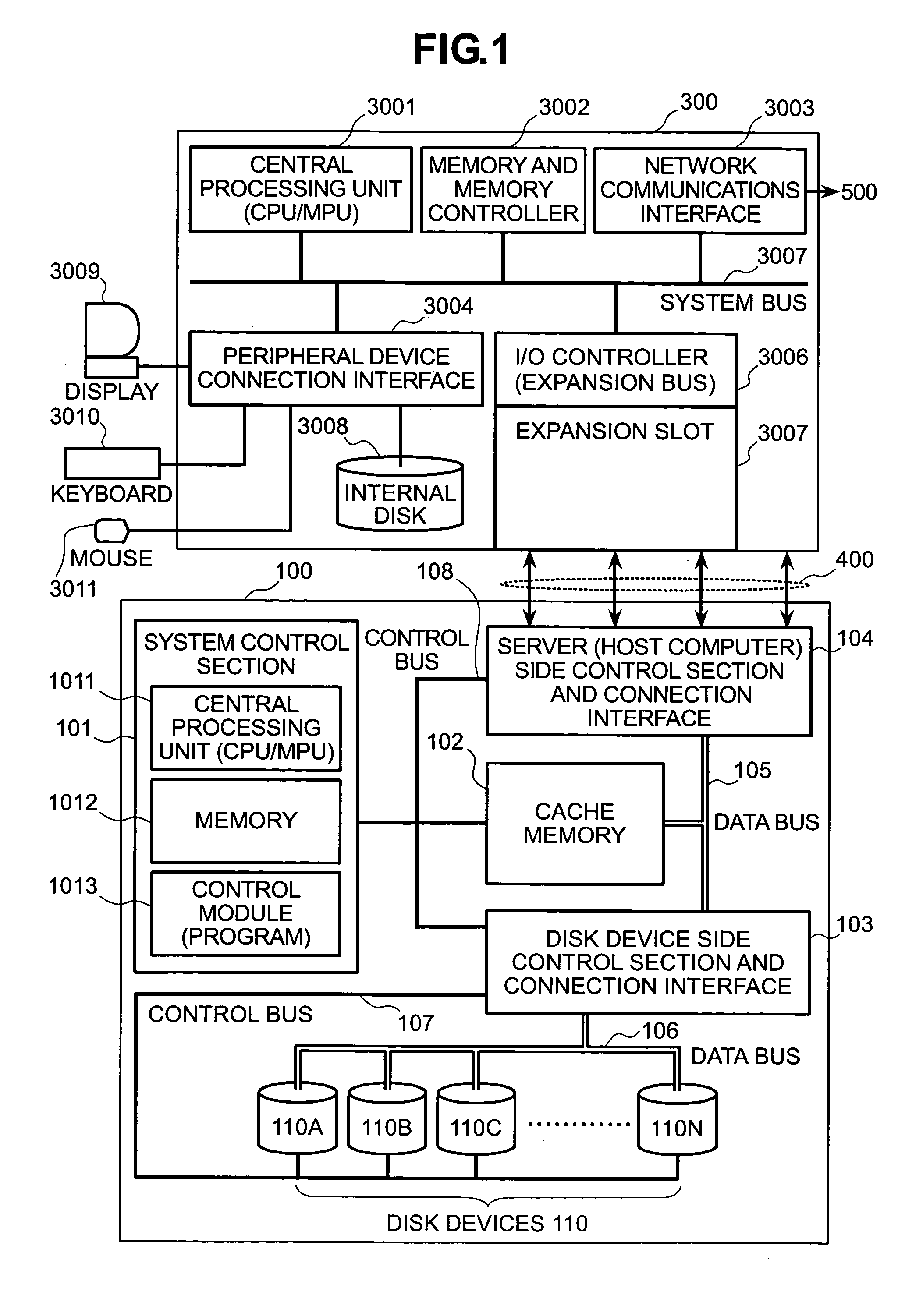
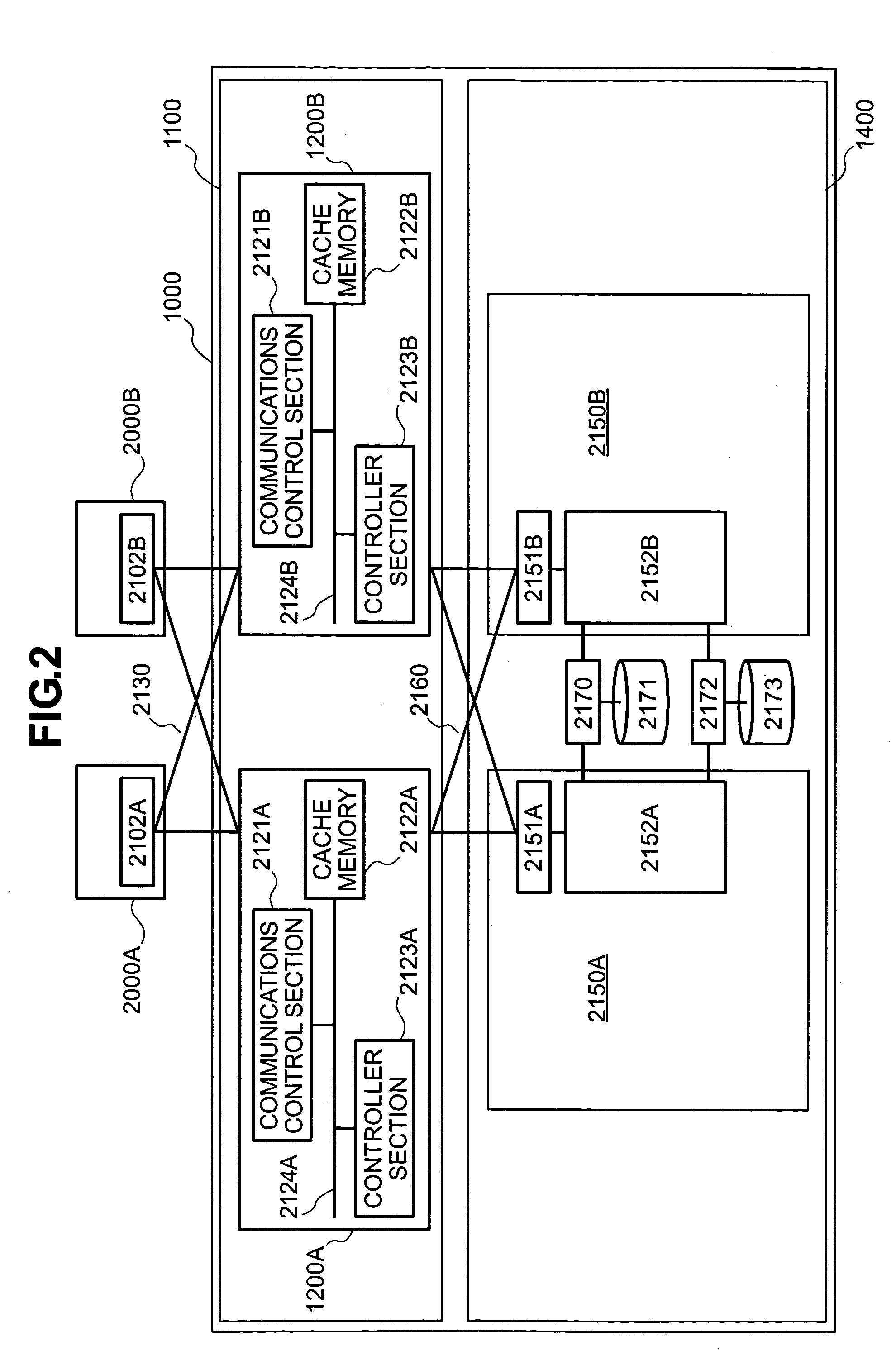
Patents
Literature
107results about How to "Exclude data" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
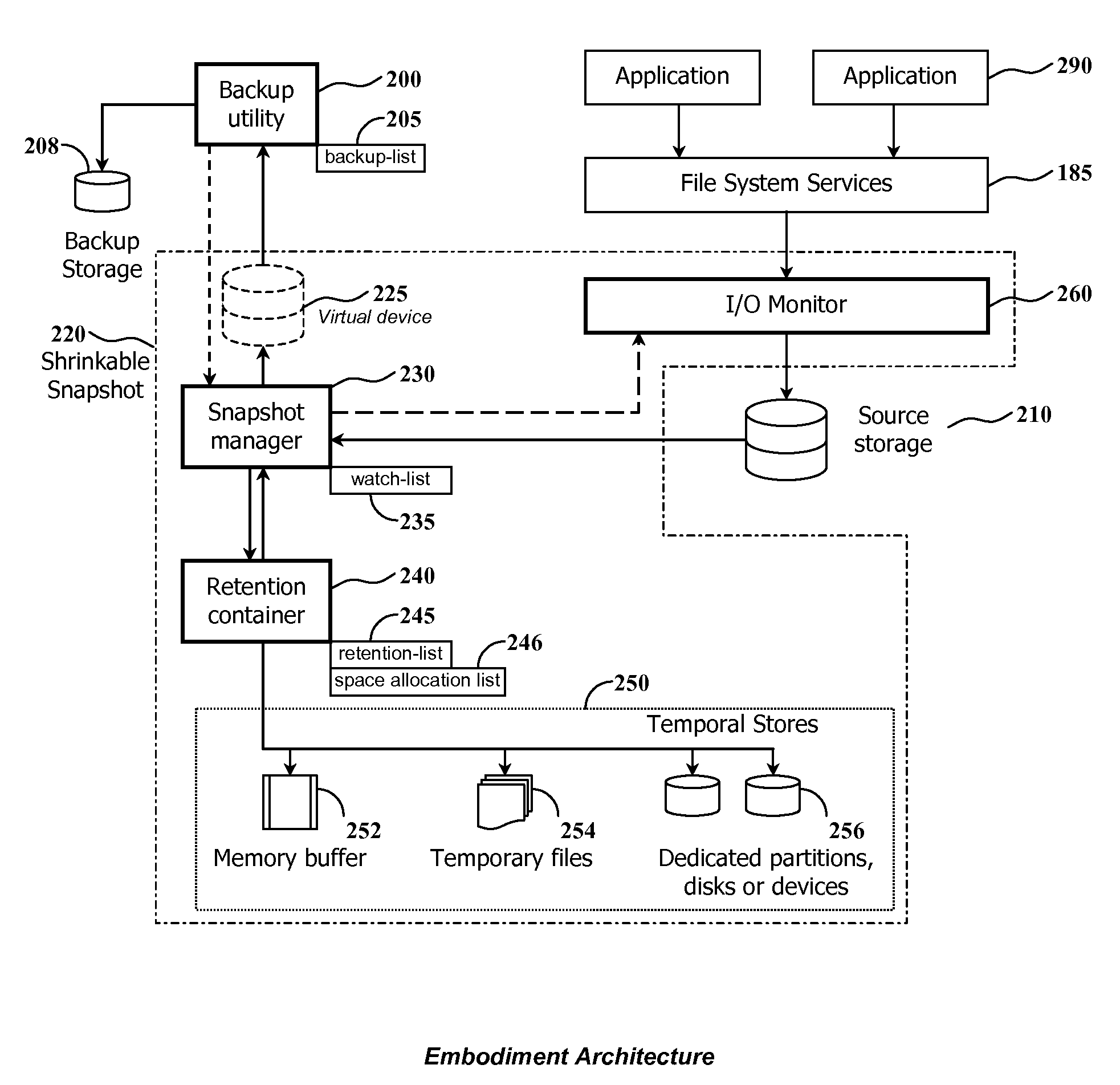
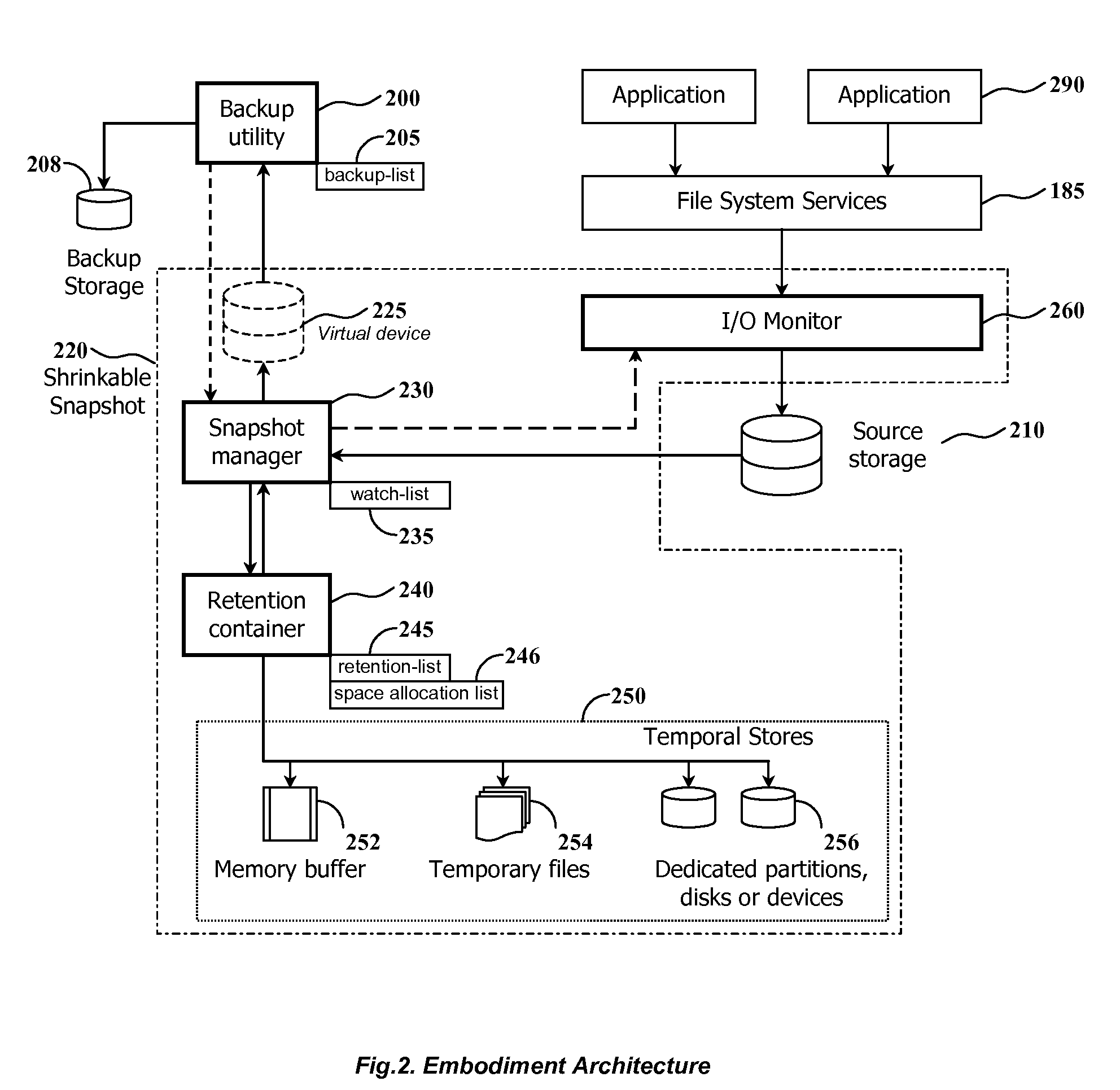
Using shrinkable read-once snapshots for online data backup
InactiveUS20080082593A1Improve performanceEasy to useDigital data information retrievalError detection/correctionRetention timeWatch list
The present invention discloses a method and system for snapshot-based online backup operations permitting reduced requirements to storage capacity and computational overhead for snapshot function.At the beginning of an online backup operation, the backup software system creates a snapshot of source data storage. The snapshot includes a watch-list used for identifying blocks of a source storage which are watched by snapshot management means for update. If a block included into the watch-list was requested for update, the snapshot management means preserve original contents of that block in a retention container for the purpose of temporary store. The retention container includes a set of temporal stores dedicated for transient storing of blocks until they are backed up.The essence of the invention is enabling to exclude blocks from the watch-list and the retention container at any moment within the period of snapshot operation. Therefore it is possible to exclude unnecessary blocks from the scope of blocks managed by the snapshot management means, for the purpose of preserving point-in-time data.Backed up blocks can be operatively excluded from the snapshot so that unchanged blocks are excluded from the watch-list and updated blocks are removed from the retention container. In the latter case temporal stores are shrunk as well. This technique allows to reduce progressively storage expenses and computational overheads required for maintenance of a snapshot being used in the online backup routine.When a volume-level online backup is performed the snapshot is switched to the read-once mode at the beginning of the data copying stage. A backup utility performs sequential read of blocks from the snapshot. The snapshot management means automatically exclude requested blocks from the scope of managed blocks.
Owner:PARAGON SOFTWARE GMBH
Method and device for acquiring snapshots and computer system with snapshot acquiring function
ActiveUS20050187982A1Easy to useEliminate unnecessary generational managementDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsComputer scienceOperating system
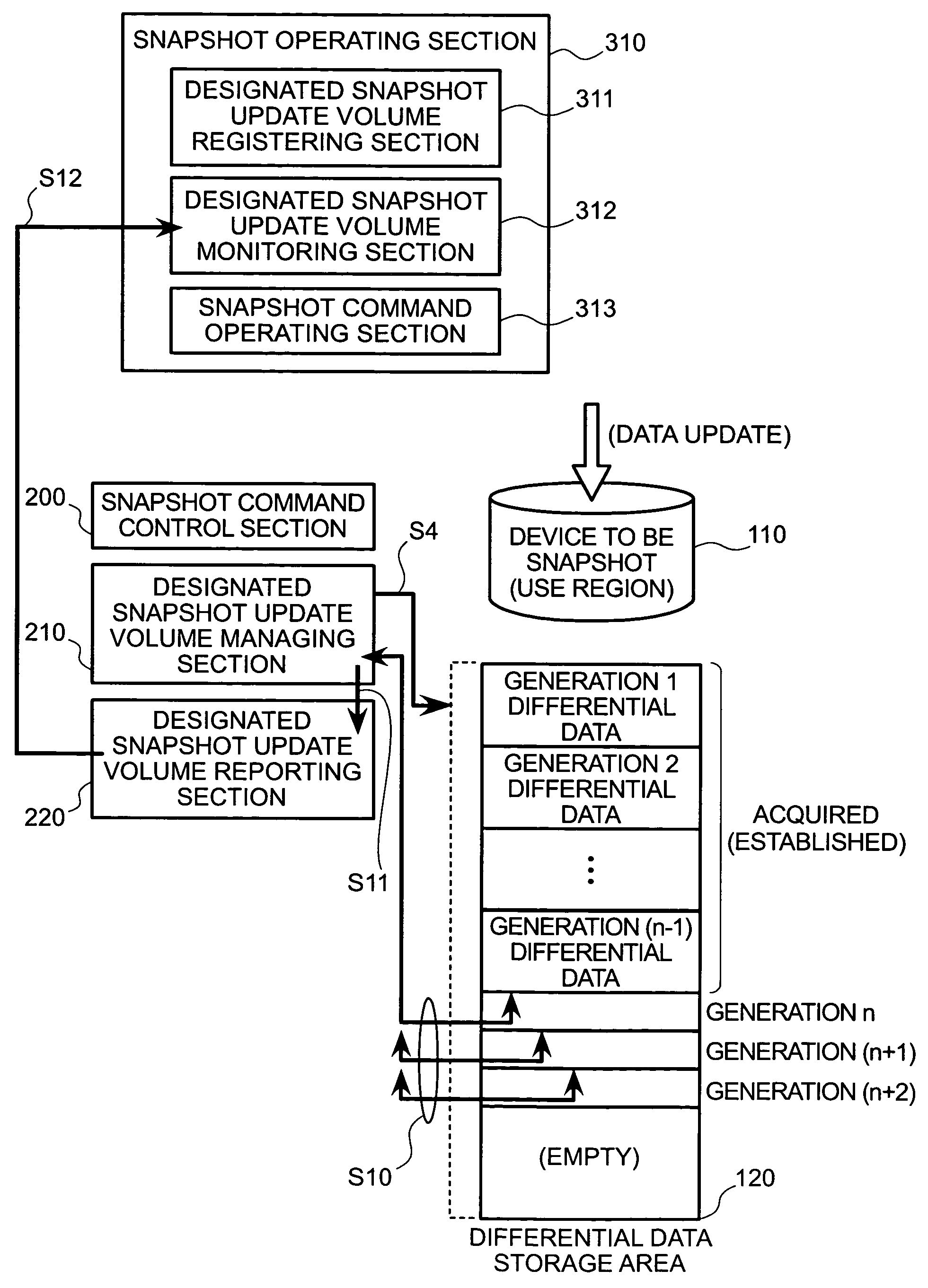
The present invention enables generational management of snapshot data while eliminating unnecessary generational management. A device to be snapshot which is a use region in actual use, and a snapshot control device capable of controlling snapshot commands are connected to a storage system connected to a server provided with a snapshot operating section. The storage system has a differential data storage area for the purpose of generational management of differential data in the device to be snapshot. A snapshot command control section carries out command processing upon receiving snapshot control command issue requests from the server. There are provided: a designated snapshot update volume managing section having the functions of managing the update differential volume for snapshot processing, comparing and judging a previously designated update volume and an actual update volume, and implementing processing for provisional generational management of the update differential in accordance with the designated update volume; and a designated snapshot volume reporting section having the functions of reporting the management status and the processing results to the server, as and when necessary, in accordance with the management of the update differential volume and the generational management.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
System and method for data management
InactiveUS7103602B2Exclude dataSmall sizeData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsOperational systemData file
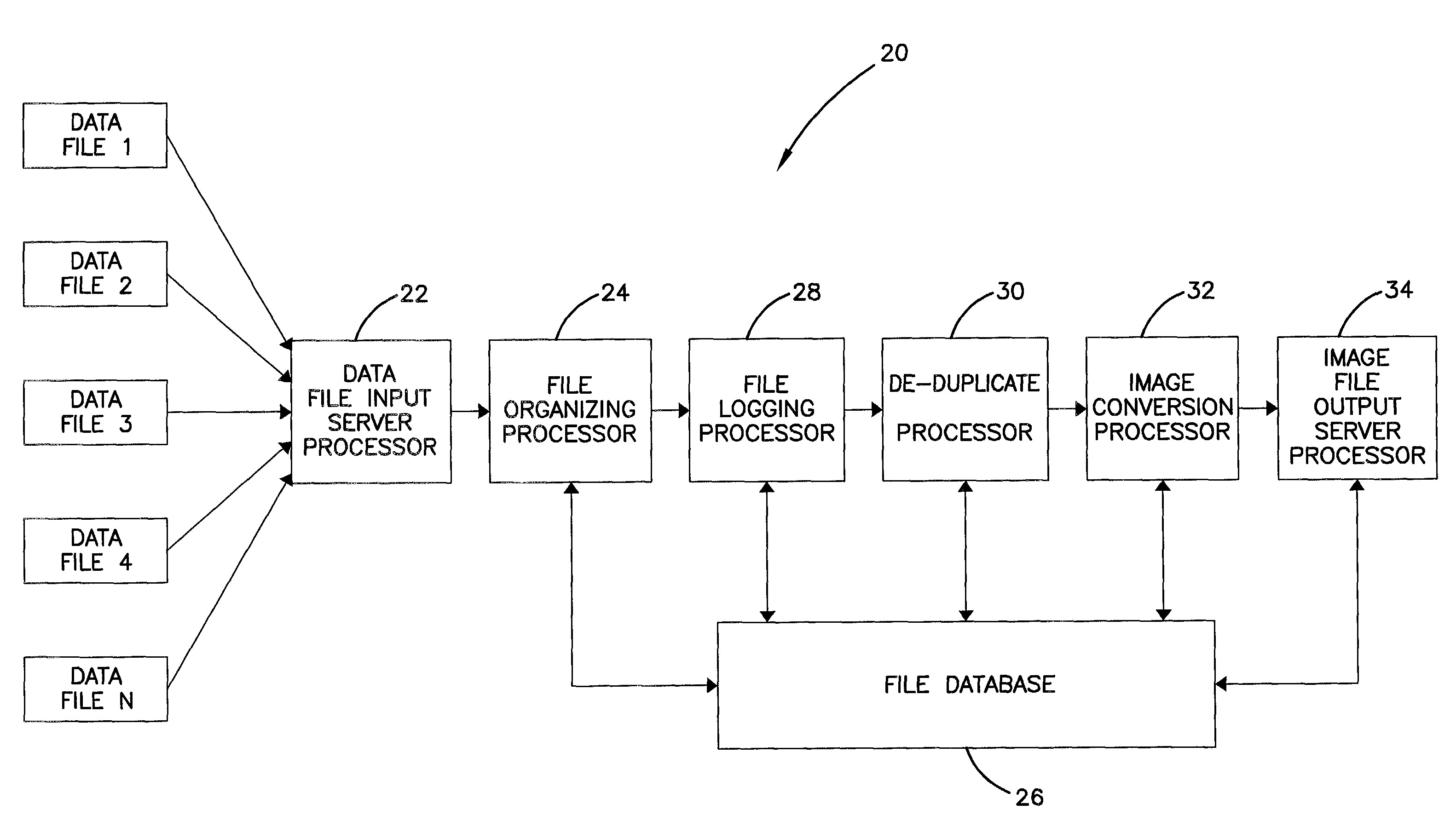
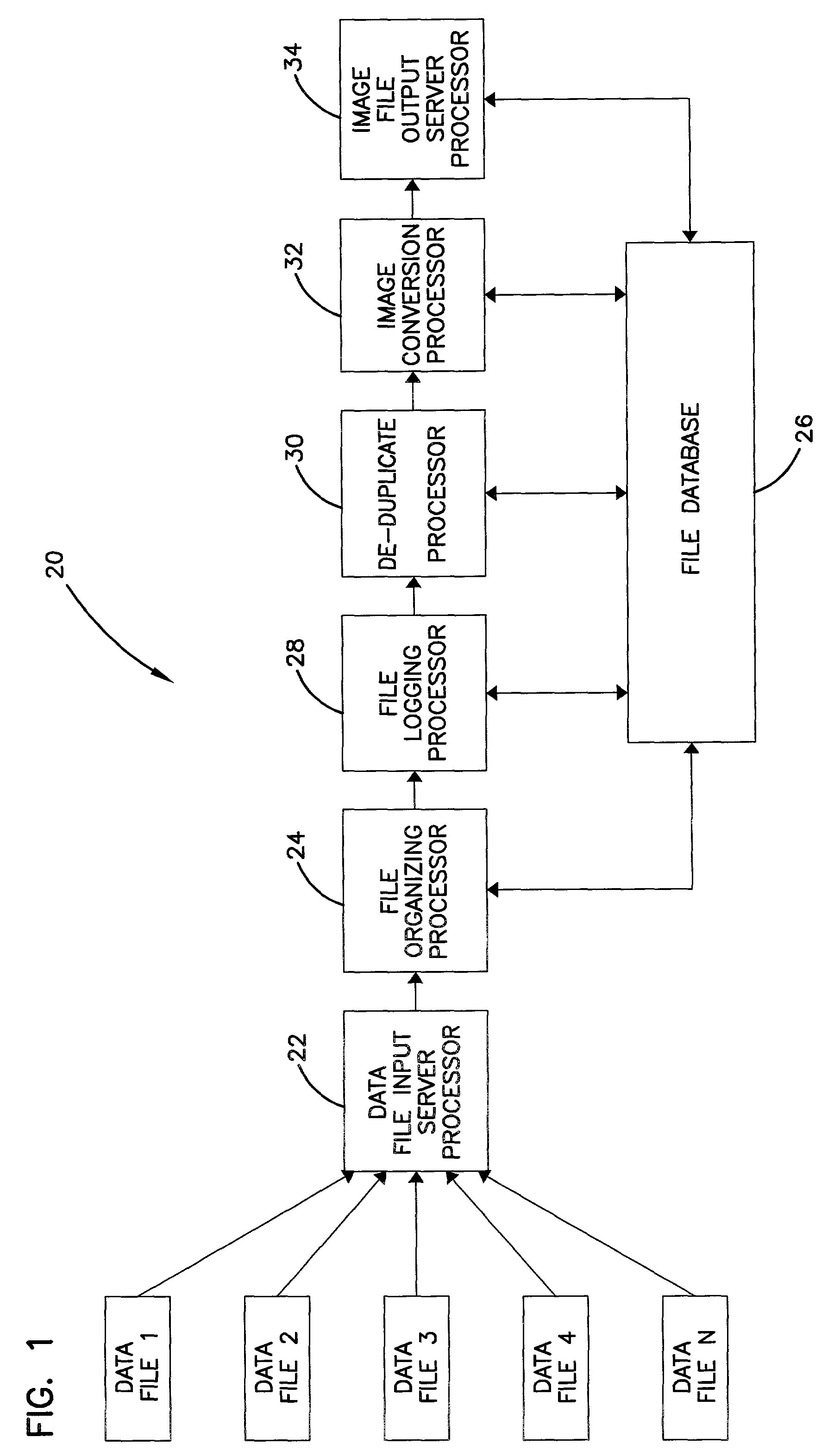
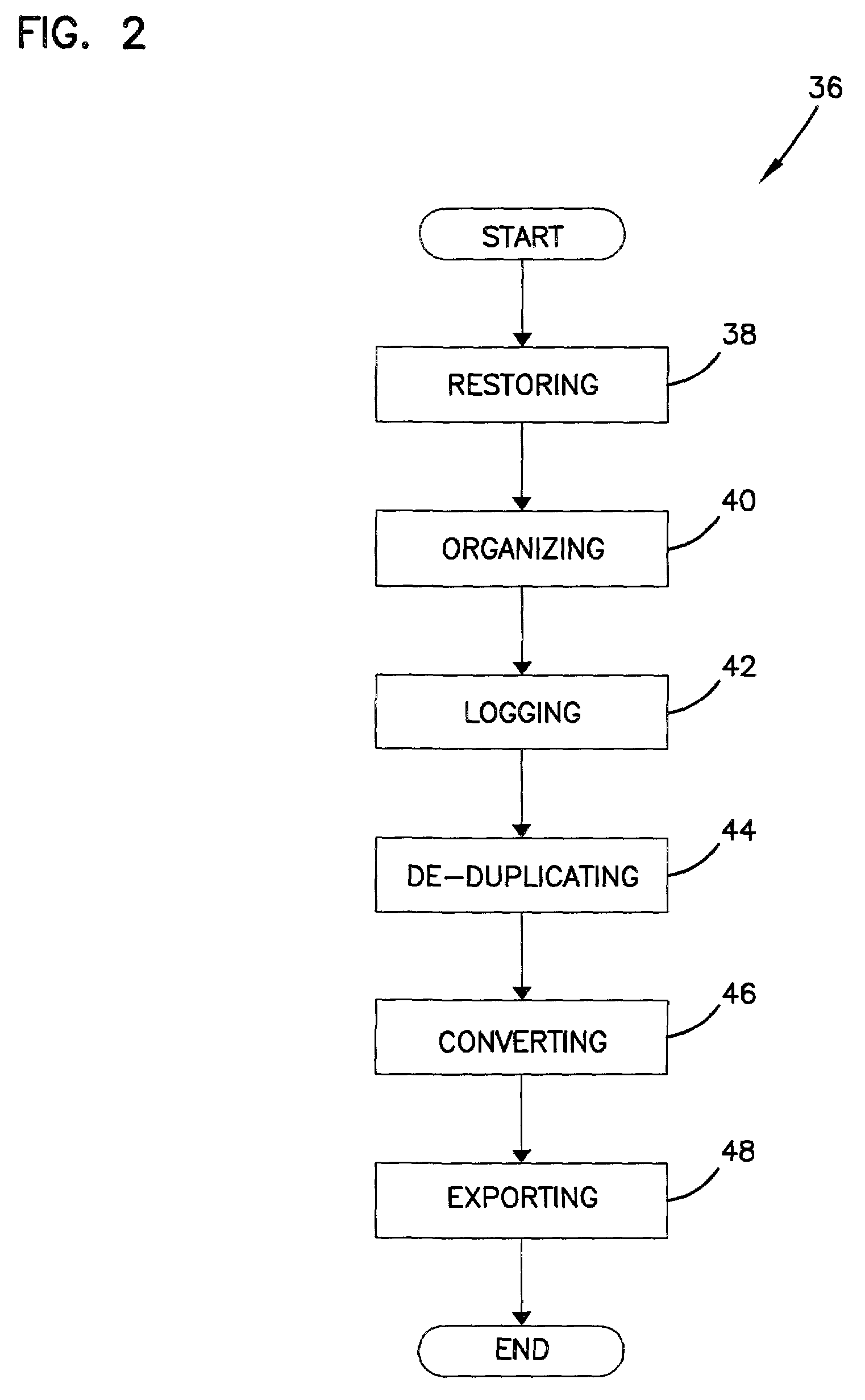
An automated data management system and method for logging, processing, and reporting a large volume of data having different file types, stored on different media, and / or run by different operating systems, includes a first server processor for restoring a plurality of received data files, the data files being capable of being different file types; a file organizing / categorizing processor for organizing the received data files, based on a predetermined user list, into a source directory structure and a destination directory structure; a file logging processor for logging the received data files into a database formed by the source and destination directory structures and identifying a file type of the received data files; a de-duplicate processor for calculating a SHA value of the received data files to determine whether the received data files have duplicates and flagging duplicated data files in the database; an image conversion processor for converting the remaining data files into image files, respectively; and a second server processor for exporting the image files.
