Patents
Literature
40 results about "Supersampling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
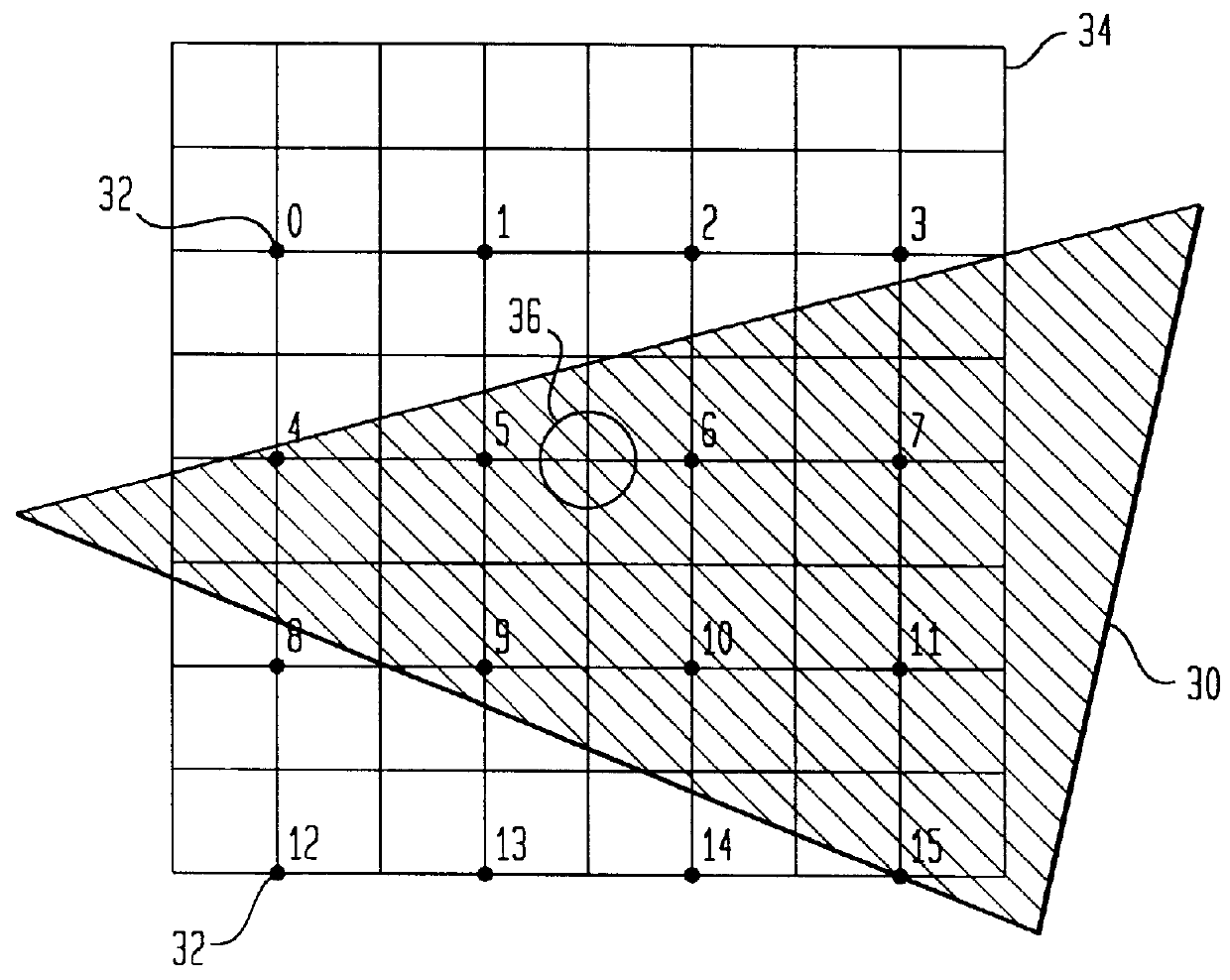
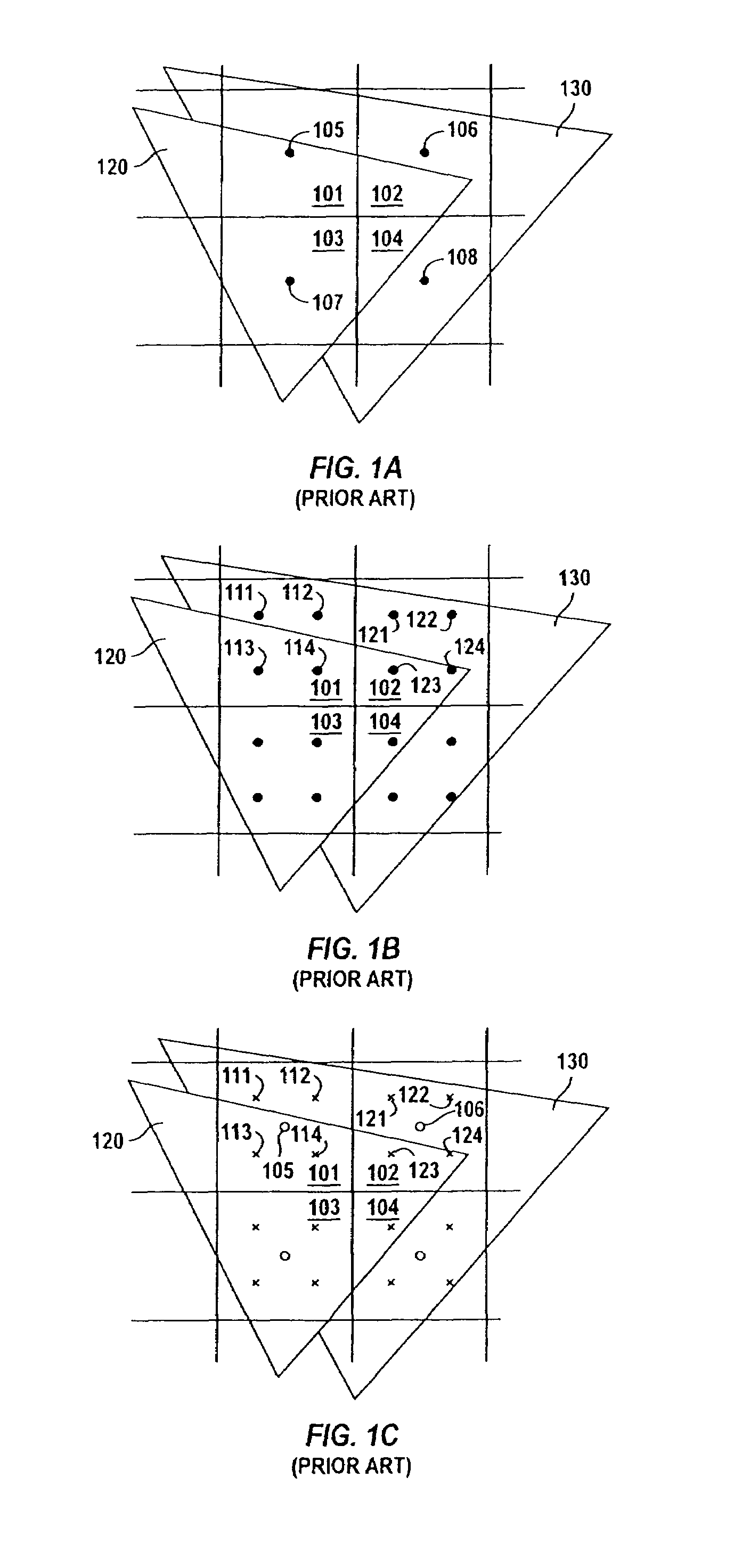
Supersampling is a spatial anti-aliasing method, i.e. a method used to remove aliasing (jagged and pixelated edges, colloquially known as "jaggies") from images rendered in computer games or other computer programs that generate imagery. Aliasing occurs because unlike real-world objects, which have continuous smooth curves and lines, a computer screen shows the viewer a large number of small squares. These pixels all have the same size, and each one has a single color. A line can only be shown as a collection of pixels, and therefore appears jagged unless it is perfectly horizontal or vertical. The aim of supersampling is to reduce this effect. Color samples are taken at several instances inside the pixel (not just at the center as normal), and an average color value is calculated. This is achieved by rendering the image at a much higher resolution than the one being displayed, then shrinking it to the desired size, using the extra pixels for calculation. The result is a downsampled image with smoother transitions from one line of pixels to another along the edges of objects.
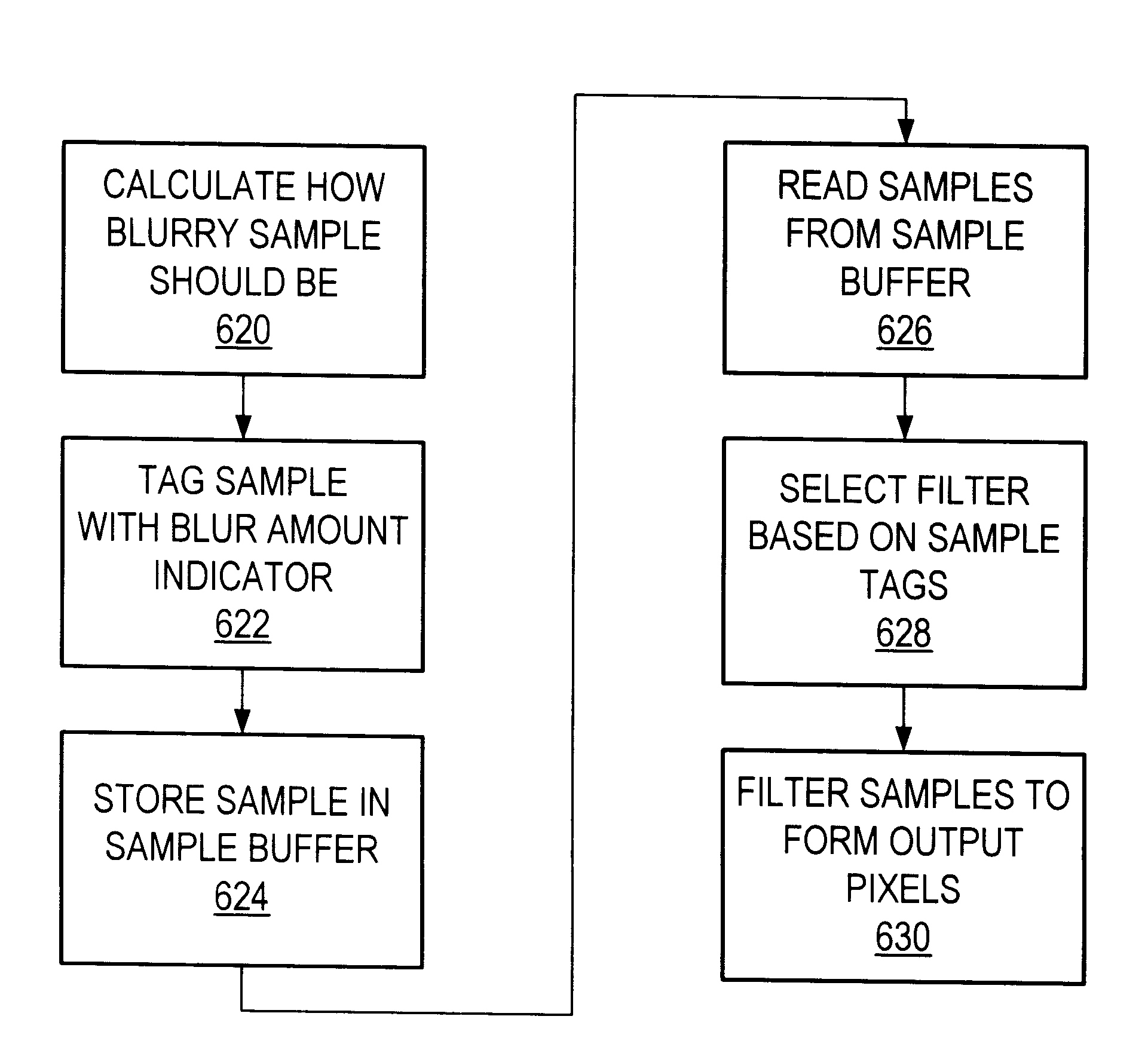
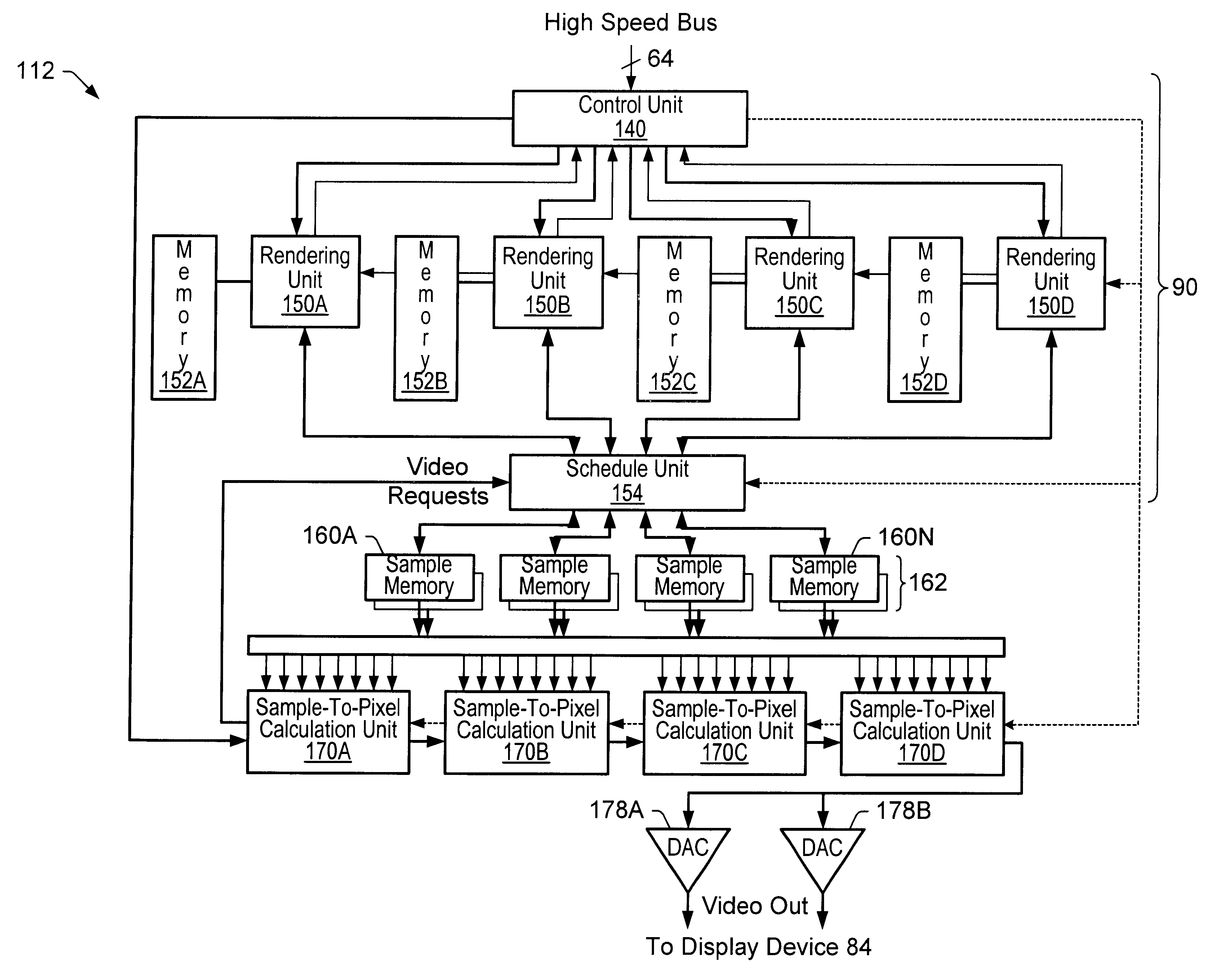
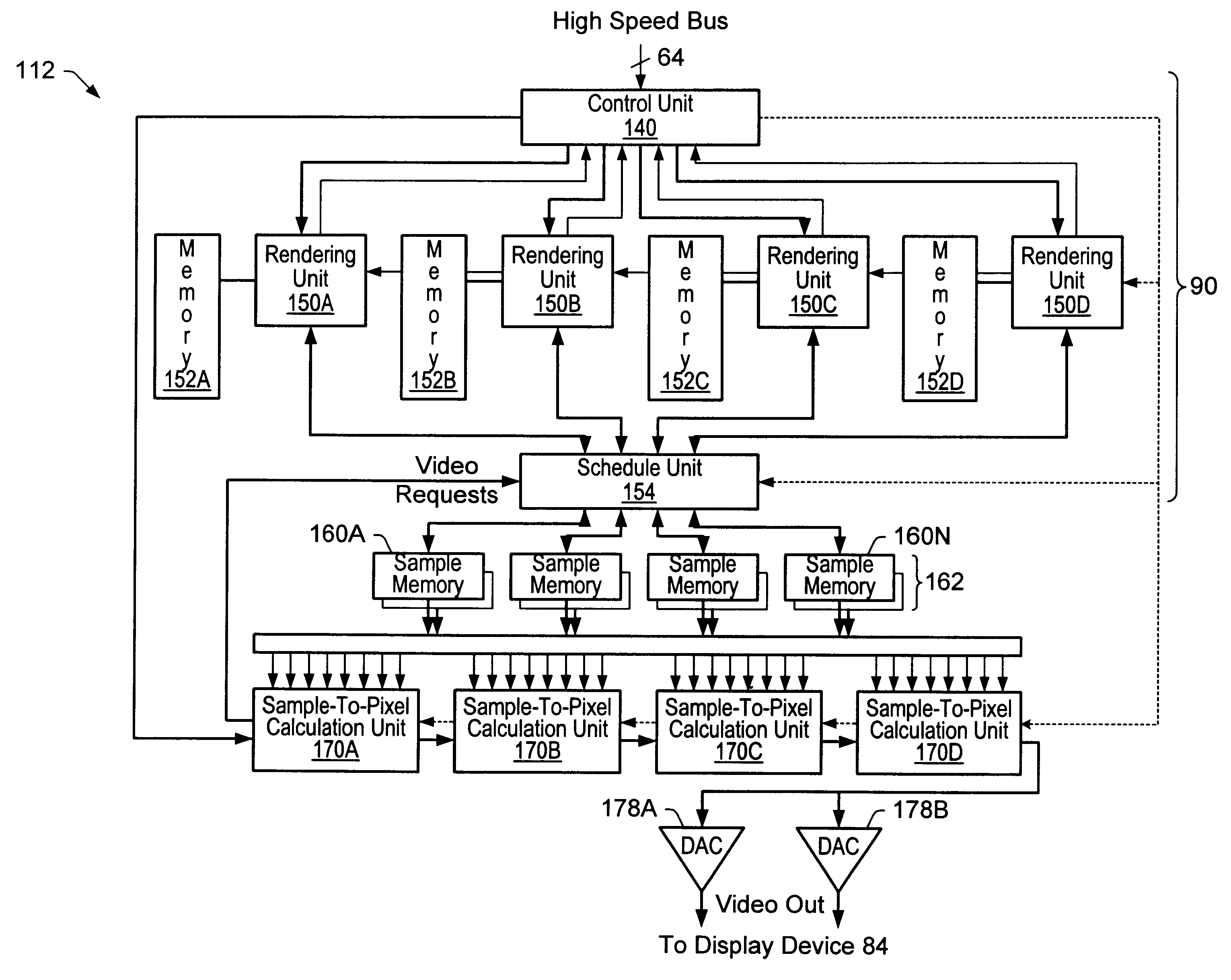
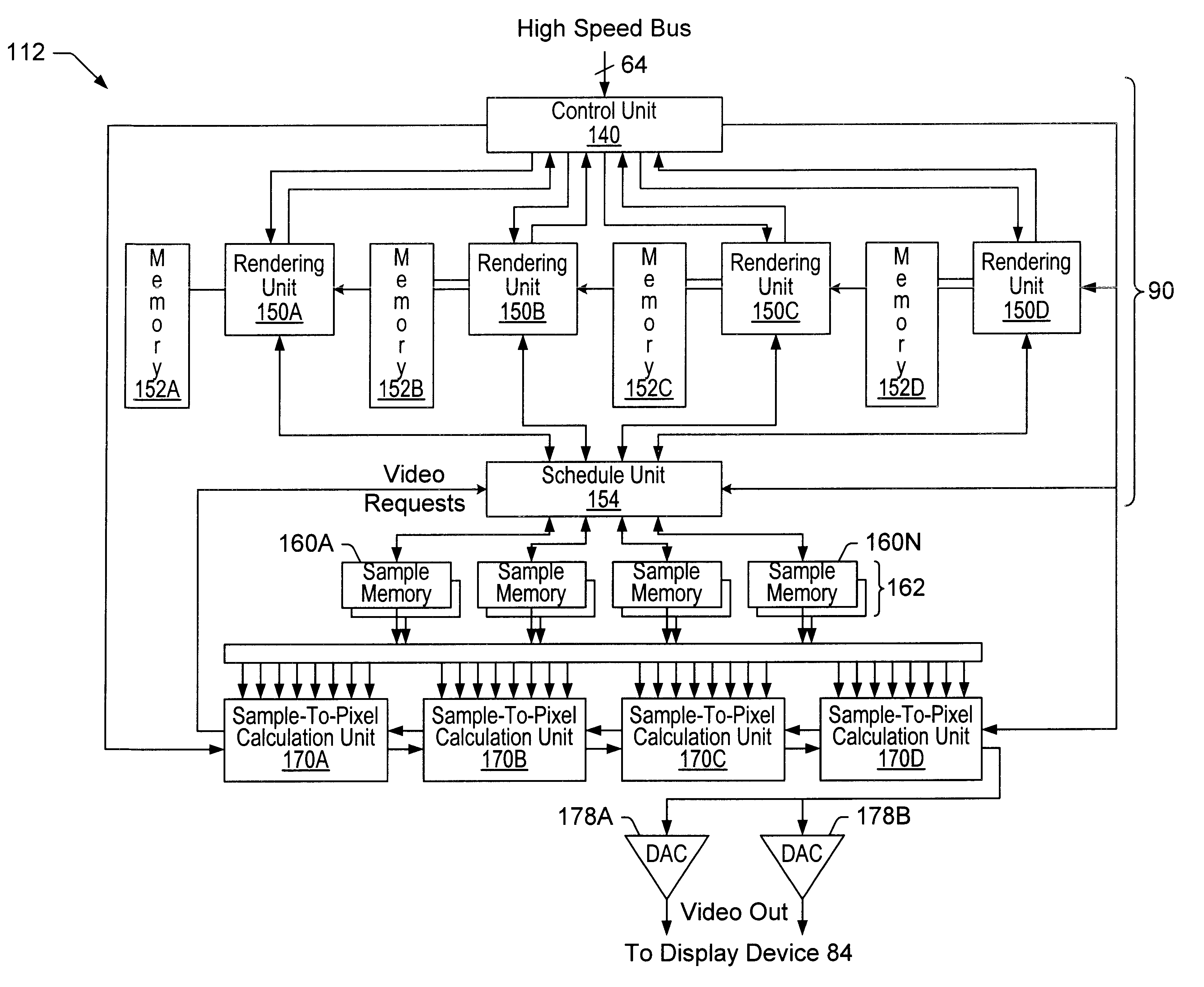
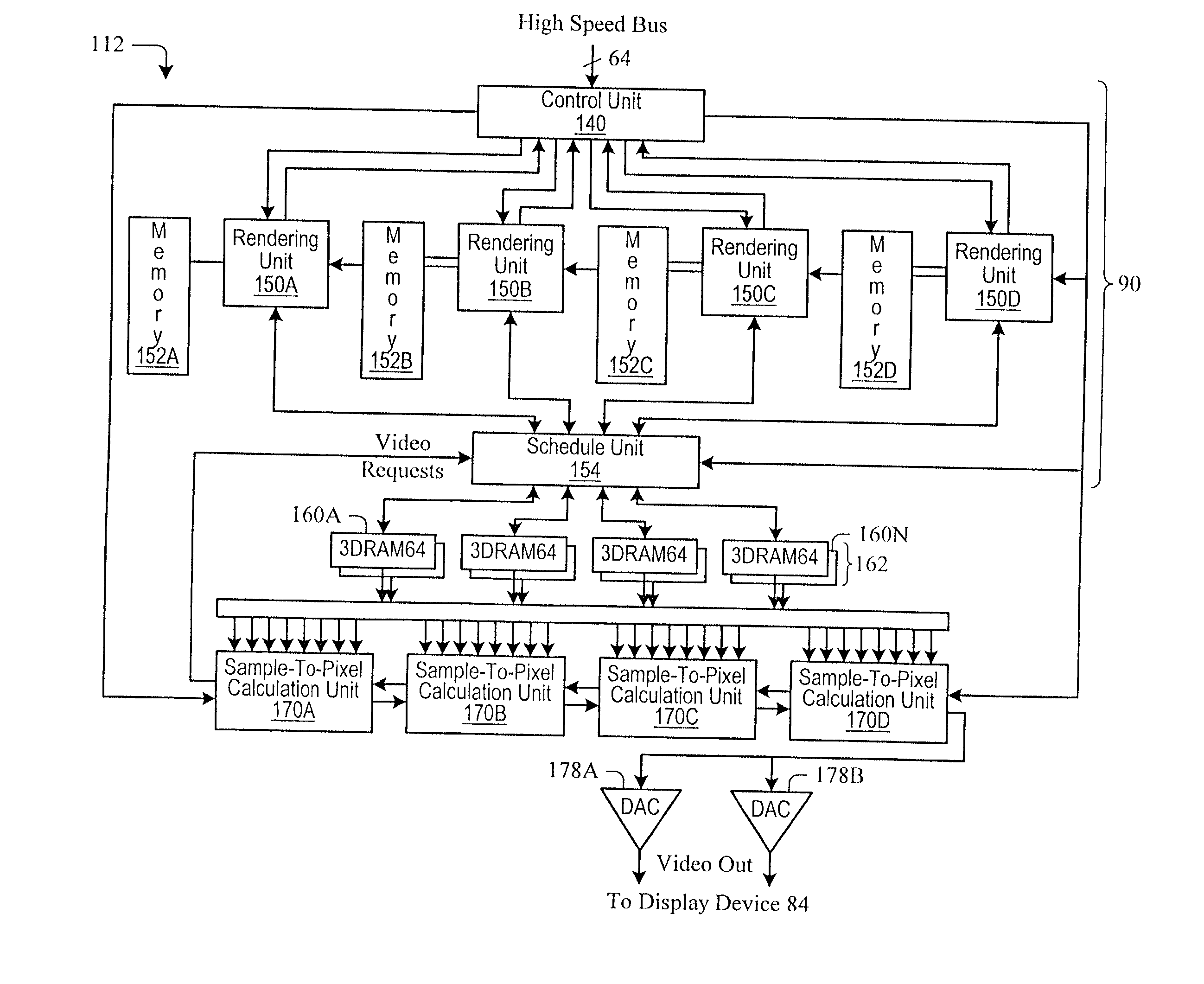
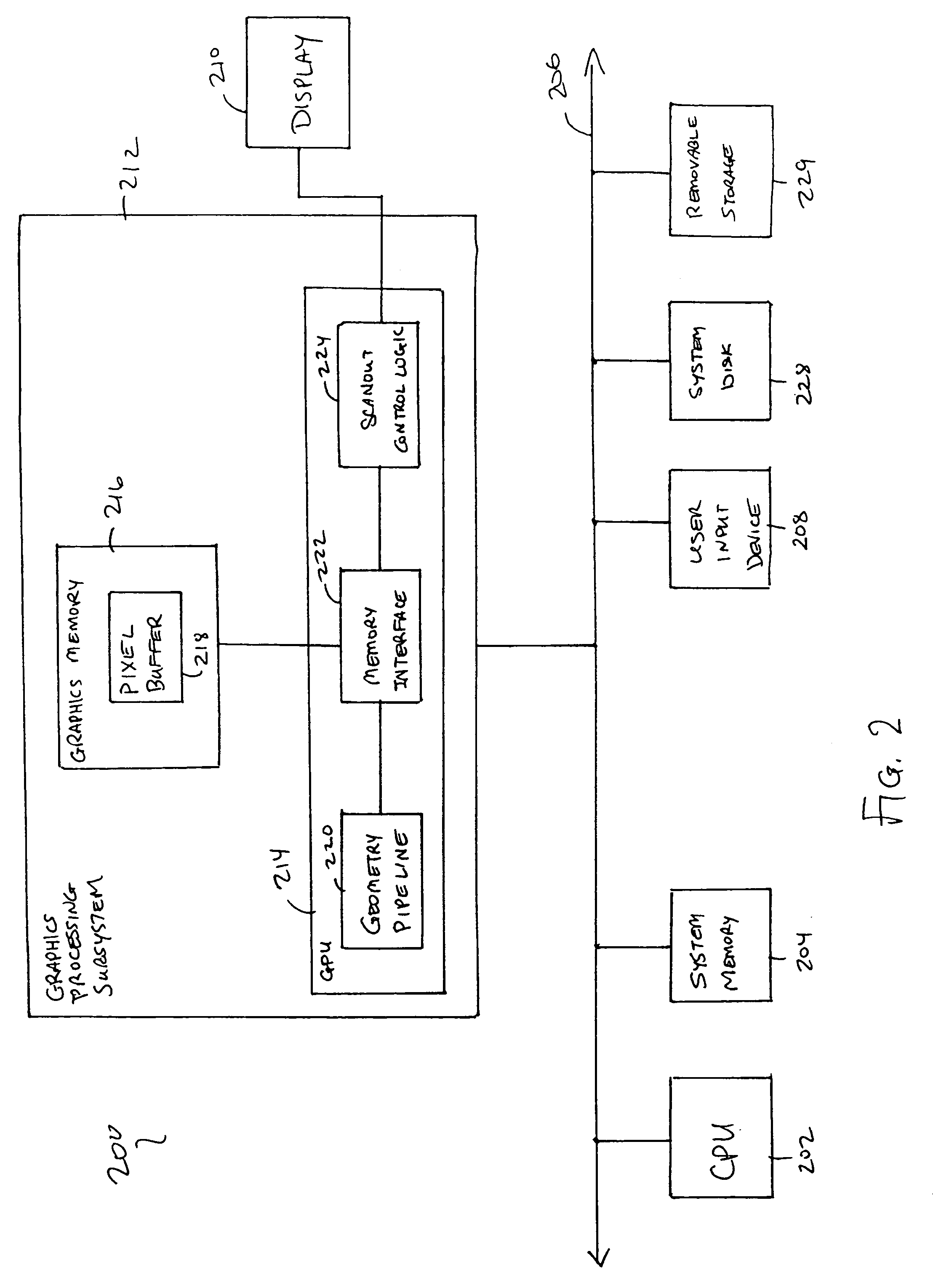
Graphics system using sample tags for blur
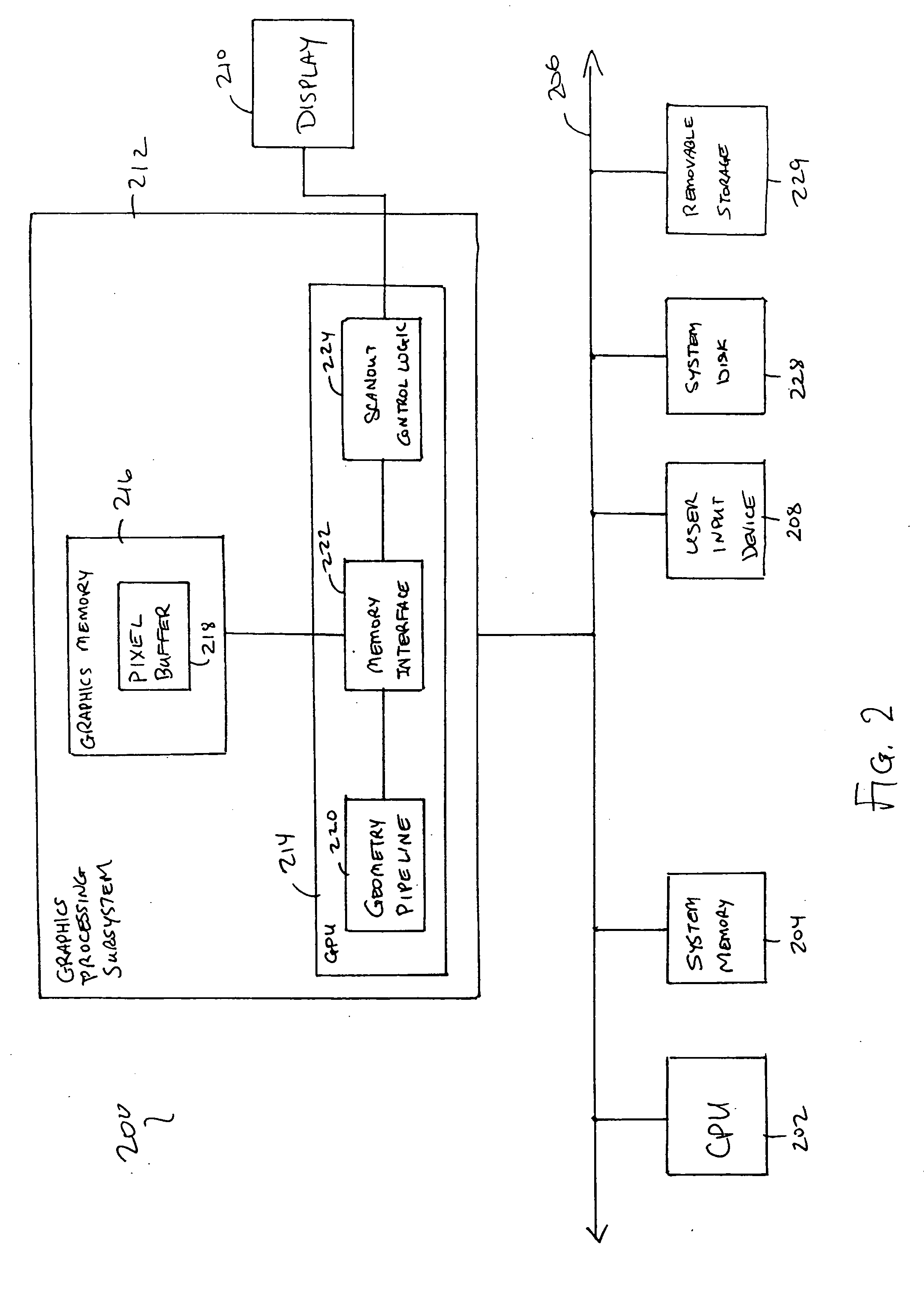
InactiveUS6426755B1Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsGraphic system
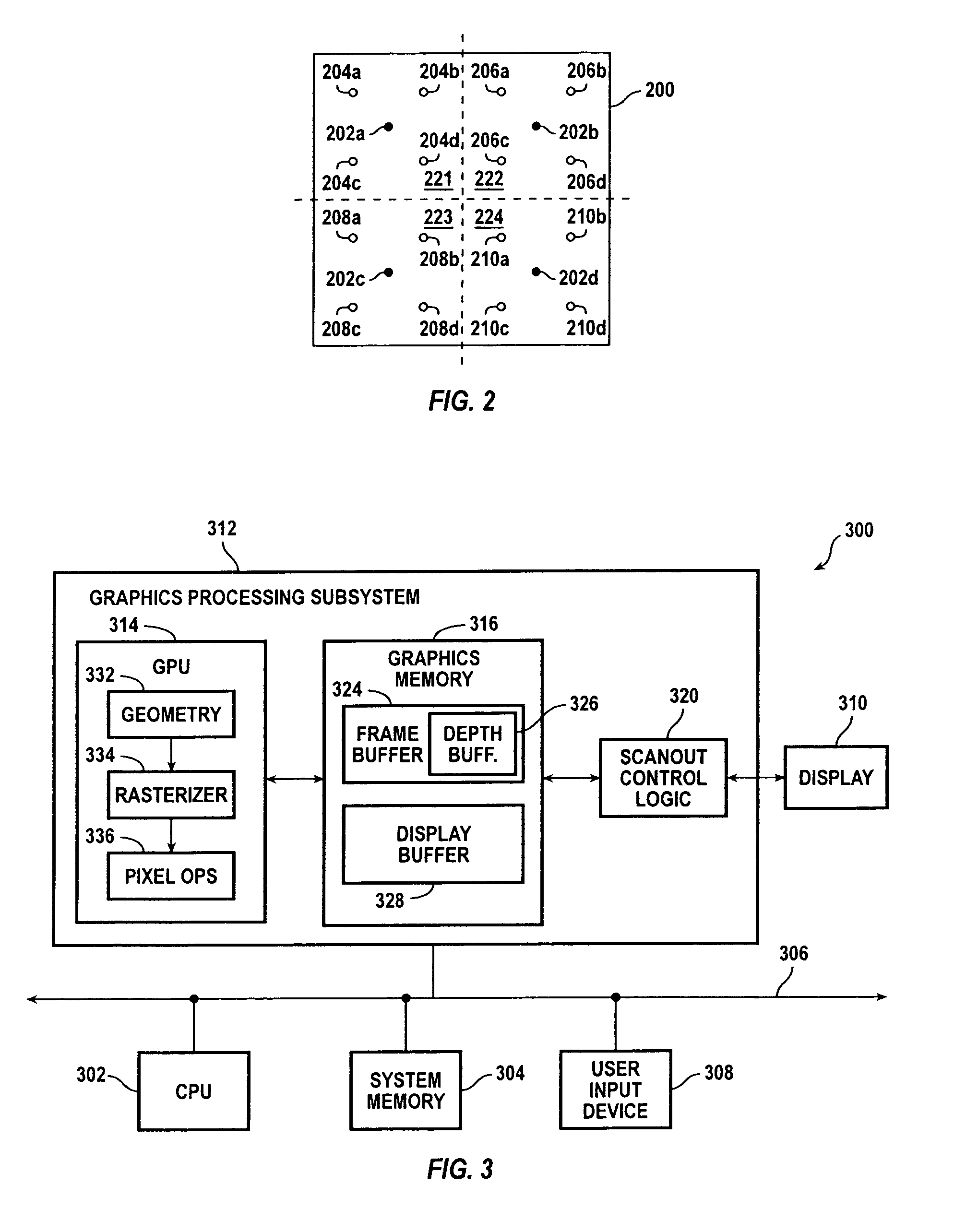
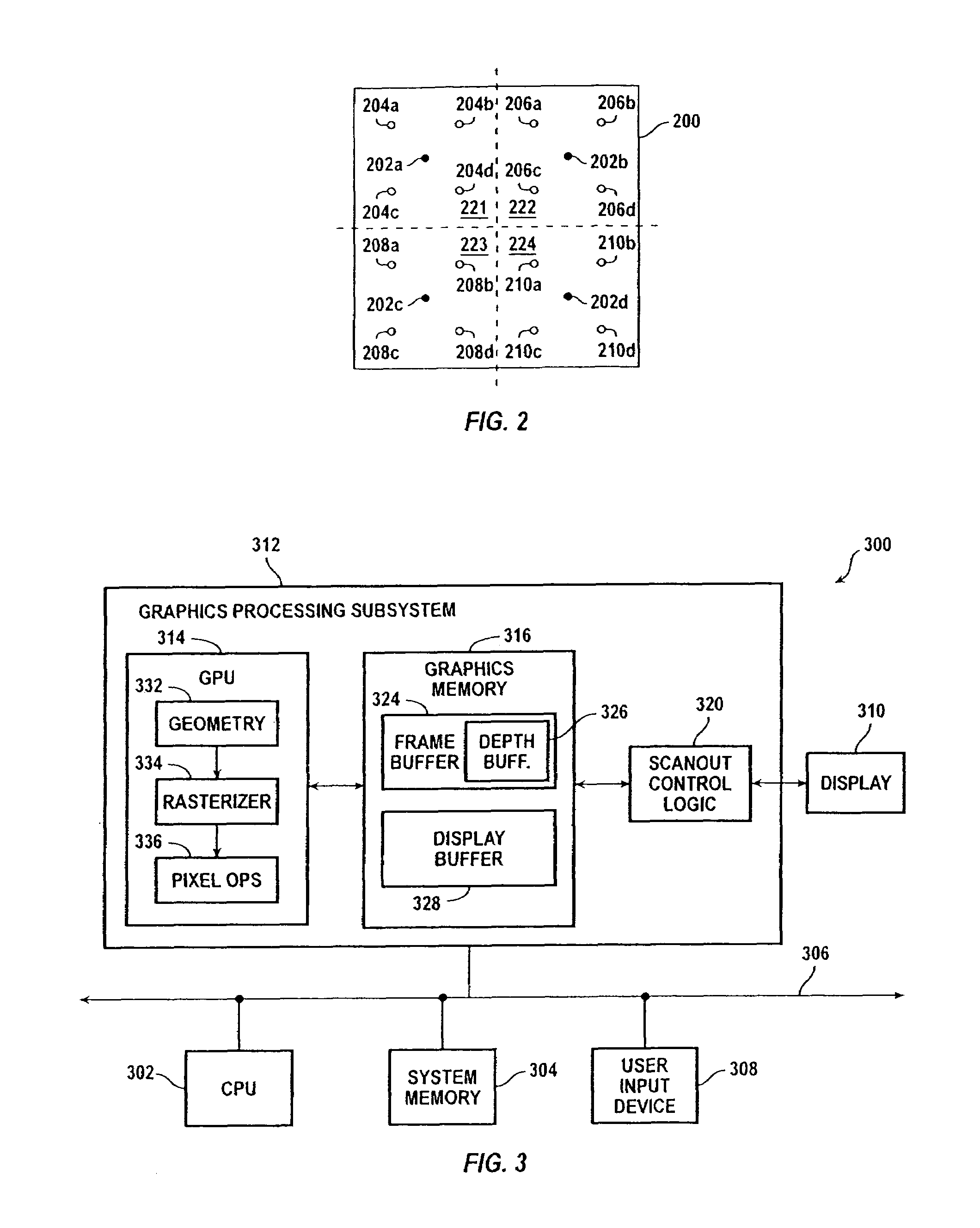
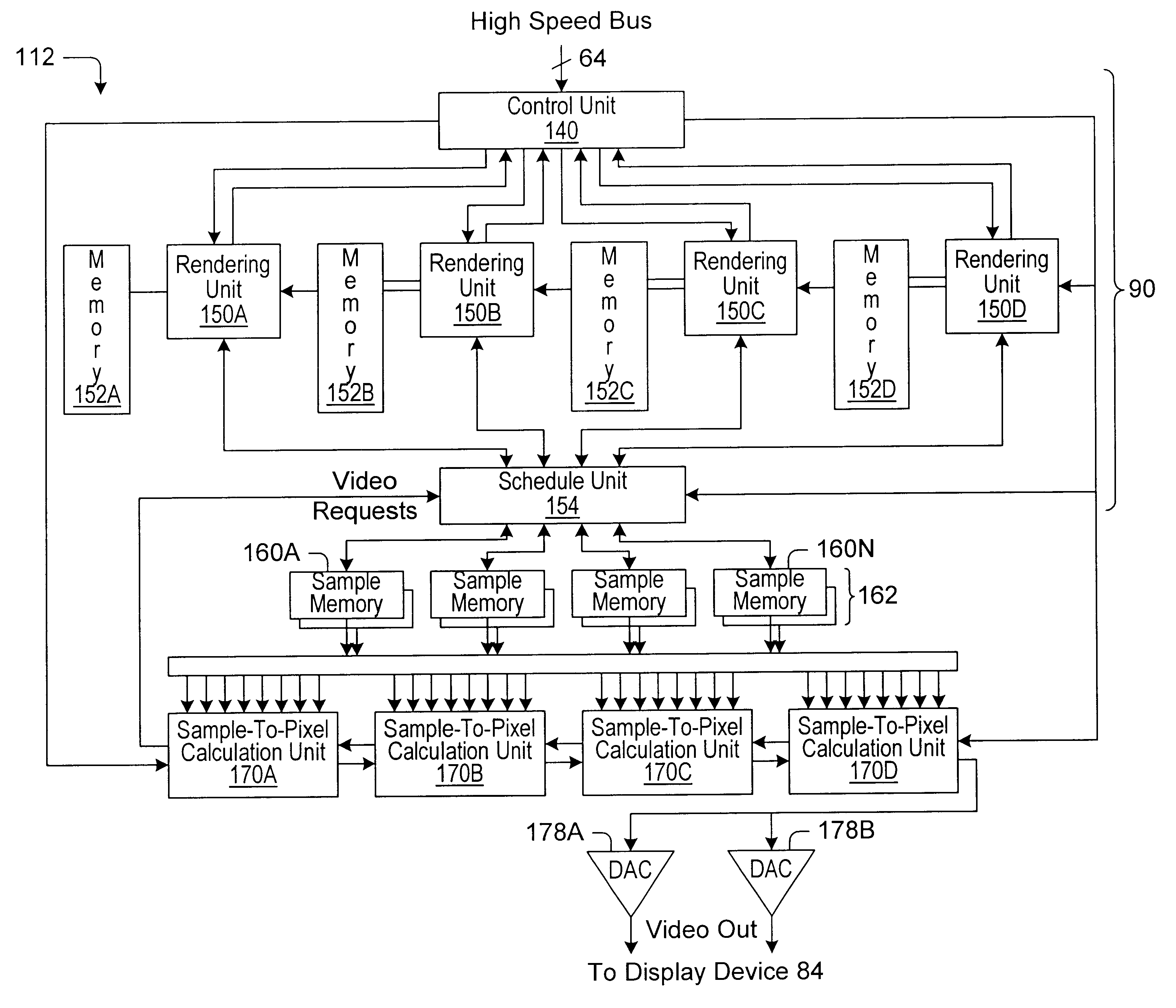
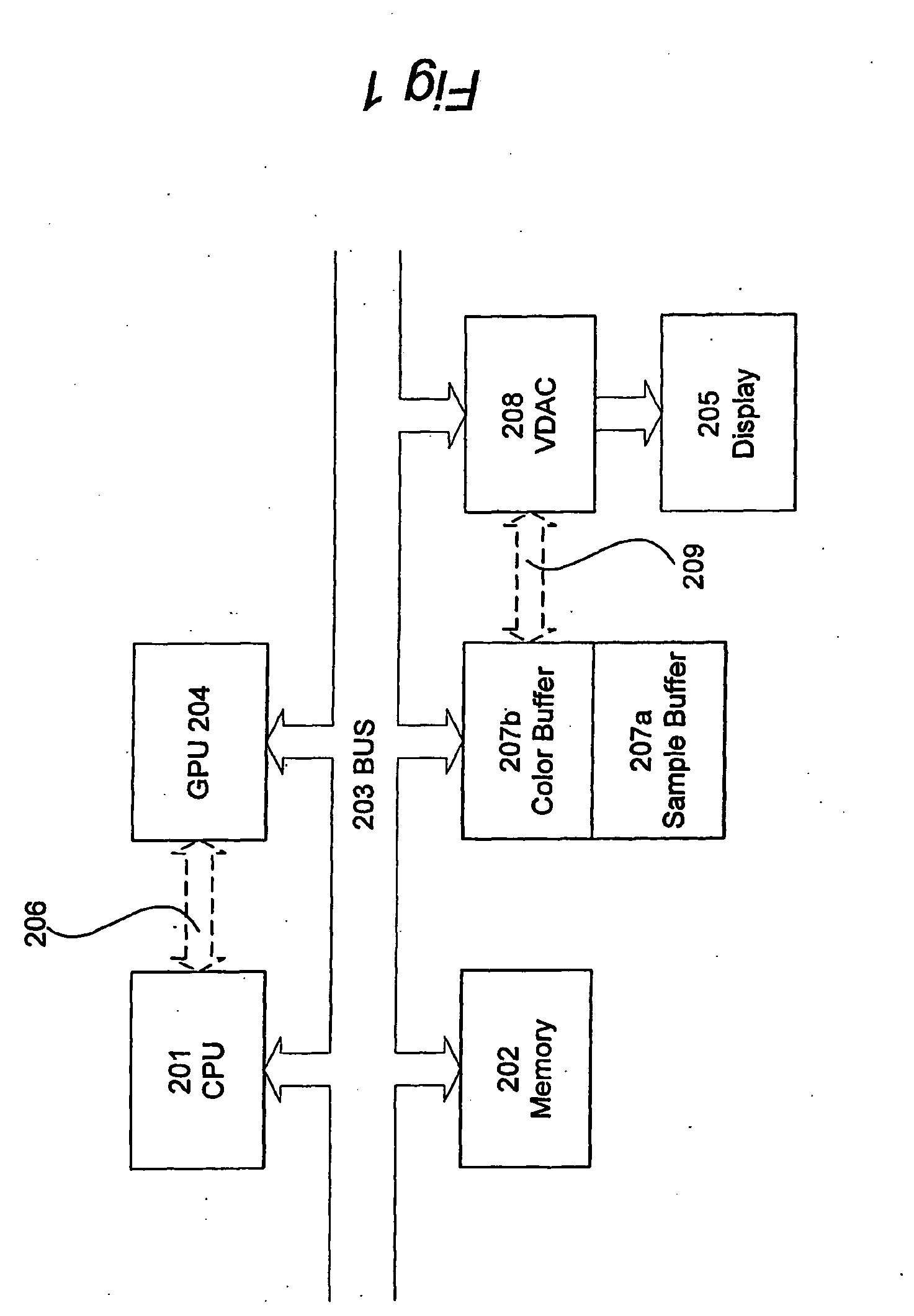
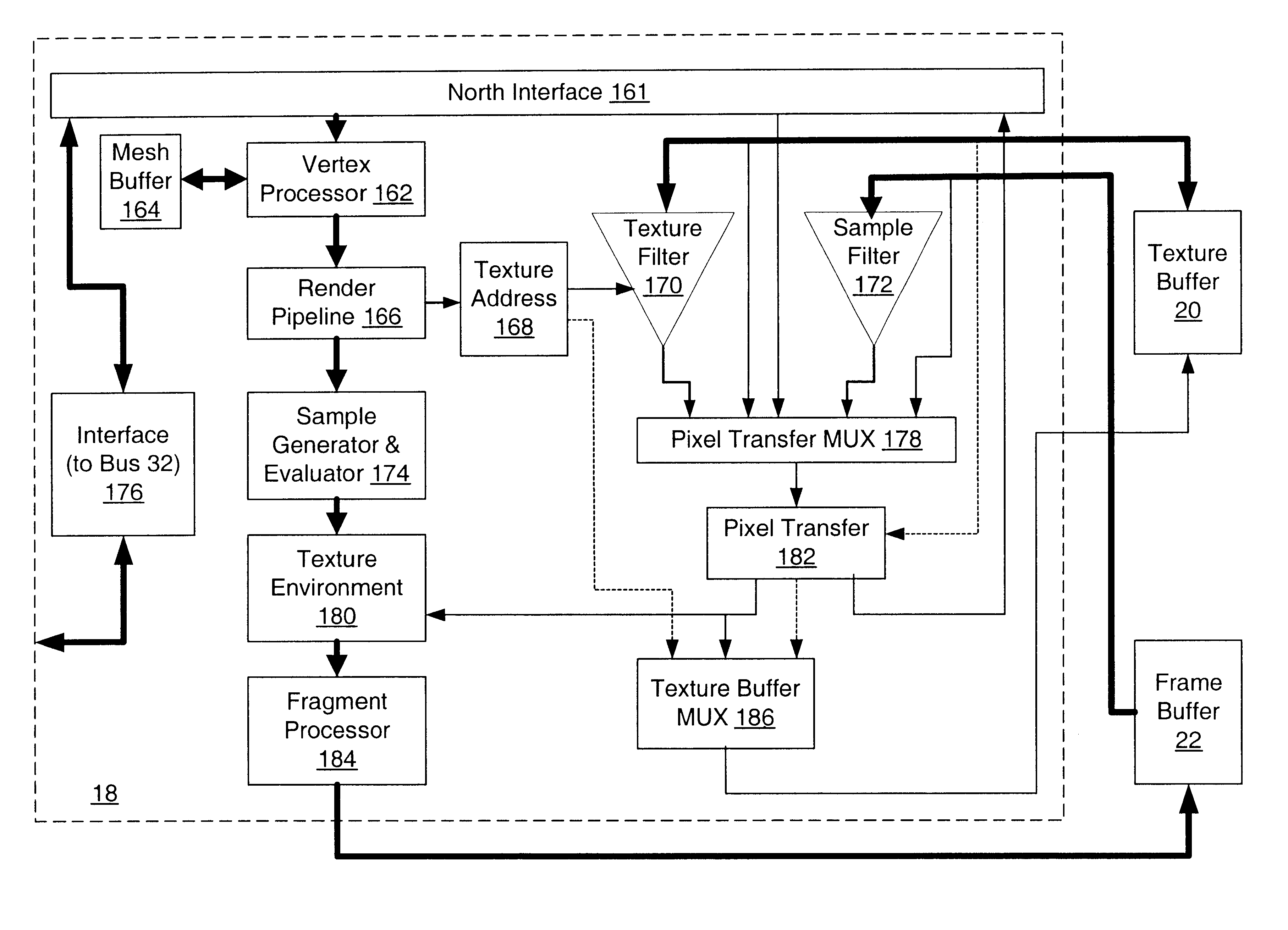
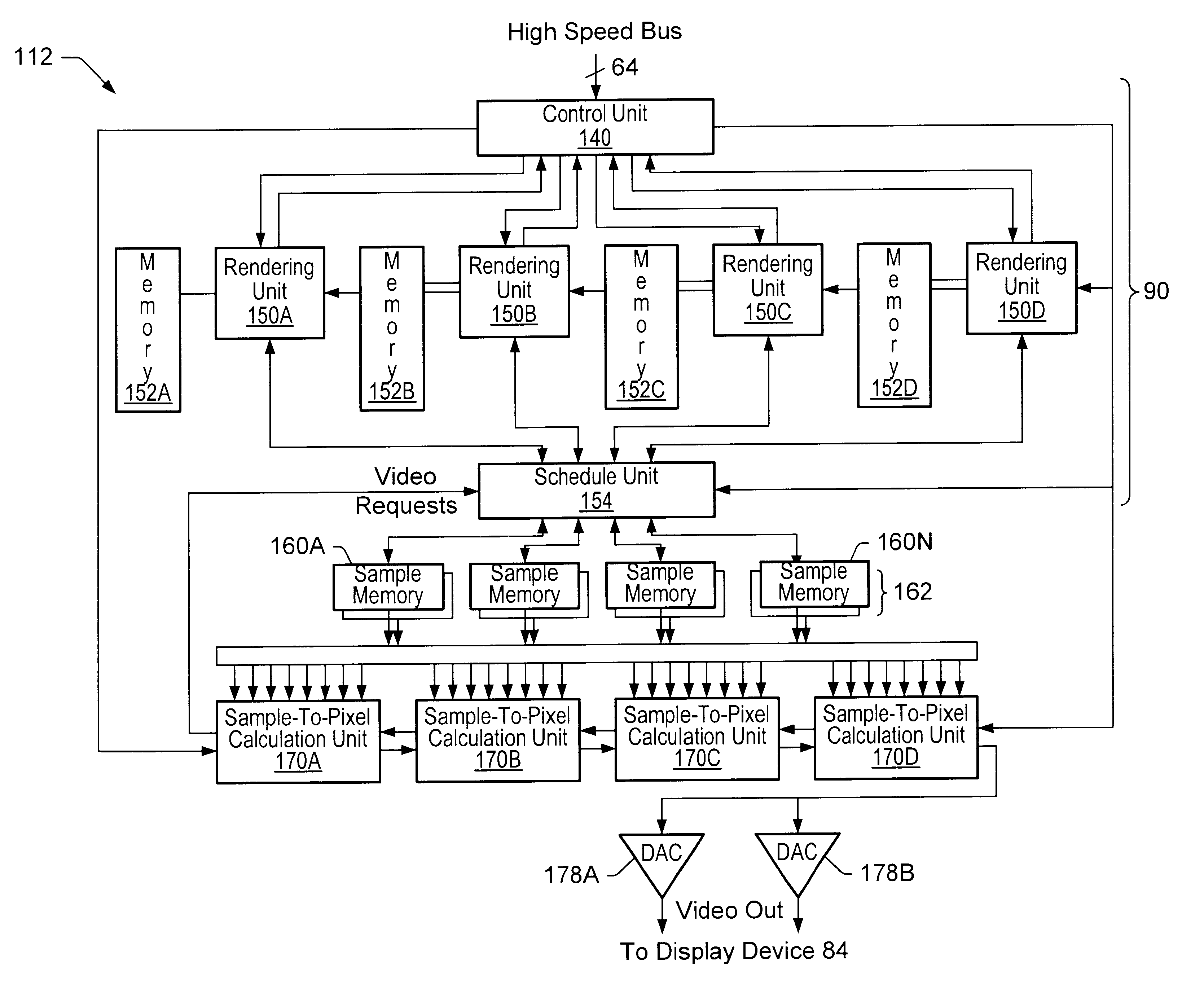
A graphics system and method for performing blur effects, including motion blur and depth of field effects, are disclosed. In one embodiment the system comprises a graphics processor, a sample buffer, and a sample-to-pixel calculation unit. The graphics processor is configured to receive a set of three-dimensional (3D) graphics data and render a plurality of samples based on the set of 3D graphics data. The processor is also configured to generate sample tags for the samples, wherein the sample tags are indicative of whether or not the samples are to be blurred. The super-sampled sample buffer is coupled to receive and store the samples from the graphics processor. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit is coupled to receive and filter the samples from the super-sampled sample buffer to generate output pixels, which in turn are displayable to form an image on a display device. The sample-to-pixel calculation units are configured to select the filter attributes used to filter the samples into output pixels based on the sample tags.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for anti-aliasing in a graphics system
InactiveUS6999100B1Low costHigh cost-effectiveImage enhancementCathode-ray tube indicatorsInterlaced videoAnti-aliasing
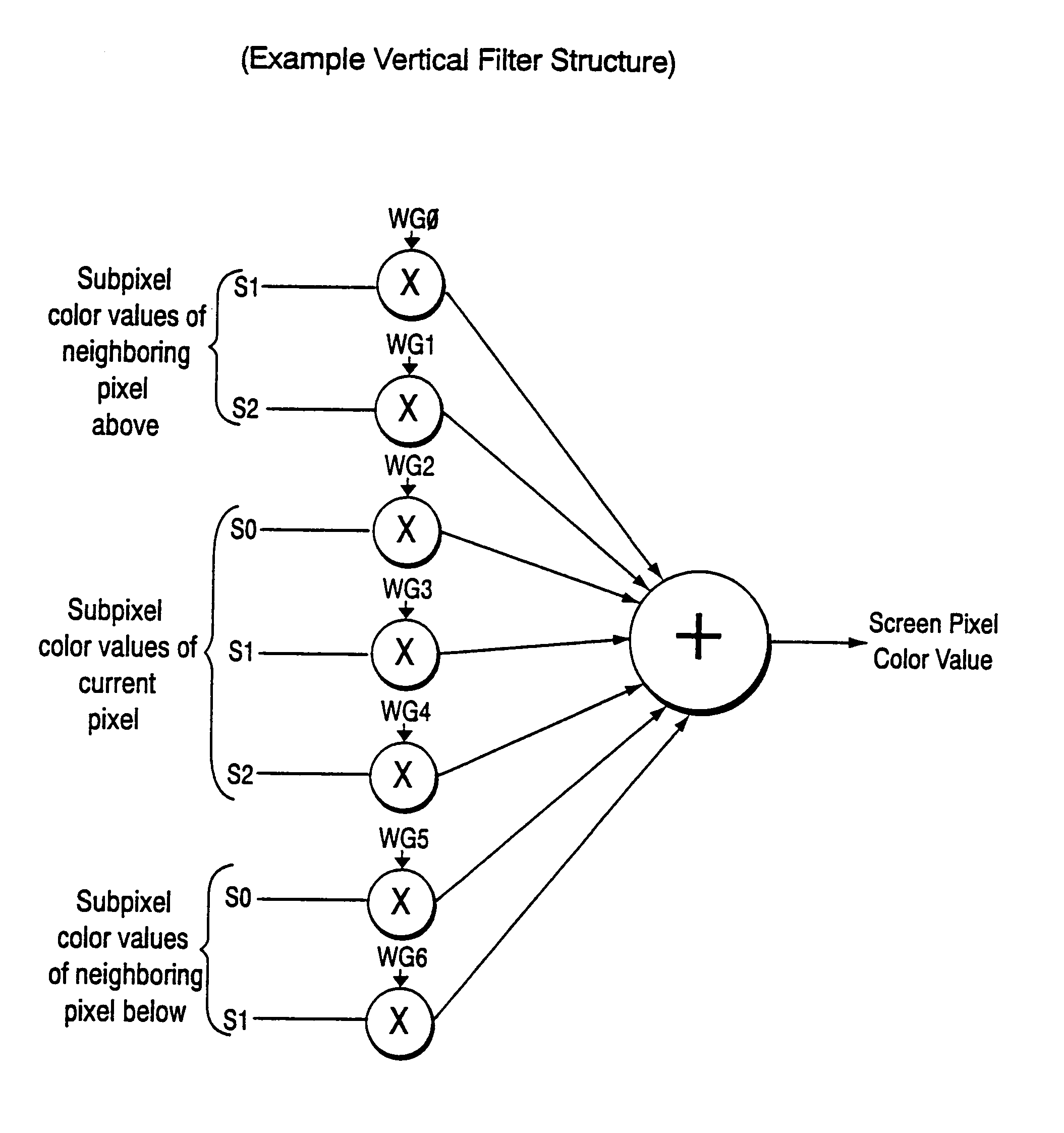
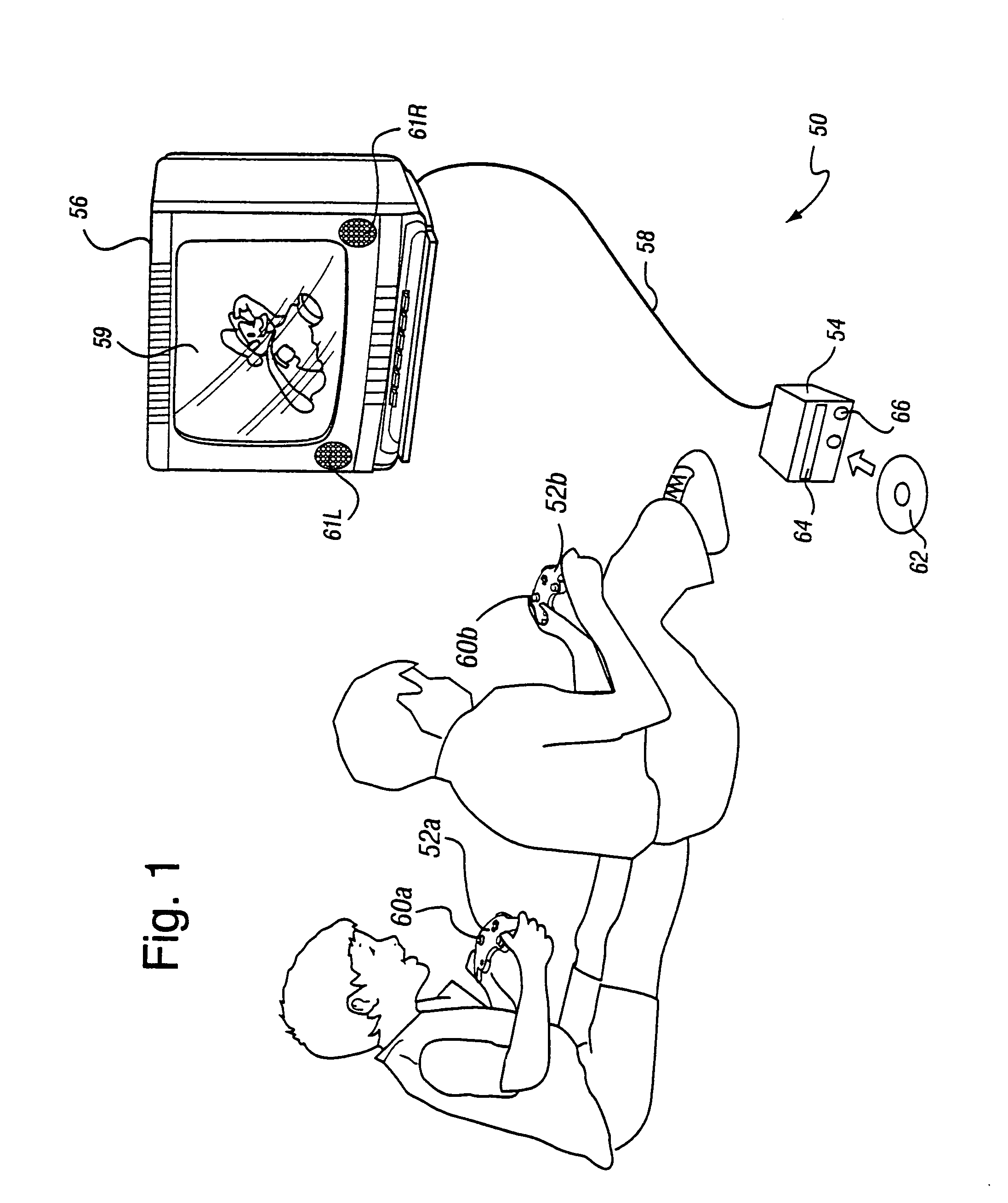
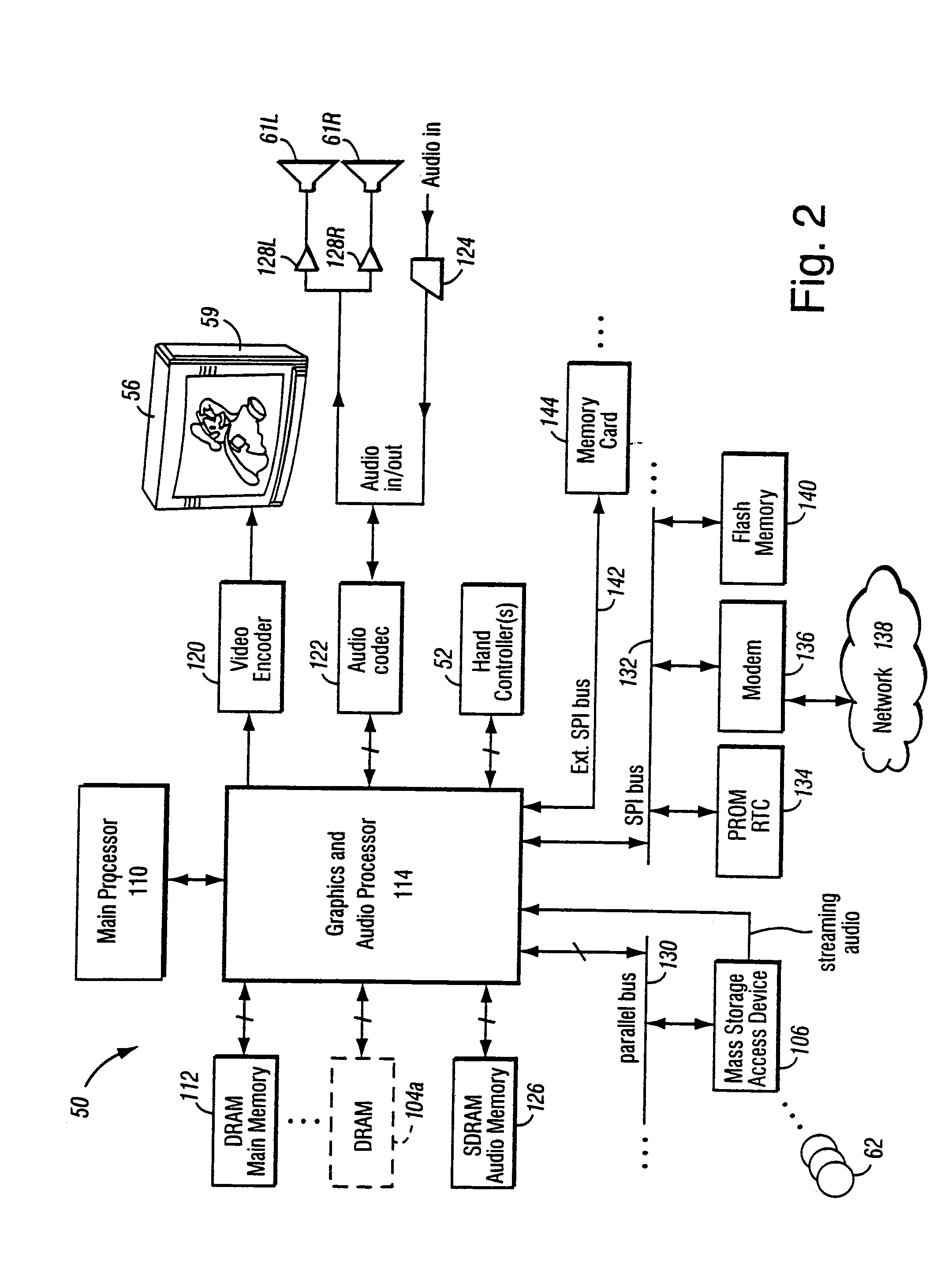
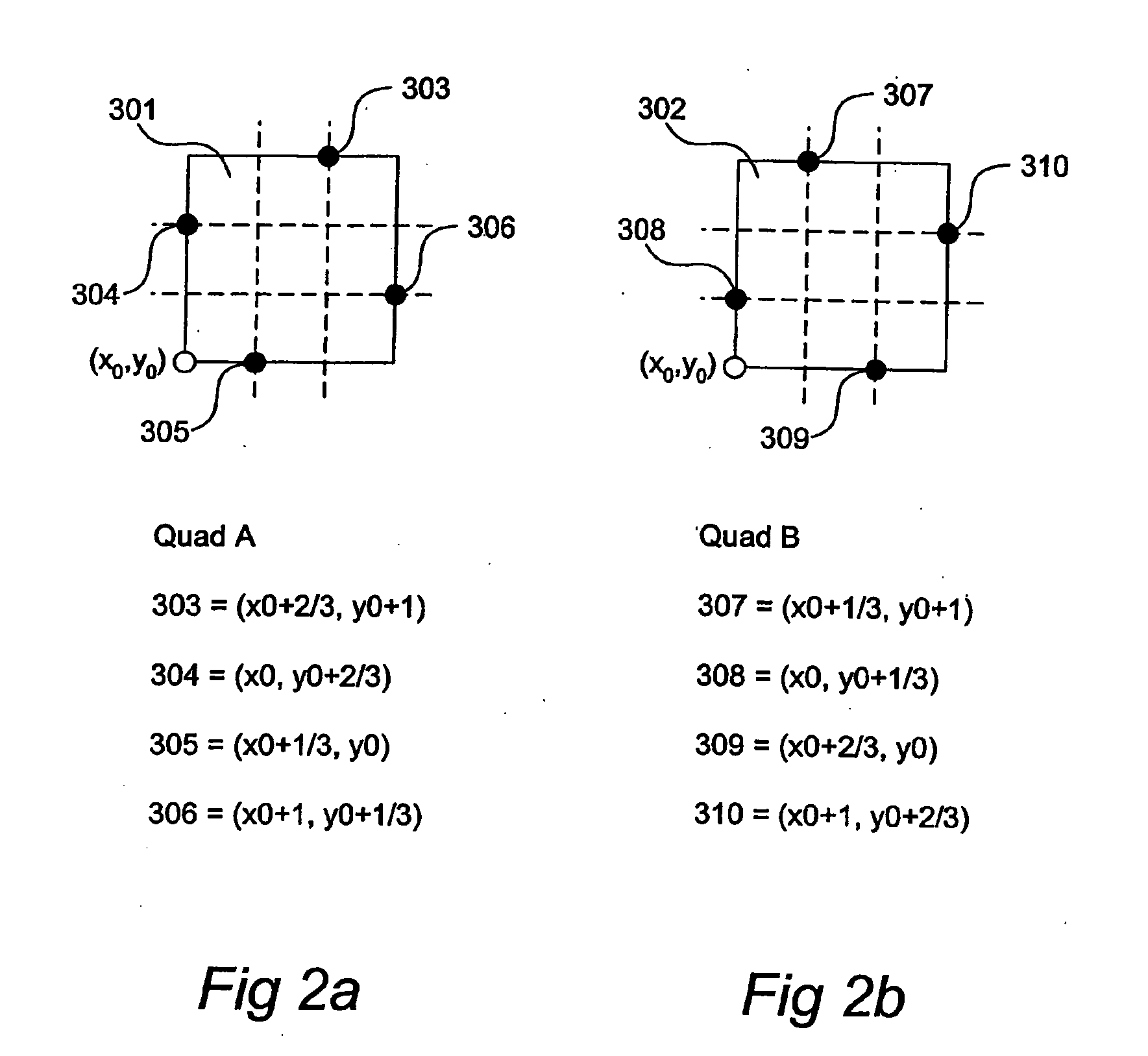
