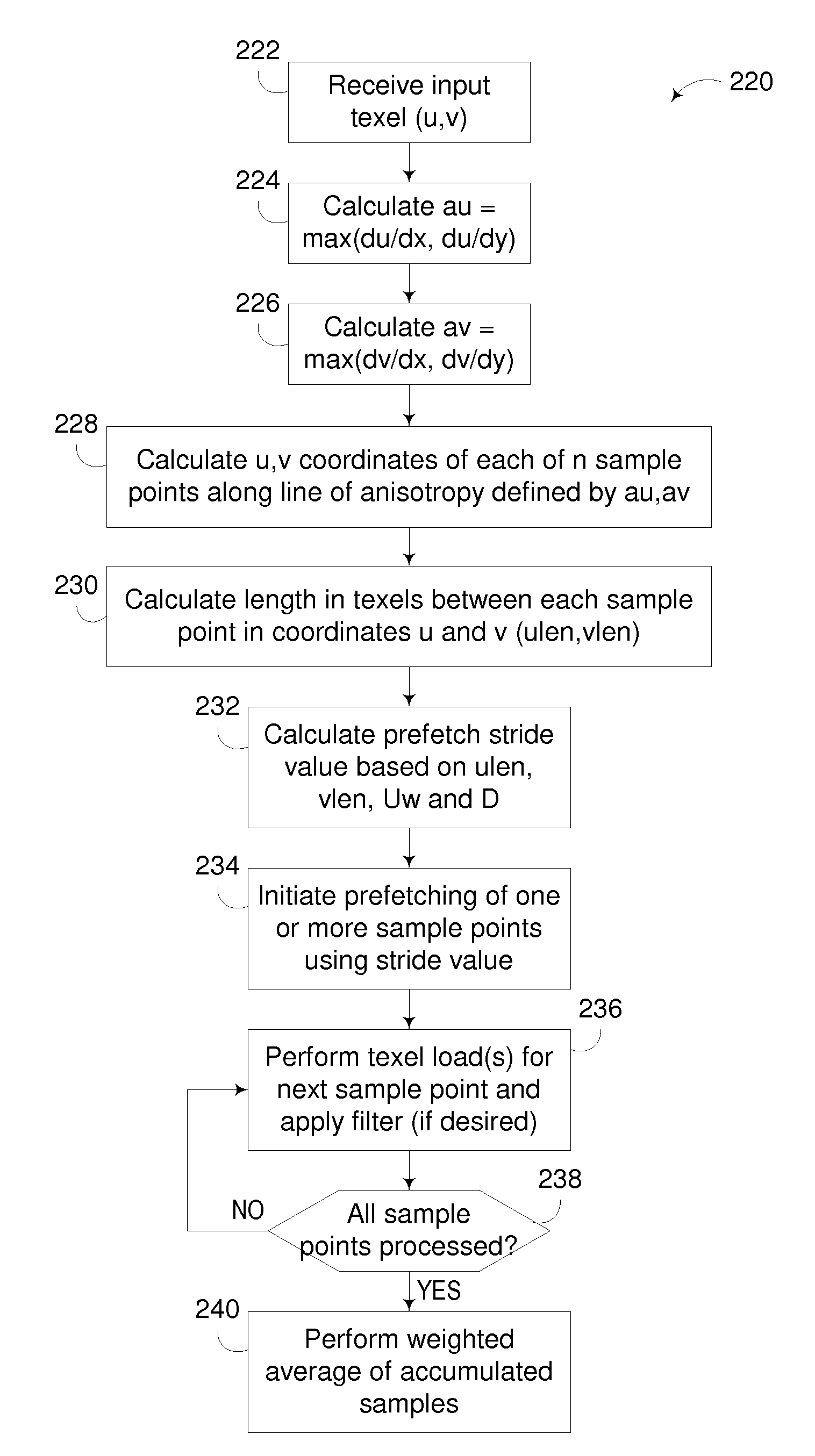
Anisotropic Texture Filtering with Texture Data Prefetching
InactiveUS20090315908A1Details involving antialiasingCharacter and pattern recognitionComputational scienceMemory address
A circuit arrangement and method utilize texture data prefetching to prefetch texture data used by an anisotropic filtering algorithm. In particular, stride-based prefetching may be used to prefetch texture data for use in anisotropic filtering, where the value of the stride, or difference between successive accesses, is based upon a distance in a memory address space between sample points taken along the line of anisotropy used in an anisotropic filtering algorithm.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
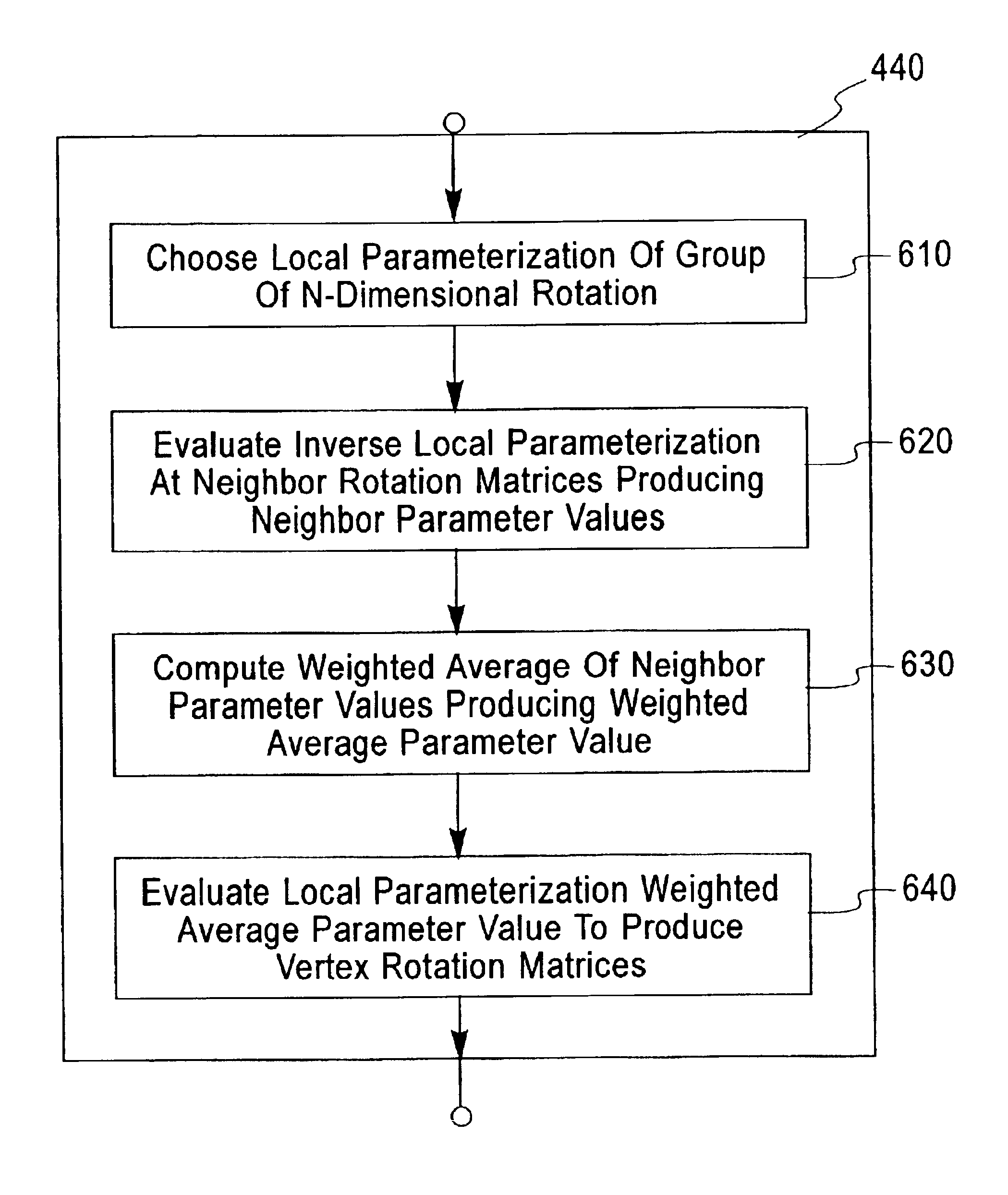
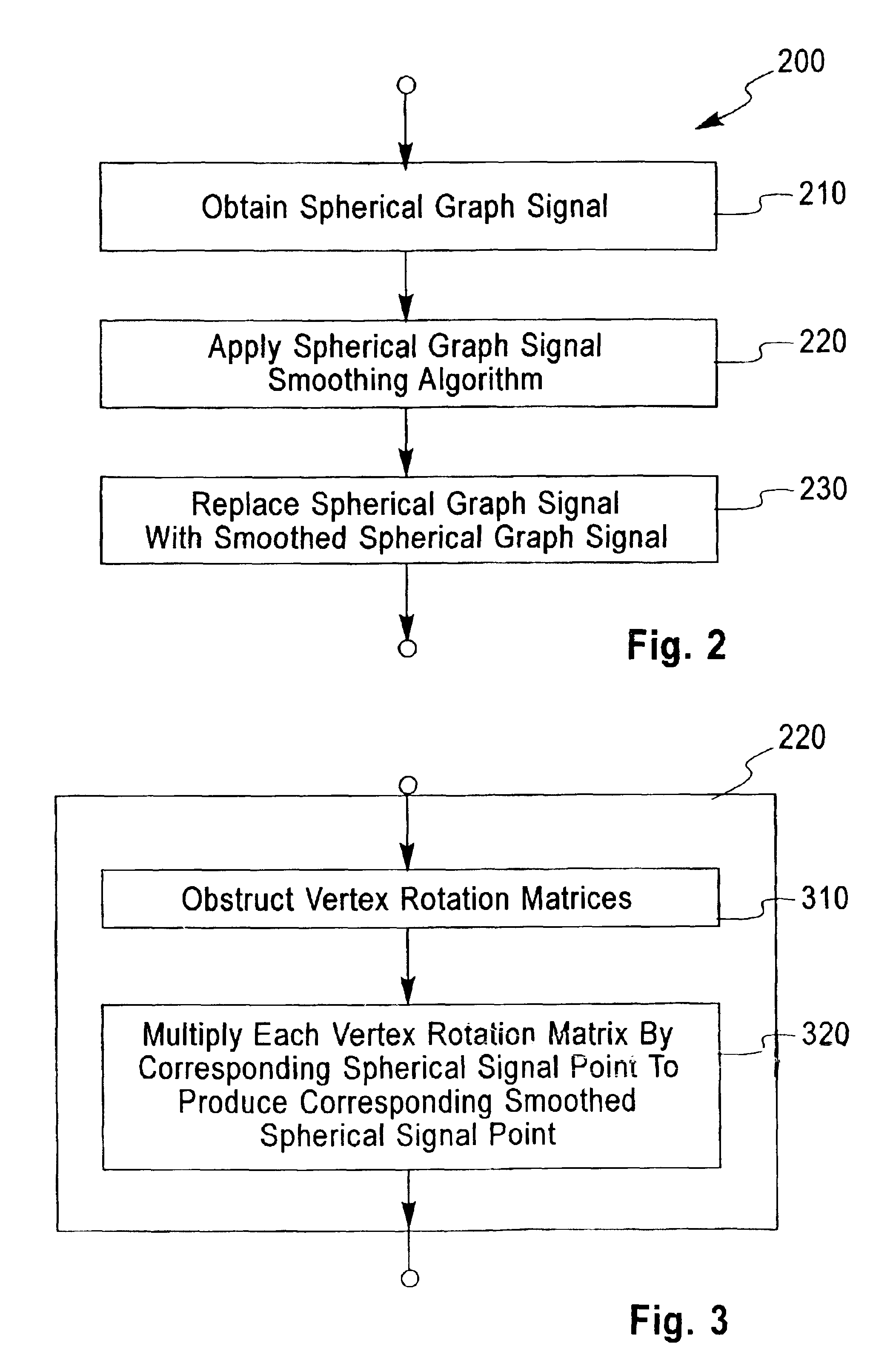
Linear anisotrophic mesh filtering
InactiveUS6987511B2Additional componentAvoid driftingImage enhancementCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsAlgorithm
The present invention smoothes a spherical graph signal composed of spherical signal points associated with graph vertices of a graph producing a smoothed spherical graph signal composed of smoothed spherical signal points. Each smoothed spherical signal point is computed by multiplying a vertex rotation matrix by the corresponding spherical signal point. The vertex rotation matrix is computed as a weighted average of neighbor rotation matrices using a local parameterization of the group of rotations. The present invention also filters anisotropically a graph signal composed signal points associated with graph vertices of a graph producing a filtered graph signal composed of filtered signal points. Each filtered signal point is computed as a weighted average of signal points corresponding to the corresponding graph vertices and neighbor graph vertices with neighbor weight matrices. The present invention also denoises the vertex positions of a polygon mesh without tangential drift. The face normals are smoothed on the dual graph of the polygon mesh. The smoothed face normals are used to construct neighbor weight matrices on the primal graph of the polygon mesh. The vertex positions are anisotropically filtered on the primal graph of the polygon mesh. The present invention also filters the vertex positions and face normals of a polygon mesh with interpolatory vertex positions and face normal constraints.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method, system, and computer program product for anisotropic filtering and applications thereof
InactiveUS6664971B1Cathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
A first copy of an object is rendered using a texture sample selected from a texture image. This texture sample is selected from the texture image according to a first set of texture coordinates. The rendered object is stored in a frame buffer. Next, a second copy of the object is rendered using a second texture sample selected from the texture image. The second texture sample is selected from the texture image according to a second set of texture coordinates calculated in accordance with the first set of texture coordinates and one or more Jitter factors. The second set of calculated texture coordinates is displaced from the first set of texture coordinates along an axis of anisotropy. This second rendered copy of the object is then blended with the first rendered copy of the object to produce an object with anisotropic filtering. In embodiments of the invention, more than two copies of the object are rendered and blended together to form an object with anisotropic filtering.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
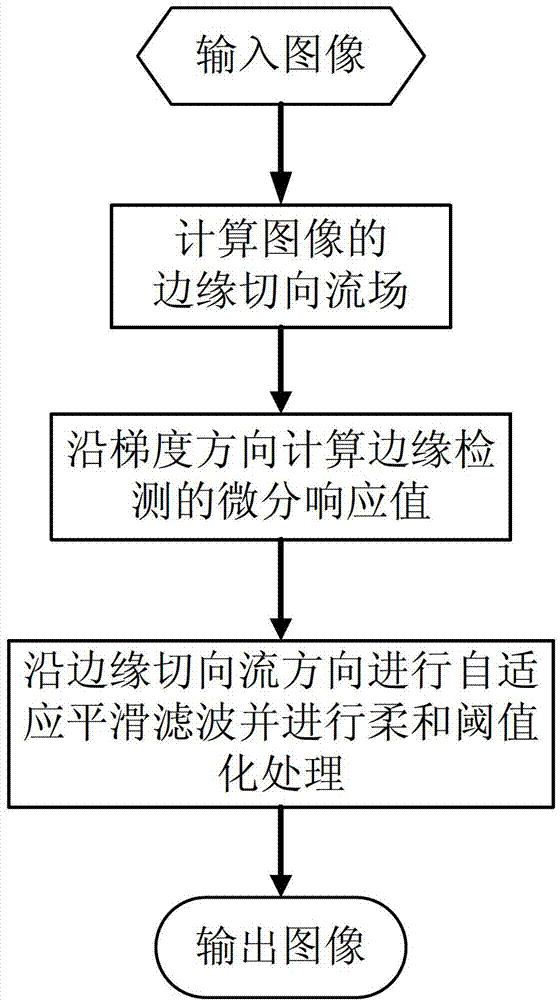
Feature flow-based method for generating abstract line drawing
InactiveCN102930576AStrong stylizationOutstanding stylized effectDrawing from basic elementsSoft thresholdingLine drawings
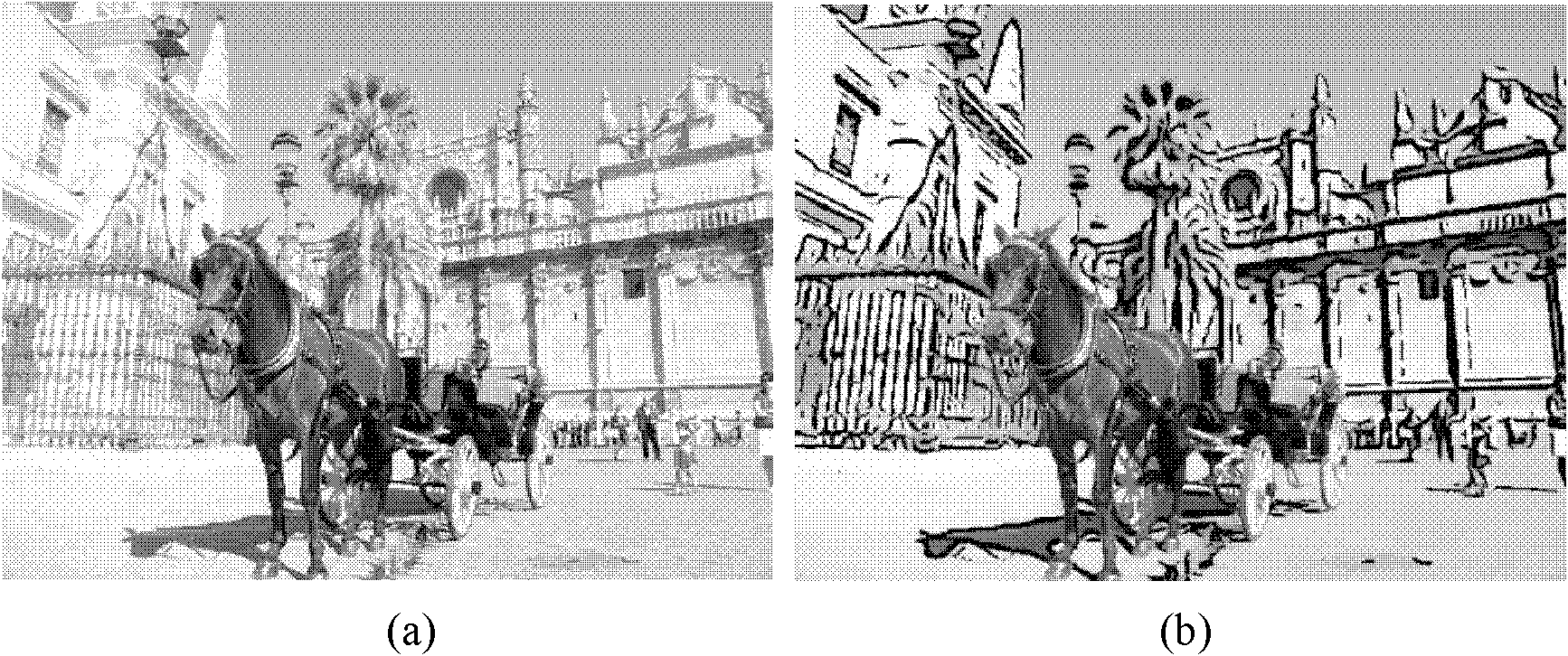
The invention relates to a feature flow-based method for generating an abstract line drawing. The invention aims to design a novel filtering method-FGaD filtering. A feature flow-based anisotropic filtering framework is referenced, a core thought is that the sum of the absolute value of Gaussian first-order filtering results and the absolute value of Gaussian difference filtering results is defined as a differential response value for edge detection, and the differential response value is subjected to soft thresholding so as to acquire a highly abstract line drawings result. According to the FGaD filtering method provided by the invention, large-scale visual features can be effectively detected, and adjacent tiny edge lines can be fused, and highly abstract line drawings with strong stylized effects are generated.
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Image enhancement and abstraction method based on anisotropic filtering
ActiveCN102800063AImprove featuresImprove sense of directionImage enhancementKuwahara filterImaging quality
The invention provides an image enhancement and abstraction method based on anisotropic filtering. The method comprises the following steps: calculating the smooth continuous characteristic-preserved edge tangential flow field of an input image by use of a structure tensor smoothing technology; performing adaptive smoothing on the image along the direction of the edge tangential flow; performing unsharp image enhancement based on a Gaussian difference mask along the gradient direction; and performing improved bilateral filtering based on characteristic flow or improved Kuwahara filtering based on characteristic flow to obtain a characteristic-enhanced abstract image. The method provided by the invention can obviously improve the generation quality of the existing image abstraction method; and the obtained abstract image has obviously-enhanced boundary characteristics, clear image quality and distinct layers.