Owner:KLDISCOVERY ONTRACK LLC
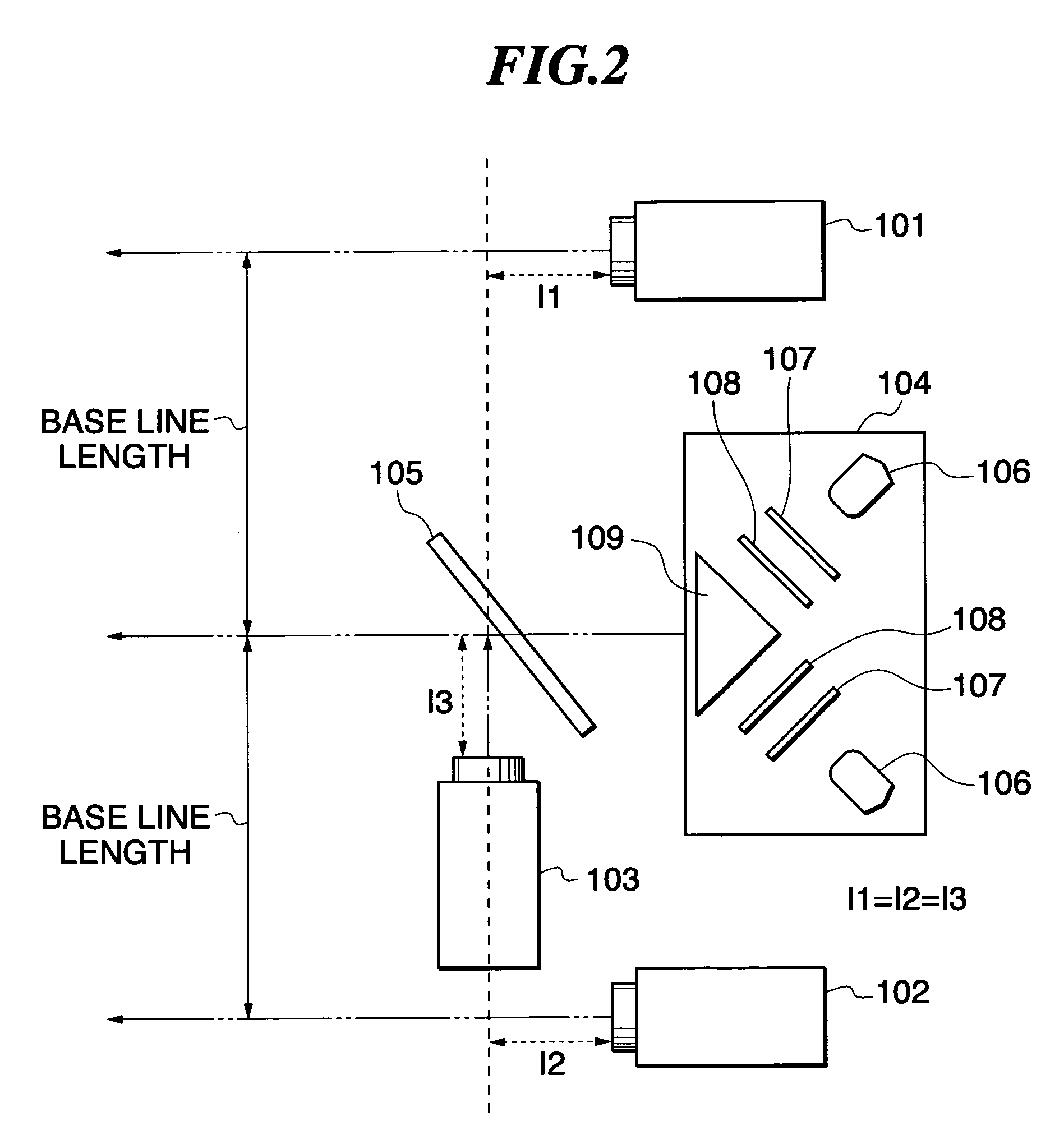
Sytem and a Method for Motion Tracking Using a Calibration Unit
ActiveUS20080262772A1Improve accuracySimple procedureProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorAnimationThree-dimensional space
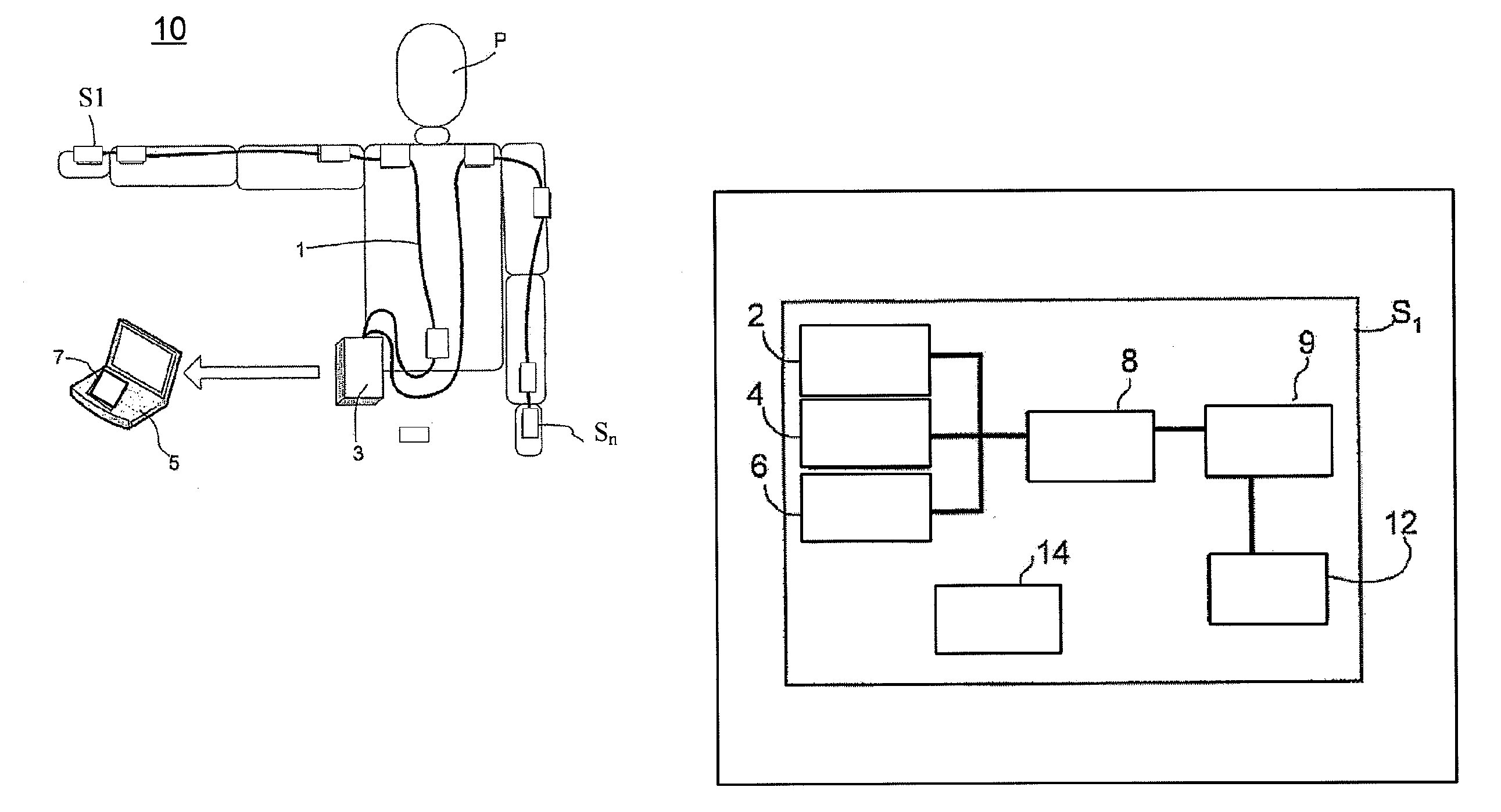
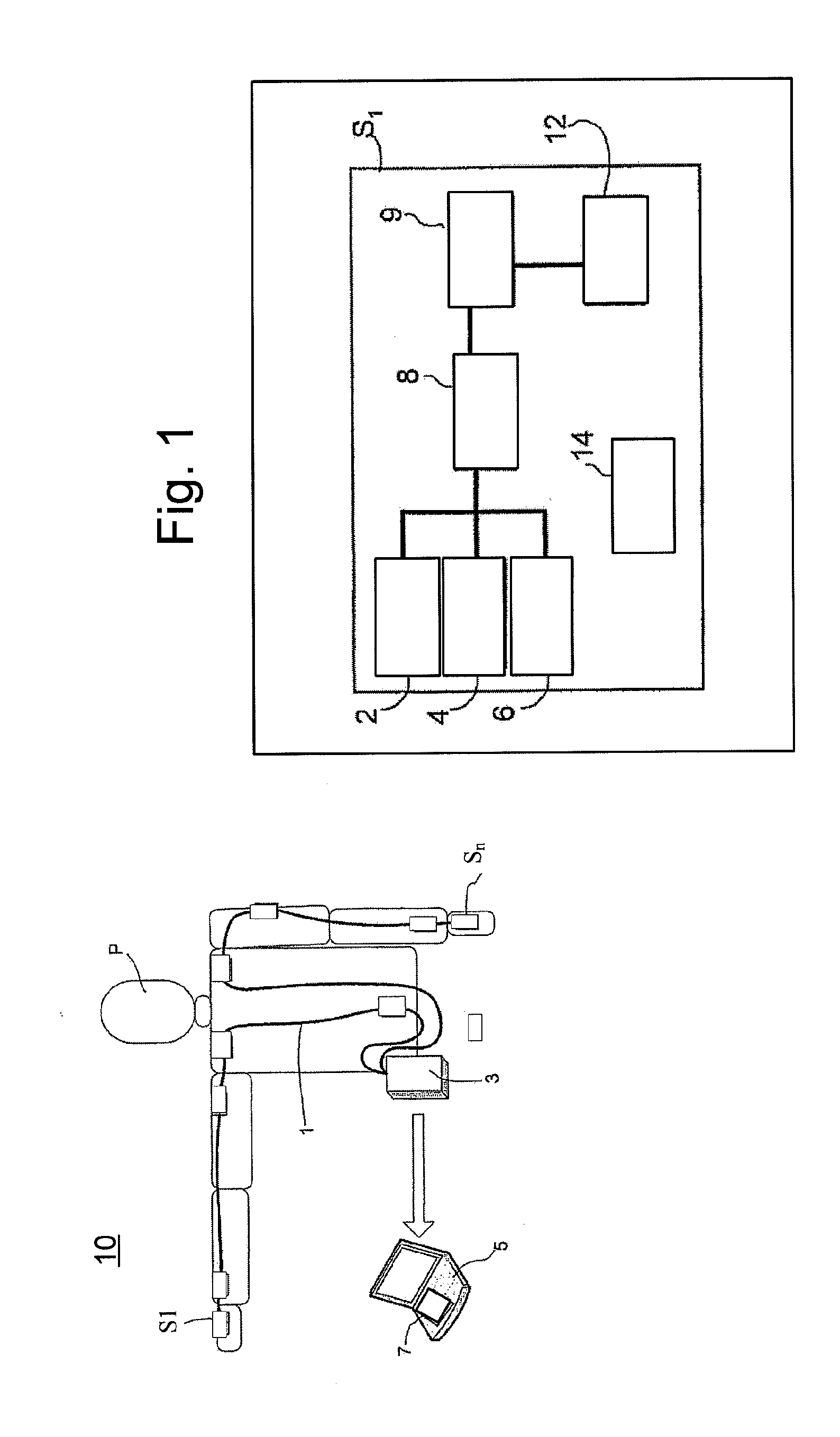
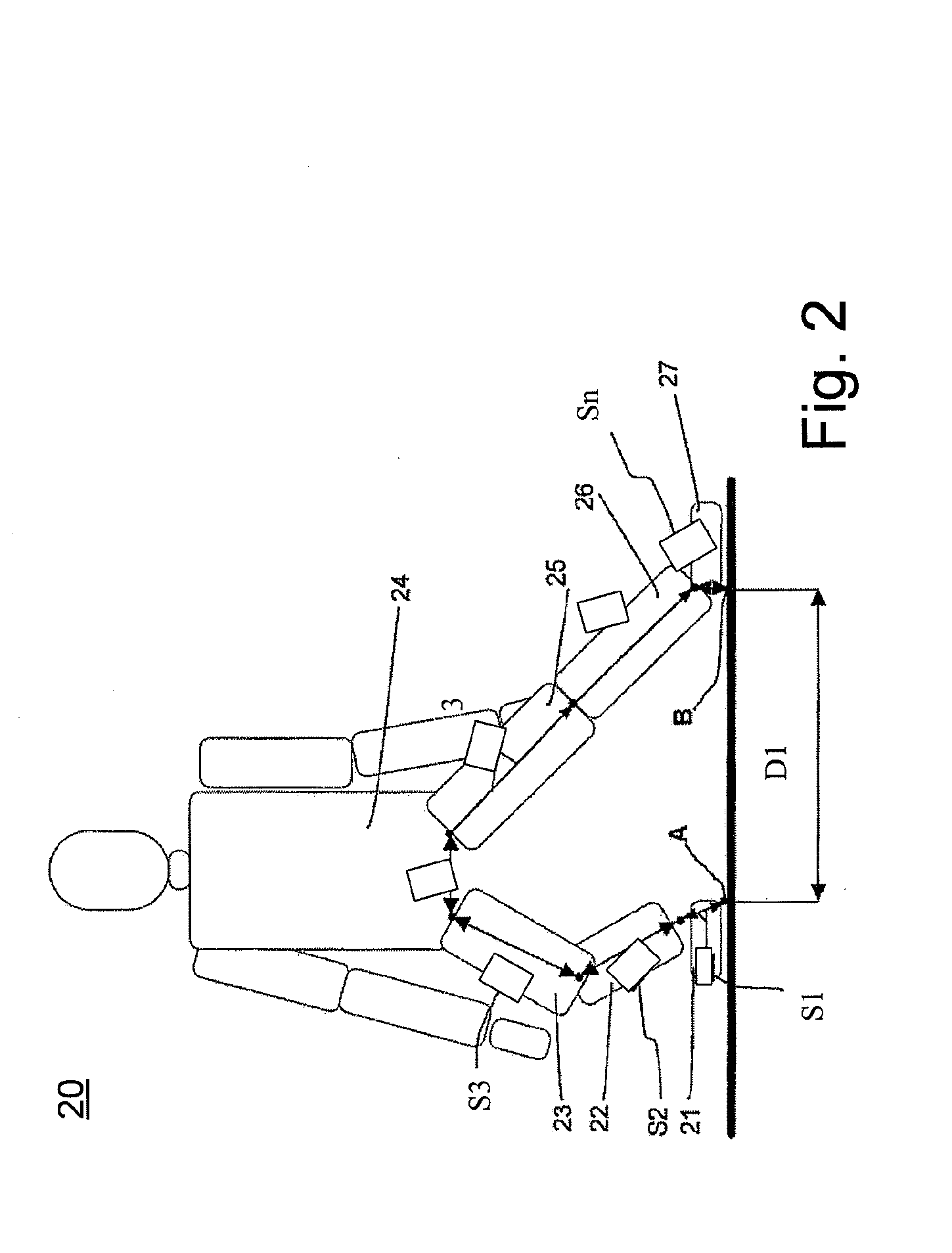
The invention relates to motion tracking system (10) for tracking a movement of an object (P) in a three-dimensional space, the said object being composed of object portions having individual dimensions and mutual proportions and being sequentially interconnected by joints the system comprising orientation measurement units (S1, S3, . . . SN) for measuring data related to at least orientation of the object portions, wherein the orientation measurement units are arranged in positional and orientational relationships with respective object portions and having at least orientational parameters; a processor (3, 5) for receiving data from the orientation measurement units, the said processor comprising a module for deriving orientation and / or position information of the object portions using the received data and a calibration unit (7) arranged to calculate calibration values based on received data and pre-determined constraints for determining at least the mutual proportions of the object portions and orientational parameters of the orientation measurement units based on received data, pre-determined constrains and additional input data. The invention further relates to a method for tracking a movement of an object, a medical rehabilitation system and an animation system.
Owner:XSENS HLDG BV
Systems and methods for knowledge discovery in spatial data
InactiveUS6865582B2Simple forecasting methodExclude dataData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsPredictive methodsStatistical analysis
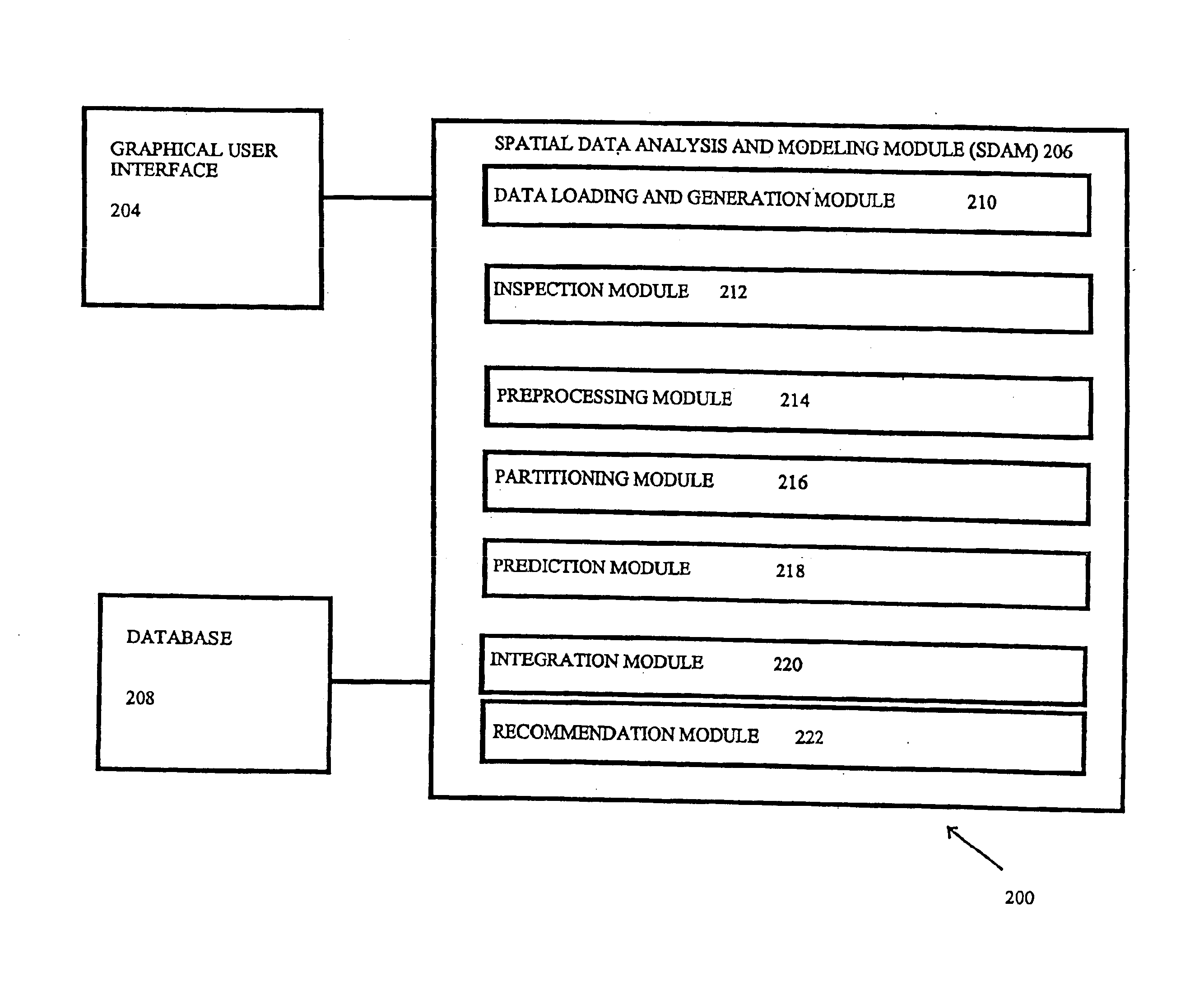
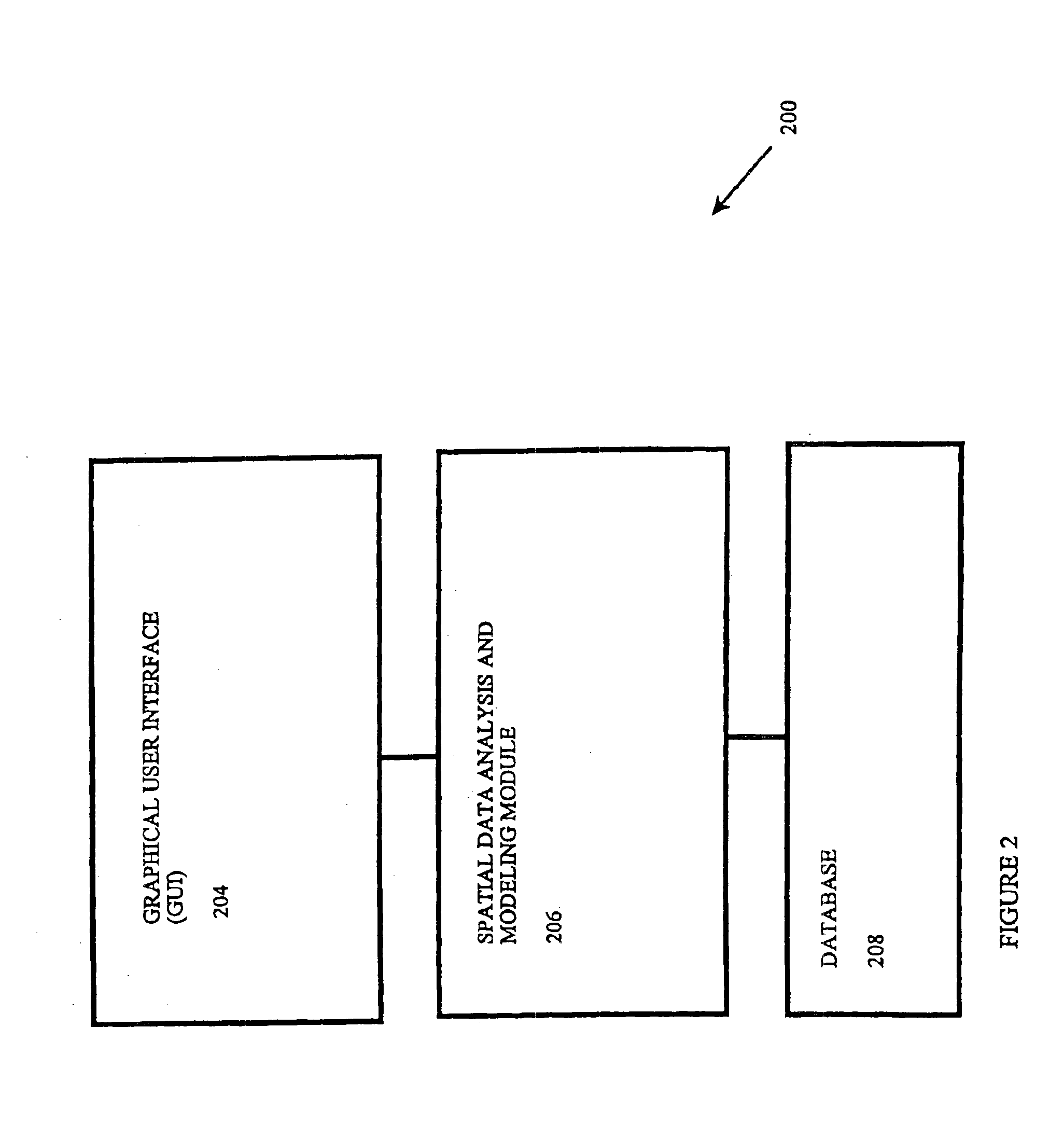
Systems and methods are provided for knowledge discovery in spatial data as well as to systems and methods for optimizing recipes used in spatial environments such as may be found in precision agriculture. A spatial data analysis and modeling module is provided which allows users to interactively and flexibly analyze and mine spatial data. The spatial data analysis and modeling module applies spatial data mining algorithms through a number of steps. The data loading and generation module obtains or generates spatial data and allows for basic partitioning. The inspection module provides basic statistical analysis. The preprocessing module smoothes and cleans the data and allows for basic manipulation of the data. The partitioning module provides for more advanced data partitioning. The prediction module applies regression and classification algorithms on the spatial data. The integration module enhances prediction methods by combining and integrating models. The recommendation module provides the user with site-specific recommendations as to how to optimize a recipe for a spatial environment such as a fertilizer recipe for an agricultural field.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Computer-implemented method for managing through symbolic abstraction of a membership expression multiple logical representations and storage structures
InactiveUS20080010241A1Maximum flexibilityImprove performanceRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsLogical representationData independence
This is a computer-implemented method for managing and enhancing data independence among multiple logical representations and storage structures of data by accessing and updating physical storage through a relational representation. The present invention supports both data independence and storage flexibility by using membership abstraction as the equalizing access for any logical representation and actual storage, while the prior art is restricted to user-supplied denotations and catalog entries.
Owner:MCGOVERAN DAVID O
Method and device for obtaining audience data on TV program
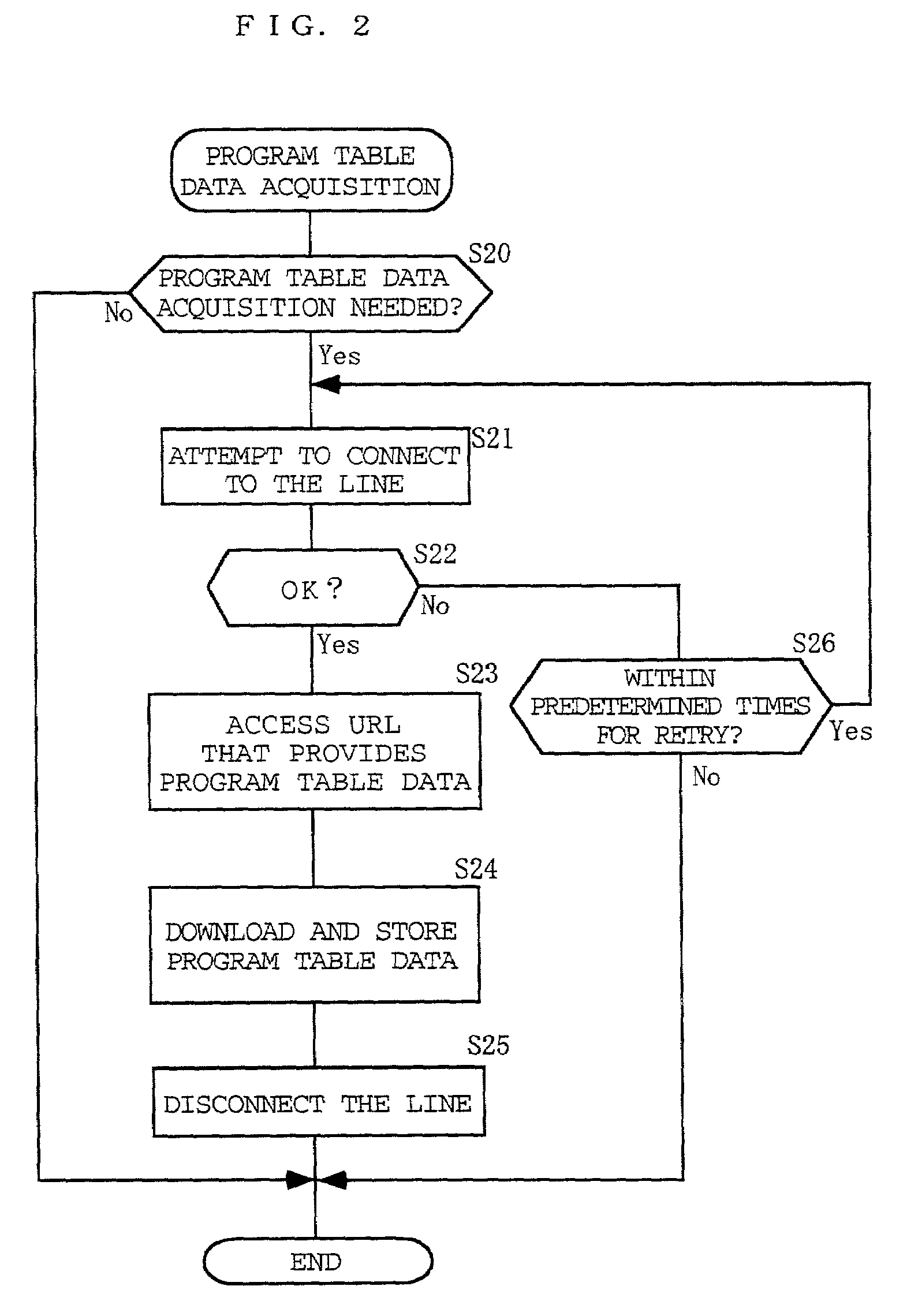
InactiveUS7039928B2Reduce congestionReduces telephone chargeTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsData packTime information
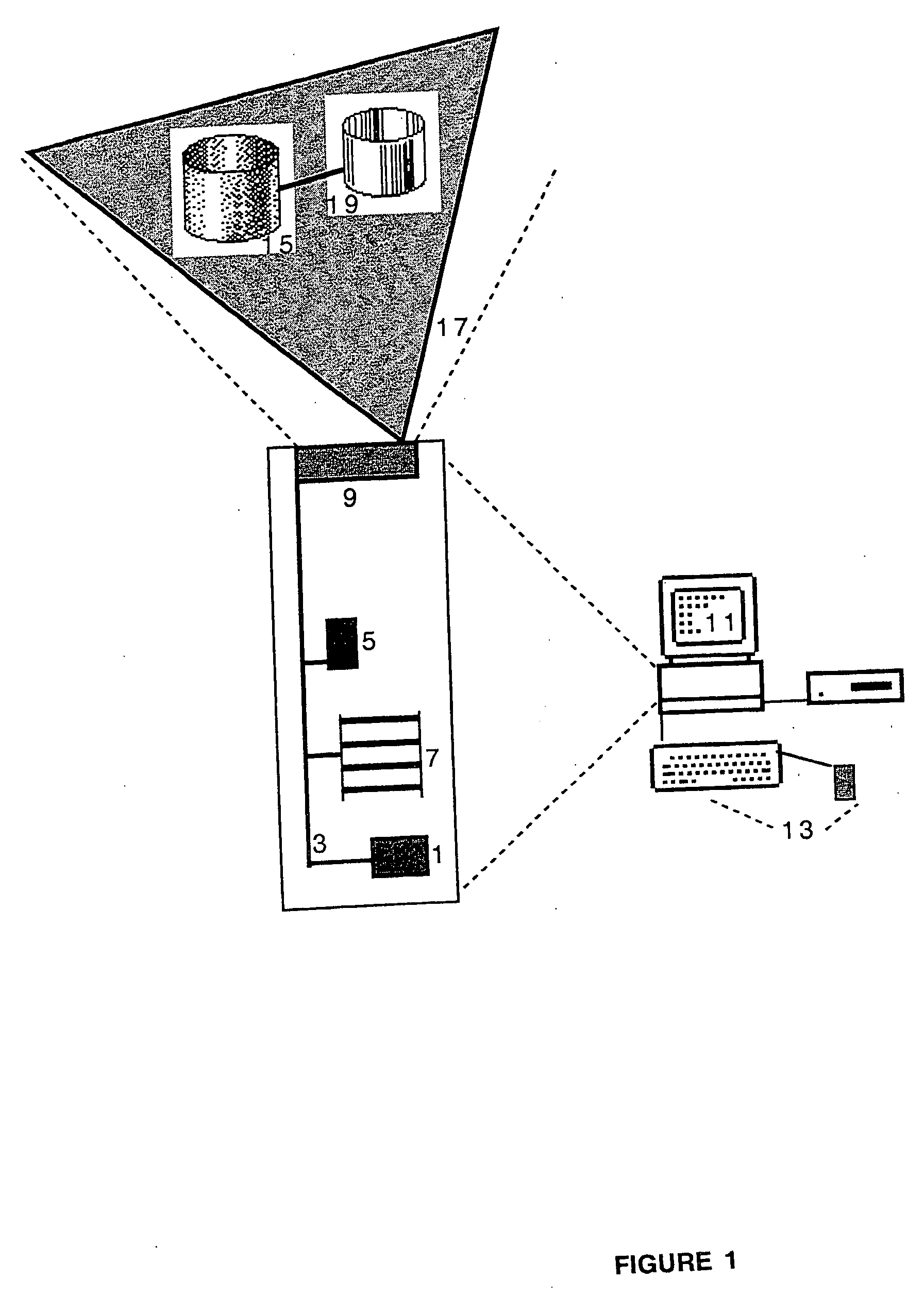
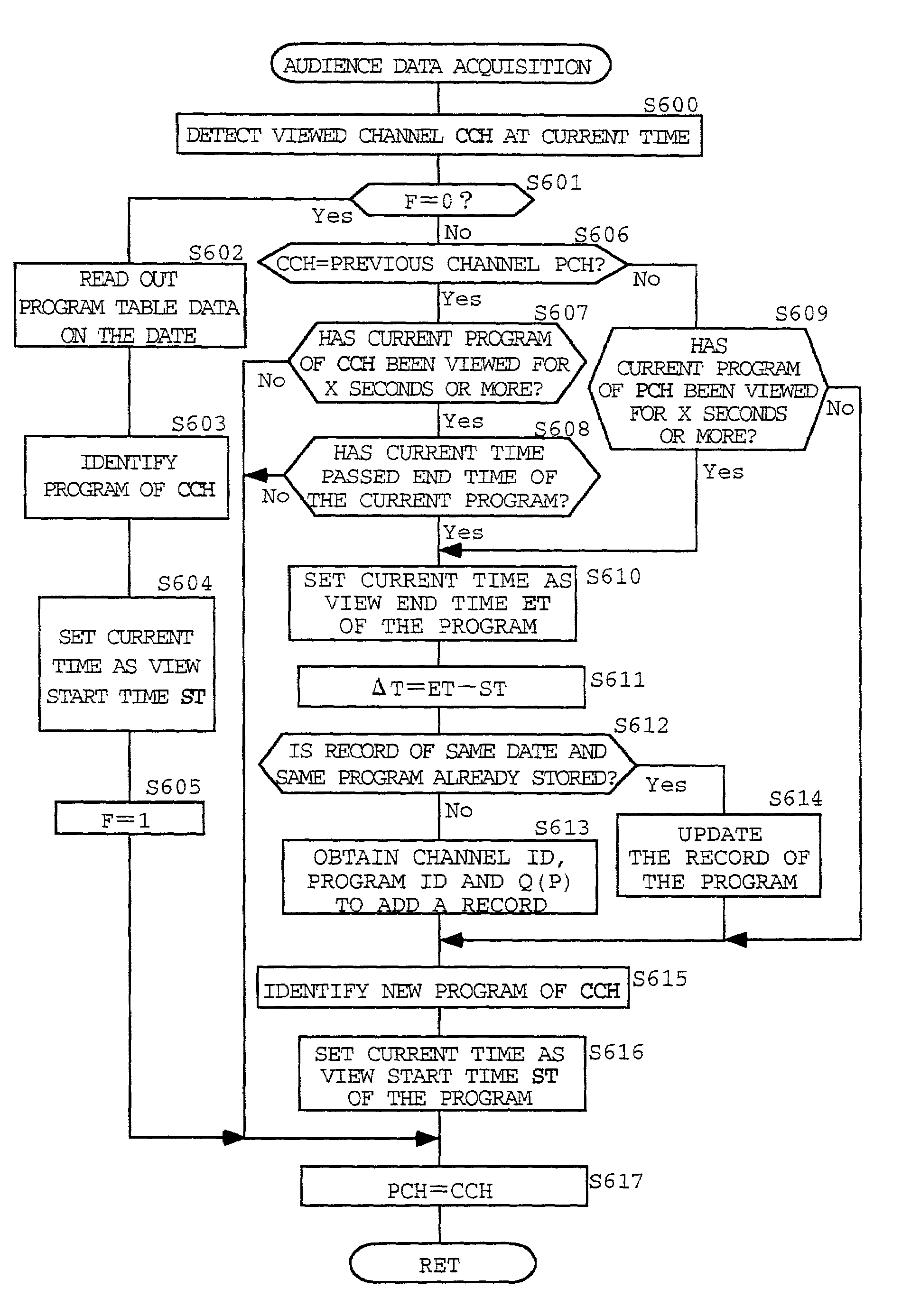
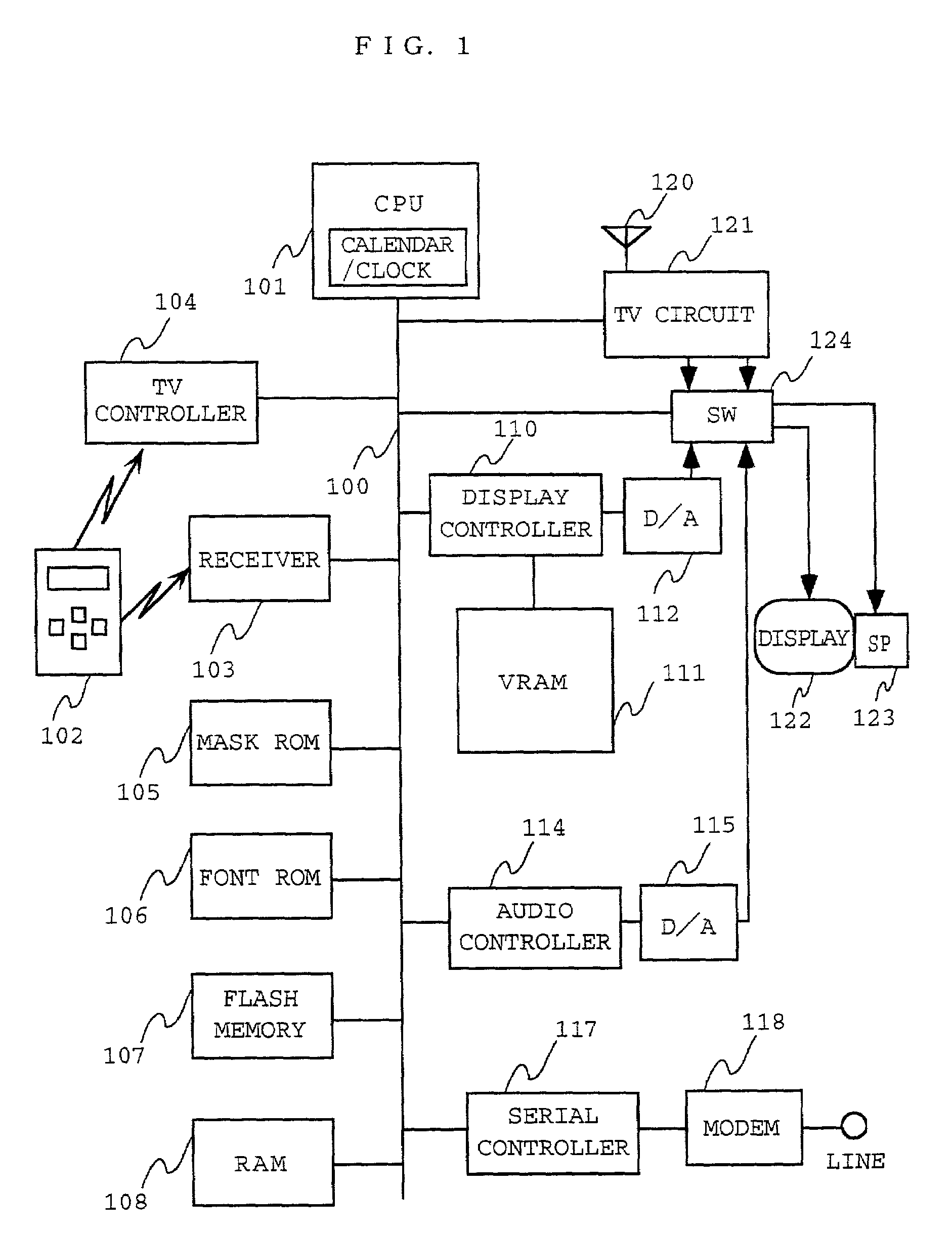
The TV program table data in the area where a viewer resides are received through the Internet or a broadcasting medium by using the TV set with an internet connection function at the viewer. While the viewer is watching a TV program, the audience data including viewed channel information and viewed time information are automatically obtained. The obtained audience data are compared with the TV program table data to identify the watched program. The program ID of the identified program and the viewed time information are transferred to a data collecting center through the Internet together with the viewer ID data. By utilizing the Internet for the distribution of the TV program table data to the viewers and for the collection of the audience data, the nationwide TV audience data can be easily collected and used to make statistics. Since viewed channel and viewed time information are correlated with programs on the viewer's side, the load of processing the data on the center side can be relieved.