A graphics system including a custom graphics and audio processor produces exciting 2D and 3D graphics and surround sound. The system includes a graphics and audio processor including a 3D graphics pipeline and an audio digital signal processor. The system achieves highly efficient full-scene anti-aliasing by implementing a programmable-location super-sampling arrangement and using a selectable-weight vertical-pixel support area blending filter. For a 2×2 pixel group (quad), the locations of three samples within each super-sampled pixel are individually selectable. A twelve-bit multi-sample coverage mask is used to determine which of twelve samples within a pixel quad are enabled based on the portions of each pixel occupied by a primitive fragment and any pre-computed z-buffering. Each super-sampled pixel is filtered during a copy-out operation from a local memory to an external frame buffer using a pixel blending filter arrangement that combines seven samples from three vertically arranged pixels. Three samples are taken from the current pixel, two samples are taken from a pixel immediately above the current pixel and two samples are taken from a pixel immediately below the current pixel. A weighted average is then computed based on the enabled samples to determine the final color for the pixel. The weight coefficients used in the blending filter are also individually programmable. De-flickering of thin one-pixel tall horizontal lines for interlaced video displays is also accomplished by using the pixel blending filter to blend color samples from pixels in alternate scan lines.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
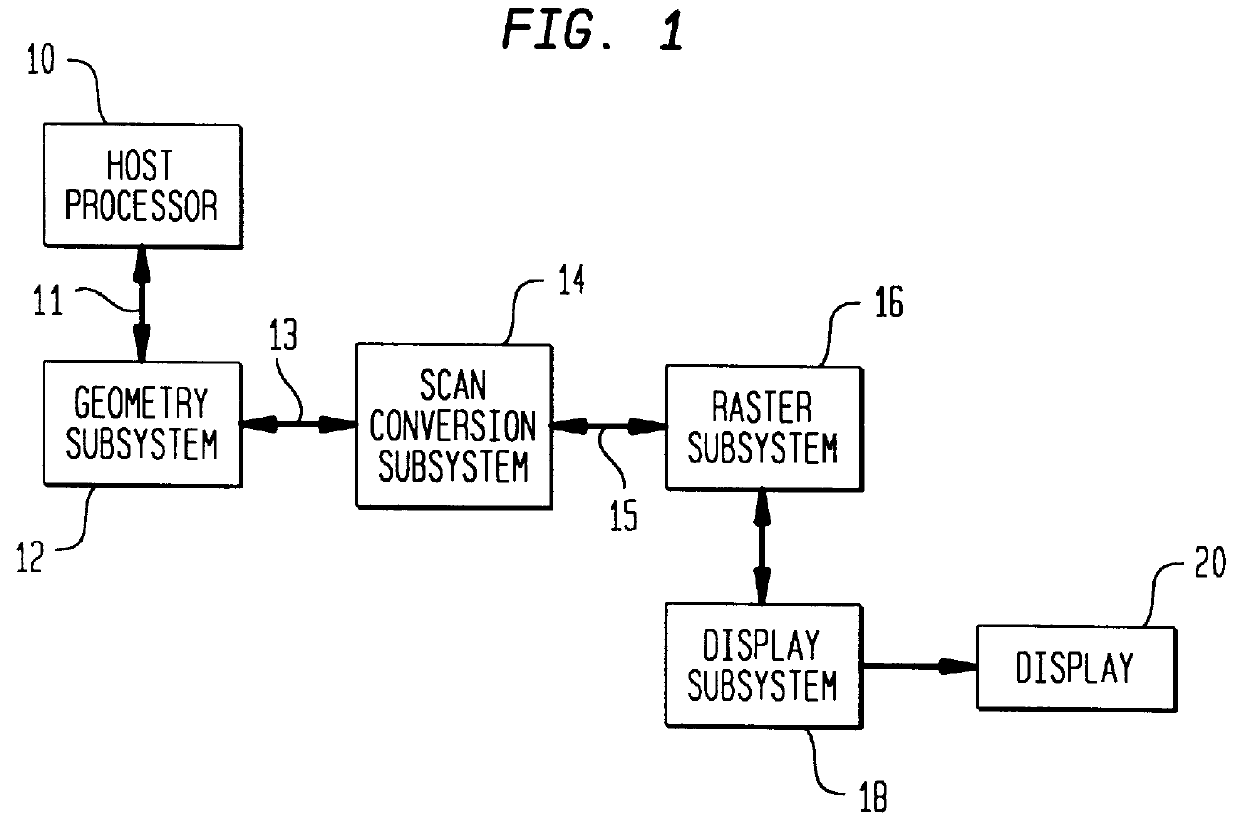
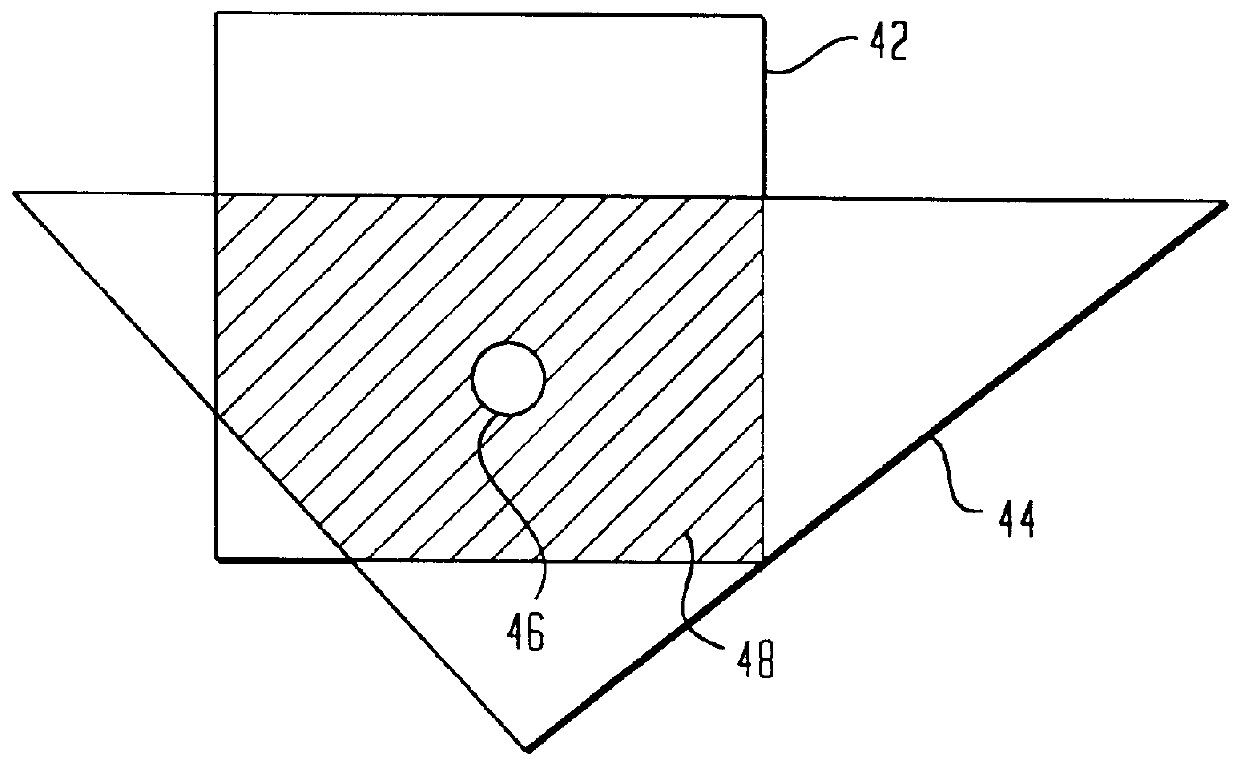
Antialiased imaging with improved pixel supersampling
An image processing system is described that receives polygonal image data at the direction of a processor and develops antialiased image data for display on a raster scanned display. In particular, the image system includes a scan convertor for converting the polygonal image data into pixel data, which includes pixel screen coordinates and at least one color value for each polygon covered pixel of the pixel data and a supersample coverage mask indicating an extent of polygon coverage within each polygon covered pixel. The image system also includes a raster system having at least one image processor for receiving the pixel data for each pixel, for developing a region mask based on the supersample coverage mask, and for storing the color value in association with the region mask as anitialiased display data in an image memory in communication with the image processor based on the pixel screen coordinates. The region mask indicates one or more, geographical regions of supersamples within each pixel covered by one or more polygons and indicates a color value stored in the image memory to be assigned to the supersamples in a region. This requires only a single color value for supersamples within a region of a covered pixel to be stored in the image memory. The image system can also be configured to develop and store Z-values, alpha values, stencil values, and texture values for each pixel for storage in the image memory in association with the region mask.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Antialiasing using hybrid supersampling-multisampling
ActiveUS6967663B1Geometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsPosition dependent
Hybrid sampling of pixels of an image involves generating shading values at multiple shading sample locations and generating depth values at multiple depth sample locations, with the number of depth sample locations exceeding the number of shading sample locations. Each shading sample location is associated with one or more of the depth sample locations. Generation and filtering of hybrid sampled pixel data can be done within a graphics processing system, transparent to an application that provides image data.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Graphics system with programmable real-time sample filtering
