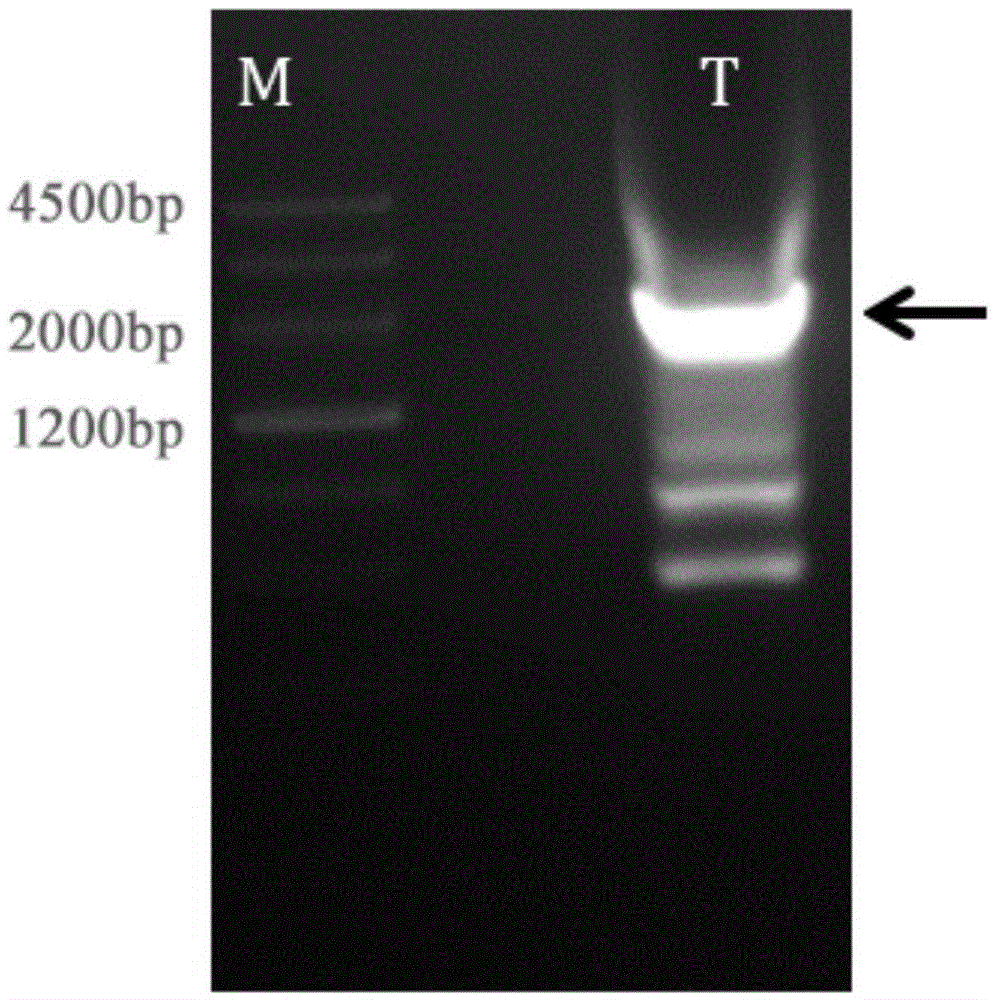
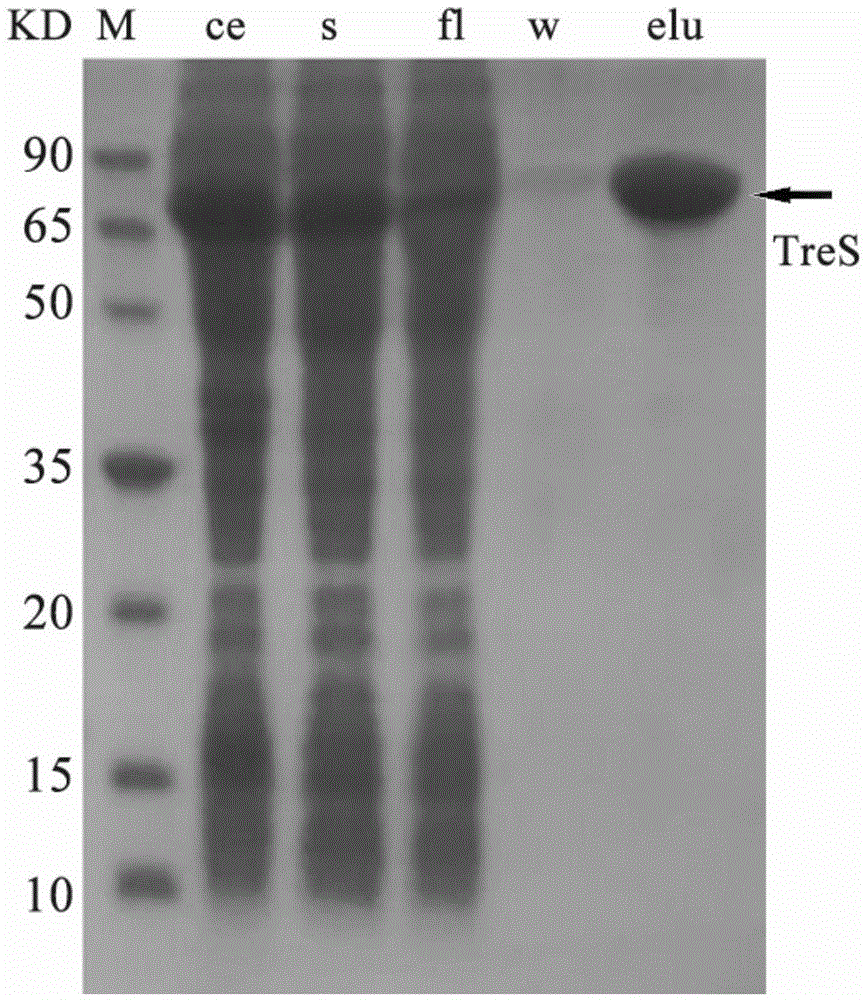
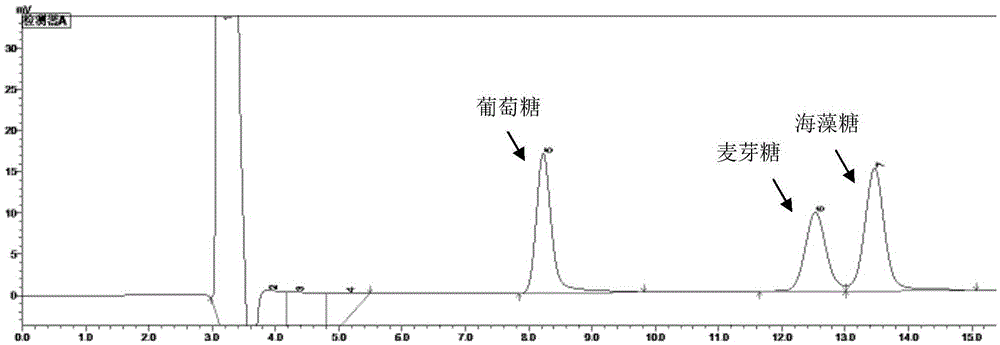
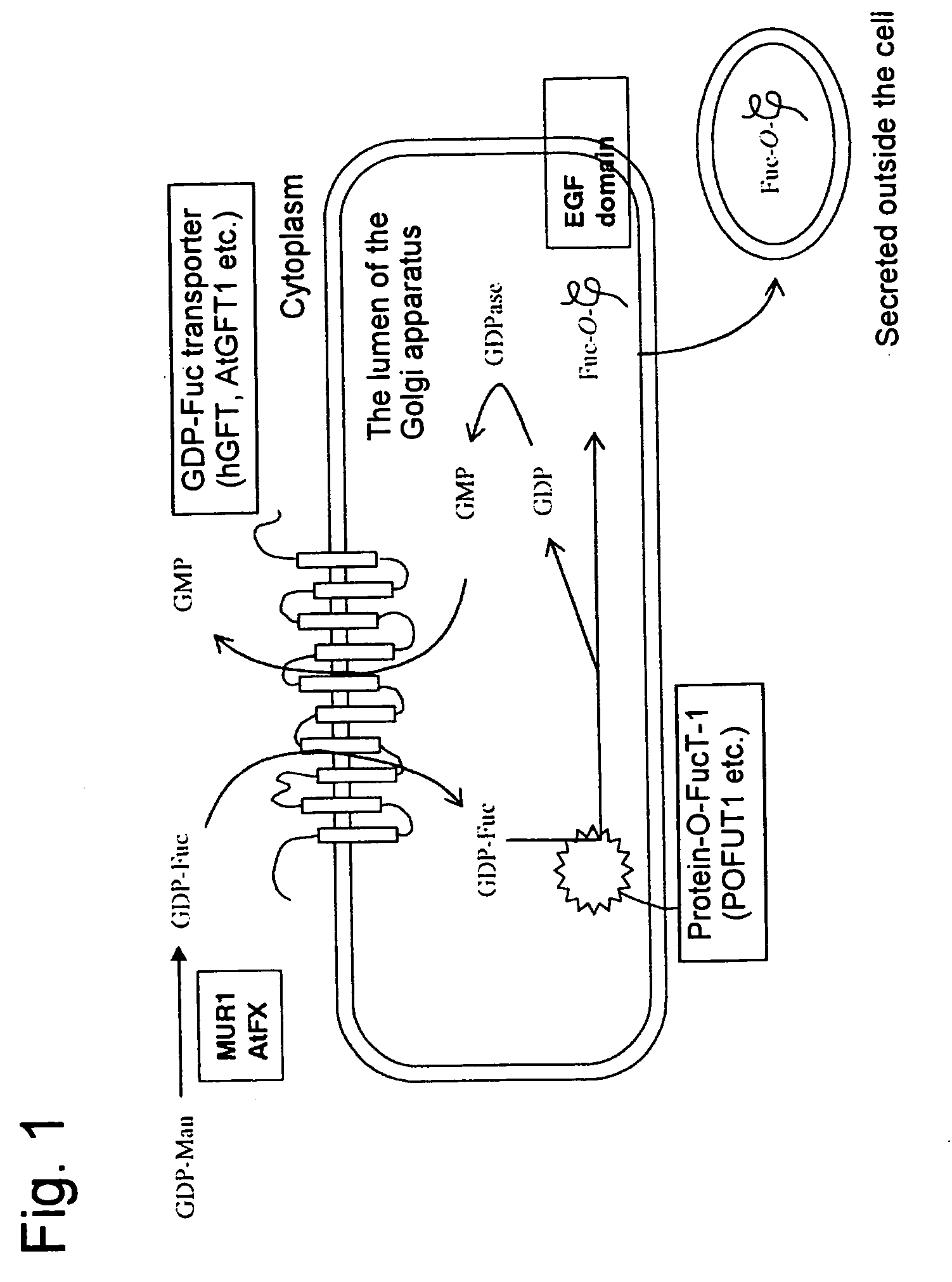
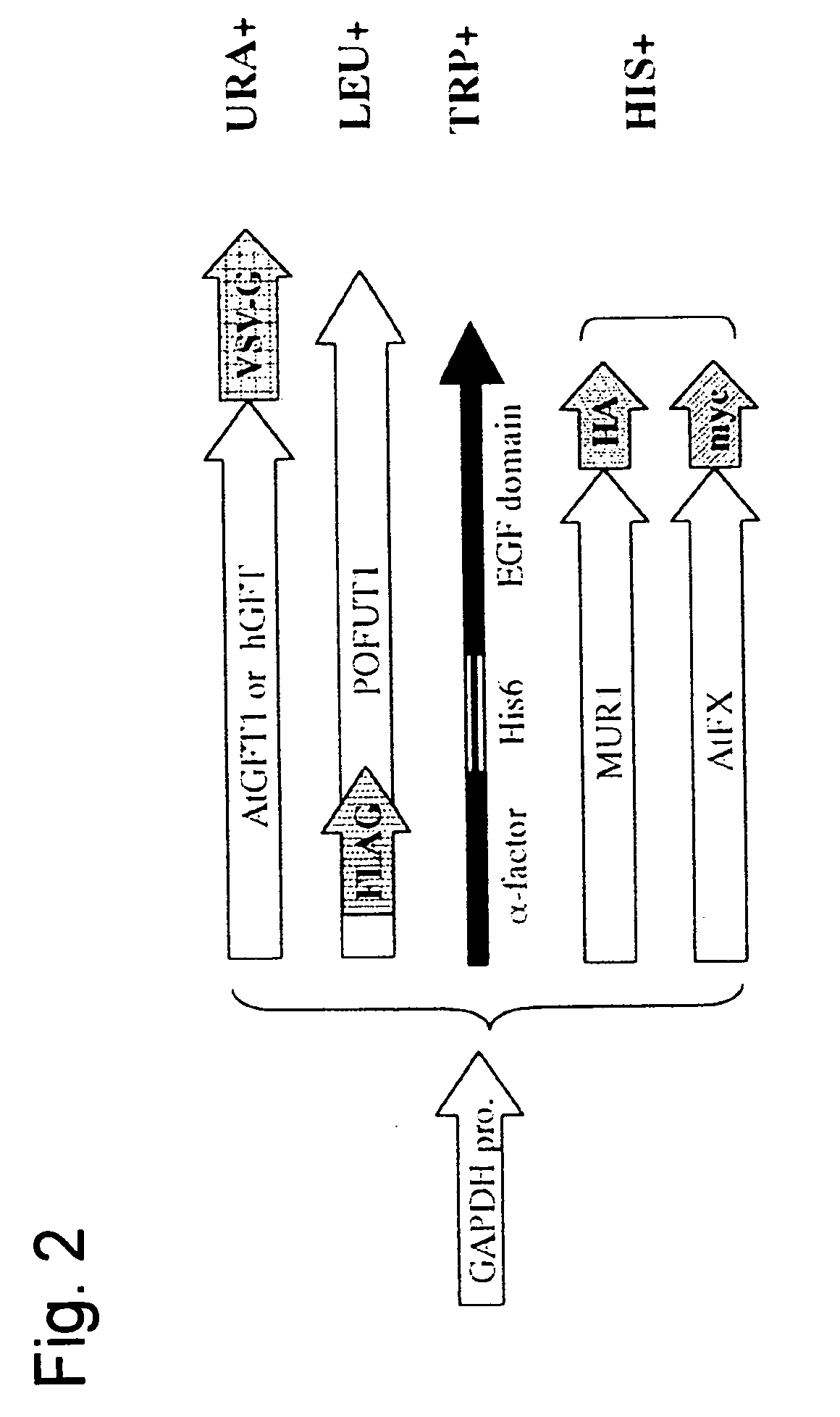
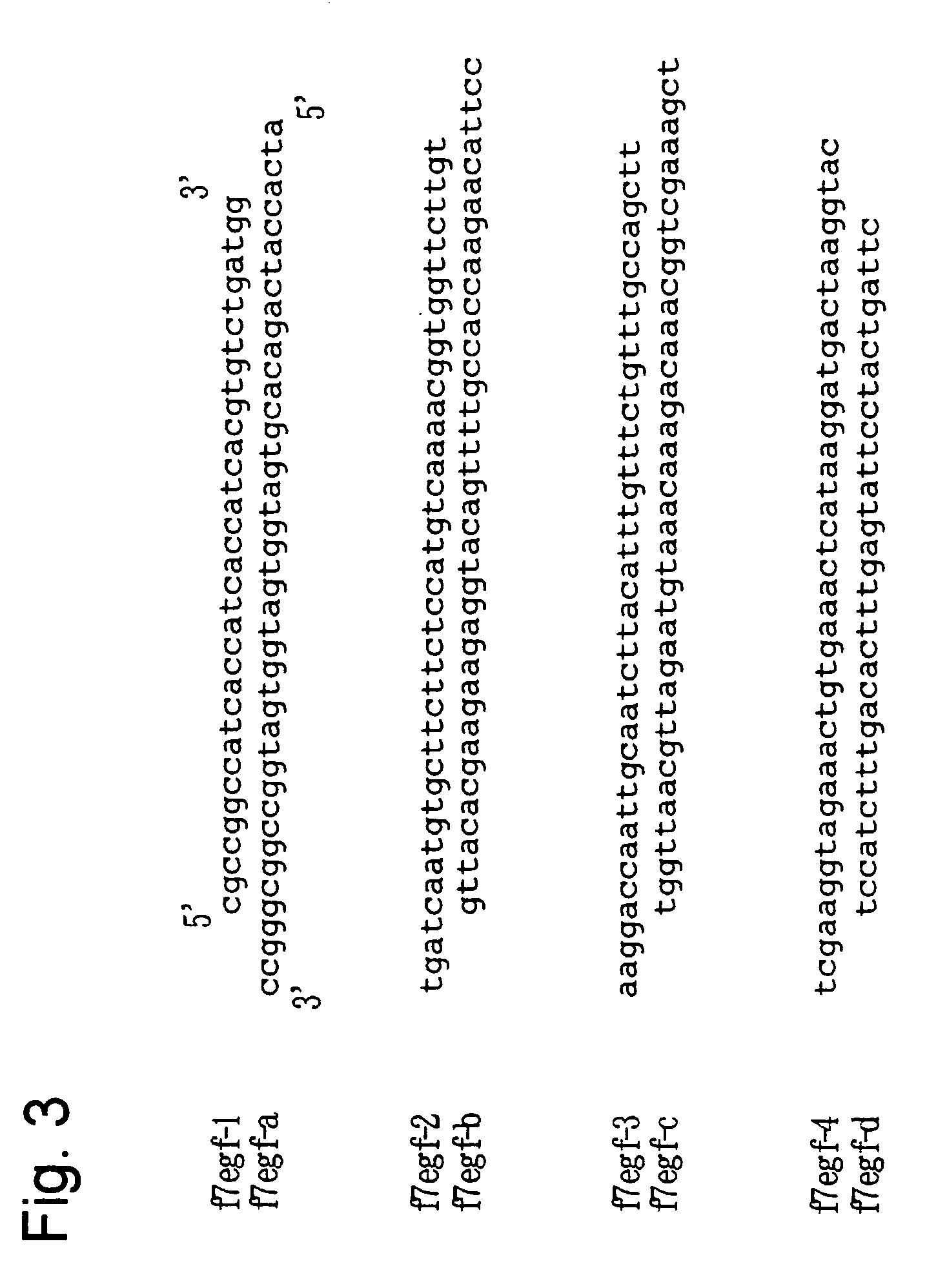
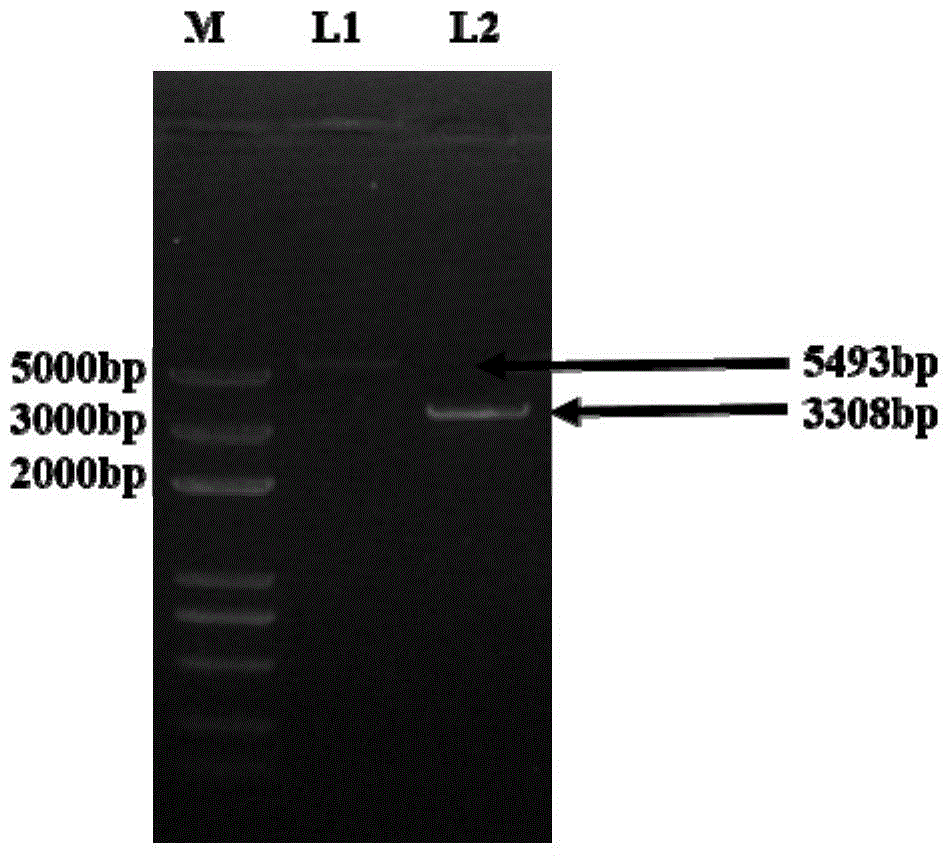
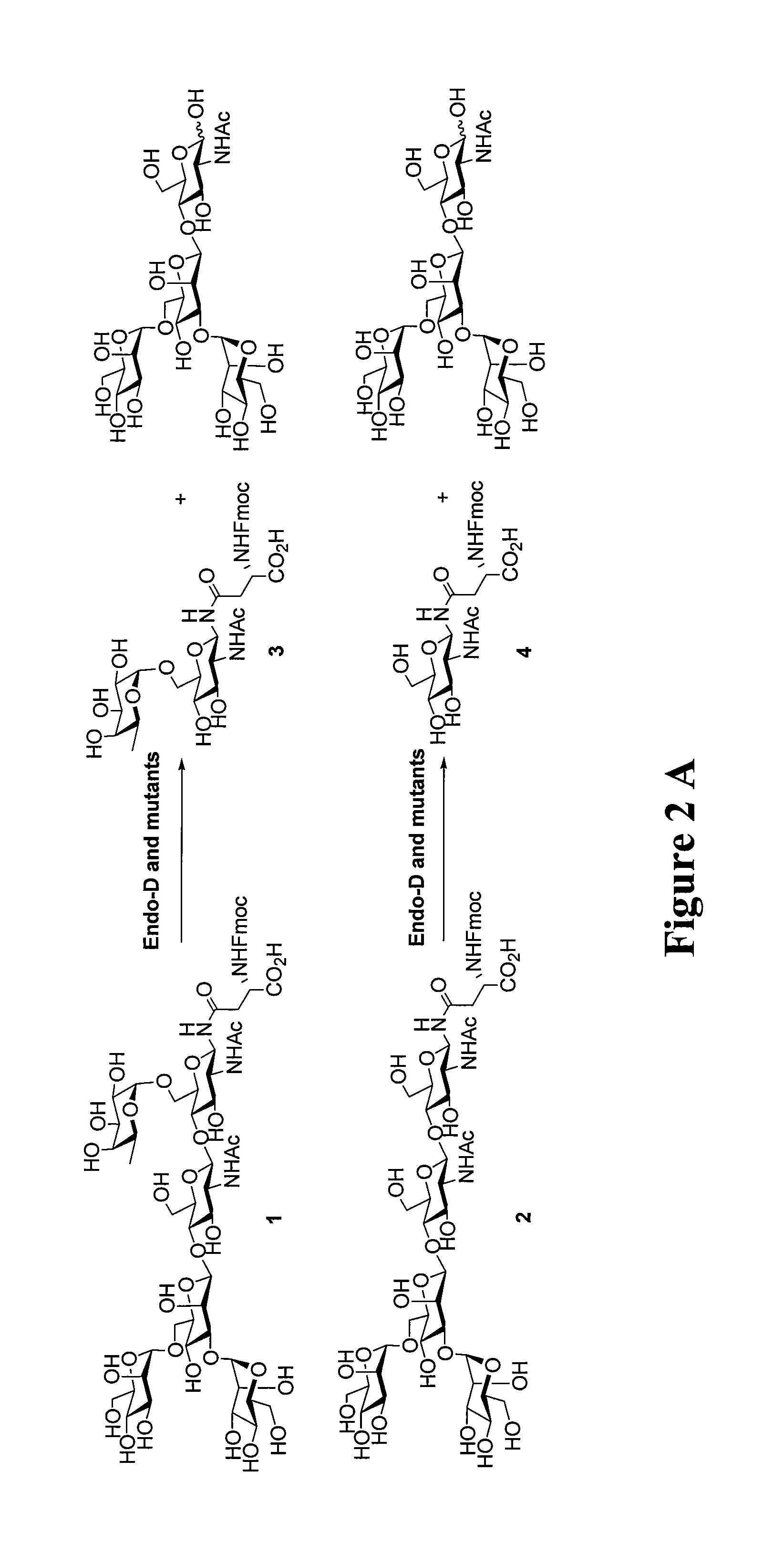
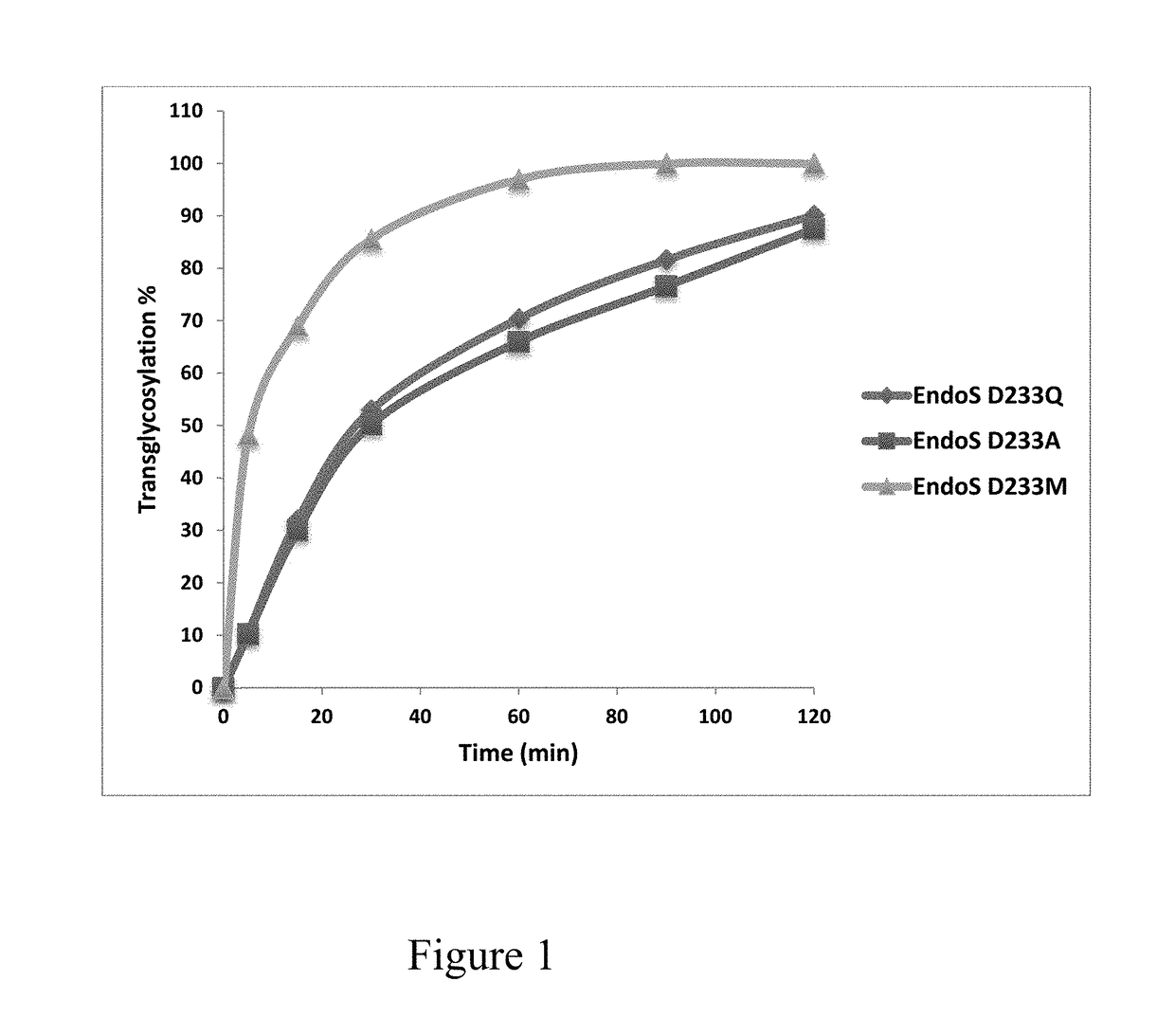
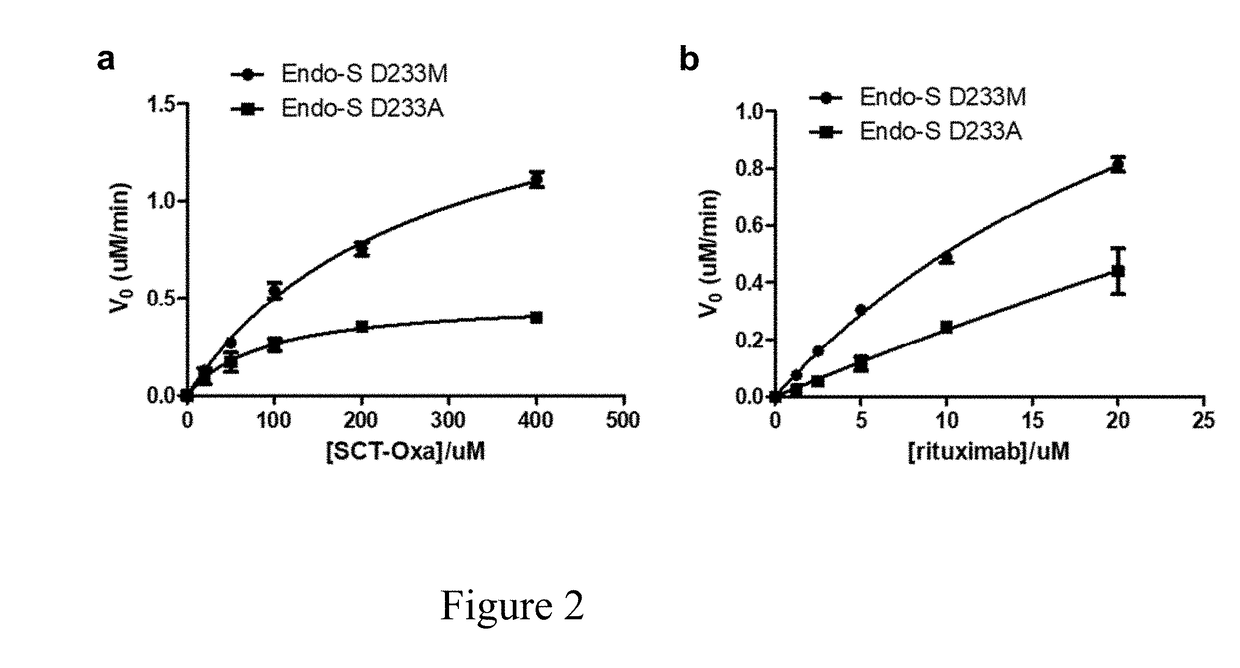
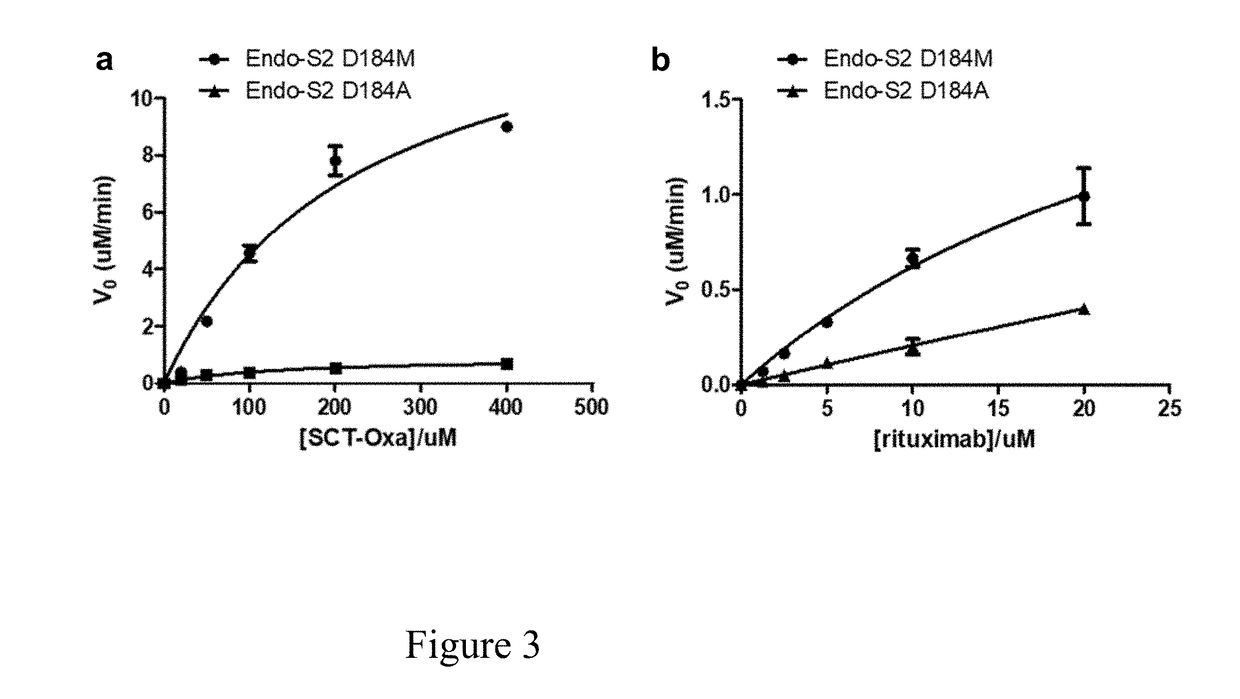
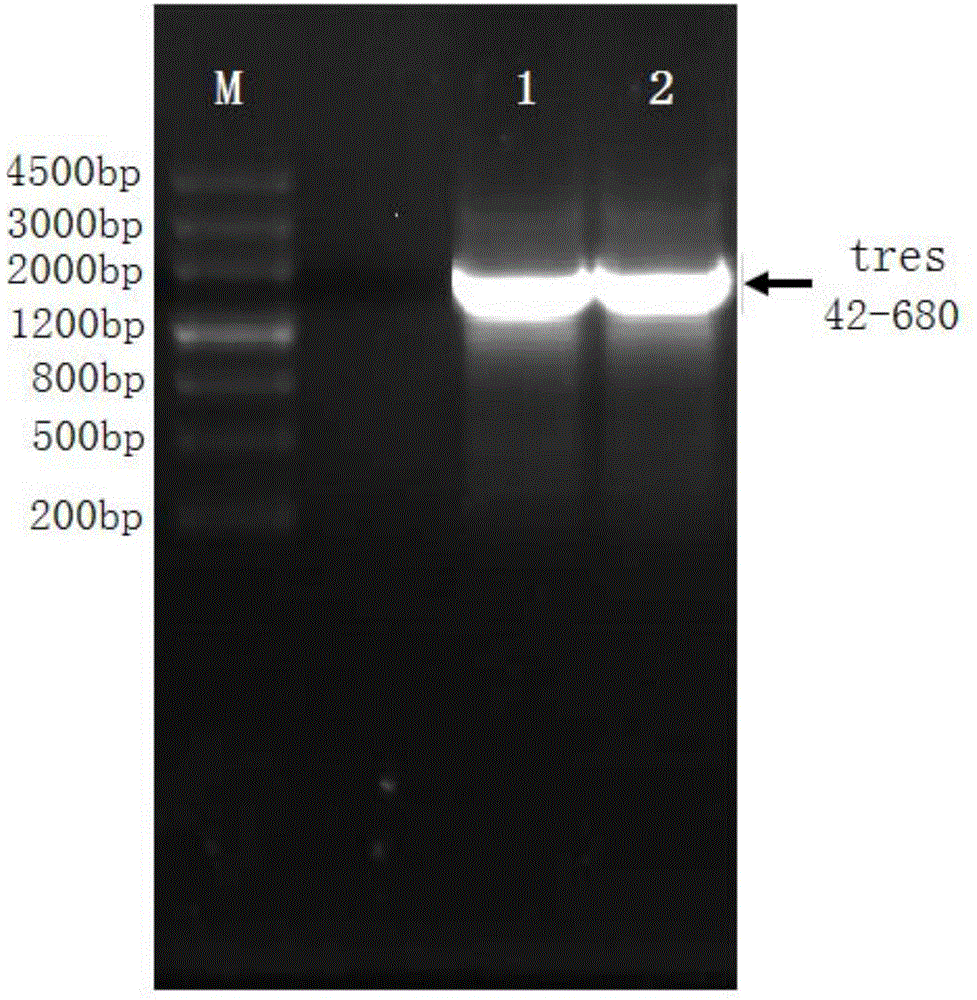
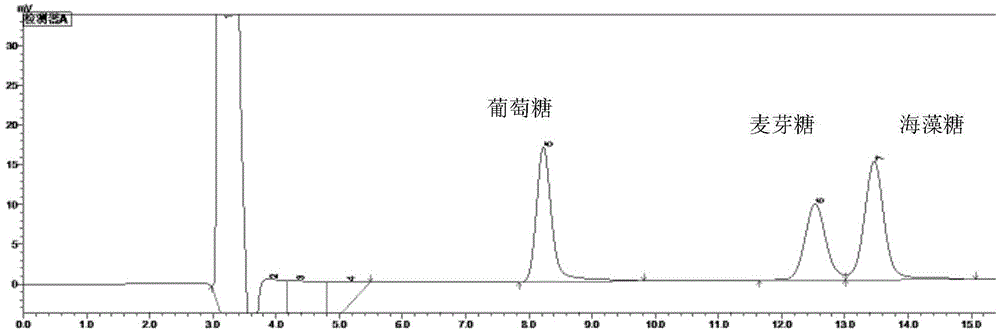
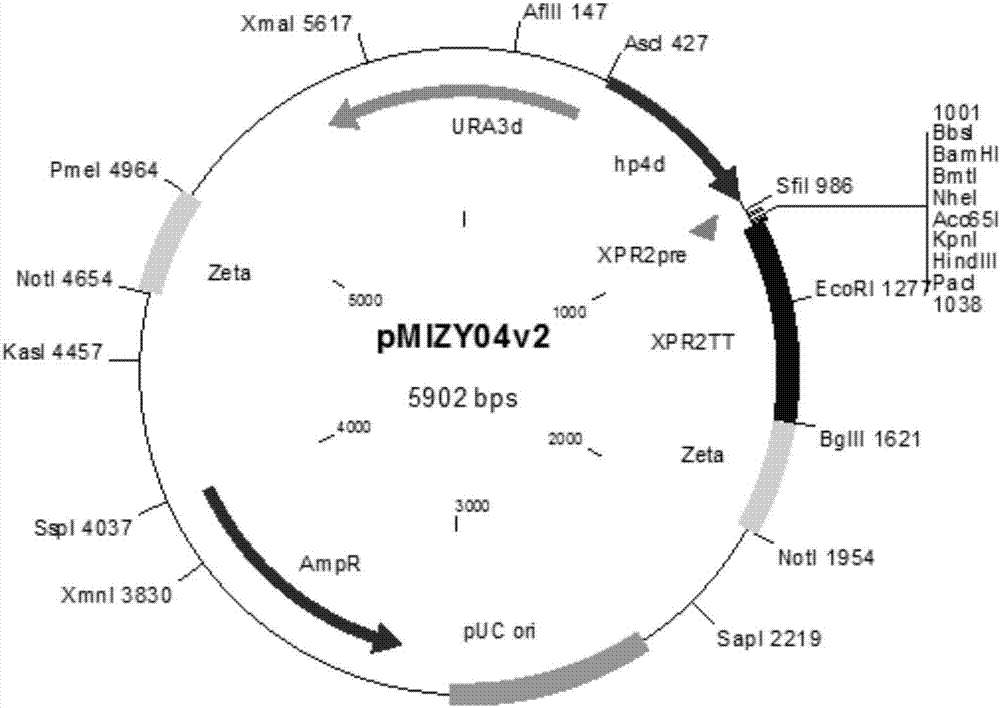
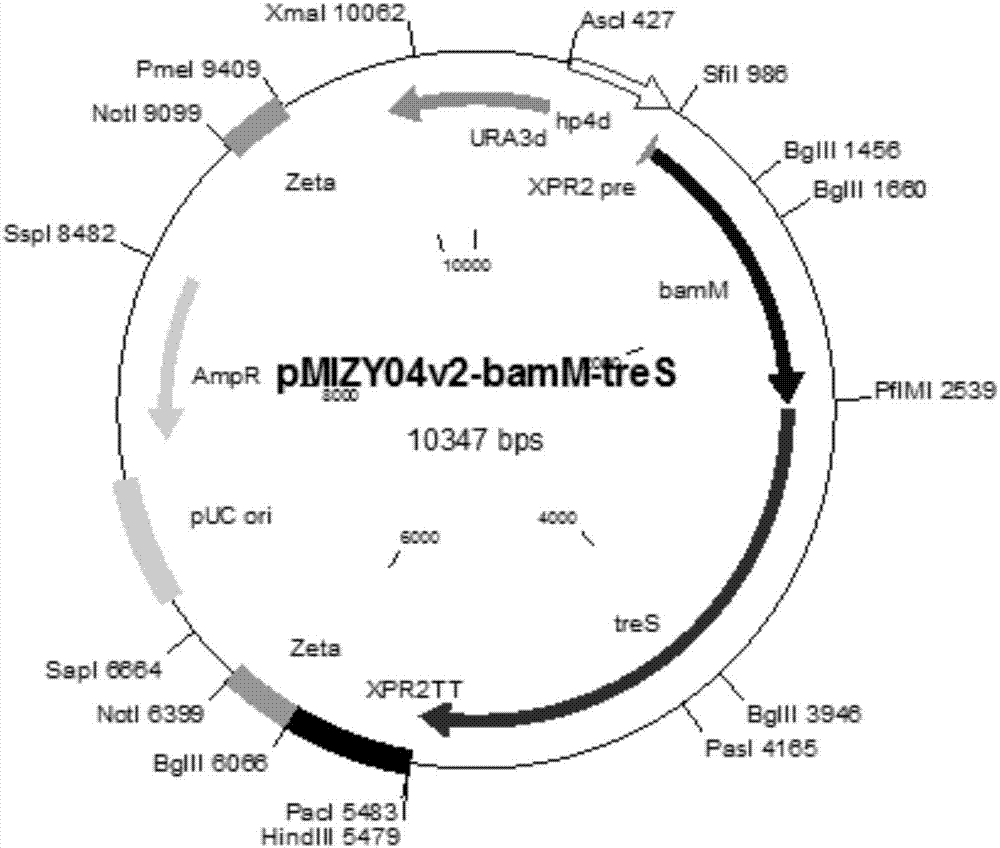
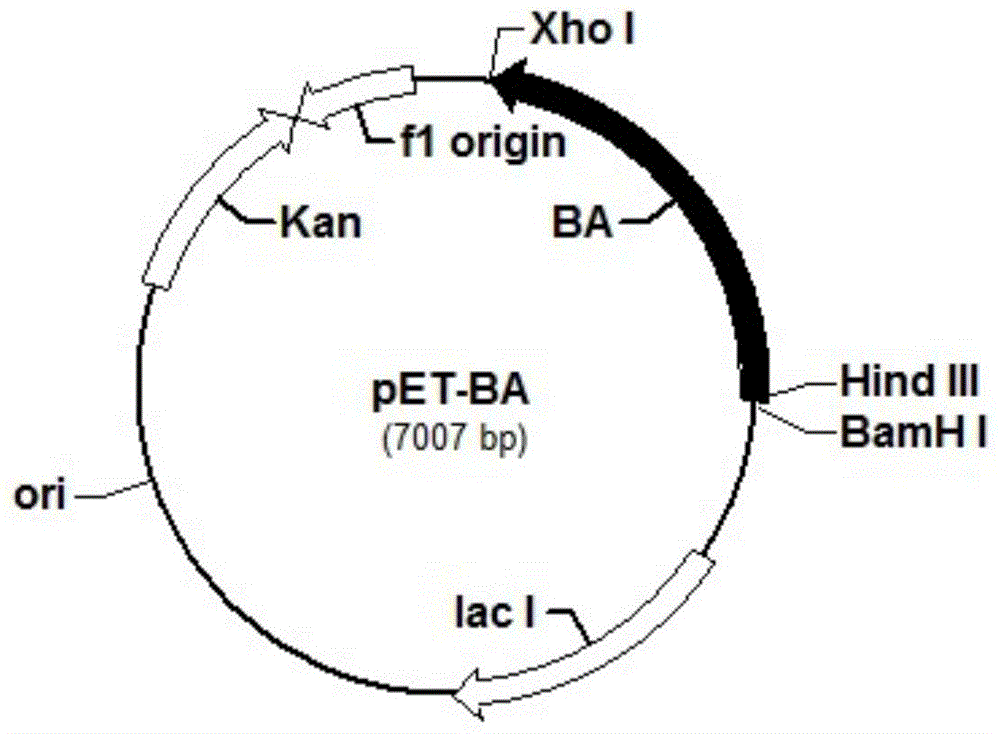
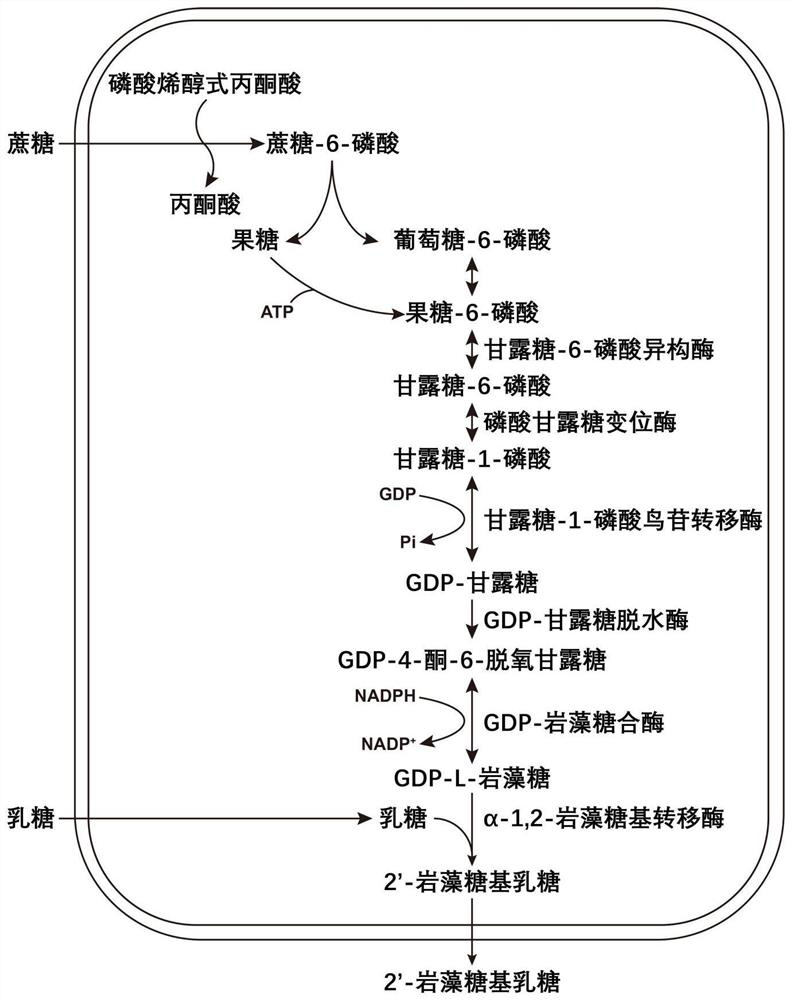
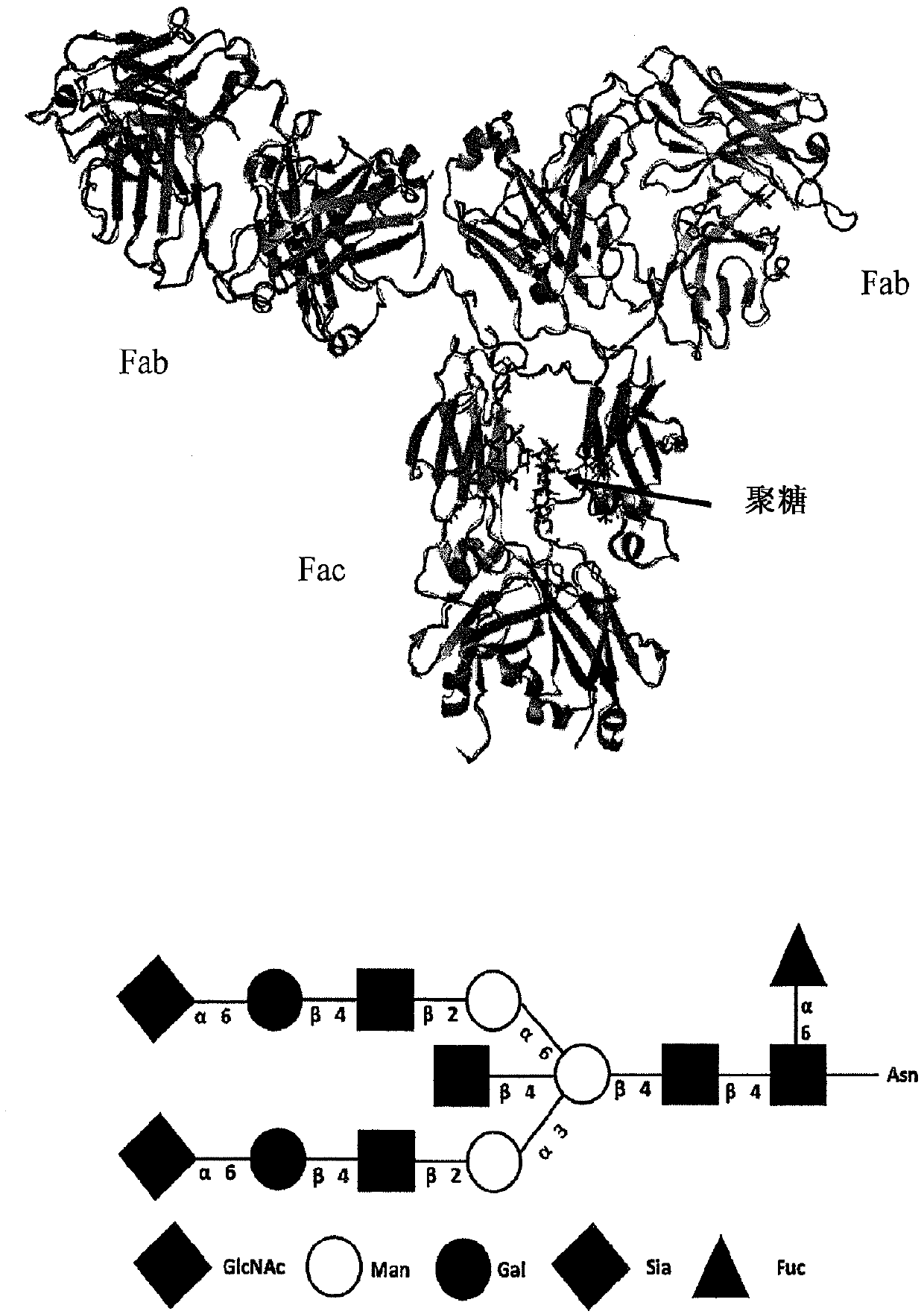