Owner:ACCESS
Method and device for acquiring snapshots and computer system with snapshot acquiring function
ActiveUS7111026B2Easy to useEliminate unnecessary generational managementData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalComputerized systemOperating system
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Human body measurement system and information provision method using the same
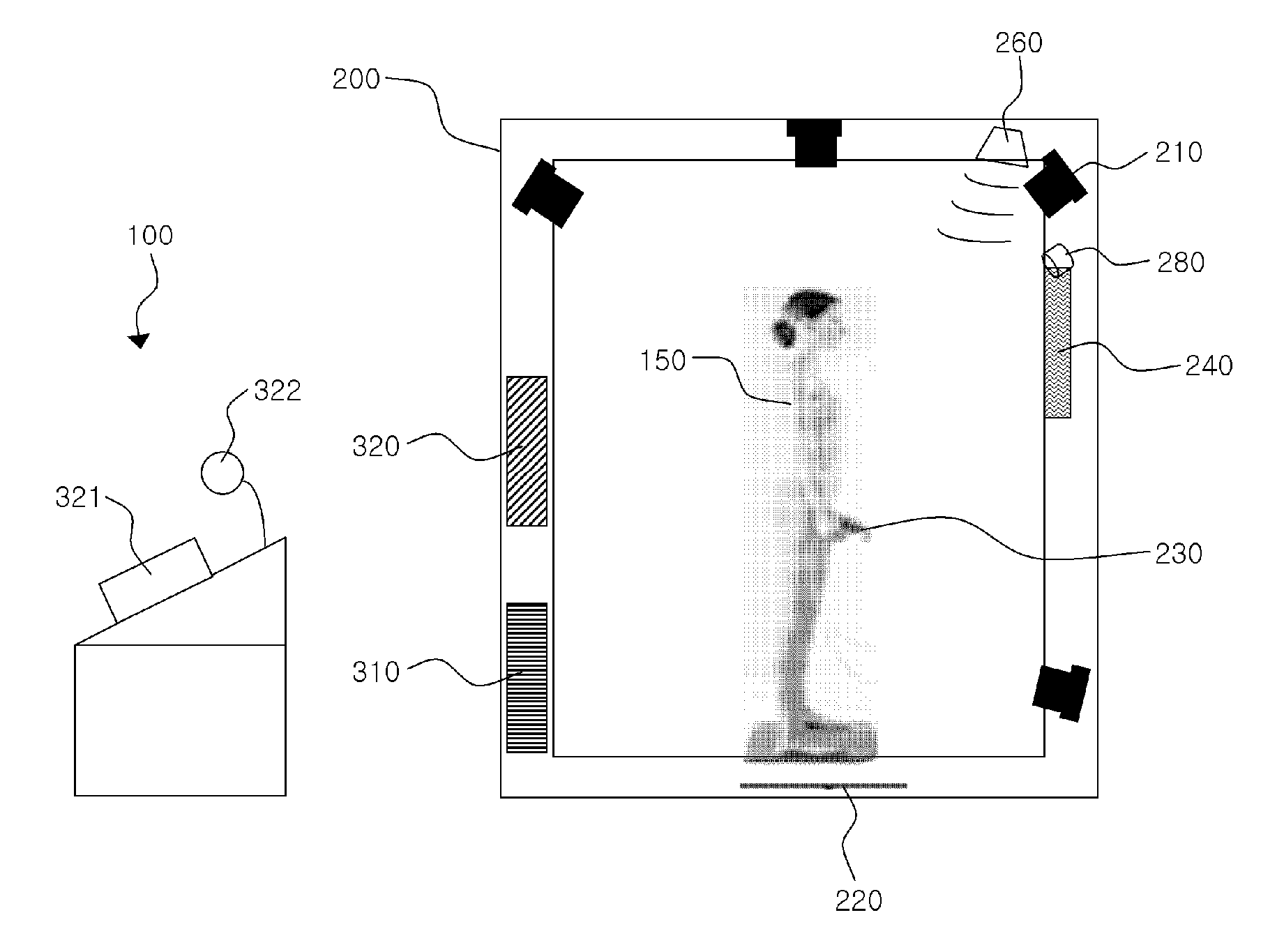
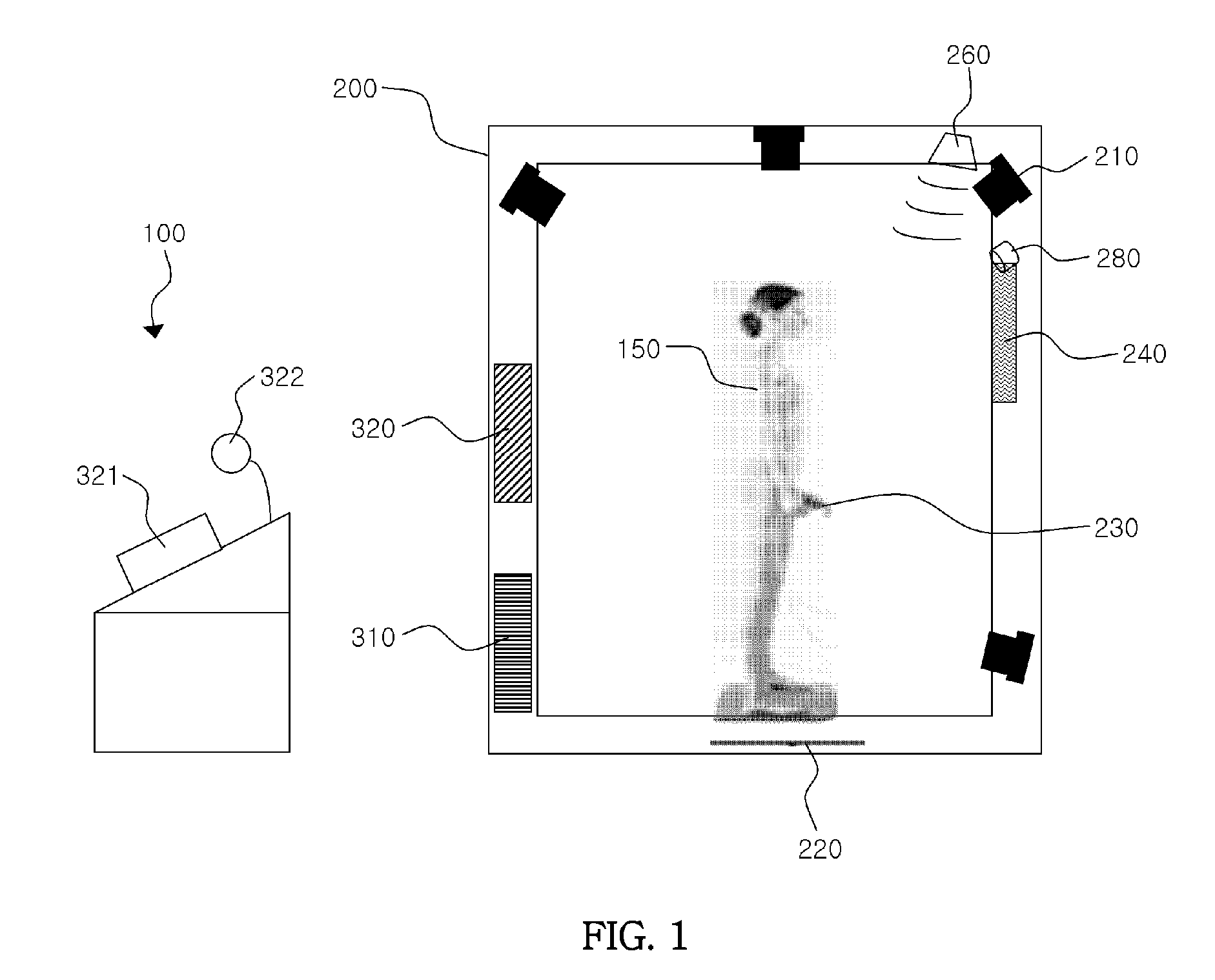
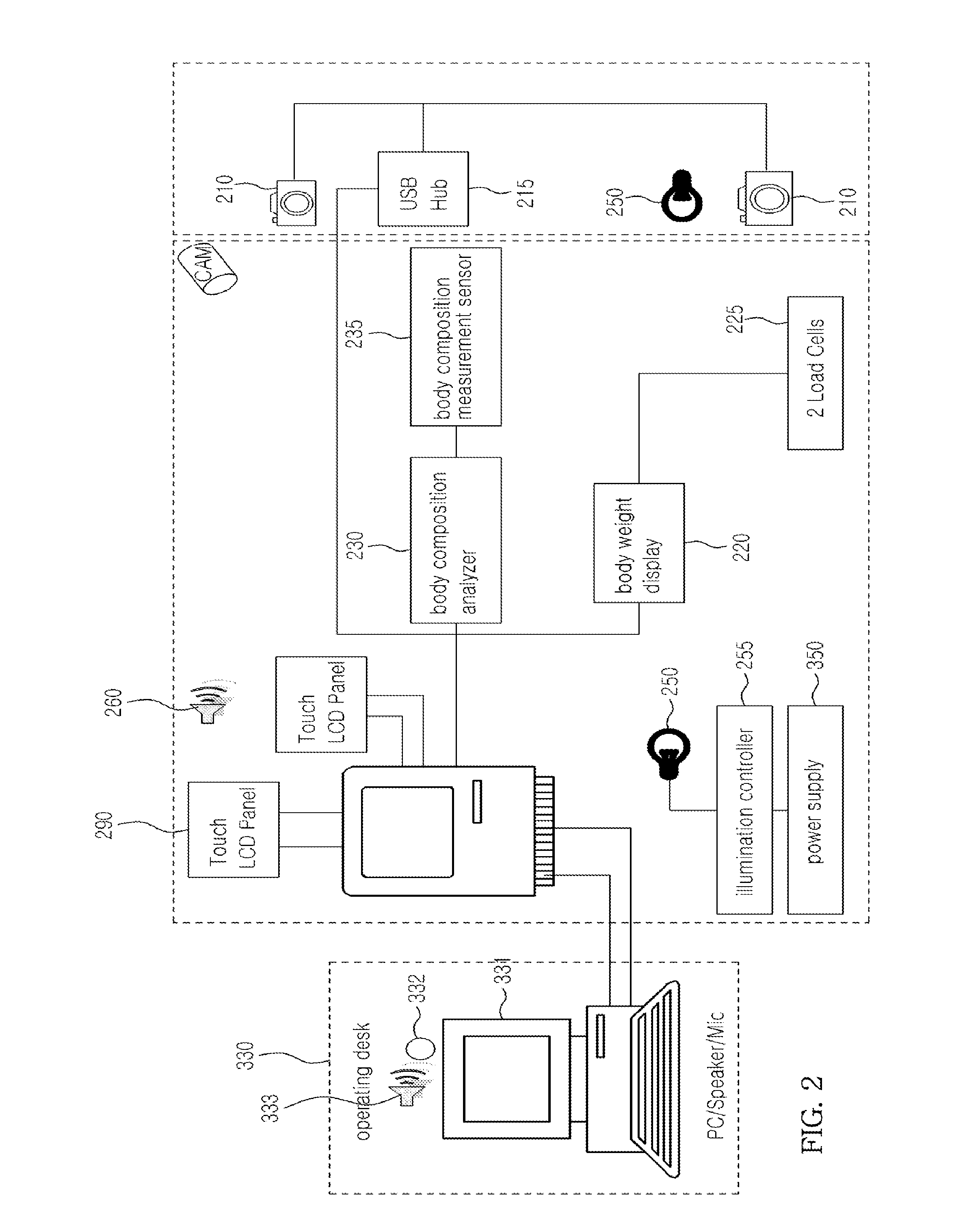
InactiveUS20100312143A1Increase speedExclude dataTelevision system detailsPerson identificationHuman bodyBody weight
A human body measurement system and a method for using such a system. The human body measurement system includes a photographing unit that includes a plurality of cameras and a hub which send images, captured by the cameras, to a PC of an integrated controller through the hub, a weight scale configured to measure body weight of a subject of measurement, and a body composition analyzer configured to measure body composition of the subject of measurement.
Owner:MINIMEDREAM
Dynamic prediction for process control
InactiveUS6370437B1Eliminate timeReduce wasteDigital computer detailsAnti-hunting elementsMotion estimationProcess control
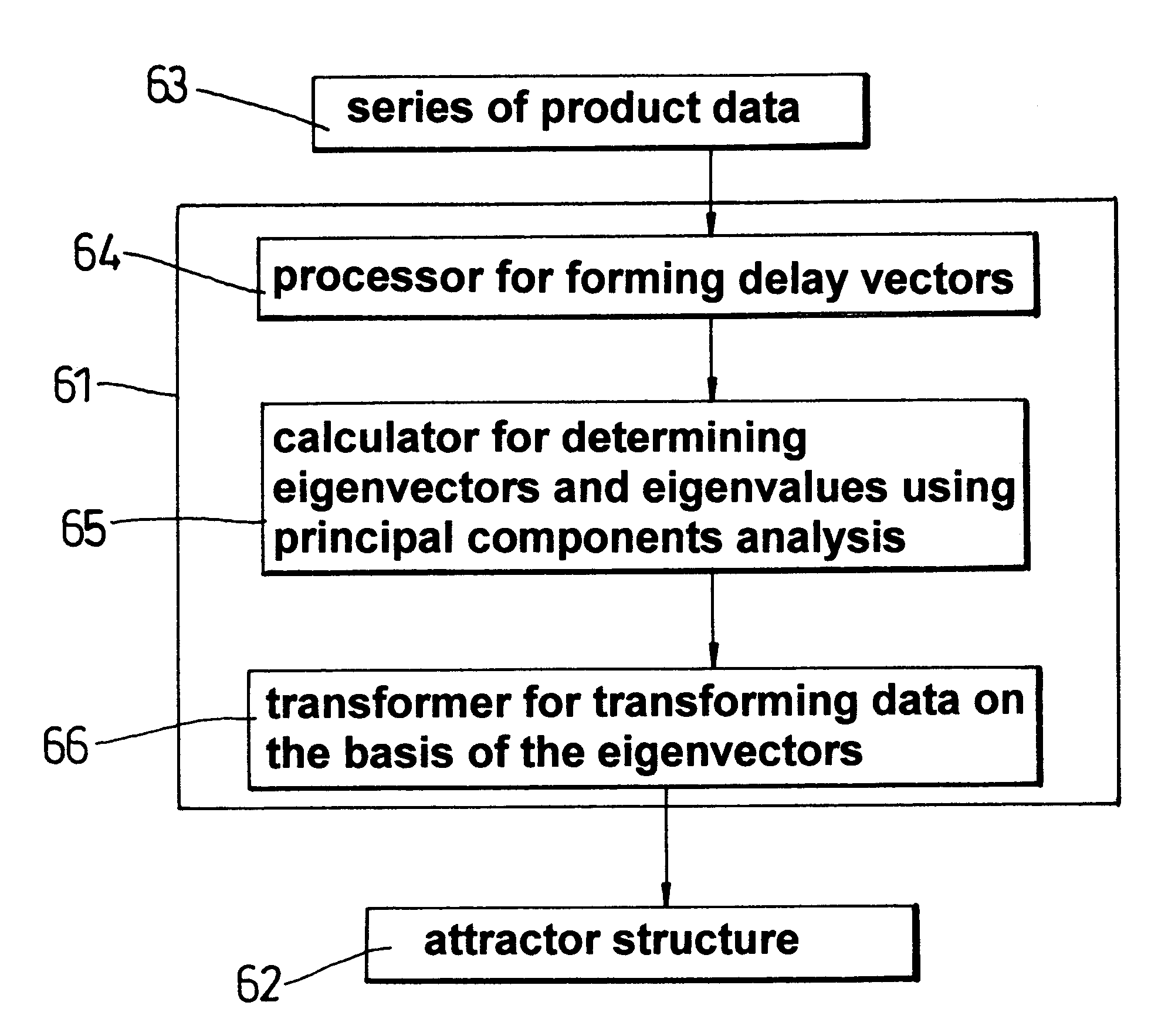
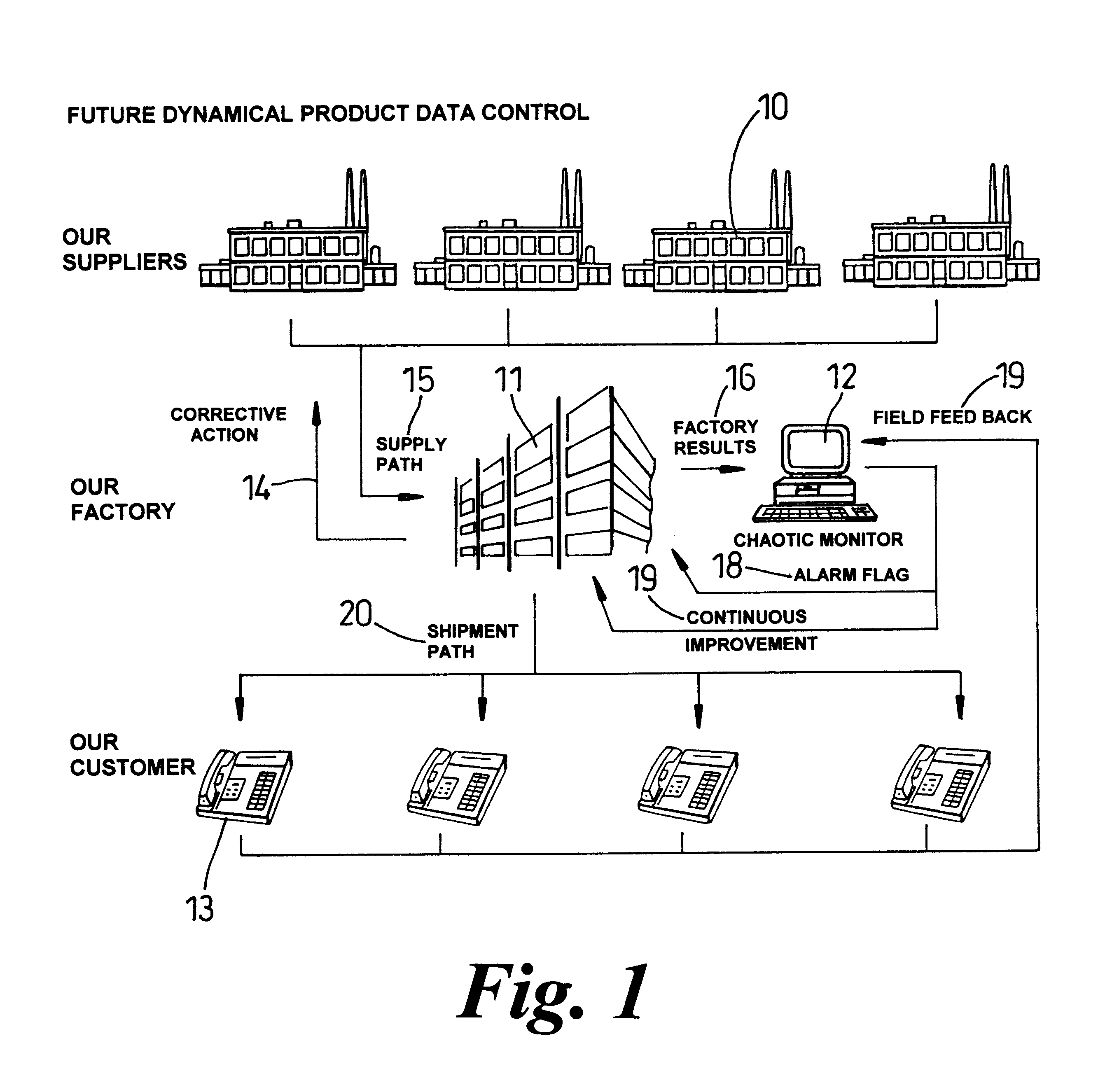
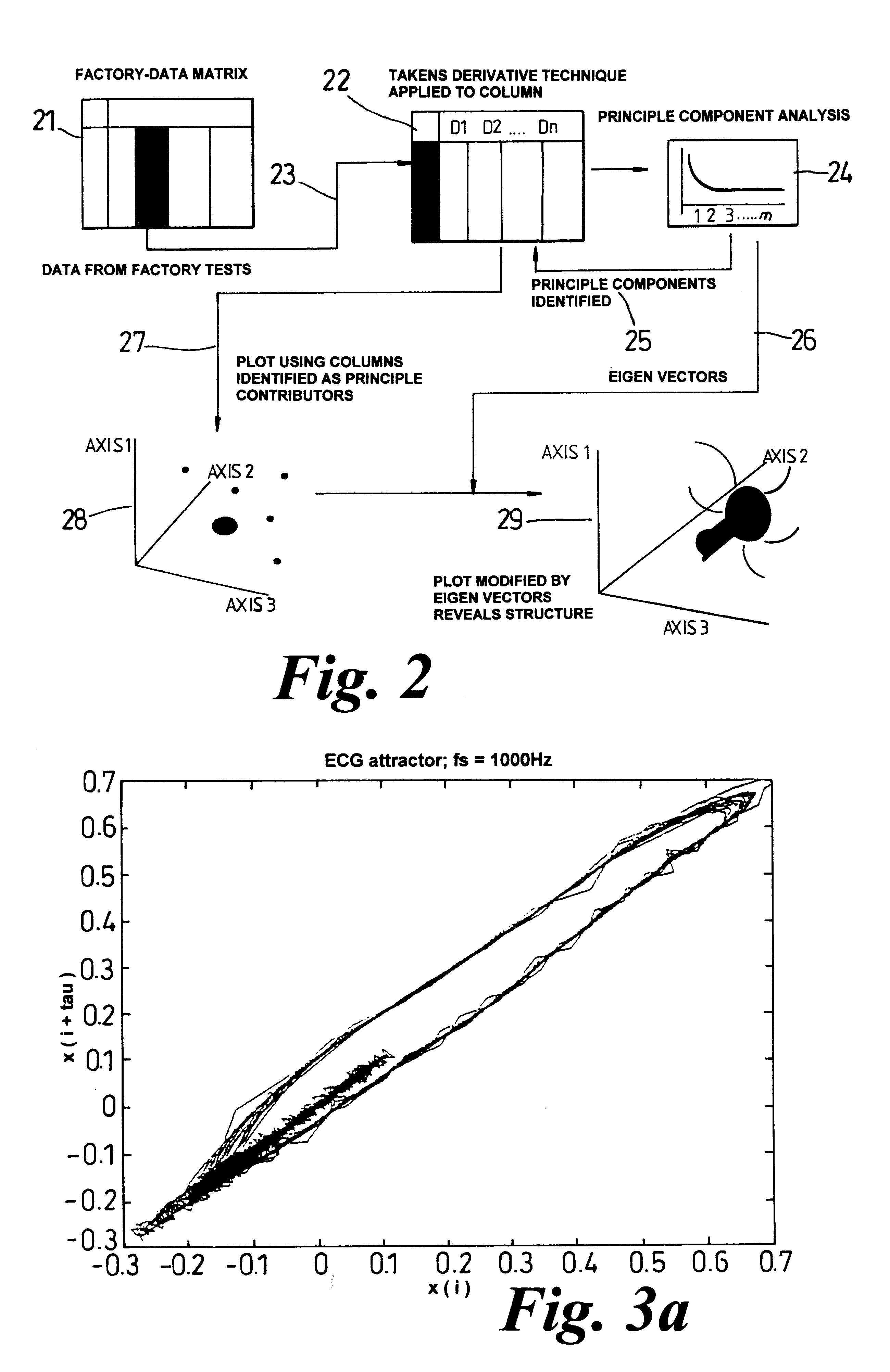
Product data from a manufacturing process is analysed using techniques adapted from the study of chaos. Future values of a series of product data are predicted and an attractor structure is determined from the product data. This enables the manufacturing process to be monitored, controlled and analysed. Action can be taken to modify the manufacturing process using the results from the prediction and attractor structure to reduce costs and improve performance and efficiency.
Owner:CALLSTAT SOLUTIONS LLC
Real-Time Social Networking
ActiveUS20130144957A1Less overall consumptionLow costDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsIn-memory databaseData element
Techniques for exploring social connections in an in-memory database include identifying an attribute in a user profile associated with a first user; executing a query against a data element stored in an in-memory database, the query including the attribute in the user profile; identifying a second user from results of the query, the second user associated with the data element based on a relationship between the second user and the first user defined by the attribute; and generating displayable information associated with the second user.