A method and computer graphics system capable of super-sampling and performing programmable real-time filtering or convolution are disclosed. In one embodiment, the computer graphics system may comprise a graphics processor, a sample buffer, and a sample-to-pixel calculation unit. The graphics processor may be configured to generate a plurality of samples. The sample buffer, which is coupled to the graphics processor, is configured to store the samples and may be configured to double-buffer at least part of the stored samples. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit is programmable to select a variable number of stored samples from the sample buffer to filter into an output pixel. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit performs the filter process in real-time, and may be programmable to use a number of different filter types in.a single frame. The sample buffer may be super-sampled, and the samples may be positioned according to a regular grid, a perturbed regular grid, or a stochastic grid.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Graphics system with programmable real-time alpha key generation
A method and graphics system capable of super-sampling and performing real-time convolution to form a soft-edge alpha key are disclosed. In one embodiment, the computer graphics system may comprise a graphics processor, a sample buffer, and a sample-to-pixel calculation unit. The graphics processor may be configured to receive 3D graphics data comprising a plurality graphics primitives and then generate a plurality of samples from the 3D graphics data. The samples may comprise both color and alpha information. The super-sampled sample buffer may be coupled to receive and store the samples from the graphics processor. The sample buffer may also be configured to double-buffer at least a portion of each stored sample. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit may be coupled to receive and filter samples from the super-sampled sample buffer to form output pixels and alpha pixels in real time, wherein the alpha pixels are usable to form an alpha key. The graphics system may be further configured to receive a video input signal and overlay the video input signal with the output pixels according to said alpha pixels.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Graphics system with a variable-resolution sample buffer
A method and computer graphics system capable of super-sampling and performing real-time convolution are disclosed. In one embodiment, the computer graphics system may comprise a graphics processor, a sample buffer, and a sample-to-pixel calculation unit. The graphics processor may be configured to generate a plurality of samples. The sample buffer, which is coupled to the graphics processor, may be configured to store the samples. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit is programmable to select a variable number of stored samples from the sample buffer to filter into an output pixel. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit performs the filter process in real-time, and may use a number of different filter types in a single frame. The sample buffer may be super-sampled, and the samples may be positioned according to a regular grid, a perturbed regular grid, or a stochastic grid.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Graphics system with programmable sample positions
