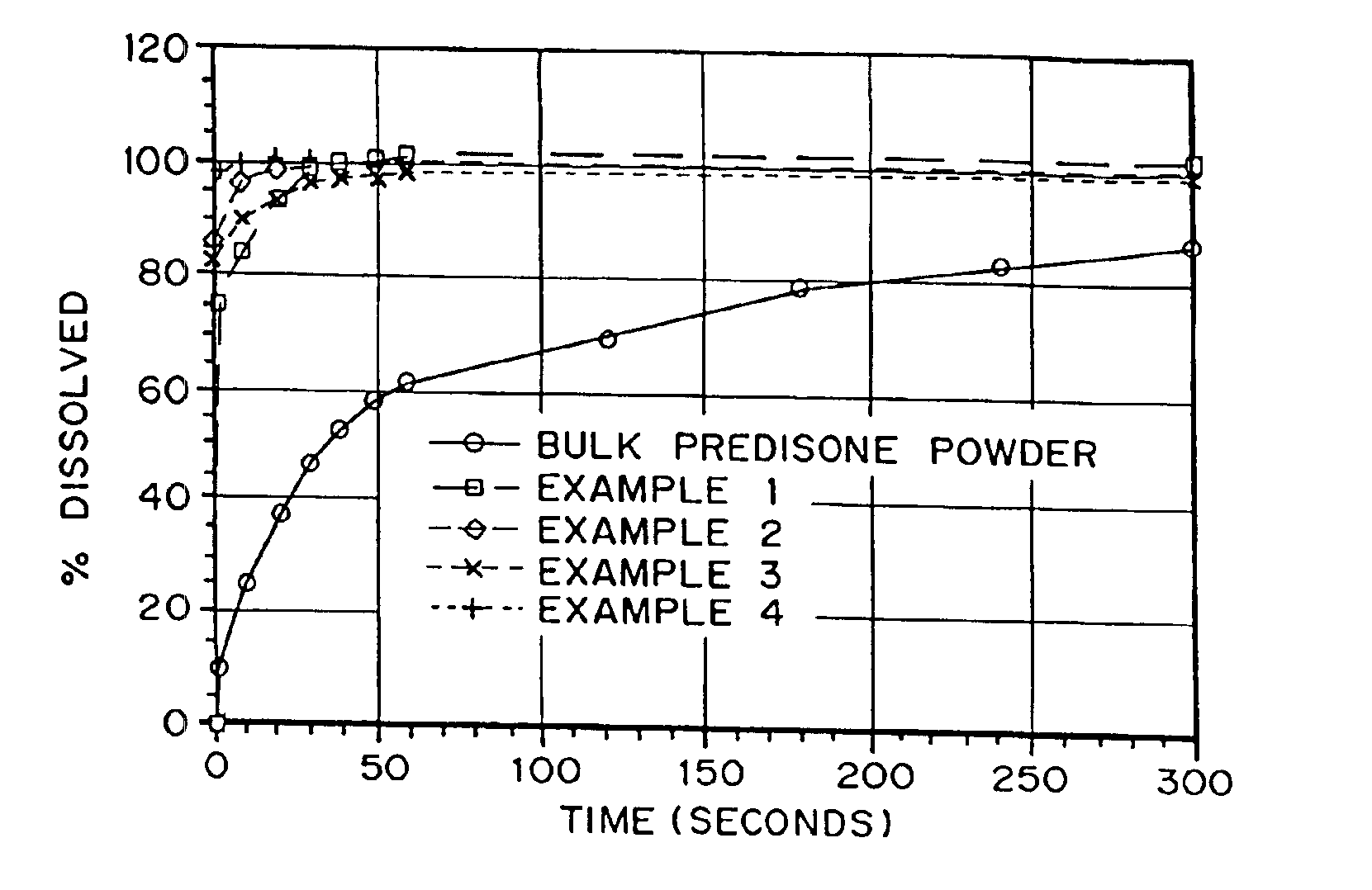
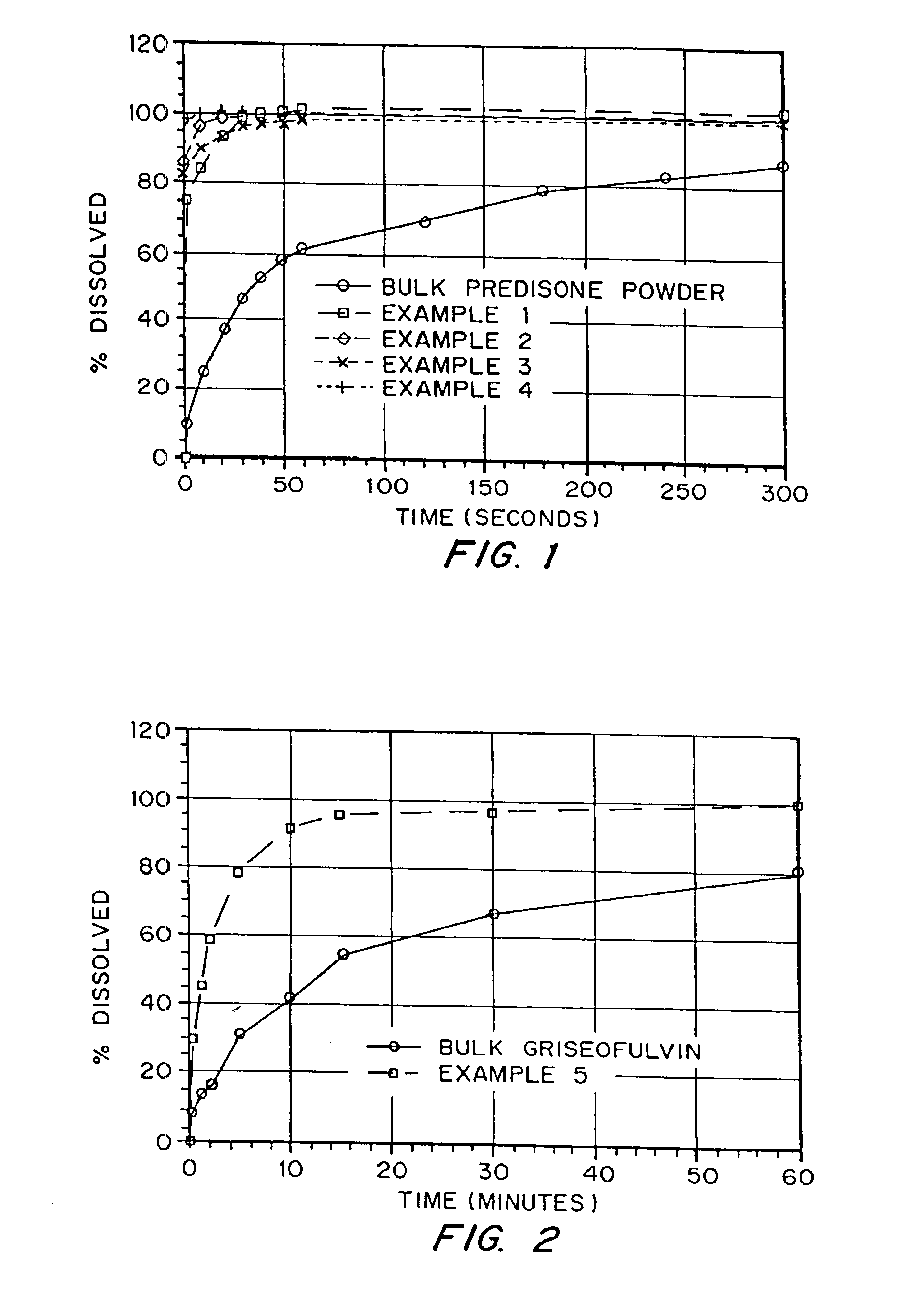
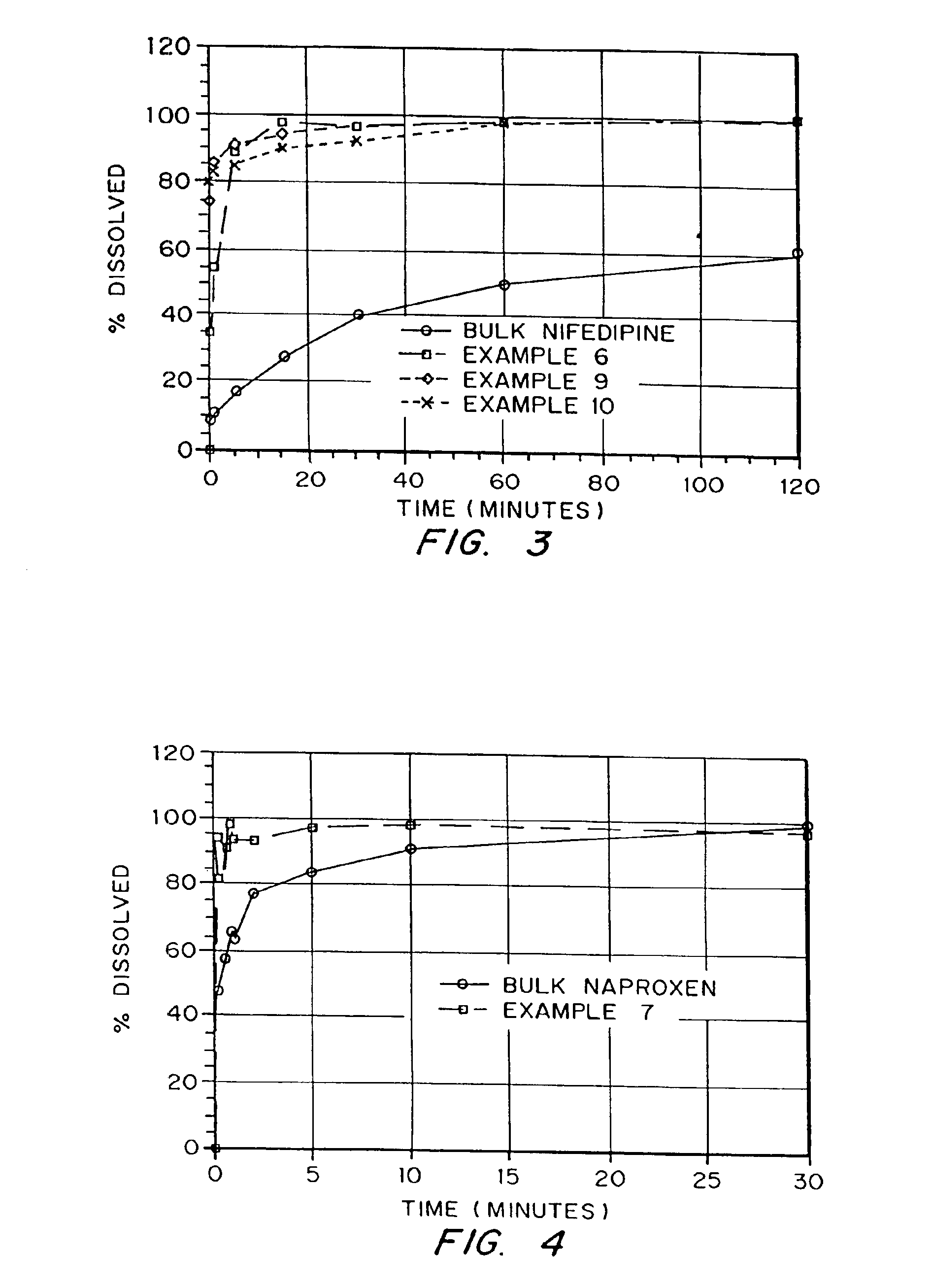
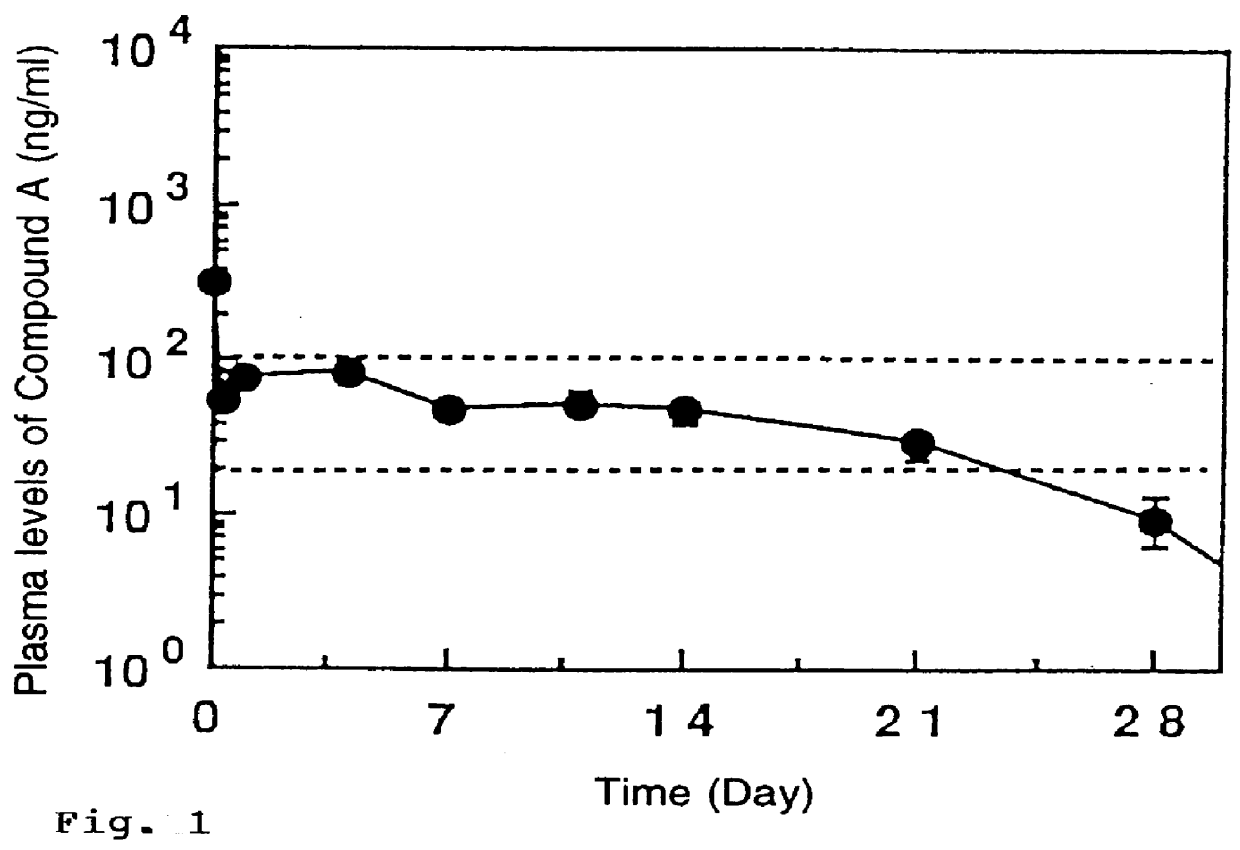
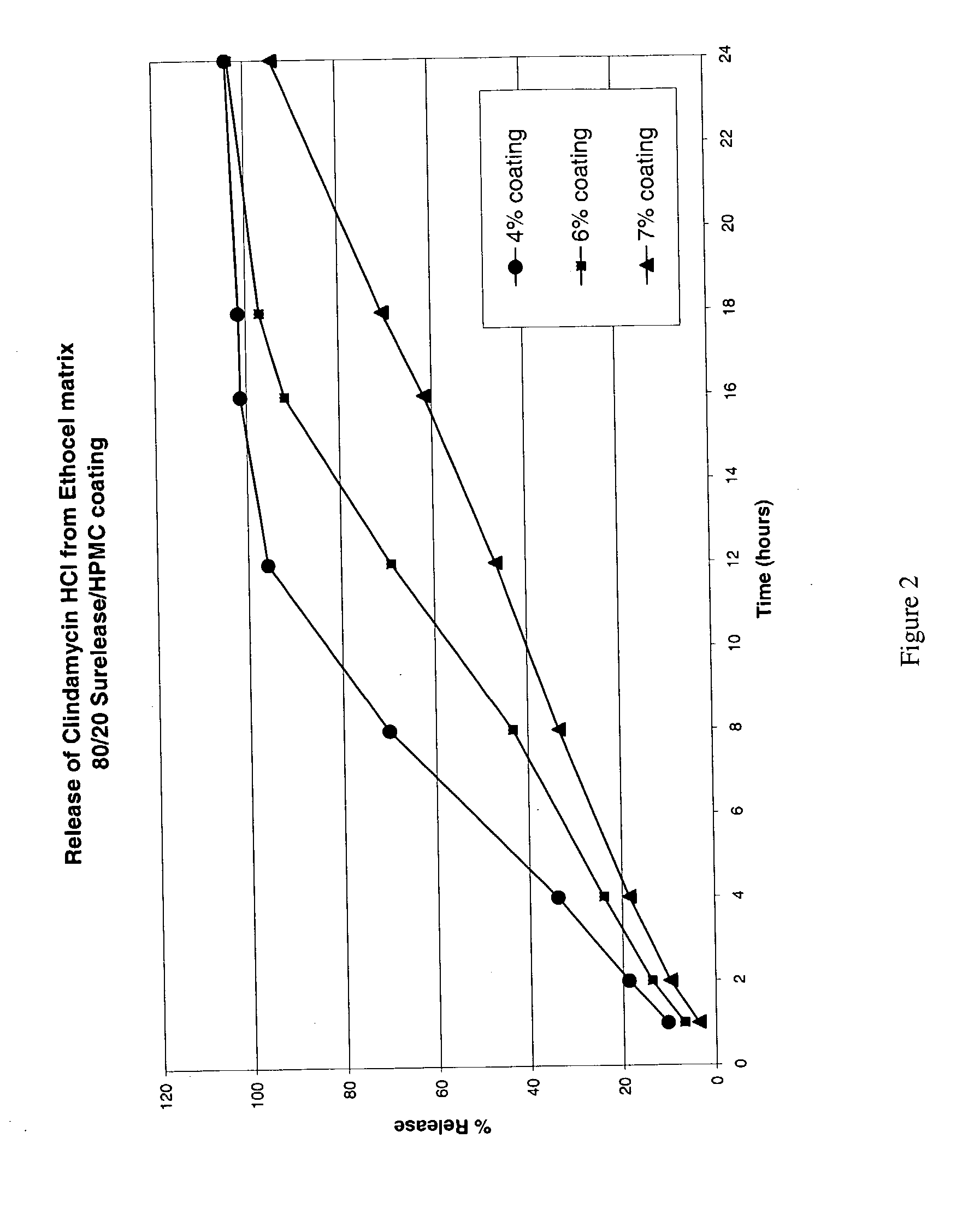
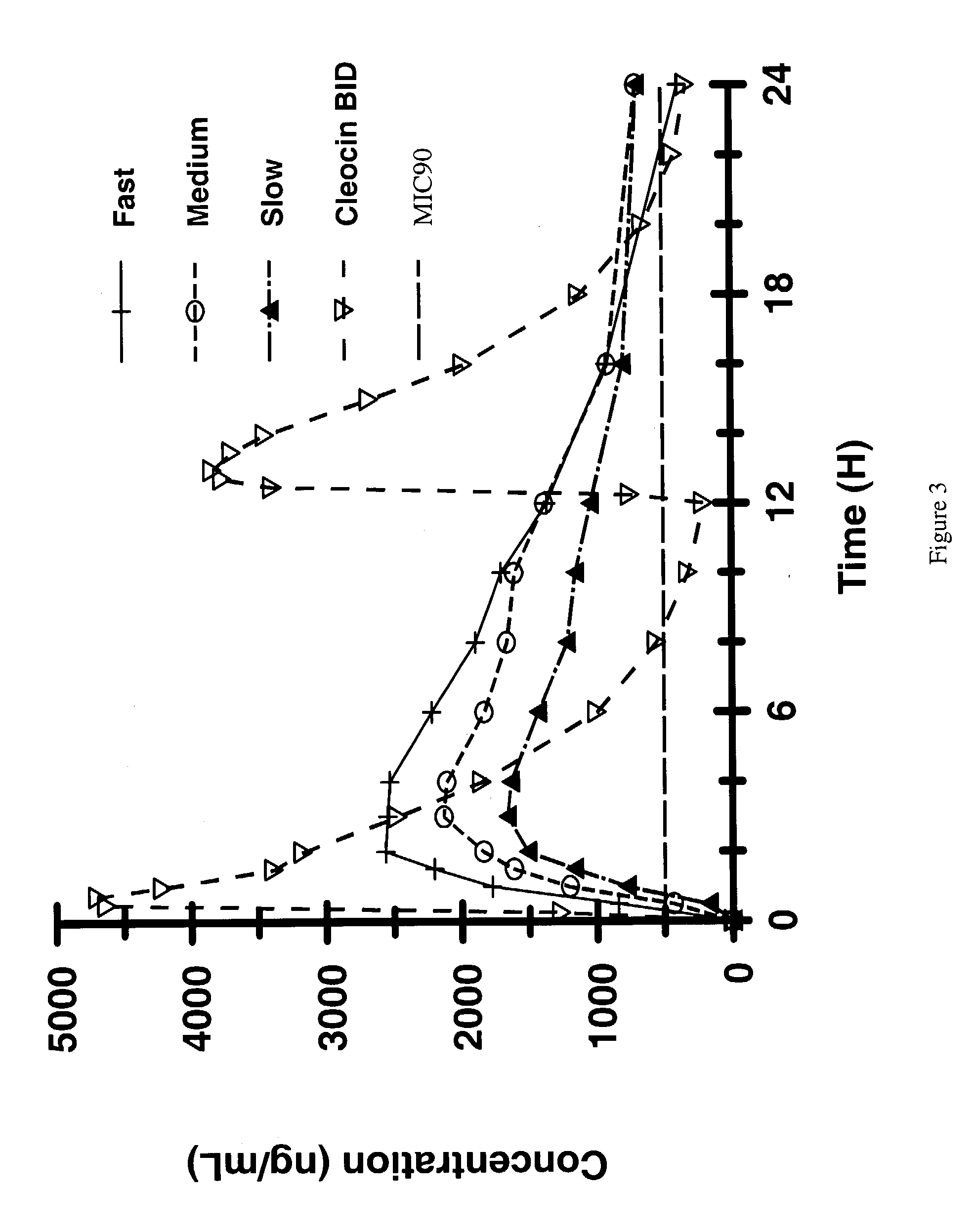
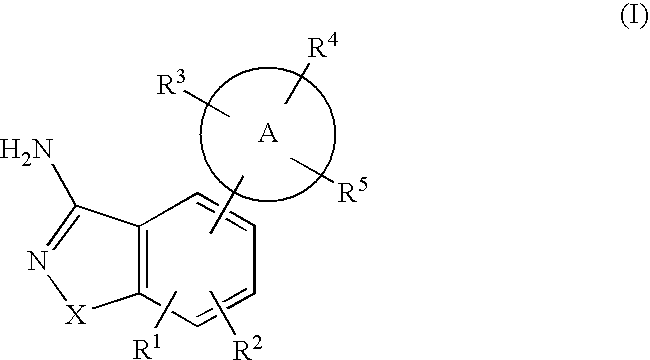
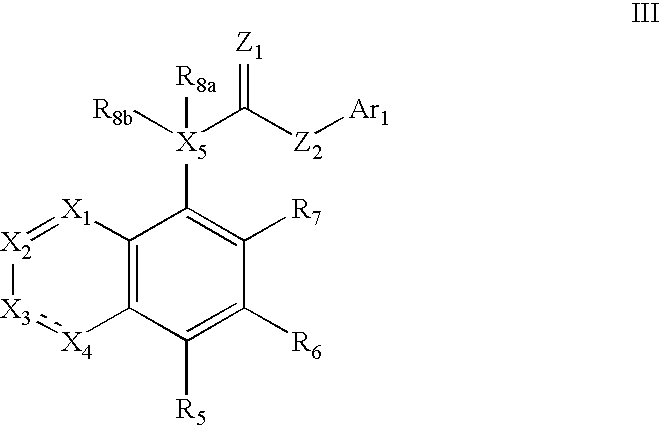
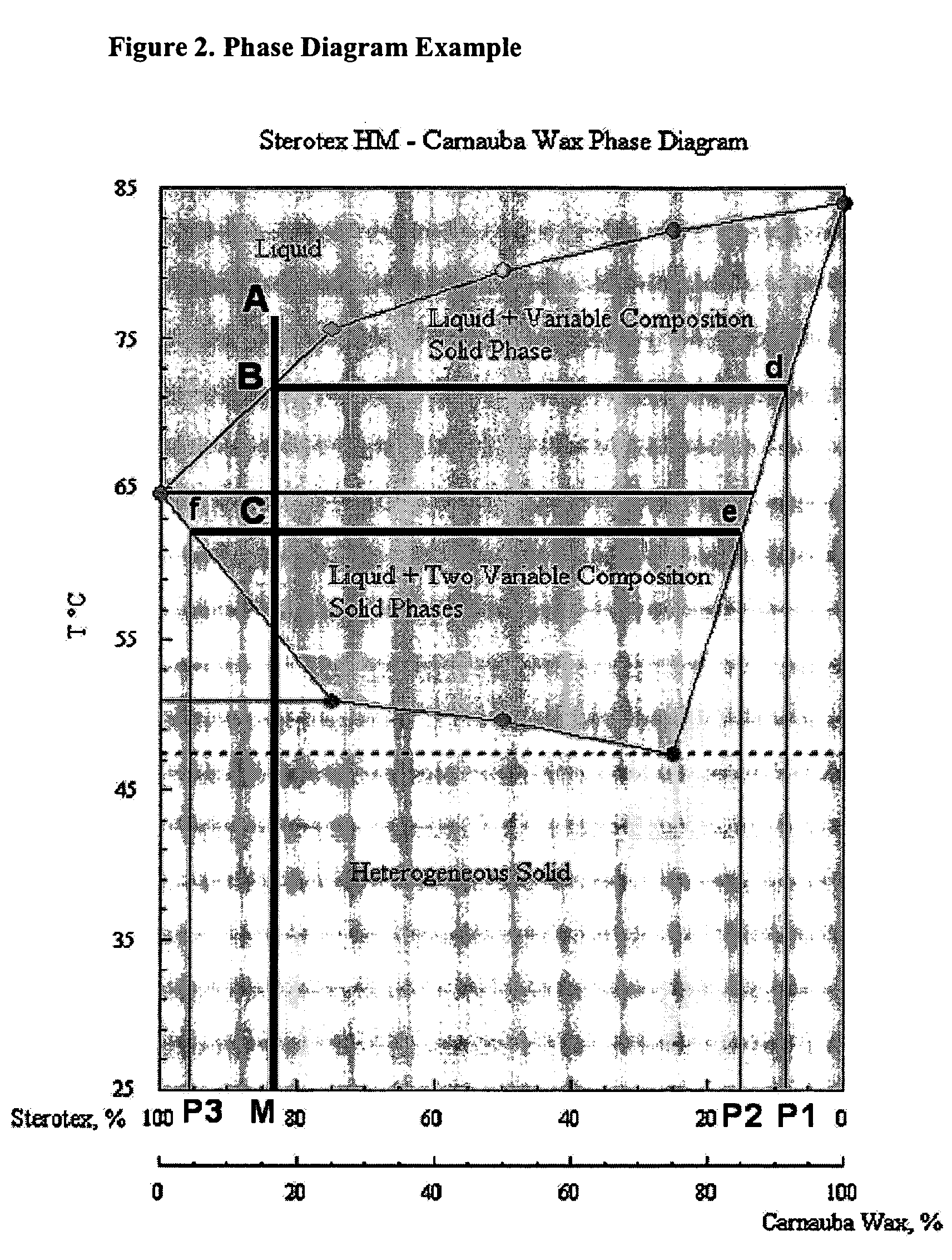
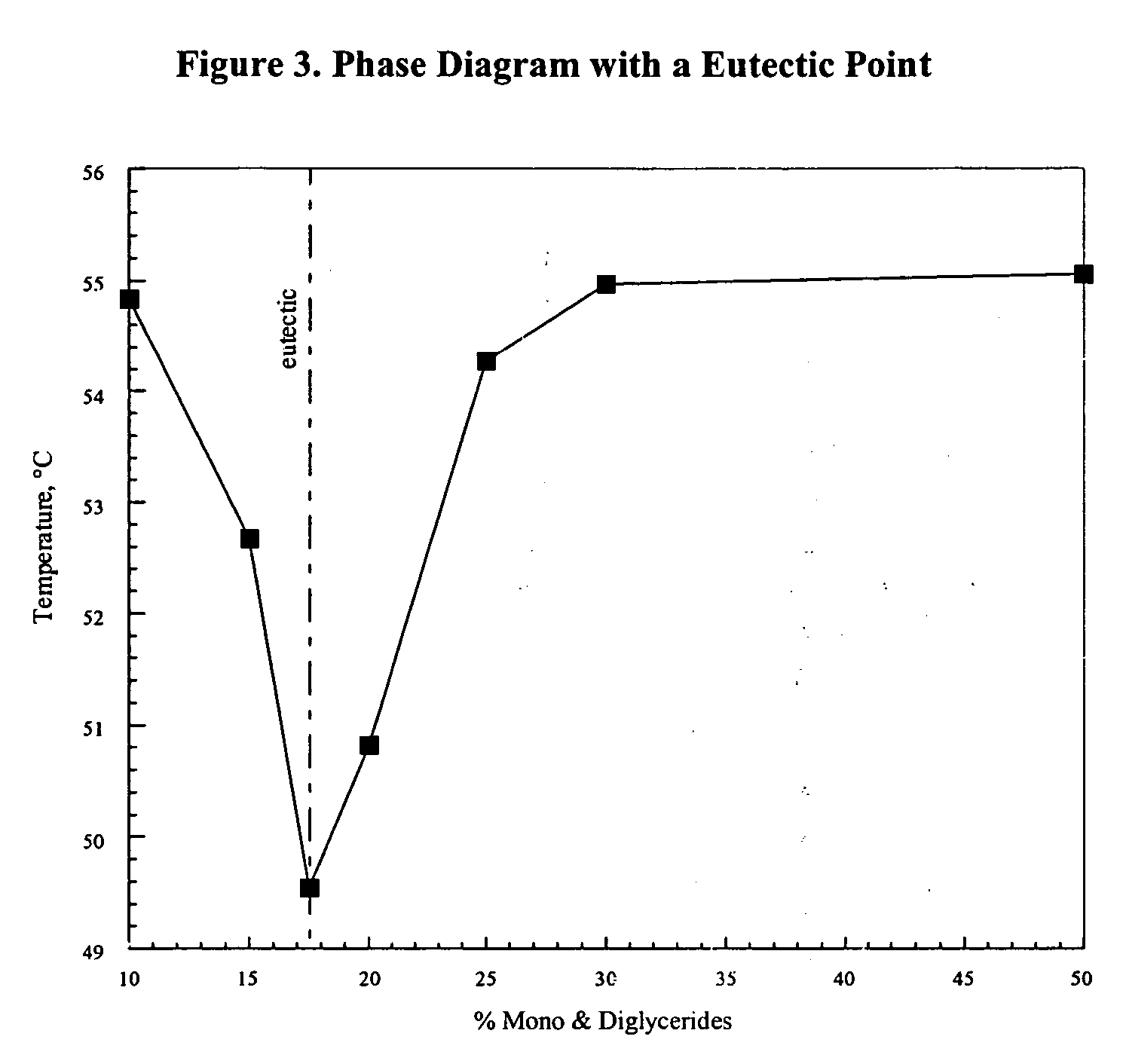
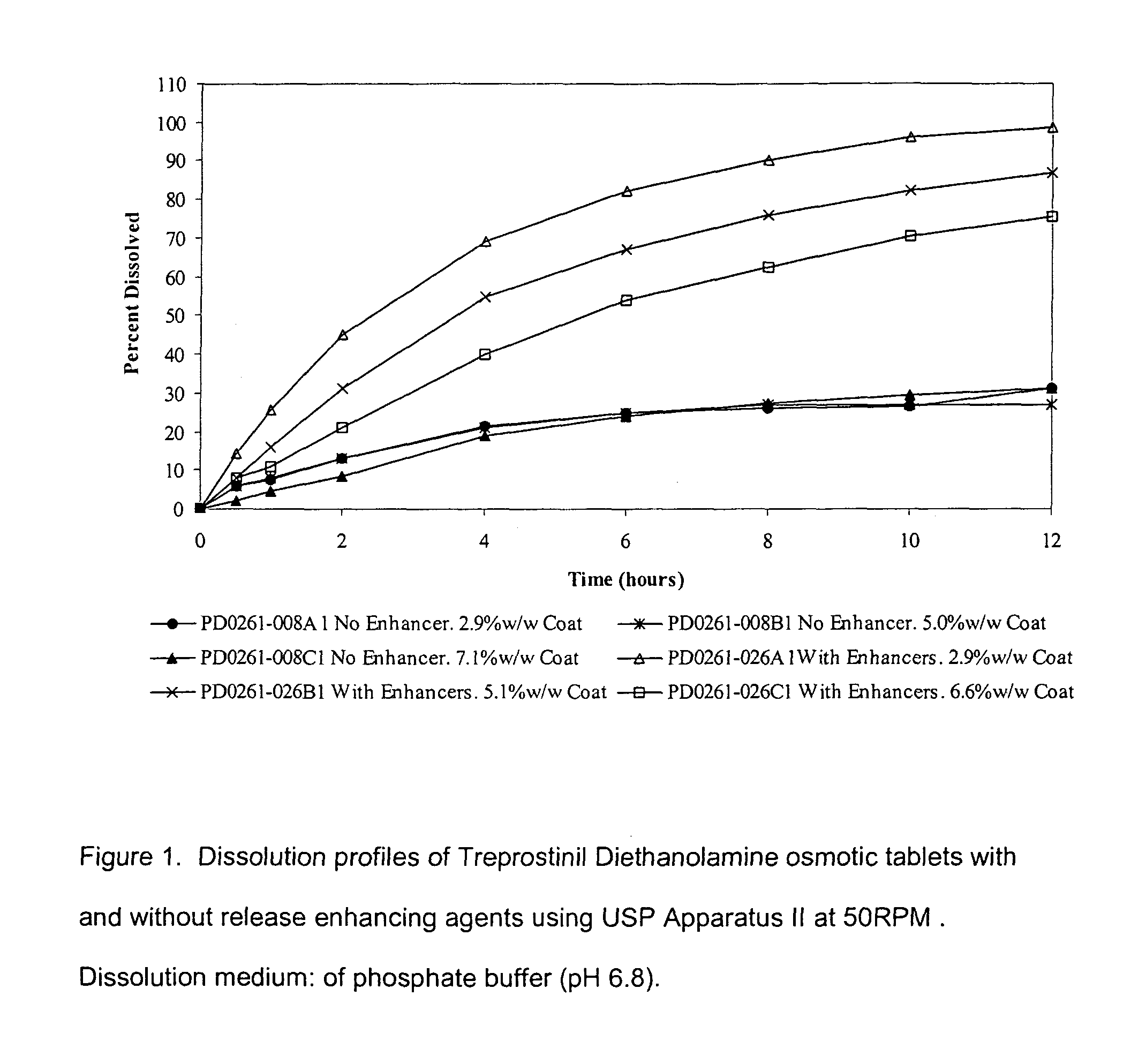
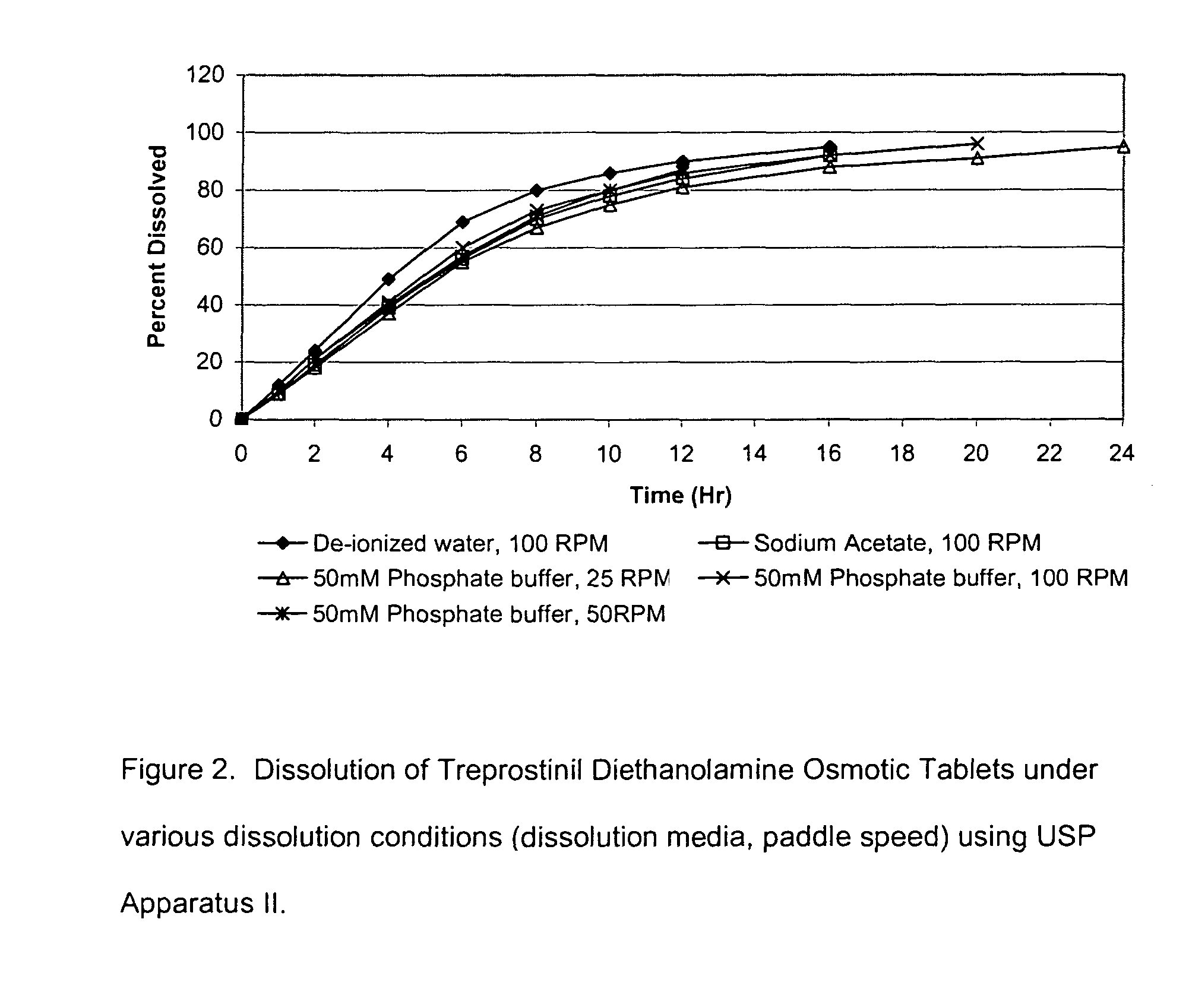