Owner:SAP PORTALS ISRAEL
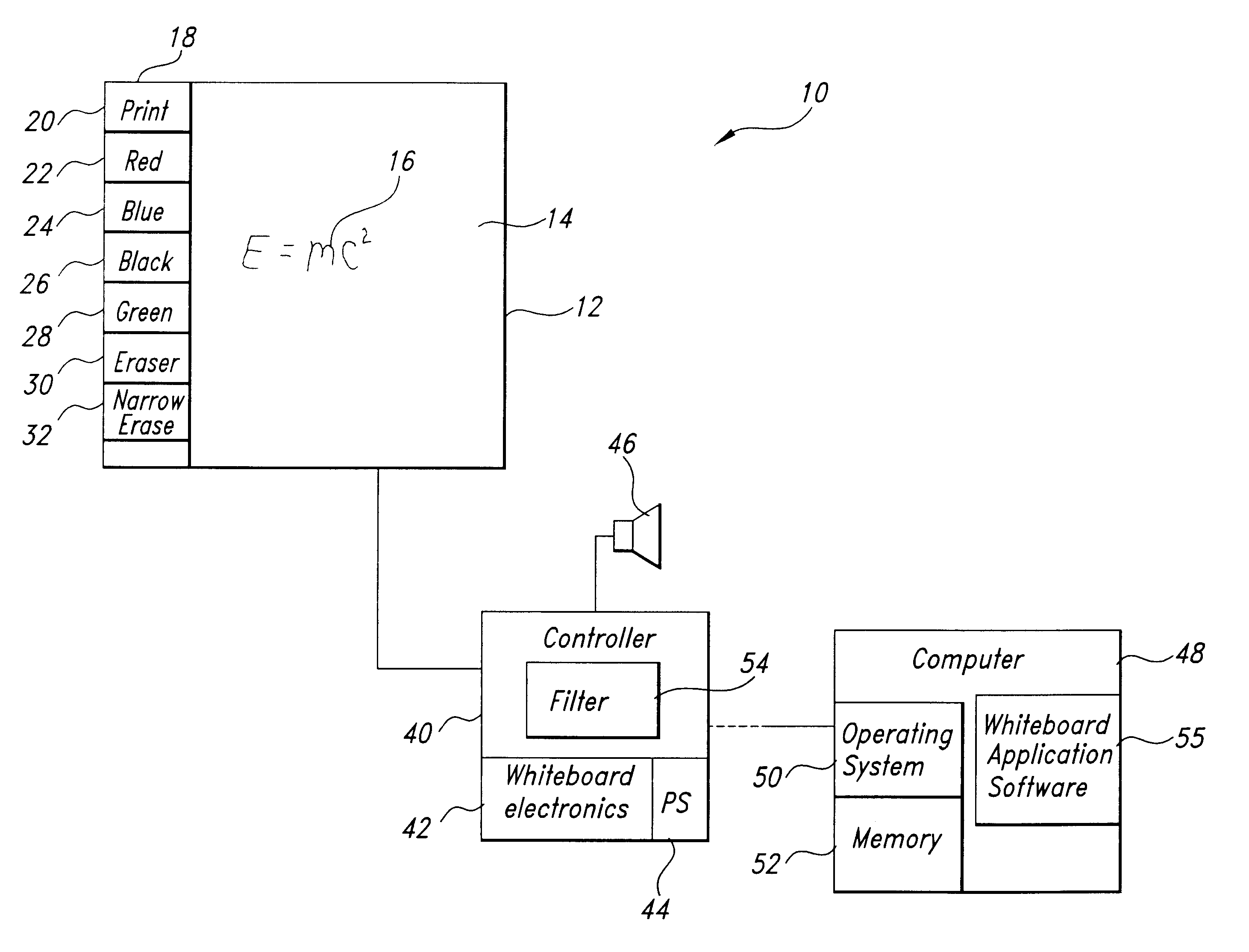
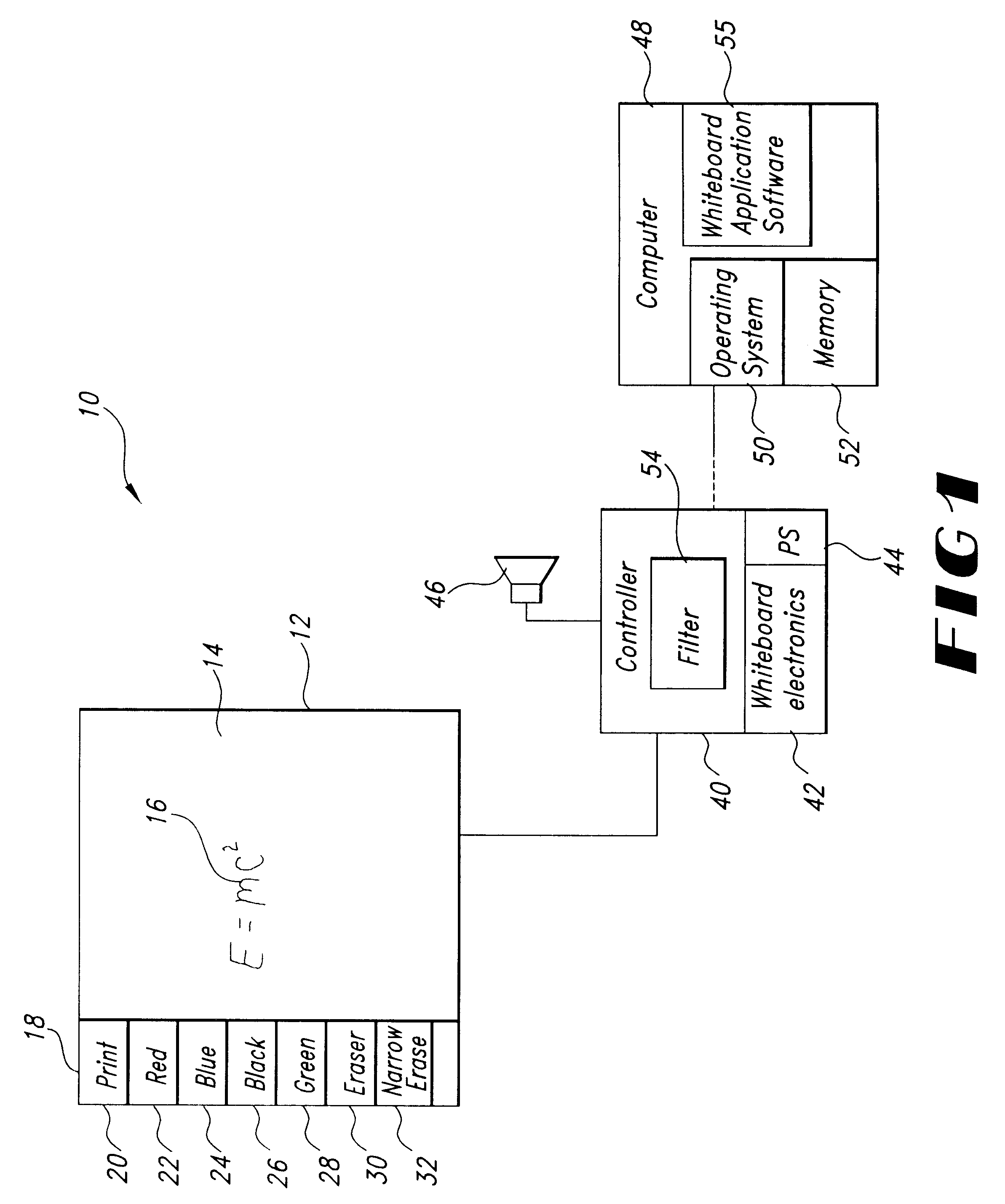
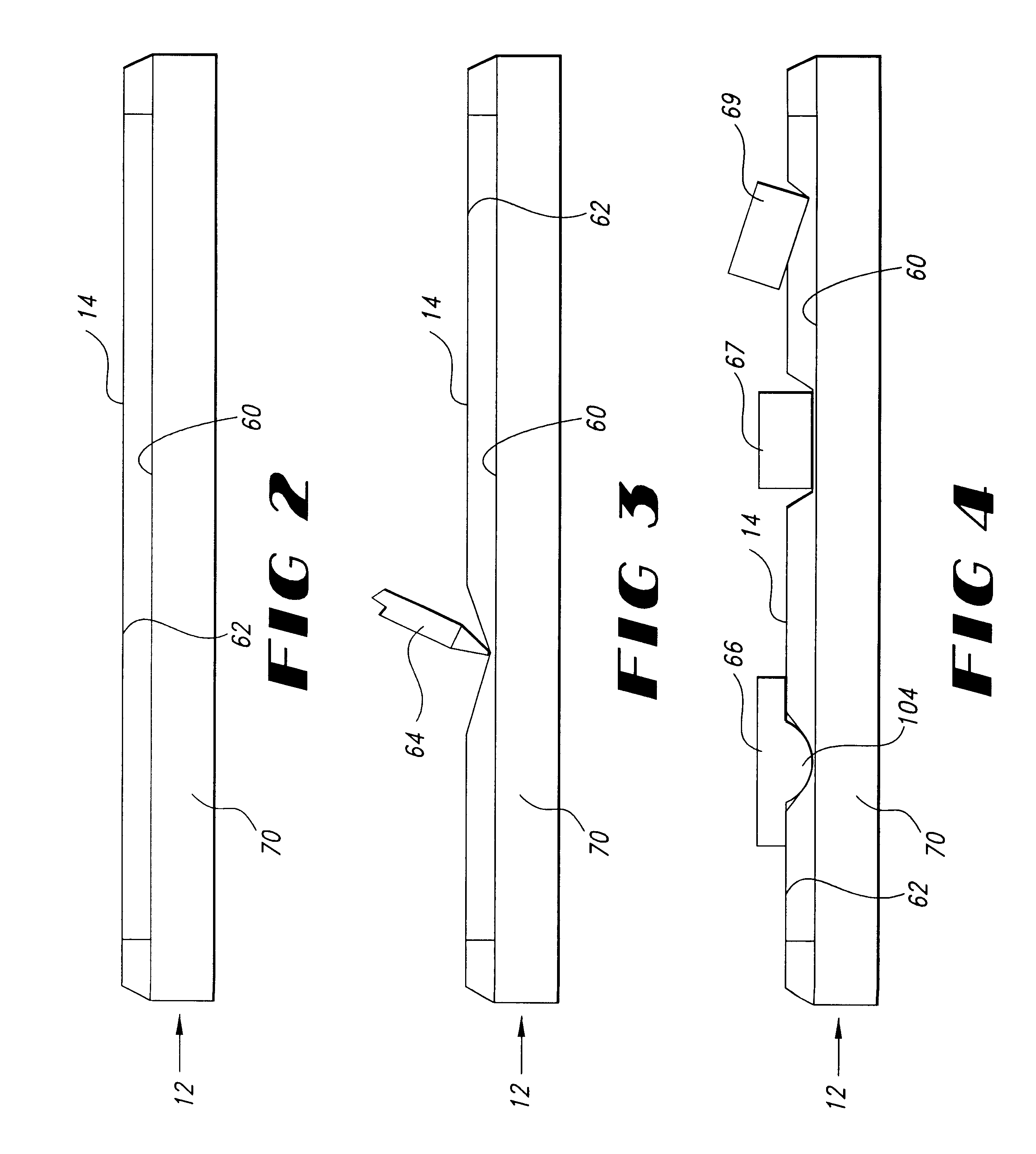
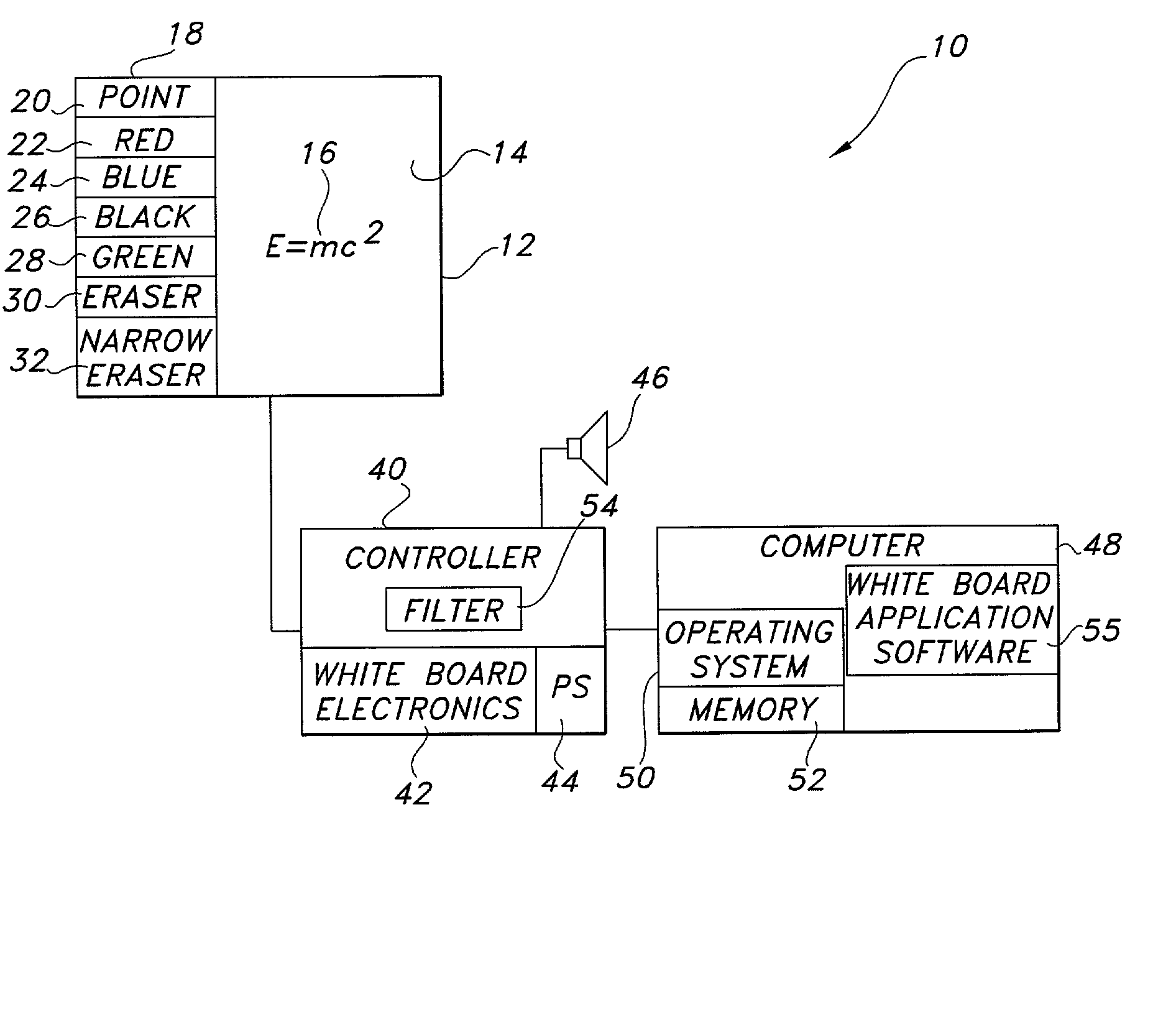
Electronic whiteboard system eraser
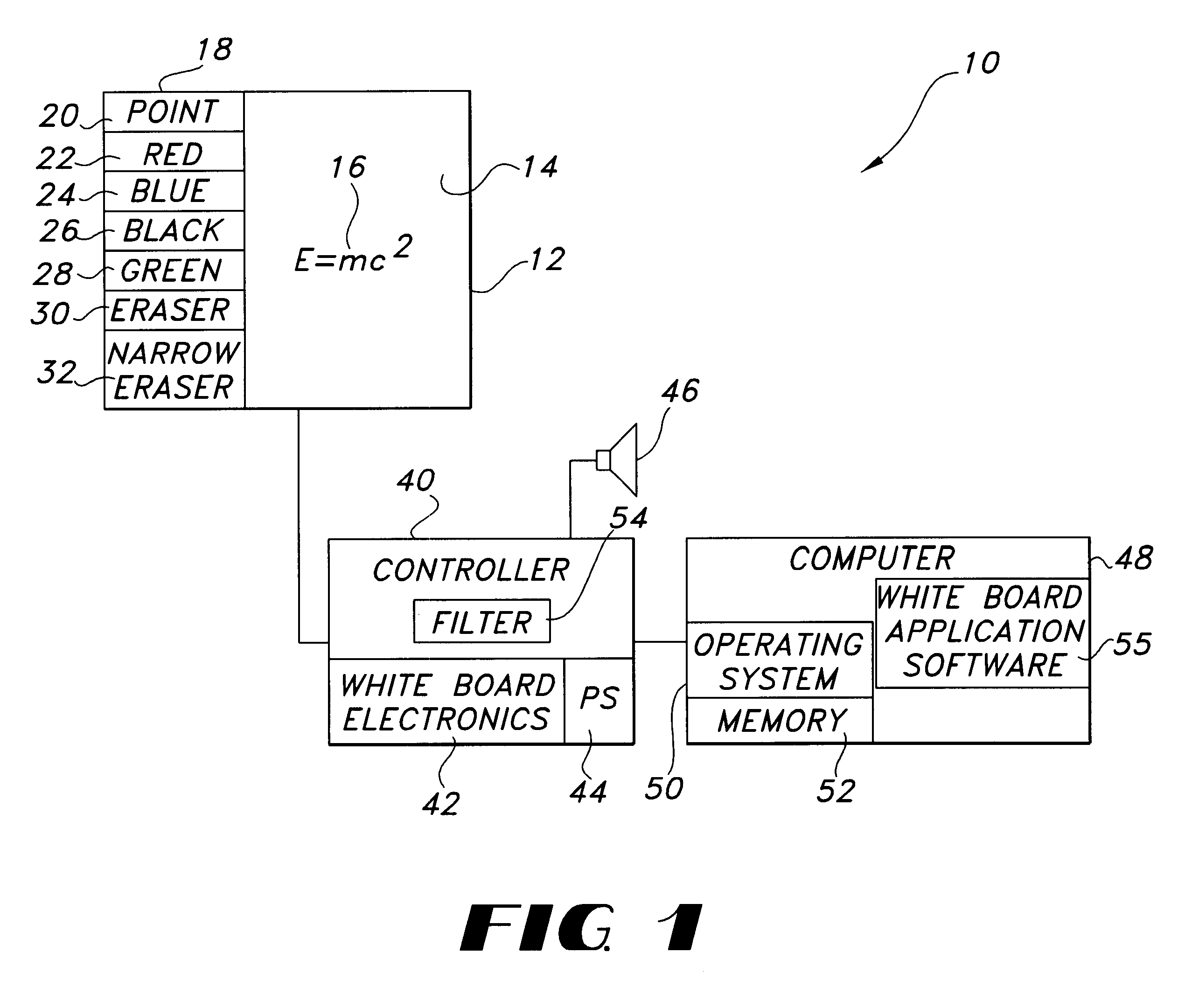
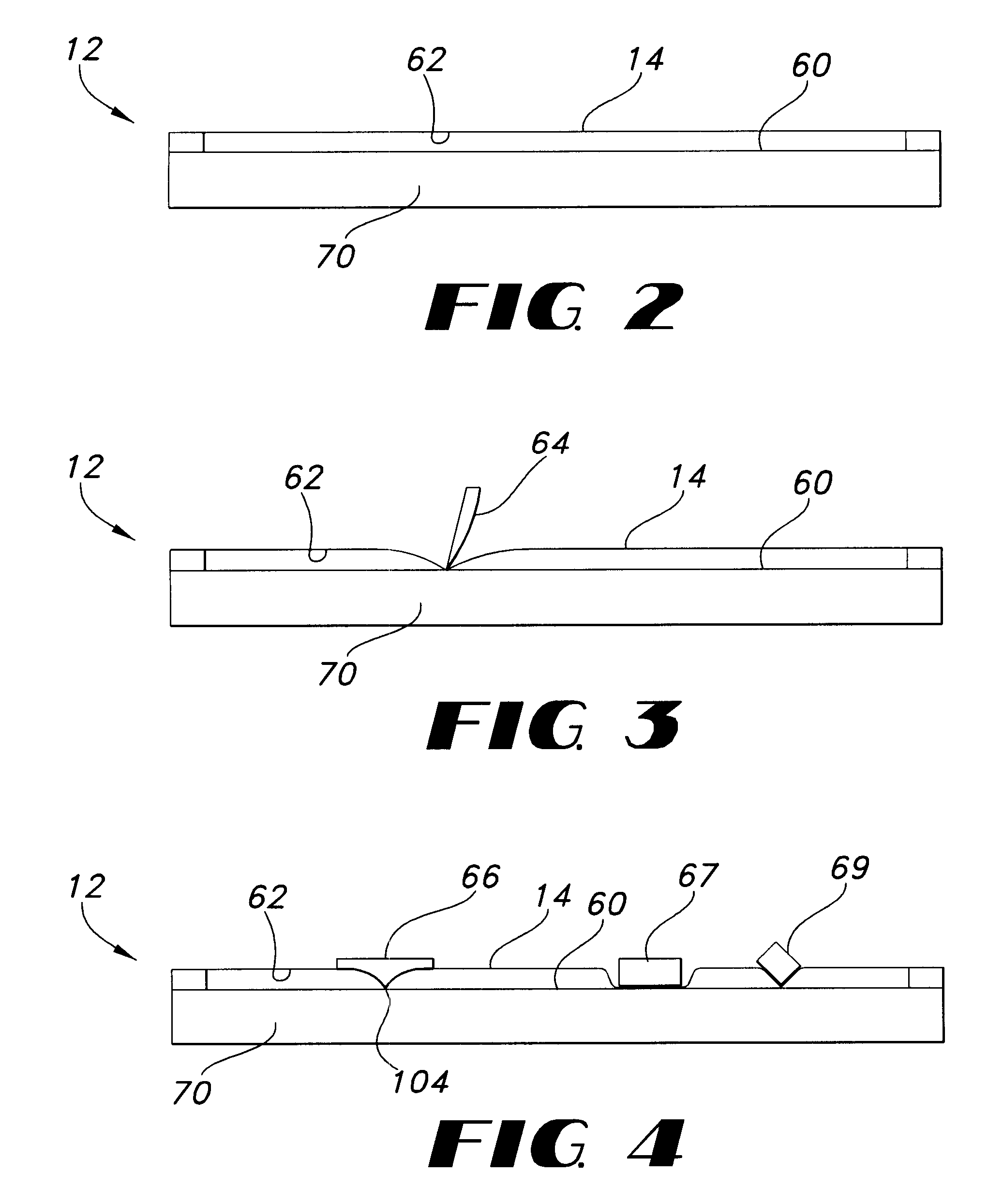
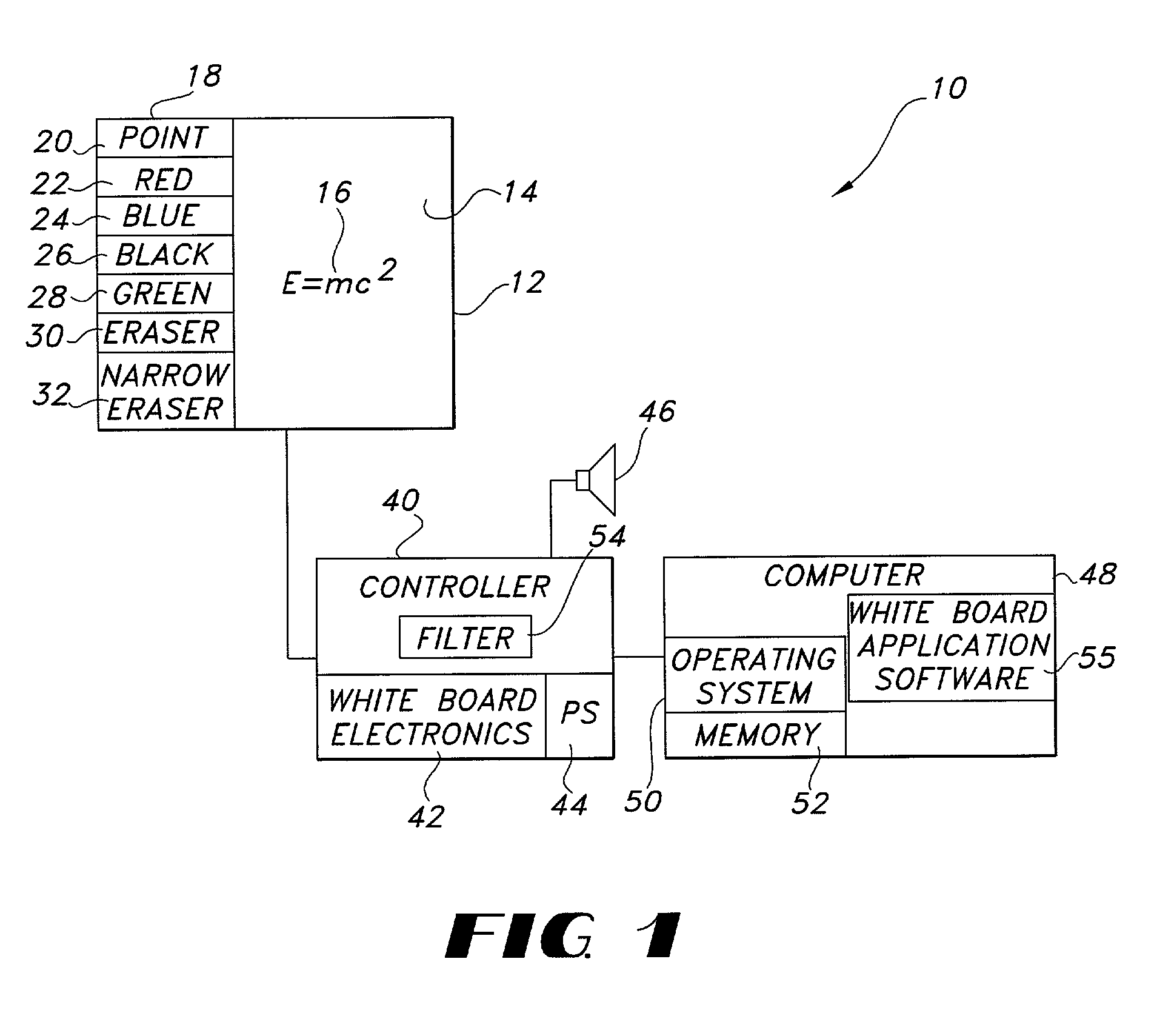
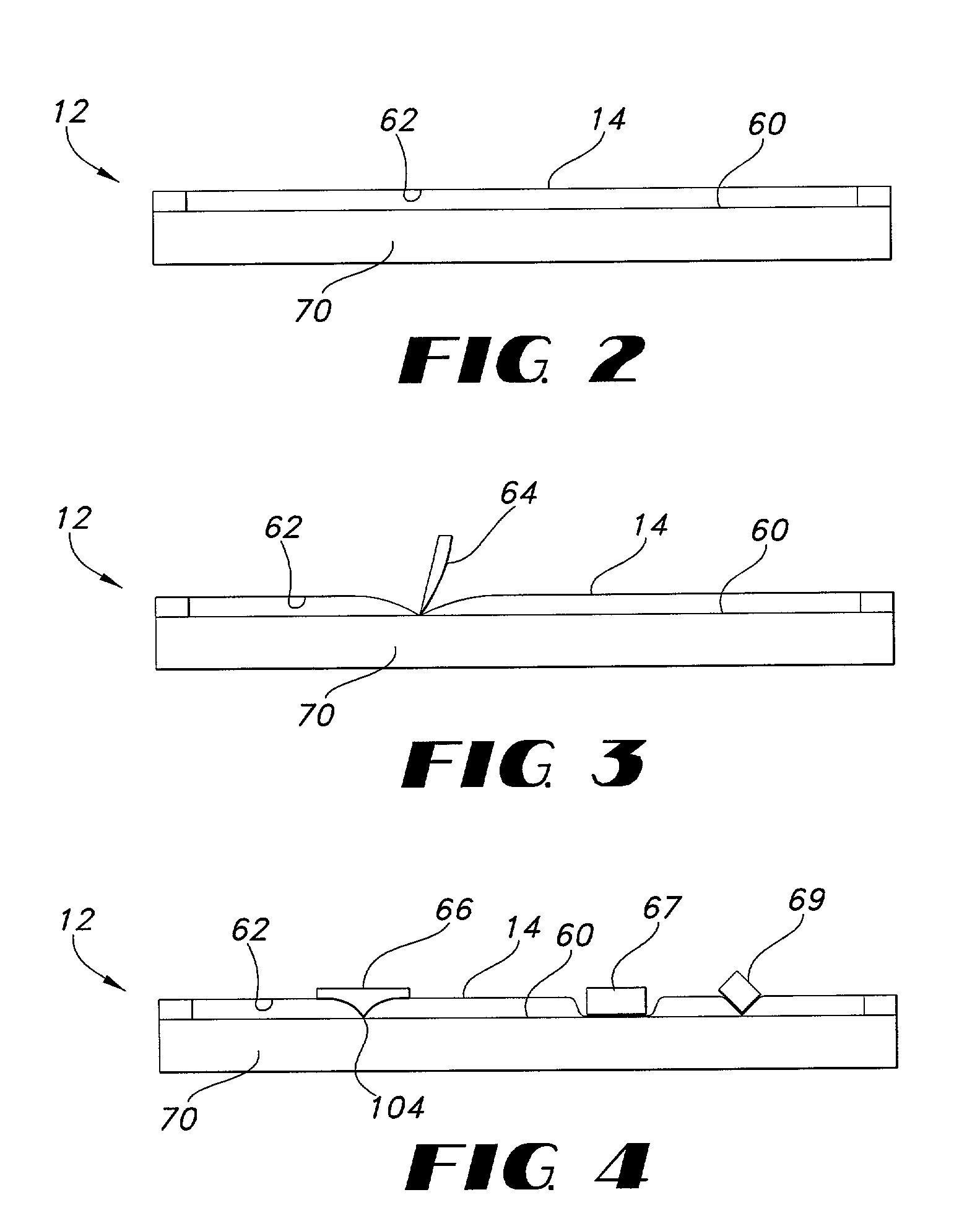
InactiveUS6445384B1Function can be cumbersomeEasy to useCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDigital dataWhiteboard
An eraser for use on an electronic whiteboard with a protrusion area on the erasing surface forming a convex area on the erasing surface for establishing a positive point of contact with the whiteboard; an electronic whiteboard system including such an eraser, a controller for storing data relating to information written on and erased from the whiteboard data, and a filter for preventing the storage of digital data relating to contacts with the whiteboard not attributable to normal writing or erasing actions.
Owner:POLYVISION CORP (US)
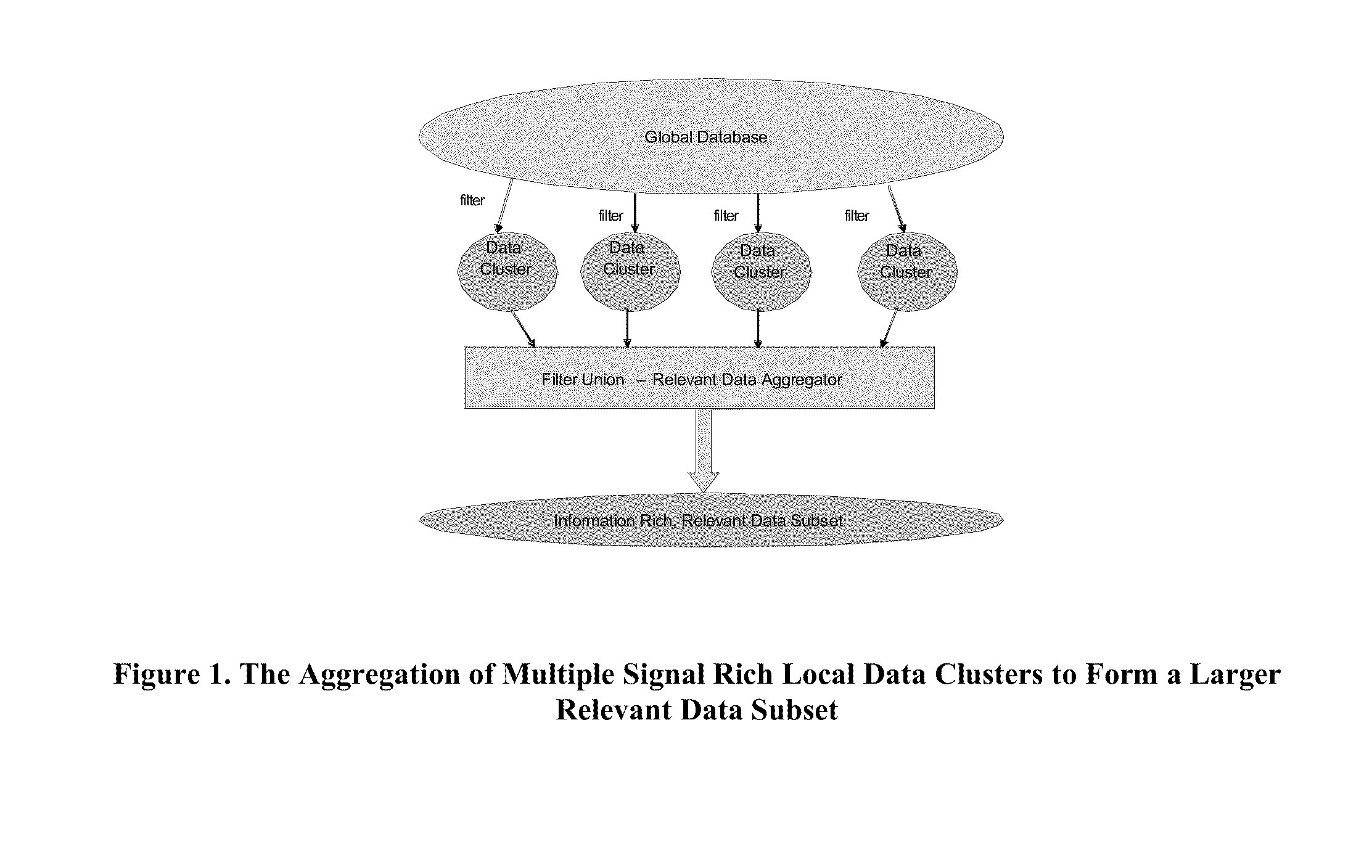
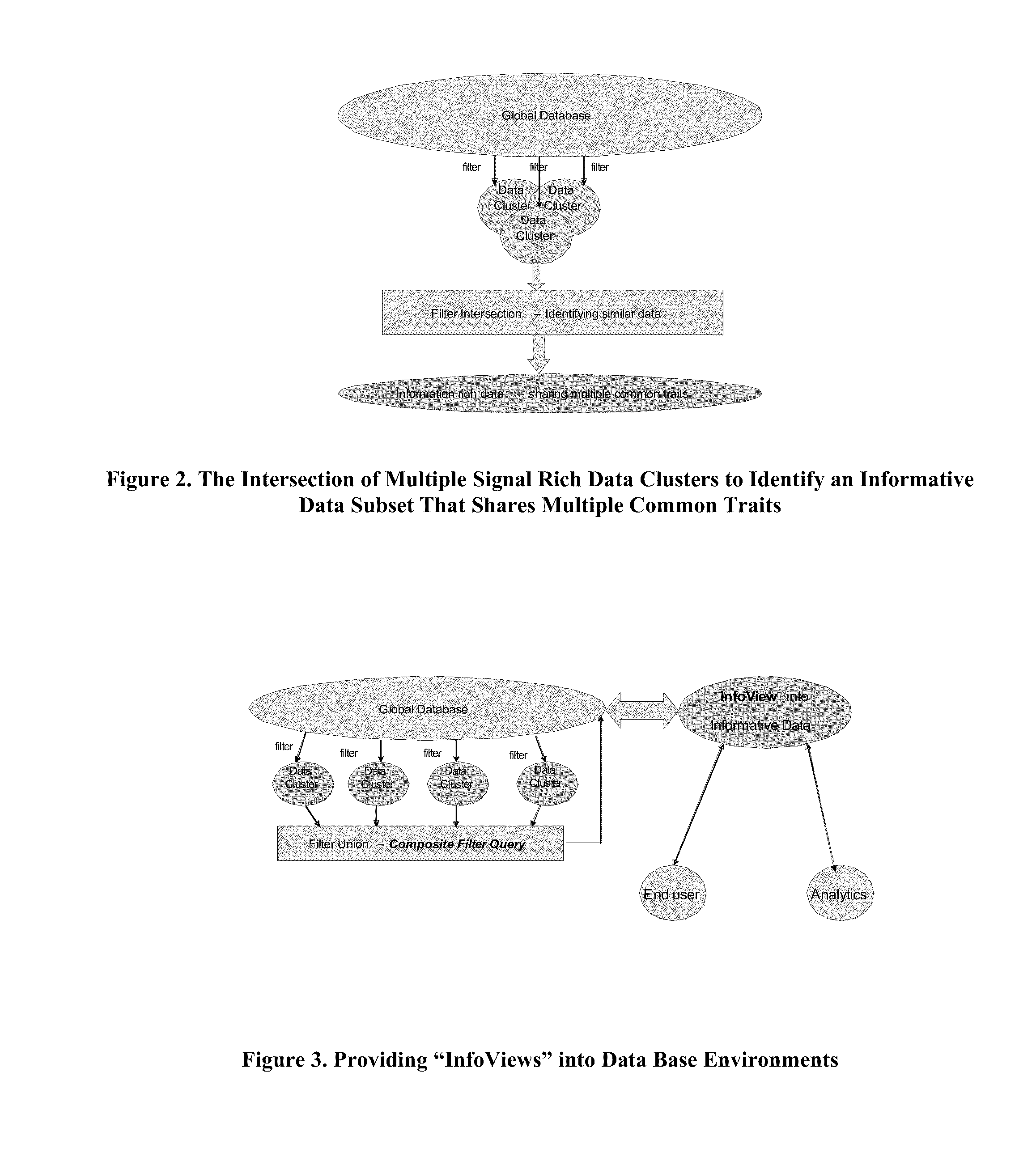
Methods for Enabling a Scalable Transformation of Diverse Data into Hypotheses, Models and Dynamic Simulations to Drive the Discovery of New Knowledge
InactiveUS20120004893A1Simple databaseReduce complexityDigital data processing detailsAnalogue computers for chemical processesHypothesisData set
The present invention relates to a method for the automatic identification of at least one informative data filter from a data set that can be used to identify at least one relevant data subset against a target feature for subsequent hypothesis generation, model building and model testing. The present invention describes methods, and an initial implementation, for efficiently linking relevant data both within and across multiple domains and identifying informative statistical relationships across this data that can be integrated into agent-based models. The relationships, encoded by the agents, can then drive emergent behavior across the global system that is described in the integrated data environment.