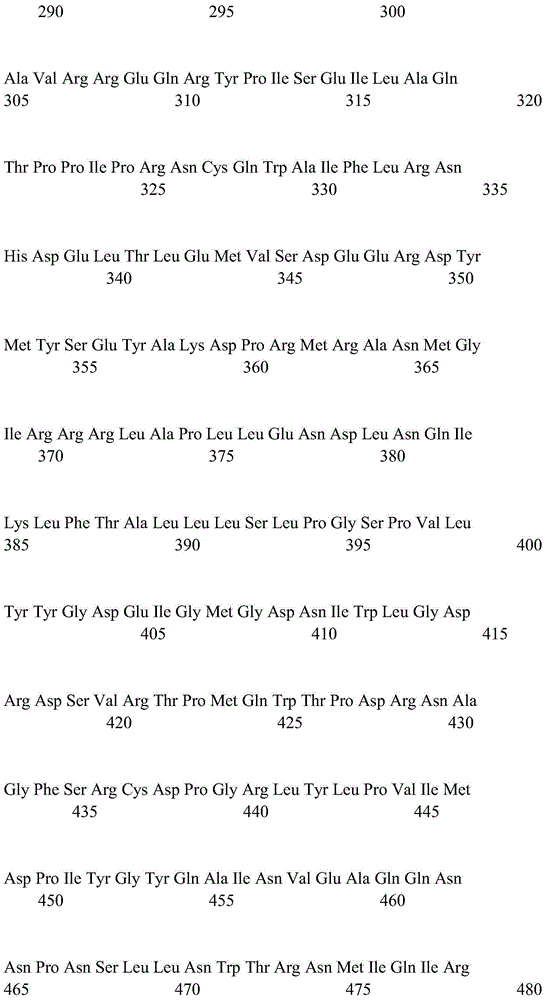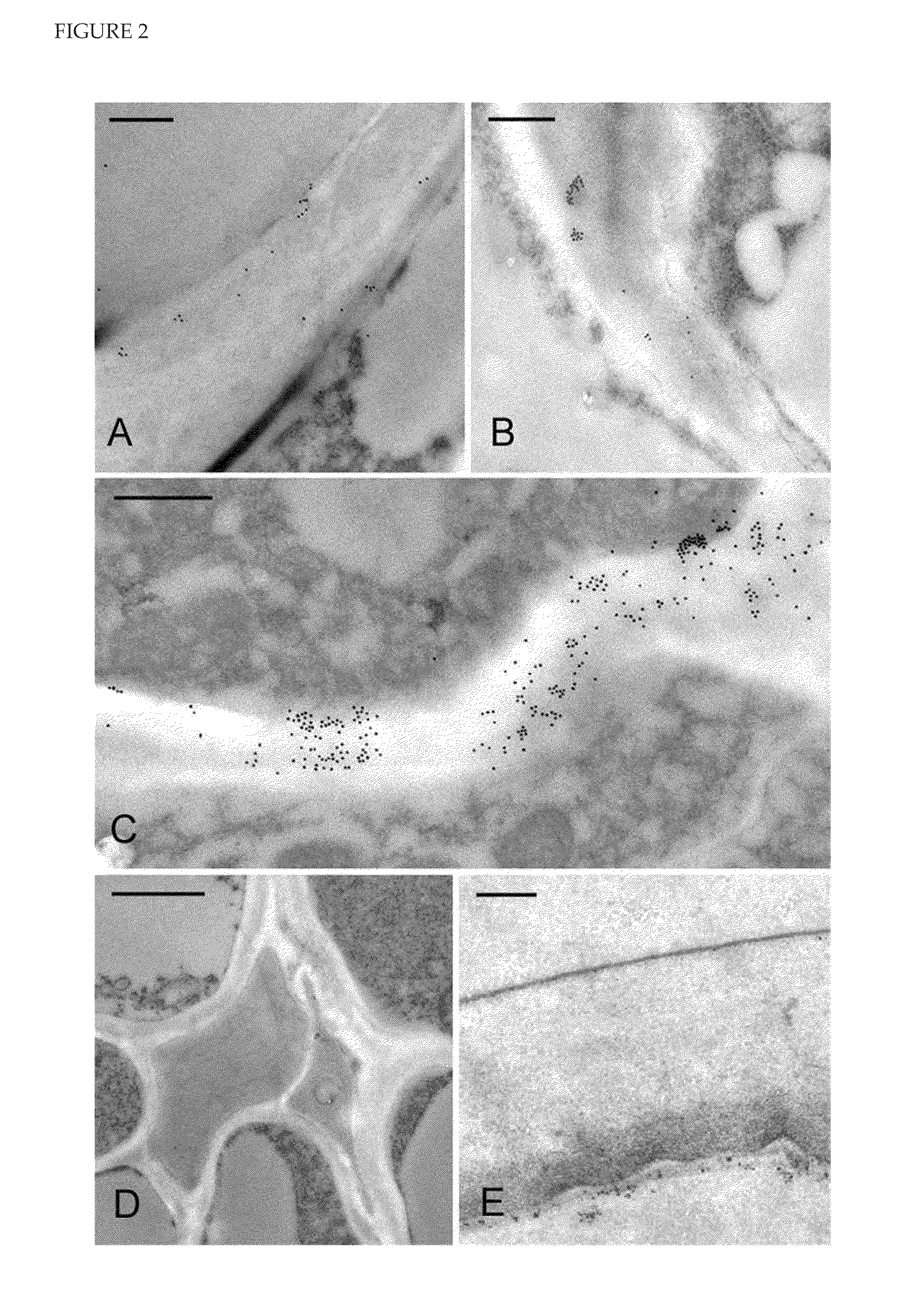Patents
Literature
61 results about "Glycosynthase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The term Glycosynthase refers to a class of proteins that have been engineered to catalyze the formation of a glycosidic bond. Glycosynthase are derived from glycosidase enzymes, which catalyze the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds. They were traditionally formed from retaining glycosidase by mutating the active site nucleophilic amino acid (usually an aspartate or glutamate) to a small non-nucleophilic amino acid (usually alanine or glycine). More modern approaches use directed evolution to screen for amino acid substitutions that enhance glycosynthase activity.