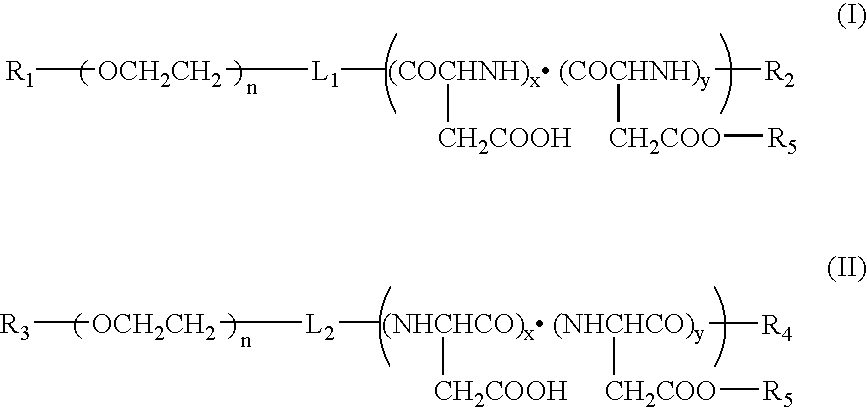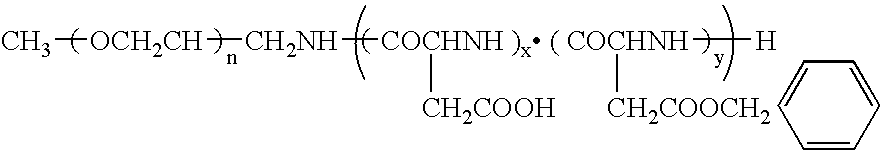Patents
Literature
607 results about "Water soluble drug" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Drugs that dissolve in water (water-soluble drugs), such as the antihypertensive drug atenolol, tend to stay within the blood and the fluid that surrounds cells (interstitial space). Drugs that dissolve in fat (fat-soluble drugs), such as the antianxiety drug clorazepate, tend to concentrate in fatty tissues.