A method and computer graphics system for rendering images using programmable sample positions is disclosed. In one embodiment, the computer graphics system may comprise a graphics processor, a sample buffer, and a sample-to-pixel calculation unit. The graphics processor may be configured to generate a plurality of samples using a sample positioning algorithm selected from a programmable memory or generated by programmable hardware. The sample buffer, which is coupled to the graphics processor, may be configured to store the samples. The sample buffer may be super-sampled and double buffered. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit is programmable to select a variable number of stored samples from the sample buffer to filter into an output pixel. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit performs the filter process in real-time, and may use a number of different filter types. The algorithms used to position the samples may position the samples according to a regular grid, a perturbed regular grid, or a stochastic grid.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Graphics system having a super-sampled sample buffer with generation of output pixels using selective adjustment of filtering for reduced artifacts
A computer graphics system that utilizes a super-sampled sample buffer and a programmable sample-to-pixel calculation unit for refreshing the display, wherein the graphics system may adjust filtering to reduce artifacts or implement display effects. In one embodiment, the graphics system may have a graphics processor, a super-sampled sample buffer, and a sample-to-pixel calculation unit. The graphics processor renders a plurality of samples and stores them into a sample buffer. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit reads the samples from the super-sampled sample buffer and filters or convolves the samples into respective output pixels which are then provided to refresh the display. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit may selectively adjust the filtering of stored samples to reduce artifacts, e.g., is operable to selectively adjust the filtering of stored samples in neighboring frames to reduce artifacts between the neighboring frames. The filter adjustment may be applied where the sample-to-pixel calculation unit generates output pixels at the same rate as the graphics processor rendering samples to the sample buffer, or at a different (e.g., higher) rate than the render rate. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit is operable to adjust filtering of stored samples to implement a display effect, such as panning, zooming, rotation, or moving scenes, among others. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit may also selectively adjust the filtering of stored samples on a fractional-pixel boundary.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Dynamically adjusting a sample-to-pixel filter in response to user input and/or sensor input
InactiveUS6850236B2LevelAvoid flickeringDrawing from basic elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsFilter tuning
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
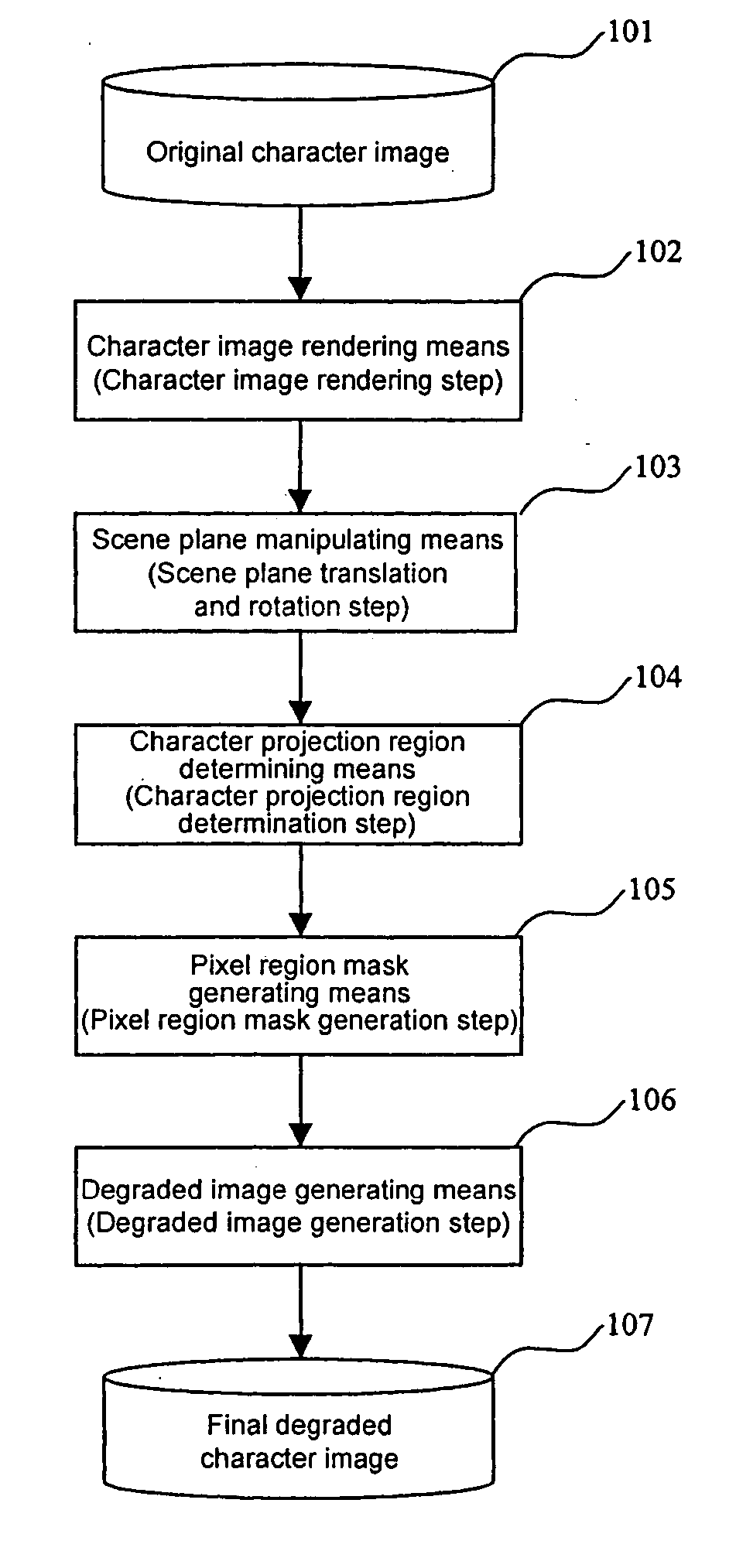
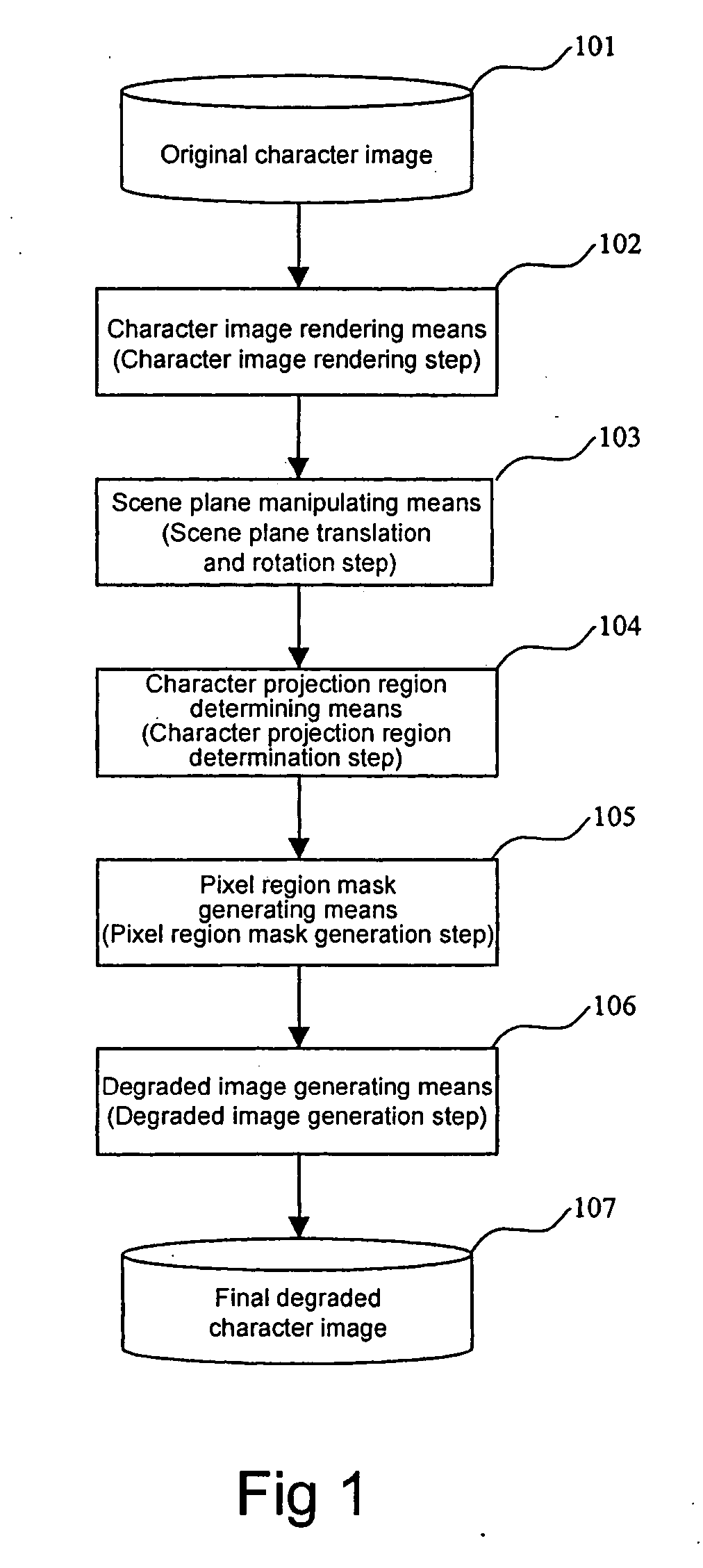
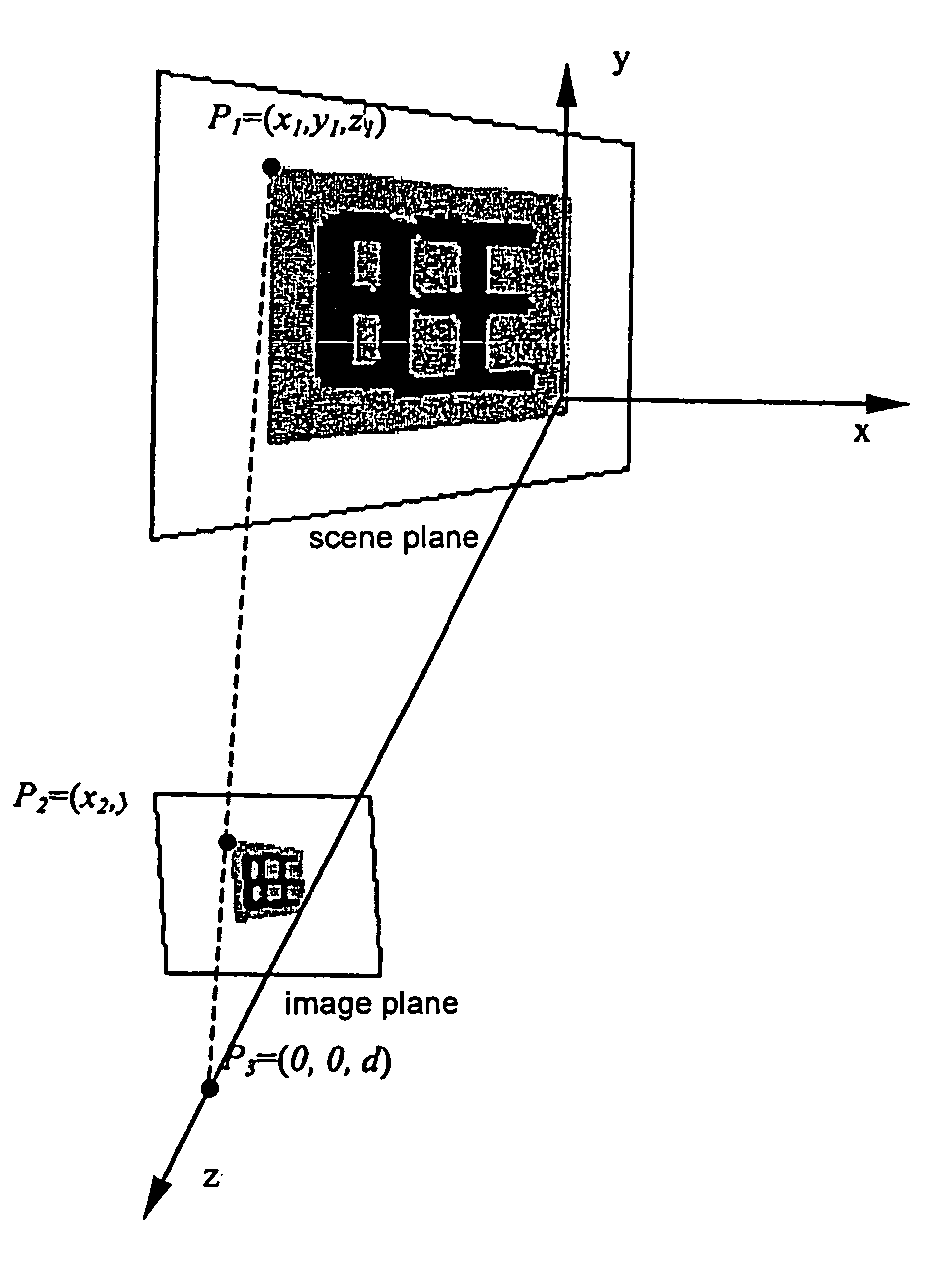
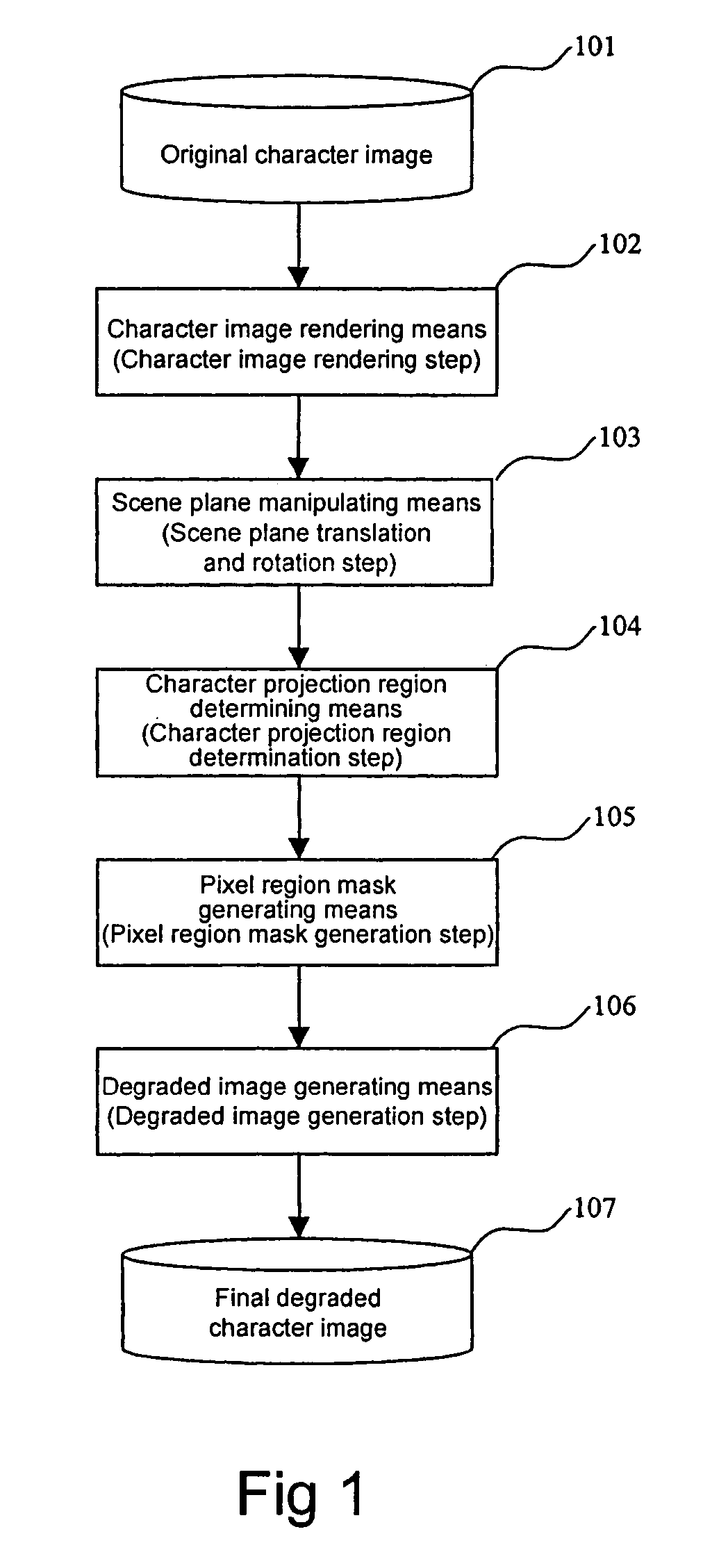
Degraded character image generation method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060056697A1Efficient identificationCharacter recognitionComputer graphics (images)Supersampling
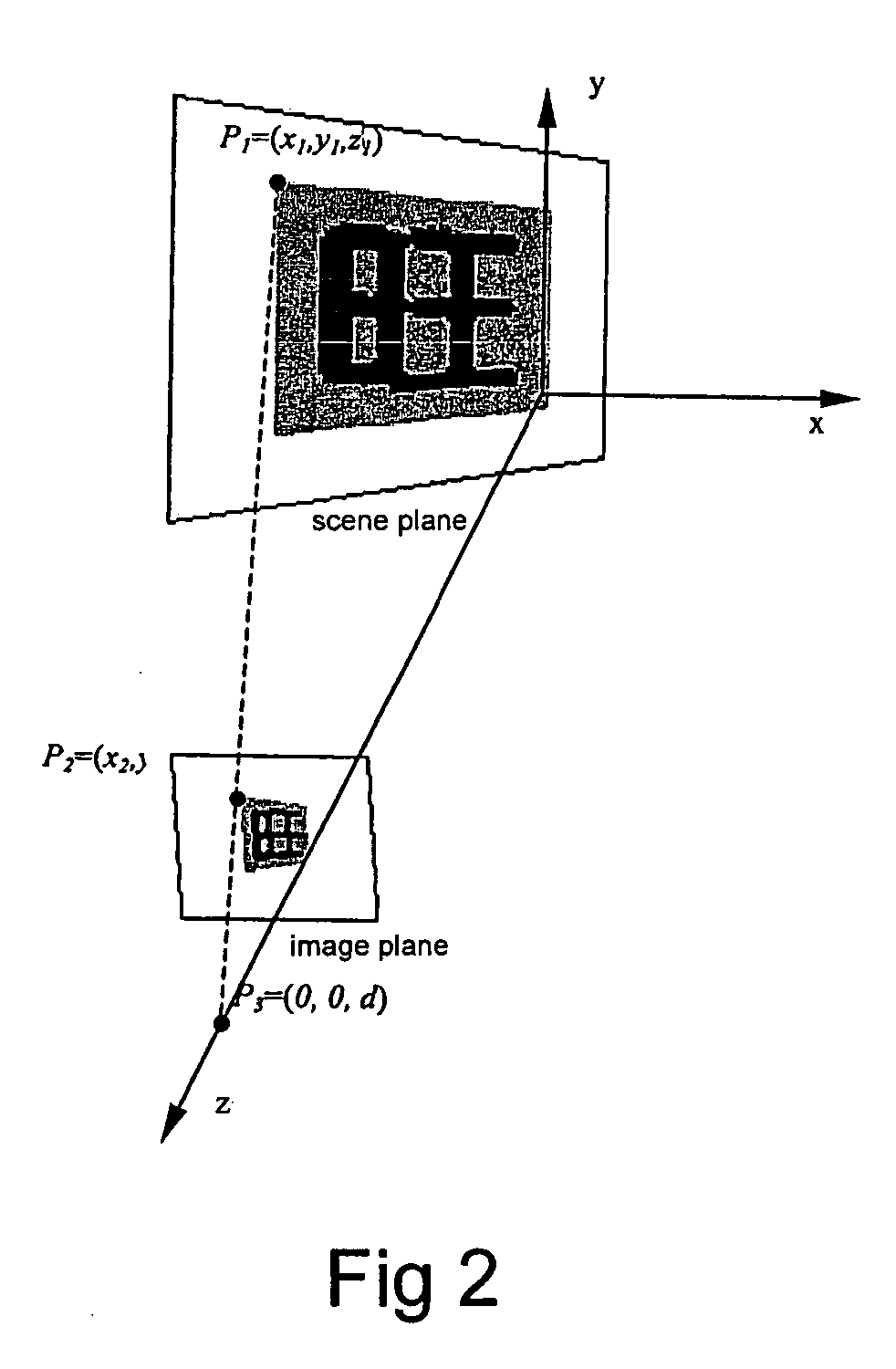
A method and apparatus for generating a degraded character image at various levels of degradation automatically is presented in this invention. The method comprises rendering the character image on a scene plane; translating and rotating the scene plane according to various parameters; determining a projection region of the character image on an image plane according to various parameters; generating a pixel region mask; and generating a final degraded image by super-sampling. Thus various degraded character images are generated on various conditions of degradation. The generated synthetic characters can be used for performance evaluation and training data augmentation in optical character recognition (OCR).