Owner:QUANTUM LEAP RES
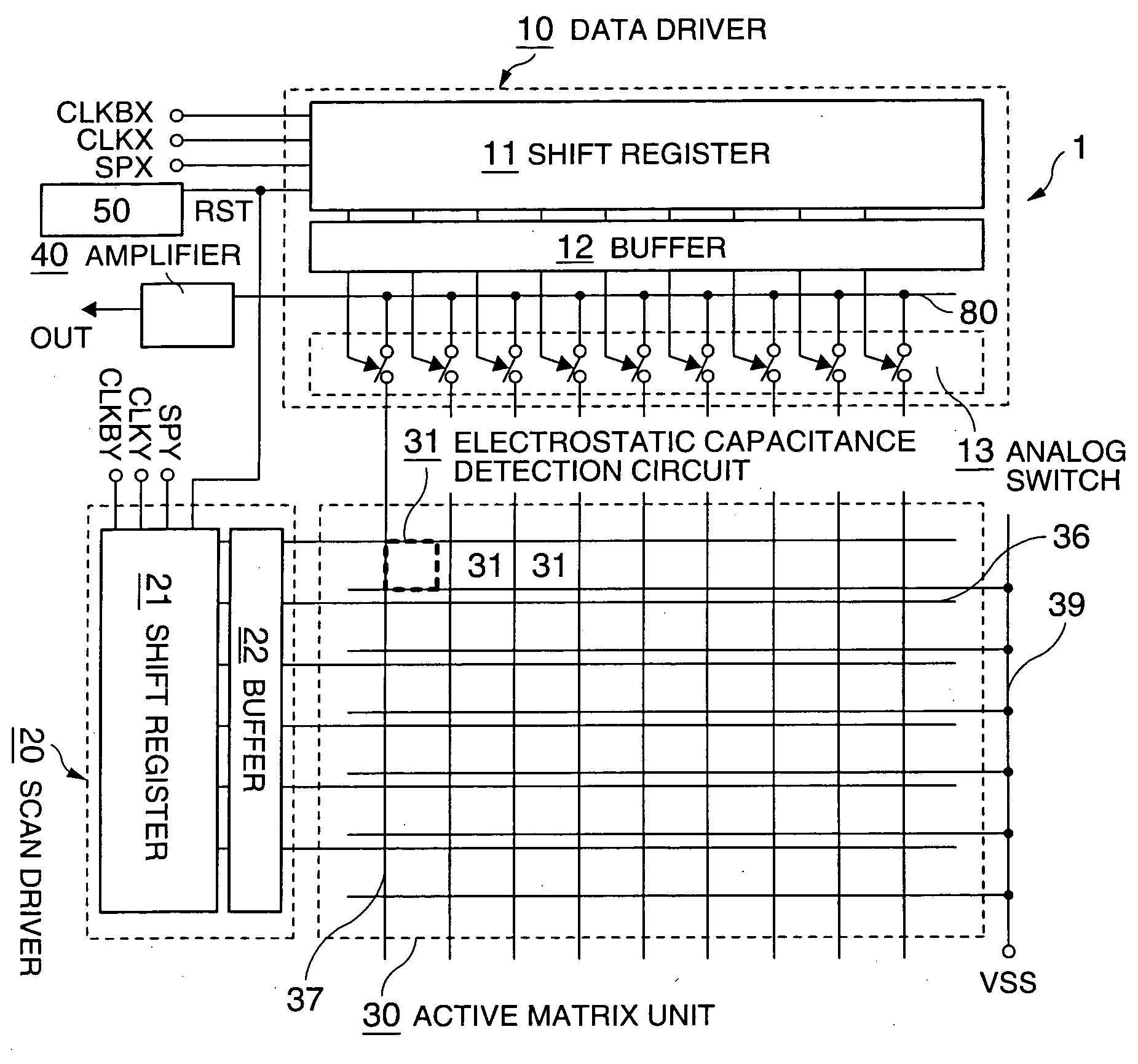
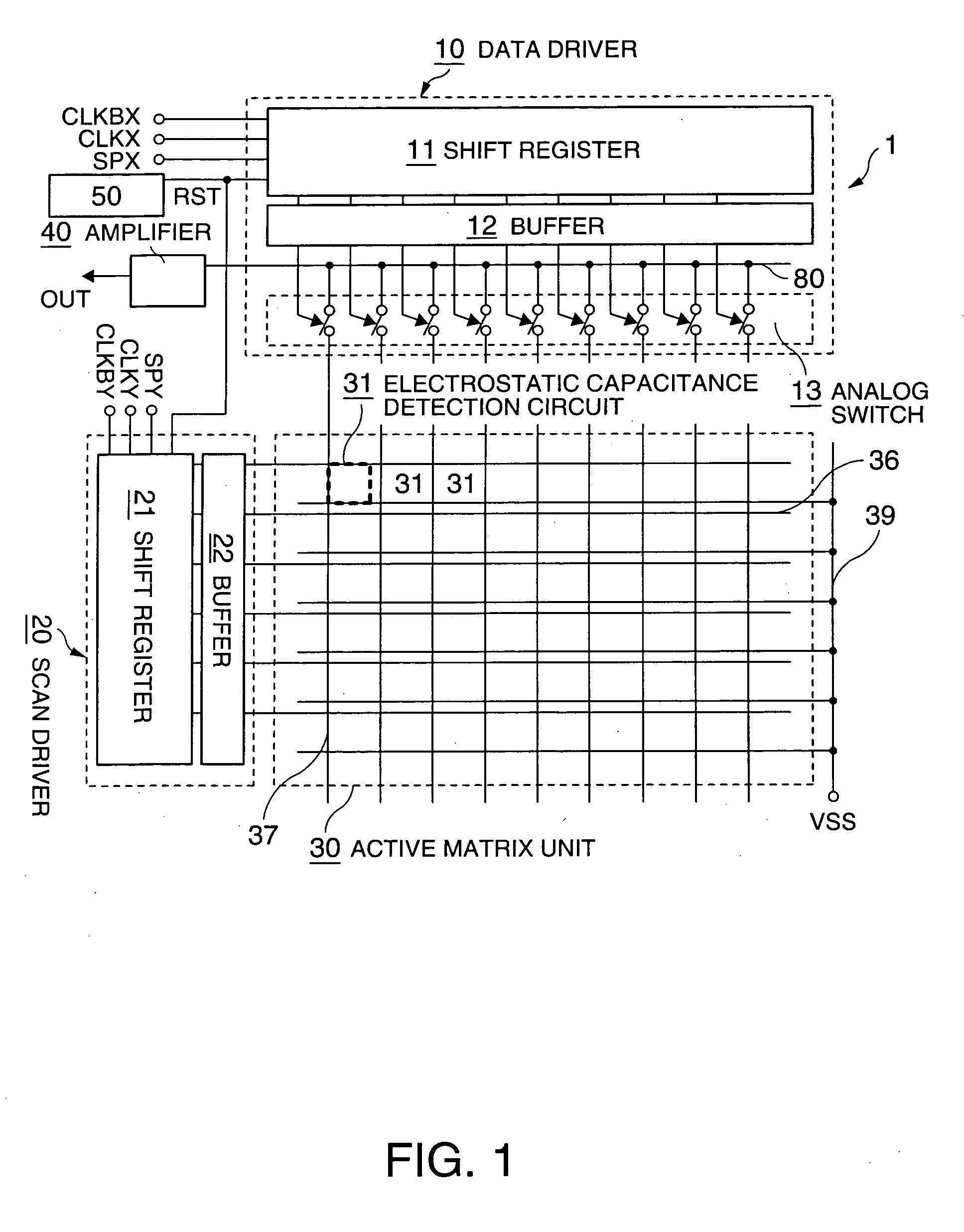
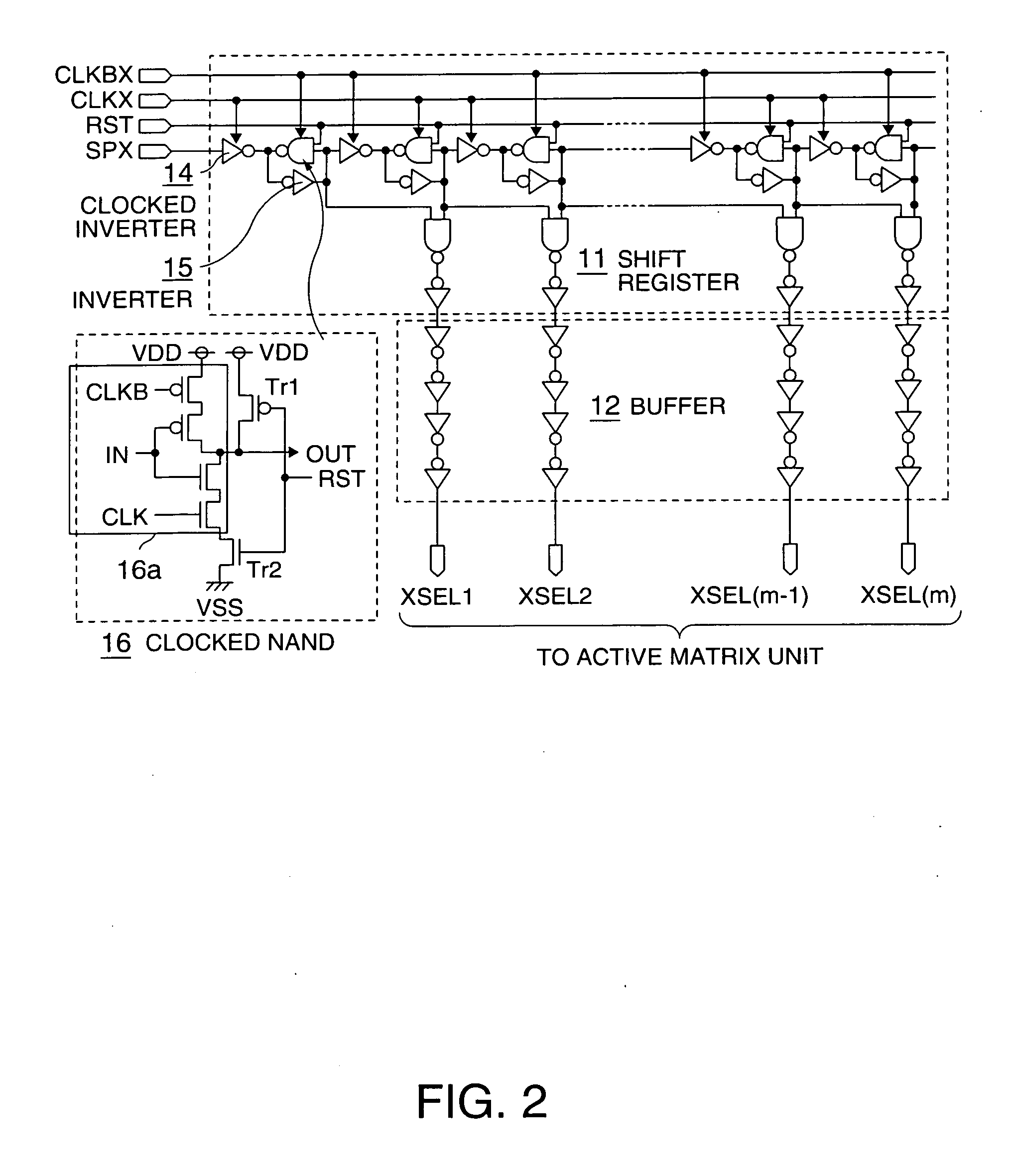
Active-matrix driving device, electrostatic capacitance detection device, and electronic equipment
ActiveUS20050083768A1Exclude dataReduce unnecessary power consumptionStatic indicating devicesElectric/magnetic contours/curvatures measurementsCapacitanceActive matrix
Aspects of the invention are intended to stabilize the initial state of an active matrix so as to reduce unnecessary power consumption and stabilize the operation. The driving device can include a selection device that is coupled to any of a plurality of row direction lines and any of a plurality of column direction lines, and by which a selected state and a non-selected state of the row direction lines or the column direction lines are switched to each other. The driving device can also include a device that switches to the non-selected state that switches the selection device coupled to the row direction lines or the selection device coupled to the column direction lines to a non-selected state. Selection by the selection device can be implemented after the selection device is switched to a non-selected state by the device that switches to the non-selected state.
Owner:138 EAST LCD ADVANCEMENTS LTD
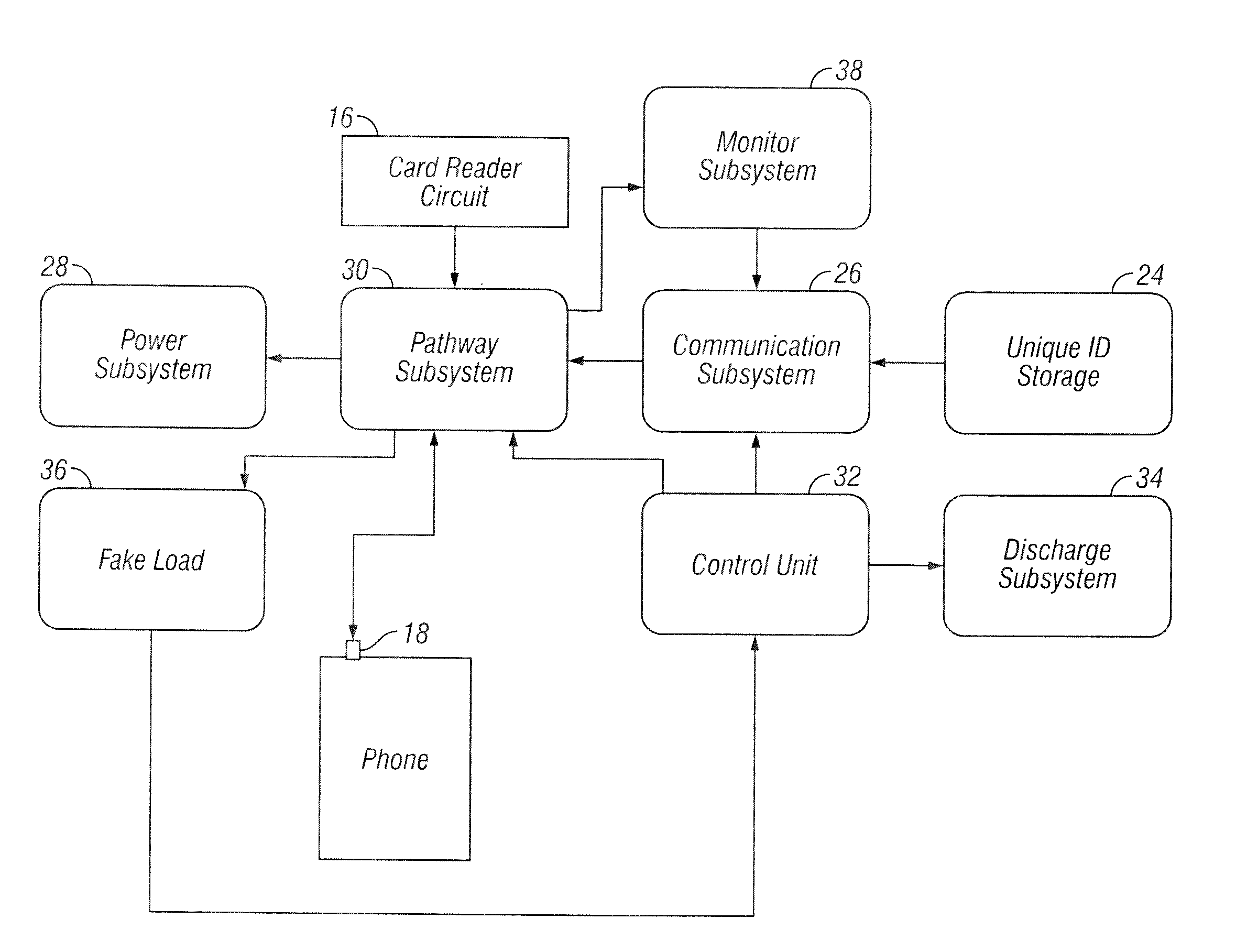
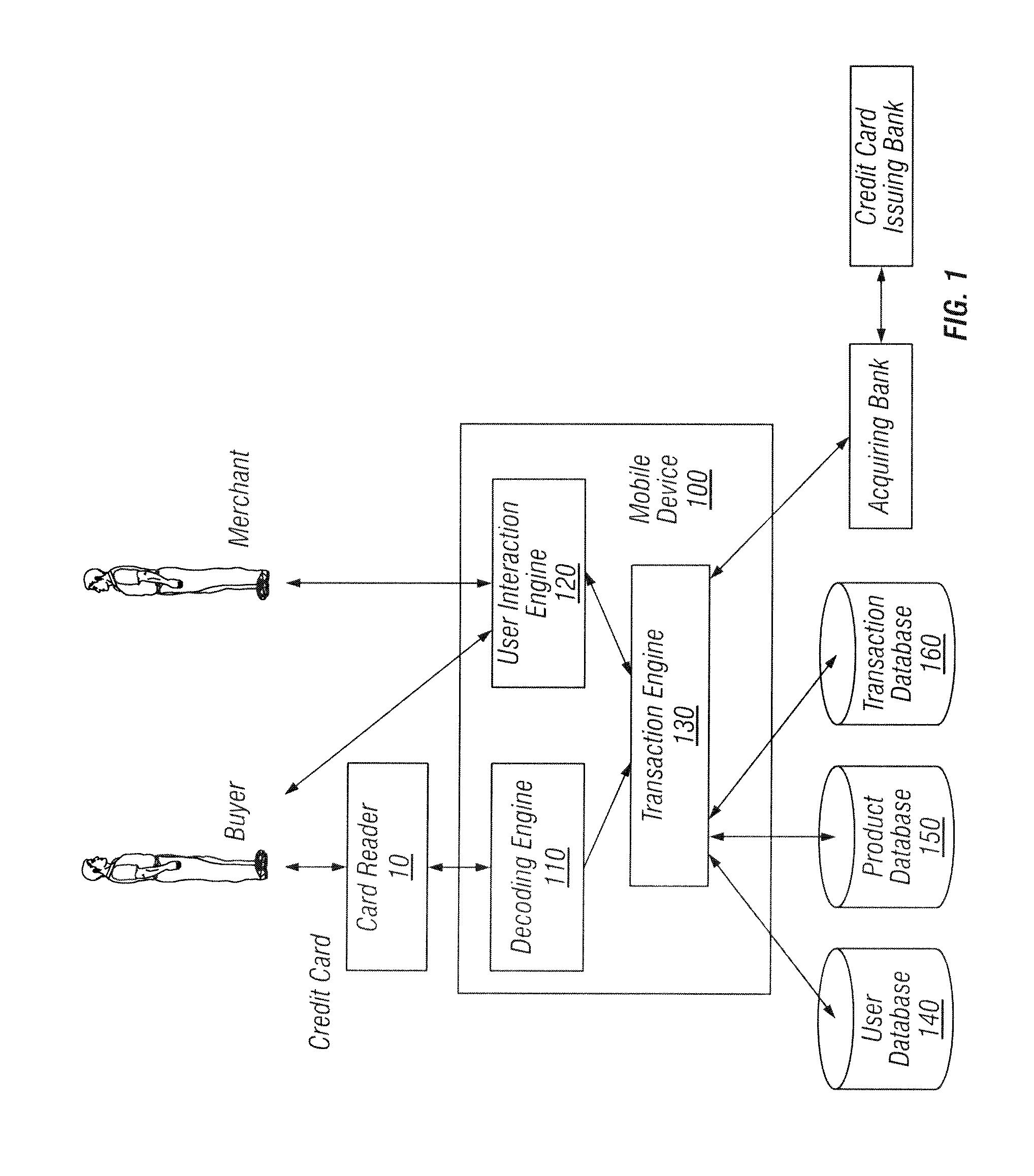
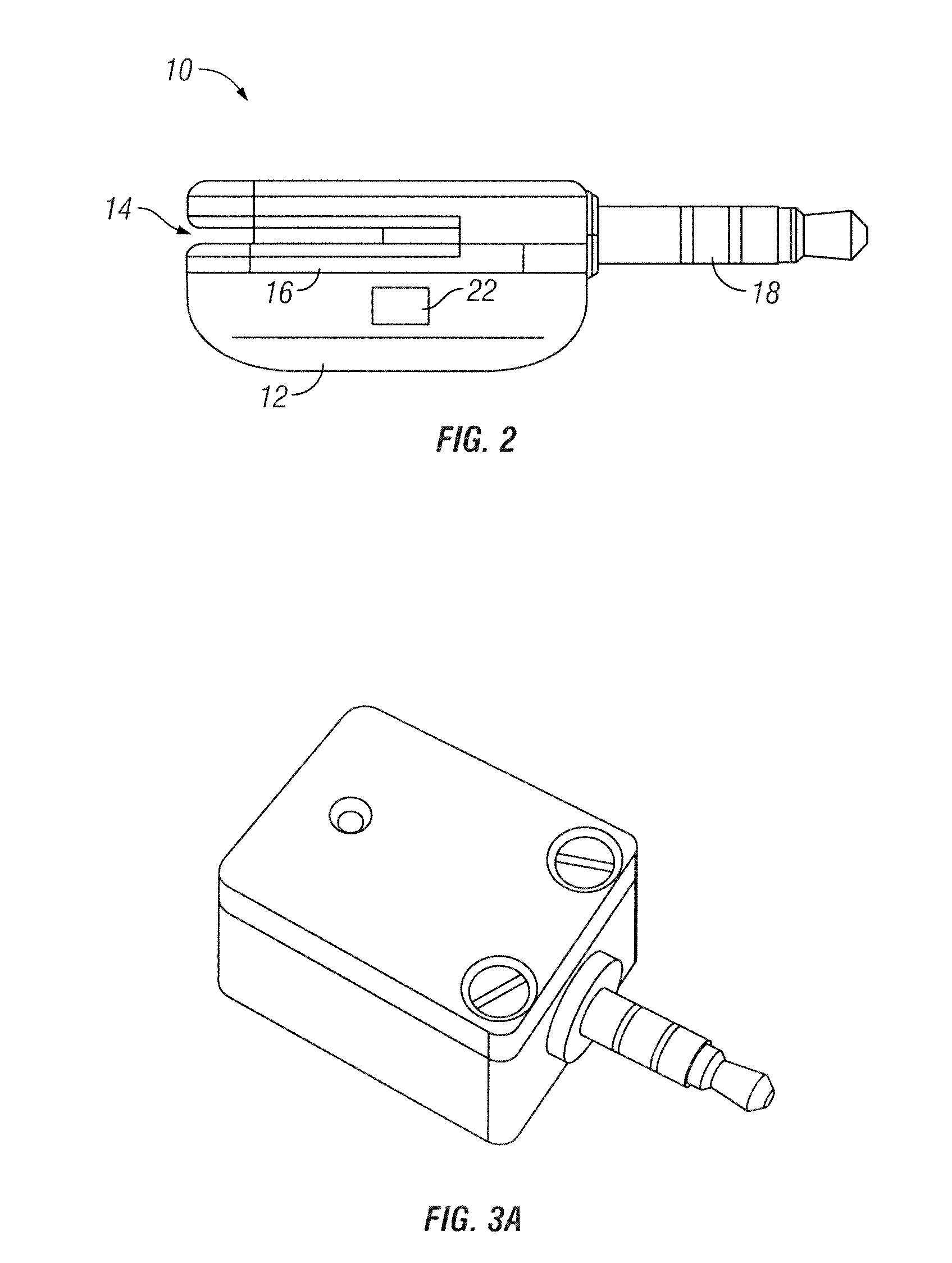
Card reader device
ActiveUS8870070B2Increase resistanceImprove the immunityFinancePayment architectureFinancial transactionData storing
A card reader device is provided that includes a housing having a slot for swiping a magnetic stripe of a financial transaction card to complete a financial transaction between a buyer and seller. A read head is positioned in the housing. The read head reads data stored on the magnetic stripe and produces a signal indicative of data stored on the magnetic stripe. The read head has sufficient impedance to set amplitude of a signal indicative of data stored on the magnetic stripe. An output jack is adapted to be inserted into a microphone input associated with a mobile device for providing the signal indicative of data stored on the magnetic stripe to the mobile device.
Owner:BLOCK INC
Systems and methods for client-based web crawling
InactiveUS7685296B2Maintain accuracyFast and accurate web crawling dataData processing applicationsWeb data indexingData validationSource Data Verification
The present invention provides systems and methods for obtaining information from a networked system utilizing a distributed web crawler. The distributed nature of clients of a server is leveraged to provide fast and accurate web crawling data. Information gathered by a server's web crawler is compared to data retrieved by clients of the server to update the crawler's data. In one instance of the present invention, data comparison is achieved by utilizing information disseminated via a search engine results page. In another instance of the present invention, data validation is accomplished by client dictionaries, emanating from a server, that summarize web crawler data. The present invention also facilitates data analysis by providing a means to resist spoofing of a web crawler to increase data accuracy.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Land partition data generating method and apparatus
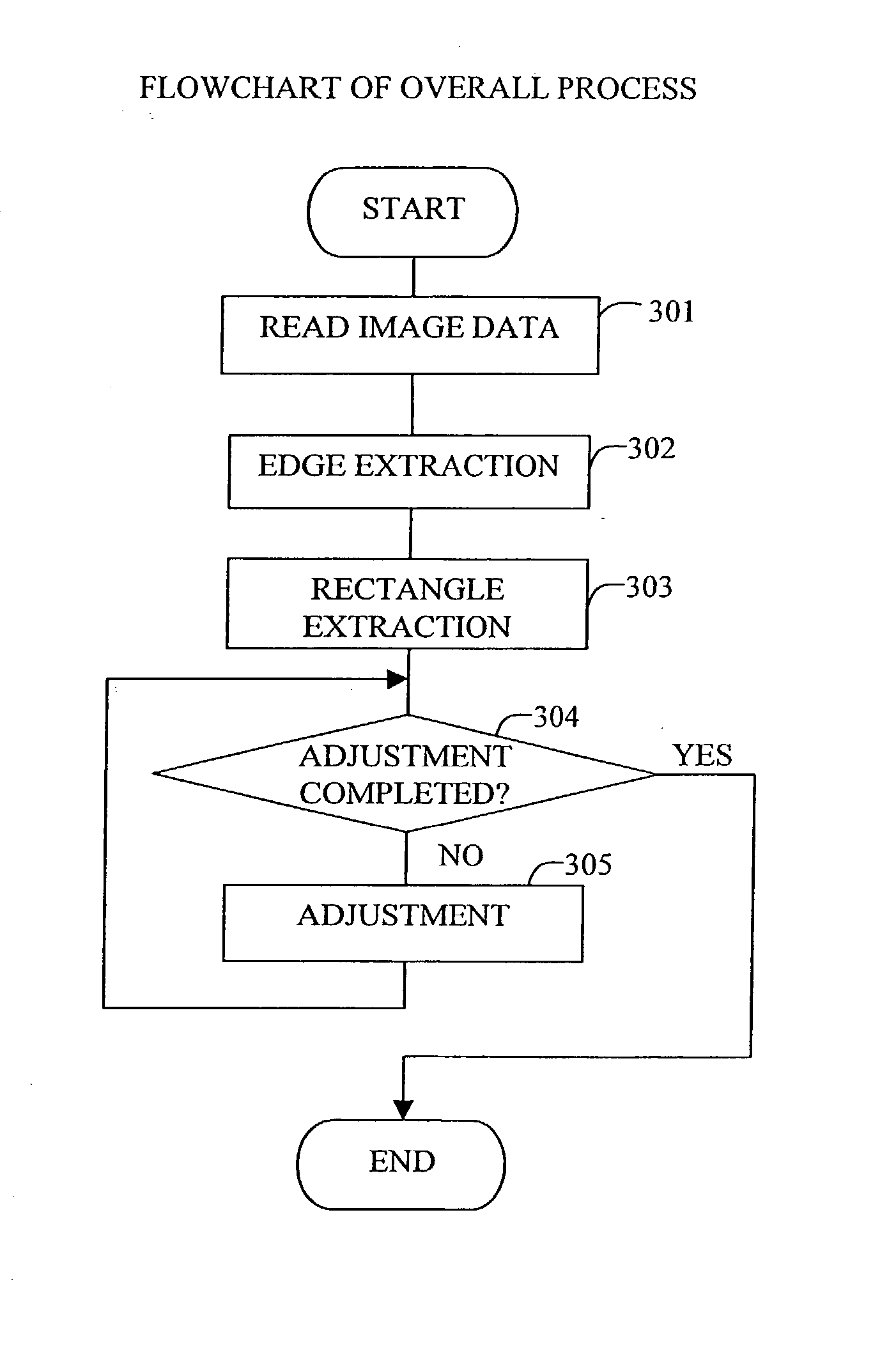
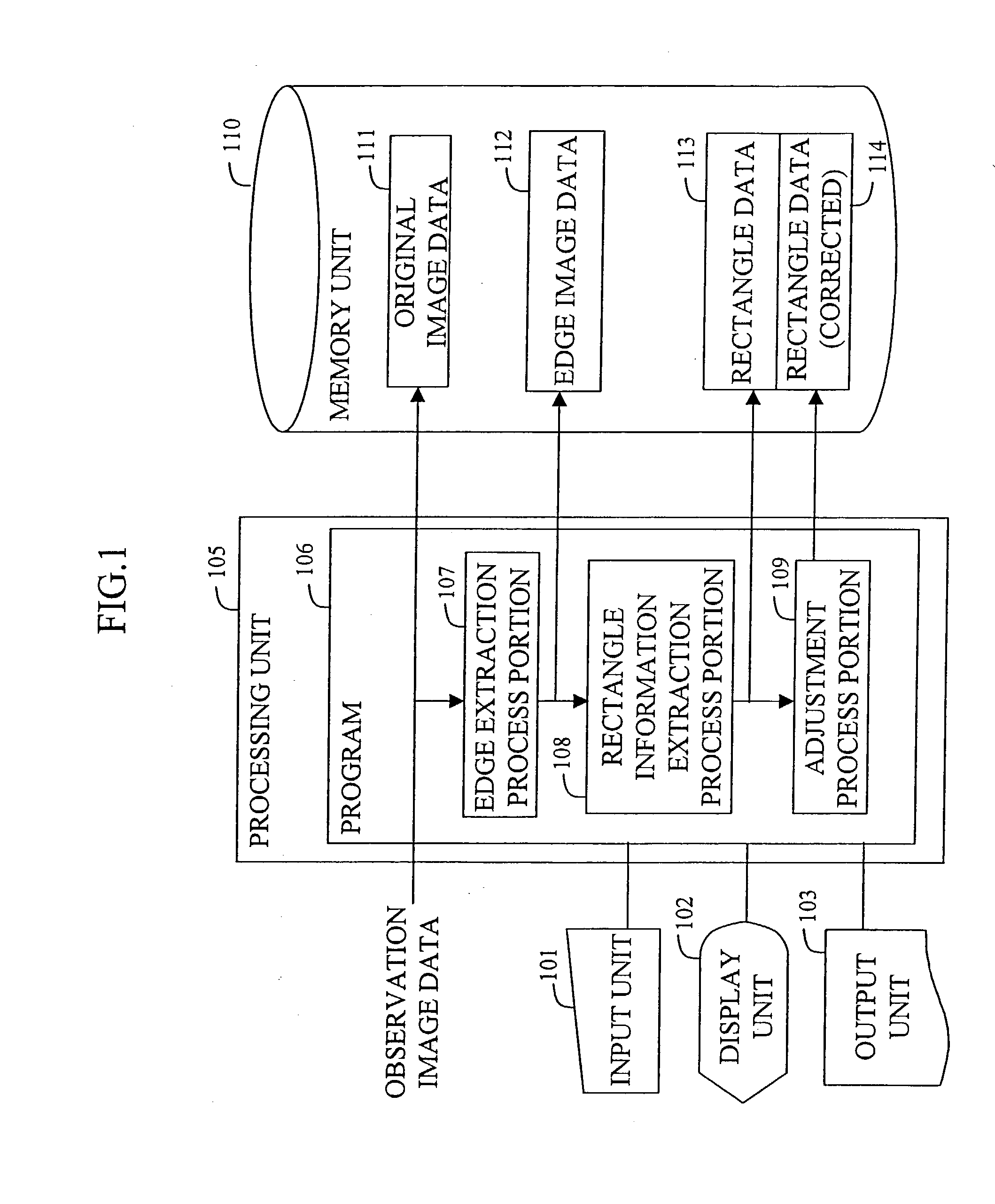
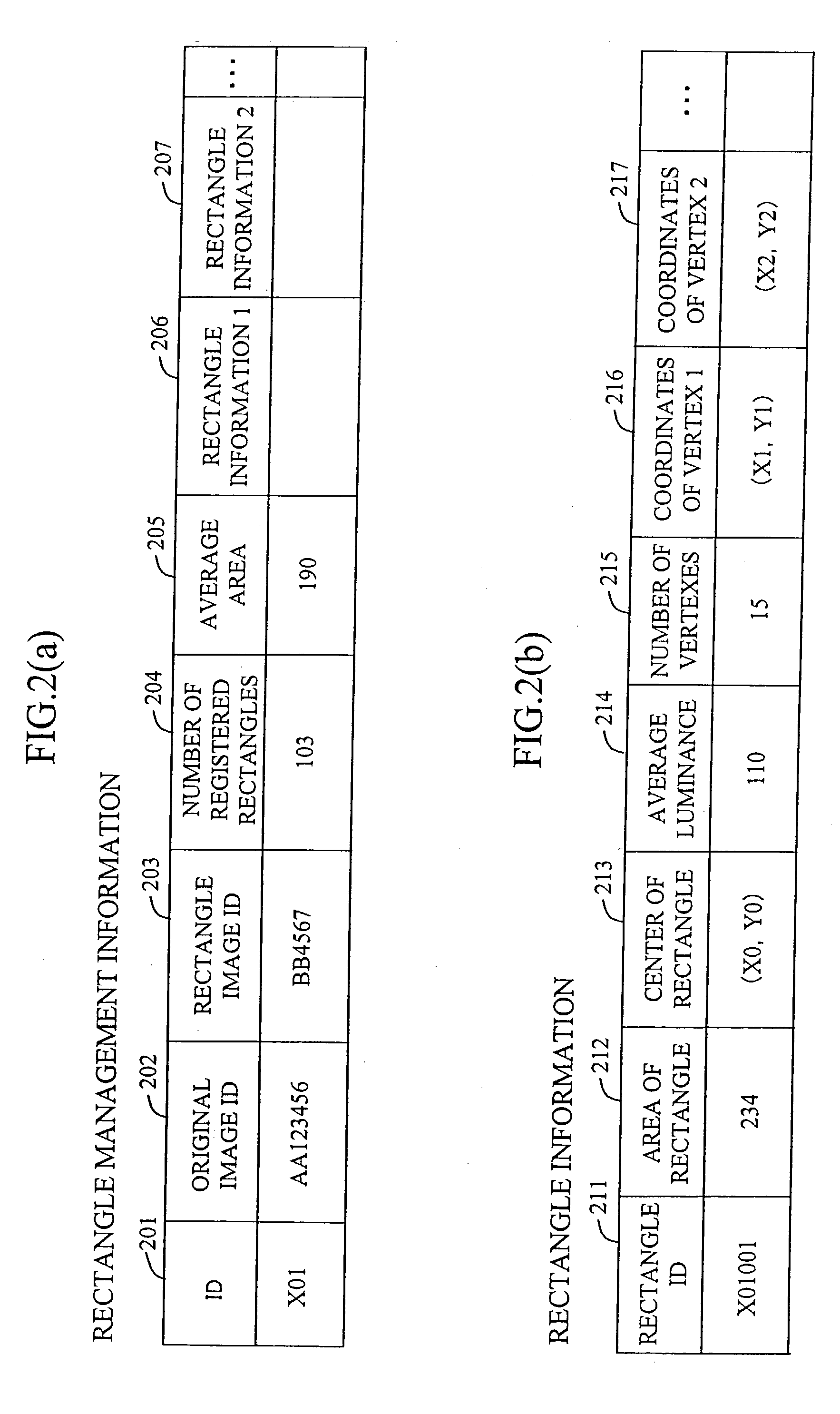
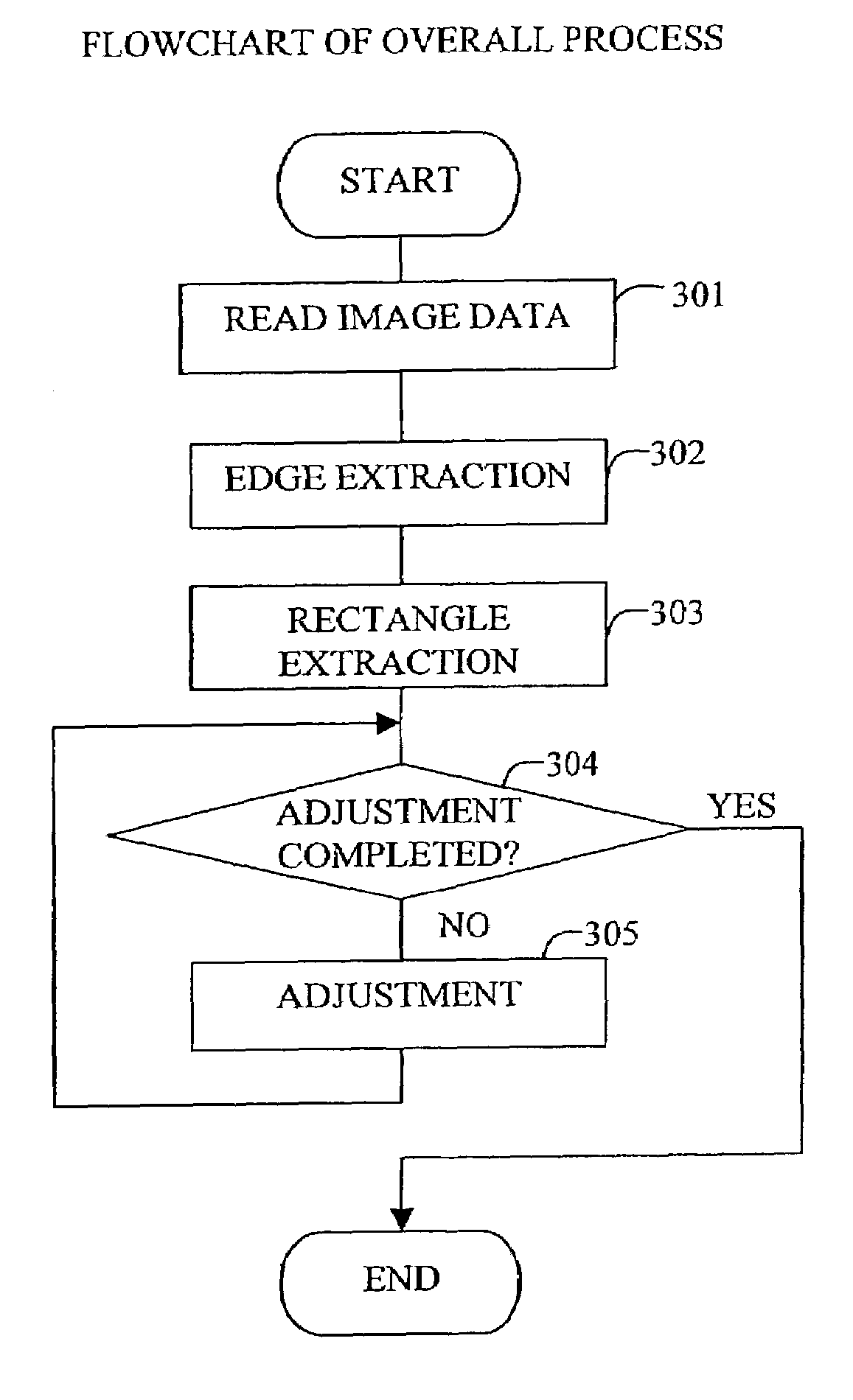
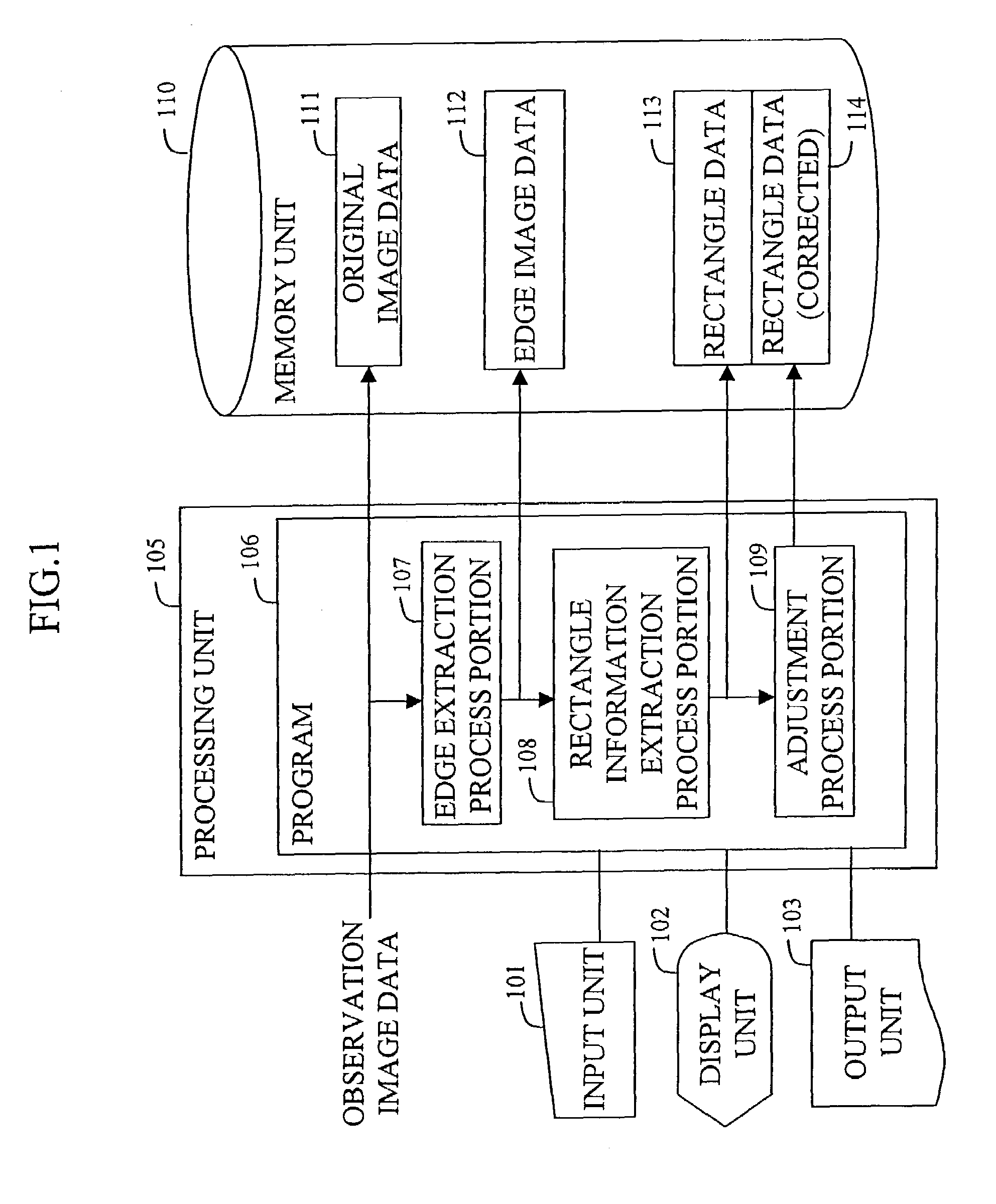
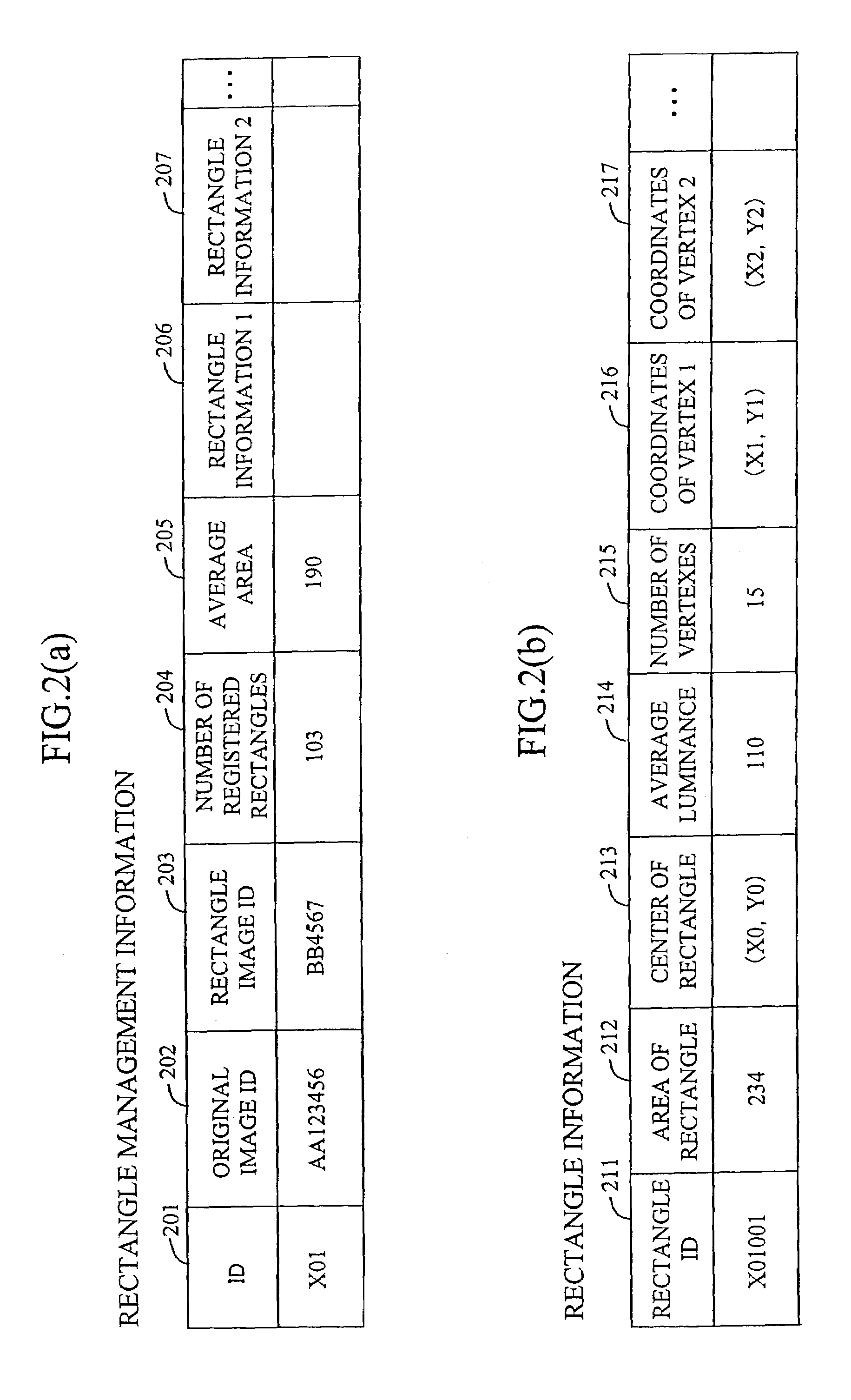