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
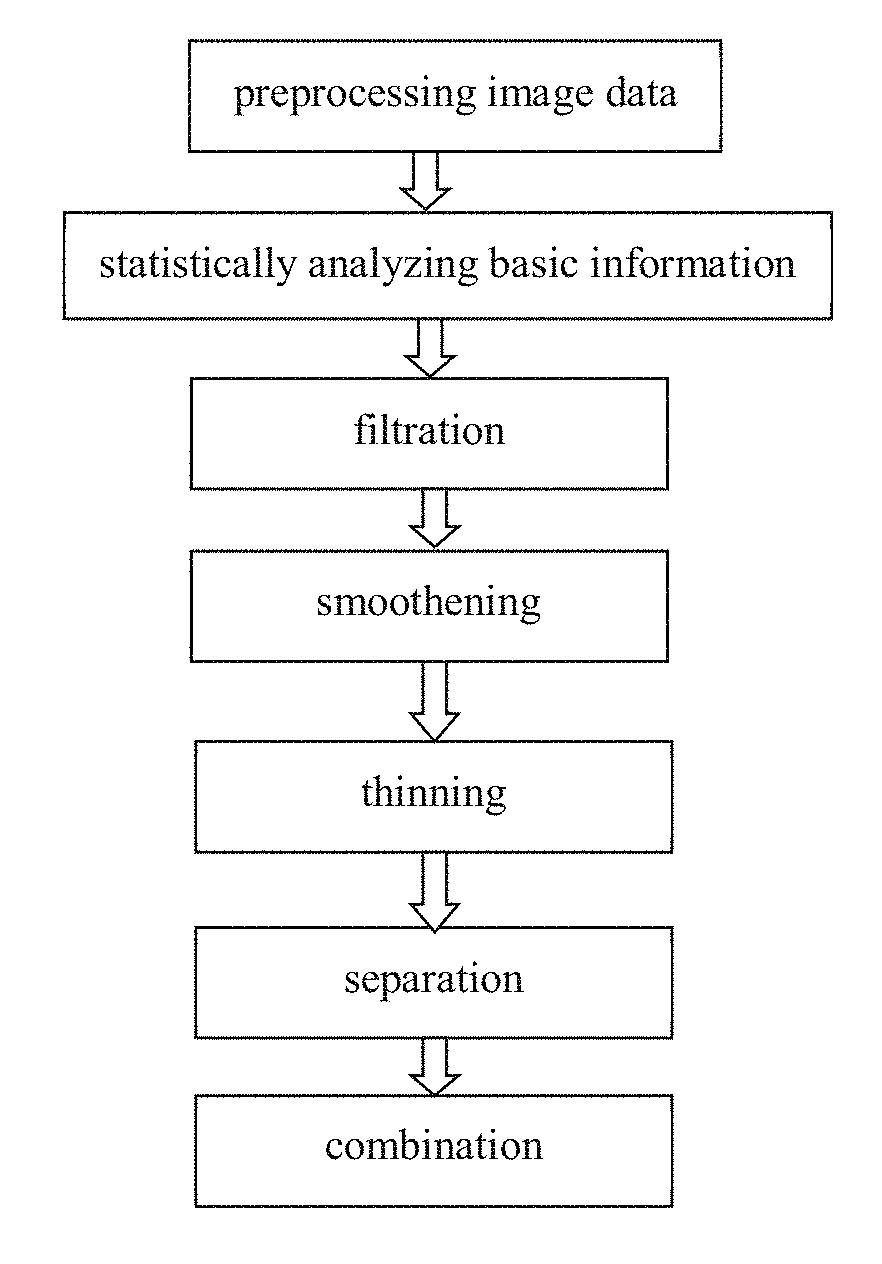
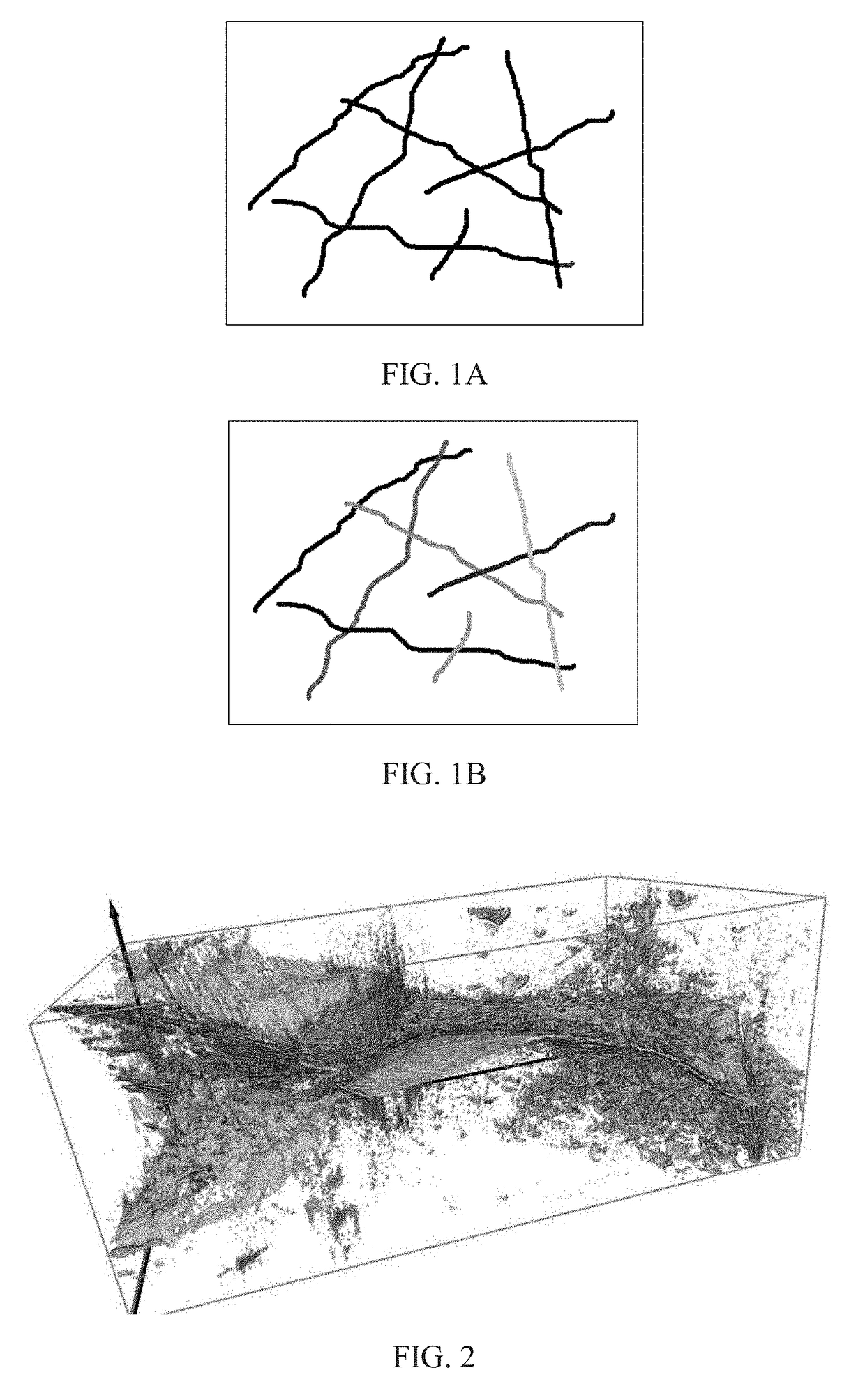
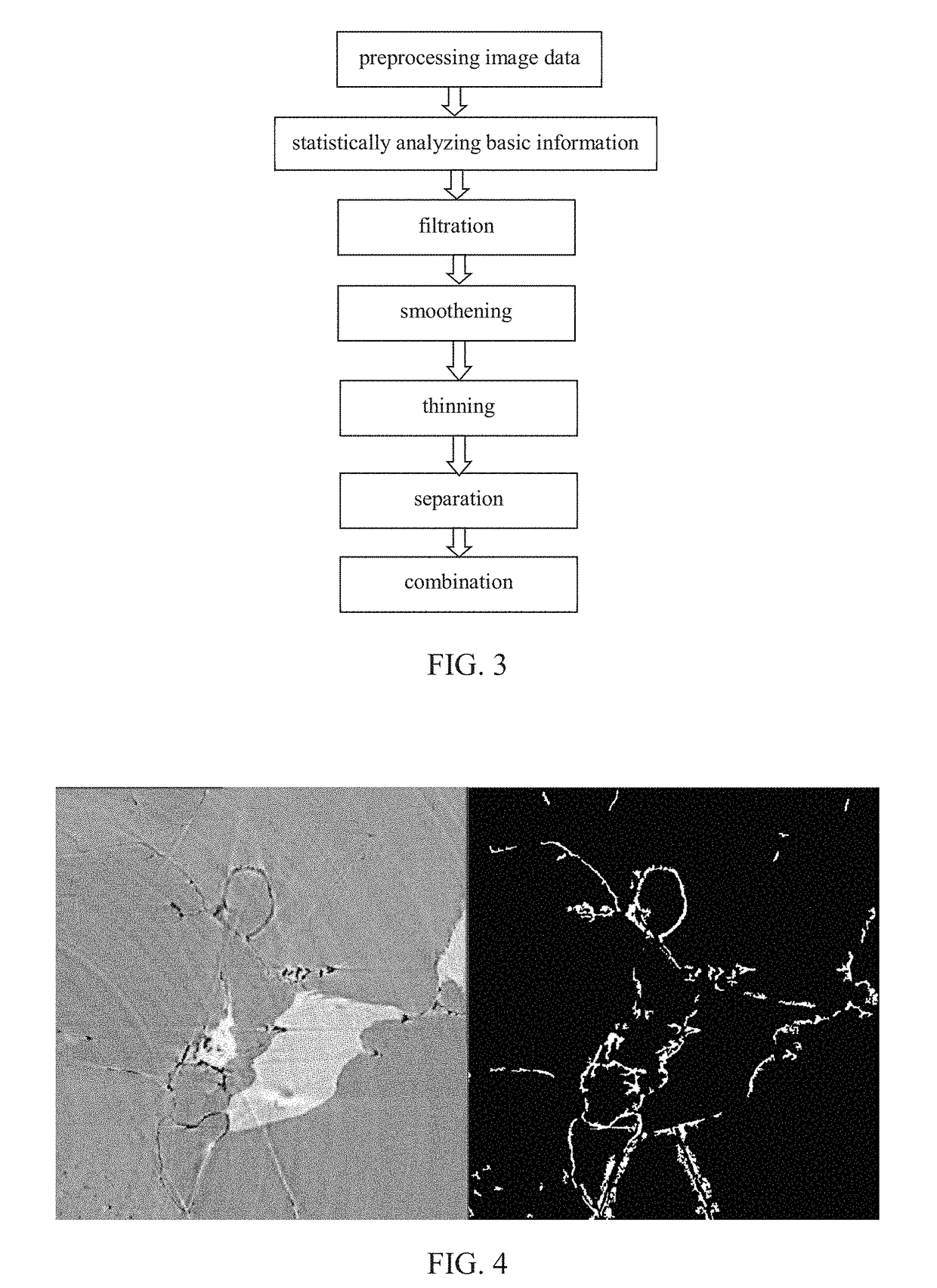
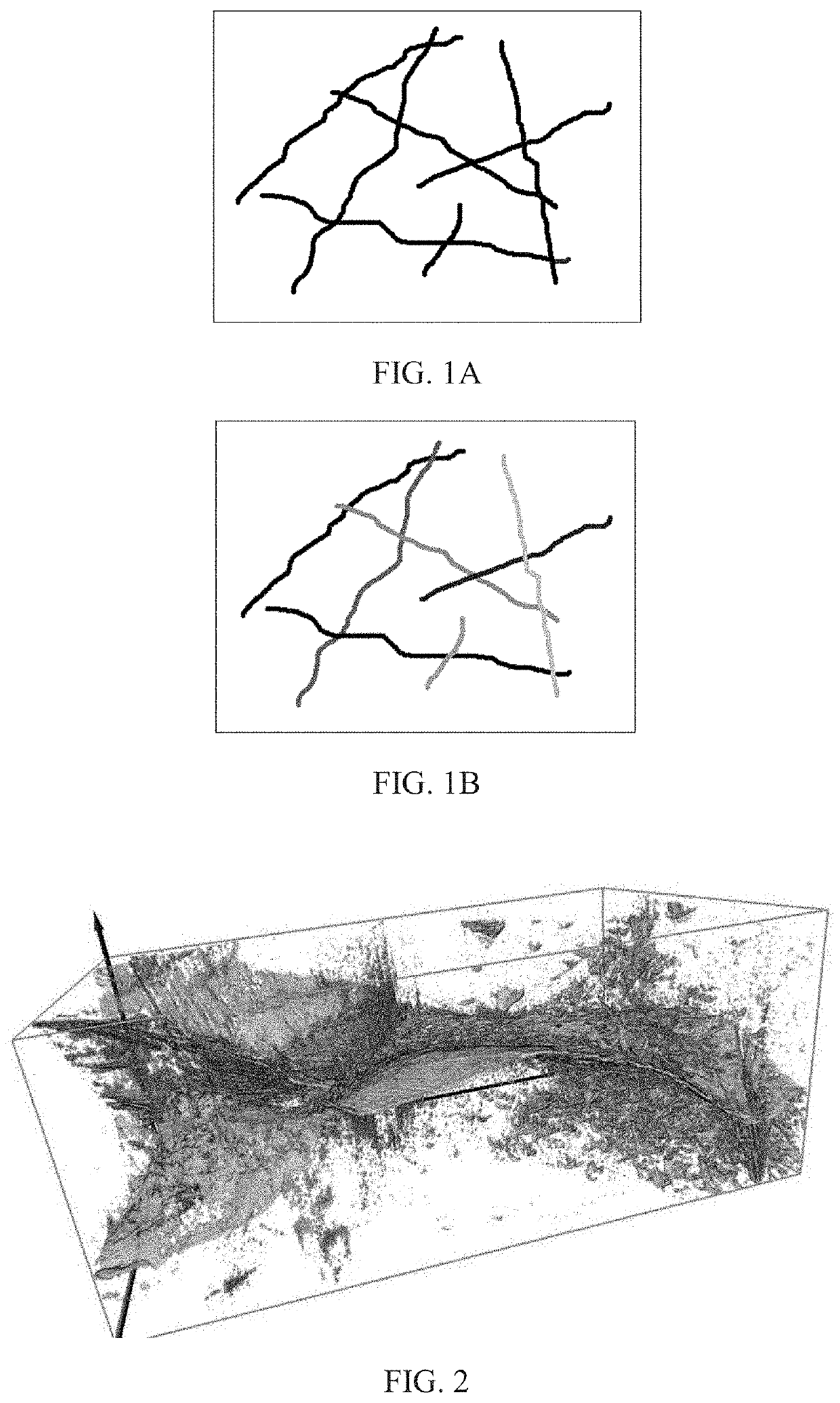
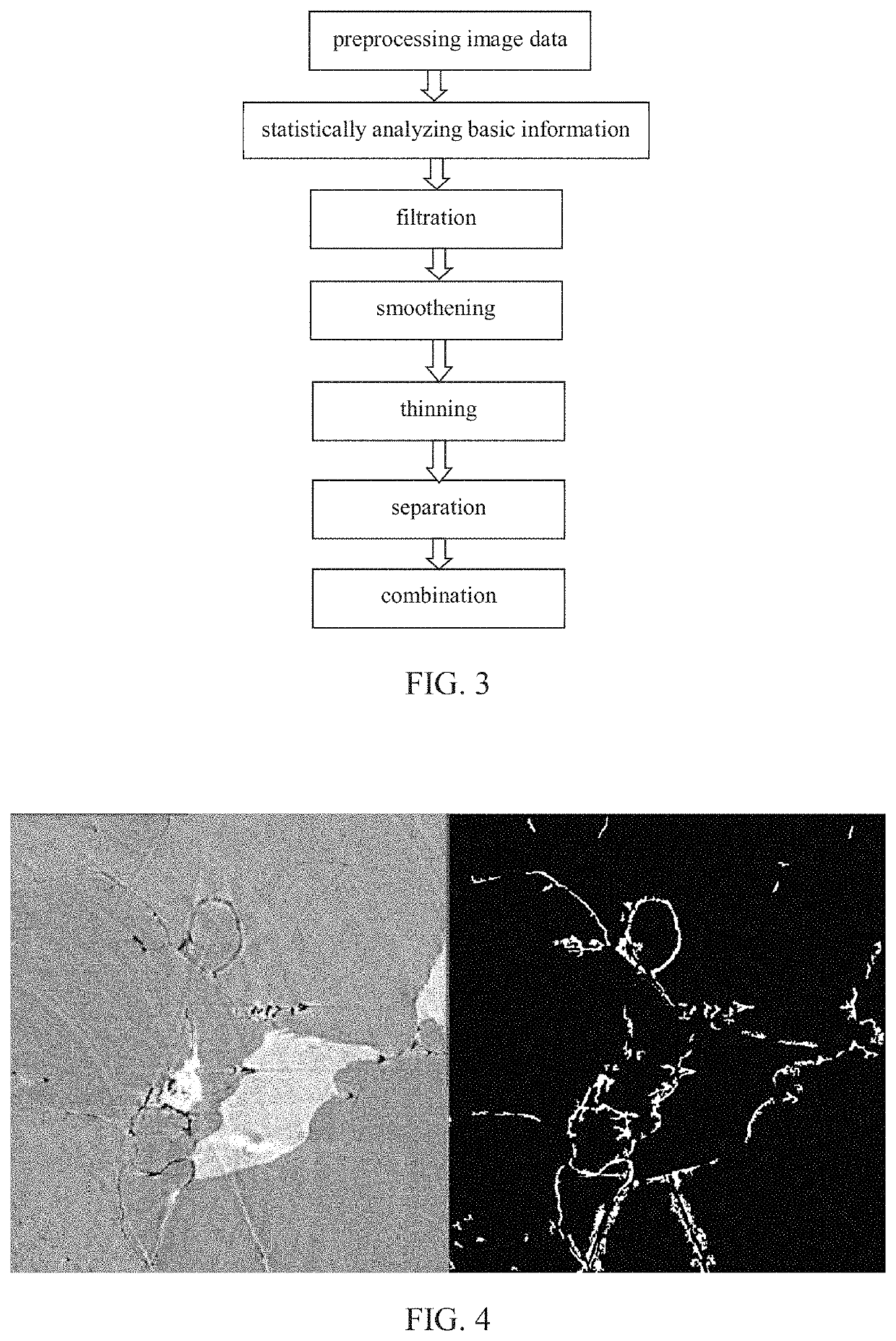
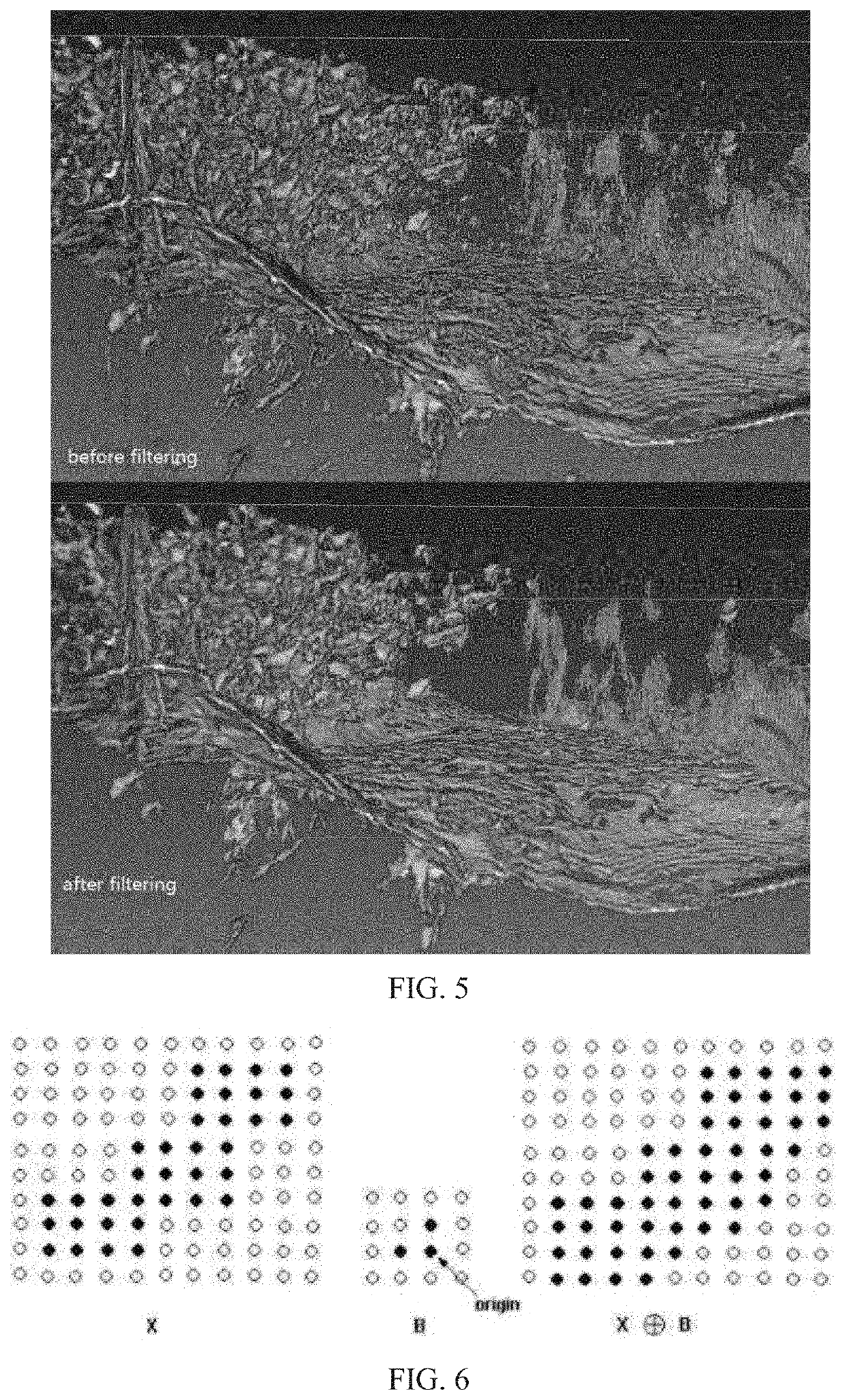
Method of separating, identifying and characterizing cracks in 3D space
ActiveUS20170372470A1Accurate calculationAccurate representationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionVoxel
The present invention discloses a method of separating, identifying and characterizing cracks in 3D space, which processes as follows to a volumetric image, so as to perform the separation, identification and the characterization of the cracks in the 3D space: 1) preprocessing digital image; 2) statistically analyzing basic information of the digital image: the basic information of the image includes porosity, connectivity of each pore, statistics of pore size, and position, size, orientation and anisotropy of each pore-structure; 3) filtration: removing non-crack structure in the image; 4) smoothening: smoothening and mending the image; 5) thinning: thinning the void structure into a thickness d (d can be any value, but more appropriate to be 2 to 3 voxels generally) in a direction with shortest extension in the 3D space; 6) separation: separating intersected cracks in a crack network by breaking the connections; 7) combination: combining those elongated cracks that are disconnected in the last step, merging tiny structures that are formed during the separation to a nearby large cluster, and restoring cracks to the thickness before thinning, and eventually giving out the characterization of the cracks. In the following expression, the wording “void” is used more, emphasizing the “empty” gap in the image rather than the rock solid. In this patent application, it is mainly for the case where the void appears in a state of crack, not excluding the case where the void appears in a state of small pore.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
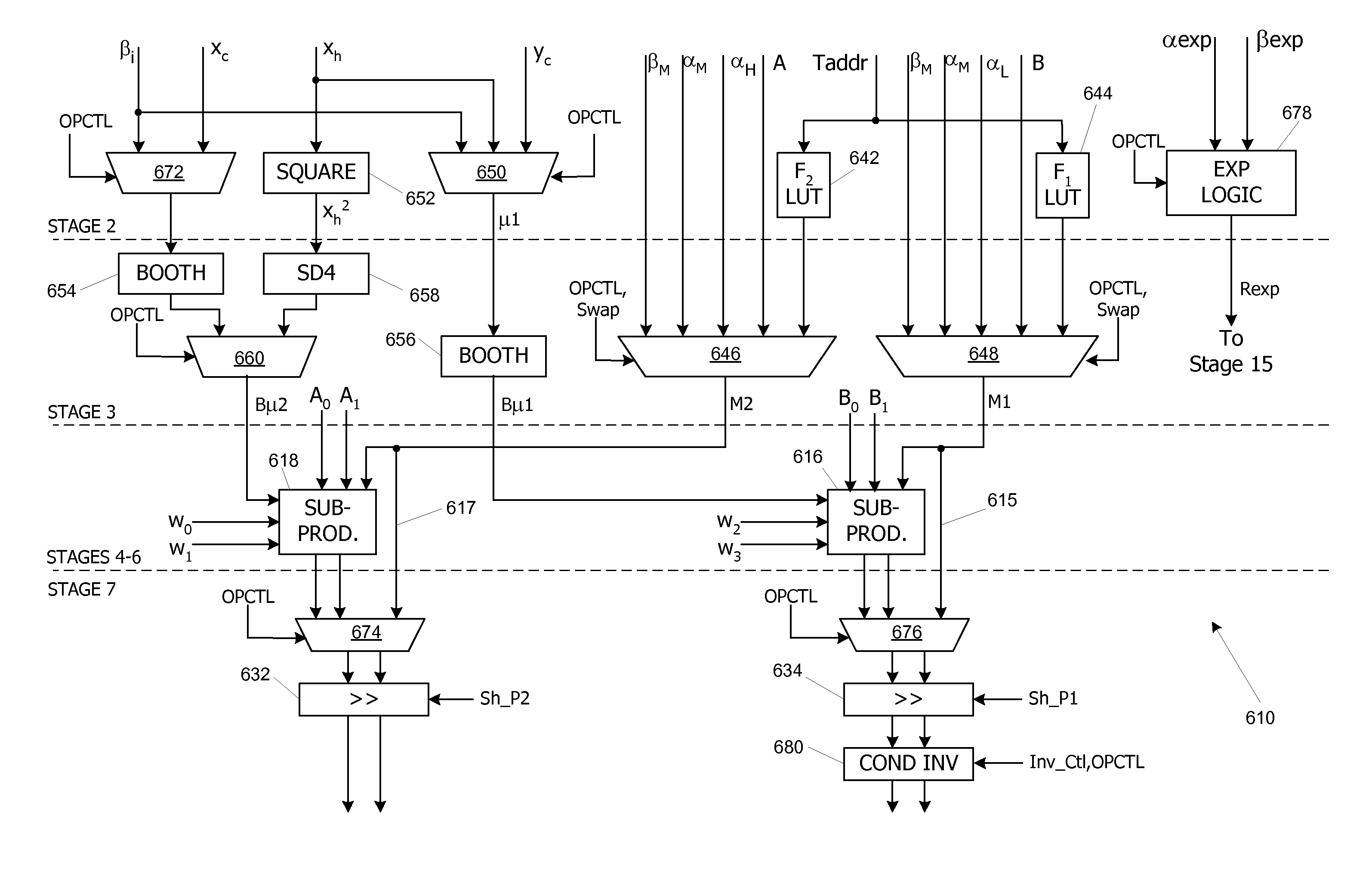
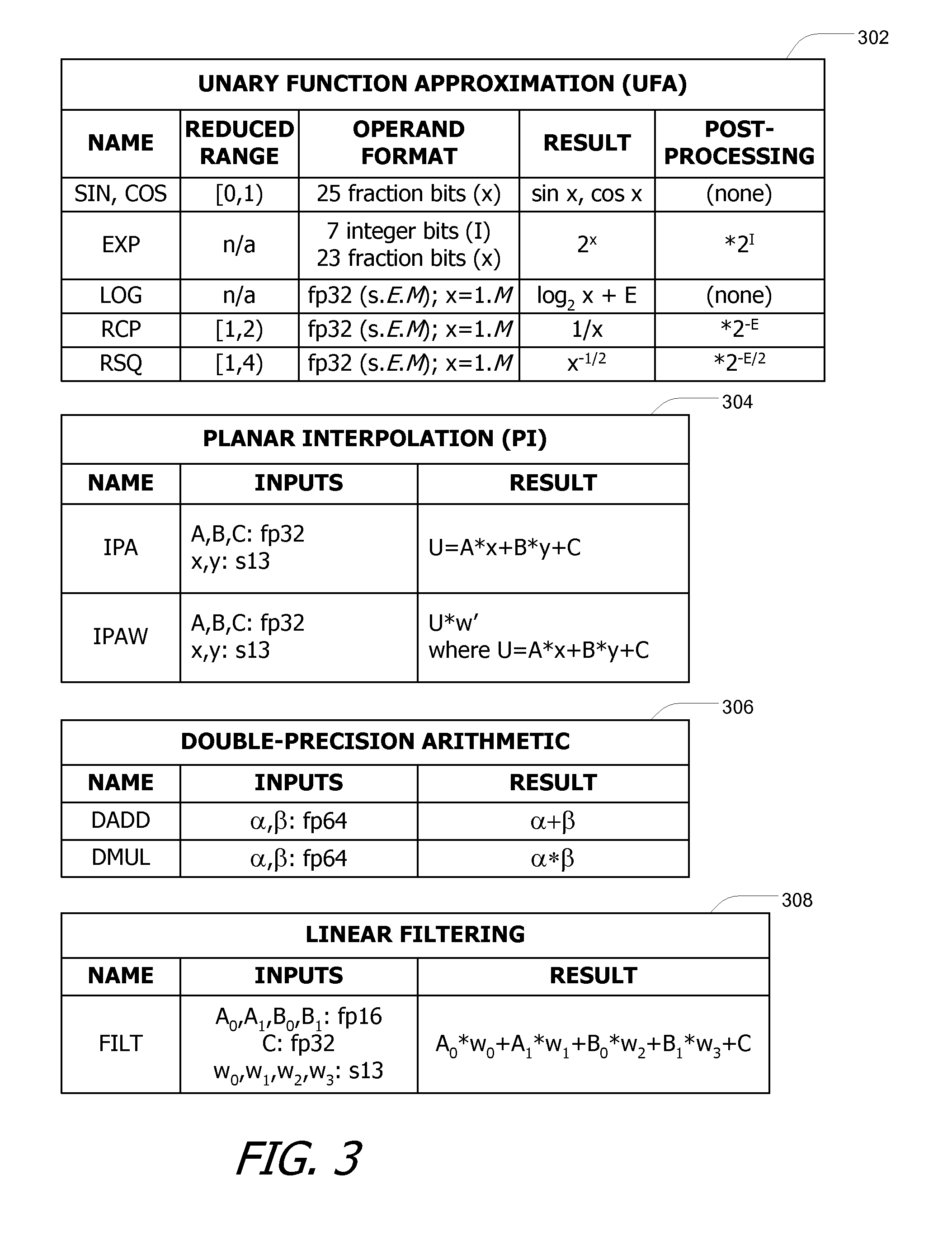
Multipurpose functional unit with double-precision and filtering operations
ActiveUS8051123B1Increase speedComputation using denominational number representationBinary multiplierProcessor register
A multipurpose arithmetic functional unit selectively performs planar attribute interpolation, unary function approximation, double-precision arithmetic, and / or arbitrary filtering functions such as texture filtering, bilinear filtering, or anisotropic filtering by iterating through a multi-step multiplication operation with partial products (partial results) accumulated in an accumulation register. Shared multiplier and adder circuits are advantageously used to implement the product and sum operations for unary function approximation and planar interpolation; the same multipliers and adders are also leveraged to implement double-precision multiplication and addition.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
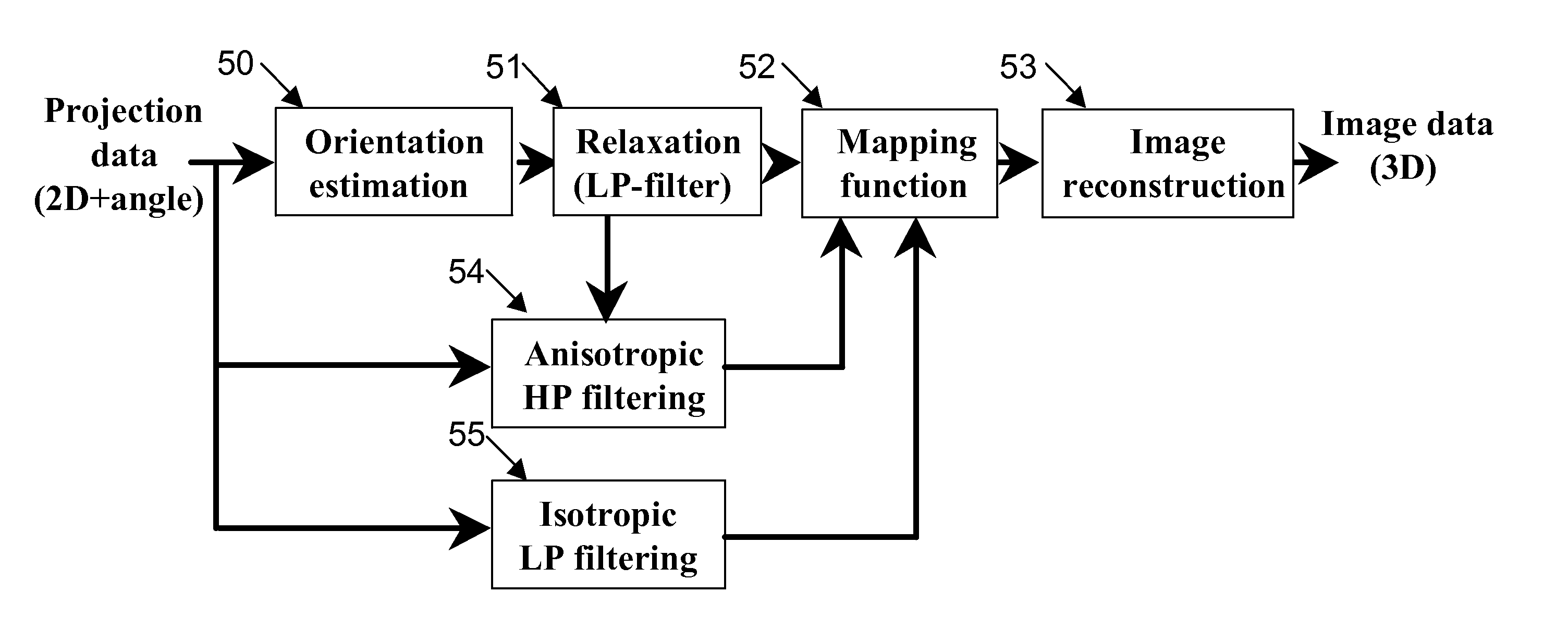
Adaptive anisotropic filtering of projection data for computed tomography
ActiveUS20080069294A1Reduce high frequency noiseReduce radiation doseImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionLow-pass filterImaging quality
CT imaging is enhanced by adaptively filtering x-ray attenuation data prior to image reconstruction. Detected x-ray projection data are adaptively and anisotropically filtered based on the locally estimated orientation of structures within the projection data from an object being imaged at a plurality of rotation positions. The detected x-ray data are uniformly low pass filtered to preserve the local mean values in the data, while the high pass filtering is controlled based on the estimated orientations. The resulting filtered data provide projection data with smoothing along the structures while maintaining sharpness along edges. Image noise and noise induced streak artifacts are reduced without increased blurring along edges in the reconstructed images. The enhanced image allows reduced x-ray dose while maintaining image quality.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