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
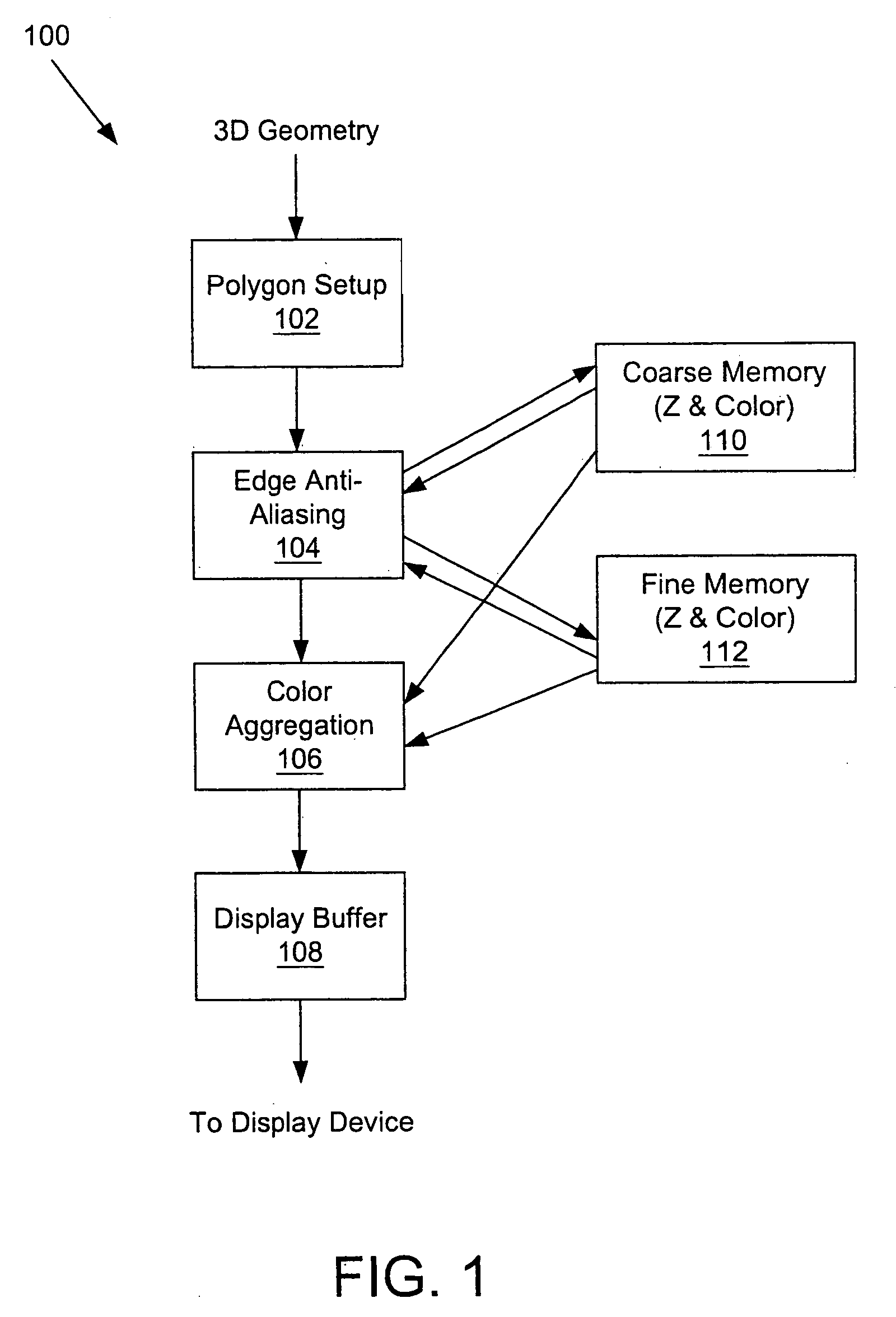
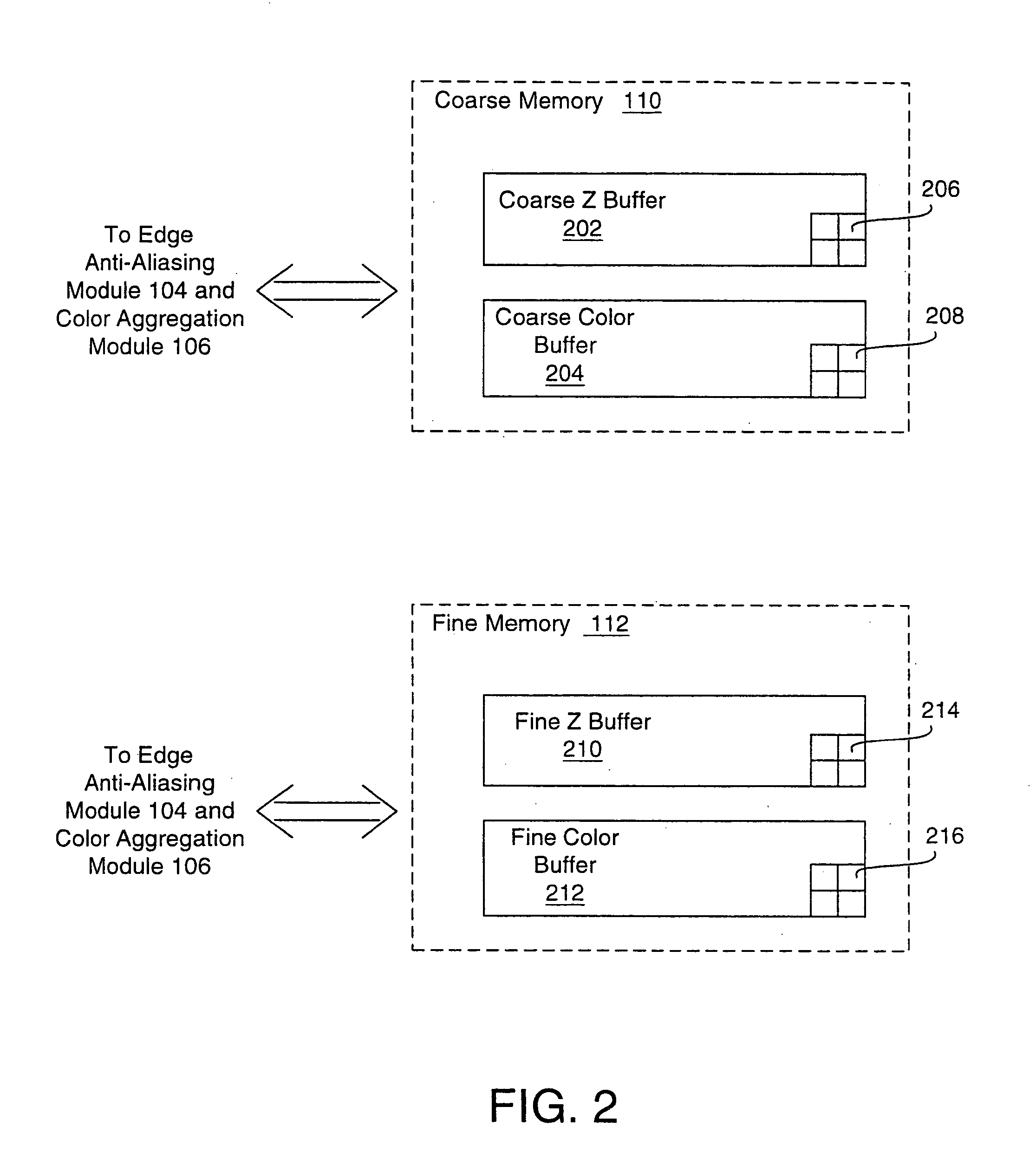
Selective super-sampling/adaptive anti-aliasing of complex 3D data
InactiveUS20050179698A1Avoid it happening againReduce trafficGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsJaggies
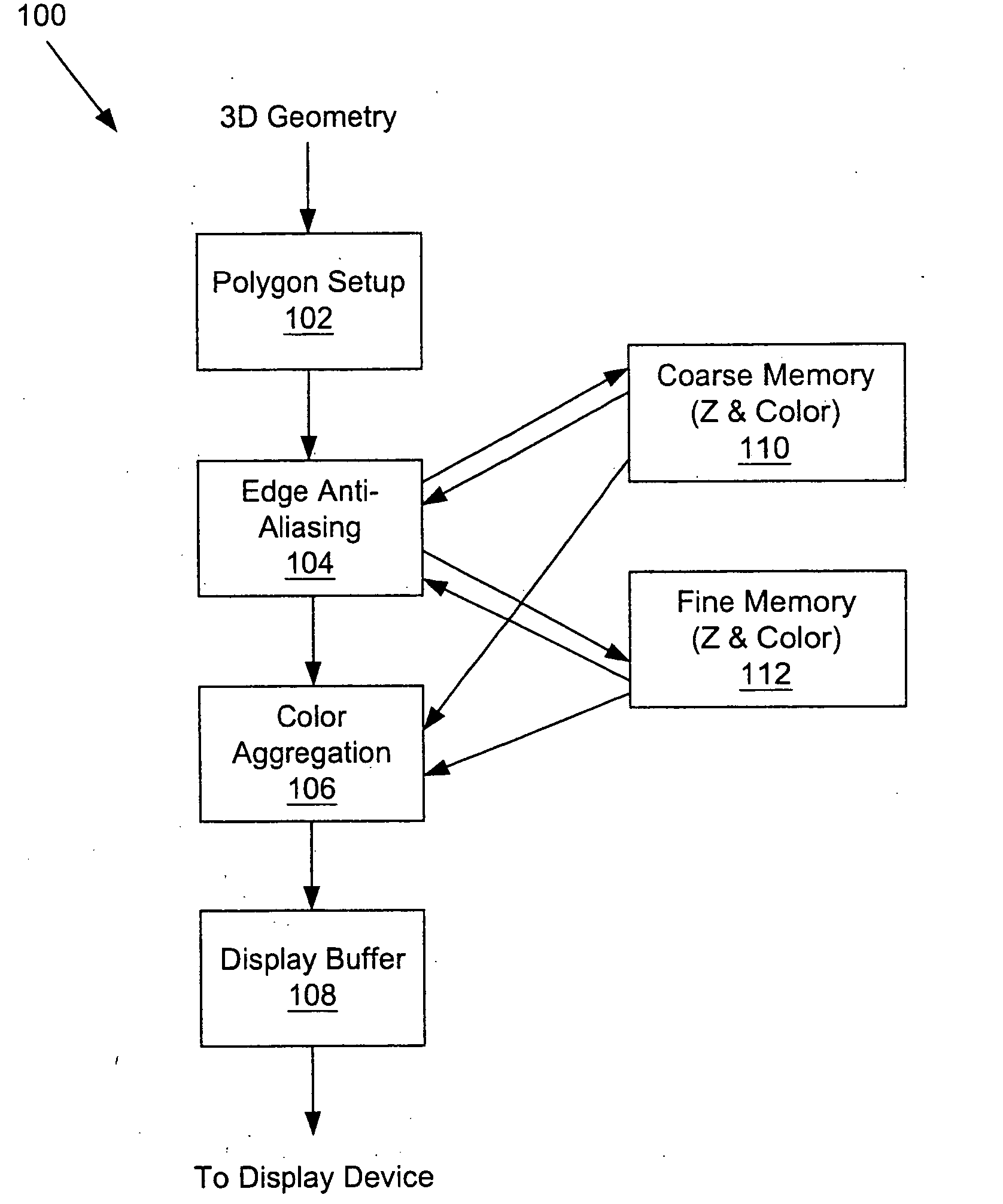
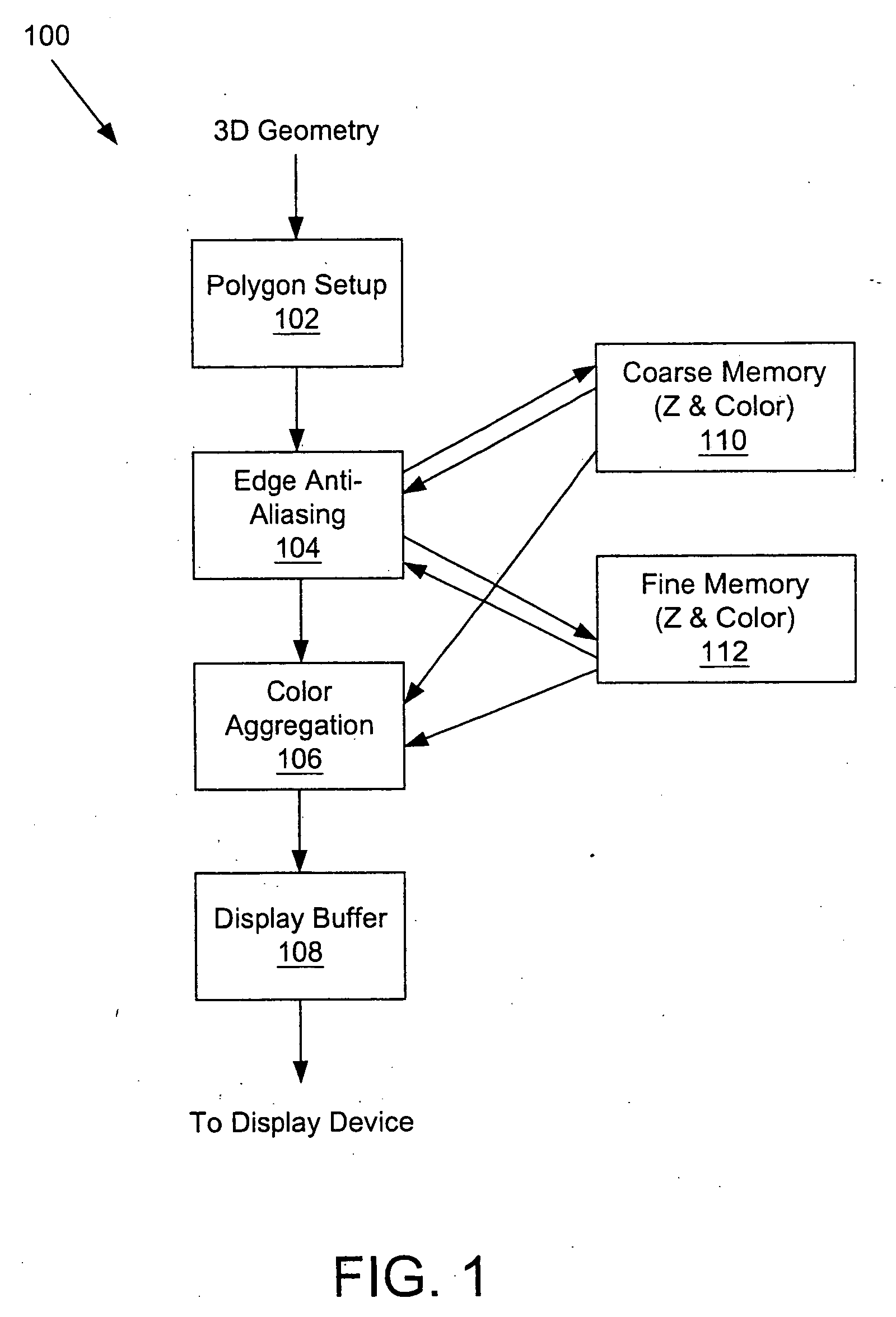
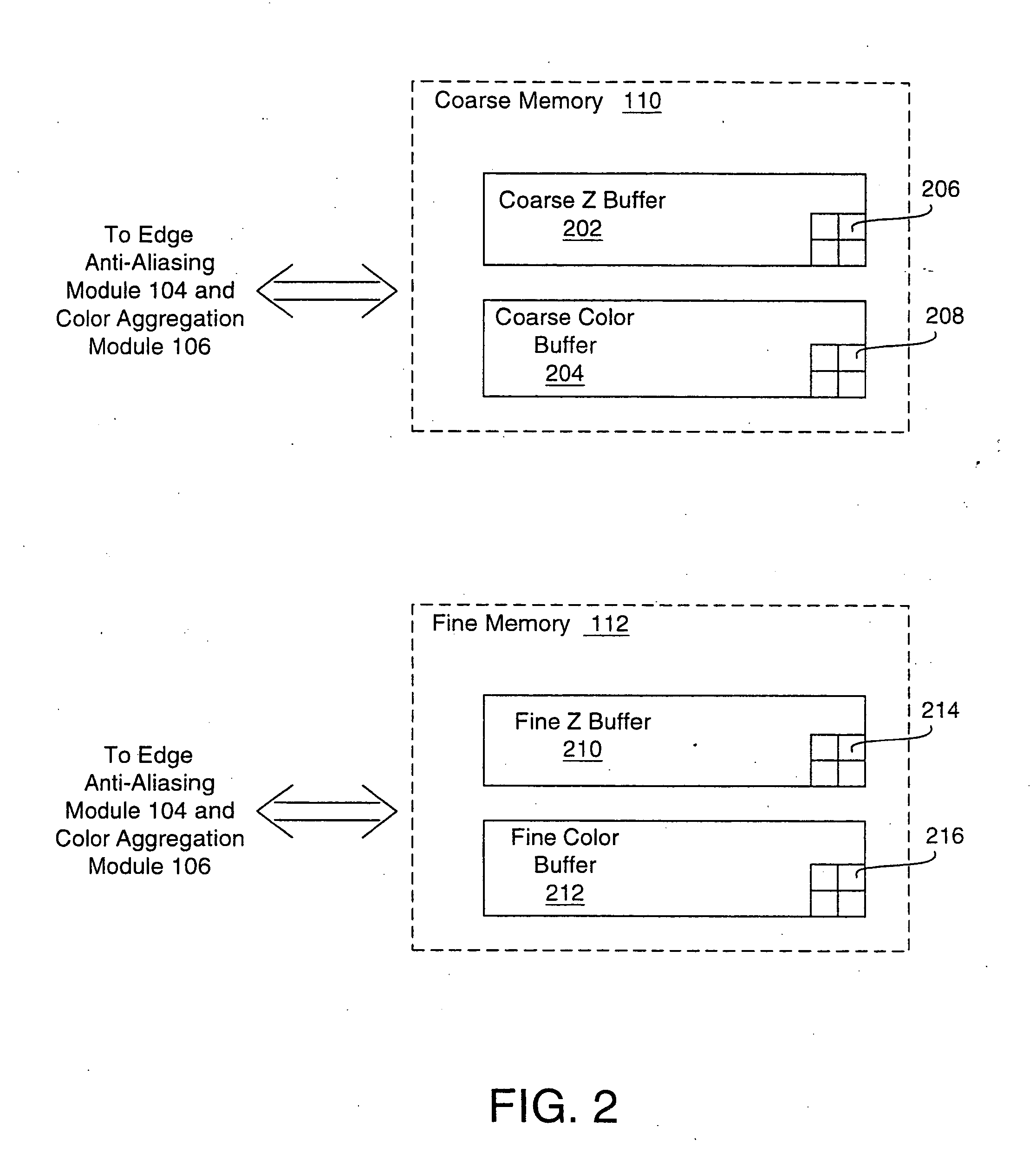
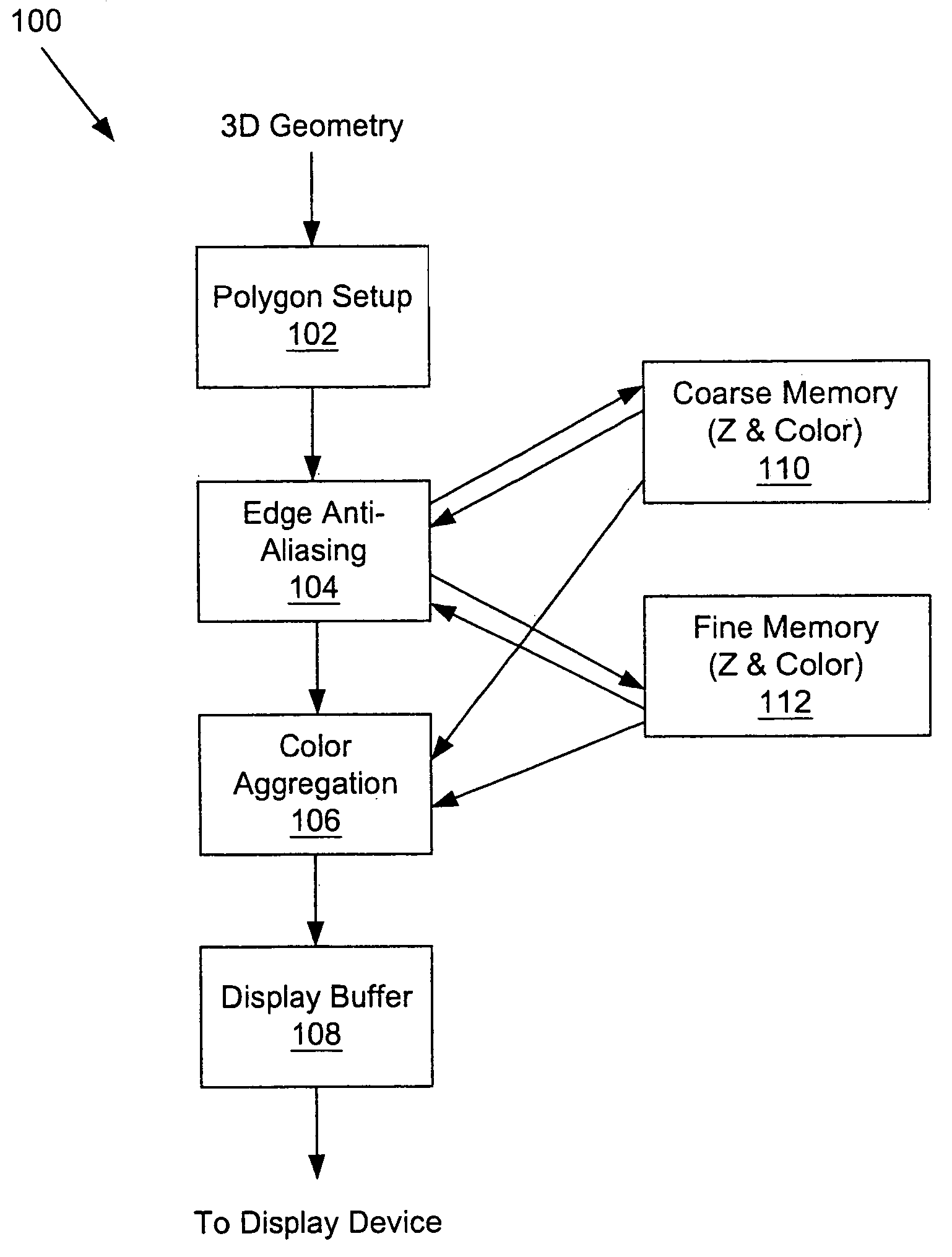
A system and method is provided for preventing the occurrence of aliasing at the edges of polygons in 3D graphics. The system may detect both polygon geometric edges and Z edges due to intersection of multiple polygons. In one embodiment, the system includes an edge anti-aliasing module configured to selectively super-sample edge portions of primitives. The system further includes a coarse memory for storing information of pixels that are not super-sampled and a fine memory for storing information of pixels that are super-sampled by the edge anti-aliasing module.
Owner:S3 GRAPHICS
Dynamically adjusting a sample-to-pixel filter in response to user input and/or sensor input
A graphics system capable of super-sampling and performing real-time convolution. The graphics system may comprise a graphics processor, a sample buffer, and a sample-to-pixel calculation unit. The graphics processor receives graphics data and generates a plurality of samples for each of a plurality of frames. The sample buffer stores the samples. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit is operable to generate output pixels by filtering the rendered samples using a filter. A display device then receives and displays the output pixels. A user may observe the displayed image and adjust properties of the filter according to the user's personal visual preferences. A display-monitoring device may be configured to capture the displayed image. The graphics system may then analyze the captured image and, in response to the captured image, perform filter adjustments.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Antialiasing using hybrid supersampling-multisampling
ActiveUS7511717B1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsFilling planer surface with attributesGraphicsPosition dependent
Hybrid sampling of pixels of an image involves generating shading values at multiple shading sample locations and generating depth values at multiple depth sample locations, with the number of depth sample locations exceeding the number of shading sample locations. Each shading sample location is associated with one or more of the depth sample locations. Generation and filtering of hybrid sampled pixel data can be done within a graphics processing system, transparent to an application that provides image data.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Graphics system having a super-sampled sample buffer with generation of output pixels using selective adjustment of filtering for implementation of display effects
A computer graphics system that utilizes a super-sampled sample buffer and a programmable sample-to-pixel calculation unit for refreshing the display, wherein the graphics system may adjust filtering to reduce artifacts or implement display effects. In one embodiment, the graphics system may have a graphics processor, a super-sampled sample buffer, and a sample-to-pixel calculation unit. The graphics processor renders a plurality of samples and stores them into a sample buffer. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit reads the samples from the super-sampled sample buffer and filters or convolves the samples into respective output pixels which are then provided to refresh the display. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit may selectively adjust the filtering of stored samples to reduce artifacts, e.g., is operable to selectively adjust the filtering of stored samples in neighboring frames to reduce artifacts between the neighboring frames. The filter adjustment may be applied where the sample-to-pixel calculation unit generates output pixels at the same rate as the graphics processor rendering samples to the sample buffer, or at a different (e.g., higher) rate than the render rate. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit is operable to adjust filtering of stored samples to implement a display effect, such as panning, zooming, rotation, or moving scenes, among others. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit may also selectively adjust the filtering of stored samples on a fractional-pixel boundary.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Graphics system with a programmable sample position memory
A method and computer graphics system capable of super-sampling and performing real-time convolution are disclosed. In one embodiment, the computer graphics system may comprise a graphics processor, a sample buffer, and a sample-to-pixel calculation unit. The graphics processor may be configured to generate a plurality of samples. The sample buffer, which is coupled to the graphics processor, may be configured to store the samples. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit is programmable to select a variable number of stored samples from the sample buffer to filter into an output pixel. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit performs the filter process in real-time, and may use a number of different filter types in a single frame. The sample buffer may be super-sampled, and the samples may be positioned according to a regular grid, a perturbed regular grid, or a stochastic grid.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Adaptive color super resolution thresholding
Methods and systems for adaptively thresholding color image pixels are based on determining a signed (e.g., a plus or minus sign) single-component gray image which can be supersampled and binarized. The method computes the distance of a given color image pixel from an idealized plane which segments the color space into two regions. The process is made adaptive by making the threshold a function of neighborhood pixels. This combines the information from all color channels, such as, for example, 3 or 4 color channels, into a high quality gray channel used for binarization.
