Plane target drone characteristic point automatic matching method for demarcating video camera
A camera calibration and planar target technology, which is applied in image analysis, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming, complicated target production, and the reduction of the number of feature points marked by ARTag in the recognition rate, so as to improve the degree of automation and calibration Efficiency, the effect of simplifying the calibration process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
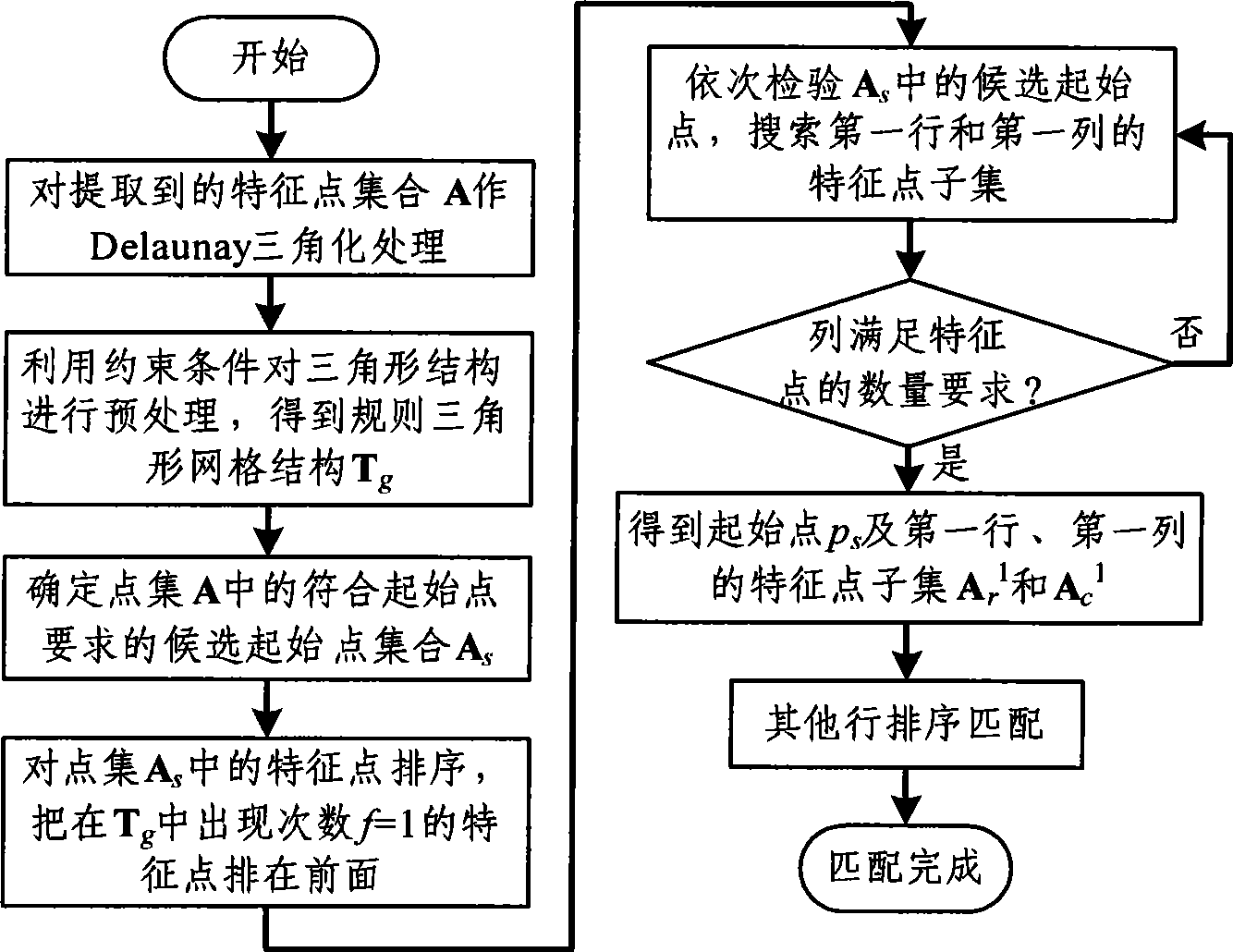
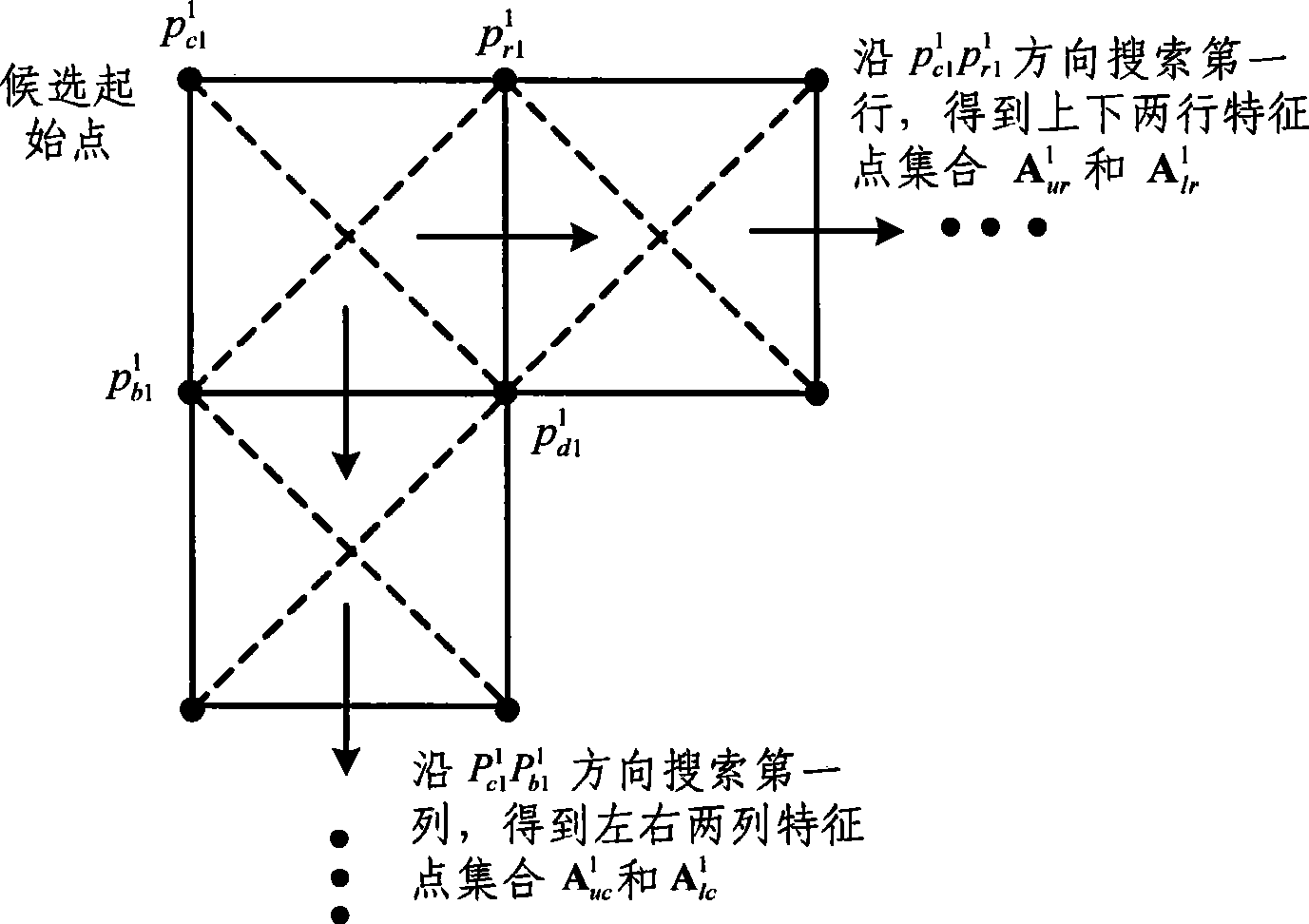
[0051] The process flow of the automatic matching method for the feature points of the plane target used for camera calibration proposed by the present invention is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the principle of using candidate starting points to search for feature points in the first row and feature points in the first column is as follows figure 2 shown.