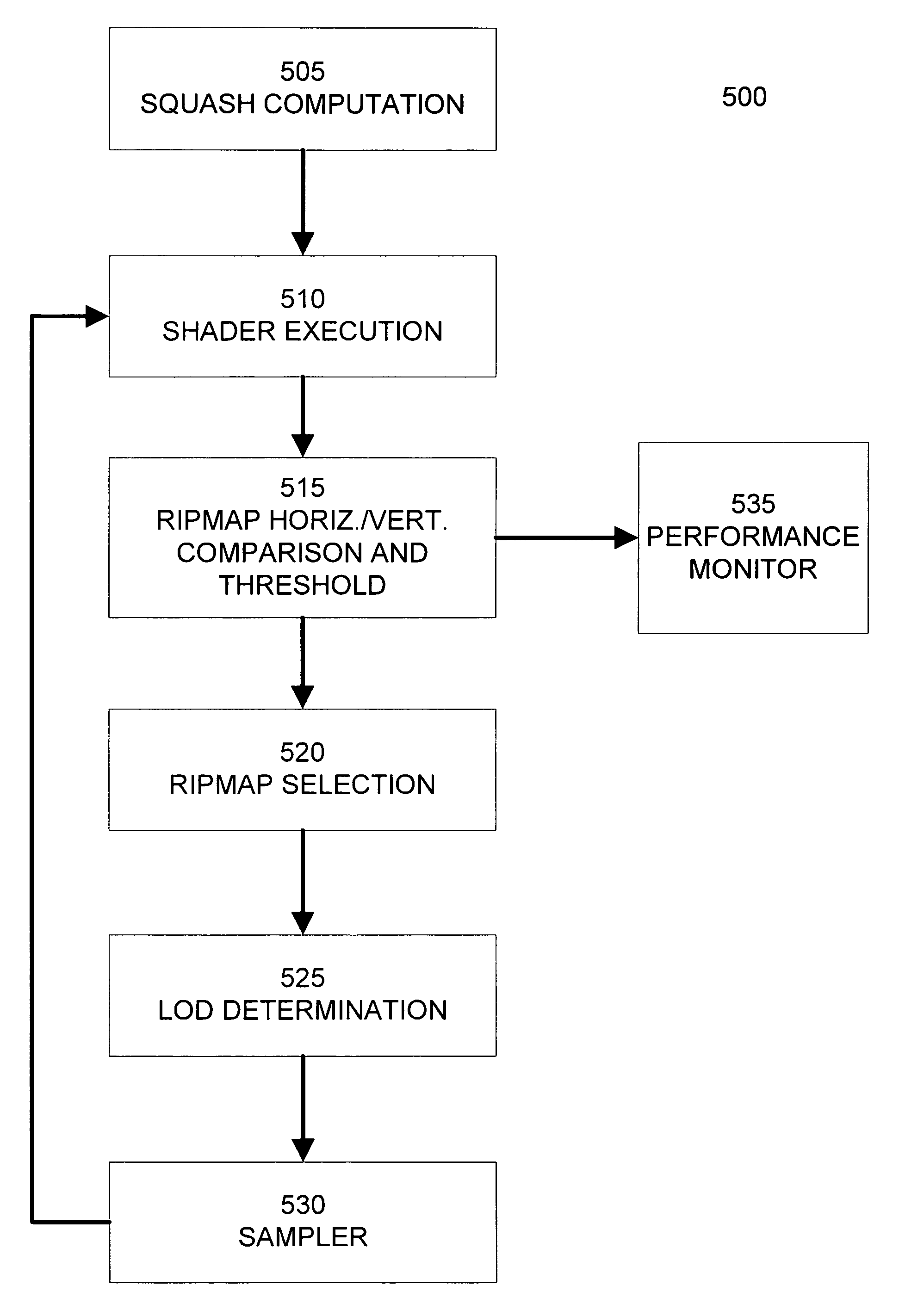
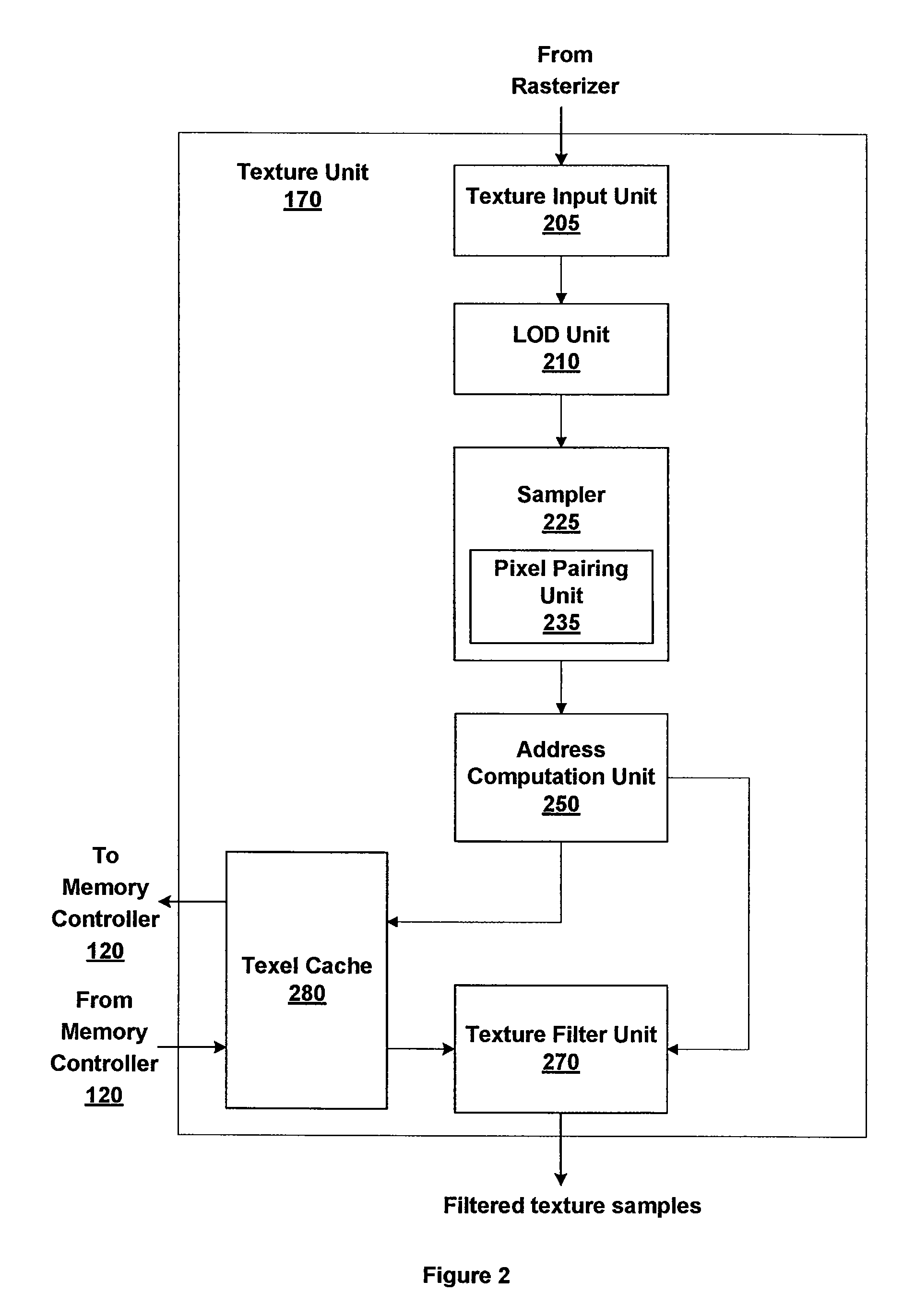
Anisotropic texture prefiltering
ActiveUS7525551B1Optimize anisotropic filteringMaximize anisotropic texture filtering performanceDetails involving antialiasingCathode-ray tube indicatorsPattern recognitionGraphics
Ripmapping and footprint assembly are used to anisotropically filter texture maps. A subset of the set of ripmaps associated with a base texture is created and stored. The subset includes ripmaps selected to maximize anisotropic texture sampling performance and to minimize the texture memory requirements. For pixel footprints not aligned with the anisotropy of ripmaps or requiring a ripmap outside of the subset, footprint assembly is used to perform anisotropic filtering by taking multiple isotropic probes from a mipmap. For texture samples aligned within a tolerance range of the anisotropy of a ripmap, footprint assembly constructs an anisotropic texture sample from one or more samples of a ripmap. Ripmap statistics are collected during texture mapping to dynamically determine an optimal subset of ripmaps, and additional ripmaps can be added to the subset on demand if warranted. A graphics driver can analyze ripmap statistics to determine the subset of ripmaps.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
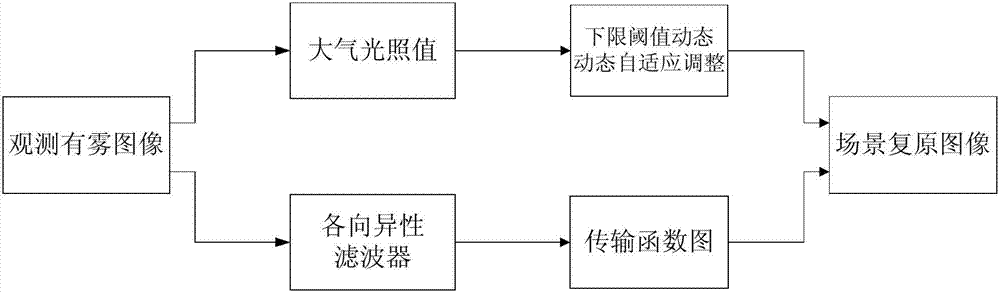
Defogging method based on anisotropic filtering
The invention relates to a defogging method based on anisotropic filtering, belonging to the field of image processing and computer vision, and providing the defogging method based on anisotropic filtering which can improve the visual effect of images taken in a foggy day, a rainy day and the like. The method comprises the following steps: 1) calculating an atmospheric light value through image guide; 2) utilizing an anisotropic filter to calculate a transfer function diagram through image guide; 3) dynamically and self-adaptively adjusting a lower threshold of defogging; and 4) according to an observed foggy image, the atmospheric light value and the atmospheric light value diagram in an atmospheric scattering physical model, recovering a scene image. The method can self-adaptively process various images taken in the foggy day, the rainy day and the like on the basis of the atmospheric scattering physical model, the defogged images have the ideal contrast and visual effect, and the overall enhancement effect is superior to the traditional image defogging method.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Automatically initialized local active contour model heart and cerebral vessel segmentation method
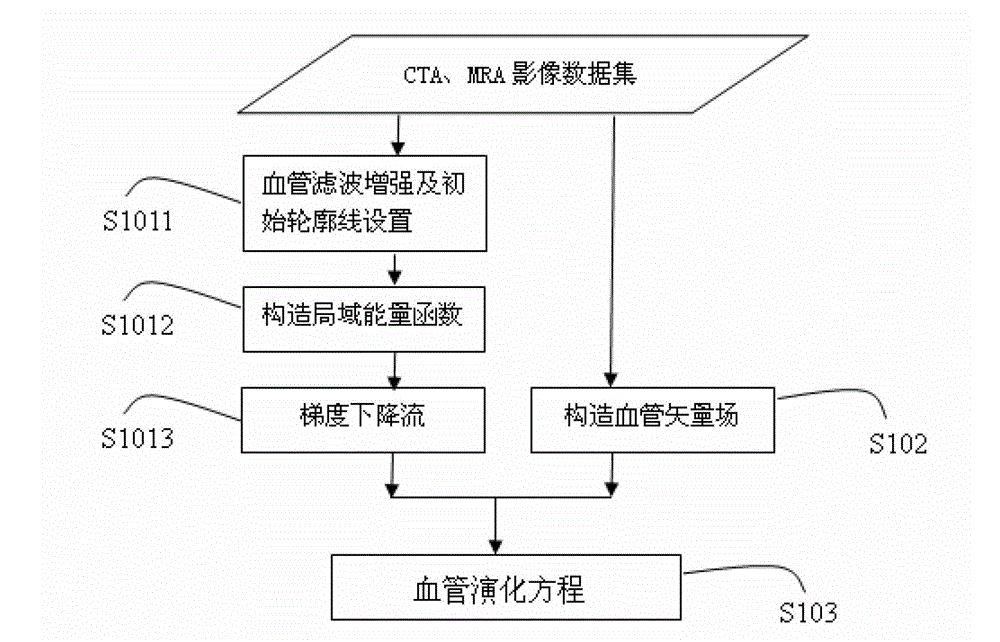
The invention provides an automatically initialized local active contour model heart and cerebral vessel segmentation method. The method comprises the following steps: performing anisotropic filtering on a three-dimensional vessel according to the tubular feature of the vessel in medical image data to acquire an initial contour line; constructing a local energy function; minimizing the local energy function by a gradient descent method to acquire the corresponding gradient descent flow; constructing a vessel vector field according to the vessel shape measurement of the medical image data; and finally combining the gradient descent flow and the vessel vector field to acquire a vessel evolution equation. The method can automatically set the initial contour line according to the vessel shape and is precise in segmentation, high in efficiency and high in robustness.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
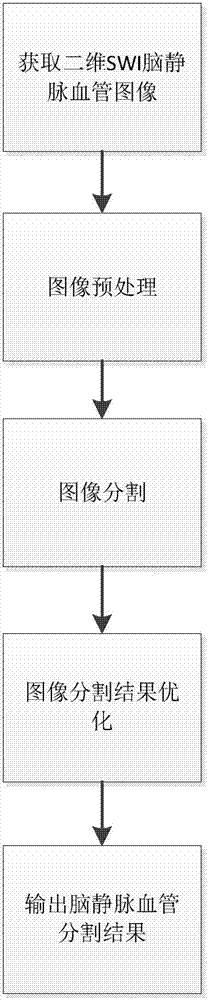
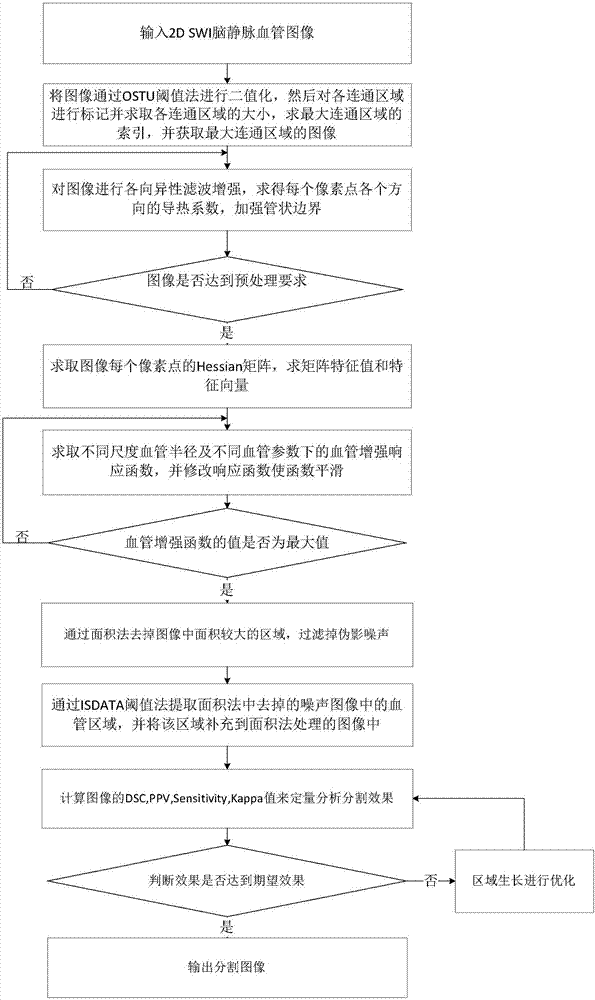
SWI (Susceptibility Weighted Imaging) image based cerebral vein vessel segmentation method
InactiveCN107248155AStrengthen the tubular structureGood removal effectImage enhancementImage analysisBoundary contourSusceptibility weighted imaging