Owner:XEROX CORP
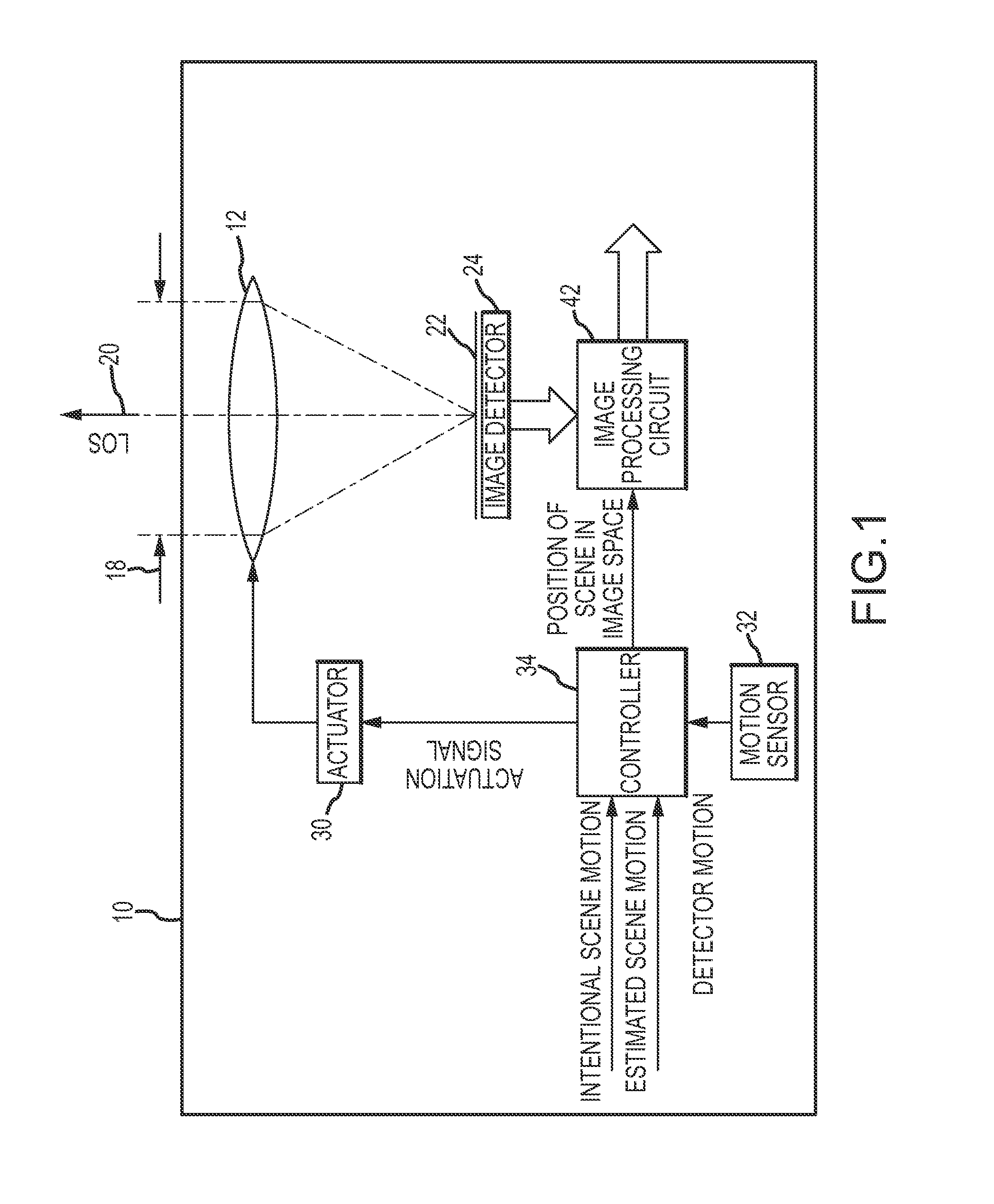
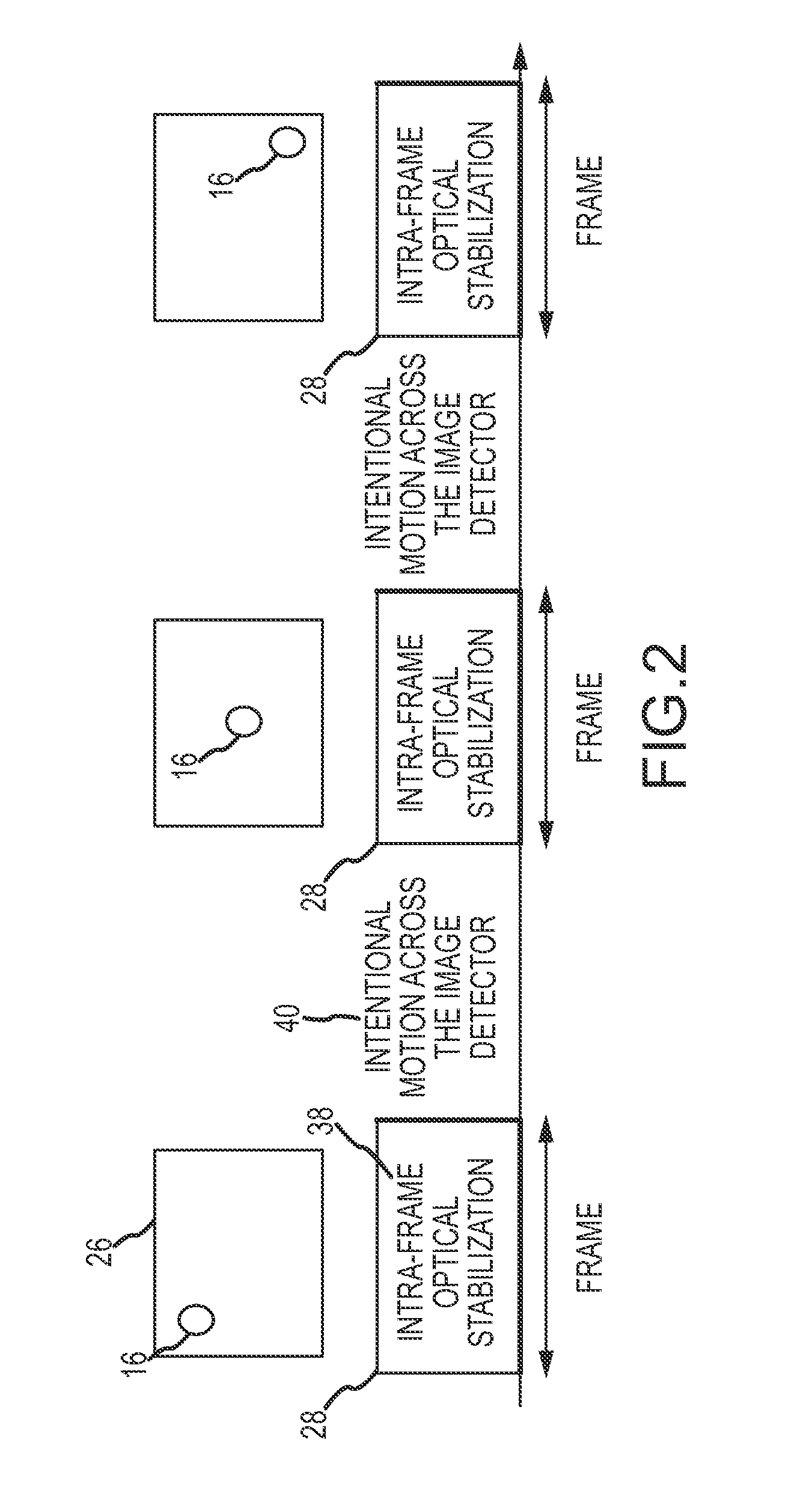
Intra-frame optical-stabilization with intentional inter-frame scene motion
ActiveUS20130235220A1Eliminates misregistrationEliminates smearing in imageTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Radiology
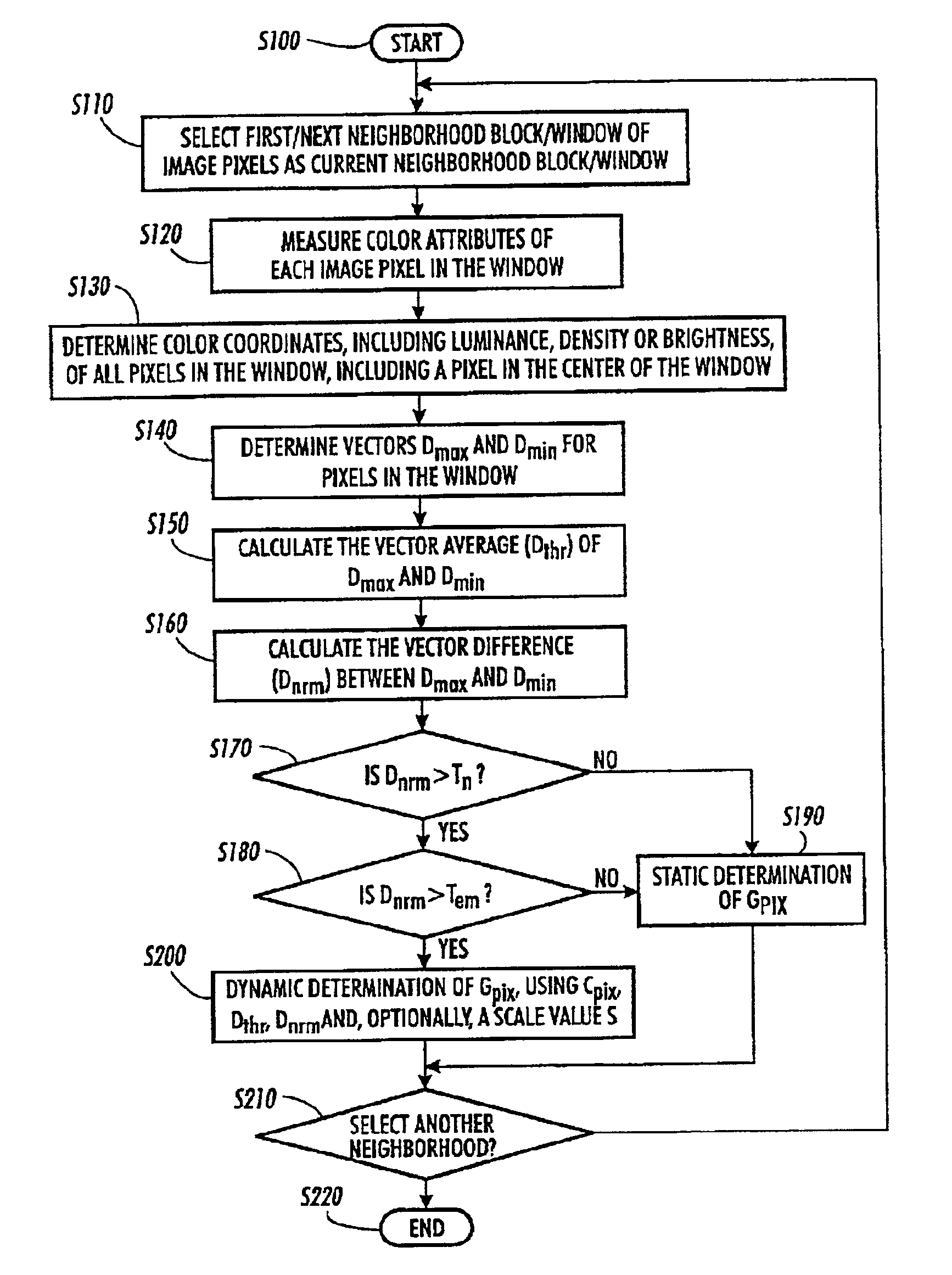
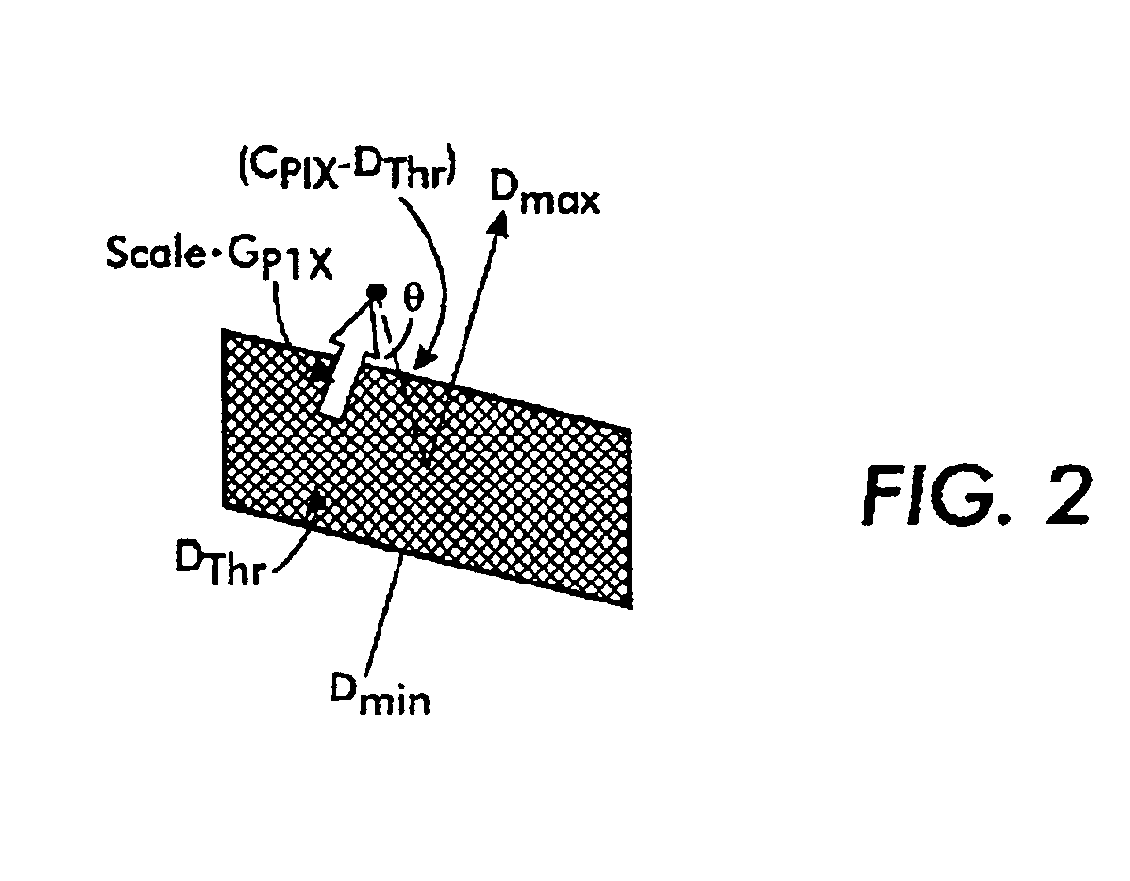
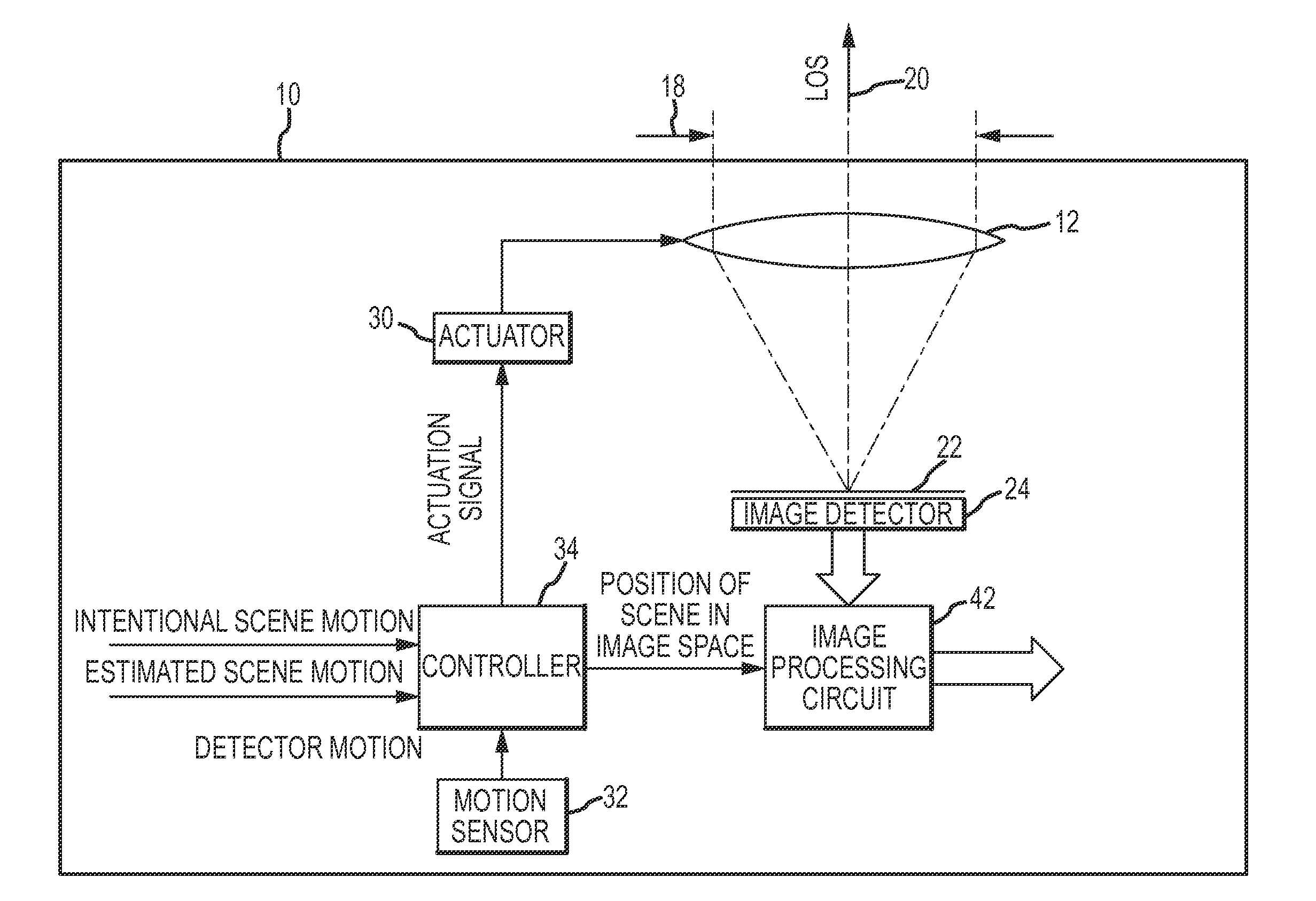
In an imaging system, intentional scene motion across the image detector from frame-to-frame, and more particularly the rate of intentional scene motion is “decoupled” from smearing of the scene in the detected image by applying the intentional scene motion in the interval between frames to produce the intentional scene motion in a discrete step across the image detector from frame-to-frame. The intentional scene motion may be quantized or provided as a sub-pixel dither signal to control the sub-pixel phase frame-to-frame. In register / sum applications, this substantially eliminates misregistration of the images and may allow for super-sampling of the images onto a higher resolution grid. The ability to decouple intentional scene motion from smearing and to control the sub-pixel phase defines a new trade space that relaxes the limitations on intentional scene motion across the image detector.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
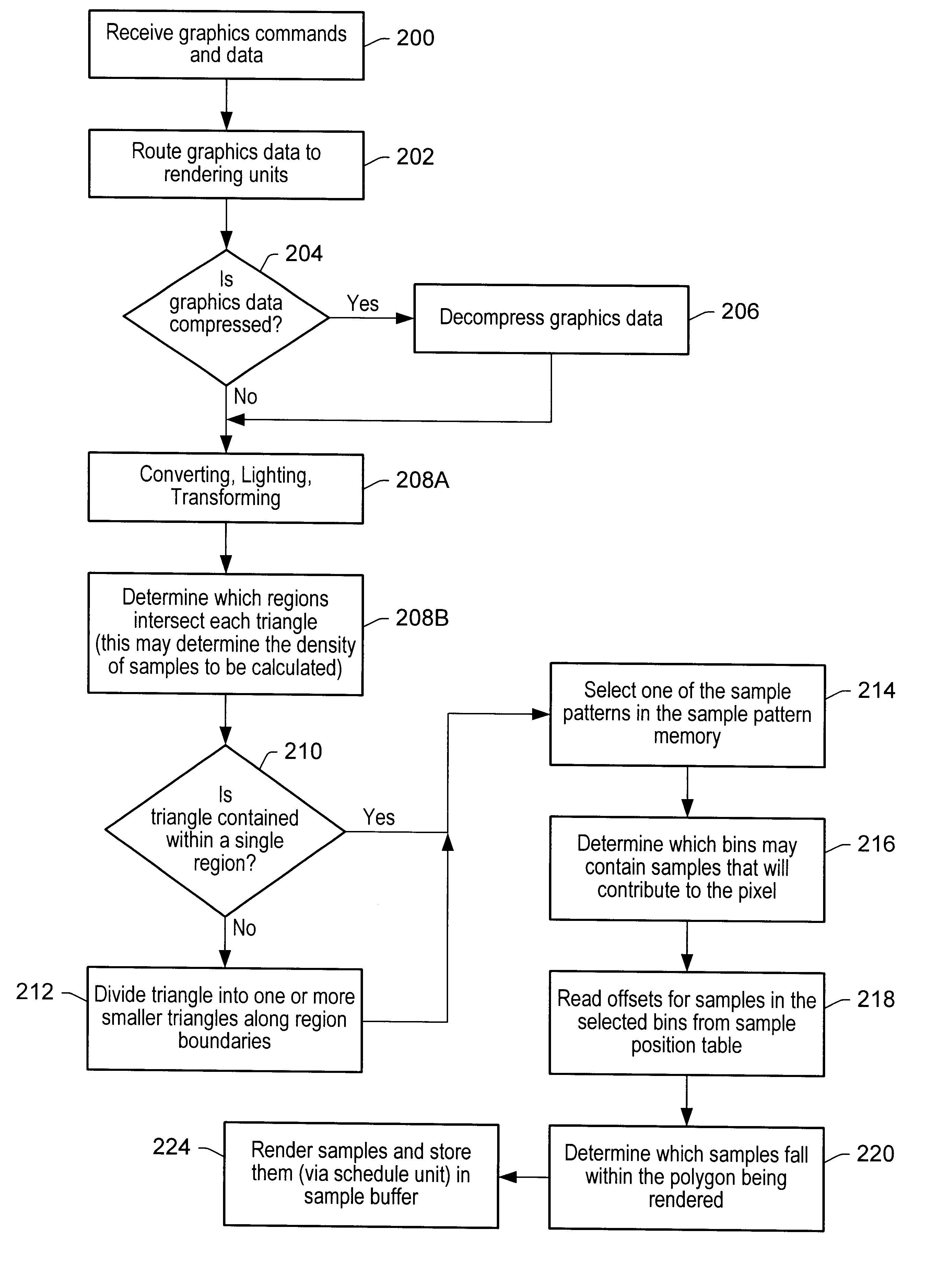
Method and system for supersampling rasterization of image data
InactiveUS20070097145A1Attenuation bandwidthReduce the burden onGeometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsAnti-aliasingComputer vision
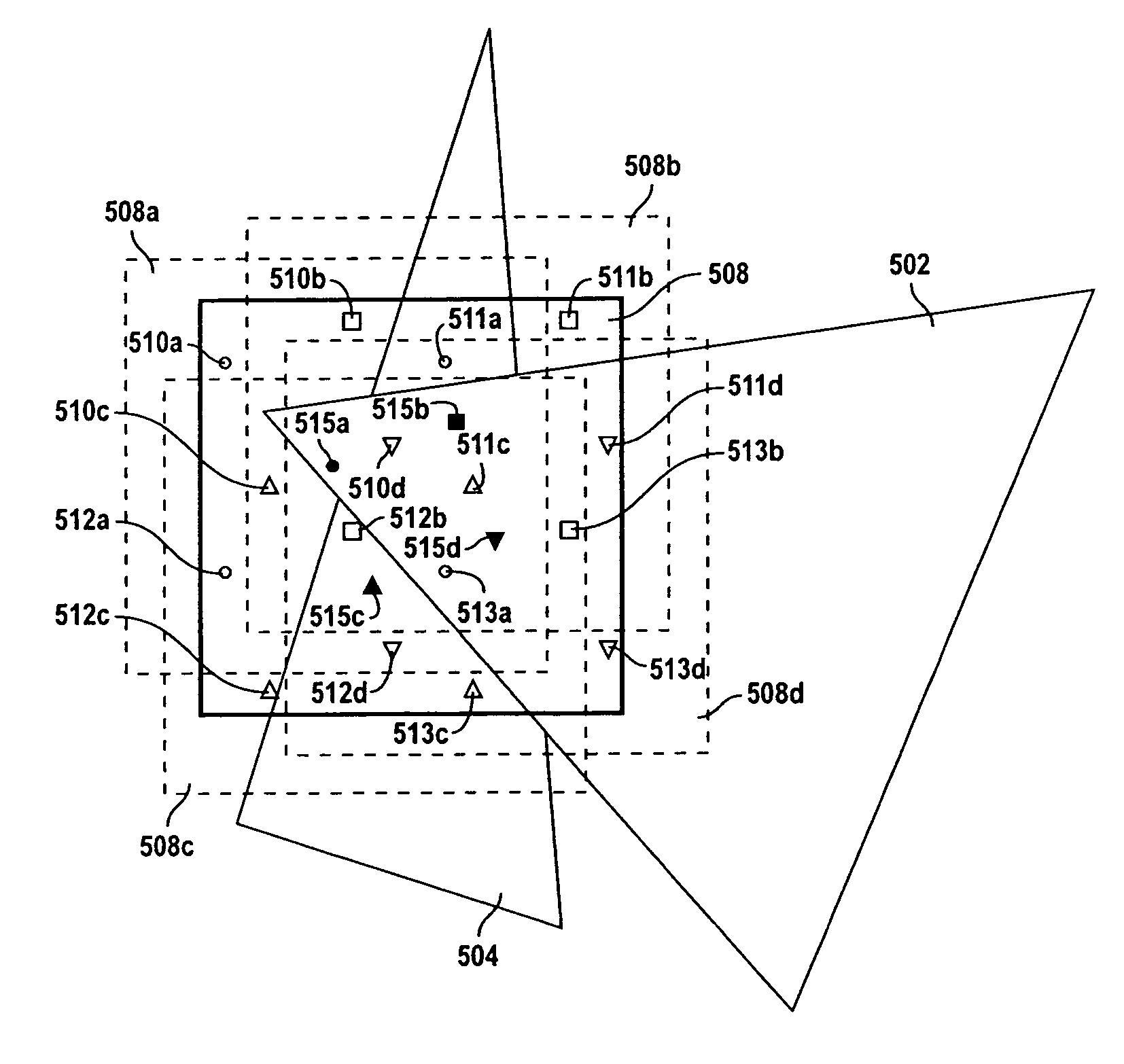
A sample-sharing pattern covering a set of pixels for use in an anti-aliasing system where each pixel has a pattern of sample points. A first sampling point is provided at a corner of the pixel, and second and third sampling points are provided at separate borders of the pixel, which do not intersect the corner sample. Moreover, the sample point pattern of each pixel is a mirror image of and different from the pattern of a neighboring pixel.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Efficient super-sampling with per-pixel shader threads
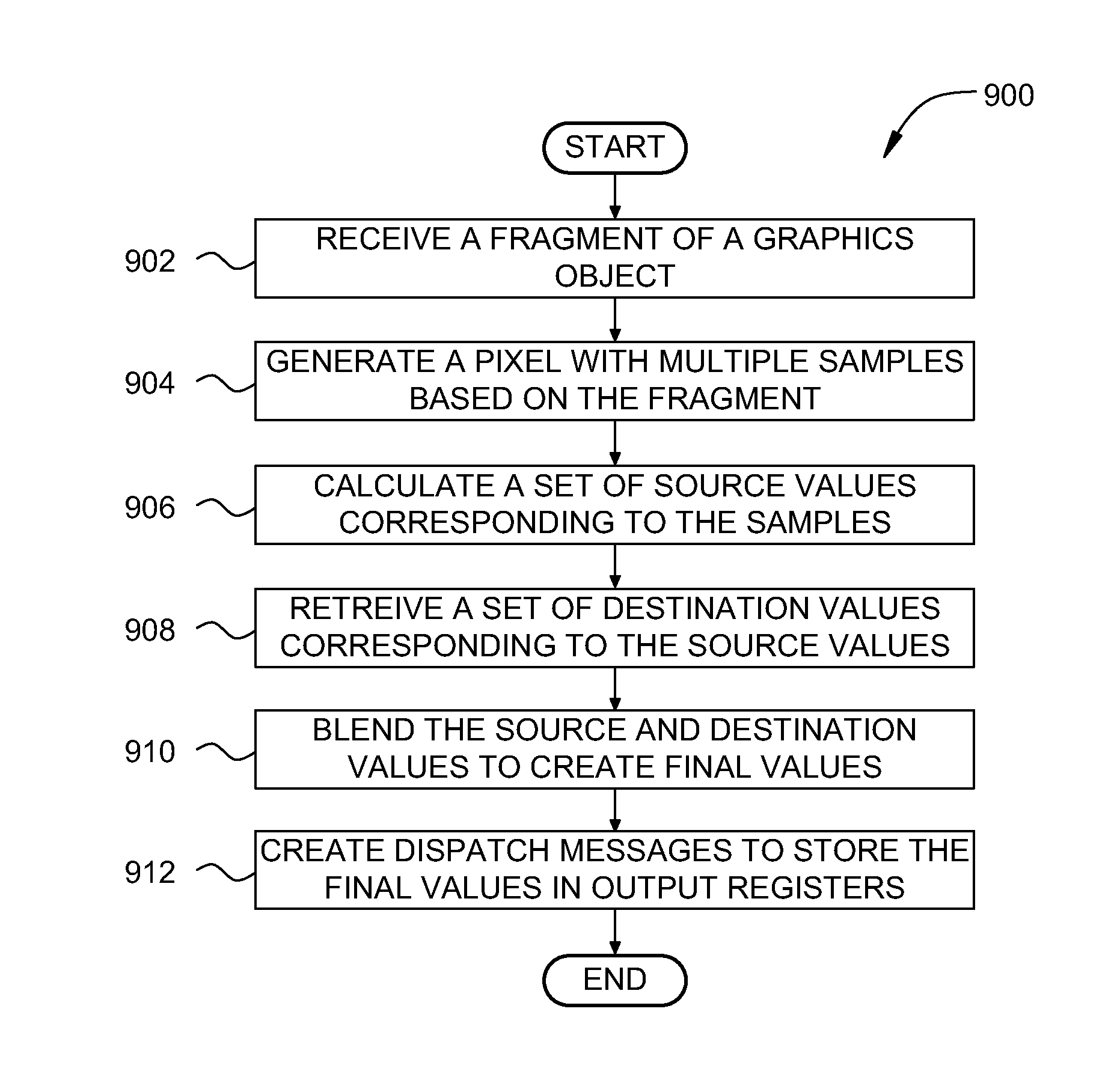
ActiveUS20140176579A1Improve efficiencyImprove image qualityProcessor architectures/configurationImage generationFragment processingComputational science
Techniques are disclosed for dispatching pixel information in a graphics processing pipeline. A fragment processing unit generates a pixel that includes multiple samples based on a first portion of a graphics primitive received by a first thread. The fragment processing unit calculates a first value for the first pixel, where the first value is calculated only once for the pixel. The fragment processing unit calculates a first set of values for the samples, where each value in the first set of values corresponds to a different sample and is calculated only once for the corresponding sample. The fragment processing unit combines the first value with each value in the first set of values to create a second set of values. The fragment processing unit creates one or more dispatch messages to store the second set of values in a set of output registers. One advantage of the disclosed techniques is that pixel shader programs perform per-sample operations with increased efficiency.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
A computational imaging method and device based on a folding mask structure
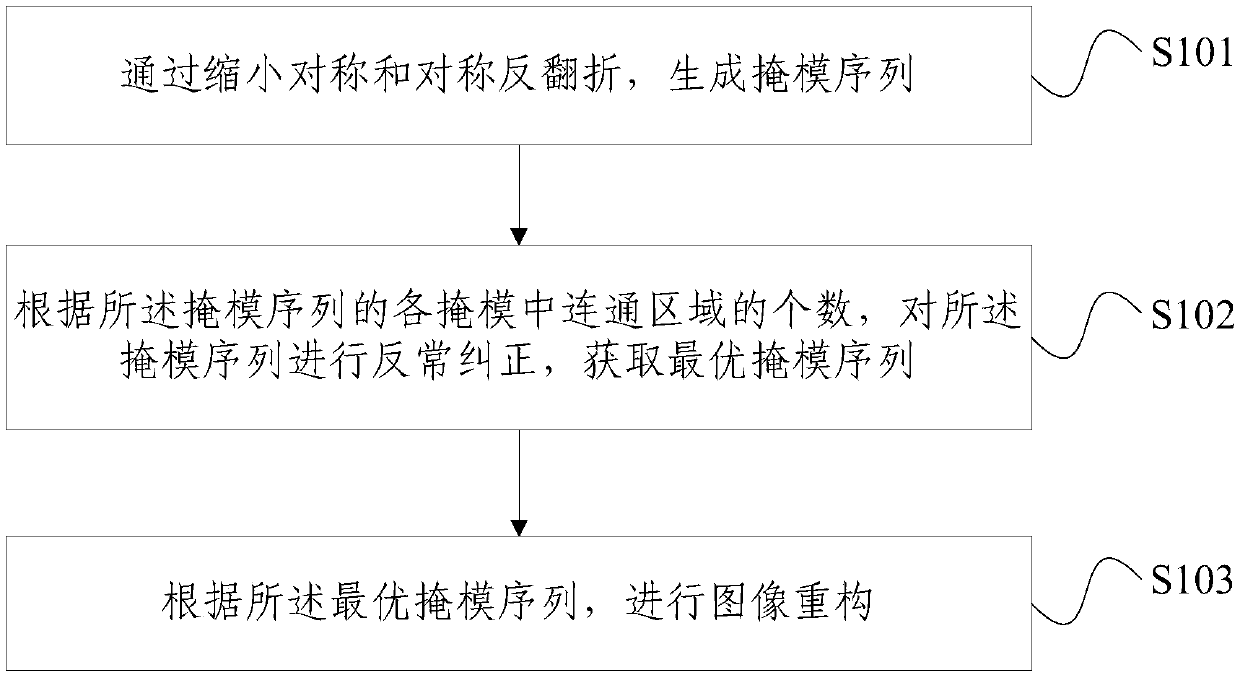
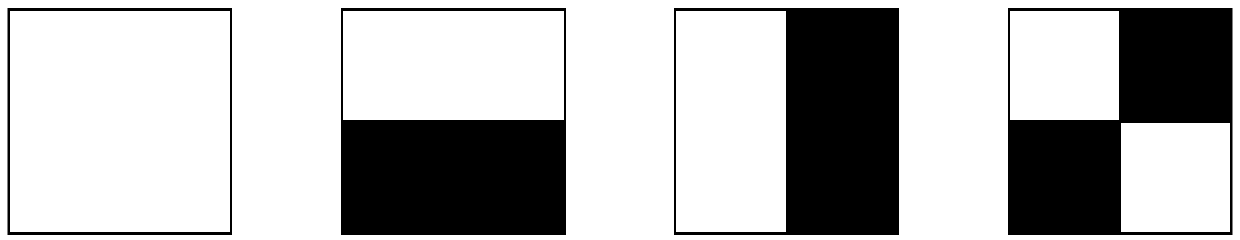
ActiveCN109035168AReduce uncertaintyQuality improvementImage enhancement2D-image generationDifferential measurementSupersampling
The invention provides a computational imaging method and device based on a folding mask structure. The method comprises the following steps: generating a mask sequence by reducing symmetry and symmetry reverse folding; according to the number of connected regions in each mask of the mask sequence, performing abnormal correction on the mask sequence to obtain an optimal mask sequence; selecting apreset number of masks from the optimal mask sequence for complementary difference measurement and image reconstruction. According to the contribution degree of the mask to the reconstruction qualityof the object to be imaged, a mask sequence is constructed by using a mask reducing symmetry and symmetry reverse fold, and the abnormal order of the mask is corrected according to the increasing order of the number of the connected regions of the mask so that the probability of emergence of masks with the same number of connected regions is reduced and the uncertainty of masks is reduced; the mask structure is optimized, and the optimized mask sequence is used for image reconstruction, which improves the quality and efficiency of image reconstruction; and the method has the advantages of supersampling, supersensitivity, low sampling dimension, high speed and real-time.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Selective super-sampling/adaptive anti-aliasing of complex 3D data
InactiveUS7095421B2Avoid it happening againReduce trafficGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsJaggies