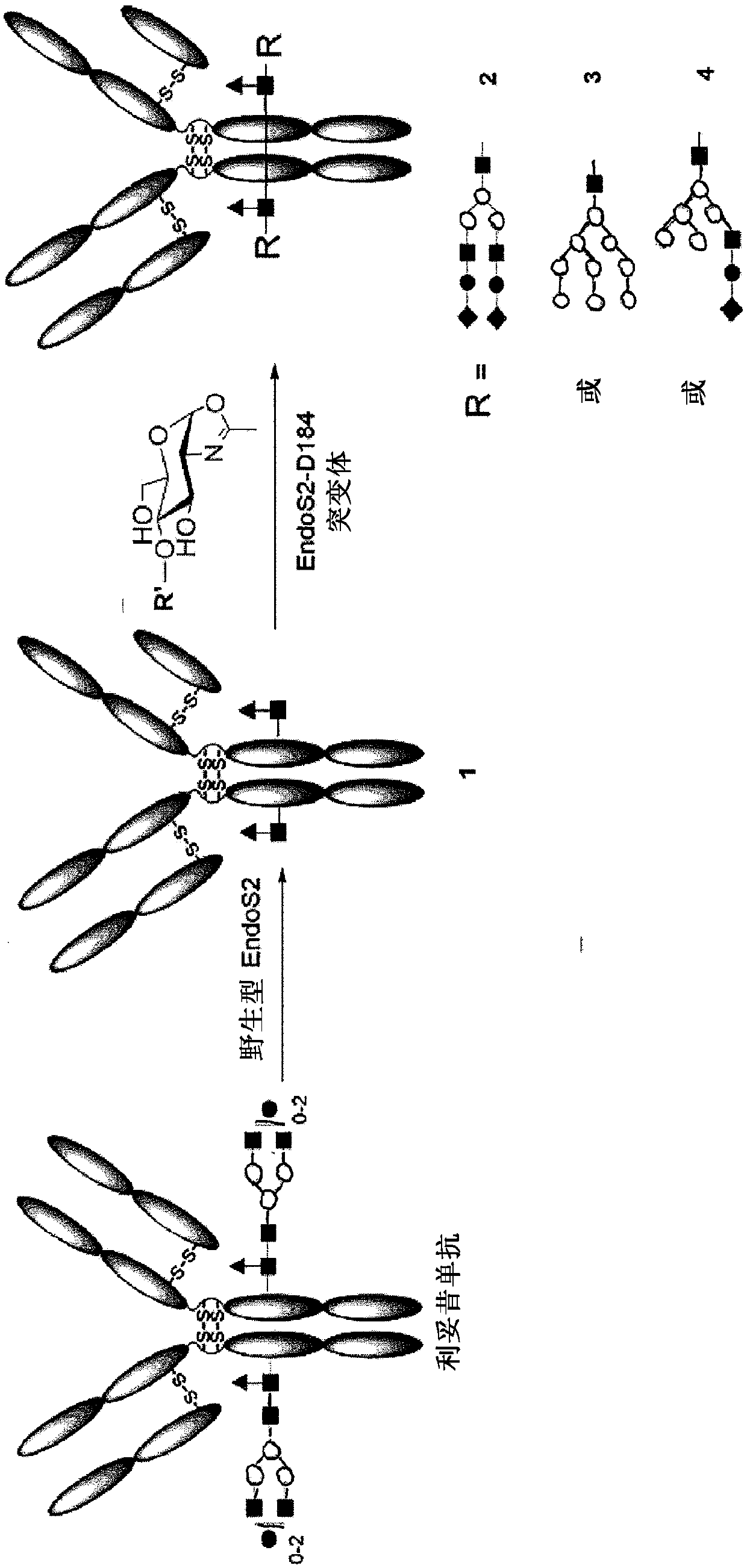
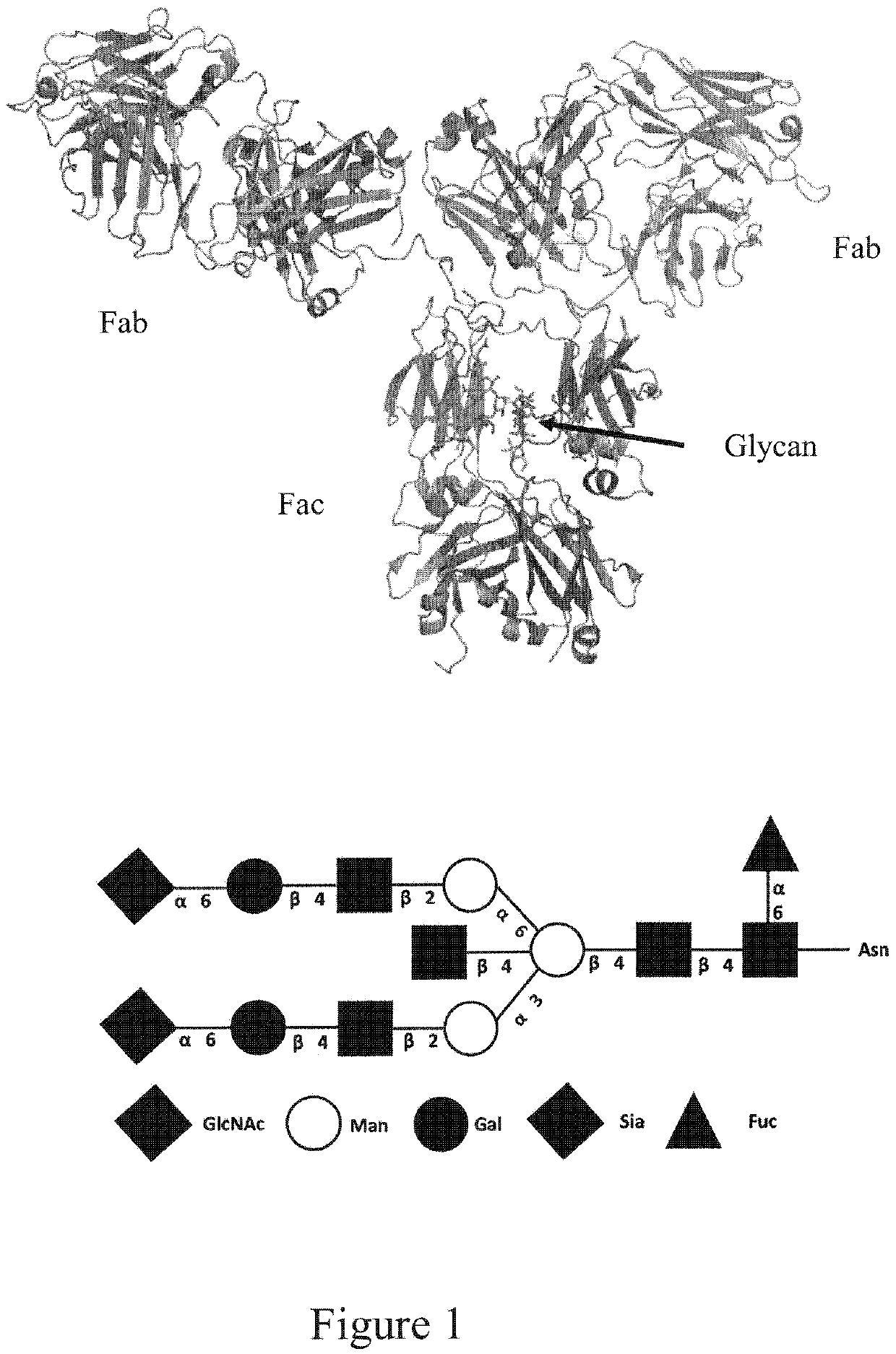
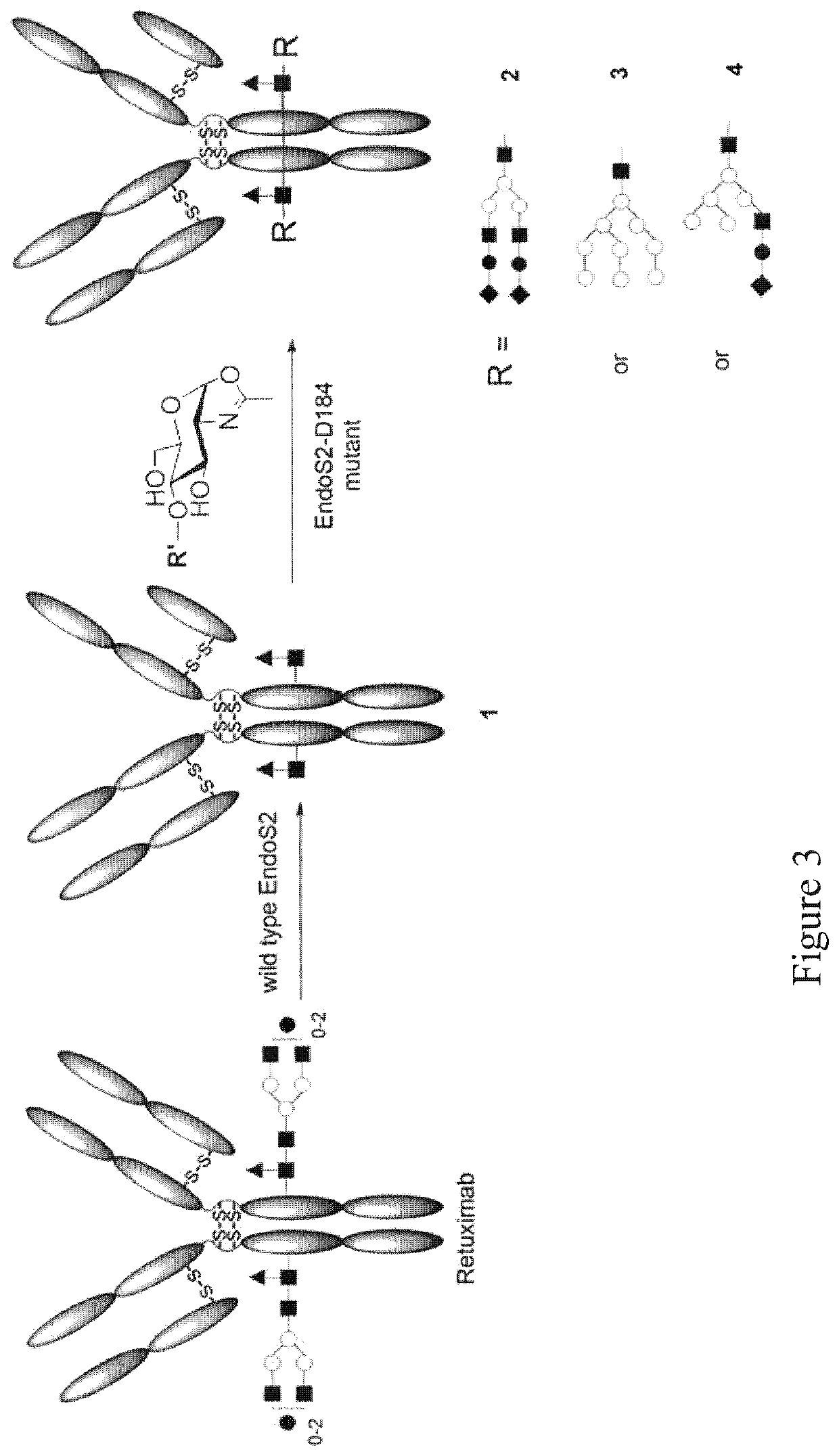
Core fucosylated glycopeptides and glycoproteins: chemoenzymatic synthesis and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120226024A1Prolonged half-life-timeLess immunogenicityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansEnzymesFucosylationEndorhamnosidase
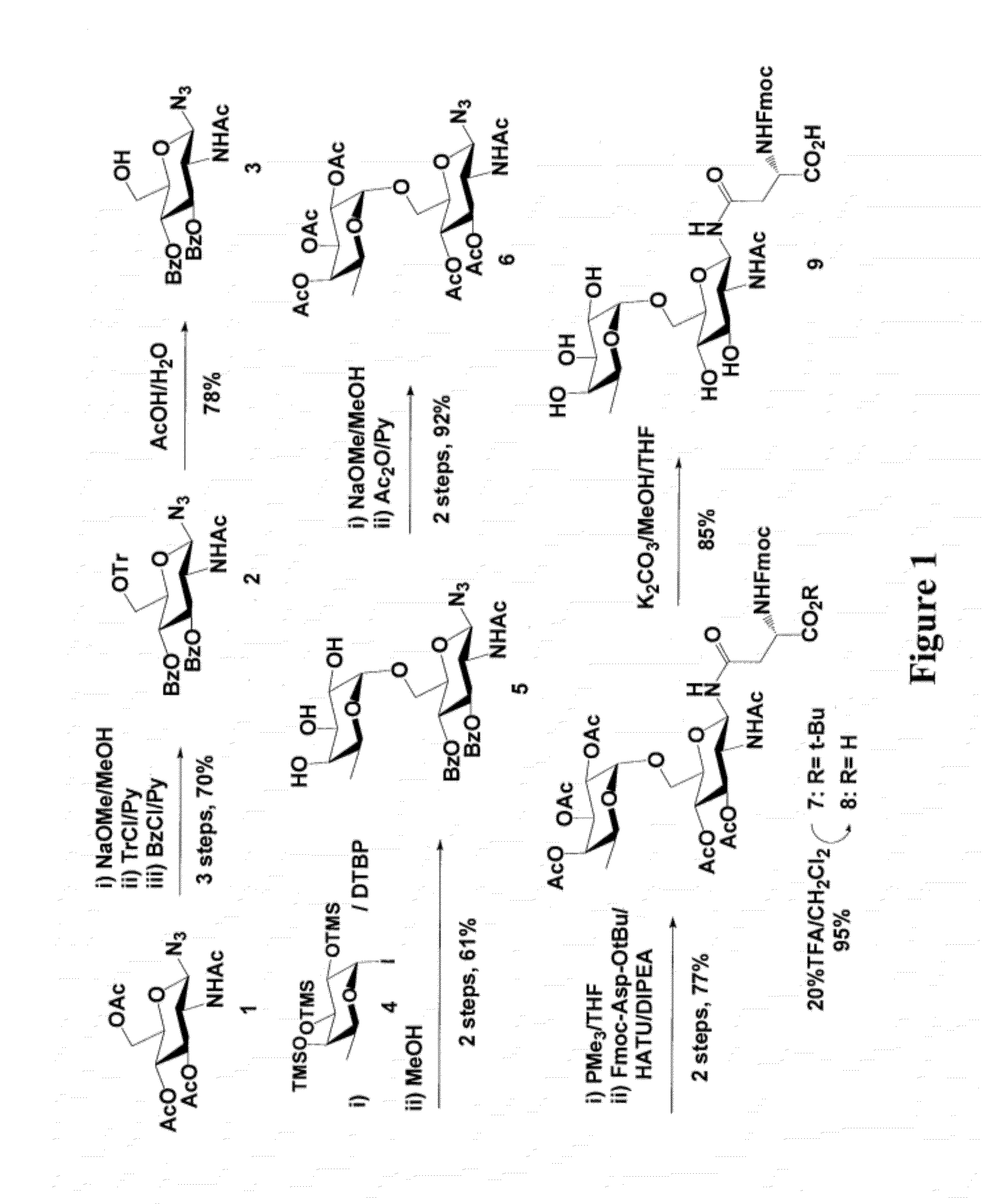
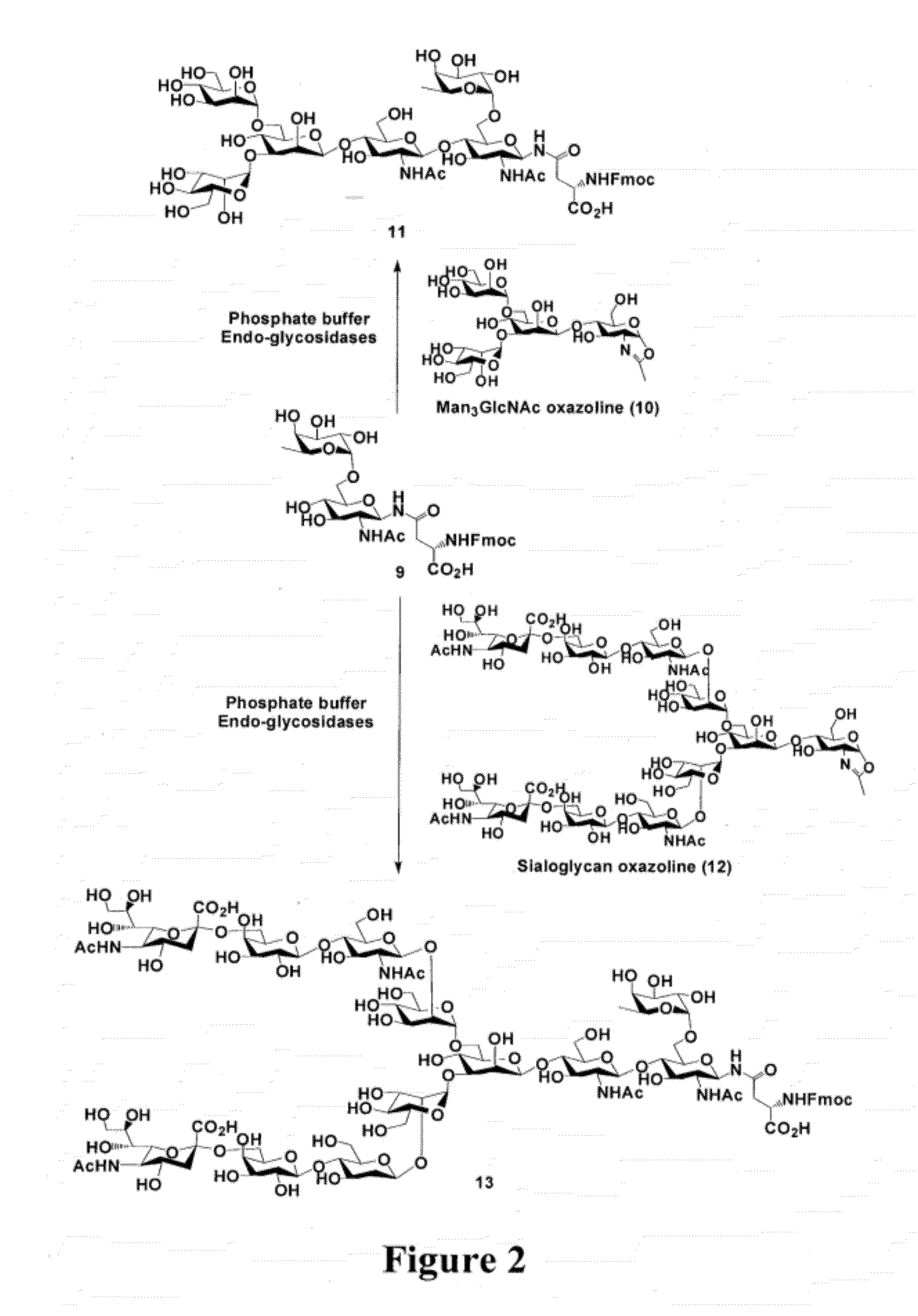
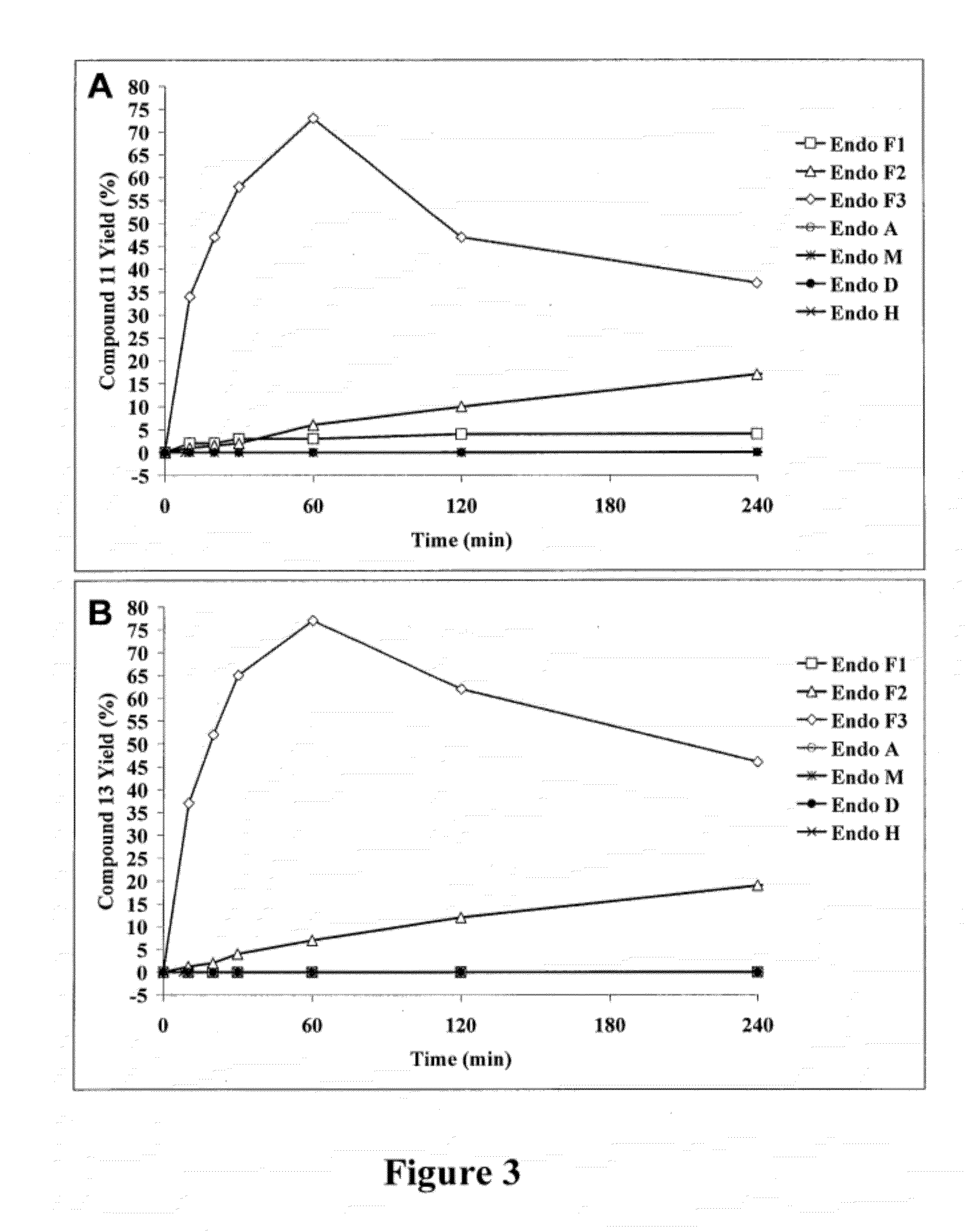
A chemoenzymatic method for the preparation of a core-fucoslyated glycoprotein or glycopeptide, including (a) providing an acceptor selected from the group consisting of a fucosylated GlcNAc-protein and fucosylated GlcNAc-peptide; and (b) reacting the acceptor with a donor substrate including an activated oligosaccharide moiety, in the presence of an endoglycosidase (ENGase) selected from Endo;F1, Endo-F2, Endo-F3, Endo-D and related glycosynthase mutants to transfer the oligosaccharide moiety to the acceptor and yield the structure defined core-fucosylated glycoprotein or glycopeptide. The donor substrate includes, in a specific implementation, a synthetic oligosaccharide oxazoline. A related method of fucosylated glycoprotein or fucosylated glycopeptide remodeling with a predetermined natural N-glycan or a tailor-made oligosaccharide moiety, and a method of remodeling an antibody to include a predetermined sugar chain to replace a heterogeneous sugar chain, are also described.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
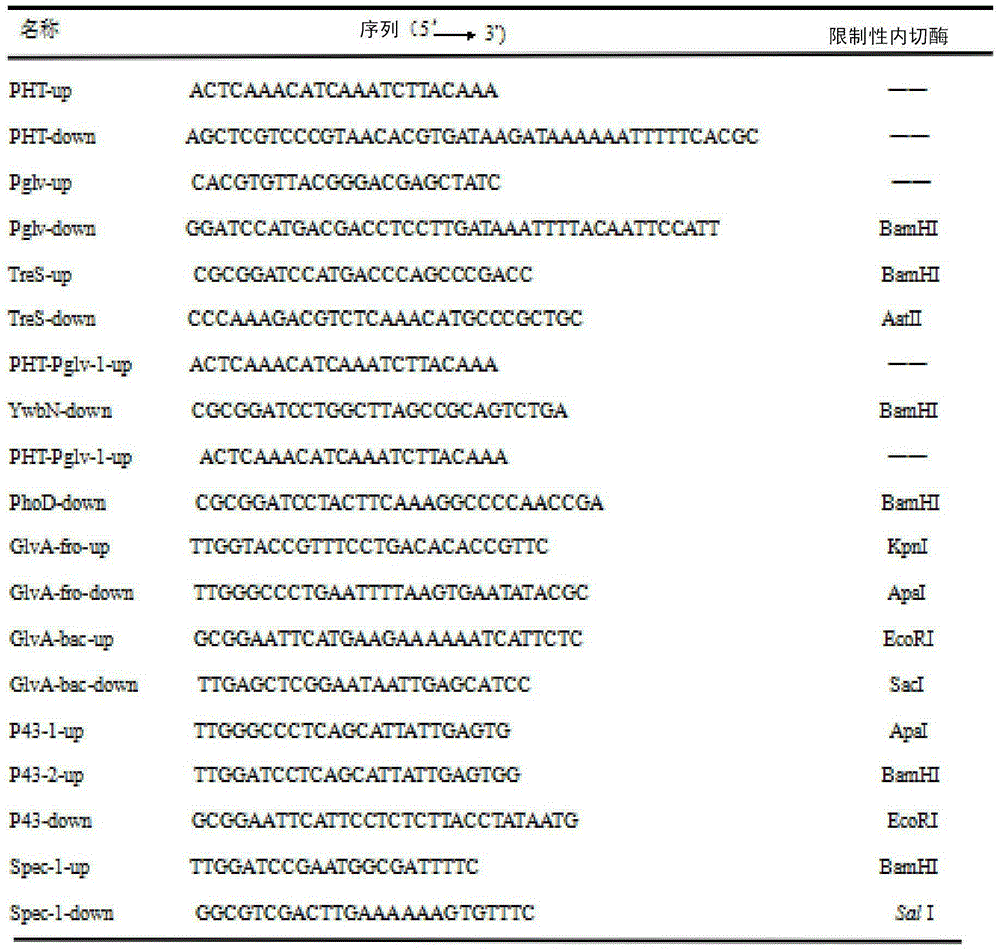
Maltose inducible trehalose synthase synthesis engineering bacterium, method for preparing same and application
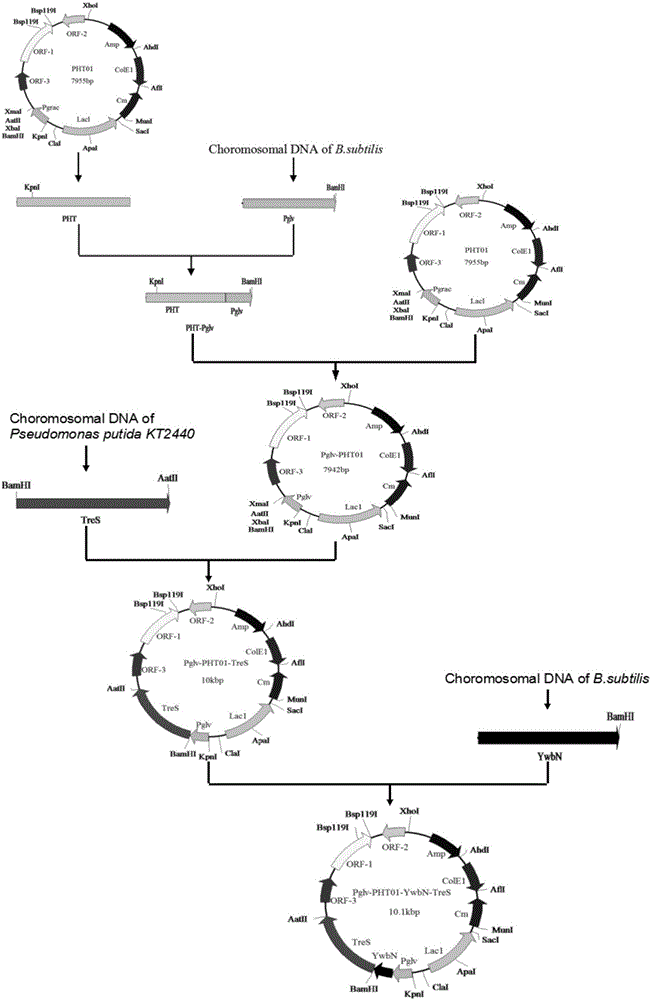
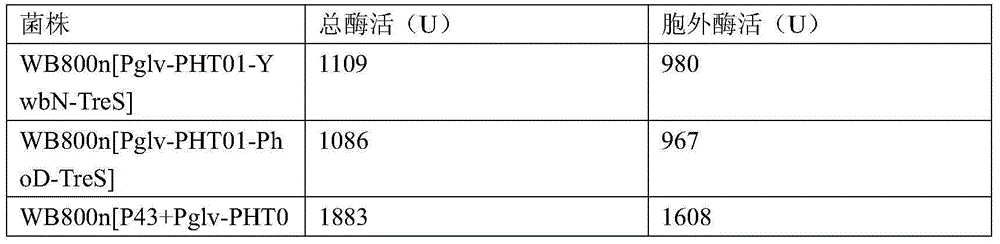
The invention relates to a maltose inducible trehalose synthase synthesis engineering bacterium, a method for preparing the same and application. The maltose inducible trehalose synthase synthesis engineering bacterium is characterized in that maltose inducible promoters are inserted in the fronts of BamHI cleavage sites of PHT01 plasmids of recombinant plasmid vectors instead of Pgrac promoters on the PHT01 plasmids, expression genes of Tat type signal peptides are inserted in the fronts of the BamHI cleavage sites, and expression genes of trehalose synthase are inserted in the rears of the BamHI cleavage sites. The maltose inducible trehalose synthase synthesis engineering bacterium, the method and the application have the advantage that expression effects realized after the maltose inducible promoters and the trehalose synthase are fused with one another are obviously superior to other inducible expression effects.