A method and apparatus generates data concerning a partition of land such as farmland based on an observation image of the surface of the earth photographed by a high-altitude flying vehicle such as a satellite or airplane at high speed while reducing the burden on the user. The method comprises the steps of extracting edges in the observation image; extracting a rectangle region on the image by determining and connecting points of intersection of a plurality of straight lines extending radially from a point on the image and the edges; and adjusting the extracted rectangle region by refining and correcting it.
Owner:HITACHI SOFTWARE ENG
Land partition data generating method and apparatus
InactiveUS7127107B2Reduce the burden onIncrease speedImage enhancementImage analysisImage generationAirplane
A method and apparatus generates data concerning a partition of land such as farmland based on an observation image of the surface of the earth photographed by a high-altitude flying vehicle such as a satellite or airplane at high speed while reducing the burden on the user. The method comprises the steps of extracting edges in the observation image; extracting a rectangle region on the image by determining and connecting points of intersection of a plurality of straight lines extending radially from a point on the image and the edges; and adjusting the extracted rectangle region by refining and correcting it.
Owner:HITACHI SOFTWARE ENG
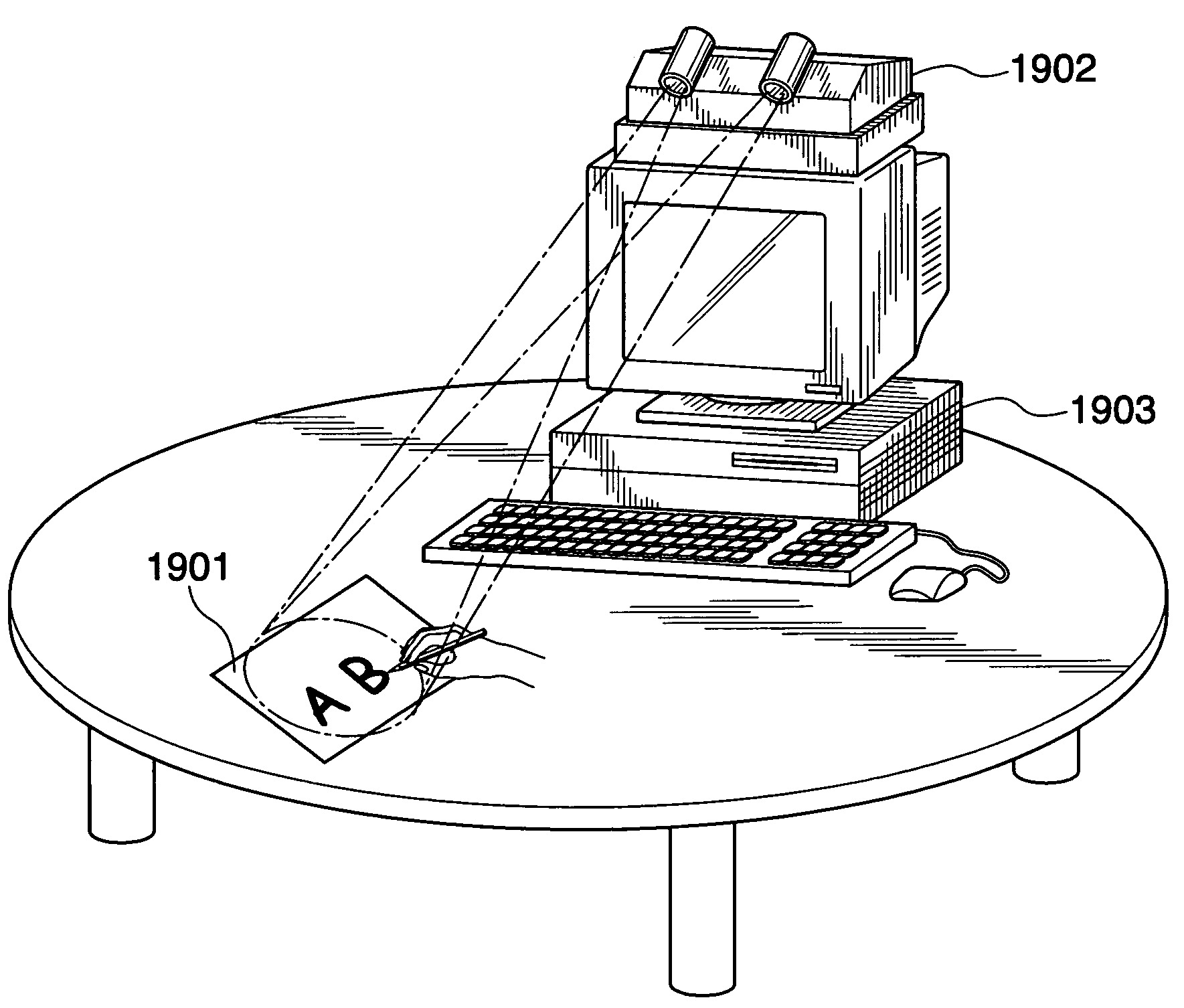
Apparatus and method for image processing of hand-written characters using coded structured light and time series frame capture
InactiveUS6970600B2Efficient identificationCancel noiseImage analysisAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsCharacter analysisWhiteboard
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
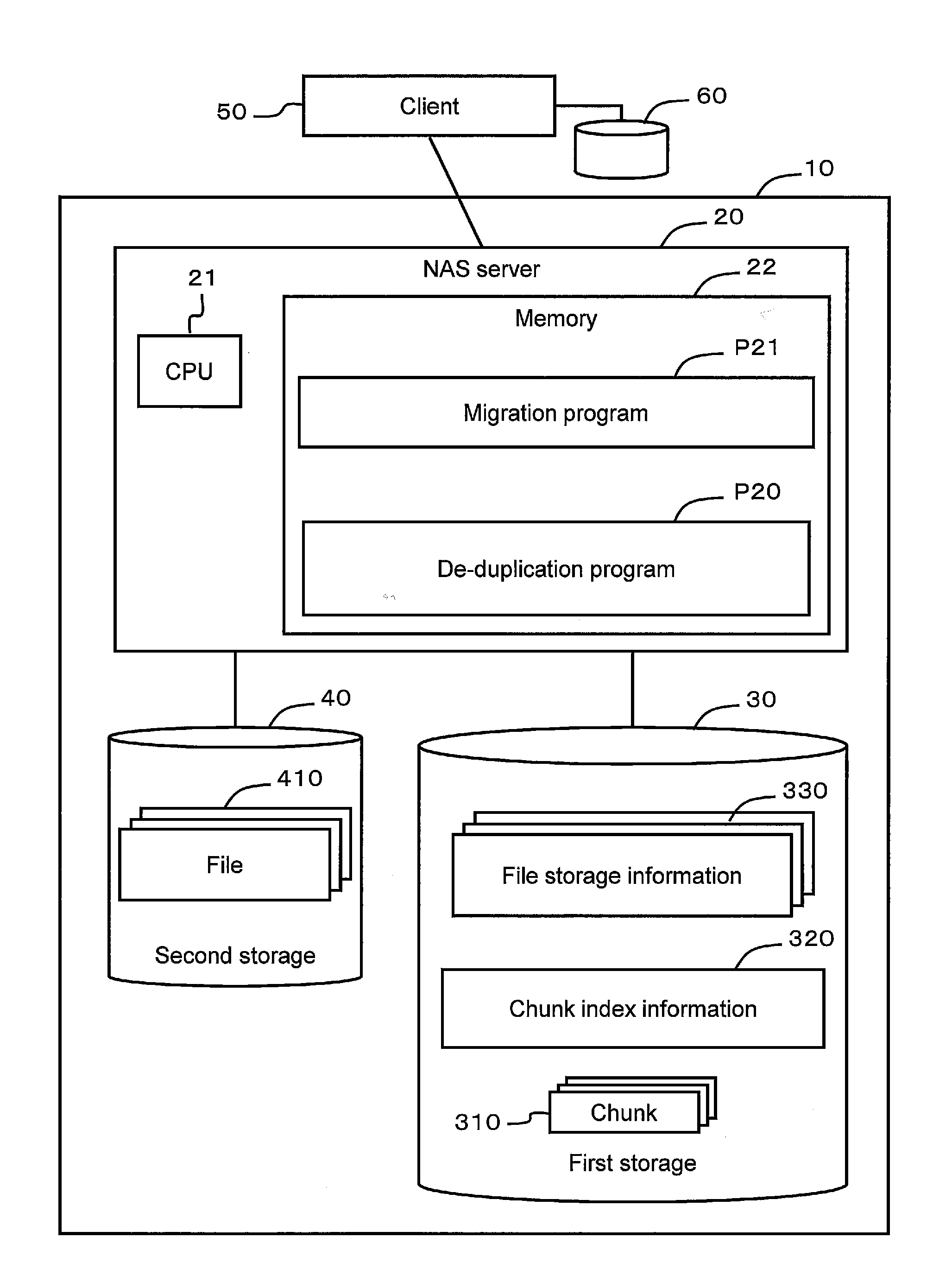
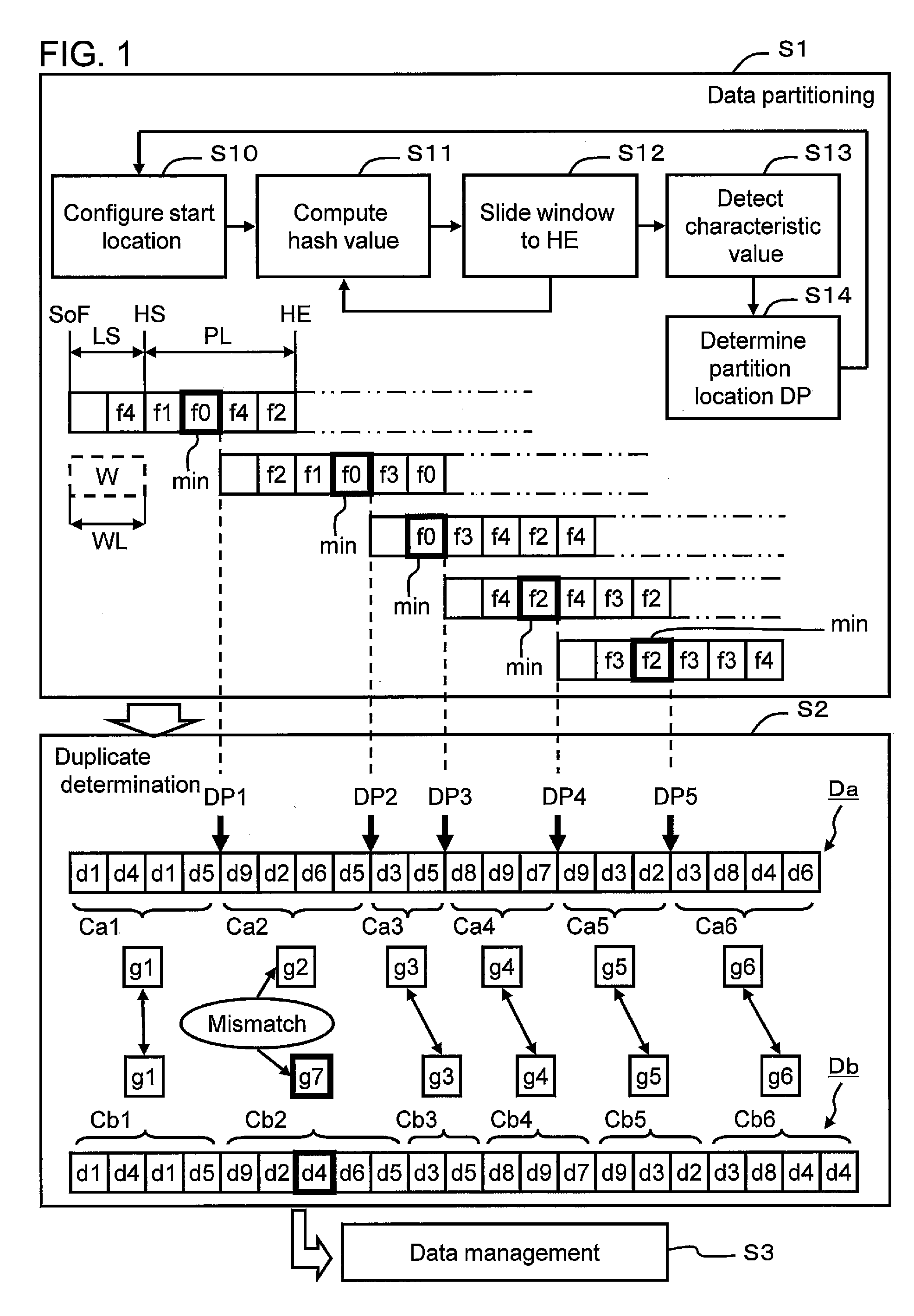
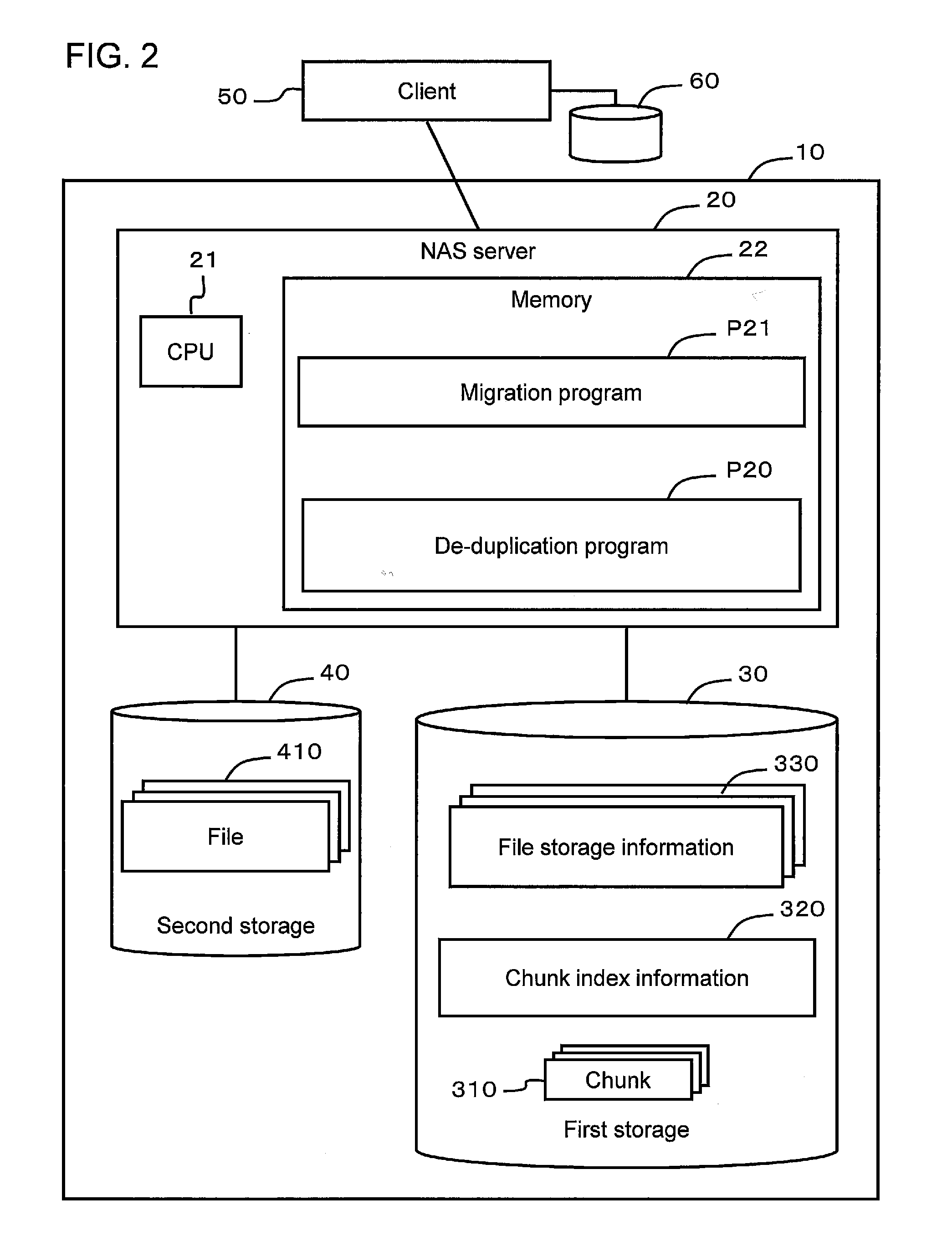
Data management method and data management system
InactiveUS20120259825A1Data duplicationExclude dataDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData managementHash table
A data management system respectively computes first hash values while sliding a window a prescribed amount at a time with respect to a prescribed range from a start location of a data block to a prescribed size. The system extracts, from among the first hash values, a first hash value, which is equivalent to a characteristic value, and partitions the data block into a first chunk of data at a location corresponding to this first hash value. The system determines coincidence between a first chunk of data and a stored second chunk of data, and prevents duplicate data from being stored twice.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
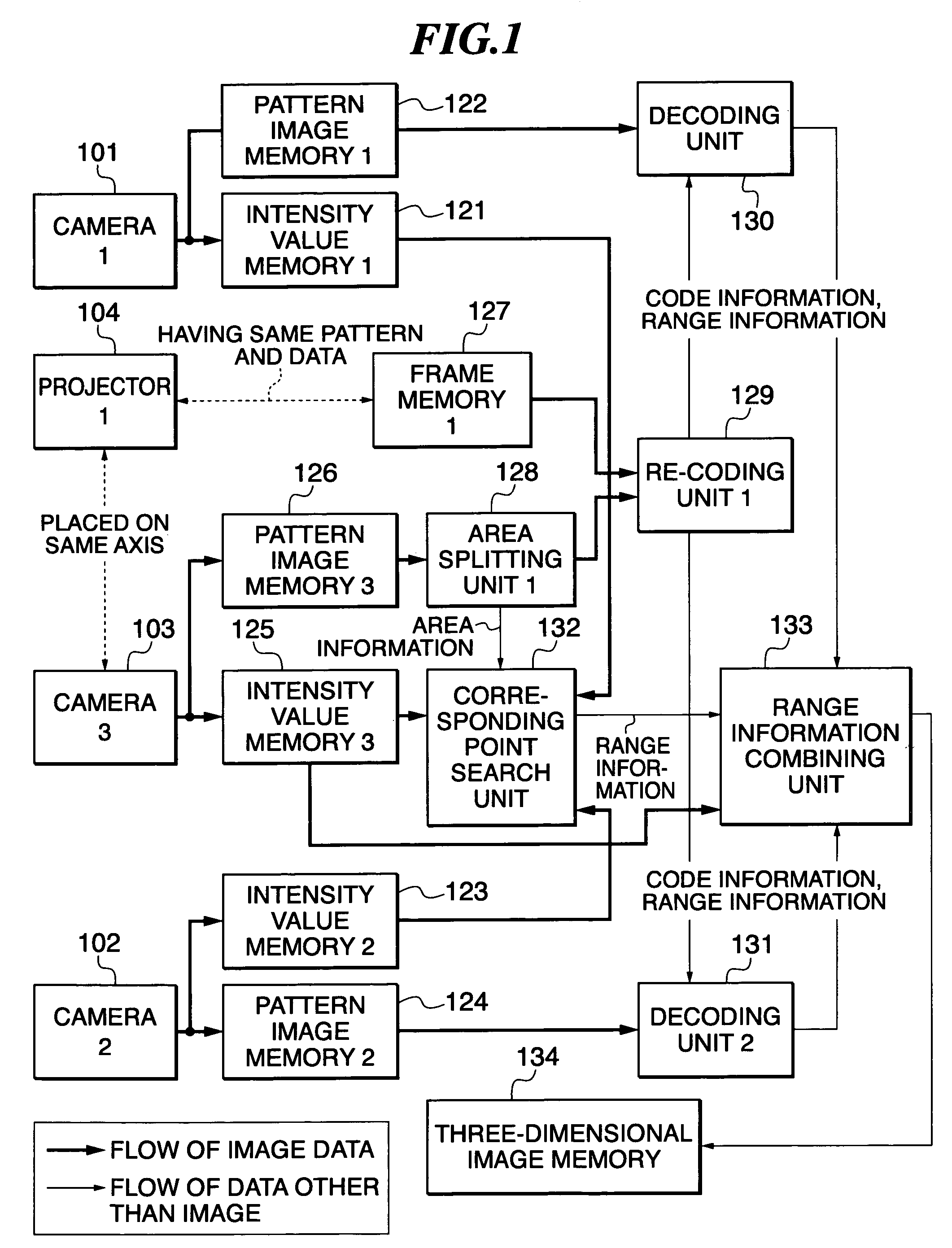
System and method for detection of acoustic shadows and automatic assessment of image usability in 3D ultrasound images
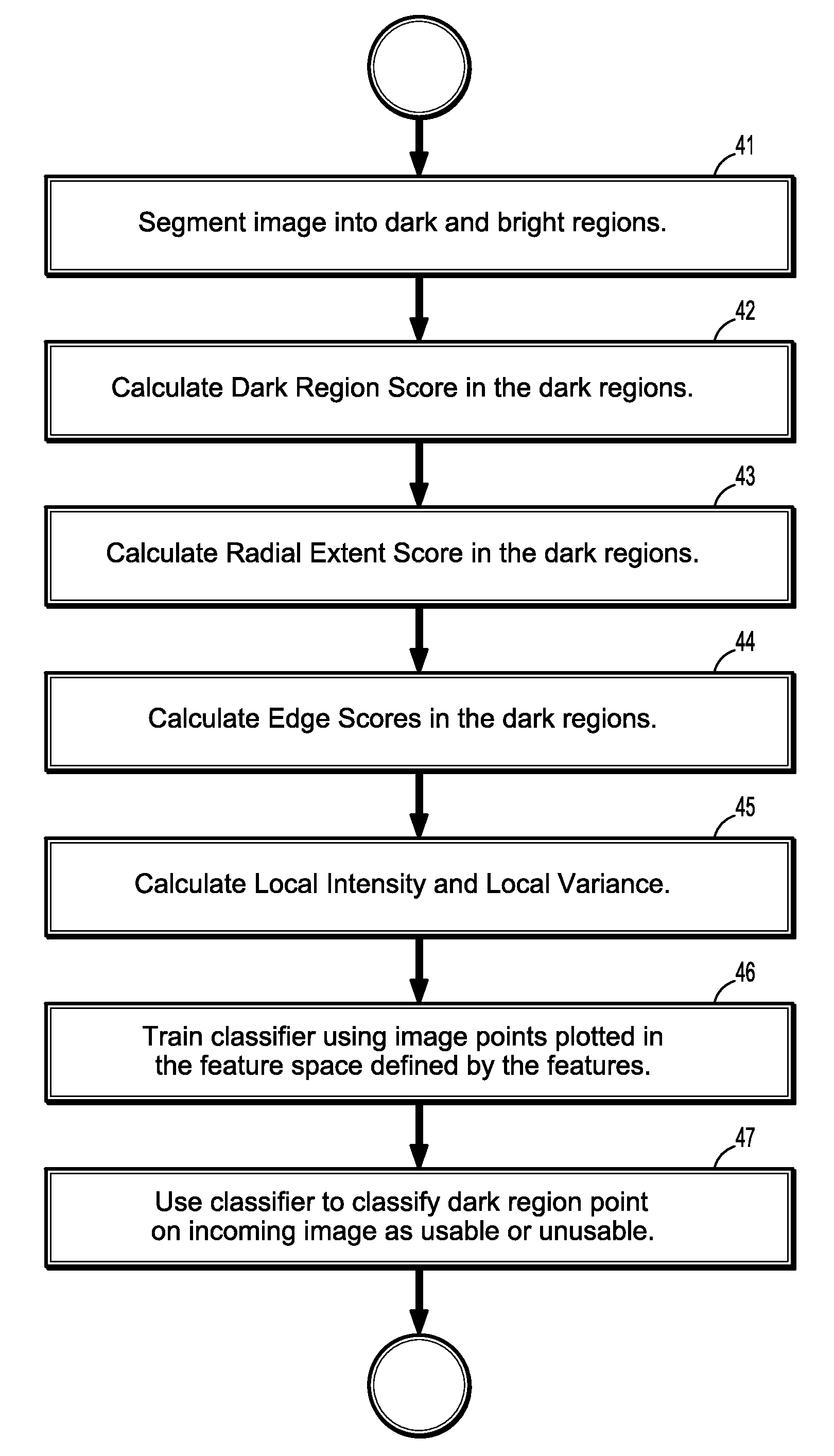
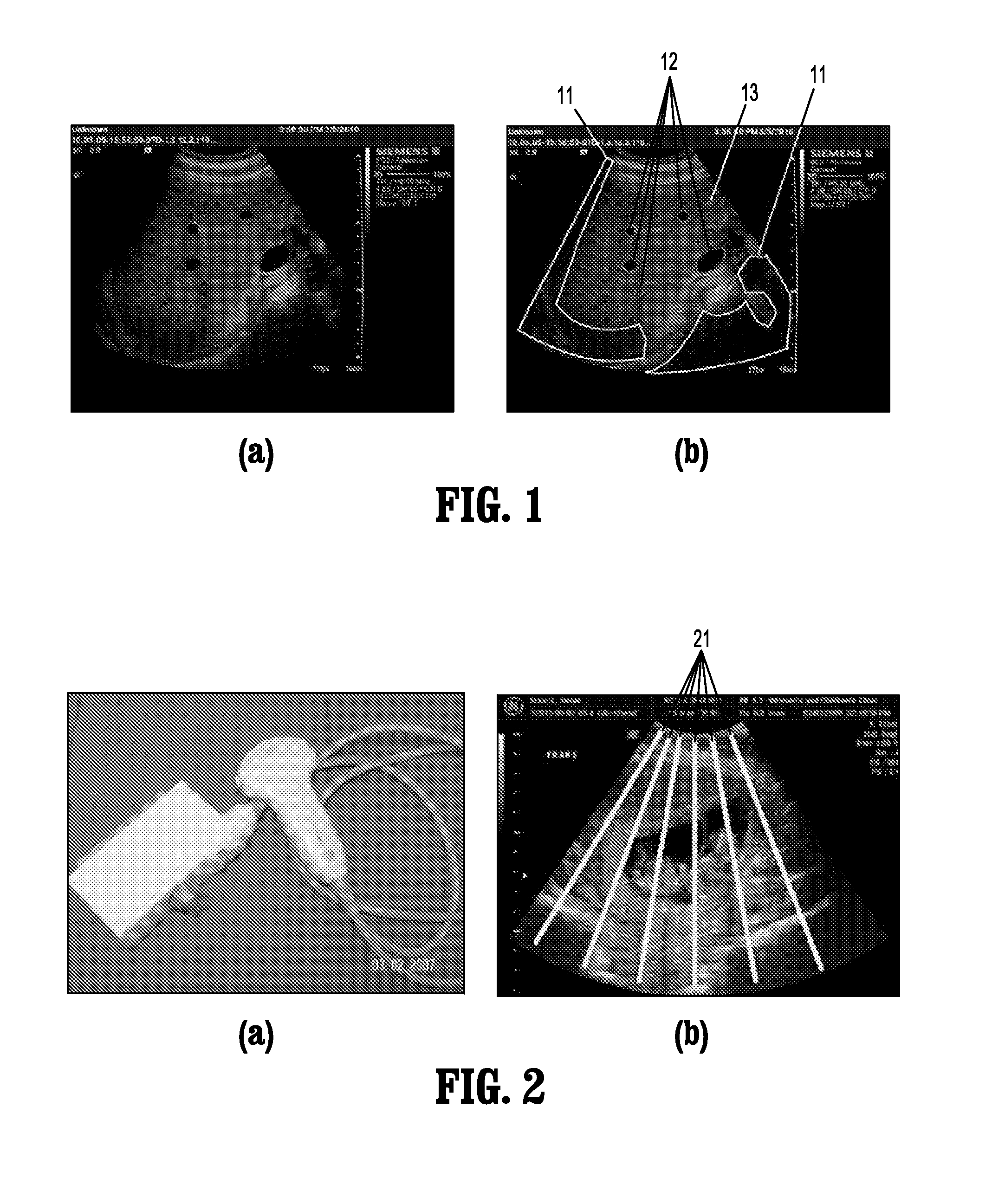
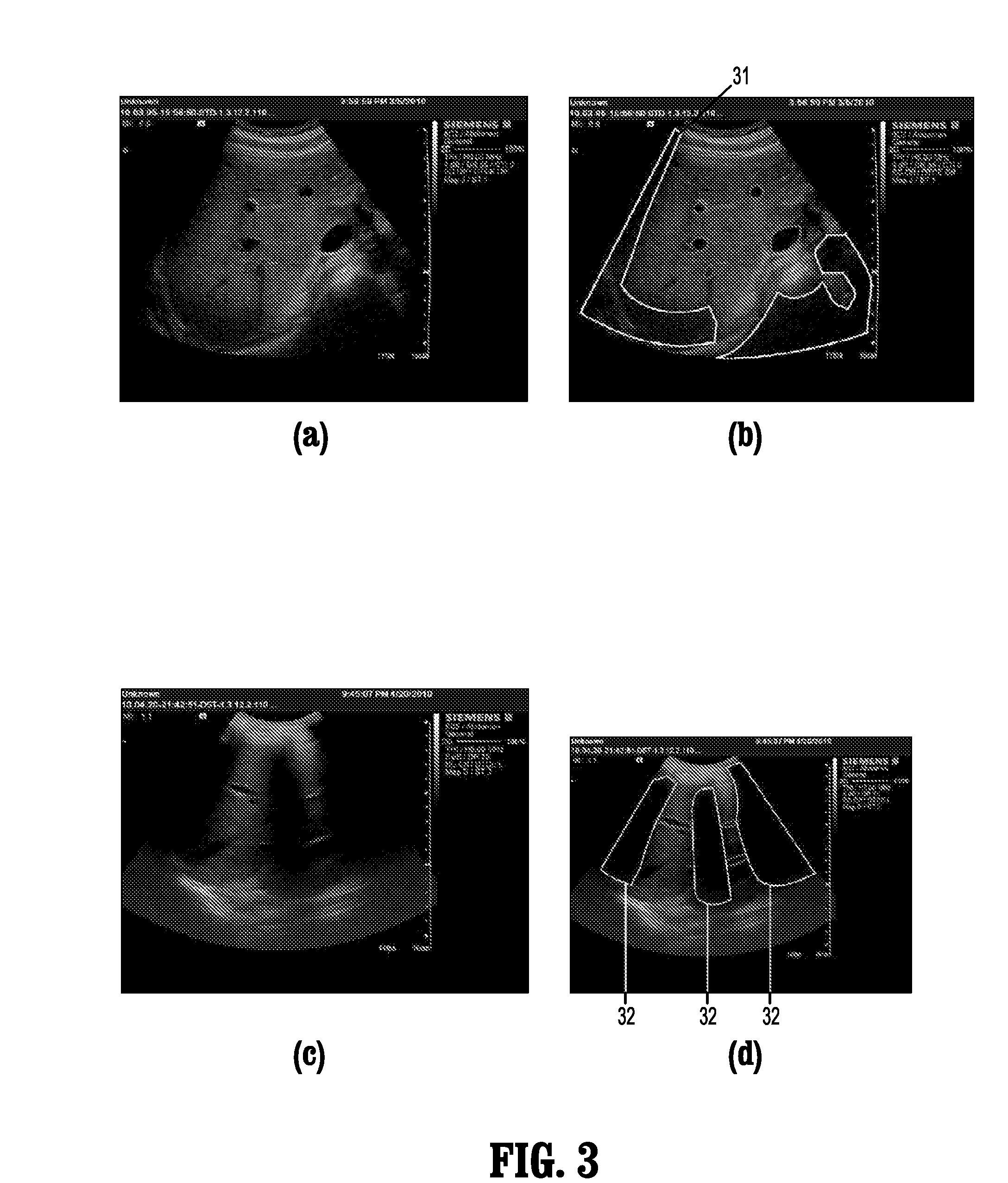
ActiveUS8582848B2Accurate separationImprove compoundImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionAnatomical structures
A method for automatically assessing medical ultrasound (US) image usability, includes extracting one or more features from at least one part of a medical ultrasound image, calculating for each feature a feature score for each pixel of the at least one part of the ultrasound image, and classifying one or more image pixels of the at least one part as either usable or unusable, based on a combination of feature scores for each pixel, where usable pixels have intensity values substantially representative of one or more anatomical structures.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Apparatus and method for canceling inter-symbol interference in a broadband wireless communication system
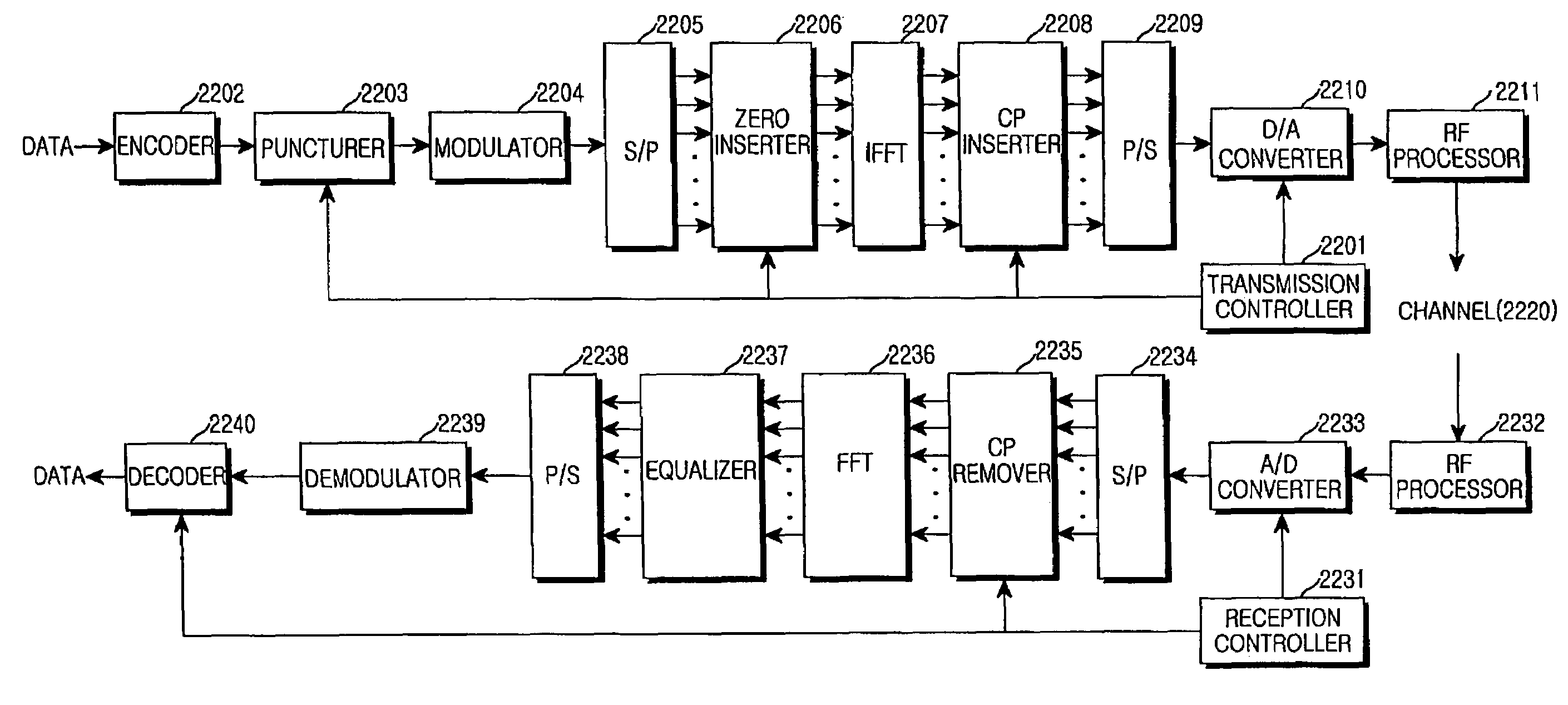