A system and method is provided for preventing the occurrence of aliasing at the edges of polygons in 3D graphics. The system may detect both polygon geometric edges and Z edges due to intersection of multiple polygons. In one embodiment, the system includes an edge anti-aliasing module configured to selectively super-sample edge portions of primitives. The system further includes a coarse memory for storing information of pixels that are not super-sampled and a fine memory for storing information of pixels that are super-sampled by the edge anti-aliasing module.
Owner:S3 GRAPHICS
Reading or writing a non-super sampled image into a super sampled buffer
A graphics system and method for storing pixel values into or reading pixel values from a sample buffer, wherein the sample buffer is configured to store a plurality of samples for each of a plurality of pixels. The graphics system comprises a sample buffer, a programmable register, and a graphics processor. The programmable register stores a value indicating a method for pixel to sample conversion, and is preferably software programmable (e.g., user programmable). The graphics processor accesses the memory to determine a method for pixel to sample conversion and stores the pixel values in the sample buffer according to the determined method. A first method for pixel to sample conversion may specify a pixel write to all of the pixel's supporting samples. A second method for pixel to sample conversion may specify a pixel write to a selected one of the pixel's supporting samples.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Low-cost supersampling rasterization
ActiveUS20060061590A1Low computational costHigh-qualityDrawing from basic elementsTexturing/coloringComputer visionAnti-aliasing
A sampling pattern covering an array of pixels for use in an anti-aliasing system is disclosed where each pixel has a pattern of sample points at the edges of the pixel. Moreover is the sample point pattern of each pixel a mirror image and different from the pattern of a directly neighboring pixel.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
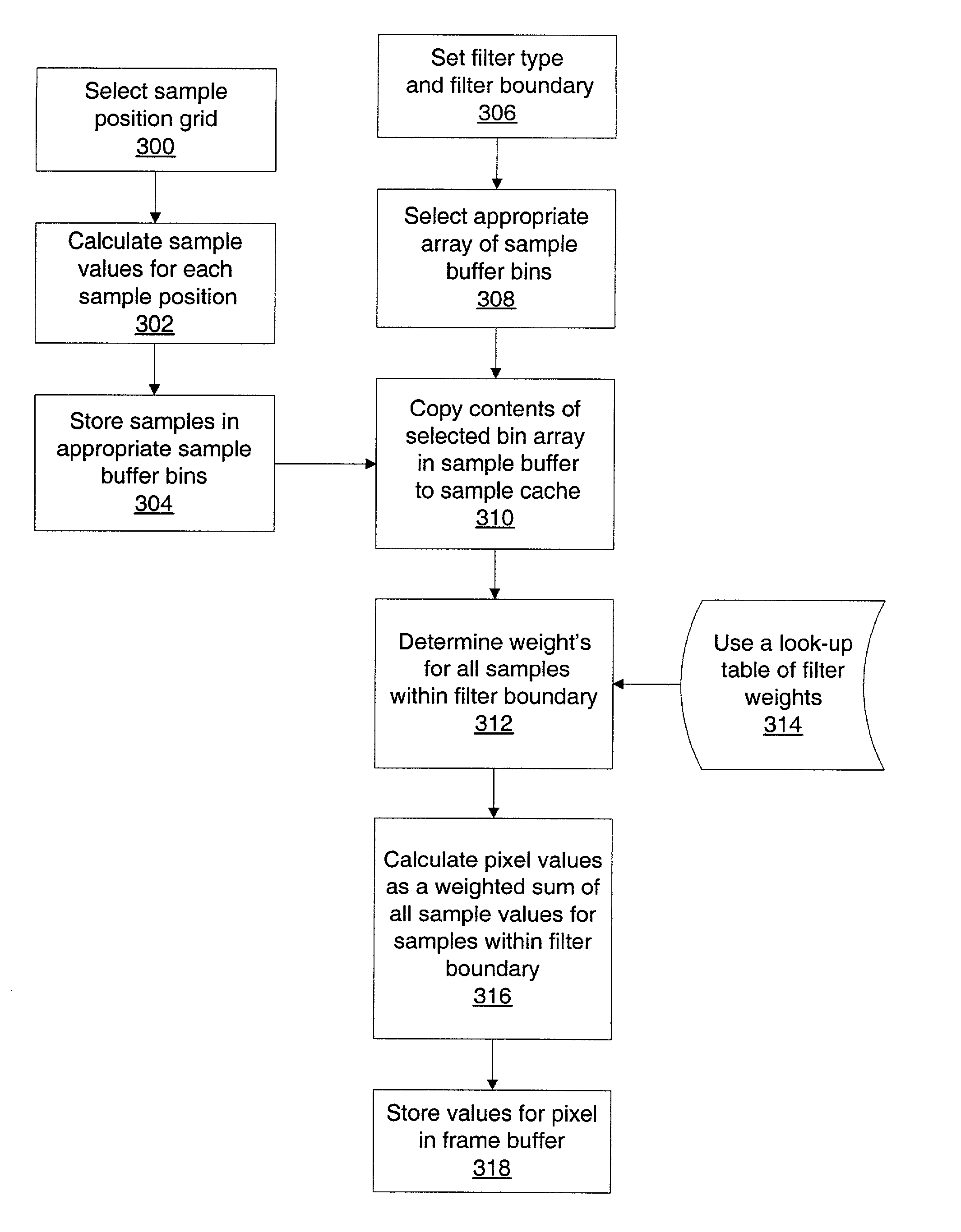
Sample cache for supersample filtering
A system and method capable of super-sampling and performing super-sample convolution are disclosed. In one embodiment, the system may comprise a graphics processor, a frame buffer, a sample cache, and a sample-to-pixel calculation unit. The graphics processor may be configured to generate a plurality of samples. The frame buffer, which is coupled to the graphics processor, may be configured to store the samples in a sample buffer. The samples may be positioned according to a regular grid, a perturbed regular grid, or a stochastic grid. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit is programmable to select a variable number of stored samples from the frame buffer, copy the selected samples to a sample cache, and filter a set of the selected samples into an output pixel. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit retains those samples in the sample cache that will be reused in a subsequent pixel calculation and replaces those samples no longer required with new samples for another filter calculation.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Sample cache for supersample filtering
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
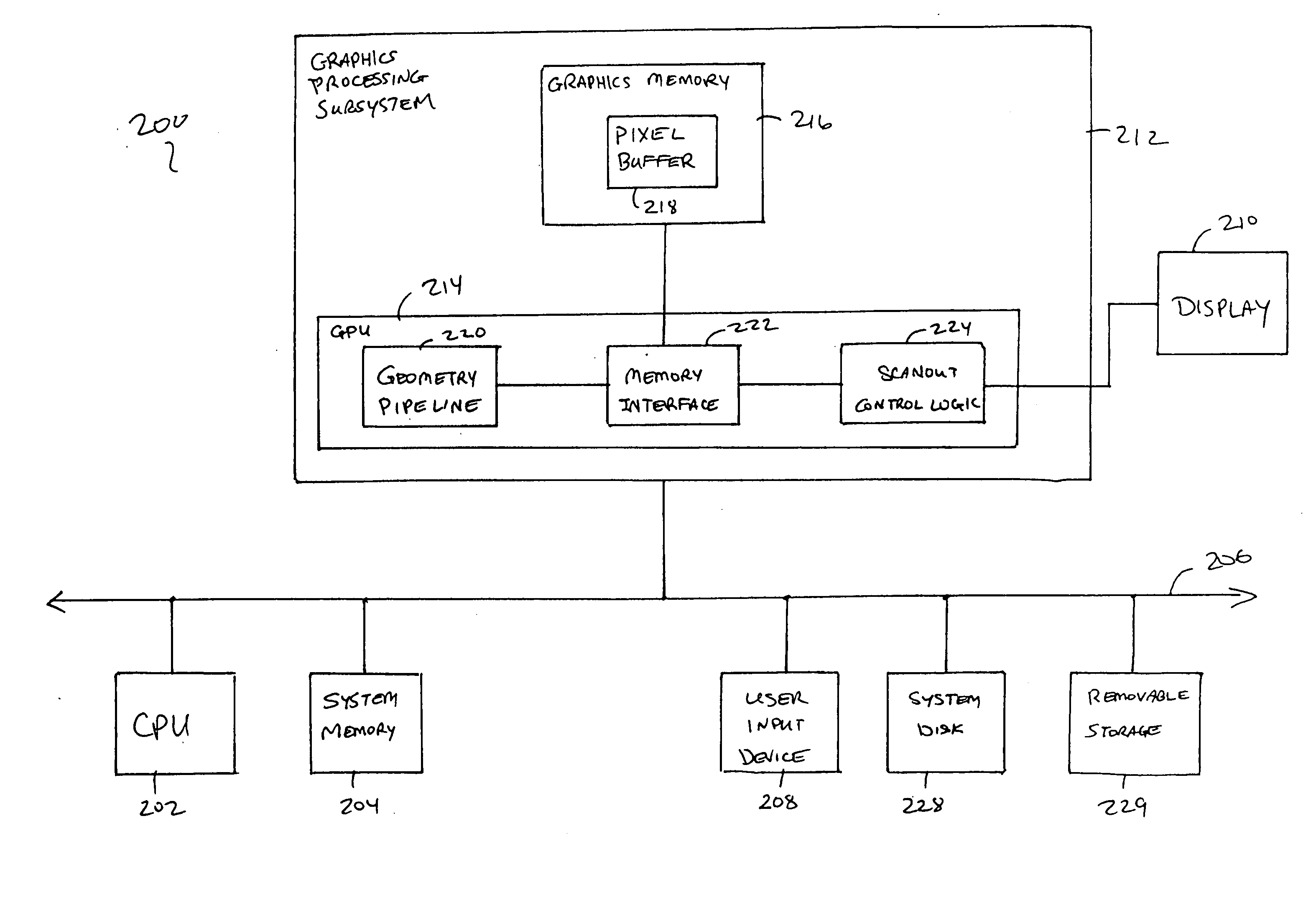
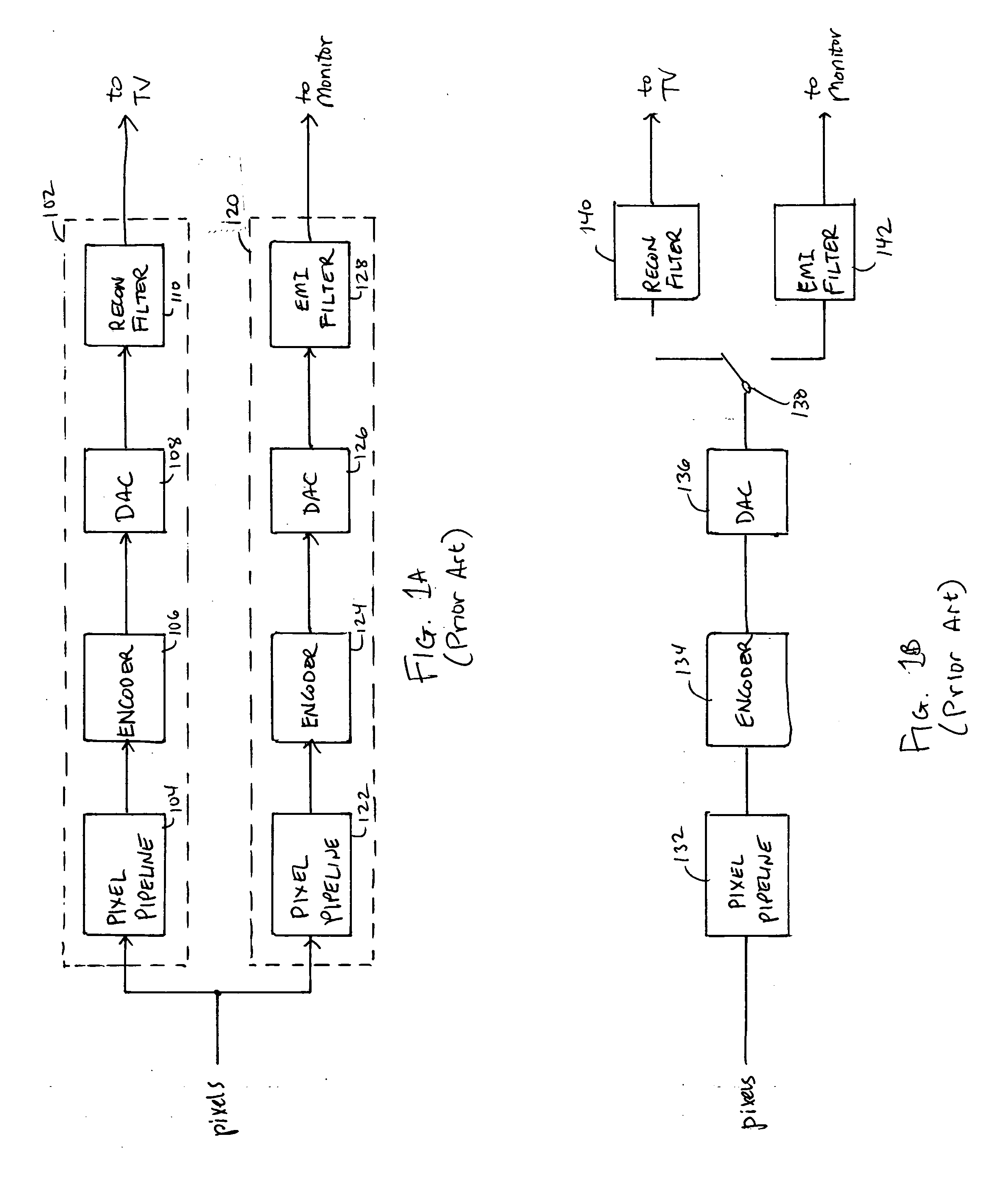
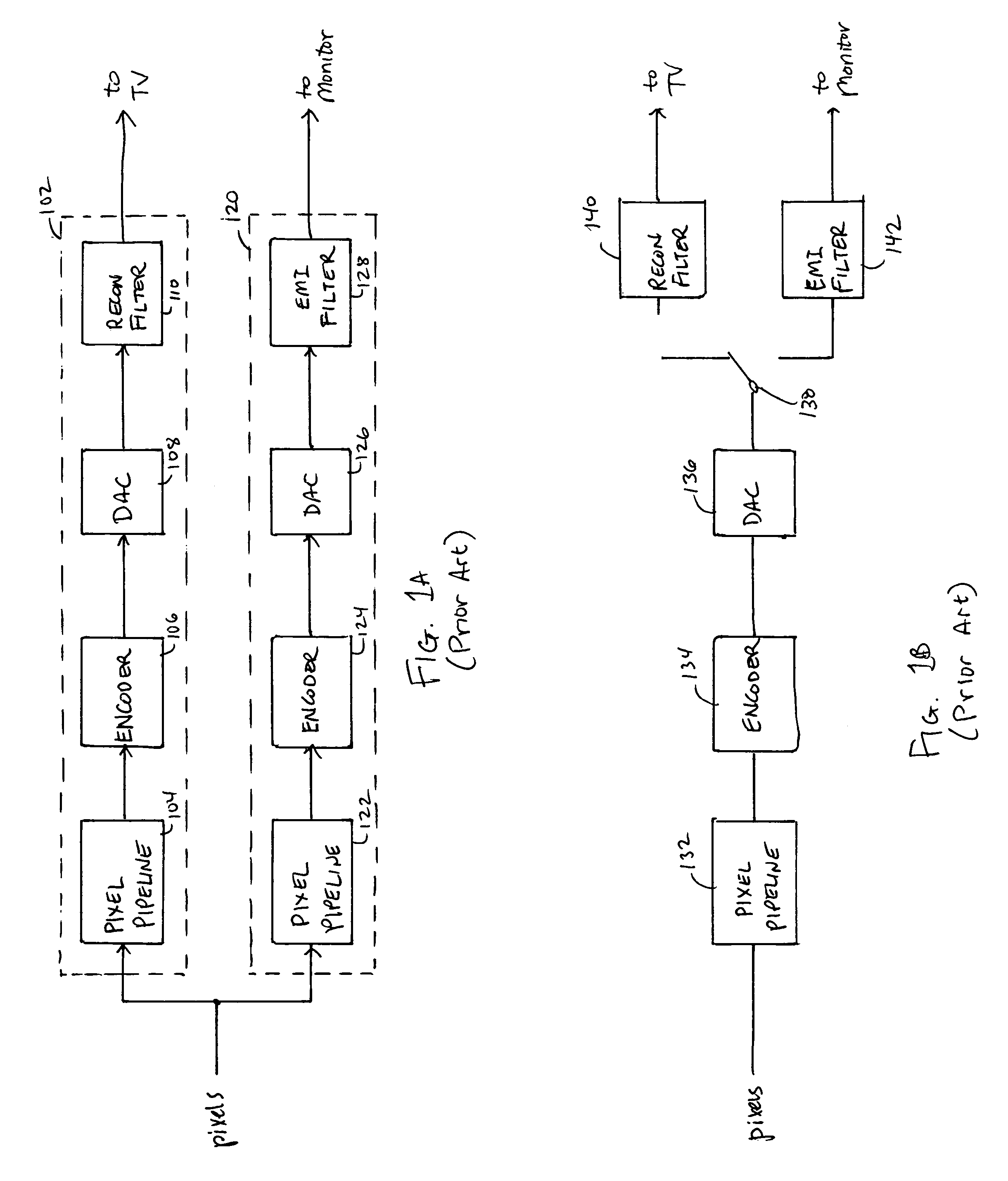
Supersampling of digital video output for multiple analog display formats
ActiveUS20050219415A1Eliminate and reduce unwanted frequency componentEasy to reconfigureTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsUltrasound attenuationDigital video
An output pipeline for a video processing device provides supersampling of the output data the digital domain to eliminate or reduce unwanted frequency components in an analog output signal. An encoder converts a pixel stream to digital sample values for a target analog signal at a base sampling rate. The base data stream is supersampled, and the supersampled data is provided to a digital to analog converter The supersampling rate can be selected so as to provide substantial attenuation of a higher frequency echo in the analog output signal.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
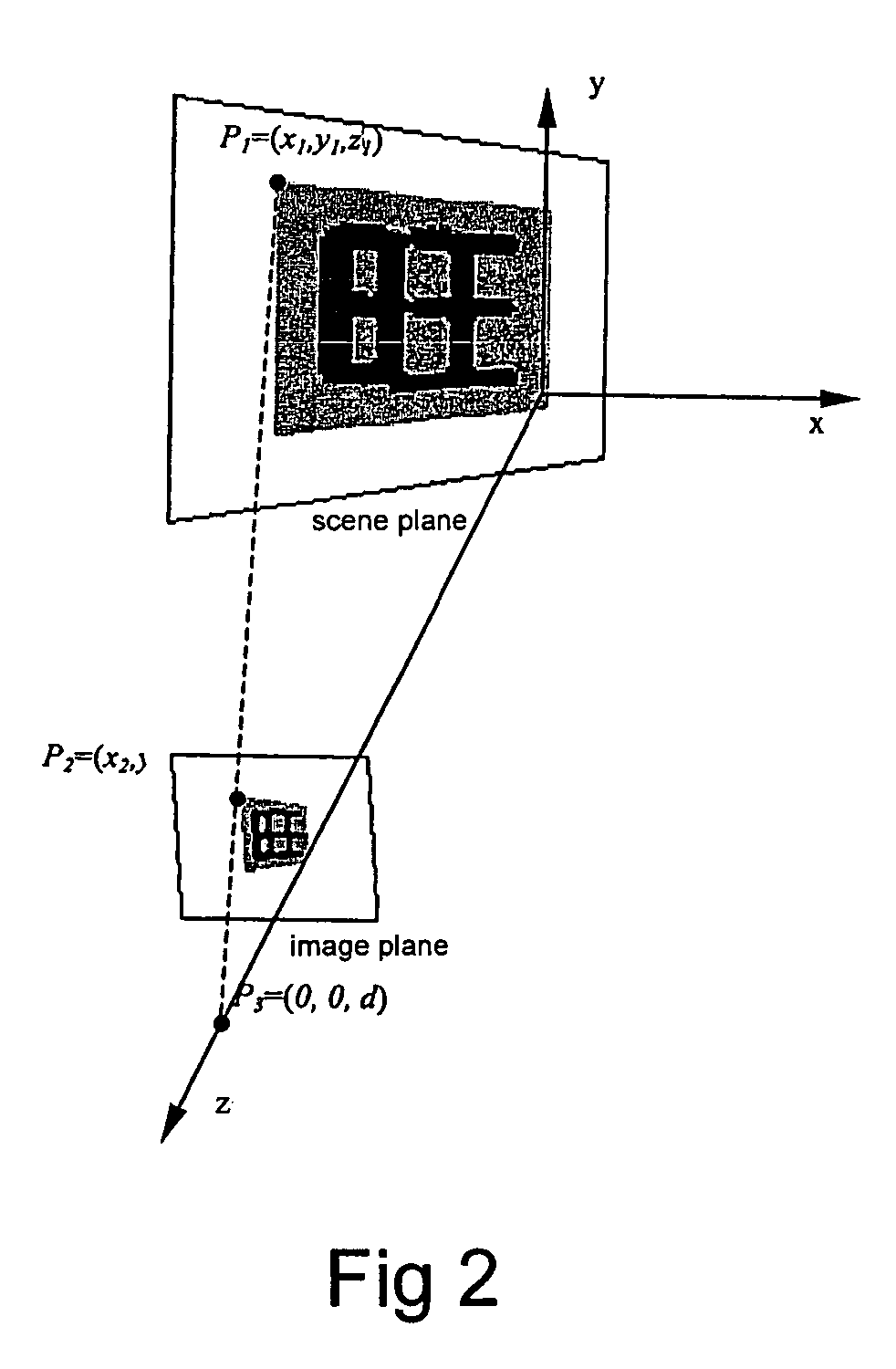
Degraded character image generation method and apparatus
InactiveUS7480409B2Efficient identificationCharacter recognitionComputer graphics (images)Supersampling
A method and apparatus for generating a degraded character image at various levels of degradation automatically is presented in this invention. The method comprises rendering the character image on a scene plane; translating and rotating the scene plane according to various parameters; determining a projection region of the character image on an image plane according to various parameters; generating a pixel region mask; and generating a final degraded image by super-sampling. Thus various degraded character images are generated on various conditions of degradation. The generated synthetic characters can be used for performance evaluation and training data augmentation in optical character recognition (OCR).