Owner:山东开盾生物科技有限公司
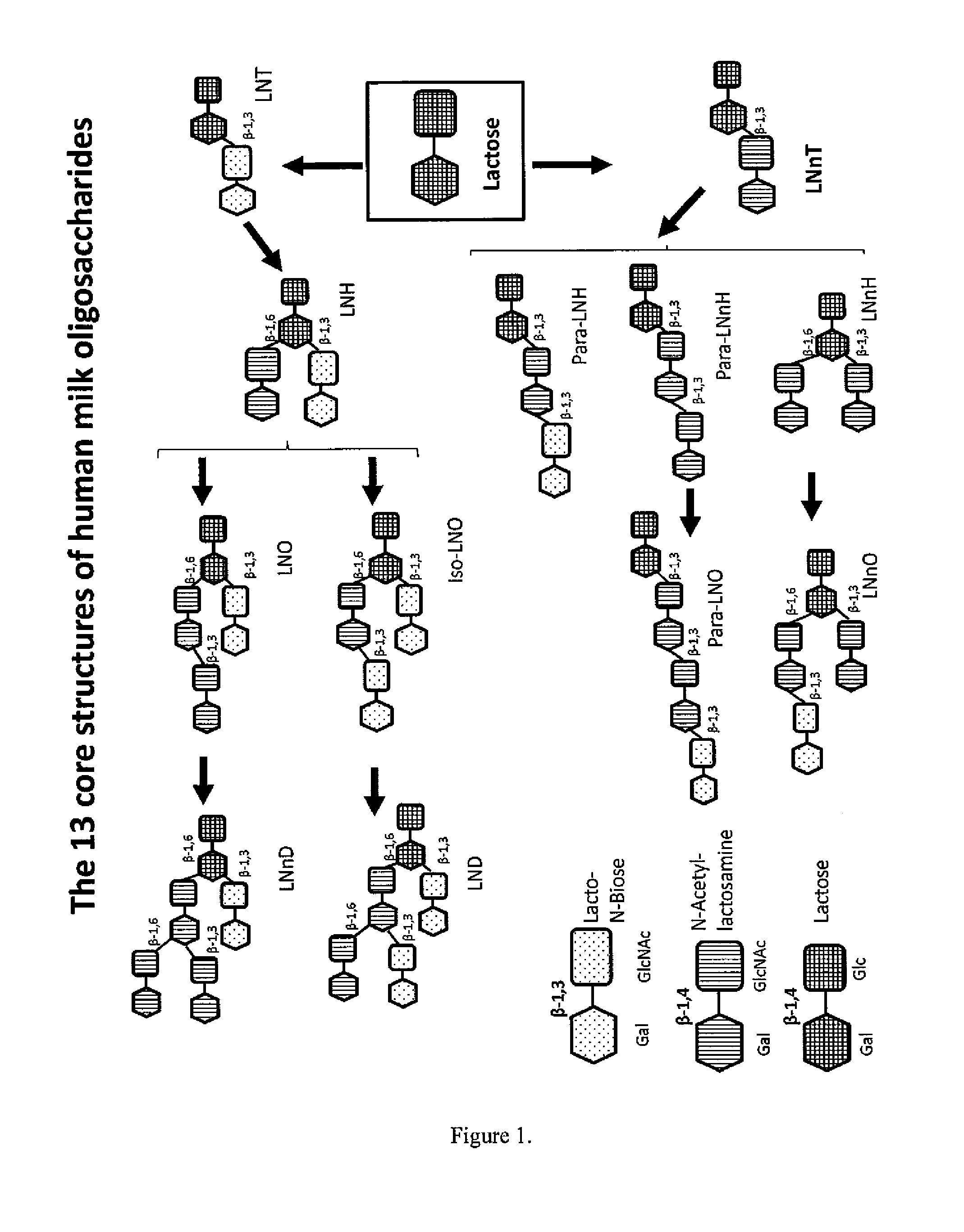
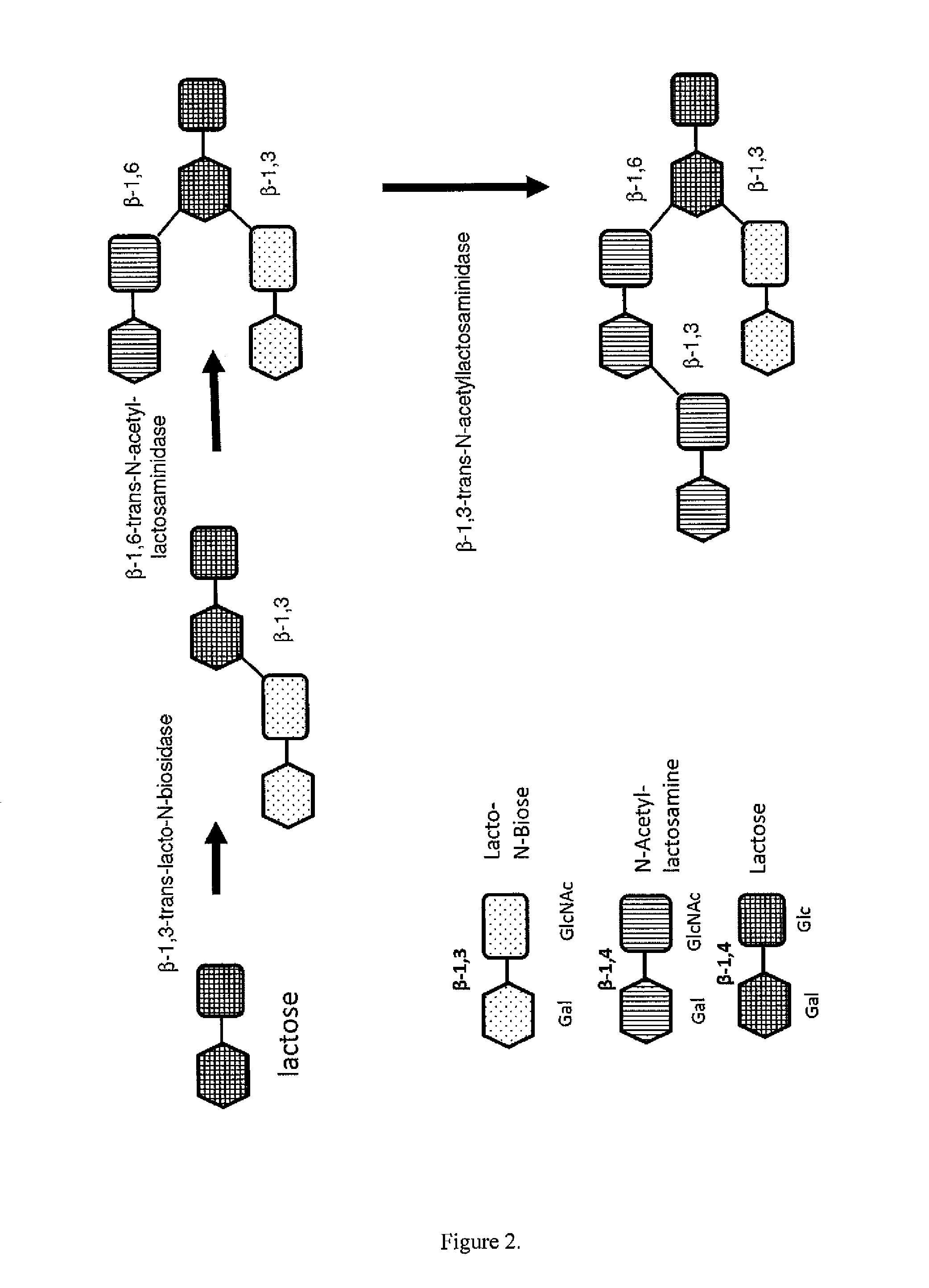
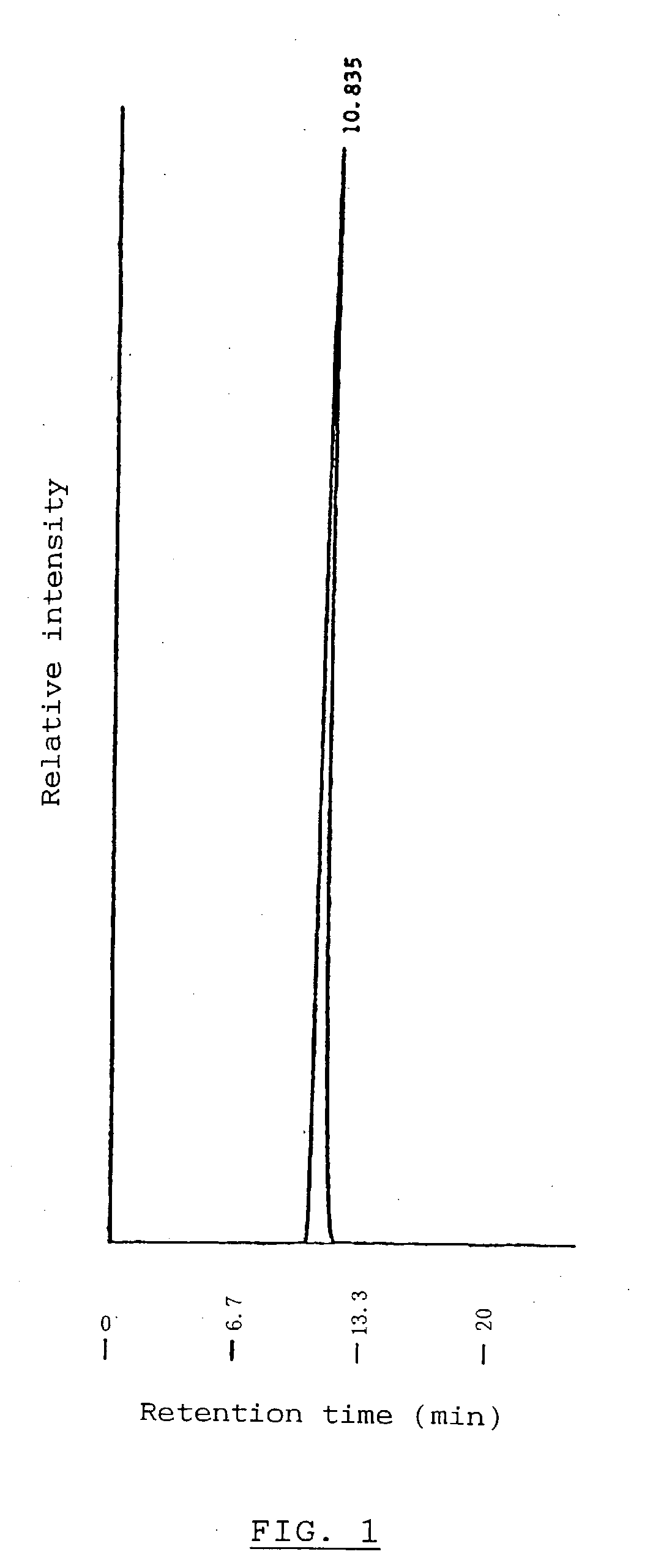
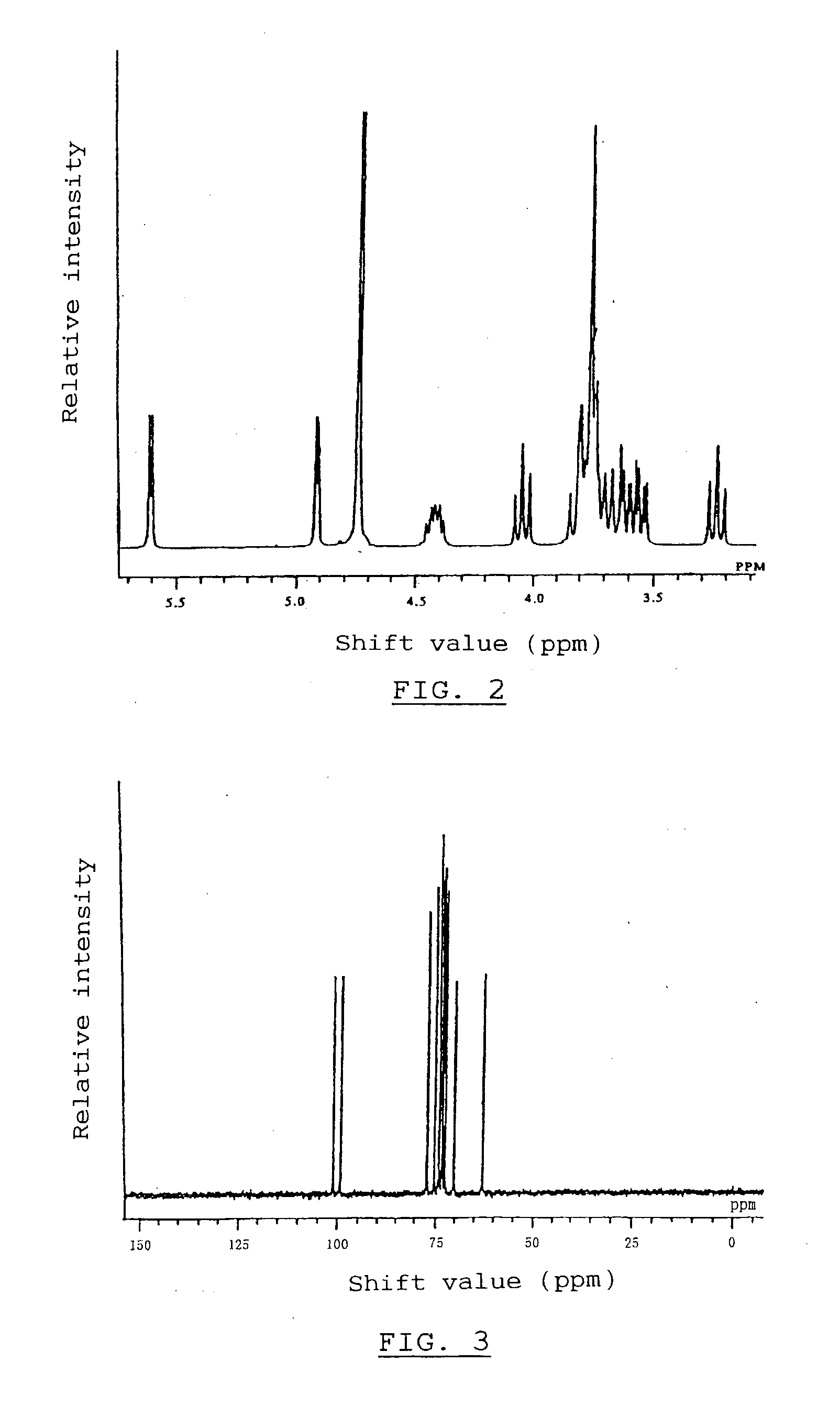
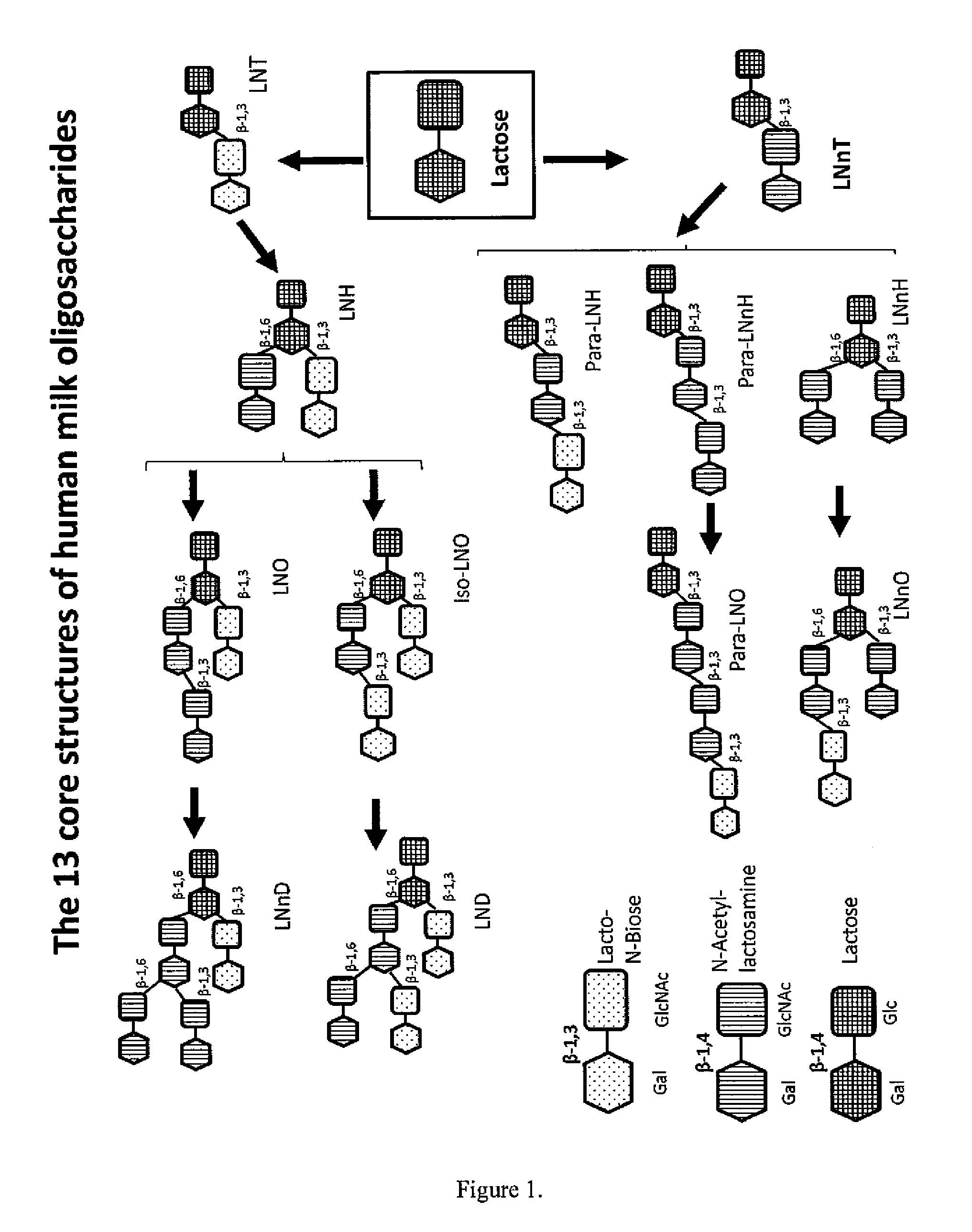
METHOD FOR GENERATING HUMAN MILK OLIGOSACCHARIDES (HMOs) OR PRECURSORS THEREOF
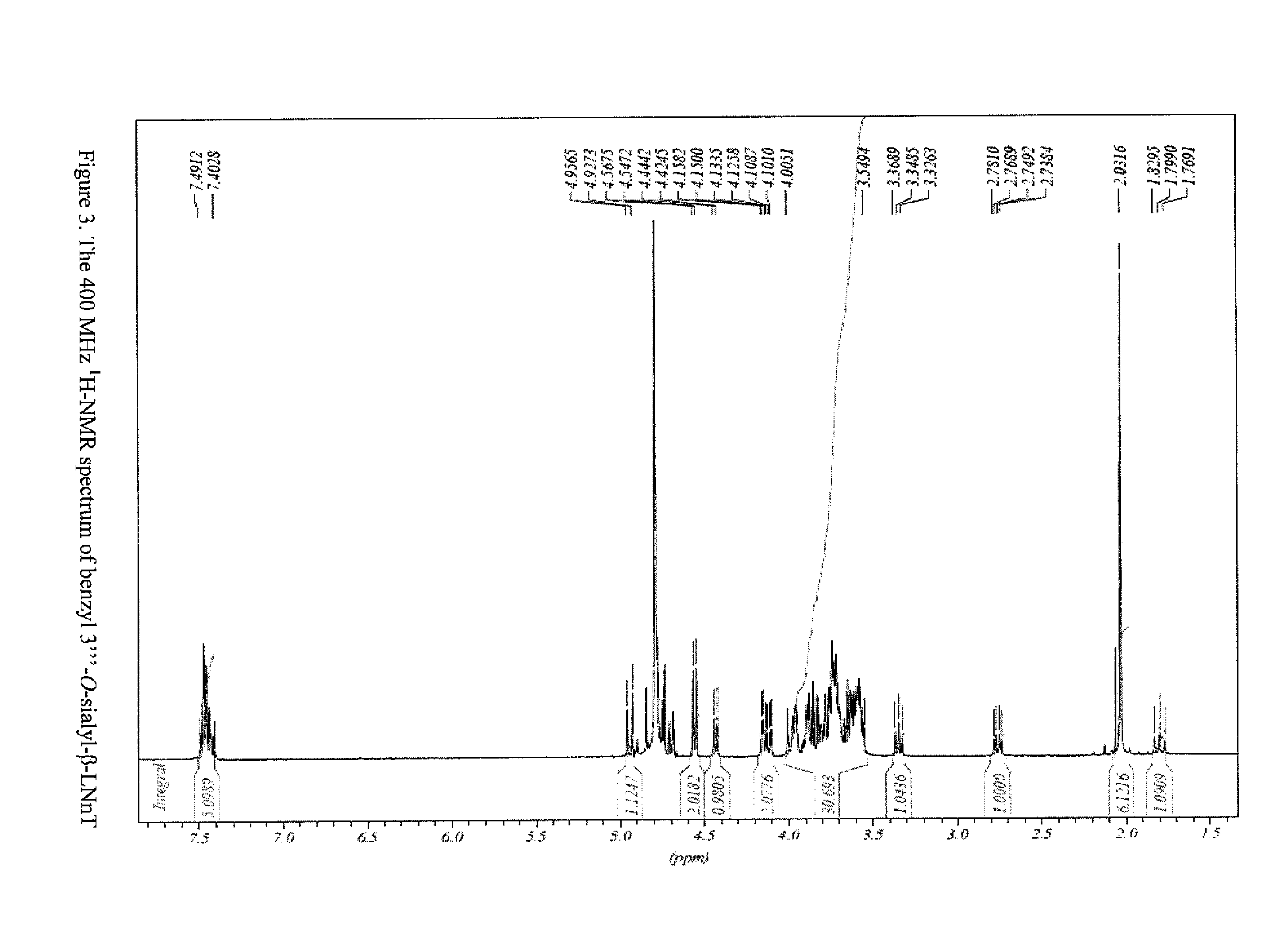
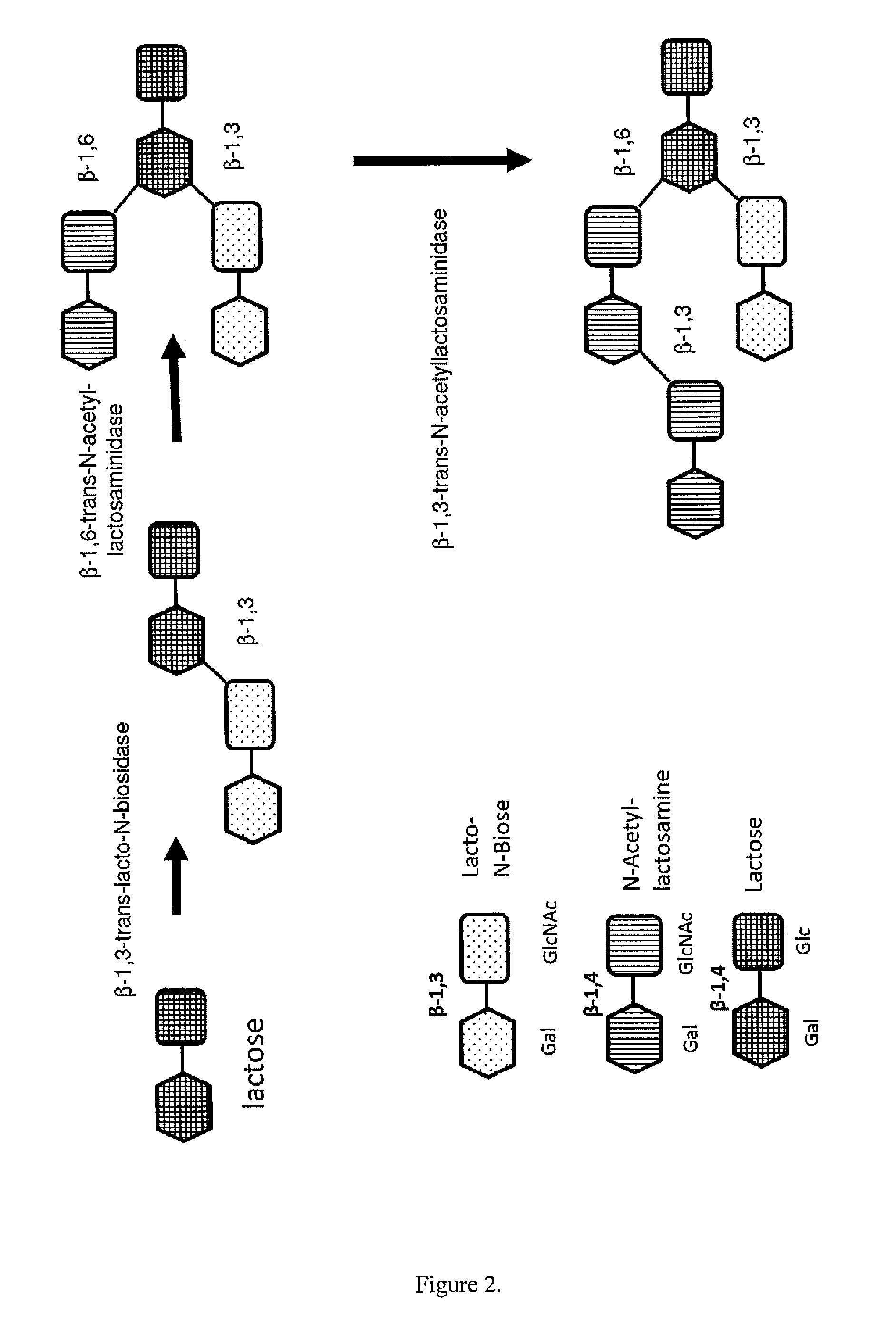
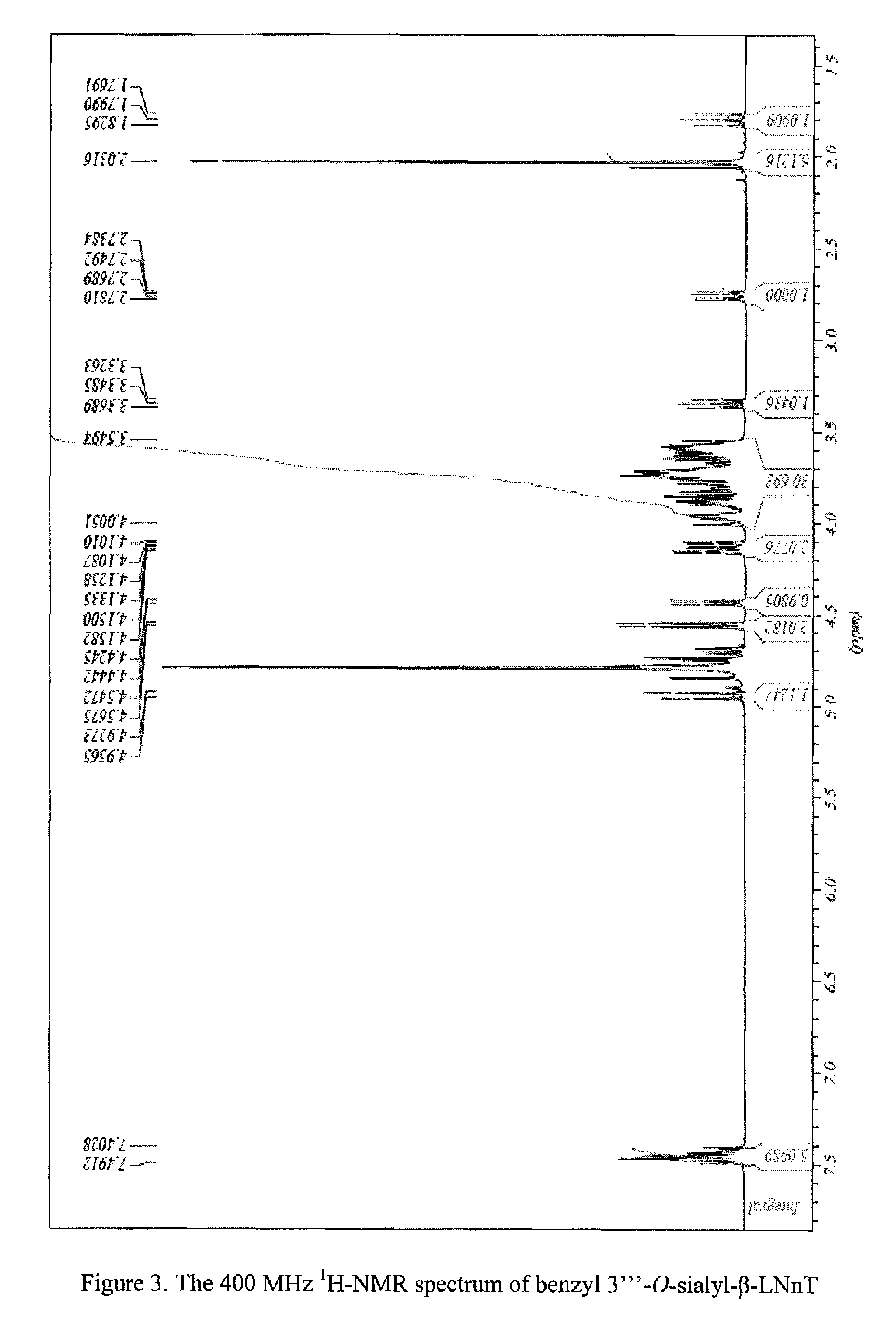
A method for generating human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) or precursors thereof, compounds obtainable by the method, and uses and compositions involving such compounds. The method comprising the steps of a) providing at least one donor selected from the group of compounds of any of formulae 5 to 10, b) providing at least one acceptor from a group of lactose, LNT, LNnT and derivatives thereof, c) providing at least one enzyme comprising a transglycosidase activity and / or a glycosynthase activity, d) preparing a mixture of the at least one donor, at least one acceptor and at least one enzyme provided in steps a), b) and c); and e) incubating the mixture prepared according to step d).
Owner:GLYCOM AS
Transglycosylation activity of glycosynthase mutants of an endo-beta-n-acetylglucosaminidase (endo-d) from streptococcus pneumoniae
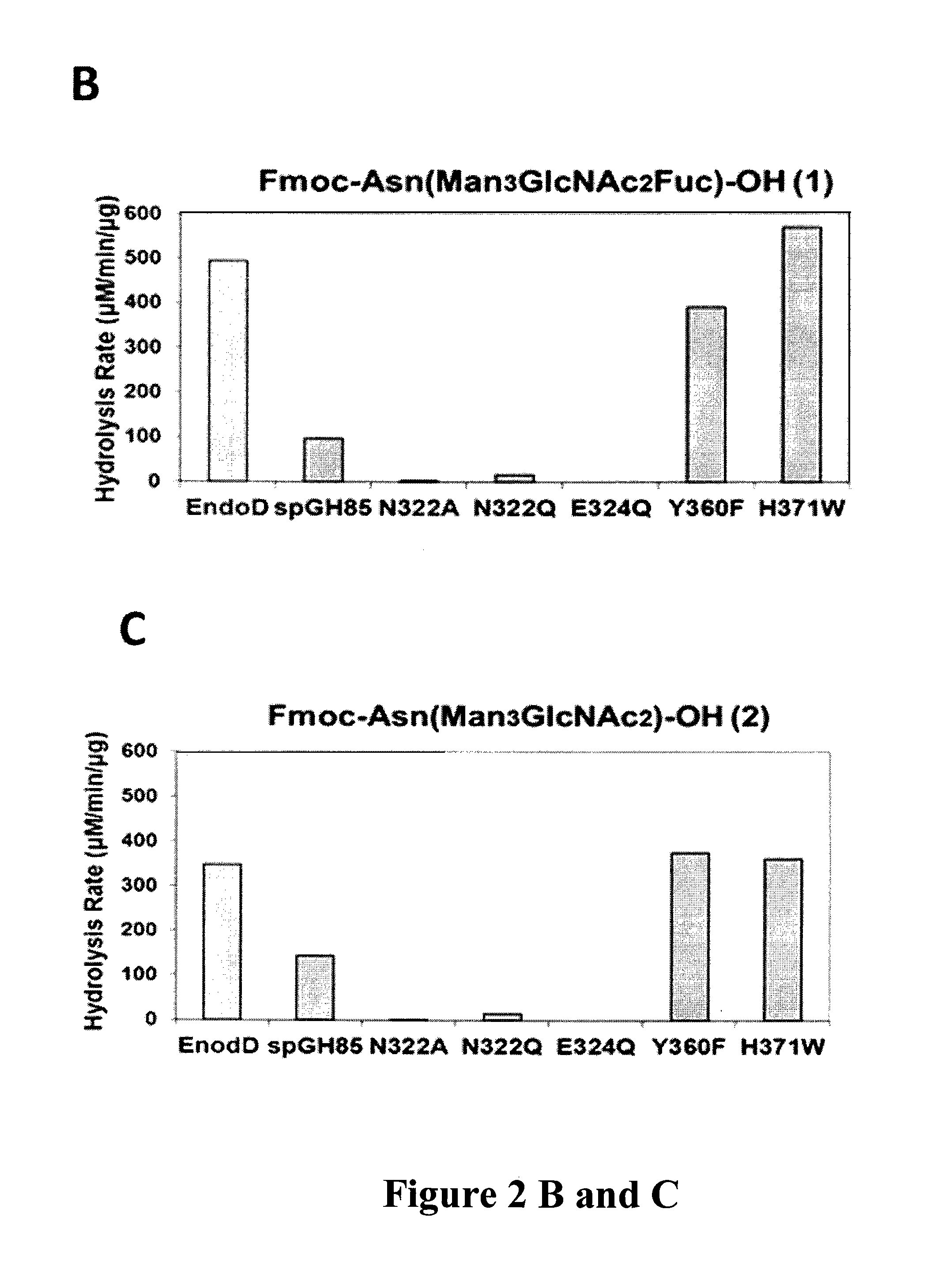
ActiveUS20130137857A1Reduced hydrolysis activityIncreased transglycosylation activityImmunoglobulinsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFucosylationStreptococcus pneumoniae
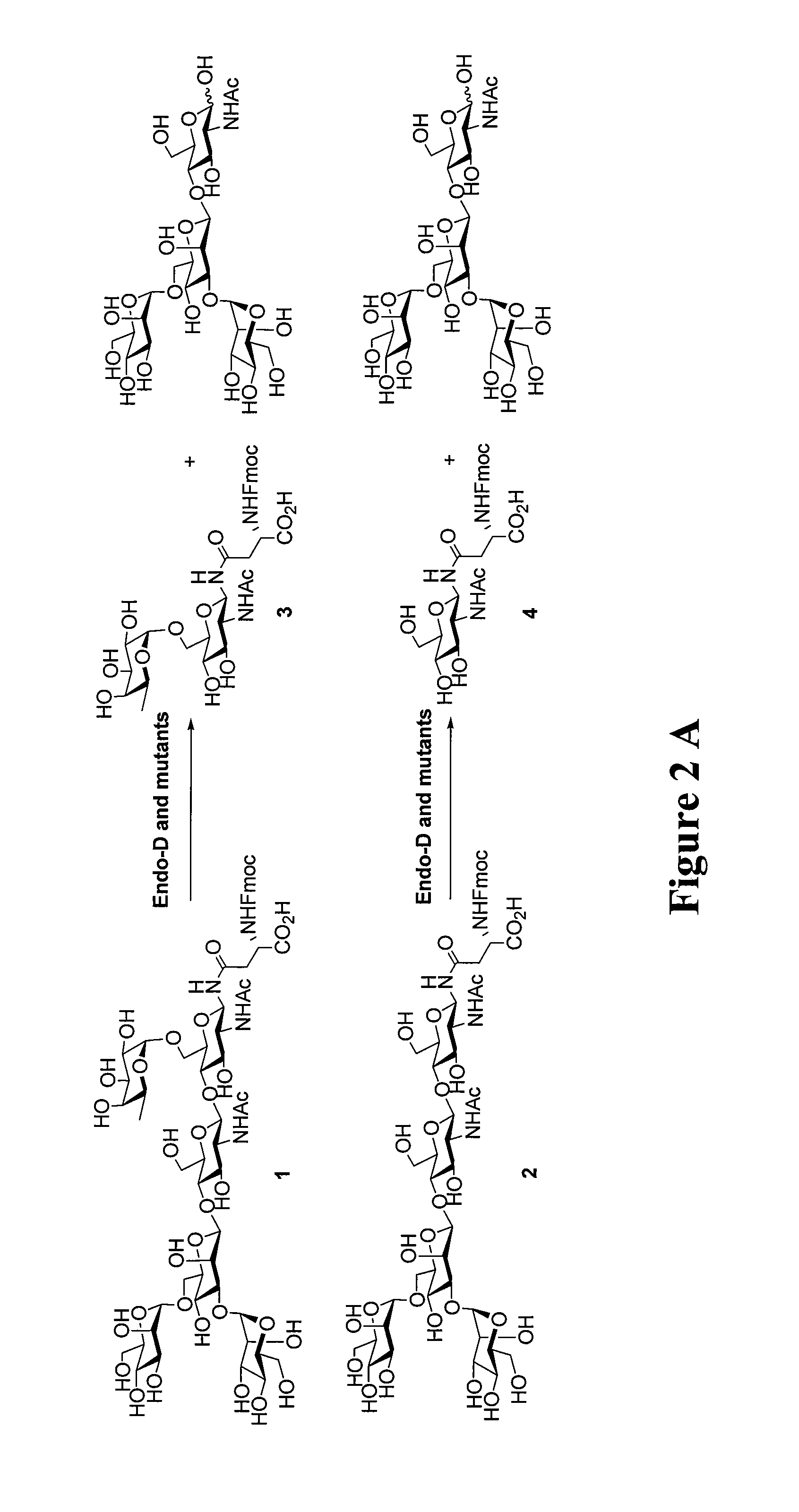
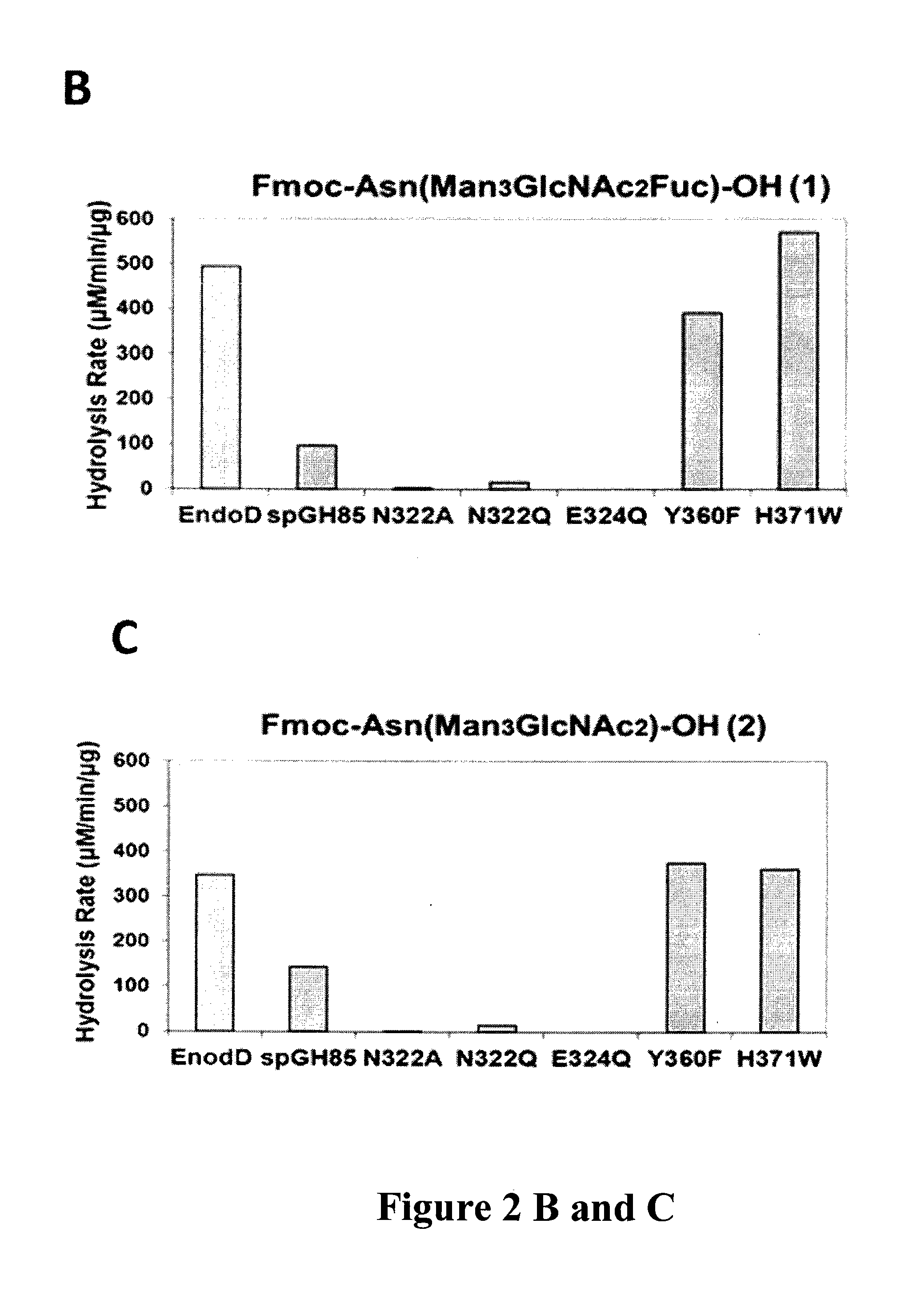
The present invention provides for recombinant Endo-D and selected mutants that exhibit reduced hydrolysis activity and increased transglycosylation activity for the synthesis of glycoproteins wherein a desired sugar chain is added to a core fucosylated or nonfucosylated GlcNAc-protein acceptor by transglycosylation. Such recombinant Endo-D and selected mutants are useful for efficient glycosylation remodeling of IgG1-Fc domain.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
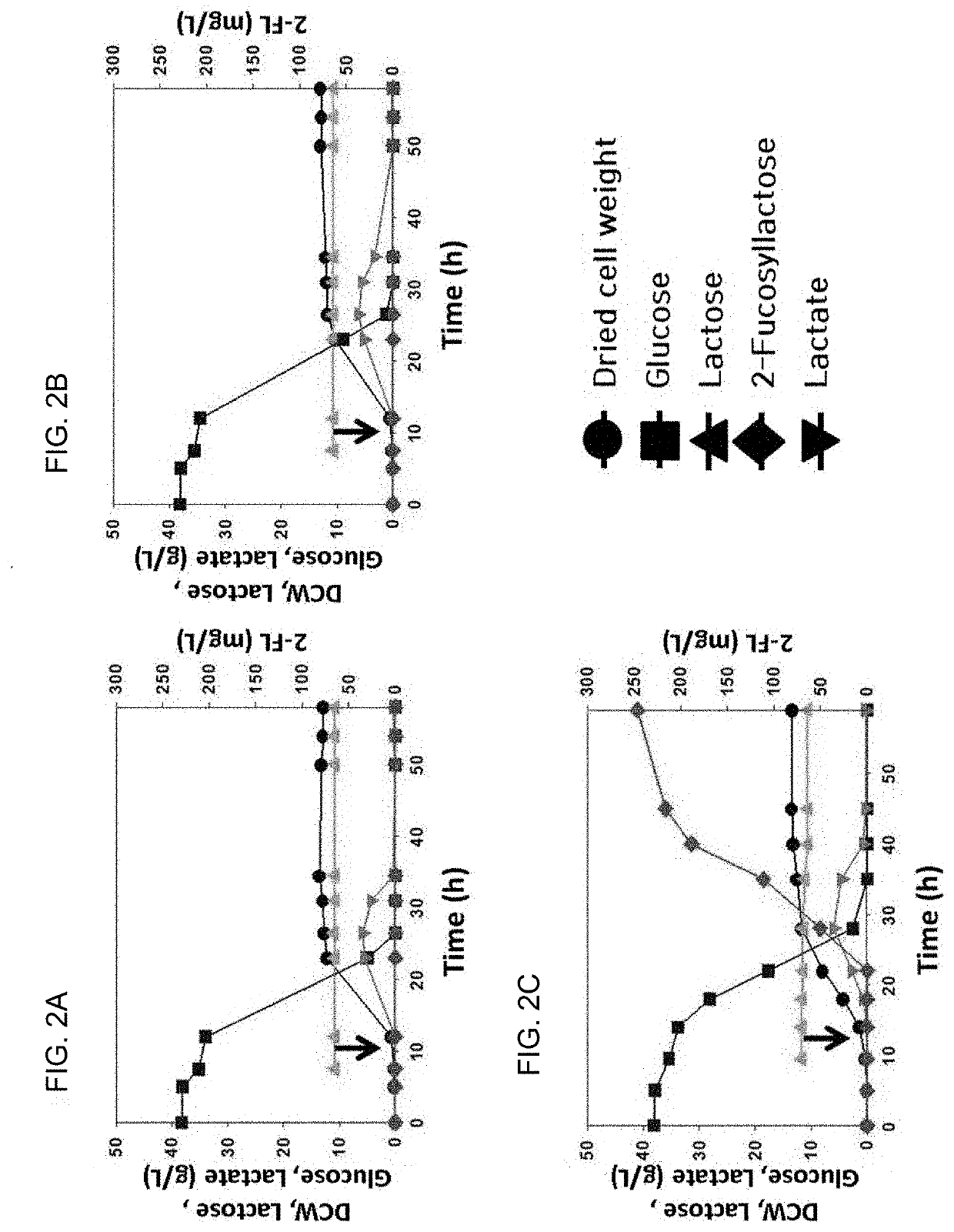