The invention relates to an SWI (Susceptibility Weighted Imaging) image based cerebral vein vessel segmentation method, which comprises the steps of reading each two-dimensional SWI cerebral vein vessel image through magnetic resonance equipment, adjusting the image resolution, and removing the skull and skin covering the periphery of the brain in the images; performing anisotropic filtering enhancement processing on the processed images; then performing improved 2D Hessian matrix filtering enhancement processing; removing a large area of noise caused by artifacts of the brain, segmenting out most small vein vessels, and removing the boundary contour of a brain image; reserving the small vein vessels mistakenly removed; and calculating a DSC value, a PPV, the sensitivity and a Kappa value of each segmented image, and performing optimization on a region with the segmentation effect being poor. The cerebral vein vessel segmentation method can acquire a stable result in different SWI brain images with great difference and under noise and interference conditions, the false positive rate is low, segmentation of a structure which does not belong to the vein is avoided, and requirements of medical images for the safety are met.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
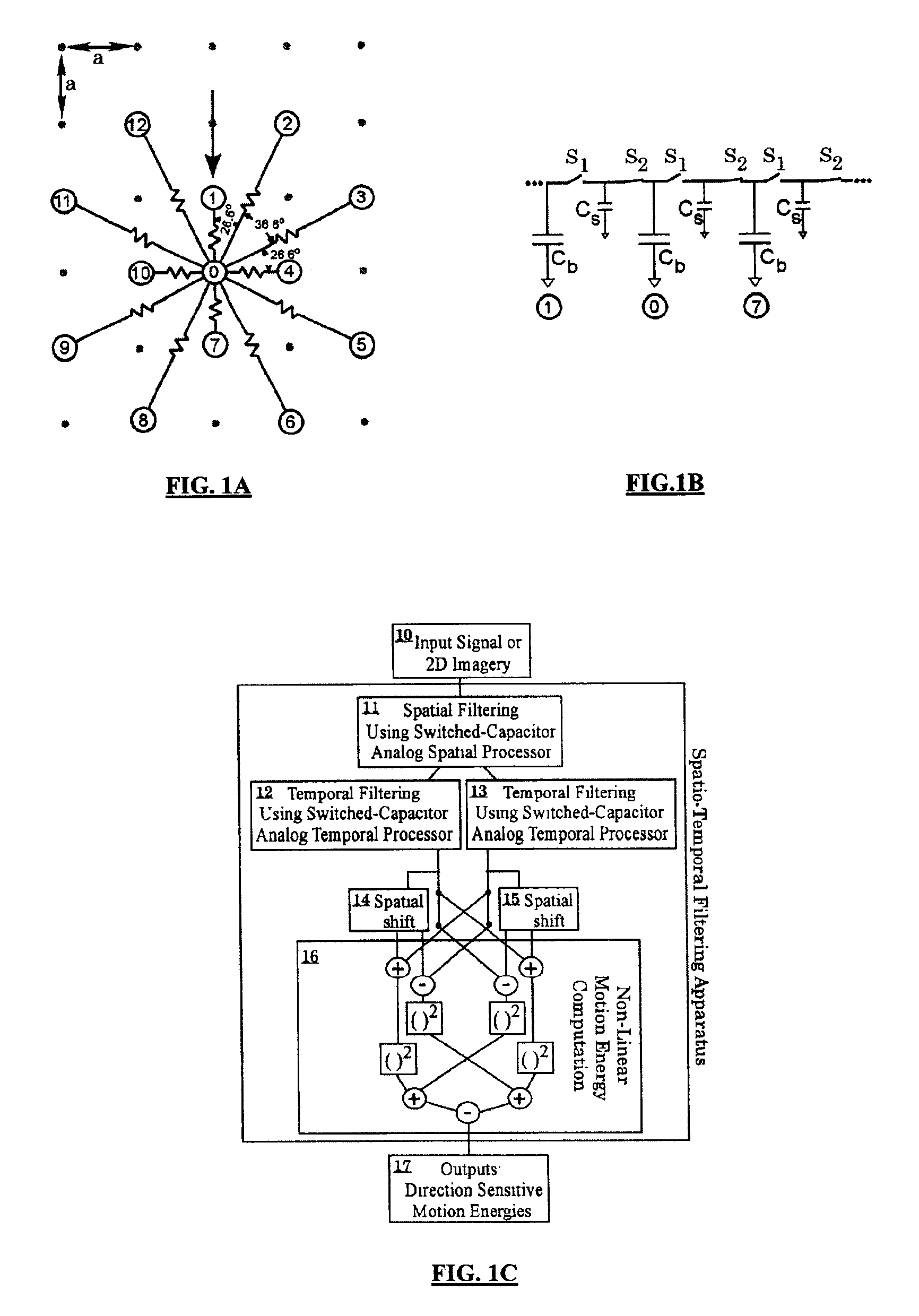
Spatio-temporal filter and method
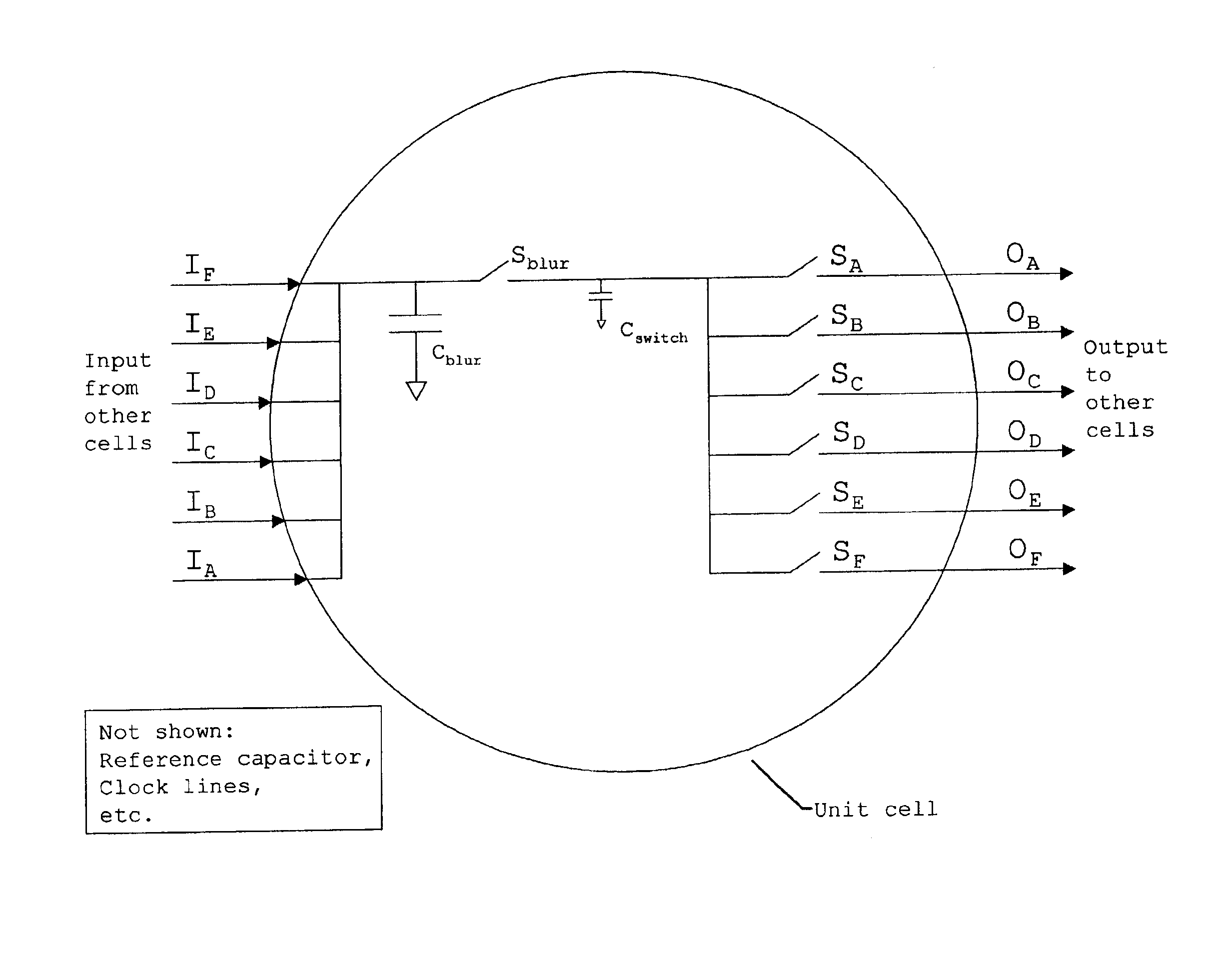
InactiveUS6910060B2Eliminates complicated polymer device processingFlexible control of blurring for spatial frequency filteringElectric/magnetic computingOptical computing devicesStreaming dataData stream
A system, apparatus and methods are disclosed for the spatial and temporal processing of time dependant array data using analog signal processors. In one embodiment, a programmable array of switched capacitors is used to provide tunable parameters for controlling the desired processing of input data streams. The switched capacitor implementation of a spatial filter provides a massively parallel device that can be programmed to perform isotropic and spatially-oriented anisotropic filtering with low power demands. The system further includes the ability to combine differently filtered output streams with independent multiplicative weights. In another embodiment, the nonlinear spatio-temporal motion energy of a two-dimensional image stream data is computed. The spatial-temporal filter is able to combine multiple analog filters, both spatial and temporal, to perform complex spatial-temporal filtering operations implemented by Gaussian kernel filtering chips. It enables the use of analog spatial-temporal filtered data provided by the chip for computing scene motion energy.
Owner:COMPUTATIONAL SENSOR
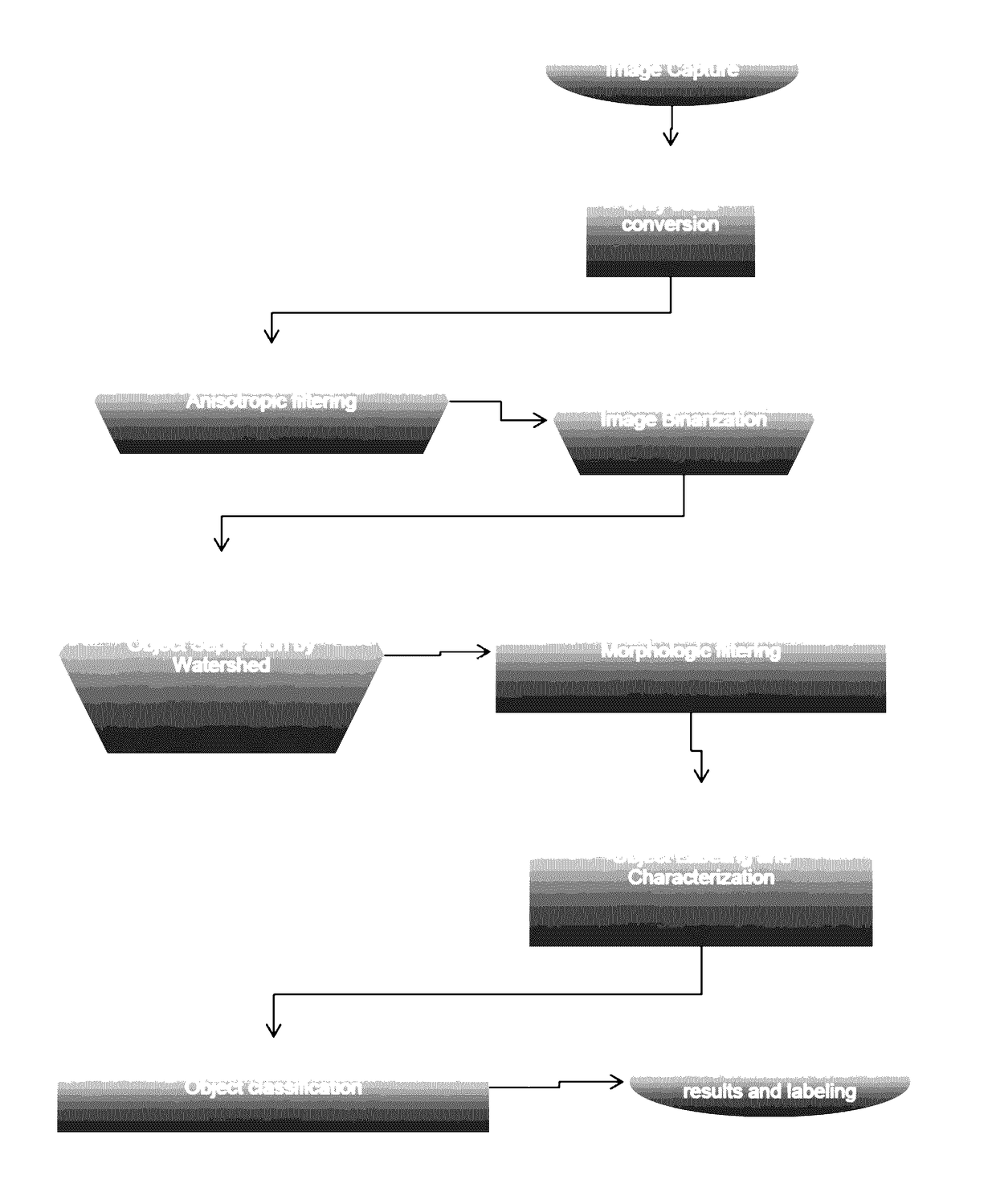
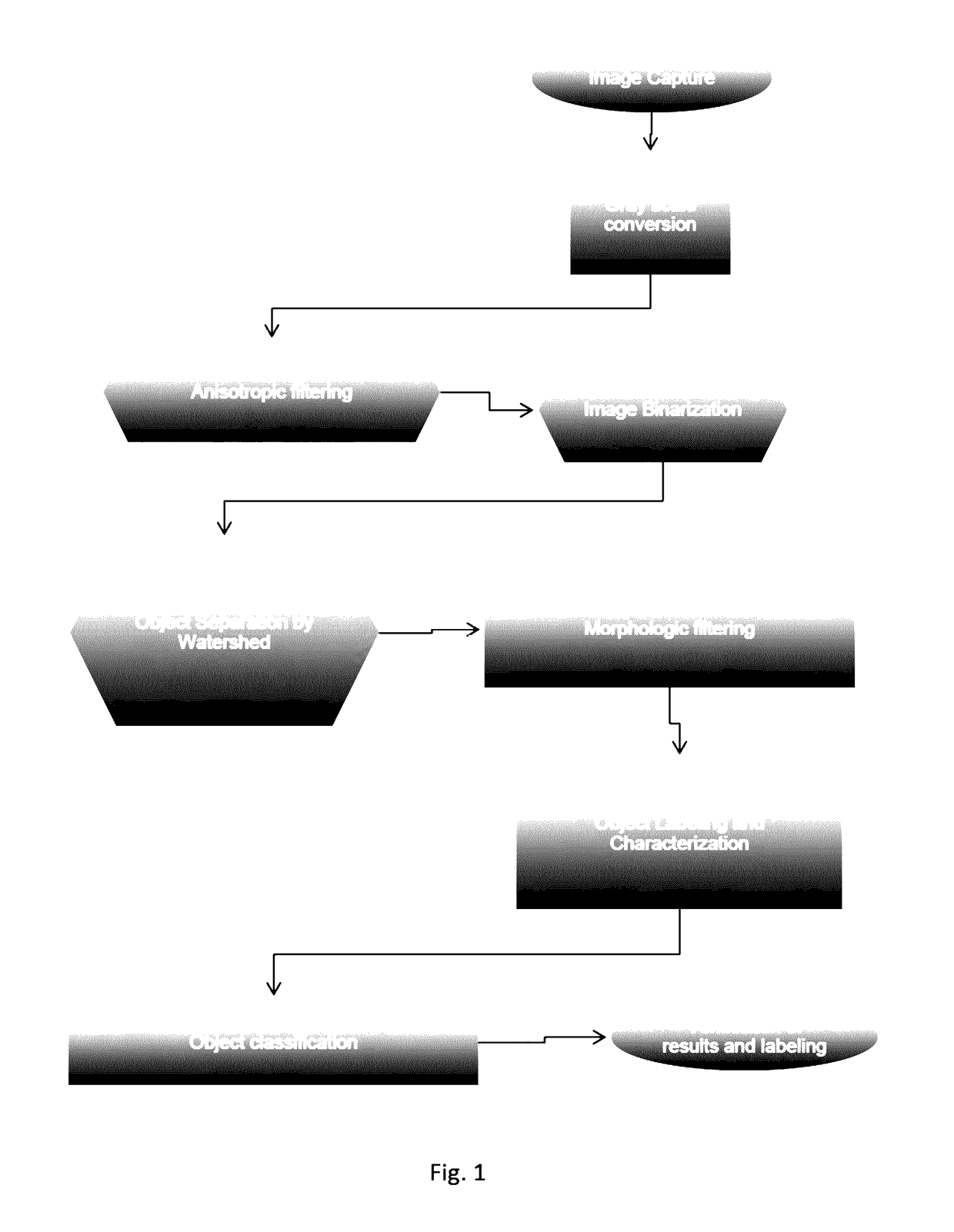
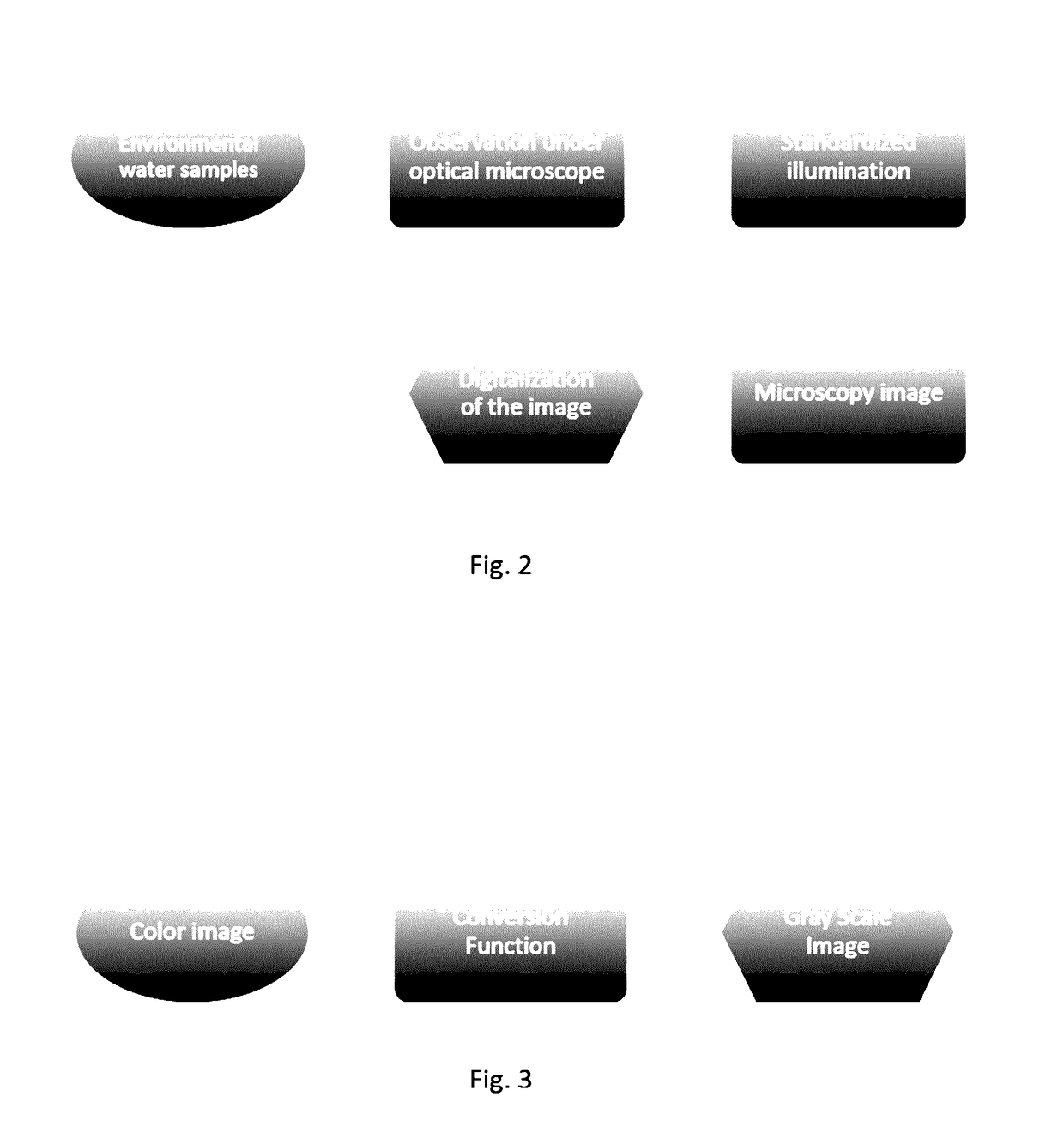
System for the identification and quantification of helminth eggs in environmental samples
ActiveUS20170103504A1Improving speed and precisionSimple and inexpensiveImage enhancementImage analysisSludgeComputer vision
Process and system for identifying and quantifying helminth eggs in water, sludge, biosolid and / or excreta samples among others, from images comprising filtering the images with an anisotropic filter maintaining the borders of the images, obtaining filtered images; filtering the filtered images applying Laplacian of Gaussian detecting changes in the filtered images, and obtaining binarized images; separating the binarized images by means of a filtered distance field Watershed filter, obtaining the images; filtering the images eliminating objects by perimeter compactness, considering the size of the objects in the images filtered again and separating the differences to avoid false positives, obtaining images with identified objects; characterizing the objects identified in the images segmenting the objects by means of gray profiles; and classifying the characterized objects according to a statistic classifier for identifying and quantifying different species of helminth eggs.