Porous drug matrices and methods of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS6932983B1Lower the volumePrevent precipitationPowder deliveryNanotechDrugs solutionWater soluble drug
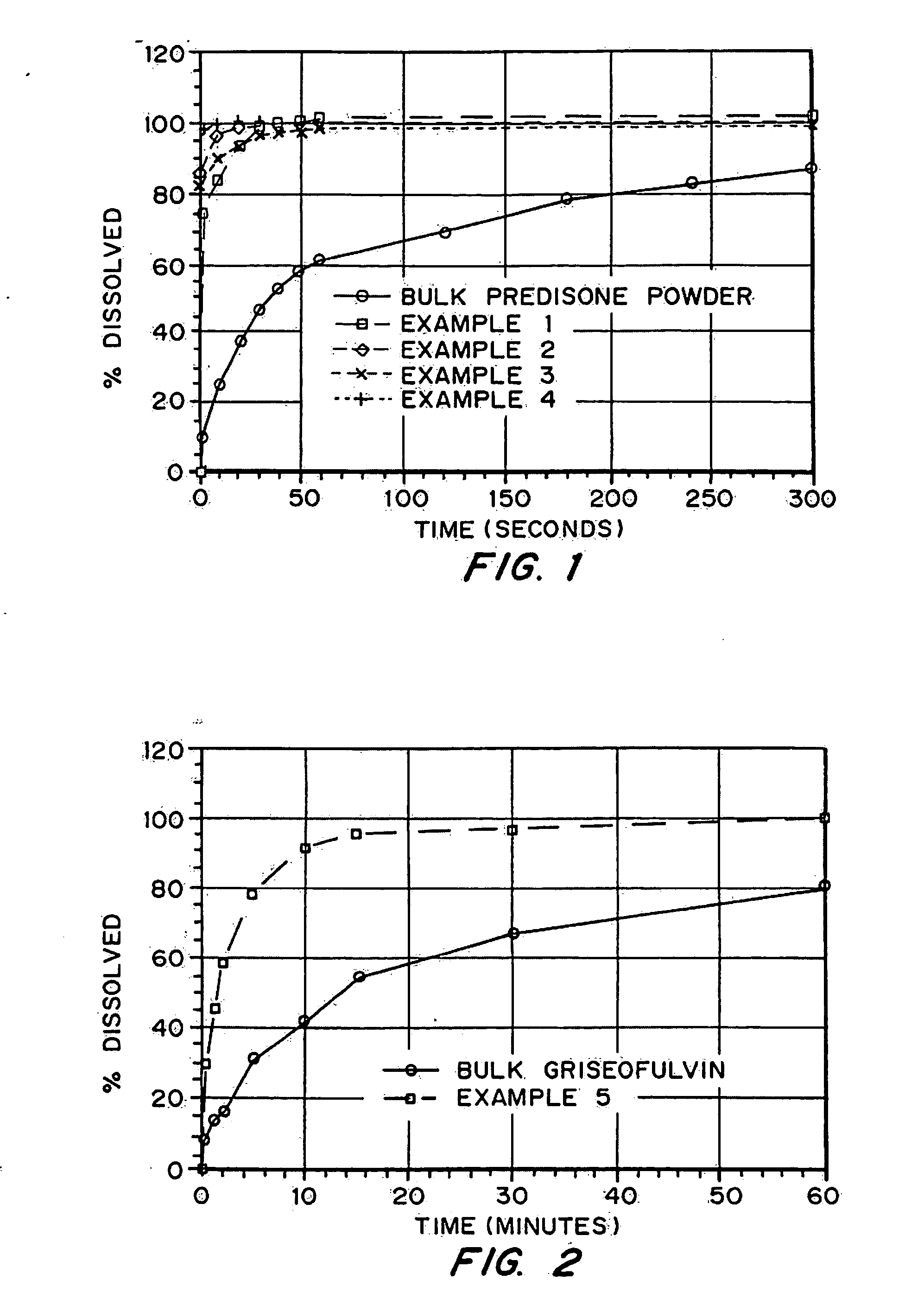
Drugs, especially low aqueous solubility drugs, are provided in a porous matrix form, preferably microparticles, which enhances dissolution of the drug in aqueous media. The drug matrices preferably are made using a process that includes (i) dissolving a drug, preferably a drug having low aqueous solubility, in a volatile solvent to form a drug solution, (ii) combining at least one pore forming agent with the drug solution to form an emulsion, suspension, or second solution, and (iii) removing the volatile solvent and pore forming agent from the emulsion, suspension, or second solution to yield the porous matrix of drug. The pore forming agent can be either a volatile liquid that is immiscible with the drug solvent or a volatile solid compound, preferably a volatile salt. In a preferred embodiment, spray drying is used to remove the solvents and the pore forming agent. The resulting porous matrix has a faster rate of dissolution following administration to a patient, as compared to non-porous matrix forms of the drug. In a preferred embodiment, microparticles of the porous drug matrix are reconstituted with an aqueous medium and administered parenterally, or processed using standard techniques into tablets or capsules for oral administration.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
Sustained-release microcapsule of amorphous water-soluble pharmaceutical active agent
InactiveUS6117455AHigh entrapment of a water-soluble drugSmall initial releaseNanotechGogglesEmulsionOrganic solvent
A sustained-release microcapsule contains an amorphous water-soluble pharmaceutical agent having a particle size of from 1 nm-10 mu m and a polymer. The microcapsule is produced by dispersing, in an aqueous phase, a dispersion of from 0.001-90% (w / w) of an amorphous water-soluble pharmaceutical agent in a solution of a polymer having a wt. avg. molecular weight of 2,000-800,000 in an organic solvent to prepare an s / o / w emulsion and subjecting the emulsion to in-water drying.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Sustained release pharmaceutical compositions for highly water soluble drugs
ActiveUS20070020335A1Reduce spreadReduce erosionPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsControlled releaseActive agent
The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions for controlled release of pharmaceutically active agents, especially those with a high water solubility, high dose, and / or short half-life. In addition, the present application provides methods for preparing and using such pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:FARNAM +1
Porous drug matrices and methods of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20050048116A1Fast dissolutionHigh dissolution ratePowder deliveryGranular deliveryDrugs solutionMicroparticle
Drugs, especially low aqueous solubility drugs, are provided in a porous matrix form, preferably microparticles, which enhances dissolution of the drug in aqueous media. The drug matrices preferably are made using a process that includes (i) dissolving a drug, preferably a drug having low aqueous solubility, in a volatile solvent to form a drug solution, (ii) combining at least one pore forming agent with the drug solution to form an emulsion, suspension, or second solution and hydrophilic or hydrophobic excipients that stabilize the drug and inhibit crystallization, and (iii) removing the volatile solvent and pore forming agent from the emulsion, suspension, or second solution to yield the porous matrix of drug. Hydrophobic or hydrophilic excipients may be selected to stabilize the drug in crystalline form by inhibiting crystal growth or to stabilize the drug in amorphous form by preventing crystallization. The pore forming agent can be either a volatile liquid that is immiscible with the drug solvent or a volatile solid-compound, preferably a volatile salt. In a preferred embodiment, spray drying is used to remove the solvents and the pore forming agent. The resulting porous matrix has a faster rate of dissolution following administration to a patient, as compared to non-porous matrix forms of the drug. In a preferred embodiment, microparticles of the porous drug matrix are reconstituted with an aqueous medium and administered parenterally, or processed using standard techniques into tablets or capsules for oral administration.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
Intravaginal drug delivery devices for the delivery of macromolecules and water-soluble drugs
ActiveUS20090004246A1Good sustained releaseViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesIntravaginal administrationPharmacy
An intravaginal drug delivery device comprises a device body comprising a hydrophobic carrier material having at least one channel defining at least one opening to the exterior of said device body, said at least one channel being adapted to receive at least one drug-containing insert; at least one drug-containing insert positioned in said at least one channel, said drug-containing insert capable of releasing a pharmaceutically effective amount of at least one drug suitable for intravaginal administration and containing about 1% to about 70% of at least one water-soluble release enhancer, both the drug and the water-soluble release enhancer dispersed in an insert carrier material; wherein said hydrophobic carrier material and said insert carrier material may be the same or different; and wherein said at least one drug-containing insert is exposed on said exterior of said device body when said intravaginal drug delivery device is in use.
Owner:APTALIS PHARMA
Liposomal products
InactiveUS6060080AHigh encapsulation efficiencyEasy to packLiposomal deliveryCholesterolWater soluble drug
A liposomal aqueous dispersion and method of making the liposomal aqueous dispersion is useful for encapsulation of drugs. The liposomal aqueous dispersion comprises: an aqueous suspension medium; multilamellar liposomes comprising an anionic phospholipid and cholesterol as essential components; neutral phospholipid in a mole ratio of 0 to 40% based on the total amount of said multilamellar liposomes; and a cation moiety-containing water-soluble drug, wherein the electrolyte concentration of said aqueous suspension medium is not more than 40 mM.
Owner:DAIICHI PHARMA CO LTD
Porous drug matrices and methods of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20050058710A1Fast dissolutionExtended half-lifePowder deliveryGranular deliveryDrugs solutionMicroparticle
Drugs, especially low aqueous solubility drugs, are provided in a porous matrix form, preferably microparticles, which enhances dissolution of the drug in aqueous media. The drug matrices preferably are made using a process that includes (i) dissolving a drug, preferably a drug having low aqueous solubility, in a volatile solvent to form a drug solution, (ii) combining at least one pore forming agent with the drug solution to form an emulsion, suspension, or second solution and hydrophilic or hydrophobic excipients that stabilize the drug and inhibit crystallization, and (iii) removing the volatile solvent and pore forming agent from the emulsion, suspension, or second solution to yield the porous matrix of drug. Hydrophobic or hydrophilic excipients may be selected to stabilize the drug in crystalline form by inhibiting crystal growth or to stabilize the drug in amorphous form by preventing crystallization. The pore forming agent can be either a volatile liquid that is immiscible with the drug solvent or a volatile solid compound, preferably a volatile salt. In a preferred embodiment, spray drying is used to remove the solvents and the pore forming agent. The resulting porous matrix has a faster rate of dissolution following administration to a patient, as compared to non-porous matrix forms of the drug. In a preferred embodiment, microparticles of the porous drug matrix are reconstituted with an aqueous medium and administered parenterally, or processed using standard techniques into tablets or capsules for oral administration.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
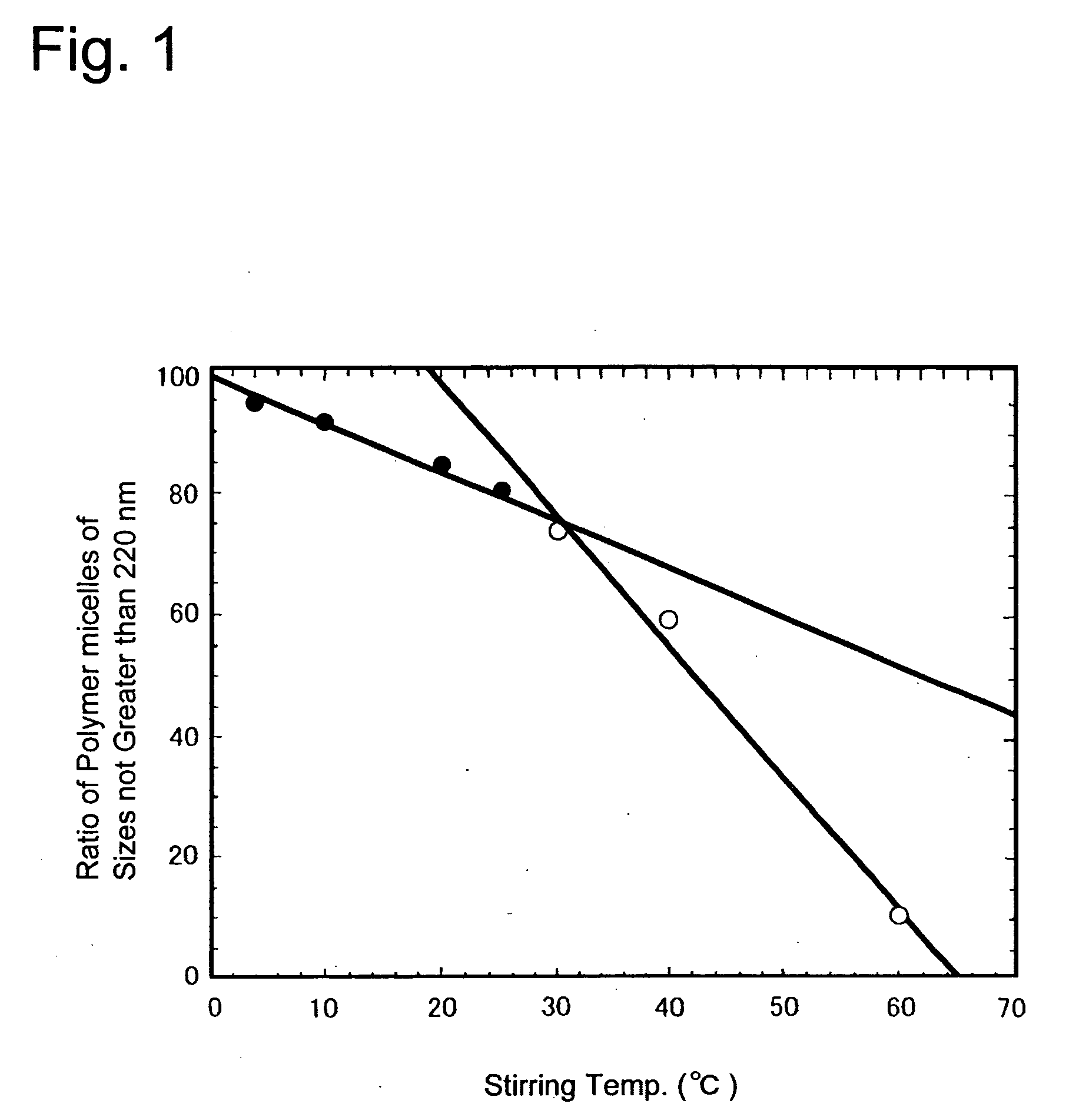
Method for preparing a polymer micelle pharmaceutical preparation containing drug for injection
InactiveUS20060057219A1Improve efficiencyThe preparation method is simple and easyHeavy metal active ingredientsPowder deliveryOrganic solventWater soluble drug
A production method of a preparation containing drug-encapsulating polymer micelles is provided, which comprises dissolving a hydrophilic-hydrophobic block copolymer and a sparingly water-soluble drug in a volatile organic solvent, then removing the solvent, and stirring the residue with water at a temperature not higher than 30° C. to dissolve the drug-encapsulating polymer micelles into the water.
