Compressive sensing method based on principal component analysis
A technique of principal component analysis and compressed sensing, applied in image data processing, instrumentation, computing, etc., can solve the problems of weak sparsity of wavelet transform, loss of details, not many, etc., to protect edge and texture information, and improve reconstruction effect , the effect of high peak signal-to-noise ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
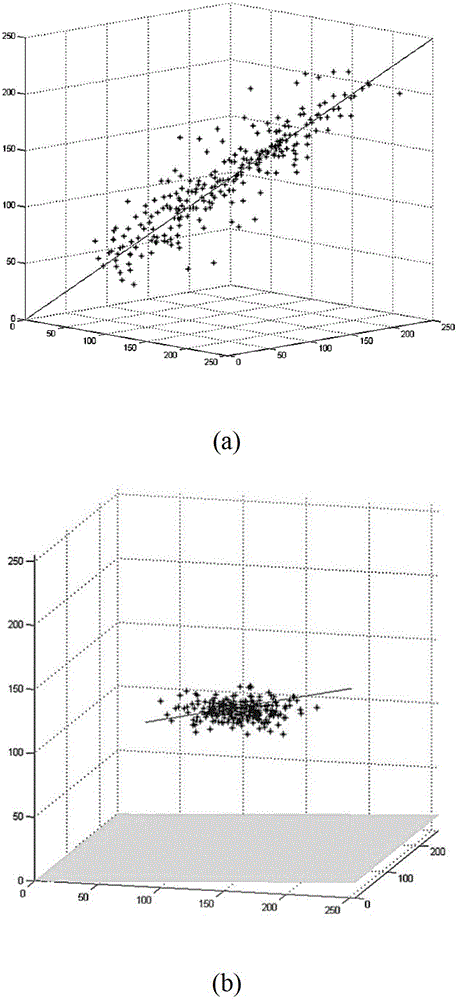
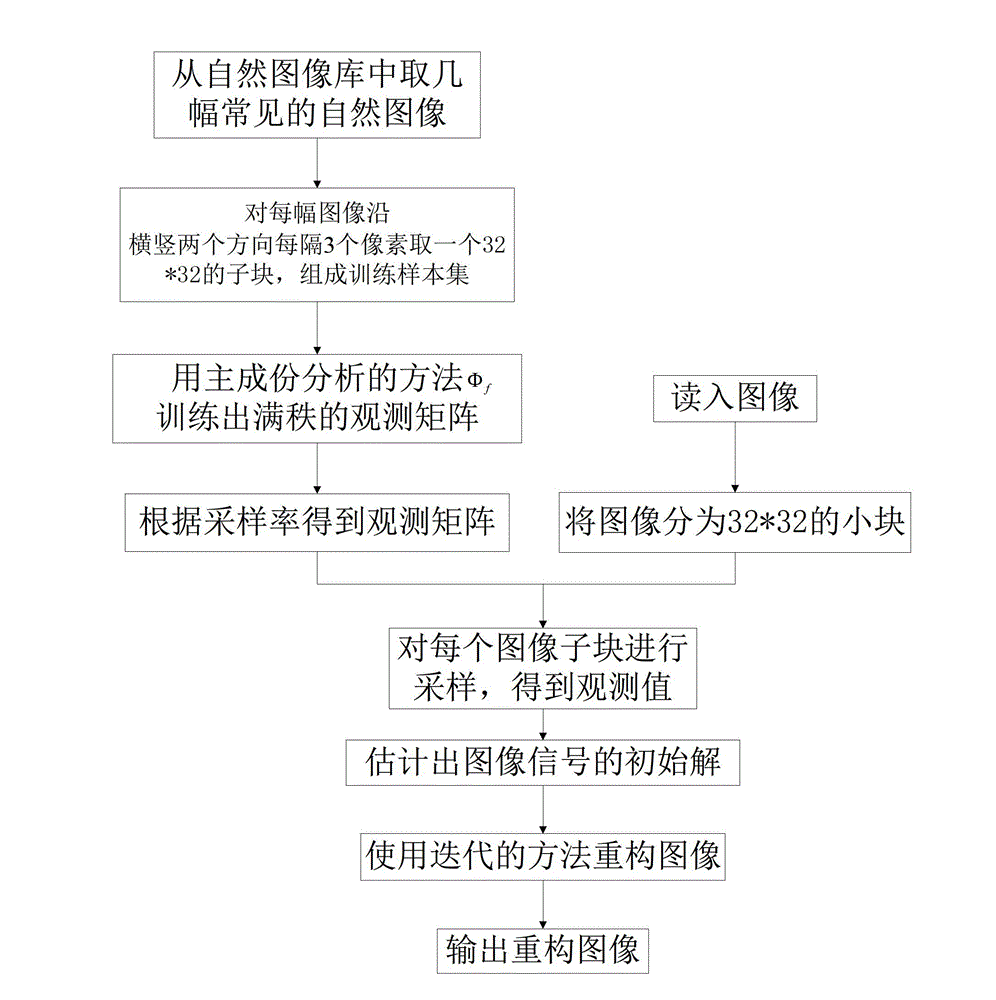
[0027] refer to figure 1 , the specific implementation steps of the present invention are as follows:
[0028] Step 1, train a full-rank observation matrix Φ f .
[0029] In order to find the commonality of image sub-blocks, the method of principal component analysis is used to train the full-rank observation matrix Φ f , the steps are as follows:
[0030] 1a) Take z common gray-scale natural images from the gray-scale natural image library, 15≤z≤25, and take a 32×32 sub-block every 3 pixels in the horizontal and vertical directions for each image taken out , forming a training sample set x 1 ,x 2 ,...,x m , where m is the number of training samples, in this experiment, z=19, m=4935;
[0031] 1b) Solve the training sample set x 1 ,x 2 ,...,x m The mean vector μ and covariance matrix of m is the number of training samples, T represents the transposition of the matrix;
[0032] 1c) Solve the eigenvalue λ of the covariance matrix E j , j=0,1,...,r-1, r is the number...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com