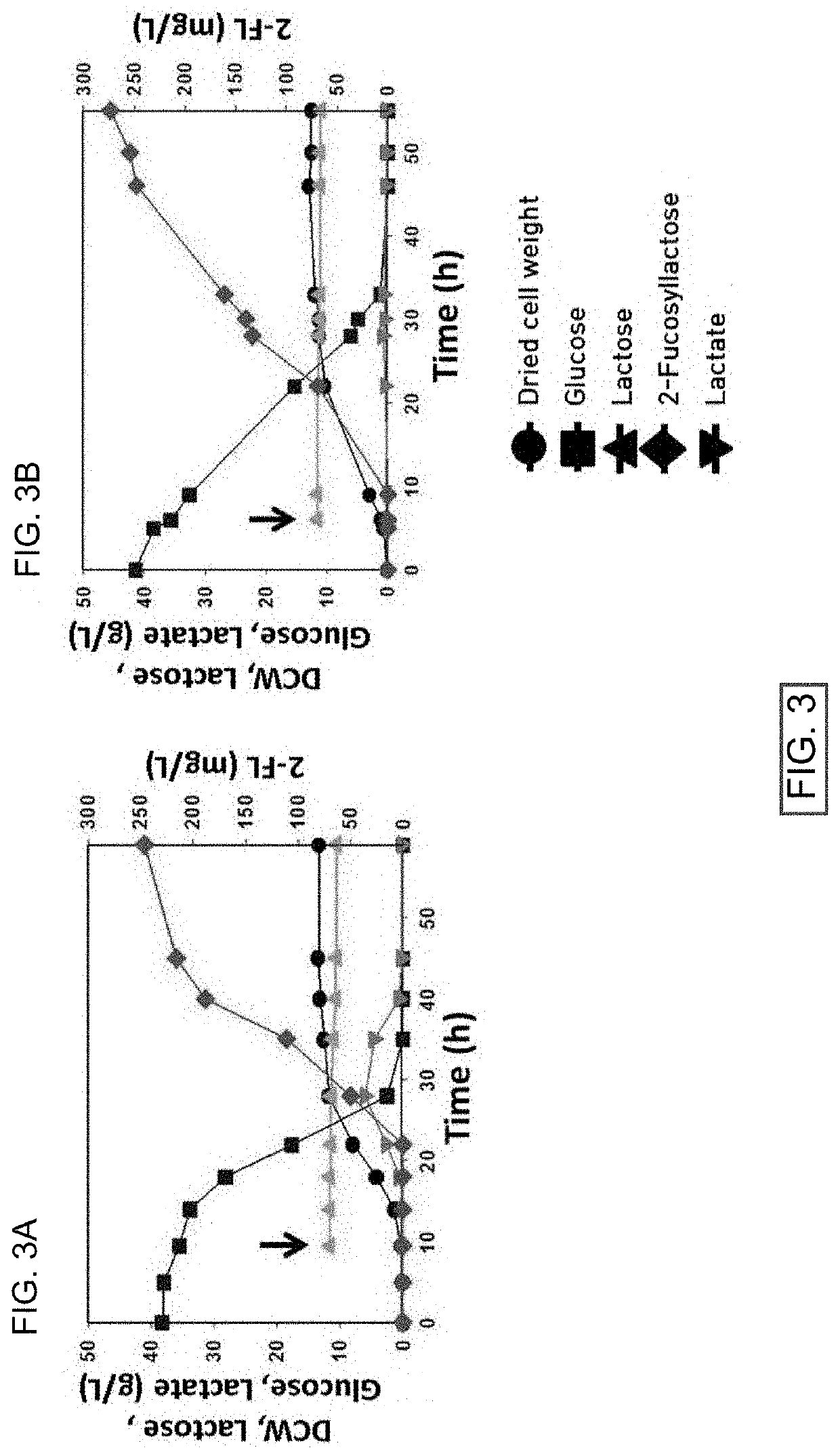
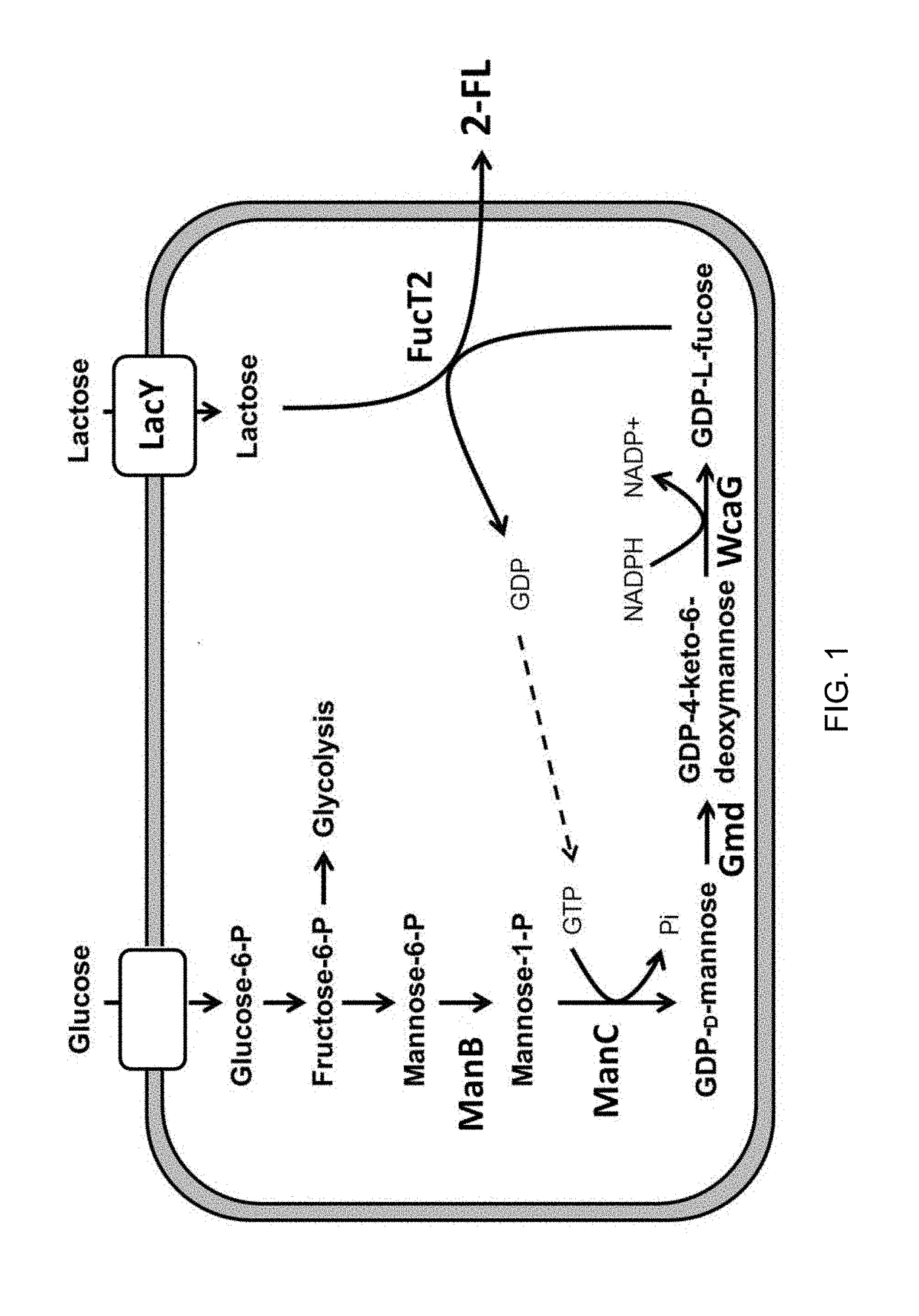
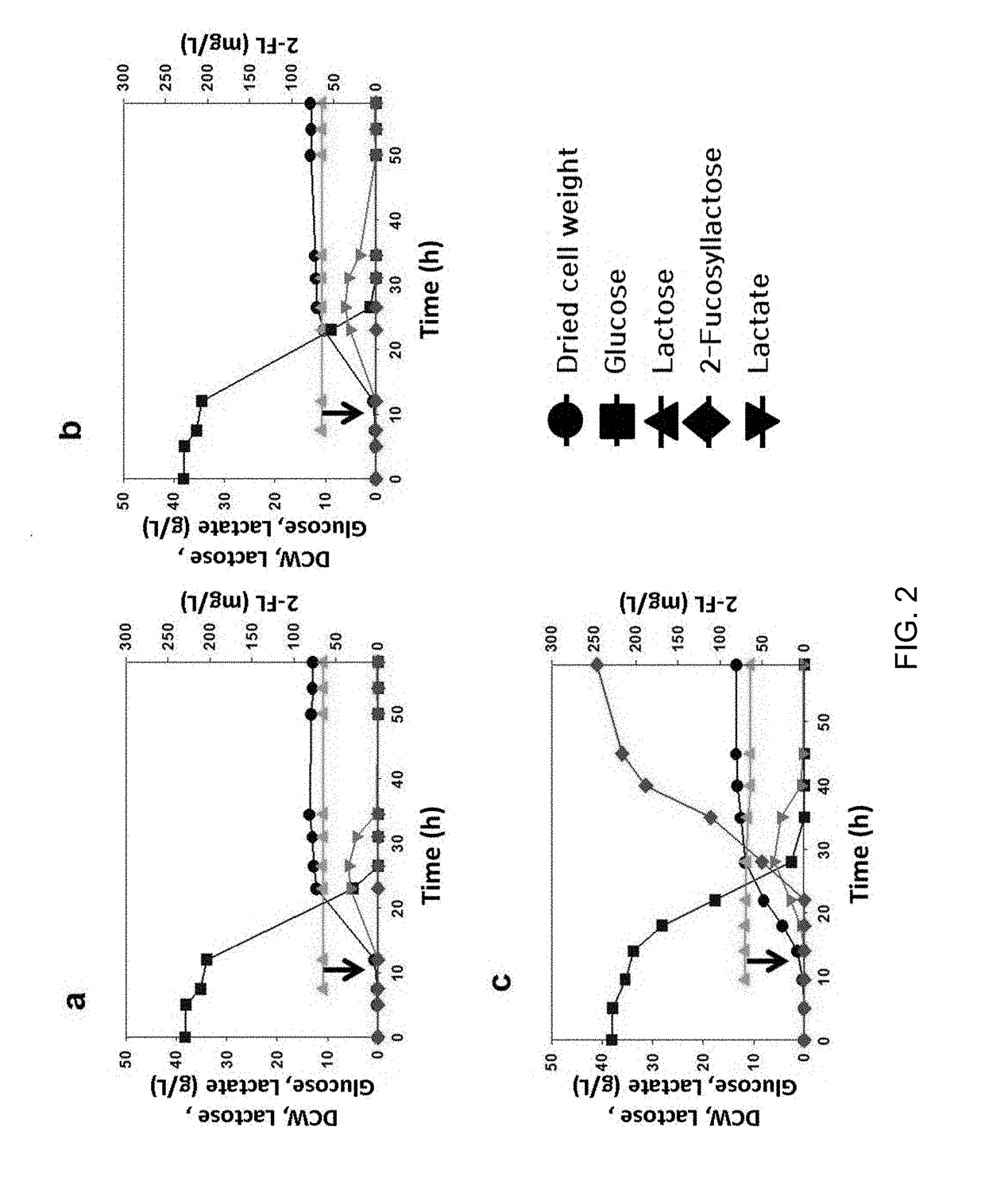
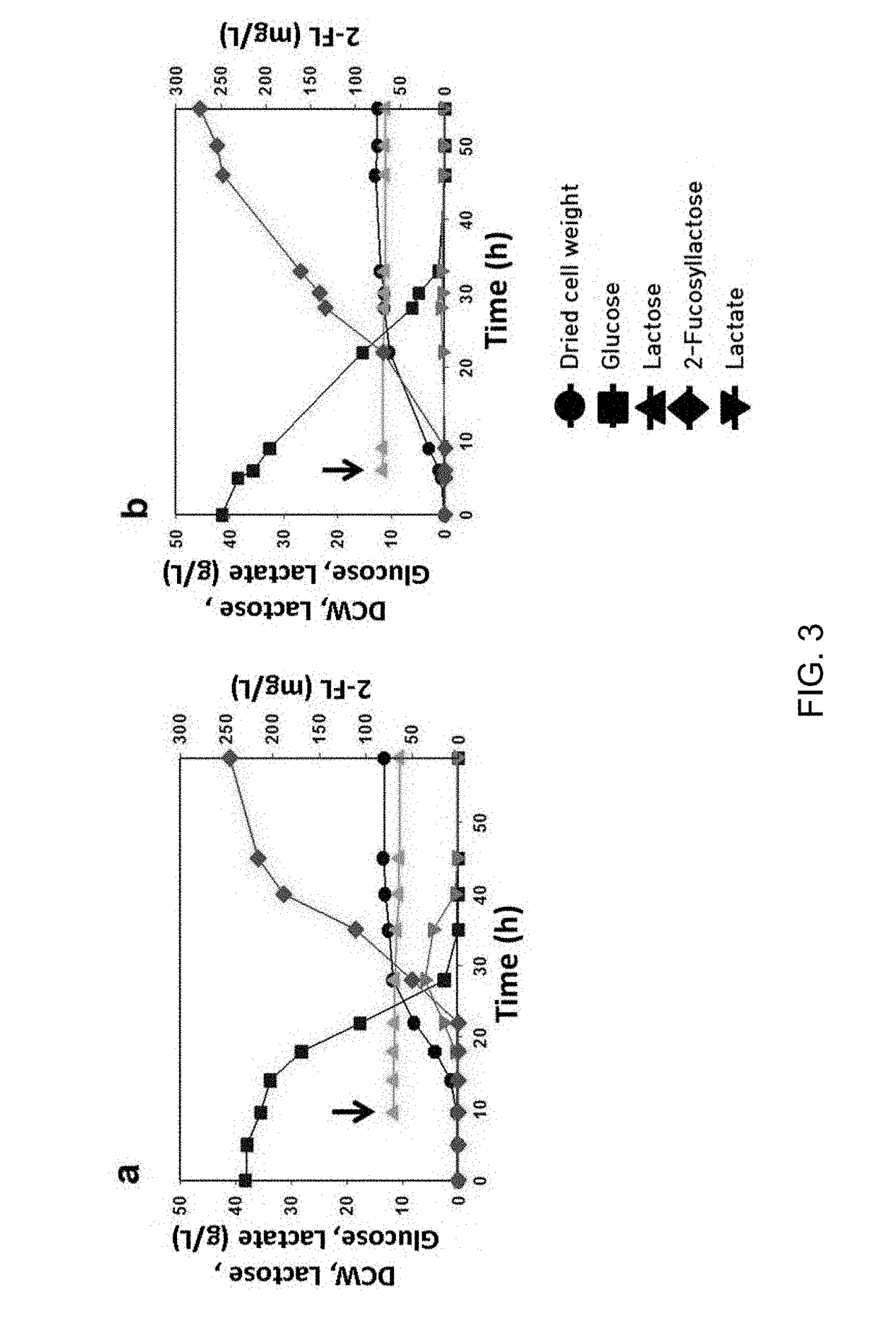
Corynebacterium glutamicum for use in producing 2'-fucosyllactose
ActiveUS20200048640A1Increase concentrationHigh yieldDepsipeptidesOxidoreductasesPhosphomannomutaseFucosyltransferase
Owner:ADVANCED PROTEIN TECH CORP
Alpha-Isomaltosylglucosaccharide synthase, process for producing the same and use thereof
InactiveUS20030194762A1High acidHigh heat-toleranceCosmetic preparationsDough treatmentIsomaltoseTransferase
The object of the present invention is to provide an alpha-isomaltosylglucosaccharide-forming enzyme, process of the same, cyclotetrasaccharide, and saccharide composition comprising the saccharide which are obtainable by using the enzyme; and is solved by establishing an alpha-isomaltosylglucosaccharide-forming enzyme which forms a saccharide, having a glucose polymerization degree of at least three and having both the alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkage as a linkage at the non-reducing end and the alpha-1,4 glucosidic linkage other than the linkage at the non-reducing end, by catalyzing the alpha-glucosyl-transfer from a saccharide having a glucose polymerization degree of at least two and having the alpha-1,4 glucosidic linkage as a linkage at the non-reducing end without substantially increasing the reducing power; alpha-isomaltosyl-transferring method using the enzyme; method for forming alpha-isomaltosylglucosaccharide; process for producing a cyclotetrasaccharide having the structure of cyclo{->6)-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->3)-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->6)-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->3)-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->} using both the alpha-isomaltosylglucosaccharide-forming enzyme and the alpha-isomaltosyl-transferring enzyme; and the uses of the saccharides obtainable therewith.
Owner:HAYASHIBARA BIOCHEMICAL LAB INC
2 '-fucosyllactose high-yield strain and preparation method and application thereof