Owner:NANOCARRIER
Polymeric drug formulations
InactiveUS7005454B2Reduce the formation of blood clotsPrevent thrombosisPowder deliveryBiocideWater insolubleMedicine
Polymeric drug formulations containing a non-releasing single-phase dispersion of a water-soluble drug in a water-insoluble tissue-compatible polymer matrix. Polymeric drug formulations are also disclosed containing a single-phase dispersion of a water-soluble drug and a water-insoluble tissue-compatible polymer matrix, and a second, phase-disrupting polymer that is non-miscible with the tissue-compatible polymer and is present in an amount sufficient to form phase-separated microdomains of the second polymer in the tissue-compatible polymer matrix, so that the release rate of the water-soluble drug from the tissue-compatible polymer matrix is related to the amount of the second polymer. Methods of preparing the polymeric drug formulations are also described, as well as methods for site-specific drug delivery utilizing the polymeric drug formulations.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY +1
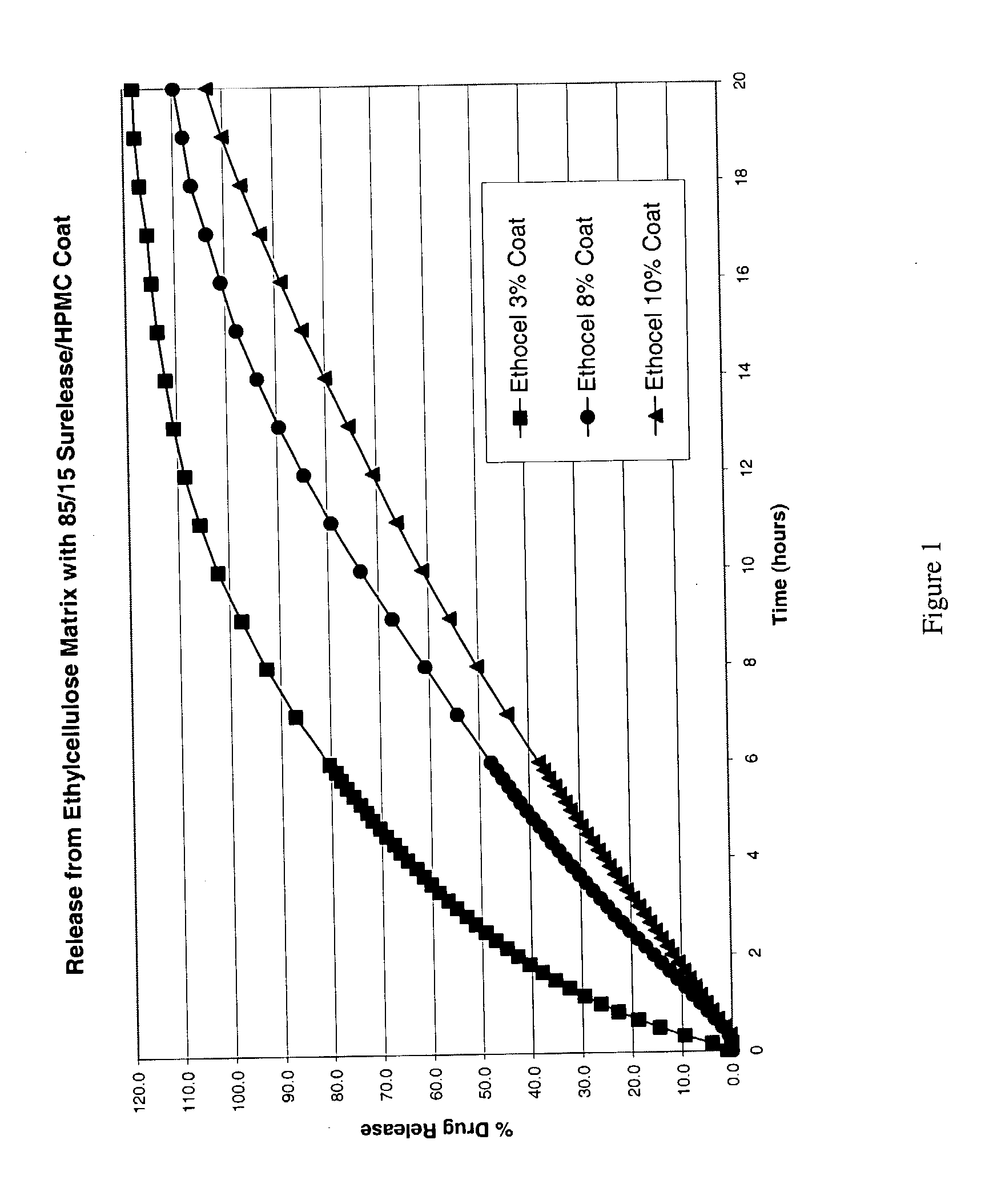
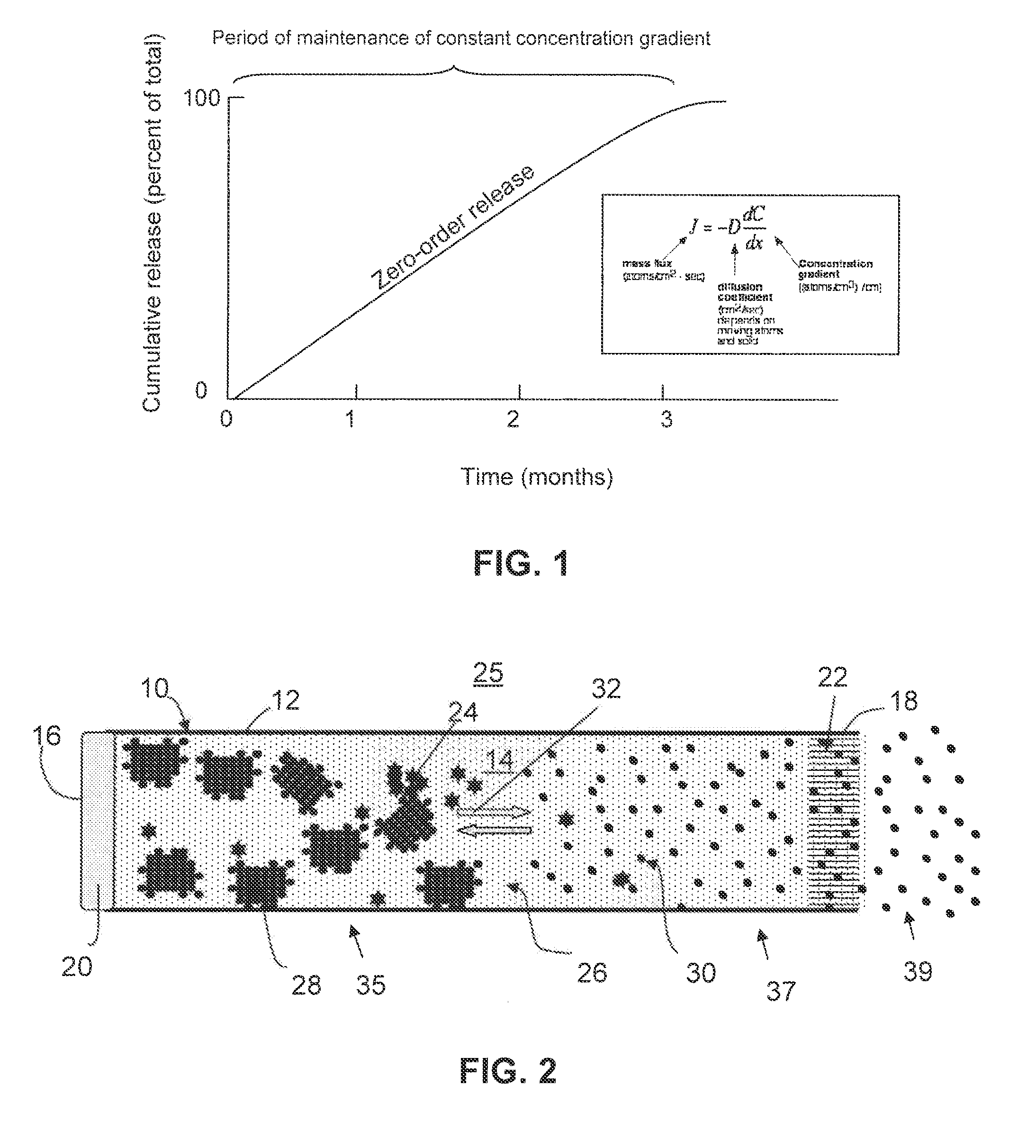
Zero-order sustained release dosage forms and method of making same
InactiveUS20030133982A1High drug loadingReduce releasePowder deliveryBiocideSustained release drugHydrophobic polymer
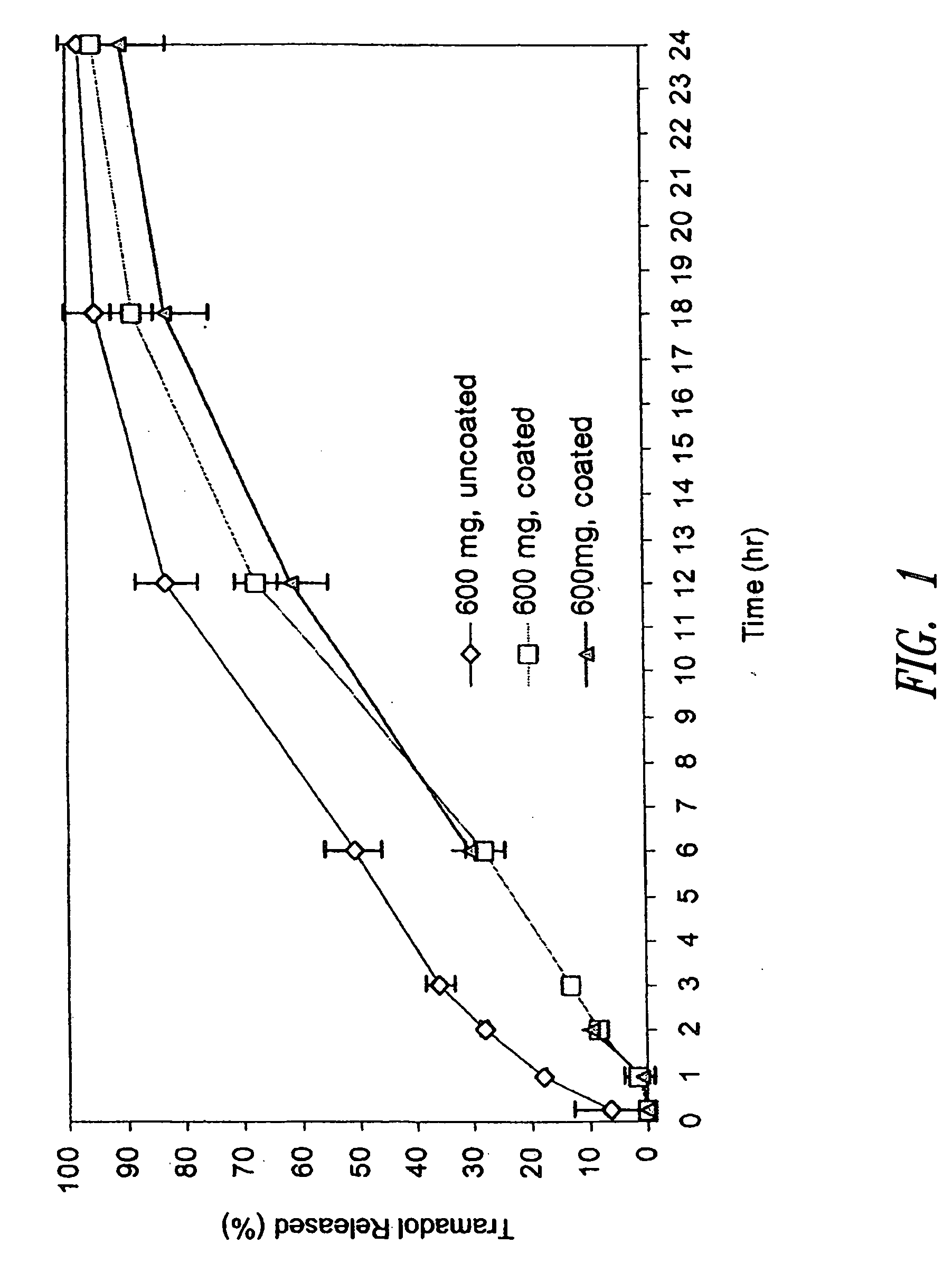
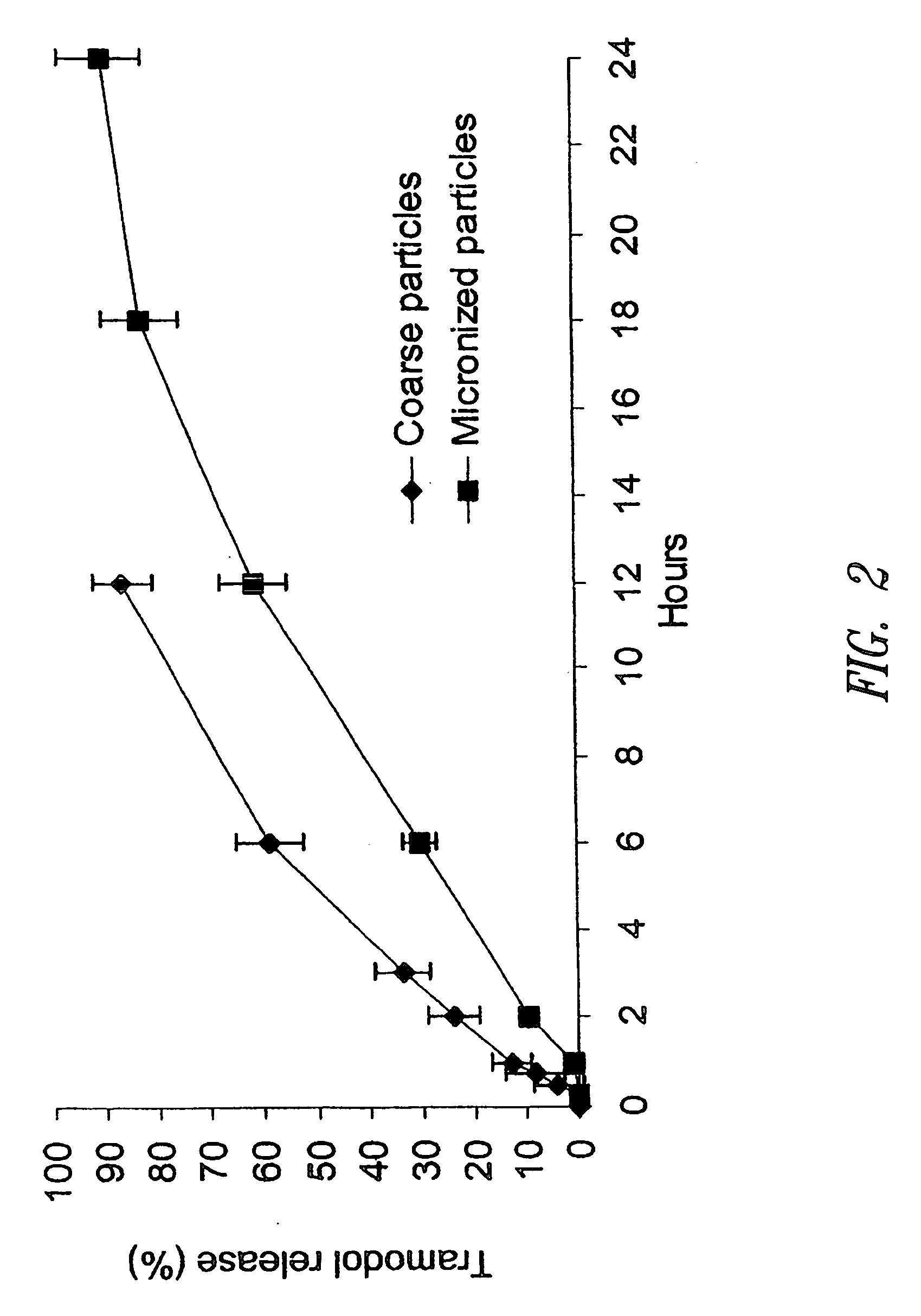
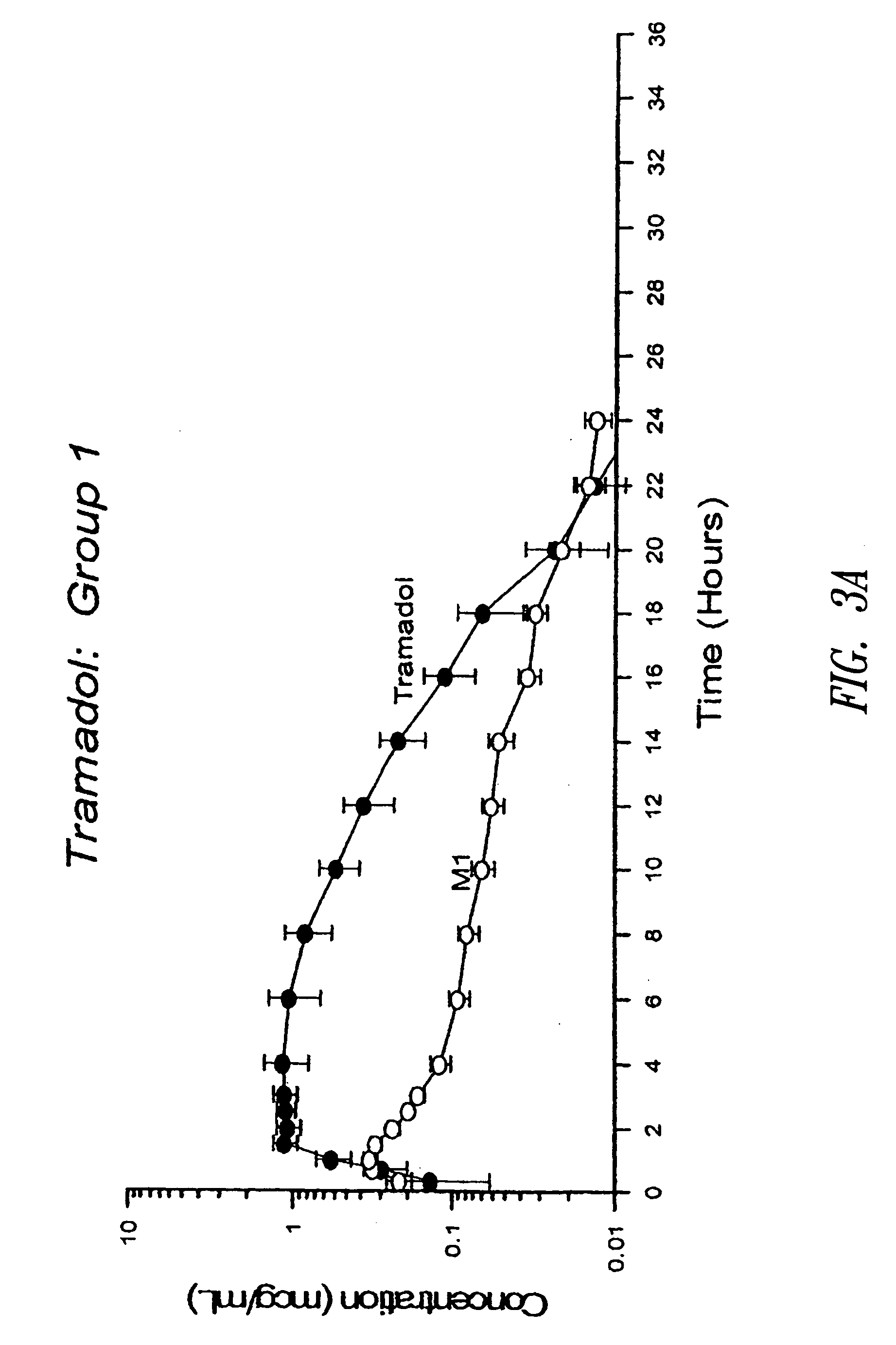
The present invention relates to zero-order sustained release solid dosage forms suitable for administration of a wide range of therapeutically active medicaments, especially those that are water-soluble, and to a process of making same. The solid dosage form comprises (a) a matrix core comprising ethylcellulose and the active agent and (b) a hydrophobic polymer coating encasing the entire matrix core.