ActiveUS7573944B2Exclude dataSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsDelay spreadAnalog signal
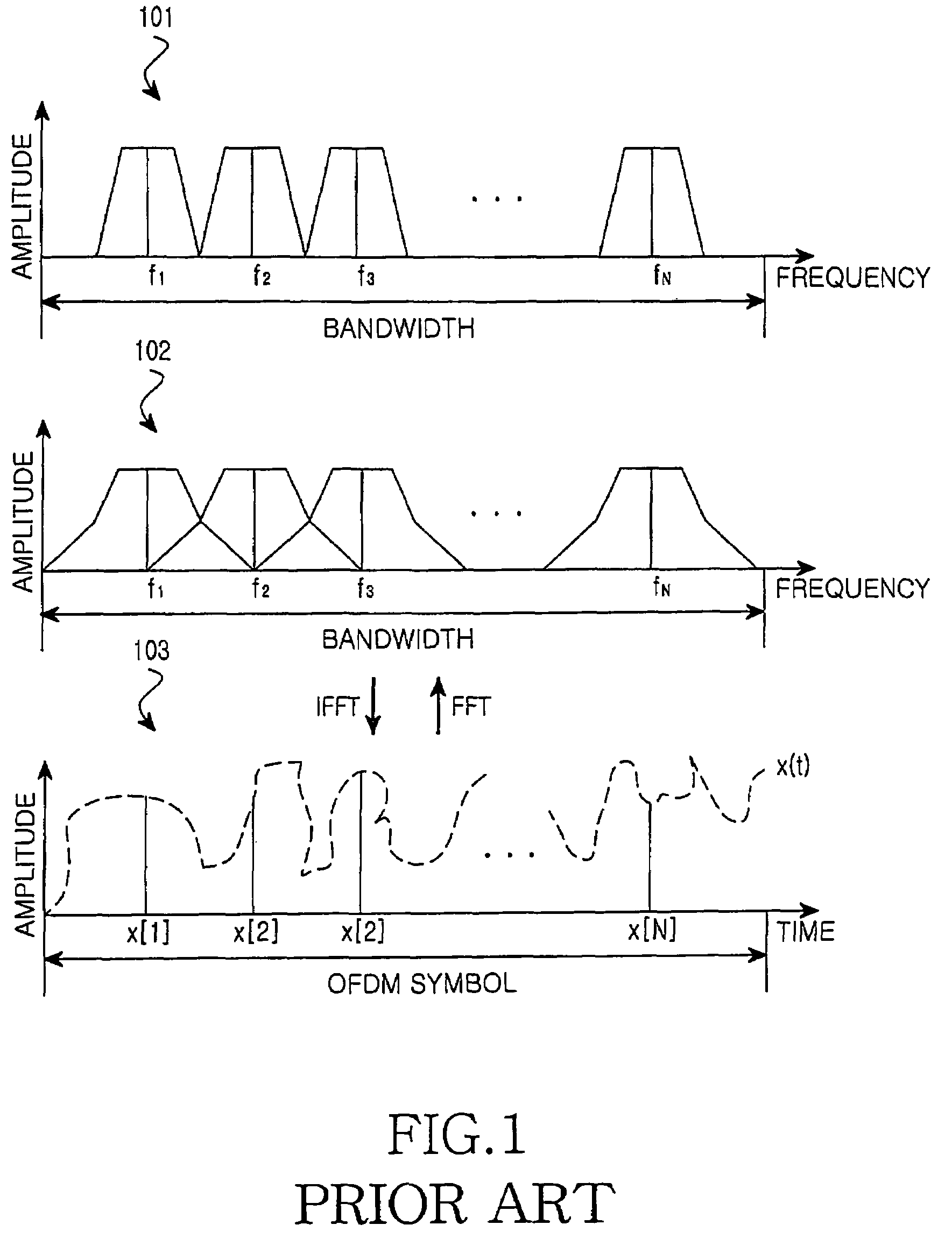
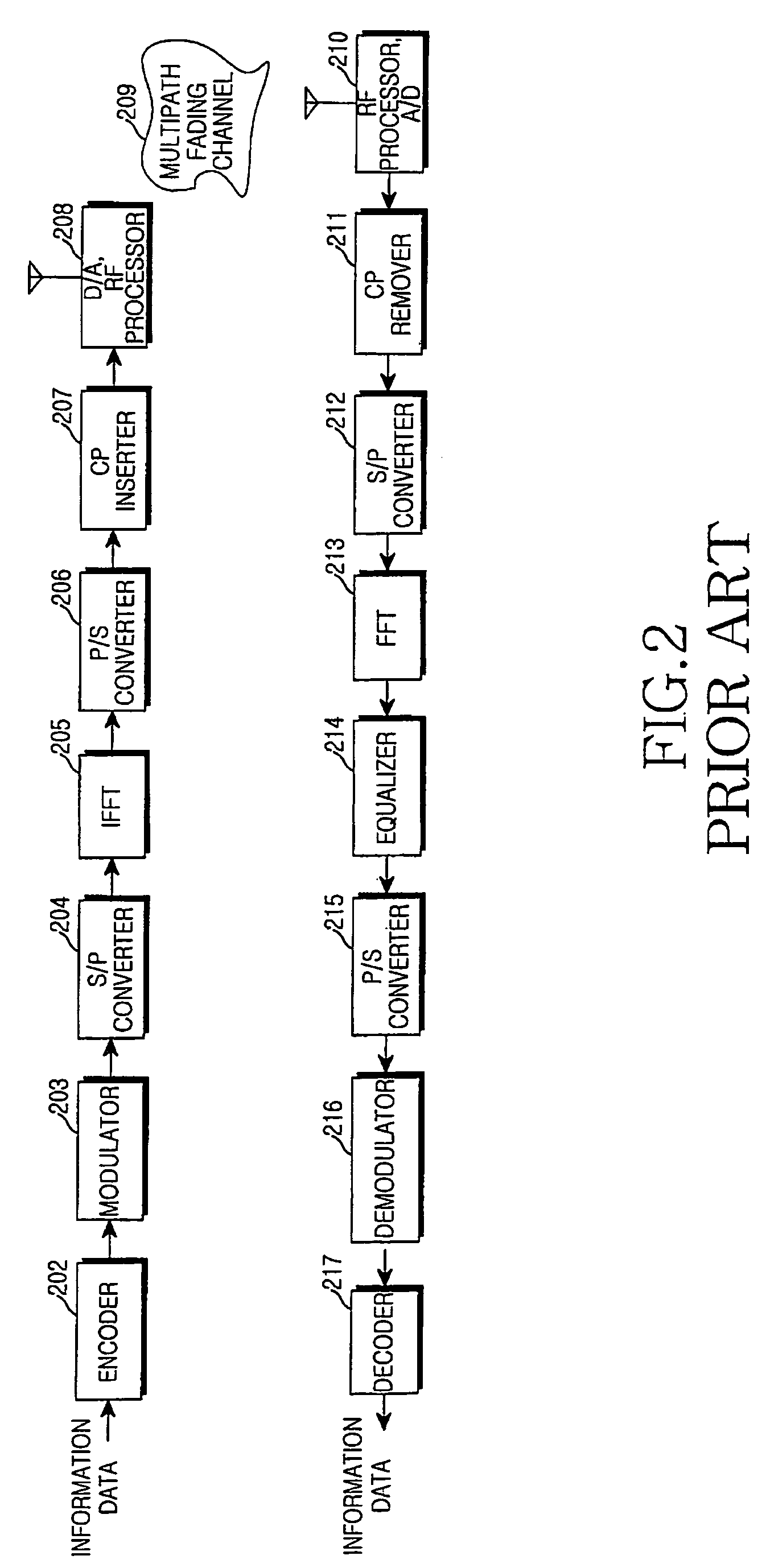
An apparatus and method for canceling ISI in a broadband wireless communication system are provided. In a transmitter of the broadband wireless communication system, a controller acquires a CP length, a puncturing pattern, and a time sample interval according to a delay spread. A puncturer punctures coded data in the puncturing pattern. An IFFT processor IFFT-processes the punctured coded data and outputs sample data. A CP inserter generates an OFDM symbol by inserting a copy of a last part of the sample data before the sample data. Here, the length of the last part of the sample data is equal to the CP length. A D / A converter converts the OFDM symbol to an analog signal at a sampling rate determined by the time sample interval.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Mounting apparatus for data storage device
InactiveUS7382610B2Exclude dataPortable framesDigital data processing detailsMechanical engineeringEngineering
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Electronic whiteboard system and method
InactiveUS6353193B1Avoid storage problemsExclude dataTransmission systemsGraph readingDigital dataWhiteboard
An eraser for use on an electronic whiteboard with a protrusion area on the erasing surface forming a convex area on the erasing surface for establishing a positive point of contact with the whiteboard; an electronic whiteboard system including such an eraser, a controller for storing data relating to information written on and erased from the whiteboard data, and a filter for preventing the storage of digital data relating to contacts with the whiteboard not attributable to normal writing or erasing actions.
Owner:STEELCASE INC
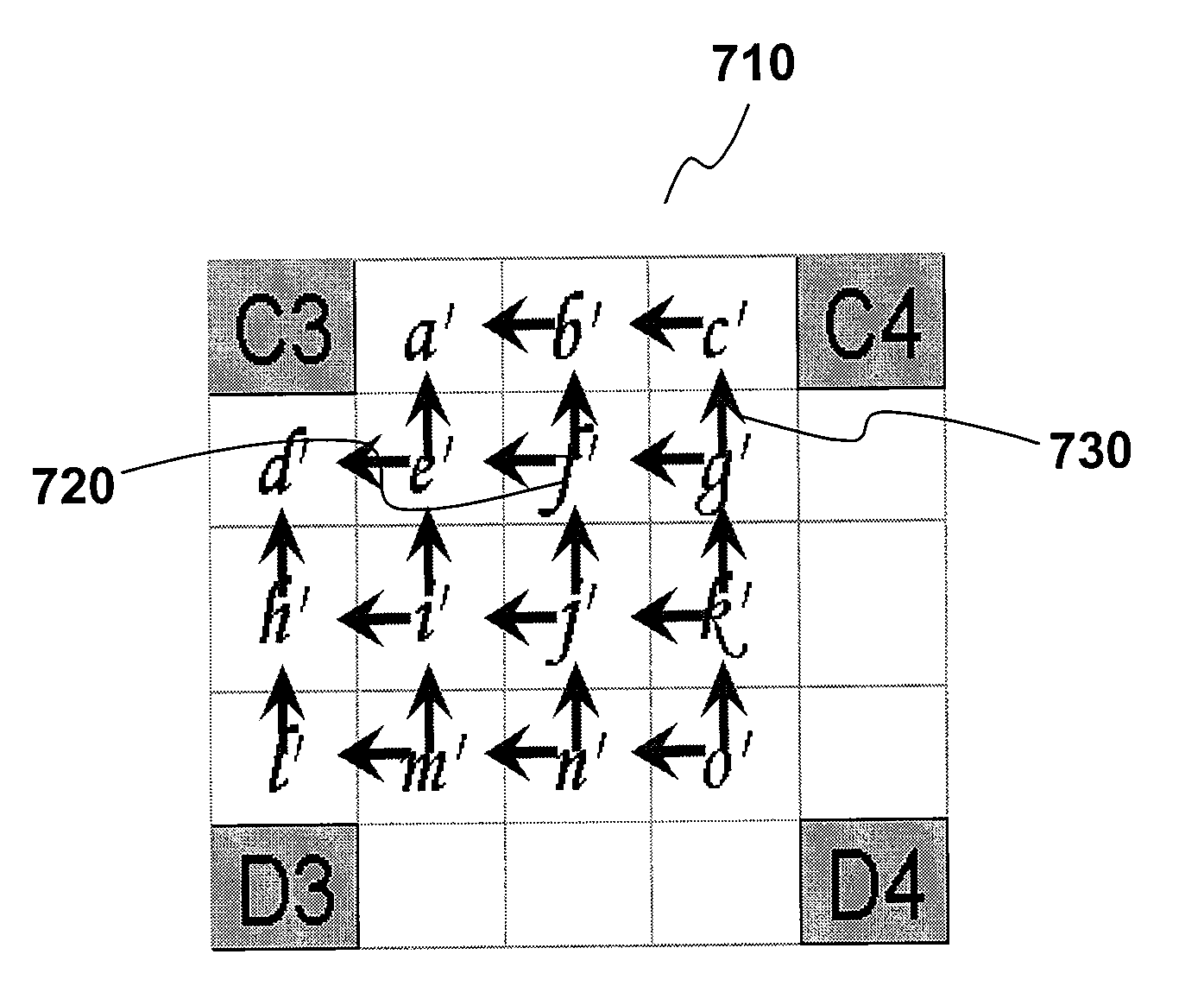
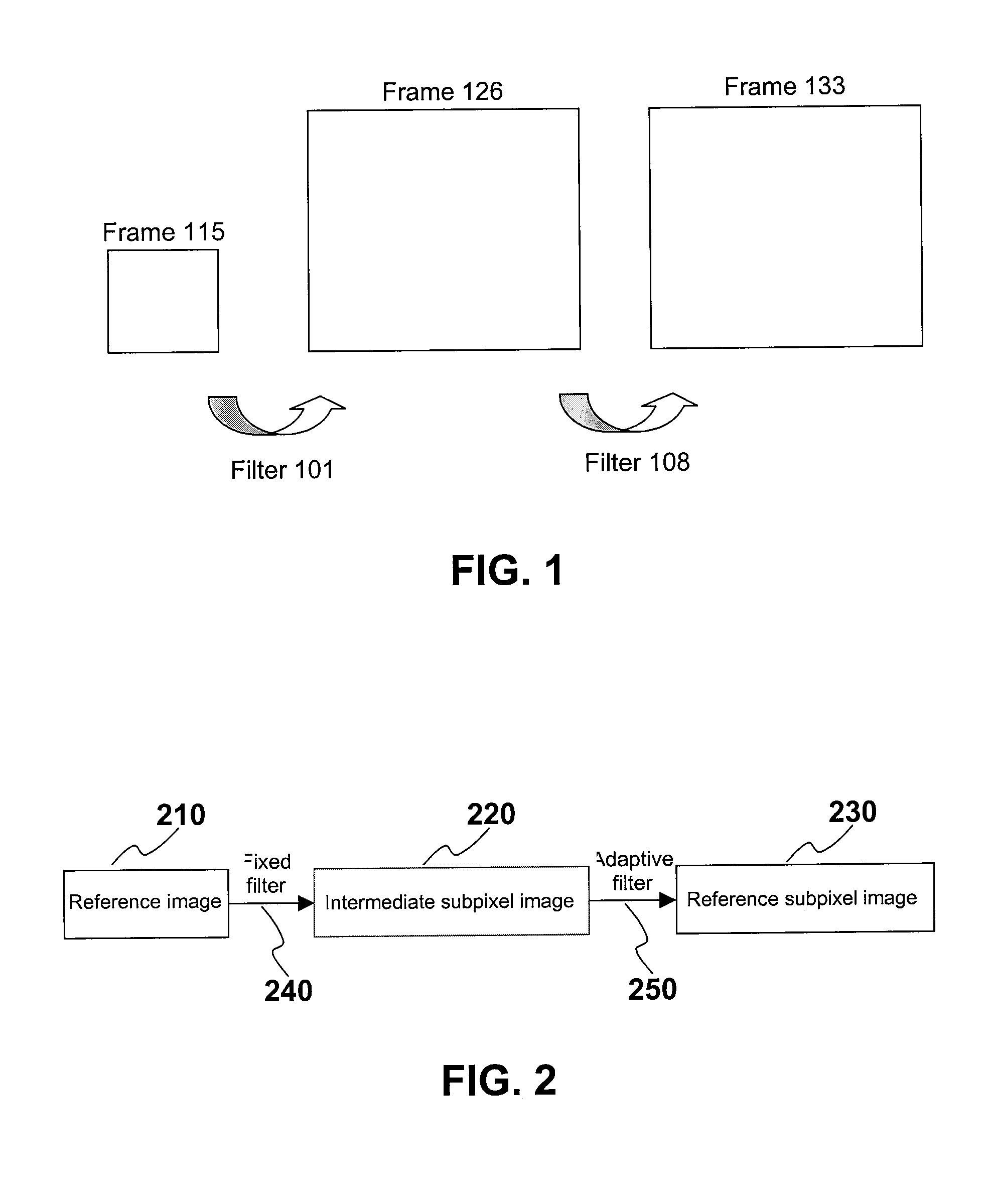
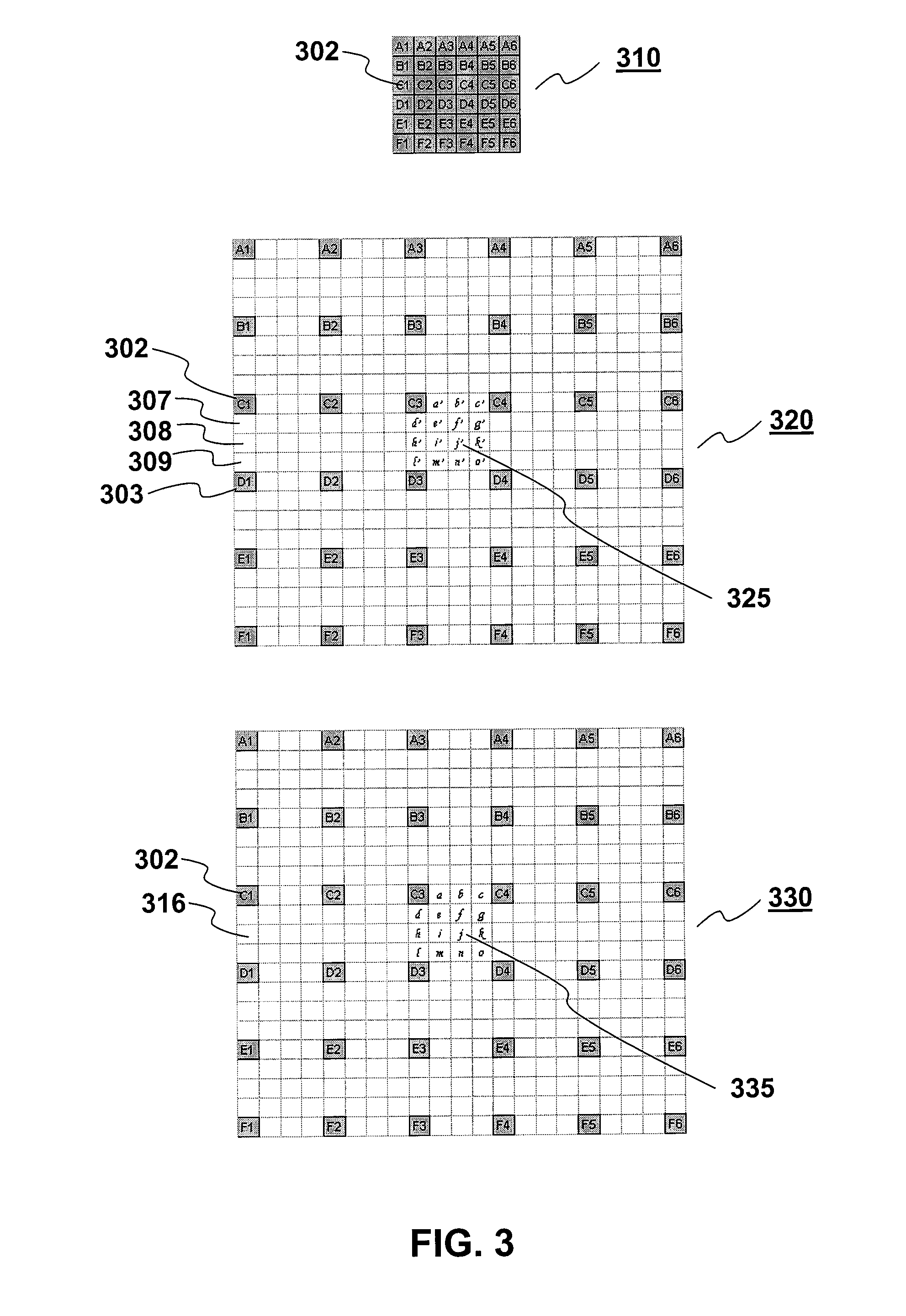
Method for motion compensation
ActiveUS20090092328A1Reduce complexityLow data requirementsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningAdaptive filterComputer graphics (images)
A method for use in video compression is disclosed. In particular, the claimed invention relates to a method of more efficient fractional-pixel interpolation in two steps by a fixed filter (240) and an adaptive filter (250) for fractional-pixel motion compensation.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
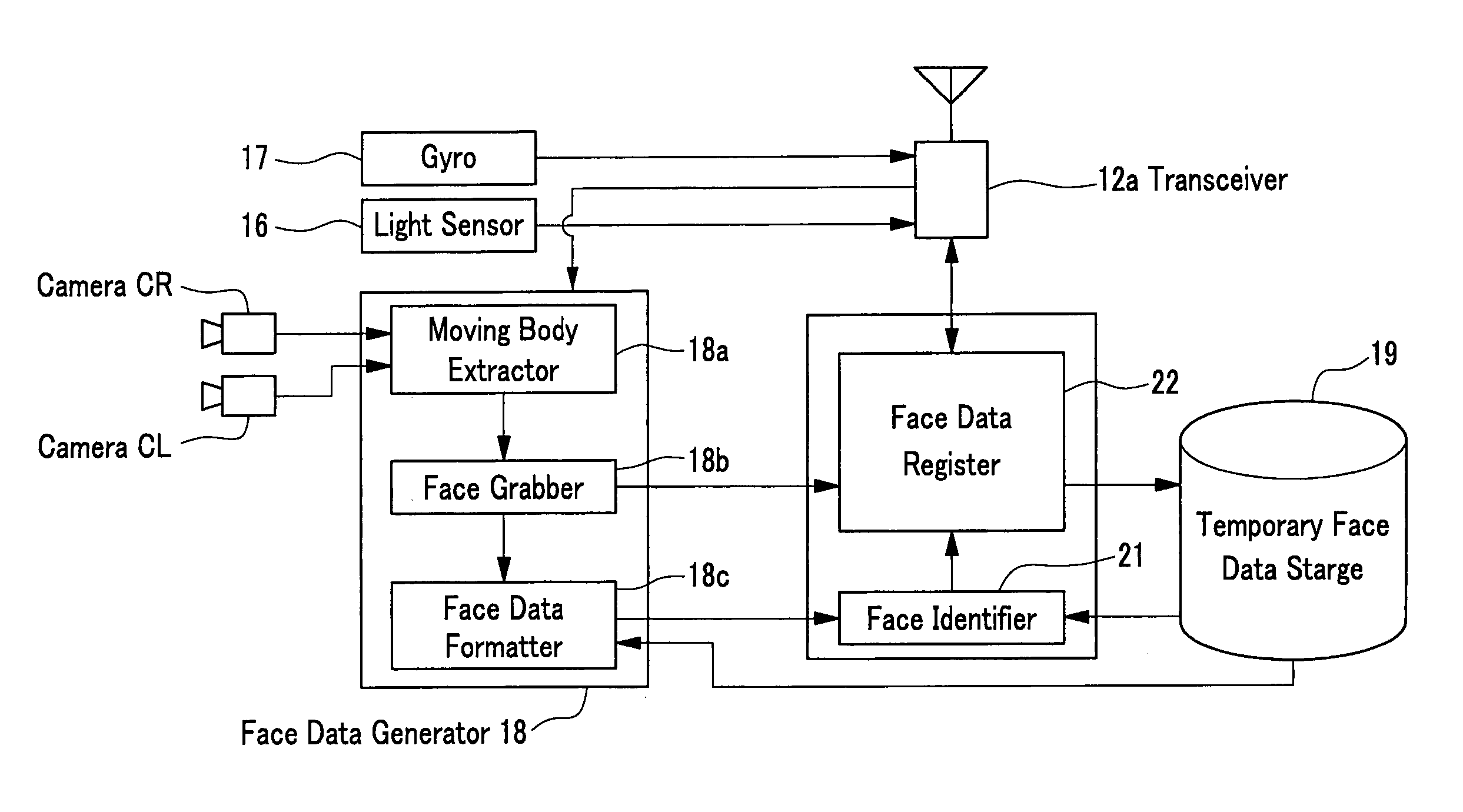
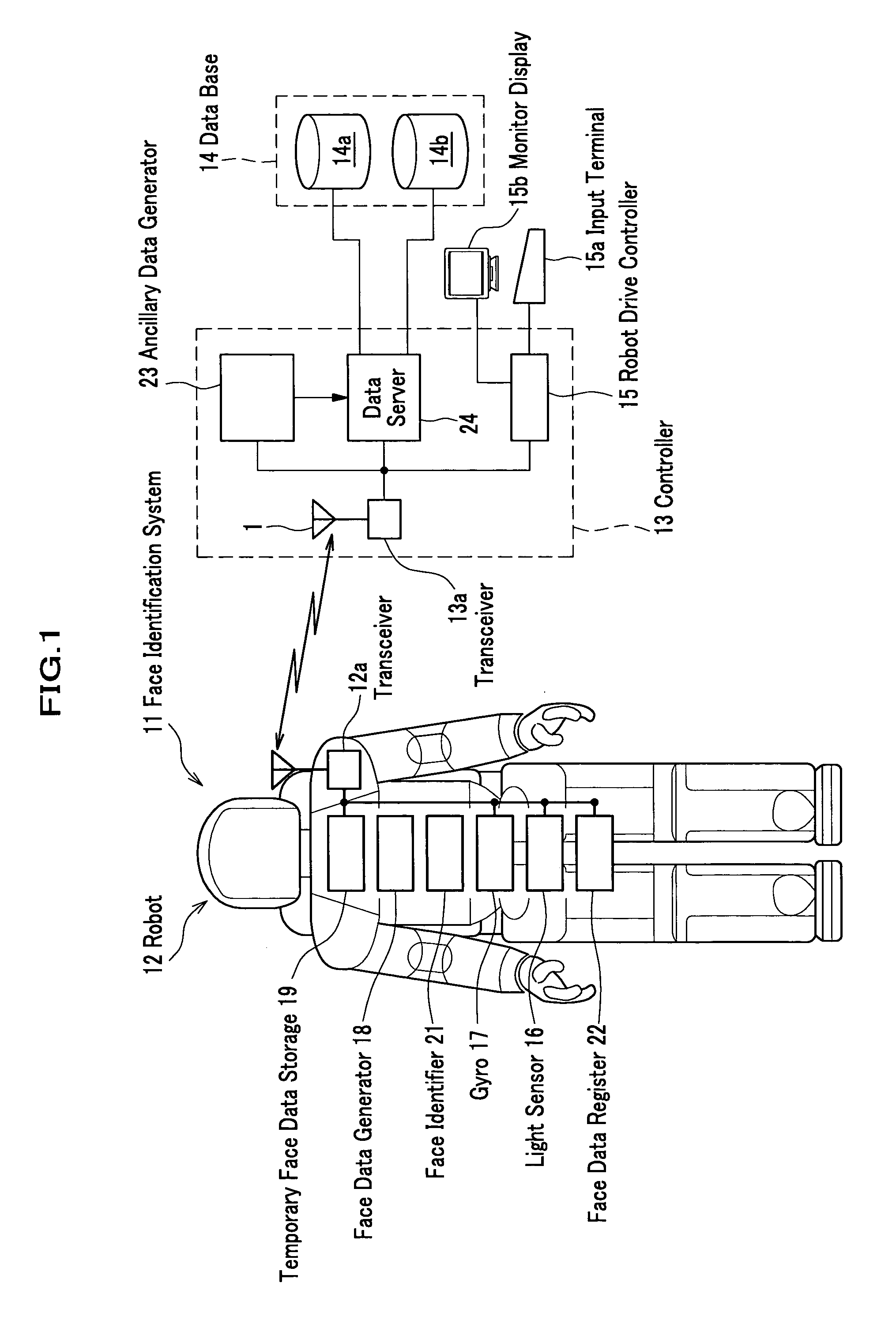
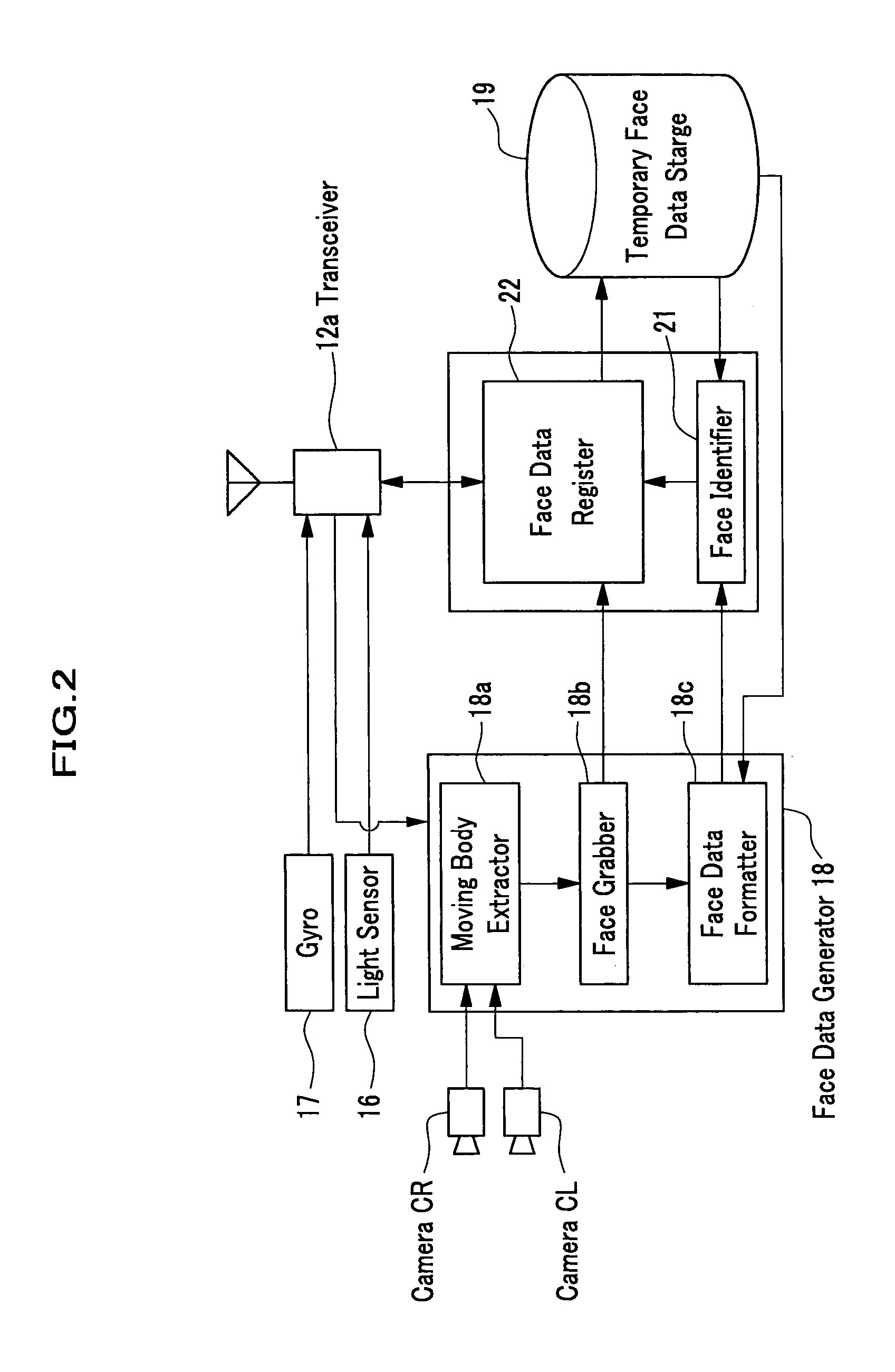
Face identification system
ActiveUS7014102B2Heavy loadReduce recognitionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFacial recognition systemSystem configuration
A face identification system includes a face data generator to generate face data of an objective person and a face data register to register the face data to be stored in a temporary face data storage, which stores the face data as reference face data. The system also includes a face identifier to identify the face of the objective person by comparing the face data with the reference face data. The system also includes a robot mechanism to move to plural areas, a data base to store face data of plural persons and a controller to transmit the retrieved face data from the data base as reference face data to the robot. By this system configuration, the face identification can be correctly carried out and improved in its process speed.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
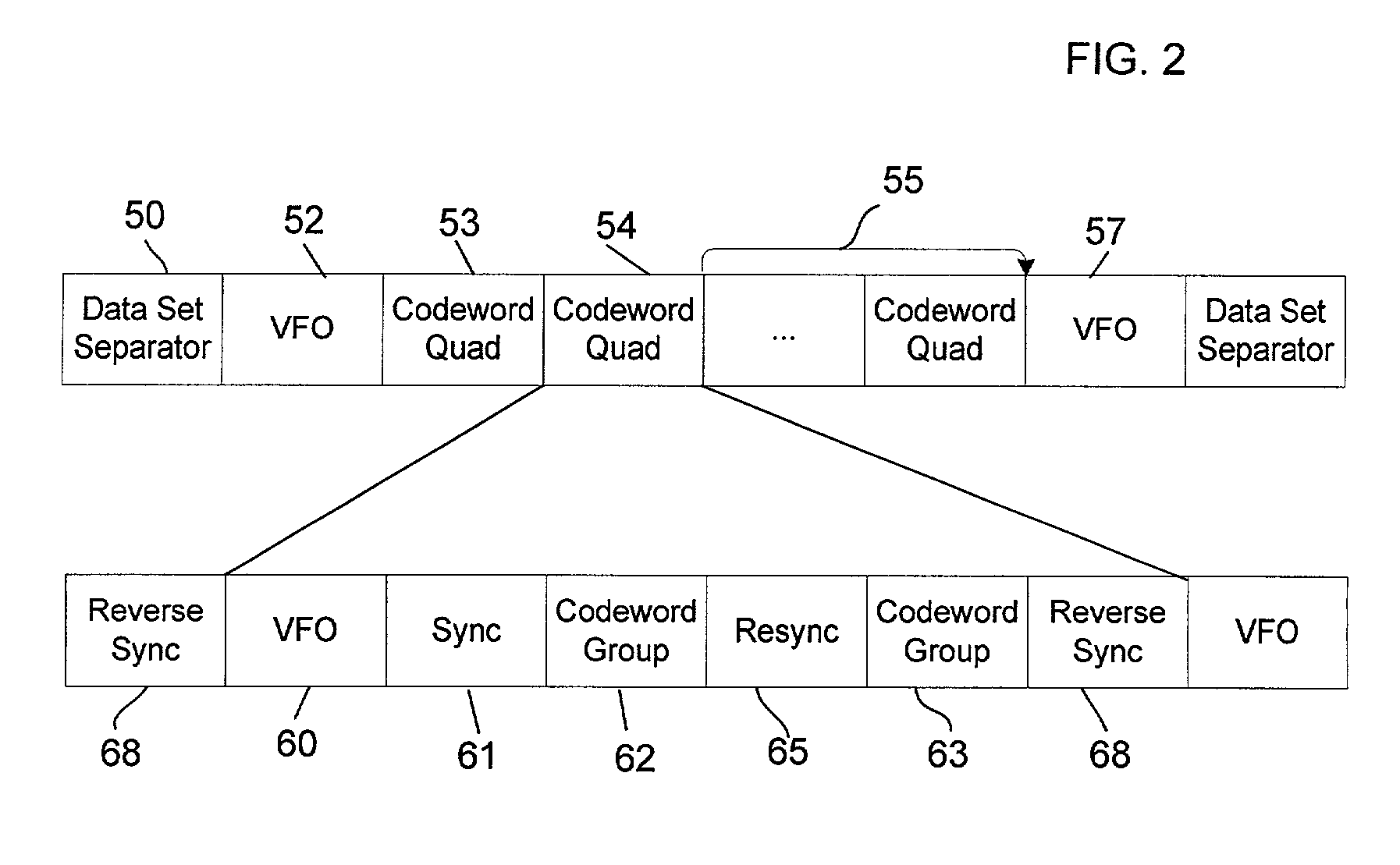
Method, system, and program for synchronization and resynchronization of a data stream
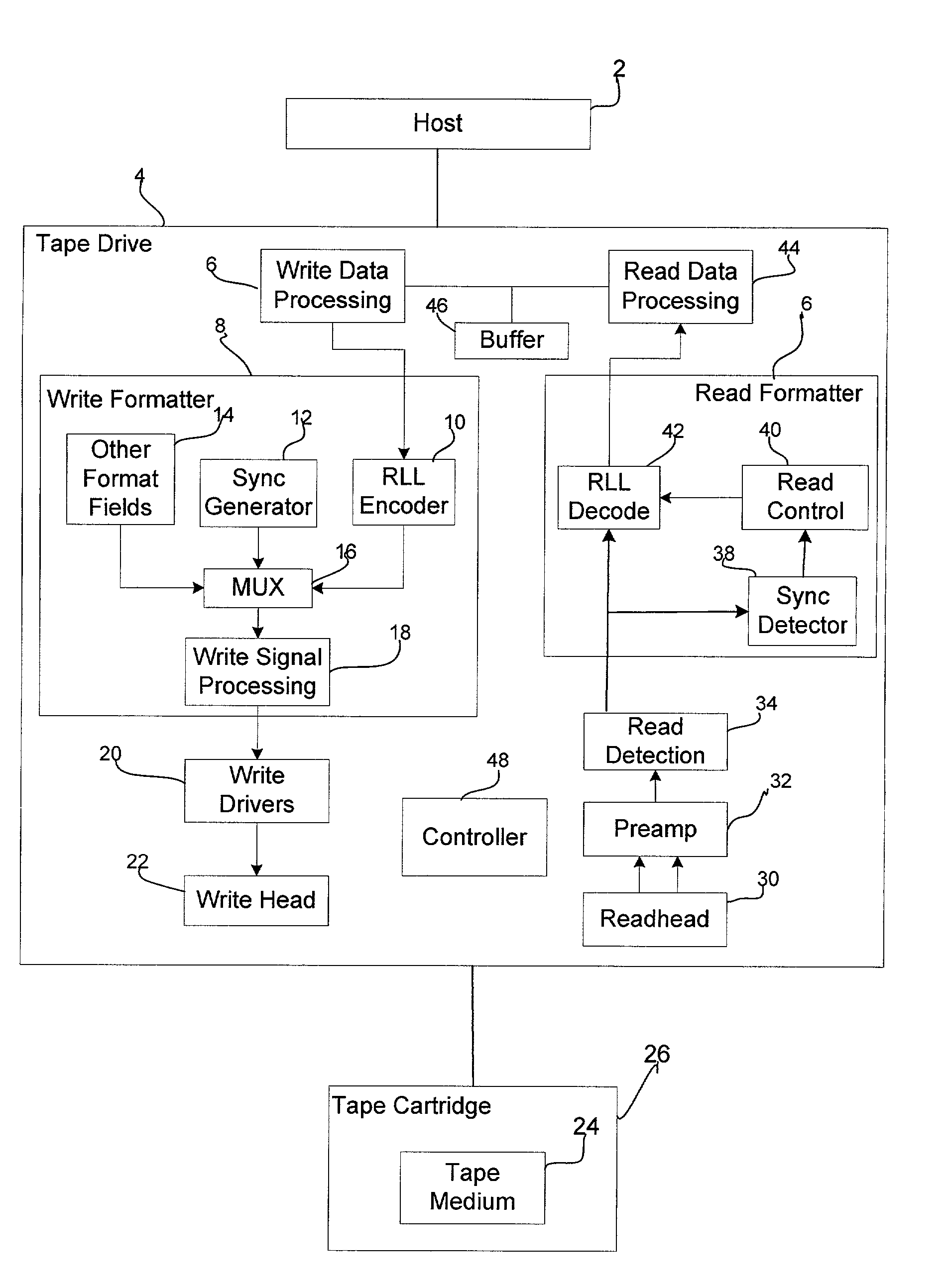