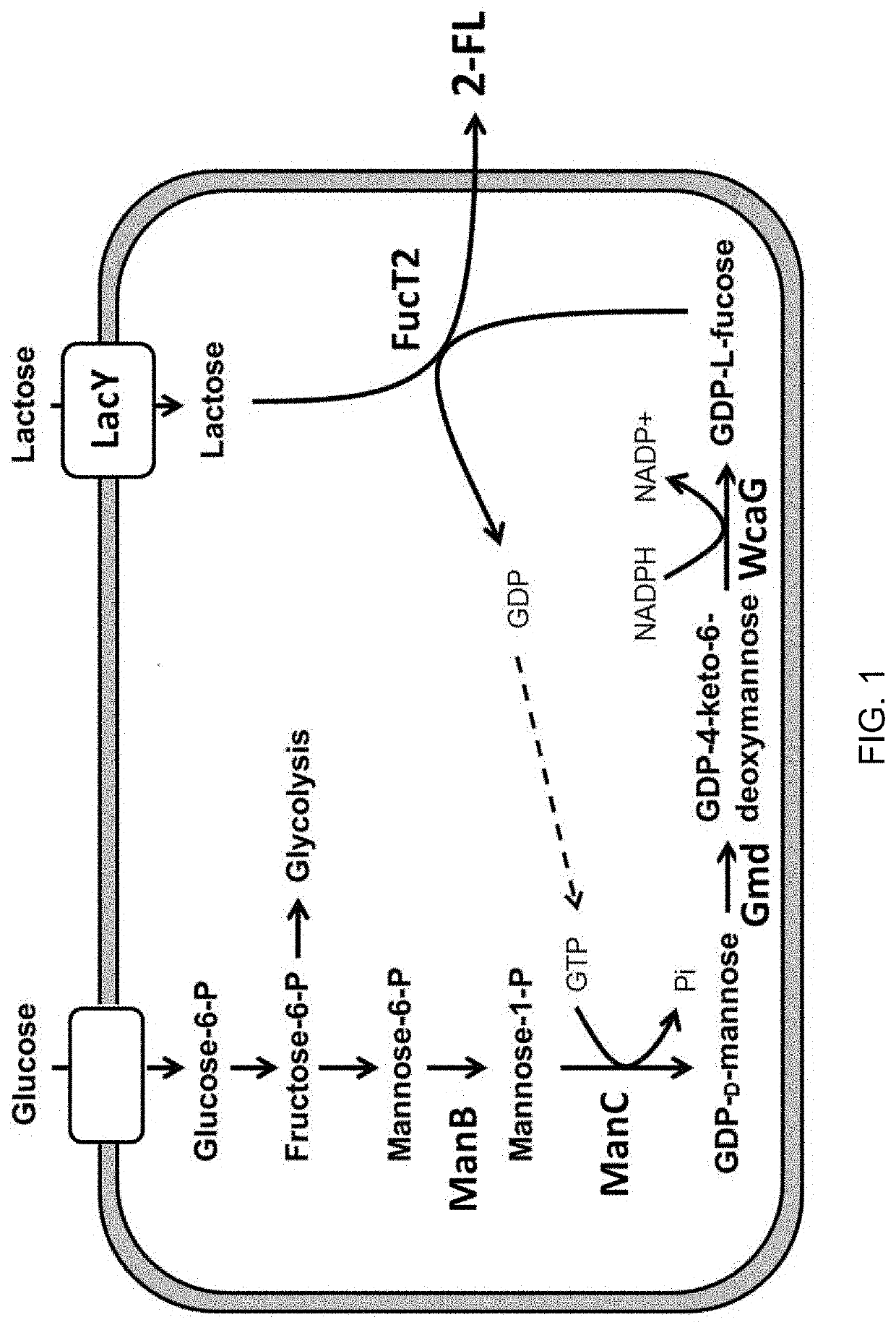
The invention discloses a 2 '-fucosyllactose high-yield strain as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No.19557. Escherichia coli E.coliBL21 (DE3) is used as a production host, and phosphomannose mutase (manB), mannose-1-phosphate phosphate guanylyltransferase (manC), GDP-mannose-4, 6-dehydratase (gmd), GDP-L-fucose synthase (flc) and alpha-1,2- fucosyltransferase (futC) are overexpressed so as to construct a synthesis path of the 2'-FL; substrate supply is improved by overexpressing sucrose transporter and lactose transporter onthe basis, the production capacity of 2 '-FL is further improved, efficient expression of 2'-FL in escherichia coli is realized, the 2 '-FL high-yield strain is improved.
Owner:江苏华燕集团有限公司
Glycosynthase variants for glycoprotein engineering and methods of use
ActiveUS20200062861A1Increased transglycosylation activityImprove enzymatic activityComponent separationImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiendomysial antibodiesReceptor
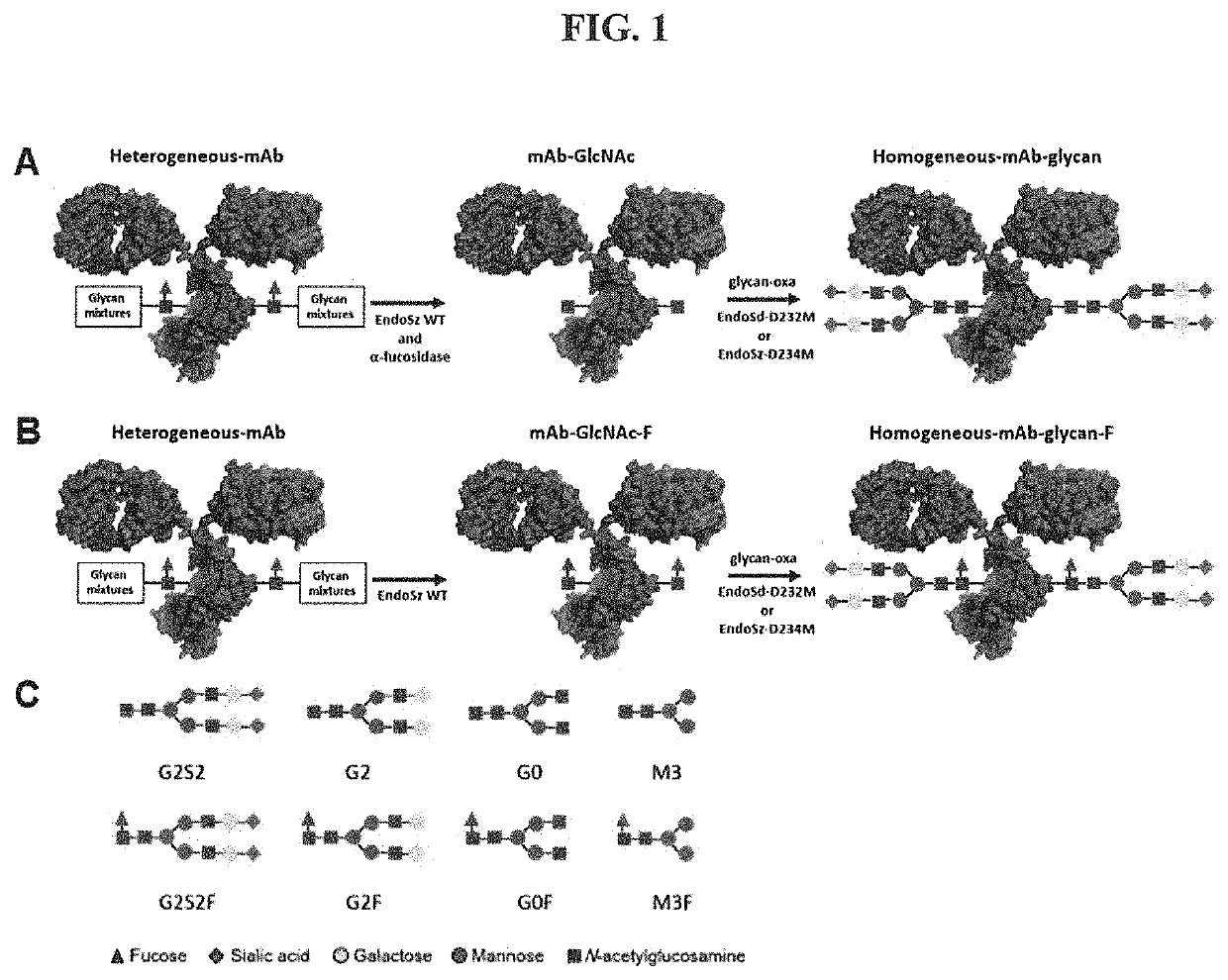
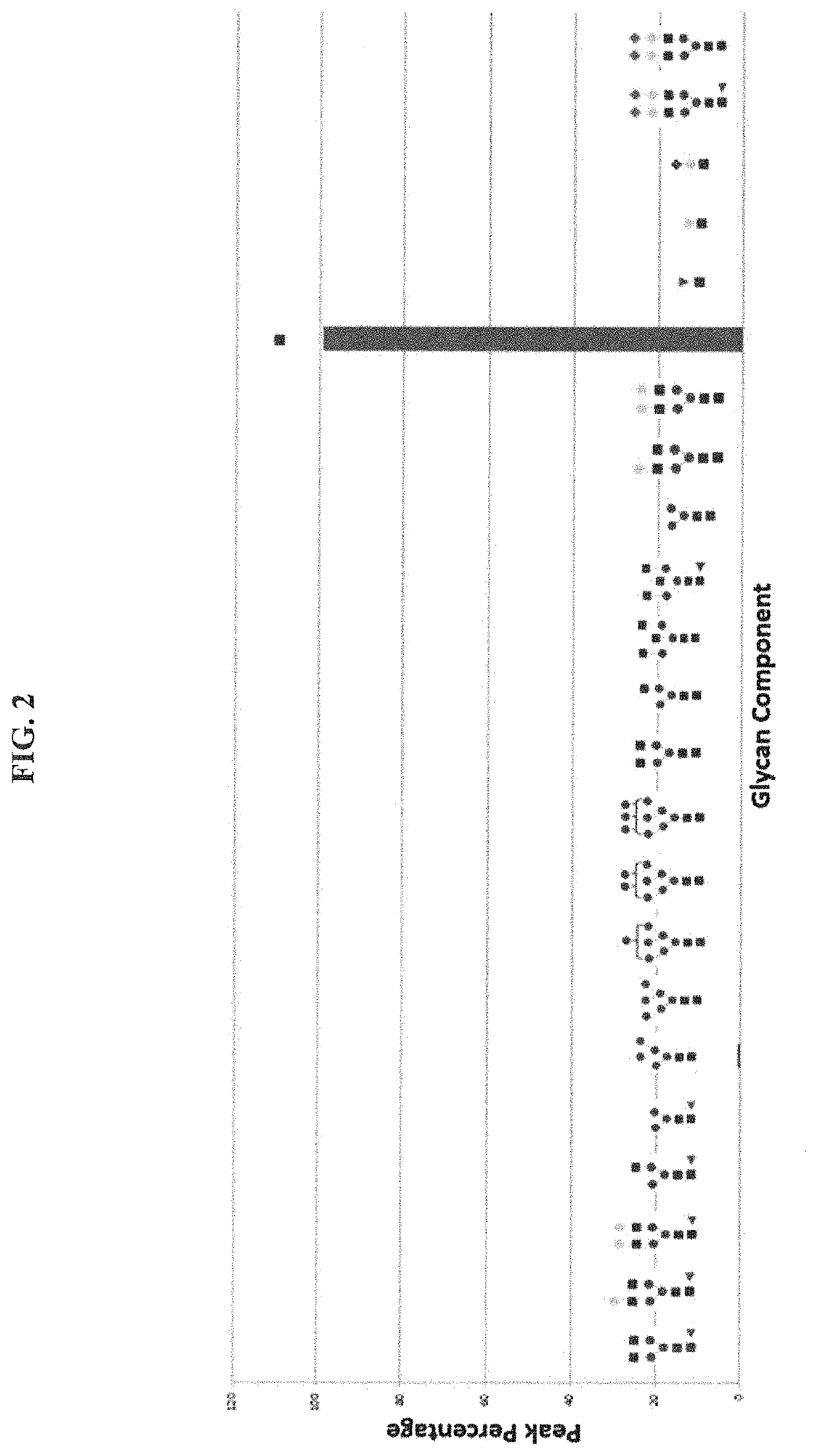
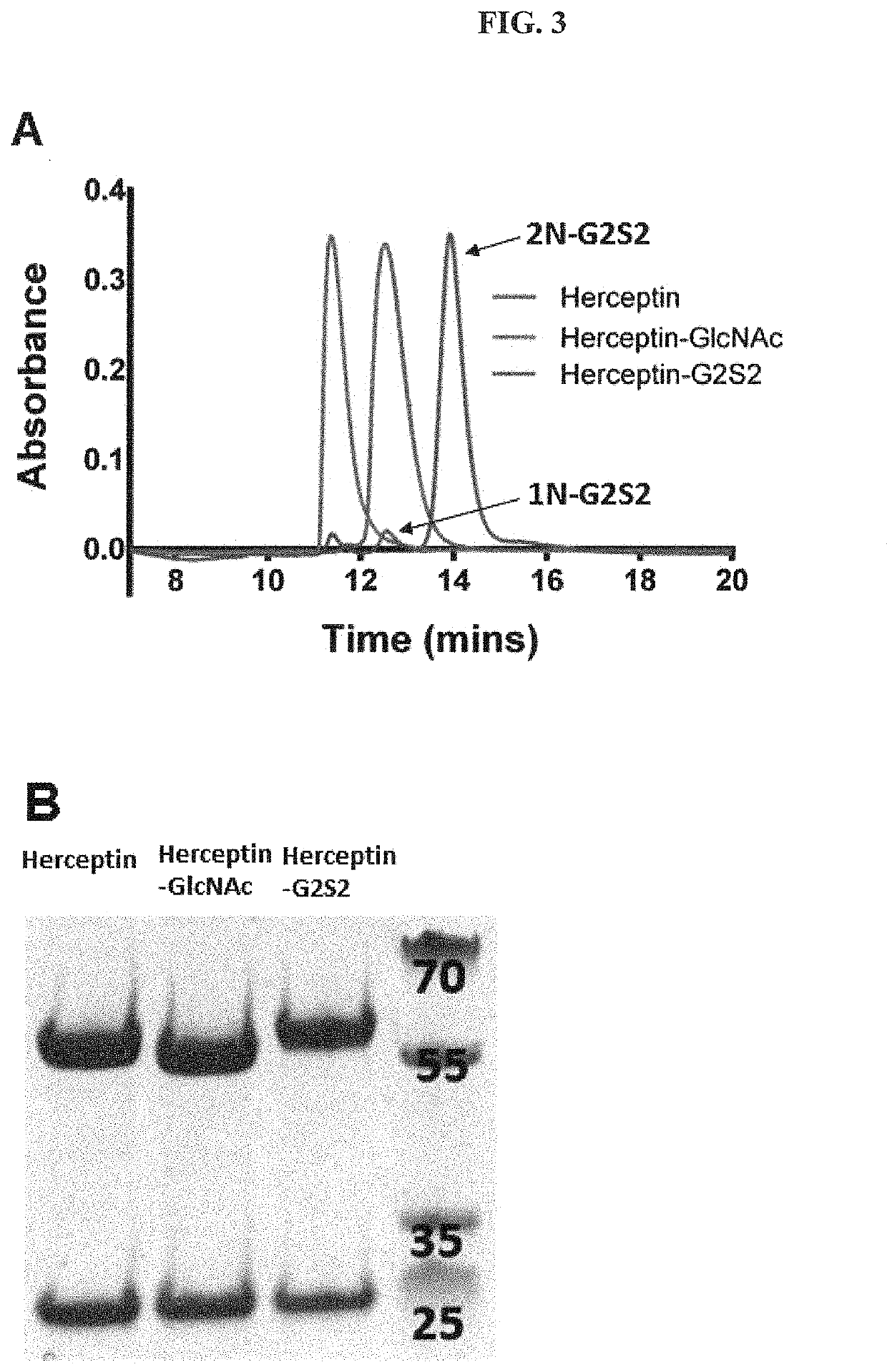
The present disclosure relates to novel glycosynthase enzymes for glycoprotein engineering and / or homogeneous antibody remodeling. The enzyme variants, termed EndoSd-D232M and EndoSz-D234M, contain the glycan conjugation and / or modification activity at the conserved N297 glycosylation site of Fc region of an exemplary antibody. It has been demonstrated that the glycosynthase activities of EndoSd-D232M and EndoSz-D234M can be applied to various mAbs targeting different receptors, including, but not limited to, Globo H, SSEA-4, SSEA-3 series of receptors (OBI-888; Globo H ganglioside), Herceptin (Her 2 receptor), Perjeta (Her 2 receptor) and Vectibix (EGFR receptor). It has been found that both mAb-GlcNAc and mAb-GlucNAc(F) were suitable substrates for both EndoSd-D232M and EndoSz-D234M. The ADCC assay of related products, OBI-888-G2S2 and Herceptin-G2S2, showed that the remodeled homogeneous antibody, mAb-G2S2, has an increased relative activity ranging from 3 to 26 folds.