Owner:UNIV NAT AUTONOMA DE MEXICO
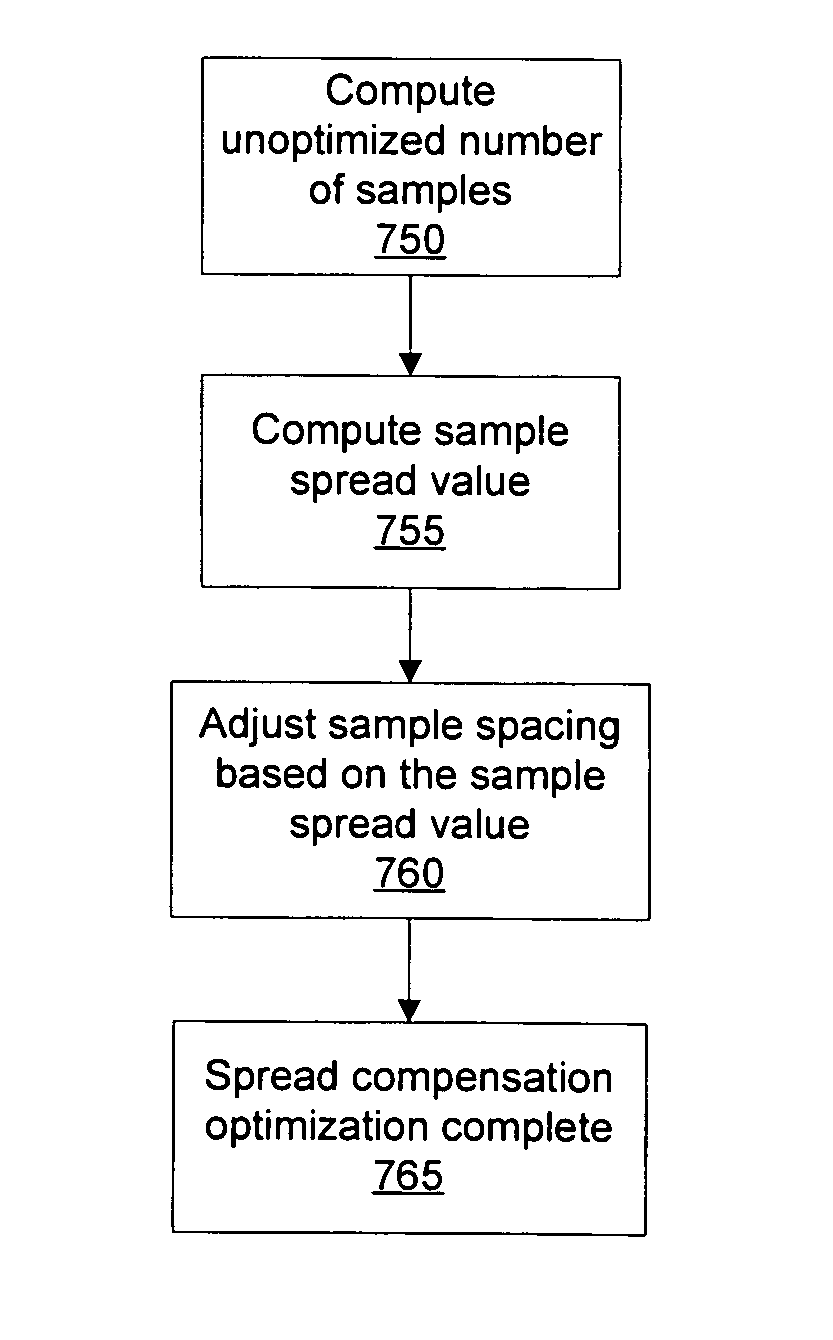
Spread-compensated anisotropic texture sampling
ActiveUS7271810B1Increase or decrease the numberBalance performanceCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingPattern recognitionGraphics
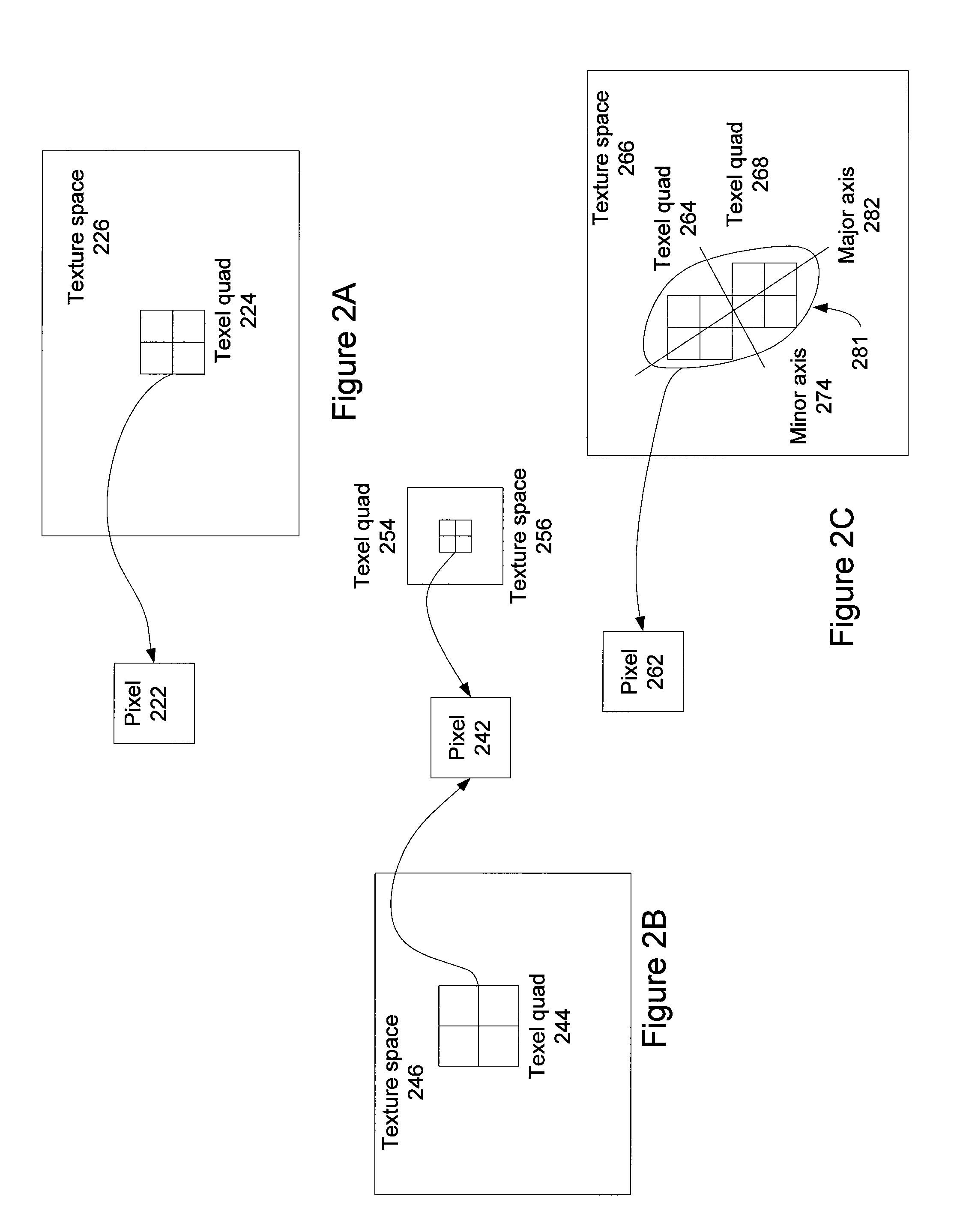
Systems and methods for determining the number of texture samples used to produce an anisotropically filtered texture mapped pixel may improve texture mapping performance or image quality. The number of texture samples may be increased or decreased based on texture state variables that may be specific to each texture map. Furthermore, the texture samples may be positioned along an axis of anisotropy to approximate an elliptical footprint, ensuring that the texture samples span the entire axis of anisotropy. A graphics driver may load the texture state variables and configure a system to modify the number of texture samples and / or position the texture samples used to produce the anisotropically filtered texture mapped pixel.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
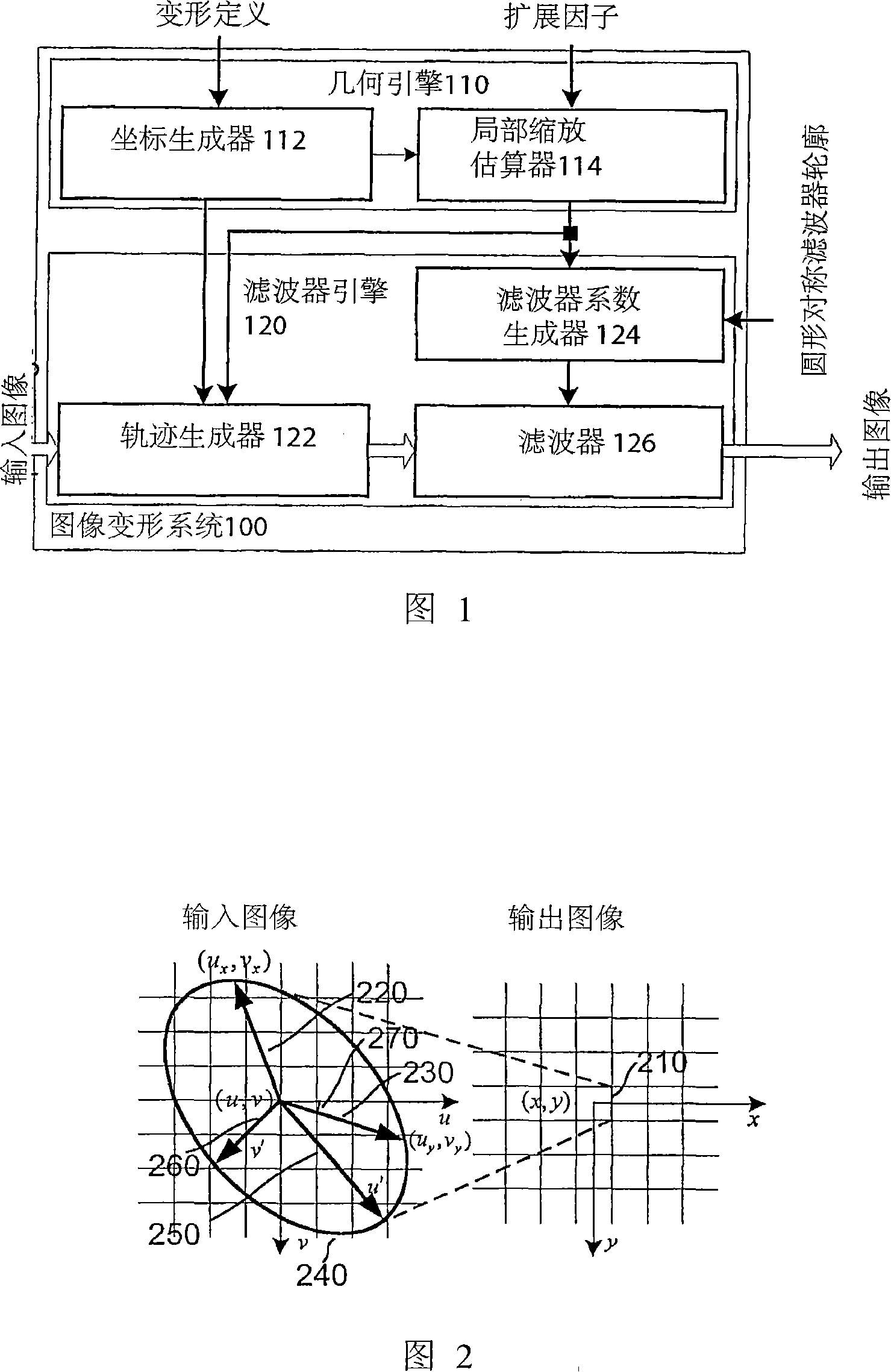
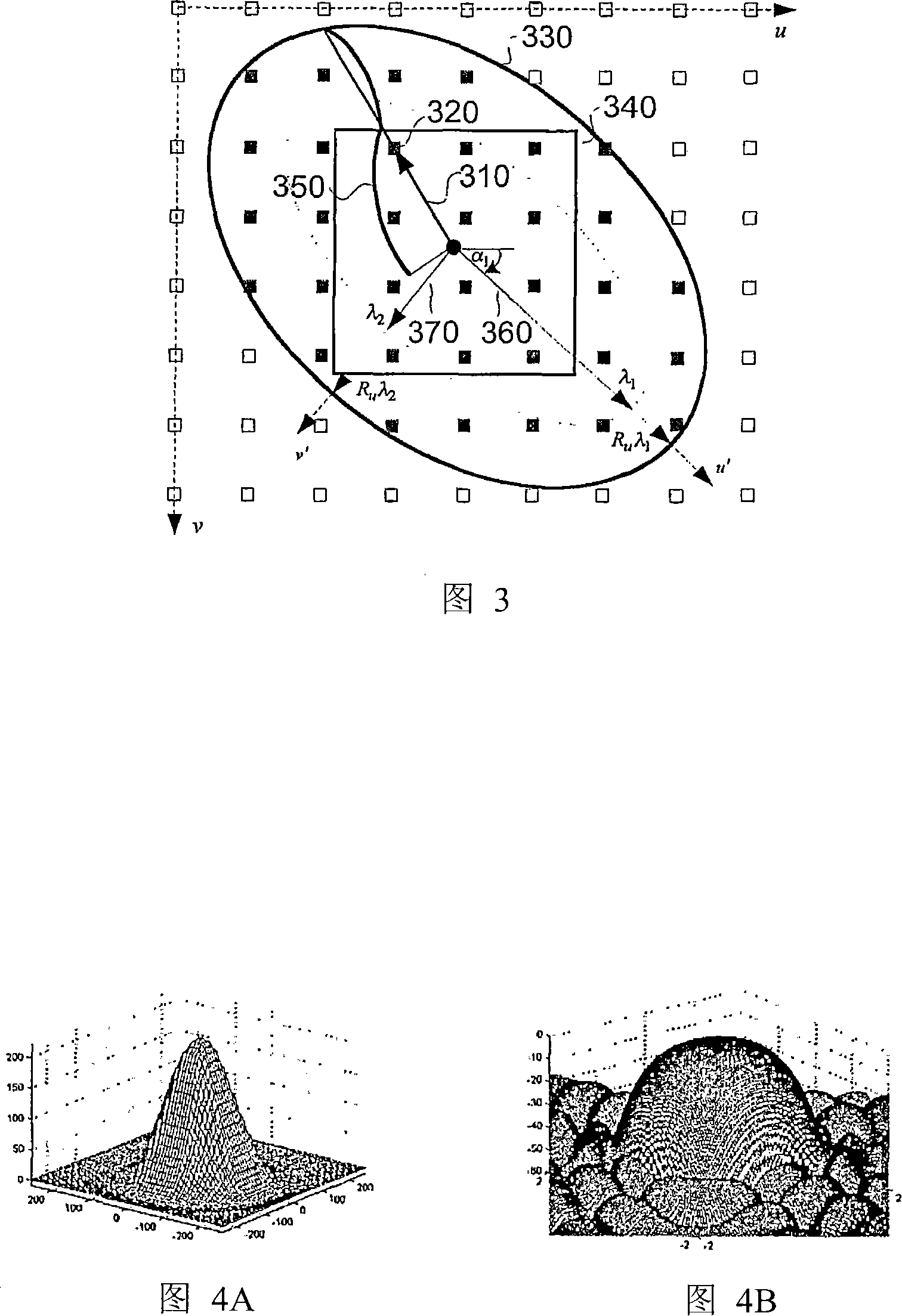
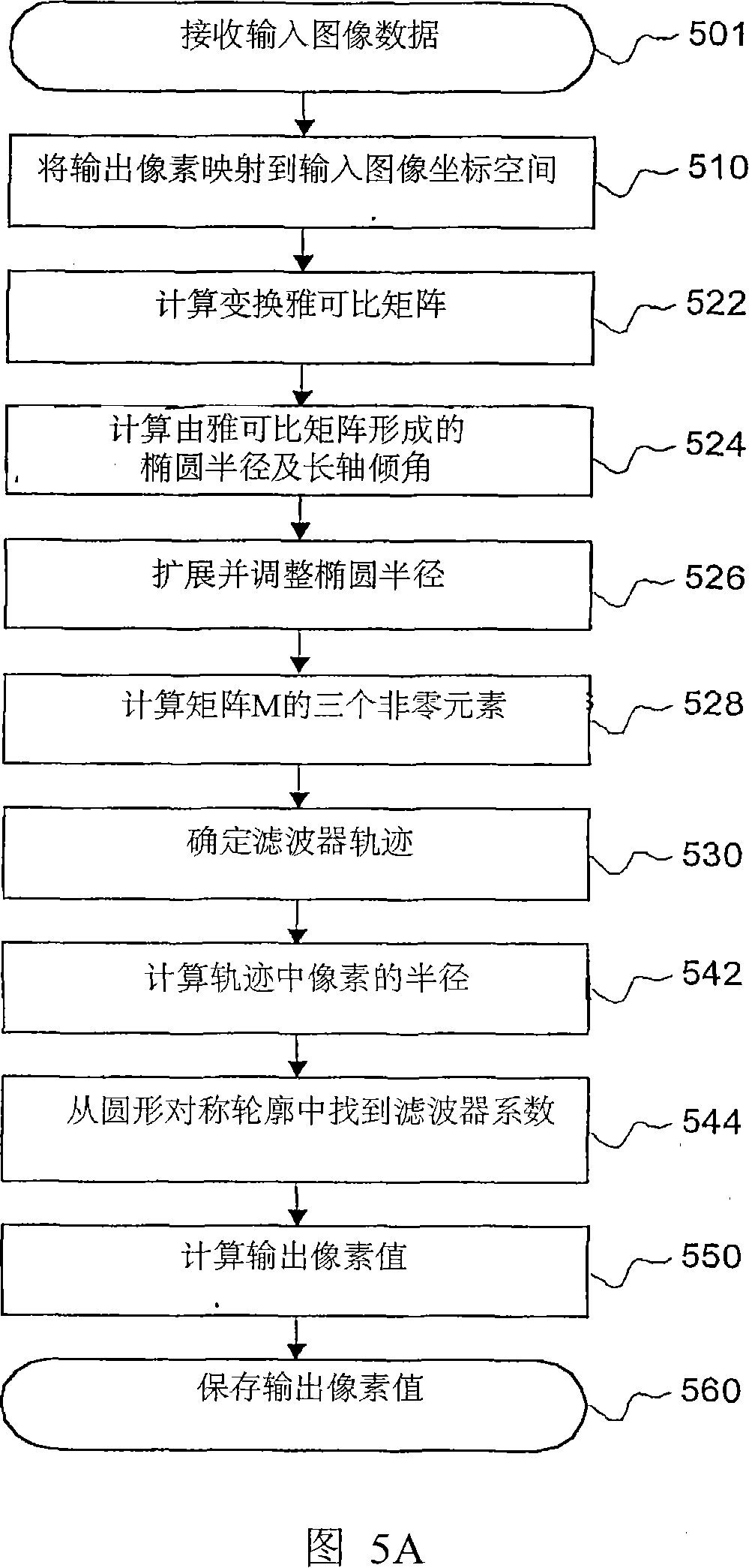
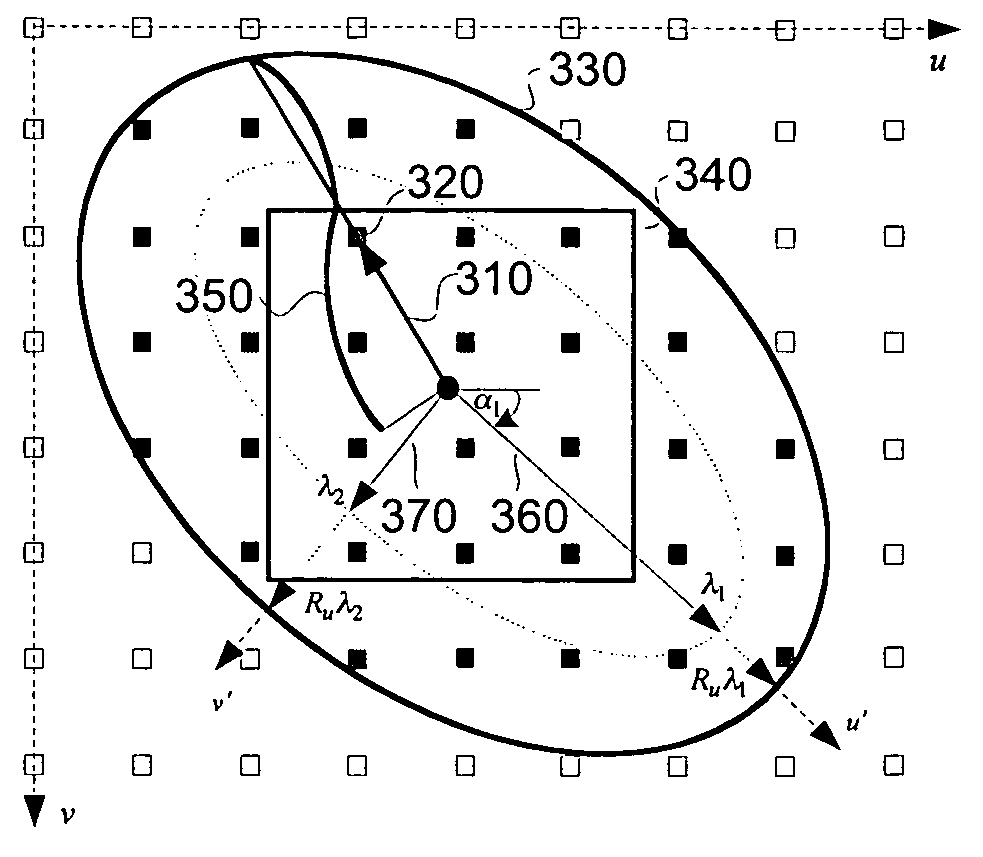
Single channel image deformation system and method using anisotropic filtering
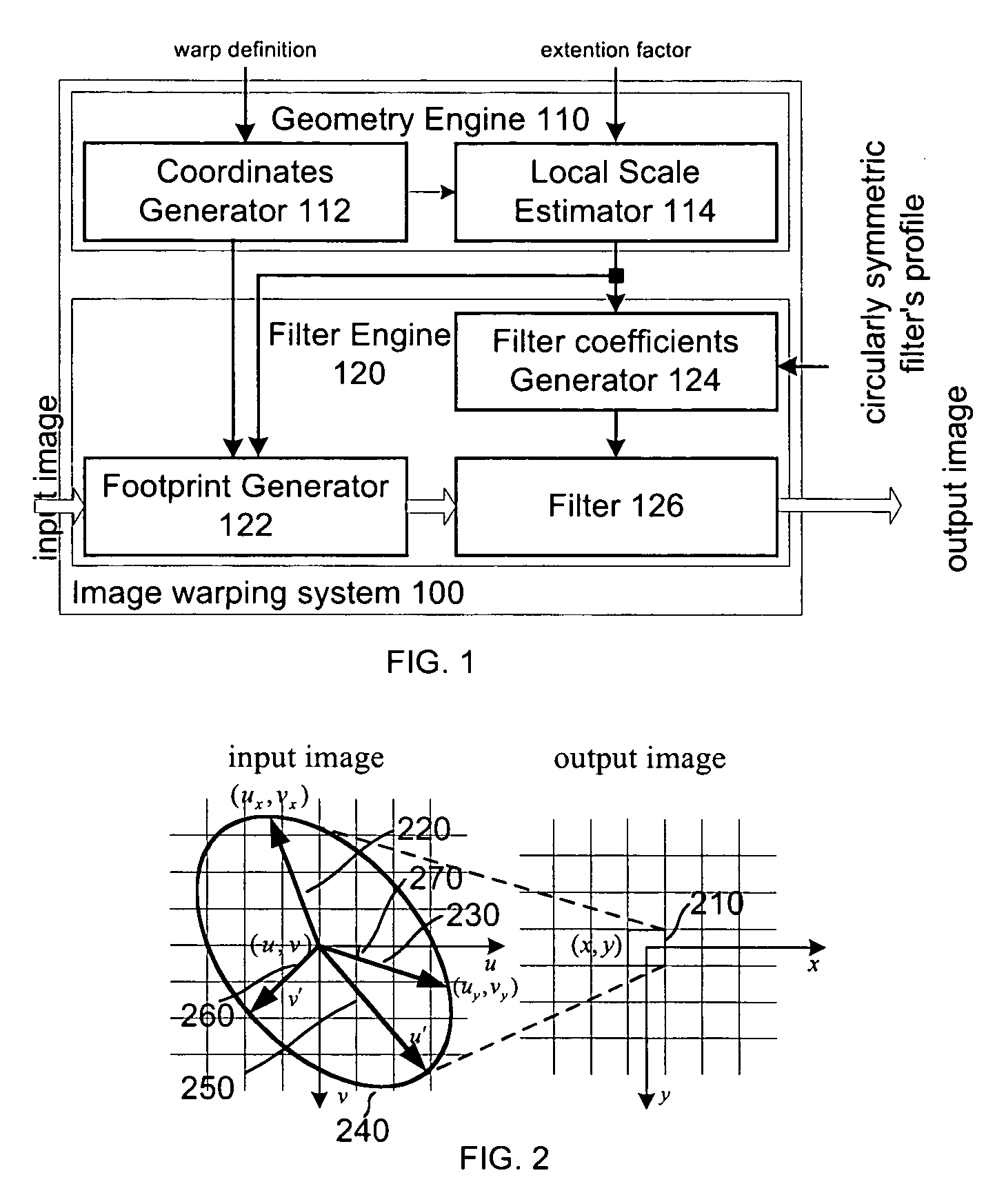
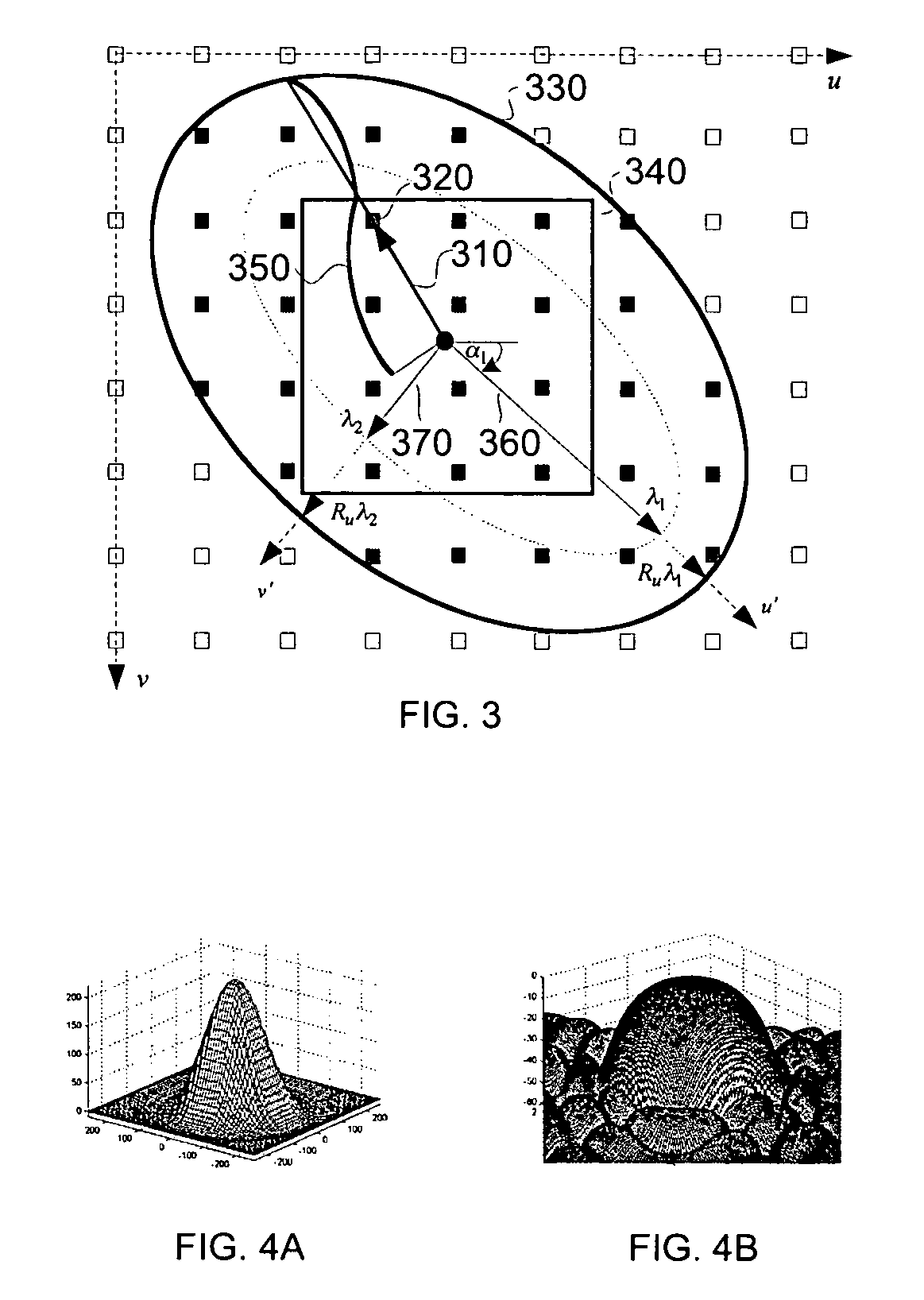
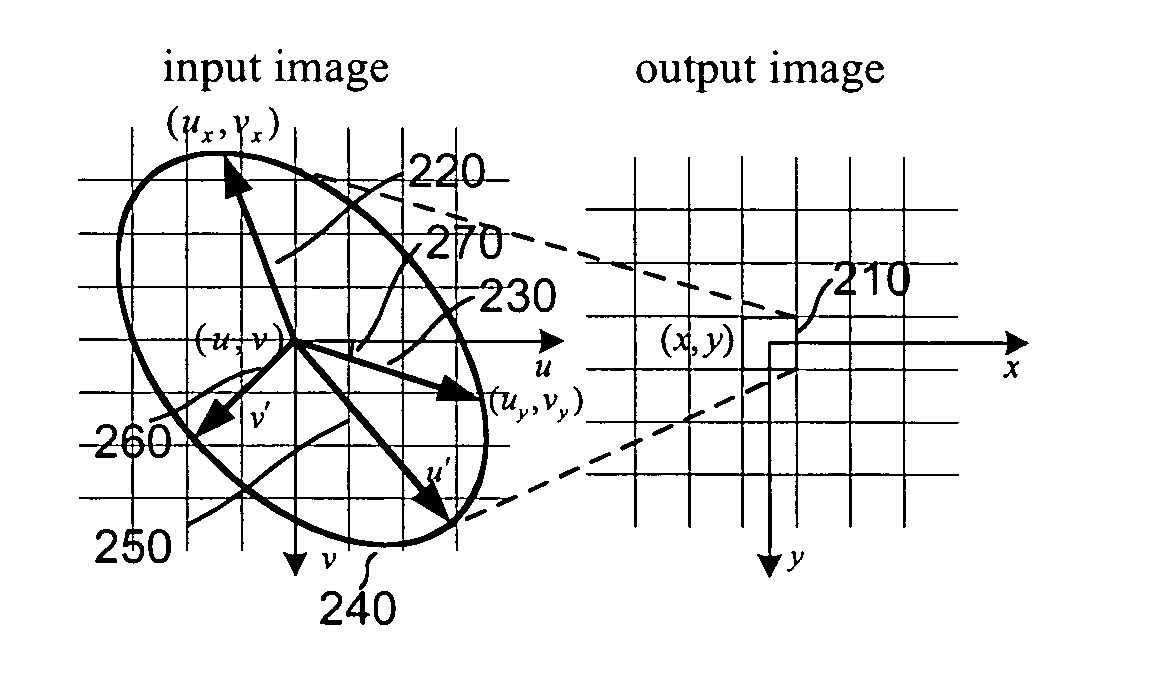
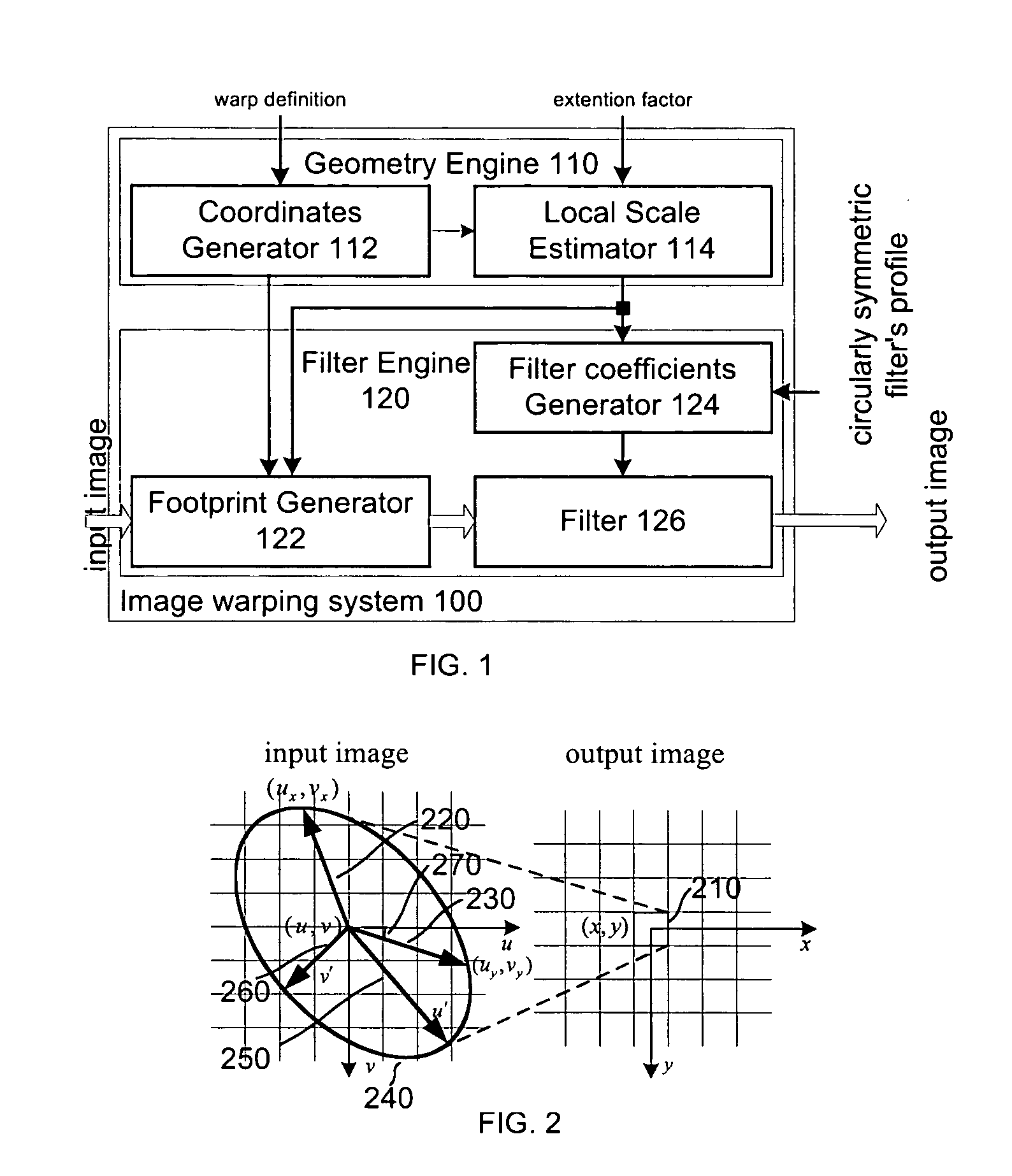
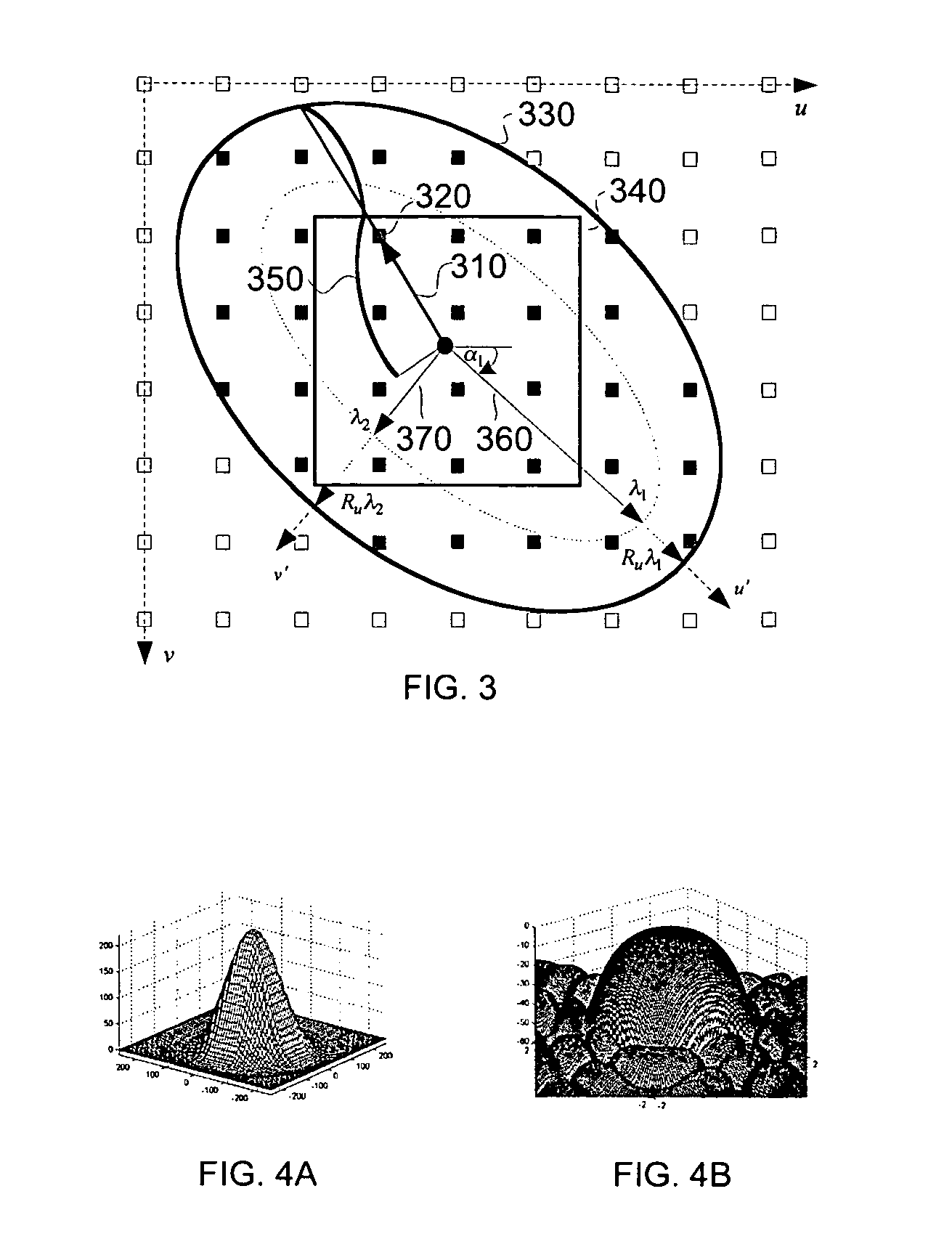
The present invention discloses a method for executing circular symmetrical anisotropic filtering in the extended ellipse or rectangular track in the single-channel digital picture deformation and a system. When the filtering is executed the ellipse is found and adjusted, and the ellipse is approximate to the non-homogeneous image scaling function at the mapping position of the output pixel in the input image space. The linear transformation from the ellipse to the unit circle in the input image space is confirmed to calculate the input image radius in the track and a corresponding wave filter coefficient as the function of the radius. Compromise is executed between the image quality and the processing speed to confirm the track shape. In one embodiment the profiles of the smooth and deformed parts are combined together to generate more clear or detail-reinforced output image. The method and system of the invention can generate lifelike output image without sawtooth distortion and at the same time the definition of the input image can be remained or reinforced.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Single-pass image resampling system and method with anisotropic filtering