Owner:PHARMACIA CORP
Compositions and methods for preparation of poorly water soluble drugs with increased stability
The present invention provides stable pharmaceutical compositions of poorly water soluble pharmaceutical agents and stabilizing agents which function to increase stability of the compositions. The use of stabilizing agents provide extended stability of nanoparticle suspensions and other formulations of poorly water soluble pharmaceutical agents such as docetaxel under certain conditions, for example upon dilution for administration.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Water-dispersible oral, parenteral, and topical formulations for poorly water soluble drugs using smart polymeric nanoparticles
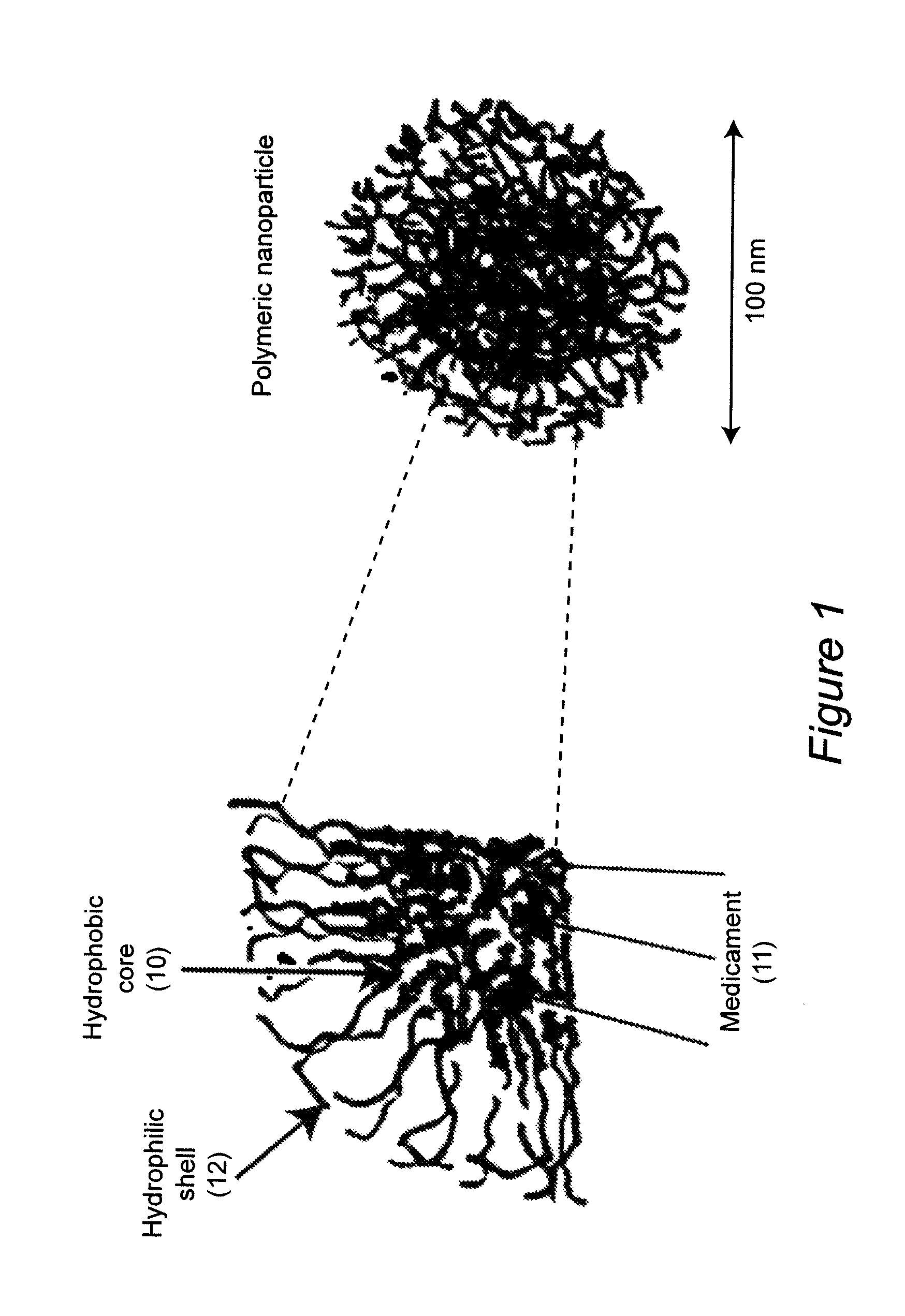
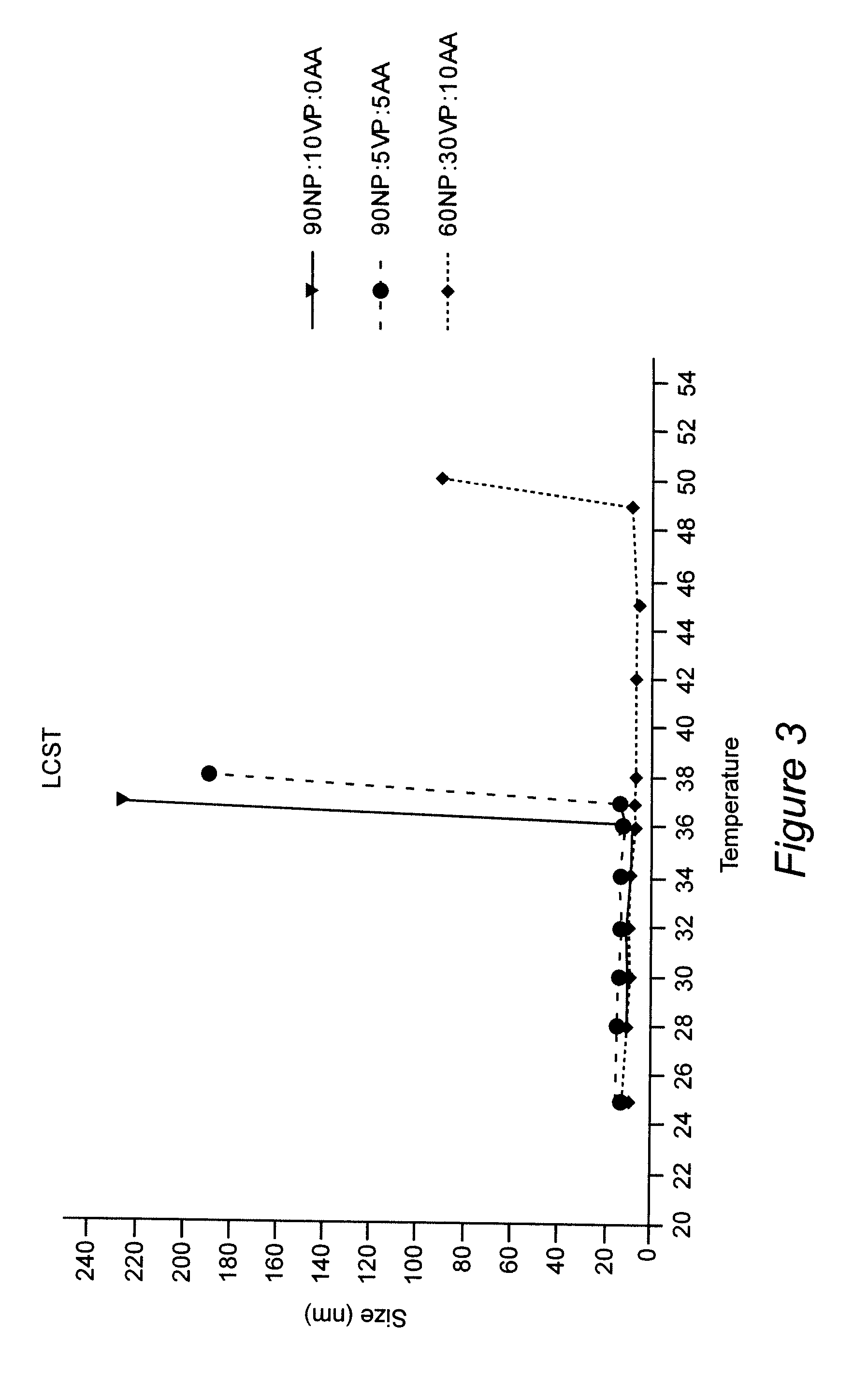
ActiveUS8313777B2Control releaseImprove bioavailabilityPowder deliveryNervous disorderWater dispersibleSmart polymer
Polymeric nanoparticles with a hydrophobic core and a hydrophilic shell are formed from: 1) N-isopropyl acrylamide (NIPAAM), at a molar ratio of about 50% to about 90%, and preferably 60% for specific delivery routes such as oral or parenteral; either water-soluble vinyl derivatives like vinylpyrolidone (VP) or vinyl acetate (VA), or water insoluble vinyl derivatives like methyl methacrylate (MMA) or styrene (ST), at a molar ratio of about 10% to about 30%; and acrylic acid (AA), at a molar ratio of about 10% to about 30%. The formed nanoparticles may be optionally surface functionalized using reactive groups present in AA, including PEGylation, or conjugation of moieties such as chemotherapeutics, contrasting agents, antibodies, radionucleides, ligands, and sugars, for diagnostic, therapeutic, and imaging purposes. The polymeric nanoparticles are preferably dispersed in aqueous solutions. The polymeric nanoparticles incorporate one or more types of medicines or bioactive agents in the hydrophobic core; on occasion, the medicine or bioactive agent may be conjugated to the nanoparticle surface via reactive functional groups. The polymeric nanoparticles are capable of delivering the said medicines or bioactive agents through oral, parenteral, or topical routes. The polymeric nanoparticles allow poorly water soluble medicines or bioactive agents, or those with poor oral bioavailability, to be formulated in an aqueous solution, and enable their convenient delivery into the systemic circulation.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Compositions of tocol-soluble therapeutics
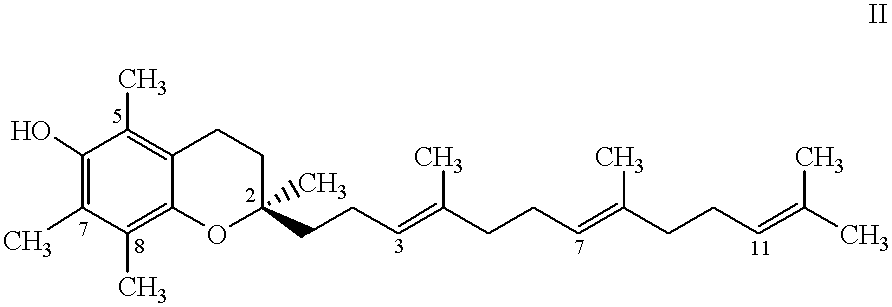
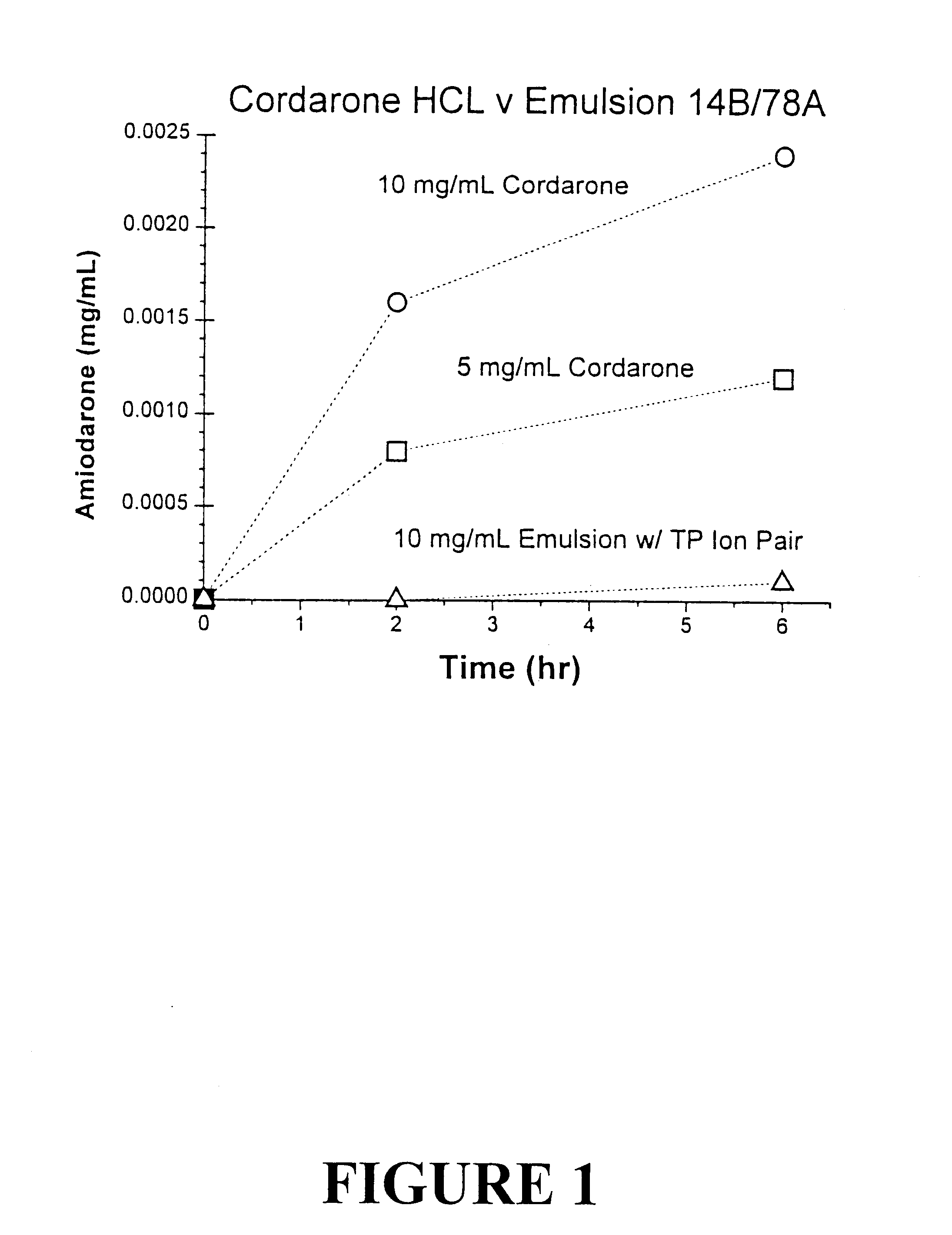
Tocol-based compositions of charged amphiphilic and water soluble pharmaceutically active compounds or their charged precursors are prepared by forming a tocol-soluble ion pair with an oppositely charged ion-pair forming compound capable of forming a tocol-soluble ion-pair with the active compound.Also disclosed are novel compounds tocopherolsuccinate-aspartate and tocopherolsuccinate-glutamate, which are useful as ion-pair forming compounds.
Owner:SONUS PHARM INC
Preparation of drug particles using evaporation precipitation into aqueous solutions
A method for preparing poorly water soluble drug particles is disclosed. The method comprises dissolving a drug in at least one organic solvent to form a drug / organic mixture, spraying the drug / organic mixture into an aqueous solution and concurrently evaporating the organic solvent in the presence of the aqueous solution to form an aqueous dispersion of the drug particles. The resulting drug particles are in the nanometer to micrometer size range and show enhanced dissolution rates and reduced crystallinity when compared to the unprocessed drug. The present invention additionally contemplates products and processes for new drug formulations of insoluble drug particles having high dissolution rates and extremely high drug-to-excipient ratios.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Polymeric drug formulations
InactiveUS7101840B2Improve performanceTrend downPowder deliverySaccharide peptide ingredientsNon solventWater insoluble
A method of forming a polymeric drug formulation in which a water-soluble drug is blended with a water-insoluble tissue-compatible polymer that is miscible in the solid phase with the drug, and with a poly(alkylene oxide), in a solvent system capable of forming a homogeneous solution of the drug, the tissue-compatible polymer and the poly(alkylene oxide), after which the solution is added to a non-solvent for the drug, the tissue-compatible polymer and the poly(alkylene oxide), so that a microdomain-separated solid co-precipitate of the drug, the tissue-compatible polymer and the poly(alkylene oxide) is formed, wherein the poly(alkylene oxide) is blended in an amount effective to form phase-separated microdomains in said co-precipitate.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY +1
Free-flowing solid formulations with improved bio-availability of poorly water soluble drugs and process for making the same
InactiveUS20070009559A1Low water solubilityPromote absorptionDispersion deliveryMetabolism disorderPolyolUnsaturated fatty acid ester
A free-flowing solid formulations of drugs or pharmaceutical agents which have poor aqueous solubility are obtained by admixing a liquid or gel composition that includes 1 to 30 percent by weight of the drug, 5 to 60 percent by weight of a surfactant, 10 to 40 percent by weight of water; 1 to 20 percent by weight of unsaturated fatty acid ester, 0 to 50 percent by weight water miscible pharmaceutically acceptable polyol and 1 to 10 percent by weight of phospholipid with a pharmaceutically acceptable suitable solid carrier and thereafter drying the admixture. The free-flowing powder is suitable for being formed into tablets or capsules. The drug or pharmaceutical agent is solubilized in the formulation and has significantly improved bio-availability when compared to the drug tested in its pure form.