Owner:OBI PHARMA
Mutant trehalose synthase as well as expression gene and application thereof
The invention relates to mutant trehalose synthase as well as an expression gene and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the expression gene of the mutant trehalose synthase is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The amino acid sequence of the mutant trehalose synthase is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. On the basis of a three-dimensional structure predicted by pseudomonas stutzeri Qlu3, the invention conducts key amino acid site-specific mutagenesis on the active center for the first time, so that the mutant protein of the trehalose synthase is obtained; the mutant trehalose synthase is simple and convenient in preparation method, high in yield, high in purity and good in thermal stability; and compared with wild trehalose synthase, the trehalose conversion rate of the mutant is improved by 4.5% and the generation amount of glucose, as a byproduct, is reduced by 69.4%.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGING BIOTECH CO LTD
Yeast transformant into which genes associated with synthesis system of O-fucosylated protein are introduced
InactiveUS20060099680A1Efficient production of O-fucosylatedFungiSugar derivativesFucosylationEnzyme Gene
An object of the present invention is to provide a means for producing O-fucosylated protein in large quantities, a means for searching for new genes associated with the synthesis system of O-fucosylated protein or the proteins expressed by the genes, and a means for elucidating the functions thereof. According to the present invention, a yeast transformant characterized in that the genes associated with the synthesis system of O-fucosylated protein are a GDP-fucose synthase gene, a GDP-fucose transporter gene, a fucosyltransferase gene, and a fucose receptor gene is provided.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Method for improving enzyme activity of trehalose synthase by C-terminal fragments of thermophilic bacteria trehalose synthase
ActiveCN104651332AIncrease productionImprove the level of enzyme catalysisTransferasesIsomerasesEnzymePseudomonas trivialis
The invention discloses a method for improving enzyme activity of trehalose synthase by C-terminal fragments of thermophilic bacteria trehalose synthase. Four C-terminal fragments of trehalose synthase from different sources connected with thermophilic bacteria-originated C-terminal gene fragments of trehalose synthase are subjected to fusion expression in escherichia coli while expressing trehalose synthase originated from pseudomonas putida, corynebacterium glutamicum, streptomyces coelicolor and thermotoga maritime by applying a molecular biological technique. Under the action of the thermophilic bacteria-originated C-termianl gene fragments of trehalose synthase, the enzyme catalytic activity of trehalose synthase is improved. According to the method disclosed by the invention, modified trehalose synthase is expressed in escherichia coli, and thus the enzyme activity of trehalose synthase is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Transglycosylation activity of glycosynthase mutants of an endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase (endo-D) from streptococcus pneumoniae
ActiveUS9175326B2Reduced activityHigh activityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide preparation methodsStreptococcus pneumoniaeFucosylation
The present invention provides for recombinant Endo-D and selected mutants that exhibit reduced hydrolysis activity and increased transglycosylation activity for the synthesis of glycoproteins wherein a desired sugar chain is added to a core fucosylated or nonfucosylated GlcNAc-protein acceptor by transglycosylation. Such recombinant Endo-D and selected mutants are useful for efficient glycosylation remodeling of IgG1-Fc domain.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Method of producing 2'-fucosyllactose using corynebacterium glutamicum
ActiveUS20180298389A1Increase concentrationHigh yieldDepsipeptidesOxidoreductasesHigh concentrationEscherichia coli
Disclosed are a recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum (C. glutamicum) for producing fucosyllactose which is transformed to express α-1,2-fucosyltransferase, GDP-D-mannose-4,6-dehydratase (Gmd), GDP-L-fucose synthase (WcaG) and lactose permease (LacY), wherein the Corynebacterium glutamicum has phosphomannomutase and GTP-mannose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase, and a method for producing fucosyllactose using the same. According to the recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum and the method for producing fucosyllactose according to the present invention, with use of a GRAS Corynebacterium glutamicum strain, which is safer than conventional Escherichia coli, 2′-fucosyllactose can be produced at a high concentration while overcoming drawbacks of conventional methods associated with industrial inapplicability resulting from low production concentrations.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND +1
Trehalose synthase mutant and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a trehalose synthase mutant and a preparation method and application thereof and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. The 271st Gln codon near the active center of trehalose synthase of trehalose synthase of Thermobifida fusca YX is converted into the Met codon, the 220th Ile codon is converted into the Val codon, the 228th Val codon is converted into the Ile codon, the 290th Cys codon is converted into Val codon, the 294th Phe codon is converted into the Tyr codon, and the 332nd Ile codon is converted into the Phe codon, so as to respectively obtain mutants Q271M, I220V, V228I, C290V, F294T and I332F. Based on the I220V, amphimutation is carried out to obtain mutants I220V / Q271M, I220V / V228I, I220V / C290V, I220V / F294Y and I220V / I332F. The mutants can be used for improving the trehalose conversion rate prepared by trehalose synthase and have relatively high industrial value.
Owner:湖南金代科技发展有限公司
Generation and comparative kinetic analysis of new glycosynthase mutants from streptococcus pyogenes fndoglycosidases for antibody glycoengineering
ActiveUS20190002945A1Reduced activityHigh activityMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesFucosylationStreptococcus pyogenes
The present invention provides for recombinant Endo-S mutants (named Endo-S glycosynthases) that exhibit reduced hydrolysis activity and increased transglycosylation activity for the synthesis of glycoproteins wherein a desired sugar chain is added to a fucosylated or nonfucosylated GlcNAc-IgG acceptor. As such, the present invention allows for the synthesis and remodeling of therapeutic antibodies thereby providing for certain biological activities, such as, prolonged half-life time in vivo, less immunogenicity, enhanced in vivo activity, increased targeting ability, and / or ability to deliver a therapeutic agent.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Glucosamine synthase producing bacterium based on CRISPR-Cas9 technology and construction method and application of glucosamine synthase producing bacterium
InactiveCN110387345AEfficient accumulationEasy to synthesizeBacteriaTransferasesMicrobiologyCompanion animal
The invention discloses a glucosamine synthase producing bacterium based on a CRISPR-Cas9 technology and a construction method and application of the glucosamine synthase producing bacterium. The glucosamine synthase producing bacterium is obtained in the modes that a glucosamine acetylase gene gnal and a glucosamine synthase gene glms are connected to a carrier pET-28a, and then a recombinant plasmid is transferred into a double-gene deletion host bacterium obtained by knocking out a glucosamine metabolism gene naggE and a glucosamine metabolism gene mannX of an E.coli BL21(DE3) genome through the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology. The recombinant bacterium is applied to fermentation culture, on a shake flask, 7.51 g / L of glucosamine can be accumulated, 3.73 g / L of acetylglucosamine canbe accumulated, and the total output is 11.24 g / L; and on a fermentor of 5 L, 7.30 g / L of the glucosamine can be accumulated, 10.53 g / L of the acetylglucosamine can be accumulated, and the total output is 17.83 g / L.
Owner:YANGZHOU RIXING BIO TECH +1
Thermostable trehalose synthase as well as expression gene and application thereof
ActiveCN104946610AImprove thermal stabilityHigh expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPseudomonas putidaExpression gene
The invention relates to a thermostable trehalose synthase as well as an expression gene and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the expression gene of the transformed thermostable trehalose synthase is shown by SEQ ID No.1; and the amino acid sequence of the transformed thermostable trehalose synthase is shown by SEQ ID No.2. In the invention, the trehalose synthase with higher stability is obtained for the first time based on the three-dimensional structure of pseudomonas putida trehalose synthase (pseudomonas putida KT2440) and by cutting the flexible area in the structure and retaining the stable structure domain at the activity center. The preparation method of the trehalose synthase is simple, the yield is large, and the purity is high; and experiments prove that the transformed trehalose synthase still keeps relatively high catalytic activity, the thermal stability is greatly improved, the production cost of trehalose can be reduced, and a foundation is laid for the industrial production of trehalose.
Owner:湖南尚道生物科技有限公司
Heat resistant beta-amylase-trehalose synthase fusion enzyme, expression gene of heat resistant beta-amylase-trehalose synthase fusion enzyme, engineering bacterium secreting fusion enzyme, and application
The invention provides a heat resistant beta-amylase-trehalose synthase fusion enzyme, an expression gene of the heat resistant beta-amylase-trehalose synthase fusion enzyme, an engineering bacterium secreting the fusion enzyme and application, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The heat resistant beta-amylase-trehalose synthase fusion enzyme comprises an amino acid sequence with SEQ ID No.1 and another amino acid sequence, and the similarity of the another amino acid sequence to the amino acid sequence with SEQ ID No.1 is 80%-100%. The expression gene of the heat resistant beta-amylase-trehalose synthase fusion enzyme comprises an amino acid sequence with SEQ ID No.2 and another amino acid sequence, and the similarity of the another amino acid sequence to the amino acid sequence with SEQ ID No.2 is 80%-100%. The obtained beta-amylase-trehalose synthase fusion enzyme has a heat resistant property, directly converts amylose into trehalose at the higher temperature, saves the complicated steps of separating and purifying endoenzyme, simplifies the production process of the trehalose, and reduces the production cost.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
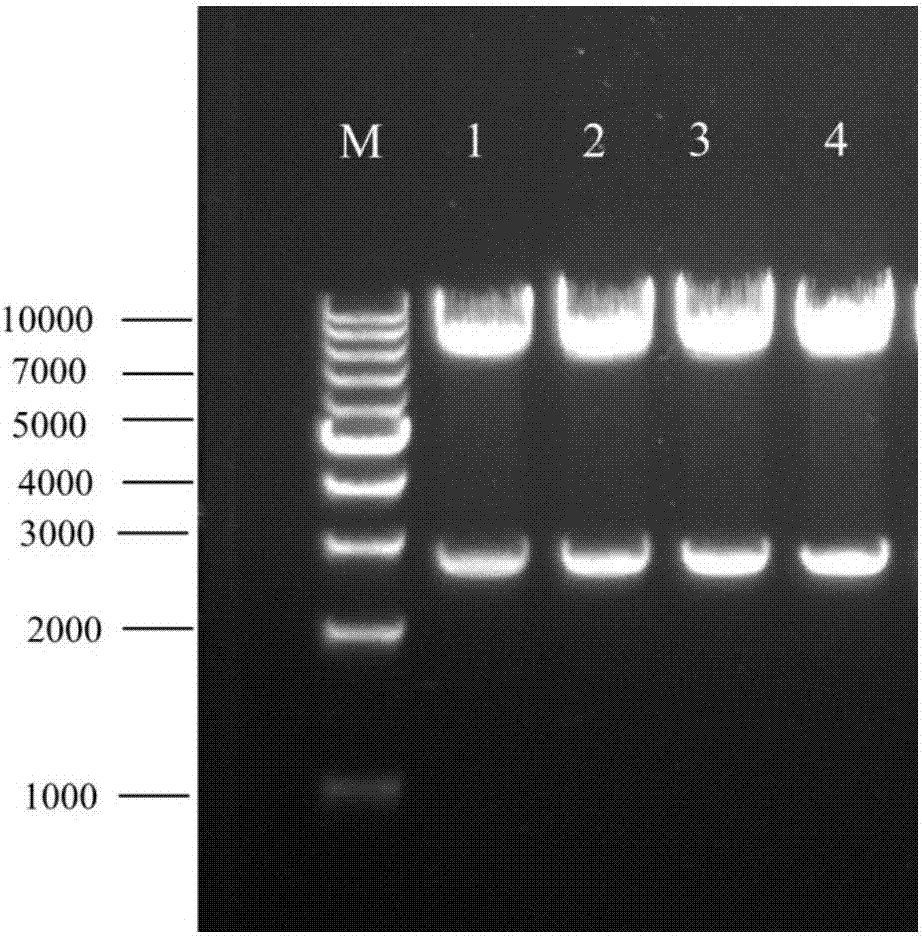
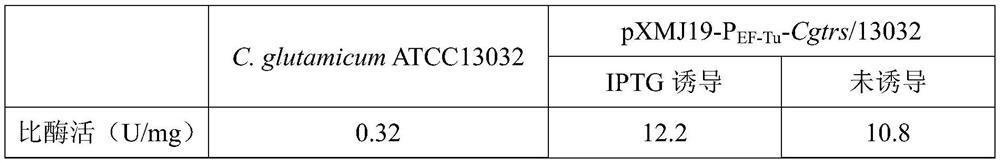
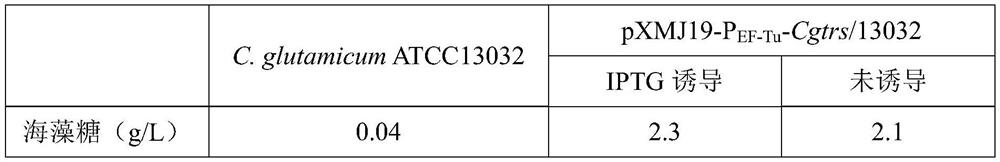
Method for expressing trehalose synthase by Corynebacterium glutamicum through an EF-Tu promoter and application of method
The invention discloses a method for expressing trehalose synthase by Corynebacterium glutamicum through an EF-Tu promoter and application of the method. The method comprises the following steps: fusing the promoter PEF-Tu of a translation elongation factor EF-Tu in Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13032 to the upstream of a trehalose synthase gene of Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13032, and cloning to a Corynebacterium glutamicum induced expression plasmid pXMJ19, and the trehalose synthase can be over-expressed in the Corynebacterium glutamicum without induction and used for converting maltose to synthesize trehalose. According to the invention, the corynebacterium glutamicum endogenous strong constitutive expression promoter is utilized to express the target protein, overexpression can be realized without induction, and the production cost can be reduced in actual production.
Owner:山东恒仁工贸有限公司
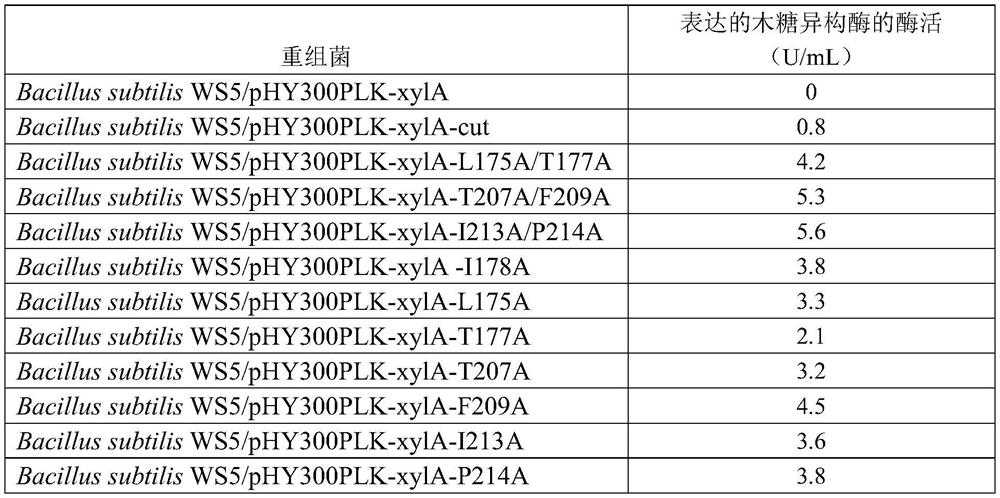
Method for promoting extracellular expression of protein in bacillus subtilis by utilizing cutinase
ActiveCN112301015ASimplify downstream purification processLow costBacteriaHydrolasesCutinaseProtein target
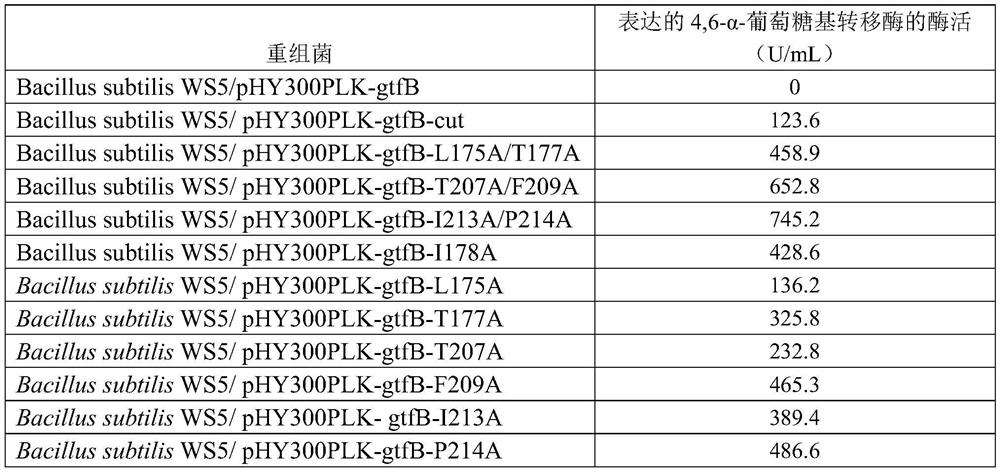
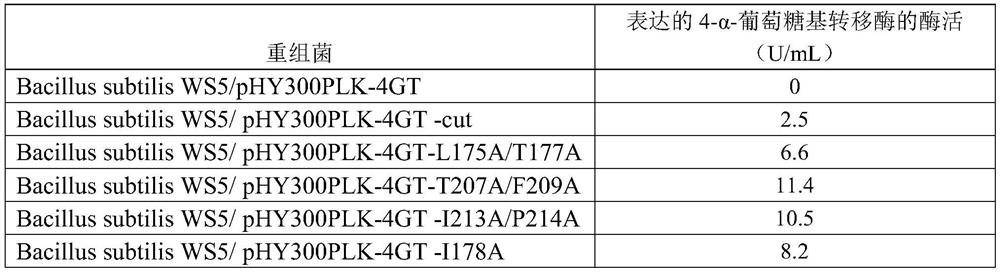
The invention discloses a method for promoting extracellular expression of protein in bacillus subtilis by utilizing cutinase, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, enzyme engineeringand microbial engineering. According to the invention, a cutinase mutant and the target protein are co-expressed in the bacillus subtilis; the target protein comprises xylose isomerase, 4,6-alpha-glucosyltransferase, 4-alpha-glucosyltransferase, trehalose synthase and branching enzyme; extracellular expression of the intracellularly localized target protein can be realized, so that the productionefficiency is improved and the post-extraction process is simplified; and the method has relatively high academic significance and application value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Beta-amylase-trehalose synthase fused enzyme and expression gene and application thereof
ActiveCN104059902AReduce the impact of separationPromote decompositionBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAmylaseExpression gene
The invention relates to a beta-amylase-trehalose synthase fused enzyme and an expression gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the beta-amylase-trehalose synthase fused enzyme is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the nucleotide sequence of the expression gene of the beta-amylase-trehalose synthase fused enzyme is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. According to the invention, beta-amylase and trehalose synthase are fused for the first time, and the obtained beta-amylase-trehalose synthase fused enzyme can be used for producing trehalose by utilizing amylose or straight-chain dextrin, and moreover the influence of substrate maltose on the separation of the product trehalose is reduced when the trehalose synthase acts on maltose to generate trehalose.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Bacillus subtilis for producing 2 '-fucosyllactose and application thereof
PendingCN114480465AIncrease supplyStrong application valueBacteriaTransferasesPhosphomannomutaseEnzyme Gene
The invention provides recombinant bacillus subtilis for producing 2 '-fucosyllactose and application of the recombinant bacillus subtilis, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the recombinant bacillus subtilis, bacillus subtilis is used as an original strain, and a mannose-6-phosphate isomerase gene manA, a phosphomannose mutase gene manB, a mannose-1-phosphoguanosine transferase gene manC, a GDP-mannose dehydratase gene gmd, a GDP-fucose synthase gene wcaG and alpha-1, 2-dihydroxy-4-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-1 The recombinant bacillus subtilis is obtained by integrating a 1, 2-fucosyl transferase gene futC onto a bacillus subtilis genome and knocking out beta-galactosidase genes yesZ and ganA. The invention also provides application of the recombinant bacillus subtilis in fermentation synthesis of the 2 '-fucosyllactose, the yield of the 2'-fucosyllactose in fermentation in a 5L fermentation tank reaches 70.08 g / L, and the recombinant bacillus subtilis has relatively high application value and industrial production potential.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for synthesizing trehalose under catalysis of co-immobilized double enzymes
InactiveCN104328107AImprove efficiencyIncrease productivityChemical industryOn/in organic carrierAmylaseEscherichia coli
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing trehalose under catalysis of co-immobilized double enzymes. According to the method, recombinant escherichia coli capable of synthesizing high-temperature-resisting trehalose synthase in a great quantity by fermentation culture is subjected to permeability treatment, and beta-amylase is added; chitosan and sodium alginate are used for co-immobilizing to form micro-spheres; starch with the weight content of 25%-30% is catalyzed by alpha-amylase and then is subjected to a contact reaction with the micro-spheres to generate the trehalose, wherein after the micro-spheres are repeatedly utilized for 8-16 times, the conversion rate of the starch can be up to 60%-65%. By adopting the method provided by the invention, the high-quality trehalose can be provided in a large-scale, low-cost and high-efficiency manner.