ActiveUS7064770B2Conservation valueImage enhancementGeometric image transformationJaggiesImaging quality
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Single-pass image warping system and method with anisotropic filtering
ActiveUS20060050083A1Conservation valueImage enhancementGeometric image transformationImaging qualityImage warping
A method and system for circularly symmetric anisotropic filtering over an extended elliptical or rectangular footprint in single-pass digital image warping are disclosed. The filtering is performed by first finding and adjusting an ellipse that approximates a non-uniform image scaling function in a mapped position of an output pixel in the input image space. A linear transformation from this ellipse to a unit circle in the output image space is determined to calculate input pixel radii inside the footprint and corresponding filter coefficient as a function of the radius. The shape of the footprint is determined as a trade-off between image quality and processing speed. In one implementation, profiles of smoothing and warping components are combined to produce sharper or detail enhanced output image. The method and system of the invention produce natural output image without jagging artifacts, while maintaining or enhancing the sharpness of the input image.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Self-adaptive surface deformation model based CT (Computed Tomography) image liver segmentation method
ActiveCN104318553ALimit oversegmentation problemAvoid balanceImage enhancementImage analysisComputed tomographyDecomposition
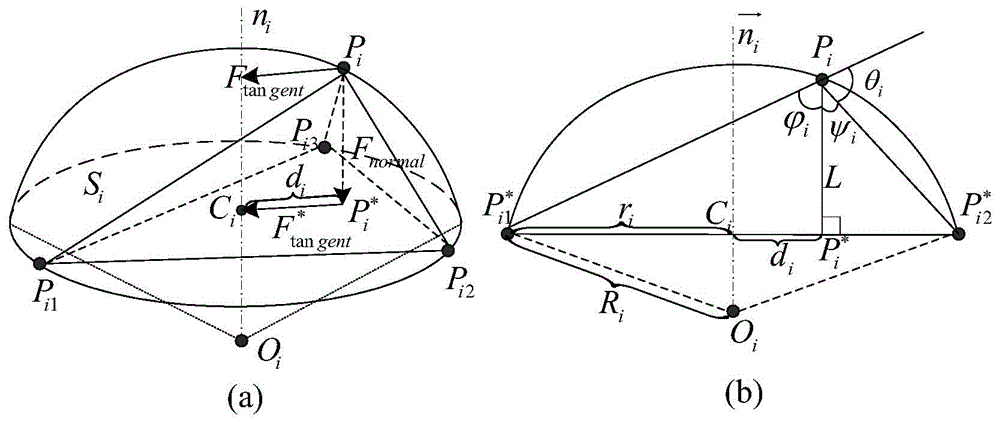
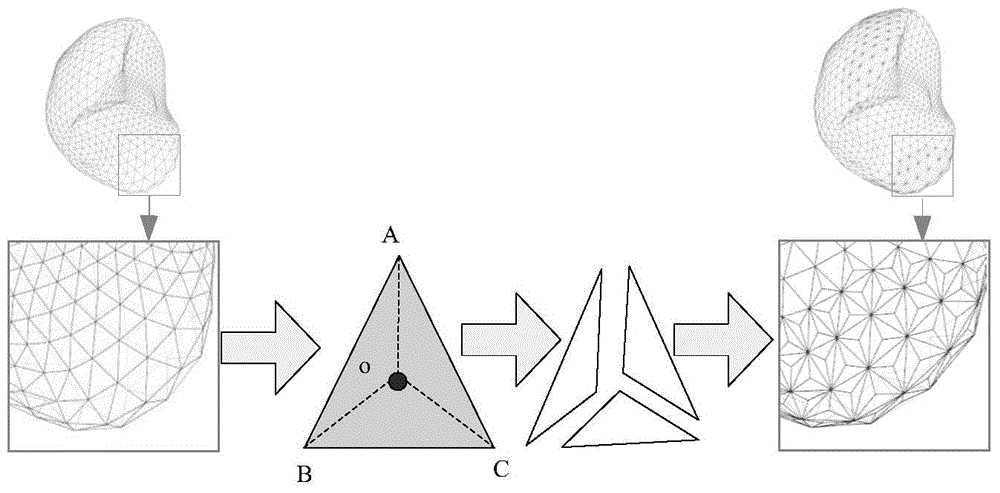
The invention provides a self-adaptive surface deformation model based CT (Computed Tomography) image liver segmentation method and a convenient tool is provided for the clinical diagnosis of liver diseases. The self-adaptive surface deformation model based CT image liver segmentation method comprises step 1, performing preprocessing on an image by an anisotropic filtering method to obtain an initial boundary image; step 2, describing the initial contour of the liver through a DSM (Deformable Simplex Model); step 3, calculating the internal force of the model according to the relation between a vertex of the model and the neighborhood of the vertex and calculating the external force of the model through the gradient and the boundary of the original image; step 4, building a constraint model of the internal force and the external force of the model; step 5, performing self-adaptive decomposition of a triangular mesh; step 6, setting the number of iterations and approximating a target area under the driving of the internal force, the external force and the balloon force; step 7, obtaining an accurate segmentation result.