Owner:LI WENJI +2
Methods of enhancing drug delivery and effectiveness of therapeutic agents
ActiveUS20120076862A1Promote absorptionConvenient treatmentPowder deliveryHeavy metal active ingredientsDiseaseCo administration
The present invention in one aspect provides methods of enhancing uptake of a therapeutic agent in a target tissue as well as methods of treating a disease (such as cancer) or enhancing effectiveness of treatment with a therapeutic agent in an individual by co-administering a composition comprising nanoparticles comprising albumin and a poorly water soluble drug such as a taxane with the therapeutic agent. The present invention in another aspect provides a method of treatment or a method of selecting patients for treatment of a disease (such as cancer) with the combination of a therapeutic agent and a composition comprising nanoparticles comprising albumin and a poorly water soluble drug such as a taxane based on one or more characteristics of the target tissue that correlates or indicates the capability of getting enhanced therapeutic agent uptake as a result of the co-administration of the taxane nanoparticle composition in the target tissue (referred to as “the drug uptake capability”). Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions, article of manufacture, and kits useful for methods described herein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Water Soluble Drug-Solubilizer Powders and Their Uses
InactiveUS20120329738A1Improve gastrointestinal absorptionEfficient processingBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsWater soluble drugGastrointestinal absorption
Enhanced methods have been discovered, using either sonication or homogenization followed by increased temperature and pressure, to solubilize compounds using diterpene glycosides and to produce a powder form of the compound-solubilizer complex than can be reconstituted in water. Without the diterpene glycoside, the compounds were insoluble or sparingly soluble in water, including some fat-insoluble vitamins. Water solutions of these compounds were made using a diterpene glycoside solubilizer, for example, rubusoside. The compound-solubilizer complex was then dehydrated to a stable powder that could then be reconstituted with water. A reconstituted drug-solubilizer complex (curcumin-rubusoside) was shown to be effective on reconstitution. In addition, the diterpene glycoside, rubusoside, was shown to be an inhibitor of permeability glycoprotein (P-gp), and will thus increase gastrointestinal absorption of certain drugs administered with rubusoside.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Nanoparticle compositions of water-soluble drugs for oral administration and preparation methods thereof
InactiveUS20070154559A1Increase ratingsIncrease resistanceAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsLipid formationOral medication
The present invention relates to an orally administrable composition containing nanoparticles with the particle size of 500 nm or less, comprising 0.1˜30 weight % of a complex of a water-soluble drug and a counter-ion substance in which the charged water-soluble drug is bonded with the counter-ion substance, 0.5˜80 weight % of a lipid, 0.5˜80 weight % of a polymer, and 1˜80 weight % of an emulsifier, wherein the weight ratio of said lipid and said polymer is in the range of 1:0.05˜3, and a preparation method thereof. The composition of the present invention has high gastrointestinal absorption rate upon oral administration, and has high drug entrapping rate in the nanoparticle, and is also stable against lipases.