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
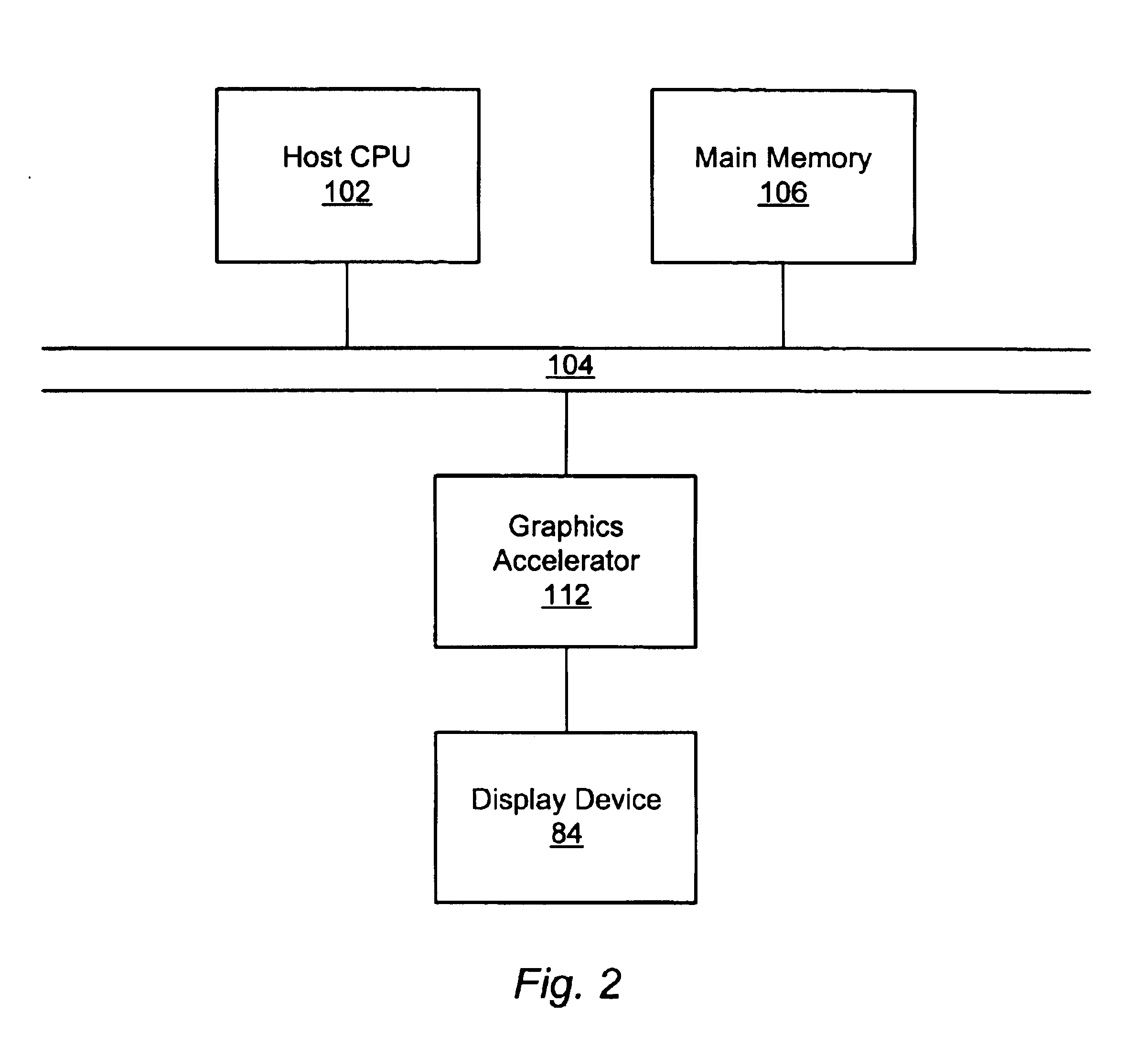
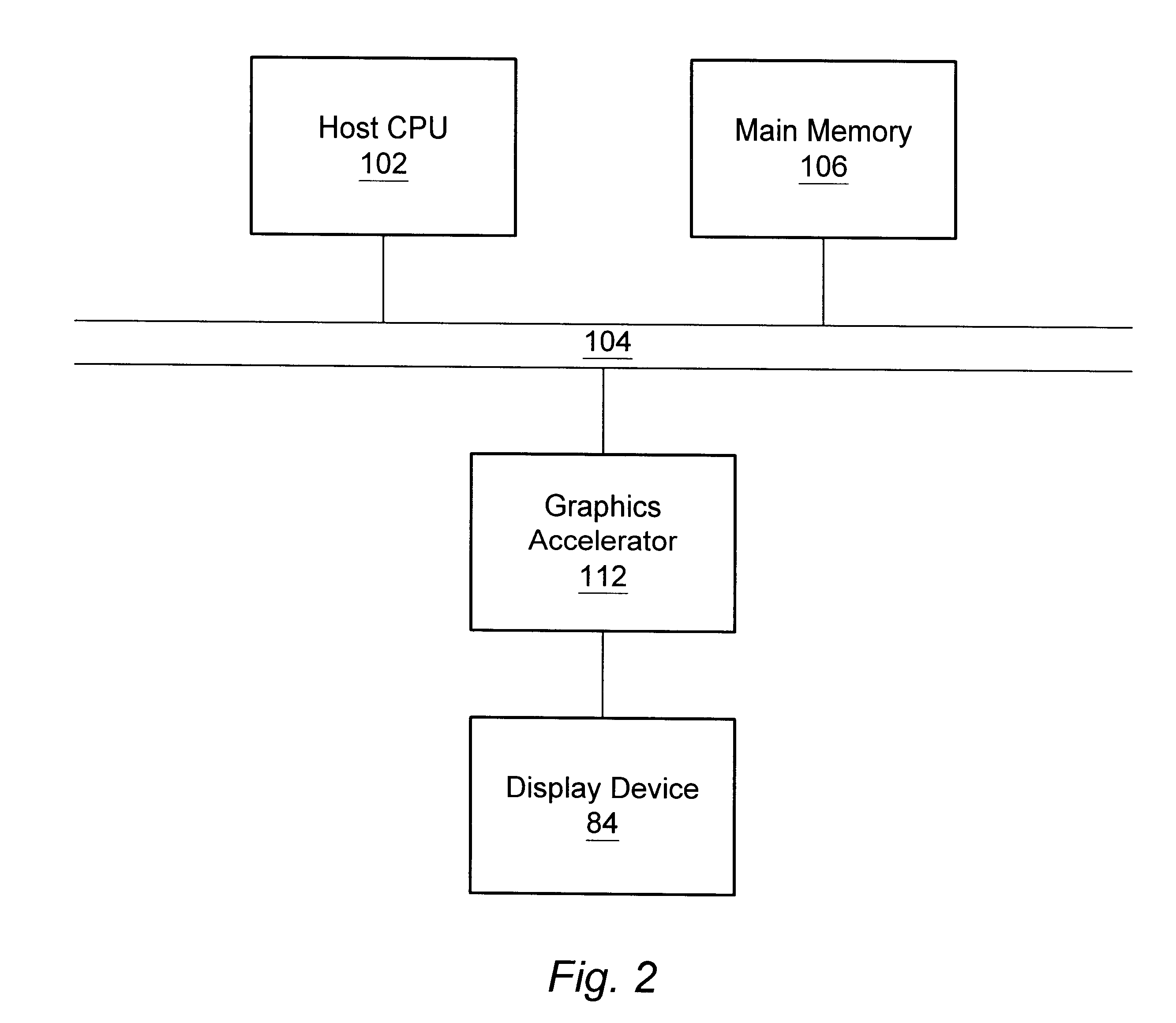
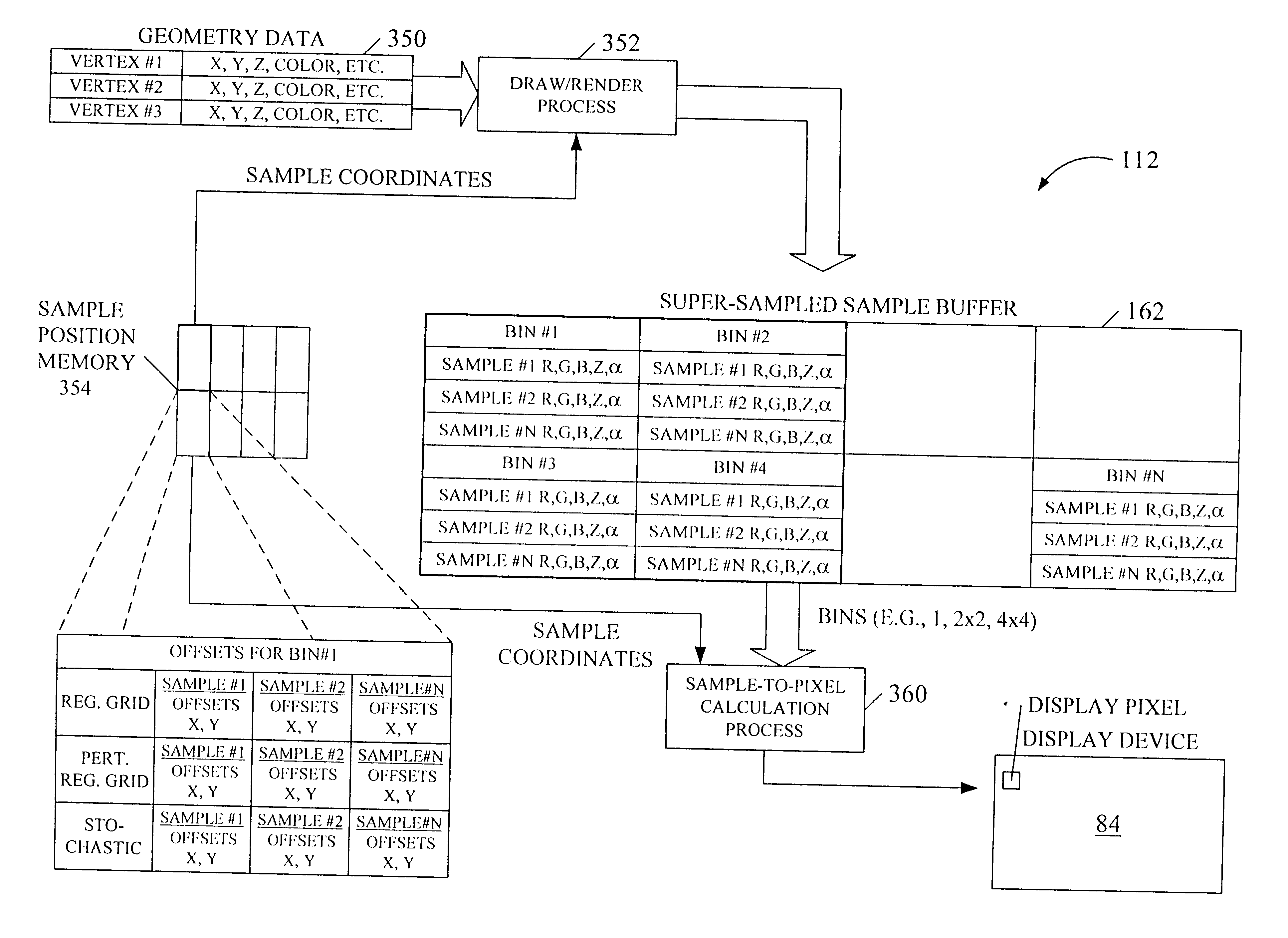
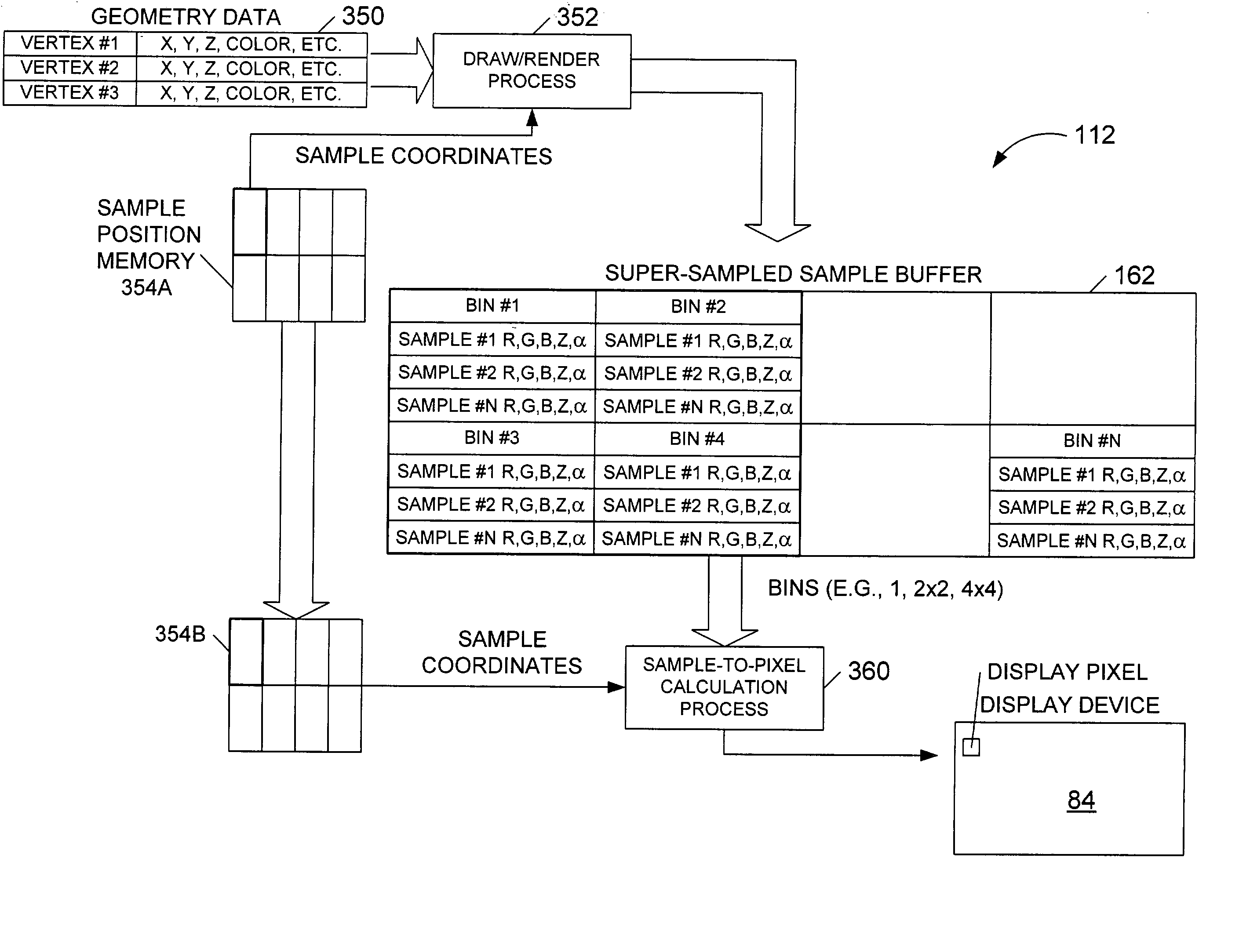
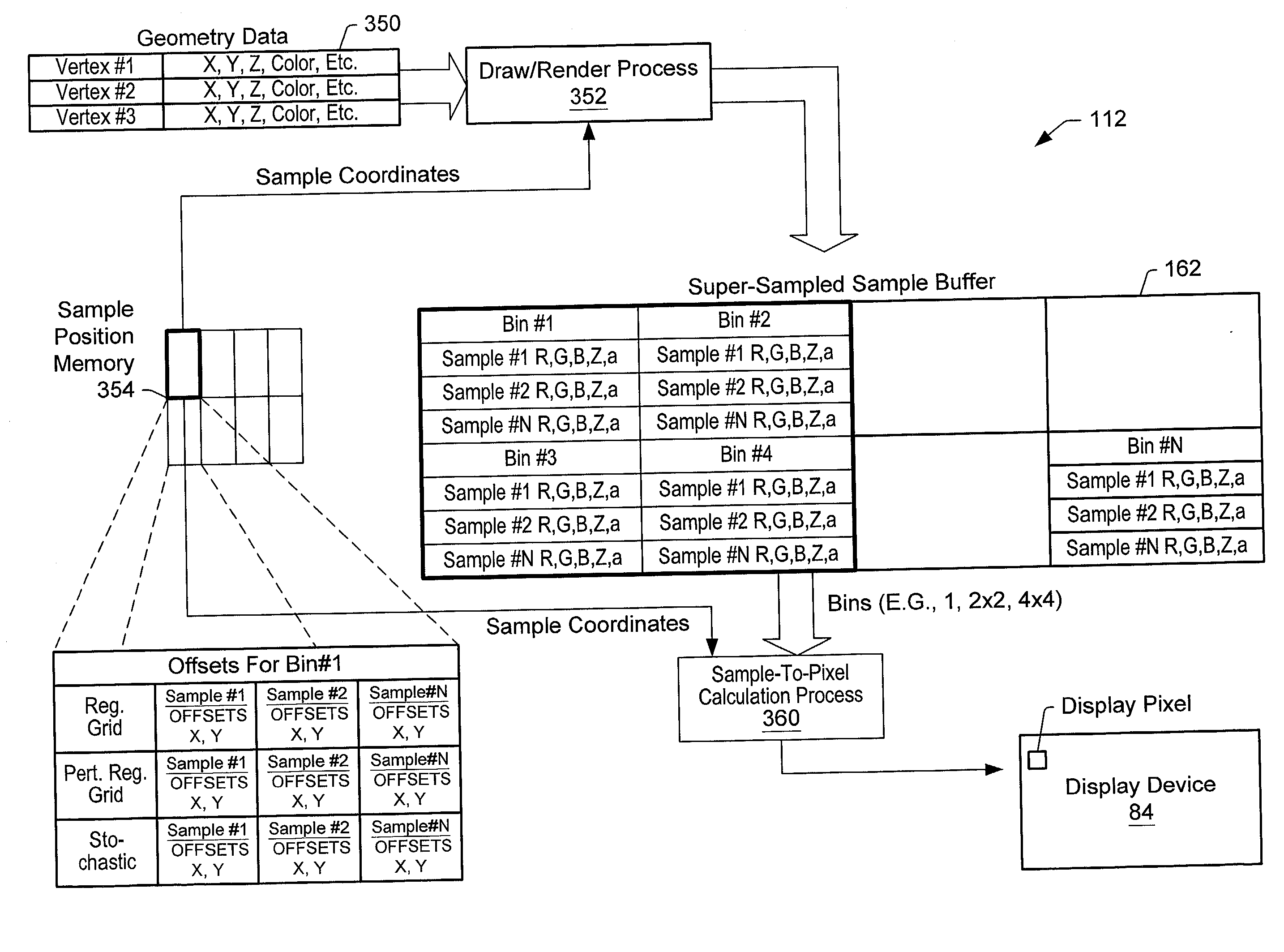
Graphics system having a super sampled-sample buffer with efficient storage of sample position information
A computer graphics system that utilizes a super-sampled sample buffer and a sample-to-pixel calculation unit for refreshing the display, wherein the graphics system may store sample position information as offsets to coordinates in the sample buffer. The graphics system may have a graphics processor, a super-sampled sample buffer, and a sample-to-pixel calculation unit. The graphics processor renders samples into the sample buffer at computed positions or locations in the sample buffer. The sample positions may be computed using various sample positioning schemes. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit uses the position information to select the samples for filtering during generation of output pixels. In one embodiment, for each sample, the position information comprises one or more offset values, such as an x-offset and a y-offset, wherein the offset values are relative to pre-defined locations in the sample buffer, such as pre-determined pixel center coordinates or predetermined bin coordinates. The position information may be stored in the sample buffer with the samples, or may be stored in a separate sample position memory coupled to the graphics processor. The samples may also be stored according to a bin ordering, wherein the bin ordering indicates a position of the samples in the respective bin. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit may use the bin ordering of the samples in the bins to index into a look-up table memory to determine the position information of the samples. The graphics system may include double buffered sample position memories.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Supersampling of digital video output for multiple analog display formats
ActiveUS7460175B2Eliminate and reduce unwanted frequency componentEasy to reconfigureTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsUltrasound attenuationDigital video
An output pipeline for a video processing device provides supersampling of the output data the digital domain to eliminate or reduce unwanted frequency components in an analog output signal. An encoder converts a pixel stream to digital sample values for a target analog signal at a base sampling rate. The base data stream is supersampled, and the supersampled data is provided to a digital to analog converter The supersampling rate can be selected so as to provide substantial attenuation of a higher frequency echo in the analog output signal.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com