Owner:ARIEMEDI MEDICAL SCI BEIJING CO LTD
Texture map coverage optimization
ActiveUS7773092B1Increasing texture filtering performanceImprove texture filtering performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer visionTexture filtering
The current invention involves new systems and methods for increasing texture filtering performance based on pixel coverage. When half of the pixels in a 2×2 pixel quad are not covered, texel coordinates for the uncovered pixels are not output. Therefore, the texels for the uncovered pixels are not read or processed, allowing the texel filtering processing throughput to be used to produce filtered results for covered pixels. This optimization is particularly useful when anisotropic filtering is used since the number of texels needed to produce a filtered result for a pixel increases as the anisotropic ratio increases. Elimination of unnecessary texel processing for uncovered pixels may improve texture filtering performance.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
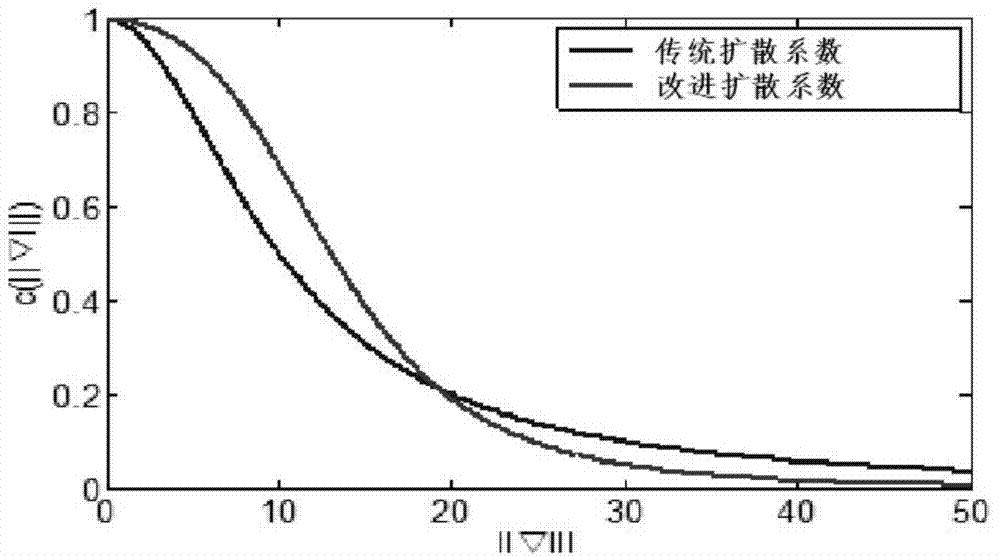
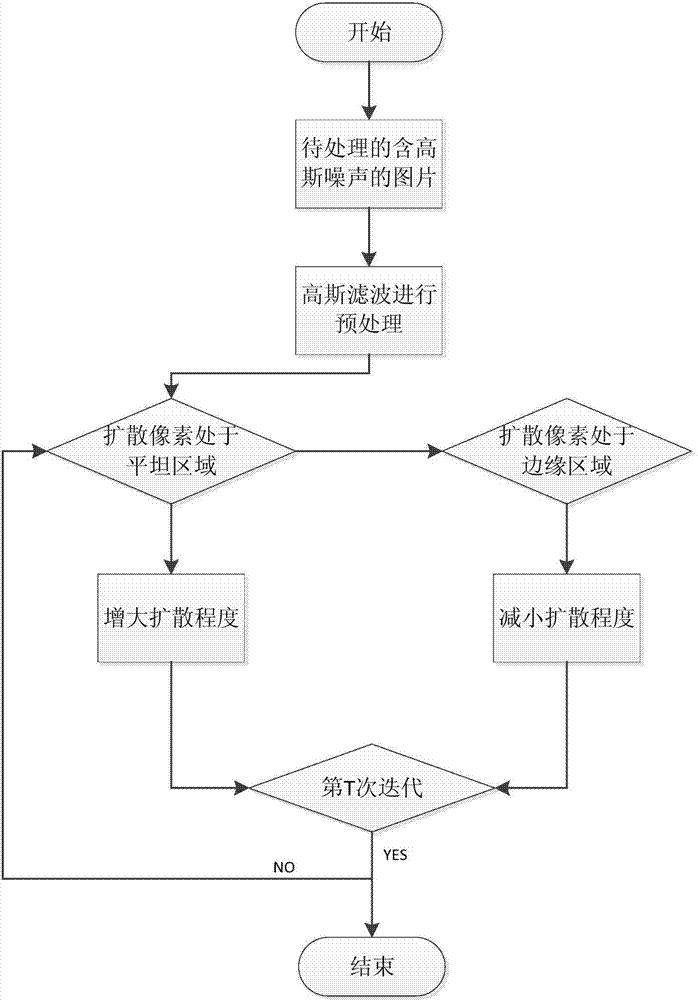
Anisotropism filtering method based on self-adaptive averaging factor
The invention relates to the technical field of digital image processing, and aims at avoiding a staircase effect and a block effect by conducting improvement on a traditional anisotropism filtering method. According to an anisotropism filtering method based on a self-adaptive averaging factor, in the image filtering process, edge fragmentary information is protected by reducing the smoothing degree of noise and marginal areas. Therefore, according to the technical scheme, the anisotropism filtering method based on the self-adaptive averaging factor comprises the steps that pretreatment is conducted on a noise image by adopting a Gaussian filter, the pretreatment formula comprises the step that an improved anisotropic filtering is utilized, the size of the value of a parameter K is determined according to differences of gradient values of each diffusion pixel to a central pixel, that is to say, a self-adaptive equation is utilized to replace the value of an original fixed parameter K, the value of the K of the improved anisotropic filtering is made to reduce on the noise and marginal areas, and the smoothing degree of the improved anisotropic filtering is reduced; the value of the K of the improved anisotropic filtering is increased on the smooth and flat areas, and the smoothing degree of the improved anisotropic filtering is increased. The anisotropism filtering method based on the self-adaptive averaging factor is mainly applied to digital image processing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Three-dimensional scattered point cloud smoothing denoising method of anisotropic diffusion filtering
InactiveCN108022221AKeep feature informationAvoid too smoothImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudEigenvalues and eigenvectors
The invention discloses a three-dimensional scattered point cloud smoothing denoising method of anisotropic diffusion filtering. A tensor matrix structure tensor matrix is obtained by tensor voting ona sampling point and effective neighboring points thereof, eigenvalues and eigenvectors are solved, according to the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the structure tensor matrix, local characteristicsof the sampling point are analyzed, the eigenvalues of a diffusion tensor matrix are designed according to different geometric feature information of the sampling point, diffusion rates are designedaccording to the different geometric feature information so that the diffusion rates in different principal feature directions are different, a modified diffusion tensor matrix is reconstructed, finally, the reconstructed diffusion tensor is substituted into a three-dimensional diffusion anisotropic filtering equation for differential solution, and after a certain number of iterations, a filteringfactor is obtained for smoothing noise. The method can effectively remove noise of the scattered point cloud and maintain feature information of an original model at the same time, thereby avoiding excessive smoothing and local distortion.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Reconfigurable dual texture pipeline with shared texture cache
ActiveUS7999821B1Rapid and efficient mannerReduce conflictCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsBilinear filteringParallel computing
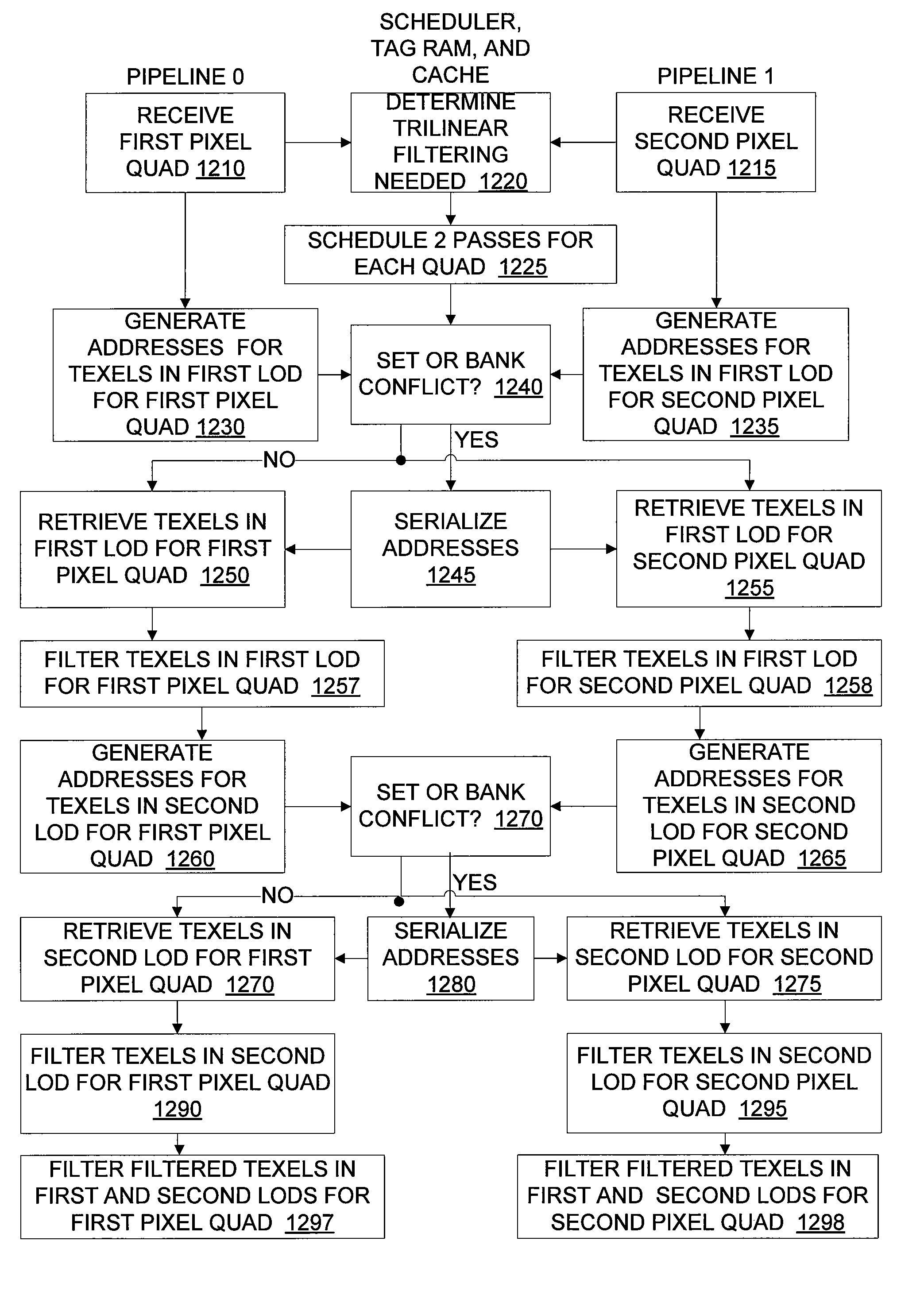
Circuits, methods, and apparatus that provide texture caches and related circuits that store and retrieve texels in an efficient manner. One such texture circuit can provide a configurable number of texel quads for a configurable number of pixels. For bilinear filtering, texels for a comparatively greater number of pixels can be retrieved. For trilinear filtering, texels in a first LOD are retrieved for a number of pixels during a first clock cycle, during a second clock cycle, texels in a second LOD are retrieved. When aniso filtering is needed, a greater number of texels can be retrieved for a comparatively lower number of pixels.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Large-depth-of-field binary defocus three-dimensional measurement method based on multi-focal projection system
ActiveCN110375673AEasy to transformAvoid failureUsing optical meansAlgorithmThree dimensional measurement
The invention discloses a large-depth-of-field binary defocus three-dimensional measurement method based on a multi-focal projection system. The method comprises the following steps: constructing themulti-focal stripe projection system which is based on an optical projection system, and realizing separation of different axial binary stripe focusing surfaces by introducing a cylindrical lens; building an anisotropic filtering model of the multi-focal stripe projection system; optimizing a binary stripe projection method on the basis of the anisotropic filtering model, and according to an optimized stripe projection algorithm, generating and projecting a plurality of phase shift binary stripe patterns; based on a binary stripe image sequence In, analyzing and calculating phase information,and obtaining continuous absolute phases through phase unwrapping; and determining system parameters of the multi-focal stripe projection system through system calibration, and restoring a three-dimensional morphology of a large-depth-of-field object on the basis of the system parameters. According to the method, the problem of failure of a focal zone of a traditional binary defocus measurement method can be effectively avoided, so that the depth-of-field measuring performance is greatly improved.
Owner:武汉斌果科技有限公司
Anisotropic texture filtering with texture data prefetching
ActiveUS20120169755A1Details involving antialiasingCathode-ray tube indicatorsMemory addressComputational science
A circuit arrangement and method utilize texture data prefetching to prefetch texture data used by an anisotropic filtering algorithm. In particular, stride-based prefetching may be used to prefetch texture data for use in anisotropic filtering, where the value of the stride, or difference between successive accesses, is based upon a distance in a memory address space between sample points taken along the line of anisotropy used in an anisotropic filtering algorithm.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