Owner:SAMYANG BIOPHARMLS CORP
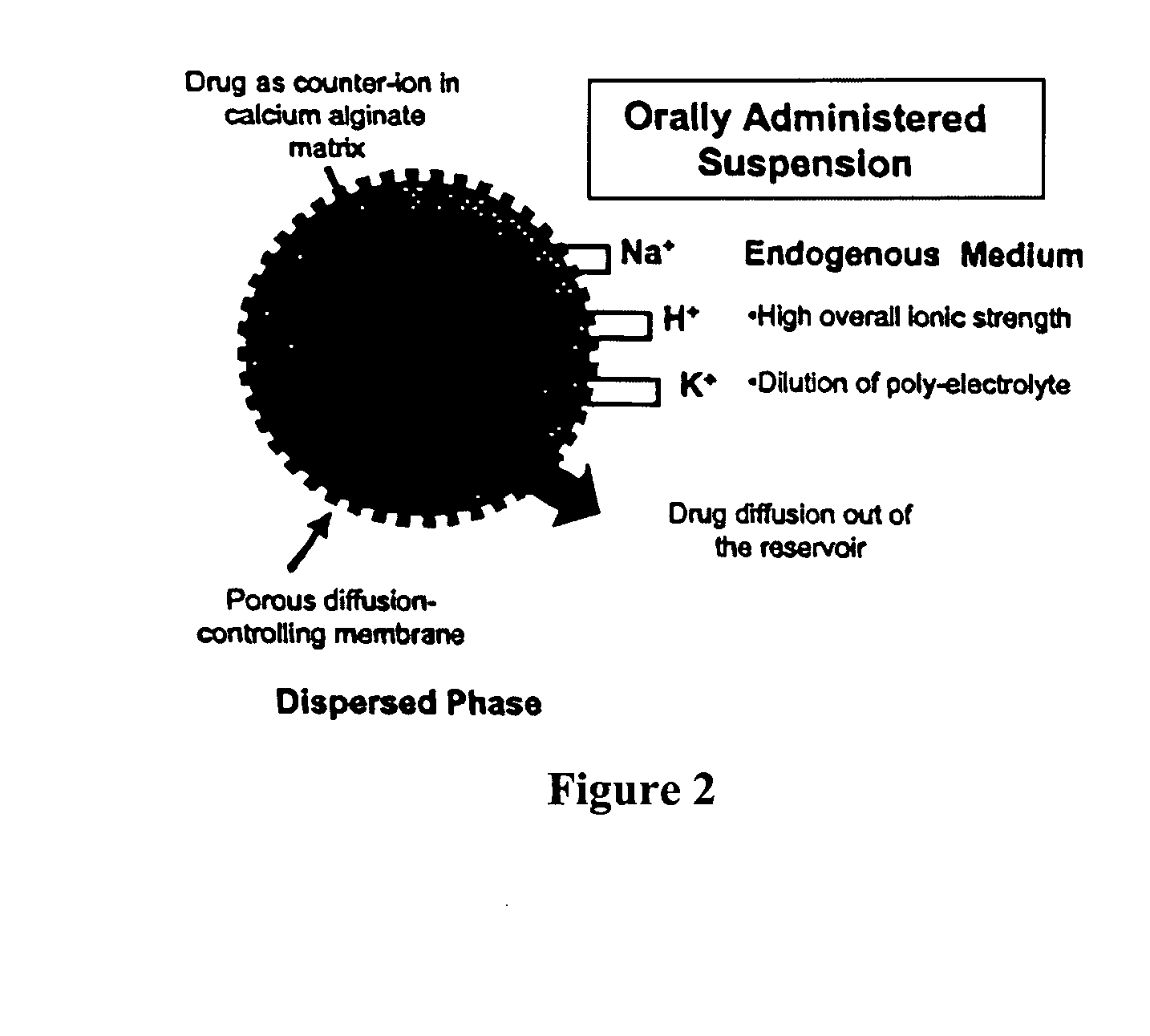
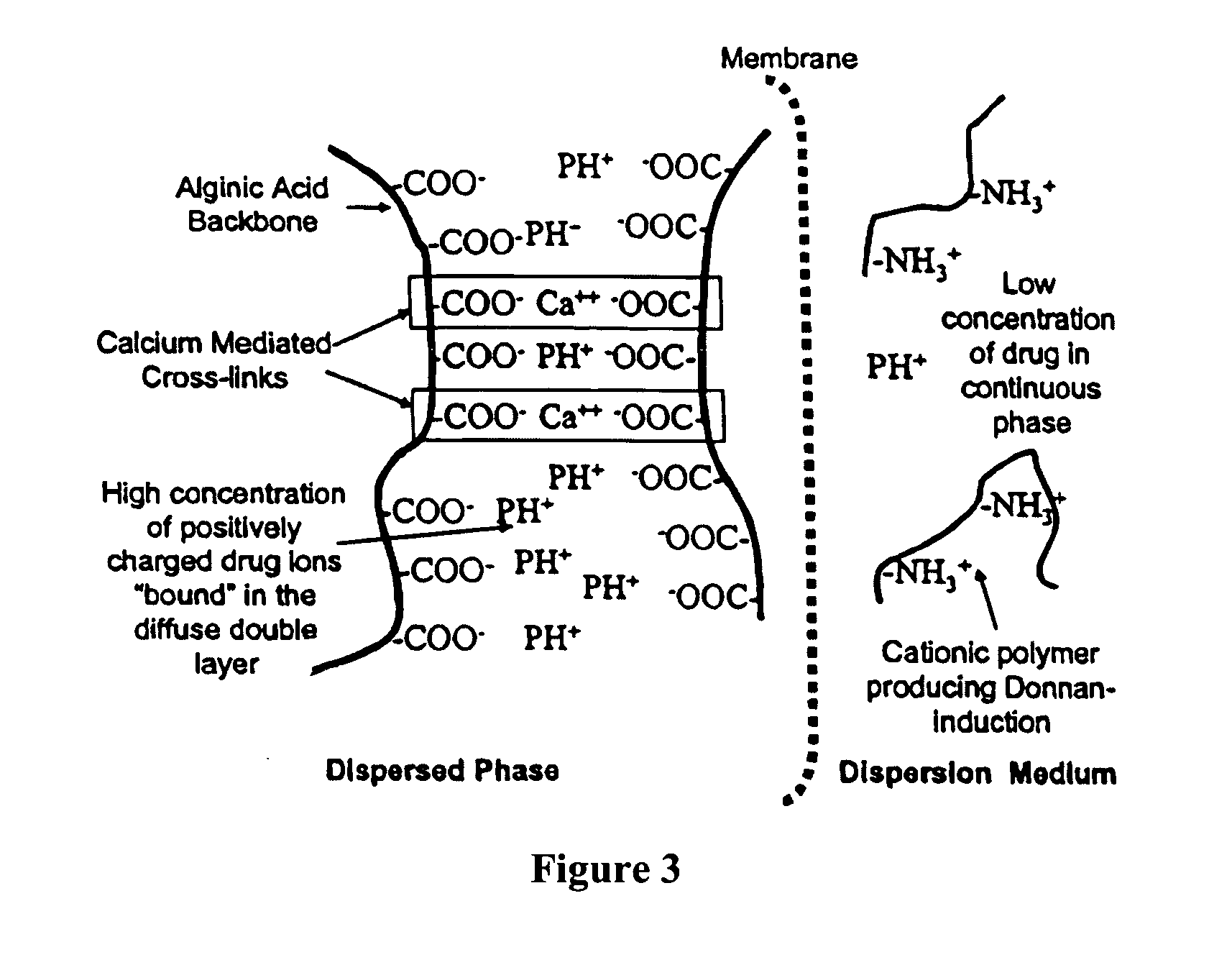
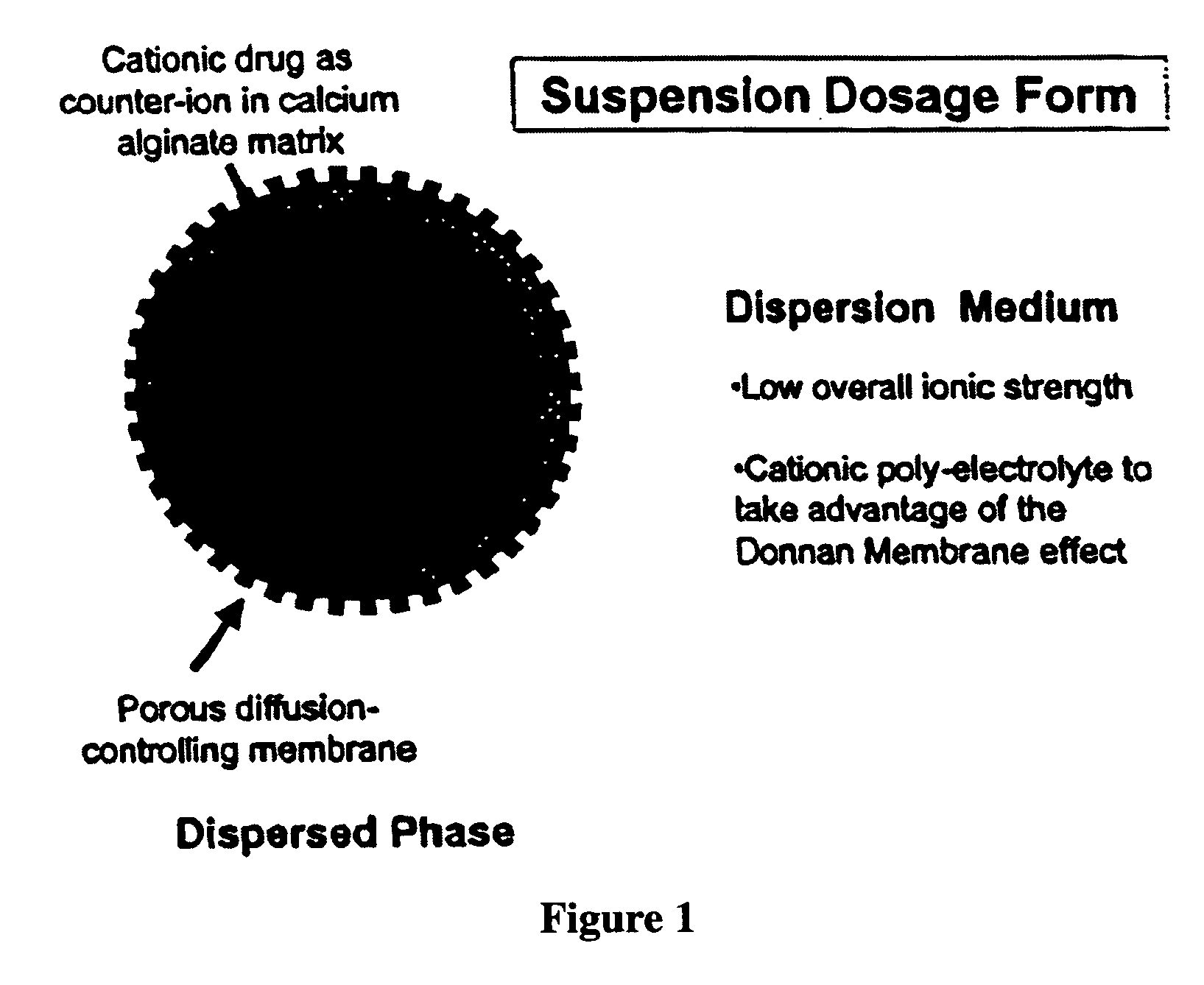
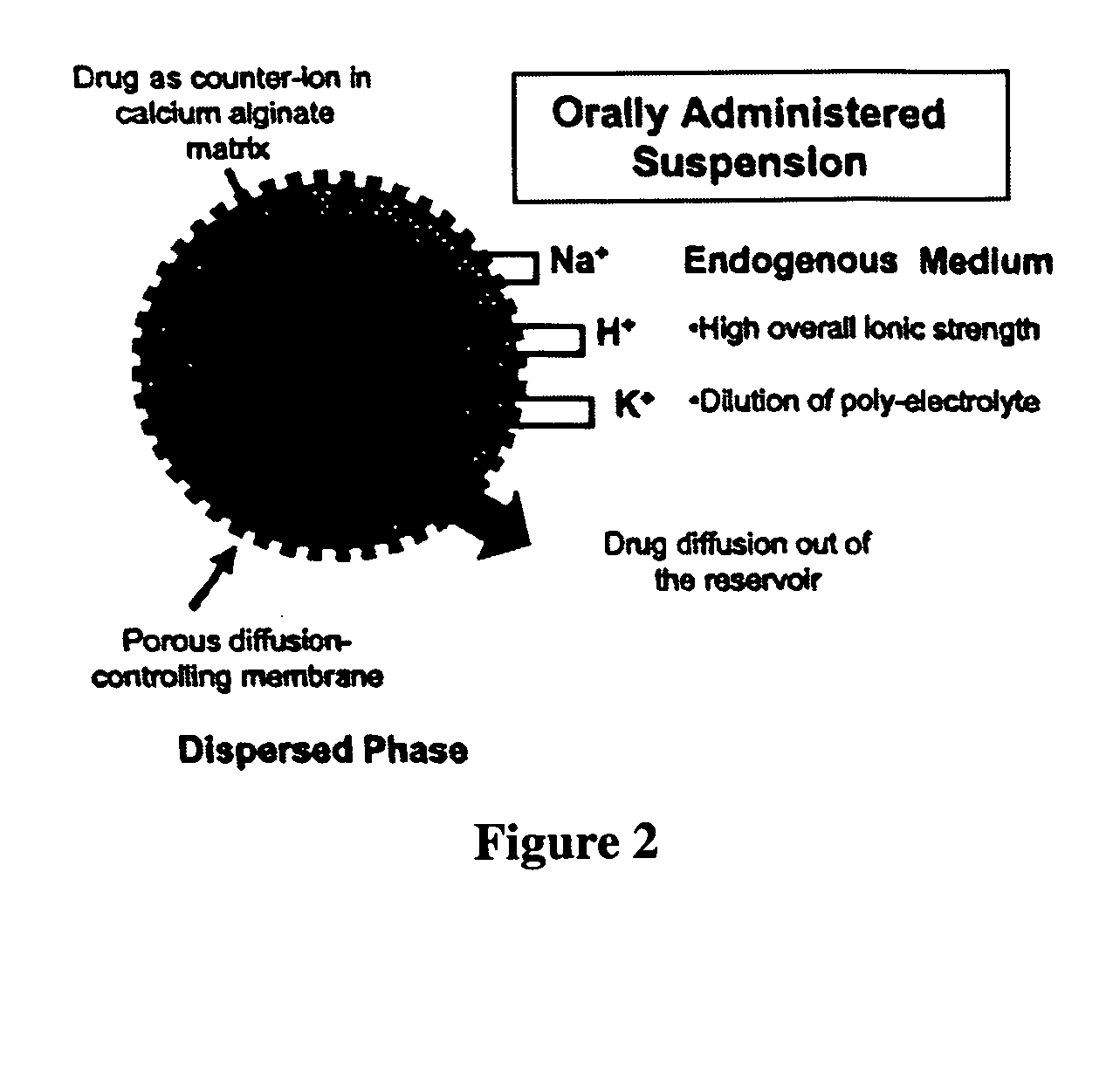
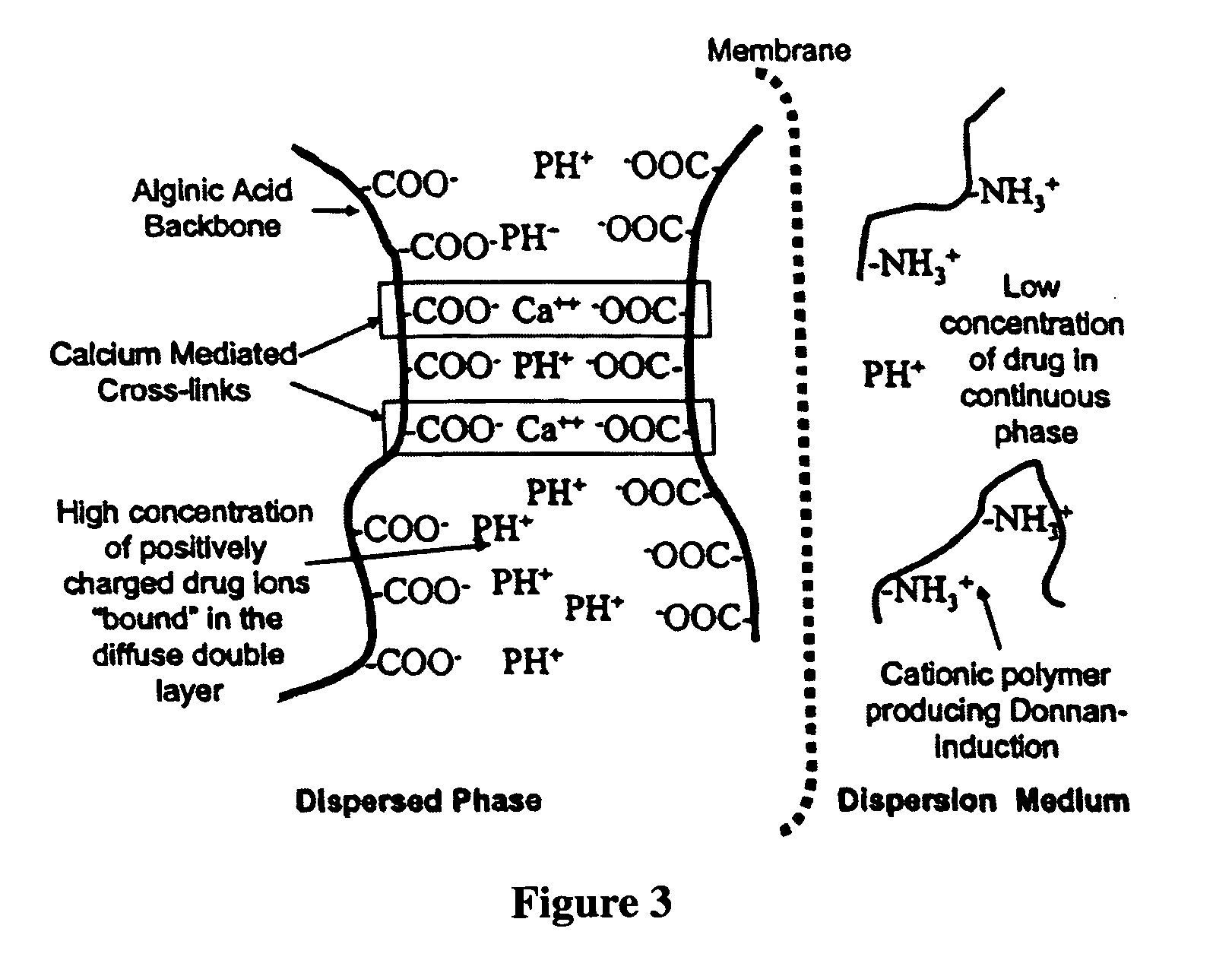
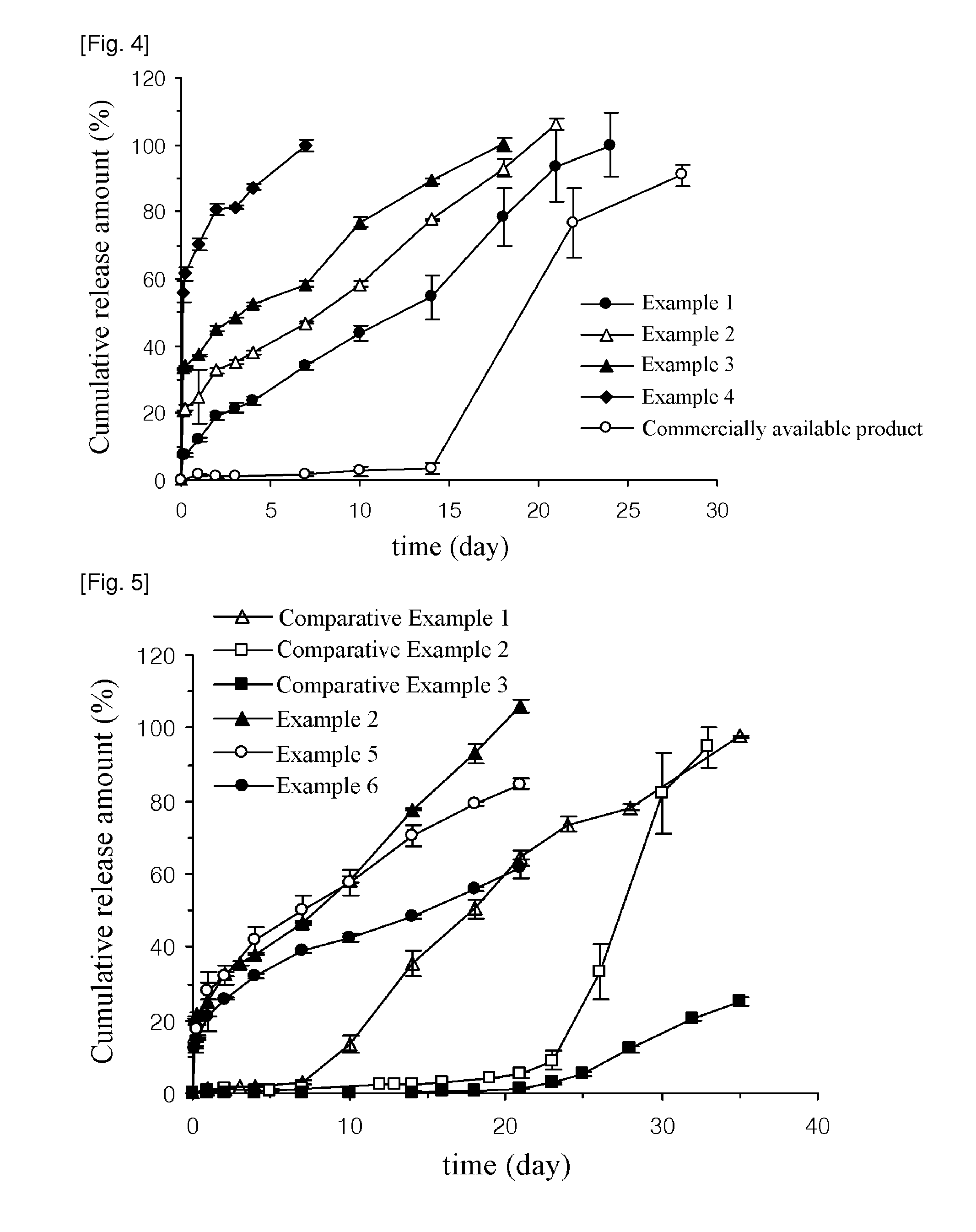
Aqueous sustained-release drug delivery system for highly water-soluble electrolytic drugs
InactiveUS20050013792A1Change in permeabilityPowder deliveryNervous disorderPolyelectrolyteSustained release drug
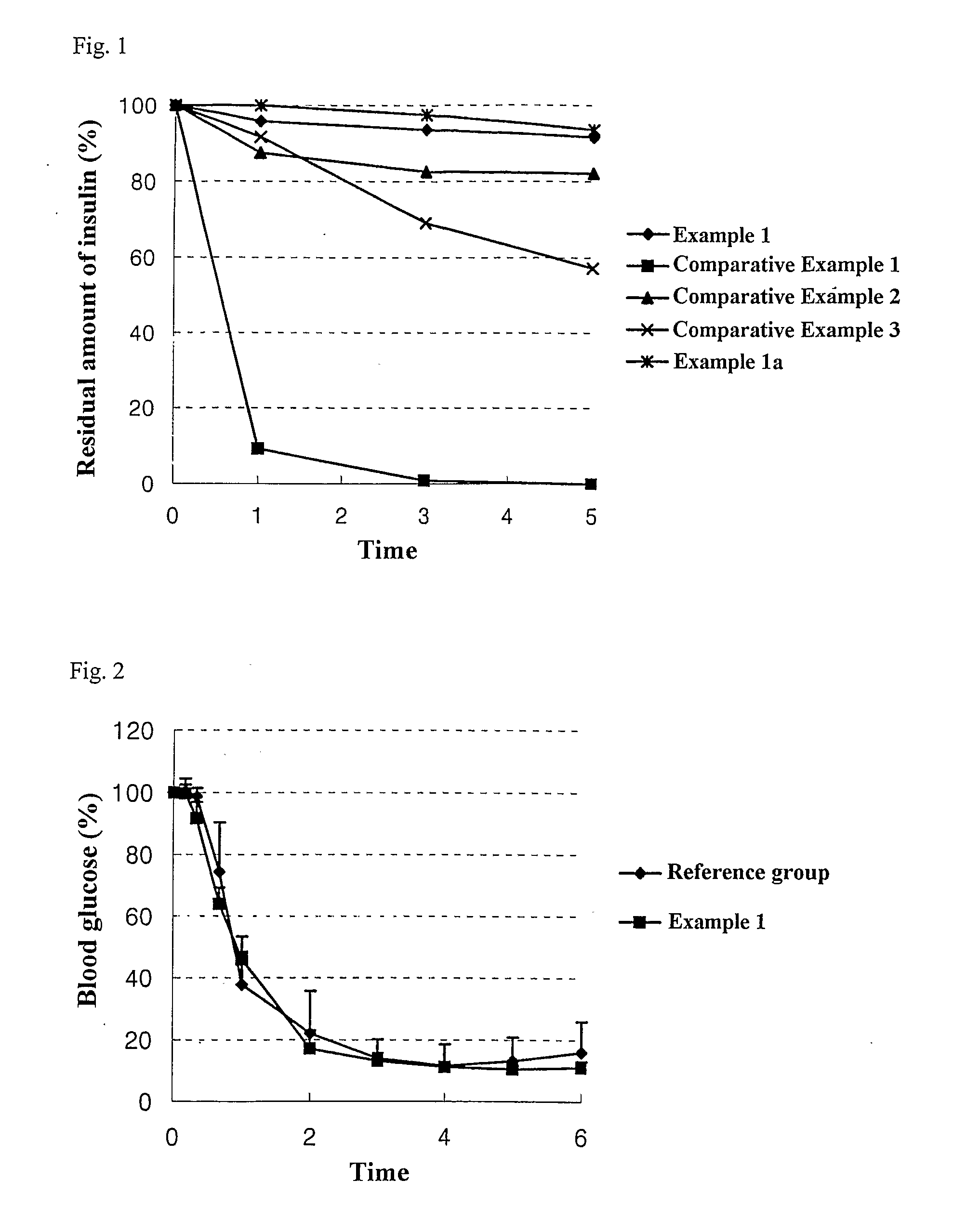
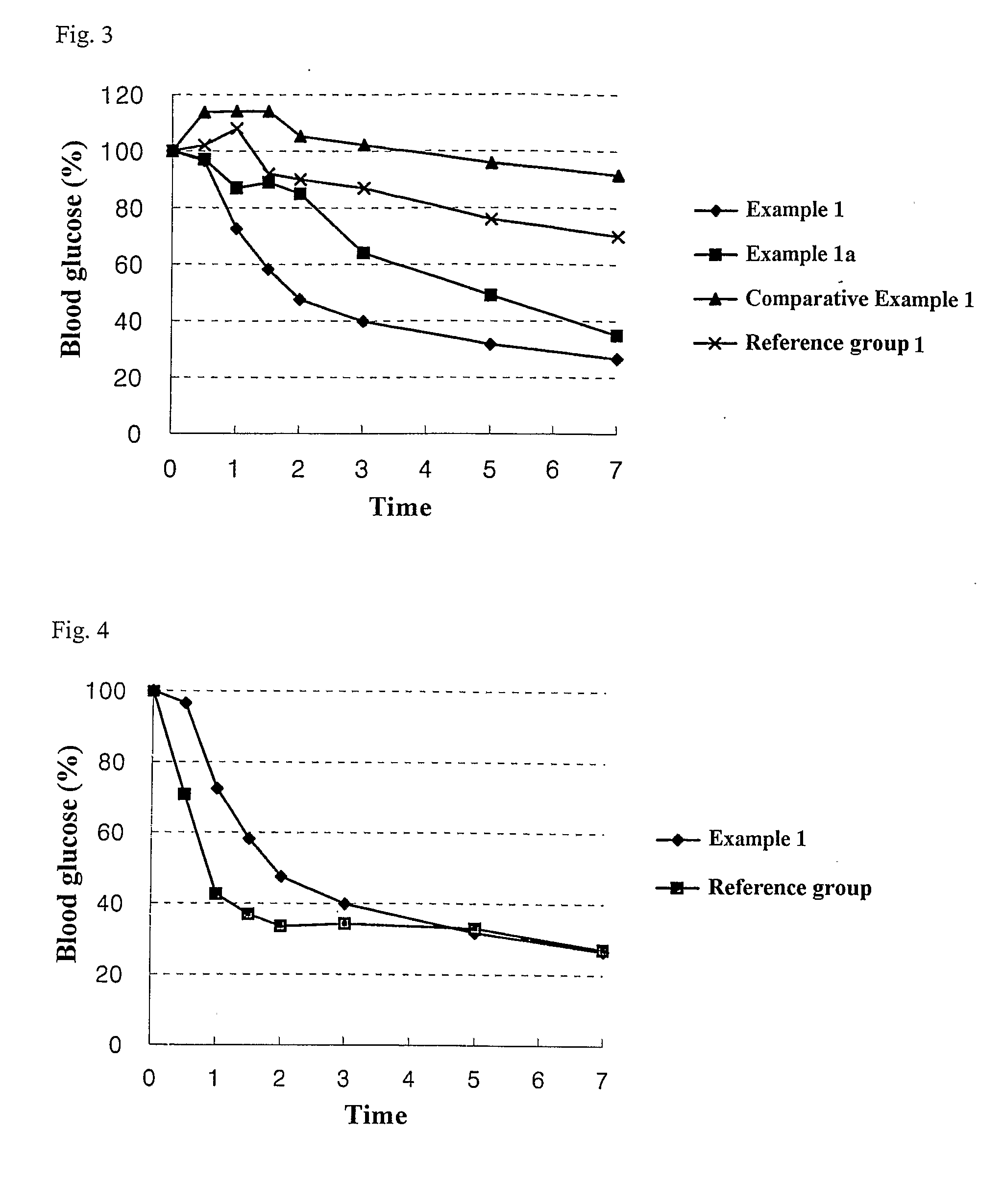
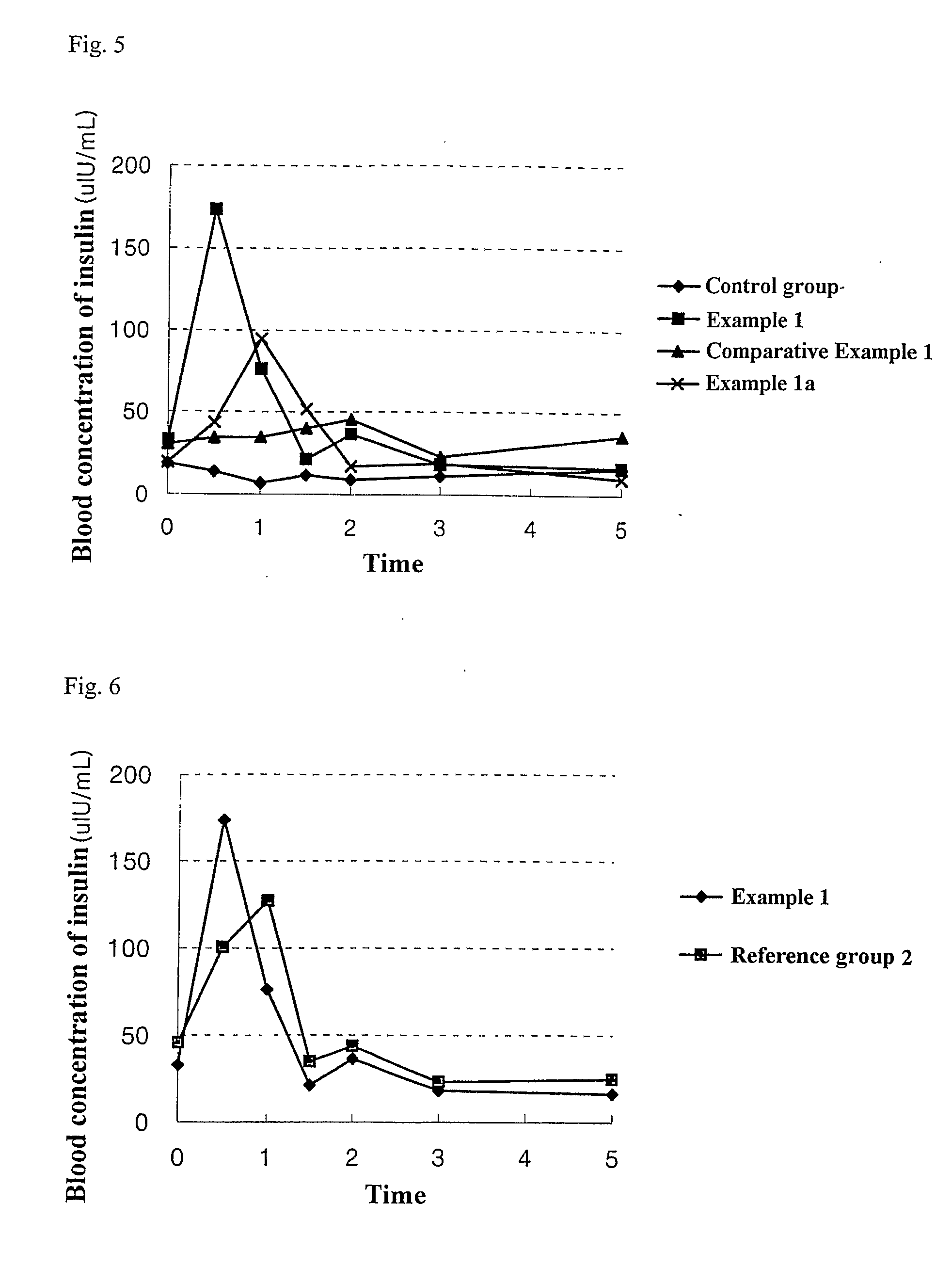
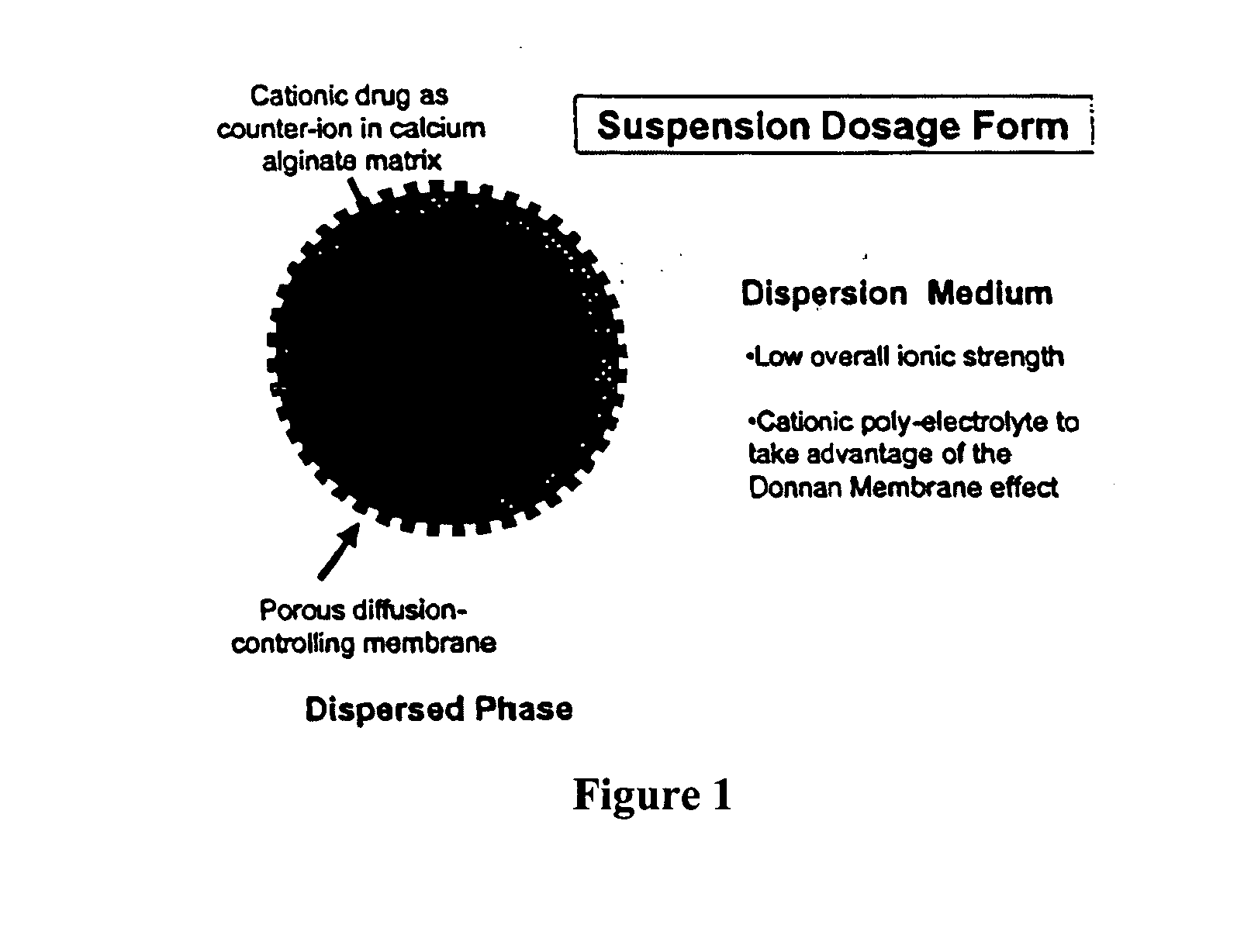
The present invention relates to liquid sustained release suspension dosage forms comprising ionized forms of water-soluble drugs. In particular, the invention encompasses a liquid form controlled release drug composition comprising a dispersed phase comprising an ion-exchange matrix drug complex comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable ion-exchange matrix and a water-soluble electrolytic drug associated with the ion-exchange matrix, wherein the surface charge of the ion-exchange matrix is opposite that of the electrolytic drug and a dispersion medium substantially free of diffusible counterions, further comprising a polyelectrolyte having the same charge as the electrolytic drug. The invention also provides methods for preparing such compositions and methods of treatment.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF BALTIMORE +1
Drug-containing nanoparticle, process for producing the same and parenterally administered preparation from the nanoparticle
InactiveUS20070077286A1Excellent sustained-releasabilityImprove targetingPowder deliveryHydroxy compound active ingredientsNanoparticleWater soluble
To provide an external preparation or injectable preparation that exerts the effect of enabling transdermal or transmucosal in viva absorption of fat-soluble drugs and water-soluble drugs not having been satisfactorily attained hitherto and that contains a highly absorbable fat-soluble / water-soluble drug, the injectable preparation especially aiming at sustained-release and target effects. In particular, drug-containing nanoparticles (secondary nanoparticles) are provided by causing primary nanoparticles containing a fat-soluble drug or fat-solubilized water-soluble drug to act with a bivalent or trivalent metal salt. Further, drug-containing nanoparticles (tertiary nanoparticles) are provided by first causing primary nanoparticles containing a fat-soluble drug or fat-solubilized water-soluble drug to act with a bivalent or trivalent metal salt to thereby obtain secondary nanoparticles and thereafter causing a monovalent to trivalent basic salt to act on the secondary nanoparticles. Still further, there are provided a process for producing these nanoparticles, and a transdermal or transmucosal external preparation or injectable preparation in which these nanoparticles are contained.