Owner:NANJING HAIHE BIOTECH
Endo-s2 mutants as glycosynthases, method of making and use for glycoengineering of glycoproteins
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
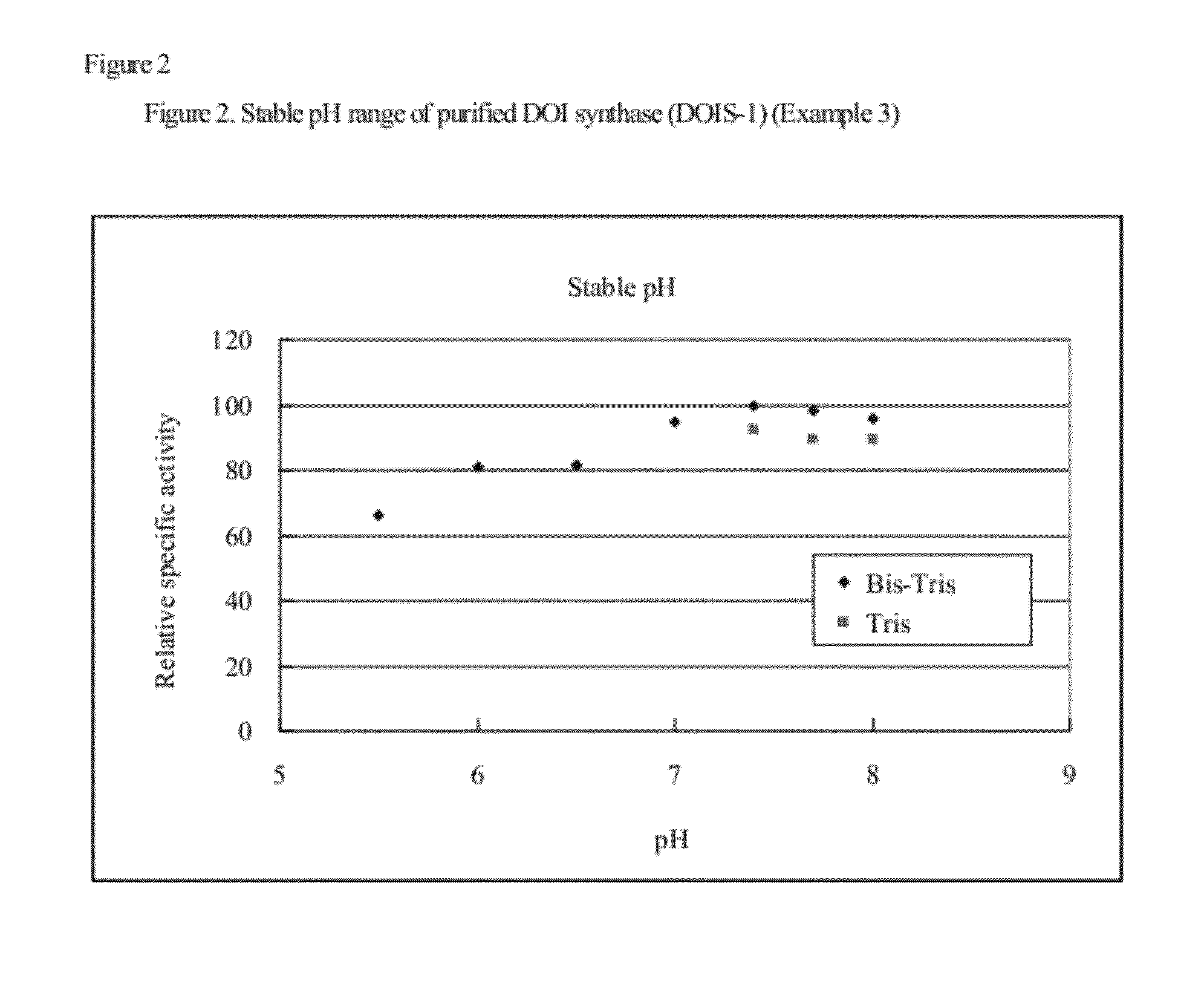
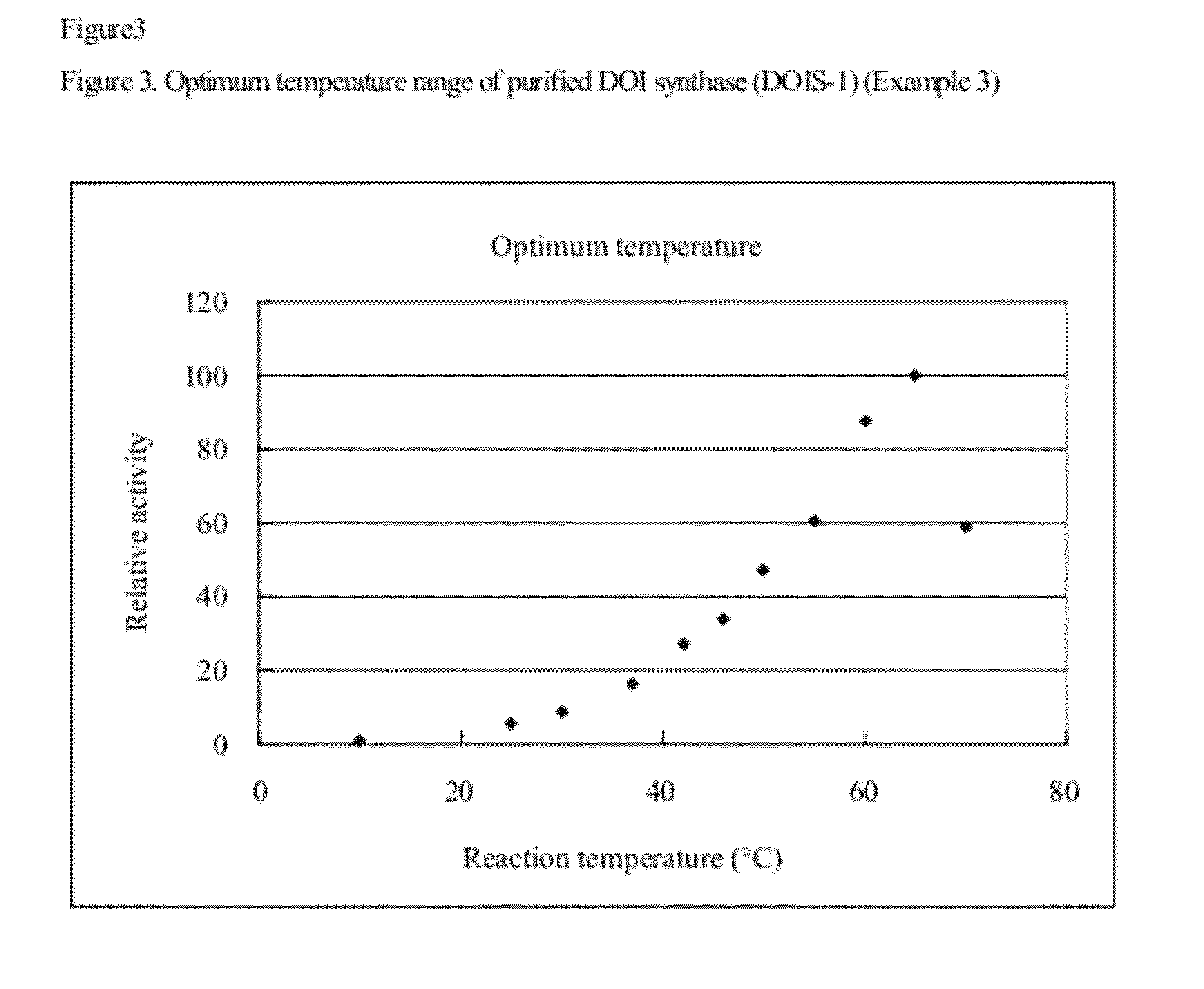
2-deoxy-scyllo-inosose synthase
An object of the present invention is to provide a DOI synthase having properties such as stability to heat and pH, which are superior to those of conventional enzymes, and a method for producing DOI using the above-mentioned enzyme. The present invention provides a 2-deoxy-scyllo-inosose synthase having the properties described in the following (1), (2), (4), (6) and (7), and also having the properties described in the following (3) and / or (5):(1) action: the enzyme has a function to convert glucose-6-phosphate to 2-deoxy-scyllo-inosose;(2) optimum pH range: pH 7.0 to 7.7;(3) stable pH range: pH 6.0 to 8.0;(4) optimum temperature range: 55° C. to 70° C.;(5) stable temperature range: 20° C. to 46° C.;(6) coenzyme used: NAD+; and(7) molecular weight: 39,000 to 42,000.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
Method for generating human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) or precursors thereof
A method for generating human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) or precursors thereof, compounds obtainable by the method, and uses and compositions involving such compounds. The method comprising the steps of a) providing at least one donor selected from the group of compounds of any of formulae 5 to 10, b) providing at least one acceptor from a group of lactose, LNT, LNnT and derivatives thereof, c) providing at least one enzyme comprising a transglycosidase activity and / or a glycosynthase activity, d) preparing a mixture of the at least one donor, at least one acceptor and at least one enzyme provided in steps a), b) and c); and e) incubating the mixture prepared according to step d).
Owner:GLYCOM AS
Endo-S2 mutants as glycosynthases, method of making and use for glycoengineering of glycoproteins
ActiveUS11008601B2Reduced activityHigh activityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiviralsFucosylationTherapeutic antibody
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Polysaccharide synthases (H)
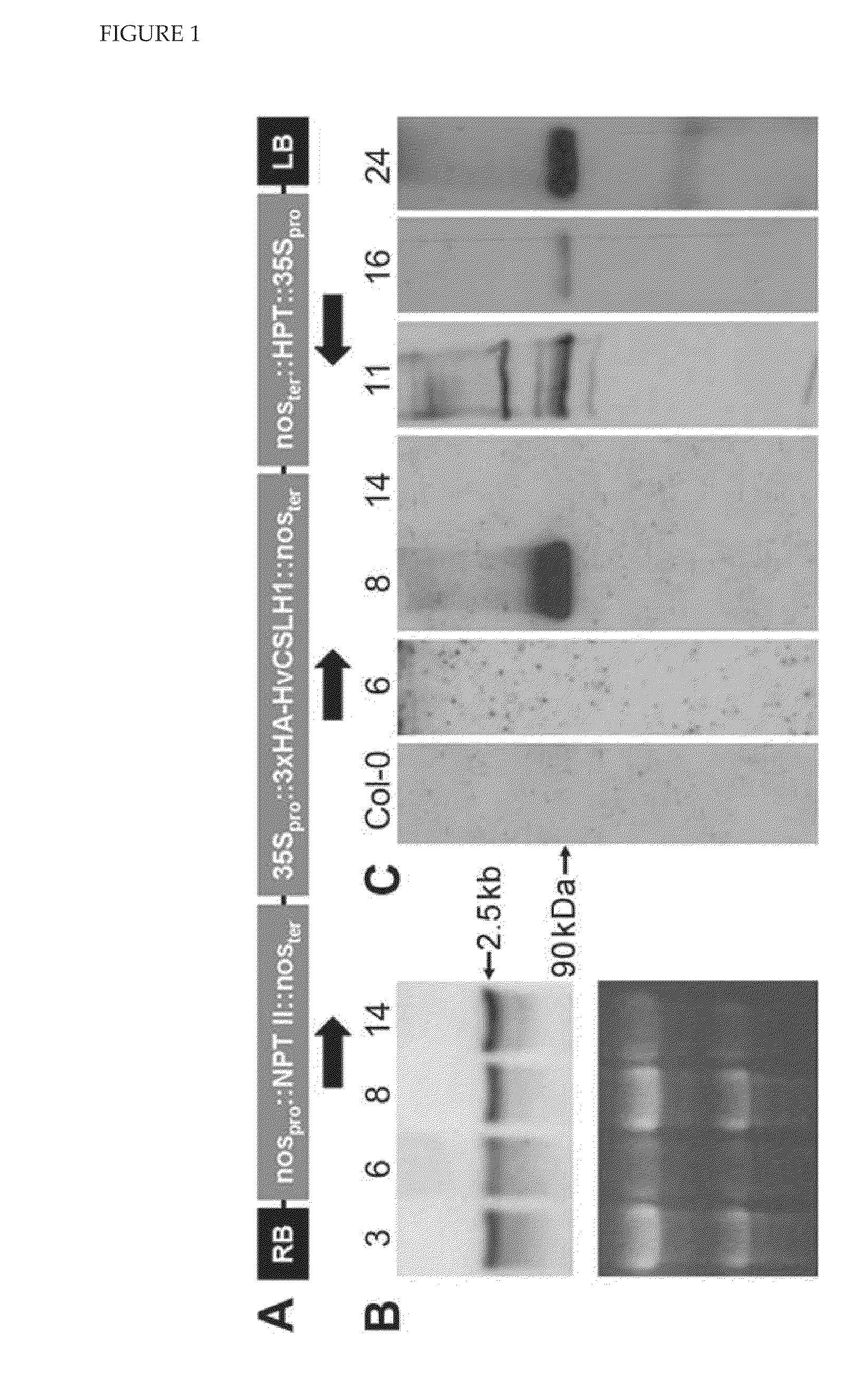
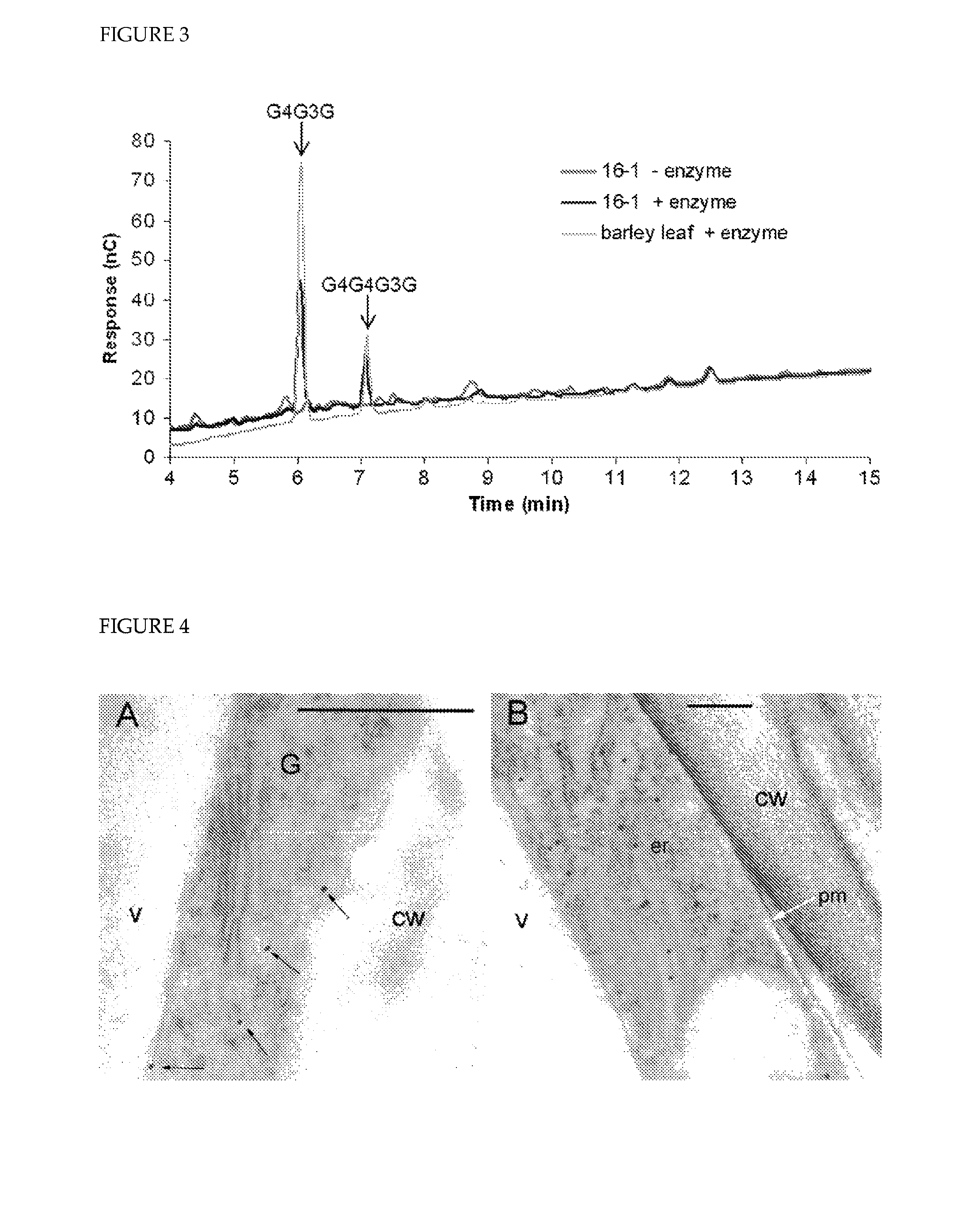
The present invention relates generally to polysaccharide synthases. More particularly, the present invention relates to (1,3;1,4)-β-D-glucan synthases. The present invention provides, among other things, methods for influencing the level of (1,3;1,4)-β-D-glucan produced by a cell and nucleic acid and amino acid sequences which encode (1,3;1,4)-β-D-glucan synthases.
Owner:DOBLIN MONIKA SUSANNE +5
A kind of trehalose synthase and its coding gene and application
ActiveCN104805104BReduce manufacturing costEasy to prepareBacteriaIsomerasesNucleotidePseudomonas stutzeri
The invention relates to a trehalose synthase and a coding gene and application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of an expression gene of the trehalose synthase is shown in SEQ ID No. 1; the amino acid sequence of the trehalose synthase is shown in SEQ ID No. 2. According to the trehalose synthase and the coding gene and application thereof, the trehalose synthase is obtained from pseudomonas stutzeri for the first time, and a preparation method of the trehalose synthase is simple and convenient and is high in yield and high in purity; proved by experiments, the thermal stability of the trehalose synthase is good, the trehalose conversion ratio can reach 70% in 1-hour reaction, and the reaction time is greatly shortened compared with that of the existing trehalose synthase, so that the production cost of trehalose can be reduced, and a foundation is laid for the industrial production of trehalose.
Owner:武汉肌赛雪生物科技有限公司
Fusion protein, as well as efficient expression method and application thereof
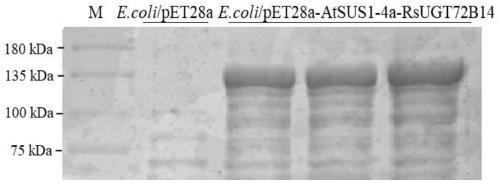
PendingCN111378630AImprove efficiencyIncrease productionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleic acid vectorEscherichia coliRhodiola sachalinensis
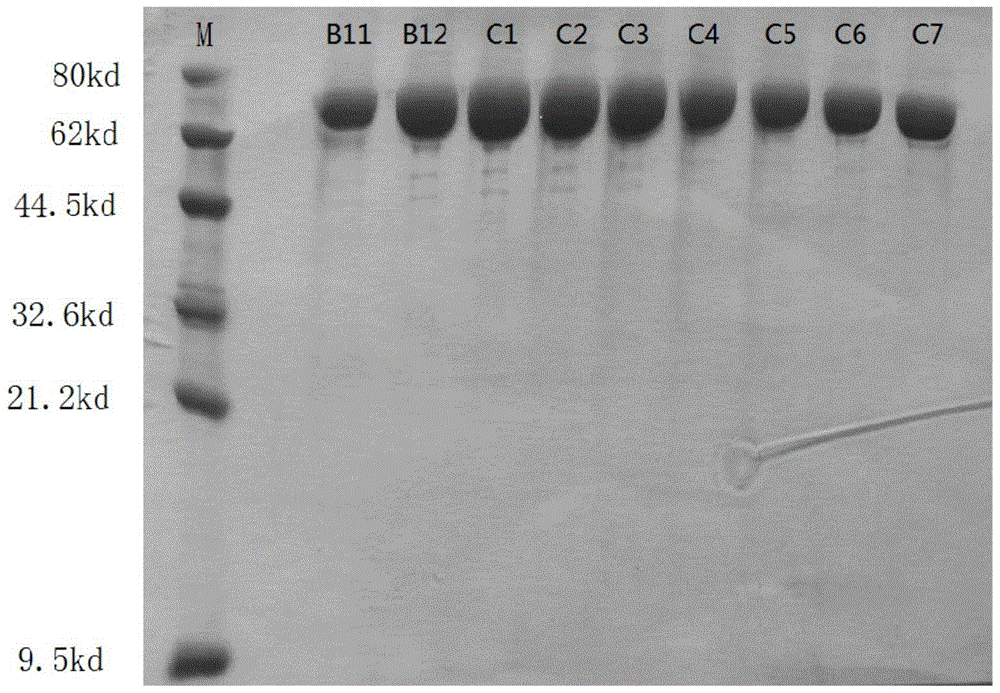
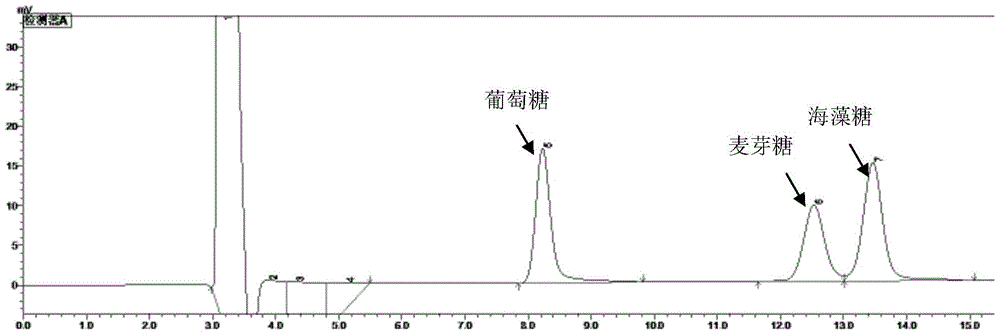
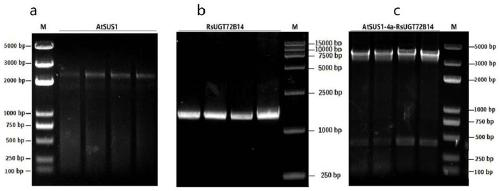
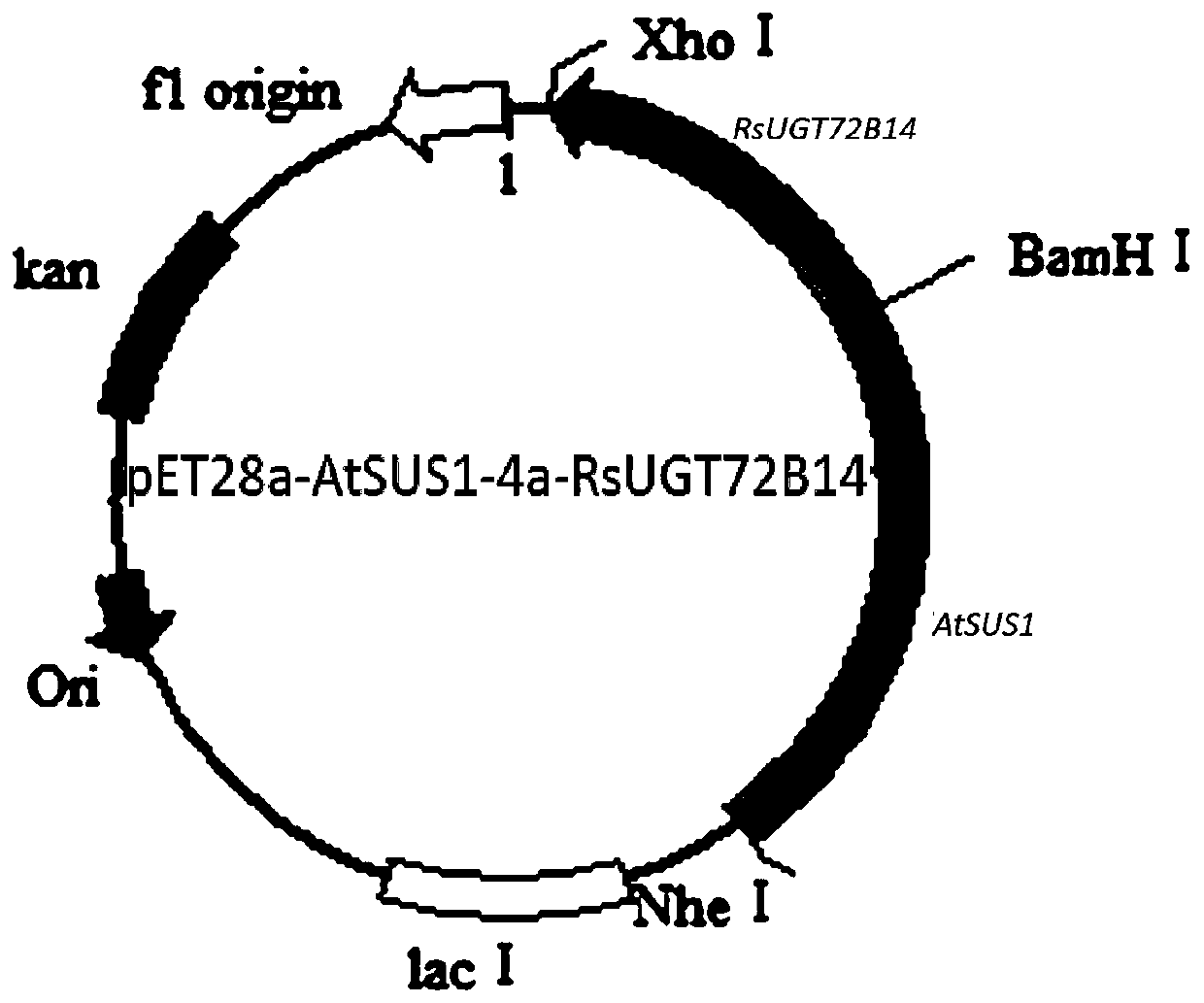
The invention discloses fusion protein, as well as an efficient expression method and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of fusion protein. The fusion protein is AtSUS1-RsUGT72B14fusion protein, including core fragments of arabidopsis thaliana sucrosesynthaseAtSUS1 and rhodiola sachalinensis uridine diphosphate glucosyl transferase RsUGT72B14. According to the codon preferenceof escherichia coli, an optimized gene sequence of the AtSUS1-RsUGT72B14 fusion protein is obtained by combining the characteristics of gene sequences of AtSUS1 and RsUGT72B14 and introducing GGSG four amino acid connecting peptide sequences by designing a restriction enzyme cutting site connection method, efficient expression of the AtSUS1-RsUGT72B14 fusion protein is realized, and the fusion protein can be used for catalytically synthesizing salidroside.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com