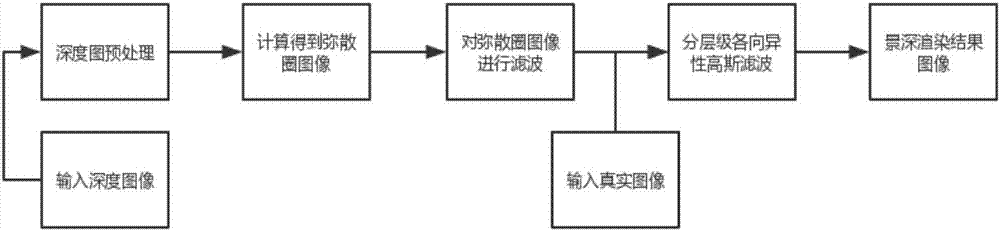
Gaussian pyramid and anisotropic filtering-based image depth of field rendering method
ActiveCN107392986AImprove subjective image qualityReduce complexityImage enhancement3D-image renderingImaging qualityImage resolution
A Gaussian pyramid and anisotropic filtering-based image depth of field rendering method disclosed by the present invention comprises the following steps of for an inputted depth image, constructing a Gaussian pyramid to pre-process; for the filtered depth image, utilizing an optical depth of field model to calculate the radius of a dispersion circle; for a focusing area in a dispersion circle image, constructing an isotropic Gaussian filtering kernel to filter; rounding and layering the filtered dispersion circle image; for the layers of the dispersion circle, constructing an anisotropic Gaussian filtering kernel and combining the inputted image to filter. According to the present invention, by constructing the Gaussian pyramid to pre-process the input scene depth image, and introducing the fuzzy and hierarchical anisotropic Gaussian filtering of the dispersion circle image, the rendering method is suitable for a scene depth image that is obtained by a mainstream depth image obtaining method, is low in resolution and has the black noisy points, and a rendering result has the better subjective image quality and a more accurate depth of field effect.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
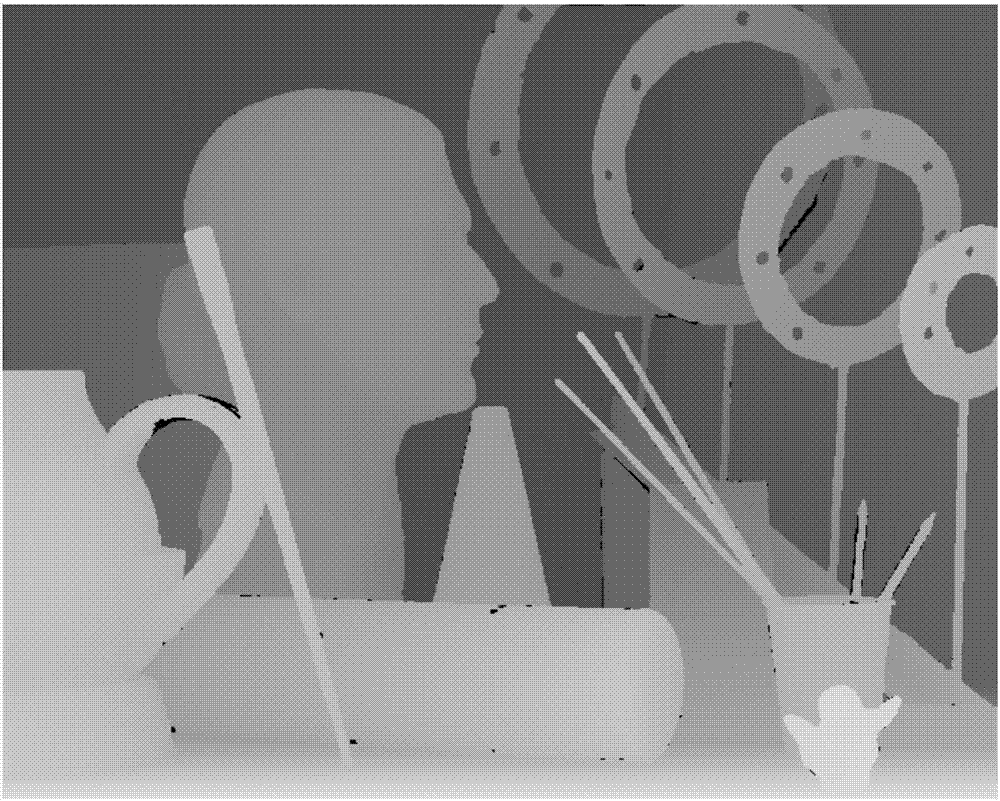
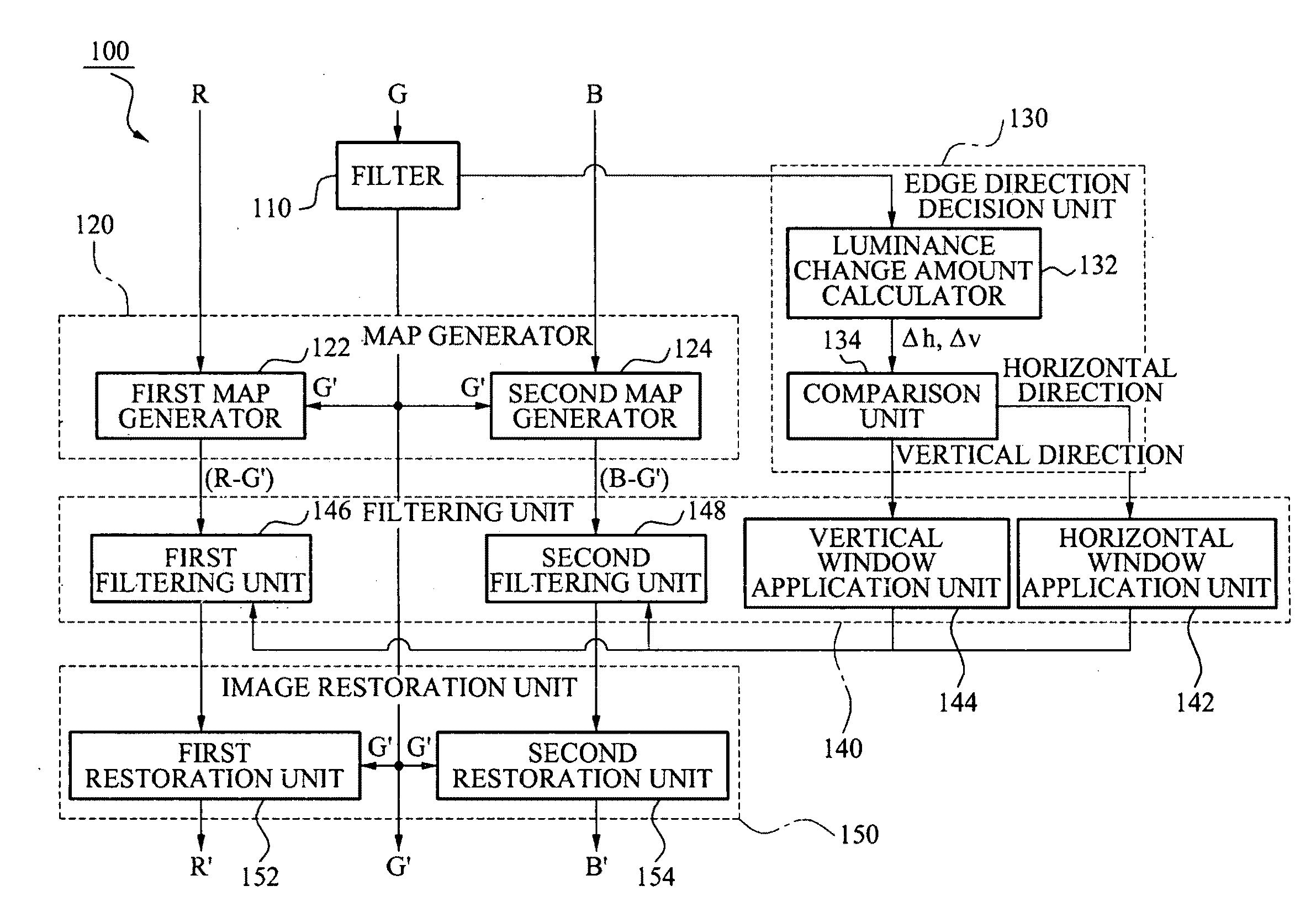
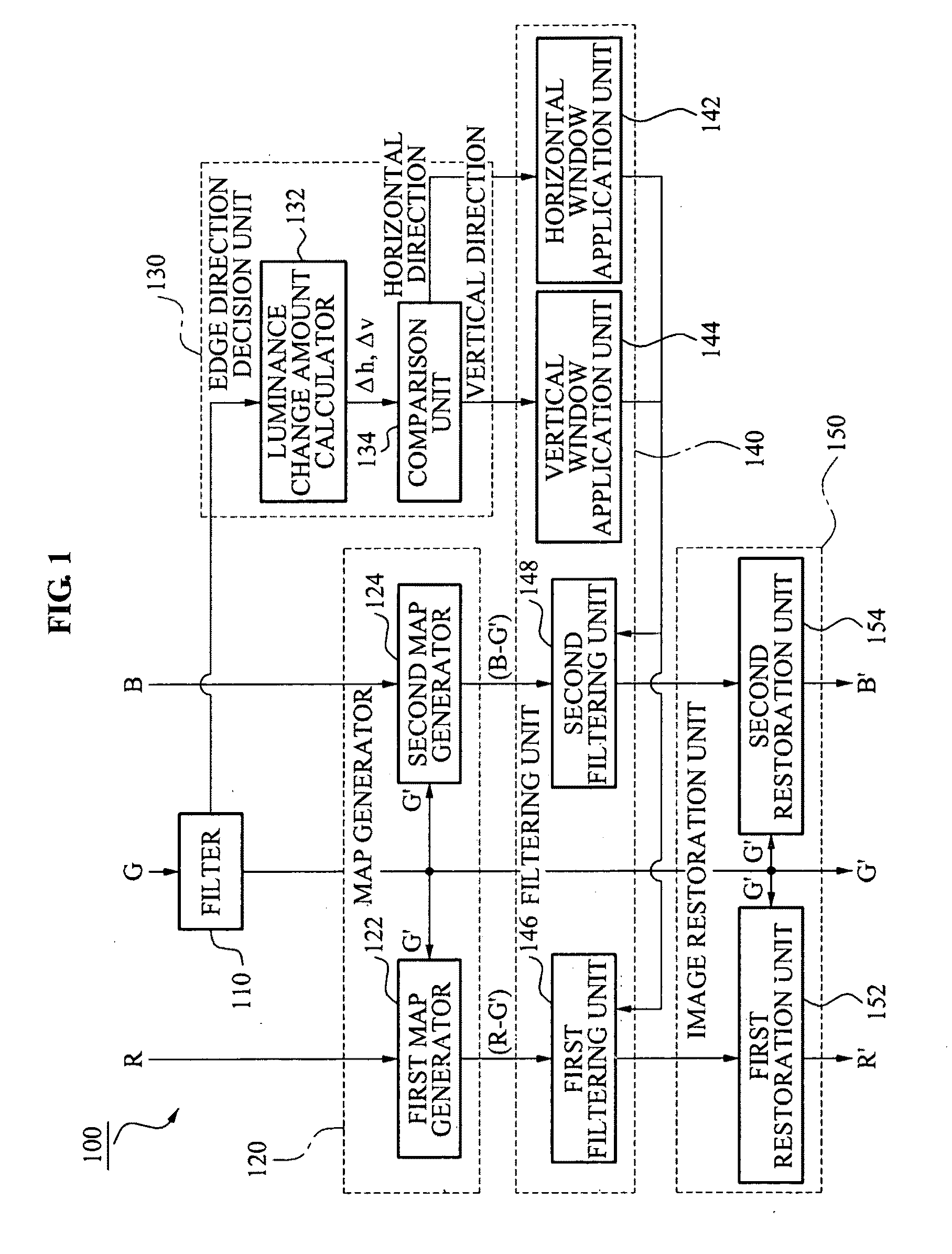
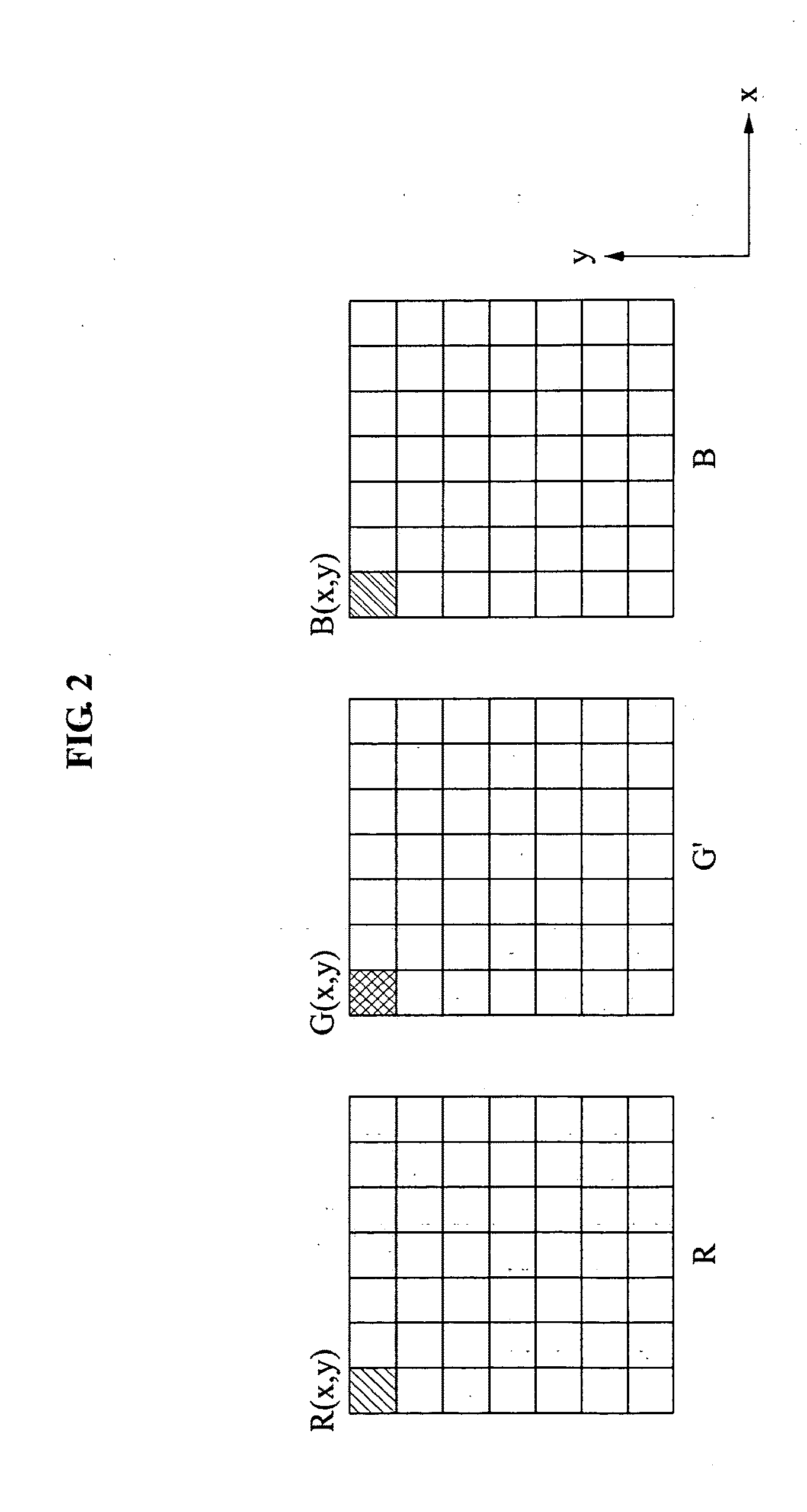
Apparatus and method of removing false color in image
An image processing method and apparatus is provided, with which a size of a filter window may be decreased by determining an edge direction of each of the pixels constituting an image and by vertically applying an anisotropic filter window to the determined edge direction.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of separating, identifying and characterizing cracks in 3D space
ActiveUS10540760B2Accurate calculationAccurate representationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionPorosity
The present invention discloses a method of separating, identifying and characterizing cracks in rocks or other materials in three-dimensional (3D) space, which processes as follows to a volumetric digital image: 1) preprocessing digital image; 2) statistically analyzing basic information of the image including porosity, connectivity of each pore, and position, size, orientation and anisotropy of each pore-structure; 3) filtration: removing non-crack structures; 4) smoothening: smoothening and mending the image; 5) thinning: thinning the void structure into a thickness d (2 to 3 voxels recommended) in a direction with shortest extension; 6) separation: separating intersected cracks in a crack network by breaking the connections; 7) combination: combining those elongated cracks that are disconnected in the last step, and restoring cracks to the thickness before thinning, and eventually giving out the characterization of the cracks.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Selective image stylizing method based on nonlinear filtering
InactiveCN102013107AIncrease contrastChange depth of field2D-image generationDepth of fieldComputer science
The invention discloses a selective image stylizing method based on nonlinear filtering, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (1) simple user interaction; (2) nonlinear filtering; (3) line extraction; and finally output of images which harmoniously combining senses of reality and unreality. In the method, nonlinear diffusion filtering is improved by the following steps of: 1. combining nonlinear diffusion filtering with bilateral filtering; 2. adding a stylizing level control item in an equation; and 3. combining isotropic filtering with anisotropic filtering, so that the nonlinear diffusion filtering can be more suitable for the application of selectivity stylizing. The invention also has the advantages of providing a new artistic style which is an artistic effect of harmonious combination of real objects and stylized scenes, ensuring that a greater contrast is formed between a foreground and a background for giving prominence to the theme of pictures, and being capable of simulating the effect of changing the depth range of fields of a camera.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Systems and methods for providing image rendering using variable rate source sampling
InactiveUS20050035973A1Eliminate gapsEliminate holesCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsHigh rate
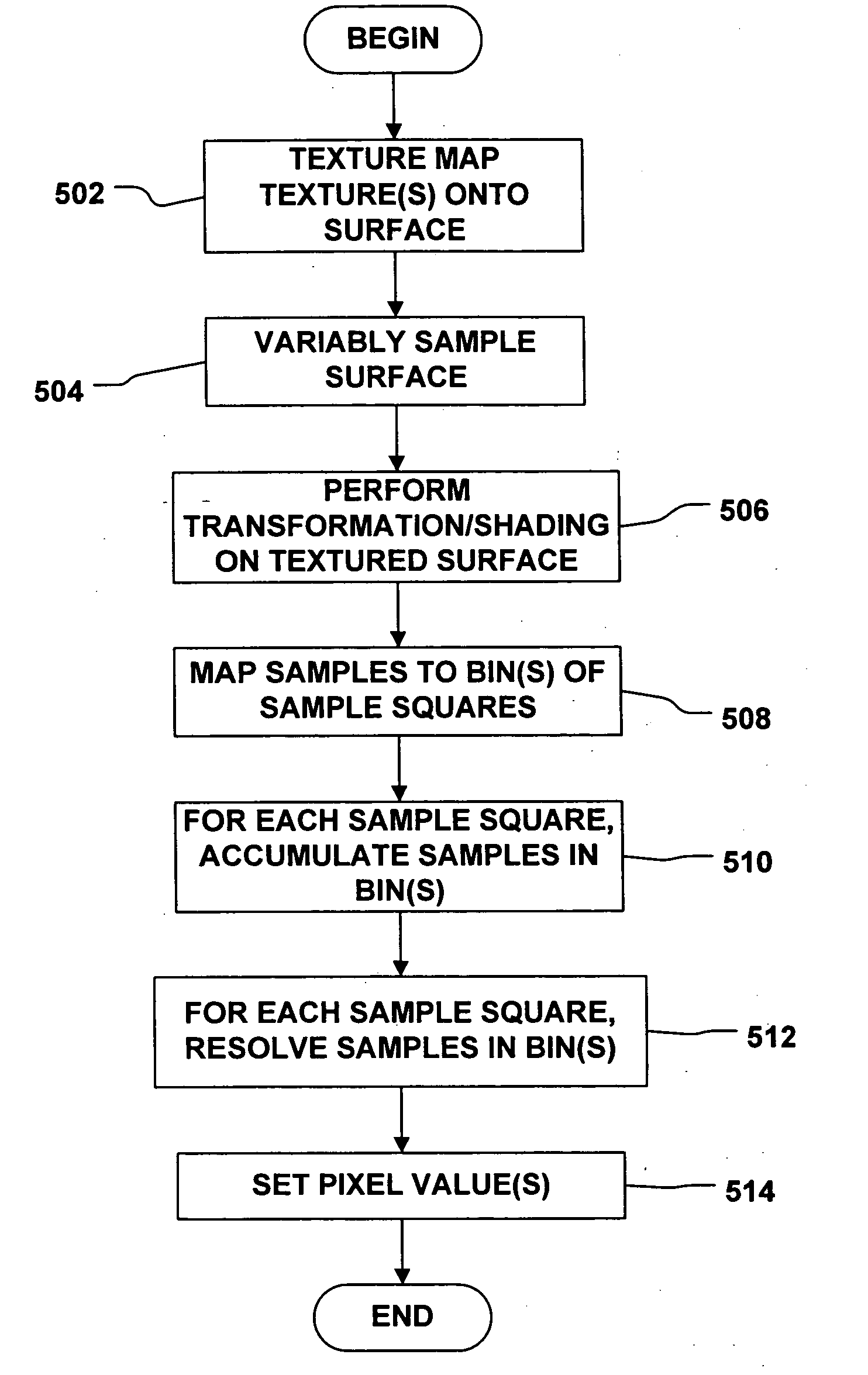
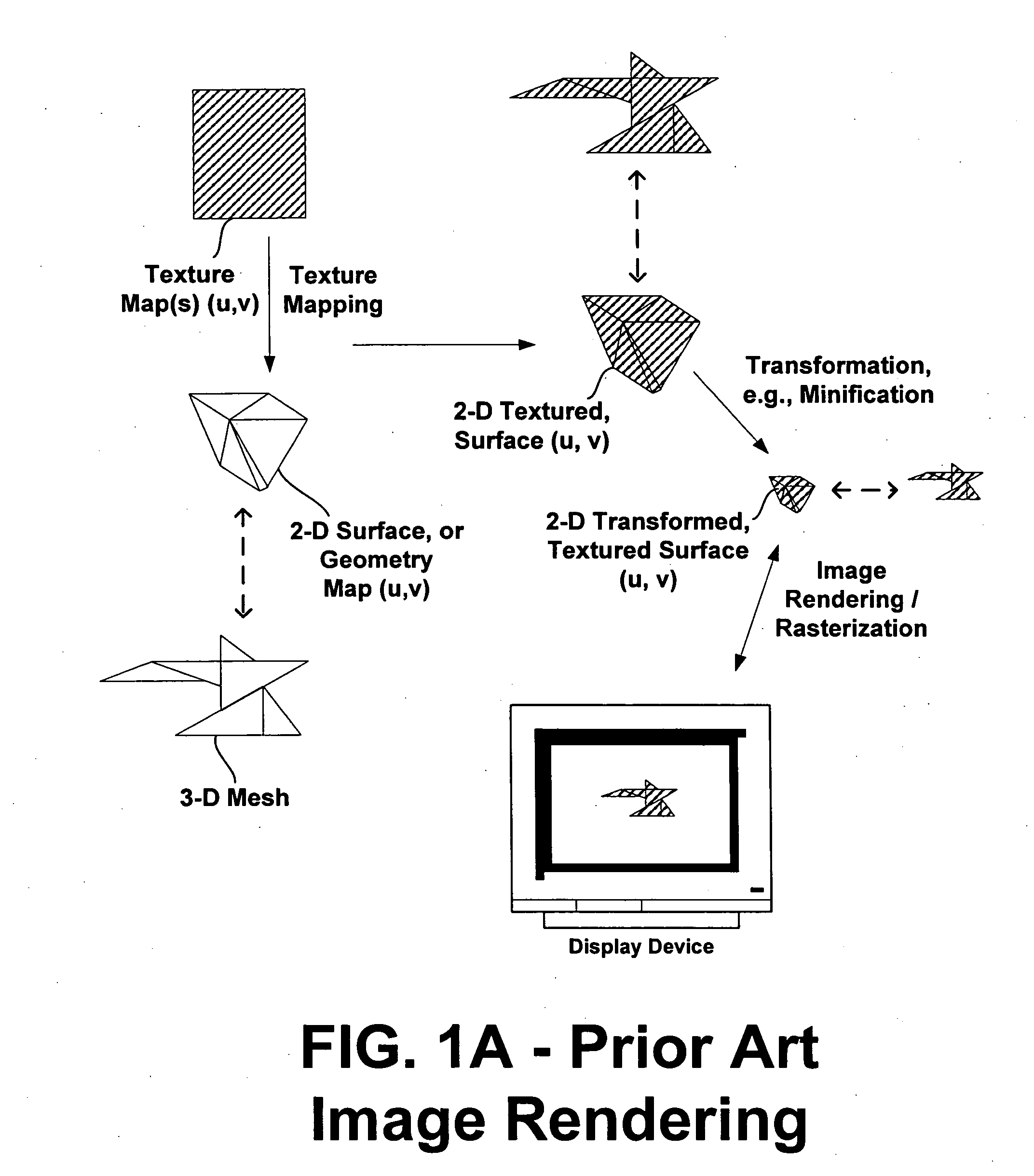
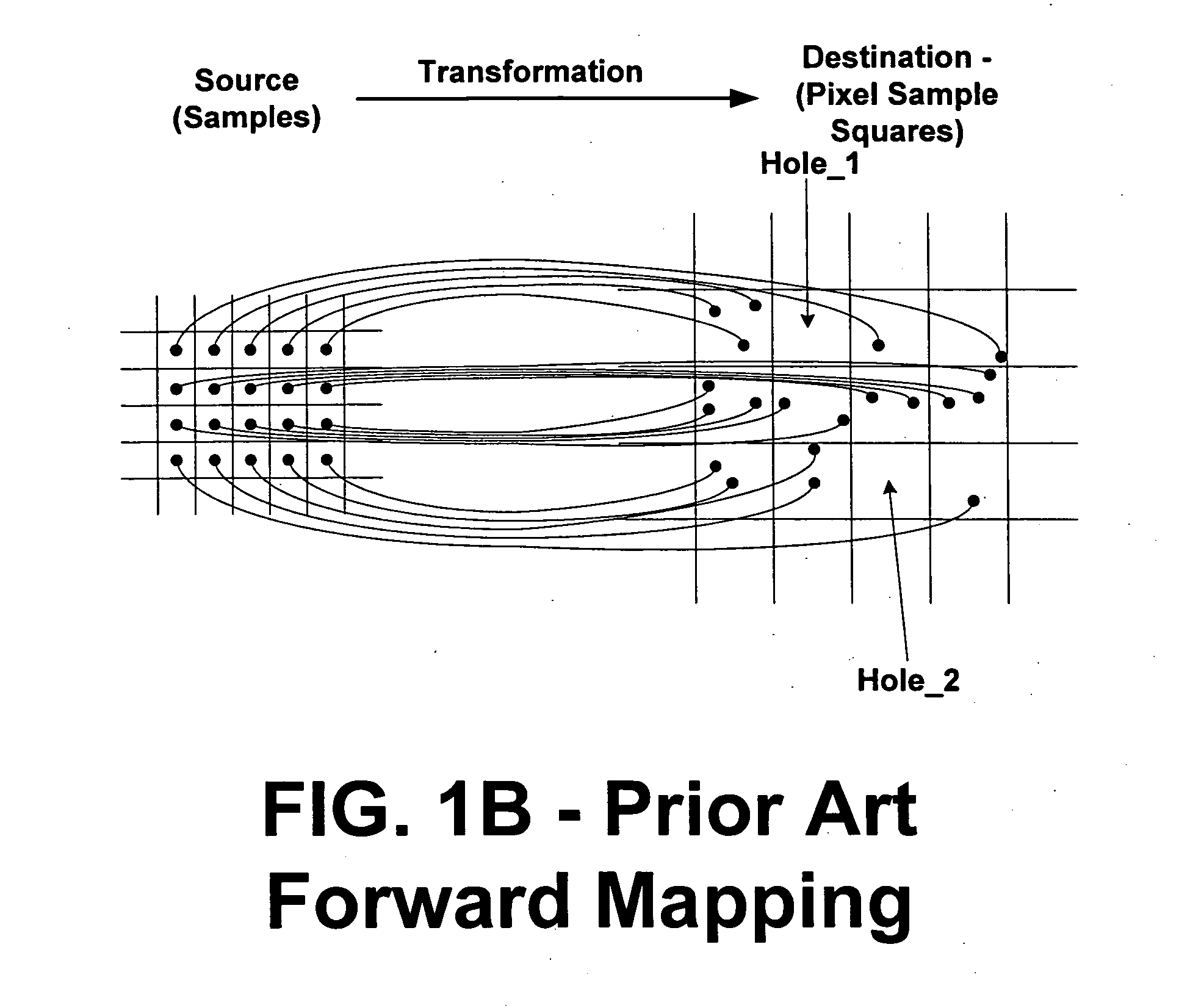
Systems and methods are provided for variable source rate sampling in connection with image rendering, which accumulate and resolve over all samples forward mapped to each pixel bin. In accordance with the invention, the textured surface to be rendered is sampled, or oversampled, at a variable rate that reflects variations in frequency among different regions, taking into account any transformation that will be applied to the surface prior to rendering and the view parameters of the display device, thus ensuring that each bin of the rendering process receives at least a predetermined minimum number of samples. In one embodiment, the sampling rate is variably set such that each bin is assured to have at least one sample point. In another embodiment, a tiling approach to division of the surface is utilized. In accordance with the architecture provided, the sample points of the surface are forward mapped to sample squares, other regions, of a rendering device, taking into account any transformations applied to the surface and the view parameters of the rendering device, such that each bin receives at least the predetermined minimum number of samples. A filter determines the value(s) to assign to each pixel based upon accumulation and resolution of all of the sample points that fall within the pixel bin(s), rather than assigning a value by selecting only the point sample that corresponds to the center of the pixel. Gaps or holes left by conventional forward-mapping techniques are eliminated by oversampling the source(s), and interpolated points are generated at a higher rate than the original source signal(s) to adequately cover the destination bins. A pixel, or sub-pixel, binning approach is used that accumulates and resolves over all samples, and performs particularly well compared to prior architectures in areas that have higher frequency content, solving the minification antialiasing problem and producing a high quality result. Anisotropic filtering is handled simply with the forward mapping approach by filtering over all samples that naturally accumulate after the forward map, and via variable control of the number of samples forward mapped to the bins. A variety of image processing applications are contemplated wherein variable rate source sampling, and accumulation and resolution of forward mapped point samples can be applied, ranging from 3-D graphics applications to applications wherein images recorded in a recording / storage environment are mapped to the arbitrary requirements of a display environment.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com