Owner:LTT BIO PHARMA
Aqueous sustained-release drug delivery system for highly water-soluble electrolytic drugs
InactiveUS20060134148A1Reduce molecular weightQuick releasePowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsElectrolysisIon exchange
Owner:HOLLENBECK R GARY
Implantable device for long-term delivery of drugs
A device for sustained delivery of a poorly water soluble drug is described. A drug reservoir within the device, when in operation, contains an aqueous suspension of the drug mixed with a suspension of an excipient that, in one embodiment, generates acidic groups for a sustained period of time to maintain a desired pH in the aqueous suspension that in turn provides a constant concentration of a soluble form of the drug.
Owner:DELPOR
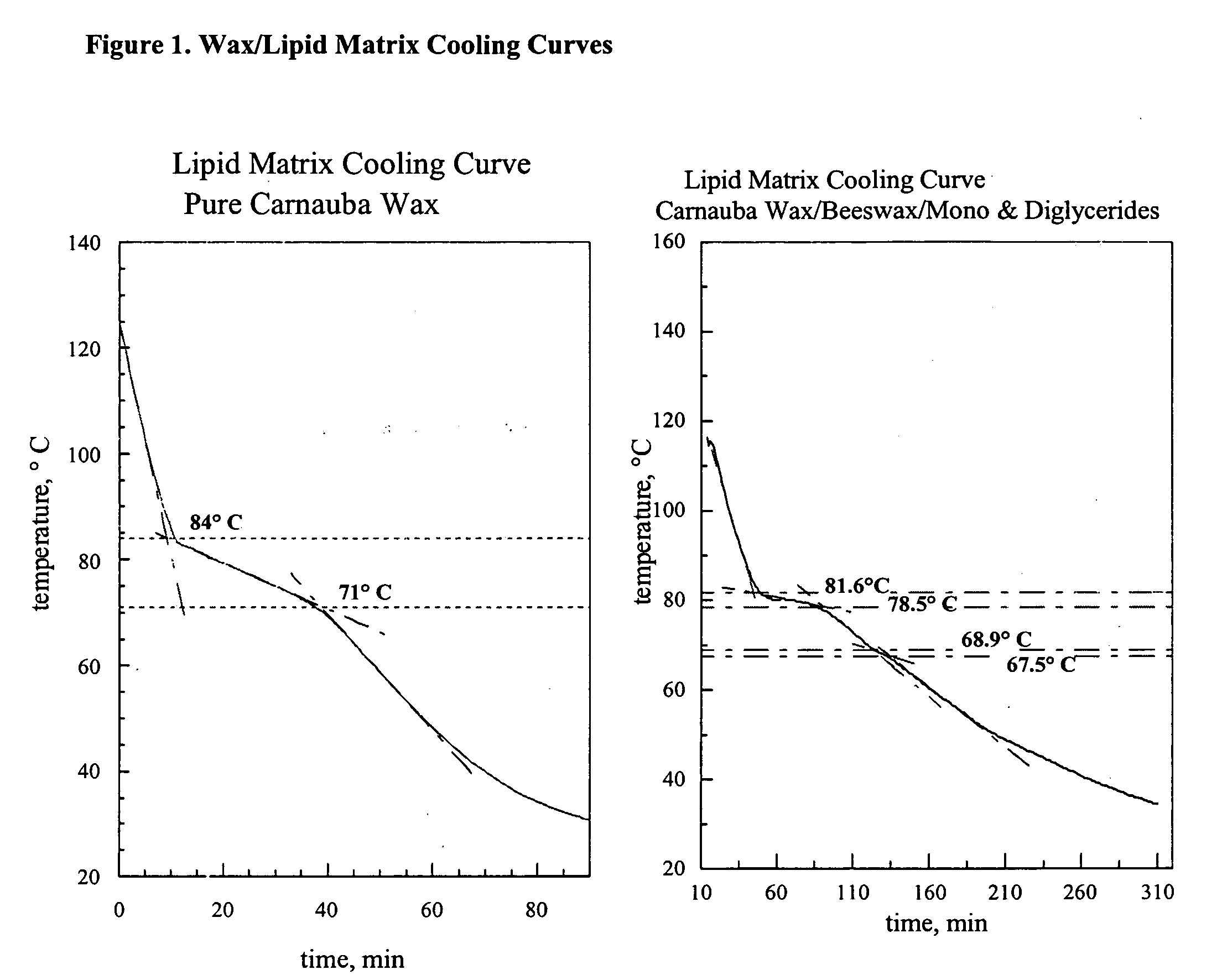
Sustained-release preparation utilizing thermal change and process for the production thereof
A sustained-release preparation which can release a highly water-soluble medicinally active ingredient over a long time and a process for the production thereof are provided. The preparation has a sustained-releasing layer formed by heating and melting a layer composed of both an aqueous ethylcellulose latex containing a plasticizer and a wax to miscibilize them.
Owner:SHIONOGI & CO LTD
Compositions and methods for preparation of poorly water soluble drugs with increased stability
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Methods of enhancing drug delivery and effectiveness of therapeutic agents
InactiveUS20140017323A1Uptake of the therapeutic agent to a target tissuePromote absorptionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseNanoparticle
The present invention in one aspect provides methods of enhancing uptake of a therapeutic agent in a target tissue as well as methods of treating a disease (such as cancer) or enhancing effectiveness of treatment with a therapeutic agent in an individual by co-administering a composition comprising nanoparticles comprising albumin and a poorly water soluble drug such as a taxane with the therapeutic agent. The present invention in another aspect provides a method of treatment or a method of selecting patients for treatment of a disease (such as cancer) with the combination of a therapeutic agent and a composition comprising nanoparticles comprising albumin and a poorly water soluble drug such as a taxane based on one or more characteristics of the target tissue that correlates or indicates the capability of getting enhanced therapeutic agent uptake as a result of the co-administration of the taxane nanoparticle composition in the target tissue (referred to as “the drug uptake capability”). Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions, article of manufacture, and kits useful for methods described herein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Sustained-release polymeric microparticles containing poorly water-soluble drug and method for preparing the same
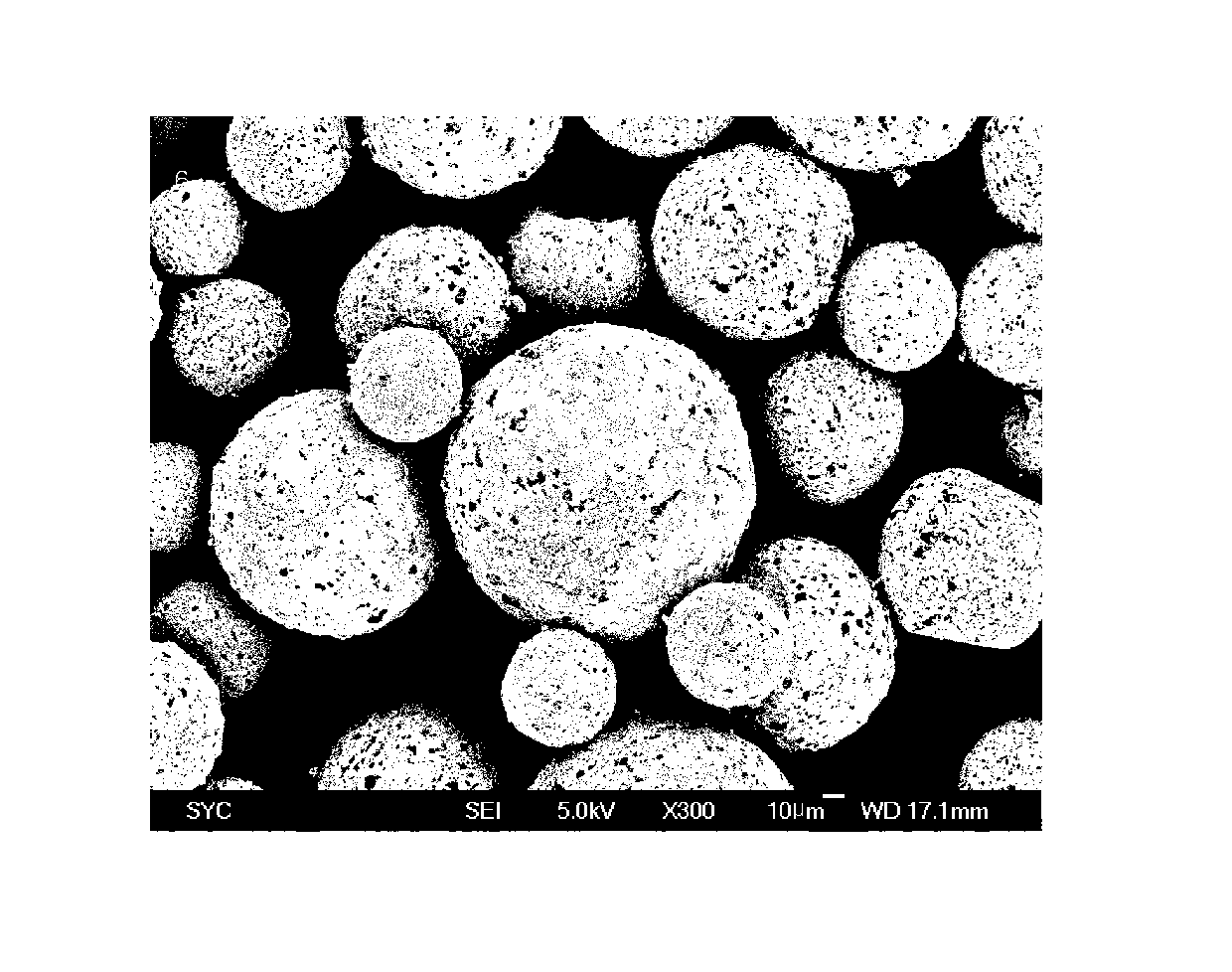
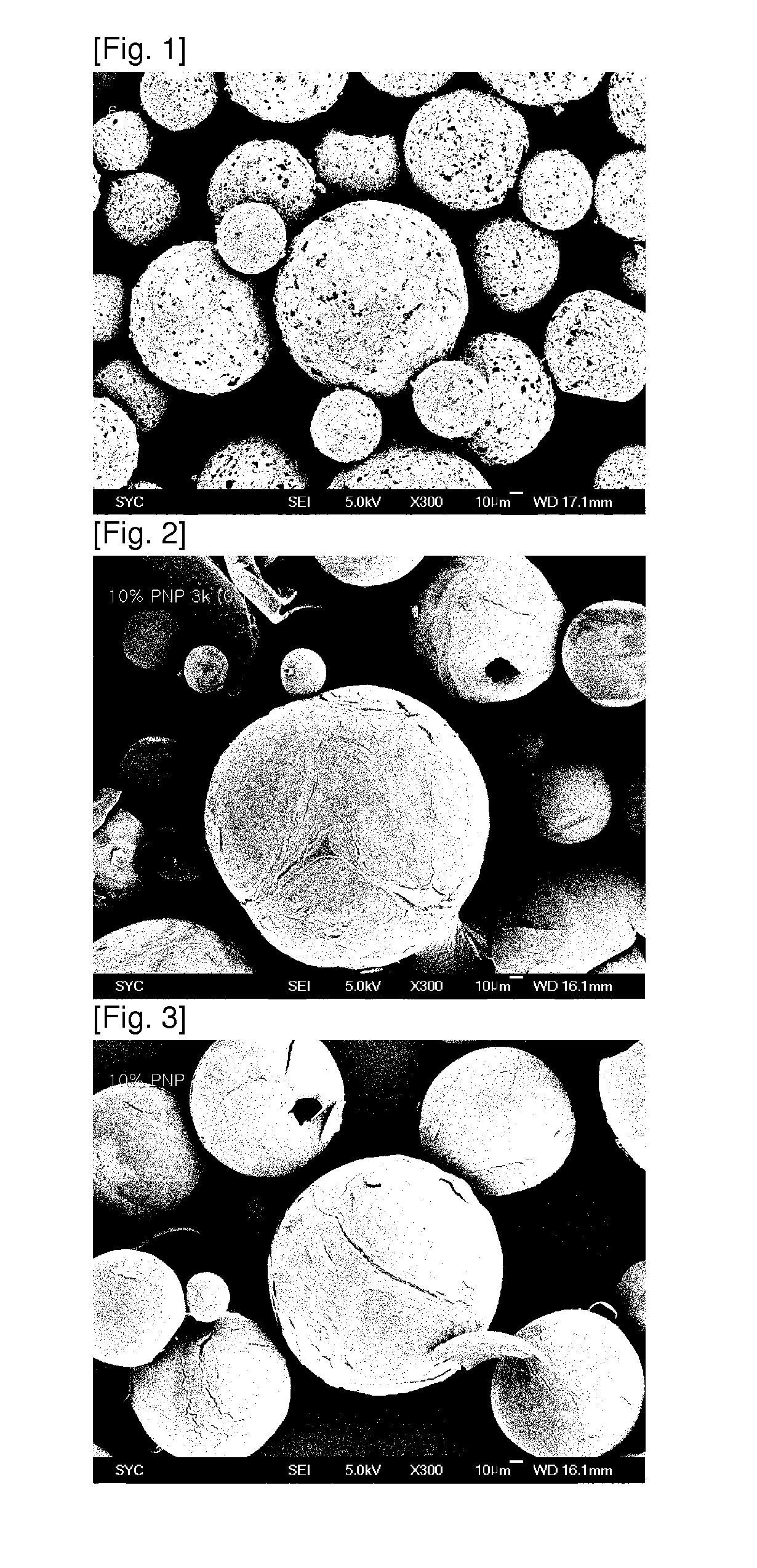
ActiveUS20130273167A1Easy to controlEffective drug concentrationBiocidePowder deliveryWater soluble drugWater soluble
Disclosed are sustained-release polymeric microparticles containing a poorly water-soluble drug and a method for preparing the same.
Owner:SAMYANG HLDG CORP
Controlled phase composition technology as an improved process for protection of drugs
InactiveUS20060008527A1Effective taste-maskingBetter conformSalicyclic acid active ingredientsPill deliveryWaxLipid formation
The present invention relates to novel processes and compositions for protecting drugs, especially water soluble drugs in aqueous environments. More specifically, this process entails coating drugs with a controlled phase composition wax / lipid middle layer for controlling migration of the drug toward the composition's surface during preparation and a polymeric outer layer.
Owner:PARTICLE DYNAMICS INT
Osmotic drug delivery system
ActiveUS8747897B2Improve solubilityIncrease surface areaBiocideSenses disorderWater soluble drugWater soluble
An oral osmotic pharmaceutical delivery system comprises a highly water-soluble drug exhibiting an erratic or an incomplete release profile when formulated in a elementary osmotic pump delivery system and at least one release enhancing agent.
Owner:SUPERNUS PHARM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com