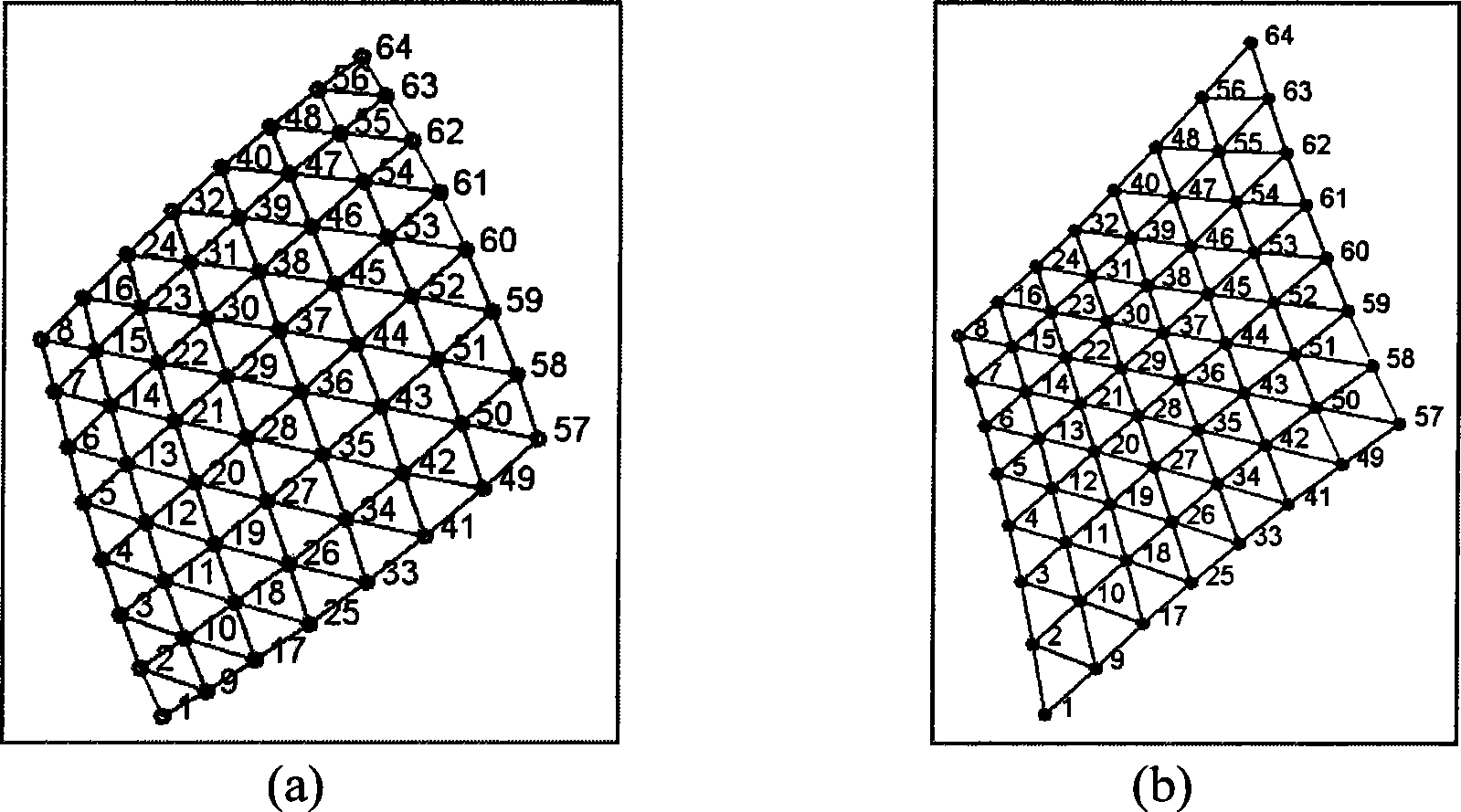
[0052] The feature points of the checkerboard target or circular target used for calibration generally have a grid array structure, so use a computer to generate 8×8 grid array feature points with a spacing of 20 mm, and the geometric center of all feature points is set to the world coordinate system origin. The simulation camera parameters are set as follows: the image resolution is 768pixel×576pixels, the effective focal length is f x = 500 pixels, f y =50 0pixels, principal point coordinate u 0 = 384 pixels, v 0 =288 pixels, the translation vector is (0, 0, 600) T , that is, the origin of the world coordinate sy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com