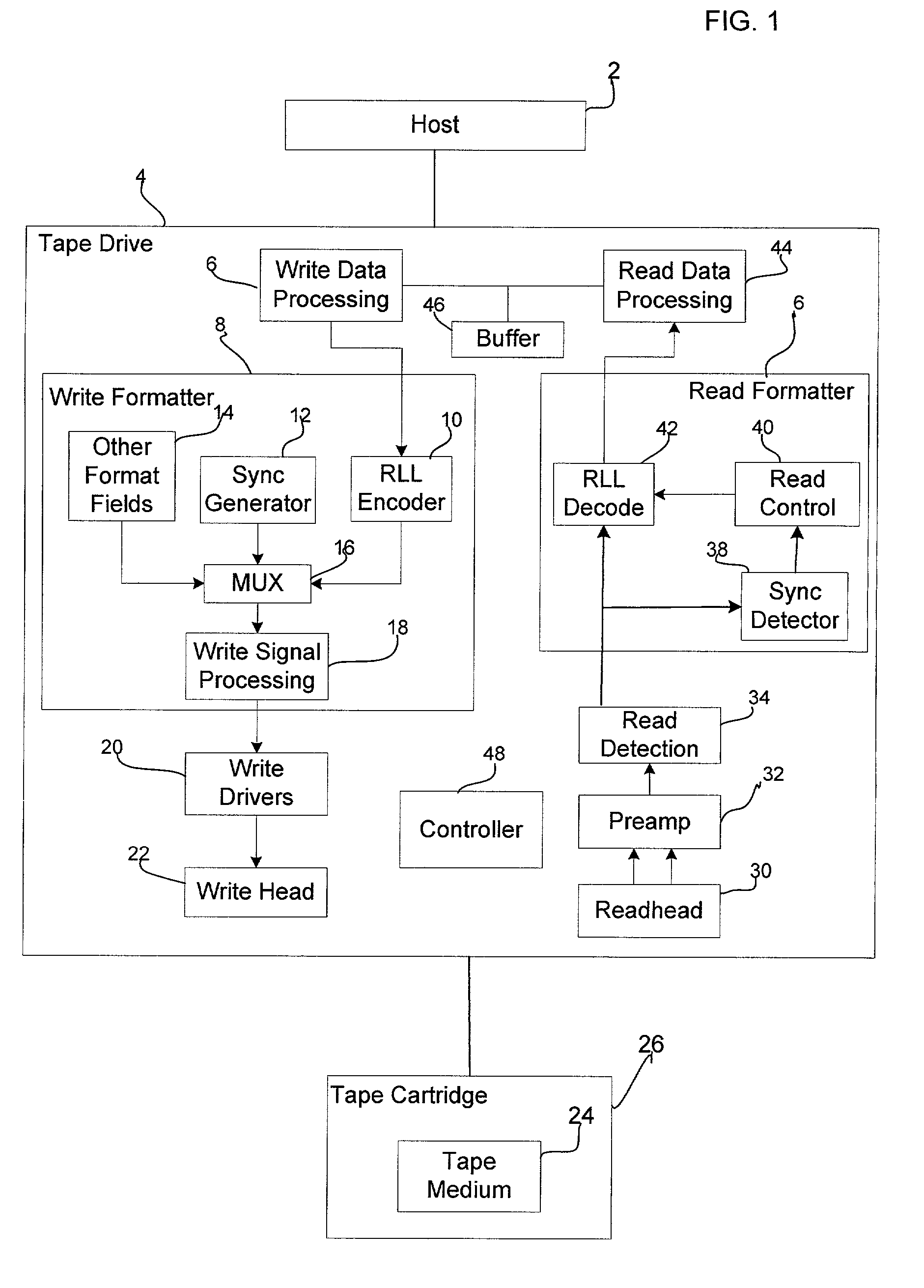
ActiveUS20030123587A1Easy to detectExclude dataCode conversionRecord information storageData streamData mining
Provided is a method, system, and program for providing synchronization in a binary data stream. A binary data stream is received. A synchronization mark having at least one isolated peak is generated into at least one point in the data stream. An encoded data stream is formed by concatenating the synchronization mark with the received binary data. During decoding, the synchronization mark is detected based on error propagation occurring adjacent to the at least one isolated peak of the synchronization mark.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Computer-implemented method for deriving, translating, and using definitional expressions for data in a database
InactiveUS20100023481A1Maximum flexibilityMinimal maintenanceRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsDerived DataData mining
A computer-implemented method is disclosed for deriving definitional expressions for data in a database from membership abstractions, and for deriving membership abstractions from definitional expressions. Definitional expressions may be partially in a natural language. By automating the translation among definitional expressions and membership abstractions, definitional expressions may then be used as database commands for the purpose of query, data update, maintenance, and the like, and may also be used to provide users with a more readable and understandable definition of both stored and derived data (e.g., the result of an ad-hoc query or data modification).
Owner:MCGOVERAN DAVD O
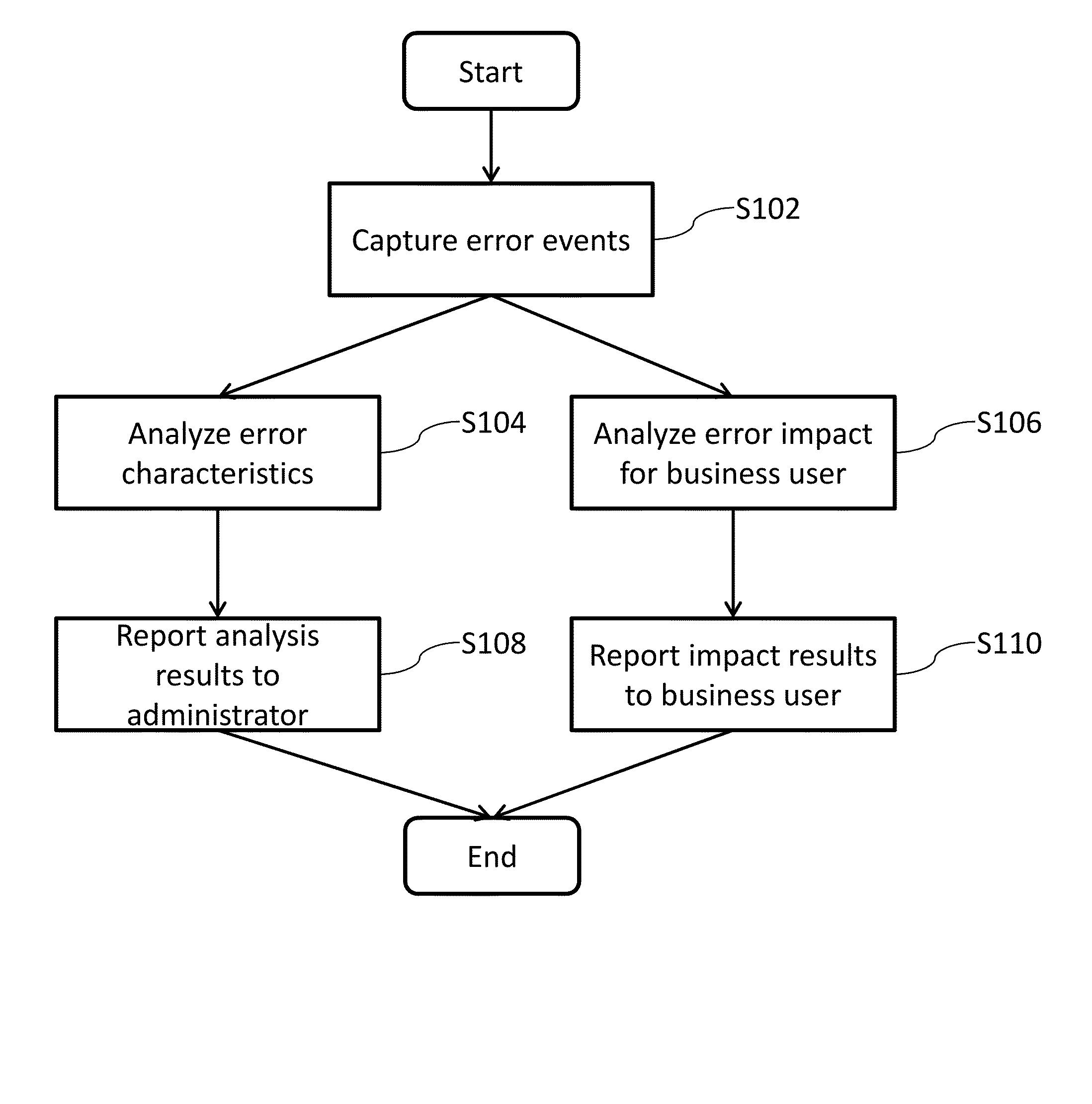
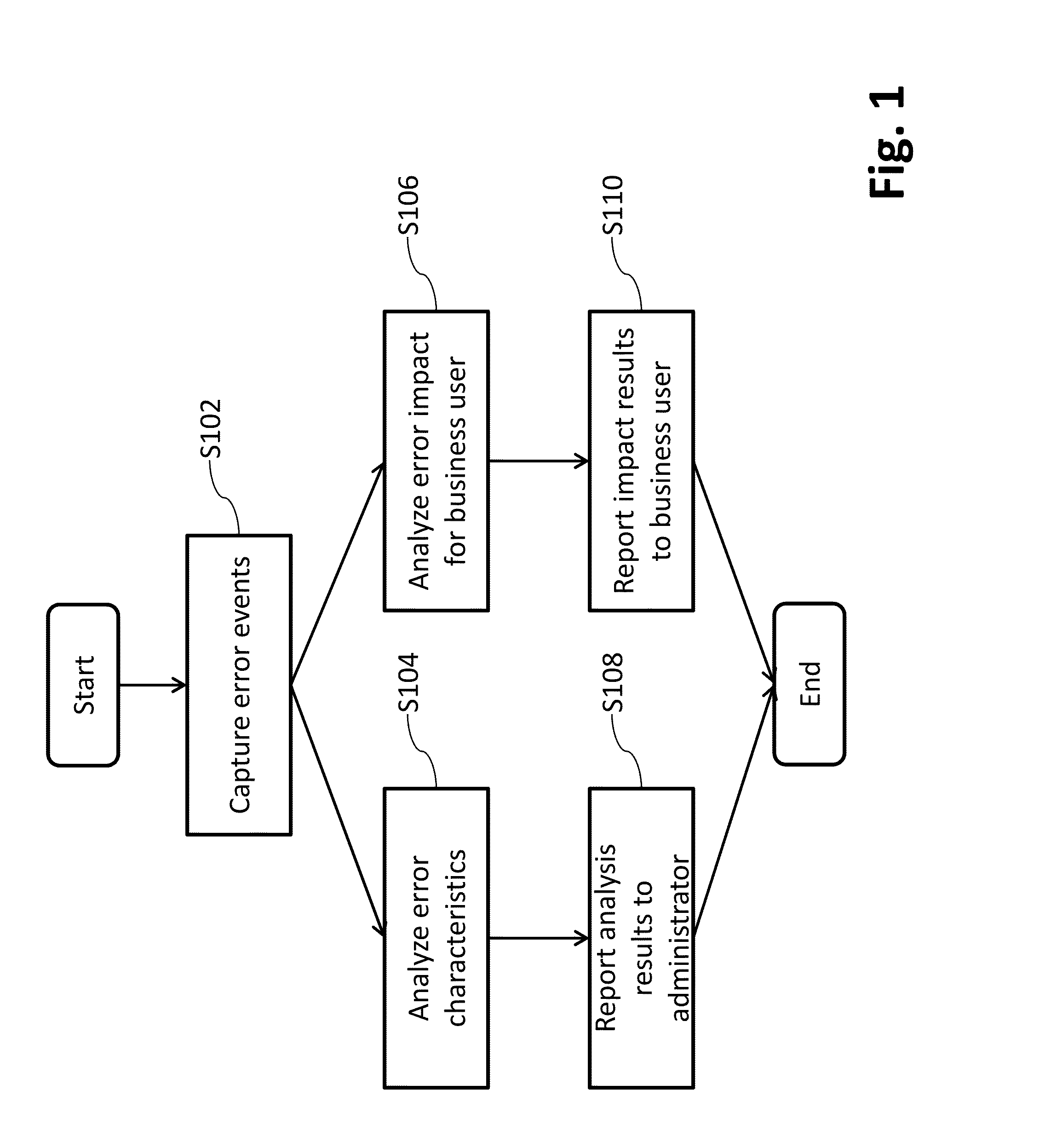
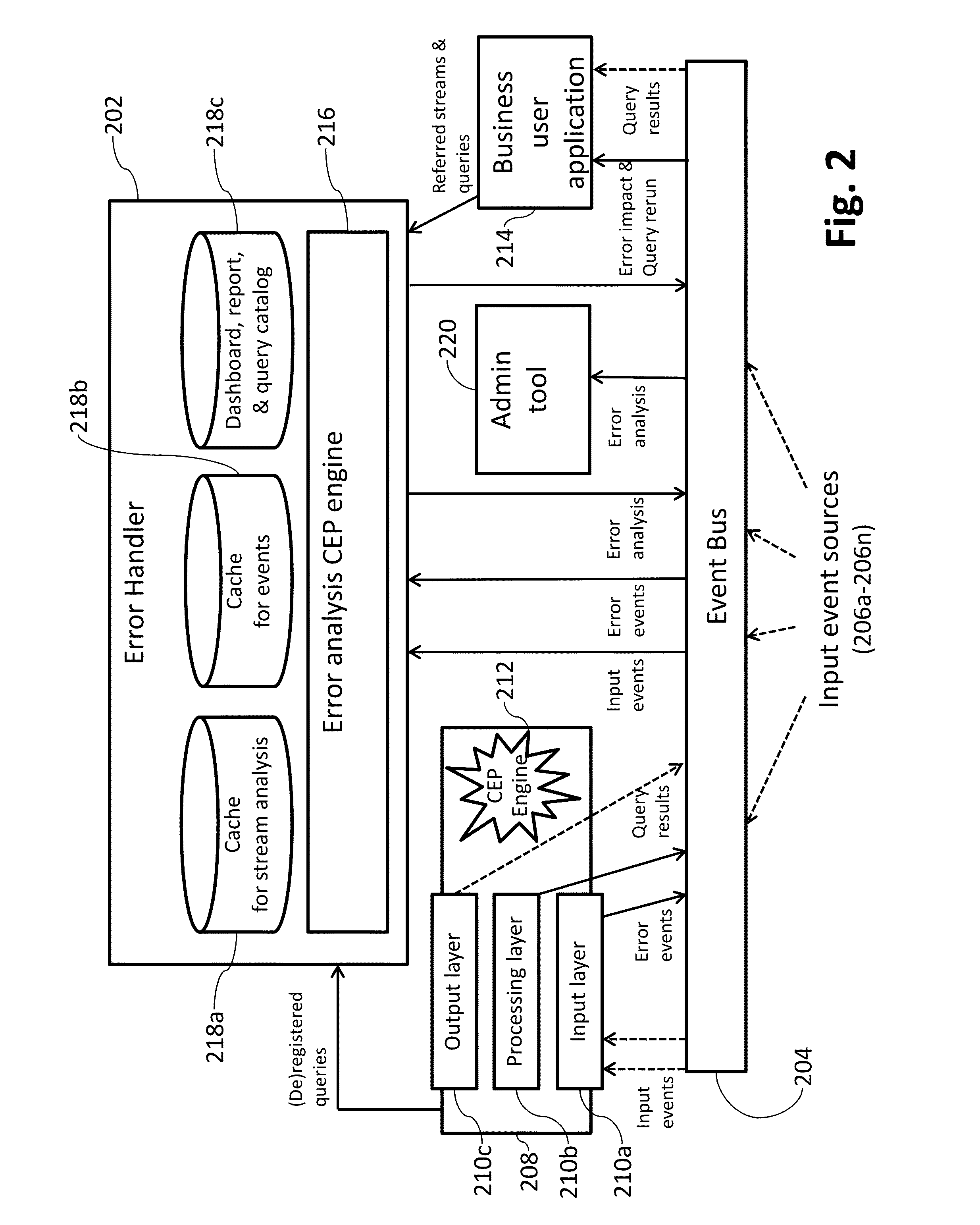
Systems and/or methods for handling erroneous events in complex event processing (CEP) applications
ActiveUS20160154692A1Improve data qualityExclude dataNon-redundant fault processingComplex event processingApplication software
Certain example embodiments address issues associated with erroneous events produced in Complex Event Processing (CEP) applications. An error handler is controlled to at least: receive, via an event bus, events from external input event sources; receive, via the event bus, error events from an application configured to process events received from the event bus, and to provide to the event bus results obtained from processing received events, and error events corresponding to errors detected at its input and / or processing layer(s); generate, for a given error, an error analysis event and an error impact event by executing a CEP query on at least a corresponding received error event; and provide to the event bus generated error analysis events and generated error impact events. Error analysis events describe for administrators detailed information analyzing corresponding errors. Error impact events describe for business users impacts corresponding errors have for their business user applications.
Owner:SOFTWARE AG
Electronic whiteboard system eraser
InactiveUS20020157880A1Exclude dataEliminate needTransmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsWhiteboardDigital data
An eraser for use on an electronic whiteboard with a protrusion area on the erasing surface forming a convex area on the erasing surface for establishing a positive point of contact with the whiteboard; an electronic whiteboard system including such an eraser, a controller for storing data relating to information written on and erased from the whiteboard data, and a filter for preventing the storage of digital data relating to contacts with the whiteboard not attributable to normal writing or erasing actions.
Owner:STEELCASE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com